Exhibit 99.1

Alterity Therapeutics (NASDAQ: A THE, AS X: A TH) AGM CEO Address 2021 Davi d Stamle r , MD CEO 1 2 Novembe r 2021

Forward Looking Statements This presentation may contain some statements that may be considered “Forward - Looking Statements”, within the meaning of the US Securities Laws. Thus, any forward - looking statement relating to financial projections or other statements relating to the Company’s plans, objectives, expectations or intentions involve risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially. For a discussion of such risks and uncertainties as they relate to us, please refer to our 2021 Form 20 - F, filed with US Securities and Exchange Commission, in particular Item 3, Section D, titled “Risk Factors.’’ 2

Alterity is dedicated to creating an alternate future for people living with neurodegenerative diseases. Alterity = the state of being different Our goal is to modify the course of disease We’re here to disrupt the trajectory of illness and improve quality of life 3

Investment Highlights Novel approach to treat the underlying pathology of disease Strong and highly experienced management team with significant R&D experience including 3 drug approvals by US FDA ATH434 is a novel drug candidate targeting key proteins implicated in neurodegeneration of Parkinson’s Disease and related disorders First therapeutic target: Multiple System Atrophy (MSA), a devastating disease with no approved treatments Orphan Drug designation in the U.S. and EU Advancing to a Phase 2 clinical trial Strong patent portfolio 4

Recent Progress Presentation of advanced quantitative MRI as potential novel biomarker in early MSA Two new US patents expand portfolio of next generation compounds for neurodegenerative diseases Publication demonstrating neuroprotective effect of ATH434 in animal model of MSA Michael J. Fox Foundation grant for ~US$500K for Parkinson’s disease EMA endorses clinical strategy for Phase 2 study in early MSA patients U S FD A pro vide s de v e lopment pathway for ATH 434 in Multiple System Atrophy Expanding bioMUSE Natural History study in early MSA 5

Experienced Leadership Team with Multiple FD A Approval s in Neurology Margaret Bradbury, Ph.D. VP, Nonclinical Development Auspex/Teva | Neurocrine | Merck • Auspex - led strategic planning and program management in Huntington Disease chorea from IND through NDA filing • Teva - led non - clinical development of several neuroscience programs Kathryn Andrews, CPA Chief Financial Officer Antisense Therapeutics | Rio Tinto | Consultant • Extensive experience advising private and public CFOs, mainly in the biotechnology sector • Prior CFO and Company Secretary o f Antisens e Therapeutics Limited • 15+ years in finance and accounting roles at Rio Tinto Limited and BP Australia Limited David Stamler, M.D. Chief Executive Officer Auspex/Teva | Abbott | Prestwick Xenoport | Fujisawa • 3 FD A Approval s i n Neurolo g y • Forme r CMO , Auspex • VP, Clinical Development & Therapeutic Head, Movement Disorders, Teva Pharmaceuticals • Part of Teva’s US$3.5 billion acquisitio n o f Auspe x i n 2015 • Led development of AUSTEDO ® (deutetrabenazine) for treatment of Huntington disease and Tardive dyskinesia, both approved in 2017 Cynthia Wong, M.P.H . Senior Director, Clinical Operations Auspex/Teva | Nextwave | Astex | Intermune | Impax Labs • Clinical Operations leadership at Auspex/Teva. • Led clinical trial activities for the registratio n stud y o f AUSTED O ® in Huntington Disease chorea. • Prior, led Phase 1 - 3 studies, including registration studies for marketing approval for Quillichew ER, Esbriet and Infergen. 6
Parkinsonian Disorders: A Significant Unmet Need Parkinsonism is a syndrome of motor symptoms that includes slowed movement, stiffness and tremor • A major source of disability Parkinsonian disorders also include atypical forms such as Multiple system atrophy (MSA) and Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) • “Atypical” as have prominent non - motor symptoms and a limited response to available treatments Current therapies treat the symptoms and NOT the underlying pathology of disease P A RKINSON’S DISEASE MSA PSP PARKINSONIAN DISORDERS 7

Discovery and Development Portfolio in Neurodegenerative Diseases Program Indication Current Status Future Plans bioMUSE Natural History Study Multiple System Atrophy Ongoing Partner: Enrolling up to 20 patients ATH434 Multiple System Atrophy Phase 1 Complete Phase 2 expected to initiate Q1 2022 ATH434 Parkinson’s Disease Preclinical studies to optimize dosing Partner: Proof of concept study in Parkinson’s disease Drug Discovery Neurodegenerative diseases Discovery ongoing Generate new IND candidates 8

Alterity’s Approach to Treating Parkinsonian Disorders 9
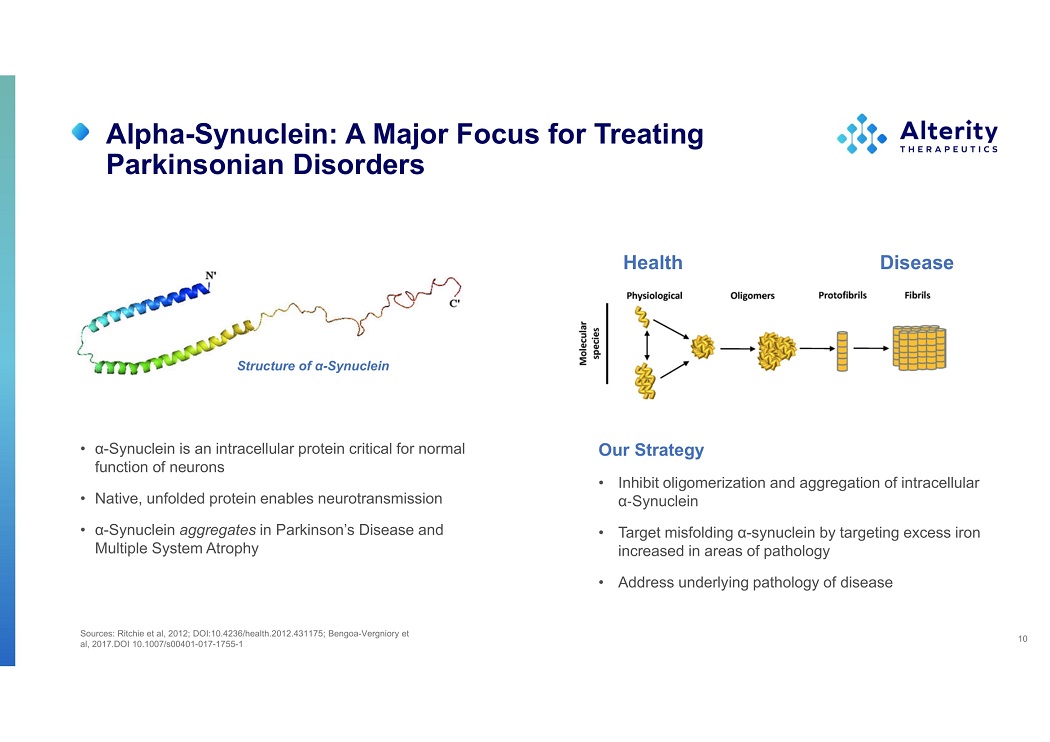
Alpha - Synuclein: A Major Focus for Treating Parkinsonian Disorders Sources: Ritchie et al, 2012; DOI:10.4236/health.2012.431175; Bengoa - Vergniory et al, 2017.DOI 10.1007/s00401 - 017 - 1755 - 1 10 • α - Synuclein is an intracellular protein critical for normal function of neurons • Native, unfolded protein enables neurotransmission • α - Synuclein aggregates in Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy Health Disease Our Strategy • Inhibit oligomerization and aggregation of intracellular α - Synuclein • Target misfolding α - synuclein by targeting excess iron increased in areas of pathology • Address underlying pathology of disease Structure of α - Synuclein

Sources: Kaindlstorfer, J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018; Rodgers, J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011 11 α - Synuclein and iron are strong contributors to the pathogenesis of MSA Prominent pathology in Oligodendroglial cells (ODG) • ODGs are vital support cells for neurons • ODGs are cells with highest iron content in the CNS • Demonstrate prominent α - synuclein pathology • Hallmark of MSA: accumulation of α - synuclein within ODGs and neuron loss in multiple brain regions Adverse impact of increased labile iron • Promotes α - synuclein aggregation • Root cause of oxidative stress which damages intracellular structures and leads to neuroinflammation Oxidative Stress Neuroinflammation Iron Dyshomeostasis Iron is Critical in the Pathogenesis of Parkinsonian Disorders

Our Approach: Dual Mode of Action to Address the Underlying Pathology of Disease 12 Bind and redistribute excess iron in the CNS of patients with Parkinsonian disorders Reduce α - synuclein aggregation and oxidative stress Rescue neurons in multiple brain regions to address underlying pathology Targeting protein misfolding aggregation by binding and redistributing iron

Increased Brain Iron in Synuclein - related Diseases 13 Dexter et al. Brain.1991 Parkinson’s disease Multiple System Atrophy Advanced Quantitative MRI to measure brain iron MSA Control Courtesy of P. Trujillo, D. Claassen n = 24 n = 13 n = 9 n = 7 * n = 3 n = 8 * 0 10000 20000 nmol iron/g of human brain 30000 Cerebral cortex Caudate nucleus Putamen (M) Putamen (L) Globus pallidus (M) Globus pallidus (L) Substantia nigra (T) Cerebellum n = 11 n = 8 n = 8 n = 8 n = 9 n = 8 n = 12 n = 8 n = 11 n = 8 * n = 9 n = 6 * 0 30000 n = 10 n = 8 * n = 10 n = 8 * 10000 20000 nmol iron/g of human brain Patients Healthy Substantia nigra (T) Substantia nigra (pc) Cerebellum

Pharmacologic Actions of ATH434 14 Reduces α - synuclein aggre g a t io n αSN+Fe αSN+Fe+ATH434 αSN Finkelstein, et al. Acta Neuropath Comm. 2017; Friedlich, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2007; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 Block s increase in brain iron Inhibits oxidative stress in vivo ATH434 redistributes excess iron Ligand Kd for Fe 3+ α - Synuclein ATH434 Ferritin T ransferrin 10 - 5 10 - 10 10 - 22 10 - 23 Iron trafficking proteins > ATH434 > α - synuclein F e (m g / k g ) Stronger binding

MPTP Mouse hA53T - syn V eh i cle A T H4 34 0 2 4 6 h A53T Mouse Finkelstein, et al. Acta Neuropath Comm. 2017 TG: transgenic, W/T: wild type, UL: unlesioned, C: control * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 ↓ α - Synuclein Preserves Neurons ** 3 0 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 1 3 10 30 80 C ATH434 (mg/kg) *** *** ** * ATH434 Reduces Alpha - Synuclein - related Neuropathology in Parkinson’s Disease Animal Models 15

Reducing excess iron led to improved motor function Source: 6 - month data from study of deferiprone in Parkinson’s disease; Adapted from Devos. Antiox. and Redox Signaling . 2014 Deferiprone • Designed to treat iron overload • Binds iron with very high affinity • Boxed Warning for hematological toxicity Ligand α - Synuclein ATH434 Ferritin Transferrin Deferip r one Kd for Fe 3+ 10 - 5 10 - 10 10 - 22 10 - 23 10 - 36 Stronger binding Clinical Strategy Supported by Proof of Concept with Iron Binding Drug in Parkinson’s Disease 16 Brain Iron by MRI S. nigra DFP PBO S . nigra Motor Symptom Severity DFP PBO Improvement Worsening
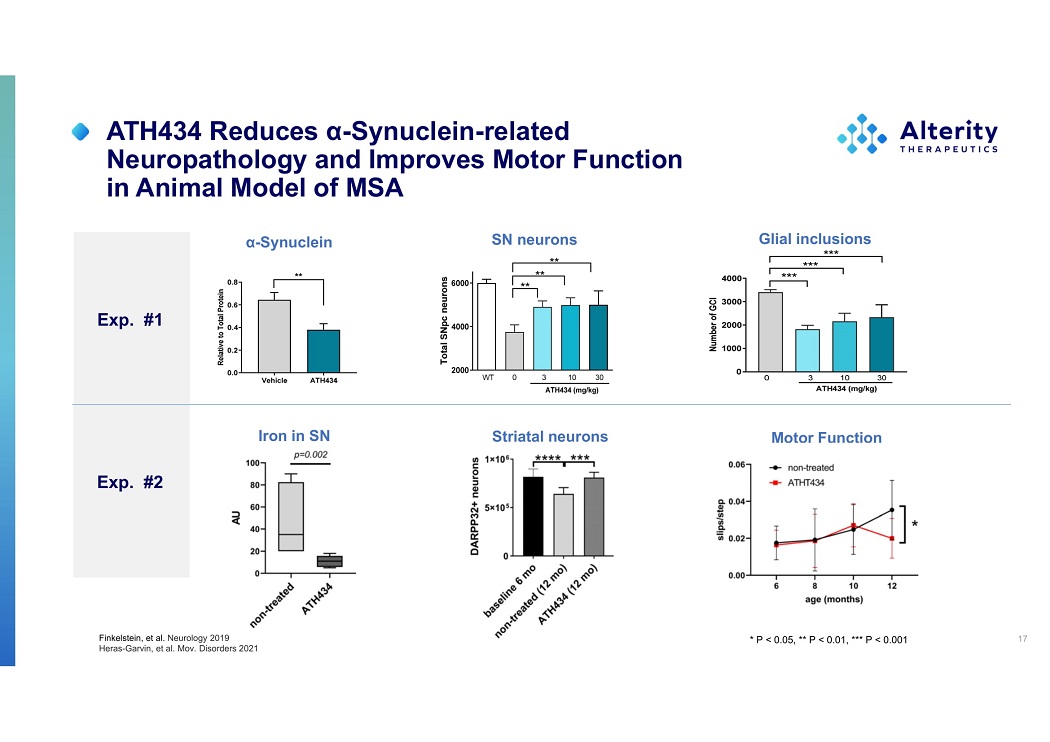
ATH434 Reduces α - Synuclein - related Neuropathology and Improves Motor Function in Animal Model of MSA 17 * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 α - Synuclein Finkelstein, et al. Neurology 2019 Heras - Garvin, et al. Mov. Disorders 2021 SN neurons Glial inclusions Motor Function Exp. #1 Striatal neurons Iron in SN Exp. #2

ATH434: Clinical Development Program 18
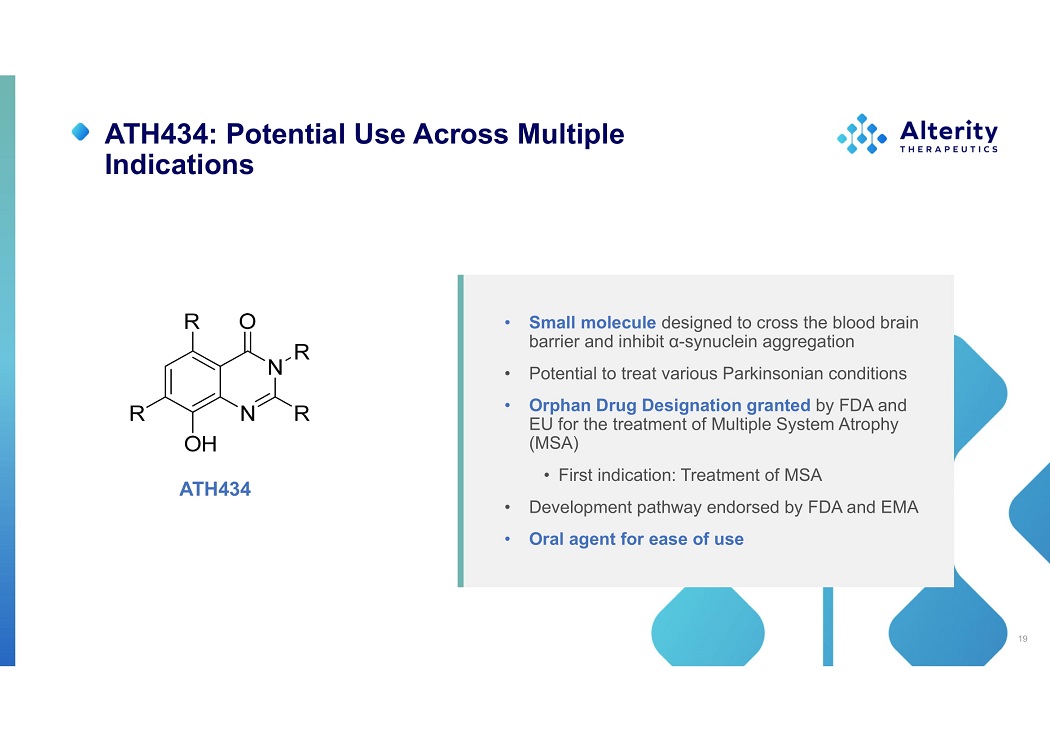
ATH434: Potential Use Across Multiple Indications • Small molecule designed to cross the blood brain barrier and inhibit α - synuclein aggregation • Potential to treat various Parkinsonian conditions • Orphan Drug Designation granted by FDA and EU for the treatment of Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) • First indication: Treatment of MSA • Development pathway endorsed by FDA and EMA • Oral agent for ease of use ATH434 19
Multiple System Atrophy (MSA) is a Rare, Neurodegenerative Disorder Characterized by Parkinsonism, autonomic instability and/or cerebellar impairments Affects the body's involuntary (autonomic) functions, including blood pressure, bladder control and bowel function Current treatments only address symptoms of MSA Alterity development strategy • Target early stage MSA patients • Explore the effect of ATH434 treatment on biomarkers and preliminary effects on clinical measures Halliday Brain 2015, based on Cykowski, Brain 2015 20

MSA is Highly Debilitating and Rapidly Progressive Fanciulli, Wenning. NEJM 2015;372:249 - 63. 60% require wheelchair confinement within 5 years 21
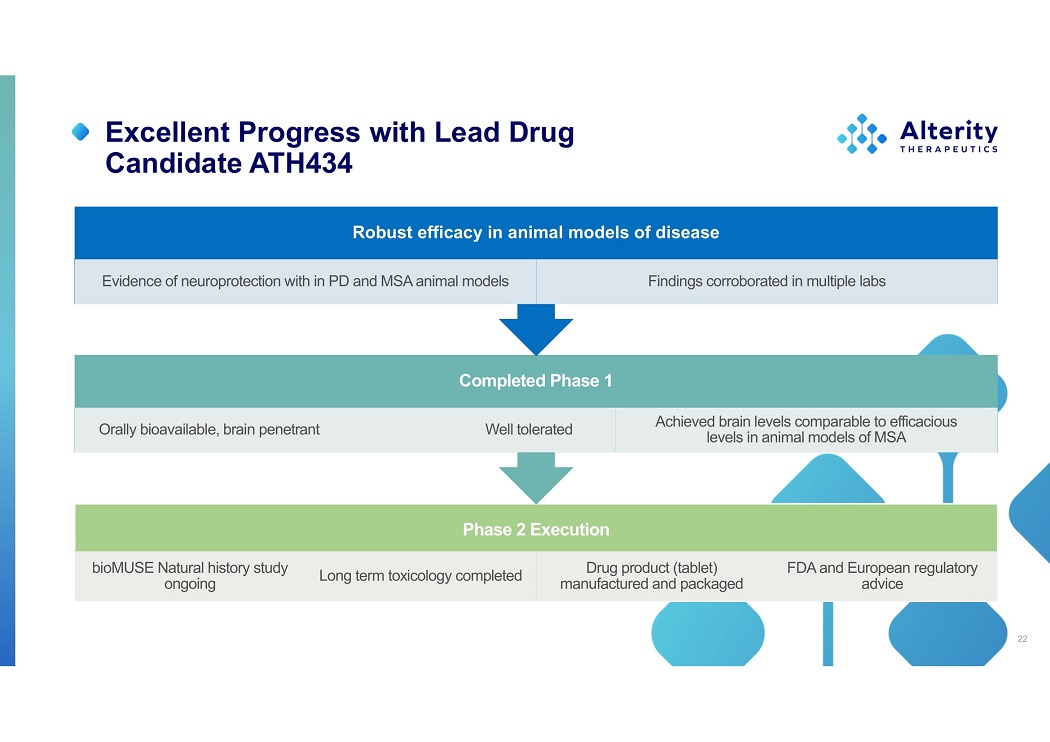
Excellent Progress with Lead Drug Candidate ATH434 Phas e 2 Execution bioMUSE Natural history study ongoing Lon g ter m toxicolog y completed Dru g produc t (tablet) manufacture d an d packaged FD A an d Europea n regulatory advice Complete d Phas e 1 Orall y bioavailable , brai n penetrant W el l tolerated Achieved brain levels comparable to efficacious level s i n anima l model s o f MSA Robust efficacy in animal models of disease Evidenc e o f neuroprotectio n wit h i n P D an d MS A anima l models Findings corroborated in multiple labs 22

Phase 1 Clinical Trial Design Design: Randomized, double blind, placebo - controlled, healthy adult and older adults (≥65 yo) Objectives: Assess safety and pharmacokinetics of ATH434 after single and multiple oral doses Plasma PK in each cohort, CSF sampled in two top multiple dose levels Safety: Adverse events, clinical labs, vital signs including orthostatics Continuous 12 - lead digital ECGs for QT assessment Multiple Ascending Doses (8A:2P/cohort) 100 mg bid 200 mg bid 250 mg bid Single Ascending Doses (6A:2P/cohort) 50 mg 600 mg 300 mg 100 mg ≥ 65 years 23
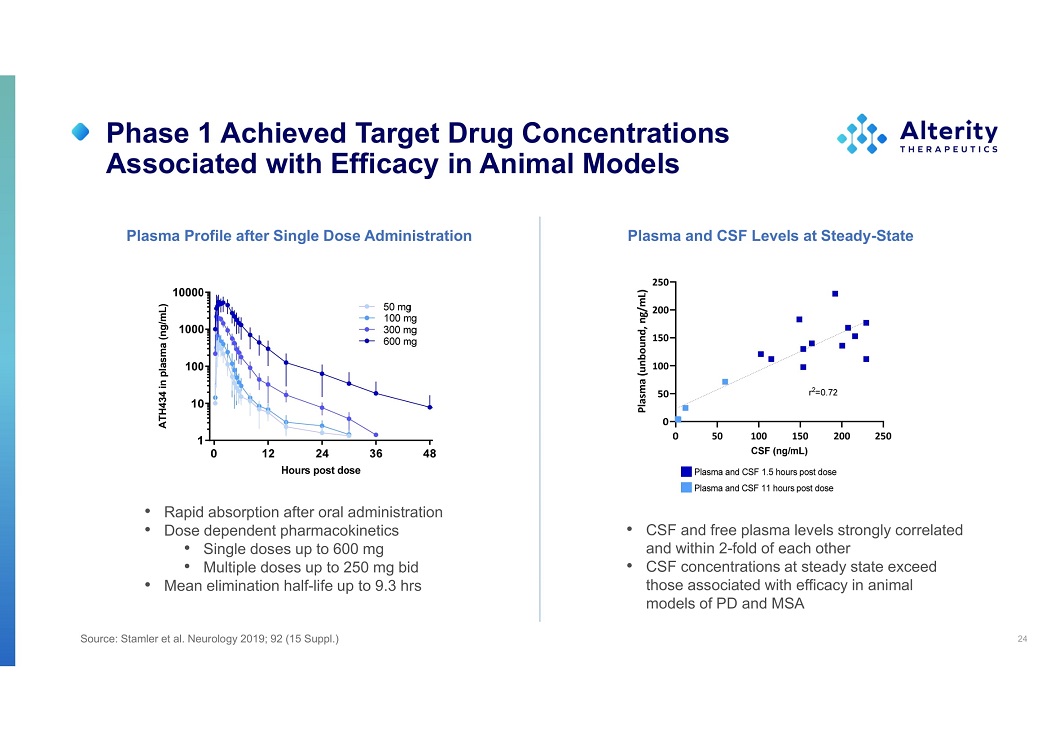
Phase 1 Achieved Target Drug Concentrations Associated with Efficacy in Animal Models 24 Plasma Profile after Single Dose Administration • Rapid absorption after oral administration • Dose dependent pharmacokinetics • Single doses up to 600 mg • Multiple doses up to 250 mg bid • Mean elimination half - life up to 9.3 hrs ATH434 in plasma (ng/mL) Plasma and CSF Levels at Steady - State • CSF and free plasma levels strongly correlated and within 2 - fold of each other • CSF concentrations at steady state exceed those associated with efficacy in animal models of PD and MSA Source: Stamler et al. Neurology 2019; 92 (15 Suppl.)
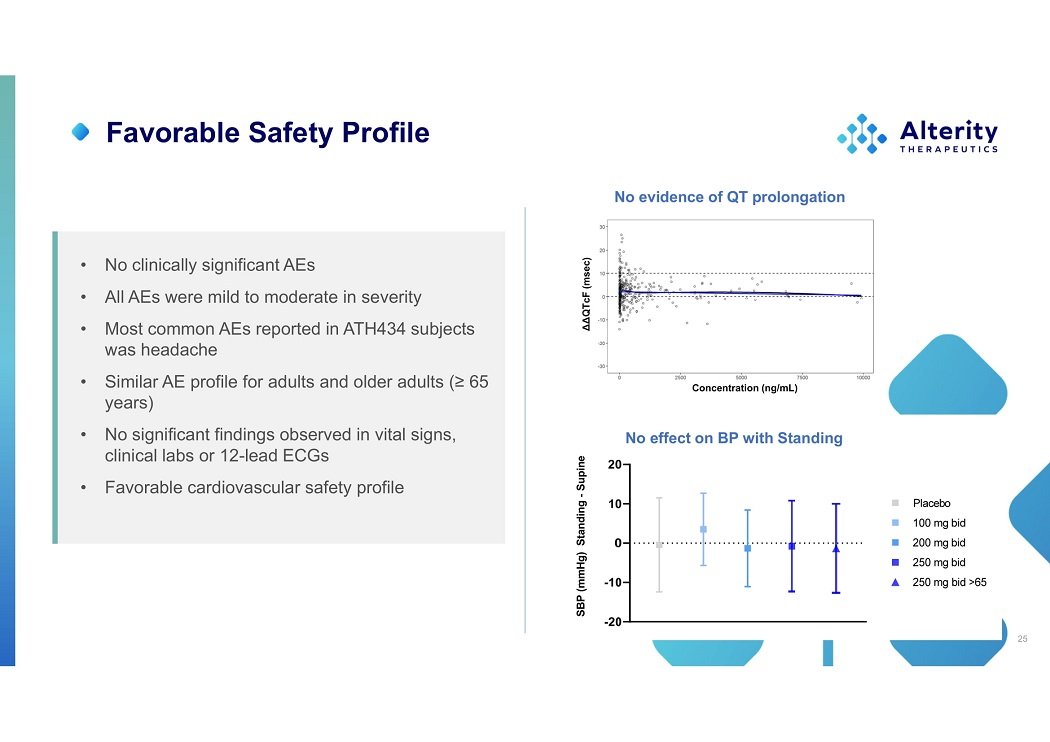
Favorable Safety Profile • N o clinicall y significan t AEs • All AEs were mild to moderate in severity • Most common AEs reported in ATH434 subjects was headache • Similar AE profile for adults and older adults (≥ 65 years) • No significant findings observed in vital signs, clinical labs or 12 - lead ECGs • Favorable cardiovascular safety profile SBP (mmHg) Standing - Supine ΔΔQT c F (msec) Concentration (ng/mL) No evidence of QT prolongation No effect on BP with Standing 25

ATH434 Well - Tolerated with No Serious Adverse Events Single Doses Placebo (N=8) 5 0 mg (N=6) 10 0 mg (N=6) 30 0 mg (N=6) 60 0 mg (N=6) Patients with ≥ 1 AE 3 (38%) 0 0 1 (17%) 1 (17%) Patients with AEs leading to Withdrawal 0 0 0 0 0 Patients with Serio u s AEs 0 0 0 0 0 Multiple Doses Placebo (N=8) 100 mg BID (N=8) 200 mg BID (N=8) 250 mg BID (N=8) 250 mg BID ≥65 (N=8) Patients with ≥ 1 AE 5 (63%) 3 (38%) 6 (75%) 4 (50%) 5 (63%) Patients with AEs leading to Withdrawal 0 0 0 0 0 Patients with Serio u s AEs 0 0 0 0 0 26

Biomarkers of Progression in Multiple System Atrophy (bioMUSE) Natural History Study Design • Observational Objectives • Inform and de - risk Phase 2 • Identify biomarker(s) suitable for endpoint in treatment study • Evaluate the change in biomarkers and clinical manifestations in patients with early MSA Population • Early - stage MSA patients similar to Phase 2 population • Expanding to n=20 subjects Observation period • 12 months Biomarkers • MRI: Iron (QSM/R2*), regional blood flow (ASL), neuromelanin, oxidative stress • Fluid: neurofilament light chain (CSF, plasma), Aggregating α - synuclein (CSF), phos - α - synuclein (skin) • Wearable movement sensors Clinical Endpoints • Clinical: Motor exam, autonomic function, activities of daily living inventory, global measures of severity and change (clinician, patient) • Functional: Timed Up and Go, 2 min Walk Test 27
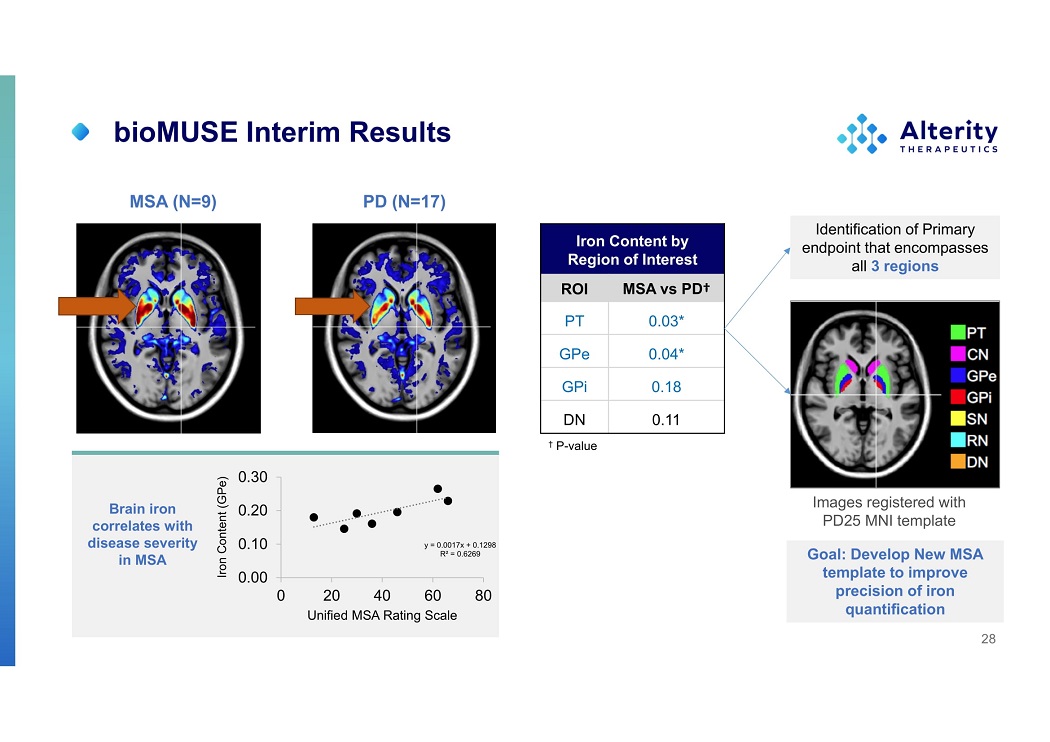
bioMUSE Interim Results Iron Content by Region of Interest ROI MSA vs PD † PT 0.03* GPe 0.04* GPi 0.18 DN 0.11 MSA (N=9) PD (N=17) † P - value Images registered with PD25 MNI template Identification of Primary endpoint that encompasses all 3 regions Goal: Develop New MSA template to improve precision of iron quantification 28 0.00 0.20 0.10 0.30 0 Iron Content (GPe) y = 0.0017x + 0.1298 R² = 0.6269 20 40 60 80 Unifie d MS A Ratin g Scale Brain iron correlates with disease severity in MSA

ATH434 Phase 2 Clinical Trial Early - Stage MSA Patients Design • Randomized, double - blind, placebo controlled Objectives • Assess efficacy and safety of ATH434 in subjects with MSA • Assess target engagement based on imaging and fluid biomarkers of disease severity • Evaluate the pharmacokinetics of ATH434 in target population Population • Early - stage patients with clinical diagnosis of MSA who are ambulatory, not severely impaired, and do not have long standing motor symptoms Sample Size • N=60 at ~30 sites in Australia, New Zealand, Europe and the U.S. Treatment • 12 - months treatment • Three groups: Two doses of ATH434 or placebo Primary Endpoint • Change in iron content as measured by brain MRI Secondary Endpoints • Additional imaging biomarkers and fluid biomarkers (aggregating α - synuclein, NFL) • Clinical measures of motor function, autonomic function, activities of daily living 29
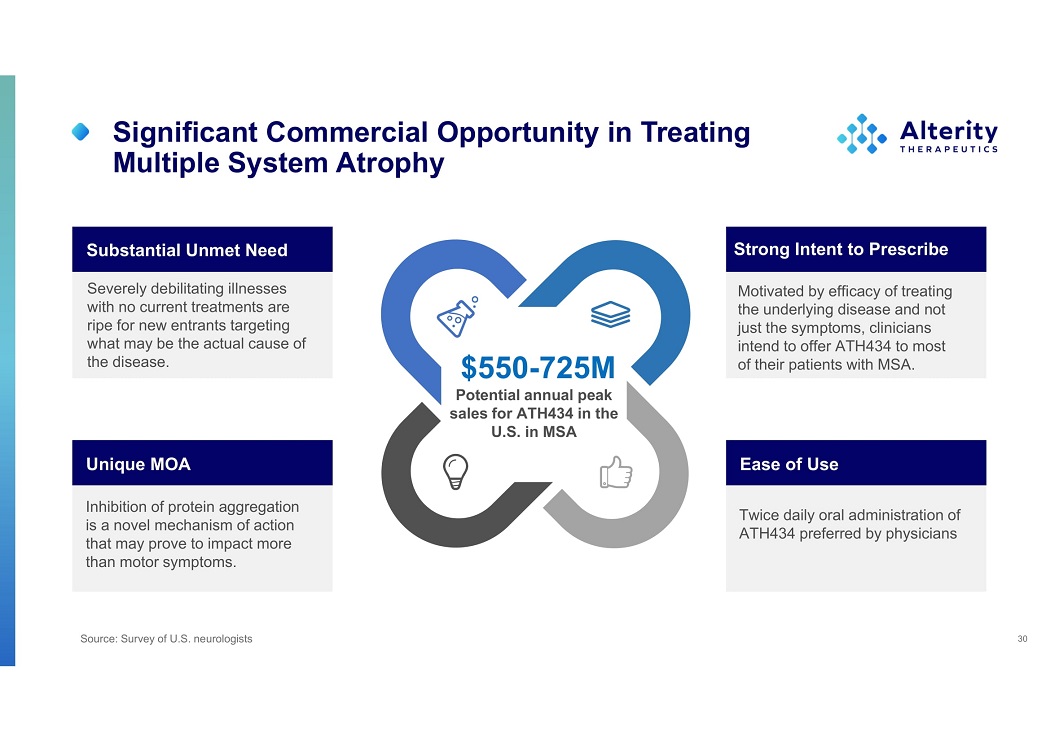
Significant Commercial Opportunity in Treating Multiple System Atrophy 30 Severely debilitating illnesses with no current treatments are ripe for new entrants targeting what may be the actual cause of the disease. Substantial Unmet Need Motivated by efficacy of treating the underlying disease and not just the symptoms, clinicians intend to offer ATH434 to most of their patients with MSA. Strong Intent to Prescribe Twice daily oral administration of ATH434 preferred by physicians Ease of Use Inhibition of protein aggregation is a novel mechanism of action that may prove to impact more than motor symptoms. Unique MOA $550 - 725M Potential annual peak sales for ATH434 in the U.S. in MSA Source: Survey of U.S. neurologists

Alterity: Poised for Progress 31 x Targeting Orphan disease with no approved treatments x Development team with proven track record and multiple FDA approvals x Lea d dru g candidat e A TH43 4 Progressin g t o Phas e 2 • Completed Phase 1 demonstrating well - tolerated safety profile and delivery of drug to site of action • Recen t publication s validatin g mechanis m o f action targetin g α - synuclein x Dru g discover y tea m generatin g patentabl e compounds a s nex t generatio n therapies x Stron g balanc e shee t wit h $41.3 M AU D a s o f 3 0 Sep t 21 Milestones x 1 H 2021 : Commenc e Phas e 2 Feasibilit y Study x Q 3 2021 : Presen t bioMUS E Natural Histor y biomarke r data x Q 4 2021 : Phas e 2 Clinica l Plan • Q 1 2022 : Initiat e Phas e 2 Clinica l T rial
