- BLUE Dashboard
- Financials
- Filings
-
Holdings
- Transcripts
- ETFs
- Insider
- Institutional
- Shorts
-
8-K Filing
bluebird bio (BLUE) 8-KRegulation FD Disclosure
Filed: 7 Dec 15, 12:00am

Transforming the Lives of Patients with Severe Genetic and Rare Diseases Making Hope a Reality Exhibit 99.4

Forward Looking Statement These slides and the accompanying oral presentation contain forward-looking statements and information. The use of words such as “may,” “might,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “project,” “intend,” “future,” “potential,” or “continue,” and other similar expressions are intended to identify forward looking statements. For example, all statements we make regarding the initiation, timing, progress and results of our preclinical and clinical studies and our research and development programs, our ability to advance product candidates into, and successfully complete, clinical studies, and the timing or likelihood of regulatory filings and approvals are forward looking. All forward-looking statements are based on estimates and assumptions by our management that, although we believe to be reasonable, are inherently uncertain. All forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from those that we expected. These statements are also subject to a number of material risks and uncertainties that are described in our most recent quarterly report on Form 10-Q, as well as our subsequent filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it was made. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. Nasdaq: BLUE
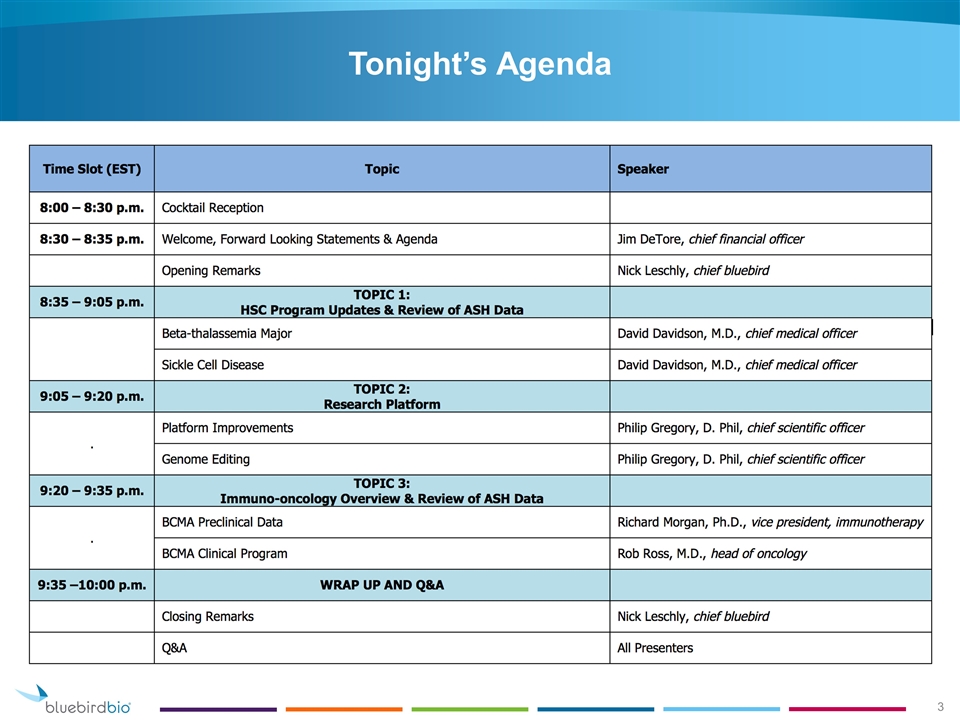
Tonight’s Agenda

bluebird bio: Why We Do What We Do Our Vision – Make Hope a Reality Seeking to transform the lives of patients with severe genetic and rare diseases through the development of innovative gene therapy products. Ethan Cameron Aidan
It’s More Than Biology…
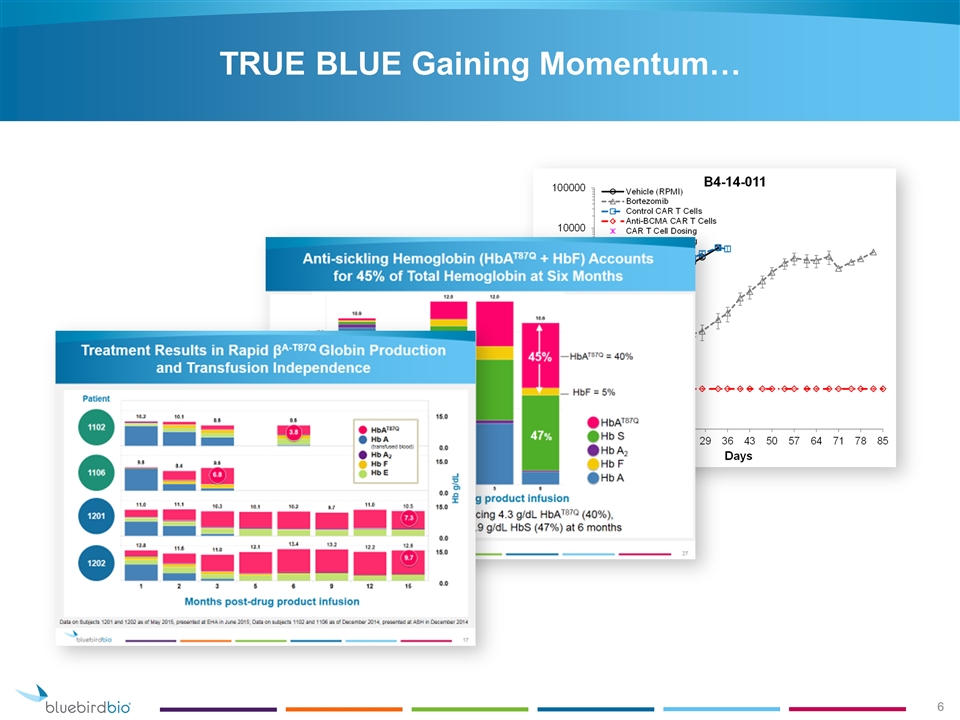
TRUE BLUE Gaining Momentum…
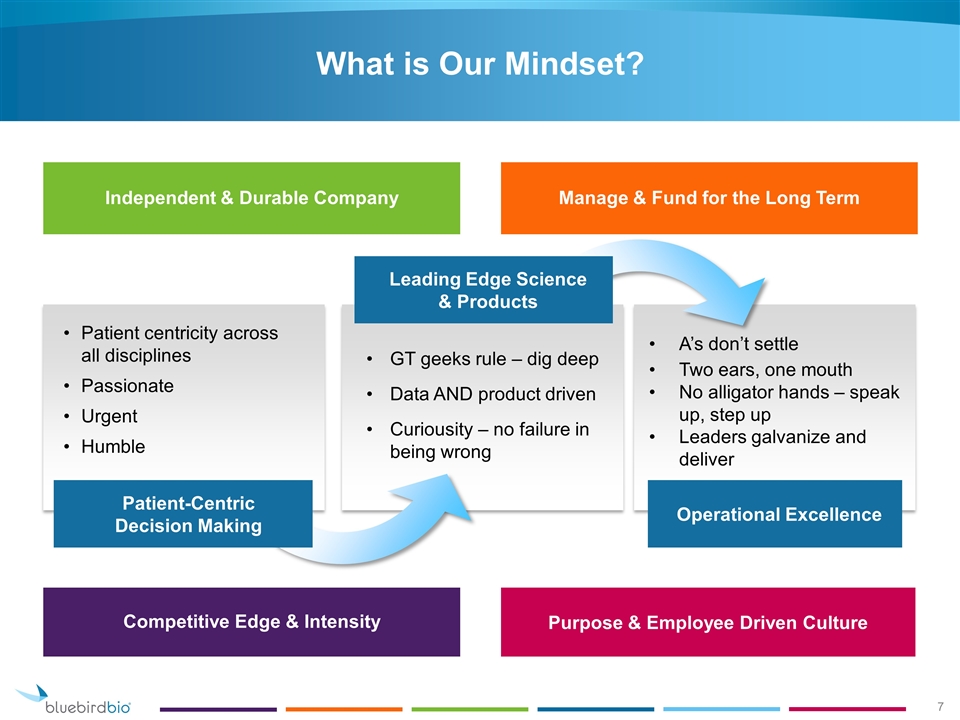
What is Our Mindset? Patient centricity across all disciplines Passionate Urgent Humble Patient-Centric Decision Making GT geeks rule – dig deep Data AND product driven Curiousity – no failure in being wrong A’s don’t settle Two ears, one mouth No alligator hands – speak up, step up Leaders galvanize and deliver Operational Excellence Independent & Durable Company Manage & Fund for the Long Term Competitive Edge & Intensity Purpose & Employee Driven Culture Leading Edge Science & Products

The Innovators Dilemma DOWNSIDE RISK & FEAR UPSIDE OPTIMISM & HUNGER “DOWNSIDE RISK OF SUCCESS IS CHOICE” Dissatisfied Optimists (and Paranoid)
Ecosystem Explosion Competition Great For All (Especially Patients) Gene Therapy (20+) CAR/TCR/T Cell (25+) Gene Editing (8+) Mustang Therapeutics CARsgen
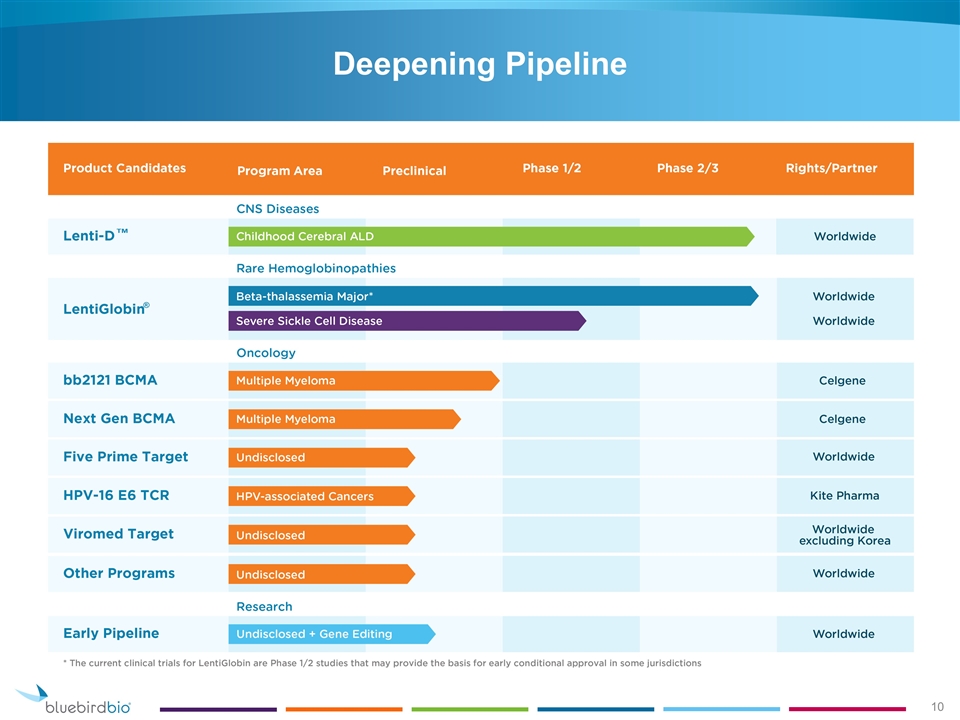
Deepening Pipeline

Asking the Important Questions What is the β-thalassemia clinical/regulatory path forward? What is the SCD data telling us? What are you doing to improve your platform? What are you doing to build a sustainable pipeline? What is the plan for oncology/BCMA?

LentiGlobin Clinical Data Update Dave Davidson, M.D. Chief Medical Officer

β-thalassemia Major

As of October 28, 2015 *reasons for ineligibility: advanced liver disease (n=3), positive HBV serology (n=1) Consented N=27 Ineligible N=4* Stem Cell Mobilization N=23 Transduction in Progress N=2 Transduction Complete N=20 Drug Product Infused N=17 Awaiting Infusion N=3 Apheresis Failure N=1 HGB-204 and HGB-205 β-Thalassemia Subjects
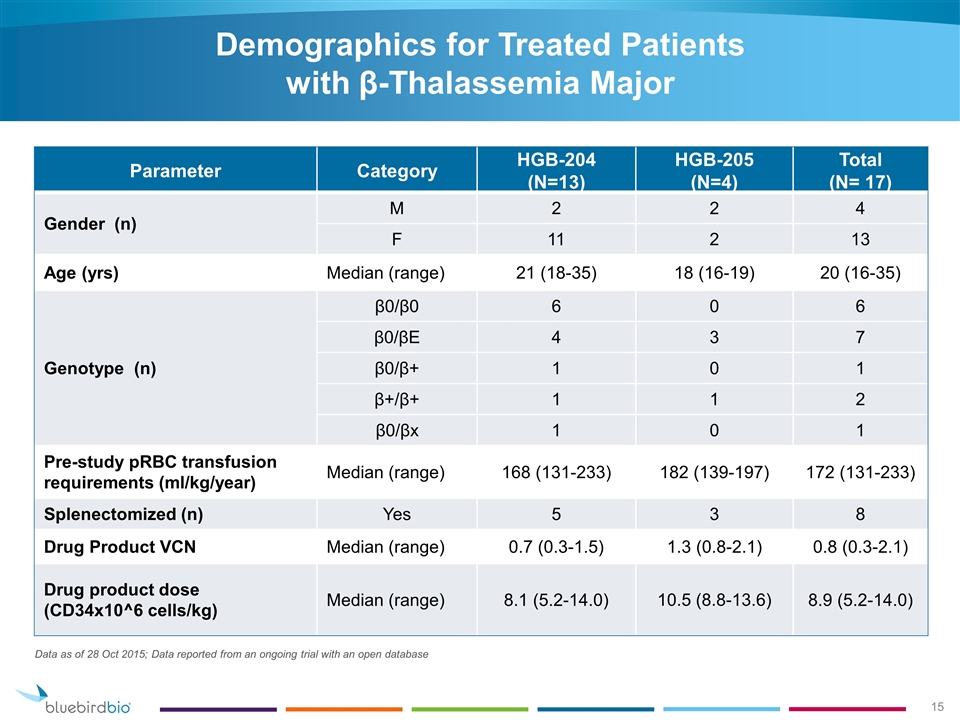
Parameter Category HGB-204 (N=13) HGB-205 (N=4) Total (N= 17) Gender (n) M 2 2 4 F 11 2 13 Age (yrs) Median (range) 21 (18-35) 18 (16-19) 20 (16-35) Genotype (n) β0/β0 6 0 6 β0/βE 4 3 7 β0/β+ 1 0 1 β+/β+ 1 1 2 β0/βx 1 0 1 Pre-study pRBC transfusion requirements (ml/kg/year) Median (range) 168 (131-233) 182 (139-197) 172 (131-233) Splenectomized (n) Yes 5 3 8 Drug Product VCN Median (range) 0.7 (0.3-1.5) 1.3 (0.8-2.1) 0.8 (0.3-2.1) Drug product dose (CD34x10^6 cells/kg) Median (range) 8.1 (5.2-14.0) 10.5 (8.8-13.6) 8.9 (5.2-14.0) Data as of 28 Oct 2015; Data reported from an ongoing trial with an open database Demographics for Treated Patients with β-Thalassemia Major
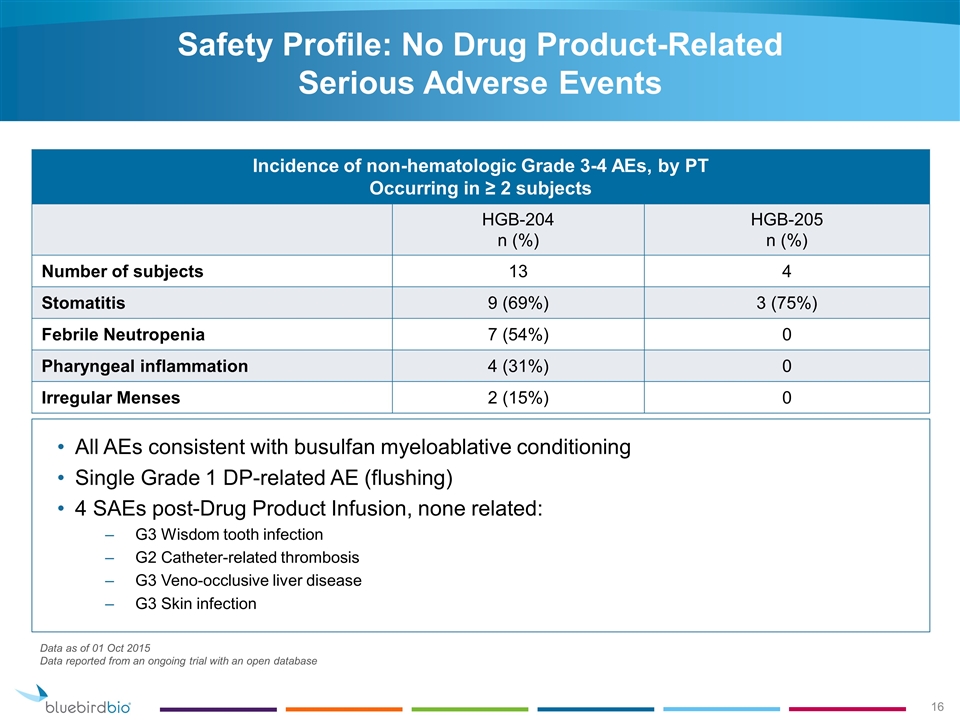
Incidence of non-hematologic Grade 3-4 AEs, by PT Occurring in ≥ 2 subjects HGB-204 n (%) HGB-205 n (%) Number of subjects 13 4 Stomatitis 9 (69%) 3 (75%) Febrile Neutropenia 7 (54%) 0 Pharyngeal inflammation 4 (31%) 0 Irregular Menses 2 (15%) 0 All AEs consistent with busulfan myeloablative conditioning Single Grade 1 DP-related AE (flushing) 4 SAEs post-Drug Product Infusion, none related: G3 Wisdom tooth infection G2 Catheter-related thrombosis G3 Veno-occlusive liver disease G3 Skin infection Data as of 01 Oct 2015 Data reported from an ongoing trial with an open database Safety Profile: No Drug Product-Related Serious Adverse Events

HGB-204 HGB-205 Follow-up period (months) Median 9 (n = 13) (range 0.2 – 19.1) Median 11.4 (n = 4) (range 1.8 – 21) Neutrophil engraftment Median Day +18 (n = 11) (range 13 - 29) Median Day +16 (n = 4) (range 13 – 28) Platelet engraftment Median Day +30 (n = 10) (range 17 - 39) Median Day +21 (n = 4) (range 17 – 24) No replication competent lentivirus detected Integration site analysis shows highly polyclonal repopulation with no clonal dominance detected at any time point HGB-204: Median of 560 (range 190-2,888) unique integration sites per subject at latest time point (3 to 12 months) HGB-205: Subjects 1201 and 1202 with 756 and 8685 unique integration sites at 12 months, respectively Data as of 01 Oct 2015 Data reported from an ongoing trial with an open database Engraftment and LVV-Specific Safety
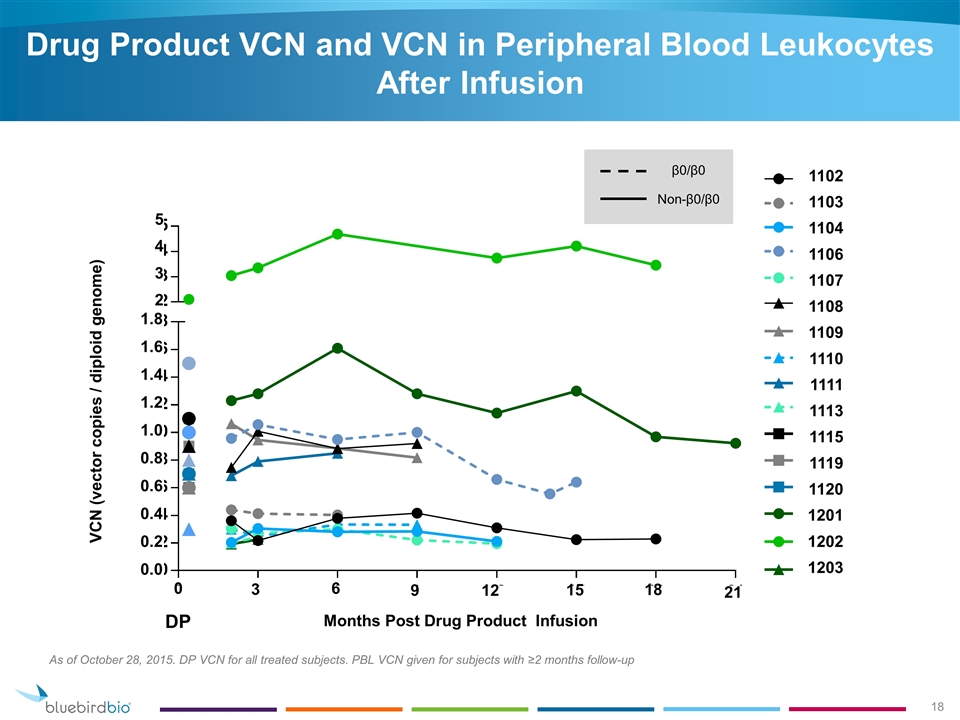
Drug Product VCN and VCN in Peripheral Blood Leukocytes After Infusion As of October 28, 2015. DP VCN for all treated subjects. PBL VCN given for subjects with ≥2 months follow-up DP β0/β0 Non-β0/β0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 5 4 3 2 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 1102 1103 1104 1106 1107 1108 1109 1110 1111 1113 1115 1119 1120 1201 1202 1203 Months Post Drug Product Infusion VCN (vector copies / diploid genome)
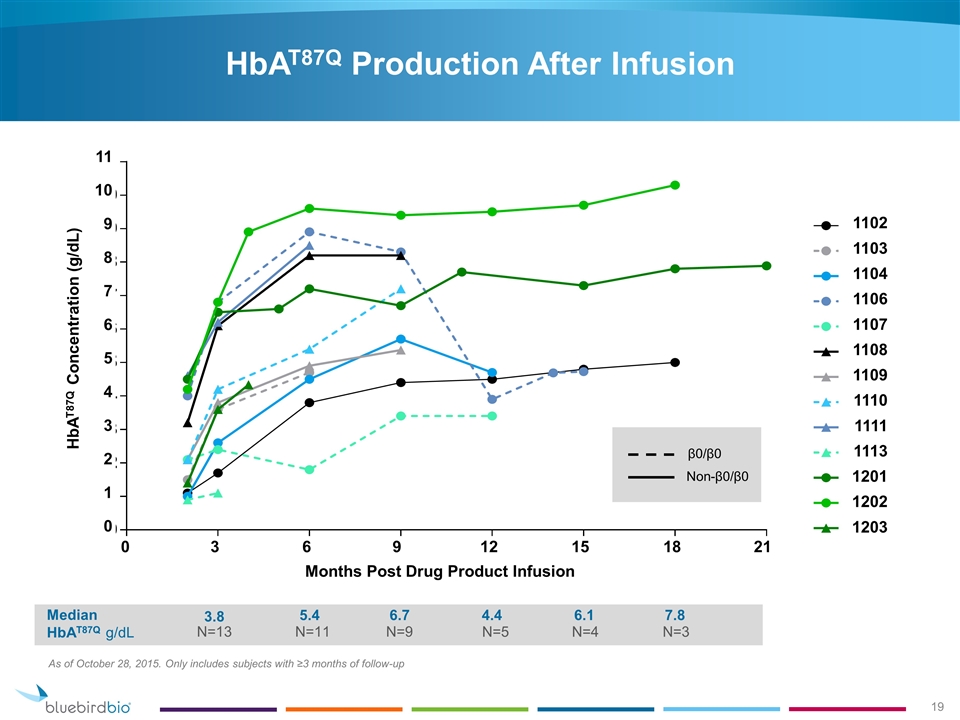
HbAT87Q Production After Infusion As of October 28, 2015. Only includes subjects with ≥3 months of follow-up Median HbAT87Q g/dL 3.8 5.4 6.7 4.4 N=9 N=13 N=11 N=5 6.1 N=4 7.8 N=3 β0/β0 Non-β0/β0 1102 1103 1104 1106 1107 1108 1109 1110 1111 1113 1201 1202 1203 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 HbAT87Q Concentration (g/dL) 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 Months Post Drug Product Infusion
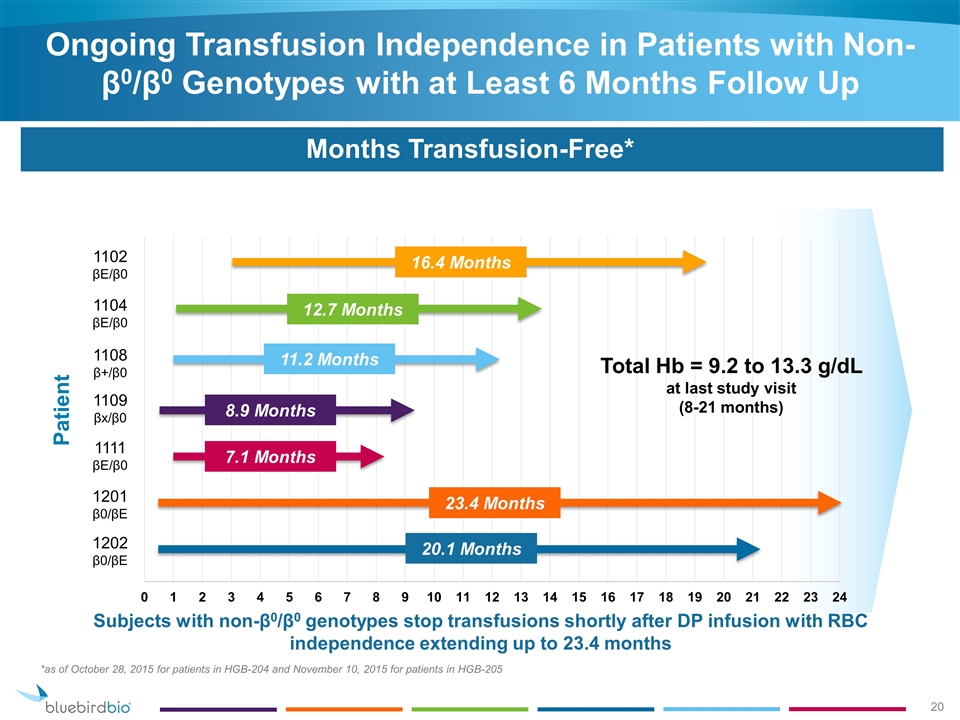
Ongoing Transfusion Independence in Patients with Non- β0/β0 Genotypes with at Least 6 Months Follow Up Days Transfusion-Free Months Transfusion-Free* *as of October 28, 2015 for patients in HGB-204 and November 10, 2015 for patients in HGB-205 Subjects with non-β0/β0 genotypes stop transfusions shortly after DP infusion with RBC independence extending up to 23.4 months Patient 1202 β0/βE 1201 β0/βE 1111 βE/β0 1109 βx/β0 1108 β+/β0 1104 βE/β0 1102 βE/β0 20.1 Months 23.4 Months 7.1 Months 8.9 Months 11.2 Months 12.7 Months 16.4 Months Total Hb = 9.2 to 13.3 g/dL at last study visit (8-21 months)
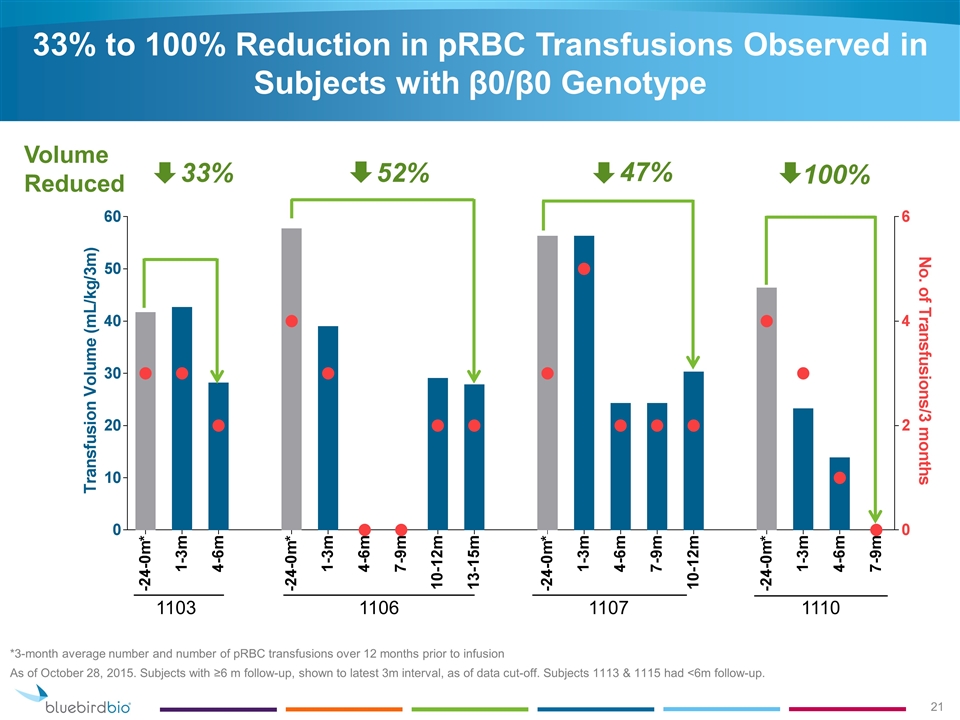
33% to 100% Reduction in pRBC Transfusions Observed in Subjects with β0/β0 Genotype As of October 28, 2015. Subjects with ≥6 m follow-up, shown to latest 3m interval, as of data cut-off. Subjects 1113 & 1115 had <6m follow-up. 52% 47% 33% 100% 1103 1106 1107 1110 Volume Reduced *3-month average number and number of pRBC transfusions over 12 months prior to infusion
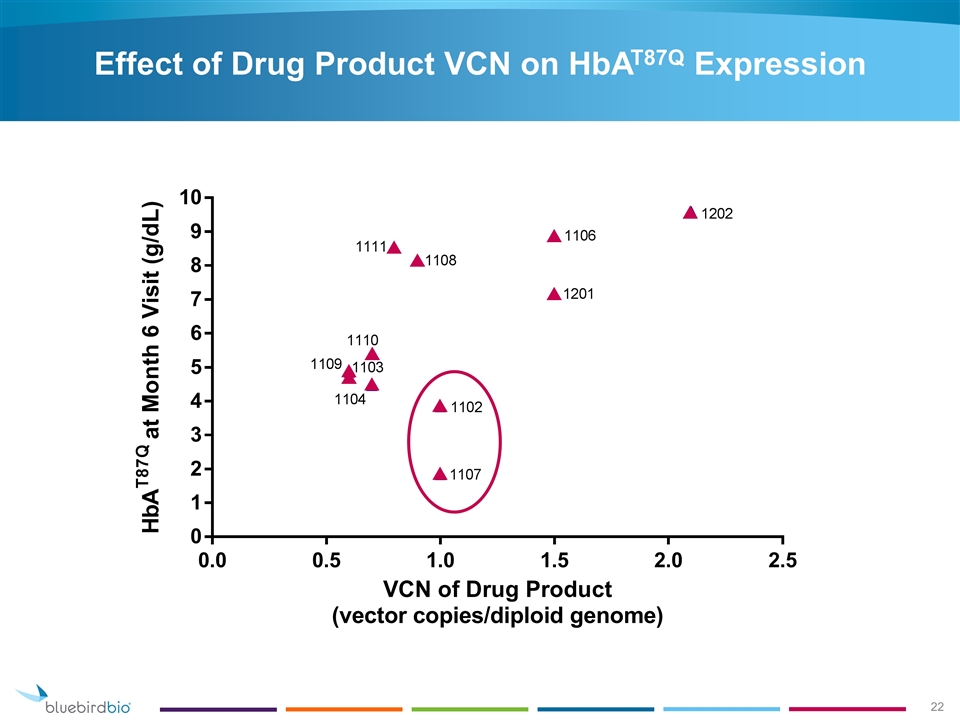
Effect of Drug Product VCN on HbAT87Q Expression
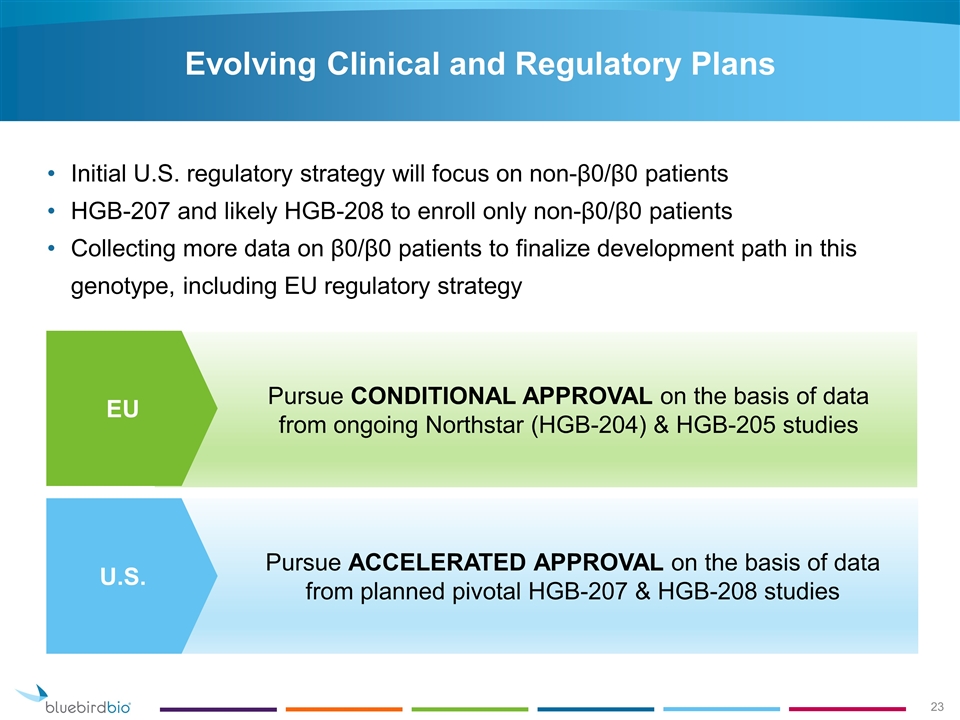
Pursue CONDITIONAL APPROVAL on the basis of data from ongoing Northstar (HGB-204) & HGB-205 studies Pursue ACCELERATED APPROVAL on the basis of data from planned pivotal HGB-207 & HGB-208 studies EU U.S. Initial U.S. regulatory strategy will focus on non-β0/β0 patients HGB-207 and likely HGB-208 to enroll only non-β0/β0 patients Collecting more data on β0/β0 patients to finalize development path in this genotype, including EU regulatory strategy Evolving Clinical and Regulatory Plans

Severe Sickle Cell Disease
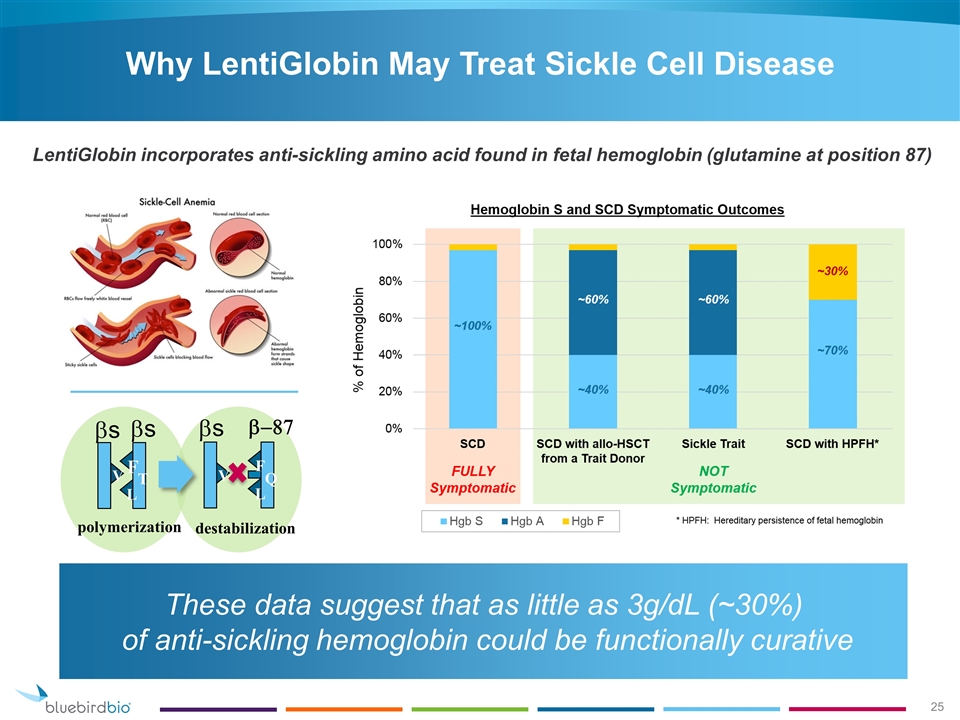
polymerization destabilization V F L T bs bs V F L Q bs b-87 Why LentiGlobin May Treat Sickle Cell Disease These data suggest that as little as 3g/dL (~30%) of anti-sickling hemoglobin could be functionally curative LentiGlobin incorporates anti-sickling amino acid found in fetal hemoglobin (glutamine at position 87)

Patients with severe sickle cell disease Open label, multi-center, U.S. based study Increased enrollment target from 8 subjects to 20 subjects to provide additional data and flexibility for regulatory strategy As of November 17, 2015, 11 subjects enrolled; bone marrow harvest completed for four subjects and in progress for five subjects Primary endpoint = Safety of gene therapy among patients with severe SCD Secondary endpoints = clinical events, including vaso-occlusive crises or acute chest syndrome HGB-206 (Severe sickle cell disease) HGB-206 Enrollment Update
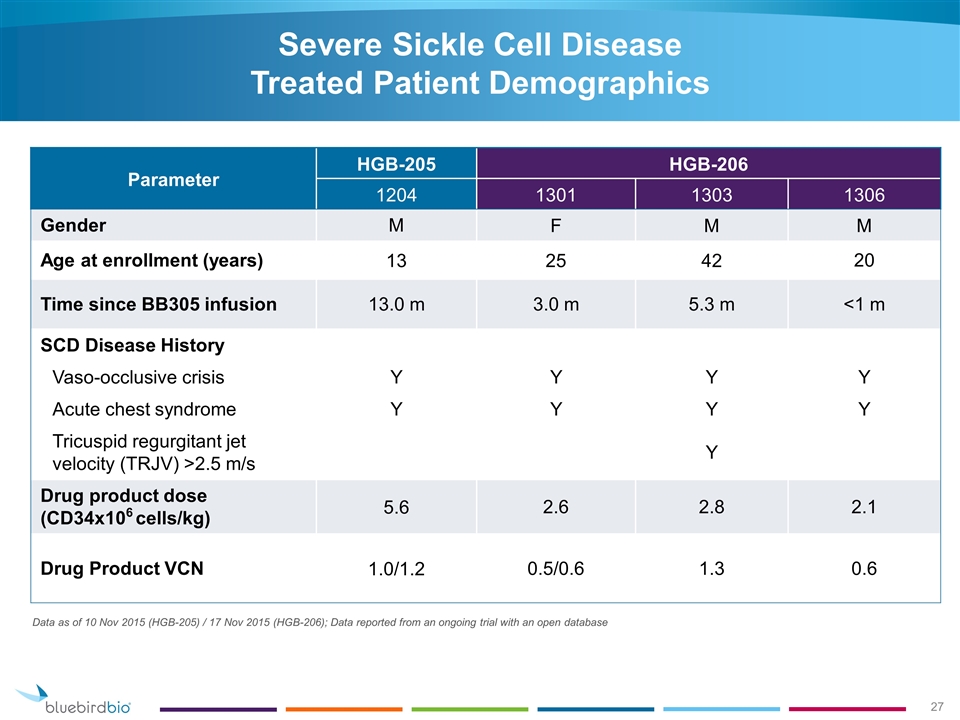
Severe Sickle Cell Disease Treated Patient Demographics Parameter HGB-205 HGB-206 1204 1301 1303 1306 Gender M F M M Age at enrollment (years) 13 25 42 20 Time since BB305 infusion 13.0 m 3.0 m 5.3 m <1 m SCD Disease History Vaso-occlusive crisis Y Y Y Y Acute chest syndrome Y Y Y Y Tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity (TRJV) >2.5 m/s Y Drug product dose (CD34x106 cells/kg) 5.6 2.6 2.8 2.1 Drug Product VCN 1.0/1.2 0.5/0.6 1.3 0.6 Data as of 10 Nov 2015 (HGB-205) / 17 Nov 2015 (HGB-206); Data reported from an ongoing trial with an open database
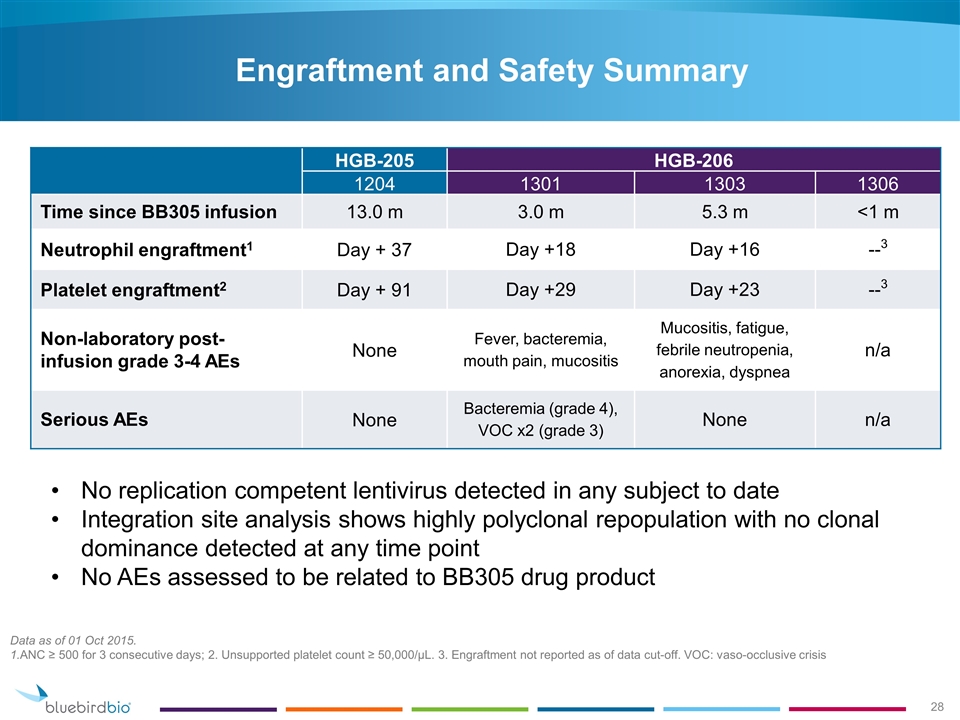
No replication competent lentivirus detected in any subject to date Integration site analysis shows highly polyclonal repopulation with no clonal dominance detected at any time point No AEs assessed to be related to BB305 drug product Data as of 01 Oct 2015. 1.ANC ≥ 500 for 3 consecutive days; 2. Unsupported platelet count ≥ 50,000/µL. 3. Engraftment not reported as of data cut-off. VOC: vaso-occlusive crisis HGB-205 HGB-206 1204 1301 1303 1306 Time since BB305 infusion 13.0 m 3.0 m 5.3 m <1 m Neutrophil engraftment1 Day + 37 Day +18 Day +16 --3 Platelet engraftment2 Day + 91 Day +29 Day +23 --3 Non-laboratory post-infusion grade 3-4 AEs None Fever, bacteremia, mouth pain, mucositis Mucositis, fatigue, febrile neutropenia, anorexia, dyspnea n/a Serious AEs None Bacteremia (grade 4), VOC x2 (grade 3) None n/a Engraftment and Safety Summary
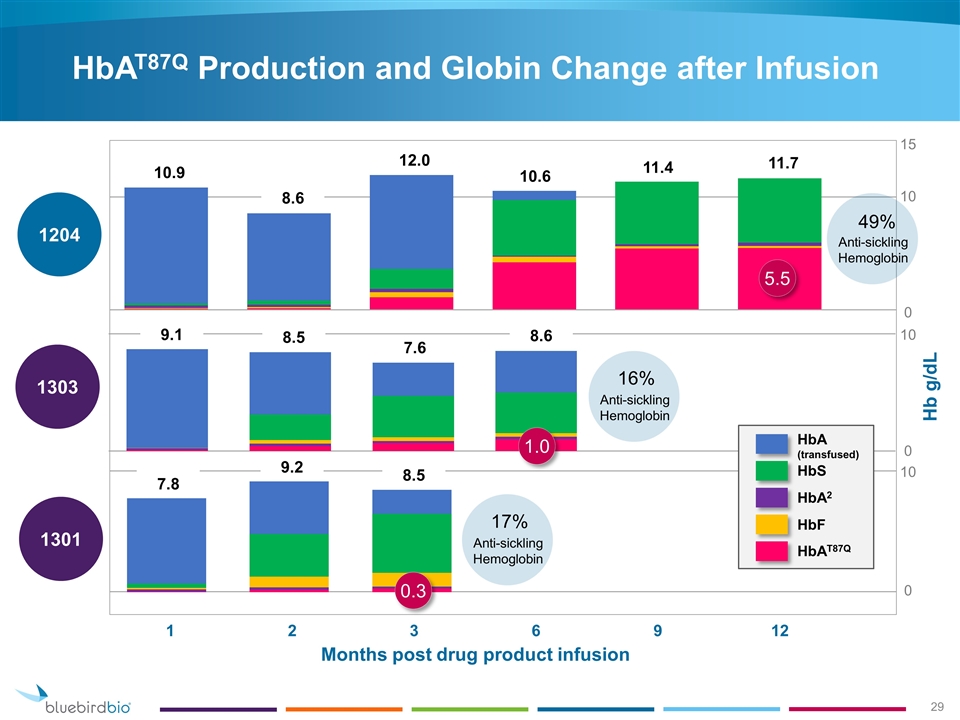
HbAT87Q Production and Globin Change after Infusion 1301 1303 1204 10 0 10 0 15 0 Months post drug product infusion Hb g/dL 1 2 3 6 9 12 10.9 12.0 10.6 11.4 11.7 9.1 8.5 7.6 5.5 10 8.6 7.8 9.2 8.5 HbAT87Q HbF HbA2 HbS HbA (transfused) 1.0 0.3 8.6 49% Anti-sickling Hemoglobin 16% Anti-sickling Hemoglobin 17% Anti-sickling Hemoglobin
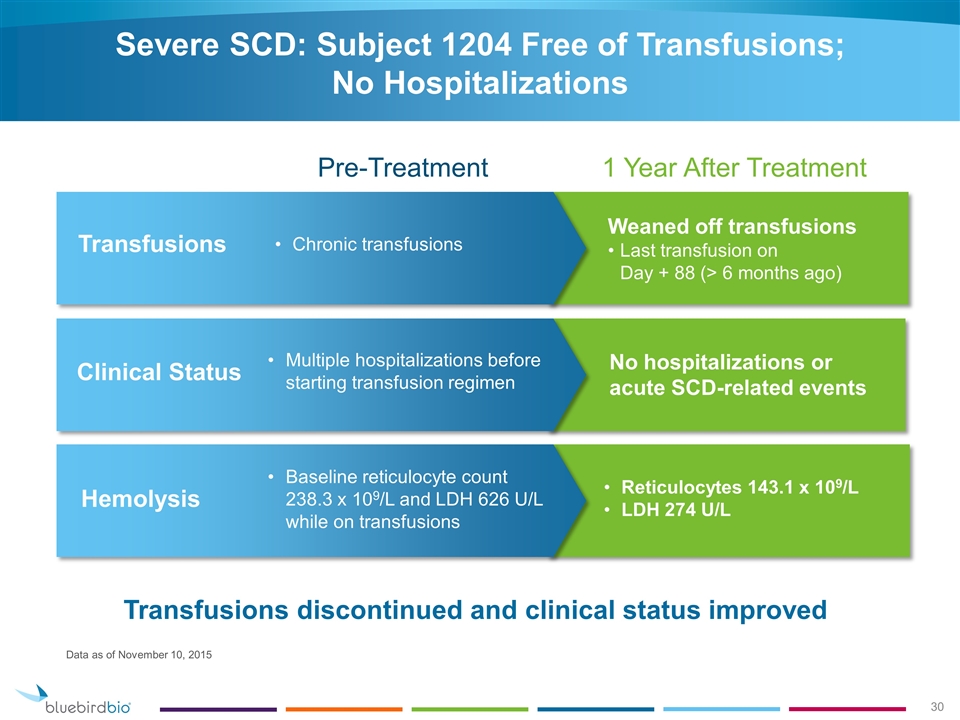
Weaned off transfusions Last transfusion on Day + 88 (> 6 months ago) Severe SCD: Subject 1204 Free of Transfusions; No Hospitalizations Transfusions Chronic transfusions Clinical Status Multiple hospitalizations before starting transfusion regimen Pre-Treatment 1 Year After Treatment Data as of November 10, 2015 Transfusions discontinued and clinical status improved Reticulocytes 143.1 x 109/L LDH 274 U/L Hemolysis Baseline reticulocyte count 238.3 x 109/L and LDH 626 U/L while on transfusions No hospitalizations or acute SCD-related events
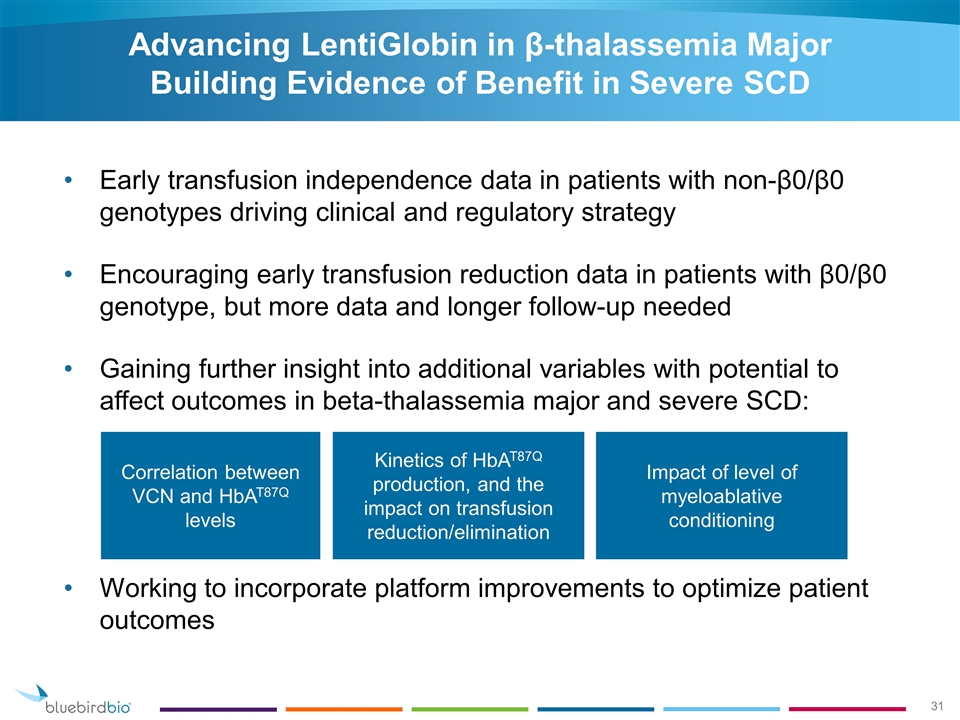
Advancing LentiGlobin in β-thalassemia Major Building Evidence of Benefit in Severe SCD Early transfusion independence data in patients with non-β0/β0 genotypes driving clinical and regulatory strategy Encouraging early transfusion reduction data in patients with β0/β0 genotype, but more data and longer follow-up needed Gaining further insight into additional variables with potential to affect outcomes in beta-thalassemia major and severe SCD: Working to incorporate platform improvements to optimize patient outcomes Correlation between VCN and HbAT87Q levels Kinetics of HbAT87Q production, and the impact on transfusion reduction/elimination Impact of level of myeloablative conditioning

Research Platform Philip Gregory, D. Phil. Chief Scientific Officer
Drive toward sustainable IND engine with ability to feed pipeline for bluebird’s future Research Platform and Strategy mRNA SynBio Lentivirus T Cell HSC Platform T Cell Platform Future Pipeline MegaTALs Strengthening existing platforms HSC Ex Vivo
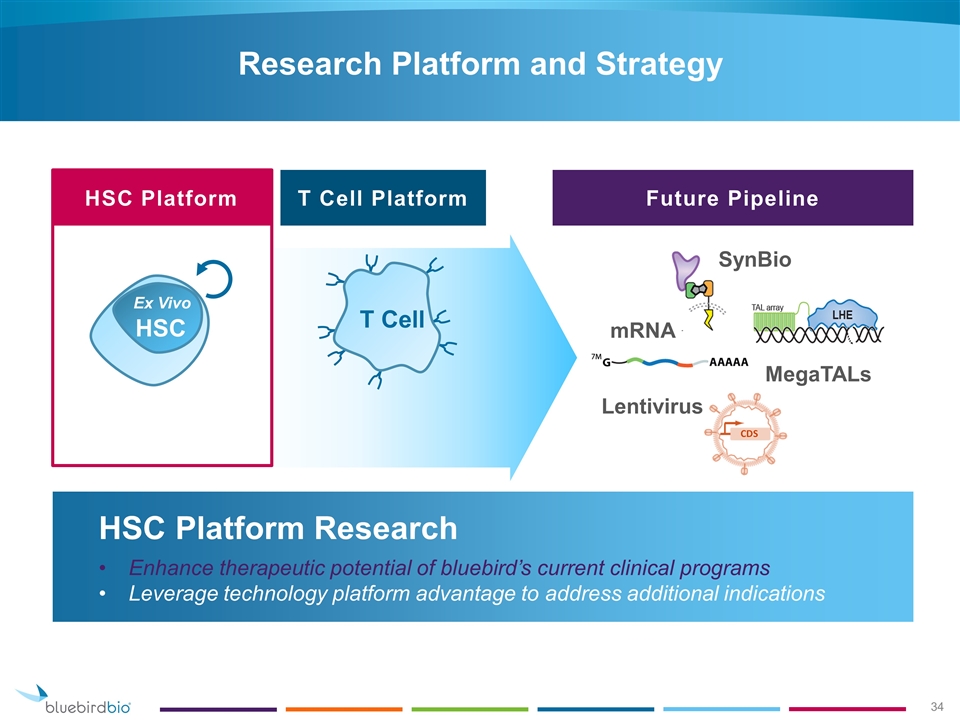
HSC Platform Research Enhance therapeutic potential of bluebird’s current clinical programs Leverage technology platform advantage to address additional indications Research Platform and Strategy HSC Ex Vivo T Cell HSC Platform T Cell Platform Future Pipeline mRNA SynBio Lentivirus MegaTALs
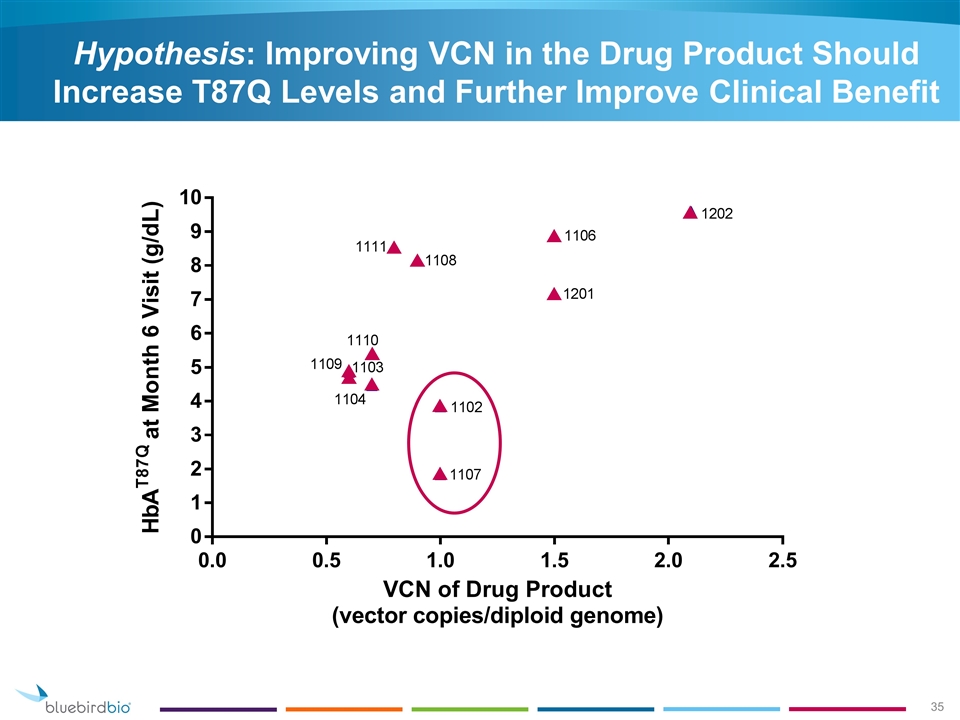
Hypothesis: Improving VCN in the Drug Product Should Increase T87Q Levels and Further Improve Clinical Benefit
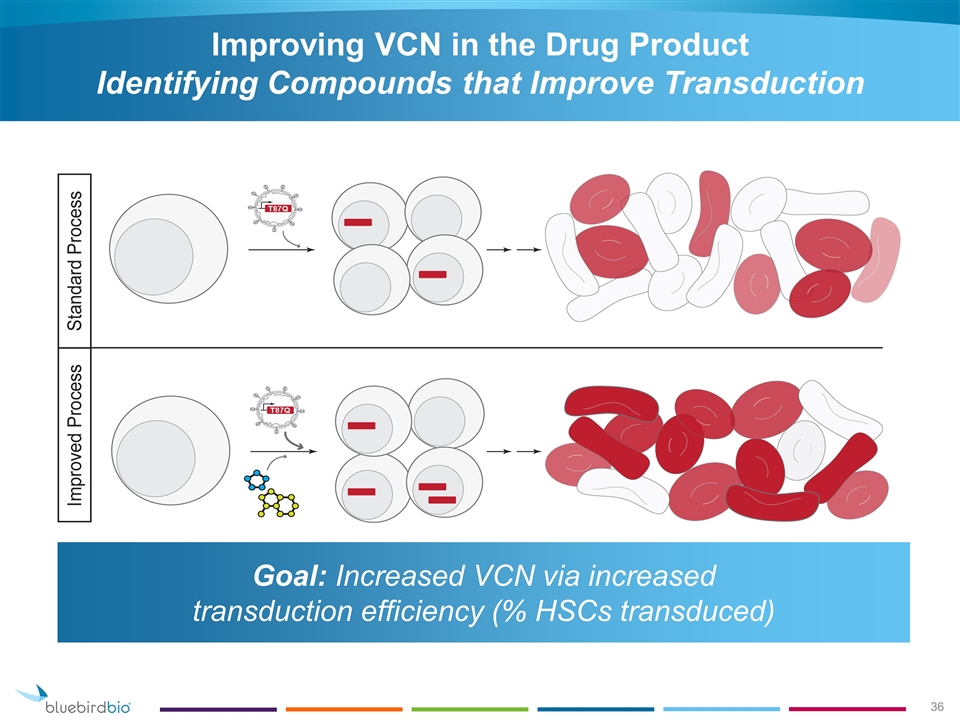
Improving VCN in the Drug Product Identifying Compounds that Improve Transduction Goal: Increased VCN via increased transduction efficiency (% HSCs transduced)
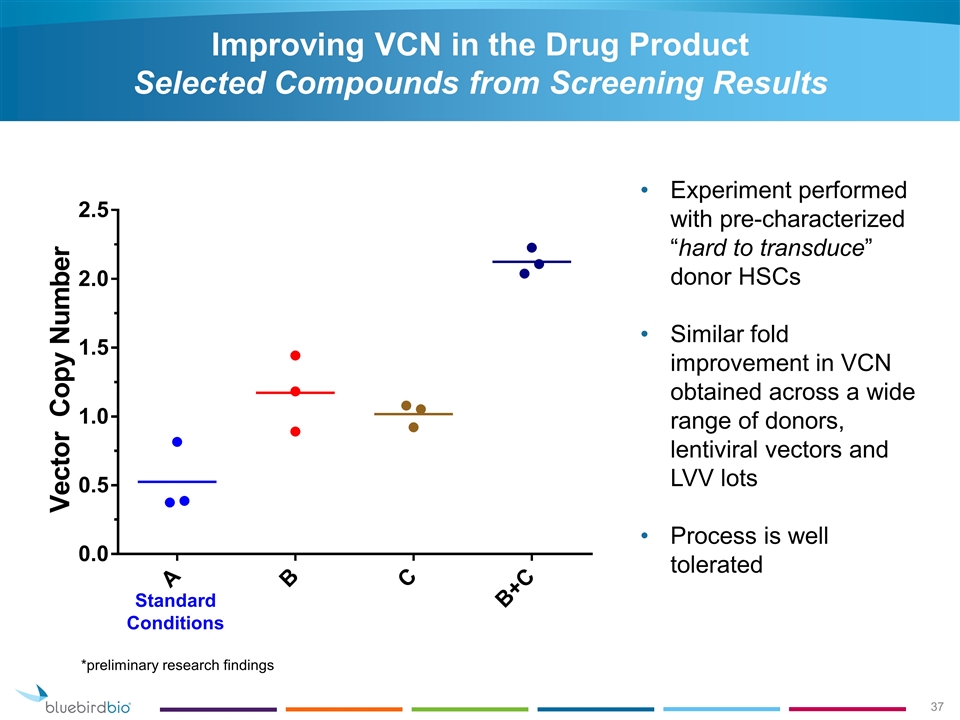
Improving VCN in the Drug Product Selected Compounds from Screening Results Experiment performed with pre-characterized “hard to transduce” donor HSCs Similar fold improvement in VCN obtained across a wide range of donors, lentiviral vectors and LVV lots Process is well tolerated Standard Conditions *preliminary research findings
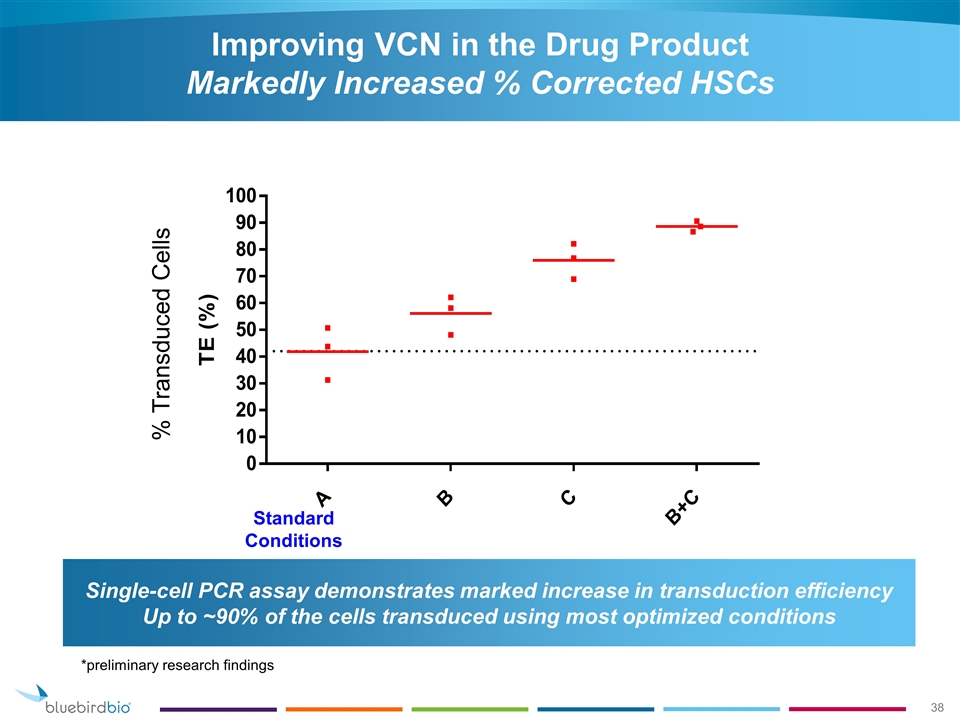
Improving VCN in the Drug Product Markedly Increased % Corrected HSCs % Transduced Cells Standard Conditions Single-cell PCR assay demonstrates marked increase in transduction efficiency Up to ~90% of the cells transduced using most optimized conditions *preliminary research findings
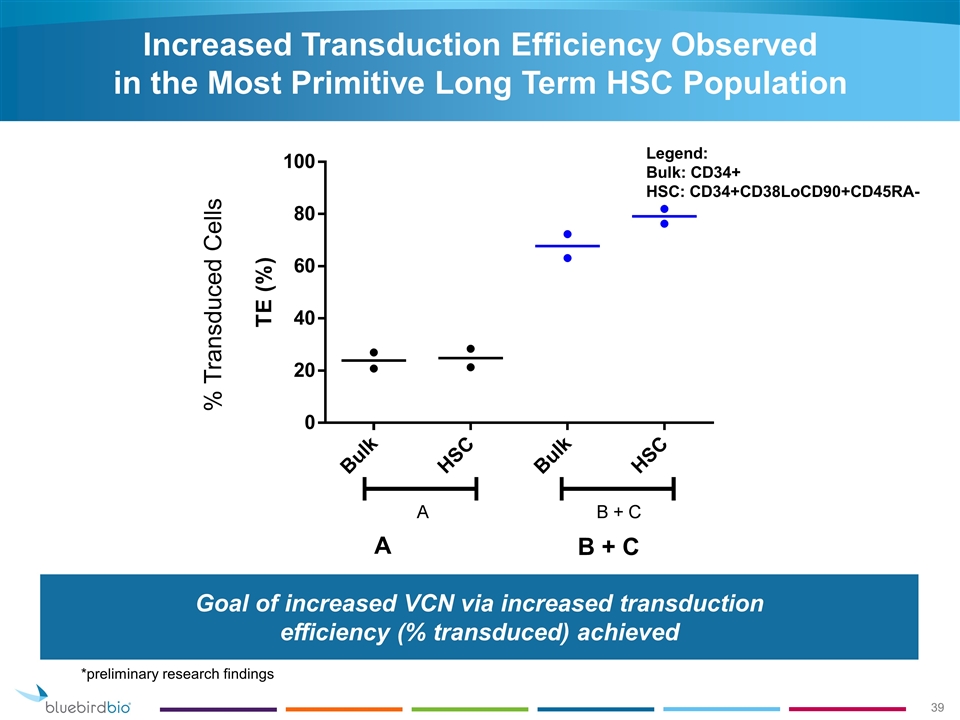
Goal of increased VCN via increased transduction efficiency (% transduced) achieved Legend: Bulk: CD34+ HSC: CD34+CD38LoCD90+CD45RA- Increased Transduction Efficiency Observed in the Most Primitive Long Term HSC Population % Transduced Cells A B + C *preliminary research findings
Improving VCN in the Drug Product Key Takeaways Several different compounds identified that increase VCN in the drug product (both alone and in combination) Importantly, increased VCN is achieved in part by increasing the number of transduced cells (% HSCs carrying LentiGlobin) Long term HSCs show a similar magnitude of improvement in both VCN and % transduced cells Improving VCN in the drug product should increase T87Q levels and further improve clinical benefit
T cell Platform Research Intensely competitive space but with potential for transformative benefit Opportunity to exploit breadth of bbb technology platforms to potentially create “best in class” differentiated products Research Platform and Strategy HSC Ex Vivo T Cell HSC Platform T Cell Platform Future Pipeline mRNA SynBio Lentivirus MegaTALs

Manufacturing of an Enhanced CAR T Cell Product by Inhibiting PI3K / AKT Pathway During T Cell Expansion Results in Improved In Vivo Efficacy of Anti-BCMA CAR T Cells Adoptive Immunotherapy Program: Oral and Poster Abstracts Session: 703. Adoptive Immunotherapy: Poster I Saturday, December 5, 2015, 5:30 PM-7:30 PM Hall A, Level 2 (Orange County Convention Center) Molly R. Perkins, D.Phil.1*, Shannon Grande, Ph.D.1*, Amanda Hamel, BS2*, Holly M. Horton, PhD2, Tracy E. Garrett, BA2*, Sara M. Miller1*, Howard J. Latimer IV, BS2*, Christopher J. Horvath, DVM, MS, DACVP2*, Michael Kuczewski, MS2*, Kevin M. Friedman, PhD2* and Richard A. Morgan, PhD2* 1bluebird bio, Cambridge, MA 2bluebird bio, Inc, Cambridge, MA Example 1: T Cell Lineages for Improved Anti-Tumor Activity
Example 2: bluebird Gene Editing Approach MegaTAL Technology Expertise in homing endonucleases (HE) and MegaTALs Robust nuclease discovery platform, proprietary database, broad IP Multiple advantages of HE and MegaTALs Naturally occurring proteins Highly specific and efficient Compact size Broad range of therapeutic applications Complementary to existing programs MegaTAL
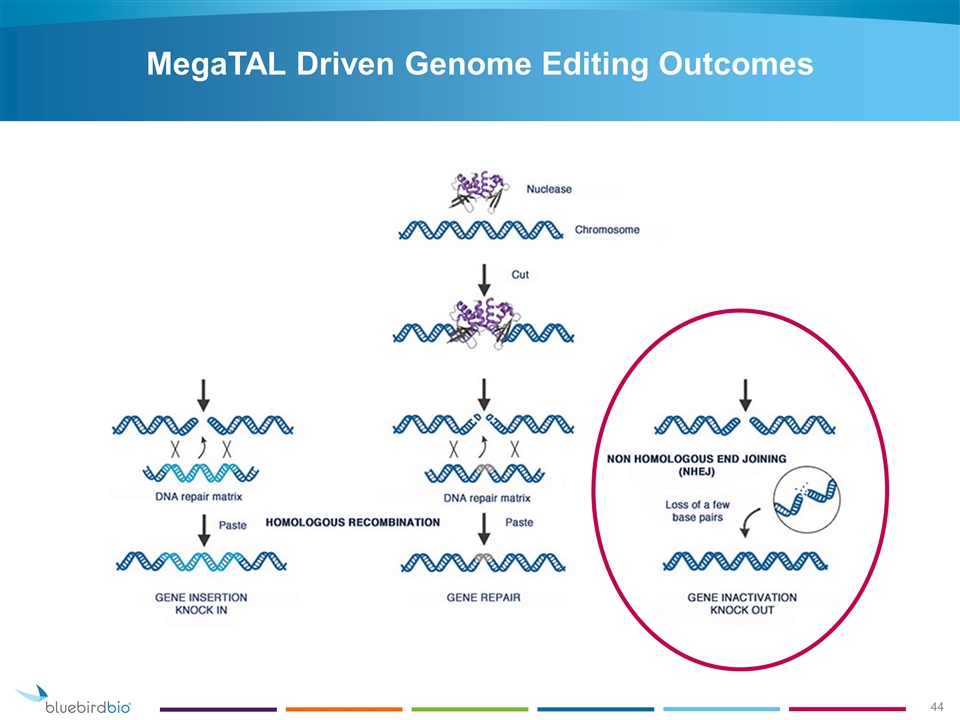
MegaTAL Driven Genome Editing Outcomes
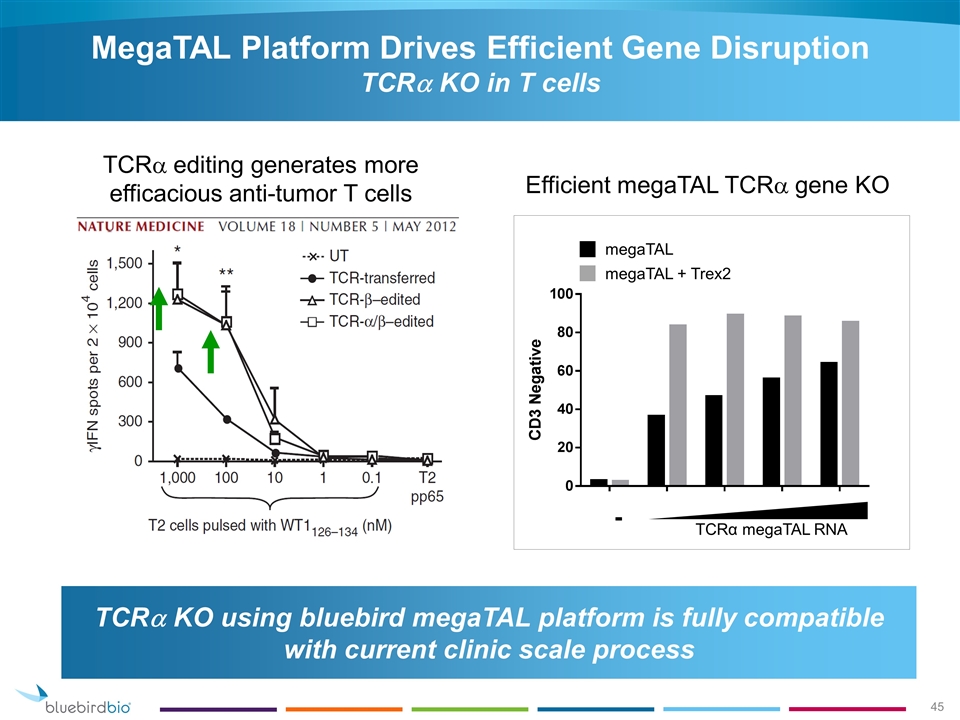
MegaTAL Platform Drives Efficient Gene Disruption TCRa KO in T cells c - TCRα megaTAL RNA megaTAL megaTAL + Trex2 Efficient megaTAL TCRa gene KO TCRa editing generates more efficacious anti-tumor T cells TCRa KO using bluebird megaTAL platform is fully compatible with current clinic scale process

Improving MegaTAL Design Density 4 bp DNA cleavage site NON-PROGRAMMABLE 12 bp TAL target recognition 18 bp HE target recognition megaTAL: 30 bp fully programmable DNA sequence recognition wild type HE central-4 targetable sequences Improved megaTAL platform enhances applicability across the universe of T cell targets and beyond bluebird expanded central-4 sequences
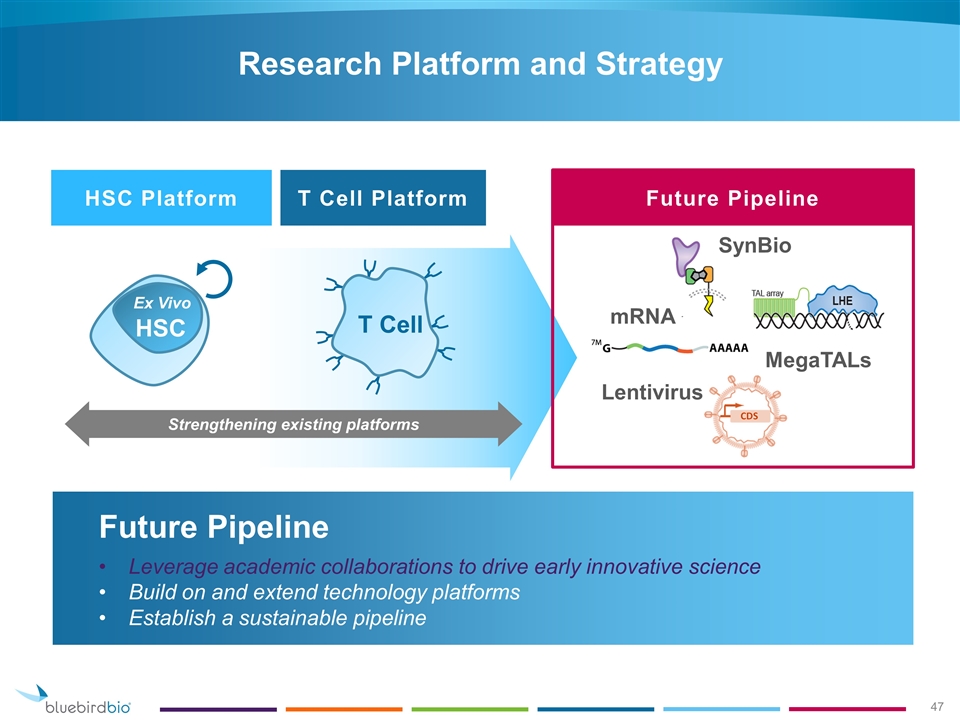
Future Pipeline Leverage academic collaborations to drive early innovative science Build on and extend technology platforms Establish a sustainable pipeline Research Platform and Strategy HSC Ex Vivo T Cell Strengthening existing platforms HSC Platform T Cell Platform Future Pipeline mRNA SynBio Lentivirus MegaTALs

Celgene, bluebird bio, and the Center for Cell and Gene Therapy Combine Strengths and Resources to Develop T-cell Based Therapies for Cancer On March 19, 2013, BCM signed an exclusive multiyear research and collaboration agreement and a platform technology license agreement with Celgene Corporation that launches the commercial development of novel immunotherapies involving manipulated T-cells that express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR CTLs)… Leveraging Select Academic Collaborations Operating at the Forefront of Innovation Seattle Children’s Research Institute Teams Up With bluebird bio to Pioneer Genome Editing and Gene Therapy Research in Pediatric Diseases 9.10.15 Gene therapy research aims to cure pediatric diseases early in life by targeting and repairing the disease-causing genes in a patient’s own genome…
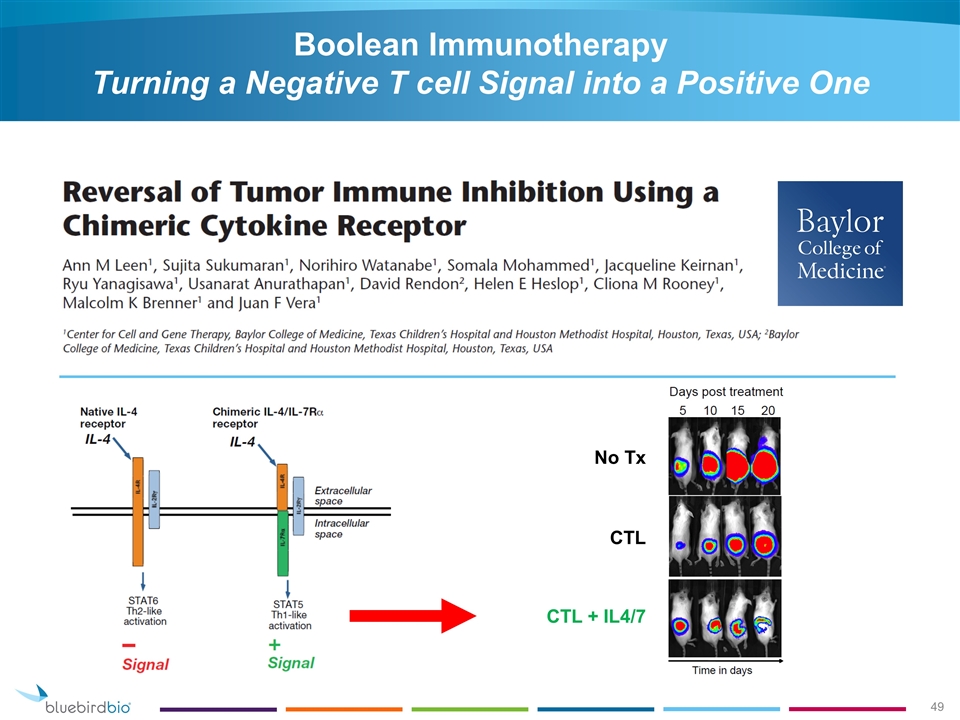
Boolean Immunotherapy Turning a Negative T cell Signal into a Positive One No Tx CTL CTL + IL4/7
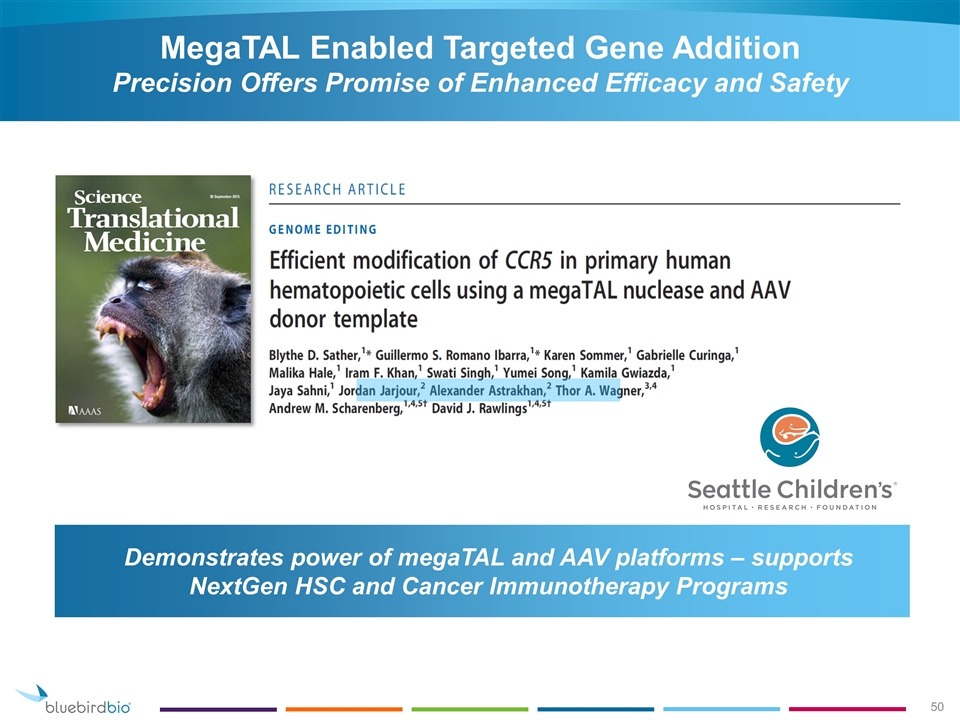
Demonstrates power of megaTAL and AAV platforms – supports NextGen HSC and Cancer Immunotherapy Programs MegaTAL Enabled Targeted Gene Addition Precision Offers Promise of Enhanced Efficacy and Safety
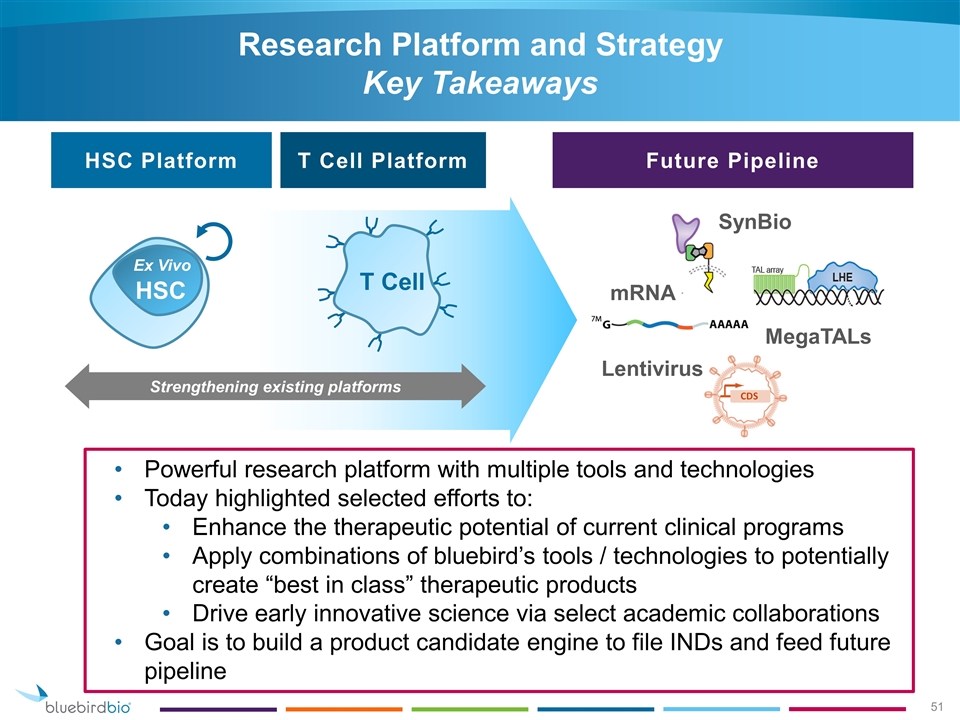
Research Platform and Strategy Key Takeaways mRNA SynBio Lentivirus T Cell HSC Platform T Cell Platform Future Pipeline MegaTALs Strengthening existing platforms HSC Ex Vivo Powerful research platform with multiple tools and technologies Today highlighted selected efforts to: Enhance the therapeutic potential of current clinical programs Apply combinations of bluebird’s tools / technologies to potentially create “best in class” therapeutic products Drive early innovative science via select academic collaborations Goal is to build a product candidate engine to file INDs and feed future pipeline

Immuno-Oncology Richard Morgan, Ph.D. Vice President, Immunotherapy Rob Ross, M.D. Head of Oncology
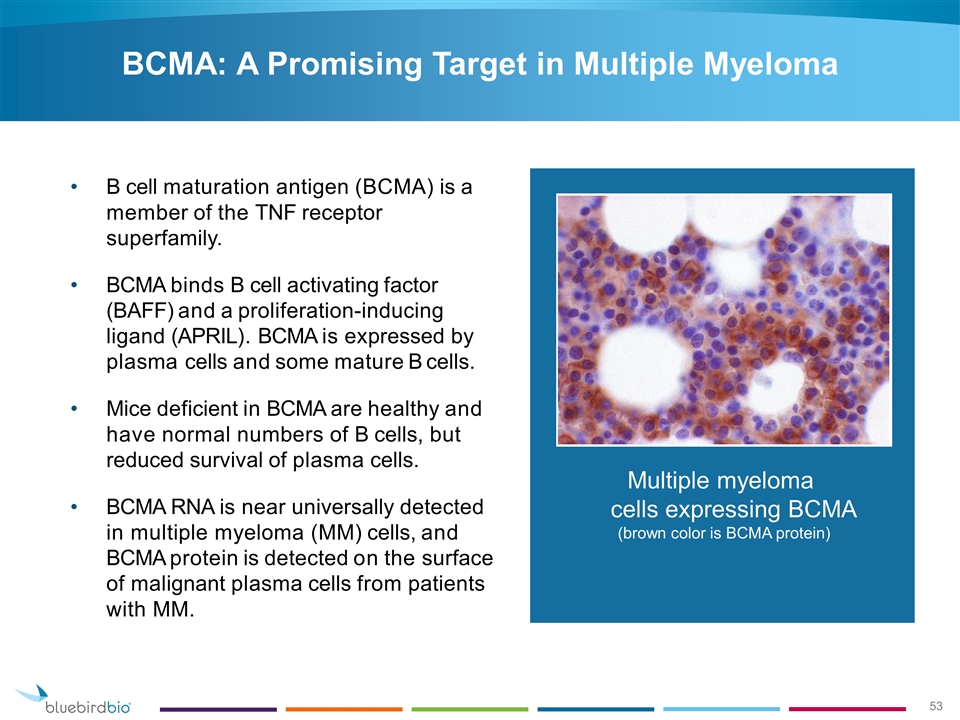
B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) is a member of the TNF receptor superfamily. BCMA binds B cell activating factor (BAFF) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL). BCMA is expressed by plasma cells and some mature B cells. Mice deficient in BCMA are healthy and have normal numbers of B cells, but reduced survival of plasma cells. BCMA RNA is near universally detected in multiple myeloma (MM) cells, and BCMA protein is detected on the surface of malignant plasma cells from patients with MM. Multiple myeloma cells expressing BCMA (brown color is BCMA protein) BCMA: A Promising Target in Multiple Myeloma
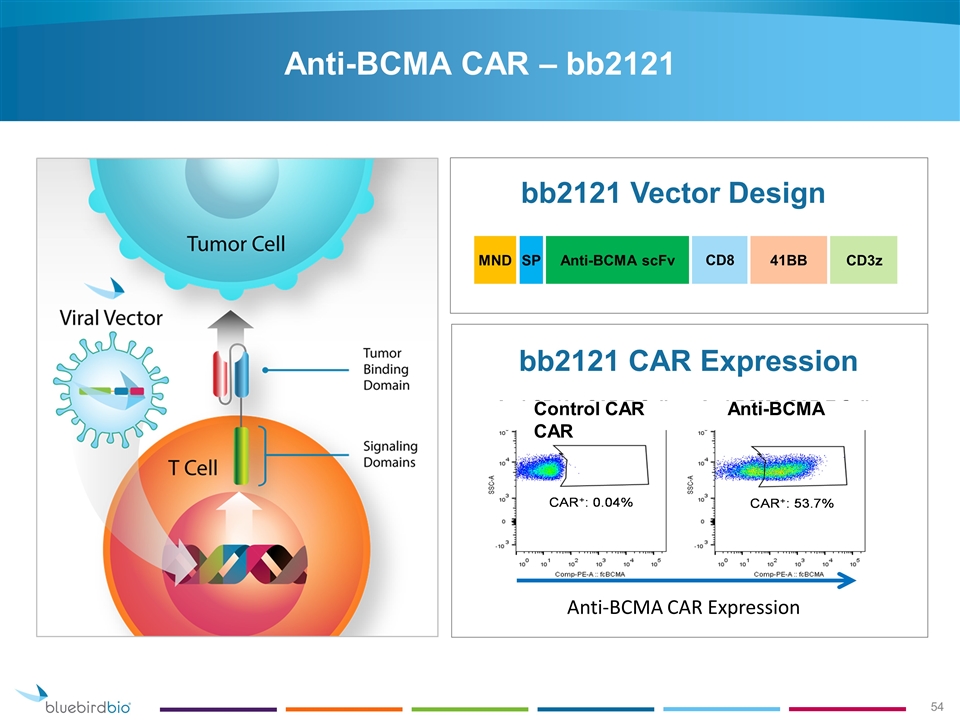
bb2121 Vector Design SP Anti-BCMA scFv CD3z 41BB MND CD8 bb2121 CAR Expression Control CAR Anti-BCMA CAR Anti-BCMA CAR Expression Anti-BCMA CAR – bb2121
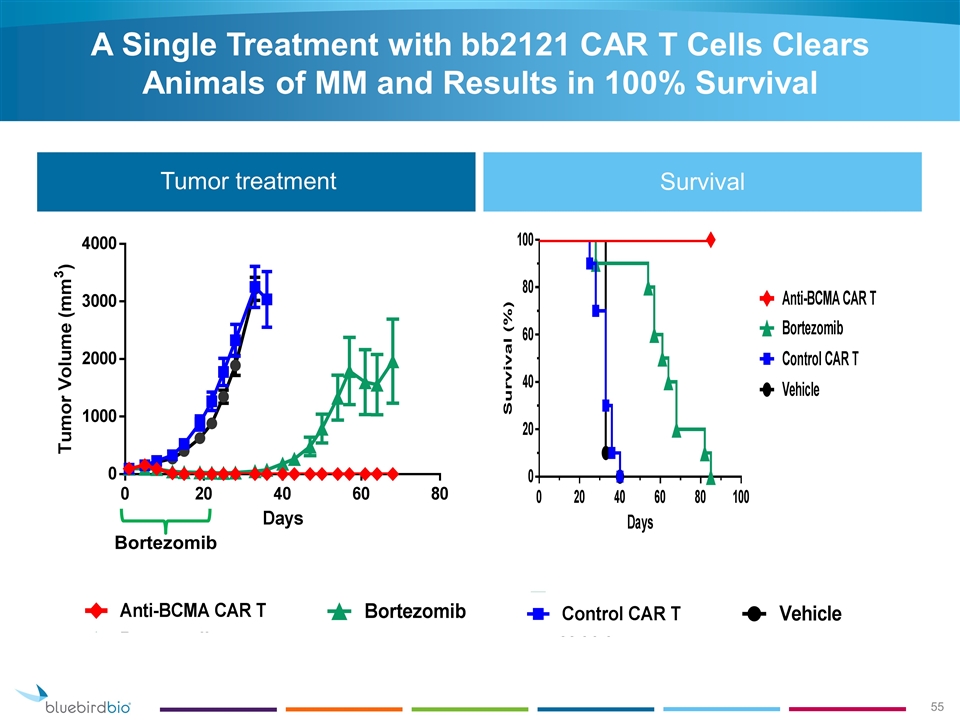
Tumor treatment Bortezomib A Single Treatment with bb2121 CAR T Cells Clears Animals of MM and Results in 100% Survival Survival
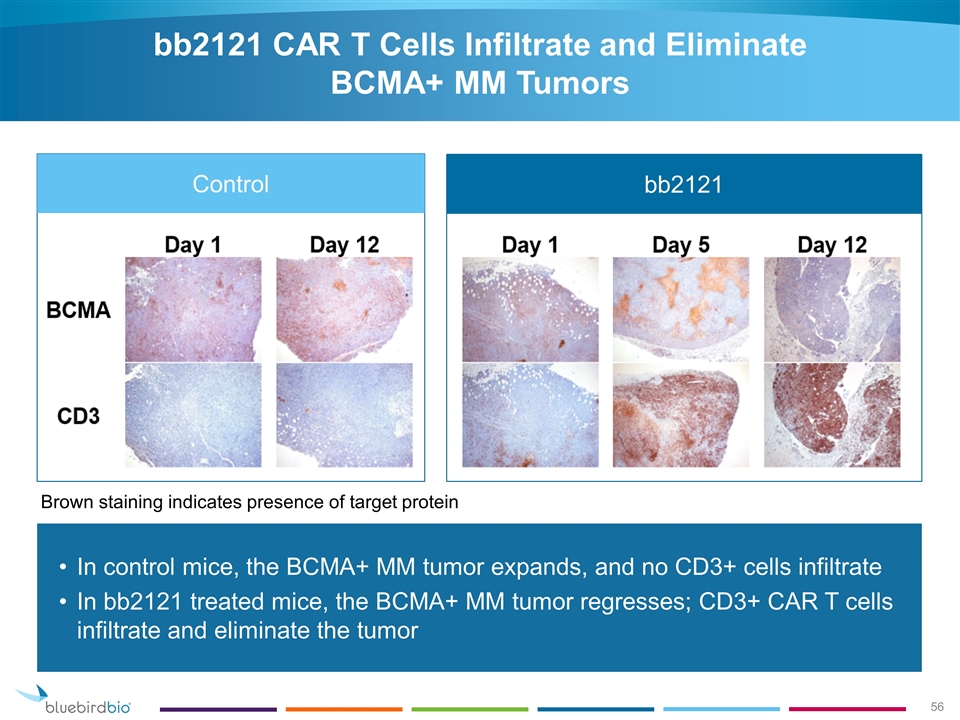
bb2121 CAR T Cells Infiltrate and Eliminate BCMA+ MM Tumors In control mice, the BCMA+ MM tumor expands, and no CD3+ cells infiltrate In bb2121 treated mice, the BCMA+ MM tumor regresses; CD3+ CAR T cells infiltrate and eliminate the tumor Brown staining indicates presence of target protein bb2121 Control
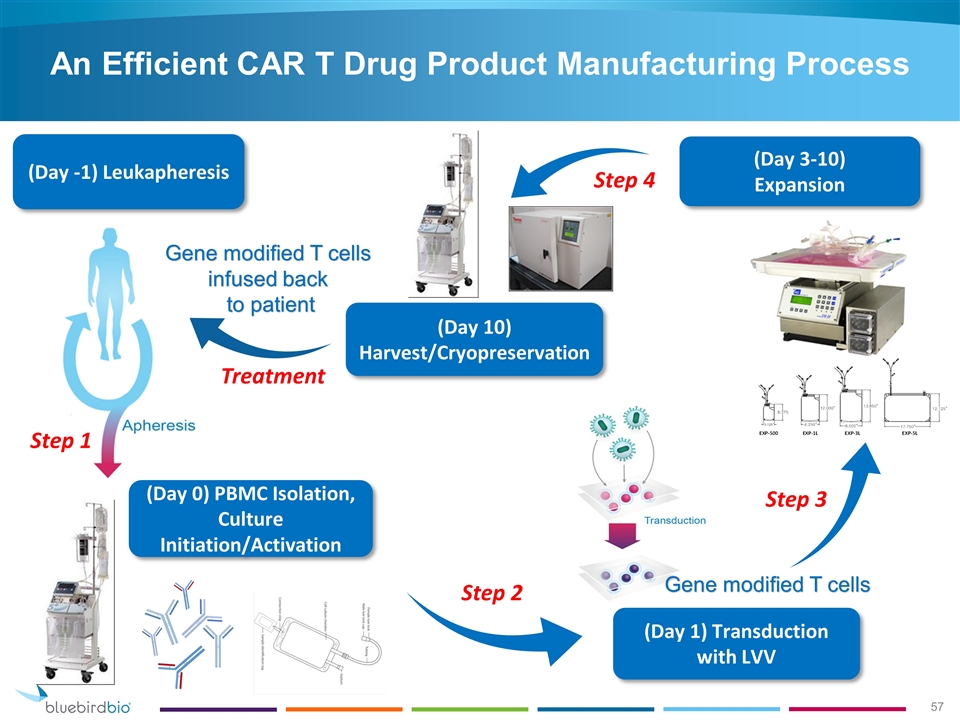
(Day 3-10) Expansion (Day 10) Harvest/Cryopreservation (Day -1) Leukapheresis Gene modified T cells infused back to patient (Day 0) PBMC Isolation, Culture Initiation/Activation (Day 1) Transduction with LVV Gene modified T cells Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Treatment An Efficient CAR T Drug Product Manufacturing Process
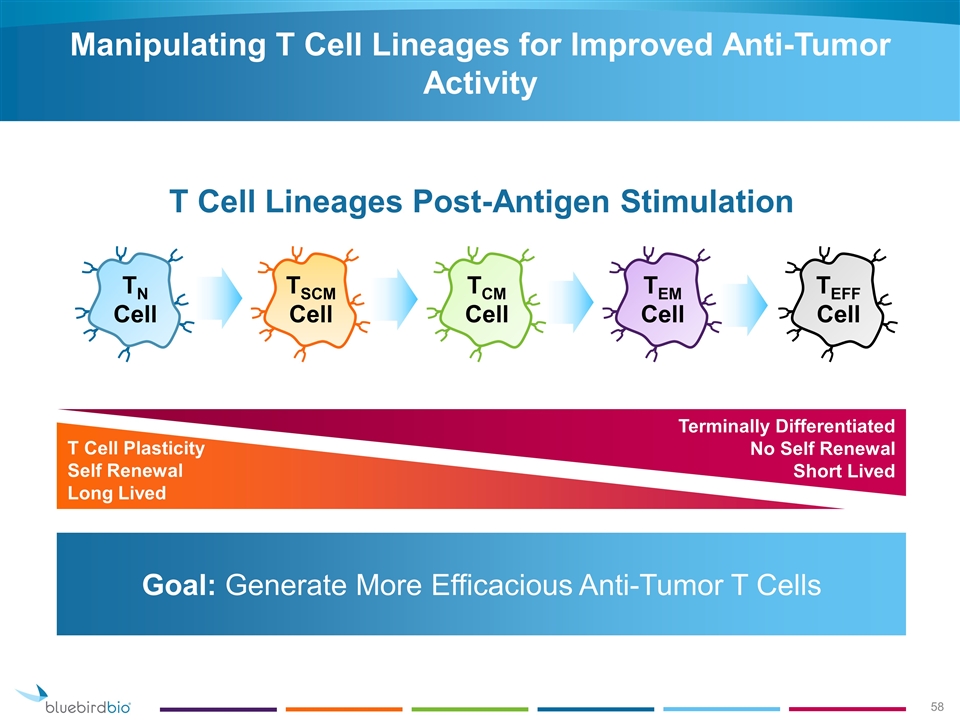
Goal: Generate More Efficacious Anti-Tumor T Cells Manipulating T Cell Lineages for Improved Anti-Tumor Activity T Cell Lineages Post-Antigen Stimulation TN Cell TSCM Cell TCM Cell TEM Cell TEFF Cell T Cell Plasticity Self Renewal Long Lived Terminally Differentiated No Self Renewal Short Lived
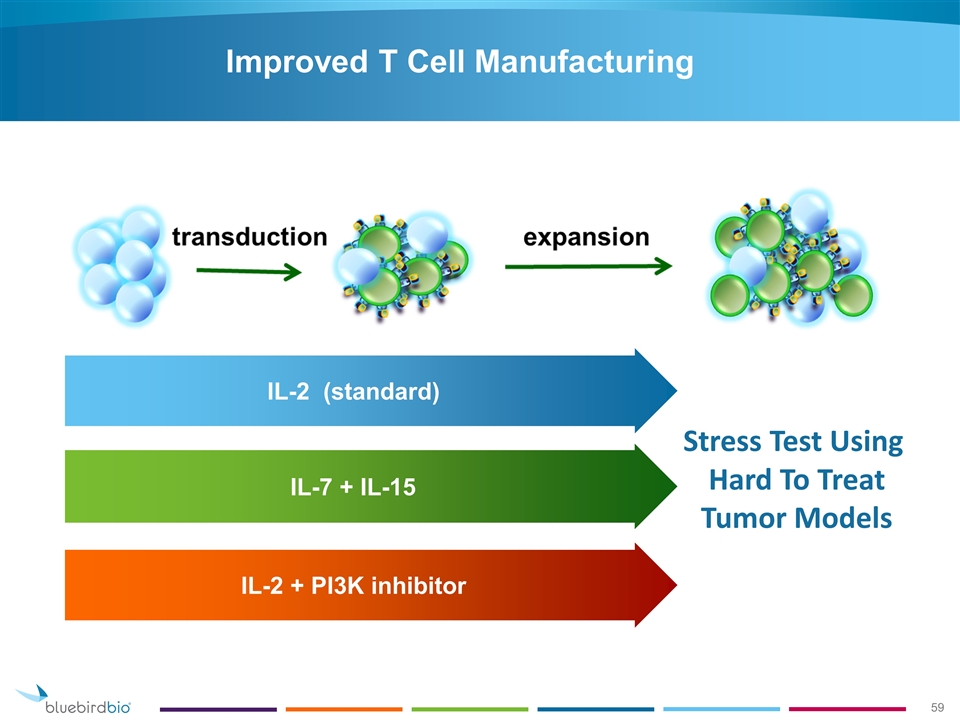
Improved T Cell Manufacturing IL-2 (standard) IL-2 + PI3K inhibitor IL-7 + IL-15 Stress Test Using Hard To Treat Tumor Models
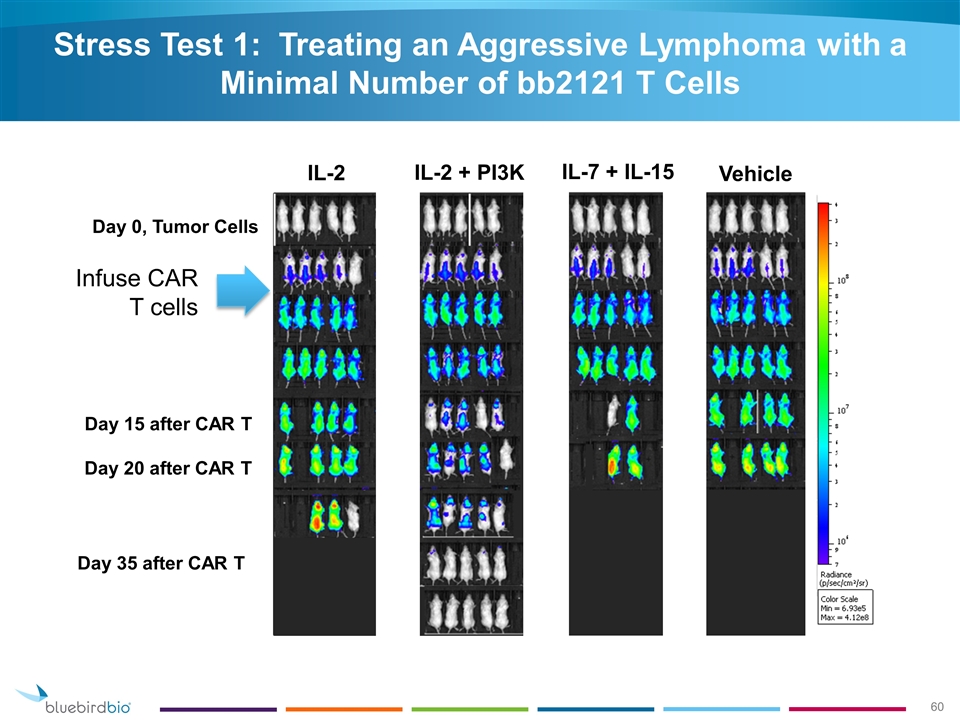
Infuse CAR T cells Day 20 after CAR T Day 35 after CAR T Day 15 after CAR T Day 0, Tumor Cells Stress Test 1: Treating an Aggressive Lymphoma with a Minimal Number of bb2121 T Cells IL-2 IL-2 + PI3K IL-7 + IL-15 Vehicle
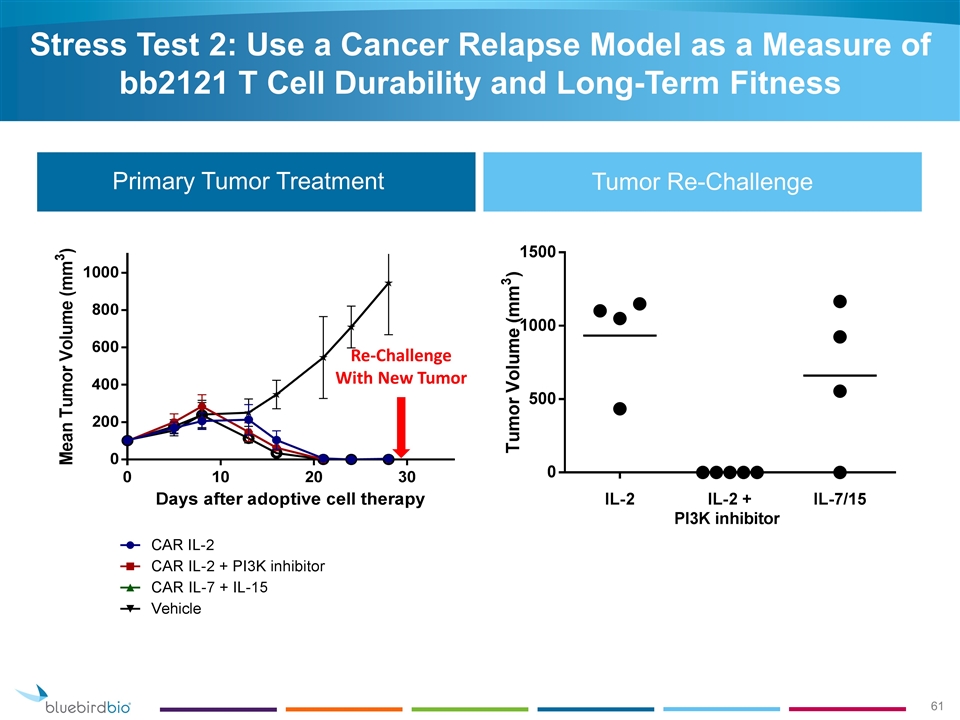
Primary Tumor Treatment Tumor Re-Challenge Re-Challenge With New Tumor Stress Test 2: Use a Cancer Relapse Model as a Measure of bb2121 T Cell Durability and Long-Term Fitness

Deepening Pipeline
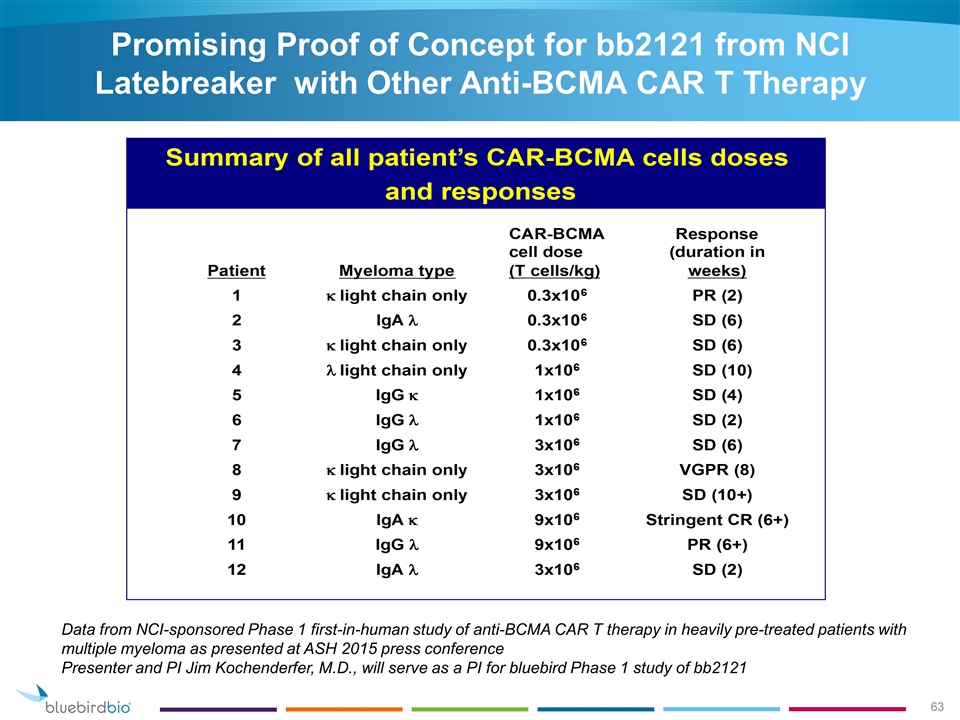
Promising Proof of Concept for bb2121 from NCI Latebreaker with Other Anti-BCMA CAR T Therapy Data from NCI-sponsored Phase 1 first-in-human study of anti-BCMA CAR T therapy in heavily pre-treated patients with multiple myeloma as presented at ASH 2015 press conference Presenter and PI Jim Kochenderfer, M.D., will serve as a PI for bluebird Phase 1 study of bb2121
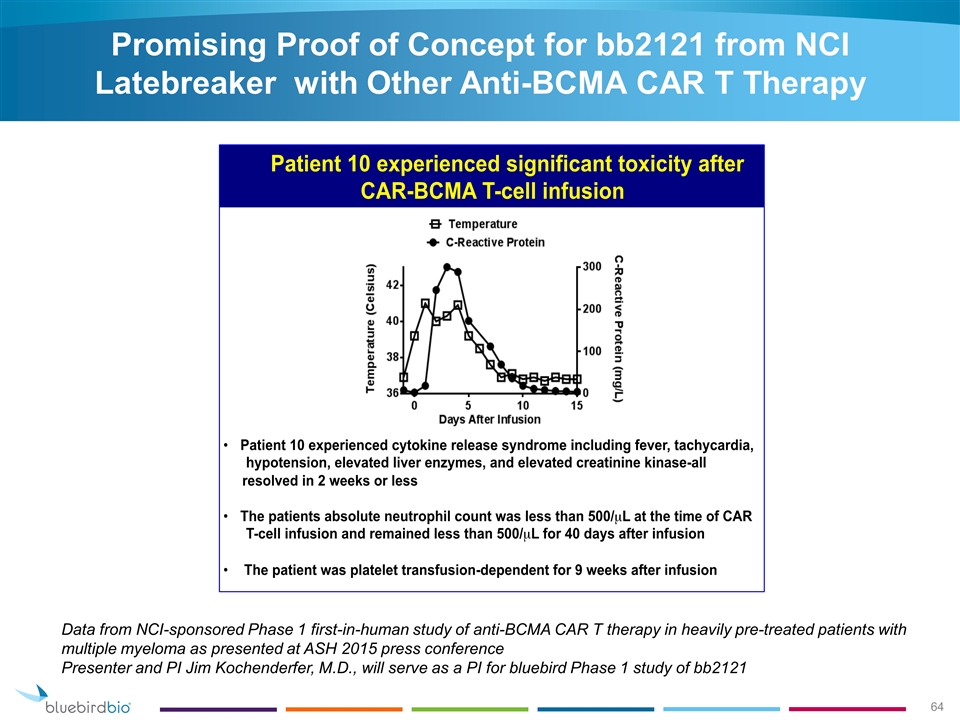
Promising Proof of Concept for bb2121 from NCI Latebreaker with Other Anti-BCMA CAR T Therapy Data from NCI-sponsored Phase 1 first-in-human study of anti-BCMA CAR T therapy in heavily pre-treated patients with multiple myeloma as presented at ASH 2015 press conference Presenter and PI Jim Kochenderfer, M.D., will serve as a PI for bluebird Phase 1 study of bb2121
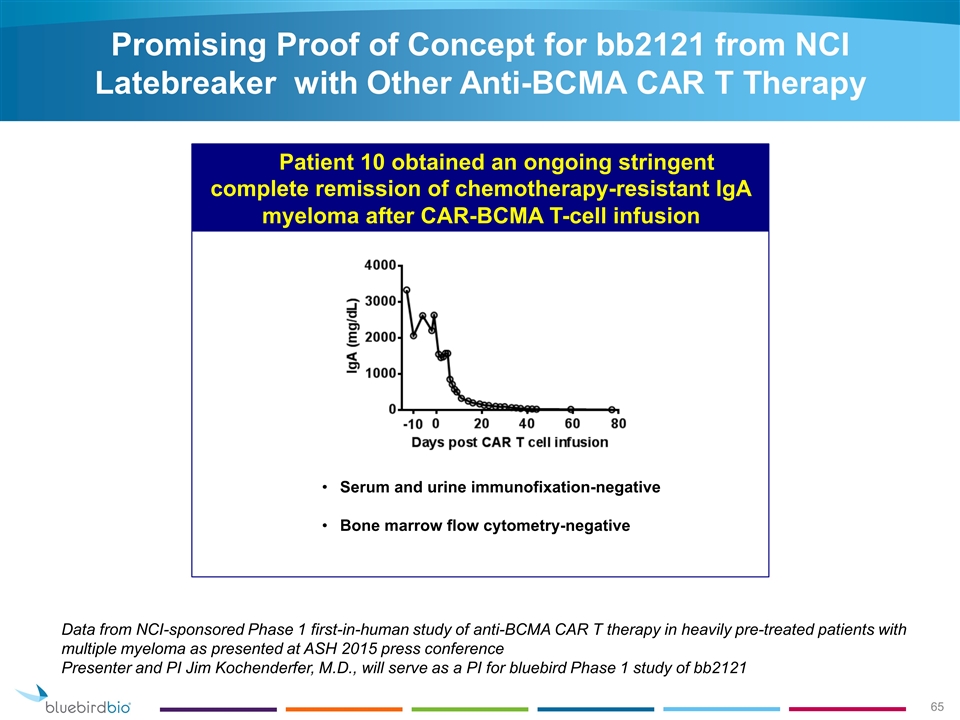
Promising Proof of Concept for bb2121 from NCI Latebreaker with Other Anti-BCMA CAR T Therapy Data from NCI-sponsored Phase 1 first-in-human study of anti-BCMA CAR T therapy in heavily pre-treated patients with multiple myeloma as presented at ASH 2015 press conference Presenter and PI Jim Kochenderfer, M.D., will serve as a PI for bluebird Phase 1 study of bb2121
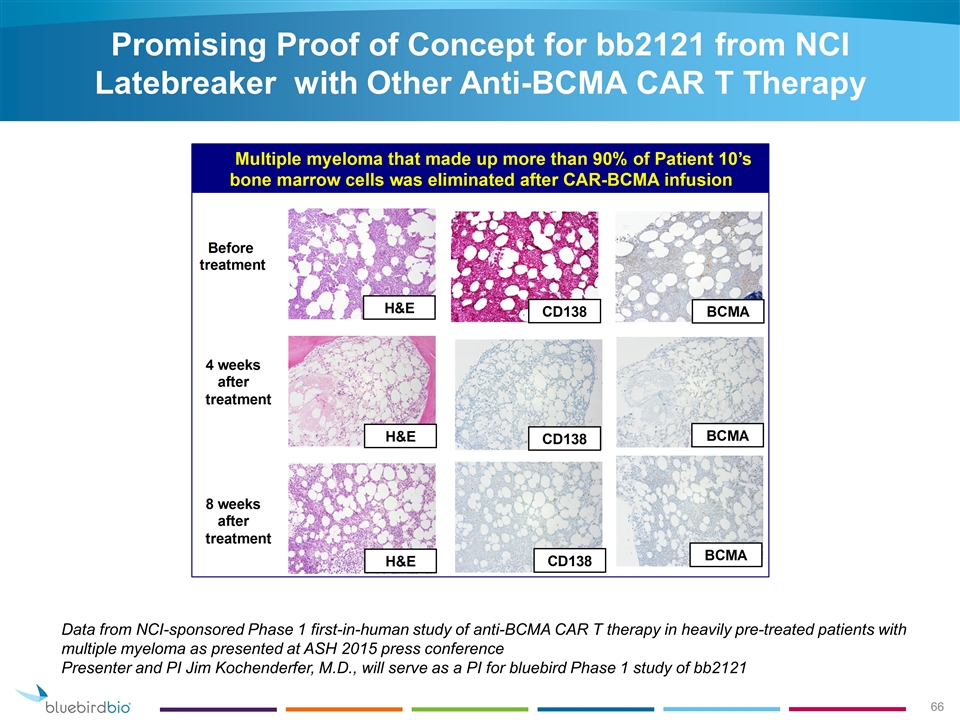
Promising Proof of Concept for bb2121 from NCI Latebreaker with Other Anti-BCMA CAR T Therapy Data from NCI-sponsored Phase 1 first-in-human study of anti-BCMA CAR T therapy in heavily pre-treated patients with multiple myeloma as presented at ASH 2015 press conference Presenter and PI Jim Kochenderfer, M.D., will serve as a PI for bluebird Phase 1 study of bb2121

U.S.-based, 6-10 clinical sites – including NCI N = 40 patients, standard 3+3 Design based on CAR+ T cells doses Primary endpoint = Determine the maximally tolerated dose and recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) Subjects must have received 3 prior regimens including a proteasome inhibitor (bortezomib, carfilzomib) and immunomodulatory agent (lenalidomide, pomalidomide) Following screening, enrolled subjects will undergo a leukapheresis procedure to collect autologous mononuclear cells for manufacturing of bb2121. Following manufacture of the drug product, subjects will receive one cycle of lymphodepletion prior to bb2121 infusion CRB-401 (Refractory Multiple Myeloma) bluebird bio’s First Oncology Clinical Trial

Deliver differentiated, best-in-class, genetically modified cellular products to patients suffering from cancer. Differentiated Oncology Approach BCMA (Partnered with Celgene) HPV Partnered with Kite Five Prime Target Viromed Target LVV Technology Manufacturing Advances (Pl3K) LVV Technology Manufacturing Advances (Pl3K) LVV Technology Manufacturing Advances (Pl3K) LVV Technology Manufacturing Advances (Pl3K) Gene Editing Technology Gene Editing Technology Synthetic Biology
Deliver differentiated, best-in-class, genetically modified cellular products to patients suffering from cancer. Five Prime Target Viromed Target BCMA (Partnered with Celgene) HPV Partnered with Kite Differentiated Oncology Approach

Closing Nick Leschly Chief Bluebird

Asking the Important Questions What is the β-thalassemia clinical/regulatory path forward? What is the SCD data telling us? What are you doing to improve your platform? What are you doing to build a sustainable pipeline? What is the plan for oncology/BCMA?
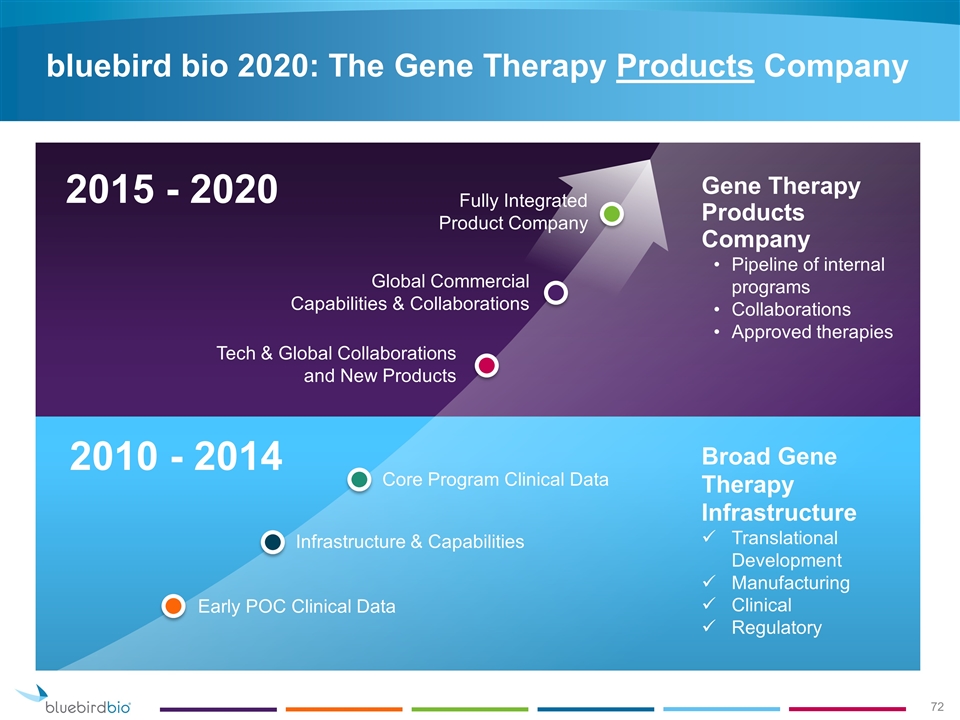
2010 - 2014 bluebird bio 2020: The Gene Therapy Products Company 2015 - 2020 Early POC Clinical Data Infrastructure & Capabilities Core Program Clinical Data Broad Gene Therapy Infrastructure Translational Development Manufacturing Clinical Regulatory Tech & Global Collaborations and New Products Global Commercial Capabilities & Collaborations Fully Integrated Product Company Gene Therapy Products Company Pipeline of internal programs Collaborations Approved therapies

Q&A