Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
x | | Annual Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of | | |
| | the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 | | |
| | | | |
| | For the fiscal year ended February 1, 2014 | | |
| | | | |
| | Or | | |
| | | | |
o | | Transition Report Pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of | | |
| | the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 | | |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 000-51315
CITI TRENDS, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware | | 52-2150697 |
(State or other jurisdiction of | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
incorporation or organization) | | |
| | |
104 Coleman Boulevard, Savannah, Georgia | | 31408 |
(Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code (912) 236-1561
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | | Name of each exchange
on which registered |
Common Stock, $.01 Par Value | | NASDAQ Stock Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer o | | Accelerated filer x |
| | |
Non-accelerated filer o
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | | Smaller reporting company o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No x
State the aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter: $211,981,707 as of August 2, 2013.
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date: Common Stock, par value $.01 per share, 15,580,948 shares outstanding as of March 25, 2014.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III incorporates information from the registrant’s definitive proxy statement, to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the close of the registrant’s fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, with respect to the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on June 4, 2014.
Table of Contents
PART I
Some statements in, or incorporated by reference into, this Annual Report on Form 10-K (this “Report”) of Citi Trends, Inc. (“we”, “us”, or the “Company”) may constitute “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). All statements other than historical facts contained in this Report, including statements regarding our future financial position, business policy and plans and objectives and expectations of management for future operations, are forward-looking statements. The words “believe,” “may,” “could,” “estimate,” “continue,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “expect,” “plan,” “project” and similar expressions, as they relate to us, are intended to identify forward-looking statements. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events, including, among other things: our ability to anticipate and respond to fashion trends, competition in our markets, consumer spending patterns, actions of our competitors or anchor tenants in the strip shopping centers where our stores are located, and anticipated fluctuations in our operating results.
These forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions, including those described in Item 1A. Risk Factors and elsewhere in this Report and the other documents we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), including our reports on Form 8-K and Form 10-Q, and any amendments thereto. Because forward-looking statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties, some of which cannot be predicted or quantified, you should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. The events and circumstances reflected in the forward-looking statements may not be achieved or occur and actual results could differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of such statements. Except as required by applicable law, including the securities laws of the United States and the rules and regulations of the SEC, we do not plan to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements contained in this Report, whether as a result of any new information, future events or otherwise.
Information is provided herein with respect to our operations related to our fiscal years ended on February 1, 2014 (“fiscal 2013”), February 2, 2013 (“fiscal 2012”) and January 28, 2012 (“fiscal 2011”).
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Overview and History
We are a value-priced retailer of urban fashion apparel and accessories for the entire family. Our merchandise offerings are designed to appeal to the fashion preferences of value-conscious consumers, particularly African-Americans. We believe that we provide merchandise at compelling values. Our goal is to provide nationally recognized branded merchandise and non-branded merchandise at discounts to department and specialty stores’ regular prices of 20% to 70%. Our stores average approximately 10,800 square feet of selling space and are typically located in neighborhood shopping centers that are convenient to low and moderate income customers. As of February 1, 2014, we operated 505 stores in both urban and rural markets in 29 states.
Our predecessor, Allied Department Stores, was founded in 1946 and grew into a chain of family apparel stores operating in the Southeast. In 1999, the Company, then consisting of 85 stores, was acquired by a private equity firm. Following this acquisition, management implemented several strategies to focus on the growing urban market and improve our operating and financial performance. After the successful implementation of these strategies and the successful growth of our chain from 85 stores to 212 stores, we completed an initial public offering of our common stock on May 18, 2005.
Our executive offices are located at 104 Coleman Boulevard, Savannah, Georgia 31408 and our telephone number is (912) 236-1561. Our Internet address is http://www.cititrends.com. The reference to our web site address in this Report does not constitute the incorporation by reference of the information contained at the web site in this Report. We make available, free of charge through publication on our web site, copies of our Annual Report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports, as soon as reasonably practicable after we have filed such materials with, or furnished such materials to, the SEC. In addition, you may read and copy any materials we file with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549 or on the SEC’s web site at http://www.sec.gov, and you may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330.
Company Strengths and Strategies
Our goal is to be the leading value-priced retailer of urban fashion apparel and accessories. We believe the following business strengths differentiate us from our competitors and are important to our success:
Focus on Urban Fashion Mix. We focus our merchandise on urban fashions, which we believe appeal to our core customers. We do not attempt to dictate trends, but rather devote considerable effort to identifying emerging trends and ensuring that our apparel assortment is considered timely and fashionable in the urban market. Our merchandising staff tests new emerging merchandise trends
3
Table of Contents
before reordering and actively manages the mix of fashion and branded products in the stores to keep our offering fresh and minimize markdowns.
Superior Value Proposition. As a value-priced retailer, we seek to offer top quality, fashionable merchandise at compelling prices in relation to department and specialty stores. We also offer products under our proprietary brands such as “Citi Steps,” “Red Ape,” “Vintage Harlem,” and “Lil Ms Hollywood.” These private brands enable us to expand our product selection, offer fashion merchandise at lower prices and enhance our product offerings.
Merchandise Mix that Appeals to the Entire Family. We merchandise our stores to create a destination environment capable of meeting the fashion needs of the entire value-conscious family. Each store offers a wide variety of products for men and women, as well as children. Our stores feature sportswear, dresses, outerwear, footwear, intimate apparel, accessories, scrubs and home décor. We believe that the breadth of our merchandise distinguishes our stores from many competitors that offer urban apparel primarily for women, and reduces our exposure to fashion trends and demand cycles in any single category.
Strong and Flexible Sourcing Relationships. We maintain strong sourcing relationships with a large group of suppliers. We have purchased merchandise from over 1,600 vendors in the past 12 months. Purchasing is controlled by a 40-plus member buying team located in one of our three buying offices - New York, New York; Los Angeles, California; and our Savannah, Georgia headquarters. We purchase merchandise through planned programs with vendors at reduced prices and opportunistically through close-outs, with the majority of our merchandise purchased for the current season and a lesser quantity held for sale in future seasons. To foster vendor relationships, we pay vendors promptly and do not ask for typical retail concessions, such as promotional and markdown allowances.
Attractive Fashion Presentation and Store Environment. We seek to provide a fashion-focused shopping environment that is similar to a specialty apparel retailer, rather than a typical off-price store. Products from nationally recognized brands are prominently displayed by brand, rather than by size, on dedicated, four-way fixtures featuring multiple sizes and styles. The remaining merchandise is arranged on hanging racks. The stores are carpeted and well-lit, with most featuring a sound system that plays urban adult and urban contemporary music throughout the store. Nearly all of our stores have either been opened or remodeled in the past ten years.
Cost-Effective Store Locations. We locate stores in high traffic strip shopping centers that are convenient to low and moderate income neighborhoods. We generally utilize previously occupied store sites which enables us to obtain attractive rents. Similarly, advertising expenses are low as we do not rely on promotion-driven sales but rather seek to build our reputation for value through everyday low prices. At the same time, from an investment perspective, we seek to design stores that are inviting and easy to shop, while limiting startup and fixturing costs.
Product Merchandising and Pricing
Products. Our merchandising strategy is to offer high quality urban apparel and accessories at attractive prices for the entire value-conscious family. We seek to maintain a diverse assortment of first quality, in-season merchandise that appeals to the distinctive tastes and preferences of our core customers. Approximately 33% of our net sales in fiscal 2013 were represented by nationally recognized brands. We also offer a wide variety of products from less recognized brands and a lesser amount representing private label products under our proprietary brands. Our private brand products enable us to expand product selection, offer merchandise at lower prices and enhance our product offerings.
Our merchandise includes apparel, accessories and home décor. Within apparel, we offer fashion sportswear for men, women and children, including offerings for newborns, infants, toddlers, boys and girls. Accessories include handbags, jewelry, footwear, belts, intimate apparel, scrubs and sleepwear.
The following table sets forth the merchandise assortment by classification as a percentage of net sales for fiscal 2013, 2012, and 2011.
| | Percentage of Net Sales | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Children’s | | 27% | | 27% | | 28% | |
Ladies’ | | 26% | | 29% | | 32% | |
Accessories | | 26% | | 23% | | 18% | |
Men’s | | 18% | | 18% | | 19% | |
Home décor | | 3% | | 3% | | 3% | |
Pricing. We purchase our merchandise at attractive prices and mark prices up less than department or specialty stores. We seek to provide nationally recognized brands at prices that are 20% to 70% below regular retail prices available in department stores and
4
Table of Contents
specialty stores. Further, we also consider the price-to-value relationships of our non-branded products to be exceptionally strong. Both branded and non-branded offerings validate our value and fashion positioning to our customers. The discount from the suggested retail price is reflected on the price tag. We review each department in our stores at least monthly for possible markdowns based on sales rates and fashion seasons to promote faster turnover of inventory and to accelerate the flow of current merchandise.
Sourcing and Allocation
The merchandising department oversees the sourcing, planning and allocation of merchandise to our stores, which allows us to utilize volume purchase discounts and maintain control over our inventory. We source our merchandise from over 1,600 vendors, consisting of domestic manufacturers and importers. Our Chief Merchandising Officer supervises a planning and allocation team consisting of 20 associates, as well as a buying team, which is comprised of over 40 merchants.
The members of our buying team have on average more than 14 years of experience in the retail business and have developed long-standing relationships with many of our vendors, including those controlling the distribution of branded apparel. Our buyers, who are based in New York, Los Angeles and Savannah, travel regularly to the major United States apparel markets, visiting major manufacturers and attending national and regional apparel trade shows, including urban-focused trade shows.
Our buyers purchase merchandise in styles, sizes and quantities to meet inventory levels developed by the planning staff. The buying staff utilizes several purchasing techniques that enable us to offer to customers branded and non-branded fashion merchandise at everyday low prices. The majority of the nationally recognized branded products we sell are purchased in-season, and we generally purchase later in the merchandising buying cycle than department and specialty stores. This allows us to take advantage of imbalances between retailers’ demands for specific merchandise and manufacturers’ supply of that merchandise. We also purchase merchandise from some vendors in advance of the selling season at reduced prices and purchase merchandise on an opportunistic basis near the end of the selling season, which we then store in our distribution centers for sale three to nine months later. Where possible, we seek to purchase items based on style or color in limited quantities on a test basis with the right to reorder as needed. Finally, we purchase private brand merchandise that we source to our specifications.
We allocate merchandise across our store base according to store-level demand. The merchandising staff utilizes a centralized management system to monitor merchandise purchasing, planning and allocation in order to maximize inventory turnover, identify and respond to changing product demands and determine the timing of markdowns to our merchandise. The buyers also regularly review the age and condition of the merchandise and manage both the reordering and clearance processes. In addition, the merchandising team communicates with regional, district and store managers to ascertain regional and store-level conditions and to better ensure that our product mix meets our consumers’ demands in terms of quality, fashion, price and availability.
We accept payment from our customers for merchandise at time of sale. Payments are made to us by cash, check, Visa™, Mastercard™ or Discover™. We do not extend credit terms to our customers; however, we do offer a layaway service.
Seasonality
The nature of our business is seasonal. Historically, sales in the first and fourth quarters have been higher than sales achieved in the second and third quarters of the fiscal year. Expenses and, to a greater extent, operating income, vary by quarter. Results of a period shorter than a full year may not be indicative of results expected for the entire year. Furthermore, the seasonal nature of our business may affect comparisons between periods.
Store Operations
Store Format. The average selling space of our existing 505 stores is approximately 10,800 square feet, which allows us the space and flexibility to departmentalize our stores and provide directed traffic patterns. We arrange most of our stores in a racetrack format with women’s sportswear in the center of each store and complementary categories adjacent to those items. Men’s and boy’s apparel is displayed on one side of the store, while dresses, footwear and accessories are displayed on the other side. Merchandise for infants, toddlers and girls, as well as home goods, are displayed along the back of the store. Impulse items, such as jewelry and sunglasses, are featured near the checkout area. Products from nationally recognized brands are prominently displayed on four-way racks at the front of each department. The remaining merchandise is displayed on hanging racks and occasionally on table displays. Large hanging signs identify each category location. The unobstructed floor plan allows the customer to see virtually all of the different product areas from the store entrance and provides us the flexibility to easily expand and contract departments in response to customer demand, seasonality and merchandise availability. Virtually all of our inventory is displayed on the selling floor. Prices are clearly marked and often have the comparative retail-selling price noted on the price tag.
In 2010, with the assistance of a retail design consulting firm, we began to test a new store format which we refer to as “Citi Lights”. We opened our first new prototype store in Savannah in July 2010 and have now opened a total of 66 new stores with the prototype design. Also, we have converted 25 of our existing stores to the new format and implemented the new format in connection with the relocation or expansion of 22 other stores, resulting in a total of 113 stores in the new format as of the end of fiscal 2013. The stores
5
Table of Contents
feature a new color palette and logo, a new layout, new fixturing, dressing room, graphics and lighting, a redesigned checkout area stocked with impulse items and an expanded footwear department. They typically have a main center drive aisle rather than the racetrack design utilized in our traditional stores. We plan to continue evaluating the performance of the Citi Lights stores before converting more of our stores to this format.
Store Management. Store operations are managed by our Senior Vice President of Store Operations, three regional vice presidents and 48 district managers, each of whom manages five to seventeen stores. The typical store is staffed with a store manager, two or three assistant managers and seven to eight part-time sales associates, all of whom rotate work days on a shift basis. Store managers and assistant store managers participate in a bonus program based on achieving predetermined levels of sales and inventory shrinkage. District managers participate in bonus programs based on achieving targeted levels of sales, profits, inventory shrinkage and payroll costs. Regional Vice Presidents participate in a bonus program based partly on a roll-up of the district managers’ bonuses and partly on the Company’s profit performance in relation to budget. Sales associates are compensated on an hourly basis with incentives. Moreover, we recognize individual performance through internal promotions and provide opportunities for advancement.
We place significant emphasis on loss prevention in order to control inventory shrinkage. Initiatives include electronic tags on most of our products, training and education of store personnel on loss prevention issues, digital video camera systems, alarm systems and motion detectors in the stores. In certain stores, we use an outside service to visually monitor the stores throughout the day using sophisticated camera systems. We also capture extensive point-of-sale data and maintain systems that monitor returns, voids and employee sales, and produce trend and exception reports to assist in identifying shrinkage issues. We have a centralized loss prevention team that focuses exclusively on implementation of these initiatives and specifically on stores that have experienced above average levels of shrinkage. We also maintain an independent, third party administered, toll-free line for reporting shrinkage concerns and any other employee concerns.
Employee Training. Our employees are critical to achieving our goals, and we strive to hire employees with high energy levels and motivation. We have well-established store operating policies and procedures and an extensive 90-day in-store training program for new store managers and assistant managers. Sales associates also participate in a 30-day customer service and store procedures training program, which is designed to enable them to assist customers in a friendly, helpful manner.
Layaway Program. We offer a layaway program that allows customers to purchase merchandise by initially paying a 20% deposit and a $2 service charge, although at various times, we have reduced the deposit requirement to 10% and waived the service charge in connection with promotional events. The customer then makes additional payments every two weeks and has 60 days within which to complete the purchase. If the purchase is not completed, the customer receives a merchandise credit for amounts paid less a re-stocking and layaway service fee.
Site Selection. Cost-effective store locations are an important part of our store profitability model. Accordingly, we look for second and third use store locations that offer attractive rents, but also meet our demographic and economic criteria. We have a dedicated real estate management team responsible for new store site selection. In selecting a location, we target both urban and rural markets. Demographic criteria used in site selection include concentrations of our core consumers. In addition, we require convenient site accessibility, as well as strong co-tenants, such as food stores, dollar stores and rent-to-own stores.
Shortly after we sign a new store lease and complete the necessary leasehold improvements to the building, we prepare the store over a three to four week period by installing fixtures, signs, dressing rooms, checkout counters and cash register systems and merchandising the initial inventory.
Advertising and Marketing
Our marketing goals are to build the “Citi Trends” brand, promote customers’ association of the “Citi Trends” brand with value, quality, fashion and everyday low prices, and drive traffic into our stores. We generally focus our advertising efforts during the first quarter (Spring/Easter), back-to-school and Christmas through the use of hip-hop radio stations, both local and syndicated. We also utilize social media as a way to engage our customers. In 2011, we started a Facebook page which has grown to over 370,000 fans. In addition, we promote new seasons and events in our window signage and through in-store announcements on our Muzak system. For store grand openings and significant remodels, we typically seek to create community awareness and consumer excitement through local radio remotes with local radio personalities broadcasting from the new location. We also distribute promotional items such as gift cards in connection with our grand openings and significant remodels.
Distribution
All merchandise sold in our stores is shipped directly from our distribution centers in Darlington, South Carolina and Roland, Oklahoma, utilizing various express package distributors. Our stores receive multiple shipments of merchandise from our distribution centers each week. The Darlington distribution center has 550,000 square feet of space, while the Roland distribution center has 460,000 square feet.
6
Table of Contents
Information Technology and Systems
We have information systems in place to support our core business functions, using an IBM iSeries as the computer platform, with enterprise software from Island Pacific, a software provider to the retail industry. This software supports purchase order management, price and markdown management, merchandise allocation, general ledger, accounts payable and sales audit functions. Our distribution centers are supported by software from Manhattan Associates.
Our stores use point-of-sale software from DataVantage, a division of MICROS Systems, Inc., to run the stores’ cash registers. The system uses bar code scanners at checkout to capture item sales and is supplemented by external pinpad/signature capture devices for the processing of charge card transactions. It also supports end-of-day processing and automatically transmits sales and transaction data to the corporate office soon after the close of business. Additionally, the software supports store time clock functions. To facilitate the marking down and re-ticketing of merchandise, employees in the stores use hand-held scanners that read UPC barcodes and prepare new price tickets for merchandise. The DataVantage software also enables us to sort, review and analyze store transaction data to assist with loss prevention activities. Software services from Workday are utilized to process our payroll and to facilitate various human capital management processes.
We believe that our information systems, with upgrades and updates over time, are adequate to support our operations for the foreseeable future.
Growth Strategy
Due to a challenging sales environment, we are taking a conservative approach to opening new stores. After opening four new stores in fiscal 2012, we opened one in fiscal 2013 and plan to open five to ten in fiscal 2014. We will continue to evaluate our growth strategy as we monitor operating results in fiscal 2014.
Competition
The markets we serve are highly competitive. The principal methods of competition in the retail business are fashion, assortment, pricing and presentation. We believe we have a competitive advantage in our offering of fashionable brands at everyday low prices. We compete against a diverse group of retailers, including national off-price retailers, mass merchants, smaller specialty retailers and dollar stores. The off-price retail companies with which we compete include TJX Companies, Inc. (“TJX Companies”), Ross Stores, Inc. (“Ross Stores”), The Cato Corporation (“Cato”), and Burlington Stores, Inc. (“Burlington”). In particular, Ross Stores’ “dd’s DISCOUNTS” stores, and Cato’s “It’s Fashion Metro” stores target lower and moderate income consumers. We believe our strategy of appealing to African-American consumers and offering urban apparel products allows us to compete successfully with these retailers. We also believe we offer a more inviting store format than the off-price retailers, including our use of carpeted floors and more prominently displayed brands. In addition, we compete with a group of smaller specialty retailers that sell only women’s products, such as Rainbow, It’s Fashion! and Simply Fashions. Our mass merchant competitors include Wal-Mart, Target and Kmart. These chains do not focus on fashion apparel and, within their apparel offering, lack the urban focus that we believe differentiates our offering and appeals to our core customers. Similarly, while some of the dollar store chains offer apparel, they typically offer a more limited selection focused on basic apparel needs. As a result, we believe there is significant demand for a value retailer that addresses the market of low and moderate income consumers generally and, particularly, African-American and other minority consumers who seek value-priced, urban fashion apparel and accessories. See Item 1A. Risk Factors in this Report for additional information.
Intellectual Property
We regard our trademarks and service marks as having significant value and as being important to our marketing efforts. We have registered “Citi Trends” as a trademark with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office on the Principal Register for retail department store services. We have also registered the following trademarks with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office on the Principal Register for various apparel: “Citi Steps,” “Citi Trends Fashion for Less,” “Diva Blue,” “Lil Citi Man,” “Lil Ms Hollywood,” “Red Ape,” “Satin in The Hood,” and “Vintage Harlem.” Our policy is to pursue registration of our marks and to oppose vigorously infringement of our marks.
Employees
As of February 1, 2014, we had approximately 2,400 full-time and approximately 2,600 part-time employees. Of these employees, approximately 4,300 are employed in our stores and the remainder are employed in our distribution centers and corporate office. We are not a party to any collective bargaining agreements, and none of our employees are represented by a labor union.
7
Table of Contents
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
You should carefully consider the following risk factors, together with the other information contained or incorporated by reference into this Report. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones we face. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we deem to be currently immaterial also may impair our business operations. The occurrence of any of the following risks could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our success depends on our ability to anticipate, identify and respond rapidly to changes in consumers’ fashion tastes, and our failure to adequately evaluate fashion trends could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The apparel industry in general and our core customer market in particular are subject to rapidly evolving fashion trends and shifting consumer demands. Accordingly, our success is heavily dependent on our ability to anticipate, identify and capitalize on emerging fashion trends, including products, styles and materials that will appeal to our target consumers. A failure on our part to anticipate, identify or react appropriately and timely to changes in styles, trends, brand preferences or desired image preferences is likely to lead to lower demand for our merchandise, which could cause, among other things, sales declines, excess inventories and higher markdowns.
If we are unsuccessful in competing with our retail apparel competitors, our market share could decline or our growth could be impaired and, as a result, our financial results could suffer.
The retail apparel market is highly competitive with few barriers to entry. We compete against a diverse group of retailers, including national off-price apparel chains such as TJX Companies, Ross Stores, Cato, and Burlington; mass merchants such as Wal-Mart, Target and Kmart; smaller discount retail chains that sell only women’s products, such as Rainbow, It’s Fashion!, and Simply Fashions; and general merchandise discount stores and dollar stores, which offer a variety of products, including apparel, for the value-conscious consumer. We also compete against local off-price and specialty retail stores, regional retail chains, traditional department stores, web-based retail stores and other direct retailers.
The level of competition we face from these retailers varies depending on the product segment, as many of our competitors do not offer apparel for the entire family. Our greatest competition is generally in women’s apparel. Many of our competitors are larger than we are and have substantially greater resources than we do and, as a result, may be able to adapt better to changing market conditions, exploit new opportunities and exert greater pricing pressures on suppliers than we can. Many of these retailers have better name recognition among consumers than we do and purchase significantly more merchandise from vendors. These retailers may be able to purchase merchandise that we cannot purchase because of their name recognition and relationships with suppliers, or they may be able to purchase merchandise with better pricing concessions than we can. Our local and regional competitors have extensive knowledge of the consumer base and may be able to garner more loyalty from customers than we can. If the consumer base we serve is satisfied with the selection, quality and price of our competitors’ products, consumers may decide not to shop in our stores. Additionally, if our existing competitors or other retailers decide to focus more on our core customers, particularly African-American consumers, we may have greater difficulty in competing effectively, our business and results of operations could be adversely affected, and the market price of our common stock could suffer.
Our ability to attract consumers to our stores depends on the success of the strip shopping centers where our stores are located.
We locate our stores primarily in strip shopping centers where we believe our consumers and potential consumers shop. The success of an individual store can depend on favorable placement within a given strip shopping center. We cannot control the development of alternative shopping destinations near our existing stores or the availability or cost of real estate within existing or new shopping destinations. If our store locations fail to attract sufficient consumer traffic or we are unable to locate replacement locations on terms acceptable to us, our business could suffer. If one or more of the anchor tenants located in the strip shopping centers where our stores are located close or leave, or if there is significant deterioration of the surrounding areas in which our stores are located, our business may be adversely affected.
We could experience a reduction in sales if we are unable to fulfill our current and future merchandising needs.
We depend on our suppliers for the continued availability and satisfactory quality of our merchandise. Most of our suppliers could discontinue selling to us at any time. Additionally, if the manufacturers or other owners of brands or trademarks terminate the license agreements under which some of our suppliers sell our products, we may be unable to obtain replacement merchandise of comparable fashion appeal or quality, in the same quantities or at the same prices. In addition, a number of our suppliers are smaller, less capitalized companies and are more likely to be impacted by unfavorable general economic and market conditions than larger and better capitalized companies. These smaller suppliers may not have sufficient liquidity during economic downturns to properly fund their businesses, and their ability to supply their products to us could be negatively impacted. If we lose the services of one or more of
8
Table of Contents
our significant suppliers or one or more of them fail to meet our merchandising needs, we may be unable to obtain replacement merchandise in a timely manner, which could negatively impact our sales and results of operations.
Our sales could decline as a result of general economic and other factors outside of our control, such as changes in consumer spending patterns and declines in employment levels.
Downturns, or the expectation of a downturn, in general economic conditions, including the effects of unemployment levels, interest rates, levels of consumer debt, inflation in food and energy prices, taxation, government stimulus, consumer confidence, and other macroeconomic factors, could adversely affect consumer spending patterns, our sales and our results of operations. Consumer confidence may also be affected by domestic and international political unrest, acts of war or terrorism, natural disasters or other significant events outside of our control, any of which could lead to a decrease in spending by consumers. Because apparel generally is a discretionary purchase, declines in consumer spending patterns may have a more negative effect on apparel retailers than some other retailers. In addition, since many of our stores are located in the southeastern United States, our operations are more susceptible to regional factors than the operations of our more geographically diversified competitors. Therefore, any adverse economic conditions that have a disproportionate effect on the southeastern United States could have a greater negative effect on our sales and results of operations than on retailers with a more geographically diversified store base.
Adverse trade restrictions may disrupt our supply of merchandise. We also face various risks because much of our merchandise is imported from abroad.
We purchase the products we sell directly from approximately 1,600 vendors, and a substantial portion of this merchandise is manufactured outside of the United States and imported by our vendors from countries such as China and other areas of the Far East. The countries in which our merchandise currently is manufactured or may be manufactured in the future could become subject to new trade restrictions imposed by the United States or other foreign governments. Trade restrictions, including increased customs restrictions and tariffs or quotas against apparel items, as well as United States or foreign labor strikes, work stoppages or boycotts, could increase the cost or reduce the supply of apparel available to us and have an adverse effect on our business. In addition, our merchandise supply could be impacted if our vendors’ imports become subject to existing or future duties and quotas, or if our vendors face increased competition from other companies for production facilities, import quota capacity and shipping capacity.
We also face a variety of other risks generally associated with relying on vendors that do business in foreign markets and import merchandise from abroad, such as:
· political instability, natural disasters, or the threat of terrorism, in particular in countries where our vendors source merchandise;
· increases in merchandise costs due to raw material price inflation or changes in purchasing power caused by fluctuations in currency exchange rates;
· enhanced security measures at United States and foreign ports, which could delay delivery of imports;
· imposition of new or supplemental duties, taxes, and other charges on imports;
· delayed receipt or non-delivery of goods due to the failure of foreign-source suppliers to comply with import regulations, organized labor strikes or congestion at United States ports; and
· local business practice and political issues, including issues relating to compliance with domestic or international labor standards.
9
Table of Contents
As an apparel retailer, we rely on numerous third parties in the supply chain to produce and deliver the products that we sell, and our business may be negatively impacted by their failure to comply with applicable law.
We rely on numerous third parties to supply the products that we sell. Violations of law by our importers, manufacturers or distributors could result in delays in shipments and receipt of goods or damage our reputation, thus causing our sales to decline. In addition, merchandise we sell in our stores is subject to regulatory standards set by various governmental authorities with respect to quality and safety. Regulations in this area may change from time to time. Issues with the quality and safety of merchandise we sell in our stores, regardless of our fault, or customer concerns about such issues, could result in damage to our reputation, lost sales, uninsured product liability claims or losses, merchandise recalls and increased costs. Further, we are susceptible to the receipt of counterfeit brands or unlicensed goods. We could incur liability with manufacturers or other owners of the brands or trademarked products if we inadvertently receive and sell counterfeit brands or unlicensed goods and, therefore, it is important that we establish relationships with reputable vendors to prevent the possibility that we inadvertently receive counterfeit brands or unlicensed goods. Although we have a quality assurance team to check merchandise in an effort to assure that we purchase only authentic brands and licensed goods and are careful in selecting our vendors, we may receive products that we are prohibited from selling or incur liability for selling counterfeit brands or unlicensed goods, which could adversely impact our results of operations.
A significant disruption to our distribution process or southeastern retail locations could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our ability to distribute our merchandise to our store locations in a timely manner is essential to the efficient and profitable operation of our business. We have distribution centers located in Darlington, South Carolina and Roland, Oklahoma. Any natural disaster or other disruption to the operation of either of these facilities due to fire, accidents, weather conditions or any other cause could damage a significant portion of our inventory and impair our ability to stock our stores adequately.
In addition, the southeastern United States, where the Darlington distribution center and many of our stores are located, is vulnerable to significant damage or destruction from hurricanes and tropical storms. Although we maintain insurance on our stores and other facilities, the economic effects of a natural disaster that affects our distribution centers and/or a significant number of our stores could increase our operating expenses, impair our cash flows and reduce our sales.
If we fail to protect our trademarks, there could be a negative effect on our brand image and limitations on our ability to penetrate new markets.
We believe that our “Citi Trends” trademark is integral to our store design and our success in building consumer loyalty to our brand. We have registered this trademark with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. We have also registered, or applied for registration of, additional trademarks with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office that we believe are important to our business. We cannot assure you that these registrations will prevent imitation of our name, merchandising concept, store design or private label merchandise or the infringement of our other intellectual property rights by others. Imitation of our name, concept, store design or merchandise in a manner that projects lesser quality or carries a negative connotation of our brand image could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, we cannot assure you that others will not try to block the manufacture or sale of our private label merchandise by claiming that our merchandise violates their trademarks or other proprietary rights since other entities may have rights to trademarks that contain the word “Citi” or may have rights in similar or competing marks for apparel and/or accessories. Although we cannot currently estimate the likelihood of success of any such lawsuit or ultimate resolution of such a conflict, such a controversy could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we fail to implement and maintain effective internal controls in our business, there could be an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and stock price.
Section 404 of the Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002 requires annual management assessments of the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting and an audit of such controls by our independent registered public accounting firm. If we fail to maintain the adequacy of our internal controls, we may be unable to conclude on an ongoing basis that we have effective internal controls over financial reporting. Moreover, effective internal controls, particularly those related to revenue recognition and accounting for inventory/cost of sales, are necessary for us to produce reliable financial reports and are important in our effort to prevent financial fraud. If we cannot produce reliable financial reports or prevent fraud, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be harmed, investors could lose confidence in our reported financial information, the market price of our stock could decline significantly and we may be unable to obtain additional financing to operate and expand our business.
Failure to attract, train, assimilate and retain skilled personnel could have an adverse effect on our financial condition.
Like most retailers, we experience significant employee turnover rates, particularly among store sales associates and managers. We therefore must continually attract, hire and train new personnel to meet our staffing needs. We constantly compete for qualified
10
Table of Contents
personnel with companies in our industry and in other industries. A significant increase in the turnover rate among our store sales associates and managers would increase our recruiting and training costs and could cause us to be unable to service our customers effectively, thus reducing our ability to operate our stores as profitably as we have in the past.
In addition, we rely heavily on the experience and expertise of our senior management team and other key management associates, and accordingly, the loss of their services could have a material adverse effect on our business strategy and results of operations.
Failure to comply with legal requirements could result in increased costs.
Compliance risks in our business include areas such as employment law, taxation, customer relations and personal injury claims, among others. Failure to comply with laws, rules and regulations could result in unexpected costs and have an adverse effect on our business and reputation.
Changes in government regulations could have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
New legal requirements, including health care legislation, could result in higher compliance costs. For instance, health care reform legislation, among other things, includes guaranteed coverage requirements, eliminates exclusions for pre-existing conditions and maximum benefits, restricts the extent to which policies can be rescinded, and imposes new taxes on health insurers and health care benefits. Such significant changes in government regulations could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Increases in the minimum wage could have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Wage rates for many of our employees are at or slightly above the minimum wage. As federal and/or state minimum wage rates increase, we may need to increase not only our employees’ wage rates that are under the new minimum, but also the wages paid to our other hourly employees. Any increase in the cost of our labor could have a material adverse effect on our operating costs, financial condition and results of operations.
Any failure of our management information systems or the inability of third parties to continue to upgrade and maintain our systems could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We depend on the accuracy, reliability and proper functioning of our management information systems, including the systems used to track our sales and facilitate inventory management. We also rely on our management information systems for merchandise planning, replenishment and markdowns, as well as other key business functions. These functions enhance our ability to optimize sales while limiting markdowns and reducing inventory risk through properly marking down slow-selling styles, reordering existing styles and effectively distributing new inventory to our stores. We do not currently have redundant systems for all functions performed by our management information systems. Any interruption in these systems could impair our ability to manage our inventory effectively, which could have an adverse effect on our business.
We depend on third-party suppliers to maintain and periodically upgrade our management information systems, including the software programs supporting our inventory management functions. If any of these suppliers is unable to continue to maintain and upgrade these software programs and/or if we are unable to convert to alternate systems in an efficient and timely manner, it could result in an adverse effect on our business.
Failure to secure our customers’ charge card information, or the private data relating to our associates or the Company, could subject us to negative publicity, government enforcement actions, or private litigation.
We have procedures and technology in place to safeguard our customers’ debit and credit card information, our associates’ private data, and the Company’s records and intellectual property. However, if we experience a data security breach, we could be exposed to costly negative publicity, governmental enforcement actions, and private litigation. In addition, our sales could be negatively impacted if our customers have security concerns and are not willing to purchase our merchandise using charge cards.
Our sales, inventory levels and earnings fluctuate on a seasonal basis, which makes our business more susceptible to adverse events that occur during the first and fourth quarters.
Our sales and earnings are significantly higher during the first and fourth quarters each year due to the importance of the spring selling season, which includes Easter, and the fall selling season, which includes Christmas. Factors negatively affecting us during the first and fourth quarters, including adverse weather, unfavorable economic conditions, reduced governmental assistance, and tax refund patterns for our customers, will have a greater adverse effect on our financial condition than if our business was less seasonal.
In order to prepare for the spring and fall selling seasons, we must order and keep in stock significantly more merchandise than during other parts of the year. This seasonality makes our business more susceptible to the risk that our inventory will not satisfy actual
11
Table of Contents
consumer demand. In addition, any unanticipated demand imbalances during these peak shopping seasons could require us to sell excess inventory at a substantial markdown or fail to satisfy our consumers. In either event, our sales may be lower and our cost of sales may be higher than historical levels, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We experience fluctuations and variability in our comparable store sales and quarterly results of operations and, as a result, the market price of our common stock may fluctuate substantially.
Our comparable store sales and quarterly results have fluctuated significantly in the past based on a number of economic, seasonal and competitive factors, and we expect them to continue to fluctuate in the future. Since the beginning of fiscal 2010, our quarter-to-quarter comparable store sales have ranged from a decrease of 11.9% to an increase of 9.6%. This variability could cause our comparable store sales and quarterly results to fall below the expectations of securities analysts or investors, which could result in a decline in the market price of our common stock.
Our stock price is subject to volatility.
Our stock price has been volatile in the past and may be influenced in the future by a number of factors, including:
· actual or anticipated fluctuations in our operating results;
· changes in securities analysts’ recommendations or estimates of our financial performance;
· changes in market valuations or operating performance of our competitors or companies similar to ours;
· announcements by us, our competitors or other retailers;
· additions and departures of key personnel;
· changes in accounting principles;
· the passage of legislation or other developments affecting us;
· the trading volume of our common stock in the public market;
· changes in economic or financial market conditions;
· natural disasters, terrorist acts, acts of war or periods of civil unrest; and
· the realization of some or all of the risks described in this section entitled “Risk Factors.”
In addition, the stock markets have experienced significant price and trading volume fluctuations from time to time, and the market prices of the equity securities of retailers have been extremely volatile and have recently experienced sharp price and trading volume changes. These broad market fluctuations may adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
We do not currently intend to pay dividends on our common stock.
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock and do not currently intend to do so for the foreseeable future.
Provisions in our certificate of incorporation and by-laws and Delaware law may delay or prevent our acquisition by a third party.
Our second amended and restated certificate of incorporation and our amended and restated by-laws contain several provisions that may make it more difficult for a third party to acquire control of us without the approval of our board of directors. These provisions include, among other things, a classified board of directors, advance notice for raising business or making nominations at stockholder meetings and “blank check” preferred stock. Blank check preferred stock enables our board of directors, without stockholder approval, to designate and issue additional series of preferred stock with such dividend, liquidation, conversion, voting or other rights, including convertible securities with no limitations on conversion, as our board of directors may determine, including rights to dividends and proceeds in a liquidation that are senior to the common stock.
12
Table of Contents
We are also subject to several provisions of the Delaware General Corporation Law that could delay, prevent or deter a merger, acquisition, tender offer, proxy contest or other transaction that might otherwise result in our stockholders receiving a premium over the market price for their common stock or may otherwise be in the best interests of our stockholders.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
Store Locations
As of February 1, 2014, we operated 505 stores located in 29 states. Our stores average approximately 10,800 square feet of selling space and are typically located in neighborhood strip shopping centers that are convenient to low and moderate income customers.
We have no franchising relationships, and all of the stores are company operated. All existing 505 stores, totaling 6.7 million total square feet and 5.5 million selling square feet, are leased under operating leases. The typical store lease is for five years with options to extend the lease term for three additional five-year periods. Nearly all store leases provide us the right to cancel following an initial three-year period in the event the store does not meet pre-determined sales levels. The table below sets forth the number of stores in each of the 29 states in which we operated as of February 1, 2014:
Alabama—29
Arkansas—8
California—9
Delaware—1
Florida—47
Georgia—61
Illinois—18
Indiana—12
Iowa—2
Kansas—1
Kentucky—6
Louisiana—33
Maryland—3
Michigan—21
Minnesota—1
Mississippi—25
Missouri—6
Nebraska—1
Nevada—3
New York—4
North Carolina—43
Ohio—26
Oklahoma—5
Pennsylvania—5
South Carolina—42
Tennessee—18
Texas—49
Virginia—20
Wisconsin—6
Support Center Facilities
We own a facility in Savannah, Georgia totaling approximately 70,000 square feet, which serves as our headquarters and, to a lesser extent, as a storage facility. We also own an approximately 550,000 square-foot distribution center in Darlington, South Carolina and a 460,000 square-foot distribution center in Roland, Oklahoma. In addition, we currently lease a 9,200 square-foot office in New York City and a 1,200 square-foot office in Los Angeles which are used for buyer operations and meetings with vendors.
13
Table of Contents
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
On August 12, 2011, we received a letter of determination from the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (the “EEOC”) commencing a conciliation process regarding alleged discrimination against males by us in our hiring and promotion practices during the years 2004 through 2006. In its letter of determination, the EEOC sought recovery in the amount of $0.2 million on behalf of a former male employee and in the additional amount of $3.8 million in a settlement fund for a class of unidentified males who sought or considered seeking manager or assistant manager positions in our stores. The EEOC also seeks certain undertakings by us with regard to our employment policies and procedures and a reporting obligation to the EEOC with respect to our compliance with these undertakings.
We have not received full documentation or information from the EEOC in support of its letter of determination, but have undertaken our own internal analysis of the EEOC’s claims and defenses to such claims and have had discussions with the EEOC in that regard. Following discussions with the EEOC regarding possible settlement, the EEOC proposed a settlement amount to be paid by us of $2.5 million, with any unclaimed funds following efforts to identify and compensate claimants to be directed to one or more charities. In the interest of reaching a satisfactory conciliation agreement with the EEOC, we proposed a total economic settlement offer of $1.0 million to cover all claims and the expenses of administering and complying with the settlement (excluding professional fees), with no reversion of unclaimed funds back to us. We continue to await the EEOC’s response to our most recent proposal regarding settlement. We are also evaluating other aspects of the conciliation process established by the EEOC.
On February 24, 2012, a suit was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of Alabama, Middle Division, by certain individuals as a purported collective action on behalf of current and former employees of the Company holding store managerial positions. The plaintiffs allege that store managers have been improperly classified as exempt from the obligation to pay overtime in violation of the Fair Labor Standards Act. We are vigorously defending the claims that have been asserted in this lawsuit. The trial court has conditionally certified a class of store managers and ruled that store managers who signed arbitration agreements are not subject to arbitration. The trial court’s ruling regarding arbitration was affirmed on appeal by a panel of the United States Court of Appeals for the Eleventh Circuit. Also, notwithstanding the initial actions by the trial court, the conditional class may be subject to decertification at the close of discovery. Because no discovery has been conducted to date, we are unable to determine the probability of any particular outcome and it is not reasonably possible to estimate a range of loss with respect to this matter. Accordingly, no accrual for costs has been recorded, and the potential impact of this matter on our financial position, results of operations and cash flows cannot be determined at this time.
We are from time to time also involved in various other legal proceedings incidental to the conduct of our business, including claims by customers, employees or former employees. Once it becomes probable that we will incur costs in connection with a legal proceeding and such costs can be reasonably estimated, we establish appropriate reserves. While legal proceedings are subject to uncertainties and the outcome of any such matter is not predictable, we are not aware of any legal proceedings pending or threatened against us that we expect to have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations or liquidity.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
14
Table of Contents
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR THE REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS ANDISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Our common stock is traded on The NASDAQ Stock Market under the symbol “CTRN”. The following table shows the high and low per share prices of our common stock for the periods indicated.
| | High | | Low | |
2012 | | | | | |
First Quarter | | 12.50 | | 8.80 | |
Second Quarter | | 16.42 | | 10.19 | |
Third Quarter | | 15.51 | | 10.53 | |
Fourth Quarter | | 14.61 | | 10.10 | |
| | | | | |
2013 | | | | | |
First Quarter | | 13.49 | | 9.73 | |
Second Quarter | | 15.65 | | 11.58 | |
Third Quarter | | 18.21 | | 13.87 | |
Fourth Quarter | | 18.45 | | 14.40 | |
On March 25, 2014, the last reported sale price of our common stock on The NASDAQ Stock Market was $16.42 per share. On March 25, 2014, there were 107 holders of record and approximately 2,500 beneficial holders of our common stock.
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock and do not intend to pay any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities.
None.
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers.
None.
Equity Compensation Plan Information.
See Item 12 of this Report.
15
Table of Contents
Stock Performance Graph
Set forth below is a line graph comparing the last five years’ percentage change in the cumulative total stockholder return on shares of our common stock against (i) the cumulative total return of companies listed on The NASDAQ Stock Market and (ii) the cumulative total return of the NASDAQ Retail Trade Index. This graph assumes that $100 was invested on January 31, 2009 in our common stock and in each of the market index and the industry index, and that all cash distributions were reinvested. Our common stock price performance shown on the graph is not indicative of future price performance.
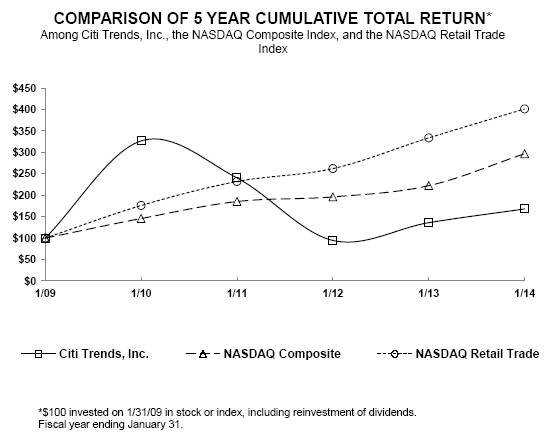
Total Return Analysis | | 1/09 | | 1/10 | | 1/11 | | 1/12 | | 1/13 | | 1/14 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Citi Trends, Inc. | | 100.00 | | 326.65 | | 240.29 | | 94.44 | | 135.78 | | 167.89 | |
NASDAQ Composite | | 100.00 | | 145.73 | | 185.35 | | 196.13 | | 222.33 | | 296.73 | |
NASDAQ Retail Trade | | 100.00 | | 176.03 | | 231.96 | | 262.10 | | 333.70 | | 401.19 | |
16
Table of Contents
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
Selected Financial and Operating Data
The following table provides selected consolidated financial and operating data for each of the fiscal years in the five-year period ended February 1, 2014, including: (a) consolidated statement of operations data for each such period, (b) additional operating data for each such period and (c) consolidated balance sheet data as of the end of each such period. The consolidated statement of operations data for the fiscal years ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012 and the consolidated balance sheet data as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Report that have been audited by KPMG LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm. The statement of operations data for the fiscal years ended January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010 and the balance sheet data as of January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010 are derived from our audited financial statements that are not included in this Report. The selected consolidated financial and operating data set forth below should be read in conjunction with, and are qualified in their entirety by reference to, the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included in Item 7 of this Report and our consolidated financial statements and related notes set forth in the financial pages of this Report. Historical results are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for any future period.
| | Fiscal Year Ended (1) | |
| | February 1,
2014 | | February 2,
2013 | | January 28,
2012 | | January 29,
2011 | | January 30,
2010 | |
| | (dollars in thousands, except per share amounts) | |
Statement of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 622,204 | | $ | 654,653 | | $ | 640,824 | | $ | 622,528 | | $ | 551,869 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of sales (exclusive of depreciation shown separately below) | | (394,445 | ) | (426,904 | ) | (420,321 | ) | (383,318 | ) | (338,898 | ) |
Selling, general and administrative expenses | | (206,146 | ) | (207,411 | ) | (207,025 | ) | (187,231 | ) | (165,166 | ) |
Depreciation | | (21,974 | ) | (23,950 | ) | (24,958 | ) | (20,324 | ) | (18,319 | ) |
Asset impairment | | (1,542 | ) | (1,177 | ) | (6,514 | ) | (211 | ) | (112 | ) |
Gain on sale of former distribution center | | 1,526 | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
(Loss) income from operations | | (377 | ) | (4,789 | ) | (17,994 | ) | 31,444 | | 29,374 | |
Interest, net | | 87 | | 48 | | 164 | | 150 | | 312 | |
(Loss) income before income taxes | | (290 | ) | (4,741 | ) | (17,830 | ) | 31,594 | | 29,686 | |
Income tax (benefit) expense | | (754 | ) | (2,516 | ) | (7,816 | ) | 10,742 | | 9,969 | |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 464 | | $ | (2,225 | ) | $ | (10,014 | ) | $ | 20,852 | | $ | 19,717 | |
Net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.03 | | $ | (0.15 | ) | $ | (0.69 | ) | $ | 1.44 | | $ | 1.36 | |
Diluted | | $ | 0.03 | | $ | (0.15 | ) | $ | (0.69 | ) | $ | 1.44 | | $ | 1.36 | |
Weighted average shares used to compute net income (loss) per share: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | 14,798,154 | | 14,671,638 | | 14,589,247 | | 14,503,418 | | 14,363,894 | |
Diluted | | 14,813,444 | | 14,671,638 | | 14,589,247 | | 14,522,662 | | 14,395,605 | |
Additional Operating Data: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Number of stores: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Opened during period | | 1 | | 4 | | 55 | | 60 | | 49 | |
Closed during period | | 9 | | 2 | | 5 | | 2 | | 3 | |
Open at end of period | | 505 | | 513 | | 511 | | 461 | | 403 | |
Selling square footage at end of period | | 5,467,021 | | 5,500,698 | | 5,473,846 | | 4,891,637 | | 4,205,046 | |
Comparable store sales (decrease) increase (2) | | (1.6 | )%(3) | (5.6 | )%(3) | (8.3 | )% | (1.8 | )% | 0.6 | % |
Average sales per store (4) | | $ | 1,222 | | $ | 1,279 | | $ | 1,319 | | $ | 1,441 | | $ | 1,452 | |
Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 58,928 | | $ | 37,263 | | $ | 41,986 | | $ | 69,231 | | $ | 62,993 | |
Short-term investments | | 6,004 | | 12,771 | | 902 | | 586 | | 33,025 | |
Long-term investments | | 19,777 | | 5,754 | | 18,840 | | 9,205 | | — | |
Total assets | | 291,308 | | 292,145 | | 314,777 | | 306,402 | | 279,986 | |
Total liabilities | | 92,437 | | 96,174 | | 118,374 | | 101,598 | | 98,643 | |
Total stockholders’ equity | | 198,871 | | 195,971 | | 196,403 | | 204,804 | | 181,343 | |
17
Table of Contents
(1) Our fiscal year ends on the Saturday closest to January 31 of each year. The years ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011, and January 30, 2010 are referred to as fiscal 2013, 2012, 2011, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Fiscal 2012 is comprised of 53 weeks, while fiscal years 2013, 2011, 2010 and 2009 are each comprised of 52 weeks.
(2) Stores included in the comparable store sales calculation for any period are those stores that were opened prior to the beginning of the preceding fiscal year and were still open at the end of such period. Relocated stores and expanded stores are included in the comparable store sales results.
(3) The Company is reporting comparable store sales on a comparable store and comparable weeks basis; for fiscal 2013, the 52 weeks ended February 1, 2014 were compared to the 52 weeks ended February 2, 2013; for fiscal 2012, the 53 weeks ended February 2, 2013 were compared to the 53 weeks ended February 4, 2012.
(4) Average sales per store is defined as net sales divided by the average number of stores open at the end of the prior fiscal year and stores open at the end of the current fiscal year.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OFOPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with the section entitled “Selected Financial and Operating Data” and our audited consolidated financial statements and the respective related notes included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. This discussion may contain forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. As a result of many factors, such as those set forth under the section entitled “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Report, our actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements.
Overview
We are a value-priced retailer of urban fashion apparel and accessories for the entire family. Our merchandise offerings are designed to appeal to the preferences of fashion conscious consumers, particularly African-Americans. We operate 505 stores in both urban and rural markets in 29 states.
Due to a challenging sales environment, we are taking a conservative approach to opening new stores. After opening four new stores in fiscal 2012, we opened one in fiscal 2013 and plan to open five to ten in fiscal 2014. We will continue to evaluate our growth strategy as we monitor operating results in fiscal 2014.
We measure performance using key operating statistics. One of the main performance measures we use is comparable store sales growth. We define a comparable store as a store that has been open for an entire fiscal year. Therefore, a store will not be considered a comparable store until its 13th month of operation at the earliest or until its 24th month at the latest. As an example, stores opened in fiscal 2012 and fiscal 2013 were not considered comparable stores in fiscal 2013. Relocated and expanded stores are included in the comparable store sales results. We also use other operating statistics, most notably average sales per store, to measure our performance. As we typically occupy existing space in established shopping centers rather than sites built specifically for our stores, store square footage (and therefore sales per square foot) varies by store. We focus on overall store sales volume as the critical driver of profitability. In addition to sales, we measure cost of sales as a percentage of sales and store operating expenses, with a particular focus on labor, as a percentage of sales. These results translate into store level contribution, which we use to evaluate overall performance of each individual store. Finally, we monitor corporate expenses against budgeted amounts. All of the statistics discussed above are critical components of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (“EBITDA”) and Adjusted EBITDA (comprised of EBITDA, excluding non-cash asset impairment expense and the 2013 gain on sale of our former distribution center), which are considered our most important operating statistics. Although EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA provide useful information on an operating cash flow basis, they are limited measures in that they exclude the impact of cash requirements for capital expenditures, income taxes and interest expense. Therefore, EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA should be used as supplements to results of operations and cash flows as reported under GAAP and should not be used as a singular measure of operating performance or as a substitute for GAAP results. Provided below is a reconciliation of net income (loss) to EBITDA and to Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal years ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012:
18
Table of Contents
| | Fiscal Year Ended | |
| | February 1, 2014 | | February 2, 2013 | | January 28, 2012 | |
| | | | | | | |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 464 | | $ | (2,225 | ) | $ | (10,014 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
Plus: | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | 194 | | 212 | | 79 | |
Depreciation | | 21,974 | | 23,950 | | 24,958 | |
| | | | | | | |
Less: | | | | | | | |
Interest income | | (281 | ) | (260 | ) | (243 | ) |
Income tax benefit | | (754 | ) | (2,516 | ) | (7,816 | ) |
EBITDA | | 21,597 | | 19,161 | | 6,964 | |
| | | | | | | |
Asset impairment | | 1,542 | | 1,177 | | 6,514 | |
Gain on sale of former distribution center | | (1,526 | ) | — | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 21,613 | | $ | 20,338 | | $ | 13,478 | |
Basis of the Presentation
Net sales consist of store sales and layaway fees, net of returns by customers. Cost of sales consists of the cost of products we sell and associated freight costs. Depreciation is not considered a component of cost of sales and is included as a separate line item in the consolidated statements of operations. Selling, general and administrative expenses are comprised of store costs, including payroll and occupancy costs, corporate and distribution center costs and advertising costs. We operate on a 52- or 53-week fiscal year, which ends on the Saturday closest to January 31. Each of our fiscal quarters consists of four 13-week periods, with an extra week added to the fourth quarter every five to six years. The years ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013, January 28, 2012, January 29, 2011, and January 30, 2010 are referred to as fiscal 2013, 2012, 2011, 2010, and 2009, respectively. Fiscal 2012 is comprised of 53 weeks, while fiscal years 2013, 2011, 2010 and 2009 are each comprised of 52 weeks.
Results of Operations
The following discussion of our financial performance is based on the consolidated financial statements set forth in the financial pages of this Report. The nature of our business is seasonal. Historically, sales in the first and fourth quarters have been higher than sales achieved in the second and third quarters of the fiscal year. Expenses and, to a greater extent, operating income, vary by quarter. Results of a period shorter than a full year may not be indicative of results expected for the entire year. Furthermore, the seasonal nature of our business may affect comparisons between periods.
19
Table of Contents
Net Sales and Additional Operating Data
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, selected consolidated statement of operations data expressed both in dollars and as a percentage of net sales:
| | Fiscal Year Ended | |
| | February 1, | | February 2, | | January 28, | |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 | |
| | (dollars in thousands) | |
Statement of Operations Data | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 622,204 | | 100.0% | | $ | 654,653 | | 100.0% | | $ | 640,824 | | 100.0% | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of sales (exclusive of depreciation shown separately below) | | (394,445 | ) | (63.4)% | | (426,904 | ) | (65.2)% | | (420,321 | ) | (65.6)% | |
Selling, general and administrative expenses | | (206,146 | ) | (33.1)% | | (207,411 | ) | (31.7)% | | (207,025 | ) | (32.3)% | |
Depreciation | | (21,974 | ) | (3.5)% | | (23,950 | ) | (3.6)% | | (24,958 | ) | (3.9)% | |
Asset impairment | | (1,542 | ) | (0.2)% | | (1,177 | ) | (0.2)% | | (6,514 | ) | (1.0)% | |
Gain on sale of former distribution center | | 1,526 | | 0.2% | | — | | 0.0% | | — | | 0.0% | |
Loss from operations | | (377 | ) | (0.0)% | | (4,789 | ) | (0.7)% | | (17,994 | ) | (2.8)% | |
Interest income | | 281 | | 0.0% | | 260 | | 0.0% | | 243 | | 0.0% | |
Interest expense | | (194 | ) | (0.0)% | | (212 | ) | (0.0)% | | (79 | ) | (0.0)% | |
Loss before income taxes | | (290 | ) | (0.0)% | | (4,741 | ) | (0.7)% | | (17,830 | ) | (2.8)% | |
Income tax benefit | | (754 | ) | (0.1)% | | (2,516 | ) | (0.4)% | | (7,816 | ) | (1.2)% | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 464 | | 0.1% | | $ | (2,225 | ) | (0.3)% | | $ | (10,014 | ) | (1.6)% | |
The following table provides information, for the years indicated, about the number of total stores open at the beginning of the year, stores opened and closed during each year, total stores open at the end of each year and comparable store sales for the years:
| | Fiscal Year Ended | |
| | February 1, | | February 2, | | January 28, | |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total stores open, beginning of year | | 513 | | 511 | | 461 | |
New stores | | 1 | | 4 | | 55 | |
Closed stores | | (9 | ) | (2 | ) | (5 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
Total stores open, end of year | | 505 | | 513 | | 511 | |
| | | | | | | |
Comparable store sales decrease (1) | | (1.6 | )%(2) | (5.6 | )%(2) | (8.3 | )% |
(1) Stores included in the comparable store sales calculation for any year are those stores that were opened prior to the beginning of the preceding fiscal year and were still open at the end of such year. Relocated stores and expanded stores are included in the comparable store sales results.
(2) The Company is reporting comparable store sales on a comparable store and comparable weeks basis; for fiscal 2013, the 52 weeks ended February 1, 2014 were compared to the 52 weeks ended February 2, 2013; for fiscal 2012, the 53 weeks ended February 2, 2013 were compared to the 53 weeks ended February 4, 2012.
20
Table of Contents
Fiscal 2013 Compared to Fiscal 2012
Net Sales. Net sales decreased $32.5 million, or 5.0%, to $622.2 million in the 52-week fiscal 2013 from $654.7 million in the 53-week fiscal 2012. The decrease in net sales was due primarily to (1) an extra week in fiscal 2012 (the first week beginning January 29, 2012) which provided a benefit of $20.7 million to that year; (2) a 1.6% decrease ($10.1 million) in comparable store sales during the 52 weeks of fiscal 2013 compared to the same 52-week period of fiscal 2012; and (3) the effect of closing 11 stores in fiscal 2012 and 2013, net of five new stores ($1.7 million).
The 1.6% decrease in comparable store sales on a 52-week basis was reflected in an average unit sale that was 7.0% lower, partially offset by a 3.4% increase in the number of customer transactions and a 2.0% increase in the average number of items per transaction. The lower average unit sale was the result of a shift in customer preferences from higher price-point branded apparel to non-branded apparel, together with the Company’s efforts to improve the value equation for our customers through an increase in the level of opportunistic buying. Comparable store sales changes on a 52-week basis, by major merchandise class, were as follows: Accessories +14%; Home +13%; Children’s -2%; Men’s -6%; and Ladies’ -13%.
Cost of Sales (exclusive of depreciation). Cost of sales (exclusive of depreciation) decreased $32.5 million, or 7.6%, to $394.4 million in fiscal 2013 from $426.9 million in fiscal 2012 due to the effect of the decrease in sales discussed above and an improvement in cost of sales as a percentage of sales to 63.4% in fiscal 2013 from 65.2% in fiscal 2012. The decrease in cost of sales as a percentage of sales was due primarily to a 160 basis points increase in the core merchandise margin (initial mark-up, net of markdowns) as the result of a reduced need for markdowns in fiscal 2013 due to a much more conservative inventory level throughout the year.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses. Selling, general and administrative expenses decreased $1.3 million, or 0.6%, to $206.1 million in fiscal 2013 from $207.4 million in fiscal 2012. Expenses decreased due primarily to approximately $3 million of expense attributable to the extra week in fiscal 2012, partially offset by an increase in incentive compensation totaling $1.7 million resulting from improved financial performance relative to budget in fiscal 2013. Selling, general and administrative expenses as a percentage of sales increased to 33.1% in fiscal 2013 from 31.7% in fiscal 2012 due primarily to the deleveraging effect associated with the $32.5 million decline in sales discussed above.
Depreciation. Depreciation expense decreased $2.0 million, or 8.3%, to $22.0 million in fiscal 2013 from $24.0 million in fiscal 2012, due to the slowing of our store opening pace in 2013 and 2012 in relation to previous years.
Asset Impairment. Impairment charges related to property and equipment at underperforming stores totaled $1.5 million and $1.2 million in fiscal 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Gain on Sale of Former Distribution Center. During the third quarter of fiscal 2013, we sold a previously closed distribution center in Savannah, Georgia for $2.9 million, resulting in a gain of $1.5 million.
Income Tax Benefit. Income tax benefit decreased to $0.8 million in fiscal 2013 from $2.5 million in fiscal 2012 due to a lower pretax loss in fiscal 2013. The tax benefit in fiscal 2013 included $1.0 million related to jobs-based tax credits, partially offset by income tax expense of $0.4 million related to the increase of a valuation allowance. The fiscal 2012 tax benefit included $0.8 million related to jobs-based tax credits.
Net Income (Loss). Net income was $0.5 million in fiscal 2013 and net loss was $2.2 million in fiscal 2012, due to the factors discussed above.
Fiscal 2012 Compared to Fiscal 2011
Net Sales. Net sales increased $13.9 million, or 2.2%, to $654.7 million in the 53-week fiscal 2012 from $640.8 million in the 52-week fiscal 2011. The increase in net sales was due primarily to 55 new store openings in fiscal 2011, for which there was not a full year of sales in fiscal 2011, and four new store openings in fiscal 2012, together with an extra week in fiscal 2012 (the last week beginning January 27, 2013) which contributed $8.8 million in sales. These sales increases were partially offset by a 4.0% decrease in comparable store sales during the first 52 weeks of fiscal 2012 (5.6% decrease on a 53 versus 53-week basis) and the closing of two stores in fiscal 2012 and five stores in fiscal 2011. In the first 52 weeks of fiscal 2012, the 55 stores opened in fiscal 2011 accounted for $28.5 million of the increase in sales and the 4 stores opened in fiscal 2012 accounted for $3.4 million of the increase, while the sales decrease in the 454 comparable stores totaled $23.8 million and the closed stores had the effect of reducing sales by $3.0 million. Comparable stores include locations that have been relocated or expanded. There were 4 stores relocated or expanded in fiscal 2012 and 14 stores relocated or expanded in fiscal 2011. In the first 52 weeks of fiscal 2012, sales in these comparable relocated and expanded stores decreased 2.1%, while sales in all other comparable stores decreased 4.1%.
The 5.6% overall decrease in comparable store sales on a 53-week basis was reflected entirely in a lower average unit sale as customer transactions and the average number of items per transaction were both up approximately 1%. The lower average unit sale resulted from the Company’s shift to a higher level of opportunistic buying in order to provide lower prices to our customers. Sales continued
21
Table of Contents
to be challenging in fiscal 2012. While we were able to improve our price competitiveness through the heightened opportunistic buying strategy, we continued to have significant declines in sales of women’s urban brands, as well as lesser decreases in the men’s and children’s businesses. Comparable store sales changes on a 53-week basis, by major merchandise class, were as follows: Accessories +9%; Home +1%; Men’s -6%; Children’s -6%; and Ladies’ -15%.
Cost of Sales (exclusive of depreciation). Cost of sales (exclusive of depreciation) increased $6.6 million, or 1.6%, to $426.9 million in fiscal 2012 from $420.3 million in fiscal 2011 as a result of the increase in sales discussed above, partially offset by an improvement in cost of sales as a percentage of sales to 65.2% in fiscal 2012 from 65.6% in fiscal 2011. The decrease in cost of sales as a percentage of sales was due to an improvement in the core merchandise margin (initial mark-up, net of markdowns) of 100 basis points, partially offset by increases in freight expense and inventory shrinkage of 30 basis points each. The improvement in the core merchandise margin was the result of steps taken to increase the level of opportunistic purchases of product at advantageous prices in fiscal 2012 and more merchandise markdowns taken in fiscal 2011 due to a higher level of negative comparable store sales.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses. Selling, general and administrative expenses increased $0.4 million, or 0.2%, to $207.4 million in fiscal 2012 from $207.0 million in fiscal 2011. The increase in expenses was due primarily to additional store level, distribution and corporate costs arising from the opening of 55 new stores in fiscal 2011 and 4 new stores in fiscal 2012, together with approximately $3 million of expense attributable to the extra week in fiscal 2012. The factors causing expenses to increase were almost completely offset by efforts to tightly manage expenses in the challenging sales environment, including the elimination of 40 positions in our corporate office, distribution centers and store organization in the third quarter of fiscal 2011. Additionally, fiscal 2011 included $1.9 million of severance expense, incurred in connection with the elimination of 40 positions and the departure of two executives. Selling, general and administrative expenses as a percentage of sales decreased to 31.7% in fiscal 2012 from 32.3% in fiscal 2011 due primarily to the expense control measures discussed above and the fiscal 2011 severance expense.
Depreciation. Depreciation expense decreased $1.0 million, or 4.0%, to $24.0 million in fiscal 2012 from $25.0 million in fiscal 2011, as a result of the Company slowing down its new store growth.
Asset Impairment. Impairment totaled $1.2 million and $6.5 million in fiscal 2012 and 2011, respectively. Impairment charges for property and equipment at certain underperforming stores were much higher in fiscal 2011 due to a significant decline in sales and an increase in cost of sales (exclusive of depreciation) as a percentage of sales in that year. In addition, goodwill of $1.4 million was fully impaired in fiscal 2011 due to a decrease in the Company’s stock price.
Income Tax Benefit. Income tax benefit decreased to $2.5 million in fiscal 2012 from $7.8 million in fiscal 2011 due to a lower pretax loss in fiscal 2012, partially offset by an increase in the effective income tax benefit rate to 53.1% in fiscal 2012 from 43.8% in fiscal 2011. The effective income tax benefit rate was higher in fiscal 2012 because the benefit from general business tax credits did not decline at the same rate as the pretax loss.
Net Loss. Net loss was $2.2 million in fiscal 2012 compared with $10.0 million in fiscal 2011, due to the factors discussed above.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our cash requirements are primarily for working capital and for capital expenditures for our stores, distribution infrastructure and information systems. Historically, we have met these cash requirements from cash flow from operations, short-term trade credit, borrowings under our revolving lines of credit, long-term debt and capital leases, and cash proceeds from our initial public offering. We expect to be able to meet future cash requirements with cash flow from operations, short-term trade credit, existing balances of cash and investment securities and, if necessary, borrowings under our revolving credit facility (described below). In fiscal 2013, there was no need to borrow under the credit facility. Due to our strong cash and cash equivalents position as of February 1, 2014 ($58.9 million), we believe that we will likely not have to borrow under the credit facility during fiscal 2014.
Cash Flows
Fiscal 2013 Compared to Fiscal 2012
As of February 1, 2014, we had total cash and cash equivalents of $58.9 million, compared with $37.3 million as of February 2, 2013. Additionally, we had $6.0 million and $19.8 million of short-term and long-term investment securities, respectively, as of February 1, 2014, compared with $12.8 million and $5.8 million, respectively, as of February 2, 2013. These securities are comprised of bank certificates of deposit and obligations of the U.S. Treasury, states and municipalities.
Inventory represented 43.4% of our total assets as of February 1, 2014, compared with 48.4% as of February 2, 2013. Management’s ability to manage our inventory can have a significant impact on our cash flows from operations during a given interim period or fiscal year. In addition, inventory purchases can be seasonal in nature, such as the purchase of warm-weather or Christmas-related merchandise.
22
Table of Contents
Cash Flows Provided by Operating Activities. Net cash provided by operating activities was $35.4 million in fiscal 2013 compared with $2.3 million in fiscal 2012. Net income, adjusted for noncash expenses such as depreciation, asset impairment, gain on sale of a former distribution center, loss on disposal of property and equipment, deferred income taxes, and stock-based compensation expense, provided cash of $24.1 million in fiscal 2013 (compared with $22.8 million in fiscal 2012). The other significant source of cash provided by operating activities in fiscal 2013 was a $15.0 million decrease in inventory (compared with an increase of $9.9 million in fiscal 2012) due to an effort to maintain a much more conservative level of inventory in fiscal 2013 in light of the challenging sales environment in recent years. Significant uses of cash included (1) Accounts payable decreased $2.7 million (compared with $16.3 million in fiscal 2012) due primarily to the aforementioned reduction in inventory. The decrease in accounts payable would typically have been higher, considering the significance of the inventory reduction; however, improved inventory turnover in fiscal 2013 had the effect of leaving a greater portion of the inventory balance in accounts payable at year end. (2) Accrued expenses and other long-term liabilities decreased $2.6 million (compared with $2.1 million in fiscal 2012) due primarily to amortization of deferred rent and tenant improvement allowances that were not offset by additions to such accounts as a result of slowing store growth in fiscal 2012 and 2013.
Cash Flows Used in Investing Activities. Cash used in investing activities was $12.8 million in fiscal 2013 compared with $6.1 million in fiscal 2012. Cash used for the purchase of property and equipment was $8.5 million in fiscal 2013 and $7.3 million in fiscal 2012. Purchases of investment securities, net of sales/redemptions, used cash of $7.2 million in fiscal 2013, while sales/redemptions of investment securities provided cash of $1.2 million in fiscal 2012. The sale of our former distribution center provided cash of $2.9 million in fiscal 2013.
Cash Flows Used in Financing Activities. Cash used in financing activities was insignificant in both fiscal 2013 and 2012.
Until required for other purposes, we maintain cash and cash equivalents in deposit or money market accounts.
Fiscal 2012 Compared to Fiscal 2011
As of February 2, 2013, we had total cash and cash equivalents of $37.3 million, compared with $42.0 million as of January 28, 2012. Additionally, we had $12.8 million and $5.8 million of short-term and long-term investment securities, respectively, as of February 2, 2013, compared with $0.9 million and $18.8 million, respectively, as of January 28, 2012. These securities are comprised of bank certificates of deposit and obligations of the U.S. Treasury, states and municipalities.
Inventory represented 48.4% of our total assets as of February 2, 2013, compared with 41.8% as of January 28, 2012. Management’s ability to manage our inventory can have a significant impact on our cash flows from operations during a given interim period or fiscal year. In addition, inventory purchases can be seasonal in nature, such as the purchase of warm-weather or Christmas-related merchandise.
Cash Flows Provided by Operating Activities. Net cash provided by operating activities was $2.3 million in fiscal 2012 compared with $22.1 million in fiscal 2011. Net loss, adjusted for noncash expenses such as depreciation, asset impairment, deferred income taxes, loss on disposal of property and equipment, and stock-based compensation expense, provided cash of $22.8 million in fiscal 2012 (compared with $24.2 million in fiscal 2011). The other significant source of cash provided by operating activities was a decrease in income tax receivable of $9.6 million (compared with an increase of $10.9 million in fiscal 2011), which is comprised of income tax refunds, net of payments, totaling $9.2 million, and current income tax expense of $0.4 million. Significant uses of cash included (1) Accounts payable decreased $16.3 million (compared with an increase of $11.0 million in fiscal 2011) due primarily to our shift back to more opportunistic buying, including making more opportunistic purchases of next-season-buy merchandise. Many of the payments to trade vendors for these opportunistic purchases had been made prior to year end, therefore, accounts payable was lower as a percentage of inventory at the end of fiscal 2012 than fiscal 2011. (2) Inventory increased $9.9 million (compared with $10.1 million in fiscal 2011) due primarily to the higher level of next-season-buy merchandise discussed above. (3) Accrued compensation decreased $2.2 million (compared with an increase of $1.7 million in fiscal 2011) due to one week of payroll being accrued at the end of fiscal 2012 compared with two weeks a year ago and as a result of fiscal 2011 severance accruals for two former officers and for employees laid off in connection with a reduction-in-force being paid in fiscal 2012. (4) Accrued expenses and other long-term liabilities decreased $2.1 million (compared with an increase of $5.2 million in fiscal 2011) due primarily to amortization of deferred rent and tenant improvement allowances that were not offset by additions to such accounts as a result of slowing store growth in fiscal 2012.
Cash Flows Used in Investing Activities. Cash used in investing activities was $6.1 million in fiscal 2012 compared with $48.4 million in fiscal 2011. Cash used for the purchase of property and equipment was $7.3 million in fiscal 2012 and $38.4 million in fiscal 2011, including capital expenditures for 4 new stores in fiscal 2012 and 55 new stores in 2011. Capital expenditures related to the new distribution center in Roland, Oklahoma totaled $5.6 million in 2011. Sales/redemptions of investment securities provided cash of $1.2 million in fiscal 2012. Purchases of investment securities, net of sales/redemptions, used cash of $10.0 million in fiscal 2011.
Cash Flows Used in Financing Activities. Cash used in financing activities was insignificant in both fiscal 2012 and 2011.
23
Table of Contents
Liquidity Sources and Requirements and Contractual Cash Requirements and Commitments
Our principal sources of liquidity consist of: (i) cash and cash equivalents (which equaled $58.9 million as of February 1, 2014); (ii) short-term and long-term investment securities (which equaled $6.0 million and $19.8 million, respectively, as of February 1, 2014); (iii) short-term trade credit; (iv) cash generated from operations on an ongoing basis as we sell our merchandise inventory; and (v) a $50 million revolving credit facility. Trade credit represents a significant source of financing for inventory purchases and arises from customary payment terms and trade practices with our vendors. Historically, our principal liquidity requirements have been for working capital and capital expenditure needs.
We believe that our existing sources of liquidity will be sufficient to fund our operations and anticipated capital expenditures for at least the next 12 months.
We anticipate that capital expenditures will be approximately $13 million to $15 million in fiscal 2014, including amounts related to five to ten new stores that we plan to open in fiscal 2014. We plan to finance these capital expenditures with cash flow from operations and existing cash balances.
The following table discloses aggregate information about our contractual obligations as of February 1, 2014 and the periods in which payments are due:
| | Payments Due by Period | |
| | | | Less than | | 1-3 | | 3-5 | | More than | |
| | Total | | 1 Year | | Years | | Years | | 5 Years | |
| | (in thousands) | |
Contractual obligations: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating leases (1) | | $ | 115,043 | | $ | 38,096 | | $ | 52,521 | | $ | 19,926 | | $ | 4,500 | |
Purchase obligations | | 66,559 | | 66,559 | | — | | — | | — | |
Total contractual cash obligations | | $ | 181,602 | | $ | 104,655 | | $ | 52,521 | | $ | 19,926 | | $ | 4,500 | |
(1) Represents fixed minimum rents in stores and does not include incremental rents which are computed as a percentage of net sales. For example, in fiscal 2013 incremental percentage rent was approximately $0.5 million, which represented 1.1% of total rent expense.
Indebtedness. On October 27, 2011, we entered into a five-year, $50 million credit facility with Bank of America to replace our prior $20 million credit facility. The facility includes a $25 million uncommitted “accordion” feature that under certain circumstances could allow us to increase the size of the facility to $75 million. Borrowings, if any, under the facility will bear interest (a) for LIBOR Rate Loans, at LIBOR plus 1.5%, or (b) for Base Rate Loans, at a rate equal to the highest of (i) the prime rate plus 0.5%, (ii) the Federal Funds Rate plus 1.0%, or (iii) LIBOR plus 1.5%. The facility is secured by our inventory, accounts receivable and related assets, but not our real estate, fixtures and equipment, and it contains one financial covenant, a fixed charge coverage ratio, which is applicable and tested only in certain circumstances. The facility has an unused commitment fee of 0.25% and permits the payment of cash dividends subject to certain limitations. We have had no borrowings under either the existing or prior facility.
Operating Leases. We lease our stores under operating leases, which generally have an initial term of five years with renewal options. The typical store lease requires a combination of both fixed monthly rents and contingent rents computed as a percentage of net sales after a certain sales threshold has been met. For fiscal 2013, rent expense was $42.1 million compared with $41.7 million in fiscal 2012 (including $0.5 million and $0.7 million of percentage rent, respectively, in fiscal 2013 and 2012).
Purchase Obligations. As of February 1, 2014, we had purchase obligations of $66.6 million, all of which were for less than one year. These purchase obligations consist of outstanding merchandise orders.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Other than the store operating leases described above, we do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Outstanding Stock Options
As of February 1, 2014, we had outstanding vested options to purchase 40,700 shares of common stock at a weighted average exercise price of $34.71 per share. There were no unvested options to purchase shares of common stock as of February 1, 2014. Based on the
24
Table of Contents
closing price of our common stock of $16.00 per share on January 31, 2014, the intrinsic value of the options outstanding on February 1, 2014 was $14,000.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of our consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. We believe the following critical accounting policies describe the more significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements:
Inventory
Inventory is stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out basis) or market as determined by the retail inventory method for store inventory and the average cost method for distribution center inventory. Under the retail inventory method, the cost of inventory is determined by calculating a cost-to-retail ratio and applying it to the retail value of inventory. Inherent in the retail inventory calculation are certain significant management judgments and estimates, including, among others, merchandise markups, markdowns and shrinkage, which impact the ending inventory valuation at cost as well as resulting cost of sales. Merchandise markdowns are reflected in the inventory valuation when the price of an item is lowered in the stores. As a result, we believe the retail inventory method results in a more conservative inventory valuation than other accounting methods. We estimate and record an allowance for shrinkage for the period between the last physical count and the balance sheet date. The estimate of shrinkage can be affected by changes in actual shrinkage trends. Inventory shrinkage as a percentage of sales has ranged from 0.9% to 1.2% during fiscal years 2011 through 2013. The allowance for estimated inventory shrinkage was $2.6 million and $2.3 million as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013, respectively. Many retailers have arrangements with vendors that provide for rebates and allowances under certain conditions, which ultimately affect the value of the inventory. We do not generally enter into such arrangements with our vendors. There were no material changes in the estimates or assumptions related to the valuation of inventory during fiscal 2013.
Property and Equipment, net
We have a significant investment in property and equipment stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the lesser of the estimated useful lives (primarily three to five years for computer equipment and furniture, fixtures and equipment, five years for leasehold improvements, seven years for major purchased software systems, and fifteen to twenty years for buildings and building improvements) of the related assets or the relevant lease term. Any reduction in these estimated useful lives would result in a higher annual depreciation expense for the related assets. There were no material changes in the estimates or assumptions related to the valuation and classification of property and equipment during fiscal 2013.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
We continually evaluate whether events and changes in circumstances warrant revised estimates of the useful lives or recognition of an impairment loss for long-lived assets. If facts and circumstances indicate that a long-lived asset may be impaired, the carrying value is reviewed. If this review indicates that the carrying value of the asset will not be recovered as determined based on projected undiscounted cash flows related to the asset over its remaining life, the carrying value of the asset is reduced to its estimated fair value. Non-cash impairment losses related to leasehold improvements and fixtures and equipment at underperforming stores totaled $1.5 million, $1.2 million and $5.1 million in fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. As of February 1, 2014, there are an additional three stores with asset carrying values totaling $0.6 million that will require close monitoring in the future. Impairment losses in the future are dependent on a number of factors such as site selection and general economic trends on a localized, regional, or national basis, and thus could be significantly different from historical results. To the extent our estimates for net sales, cost of sales and store expenses are not realized, future assessments of recoverability could result in impairment charges. There were no changes in our impairment loss methodology during fiscal 2013.
Insurance Liabilities
We are largely self-insured for workers’ compensation costs and employee medical claims. Our self-insurance liabilities are based on the total estimated costs of claims filed and estimates of claims incurred but not reported, less amounts paid against such claims. We use current and historical claims data, together with information from actuarial studies, in developing our estimates. The insurance liabilities we record are primarily influenced by the frequency and severity of claims and the Company’s growth. If the underlying facts and circumstances related to the claims change, then we may be required to record more or less expense which could be material in relation to our results of operations. Our self-insurance liabilities totaled $2.7 million ($1.6 million current and $1.1 million noncurrent) as of February 1, 2014 and $2.4 million ($1.6 million current and $0.8 million noncurrent) as of February 2, 2013. There were no material changes in the estimates or assumptions related to insurance liabilities during fiscal 2013.
25
Table of Contents
Operating Leases
We lease all of our store properties and account for the leases as operating leases. Many lease agreements contain tenant improvement allowances, rent holidays, rent escalation clauses and/or contingent rent provisions. For purposes of recognizing incentives and minimum rent expense on a straight-line basis over the terms of the leases, we use the date of initial possession to begin amortization, which is generally when we enter the space and begin to make improvements in preparation of intended use.
For scheduled rent escalation clauses during the lease terms or for rental payments commencing “rent holidays” at a date other than the date of initial occupancy, we record minimum rent expense on a straight-line basis over the terms of the leases. Tenant improvement allowances are included in accrued expenses (current portion) and other long-term liabilities (noncurrent portion) and are amortized over the lease term. Changes in the balances of tenant improvement allowances are included as a component of operating activities in the consolidated statements of cash flows.
Certain leases provide for contingent rents that are not measurable at inception. These contingent rents are primarily based on a percentage of net sales that are in excess of a predetermined level. These amounts are excluded from minimum rent and are included in the determination of total rent expense when it is probable that the expense has been incurred and the amount is reasonably estimable. There were no material changes in the estimates or assumptions related to operating leases during fiscal 2013.
Accounting for Income Taxes
We account for income taxes under the asset and liability method. The computation of income taxes is subject to estimation due to the judgment required and the uncertainty related to the recoverability of deferred tax assets or the outcome of tax audits. We adjust our income tax provision in the period it is determined that actual results will differ from our estimates. Tax law and rate changes are reflected in the income tax provision in the year in which such changes are enacted. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, and tax planning strategies in making an assessment as to the realization of these assets. Based upon the level of historical taxable income and projections for future taxable income over the periods in which the deferred tax assets are deductible and income tax credits and net operating losses may be utilized, management may determine that some or all of the Company’s deferred tax assets may not ultimately be deductible and income tax credits and net operating losses may expire unused. Should such an assessment be made, a valuation allowance against some or all of the Company’s $11.6 million in deferred tax assets would have to be recorded with a resulting charge to income tax expense. There were no material changes in the estimates or assumptions related to income taxes during fiscal 2013.
The above listing is not intended to be a comprehensive list of all our accounting policies. In many cases the accounting treatment of a particular transaction is specifically dictated by U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, with no need for management’s judgment in their application. There are also areas in which management’s judgment in selecting any available alternative would not produce a materially different result.
26
Table of Contents
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURE ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to financial market risks related to changes in interest rates earned on our investments. We cannot predict market fluctuations in interest rates. As a result, future results may differ materially from estimated results due to changes in interest rates. A hypothetical 100 basis point change in prevailing market interest rates would not have materially impacted our financial position, results of operations or cash flows for fiscal 2013. We do not engage in financial transactions for trading or speculative purposes and have not entered into any interest rate hedging contracts. Interest rates on our credit facility did not impact us in fiscal 2013 because we did not borrow during the year.
We source all of our product from apparel markets in the United States in U.S. Dollars and, therefore, are not directly subject to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. However, fluctuations in currency exchange rates could affect our purchasing power with vendors that import merchandise to sell to us. We have not entered into forward contracts to hedge against fluctuations in foreign currency prices.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The financial statements required by this item and the report of the independent accountant thereon required by Item 14(a)(2) appear beginning on page F-2 of this Report. See accompanying Index to the consolidated financial statements on page F-1. The supplementary financial data required by Item 302 of Regulation S-K appears in note 13 to the consolidated financial statements.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We carried out an evaluation under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this Report pursuant to Rules 13a-15 and 15d-15 of the Exchange Act. Based on that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer each concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information has been accumulated and communicated to our management, including the officers who certify our financial reports, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding the required disclosures.
Our disclosure controls and procedures are designed to provide reasonable assurance that the controls and procedures will meet their objectives. Management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the fiscal quarter ended February 1, 2014 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
For the Report of Management on Internal Control over Financial Reporting and the report of our independent registered public accounting firm on Internal Control over Financial Reporting, see “Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting” on page F-2 of this Report and “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” on page F-4 of this Report.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
27
Table of Contents
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The information required by this Item with respect to our executive officers and directors, compliance by our directors, executive officers and certain beneficial owners of our common stock with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, the committees of our Board of Directors, our Audit Committee Financial Expert and our Code of Ethics is incorporated herein by reference to information under the captions entitled “Board of Directors and Committees of the Board of Directors,” “Executive Officers,” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in our definitive proxy statement (to be filed hereafter) in connection with our 2014 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and possibly elsewhere in the proxy statement (or will be filed by amendment to this Report).
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to information under the captions entitled “Executive Compensation,” “Board of Directors and Committees of the Board of Directors” and “Compensation Committee Report” in our definitive proxy statement (to be filed hereafter) in connection with our 2014 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and possibly elsewhere in the proxy statement (or will be filed by amendment to this Report).
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information required by this Item with respect to ownership of our common stock is incorporated herein by reference to the information under the caption entitled “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” in our definitive proxy statement (to be filed hereafter) in connection with our 2014 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and possibly elsewhere in the proxy statement (or will be filed by amendment to this Report).
Equity Compensation Plan Information. The following table represents those securities authorized for issuance as of February 1, 2014 under our existing equity compensation plans.
Plan category | | Number of securities to
be issued upon exercise
of outstanding options,
warrants and rights (1)
(a) | | Weighted average
exercise price of
outstanding options,
warrants and rights (2)
(b) | | Number of securities
remaining available for
future issuance under
equity compensation
plans (excluding
securities reflected in
column (a)) (3) (c) | |
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | | 40,700 | | $ | 34.71 | | 1,068,065 | |
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | | — | | — | | — | |
Total | | 40,700 | | $ | 34.71 | | 1,068,065 | |
(1) Includes 40,700 outstanding options issued under the Citi Trends, Inc. 2005 Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “2005 Plan”). The Citi Trends, Inc. 2012 Incentive Plan (the “2012 Plan”) became effective in May 2012 as a successor to the 2005 Plan. The 2012 Plan provides for the issuance of up to 1,600,000 shares of common stock, plus a number of additional shares (not to exceed 300,000) underlying awards outstanding under prior plans that later terminate or expire unexercised. Such shares will be issued upon the exercise of stock options or as awards of nonvested restricted stock and other performance awards. Does not include nonvested restricted stock grants issued under the 2005 Plan and 2012 Plan totaling 96,000 and 518,000, respectively.
(2) The weighted average exercise price is for options only and does not include nonvested restricted stock.
(3) Consists of shares available for awards of options, restricted stock and other performance awards under the 2012 Plan.
28
Table of Contents
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the information under the captions entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions” and “Board of Directors and Committees of the Board of Directors” in our definitive proxy statement (to be filed hereafter) in connection with our 2014 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and possibly elsewhere in the proxy statement (or will be filed by amendment to this Report).
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the information under the caption entitled “Ratification of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in our definitive proxy statement (to be filed hereafter) in connection with our 2014 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and possibly elsewhere in the proxy statement (or will be filed by amendment to this Report).
29
Table of Contents
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a)(1) Financial Statements
See accompanying Financial Statements beginning on page F-1.
(a)(2) Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulations of the SEC are not required under the related instructions, are inapplicable or the information is included in the Financial Statements, and therefore, have been omitted.
(a)(3) Exhibits
Exhibit Index
Exhibit No. | | Description |
3.1 | | Second Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, as amended by the Certificate of Amendment dated June 22, 2006 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended July 29, 2006) |
| | |
3.2 | | Amended and Restated By-laws (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (File No. 333-125611) filed with the SEC on June 8, 2005) |
| | |
4.1 | | Specimen certificate for shares of common stock, $.01 par value (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Amendment No. 2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-123028) filed with the SEC on April 29, 2005) |
| | |
*10.1 | | Allied Fashion, Inc. Amended and Restated 1999 Stock Option Plan (as previously amended and restated effective as of June 17, 2004) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (File No. 333-125611) filed with the SEC on June 8, 2005) |
| | |
*10.2 | | Amendment to the 1999 Allied Fashion, Inc. Stock Option Plan (as previously amended and restated effective as of June 17, 2004) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended October 28, 2006) |
| | |
*10.3 | | Citi Trends, Inc. Amended and Restated 2005 Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “2005 Plan”) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 2, 2008) |
| | |
*10.4 | | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Employees under the 2005 Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 2, 2008) |
| | |
*10.5 | | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Directors under the 2005 Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.19 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 3, 2007) |
| | |
*10.6 | | Form of Stock Option Agreement for Employees under the 2005 Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 3, 2007) |
| | |
*10.7 | | Form of Stock Option Agreement for Directors under the 2005 Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 3, 2007) |
| | |
*10.8 | | Offer Letter to Ivy Council dated December 6, 2006 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 2, 2008) |
| | |
*10.9 | | Offer Letter to Bruce D. Smith dated March 5, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended May 5, 2007) |
| | |
10.10 | | Credit Agreement, dated March 26, 2008 among Citi Trends, Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiaries of the Borrower identified therein, as the Guarantors, and Bank of America, N.A., as Lender (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.25 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 2, 2008) |
30
Table of Contents
10.11 | | UBS Offer Letter, dated October 8, 2008, together with Acceptance Form of Citi Trends, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended November 1, 2008) |
| | |
10.12 | | First Amendment to Credit Agreement, dated as of March 25, 2009, by and between Citi Trends, Inc. and Bank of America, N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.28 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 31, 2009) |
| | |
*10.13 | | Citi Trends, Inc. Annual Incentive Bonus Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 1, 2009) |
| | |
*10.14 | | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Employees under the 2005 Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended October 31, 2009) |
| | |
*10.15 | | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Directors under the 2005 Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended October 31, 2009) |
| | |
10.16 | | Second Amendment to Credit Agreement, dated as of March 22, 2010, by and between Citi Trends, Inc. and Bank of America, N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.37 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 30, 2010) |
| | |
*10.17 | | Offer Letter to Charles D. Crowell dated February 3, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.29 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 28, 2012) |
| | |
*10.18 | | Third Amendment to Credit Agreement, dated as of July 27, 2011, by and between Citi Trends, Inc., the Guarantor identified therein and Bank of America, N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended July 30, 2011) |
| | |
10.19 | | Credit Agreement, dated October 27, 2011 among Citi Trends, Inc., as Borrower, its wholly owned subsidiary, as Guarantor, and Bank of America, N.A., as Lender (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended October 29, 2011) |
| | |
*10.20 | | Summary of terms of employment for R. Edward Anderson (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.34 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 28, 2012) |
| | |
*10.21 | | Employment Non-Compete, Non-Solicit and Confidentiality Agreement between the Company and R. Edward Anderson dated February 7, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on February 10, 2012) |
| | |
*10.22 | | Severance Agreement between the Company and R. Edward Anderson dated February 7, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.36 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 28, 2012) |
| | |
*10.23 | | Offer Letter to Jason T. Mazzola dated January 18, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.37 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 28, 2012) |
| | |
*10.24 | | Employment Non-Compete, Non-Solicit and Confidentiality Agreement between the Company and Jason T. Mazzola dated February 13, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.38 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 28, 2012) |
| | |
*10.25 | | Severance Agreement between the Company and Jason T. Mazzola dated February 13, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.39 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 28, 2012) |
| | |
*10.26 | | Citi Trends, Inc. 2012 Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended July 28, 2012) |
| | |
*10.27 | | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Employees under the Citi Trends, Inc. 2012 Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended July 28, 2012) |
| | |
*10.28 | | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Directors under the Citi Trends, Inc. 2012 Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended July 28, 2012) |
| | |
*10.29 | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement for Employees under the Citi Trends, Inc. 2012 Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.37 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 2, 2013) |
31
Table of Contents
*10.30 | | Employment Non-Compete, Non-Solicit and Confidentiality Agreement between the Company and Bruce D. Smith dated May 1, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 3, 2013) |
| | |
*10.31 | | Employment Non-Compete, Non-Solicit and Confidentiality Agreement between the Company and Ivy D. Council dated May 1, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 3, 2013) |
| | |
*10.32 | | Employment Non-Compete, Non-Solicit and Confidentiality Agreement between the Company and James A. Dunn dated May 1, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 3, 2013) |
| | |
*10.33 | | Employment Non-Compete, Non-Solicit and Confidentiality Agreement between the Company and Charles D. Crowell dated May 1, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 3, 2013) |
| | |
*10.34 | | Severance Agreement between the Company and Bruce D. Smith dated May 1, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 3, 2013) |
| | |
*10.35 | | Severance Agreement between the Company and Ivy D. Council dated May 1, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 3, 2013) |
| | |
*10.36 | | Severance Agreement between the Company and James A. Dunn dated May 1, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 3, 2013) |
| | |
*10.37 | | Severance Agreement between the Company and Charles D. Crowell dated May 1, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended August 3, 2013) |
| | |
21.1 | | Subsidiary of the Registrant |
| | |
23.1 | | Consent of KPMG LLP |
| | |
31.1 | | Certification of R. Edward Anderson, Chief Executive Officer, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| | |
31.2 | | Certification of Bruce D. Smith, Chief Financial Officer, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| | |
32.1 | | Certification of R. Edward Anderson, Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| | |
32.2 | | Certification of Bruce D. Smith, Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| | |
101 | | The following financial statements from Citi Trends, Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 1, 2014, formatted in XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language): (i) Consolidated Statements of Operations, (ii) Consolidated Balance Sheets, (iii) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, (iv) Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity and (v) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.^ |
* Indicates management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
^ In accordance with Regulation S-T, the XBRL-related information in Exhibit 101 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K shall be deemed “furnished” and not “filed”.
32
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| CITI TRENDS, INC. | |
| (Registrant) | |
| | |
Date April 16, 2014 | By | /s/ R. Edward Anderson | | /s/ Bruce D. Smith |
| | R. Edward Anderson | | Bruce D. Smith |
| | Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | | | |
/s/ R. Edward Anderson | | Chief Executive Officer | | April 16, 2014 |
R. Edward Anderson | | (Principal Executive Officer) and Chairman
of the Board of Directors | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Bruce D. Smith | | Executive Vice President and | | April 16, 2014 |
Bruce D. Smith | | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Brian P. Carney | | Director | | April 16, 2014 |
Brian P. Carney | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Laurens M. Goff | | Director | | April 16, 2014 |
Laurens M. Goff | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ Lawrence E. Hyatt | | Director | | April 16, 2014 |
Lawrence E. Hyatt | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ John S. Lupo | | Director | | April 16, 2014 |
John S. Lupo | | | | |
33
Table of Contents
Citi Trends, Inc.
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS OF AND FOR THE YEARS ENDED FEBRUARY 1, 2014, FEBRUARY 2, 2013 AND JANUARY 28, 2012
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting | F-2 |
| |
Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | F-3 |
| |
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 | F-5 |
| |
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Years Ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012 | F-6 |
| |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012 | F-7 |
| |
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the Years Ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012 | F-8 |
| |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for the Years Ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012 | F-9 |
F-1
Table of Contents
MANAGEMENT’S ANNUAL REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Our internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of consolidated financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
· pertain to maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company;
· provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and
· provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
Under the supervision and with the participation of management, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, we assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of February 1, 2014, based on the criteria described in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992), issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). Based on this assessment, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective based on those criteria as of February 1, 2014.
Our independent registered public accounting firm, KPMG LLP, audited the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of February 1, 2014, as stated in their report which is included herein.
F-2
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Citi Trends, Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Citi Trends, Inc. and subsidiary as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for the years ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Citi Trends, Inc. and subsidiary as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Citi Trends, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of February 1, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated April 16, 2014, expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP | |
| |
Jacksonville, FL | |
April 16, 2014 | |
Certified Public Accountants | |
F-3
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Citi Trends, Inc.:
We have audited Citi Trends, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of February 1, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Citi Trends, Inc.’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, Citi Trends, Inc. maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of February 1, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of Citi Trends, Inc. and subsidiary as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for the years ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012 and our report dated April 16, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
/s/ KPMG LLP | |
| |
Jacksonville, FL | |
April 16, 2014 | |
Certified Public Accountants | |
F-4
Table of Contents
Citi Trends, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013
(in thousands, except share data)
| | February 1,
2014 | | February 2,
2013 | |
Assets | | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 58,928 | | $ | 37,263 | |
Short-term investment securities | | 6,004 | | 12,771 | |
Inventory | | 126,501 | | 141,473 | |
Prepaid and other current assets | | 11,221 | | 10,648 | |
Income tax receivable | | 394 | | 1,134 | |
Deferred tax asset | | 4,711 | | 6,088 | |
Assets held for sale | | — | | 1,415 | |
Total current assets | | 207,759 | | 210,792 | |
Property and equipment, net | | 56,154 | | 70,995 | |
Long-term investment securities | | 19,777 | | 5,754 | |
Deferred tax asset | | 6,932 | | 3,863 | |
Other assets | | 686 | | 741 | |
Total assets | | $ | 291,308 | | $ | 292,145 | |
| | | | | |
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | | | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | | | |
Accounts payable | | $ | 60,037 | | $ | 62,690 | |
Accrued expenses | | 14,651 | | 14,435 | |
Accrued compensation | | 9,548 | | 8,129 | |
Layaway deposits | | 515 | | 660 | |
Total current liabilities | | 84,751 | | 85,914 | |
Other long-term liabilities | | 7,686 | | 10,260 | |
Total liabilities | | 92,437 | | 96,174 | |
| | | | | |
Stockholders’ equity: | | | | | |
Common stock, $0.01 par value. Authorized 32,000,000 shares; 15,604,805 shares issued as of February 1, 2014 and 15,295,780 shares issued as of February 2, 2013; 2012; 15,439,055 shares outstanding as of February 1, 2014 and 15,130,030 shares outstanding as of February 2, 2013 | | 150 | | 149 | |
Paid in capital | | 82,815 | | 80,380 | |
Retained earnings | | 116,071 | | 115,607 | |
Treasury stock, at cost; 165,750 shares as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 | | (165 | ) | (165 | ) |
Total stockholders’ equity | | 198,871 | | 195,971 | |
| | | | | |
Commitments and contingencies (note 11) | | | | | |
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | $ | 291,308 | | $ | 292,145 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
F-5
Table of Contents
Citi Trends, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
Years Ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013, and January 28, 2012
(in thousands, except per share data)
| | Fiscal 2013 | | Fiscal 2012 | | Fiscal 2011 | |
Net sales | | $ | 622,204 | | $ | 654,653 | | $ | 640,824 | |
| | | | | | | |
Cost of sales (exclusive of depreciation shown separately below) | | (394,445 | ) | (426,904 | ) | (420,321 | ) |
Selling, general and administrative expenses | | (206,146 | ) | (207,411 | ) | (207,025 | ) |
Depreciation | | (21,974 | ) | (23,950 | ) | (24,958 | ) |
Asset impairment | | (1,542 | ) | (1,177 | ) | (6,514 | ) |
Gain on sale of former distribution center | | 1,526 | | — | | — | |
Loss from operations | | (377 | ) | (4,789 | ) | (17,994 | ) |
Interest income | | 281 | | 260 | | 243 | |
Interest expense | | (194 | ) | (212 | ) | (79 | ) |
Loss before income taxes | | (290 | ) | (4,741 | ) | (17,830 | ) |
Income tax benefit | | (754 | ) | (2,516 | ) | (7,816 | ) |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 464 | | $ | (2,225 | ) | $ | (10,014 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
Basic net income (loss) per common share | | $ | 0.03 | | $ | (0.15 | ) | $ | (0.69 | ) |
Diluted net income (loss) per common share | | $ | 0.03 | | $ | (0.15 | ) | $ | (0.69 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
Weighted average number of shares outstanding | | | | | | | |
Basic | | 14,798 | | 14,672 | | 14,589 | |
Diluted | | 14,813 | | 14,672 | | 14,589 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
F-6
Table of Contents
Citi Trends, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013, and January 28, 2012
(in thousands)
| | Fiscal 2013 | | Fiscal 2012 | | Fiscal 2011 | |
Operating activities: | | | | | | | |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 464 | | $ | (2,225 | ) | $ | (10,014 | ) |
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | |
Depreciation | | 21,974 | | 23,950 | | 24,958 | |
Asset impairment | | 1,542 | | 1,177 | | 6,514 | |
Deferred income taxes | | (1,692 | ) | (2,899 | ) | (144 | ) |
Gain on sale of former distribution center | | (1,526 | ) | — | | — | |
Loss on disposal of property and equipment | | 1 | | 42 | | 320 | |
Noncash stock-based compensation expense | | 3,355 | | 2,743 | | 2,573 | |
Excess tax benefits from stock-based payment arrangements | | 305 | | 428 | | 268 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | |
Inventory | | 14,972 | | (9,947 | ) | (10,094 | ) |
Prepaid and other current assets | | (573 | ) | (126 | ) | 716 | |
Other assets | | 55 | | 57 | | (190 | ) |
Accounts payable | | (2,653 | ) | (16,251 | ) | 11,007 | |
Accrued expenses and other long-term liabilities | | (2,565 | ) | (2,081 | ) | 5,221 | |
Accrued compensation | | 1,419 | | (2,216 | ) | 1,748 | |
Income tax receivable | | 435 | | 9,633 | | (10,939 | ) |
Layaway deposits | | (145 | ) | 57 | | 159 | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | 35,368 | | 2,342 | | 22,103 | |
| | | | | | | |
Investing activities: | | | | | | | |
Purchases of investment securities | | (24,548 | ) | — | | (11,380 | ) |
Sales/redemptions of investment securities | | 17,292 | | 1,217 | | 1,429 | |
Proceeds from sale of former distribution center | | 2,941 | | — | | — | |
Purchases of property and equipment | | (8,469 | ) | (7,332 | ) | (38,437 | ) |
Net cash used in investing activities | | (12,784 | ) | (6,115 | ) | (48,388 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
Financing activities: | | | | | | | |
Excess tax benefits from stock-based payment arrangements | | (305 | ) | (428 | ) | (268 | ) |
Cash used to settle withholding taxes on stock option exercises and the vesting of nonvested restricted stock | | (668 | ) | (522 | ) | (732 | ) |
Proceeds from the exercise of stock options | | 54 | | — | | 40 | |
Net cash used in financing activities | | (919 | ) | (950 | ) | (960 | ) |
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | 21,665 | | (4,723 | ) | (27,245 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | | | | |
Beginning of year | | 37,263 | | 41,986 | | 69,231 | |
End of year | | $ | 58,928 | | $ | 37,263 | | $ | 41,986 | |
| | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | | | | | | | |
Cash paid for interest | | $ | 127 | | $ | 141 | | $ | 54 | |
Cash payments (refunds) of income taxes | | $ | 503 | | $ | (9,250 | ) | $ | 3,267 | |
Supplemental disclosures of noncash investing activities: | | | | | | | |
Increase (decrease) in accrual for purchases of property and equipment | | $ | 207 | | $ | (1,709 | ) | $ | (1,359 | ) |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
F-7
Table of Contents
Citi Trends, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
Years Ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013, and January 28, 2012
(in thousands, except share amounts)
| | Common Stock | | Paid in | | Retained | | Treasury Stock | | | |
| | Shares | | Amount | | Capital | | Earnings | | Shares | | Amount | | Total | |
Balances—January 29, 2011 | | 14,989,535 | | $ | 147 | | $ | 76,976 | | $ | 127,846 | | 165,750 | | $ | (165 | ) | $ | 204,804 | |
Exercise of stock options | | 13,049 | | 1 | | 39 | | | | | | | | 40 | |
Excess tax benefits from stock based payment arrangements | | | | | | (268 | ) | | | | | | | (268 | ) |
Issuance of nonvested shares to employees and directors under incentive plan | | 242,277 | | | | | | | | | | | | — | |
Forfeiture of nonvested shares by employees and directors | | (149,600 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | — | |
Stock-based compensation expense | | | | | | 2,573 | | | | | | | | 2,573 | |
Net share settlement of options | | | | | | (61 | ) | | | | | | | (61 | ) |
Net share settlement of nonvested shares | | (32,961 | ) | | | (671 | ) | | | | | | | (671 | ) |
Net loss | | | | | | | | (10,014 | ) | | | | | (10,014 | ) |
Balances—January 28, 2012 | | 15,062,300 | | 148 | | 78,588 | | 117,832 | | 165,750 | | (165 | ) | 196,403 | |
Vesting of nonvested shares | | | | 1 | | | | | | | | | | 1 | |
Excess tax benefits from stock based payment arrangements | | | | | | (428 | ) | | | | | | | (428 | ) |
Issuance of nonvested shares to employees and directors under incentive plan | | 334,564 | | | | | | | | | | | | — | |
Forfeiture of nonvested shares by employees and directors | | (56,865 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | — | |
Stock-based compensation expense | | | | | | 2,743 | | | | | | | | 2,743 | |
Net share settlement of nonvested shares | | (44,219 | ) | | | (523 | ) | | | | | | | (523 | ) |
Net loss | | | | | | | | (2,225 | ) | | | | | (2,225 | ) |
Balances—February 2, 2013 | | 15,295,780 | | 149 | | 80,380 | | 115,607 | | 165,750 | | (165 | ) | 195,971 | |
Exercise of stock options | | 6,525 | | | | 54 | | | | | | | | 54 | |
Vesting of nonvested restricted stock units | | 29,166 | | 1 | | | | | | | | | | 1 | |
Excess tax benefits from stock based payment arrangements | | | | | | (305 | ) | | | | | | | (305 | ) |
Issuance of nonvested shares to employees and directors under incentive plan | | 392,466 | | | | | | | | | | | | — | |
Forfeiture of nonvested shares by employees and directors | | (63,060 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | — | |
Stock-based compensation expense | | | | | | 3,355 | | | | | | | | 3,355 | |
Net share settlement of nonvested shares | | (56,072 | ) | | | (669 | ) | | | | | | | (669 | ) |
Net loss | | | | | | | | 464 | | | | | | 464 | |
Balances—February 1, 2014 | | 15,604,805 | | $ | 150 | | $ | 82,815 | | $ | 116,071 | | 165,750 | | $ | (165 | ) | $ | 198,871 | |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements
F-8
Table of Contents
Citi Trends, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012
(1) Organization and Business
Citi Trends, Inc. and its subsidiary (the “Company”) operate as a value-priced retailer of urban fashion apparel and accessories for the entire family. As of February 1, 2014, the Company operated 505 stores in 29 states.
(2) Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
(a) Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiary. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
(b) Fiscal Year
The Company’s fiscal year ends on the Saturday closest to January 31 of each year. The years ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013, and January 28, 2012 are referred to as fiscal 2013, fiscal 2012, and fiscal 2011, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. Fiscal year 2012 is comprised of 53 weeks, while fiscal years 2013 and 2011 are each comprised of 52 weeks.
(c) Cash and Cash Equivalents/Concentration of Credit Risk
For purposes of the consolidated balance sheets and consolidated statements of cash flows, the Company considers all highly liquid investments with maturities at date of purchase of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to a concentration of credit risk consist principally of cash and cash equivalents. The Company places its cash and cash equivalents in what it believes to be high credit quality banks and institutional money market funds. The Company maintains cash accounts that exceed federally insured limits.
(d) Inventory
Inventory is stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out basis) or market as determined by the retail inventory method for store inventory and the average cost method for distribution center inventory. Under the retail inventory method, the cost of inventory is determined by calculating a cost-to-retail ratio and applying it to the retail value of inventory. Merchandise markdowns are reflected in the inventory valuation when the retail price of an item is lowered in the stores. Inventory is recorded net of an allowance for shrinkage based on the most recent physical inventory counts.
(e) Property and Equipment, net
Property and equipment, net are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the lesser of the estimated useful lives (primarily three to five years for computer equipment and furniture, fixtures and equipment, five years for leasehold improvements, seven years for major purchased software systems, and fifteen to twenty years for buildings and building improvements) of the related assets or the relevant lease term.
(f) Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
If facts and circumstances indicate that a long-lived asset may be impaired, the carrying value is reviewed. If this review indicates that the carrying value of the asset will not be recovered as determined based on projected undiscounted cash flows related to the asset over its remaining life, the carrying value of the asset is reduced to its estimated fair value.
(g) Insurance Liabilities
The Company is largely self-insured for workers’ compensation costs and employee medical claims. The Company’s self-insured retention or deductible, as applicable, for each claim involving workers’ compensation and employee medical is limited to $250,000 and $65,000, respectively. Self-insurance liabilities are based on the total estimated costs of claims filed and estimates of claims incurred but not reported, less amounts paid against such claims. Current and historical claims data, together with information from actuarial studies, are used in developing the estimates. The insurance liabilities that are recorded are primarily influenced by the frequency and severity of claims and the Company’s growth. If the underlying facts and circumstances related to the claims change, then the Company may be required to record more or less expense which could be material in relation to results of operations.
F-9
Table of Contents
(h) Stock-Based Compensation
The Company recognizes compensation expense associated with all nonvested restricted stock and stock options based on an estimate of the grant-date fair value of each equity award. Grants of time-based nonvested restricted stock are valued based on the closing stock price on the grant date, while grants of performance-based restricted stock units are valued at an estimate of fair market value using a lattice model. The fair values of options issued are estimated at each grant date using the Black-Scholes Merton option pricing model. See Note 10 for additional information on the Company’s stock-based compensation plans.
(i) Revenue Recognition
Revenue from retail sales net of sales taxes is recognized at the time the customer takes possession of and pays for merchandise, less an allowance for returns. The Company allows customers to return merchandise for up to thirty days after the date of sale and the Company reduces revenues for each fiscal year using a combination of actual and estimated return information for the returns in the thirty days after the year ends. The provision for returns was $0.1 million as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013. Revenue from layaway sales is recognized when the customer has paid for and received the merchandise. If the merchandise is not fully paid for within sixty days, the customer is given a store credit for merchandise payments made, less a re-stocking and layaway service fee. Such fees, which are non-refundable, are recognized in revenue when collected. The introduction of gift cards to all stores was completed in 2010. Proceeds from the sale of gift cards are deferred until the customers use the cards to purchase merchandise. No amounts have yet been amortized into income for gift cards that were sold and are not expected to be redeemed (“breakage”) due to the lack of time that has lapsed since cards began being sold under the program and the relative immateriality of the total gift card liability ($0.6 million and $0.5 million as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013, respectively). All sales are from cash, check or major credit card company transactions. The Company does not offer company-sponsored customer credit accounts.
(j) Cost of Sales
Cost of sales includes the cost of inventory sold during the period and transportation costs, including inbound freight related to inventory sold and freight from the distribution centers to the stores, net of discounts and allowances. Distribution center costs, store occupancy expenses and advertising expenses are not considered components of cost of sales and are included as part of selling, general and administrative expenses. Depreciation is also not considered a component of cost of sales and is included as a separate line item in the consolidated statements of operations. Distribution center costs (exclusive of depreciation) for fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011 were $13.2 million, $13.4 million and $12.3 million, respectively.
(k) Earnings per Share
Basic earnings per common share amounts are calculated using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per common share amounts are calculated using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding plus the additional dilution for all potentially dilutive securities, such as nonvested restricted stock and stock options. During loss periods, diluted loss per share amounts are based on the weighted average number of common shares outstanding because the inclusion of common stock equivalents would be antidilutive.
The following table provides a reconciliation of the number of average common shares outstanding used to calculate basic earnings per share to the number of common shares and common stock equivalents outstanding used in calculating diluted earnings per share for fiscal 2013, 2012, and 2011:
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Average number of common shares outstanding | | 14,798,154 | | 14,671,638 | | 14,589,247 | |
Incremental shares from assumed exercises of stock options | | 1,187 | | — | | — | |
Incremental shares from assumed vesting of nonvested restricted stock | | 14,103 | | — | | — | |
Average number of common shares and common stock equivalents outstanding | | 14,813,444 | | 14,671,638 | | 14,589,247 | |
The dilutive effect of stock-based compensation arrangements is accounted for using the treasury stock method. This method assumes that the proceeds the Company receives from the exercise of stock options are used to repurchase common shares in the market. The Company includes as assumed proceeds the amount of compensation cost attributed to future services and not yet recognized, and the amount of tax benefits, if any, that would be credited to additional paid-in capital assuming exercise of outstanding options and vesting of nonvested restricted stock. For fiscal 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively, there were 41,000, 47,000, and 53,000 options outstanding to purchase shares of common stock excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share because of antidilution. For fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively, there were 607,000, 402,000 and 361,000 shares of nonvested restricted stock, respectively, excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share because of antidilution.
F-10
Table of Contents
(l) Advertising
The Company expenses advertising as incurred. Advertising expense for fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $2.4 million, $3.1 million and $3.2 million, respectively.
(m) Operating Leases
The Company leases all of its store properties and accounts for the leases as operating leases. Many lease agreements contain tenant improvement allowances, rent holidays, rent escalation clauses and/or contingent rent provisions. For purposes of recognizing incentives and minimum rent expense on a straight-line basis over the terms of the leases, the Company uses the date of initial possession to begin amortization, which is generally when the Company enters the space and begins to make improvements in preparation of intended use.
For scheduled rent escalation clauses during the lease terms or for rental payments commencing “rent holidays” at a date other than the date of initial occupancy, the Company records minimum rent expense on a straight-line basis over the terms of the leases. Tenant improvement allowances are included in accrued expenses (current portion) and other long-term liabilities (noncurrent portion) and are amortized over the lease term. Changes in the balances of tenant improvement allowances are included as a component of operating activities in the consolidated statements of cash flows.
Certain leases provide for contingent rents that are not measurable at inception. These contingent rents are primarily based on a percentage of net sales that are in excess of a predetermined level. These amounts are excluded from minimum rent and are included in the determination of total rent expense when it is probable that the expense has been incurred and the amount is reasonably estimable.
The Company is required to recognize a liability for the fair value of a conditional asset retirement obligation when incurred if the liability’s fair value can be reasonably estimated. As of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013, the Company included a liability of $0.7 million in other long-term liabilities, representing estimated expenses that would be incurred upon the termination of the Company’s operating leases.
(n) Store Opening and Closing Costs
New and relocated store opening period costs are charged directly to expense when incurred. When the Company decides to close or relocate a store, the Company records an expense for the present value of expected future rent payments, net of sublease income, if any, in the period that a store closes or relocates. All store opening and closing costs are included in selling, general and administrative expenses.
(o) Income Taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
(p) Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and use assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
The most significant estimates made by management include those used in the valuation of inventory, property and equipment, self-insurance liabilities, leases and income taxes. Management periodically evaluates estimates used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements for continued reasonableness. Appropriate adjustments, if any, to the estimates used are made prospectively based on such periodic evaluations.
F-11
Table of Contents
(q) Business Reporting Segments
The Company is a value-priced retailer of urban fashion apparel and accessories for the entire family. The retail operations represent a single operating segment based on the way the Company manages its business. Operating decisions and resource allocation decisions are made at the Company level in order to maintain a consistent retail store presentation. The Company’s retail stores sell similar products, use similar processes to sell those products, and sell their products to similar classes of customers. All sales and assets are located within the United States. The Company’s merchandise assortment by classification as a percentage of net sales for fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011 is as follows:
| | Percentage of Net Sales | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Children’s | | 27% | | 27% | | 28% | |
Ladies’ | | 26% | | 29% | | 32% | |
Accessories | | 26% | | 23% | | 18% | |
Men’s | | 18% | | 18% | | 19% | |
Home décor | | 3% | | 3% | | 3% | |
(3) Impairment
Goodwill
Goodwill impairment is determined using a two-step process. The first step is to identify if a potential impairment exists by comparing the Company’s fair value with its carrying amount, including goodwill. In the Company’s case, there is only one reporting unit, therefore, fair value and carrying value used in the test are at the consolidated level. If fair value exceeds the carrying amount, goodwill is not considered to have a potential impairment and the second step of the impairment test is not necessary.
The goodwill impairment testing done as of January 28, 2012 indicated that the Company’s carrying value exceeded fair value, requiring that the second step of the test be performed. The second step compares the carrying value of goodwill to an implied fair value of goodwill, which is derived by performing a hypothetical purchase price allocation for the Company as of year-end, allocating the Company’s estimated fair value to its assets and liabilities. The residual amount, if any, from performing this allocation represents the implied fair value of goodwill, and if such value is less than the carrying value of goodwill, an impairment charge is recorded for the difference. The results of the second step of the test indicated that goodwill, totaling $1.4 million, should be fully impaired, resulting in a non-cash charge to asset impairment expense in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2011.
Long-Lived Assets
Non-cash impairment expense related primarily to leasehold improvements and fixtures and equipment at underperforming stores totaled $1.5 million, $1.2 million and $5.1 million in fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
(4) Closure and Sale of Distribution Center
The Company closed its distribution center in Savannah, Georgia in June 2011. A real estate broker was engaged to sell the Savannah land and building; accordingly, the net book value of the related assets was classified as assets held for sale in the February 2, 2013 consolidated balance sheet. The closure of the distribution center required the Company to test the asset for potential impairment. The Company evaluated the fair value of the distribution center, including estimates by real estate brokers, and determined that estimated fair value was in excess of the $1.4 million net book value, therefore, no impairment charge was necessary.
In connection with the closure of the distribution center, the Company incurred $0.6 million of expenses in fiscal 2011, and such amount was recorded in selling, general and administrative expenses within the consolidated statement of operations for the year ended January 28, 2012.
In August 2013, the Company sold the distribution center for $2.9 million, resulting in a gain on sale of $1.5 million.
F-12
Table of Contents
(5) Property and Equipment, net
The components of property and equipment as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 are as follows (in thousands):
| | February 1, | | February 2, | |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | |
Land | | $ | 246 | | $ | 246 | |
Buildings | | 23,437 | | 22,027 | |
Leasehold improvements | | 73,276 | | 73,212 | |
Furniture, fixtures and equipment | | 95,671 | | 93,772 | |
Computer equipment | | 24,502 | | 23,019 | |
Construction in progress | | 890 | | 1,489 | |
| | 218,022 | | 213,765 | |
Accumulated depreciation | | (161,868 | ) | (142,770 | ) |
| | $ | 56,154 | | $ | 70,995 | |
(6) Fair Value Measurements
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants in the principal or most advantageous market at the measurement date. Fair value is established according to a hierarchy that prioritizes observable and unobservable inputs used to measure fair value into three broad levels, which are described below:
Level 1: Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets that are accessible at the measurement date for assets or liabilities. The fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to Level 1 inputs.
Level 2: Observable prices that are based on inputs not quoted on active markets, but corroborated by market data.
Level 3: Unobservable inputs are used when little or no market data is available. Level 3 inputs are given the lowest priority in the fair value hierarchy.
As of February 1, 2014, the Company’s investment securities are classified as held-to-maturity since the Company has the intent and ability to hold the investments to maturity. Such securities are carried at amortized cost plus accrued interest and consist of the following (in thousands):
| | Amortized
Cost | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | Gross
Unrealized
Losses | | Fair Market
Value | |
Short-term: | | | | | | | | | |
Bank certificates of deposit (Level 2) | | $ | 6,004 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 6,004 | |
| | $ | 6,004 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 6,004 | |
Long-term: | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of the U. S. Treasury (Level 1) | | $ | 15,152 | | $ | 19 | | $ | — | | $ | 15,171 | |
Bank certificates of deposit (Level 2) | | 4,625 | | — | | — | | 4,625 | |
| | $ | 19,777 | | $ | 19 | | $ | — | | $ | 19,796 | |
The amortized cost and fair market value of investment securities as of February 1, 2014 by contractual maturity are as follows (in thousands):
| | Amortized
Cost | | Fair
Market
Value | |
Mature in one year or less | | $ | 6,004 | | $ | 6,004 | |
Mature after one year through five years | | 19,777 | | 19,796 | |
| | $ | 25,781 | | $ | 25,800 | |
F-13
Table of Contents
As of February 2, 2013, the Company’s investment securities were classified as held-to-maturity and consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | Amortized
Cost | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | Gross Unrealized
Losses | | Fair
Market
Value | |
Short-term: | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of the U. S. Treasury (Level 1) | | $ | 4,993 | | $ | 39 | | $ | — | | $ | 5,032 | |
Obligations of states and municipalities (Level 2) | | 1,731 | | 9 | | — | | 1,740 | |
Bank certificates of deposit (Level 2) | | 6,047 | | — | | — | | 6,047 | |
| | $ | 12,771 | | $ | 48 | | $ | — | | $ | 12,819 | |
Long-term: | | | | | | | | | |
Bank certificates of deposit (Level 2) | | $ | 5,754 | | $ | 6 | | $ | — | | $ | 5,760 | |
The amortized cost and fair market value of investment securities as of February 2, 2013 by contractual maturity were as follows (in thousands):
| | Amortized
Cost | | Fair
Market
Value | |
Mature in one year or less | | $ | 12,771 | | $ | 12,819 | |
Mature after one year through five years | | 5,754 | | 5,760 | |
| | $ | 18,525 | | $ | 18,579 | |
There were no changes among the levels in the three fiscal years ended February 1, 2014.
Fair market values of Level 2 investments are determined by management with the assistance of a third party pricing service. Since quoted prices in active markets for identical assets are not available, these prices are determined by the third party pricing service using observable market information such as quotes from less active markets and quoted prices of similar securities.
(7) Revolving Line of Credit
On October 27, 2011, the Company entered into a five-year, $50 million credit facility with Bank of America to replace its prior $20 million credit facility. The facility includes a $25 million uncommitted “accordion” feature that under certain circumstances could allow the Company to increase the size of the facility to $75 million. Borrowings, if any, under the facility will bear interest (a) for LIBOR Rate Loans, at LIBOR plus 1.5%, or (b) for Base Rate Loans, at a rate equal to the highest of (i) the prime rate plus 0.5%, (ii) the Federal Funds Rate plus 1.0%, or (iii) LIBOR plus 1.5%. The facility is secured by the Company’s inventory, accounts receivable and related assets, but not its real estate, fixtures and equipment, and it contains one financial covenant, a fixed charge coverage ratio, which is applicable and tested only in certain circumstances. The facility has an unused commitment fee of 0.25% and permits the payment of cash dividends subject to certain limitations, including a requirement that there were no borrowings outstanding in the 30 days prior to the dividend payment and no borrowings are expected in the 30 days subsequent to the payment. The Company has had no borrowings under either the existing or prior facility.
F-14
Table of Contents
(8) Income Taxes
Income tax (benefit) expense for fiscal 2013, 2012, and 2011 consists of the following (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Current: | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 637 | | $ | 70 | | $ | (6,809 | ) |
State | | 301 | | 313 | | (863 | ) |
Total current | | 938 | | 383 | | (7,672 | ) |
Deferred: | | | | | | | |
Federal | | (1,882 | ) | (2,281 | ) | (499 | ) |
State | | 190 | | (618 | ) | 355 | |
Total deferred | | (1,692 | ) | (2,899 | ) | (144 | ) |
Total income tax benefit | | $ | (754 | ) | $ | (2,516 | ) | $ | (7,816 | ) |
Income tax (benefit) expense computed using the federal statutory rate is reconciled to the reported income tax (benefit) expense as follows for fiscal 2013, 2012, and 2011 (in thousands):
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | |
Statutory rate applied to loss before income taxes | | $ | (102 | ) | $ | (1,659 | ) | $ | (6,241 | ) |
State income taxes, net of federal benefit | | (9 | ) | (182 | ) | (684 | ) |
State tax credits | | (144 | ) | (106 | ) | (342 | ) |
State tax credits - valuation allowance (net of federal benefit) | | 359 | | — | | 810 | |
Tax exempt interest | | (63 | ) | (7 | ) | (9 | ) |
General business credits | | (886 | ) | (691 | ) | (1,477 | ) |
Other | | 91 | | 129 | | 127 | |
Income tax benefit | | $ | (754 | ) | $ | (2,516 | ) | $ | (7,816 | ) |
The components of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 are as follows (in thousands):
| | February 1, | | February 2, | |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | |
Deferred tax assets: | | | | | |
Deferred rent amortization | | $ | 1,322 | | $ | 1,773 | |
Inventory capitalization | | 2,238 | | 2,628 | |
Federal jobs credits | | 2,072 | | 1,438 | |
Book and tax depreciation differences | | 1,915 | | — | |
Vacation liability | | 828 | | 850 | |
State tax credits | | 1,539 | | 1,528 | |
Stock compensation | | 1,369 | | 1,204 | |
Legal expense reserve | | 595 | | 604 | |
Insurance liabilities | | 851 | | 803 | |
Other | | 478 | | 486 | |
Subtotal deferred tax assets | | 13,207 | | 11,314 | |
Less: State tax credits valuation allowance - net | | (1,169 | ) | (810 | ) |
Total deferred tax assets | | 12,038 | | 10,504 | |
| | | | | |
Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | |
Book and tax depreciation differences | | — | | (232 | ) |
Prepaid expenses | | (395 | ) | (321 | ) |
Total deferred tax liabilities | | (395 | ) | (553 | ) |
Net deferred tax asset | | $ | 11,643 | | $ | 9,951 | |
F-15
Table of Contents
The Company files income tax returns in U.S. federal and state jurisdictions where it does business and is subject to examinations by the IRS and other taxing authorities. With a few exceptions, the Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal and state income tax examinations by tax authorities for years prior to fiscal 2010. The Company reviews and assesses uncertain tax positions, if any, with recognition and measurement of tax benefit based on a “more-likely-than-not” standard with respect to the ultimate outcome, regardless of whether this assessment is favorable or unfavorable. As of February 1, 2014, there were no benefits taken on the Company’s income tax returns that do not qualify for financial statement recognition. If a tax position does not meet the minimum statutory threshold to avoid payment of penalties and interest, a company is required to recognize an expense for the amount of the interest and penalty in the period in which the company claims or expects to claim the position on its tax return. For financial statement purposes, companies are allowed to elect whether to classify such charges as either income tax expense or another expense classification. Should such expense be incurred in the future, the Company will classify such interest as a component of interest expense and penalties as a component of income tax expense.
In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, and tax planning strategies in making this assessment. Based upon the level of historical taxable income and projections for future taxable income over the periods in which the deferred tax assets are deductible and income tax credits may be utilized, management believes it is more likely than not that the Company will realize the benefits of these deductible differences with the exception of certain tax credits available in one state. Losses incurred in 2011 caused the Company to conclude that its ability to utilize a portion of such state’s tax credits was no longer more likely than not, necessitating a charge to income tax expense and a reduction in deferred tax assets totaling $0.8 million in connection with the establishment of a valuation allowance. In 2013, the Company increased the valuation allowance by $0.4 million when it concluded that its ability to utilize most of the remaining portion of such credits was no longer more likely than not.
The effective income tax rate for fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011 included the recognition of benefits arising from various federal and state tax credits. Under current IRS and state income tax regulations, these credits may be carried back for two years or carried forward for periods up to 20 years. The income tax benefit in fiscal 2013 included $1.0 million related to such credits, partially offset by the aforementioned $0.4 million increase in a valuation allowance. The income tax benefit in fiscal 2012 included $0.8 million related to such credits. The income tax benefit in fiscal 2011 included $1.8 million related to such credits, partially offset by the aforementioned $0.8 million establishment of a valuation allowance.
A number of U.S. income tax provisions expired on December 31, 2013. Included in the expiring tax provisions are certain employment tax credits, including the work opportunity tax credit, as well as provisions which allow for accelerated depreciation on qualified leasehold improvements and other qualified property. If not renewed, the expiration of certain employment credits will adversely impact the Company’s income tax expense beginning in the first quarter of 2014.
(9) Other Long-Term Liabilities
The components of other long-term liabilities as of February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 are as follows (in thousands):
| | February 1,
2014 | | February 2,
2013 | |
Deferred rent | | $ | 2,051 | | $ | 3,342 | |
Tenant improvement allowances | | 3,823 | | 5,384 | |
Other | | 1,812 | | 1,534 | |
| | $ | 7,686 | | $ | 10,260 | |
(10) Stockholders’ Equity
Stock-Based Compensation
On April 6, 2012, the Company adopted the Citi Trends, Inc. 2012 Incentive Plan (the “2012 Plan”), which became effective upon approval by the Company’s stockholders on May 23, 2012. The 2012 Plan is a successor plan to the 2005 Citi Trends, Inc. Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “2005 Plan”), which became effective upon the consummation of the Company’s initial public offering in May 2005. The 2005 Plan superseded and replaced the 1999 Allied Fashion Stock Option Plan (the “1999 Plan”).
The 1999 Plan provided for the grant of incentive and nonqualified options to key employees and directors, while the 2005 Plan provided for the grant of incentive and nonqualified options, nonvested restricted stock and other forms of stock-based compensation
F-16
Table of Contents
to key employees and directors. The 2012 Plan provides for the grant of incentive and nonqualified options, nonvested restricted stock and other forms of stock-based and cash-based compensation to key employees and directors.
Shares of time-based nonvested restricted stock granted to employees vest in either equal installments over three or four years from the date of grant, or over three years at 25% on the first and second anniversaries and 50% on the third anniversary. Shares issued to directors vest one or two years from the date of grant. The Company records compensation expense for grants of time-based nonvested restricted stock on a straight line basis over the requisite service period of the stock recipients which is equal to the vesting period of the stock. Total compensation cost for such stock is calculated based on the closing market price on the date of grant multiplied by the number of shares granted. Using an estimated forfeiture rate equal to 12.8%, the Company expects to recognize $4.5 million in future compensation expense from the grants of time-based restricted stock over the requisite service period of up to four years. Compensation costs for grants of performance-based restricted stock units (RSU’s) are recorded in full on the date of grant using a lattice model to estimate fair market value. During fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011, compensation expense arising from time-based nonvested restricted stock grants and performance-based RSU’s totaled $3.4 million, $2.7 million and $2.6 million, respectively.
A summary of activity related to time-based nonvested restricted stock grants during fiscal year 2013 is as follows:
| | Nonvested
Restricted
Shares | | Weighted Average
Grant Date
Fair Value | |
Outstanding as of February 2, 2013 | | 425,946 | | $ | 16.51 | |
Granted | | 392,466 | | 11.02 | |
Vested | | (141,625 | ) | 17.60 | |
Forfeited | | (63,060 | ) | 14.13 | |
Outstanding as of February 1, 2014 | | 613,727 | | $ | 12.98 | |
In March 2013, the Company granted 38,889 RSU’s to one employee. The RSU’s have performance vesting criteria which are based upon the closing price of the Company’s stock achieving certain thresholds. The shares vest 25% upon achieving a closing stock price for a 20 consecutive day period of $11; $13; $16; and $20, respectively. The award expires 3 years from the date of grant. On the date of grant, the Company expensed $219,000 which was the estimated fair market value. The first three thresholds were achieved in 2013, resulting in the vesting of 29,166 shares during the year and an unvested balance of 9,723 shares as of February 1, 2014.
Cash flows resulting from tax deductions in excess of the cumulative compensation cost recognized for options exercised and vesting of restricted shares (“excess tax benefits”) are classified as financing cash flows. Decrease in such excess tax benefits was $0.3 million, $0.4 million and $0.3 million in fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Compensation expense associated with stock options is based on an estimate of the fair value of each option award on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes Merton option pricing model. Expected volatility is based on estimated future volatility of the Company’s common stock price. No compensation expense for stock options was recorded during fiscal 2013, 2012 or 2011 as the last grant vested prior to the beginning of fiscal 2011.
As of February 1, 2014, there remained outstanding 40,700 options, issued under the 2005 Plan. No options have been issued under the 2012 Plan. The Board of Directors determined the exercise prices of the option grants. Option grants generally vested in equal installments over four years from the date of grant for employees and over one to three years for directors and were generally exercisable up to ten years from the date of grant. The exercise price of stock options may be satisfied through net share settlements. A summary of the status of stock options under the Company’s stock option plans and changes during fiscal 2013 is presented in the table below:
F-17
Table of Contents
| | 2013 | |
| | | | | | Weighted Average | | | |
| | | | Weighted Average | | Remaining | | Aggregate | |
| | | | Exercise | | Contractual | | Intrinsic | |
| | Options | | Price | | Term (Years) | | Value | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding as of February 2, 2013 | | 51,025 | | $ | 31.69 | | 2.8 | | $ | 32,871 | |
Granted | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
Exercised | | (6,525 | ) | 8.30 | | 0.4 | | 7.49 | |
Net shares settled | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
Forfeited | | (3,800 | ) | 39.40 | | 2.1 | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding as of February 1, 2014 | | 40,700 | | $ | 34.71 | | 2.0 | | $ | 14,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Vested as of February 1, 2014 | | 40,700 | | $ | 34.71 | | 2.0 | | $ | 14,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Exercisable as of February 1, 2014 | | 40,700 | | $ | 34.71 | | 2.0 | | $ | 14,000 | |
As of February 1, 2014, the range of exercise prices was $14.00 to $44.03. As of February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012, the range of exercise prices was $4.46 to $44.03.
Cash received from options exercised totaled $54,000 in fiscal 2013, $0 in fiscal 2012, and $40,000 in 2011. The intrinsic value of the options exercised in fiscal 2013 and 2011 was $49,000 and $231,000, respectively.
(11) Commitments and Contingencies
The Company leases its stores under operating leases, which generally have an initial term of five years with renewal options. Future minimum rent payments under operating leases having noncancellable lease terms as of February 1, 2014 are as follows (in thousands):
Fiscal Year: | | | |
2014 | | $ | 38,096 | |
2015 | | 30,860 | |
2016 | | 21,661 | |
2017 | | 12,906 | |
2018 | | 7,020 | |
Thereafter | | 4,500 | |
Total future minimum lease payments | | $ | 115,043 | |
Certain operating leases provide for fixed monthly rents, while others provide for contingent rents computed as a percentage of net sales and others provide for a combination of both fixed monthly rents and contingent rents computed as a percentage of net sales. Rent expense was $42.1 million, $41.7 million and $39.8 million in fiscal 2013, 2012 and 2011 (including $0.5 million, $0.7 million and $0.9 million of percentage rent), respectively.
On August 12, 2011, the Company received a letter of determination from the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (the “EEOC”) commencing a conciliation process regarding alleged discrimination against males by the Company in its hiring and promotion practices during the years 2004 through 2006. In its letter of determination, the EEOC sought recovery in the amount of $0.2 million on behalf of a former male employee and in the additional amount of $3.8 million in a settlement fund for a class of unidentified males who sought or considered seeking manager or assistant manager positions in the Company’s stores. The EEOC also seeks certain undertakings by the Company with regard to its employment policies and procedures and a reporting obligation to the EEOC with respect to the Company’s compliance with these undertakings.
The Company has not received full documentation or information from the EEOC in support of its letter of determination, but has undertaken its own internal analysis of the EEOC’s claims and defenses to such claims and has had discussions with the EEOC in that regard. Following discussions with the EEOC regarding possible settlement, the EEOC proposed a settlement amount to be paid by the Company of $2.5 million, with any unclaimed funds following efforts to identify and compensate claimants to be directed to one or more charities. In the interest of reaching a satisfactory conciliation agreement with the EEOC, the Company proposed a total economic settlement offer of $1.0 million to cover all claims and the expenses of administering and complying with the settlement
F-18
Table of Contents
(excluding professional fees), with no reversion of unclaimed funds back to the Company. The Company continues to await the EEOC’s response to the Company’s most recent proposal regarding settlement. The Company is also evaluating other aspects of the conciliation process established by the EEOC.
On February 24, 2012, a suit was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of Alabama, Middle Division, by certain individuals as a purported collective action on behalf of current and former employees of the Company holding store managerial positions. The plaintiffs allege that store managers have been improperly classified as exempt from the obligation to pay overtime in violation of the Fair Labor Standards Act. The Company is vigorously defending the claims that have been asserted in this lawsuit. The trial court has conditionally certified a class of store managers and ruled that store managers who signed arbitration agreements are not subject to arbitration. The trial court’s ruling regarding arbitration was affirmed on appeal by a panel of the United States Court of Appeals for the Eleventh Circuit. Also, notwithstanding the initial actions by the trial court, the conditional class may be subject to decertification at the close of discovery. Because no discovery has been conducted to date, the Company is unable to determine the probability of any particular outcome and it is not reasonably possible to estimate a range of loss with respect to this matter. Accordingly, no accrual for costs has been recorded, and the potential impact of this matter on the Company’s financial position, results of operations and cash flows cannot be determined at this time.
The Company from time to time is also involved in various other legal proceedings incidental to the conduct of its business, including claims by customers, employees or former employees. Once it becomes probable that the Company will incur costs in connection with a legal proceeding and such costs can be reasonably estimated, it establishes appropriate reserves. While legal proceedings are subject to uncertainties and the outcome of any such matter is not predictable, the Company is not aware of any legal proceedings pending or threatened against it that it expects to have a material adverse effect on its financial condition, results of operations or liquidity.
(12) �� Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
The following table summarizes the allowance for inventory shrinkage (in thousands):
| | Allowance for
Inventory
Shrinkage | | Allowance for
Deferred Tax
Assets | |
Balance as of January 29, 2011 | | $ | 1,922 | | $ | — | |
Additions charged to costs and expenses | | 5,758 | | 810 | |
Deductions | | (5,693 | ) | — | |
Balance as of January 28, 2012 | | 1,987 | | 810 | |
Additions charged to costs and expenses | | 7,608 | | — | |
Deductions | | (7,260 | ) | — | |
Balance as of February 2, 2013 | | 2,335 | | 810 | |
Additions charged to costs and expenses | | 7,535 | | 359 | |
Deductions | | (7,302 | ) | — | |
Balance as of February 1, 2014 | | $ | 2,568 | | $ | 1,169 | |
For the allowance for inventory shrinkage, additions charged to costs and expenses are the result of estimated inventory shrinkage,while deductions represent actual inventory shrinkage incurred from physical inventories taken during the fiscal year.
For the deferred tax asset valuation allowance, additions charged to costs and expenses represent the establishment of a valuation allowance when management determines that its ability to utilize certain tax credits included in deferred tax assets is no longer more likely than not.
F-19
Table of Contents
(13) Unaudited Quarterly Results of Operations
| | Quarter Ended | |
| | Feb. 1 | | Nov. 2 | | Aug. 3 | | May 4 | | Feb. 2 | | Oct. 27 | | Jul. 28 | | Apr. 28 | |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2013 | | 2013 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2012 | | 2012 | |
| | (in thousands, except per share and share amounts) | |
Statement of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | | $ | 157,193 | | $ | 145,362 | | $ | 137,821 | | $ | 181,828 | | $ | 175,656 | | $ | 148,985 | | $ | 132,318 | | $ | 197,694 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of sales (exclusive of depreciation shown separately below) | | (99,567 | ) | (92,074 | ) | (88,299 | ) | (114,505 | ) | (118,165 | ) | (97,808 | ) | (87,903 | ) | (123,028 | ) |
Selling, general and administrative expenses | | (50,170 | ) | (52,148 | ) | (51,920 | ) | (51,908 | ) | (52,678 | ) | (51,132 | ) | (50,932 | ) | (52,669 | ) |
Depreciation | | (5,258 | ) | (5,454 | ) | (5,667 | ) | (5,595 | ) | (5,797 | ) | (5,970 | ) | (6,038 | ) | (6,145 | ) |
Asset impairment | | (305 | ) | (556 | ) | (654 | ) | (27 | ) | (517 | ) | (660 | ) | — | | — | |
Gain on sale of former distribution center | | — | | 1,526 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) from operations | | 1,893 | | (3,344 | ) | (8,719 | ) | 9,793 | | (1,501 | ) | (6,585 | ) | (12,555 | ) | 15,852 | |
Interest, net | | 19 | | 29 | | 18 | | 21 | | 17 | | 16 | | 2 | | 13 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) before income taxes | | 1,912 | | (3,315 | ) | (8,701 | ) | 9,814 | | (1,484 | ) | (6,569 | ) | (12,553 | ) | 15,865 | |
Income tax expense (benefit) | | 447 | | (1,643 | ) | (3,208 | ) | 3,650 | | (780 | ) | (2,869 | ) | (4,628 | ) | 5,761 | |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 1,465 | | $ | (1,672 | ) | $ | (5,493 | ) | $ | 6,164 | | $ | (704 | ) | $ | (3,700 | ) | $ | (7,925 | ) | $ | 10,104 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.10 | | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.42 | | $ | (0.05 | ) | $ | (0.25 | ) | $ | (0.54 | ) | $ | 0.69 | |
Diluted | | $ | 0.10 | | $ | (0.11 | ) | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.42 | | $ | (0.05 | ) | $ | (0.25 | ) | $ | (0.54 | ) | $ | 0.69 | |
Weighted average shares used to compute net income (loss) per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | 14,824,656 | | 14,815,107 | | 14,801,217 | | 14,751,637 | | 14,698,736 | | 14,676,817 | | 14,673,403 | | 14,635,509 | |
Diluted | | 14,881,752 | | 14,815,107 | | 14,801,217 | | 14,753,048 | | 14,698,736 | | 14,676,817 | | 14,673,403 | | 14,636,918 | |
Net income (loss) per share is computed independently for each period presented. As a result, the total of net income (loss) per share for the four quarters may not equal the annual amount.
F-20
