UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007 |
or
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | For the transition period from to |
Commission file number 0-50854
Thomas Properties Group, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | |
| Delaware | | 20-0852352 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (IRS employer identification number) |
| |
515 South Flower Street, Sixth Floor, Los Angeles, CA | | 90071 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | Zip Code |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code
(213) 613-1900
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of Each Class
Common Stock, $0.01 par value
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company, See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | | Accelerated filer x | | Non-accelerated filer ¨ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is an accelerated filer (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $379,492,017 based on the closing price on the Nasdaq Global Market for such shares on June 30, 2007.
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the issuer’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date.
| | |
Class | | Outstanding at March 14, 2008 |
Common Stock, $.01 par value per share | | 23,747,936 |
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s Proxy Statement with respect to its 2008 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed not later than 120 days after the end of the registrant’s fiscal year are incorporated by reference into Part III hereof as noted therein.
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC.
FORM 10-K
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | | | |
| | | | | Page No. |
PART I. | | | | |
Item 1. | | Business | | 3 |
Item 1A. | | Risk Factors | | 7 |
Item 1B. | | Unresolved Staff Comments | | 20 |
Item 2. | | Properties | | 20 |
Item 3. | | Legal Proceedings | | 24 |
Item 4. | | Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders | | 24 |
| | |
PART II. | | | | |
Item 5. | | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | | 25 |
Item 6. | | Selected Financial Data | | 26 |
Item 7. | | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | | 29 |
Item 7A. | | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | | 44 |
Item 8. | | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | | 45 |
Item 9. | | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | | 45 |
Item 9A. | | Controls and Procedures | | 45 |
Item 9B. | | Other Information | | 48 |
| | |
PART III. | | | | |
Item 10. | | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | | 49 |
Item 11. | | Executive Compensation | | 52 |
Item 12. | | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | | 52 |
Item 13. | | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions and Director Independence | | 52 |
Item 14. | | Principal Accounting Fees and Services | | 52 |
| | |
PART IV. | | | | |
Item 15. | | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules | | 53 |
| |
SIGNATURES | | 124 |
2
PART 1
General
The terms “Thomas Properties Group,” “we,” “us” and “our company” refer to Thomas Properties Group, Inc., together with our operating partnership, Thomas Properties Group, L.P. (the “Operating Partnership”). We are a full-service real estate company that owns, acquires, develops and manages primarily office, as well as mixed-use and residential properties on a nationwide basis. Our company’s primary areas of focus are the acquisition and ownership of premier properties, both on a consolidated basis and through strategic joint ventures, property development and redevelopment, and property management activities. Property operations comprise our primary source of cash flow and provide revenue through rental operations, property management, asset management, leasing and other fee income. Our acquisitions program targets properties purchased both for our own account and that of third parties, targeted at core, core plus, and value-add properties. We engage in property development and redevelopment as market conditions warrant. As part of our investment management activities, we earn fees for advising institutional investors on property portfolios.
Our properties are located in Southern California and Sacramento, California; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Northern Virginia; Houston, Texas; and Austin, Texas. As of December 31, 2007, we own interests in and asset manage 25 operating properties with 13.0 million rentable square feet and provide asset and/or property management services on behalf of third parties for an additional four operating properties with 2.2 million rentable square feet. We also have a development pipeline of approximately 7.5 million square feet of primarily office development and 3,200 residential units, including approximately 192,000 square feet of office space and 302 residential units currently under construction.
As of March 14, 2008, we had approximately 180 employees. Our executive management team is based in our Los Angeles and Philadelphia offices. None of our employees are currently represented by a labor union.
We were incorporated in the State of Delaware on March 9, 2004 .We maintain offices in Los Angeles, Newport Beach and Sacramento, California; Austin and Houston, Texas; Northern Virginia and Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Our corporate headquarters are located at City National Plaza, 515 South Flower Street, Sixth Floor, Los Angeles, California 90071 and our phone number is (213) 613-1900. Our website is www.tpgre.com. We make available through our website our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to such reports filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), as soon as reasonably practicable after we file them with or furnish them to the SEC. You may also read and copy any materials we file with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room located at 100 F Street NE, Washington, DC 20549. Information on the operations of the Public Reference Room may be obtained by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. You may also download these materials from the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
Business Focus
Portfolio Enhancement: We focus on increasing net revenues from the properties in which we own an interest or which we manage for third parties through proactive management. As part of portfolio management, we maintain strong tenant relationships through our commitment to service in marketing, lease negotiations, building design and property management.
Property Acquisitions: We seek to acquire “core,” “core plus,” and “value-add” properties for our own account and/or in joint ventures with others where such acquisitions provide us with attractive risk-adjusted returns. Core plus properties consist of under-performing properties that we believe can be brought to market potential through improved management. Value-add properties are characterized by unstable net revenues for an extended period of time, occupancy less than 90% and/or physical or management problems which we believe can be improved by investing additional capital and/or improving management.
3
Partnerships and Joint Ventures: We leverage our property acquisition and development expertise through partnerships and joint ventures. These entities provide us with additional capital for investment, shared risk exposure, and earned fees for asset management, property management, leasing and other services. We are the general partner and hold an ownership interest of 25% in TPG/CalSTRS, LLC (“TPG/CalSTRS”), a joint venture with the California State Teachers’ Retirement System (“CalSTRS”), which owns 12 office properties. In addition, TPG/CalSTRS is the general partner and holds a 25% interest in a joint venture between TPG/CalSTRS, Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc. (“Lehman”) and another institutional investor (the “Austin Portfolio Joint Venture”), which owns ten office properties in Austin, Texas. We are also the general partner and hold an interest in the Thomas High Performance Green Fund, L.P. (the “Green Fund”), which will develop, redevelop and invest in high performance, sustainable commercial buildings.
Development and Redevelopment: We develop and redevelop projects in diversified geographic markets using pre-leasing, guaranteed maximum cost construction contracts and other measures to reduce development risk. We have development properties in Los Angeles and El Segundo, California; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; and Houston and Austin, Texas.
Recent Developments
Partnerships and Joint Ventures:In January 2007, TPG/CalSTRS acquired two properties totaling approximately 601,000 square feet in Fairfax, Virginia for $166.5 million. The acquisition and closing costs were funded with $135.3 million of mortgage financing proceeds and approximately $43.1 million of equity provided by TPG/CalSTRS. In May 2007, TPG/CalSTRS sold Intercontinental Center located in Houston, Texas for $24.2 million and recognized a gain of $7.9 million from this sale. In June 2007, TPG/CalSTRS acquired its interest in the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture, which acquired ten office properties in Austin, Texas for a purchase price of $1.15 billion. The acquisition and closing costs and operating reserves were funded with $907.5 million of debt financing proceeds and $295 million of equity, with TPG/CalSTRS funding 25% of the equity, or approximately $74 million. TPG/CalSTRS has total capital commitments of $378.3 million, of which approximately $30 million was unfunded at March 14, 2008.
The Green Fund has received initial capital commitments of $150 million, $100 million and $50 million from CalSTRS and ourselves, respectively, to be used to develop, redevelop, and invest in high performance, sustainable commercial buildings.
Consolidated Properties:On December 31, 2007, we exercised our option to purchase the remaining 11% interest in One Commerce Square for $2.0 million, resulting in our 100% ownership of One Commerce Square. We intend to exercise our option to purchase the remaining 11% interest in Two Commerce Square in 2008.
Development Pipeline:The construction of Murano, a 302-unit high-rise residential condominium project in Philadelphia, commenced in the second quarter of 2006. We expect that approximately 50% of the condominium units will be completed in the second quarter of 2008 and the remaining units are expected to be completed in the third quarter of 2008.
We commenced construction of two office buildings totaling approximately 192,000 square feet at Four Points Centre in Austin, Texas in the second quarter of 2007. We expect construction to be substantially complete in the third quarter of 2008.
We are presently entitling approximately 14.4 acres in Los Angeles, California, for office, production facility, residential and retail uses. The project, called Metro Studio @ Lankershim, will include approximately 1.5 million square feet for office, production facility, residential and retail development. We expect to enter into a long-term ground lease with the Los Angeles Metropolitan Transportation Authority, which owns the land, upon completion of entitlements. We are pre-leasing the first phase of the development, which is expected to utilize approximately half of the project’s total square footage for the construction of office and entertainment production studio facilities.
4
We have been engaged by NBC/Universal to entitle 124 acres in Los Angeles, California, as a residential and retail town center, located adjacent to Universal City.
Competition
The real estate business is highly competitive. There are numerous other acquirers, developers, managers and owners of commercial and mixed-use real estate that compete with us nationally, regionally and locally, some of whom may have greater financial resources. They compete with us for acquisition opportunities, management and leasing revenues, land for development, tenants for properties and prospective investors in acquisition or development funds we may establish through our investment advisory business.
Our properties compete for tenants with similar properties primarily on the basis of property quality, location, total occupancy costs (including base rent and operating expenses), services provided, building quality and the design and condition of any planned improvements or tenant improvements we may negotiate. The number and type of competing properties or available rentable space in a particular market or submarket could have a material effect on our ability to lease space and maintain or increase occupancy or rents in our existing properties. We believe, however, that the quality services and individualized attention that we offer our tenants, together with our property management services on site, enhance our ability to attract and retain tenants for the office properties we own an interest in or manage.
In addition, in many of our submarkets, institutional investors and owners and developers of properties (including other real estate operating companies and REITs) compete for the acquisition and development, or redevelopment, of land and space. Many of these entities have substantial resources and experience. Competition in acquiring existing properties and land, both from institutional capital sources, other real estate operating companies and from REITs, has been very strong over the past several years. We may compete for investors in potential property acquisitions with other property investment managers with larger or more established operations. Additionally, our ability to compete depends upon trends in the economies of our markets in which we operate or own interests in properties, investment alternatives, financial condition and operating results of current and prospective tenants, availability and cost of capital and debt financing, construction and renovation costs, land availability, completion of construction approvals, taxes and governmental regulations.
Regulatory Issues
Environmental Matters
Under various federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations, a current or previous owner, manager or tenant of real estate may be required to investigate and clean up hazardous or toxic substances at the property, and may be held liable to a government entity or to third parties for property damage and for investigation, clean-up and monitoring costs incurred by the parties in connection with the actual or threatened contamination.
Federal regulations require building owners and those exercising control over a building’s management to identify and warn, via signs and labels, of potential hazards posed by workplace exposure to installed asbestos- containing materials and potentially asbestos-containing materials in their building. The regulations also set forth employee training, record keeping and due diligence requirements pertaining to asbestos-containing materials and potentially asbestos-containing materials. Federal, state and local laws and regulations also govern the removal, encapsulation, disturbance, handling and/or disposal of asbestos-containing materials and potentially asbestos-containing materials when the materials are in poor condition or in the event of construction, remodeling or renovation of a building.
We are aware of potentially environmentally hazardous or toxic materials at three of the properties in which we hold an ownership interest. Prior to commencing construction at our Murano development property, we
5
engaged in remediation efforts as a result of a gasoline spill that occurred on the premises in April 2002, due to an accident caused by the former tenant’s agent. All soil remediation work has been completed. We are operating under a regulatory requirement to monitor the ground water to achieve four consecutive quarters of acceptable sample results.
With respect to asbestos-containing materials present at our City National Plaza and Brookhollow properties, these materials have been removed or abated from certain tenant and common areas of the building structures. We continue to remove or abate asbestos-containing materials from various areas of the building structures and as of December 31, 2007, have accrued $2.6 million and $0.2 million for estimated future costs of such removal or abatement at City National Plaza and Brookhollow, respectively.
Americans with Disabilities Act
Our properties must comply with Title III of the Americans with Disabilities Act, or ADA, to the extent that the properties are “public accommodations” as defined by the ADA. The ADA may require removal of structural barriers to access by persons with disabilities in public areas of our properties where the removal is readily achievable. The obligation to make readily achievable accommodations is an ongoing one, and we assess our properties and make alterations as appropriate.
Insurance
We carry comprehensive liability, fire, flood, extended coverage, wind, earthquake, terrorism, pollution legal liability, business interruption and rental loss insurance under our blanket policy covering all of the properties which we own an interest in or manage for third parties, including our development properties (although we carry only liability insurance for the California Environmental Protection Agency (“CalEPA”) headquarters building under our blanket policy because the tenant has the right to provide all other forms of coverage it deems necessary, and it has elected to do so). We believe the policy specifications and insured limits are appropriate given the relative risk of loss, the cost of the coverage and industry practice. In the opinion of our management team, the properties in our portfolio are adequately insured. Our terrorism insurance is subject to exclusions for loss or damage caused by nuclear substances, pollutants, contaminants, and biological and chemical weapons. We carry earthquake insurance on our properties located in seismically active areas, which includes our Southern California properties, and terrorism insurance on all of our properties, in amounts and with deductibles which we believe are commercially reasonable.
Foreign Operations
We do not engage in any non-U.S. operations or derive any revenue from sources outside the United States.
Segment Financial Information
We operate in one business segment: the acquisition, development, ownership and management of commercial and mixed-use real estate. Additionally, we operate in one geographic area: the United States. Our office portfolio generates revenues from the rental of office space to tenants, parking, rental of storage space and other tenant services. Our management activities generate revenues from third parties from property and asset management fees, acquisition fees and disposition fees. For a further discussion of segment financial information, see the financial statements commencing on page 56.
Forward-Looking Statements
This report contains statements that constitute forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements involve numerous risks and uncertainties and you should not rely on them as predictions of future events. Forward-looking statements depend on assumptions, data or methods which may be incorrect or imprecise and we may not be able to realize them. These statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties that could
6
cause actual results to differ materially from those anticipated. Although the information is based on our current estimations, actual results could vary. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on this information as we cannot guarantee that any future expectations and events described will happen as described or that they will happen at all. You can identify forward-looking statements by the use of forward-looking terminology such as “believes,” “expects,” “may,” “will,” “should,” “seeks,” “approximately,” “intends,” “plans,” “pro forma,” “estimates” or “anticipates” or the negative of these words and phrases or similar words or phrases. You can also identify forward-looking statements by discussions of strategy, plans or intentions.
Risks Related to Our Properties and Our Business
We generate a significant portion of our revenues as a result of our relationships with CalSTRS. If we were to lose these relationships, our financial results and growth prospects would be significantly negatively affected.
Our relationships with CalSTRS are a significant factor in our ability to achieve our intended business growth. Our separate account and joint venture relationships with CalSTRS, including our Austin Portfolio Joint Venture, provide us with substantial fee revenues. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, approximately 31.5%, 22.2% and 15.7%, respectively of our revenue has been derived from fees earned from these relationships. We expect in the future to earn fee revenues from the Green Fund as a result of CalSTRS’ investment in that partnership.
We cannot assure you that our relationships with CalSTRS will continue and we may not be able to replace these relationships with other strategic alliances that would provide comparable revenues. Our interest in TPG/CalSTRS is subject to a buy-sell provision, and is subject to purchase by CalSTRS upon the occurrence of certain events. Under the buy-sell provision either our Operating Partnership or CalSTRS can initiate a buy-out by delivering a notice to the other specifying a purchase price for all the joint venture’s assets; the other venture partner then has the option to sell its joint venture interest or purchase the interest of the initiating venture partner. The purchase price is based on what each venture partner would receive on liquidation if the joint venture’s assets were sold for the specified price and the joint venture’s liabilities paid and the remaining assets distributed to the joint venture partners. In addition, CalSTRS has the ability to initiate this provision upon an event of default by us under the joint venture agreement or related management and development agreements or upon bankruptcy of our Operating Partnership, or upon the death or disability of either James A. Thomas, our Chairman, President and CEO, or John R. Sischo, one of our Executive Vice Presidents, or the failure of either of them to devote the necessary time to perform their duties (unless replaced by an individual approved by CalSTRS) (a “Buyout Default”), or upon any transfer of stock of our company or limited partnership units in our Operating Partnership resulting in Mr. Thomas, his immediate family and controlled entities owning less than 30% of our securities entitled to vote for the election of directors. Our Operating Partnership has the ability to initiate the buy-sell provision upon an event of default of CalSTRS, such as a failure to contribute capital in accordance with capital calls. Upon the occurrence of a Buyout Default, the non-defaulting member may elect to purchase the other member’s joint venture interest based on a three percent discount to the appraised fair market value.
Most of our fee arrangements under our separate account relationship with CalSTRS are terminable on 30 days’ notice. Termination of either our joint venture or separate account relationship with CalSTRS could adversely affect our revenue and profitability and our ability to achieve our business plan by reducing our fee income and access to co-investment capital to acquire additional properties.
Our joint venture investments may be adversely affected by our lack of control or input on decisions or shared decision-making authority or disputes with our co-venturers.
We hold interests in each of our operating properties in a joint venture or partnership. As a result, we do not exercise sole decision-making authority regarding the property, joint venture or other entity, including with
7
respect to cash distributions or the sale of the property. Furthermore, we expect to co-invest in the future through other partnerships, joint ventures or other entities, acquiring non-controlling interests or in sharing responsibility for managing the affairs of a property, partnership or joint venture. Investments in partnerships, joint ventures or other entities may, under certain circumstances, involve risks including partners who may have economic or other business interests or goals which are inconsistent with our business interests or goals and may be in a position to take actions contrary to our policies or objectives. These investments may also have the risk of impasses on significant decisions, because neither we nor our partner or co-venturer would have full control over the partnership or joint venture. Disputes between us and our partners or co-venturers may result in litigation or arbitration that would increase our expenses and prevent our officers and/or directors from focusing their full time and effort on our business. In addition, under the principles of agency and partnership law, we may in certain circumstances be liable for the actions of our third-party partners or co-venturers such as if a partner or co-venturer were to become bankrupt and default on its reimbursement and contribution obligations to us, were to subject property owned by the partnership or joint venture to liabilities in excess of those contemplated by the partnership or joint venture agreement or were to incur debts or liabilities on behalf of the partnership or joint venture in excess of the authority otherwise granted by the partnership or joint venture agreement. In some joint ventures or other investments we make, if the entity in which we invest is a limited partnership, we have acquired and may acquire in the future all or a portion of our interest in such partnership as a general partner. In such event, we may be liable for all the liabilities of the partnership, although we attempt to limit such liability to our investment in the partnership by investing through a subsidiary.
Our joint venture partners have rights under our joint venture agreements that could adversely affect us.
As of March 14, 2008, we hold interests in 22 of our properties through TPG/CalSTRS, 10 of which are held indirectly through TPG/CalSTRS’ interest in the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture. TPG/CalSTRS requires a unanimous vote of the joint venture’s management committee on certain major decisions, including approval of annual business plans and budgets, financings and refinancings, and additional capital calls not in compliance with an approved annual plan. All other decisions, including sales of properties, are made based upon a majority decision of the management committee, which currently consists of two members appointed by CalSTRS and one member appointed by us. Thus CalSTRS has the ability to control certain decisions for the joint venture that may result in an outcome contrary to our interests. In addition to CalSTRS’ ability to control certain decisions relating to the joint venture, our joint venture agreement with CalSTRS includes provisions negotiated for the benefit of CalSTRS that could adversely affect us. Unless otherwise determined by the management committee of the joint venture, we are required to use diligent efforts to sell each joint venture property generally within five years of that property reaching stabilization, except that the holding period for Reflections I and Reflections II, both of which are 100% leased, will be separately determined by the joint venture management committee. With respect to these two properties, we are required to perform a hold/sell analysis at least annually, and make a recommendation to the management committee regarding the appropriate holding period, which could be less than five years. We have a right of first offer to purchase a joint venture property upon a required sale at a price we propose, and if CalSTRS accepts our offer we must close within 90 days. If we do not exercise the right of first offer and we subsequently fail to effect a sale by the end of the specified holding period, CalSTRS has the right to assume control of the sale process. This may require us to sell a substantial portion of our assets at an inopportune time, or for prices that are lower than could be achieved if we had more flexibility in the timing for effecting sales.
TPG/CalSTRS is the general partner of the partnership that owns ten properties in Austin, Texas. The limited partners in this partnership have certain approval rights similar to CalSTRS’ rights described above. These rights include but are not limited to the right to approve annual business plans and budgets, financings and refinancings, sales of properties, additional capital calls not in compliance with an approved annual plan, and agreements with affiliates. The limited partners also have the right to remove the general partner under certain circumstances. These rights could adversely affect us.
8
We may not be able to find syndication investors for the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture.
TPG/CalSTRS has entered into a partnership agreement and syndication agreement with Lehman in relation to the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture that requires us to syndicate a significant portion of Lehman’s current equity position by June 1, 2008. As of December 31, 2007, 33% of Lehman’s original equity in the joint venture had been sold to an unrelated institutional investor. There is a risk that we will be unable to successfully sell Lehman’s remaining equity to investors or to extend the syndication period. The consequences of a failed syndication are that certain expected fees on any unsold equity, such as a promote, administration fees and disposition fees, could be reduced or eliminated for us, and Lehman will retain control rights with respect to major decisions of the joint venture.
We depend on significant tenants, and their failure to pay rent could seriously harm our operating results and financial condition.
As of December 31, 2007, the 20 largest tenants for properties in which we hold an ownership interest collectively leased 35.7% of the rentable square feet of space, representing 42.3% of the total annualized rent generated by these properties. Consolidated Rail Corporation, together with its wholly-owned subsidiary New York Central Lines, LLC (“Conrail”), leases the substantial majority of space at Two Commerce Square and accounted for approximately 10.4% of the total annualized rent generated by all of our consolidated and unconsolidated properties as of December 31, 2007. In addition, Conrail’s rental revenues and tenant reimbursements accounted for approximately 16.8% of total consolidated revenue for the year ended December 31, 2007.
We rely on rent payments from our tenants as a source of cash to finance our business. Any of our tenants may experience a downturn in its business that may weaken its financial condition. As a result, a tenant may delay lease commencement, fail to make rental payments when due, decline to extend a lease upon its expiration, become insolvent or declare bankruptcy. Any tenant bankruptcy or insolvency, leasing delay or failure to make rental payments when due could result in the termination of the tenant’s lease and material losses to our company.
In particular, if any of our significant tenants becomes insolvent, suffers a downturn in its business and decides not to renew its lease or vacates a property, it may seriously harm our business. Failure on the part of a tenant to comply with the terms of a lease may give us the right to terminate the lease, repossess the applicable property and enforce the payment obligations under the lease. In those circumstances, we would be required to find another tenant. We cannot assure you that we would be able to find another tenant without incurring substantial costs, or at all, or that if another tenant were found, we would be able to enter into a new lease on favorable terms. We are not aware of an insolvency issue with any of our significant tenants.
Bankruptcy filings by or relating to one of our tenants could bar us from collecting pre-bankruptcy debts from that tenant or their property. A tenant bankruptcy would delay our efforts to collect past due balances under the relevant leases, and could ultimately preclude full collection of these amounts. If a lease is assumed by the tenant in bankruptcy, all pre-bankruptcy amounts due under the lease must be paid to us in full. However, if a lease is rejected by a tenant in bankruptcy, we would have only a general unsecured claim for damages. Any unsecured claim we hold against a bankrupt entity may be paid only to the extent that funds are available and only in the same percentage as is paid to all other holders of unsecured claims. We may recover substantially less than the full value of any unsecured claims in the event of the bankruptcy of a large tenant, which would adversely impact our financial condition.
Our operating results depend upon the regional economies in which our properties are located and the demand for office and other mixed-use space, and an economic downturn in these regions could harm our operating results.
Our operating and development properties are located in three geographic regions of the United States: the West Coast, Southwest and Mid-Atlantic regions. Historically, the largest part of our revenues has been derived
9
from our ownership and management of properties consisting primarily of office buildings. A decrease in the demand for office space in these geographic regions, and Class A office space in particular, may have a greater adverse effect on our business and financial condition than if we owned a more diversified real estate portfolio. We are susceptible to adverse developments in these regions and in the national office market, such as business layoffs or downsizing, industry slowdowns, relocations of businesses, changing demographics, terrorist targeting of high-rise structures, infrastructure quality, increases in real estate and other taxes, costs of complying with government regulations or increased regulation and other factors, and oversupply of or reduced demand for office space. Some of the regional issues we face include the more highly regulated and taxed economy of Southern California and high local and municipal taxes for our Philadelphia properties. Any adverse economic or real estate developments in a local region, or any decrease in demand for office space resulting from the local regulatory environment, business climate or energy or fiscal problems, could adversely impact our revenue and profitability, thereby causing a significant downturn in our financial condition, results of operations, cash flow, the trading price of our common stock and impairing our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations.
Our debt service obligations reduce cash available to fund business growth and may expose us to the risk of default under our debt obligations.
As of December 31, 2007, our total consolidated indebtedness is approximately $396.0 million. In addition, we own interests in unconsolidated entities subject to total indebtedness in the amount of $2.2 billion as of December 31, 2007. Mortgage loans, which comprise a portion of both the consolidated and unconsolidated indebtedness, are secured by first deeds of trust in the related real property. Mezzanine loans and other secured loans are secured by our direct or indirect ownership interest in the entity that owns the related real property. We may need to incur significant additional debt to finance future acquisition and development activities. It is possible the required payments of principal and interest on borrowings may leave us with insufficient cash to operate our properties profitably. Our need for debt financing, our existing level of debt and the limitations imposed on us by our debt agreements could have significant adverse consequences, including the following:
| | • | | our cash flow may be insufficient to meet our required principal and interest payments or to pay dividends; |
| | • | | we may be unable to borrow additional funds as needed or on favorable terms; |
| | • | | we may be unable to refinance our indebtedness at maturity or the refinancing terms may be less favorable than the terms of our original indebtedness; |
| | • | | we may be unable to distribute funds from a property to our Operating Partnership or apply such funds to cover expenses related to another property; |
| | • | | we could be required to dispose of one or more of our properties, possibly on disadvantageous terms and/or at disadvantageous times; |
| | • | | we could default on our obligations and the lenders or mortgagees may foreclose on our properties that secure their loans and receive an assignment of rents and leases; |
| | • | | we could violate covenants in our loan documents, including provisions that may limit our ability to further mortgage a property, make distributions, acquire additional properties, repay indebtedness prior to a set date without payment of a premium or other pre-payment penalties, all of which would entitle the lenders to accelerate our debt obligations; |
| | • | | a default under any one of our mortgage loans with cross default provisions could result in a default on other indebtedness; and |
| | • | | because we have agreed to use commercially reasonable efforts to maintain certain debt levels to provide the ability for Mr. Thomas and entities controlled by him to guarantee debt of $210 million, including $11 million of debt available for guarantee by Mr. Edward Fox, one of our non-employee directors, and by Mr. Richard Gilchrist, an individual formerly affiliated with Maguire Thomas |
10
| | Partners, we may not be able to refinance our debt when it would otherwise be advantageous to do so or to reduce our indebtedness when our board of directors thinks it is prudent. |
If any one of these events were to occur, our revenue and profitability could be adversely impacted, causing a significant downturn in our financial condition, results of operations, cash flow, and the trading price of our common stock and impairing our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations.
We have a substantial amount of debt which bears interest at variable rates. Our failure to hedge effectively against interest rate changes may adversely affect our results of operations.
As of December 31, 2007, $112.4 million of our consolidated debt and $1.1 billion of our unconsolidated debt was at variable interest rates. As of December 31, 2007, interest rate caps have been purchased for $873.8 million of the unconsolidated floating rate loans.
We intend to generally limit our exposure to interest rate volatility by using interest rate hedging arrangements and swap agreements to cap our interest rate exposure. These arrangements involve risks, including that our hedging or swap transactions might not achieve the desired effect in eliminating the impact of interest rate fluctuations, or that counterparties may fail to honor their obligations under these arrangements. As a result, these arrangements may not be effective in reducing our exposure to interest rate fluctuations and this could reduce our revenue, require us to modify our leverage strategy, and adversely affect our expected investment returns.
We may be unable to complete acquisitions necessary to grow our business, and even if consummated, we may fail to successfully operate these acquired properties.
Our planned growth strategy includes the acquisition of additional properties as opportunities arise. We regularly evaluate approximately 20 markets in the United States for office, mixed-use and other properties for strategic opportunities. Our ability to acquire properties on favorable terms and successfully operate them is subject to the following significant risks:
| | • | | we may be unable to acquire a desired property because of competition from other real estate investors with more available capital, including other real estate operating companies, real estate investment trusts and investment funds; |
| | • | | we may be unable to generate sufficient cash from operations, or obtain the necessary debt or equity to consummate an acquisition or, if obtainable, it may not be on favorable terms; |
| | • | | we may need to spend more than budgeted amounts to make necessary improvements or renovations to acquired properties; |
| | • | | competition from other potential acquirers may significantly increase the purchase price, even if we are able to acquire a desired property; |
| | • | | agreements for the acquisition of office properties are typically subject to customary conditions to closing, including satisfactory completion of due diligence investigations, and we may spend significant time and money on a potential acquisition we eventually decide not to pursue; |
| | • | | we may be unable to quickly and efficiently integrate new acquisitions, particularly acquisitions of portfolios of properties, into our existing operations; |
| | • | | market conditions may result in higher than expected vacancy rates and lower than expected rental rates; and |
| | • | | we may acquire properties subject to liabilities without any recourse, or with only limited recourse, for unknown liabilities such as clean-up of undisclosed environmental contamination, claims by tenants, vendors or other persons dealing with the former owners of the properties and claims for indemnification by general partners, directors, officers and others indemnified by the former owners of the properties. |
11
If we cannot complete property acquisitions on favorable terms, or operate acquired properties to meet our expectations, our revenue and profitability could be adversely impacted, causing a significant downturn in our financial condition, results of operations, trading price of our common stock, and impairing our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations.
Our real estate acquisitions may result in disruptions to our business as a result of the burden in integrating operations placed on our management.
Our business strategy includes acquisitions and investments in real estate on an ongoing basis. These acquisitions may cause disruptions in our operations and divert management’s attention from day-to-day operations, which could impair our relationships with our current tenants and employees. In addition, if we acquire real estate by acquiring another entity, we may be unable to effectively integrate the operations and personnel of the acquired business. In addition, we may be unable to train, retain and motivate any key personnel from the acquired business. If our management is unable to effectively implement our acquisition strategy, we may experience disruptions to our business.
As a result of the limited time during which we have to perform due diligence of many of our acquired properties, we may become subject to significant unexpected liabilities and our properties may not meet projections.
When we enter into an agreement to acquire a property or portfolio of properties, we often have limited time to complete our due diligence prior to acquiring the property. To the extent we underestimate or fail to investigate or identify risks and liabilities associated with the properties we acquire, we may incur unexpected liabilities or the property may fail to perform as we expected. If we do not accurately assess the liabilities associated with properties prior to their acquisition, we may pay a purchase price that exceeds the current fair value of the net identifiable assets of the acquired property. As a result, intangible assets would be required to be recorded, which could result in significant accounting charges in future periods. These charges, in addition to the financial impact of significant liabilities that we may assume, could adversely impact our revenue and profitability, causing a significant downturn in our financial condition, results of operations, trading price of our common stock and impairing our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations.
We may be unable to successfully complete and operate properties under development, which would impair our financial condition and operating results.
A significant part of our business is devoted to the development of office, mixed-use and other properties, including the redevelopment of core plus and value-add properties. Our development, construction and redevelopment activities involve the following significant risks:
| | • | | we may be unable to obtain construction or redevelopment financing on favorable terms or at all; |
| | • | | if we finance development projects through construction loans, we may be unable to obtain permanent financing at all or on advantageous terms; |
| | • | | we may not complete development projects on schedule or within budgeted amounts; |
| | • | | we may underestimate the expected costs and time necessary to achieve the desired result with a redevelopment project; |
| | • | | we may discover structural, environmental or other feasibility issues with properties acquired as redevelopment projects following our acquisition, which may render the redevelopment as planned not possible; |
| | • | | we may encounter delays or refusals in obtaining all necessary zoning, land use, building, occupancy, and other required governmental permits and authorizations; |
| | • | | occupancy rates and rents at newly developed or renovated properties may fluctuate depending on a number of factors, including market and economic conditions, and may result in our investment not being profitable; |
12
| | • | | adverse weather that damages the project or causes delays; |
| | • | | changes to the plans or specifications; |
| | • | | shortages of materials and skilled labor; |
| | • | | increases in material and labor costs; |
| | • | | shortages of qualified employees; |
| | • | | fire, flooding and other natural disasters; and |
| | • | | inability to sell or close on the sale of condominium units at Murano. |
If we are not successful in our property development initiatives, it could adversely impact our revenue and profitability, causing a significant downturn in our business, including our financial condition, results of operations, trading price of our common stock and impairing our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations. Further, our Murano project is the development of a high-rise residential condominium building. Historically, our development and property management activities have centered on office properties. In developing a residential project, we may encounter unfamiliar problems that adversely impact our ability to complete the project on a timely basis. During 2007 the residential housing market has experienced a decline and we could experience difficulties in selling or closing on the sale of condominium units at Murano.
Our efforts to expand our geographic presence and diversify into other regional real estate markets may not be successful, thereby constraining our growth to markets in which we currently operate.
We intend to expand our business to new geographic regions where we expect the development, ownership and management of property to result in favorable risk-adjusted investment returns. In order for us to achieve economies of scale, we generally target ownership of 500,000 or more rentable square feet in a market. It may be difficult for us to achieve this level of ownership and our initial entry into a particular market may result in higher administrative expenses for us initially. Presently, we do not possess the same level of familiarity with the development, ownership and management of properties in locations other than the West Coast, Southwest and Mid-Atlantic regions in the United States, which could adversely affect our ability to develop properties outside these regions successfully or at all or to achieve expected performance.
We face significant competition, which may decrease or prevent increases of the occupancy and rental rates of our properties.
We face significant competition from other developers, managers and owners of office and mixed-use real estate, many of which own properties similar to ours in the same regional markets in which our properties are located. We also compete with other diversified real estate companies and companies focused solely on offering property investment management and brokerage services. A number of our competitors are larger and better able to take advantage of efficiencies created by size, and have better financial resources, or increased access to capital at lower costs, and may be better known in regional markets in which we compete. Our smaller size as compared to some of our competition may increase our susceptibility to economic downturns and pressures on rents. Our failure to compete successfully in our industry would materially affect our business prospects.
We may be unable to renew leases, lease vacant space or re-lease space as leases expire resulting in increased vacancy rates, lower revenue and an adverse effect on our operating results.
As of December 31, 2007, leases representing 11.8% and 7.2% of the rentable square feet of the office and mixed-use properties in which we hold an ownership interest will expire in 2008 and 2009, respectively. Further, an additional 12.0% of the square feet of these properties was available for lease as of December 31, 2007. Rental rates on existing leases above the current market rate at some of the properties in our office and mixed-use portfolio may require us to renew or re-lease some expiring leases at lower rates. If the rental rates for our properties decrease, our existing tenants do not renew their leases or we do not re-lease a significant portion of
13
our available space and space for which leases will expire, our revenue and profitability could be adversely impacted, causing a significant downturn in our financial condition, results of operations, cash flow, and the trading price of our common stock and impairing our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations. In particular, a significant amount of space at our Two Commerce Square property has historically been leased to Conrail. This lease expires in two stages in 2008 and 2009. Conrail currently subleases substantially all of its space to a number of subtenants. While we have entered into agreements with many of the subtenants for direct leases once their sublease term expires, the rental rates are lower than paid by the current tenant. As a result, we currently expect our aggregate revenues from this property will be lower following the expiration of the Conrail lease in 2008 and 2009. If we are unable to lease the remaining portion of the space currently leased by Conrail in Two Commerce Square prior to the expiration of the lease and assuming all subtenants to the Conrail lease exercise no renewal options and exercise all early termination options, our rental revenue (excluding tenant reimbursements revenue) computed in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) would decrease by $1.5 million in 2008 as compared to 2007, $2.8 million in 2009 as compared to 2008, and $1.4 million in 2010 as compared to 2009.
Our growth depends on external sources of capital, some of which are outside of our control. If we are unable to access capital from external sources, we may not be able to implement our business strategy.
Our business strategy requires us to rely significantly on third-party sources to fund our capital needs. We may not be able to obtain debt or equity on favorable terms or at all. During the second half of 2007, we experienced a significant tightening of the credit markets, and we may experience difficulty refinancing existing debt or obtaining new debt to complete acquisitions. Any additional debt we incur will increase our leverage. Any issuance of equity by our company will cause dilution to our existing stockholders, and could have a negative impact on our stock price. Our access to third-party sources of capital depends, in part, on:
| | • | | our current debt levels, which were $396 million of consolidated debt and $2.2 billion of unconsolidated debt as of December 31, 2007; |
| | • | | our current cash flow from operating activities, which was $45.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2007; |
| | • | | our current and expected future earnings; |
| | • | | the market’s perception of our growth potential; |
| | • | | the market price per share of our common stock; |
| | • | | the perception of the value of an investment in our common stock; and |
| | • | | general market conditions. |
If we cannot obtain capital from third-party sources, we may not be able to acquire or develop properties when strategic opportunities exist, satisfy our debt service obligations or continue to fund operations.
We could incur significant costs related to government regulation and private litigation over environmental matters, including with respect to clean-up of contaminated properties and litigation from any harm caused by environmental hazards on our properties.
Under various federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations, a current or previous owner, manager or tenant of real estate may be required to investigate and clean up hazardous or toxic substances at the property, and may be held liable to a government entity or to third parties for property damage and for investigation, clean-up and monitoring costs incurred by the parties in connection with the actual or threatened contamination. These laws typically impose clean-up responsibility and liability without regard to fault, or whether or not the owner, operator or tenant knew of or caused the presence of the contamination. The liability under the laws may be joint and several for the full amount of the investigation, clean-up and monitoring costs incurred or to be incurred or actions to be undertaken, although a party held jointly and severally liable may
14
obtain contributions from other identified, solvent, responsible parties of their fair share toward these costs to the extent such contributions are possible to obtain. These costs may be substantial, and may exceed the value of the property. The presence of contamination, or the failure to properly remediate contamination on a property may limit the ability of the owner, operator or tenant to sell or rent that property or to borrow using the property as collateral, and may cause our investment in that property to decline in value.
Federal regulations require building owners and those exercising control over a building’s management to identify and warn of, by signs and labels, potential hazards posed by workplace exposure to installed asbestos-containing materials and potentially asbestos-containing materials in their building. The regulations also set forth employee training, record keeping and due diligence requirements pertaining to asbestos-containing materials and potentially asbestos-containing materials. Significant fines can be assessed for violation of these regulations. Building owners and managers may be subject to an increased risk of personal injury lawsuits by workers and others exposed to asbestos-containing materials and potentially asbestos-containing materials as a result of these regulations. The regulations may affect the value of a building incorporating asbestos-containing materials or potentially asbestos-containing materials that we own or manage.
We are aware of potentially environmentally hazardous or toxic materials at three of our properties in which we hold an ownership interest. Prior to commencing construction at our Murano development property, we engaged in remediation efforts as a result of a gasoline spill that occurred on the premises in April 2002, due to an accident caused by the former tenant’s agent. All soil remediation work has been completed. We are operating under a regulatory requirement to monitor the ground water to achieve four consecutive quarters of acceptable sample results.
With respect to asbestos-containing materials present at our City National Plaza and Brookhollow properties, these materials have been removed or abated from certain tenant and common areas of the building structures. We continue to remove or abate asbestos-containing materials from various areas of the building structures and as of December 31, 2007, have accrued $2.6 million and $0.2 million for estimated future costs of such removal or abatement at City National Plaza and Brookhollow, respectively.
Federal, state and local laws and regulations also govern the removal, encapsulation, disturbance, handling and/or disposal of asbestos-containing materials and potentially asbestos-containing materials. These laws may impose liability for improper handling or a release to the environment of asbestos-containing materials and potentially asbestos-containing materials. In addition, fines may be imposed on owners or managers of real properties for personal injury or improper work exposure associated with asbestos-containing materials and potentially asbestos-containing materials.
Tax indemnification obligations that may arise in the event we or our Operating Partnership sell an interest in either of two of our properties could limit our operating flexibility.
We and our Operating Partnership have agreed to indemnify Mr. Thomas against adverse direct and indirect tax consequences in the event that our Operating Partnership or the underlying property joint venture directly or indirectly sells, exchanges or otherwise disposes (including by way of merger, sale of assets or otherwise) of any portion of its interests, in a taxable transaction, in either One Commerce Square or Two Commerce Square. These two properties represented 20.4% of annualized rent for properties in which we hold an ownership interest as of December 31, 2007. This indemnification period will expire in October 2008, unless Mr. Thomas and related entities contribute the remaining 11% minority interest in Two Commerce Square to us prior to October 13, 2008 for not more than $2 million, in which event the indemnification period will expire on October 13, 2013, which may be extended to October 13, 2016 provided Mr. Thomas and his controlled entities collectively retain at least 50% of the Operating Partnership units received by them in connection with our formation transactions at the time of our initial public offering.
We have also agreed to use commercially reasonable efforts to make approximately $210 million of debt available to be guaranteed by entities controlled by Mr. Thomas, by Mr. Fox, a non-employee member of our
15
board of directors, and by Mr. Gilchrist, an individual formerly affiliated with Maguire Thomas Partners. We agreed to make this debt available for guarantee in order to assist Mr. Thomas and these other persons in preserving their tax position after their contributions at the time of our initial public offering.
Risks Related to the Real Estate Industry
Illiquidity of real estate investments and the susceptibility of the real estate industry to economic conditions could significantly impede our ability to respond to adverse changes in the performance of our properties.
Our ability to achieve desired and projected results for growth of our business depends on our ability to generate revenues in excess of expenses, and make scheduled principal payments on debt and fund capital expenditure requirements. Events and conditions generally applicable to owners and operators of real property that are beyond our control may adversely impact results of operations and the value of our properties. These events include:
| | • | | vacancies or our inability to rent space on favorable terms; |
| | • | | inability to collect rent from tenants; |
| | • | | difficulty in accessing credit in the present economic environment, in particular for larger mortgage loans; |
| | • | | inability to finance property development and acquisitions on favorable terms; |
| | • | | increased operating costs, including real estate taxes, insurance premiums and utilities; |
| | • | | local oversupply, increased competition or reduction in demand for office space; |
| | • | | costs of complying with changes in governmental regulations; |
| | • | | the relative illiquidity of real estate investments; |
| | • | | changing submarket demographics; and |
| | • | | the significant transaction costs related to property sales, including a high transfer tax rate in the City of Philadelphia. |
In addition, periods of economic slowdown or recession, rising interest rates or declining demand for real estate, or the public perception that any of these events may occur, could result in a general decline in rents or an increased incidence of defaults under existing leases. If any of these events were to happen, our revenue and profitability could be impaired, causing a significant downturn in our financial condition, results of operations, cash flow, and trading price of our common stock and our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations could be impaired.
Compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act and fire, safety and other regulations may require us to make unintended expenditures that adversely impact our financial condition.
All of our commercial properties are required to comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act, or ADA. The ADA has separate compliance requirements for “public accommodations” and “commercial facilities,” but generally requires that buildings be made accessible to people with disabilities. The obligation to make readily achievable accommodations is an ongoing one, and we assess our properties and make alterations as appropriate. Compliance with the ADA requirements could require removal of access barriers. Non-compliance could result in imposition of fines by the U.S. government or an award of damages to private litigants, or both. Typically, we are responsible for changes to a building structure that are required by the ADA, which can be costly. In addition, we are required to operate our properties in compliance with fire and safety regulations, building codes and other land use regulations. We may be required to make substantial capital expenditures to comply with these requirements thereby limiting the funds available to operate, develop and redevelop our properties and acquire additional properties. As a result, these expenditures could negatively impact our revenue and profitability.
16
Potential losses may not be covered by insurance and may result in our inability to repair damaged properties and we could lose invested capital.
We carry comprehensive liability, fire, flood, extended coverage, wind, earthquake, terrorism, pollution legal liability, business interruption and rental loss insurance under our blanket policy covering all of the properties which we own an interest in or manage for third parties, including our development properties (although we carry only liability insurance for the CalEPA headquarters building under our blanket policy because the tenant has the right to provide all other forms of coverage it deems necessary, and it has elected to do so). We believe the policy specifications and insured limits are appropriate and adequate given the relative risk of loss, the cost of the coverage and industry practice. We carry earthquake insurance on our properties located in seismically active areas, which includes our Southern California properties, and terrorism insurance on all of our properties. Our terrorism insurance is subject to exclusions for loss or damage caused by nuclear substances, pollutants, contaminants, and biological and chemical weapons as more specifically excluded under the actual terrorism policies. Some of our policies, like those covering losses due to earthquakes and terrorism, are subject to limitations involving deductibles and policy limits which may not be sufficient to cover losses. We either own or have interests in a number of properties in Southern California, an area especially prone to earthquakes.
Under their leases, tenants are generally required to indemnify us from liabilities resulting from injury to persons, air, water, land or property, on or off the premises due to activities conducted by them on our properties. There is an exception for claims arising from the negligence or intentional misconduct by us or our agents. Additionally, tenants are generally required, with the exception of governmental entities and other entities that are self-insured, to obtain and keep in force during the term of the lease liability and property damage insurance policies issued by companies holding ratings at a minimum level at their own expense.
Although we have not experienced such a loss to date, if we experience a loss that is uninsured or that exceeds policy limits, we could lose the capital invested in the damaged property as well as the anticipated future cash flows from that property, including lost revenue from unpaid rent from tenants. In addition, if the damaged property is subject to recourse indebtedness, we would continue to be liable for the indebtedness, even if this property was irreparably damaged. In the event of a significant loss at one or more of the properties covered by the blanket policy, the remaining insurance under our policy, if any, could be insufficient to adequately insure our remaining properties. In this event, securing additional insurance, if possible, could be significantly more expensive than our current policy.
Risks Related to Our Organization and Structure
Our senior management has existing conflicts of interest with us and our public stockholders that could result in decisions adverse to our company.
As of December 31, 2007, Mr. Thomas owns or controls a very significant interest in our Operating Partnership consisting of 14,496,666 units, or a 37.0% interest (including units beneficially owned by other senior executive officers) as of such date. In addition, our senior executive officers, excluding Mr. Thomas, collectively hold an interest in Operating Partnership units and incentive units (vested and unvested) aggregating a 4.4% interest in our company.
The various terms of these equity and incentive interests could create conflicts of interest with our public stockholders. Members of executive management could be required to make decisions that could have different implications for our Operating Partnership and for us, including:
| | • | | potential acquisitions or sales of properties; |
| | • | | the issuance or disposition of shares of our common stock or units in our Operating Partnership; and |
| | • | | the payment of dividends by us. |
For example, an acquisition in exchange for the issuance by our Operating Partnership of additional Operating Partnership units would dilute the interests of members of our management team as limited partners in
17
our Operating Partnership. Dispositions could trigger our tax indemnification obligations with respect to Mr. Thomas. Dividends paid by us to our public stockholders decrease our funds available to reinvest in our business.
We have a holding company structure and rely upon funds received from our Operating Partnership to pay liabilities.
We are a holding company. Our primary asset is our general partnership interest in our Operating Partnership. We have no independent means of generating revenues. To the extent we require funds to pay taxes or other liabilities incurred by us, to pay dividends or for any other purpose, we must rely on funds received from our Operating Partnership. If our Operating Partnership should become unable to distribute funds to us, we would be unable to continue operations after a short period. Most of the properties owned by our subsidiaries and joint ventures are encumbered by loans that restrict the distribution of funds to our Operating Partnership. The loans generally contain lockbox arrangements, reserve requirements, financial covenants and other restrictions and provisions that prior to an event of default may prevent the distribution of funds from the subsidiaries who own these properties to our Operating Partnership. In the event of a default under these loans, the defaulting subsidiary or joint venture would be prohibited from distributing cash to our Operating Partnership. As a result, our Operating Partnership may be unable to distribute funds to us and we may be unable to use funds from one property to support the operation of another property. As we acquire new properties and refinance our existing properties, we may finance these properties with new loans that contain similar provisions. Some of the loans to our subsidiaries and joint ventures may contain provisions that restrict us from loaning funds to our subsidiaries or joint ventures. If we are permitted to loan funds to our subsidiaries or joint ventures, our loans generally will be subordinated to the existing debt on our properties.
Mr. Thomas has a significant vote in certain matters as a result of his ownership of 100% of our limited voting stock.
Each entity that received Operating Partnership units in our formation transactions received shares of our limited voting stock that are paired with units in our Operating Partnership on a one-for-one basis. All of these entities are directly or indirectly controlled by Mr. Thomas, and, as a result, Mr. Thomas controls 100% of our outstanding limited voting stock, or 40.1% of our outstanding voting stock (including outstanding shares of common stock owned by Mr. Thomas and his affiliates) as of December 31, 2007. These limited voting shares are entitled to vote in the election of directors, for the approval of certain extraordinary transactions including any merger or sale of the company, amendments to our certificate of incorporation and any other matter required to be submitted to a separate class vote under Delaware law. Mr. Thomas may have interests that differ from that of our public stockholders, including by reason of his interests held in Operating Partnership units, and may accordingly vote as a stockholder in ways that may not be consistent with the interests of our public stockholders. This significant voting influence over certain matters may have the effect of delaying, preventing or deterring a change of control of our company, or could deprive our stockholders of an opportunity to receive a premium for their common stock as part of a sale of our company.
Our success depends on key personnel, the loss of whom could impair our ability to operate our business successfully.
We depend on the efforts of key personnel, particularly Mr. Thomas, our Chairman, Chief Executive Officer, and President. Among the reasons that Mr. Thomas is important to our success is that he has an industry reputation developed over more than 25 years in the real estate industry that attracts business and investment opportunities and assists us in negotiations with lenders, existing and potential tenants and industry personnel. If we lost his services, our relationships with these parties could diminish. Mr. Thomas is 71 and, although he has informed us that he does not currently plan to retire, we cannot be certain how long he will continue working on a full-time basis.
18
Many of our other senior executives also have significant real estate industry experience. Mr. Scott has extensive development and management experience on several large-scale projects, including the development, construction and management of One Commerce Square and Two Commerce Square. Mr. Sischo and Mr. Scott are jointly responsible for oversight of our relationship with CalSTRS. Mr. Sischo is responsible for our acquisition efforts. Mr. Ricci has been extensively involved in the development of large, mixed-use and commercial projects. Ms. Laing has served as chief financial officer of two publicly-traded real estate investment trusts. While we believe that we could find acceptable replacements for these executives, the loss of their services could materially and adversely affect our operations because of diminished relationships with lenders, existing and prospective tenants and industry personnel. A departure of either Mr. Thomas or Mr. Sischo could also have adverse effects on our joint venture relationship with CalSTRS, including the possible sale of our joint venture interest to CalSTRS at 97% of fair value.
Some provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws may deter takeover attempts, which may limit the opportunity of our stockholders to sell their shares at a favorable price.
Some of the provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire us, even if doing so might be beneficial to our stockholders by providing them with the opportunity to possibly sell their shares at a premium over the then market price. Our certificate of incorporation and bylaws contain provisions including the following:
| | • | | vacancies on our board of directors may only be filled by the remaining directors; |
| | • | | only the board of directors can change the number of directors; |
| | • | | there is no provision for cumulative voting for directors; |
| | • | | directors may only be removed for cause; and |
| | • | | our stockholders are not permitted to act by written consent. |
In addition, our certificate of incorporation authorizes the board of directors to issue up to 25,000,000 shares of preferred stock. The preferred stock may be issued in one or more series, the terms of which will be determined at the time of issuance by our board of directors without further action by the stockholders. These terms may include voting rights, including the right to vote as a series on particular matters, preferences as to dividends and liquidation, conversion rights, redemption rights and sinking fund provisions. The issuance of any preferred stock could diminish the rights of holders of our common stock, and therefore could reduce the value of our common stock. In addition, specific rights granted to future holders of preferred stock could be used to restrict our ability to merge with, or sell assets to, a third party. The ability of our board of directors to issue preferred stock could make it more difficult, delay, discourage, prevent or make it more costly to acquire or effect a change in control, thereby preserving the current stockholders’ control of our company.
Finally, we are also subject to Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law which, subject to certain exceptions, prohibits a Delaware corporation from engaging in any business combination with any interested stockholder for a period of three years following the date that the stockholder became an interested stockholder.
The provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, described above, as well as Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, could discourage potential acquisition proposals, delay or prevent a change of control and prevent changes in our management, even if these events would be in the best interests of our stockholders.
We could authorize and issue stock without stockholder approval, which could cause our stock price to decline and dilute the holdings of our existing stockholders.
Our certificate of incorporation authorizes our board of directors to issue authorized but unissued shares of our common stock or preferred stock and to classify or reclassify any unissued shares of our common stock or
19
preferred stock and to set the preferences, rights and other terms of the classified or unclassified shares. Although our board of directors has no intention at the present time, it could establish a series of preferred stock that could, depending on the terms of the series, delay, defer or prevent a transaction or a change of control that might involve a premium price for our common stock or otherwise be in the best interest of our stockholders.
| ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
Our Ownership Interest Properties
Our properties are located in the West Coast, Southwest, and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States, consisting primarily of office space and also including mixed-use, multi-family and retail properties. On December 31, 2007, we exercised our option to purchase the remaining 11% minority interest held by Mr. Thomas in One Commerce Square for $2.0 million, resulting in our 100% ownership of One Commerce Square. We intend to exercise our option to purchase the remaining 11% minority interest held by Mr. Thomas in Two Commerce Square in 2008. We hold a 50% interest in 2121 Market Street; the other 50% interest is held by an entity owned by Philadelphia Management, an unaffiliated Philadelphia-based real estate developer. As of December 31, 2007, we provide asset and/or property management services for three properties on behalf of CalSTRS under a separate account relationship, and one property on behalf of the City of Sacramento. We have an ownership interest of 25% in TPG/CalSTRS, which holds a 100% ownership interest in eleven properties, an 85% interest in City National Plaza, and a 25% interest in ten properties in Austin, Texas. Our indirect interest in City National Plaza is 21.3% and our indirect interest in the ten properties in Austin, Texas is 6.25%.
20
An overview of these properties as of December 31, 2007, including development properties, is presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consolidated properties: | | Location | | Percentage
Interest | | | Rentable
Square Feet
(1) | | Percent
Leased
(2) | | | Annualized
Rent (3) | | Annualized
Net Rent
Per Leased
Square
Foot (4) |
One Commerce Square | | Philadelphia, PA | | 100.0 | % | | 942,866 | | 95.1 | % | | $ | 12,177,000 | | | 13.49 |
Two Commerce Square | | Philadelphia, PA | | 89.0 | | | 953,276 | | 99.4 | | | | 19,961,000 | | | 20.21 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total/Weighted Average: | | | 1,896,142 | | 97.8 | | | $ | 32,138,000 | | $ | 17.00 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
Unconsolidated properties: | | Location | | Percentage
Interest | | | Rentable
Square Feet
(1) | | Percent
Leased | | | Annualized
Rent (3) | | Annualized
Net Rent
Per Leased
Square
Foot (4) |
2121 Market Street (5) | | Philadelphia, PA | | 50.0 | % | | 22,136 | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 356,000 | | | 17.10 |
Reflections I | | Reston, VA | | 25.0 | | | 123,546 | | 100.0 | | | | 2,858,000 | | | 23.13 |
Reflections II | | Reston, VA | | 25.0 | | | 64,253 | | 100.0 | | | | 1,086,000 | | | 16.90 |
2500 City West | | Houston, TX | | 25.0 | | | 578,284 | | 95.5 | | | | 4,253,000 | | | 7.79 |
Fair Oaks Plaza | | Fairfax, VA | | 25.0 | | | 179,688 | | 85.9 | | | | 2,179,000 | | | 14.12 |
City National Plaza | | Los Angeles, CA | | 21.3 | | | 2,496,084 | | 81.4 | | | | 28,750,000 | | | 14.21 |
Four Falls Corporate Center | | Conshohocken, PA | | 25.0 | | | 253,985 | | 78.3 | | | | 3,113,000 | | | 15.63 |
Oak Hill Plaza | | King of Prussia, PA | | 25.0 | | | 164,360 | | 92.9 | | | | 1,794,000 | | | 11.72 |
Walnut Hill Plaza | | King of Prussia, PA | | 25.0 | | | 150,573 | | 83.3 | | | | 1,229,000 | | | 9.80 |
San Felipe Plaza | | Houston, TX | | 25.0 | | | 980,472 | | 97.6 | | | | 7,053,000 | | | 7.21 |
Brookhollow Central I, II and III | | Houston, TX | | 25.0 | | | 804,181 | | 66.5 | | | | 5,078,000 | | | 6.20 |
CityWestPlace | | Houston, TX | | 25.0 | | | 1,473,020 | | 97.5 | | | | 18,742,000 | | | 12.57 |
Centerpointe I & II | | Fairfax, VA | | 25.0 | | | 421,651 | | 87.0 | | | | 3,389,000 | | | 9.30 |
San Jacinto Center | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 403,329 | | 91.8 | | | | 4,730,000 | | | 12.53 |
Frost Bank Tower | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 530,533 | | 84.7 | | | | 8,885,000 | | | 20.09 |
One Congress Plaza | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 517,849 | | 85.1 | | | | 6,005,000 | | | 13.70 |
One American Center | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 505,770 | | 80.1 | | | | 6,199,000 | | | 15.24 |
300 West 6th Street | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 446,637 | | 85.2 | | | | 8,127,000 | | | 21.14 |
Research Park Plaza I & II | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 271,882 | | 88.6 | | | | 3,741,000 | | | 15.49 |
Park 22 I-III | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 203,716 | | 90.1 | | | | 2,639,000 | | | 14.55 |
Great Hills Plaza | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 135,333 | | 55.2 | | | | 929,000 | | | 12.44 |
Stonebridge Plaza II | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 193,131 | | 98.1 | | | | 2,700,000 | | | 14.35 |
Westech 360 I-IV | | Austin, TX | | 6.3 | | | 178,777 | | 80.1 | | | | 1,287,000 | | | 8.61 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total/Weighted Average: | | | 11,099,190 | | 86.5 | % | | $ | 125,122,000 | | $ | 12.58 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | For purposes of the tables above, both on-site and off-site parking is excluded. Total portfolio square footage includes office properties and mixed-use space (including retail), but excludes 168 apartment units at 2121 Market Street. Some of the properties have been re-measured in accordance with Building Owners and Managers Association (BOMA) 1996 standards, and the rentable area for these properties reflects the BOMA 1996 measurement guidelines. We are in the process of confirming that the square footage of the properties held in the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture are measured in accordance with the general requirements of BOMA 1996 standards. For all other properties, the rentable area is calculated consistent with leases in place on the property and local market conventions. |
| (2) | Percent leased represents the sum of the square footage of the existing leases as a percentage of rentable area described in (1) above. |
21
| (3) | Annualized rent represents the annualized monthly contractual rent under existing leases as of December 31, 2007 for 100% of the property. For leases with a remaining term of less than one year, annualized rent includes only the amounts through the expiration of the lease. Annualized rent reflects total base rent before any one-time or non-recurring rent abatements, but after annually recurring rent credits and is shown on a net basis. For any tenant under a partial gross lease (which requires the tenant to reimburse the landlord for its pro-rata share of operating expenses in excess of a stated expense stop) or under a full gross lease (which does not require the tenant to reimburse the landlord for any operating expenses) the unreimbursed portion of current year operating expenses (which may be estimates as of such date) are subtracted from gross rent. Total projected recurring rent credits for leases in effect as of December 31, 2007 for the twelve months ending December 31, 2008 are $1.8 million. There are no operating expense credits. |
| (4) | Annualized net rent per leased square foot represents annualized rent as computed above, divided by the total square footage under lease as of the same date. |
| (5) | The square footage and occupancy information presented for 2121 Market Street represents the information for two retail/office tenants only, and excludes the 168 residential units comprising 132,823 square feet. |
Our development pipeline as of December 31, 2007 is presented below.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Development Properties | | Location | | Percentage
Interest | | | Number
of Acres | | Potential Property Types | | Potential
Square Feet/
Units Upon
Completion | |
Four Points Centre | | Austin, TX | | 100.0 | % | | 259.8 | | Office/Retail/R&D/Hotel | | 1,660,000 | (1) |
2100 JFK Boulevard | | Philadelphia, PA | | 100.0 | | | 0.7 | | Office/Retail/Residential | | 366,000 | |
Campus El Segundo | | El Segundo, CA | | 100.0 | | | 26.1 | | Office/Retail/R&D/Hotel | | 1,925,000 | |
2500 City West land | | Houston, TX | | 25.0 | | | 6.3 | | Office/Retail/Hotel/Residential | | 500,000 | |
CityWestPlace land | | Houston, TX | | 25.0 | | | 24.0 | | Office/Retail/Hotel/Residential | | 1,500,000 | |
Metro Studio @ Lankershim | | Los Angeles, CA | | N/A | | | 14.4 | | Office/Production Facility/Residential/Retail | | 1,500,000 | (2) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Subtotal Projected Office Developments (3) | | | | | | | 331.3 | | | | 7,451,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Murano | | Philadelphia, PA | | 73.0 | (4) | | 1.1 | | Residential-condominium | | 302 | (5) |
Universal Village | | Los Angeles, CA | | N/A | | | 124.0 | | Residential/Retail | | 2,937 | (6) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Subtotal Projected Residential
Developments (3) | | | | | | | 125.1 | | | | 3,239 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | | | | | 456.4 | | | | 7,451,000 | Sq. Ft. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | 3,239 | Units |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | We commenced construction of two buildings totaling approximately 192,000 square feet at Four Points Centre in the second quarter of 2007. We expect construction to be substantially complete in the third quarter of 2008. |
| (2) | This property is currently being entitled for a mixed-use development. We expect to enter into a long-term ground lease with the Los Angeles Metropolitan Transportation Authority, which owns the land, upon completion of entitlements. We are pre-leasing the first phase of the development, which is expected to utilize approximately half of the project’s total square footage, for the construction of office and entertainment production studio facilities. |
| (3) | These potential office and residential development properties may also result in other uses depending on market and other conditions at the time of commencement of construction. |
| (4) | We have a $20.5 million preferred equity interest in Murano. Excluding the preferred equity interest, we own a 73.0% ownership interest in Murano. |
| (5) | The construction of Murano, a 302-unit high-rise residential condominium project, commenced in the second quarter of 2006. We expect that approximately 50% of the condominium units will be completed in the second quarter of 2008 and the remaining units are expected to be completed in the third quarter of 2008. |
22
| (6) | We have been engaged by NBC/Universal to entitle 124 acres for the development of a residential and retail town center located adjacent to Universal City. |
Our portfolio in which we presently have an ownership interest includes approximately 27,056 vehicle spaces which are revenue generating within on-site and off-site parking facilities. The following table presents an overview of these garage properties as of December 31, 2007.
| | | | | | | | | |
On-Site/Off-Site Parking | | Square
Footage | | Vehicle
Capacity | | Vehicles
Under
Monthly
Contract (1) | | Percentage
of Vehicle
Capacity
Under
Monthly
Contract | |
On-Site Parking (2) | | 8,058,541 | | 24,571 | | 15,038 | | 61.2 | % |
Off-Site Parking (3) | | 1,056,000 | | 2,485 | | 3,198 | | 128.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total | | 9,114,541 | | 27,056 | | 18,236 | | 67.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | Includes vehicle spaces provided to tenants under lease agreements. |
(2) | Includes garage space at One Commerce Square in which we have a 100% ownership interest, at Two Commerce Square in which we have an 89% ownership interest, at City National Plaza, in which we have an indirect 21.3% ownership interest, at San Felipe Plaza, 2500 City West, Brookhollow Central I, II and III, 2101 CityWestPlace, Centerpointe I & II, and Fair Oaks Plaza, in which we have an indirect 25% ownership interest and at San Jacinto Center, Frost Bank Tower, One Congress Plaza, One American Center, 300 West 6th Street, Research Park Plaza I & II, Park 22 I-III, Great Hills Plaza, Stonebridge Plaza II, and Westech 360 I-IV in which we have an indirect 6.25% ownership interest. |
| (3) | Includes off-site garage space for City National Plaza in which we have an indirect 21.3% ownership interest. |
Our Managed Properties
In addition to our portfolio of operating and development properties in which we hold an ownership interest, we provide asset and/or property management services for four properties as a fee service for third parties. We asset and property manage three properties through our separate account relationship with CalSTRS. We developed and continue to property manage the CalEPA headquarters building. The table below presents an overview of those properties which we manage for third parties as of December 31, 2007. In addition, we provide asset and/or property management services for twelve properties held by TPG/CalSTRS and ten properties held by the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture as of December 31, 2007.
| | | | | | | |
Managed Properties | | Location | | Rentable
Square
Feet (1) | | Percent
Leased (2) | |
800 South Hope Street | | Los Angeles, CA | | 242,176 | | 90.1 | % |
Pacific Financial Plaza | | Newport Beach, CA | | 279,474 | | 99.0 | |
1835 Market Street | | Philadelphia, PA | | 686,503 | | 82.4 | |
CalEPA Headquarters | | Sacramento, CA | | 950,939 | | 100.0 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total/Weighted Average | | 2,159,092 | | 93.2 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| (1) | For purposes of the table above, both on-site and off-site parking are excluded. Total portfolio square footage includes office properties and retail. The rentable area is calculated consistent with leases in place on the property and local market conventions. |
| (2) | 800 South Hope Street, Pacific Financial Plaza and the CalEPA headquarters building are core properties. 1835 Market Street was repositioned by us during 2006 from a core plus property to a core property. |
23
We have been named as a defendant in a number of lawsuits in the ordinary course of business. Management believes that the resolution of these suits will not have a materially adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations.
| ITEM 4. | SUBMISSION OF MATTERS TO A VOTE OF SECURITY HOLDERS |
None
24
PART II.
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Our common stock trades on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “TPGI”. As of March 14, 2008, there were seven stockholders of record. This figure does not reflect the beneficial ownership of shares held in the name of CEDE & Co. The following table sets forth, for the period indicated, the intra-day high and low per share sales prices in dollars on the Nasdaq Global Market for our common stock.
| | | | | | |
| | | High | | Low |
4th quarter 2007 | | $ | 13.12 | | $ | 9.49 |
3rd quarter 2007 | | | 16.40 | | | 11.75 |
2nd quarter 2007 | | | 17.64 | | | 14.93 |
1st quarter 2007 | | | 16.62 | | | 14.71 |
4th quarter 2006 | | | 16.24 | | | 12.85 |
3rd quarter 2006 | | | 13.21 | | | 11.47 |
2nd quarter 2006 | | | 14.20 | | | 11.50 |
1st quarter 2006 | | | 14.48 | | | 11.55 |
The closing price of our common stock as of March 14, 2008 was $8.33.
In 2007, we paid quarterly dividends of $0.06 per common share. The actual amount and timing of distributions is at the discretion of our board of directors and depends upon our financial condition, and no assurance can be given as to the amounts or timing of future distributions. Factors that could influence our ability to declare and pay dividends are discussed in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources.”
There were no issuer purchases of equity securities during the year ended December 31, 2007.
Equity compensation plan information is discussed under the heading “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.”
25
Performance Measurement Comparison
The following graph provides a comparison of cumulative total stockholder return for the period from October 7, 2004 (the date upon which our Common Stock began publicly trading) through December 31, 2007, for the common stock of our company, Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index (S&P 500) and the Dow Jones Wilshire Real Estate Securities Index (DWRS). The stock performance graph assumes an investment of $100.00 in each of our common stock and the two indices, and the reinvestment of any dividends. The historical information set forth below is not necessarily indicative of future performance. The data shown is based on the closing share prices or index values, as applicable, at the end of the last day of each month shown (except for the initial date, October 7, 2004).
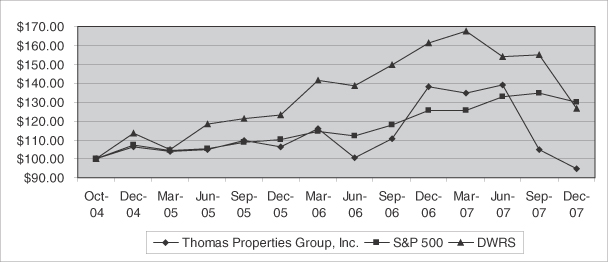
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Oct-04 | | Dec-04 | | Mar-05 | | Jun-05 | | Sep-05 | | Dec-05 | | Mar-06 | | Jun-06 | | Sep-06 | | Dec-06 | | Mar-07 | | Jun-07 | | Sep-07 | | Dec-07 |
Thomas Properties Group, Inc. | | $ | 100.00 | | $ | 106.17 | | $ | 104.00 | | $ | 105.17 | | $ | 109.88 | | $ | 106.16 | | $ | 116.10 | | $ | 100.83 | | $ | 110.69 | | $ | 138.43 | | $ | 134.71 | | $ | 139.23 | | $ | 105.07 | | $ | 94.92 |
S&P 500 | | $ | 100.00 | | $ | 107.19 | | $ | 104.42 | | $ | 105.37 | | $ | 108.68 | | $ | 110.40 | | $ | 114.52 | | $ | 112.31 | | $ | 118.15 | | $ | 125.44 | | $ | 125.67 | | $ | 132.96 | | $ | 135.03 | | $ | 129.87 |
DWRS | | $ | 100.00 | | $ | 113.50 | | $ | 104.87 | | $ | 118.40 | | $ | 121.27 | | $ | 123.29 | | $ | 141.45 | | $ | 138.44 | | $ | 149.79 | | $ | 167.44 | | $ | 167.47 | | $ | 154.26 | | $ | 154.84 | | $ | 126.87 |
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
The following table sets forth selected consolidated financial and operating data on a historical basis for our company and on a combined historical basis for the affiliated group of companies which constitute our predecessor prior to October 13, 2004 (“TPGI Predecessor”). We have not presented historical information for our company prior to October 13, 2004, the date on which we consummated our initial public offering, because during the period from our formation until the offering, we did not have any material corporate activity.
The following data should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and notes thereto and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this Form 10-K.
TPGI Predecessor’s historical combined financial data includes the following operations and properties for periods prior to October 13, 2004:
| | • | | the investment advisory, property management, leasing and real estate development operations of TPGI Predecessor (for all periods presented); |
26
| | • | | the real estate operations of the affiliates that currently own interests in Four Points Centre, Two Commerce Square and 2100 JFK Boulevard (for all periods presented), Campus El Segundo (beginning February 2001), and One Commerce Square (beginning June 2004); and |
| | • | | investment and equity in income or loss from the operations of the affiliates that currently own interests in One Commerce Square (through May 2004), 2121 Market Street (beginning with formation in January 2001 and operations in September 2001) and City National Plaza (beginning January 2003). |
Thomas Properties Group, Inc. and TPGI Predecessor
(dollars in thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Thomas Properties Group, Inc. | | | TPGI Predecessor | |
| | | Year ended
December 31,
2007 | | | Year ended
December 31,
2006 | | | Year ended
December 31,
2005 | | | Period from
October 13,
2004 through
December 31,
2004 | | | Period from
January 1,
2004
through
October 12,
2004 | | | Year ended
December 31,
2003 | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Rental | | $ | 32,646 | | | $ | 33,076 | | | $ | 32,618 | | | $ | 7,356 | | | $ | 20,611 | | | $ | 20,418 | |
Tenant reimbursements | | | 26,371 | | | | 25,197 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 5,056 | | | | 14,289 | | | | 12,932 | |
Parking and other | | | 3,917 | | | | 3,837 | | | | 4,151 | | | | 793 | | | | 2,103 | | | | 1,981 | |
Investment advisory, management, leasing, and development services | | | 13,535 | | | | 7,913 | | | | 4,633 | | | | 1,427 | | | | 5,089 | | | | 8,815 | |
Investment advisory, management, leasing, and development services—unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 21,013 | | | | 14,241 | | | | 8,876 | | | | 969 | | | | 4,494 | | | | 5,021 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues | | | 97,482 | | | | 84,264 | | | | 75,238 | | | | 15,601 | | | | 46,586 | | | | 49,167 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Rental property operating and maintenance | | | 22,690 | | | | 20,805 | | | | 20,593 | | | | 4,521 | | | | 11,888 | | | | 10,166 | |
Real estate taxes | | | 6,087 | | | | 5,904 | | | | 5,803 | | | | 1,267 | | | | 3,392 | | | | 3,299 | |
Investment advisory, management, leasing, and development services | | | 15,359 | | | | 9,759 | | | | 6,218 | | | | 904 | | | | 5,203 | | | | 6,596 | |
Rent—unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 241 | | | | 227 | | | | 233 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest | | | 17,721 | | | | 20,570 | | | | 20,784 | | | | 5,611 | | | | 18,695 | | | | 21,362 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 11,604 | | | | 12,661 | | | | 12,408 | | | | 2,614 | | | | 6,206 | | | | 5,795 | |
General and administrative | | | 18,937 | | | | 17,202 | | | | 12,914 | | | | 2,095 | | | | 4,487 | | | | 3,467 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total expenses | | | 92,639 | | | | 87,128 | | | | 78,953 | | | | 17,012 | | | | 49,871 | | | | 50,685 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gain on purchase of other secured loan | | | — | | | | — | | | | 25,776 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Gain on sale of real estate | | | 4,441 | | | | 10,640 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 975 | | | | — | |
Loss from early extinguishment of debt | | | — | | | | (360 | ) | | | (4,497 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | | |
Interest income | | | 6,014 | | | | 2,974 | | | | 1,268 | | | | 300 | | | | 17 | | | | 51 | |
Equity in net (loss) of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (14,853 | ) | | | (12,909 | ) | | | (16,259 | ) | | | (988 | ) | | | (1,099 | ) | | | (1,088 | ) |
Minority interests—unitholders in the Operating Partnership | | | (249 | ) | | | 1,577 | | | | (1,559 | ) | | | 1,128 | | | | (1,614 | ) | | | — | |
Minority interests in consolidated real estate entities | | | 122 | | | | (472 | ) | | | 328 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) before (provision) benefit for income taxes | | | 318 | | | | (1,414 | ) | | | 1,342 | | | | (971 | ) | | | (5,006 | ) | | | (2,555 | ) |
(Provision) benefit for income taxes | | | (1,221 | ) | | | (635 | ) | | | (698 | ) | | | 390 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net (loss) income | | $ | (903 | ) | | $ | (2,049 | ) | | $ | 644 | | | $ | (581 | ) | | $ | (5,006 | ) | | $ | (2,555 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Loss) earnings per share-basic and diluted | | $ | (0.04 | ) | | $ | (0.14 | ) | | $ | 0.05 | | | $ | (0.04 | ) | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding—basic | | | 20,739,371 | | | | 14,339,032 | | | | 14,301,932 | | | | 14,290,097 | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding—diluted | | | 20,739,371 | | | | 14,339,032 | | | | 14,308,087 | | | | 14,290,097 | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating activities | | $ | 45,507 | | | $ | 20,628 | | | $ | 20,820 | | | $ | (5,435 | ) | | $ | 11,255 | | | $ | 13,374 | |
Investing activities | | | (144,672 | ) | | | (18,524 | ) | | | (54,510 | ) | | | (88,746 | ) | | | 5,380 | | | | (9,117 | ) |
Financing activities | | | 161,469 | | | | (1,676 | ) | | | 41,099 | | | | 147,154 | | | | (16,692 | ) | | | (4,513 | ) |
27
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | Thomas Properties Group, Inc. | | TPGI Predecessor | |
| | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | | 2004 | | 2003 | |
Balance Sheet Data (at year end): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investments in real estate, net | | $ | 463,364 | | $ | 336,154 | | $ | 313,161 | | $ | 282,485 | | $ | 166,701 | |
Total assets | | | 720,892 | | | 518,080 | | | 482,447 | | | 451,854 | | | 229,725 | |
Mortgages, other secured, and unsecured loans | | | 396,007 | | | 331,828 | | | 325,179 | | | 295,890 | | | 225,841 | |
Total liabilities | | | 478,496 | | | 375,152 | | | 344,690 | | | 307,760 | | | 231,462 | |
Minority interests | | | 99,826 | | | 80,678 | | | 74,125 | | | 77,909 | | | 1,133 | |
Stockholders’ equity (owners’ deficit) | | | 142,570 | | | 62,250 | | | 63,632 | | | 66,185 | | | (2,870 | ) |
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity (owners’ deficit) | | | 720,892 | | | 518,080 | | | 482,447 | | | 451,854 | | | 229,725 | |
28
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with the financial statements and notes thereto appearing elsewhere in this report. We make statements in this section that are forward-looking statements within the meaning of the federal securities laws. For a complete discussion of forward-looking statements, see the section in this Form 10-K entitled “Forward-Looking Statements.” Certain risk factors may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to differ materially from those expressed or implied by the following discussion. For a discussion of such risk factors, see the section in this report entitled “Risk Factors.”
Overview and Background
We are a full-service real estate operating company that owns, acquires, develops and manages office, retail and multi-family properties on a nationwide basis. We conduct our business through our Operating Partnership, of which we own 60.5% at December 31, 2007. We have control over the major decisions of the Operating Partnership.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Accounting estimates. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses for the relevant reporting periods. Certain accounting policies are considered to be critical accounting estimates, as these policies require us to make assumptions about matters that are highly uncertain at the time the estimate is made and changes in the accounting estimate are reasonably likely to occur from period to period. We believe the following accounting policies reflect the more significant estimates used in the preparation of our financial statements. For a summary of significant accounting policies, see note 3 to our financial statements, included elsewhere in this report.
Investments in real estate. The price that we pay to acquire a property is impacted by many factors including the condition of the buildings and improvements, the occupancy of the building, the existence of above and below market tenant leases, the creditworthiness of the tenants, favorable or unfavorable financing, above or below market ground leases and numerous other factors. Accordingly, we are required to make subjective assessments to allocate the purchase price paid to acquire investments in real estate among the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on our estimate of the fair values of such assets and liabilities. This includes determining the value of the buildings and improvements, land, any ground leases, tenant improvements, in-place tenant leases, tenant relationships, the value (or negative value) of above (or below) market leases and any debt assumed from the seller or loans made by the seller to us. Each of these estimates requires a great deal of judgment and some of the estimates involve complex calculations. Our calculation methodology is summarized in Note 3 to our consolidated financial statements. These allocation assessments have a direct impact on our results of operations because if we were to allocate more value to land there would be no depreciation with respect to such amount or if we were to allocate more value to the buildings as opposed to allocating to the value of tenant leases, this amount would be recognized as an expense over a much longer period of time, since the amounts allocated to buildings are depreciated over the estimated lives of the buildings whereas amounts allocated to tenant leases are amortized over the terms of the leases. Additionally, the amortization of value (or negative value) assigned to non-market rate leases is recorded as an adjustment to rental revenue as compared to amortization of the value of in-place leases and tenant relationships, which is included in depreciation and amortization in our consolidated statements of operations.
We are required to make subjective assessments as to the useful lives of our properties for purposes of determining the amount of depreciation to record on an annual basis with respect to our investments in real estate. These assessments have a direct impact on our net income because if we were to shorten the expected useful lives of our investments in real estate we would depreciate such investments over fewer years, resulting in more depreciation expense and lower net income on an annual basis.
29
We evaluate a property for potential impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the current book value of the property may not be recoverable. In the event that these periodic assessments result in a determination that the carrying amount of a property exceeds the sum of the undiscounted cash flows (excluding interest) that are expected to result from the use and eventual disposition of the property, we would recognize an impairment loss to the extent the carrying amount exceeded the estimated fair value of the property. Estimates of expected future net cash flows are inherently uncertain and are based on assumptions dependent upon future and current market conditions and events that affect the ultimate value of the property. These estimates require us to make assumptions relating to, among other things, future rental rates, tenant allowances, operating expenditures, property taxes, capital improvements, occupancy levels, and the estimated proceeds generated from the future sale of the property.
Revenue recognition. Leases with tenants are accounted for as operating leases. Rental income is recognized as earned based upon the contractual terms of the leases with tenants. Minimum annual rents are recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term regardless of when the payments are made. The deferred rents asset on our balance sheets represents the aggregate excess rental revenue recognized on a straight-line basis over the cash received under the applicable lease provisions. Our leases generally contain provisions that require tenants to reimburse us for a portion of property operating expenses and real estate related taxes associated with the property. These reimbursements are recognized as revenues in the period the related expenses are incurred. Real estate commissions on leases we charge to third party owners of rental properties are generally recorded as income after we satisfy all obligations under the commission agreement. A typical commission agreement provides that we earn 50% of the lease commission upon the execution of the lease agreement by the tenant. The remaining 50% of the lease commission is earned at a later date, usually upon tenant occupancy. The existence of any significant future contingencies will delay recognition of commission revenue until those contingencies are satisfied. In addition, we eliminate lease commissions we charge on our ownership share of rental properties. Investment advisory, property management and development services fees are recognized when earned under the provisions of the related agreements.
Allowances for uncollectible current tenant receivables and unbilled deferred rents receivable. Tenant receivables and unbilled deferred rent receivables are carried net of the allowances for estimated uncollectible tenant receivables and unbilled deferred rent. Our determination of the adequacy of these allowances requires significant judgments and estimates. Unbilled deferred rents receivable represents the amount that the cumulative straight-line rental revenue recorded to date exceeds cash rents billed to date under the lease agreements. Given the longer-term nature of these types of receivables, our determination of the adequacy of the allowance for unbilled deferred rents receivables is based primarily on historical loss experience. We evaluate the allowance for unbilled deferred rents receivable using a specific identification methodology for our company’s significant tenants, assessing a tenant’s financial condition and the tenant’s ability to meet its lease obligations. In addition, the allowance includes a reserve based upon our historical experience and current and anticipated future economic conditions that are not associated with any specific tenant.
Depreciable lives of leasing costs. We incur certain capital costs in connection with leasing our properties. These costs consist primarily of lease commissions and tenant improvements. Lease costs are amortized on the straight-line method over the shorter of the estimated useful life of the asset or the estimated remaining term of the lease, ranging from one to 15 years. We reevaluate the remaining useful life of these costs as the creditworthiness of our tenants changes. If we determine that the estimated remaining life of the respective lease has changed, we adjust the amortization period and, therefore, the amortization or depreciation expense recorded each period may fluctuate. If we experience increased levels of amortization or depreciation expense due to changes in the estimated useful lives of leasing costs, our results of operations may be adversely affected.
Income taxes. We are subject to federal income taxes in the United States, and also in states and local jurisdictions in which we operate. We account for income taxes according to Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 109, Accounting for Income Taxes. SFAS 109 requires the recognition of deferred tax assets, net of applicable reserves, related to net operating loss carryforwards and certain temporary differences.
30
The standard requires recognition of a future tax benefit to the extent that realization of such benefit is more likely than not. Otherwise, a valuation allowance is applied.
In accordance with the criteria of SFAS No. 5, “Accounting for Contingencies”, we record tax contingencies when the exposure item becomes probable and reasonably estimable. We assess the tax uncertainties on a quarterly basis and maintain the required tax reserves until the underlying issue is resolved or upon the expiration of the statute of limitations. Our estimate of potential outcome of any uncertain tax issue is highly judgmental and we believe we have adequately provided for any reasonable and foreseeable outcomes related to uncertain tax matters.
In July 2006, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued FASB Interpretation No. 48 (FIN 48), “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes, an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109, Accounting for Income Taxes,” which was effective for our company on January 1, 2007. FIN 48 clarifies the accounting for uncertainty in tax positions and requires that we recognize the impact of a tax position in our financial statements if that position would more likely than not be sustained on audit, based on the technical merits of the position. We recorded the cumulative effect of this change in accounting principle as an adjustment to opening retained earnings at January 1, 2007.
Factors That May Influence Future Results of Operations
The following is a summary of the more significant factors we believe may affect our results of operations. For a more detailed discussion regarding the factors that you should consider before making a decision to acquire shares of our common stock, see the information under the caption “Risk Factors” elsewhere in this report.
Rental income. The amount of net rental income generated by our properties depends principally on our ability to maintain the occupancy rates of currently leased space, to lease currently available space as well as space in newly developed or redeveloped properties and space available from unscheduled lease terminations. The amount of rental income we generate also depends on our ability to maintain or increase rental rates in the submarkets where our properties are located.
Los Angeles, Philadelphia, Austin, and Houston—Submarket Information. A significant portion of our income is derived from properties located in Los Angeles, Philadelphia, Austin and Houston. The market conditions in these submarkets have a significant impact on our results of operations.
Information regarding significant tenants—Conrail. Currently, the largest tenant in our portfolio is Conrail. Conrail leased 753,000 rentable square feet of office space in Two Commerce Square as of December 31, 2007. This lease represents 16.8% of our consolidated annual rental and tenant reimbursements revenues for the year ended December 31, 2007. The lease has staggered expirations, with 375,000 square feet expiring in 2008 and the remaining 378,000 square feet expiring in 2009. We have entered into leases with tenants currently subleasing this space covering 163,000 square feet commencing 2008, and 378,000 square feet commencing 2009. Of the leases commencing 2008 and 2009, 1,800 square feet will expire in 2008, 57,000 square feet will expire in 2009, 73,000 square feet will expire in 2010, 14,000 square feet will expire in 2011, 33,000 square feet will expire in 2012, 6,000 square feet will expire in 2013, 339,000 square feet will expire in 2015 and 17,000 square feet will expire in 2016. A lease for 214,000 square feet expiring in 2015 has an early termination option in 2010. Because of these direct leases, we believe we have mitigated some of the risks associated with the Conrail tenant concentration.
Development and redevelopment activities. We believe that our development activities present growth opportunities for us over the next several years. We continually evaluate the size, timing and scope of our development and redevelopment initiatives and, as necessary, sales activity to reflect the economic conditions and the real estate fundamentals that exist in our submarkets. However, we may not be able to lease committed development or redevelopment properties at expected rental rates or within projected time frames or complete
31
projects on schedule or within budgeted amounts. The occurrence of one or more of these events could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. We currently own interests in four development projects, and TPG/CalSTRS includes six redevelopment properties and two development sites. As of December 31, 2007, we had incurred, on a consolidated basis, approximately $135.4 million in construction costs related to our development projects. To the extent that we, or joint ventures we are a partner in, do not proceed with projects as planned, development and/or redevelopment costs would need to be evaluated for impairment.
Results of Operations
The results of operations reflect the consolidation of the affiliates that own One Commerce Square (beginning June 1, 2004), Two Commerce Square, Murano, 2100 JFK Boulevard, Four Points Centre, Campus El Segundo and our investment advisory, property management, leasing and real estate development operations. The following properties are accounted for using the equity method of accounting:
2121 Market Street (for all periods presented)
City National Plaza (as of January 2003, the date of acquisition)
One Commerce Square (through May 2004)
Reflections I (as of October 2004, the date of acquisition)
Reflections II (as of October 2004, the date of acquisition)
Murano (as of March 2005, the date of formation, through August 1, 2006)
Four Falls Corporate Center (as of March 2005, the date of acquisition)
Oak Hill Plaza (as of March 2005, the date of acquisition)
Walnut Hill Plaza (as of March 2005, the date of acquisition)
Valley Square Office Park (as of March 2005, the date of acquisition, through April 2006, the date of disposition)
San Felipe Plaza (as of August 2005, the date of acquisition)
2500 City West (as of August 2005, the date of acquisition)
Brookhollow Central I, II, and III (as of August 2005, the date of acquisition)
Intercontinental Center (as of August 2005, the date of acquisition through May 2007, the date of disposition)
2500 City West land (as of December 2005, the date of acquisition)
CityWestPlace (as of June 2006, the date of acquisition)
CityWestPlace land (as of June 2006, the date of acquisition)
Centerpointe I & II (as of January 2007, the date of acquisition)
Fair Oaks Plaza (as of January 2007, the date of acquisition)
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC also owns a 25% interest in the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture which owns the following properties (“Austin Portfolio Properties”):
San Jacinto Center (purchased June 2007)
Frost Bank Tower (purchased June 2007)
One Congress Plaza (purchased June 2007)
One American Center (purchased June 2007)
300 West 6th Street (purchased June 2007)
Research Park Plaza I & II (purchased June 2007)
Park 22 I-III (purchased June 2007)
Great Hills Plaza (purchased June 2007)
Stonebridge Plaza II (purchased June 2007)
Westech 360 I-IV (purchased June 2007)
Comparison of the year ended December 31, 2007 to the year ended December 31, 2006.
Total revenues. Total revenues increased by $13.2 million, or 15.7%, to $97.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $84.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The significant components of revenue are discussed below.
32
Rental revenues. Rental revenue remained consistent for each of the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2007 and 2006.
Tenant reimbursements.Tenant reimbursements remained consistent for each of the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2007 and 2006.
Parking and other revenues. Revenues from parking and other remained consistent for each of the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2007 and 2006.
Investment advisory, management, leasing and development services revenues. This caption represents revenues earned from services provided to unaffiliated entities in which we have no ownership interest. Revenues from these services increased by $5.6 million, or 70.9%, to $13.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $7.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The increase was primarily due to a disposition fee of $5.5 million related to the sale of an unaffiliated fee managed property.
Investment advisory, management, leasing and development services revenues—unconsolidated real estate entities.This caption represents revenues earned from services provided to entities in which we use the equity method to account for our ownership interest since we have significant influence, but not control over the entities. Revenues from these services from unconsolidated real estate entities increased by $6.8 million, or 47.9%, to $21.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $14.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. This increase was primarily the result of an increase in fee income of $1.5 million related to the property investments in Fairfax, Virginia acquired on January 31, 2007 by TPG/CalSTRS and $4.4 million related to the properties in Austin, Texas acquired on June 1, 2007 by the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture. The increase was also due to an increase in fee income of $0.5 million relating to higher asset management fees from City National Plaza.
Total expenses. Total expenses increased by $5.5 million, or 6.3%, to $92.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $87.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The significant components of expense are discussed below.
Rental property operating and maintenance expense.Rental property operating and maintenance expense increased by $1.9 million, or 9.1%, to $22.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 as compared to $20.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The increase is primarily due to an increase in various operating expenses, such as professional services, engineering, utilities and business property taxes.
Real estate taxes. Real estate taxes remained consistent for each for the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2007 and 2006.
Investment advisory, management, leasing and development services expenses.These expenses increased by $5.6 million, or 57.1%, to $15.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 as compared to $9.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2006, primarily due to an increase in salaries and employment-related costs due to an increase in the number of personnel, and leasing expenses related to increased leasing volume in our Houston portfolio.
Interest expense. Interest expense decreased by $2.9 million or 14.1% to $17.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 as compared to $20.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The decrease is primarily due to increased capitalized interest of $1.5 million in 2007 compared to 2006 related to our developments. In addition, there was a decrease in interest expense relating to Two Commerce Square of $0.8 million primarily due to the amortizing loan balances for the mortgage and mezzanine loans.
Depreciation and amortization expense.Depreciation and amortization expense decreased by $1.1 million or 8.7% to $11.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $12.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The decrease primarily was due to assets which were fully depreciated during 2007.
33
General and administrative. General and administrative expense increased by $1.7 million, or 9.9%, to $18.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $17.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The increase is primarily due to an increase in salaries and employment related costs due to an increase in the number of personnel.
Gain on sale of real estate. Gain on sale of real estate decreased by $6.2 million, or 58.5%, to $4.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $10.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. A 14.1 acre parcel at Campus El Segundo was sold in 2006 for $24.6 million resulting in a total gain of $18.4 million. We were obligated to fund certain infrastructure improvements of approximately $2.7 million with respect to the development of the sold parcel; therefore we recorded a deferred gain of $8.1 million. The remaining deferred gain as of December 31, 2007 was $3.4 million, which will be recognized on a percentage of completion basis as we complete the remaining infrastructure improvements of approximately $1.1 million.
Interest income. Interest income increased $3.0 million, or 100.0%, to $6.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $3.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2006, primarily due to higher average cash balances invested at higher rates.
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities.Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities increased by $2.0 million, or 15.5%, to a net loss of $14.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to a net loss of $12.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. Set forth below is a summary of the unconsolidated condensed financial information for the unconsolidated real estate entities and our share of net loss and equity in net loss for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Revenue | | $ | 258,512 | | | $ | 140,796 | |
Operating and other expenses | | | (138,942 | ) | | | (89,931 | ) |
Interest expense | | | (118,182 | ) | | | (56,795 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization | | | (107,633 | ) | | | (55,501 | ) |
Minority interest | | | (104 | ) | | | (1,650 | ) |
Income from discontinued operations | | | 7,662 | | | | 4,722 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Net Loss | | $ | (98,687 | ) | | $ | (58,359 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Thomas Properties’ share of net loss | | $ | (17,465 | ) | | $ | (14,473 | ) |
Intercompany eliminations | | | 2,612 | | | | 1,564 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | $ | (14,853 | ) | | $ | (12,909 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Aggregate revenue attributable to, and operating and other expenses for unconsolidated real estate entities for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to the year ended December 31, 2006 increased primarily due to the acquisition of our interests in City West Place in June 2006, the two properties in Fairfax, Virginia in January 2007 and the Austin Portfolio Properties in June 2007.
Aggregate interest expense increased by $61.4 million, or 108.1%, to $118.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $56.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 primarily as a result of an increase in interest expense of $6.3 million relating to the debt obligations of City West Place, $8.9 million relating to the debt obligations of the Fairfax, Virginia properties and $35.8 million relating to the debt obligations of the Austin Portfolio Properties. The increase was also due to refinancing of the City National Plaza mortgage and mezzanine loans in July 2006, resulting in higher additional borrowings in 2007, which resulted in an increase in interest expense of $9.4 million.
Aggregate depreciation and amortization expense increased by $52.1 million, or 93.9%, to $107.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $55.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2006
34
primarily as a result of additional depreciation and amortization expense of $7.6 million due to the acquisition of City West Place in June 2006, $7.9 million due to the acquisition of the two Fairfax, Virginia properties in January 2007 and $38.7 million due to the acquisition of the Austin Portfolio Properties in June 2007. In addition, there was an increase of $4.0 million for City National Plaza due to additional capital expenditures in 2007, offset by a $5.7 million decrease in depreciation and amortization expense related to a previous operational building, which is now under redevelopment at our Brookhollow property.
(Provision) benefit for income taxes. Provision for income taxes increased $586,000, or 92.3%, to a provision of $1,221,000 for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to a provision of $635,000 for the year ended December 31, 2006. Of this increase, approximately $335,000 is attributable to the interest on unrecognized benefits, which is recorded as a component of income tax expense, and the remainder is attributable to an increase in book income for the year ended December 31, 2007.
Comparison of the year ended December 31, 2006 to the year ended December 31, 2005.
Total revenues. Total revenues increased by $9.1 million, or 12.1%, to $84.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $75.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. The significant components of revenue are discussed below.
Rental revenues. Rental revenue remained consistent for each of the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2006 and 2005.
Tenant reimbursements.Revenues remained consistent for each of the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2006 and 2005.
Parking and other revenues. Revenues from parking and other decreased by $314,000, or 7.6%, to $3.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $4.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2005, as a result of a decrease $267,000 in parking revenues related to the 2101 Market Street property following our commencement of construction of the Murano project during the second quarter of 2006. Beginning in May 2005, upon commencement of the development activities of Murano, the incidental parking revenues are accounted for as a reduction of capitalized project costs. In addition, for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005, there was $478,000 and $489,000, respectively, in lease termination fees from tenants at One Commerce Square.
Investment advisory, management, leasing and development services revenues. This caption represents revenues earned from services provided to unaffiliated entities in which we have no ownership interest. Revenues from these services increased by $3.3 million, or 71.7%, to $7.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $4.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. The increase was primarily due to an increase of $3.3 million in development fees relating to a professional services agreement with NBC Universal, Inc. to advise on a plan for future development at its Universal City property in Los Angeles. This agreement was entered into in March 2006.
Investment advisory, management, leasing and development services revenues—unconsolidated real estate entities.This caption represents revenues earned from services provided to entities in which we use the equity method to account for our ownership interest since we have significant influence, but not control over the entities. Revenues from these services from unconsolidated real estate entities increased by $5.3 million, or 59.6%, to $14.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $8.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. This increase was primarily a result of fee income related to the investments in Houston and suburban Philadelphia, which were acquired in August 2005 and March 2005, respectively, by TPG/CalSTRS. Investment advisory, management, leasing and development fees increased by $3.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2006 relating to a full year of operations for these acquired properties. In addition, the increase
35
was a result of an acquisition fee of $1.1 million and leasing, property management and advisor fees of $1.6 million related to the acquisition of CityWestPlace in June 2006. Furthermore, the asset management fees and property management fees for City National Plaza increased $0.7 million due to a higher asset valuation and increased revenue, respectively. The increase was partially offset by acquisition fees of $1.1 million and $0.7 million in the year ended December 31, 2005 related to the August 2005 Houston portfolio acquisition and the March 2005 suburban Philadelphia portfolio acquisition, respectively.
Total expenses. Total expenses increased by $8.1 million, or 10.3%, to $87.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $79.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. The significant components of expense are discussed below.
Rental property operating and maintenance expense.Rental property operating and maintenance expense remained consistent for each of the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2006 and 2005.
Real estate taxes. Real estate taxes remained consistent of each for the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2006 and 2005.
Investment advisory, management, leasing and development services expenses.These expenses increased by $3.6 million, or 58.1%, to $9.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 as compared to $6.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2005, primarily due to an increase in salaries and employment related costs due to an increase in the number of personnel; leasing agency fees related to increased leasing volume in our Houston portfolio; and expenses related to our engagement to provide entitlement advisory services to NBC Universal, Inc., which began in March 2006.
Interest expense. Interest expense remained consistent for each for the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2006 and 2005.
Depreciation and amortization expense.Depreciation and amortization expense remained consistent for each for the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2006 and 2005.
General and administrative. General and administrative expense increased by $4.3 million, or 33.3%, to $17.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $12.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. The increase is primarily due to an increase in salaries and employment related costs due to an increase in the number of employees, and non-cash compensation expense related to our restricted incentive unit awards, offset by a decrease in professional fees related to Sarbanes-Oxley compliance as well as external tax and audit services fees.
Gain on sale of real estate. Gain on sale of real estate was $10.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 due to the sale of a 14.1 acre parcel at Campus El Segundo in 2006. The parcel was sold for $24.6 million resulting in a total gain of $18.4 million. We are obligated to fund certain infrastructure improvements with respect to the development of the sold parcel of which the remaining amount is approximately $2.5 million; therefore we recorded a deferred gain, which has a balance of approximately $7.8 million as of December 31, 2006. We also sold a 5.4 acre parcel and deeded a 1.0 acre parcel to the City of El Segundo, which resulted in no gain or loss.
Gain on purchase of other secured loan.Gain on purchase of other secured loan was $25.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 due to the purchase of the Two Commerce Square Junior B mezzanine loan in April 2005 at a discount to face amount and accrued interest.
Loss from early extinguishment of debt. Loss from early extinguishment of debt is comprised of defeasance costs related to the One Commerce Square mortgage loan. These defeasance costs decreased by $4.1 million, or 91.1%, to a loss of $360,000 for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to a loss of $4.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2005.
36
Interest income. Interest income increased $1.7 million, or 130.8%, to $3 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $1.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2005, primarily due to higher average cash balances invested at higher rates.
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities.Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities decreased by $3.4 million, or 20.9%, to a net loss of $12.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to a net loss of $16.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. Set forth below is a summary of the unconsolidated condensed financial information for the unconsolidated real estate entities and our share of net loss and equity in net loss for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
Revenue | | $ | 140,796 | | | $ | 77,201 | |
Operating and other expenses | | | (89,931 | ) | | | (53,406 | ) |
Interest expense | | | (56,795 | ) | | | (29,398 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization | | | (55,501 | ) | | | (31,632 | ) |
Minority interest | | | (1,650 | ) | | | 3,910 | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | 4,722 | | | | (3,157 | ) |
Cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle | | | — | | | | (1,279 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (58,359 | ) | | $ | (37,761 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Thomas Properties’ share of net loss | | $ | (14,473 | ) | | $ | (17,112 | ) |
Intercompany eliminations | | | 1,564 | | | | 853 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | $ | (12,909 | ) | | $ | (16,259 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Aggregate revenue attributable to, and operating and other expenses for unconsolidated real estate entities for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to the year ended December 31, 2005 increased primarily due to the acquisition of our interests in the four properties in suburban Philadelphia in March 2005, the four properties in Houston in August 2005, and CityWestPlace in Houston in June 2006. Additionally, the various revenue and operating expense accounts increased due to increased occupancy at City National Plaza.
Aggregate interest expense increased by $27.4 million, or 93.2%, to $56.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $29.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 primarily as a result of an increase in interest expense of $16.5 million related to the acquisition of the five properties in Houston, and an increase of $1.6 million related to the acquisition of the suburban Philadelphia properties. The increase was also due to refinancing of the City National Plaza mortgage and mezzanine loans in July 2006, resulting in higher additional borrowings in 2006, which resulted in an increase in interest expense of $9.6 million.
Aggregate depreciation and amortization expense increased by $23.9 million, or 75.6%, to $55.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $31.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 primarily as a result of additional depreciation and amortization expense of $19.4 million due to the acquisition of the five properties in Houston. In addition, the increase is a result of additional real estate improvements at City National Plaza during 2006, which resulted in an increase of $3.5 million in depreciation and amortization expense for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to the year ended December 31, 2005.
Income (loss) from discontinued operations is the result of the classification of one of the properties in suburban Philadelphia as held for sale in November 2005. The increase of $7.9 million was primarily due to a gain of $6.3 million resulting from the sale of the property in April 2006. The increase was also due to a decrease in depreciation and amortization expense, which ceased when the property was classified as held for sale beginning November 2005. Depreciation and amortization expense was $0 and $2.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2006 and December 31, 2005, respectively.
37
The cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle is the result of the adoption of FIN 47, “Accounting for Conditional Asset Retirement Obligations, an interpretation of SFAS No. 143,” an accounting principle that provided clarification with respect to the timing of liability recognition for legal obligations associated with the removal of asbestos when the timing and/or method of settlement of the obligation is conditional on a future event. This accounting principle was adopted in 2005 and relates to City National Plaza and Brookhollow.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, 2007, we have unrestricted cash and cash equivalents of $126.6 million. Our management believes that our company will have sufficient capital to satisfy our liquidity needs over the next 12 months through working capital and net cash provided by operations. We expect to meet our long-term liquidity requirements, including property and undeveloped land acquisitions and additional future development and redevelopment activity, through cash flow from operations, additional secured and unsecured long-term borrowings, dispositions of assets, and the issuance of common or preferred equity securities, including additional interests in our Operating Partnership, convertible securities or debt securities. However, at present there is a lack of readily available debt financing for acquisitions. We do not have any present intent to reserve funds to retire existing debt upon maturity. We will instead seek to refinance this debt at maturity or retire the long-term debt through the issuance of securities, as market conditions permit.
Subsequent to year-end, the TPG/CalSTRS joint venture agreement was amended to increase the capital commitments by $25 million. As of March 14, 2008, TPG/CalSTRS had unfunded capital commitments of approximately $30 million, of which our share was $7.4 million. Also, as of March 14, 2008, the Green Fund had $150 million in capital commitments, $100 million and $50 million from CalSTRS and us, respectively, all of which is presently unfunded.
We intend to declare and pay annual dividends on our common stock. The availability of funds to pay dividends is impacted by property-level restrictions on cash flows. Two Commerce Square is subject to debt financing covenants containing lock-box arrangements. Funds generated by Two Commerce Square cannot be distributed to us under the terms of the lock-box arrangements established for the existing lenders for the property. In addition, our joint venture with CalSTRS is subject to debt financing with a lockbox arrangement. With respect to our joint venture properties, we do not control decision making with respect to these properties, and may not be able to obtain monies from these properties even if funds are available for distribution to us. In addition, future financing arrangements we may enter into may contain restrictions on our use of cash generated from our properties.
Development and Redevelopment Projects
We currently own interests in four development projects and our joint venture with CalSTRS includes six redevelopment properties and two development sites. The construction of Murano, a 302-unit high-rise residential condominium project, commenced in the second quarter of 2006. We expect that approximately 50% of the condominium units will be completed in the second quarter of 2008 and the remaining units are expected to be completed in the third quarter of 2008. We commenced construction of two buildings totaling approximately 192,000 square feet at Four Points Centre in the second quarter of 2007. We expect construction to be substantially complete in the third quarter of 2008. We are presently entitling approximately 14.4 acres in Los Angeles, California, for office, production facility, residential and retail uses. The project, called Metro Studio @ Lankershim, will include approximately 1.5 million square feet. Upon completion of entitlements, we expect to enter into a long-term ground lease with the Los Angeles Metropolitan Transportation Authority, which owns the land. Also, we have been engaged by NBC/Universal to entitle 124 acres located adjacent to Universal City in Los Angeles for the development of a residential and retail town center. We anticipate completing the development of these projects as market feasibility permits. We also anticipate seeking to mitigate development risk by obtaining significant pre-leasing and guaranteed maximum cost construction contracts. There can be no assurance we will be able to successfully implement these risk mitigation measures.
38
The amount and timing of costs associated with our development and redevelopment projects is inherently uncertain due to market and economic conditions. We presently intend to fund development and redevelopment expenditures primarily through construction or refurbishment financing. In 2006, we refinanced the loan for City National Plaza, which provides proceeds to cover the estimated future redevelopment costs for this property. Construction of the Murano is financed in part with a $142.5 million construction loan. Repayment of this loan is expected to be made with proceeds from the sales of condominium units. The development at Four Points is financed in part with a $42.7 million construction loan. Presently, we have not obtained construction financing for the development at Campus El Segundo. If we finance these development projects through construction loans and are unable to obtain permanent financing on advantageous terms or at all, we would need to fund these obligations from cash flow from operations or seek alternative capital sources. If unsuccessful, this could adversely impact our financial condition and results of operations and impair our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations. If we are successful in obtaining construction or refurbishment financing and permanent financing, we anticipate that the corresponding interest costs would represent both a significant use of our cash flow and a material component of our results of operations.
Leasing, Tenant Improvement and Capital Needs
In addition to our development and redevelopment projects, we also own One Commerce Square and a majority interest in Two Commerce Square. These properties are substantially leased and have significant stabilized cash flows. These properties require routine capital maintenance in the ordinary course of business. The properties also require that we incur expenditures for leasing commissions and tenant improvement costs. The level of these expenditures varies from year to year based on several factors, including lease expirations. Based upon historical expenditure levels, the leasing activity for the properties and the current rent roll, we anticipate incurring expenditures of approximately $2.7 million in capital improvements, tenant improvements, and leasing costs for the One Commerce Square and Two Commerce Square properties collectively during 2008 through 2010.
Annual capital expenditures may fluctuate in response to the nature, extent and timing of improvements required to maintain our properties. Tenant improvements and leasing costs may also fluctuate depending upon other factors, including the type of property involved, the existing tenant base, terms of leases, types of leases, the involvement of leasing agents and overall market conditions.
Contractual Obligations
A summary of our contractual obligations at December 31, 2007 is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Payments Due by Period |
| | | 2008 | | 2009 | | 2010 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | Thereafter | | Total |
Regularly scheduled principal payments | | $ | 3,200 | | $ | 500 | | $ | 492 | | $ | 1,971 | | $ | 2,160 | | $ | 5,826 | | $ | 14,149 |
Balloon principal payments due at maturity | | | 28,138 | | | 81,089 | | | 43,188 | | | — | | | — | | | 227,655 | | | 380,070 |
Interest payments - fixed rate debt | | | 21,356 | | | 21,906 | | | 14,928 | | | 14,290 | | | 14,205 | | | 24,806 | | | 111,491 |
Interest payments - variable rate debt (1) | | | 1,825 | | | 2,690 | | | 34 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 4,549 |
Capital commitments (2) | | | 16,496 | | | 18,854 | | | 17,523 | | | 8,333 | | | — | | | — | | | 61,206 |
Purchase commitment (3) | | | 1,918 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,918 |
Operating lease (4) | | | 127 | | | 53 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 180 |
FIN 48 obligations, including interest and penalties (5) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 73,060 | | $ | 125,092 | | $ | 76,165 | | $ | 24,594 | | $ | 16,365 | | $ | 258,287 | | $ | 573,563 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | The interest payments on the Four Points Centre construction loan and El Segundo mortgage loans are based on the prime rate or LIBOR. The interest rate for the Four Points Centre construction loan was 7.25% as of December 31, 2007. For the El Segundo mortgage loan, $17.3 million bears interest at 7.47% as of December 31, 2007. The Murano construction loan bears interest at the greater of 7.0% or the three month LIBOR rate plus 3.25%. The interest rate for this loan as of December 31, 2007 was 7.85%. Accrued interest related to these loans is reflected in the year in which we expect it to be due. |
39
| (2) | Capital commitments of our company and consolidated subsidiaries include approximately $2.5 million of tenant improvement allowances and leasing commissions for certain tenants in One Commerce Square and Two Commerce Square and building improvements of $0.2 million for One Commerce Square. As part of the sale of two parcels at El Segundo in 2006, we were obligated to fund $3 million in infrastructure improvements. We expect that the remaining obligation of $1.1 million will be incurred in 2008. We have an unfunded capital commitment of $7.4 million to TPG/CalSTRS, which we estimate we will fund $5.2 million in 2008 and $2.2 million in 2009. Additionally, we have an unfunded capital commitment of $50.0 million to the Green Fund, which we estimate we will fund $8.3 million, $16.7 million, $16.7 million, and $8.3 million in 2008, 2009, 2010, and 2011, respectively, subject to the identification and approval of projects. These cash requirements could be reduced by contributions to the Green Fund by us of assets in which we have an interest. |
| (3) | We entered into an agreement to purchase a commercial condominium unit for $2.2 million on November 30, 2007. This space will serve as a marketing office and an interim property management office for the adjacent development at Campus El Segundo. As of December 31, 2007, we made a $200,000 deposit and the remaining balance is due upon closing which is expected to occur in the first half of 2008. |
| (4) | Represents the future minimum lease payments on our long-term operating lease for our corporate offices at City National Plaza. The table does not reflect available maturity extension options. |
| (5) | The FIN 48 obligations in the table above should represent amounts associated with uncertain tax positions related to temporary differences. However, reasonable estimates cannot be made about the amount and timing of payment for these obligations. As of December 31, 2007, $16.3 million of unrecognized tax benefits have been recorded as liabilities in accordance with FIN 48, and we are uncertain as to if and when such amounts may be settled. We have recorded $728,000 of accrued interest with respect to unrecognized tax benefits. We have not recorded any penalties with respect to unrecognized tax benefits. |
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements—Indebtedness of Unconsolidated Real Estate Entities
As of December 31, 2007, our company had investments in entities owning unconsolidated properties with stated ownership percentages ranging from 6.25% to 50.0%. We do not have control of these entities, and none of the entities are considered variable interest entities. Therefore, we account for them using the equity method of accounting. The table below summarizes the outstanding debt for the properties as of December 31, 2007 (in thousands). We have not guaranteed any of the debt.
40
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Interest Rate | | | | | Principal
Amount | | | Maturity
Date |
City National Plaza (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan | | LIBOR | | + | | 1.07 | % | | (2)(23) | | $ | 355,300 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan-Note A (3) | | LIBOR | | + | | 2.59 | % | | (23) | | | 42,673 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan-Note B | | LIBOR | | + | | 1.90 | % | | (2)(23) | | | 24,000 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan-Note C | | LIBOR | | + | | 2.25 | % | | (2)(23) | | | 24,000 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan-Note D | | LIBOR | | + | | 2.50 | % | | (2)(23) | | | 24,000 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan-Note E | | LIBOR | | + | | 3.05 | % | | (2)(23) | | | 22,700 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Junior mezzanine loan (4) | | LIBOR | | + | | 5.00 | % | | (23) | | | 36,576 | | | 7/17/2008 |
CityWestPlace | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fixed | | | | | | 6.16 | % | | | | | 121,000 | | | 7/6/2016 |
Floating | | LIBOR | | + | | 1.25 | % | | (2)(22) | | | 82,400 | | | 7/1/2008 |
Floating | | LIBOR | | + | | 1.25 | % | | (22) | | | 7,825 | | | 7/1/2008 |
San Felipe Plaza | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loan-Note A | | | | | | 5.28 | % | | | | | 101,500 | | | 8/11/2010 |
Mortgage loan-Note B (5) | | LIBOR | | + | | 3.00 | % | | | | | 9,655 | | | 8/11/2010 |
2500 City West | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loan-Note A | | | | | | 5.28 | % | | | | | 70,000 | | | 8/11/2010 |
Mortgage loan-Note B (6) | | LIBOR | | + | | 3.00 | % | | | | | 9,671 | | | 8/11/2010 |
Brookhollow Central I, II and III | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loan-Note A | | LIBOR | | + | | 0.44 | % | | (2)(23) | | | 24,154 | | | 8/9/2008 |
Mortgage loan-Note B (7) | | LIBOR | | + | | 3.25 | % | | (23) | | | — | | | 8/9/2008 |
Mortgage loan-Note C | | LIBOR | | + | | 4.86 | % | | (2)(23) | | | 16,746 | | | 8/9/2008 |
Four Falls Corporate Center | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loan-Note A | | | | | | 5.31 | % | | | | | 42,200 | | | 3/6/2010 |
Mortgage loan-Note B (8) (9) | | LIBOR | | + | | 3.25 | % | | (2)(11) | | | 9,867 | | | 3/6/2010 |
Oak Hill Plaza/Walnut Hill Plaza | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loan-Note A | | | | | | 5.31 | % | | | | | 35,300 | | | 3/6/2010 |
Mortgage loan-Note B (9) (10) | | LIBOR | | + | | 3.25 | % | | (2)(11) | | | 9,152 | | | 3/6/2010 |
2121 Market Street mortgage loan (12) | | | | | | 6.05 | % | | | | | 19,124 | | | 8/1/2033 |
Reflections I mortgage loan | | | | | | 5.23 | % | | | | | 22,527 | | | 4/1/2015 |
Reflections II mortgage loan | | | | | | 5.22 | % | | | | | 9,386 | | | 4/1/2015 |
Centerpointe I & II | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan | | LIBOR | | + | | .60 | % | | (2) | | | 55,000 | | | 2/9/2009 |
Mezzanine loan (Note A) (13) (14) | | LIBOR | | + | | 1.50 | % | | (2) | | | 13,085 | | | 2/9/2009 |
Mezzanine loan (Note B) (13) (15) | | LIBOR | | + | | 4.79 | % | | (2) | | | 11,315 | | | 2/9/2009 |
Mezzanine loan (Note C) (13) (16) | | LIBOR | | + | | 3.26 | % | | (2) | | | 11,600 | | | 2/9/2009 |
Fair Oaks Plaza (17) | | | | | | 5.52 | % | | | | | 44,300 | | | 2/9/2017 |
Austin Portfolio Properties: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
San Jacinto Center | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loan-Note A | | | | | | 6.05 | % | | | | | 43,000 | | | 6/11/2017 |
Mortgage loan-Note B | | | | | | 6.05 | % | | | | | 58,000 | | | 6/11/2017 |
Frost Bank Tower | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loan-Note A | | | | | | 6.06 | % | | | | | 61,300 | | | 6/11/2017 |
Mortgage loan-Note B | | | | | | 6.06 | % | | | | | 88,700 | | | 6/11/2017 |
One Congress Plaza | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loan-Note A | | | | | | 6.08 | % | | | | | 57,000 | | | 6/11/2017 |
Mortgage loan-Note B | | | | | | 6.08 | % | | | | | 71,000 | | | 6/11/2017 |
One American Center | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loan-Note A | | | | | | 6.03 | % | | | | | 50,900 | | | 6/11/2017 |
Mortgage loan-Note B | | | | | | 6.03 | % | | | | | 69,100 | | | 6/11/2017 |
300 West 6th Street | | | | | | 6.01 | % | | | | | 127,000 | | | 6/11/2017 |
Research Park Plaza I & II | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan | | LIBOR | | + | | 1.34 | % | | (2)(24) | | | 27,000 | | | 6/9/2009 |
Mezzanine loan | | LIBOR | | + | | 1.34 | % | | (2)(24) | | | 24,500 | | | 6/9/2009 |
Stonebridge Plaza II | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan | | LIBOR | | + | | 1.16 | % | | (2)(24) | | | 19,800 | | | 6/9/2009 |
Mezzanine loan | | LIBOR | | + | | 1.16 | % | | (2)(24) | | | 17,700 | | | 6/9/2009 |
Austin Bank Term Loan | | LIBOR | | + | | 3.25 | % | | (18)(19) | | | 192,500 | | | 6/1/2013 |
Revolving Credit Facility | | LIBOR | | + | | 3.25 | % | | (20) | | | — | | | 6/1/2012 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Subtotal – Austin, TX Portfolio: | | $ | 907,500 | (21) | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | $ | 2,162,556 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
41
| (1) | The City National Plaza loans collectively have maximum borrowings of $580 million. The senior mortgage loan and Notes B, C, D and E under the senior mezzanine loans are subject to exit fees equal to .25% of the loan amounts. Note A under the senior mezzanine loan and the junior mezzanine loan are subject to an exit fee equal to .50% of the loan amount. Under certain circumstances all of the exit fees will be waived. All of the City National Plaza loans have two one-year extension options at our election. We plan to exercise the extension options in 2008. |
| (2) | The partnership that owns each property has purchased interest rate cap agreements for the funded portion of these loans. |
| (3) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $27.3 million. |
| (4) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $23.4 million. |
| (5) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $6.5 million under this loan. |
| (6) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $5.8 million under this loan. |
| (7) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $26.7 million under this loan. |
| (8) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $3.0 million under this loan. |
| (9) | These loans are subject to exit fees equal to 1% of the loan amounts, however, under certain circumstances the exit fees will be waived. |
| (10) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow up to $4.2 million under this loan. |
| (11) | These loans bear interest at the greater of the one month LIBOR or 2.25% per annum, plus the applicable margin. As of December 31, 2007, one month LIBOR exceeds 2.25%, per annum. |
| (12) | The 2121 Market Street mortgage loan is prepayable without penalty after May 1, 2013, at which date the outstanding principal amount of this loan will be approximately $17.2 million. The interest rate will increase to the greater of 8.1% or the treasury rate plus 2.0% on August 1, 2013. Any amounts over the initial interest rate may be deferred to the extent excess cash is not available to make such payments. Provided there is no deferred interest, the loan balance will be fully amortized on August 1, 2033, the maturity date of the loan. |
| (13) | The loans are subject to exit fees of up to 1.0% through February 9, 2009. The Centerpointe I & II senior mortgage loan bears interest at a rate equal to one month LIBOR plus 0.60%. The mezzanine loans bear interest at a rate such that the weighted average of the rate on these loans and the rate on the senior mortgage loan secured by Centerpointe I & II equals LIBOR plus 1.59% per annum. The effective interest rate on the senior mezzanine loan as of December 31, 2007 was 8.5% per annum. The weighted average interest rate on all of the loans was 6.19% per annum. All of these loans have three one-year extension options at our election. |
| (14) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $11.9 million under this loan. |
| (15) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $10.3 million under this loan. |
| (16) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $10.6 million under this loan. |
| (17) | This loan may be defeased in full after three years, or prepaid in full after 9 years and 8 months. |
| (18) | The Austin Portfolio Joint Venture entered into an interest rate collar agreement for 50% of the loan balance, or $96.25 million, in which we bought a cap and sold a floor. |
| (19) | The margin above LIBOR on the bank term loan is subject to adjustment under certain circumstances. The term loan is secured by mortgages on three of the Austin Portfolio Properties, a pledge of equity interests in the remaining seven Austin Portfolio Properties and guarantees of certain other Austin Portfolio Properties. |
| (20) | The Austin Portfolio Joint Venture has obtained a $100 million secured revolving credit commitment to fund future capital requirements, bearing interest at LIBOR plus 3.25%. The margin above LIBOR on this facility is subject to adjustment under certain circumstances. As of December 31, 2007, this revolving credit facility was undrawn. |
42
| (21) | The Austin Portfolio Joint Venture, a limited partnership between Lehman, TPG/CalSTRS and other institutional investors, has agreed to compensate Lehman at a net profit margin of 1% of the amount of the financing provided by Lehman. |
| (22) | These loans have three one-year extension options at our election. We plan to exercise our extension options in 2008. |
| (23) | These loans have two one-year extension options at our election. We plan to exercise our extension options in 2008. |
| (24) | These loans have three one-year extension options at our election. |
Cash Flows
Comparison of year ended December 31, 2007 to year ended December 31, 2006
Cash and cash equivalents were $126.7 million as of December 31, 2007 and $64.3 million as of December 31, 2006.
Operating Activities—Net cash provided by operating activities increased by $24.9 million to $45.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $20.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The increase was primarily in changes in assets and liabilities of $15.2 million, an increase in net income (loss) of $1.1 million, an increase in minority interest of $1.2 million, and the change of the deferred gain on sale of real estate of $6.2 million related to Campus El Segundo.
Investing Activities—Net cash used in investing activities increased by $126.2 million to $144.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $18.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The increase was primarily the result of an increase in real estate improvements of $96.2 million, a decrease in return of capital distributions from unconsolidated entities of $19.7 million, and a decrease of $29.5 million due to less proceeds from the sale of real estate. The increases were offset by $5.4 million used for the purchase of interests in unconsolidated real estate entities and a decrease of $19.9 million from fewer contributions to unconsolidated real estate entities.
Financing Activities—Net cash provided by financing activities increased by $163.1 million to $161.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $1.7 million used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2006. The increase was primarily the result of proceeds from our April 2007 public offering, net of offering costs, of $139.3 million. There was an increase of loan draws of $66.8 million for the construction loans at Four Points and Murano, which was offset by an increase in principal payments of mortgage and other secured loans of $9.3 million related to the land loan at Four Points, the Murano preferred equity loan, and the loans at Two Commerce Square. The increases were offset by a decrease of $33.6 million related to payments for the redemption of operating units.
Comparison of year ended December 31, 2006 to year ended December 31, 2005
Cash and cash equivalents were $64.3 million as of December 31, 2006 and $63.9 million as of December 31, 2005.
Operating Activities—Net cash provided by operating activities decreased by $0.2 million to $20.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $20.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. Net income (loss) decreased by $2.6 million, from a net income of $0.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 to a net loss of $2.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. Non-cash income increased by $9.9 million from $13.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2005, to $23.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. This increase was primarily a result of 2005 activities which included the $25.8 million gain from the purchase of the Two Commerce Square Junior B Mezzanine loan, offset by a $4.5 million loss from early extinguishment of the loan and a 2006 increase due to the gain of $10.6 million for the sale of a 14 acre parcel of El Segundo.
43
Distributions of income from unconsolidated real estate entities decreased by $1.1 million from $2.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 to $1.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2006.
Further, net cash provided by operations decreased due to net changes in assets and liabilities of $6.2 million. This decrease was primarily a result of $3.1 million decrease for prepaid rent and $4.7 million decrease for accounts payable and other liabilities offset by a $1.9 million increase in due to affiliates.
Investing Activities—Net cash used in investing activities decreased by $35.9 million to $18.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $54.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. The decrease was the result of the receipt of $29.5 million related to the sale of the El Segundo parcel during the year ended December 31, 2006, compared with a use of cash of $31.1 million associated with the exercise of the El Segundo purchase option in 2005. Expenditures for improvements to real estate increased by $22.2 million to $29.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 from $7.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. Return of capital from unconsolidated real estate increased $18.5 million to $26.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 from $8.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2005, reflecting the receipt of a distribution of the net proceeds of refinancing City National Plaza during 2006. Contributions to unconsolidated real estate entities increased by $11.5 million to $22.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 from $10.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. The change in restricted cash and short-term investments decreased by $10.9 million to $0.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared with $11.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2005.
Financing Activities—Net cash provided by financing activities decreased by $42.8 million to net cash used in financing activities of $1.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $41.1 million provided by financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2005. The decrease was primarily a result of activities from the year ended December 31, 2005 which include the repayment of the One Commerce Square mezzanine loan of $9.3 million, repayment of the 2101 Market Street mortgage loan of $3.5 million, and the refinancing of One Commerce Square in which the $72.2 million mortgage loan was defeased and $4.8 million in defeasance costs were incurred, offset by the new mortgage loan proceeds of $130.0 million.
Inflation
Substantially all of our office leases provide for tenants to reimburse us for increases in real estate taxes and operating expenses related to the leased space at the applicable property. In addition, many of the leases provide for increases in fixed base rent. We believe that inflationary increases may be partially offset by the contractual rent increases and expense reimbursements as described above. We have one multi-family residential rental property and are in construction on Murano, a high-rise residential tower in Philadelphia. The existing residential property is located in the Philadelphia central business district and subject to short-term leases. Inflationary increases can often be offset by increased rental rates, however, a weak economic environment may restrict our ability to raise rental rates.
| ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
A primary market risk faced by our company is interest rate risk. Our strategy is to match as closely as possible the expected holding periods and income streams of our assets with the terms of our debt. In general, we intend to use floating rate debt on assets with higher growth prospects and less stability to their income streams. Correspondingly, with respect to stabilized assets with lower growth rates, we will generally use longer-term fixed-rate debt. As of December 31, 2007, our company had $112.4 million of outstanding consolidated floating rate debt.
The unconsolidated real estate entities have total debt of $2.2 billion, of which $1.1 billion bears interest at floating rates. As of December 31, 2007, interest rate caps have been purchased for $873.8 million of the unconsolidated floating rate loans.
44
Our fixed and variable rate long-term debt at December 31, 2007 consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year of Maturity | | Fixed Rate | | | Variable
Rate | | | Total | |
2008 | | $ | 3,200 | | | $ | 28,138 | | | $ | 31,338 | |
2009 | | | 4,400 | | | | 79,321 | | | | 83,721 | |
2010 | | | 38,441 | | | | 4,895 | | | | 43,336 | |
2011 | | | 1,971 | | | | — | | | | 1,971 | |
2012 | | | 2,160 | | | | — | | | | 2,160 | |
Thereafter | | | 233,481 | | | | — | | | | 233,481 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 283,653 | | | $ | 112,354 | | | $ | 396,007 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average interest rate | | | 7.63 | % | | | 7.50 | % | | | 7.59 | % |
We utilize sensitivity analyses to assess the potential effect of our variable rate debt. At December 31, 2007, our variable rate long-term debt represents 28.4% of our total long-term debt. If interest rates were to increase by 75 basis points, or by approximately 10% of the weighted average variable rate at December 31, 2007, the net impact would be increased costs of $843,000 per year.
As of December 31, 2007, the fair value of our mortgage and other secured loans aggregates $399.3 million, compared to the aggregate carrying value of $396 million.
| ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
The financial statements and supplementary data required by this Item 8 are filed with this report on Form 10-K commencing on page 56.
| ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
| ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We carried out an evaluation required by the Exchange Act, under the supervision and with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) of the Exchange Act, as of December 31, 2007. Based on this evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that, as of December 31, 2007, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the Securities and Exchange Commission and to provide reasonable assurance that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Management has assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2007 based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway
45
Commission. As a result of this assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2007, our internal control over financial reporting was effective in providing reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. The attestation report of the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting is included below under the caption “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.”
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2007 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Limitations on Controls
Management does not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal control over financial reporting will prevent or detect all error and fraud. Any control system, no matter how well designed and operated, is based upon certain assumptions and can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that its objectives will be met. Further, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that misstatements due to error or fraud will not occur or that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within the Company have been detected.
46
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Thomas Properties Group, Inc.:
We have audited Thomas Properties Group, Inc. and Subsidiaries’ (the “Company”) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2007, based on criteria established inInternal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying management’s report on Internal Control’s over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on management’s assessment and an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control, based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2007, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (owners’ deficit) and cash flows for the years ended, and our report dated March 14, 2008 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
ERNST & YOUNG LLP
Los Angeles, California
March 14, 2008
47
| ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
48
PART III
| ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
Executive officers are elected annually by the Board of Directors and serve at the discretion of the Board. The following table sets forth certain information regarding our directors and executive officers as of March 14, 2008. The information concerning Section 16(a) beneficial ownership reporting and corporate governance, including our nominating committee process, and audit committee members, will be included in the Proxy Statement to be filed relating to our 2008 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
| | | | |
Name | | Age | | Position |
James A. Thomas | | 71 | | Chairman of the Board, President and Chief Executive Officer |
R. Bruce Andrews | | 67 | | Director |
Edward D. Fox | | 60 | | Director |
Winston H. Hickox | | 65 | | Director |
John Goolsby | | 66 | | Director |
Randall L. Scott | | 52 | | Executive Vice President and Director |
John R. Sischo | | 51 | | Executive Vice President and Director |
Diana M. Laing | | 53 | | Chief Financial Officer and Secretary |
Thomas S. Ricci | | 50 | | Executive Vice President |
Robert D. Morgan | | 42 | | Senior Vice President, Accounting and Administration |
James A. Thomas serves as our Chairman of the Board, President and Chief Executive Officer. Mr. Thomas has served on our Board of Directors since the Company was organized in March 2004. Mr. Thomas founded our predecessor group of entities, and served as the Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer of our predecessor group of entities from 1996 to the commencement of our operations in October 2004. Prior to founding our predecessor group of entities, Mr. Thomas served as a co-managing partner of Maguire Thomas Partners, a national full-service real estate operating company from 1983 to 1996. In 1996, Maguire Thomas Partners was divided into two companies with Mr. Thomas forming our predecessor group of entities with other key members of the former executive management at Maguire Thomas Partners. Mr. Thomas also served as Chief Executive Officer and principal owner of the Sacramento Kings NBA Basketball team and the ARCO Arena from 1992 until 1999. Mr. Thomas is the Chairman of the board of directors of Townhall Los Angeles, and serves on the board of directors of the SOS Coral Trees, Los Angeles Chamber of Commerce, Center Theatre Group, and the National Advisory Council of the Cleveland Marshall School of Law. He serves on the board of trustees of the Ralph M. Parsons Foundation and I Have a Dream Foundation in Los Angeles, Baldwin Wallace College in Cleveland, the Los Angeles County Museum of Art, and St. John’s Health Center Foundation in Santa Monica, California. Mr. Thomas also serves on the board of governors of the Music Center of Los Angeles County and is a member of the Rand Advisory Board. He is a member of the Chairman Council of the Weingart Center Association, and the Colonial Williamsburg National Council. Mr. Thomas received his Bachelor of Arts degree in economics and political science with honors from Baldwin Wallace College in 1959. He graduatedmagna cum laude with a juris doctorate degree in 1963 from Cleveland Marshall Law School.
R. Bruce Andrews has been a member of our Board of Directors since October 2004. Until his retirement in April 2004, Mr. Andrews served as the President and Chief Executive Officer of Nationwide Health Properties, Inc., a real estate investment trust, which position he had held since September 1989. Mr. Andrews’ previous experience includes serving in various capacities including Chief Financial Officer, Chief Operating Officer and Director of American Medical International. He began his career as an auditor with Arthur Andersen and Company. Mr. Andrews currently serves on the board of directors for Nationwide Health Properties, Inc. Mr. Andrews graduated from Arizona State University with a Bachelor of Science degree in accounting.
49
Edward D. Fox has been a member of our Board of Directors since October 2004. Since January 2003, Mr. Fox has served as Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Vantage Property Investors, LLC, a private real estate investment and development company. Prior to 2003, Mr. Fox was Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Center Trust, a real estate investment trust, from 1998 to January 2003 when Center Trust was acquired by Pan Pacific Retail Properties. Mr. Fox co-founded and served as the Chairman of CommonWealth Partners, a fully integrated real estate operating company, from 1995 through October 2003. Prior to forming CommonWealth Partners, Mr. Fox was a senior partner with Maguire Thomas Partners. A certified public accountant, Mr. Fox started his career in public accounting specializing in real estate transactions. Mr. Fox serves on the Dean’s advisory council for the USC School of Architecture and the board of directors of the Orthopaedic Hospital Foundation and the Los Angeles Boy Scouts. He is a member of the International Council of Shopping Centers, Urban Land Institute and the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants. He received a bachelor’s degree in accounting and a master’s degree in business, both with honors, from the University of Southern California.
Winston H. Hickox has been a member of our Board of Directors since October 2004. Since September 2006 he has been a partner in the government affairs consulting firm California Strategies, LLC. From June 2004 to July 2006, he was a Senior Portfolio Manager for the California Public Employees Retirement System, responsible for the design and implementation of environmental investment initiatives. From January 1999 to November 2003, Mr. Hickox served as Secretary of the California Environmental Protection Agency, and was responsible for a broad range of programs created to protect California’s human and environmental health. From December 1994 to May 1998, Mr. Hickox was a partner in LaSalle Advisors, Ltd. Prior to joining LaSalle Advisors, Ltd., Mr. Hickox was a Managing Director with Alex, Brown Kleinwort Benson Realty Advisors Corp. From April 1997 to January 1999, Mr. Hickox served as an alternate Commissioner on the California Coastal Commission. He was President of the California League of Conservation Voters from 1990 to 1994. He is currently a member of the board of Cadiz, Inc. and the Sacramento County Employees’ Retirement System. Mr. Hickox is a graduate of the California State University at Sacramento with a bachelor of science degree in business administration in 1965, and obtained a master of business administration degree in 1972 from Golden Gate University.
John Goolsby has been a member of the Board of Directors since May 2006. He is a private investor and from 1988 until his retirement in 1998, he served as the President and Chief Executive Officer of The Howard Hughes Corporation, a real estate development company. He currently serves as a director of Tejon Ranch Company.
Randall L. Scott serves us as an Executive Vice President and Director. Mr. Scott has been a member of our Board of Directors since April 2004. Mr. Scott directed asset management operations nationally and East Coast development activity for our predecessor group of entities from its inception in 1996 until the commencement of our operations in October 2004. Prior to the formation of our predecessor group of entities, Mr. Scott was with Maguire Thomas Partners from 1986 to August 1996. As a senior executive at Maguire Thomas Partners, Mr. Scott worked on several large-scale development projects, including One Commerce Square in Philadelphia and The Gas Company Tower in Los Angeles. Mr. Scott was also on the pre-development team for the CalEPA project in Sacramento and served in a general business development capacity. Mr. Scott is currently involved in various civic and professional organizations and serves on the board of directors of the Center City District, a Philadelphia non-profit special services organization. Mr. Scott holds a bachelor’s degree in business administration and economics from Butler University in Indianapolis.
John R. Sischo serves us as an Executive Vice President and Director. Mr. Sischo has been a member of our Board of Directors since April 2004. He is responsible for our investment management services, including oversight of our relationship with CalSTRS, acquisition efforts and our capital market relationships. He served as Chief Financial Officer of our predecessor group of entities from April 1998 until May 2004. Prior to joining our predecessor group of entities, Mr. Sischo was with Banker’s Trust from 1989 to 1998 where he was instrumental in developing Bankers Trust’s real estate investment management practice. Prior to 1989, Mr. Sischo was with
50
Security Pacific Corporation’s real estate investment banking practice. He began his career at Merrill Lynch Capital Markets. Mr. Sischo is on the board of directors of the Center City Association, a Los Angeles non-profit special services organization. Mr. Sischo received a bachelor’s degree in political science from the University of California at Los Angeles.
Diana M. Laing serves as our Chief Financial Officer and Secretary, which positions she has held since May 2004. She is responsible for financial reporting oversight, capital markets transactions and investor relations. Prior to becoming a member of our senior management team, Ms. Laing served as Chief Financial Officer of Triple Net Properties, LLC from January 2004 through April 2004. From December 2001 to December 2003, Ms. Laing served as Chief Financial Officer of New Pacific Realty Corporation, and held this position at Firstsource Corp. from July 2000 to May 2001. Previously, Ms. Laing was Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Arden Realty, Inc., a publicly-traded REIT, from August 1996 to July 2000. From 1982 to August 1996, she was Chief Financial Officer of Southwest Property Trust, Inc., a publicly-traded multi-family REIT. She is a member of the board of directors, chairman of the audit committee and a member of the compensation committee for The Macerich Company, a publicly-traded REIT. She also serves on the board of the Big Brothers/Big Sisters of Greater Los Angeles and the Inland Empire. Ms. Laing holds a bachelor of science degree in accounting from Oklahoma State University and is a certified public accountant in Texas.
Thomas S. Ricci has served us as an Executive Vice President since April 2004. He served as Senior Vice President of our predecessor group of entities from May 1998 to the commencement of our operations in October 2004, with oversight of business development and development services. From February 1992 through May 1998, Mr. Ricci was the vice president of planning and entitlements at Maguire Thomas Partners, Playa Capital Company division. As a senior executive at Maguire Thomas Partners, Mr. Ricci worked on several large mixed-use and commercial projects. Prior to joining Maguire Thomas Partners in 1987, Mr. Ricci was a Captain in the U.S. Air Force, where he was involved in planning, programming, design and construction of medical facilities at locations in the United States and abroad. Mr. Ricci is currently involved in various civic and professional organizations and serves as a member of the board of trustees of Marymount College in Rancho Palos Verdes, California. Mr. Ricci holds a bachelor of science degree and a bachelor of architecture degree with honors from the New York Institute of Technology.
Robert D. Morgan serves us as a Senior Vice President responsible for accounting and administration. He served us as a Vice President from April 2004 to December 2006 in the same capacity. Mr. Morgan joined our predecessor group of entities in March 2000 from Arthur Andersen LLP, where he spent 10 years in the real estate service group. At Arthur Andersen, Mr. Morgan was a Senior Manager specializing in providing audit and transaction due diligence services to real estate developers, owners, lenders and operators. Mr. Morgan earned a bachelor of science degree in business administration with a concentration in accounting from California Polytechnic State University at San Luis Obispo. Mr. Morgan is a certified public accountant, licensed by the State of California.
The information concerning our audit committee financial expert required by Item 10 will be included in the Proxy Statement to be filed relating to our 2008 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that applies to all of our directors, officers and employees. This code is publicly available on our web site at www.tpgre.com. Any substantive amendments to the code and any grant of waiver from a provision of the code requiring disclosure under applicable SEC or Nasdaq rules will be disclosed by us in a report on Form 8-K.
51
| ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information concerning our executive compensation and director compensation required by Item 11 will be included in the Proxy Statement to be filed relating to our 2008 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information concerning our security ownership of certain beneficial owners and management required by Item 12 will be included in the Proxy Statement to be filed relating to our 2008 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Incentive Plans
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table sets forth information with respect to our 2004 Equity Incentive Plan (“Incentive Plan”) and our Non-employee Directors Restricted Stock Plan under which equity securities of our company are authorized for issuance. The Incentive Plan provides incentives to our employees and is intended to attract, reward and retain personnel. Our Incentive Plan permits the granting of awards in the form of options to purchase common stock, restricted shares of common stock and restricted incentive units in our Operating Partnership. Our Non-employee Directors Restricted Stock Plan provides for initial and annual grants to our non-employee directors.
Under the original Plan, we were allowed to issue up to 1,392,858 shares reserved under the Incentive Plan as either restricted stock awards or incentive unit awards and up to 619,048 shares upon the exercise of options granted pursuant to the Incentive Plan. At the Annual Meeting of shareholders in May 2007, the shareholders approved an increase in the number of shares of common stock reserved for issuance or transfer under the Plan from 2,011,906 shares to a total of 2,361,906. In addition, the restrictions on the aggregate number of shares that may be issued or transferred with respect to specified awards granted under the Plan were eliminated. The total number of shares under the Non-employee Directors Restricted Stock Plan available for grant is 60,000. The shares under each of our plans entitle the holder to full voting rights and the holder will receive any dividends paid.
We have no equity compensation plans that were not approved by our security holders.
| | | | | | | |
Plan category | | Number of securities
to be issued upon
exercise of
outstanding options,
warrants and rights | | Weighted-average
exercise price of
outstanding
options, warrants
and rights | | Number of securities
remaining available
for future issuance
under compensation
plans |
Equity compensation plans approved by securityholders at December 31, 2007 | | 501,197 | | $ | 13.52 | | 590,218 |
Non-employee director plan approved by securityholders at December 31, 2007 | | 6,482 | | $ | 14.86 | | 35,033 |
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information concerning certain relationships and related transactions and director independence required by Item 13 will be included in the Proxy Statement to be filed relating to our 2008 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
The information concerning our principal accounting fees and services required by Item 14 will be included in the Proxy Statement to be filed relating to our 2008 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
52
PART IV
| ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
(a) Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedules
The following consolidated financial information is included as a separate section of this report on Form 10-K:
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| | |
| | | Page |
Thomas Properties Group, Inc. and Subsidiaries: | | |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | | 56 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | | 57 |
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 | | 58 |
Consolidated Statements of Operations for Thomas Properties Group, Inc. and Subsidiaries for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 | | 59 |
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for Thomas Properties Group, Inc. and Subsidiaries for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 | | 60 |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for Thomas Properties Group, Inc. and Subsidiaries for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 | | 61 |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Information | | 63 |
Schedule III: Investments in Real Estate | | 97 |
| |
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC: | | |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | | 98 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | | 99 |
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 (As restated, Note 8) | | 100 |
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 (As restated, Note 8) | | 101 |
Consolidated Statements of Members’ Equity and Comprehensive Loss for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 (As restated, Note 8) | | 102 |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 (As restated, Note 8) | | 103 |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Information | | 104 |
(b) Exhibits
| | |
| 3.1 | | Second Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Registrant. (1) |
| |
| 3.2 | | Amended and Restated Bylaws of the Registrant. (2) |
| |
| 10.1* | | 2004 Equity Incentive Plan of Thomas Properties Group, Inc. (3) |
| |
| 10.2 | | Operating Partnership Agreement. (4) |
| |
| 10.3 | | Master Contribution Agreement entered into by James A. Thomas and the other contributors party thereto. (4) |
| |
| 10.4 | | Non-employee Directors Restricted Stock Plan. (4) |
| |
| 10.5 | | Pairing Agreement between the Registrant and its Operating Partnership. (4) |
| |
| 10.6 | | Form of Indemnification Agreement entered into by the Registrant and each of its directors and executive officers. (5) |
53
| | |
| 10.7* | | Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Mr. James A Thomas. (4) |
| |
| 10.8* | | Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Mr. Thomas S. Ricci. (4) |
| |
| 10.9* | | Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Mr. Randall L. Scott. (4) |
| |
| 10.10* | | Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Mr. John R. Sischo. (4) |
| |
| 10.11* | | Employment Agreement between the Registrant and Ms. Diana M. Laing. (4) |
| |
| 10.12+ | | Second Amended and Restated Operating Agreement of TPG/CalSTRS, LLC. (5) |
| |
| 10.13 | | Registration Rights Agreement between the Registrant and the parties thereto. (4) |
| |
| 10.14 | | Loan Agreement dated as of July 31, 2003 between Philadelphia Plaza-Phase II, LP as Borrower and Morgan Stanley Mortgage Capital, Inc. as Lender. (5) |
| |
| 10.15 | | Senior Mezzanine Loan Agreement dated as of July 31, 2003 by and among Philadelphia Plaza-Phase II, LP as Borrower, TCS SPE 1, LP as Guarantor and DB Realty Mezzanine Investment Fund II, LLC as Lender. (5) |
| |
| 10.16 | | Junior A Mezzanine Loan Agreement dated as of July 31, 2003 by and among Philadelphia Plaza-Phase II, LP as Borrower, TCS SPE 2, LP as Guarantor and DB Realty Mezzanine Parallel Fund II, LLC as Lender. (5) |
| |
| 10.17 | | Junior B Mezzanine Loan Agreement dated as of July 31, 2003 by and among Philadelphia Plaza-Phase II, LP as Borrower, TCS SPE 3, LP as Guarantor and DB Realty Mezzanine Parallel Fund II, LLC as Lender. (5) |
| |
| 10.18 | | Thomas Properties Group, Inc. Form of Restricted Shares Award Agreement. (6) |
| |
| 10.19 | | Thomas Properties Group, Inc., Form of Incentive Unit Award Agreement. (6) |
| |
| 10.20 | | Thomas Properties Group, Inc. Form of Non-Qualified Option Award Agreement. (6) |
| |
| 10.21 | | Thomas Properties Group, Inc. Form of Non-employee Directors’ Restricted Shares Award Agreement. (6) |
| |
| 10.22 | | Loan Agreement between TPG Oak Hill/Walnut Hill, LLC and Greenwich Capital Financial Products, Inc. (6) |
| |
| 10.23 | | Loan Agreement between TPG Four Falls, LLC and Greenwich Capital Financial Products, Inc. (6) |
| |
| 10.24 | | Loan Agreement between TPG—San Felipe Plaza, L.P. and Nomura Credit & Capital, Inc. (7) |
| |
| 10.25 | | Loan Agreement between TPG—2500 City West, L.P. and Nomura Credit & Capital, Inc. (7) |
| |
| 10.26 | | Loan Agreement between TPG—BH/ICC, L.P. and Nomura Credit & Capital, Inc. (7) |
| |
| 10.27 | | Loan Agreement between TPG—Commerce Square Partners—Philadelphia Plaza, L.P. as borrower and Greenwich Capital Financial Products, Inc. as lender. (8) |
| |
| 10.28 | | Loan Agreement between TPG-2101 CityWest 1&2, L.P. and Greenwich Capital Financial Products, Inc. (9) |
| |
| 10.29 | | Loan Agreement between TPG-2101 CityWest 3&4, L.P. and Greenwich Capital Financial Products, Inc. (9) |
| |
| 10.30 | | Loan Agreement between 515/555 Flower Associates, LLC and Citigroup Global Markets Realty Corp. (9) |
| |
| 10.31 | | Loan Agreement between 515/555 Flower Mezzanine Associates, LLC and Citigroup Global Markets Realty Corp. (9) |
54
| | |
| 10.32 | | Loan Agreement between 515/555 Flower Junior Mezzanine Associates, LLC and Citigroup Global Markets Realty Corp. (9) |
| |
| 10.33 | | First Amendment to Second Amended and Restated Operating Agreement of TPG/CalSTRS, LLC. (10) |
| |
| 10.34 | | Second Amendment to Second Amended and Restated Operating Agreement of TPG/CalSTRS, LLC. (11) |
| |
| 10.35 | | Third Amendment to Second Amended and Restated Operating Agreement of TPG/CalSTRS, LLC. |
| |
| 10.36 | | Limited Partnership Agreement of Thomas High Performance Green Fund, L.P. |
| |
| 10.37+ | | Letter Agreement Relating to Thomas High Performance Green Fund, L.P. with California State Teachers’ Retirement System. |
| |
| 21.1 | | Subsidiaries of the Registrant. |
| |
| 23.1 | | Consent of Ernst & Young, LLP. |
| |
| 23.2 | | Consent of Deloitte & Touche, LLP. |
| |
| 31.1 | | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| |
| 31.2 | | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
|
| In accordance with SEC Release 33-8212, the following exhibits are being furnished, and are not being filed aspart of this report or as a separate disclosure document, and are not being incorporated by reference into anyregistration statement filed under the Securities Act of 1933. |
| |
| 32.1 | | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| |
| 32.2 | | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed October 18, 2004. |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed January 4, 2008. |
| (3) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement filed April 30, 2007. |
| (4) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q filed November 22, 2004. |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference from Registration Statement file number 333-11452. |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K filed March 30, 2005. |
| (7) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q filed August 10, 2005. |
| (8) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Report on Form 8-K filed January 5, 2006. |
| (9) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q filed August 9, 2006. |
| (10) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Report on Form 10-K filed April 2, 2007. |
| (11) | Incorporated by reference from the Registrant’s Report on Form 10-Q filed August 9, 2007. |
| + | Confidential treatment requested. |
| * | Managerial compensatory plan or arrangement. |
55
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Thomas Properties Group, Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Thomas Properties Group, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (owners’ deficit), and cash flows of the Company for the years then ended. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at item 15(a). These financial statements and the financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the financial statements and the financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated position of the Company at December 31, 2007 and 2006, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly in all material respects the information set forth therein.
As discussed in Note 3 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed its method of accounting for Share-Based Payments in accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 123 (revised 2004) on January 1, 2006.
As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, as of January 1, 2006, the Company changed its method of accounting for a deferred tax asset recorded upon the Company’s initial formation transaction.
As discussed in Note 10 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company adopted FIN 48 on January 1, 2007.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Thomas Properties Group, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2007, based on the criteria established inInternal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated March 14, 2008 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
ERNST & YOUNG LLP
Los Angeles, California
March 14, 2008
56
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Thomas Properties Group, Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows of Thomas Properties Group, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) for the year ended December 31, 2005. Our audit also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index to the Financial Statements. These financial statements and the financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the financial statements and the financial statement schedule based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the results of operations and cash flows of the Company for the year ended December 31, 2005 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly in all material respects the information set forth therein.
As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, as of January 1, 2006, the Company changed its method of accounting for the deferred tax asset recorded for differences between the tax basis and reported amounts related to Thomas Properties Group, L.P. and retrospectively adjusted the accompanying financial statements to give effect to the accounting change.
DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Los Angeles, California
March 15, 2006 (April 2, 2007 as to Note 2 and March 17, 2008 as to the reclassification discussed under the revenue recognition caption in Note 3)
57
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except share data)
December 31, 2007 and 2006
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
Investments in real estate: | | | | | | | | |
Land and improvements | | $ | 35,499 | | | $ | 35,499 | |
Land improvements—development properties | | | 85,253 | | | | 65,526 | |
Construction in progress | | | 135,396 | | | | 25,403 | |
Buildings and improvements | | | 259,031 | | | | 254,539 | |
Tenant improvements | | | 59,804 | | | | 61,831 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 574,983 | | | | 442,798 | |
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | | (111,619 | ) | | | (106,644 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 463,364 | | | | 336,154 | |
Investments in unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 49,199 | | | | 52,364 | |
Cash and cash equivalents, unrestricted | | | 126,647 | | | | 64,343 | |
Restricted cash | | | 26,251 | | | | 21,500 | |
Rents and other receivables, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $558 and $419 as of 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 2,352 | | | | 2,195 | |
Receivables—unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 6,640 | | | | 4,074 | |
Deferred rents | | | 14,696 | | | | 17,918 | |
Deferred leasing and loan costs, net of accumulated amortization of $8,874 and $7,783 as of 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 13,051 | | | | 14,399 | |
Other assets | | | 18,692 | | | | 5,133 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 720,892 | | | $ | 518,080 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loans | | $ | 257,278 | | | $ | 265,823 | |
Other secured loans | | | 134,829 | | | | 62,105 | |
Unsecured loan | | | 3,900 | | | | 3,900 | |
Accounts payable and other liabilities | | | 74,733 | | | | 35,458 | |
Dividends and distributions payable | | | 2,354 | | | | 1,916 | |
Due to affiliate | | | 2,000 | | | | — | |
Prepaid rent | | | 3,402 | | | | 3,558 | |
Deferred tax liability | | | — | | | | 2,392 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 478,496 | | | | 375,152 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Minority Interests: | | | | | | | | |
Unitholders in the Operating Partnership | | | 95,245 | | | | 76,390 | |
Minority interests in consolidated real estate entities | | | 4,581 | | | | 4,288 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total minority interests | | | 99,826 | | | | 80,678 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Commitments and contingencies | | | | | | | | |
| | |
Stockholders’ equity: | | | | | | | | |
Preferred stock, $.01 par value, 25,000,000 shares authorized, none issued or outstanding as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 | | | — | | | | — | |
Common stock, $.01 par value, 75,000,000 shares authorized, 23,747,936 and 14,418,261 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 237 | | | | 144 | |
Limited voting stock, $.01 par value, 20,000,000 shares authorized, 14,496,666 and 16,666,666 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 145 | | | | 167 | |
Additional paid-in capital | | | 157,799 | | | | 71,095 | |
Deficit and dividends, including $201 of other comprehensive loss as of December 31, 2007 | | | (15,611 | ) | | | (9,156 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Total stockholders’ equity | | | 142,570 | | | | 62,250 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | $ | 720,892 | | | $ | 518,080 | |
| | | | | | | | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial information.
58
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended
December 31,
2007 | | | Year ended
December 31,
2006 | | | Year ended
December 31,
2005 | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Rental | | $ | 32,646 | | | $ | 33,076 | | | $ | 32,618 | |
Tenant reimbursements | | | 26,371 | | | | 25,197 | | | | 24,960 | |
Parking and other | | | 3,917 | | | | 3,837 | | | | 4,151 | |
Investment advisory, management, leasing, and development services | | | 13,535 | | | | 7,913 | | | | 4,633 | |
Investment advisory, management, leasing, and development services—unconsolidated real estate entities unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 21,013 | | | | 14,241 | | | | 8,876 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues | | | 97,482 | | | | 84,264 | | | | 75,238 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Rental property operating and maintenance | | | 22,690 | | | | 20,805 | | | | 20,593 | |
Real estate taxes | | | 6,087 | | | | 5,904 | | | | 5,803 | |
Investment advisory, management, leasing, and development services | | | 15,359 | | | | 9,759 | | | | 6,218 | |
Rent—unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 241 | | | | 227 | | | | 233 | |
Interest | | | 17,721 | | | | 20,570 | | | | 20,784 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 11,604 | | | | 12,661 | | | | 12,408 | |
General and administrative | | | 18,937 | | | | 17,202 | | | | 12,914 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total expenses | | | 92,639 | | | | 87,128 | | | | 78,953 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gain on purchase of other secured loan | | | — | | | | — | | | | 25,776 | |
Gain on sale of real estate | | | 4,441 | | | | 10,640 | | | | — | |
Loss from early extinguishment of debt | | | — | | | | (360 | ) | | | (4,497 | ) |
Interest income | | | 6,014 | | | | 2,974 | | | | 1,268 | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (14,853 | ) | | | (12,909 | ) | | | (16,259 | ) |
Minority interests—unitholders in the Operating Partnership | | | (249 | ) | | | 1,577 | | | | (1,559 | ) |
Minority interests in consolidated real estate entities | | | 122 | | | | (472 | ) | | | 328 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) before provision for income taxes | | | 318 | | | | (1,414 | ) | | | 1,342 | |
Provision for income taxes | | | (1,221 | ) | | | (635 | ) | | | (698 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net (loss) income | | $ | (903 | ) | | $ | (2,049 | ) | | $ | 644 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Loss) earnings per share-basic and diluted | | $ | (0.04 | ) | | $ | (0.14 | ) | | $ | 0.05 | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding—basic | | | 20,739,371 | | | | 14,339,032 | | | | 14,301,932 | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding—diluted | | | 20,739,371 | | | | 14,339,032 | | | | 14,308,087 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial information.
59
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(In thousands, except share data)
Years Ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Common Stock | | Limited
Voting
Stock | | | Additional
Paid-In
Capital | | | Deficit | | | Unearned
Compensation,
net | | | Other
Comprehensive
Loss | | | Total | |
| | | Shares | | Amount | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2004 | | 14,342,481 | | $ | 143 | | $ | 167 | | | $ | 66,925 | | | $ | (581 | ) | | $ | (469 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | 66,185 | |
Issuance of unvested restricted stock, net of minority interests | | 4,984 | | | — | | | — | | | | 40 | | | | — | | | | (28 | ) | | | — | | | | 12 | |
Vesting of restricted stock, net of minority interests | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 127 | | | | — | | | | 127 | |
Vesting of stock options, net of minority interests | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 106 | | | | — | | | | 106 | |
Dividends | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3,442 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3,442 | ) |
Net income | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | 644 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 644 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2005 | | 14,347,465 | | $ | 143 | | $ | 167 | | | $ | 66,965 | | | $ | (3,379 | ) | | $ | (264 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | 63,632 | |
Beginning balance adjustment | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | 4,603 | | | | (269 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 4,334 | |
Reclass due to adoption of SFAS No. 123 R | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | (264 | ) | | | — | | | | 264 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Issuance of unvested restricted stock, net of minority interests | | 66,419 | | | 1 | | | — | | | | 408 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 409 | |
Vesting of restricted stock, net of minority interests | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | 235 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 235 | |
Vesting of stock options, net of minority interests | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | 77 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 77 | |
Vesting of incentive units, net of minority interests | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | 1,390 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,390 | |
Change in minority interest (see Note 3) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | (2,373 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,373 | ) |
Stock option exercise, net of minority interest | | 4,377 | | | — | | | — | | | | 54 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 54 | |
Dividends | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3,459 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3,459 | ) |
Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,049 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,049 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2006 | | 14,418,261 | | $ | 144 | | $ | 167 | | | $ | 71,095 | | | $ | (9,156 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 62,250 | |
Adoption of FIN 48 | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (120 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (120 | ) |
Issuance of unvested restricted stock, net of minority interests | | 103,564 | | | 1 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | |
Vesting of restricted stock, net of minority interests | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | 1,354 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,354 | |
Vesting of stock options, net of minority interests | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | 465 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 465 | |
Vesting of incentive units, net of minority interests | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | 1,481 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,481 | |
Change in minority interest (see Note 3) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | (22,272 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (22,272 | ) |
Stock option exercise, net of minority interest | | 26,111 | | | — | | | — | | | | 320 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 320 | |
Proceeds from sale of common stock, net of offering expenses | | 9,200,000 | | | 92 | | | — | | | | 139,316 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 139,408 | |
Syndication fee | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | (314 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (314 | ) |
Redemption of Operating Partnership units | | — | | | — | | | (22 | ) | | | (33,646 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (33,668 | ) |
Dividends | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (5,278 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (5,278 | ) |
Tax benefit for uncertain tax provision | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | 47 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 47 | |
Other comprehensive loss recognized, net of minority interests | | — | | | | | | | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (201 | ) | | | (201 | ) |
Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (903 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (903 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2007 | | 23,747,936 | | $ | 237 | | $ | 145 | | | $ | 157,799 | | | $ | (15,410 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | (201 | ) | | $ | 142,570 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial information.
60
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended
December 31,
2007 | | | Year ended
December 31,
2006 | | | Year ended
December 31,
2005 | |
Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income/(loss) | | $ | (903 | ) | | $ | (2,049 | ) | | $ | 644 | |
Adjustments to reconcile net income/(loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gain on sale of real estate | | | (4,441 | ) | | | (10,640 | ) | | | — | |
Gain on purchase of other secured loan | | | — | | | | — | | | | (25,776 | ) |
Loss from early extinguishment of debt | | | — | | | | 360 | | | | 4,475 | |
Loss from early extinguishment of debt applied to loan premiums | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,098 | ) |
Reversal of deferred interest on other secured loan | | | — | | | | — | | | | (515 | ) |
Write off of unamortized loan costs | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,120 | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 14,853 | | | | 12,909 | | | | 16,259 | |
Deferred rents | | | 5,896 | | | | 5,543 | | | | 5,355 | |
Depreciation and amortization expense | | | 11,604 | | | | 12,661 | | | | 12,408 | |
Amortization of loan costs | | | 327 | | | | 488 | | | | 563 | |
Amortization of loan premium | | | — | | | | — | | | | (459 | ) |
Amortization of above and below market leases, net | | | (16 | ) | | | (259 | ) | | | (284 | ) |
Vesting of stock options and restricted stock | | | 3,764 | | | | 3,754 | | | | 505 | |
Minority interests | | | 127 | | | | (1,105 | ) | | | 1,231 | |
Distributions of income from unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 1,113 | | | | 980 | | | | 2,108 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Rents and other receivables | | | (157 | ) | | | (752 | ) | | | 912 | |
Receivables—unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (2,566 | ) | | | (739 | ) | | | (2,578 | ) |
Deferred leasing and loan costs | | | (599 | ) | | | (419 | ) | | | (1,115 | ) |
Deferred tax asset | | | — | | | | 635 | | | | 698 | |
Other assets | | | (12,558 | ) | | | 28 | | | | 1,151 | |
Deferred interest payable | | | 177 | | | | 177 | | | | 195 | |
Accounts payable and other liabilities | | | 29,434 | | | | (749 | ) | | | 3,961 | |
Due to affiliate | | | 2,000 | | | | — | | | | (1,852 | ) |
Prepaid rent | | | (156 | ) | | | (195 | ) | | | 2,912 | |
Deferred tax liability | | | (2,392 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by operating activities: | | | 45,507 | | | | 20,628 | | | | 20,820 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenditures for improvements to real estate | | | (125,481 | ) | | | (29,257 | ) | | | (6,981 | ) |
Exercise of El Segundo purchase option and buy-out of minority partner | | | — | | | | — | | | | (31,100 | ) |
Purchases of interests in unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (18,797 | ) | | | (24,150 | ) | | | (25,733 | ) |
Proceeds from sale of real estate | | | — | | | | 29,450 | | | | — | |
Return of capital from unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 7,166 | | | | 26,853 | | | | 8,386 | |
Contributions to unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (2,059 | ) | | | (21,980 | ) | | | (10,520 | ) |
Payments for purchase of naming rights | | | (750 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Change in restricted cash | | | (4,751 | ) | | | 560 | | | | (2,562 | ) |
Change in short term investments | | | — | | | | — | | | | 14,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in investing activities | | | (144,672 | ) | | | (18,524 | ) | | | (54,510 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
61
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS—(Continued)
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended
December 31,
2007 | | | Year ended
December 31,
2006 | | | Year ended
December 31,
2005 | |
Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from equity offering | | | 139,818 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Payment of offering costs | | | (432 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Payment for redemption of operating units | | | (33,646 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Minority interest contributions | | | — | | | | 52 | | | | — | |
Minority interest distributions | | | (36 | ) | | | (550 | ) | | | — | |
Payment of dividends to common stockholders and distributions to limited partners of the Operating Partnership | | | (8,557 | ) | | | (7,653 | ) | | | (5,715 | ) |
Principal payments of mortgage and other secured loans | | | (20,215 | ) | | | (10,962 | ) | | | (8,995 | ) |
Repayment of notes payable, including principal defeased and defeasance costs | | | — | | | | — | | | | (89,798 | ) |
Purchase of Two Commerce Square Junior B Mezzanine loan | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,500 | ) |
Proceeds from mortgage and other secured loans | | | 84,217 | | | | 17,434 | | | | 149,500 | |
Payments of loan costs | | | — | | | | (51 | ) | | | (1,393 | ) |
Proceeds from exercise of stock options | | | 320 | | | | 54 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | | | 161,469 | | | | (1,676 | ) | | | 41,099 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | 62,304 | | | | 428 | | | | 7,409 | |
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | | | 64,343 | | | | 63,915 | | | | 56,506 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | | $ | 126,647 | | | $ | 64,343 | | | $ | 63,915 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash paid for interest, net of capitalized interest of $3,495, $4,710, and $2,165 for the year ended December 31, 2007, December 31, 2006 and December 31, 2005 | | $ | 17,866 | | | $ | 19,180 | | | $ | 27,201 | |
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accrual for declaration of dividends to common shareholders and distributions to limited partners of the Operating Partnership | | $ | 2,354 | | | $ | 1,916 | | | $ | 1,905 | |
Investments in real estate included in accounts payable and other liabilities | | | 13,503 | | | | 5,789 | | | | 692 | |
Decrease in investments in real estate and accumulated depreciation for removal of fully amortized improvements | | | 4,540 | | | | 8,730 | | | | — | |
Increase in investments in real estate for the consolidation of Murano | | | — | | | | 7,436 | | | | — | |
Financing provided by minority partner relating to acquisition of minority partner's interest | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,900 | |
Reclassification of minority interest for limited partnership units in the Operating Partnership from additional paid in capital | | | 22,272 | | | | 2,373 | | | | 20,238 | |
Other comprehensive income | | | 329 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Syndication fee related to investment in Austin Portfolio Properties | | | 560 | | | | — | | | | — | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial information.
62
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
December 31, 2007, 2006, and 2005
(Tabular amounts in thousands)
1. Organization and Description of Business
The terms “Thomas Properties”, “us”, “we” and “our” as used in this report refer to Thomas Properties Group, Inc. together with our Operating Partnership, Thomas Properties Group, L.P.
We were formed to succeed to certain businesses of the Thomas Properties predecessor (Thomas Properties Group, Inc. Predecessor, or “TPGI Predecessor”), which was not a legal entity but rather a combination of real estate entities and operations. We own, manage, lease, acquire and develop real estate, consisting primarily of office properties and related parking garages, located in Southern California; Sacramento, California; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Northern Virginia; Houston, Texas; and Austin, Texas. The owners of TPGI Predecessor were Mr. James A. Thomas, our Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President, and certain others who had minor ownership interests.
We were incorporated in the State of Delaware on March 9, 2004. On October 13, 2004, we completed our initial public offering (the “Offering”). Concurrent with the consummation of the Offering, Thomas Properties and the Operating Partnership, together with the partners and members of the affiliated partnerships and limited liability companies of TPGI Predecessor and other parties which held direct or indirect ownership interests in the properties engaged in certain formation transactions. The formation transactions were designed to (i) continue the operations of TPGI Predecessor, (ii) enable us to raise the necessary capital to acquire increased interests in certain of the properties and repay certain property level indebtedness, (iii) fund joint venture capital commitments, (iv) provide capital for future acquisitions, and (v) fund future development costs at our development properties.
On April 25, 2007, the Company completed the sale of 9.2 million shares of common stock at $16.00 per share. The net proceeds, after deducting underwriting discounts, commissions and offering expenses were $139.4 million, of which $33.7 million was used to redeem 2,170,000 units in our Operating Partnership held by our CEO and 45,000 units held by another senior executive.
Our operations are carried on through our Operating Partnership. We are the sole general partner in the Operating Partnership. Pursuant to contribution agreements among the owners of TPGI Predecessor and the Operating Partnership, the Operating Partnership received a contribution of interests in the real estate properties, as well as the investment advisory, property management, leasing and real estate development operations of TPGI Predecessor in exchange for limited partnership units (“Units”) in the Operating Partnership issued to the contributors and the assumption of debt and other specified liabilities. As of December 31, 2007, we held a 60.5% interest in the Operating Partnership which we consolidated, as we have control over the major decisions of the Operating Partnership.
63
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
As of December 31, 2007, we were invested in the following real estate properties:
| | | | |
Property | | Type | | Location |
Consolidated properties: | | | | |
One Commerce Square | | High-rise office | | Philadelphia Central Business District, Pennsylvania (“PCBD”) |
Two Commerce Square | | High-rise office | | PCBD |
Murano | | Construction in progress; Residential condominiums | | PCBD |
2100 JFK Boulevard | | Undeveloped land; Residential/Office/Retail | | PCBD |
Four Points Centre | | Construction in progress and undeveloped land; Office/Retail/Research and Development/Hotel | | Austin, Texas |
Campus El Segundo | | Site infrastructure in progress and undeveloped land; Office/Retail/ Research and Development/Hotel | | El Segundo, California |
Metro Studio@Lankershim | | Entitlements and pre-development in progress; Office/Studio/Production/Retail | | Los Angeles, California |
| | |
Unconsolidated properties: | | | | |
2121 Market Street | | Residential and Retail | | PCBD |
| | |
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC: | | | | |
City National Plaza | | High-rise office | | Los Angeles Central Business District, California |
Reflections I | | Suburban office—single tenancy | | Reston, Virginia |
Reflections II | | Suburban office—single tenancy | | Reston, Virginia |
Four Falls Corporate Center | | Suburban office | | Conshohocken, Pennsylvania |
Oak Hill Plaza | | Suburban office | | King of Prussia, Pennsylvania |
Walnut Hill Plaza | | Suburban office | | King of Prussia, Pennsylvania |
San Felipe Plaza | | High-rise office | | Houston, Texas |
2500 City West | | Suburban office and undeveloped land | | Houston, Texas |
Brookhollow Central I, II and III | | Suburban office | | Houston, Texas |
CityWestPlace | | Suburban office and undeveloped land | | Houston, Texas |
Centerpointe I & II | | Suburban office | | Fairfax, Virginia |
Fair Oaks Plaza | | Suburban office | | Fairfax, Virginia |
San Jacinto Center | | High-rise office | | Austin Central Business District, Texas, (“ACBD”) |
64
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
| | | | |
Property | | Type | | Location |
| | |
Frost Bank Tower | | High-rise office | | ACBD |
| | |
One Congress Plaza | | High-rise office | | ACBD |
| | |
One American Center | | High-rise office | | ACBD |
| | |
300 West 6th Street | | High-rise office | | ACBD |
| | |
Research Park Plaza I & II | | Suburban Office | | Austin, Texas |
| | |
Park 22 I-III | | Suburban Office | | Austin, Texas |
| | |
Great Hills Plaza | | Suburban Office | | Austin, Texas |
| | |
Stonebridge Plaza II | | Suburban Office | | Austin, Texas |
| | |
Westech 360 I-IV | | Suburban Office | | Austin, Texas |
2100 JFK Boulevard includes a surface parking lot that services One Commerce Square, Two Commerce Square and other unrelated properties. The City National Plaza property also includes an off-site garage that provides parking for City National Plaza and other properties. The office properties typically include on-site parking, retail and storage space.
From the late 1980s through 2000, TPGI Predecessor developed One Commerce Square, Two Commerce Square, 2121 Market Street and the California Environmental Protection Agency (“CalEPA”) headquarters building in Sacramento, California. We have the responsibility for the day-to-day operations of CalEPA building, but have no ownership interest in the property. We provide investment advisory services for the California State Teachers Retirement System (“CalSTRS”) with respect to three properties that are wholly owned by CalSTRS— 800 South Hope Street, 1835 Market Street and Pacific Financial Plaza—as well as the properties owned in a joint venture between CalSTRS and us (“TPG/CalSTRS”). In addition, we provide property management, leasing and development services to the properties discussed above, except we do not provide property management services for 2121 Market Street and Reflections I.
In 2001, TPGI Predecessor formed a joint venture with a third party, which entered into an agreement to purchase the land commonly referred to as Campus El Segundo. In October 2005, we purchased the entire interest of our unaffiliated minority partner in the joint venture and exercised the option to acquire the land.
Effective October 13, 2004, Mr. Thomas owned an 11% ownership interest in One Commerce Square and Two Commerce Square. On December 31, 2007, we exercised our option to purchase Mr. Thomas’ 11% ownership interest in One Commerce Square for $2 million. As of December 31, 2007, Mr. Thomas owns an 11% ownership interest in Two Commerce Square, which we intend to acquire in 2008.
As of December 31, 2007, we hold a 73% interest in Murano, which was formed to hold a general partnership interest in the Murano development project. As of August 2, 2006, we consolidated this entity.
2. Change in Method of Accounting for Deferred Tax Asset
As of January 1, 2006, we elected to change the method of accounting for the deferred tax effects of Thomas Properties Group, Inc.’s investment in its consolidated Operating Partnership. Paragraph 34 of SFAS No. 109, Accounting for Income Taxes (SFAS No. 109), notes that a deferred tax asset related to an investment in a consolidated subsidiary or corporate joint venture should not be recorded unless it is apparent it will reverse in
65
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
the foreseeable future. Because partnerships are not taxable entities and their tax consequences flow through to their investors they generally are not considered consolidated subsidiaries or corporate joint ventures. However, because the deferred tax assets related to the outside basis difference of the Company’s investment in the Operating Partnership bears the same attributes as the outside basis difference of a consolidated subsidiary, we have adopted, as a change in accounting policy, a limitation on recording deferred tax assets related to the investment in consolidated partnerships unless the temporary difference will reverse in the foreseeable future. This preferable alternative results in an application whereby we do not recognize a deferred tax asset related to these temporary differences as they will not reverse in the foreseeable future. In accordance with SFAS No. 154, Accounting Changes and Error Corrections (SFAS No. 154), we have retrospectively applied this preferable alternative and adjusted our previously issued consolidated financial statements. The following financial statement line items within our consolidated statement of stockholders’ equity for the year ended December 31, 2005 were affected by the change in accounting principle.
Consolidated Statement of Stockholders’ Equity
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As
Originally
Reported | | As
Adjusted | | Effect of
Change | |
Balance, December 31, 2004 | | $ | 105,933 | | $ | 66,185 | | $ | (39,748 | ) |
Balance, December 31, 2005 | | | 103,380 | | | 63,632 | | | (39,748 | ) |
3. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation and Combination
The accompanying consolidated financial statements of our company include all the accounts of Thomas Properties Group, Inc., the Operating Partnership and the subsidiaries of the Operating Partnership. Property interests contributed to the Operating Partnership by Mr. Thomas and entities majority owned by him in exchange for Units have been accounted for as a reorganization of entities under common control in a manner similar to a pooling of interests. Accordingly, the contributed assets and assumed liabilities were recorded at TPGI Predecessor’s historical cost basis, except for the minority owners’ share. The pooling-of-interests method of accounting also requires the reporting of results of operations, for the period in which the combination occurred as though the entities had been combined at either the beginning of the period or inception. Prior to the Offering, Thomas Properties Group, Inc. and the Operating Partnership had no operations. The combination did not require any material adjustments to conform the accounting policies of the separate entities. The remaining interests, which were acquired for cash and Units, have been accounted for as a purchase, and the excess of the purchase price over the related historical cost basis has been allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed.
The real estate entities included in the consolidated financial statements have been consolidated only for the periods that such entities were under control by us or TPGI Predecessor, or were considered a variable interest entity. The equity method of accounting is utilized to account for investments in real estate entities over which we have significant influence, but not control over major decisions, including the decision to sell or refinance the properties owned by such entities. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in the consolidated financial statements.
The interests in One Commerce Square (beginning June 1, 2004 through December 31, 2006), Two Commerce Square (beginning October 13, 2004), and Campus El Segundo (through October 11, 2005), not owned by us are reflected as minority interest. On December 31, 2007, we exercised our option to purchase the
66
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
remaining 11% interest in One Commerce Square for $2.0 million, resulting in our 100% ownership of One Commerce Square. For the period from October 13, 2004 through December 31, 2007, no losses of Two Commerce Square have been allocated to Mr. Thomas, as no further contributions are required from Mr. Thomas. The unrecognized minority interest in the deficit of Two Commerce Square is $847,000 and $762,000 at December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Future income allocable to Mr. Thomas will be reduced by such unrecognized losses.
We have a $20,510,000 preferred equity interest in Murano. Excluding the preferred equity interest, a third party has a 27.0% ownership interest in Murano.
Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents consist of highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less when acquired.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash consists of security deposits from tenants and deposits from prospective condominium buyers as well as funds required under the terms of certain secured notes payable. There are restrictions on our ability to withdraw these funds other than for their specified usage. See Note 5 for additional information on restrictions under the terms of certain secured notes payable.
Investments in Real Estate
Investments in real estate are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are recorded on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives as follows:
| | |
Buildings | | 40 to 50 years |
Building improvements | | 5 to 40 years |
Tenant improvements | | Shorter of the useful lives or the terms of the related leases |
Improvements and replacements are capitalized when they extend the useful life, increase capacity or improve the efficiency of the asset. Repairs and maintenance are charged to expense as incurred.
Costs related to the acquisition, development, construction and improvement of properties are capitalized. Interest, real estate taxes, insurance and other development related costs incurred during construction periods are capitalized and depreciated on the same basis as the related assets. Included in investments in real estate is capitalized interest of $16.3 million and $8.1 million as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
We consider assets to be held for sale pursuant to the provisions of SFAS No. 144, Impairments of Long-Lived Assets and Discontinued Operations (“SFAS 144”). We evaluate the held for sale classification of real estate owned each quarter.
Unconsolidated Real Estate Entities
Investments in unconsolidated real estate entities are accounted for using the equity method of accounting whereby our investments in partnerships and limited liability companies are recorded at cost and the investment accounts are adjusted for our share of the entities’ income or loss and for distributions and contributions.
67
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
We use the equity method to account for our unconsolidated real estate entities since we have significant influence but not control over the entities and none of the entities, other than Murano, effective August 1, 2006, are considered variable interest entities.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
We assess whether there has been impairment in the value of our long-lived assets whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount to the future net cash flows, undiscounted and without interest, expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. Assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value, less costs to sell. Management believes no impairment in the net carrying values of the investments in real estate and investments in unconsolidated real estate entities has occurred for the periods presented.
Deferred Leasing and Loan Costs
Deferred leasing commissions and other direct costs associated with the acquisition of tenants are capitalized and amortized on a straight-line basis over the terms of the related leases. Costs associated with unsuccessful leasing opportunities are expensed. Leasing costs, net of related amortization, totaled $11,064,000 and $12,084,000 as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively, and are included in deferred leasing and loan costs, net of accumulated amortization, in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. For the years ended 2007 and 2006, amortization of leasing costs was $2,580,000 and $1,720,000, respectively.
Loan costs are capitalized and amortized to interest expense over the terms of the related loans using a method that approximates the effective-interest method. Loan costs, net of related amortization, totaled $1,987,000 and $2,315,000 as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively, and are included in deferred leasing and loan costs, net of accumulated amortization, in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Deferred leasing and loan costs also include the carrying value of acquired in-place leases, which are discussed below.
Purchase Accounting for Acquisition of Interests in Real Estate Entities
Purchase accounting was applied, on a pro rata basis, to the assets and liabilities related to real estate entities for which we or TPGI Predecessor acquired interests, based on the percentage interest acquired. For purchases of additional interests that were consummated subsequent to June 30, 2001, the effective date of SFAS No. 141, Business Combinations, the fair value of the real estate acquired is allocated to the acquired tangible assets, consisting of land, building, tenant and site improvements, and identified intangible assets and liabilities, consisting of the value of above-market and below-market leases, other value of in-place leases and value of tenant relationships, based in each case on their fair values. Loan premiums, in the case of any above market rate loans, or loan discounts, in the case of below market loans, are recorded based on the fair value of any loans assumed in connection with acquiring the real estate.
The fair value of the tangible assets of an acquired property (which includes land, building, tenant and site improvements) is determined by valuing the property as if it were vacant, and the “as-if-vacant” value is then allocated to land, building, tenant and site improvements based on management’s determination of the relative fair values of these assets. Management determines the as-if-vacant fair value of a property using methods
68
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
similar to those used by independent appraisers. Factors considered by management in performing these analyses include an estimate of carrying costs during the expected lease-up periods considering current market conditions and costs to execute leases. In estimating carrying costs, management includes real estate taxes, insurance and other operating expenses and estimates of lost rental revenue during the expected lease-up periods based on current market demand. Management also estimates costs to execute leases including leasing commissions, legal and other related costs.
In allocating the fair value of the identified intangible assets and liabilities of an acquired property, above-market and below-market in-place lease values are recorded based on the present value (using an interest rate which reflects the risks associated with the leases acquired) of the difference between (i) the contractual amounts to be paid pursuant to the in-place leases and (ii) management’s estimate of fair market lease rates for the corresponding in-place leases, measured over a period equal to the remaining non-cancelable term of the lease. The capitalized above-market lease values, included in other assets, are amortized as a reduction of rental income over the remaining non-cancelable terms of the respective leases. The capitalized below-market lease values, included in other liabilities, are amortized as an increase to rental income over the terms in the respective leases. As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, we had an asset related to above market leases of $1,148,000 and 1,378,000, respectively, net of accumulated amortization of $658,000 and $533,000, respectively, and a liability related to below market leases of $946,000 and $1,191,000, respectively, net of accumulated accretion of $1,110,000 and $892,000, respectively. The weighted average amortization period for our above and below market leases was approximately 7.7 and 7.4 years as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
The aggregate value of other acquired intangible assets, consisting of in-place leases and tenant relationships, is measured by the excess of (i) the purchase price paid for a property after adjusting existing in-place leases to market rental rates over (ii) the estimated fair value of the property as if vacant, determined as set forth above. This aggregate value is allocated between in-place lease values and tenant relationships based on management’s evaluation of the specific characteristics of each tenant’s lease; however, the value of tenant relationships has not been separated from in-place lease value for the additional interests in real estate entities acquired by us and TPGI Predecessor because such value and its consequence to amortization expense is immaterial for these particular acquisitions. Should future acquisitions of properties result in allocating material amounts to the value of tenant relationships, an amount would be separately allocated and amortized over the estimated life of the relationship. The value of in-place leases exclusive of the value of above-market and below-market in-place leases is amortized to depreciation and amortization expense over the remaining non-cancelable periods of the respective leases. If a lease were to be terminated prior to its stated expiration, all unamortized amounts relating to that lease would be written off.
The table below presents the expected amortization related to the acquired in-place lease value and acquired above and below market leases at December 31, 2007:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2009 | | | 2010 | | | 2011 | | | 2012 | | | Thereafter | | | Total | |
Amortization expense: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Acquired in-place lease value | | $ | 435 | | | $ | 655 | | | $ | 631 | | | $ | 624 | | | $ | 526 | | | $ | 521 | | | $ | 3,392 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjustments to rental revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Above market leases | | $ | (197 | ) | | $ | (197 | ) | | $ | (197 | ) | | $ | (196 | ) | | $ | (194 | ) | | $ | (167 | ) | | $ | (1,148 | ) |
Below market leases | | | 222 | | | | 206 | | | | 191 | | | | 183 | | | | 107 | | | | 37 | | | | 946 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net adjustment to rental revenues | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 9 | | | $ | (6 | ) | | $ | (13 | ) | | $ | (87 | ) | | $ | (130 | ) | | $ | (202 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
69
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Minority Interests of Unitholders in the Operating Partnership
Minority interests of unitholders in the Operating Partnership represent the interests in the Operating Partnership units which are held primarily by entities affiliated with Mr. Thomas. The ownership percentage of the minority interest is determined by dividing the number of Operating Partnership units by the total number of shares of common stock and Operating Partnership units outstanding. Net income is allocated based on the ownership percentages. The issuance of additional shares of common stock or Operating Partnership units results in changes to the minority interest of the Operating Partnership percentage as well as the total net assets to the Company. As a result, all common transactions result in an allocation between the stockholders’ equity and minority interest of the Operating Partnership in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets to account for the change in the minority interest of the Operating Partnership ownership percentage as well as the change in total net assets of the company.
Revenue Recognition
All leases are classified as operating leases and minimum rents are recognized on a straight-line basis over the terms of the leases. The impact of the straight line rent adjustment decreased revenue by $5,895,000, $5,543,000, and $5,355,000 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively. Additionally, the net impact of the amortization of acquired above market leases and acquired below market leases increased revenue by $16,000, $259,000 and $284,000 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively. The excess of rents recognized over amounts contractually due pursuant to the underlying leases is included in deferred rents in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and contractually due but unpaid rents are included in rents and other receivables. We also maintain an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses resulting from the inability of tenants to make required rent payments. The computation of this allowance is based on the tenants’ payment history and current credit status, as well as certain industry or specific credit considerations. If estimates of collectability differ from the cash received, then the timing and amount of our reported revenue could be impacted. The credit risk is mitigated by the high quality of the existing tenant base, reviews of prospective tenant’s risk profiles prior to lease execution and continual monitoring of our tenant portfolio to identify potential problem tenants.
Tenant reimbursements for real estate taxes, common area maintenance and other recoverable costs are recognized in the period that the expenses are incurred. Amounts allocated to tenants based on relative square footage are included in the tenant reimbursements caption on the consolidated statements of operations. Revenues generated from requests from tenants, which result in over-standard usage of services are directly billed to the tenants and are also included in the tenant reimbursements caption on the consolidated statements of operations. Lease termination fees, which are included in other income in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations, are recognized when the related leases are canceled and we have no continuing obligation to provide services to such former tenants.
During the fourth quarter of 2007, our management concluded that the accounting for certain reimbursements (primarily tenants’ over-standard usage of certain operating expenses such as electricity and business use and occupancy taxes) related to our property operations, should have been presented on a gross basis versus a net revenue basis, pursuant to EITF 99-19, “Reporting Revenue Gross as a Principal versus Net as an Agent”, and that revenues should have been presented in tenant reimbursements instead of parking and other. Accordingly, we reclassified such reimbursements from the parking and other revenue caption to the tenant reimbursements revenue caption, and we reclassified the corresponding expense from the parking and other revenue caption to the rental property operating and maintenance expense caption for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 to be consistent with the presentation for the year ended December 31, 2007. As a result, amounts reflected as “tenant reimbursements”, “parking and other” and “rental property operating and
70
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
maintenance” in the consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2006 have increased (decreased) from the amounts previously reported by $5.8 million, $(0.1) million, and $5.7 million, respectively, and for the year ended December 31, 2005 have increased (decreased) from the amounts previously reported by $6.1 million, $(0.1) million, and $6.0 million, respectively. This reclassification had no impact on operating income, net income, and earnings per share or stockholders’ equity.
We recognize gains on sales of real estate when the recognition criteria in SFAS No. 66 “Accounting for Sales of Real Estate” (“SFAS 66”) have been met, generally at the time title is transferred and we no longer have substantial continuing involvement with the real estate asset sold. If the criteria for profit recognition under the full-accrual method are not met, we defer gain recognition and account for the continued operations of the property by applying the deposit or percentage of completion method, as appropriate, until the appropriate criteria are met. With respect to a parcel we sold at Campus El Segundo in 2006, we deferred a portion of the gain as we are obligated to fund certain infrastructure improvements with respect to the sold parcel; therefore we are recognizing the deferred gain on the percentage of completion method.
Investment advisory fees are based on a percentage of net operating income earned by a property under management and are recorded on a monthly basis as earned. Property management fees are based on a percentage of the revenue earned by a property under management and are recorded on a monthly basis as earned. Generally, 50% of leasing fees are recognized upon the execution of the lease and the remainder upon tenant occupancy unless significant future contingencies exist. Development fees are recognized as the real estate development services are rendered using the percentage-of-completion method of accounting based on total project costs incurred to total estimated costs.
Opening Additional Paid in Capital and Retained Deficit Adjustment and Reclassifications
In accordance with SAB 108, we adjusted our opening stockholders’ equity and minority interest of unitholders in the Operating Partnership for 2006 and financial results in the accompanying consolidated financial statements to reflect (1) a change in the allocation of depreciation expense relating to our investment in TPG/CalSTRS, and (2) expense attributable to incentive units in our Operating Partnership. See Notes 4 and 8 for additional information regarding the allocation of depreciation expense and incentive unit expense, respectively, and Note 16 for additional information on SAB 108.
Equity Offering Costs
Underwriting commissions and costs and expenses from our October 2004 initial public offering and our April 2007 public offering are reflected as a reduction to additional paid-in-capital.
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes using the asset and liability approach, the objective of which is to establish deferred tax assets and liabilities for the temporary differences between the financial reporting basis and the tax basis of our assets and liabilities, as measured by applying currently enacted tax laws. A valuation allowance is established for deferred tax assets if, based on the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Earnings (loss) per share
Earnings (loss) per share is calculated based on the weighted average number of shares of our common stock outstanding during the period. The assumed exercise of outstanding stock options and the effect of the vesting of unvested restricted stock that has been granted or has been committed to be granted, all using the treasury stock method, are not dilutive for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006.
71
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Stock-based Compensation
On January 1, 2006, in connection with the adoption of SFAS No. 123R using the modified prospective method, we reclassified $264,000 to net the unearned compensation line item within equity against additional paid in capital. Under SFAS No. 123R, an equity instrument is not recorded to stockholders’ equity until the related compensation expense is recorded over the requisite service period of the award. Prior to the adoption of SFAS No. 123R, and in accordance with the previous accounting guidance, we recorded the full fair value of all issued but nonvested stock options and restricted shares in additional paid in capital and recorded an offsetting deferred compensation balance on a separate line item within equity for the amount of compensation costs not yet recognized for these nonvested instruments. We use the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model to estimate the fair value of granted options. This model takes into account the option’s exercise price, the option’s expected life, the current price of the underlying stock, the expected volatility of the underlying stock, expected dividends, and a risk-free interest rate.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In July 2006, FASB issued FASB Interpretation No. 48 “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes, an Interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109” (“FIN 48”), which is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2006, and clarifies the accounting for uncertainty in tax positions. FIN 48 requires that we recognize the impact of a tax position in our financial statements if that position would more likely than not be sustained on audit, based on the technical merits of the position. See Note 10 for further details regarding the adoption of FIN 48.
In September 2006, FASB issued FASB Statement No. 157 “Fair Value Measurement” (“SFAS 157”), which defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in generally accepted accounting principles and provides for expanded disclosure about fair value measurements. This statement applies under other accounting pronouncements that require or permit fair value measurements. This guidance was issued to increase consistency and comparability in fair value measurements and to expand disclosures about fair value measurements. This statement is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007. We do not expect that the adoption of SFAS 157 will have a material impact on our financial statements.
In February 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. 157-1, “Application of FASB Statement No. 157 to FASB Statement No. 13 and Other Accounting Pronouncements That Address Fair Value Measurements for Purposes of Lease Classification or Measurement under Statement 13” (“SFAS 157-1”). SFAS No. 157-1 amends SFAS 157, to exclude the FASB issued FASB Statement No. 13, “Accounting for Leases” (“SFAS 13”), and other accounting pronouncements that address fair value measurements for purposes of lease classification or measurement under SFAS 13. However, this scope exception does not apply to assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination that are required to be measured at fair value under FASB Statement No. 141 (R), “Business Combinations” (“SFAS 141R”), regardless of whether those assets and liabilities are related to leases. We are evaluating SFAS 157-1 and have not yet determined the impact the adoption will have on our financial position or results of operations.
In September 2006, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) released Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 108 (SAB 108) “Considering the Effects of Prior Year Misstatements when Quantifying Misstatements in Current Year Financial Statements,” to address diversity in practice regarding consideration of the effects of prior year errors when quantifying misstatements in current year financial statements. The SEC staff concluded that registrants should quantify financial statement errors using both a balance sheet approach and an income statement approach and evaluate whether either approach results in quantifying a misstatement that, when all
72
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
relevant quantitative and qualitative factors are considered, is material. SAB 108 states that if correcting an error in the current year materially affects the current year’s income statement, the prior period financial statements must be restated. SAB 108 is effective for fiscal years ending after November 15, 2006, and we elected early application of SAB 108 as of September 30, 2006. See Note 16 for the impact of SAB 108 on our financial statements.
In September 2006, the Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) of the FASB issued EITF Issue No. 06-8, “Applicability of the Assessment of a Buyer’s Continuing Investment under SFAS No. 66 for the Sale of Condominiums” (“EITF 06-8”). EITF 06-8 states that in assessing the collectability of the sales price pursuant to SFAS 66, an entity should evaluate the adequacy of the buyer’s initial and continuing investment to conclude that the sales price is collectible. If an entity is unable to meet the criteria of SFAS 66, including an assessment of collectability using the initial and continuing investment tests described in SFAS 66, then the entity should apply the deposit method as described in SFAS 66. In November 2006, the FASB ratified the EITF’s recommendation. This statement is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after March 15, 2007. We are currently applying the deposit method on our Murano residential project, and will continue to evaluate this method versus the percentage of completion method in future periods.
In February 2007, the FASB issued FASB Statement No. 159 “The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities” (“SFAS 159”). SFAS 159 permits all entities to choose to measure eligible items at fair value at specified election dates. SFAS 159 is effective as of the beginning of an entity’s first fiscal year that begins after November 15, 2007. We are evaluating SFAS 159 and have not yet determined the impact the adoption will have on our financial position or results of operations.
In December 2007, FASB issued SFAS 141R, to create greater consistency in the accounting and financial reporting of business combinations. SFAS 141R requires a company to recognize the assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquired entity to be measured at their fair values as of the acquisition date. SFAS 141R also requires companies to recognize the fair value of assets acquired, the liabilities assumed and any noncontrolling interest in acquisitions of less than a one hundred percent interest when the acquisition constitutes a change in control of the acquired entity. In addition, SFAS 141R requires that acquisition-related costs and restructuring costs be recognized separately from the business combination and expensed as incurred. SFAS 141R is effective for business combinations for which the acquisition date is on or after the beginning of the first annual reporting period beginning after December 15, 2008. We are evaluating SFAS 141R and have not yet determined the impact the adoption will have on our financial position or results of operations.
In December 2007, FASB issued FASB Statement No. 160, “Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements - an Amendment of Accounting Research Bulletin No. 51” (“SFAS 160”). SFAS 160 requires all entities to report noncontrolling interests in subsidiaries within equity in the consolidated financial statements, but separate from the parent shareholders’ equity. SFAS No. 160 also requires any acquisitions or dispositions of noncontrolling interests that do not result in a change of control to be accounted for as equity transactions. In addition, SFAS No. 160 requires that a parent company recognize a gain or loss in net income when a subsidiary is deconsolidated upon a change in control. SFAS No. 160 applies to fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008 and is adopted prospectively. The presentation and disclosure requirements shall be applied retrospectively for all periods presented. The adoption of SFAS 160 will result in a reclassification of minority interest to a separate component of total equity and net income attributable to noncontrolling interests will no longer be treated as a reduction to net income but will be shown as a reduction from net income in calculating net income available to common stockholders. We are evaluating SFAS 160 and have not yet determined the impact the adoption will have on our financial position or results of operations.
73
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Management’s Estimates and Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
We have identified certain critical accounting policies that affect management’s more significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate estimates related to critical accounting policies, including those related to revenue recognition and the allowance for doubtful accounts receivable and investments in real estate and asset impairment. The estimates are based on information that is currently available to us and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances.
We must make estimates related to the collectability of accounts receivable related to minimum rent, deferred rent, expense reimbursements, lease termination fees and other income. We specifically analyze accounts receivable and historical bad debts, tenant concentrations, tenant creditworthiness, and current economic trends when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts receivable. These estimates have a direct impact on our net income, because a higher bad debt allowance would result in lower net income.
We are required to make subjective assessments as to the useful lives of the properties for purposes of determining the amount of depreciation to record on an annual basis with respect to our investments in real estate. These assessments have a direct impact on our net income because if we were to shorten the expected useful lives of our investments in real estate, we would depreciate such investments over fewer years, resulting in more depreciation expense and lower net income on an annual basis.
We are required to make subjective assessments as to whether there are impairments in the values of our investments in real estate, including real estate held by the unconsolidated real estate entities accounted for using the equity method. These assessments have a direct impact on our net income because recording an impairment loss results in a negative adjustment to net income.
We are required to make subjective assessments as to the fair value of assets and liabilities in connection with purchase accounting related to interests in real estate entities acquired by us. These assessments have a direct impact on our net income subsequent to the acquisition of the interests as a result of depreciation and amortization being recorded on these assets and liabilities over the expected lives of the related assets and liabilities. We estimate the fair value of rental properties utilizing a discounted cash flow analysis that includes projections of future revenues, expenses and capital improvement costs, similar to the income approach that is commonly utilized by appraisers.
Segment Disclosure
SFAS No. 131, Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information established standards for disclosure about operating segments and related disclosures about products and services, geographic areas and major customers. We currently operate in one operating segment: the acquisition, development, ownership, and management of commercial real estate. Additionally, we operate in one geographic area: the United States.
Our office portfolio includes revenues from the rental of office space to tenants, parking, rental of storage space and other tenant services.
74
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that subject us to credit risk consist primarily of cash and accounts receivable. We maintain our unrestricted cash and restricted cash on deposit with high quality financial institutions. Accounts at each institution are insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) up to $100,000. There is a concentration of risk related to amounts that exceed the FDIC insurance coverage. We believe that the risk is not significant. Our cash equivalents are typically invested in AAA-rated short-term instruments, which provide daily liquidity. These instruments are not insured.
We have two operating properties and one unconsolidated operating property located in downtown Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. In addition, the Murano residential high-rise project is under construction in downtown Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The ability of the tenants to honor the terms of their respective leases, and the ability of prospective buyers to close on the acquisition of a condominium unit, is dependent upon the economic, regulatory and social factors affecting the communities in which the tenants operate.
We generally require either a security deposit, letter of credit or a guarantee from our tenants. We require a 15% cumulative deposit of prospective buyers of our Murano condominium project, which is essentially non-refundable except in cases of our non-performance.
4. Unconsolidated Real Estate Entities
The unconsolidated real estate entities include the entities that own 2121 Market Street, Harris Building Associates, TPG/CalSTRS, and Murano (through July 31, 2006, as this entity was considered to be a variable interest entity on August 1, 2006). TPG/CalSTRS owns the following properties:
City National Plaza (purchased January 2003)
Reflections I (purchased October 2004)
Reflections II (purchased October 2004)
Four Falls Corporate Center (purchased March 2005)
Oak Hill Plaza (purchased March 2005)
Walnut Hill Plaza (purchased March 2005)
Valley Square Office Park (purchased March 2005, sold April 2006)
San Felipe Plaza (purchased August 2005)
2500 City West (purchased August 2005)
Brookhollow Central I, II and III (purchased August 2005)
Intercontinental Center (purchased August 2005, sold May 2007)
2500 City West land (purchased December 2005)
CityWestPlace (purchased June 2006)
Centerpointe I & II (purchased January 2007)
Fair Oaks Plaza (purchased January 2007)
TPG/CalSTRS also owns a 25% interest in the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture which owns the following properties (“Austin Portfolio Properties”):
San Jacinto Center (purchased June 2007)
Frost Bank Tower (purchased June 2007)
One Congress Plaza (purchased June 2007)
One American Center (purchased June 2007)
300 West 6th Street (purchased June 2007)
Research Park Plaza I & II (purchased June 2007)
75
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Park 22 I-III (purchased June 2007)
Great Hills Plaza (purchased June 2007)
Stonebridge Plaza II (purchased June 2007)
Westech 360 I-IV (purchased June 2007)
Capital contributions, distributions, and profits and losses of the real estate entities are allocated in accordance with the terms of the applicable partnership and limited liability company agreements. Such allocations may differ from the stated ownership percentage interests in such entities as a result of preferred returns and allocation formulas as described in the partnership and limited liability company agreements. Following are the stated ownership percentages, prior to any preferred or special allocations, as of July 31, 2006 for Murano (after which date this entity was consolidated) and as of December 31, 2007 for all other entities:
| | | |
2121 Market Street | | 50.0 | % |
Harris Building Associates | | 0.1 | %(1) |
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC: | | | |
City National Plaza | | 21.3 | %(2) |
All other properties, excluding Austin Portfolio Properties | | 25.0 | %(3) |
Austin Portfolio Properties | | 6.3 | % |
Murano | | 73.0 | % |
| (1) | The partnership that owns 2121 Market Street entered into a master lease for the property with Harris Building Associates designed to allow a third party investor to take advantage of the historic tax credits for the property through December 31, 2007. Our Operating Partnership and an unrelated party each held a 0.05% general partnership interest in Harris Building Associates. The 99.9% limited partner of Harris Building Associates contributed $3.5 million and no further contributions were required. In addition, this partner was entitled to various distributions, fees, and priority returns. During 2004, the accumulated losses and distributions for this limited partner exceeded their contribution amount and priority return. As such, net loss was allocated equally to the general partners, resulting in an allocation of 50% of the net loss to us. Effective December 31, 2007, we and our co-general partner acquired the limited partner interest held by the historic tax credit investor. Our share of the total purchase price of $1.2 million was $600,000. The remaining interests in this project are held equally by us and our co-general partner. |
| (2) | In accordance with the limited liability agreement, prior to January 1, 2006, the minority owner of City National Plaza and the Operating Partnership were initially allocated depreciation expense of City National Plaza ahead of CalSTRS. This resulted in the allocation to us of 22.5% of City National Plaza’s depreciation expense and 21.3% of City National Plaza’s net income/loss (excluding depreciation expense). |
During 2005, the accumulated losses and distributions for the minority owner equaled their contribution amount. As such, net income/loss is allocated to the Operating Partnership and CalSTRS.
Beginning January 1, 2006, the Operating Partnership is allocated 25% of net income/loss, including depreciation expense. See Note 16 for discussion of the adjustment to opening retained deficit as of January 1, 2006 as a result of the change in allocation of depreciation expense.
| (3) | In accordance with the limited liability agreement, prior to January 1, 2006, the Operating Partnership was allocated depreciation expense of the properties ahead of CalSTRS, resulting in the allocation to us of 100% of depreciation expense and 25% of net income/loss (excluding depreciation expense) of the properties. Beginning January 1, 2006, the Operating Partnership is allocated 25% of net income/loss, including depreciation expense, which is equal to the economic ownership of the Operating Partnership. See Note 16 for discussion of the adjustment to opening retained deficit as of January 1, 2006 as a result of the change in allocation of depreciation expense. |
76
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Investments in unconsolidated real estate entities as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2007 | | | December 31, 2006 | |
TPG/CalSTRS | | | | | | | | |
City National Plaza | | $ | (9,168 | ) | | $ | (766 | ) |
Reflections I | | | 1,402 | | | | 1,525 | |
Reflections II | | | 1,609 | | | | 1,778 | |
Four Falls Corporate Center | | | 1,069 | | | | 1,989 | |
Oak Hill Plaza/Walnut Hill Plaza | | | 700 | | | | 1,532 | |
Valley Square Office Park | | | (9 | ) | | | 60 | |
San Felipe Plaza | | | 4,450 | | | | 6,514 | |
2500 City West | | | 1,962 | | | | 3,874 | |
Brookhollow Central I, II and III/ Intercontinental Center | | | 1,934 | | | | 2,942 | |
CityWestPlace | | | 21,280 | | | | 23,328 | |
Centerpointe I & II | | | 6,526 | | | | — | |
Fair Oaks Plaza | | | 2,957 | | | | — | |
Austin Portfolio Investor | | | (472 | ) | | | — | |
Frost Bank Tower | | | 3,057 | | | | — | |
300 West 6th Street | | | 2,611 | | | | — | |
San Jacinto Center | | | 2,059 | | | | — | |
One Congress Plaza | | | 2,587 | | | | — | |
One American Center | | | 2,411 | | | | — | |
Stonebridge Plaza II | | | 762 | | | | — | |
Park 22 I-III | | | 671 | | | | — | |
Research Park Plaza I & II | | | 1,002 | | | | — | |
Westech 360 I-IV | | | 540 | | | | — | |
Great Hills Plaza | | | 397 | | | | — | |
TPG/CalSTRS | | | 51 | | | | 10,912 | |
2121 Market Street and Harris Building Associates | | | (1,189 | ) | | | (1,324 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 49,199 | | | $ | 52,364 | |
| | | | | | | | |
77
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The following is a summary of the investments in unconsolidated real estate entities for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006, and 2005:
| | | | |
Investment balance, December 31, 2004 | | $ | 31,624 | |
Contributions, including $25,733 for acquisition of new properties | | | 36,253 | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (16,259 | ) |
Distributions | | | (10,494 | ) |
| | | | |
Investment balance, December 31, 2005 | | $ | 41,124 | |
Beginning balance adjustment for recalculated depreciation expense allocation | | | 9,836 | |
Contributions, including $24,150 for acquisition of new properties | | | 46,130 | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (12,909 | ) |
Distributions | | | (31,817 | ) |
| | | | |
Investment balance, December 31, 2006 | | $ | 52,364 | |
Contributions, including $18,797 for acquisition of new properties | | | 20,296 | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (14,853 | ) |
Other comprehensive income/loss | | | (329 | ) |
Distributions | | | (8,279 | ) |
| | | | |
Investment balance, December 31, 2007 | | $ | 49,199 | |
| | | | |
TPG/CalSTRS was formed to acquire office properties on a nationwide basis classified as moderate risk (core plus) and high risk (value add) properties. Core plus properties consist of under-performing properties that we believe can be brought to market potential through improved management. Value-add properties are characterized by unstable net operating income for an extended period of time, occupancy less than 90% and/or physical or management problems which we believe can be positively impacted by introduction of new capital and/or management. We are required to use diligent efforts to sell each joint venture property within five years of that property reaching stabilization, except for certain stabilized properties, as to which, we are required to perform a hold/sell analysis at least annually and make a recommendation to the TPG/CalSTRS’ management committee regarding the appropriate holding period.
The total initial capital commitment to the joint venture was $333.3 million. As of December 31, 2007, there were unfunded capital commitments of approximately $3.25 million and $1.15 million by CalSTRS and us, respectively. On February 1, 2008, we revised our agreement with CalSTRS providing for $25 million in additional capital commitments, $18.75 million and $6.25 million from CalSTRS and us, respectively.
A buy-sell provision may be exercised by either CalSTRS or us. Under this provision, the initiating party sets a price for its interest in the joint venture, and the other party has a specified time to either elect to buy the initiating party’s interest, or to sell its own interest to the initiating party. Upon the occurrence of certain events, CalSTRS also has a buy-out option to purchase our interest in the joint venture. The buyout price is based upon a 3% discount to the appraised fair market value. In addition, the minority owner of City National Plaza has the option to require the joint venture to purchase its interests for an amount equal to what would be payable to it upon liquidation of the assets at fair market value.
78
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Following is summarized financial information for the unconsolidated real estate entities as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 and for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005:
Summarized Balance Sheets
| | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | 2006 |
| ASSETS | | | | | | |
Investments in real estate, net | | $ | 2,326,679 | | $ | 1,007,854 |
Land held for sale | | | 3,418 | | | 3,358 |
Assets associated with discontinued operations | | | 28 | | | 14,767 |
Receivables including deferred rents | | | 62,954 | | | 40,754 |
Other assets | | | 330,537 | | | 202,064 |
| | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 2,723,616 | | $ | 1,268,797 |
| | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND OWNERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | |
Mortgage and other secured loans | | $ | 2,162,556 | | $ | 1,037,491 |
Other liabilities | | | 208,977 | | | 72,664 |
Liabilities associated with discontinued operations | | | 23 | | | 13,676 |
| | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 2,371,556 | | | 1,123,831 |
| | | | | | |
Minority interest | | | — | | | — |
Owners’ equity: | | | | | | |
Thomas Properties, including $272 and $258 of other comprehensive loss as of 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 54,041 | | | 55,700 |
Other owners, including $2,612 and $1,199 of other comprehensive loss as of 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 298,019 | | | 89,266 |
| | | | | | |
Total owners’ equity | | | 352,060 | | | 144,966 |
| | | | | | |
Total liabilities and owners’ equity | | $ | 2,723,616 | | $ | 1,268,797 |
| | | | | | |
Summarized Statements of Operations
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
Revenues | | $ | 258,512 | | | $ | 140,796 | | | $ | 77,201 | |
Expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating and other expenses | | | 138,942 | | | | 89,931 | | | | 53,407 | |
Interest expense | | | 118,182 | | | | 56,795 | | | | 29,398 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 107,633 | | | | 55,501 | | | | 31,631 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total expenses | | | 364,757 | | | | 202,227 | | | | 114,436 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (106,245 | ) | | | (61,431 | ) | | | (37,235 | ) |
Minority interest | | | (104 | ) | | | (1,650 | ) | | | 3,910 | |
Gain on sale of real estate | | | 7,932 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | (270 | ) | | | 4,722 | | | | (3,157 | ) |
Cumulative effect of change in accounting policy | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,279 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (98,687 | ) | | $ | (58,359 | ) | | $ | (37,761 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Thomas Properties’ share of net loss, prior to intercompany eliminations | | $ | (17,465 | ) | | $ | (14,473 | ) | | $ | (17,112 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
79
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Included in the preceding summarized balance sheets as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, are the following balance sheets of TPG/CalSTRS, LLC:
| | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | 2006 |
| ASSETS | | | | | | |
Investments in real estate, net | | $ | 1,194,028 | | $ | 989,958 |
Land held for sale | | | 3,418 | | | 3,358 |
Assets associated with discontinued operations | | | 28 | | | 14,767 |
Receivables including deferred rents | | | 55,582 | | | 38,738 |
Investments in unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 61,662 | | | — |
Other assets | | | 174,383 | | | 198,864 |
| | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 1,489,101 | | $ | 1,245,685 |
| | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | |
Mortgage and other secured loans | | $ | 1,235,932 | | $ | 1,018,087 |
Other liabilities | | | 83,914 | | | 67,455 |
Liabilities associated with discontinued operations | | | 23 | | | 13,673 |
| | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 1,319,869 | | | 1,099,215 |
| | | | | | |
Members’ equity: | | | | | | |
Thomas Properties, including $272 and $258 of other comprehensive loss as of December 31, 2007 and December 31, 2006, respectively | | | 54,250 | | | 56,174 |
CalSTRS, including $1,171 and $1,199 of other comprehensive loss as of December 31, 2007 and December 31, 2006, respectively | | | 114,982 | | | 90,296 |
| | | | | | |
Total members’ equity | | | 169,232 | | | 146,470 |
| | | | | | |
Total liabilities and members’ equity | | $ | 1,489,101 | | $ | 1,245,685 |
| | | | | | |
80
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Following is summarized financial information by real estate entity for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, 2007 | |
| | | 2121 Market
Street and Harris
Building
Associates | | | TPG/
CalSTRS,
LLC | | | Austin
Portfolio
Properties | | | Eliminations | | Total | |
| | | Unaudited | |
Revenues | | $ | 5,712 | | | $ | 185,773 | | | $ | 67,027 | | | $ | — | | $ | 258,512 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating and other expenses | | | 3,515 | | | | 106,865 | | | | 28,562 | | | | — | | | 138,942 | |
Interest expense | | | 1,182 | | | | 81,247 | | | | 35,753 | | | | — | | | 118,182 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 962 | | | | 67,955 | | | | 38,716 | | | | — | | | 107,633 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total expenses | | | 5,659 | | | | 256,067 | | | | 103,031 | | | | — | | | 364,757 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) from continuing operations | | | 53 | | | | (70,294 | ) | | | (36,004 | ) | | | — | | | (106,245 | ) |
Minority interest | | | (104 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | (104 | ) |
Gain on sale of real estate | | | — | | | | 7,932 | | | | — | | | | — | | | 7,932 | |
Loss from discontinued operations | | | — | | | | (270 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | (270 | ) |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | — | | | | (9,001 | ) | | | — | | | | 9,001 | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net (loss) income | | $ | (51 | ) | | $ | (71,633 | ) | | $ | (36,004 | ) | | $ | 9,001 | | $ | (98,687 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Thomas Properties’ share of net loss | | $ | (25 | ) | | $ | (15,190 | ) | | $ | (2,250 | ) | | $ | — | | $ | (17,465 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Intercompany eliminations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,612 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | (14,853 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, 2006 | |
| | | 2121 Market
Street and Harris
Building
Associates | | | Murano | | | TPG/
CalSTRS,
LLC | | | Total | |
| | | Unaudited | |
Revenues | | $ | 5,607 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 135,189 | | | $ | 140,796 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating and other expenses | | | 3,463 | | | | 418 | | | | 86,050 | | | | 89,931 | |
Interest expense | | | 1,199 | | | | — | | | | 55,596 | | | | 56,795 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 1,082 | | | | 452 | | | | 53,967 | | | | 55,501 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total expenses | | | 5,744 | | | | 870 | | | | 195,613 | | | | 202,227 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (137 | ) | | | (870 | ) | | | (60,424 | ) | | | (61,431 | ) |
Minority interest | | | (104 | ) | | | — | | | | (1,546 | ) | | | (1,650 | ) |
Gain on sale of real estate | | | — | | | | — | | | | 6,328 | | | | 6,328 | |
Loss from discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,606 | ) | | | (1,606 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (241 | ) | | $ | (870 | ) | | $ | (57,248 | ) | | $ | (58,359 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Thomas Properties’ share of net loss | | $ | (120 | ) | | $ | (435 | ) | | $ | (13,918 | ) | | $ | (14,473 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Intercompany eliminations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,564 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | (12,909 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
81
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, 2005 | |
| | | 2121 Market
Street and Harris
Building
Associates | | | Murano | | | TPG/
CalSTRS,
LLC | | | Total | |
| | | Unaudited | |
Revenues | | $ | 5,324 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 71,877 | | | $ | 77,201 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating and other expenses | | | 3,344 | | | | 412 | | | | 49,650 | | | | 53,406 | |
Interest expense | | | 1,212 | | | | — | | | | 28,186 | | | | 29,398 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 1,135 | | | | — | | | | 30,497 | | | | 31,632 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total expenses | | | 5,691 | | | | 412 | | | | 108,333 | | | | 114,436 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (367 | ) | | | (412 | ) | | | (36,456 | ) | | | (37,235 | ) |
Minority interest | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,910 | | | | 3,910 | |
Loss from discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3,157 | ) | | | (3,157 | ) |
Cumulative effect of change in accounting policy | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,279 | ) | | | (1,279 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (367 | ) | | $ | (412 | ) | | $ | (36,982 | ) | | $ | (37,761 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Thomas Properties’ share of net loss | | $ | (183 | ) | | $ | (206 | ) | | $ | (16,723 | ) | | $ | (17,112 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Intercompany eliminations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 853 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | (16,259 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, one tenant accounted for approximately 10.2%, 12.2% and 10.1%, respectively, of rent and tenant reimbursements (excluding tenant reimbursements for over-standard usage of certain operating expenses) of TPG/CalSTRS.
Following is a reconciliation of our share of owners’ equity of the unconsolidated real estate entities as shown above to amounts recorded by us as of December 31, 2007 and 2006:
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Our share of owners’ equity recorded by unconsolidated real estate entities | | $ | 54,041 | | | $ | 55,700 | |
Intercompany eliminations and other adjustments | | | (4,842 | ) | | | (3,336 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Investments in unconsolidated real estate entities | | $ | 49,199 | | | $ | 52,364 | |
| | | | | | | | |
82
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
5. Mortgage and Other Secured Loans
A summary of the outstanding mortgage and other secured loans as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Outstanding debt | | Maturity
date |
Secured debt | | Interest Rate | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
One Commerce Square mortgage loan (1) | | 5.67% | | $ | 130,000 | | $ | 130,000 | | 1/6/2016 |
Two Commerce Square: | | | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage Loan (2) | | 6.30 | | | 110,019 | | | 114,564 | | 5/9/2013 |
Senior mezzanine loan (3) (4) | | 18.32 | | | 35,449 | | | 40,564 | | 1/9/2010 |
Junior mezzanine loan (3) (5) | | 15.00 | | | 4,285 | | | 4,107 | | 1/9/2010 |
Campus El Segundo mortgage loan (6) | | Prime Rate or LIBOR + 2.25 | | | 17,259 | | | 17,259 | | 10/10/2008 |
Four Points Centre Construction Loan (7) | | Prime Rate or LIBOR + 1.50 | | | 4,895 | | | 4,000 | | 6/11/2010 |
Murano construction loan (8) | | 7.00 or LIBOR + 3.25 | | | 79,321 | | | — | | 7/31/2009 |
Loan secured by our preferred equity interest in Murano (9) | | LIBOR + 4.00 | | | 10,879 | | | 17,434 | | 7/7/2008 |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Total mortgage loans and other secured loans | | | | $ | 392,107 | | $ | 327,928 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | The mortgage loan is subject to interest only payments for the first five years, and thereafter, principal and interest payments are due based on a thirty-year amortization schedule. The loan is subject to yield maintenance payments for any prepayments prior to October 2015, and beginning January 2009, may be defeased. |
| (2) | The mortgage loan may be defeased, and beginning February 2012, may be prepaid. |
| (3) | These loans are guaranteed by Mr. Thomas up to an aggregate maximum of $7.5 million. We have agreed to indemnify Mr. Thomas in the event his guarantees are called upon. |
| (4) | The senior mezzanine loan bears interest at a rate such that the weighted average of the rate on this loan and the rate on the mortgage loan secured by Two Commerce Square equals 9.2% per annum. The effective interest rate on this loan as of December 31, 2007 was 18.3% per annum. The loan may not be prepaid prior to August 9, 2009, and thereafter is subject to yield maintenance payments unless the loan is prepaid within 60 days of maturity. The loan is secured by our ownership interest in the real estate entities that own Two Commerce Square. |
| (5) | Interest at a rate of 10% per annum is payable currently, and additional interest of 5% per annum is deferred until maturity. The loan is subject to a prepayment penalty in the amount of the greater of 3% of the principal amount or a yield maintenance premium. The loan is secured by our ownership interest in the real estate entities that own Two Commerce Square. |
| (6) | The weighted average interest rate as of December 31, 2007 was 7.47% per annum. The loan has two one-year extension options at our election. |
| (7) | The interest rate as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 was 7.25% and 8.25% per annum, respectively. |
| (8) | We may borrow an additional $63.2 million under this construction loan. This loan has two six-month extension options. The interest rate for this loan as of December 31, 2007 was 7.85%. |
| (9) | A subsidiary of our Operating Partnership pledged its preferred equity interest in Murano to a lender for $17,434,000. During the fourth quarter of 2007, we paid $6.6 million to reduce the principal balance on this loan. In addition, the loan was extended through July 7, 2008 and requires monthly payments of $1.6 million. The loan will be fully amortized by the maturity date. The Operating Partnership has guaranteed this loan. |
83
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The loan agreement for Two Commerce Square requires that all receipts collected from this property be deposited in lockbox accounts under the control of the lenders to fund reserves, debt service and operating expenditures. Included in restricted cash at December 31, 2007 and 2006 is $3,263,000 and $3,071,000, respectively, which has been deposited in the lockbox account.
Certain mortgage and other secured loans were repaid or defeased, which resulted in repayment and defeasance costs. Such costs, along with the write-off of unamortized loan costs, net of loan premiums recorded, are presented as loss from early extinguishment of debt in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
As of December 31, 2007, principal payments due for the secured and unsecured outstanding debt are as follows:
| | | |
2008 | | $ | 31,338 |
2009 | | | 83,721 |
2010 | | | 43,336 |
2011 | | | 1,971 |
2012 | | | 2,160 |
Thereafter | | | 233,481 |
| | | |
| | $ | 396,007 |
| | | |
6. Unsecured Loan
In October 2005, we purchased the entire interest of our unaffiliated minority partner in TPG-El Segundo Partners, LLC, $3,900,000 of which was financed with an unsecured loan from the former minority partner. The loan bears interest at 5% per annum. Principal and interest is payable at maturity on October 12, 2009.
7. Earnings (loss) per Share
The following is a summary of the elements used in calculating basic and diluted earnings (loss) per share for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006, and 2005 (in thousands except share and per share amounts):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 |
Net (loss) income attributable to common shares | | $ | (903 | ) | | $ | (2,049 | ) | | $ | 644 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average common shares outstanding - basic | | | 20,739,371 | | | | 14,339,032 | | | | 14,301,932 |
Potentially dilutive common shares (1): | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock options | | | — | | | | — | | | | 4,675 |
Restricted stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,480 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjusted weighted average common shares outstanding - diluted | | | 20,739,371 | | | | 14,339,032 | | | | 14,308,087 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
(Loss) earnings per share - basic and diluted | | $ | (0.04 | ) | | $ | (0.14 | ) | | $ | 0.05 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | For the year ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, the potentially dilutive shares were not included in the loss per share calculation as their effect is antidilutive. |
8. Stockholders’ Equity
We adopted the 2004 Equity Incentive Plan of Thomas Properties Group, Inc. (the “Incentive Plan”) concurrent with the closing of our initial public offering. The Incentive Plan provides incentives to our
84
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
employees and serves to attract, reward and retain personnel. Our Incentive Plan permits the granting of awards in the form of options to purchase common stock, restricted shares of common stock and restricted incentive units in our Operating Partnership. The Incentive Plan originally allowed us to issue up to 1,392,858 shares reserved under the Incentive Plan as either restricted stock awards or incentive unit awards and up to 619,048 shares upon the exercise of options granted pursuant to the Incentive Plan. At the Annual Meeting of shareholders in May 2007, the shareholders approved an increase in the number of shares of common stock reserved for issuance or transfer under the Incentive Plan from 2,011,906 shares to a total of 2,361,906. In addition, the restrictions on the aggregate number of shares that may be issued or transferred with respect to specified awards granted under the Plan were eliminated. We also adopted the Non-employee Directors Restricted Stock Plan (“the Non-employee Directors Plan”) concurrent with the consummation of our initial public offering, under which a total of 60,000 shares are available for grant. A total of 24,967 shares have been granted to non-employee directors and 18,485 of those shares have vested as of December 31, 2007.
A Unit and a share of our common stock have essentially the same economic characteristics as they share equally in the total net income or loss and distributions of the Operating Partnership. A Unit may be redeemed for cash, or exchanged for shares of common stock at our election, on a one-for-one basis after December 13, 2005.
As mentioned above, our incentive plan permits the granting of restricted incentive units. We issued 730,003 incentive units on October 13, 2004, which fully vested as of October 13, 2007. In March 2007 and February 2006 we issued 183,333 and 120,000 incentive units, respectively, to certain employees. Incentive units represent a profits interest in the Operating Partnership and generally will be treated as regular units in our Operating Partnership and rank pari passu with the Units as to payment of regular and special periodic and other distributions and distributions of assets upon liquidation. Incentive units are subject to vesting, forfeiture and additional restrictions on transfer as may be determined by us as general partner of our Operating Partnership. The holder of an incentive unit has the right to convert all or a part of his vested incentive units into Units, but only to the extent of the incentive units’ economic capital account balance. As general partner, we may also cause any number of vested incentive units to be converted into Units to the extent of the incentive units’ economic capital account balance. We had 23,747,936 and 14,418,261 shares of common stock, and 14,496,666 and 16,666,666 Units outstanding as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Beginning as of January 1, 2006, we record compensation expense for the incentive units based on the fair value of the units recognized ratably over the applicable vesting period. See Note 16 for discussion of the adjustment to opening stockholders’ equity as a result of the change in recording incentive unit expense. For the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, we recognized incentive unit expense of $2,645,000 and $3,068,000, respectively. We did not recognize any tax benefit related to this compensation expense. As of December 31, 2007, there was $1,931,000 of total unrecognized compensation cost related to the nonvested incentive units.
Under the Incentive Plan, we issued 46,667 shares of restricted stock with an aggregate value of $560,004 in March 2005, which shares fully vested in October 2007. In March 2007 and February 2006, we issued 100,000 and 60,000 shares of restricted stock, respectively, with an aggregate value of $1,580,000 and $740,400, respectively, which shares will fully vest 24 months from grant date, subject to continued service. The February 2006 grant vested in February 2008. Under the Non-employee Directors Plan, we have issued 24,967 restricted shares with an aggregate value of $322,000, 18,485 of those shares have fully vested and 6,482 shares will vest upon the closing of our Annual Meeting of Stockholders in 2008. The holders of all restricted shares have full voting rights and receive all dividends paid. We recorded deferred compensation charges totaling $896,000, $517,000 and $276,000 for the amortization of the restricted stock grants for the year ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively. The total tax benefit recognized in the statements of operations related to restricted stock compensation expense for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 was $385,000, $212,000 and $113,000, respectively. As of December 31, 2007, there was $1,462,000 of total unrecognized compensation cost related to the nonvested restricted stock.
85
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
We granted 360,000 stock options in March 2005 under our Incentive Plan with an exercise price of $12.26, and the options were fully vested October 13, 2007 and expire ten years after the date of commencement of vesting. During 2007 and 2006, 13,333 and 13,817, respectively, of the options were forfeited and 26,111 and 4,377 of the options were exercised in 2007 and 2006, respectively. The fair market value of each option granted was estimated on the date of the grant using the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model, see table below.
We granted 15,000 stock options on February 2, 2006 under our Incentive Plan with an exercise price of $12.36, and 58,333 stock options on May 5, 2006 with an exercise price of $13.25 and the options vest over the course of a three year period commencing February 2, 2006 and May 5, 2006, respectively. The options vest at the rate of one third per year and expire ten years after the date of commencement of vesting. During 2007 and 2006, none of these options were forfeited. The fair market value of each option granted was estimated on the date of the grant using the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model, see table below.
We granted 101,475 stock options on March 7, 2007 under our Incentive Plan with an exercise price of $15.45. The options vest over the course of a three year period commencing with the grant date at the rate of one third per year and expire ten years after the date of commencement of vesting. We granted 50,000 stock options on June 1, 2007 with an exercise price of $17.19 and the options vest eighteen months after the date of grant. During 2007, none of these options were forfeited. The fair market value of existing option granted was estimated on the date of the grant using the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model, see table below.
| | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 |
Dividend yield | | 1.55% | | 2.00% | | 2.00% |
Expected life of option | | 2 to 4 years | | 1 to 3 years | | 1 to 3 years |
Risk-free interest rate | | 4.62% | | 4.40% | | 2.88% |
Expected stock price volatility, historical basis | | 13% | | 15% | | 20% |
The following is a summary of stock option activity under our Incentive Plan as of and for the year ended December 31, 2007:
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Shares | | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted Average
Remaining
Contractual Term
(in years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value |
Outstanding at January 1, 2007 | | 389,166 | | | $ | 12.42 | | | | |
Granted-March | | 101,475 | | | | 15.45 | | | | |
Granted-June | | 50,000 | | | | 17.19 | | | | |
Forfeitures | | (13,333 | ) | | | 12.26 | | | | |
Exercised | | (26,111 | ) | | | 12.26 | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2007 | | 501,197 | | | | 13.52 | | 6.9 | | — |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Options exercisable at December 31, 2007 | | 300,833 | | | | 12.33 | | 7.0 | | — |
| | | | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2007, there was $173,000 of total unrecognized compensation cost related to the nonvested stock options. The cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 1.3 years. The total fair value of shares vested during the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006 was $1,557,000 and $2,022,000, respectively. The weighted-average grant date fair value of options granted during the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006 was $1.89 and $1.50, respectively. The options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006 had an intrinsic value of $98,000 and $2,000.
Included in the consolidated statement of operations for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 is $223,000, $169,000 and $229,000, respectively, in stock compensation expense related to stock options. The
86
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
total income tax benefit recognized in the statements of operations related to this compensation expense was $96,000, $69,000 and $94,000, for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively.
9. Related Party Transactions
As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, we advanced TPG/CalSTRS $2,782,000 and $1,758,000 respectively, and these amounts were repaid in January of the following year.
On December 31, 2007, we exercised our option to purchase the remaining 11% interest held by an affiliate of Mr. Thomas in One Commerce Square for $2.0 million, resulting in our 100% ownership of One Commerce Square. This obligation is reflected in the due to affiliate caption on our consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2007. We have not allocated the fair value of this acquired interest to the acquired tangible assets and identified intangible assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2007. We will do so in 2008.
An affiliate of Mr. Thomas leases retail space located at One Commerce Square and Two Commerce Square through December 31, 2008, for which rent is based on a percentage of the restaurant’s sales. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, we earned rental revenues and tenant reimbursements from this affiliate of $165,000, $56,000, and $81,000 respectively, of which $162,000, $51,000, and $0, respectively, was reserved as bad debt expense. The One Commerce Square partnership incurred approximately $199,000 in 2007 primarily related to furniture, equipment and design improvements for the restaurant. These costs will be fully amortized by December 31, 2008.
Mr. Thomas has guaranteed up to $7,500,000 with respect to the mezzanine loans on Two Commerce Square and we have agreed to indemnify Mr. Thomas (see Note 5).
10. Income Taxes
All operations are carried on through the Operating Partnership and its subsidiaries. The Operating Partnership is not subject to income tax, and all of the taxable income, gains, losses, deductions and credits are passed through to its partners. We are responsible for our share of taxable income or loss of the Operating Partnership allocated to us in accordance with the Operating Partnership’s Agreement of Limited Partnership. As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, we held a 60.5% and 45.15%, respectively, capital interest in the Operating Partnership. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, we were allocated 55.5%, 45.15% and 46.3%, respectively, of the income and losses from the Operating Partnership.
Our effective tax rate is 384%, (45)% and 52%, respectively, for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005. The higher effective tax rate compared to the federal statutory rate of 35% is primarily due to the amortization of the incentive units granted and the interest related to our unrecognized tax benefits.
The provision for income taxes is based on reported income before income taxes. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities reflect the impact of temporary differences between the amounts of assets and liabilities recognized for financial reporting purposes and the amount recognized for tax purposes, as measured by applying the currently enacted tax laws.
87
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The provision for income taxes consists of the following for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
Current income taxes | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | (5,616 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
State | | | (1,177 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total current income taxes | | $ | (6,793 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deferred income tax provision: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | | 4,728 | | | | (541 | ) | | | (551 | ) |
State | | | 1,179 | | | | (94 | ) | | | (147 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total deferred income tax (provision) benefit | | $ | 5,907 | | | $ | (635 | ) | | $ | (698 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense, gross of related tax effects | | | (335 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Provision for income taxes | | $ | (1,221 | ) | | $ | (635 | ) | | $ | (698 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
A reconciliation of the provision for income taxes with amounts determined by applying the statutory U.S. federal income tax rate to income (loss) before income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
Tax (provision) benefit at statutory rate of 35% | | $ | (111 | ) | | $ | 495 | | | $ | (470 | ) |
State income taxes, net of federal tax benefit & reduction in state valuation allowance | | | 15 | | | | (149 | ) | | | (73 | ) |
Restricted incentive unit compensation | | | (521 | ) | | | (1,073 | ) | | | (43 | ) |
Interest expense, gross of related tax effects | | | (335 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Other | | | (269 | ) | | | 92 | | | | (112 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Provision for income taxes | | $ | (1,221 | ) | | $ | (635 | ) | | $ | (698 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Effective income tax rate | | | 384 | % | | | (45 | )% | | | 52 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
The significant components of the net deferred tax (asset) and liability as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Deferred tax (asset) liability: | | | | | | | | |
Net operating loss carry forward | | $ | (7,113 | ) | | $ | (4,212 | ) |
State taxes | | | 325 | | | | (507 | ) |
Stock compensation | | | (662 | ) | | | (546 | ) |
(Loss) income from Operating Partnership | | | (2,403 | ) | | | 9,472 | |
Interest income from loan receivable | | | (2,708 | ) | | | (1,764 | ) |
Other, net | | | (59 | ) | | | (51 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Deferred tax (asset) liability, net | | $ | (12,620 | ) | | $ | 2,392 | |
| | | | | | | | |
The net deferred tax liability as of December 31, 2006 of approximately $2.4 million in the above reconciliation does not reflect the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits of approximately $9 million, which resulted in a reduction to the opening balance of the net deferred tax liability upon the Company’s adoption of FIN 48 on January 1, 2007, which comparatively, resulted in a net deferred tax asset.
88
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The net deferred tax asset is included with other assets on the Company’s balance sheet. The future tax benefits of the net operating loss carryforwards expire in 2015-2027.
FASB Statement No. 109, “Accounting for Income Taxes” (SFAS No. 109), requires that deferred tax assets be reduced by a valuation allowance if it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax asset will not be realized. Realization of the deferred tax asset is dependent on us generating sufficient taxable income in future years as the deferred income tax charges become currently deductible for tax reporting purposes. Although realization is not assured, management believes that it is more likely than not that the net deferred tax asset will be realized.
In June 2006, the FASB issued Financial Interpretation No. 48, “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes” (FIN 48), which clarifies the accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in a company’s financial statements in accordance with SFAS No. 109. The interpretation prescribes a recognition threshold and measurement attribute criteria for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The interpretation also provides guidance on derecognition, classification, interest and penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosure and transition.
The Company files U.S. federal income tax returns and returns in various states jurisdictions. The Company’s policy is to recognize interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as a component of income tax expense. As of December 31, 2007, we recorded $335,000 of interest related to unrecognized tax benefits as a component of income tax expense.
The Company adopted the provisions of FIN 48 on January 1, 2007, which resulted in unrecognized tax benefits of approximately $9 million and accrued interest of $200,000, of which $120,000 was recorded as a reduction to the opening deficit balance within stockholders’ equity, and if recognized, would affect our effective tax rate.
As of December 31, 2007, the Company has recorded unrecognized tax benefits of approximately $15.6 million, and if recognized, would not affect our effective tax rate.
As of December 31, 2007, the Company has recorded $728,000 of accrued interest with respect to unrecognized tax benefits. We have not recorded any penalties with respect to unrecognized tax benefits. We do not anticipate any significant increases or decreases to the amounts of unrecognized tax benefits within the next twelve months.
We conduct business in California, Pennsylvania, Texas and Virginia. For federal and state purposes, the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005, 2006, and 2007 remain subject to examination by the respective tax jurisdictions.
A reconciliation of the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits are as follows on December 31, 2007:
| | | | |
Unrecognized Tax Benefits—Opening Balance | | $ | 9,022 | |
Gross increases—tax positions in prior period | | | 437 | |
Gross decreases—tax positions in prior period | | | (62 | ) |
Gross increases—current period tax positions | | | 6,676 | |
Gross decreases—current period tax positions | | | (496 | ) |
Settlements | | | — | |
Lapse of statute of limitations | | | — | |
| | | | |
| | $ | 15,577 | |
| | | | |
89
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
11. Fair Value of Financial Instruments
SFAS No. 107, Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments, requires us to disclose fair value information about all financial instruments, whether or not recognized in the balance sheets, for which it is practicable to estimate fair value.
Our estimates of the fair value of financial instruments at December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively, were determined using available market information and appropriate valuation methods. Considerable judgment is necessary to interpret market data and develop estimated fair value. The use of different market assumptions or estimation methods may have a material effect on the estimated fair value amounts.
The carrying amounts for cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, rents and other receivables, due from affiliates, accounts payable and other liabilities approximate fair value because of the short-term nature of these instruments.
As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, the fair value of our mortgage and other secured loans and unsecured loan aggregates $399,295,000 and $325,886,000, respectively, compared to the aggregate carrying value of $396,007,000 and $331,828,000, respectively.
12. Minimum Future Lease Rentals
We have entered into various lease agreements with tenants as of December 31, 2007. The minimum future cash rents receivable under non-cancelable operating leases in each of the next five years and thereafter are as follows:
| | | |
Year ending December 31, | | | |
2008 | | $ | 34,632 |
2009 | | | 28,839 |
2010 | | | 26,061 |
2011 | | | 26,413 |
2012 | | | 23,476 |
Thereafter | | | 48,300 |
| | | |
| | $ | 187,721 |
| | | |
The leases generally also require reimbursement of the tenant’s proportional share of common area, real estate taxes and other operating expenses, which are not included in the amounts above.
13. Revenue Concentrations
(a) Rental revenue concentrations:
A significant portion of our rental revenues and tenant reimbursements were generated from one tenant, Conrail. The revenue recognized related to this tenant for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006, and 2005 were $25,320,000, $24,920,000, and $24,648,000, respectively.
In March 1990, Two Commerce Square entered into a long-term lease agreement with Conrail to occupy approximately 753,000 square feet of office space in Two Commerce Square, a portion of which expires in 2008 and the remainder in 2009. As an inducement to enter into the lease, Two Commerce Square agreed to pay Conrail $34,000,000 no later than the fifth anniversary of the commencement of the lease, as defined, plus accrued interest at 8% per annum, compounded annually, under certain circumstances.
90
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
In accordance with the agreement, $34,000,000 was paid to Conrail in 1997. This lease concession has been reflected in the accompanying financial statements as a deferred rent receivable, and is being recognized ratably over Conrail’s lease period as a reduction in rental revenue. Interest is payable only in the event of sufficient cash flow from Two Commerce Square, as defined. We have not paid any interest through December 31, 2007 and believe that an accrual for interest expense at December 31, 2007 is not required. Conrail has entered into sublease agreements for substantially all of the space leased.
As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, $5,583,000 and $11,242,000 respectively, of the deferred rents relates to Conrail. As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, we had received prepaid rents of $2,581,000 and $2,560,000 respectively, from Conrail.
(b) Concentrations related to investment advisory, property management, leasing and development services revenue:
Under agreements with CalSTRS, we provide property acquisition, investment advisory, property management, leasing and development services for CalSTRS under a separate account relationship and through a joint venture relationship. At December 31, 2007 and 2006, there were three and four office properties, respectively, subject to the separate account relationship. At December 31, 2007 and 2006, there were twenty-two and eleven office properties, respectively, subject to the joint venture relationship. We asset manage all of these properties.
Under the separate account relationship, we earn acquisition fees over the first three years after a property is acquired, if the property meets or exceeds the pro forma operating results that were submitted at the time of acquisition and a performance index associated with the region in which the property is located. Under the joint venture relationship, we are paid acquisition fees at the time a property is acquired, as a percent of the total acquisition price. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006, and 2005, we earned acquisition fees of $7,265,000, $1,106,000 and $1,802,000, respectively, including $1,703,000, $1,106,000 and $1,802,000 from TPG/CalSTRS.
Under the separate account relationship, we earn asset management fees paid on a quarterly basis, based on the annual net operating income of the properties. Under the joint venture relationship, asset management fees are paid on a monthly basis, initially based upon a percentage of a property’s annual appraised value for properties that are unstabilized at the time of acquisition. At the point of stabilization of the property, asset management fees are calculated based on net operating income. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, we earned asset management fees under these agreements of $5,978,000, $4,349,000 and $2,899,000, respectively, including $5,211,000, $3,379,000 and $1,905,000, respectively, from TPG/CalSTRS.
We perform property management and leasing services for fourteen of the fifteen properties subject to the asset management agreements with CalSTRS. We are entitled to property management fees calculated based on 2% or 3% of the gross revenues of the particular property, paid on a monthly basis. In addition, we are reimbursed for compensation paid to certain of our employees and direct out-of-pocket expenses. The management and leasing agreements expire on the third anniversary of each property’s acquisition. The agreements are automatically renewed for successive periods of one year each, unless we elect not to renew the agreements. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, we earned property management fees under these agreements of $6,455,000, $3,960,000 and $2,604,000, respectively, including $5,586,000, $2,891,000 and $1,573,000, respectively, from TPG/CalSTRS. In addition, for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, we were reimbursed $3,524,000, $2,265,000 and $2,074,000, respectively, including $2,928,000, $1,639,000 and $1,072,000, respectively, from TPG/CalSTRS. The reimbursements represent primarily the cost of on-site property management personnel incurred on behalf of the managed properties.
91
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
For properties in which we are responsible for the leasing and development services, we are entitled to receive market leasing commissions and development fees as defined in the agreements with CalSTRS. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, we earned leasing commissions under the agreements of $4,289,000, $4,450,000 and $2,093,000, respectively, including $4,126,000, $4,084,000 and $1,784,000, respectively, from TPG/CalSTRS. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, we earned development fees under these agreements of $1,387,000, $1,291,000 and $842,000, respectively, including $1,297,000, $1,142,000 and $739,000, respectively, from our joint venture with CalSTRS.
Under the separate account relationship, we receive incentive compensation based upon performance above a minimum hurdle rate, at which time we begin to participate in cash flow from the relevant property. Incentive compensation is paid at the time an investment is sold. For the year ended December 31, 2007, we earned incentive compensation of $5,713,000 related to the sale of Valencia Town Center. None was earned during the years ended December 31, 2006 or 2005. Under the joint venture relationship, incentive compensation is based on a minimum return on investment to CalSTRS, following which we participate in cash flow above the stated return, subject to a clawback provision if returns for a property fall below the stated return. We earned incentive compensation fee $571,000 related to the sale of our joint venture property, Intercontinental Center, during the year ended December 31, 2007. We earned incentive compensation of $521,000 related to the sale of our joint venture property, Valley Square, during the year ended December 31, 2006. None was earned during the year ended December 31, 2005. Of these amounts, 25% was eliminated in consolidation and the remaining 75% was recorded as deferred revenue due to the clawback provision.
At December 31, 2007 and 2006, we had accounts receivable under the above agreements of $7,073,000 and $4,456,000, respectively, including $6,610,000 and $4,068,000, respectively, due from TPG/CalSTRS.
We also provide property management and leasing services for the CalEPA building for the City of Sacramento. The property management agreement expires on June 30, 2016, is extendable for an additional 5 years through June 30, 2020 and is subject to early termination on June 30, 2011 based on the terms in the agreement. Property management fees are $74,000 per month. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, we earned property management fees from the City of Sacramento of $894,000, $970,000 and $1,046,000, respectively, and were reimbursed $353,000, $355,000 and $375,000, respectively. The reimbursements represent the cost of on-site property management personnel incurred on behalf of the managed property. At December 31, 2007 and 2006, we had accounts receivable from the CalEPA building of $29,000 and $45,000, respectively.
We obtain insurance under a master insurance policy that includes all the properties in which we have an investment and for which we perform investment advisory or property management services. Property insurance premiums are allocated based on estimated insurable values. Liability insurance premiums are allocated to the properties based on relative square footage. The allocated expense to us for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 was $1,813,000, $1,851,000 and $1,947,000, respectively, and is included in rental property operating and maintenance expense.
14. Commitments and Contingencies
We have been named as a defendant in a number of lawsuits in the ordinary course of business. We believe that the ultimate settlement of these suits will not have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations.
92
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
We sponsor a 401(k) plan for our employees. Our contributions were $688,000, $322,000 and $352,000 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively. Our contributions increased by approximately 214% in 2007 compared to 2006 primarily due to an increase in personnel related to property acquisitions in 2007, and a revision to our 401(k) plan, which allows eligible personnel to participate sooner.
We are a tenant in City National Plaza through May 2009 and in One Commerce Square through December 2009. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006, and 2005 we incurred rent expense of $241,000, $227,000 and $233,000, respectively, to City National Plaza. These expense amounts are included in rent—unconsolidated real estate entities. The rent expense related to One Commerce Square is eliminated in consolidation.
The minimum future rents payable under the City National Plaza lease in each of the next two years are as follows:
| | | |
Year ending December 31, | | | |
2008 | | $ | 127 |
2009 | | | 53 |
Thereafter | | | — |
| | | |
| | $ | 180 |
| | | |
In connection with the ownership, operation and management of the real estate properties, we may be potentially liable for costs and damages related to environmental matters. We have not been notified by any governmental authority of any non-compliance, liability or other claim in connection with any of the properties, and we are not aware of any other existing environmental condition with respect to any of the properties that management believes will have a material adverse effect on our assets or results of operations.
A mortgage loan, with an outstanding balance of $19,122,000 and $19,404,000 as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively, secured by a first trust deed on 2121 Market Street is guaranteed by our Operating Partnership and our co-general partner in the partnership that owns 2121 Market Street, up to a maximum amount of $3.3 million. Additionally, our Operating Partnership has separately guaranteed the repayment of up to $3.5 million on this same loan.
In connection with our Campus El Segundo mortgage loan (see Note 5), we have guaranteed and promised to pay the principal, interest and any other sum payable under the loan in the event the borrower, a wholly-owned entity of our Operating Partnership, does not do so.
In connection with our Murano construction loan (see Note 5), we and two individuals affiliated with our unaffiliated limited partner in the Murano development project, collectively agreed to guarantee the completion of the required work, as defined in the applicable agreement, in favor of the construction loan lender, in the event of any default of the borrower. If the borrower, which is a consolidated subsidiary for us, fails to complete the required work, the guarantor agrees to perform timely all of the completion obligations, as defined in the guaranty agreement.
In connection with the loan secured by our preferred equity interest in Murano (see Note 5), we have guaranteed and promised to pay the principal, interest and any other sum payable to the lender in the event the borrower, a wholly-owned entity of our Operating Partnership, does not do so.
In connection with our Four Points Centre construction loan (see Note 5), we have guaranteed in favor of and promised to pay to the lender 46.5% of the principal, interest and any other sum payable under the loan in the
93
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
event the borrower, a wholly-owned entity of our Operating Partnership, does not do so. Upon the occurrence of certain events, as defined in the repayment and completion guaranty agreement, our maximum liability as guarantor will be reduced to 31.5% of all sums payable under the loan, and upon the occurrence of even further events, as defined, our maximum liability as guarantor will be reduced to 25.0% of all sums payable under the loan. Furthermore, we agreed to guarantee the completion of the construction improvements, as defined in the agreement, in the event of any default of the borrower. If the borrower fails to complete the required work, the guarantor agrees to perform timely all of the completion obligations, as defined in the agreement.
In connection with a standby letter of credit (the “Credit”) issued by the lender on City National Plaza, one of our unconsolidated real entities, for the benefit of the trustee under a certain pooling and servicing agreement established in connection with commercial mortgage pass-through certificates, we have agreed to reimburse the lender in an amount not to exceed $3,773,065 for the amount of each payment the lender makes on the Credit. The Credit expires on July 17, 2008, and may be renewed under certain circumstances, but in no event beyond July 17, 2010.
We entered into an agreement to purchase a commercial condominium unit for $2.2 million on November 30, 2007. This space will serve as a marketing office and an interim property management office for the adjacent development at Campus El Segundo. As of December 31, 2007 we made a $200,000 deposit and the remaining balance is due upon closing which is expected to occur in the first half of 2008.
15. Quarterly Financial Information
The tables below reflect the selected quarterly information for us for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006. Certain amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation (in thousands, except for share and per share amounts) (unaudited).
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Three Months Ended | |
| | | December 31,
2007 | | | September 30,
2007 | | | June 30,
2007 | | March 31,
2007 | |
Total revenue | | $ | 23,398 | | | $ | 28,521 | | | $ | 23,262 | | $ | 22,301 | |
(Loss) income before gain on sale of real estate, interest income, equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities, and minority interests | | | (1,238 | ) (1) | | | 5,481 | | | | 343 | | | 257 | |
(Loss) income before minority interests and provision/benefit for income taxes | | | (4,006 | ) | | | 3,425 | | | | 2,130 | | | (1,104 | ) |
Net income (loss) | | | (1,569 | ) | | | (271 | ) | | | 650 | | | (255 | ) |
Net income (loss) per share-basic | | $ | (0.07 | ) | | $ | 0.01 | | | $ | 0.03 | | $ | (0.02 | ) |
Net income (loss) per share-diluted | | $ | (0.07 | ) | | $ | 0.01 | | | $ | 0.03 | | $ | (0.02 | ) |
Weighted-average shares outstanding-basic | | | 23,643,502 | | | | 23,626,645 | | | | 20,540,116 | | | 14,373,318 | |
Weighted-average shares outstanding-diluted | | | 23,643,502 | | | | 23,645,563 | | | | 20,611,368 | | | 14,373,318 | |
| (1) | Certain unrecorded expenses, primarily interest, related to the first, second and third quarters were recorded in the fourth quarter. We believe the amounts were not material. |
94
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Three Months Ended | |
| | | December 31,
2006 | | | September 30,
2006 | | | June 30,
2006 | | | March 31,
2006 | |
Total revenue | | $ | 22,119 | | | $ | 20,706 | | | $ | 22,299 | | | $ | 19,140 | |
Loss before early extinguishment of debt, interest income, equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities, and minority interests | | | (236 | ) | | | (397 | ) | | | (392 | ) | | | (1,839 | ) |
(Loss) income before minority interests and provision/benefit for income taxes | | | (1,497 | ) | | | 4,632 | | | | (1,159 | ) | | | (4,495 | ) |
Net income (loss) | | | (1,568 | ) | | | 1,283 | | | | (336 | ) | | | (1,428 | ) |
Net income (loss) per share-basic | | $ | (0.11 | ) | | $ | 0.09 | | | $ | (0.02 | ) | | $ | (0.10 | ) |
Net income (loss) per share-diluted | | $ | (0.11 | ) | | $ | 0.09 | | | $ | (0.02 | ) | | $ | (0.10 | ) |
Weighted-average shares outstanding-basic | | | 14,354,703 | | | | 14,338,050 | | | | 14,332,397 | | | | 14,320,779 | |
Weighted-average shares outstanding-diluted | | | 14,354,703 | | | | 14,352,687 | | | | 14,332,397 | | | | 14,320,779 | |
16. Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 108
In September 2006, the SEC released SAB 108, which permits a company to adjust for the cumulative effect of immaterial errors relating to prior years in the carrying amount of assets and liabilities as of the beginning of the current fiscal year, with an offsetting adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings in the year of adoption. SAB 108 also requires the adjustment of any prior quarterly financial statements within the fiscal year of adoption for the effects of such errors. Such adjustments do not require previously filed reports with the SEC to be amended. Effective September 30, 2006, we elected early application of SAB 108.
Accounting for Investments in TPG/CalSTRS
In accordance with SAB 108, we have adjusted our opening retained earnings for 2006 as a result of the change in the allocation of depreciation expense relating to our investment in TPG/CalSTRS. Depreciation expense was previously allocated to the members in accordance with the operating agreement of the limited liability company. For all properties excluding City National Plaza, the Operating Partnership was initially allocated depreciation expense ahead of CalSTRS. For City National Plaza, the minority owner and the Operating Partnership were initially allocated depreciation expense ahead of CalSTRS. Based on the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (“AICPA”) Statement of Position 78-9 “Accounting for Investments in Real Estate Ventures,” we determined that the allocation of net income/loss, including depreciation expense, to the members should be based on the allocation of cash distributions and liquidating distributions, not the profit and loss allocation ratios as specified in the operating agreement. We consider these adjustments to be immaterial to prior periods.
The impact on the 2006 opening additional paid in capital and deficit was $4,334,000. The pro forma impact to the statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2005 is an increase in net income of $1,986,000.
95
THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The aggregate pro forma impact of these adjustments is summarized below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As
Reported | | | Pro Forma
Adjustment | | | Pro
Forma | |
As of and for the 12 months ended December 31, 2005 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investments in unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 41,124 | | | | 9,836 | | | | 50,960 | |
Deferred tax liability | | | 308 | | | | 1,449 | | | | 1,757 | |
Minority interests – unitholders in the Operating Partnership | | | 74,099 | | | | 4,053 | | | | 78,152 | |
Stockholders’ equity | | | 63,632 | | | | 4,334 | | | | 67,966 | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (16,259 | ) | | | 7,350 | | | | (8,909 | ) |
Minority interests – unitholders income in the Operating Partnership | | | (1,559 | ) | | | (3,950 | ) | | | (5,509 | ) |
Provision for income taxes | | | (698 | ) | | | (1,414 | ) | | | (2,112 | ) |
Net income | | | 644 | | | | 1,986 | | | | 2,630 | |
Income per share – basic and diluted | | $ | 0.05 | | | $ | 0.13 | | | $ | 0.18 | |
Incentive Units
Also in accordance with SAB 108, we adjusted our opening stockholders’ equity and minority interests of unitholders in the Operating Partnership for 2006 as a result of a change in recognizing compensation expense for incentive units issued in our Operating Partnership. Previously, we did not record compensation expense until a book-up event occurred. Based on SFAS 123, we determined that compensation expense should be recorded based on the fair value of the units recognized ratably over the applicable vesting period. We consider these adjustments to be immaterial to prior periods.
The impact on the 2006 opening deficit and minority interests of unitholders in the Operating Partnership was $2,308,000 and $2,682,000, respectively. The pro forma impact to the statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2005, is a decrease in net income of $1,829,000.
The aggregate pro forma impact of these adjustments is summarized below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As
Reported | | | Pro Forma
Adjustment | | | Pro
Forma | |
As of and for the 12 months ended December 31, 2005 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
General and administrative expense | | $ | 12,914 | | | $ | 3,954 | | | $ | 16,868 | |
Minority interests – unitholders income in the Operating Partnership | | | (1,559 | ) | | | (2,125 | ) | | | (3,684 | ) |
Provision for income taxes | | | (698 | ) | | | — | | | | (698 | ) |
Net income (loss). | | | 644 | | | | (1,829 | ) | | | (1,185 | ) |
Income (loss) per share – basic and diluted | | $ | 0.05 | | | $ | (0.13 | ) | | $ | (0.08 | ) |
17. Issuance of Common Stock and Change in Limited Voting Stock
On April 25, 2007, we sold 9.2 million shares of common stock (including the shares issued upon exercise of the underwriters’ over-allotment option), pursuant to an effective registration statement previously filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, at $16.00 per share. We received net proceeds, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses, of $139.4 million from this offering of which $33.7 million was used to redeem 2,170,000 units in our Operating Partnership held by our CEO, and 45,000 units held by another senior executive. The redemption in Operating Partnership units, which are paired with limited voting stock on a one-for-one basis, resulted in a decrease in the total limited voting stock from $167 at December 31, 2006 to $145 at December 31, 2007. Following the closing of the offering, we held a 60.5% interest in our Operating Partnership at April 25, 2007.
96
SCHEDULE III—INVESTMENTS IN REAL ESTATE
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | One
Commerce
Square | | | Two
Commerce
Square | | | Murano | | | 2100 JFK
Boulevard | | | Four Points
Centre | | Campus El
Segundo | | Metro Studio
@
Lankershim |
| Property Type | | High-rise
office | | | High-rise
office | | | Residential/
Development | | | Parking lot | | | Office/
Retail/Hotel/
Development | | Office/
Retail/Hotel/
Development | | Office/Prod.
Studio/
Residential/
Retail |
| Location | | Philadelphia,
PA | | | Philadelphia,
PA | | | Philadelphia,
PA | | | Philadelphia,
PA | | | Austin,
TX | | El Segundo,
CA | | Los Angeles,
CA |
Encumbrances, net | | $ | 130,000 | | | $ | 149,753 | | | $ | 90,200 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4,895 | | $ | 17,259 | | $ | — |
Initial cost to the real estate entity that acquired
the property: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Land and improvements | | | 14,259 | | | | 15,758 | | | | 6,213 | | | | 4,872 | | | | 10,523 | | | 39,937 | | | — |
Buildings and improvements | | | 87,653 | | | | 147,951 | | | | — | | | | | | | | — | | | — | | | — |
Cost capitalized subsequent to acquisition: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Land and improvements | | | — | | | | — | | | | 124,194 | | | | — | | | | 25,654 | | | 8,421 | | | 6,317 |
Buildings and improvements | | | 31,075 | (2) | | | 52,156 | (3) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — |
Gross amount at which carried at close of period: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Land and improvements | | | 14,259 | | | | 15,758 | | | | 130,407 | | | | 4,872 | | | | 36,177 | | | 48,358 | | | 6,317 |
Buildings and improvements | | | 118,728 | | | | 200,107 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — |
Accumulated depreciation and amortization (4) | | | (25,705 | ) | | | (85,241 | ) | | | (658 | ) | | | (15 | ) | | | — | | | — | | | — |
Date construction completed | | | 1987 | | | | 1992 | | | | N/A | | | | N/A | | | | N/A | | | N/A | | | N/A |
| | | | | | | |
Investments in real estate: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, beginning of the year | | $ | 442,798 | | | $ | 417,486 | | | $ | 377,529 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Additions during the year | | | 136,725 | | | | 34,042 | | | | 41,377 | (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Retirements during the year | | | (4,540 | ) | | | (8,730 | ) | | | (1,420 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, end of the year | | $ | 574,983 | | | $ | 442,798 | | | $ | 417,486 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accumulated depreciation related to investments in real estate: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, beginning of the year | | $ | (106,644 | ) | | $ | (104,325 | ) | | $ | (95,044 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Additions during the year | | | (9,515 | ) | | | (11,049 | ) | | | (10,701 | )(1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Retirements during the year | | | 4,540 | | | | 8,730 | | | | 1,420 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, end of the year | | $ | (111,619 | ) | | $ | (106,644 | ) | | $ | (104,325 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | The additions during 2005 include the exercise of the Campus El Segundo purchase option. |
| (2) | Included in the total are write-offs of $2.9 million for fully depreciated tenant improvements |
| (3) | Included in the total are write-offs of $1.6 million for fully depreciated tenant improvements. |
| (4) | The depreciable life for buildings ranges from 40 to 50 years, 5 to 40 years for building improvements, and the shorter of the useful lives or the terms of the related leases for tenant improvements. |
The aggregate gross cost of our investments in real estate for federal income tax purposes approximated $399.5 million as of December 31, 2007 (unaudited).
97
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The Members
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of TPG/CalSTRS, LLC (a Delaware limited liability company) (“TPG/CalSTRS”) as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, and the related consolidated statements of operations, members’ equity and comprehensive loss and cash flows for the years then ended. These financial statements are the responsibility of TPG/CalSTRS’ management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform audits of TPG/CalSTRS’s internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of TPG/CalSTRS’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of TPG/CalSTRS at December 31, 2007 and 2006, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for the periods then ended, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
ERNST & YOUNG LLP
Los Angeles, California
March 14, 2008
98
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The Members
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of operations, members’ equity and comprehensive loss and cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2005 of TPG/CalSTRS, LLC (a Delaware limited liability company) (“TPG/CalSTRS”). These financial statements are the responsibility of TPG/CalSTRS’ management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. TPG/CalSTRS is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audit included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of TPG/CalSTRS’ internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the results of operations and cash flows of TPG/CalSTRS for the year ended December 31, 2005 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
As discussed in Note 8, TPG/CalSTRS has restated its consolidated statements of operations and members’ equity and comprehensive loss for the year ended December 31, 2005.
DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Los Angeles, California
March 15, 2006 (April 2, 2007 as to Note 8 and March 17, 2008 as to the reclassification discussed under the revenue recognition caption in Note 2 and as to Note 5)
99
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2007 and 2006
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
Investments in real estate: | | | | | | | | |
Land and improvements | | $ | 119,876 | | | $ | 84,012 | |
Land improvements—development properties | | | 24,496 | | | | 23,689 | |
Buildings and improvements | | | 981,720 | | | | 821,806 | |
Tenant improvements | | | 168,821 | | | | 122,852 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 1,294,913 | | | | 1,052,359 | |
Less accumulated depreciation | | | (100,885 | ) | | | (62,401 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 1,194,028 | | | | 989,958 | |
Investment in real estate—land held for sale | | | 3,418 | | | | 3,358 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 1,197,446 | | | | 993,316 | |
Investments in unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 61,662 | | | | — | |
Cash and cash equivalents, unrestricted | | | 6,813 | | | | 9,472 | |
Restricted cash | | | 57,268 | | | | 60,736 | |
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $59 and $649 as of 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 4,947 | | | | 8,036 | |
Deferred leasing costs and value of in-place leases, net of accumulated amortization of $47,709 and $32,417 as of 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 98,606 | | | | 98,964 | |
Deferred loan costs, net of accumulated amortization of $7,659 and $3,070 as of 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 5,526 | | | | 7,895 | |
Deferred rents | | | 50,101 | | | | 29,729 | |
Acquired above market leases, net of accumulated amortization of $5,012 and $3,941 as of 2007 and 2006 respectively | | | 3,531 | | | | 4,755 | |
Prepaid expenses and other assets | | | 3,173 | | | | 18,015 | |
Assets associated with discontinued operations | | | 28 | | | | 14,767 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 1,489,101 | | | $ | 1,245,685 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Mortgage loans | | $ | 1,141,232 | | | $ | 923,388 | |
Other secured loans | | | 94,700 | | | | 94,700 | |
Accounts payable and other liabilities | | | 56,088 | | | | 44,702 | |
Due to affiliate | | | 7,098 | | | | 5,263 | |
Acquired below market leases, net of accumulated amortization of $10,300 and $5,686 as of 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 15,211 | | | | 13,365 | |
Prepaid rent | | | 5,517 | | | | 4,124 | |
Liabilities associated with discontinued operations | | | 23 | | | | 13,673 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 1,319,869 | | | | 1,099,215 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Members’ equity, including $1,443 and $1,457 accumulated other comprehensive loss as of 2007 and 2006, respectively | | | 169,232 | | | | 146,470 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and members’ equity | | $ | 1,489,101 | | | $ | 1,245,685 | |
| | | | | | | | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial information.
100
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Years Ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Rental | | $ | 127,570 | | | $ | 92,338 | | | $ | 54,008 | |
Tenant reimbursements | | | 36,143 | | | | 25,056 | | | | 8,982 | |
Parking | | | 13,934 | | | | 11,578 | | | | 8,197 | |
Interest income | | | 2,761 | | | | 1,609 | | | | 428 | |
Other | | | 5,365 | | | | 4,608 | | | | 262 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues | | | 185,773 | | | | 135,189 | | | | 71,877 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating | | | 93,847 | | | | 75,085 | | | | 43,463 | |
General and administrative | | | 10,412 | | | | 8,401 | | | | 4,144 | |
Parking | | | 2,606 | | | | 2,564 | | | | 2,043 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 67,955 | | | | 53,967 | | | | 30,497 | |
Interest | | | 81,247 | | | | 55,596 | | | | 28,186 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total expenses | | | 256,067 | | | | 195,613 | | | | 108,333 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations before minority interest | | | (70,294 | ) | | | (60,424 | ) | | | (36,456 | ) |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (9,001 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Minority interest attributable to continuing operations | | | — | | | | (1,546 | ) | | | 3,398 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (79,295 | ) | | | (61,970 | ) | | | (33,058 | ) |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | 7,662 | | | | 4,722 | | | | (3,157 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss before cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle | | | (71,633 | ) | | | (57,248 | ) | | | (36,215 | ) |
Cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,279 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (71,633 | ) | | $ | (57,248 | ) | | $ | (37,494 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial information.
101
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF MEMBERS’ EQUITY AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
Years Ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | CalSTRS | | | TPG | | | Total | |
Balance-December 31, 2004 (As restated, see Note 8) | | $ | 66,787 | | | $ | 35,271 | | | $ | 102,058 | |
Contribution | | | 96,827 | | | | 34,459 | | | | 131,286 | |
Distribution | | | (28,701 | ) | | | (8,840 | ) | | | (37,541 | ) |
| | | |
Net loss (As restated, see Note 8) | | | (28,121 | ) | | | (9,373 | ) | | | (37,494 | ) |
Other comprehensive income | | | 19 | | | | 6 | | | | 25 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive loss | | | (28,102 | ) | | | (9,367 | ) | | | (37,469 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance-December 31, 2005 (As restated, see Note 8) | | | 106,811 | | | | 51,523 | | | | 158,334 | |
Contribution | | | 99,806 | | | | 43,001 | | | | 142,807 | |
Distribution | | | (71,847 | ) | | | (24,470 | ) | | | (96,317 | ) |
| | | |
Net loss | | | (43,328 | ) | | | (13,920 | ) | | | (57,248 | ) |
Other comprehensive loss | | | (770 | ) | | | (336 | ) | | | (1,106 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive loss | | | (44,098 | ) | | | (14,256 | ) | | | (58,354 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance-December 31, 2006 | | | 90,672 | | | | 55,798 | | | | 146,470 | |
Contribution | | | 90,904 | | | | 20,566 | | | | 111,470 | |
Distribution | | | (10,692 | ) | | | (4,161 | ) | | | (14,853 | ) |
Syndication fee | | | (1,678 | ) | | | (559 | ) | | | (2,237 | ) |
| | | |
Net loss | | | (54,193 | ) | | | (17,440 | ) | | | (71,633 | ) |
Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | (31 | ) | | | 46 | | | | 15 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive loss | | | (54,224 | ) | | | (17,394 | ) | | | (71,618 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance-December 31, 2007 | | $ | 114,982 | | | $ | 54,250 | | | $ | 169,232 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial information.
102
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Years Ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (71,633 | ) | | $ | (57,248 | ) | | $ | (37,494 | ) |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gain on sale of real estate | | | (7,932 | ) | | | (6,133 | ) | | | — | |
Cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,279 | |
Gain on purchase of other secured loan | | | — | | | | 1,546 | | | | (3,398 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization expense | | | 67,955 | | | | 55,283 | | | | 34,018 | |
Amortization of above and below market leases, net | | | (4,422 | ) | | | 317 | | | | (585 | ) |
Amortization of loan costs | | | 4,681 | | | | 4,409 | | | | 3,600 | |
Equity in net loss in unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 9,001 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Deferred rents | | | (12,281 | ) | | | (15,518 | ) | | | (5,777 | ) |
Changes in assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts receivable | | | 3,243 | | | | (4,310 | ) | | | (3,209 | ) |
Prepaid expenses and other assets | | | 14,922 | | | | (16,600 | ) | | | 1,178 | |
Deferred lease costs | | | (16,825 | ) | | | (19,884 | ) | | | (8,726 | ) |
Accounts payable and other liabilities | | | 1,575 | | | | 126 | | | | 15,811 | |
Prepaid rent | | | 1,393 | | | | 1,857 | | | | 1,428 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in operating activities | | | (10,323 | ) | | | (56,155 | ) | | | (1,875 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenditures for real estate | | | (246,543 | ) | | | (352,183 | ) | | | (479,024 | ) |
Proceeds from sale of real estate | | | 23,594 | | | | 11,362 | | | | — | |
Distributions received from unconsolidated real estate entities | | | 369 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Purchases of interests in unconsolidated real estate entities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Investments in unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (73,750 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Change in restricted cash | | | 3,202 | | | | (28,162 | ) | | | (17,828 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in investing activities | | | (293,128 | ) | | | (368,983 | ) | | | (496,852 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from mortgage and other secured loans | | | 219,886 | | | | 719,236 | | | | 412,542 | |
Repayment of mortgage loan | | | (14,570 | ) | | | (316,909 | ) | | | — | |
Principal payments on mortgage loans | | | — | | | | — | | | | (291 | ) |
Members' contribution | | | 111,472 | | | | 142,807 | | | | 131,286 | |
Members distributions | | | (14,853 | ) | | | (96,317 | ) | | | (37,541 | ) |
Minority interest contributions | | | — | | | | 2,379 | | | | 2,343 | |
Minority interest distributions | | | — | | | | (13,500 | ) | | | — | |
Payment of loan costs | | | (1,591 | ) | | | (8,448 | ) | | | (5,417 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by financing activities | | | 300,344 | | | | 429,248 | | | | 502,922 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | (3,107 | ) | | | 4,110 | | | | 4,195 | |
Cash and cash equivalents, at beginning of period | | | 9,920 | | | | 5,810 | | | | 1,615 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents, at end of period | | $ | 6,813 | | | $ | 9,920 | | | $ | 5,810 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash paid during the period for interest, including capitalized interest of $3,075, $4,345 and $2,005 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 | | $ | 78,546 | | | $ | 55,576 | | | $ | 25,330 | |
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investments in real estate included in accounts payable and other liabilities | | | 3,855 | | | | 2,357 | | | | 12,932 | |
Decrease in investments in real estate and accumulated depreciation for removal of fully amortized improvements | | | 4,887 | | | | 2,042 | | | | — | |
Other comprehensive income | | | 15 | | | | (1,107 | ) | | | 25 | |
Syndication fee related to the investment in Austin Portfolio Properties | | | 2,237 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Increase in lease inducements included in deferred rent | | | 6,668 | | | | — | | | | — | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial information.
103
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Years Ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005
(Tabular amounts in thousands)
1. Organization
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC (“TPG/CalSTRS” or “the Company”) was formed on December 23, 2002 as a Delaware limited liability company for the purpose of acquiring office properties on a nationwide basis classified as moderate risk (core plus) and high risk (value add) properties. Core plus properties consist of under-performing properties that we believe can be brought to market potential through improved management. Value add properties are characterized by unstable net operating income for an extended period of time, occupancy less than 90% and/or physical or management problems which can be positively impacted by introduction of new capital and/or management.
The original members of TPG/CalSTRS were Thomas Properties Group, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, with a 5% ownership interest and California State Teachers’ Retirement System (“CalSTRS”), with a 95% ownership interest.
TPG/CalSTRS is the sole member of TPGA, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, which is the managing member of TPG Plaza Investments, LLC (“TPG Plaza”), a Delaware limited liability company. TPGA, LLC has an 85.4% ownership interest in TPG Plaza. TPG/CalSTRS’ financial statements are consolidated with the accounts of TPGA, LLC and TPG Plaza. The ownership interests of the other members of TPG Plaza are reflected in the accompanying balance sheets as minority interest.
On January 28, 2003, TPG Plaza purchased an office building complex located in Los Angeles, California, commonly known as City National Plaza. On October 13, 2004, Thomas Properties Group, LLC contributed its interest in TPG/CalSTRS to Thomas Properties Group, L.P. (“TPG”), a Maryland limited partnership, in connection with the initial public offering of TPG’s sole general partner, Thomas Properties Group, Inc. CalSTRS contributed to TPG/CalSTRS its interest in office buildings located in Reston, Virginia, commonly known as Reflections I and Reflections II. In addition, TPG increased its ownership interest in TPG/CalSTRS from 5% to 25%. TPG acts as the managing member of TPG/CalSTRS. During 2005, TPG/CalSTRS acquired four properties in suburban Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and four properties in Houston, Texas, including a 6.3 acre (unaudited) development site in Houston, Texas. During 2006, TPG/CalSTRS sold a suburban office property in suburban Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and acquired a four-building campus and 24.0 acre (unaudited) development site in Houston, Texas. During 2007, TPG/CalSTRS acquired two suburban office properties in Fairfax, Virginia and sold one office property in Houston Texas. In addition, TPG/CalSTRS acquired a 25% interest in a joint venture which owns a portfolio of ten office properties in Austin, Texas.
104
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
As of December 31, 2007, TPG/CalSTRS owned an interest in the following properties:
| | | | |
Property | | Type | | Location |
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC: | | | | |
| | |
City National Plaza | | High-rise office | | Los Angeles Central Business
District, California |
Reflections I | | Suburban office – single tenancy | | Reston, Virginia |
Reflections II | | Suburban office – single tenancy | | Reston, Virginia |
Four Falls Corporate Center | | Suburban office | | Conshohocken, Pennsylvania |
Oak Hill Plaza | | Suburban office | | King of Prussia, Pennsylvania |
Walnut Hill Plaza | | Suburban office | | King of Prussia, Pennsylvania |
San Felipe Plaza | | High-rise office | | Houston, Texas |
2500 City West | | Suburban office and undeveloped land | | Houston, Texas |
Brookhollow Central I, II and III | | Suburban office | | Houston, Texas |
CityWestPlace | | Suburban office and undeveloped land | | Houston, Texas |
Centerpointe I & II | | Suburban office | | Fairfax, Virginia |
Fair Oaks Plaza | | Suburban office | | Fairfax, Virginia |
|
| TPG/CalSTRS, LLC also owns a 25% interest in a joint venture which owns the following properties (“Austin Portfolio Properties”): |
| | |
San Jacinto Center | | High-rise office | | Austin Central Business
District, Texas,(“ACBD”) |
Frost Bank Tower | | High-rise office | | ACBD |
One Congress Plaza | | High-rise office | | ACBD |
One American Center | | High-rise office | | ACBD |
300 West 6th Street | | High-rise office | | ACBD |
Research Park Plaza I & II | | Suburban office | | Austin, Texas |
Park 22 I—III | | Suburban office | | Austin, Texas |
Great Hills Plaza | | Suburban office | | Austin, Texas |
Stonebridge Plaza II | | Suburban office | | Austin, Texas |
Westech 360 I—IV | | Suburban office | | Austin, Texas |
105
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The minority members of TPG Plaza have the option to require TPG Plaza or TPGA, LLC to redeem or purchase, as applicable, their member interests for an amount equal to what would be payable to them upon liquidation of the assets of TPG Plaza at fair market value.
Either member of TPG/CalSTRS may trigger a buy-sell provision. Under this provision, the initiating party sets a price for its interest in TPG/CalSTRS, and the other party has a specified time to either elect to buy the initiating party’s interest, or sell its own interest to the initiating party. Under certain events, CalSTRS has a buy-out option to purchase TPG’s interest in TPG/CalSTRS. The buy-out price is generally based on a 3% discount to appraised fair market value.
TPG is required to use diligent efforts to sell each joint venture property within five years of that property reaching stabilization, except that for stabilized properties, TPG is required to perform a hold/sell analysis at least annually, and make a recommendation to the management committee regarding the appropriate holding period for these properties.
Capital contributions, distributions, and profits and losses of the real estate entities are allocated in accordance with the terms of the applicable limited liability company agreements. Such allocations may differ from the stated ownership percentage interests in such entities as a result of preferred returns and allocation formulas as described in the limited liability company agreements. Following are the stated ownership percentages, prior to any preferred or special allocations, as of December 31, 2007:
| | | |
City National Plaza (1): | | | |
CalSTRS | | 64.1 | % |
TPG | | 21.3 | % |
Other members | | 14.6 | % |
All Other Properties (2): | | | |
CalSTRS | | 75.0 | % |
TPG | | 25.0 | % |
| (1) | Prior to January 1, 2006, the minority owner of City National Plaza and TPG were allocated depreciation expense of City National Plaza ahead of CalSTRS, resulting in the allocation to TPG of 22.5% of City National Plaza’s depreciation expense and 21.3% of City National Plaza’s net income/loss (excluding depreciation expense). During 2005, the accumulated losses and distributions for the minority owner equaled their contribution amount. As such, net income/loss is allocated to TPG and CalSTRS. |
Beginning January 1, 2006, TPG is allocated 25% of net income/loss, including depreciation expense. See Note 8 for discussion of the adjustment to opening members’ equity and statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2005 as a result of the change in allocation of depreciation expense.
| (2) | Prior to January 1, 2006, TPG was allocated depreciation expense of the properties ahead of CalSTRS, resulting in the allocation to us of 100% of depreciation expense and 25% of net income/loss (excluding depreciation expense) of the properties. Beginning January 1, 2006, TPG is allocated 25% of net income/loss, including depreciation expense, which is equal to the economic ownership of TPG. See Note 8 for discussion of the adjustment to opening members’ equity as a result of the change in allocation of depreciation expense. |
106
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Principles of Consolidation
All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Cash Equivalents
TPG/CalSTRS considers all highly liquid financial instruments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash consists of property lockbox deposits under the control of lenders to fund reserves, debt service and operating expenditures. See Note 3 for additional information on restrictions under the terms of certain secured notes payable.
Investments in Real Estate
Investments in real estate are carried at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are recorded on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives as follows:
| | |
Buildings | | 40 years |
Building improvements | | 5 to 40 years |
Tenant improvements | | Shorter of the useful lives or the terms of the related leases. |
Improvements and replacements are capitalized when they extend the useful life, increase capacity or improve the efficiency of the asset. Repairs and maintenance are charged to expense as incurred.
Costs related to the acquisition, development, construction and improvement of properties are capitalized. Interest, real estate taxes, insurance and other development related costs incurred during construction periods are capitalized and depreciated on the same basis as the related assets. Included in investments in real estate is capitalized interest of $2,809,000 and $6,397,000 as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Investments in Real Estate- Land held for sale
TPG/CalSTRS considers assets to be held for sale pursuant to the provisions of SFAS No. 144, Impairments of Long-Lived Assets and Discontinued Operations (“SFAS 144”). The held for sale classification for real estate owned is evaluated quarterly.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
TPG/CalSTRS assesses whether there has been impairment in the value of its long-lived assets whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount to the future net
107
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
cash flows, undiscounted and without interest, expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. Assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value, less costs to sell. Management believes no impairment in the net carrying values of the investments in real estate has occurred for the periods presented.
Deferred Leasing and Loan Costs
Deferred leasing commissions and other direct costs associated with the acquisition of tenants are capitalized and amortized on a straight-line basis over the terms of the related leases. Costs associated with unsuccessful leasing opportunities are expensed. Loan costs are capitalized and amortized to interest expense over the terms of the related loans using a method that approximates the effective-interest method.
Purchase Accounting for Acquisition of Interests in Real Estate Entities
Purchase accounting was applied, on a pro rata basis, to the assets and liabilities related to real estate entities for which TPG/CalSTRS acquired interests, based on the percentage interest acquired. For purchases of additional interests that were consummated subsequent to June 30, 2001, the effective date of SFAS No. 141, Business Combinations, the fair value of the real estate acquired is allocated to the acquired tangible assets, consisting of land, building, tenant and site improvements, and identified intangible assets and liabilities, consisting of the value of above-market and below-market leases, other value of in-place leases and value of tenant relationships, based in each case on their fair values.
The fair value of the tangible assets of an acquired property (which includes land, building, tenant and site improvements) is determined by valuing the property as if it were vacant, and the “as-if-vacant” value is then allocated to land, building, tenant and site improvements based on management’s determination of the relative fair values of these assets. Management determines the as-if-vacant fair value of a property using methods similar to those used by independent appraisers. Factors considered by management in performing these analyses include an estimate of carrying costs during the expected lease-up periods considering current market conditions and costs to execute leases. In estimating carrying costs, management includes real estate taxes, insurance and other operating expenses and estimates of lost rental revenue during the expected lease-up periods based on current market demand. Management also estimates costs to execute leases including leasing commissions, legal and other related costs.
In allocating the fair value of the identified intangible assets and liabilities of an acquired property, above-market and below-market in-place lease values are recorded based on the present value (using an interest rate which reflects the risks associated with the leases acquired) of the difference between (i) the contractual amounts to be paid pursuant to the in-place leases and (ii) management’s estimate of fair market lease rates for the corresponding in-place leases, measured over a period equal to the remaining non-cancelable term of the lease. The capitalized above-market lease values are amortized as a reduction of rental income over the remaining non-cancelable terms of the respective leases. The capitalized below-market lease values are amortized as an increase to rental income over the terms in the respective leases. As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, we had an asset related to above market leases of $3,532,000 and $4,779,000, respectively, net of accumulated amortization of $5,013,000 and $3,941,000, respectively, and a liability related to below market leases of $15,211,000 and $13,365,000, respectively, net of accumulated accretion of $10,300,000 and $5,686,000, respectively. The weighted average amortization period for the above and below market leases was approximately 4.5 and 3.9 years as of December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
108
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The aggregate value of other acquired intangible assets, consisting of in-place leases and tenant relationships, is measured by the excess of (i) the purchase price paid for a property after adjusting existing in-place leases to market rental rates over (ii) the estimated fair value of the property as if vacant, determined as set forth above. This aggregate value is allocated between in-place lease values and tenant relationships based on management’s evaluation of the specific characteristics of each tenant’s lease; however, the value of tenant relationships has not been separated from in-place lease value for the additional interests in real estate entities acquired by TPG/CalSTRS because such value and its consequence to amortization expense is immaterial for these particular acquisitions. Should future acquisitions of properties result in allocating material amounts to the value of tenant relationships, an amount would be separately allocated and amortized over the estimated life of the relationship. The value of in-place leases exclusive of the value of above-market and below-market in-place leases is amortized to expense over the remaining non-cancelable periods of the respective leases. If a lease were to be terminated prior to its stated expiration, all unamortized amounts relating to that lease would be written off.
The table below presents the expected amortization related to the acquired in-place lease value and acquired above and below market leases at December 31, 2007:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2009 | | | 2010 | | | 2011 | | | 2012 | | | Thereafter | | | Total | |
Amortization expense: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Acquired in-place lease value | | $ | 11,636 | | | $ | 8,675 | | | $ | 6,977 | | | $ | 5,734 | | | $ | 5,011 | | | $ | 16,522 | | | $ | 54,555 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjustments to rental revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Above market leases | | $ | (1,081 | ) | | $ | (639 | ) | | $ | (451 | ) | | $ | (401 | ) | | $ | (293 | ) | | $ | (667 | ) | | $ | (3,532 | ) |
Below market leases | | | 2,611 | | | | 2,314 | | | | 2,156 | | | | 1,956 | | | | 1,747 | | | | 4,427 | | | | 15,211 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net adjustment to rental revenues | | $ | 1,530 | | | $ | 1,675 | | | $ | 1,705 | | | $ | 1,555 | | | $ | 1,454 | | | $ | 3,760 | | | $ | 11,679 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue Recognition
All leases are classified as operating leases and minimum rents are recognized on a straight-line basis over the terms of the leases. The impact of the straight line rent adjustment increased revenue by $12,135,000, $13,759,000, and $5,777,000 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006, and 2005, respectively. Additionally, the net impact of the amortization of acquired above market leases and acquired below market leases increased revenue by $5,810,000 for the year ended December 31, 2007, decreased revenue by $319,000 for the year ended December 31, 2006, and increased revenue by $585,000 for the year ended December 31, 2005. The excess of rents recognized over amounts contractually due pursuant to the underlying leases is included in deferred rents in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and contractually due but unpaid rents are included in accounts receivable. TPG/CalSTRS also maintains an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses resulting from the inability of tenants to make required rent payments. The computation of this allowance is based on the tenants’ payment history and current credit status, as well as certain industry or specific credit considerations. If estimates of collectability differ from the cash received, then the timing and amount of our reported revenue could be impacted. The credit risk is mitigated by the reviews of prospective tenant’s risk profiles prior to lease execution and continual monitoring of our tenant portfolio to identify potential problem tenants.
Tenant reimbursements for real estate taxes, common area maintenance and other recoverable costs are recognized in the period that the expenses are incurred. Amounts allocated to tenants based on relative footage are included in the tenant reimbursements caption on the consolidated statements of operations. Revenues generated from requests from tenants, which result in over-standard usage of services are directly billed to the
109
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
tenants and are also included in the tenant reimbursements caption on the consolidated statements of operations. Lease termination fees, which are included in other income in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations, are recognized when the related leases are canceled and TPG/CalSTRS has no continuing obligation to provide services to such former tenants.
During the fourth quarter of 2007, our management concluded that the accounting for certain reimbursements (primarily tenants’ over-standard usage of certain operating expenses such as electricity and business use and occupancy taxes) related to our property operations, should have been presented on a gross basis versus a net revenue basis, pursuant to EITF 99-19, “Reporting Revenue Gross as a Principal versus Net as an Agent”, and that the revenues should have been presented in tenant reimbursements instead of other. Accordingly, we reclassified such reimbursements from the other revenue caption to the tenant reimbursements revenue caption, and the corresponding expense from the other revenue caption to the operating expense caption for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 to be consistent with the presentation for the year ended December 31, 2007. As a result, amounts reflected as “tenant reimbursements”, “other” and “operating” in the consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2006 have increased (decreased) from the amounts previously reported by $5.4 million, $(0.2) million, and $5.2 million, respectively, and for the year ended December 31, 2005 have increased (decreased) from the amounts previously reported by $2.5 million, $(0.1) million, and $2.4 million, respectively. This reclassification had no impact on operating income and net income or members’ equity.
We recognize gains on sales of real estate when the recognition criteria in SFAS No. 66 “Accounting for Sales of Real Estate” (“SFAS 66”) have been met, generally at the time title is transferred and we no longer have substantial continuing involvement with the real estate asset sold.
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
SFAS No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities, as amended and interpreted by SFAS No. 149, Amendment of Statement 133 on Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities, establishes accounting and reporting standards for derivative instruments, including certain derivative instruments embedded in other contracts, and for hedging activities. As required by SFAS No. 133, TPG/CalSTRS records all derivatives on the balance sheet at fair value. The accounting for changes in the fair value of derivatives depends on the intended use of the derivative and the resulting designation. Derivatives used to hedge the exposure to changes in the fair value of an asset, liability, or firm commitment attributable to a particular risk, such as interest rate risk, are considered fair value hedges. Derivatives used to hedge the exposure to variability in expected future cash flows, or other types of forecasted transactions, are considered cash flow hedges.
For derivatives designated as fair value hedges, changes in the fair value of the derivative and the hedged item related to the hedged risk are recognized in earnings. For derivatives designated as cash flow hedges, the effective portion of changes in the fair value of the derivative is initially reported in other comprehensive income, outside of earnings, and subsequently reclassified to earnings when the hedged transaction affects earnings, and the ineffective portion of changes in the fair value of the derivative is recognized directly in earnings. TPG/CalSTRS assesses the effectiveness of each hedging relationship by comparing the changes in fair value or cash flows of the derivative hedging instrument with the changes in fair value or cash flows of the designated hedged item or transaction. For derivatives not designated as hedges, changes in fair value are recognized in earnings. We use a variety of methods and assumptions based on market conditions and risks existing at each balance sheet date to determine the approximate fair values of our cash flow hedges.
110
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The objective in using derivatives is to add stability to interest expense and to manage its exposure to interest rate movements or other identified risks. To accomplish this objective, TPG/CalSTRS primarily uses interest rate caps as part of its cash flow hedging strategy. Under SFAS No. 133, our interest rate caps qualify as cash flow hedges. No derivatives were designated as fair value hedges or hedges of net investments in foreign operations. Additionally, TPG/CalSTRS does not use derivatives for trading or speculative purposes and currently does not have any derivatives that are not designated as hedges.
At December 31, 2007 and 2006, derivatives with a fair value of $10,000 and $468,000, respectively, were included in deferred loan costs. The change in net unrealized gain (loss) of $15,000, $(1,106,000) and $25,000 in 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively, for derivatives designated as cash flow hedges is separately disclosed in the statements of members’ equity and comprehensive loss. At December 31, 2007, derivatives with a notional amount of $661.1 million, $189.2 million and $106.1 million expire in 2008, 2009 and 2010, respectively.
Asset Retirement Obligation
In March 2005, the FASB issued FIN 47, “Accounting for Conditional Asset Retirement Obligations, an interpretation of SFAS No. 143”, which provides clarification with respect to the timing of liability recognition for legal obligations associated with the retirement of tangible long-lived assets when the timing and/or method of settlement of the obligation is conditional on a future event. FIN 47 requires that the fair value of a liability for a conditional asset retirement obligation be recognized in the period in which it was incurred if a reasonable estimate of fair value can be made. TPG/CalSTRS has determined that conditional legal obligations exist for City National Plaza related primarily to asbestos-containing materials. TPG/CalSTRS adopted this interpretation on December 31, 2005 and recorded a non cash impact of $1,279,000, which is reported as a cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle in the statement of operations, and a liability for conditional asset retirement obligations of $4,239,000.
The following table illustrates the effect on net loss as if FIN 47 had been applied during the year ended December 31, 2005:
| | | | |
| | | 2005 | |
Loss from continuing operations before minority interest, as reported | | $ | (36,456 | ) |
Less: depreciation and accretion expense | | | (431 | ) |
| | | | |
Pro forma loss from continuing operations before minority interest | | | (36,887 | ) |
Pro forma minority interest attributable to continuing operations | | | 3,274 | |
| | | | |
Pro forma loss from continuing operations | | | (33,613 | ) |
Loss from discontinued operations | | | (1,566 | ) |
| | | | |
Pro forma loss | | $ | (35,179 | ) |
| | | | |
As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, the liability for conditional asset retirement obligations for City National Plaza and Brookhollow Central I, II and III is $2.6 million and $0.2 million, respectively, and $4.0 million and $0.2 million, respectively.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are not recorded by TPG/CalSTRS. TPG/CalSTRS is not subject to federal or state income taxes, except certain California corporate franchise taxes. Income or loss is allocated to the members and included in their respective income tax returns.
111
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Management’s Estimates and Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
TPG/CalSTRS has identified certain critical accounting policies that affect management’s more significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements. On an ongoing basis, TPG/CalSTRS will evaluate estimates related to critical accounting policies, including those related to revenue recognition and the allowance for doubtful accounts receivable and investments in real estate and asset impairment. The estimates are based on information that is currently available and on various other assumptions that TPG/CalSTRS believes is reasonable under the circumstances.
TPG/CalSTRS must make estimates related to the collectability of accounts receivable related to minimum rent, deferred rent, expense reimbursements, lease termination fees and other income. TPG/CalSTRS specifically analyze accounts receivable and historical bad debts, tenant concentrations, tenant creditworthiness, and current economic trends when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts receivable. These estimates have a direct impact on our net income, because a higher bad debt allowance would result in lower net income.
TPG/CalSTRS is required to make subjective assessments as to the useful lives of the properties for purposes of determining the amount of depreciation to record on an annual basis with respect to its investments in real estate. These assessments have a direct impact on net income because if TPG/CalSTRS were to shorten the expected useful lives of its investments in real estate, TPG/CalSTRS would depreciate such investments over fewer years, resulting in more depreciation expense and lower net income on an annual basis.
TPG/CalSTRS is required to make subjective assessments as to whether there are impairments in the values of its investments in real estate. These assessments have a direct impact on net income because recording an impairment loss results in a negative adjustment to net income.
TPG/CalSTRS is required to make subjective assessments as to the fair value of assets and liabilities in connection with purchase accounting related to interests in real estate entities acquired. These assessments have a direct impact on net income subsequent to the acquisition of the interests as a result of depreciation and amortization being recorded on these assets and liabilities over the expected lives of the related assets and liabilities. TPG/CalSTRS estimates the fair value of rental properties utilizing a discounted cash flow analysis that includes projections of future revenues, expenses and capital improvement costs, similar to the income approach that is commonly utilized by appraisers.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that subject TPG/CalSTRS to credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable.
For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, one tenant accounted for approximately 10.2%, 12.2% and 10.1%, respectively, of rent and tenant reimbursements (excluding tenant reimbursements for over-standard usage of certain operating expenses) of TPG/CalSTRS.
TPG/CalSTRS generally requires either a security deposit, letter of credit or a guarantee from its tenants.
112
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Expenses
Expenses include all costs incurred by TPG/CalSTRS in connection with the management, operation, maintenance and repair of the properties and are expensed as incurred.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In September 2006, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) released Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 108 (SAB 108) “Considering the Effects of Prior Year Misstatements when Quantifying Misstatements in Current Year Financial Statements,” to address diversity in practice regarding consideration of the effects of prior year errors when quantifying misstatements in current year financial statements. The SEC staff concluded that registrants should quantify financial statement errors using both a balance sheet approach and an income statement approach and evaluate whether either approach results in quantifying a misstatement that, when all relevant quantitative and qualitative factors are considered, is material. SAB 108 states that if correcting an error in the current year materially affects the current year’s income statement, the prior period financial statements must be restated. SAB 108 is effective for fiscal years ending after November 15, 2006, and the Company elected early application of SAB 108 as of September 30, 2006. See Note 8 for the impact of SAB 108 on our financial statements.
In September 2006, FASB issued FASB Statement No. 157 “Fair Value Measurement” (“SFAS 157”), which defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in generally accepted accounting principles and provides for expanded disclosure about fair value measurements. This statement applies under other accounting pronouncements that require or permit fair value measurements. This guidance was issued to increase consistency and comparability in fair value measurements and to expand disclosures about fair value measurements. This statement is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007. The Company does not expect that the adoption of SFAS 157 will have a material impact on its financial statements.
In February 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. 157-1, “Application of FASB Statement No. 157 to FASB Statement No. 13 and Other Accounting Pronouncements That Address Fair Value Measurements for Purposes of Lease Classification or Measurement under Statement 13” (“SFAS 157-1”). SFAS No. 157-1 amends SFAS 157, to exclude the FASB issued FASB Statement No. 13, “Accounting for Leases” (“SFAS 13”), and other accounting pronouncements that address fair value measurements for purposes of lease classification or measurement under SFAS 13. However, this scope exception does not apply to assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination that are required to be measured at fair value under FASB Statement No. 141(R), “ Business Combinations” (“SFAS 141R”), regardless of whether those assets and liabilities are related to leases. The Company is evaluating SFAS 157-1 and has not yet determined the impact the adoption will have on the Company’s financial position or results of operations.
In December 2007, FASB issued SFAS 141R, to create greater consistency in the accounting and financial reporting of business combinations. SFAS 141R requires a company to recognize the assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquired entity to be measured at their fair values as of the acquisition date. SFAS 141R also requires companies to recognize the fair value of assets acquired, the liabilities assumed and any noncontrolling interest in acquisitions of less than a one hundred percent interest when the acquisition constitutes a change in control of the acquired entity. In addition, SFAS 141R requires that acquisition-related costs and restructuring costs be recognized separately from the business combination and expensed as incurred. SFAS 141R is effective for business combinations for which the acquisition date is on or after the beginning of the first annual reporting period beginning after December 15, 2008. The Company is
113
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
evaluating SFAS 141R and has not yet determined the impact the adoption will have on its financial position or results of operations.
In December 2007, FASB issued FASB Statement No. 160, “Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements - an Amendment of Accounting Research Bulletin No. 51” (“SFAS 160”). SFAS 160 requires all entities to report noncontrolling interests in subsidiaries within equity in the consolidated financial statements, but separate from the parent shareholders’ equity. SFAS No. 160 also requires any acquisitions or dispositions of noncontrolling interests that do not result in a change of control to be accounted for as equity transactions. In addition, SFAS No. 160 requires that a parent company recognize a gain or loss in net income when a subsidiary is deconsolidated upon a change in control. SFAS No. 160 applies to fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008 and is adopted prospectively. The presentation and disclosure requirements shall be applied retrospectively for all periods presented. The adoption of SFAS 160 will result in a reclassification of minority interest to a separate component of total equity and net income attributable to noncontrolling interests will no longer be treated as a reduction to net income but will be shown as a reduction from net income in calculating net income available to common stockholders. The Company is evaluating SFAS 160 and has not yet determined the impact the adoption will have on its financial position or results of operations.
In February 2007, the FASB issued FASB Statement No. 159 “The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities” (“SFAS 159”). SFAS 159 permits all entities to choose to measure eligible items at fair value at specified election dates. SFAS 159 is effective as of the beginning of an entity’s first fiscal year that begins after November 15, 2007. The Company is evaluating SFAS 159 and has not yet determined the impact the adoption will have on the Company’s financial position or results of operations.
114
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
3. Mortgage and Other Secured Loans
A summary of the outstanding mortgage and other secured loans as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Interest Rate | | | Outstanding Debt | | | Maturity Date |
| | | | 2007 | | 2006 | | |
City National Plaza (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan | | LIBOR + 1.07 | %(2) | | $ | 355,300 | | $ | 355,300 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan (Note A) (3) | | LIBOR + 2.59 | % | | | 42,673 | | | 12,026 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan (Note B) | | LIBOR + 1.90 | %(2) | | | 24,000 | | | 24,000 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan (Note C) | | LIBOR + 2.25 | %(2) | | | 24,000 | | | 24,000 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan (Note D) | | LIBOR + 2.50 | %(2) | | | 24,000 | | | 24,000 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Senior mezzanine loan (Note E) | | LIBOR + 3.05 | %(2) | | | 22,700 | | | 22,700 | | | 7/17/2008 |
Junior mezzanine loan (4) | | LIBOR + 5.00 | % | | | 36,576 | | | 10,307 | | | 7/17/2008 |
CityWestPlace | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fixed | | 6.16 | % | | | 121,000 | | | 121,000 | | | 7/6/2016 |
Floating | | LIBOR + 1.25 | %(2)(12) | | | 82,400 | | | 82,400 | | | 7/1/2008 |
Floating | | LIBOR + 1.25 | %(12) | | | 7,825 | | | — | | | 7/1/2008 |
San Felipe Plaza | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan | | 5.28 | % | | | 101,500 | | | 101,500 | | | 8/11/2010 |
Senior mortgage loan (5) | | LIBOR + 3.00 | % | | | 9,655 | | | 2,120 | | | 8/11/2010 |
2500 City West | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan | | 5.28 | % | | | 70,000 | | | 70,000 | | | 8/11/2010 |
Senior mortgage loan (6) | | LIBOR + 3.00 | % | | | 9,671 | | | 3,113 | | | 8/11/2010 |
Brookhollow Central I, II and
III/Intercontinental Center | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan (Note A) | | LIBOR + 0.44 | %(2)(13) | | | 24,154 | | | 53,000 | | �� | 8/9/2008 |
Mezzanine loan (Note B) (7) | | LIBOR + 3.25 | %(13) | | | — | | | — | | | 8/9/2008 |
Senior mortgage loan (Note C) | | LIBOR + 4.86 | %(2)(13) | | | 16,746 | | | 1,984 | | | 8/9/2008 |
Four Falls Corporate Center | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan (Note A) | | 5.31 | % | | | 42,200 | | | 42,200 | | | 3/6/2010 |
Senior mezzanine loan (Note B) (8) (9) | | LIBOR + 3.25 | %(2)(11) | | | 9,867 | | | 7,867 | | | 3/6/2010 |
Oak Hill Plaza/Walnut Hill Plaza | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan (Note A) | | 5.31 | % | | | 35,300 | | | 35,300 | | | 3/6/2010 |
Senior mezzanine loan (Note B) (9) (10) | | LIBOR + 3.25 | %(2)(11) | | | 9,152 | | | 5,400 | | | 3/6/2010 |
Reflections I mortgage loan | | 5.23 | % | | | 22,527 | | | 22,870 | | | 4/1/2015 |
Reflections II mortgage loan | | 5.22 | % | | | 9,386 | | | 9,529 | | | 4/1/2015 |
Centerpointe I & II | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Senior mortgage loan | | LIBOR + .60 | %(2) | | | 55,000 | | | — | | | 2/9/2009 |
Mezzanine loan (Note A) (14) (15) | | LIBOR + 1.50 | %(2) | | | 13,085 | | | — | | | 2/9/2009 |
Mezzanine loan (Note B) (14) (16) | | LIBOR + 4.79 | %(2) | | | 11,315 | | | — | | | 2/9/2009 |
Mezzanine loan (Note C) (14) (17) | | LIBOR + 3.26 | %(2) | | | 11,600 | | | — | | | 2/9/2009 |
Fair Oaks Plaza (18) | | 5.52 | % | | | 44,300 | | | — | | | 2/9/2017 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | $ | 1,235,932 | | $ | 1,030,616 | (19) | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
The LIBOR rate for the loans above was 4.6% at December 31, 2007.
| (1) | The City National Plaza loans collectively have maximum borrowings of $580 million. The senior mortgage loan and Notes B, C, D and E under the senior mezzanine loan are subject to exit fees equal to .25% of the loan amounts. Note A under the senior mezzanine loan and the junior mezzanine loan are subject to an exit |
115
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
| | fee equal to .50% of the loan amounts. Under certain circumstances all of the exit fees will be waived. All of the City National Plaza loans have two one-year extension options at our election. The Company plans to exercise the extension options in 2008. |
| (2) | The partnership that owns each property has purchased interest rate cap agreements for the funded portion of these loans. TPG/CalSTRS has purchased interest rate caps aggregating $873.8 million on its loan portfolio. |
| (3) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $27.3 million. |
| (4) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $23.4 million. |
| (5) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $6.5 million under this loan. |
| (6) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $5.8 million under this loan. |
| (7) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $26.7 million under this loan. |
| (8) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $3.0 million under this loan. |
| (9) | These loans are subject to exit fees equal to 1% of the loan amounts, however, under certain circumstances the exit fees will be waived. |
| (10) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow up to $4.2 million under this loan. |
| (11) | These loans bear interest at the greater of the one month LIBOR or 2.25% per annum, plus the applicable margin. As of December 31, 2007, one month LIBOR exceeds 2.25%, per annum. |
| (12) | These loans have three one-year extension options. The Company plans to exercise the extension options in 2008. |
| (13) | These loans have two one-year extension options. The Company plans to exercise the extension options in 2008. |
| (14) | The loans are subject to exit fees of up to 1.0% through February 9, 2009. The Centerpointe I & II senior mortgage loan bears interest at a rate equal to one month LIBOR plus 0.60%. The mezzanine loans bear interest at a rate such that the weighted average of the rate on these loans and the rate on the senior mortgage loan secured by Centerpointe I & II equals LIBOR plus 1.59% per annum. The effective interest rate on the senior mezzanine loan as of December 31, 2007 was 8.5% per annum. The weighted average interest rate on all of the loans was 6.19% per annum. All of these loans have three one-year extension options at our election. |
| (15) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $11.9 million under this loan. |
| (16) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $10.3 million under this loan. |
| (17) | TPG/CalSTRS may borrow an additional $10.6 million under this loan. |
| (18) | This loan may be defeased in full after three years, or prepaid in full after 9 years and 8 months. |
| (19) | Approximately $12.5 million of this total outstanding debt amount as of December 31, 2006 relates to the Brookhollow Central I, II and III/Intercontinental Center loans, and is classified on the consolidated balance sheets in the liabilities associated with discontinued operations caption as of December 31, 2006, for the portion related to Intercontinental Center. |
The loan agreements generally require that all receipts collected from the properties be deposited in a lockbox account under the control of the lender to fund reserves, debt service and operating expenditures.
116
As of December 31, 2007, scheduled principal payments for the secured outstanding debt are as follows:
| | | | |
2008 | | $ | 660,374 | (1) |
2009 | | | 91,000 | |
2010 | | | 287,345 | |
2011 | | | — | |
2012 | | | — | |
Thereafter | | | 197,213 | |
| | | | |
| | $ | 1,235,932 | |
| | | | |
| (1) | TPG/CalSTRS has extension options for this full amount, and it plans to exercise these options. |
4. Related Party Transactions
TPG/CalSTRS incurred acquisition fees to an affiliate of TPG of $833,000, $1,475,000 and $2,384,000 for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively, which have been capitalized to real estate. Such fees were paid upon acquisition of two properties in 2007, one property in 2006 and eight properties and undeveloped land in 2005. During the year ended December 31, 2007, an acquisition fee of $1,438,000 was incurred upon the acquisition of a 25% equity investment in the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture, which owns a portfolio of 10 properties.
TPG provides asset management services to TPG/CalSTRS. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, TPG/CalSTRS incurred asset management fees of$6,256,000, $4,402,000, and $2,471,000, respectively, to TPG, which are included in general and administrative expenses and loss from discontinued operations. An additional $544,000 was incurred for asset management fees for the Austin Portfolio Properties for the year ended December 31, 2007.
Pursuant to a management and leasing agreement, TPG performs property management and leasing services for TPG/CalSTRS. TPG is entitled to property management fees calculated based on 3% of gross property revenues, paid on a monthly basis. In addition, TPG is reimbursed for compensation paid to certain of its employees and direct out-of-pocket expenses. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, TPG charged TPG/CalSTRS $5,030,000, $3,792,000, and $2,048,000, respectively, for property management fees and $2,140,000, $1,639,000, and $1,072,000, respectively, representing the cost of on-site property management personnel incurred on behalf of TPG/CalSTRS, which are included in operating expenses and loss from operations. An additional $1,871,000 was incurred for property management fees and $596,000 for costs of on-site property management personnel for the Austin Portfolio Properties for the year ended December 31, 2007.
For new leases entered into by TPG/CalSTRS, TPG is entitled to leasing commissions, calculated at 4% of base rent during years 1 through 10 of a lease and 3% of base rent thereafter, where TPG acts as the procuring broker, and 2% of lease rent during years 1 through 10 of a lease and 1.5% of base rent thereafter, where TPG acts as the co-operating broker. For lease renewals, where TPG is the procuring broker and there is no co-operating broker, TPG is entitled to leasing commissions, calculated at 4% of base rent. For lease renewals, where there is both a procuring and co-operating broker, if TPG is the procuring broker, it is entitled to receive 3% of base rents and if it’s the co-operating broker, it is entitled to receive 1.5% of base rents. Commissions are paid 50% at signing and 50% upon occupancy. The leasing commissions will be split on the customary basis between TPG and tenant representative when applicable. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, TPG/CalSTRS incurred leasing commissions to TPG of $5,002,000, $5,347,000 and $2,318,000, respectively, which are included in deferred leasing costs. An additional $326,000 was incurred for leasing commissions for the Austin Portfolio Properties for the year ended December 31, 2007. At December 31, 2007 and 2006, $1,358,000 and $2,079,000, respectively, is payable to TPG pursuant to the management and leasing agreement.
117
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The management and leasing agreement expires on January 27, 2009, and is automatically renewed for successive periods of one year each, unless TPG elects not to renew the agreement.
TPG receives incentive compensation based on a minimum return on investment to CalSTRS, following which TPG would participate in cash flow above the stated return, subject to a clawback provision in the joint venture agreement if returns for a property fall below the stated return. TPG earned incentive compensation of $571,000 related to the sale of Intercontinental Center during the year ended December 31, 2007. For the year ended December 31, 2006, TPG earned incentive compensation of $521,000 related to the sale of Valley Square.
TPG acts as the development manager for the properties. TPG/CalSTRS pays TPG a fee based upon a market rate percentage of the total direct and indirect costs of the property, including the cost of all tenant improvements therein. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, TPG/CalSTRS incurred development management fees of $1,600,000, $1,472,000, and $948,000, respectively, to TPG, which have been capitalized to real estate. An additional $66,000 was incurred for the Austin Portfolio Properties for the year ended December 31, 2007.
TPG/CalSTRS obtains insurance as part of a master insurance policy that includes all the properties in which TPG and affiliated entities have an investment and for which they perform investment advisory or property management services. Property insurance premiums are allocated to TPG/CalSTRS based on estimated insurable values. Liability insurance premiums are allocated to TPG/CalSTRS based on relative square footage. The allocated premium for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 is $7,131,000, $6,720,000, and $3,256,000, respectively, and is included in operating expenses and loss from discontinued operations.
TPG is a tenant in City National Plaza through May 2009. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2006, and 2005, rental revenues from TPG were $306,000, $289,000, and $296,000, respectively.
5. Discontinued Operations
In January 2007, TPG/CalSTRS classified Intercontinental Center as held for sale, upon the decision to market the property for sale. In accordance with SFAS No. 144, Accounting for Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets, the results of operations for Intercontinental Center are reflected in the consolidated statements of operations as discontinued operations since acquisition of the property in August 2005. The property was sold in April 2007. The residual amounts for the sale of Valley Square Office Park in 2006 are also reflected in discontinued operations for 2007. The results of operations for Valley Square Office Park are reflected in the consolidated statements of operations as discontinued operations from acquisition of the property in March 2005 through the date of sale in April 2006.
118
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The following table summarizes the income and expense components that comprise income (loss) from discontinued operations before minority interests for the year ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005:
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | |
Rental | | $ | 1,002 | | $ | 3,969 | | $ | 4,713 | |
Tenant reimbursements | | | 146 | | | 320 | | | 322 | |
Other | | | 29 | | | 124 | | | 109 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues | | | 1,177 | | | 4,413 | | | 5,144 | |
Expenses: | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating and other expenses | | | 1,022 | | | 2,740 | | | 2,835 | |
Interest expense | | | 425 | | | 1,768 | | | 1,945 | |
Deprecation and amortization | | | — | | | 1,316 | | | 3,521 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Total expenses | | | 1,447 | | | 5,824 | | | 8,301 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Gain on sale of property | | $ | 7,932 | | $ | 6,133 | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | $ | 7,662 | | $ | 4,722 | | $ | (3,157 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
The following table summarizes the components that comprise the assets and liabilities associated with discontinued operations as of December 31, 2007 and 2006:
| | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | 2006 |
| ASSETS | | | | | | |
Investments in real estate, net | | $ | — | | $ | 11,268 |
Receivables including deferred rents | | | 16 | | | 1,422 |
Other assets | | | 12 | | | 2,077 |
| | | | | | |
Total assets associated with discontinued operations | | $ | 28 | | $ | 14,767 |
| | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | |
Liabilities: | | | | | | |
Mortgage loans | | $ | — | | $ | 12,528 |
Other liabilities | | | 23 | | | 1,146 |
| | | | | | |
Total liabilities associated with discontinued operations | | | 23 | | | 13,674 |
| | | | | | |
Members’ equity | | | 5 | | | 1,093 |
| | | | | | |
Total liabilities and members' equity associated with discontinued operations | | $ | 28 | | $ | 14,767 |
| | | | | | |
119
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
6. Minimum Future Lease Rentals
TPG/CalSTRS has entered into various lease agreements with tenants as of December 31, 2007. The minimum future cash rents receivable on non-cancelable leases, including leases relating to the property held for sale, in each of the next five years and thereafter are as follows:
| | | |
Year ending December 31, | | | |
2008 | | $ | 118,877 |
2009 | | | 118,311 |
2010 | | | 115,083 |
2011 | | | 108,696 |
2012 | | | 101,049 |
Thereafter | | | 504,753 |
| | | |
| | $ | 1,066,769 |
| | | |
The leases generally also require reimbursement of the tenant’s proportionate share of common area, real estate taxes and other operating expenses, which are not included in the amounts above.
7. Commitments and Contingencies
TPG/CalSTRS has been named as a defendant in a number of lawsuits in the ordinary course of business. TPG/CalSTRS believes that the ultimate settlement of these suits will not have a material adverse effect on its financial position and results of operations.
In connection with the ownership, operation and management of the real estate properties, TPG/CalSTRS may be potentially liable for costs and damages related to environmental matters. TPG/CalSTRS has not been notified by any governmental authority of any noncompliance, liability or other claim in connection with any of the properties, and TPG/CalSTRS is not aware of any other environmental condition with respect to any of the properties that management believes will have a material adverse effect on TPG/CalSTRS’ assets or results of operations.
8. Restatement
We have restated TPG/CalSTRS’ 2005 consolidated financial statements as a result of the change in the allocation of depreciation expense relating to TPG and CalSTRS. Depreciation expense was previously allocated to the members in accordance with the operating agreement of the limited liability company. For all properties excluding City National Plaza, TPG was initially allocated depreciation expense ahead of CalSTRS. For City National Plaza, the minority owner and TPG were initially allocated depreciation expense ahead of CalSTRS. Based on AICPA Statement of Position 78-9 “Accounting for Investments in Real Estate Ventures,” we determined that the allocation of net income/loss, including depreciation expense, to the members should be based on the allocation of cash distributions and liquidating distributions, not the profit and loss allocation ratios as specified in the operating agreement.
120
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
The following table presents the effects of the change in allocation of depreciation expense made to the previously reported consolidated statement of members’ equity and comprehensive loss of TPG/CalSTRS for the year ended December 31, 2005 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As Previously
Reported | | | Restatement | | | As
Restated | |
Balance, December 31, 2004 | | $ | 111,120 | | | $ | (9,062 | ) | | $ | 102,058 | |
Net loss | | | (36,982 | ) | | | (512 | ) | | | (37,494 | ) |
Balance, December 31, 2005 | | | 167,908 | | | | (9,574 | ) | | | 158,334 | |
The following table presents the effects of the change in allocation of depreciation expense made to the previously reported consolidated statement of operations in TPG/CalSTRS for the year ended December 31, 2005 (in thousands).
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As Previously
Reported | | | Restatement | | | As
Restated | | | As
Reclassified(1) | |
Revenues | | $ | 70,521 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 70,521 | | | $ | 71,877 | |
Expenses | | | 108,568 | | | | — | | | | 108,568 | | | | 108,333 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations before minority interest | | | (38,047 | ) | | | — | | | | (38,047 | ) | | | (36,456 | ) |
Minority interest attributable to continuing operations | | | 3,910 | | | | (512 | ) | | | 3,398 | | | | 3,398 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (34,137 | ) | | | (512 | ) | | | (34,649 | ) | | | (33,058 | ) |
Loss from discontinued operations | | | (1,566 | ) | | | — | | | | (1,566 | ) | | | (3,157 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss before cumulative effect of change in accounting principle | | | (35,703 | ) | | | (512 | ) | | | (36,215 | ) | | | (36,215 | ) |
Cumulative effect of change in accounting principle | | | (1,279 | ) | | | — | | | | (1,279 | ) | | | (1,279 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (36,982 | ) | | $ | (512 | ) | | $ | (37,494 | ) | | $ | (37,494 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | The “As Restated” amounts have been adjusted to reflect the reclassifications related to certain reimbursements (see Note 2) and discontinued operations (see Note 5). |
The restatement did not change any amounts in net cash used in operating activities and investing activities, and provided by financing activities in previously reported consolidated statement of cash flows.
121
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
9. Unconsolidated Real Estate Entities
TPG/CalSTRS owns a 25% interest in the Austin Portfolio Joint Venture which owns the following ten properties all of which were purchased on June 1, 2007 (“Austin Portfolio Properties”):
San Jacinto Center
Frost Bank Tower
One Congress Plaza
One American Center
300 West 6th Street
Research Park Plaza I & II
Park 22 I-III
Great Hills Plaza
Stonebridge Plaza II
Westech 360 I-IV
Capital contributions, distributions, and profits and losses of the real estate entities are allocated in accordance with the terms of the applicable partnership and limited liability company agreements. Such allocations may differ from the stated ownership percentage interests in such entities as a result of preferred returns and allocation formulas as described in the partnership and limited liability company agreements.
The following is a summary of the investments in unconsolidated real estate entities for the period from inception (June 1, 2007) to December 31, 2007:
| | | | |
Investment balance, June 1, 2007 (date of acquisition) | | $ | 71,512 | |
Contributions | | | — | |
Equity in net loss of unconsolidated real estate entities | | | (9,001 | ) |
Other comprehensive income/loss | | | (481 | ) |
Distributions | | | (368 | ) |
| | | | |
Investment balance, December 31, 2007 | | $ | 61,662 | |
| | | | |
122
TPG/CalSTRS, LLC
(A Delaware Limited Liability Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION—(Continued)
Following is summarized financial information for the unconsolidated real estate entities as of December 31, 2007 and for the period from June 1, 2007 (date of inception) to December 31, 2007:
Summarized Balance Sheet
| | | |
| ASSETS | | | |
Investments in real estate, net | | $ | 1,115,672 |
Receivables including deferred rents | | | 4,140 |
Other assets | | | 153,619 |
| | | |
Total assets | | $ | 1,273,431 |
| | | |
| |
| LIABILITIES AND OWNERS’ EQUITY | | | |
Mortgage and other secured loans | | $ | 907,500 |
Other liabilities | | | 119,283 |
| | | |
Total liabilities | | | 1,026,783 |
| | | |
Owners’ equity: | | | |
TPG/CalSTRS, including $481 of other comprehensive loss | | | 61,662 |
Other owners, including $1,442 of other comprehensive loss | | | 184,986 |
| | | |
Total owners’ equity | | | 246,648 |
| | | |
Total liabilities and owners’ equity | | $ | 1,273,431 |
| | | |
Summarized Statement of Operations
| | | | |
Revenues | | $ | 67,027 | |
Expenses: | | | | |
Operating and other expenses | | | 28,562 | |
Interest expense | | | 35,753 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 38,716 | |
| | | | |
Total expenses | | | 103,031 | |
| | | | |
Net loss | | | (36,004 | ) |
| | | | |
TPG/CalSTRS’ share of net loss | | $ | (9,001 | ) |
| | | | |
123
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
Dated: March 18, 2008
| | |
| THOMAS PROPERTIES GROUP, INC. |
| |
| By: | | /S/ JAMES A. THOMAS |
| | James A. Thomas Chief Executive Officer |
124
POWER OF ATTORNEY
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each individual whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints James A. Thomas and Diana M. Laing, his or her true and lawful attorneys-in-fact each acting alone, with full power of substitution and re-substitution, for him or her and in his or her name, place and stead in any and all capacities to sign any or all amendments to this report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in and about the premises, as fully to all intents and purposes as he or she might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact, or their substitutes, each acting alone, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed by the following persons in the capacities indicated below.
| | | | |
Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | |
/S/ JAMES A. THOMAS James A. Thomas | | Chairman of the Board, President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | | March 18, 2008 |
| | |
/S/ R. BRUCE ANDREWS R. Bruce Andrews | | Director | | March 18, 2008 |
| | |
/S/ EDWARD D. FOX Edward D. Fox | | Director | | March 18, 2008 |
| | |
/S/ WINSTON H. HICKOX Winston H. Hickox | | Director | | March 18, 2008 |
| | |
/S/ JOHN GOOLSBY John Goolsby | | Director | | March 18, 2008 |
| | |
/S/ RANDALL L. SCOTT Randall L. Scott | | Executive Vice President and Director | | March 18, 2008 |
| | |
/S/ JOHN R. SISCHO John R. Sischo | | Executive Vice President and Director | | March 18, 2008 |
| | |
/S/ DIANA M. LAING Diana M. Laing | | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | | March 18, 2008 |
| | |
/S/ ROBERT D. MORGAN Robert D. Morgan | | Senior Vice President (Principal Accounting Officer) | | March 18, 2008 |
125
