Exhibit 99.1

Alterity Therapeutics (NASDAQ: A THE , ASX: A T H) Jun e 2021 Davi d Stamle r , MD CEO

Forward Looking Statements This presentation may contain some statements that may be considered “Forward - Looking Statements”, within the meaning of the US Securities Laws. Thus, any forward - looking statement relating to financial projections or other statements relating to the Company’s plans, objectives, expectations or intentions involve risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially. For a discussion of such risks and uncertainties as they relate to us, please refer to our 2020 Form 20 - F, filed with US Securities and Exchange Commission, in particular Item 3, Section D, titled “Risk Factors.’’ 2
Our Purpose We exist to create an alternate future for people living with neurodegenerative diseases. An alternate, healthier life. We’re here to disrupt the trajectory for people with these diseases. 3
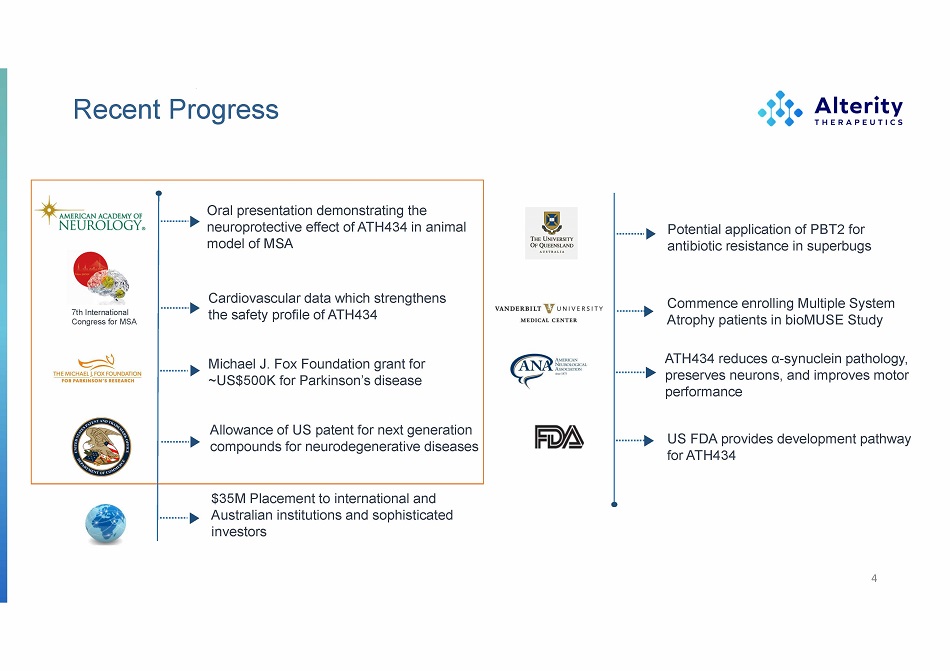
Recent Progress 4 Potential application of PBT2 for antibiotic resistance in superbugs Commence enrolling Multiple System Atrophy patients in bioMUSE Study ATH 434 reduces α - synuclein pathology, preserves neurons, and improves motor performance US FDA provides development pathway for ATH 434 Michael J. Fox Foundation grant for ~US$500K for Parkinson’s disease Allowance of US patent for next generation compounds for neurodegenerative diseases $35M Placement to international and Australian institutions and sophisticated investors Cardiovascular data which strengthens the safety profile of ATH434 7th International Congress for MSA Oral presentation demonstrating the neuroprotective effect of ATH434 in animal model of MSA
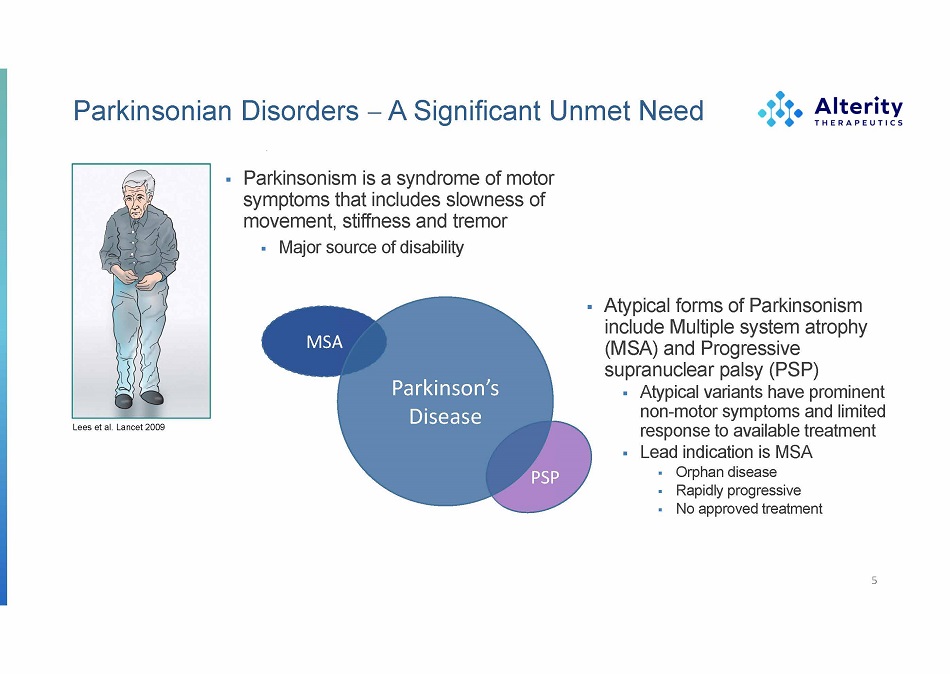
Parkinsonian Disorders A Significant Unmet Need ▪ Parkinsonism is a syndrome of motor symptoms that includes slowness of movement, stiffness and tremor ▪ Major source of disability 5 MS A P arkinson ’ s Disease PSP ▪ Atypica l form s o f Parkinsonism includ e Multipl e syste m atrophy (MSA) and Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) ▪ Atypical variants have prominent non - motor symptoms and limited response to available treatment ▪ Lead indication is MSA ▪ Orpha n disease ▪ Rapidl y progres s i v e ▪ N o approve d treatment Lees et al. Lancet 2009

Leadershi p o f 3 FDA Approvals i n Neurology David Stamler, M.D. • 3 FDA Approvals in Neurology • Led FDA Advisory Committee and approval of Xenazine ® in Huntington’s disease in 2008 • Led clinical development and approval of Austedo ® in Huntington’s disease and Tardive dyskinesia, both approved in 2017 • Former Chief Medical O f fice r , Auspex Pharmaceuticals and VP, Clinical Development & Therapeutic Head, Movement Disorders, Teva Pharmaceuticals • Part of Teva’s US$3.5 billion acquisition of Auspex in 2015 • Development leadership from Auspex joined Alterity in 2017 FD A Advisor y Committe e V ote s Unanimo usl y t o Recommend Approval of Tetrabenazine for Chorea Associated With Huntington Disease Dec 7, 2007 XENAZINE® (Tetrabenazine) Approved by FDA for Patients with Chorea Associated with Huntington's Disease Aug 15, 2008 FDA approves Teva’s Austedo ® for Tardive Dyskinesia Aug 31, 2017 Teva’s Austedo is now the first and only therapy approved in the US to treat both tardive dyskinesia and chorea associated with Huntington’s disease 6
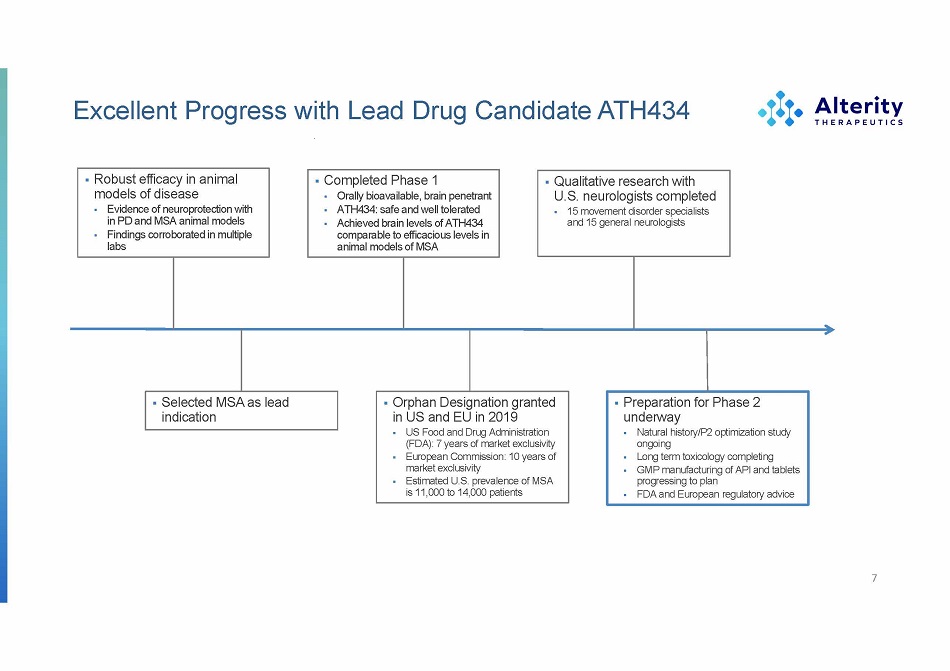
Excellent Progress with Lead Drug Candidate ATH434 7 ▪ Robus t e f ficac y i n animal model s o f disease ▪ Evidenc e o f neurop r o t e c t io n with i n P D an d M S A anima l models ▪ Finding s corrobo ra t e d i n multiple labs ▪ Orpha n Designatio n granted i n U S an d E U i n 2019 ▪ U S Foo d an d Dru g Administrat i o n (FDA) : 7 year s o f marke t exclusivity ▪ Europ ea n Commis s ion : 1 0 year s of marke t exclusivi t y ▪ Estimated U.S. prevalence of MSA i s 11,00 0 t o 14,00 0 patients ▪ Complete d Phas e 1 ▪ Orally bioavailable, brain penetrant ▪ ATH434 : saf e an d w el l tolerated ▪ Achieve d brai n level s o f ATH434 compara bl e t o efficaciou s level s in anima l model s o f M S A ▪ Preparatio n fo r Phas e 2 underway ▪ Natura l history/P 2 optimizat io n study ongoing ▪ Lon g ter m toxicolo g y complet i n g ▪ GM P manufactu r in g o f AP I an d tablets progress in g t o plan ▪ FD A an d Europe a n regu l ato r y advice ▪ Qualitativ e researc h with U.S . neurologist s completed ▪ 1 5 movem e n t disord e r specialists an d 1 5 gene r a l neuro log ists ▪ Selecte d MS A a s lead indication

8 I 3 STRATEGY PARTNERS CONFIDENTIAL Comme r cial Oppo r tunity Multiple Syste m At r op h y Independent Ana l ysis *Does not include spontaneous use in PD Severely debilitating, fatal illnesses with no current treatments are ripe for new entrants targeting what may be the actual cause of the disease. SUBSTANTIAL UNMET NEED Motivated by efficacy in treating the underlying disease and not just the symptoms, clinicians intend to offer ATH434 to most of their patients with MSA. STRONG INTENT TO PRESCRIBE Given similar efficacy, clinicians will likely prefer ATH434’s once or twice daily oral administration vs. the monthly IV infusions or injections required for alpha-synuclein antibodies that come to market. EASE OF USE Inhibition of protein accumulation and aggregation is a novel mechanism of action that may ultimately prove in clinical practice to impact more than motor symptoms. UNIQUE MOA $550 - 725M Potential annual peak sales for ATH434 in the U.S. in MSA*
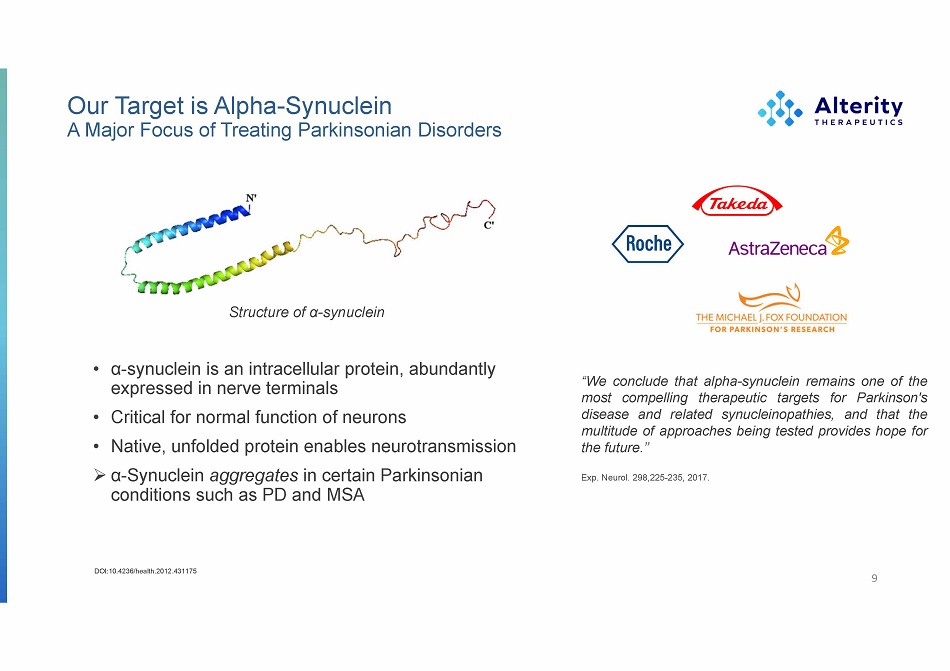
Our Target is Alpha - Synuclein A Major Focus of Treating Parkinsonian Disorders • α - synuclein is an intracellular protein, abundantly expressed in nerve terminals • Critical for normal function of neurons • Native, unfolded protein enables neurotransmission » α - Synuclein aggregates in certain Parkinsonian conditions such as PD and MSA 9 DOI:10.4236/health.2012.431175 Structure of α - synuclein “We conclude that alpha - synuclein remains one of the most compelling therapeutic targets for Parkinson's disease and related synucleinopathies, and that the multitude of approaches being tested provides hope for the future . ’’ Exp. Neurol. 298,225 - 235, 2017.
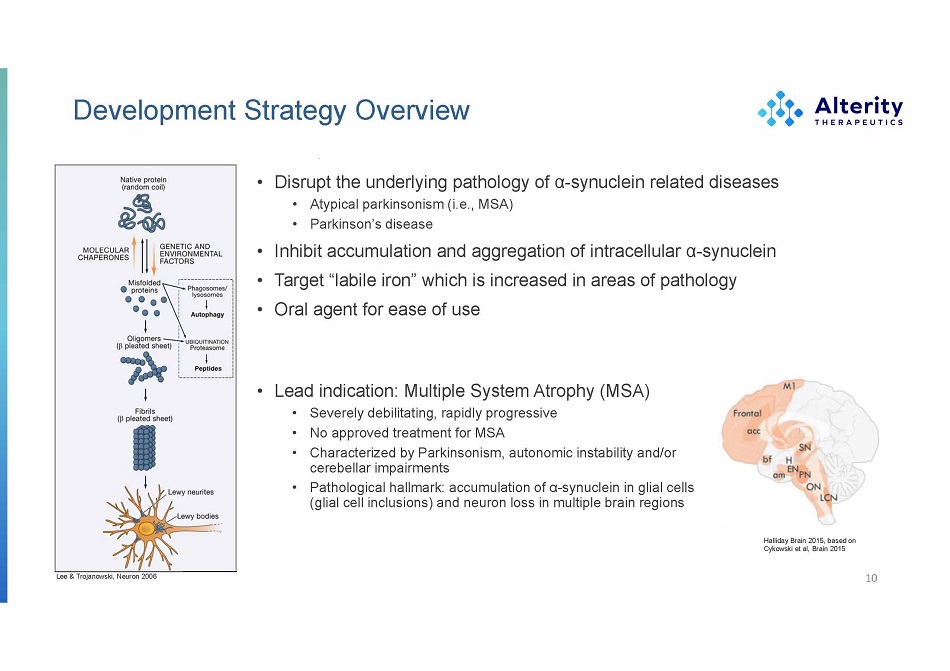
Development Strategy Overview • Disrupt the underlying pathology of α - synuclein related diseases • Atypical parkinsonism (i.e., MSA) • Parkinson’s disease • Inhibit accumulation and aggregation of intracellular α - synuclein • Target “labile iron” which is increased in areas of pathology • Oral agent for ease of use 10 Lee & Trojanowski, Neuron 2006 Halliday Brain 2015, based on Cykowski et al, Brain 2015 • Lead indication: Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) • Severely debilitating, rapidly progressive • No approved treatment for MSA • Characterized by Parkinsonism, autonomic instability and/or cerebellar impairments • Pathological hallmark: accumulation of α - synuclein in glial cells (glial cell inclusions) and neuron loss in multiple brain regions

Increased Brain Iron in Synuclein - related Diseases 11 Dexter et al. Brain.1991 Parkinson’s disease Multiple System Atrophy Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (MRI) to assess brain iron MSA Control Courtesy of P. Trujillo, D. Claassen n = 24 n = 13 n = 9 n = 7 * n = 3 n = 8 * 0 10000 20000 nmol iron/g of human brain 30000 Cerebral cortex Caudate nucleus Putamen (M) Putamen (L) Globus pallidus (M) Globus pallidus (L) Substantia nigra (T) Cerebellum n = 11 n = 8 n = 8 n = 8 n = 9 n = 8 n = 12 n = 8 n = 11 n = 8 * n = 9 n = 6 * 0 30000 n = 10 n = 8 * n = 10 n = 8 * 10000 20000 nmol iron/g of human brain Healthy Patients Substantia nigra (T) Substantia nigra (pc) Cerebellum
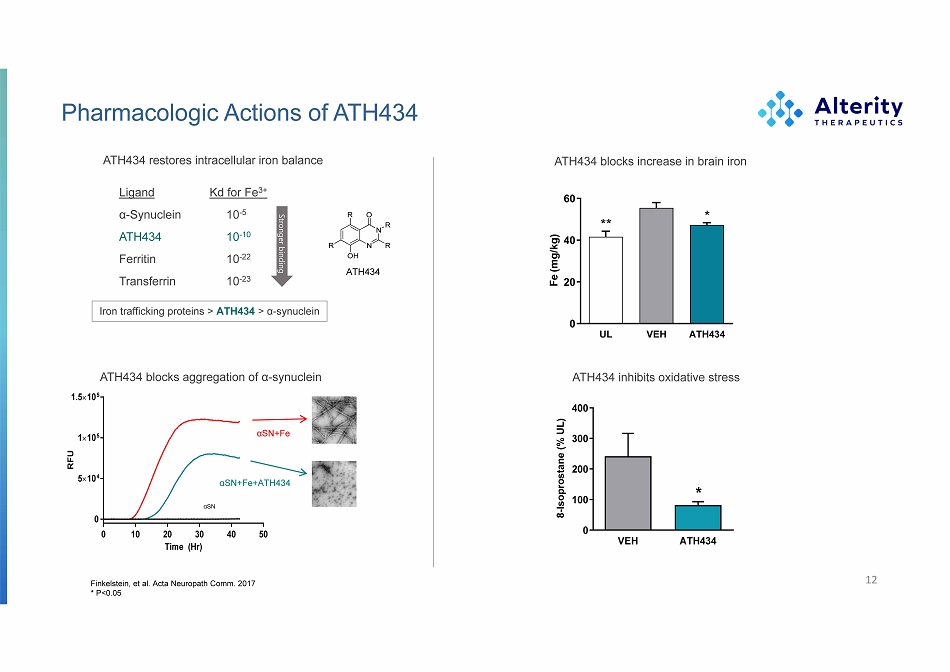
Pharmacologic Actions of ATH434 ATH434 blocks aggregation of α - synuclein αSN+Fe+ATH434 αSN+Fe αSN Finkelstein, et al. Acta Neuropath Comm. 2017 * P<0.05 ATH434 blocks increase in brain iron ATH434 inhibits oxidative stress 12 F e (m g / k g ) Ligand α - Synuclein ATH434 Ferritin T ransferrin Kd for Fe 3+ 10 - 5 10 - 10 10 - 22 10 - 23 Str onger binding ATH434 restores intracellular iron balance Iron trafficking proteins > ATH434 > α - synuclein ATH434

ATH434 Reduces Alpha - Synuclein - related Neuropathology and Improves Motor Function in Parkinson’s Disease Animal Models Vehicle ATH434 ATH434 Dose: 30 mg/kg MPTP Mouse Preserves nigral neurons ↓ α - Synuclein Improves motor function h A53T Mouse Finkelstein, et al. Acta Neuropath Comm. 2017 TG: transgenic, W/T: wild type, UL: unlesioned, C: control * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 hA53T - syn 0 2 4 6 ** VEH ATH434 VEH ATH434 0 50 1 0 0 TG W / T P<0.001 0 1 3 10 30 80 C 0 3 0 0 0 6 0 0 0 AT H 43 4 ( mg /k g ) *** *** ** * 0 1 3 10 30 80 C 0 6 12 A T H 4 3 4 (mg / k g ) ** * 13
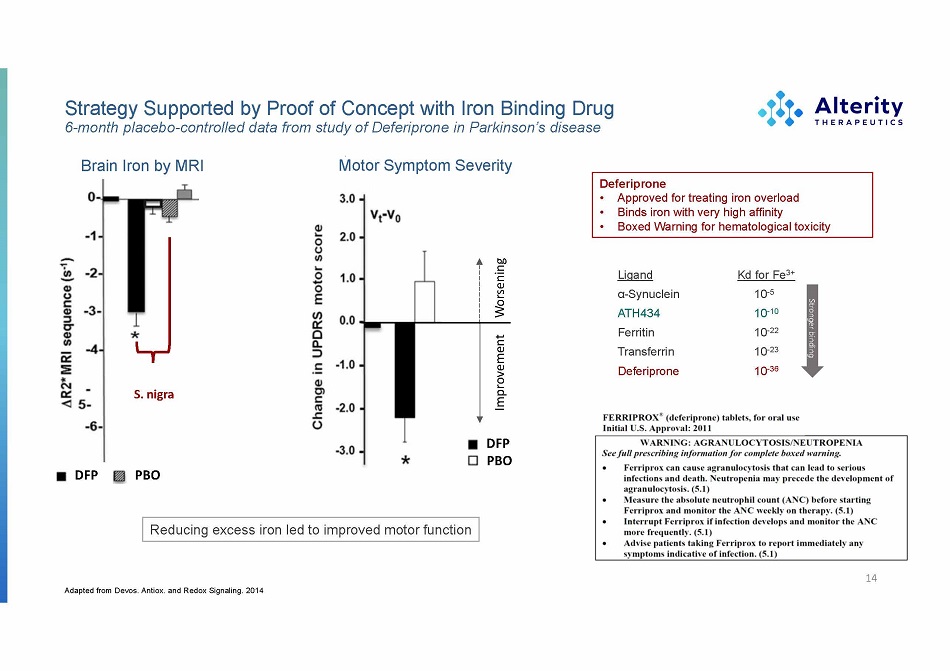
Strategy Supported by Proof of Concept with Iron Binding Drug 6 - month placebo - controlled data from study of Deferiprone in Parkinson’s disease 14 Adapted from Devos. Antiox. and Redox Signaling. 2014 Brain Iron by MRI Motor Symptom Severity S . nig r a DFP PBO S. nigra Deferiprone • Approved for treating iron overload • Binds iron with very high affinity • Boxed Warning for hematological toxicity Reducing excess iron led to improved motor function DFP PBO Improvement Worsening Ligand α - Synuclein ATH434 Ferritin T ransferrin Deferiprone Kd for Fe 3+ 10 - 5 10 - 10 10 - 22 10 - 23 10 - 36 Str onger binding
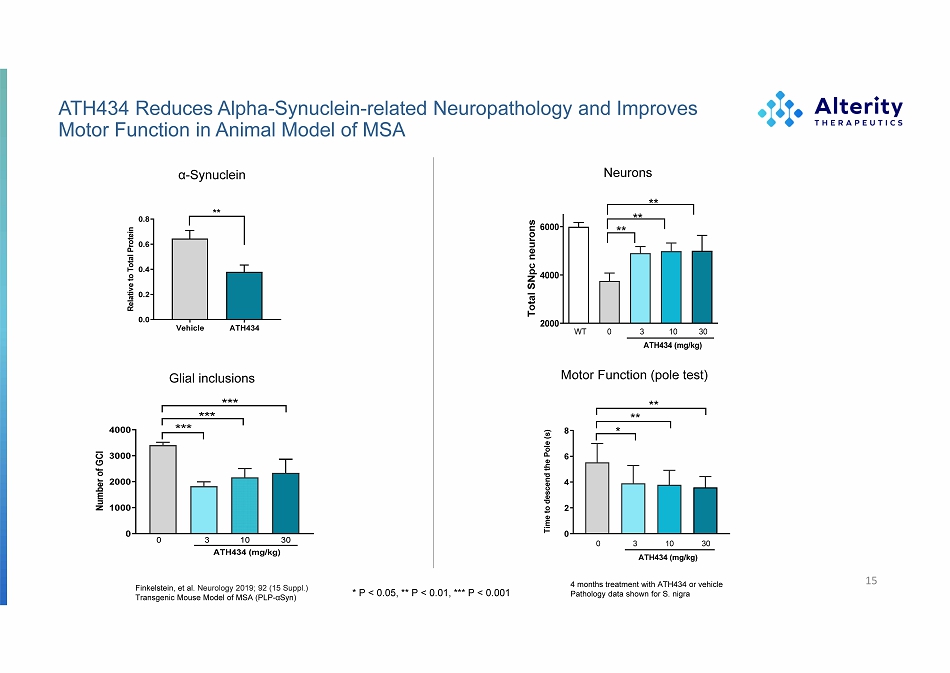
ATH434 Reduces Alpha - Synuclein - related Neuropathology and Improves Motor Function in Animal Model of MSA 15 * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 Neurons Motor Function (pole test) Glial inclusions α - Synuclein Finkelstein, et al. Neurology 2019; 92 (15 Suppl.) Transgenic Mouse Model of MSA (PLP - αSyn) 4 months treatment with ATH434 or vehicle Pathology data shown for S. nigra

Clinical Development 16
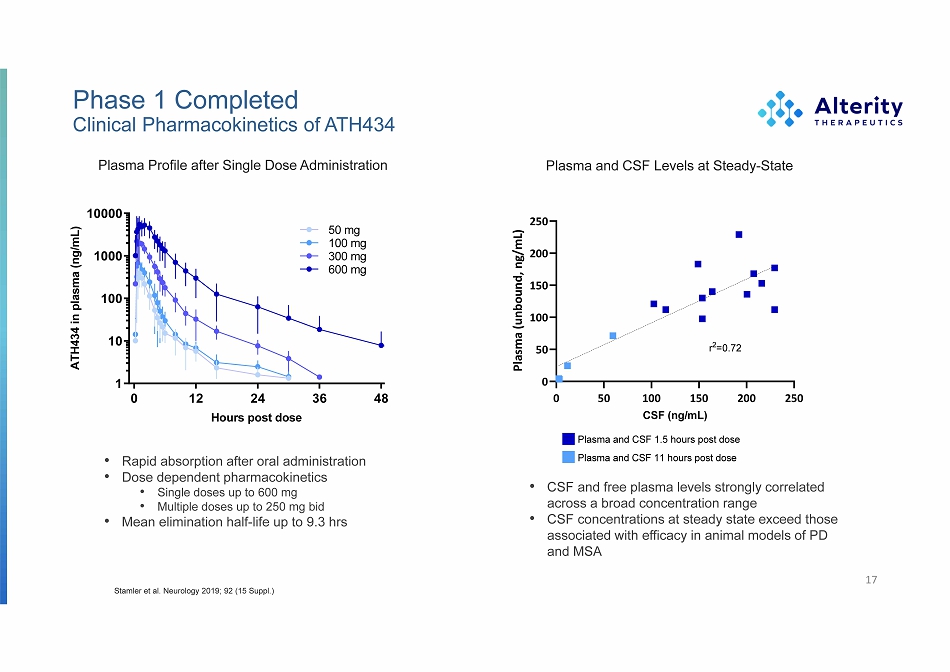
Phase 1 Completed Clinical Pharmacokinetics of ATH434 Plasma Profile after Single Dose Administration • CSF and free plasma levels strongly correlated across a broad concentration range • CSF concentrations at steady state exceed those associated with efficacy in animal models of PD and MSA 17 Stamler et al. Neurology 2019; 92 (15 Suppl.) • Rapid absorption after oral administration • Dose dependent pharmacokinetics • Single doses up to 600 mg • Multiple doses up to 250 mg bid • Mean elimination half - life up to 9.3 hrs ATH434 in plasma (ng/mL) Plasma and CSF Levels at Steady - State
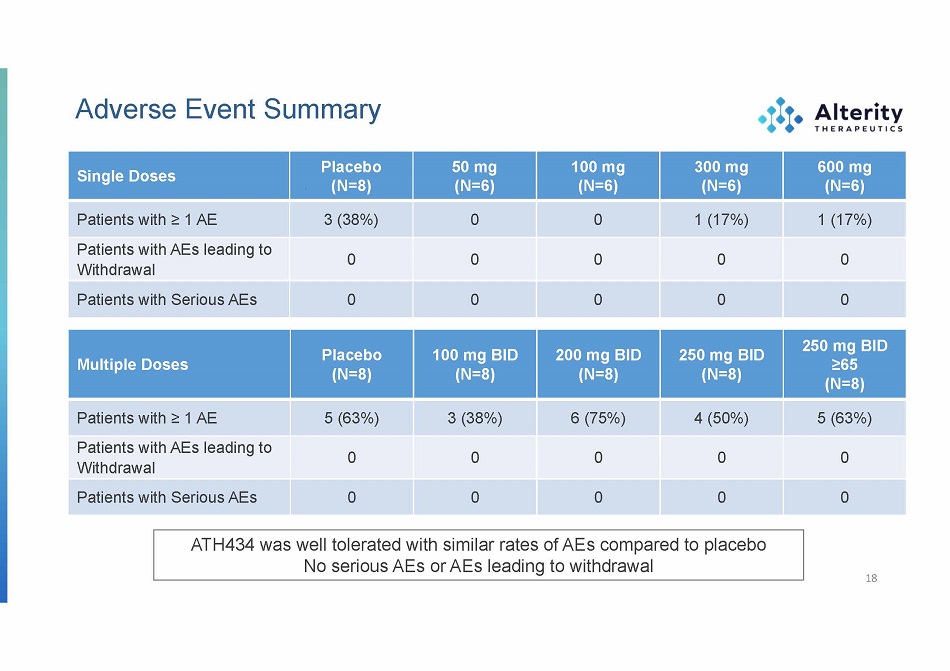
Adverse Event Summary Single Doses Placebo (N=8) 50 mg (N=6) 100 mg (N=6) 300 mg (N=6) 600 mg (N=6) Patients with ≥ 1 AE 3 (38%) 0 0 1 (17%) 1 (17%) Patients with AEs leading to Withdrawal 0 0 0 0 0 Patient s wit h Seriou s AEs 0 0 0 0 0 ATH434 was well tolerated with similar rates of AEs compared to placebo No serious AEs or AEs leading to withdrawal Multiple Doses Placebo (N=8) 100 mg BID (N=8) 200 mg BID (N=8) 250 mg BID (N=8) 250 mg BID ≥65 (N=8) Patients with ≥ 1 AE 5 (63%) 3 (38%) 6 (75%) 4 (50%) 5 (63%) Patients with AEs leading to Withdrawal 0 0 0 0 0 Patient s wit h Seriou s AEs 0 0 0 0 0 18
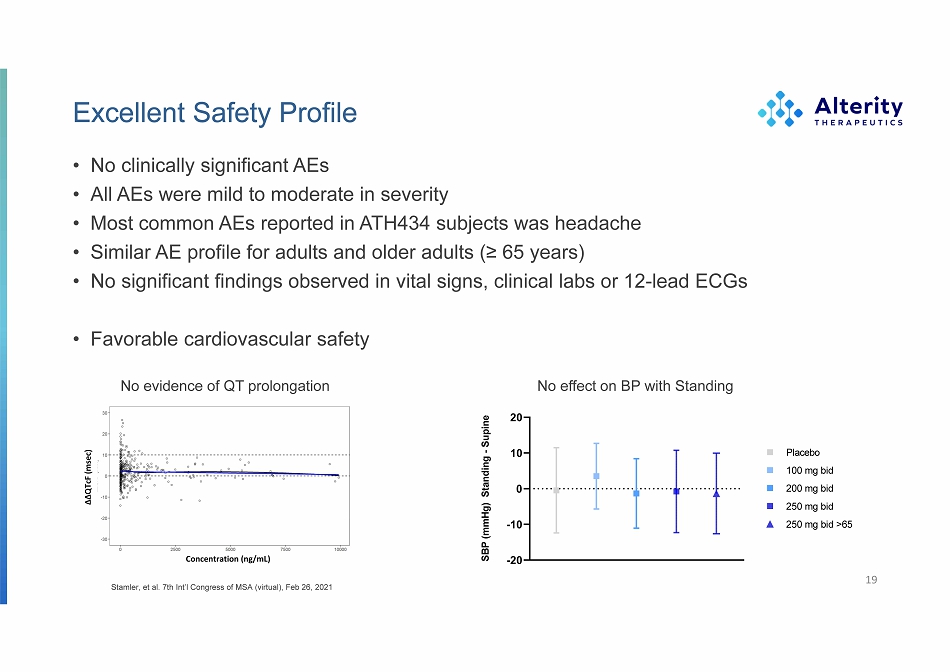
Excellent Safety Profile • No clinically significant AEs • All AEs were mild to moderate in severity • Most common AEs reported in ATH434 subjects was headache • Similar AE profile for adults and older adults (≥ 65 years) • No significant findings observed in vital signs, clinical labs or 12 - lead ECGs • Favorable cardiovascular safety 19 SBP (mmHg) Standing - Supine ΔΔ Q Tc F (msec) Concentration (ng/mL) No evidence of QT prolongation No effect on BP with Standing Stamler, et al. 7th Int’l Congress of MSA (virtual), Feb 26, 2021

bioMUSE Natural History Study • Design: Observational (no treatment) • Objective: De - risk Phase 2 study • Identify biomarker(s) suitable for endpoint in treatment study • Evaluate the change in biomarkers and clinical scales in patients with early MSA to track disease progression • Population: Early MSA patients similar to Phase 2 population • Observation period: 12 months • Sample size: 10 • Biomarkers • MRI: Iron content, regional blood flow/metabolism, neuromelanin, oxidative stress • Protein: neurofilament light protein (CSF, plasma), Aggregating α - synuclein (CSF), phos - α - synuclein (skin) • Wearable movement sensors • Clinical Endpoints • Clinical: Motor exam, UMSARS (function/ADL inventory), global assessments of severity and change (clinician, patient) • Functional: Timed Up and Go 20
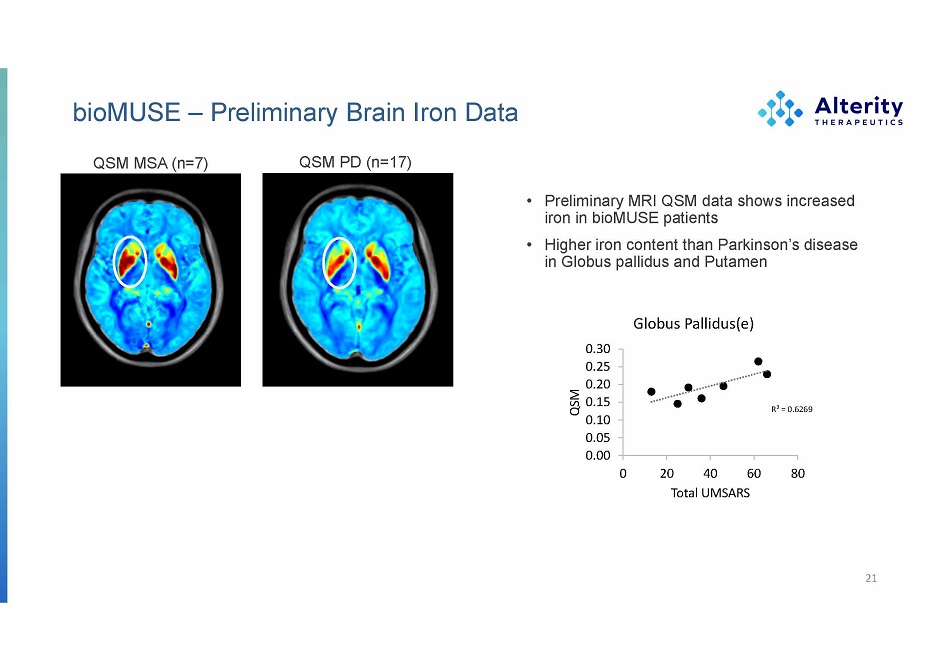
bioMUSE – Preliminary Brain Iron Data 21 QSM MSA (n=7) QSM PD (n=17) • Preliminary MRI QSM data shows increased iron in bioMUSE patients • Higher iron content than Parkinson’s disease in Globus pallidus and Putamen Globus Pallidus(e) R² = 0.6269 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 0 20 40 60 80 QSM T o t al UM S A R S

Phase 2 Design • Design: Randomized, double - blind, placebo controlled • Objectives: • Assess efficacy, safety and tolerability of ATH434 in subjects with MSA • Assess target engagement based on imaging and fluid biomarkers of disease progression • Evaluate the pharmacokinetics of ATH434 in target population • Population: Early MSA patients • Parkinsonism, motor symptom onset < 3 years, ambulatory (assistance ok) • No severe impairment on speech, swallowing, walking, falls • Sample size: 60 • Sites: 25 • Treatment: 6 months • ATH434 high dose BID • ATH434 low dose BID • Placebo • Efficacy Endpoints • MRI: Iron by QSM/R2*, neuromelanin, regional blood flow/cerebral metabolism, oxidative stress • Fluid/tissue biomarkers: Neurofilament light protein (CSF, plasma), Aggregating α - synuclein (CSF), phos - α - synuclein (skin) • Wearable movement sensors • Clinical: Motor exam, UMSARS (function/ADL inventory), levodopa dose equivalents, global assessments of severity and change • Functional: Timed Up and Go • Safety Endpoints: AE reporting, clinical laboratory parameters, 12 - lead ECGs 22

Clinical Development Timeline ATH434 in Multiple System Atrophy 23 2H ’21 First patient enrolled in Phase 2 1 H ’ 22 Last patient enrolled in Phase 2 2H ’20 European National Meetings Natural History Study in early MSA Phase 2 Optimization 2021 2022 2H ’22 T o p line Data 1H ’21 Phase 2 Feasibili ty Phase 2 Study in early MSA E.g., Data to inform P2
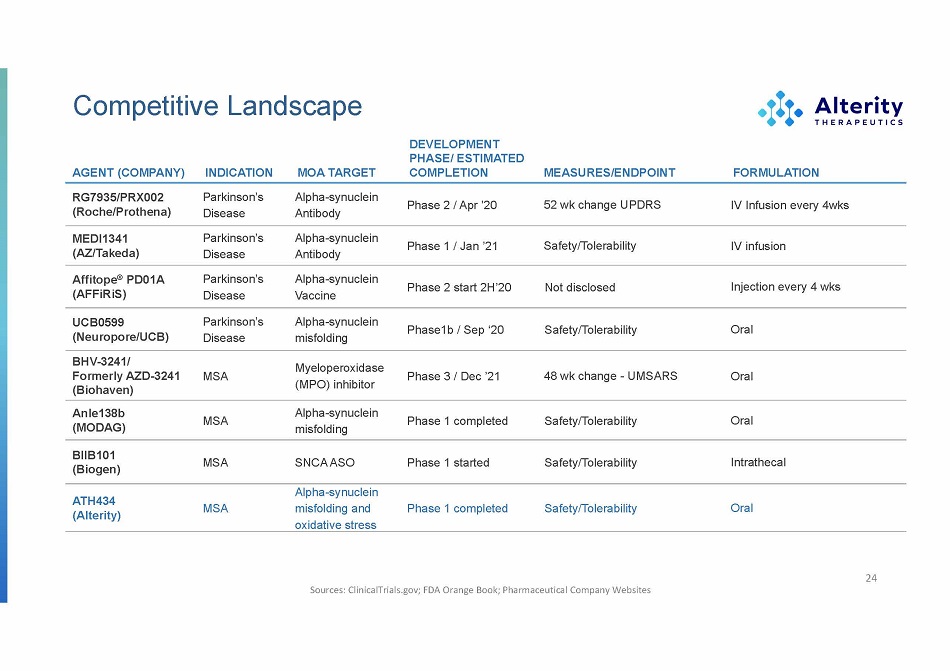
Competitive Landscape (Roche/Prothena) Disease Antibody (AZ/Takeda) Disease Antibody (AFFiRiS) Disease V a ccine (Neuropore/UCB) Disease misfolding (Biohaven) (MODAG) misfolding (Biogen) (Alterity) DEVELOPMENT PHASE/ ESTIM A TED AGENT (COMPANY) INDICATION MOA TARGET COMPLETION MEASURES/ENDPOINT FORMULATION RG7935/PRX002 Parkinson’s Alpha - synuclein Phase 2 / Apr ’20 52 wk change UPDRS IV Infusion every 4wks MEDI1341 Parkinson’s Alpha - synuclein Phase 1 / Jan ’21 Safety/Tolerability IV infusion Affitope ® PD01A Parkinson’s Alpha - synuclein Phase 2 start 2H’20 Not disclosed Injection every 4 wks UCB0599 Parkinson’s Alpha - synuclein Phase1b / Sep ‘20 Safety/Tolerability Oral BHV - 3241/ Myeloperoxidase Formerly AZD - 3241 MSA (MPO) inhibitor Phase 3 / Dec ’21 48 wk change - UMSARS Oral Anle138b MSA Alpha - synuclein Phase 1 completed Safety/Tolerability Oral BIIB101 MSA SNCA ASO Phase 1 started Safety/Tolerability Intrathecal Alpha - synuclein ATH434 MSA misfolding and Phase 1 completed Safety/Tolerability Oral oxidative stress Sources: ClinicalTrials.gov; FDA Orange Book; Pharmaceutical Company Websites 24

Investment Summary x Targeting Orphan disease with no approved treatments • ATH434 has potential U.S. peak sales up to US$ 725 million x Development team with proven track record at FDA x Lea d dru g candidat e A TH434 • Completed Phase 1 with excellent safety profile • Achieved CSF concentrations associated with robust efficacy in MSA animal model • Novel mechanism targets α - synuclein aggregation and root cause of oxidative stress x Phase 2 program • Ongoing Natural History study to de - risk P2 study • Enrollment to start 2H ‘21 x Strong pipeline potential with new patent family supporting next generation therapies 25


























