UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008
OR
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For transition period from to
Commission File Number 001-33622
VMWARE, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | |
| Delaware | | 94-3292913 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
| |
3401 Hillview Avenue Palo Alto, CA | | 94304 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
(650) 427-5000
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | |
Title of each class | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Class A Common Stock, par value $0.01 | | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | |
Large accelerated filer x | | Accelerated filer ¨ | | Non-accelerated filer ¨ | | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
| | | | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
At June 30, 2008, the aggregate market value of the registrant’s Class A common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant (based upon the closing sale price of such shares on the New York Stock Exchange on June 30, 2008) was approximately $2,439,767,515. Shares of the registrant’s Class A common stock and Class B common stock held by each executive officer and director and by each entity or person, other than investment companies, that, to the registrant’s knowledge, owned 5% or more of the registrant’s outstanding Class A common stock as of June 30, 2008 have been excluded in that such persons may be deemed to be affiliates of the registrant. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
As of February 19, 2009, the number of shares of common stock, par value $.01 per share, of the registrant outstanding was 390,654,149, of which 90,654,149 shares were Class A common stock and 300,000,000 were Class B common stock.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Information required in response to Part III of Form 10-K (Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14) is hereby incorporated by reference to portions of the registrant’s Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held in 2009. The Proxy Statement will be filed by the registrant with the Securities and Exchange Commission no later than 120 days after the end of the registrant’s fiscal year ended December 31, 2008.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FACTORS THAT MAY AFFECT FUTURE RESULTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements, within the meaning of the federal securities laws, about our business and prospects. The forward-looking statements do not include the potential impact of any mergers, acquisitions, divestitures, securities offerings or business combinations or other developments in our business that may be announced or consummated after the date hereof. Any statements contained herein that are not statements of historical fact may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. Without limiting the foregoing, the words “outlook,” “believes,” “plans,” “intends,” “expects,” “goals,” “potential,” “continues,” “may,” “will,” “should,” “seeks,” “predicts,” “estimates,” “anticipates,” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these words. Our future results may differ materially from our past results and from those projected in the forward-looking statements due to various uncertainties and risks, including those described in Item 1A of Part I (Risk Factors). The forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report and undue reliance should not be placed on these statements. We disclaim any obligation to update any forward-looking statements contained herein after the date of this Annual Report.
i
PART I
VMware is the leading provider of virtualization solutions from the desktop to the data center. Our virtualization solutions represent a pioneering approach to computing that separates application software from the underlying hardware to achieve significant improvements in efficiency, availability, flexibility, and manageability. Our broad and proven suite of virtualization solutions addresses a range of complex information technology (“IT”) problems that include cost and operational inefficiencies, business continuity, software lifecycle management, and desktop management. The benefits to our customers include substantially lower IT costs, cost-effective high availability across a wide range of applications, and a more automated and resilient systems infrastructure capable of responding dynamically to variable business demands. Our customer base includes organizations of all sizes across numerous industries and includes 100% of the Fortune 100 and approximately 95% of the Fortune 1000.
Our solutions enable organizations to aggregate multiple servers, storage infrastructure, and networks together into shared pools of capacity that can be allocated dynamically, securely, and reliably to applications as needed, increasing hardware utilization and reducing spending. In the ten years since the introduction of our first virtualization platform, we have expanded our product offerings to address distributed and heterogeneous infrastructure challenges such as planned and unplanned downtime management, system recoverability and reliability, backup and recovery, resource provisioning and management, capacity and performance management, and security.
We work closely with more than 900 technology partners, including leading server, microprocessor, storage, networking and software vendors. We have shared the economic opportunities surrounding virtualization with our partners by facilitating solution development through open Application Programming Interface (“APIs”) formats and protocols and providing access to our source code and technology. The endorsement and support of our partners have further enhanced the awareness, reputation, and adoption of our virtualization solutions.
We have developed a multi-channel distribution model to expand our presence and reach various segments of the market. We derive a significant majority of our revenues from our large indirect sales channel that include distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors, and systems integrators. We believe that our partners benefit greatly from the sale of our solutions through additional services, software, and hardware sales opportunities. We have trained a large number of partners and end users to deploy and leverage our solutions.
We were incorporated as a Delaware corporation in 1998 and continued to operate in large measure as a stand-alone company following our acquisition by EMC Corporation (“EMC”) in 2004 and following our initial public offering (“IPO”) of our Class A common stock in August 2007. EMC continues to hold 84% of our outstanding Class A common stock and all of our Class B common stock, and we are considered a “controlled company” under the rules of the New York Stock Exchange. Total revenues in 2008 increased 42% to $1,881.0 million. This included license revenues of $1,178.1 million and services revenues of $702.9 million. In the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, over 90% of our license revenues were from our data center solutions with the balance from our other solutions. Of our total services revenues in 2008, 79% were software maintenance revenues and 21% were professional services revenues. For additional financial information, see Note M to the consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this filing. Our corporate headquarters are located at 3401 Hillview Avenue, Palo Alto, California and we have approximately 70 offices worldwide.
We began shipping our first product in 1999, and today we offer multiple products from the desktop to the data center. Our business is organized around providing solutions for three major IT predicaments: Reducing costs and increasing operational efficiency in data centers, providing easy access to “cloud computing” capacity and simplifying management and control of corporate client computing.
1
Overview of Virtualization
Virtualization was first introduced in the 1970s to enable multiple business applications to share and fully harness the centralized computing capacity of mainframe systems. Virtualization was effectively abandoned during the 1980s and 1990s when client-server applications and inexpensive x86 servers and personal computers established the model of distributed computing. Rather than sharing resources centrally in the mainframe model, organizations used the low cost of distributed systems to build up islands of computing capacity, providing some benefits but also introducing new challenges. Some of these challenges include a gross underutilization of hardware resources, inability to easily assure quality of service to applications, and unwieldy management processes made cumbersome by the tight coupling of applications to the underlying hardware.
Data Center Virtualization
Today, x86 hardware is becoming increasingly proficient with multi-core processors, growing memory capacity, and higher speed interconnects shipping in standard servers. Complexity of applications is on the rise with multi-element, mixed operating system (“OS”) applications becoming increasingly common, making it difficult to provide a uniform quality of service across all components. Virtualization is being overwhelmingly accepted as the standard way of computing in data centers for the most efficient utilization of hardware.
VMware server virtualization technology is categorized as a virtual data center operating system (“VDC-OS”). A VDC-OS not only decouples the entire software environment from its underlying hardware infrastructure, but also enables the aggregation of multiple servers, storage infrastructure, and networks into shared pools of resources that can be delivered dynamically, securely, and reliably to applications as needed. This approach enables organizations to build a computing infrastructure with high levels of utilization, availability, automation, and flexibility using building blocks of inexpensive industry-standard servers.
In addition to providing abstraction from the underlying hardware, a VDC-OS is also able to deliver services to applications running inside virtual machines, in an OS and application agnostic manner. This not only increases operational efficiency, since these services are built-in and easily enabled, but also allows mixed-element, multi-OS applications to get standard service levels delivered by the infrastructure, broadening customer deployment choices.
A VDC-OS effectively creates “internal clouds” of resources, shareable by many applications, with applications moving across resources without disruption or downtime to ensure the right quality of service to every application dynamically. This enables service-level guarantees from the infrastructure to applications. Greater levels of operational automation benefits are achievable in this environment because of the inherent standardization of virtual machines and can only be realized by using management services that are aware of the unique flexibility and dynamism of a VDC-OS.
In 2008, we announced our vCloud initiative in order to leverage our platform to allow enterprises with internal clouds to easily access external cloud capacity on demand, without the need to customize or change their applications. The objective of the vCloud initiative is to enable hosting and cloud computing vendors to deliver enterprise-class cloud computing by federating on demand compute capacity between virtual data centers and cloud service providers on a common VMware platform. The initiative is aimed at providing users choice in where they deploy applications by providing a common set of cloud computing services for businesses and service providers, with support for any application or OS and the ability to choose where applications live, on or off premise.
2
Data Center Products and Technology
VMware Infrastructure is our flagship VDC-OS product. Users can choose to deploy the VMware ESX or VMware ESXi hypervisor when they purchase VMware Infrastructure. VMware ESX is the industry’s most mature hypervisor. VMware ESXi is a compact, 32MB footprint version of VMware ESX with the same functionality and performance. Other components of VMware Infrastructure include capabilities such as the following:
| | • | | VMware VMotion and Storage VMotion, the live migration of live running virtual machines across servers or storage locations without disruption or downtime. |
| | • | | VMware High Availability, cost-effective high availability for all applications against hardware failures and operating systems. |
| | • | | VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler, continuous monitoring of virtual machines that ensure optimal placement on hardware based on resource requirements and priorities. |
Management of the VDC-OS is provided by the vCenter family of products, which simplify and automate management tasks. Key vCenter products include the following:
| | • | | vCenter Server, the central management and control point for VMware Infrastructure environments. |
| | • | | vCenter Site Recovery Manager, one-button disaster recovery for virtualized environments. |
| | • | | vCenter Lifecycle Manager, an automated process for managing the lifecycle of virtual machines in the data center. |
| | • | | vCenter Lab Manager, an automated process for software development environments. |
We also offer free data center products such as VMware Server and VMware ESXi that encourage the trial, usage, and adoption of VMware virtualization in data centers of all sizes. VMware Server is a virtualization platform that runs on top of an OS (a “hosted” product) available for trial and download by customers so they can test virtualization before they move to the bare-metal products.
Desktop Virtualization
Personal computing and personal computing devices are undergoing change as users increasingly use multiple devices including desktop personal computers, laptop computers, thin clients, and mobile internet devices to access data and applications. In addition, users are employing various desktop operating systems including Windows, Apple OS X, and Linux to access applications that may run locally on a computer, centrally on a server, or accessed through a web page. This heterogeneity is becoming increasingly common, making it difficult to manage and secure customers’ desktop environments.
VMware desktop virtualization technology is categorized as a universal client solution. A universal client solution decouples the entire desktop environment from its underlying device, enabling customers to create user-centric instead of device-centric desktop environments. There are two main approaches to desktop virtualization: Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (“VDI”), where the desktop virtual machine runs on a server and is accessed remotely using a display protocol, and client-hosted virtual desktops, where a desktop virtual machine runs locally on a computer and is able to use the local hardware and peripherals. We have products in both of these categories, as well as offerings that combine both approaches. VDI enables customers to provide central management and control over their desktop environments by moving the entire desktop environments off the end-point device and into a virtual machine running on a VDC-OS. This enables customers to quickly provision new desktop environments to local and remote users while enabling centralized security, updating, and control over these environments. VDI can also take advantage of the other tools and technologies that surround a VDC-OS, including high availability and disaster recovery.
3
Client-hosted desktop virtualization enables users to run one or more virtual machines on a single desktop or laptop computer. Technical professionals have been using our technology for testing and development because it allows them to run multiple operating systems on a single computer for securely testing new operating systems, patches, and applications. Client-hosted desktop virtualization also allows individual users to run applications that require a different operating system such as a Windows application on an Apple OS X. In addition, users can leverage desktop virtualization to run a virtual work desktop on an employee-owned home computer and use the isolation attribute of virtualization to create a secure barrier between the two environments.
In 2008, VMware announced its vClient initiative, which consists of both product and partnering efforts aimed at delivering universal clients, that is desktops that follow users to any end-point, that are secure, cost-effective, and easy for IT to manage. Our vClient partnering efforts involve a network of hardware, systems, and software partners to deliver a complete universal client virtualization solution to customers.
Desktop Products and Technologies
Our desktop products leverage our virtualization technology to deliver desktop virtualization to both enterprise users and personal users.
VMware View is our enterprise desktop virtualization platform. VMware View incorporates and extends VMware Infrastructure, VMware’s VDC-OS, into both a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure and a client-hosted virtualization solution that allows a desktop virtual machine to run centrally or locally. Major components of VMware View include:
| | • | | View Managerprovides session management and security between a user connecting from a personal computer or a thin client to a virtual desktop running on VMware Infrastructure or to a terminal session running on Windows Terminal Services or to a physical PC. |
| | • | | View Composer provides desktop image provisioning, management, and storage reduction for desktop virtual machines running on VMware Infrastructure and managed by View Manager. |
| | • | | VMware ThinApp is an application virtualization solution that customers can purchase separately or with VMware View. Application virtualization packages individual applications into separate containers allowing quicker application delivery and reduced management costs. |
VMware also sells a range of personal client-hosted desktop virtualization products including:
| | • | | Workstation enables technical professionals to create multiple secure virtual sandboxes on a single computer for running and testing multiple operating systems and applications. |
| | • | | Fusion enables Apple users to seamlessly run Windows and Windows applications on an Intel processor powered Apple OS X Macintosh computer. |
Other desktop products include VMware ACE, which provides a layer of management around client-hosted desktops, and VMware Player, a free client-hosted virtual desktop runtime that encourages trial of desktop virtualization.
Support and Services
We believe that our strong services organization and frequent customer touch points help establish loyal customers that provide references and help promote our technology across various industries. We have implemented a broad services strategy that leverages the professional services organizations of our partners. We have also established our own services offerings to complement our partners’ services offerings and to ensure customer satisfaction, drive additional sales, and promote renewals and upgrades. Our services offerings include customized solutions and onsite support that enable us and our channel partners to provide a positive overall customer experience.
4
We have established our global customer support organization, VMware Global Support Services, to align with and support our expanding customer base.
| | • | | VMware Global Support Services.We offer a suite of proactive, top-quality support packages backed by industry-leading expertise. We offer three support and subscription programs (Platinum, Gold, and Silver) on an annual or multi-year subscription basis, that include VMware support along with access to periodic updates, bug fixes, and enhancements to our products. Complementing our Platinum support and subscription program, we offer Business Critical Support which provides customers personalized technical support delivered by a designated team of experts familiar with a customer’s specific system configuration, past support experience, and business needs. A majority of our server customers purchase Platinum support. In addition to phone support, our customers have access to an online product knowledge database for help with troubleshooting and operational questions. Our support teams, located in California, Denver, Canada, Ireland, India, and Japan, provide first response and manage the resolution of customer issues. In addition, we have authorized certain systems vendors and independent service providers to provide support for our products on our behalf. |
We also offer a range of professional services under our VMware Professional Services offering, which includes the following:
| | • | | VMware Consulting Services.VMware Certified Professionals (“VCPs”) provide on-site assistance throughout the virtualization adoption lifecycle to accelerate the implementation of our virtualization solutions. VCPs conduct initial assessments and upgrade workshops and prepare detailed implementation project plans. Once customers are ready for standardization across their enterprise, VCPs help integrate virtual infrastructure into enterprise systems and processes. VCPs include VMware employees, partners, and customers that have completed training and have successfully passed our VCP exam. |
| | • | | VMware Education Services.Our courses provide extensive hands-on labs, case study examples, and course materials. Customers work in teams of two on servers located offsite using a variety of remote access technologies. |
| | • | | VMware Technical Account Manager (“TAM”). TAM service provides our customers with a dedicated VMware expert, which enables customers to accelerate standardization of VMware products by assessing their unique environment, proactively recommending solutions, and identifying unforeseen circumstances that may cause delays in deployment. |
Technology Alliances
Consistent with our partner-centric strategy, we have engaged a broad group of hardware and software vendors to cooperatively advance virtualization technology through joint marketing, product interoperability, collaboration, and co-development. We create opportunity for partners by enabling them to build products that utilize our virtualization technology and create differentiated value through joint solutions.
We have more than 900 technology partners with whom we bring joint offerings to the marketplace. We classify our partners as follows:
| | • | | Independent Hardware Vendors (“IHVs”). We have established strong relationships with large system vendors, including Dell, Fujitsu, Fujitsu-Siemens, HP, IBM, Lenovo, NEC, and Sun, for joint certification and co-development. We also work closely with AMD, Cisco, Intel, and other IHVs to provide input on product development to enable them to deliver hardware advancements that benefit virtualization users. We coordinate with the leading storage and networking vendors to ensure joint interoperability, as well as to enable our software to access their differentiated functionality. |
| | • | | Independent Software Vendors (“ISVs”). We partner with leading systems management, infrastructure software, and application software vendors to enable them to deliver value-added |
5
| | products that integrate with our VMware Infrastructure suite of products. The VMware Technology Alliance Partner Program facilitates joint solution creation and coordinated go-to-market activities with our partners. Our ISV partners have distributed more than 900 software applications as virtual appliances. |
In addition to developing open APIs, formats, and protocols at multiple levels in our products, we provide source code access to select partners in our “Community Source” program to facilitate joint development and partner differentiation. We provide access to our ESX source code to more than 500 developers from more than 40 partners for joint development projects. We also work with our industry partners to promote and foster the adoption of industry standards.
We invest significant capital in testing and certification infrastructure to rigorously ensure our software works well with major hardware and software products. We have introduced VMware Ready, an expanded and unified program for interoperable and optimized partner solutions. We have more than 2,000 server, storage, I/O, and thin-client devices from more than 150 companies that are VMware Ready Certified. We have successfully tested more than 90 operating systems for use with our solutions. We believe that the scale and scope of this effort is a significant competitive advantage.
Research and Development
We have made and intend to make significant investments in research and development (“R&D”). We have assembled a strong group of developers with system-level and system management software expertise. We also have strong ties to leading academic institutions around the world and we support academic programs that range from shared source code for research to sabbatical programs for visiting professors.
We prioritize our product development efforts through a combination of engineering-driven innovation and customer and market-driven feedback. Our R&D culture places high value on innovation, quality, and open collaboration with our partners. We currently participate in numerous standards groups and VMware employees hold a variety of standards organization leadership positions, including the Distributed Management Task Force and the Standard Performance Evaluation Corporation. We believe the strength of our R&D organization is a competitive differentiator.
Our R&D expenses totaled $429.2 million, $285.9 million and $152.0 million in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Sales and Marketing
We sell and market our products largely through a network of channel partners, which includes distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors, and systems integrators, with over 75% of our revenue in 2008 derived from this indirect network.
We have established ongoing business relationships with our distributors. Our distributors purchase software licenses and software support from us for resale to end user customers via resellers.
A substantial majority of our resellers obtain software licenses and software support from our distributors and market and sell them to our end user customers. The majority of these resellers are part of our VIP Partner Program, which offers these resellers sales and product training and pricing incentives and rebates and access to the worldwide network of VMware distributors and access to the VMware Partner Central Web portal.
We offer several levels of membership in our VIP reseller network depending on a reseller’s interest and capability of providing demand generation, fulfillment, service delivery, and education to customers and prospects. We also have certain resellers, as well as systems integrators, who obtain software licenses and software support directly from VMware. The VIP network agreements signed by the resellers carry no obligation to purchase or sell VMware products and can be terminated at any time by either party.
6
We have a direct sales force that complements our channel partners’ efforts. Our sales force works with our channel partners to introduce them to end user customer accounts and new sales opportunities. Our channel partners also introduce our sales force to their end user customers.
In addition, our channel partner network includes certain system integrators and resellers trained and certified to deliver consulting services and solutions leveraging VMware products.
Our strategy is to position our products within a variety of organizations where end user customers might consider buying virtualization solutions. We provide product training and marketing assistance to our channel partner network.
We generally do not have long-term contracts or minimum purchase commitments with our distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors, systems integrators, and our contracts with these channel partners do not prohibit them from offering products or services that compete with ours.
We primarily sell our software under perpetual licenses, and our sales contracts generally require end user customers to purchase maintenance for the first year. Software maintenance is sold both directly to end user customers and via our network of channel partners, and the majority of professional services are sold directly, with some professional services sold via our channel partners. End users can obtain licenses to our products through individual discrete purchases to meet their immediate needs or through the adoption of enterprise license agreements (“ELAs”). ELAs are comprehensive volume license offerings that provide for multi-year maintenance and support at discounted prices. ELAs enable us to build long-term relationships with our customers as they commit to VMware’s virtual infrastructure solutions in their data centers. Our sales cycle with end user customers ranges from less than 90 days to over a year depending on several factors, including the size and complexity of the customer’s infrastructure.
The competitive landscape in which we operate includes not only other software virtualization vendors, but also traditional hardware solutions. In establishing prices for our products, we take into account, among other factors, the value our products and solutions deliver, and the cost of both alternative virtualization and hardware solutions. We believe the significant number of customers who also purchase our software services reflects a clear customer perception as to the value of our software services.
Our marketing efforts focus on communicating the benefits of our solutions and educating our customers, distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors, systems integrators, the media, and analysts about the advantages of our innovative virtualization technology.
We raise the awareness of our company, market our products, and generate sales leads through industry events, public relations efforts, marketing materials, free downloads, and our website. On average, our website receives approximately 875,000 unique visits to www.vmware.com each week, as measured by a third-party tracking system. We also have created an online community called VMware Technology Network (“VMTN”) that enables customers and partners to share and discuss sales and development resources, implementation best practices, and industry trends among other topics. Attendance at VMworld in the U.S., the largest virtualization conference hosted by VMware, has grown from approximately 1,400 attendees in 2004 to nearly 14,000 attendees in 2008. In 2008, we also had our first VMworld conference in Europe with approximately 4,500 attendees. We also offer management presentations, seminars, and webinars on our products and topics of virtualization. We believe a combination of these efforts strengthens our brand and enhances our leading market position in our industry.
Customers
Our customers include 100% of the Fortune 100 and approximately 95% of the Fortune 1000. Our customer deployments range in size from a single virtualized server for small businesses to up to thousands of virtual machines for our largest enterprise customers. In periodic third-party surveys commissioned by us, our customers indicate very high satisfaction rates with our products and many have indicated a strong preference for repeat purchases.
7
One of our distribution relationships is with Ingram Micro, which accounted for 18% of our worldwide revenues in 2008. The agreement under which we receive the substantial majority of our Ingram Micro revenues is terminable by either party upon 90 days’ prior written notice to the other party, and neither party has any obligation to purchase or sell any products under the agreement. Additionally, Arrow Electronics, Inc and Hewlett Packard Company accounted for 16% and 11% of revenues in 2008, respectively. No other channel partner accounted for more than 10% of our revenues in 2008.
Competition
The virtualization market is evolving, and during 2008 we experienced increased competition and expect competition to significantly intensify in the future. We compete with large and small companies in different segments of the virtualization market, and expect that new entrants will continue to enter the market and develop technologies that, if commercialized, may compete with our products.
We believe that the key competitive factors in the virtualization market include:
| | • | | the level of reliability and new functionality of product offerings; |
| | • | | the ability to provide full virtual infrastructure solutions; |
| | • | | the ability to offer products that support multiple hardware platforms and operating systems; |
| | • | | the proven track record of formulating and delivering a roadmap of virtualization capabilities; |
| | • | | pricing of products, individually and in bundles; |
| | • | | the ability to attract and preserve a large installed base of customers; |
| | • | | the ability to create and maintain partnering opportunities with hardware and infrastructure software vendors and development of robust indirect sales channels; and |
| | • | | the ability to attract and retain virtualization and systems experts as key employees. |
Microsoft is our primary competitor for data center virtualization solutions. In 2008, Microsoft released virtual infrastructure and virtual management products and recently announced a cloud-based computing initiative. Microsoft’s offerings are positioned to compete with our virtual infrastructure, virtualization management, and some of our free data center product offerings. We believe our server virtualization approach and roadmap is differentiated from Microsoft’s and delivers significant flexibility, functionality, reliability, and superior economic value to customers. Unlike Microsoft, we have developed our virtualization solutions as a software layer between the hardware and the operating system that is not tied to a specific operating system.
We also compete with Citrix for desktop virtualization solutions and with companies whose virtualization products are based on emerging open-source technologies. In addition, we compete with companies that take different approaches to virtualization. However, we believe these solutions offer limited support for heterogeneous operating system deployments. Furthermore, our VMware Infrastructure suite competes with products that provide high availability clustering, workload management, and resource management.
We also expect to compete with new entrants to the virtualization market, which may include parties currently selling our products or our current technology partners. Existing and future competitors may introduce products in the same markets we serve or intend to serve, and competing products may have better performance, lower prices, better functionality, and broader acceptance than our products. Our competitors may also add features to their virtualization products similar to features that presently differentiate our product offerings from theirs. Additionally, some of our competitors may make acquisitions or enter into partnerships or other strategic relationships with one another to offer a more comprehensive virtualization solution than they individually had offered. Some competitors have in the past and may in the future take advantage of their existing relationships with our business partners to engage in business practices such as distribution and license restrictions that make
8
our products less attractive to our channel partners and end users. A number of companies have recently announced initiatives in these areas. In addition, competitors with existing relationships with our current or prospective end users could in the future integrate competitive capabilities into their existing products and make them available without additional charge. Many of our current and future competitors have longer operating histories, greater name recognition, a larger customer base, and significantly greater financial, technical, sales and marketing, and other resources than we do.
We believe our market leadership, large customer base, strong partner network, broad and innovative solutions suite, and platform-agnostic approach position us favorably to compete effectively for the foreseeable future.
Intellectual Property
To date, the United States Patent and Trademark Office has issued us 48 patents covering various aspects of our server virtualization and other technologies. The granted United States patents will expire beginning in 2018, with the latest granted patent expiring in 2027. We also have numerous United States provisional and non-provisional patent applications pending that cover other aspects of our virtualization and other technologies.
We have been issued trademark registrations in the United States, the European Community, and Japan covering the trademarks VMWARE for use in connection with computer software, clothing, and reference materials, and VMWORLD for use in connection with educational seminars. VMWARE also is our registered trademark in Australia, Canada, India, Israel, the Republic of Korea, Mexico, Singapore, and Taiwan. We also have a trademark application pending to register the VMWARE trademark in China. We have trademark applications pending to register the VMWARE FUSION trademark in Australia, Canada, China, the European Community, Hong Kong, Japan, New Zealand, the Russian Federation, the Republic of Korea, and the United States. We also have trademark applications pending to register the VMMARK trademark in the United States, China, European Community, India, Israel, Japan, and the Russian Federation. In addition, we have registered trademarks for GSX SERVER and P2V in the United States and for MULTIPLEWORLDS in Japan.
We also rely on intellectual property protections such as copyrights and trade secrets.
Despite our efforts, the steps we have taken to protect our proprietary rights may not be adequate to preclude misappropriation of our proprietary information or infringement of our intellectual property rights, and our ability to police such misappropriation or infringement is uncertain, particularly in countries outside of the United States. United States patent filings are intended to provide the holder with a right to exclude others from making, using, selling, or importing in the United States the inventions covered by the claims of granted patents. Our granted United States patents, and any future patents (to the extent they are issued), may be contested, circumvented, or invalidated in the future. Moreover, the rights granted under any issued patents may not provide us with proprietary protection or competitive advantages, and we may not be able to prevent third parties from infringing these patents. Therefore, the exact effect of our patents and the other steps we have taken to protect our intellectual property cannot be predicted with certainty.
Employees
As of December 31, 2008, we had approximately 6,700 employees in offices worldwide, including employees contracted through EMC as discussed below. None of our employees are represented by labor unions, and we consider current employee relations to be good.
We contract with EMC to utilize personnel who are dedicated to work for VMware on a full-time basis. These individuals are located in countries in which we do not currently have an operating subsidiary and are predominantly dedicated to our marketing efforts. We use contractors from time to time for temporary assignments and in locations in which we do not currently have operating subsidiaries. In the event that these contractor resources were not available, we do not believe that this would have a material adverse effect on our operations.
9
Available Information
Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to reports filed pursuant to Sections 13(a) and 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), are made available free of charge on or through our website at www.vmware.com as soon as reasonably practicable after such reports are filed with, or furnished to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). Copies of the (i) charters for our Audit Committee, Compensation and Corporate Governance Committee, and Mergers and Acquisitions Committee, (ii) our Business Conduct Guidelines (code of business conduct and ethics), and (iii) our Corporate Governance Guidelines, are available on the Investor Relations page of our website at www.vmware.com. Copies will be provided to any shareholder upon request. Please send a written request to VMware Investor Relations, 3401 Hillview Avenue, Palo Alto, California 94304. None of the information posted on or accessible through our website is incorporated by reference into this Annual Report.
The risk factors that appear below could materially affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only risks and uncertainties facing us. Our business is also subject to general risks and uncertainties that affect many other companies.
Risks Related to Our Business
The virtualization products and services we sell are based on an emerging technology and therefore the potential market for our products remains uncertain.
The virtualization products and services we develop and sell are based on an emerging technology platform and our success depends on organizations and customers perceiving technological and operational benefits and cost savings associated with adopting virtual infrastructure solutions. Our relatively limited operating history and the relatively limited extent to which virtual infrastructure solutions have been currently adopted may make it difficult to evaluate our business because the potential market for our products remains uncertain. The markets for our virtualization products are new and have grown rapidly from a small base. This has resulted in significant percentage increases in our product sales in recent periods. As the markets for our products mature and the scale of our business increases, the rate of growth in our product sales may be lower than those we have experienced in recent periods. In addition, to the extent that rates of adoption of virtualization infrastructure solutions occur more slowly or less comprehensively than we expect, our revenue growth rates may slow materially or our revenue may decline substantially.
We expect to face increasing competition that could result in a loss of customers, reduced revenues or decreased operating margins.
The market for our products is competitive and we expect competition to significantly intensify in the future. For example, Microsoft currently provides products that compete with some of our free offerings, and has released virtual infrastructure and virtual management products during 2008, announced plans to add higher-end features to those products and recently announced a cloud-based computing initiative. Microsoft’s offerings are positioned to compete with our virtual infrastructure and other virtualization product offerings. We also face competition from other companies and there have been a number of announcements of new product initiatives, alliances and consolidation efforts by our competitors. For example, Citrix Systems recently released new versions of the server virtualization product acquired in conjunction with its 2007 XenSource acquisition and its virtual desktop offering, RedHat recently acquired Qumranet, a developer of virtual infrastructure solutions software, Sun Microsystems and IBM announced new cloud computing initiatives and Oracle announced enhancements to their Xen-based products. Symantec Corporation also announced a competitive Xen-based product. Existing and future competitors may introduce products in the same markets we serve or intend to serve, and competing products may have better performance, lower prices, better functionality and broader acceptance
10
than our products. Our competitors may also add features to their virtualization products similar to features that presently differentiate our product offerings from theirs. Many of our current or potential competitors also have longer operating histories, greater name recognition, larger customer bases and significantly greater financial, technical, sales, marketing and other resources than we do. This competition could result in increased pricing pressure and sales and marketing expenses, thereby materially reducing our operating margins, and could harm our ability to increase, or cause us to lose, market share. Increased competition also may prevent us from entering into or renewing service contracts on terms similar to those that we currently offer and may cause the length of our sales cycle to increase.
Some of our competitors and potential competitors supply a wide variety of products to, and have well-established relationships with, our current and prospective end users. Some of these competitors have in the past and may in the future take advantage of their existing relationships to engage in business practices that make our products less attractive to our end users. For example, Microsoft has implemented distribution arrangements with x86 system vendors and independent software vendors, or ISVs, related to certain of their operating systems that only permit the use of Microsoft’s virtualization format and do not allow the use of our corresponding format. Microsoft has also implemented pricing policies that require customers to pay additional license fees based on certain uses of virtualization technology. These distribution and licensing restrictions, as well as other business practices that may be adopted in the future by our competitors, could materially impact our prospects regardless of the merits of our products. In addition, competitors with existing relationships with our current or prospective end users could in the future integrate competitive capabilities into their existing products and make them available without additional charge. For example, Oracle provides free server virtualization software intended to support Oracle and non-Oracle applications and Microsoft offers its own server virtualization software packaged with the 2008 release of its Windows server product. By engaging in such business practices, our competitors can diminish competitive advantages we may possess by incentivizing end users to choose products that lack some of the technical advantages of our own offerings.
We also face potential competition from our partners. For example, third parties currently selling our products could build and market their own competing products and services or market competing products and services of third parties. If we are unable to compete effectively, our growth and our ability to sell products at profitable margins could be materially and adversely affected.
The current economic downturn and ongoing uncertainty in global economic conditions could result in reduced information technology spending and may adversely impact our revenues, end user adoption of new products and product upgrades and adversely impact our competitive position.
Our business depends on the overall demand for information technology and on the economic health of our current and prospective customers. The purchase of our products is often discretionary and may involve a significant commitment of capital and other resources. Weak economic conditions, or a reduction in information technology spending even if economic conditions improve, would likely adversely impact our business, financial condition and results of operations in a number of ways, including by lengthening sales cycles (for example, for enterprise license agreements (“ELAs”)), lowering prices for our products and services, reducing unit sales, decreasing or reversing quarterly growth in our revenues, reducing the rate of adoption of our products by new customers and the willingness of current customers to purchase upgrades to our existing products.
The current global economic crisis has also caused a general tightening in the credit markets, lower levels of liquidity, increases in the rates of default and bankruptcy, and extreme volatility in credit, equity and fixed income markets. For example, current or potential customers may be unable to fund software purchases, which could cause them to delay, decrease or cancel purchases of our products and services. Even if customers are willing to purchase our products and services, if they do not meet our credit requirements, we may not be able to record accounts receivable or deferred revenue or recognize revenues from these customers until we receive payment, which could adversely affect the amount of revenues we are able recognize in a particular period.
11
Additionally, while we plan to continue making strategic investments in our business during the economic downturn, many of our competitors have significantly greater financial, technical and other resources than us and if economic conditions continue to worsen, they may be better positioned to sustain investment in competitive technologies.
Industry alliances or consolidation may result in increased competition.
Some of our competitors have made acquisitions or entered into partnerships or other strategic relationships with one another to offer a more comprehensive virtualization solution than they individually had offered. For example, Red Hat recently acquired Qumranet, a developer of virtual infrastructure solutions, Citrix and Intel recently announced a desktop virtualization collaboration and during 2008, Microsoft announced an expansion of its alliance with Citrix. We expect these trends to continue as companies attempt to strengthen or maintain their market positions in the evolving virtualization infrastructure industry. Many of the companies driving this trend have significantly greater financial, technical and other resources than we do and may be better positioned to acquire and offer complementary products and technologies. The companies resulting from these possible combinations may create more compelling product offerings and be able to offer greater pricing flexibility than we can or may engage in business practices that make it more difficult for us to compete effectively, including on the basis of price, sales and marketing programs, technology or product functionality. These pressures could result in a substantial loss of customers or a reduction in our revenues.
Our operating results may fluctuate significantly, which makes our future results difficult to predict and may result in our operating results falling below expectations or our guidance, which could cause the price of our Class A common stock to decline.
Our operating results may fluctuate due to a variety of factors, many of which are outside of our control. As a result, comparing our operating results on a period-to-period basis may not be meaningful. Our past results should not be relied upon as an indication of our future performance. In addition, a significant portion of our quarterly sales typically occurs during the last month of the quarter, which we believe generally reflects customer buying patterns for enterprise technology. As a result, our quarterly operating results are difficult to predict even in the near term. If our revenues or operating results fall below the expectations of investors or securities analysts or below any guidance we may provide to the market, the price of our Class A common stock would likely decline substantially.
In addition, factors that may affect our operating results include, among others:
| | • | | fluctuations in demand, adoption rates, sales cycles and pricing levels for our products and services; |
| | • | | fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates; |
| | • | | changes in customers’ budgets for information technology purchases and in the timing of their purchasing decisions; |
| | • | | the timing of recognizing revenues in any given quarter, which, as a result of software revenue recognition policies, can be affected by a number of factors, including product announcements and beta programs; |
| | • | | the sale of our products in the timeframes we anticipate, including the number and size of orders in each quarter; |
| | • | | our ability to develop, introduce and ship in a timely manner new products and product enhancements that meet customer demand, certification requirements and technical requirements; |
| | • | | the timing of the announcement or release of upgrades or new products by us or by our competitors; |
| | • | | our ability to implement and maintain scalable internal systems for reporting, order processing, license fulfillment, product delivery, purchasing, billing and general accounting, among other functions; |
12
| | • | | our ability to control costs, including our operating expenses; |
| | • | | changes to our effective tax rate; |
| | • | | the increasing scale of our business and its effect on our ability to maintain historical rates of growth; |
| | • | | our ability to attract and retain highly skilled employees, particularly those with relevant experience in software development and sales; |
| | • | | general economic conditions in our domestic and international markets; |
| | • | | the timing and amount of capitalized software development costs as a result of establishing technological feasibility; and |
| | • | | the recoverability of benefits from goodwill and intangible assets and the potential impairment of these assets. |
If operating system and hardware vendors do not cooperate with us or we are unable to obtain early access to their new products, or access to certain information about their new products to ensure that our solutions interoperate with those products, our product development efforts may be delayed or foreclosed.
Our products interoperate with Windows, Linux and other operating systems and the hardware devices of numerous manufacturers. Developing products that interoperate properly requires substantial partnering, capital investment and employee resources, as well as the cooperation of the vendors or developers of the operating systems and hardware. Operating system and hardware vendors may not provide us with early access to their technology and products, assist us in these development efforts or share with or sell to us any application protocol interfaces (“APIs”), formats, or protocols we may need. If they do not provide us with the necessary early access, assistance or proprietary technology on a timely basis, we may experience product development delays or be unable to expand our products into other areas. To the extent that software or hardware vendors develop products that compete with ours or those of our controlling stockholder, EMC, they may have an incentive to withhold their cooperation, decline to share access or sell to us their proprietary APIs, protocols or formats or engage in practices to actively limit the functionality, or compatibility, and certification of our products. In addition, hardware or operating system vendors may fail to certify or support or continue to certify or support, our products for their systems. If any of the foregoing occurs, our product development efforts may be delayed or foreclosed and our business and results of operations may be adversely affected.
Our product and technology initiatives subject us to additional business, legal and competitive risks.
We recently announced new product and technology initiatives which aim to leverage our virtual infrastructure products into the emerging areas of cloud and virtual desktop computing as alternatives to the provisioning of physical computing resources. These initiatives may present new and difficult technology challenges, end users may choose not to adopt our new product or service offerings, and we may be subject to claims if customers of these offerings experience service disruptions or failures, security breaches or other quality issues. Further, the success of these new offerings depends upon the cooperation of hardware, software and cloud hosting vendors to ensure interoperability with our products and offer compatible products and services to end users.
Both the cloud computing and virtual desktop markets are in early stages of development. Other companies seeking to enter and develop competing standards for the cloud computing market such as Microsoft, IBM, Oracle and Amazon and the virtual desktop market such as Microsoft and Citrix have introduced or are likely to introduce their own initiatives that may compete with or not be compatible with our cloud and virtual desktop computing initiatives which could limit the degree to which other vendors develop products and services around our offerings and end users adopt our platforms. Additionally, our operating margins in our newer initiatives may be lower than those we have achieved in the markets we currently serve, and we may not be successful enough in these newer activities to recoup our investments in them. If any of this were to occur, it could damage our reputation, limit our growth and negatively affect our operating results.
13
We rely on distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors and systems integrators to sell our products, and our failure to effectively develop, manage or prevent disruptions to our distribution channels and the processes and procedures that support them could cause a reduction in the number of end users of our products.
Our future success is highly dependent upon maintaining and increasing the number of our relationships with distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors and systems integrators. By relying on distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors and systems integrators, we may have little or no contact with the ultimate users of our products, thereby making it more difficult for us to establish brand awareness, ensure proper delivery and installation of our products, service ongoing customer requirements, estimate end user demand and respond to evolving customer needs.
Recruiting and retaining qualified channel partners and training them in the use of our technology and product offerings requires significant time and resources. In order to develop and expand our distribution channel, we must continue to expand and improve our processes and procedures that support our channel, including our investment in systems and training, and those processes and procedures may become increasingly complex and difficult to manage. The time and expense required for sales and marketing organizations of our channel partners to become familiar with our product offerings, including our new product developments, may make it more difficult to introduce those products to end users and delay end user adoption of our product offerings. We generally do not have long-term contracts or minimum purchase commitments with our distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors and systems integrators, and our contracts with these channel partners do not prohibit them from offering products or services that compete with ours. Our competitors may be effective in providing incentives to existing and potential channel partners to favor products of our competitors or to prevent or reduce sales of our products. Certain x86 system vendors now offer competing virtualization products preinstalled on their server products. Additionally, our competitors could attempt to require key distributors to enter into exclusivity arrangements with them or otherwise apply their pricing or marketing leverage to discourage distributors from offering our products. Accordingly, our channel partners and x86 system vendors may choose not to offer our products exclusively or at all. Our failure to maintain and increase the number of relationships with channel partners would likely lead to a loss of end users of our products which would result in us receiving lower revenues from our channel partners. One of the Company’s distribution agreements is with Ingram Micro, which accounted for 18% and 23% of our revenues in fiscal year 2008 and 2007. The agreement with Ingram Micro under which the Company receives the substantial majority of its Ingram Micro revenues is terminable by either party upon 90 days’ prior written notice to the other party, and neither party has any obligation to purchase or sell any products under the agreement. The terms of this agreement between Ingram Micro and us are substantially similar to the terms of the agreements we have with other distributors, except for certain differences in shipment and payment terms, indemnification obligations and product return rights. While we believe that we have in place, or would have in place by the date of any such termination, agreements with other distributors sufficient to maintain our revenues from distribution, if we were to lose Ingram Micro’s distribution services, such loss could have a negative impact on our results of operations until such time as we arrange to replace these distribution services with the services of existing or new distributors.
The concentration of our product sales among a limited number of distributors and the weakness in credit markets increases our potential credit risk and could cause significant fluctuations or declines in our product revenues.
One distributor accounted for 18% and 23% of revenues in fiscal year 2008 and 2007. Additionally, another distributor accounted for 16% and 12% of revenues in fiscal year 2008 and 2007. We anticipate that sales of our products to a limited number of distributors will continue to account for a significant portion of our total product revenues for the foreseeable future. The concentration of product sales among certain distributors increases our potential credit risks. For example, approximately 42% of our total accounts receivable as of December 31, 2008 was from two distributors. Some of our distributors may experience financial difficulties, which could adversely impact our collection of accounts receivable. One or more of these distributors could delay payments or default on credit extended to them. Our exposure to credit risks of our distributors may increase if our distributors and
14
their customers are adversely affected by the current global economic downturn, or if there is a continuation or worsening of the downturn. Any significant delay or default in the collection of significant accounts receivable could result in an increased need for us to obtain working capital from other sources, possibly on worse terms than we could have negotiated if we had established such working capital resources prior to such delays or defaults. Any significant default could result in a negative impact on our results of operations.
The large majority of our revenues have come from our data center virtualization products including our flagship VDC-OS, Virtual Infrastructure product line. Decreases in demand for Virtual Infrastructure products could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Revenues from our data center virtualization products have consistently constituted over 90% of our license revenues. Although we are continuing to develop applications for our virtualization technology such as our desktop virtualization products, we expect our Virtual Infrastructure product line and related enhancements and upgrades will constitute a majority of our revenue for the foreseeable future. Declines and variability in demand for our Virtual Infrastructure products could occur as a result of:
| | • | | an improved version of products being offered by competitors in the market in which we participate; |
| | • | | competitive pressures on our pricing models; |
| | • | | a failure to release new or enhanced versions of our Virtual Infrastructure products on a timely basis; |
| | • | | technological change that we are unable to address with our Virtual Infrastructure products; |
| | • | | general economic conditions; or |
| | • | | increased pressure from competitors that offer broader product lines. |
Due to our product concentration, our business, results of operations, financial condition, and cash flows would therefore be adversely affected by a decline in demand for our Virtual Infrastructure product line.
Our revenues and our collection of accounts receivable may be adversely impacted by fluctuation of foreign currency exchange rates.
Our revenues and our collection of accounts receivable may be adversely impacted as a result of fluctuations in the exchange rates between the U.S. Dollar and foreign currencies. For example, we have distributors in foreign countries that may incur higher costs due to the recent strengthening of the U.S. Dollar. One or more of these distributors could delay payments or default on credit extended to them. Any significant delay or default in the collection of significant accounts receivable could result in an increased need for us to obtain working capital from other sources. If we determine that the amount of accounts receivable to be uncollectible is greater than our estimates, we would recognize an increase in bad debt expense, which would have a negative impact on our results of operations. In addition, in periods when the value of the Dollar strengthens, we may need to offer additional discounts, reduce prices or offer other incentives to mitigate the negative effect on demand.
We are dependent on our management and our key development personnel, and the loss of key personnel may prevent us from implementing our business plan in a timely manner.
Our success depends largely upon the continued services of our existing management. We are also substantially dependent on the continued service of our key development personnel for product innovation. We generally do not have employment or non-compete agreements with our existing management or development personnel and, therefore, they could terminate their employment with us at any time without penalty and could pursue employment opportunities with any of our competitors. Changes to management and key employees can also lead to additional unplanned losses of key employees. The loss of key employees could seriously harm our ability to release new products on a timely basis and could significantly help our competitors.
15
Because competition for our target employees is intense, we may not be able to attract and retain the highly skilled employees we need to support our planned growth and our compensation expenses may increase.
To execute our growth plan, we must attract and retain highly qualified personnel. Competition for these personnel is intense, especially for engineers with high levels of experience in designing and developing software and senior sales executives. We may not be successful in attracting and retaining qualified personnel. We have from time to time in the past experienced, and we expect to continue to experience in the future, difficulty in hiring and retaining highly skilled employees with appropriate qualifications. Many of the companies with which we compete for experienced personnel have greater resources than we have. In addition, in making employment decisions, particularly in the high-technology industry, job candidates often consider the value of the stock options, restricted stock grants or other stock-based compensation they are to receive in connection with their employment. The declines in the value of our stock during 2008 could adversely affect our ability to attract or retain key employees and result in increased employee compensation expenses. If we fail to attract new personnel or fail to retain and motivate our current personnel, our business and future growth prospects could be severely harmed.
If we are unable to protect our intellectual property rights, our competitive position could be harmed or we could be required to incur significant expenses to enforce our rights.
We depend on our ability to protect our proprietary technology. We rely on trade secret, patent, copyright and trademark laws and confidentiality agreements with employees and third parties, all of which offer only limited protection. As such, despite our efforts, the steps we have taken to protect our proprietary rights may not be adequate to preclude misappropriation of our proprietary information or infringement of our intellectual property rights, and our ability to police such misappropriation or infringement is uncertain, particularly in countries outside of the United States. Further, with respect to patent rights, we do not know whether any of our pending patent applications will result in the issuance of patents or whether the examination process will require us to narrow our claims. Even if patents are issued from our patent applications, which is not certain, they may be contested, circumvented or invalidated in the future. Moreover, the rights granted under any issued patents may not provide us with proprietary protection or competitive advantages, and, as with any technology, competitors may be able to develop similar or superior technologies to our own now or in the future. In addition, we rely on contractual agreements and ELAs with third parties in connection with their use of our products and technology. There is no guarantee that such parties will abide by the terms of such agreements or that we will be able to adequately enforce our rights, in part because we rely on “click-wrap” and “shrink-wrap” licenses in some instances.
Detecting and protecting against the unauthorized use of our products, technology and proprietary rights is expensive, difficult and, in some cases, impossible. Litigation may be necessary in the future to enforce or defend our intellectual property rights, to protect our trade secrets or to determine the validity and scope of the proprietary rights of others. Such litigation could result in substantial costs and diversion of management resources, either of which could harm our business, financial condition and results of operations, and there is no guarantee that we would be successful. Furthermore, many of our current and potential competitors have the ability to dedicate substantially greater resources to protecting their technology or intellectual property rights than we do. Accordingly, despite our efforts, we may not be able to prevent third parties from infringing upon or misappropriating our intellectual property, which could result in a substantial loss of our market share.
We provide access to our hypervisor and other selected source code to partners, which creates additional risk that our competitors could develop products that are similar or better than ours.
Our success and ability to compete depend substantially upon our internally developed technology, which is incorporated in the source code for our products. We seek to protect the source code, design code, documentation and other written materials for our software, under trade secret and copyright laws. However, we have chosen to provide access to our hypervisor and other selected source code to more than 50 of our partners for
16
co-development, as well as for open APIs, formats and protocols. Though we generally control access to our source code and other intellectual property, and enter into confidentiality or ELAs with such partners, as well as with our employees and consultants, our safeguards may be insufficient to protect our trade secrets and other rights to our technology. Our protective measures may be inadequate, especially because we may not be able to prevent our partners, employees or consultants from violating any agreements or licenses we may have in place or abusing their access granted to our source code. Improper disclosure or use of our source code could help competitors develop products similar to or better than ours.
Claims by others that we infringe their proprietary technology could force us to pay damages or prevent us from using certain technology in our products.
Third parties could claim that our products or technology infringe their proprietary rights. This risk may increase as the number of products and competitors in our market increases and overlaps occur. In addition, to the extent that we gain greater visibility and market exposure as a public company, we face a higher risk of being the subject of intellectual property infringement claims. Any claim of infringement by a third party, even one without merit, could cause us to incur substantial costs defending against the claim, and could distract our management from our business. Furthermore, a party making such a claim, if successful, could secure a judgment that requires us to pay substantial damages. A judgment could also include an injunction or other court order that could prevent us from offering our products. In addition, we might be required to seek a license for the use of such intellectual property, which may not be available on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Alternatively, we may be required to develop non-infringing technology, which could require significant effort and expense and may ultimately not be successful. Any of these events could seriously harm our business, operating results and financial condition. Third parties may also assert infringement claims against our customers and channel partners. Any of these claims could require us to initiate or defend potentially protracted and costly litigation on their behalf, regardless of the merits of these claims, because we generally indemnify our customers and channel partners from claims of infringement of proprietary rights of third parties in connection with the use of our products. If any of these claims succeed, we may be forced to pay damages on behalf of our customers or channel partners, which could materially reduce our income.
Our use of “open source” software could negatively affect our ability to sell our products and subject us to possible litigation.
A significant portion of the products or technologies acquired, licensed or developed by us may incorporate so-called “open source” software, and we may incorporate open source software into other products in the future. Such open source software is generally licensed by its authors or other third parties under open source licenses, including, for example, the GNU General Public License, the GNU Lesser General Public License, “Apache-style” licenses, “Berkeley Software Distribution,” “BSD-style” licenses and other open source licenses. We monitor our use of open source software in an effort to avoid subjecting our products to conditions we do not intend. Although we believe that we have complied with our obligations under the various applicable licenses for open source software that we use such that we have not triggered any such conditions, there is little or no legal precedent governing the interpretation of many of the terms of certain of these licenses, and therefore the potential impact of these terms on our business is somewhat unknown and may result in unanticipated obligations regarding our products and technologies. For example, we may be subjected to certain conditions, including requirements that we offer our products that use the open source software for no cost, that we make available source code for modifications or derivative works we create based upon, incorporating or using the open source software and/or that we license such modifications or derivative works under the terms of the particular open source license.
If an author or other third party that distributes such open source software were to allege that we had not complied with the conditions of one or more of these licenses, we could be required to incur significant legal expenses defending against such allegations. If our defenses were not successful, we could be subject to significant damages, enjoined from the distribution of our products that contained the open source software and
17
required to comply with the foregoing conditions, which could disrupt the distribution and sale of some of our products. In addition, if we combine our proprietary software with open source software in a certain manner, under some open source licenses we could be required to release the source code of our proprietary software, which could substantially help our competitors develop products that are similar to or better than ours.
In addition to risks related to license requirements, usage of open source software can lead to greater risks than use of third party commercial software, as open source licensors generally do not provide warranties or assurance of title or controls on origin of the software. We have established processes to help alleviate these risks, including a review process for screening requests from our development organizations for the use of open source, but we cannot be sure that all open source software is submitted for approval prior to use in our products. In addition, many of the risks associated with usage of open source such as the lack of warranties or assurances of title, cannot be eliminated, and could, if not properly addressed, negatively affect our business.
Our sales cycles can be long and unpredictable, our sales efforts require considerable time and expense and timing of sales is subject to changing purchasing behaviors of our customers. As a result, our sales are difficult to predict and may vary substantially from quarter to quarter, which may cause our operating results to fluctuate significantly.
The timing of our revenues is difficult to predict. Our sales efforts involve educating our customers about the use and benefit of our products, including their technical capabilities, potential cost savings to an organization and advantages compared to lower-cost products offered by our competitors. Customers typically undertake a significant evaluation process that has in the past resulted in a lengthy sales cycle, which typically lasts several months, and may last a year or longer. We spend substantial time, effort and money on our sales efforts without any assurance that our efforts will produce any sales. In addition, product purchases are frequently subject to budget constraints, multiple approvals, and unplanned administrative, processing and other delays. Additionally, the greater number of competitive alternatives, as well as announcements by our competitors that they intend to introduce competitive alternatives at some point in the future, can lengthen customer procurement cycles, cause us to spend additional time and resources to educate end users on the advantages of our product offerings and delay product sales. These factors can have a particular impact on the timing and length of our ELA sales cycles.
Additionally, our quarterly sales have historically reflected an uneven pattern in which a disproportionate percentage of a quarter’s total sales occur in the last month, weeks and days of each quarter. This pattern makes prediction of revenues, earnings and working capital for each financial period especially difficult and uncertain and increases the risk of unanticipated variations in financial condition and results of operations. We believe this uneven sales pattern is a result of many factors including the following:
| | • | | the tendency of customers to wait until late in a quarter to commit to a purchase in the hope of obtaining more favorable pricing; |
| | • | | the fourth quarter influence of customers spending their remaining capital budget authorization prior to new budget constraints in the first nine months of the following year; and |
If sales expected from a specific customer for a particular quarter are not realized in that quarter or at all, our results could fall short of public expectations and our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Our current research and development efforts may not produce significant revenues for several years, if at all.
Developing our products is expensive. Our investment in research and development may not result in marketable products or may result in products that take longer to generate revenues, or generate less revenues, than we anticipate. Our research and development expenses were $429.2 million, or 23% of our total revenues, in
18
2008, and $285.9 million, or 22% of our total revenues, in 2007. Our future plans include significant investments in software research and development and related product opportunities. We believe that we must continue to dedicate a significant amount of resources to our research and development efforts to maintain our competitive position. However, we may not receive significant revenues from these investments for several years, if at all.
We may not be able to respond to rapid technological changes with new solutions and services offerings, which could have a material adverse effect on our sales and profitability.
The markets for our software solutions are characterized by rapid technological changes, changing customer needs, frequent new software product introductions and evolving industry standards. The introduction of third-party solutions embodying new technologies and the emergence of new industry standards could make our existing and future software solutions obsolete and unmarketable. We may not be able to develop updated products that keep pace with technological developments and emerging industry standards and that address the increasingly sophisticated needs of our customers or that interoperate with new or updated operating systems and hardware devices or certify our products to work with these systems and devices. There is no assurance that any of our new offerings would be accepted in the marketplace. Significant reductions in server-related costs or the rise of more efficient infrastructure management software could also affect demand for our software solutions. As hardware and processors become more powerful, we will have to adapt our product and service offerings to take advantage of the increased capabilities. For example, while the introduction of more powerful servers presents an opportunity for us to provide better products for our customers, the migration of servers from dual-core to quad-core and greater multi-core microprocessor technology will also allow an end user with a given number of licensed copies of our software to more than double the number of virtualization machines run per server socket without having to purchase additional licenses from us. As a result, we may not be able to accurately predict the lifecycle of our software solutions, and they may become obsolete before we receive the amount of revenues that we anticipate from them. If any of the foregoing events were to occur, our ability to retain or increase market share and revenues in the virtualization software market could be materially adversely affected.
Our success depends upon our ability to develop new products and services, integrate acquired products and services and enhance our existing products and services.
If we are unable to develop new products and services, or to enhance and improve our products and support services in a timely manner or to position and/or price our products and services to meet market demand, customers may not buy new software licenses or renew software license updates and product support. In addition, information technology standards from both consortia and formal standards-setting forums as well as de facto marketplace standards are rapidly evolving. We cannot provide any assurance that the standards on which we choose to develop new products will allow us to compete effectively for business opportunities in emerging areas such as cloud computing.
New product development and introduction involves a significant commitment of time and resources and is subject to a number of risks and challenges including:
| | • | | managing the length of the development cycle for new products and product enhancements, which has frequently been longer than we originally expected; |
| | • | | managing customers’ transitions to new products, which can result in delays in their purchasing decisions; |
| | • | | adapting to emerging and evolving industry standards and to technological developments by our competitors and customers; |
| | • | | entering into new or unproven markets with which we have limited experience; |
| | • | | incorporating and integrating acquired products and technologies; and |
| | • | | developing or expanding efficient sales channels. |
19
In addition, if we cannot adapt our business models to keep pace with industry trends, our revenues could be negatively impacted.
Our ability to sell our products is dependent on the quality of our support and services offerings, and our failure to offer high-quality support and services could have a material adverse effect on our sales and results of operations.
Once our products are integrated within our customers’ hardware and software systems, our customers may depend on our support organization to resolve any issues relating to our products. A high level of support is critical for the successful marketing and sale of our products. If we or our channel partners do not effectively assist our customers in deploying our products, succeed in helping our customers quickly resolve post-deployment issues, and provide effective ongoing support, our ability to sell our products to existing customers would be adversely affected, and our reputation with potential customers could be harmed. In addition, as we expand our operations internationally, our support organization will face additional challenges, including those associated with delivering support, training and documentation in languages other than English. As a result, our failure to maintain high-quality support and services, or to adequately assist our channel partners in providing high-quality support and services, could result in customers choosing to use our competitors’ products instead of ours in the future.
We may engage in future acquisitions that could disrupt our business, cause dilution to our stockholders and harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In the future we may seek to acquire other businesses, products or technologies. However, we may not be able to find suitable acquisition candidates and we may not be able to complete acquisitions on favorable terms, if at all. If we do complete acquisitions, we may not ultimately strengthen our competitive position or achieve our goals, or they may be viewed negatively by customers, financial markets or investors. Acquisitions may disrupt our ongoing operations, divert management from day-to-day responsibilities, increase our expenses and adversely impact our business, financial condition and results of operations. Future acquisitions may reduce our cash available for operations and other uses and could result in an increase in amortization expense related to identifiable intangible assets acquired, potentially dilutive issuances of equity securities or the incurrence of debt. We have limited historical experience with the integration of acquired companies. There can be no assurance that we will be able to manage the integration of acquired businesses effectively or be able to retain and motivate key personnel from these businesses. Any difficulties we encounter in the integration process could divert management from day-to-day responsibilities, increase our expenses and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, we review our amortizable intangible assets annually for impairment, or more frequently, when events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable, and we are required to test goodwill for impairment at least annually. We may be required to record a significant charge to earnings in our financial statements during the period in which any impairment of our goodwill or amortizable intangible assets resulting from an acquisition or otherwise is determined, resulting in an adverse impact on our results of operations.
Operating in foreign countries subjects us to additional risks that may harm our ability to increase or maintain our international sales and operations.
In 2007, we derived approximately 46%, and in 2008, we derived approximately 48%, of our revenues from customers outside the United States. We have sales and technical support personnel in numerous countries worldwide. We expect to continue to add personnel in additional countries. Our international operations subject us to a variety of risks, including:
| | • | | the difficulty of managing and staffing international offices and the increased travel, infrastructure and legal compliance costs associated with multiple international locations; |
| | • | | increased exposure to foreign currency exchange rate risk; |
20
| | • | | difficulties in enforcing contracts and collecting accounts receivable, and longer payment cycles, especially in emerging markets; |
| | • | | difficulties in delivering support, training and documentation in certain foreign markets; |
| | • | | tariffs and trade barriers and other regulatory or contractual limitations on our ability to sell or develop our products in certain foreign markets; |
| | • | | economic or political instability and security concerns in countries that are important to our international sales and operations; |
| | • | | the overlap of different tax structures or changes in international tax laws; |
| | • | | reduced protection for intellectual property rights, including reduced protection from software piracy in some countries; |
| | • | | difficulties in transferring funds from certain countries; and |
| | • | | difficulties in maintaining appropriate controls relating to revenue recognition practices. |
As we continue to expand our business globally, our success will depend, in large part, on our ability to anticipate and effectively manage these and other risks associated with our international operations. We expect a significant portion of our growth to occur in foreign countries which can add to the difficulties in establishing and maintaining adequate management systems and internal controls over financial reporting and increase challenges in managing an organization operating in various countries.
Our failure to manage any of these risks successfully could harm our international operations and reduce our international sales.
Our products are highly technical and may contain errors, which could cause harm to our reputation and adversely affect our business.
Our products are highly technical and complex and, when deployed, have contained and may contain errors, defects or security vulnerabilities. Some errors in our products may only be discovered after a product has been installed and used by customers. Any errors, defects or security vulnerabilities discovered in our products after commercial release could result in loss of revenues or delay in revenue recognition, loss of customers and increased service and warranty cost, any of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. Undiscovered vulnerabilities in our products could expose them to hackers or other unscrupulous third parties who develop and deploy viruses, worms, and other malicious software programs that could attack our products. Actual or perceived security vulnerabilities in our products could harm our reputation and lead some customers to return products, to reduce or delay future purchases or use competitive products. End users, who rely on our products and services for the interoperability of enterprise servers and applications that are critical to their information systems, may have a greater sensitivity to product errors and security vulnerabilities than customers for software products generally. Any security breaches could lead to interruptions, delays and data loss and protection concerns. In addition, we could face claims for product liability, tort or breach of warranty, including claims relating to changes to our products made by our channel partners. Our contracts with customers contain provisions relating to warranty disclaimers and liability limitations, which may not be upheld. Defending a lawsuit, regardless of its merit, is costly and time-consuming and may divert management’s attention and adversely affect the market’s perception of us and our products. In addition, if our business liability insurance coverage proves inadequate or future coverage is unavailable on acceptable terms or at all, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely impacted.
21
If we fail to maintain an effective system of internal controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results or prevent fraud. As a result, our stockholders could lose confidence in our financial reporting, which could harm our business and the trading price of our common stock.
We have prepared for compliance with Section 404 by assessing, strengthening and testing our system of internal controls. Even after implementing internal controls that achieve compliance with Section 404, we will need to continue to maintain our processes and systems and adapt them to changes as our business continues to expand and we rearrange management responsibilities and reorganize our business accordingly. The continuous process of maintaining and adapting our internal controls and complying with Section 404 is expensive and time-consuming, and requires significant management attention. We cannot be certain that these measures will continue to provide adequate control over our financial processes and reporting. If we are not able to automate these processes in a timely fashion, we will not be able to ensure ongoing compliance. Furthermore, as we grow our business, our internal controls will become more complex and we will require significantly more resources to ensure our internal controls overall remain effective. Failure to implement required new or improved controls, or difficulties encountered in their implementation, could harm our operating results or cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations. If we or our independent registered public accounting firm identify material weaknesses, the disclosure of that fact, even if quickly remedied, could reduce the market’s confidence in our financial statements and harm our stock price. In addition, if we are unable to continue to comply with Section 404, our non-compliance could subject us to a variety of administrative sanctions, including the suspension or delisting of our common stock from the New York Stock Exchange and the inability of registered broker-dealers to make a market in our common stock, which could further reduce our stock price.
Problems with our information systems could interfere with our business and operations.
We rely on our information systems and those of third parties for processing customer orders, delivery of products, providing services and support to our customers, billing and tracking our customers, fulfilling contractual obligations, and otherwise running our business. Any disruption in our information systems and those of the third parties upon whom we rely could have a significant impact on our business. In addition, we are in the process of enhancing our information systems. The implementation of these types of enhancements is frequently disruptive to the underlying business of an enterprise, which may especially be the case for us due to the size and complexity of our businesses. Any disruptions relating to our systems enhancements, particularly any disruptions impacting our operations during the implementation period, could adversely affect our business in a number of respects. Even if we do not encounter these adverse effects, the implementation of these enhancements may be much more costly than we anticipated. If we are unable to successfully implement the information systems enhancements as planned, our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows could be negatively impacted.
If we fail to manage future growth effectively, we may not be able to meet our customers’ needs or be able to meet our future reporting obligations.
We have expanded our operations significantly since inception and anticipate further expansion in the future. This future growth, if it occurs, will place significant demands on our management, infrastructure and other resources. Additionally, further international growth may occur in regions where we presently have little or no infrastructure. To manage any future growth, we will need to hire, integrate and retain highly skilled and motivated employees. We will also need to continue to improve our financial and management controls, reporting and operational systems and procedures. If we do not effectively manage our growth we may not be able to meet our customers’ needs, thereby adversely affecting our sales, or be able to meet our future reporting obligations.
Our financial results may be adversely impacted by higher than expected tax rates and we may have exposure to additional tax liabilities.
As a multinational corporation, we are subject to income taxes as well as non-income based taxes, in both the United States and various foreign jurisdictions. Our domestic and international tax liabilities are subject to the
22
allocation of revenues and expenses in different jurisdictions and the timing of recognizing revenues and expenses. Additionally, the amount of income taxes paid is subject to our interpretation of applicable tax laws in the jurisdictions in which we file and changes to tax laws. Significant judgment is required in determining our worldwide provision for income taxes and other tax liabilities. From time to time, we are subject to income tax audits. While we believe we have complied with all applicable income tax laws, there can be no assurance that a governing tax authority will not have a different interpretation of the law and assess us with additional taxes. Should we be assessed with additional taxes, there could be a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
Our future effective tax rate may be affected by such factors as changes in tax laws, regulations or rates, changing interpretation of existing laws or regulations, the impact of accounting for stock-based compensation, the impact of accounting for business combinations under the new accounting standard FAS No. 141R, changes in our international organization, and changes in overall levels of income before tax. In addition, in the ordinary course of a global business, there are many intercompany transactions and calculations where the ultimate tax determination is uncertain. Although we believe that our tax estimates are reasonable, we cannot assure you that the final determination of tax audits or tax disputes will not be different from what is reflected in our historical income tax provisions and accruals.
We are also subject to non-income taxes, such as payroll, sales, use, value-added, net worth, property and goods and services taxes, in both the United States and various foreign jurisdictions. We are under audit from time to time by tax authorities with respect to these non-income taxes and may have exposure to additional non-income tax liabilities.
Our business is subject to the risks of earthquakes, fire, floods and other natural catastrophic events, and to interruption by man-made problems, such as computer viruses or terrorism, which could result in delays or cancellations of customer orders or the deployment of our products.
Our corporate headquarters are located in the San Francisco Bay Area, a region known for seismic activity. A significant natural disaster, such as an earthquake, fire or a flood, could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations. As we continue to grow internationally, increasing amounts of our business will be located in foreign countries that may be more subject to political or social instability that could disrupt operations. In addition, our servers are vulnerable to computer viruses, break-ins and similar disruptions from unauthorized tampering with our computer systems. Furthermore, acts of terrorism or war could cause disruptions in our or our customers’ business or the economy as a whole. To the extent that such disruptions result in delays or cancellations of customer orders, or the deployment of our products, our revenues would be adversely affected.
Risks Related to Our Relationship with EMC
As long as EMC controls us, holders of our Class A common stock will have limited ability to influence matters requiring stockholder approval.
As of December 31, 2008, EMC owned 27,000,000 shares of our Class A common stock and all 300,000,000 shares of our Class B common stock, representing approximately 84% of the total outstanding shares of common stock or 98% of the voting power of outstanding common stock. The holders of our Class A common stock and our Class B common stock have identical rights, preferences and privileges except with respect to voting and conversion rights, the election of directors, certain actions that require the consent of holders of Class B common stock and other protective provisions as set forth in our certificate of incorporation. Holders of our Class B common stock are entitled to 10 votes per share of Class B common stock on all matters except for the election of our Group II directors, in which case they are entitled to one vote per share, and the holders of our Class A common stock are entitled to one vote per share of Class A common stock. The holders of Class B common stock, voting separately as a class, are entitled to elect 80% of the total number of directors on
23
our board of directors that we would have if there were no vacancies on our board of directors at the time. These are our Group I directors. Subject to any rights of any series of preferred stock to elect directors, the holders of Class A common stock and the holders of Class B common stock, voting together as a single class, are entitled to elect our remaining directors, which at no time will be less than one director—our Group II director(s). Shares of Class B common stock are entitled to one vote per share when voting for such remaining directors. Accordingly, the holders of our Class B common stock currently are entitled to elect 7 of our 8 directors. If EMC transfers shares of our Class B common stock to any party other than a successor-in-interest or a subsidiary of EMC (other than in a distribution to its stockholders under Section 355 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, or in transfers following such a distribution), those shares will automatically convert into Class A common stock. For so long as EMC or its successor-in-interest beneficially owns shares of our common stock representing at least a majority of the votes entitled to be cast by the holders of outstanding voting stock, EMC will be able to elect all of the members of our board of directors.
In addition, until such time as EMC or its successor-in-interest beneficially owns shares of our common stock representing less than a majority of the votes entitled to be cast by the holders of outstanding voting stock, EMC will have the ability to take stockholder action without the vote of any other stockholder and without having to call a stockholder meeting, and holders of our Class A common stock will not be able to affect the outcome of any stockholder vote during this period. As a result, EMC will have the ability to control all matters affecting us, including:
| | • | | the composition of our board of directors and, through our board of directors, any determination with respect to our business plans and policies; |
| | • | | any determinations with respect to mergers, acquisitions and other business combinations; |
| | • | | our acquisition or disposition of assets; |
| | • | | our financing activities; |
| | • | | certain changes to our certificate of incorporation; |
| | • | | changes to the agreements providing for our transition to becoming a public company; |
| | • | | corporate opportunities that may be suitable for us and EMC; |
| | • | | determinations with respect to enforcement of rights we may have against third parties, including with respect to intellectual property rights; |
| | • | | the payment of dividends on our common stock; and |
| | • | | the number of shares available for issuance under our stock plans for our prospective and existing employees. |
Our certificate of incorporation and the master transaction agreement between us and EMC also contain provisions that require that as long as EMC beneficially owns at least 20% or more of the outstanding shares of our common stock, the prior affirmative vote or written consent of EMC (or its successor-in-interest) as the holder of the Class B common stock is required (subject in each case to certain exceptions) in order to authorize us to:
| | • | | consolidate or merge with any other entity; |
| | • | | acquire the stock or assets of another entity in excess of $100 million; |
| | • | | issue any stock or securities except to our subsidiaries or pursuant to our employee benefit plans; |
| | • | | establish the aggregate annual amount of shares we may issue in equity awards; |
| | • | | dissolve, liquidate or wind us up; |
| | • | | declare dividends on our stock; |
24
| | • | | enter into any exclusive or exclusionary arrangement with a third party involving, in whole or in part, products or services that are similar to EMC’s; and |
| | • | | amend, terminate or adopt any provision inconsistent with certain provisions of our certificate of incorporation or bylaws. |
If EMC does not provide any requisite consent allowing us to conduct such activities when requested, we will not be able to conduct such activities and, as a result, our business and our operating results may be harmed.
EMC’s voting control and its additional rights described above may discourage transactions involving a change of control of us, including transactions in which holders of our Class A common stock might otherwise receive a premium for their shares over the then-current market price. EMC is not prohibited from selling a controlling interest in us to a third party and may do so without the approval of the holders of our Class A common stock and without providing for a purchase of any shares of Class A common stock held by persons other than EMC. Accordingly, shares of Class A common stock may be worth less than they would be if EMC did not maintain voting control over us or have the additional rights described above.
In the event EMC is acquired or otherwise undergoes a change of control, any acquirer or successor will be entitled to exercise the voting control and contractual rights of EMC, and may do so in a manner that could vary significantly from that of EMC.
By becoming a stockholder in our company, holders of our Class A common stock are deemed to have notice of and have consented to the provisions of our certificate of incorporation and the master transaction agreement with respect to the limitations that are described above.
Our business and that of EMC overlap, and EMC may compete with us, which could reduce our market share.
EMC and we are both IT infrastructure companies providing products related to storage management, back-up, disaster recovery, security, system management and automation, provisioning and resource management. There can be no assurance that EMC will not engage in increased competition with us in the future. In addition, the intellectual property agreement that we have entered into with EMC will provide EMC the ability to use our source code and intellectual property, which, subject to limitations, it may use to produce certain products that compete with ours. EMC’s rights in this regard extend to its majority-owned subsidiaries, which could include joint ventures where EMC holds a majority position and one or more of our competitors hold minority positions.
EMC could assert control over us in a manner which could impede our growth or our ability to enter new markets or otherwise adversely affect our business. Further, EMC could utilize its control over us to cause us to take or refrain from taking certain actions, including entering into relationships with channel, technology and other marketing partners, enforcing our intellectual property rights or pursuing corporate opportunities or product development initiatives that could adversely affect our competitive position, including our competitive position relative to that of EMC in markets where we compete with them. In addition, EMC maintains significant partnerships with certain of our competitors, including Microsoft.
EMC’s competition in certain markets may affect our ability to build and maintain partnerships.
Our existing and potential partner relationships may be affected by our relationship with EMC. We partner with a number of companies that compete with EMC in certain markets in which EMC participates. EMC’s majority ownership in us might affect our ability to effectively partner with these companies. These companies may favor our competitors because of our relationship with EMC.
EMC competes with certain of our significant channel, technology and other marketing partners, including IBM and Hewlett-Packard. Pursuant to our certificate of incorporation and other agreements that we have with
25
EMC, EMC may have the ability to impact our relationship with those of our partners that compete with EMC, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations or our ability to pursue opportunities which may otherwise be available to us.
Our historical financial information as a business segment of EMC may not be representative of our results as an independent public company.
Our historical financial information we have included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K does not necessarily reflect what our financial position, results of operations or cash flows would have been had we been an independent entity during those historical periods. The historical costs and expenses reflected in our consolidated financial statements prior to 2008 include an allocation for certain corporate functions historically provided by EMC, including tax, accounting, treasury, legal and human resources services. Although we have transitioned most of these corporate functions to VMware personnel, in certain geographic regions where we do not have an established legal entity, we contract with EMC subsidiaries for support services and EMC employees who are managed by VMware personnel. The costs incurred by EMC on VMware’s behalf related to these employees include an estimated arm’s-length mark-up and are included as expenses in our financial statements. Our historical financial information is not necessarily indicative of what our financial position, results of operations or cash flows will be in the future if and when we contract at arm’s-length with independent third parties for the services we have received and currently receive from EMC. For additional information, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our historical consolidated financial statements and notes thereto.
In order to preserve the ability for EMC to distribute its shares of our Class B common stock on a tax-free basis, we may be prevented from pursuing opportunities to raise capital, to effectuate acquisitions or to provide equity incentives to our employees, which could hurt our ability to grow.
Beneficial ownership of at least 80% of the total voting power and 80% of each class of nonvoting capital stock is required in order for EMC to effect a tax-free spin-off of VMware or certain other tax-free transactions. We have agreed that for so long as EMC or its successor-in-interest continues to own greater than 50% of the voting control of our outstanding common stock, we will not knowingly take or fail to take any action that could reasonably be expected to preclude EMC’s or its successor-in-interest’s ability to undertake a tax-free spin-off. Additionally, under our certificate of incorporation and the master transaction agreement we entered into with EMC, we must obtain the consent of EMC or its successor-in-interest, as the holder of our Class B common stock, to issue stock or other VMware securities, excluding pursuant to employee benefit plans (provided that we obtain Class B common stockholder approval of the aggregate annual number of shares to be granted under such plans), which could cause us to forgo capital raising or acquisition opportunities that would otherwise be available to us. As a result, we may be precluded from pursuing certain growth initiatives.
Third parties may seek to hold us responsible for liabilities of EMC, which could result in a decrease in our income.
Third parties may seek to hold us responsible for EMC’s liabilities. Under our master transaction agreement with EMC, EMC will indemnify us for claims and losses relating to liabilities related to EMC’s business and not related to our business. However, if those liabilities are significant and we are ultimately held liable for them, we cannot be certain that we will be able to recover the full amount of our losses from EMC.
Although we have entered into a tax sharing agreement with EMC under which our tax liabilities effectively will be determined as if we were not part of any consolidated, combined or unitary tax group of EMC Corporation and/or its subsidiaries, we nonetheless could be held liable for the tax liabilities of other members of these groups.
We have historically been included in EMC’s consolidated group for U.S. federal income tax purposes, as well as in certain consolidated, combined or unitary groups that include EMC Corporation and/or certain of its subsidiaries for state and local income tax purposes. Pursuant to our tax sharing agreement with EMC, we and
26
EMC generally will make payments to each other such that, with respect to tax returns for any taxable period in which we or any of our subsidiaries are included in EMC’s consolidated group for U.S. federal income tax purposes or any other consolidated, combined or unitary group of EMC Corporation and/or its subsidiaries, the amount of taxes to be paid by us will be determined, subject to certain adjustments, as if we and each of our subsidiaries included in such consolidated, combined or unitary group filed our own consolidated, combined or unitary tax return.
Prior to our IPO in August 2007, we were included in the EMC consolidated group for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and expect to continue to be included in such consolidated group for periods in which EMC owned at least 80% of the total voting power and value of our outstanding stock. Each member of a consolidated group during any part of a consolidated return year is jointly and severally liable for tax on the consolidated return of such year and for any subsequently determined deficiency thereon. Similarly, in some jurisdictions, each member of a consolidated, combined or unitary group for state, local or foreign income tax purposes is jointly and severally liable for the state, local or foreign income tax liability of each other member of the consolidated, combined or unitary group. Accordingly, for any period in which we are included in the EMC consolidated group for U.S. federal income tax purposes or any other consolidated, combined or unitary group of EMC Corporation and/or its subsidiaries, we could be liable in the event that any income tax liability was incurred, but not discharged, by any other member of any such group.
Any inability to resolve favorably any disputes that arise between us and EMC with respect to our past and ongoing relationships may result in a significant reduction of our revenues and earnings.
Disputes may arise between EMC and us in a number of areas relating to our ongoing relationships, including:
| | • | | labor, tax, employee benefit, indemnification and other matters arising from our separation from EMC; |
| | • | | employee retention and recruiting; |
| | • | | business combinations involving us; |
| | • | | our ability to engage in activities with certain channel, technology or other marketing partners; |
| | • | | sales or dispositions by EMC of all or any portion of its ownership interest in us; |
| | • | | the nature, quality and pricing of services EMC has agreed to provide us; |
| | • | | arrangements with third parties that are exclusionary to EMC; |
| | • | | business opportunities that may be attractive to both EMC and us; and |
| | • | | product or technology development or marketing activities or customer agreements which may require the consent of EMC. |
We may not be able to resolve any potential conflicts, and even if we do, the resolution may be less favorable than if we were dealing with an unaffiliated party.
The agreements we entered into with EMC in connection with our IPO may be amended upon agreement between the parties. While we are controlled by EMC, we may not have the leverage to negotiate amendments to these agreements if required on terms as favorable to us as those we would negotiate with an unaffiliated third party.
Some of our directors and executive officers own EMC common stock, restricted shares of EMC common stock and/ or options to acquire EMC common stock and hold management positions with EMC, which could cause conflicts of interests that result in our not acting on opportunities we otherwise may have.
Some of our directors and executive officers own EMC common stock and/or options to purchase EMC common stock. In addition, some of our directors are executive officers and/or directors of EMC. Ownership of EMC common stock, restricted shares of EMC common stock and options to purchase EMC common stock by
27
our directors and officers and the presence of executive officers or directors of EMC on our board of directors could create, or appear to create, conflicts of interest with respect to matters involving both us and EMC that could have different implications for EMC than they do for us. Provisions of our certificate of incorporation and the master transaction agreement between EMC and us address corporate opportunities that are presented to our directors or officers that are also directors or officers of EMC. There can be no assurance that the provisions in our certificate of incorporation or the master transaction agreement will adequately address potential conflicts of interest or that potential conflicts of interest will be resolved in our favor or that we will be able to take advantage of corporate opportunities presented to individuals who are officers or directors of both us and EMC. As a result, we may be precluded from pursuing certain growth initiatives.
EMC’s ability to control our board of directors may make it difficult for us to recruit independent directors.
So long as EMC beneficially owns shares of our common stock representing at least a majority of the votes entitled to be cast by the holders of outstanding voting stock, EMC can effectively control and direct our board of directors. Further, the interests of EMC and our other stockholders may diverge. Under these circumstances, persons who might otherwise accept our invitation to join our board of directors may decline.
We are a “controlled company” within the meaning of the New York Stock Exchange rules, and, as a result, are relying on exemptions from certain corporate governance requirements that provide protection to stockholders of companies that are not “controlled companies.”
EMC owns more than 50% of the total voting power of our common shares and, as a result, we are a “controlled company” under the New York Stock Exchange corporate governance standards. As a controlled company, we are exempt under the New York Stock Exchange standards from the obligation to comply with certain New York Stock Exchange corporate governance requirements, including the requirements:
| | • | | that a majority of our board of directors consists of independent directors; |
| | • | | that we have a corporate governance and nominating committee that is composed entirely of independent directors with a written charter addressing the committee’s purpose and responsibilities; |
| | • | | that we have a compensation committee that is composed entirely of independent directors with a written charter addressing the committee’s purpose and responsibilities; and |
| | • | | for an annual performance evaluation of the nominating and governance committee and compensation committee. |
While we have voluntarily caused our Compensation and Corporate Governance Committee to currently be composed entirely of independent directors in compliance with the requirements of the New York Stock Exchange, we are not required to maintain the independent composition of the committee. As a result of our use of the “controlled company” exemptions, holders of our Class A common stock will not have the same protection afforded to stockholders of companies that are subject to all of the New York Stock Exchange corporate governance requirements.
Risks Related to Owning Our Class A Common Stock
Our Class A common stock has only been publicly traded since August 14, 2007 and the price of our Class A common stock has fluctuated substantially since then and may fluctuate substantially in the future.
Our Class A common stock has only been publicly traded since our IPO on August 14, 2007. The trading price of our Class A common stock has fluctuated significantly since then. For example, during 2008, the closing trading price of our Class A common stock was very volatile, ranging between $17.88 and $84.60 per share. Our trading price could fluctuate substantially in the future due to the factors discussed in this Risk Factors section and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
28
Substantial amounts of Class A common stock are held by our employees, EMC, Intel Corporation (“Intel”) and Cisco Systems (“Cisco”), and all of the shares of our Class B common stock, which may be converted to Class A common stock upon request of the holder, are held by EMC. Contractual restrictions on the sale of shares held by EMC Cisco and Intel expired in 2008. During 2008, following expiration of the contractual restrictions on its sale of VMware stock, Intel sold approximately 3.4 million of the 9.5 million shares of Class A common stock it had originally purchased and disclosed plans to sell approximately 1.4 million additional shares. Cisco and EMC each purchased 500,000 of the shares sold by Intel during 2008, thereby increasing their holdings. Shares of Class A common stock held by EMC (including shares of Class A common stock that might be issued upon the conversion of Class B common stock) are eligible for sale subject to the volume, manner of sale and other restrictions of Rule 144 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1933 which allow the holder to sell up to the greater of 1% of our outstanding Class A common stock or our average weekly trading volume during any three-month period and following the expiration of their contractual restrictions. Additionally, EMC possesses registration rights with respect to the shares of our common stock that it holds. If EMC chooses to exercise such rights, its sale of the shares that are registered would not be subject to the Rule 144 limitations. If a significant amount of the shares that become eligible for resale enter the public trading markets in a short period of time, the market price of our Class A common stock may decline.
Additionally, broad market and industry factors may decrease the market price of our Class A common stock, regardless of our actual operating performance. The stock market in general, and technology companies in particular, also have often experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations. In addition, in the past, following periods of volatility in the overall market and the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation has often been instituted, including against us, and, if not resolved swiftly, can result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish or cease publishing research or reports about us, our business or our market, or if they change their recommendations regarding our stock adversely, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our Class A common stock will be influenced by the research and reports that industry or securities analysts may publish about us, our business, our market or our competitors. If any of the analysts who may cover us change their recommendation regarding our stock adversely, or provide more favorable relative recommendations about our competitors, our stock price would likely decline. If any analyst who may cover us were to cease coverage of our company or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause our stock price or trading volume to decline.
Delaware law and our certificate of incorporation and bylaws contain anti-takeover provisions that could delay or discourage takeover attempts that stockholders may consider favorable.
Provisions in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws will have the effect of delaying or preventing a change of control or changes in our management. These provisions include the following:
| | • | | the division of our board of directors into three classes, with each class serving for a staggered three-year term, which would prevent stockholders from electing an entirely new board of directors at any annual meeting; |
| | • | | the right of the board of directors to elect a director to fill a vacancy created by the expansion of the board of directors; |
| | • | | following a distribution of Class B common stock by EMC to its stockholders, the restriction that a beneficial owner of 10% or more of our Class B common stock may not vote in any election of directors unless such person or group also owns at least an equivalent percentage of Class A common stock or obtains approval of our board of directors prior to acquiring beneficial ownership of at least 5% of Class B common stock; |
29
| | • | | the prohibition of cumulative voting in the election of directors or any other matters, which would otherwise allow less than a majority of stockholders to elect director candidates; |
| | • | | the requirement for advance notice for nominations for election to the board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon at a stockholders’ meeting; |
| | • | | the ability of the board of directors to issue, without stockholder approval, up to 100,000,000 shares of preferred stock with terms set by the board of directors, which rights could be senior to those of common stock; and |
| | • | | in the event that EMC or its successor-in-interest no longer owns shares of our common stock representing at least a majority of the votes entitled to be cast in the election of directors, stockholders may not act by written consent and may not call special meetings of the stockholders. |
Until such time as EMC or its successor-in-interest ceases to beneficially own 20% or more of the outstanding shares of our common stock, the affirmative vote or written consent of the holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of the Class B common stock will be required to:
| | • | | amend certain provisions of our bylaws or certificate of incorporation; |
| | • | | make certain acquisitions or dispositions; |
| | • | | declare dividends, or undertake a recapitalization or liquidation; |
| | • | | adopt any stockholder rights plan, “poison pill” or other similar arrangement; |
| | • | | approve any transactions that would involve a merger, consolidation, restructuring, sale of substantially all of our assets or any of our subsidiaries or otherwise result in any person or entity obtaining control of us or any of our subsidiaries; or |
| | • | | undertake certain other actions. |
In addition, we have elected to apply the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law. These provisions may prohibit large stockholders, in particular those owning 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock, from merging or combining with us. These provisions in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws and under Delaware law could discourage potential takeover attempts and could reduce the price that investors might be willing to pay for shares of our common stock.
Intel’s and Cisco’s ownership relationship with us and the membership on our board of individuals proposed by Intel and Cisco may create actual or potential conflicts of interest.
As a result of an investment by Intel Capital in our Class A common stock in August 2007, Intel has an ownership interest in us and pursuant to Intel’s right to designate a director acceptable to our board of directors, we appointed an Intel executive to our board of directors. Cisco, pursuant to its purchase of our Class A common stock from EMC, also has an ownership relationship with us, and we appointed an executive officer of Cisco (since retired from that position) proposed by Cisco as one of our directors. These relationships may create actual or potential conflicts of interest and the best interests of Intel or Cisco may not reflect the best interests of other holders of our Class A common stock.
| ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
30
As of December 31, 2008, we owned or leased the facilities described below:
| | | | | | |
Location | | | | Approximate
Sq. Ft.* | | Principal Use(s) |
Palo Alto, CA | | owned: | | 462,000 | | Executive and administrative offices, sales and |
| | leased: | | 371,000 | | marketing, R&D, and data center |
| | | |
North and Latin American region
(excluding Palo Alto, CA) | | leased: | | 356,000 | | Administrative offices, sales and marketing, R&D, and data center |
| | | |
Europe, Middle East, and Africa region | | leased: | | 220,000 | | Administrative offices, sales and marketing, and R&D |
| | | |
Asia Pacific region | | leased: | | 205,000 | | Administrative offices, sales and marketing, and R&D |
| * | Of the total square feet leased, approximately 45,000 square feet were under construction as of December 31, 2008. |
In April 2008, VMware entered into an agreement to lease space for a data center facility. The lease has a term of 16 years with a termination option at the end of the tenth year and the option to take over additional building space. As of December 31, 2008, approximately 30,000 square feet remained under construction. For accounting purposes, VMware is considered to be the owner of the data center. See Note E and Note G to our consolidated financial statements.
In August 2007, we used a portion of the net proceeds from our initial public offering of our Class A common stock to purchase our new corporate headquarters facilities in Palo Alto, California from EMC Corporation (“EMC”) for $132.6 million, which is equal to the cost expended by EMC in the construction of those facilities through the date of purchase. As of December 31, 2008, approximately 18,000 square feet remained under construction. Although we own the building and improvements, the land is leased. The ground lease relating to our new corporate headquarters expires in 2057.
We believe that our current facilities are suitable for our current employee headcount and will sustain us through 2009. In global locations such as China and India where we expect some headcount growth, we intend to expand facilities commensurate with the increase in headcount.
For further information regarding our lease obligations, see Note G to our consolidated financial statements.
VMware is named from time to time as a party to lawsuits in the normal course of its business. In such cases it is our policy to defend against such claims, or if considered appropriate, negotiate a settlement on commercially reasonable terms. However, no assurance can be given that we will be able to negotiate settlements on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, or that any litigation resulting from such claims would not have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial position, and cash flows, or consolidated financial statements taken as a whole.
| ITEM 4. | SUBMISSION OF MATTERS TO A VOTE OF SECURITY HOLDERS |
No matter was submitted to a vote of our stockholders during the fourth quarter of 2008.
31
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
The names of our executive officers and their ages as of February 20, 2009 are as follows:
| | | | |
Name | | Age | | Positions(s) |
Paul Maritz | | 53 | | President, Chief Executive Officer and Director |
Tod Nielsen | | 43 | | Chief Operating Officer |
Mark S. Peek | | 51 | | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
Carl M. Eschenbach | | 42 | | Executive Vice President of Worldwide Operations |
Rashmi Garde | | 43 | | Vice President and General Counsel |
Paul Maritz has been the President and Chief Executive Officer and a Director at VMware since July 2008. Prior to joining VMware, he served as President, Cloud Infrastructure and Services Division of EMC Corporation (“EMC”), VMware’s parent company and controlling stockholder. Mr. Maritz joined EMC in February 2008 when EMC acquired Pi Corporation (“Pi”), which he had founded in 2003 and where he served as CEO. Pi was a software company focused on building cloud-based solutions for new ways of doing personal information management. Prior to founding Pi, he spent 14 years working at Microsoft Corporation (“Microsoft”), where he served as a member of the five-person Executive Committee that managed the overall company prior to his retirement in 2000. At Microsoft, Mr. Maritz managed the development and marketing of many of the company’s major products, including such releases as Windows 95, Windows NT, Database, Tools and Applications. He also serves as Chairman of the Board of the Grameen Foundation, which supports microfinance around the world.
Tod Nielsen has been the Chief Operating Officer at VMware since January 2009. Prior to joining VMware, he served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Borland Software Corporation (“Borland”) since November 2005. From June 2005 to November 2005, Mr. Nielsen served as Senior Vice President, Marketing and Global Sales Support for Oracle Corporation, an enterprise software company. From August 2001 to August 2004, he served in various positions at BEA Systems, Inc. (“BEA Systems”), a provider of application infrastructure software, including Chief Marketing Officer and Executive Vice President, Engineering. He joined BEA Systems after the acquisition of his private company, Crossgain, Inc., where he served as its Chief Executive Officer from June 2000 to August 2001. Mr. Nielsen also spent 12 years with Microsoft in various roles, including General Manager of Database and Developer Tools, Vice President of Developer Tools, and at the time of his departure, Vice President of Microsoft’s platform group. Throughout his tenure with Microsoft, he worked on many parts of the business, with an emphasis on infrastructure and developer-oriented technologies. Mr. Nielsen is a member of the Board of Directors of Borland.
Mark S. Peek has been the Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer at VMware since April 2007. Prior to joining VMware, he served as Senior Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer of Amazon.com, Inc. since July 2002. Prior to joining Amazon.com in April 2000, Mr. Peek spent 19 years at Deloitte & Touche, the last ten years as a partner.
Carl M. Eschenbachhas been the Executive Vice President of Worldwide Field Operations at VMware since May 2005. Prior to joining VMware in 2002, he was Vice President of North America Sales at Inktomi from 2000 to 2002. He also held various sales management positions with 3Com Corporation, Lucent Technologies, and EMC.
Rashmi Gardehas been the Vice President and General Counsel at VMware since September 2005. She joined the Company in 2001. Prior to joining VMware, she was Senior Corporate Counsel at Electronics for Imaging, Inc., a printing technology company, and was an associate with Graham & James LLP and Fenwick & West LLP.
32
PART II
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS, AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Market Information
Our Class A common stock, par value $0.01 per share, trades on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol VMW.
The following table sets forth the range of high and low sales prices of our common stock since August 14, 2007, the date our Class A common stock commenced trading on the New York Stock Exchange. Our Class B common stock is not publicly traded.
| | | | | | |
| | | Market Prices |
| | | High | | Low |
Year ended December 31, 2008 | | | | | | |
First Quarter | | $ | 86.93 | | $ | 41.41 |
Second Quarter | | | 72.08 | | | 42.05 |
Third Quarter | | | 57.00 | | | 22.67 |
Fourth Quarter | | | 32.75 | | | 17.25 |
Year ended December 31, 2007 | | | | | | |
Third Quarter | | $ | 85.52 | | $ | 51.50 |
Fourth Quarter | | | 125.25 | | | 71.00 |
Holders
We had 39 holders of record of our Class A common stock, and one holder of record, EMC Corporation (“EMC”), of our Class B common stock as of February 19, 2009.
Dividends
In April 2007, we declared an $800.0 million dividend to EMC paid in the form of a note payable. Subsequent to receiving the proceeds from the initial public offering (“IPO”) of our Class A common stock in August 2007, we repaid $350.0 million of principal on the note.
Subsequent to our IPO, we have not declared or paid cash dividends on our common stock. We currently do not anticipate declaring any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination to declare cash dividends will be made at the discretion of our board of directors, subject to the consent of the holders of our Class B common stock pursuant to our certificate of incorporation. Holders of our Class A common stock and our Class B common stock will share equally on a per share basis in any dividend declared on our common stock by our board of directors.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
33
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Issuer purchases of equity securities during the quarter ended December 31, 2008:
| | | | | | | | | | |
Period | | Total Number
of Shares
Purchased | | Average Price
Paid Per Share | | Total Number of
Shares Purchased
as Part of Publicly
Announced Plans
or Programs | | Approximate Dollar Value
of Shares That May Yet Be
Purchased Under the
Publicly Announced Plans
or Programs |
October 1 – October 31, 2008 | | 26,936 | | $ | 31.00 | | — | | $ | — |
November 1 – November 30, 2008 | | 26,825 | | | 19.35 | | — | | | — |
December 1 – December 31, 2008 | | 28,840 | | | 23.77 | | — | | | — |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | 82,601 | | | 24.69 | | — | | $ | — |
| | | | | | | | | | |
We do not have a publicly announced stock repurchase program. All shares referenced in the above table were withheld through net share settlements during the quarter ending December 31, 2008 upon the vesting of restricted stock and restricted stock units under our equity compensation plan to satisfy tax withholding obligations.
Use of Proceeds
None.
34
Stock Performance Graph
The graph below compares the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock with the cumulative total return on the S&P 500 Index and the S&P 500 Systems Software Index for the period beginning on August 14, 2007 (the date our Class A common stock commenced trading on the New York Stock Exchange) through December 31, 2008, assuming an initial investment of $100. While the IPO price of our common stock was $29.00 per share, the graph assumes the initial value of our common stock on August 14, 2007 was the closing sales price of $51.00 per share. Data for the S&P 500 Index and the S&P 500 Systems Software Index assume reinvestment of dividends.
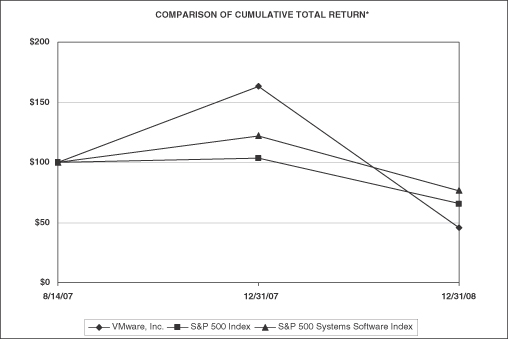
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Base Period
8/14/07 | | 12/31/07 | | 12/31/08 |
VMware, Inc. | | $ | 100.00 | | $ | 166.65 | | $ | 46.45 |
S&P 500 Index | | $ | 100.00 | | $ | 103.83 | | $ | 65.42 |
S&P 500 Systems Software Index | | $ | 100.00 | | $ | 121.87 | | $ | 76.12 |
| * | $100 invested on August 14, 2007 in VMware common stock, S&P 500 Index and S&P 500 Systems Software Index, including reinvestment of dividends, if any. |
Note: The stock price performance shown on the graph above is not necessarily indicative of future price performance. This graph shall not be deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act or otherwise subject to the liabilities of that section nor shall it be deemed incorporated by reference in any filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Exchange Act, regardless of any general incorporation language in such filing.
35
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
FIVE-YEAR SELECTED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL DATA
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Successor Company | | | | | Predecessor Company | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | | Period from
January 9, 2004 to
December 31, 2004 | | | | | February 1, 2003 to
January 8, 2004
(unaudited) | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | | 2005 | | | | |
Summary of Operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
License | | $ | 1,178,142 | | $ | 905,368 | | $ | 491,902 | | | $ | 287,006 | | | $ | 178,873 | | | | | $ | 61,980 | |
Services | | | 702,885 | | | 420,443 | | | 212,002 | | | | 100,068 | | | | 39,883 | | | | | | 12,220 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues | | $ | 1,881,027 | | $ | 1,325,811 | | $ | 703,904 | | | $ | 387,074 | | | $ | 218,756 | | | | | $ | 74,200 | |
Operating income (1) | | $ | 312,525 | | $ | 235,341 | | $ | 120,639 | | | $ | 93,595 | | | $ | 35,207 | | | | | $ | 6,032 | |
Net income | | $ | 290,133 | | $ | 218,137 | | $ | 85,890 | | | $ | 66,775 | | | $ | 16,781 | | | | | $ | 4,620 | |
Net income per weighted average share, basic, for Class A and Class B | | $ | 0.75 | | $ | 0.62 | | $ | 0.26 | | | $ | 0.20 | | | $ | 0.05 | | | | | | Not applicable | |
Net income per weighted average share, diluted, for Class A and Class B | | $ | 0.73 | | $ | 0.61 | | $ | 0.26 | | | $ | 0.20 | | | $ | 0.05 | | | | | | Not applicable | |
Weighted average shares, basic, for Class A and Class B | | | 385,068 | | | 350,493 | | | 332,500 | | | | 332,500 | | | | 332,500 | | | | | | Not applicable | |
Weighted average shares, diluted, for Class A and Class B | | | 397,185 | | | 359,189 | | | 332,500 | | | | 332,500 | | | | 332,500 | | | | | | Not applicable | |
| | | |
| | | Successor Company | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | | | | | Predecessor Company | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | | 2005 | | | 2004 | | | | | January 8, 2004 | |
Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents (2) | | $ | 1,840,812 | | $ | 1,231,168 | | $ | 176,134 | | | $ | 38,653 | | | $ | 36,059 | | | | | $ | 49,883 | |
Working capital (deficiency) (2) | | $ | 1,510,338 | | $ | 935,162 | | $ | (55,318 | ) | | $ | (134,198 | ) | | $ | (29,166 | ) | | | | $ | 12,189 | |
Total assets (2) | | $ | 3,839,205 | | $ | 2,695,700 | | $ | 1,145,950 | | | $ | 799,803 | | | $ | 697,675 | | | | | $ | 82,015 | |
Long-term obligations (3)(4) | | $ | 469,770 | | $ | 450,000 | | $ | 800,000 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | — | |
Stockholders’ equity (deficit) (2)(3) | | $ | 2,070,067 | | $ | 1,340,617 | | $ | (230,812 | ) | | $ | 453,829 | | | $ | 560,282 | | | | | $ | (27,455 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
Cash Flow Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | $ | 800,131 | | $ | 552,436 | | $ | 279,863 | | | $ | 238,247 | | | $ | 93,994 | | | | | | Not applicable | |
| (1) | In evaluating our results, we also focus on operating margin excluding stock-based compensation, employer taxes on employee stock transactions, amortization of intangible assets, the write-off of in-process research and development, and the net effect of the amortization and capitalization of software development costs as we believe this measure reflects our ongoing business in a manner that allows meaningful period-to-period comparisons. |
36
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Successor Company | | | | | Predecessor Company |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | | Period from
January 9, 2004 to
December 31, 2004 | | | | | Period from
February 1, 2003 to
January 8, 2004 |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | | | | |
Cost of license revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation | | $ | 1,120 | | | $ | 558 | | | $ | 99 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | — |
Employer payroll tax on employee stock transactions | | | 28 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | | — |
Acquisition-related intangible amortization | | | 11,278 | | | | 21,172 | | | | 21,840 | | | | 23,357 | | | | 25,487 | | | | | | — |
Capitalized software development costs amortization | | | 51,641 | | | | 36,407 | | | | 22,299 | | | | 6,159 | | | | 1,317 | | | | | | — |
| | | | | | | |
| Cost of services revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation | | | 13,485 | | | | 6,070 | | | | 2,384 | | | | 1,299 | | | | 1,061 | | | | | | — |
Employer payroll tax on employee stock transactions | | | 224 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | | — |
| | | | | | | |
| Research and development | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation not capitalized | | | 77,992 | | | | 42,934 | | | | 26,342 | | | | 14,656 | | | | 10,292 | | | | | | — |
Employer payroll tax on employee stock transactions | | | 2,814 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | | — |
In-process research and development | | | 6,576 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | | — |
Total capitalized software development costs | | | (113,649 | ) | | | (56,840 | ) | | | (43,012 | ) | | | (25,103 | ) | | | (8,155 | ) | | | | | — |
Stock-based compensation included in total capitalized software development costs above | | | 22,749 | | | | 9,105 | | | | 10,489 | | | | 3,545 | | | | — | | | | | | — |
| | | | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation | | | 49,762 | | | | 26,288 | | | | 12,020 | | | | 5,341 | | | | 4,672 | | | | | | — |
Employer payroll tax on employee stock transactions | | | 1,257 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | | — |
Acquisition-related intangible amortization | | | 3,586 | | | | 2,597 | | | | 2,188 | | | | 1,785 | | | | — | | | | | | — |
| | | | | | | |
| General and administrative | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation | | | 24,157 | | | | 16,556 | | | | 10,381 | | | | 5,775 | | | | 3,518 | | | | | | — |
Employer payroll tax on employee stock transactions | | | 519 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | | — |
Acquisition-related intangible amortization | | | 2,599 | | | | 1,972 | | | | 1,494 | | | | 1,000 | | | | 773 | | | | | | — |
| (2) | In August 2007, we completed our IPO in which we sold 37,950,000 shares (including 4,950,000 shares pursuant to the underwriters’ full exercise of their over-allotment option) of our Class A common stock at a price to the public of $29.00 per share. The net proceeds to us were $1,035.2 million. Subsequent to receiving the proceeds, we purchased our new headquarters facilities from EMC for $132.6 million, which is equal to the cost expended by EMC through the date of purchase. We also repaid $350.0 million of principal on the note payable to EMC. Also in August 2007, we sold 9.5 million shares of our Class A common stock to Intel Capital at $23.00 per share. The net proceeds to us from that transaction were $218.3 million. See Note K to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. |
| (3) | In April 2007, we declared an $800.0 million dividend to EMC paid in the form of a note. This dividend was given retroactive effect as of December 31, 2006. Subsequent to receiving the proceeds from the IPO in August 2007, we repaid $350.0 million of principal on the note. See Note G to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. In 2005, we declared and paid a cash dividend of $190.0 million to EMC. |
| (4) | In April 2008, we entered into an agreement to lease space for a data center facility. Significant leasehold improvements were under construction at December 31, 2008 as the building had never been occupied or improved for occupancy. For accounting purposes, we are considered to be the owner of the data center. Therefore, we capitalized the fair value of the portion of the building that it leases with a corresponding credit to a financing liability. As of December 31, 2008, the financing liability was approximately $19.8 million. See Note G to the consolidated financial statements for additional information. |
37
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATION |
This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (“MD&A”) should be read in conjunction with our annual consolidated financial statements and notes thereto which appear elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
This section and other parts of this Annual Report on Form 10-K contain forward-looking statements, within the meaning of the federal securities laws, about our business and prospects. The forward-looking statements do not include the potential impact of any mergers, acquisitions, divestitures, securities offerings or business combinations or other developments in our business that may be announced or consummated after the date hereof. Any statements contained herein that are not statements of historical fact may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. Without limiting the foregoing, the words “outlook,” “believes,” “plans,” “intends,” “expects,” “goals,” “potential,” “continues,” “may,” “will,” “should,” “seeks,” “predicts,” “estimates,” “anticipates” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these words. Our future results may differ materially from our past results and from those projected in the forward-looking statements due to various uncertainties and risks, including those described in Item 1A of Part I (Risk Factors). The forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report and undue reliance should not be placed on these statements. We disclaim any obligation to update any forward-looking statements contained herein after the date of this Annual Report.
All dollar amounts expressed as numbers in this MD&A (except per share amounts) are in millions.
Certain tables may not add due to rounding.
Overview
Our primary source of revenues is the licensing of virtual infrastructure software solutions and related support and services through a variety of distribution channels for use by businesses and organizations of all sizes and across numerous industries in their information technology infrastructure. Our virtual infrastructure software solutions run on industry-standard desktops and servers and support a wide range of operating system and application environments, as well as networking and storage infrastructures. We have developed a multi-channel distribution model to expand our presence and to reach various segments of the industry. In 2008, 2007 and 2006 we derived over 75% of our revenues from our channel partners, which include distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors and system integrators. We have also developed a network of indirect channel partners who fulfill orders through our direct channel partners. The majority of our revenues result from contracts that include both perpetual software licenses and ongoing software maintenance contracts. License revenues are recognized when the elements of revenue recognition are complete. Software maintenance revenues are recognized ratably over the term of the software maintenance period, and include renewals of software maintenance sold after the initial software maintenance period expires. We also recognize revenues from professional services provided to our customers.
We have achieved significant revenue growth to date by focusing on delivering new virtual infrastructure software solutions technology and products, expanding our network of technology and distribution partners, increasing product awareness, promoting the adoption of virtualization and building long-term relationships with our customers through the adoption of enterprise license agreements (“ELAs”).
Our current financial focus is on revenue growth to generate cash flows to fund our expansion of industry segment share and our development of virtualization-based products for data centers, desktops and cloud computing. We expect to continue our revenue growth by broadening our virtual infrastructure software solutions technology and product portfolio. We experienced growth in our channel partner transaction business and in the acquisition of new customers during 2008 as compared to 2007. However, since the end of the second quarter of 2008 we have observed that customers are subjecting larger orders, such as ELAs, to a longer review process and
38
in certain cases are purchasing products through the channel to meet their immediate needs, forgoing larger discounts offered under ELAs. We believe this trend primarily correlated to the recent global economic uncertainty and may continue throughout 2009 and perhaps longer.
We believe the use of virtual infrastructure solutions is at early stages by customers. Although we are currently the leading provider of virtual infrastructure solutions, we face competitive threats to our leadership from a number of companies, some of which have significantly greater resources than we do, which could result in increased pressure to reduce prices on our offerings. As a result, we believe it is important to continue to invest in strategic initiatives related to product research and development, market expansion and associated support functions to expand our industry leadership. These investments could result in contracting operating margins as we invest in our future. We believe that we will be able to continue to meet our product development objectives through continued investment in our current resources, supplemented with strategic hires and acquisitions, funded through the operating cash flows generated from the sale of our existing products and services. We believe this is the appropriate priority for the long-term health of our business.
In evaluating our results, we also focus on operating margin excluding stock-based compensation, employer taxes on employee stock transactions, amortization of intangible assets, the write-off of in-process research and development, and the net effect of the amortization and capitalization of software development costs as we believe this measure reflects our ongoing business in a manner that allows meaningful period-to-period comparisons. A portion of our services revenues is recognized in periods of up to five years subsequent to the initial contract, whereas most of our license revenues are recognized within the first quarter of contract signing. As a result, variability in operating margin can result from differences in when we price our service and when the cost is incurred. Substantially all of our international revenues are for contracts in U.S. Dollars to international channel partners. A portion of our operating expenses is in currencies other than the U.S. Dollar. This difference may cause variability in operating margins due to fluctuations in the U.S. Dollar compared to other currencies. We are not currently focused on short-term operating margin expansion, but rather on investing at appropriate rates to support our growth and future product offerings in what may be a substantially more competitive environment; as a result, our future operating margins may decline from current levels.
Prior to our initial public offering (“IPO”) in August 2007, we were a wholly-owned subsidiary of EMC Corporation (“EMC”), and as such we relied on EMC to provide a number of administrative support services and facilities in other countries. Although we continue to operate under an administrative services agreement and continue to receive support from EMC, we have invested in our own administrative functions, including our finance, legal and human resources functions. We are also incurring additional costs as a public company, including audit, investor relations, expanded information systems, stock administration and regulatory compliance costs.
Our Relationship with EMC
As of December 31, 2008, EMC owned 27,000,000 shares of Class A common stock and all 300,000,000 shares of Class B common stock, representing approximately 84% of our total outstanding shares of common stock and 98% of the combined voting power of our outstanding common stock.
In 2008, 2007 and 2006, we recognized professional services revenues of $16.9, $11.8 and $1.4, respectively, for services provided to EMC’s customers pursuant to our contractual agreements with EMC.
In 2008, we recognized revenues from server and desktop products and services purchased by EMC for internal use of $4.1 pursuant to our contractual agreements with EMC. As of December 31, 2008 and 2007, $1.8 and $4.3, respectively, of revenues from server and desktop products and services purchased by EMC for internal use were included in deferred revenue.
We purchased storage systems from EMC for $24.0, $7.2 and $2.9 in the years ended 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Through the third quarter of 2007, the systems purchased from EMC were at EMC’s cost. Since the fourth quarter of 2007, the systems purchased from EMC were at a discount off of EMC’s list price.
39
For certain corporate functions provided by EMC, $7.7 and $5.1 of expenses were allocated to us by EMC in 2007 and 2006, respectively. In 2008, this amount was not significant.
In certain geographic regions where we do not have an established legal entity, we contract with EMC subsidiaries for support services and EMC employees who are managed by our personnel. The costs incurred by EMC on our behalf related to these employees include an estimated arm’s-length mark-up and were included as expenses in our financial statements. These costs include expenses for salaries and benefits, travel, and rent. Additionally, EMC incurs certain costs on our behalf in the U.S., which primarily relate to shared systems for travel. The total of these costs were $139.8, $116.1 and $69.6 in the years ended 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
As part of our tax sharing agreement, we paid EMC income taxes of $64.3, $86.4 and $63.1 in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively, for our portion of their consolidated federal income taxes. These amounts differed from the amounts owed on a stand-alone basis and the differences are presented as a component of stockholders’ equity. In 2008, the difference between the amount of tax calculated on a stand-alone basis and the amount of tax calculated per the tax sharing agreement was recorded as an increase in stockholders’ equity of $5.2. In 2007 and 2006, this difference was recorded as a decrease in stockholders’ equity of $2.5 and $32.3, respectively.
Interest income (expense) with EMC, net, primarily consists of interest expense on the note payable to EMC, offset by interest income that has been earned on our intercompany balance with EMC. In 2008 and 2007, $18.6 and $26.6, respectively, of interest expense was recorded related to the note payable to EMC and was included in the $18.3 and $17.8, respectively, of interest expense with EMC, net, recorded on the consolidated statements of income. In 2006, we earned interest income with EMC, net, of $0.3. Our interest income and our expenses as a separate, stand-alone company may be higher or lower than the amounts reflected in the financial statements.
In 2008, we resolved with EMC certain acquisition-related intercompany liabilities due to EMC. As a result, intercompany liabilities due to EMC of $9.7 were recorded as a capital contribution from EMC in additional paid-in capital without the issuance of additional equity by us or remittance of any cash.
Prior to March 2008, our employees participated in the EMC Corporation 401(k) Savings Plan. EMC cross-charged us for the costs associated with our employees who participated in the EMC Plan. In March 2008, our employees began participating in our 401(k) Savings Plan and ceased participation in the EMC Plan. See Note I to our consolidated financial statements.
As of December 31, 2008, we had $38.4 due to EMC, which was partially offset by $5.0 due from EMC. As of December 31, 2007, we had $55.5 due to EMC, which was partially offset by $52.7 due from EMC. The net amounts due to EMC in 2008 and 2007 were $33.4 and $2.8, respectively, and resulted from the related party transactions described above. As of December 31, 2008, we had $111.1 of income taxes receivable due from EMC and $3.6 of income taxes payable due to EMC. As of December 31, 2007, we had $65.4 of income taxes payable due to EMC. Balances due to or from EMC which are unrelated to tax obligations are generally settled in cash within 60 days of each quarter end. The timing of the tax payments due to and from EMC is governed by the tax sharing agreement with EMC.
Given that the amounts we recorded for our intercompany transactions with EMC did not arise from transactions negotiated at arm’s-length with an unrelated third party, the financial statements included herein may not necessarily reflect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows had we engaged in such transactions with an unrelated third party during all periods presented. Accordingly, our historical results should not be relied upon as an indicator of our future performance as a stand-alone company.
40
Income Statement Presentation
Sources of Revenues
License revenues
Our license revenues consist of revenues earned from the licensing of our software products. These products are generally licensed on a perpetual basis and are generally priced based upon the number of physical desktops or server processors on which our software runs.
Software maintenance revenues
Software maintenance revenues are recognized ratably over the contract period. Typically, our contract periods range from one to five years. Customers receive various types of technical support based on the level of support purchased. Customers who are party to software maintenance agreements with us are entitled to receive product updates and upgrades on a when-and-if-available basis.
Professional services revenues
Professional services include design, implementation and training. Professional services are not considered essential to the functionality of our products, as these services do not alter the product capabilities and may be performed by our customers or other vendors. Professional services engagements for which we are able to make reasonably dependable estimates of progress toward completion are recognized on proportional performance to date based upon the hours incurred. Revenues on all other professional services engagements are recognized upon completion.
Operating Expenses
Cost of license revenues
Our cost of license revenues principally consists of amortization of capitalized software development costs and the cost of fulfillment of our software. This cost of fulfillment of our software includes product packaging, personnel costs and related overhead associated with the physical and electronic delivery of our software products.
Cost of services revenues
Our cost of services revenues includes the costs of personnel and related overhead to deliver technical support on our products and to provide our professional services.
Research and development expenses
Our research and development (“R&D”) expenses include the personnel and related overhead associated with the research and development of new product offerings, including depreciation expense, and the enhancement of our existing software offerings.
Sales and marketing expenses
Our sales and marketing expenses include personnel costs and related overhead associated with the sale and marketing of our license and services offerings, as well as the cost of certain marketing initiatives, including our semi-annual VMworld conference.
General and administrative expenses
Our general and administrative expenses include personnel and related overhead costs to support the overall business. These expenses include the costs associated with our finance, facilities, human resources, IT infrastructure, and legal departments.
41
Results of Operations
Revenues
Our revenues for the years ended 2008, 2007 and 2006 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
License | | $ | 1,178.1 | | | $ | 905.4 | | | $ | 491.9 | |
Services: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Software maintenance | | | 555.9 | | | | 330.0 | | | | 164.5 | |
Professional services | | | 147.0 | | | | 90.4 | | | | 47.5 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total services | | | 702.9 | | | | 420.4 | | | | 212.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 1,881.0 | | | $ | 1,325.8 | | | $ | 703.9 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Percentage of revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
License | | | 62.6 | % | | | 68.3 | % | | | 69.9 | % |
Services: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Software maintenance | | | 29.6 | | | | 24.9 | | | | 23.4 | |
Professional services | | | 7.8 | | | | 6.8 | | | | 6.7 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total services | | | 37.4 | | | | 31.7 | | | | 30.1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
United States | | $ | 987.6 | | | $ | 720.6 | | | $ | 391.6 | |
International | | | 893.4 | | | | 605.2 | | | | 312.3 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 1,881.0 | | | $ | 1,325.8 | | | $ | 703.9 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Percentage of revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
United States | | | 52.5 | % | | | 54.4 | % | | | 55.6 | % |
International | | | 47.5 | | | | 45.6 | | | | 44.4 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues were $1,881.0 in 2008, $1,325.8 in 2007 and $703.9 in 2006, representing year-over-year increases of $555.2 or 42% in 2008 and $621.9 or 88% in 2007. The growth in revenues in 2008 reflected an increase of $272.8 in license revenues and an increase of $282.4 in services revenues as compared to 2007. The growth in revenues in 2007 reflected an increase of $413.5 in license revenues and an increase of $208.4 in services revenues as compared to 2006. International revenues as a percentage of total revenues increased to 48% in 2008, from 46% in 2007 and 44% in 2006.
Our revenue contracts with international customers are denominated in U.S. Dollars. During the last four months of 2008, exchange rates between the U.S. Dollar, the Euro, British Pound and Australian Dollar experienced a significant degree of volatility. Our distributors and resellers generally quote to end user customers in local currency, and accordingly, uncertainty of short-term exchange rates may disrupt regular quoting of orders as distributors are subject to higher degrees of exchange risk.
Given the recent economic downturn and global financial crisis, we have applied additional scrutiny and analysis around the collectibility of transactions with certain customers, including but not limited to those customers in the financial services, insurance, and automotive industries and we continue to monitor the appropriateness of established customer credit limits. We do not record accounts receivable or deferred revenue
42
or recognize revenue relating to transactions where collectibility is not probable. We experienced an increase in these transactions in the fourth quarter of 2008. We recognize such transactions upon cash collection and recognize revenue as earned in accordance with our revenue recognition policies.
The current economic situation is creating a high degree of uncertainty around how much money will be spent on information technology (“IT”) over the foreseeable future. We believe the uncertainty is causing customers to be conservative and preserve their cash. Given these global economic conditions, we expect total revenues to increase in 2009 compared to 2008, but at a lower rate of growth. We also expect our license and professional services revenues growth rate to decelerate, and potentially contract, compared to 2008.
License Revenues
Software license revenues were $1,178.1 in 2008, $905.4 in 2007 and $491.9 in 2006, representing year-over-year increases of $272.8 or 30% in 2008 and $413.5 or 84% in 2007. We believe a significant majority of the revenue growth in 2008 compared to 2007, as well as 2007 compared to 2006, is the result of greater demand for our virtualization product offerings attributable to wider industry acceptance of virtualization as part of organizations’ IT infrastructure, a broadened product portfolio and expansion of our network of indirect channel partners. We expect the rate of growth in our license revenues to decelerate or contract due primarily to the size and scale of our business and lengthened sales cycles attributable to challenges our customers may face in the current uncertain economic environment, such as decreases in IT budgets and difficulties in obtaining financing. We expect that license revenues will be lower in the first quarter of 2009 than the comparable quarter of 2008. Due to the unprecedented level of uncertainty regarding future IT spending, we lack visibility into whether or how long this trend will continue.
ELAs continue to be a significant component of our revenue growth and are offered both direct and through certain channel partners. ELAs are core to our strategy to build long-term relationships with customers as they commit to our virtual infrastructure solutions in their data centers. ELAs provide a base from which to sell additional products, such as our application and infrastructure management suite and our disaster recovery products. Under a typical ELA, a portion of the revenues is attributed to the license and recognized immediately, but the majority is deferred and recognized as services revenues in future periods.
At the end of the fourth quarter of 2008, we observed seasonal strength in our ELAs from our enterprise accounts and comparative weakness in the transactional business especially with price-sensitive customers, such as the academic market and smaller businesses. We expect to continue to observe the lengthening of the sales cycle on ELAs that management believes is primarily correlated to economic uncertainty. During the second half of the year, customers began purchasing our solutions in smaller quantities through the channel to meet their immediate needs, forgoing larger discounts offered under ELAs. We expect that customers may continue smaller purchases through the channel at least through the first quarter of 2009, and perhaps longer.
We sell our products through a network of channel partners, which includes distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors and systems integrators. As we expand geographically, we may add additional direct channel partners. The increases in revenues in 2008 primarily resulted from increased sales volumes through our existing direct channel partners. These increases were driven by several factors, including greater demand for our virtualization product offerings, wider industry acceptance of virtualization as part of an organization’s IT infrastructure, a broadened product portfolio and expansion of our indirect channel partner network which purchase products from our direct partners.
We divide our license revenues into two classes: (1) Data center products and (2) Other products. Our data center products include a hypervisor for system-partitioning the software environment from its underlying hardware infrastructure and additional tools that enable the aggregation of multiple servers, storage infrastructure and networks into shared pools of resources that can be delivered dynamically, securely and reliably to applications as needed. Other products primarily include desktop virtualization products which decouple the
43
entire desktop environment from its underlying device, enabling customers to create user-centric instead of device-centric desktop environments. Revenues from data center products were $1,112.1, $875.6, and $451.3 in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. As a percentage of license revenues, revenues from data center products were 94%, 97% and 92% in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Revenues from other products were $66.0, $29.8, and $40.6 in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. As a percentage of license revenues, revenues from other products were 6%, 3% and 8% in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Our indirect channel partners obtain software licenses and services from our distributors and x86 system vendors and market and sell them to end user customers. In the first quarter of 2008, we introduced new programs for these channel partners to assist them to quickly establish and expand their virtualization practices and drive new customer acquisition. We believe these programs encourage channel loyalty and may facilitate our ability to reach additional industry segments and acquire new customers. In addition, we have a direct sales force that complements these efforts. Our sales force works with our channel partners to introduce them to customers and new sales opportunities. Our channel partners also introduce our sales force to their customers.
Services Revenues
Services revenues were $702.9 in 2008, $420.4 in 2007 and $212.0 in 2006, representing year-over-year increases of $282.4 or 67% in 2008 and $208.4 or 98% in 2007. We expect that services revenues will compose a larger proportion of our revenue mix and revenue growth in 2009. The increase in services revenues in 2008 was primarily attributable to growth in our software maintenance revenues.
Software maintenance revenues were $555.9 in 2008, $330.0 in 2007 and $164.5 in 2006, representing year-over-year increases of $225.9 or 69% in 2008 and $165.5 or 101% in 2007. This growth reflects the increase in our license revenues, as software maintenance services are generally purchased with licenses, the benefit from multi-year software maintenance contracts sold in previous periods and renewals of existing customer software maintenance contracts.
Professional services revenues were $147.0 in 2008, $90.4 in 2007 and $47.5 in 2006, representing year-over-year increases of $56.5 or 63% in 2008 and $42.9 or 90% in 2007. Professional services revenues increased due to growing demand for design and implementation services and training programs, as end user organizations deployed virtualization across their organizations. Although, professional services revenues increased year-over-year, professional services revenues in the fourth quarter of 2008 were flat sequentially to the third quarter due to our transitioning some of this business to our partners. Although we will continue to serve our customers directly, we encourage our partners to build their professional services businesses which we believe will leverage our license sales through this channel.
44
Operating Expenses, GAAP and Non-GAAP
Information about our operating expenses with and without stock-based compensation is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, | | | Non-
GAAP,
As
Adjusted
Change | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | |
| | | GAAP | | | Stock-
Based
Compen-
sation | | | Non-
GAAP,
As
Adjusted | | | GAAP | | | Stock-
Based
Compen-
sation | | | Non-
GAAP,
As
Adjusted | | |
Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of license revenues (1) | | $ | 88.2 | | | $ | (1.1 | ) | | $ | 87.1 | | | $ | 80.9 | | | $ | (0.6 | ) | | $ | 80.3 | | | $ | 6.8 | | 8 | % |
Cost of services revenues | | | 215.9 | | | | (13.5 | ) | | | 202.4 | | | | 137.8 | | | | (6.1 | ) | | | 131.7 | | | | 70.7 | | 54 | % |
Research and development (2) | | | 429.2 | | | | (78.0 | ) | | | 351.2 | | | | 285.9 | | | | (42.9 | ) | | | 243.0 | | | | 108.2 | | 45 | % |
Sales and marketing | | | 654.1 | | | | (49.8 | ) | | | 604.3 | | | | 450.2 | | | | (26.2 | ) | | | 424.0 | | | | 180.3 | | 43 | % |
General and administrative | | | 181.1 | | | | (24.1 | ) | | | 157.0 | | | | 135.7 | | | | (16.6 | ) | | | 119.1 | | | | 37.9 | | 32 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating expenses | | $ | 1,568.5 | | | $ | (166.5 | ) | | $ | 1,402.0 | | | $ | 1,090.5 | | | $ | (92.4 | ) | | $ | 998.1 | | | $ | 403.9 | | 40 | % |
| | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | $ | 312.5 | | | $ | 166.5 | | | $ | 479.0 | | | $ | 235.3 | | | $ | 92.4 | | | $ | 327.7 | | | $ | 151.3 | | 46 | % |
| | | | | | | | |
Percentage of revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of license revenues | | | 4.7 | % | | | | | | | 4.6 | % | | | 6.1 | % | | | | | | | 6.1 | % | | | | | | |
Cost of services revenues | | | 11.5 | | | | | | | | 10.8 | | | | 10.4 | | | | | | | | 9.9 | | | | | | | |
Research and development | | | 22.8 | | | | | | | | 18.7 | | | | 21.6 | | | | | | | | 18.3 | | | | | | | |
Sales and marketing | | | 34.8 | | | | | | | | 32.1 | | | | 34.0 | | | | | | | | 32.0 | | | | | | | |
General and administrative | | | 9.6 | | | | | | | | 8.3 | | | | 10.2 | | | | | | | | 9.0 | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating expenses | | | 83.4 | % | | | | | | | 74.5 | % | | | 82.3 | % | | | | | | | 75.3 | % | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Operating margin | | | 16.6 | % | | | | | | | 25.5 | % | | | 17.7 | % | | | | | | | 24.7 | % | | | | | | |
| | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, | | | Non-
GAAP,
As
Adjusted
Change | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | |
| | | GAAP | | | Stock-
Based
Compen-
sation | | | Non-
GAAP,
As
Adjusted | | | GAAP | | | Stock-
Based
Compen-
sation | | | Non-
GAAP,
As
Adjusted | | |
Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of license revenues (1) | | $ | 80.9 | | | $ | (0.6 | ) | | $ | 80.3 | | | $ | 59.2 | | | $ | (0.1 | ) | | $ | 59.1 | | | $ | 21.2 | | 36 | % |
Cost of services revenues | | | 137.8 | | | | (6.1 | ) | | | 131.7 | | | | 64.2 | | | | (2.4 | ) | | | 61.8 | | | | 69.9 | | 113 | % |
Research and development (2) | | | 285.9 | | | | (42.9 | ) | | | 243.0 | | | | 152.0 | | | | (26.3 | ) | | | 125.7 | | | | 117.3 | | 93 | % |
Sales and marketing | | | 450.2 | | | | (26.2 | ) | | | 424.0 | | | | 238.3 | | | | (12.0 | ) | | | 226.3 | | | | 197.7 | | 87 | % |
General and administrative | | | 135.7 | | | | (16.6 | ) | | | 119.1 | | | | 69.6 | | | | (10.4 | ) | | | 59.2 | | | | 59.9 | | 101 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating expenses | | $ | 1,090.5 | | | $ | (92.4 | ) | | $ | 998.1 | | | $ | 583.3 | | | $ | (51.2 | ) | | $ | 532.1 | | | $ | 466.0 | | 88 | % |
| | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | $ | 235.3 | | | $ | 92.4 | | | $ | 327.7 | | | $ | 120.6 | | | $ | 51.2 | | | $ | 171.8 | | | $ | 155.9 | | 91 | % |
| | | | | | | | |
Percentage of revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of license revenues | | | 6.1 | % | | | | | | | 6.1 | % | | | 8.4 | % | | | | | | | 8.4 | % | | | | | | |
Cost of services revenues | | | 10.4 | | | | | | | | 9.9 | | | | 9.1 | | | | | | | | 8.8 | | | | | | | |
Research and development | | | 21.6 | | | | | | | | 18.3 | | | | 21.6 | | | | | | | | 17.9 | | | | | | | |
Sales and marketing | | | 34.0 | | | | | | | | 32.0 | | | | 33.9 | | | | | | | | 32.1 | | | | | | | |
General and administrative | | | 10.2 | | | | | | | | 9.0 | | | | 9.9 | | | | | | | | 8.4 | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating expenses | | | 82.3 | % | | | | | | | 75.3 | % | | | 82.9 | % | | | | | | | 75.6 | % | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Operating margin | | | 17.7 | % | | | | | | | 24.7 | % | | | 17.1 | % | | | | | | | 24.4 | % | | | | | | |
| (1) | Included in the cost of license revenues is the amortization of capitalized software development costs of $51.6, $36.4 and $22.3 in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. |
| (2) | Included in R&D is the capitalization of software development costs of $113.6 (including $22.7 of stock-based compensation) in 2008, $56.8 (including $9.1 of stock-based compensation) in 2007, and $43.0 (including $10.5 of stock-based compensation) in 2006. |
45
Operating expenses without stock-based compensation are non-GAAP financial measures. See—”Non-GAAP Financial Measures” below. Aside from the effects of stock-based compensation shown in the table above, the following discussion highlights additional factors that impacted our results of operations.
Cost of License Revenues
The decreases in our cost of license revenues as a percentage of revenues were primarily attributable to decreased amortization of intangible assets. As a percentage of revenues, amortization of intangible assets decreased by 1.0 percentage point of revenues to 0.6% of revenues in 2008 as compared with 1.6% in 2007, and decreased by 1.5 percentage points of revenues in 2007 as compared with 3.1% in 2006. The cost of fulfillment of our software, which includes product packaging, personnel costs and related overhead associated with the physical and electronic delivery of our software products remained relatively flat.
In the future when recently capitalized software development costs begin to amortize as a component of cost of license revenues, our cost of license revenues will increase in absolute dollars.
Cost of Services Revenues
The increases in our cost of services revenues were primarily attributable to the increased direct support, professional services personnel and third-party professional services costs to support the increased services revenues.
Research and Development Expenses
The increases in R&D expenses were primarily attributable to increased facilities, salaries and benefits expenses resulting from incremental headcount added in support of feature functionality development, sustainment of existing products, and new product development, which are intended to grow our future business. Partially offsetting this increase in expenses was an increase in software capitalization by $56.8 to $113.6 (including $22.7 of stock-based compensation) in 2008 as compared with 2007, and by $13.8 to $56.8 (including $9.1 of stock-based compensation) in 2007 as compared with $43.0 (including $10.5 of stock-based compensation) in 2006. As the number of future projects requiring capitalization may decrease, our future R&D expenses could increase.
Included in our R&D expenses, we had in process research and development (“IPR&D”) expense of $6.6, related to acquisitions in 2008. We had no IPR&D expense in 2007. In 2006, IPR&D expense was $3.7.
Sales and Marketing Expenses
The increases in sales and marketing expenses in absolute dollars consisted primarily of higher salaries and benefits expenses due to both increases in sales and marketing personnel and higher commission expense resulting from increased sales volumes. Our sales and marketing expenses also increased due to marketing expenses related to our ongoing international market expansion and marketing expenses related to our branding initiative in 2008. A portion of our sales and marketing expenses is denominated in foreign currencies and thus exposed to foreign exchange rate fluctuations. Upon consolidation, as exchange rates vary, the amount of sales and marketing expenses may fluctuate in response to changes in the exchange rate between the U.S. Dollar and the foreign currencies in which the expenses are payable.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses increased in absolute dollars primarily as a result of additional salaries and benefits expenses resulting from the additional resources to support the growth of our business and to expand our own administrative functions.
46
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, | | 2008
versus
2007 | | | 2007
versus
2006 | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | |
Stock-based compensation, excluding amounts capitalized under FAS 86 | | $ | 166.5 | | $ | 92.4 | | $ | 51.2 | | 80 | % | | 80 | % |
Stock-based compensation capitalized under FAS 86 | | | 22.7 | | | 9.1 | | | 10.5 | | 149 | % | | -13 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation, including amounts capitalized under FAS 86 | | $ | 189.2 | | $ | 101.5 | | $ | 61.7 | | 86 | % | | 65 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation expenses, excluding amounts capitalized under FAS 86, increased primarily due to broad-based stock option and restricted stock unit grants made under the VMware 2007 Equity and Incentive Plan beginning in the second quarter of 2007. Between the time of our acquisition by EMC in January 2004 and June 2007, we did not issue equity awards in our stock to our employees. During this period, employees received stock-based compensation in the form of EMC stock options and restricted stock awards and units as a result of grants made by EMC’s Board of Directors. Beginning in June 2007, we granted equity incentive awards under our 2007 Equity and Incentive Plan in anticipation of our IPO. In connection with the IPO in August 2007, we conducted an exchange offer pursuant to which we offered our eligible employees the ability to exchange their existing EMC options and restricted stock awards for options to purchase our Class A common stock and restricted stock awards of our Class A common stock, respectively.
In September 2008, we completed an offer to exchange certain employee stock options issued under the VMware 2007 Equity and Incentive Plan (“2008 Exchange Offer”). Certain previously granted options were exchanged for new, lower-priced stock options granted on a one-for-one basis. Executive officers and members of our Board of Directors were excluded from participating in the 2008 Exchange Offer. Options for an aggregate of 4.1 million shares of our Class A common stock were exchanged with a weighted average exercise price per share of $71.60. Options granted pursuant to the 2008 Exchange Offer have an exercise price of $33.95 per share, vest pro rata over four years beginning September 10, 2008 with no credit for past vesting and have a new six-year option term. The 2008 Exchange Offer resulted in incremental stock-based compensation expense of $18.0 to be recognized over the four-year vesting term.
In September 2008, we awarded 5.3 million restricted stock units to certain employees, including a portion for international employees who were not eligible to participate in the 2008 Exchange Offer and a portion for retention purposes. These awards generally will vest over a three-year or four-year period. These awards resulted in stock-based compensation expense of $164.5 to be recognized over the three-year or four-year vesting term.
As of December 31, 2008, the total unamortized fair value of our outstanding equity-based awards and EMC equity-based awards held by our employees was approximately $522.6. This amount will be recognized over the awards’ requisite service periods, and is expected to result in stock-based compensation expense of approximately $204.1, $182.0, $109.9 and $26.6 for 2009, 2010, 2011 and 2012, respectively.
In future quarters, our stock-based compensation expense is expected to increase as a result of additional equity grants in future periods. During 2009, we expect to issue equity awards through refresh grants to our employees. The stock-based compensation expense is subject to the amount of stock-based compensation that may be capitalized as costs incurred for the development of new software products, software developed for internal use and the amount of awards that ultimately vest.
47
Intangible Assets
Amortization expense was lower in 2008 as compared to 2007, and flat in 2007 compared to 2006, due primarily to decreasing amortization for intangible assets resulting from EMC’s acquisition of us, offset in part by additional amortization for new acquisitions. The amortization expense was classified as follows in the consolidated income statements:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
Cost of license revenues | | $ | 11.3 | | $ | 21.2 | | $ | 21.8 |
Sales and marketing | | | 3.6 | | | 2.6 | | | 2.2 |
General and administrative | | | 2.6 | | | 1.9 | | | 1.5 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total intangible amortization expense | | $ | 17.5 | | $ | 25.7 | | $ | 25.5 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Operating Income
The operating margin in 2008 increased primarily as a result of a decrease in expense from the net effect of capitalizing and amortizing software development costs.
A portion of our costs of revenues, primarily the costs of personnel to deliver technical support on our products and professional services, and a portion of our operating expenses mainly related to sales, sales support and R&D, are denominated in foreign currencies, primarily the Euro, the British Pound, the Australian Dollar, the Canadian Dollar, the Indian Rupee, and the Japanese Yen. These costs and the resulting effect on operating income are exposed to foreign exchange rate fluctuations. To quantify the effect on our operating income of fluctuations in the exchange rates between the U.S. Dollar and foreign currencies, we translate our non-U.S. Dollar operating expenses into local currency using current period average exchange rates. Operating expenses are then reconverted into the U.S. Dollar using the prior period average exchange rates and the results are compared to quantify the impact. As a result of fluctuations in the exchange rates between the U.S. Dollar and foreign currencies, operating income decreased by $10.6 in 2008, $18.6 in 2007 and $2.8 in 2006. If the Dollar weakens or strengthens in relation to other currencies, such as the Euro, we expect this to have a negative or positive effect, respectively, on our operating margins.
The current economic situation is creating a high degree of uncertainty around how much money will be spent on IT over the foreseeable future. We continue to expect that our operating expenses will increase in absolute terms and could increase as a percentage of revenues as we intend to continue our strategic investments in product development and expansion into strategic geographic markets.
Investment Income
Investment income was $28.3 in 2008, $22.9 in 2007 and $2.5 in 2006. Investment income consists of interest earned on cash and cash equivalent balances. Investment income increased in 2008 compared to 2007 due to higher cash and cash equivalent balances, primarily as a result of cash provided by operating activities, as well as a full year of interest earned on proceeds we received in the middle of the third quarter of 2007 from our IPO and the sale of shares of our Class A common stock to Intel Capital. The increase in interest income earned on our cash and cash equivalent balances was partially offset by the negative impact of lower interest rates in 2008. Investment income increased in 2007 compared to 2006 due to higher cash and cash equivalent balances, primarily as a result of the proceeds we received from our IPO and the sale of shares of our Class A common stock to Intel Capital. We expect investment income in the first quarter of 2009 to decrease as compared with the fourth quarter of 2008 due to an anticipated decline in investments yields as a result of decreasing interest rates.
48
Interest Income (Expense) with EMC, Net
Interest expense with EMC, net, was $18.3 in 2008 and $17.8 in 2007. Interest income with EMC, net, was $0.3 in 2006. In 2008 and 2007, interest expense with EMC, net, consisted primarily of $18.6 and $26.6, respectively, of interest expense incurred on the note issued to EMC in April 2007, net of interest income earned on intercompany balances. The decrease in interest expense in 2008 was due to a lower weighted-average interest rate on the note of 4.14% in 2008 as compared to 5.86% in 2007, as well as a repayment of $350.0 of the principal balance in August of 2007. The interest rate on the note payable resets quarterly and is determined using the 90-day LIBOR rate plus 55 basis points, two business days prior to the first day of each fiscal quarter.
Income Tax Provision
Our effective tax rate for 2008 was 9.1% compared to 9.3% for 2007 and 30.1% for 2006. The slightly lower effective tax rate in 2008 was mainly attributable to a net benefit resulting from an increase in tax credits.
The change in the effective rate which decreased to 9.3% in 2007 from 30.1% in 2006 was primarily attributable to the decrease in the other non-deductible permanent differences of 17.2 percentage points from 2006 to 2007. This decrease was primarily attributable to the change of our tax structure, whereby income in 2007 earned abroad principally qualified for deferral from U. S. taxation, whereas in 2006 the income was principally taxed in the United States. The other significant contributing factor to the decrease in the effective tax rate from 2006 to 2007 was that our aggregate income tax rate in foreign jurisdictions, which is typically lower than our income tax rate in the United States, resulted in an increase of a favorable tax benefit of 4 percentage points from 2006 to 2007. Offsetting this favorable tax benefit was the decrease in the generated tax credits by 0.4 percentage points from 2006 to 2007.
The 2009 tax rate is expected to be higher than the 2008 tax rate primarily due to a forecasted shift of earnings from low-tax non-U.S. jurisdictions to the United States and an increase in unrecognized tax positions relative to income before tax. The effective tax rate for 2009 is based upon the income for the year, the composition of the income in different countries, and adjustments, if any, for the potential tax consequences, benefits, resolutions of audits or other tax contingencies. Our aggregate income tax rate in foreign jurisdictions is lower than our income tax rate in the United States.
Our future effective tax rate may be affected by such factors as changes in tax laws, regulations or rates, changing interpretation of existing laws or regulations, the impact of accounting for stock-based compensation, the impact of accounting for business combinations under the new Financial Accounting Standard No. 141 (revised 2007), “Business Combinations” (“FAS No. 141R”), changes in our international organization, and changes in overall levels of income before tax.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
Regulation S-K Item 10(e), “Use of Non-GAAP Financial Measures in Commission Filings,” and other Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) regulations define and prescribe the conditions for use of certain non-GAAP financial information. Our measures of operating expenses and operating income without stock-based compensation meet the definition of non-GAAP financial measures. These non-GAAP financial measures, which are used as measures of our performance, should be considered in addition to, not as a substitute for or in isolation from, measures of our financial performance prepared in accordance with GAAP. We provide this information to show the impact of stock-based compensation on our results of operations, as it is excluded from our internal operating plans and measurement of financial performance (although we consider the dilutive impact to our shareholders when awarding stock-based compensation and value such awards accordingly) and because determining the fair value of the related equity awards involves a high degree of judgment and estimation.
When evaluating the performance of our individual functional groups, we do not consider stock-based compensation charges. Likewise, we exclude stock-based compensation expense from our short and long-term
49
operating plans. Our management team is held accountable for cash-based compensation and such amounts are included in their operating plans. Due to its nature, individual managers generally are unable to project the impact of stock-based compensation and accordingly they are not held accountable for the impact of equity award grants. Although we acknowledge that stock-based compensation is necessary to attract and retain quality employees, our consideration of stock based compensation places its primary emphasis on overall shareholder dilution rather than the accounting charges associated with such grants. For comparability purposes, we believe it is useful to provide a non-GAAP financial measure that excludes stock-based compensation in order to better understand the long-term performance of our core business and to facilitate the comparison of our results to the results of our peer companies because of varying available valuation methodologies and the variety of award types that companies can use under Financial Accounting Standard No. 123R, “Share-Based Payment,” or FAS No. 123R. Furthermore, unlike cash compensation, the value of stock-based compensation is determined using a complex formula that incorporates factors, such as market volatility, that are beyond our control. Accordingly, we believe that the presentation of non-GAAP operating expenses and operating income when read in conjunction with our reported GAAP operating expenses and operating income can provide useful supplemental information to our management and to investors regarding financial and business trends relating to our financial condition and results of operations.
Operating expenses without stock-based compensation have limitations due to the fact that they do not include all expenses related to the compensation of our people. More specifically, if we did not pay out a portion of our compensation in the form of stock-based compensation, it is likely that cash-based compensation expense included in our operating expenses would be higher. We compensate for this limitation by providing supplemental information about outstanding stock-based awards in the footnotes to our financial statements. Stock-based compensation programs are an important element of our compensation structure and all forms of stock-based awards are valued and included as appropriate in results of operations. Management strongly encourages stockholders to review our financial statements and publicly-filed reports in their entirety and not to rely on any single financial measure.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
| | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 1,840.8 | | $ | 1,231.2 |
Our cash flows for 2008, 2007 and 2006 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | $ | 800.1 | | | $ | 552.4 | | | $ | 279.9 | |
Net cash used in investing activities | | $ | (421.9 | ) | | $ | (403.7 | ) | | $ | (142.4 | ) |
Net cash provided by financing activities | | $ | 231.4 | | | $ | 906.3 | | | $ | — | |
Our operating activities for each year in the three years ended December 31, 2008 have generated adequate cash to meet our operating needs. As of December 31, 2008, we had cash and cash equivalents totaling $1,840.8, compared to $1,231.2 as of December 31, 2007. During the year ended December 31, 2008, key drivers in the increase of cash included the generation of $800.1 of cash from operating activities and $190.1 from issuance of common stock, primarily as a result of the exercise of employee stock options. In 2008, we invested $138.6 of cash for business acquisitions and used $191.6 of cash for capital expenditures.
We invest excess cash predominantly in money market securities that are liquid and of high-quality investment grade. The fair value for securities is determined based on quoted market prices as of the valuation date. We limit the amount of our domestic and international investments with any one issuer and also monitor the
50
portfolio so that investments are placed in funds with dissimilar economic characteristics, thereby diversifying the credit risk. As of December 31, 2008, all of our domestic money market funds were participating in the Temporary Guarantee Program for Money Market Funds, which is backed by the U.S. Treasury Department but limited to the balance in our money market funds as of September 19, 2008. The Temporary Guarantee Program for Money Market Funds expires on April 30, 2009. As of December 31, 2008, these guaranteed funds represented 42% of our cash and cash equivalents balance. Our international money market funds comprise 18% of our cash and cash equivalents balance and are invested in offshore money market funds and time deposits. In addition to investment in money market securities, we also use excess cash to support our growing infrastructure needs, to expand our operations and as consideration for acquisitions and strategic investments.
We expect to continue to generate positive cash flow from operations in 2009 and will use cash generated by operations as our primary source of liquidity. We believe that existing cash and cash equivalents, together with any cash generated from operations will be sufficient to meet normal operating requirements including strategic acquisitions and capital expenditures for at least the next twelve months.
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Cash provided by operating activities is driven by our net income, adjusted for non-cash items and changes in assets and liabilities. Non-cash adjustments include depreciation, amortization of intangible assets, stock-based compensation expense, tax benefits from stock-based compensation and other adjustments. In the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, there were significant increases in deferred revenue that positively impacted cash flow from operating activities. These increases were largely driven by an increase in deferred maintenance revenue for which we are typically paid when the product is sold. In each of the three years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 cash flows from operating activities were negatively impacted by the increase in our accounts receivable balance, which resulted from increases in our revenues. However, the decrease in the days of sales outstanding metric over each of the three years partially offset the negative impact of the increase in accounts receivable. Additionally, cash flow from operating activities was negatively affected by $111.1 for an increase in income tax receivable from EMC in 2008.The receivable arose because we had a stand-alone taxable loss for the year-ended December 31, 2008, which was primarily attributable to tax deductions arising from both non-qualified stock option exercises and from the vesting of restricted stock. Under the tax sharing agreement with EMC, EMC is obligated to pay us an amount equal to the tax benefit that EMC will recognize on its consolidated tax return.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
Cash used in investing activities is primarily attributable to business acquisitions, capital expenditures, and capitalized software development costs. We invested $138.6 for acquisitions in 2008, compared to $82.5 for acquisitions in 2007 and $46.5 for an acquisition in 2006. Acquisitions are an important element of our corporate strategy and we expect to continue to invest in strategic acquisitions in the future.
Our capital expenditures totaled $191.6, $269.0, and $52.6 in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. During 2008, our capital expenditures primarily related to the construction at our headquarters facility and our data center and investing in computer and network equipment to support increased personnel and related infrastructure requirements both domestically and internationally. Capital expenditures in 2007 were higher compared to other years, primarily due to our investment in our new headquarters facility. We purchased from EMC buildings already under construction for $132.6, which was the cost expended by EMC during construction. We also purchased furniture and fixtures for the new facilities and invested cash in the remaining buildings under development. In addition to the investment in our headquarters facilities in 2007, we purchased computer and network equipment to support increased personnel and related infrastructure requirements.
Our capitalized software development costs, excluding stock-based compensation expense, totaled $90.9, $47.7, and $32.5 in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. The increase in capitalized software development costs was the result of the deployment of additional resources to support the development of software products, as well as the timing of when those products reached technological feasibility.
51
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
In 2008, cash provided by financing activities was primarily driven by $190.1 of issuances of our common stock from the exercise of options and issuance of shares under our 2007 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”). Between the time of our acquisition by EMC in January 2004 and June 2007, we did not issue equity awards in our stock to our employees. During this period, employees received stock-based compensation in the form of EMC stock options and restricted stock awards and units as a result of grants made by EMC’s Board of Directors. Beginning in June 2007, we granted equity incentive awards under our 2007 Equity and Incentive Plan in anticipation of our IPO. As such, we had no financing activities in 2006 and $2.8 of financing activities in 2007 related to the exercise of options.
Upon adoption of FAS No. 123R on January 1, 2006, we have included as part of our cash flows from financing activities the benefit of tax deductions related to stock-based compensation in excess of the tax benefits expected at the grant date of the related stock-based awards. This amount is shown as a reduction to cash flows from operating activities and an increase to cash flows from financing activities. Net cash flows remain unchanged from what would have been reported prior to the adoption of FAS No. 123R.
Future cash proceeds from issuances of common stock and the excess tax benefit from stock-based compensation will depend upon and could fluctuate significantly from period to period based upon the market value of our stock, the number of awards exercised, sold or vested, the tax benefit realized and the tax-affected compensation recognized.
The above described financing cash inflows were partially offset by $44.5 of shares repurchased in 2008 to cover tax withholding obligations in conjunction with the net share settlement upon the vesting of restricted stock.
In 2007, as a result of the completion of our IPO, we received net proceeds of $1,035.2 from issuance of our Class A common stock. We also received net proceeds of $218.3 from the sale of our Class A common stock to Intel Capital in 2007. We used a portion of these proceeds to pay $350.0 of principal on the intercompany note payable owed to EMC. There were no financing cash flows from financing activities in 2006.
To date, inflation has not had a material impact on our financial results.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, Contractual Obligations, Contingent Liabilities and Commitments
Guarantees and Indemnification Obligations
We enter into agreements in the ordinary course of business with, among others, distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors and system integrators. Most of these agreements require us to indemnify the other party against third-party claims alleging that one of our products infringes or misappropriates a patent, copyright, trademark, trade secret and/or other intellectual property right. Certain of these agreements require us to indemnify the other party against certain claims relating to property damage, personal injury or the acts or omissions by us, our employees, agents or representatives. In addition, from time to time we have made certain guarantees regarding the performance of our systems to our customers.
52
Contractual Obligations
We have various contractual obligations impacting our liquidity. The following represents our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2008:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Payments Due by Period |
| | | Total | | Less than
1 year | | 1-3
years (1) | | 3-5
years(2) | | More than
5 years |
Note payable to EMC(3) | | $ | 450.0 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 450.0 | | $ | — |
Operating leases | | | 376.0 | | | 29.5 | | | 50.8 | | | 25.2 | | | 270.5 |
Purchase orders | | | 120.9 | | | 119.7 | | | 1.2 | | | — | | | — |
FIN 48 (4) | | | 46.8 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — |
Other agreements(5) | | | 28.1 | | | 13.7 | | | 9.7 | | | 4.7 | | | — |
Financing liability related to data center(6) | | | 19.8 | | | — | | | 0.2 | | | 0.5 | | | 19.1 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 1,041.6 | | $ | 162.9 | | $ | 61.9 | | $ | 480.4 | | $ | 289.6 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | Includes payments from January 1, 2010 through December 31, 2011. |
| (2) | Includes payments from January 1, 2012 through December 31, 2013. |
| (3) | The note is due and payable in full on or before April 16, 2012, however, we can pay down the note at an earlier date in full or in part at our election. |
| (4) | As of December 31, 2008, we had $46.8 of non-current net unrecognized tax benefits under FIN 48. We are not able to provide a reasonably reliable estimate of the timing of future payments relating to these obligations. |
| (5) | Includes various contractual agreements, primarily relating to royalties and subscriptions. |
| (6) | Relates to an agreement to lease space for a data center facility. See Note G to our consolidated financial statements. |
Our operating leases are primarily for office space around the world. While our purchase orders are generally cancelable without penalty, certain vendor agreements provide for percentage-based cancellation fees or minimum restocking charges based on the nature of the product or service.
Critical Accounting Policies
Our consolidated financial statements are based on the selection and application of generally accepted accounting principles that require us to make estimates and assumptions about future events that affect the amounts reported in our financial statements and the accompanying notes. Future events and their effects cannot be determined with certainty. Therefore, the determination of estimates requires the exercise of judgment. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and any such differences may be material to our financial statements. We believe that the policies set forth below may involve a higher degree of judgment and complexity in their application than our other accounting policies and represent the critical accounting policies used in the preparation of our financial statements. If different assumptions or conditions were to prevail, the results could be materially different from our reported results. Our significant accounting policies are presented within Note A to our consolidated financial statements.
Accounting for Stock Options
In 2006, we adopted FAS No. 123R, to account for stock-based compensation expense. FAS No. 123R requires recognizing compensation costs for all share-based payment awards made to employees based upon the awards’ estimated grant date fair value. Additionally, we applied the provisions of Security and Exchange Commission’s Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107 on Share-Based Payment to our adoption of FAS No. 123R. Our financial statements include the adoption of FAS No. 123R using the modified prospective transition method of adoption, which does not result in the restatement of results from prior periods.
53
We elected to estimate the fair value of employee stock option awards and the ESPP using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The determination of the fair value of our share-based payment awards on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model is affected by our stock price, as well as assumptions regarding a number of subjective variables. These variables include the expected stock price volatility over the term of the awards, the risk-free interest rate associated with the expected term of the awards, expected dividends and actual and projected employee stock option exercise behaviors. If any of the assumptions used in the Black-Scholes option pricing model change significantly, stock-based compensation expense may differ materially in the future from that recorded in the current period.
The estimation of stock awards that will ultimately vest requires judgment, and to the extent actual results or updated estimates differ from our current estimates, such amounts will be recorded as an adjustment in the period the estimates are revised. Should our actual forfeitures differ from our estimates, this could have a material impact on our financial statements.
Revenue Recognition
We derive revenues from the licensing of software and related services. We recognize revenues for software products and related services in accordance with the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants’ Statement of Position (SOP) 97-2, “Software Revenue Recognition,” as amended. We recognize revenues when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, delivery has occurred, the sales price is fixed or determinable and collectibility is probable. However, determining whether and when some of these criteria have been satisfied often involves assumptions and judgments that can have a significant impact on the timing and amount of revenue we report.
Given the recent economic downturn and global financial crisis, we have applied additional scrutiny and analysis around the collectibility of transactions with certain customers, including but not limited to those customers in the financial services, insurance and automotive industries, and we continue to monitor the appropriateness of established customer credit limits. Our assessment of likelihood of collection is a critical element in determining the timing of revenue recognition. We do not record accounts receivable or deferred revenue or recognize revenue relating to transactions where collectibility is not probable. We experienced an increase in these transactions in the fourth quarter of 2008. We recognize such transactions upon cash collection and recognize revenue as earned in accordance with our revenue recognition policies.
We recognize license revenues from the sale of software when risk of loss transfers, which is generally upon electronic shipment. We license our software under perpetual licenses through our direct sales force and through our channel of distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors and systems integrators. We defer revenues relating to products that have shipped into our channel until our products are sold through the channel. We estimate and record reserves for products that are not sold through the channel based on historical trends and relevant current information. We obtain sell-through information from distributors and certain resellers on a monthly basis and reconcile any estimates, if necessary, made in the previous month. Historically, actual information has not differed materially from the related estimate. For our channel partners who do not report sell-through data, we determine sell-through based on payment of such distributors’ and certain resellers’ accounts receivable balances and other relevant factors. For software sold by x86 system vendors and bundled with their hardware, unless we have a separate license agreement with the end user, revenues are recognized in arrears upon the receipt of binding royalty reports. The accuracy of our reserves depends on our ability to estimate the product sold through the channels and could have a significant impact on the timing and amount of revenue we report.
We offer rebates to certain channel partners, which are recognized as a reduction of revenue at the time the related product sale is recognized. When rebates are based on the set percentage of actual sales, we recognize the costs of the rebates as a reduction of revenue when the underlying revenue is recognized. In cases where rebates are earned if a cumulative level of sales is achieved, we recognize the cost of the rebates as a reduction of revenue proportionally for each sale that is required to achieve the target. The estimated reserves for channel
54
rebates and sales incentives are based on channel partners’ actual performance against the terms and conditions of the programs, historical trends and the value of the rebates. The accuracy of these reserves for these rebates and sales incentives depends on our ability to estimate these items and could have a significant impact on the timing and amount of revenue we report.
With the exception of one of our desktop products, our return policy does not allow end users to return products for a refund. Certain distributors and resellers may rotate stock when new versions of a product are released. We estimate future product returns at the time of sale. Our estimate is based on historical return rates, levels of inventory held by distributors and resellers and other relevant factors. The accuracy of these reserves depends on our ability to estimate sales returns and stock rotation among other criteria. If we were to change any of these assumptions or judgments, it could cause a material increase or decrease in the amount of revenue that we report in a particular period. Returns have not been material to date and have been in line with our expectations.
Our services revenues consist of software maintenance and professional services. We recognize software maintenance revenues ratably over the contract period. Professional services include design, implementation and training. Professional services are not considered essential to the functionality of our products because these services do not alter the product capabilities and may be performed by customers or other vendors. Professional services engagements for which we are able to make reasonably dependable estimates of progress toward completion are recognized on a proportional performance basis based upon the hours incurred. Revenues on all other professional services engagements are recognized upon completion. However, if we were to change any of these assumptions or judgments, it could cause a material increase or decrease in the amount of revenue that we report in a particular period.
Our software products are typically sold with software maintenance and/or professional services. Vendor-specific objective evidence (“VSOE”) of fair value for professional services is based upon the standard rates we charge for such services when sold separately. VSOE of fair value for software maintenance services is established by the rates charged in stand-alone sales of software maintenance contracts or the stated renewal rate for software maintenance included in the license agreement. The revenues allocated to the software license included in multiple element contracts represent the residual amount of the contract after the fair value of the other elements has been determined.
Customers under software maintenance agreements are entitled to receive updates and upgrades on a when-and-if-available basis. In the event specific features, entitlements or release number of an upgrade or new product have been announced but not delivered, and customers will receive that upgrade or new product as part of a current software maintenance contract, a specified upgrade is deemed created and product revenues are deferred on purchases made after the announcement date until delivery of the upgrade or new product. The amount and elements to be deferred are dependent on whether the company has established VSOE of fair value for the upgrade or new product. VSOE of fair value of these upgrades or new products is established based upon the price set by management. We have a history of selling these upgrades or new products on a stand-alone basis. We are required to exercise judgment in determining whether VSOE exists for each undelivered element based on whether our pricing for these elements is sufficiently consistent with the sale of these elements on a stand-alone basis. This could cause a material increase or decrease in the amount of revenue that we report in a particular period.
Capitalized Software Development Costs
Costs related to R&D are generally charged to expense as incurred. Capitalization of material development costs of software to be sold, leased, or otherwise marketed are subject to capitalization beginning when our products’ technological feasibility has been established, which is at the earlier of completion of a detailed product design or a working model, and ending when the product is available for general release, in accordance with the provisions of Financial Accounting Standard No. 86, “Accounting for the Costs of Computer Software to be Sold, Leased, or Otherwise Marketed” (“FAS No. 86”). Judgment is required in determining when
55
technological feasibility of a product is established. Changes in judgment as to when technological feasibility is established, or changes in our business, including our go-to-market strategy, would likely materially impact the amount of costs capitalized. For example, if the length of time between technological feasibility and general availability is less in the future, the amount of costs capitalized would likely decrease. In addition, our R&D expenses and amounts capitalized as software development costs may not be comparable to our peer companies due to differences in judgment as to when a detailed product design or a working model has been completed or differences in judgment regarding when the product is available for general release. FAS No. 86 requires annual amortization expense of capitalized software development costs to be the greater of the amounts computed using the ratio of current gross revenue to a products’ total current and anticipated revenues, or the straight-line method over the product’s remaining estimated economic life. To date, we have amortized these costs using the straight-line method as it is the greater of the two amounts. The ongoing assessment of the recoverability of these costs requires considerable judgment by management with respect to certain external factors such as anticipated future revenue, estimated economic life, and changes in software and hardware technologies. Changes in the periods over which we actually generate revenues or the amounts of revenues generated could result in materially different amounts of amortization.
Amounts capitalized under FAS No. 86 are primarily related to salaries and stock-based compensation of our employees. Because of the significant judgment necessary in applying FAS No. 86, our internal measurements of performance, including our cash bonus programs, are based on results excluding the net effect of amounts capitalized and amortized pursuant to FAS No. 86.
Asset Valuation
Asset valuation includes assessing the recorded value of certain assets, including accounts receivable, other intangible assets, and goodwill. We use a variety of factors to assess valuation, depending upon the asset. Accounts receivable are evaluated based upon the creditworthiness of our customers, historical experience, the age of the receivable and current market and economic conditions. Should current market and economic conditions deteriorate, our actual bad debt experience could exceed our estimate. Other intangible assets are evaluated based upon the expected period during which the asset will be utilized, forecasted cash flows, changes in technology and customer demand. Changes in judgments on any of these factors could materially impact the value of the asset. Our goodwill valuation is based upon a discounted cash flow analysis. The analysis considers estimated revenue and expense growth rates. The estimates are based upon our historical experience and projections of future activity, considering customer demand, changes in technology and a cost structure necessary to achieve the related revenues. Changes in judgments on any of these factors could materially impact the value of the asset.
Accounting for Income Taxes
In calculating our income tax expense, management judgment is necessary to make certain estimates and judgments for financial statement purposes that affect the recognition of tax assets and liabilities.
In order for us to realize our deferred tax assets, we must be able to generate sufficient taxable income in those jurisdictions where the deferred tax assets are located. We record a valuation allowance to reduce our deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized. We consider future market growth, forecasted earnings, future taxable income, and prudent and feasible tax planning strategies in determining the need for a valuation allowance. In the event we were to determine that we would not be able to realize all or part of our net deferred tax assets in the future, an adjustment to the deferred tax assets would be charged to earnings in the period in which we make such determination. Likewise, if we later determine that it is more likely than not that the net deferred tax assets would be realized, we would reverse the applicable portion of the previously provided valuation allowance.
We calculate our current and deferred tax provision based on estimates and assumptions that could differ from the actual results reflected in income tax returns filed during the subsequent year. Adjustments based on filed returns are generally recorded in the period when the tax returns are filed.
56
The amount of income tax we pay is subject to audits by federal, state and foreign tax authorities, which may result in proposed assessments. Our estimate of the potential outcome for any uncertain tax issue is highly judgmental. We believe we have adequately provided for any reasonably foreseeable outcome related to these matters. However, our future results may include favorable or unfavorable adjustments to our estimated tax liabilities in the period the assessments are made or resolved, audits are closed or when statutes of limitation on potential assessments expire. Additionally, the jurisdictions in which our earnings or deductions are realized may differ from our current estimates. As a result, our effective tax rate may fluctuate significantly on a quarterly basis.
We do not provide for a U.S. income tax liability on undistributed earnings of our foreign subsidiaries. The earnings of non-U.S. subsidiaries, which reflect full provision for non-U.S. income taxes, are indefinitely reinvested in non-U.S. operations or will be remitted substantially free of additional tax.
Income taxes are calculated on a separate tax return basis, although we are included in the consolidated tax return of EMC. The difference between the income taxes payable that is calculated on a separate return basis and the amount actually paid to EMC pursuant to our tax sharing agreement with EMC is presented as a component of additional paid-in capital.
New Accounting Pronouncements
We adopted Financial Accounting Standards (“FAS”) No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements” (“FAS No. 157”) on January 1, 2008. FAS No. 157 defines fair value, establishes a methodology for measuring fair value and expands the required disclosure for fair value measurements. The adoption of FAS No. 157 did not have a material impact on our financial position and results of operations. In February 2008, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued FASB Staff Position No. FAS 157-2, “Effective Date of FASB Statement No. 157” (“FSP FAS No. 157-2”), which delays the effective date of FAS No. 157 from 2008 to 2009 for non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities, except for items that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a recurring basis (at least annually). Although we will continue to evaluate the application of FAS 157-2, we do not currently believe adoption will have a material impact on our financial position and results of operations.
In December 2007, the FASB issued FAS No. 141R. This statement establishes principles and requirements for how the acquirer in a business combination (i) recognizes and measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree, (ii) recognizes and measures the goodwill acquired in the business combination or a gain from a bargain purchase, and (iii) determines what information to disclose to enable users of the financial statements to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the business combination. We adopted FAS No. 141R, which is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The impact of the standard on our financial position and results of operation will be dependent upon the number of and magnitude of acquisitions that are consummated subsequent to adoption.
In December 2007, the FASB issued FAS No. 160, “Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements—an amendment of ARB No. 51” (“FAS No. 160”). The objective of this statement is to improve the relevance, comparability, and transparency of the financial information that a reporting entity provides in its consolidated financial statements by establishing accounting and reporting standards for the noncontrolling interest in a subsidiary and therefore deconsolidation of a subsidiary. FAS No. 160 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. We do not expect the standard to have a material impact on our financial position and results of operations.
In April 2008, the FASB issued a new position on FAS No. 142-3 titled “Determination of the Useful Life of Intangible Assets.” It amends the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under FAS No. 142, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets.” The intent is to improve the consistency between the useful life of a recognized
57
intangible asset under FAS No. 142 and the period of expected cash flows used to measure the fair value of the asset under FAS No. 141R, “Business Combinations”, and other U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. This position is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. We do not expect the standard to have a material impact on our financial position and results of operations.
In November 2008, the FASB ratified EITF Issue No. 08-7, “Accounting for Defensive Intangible Assets” (“EITF 08-7”). EITF 08-7 applies to defensive intangible assets, which are acquired intangible assets that the acquirer does not intend to actively use but intends to hold to prevent its competitors from obtaining access to them. As these assets are separately identifiable, EITF 08-7 requires an acquiring entity to account for defensive intangible assets as a separate unit of accounting. Defensive intangible assets must be recognized at fair value in accordance with FAS No. 141R and FAS No. 157. EITF 08-7 is effective for defensive intangible assets acquired in fiscal years beginning on or after December 15, 2008. The impact of the standard on our financial position and results of operation will be dependent upon the type of acquisitions that are consummated subsequent to adoption.
| ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Foreign Exchange Risk
International revenues as a percentage of total revenues were 48% in 2008, 46% in 2007 and 44% in 2006. Our revenue contracts are denominated in U.S. Dollars and the vast majority of our purchase contracts are denominated in U.S. Dollars. A portion of our cost of revenues, primarily the cost of personnel to deliver technical support on our products and professional services, and a portion of our operating expenses related to sales and sales support and research and development, are denominated in foreign currencies, primarily the Euro, the British Pound, the Canadian Dollar, the Australian Dollar, the Indian Rupee, and the Japanese Yen. These costs and the resulting effect on operating income are exposed to foreign exchange rate fluctuations. Upon consolidation, as exchange rates vary, operating expenses may differ materially from expectations. For example, the amount of our operating lease commitments may fluctuate in response to changes in the exchange rate between the U.S. Dollar and foreign currencies as several of our operating leases are payable in foreign currencies.
We do not hedge our exposure to foreign currency fluctuation. As a result of fluctuations in the exchange rates between the U.S. Dollar and foreign currencies, operating income was negatively impacted by $10.6 million in 2008, $18.6 million in 2007 and $2.8 million in 2006. Based upon planned spending in 2009, if the Dollar weakened by 10% in 2009 in relation to the Euro, the British Pound, the Japanese Yen, the Indian Rupee, the Australian Dollar, and the Canadian Dollar, this would result in additional expense of approximately $35 million.
Interest Rate Risk
Our exposure to market risk relates primarily to the variable interest obligation on the note we incurred to fund an $800.0 million dividend to EMC Corporation. The dividend was declared in April 2007, but given retroactive effect as of December 31, 2006. The note may be repaid, without penalty, at any time. Subsequent to receiving the proceeds from our IPO in August 2007, we repaid $350.0 million of principal on the note. No repayments of principal were made during 2008. The note matures in April 2012 and bears an interest rate of the 90-day LIBOR plus 55 basis points, with interest payable quarterly in arrears. The interest rate on the note resets quarterly and is determined on the two business days prior to the first day of each fiscal quarter. The interest rate on the note payable as of December 31, 2008 was 4.43%, and the weighted-average interest rate on the note payable for 2008 was 4.14%. We expect our interest expense on the note payable to decrease in the first quarter of 2009 as a result of an approximately 245 basis point decrease in the first quarter interest rate from the rate used in the fourth quarter of 2008. If the interest rate on the note payable were to change 100 basis points from the December 31, 2008 rate and assuming no payments on the principal were made during 2009, our annual interest expense would change by $4.5 million.
58
| ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
VMware, Inc.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SCHEDULE
Note: All other financial statement schedules are omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is included in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
59
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors of VMware, Inc.:
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the accompanying index present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of VMware, Inc. and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2008 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule listed in the accompanying index presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedule, and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits (which was an integrated audit in 2008). We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company, (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company, and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
San Jose, California
February 20, 2009
60
VMware, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 1,840,812 | | $ | 1,231,168 | |
Accounts receivable, less allowance for doubtful accounts of $1,690 and $1,603 | | | 338,014 | | | 283,824 | |
Deferred tax asset, current portion | | | 44,573 | | | 54,386 | |
Income taxes receivable from EMC | | | 111,050 | | | — | |
Other current assets | | | 55,639 | | | 33,956 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total current assets | | | 2,390,088 | | | 1,603,334 | |
Property and equipment, net | | | 418,212 | | | 276,983 | |
Other assets, net | | | 134,553 | | | 71,695 | |
Deferred tax asset, net of current portion | | | 68,280 | | | 72,249 | |
Intangible assets, net | | | 56,984 | | | 32,073 | |
Goodwill | | | 771,088 | | | 639,366 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 3,839,205 | | $ | 2,695,700 | |
| | | | | | | |
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | | |
| | |
Current liabilities: | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable | | $ | 88,647 | | $ | 61,503 | |
Accrued expenses | | | 197,580 | | | 171,770 | |
Due to EMC, net | | | 33,407 | | | 2,759 | |
Income taxes payable | | | 15,761 | | | 68,823 | |
Deferred revenue, current portion | | | 544,355 | | | 363,317 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total current liabilities | | | 879,750 | | | 668,172 | |
Note payable to EMC | | | 450,000 | | | 450,000 | |
Deferred revenue, net of current portion | | | 325,634 | | | 189,479 | |
Deferred tax liability | | | 47,825 | | | 27,327 | |
Other liabilities | | | 65,929 | | | 20,105 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 1,769,138 | | | 1,355,083 | |
Commitments and contingencies (see Note J) | | | | | | | |
Stockholders’ equity: | | | | | | | |
Class A common stock, par value $.01; authorized 2,500,000 shares; issued and outstanding 90,448 and 82,924 shares | | | 904 | | | 829 | |
Class B convertible common stock, par value $.01; authorized 1,000,000 shares; issued and outstanding 300,000 shares | | | 3,000 | | | 3,000 | |
Additional paid-in capital | | | 1,836,513 | | | 1,352,788 | |
Retained earnings (accumulated deficit) | | | 229,650 | | | (16,000 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
Total stockholders’ equity | | | 2,070,067 | | | 1,340,617 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | $ | 3,839,205 | | $ | 2,695,700 | |
| | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
61
VMware, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
License | | $ | 1,178,142 | | | $ | 905,368 | | | $ | 491,902 | |
Services | | | 702,885 | | | | 420,443 | | | | 212,002 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 1,881,027 | | | | 1,325,811 | | | | 703,904 | |
Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of license revenues | | | 88,156 | | | | 80,876 | | | | 59,202 | |
Cost of services revenues | | | 215,949 | | | | 137,798 | | | | 64,180 | |
Research and development | | | 429,204 | | | | 285,941 | | | | 151,954 | |
Sales and marketing | | | 654,083 | | | | 450,195 | | | | 238,327 | |
General and administrative | | | 181,110 | | | | 135,660 | | | | 69,602 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | | 312,525 | | | | 235,341 | | | | 120,639 | |
Investment income | | | 28,301 | | | | 22,942 | | | | 2,497 | |
Interest income (expense) with EMC, net | | | (18,316 | ) | | | (17,757 | ) | | | 293 | |
Other expense, net | | | (3,225 | ) | | | (48 | ) | | | (882 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income taxes | | | 319,285 | | | | 240,478 | | | | 122,547 | |
Income tax provision | | | 29,152 | | | | 22,341 | | | | 36,832 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income before cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle | | | 290,133 | | | | 218,137 | | | | 85,715 | |
Cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle, net of tax of $108 | | | — | | | | — | | | | 175 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 290,133 | | | $ | 218,137 | | | $ | 85,890 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income per weighted-average share, basic for Class A and Class B: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income per share before cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle | | $ | 0.75 | | | $ | 0.62 | | | $ | 0.26 | |
Cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income per share | | $ | 0.75 | | | $ | 0.62 | | | $ | 0.26 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income per weighted-average share, diluted for Class A and Class B: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income per share before cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle | | $ | 0.73 | | | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.26 | |
Cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income per share | | $ | 0.73 | | | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.26 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average shares, basic for Class A and Class B | | | 385,068 | | | | 350,493 | | | | 332,500 | |
Weighted-average shares, diluted for Class A and Class B | | | 397,185 | | | | 359,189 | | | | 332,500 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
62
VMware, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 290,133 | | | $ | 218,137 | | | $ | 85,890 | |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 158,628 | | | | 104,027 | | | | 66,573 | |
Stock-based compensation, excluding amounts capitalized | | | 166,516 | | | | 92,406 | | | | 51,226 | |
Excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation | | | (85,776 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Other adjustments | | | 8,663 | | | | (167 | ) | | | 8,776 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts receivable | | | (52,527 | ) | | | (88,969 | ) | | | (97,992 | ) |
Other assets | | | (21,910 | ) | | | (977 | ) | | | (9,076 | ) |
Due to/from EMC, net | | | 40,348 | | | | 5,004 | | | | (48,365 | ) |
Accounts payable | | | 7,713 | | | | 15,571 | | | | 31,762 | |
Accrued expenses | | | 18,229 | | | | 61,620 | | | | 60,904 | |
Income taxes receivable from EMC | | | (111,050 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Income taxes payable | | | 26,623 | | | | (17,812 | ) | | | (6,006 | ) |
Deferred income taxes, net | | | 38,908 | | | | (78,486 | ) | | | (21,888 | ) |
Deferred revenue | | | 315,633 | | | | 242,082 | | | | 158,059 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 800,131 | | | | 552,436 | | | | 279,863 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Additions to property and equipment | | | (191,596 | ) | | | (136,395 | ) | | | (52,574 | ) |
Purchase of headquarters facilities from EMC | | | — | | | | (132,564 | ) | | | — | |
Capitalized software development costs | | | (90,900 | ) | | | (47,735 | ) | | | (32,523 | ) |
Purchase of long-term investment | | | (1,750 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Business acquisitions, net of cash acquired | | | (138,569 | ) | | | (82,535 | ) | | | (46,541 | ) |
Decrease (increase) in restricted cash | | | 928 | | | | (4,466 | ) | | | (10,744 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in investing activities | | | (421,887 | ) | | | (403,695 | ) | | | (142,382 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from issuance of common stock | | | 190,107 | | | | 1,256,293 | | | | — | |
Excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation | | | 85,776 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Shares repurchased for tax withholdings on vesting of restricted stock | | | (44,483 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Repayment of note payable to EMC | | | — | | | | (350,000 | ) | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by financing activities | | | 231,400 | | | | 906,293 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | 609,644 | | | | 1,055,034 | | | | 137,481 | |
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period | | | 1,231,168 | | | | 176,134 | | | | 38,653 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period | | $ | 1,840,812 | | | $ | 1,231,168 | | | $ | 176,134 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash paid for interest | | $ | 20,180 | | | $ | 19,991 | | | $ | 481 | |
Cash paid for taxes | | $ | 74,549 | | | $ | 118,413 | | | $ | 64,074 | |
| | | |
Non-cash items: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Changes in capital additions, accrued but not paid | | $ | 19,566 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Capitalization of facilities under financing lease transaction | | $ | 19,077 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Dividends declared via note payable to EMC | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 800,000 | |
Fair value of stock options issued in acquisition | | $ | 2,388 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 689 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
63
VMware, Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Class A
Common Stock | | | Class B
Convertible
Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-in
Capital | | | Deferred
Compensation | | | Retained
Earnings
(Accumulated
Deficit) | | | Stockholders’
Equity
(Deficit) | |
| | | Shares | | | Par Value | | | Shares | | Par Value | | | | |
Balance, January 1, 2006 | | 32,500 | | | $ | 325 | | | 300,000 | | $ | 3,000 | | $ | 560,649 | | | $ | (110,145 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | 453,829 | |
Cumulative effect of change in accounting principle | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,060 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,060 | |
EMC stock options issued in acquisitions | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 689 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 689 | |
Stock-based compensation | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 60,006 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 60,006 | |
Reclassification of deferred compensation | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (110,145 | ) | | | 110,145 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Charge from tax sharing arrangement (see Note A) | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (32,286 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (32,286 | ) |
Dividends declared | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (479,973 | ) | | | — | | | | (320,027 | ) | | | (800,000 | ) |
Net income | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | 85,890 | | | | 85,890 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2006 | | 32,500 | | | | 325 | | | 300,000 | | | 3,000 | | | — | | | | — | | | | (234,137 | ) | | | (230,812 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issuance of Class A common stock in IPO, net of underwriter fees of $60,530 and other issuance costs of $4,787 | | 37,950 | | | | 380 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,034,853 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,035,233 | |
Issuance of Class A common stock to Intel Capital, net of issuance costs of $200 | | 9,500 | | | | 95 | | | — | | | — | | | 218,205 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 218,300 | |
Issuance of restricted stock, net of cancellations | | 2,974 | | | | 29 | | | — | | | — | | | (29 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Stock-based compensation | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 102,290 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 102,290 | |
Charge from tax sharing arrangement (see Note A) | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,531 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,531 | ) |
Net income | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | 218,137 | | | | 218,137 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2007 | | 82,924 | | | | 829 | | | 300,000 | | | 3,000 | | | 1,352,788 | | | | — | | | | (16,000 | ) | | | 1,340,617 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from issuance of common stock | | 8,247 | | | | 82 | | | — | | | — | | | 190,025 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 190,107 | |
Issuance of stock options in acquisition | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 2,388 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,388 | |
Issuance of restricted stock, net of cancellations | | 104 | | | | 1 | | | — | | | — | | | (1 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Shares repurchased for tax withholdings on vesting of restricted stock | | (827 | ) | | | (8 | ) | | — | | | — | | | 8 | | | | — | | | | (44,483 | ) | | | (44,483 | ) |
Stock-based compensation | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 190,622 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 190,622 | |
Excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 85,776 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 85,776 | |
Credit from tax sharing arrangement (see Note A) | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 5,242 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5,242 | |
Capital contribution by EMC (see Note L) | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 9,665 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 9,665 | |
Net income | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | 290,133 | | | | 290,133 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2008 | | 90,448 | | | $ | 904 | | | 300,000 | | $ | 3,000 | | $ | 1,836,513 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 229,650 | | | $ | 2,070,067 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
64
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
A. The Company and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Company and Background
VMware, Inc. (“VMware” or the “Company”) is the leading provider of virtual infrastructure software solutions from the desktop to the data center. VMware’s virtual infrastructure software solutions run on industry-standard desktops and servers and support a wide range of operating system and application environments, as well as networking and storage infrastructures.
Initial Public Offering
In August 2007, VMware completed its initial public offering (the “IPO”) in which the Company sold 37,950,000 shares (including 4,950,000 shares pursuant to the underwriters’ full exercise of their over-allotment option) of its Class A common stock at a price to the public of $29.00 per share. The net proceeds of the IPO to the Company were $1,035.2 million after deducting the offering expenses and underwriters’ discounts (see Note K). As of December 31, 2008, EMC Corporation (“EMC”) holds approximately 30% of VMware’s Class A common stock and 100% of VMware’s Class B common stock, representing approximately 84% of VMware’s outstanding common stock and 98% of the combined voting power of VMware’s outstanding common stock. As a result, EMC continues to control the Company and is able to exercise control over all matters requiring stockholder approval, including the election of directors and approval of significant corporate transactions.
Accounting Principles
The financial statements and accompanying notes are prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis of Presentation
VMware historically has received, and continues to receive, certain administrative services from EMC, and VMware and EMC engage in certain intercompany transactions. The consolidated financial statements include expense allocations for certain corporate functions provided to VMware by EMC. These allocations were based on estimates of the level of effort or resources incurred on behalf of VMware. Additionally, certain other costs incurred by EMC for the direct benefit of VMware, such as rent, salaries and benefits, plus an estimated arm’s-length mark-up, have been included in VMware’s financial statements. Management believes the assumptions underlying the financial statements and the above allocations are reasonable. However, given that these intercompany transactions did not arise from transactions negotiated at arm’s-length with an unrelated third party, the financial statements included herein may not necessarily reflect results of operations, financial position, and cash flows had VMware engaged in such transactions with an unrelated third party during all periods presented. Accordingly, VMware’s historical financial information is not necessarily indicative of what the Company’s results of operations, financial position, or cash flows will be in the future if and when VMware contracts at arm’s-length with independent third parties for the services the Company has received and currently receives from EMC.
Prior period financial statements have been reclassified to conform to current period presentation.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of VMware and its subsidiaries. All intercompany transactions and balances between VMware and its subsidiaries have been eliminated. All intercompany transactions with EMC in the consolidated statements of cash flows will be settled in cash, and changes in the intercompany balances are presented as a component of cash flows from operating activities.
65
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Use of Accounting Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods, and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements. Estimates are used for, but not limited to, receivable valuation, certain accrued liabilities, useful lives of fixed assets, valuation of acquired intangibles, income taxes, stock-based compensation, and contingencies. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition
VMware derives revenues from the licensing of software and related services. VMware recognizes revenues for software products and related services in accordance with the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants’ Statement of Position (“SOP”) 97-2, “Software Revenue Recognition,” as amended. VMware recognizes revenues when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, delivery has occurred, the sales price is fixed or determinable, and collectibility is probable.
The following summarizes the major terms of VMware’s contractual relationships with customers and the manner in which VMware accounts for sales transactions.
License revenues
VMware recognizes revenues from the sale of software when risk of loss transfers, which is generally upon electronic shipment.
VMware licenses its software under perpetual licenses through its direct sales force and through its channel of distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors, and systems integrators. VMware defers revenues relating to products that have shipped into its channel until its products are sold through the channel. VMware obtains sell-through information from distributors and certain resellers on a monthly basis. For VMware’s channel partners who do not report sell-through data, VMware determines sell-through based on payment of such distributors’ and certain resellers’ accounts receivable balances and other relevant factors. For software sold by x86 system vendors that is bundled with their hardware, unless the Company has a separate license agreement with the end user, revenue is recognized in arrears upon the receipt of binding royalty reports.
For all sales, VMware uses one of the following to constitute evidence of an arrangement:
| | • | | a purchase order or equivalent; |
| | • | | a license agreement and a purchase order or equivalent; |
| | • | | a license agreement which includes language that the agreement also serves as the purchase order; or |
| | • | | a master agreement and a binding royalty report. |
Sales through distributors and resellers are evidenced by a master distribution agreement, together with purchase orders or equivalent, on a transaction-by-transaction basis.
With the exception of one of VMware’s desktop products, VMware’s return policy does not allow end users to return products for a refund. Certain distributors and resellers may rotate stock when new versions of a product are released. VMware estimates future product returns at the time of sale. VMware’s estimate is based on historical return rates, levels of inventory held by distributors and resellers, and other relevant factors. Returns have not been material to date and have been in line with the Company’s expectations.
66
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
VMware offers rebates to certain channel partners. When rebates are based on a set percentage of actual sales, VMware recognizes the cost of the rebates as a reduction of revenues when the underlying revenue is recognized. When rebates are earned only if a cumulative level of sales is achieved, VMware recognizes the cost of the rebates as a reduction of revenues proportionally for each sale that is required to achieve the target.
VMware also offers marketing development funds to certain channel partners. VMware records the cost of the marketing development funds, based on the maximum potential liability, as a reduction of revenues at the time the underlying revenue is recognized.
Services revenues
Services revenues consist of software maintenance and professional services. VMware recognizes software maintenance revenues ratably over the contract period. Professional services include design, implementation, and training. Professional services are not considered essential to the functionality of VMware’s products as these services do not alter the product capabilities and may be performed by customers or other vendors. Professional services engagements for which VMware is able to make reasonably dependable estimates of progress toward completion are recognized on a proportional performance basis based upon the hours incurred. Revenues on all other professional services engagements are recognized upon completion.
Multiple element arrangements
VMware’s software products are typically sold with software maintenance and/or professional services. Vendor-specific objective evidence (“VSOE”) of fair value for professional services is based upon the standard rates VMware charges for such services when sold separately. VSOE of fair value for software maintenance services is established by the rates charged in stand-alone sales of software maintenance contracts or the stated renewal rate for software maintenance included in the license agreement. The revenues allocated to the software license included in multiple element contracts represent the residual amount of the contract after the fair value of the other elements has been determined.
Customers under software maintenance agreements are entitled to receive updates and upgrades on a when-and-if-available basis. In the event specific features, entitlements, or release number of an upgrade or new product have been announced but not delivered, and customers will receive that upgrade or new product as part of a current software maintenance contract, a specified upgrade is deemed created and product revenues are deferred on purchases made after the announcement date until delivery of the upgrade or new product. The amount and elements to be deferred are dependent on whether the company has established VSOE of fair value for the upgrade or new product. VSOE of fair value of these upgrades or new products is established based upon the price set by management. VMware has a history of selling these upgrades or new products on a stand-alone basis.
Deferred revenues include unearned software maintenance fees, professional services fees, and license fees.
Foreign Currency Translation
The U.S. Dollar is the functional currency of VMware’s foreign subsidiaries. Gains and losses from foreign currency transactions are included in other expense, net and were not material in any period presented.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include highly liquid investments with a maturity of 90 days or less at the time of purchase. Cash equivalents consist of money market funds and time deposits. Money market funds are
67
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
considered financial instruments and are subject to the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards (“FAS”) No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements” (“FAS No. 157”). See Note C to VMware’s consolidated financial statements.
Under the terms of various agreements, VMware has restricted cash included in other current assets and other assets, net. The amounts were not material in any period presented.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
VMware maintains an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated probable losses on uncollectible accounts receivable. The allowance is based upon the creditworthiness of VMware’s customers, historical experience, the age of the receivable, and current market and economic conditions. Uncollectible amounts are charged against the allowance account.
Property and Equipment, net
Property and equipment, net are recorded at cost. Depreciation commences upon placing the asset in service and is recognized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets, as follows:
| | |
Buildings | | 39 to 51 years |
Land improvements | | 15 years |
Furniture and fixtures | | 5 years |
Equipment | | 2 to 5 years |
Leasehold improvements | | Lease term, not to exceed 5 years |
Upon retirement or disposition, the asset cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed with any gain or loss recognized as operating expenses in the consolidated statements of income. Repair and maintenance costs that do not extend the economic life of the underlying assets are expensed as incurred.
Research and Development and Capitalized Software Development Costs
Costs related to research and development (“R&D”) are generally charged to expense as incurred. Capitalization of material development costs of software to be sold, leased, or otherwise marketed are subject to capitalization beginning when the Company’s products’ technological feasibility has been established, which is at the earlier of completion of a detailed product design or a working model, and ending when the product is available for general release, in accordance with the provisions of FAS No. 86, “Accounting for the Costs of Computer Software to be Sold, Leased, or Otherwise Marketed.” Judgment is required in determining when technological feasibility of a product is established. Changes in judgment as to when technological feasibility is established, or changes in the Company’s business, including VMware’s go-to-market strategy, would likely materially impact the amount of costs capitalized. For example, if the length of time between technological feasibility and general availability is less in the future, the amount of costs capitalized would likely decrease. In addition, VMware’s R&D expenses and amounts capitalized as software development costs may not be comparable to VMware’s peer companies due to differences in judgment as to when a detailed product design or a working model has been completed or differences in judgment regarding when the product is available for general release. FAS No. 86 requires annual amortization expense of capitalized software development costs to be the greater of the amounts computed using the ratio of current gross revenue to a products’ total current and anticipated revenues, or the straight-line method over the product’s remaining estimated economic life. To date, VMware has amortized these costs using the straight-line method as it is the greater of the two amounts. The
68
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
costs are amortized over periods ranging from 18 to 24 months, which represent the product’s remaining estimated economic life. The ongoing assessment of the recoverability of these costs requires considerable judgment by management with respect to certain external factors such as anticipated future revenue, estimated economic life, and changes in software and hardware technologies. Changes in the periods over which VMware actually generates revenues or the amounts of revenues generated could result in materially different amounts of amortization.
Unamortized software development costs were $128.8 million and $66.8 million as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively, and are included in other assets, net.
For the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, VMware capitalized $113.6 million (including $22.7 million of stock-based compensation), $56.8 million (including $9.1 million of stock-based compensation), and $43.0 million (including $10.5 million of stock-based compensation), respectively, of costs incurred for the development of software products. These amounts have been excluded from R&D on the Company’s accompanying consolidated statements of income. Amortization expense from capitalized amounts was $51.6 million, $36.4 million and $22.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively, and are included in cost of license revenues on the Company’s accompanying consolidated statements of income.
Long-Lived Assets
Intangible assets, other than goodwill, are amortized over their estimated useful lives, during which the assets are expected to contribute directly or indirectly to future cash flows, and which range from one to eleven years. In the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, VMware amortized $17.5 million, $25.7 million, and $25.5 million, respectively, for intangible assets.
VMware reviews long-lived assets for impairment in accordance with FAS No. 144 “Accounting for Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets.” VMware reviews annually for impairment, or more frequently if events or changes in business circumstances indicate that the carrying amounts of the assets may not be fully recoverable or that the useful lives of these assets are no longer appropriate.
Goodwill is carried at its historical cost. VMware tests goodwill for impairment in accordance with FAS No. 142 “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets,” in the fourth quarter of each year or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired.
To date, there have been no impairments of goodwill or other intangible assets.
Advertising
Advertising production costs are expensed as incurred. Advertising expense was $9.4 million, $2.5 million and $1.6 million in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Income Taxes
Income taxes as presented herein are calculated on a separate tax return basis, although VMware is included in the consolidated tax return of EMC. Deferred tax liabilities and assets are recognized for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Deferred tax liabilities and assets are determined based on the difference between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to
69
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
reverse. Tax credits are generally recognized as reductions of income tax provisions in the year in which the credits arise. The measurement of deferred tax assets is reduced by a valuation allowance if, based upon available evidence, it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
VMware does not provide for a U.S. income tax liability on undistributed earnings of VMware’s foreign subsidiaries. The earnings of non-U.S. subsidiaries, which reflect full provision for non-U.S. income taxes, are currently indefinitely reinvested in non-U.S. operations or will be remitted substantially free of additional tax.
The difference between the income taxes payable that is calculated on a separate return basis and the amount actually paid to EMC pursuant to VMware’s tax sharing agreement (see Note H) is presented as a component of additional paid-in capital.
Earnings per Share
Basic net income per share is calculated using the weighted-average number of shares of VMware’s common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share is calculated using the weighted-average number of common shares including the dilutive effect of equity awards as determined under the treasury stock method. For purposes of calculating earnings per share, VMware uses the two-class method. As both classes share the same rights in dividends, basic and diluted earnings per share are the same for both classes.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income is equal to net income.
Concentrations of Risks
Financial instruments, which potentially subject VMware to concentrations of credit risk, consist principally of cash and cash equivalents and accounts receivable. Cash on deposit with banks exceeds the amount of insurance provided on such deposits. These deposits may be redeemed upon demand. VMware places cash and cash equivalents primarily in money market funds and limits the amount of investment with any one issuer. As of December 31, 2008, all of VMware’s domestic money market funds were participating in the Temporary Guarantee Program for Money Market Funds, which is backed by the U.S. Treasury Department but limited to the balance in the money market fund as of September 19, 2008. The Temporary Guarantee Program for Money Market Funds expires on April 30, 2009. VMware monitors the money market portfolio so that investments are placed in funds with dissimilar economic characteristics, thereby diversifying the credit risk. In addition, VMware monitors the counterparty risk to ensure adequate diversification amongst the financial institutions holding the Company’s funds.
VMware provides credit to distributors, resellers, and certain end user customers in the normal course of business. Credit is generally extended to new customers based upon a credit evaluation. Credit is extended to existing customers based on ongoing credit evaluations, prior payment history, and demonstrated financial stability. Given the recent economic downturn and global financial crisis, VMware has applied additional scrutiny and analysis around the collectibility of transactions with certain customers, including but not limited to those customers in the financial services, insurance, and automotive industries, and the Company continues to monitor the appropriateness of established customer credit limits. VMware does not record accounts receivable or deferred revenue or recognize revenue relating to transactions where collectibility is not probable. During the fourth quarter of 2008, VMware experienced an increase in transactions where the Company did not believe collection was probable at the time of sale. The Company recognizes such transactions upon cash collection and recognizes revenue as earned in accordance with the Company’s revenue recognition policies.
70
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
As of December 31, 2008, two distributors accounted for 22% and 20%, respectively, of VMware’s accounts receivable balance. As of December 31, 2007, two distributors accounted for 23% and 19%, respectively, of VMware’s accounts receivable balance.
One distributor accounted for 18%, 23%, and 29% of revenues in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively, and another distributor accounted for 16% and 12% of revenues in 2008 and 2007, respectively. One channel partner accounted for 11% of revenues in both 2008 and 2007, respectively.
Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation
Prior to the adoption of VMware’s Equity and Incentive Plan in June 2007, VMware employees were granted stock options for and restricted stock awards of EMC’s common stock. On January 1, 2006, FAS No. 123R, “Share-Based Payment” (“FAS No. 123R”), became effective. The standard requires recognizing compensation costs for all share-based payment awards made to employees based upon the awards’ estimated grant date fair value. Additionally, VMware applied the provisions of the Securities and Exchange Commission’s (the “SEC”) Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107 on Share-Based Payment to VMware’s adoption of FAS No. 123R. For equity awards made in EMC’s common stock prior to June 2007, and for equity awards made under VMware’s Equity and Incentive Plan, all compensation related to these equity grants has been included as a component of stockholders’ equity for purposes of presentation within these financial statements.
FAS No. 123R was adopted using the modified prospective transition method. Under the modified prospective transition method, FAS No. 123R applies to new equity awards and to equity awards modified, repurchased, or canceled after the adoption date. Additionally, compensation cost for the portion of awards granted prior to the adoption date for which the requisite service has not been rendered as of the adoption date is recognized as the requisite service is rendered. The compensation cost for that portion of awards is based on the grant-date fair value of those awards as calculated in the prior period pro forma disclosures under FAS No. 123, “Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation” (“FAS No. 123”), as reported by EMC. The compensation cost for those earlier awards is attributed to periods beginning on or after the adoption date using the attribution method that was used under FAS No. 123, which was the straight-line method. Instead of recognizing forfeitures only as they occur under FAS No. 123, VMware estimates an expected forfeiture rate which is utilized to determine VMware’s expense. Deferred compensation which related to those earlier awards was eliminated against additional paid-in capital in conjunction with the adoption of FAS No. 123R.
For stock options, VMware has utilized the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to determine the fair value of VMware’s stock option awards. For equity-based awards, VMware recognizes compensation cost on a straight-line basis over the awards’ vesting periods for those awards which contain only a service vesting feature. For awards with performance conditions, management evaluates the criteria in each grant to determine the probability that the performance condition will be achieved.
New Accounting Pronouncements
VMware adopted FAS No. 157 on January 1, 2008. FAS No. 157 defines fair value, establishes a methodology for measuring fair value and expands the required disclosure for fair value measurements. The adoption of FAS No. 157 did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations. In February 2008, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued FASB Staff Position No. FAS 157-2, “Effective Date of FASB Statement No. 157” (“FSP FAS No. 157-2”), which delays the effective date of FAS No. 157 from 2008 to 2009 for non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities, except for items that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a recurring basis (at least
71
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
annually). Although VMware will continue to evaluate the application of FAS 157-2, the Company does not currently believe adoption will have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations.
In December 2007, the FASB issued FAS No. 141 (revised 2007), “Business Combinations” (“FAS No. 141R”). This statement establishes principles and requirements for how the acquirer in a business combination (i) recognizes and measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree, (ii) recognizes and measures the goodwill acquired in the business combination or a gain from a bargain purchase, and (iii) determines what information to disclose to enable users of the financial statements to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the business combination. VMware adopted FAS No. 141R, which is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. The impact of the standard on VMware’s financial position and results of operation will be dependent upon the number of and magnitude of acquisitions that are consummated subsequent to adoption.
In December 2007, the FASB issued FAS No. 160, “Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements—an amendment of ARB No. 51” (“FAS No. 160”). The objective of this statement is to improve the relevance, comparability, and transparency of the financial information that a reporting entity provides in its consolidated financial statements by establishing accounting and reporting standards for the noncontrolling interest in a subsidiary and therefore deconsolidation of a subsidiary. FAS No. 160 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008. VMware does not expect the standard to have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations.
In April 2008, the FASB issued a new position on FAS No. 142-3 titled “Determination of the Useful Life of Intangible Assets.” It amends the factors that should be considered in developing renewal or extension assumptions used to determine the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under FAS No. 142, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets.” The intent is to improve the consistency between the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under FAS No. 142 and the period of expected cash flows used to measure the fair value of the asset under FAS No. 141R, and other U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. This position is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. VMware does not expect the standard to have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations.
In November 2008, the FASB ratified EITF Issue No. 08-7, “Accounting for Defensive Intangible Assets” (“EITF 08-7”). EITF 08-7 applies to defensive intangible assets, which are acquired intangible assets that the acquirer does not intend to actively use but intends to hold to prevent its competitors from obtaining access to them. As these assets are separately identifiable, EITF 08-7 requires an acquiring entity to account for defensive intangible assets as a separate unit of accounting. Defensive intangible assets must be recognized at fair value in accordance with FAS No. 141R and FAS No. 157. EITF 08-7 is effective for defensive intangible assets acquired in fiscal years beginning on or after December 15, 2008. The impact of the standard on the Company’s financial position and results of operation will be dependent upon the type of acquisitions that are consummated subsequent to adoption.
B. Net Income per Share
Basic net income per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period. For purposes of computing basic net income per share, the weighted-average number of outstanding shares of common stock excludes potentially dilutive securities. Diluted net income per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of common shares
72
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
outstanding and potentially dilutive securities outstanding during the period. Potentially dilutive securities include stock options, unvested restricted stock units, unvested restricted stock awards, and other unvested restricted stock, using the treasury stock method. Securities are excluded from the computations of diluted net income per share if their effect would be anti-dilutive. As of December 31, 2008, VMware had 89.5 million shares of Class A common stock and 300.0 million shares of Class B common stock outstanding that were included in the calculation of basic earnings per share. For purposes of calculating earnings per share, VMware uses the two-class method. As both classes share the same rights in dividends, basic and diluted earnings per share are the same for both classes.
The following table sets forth the computations of basic and diluted net income per share (in thousands, except per share data):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
Net income | | $ | 290,133 | | $ | 218,137 | | $ | 85,890 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average shares, basic for Class A and Class B | | | 385,068 | | | 350,493 | | | 332,500 |
Effect of dilutive securities | | | 12,117 | | | 8,696 | | | — |
| | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average shares, diluted for Class A and Class B | | | 397,185 | | | 359,189 | | | 332,500 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Net income per weighted-average share, basic for Class A and Class B | | $ | 0.75 | | $ | 0.62 | | $ | 0.26 |
Net income per weighted-average share, diluted for Class A and Class B | | $ | 0.73 | | $ | 0.61 | | $ | 0.26 |
For the year ended December 31, 2008, 11.4 million stock options to acquire VMware Class A common stock and 5.4 million shares of restricted stock were excluded from the diluted earnings per share calculations because their effect would have been anti-dilutive. For the year ended December 31, 2007, stock options to acquire 2.2 million of VMware Class A common stock were excluded from the diluted earnings per share calculations because their effect would have been anti-dilutive. For the year ended December 31, 2006, there was no difference between basic and diluted earnings per share because there were no outstanding options to purchase shares of VMware common stock or other potentially dilutive securities outstanding.
C. Fair Value Measurements
FAS No. 157 clarifies that fair value is an exit price, representing the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. As such, fair value is a market-based measurement that should be determined based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. As a basis for considering such assumptions, FAS No. 157 establishes a three-tier value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value as follows: (Level 1) observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets, (Level 2) inputs other than the quoted prices in active markets that are observable either directly or indirectly, and (Level 3) unobservable inputs in which there is little or no market data, which requires VMware to develop its own assumptions. This hierarchy requires VMware to use observable market data, when available, and to minimize the use of unobservable inputs when determining fair value.
VMware’s cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2008 were $1,840.8 million and included $1,359.0 million of money market securities, which are classified within Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy because the securities are valued using quoted prices in active markets for identical assets. There were no other financial assets or liabilities carried at fair value as of December 31, 2008.
73
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
D. Business Acquisitions, Goodwill, and Intangible Assets
Business Acquisitions
On July 1, 2008, VMware acquired all of the outstanding capital stock of a privately-held application performance management software company with headquarters in San Mateo, California, and principal R&D facilities in Herzliya, Israel. The results of this company’s operations have been included in VMware’s consolidated financial statements since that date.
The following table summarizes the estimated fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed in this acquisition as of December 31, 2008 (in thousands):
| | | | |
Cash | | $ | 216 | |
Intangible assets | | | 18,503 | |
Goodwill | | | 56,483 | |
Assets acquired | | | 2,831 | |
Total liabilities assumed | | | (17,209 | ) |
| | | | |
Total purchase price | | $ | 60,824 | |
| | | | |
Cash consideration | | $ | 58,436 | |
Value of options assumed | | | 2,388 | |
| | | | |
Total consideration | | $ | 60,824 | |
| | | | |
In addition to the above acquisition, VMware acquired six companies during 2008 for aggregate cash consideration of $80.3 million, net of cash acquired and including transaction costs. In connection with these acquisitions, the Company acquired technologies that are complementary to VMware’s core virtualization technology. The results of operations of all acquired companies have been included in VMware’s consolidated financial statements since their respective acquisition dates. Acquired intangibles totaled $23.9 million, consisted primarily of purchased technology, and have a weighted-average estimated useful life of 7.1 years. The excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired was $69.9 million and is classified as goodwill on the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2008.
The purchase prices for the companies acquired in 2008 have been allocated to the assets acquired and the liabilities assumed based on estimated fair values as of the respective acquisition dates. The purchase price allocations may be adjusted. On January 1, 2009, VMware adopted FAS No. 141R, which requires that any adjustments recognized within the measurement period are recorded to goodwill. Adjustments recognized outside the measurement period are recorded as reductions to VMware’s consolidated statements of income. While VMware does not expect any adjustments to be material, a final determination of required purchase accounting adjustments will be made upon finalization of integration activities and resolution of certain tax contingencies.
In 2007, VMware acquired four companies for aggregate cash consideration of $82.5 million, net of cash acquired and including transaction costs. None of the acquisitions were individually material. Acquired intangibles totaled $14.3 million and have a weighted-average estimated useful life of 6.2 years. The excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired was $81.1 million and is classified as goodwill on the consolidated balance sheets, which reflects adjustments in 2008 to finalize the purchase price allocation.
Pro forma results of operations have not been presented for the aforementioned acquisitions as the results of the acquired companies, either individually or in the aggregate, were not material to the Company’s consolidated results of operations in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006.
74
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Goodwill
Changes in the carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 consist of the following (table in thousands):
| | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended
December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 |
Balance, beginning of the year | | $ | 639,366 | | $ | 560,482 |
Goodwill acquired | | | 126,393 | | | 75,843 |
Adjustments to purchase price allocations | | | 5,329 | | | 3,041 |
| | | | | | |
Balance, end of the year | | $ | 771,088 | | $ | 639,366 |
| | | | | | |
Intangible Assets, net
Intangible assets, net, excluding goodwill, as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, consist of the following (dollar amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
2008 | | Weighted-
Average
Useful
Lives
(in years) | | Gross Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | | Net Book
Value |
Purchased technology | | 5.3 | | $ | 151,922 | | $ | (103,135 | ) | | $ | 48,787 |
Trademarks and tradenames | | 5.0 | | | 7,580 | | | (7,580 | ) | | | — |
Customer relationships and customer lists | | 6.8 | | | 11,994 | | | (4,629 | ) | | | 7,365 |
Other | | 4.6 | | | 6,618 | | | (5,786 | ) | | | 832 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total intangible assets, net, excluding goodwill | | | | $ | 178,114 | | $ | (121,130 | ) | | $ | 56,984 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
2007 | | Weighted-
Average
Useful
Lives
(in years) | | Gross Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | | Net Book
Value |
Purchased technology | | 5.1 | | $ | 115,210 | | $ | (91,857 | ) | | $ | 23,353 |
Trademarks and tradenames | | 5.0 | | | 7,580 | | | (5,146 | ) | | | 2,434 |
Customer relationships and customer lists | | 7.2 | | | 7,290 | | | (2,886 | ) | | | 4,404 |
Other | | 5.0 | | | 5,660 | | | (3,778 | ) | | | 1,882 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total intangible assets, net, excluding goodwill | | | | $ | 135,740 | | $ | (103,667 | ) | | $ | 32,073 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Amortization expense on intangibles was $17.5 million, $25.7 million and $25.5 million in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Based on intangible assets recorded as of December 31, 2008 and assuming no subsequent additions or impairment of the underlying assets, the remaining estimated annual amortization expense is expected to be as follows (table in thousands):
| | | |
2009 | | $ | 13,113 |
2010 | | | 11,853 |
2011 | | | 11,799 |
2012 | | | 10,590 |
2013 | | | 3,540 |
Thereafter | | | 6,089 |
| | | |
Total | | $ | 56,984 |
| | | |
75
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
E. Property and Equipment, net
Property and equipment, net, as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 consist of the following (table in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
Equipment and software | | $ | 284,458 | | | $ | 156,641 | |
Buildings and improvements | | | 182,118 | | | | 129,752 | |
Construction in progress | | | 66,663 | | | | 32,097 | |
Furniture and fixtures | | | 45,904 | | | | 30,678 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total property and equipment | | | 579,143 | | | | 349,168 | |
Accumulated depreciation | | | (160,931 | ) | | | (72,185 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Total property and equipment, net | | $ | 418,212 | | | $ | 276,983 | |
| | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2008, construction in progress includes $53.3 million related to both costs paid directly by the Company and costs paid by the builder (lessor) on a leased data center facility for which VMware is considered to be the owner for accounting purposes. See Note G to VMware’s consolidated financial statements.
Depreciation expense was $89.5 million, $41.9 million and $18.7 million in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
During the second quarter of 2008, VMware reviewed and revised the estimated useful lives of certain assets after considering (i) the estimated future benefits the Company expects to receive from those assets, (ii) the pattern of consumption of those benefits, and (iii) the information available regarding those benefits, and prospectively increased the estimated useful lives of computers and other related equipment from 2 years to 3 years to match the length of the related warranty contracts. In the year ended December 31, 2008, these changes in estimates reduced depreciation expense by $10.4 million and increased both basic and diluted earnings per share by $0.02, from what would have been reported otherwise in the year ended December 31, 2008.
In August 2007, VMware used a portion of the net IPO proceeds to purchase its new headquarters facilities from EMC for $132.6 million.
F. Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 consist of the following (table in thousands):
| | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 |
Salaries, commissions, and benefits | | $ | 105,529 | | $ | 93,678 |
Accrued partner liabilities | | | 52,914 | | | 42,852 |
Other | | | 39,137 | | | 35,240 |
| | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 197,580 | | $ | 171,770 |
| | | | | | |
Accrued partner liabilities referenced in the table above relate to rebates and marketing development fund accruals for channel partners, x86 system vendors, and system integrators.
76
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
G. Long-Term Debt
Note Payable to EMC
In April 2007, VMware declared an $800.0 million dividend to EMC paid in the form of a note payable. This dividend was given retroactive effect as of December 31, 2006. The dividend was first applied against retained earnings until that was reduced to zero, then applied against additional paid-in capital until that was reduced to zero, with the remainder then allocated as a further reduction of retained earnings. The note matures in April 2012, with interest payable quarterly in arrears commencing June 30, 2007. The interest rate resets quarterly and bears an interest rate of the 90-day LIBOR plus 55 basis points. The weighted-average interest rate for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 was 4.14% and 5.86%, respectively. In the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, $18.6 million and $26.6 million of interest expense was recorded related to the note payable. The note may be repaid, without penalty, at any time commencing July 2007. Subsequent to receiving the proceeds from the IPO in August 2007, VMware repaid $350.0 million of principal on the note. No repayments of principal were made during 2008.
Financing Liability Related to Data Center
In April 2008, VMware entered into an agreement to lease space for a data center facility. The lease has a term of 16 years with a termination option at the end of the tenth year and the option to take over additional building space. Significant leasehold improvements were under construction at December 31, 2008 as the building had never been occupied or improved for occupancy prior to VMware’s occupation of the facility.
VMware is considered to be the owner of the construction project for accounting purposes under Emerging Issues Task Force Issue No. 97-10, “The Effect of Lessee Involvement in Asset Construction” (“EITF 97-10”) as the tenant improvements are considered structural in nature and VMware is primarily responsible for the cost of these improvements.
In accordance with EITF 97-10, VMware capitalized the fair value of the portion of the building that it leases with a corresponding credit to a financing liability. The capitalized fair value was determined using the cost approach, which measures the value of an asset as the cost to reconstruct or replace it with another asset of like utility. As of December 31, 2008, the fair value of the building was $19.1 million and the corresponding financing liability related to the data center was approximately $19.8 million. The fair value of the building is included in property and equipment, net, and the financing liability is included in other liabilities on the Company’s accompanying consolidated balance sheet.
H. Income Taxes
The domestic and foreign components of income before provisions for income taxes were as follows (table in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
Domestic | | $ | 63,588 | | $ | 42,877 | | $ | 40,569 |
International | | | 255,697 | | | 197,601 | | | 81,978 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 319,285 | | $ | 240,478 | | $ | 122,547 |
| | | | | | | | | |
77
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
VMware’s provision for income taxes consists of the following (table in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | �� | For the Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Federal: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Current | | $ | (27,524 | ) | | $ | 86,279 | | | $ | 53,101 | |
Deferred | | | 38,348 | | | | (74,640 | ) | | | (20,083 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 10,824 | | | | 11,639 | | | | 33,018 | |
State: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Current | | | (824 | ) | | | 5,413 | | | | 3,096 | |
Deferred | | | 4,044 | | | | (3,846 | ) | | | (2,184 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 3,220 | | | | 1,567 | | | | 912 | |
Foreign: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Current | | | 18,592 | | | | 9,135 | | | | 2,902 | |
Deferred | | | (3,484 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 15,108 | | | | 9,135 | | | | 2,902 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total provision for income taxes | | $ | 29,152 | | | $ | 22,341 | | | $ | 36,832 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
A reconciliation of VMware’s income tax rate to the statutory federal tax rate is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Statutory federal tax rate | | 35.0 | % | | 35.0 | % | | 35.0 | % |
State taxes, net of federal benefit | | 1.0 | % | | 0.7 | % | | 0.7 | % |
Tax rate differential for international jurisdictions | | (23.3 | %) | | (25.0 | %) | | (21.0 | %) |
U.S. tax credits | | (6.7 | %) | | (4.5 | %) | | (4.9 | %) |
Permanent items and other | | 3.1 | % | | 3.1 | % | | 20.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
Effective tax rate | | 9.1 | % | | 9.3 | % | | 30.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
78
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
The components of the current and non-current deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows (table in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
| | | Deferred Tax
Asset | | | Deferred Tax
Liability | | | Deferred Tax
Asset | | Deferred Tax
Liability | |
Current: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accruals and allowances | | $ | 18,169 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 8,839 | | $ | — | |
Deferred revenue | | | 29,451 | | | | — | | | | 44,683 | | | — | |
Net operating loss carryforwards | | | 2,888 | | | | — | | | | 864 | | | — | |
Valuation allowance | | | (5,935 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total current | | | 44,573 | | | | — | | | | 54,386 | | | — | |
| | | | |
Non-current: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Property, plant and equipment, net | | | — | | | | (16,927 | ) | | | — | | | (571 | ) |
Intangible and other, net | | | — | | | | (30,898 | ) | | | — | | | (26,756 | ) |
Stock-based compensation | | | 34,756 | | | | — | | | | 23,434 | | | — | |
Deferred revenue | | | 17,116 | | | | — | | | | 44,068 | | | — | |
Tax credit and net operating loss carryforwards | | | 25,867 | | | | — | | | | 4,747 | | | — | |
Valuation allowance | | | (9,459 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total non-current | | | 68,280 | | | | (47,825 | ) | | | 72,249 | | | (27,327 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total deferred tax assets and liabilities | | $ | 112,853 | | | $ | (47,825 | ) | | $ | 126,635 | | $ | (27,327 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
VMware has federal net operating loss carryforwards of $29.2 million from acquisitions in 2008, 2007 and 2006. These carryforwards expire at different periods through 2027. Portions of these carryforwards are subject to annual limitations. VMware expects to be able to fully use these net operating losses against future income. Also resulting from 2008, 2007 and 2006 acquisitions, VMware has state net operating loss carryforwards of $25.2 million expiring at different periods through 2029. A valuation allowance was recorded to reduce gross deferred tax assets to an amount VMware believes is more likely than not to be realized. The valuation allowance is attributable to the uncertainty regarding the realization of state tax credit carryforward benefits. VMware has non-U.S. net operating losses of $10.8 million resulting from non-U.S. acquisitions in 2008 and 2007. Certain of these net operating losses will begin to expire in 2012, while others have an unlimited carryforward period. VMware expects to be able to fully use these net operating losses against future non-U.S. income.
U.S. income taxes have not been provided on certain undistributed earnings of non-U.S. subsidiaries of approximately $426.9 million and $181.9 million at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively, because such earnings are considered to be reinvested indefinitely outside of the U.S., and it is not practicable to estimate the amount of tax that may be payable upon distribution. Income before income taxes from foreign operations in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 was $255.7 million, $197.6 million and $82.0 million, respectively.
As of December 31, 2008, VMware had a net income tax receivable of $111.1 million, which was principally comprised of amounts due from EMC. The receivable arose because VMware had a stand-alone taxable loss for the year ended December 31, 2008, which was primarily attributable to tax deductions arising from both non-qualified stock option exercises and from restricted stock when the restrictions lapsed. Under the tax sharing agreement with EMC, EMC is obligated to pay to VMware an amount equal to the tax benefit that EMC will recognize on its consolidated tax return.
79
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
The difference between the income taxes payable that is calculated on a separate return basis and the amount actually paid to EMC pursuant to VMware’s tax sharing agreement is presented as a component of additional paid-in capital. These differences resulted in an increase in additional paid-in capital of $5.2 million in the year ended December 31, 2008 and a decrease in additional paid-in capital of $2.5 million in the year ended December 31, 2007.
VMware adopted FASB Interpretation No. 48, “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes” (“FIN 48”), on January 1, 2007.
As of December 31, 2007, VMware had $18.3 million of net unrecognized tax benefits, of which, if recognized, $12.3 million would be a reduction to income tax expense impacting the effective income tax rate and $5.9 million would be a reduction to goodwill. As of December 31, 2008, VMware had $46.8 million of net unrecognized tax benefits (net of federal tax benefit), of which, if recognized, $30.1 million would be a reduction to income tax expense impacting the effective income tax rate and $16.7 million would be a reduction to goodwill. As noted below, VMware adopted FAS No. 141R on January 1, 2009. As a result, some portion of the $16.7 million will be a reduction to goodwill if recognized within the measurement period. Any remaining amount that is recognized outside the measurement period will be a reduction to tax expense. The Company cannot reasonably estimate the amounts that would be recorded to goodwill and the Company’s consolidated statement of income. It is reasonably possible that VMware may pay an immaterial amount of the $46.8 million of net unrecognized tax benefits within the next 12 months. However, based on the status of audit examinations and the protocol of finalizing audits, it is not possible to estimate the amount to be paid within the next 12 months. The $46.8 million of net unrecognized tax benefits were classified as a non-current liability on the consolidated balance sheet. As discussed in Note A, VMware adopted FAS No. 141R on January 1, 2009. FAS No. 141R amends the guidance in FAS No. 109, “Accounting for Income Taxes” (“FAS No. 109”) and FIN 48 on the accounting for changes in assumed liabilities for acquired income tax uncertainties. As a result of the amendments, the manner in which changes in liabilities for income tax uncertainties are recognized is consistent with the general requirements of FAS No. 141R for adjustments during the measurement period, which adjust the accounting for the business combination, and adjustments outside of the measurement period, which do not result in adjustments to the accounting for the business combination. Accordingly, changes in a liability for an assumed income tax uncertainty will be recognized as an element of the business combination if the change occurs during the measurement period, or as an adjustment to income tax expense and not as an adjustment to the accounting for the business combination. This represents a significant change from the requirements under FAS No. 141, “Business Combinations”, and FAS No. 109, before the effective date of FAS No. 141R. Under that literature, changes in liabilities for acquired income tax uncertainties were accounted for as an element of the business combination, generally as a reduction to goodwill.
VMware recognizes interest expense and penalties related to income tax matters in the income tax provision. VMware had accrued $0.3 million of interest as of January 1, 2008 and $1.2 million of interest as of December 31, 2008 associated with unrecognized tax benefits. These amounts are included as components of the $18.3 million net unrecognized tax benefits and $46.8 million net unrecognized tax benefits, respectively, as noted above. Income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2008 included interest of $0.9 million associated with uncertain tax positions.
80
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of gross unrecognized tax benefits, excluding interest associated with unrecognized tax benefits, is as follows (table in thousands):
| | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended
December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 |
Balance, beginning of the year | | $ | 19,198 | | | $ | 5,160 |
Tax positions related to current year: | | | | | | | |
Additions | | | 30,089 | | | | 14,038 |
Tax positions related to prior years: | | | | | | | |
Additions | | | 503 | | | | — |
Foreign currency effects | | | (1,383 | ) | | | — |
| | | | | | | |
Balance, end of the year | | $ | 48,407 | | | $ | 19,198 |
| | | | | | | |
There were no settlements during 2008. Due to the increased complexity in international operations, including judgments in determining the appropriate tax jurisdictions for revenue and expense items, the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits will likely increase in 2009. The Company cannot reasonably estimate the increase.
VMware is subject to U.S. federal income tax and various states, local, and international income taxes in numerous jurisdictions. VMware’s domestic and international tax liabilities are subject to the allocation of revenues and expenses in different jurisdictions and the timing of recognizing revenues and expenses. Additionally, the amount of income taxes paid is subject to the VMware’s interpretation of applicable tax laws in the jurisdictions in which it files.
VMware’s 2005 and 2006 federal income tax audits are ongoing and are expected to conclude in 2009. The U.S. federal income tax audit for 2007 and 2008 is expected to commence during 2009. VMware has income tax audits in progress in numerous states, local and international jurisdictions in which it operates. In the VMware international jurisdictions that comprise a significant portion of its operations, the years that may be examined vary, with the earliest year being 2004. Based on the outcome of examinations of VMware, the result of the expiration of statutes of limitations for specific jurisdictions or the result of ruling requests from taxing authorities, it is reasonably possible that the related unrecognized tax benefits could change from those recorded in the statement of financial position. It is possible that one or more of these audits may be finalized within the next twelve months. However, based on the status of examinations, and the protocol of finalizing audits, it is not possible to estimate the impact of such changes, if any, to the previously recorded uncertain tax positions.
I. 401(k) Plan
Prior to March 2008, VMware employees participated in the EMC Corporation 401(k) Savings Plan (the “EMC Plan”), and EMC cross-charged VMware for the costs associated with VMware employees who participated in the EMC Plan.
In 2008, VMware established a defined contribution retirement savings program, the VMware Inc. 401(k) Savings Plan (the “VMware Plan”), which is qualified under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 (the “Code”). This plan is available solely to employees of VMware. In March 2008, VMware employees began participating in the VMware Plan and ceased participation in the EMC Plan. In March 2008, $96.4 million of assets and $1.1 million of participant loans were transferred from the EMC Plan into the VMware Plan.
81
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
VMware has matched pre-tax employee contributions up to 6% of eligible compensation during each pay period, subject to a $750 maximum match each quarter per employee. Matching contributions are immediately 100% vested. VMware contributions for employees were $9.0 million, $5.8 million and $3.1 million in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Employees may elect to invest their contributions in a variety of funds. VMware’s matching contribution mirrors the investment allocation of the employee’s contribution.
Beginning January 1, 2009, VMware suspended its company match of pre-tax employee contributions.
J. Commitments and Contingencies
Litigation
VMware is named from time to time as a party to lawsuits in the normal course of its business. In such cases it is the Company’s policy to defend against such claims, or if considered appropriate, negotiate a settlement on commercially reasonable terms. However, no assurance can be given that the Company will be able to negotiate settlements on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, or that any litigation resulting from such claims would not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position, and cash flows, or consolidated financial statements taken as a whole.
Operating Lease Commitments
VMware leases office facilities and equipment under various operating leases. Facility leases generally include renewal options. Rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 was $38.0 million, $20.2 million and $14.0 million, respectively. VMware’s future lease commitments at December 31, 2008 are as follows (table in thousands):
| | | |
2009 | | $ | 29,491 |
2010 | | | 26,573 |
2011 | | | 24,200 |
2012 | | | 14,321 |
2013 | | | 10,894 |
Thereafter | | | 270,530 |
| | | |
Total minimum lease payments | | $ | 376,009 |
| | | |
The amount of the future lease commitments after 2013 is primarily for the ground lease on VMware’s Palo Alto, California headquarters facilities, which expires in 2057. As several of VMware’s operating leases are payable in foreign currencies, the amount of operating lease commitments may fluctuate in response to changes in the exchange rate between the U.S. Dollar and the foreign currencies in which the commitments are payable.
Outstanding Obligations
At December 31, 2008, VMware had outstanding purchase orders aggregating $120.9 million. While the purchase orders are generally cancelable without penalty, certain vendor agreements provide for percentage-based cancellation fees or minimum restocking charges based on the nature of the product or service. In addition, at December 31, 2008, VMware had various contractual commitments aggregating $28.1 million, primarily relating to royalties and subscriptions.
82
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Guarantees and Indemnification Obligations
VMware enters into agreements in the ordinary course of business with, among others, customers, distributors, resellers, x86 system vendors, and systems integrators. Most of these agreements require VMware to indemnify the other party against third-party claims alleging that a VMware product infringes or misappropriates a patent, copyright, trademark, trade secret, and/or other intellectual property right. Certain of these agreements require VMware to indemnify the other party against certain claims relating to property damage, personal injury, or the acts or omissions of VMware, its employees, agents, or representatives.
VMware has agreements with certain vendors, financial institutions, lessors, and service providers pursuant to which VMware has agreed to indemnify the other party for specified matters, such as acts and omissions of VMware, its employees, agents, or representatives.
VMware has procurement or license agreements with respect to technology that is used in VMware’s products and agreements in which VMware obtains rights to. Under some of these agreements, VMware has agreed to indemnify the supplier for certain claims that may be brought against such party with respect to VMware’s acts or omissions relating to the supplied products or technologies.
VMware has agreed to indemnify the directors and officers of VMware and VMware’s subsidiaries, to the extent legally permissible, against all liabilities reasonably incurred in connection with any action in which such individual may be involved by reason of such individual being or having been a director or officer. VMware also indemnifies certain employees who provide service with respect to employee benefits plans, including the members of the VMware 401(k) Savings Plan Committee.
In connection with certain acquisitions, VMware has agreed to indemnify the former directors and officers of the acquired company in accordance with the acquired company’s by-laws and charter in effect immediately prior to the acquisition or in accordance with indemnification or similar agreements entered into by the acquired company and such persons. VMware typically purchases a “tail” directors’ and officers’ insurance policy, which should enable VMware to recover a portion of any future indemnification obligations related to the former officers and directors of an acquired company.
It is not possible to determine the maximum potential amount under these indemnification agreements due to the Company’s limited history with prior indemnification claims and the unique facts and circumstances involved in each particular agreement. Historically, payments made by the Company under these agreements have not had a material effect on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position, or cash flows.
K. Stockholders’ Equity
Initial Public Offering
In August 2007, VMware completed its IPO in which the Company sold 37,950,000 shares (including 4,950,000 shares pursuant to the underwriters’ full exercise of their over-allotment option) of its Class A common stock at a price to the public of $29.00 per share. The net proceeds of the IPO to the Company were $1,035.2 million after deducting the offering expenses and underwriters’ discounts. In August 2007, VMware used a portion of the proceeds to repay $350.0 million of principal on the note payable owed to EMC. VMware also purchased its new headquarters facilities from EMC for $132.6 million, which is equal to the cost expended by EMC in the construction of those facilities.
83
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Intel Ownership in VMware Class A Common Stock
In July 2007, VMware entered into a stock purchase agreement with Intel Corporation (“Intel”), pursuant to which Intel, through its affiliate, Intel Capital Corporation (“Intel Capital”), agreed to purchase 9.5 million shares of VMware’s Class A common stock at $23.00 per share for an aggregate offering price of $218.5 million. Intel Capital’s purchase of the 9.5 million shares of Class A common stock closed in August 2007.
In October 2008, Intel sold 0.5 million of these shares to EMC, increasing EMC’s Class A common stock holdings to 27.0 million shares. As of December 31, 2008, Intel held 6.1 million shares of the Company’s Class A common stock.
Cisco Ownership in VMware Class A Common Stock
In July 2007, VMware was a party to a stock purchase agreement with Cisco Systems, Inc. (“Cisco”) and EMC, pursuant to which Cisco agreed to purchase 6.0 million shares of VMware Class A common stock from EMC at $25.00 per share for an aggregate offering price of $150.0 million. VMware received no proceeds from this transaction. Cisco’s purchase of the 6.0 million shares of Class A common stock closed in August 2007.
In October 2008, Cisco purchased 0.5 million shares of VMware Class A common stock from Intel. As of December 31, 2008, Cisco held 6.5 million shares of the Company’s Class A common stock.
VMware Class B Common Stock Conversion Rights
Each share of Class B common stock is convertible while held by EMC or its successor-in-interest at the option of EMC or its successor-in-interest into one share of Class A common stock. If VMware’s Class B common stock is distributed to security holders of EMC in a transaction (including any distribution in exchange for shares of EMC’s or its successor-in-interest’s common stock or other securities) intended to qualify as a distribution under Section 355 of the Code, or any corresponding provision of any successor statute, shares of VMware’s Class B common stock will no longer be convertible into shares of Class A common stock. Prior to any such distribution, all shares of Class B common stock will automatically be converted into shares of Class A common stock upon the transfer of such shares of Class B common stock by EMC other than to any of EMC’s successors or any of its subsidiaries (excluding VMware). If such a distribution has not occurred, each share of Class B common stock will also automatically convert at such time as the number of shares of common stock owned by EMC or its successor-in-interest falls below 20% of the outstanding shares of VMware’s common stock. Following any such distribution, VMware may submit to its stockholders a proposal to convert all outstanding shares of Class B common stock into shares of Class A common stock, provided that VMware has received a favorable private letter ruling from the Internal Revenue Service satisfactory to EMC to the effect that the conversion will not affect the intended tax treatment of the distribution. In a meeting of VMware stockholders called for this purpose, the holders of VMware Class A common stock and VMware Class B common stock will be entitled to one vote per share and, subject to applicable law, will vote together as a single class, and neither class of common stock will be entitled to a separate class vote. All conversions will be effected on a share-for-share basis.
VMware Equity Plans
In June 2007, VMware adopted its 2007 Equity and Incentive Plan (the “2007 Plan”). Awards under the 2007 Plan may be in the form of stock options or other stock-based awards, including awards of restricted stock. The maximum number of shares of the VMware Class A common stock reserved for the grant or settlement of awards under the 2007 Plan is 80.0 million. The exercise price for a stock option awarded under the 2007 Plan
84
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
shall not be less than 100% of the fair market value of VMware Class A common stock on the date of grant. Most options granted under the 2007 Plan vest 25% after the first year and then monthly thereafter over the following three years. All options granted pursuant to the 2007 Plan expire between six and seven years from the date of grant. Most restricted stock awards granted under the 2007 Plan have a three-year to four-year period over which they vest. VMware utilizes both authorized and unissued shares to satisfy all shares issued under the 2007 Plan.
VMware Stock Purchase Plan
In June 2007, VMware adopted its 2007 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”) that is intended to be qualified under Section 423 of the Code. A total of 6.4 million shares of VMware Class A common stock were reserved for future issuance. Under the ESPP, eligible VMware employees are granted options to purchase shares at the lower of 85% of the fair market value of the stock at the time of grant or 85% of the fair market value at the time of exercise. Options to purchase shares were first granted under the ESPP on August 13, 2007, the date on which VMware’s Form S-1 Registration Statement was declared effective by the SEC, and became exercisable on December 31, 2007. Options to purchase shares are generally granted twice yearly.
In 2008, 1.7 million shares of Class A common stock were purchased under the ESPP at a weighted-average purchase price per share of $28.05. The total cash proceeds from the purchase of these shares under the ESPP were $46.9 million. As part of the 1.7 million shares purchased in 2008, employees purchased 0.6 million shares under the ESPP at a purchase price per share of $24.65. The purchase of 0.6 million shares related to the December 31, 2007 purchase, which was completed in January 2008. The total cash proceeds from the December 31, 2007 purchase under the ESPP were $15.7 million. In 2007, no shares were purchased under the ESPP.
EMC Exchange Offer
In August 2007, VMware and EMC completed an exchange offer (the “EMC Exchange Offer”) enabling eligible VMware employees to exchange their options to acquire EMC common stock for options to acquire VMware Class A common stock and to exchange restricted stock awards of EMC’s common stock for restricted stock awards of VMware’s Class A common stock. The formulaic exchange ratio applied to the exchange was determined by dividing the two-day volume weighted-average price of EMC’s common stock for the last two full days of the EMC Exchange Offer by the IPO price of VMware Class A common stock. The EMC Exchange Offer was structured to generally retain the intrinsic value of the tendered EMC securities. The number of VMware options received in exchange for EMC options was determined by multiplying the number of tendered EMC options by the exchange ratio. The exercise price of the VMware options received in exchange was the exercise price of the tendered EMC options divided by the exchange ratio. The VMware options received in the exchange retained their original term of ten years from the date of grant. The number of shares of VMware restricted stock received in exchange for EMC restricted stock was determined by multiplying the number of tendered EMC restricted shares by the exchange ratio. The EMC Exchange Offer resulted in a reduction in diluted earnings per share due to the inclusion of the VMware Class A common stock shares issued in the exchange. VMware employees that did not elect to exchange their EMC options and EMC restricted stock for options to purchase VMware Class A common stock and restricted stock awards of VMware Class A common stock, respectively, continue to have their existing grants governed under EMC’s stock plans.
There were approximately 6.7 million options to purchase VMware Class A common stock issued in the exchange with a weighted-average exercise price per share of $19.94 and approximately 2.9 million shares of VMware restricted stock issued in the exchange. The total incremental stock-based compensation expense resulting from the exchange of equity instruments was not material.
85
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
2008 Exchange Offer
In September 2008, VMware completed an offer to exchange certain employee stock options issued under VMware’s 2007 Equity and Incentive Plan (“2008 Exchange Offer”). Certain previously granted options were exchanged for new, lower-priced stock options granted on a one-for-one basis. Executive officers and members of the Company’s Board of Directors were excluded from participating in the 2008 Exchange Offer. Options for an aggregate of 4.1 million shares of VMware’s Class A common stock were exchanged with a weighted-average exercise price per share of $71.60. Options granted pursuant to the 2008 Exchange Offer have an exercise price of $33.95 per share, vest pro rata over four years beginning September 10, 2008 with no credit for past vesting and have a new six-year option term. The 2008 Exchange Offer resulted in incremental stock-based compensation expense of $18.0 million to be recognized over the four-year vesting term.
VMware Stock Options
The following table summarizes option activity since January 1, 2007 for VMware stock options (shares in thousands):
| | | | | | |
| | | Number
of
Shares | | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise Price
(per share) |
Outstanding, January 1, 2007 | | — | | | $ | — |
Granted | | 39,271 | | | | 27.88 |
Exchanged from EMC stock options | | 6,732 | | | | 19.94 |
Forfeited | | (539 | ) | | | 24.50 |
Expired | | (5 | ) | | | 24.64 |
Exercised | | (120 | ) | | | 23.00 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2007 | | 45,339 | | | | 26.76 |
Granted(1) | | 11,741 | | | | 40.48 |
Forfeited(1) | | (8,033 | ) | | | 51.74 |
Expired | | (37 | ) | | | 24.26 |
Exercised | | (6,574 | ) | | | 21.64 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2008 | | 42,436 | | | | 26.54 |
| | | | | | |
Exercisable, December 31, 2008 | | 10,889 | | | $ | 24.04 |
Vested and expected to vest, December 31, 2008 | | 38,319 | | | $ | 26.03 |
| (1) | Includes options for 4,107 shares exchanged in the 2008 Exchange Offer. |
As of December 31, 2008, the weighted-average remaining contractual term was 4.7 years and the aggregate intrinsic value was $20.4 million for the 10.9 million exercisable shares. For the 38.3 million shares vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2008, the weighted-average remaining contractual term was 4.9 years and the aggregate intrinsic value was $41.5 million. These aggregate intrinsic values represent the total pre-tax intrinsic values based on VMware’s closing stock price of $23.69 as of December 31, 2008, which would have been received by the option holders had all in-the-money options been exercised as of that date.
Cash proceeds from the exercise of stock options for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 were $143.2 million and $2.8 million, respectively. The options exercised in 2008 had a pre-tax intrinsic value of $219.6 million and income tax benefits realized from the exercise of stock options of $71.4 million. There was no pre-tax intrinsic value to the options exercised or related income tax benefits realized in 2007.
86
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
In June 2007, options were granted to non-employee directors to purchase 120,000 shares of Class A common stock with an exercise price of $23.00 per share. The options were exercisable immediately, subjected to termination if not exercised within one year from the date of grant, and vest pro rata annually over the first three years of the grant. In July 2007, the 120,000 options to purchase shares of Class A common stock were exercised prior to vesting, resulting in the outstanding shares being subject to repurchase and hence restricted until such time as the underlying options vest. As of December 31, 2008 and 2007, $1.8 million and $2.8 million, respectively, of the proceeds from the exercise of the options remain classified as a liability on the consolidated balance sheets. The proceeds are reclassified to stockholders’ equity as vesting occurs and the shares are no longer subject to repurchase.
VMware Restricted Stock
VMware restricted stock includes restricted stock awards, restricted stock units, and other restricted stock. Other restricted stock includes options exercised by non-employee directors that were required to be exercised within one year of grant, but are subject to a three-year vesting provision. The exercise of those options prior to vesting resulted in the outstanding shares being subject to repurchase and hence restricted until such time as the respective options vest.
In September 2008, VMware awarded 5.3 million restricted stock units to certain employees, including a portion for international employees who were not eligible to participate in the 2008 Exchange Offer and a portion for retention purposes. These awards generally will vest over a three-year or four-year period. These awards resulted in stock-based compensation expense of $164.5 million to be recognized over the three-year or four-year vesting term.
The following table summarizes restricted stock activity since January 1, 2007 for VMware restricted stock (shares in thousands):
| | | | | | |
| | | Number
of
Shares | | | Weighted-
Average Grant
Date Fair
Value
(per share) |
Restricted stock at January 1, 2007 | | — | | | $ | — |
Granted | | 596 | | | | 39.99 |
Exchanged from EMC restricted stock | | 2,872 | | | | 21.48 |
Exercised stock options, subject to repurchase | | 120 | | | | 23.00 |
Vested | | (5 | ) | | | 20.24 |
Forfeited | | (18 | ) | | | 20.19 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2007 | | 3,565 | | | | 24.64 |
Granted | | 6,619 | | | | 35.14 |
Vested | | (2,153 | ) | | | 22.58 |
Forfeited | | (405 | ) | | | 61.90 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2008 | | 7,626 | | | | 32.35 |
| | | | | | |
The total fair value of restricted stock that vested in 2008 and 2007 was $116.3 million and $0.6 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2008, 7.6 million shares of VMware restricted stock were outstanding, with an aggregate intrinsic value of $178.8 million. These shares are scheduled to vest through 2012.
The restricted stock awards are valued based on the VMware stock price on the date of grant. The majority of VMware’s restricted stock awards have pro rata vesting over three or four years.
87
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Shares Repurchased for Tax Withholdings
In 2008, VMware repurchased 826,731 shares of Class A common stock for $44.5 million to cover employee tax withholding obligations. Pursuant to the respective agreements, these shares were repurchased in conjunction with the net share settlement upon the vesting of restricted stock and restricted stock units during the quarter. The $44.5 million is recorded as a reduction to retained earnings as of December 31, 2008. In 2007, no shares were repurchased for tax withholdings.
EMC Stock Purchase Plan
Under EMC’s 1989 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “1989 Plan”), eligible VMware employees were allowed to purchase shares of EMC’s common stock through payroll deductions at the lower of 85% of the fair market value of the stock at the time of grant or 85% of the fair market value at the time of exercise. Options to purchase shares were granted twice yearly, on January 1 and July 1, and were exercisable on the succeeding June 30 or December 31. As a result of the completion of the IPO in August 2007, employees eligible for the VMware 2007 Employee Stock Purchase Plan were no longer able to participate in the EMC 1989 Employee Stock Purchase Plan after the June 30, 2007 purchase. In 2007 and 2006, 0.6 million shares and 1.0 million shares, respectively, were purchased under the 1989 Plan by VMware employees at a weighted-average purchase price per share of $11.36 and $9.32, respectively. Total cash proceeds to EMC from the purchase of shares under the 1989 Plan by VMware employees in 2007 and 2006 were $7.2 million and $9.0 million, respectively. These amounts were not material in 2008.
EMC Stock Options
The following table summarizes option activity for VMware employees in EMC stock options since January 1, 2006 (shares in thousands):
| | | | | | |
| | | Number
of
Shares | | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise Price
(per share) |
Outstanding, January 1, 2006 | | 10,585 | | | $ | 9.59 |
Options relating to employees transferred from EMC | | 293 | | | | 23.59 |
Options exchanged in a business acquisition | | 265 | | | | 0.40 |
Granted | | 4,941 | | | | 12.51 |
Forfeited | | (847 | ) | | | 12.22 |
Expired | | (114 | ) | | | 14.80 |
Exercised | | (1,298 | ) | | | 2.35 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2006 | | 13,825 | | | | 11.23 |
Options relating to employees transferred from EMC | | 678 | | | | 21.21 |
Granted | | 879 | | | | 13.91 |
Exchanged to VMware stock options | | (11,009 | ) | | | 12.19 |
Forfeited | | (410 | ) | | | 12.65 |
Expired | | (24 | ) | | | 12.66 |
Exercised | | (1,184 | ) | | | 7.16 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2007 | | 2,755 | | | | 12.22 |
Options relating to employees transferred from EMC | | 3,411 | | | | 15.35 |
Granted | | — | | | | — |
Forfeited | | (115 | ) | | | 13.03 |
Expired | | (21 | ) | | | 15.70 |
Exercised | | (295 | ) | | | 6.49 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2008 | | 5,735 | | | | 14.35 |
| | | | | | |
Exercisable, December 31, 2008 | | 1,425 | | | $ | 14.02 |
Vested and expected to vest, December 31, 2008 | | 5,559 | | | $ | 14.39 |
88
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
As of December 31, 2008, the weighted-average remaining contractual term was 5.2 years and the aggregate intrinsic value was $2.6 million for the 1.4 million exercisable shares. For the 5.6 million shares vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2008, the weighted-average remaining contractual term was 7.8 years and the aggregate intrinsic value was $2.7 million. These aggregate intrinsic values represent the total pre-tax intrinsic values based on EMC’s closing stock price of $10.47 as of December 31, 2008 which would have been received by the option holders had all in-the-money options been exercised as of that date.
The pre-tax intrinsic value of EMC options held by VMware employees that were exercised during the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 were $2.8 million, $12.3 million and $13.2 million, respectively. Cash proceeds from the exercise of these stock options paid to EMC were $1.9 million, $8.5 million and $3.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006.
EMC Restricted Stock
EMC restricted stock includes restricted stock awards and restricted stock units. The following table summarizes restricted stock for grants to VMware employees of EMC restricted stock since January 1, 2006 (shares in thousands):
| | | | | | |
| | | Number
of
Shares | | | Weighted-
Average Grant
Date Fair
Value
(per share) |
Restricted Stock at January 1, 2006 | | 7,902 | | | $ | 13.94 |
Granted | | 3,303 | | | | 12.19 |
Vested | | (1,967 | ) | | | 13.70 |
Forfeited | | (425 | ) | | | 13.94 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2006 | | 8,813 | | | | 13.34 |
Granted | | 48 | | | | 13.93 |
Exchanged to VMware restricted stock | | (4,697 | ) | | | 13.14 |
Vested | | (2,661 | ) | | | 13.47 |
Forfeited | | (221 | ) | | | 13.72 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2007 | | 1,282 | | | | 13.72 |
Granted | | — | | | | — |
Vested | | (1,144 | ) | | | 13.91 |
Forfeited | | (22 | ) | | | 12.35 |
| | | | | | |
Outstanding, December 31, 2008 | | 116 | | | | 12.16 |
| | | | | | |
The total fair value of EMC restricted stock granted to VMware employees that vested in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 was $18.2 million, $39.6 million and $26.9 million, respectively.
As of December 31, 2008, 0.1 million shares of EMC restricted stock granted to VMware employees were outstanding, with an aggregate intrinsic value of $1.2 million. These shares are scheduled to vest through 2011.
The EMC restricted stock awards have various vesting terms, including pro rata vesting over three years and cliff vesting at the end of five years from the date of grant with acceleration in each of the first three or four years for achieving specified performance criteria.
89
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
The following table summarizes the components of total stock-based compensation expense included in VMware’s consolidated statements of income for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 (table in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended
December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
Cost of license revenues | | $ | 1,120 | | $ | 558 | | $ | 99 |
Cost of services revenues | | | 13,485 | | | 6,070 | | | 2,384 |
Research and development | | | 77,992 | | | 42,934 | | | 26,342 |
Sales and marketing | | | 49,762 | | | 26,288 | | | 12,020 |
General and administrative | | | 24,157 | | | 16,556 | | | 10,381 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation expense | | | 166,516 | | | 92,406 | | | 51,226 |
Income tax benefit | | | 33,020 | | | 21,227 | | | 12,229 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total stock-based compensation expense, net of tax | | $ | 133,496 | | $ | 71,179 | | $ | 38,997 |
| | | | | | | | | |
In connection with the adoption of FAS No. 123R on January 1, 2006, VMware recorded to its income statement, a cumulative effect adjustment, net of taxes, of $0.2 million to record an amount for the reversal of the previously recognized compensation expense related to outstanding restricted stock awards that are not expected to vest, based on an estimate of forfeitures as of the date of adoption of FAS No. 123R. Additionally, VMware recorded to stockholders’ equity, a cumulative effect adjustment, net of taxes, of $1.1 million to capitalize amounts associated with software development costs that were previously capitalized in VMware’s pro forma compensation disclosures prior to adoption.
For the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, VMware capitalized $22.7 million, $9.1 million and $10.5 million, respectively, of stock-based compensation expense associated with capitalized software development. For the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, VMware capitalized an additional $1.4 million and $0.8 million, respectively, of stock-based compensation expense associated with software developed for internal use. The amount of stock-based compensation expense capitalized for software developed for internal use was not material in 2006.
As of December 31, 2008, the total unrecognized compensation cost for both VMware stock options and restricted stock and EMC stock options and restricted stock was $522.6 million. This non-cash expense will be recognized through 2012 with a weighted-average remaining period of 1.4 years.
Fair Value of VMware Options
The fair value of each option to acquire VMware Class A common stock granted during the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
| | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended
December 31, | |
VMware Stock Options | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
Dividend yield | | | None | | | | None | |
Expected volatility | | | 39.4 | % | | | 39.2 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | | 2.5 | % | | | 4.9 | % |
Expected term (in years) | | | 3.4 | | | | 3.4 | |
Weighted-average fair value at grant date | | $ | 17.88 | | | $ | 27.88 | |
90
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
| | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended
December 31, | |
VMware Employee Stock Purchase Plan | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
Dividend yield | | | None | | | | None | |
Expected volatility | | | 39.3 | % | | | 34.8 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | | 2.7 | % | | | 4.8 | % |
Expected term (in years) | | | 0.5 | | | | 0.4 | |
Weighted-average fair value at grant date | | $ | 18.06 | | | $ | 6.99 | |
For all equity awards granted in 2008 and 2007, volatility was based on an analysis of historical stock prices and implied volatility of publicly-traded companies with similar characteristics, including industry, stage of life cycle, size, and financial leverage. The expected term was calculated based on the historical experience that VMware employees have had with EMC stock option grants as well as the expected term of similar grants of comparable companies. The risk-free interest rate was based on a treasury instrument whose term is consistent with the expected term of the stock options.
For the equity awards granted prior to the Company’s IPO, VMware performed a contemporaneous valuation of the Company’s Class A common stock each time an equity grant of common stock was made. In determining the fair value of the equity, VMware analyzed general market data, including economic, governmental, and environmental factors; considered its historic, current, and future state of its operations; analyzed its operating and financial results; analyzed its forecasts; gathered and analyzed available financial data for publicly traded companies engaged in the same or similar lines of business to develop appropriate valuation multiples and operating comparisons, and analyzed other facts and data considered pertinent to the valuation to arrive at an estimated fair value.
VMware utilized both the income approach and the market approach in estimating the value of the equity. The market approach estimates the fair value of a company by applying to the company’s historical and/or projected financial metrics market multiples of the corresponding financial metrics of publicly traded firms in similar lines of business. The use of the market approach requires judgments regarding the comparability of companies that are similar to VMware. If different comparable companies had been used, the market multiples and resulting estimates of the fair value of the Company’s stock also would have been different. The income approach involves applying appropriate risk-adjusted discount rates to estimated debt-free cash flows, based on forecasted revenues and costs. The projections used in connection with this valuation were based on the Company’s expected operating performance over the forecast period. There is inherent uncertainty in these estimates. If different discount rates or other assumptions had been used, the resulting estimates of the fair value of the Company’s stock would have been different. Due to the prospect of an imminent public offering, VMware did not apply a marketability discount in carrying out either approach. Further, VMware did not apply a minority interest discount in concluding on fair value.
In reaching its estimated valuation range, VMware considered the indicated values derived from each valuation approach in relation to the relative merits of each approach, the suitability of the information used, and the uncertainties involved. The results of the approaches overlapped, with the income approach results falling within a narrower range, which VMware ultimately relied on in its concluding estimate of value.
In addition to the aforementioned analysis, with respect to grants of options to purchase Class A common stock with an exercise price of $23.00 per share, the Company believes that the fair value of its equity at that time was further substantiated by the arm’s-length transaction with Intel Capital, whereby Intel agreed to purchase 9.5 million shares of VMware’s Class A common stock at $23.00 per share, subject to adjustment if the price in the offering were below $23.00 per share. VMware believes that the fair value of its equity at the time of
91
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
the grant of options at $25.00 per share was substantiated by the contemporaneous arm’s-length transaction whereby Cisco agreed to purchase 6.0 million shares of VMware’s Class A common stock from EMC at $25.00 per share. The Company believes that the fair value of VMware’s equity at the time of the grant of options at $29.00 per share was substantiated by the proximity to the IPO.
The fair value of each VMware option granted at $23.00 was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
| | | |
Dividend yield | | None | |
Expected volatility | | 39.2 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | 5.0 | % |
Expected term (in years) | | 3.4 | |
The fair value of each VMware option granted at $25.00 was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
| | | |
Dividend yield | | None | |
Expected volatility | | 38.2 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | 4.8 | % |
Expected term (in years) | | 3.4 | |
The fair value of each VMware option granted at $29.00 was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
| | | |
Dividend yield | | None | |
Expected volatility | | 39.6 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | 4.5 | % |
Expected term (in years) | | 3.4 | |
Fair Value of EMC Options
There were no EMC stock option grants to VMware employees subsequent to the first quarter of 2007. VMware employees eligible to participate in the VMware employee stock purchase plan were able to participate in the EMC employee stock purchase plan up through the date of the IPO, at which time they were withdrawn from the plan. The fair value of each EMC option granted during the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006 was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
| | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended
December 31, | |
EMC Stock Options | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Dividend yield | | | None | | | | None | |
Expected volatility | | | 30.1 | % | | | 34.4 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | | 4.7 | % | | | 4.8 | % |
Expected life (in years) | | | 4.2 | | | | 4.0 | |
Weighted-average fair value at grant date | | $ | 4.45 | | | $ | 4.28 | |
92
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
| | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended
December 31, | |
EMC Employee Stock Purchase Plan | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Dividend yield | | | None | | | | None | |
Expected volatility | | | 25.3 | % | | | 27.6 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | | 5.0 | % | | | 4.9 | % |
Expected life (in years) | | | 0.5 | | | | 0.5 | |
Weighted-average fair value at grant date | | $ | 3.07 | | | $ | 2.86 | |
Expected volatilities were based on historical stock prices and implied volatilities from traded options in EMC’s stock. VMware used EMC historical data to estimate the expected term of options granted within the valuation model. The risk-free interest rates were based on treasury instruments whose terms were consistent with the expected term of the stock options.
L. Related Party Transactions
Transactions with EMC
In 2008, 2007 and 2006, VMware recognized professional services revenues of $16.9 million, $11.8 million and $1.4 million, respectively, for services provided to EMC’s customers pursuant to VMware’s contractual agreements with EMC.
In 2008, VMware recognized revenues from server and desktop products and services purchased by EMC for internal use of $4.1 million pursuant to VMware’s contractual agreements with EMC. As of December 31, 2008 and 2007, $1.8 million and $4.3 million, respectively, of revenues from server and desktop products and services purchased by EMC for internal use were included in deferred revenue.
VMware purchased storage systems from EMC for $24.0 million, $7.2 million and $2.9 million in the years ended 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Through the third quarter of 2007, the systems purchased from EMC were at EMC’s cost. Since the fourth quarter of 2007, the systems purchased from EMC were at a discount off of EMC’s list price.
For certain corporate functions provided by EMC, $7.7 million and $5.1 million of expenses were allocated to VMware by EMC in 2007 and 2006, respectively. In 2008, this amount was not significant.
In certain geographic regions where VMware does not have an established legal entity, VMware contracts with EMC subsidiaries for support services and EMC employees who are managed by VMware personnel. The costs incurred by EMC on VMware’s behalf related to these employees include an estimated arm’s-length mark-up and were included as expenses in VMware’s financial statements. These costs include expenses for salaries and benefits, travel, and rent. Additionally, EMC incurs certain costs on VMware’s behalf in the U.S., which primarily relate to shared systems for travel. The total of these costs were $139.8 million, $116.1 million and $69.6 million in the years ended 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
As part of VMware’s tax sharing agreement, VMware paid EMC income taxes of $64.3 million, $86.4 million and $63.1 million in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively, for VMware’s portion of their consolidated federal income taxes. These amounts differed from the amounts owed on a stand-alone basis and the differences are presented as a component of stockholders’ equity. In 2008, the difference between the amount of tax calculated on a stand-alone basis and the amount of tax calculated per the tax sharing agreement was recorded as an increase in stockholders’ equity of $5.2 million. In 2007 and 2006, this difference was recorded as a decrease in stockholders’ equity of $2.5 million and $32.3 million, respectively.
93
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Interest income (expense) with EMC, net, primarily consists of interest expense on the note payable to EMC, offset by interest income that has been earned on VMware’s intercompany balance with EMC. In 2008 and 2007, $18.6 million and $26.6 million, respectively, of interest expense was recorded related to the note payable to EMC and was included in the $18.3 million and $17.8 million, respectively, of interest expense with EMC, net, recorded on the consolidated statements of income. In 2006, VMware earned interest income with EMC, net, of $0.3 million. VMware’s interest income and VMware’s expenses as a separate, stand-alone company may be higher or lower than the amounts reflected in the financial statements.
In 2008, VMware and EMC resolved certain acquisition-related intercompany liabilities due to EMC. As a result, intercompany liabilities due to EMC of $9.7 million were recorded as a capital contribution from EMC in additional paid-in capital without the issuance of additional equity by VMware or remittance of any cash.
Prior to March 2008, VMware employees participated in the EMC Corporation 401(k) Savings Plan. EMC cross-charged VMware for the costs associated with VMware employees who participated in the EMC Plan. In March 2008, VMware employees began participating in VMware’s 401(k) Savings Plan and ceased participation in the EMC Plan. See Note I to VMware’s consolidated financial statements.
As of December 31, 2008, VMware had $38.4 million due to EMC, which was partially offset by $5.0 million due from EMC. As of December 31, 2007, VMware had $55.5 million due to EMC, which was partially offset by $52.7 million due from EMC. The net amounts due to EMC for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 were $33.4 million and $2.8 million, respectively, and resulted from the related party transactions described above. As of December 31, 2008, VMware had $111.1 million of income taxes receivable due from EMC and $3.6 million of income taxes payable due to EMC. As of December 31, 2007, VMware had $65.4 million of income taxes payable due to EMC. Balances due to or from EMC which are unrelated to tax obligations are generally settled in cash within 60 days of each quarter end. The timing of the tax payments due to and from EMC is governed by the tax sharing agreement with EMC.
Transactions with Other Related Parties
In connection with Intel Capital’s purchase in 2007 of 9.5 million shares of VMware’s Class A common stock, the Company agreed to the appointment of an Intel executive acceptable to VMware’s Board of Directors. In connection with Cisco’s purchase in 2007 of 6.0 million shares from EMC, the Company agreed to consider the appointment of a Cisco executive to the Board of Directors. In November 2007, both an Intel executive and a Cisco executive were appointed to VMware’s Board. In October 2008, Intel sold 0.5 million shares of VMware’s Class A common stock to EMC and an additional 0.5 million shares to Cisco in separate transactions, increasing EMC’s Class A common stock holdings to 27.0 million shares and Cisco’s holdings to 6.5 million shares. As of December 31, 2008, Intel held 6.1 million shares of the Company’s Class A common stock.
VMware has in the past done business, and expects to continue to do business, with Intel and Cisco on a regular arm’s-length basis, on the same or similar terms as would be negotiated with unrelated third parties. The transactions with Intel and Cisco in 2008 and 2007 were not material to VMware’s consolidated financial statements.
In addition, from time to time, VMware may purchase or sell goods and services in the ordinary course of business with financial institutions that beneficially own 5% or more of VMware’s Class A common stock. VMware has in the past done business, and expects to continue to do business, with entities affiliated with FMR LLC and UBS AG, financial institutions that beneficially own 5% or more of the Company’s Class A common stock, on regular, arm’s-length basis, on the same or similar terms as would be negotiated with
94
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
unrelated third parties. During 2008, VMware invoiced entities believed to be affiliated with FMR LLC and UBS AG for goods and services sold by VMware. In addition, the Company’s 401(k) plan is also administered by Fidelity Investments, an affiliate of FMR LLC, and UBS Financial Services, Inc., an affiliate of UBS, is VMware’s stock plan administrator. Transactions with FMR LLC and with UBS AG were not material to VMware’s 2008 and 2007 consolidated financial statements.
In 2007, VMware entered into an agreement to license software from Softrax Corporation (“Softrax”). A member of the Company’s Board of Directors is a managing partner and general partner in a limited partnership which has an equity interest in Softrax of greater than 10%. The amounts expensed or paid to Softrax in 2008 and 2007 were not material to VMware’s consolidated financial statements.
M. Segment Information
VMware operates in one reportable segment in accordance with the provisions of FAS No. 131, “Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information.” Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise about which separate financial information is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker in deciding how to allocate resources and assessing performance. The chief operating decision maker is the President and Chief Executive Officer. VMware operates in one segment, therefore all financial segment information required by FAS No. 131 can be found in the consolidated financial statements.
Revenues by geographic area are as follows (table in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
United States | | $ | 987,604 | | $ | 720,620 | | $ | 391,614 |
International | | | 893,423 | | | 605,191 | | | 312,290 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 1,881,027 | | $ | 1,325,811 | | $ | 703,904 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Long-lived assets, which include property and equipment, net, and other assets, net, excluding capitalized software and financial instruments, in the United States at December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, were $325.4 million, $236.5 million and $40.6 million, respectively. Long-lived assets internationally at December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 were $44.5 million, $22.8 million and $5.2 million, respectively. No country other than the United States accounted for 10% or more of these assets at December 31, 2008, 2007 or 2006.
VMware groups its products into portfolios that are categorized into the following classes:
Data center products. The Company’s data center products include a hypervisor for system-partitioning the software environment from its underlying infrastructure and products that enable the aggregation of multiple servers, storage infrastructure, and networks into shared pools of resources that can be delivered dynamically, securely, and reliably to applications as needed. The data center products include VMware VMotion and Storage VMotion, VMware High Availability, VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler, and virtualization management products such as VMware vCenter Server, VMware vCenter Site Recovery Manager, VMware vCenter Lab Manager, VMware vCenter Stage Manager, and VMware vCenter Lifecycle Manager.
Other Products. The Company’s other products include primarily desktop virtualization products, which decouple the entire desktop environment from its underlying device, enabling customers to create user-centric instead of device-centric desktop environments. The other products include View Manager, View Composer, Workstation, and Fusion.
95
VMWARE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Revenues by class of products or services were as follows (table in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
Data center products | | $ | 1,112,070 | | $ | 875,590 | | $ | 451,338 |
Other products | | | 66,072 | | | 29,778 | | | 40,564 |
| | | | | | | | | |
License revenues | | | 1,178,142 | | | 905,368 | | | 491,902 |
Services revenues | | | 702,885 | | | 420,443 | | | 212,002 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 1,881,027 | | $ | 1,325,811 | | $ | 703,904 |
| | | | | | | | | |
One distributor accounted for 18%, 23% and 29% of revenues in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Additionally, another distributor accounted for 16% and 12% of revenues in 2008 and 2007, respectively. One channel partner accounted for 11% of revenues in both 2008 and 2007, respectively.
N. Selected Quarterly Financial Data (unaudited)
Quarterly financial data for 2008 and 2007 is as follows (tables in millions, except per share amounts):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
2008 | | Q1 2008 | | Q2 2008 | | Q3 2008 | | Q4 2008 |
Revenues | | $ | 438.2 | | $ | 456.1 | | $ | 472.1 | | $ | 514.6 |
Net income | | $ | 43.1 | | $ | 52.3 | | $ | 83.3 | | $ | 111.5 |
Net income per share, basic | | $ | 0.11 | | $ | 0.14 | | $ | 0.21 | | $ | 0.29 |
Net income per share, diluted | | $ | 0.11 | | $ | 0.13 | | $ | 0.21 | | $ | 0.29 |
| | | | |
2007 | | Q1 2007 | | Q2 2007 | | Q3 2007 | | Q4 2007 |
Revenues | | $ | 258.7 | | $ | 296.8 | | $ | 357.8 | | $ | 412.5 |
Net income | | $ | 41.1 | | $ | 34.2 | | $ | 64.7 | | $ | 78.2 |
Net income per share, basic | | $ | 0.12 | | $ | 0.10 | | $ | 0.18 | | $ | 0.21 |
Net income per share, diluted | | $ | 0.12 | | $ | 0.10 | | $ | 0.18 | | $ | 0.19 |
| ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
| ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We carried out an evaluation required by the Exchange Act, under the supervision and with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) of the Exchange Act, as of December 31, 2008. Based on this evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that, as of December 31, 2008, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the Security and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms and to provide reasonable assurance that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures.
96
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Management has assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008 based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. As a result of this assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2008, our internal control over financial reporting was effective in providing reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers, LLP our independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which appears in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2008 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Limitations on Controls
Our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting are designed to provide reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives as specified above. Management does not expect, however, that our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal control over financial reporting will prevent or detect all error and fraud. Any control system, no matter how well designed and operated, is based upon certain assumptions and can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that its objectives will be met. Further, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that misstatements due to error or fraud will not occur or that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within the Company have been detected.
| ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
97
PART III
| ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS, AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
We will furnish to the Securities and Exchange Commission a definitive Proxy Statement no later than 120 days after the close of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008. The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement. Also see “Executive Officers of the Registrant” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
On August 28, 2008, we submitted to the New York Stock Exchange the Annual CEO Certification required pursuant to Section 303A.12(a) of the New York Stock Exchange Listed Company Manual.
We have a code of ethics that applies to all of our employees, including our executive officers. Our Business Conduct Guidelines (available on our website) satisfy the requirements set forth in Item 406 of Regulation S-K and apply to all relevant persons set forth therein. We intend to disclose on our website at www.vmware.com amendments to, and, if applicable, waivers of, our code of ethics.
| ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT, AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement and is included in Note L to the consolidated financial statements.
| ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Proxy Statement.
98
PART IV
| ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULE |
| (a) | Documents filed as a part of this report: |
The financial statements listed in the Index to Consolidated Financial Statements are filed as part of this report (refer to Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data).
| | 2. | Financial statement schedule |
Schedule II—Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
All other schedules have been omitted because the required information is included in the consolidated financial statements or the notes thereto, or is not applicable or required.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Incorporated by Reference |
Exhibit
Number | | Exhibit Description | | Filed
Herewith | | Form/File
No. | | Date |
| 3.1 | | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 3.2 | | Amended and Restated Bylaws | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 4.1 | | Form of specimen common stock certificate | | | | S-1/A-4 | | 7/27/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.1 | | Form of Master Transaction Agreement between VMware, Inc. and EMC Corporation | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.2 | | Form of Administrative Services Agreement between VMware, Inc. and EMC Corporation | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.3 | | Form of Tax Sharing Agreement between VMware, Inc. and EMC Corporation | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.4 | | Form of Intellectual Property Agreement between VMware, Inc. and EMC Corporation | | | | S-1/A-1 | | 6/11/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.5 | | Form of Employee Benefits Agreement between VMware, Inc. and EMC Corporation | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.6 | | Form of Real Estate License Agreement between VMware, Inc. and EMC Corporation | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.7+ | | Letter Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Mark Peek dated March 16, 2007 | | | | S-1/A-1 | | 6/11/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.8+ | | Form of Indemnification Agreement for directors and executive officers | | | | S-1/A-1 | | 6/11/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.9+ | | 2007 Equity and Incentive Plan, as amended December 3, 2008 | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 10.10 | | Promissory Note between VMware, Inc. and EMC Corporation dated April 16, 2007 | | | | S-1 | | 6/11/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.11 | | Form of Insurance Matters Agreement between VMware, Inc. and EMC Corporation | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.12+ | | Form of Option Agreement | | | | S-1/A-1 | | 6/11/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.13+ | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement | | | | S-1/A-1 | | 6/11/2007 |
99
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Incorporated by Reference |
Exhibit
Number | | Exhibit Description | | Filed
Herewith | | Form/File
No. | | Date |
| 10.14 | | 2007 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as amended and restated December 10, 2007 and as further amended February 4, 2009 | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 10.15+ | | Letter Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Mark Peek dated June 13, 2007 | | | | 10-K | | 2/29/2008 |
| | | | |
| 10.16# | | Distributor Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Ingram Micro, Inc. dated May 17, 2002 | | | | S-1/A-5 | | 8/3/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.17 | | Amendment No. 11 dated June 5, 2008 to Distributor Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Ingram Micro, Inc. | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 10.18 | | Form of Real Estate Purchase and Sale Agreement between VMware, Inc. and EMC Corporation | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.19 | | Class A Common Stock Purchase Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Intel Capital Corporation dated July 9, 2007 | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.20 | | Investor Rights Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Intel Capital Corporation dated July 9, 2007 | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.21+ | | Form of Early Exercise Option Agreement | | | | S-1/A-2 | | 7/9/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.22 | | Class A Common Stock Purchase Agreement among VMware, Inc., EMC Corporation, and Cisco Systems, Inc. dated July 26, 2007 | | | | S-1/A-4 | | 7/27/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.23 | | Investor Rights Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Cisco Systems, Inc. dated July 26, 2007 | | | | S-1/A-4 | | 7/27/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.24+ | | Employment Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Diane Greene dated July 26, 2007 | | | | 10-Q | | 9/17/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.25+ | | Letter Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Dev R. (Richard) Sarwal dated November 29, 2007 | | | | 10-K | | 2/29/2008 |
| | | | |
| 10.26+ | | EMC Corporation 2003 Stock Plan, as amended | | | | DEF 14/A | | 3/11/2005 |
| | | | |
| 10.27+ | | Form of Stock Option Agreement under the EMC 2003 Stock Plan | | | | 10-Q filed by
EMC | | 11/3/2004 |
| | | | |
| 10.28+ | | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement under the EMC 2003 Stock Plan | | | | 10-Q filed by
EMC | | 11/3/2004 |
| | | | |
| 10.29+ | | Letter Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Thomas J. Jurewicz dated June 24, 1999 | | | | S-1/A-1 | | 6/11/2007 |
| | | | |
| 10.30+ | | Letter Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Carl Eschenbach dated May 25, 2005 | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 10.31+ | | Letter Agreement and Release with Diane Greene entered into on August 25, 2008 | | | | 8-K | | 8/29/2008 |
| | | | |
| 10.32+ | | Letter Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Paul Maritz dated September 11, 2008 | | | | 8-K | | 9/12/2008 |
| | | | |
| 10.33+ | | Letter Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Mark Peek dated November 24, 2008 | | X | | | | |
100
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Incorporated by Reference |
Exhibit
Number | | Exhibit Description | | Filed
Herewith | | Form/File
No. | | Date |
| 10.34+ | | Letter Agreement between VMware, Inc. and Tod Nielsen | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 10.35+ | | 2009 Executive Bonus Program | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 21.1 | | List of subsidiaries | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 23.1 | | Consent of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 31.1 | | Certification of Principal Executive Officer required by Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 31.2 | | Certification of Principal Financial Officer required by Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 32.1 | | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | | X | | | | |
| | | | |
| 32.2 | | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | | X | | | | |
| + | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| # | Confidential treatment requested for certain portions of this Exhibit pursuant to Rule 406 promulgated under the Securities Act, which portions are omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
101
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | |
| | VMWARE, INC. |
| | |
| Dated: February 25, 2009 | | By: | | /s/ PAUL MARITZ |
| | | | Paul Maritz President and Chief Executive Officer |
| |
| | VMWARE, INC. |
| | |
| Dated: February 25, 2009 | | By: | | /s/ MARK S. PEEK |
| | | | Mark S. Peek Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | |
Date | | Signature | | Title |
| | |
| February 25, 2009 | | /s/ PAUL MARITZ Paul Maritz | | President and Chief Executive Officer, Director (Principal Executive Officer) |
| | |
| February 25, 2009 | | /s/ MARK S. PEEK Mark S. Peek | | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
| | |
| February 25, 2009 | | /s/ JOSEPH M. TUCCI Joseph M. Tucci | | Chairman |
| | |
| February 25, 2009 | | /s/ MICHAEL W. BROWN Michael W. Brown | | Director |
| | |
| February 25, 2009 | | /s/ JOHN R. EGAN John R. Egan | | Director |
| | |
| February 25, 2009 | | /s/ DAVID I. GOULDEN David I. Goulden | | Director |
| | |
| February 25, 2009 | | /s/ RENEE J. JAMES Renee J. James | | Director |
| | |
| February 25, 2009 | | /s/ DENNIS D. POWELL Dennis D. Powell | | Director |
| | |
| February 25, 2009 | | /s/ DAVID N. STROHM David N. Strohm | | Director |
102
VMWARE, INC.
SCHEDULE II—VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for Bad Debts | | Balance at
Beginning
of Period | | Allowance for Bad
Debts Charged to
Selling, General,
and Administrative
Expenses | | | Charged to
Other Accounts | | Bad Debts
Write-Offs | | | Balance at
End of
Period |
Year ended December 31, 2008 allowance for doubtful accounts | | $ | 1,603 | | $ | 254 | | | $ | — | | $ | (167 | ) | | $ | 1,690 |
Year ended December 31, 2007 allowance for doubtful accounts | | | 2,139 | | | (316 | ) | | | — | | | (220 | ) | | | 1,603 |
Year ended December 31, 2006 allowance for doubtful accounts | | | 1,589 | | | 763 | | | | — | | | (213 | ) | | | 2,139 |
| | | | | |
Tax Valuation Allowance | | Balance at
Beginning
of Period | | Tax Valuation
Allowance
Charged to Income
Tax Provision | | | Charged to
Other Accounts | | Valuation
Allowance
Credited to
Income Tax
Provision | | | Balance at
End of
Period |
Year ended December 31, 2008 income tax valuation allowance | | $ | — | | $ | 15,394 | | | $ | — | | $ | — | | | $ | 15,394 |
103
