| | Daniel M. Miller Partner (604) 630-5199 FAX (604) 687-8504 miller.dan@dorsey.com |
January 4, 2013
Division of Corporation Finance
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission
100 F Street N.E.
Washington, D.C. 20549
USA
Attention: H. Roger Schwall, Assistant Director
| Re: | Dejour Energy Inc. |
| | Registration Statement on Form F-3 |
| | Filed August 27, 2012 |
| | |
| | File No. 333-183587 |
| | Form 20-F for Fiscal Year ended December 31, 2011 |
| | Filed April 30, 2012 |
| | File No. 001-33491 |
Dear Sirs and Mesdames:
On behalf of our client, Dejour Energy Inc. (the “Company”), and pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Act”), and the rules and regulations thereunder, we transmit for your review the Company’s responses, as we have been informed by the Company, to the Staff’s letters of comments, dated September 14, 2012 and September 25, 2012 (the “Comment Letters”), in respect of the above noted filings. The Company’s responses below are keyed to the headings and comment numbers contained in the Comment Letters.
Comment Letter Dated September 14, 2012
Form 20-F for Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2011
Item 3, Key Information, page 7
Selected Financial Data, page 7


January 4, 2013
Page 2
| 1. | We note your presentation of selected financial data under Canadian GAAP for 2007, 2008 and 2009, and under International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) for 2010 and 2011. Please revise your presentation to disclose that the information based on previous GAAP is not comparable to the information based on IFRS. In addition, please revise your presentation so financial data determined under Canadian GAAP or US GAAP is not presented side-by-side with IFRS financial data here and throughout your Form 20-F. Refer to Form 20-F General Instruction G(h)(1) and G(h)(3). |
| | The requested revisions will be made in Amendment No. 2 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011 (the “Amendment”), a draft of which is included herewith, under the heading “Item.3. Key Information – Selected Financial Information” beginning on page 8. |
Item 4, Information on the Company, page 19
Reserves Price Sensitivity, page 34
| 2. | We note your disclosure of the non-GAAP measure PV-10 in the tables presented on page 35. It does not appear that you have presented a reconciliation to the most directly comparable GAAP measure (i.e., the standardized measure of future net discounted cash flows presented in accordance with Item 302(B) of Regulation S-K). Please revise your disclosure accordingly. Refer to Item 10(e) of Regulation S-K. |
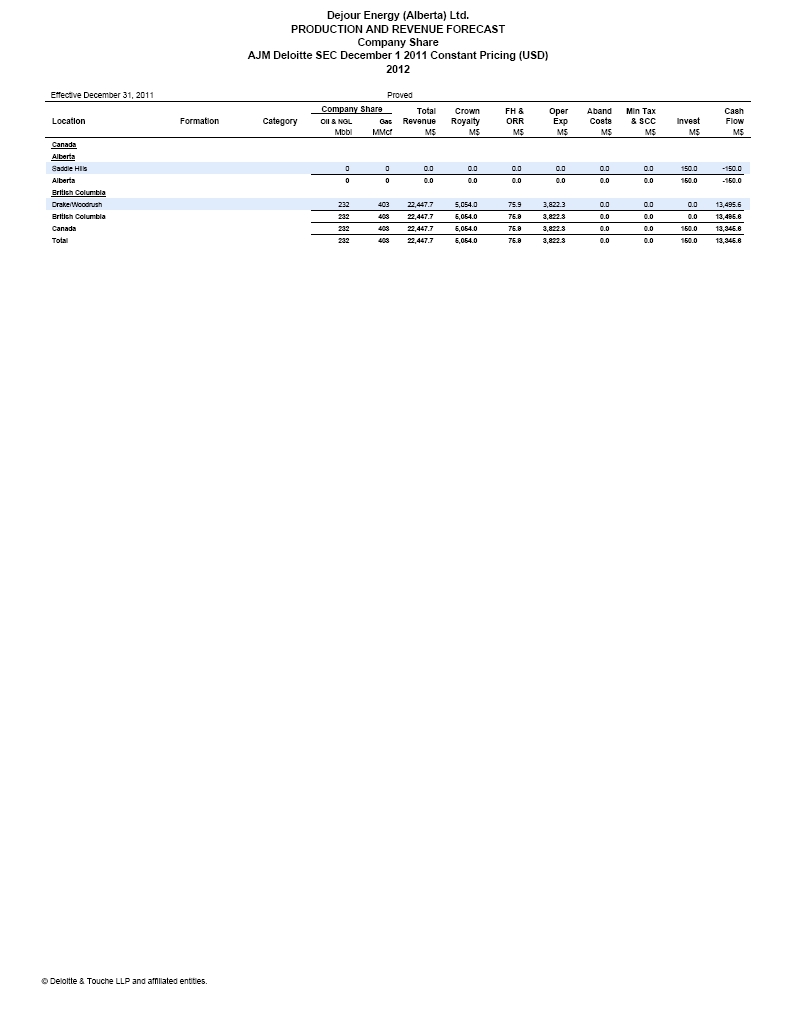
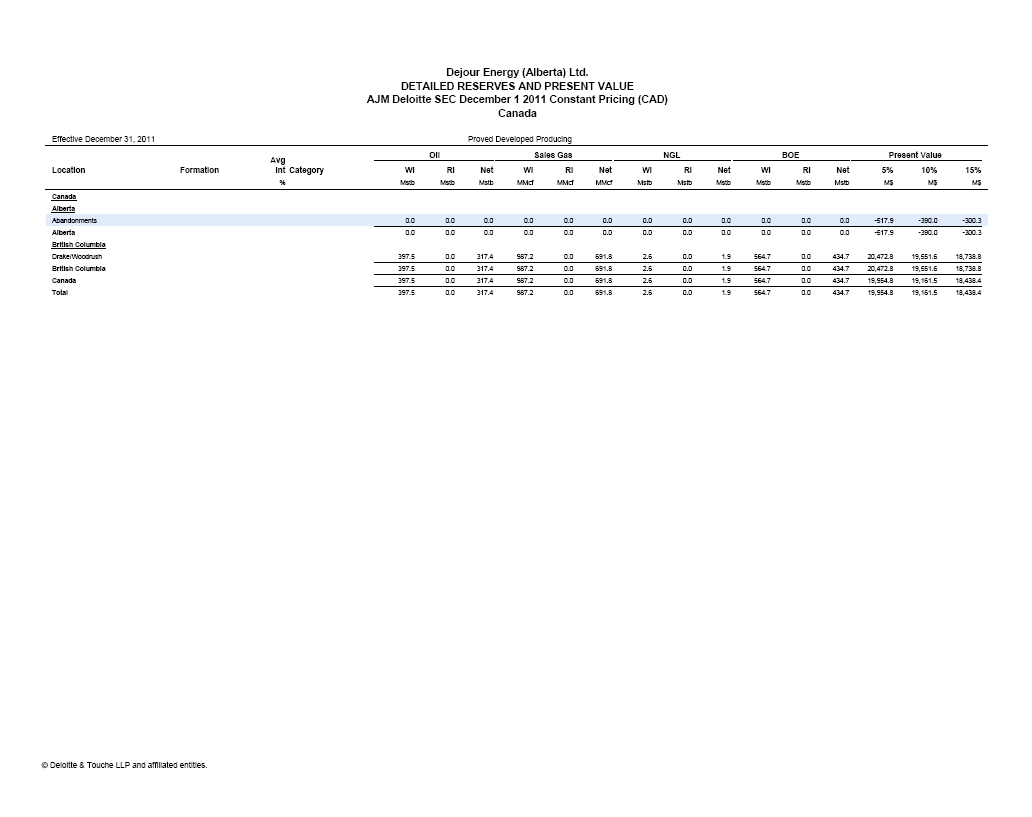
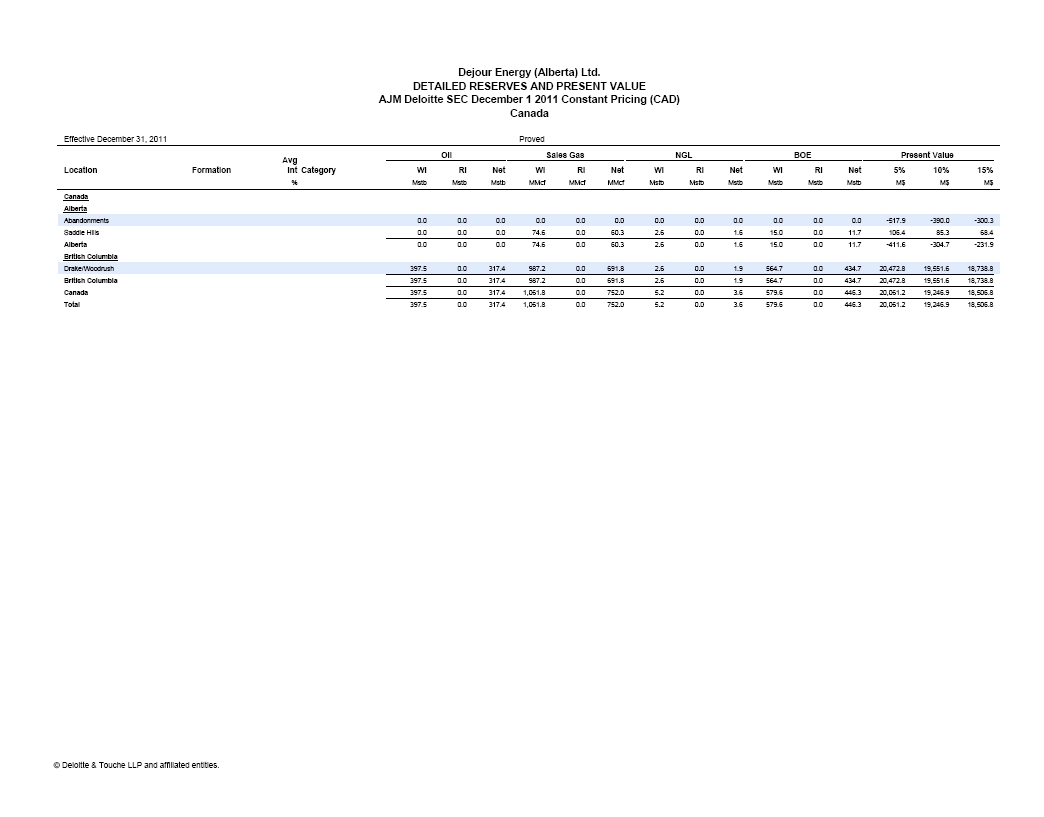
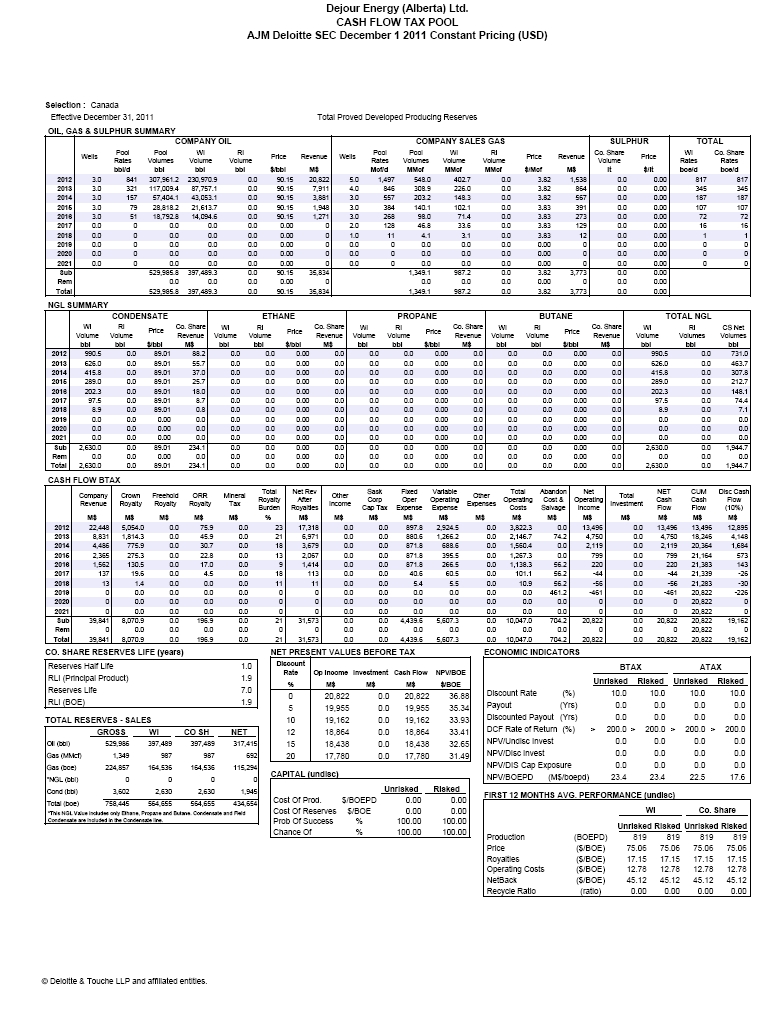
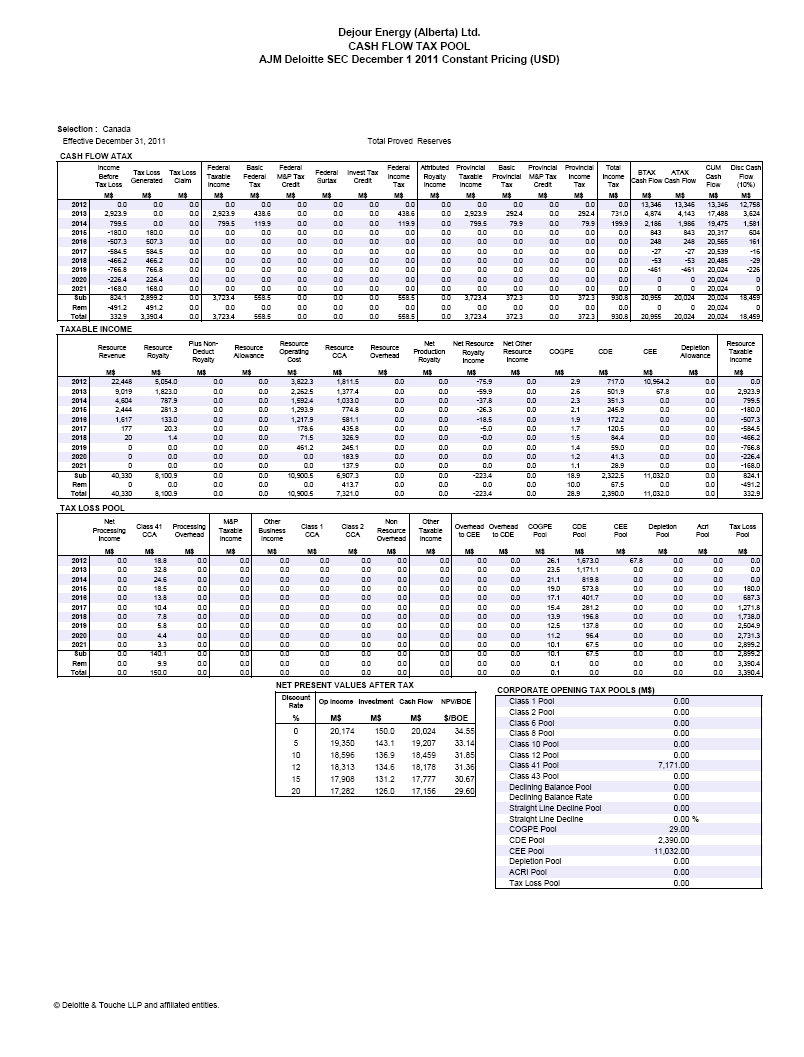
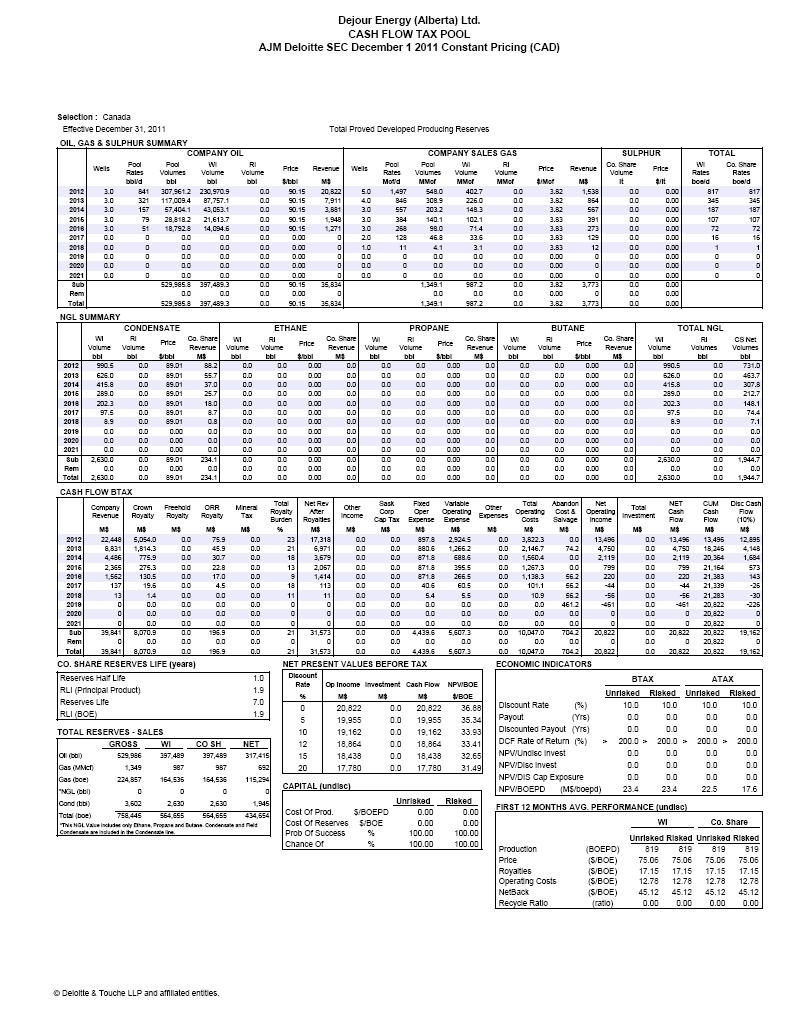
| | The requested reconciliation to the standardized measure of future net discounted cash flows has been included in the draft Amendment under the heading “Item 4. Information on the Company – D. Property, Plant and Equipment – Summary of Oil and Gas Reserves as of Fiscal Year-End Based on Average Fiscal Year Prices – Total Proved Reserves”, on page 38. |
Independent Auditor’s Report, page F-2
| 3. | We note the report issued by your independent accountant states: “In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Dejour Energy Inc…in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards.” Please obtain a revised report which complies with Item 17(c) of Form 20-F and explicitly states, if true, the financial statements comply with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board. |
| | A revised and corrected audit report has been included with the financial statements that are included beginning on page F-1 of the draft Amendment. |
| 4. | We note the report issued by your independent accountant states that their audit was conducted in accordance with Canadian generally accepted auditing standards. Please obtain a revised report which includes a statement that the audit was conducted “in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States).: Refer to Instruction 2 to Item 8.A.2 of Form 20-F. |


January 4, 2013
Page 3
| | A revised and corrected audit report has been included with the financial statements that are included beginning on page F-1 of the draft Amendment. |
| 5. | We also note the report issued by your independent accountant appears to use going concern language that is not consistent with PCAOB standards. Please obtain a revised report that uses the term “substantial doubt” in referencing a going concern matter. Refer to AU 341. |
| | A revised and corrected audit report has been included with the financial statements that are included beginning on page F-1 of the draft Amendment. |
Comment Letter Dated September 25, 2012
Form 20-F for Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2011
Information on the Company, page 19
Summary of Oil and Gas Reserves as of Fiscal-Year End Based on Average Fiscal-Year Prices, page 34
| 1. | We note your disclosure of the $7 million in costs incurred during 2011 to convert proved undeveloped reserves to proved developed reserves as required by Item 1203(c) of Regulation S-K. Expand your disclosure to also address the material changes in your proved undeveloped reserves, including the quantities converted into proved developed reserves during the year. See Item 1203(b) of Regulation S-K. |
| | The requested disclosure has been provided in the draft Amendment under the heading “Item 4. Information on the Company – D. Property, Plant and Equipment – Summary of Oil and Gas Reserves as of Fiscal Year-End Based on Average Fiscal Year Prices – Proved Undeveloped Reserves”, on page 37. |
Reserves Price Sensitivity, page 34
| 2. | Your cautionary note on page 34 states “the following table contains reserve sensitivity pricing” and further states this is “intended to illustrate certain reserve sensitivities to the commodity prices and should not be confused with “SEC Pricing Proved Reserves” and does not comply with SEC pricing assumptions.” Based on the information contained in footnote (1) to the table, it appears to us that the prices used do conform to the requirements in Rule 4-10(a)(22)(v) of Regulation S-X and are not related to an alternative commodity price. Please tell us why the information presented constitutes a reserves sensitivity analysis under Item 1202(b) of Regulation S-K. |


January 4, 2013
Page 4
The cautionary note has been deleted from the draft Amendment.
Oil and Gas Properties, Wells, Operations, page 37
| 3. | We note your filing does not appear to include the disclosures relating to the total gross and net developed and undeveloped acreage or the minimum remaining terms of your leases. Please amend your filing to address the requirements contained in Items 1208(a) and 1208(b) of Regulation S-K. |
Except as noted in the following paragraph, the requested disclosure has been provided in the draft Amendment under the heading “Item 4. Information on the Company – D. Property, Plant and Equipment – Summary of Oil and Gas Reserves as of Fiscal Year-End Based on Average Fiscal Year Prices – Interest in Oil and Gas Properties”, on page 41.
The Company supplementally advises the Staff that due to the unavailability of the required detailed information, the Company is unable to disclose the exact breakdown in acres between oil properties and gas properties. However, the Company supplementally advised the Staff that its interest in oil and gas properties in Canada are primarily related to oil properties, while its interest in oil and gas properties in the United States is primarily related to gas properties.
Supplementary Oil and Gas Reserves Estimation and Disclosures-ASC 932 (Unaudited), page F-49
Net Proved Developed and Proved Undeveloped Reserves, page F-50
| 4. | We note your disclosure of the changes in net quantities of your proved reserves; however, your filing does not appear to include any explanation of the significant changes in your reserves also required in FASB ASC 932-235-50-5. Please amend your filing to include an appropriate explanation. |
The requested disclosure has been provided in the draft Amendment under the heading “Supplemental Oil and Gas Reserve Estimation and Disclosures – ASC 932 – (a) CONSTANT PRICES AND COSTS – YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2011”, on page F-50.
Exhibit 99.1
| 5. | The second paragraph of your letter states that the report “has been prepared for the exclusive use of Dejour Energy (Alberta) Ltd. for corporate reporting purposes and no part thereof shall be reproduced, distributed or made available to any other person, company, regulatory body or organization pursuant to Part 5 Section 5.7 of NI 51-101” and further states “AJM Deloitte hereby gives its consent to the use of its name and to the said estimates pursuant to Part 5 Section 5.7 of NI 51-101.” As Item 1202(a)(8) of Regulation S-K requires the report, the letter should contain no language that could suggest either a limited audience or a limit on potential investor reliance. |


January 4, 2013
Page 5
| | The requested revisions have been made to the letter, which will be re-filed as part of Exhibit 99.1 to the Amendment and is included herewith. |
| 6. | We note the reserve report includes information relating to probable reserves; whereas, information relating to probable reserves is not disclosed in Form 20-F. Either file a revised report which does not include the information relating to probable reserves or amend the Form 20-F to include that information. |
| | Information relating to probable reserves has been removed from the report, which will be re-filed as Exhibit 99.1 to the Amendment and is included herewith. |
| 7. | We note under the section entitled “Production Forecasts” on page 13 you state that “if the reserves were located in a remote location and/or the reserve volume was of higher risk, the reserves were forecast to come on-stream beyond five years from the effective date” when the company could not provide specific on-stream date information. Please tell us if you have used on-stream dates for any of the proved undeveloped reserves contained in your report that are beyond five years of the effective date of the report or since disclosure of such reserves by Dejour in a filing made with the SEC. |
| | The Company supplementally advises the Staff that it has not used any on-stream dates for any of the proved undeveloped reserves contained in the report that are beyond five years of the effective date of the report or since disclosure of such reserves by the Company in a filing made with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| 8. | We note the reserve report does not include the following disclosures required in Item 1202(a)(8) of Regulation S-K: |
| | | |
| · | The reserve report does not clearly state it was prepared for the purpose of inclusion as an exhibit in a filing made with the SEC as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(í) of Regulation S-K. |
| · | The reserve report does not state the date on which the report was completed as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(ii) of Regulation S-K. |
| · | The reserve report does not state the proportion of the registrant’s total reserves covered by the report as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(iii) of Regulation S-K. |
| · | The reserve report does not include a statement that the assumptions, data, methods and procedures are appropriate for the purpose served by the report as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(iv) of Regulation S-K. |
| · | The reserve report does not include a summary of the prices actually used in the estimation of the reserves in accordance with 210.4-10(a)(22)(v) of Regulation S-X as part of the disclosure of the primary economic assumptions under Item 1202(a)(8)(v) of Regulation S-K. |


January 4, 2013
Page 6
| · | The reserve report does not include the net quantities of proved reserves estimated in accordance with 210.4-10(a)(22)(v) of Regulation S-X as required under Item 1202(a)(8)(ix) of Regulation S-K. |
Please amend the report to include the disclosures noted as requirements under Item 1202(a)(8) of Regulation S-K. See Instruction 2 to Item 4 of the Form 20-F.
| | The requested revisions have been made to the report, which will be re-filed as Exhibit 99.1 to the Amendment and has been included herewith. |
Exhibit 99.2
| 9. | In reference to your discussion of the Kokopelli Field, we note you state that the proved undeveloped reserves are “limited to the number of wells in Dejour’s five-year plan.” Please refer to Item 1203(d) of Regulation S-K and tell us if any of your proved undeveloped reserves will remain undeveloped for five years or more since disclosure by Dejour in a filing made with the SEC. |
| | The Company supplementally advises the Staff that none of the Company provided undeveloped reserves are currently expected to remain undeveloped for five years or more since disclosure by the Company in a filing made with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| 10. | We note the reserve report does not include the following disclosures required in Item 1202(a)(8) of Regulation S-K: |
| · | The reserve report does not clearly state it was prepared for the purpose of inclusion as an exhibit in a filing made with the SEC as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(i) of Regulation S-K. |
| · | The reserve report does not state the date on which the report was completed as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(ii) of Regulation S-K. |
| · | The reserve report does note state the proportion of the registrant’s total reserves covered by the report as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(iii) of Regulation S-K. |
| · | The reserve report does not include a statement that the assumptions, data, methods and procedures are appropriate for the purpose served by the report as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(iv) of Regulation S-K. |
| · | The reserve report does not include a discussion of the possible effects of regulation on the ability of the registrant to recover the estimated reserves as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(vi) of Regulation S-K. |
| · | The reserve report does not include a statement that the third party has used all methods and procedures as it considered necessary under the circumstances to prepare the report as required in Item 1202(a)(8)(viii) of Regulation S-K. |


January 4, 2013
Page 7
| · | The reserve report does not include the qualifications of the technical person primarily responsible for overseeing the preparation of the reserves estimates. If the registrant files a report of the third party as an exhibit, the third party must include in that report a disclosure under Item 1202(a)(7) of Regulation S-K. |
Please amend the report to include the disclosures noted as requirements under Items 1202(a)(7) and 1202(a)(8) of Regulation S-K.
| | The requested revisions have been made to the report, which will be re-filed as Exhibit 99.2 to the Amendment and has been included herewith. |
* * *
As always, should you have further comments or require further information, or if any questions should arise in connection with this submission, please call the undersigned at (604) 630-5199. You also may email me atmiller.dan@dorsey.com or fax me at (604) 687-8504.
| | Yours truly, |
| | |
| | /s/ Daniel M. Miller |
| | Daniel M. Miller |
| cc: Mathew Wong | |
| Dejour Energy Inc. | |

UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Amendment No. 2
To
Form 20-F
| ¨ | | REGISTRATION STATEMENT PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OR (g) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| OR |
| x | | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011 |
| OR |
| ¨ | | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the transition period from ____ to ______ |
| |
| OR |
| ¨ | | SHELL COMPANY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| Date of event requiring this shell company report: |
Commission file number: 001-33491

DEJOUR ENERGY INC.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
Province of British Columbia, Canada
(Jurisdiction of incorporation or organization)
598 - 999 Canada Place
Vancouver, British Columbia V6C 3E1
(Address of principal executive offices)
Mathew Wong
598 - 999 Canada Place
Vancouver, British Columbia V6C 3E1
Tel: (604) 638-5050
Facsimile: (604) 638-5051
(Name, Telephone, E-mail and/or Facsimile number and Address of Company Contact Person)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| | | |
| Common Shares, without par value | | NYSE Amex Equities |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:None
Securities for which there is a reporting obligation pursuant to Section 15(d) of the Act:None
Indicate the number of outstanding shares of each of the Registrant’s classes of capital or common stock as of the close of the period covered by the annual report:130,786,069 common shares as at April 26, 2012
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. YesoNox
If this report is an annual or transition report, indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.YesoNox
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.YesxNoo
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).YesoNoo
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, or a non-accelerated filer. See definition of “accelerated filer and large accelerated filer” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one)
Large accelerated filero Accelerated filero Non-accelerated filerx
Indicate by check mark which basis of accounting the registrant has used to prepare the financial statements included in this filing:
| | U.S. GAAPo | International Financial Reporting Standards as issued | x |
| | Othero | | |
| | | by the International Accounting Standards Board | |
If “Other” has been checked in response to the previous question, indicate by check mark which financial statement item the registrant has elected to follow:
Item 17o Item 18o
If this is an annual report, indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yeso Nox
EXPLANATORY NOTE
This Amendment No. 2 (“Amendment No. 2”) to the Annual Report on Form 20-F of Dejour Energy Inc. (the “Company”) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, originally filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) on April 30, 2012 (the “Original Report”) and amended on May 23, 2012, is being filed in order to address certain comments received from the Staff of the SEC.
This Amendment No. 2 speaks as of the initial filing date of the Original Report, as amended. Other than as expressly set forth above, no part of the Original Report, as amended, is being amended. Accordingly, other than as discussed above, this Amendment No. 2 does not purport to amend, update or restate any other information or disclosure included in the Original Report, as amended, or reflect any events that have occurred after the initial filing date of the Original Report, as amended. As a result, the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, as amended, continues to speak as of April 26, 2012 or, to the extent applicable, such other date as may be indicated in the Original Report, as amended.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| GENERAL INFORMATION | 4 |
| CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS | 4 |
| CURRENCY AND EXCHANGE RATES | 6 |
| ABBREVIATIONS | 6 |
| PART I | 8 |
| ITEM 1. IDENTITY OF DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND ADVISORS. | 8 |
| ITEM 2. OFFER STATISTICS AND EXPECTED TIMETABLE. | 8 |
| ITEM 3. KEY INFORMATION. | 8 |
| ITEM 4. INFORMATION ON THE COMPANY | 20 |
| ITEM 4A. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS | 42 |
| ITEM 5. OPERATING AND FINANCIAL REVIEW AND PROSPECTS | 42 |
| ITEM 6. DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND EMPLOYEES. | 50 |
| ITEM 7. MAJOR SHAREHOLDERS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS. | 65 |
| ITEM 8. FINANCIAL INFORMATION. | 68 |
| ITEM 9. THE OFFER AND LISTING | 69 |
| ITEM 10. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION | 72 |
| ITEM 11. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK | 89 |
| ITEM 12. DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES OTHER THAN EQUITY SECURITIES | 91 |
| PART II | 92 |
| ITEM 13. DEFAULTS, DIVIDEND ARREARAGES AND DELINQUENCIES | 92 |
| ITEM 14. MATERIAL MODIFICATIONS TO THE RIGHTS OF SECURITY HOLDERS AND USE OF PROCEEDS | 92 |
| ITEM 15. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES | 92 |
| ITEM 16. [RESERVED] | 93 |
| ITEM 16A. AUDIT COMMITTEE FINANCIAL EXPERT | 93 |
| ITEM 16B. CODE OF ETHICS | 93 |
| ITEM 16C. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES | 94 |
| ITEM 16D. EXEMPTIONS FROM THE LISTING STANDARDS FOR AUDIT COMMITTEES | 94 |
| ITEM 16E. PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER AND AFFILIATED PERSONS | 95 |
| ITEM 16F. CHANGE IN REGISTRANT’S CERTIFYING ACCOUNTANT | 95 |
| ITEM 16G. CORPORATE GOVERNANCE | 95 |
| ITEM 16H. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE | 96 |
| PART III | 97 |
| ITEM 17. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS | 97 |
| ITEM 18. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS | 97 |
| ITEM 19. EXHIBITS | 98 |
| SIGNATURES | 100 |
GENERAL INFORMATION
All references in this annual report on Form 20-F to the terms “we”, “our”, “us”, “the Company” and “Dejour” refer to Dejour Energy Inc.
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This annual report on Form 20-F and the documents incorporated herein by reference contain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Such forward-looking statements concern our anticipated results and developments in the our operations in future periods, planned exploration and, if warranted, development of our properties, plans related to our business and other matters that may occur in the future. These statements relate to analyses and other information that are based on forecasts of future results, estimates of amounts not yet determinable and assumptions of management.
Any statements that express or involve discussions with respect to predictions, expectations, beliefs, plans, projections, objectives, assumptions or future events or performance (often, but not always, using words or phrases such as “expects” or “does not expect”, “is expected”, “anticipates” or “does not anticipate”, “plans”, “estimates” or “intends”, or stating that certain actions, events or results “may”, “could”, “would”, “might” or “will” be taken, occur or be achieved) are not statements of historical fact and may be forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements contained in this annual report on Form 20-F concern, among other things:
| · | drilling inventory, drilling plans and timing of drilling, re-completion and tie-in of wells; |
| · | productive capacity of wells, anticipated or expected production rates and anticipated dates of commencement of production; |
| · | drilling, completion and facilities costs; |
| · | results of our various projects; |
| · | ability to lower cost structure in certain of our projects; |
| · | our growth expectations; |
| · | timing of development of undeveloped reserves; |
| · | the performance and characteristics of the Company’s oil and natural gas properties; |
| · | oil and natural gas production levels; |
| · | the quantity of oil and natural gas reserves; |
| · | capital expenditure programs; |
| · | supply and demand for oil and natural gas and commodity prices; |
| · | the impact of federal, provincial, and state governmental regulation on Dejour; |
| · | expected levels of royalty rates, operating costs, general administrative costs, costs of services and other costs and expenses; |
| · | expectations regarding our ability to raise capital and to continually add to reserves through acquisitions, exploration and development; |
| · | treatment under governmental regulatory regimes and tax laws; and |
| · | realization of the anticipated benefits of acquisitions and dispositions. |
These statements relate to analyses and other information that are based on forecasts of future results, estimates of amounts not yet determinable and assumptions of our management.
Forward-looking statements are subject to a variety of known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that could cause actual events or results to differ from those expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements, including, without limitation:
| · | risks related to the marketability and price of oil and natural gas being affected by factors outside our control; |
| · | risks related to world oil and natural gas prices being quoted in U.S. dollars and our production revenues being adversely affected by an appreciation in the Canadian dollar; |
| · | risks related to our ability to execute projects being dependent on factors outside our control; |
| · | risks related to oil and gas exploration having a high degree of risk and exploration efforts failing; |
| · | risks related to cumulative unsuccessful exploration efforts; |
| · | risks related to oil and natural gas operations involving hazards and operational risks; |
| · | risks related to seasonal factors and unexpected weather; |
| · | risks related to competition in the oil and gas industry; |
| · | risks related to the fact that we do not control all of the assets that are used in the operation of our business; |
| · | risks related to our ability to market oil and natural gas depending on its ability to transport the product to market; |
| · | risks related to high demand for drilling equipment; |
| · | risks related to title to our properties; |
| · | risks related to our ability to continue to meet its oil and gas lease or license obligations; |
| · | risks related to our anticipated substantial capital needs for future acquisitions; |
| · | risks related to our cash flow from reserves not being sufficient to fund its ongoing operations; |
| · | risks related to covenants in issued debt restricting the ability to conduct future financings; |
| · | risks related to our being exposed to third party credit risks; |
| · | risks related to our being able to find, acquire, develop and commercially produce oil and natural gas; |
| · | risks related to our properties not producing as projected; |
| · | risks related to our estimated reserves being based upon estimates; |
| · | risks related to future oil and gas revenues not resulting in revenue increases; |
| · | risks related to our managing growth; |
| · | risks related to our being dependent on key personnel; |
| · | risks related to our operations being subject to federal, state, local and other laws, controls and regulations; |
| · | risks related to uncertainty regarding claims of title and right of aboriginal people; |
| · | risks related to environmental laws and regulations; |
| · | risks related to our facilities, operations and activities emitting greenhouse gases; |
| · | risks related to our not having paid dividends to date; |
| · | risks related to our stock price being volatile; and |
| · | risks related to our being a foreign private issuer. |
This list is not exhaustive of the factors that may affect any of our forward-looking statements. Some of the important risks and uncertainties that could affect forward-looking statements are described further under the section heading “Item 3. Key Information – D. Risk Factors” below. If one or more of these risks or uncertainties materializes, or if underlying assumptions prove incorrect, our actual results may vary materially from those expected, estimated or projected. Forward-looking statements in this document are not a prediction of future events or circumstances, and those future events or circumstances may not occur. Given these uncertainties, users of the information included herein, including investors and prospective investors are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such forward-looking statements. Investors should consult our quarterly and annual filings with Canadian and U.S. securities commissions for additional information on risks and uncertainties relating to forward-looking statements. We do not assume responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of these statements.
Forward-looking statements are based on our beliefs, opinions and expectations at the time they are made, and we do not assume any obligation to update our forward-looking statements if those beliefs, opinions, or expectations, or other circumstances, should change, except as required by applicable law.
We qualify all the forward-looking statements contained in this annual report on Form 20-F by the foregoing cautionary statements.
CURRENCY AND EXCHANGE RATES
Canadian Dollars Per U.S. Dollar
Unless otherwise indicated, all references in this annual report are to Canadian dollars ("$" or "Cdn$").
The following tables set forth the number of Canadian dollars required to buy one United States dollar (US$) based on the average, high and low nominal noon exchange rate as reported by the Bank of Canada for each of the last five fiscal years and each of the last six months. The average rate means the average of the exchange rates on the last day of each month during the period.
| | | Canadian Dollars Per One U.S. Dollar | |
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
| Average for the period | | | 0.9891 | | | | 1.0345 | | | | 1.1416 | | | | 1.0592 | | | | 1.0697 | |
| | | March | | | February | | | January | | | December | | | November | | | October | |
| | | 2012 | | | 2012 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | 2011 | | | 2011 | |
| High for the period | | | 1.0015 | | | | 1.0016 | | | | 1.0272 | | | | 1.0406 | | | | 1.0487 | | | | 1.0604 | |
| Low for the period | | | 0.9849 | | | | 0.9866 | | | | 0.9986 | | | | 1.0105 | | | | 1.0126 | | | | 0.9935 | |
Exchange rates are based on the Bank of Canada nominal noon exchange rates.The nominal noon exchange rate on April 26, 2012 as reported by the Bank of Canada for the conversion of United States dollars into Canadian dollars was US$1.00 = Cdn$0.9841.
ABBREVIATIONS
| Oil and Natural Gas Liquids | Natural Gas |
| bbl | barrel | Mcf | thousand cubic feet |
| bbls | barrels | MCFD | thousand cubic feet per day |
| BOPD | barrels per day | MMcf | million cubic feet |
| Mbbls | thousand barrels | MMcf/d | million cubic feet per day |
| Mmbtu | million British thermal units | Mcfe | Thousand cubic feet of gas equivalent |
| Other | |
| AECO | Intra-Alberta Nova Inventory Transfer Price (NIT net price of natural gas). |
| BOE | Barrels of oil equivalent. A barrel of oil equivalent is determined by converting a volume of natural gas to barrels using the ratio of 6 Mcf to one barrel. |
| BOE/D | Barrels of oil equivalent per day. |
| BCFE | Billion cubic feet equivalent |
| MBOE | Thousand barrels of oil equivalent. |
| NYMEX | New York Mercantile Exchange. |
| WTI | West Texas Intermediate, the reference price paid in U.S. dollars at Cushing Oklahoma for crude oil of standard grade. |
PART I
ITEM 1. IDENTITY OF DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND ADVISORS
Not applicable.
ITEM 2. OFFER STATISTICS AND EXPECTED TIMETABLE
Not applicable.
ITEM 3. KEY INFORMATION
| A. | Selected Financial Data |
Our selected financial data and the information in the following tables for the years ended December 31, 2007 - 2011 was derived from our audited consolidated financial statements. These audited consolidated financial statements have been audited by BDO Canada LLP, Chartered Accountants, for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010, and Dale Matheson Carr-Hilton LaBonte LLP, Chartered Accountants, for the years ended December 31, 2007 - 2009. Certain prior years’ comparative figures have been reclassified, if necessary.
The information in the following table should be read in conjunction with the information appearing under the heading “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects” and our audited consolidated financial statements under the heading "Item 18. Financial Statements".
On January 1, 2011, the Company adopted International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) for financial reporting purposes, using a transition date of January 1, 2010. The Company’s annual audited Consolidated Financial Statements for the year ended December 31, 2011, including 2010 required comparative information, have been prepared in accordance with IFRS, as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”) and interpretations of the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (“IFRIC”). Financial statements prior to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010 were prepared in accordance with Canadian generally accepted accounting principles (“Canadian GAAP”). Reference is made to Note 21 of our audited consolidated financial statements as at December 31, 2010 and 2009 and for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 for a discussion of the material measurement differences between Canadian GAAP and United States generally accepted accounting principles (“U.S. GAAP”), and their effect on our financial statements.
Financial information included in this annual report on Form 20-F for the years 2011 and 2010 is determined using IFRS, which differ from U.S. GAAP and Canadian GAAP. Unless otherwise indicated, financial information included in this annual report on Form 20-F prior to year 2010 were in accordance with Canadian GAAP.
We have not declared any dividends since incorporation and do not anticipate that we will do so in the foreseeable future. Our present policy is to retain all available funds for use in our operations and the expansion of our business.
The following table is a summary of selected audited consolidated financial information of the Company for each of the two most recently completed financial years. The information presented is presented in accordance with IFRS:
| (Cdn$ in 000, except per share data) | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| Revenue (Oil and natural gas) | | $ | 8,824 | | | $ | 8,086 | |
| Net Loss for the Year | | $ | (11,043 | ) | | $ | (5,124 | ) |
| Loss Per Share | | $ | (0.09 | ) | | $ | (0.05 | ) |
| Dividends Per Share | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Weighted Avg. Shares, basic (,000) | | | 120,300 | | | | 99,789 | |
| Weighted Avg. Shares, diluted (,000) | | | 120,300 | | | | 99,789 | |
| Year-end Shares (,000) | | | 126,892 | | | | 110,181 | |
| Working Capital (Deficiency) | | $ | (7,756 | ) | | $ | (3,264 | ) |
| Resource Properties | | $ | 25,043 | | | $ | 24,432 | |
| Long-term Investments | | | - | | | | - | |
| Long-term Liabilities | | $ | 1,383 | | | $ | 738 | |
| Capital Stock | | $ | 85,076 | | | $ | 79,386 | |
| Retained Earnings (Deficit) | | $ | (76,510 | ) | | $ | (65,467 | ) |
| Total Assets | | $ | 29,438 | | | $ | 30,413 | |
The following table is a summary of selected audited consolidated financial information of the Company for the three fiscal years ended December 31, 2009. The information presented is presented in accordance with Canadian GAAP and is not comparable to the financial information presented in accordance with IFRS.
| (Cdn$ in 000, except per share data) | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue (Oil and natural gas) | | $ | 6,471 | | | $ | 5,766 | | | | Nil | |
| Net Loss for the Year | | $ | (12,807 | ) | | $ | (20,891 | ) | | $ | (26,810 | ) |
| Loss Per Share | | $ | (0.16 | ) | | $ | (0.29 | ) | | $ | (0.40 | ) |
| Dividends Per Share | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Weighted Avg. Shares, basic (,000) | | | 78,926 | | | | 72,211 | | | | 66,588 | |
| Weighted Avg. Shares, diluted (,000) | | | 78,926 | | | | 72,211 | | | | 66,588 | |
| Year-end Shares (,000) | | | 95,791 | | | | 73,652 | | | | 70,128 | |
| Working Capital (Deficiency) | | $ | (20 | ) | | $ | (12,712 | ) | | $ | 11,335 | |
| Resource Properties | | $ | 41,758 | | | $ | 57,684 | | | $ | 35,411 | |
| Long-term Investments | | | - | | | $ | 2,722 | | | $ | 12,600 | |
| Long-term Liabilities | | $ | 2,594 | | | $ | 3,446 | | | | Nil | |
| Capital Stock | | $ | 72,560 | | | $ | 64,939 | | | $ | 61,394 | |
| Retained Earnings (Deficit) | | $ | (39,386 | ) | | $ | (26,579 | ) | | $ | (5,688 | ) |
| Total Assets | | $ | 45,886 | | | $ | 62,643 | | | $ | 63,143 | |
Canadian GAAP Adjusted to United States Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
Under U.S. GAAP the following financial information would be adjusted from Canadian GAAP, and certain prior years’ comparative figures have been reclassified or restated, if necessary. The following table is a summary of selected audited consolidated financial information of the Company for the three fiscal years ended December 31, 2009. The information presented is presented in accordance with U.S. GAAP:
| (Cdn$ in 000, except per share data) | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
| Net Loss for the Year | | $ | (10,270 | ) | | $ | (34,181 | ) | | $ | (29,523 | ) |
| Loss Per Share | | $ | (0.13 | ) | | $ | (0.47 | ) | | $ | (0.44 | ) |
| Resource Properties | | $ | 31,041 | | | $ | 44,232 | | | $ | 34,783 | |
| Retained Earnings (Deficit) | | $ | (54,785 | ) | | $ | (44,515 | ) | | $ | (10,334 | ) |
| Total Assets | | $ | 35,169 | | | $ | 49,192 | | | $ | 62,515 | |
Exchange Rate History
See the disclosure under the heading "Currency and Exchange Rates" above.
Recently Adopted Accounting Policies and Future Accounting Pronouncements
IFRS
On January 1, 2011, we adopted IFRS and the accounting policies have been applied in preparing the consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2011, the consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2010 and the opening IFRS balance sheet on January 1, 2010. The detail accounting policies in accordance with IFRS are disclosed in Note 3 of the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements and the details of transition to IFRS are disclosed in Note 25 of the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements under the heading "Item 18. Financial Statements", below.
Future Accounting Pronouncements
Certain pronouncements were issued by the IASB or the IFRIC that are mandatory for accounting periods beginning after January 1, 2011 or later periods.
The Company has early adopted the amendments to IFRS 1 which replaces references to a fixed date of ‘1 January 2004’ with ‘the date of transition to IFRS’. This eliminates the need for the Company to restate derecognition transactions that occurred before the date of transition to IFRS. The amendment is effective for year-ends beginning on or after July 1, 2011; however, the Company has early adopted the amendment. The impact of the amendment and early adoption is that the Company only applies IAS 39 derecognition requirements to transactions that occurred after the date of transition.
The following are new standards, amendments and interpretations, that have not been early adopted in these consolidated annual financial statements. The Company is currently assessing the impact, if any, of this new guidance on the Company’s future results and financial position:
| · | IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Disclosures, which requires disclosure of both gross and net information about financial instruments eligible for offset in the balance sheet and financial instruments subject to master netting arrangements. Concurrent with the amendments to IFRS 7, the IASB also amended IAS 32, Financial Instruments: Presentation to clarify the existing requirements for offsetting financial instruments in the balance sheet. The amendments to IAS 32 are effective as of January 1, 2014. |
| · | IFRS 9 Financial Instruments is part of the IASB's wider project to replace IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement. IFRS 9 retains but simplifies the mixed measurement model and establishes two primary measurement categories for financial assets: amortized cost and fair value. The basis of classification depends on the entity's business model and the contractual cash flow characteristics of the financial asset. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2015. |
| · | IFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements is the result of the IASB’s project to replace Standing Interpretations Committee 12, Consolidation – Special Purpose Entities and the consolidation requirements of IAS 27, Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements. The new standard eliminates the current risk and rewards approach and establishes control as the single basis for determining the consolidation of an entity. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013. |
| · | IFRS 11 Joint Arrangements is the result of the IASB’s project to replace IAS 31, Interests in Joint Ventures. The new standard redefines joint operations and joint ventures and requires joint operations to be proportionately consolidated and joint ventures to be equity accounted. Under IAS 31, joint ventures could be proportionately consolidated. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013. |
| · | IFRS 12 Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities outlines the required disclosures for interests in subsidiaries and joint arrangements. The new disclosures require information that will assist financial statement users to evaluate the nature, risks and financial effects associated with an entity’s interests in subsidiaries and joint arrangements. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013. |
| · | IFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement defines fair value, requires disclosures about fair value measurements and provides a framework for measuring fair value when it is required or permitted within the IFRS standards. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013. |
| · | IFRIC 20 Stripping costs in the production phase of a mine, IFRIC 20 clarifies the requirements for accounting for the costs of the stripping activity in the production phase when two benefits accrue: (i) unusable ore that can be used to produce inventory and (ii) improved access to further quantities of material that will be mined in future periods. IFRIC 20 is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013 with earlier application permitted and includes guidance on transition for pre-existing stripping assets. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the new guidance is expected to have on its consolidated financial statements. |
The following new standards, amendments and interpretations that have not been early adopted in these consolidated financial statements, are not expected to have an effect on the Company’s future results and financial position:
| · | IFRS 1: Severe Hyperinflation (Effective for periods beginning on or after July 1, 2011) |
| · | IAS 12: Deferred Tax: Recovery of Underlying Assets (Amendments to IAS 12 (Effective for periods beginning on or after January 1, 2012) |
| B. | Capitalization and Indebtedness |
Not Applicable.
| C. | Reasons for the Offer and Use of Proceeds |
Not Applicable.
An investment in a company engaged in oil and gas exploration involves an unusually high amount of risk, both unknown and known, present and potential, including, but not limited to the risks enumerated below. An investment in our common shares is highly speculative and subject to a number of known and unknown risks. Only those persons who can bear the risk of the entire loss of their investment should purchase our securities. An investor should carefully consider the risks described below and the other information that we file with the SEC and with Canadian securities regulators before investing in our common shares. The risks described below are not the only ones faced. Additional risks that we are not currently aware of or that we currently believe are immaterial may become important factors that affect our business. The risk factors set forth below and elsewhere in this annual report, and the risks discussed in our other filings with the SEC and Canadian securities regulators, may have a significant impact on our business, financial condition and/or results of operations and could cause actual results to differ materially from those projected in any forward-looking statements. See “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements”.
Our failure to successfully address the risks and uncertainties described below would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and/or results of operations, and the trading price of our common stock may decline and investors may lose all or part of their investment. We cannot assure you that we will successfully address these risks or other unknown risks that may affect our business.
Risks related to commodity price fluctuations
The marketability and price of oil and natural gas are affected by numerous factors outside of our control. Material fluctuations in oil and natural gas prices could adversely affect our net production revenue and oil and natural gas operations.
Prices for oil and natural gas may fluctuate widely in response to relatively minor changes in the supply of and demand for oil and natural gas, market uncertainty and a variety of additional factors that are beyond our control, such as:
| · | the domestic and foreign supply of and demand for oil and natural gas; |
| · | the price and quantity of imports of crude oil and natural gas; |
| · | overall domestic and global economic conditions; |
| · | political and economic conditions in other oil and natural gas producing countries, including embargoes and continued hostilities in the Middle East and other sustained military campaigns, and acts of terrorism or sabotage; |
| · | the ability of members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries to agree to and maintain oil price and production controls; |
| · | the level of consumer product demand; |
| · | the impact of the U.S. dollar exchange rates on oil and natural gas prices; and |
| · | the price and availability of alternative fuels. |
Our ability to market our oil and natural gas depends upon our ability to acquire space on pipelines that deliver such commodities to commercial markets. We are also affected by deliverability uncertainties related to the proximity of our reserves to pipelines and processing and storage facilities and operational problems affecting such pipelines and facilities, as well as extensive governmental regulation relating to price, taxes, royalties, land tenure, allowable production, the export of oil and natural gas and many other aspects of the oil and natural gas business.
Both oil and natural gas prices are unstable and are subject to fluctuation. Any material decline in prices could result in a reduction of our net production revenue. The economics of producing from some wells may change as a result of lower prices, which could result in reduced production of oil or natural gas and a reduction in the volumes and net present value of our reserves. We might also elect not to produce from certain wells at lower prices. All of these factors could result in a material decrease in our net production revenue and a reduction in our oil and natural gas acquisition, development and exploration activities.
Because world oil and natural gas prices are quoted in U.S. dollars, our production revenues could be adversely affected by an appreciation of the Canadian dollar.
World oil and natural gas prices are quoted in U.S. dollars, and the price received by Canadian producers, including us, is therefore affected by the Canadian/U.S. dollar exchange rate, which will fluctuate over time. In recent years, the Canadian dollar has increased materially in value against the U.S. dollar, which may negatively affect our production revenues. Further material increases in the value of the Canadian dollar would exacerbate this potential negative effect and could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. An increase in the exchange rate for the Canadian dollar and future Canadian/U.S. exchange rates could also negatively affect the future value of our reserves as determined by independent petroleum reserve engineers.
Risks related to operating an exploration, development and production company
Our ability to execute projects will depend on certain factors outside of our control. If we are unable to execute projects on time, on budget or at all, we may not be able to effectively market the oil and natural gas that we produce.
We manage a variety of small and large projects in the conduct of our business. Our ability to execute projects and market oil and natural gas will depend upon numerous factors beyond our control, including:
| · | the availability of adequate financing; |
| · | the availability of processing capacity; |
| · | the availability and proximity of pipeline capacity; |
| · | the availability of storage capacity; |
| · | the supply of and demand for oil and natural gas; |
| · | the availability of alternative fuel sources; |
| · | the effects of inclement weather; |
| · | the availability of drilling and related equipment; |
| · | changes in governmental regulations; and |
| · | the availability and productivity of skilled labor. |
Because of these factors, we could be unable to execute projects on time, on budget or at all, and may not be able to effectively market the oil and natural gas that we produce.
Oil and gas exploration has a high degree of risk and our exploration efforts may be unsuccessful, which would have a negative effect on our operations.
There is no certainty that the expenditures to be made by us in the exploration of our current projects, or any additional project interests we may acquire, will result in discoveries of recoverable oil and gas in commercial quantities. An exploration project may not result in the discovery of commercially recoverable reserves and the level of recovery of hydrocarbons from a property may not be a commercially recoverable (or viable) reserve that can be legally and economically exploited. If exploration is unsuccessful and no commercially recoverable reserves are defined, we would be required to evaluate and acquire additional projects that would require additional capital, or we would have to cease operations altogether.
Cumulative unsuccessful exploration efforts could result in us having to cease operations.
The expenditures to be made by us in the exploration of our properties may not result in discoveries of oil and natural gas in commercial quantities. Many exploration projects do not result in the discovery of commercially recoverable oil and gas deposits, and this occurrence could ultimately result in us having to cease operations.
Oil and natural gas operations involve many hazards and operational risks, some of which may not be fully covered by insurance. If a significant accident or event occurs for which we are not fully insured, our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could be adversely affected.
Our involvement in the oil and natural gas exploration, development and production business subjects us to all of the risks and hazards typically associated with those types of operations, including hazards such as fire, explosion, blowouts, sour gas releases and spills, each of which could result in substantial damage to oil and natural gas wells, production facilities, other property and the environment or personal injury. In particular, we may explore for and produce sour natural gas in certain areas. An unintentional leak of sour natural gas could result in personal injury, loss of life or damage to property, and may necessitate an evacuation of populated areas, all of which could result in liability to us. In accordance with industry practice, we are not fully insured against all of these risks. Although we maintain liability insurance in an amount that we consider consistent with industry practice, the nature of these risks is such that liabilities could exceed policy limits, in which event we could incur significant costs that could have a material adverse effect upon our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. In addition, the risks we face are not, in all circumstances, insurable and, in certain circumstances, we may elect not to obtain insurance to deal with specific risks due to the high premiums associated with such insurance or other reasons. For instance, we do not have insurance to protect against the risk from terrorism. Oil and natural gas production operations are also subject to all of the risks typically associated with those operations, including encountering unexpected geologic formations or pressures, premature decline of reservoirs and the invasion of water into producing formations. Losses resulting from the occurrence of any of these risks could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Seasonal factors and unexpected weather patterns may lead to declines in exploration and production activity.
The level of activity in the Canadian oil and natural gas industry is influenced by seasonal weather patterns. Oil and natural gas development activities, including seismic and drilling programs in northern Alberta and British Columbia, are restricted to those months of the year when the ground is frozen. Wet weather and spring thaw may make the ground unstable. Consequently, municipalities and provincial transportation departments enforce road bans that restrict the movement of rigs and other heavy equipment, thereby reducing activity levels. In addition, certain oil and natural gas producing areas are located in areas that are inaccessible other than during the winter months because the ground surrounding the sites in these areas consists of swampy terrain, and additional seasonal weather variations will also affect access to these areas. Seasonal factors and unexpected weather patterns may lead to declines in exploration and production activity during certain parts of the year.
The petroleum industry is highly competitive, and increased competitive pressures could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The petroleum industry is competitive in all of its phases. We compete with numerous other organizations in the search for, and the acquisition of, oil and natural gas properties and in the marketing of oil and natural gas. Our competitors include oil and natural gas companies that have substantially greater financial resources, staff and facilities than us. Our ability to increase our reserves in the future will depend not only upon our ability to explore and develop our present properties, but also upon our ability to select and acquire other suitable producing properties or prospects for exploratory drilling. Competitive factors in the distribution and marketing of oil and natural gas include price and methods and reliability of delivery and storage.
We do not control all of the assets that are used in the operation of our business and, therefore, cannot ensure that those assets will be operated in a manner favorable to us.
Other companies operate some of the assets in which we have an interest. As a result, we have a limited ability to exercise influence over the operation of those assets or their associated costs, which could adversely affect our financial performance. Our return on assets operated by others will therefore depend upon a number of factors that may be outside of our control, including the timing and amount of capital expenditures, the operator's expertise and financial resources, the approval of other participants, the selection of technology and risk management practices.
Our ability to market oil and natural gas depends on our ability to transport our product to market. If we are unable to expand and develop the infrastructure in the areas surrounding certain of our assets, we may not be able to effectively market the oil and natural gas that we produce.
Due to the location of some of our assets, both in Canada and the United States, there is minimal infrastructure currently available to transport oil and natural gas from our existing and future wells to market. As a result, even if we are able to engage in successful exploration and production activities, we may not be able to effectively market the oil and natural gas that we produce, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Demand and competition for drilling equipment could delay our exploration and production activities, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Oil and natural gas exploration and development activities depend upon the availability of drilling and related equipment (typically leased from third parties) in the particular areas where such activities will be conducted. Demand for such limited equipment or access restrictions may affect the availability of such equipment to us and may delay exploration and development activities. To the extent we are not the operator of our oil and natural gas properties, we depend upon the operators of the properties for the timing of activities related to the properties and are largely unable to direct or control the activities of the operators.
Title to our oil and natural gas producing properties cannot be guaranteed and may be subject to prior recorded or unrecorded agreements, transfers, claims or other defects.
Although title reviews may be conducted prior to the purchase of oil and natural gas producing properties or the commencement of drilling wells, those reviews do not guarantee or certify that an unforeseen defect in the chain of title will not arise to defeat our claim. Unregistered agreements or transfers, or native land claims, may affect title. If title is disputed, we will need to defend our ownership through the courts, which would likely be an expensive and protracted process and have a negative effect on our operations and financial condition. In the event of an adverse judgment, we would lose our property rights. A defect in our title to any of our properties may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We may be unable to meet all of the obligations necessary to successfully maintain each of the licenses and leases and working interests in licenses and leases related to its properties, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Our properties are held in the form of licenses and leases and working interests in licenses and leases. If we or the holder of the license or lease fails to meet the specific requirement of a license or lease, the license or lease may terminate or expire. None of the obligations required to maintain each license or lease may be met. The termination or expiration of our licenses or leases or the working interests relating to a license or lease may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. Certain leases in our Kokopelli (formerly Gibson Gulch) and South Rangley properties will expire in 2012 and 2013.
Risks related to financing continuing and future operations
We have a working capital deficiency and will be required to raise capital through financings. We may not be able to obtain capital or financing on satisfactory terms, or at all.
As of December 31, 2011, the Company had a working capital deficiency of approximately $7.8 million. Excluding the non-cash warrant liability of $2.2 million related to the fair value of US$ denominated warrants issued in previous equity financings, the working capital deficiency includes a $5.5 million used demand line of credit. As at December 31, 2011, $1.5 million of the demand line of credit remains unused. We expect to incur general and administration expenses of approximately $3.5 million over the next twelve months. The next review date for the demand line of credit is scheduled on or before May 1, 2012. If we are unable to extend or refinance the bank line of credit or meet our general and administration expenses or our share of the joint venture costs through revenues and field operating netback from our oil and gas operations, we will need to raise capital through debt or equity financings. We cannot assure you that debt or equity financing will be available to us, and even if debt or equity financing is available, it may not be on terms acceptable to us. Our inability to access sufficient capital for our operations would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The Company's ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon attaining profitable operations and obtaining sufficient financing to meet obligations and continue exploration and development activities. Whether and when the Company can attain profitability is uncertain. These uncertainties cast significant doubt upon the Company’s ability to continue as going concern.
In the course of our development activities, we have sustained losses and expect losses in the year ended December 31, 2012. We expect to finance our operations primarily through our existing cash and any future financing. Whether and when the Company can attain profitability is uncertain. These uncertainties cast substantial doubt upon the Company’s ability to continue as going concern in the next twelve months, because we will be required to obtain additional capital in the future to continue our operations and there is no assurance that we will be able to obtain such capital, through equity or debt financing, or any combination thereof, or on satisfactory terms or at all. Our independent auditors have included an explanatory paragraph in their report on our consolidated financial statements that describes uncertainties that cast substantial doubt about our ability to continue as agoing concern. Our audited consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board applicable to a going concern, which implies we will continue to meet our obligations and continue our operations for the next twelve months. Realization values may be substantially different from carrying values as shown, and our consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability orclassification of recorded asset amounts or the amount and classification of liabilities that might be necessary as a result of the going concern uncertainty.
We anticipate making substantial capital expenditures for future acquisition, exploration, development and production projects. We may not be able to obtain capital or financing necessary to support these projects on satisfactory terms, or at all.
We anticipate making substantial capital expenditures for the acquisition, exploration, development and production of oil and natural gas reserves in the future. If our revenues or reserves decline, we may not have access to the capital necessary to undertake or complete future drilling programs. Debt or equity financing, or cash generated by operations, may not be available to us or may not be sufficient to meet our requirements for capital expenditures or other corporate purposes. Even if debt or equity financing is available, it may not be on terms acceptable to us. Our inability to access sufficient capital for our operations could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Our cash flow from our reserves may not be sufficient to fund our ongoing activities at all times, thereby causing us to forfeit our interest in certain properties, miss certain acquisition opportunities and reduce or terminate our operations.
Our cash flow from our reserves may not be sufficient to fund our ongoing activities at all times and we are currently utilizing our bank line of credit to fund our working capital deficit. From time to time, we may require additional financing in order to carry out our oil and gas acquisition, exploration and development activities. Failure to obtain such financing on a timely basis could cause us to forfeit its interest in certain properties, not be able to take advantage of certain acquisition opportunities and reduce or terminate our level of operations. If our revenues from our reserves decrease as a result of lower oil and natural gas prices or otherwise, our ability to expend the necessary capital to replace our reserves or to maintain our production will be impaired. If our cash flow from operations is not sufficient to satisfy our capital expenditure requirements, there can be no assurance that additional debt or equity financing will be available to meet these requirements or, if available, on favorable terms.
Debt that we incur in the future may limit our ability to obtain financing and to pursue other business opportunities, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
From time to time, we may enter into transactions to acquire assets or equity of other organizations. These transactions may be financed in whole or in part with debt, which may increase our debt levels above industry standards for oil and natural gas companies of a similar size. Depending upon future exploration and development plans, we may require additional equity and/or debt financing that may not be available or, if available, may not be available on acceptable terms. None of our organizational documents currently limit the amount of indebtedness that we may incur. The level of our indebtedness from time to time could impair our ability to obtain additional financing on a timely basis to take advantage of business opportunities that may arise.
We may be exposed to the credit risk of third parties through certain of our business arrangements. Non-payment or non-performance by any of these third parties could have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
We may be exposed to third-party credit risk through our contractual arrangements with our current or future joint venture partners, marketers of our petroleum and natural gas production and other parties. In the event those entities fail to meet their contractual obligations to us, those failures could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. In addition, poor credit conditions in the industry and of joint venture partners may affect a joint venture partner's willingness to participate in our ongoing capital program, potentially delaying the program and the results of the program until we find a suitable alternative partner.
Risks related to maintaining reserves and acquiring new sources of oil and natural gas
Our success depends upon our ability to find, acquire, develop and commercially produce oil and natural gas, which depends upon factors outside of our control.
Oil and natural gas operations involve many risks that even a combination of experience, knowledge and careful evaluation may not be able to overcome. Our long-term commercial success depends upon our ability to find, acquire, develop and commercially produce oil and natural gas. We have only recently commenced production of oil and natural gas. There is no assurance that our other properties or future properties will achieve commercial production. Without the continual addition of new reserves, our existing reserves and our production will decline over time as our reserves are exploited. A future increase in our reserves will depend not only upon our ability to explore and develop any properties we may have from time to time, but also upon our ability to select and acquire new suitable producing properties or prospects. No assurance can be given that we will be able to locate satisfactory properties for acquisition or participation. Moreover, if acquisitions or participations are identified, we may determine that current market conditions, the terms of any acquisition or participation arrangement, or pricing conditions, may make the acquisitions or participations uneconomical, and further commercial quantities of oil and natural gas may not be produced, discovered or acquired by us, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Properties that we acquire may not produce as projected, and we may be unable to determine reserve potential, identify liabilities associated with the properties or obtain protection from sellers against such liabilities.
Our long-term commercial success depends upon our ability to find, acquire, develop and commercially produce oil and natural gas reserves. However, our review of acquired properties is inherently incomplete, as it generally is not feasible to review in depth every individual property involved in each acquisition. Even a detailed review of records and properties may not necessarily reveal existing or potential problems, nor will it permit a buyer to become sufficiently familiar with the properties to assess fully their deficiencies and potential. Inspections may not always be performed on every well, and environmental problems, such as ground water contamination, are not necessarily observable even when an inspection is undertaken.
Our estimated reserves are based on many assumptions that may prove to be inaccurate. Any material inaccuracies in the reserve estimates or the underlying assumptions may adversely affect the quantities and present value of our reserves.
There are numerous uncertainties inherent in estimating quantities of oil, natural gas reserves and the future cash flows attributed to the reserves. Our reserve and associated cash flow estimates are estimates only. In general, estimates of economically recoverable oil and natural gas reserves and the associated future net cash flows are based upon a number of variable factors and assumptions, such as historical production from the properties, production rates, ultimate reserve recovery, timing and amount of capital expenditures, marketability of oil and gas, royalty rates, the assumed effects of regulation by governmental agencies and future operating costs, all of which may vary materially from actual results. All estimates are to some degree speculative, and classifications of reserves are only attempts to define the degree of speculation involved. For those reasons, estimates of the economically recoverable oil and natural gas reserves attributable to any particular group of properties, classification of such reserves based on risk of recovery and estimates of future net revenues associated with reserves prepared by different engineers, or by the same engineers at different times, may vary. Our actual production, revenues, taxes and development and operating expenditures with respect to our reserves will vary from our estimates of them, and those variations could be material.
Estimates of proved reserves that may be developed and produced in the future are often based upon volumetric calculations and upon analogy to similar types of reserves rather than actual production history. Recovery factors and drainage areas are estimated by experience and analogy to similar producing pools. Estimates based on these methods are generally less reliable than those based on actual production history. Subsequent evaluation of the same reserves based upon production history and production practices will result in variations in the estimated reserves, and those variations could be material.
Our future oil and natural gas production may not result in revenue increases and may be adversely affected by operating conditions, production delays, drilling hazards and environmental damages.
Future oil and natural gas exploration may involve unprofitable efforts, not only from dry wells, but also from wells that are productive but do not produce sufficient petroleum substances to return a profit after drilling, operating and other costs. Completion of a well does not assure a profit on the investment or recovery of drilling, completion and operating costs. In addition, drilling hazards or environmental damage could greatly increase the cost of operations, and various field operating conditions may adversely affect the production from successful wells. These conditions include delays in obtaining governmental approvals or consents, shut-ins of connected wells resulting from extreme weather conditions, insufficient storage or transportation capacity or other geological and mechanical conditions. While diligent well supervision and effective maintenance operations can contribute to maximizing production rates over time, production delays and declines from normal field operating conditions cannot be eliminated and can be expected to adversely affect revenue and cash flow levels to varying degrees.
Risks related to management of the Company
We may experience difficulty managing our anticipated growth.
We may be subject to growth-related risks including capacity constraints and pressure on our internal systems and controls. Our ability to manage growth effectively will require us to continue to implement and improve our operational and financial systems and to attract and retain qualified management and technical personnel to meet the needs of our anticipated growth. Our inability to deal with this growth could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We depend upon key personnel and the absence of any of these individuals could result in us having to cease operations.
Our ability to continue our operation business depends, in large part, upon our ability to attract and maintain qualified key management and technical personnel. Competition for such personnel is intense and we may not be able to attract and retain such personnel.
Strategic relationships upon which we may rely are subject to change, which may diminish our ability to conduct our operations.
Our ability to successfully acquire additional licenses, to discover reserves, to participate in drilling opportunities and to identify and enter into commercial arrangements depends on developing and maintaining close working relationships with industry participants and government officials and on our ability to select and evaluate suitable properties and to consummate transactions in a highly competitive environment. We may not be able to establish these strategic relationships, or if established, we may not be able to maintain them. In addition, the dynamics of our relationships with strategic partners may require us to incur expenses or undertake activities we would not otherwise be inclined to undertake in order to fulfill our obligations to these partners or maintain our relationships. If our strategic relationships are not established or maintained, our business prospects may be limited, which could diminish our ability to conduct our operations.
We cannot be certain that current expected expenditures and any current or planned completion/testing programs will be realized.
We believe that the costs used to prepare internal budgets are reasonable, however, there are assumptions, uncertainties, and risk that may cause our allocated funds on a per well basis to change as a result of having to alter certain activities from those originally proposed or programmed to reduce and mitigate uncertainties and risks. These assumptions, uncertainties, and risks are inherent in the completion and testing of wells and can include but are not limited to: pipe failure, casing collapse, unusual or unexpected formation pressure, environmental hazards, and other operating or production risk intrinsic in oil and or gas activities. Any of the above may cause a delay in any of our completion/testing programs or our ability to determine reserve potential.
Risks related to federal, state, local and other laws, controls and regulations
We are subject to complex federal, provincial, state, local and other laws, controls and regulations that could adversely affect the cost, manner and feasibility of conducting our oil and natural gas operations.
Oil and natural gas exploration, production, marketing and transportation activities are subject to extensive controls and regulations imposed by various levels of government, which may be amended from time to time. Governments may regulate or intervene with respect to price, taxes, royalties and the exportation of oil and natural gas. Regulations may be changed from time to time in response to economic or political conditions. The implementation of new regulations or the modification of existing regulations affecting the oil and natural gas industry could reduce demand for crude oil and natural gas and increase our costs, any of which may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. In addition, in order to conduct oil and natural gas operations, we require licenses from various governmental authorities. We cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain all of the licenses and permits that may be required to conduct operations that we may desire to undertake.
There is uncertainty regarding claims of title and rights of the aboriginal people to properties in certain portions of western Canada, and such a claim, if made in respect of our property or assets, could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Aboriginal peoples have claimed aboriginal title and rights to a substantial portion of western Canada. We are not aware that any claims have been made in respect of its property and assets. However, if a claim arose and was successful it would have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We are subject to stringent environmental laws and regulations that may expose us to significant costs and liabilities, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
All phases of the oil and natural gas business present environmental risks and hazards and are subject to environmental regulation under a variety of federal, provincial, state and local laws and regulations. Environmental legislation provides for, among other things, restrictions and prohibitions on spills, releases or emissions of various substances produced in association with oil and natural gas operations. The legislation also requires that wells and facility sites be operated, maintained, abandoned and reclaimed to the satisfaction of applicable regulatory authorities. Compliance with legislation can require significant expenditures, and a breach of applicable environmental legislation may result in the imposition of fines and penalties, some of which may be material. Environmental legislation is evolving in a manner expected to result in stricter standards and enforcement, larger fines and liability and potentially increased capital expenditures and operating costs. The discharge of oil, natural gas or other pollutants into the air, soil or water may give rise to liabilities to governments and third parties and may require us to incur costs to remedy any discharge. Environmental laws may result in a curtailment of production or a material increase in the costs of production, development or exploration activities, or otherwise adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
As a public company, our compliance costs and risks have increased in recent years.
Legal, accounting and other expenses associated with public company reporting requirements have increased significantly in the past few years. We anticipate that general and administrative costs associated with regulatory compliance will continue to increase with on-going compliance requirements under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as well as any new rules implemented by the SEC, Canadian Securities Administrators, the NYSE Amex Equities and the Toronto Stock Exchange in the future. These rules and regulations have significantly increased our legal and financial compliance costs and made some activities more time-consuming and costly. We cannot assure you that we will continue to effectively meet all of the requirements of these regulations, including Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and National Instrument 52-109 of the Canadian Securities Administrators. Any failure to effectively implement internal controls, or to resolve difficulties encountered in their implementation, could harm our operating results, cause us to fail to meet reporting obligations, or result in our principal executive officer and principal financial officer being required to give a qualified assessment of our internal control over financial reporting. Any such result could cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information, which could have a material adverse effect on the trading price of our common shares and our ability to raise capital. These rules and regulations have made it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain the same or similar coverage in the future. As a result, it may be more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified individuals to serve on our board of directors or as executive officers.
Risks Related to Our Being a Foreign Private Issuer
As a foreign private issuer, our shareholders may receive less complete and timely data.
We are a “foreign private issuer” as defined in Rule 3b-4 under the United States Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Our equity securities are accordingly exempt from Sections 14(a), 14(b), 14(c), 14(f) and 16 of the Exchange Act, pursuant to Rule 3a12-3 of the Exchange Act. Therefore, we are not required to file a Schedule 14A proxy statement in relation to our annual meetings of shareholders. The submission of proxy and annual meeting of shareholder information on Form 6-K may result in shareholders having less complete and timely information in connection with shareholder actions. The exemption from Section 16 rules regarding reports of beneficial ownership and purchases and sales of common shares by insiders and restrictions on insider trading in our securities may result in shareholders having less data and there being fewer restrictions on insiders’ activities in our securities.
It may be difficult to enforce judgments or bring actions outside the United States against us and certain of our directors and officers.
It may be difficult to bring and enforce suits against us. We are incorporated in British Columbia, Canada. Many of our directors and officers are not residents of the United States and some of our assets are located outside of the United States. As a result, it may be difficult for U.S. holders of our common shares to effect service of process on these persons within the United States or to enforce judgments obtained in the U.S. based on the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities laws against us or our officers and directors. In addition, a shareholder should not assume that the courts of Canada (i) would enforce judgments of U.S. courts obtained in actions against us or our officers or directors predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities laws or other laws of the United States, or (ii) would enforce, in original actions, liabilities against us or our officers or directors predicated upon the U.S. federal securities laws or other laws of the United States.
Risks related to investing in our common shares
We have not paid any dividends on our common shares. Consequently, your only opportunity currently to achieve a return on your investment will be if the market price of our common shares appreciates above the price that you pay for our common shares.
We have not declared or paid any dividends on our common shares since our incorporation. Any decision to pay dividends on our common shares will be made by our board of directors on the basis of our earnings, financial requirements and other conditions existing at such future time. Consequently, your only opportunity to achieve a return on your investment in our securities will be if the market price of our common shares appreciates and you are able to sell your common shares at a profit.
Our common share price has been volatile and your investment in our common shares could suffer a decline in value.
Our common shares are traded on the Toronto Stock Exchange and the NYSE Amex Equities. The market price of our common shares may fluctuate significantly in response to a number of factors, some of which are beyond our control. These factors include price fluctuations of precious metals, government regulations, disputes regarding mining claims, broad stock market fluctuations and economic conditions in the United States.
Dilution through officer, director, employee, consultant or agent options could adversely affect our shareholders.
Because our success is highly dependent upon our officers, directors, employees, consultants and agents, we have granted to some or all of our key officers, directors, employees, consultants and agents options to purchase common shares as non-cash incentives. To the extent that we grant significant numbers of options and those options are exercised, the interests of our other shareholders may be diluted. As of April 26, 2012, there were 9,329,001 common share purchase options outstanding, of which 7,201,506 common share purchase options are vested and exercisable. If all the vested options were exercised, it would result in an additional 7,201,506 common shares being issued and outstanding.
The issuance of additional common shares may negatively affect the trading price of our common shares.
We have issued equity securities in the past and may continue to issue equity securities to finance our activities in the future, including to finance future acquisitions, or as consideration for acquisitions of businesses or assets. In addition, outstanding options and warrants to purchase our common shares may be exercised, resulting in the issuance of additional common shares. The issuance by us of additional common shares would result in dilution to our shareholders, and even the perception that such an issuance may occur could have a negative effect on the trading price of our common shares.
ITEM 4. INFORMATION ON THE COMPANY
| A. | History and Development of the Company |
Introduction
Our executive office is located at:
598 – 999 Canada Place
Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada V6C 3E1
Telephone: (604) 638-5050
Facsimile: (604) 638-5051
Website: www.dejour.com
Email: rhodgkinson@dejour.com or mwong@dejour.com
The contact person is: Mr. Robert L. Hodgkinson, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer or Mr. Mathew H. Wong, Chief Financial Officer and Corporate Secretary.
Our common shares trade on the Toronto Stock Exchange and the NYSE Amex Equities Stock Exchange under the symbol “DEJ”.
Our authorized capital consists of three classes of shares: an unlimited number of common shares; an unlimited number of preferred shares designated as First Preferred Shares, issuable in series; and an unlimited number of preferred shares designated as Second Preferred Shares, issuable in series. There are no indentures or agreements limiting the payment of dividends and there are no conversion rights, special liquidation rights, pre-emptive rights or subscription rights.
The First Preferred Shares have priority over the Common Shares and the Second Preferred Shares with respect to the payment of dividends and in the distribution of assets in the event of a winding up of Dejour. The Second Preferred Shares have priority over the Common Shares with respect to dividends and surplus assets in the event of a winding up of Dejour.
As of December 31, 2011, there were 126,892,386 common shares issued and outstanding. As of December 31, 2011, there were no First Preferred Shares and no Second Preferred Shares issued and outstanding.
Incorporation and Name Changes
Dejour Energy Inc. (formerly Dejour Enterprises Ltd.) is incorporated under the laws of British Columbia, Canada. The Company was originally incorporated as “Dejour Mines Limited” on March 29, 1968 under the laws of the Province of Ontario. By articles of amendment dated October 30, 2001, the issued shares were consolidated on the basis of one (1) new for every fifteen (15) old shares and the name of the Company was changed to Dejour Enterprises Ltd. On June 6, 2003, the shareholders approved a resolution to complete a one-for-three-share consolidation, which became effective on October 1, 2003. In 2005, the Company was continued in British Columbia under theBusiness Corporations Act(British Columbia). On March 9, 2011, the Company changed its name from Dejour Enterprises Ltd. to Dejour Energy Inc.
Financings
We have financed our operations through funds from loans, public/private placements of common shares, common shares issued for property, common shares issued in debt settlements, and shares issued upon exercise of stock options and share purchase warrants. The following table summarizes our financings for the past three fiscal years.
| Fiscal Year | | Nature of Share Issuance | | Number of Shares | | | Gross Proceeds
(Cdn$) | |
| Fiscal 2009 | | Exercise of Stock Options | | | 631,856 | | | | 273,223 | |
| | | Private Placement(1) | | | 2,710,332 | | | | 1,626,199 | |
| | | Public Offering(2) | | | 10,766,665 | | | | 3,425,060 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fiscal 2010 | | Private Placement(3) | | | 2,907,334 | | | | 1,017,567 | |
| | | Private Placement(4) | | | 2,000,000 | | | | 750,000 | |
| | | Public Offering/Private Placement (5) | | | 7,142,858 | | | | 2,000,000 | |
| | | Private Placement (6) | | | 2,339,315 | | | | 888,940 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fiscal 2011 | | Public Offering (7) | | | 11,010,000 | | | | 3,288,641 | |
| | | Exercise of Warrants | | | 4,551,841 | | | | 1,688,147 | |
| | | Exercise of Options | | | 1,150,000 | | | | 402,500 | |
| (1) | In October 2009, we completed a private placement and issued 2,710,332 flow-through shares (“FTS”) at Cdn$0.60 per share. Gross proceeds raised were Cdn$1,626,199. In connection with this private placement, we paid finders’ fees of Cdn$83,980 and other related costs of Cdn$73,427. |
| (2) | In December 2009, we completed a public offering and issued 10,766,665 units at US$0.30 per unit. Each unit consists of 10,766,665 common shares and 8,075,000 share purchase warrants, exercisable at US$0.40 per share on or before December 23, 2014. Gross proceeds raised were Cdn$3,425,060 (US$3,230,000). In connection with this public offering, we paid finders’ fees of Cdn$203,180 and other related costs of Cdn$140,790. We also issued 645,999 agent’s warrants, exercisable at US$0.46 per share on or before November 3, 2014. The grant date fair values of the warrants and agent’s warrants, estimated to be $888,250 and $71,060 respectively, have been included in share capital on a net basis and accordingly have not been recorded as a separate component of shareholders’ equity. |
| (3) | In March 2010, we completed a private placement and issued 2,907,334 flow-through units at Cdn$0.35 per unit. Each unit consists of 2,907,334 common shares and 1,453,667 share purchase warrants, exercisable at $0.45 per share on or before March 3, 2011. Gross proceeds raised were Cdn$1,017,567. In connection with this private placement, we paid finders’ fees of Cdn$54,575 and other related costs of $52,819. We also issued 37,423 agent’s warrants, exercisable at Cdn$0.45 per share on or before March 3, 2011. |
| (4) | In September 2010, we completed a private placement and issued 2,000,000 flow-through shares at Cdn$0.375 per share. Gross proceeds raised were Cdn$750,000. In connection with this private placement, we paid finders’ fees of Cdn$37,500 and other related costs of Cdn$38,890. |
| (5) | In November 2010, we completed an offering of 7,142,858 units at Cdn$0.28 per unit, partially pursuant to a public offering and partially pursuant to a private placement. Each unit consists of one common share and 0.65 of a common share purchase warrant. Each whole common share purchase warrant is exercisable into one common share at Cdn$0.40 per share on or before November 17, 2015. Gross proceeds raised were Cdn$2,000,000. In connection with this offering, we paid finders’ fees of Cdn$120,000 and other related costs of Cdn$123,423. |
| (6) | In December 2010, we completed a private placement and issued 2,339,315 flow-through shares at Cdn$0.38 per share. Gross proceeds raised were Cdn$888,940. In connection with this private placement, we paid finders’ fees of Cdn$53,337 and other related costs of Cdn$61,862. We also issued 140,359 agent’s warrants, exercisable at Cdn$0.38 per share on or before December 23, 2011. Directors and Officers of the Company purchased 513,157 shares of this offering. |
| (7) | In February 2011, we completed a public offering of 11,010,000 units at US $0.30 per unit. Each unit consists of one common share and one-half of one common share purchase warrant. Each whole warrant entitles the holder to acquire one additional common share of the Company at US$0.35 per common share on or before February 10, 2012. Gross proceeds raised were Cdn$3,288,641 (US$3,303,000). In connection with this private placement, the Company paid finders’ fees of Cdn$196,694 (US$199,710) in cash and other related costs of Cdn$119,602 in cash. |
Past Capital Expenditures
| Fiscal Year | | Cash flows used for equipment and resource properties | |
| | | | | |
| Fiscal 2009 (Canadian GAAP) | | Cdn$ | 2,626,488 | (1) |
| Fiscal 2010 (IFRS) | | Cdn$ | 5,038,711 | (2) |
| Fiscal 2011 (IFRS) | | Cdn$ | 8,360,376 | (3) |
| (1) | $39,279 of these funds was spent on the purchase of corporate and other assets; and $2,587,209 was spent on our resource properties. (For a breakdown on the resource property expenditures, see Note 6 to our audited consolidated financial statements for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009, filed with our annual report on Form 20-F on June 30, 2010.) |
| (2) | $26,945 of these funds was spent on the purchase of corporate and other assets; and $5,011,766 was spent on our resource properties. (For a breakdown on the resource property expenditures, see Notes 5 and 6 to our audited consolidated financial statements for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, filed with this annual report on Form 20-F.) |
| (3) | $28,867 of these funds was spent on the purchase of corporate and other assets; and $8,331,509 was spent on our resource properties. (For a breakdown on the resource property expenditures, see Notes 5 and 6 to our audited consolidated financial statements for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, filed with this annual report on Form 20-F.) |
Capital Expenditures
Additions to property and equipment, and exploration and evaluation assets:
| | | Three months ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| | | $ | | | $ | | | $ | | | $ | |
| Land acquisition and retention | | | 37,197 | | | | 31,337 | | | | 241,911 | | | | 272,837 | |
| Drilling and completion | | | 1,853,487 | | | | 1,113,000 | | | | 4,397,819 | | | | 2,206,270 | |
| Facility and pipelines | | | 290,381 | | | | 331,799 | | | | 2,949,008 | | | | 1,243,616 | |
| Capitalized general and administrative | | | 168,403 | | | | 145,620 | | | | 742,771 | | | | 1,289,043 | |
| Other assets | | | 148 | | | | (15,261 | ) | | | 28,867 | | | | 26,945 | |
| | | | 2,349,616 | | | | 1,606,495 | | | | 8,360,376 | | | | 5,038,711 | |
During 2011, the Company further refined its focus toward the conversion of resources into reserves. As a result, the Company’s asset characterization has moved toward more tangible low risk near term development projects, moderate risk appraisal opportunities and moderate to high risk exploration potential.
In 2011, the Company’s focus was on production optimization of the Drake/Woodrush property, while finalizing pre-drilling activities for the Kokopelli development and drilling a discovery well at South Rangely.
Most of the waterflood capital expenditures have already been spent in fiscal 2011. Future capital expenditures at Woodrush in the upcoming year of 2012 are expected to be approximately $1.2 to $1.5 million and funded through its cash flow from operations and the undrawn line of credit. In the U.S., the Company plans to drill up to eight wells during 2012 and its share of expenditures ranges from $6.5 to $11 million. The Company plans to fund the expenditures through additional financing, including debt, equity or joint venture financing, or disposal of non-core assets.
DAILY PRODUCTION
| | | Three months ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| By Product | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Natural gas (mcf/d) | | | 1,376 | | | | 1,614 | | | | 1,184 | | | | 1,504 | |
| Oil and natural gas liquids (bbls/d) | | | 242 | | | | 149 | | | | 223 | | | | 236 | |
| Total (boe/d) | | | 471 | | | | 418 | | | | 421 | | | | 487 | |
The decrease in natural gas production for the year ended December 31, 2011 (“fiscal 2011”) was primarily the result of the temporary curtailment of production due to maintenance related downtime at the regional gas processing plant in the 2nd quarter of 2011 and extended to the third week of July 2011. This regional gas processing plant is operated by a third party and is not under the Company’s control. Gas production resumed during the third week of July 2011. The decrease in natural gas production for the current quarter was because gas production is restricted to a maximum daily limit, due to 100% compressor capacity.
The decrease in oil production for the current year was the result of production restrictions imposed by the Oil and Gas Conservation Commission of British Columbia (“OGC”) on the Company’s Woodrush property prior to the successful implementation of the waterflood in the Halfway “E” Pool.
General
The Company is in the business of acquiring, exploring and developing energy projects with a focus on oil and gas exploration in Canada and the United States. The Company holds approximately 113,000 net acres of oil and gas leases in the following regions:
| · | The Peace River Arch of northwestern British Columbia and northeastern Alberta, Canada |
| · | The Piceance, Paradox and Uinta Basins in the US Rocky Mountains |
Summary
Over the past three years, the Company has evolved its forward focus from acquiring resource potential toward conversion of resources into reserves. This process involved several distinct steps on the same continuum including:
| · | Classification and prioritization of acreage based on economic promise, technical robustness, infrastructural and logistic advantage and commercial maturity |
| · | Evaluation and development planning for top tier acreage positions |
| · | Developing partnerships within financial and industry circles to speed the exploitation process, and |
| · | Aggressively bringing production on line where feasible |
As a result of these moves, the Company’s asset characterization has moved toward more tangible low risk near term development projects, moderate risk appraisal opportunities and moderate to high risk exploration potential.
Our business objective is to grow our oil and gas production and generate sufficient cash flow to continue to expand company operations and enhance shareholder value.
Specialized Skill and Knowledge:Exploration for and development of petroleum and natural gas resources requires specialized skills and knowledge including in the areas of petroleum engineering, geophysics, geology and title. The Company and its subsidiaries have obtained personnel with the required specialized skills and knowledge to carry out their respective operations. While the current labour market in the industry is highly competitive, the Company expects to be able to attract and maintain appropriately qualified employees for fiscal 2012.
Cycles:All of the Company's operations in Canada are affected by seasonal operating conditions. Dejour Energy (Alberta) Ltd., our wholly owned subsidiary, holds properties in northwestern Alberta and northeastern British Columbia which are accessible to heavy equipment in winter only when the ground is frozen, typically between December to early April. For this reason drilling and pipeline construction ceases over the remainder of the year, limiting growth to winter only. Production operations continue year round in these areas once production is established. The prices that the Company will receive for oil and gas production in the future are weighted to world benchmark prices and may be adversely affected by mild weather conditions. Recently there has been a significant change in the supply demand balance and commodity prices have fallen dramatically. The Company expects this condition to persist for several months but the Company believes that a balance between production and consumption and a stable price environment will be reestablished by the end of 2012. See"Risk Factors – Risks related to operating an exploration, development and production company".
Environmental Protection:The Company's operations are subject to environmental regulations (including regular environmental impact assessments and permitting) in the jurisdictions in which it operates. Such regulations cover a wide variety of matters, including, without limitation, emission of greenhouse gases, prevention of waste, pollution and protection of the environment, labour regulations and worker safety. Under such regulations there are preventative obligations, clean-up costs and liabilities for toxic or hazardous substances which may exist on or under any of its properties or which may be produced as a result of its operations. Environmental legislation and legislation relating to exploration and production of oil and natural gas will require stricter standards and enforcement, increased fines and penalties for non-compliance, more stringent environmental assessments of proposed projects and a heightened degree of responsibility for companies and their directors and employees. Such stricter standards could impact the Company's costs and have an adverse effect on results of operations. The Company expects to incur abandonment and site reclamation costs as existing oil and gas properties are abandoned and reclaimed; however, the Company does not anticipate making material expenditures beyond normal compliance with environmental regulations in 2012 and future years.
Employees:The Company had the equivalent of approximately 18 full-time employees and consultants during 2011.
Social or Environmental Policies:The health and safety of employees, contractors and the public, as well as the protection of the environment, is of utmost importance to the Company. The Company endeavors to conduct its operations in a manner that will minimize adverse effects of emergency situations by:
| • | complying with government regulations and standards; |
| • | following industry codes, practices and guidelines; |
| • | ensuring prompt, effective response and repair to emergency situations and environmental incidents; and |
| • | educating employees and contractors of the importance of compliance with corporate safety and environmental rules and procedures. |
The Company believes that all Company personnel have a vital role in achieving excellence in environmental, health and safety performance. This is best achieved through careful planning and the support and active participation of everyone involved.
Competitive Conditions: The Company operates in geographical areas where there is strong competition by other companies for reserve acquisitions, exploration leases, licences and concessions and skilled industry personnel. The Company’s competitors include major integrated oil and natural gas companies and numerous other independent oil and natural gas companies and individual producers and operators, many of whom have greater financial and personnel resources than the Company. The Company’s ability to acquire additional property rights, to discover reserves, to participate in drilling opportunities and to identify and enter into commercial arrangements with customers is dependent upon developing and maintaining close working relationships with its current industry partners and joint operators, and its ability to select and evaluate suitable properties and to consummate transactions in a highly competitive environment.
Three Year History
2011
In 2011, the Company’s focus was on production optimization of the Drake/Woodrush property, while finalizing pre-drilling activities for the Kokopelli development and drilling a discovery well at South Rangely.
During the year, the Company achieved the following major objectives and also made significant progress on key strategic initiatives that resulted in:
| (1) | Successful implementation and expansion of the Halfway “E” oil pool waterflood on the Company’s Woodrush property. |
| (2) | Obtained a $7 million line of credit from a Canadian bank to refinance the bridge loan and to provide funds for general corporate purposes. |
| (3) | Generated positive operating cash flow for the second half of the year. |
| (4) | Completed all requirements for drilling on the Company’s federal leases at Gibson Gulch, Piceance Basin, Colorado, resulting in the first drilling permits being issued in the fourth quarter of the year. |
| (5) | Completed and tested a discovery well at South Rangely. After the well was successfully fractured and stimulated, the well flowed rich gas from the Mancos "B" Sand in commercial quantities. |
2010
In 2010, the Company’s focus was on increasing production, reserves, and operational efficiency at the Drake/Woodrush properties, while maintaining all prospective acreage holdings and positioning for renewed drilling activities as both the business environment and commodity prices improved.
During the year, the Company achieved the following major objectives and also made significant progress on key strategic initiatives that resulted in:
| (1) | Extended the limits of the Woodrush halfway pool by drilling three successful development wells in 2010. |
| (2) | Received approval from the British Columbia Oil and Gas Commission to implement a waterflood in the Halfway “E” oil pool at Woodrush and began project implementation in October. |
| (3) | Raised gross proceeds of $4.7 million in equity, allowing the Company to support the development of oil and gas properties in the Drake/Woodrush properties. |
| (4) | Obtained a bridge loan credit facility of up to $5 million, allowing the Company to refinance its existing bank facility and fund its working capital and capital expenditures. |
2009
In 2009, the Company’s focus was on the restructuring of current assets and operations to reduce debt and lower operating costs while maintaining all prospective acreage holdings and positioning for renewed drilling activities as both the business environment and commodity prices improved.
Despite the difficult environment faced in 2009, the Company was able to achieve all major objectives and also make significant progress on key strategic initiatives that resulted in the following:
| (1) | Increased Net Proved and Probable Reserves by more than 3,500% from slightly more than 6 BCFE to over 217 BCFE. The before tax discounted (NPV10) value of the Company’s proved and probable reserves, net of all future costs for development is now valued at $324 million. This is up from $31 million as at December 31, 2008. The major increase in reserves results from developments in the Gibson Gulch field in the Piceance Basin where the Company holds a 72% working interest in 2200 gross acres. This property is discussed in more detail later in this report. |
| (2) | Reduced total liabilities from $18.3 million to $6.2 million |
| (3) | Reduced working capital deficit of $12.7 million at the end of 2008 to $20.0 thousand at the end of 2009 |
| (4) | Raised $5 million of equity, allowing the Company to execute its winter drilling program in Woodrush Field. |
| (5) | Strengthening our Board of Directors with the addition of Stephen Mut as Co-Chairman of the Board and Darren Devine as Director. |
| (6) | We disposed of all of our holdings in Titan Uranium for proceeds of $2,305,491. We retained a 10% carried interest and a 1% net smelter return on approximately 578,365 acres of uranium leases. |
United States vs. Foreign Sales/Assets
Commencing the second quarter of fiscal 2008, we recorded our reported oil and gas revenue.
| Gross Revenue for fiscal year ended: | | Canada | | | United States | |
| | | | | | | |
| 12/31/2009 (Canadian GAAP) | | $ | 6,470,725 | | | | — | |
| 12/31/2010 (IFRS) | | $ | 8,085,627 | | | | — | |
| 12/31/2011 (IFRS) | | $ | 8,824,345 | | | | — | |
| Asset Location as of: | | Canada | | | United States | |
| | | | | | | |
| 12/31/2009 (Canadian GAAP) | | $ | 16,874,298 | | | $ | 29,011,578 | |
| 12/31/2010 (IFRS) | | $ | 18,563,424 | | | $ | 11,849,967 | |
| 12/31/2011 (IFRS) | | $ | 20,622,433 | | | $ | 8,816,003 | |
Commodity Price Environment
Generally, the demand for, and the price of, natural gas increases during the colder winter months and decreases during the warmer summer months. Pipelines, utilities, local distribution companies and industrial users utilize natural gas storage facilities and purchase some of their anticipated winter requirements during the summer, which can lessen seasonal demand fluctuations. Crude oil and the demand for heating oil are also impacted by seasonal factors, with generally higher prices in the winter. Seasonal anomalies, such as mild winters, sometimes lessen these fluctuations.
Our results of operations and financial condition are significantly affected by oil and natural gas commodity prices, which can fluctuate dramatically. The market for oil and natural gas is beyond our control and prices are difficult to predict.
Forward Contracts
The Company is not bound by an agreement (including any transportation agreement) directly or through an aggregator, under which it may be precluded from fully realizing, or may be protected from the full effect of, future market prices for oil and gas.
The following table summarizes the Company’s crude oil risk management positions at December 31, 2011:
| Instrument type | | Contract Month | | Volume | | Price per
barrel | |
| Western Texas Instrument (“WTI”) Sold Futures | | February 2012 | | 4,000 barrels per month | | US$ | 98 | |
| Western Texas Instrument (“WTI”) Sold Futures | | March 2012 | | 4,000 barrels per month | | US$ | 98 | |
| Western Texas Instrument (“WTI”) Sold Futures | | April 2012 | | 4,000 barrels per month | | US$ | 98 | |
Additional Information Concerning Abandonment and Reclamation Costs
For the Company’s Canadian and US oil and gas interests, the well abandonment costs for all wells with reserves have been included at the property level. The Company estimated the total undiscounted amount of the cash flows required to settle the retirement obligations to be approximately $1,635,000. These obligations are expected to be settled over the next 20 years with the majority of costs incurred between 2018 and 2025. Additional abandonment costs associated with non-reserves wells, lease reclamation costs and facility abandonment and reclamation expenses have not been included.
Government Regulations
Our oil and natural gas exploration, production and related operations, when developed, are subject to extensive laws and regulations promulgated by federal, state, tribal and local authorities and agencies. These laws and regulations often require permits for drilling operations, drilling bonds and reports concerning operations, and impose other requirements relating to the exploration for and production of oil and natural gas. Many of the laws and regulations govern the location of wells, the method of drilling and casing wells, the plugging and abandoning of wells, the restoration of properties upon which wells are drilled, temporary storage tank operations, air emissions from flaring, compression, the construction and use of access roads, sour gas management and the disposal of fluids used in connection with operations.
Our operations are subject to environmental regulations (including regular environmental impact assessments and permitting) in the jurisdictions in which it operates. Such regulations cover a wide variety of matters, including, without limitation, emission of greenhouse gases, prevention of waste, pollution and protection of the environment, labour regulations and worker safety. Under such regulations there are preventative obligations, clean-up costs and liabilities for toxic or hazardous substances which may exist on or under any of its properties or which may be produced as a result of its operations. Environmental legislation and legislation relating to exploration and production of oil and natural gas will require stricter standards and enforcement, increased fines and penalties for non-compliance, more stringent environmental assessments of proposed projects and a heightened degree of responsibility for companies and their directors and employees. Such stricter standards could impact our costs and have an adverse effect on results of operations.
The Comprehensive Environmental, Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, or CERCLA, and comparable state statutes impose strict, joint and several liability on owners and operators of sites and on persons who disposed of or arranged for the disposal of "hazardous substances" found at such sites. It is not uncommon for the government to file claims requiring cleanup actions, demands for reimbursement for government-incurred cleanup costs, or natural resource damages, or for neighboring landowners and other third parties to file claims for personal injury and property damage allegedly caused by hazardous substances released into the environment. The Federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, or RCRA, and comparable state statutes govern the disposal of "solid waste" and "hazardous waste" and authorize the imposition of substantial fines and penalties for noncompliance, as well as requirements for corrective actions. Although CERCLA currently excludes petroleum from its definition of "hazardous substance," state laws affecting our operations may impose clean-up liability relating to petroleum and petroleum-related products. In addition, although RCRA classifies certain oil field wastes as "non-hazardous," such exploration and production wastes could be reclassified as hazardous wastes thereby making such wastes subject to more stringent handling and disposal requirements. CERCLA, RCRA and comparable state statutes can impose liability for clean-up of sites and disposal of substances found on drilling and production sites long after operations on such sites have been completed. Other statutes relating to the storage and handling of pollutants include the Oil Pollution Act of 1990, or OPA, which requires certain owners and operators of facilities that store or otherwise handle oil to prepare and implement spill response plans relating to the potential discharge of oil into surface waters. The OPA, contains numerous requirements relating to prevention of, reporting of, and response to oil spills into waters of the United States. State laws mandate oil cleanup programs with respect to contaminated soil. A failure to comply with OPA's requirements or inadequate cooperation during a spill response action may subject a responsible party to civil or criminal enforcement actions.
The Endangered Species Act, or ESA, seeks to ensure that activities do not jeopardize endangered or threatened animal, fish and plant species, or destroy or modify the critical habitat of such species. Under the ESA, exploration and production operations, as well as actions by federal agencies, may not significantly impair or jeopardize the species or its habitat. The ESA has been used to prevent or delay drilling activities and provides for criminal penalties for willful violations of its provisions. Other statutes that provide protection to animal and plant species and that may apply to our operations include, without limitation, the Fish and Wildlife Coordination Act, the Fishery Conservation and Management Act, the Migratory Bird Treaty Act. Although we believe that our operations are in substantial compliance with these statutes, any change in these statutes or any reclassification of a species as threatened or endangered or re-determination of the extent of "critical habit" could subject us to significant expenses to modify our operations or could force us to discontinue some operations altogether.
The National Environmental Policy Act, or NEPA, requires a thorough review of the environmental impacts of "major federal actions" and a determination of whether proposed actions on federal and certain Indian lands would result in "significant impact." For purposes of NEPA, "major federal action" can be something as basic as issuance of a required permit. For oil and gas operations on federal and certain Indian lands or requiring federal permits, NEPA review can increase the time for obtaining approval and impose additional regulatory burdens on the natural gas and oil industry, thereby increasing our costs of doing business and our profitability.
The Clean Water Act, or CWA, and comparable state statutes, impose restrictions and controls on the discharge of pollutants, including spills and leaks of oil and other substances, into waters of the United States. The discharge of pollutants into regulated waters is prohibited, except in accordance with the terms of a permit issued by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) or an analogous state agency. The CWA regulates storm water run-off from oil and natural gas facilities and requires a storm water discharge permit for certain activities. Such a permit requires the regulated facility to monitor and sample storm water run-off from its operations. The CWA and regulations implemented thereunder also prohibit discharges of dredged and fill material in wetlands and other waters of the United States unless authorized by an appropriately issued permit. The CWA and comparable state statutes provide for civil, criminal and administrative penalties for unauthorized discharges for oil and other pollutants and impose liability on parties responsible for those discharges for the costs of cleaning up any environmental damage caused by the release and for natural resource damages resulting from the release.
The Safe Drinking Water Act, or SDWA, and the Underground Injection Control (UIC) program promulgated thereunder, regulate the drilling and operation of subsurface injection wells. EPA directly administers the UIC program in some states and in others the responsibility for the program has been delegated to the state. The program requires that a permit be obtained before drilling a disposal well. Violation of these regulations and/or contamination of groundwater by oil and natural gas drilling, production, and related operations may result in fines, penalties, and remediation costs, among other sanctions and liabilities under the SWDA and state laws. In addition, third party claims may be filed by landowners and other parties claiming damages for alternative water supplies, property damages, and bodily injury.
The Clean Air Act, as amended, restricts the emission of air pollutants from many sources, including oil and gas operations. New facilities may be required to obtain permits before work can begin, and existing facilities may be required to incur capital costs in order to remain in compliance. In addition, the EPA has promulgated more stringent regulations governing emissions of toxic air pollutants from sources in the oil and gas industry, and these regulations may increase the costs of compliance for some facilities.
Significant studies and research have been devoted to climate change and global warming, and climate change has developed into a major political issue in the United States and globally. Certain research suggests that greenhouse gas emissions contribute to climate change and pose a threat to the environment. Recent scientific research and political debate has focused in part on carbon dioxide and methane incidental to oil and natural gas exploration and production. Many state governments have enacted legislation directed at controlling greenhouse gas emissions, and future state and federal legislation and regulation could impose additional restrictions or requirements in connection with our operations and favor use of alternative energy sources, which could increase operating costs and demand for oil products. As such, our business could be materially adversely affected by domestic and international legislation targeted at controlling climate change.
We expect to incur abandonment and site reclamation costs as existing oil and gas properties are abandoned and reclaimed; however, we do not anticipate making material expenditures beyond normal compliance with environmental regulations in 2012 and future years.
The health and safety of employees, contractors and the public, as well as the protection of the environment, is of utmost importance to us. We endeavour to conduct our operations in a manner that will minimize adverse effects of emergency situations by:
| · | complying with government regulations and standards; |
| · | following industry codes, practices and guidelines; |
| · | ensuring prompt, effective response and repair to emergency situations and environmental incidents; and |
| · | educating employees and contractors of the importance of compliance with corporate safety and environmental rules and procedures. |
We believe that all of our personnel have a vital role in achieving excellence in environmental, health and safety performance. This is best achieved through careful planning and the support and active participation of everyone involved.
Competition
We operate in geographical areas where there is strong competition by other companies for reserve acquisitions, exploration leases, licences and concessions and skilled industry personnel. Our competitors include major integrated oil and natural gas companies and numerous other independent oil and natural gas companies and individual producers and operators, many of whom have greater financial and personnel resources than us. Our ability to acquire additional property rights, to discover reserves, to participate in drilling opportunities and to identify and enter into commercial arrangements with customers is dependent upon developing and maintaining close working relationships with its current industry partners and joint operators, and its ability to select and evaluate suitable properties and to consummate transactions in a highly competitive environment.
We compete with many companies possessing greater financial resources and technical facilities for the acquisition of oil and gas properties, exploration and production equipment, as well as for the recruitment and retention of qualified employees.
Seasonality
All of our operations in Canada are affected by seasonal operating conditions. Dejour Energy (Alberta) Ltd., our wholly owned subsidiary, holds properties in northwestern Alberta and northeastern British Columbia which are accessible to heavy equipment in winter only when the ground is frozen, typically between December to early April. For this reason drilling and pipeline construction ceases over the remainder of the year, limiting growth to winter only. Production operations continue year round in these areas once production is established. The prices that we will receive for oil and gas production in the future are weighted to world benchmark prices and may be adversely affected by mild weather conditions.
| C. | Organizational Structure |
Dejour Energy Inc. (formerly Dejour Enterprises Ltd.) is incorporated under the laws of British Columbia, Canada. The Company was originally incorporated as “Dejour Mines Limited” on March 29, 1968 under the laws of the Province of Ontario. By articles of amendment dated October 30, 2001, the issued shares were consolidated on the basis of one (1) new for every fifteen (15) old shares and the name of the Company was changed to Dejour Enterprises Ltd. On June 6, 2003, the shareholders approved a resolution to complete a one-for-three-share consolidation, which became effective on October 1, 2003. In 2005, the Company was continued in British Columbia under theBusiness Corporations Act(British Columbia). On March 9, 2011, the Company changed its name from Dejour Enterprises Ltd. to Dejour Energy Inc.
Intercorporate Relationships
We have four 100% owned subsidiaries:
| · | Dejour Energy (USA) Corp. (“Dejour USA”), a Nevada corporation, holds Dejour's United States oil and gas interests, |
| · | Dejour Energy (Alberta) Ltd. (“DEAL”), an Alberta corporation, holds its Canadian oil and gas interests in northwestern Alberta and northeastern British Columbia; |
| · | Wild Horse Energy Ltd. (“Wild Horse”), an inactive Alberta corporation, and |
| · | 0855524 B.C. Ltd. (“0855524”), a British Columbia Corporation, which had disposed of its Montney (Buick Creek) property during 2010 and is currently inactive. |
| D. | Property, Plant and Equipment |
Our executive offices are located in rented premises of approximately 2,519 sq. ft. at 598 – 999 Canada Place, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6C 3E1. We began occupying these facilities on July 1, 2009. Current monthly base rent is $6,088.
Resource Properties
Our current focus is on oil and gas properties located in the United States and Canada. We formerly had direct interest in uranium exploration properties, which we sold to Titan Uranium Inc. in 2006 for Titan common shares. We sold all of our Titan common shares in 2009, but retained a 1% NSR on all the properties sold to Titan, and a 10% working interest in each claim, carried by Titan to a completed bankable feasibility study after which we may elect to participate as to its 10% interest or convert to an additional 1% NSR.
We currently haveoil and gas leases in the following regions:
| · | The Piceance, Paradox and Uinta Basins in the US Rocky Mountains. |
| · | The Peace River Arch of northeastern British Columbia and north western Alberta, Canada. |
United States Oil and Gas Properties
In July 2006, our U.S. subsidiary, Dejour USA, entered into a participation agreement (the “2006 Retamco Agreement”) with Retamco Operating, Inc. (“Retamco”), a U.S. privately owned oil and gas corporation, and Brownstone Ventures (US) Inc. (“Brownstone”), a subsidiary of Brownstone Ventures Inc., a Canadian company listed on the TSX-V. Under the agreement, Dejour USA and Brownstone agreed to participate in the ownership of specified oil and gas leasehold interests and related exploration and development of those leases located in the Piceance, Uinta and Paradox Basins of western Colorado and eastern Utah.
In June 2008, Dejour USA entered into a further purchase and sale agreement with Retamco resulting in Dejour USA acquiring an additional 64,000 net acres involving the same properties in which it purchased an interest in the 2006 Retamco Agreement. Additionally, as a part of this latter agreement Dejour USA sold its 25% working interests in two wells in the North Barcus Creek Prospect (located in Piceance Basin, Colorado) and its lease interest in the Rio Blanco Deep Prospect (located in northern Colorado).
Certain leases expired or sold, and the Company currently has approximately 100,000 net acres in the Piceance, Paradox and Uinta Projects.
Kokopelli (Gibson Gulch)
The Company continued working with its partners to bring this project into production. Dejour has a 71.43% working interest in this 2,200 acre project which is ideally situated for exploitation of both the Williams Fork and Mancos shale bodies. The Williams Companies, Inc. and Bill Barrett Corporation are developing and producing on adjacent acreage to the east, west and north of the Company’s acreage. Dejour USA has worked closely with important constituents including local citizenry and government, the Bureau of Land Management and the Colorado Division of Wildlife to develop a mutually acceptable development plan for this environmentally sensitive area. In 2010, we were granted approval to develop a 660 acre portion of the leases with 10-acre spacing. Approval of this spacing on the remainder of the lease acreage has enabled us and our partner to drill up to 220 wells (158 wells net to us) from a few multi-well drilling pads to optimally exploit the gas reserves in the subsurface. Construction of the first drilling pad commenced in the fourth quarter of 2011 with production expected to begin in the second half of 2012.
South Rangely
The Rangely Prospect Area is just south of Rangely Field near the Utah border. In the Rangely prospect area, fractured Mancos Shale is producing gas. The Mancos also contains sandstone intervals, Mancos A and Mancos B, which can be productive. The eastern shoulder of the Douglas Creek Arch and the flanks of the Rangely Anticline as well as other areas of the basin are being explored for this Cretaceous age strata. The Mancos is also considered a source rock in the area.
Evaluation and subsequent exploitation of an oil prospect at South Rangely, was deferred from the fourth quarter of 2010 to the second quarter of 2011, as a result of minor delays in the permitting process that prevented drilling from occurring before the winter drilling prohibitions designed to protect big game habitat. Despite a minor delay, we did not alter our plans to drill an evaluation well on the 7,000 acre lease located just south of Rangely field. Recent advances in horizontal drilling and fracture stimulation technology have moved this previously marginal development into robust economic status. Success at South Rangely may allow us to revisit plans to evaluate and potentially exploit a 22,000 acre tract at our North Rangely prospect.
In May 2011, we announced that we and our partners had executed a development alliance with a private Dallas based US E&P with adjacent properties and in June 2011, we announced that it has drilled and set casing on an initial vertical well to test the Mancos/Niobrara potential on its South Rangely. After a thorough review of the well data the well will be completed, fractured and flow tested to determine the commercial potential of the Lower Mancos “C” Sand in this area
In June 2011, the Company drilled and cased an evaluation well on this 5,500 gross acre (3,300 net acre) lease which is located just south of the Rangely field. The well was drilled and casing set on approximately 90 feet of gross Mancos "B" Sand and later successfully fractured and stimulated. The well flowed rich gas from the Mancos "B" Sand in commercial quantities. Analysis of the gas showed a higher natural gas liquid (“NGL”) yield from the South Rangely discovery than that expected from our NGL development at Kokopelli (formerly Gibson Gulch).
West Grand Valley (Piceance Basin)
On the Company’s West Grand Valley property, Dejour operates approximately 5,180 acres (gross) with a 71.43% working interest in an area of active drilling by EnCana, Laramie Partners II and Axia. Success in developing the gas in the Lower Mancos (Niobrara) section has revitalized drilling interest in this area of the Piceance Basin. Included in the West Grand Valley property acreage is the 1400+ acre Roan Creek evaluation project. This project is located very close to and sandwiched between existing Williams Fork gas fields operated by Occidental and Chevron. While it is likely that the Williams Fork at Roan Creek will be somewhat thinner than is found to the east and west, Roan Creek has Mancos potential which can be tested via an exploratory tail to a Williams Fork appraisal well. During 2009, the various geologic and commercial studies conducted by us highlighted the potential at Roan Creek. As a result of those studies, we began to make plans for a single well drilling program. The permitting process is underway and drilling at Roan Creek will follow the first increment of drilling at Kokopelli.
Future Exploration and Evaluation
As a result of a reasonably comprehensive geologic and commercial study in 2009, Dejour has high graded two future development and appraisal projects including:
| · | Plateau (Piceance Basin) – We have 71.43% working interest in this 3,014 acre (gross) project located south of Roan Creek has Williams Fork potential as evidenced by successful drilling by EnCana Corporation at acreage adjacent to the Company’s holdings. |
| | |
| · | North Rangely – We have 71.43% working interest in this 18,000 acre (gross) project located north of the Rangely Field, is prospective for oil in the Lower Mancos (Niobrara), Dakota, Morrison and Phosphoria formations. |
These potential developments will be deferred to at least 2013 as the current natural gas price has caused Dejour to delay the start of investments on its other leases in Colorado. Exploitation of these opportunities will in all likelihood proceed once developments at Kokopelli, South Rangely and Roan Creek have been advanced to the point that Company’s cash flow and proved producing reserve base can support the additional development costs.
Other Prospect Areas
We have approximately 77,403 net acres in the following prospect areas, which are considered as non-core projects of the Company.
| Area | | Prospect | | Net acres to Dejour | |
| Piceance | | Book Cliffs | | | 11,524 | |
| | | Gunnison | | | 753 | |
| Paradox | | San Juan | | | 169 | |
| Uinta | | Bitter Creek | | | 240 | |
| | | Bonanza | | | 262 | |
| | | Cisco | | | 5,071 | |
| | | Displacement | | | 4,125 | |
| | | Gorge Spring | | | 986 | |
| | | Oil shale | | | 899 | |
| | | Seep Ridge | | | 160 | |
| | | Tri County | | | 677 | |
| Northern Colorado | | Meeker | | | 2,329 | |
| | | Pinyon | | | 4,637 | |
| | | Waddle Creek | | | 80 | |
| Sub-Thrust | | Dinosaur | | | 44,878 | |
| | | Ashley | | | 480 | |
| Sand Wash | | Sand Wash | | | 133 | |
| Total | | | | | 77,403 | |
Canadian Oil and Gas Properties
Our wholly-owned subsidiary, Dejour Energy (Alberta) Ltd. (“DEAL”), currently has interests in oil and gas properties in the Peace River Arch located principally in northeastern British Columbia. DEAL’s holdings approximately 11,000 net acres concentrated in the Peace River Arch.
Summary of Operational Highlights
Production and Netback Summary
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| Production Volumes: | | | | | | | | |
| Oil and natural gas liquids (bbls) | | | 81,468 | | | | 86,119 | |
| Gas (mcf) | | | 432,199 | | | | 548,890 | |
| Total (BOE) | | | 153,501 | | | | 177,599 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Average Price Received: | | | | | | | | |
| Oil and natural gas liquids ($/bbls) | | | 88.98 | | | | 67.46 | |
| Gas ($/mcf) | | | 3.64 | | | | 4.13 | |
| Total ($/BOE) | | | 57.49 | | | | 45.53 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Royalties ($/BOE) | | | 10.61 | | | | 7.39 | |
| Operating and Transportation Expenses ($/BOE) | | | 16.18 | | | | 14.67 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Operating Netbacks ($/BOE)* | | | 30.70 | | | | 23.48 | |
*NON-GAAP MEASURES
Non-GAAP measures are commonly used in the oil and gas industry. Certain measures in this Form 20-F includes disclosures of Call Cash Flow from Operating Activities, Operating Netback, Operating Loss, and EBITDA, which are financial measures not prepared in accordance with IFRS, and therefore are considered non-GAAP measures. A non-GAAP financial measure is a numerical measure of historical or future financial performance, financial position or cash flows that excludes or includes amounts that are required to be disclosed by GAAP.The presentation of this additional information is not meant to be considered in isolation or as a substitute for the numbers prepared in accordance with GAAP.These measures may not be comparable to similar measures presented by other issuers. These measures have been described and presented in this document in order to provide shareholders and potential investors with additional information regarding our liquidity and our ability to generate funds to finance our operations. The reconciliations of non-GAAP financial measures are included in the table below and elsewhere if there are any non-GAAP measures.
Operating Netback is a non-GAAP measure defined as revenues less royalties and operating and transportation expenses.
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| | | $ | | | $ | |
| Revenues | | | 8,824,000 | | | | 8,086,000 | |
| Less: Royalties | | | (1,628,000 | ) | | | (1,312,000 | ) |
| Less: Operating and transportation expenses | | | (2,499,000 | ) | | | (2,609,000 | ) |
| Operating Netback | | | 4,697,000 | | | | 4,165,000 | |
The decrease in natural gas production in 2011 was primarily the result of the temporary shut-in of gas production in the summer of 2011 due to maintenance related downtime at the regional gas processing plant that is operated by a third party and is not under the Company’s control.
Production and Development Projects
Drake/Woodrush
2011
In December 2010, a waterflood project application was expedited and approval was received. The project was implemented in early 2011 with water injection commencing in March 2011. In the first quarter of 2011, gross production from the field was reduced to approximately 544 barrels of oil equivalent/day (“BOED”) (408 BOED net) in response to the decreasing pressure in the Halfway oil sand. In October 2011, Dejour received approval to operate the waterflood on a voidage replacement basis and in December drilled a third production well while increasing total injection from 1200 BWPD to 2400 BWPD. The start-up and subsequent enhancement of the waterflood marked the end of major capital investments in Woodrush. Dejour will concentrate on optimizing injection and production in the waterflood, controlling cost and increasing margins on oil production.
Effective December 31, 2011, the Company's reserve evaluation valued the before tax discounted net present value 10% (NPV10) of remaining proved reserves in the Woodrush oil pool at $19 million net to Dejour’s 75% working interest. The reserve evaluation was conducted by an independent firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP (“AJM Deloitte” or “AJM”) of Calgary, Alberta.
2010
After completing a 3-D seismic program over the field in January 2010, we finalized drilling plans and in March 2010 commenced drilling of two development wells. The first found the target Halfway sand tight, but encountered a new Gething Gas pool that was subsequently put on production at more than 1,000 MCFD (100% gross). The second development well encountered the Halfway sand as expected, was completed and flow tested at rates in excess of 500 BOPD (100% gross).
With the success of the drilling in March 2010, field production reached a record level in May 2010, averaging 970 BOED (100% gross), where 75% is oil. In the fourth quarter of 2010, production from the field was reduced to approximately 560 BOED (100% gross) in response to increasing gas production resulting from the decreasing pressure in the Halfway oil sand. In October 2010, the first water injection well was drilled to the southeast limit of the reservoir. This well was produced briefly without the assistance of at 60 BOPD prior to conversion to injection. In December 2010, a waterflood project application was expedited and approval was received. The project was fully implemented in early 2011 with water injection commencing in March 2011. Water injection will be gradually ramped up to a level of 1,500 to 2,000 BWPD with the resulting oil production expected to reach a peak of approximately 900 BOPD (100% gross) in the second half of 2012.
In 2011 Dejour concentrated on optimizing injection and production in the waterflood, controlling cost and increasing margins on gas production as the oil production is gradually ramped up to its maximum level in the second half of 2012.
2009
DEAL was the successful bidder for 1,579 net acres of Crown land located adjacent to the northern boundary of the Woodrush lease which was offered for lease in November 2009. The price paid for this acquisition was approximately $340,000.
Late in 2009, we began preparations for a 3-D seismic survey designed to investigate the northern portion of the Woodrush lease and the southern portion of the newly acquired acreage. The survey was shot, processed and interpreted in late 2009/early 2010 with several drilling locations identified. Rigs were contracted and two or three wells are anticipated to be drilled before activity is truncated at time of “break-up” in the water prone areas which overlay the prospective oil and gas deposits.
In late 2009 and prior to the seismic survey, DEAL drilled, sidetracked and suspended an oil and gas well with hydrocarbon shows in several intervals. The well location was based upon previously acquired seismic data.
During 2009, DEAL sold 25% of its interest in Woodrush/Drake for $4,500,000 in cash. Proceeds from the sale of the interest were used to fund expanded Woodrush/Drake investments and to reduce our outstanding bank line of credit. DEAL’s working interest in Woodrush/Drake was 75% as at December 31, 2009.
Buick Creek (Montney)
In December 2010, we sold our entire 90% interest in this area for net proceeds of approximately $952,000.
Reserve Data
The standards of the SEC require that proved reserves be estimated using existing economic conditions (constant pricing). Based on this methodology, the Company’s results have been calculated utilizing the 12-month average price for each of the years presented.
The Company reports in Canadian currency and therefore the Reserves Data set forth in the tables below has been converted to Canadian dollars at the prevailing conversion rate at December 31, 2011. The conversion rate used per Bank of Canada is 1.0170.
In 2011, AJM Deloitte, independent petroleum engineering consultants based in Calgary, Alberta was retained by the Company to evaluate the Canadian properties of the Company. Their report, titled “Reserve Estimation and Economic Evaluation, Dejour Energy (Alberta) Ltd.”, is dated March 23, 2012 and has an effective date of December 31, 2011.
Gustavson Associates LLP, an independent petroleum engineering consulting firm based in Boulder, Colorado has been retained by the Company to evaluate the US properties of the Company. Their 2011 report, titled “Reserves Evaluation Report, Dejour Energy (USA) Corp., Leasehold Garfield county, Colorado, USA” is dated February 15, 2012 and has an effective date of January 1, 2012.
In 2010, GLJ Petroleum Consultants (“GLJ”), independent petroleum engineering consultants based in Calgary, Alberta were retained by to evaluate our Canadian properties. Their report, titled “Reserves Assessment and Evaluation of Canadian Oil and Gas Properties”, is dated March 22, 2011 and has an effective date of December 31, 2010.
The reserves data set forth below (the "Reserves Data"), derived from AJM Deloitte and Gustavson’s reports, summarizes our oil, liquids and natural gas reserves.
The AJM Deloitte and Gustavson reports are based on certain factual data supplied by the Company, and AJM Deloitte and Gustavson's opinion of reasonable practice in the industry. The extent and character of ownership and all factual data pertaining to the Company’s petroleum properties and contracts (except for certain information residing in the public domain) were supplied by the Company to AJM and Gustavson and accepted without any further investigation. AJM and Gustavson accepted this data as presented and neither title searches nor field inspections were conducted. All statements relating to the activities of the Company for the year ended December 31, 2011 include a full year of operating data on the properties of the Company.
The reserve estimates of crude oil, natural gas liquids and natural gas reserves provided herein are estimates only and there is no guarantee that the estimated reserves will be recovered. Actual crude oil, natural gas liquids and natural gas reserves may be greater than or less than the estimates provided herein.
Controls Over Reserve Report Preparation
Our reserve estimates reports as of December 31, 2011 are prepared by our independent qualified reserve evaluators, AJM and Gustavson. To ensure accuracy and completeness of the data prior to disclosure of reserve estimates to the public, our reserves committee does the following: (1) reviews our procedures for providing information to the independent qualified reserve evaluators, (2) meets with the independent qualified reserves evaluators to determine whether any restrictions affected the ability of the qualified reserves evaluators to report without reservation, (3) reviews the reserves data with management and the independent qualified reserves evaluator. If the reserve committee is satisfied with results of its evaluation it will approve the content of our reserve disclosure. If any concerns arise in the reserve committee’s evaluation, the reserve committee will work with our management and the independent qualified reserves evaluators to resolve the issues before disclosure of reserves is made public.
As of December 31, 2011, the Company’s reserve committee was composed of: Harrison Blacker, Robert Holmes and Richard Patricio. Please see “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees, A. Directors and Senior Management” for biographical information on the members of the reserve committee.
Summary of Oil and Gas Reserves as of Fiscal Year-End Based on Average Fiscal Year Prices
| | | Net Reserves | |
| Reserves Category | | Oil
(Mbbl) | | | Condensate
(MBO) | | | Natural Gas
(Mmcf) | | | Natural Gas
Liquids
(Mbbl) | |
| PROVED | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Developed | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Canada | | | 317 | | | | - | | | | 752 | | | | 4 | |
| United States | | | - | | | | - | | | | 158 | | | | 14 | |
| Undeveloped | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Canada | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| United States | | | - | | | | 287 | | | | 41,156 | | | | 3,849 | |
| TOTAL PROVED | | | 317 | | | | 287 | | | | 42,066 | | | | 3,867 | |
Proved Undeveloped Reserves
| | | Total Proved Undeveloped Reserves |
Oil
(Mbbl) | | Condensate
(MBO) | | | Natural Gas
(Mmcf) | | | | Natural Gas
Liquids
(Mbbl) | |
| - | | 287 | | | 41,156 | | | | 3,849 | |
The significant majority of the undeveloped reserves are scheduled to be developed within the next five years. Our proved undeveloped reserves for natural gas decreased by 4,152 Mmcf, mainly due to a decrease in natural gas in the Kokopelli (formerly Gibson Gulch) property resulting from technical revisions. Our proved undeveloped reserves for natural gas liquids increased by 3,849 Mbbl, mostly due to increase in natural gas liquids in the Kokopelli (formerly Gibson Gulch) property from technical revision.
In 2011, we incurred approximately $7 million in expenditures mainly for development of proved undeveloped reserves to convert 92 Mbbl proved undeveloped reserves of oil into 243 Mbbl proved developed reserves in the Woodrush property.
Total Proved Reserves
The table below compares our estimated proved reserves and associated present value (discounted at an annual rate of 10%) of the estimated future revenue before income tax.
| | | December 31, 2011 | |
| | | Natural | | | | | | Natural | | | | | | | |
| Canada (Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves) | | Gas | | | Oil | | | Gas Liquids | | | Total | | | PV-10(2) | |
| | | | (Mmcf) | | | | (Mbbl) | | | | (Mbbl) | | | | (Mmcfe) | | | | (in thousands Cdn$) | |
| 2011 12-month average prices (SEC)(1) | | | 752 | | | | 317 | | | | 4 | | | | 2,678 | | | $ | 19,247 | |
| | | | |
| | | December 31, 2011 | |
| | | Natural | | | | | | Natural | | | | | | | |
| United States (Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves) | | Gas | | | Condensate | | | Gas Liquids | | | Total | | | PV-10(2) | |
| | | | (Mmcf) | | | | (Mbbl) | | | | (Mbbl) | | | | (Mmcfe) | | | | (in thousands Cdn$) | |
| 2011 12-month average prices (SEC)(1) | | | 41,314 | | | | 287 | | | | 3,863 | | | | 66,214 | | | $ | 33,462 | |
| | | December 31, 2011 | |
| | | Natural | | | | | | | | | Natural | | | | | | | |
| Total (Proved Developed and Undeveloped Reserves) | | Gas | | | Oil | | | Condensate | | | Gas Liquids | | | Total | | | PV-10(2) | |
| | | (Mmcf) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mmcfe) | | | (in thousands Cdn$) | |
| 2011 12-month average p rices (SEC)(1) | | | 42,066 | | | | 317 | | | | 287 | | | | 3,867 | | | | 68,892 | | | $ | 52,709 | |
Reconciliation to Standardized Measure
As at December 31, 2011
| (in thousands of Canadian dollars) | | Canada | | | USA | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Future cash from revenues after royalties | | $ | 32,005 | | | $ | 298,776 | | | $ | 330,781 | |
| Future production costs | | | (10,900 | ) | | | (72,833 | ) | | | (83,733 | ) |
| Future development costs | | | (150 | ) | | | (88,377 | ) | | | (88,527 | ) |
| Less: 10% annual discount factor | | | (1,708 | ) | | | (104,104 | ) | | | (105,812 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Standardized measure of discounted future net cash flow | | $ | 19,247 | | | $ | 33,462 | | | $ | 52,709 | |
Notes:
(1) The 12-month average prices (SEC) are calculated based on an average of the first price on the first day of each month in 2011, adjusted for wellhead differential and current costs prevailing at December 31, 2011. The 12-month average prices (SEC) used for Canadian properties were Cdn$90.15 per barrel of oil and Cdn$3.82 per Mcf of natural gas. The 12-month average prices (SEC) used for US properties were US$89.19 per barrel of condensate, US$30.24 per barrel of ethane, US$43.18 per barrel of heavy NGLs, and US$3.14 per Mcf of natural gas.
(2) Present value of estimated future net cash flows before income taxes (PV-10) is considered a non-GAAP financial measure as defined by the SEC. We believe that our PV-10 presentation is relevant and useful to our investors because it presents the discounted future net cash flows attributable to our proved reserves before taking into account the related deferred income taxes, as such taxes may differ among various companies because of differences in the amounts and timing of deductible basis, net operating loss carryforwards and other factors. We believe investors and creditors use our PV-10, before tax, as a basis for comparison of the relative size and value of our proved reserves to the reserve estimates of other companies. PV-10 is not a measure of financial or operating performance under GAAP and is not intended to represent the current market value of our estimated oil and natural gas reserves. PV-10, before tax, should not be considered in isolation or as a substitute for the standardized measure of discounted future net cash flows as defined under GAAP.
(3) US dollars are converted into Canadian dollars using the closing exchange rate on December 31, 2011, which is US$1.00 = Cdn$1.017.
Oil and Gas Production, Production Prices and Production Costs
The following is our total net oil and gas production for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009. All production came from our Canadian properties. There was no production from our United States properties in the fiscal years ended December 31, 2011, 2010, or 2009.
| Production | |
| Fiscal Year Ended | | Oil
(bbls) | | | Natural Gas
(Mcf) | | | Natural Gas Liquids
(bbls) | |
| December 31, 2011 | | | 80,113 | | | | 432,199 | | | | 1,355 | |
| December 31, 2010 | | | 84,197 | | | | 548,890 | | | | 1,922 | |
| December 31, 2009 | | | 72,254 | | | | 566,158 | | | | 2,028 | |
The following table includes the average prices the Company received for its production for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009.
| Average Sales Prices | |
| Fiscal Year Ended | | Oil
($/bbls) | | | Natural Gas
($/Mcf) | | | Natural Gas Liquids
($/bbls) | |
| December 31, 2011 | | | 88.72 | | | | 3.64 | | | | 104.19 | |
| December 31, 2010 | | | 67.67 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 64.04 | |
| December 31, 2009 | | | 54.67 | | | | 4.35 | | | | 52.91 | |
The following table includes the average production cost, not including ad valorem and severance taxes, per unit of production for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2011, 2010 and 2009.
| Average Production Costs | |
| Fiscal Year Ended | | Oil
($/bbls) | | | Natural Gas
($/Mcf) | | | Natural Gas Liquids
($/bbls) | |
| December 31, 2011 | | | 16.66 | | | | 2.60 | | | | 14.02 | |
| December 31, 2010 | | | 13.01 | | | | 2.77 | | | | 13.01 | |
| December 31, 2009 | | | 23.38 | | | | 3.11 | | | | 16.12 | |
Drilling and Other Exploratory and Development Activities
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, we drilled the following wells:
| | | Net Exploratory Wells | | | Net Development Wells | |
| Canada | | Productive | | | Dry | | | Productive | | | Dry | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oil | | | - | | | | - | | | | 0.75 | | | | - | |
| Natural Gas | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Dry Wells | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Service Wells | | | 1.50 | | | | - | | | | 2.25 | | | | - | |
| Suspended | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Wells | | | 1.50 | | | | - | | | | 3.00 | | | | - | |
| | | Net Exploratory Wells | | | Net Development Wells | |
| U.S.A | | Productive | | | Dry | | | Productive | | | Dry | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Natural Gas (1) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 0.50 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Wells | | | - | | | | - | | | | 0.50 | | | | - | |
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010, we drilled the following wells:
| | | Net Exploratory Wells | | | Net Development Wells | |
| Canada | | Productive | | | Dry | | | Productive | | | Dry | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oil | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1.50 | | | | - | |
| Natural Gas | | | 0.75 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Dry Wells | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Service Wells | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Suspended | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Wells | | | 0.75 | | | | - | | | | 1.50 | | | | - | |
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009, we drilled the following wells:
| | | Net Exploratory Wells | | | Net Development Wells | |
| Canada | | Productive | | | Dry | | | Productive | | | Dry | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oil | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Natural Gas | | | 0.75 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Dry Wells | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Service Wells | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Suspended | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Wells | | | 0.75 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Delivery Commitments
We have no current delivery commitments for either oil or natural gas.
Oil and Gas Properties and Wells
As of December 31, 2011, we had 10 gross (7.13 net) producing oil or natural gas wells.
| | | Oil | | | Natural Gas | |
| Canada | | Gross | | | Net | | | Gross | | | Net | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Producing | | | 3 | | | | 2.25 | | | | 5 | | | | 3.63 | |
| Shut-In | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 0.75 | |
| TOTAL | | | 3 | | | | 2.25 | | | | 6 | | | | 4.38 | |
| | | Oil | | | Natural Gas | |
| U.S.A | | Gross | | | Net | | | Gross | | | Net | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Shut-In (1) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 0.50 | |
| TOTAL | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 0.50 | |
As of December 31, 2010, we had 9 gross (6.63 net) producing oil or natural gas wells.
| | | Oil | | | Natural Gas | |
| Canada | | Gross | | | Net | | | Gross | | | Net | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Producing | | | 3 | | | | 2.25 | | | | 3 | | | | 2.19 | |
| Shut-In | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3 | | | | 2.19 | |
| TOTAL | | | 3 | | | | 2.25 | | | | 6 | | | | 4.38 | |
Interest in Oil and Gas Properties
The following table summarizes our landholdings as of December 31, 2011:
| Landholdings | | Developed | | | Undeveloped(1) | | | Total | |
| (in acres) | | Gross | | | Net | | | Gross | | | Net | | | Gross | | | Net | |
| Canada | | | 10,280 | | | | 6,516 | | | | 21,530 | | | | 5,838 | | | | 16,796 | | | | 12,354 | |
| U.S.A | | | 7,176 | | | | 3,896 | | | | 201,164 | | | | 99,019 | | | | 208,340 | | | | 102,915 | |
| TOTAL | | | 17,456 | | | | 10,412 | | | | 222,694 | | | | 104,857 | | | | 225,136 | | | | 115,269 | |
(1) Undeveloped properties are properties for which the Company has no attributed reserves.
Uranium Properties
In 2009, we disposed of all of our 16,750,000 shares in Titan Uranium inc. for proceeds of $2,305,491. We have 10% carried interest and 1% Net Smelter Return on certain uranium exploration leases in Saskatchewan operated by Titan Uranium Inc. However, we no longer maintain the right of first refusal on future financings, we are no longer required to provide geologists to Titan, and our representatives have since resigned from the Titan Board of Directors.
ITEM 4A. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
Not Applicable.
ITEM 5. OPERATING AND FINANCIAL REVIEW AND PROSPECTS
The following is a discussion of our consolidated operating results and financial position, including all our wholly-owned subsidiaries. It should be read in conjunction with our audited consolidated financial statements and notes for the year ended December 31, 2011 and related notes included therein under the heading "Item 18. Financial Statements" below.
The financial statements of the Company for the year ended December 31, 2011 are prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”) and interpretations of the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (“IFRIC”). These are the Company’s first consolidated annual financial statements presented in accordance with IFRS.
The preparation of these consolidated financial statements resulted in changes to the accounting policies as compared with the most recent annual financial statements prepared under Canadian generally accepted accounting principles (“Canadian GAAP”). These consolidated financial statements should be read in conjunction with the Company’s 2010 annual financial statements and the explanation of how the transition to IFRS has affected the reported financial position, financial performance and cash flows of the Company provided in note 25 of the Company’s consolidated financial statements included therein under the heading "Item 18. Financial Statements" below.
Certain forward-looking statements are discussed in this Item 5 with respect to our activities and future financial results. These are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause projected results or events to differ materially from actual results or events. Readers should also read the "Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements" above and “Item 3. Key Information - Risk Factors.”
INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARDS
On January 1, 2011, the Company adopted IFRS for financial reporting purposes, with a transition date of January 1, 2010. The consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2011, including required comparative information, have been prepared in accordance with IFRS. Previously, the Company prepared its financial statements in accordance with Canadian GAAP. Unless otherwise noted, 2010 comparative financial statement information has been prepared in accordance with IFRS.
The adoption of IFRS has not had a material impact on the Company’s operations, strategic decisions, cash flow and capital expenditures. The most significant changes to the Company’s accounting policies related to the accounting for its property, plant and equipment and accounting for derivative financial instruments. Other impacted areas include stock-based compensation, foreign currency translation and accounting for flow through shares.
Further information on the IFRS accounting policies, impacts and reconciliation between previous Canadian GAAP and IFRS are provided in Note 3 and Note 25 to the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements for the year ended December 31, 2011. The reconciliations include the Consolidated Balance Sheets as at January 1, 2010 and December 31, 2010, Consolidated Statement of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity for the year ended December 31, 2010, and Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Loss for the year ended December 31, 2010.
The following provides a summary of the significant IFRS accounting policy changes.
Exploration and Evaluation Assets
Under Canadian GAAP, the Company followed the Canadian Institute of Chartered Accountants (“CICA”) guideline on full cost accounting in which all costs directly associated with the acquisition of, the exploration for, and the development of natural gas and crude oil reserves are capitalized on a country-by-country cost centre basis. Costs accumulated within each country cost centre were depleted using the unit-of-production method based on proved reserves determined using estimated future prices and costs. Under IFRS, the Company adopted new accounting policies for its oil and gas activities, including pre-exploration costs, exploration and evaluation costs and development costs.
Under IFRS, pre-exploration costs are expensed and exploration and evaluation (“E&E”) costs are those expenditures for an area or project for which technical feasibility and commercial viability have not yet been determined. The technical feasibility and commercial viability of extracting a mineral resource is considered to be determinable when proven reserves are determined to exist. Development (“D&P”) costs include those expenditures for areas or projects where technical feasibility and commercial viability have been determined. Under Canadian GAAP, all costs, including E&E assets were capitalized as Property and Equipment (“D&P”). Under IFRS, E&E costs and D&P are disclosed as different class of assets.
Impairment
Under Canadian GAAP, the Company was required to recognize an impairment loss if the carrying amount exceeds the undiscounted cash flows from proved reserves for the country cost centre. If an impairment loss was to be recognized, it was then measured as the amount that the carrying value exceeded the sum of the estimated fair value of the proved and probable reserves and the costs of unproved properties. Impairments recognized under Canadian GAAP could not be reversed.
Under IFRS, the Company is required to recognize and measure an impairment loss if the carrying value exceeds the recoverable amount for a cash-generating unit (“CGU”). Oil and gas assets are grouped into CGUs based on their ability to generate largely independent cash flows. Under IFRS, the recoverable amount is the higher of the estimated fair value less cost to sell and value in use. Impairment losses, other than goodwill, can be reversed when there is a subsequent increase in the recoverable amount.
Upon adoption of IFRS, the Company recognized an additional impairment charge of $14.7 million to the opening deficit at January 1, 2010, relating to certain non-core E&E assets in the US. The impairment charge was based on the difference between the net book value of the assets and the estimated recoverable amount. The recoverable amount was determined using the fair value less costs to sell based on the expected amount for which the asset could be sold in an arm’s length transaction. Under Canadian GAAP, these assets were included in the US country cost centre ceiling test, which was not impaired as at December 31, 2009.
Warrant Liabilities
The Company issued US$ denominated warrants as part of equity financings, while the Company’s functional currency is the CAD$. Under Canadian GAAP, common share purchase warrants were classified as equity.
Under IFRS, the Company determined that the warrants denominated in US$ outstanding at the date of transition must be treated as warrant liabilities in the Company’s statement of financial position. Any issuance costs related to the warrants denominated in a foreign currency are expensed upon initial issuance. Prospectively, these warrants are re-measured at each balance sheet date based on estimated fair value, and any resultant changes in fair value are recorded as non-cash valuation adjustments as income or loss in the respective period.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
The Company makes estimates and assumptions about the future that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities. Estimates and judgments are continually evaluated based on historical experience and other factors, including expectations of future events that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. In the future, actual experience may differ from these estimates and assumptions.
The effect of a change in an accounting estimate is recognized prospectively by including it in profit or loss in the period of the change, if the change affects that period only; or in the period of the change and future periods, if the change affects both.
Information about critical judgments in applying accounting policies that have the most significant risk of causing material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities recognized in the condensed interim consolidated financial statements within the next financial year are discussed below:
Reserves
The estimate of reserves is used in forecasting the recoverability and economic viability of the Company’s oil and gas properties, and in the depletion and impairment calculations. The process of estimating reserves is complex and requires significant interpretation and judgment. It is affected by economic conditions, production, operating and development activities, and is performed using available geological, geophysical, engineering, and economic data. Reserves are evaluated at least annually by the Company’s independent reserve evaluators and updates to those reserves, if any, are estimated internally. Future development costs are estimated using assumptions as to the number of wells required to produce the commercial reserves, the cost of such wells and associated production facilities and other capital costs.
Exploration and evaluation expenditures
The application of the Company’s accounting policy for exploration and evaluation expenditure requires judgment in determining whether it is likely that future economic benefits will flow to the Company, which is based on assumptions about future events or circumstances. Estimates and assumptions made may change if new information becomes available. If, after expenditure is capitalized, information becomes available suggesting that the recovery of the expenditure is unlikely, the amount capitalized is written off in profit or loss in the period the new information becomes available.
Impairment
A CGU is defined as the lowest grouping of integrated assets that generate identifiable cash inflows that are largely independent of the cash inflows of other assets or groups of assets. The allocation of assets into CGUs requires significant judgment and interpretations with respect to the integration between assets, the existence of active markets, similar exposure to market risks, shared infrastructures, and the way in which management monitors the operations. The recoverable amounts of CGUs and individual assets have been determined based on the higher of fair value less costs to sell or value-in-use calculations. The key assumptions the Company uses in estimating future cash flows for recoverable amounts are anticipated future commodity prices, expected production volumes, future operating and development costs. Changes to these assumptions will affect the recoverable amounts of CGUs and individual assets and may then require a material adjustment to their related carrying value.
Derivative Financial Instruments
When estimating the fair value of derivative financial instruments, the Company uses third-party models and valuation methodologies that utilize observable market data. In addition to market information, the Company incorporates transaction specific details that market participants would utilize in a fair value measurement, including the impact of non-performance risk. However, these fair value estimates may not necessarily be indicative of the amounts that could be realized or settled in a current market transaction.
Decommissioning liability
Decommissioning provisions have been recognized based on the Company’s internal estimates. Assumptions, based on the current economic environment, have been made which management believes are a reasonable basis upon which to estimate the future liability. These estimates take into account any material changes to the assumptions that occur when reviewed regularly by management. Estimates are reviewed at least annually and are based on current regulatory requirements. Significant changes in estimates of contamination, restoration standards and techniques will result in changes to provisions from period to period. Actual decommissioning costs will ultimately depend on future market prices for the decommissioning costs which will reflect the market conditions at the time the decommissioning costs are actually incurred. The final cost of the currently recognized decommissioning provisions may be higher or lower than currently provided for.
Income taxes
The Company recognizes the net future tax benefit related to deferred tax assets to the extent that it is probable that the deductible temporary differences will reverse in the foreseeable future. Assessing the recoverability of deferred tax assets requires the Company to make significant estimates related to expectations of future taxable income. Estimates of future taxable income are based on forecast cash flows from operations and the application of existing tax laws in each jurisdiction. To the extent that future cash flows and taxable income differ significantly from estimates, the ability of the Company to realize the net deferred tax assets recorded at the reporting date could be impacted. Additionally, future changes in tax laws in the jurisdictions in which the Company operates could limit the ability of the Company to obtain tax deductions in future periods. All tax filings are subject to audit and potential reassessment. Accordingly, the actual income tax liability may differ significantly from the estimated and recorded amounts.
Share-based payment transactions
The Company measures the cost of equity-settled transactions with employees by reference to the fair value of the equity instruments at the date at which they are granted. Estimating fair value for share-based payment transactions requires determining the most appropriate valuation model, which is dependent on the terms and conditions of the grant. This estimate also requires determining the most appropriate inputs to the valuation model including the expected life of the share option, volatility and dividend yield.
Future Accounting Pronouncements
Certain pronouncements were issued by the IASB or the IFRIC that are mandatory for accounting periods beginning after January 1, 2011 or later periods.
The Company has early adopted the amendments to IFRS 1 which replaces references to a fixed date of ‘1 January 2004’ with ‘the date of transition to IFRS’. This eliminates the need for the Company to restate derecognition transactions that occurred before the date of transition to IFRS. The amendment is effective for year-ends beginning on or after July 1, 2011; however, the Company has early adopted the amendment. The impact of the amendment and early adoption is that the Company only applies IAS 39 derecognition requirements to transactions that occurred after the date of transition.
The following new standards, amendments and interpretations, that have not been early adopted in these consolidated annual financial statements. The Company is currently assessing the impact, if any, of this new guidance on the Company’s future results and financial position:
| · | IFRS 7, Financial Instruments: Disclosures, which requires disclosure of both gross and net information about financial instruments eligible for offset in the balance sheet and financial instruments subject to master netting arrangements. Concurrent with the amendments to IFRS 7, the IASB also amended IAS 32, Financial Instruments: Presentation to clarify the existing requirements for offsetting financial instruments in the balance sheet. The amendments to IAS 32 are effective as of January 1, 2014. |
| · | IFRS 9 Financial Instruments is part of the IASB's wider project to replace IAS 39 Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement. IFRS 9 retains but simplifies the mixed measurement model and establishes two primary measurement categories for financial assets: amortized cost and fair value. The basis of classification depends on the entity's business model and the contractual cash flow characteristics of the financial asset. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2015. |
| · | IFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements is the result of the IASB’s project to replace Standing Interpretations Committee 12, Consolidation – Special Purpose Entities and the consolidation requirements of IAS 27, Consolidated and Separate Financial Statements. The new standard eliminates the current risk and rewards approach and establishes control as the single basis for determining the consolidation of an entity. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013. |
| · | IFRS 11 Joint Arrangements is the result of the IASB’s project to replace IAS 31, Interests in Joint Ventures. The new standard redefines joint operations and joint ventures and requires joint operations to be proportionately consolidated and joint ventures to be equity accounted. Under IAS 31, joint ventures could be proportionately consolidated. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013. |
| · | IFRS 12 Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities outlines the required disclosures for interests in subsidiaries and joint arrangements. The new disclosures require information that will assist financial statement users to evaluate the nature, risks and financial effects associated with an entity’s interests in subsidiaries and joint arrangements. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013. |
| · | IFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement defines fair value, requires disclosures about fair value measurements and provides a framework for measuring fair value when it is required or permitted within the IFRS standards. The standard is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013. |
| · | IFRIC 20 Stripping costs in the production phase of a mine, IFRIC 20 clarifies the requirements for accounting for the costs of the stripping activity in the production phase when two benefits accrue: (i) unusable ore that can be used to produce inventory and (ii) improved access to further quantities of material that will be mined in future periods. IFRIC 20 is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013 with earlier application permitted and includes guidance on transition for pre-existing stripping assets. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the new guidance is expected to have on its consolidated financial statements. |
The following new standards, amendments and interpretations that have not been early adopted in these consolidated financial statements, are not expected to have an effect on the Company’s future results and financial position:
| · | IFRS 1: Severe Hyperinflation (Effective for periods beginning on or after July 1, 2011) |
| · | IAS 12: Deferred Tax: Recovery of Underlying Assets (Amendments to IAS 12 (Effective for periods beginning on or after January 1, 2012) |
A. Operating Results
On January 1, 2011, the Company adopted IFRS for financial reporting purposes, using a transition date of January 1, 2010. The Company’s annual audited Consolidated Financial Statements for the year ended December 31, 2011, including 2010 required comparative information, have been prepared in accordance with IFRS. Financial statements prior to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010 were prepared in accordance with Canadian generally accepted accounting principles (“Canadian GAAP”). Certain comparative figures for 2010 were restated under IFRS.
All financial information is stated in Canadian dollars, the Company’s presentation currency, unless otherwise noted. Some numbers have been rounded to the nearest thousand for discussion purposes.
Revenues
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| Revenue | | | | | | | | |
| Gross revenues | | $ | 8,824,000 | | | $ | 8,086,000 | |
| Royalties | | | (1,628,000 | ) | | | (1,312,000 | ) |
| Revenues, net of royalties | | | 7,196,000 | | | | 6,774,000 | |
| Financial instrument gain (loss) | | | (59,000 | ) | | | 68,000 | |
| Other income | | | 34,000 | | | | 36,000 | |
| Total revenue | | $ | 7,171,000 | | | $ | 6,878,000 | |
For fiscal 2011, the Company recorded $8,824,000 in oil and natural gas sales as compared to $8,086,000 in oil, natural gas and natural gas liquids sales for the year ended December 31, 2010 (“fiscal 2010”). The increase in gross revenues was due to higher realized oil prices in 2011. This was partly offset by lower oil and gas production for the current year.
Royalties for fiscal 2011 increased to $1,628,000 from $1,312,000 for fiscal 2010. The increase was attributable to higher oil revenue and the increase in the proportion of revenue attributed to oil. Oil production is subject to higher royalty rate compared to the royalty rate for natural gas.
The following table summarizes the commodity prices realized by the Company and the crude oil and natural gas benchmark prices for the year ended December 31, 2011 and 2010:
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| Dejour Realized Average Prices | | | | | | |
| Natural gas ($/mcf) | | $ | 3.64 | | | $ | 4.13 | |
| Oil and natural gas liquids ($/bbl) | | | 88.98 | | | | 67.46 | |
| Total average price ($/boe) | | $ | 57.49 | | | $ | 45.53 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Average Benchmark Prices | | | | | | | | |
| Edmonton Par ($/bbl) | | $ | 95.16 | | | $ | 77.81 | |
| Natural gas - AECO-C Spot ($ per mcf) | | $ | 3.67 | | | $ | 4.13 | |
In 2011, the Company changed the benchmark prices from Western Canada Select to Edmonton Par. This is because Edmonton Par is more comparable to the Company’s oil revenue sales.
For the current year, Dejour’s average realized natural gas prices reflected lower benchmark prices compared to fiscal 2010. Oil prices received for fiscal 2011 increased to $88.98 per barrel (“bbl”), compared to $67.46 per bbl for fiscal 2010.
Operating and Transportation Expenses
Operating and transportation expenses include all costs associated with the production of oil and natural gas and the transportation of oil and natural gas to the processing plants. The major components of operating expenses include labour, equipment maintenance, workovers, fuel and power. Operating and transportation expenses for fiscal 2011 decreased to $2,499,000 from $2,609,000 for fiscal 2010. The decrease was due to lower oil and gas production. Operating costs per BOE for both years were comparable despite lower oil and gas production.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses for fiscal 2011 increased to $4,042,000 from $3,383,000 for fiscal 2010. The comparative figures for 2010 were restated under IFRS. The increase was mainly due to the year-end bonus accrual for fiscal 2011 andthe non-recurring professional fees associated with the required conversion to the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Finance Costs and Change in Fair Value of Warrant Liability
Finance costs for fiscal 2011 decreased to $868,000 from $1,092,000 for fiscal 2010. The decrease was attributable to the line of credit facility obtained in September 2011 that bears a lower interest rate, compared to the bridge loan with a relatively higher interest rate.
The non-cash change in fair value of warrant liability for fiscal 2011 was a loss of $1,580,000, compared to a gain of $68,000 for fiscal 2010. The warrant liability relates to the fair value of certain warrants that were issued in the previous equity financings. These warrants are denominated in US dollars, which is different than the functional currency of the Company. Under IFRS, they are classified as liabilities and any change in the fair value is recognized in the profit or loss. Changes in fair value result from volatility in the Company’s share prices and fluctuations in the US/Canadian dollar exchange rates. Due to higher market prices for the Company’s common shares towards the end of the year, this resulted in higher valuation for these warrants and a non-cash valuation loss for fiscal 2011.
Amortization, Depletion and Impairment Losses
For fiscal 2011, amortization, depletion and impairment losses were $8,652,000, compared to $4,685,000 for fiscal 2010. The comparative figures for 2010 were restated under IFRS. Amortization and depletion of property and equipment for fiscal 2011 was $2,404,000, compared to $3,493,000 for fiscal 2010. The decrease in amortization and depletion expenses was mainly due to the increased reserves in the Woodrush property at December 31, 2011 and the decrease in production. Impairment losses of $6,248,000 for fiscal 2011 were recognized because the carrying value of certain property and equipment and exploration and evaluation assets exceeded their recoverable amounts, while the impairment losses of $1,192,000 for fiscal 2010 were recognized upon the expiry of certain leases for exploration and evaluation assets and property and equipment.
Net Loss and Operating Loss
The Company’s net loss for fiscal 2011 was $11,043,000 or $0.092 per share, compared to a net loss of $5,124,000 or $0.051 per share for fiscal 2010. The comparative figures for 2010 were restated under IFRS. The increase in net loss was primarily due to the recognition of non-cash impairment losses of $6,248,000 and non-cash valuation loss of $1,580,000 from the increase in fair value of warrant liability. This was partly offset by the increase in revenues.
The Company’s operating loss for fiscal 2011 was $3,215,000, compared to $4,000,000 for fiscal 2010. The decrease was primarily due to lower amortization and depletion of property and equipment for the current year, as a result of the increased reserves in the Company’s Woodrush property.
The operating loss is a non-GAAP measure defined as net income (loss) excluding non-cash items that management believes affects the comparability of operating results. These items may include, but are not limited to, unrealized financial instrument gain (loss), impairment losses and impairment reversals, gain (loss) on divestitures, and change in fair value of financial instruments.
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| | | | $ | | | | $ | |
| Net loss | | | (11,043,000 | ) | | | (5,124,000 | ) |
| Add back (losses) and deduct gains: | | | | | | | | |
| Impairment losses | | | 6,248,000 | | | | 1,192,000 | |
| Change in fair value of warrant liability | | | 1,580,000 | | | | (68,000 | ) |
| Operating Loss – NonGAAP | | | (3,215,000 | ) | | | (4,000,000 | ) |
Financial Instruments and Risk Management
The Company’s financial instruments consist of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, bank line of credit, and accounts payable and accrued liabilities. Management has determined that the fair value of these financial instruments approximates their carrying values due to their immediate or short-term maturity.Net smelter royalties and related rights to earn or relinquish interests in mineral properties constitute derivative instruments. No value or discounts have been assigned to such instruments as there is no reliable basis to determine fair value until properties are in development or production and reserves have been determined.
From time to time, the Company enters into derivative contracts such as forwards, futures and swaps in an effort to mitigate the effects of volatile commodity prices and protect cash flows to enable funding of its exploration and development programs. Commodity prices can fluctuate due to political events, meteorological conditions, disruptions in supply and changes in demand.
The primary risks and how the Company mitigates them are disclosed inItem 11 – Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk, below.
Stock Based Compensation
For fiscal 2011, the Company recorded non-cash stock based compensation expense of $662,000 compared to $765,000 for fiscal 2010. The decrease in stock based compensation expense was because many of the stock options previously granted had been fully vested.
| B. | Liquidity and Capital Resources |
Cash Balance and Cash Flow
The Company had cash and cash equivalents of $2,488,000 as at December 31, 2011. In addition to the cash balance, the Company has an unused line of credit of $1.5 million from a Canadian Bank.
Bank Line of Credit Financing
In September 2011, the Company obtained a $7 million revolving operating demand loan (“line of credit”), including a letter of credit facility to a maximum of $700,000 for a maximum one year term, from a Canadian Bank to refinance the bridge loan and to provide operating funds. The line of credit is at an interest rate of Prime + 1% (total 4% p.a. currently) and collateralized by a $10,000,000 debenture over all assets of DEAL and a $10,000,000 guarantee from Dejour Energy Inc. In December 2011, the Company renewed the line of credit with the Canadian Bank. The next review date is scheduled on or before May 1, 2012, but subject to change at the discretion of the bank. As at December 31, 2011, a total of $5.5 million of this facility was utilized.
According to the terms of the facility, DEAL is required to maintain a working capital ratio of greater than 1:1 at all times. The working capital ratio is defined as the ratio of (i) current assets (including any undrawn and authorized availability under the facility) less unrealized hedging gains to (ii) current liabilities (excluding current portion of outstanding balances of the facility) less unrealized hedging losses. As at December 31, 2011, the Company is in compliance with the working capital ratio requirement.
Working Capital Position
| As at December 31, 2011 | | $ | |
| Working capital deficit | | | (7,756,000 | ) |
| Non-cash warrant liability | | | 2,245,000 | |
| Net cash working capital deficit | | | (5,511,000 | ) |
As at December 31, 2011, the Company had a working capital deficit of $7,756,000. Excluding the non-cash warrant liability of $2,245,000 related to the fair value of US$ denominated warrants issued in previous equity financings, the working capital deficit includes a $5.5 million used demand line of credit with a $7 million credit limit. As at December 31, 2011, $1.5 million remains unused. The Company plans to remedy the deficiency through the following:
| · | Subsequent to December 31, 2011, the Company received $1,200,000 from the exercise of warrants and options. |
| · | Beginning in June 2011, oil production increased as a result of the waterflood at Woodrush. Oil production is expected to increase in 2012, generating more cash flow for the Company. |
| · | If necessary and at the right market conditions, the Company may fund its working capital through additional debt, equity or joint venture financing, or disposal of non-core assets. |
Capital Resources
During the year ended December 31, 2011, the Company continued to optimize the waterflood at its Woodrush property in Canada. Most of the waterflood capital expenditures have already been spent in fiscal 2011. Future capital expenditures at Woodrush in 2012 are expected to be approximately $1.2 to $1.5 million and funded through its cash flow from operations and the undrawn line of credit. In the U.S., the Company plans to drill up to eight wells during 2012 and its share of expenditures ranges from $6.5 to $11 million. The Company plans to fund the expenditures through additional financing, including debt, equity or joint venture financing, or disposal of non-core assets.
| C. | Research and Development, Patents and Licenses, Etc. |
None.
Oil currently has risen near $100 per barrel and the Company’s revenue from oil sales increased. On the other hand, the price of natural gas declined to low $2 range, lowering the Company’s gas revenue and the economics of natural gas properties. The marketability and price of oil and natural gas are affected by numerous factors outside of the Company’s control, including domestic and foreign supply and demand, economics and political conditions, weather and US$ exchange rate. (See risks factors disclosure). Some or all of these [situations] are likely to have a material effect upon our net sales or revenues, income from continuing operations, profitability, liquidity or capital resources, or cause reported financial information not necessarily to be indicative of future operating results or financial condition.
| E. | Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements |
The Company has no material undisclosed off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have, a current or future effect on our results of operations or financial condition at December 31, 2011.
| F. | Tabular Disclosure of Contractual Obligations |
As of December 31, 2011, and in the normal course of business we have obligations to make future payments, representing contracts and other commitments that are known and committed.
| Contractual Obligations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands of dollars) | | 2012 | | | 2013 | | | 2014 | | | 2015 | | | 2016 | | | Thereafter | | | Total | |
| | | $ | | | $ | | | $ | | | $ | | | $ | | | $ | | | $ | |
| Operating Lease Obligations | | | 223 | | | | 107 | | | | 49 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | Nil | | | | 379 | |
| Bank line of credit | | | 5,545 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | Nil | | | | 5,545 | |
| Total | | | 5,768 | | | | 107 | | | | 49 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | Nil | | | | 5,924 | |
The Company seeks safe harbor for our forward-looking statements contained in Items 5.E and F. See the heading “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” above.
ITEM 6. DIRECTORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT AND EMPLOYEES
| A. | Directors and Senior Management |
The following table sets forth all current directors and executive officers of Dejour as of the date of this annual report on Form 20-F, with each position and office held by them in the Company and the period of service as such.
Name, Jurisdiction of Residence and Position(1) | | Principal occupation or employment during the past 5 years | | Number of Dejour Common Shares beneficially owned, directly or indirectly, or controlled or directed (2) | | Percentage of Dejour Common Shares beneficially owned, directly or indirectly, or controlled or directed (2) | | Director Since |
| | | | | | | | | |
Robert L. Hodgkinson British Columbia, Canada Director, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer (Age: 62) | | President of a private company, Hodgkinson Equities Corporation, which provides consulting services to emerging businesses in the petroleum resource industry. Formerly a director of Titan Uranium (TSX-V:TUE). | | 7,187,840 | | 5.5% | | May 18/04 |
Name, Jurisdiction of Residence and Position(1) | | Principal occupation or employment during the past 5 years | | Number of Dejour Common Shares beneficially owned, directly or indirectly, or controlled or directed (2) | | Percentage of Dejour Common Shares beneficially owned, directly or indirectly, or controlled or directed (2) | | Director Since |
| | | | | | | | | |
Stephen Mut Colorado, USA Director and Co-Chairman (Age: 61) | | Mr. Mut has served as CEO of Nycon Energy Consulting since his retirement from Shell in mid 2009. At Shell, Mr. Mut served as chief executive officer of a unit of Shell Exploration and Production Company from 2000 until his retirement in 2009. Prior to that, Mr. Mut served in various executive roles at Atlantic Richfield Corporation. | | 1,701,001 | | 1.3% | | Dec 17/09 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Harrison Blacker(4) Colorado, U.S.A. Director, President and Chief Operating Officer of Dejour Energy (USA) Inc. (Age: 61) | | President of Dejour Energy (USA) Inc. since April 2008. Over 30 years of expertise managing oil and gas operations. Held the positions of Chief Executive Officer with China Oman Energy Company and Portfolio Manager, Latin American Business Unit and General Manager/ President of Venezuela Energy with Atlantic Richfield Corporation prior to joining Dejour USA. | | 525,678 | | 0.4% | | Apr 2/08 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Richard Patricio(4) Ontario, Canada Director (Age: 38) | | Vice President of Corporate & Legal Affairs and Secretary of Pinetree Capital Ltd. (investment and merchant banking firm). Prior to joining Pinetree Capital, practiced law at a top tier law firm in Toronto and worked as in-house General Counsel for a senior TSX listed company. Mr. Patricio is a lawyer qualified to practice in the Province of Ontario. | | - | | - | | Oct 17/08 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Robert Holmes(3) , (4) California, U.S.A Director (Age: 68) | | Began career as an Investment Executive with Merrill, Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, and held various senior executive positions with the firm Blyth, Eastman, Dillon & Company. In 1980, co-founded Gilford Securities, Inc., a member of the NYSE, and in 1992 founded a hedge fund, Gilford Partners. Has served on several boards including the North Central College Trustees in Naperville, Illinois; Board of Trustees Sacred Heart Schools Chicago; Crested Butte Academy in Crested Butte, Colorado; and Mary Wood Country Day School in Rancho Mirage, California. | | 1,663,000 | | 1.3% | | Oct 17/08 |
Name, Jurisdiction of Residence and Position(1) | | Principal occupation or employment during the past 5 years | | Number of Dejour Common Shares beneficially owned, directly or indirectly, or controlled or directed (2) | | Percentage of Dejour Common Shares beneficially owned, directly or indirectly, or controlled or directed (2) | | Director Since |
| | | | | | | | | |
Craig Sturrock(3) British Columbia, Canada Director (Age: 68) | | Tax lawyer since 1971. Currently, he is a partner at Thorsteinssons LLP, and his practice focuses primarily on civil and criminal tax litigation. | | 650,000 | | 0.5% | | Aug 22/05 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Darren Devine(3) British Columbia, Canada Director (Age: 44) | | Since 2003, Mr. Devine has been the principal of Chelmer Consulting Corp., a corporate finance consultancy. Prior to founding Chelmer Consulting, Mr. Devine practiced law with the firm of Du Moulin Black LLP, in Vancouver, British Columbia. Mr. Devine is a qualified Barrister and Solicitor in British Columbia, and a qualified solicitor in England and Wales. | | - | | - | | Dec 17/09 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Mathew Wong British Columbia, Canada Chief Financial Officer (Age: 37) | | Chartered Accountant worked at Ernst & Young LLP from 1995 to 2000. Since then, he worked as the Corporate Accounting Manager for Mitsubishi Canada Limited and CFO for Dejour Enterprise Ltd. Mr. Wong is a Chartered Accountant (CA) in British Columbia, Canada, a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) in Washington State, USA and a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA). | | 122 | | - | | N/A |
| | | | | | | | | |
Phil Bretzloff, BA, LLB British Columbia, Canada Vice President and General Counsel (Age: 63) | | Mr. Bretzloff has acted for oil, gas and energy companies, including extensive work for Canadian and offshore private and public corporations. Between 1980 and 1995, he was Senior Counsel for Petro-Canada. Subsequently, he was a Partner for 8 years with Cumming Blackett Bretzloff Todesco, Gowlings, and Baker & McKenzie, where his clients included PetroChina, Shell, Exxon Mobil, GazProm and Veba Oil and Gas. | | 59,500 | | 0.04% | | N/A |
| | | | | | | | | |
Neyeska Mut EVP Operations, Dejour Energy (USA) Corp. (Age: 54) | | Engineer. Since 2000, she has been President of Nycon Energy Consulting working as an advisor to two major oil companies. Prior to forming Nycon Energy Consulting Mrs. Mut pursued international opportunities with Atlantic Richfield Corporation. Mr. Mut has been with Dejour since 2008. | | 50,001 | | 0.04% | | N/A |
| (1) | Each director will serve until the next annual general meeting of the Company or until a successor is duly elected or appointed in accordance with the Notice of Articles and Articles of the Company and theBusiness Corporations Act(British Columbia). |
| (2) | The number of common shares beneficially owned, directly or indirectly, or over which control or direction is exercised is based upon information furnished to the Company by individual directors and executive officers. |
| (3) | Member of audit committee. |
| (4) | Member of reserve committee. |
Board of Directors
Brief biographies for each member of Dejour's board of directors are set forth below:
Robert L. Hodgkinson:Mr. Hodgkinson was the founder and Chairman of Optima Petroleum, which drilled wells in Alberta and the Gulf of Mexico before merging to form Petroquest Energy, a NASDAQ traded company. Subsequently, he founded and was CEO of Australian Oil Fields, which would later merge to become Resolute Energy/Cardero Energy Inc. Mr. Hodgkinson was also a Vice-President and partner of Canaccord Capital Corporation, and an early stage investor and original lease financier in Synenco Energy's Northern Lights Project in the Alberta oil sands.
Stephen Mut: Mr. Mut most recently served as chief executive officer of a unit of Shell Exploration and Production Company. Prior to joining Shell in 2000, Mr. Mut dedicated much of his career to operational and new business venture activities in the oil and gas, refining and marketing, and chemical and mining sectors at Atlantic Richfield Corporation, where he served in various internationally based executive roles in both upstream and downstream businesses. His global expertise has contributed to industry successes in Europe, South America, the Asia Pacific and the United States.
HarrisonBlacker:Mr. Blacker is an accomplished senior executive with over 30 years of expertise managing oil and gas operations with major corporations in the United States, South America, China and the Middle East. Prior to joining Dejour, Mr. Blacker was CEO of China Oman Energy Company, a joint venture between Oman Oil Company, IPIC and China Gas Holdings, importing and distributing LNG and LPG from the Middle East into China. Mr. Blacker held positions as VP of Business Development and Senior Investor Advisor with Oman Oil Company and Portfolio Manager, Latin American Business Unit and General Manager/ President of Venezuela Energy with Atlantic Richfield Corporation. Mr. Blacker began his career with Amoco Production Company working in offshore construction and field operations in the Gulf of Mexico.
RichardPatricio:Mr. Patricio is Vice President Corporate & Legal Affairs and Secretary of Pinetree Capital Ltd. and Brownstone Ventures Inc. Mr. Patricio previously practiced law at a top tier law firm in Toronto and worked as in-house General Counsel for a senior TSX listed company. Mr. Patricio is a lawyer qualified to practice in the Province of Ontario.
RobertHolmes:Mr. Holmes began his career as an Investment Executive with Merrill, Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, and subsequently held various senior executive positions with the firm Blyth, Eastman, Dillon & Company (purchased by Paine Webber & Co.). In 1980, Mr. Holmes co-founded Gilford Securities, Inc., a member of the NYSE, and in 1992 founded a hedge fund, Gilford Partners. He has served on several boards including the North Central College Trustees in Naperville, Illinois; Board of Trustees Sacred Heart Schools Chicago; Crested Butte Academy in Crested Butte, Colorado; and Mary Wood Country Day School in Rancho Mirage, California. He graduated with a BA from North Central College in 1965.
Craig Sturrock:Mr. Sturrock has served as a director and founding member of various public and private companies. Admitted to the British Columbia Bar in 1969, he joined Thorsteinssons LLP, tax lawyers in 1971. He served for 15 years as a tax lawyer and partner at Birnie, Sturrock & Company returning to Thorsteinssons as a partner in 1989. He is an author and speaker for the Canadian and British Columbia Bar Associations, the Continuing Legal Education Society of British Columbia and the Canadian Tax Foundation. He is also a former member of the Board of Governors of the Canadian Tax Foundation.
Darren Devine: Mr. Devine is the principal of Chelmer Consulting Corp., which provides corporate finance advisory services to private and public companies. Mr. Devine is a qualified Barrister and Solicitor in British Columbia, and a qualified solicitor in England and Wales. Prior to forming Chelmer Consulting, Mr. Devine practiced exclusively in the areas of corporate finance and securities law with a focus on cross-border finance, stock exchange listings and mergers and acquisitions with the firm DuMoulin Black LLP in Vancouver, British Columbia.
Family Relationships
There are no family relationships between any directors or executive officers of the Company.
Arrangements
There are no known arrangements or understandings with any major shareholders, customers, suppliers or others, pursuant to which any of the Company’s officers or directors was selected as an officer or director of the Company, other than indicated immediately above and at “Item 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions - Related Party Transactions.”
Cease Trade Orders, Bankruptcies, Penalties or Sanctions
To the knowledge of the Company, no director or executive officer of the Company is, or has been in the last ten years, a director, chief executive officer or chief financial officer of an issuer that, while that person was acting in that capacity, (a) was the subject of a cease trade order or similar order or an order that denied the issuer access to any exemptions under Canadian securities legislation, for a period of more than 30 consecutive days, or (b) was subject to an event that resulted, after that person ceased to be a director, chief executive officer or chief financial officer, in the issuer being the subject of a cease trade or similar order or an order that denied the issuer access to any exemption under Canadian securities legislation, for a period of more than 30 consecutive days. To the knowledge of the Company, no director or executive officer of the Company, or a shareholder holding a sufficient number of securities in the Company to affect materially the control of the Company, is or has been in the last ten years, a director or executive officer of an issuer that, while or acting in that capacity within a year of that person ceasing to act in that capacity, became bankrupt, made a proposal under any legislation relating to bankruptcy or insolvency or was subject to or instituted any proceedings, arrangement or compromise with creditors or had a receiver, receiver manager or trustee appointed to hold its assets. To the knowledge of the Company, in the past ten years, no such person has become bankrupt, made a proposal under any legislation related to bankruptcy or insolvency, or was subject to or instituted any proceedings, arrangement or compromise with creditors, or had a receiver, receiver manager or trustee appointed to hold their assets.
Conflicts of Interest
Certain of the Company's directors and officers serve or may agree to serve as directors or officers of other reporting companies or have significant shareholdings in other reporting companies and, to the extent that such other companies may participate in ventures in which the Company may participate, the directors of the Company may have a conflict of interest in negotiating and concluding terms respecting the extent of such participation. In the event that such a conflict of interest arises at a meeting of the Company's directors, a director who has such a conflict will abstain from voting for or against the approval of such participation or such terms and such director will not participate in negotiating and concluding terms of any proposed transaction. From time to time, several companies may participate in the acquisition, exploration and development of natural resource properties thereby allowing for their participation in larger programs, permitting involvement in a greater number of programs and reducing financial exposure in respect of any one program. It may also occur that a particular company will assign all or a portion of its interest in a particular program to another of these companies due to the financial position of the company making the assignment. Under the laws of the Province of British Columbia, the directors of the Company are required to act honestly, in good faith and in the best interests of the Company. In determining whether or not the Company will participate in a particular program and the interest therein to be acquired by it, the directors will primarily consider the degree of risk to which the Company may be exposed and its financial position at that time. See also "Description of the Business – Risk Factors".
Basis of Compensation for Executive Officers
The Company compensates its executive officers through a combination of base compensation, bonuses and Common Stock options. The base compensation provides an immediate cash incentive for the executive officers. Bonuses encourage and reward exceptional performance over the financial year. Common Stock options ensure that the executive officers are motivated to achieve long term growth of the Company and continuing increases in shareholder value. In terms of relative emphasis, the Company places more importance on Common Stock options as long term incentives. Bonuses are related to performance and may form a greater or lesser part of the entire compensation package in any given year. Each of these means of compensation is briefly reviewed in the following sections.
Base Compensation
Base compensation, including that of the Chief Executive Officer, are set by the Compensation Committee and approved by the Board of Directors on the basis of the applicable executive officer’s responsibilities, experience and past performance. The compensation program is intended to provide a base compensation competitive among companies of a comparable size and character in the oil and gas industry. In making such an assessment, the Board considers the objectives set forth in the Company’s business plan and the performance of executive officers and employees in executing the plan in combination with the overall result of the activities undertaken.
Common Stock Options
The Company provides long term incentive compensation to its executive officers through the Common Stock Option Plan, which is considered an integral part of the Company’s compensation program. Upon the recommendation of management and approval by the Board of Directors, stock options are granted under the Company’s Option Plan to new directors, officers and key employees, usually upon their commencement of employment with the Company. The Board approves the granting of additional stock options from time to time based on its assessment of the appropriateness of doing so in light of the long term strategic objectives of the Company, its current stage of development, the need to retain or attract key technical and managerial personnel in a competitive industry environment, the number of stock options already outstanding, overall market conditions, and the individual’s level of responsibility and performance within the Company.
The Board views the granting of stock options as a means of promoting the success of the Company and creating and enhancing returns to its shareholders. As such, the Board does not grant stock options in excessively dilutive numbers. Total options outstanding are presently limited to 10% of the total number of shares outstanding under the rules of the TSX. Grant sizes are, therefore, determined by various factors including the number of eligible individuals currently under the Option Plan and future hiring plans of the Company.
The Board granted a total of 2,046,000 stock options to the executive officers in 2011.
| | | Annual Compensation | | | Long Term Compensation | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Awards | | | Payouts | | | | |
Name and
Principal Position | | Year | | | Annual
Salary | | | Consulting
Fees
($) | | | Bonus
($) | | | Securities
Under
Option/
SAR's
Granted
(#) | | | Shares/
Units
Subject to
Resale
Restrictions
($) | | | LTIP
Pay-
outs ($) | | | All Other
Compensation
($) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Robert L. | | | 2011 | | | $ | 78,000 | | | $ | 177,000 | | | $ | 100,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Hodgkinson, | | | 2010 | | | $ | 78,000 | | | $ | 177,000 | | | | Nil | | | | 369,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Chief Executive Officer | | | 2009 | | | $ | 78,000 | | | $ | 177,000 | | | | Nil | | | | 275,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Mathew Wong, | | | 2011 | | | $ | 78,000 | | | $ | 151,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Chief Financial | | | 2010 | | | $ | 78,000 | | | $ | 151,000 | | | | 12,000 | | | | 217,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Officer | | | 2009 | | | $ | 78,000 | | | $ | 140,000 | | | | Nil | | | | 125,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Harrison Blacker, | | | 2011 | | | US$ | 295,000 | | | | Nil | | | US$ | 135,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 58,000 | * |
| Director and | | | 2010 | | | US$ | 250,000 | | | | Nil | | | US$ | 60,000 | | | | 433,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| President of Dejour Energy (USA) | | | 2009 | | | US$ | 203,646 | | | | Nil | | | US$ | 98,553 | | | | 300,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Craig Sturrock, | | | 2011 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 100,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 7,000 | |
| Director | | | 2010 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 150,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 5,500 | |
| | | | 2009 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 50,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 10,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Robert Holmes, | | | 2011 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 100,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 7,500 | |
| Director | | | 2010 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 150,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 6,500 | |
| | | | 2009 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 50,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 10,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Richard Patricio, | | | 2011 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 100,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 5,000 | |
| Director | | | 2010 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 150,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 5,500 | |
| | | | 2009 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 50,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | $ | 10,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stephen Mut, | | | 2011 | | | | Nil | | | US$ | 138,573 | | | | Nil | | | | 300,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Director & Co- | | | 2010 | | | | Nil | | | US$ | 120,000 | | | | Nil | | | | 250,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Chairman | | | 2009 | | | | Nil | | | US$ | 14,286 | | | | Nil | | | | 100,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Darren Devine, | | | 2011 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 100,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 7,000 | |
| Director | | | 2010 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 200,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 5,500 | |
| | | | 2009 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Neyeska Mut, | | | 2011 | | | US$ | 200,470 | | | | Nil | | | US$ | 100,000 | | | | 306,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| EVP Operations | | | 2010 | | | US$ | 200,470 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | 194,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Of Dejour Energy (USA) | | | 2009 | | | US$ | 163,300 | | | | Nil | | | US$ | 30,763 | | | | 80,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Phil Bretzloff | | | 2011 | | | | Nil | | | $ | 130,984 | | | $ | 13,320 | | | | 140,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| Vice President & | | | 2010 | | | | Nil | | | $ | 77,401 | | | | Nil | | | | 110,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| General Counsel | | | 2009 | | | | Nil | | | $ | 74,635 | | | $ | 7,200 | | | | 75,000 | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
*US$58,000 was paid for relocation expenses reimbursement.
Stock Option Grants
| Name | | Number of
Options Granted | | | Exercise Price
per Share | | | Grant Date | | Expiration Date |
| Robert Hodgkinson | | | 300,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Mathew Wong | | | 300,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Harrison Blacker | | | 300,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Craig Sturrock | | | 100,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Robert Holmes | | | 100,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Richard Patricio | | | 100,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Darren Devine | | | 100,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Stephen Mut | | | 300,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Neyeska Mut | | | 306,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Phil Bretzloff | | | 140,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
| Employees and Consultants | | | 200,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | January 4, 2011 | | January 3, 2012 |
| | | | 280,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | January 4, 2011 | | January 3, 2013 |
| | | | 686,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | March 16, 2011 | | March 15, 2014 |
Director Compensation
The Company has compensation agreements for its Directors who are not executive officers. Under the agreements, Directors receive $2,500 per meeting for the first 4 meetings each year, and $1,500 for each meeting thereafter. The Board of Directors may award special remuneration to any Director undertaking any special services on behalf of the Company other than services ordinarily required of a Director. Per an amendment to the agreements approved by the Board of Directors, effective January 1, 2010, the Directors received $1,000 per quarter plus $500 for each meeting.
Long Term Incentive Plan Awards
Long term incentive plan awards ("LTIP") means any plan providing compensation intended to serve as an incentive for performance to occur over a period longer than one financial year, whether the performance is measured by reference to financial performance of the Company or an affiliate of the Company, the price of the Company's shares, or any other measure, but does not include option or stock appreciation rights plans or plans for compensation through restricted shares or units. The Company did not award any LTIPs to any executive officer during the most recently completed financial year ended December 31, 2011. There are no pension plan benefits in place for the executive officers.
Stock Appreciation Rights
Stock appreciation rights ("SARs") means a right, granted by the Company or any of its subsidiaries as compensation for services rendered or in connection with office or employment, to receive a payment of cash or an issue or transfer of securities based wholly or in part on changes in the trading price of the Company's shares. No SARs were granted to, or exercised by, any executive officer of the Company during the most recently completed financial year ended December 31, 2011.
Termination and Change of Control Remuneration
The Company has management contracts with the following executive officers or the companies controlled by the executive officers:
Named Executive
Officer | | Annual Base
Salary and / or
Consulting
Fees | | | Compensation Package on
Termination of Contract,
other than for termination
with cause | | Compensation Package
on Termination of Contract, in
the event of a change in control |
| | | | | | | | |
| Robert Hodgkinson | | $ | 255,000 | | | 1 times annual base salary and consulting fee | | 2 times annual base salary and consulting fee |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Mathew Wong | | $ | 229,000 | | | 1 times annual base salary and consulting fee | | 2 times annual base salary and consulting fee |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Harrison Blacker | | US$ | 310,000 | | | 1 times annual base salary | | 2 times annual base salary |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Neyeska Mut | | US$ | 200,470 | | | 1 times annual base salary | | 2 times annual base salary |
Bonus/Profit Sharing/Non-Cash Compensation
The Board adopted a bonus plan for eligible executives, which include the senior executives of the Company or any subsidiary of the Company, including but not limited to the CEO, President, Executive Vice-President and CFO who, by the nature of their positions are, in the opinion of the Committee, in a senior position to contribute to the success of the Company.
The bonus plan includes both non-discretionary and discretionary portions.
| A) | Executives Non-Discretionary; |
Each Eligible Executives will receive a USD$100,000 award should:
| i) | Total Shareholder Return % exceeds Total XEG Return % by a minimum of 10% and in addition; |
| ii) | Total Shareholder Return is positive (the share price of Dejour shares is higher at the end of the year, in comparison to, the price of the shares at the beginning of the year). |
For example, for fiscal 2011, if Total Shareholder Return % is 20%, while Total XEG Return is 5%, then Dejour’s stock outperformed the XEG by 15% and a USD$100,000 award is payable to each executives. However, this award would only be payable in the event that during the same period shareholder return is positive.
| B) | Executives Discretionary; |
The Compensation Committee, upon the recommendation of the CEO, shall review (i) performance goals and objectives (“Performance Targets') for the Company and the subsidiaries for such period and (ii) target awards (“Target Awards') for each Participant which shall be based on, up to 30% of the Participant's base compensation, provided however, the Performance Targets for each Executive Participants shall be exactly the same during each year, calculated based on the same percentage of each Participants base compensation, unless otherwise agreed by the Participants.
Such Performance Targets shall include but not be limited to the following:
| · | Increase in oil & gas production; |
| · | Achievement of financial stability and working capital position including compliance with the Company loan covenants; |
| · | Increase in Proved Developed Production (PDP) Reserves; |
| · | Increase in Proved and Probable (2P) reserves; |
| · | Creating significant positive impact on the Company business as demonstrated by significant accomplishments not in the base budget/business plan; |
| · | Increase in Operating Cash flow and Adjusted EBITDA; |
| · | Reducing overhead costs; |
| · | Other factors or extraordinary success, that in the opinion of the Committee, enhance shareholder value |
For purposes of the bonus plan, “XEG” is definedas the iShares™ CDN Energy Sector Index Fund, trading under the symbol “XEG” on the TSX. Total Shareholder Return and Total XEG Return are based on the 20 days average closing shares price of Dejour shares and XEG on the TSX at the end of each fiscal year.
Pension/Retirement Benefits
No funds were set aside or accrued by the Company during Fiscal 2011 to provide pension, retirement or similar benefits for Directors or Senior Management.
Compensation Committee
The Company has a Compensation Committee composed of three Directors, Robert Holmes, Craig Sturrock and Richard Patricio.
Role of the Compensation Committee
The Compensation Committee exercises general responsibility regarding overall executive compensation. The Board of Directors sets the annual compensation, bonus and other benefits of the Chief Executive Officer and approves compensation for all other executive officers of the Company after considering the recommendations of the Compensation Committee.
Audit Committee
The Company’s Board of Directors has a separately-designated standing Audit Committee established for the purpose of overseeing the accounting and financial reporting processes of the Company and audits of the Company’s annual financial statements in accordance with Section 3(a)(58)(A) of the Exchange Act. As of the date of this annual report on Form 20-F, the Company’s Audit Committee is comprised of Craig Sturrock, Robert Holmes and Darren Devine.
In the opinion of the Company’s Board of Directors, all the members of the Audit Committee are independent (as determined under Rule 10A-3 of the Exchange Act and Section 803A of the NYSE Amex Company Guide). The Audit Committee meets the composition requirements set forth by Section 803B(2) of the NYSE Amex Company Guide. All three members of the Audit Committee are financially literate, meaning they are able to read and understand the Company’s financial statements and to understand the breadth and level of complexity of the issues that can reasonably be expected to be raised by the Company’s financial statements.
The members of the Audit Committee do not have fixed terms and are appointed and replaced from time to time by resolution of the Board of Directors.
Terms of Reference for the Audit Committee
Audit Committee Mandate
The primary function of the audit committee is to assist the Board in fulfilling its financial oversight responsibilities by reviewing the financial reports and other financial information provided by the Company to regulatory authorities and Shareholders, the Company’s systems of internal controls regarding finance and accounting and the Company’s auditing, accounting and financial reporting processes. Consistent with this function, the audit committee will encourage continuous improvement of, and should foster adherence to, the Company’s policies, procedures and practices at all levels. The audit committee’s primary duties and responsibilities are to:
| · | Serve as an independent and objective party to monitor the Company’s financial reporting and internal control system and review the Company’s financial statements; |
| · | Review and appraise the performance of the Company’s external auditors; and |
| · | Provide an open avenue of communication among the Company’s auditors, financial and senior management and the Board. |
Composition
The audit committee shall be comprised of three Directors as determined by the Board, the majority of whom shall be free from any relationship that, in the opinion of the Board, would interfere with the exercise of his or her independent judgment as a member of the audit committee.
At least one member of the audit committee shall have accounting or related financial management expertise. All members of the audit committee that are not financially literate will work towards becoming financially literate to obtain a working familiarity with basic finance and accounting practices. For the purposes of the Company's Charter, the definition of “financially literate” is the ability to read and understand a set of financial statements that present a breadth and level of complexity of accounting issues that are generally comparable to the breadth and complexity of the issues that can presumably be expected to be raised by the Company's financial statements.
The members of the audit committee shall be elected by the Board at its first meeting following the annual Shareholders’ meeting. Unless a Chair is elected by the full Board, the members of the audit committee may designate a Chair by a majority vote of the full audit committee membership.
Meetings
The audit committee shall meet a least twice annually, or more frequently as circumstances dictate. As part of its job to foster open communication, the audit committee will meet at least annually with the Chief Financial Officer and the external auditors in separate sessions.
Responsibilities and Duties
To fulfill its responsibilities and duties, the audit committee shall:
Documents/Reports Review
| (a) | Review and update this Charter annually. |
| (b) | Review the Company's financial statements, MD&A and any annual and interim earnings, press releases before the Company publicly discloses this information and any reports or other financial information (including quarterly financial statements), which are submitted to any governmental body, or to the public, including any certification, report, opinion, or review rendered by the external auditors. |
| (c) | Approve, on behalf of the Board, the Corporation’s interim financial statements to be filed pursuant to section 4.3 of NI 51-102, before the Corporation publicly discloses such information. |
External Auditors
| (a) | Review annually, the performance of the external auditors who shall be ultimately accountable to the Board and the audit committee as representatives of the Shareholders of the Company. |
| (b) | Obtain annually, a formal written statement of external auditors setting forth all relationships between the external auditors and the Company, consistent with Independence Standards Board Standard 1. |
| (c) | Review and discuss with the external auditors any disclosed relationships or services that may impact the objectivity and independence of the external auditors. |
| (d) | Take, or recommend that the full Board take, appropriate action to oversee the independence of the external auditors. |
| (e) | Recommend to the Board the selection and, where applicable, the replacement of the external auditors nominated annually for Shareholder approval. |
| (f) | At each meeting, consult with the external auditors, without the presence of management, about the quality of the Company’s accounting principles, internal controls and the completeness and accuracy of the Company's financial statements. |
| (g) | Review and approve the Company's hiring policies regarding partners, employees and former partners and employees of the present and former external auditors of the Company. |
| (h) | Review with management and the external auditors the audit plan for the year-end financial statements and intended template for such statements. |
| (i) | Review and pre-approve all audit and audit-related services and the fees and other compensation related thereto, and any non-audit services, provided by the Company’s external auditors. The pre-approval requirement is waived with respect to the provision of non-audit services if: |
| i. | the aggregate amount of all such non-audit services provided to the Company constitutes not more than five percent of the total amount of revenues paid by the Company to its external auditors during the fiscal year in which the non-audit services are provided; |
| ii. | such services were not recognized by the Company at the time of the engagement to be non-audit services; and |
| iii. | such services are promptly brought to the attention of the audit committee by the Company and approved prior to the completion of the audit by the audit committee or by one or more members of the audit committee who are members of the Board to whom authority to grant such approvals has been delegated by the audit committee. |
Provided the pre-approval of the non-audit services is presented to the audit committee's first scheduled meeting following such approval such authority may be delegated by the audit committee to one or more independent members of the audit committee.
Financial Reporting Processes
| (a) | In consultation with the external auditors, review with management the integrity of the Company's financial reporting process, both internal and external. |
| (b) | Consider the external auditors’ judgments about the quality and appropriateness of the Company’s accounting principles as applied in its financial reporting. |
| (c) | Consider and approve, if appropriate, changes to the Company’s auditing and accounting principles and practices as suggested by the external auditors and management. |
| (d) | Review significant judgments made by management in the preparation of the financial statements and the view of the external auditors as to appropriateness of such judgments. |
| (e) | Following completion of the annual audit, review separately with management and the external auditors any significant difficulties encountered during the course of the audit, including any restrictions on the scope of work or access to required information. |
| (f) | Review any significant disagreement among management and the external auditors in connection with the preparation of the financial statements. |
| (g) | Review with the external auditors and management the extent to which changes and improvements in financial or accounting practices have been implemented. |
| (h) | Review any complaints or concerns about any questionable accounting, internal accounting controls or auditing matters. |
| (i) | Review certification process. |
| (j) | Establish a procedure for the confidential, anonymous submission by employees of the Company of concerns regarding questionable accounting or auditing matters. |
Other
Review any related-party transactions
Audit Committee Oversight
At no time since the commencement of the Company’s most recently completed financial year was a recommendation of the audit committee to nominate or compensate an external auditor not adopted by the Board of Directors.
The Company had the equivalent of approximately 18 full-time employees and consultants during 2011, of which 10 are located in Canada and 8 in USA.
Directors and Officer Beneficial Ownership
The following table discloses as of April 26, 2012, Directors and Senior Management who beneficially own the Company's voting securities, consisting solely of common shares, and the amount of the Company's voting securities owned by the Directors and Senior Management as a group.
Shareholdings of Directors and Senior Management as of April 26, 2012
Title of
Class | | Name of Beneficial Owner | | Notes | | | Amount and Nature
of Beneficial
Ownership | | | Percent of
Class | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common | | Robert L. Hodgkinson | | | (1) | | | | 8,783,658 | | | | 6.72 | % |
| Common | | Harrison Blacker | | | (2) | | | | 1,618,678 | | | | 1.24 | % |
| Common | | Mathew H. Wong | | | (3) | | | | 605,872 | | | | 0.46 | % |
| Common | | Craig Sturrock | | | (4) | | | | 1,092,500 | | | | 0.84 | % |
| Common | | Robert Holmes | | | (5) | | | | 2,708,000 | | | | 2.07 | % |
| Common | | Richard Patricio | | | (6) | | | | 295,000 | | | | 0.23 | % |
| Common | | Stephen Mut | | | (7) | | | | 2,676,001 | | | | 2.05 | % |
| Common | | Darren Devine | | | (8) | | | | 250,000 | | | | 0.19 | % |
| Common | | Neyeska Mut | | | (9) | | | | 523,001 | | | | 0.40 | % |
| Common | | Phil Bretzloff | | | (10) | | | | 333,250 | | | | 0.25 | % |
| | | Total Directors/Management | | | | | | | 18,885,960 | | | | 14.44 | % |
| (1) | Of these shares, 7,187,840 are represented by common shares, 914,000 are represented by vested stock options and 681,818 are represented by currently exercisable share purchase warrants. 1,500,000 of these shares are owned by 7804 Yukon Inc., a private company owned by Robert Hodgkinson; 3,600,499 are common shares owned by Hodgkinson Equities Corp., a private company owned by Robert Hodgkinson. A further 405,000 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
| (2) | Of these shares, 525,678 are represented by common shares, 943,000 are represented by vested stock options and 150,000 are represented by currently exercisable share purchase warrants. A further 390,000 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
| (3) | Of these shares, 122 are represented by common shares, 549,500 are represented by vested stock options and 56,250 are represented by currently exercisable share purchase warrants. 98 of these common shares are held by 390855 BC Ltd., a private company owned by Mathew Wong; 24 common shares are owned by Pui Ngor Lee, Mr. Wong’s mother. A further 267,500 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
| (4) | Of these shares, 650,000 are represented by common shares, 292,500 are represented by vested stock options and 150,000 are represented by currently exercisable share purchase warrants. A further 107,500 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
| (5) | Of these shares, 1,663,000 are represented by common shares, 295,000 are represented by vested stock options and 750,000 are represented by currently exercisable share purchase warrants. A further 105,000 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
| (6) | Of these shares, 295,000 are represented by vested stock options. A further 105,000 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
| (7) | Of these shares, 1,701,001 are represented by common shares, 600,000 are represented by vested stock options and 375,000 are represented by currently exercisable share purchase warrants. A further 50,000 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
| (8) | Of these shares, 250,000 are represented by vested stock options. A further 50,000 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
| (9) | Of these shares, 50,001 are represented by common shares and 473,000 are represented by vested stock options. A further 227,000 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
| (10) | Of these shares, 59,500 are represented by common shares and 273,750 are represented by vested stock options. A further 126,250 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
All percentages based on 130,786,069 shares outstanding as of April 26, 2012.
Stock Option Plan
We have a Stock Option Plan (the “Option Plan”), the principal purposes of whichis to (i) advance our interests by aiding us, and our subsidiaries, in motivating, attracting and retaining key employees and directors capable of assuring the future success of the Company; and (ii) secure for us and our shareholders the benefits inherent in the ownership of our common shares by key employees and directors of the Company and our subsidiaries. We also have a United States stock incentive sub-plan that was initially approved in 2009 and amended in 2012 (the “Sub-Plan”) and forms a part of the Option Plan. Any option granted under the Sub-Plan is also subject to the terms and conditions of the Option Plan. Where there is a conflict between the terms and conditions of the Sub-Plan and the terms and conditions of the Option Plan, the terms and conditions of the Option Plan govern.
Directors, officers, employees and other insiders of us or any of our subsidiaries, as well as any person or corporation engaged to provide services for us or for any entity controlled by us for an initial, renewable or extended period of twelve months or more (or a lesser period of time if approved by the committee that administers the Option Plan and acceptable to the Toronto Stock Exchange (the “TSX”) (including individuals employed by such person or corporation), are eligible to participate in the Option Plan. Eligible participants who are natural persons resident in the United States, United States citizens, or are otherwise subject to United States tax law may participate in the Sub-Plan.
At the time of grant of any option, the aggregate number of common shares reserved for issuance under the Option Plan (which includes the Sub-Plan) that may be made subject to options any time and from time to time, together with common shares reserved for issuance at that time under any of our other share compensation arrangements, may not exceed 10% of the total number of issued and outstanding common shares, on a non-diluted basis, on the date of grant of the option. Of this 10%, the number of common shares reserved for issuance to any one participant pursuant to the Sub-Plan in any year may not exceed 5% of our total outstanding common shares on a non-diluted basis. Common shares subject to any option (or portion thereof) under the Option Plan that has been cancelled or otherwise terminated prior to the issuance or transfer of such common shares will again be available for options under the Option Plan. The number of common shares authorized under the Option Plan may be increased, decreased or fixed by the Board of Directors. Subject to adjustment in accordance with the Sub-Plan, an aggregate of 12,800,000 common shares, less those common shares issued under the Option Plan, may be issued pursuant to stock options issued under the Sub-Plan. If a stock option terminates, is forfeited or is cancelled without the issuance of any common shares, or any common shares covered by a stock option or to which a stock option relates are not issued for any other reason, then the number of common shares counted against the aggregate number of common shares available under the Sub-Plan with respect to such stock option, to the extent of any such termination, forfeiture, cancellation or other event, will again be available for granting stock options under the Sub-Plan.
The option exercise price will be determined by the committee that administers the Option Plan or the Sub-Plan administrator, as applicable. The exercise price may not be less than the last closing price per common share on the TSX on the trading day immediately preceding the day the options are granted, or if the common shares are not listed on the TSX, on the most senior of any other exchange on which the common shares are then traded, on the last trading day immediately preceding the date of grant of such options.
The Option Plan may be terminated by the committee that administers the Option Plan at any time. The Sub-Plan terminates at midnight on January 5, 2022, unless it is terminated before then by our Board of Directors. Any option outstanding under the Option Plan or Sub-Plan at the time of termination shall remain in effect until such option has been exercised, has expired, has been surrendered to us or has been terminated.
A copy of the Option Plan and Sub-Plan is incorporated by reference into this Form 20-F as Exhibits 4.17 and 4.18, respectively.
Stock Options Outstanding
The names and titles of the Directors/Executive Officers of the Company to whom outstanding stock options have been granted and the number of common shares subject to such options is set forth in the following table as of April 26, 2012:
Stock Options Outstanding as of April 26, 2012
| Name | | Number of
Options Held | | | Number of
Options
Vested | | | Exercise Price per
Share | | | Grant Date | | Expiration Date |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Robert Hodgkinson | | | 375,000 | | | | 262,500 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 10/28/2008 | | 10/28/2013 |
| | | | 275,000 | | | | 165,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 5/5/2009 | | 5/4/2014 |
| | | | 350,000 | | | | 350,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 19,000 | | | | 19,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/16/2010 | | 2/15/2015 |
| | | | 300,000 | | | | 187,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Harrison Blacker | | | 300,000 | | | | 210,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 10/28/2008 | | 10/28/2013 |
| | | | 300,000 | | | | 180,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 5/5/2009 | | 5/4/2014 |
| | | | 400,000 | | | | 400,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 33,000 | | | | 33,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/16/2010 | | 2/15/2015 |
| | | | 300,000 | | | | 187,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Mathew Wong(1) | | | 175,000 | | | | 122,500 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 10/28/2008 | | 10/28/2013 |
| | | | 125,000 | | | | 75,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 5/5/2009 | | 5/4/2014 |
| | | | 200,000 | | | | 200,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 17,000 | | | | 17,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/16/2010 | | 2/15/2015 |
| | | | 300,000 | | | | 187,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Craig Sturrock | | | 100,000 | | | | 70,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 10/28/2008 | | 10/28/2013 |
| | | | 50,000 | | | | 30,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 5/5/2009 | | 5/4/2014 |
| | | | 150,000 | | | | 150,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 100,000 | | | | 62,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Robert Holmes | | | 100,000 | | | | 70,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 10/28/2008 | | 10/28/2013 |
| | | | 50,000 | | | | 32,500 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 02/12/2009 | | 02/12/2014 |
| | | | 150,000 | | | | 150,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 100,000 | | | | 62,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Richard Patricio | | | 100,000 | | | | 70,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 10/28/2008 | | 10/28/2013 |
| | | | 50,000 | | | | 32,500 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 02/12/2009 | | 02/12/2014 |
| | | | 150,000 | | | | 150,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 100,000 | | | | 62,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Stephen Mut | | | 100,000 | | | | 100,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 6/29/2009 | | 6/29/2014 |
| | | | 250,000 | | | | 250,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 300,000 | | | | 262,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Darren Devine (2) | | | 200,000 | | | | 200,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 100,000 | | | | 62,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Neyeska Mut | | | 120,000 | | | | 84,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 10/28/2008 | | 10/28/2013 |
| | | | 80,000 | | | | 52,000 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 2/12/2009 | | 2/12/2014 |
| | | | 175,000 | | | | 175,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 19,000 | | | | 19,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/16/2010 | | 2/15/2015 |
| | | | 306,000 | | | | 191,250 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Phil Bretzloff | | | 75,000 | | | | 52,500 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 10/28/2008 | | 10/28/2013 |
| | | | 75,000 | | | | 48,750 | | | $ | 0.45 | | | 2/12/2009 | | 2/12/2014 |
| | | | 110,000 | | | | 110,000 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 2/4/2010 | | 2/3/2015 |
| | | | 140,000 | | | | 87,500 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | 3/16/2011 | | 3/15/2014 |
| Total Officers/Directors | | | 6,719,000 | | | | 5,234,000 | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | 125,000 options granted on May 5, 2009 were issued to 390855 B.C. Ltd., a private company owned by Mathew Wong. |
| (2) | 200,000 options granted on February 4, 2010 were issued to Chelmer Investments Corp., a private company owned by Darren Devine. On October 25, 2010, these options were re-issued to the name of Darren Devine with the same exercise price, vesting term and expiration date. |
ITEM 7. MAJOR SHAREHOLDERS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS.
Shareholders
The Company is aware of one person who each beneficially own 5% or more of the Registrant's voting securities. The following table lists as of April 26, 2012 persons and/or companies holding 5% or more beneficial interest in the Company’s outstanding common stock.
5% or Greater Shareholders as of April 26, 2012
| Title of Class | | Name of Owner | | Amount and Nature of
Beneficial Ownership | | | Percent of Class | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common | | Robert L. Hodgkinson (1) | | | 8,783,658 | | | | 6.72 | % |
| (1) | Of these shares, 7,187,840 are represented by common shares, 914,000 are represented by vested stock options and 681,818 are represented by currently exercisable share purchase warrants. 1,500,000 of these shares are owned by 7804 Yukon Inc., a private company owned by Robert Hodgkinson; 3,600,499 are common shares owned by Hodgkinson Equities Corp., a private company owned by Robert Hodgkinson. A further 405,000 stock options have been granted but not yet vested. |
All percentages based on 130,786,069 shares outstanding as of April 26, 2012.
Changes in ownership by major shareholders
To the best of the Company’s knowledge there have been no changes in the ownership of the Company’s shares other than disclosed herein.
Voting Rights
The Company’s major shareholders do not have different voting rights.
Shares Held in the United States
As of April 26, 2012, there were approximately 7,534 registered holders of the Company’s shares in the United States, with combined holdings of 90,890,625 common shares.
Change of Control
As of April 26, 2012, there were no arrangements known to the Company which may, at a subsequent date, result in a change of control of the Company.
Control by Others
To the best of the Company’s knowledge, the Company is not directly or indirectly owned or controlled by another corporation, any foreign government, or any other natural or legal person, severally or jointly.
| B. | Related Party Transactions |
Other than as disclosed below, from January 1, 2009 through December 31, 2011, the Company did not enter into any transactions or loans between the Company and any (a) enterprises that directly or indirectly through one or more intermediaries, control or are controlled by, or are under common control with the Company; (b) associates; (c) individuals owning, directly or indirectly, an interest in the voting power of the Company that gives them significant influence over the Company, and close members of any such individual’s family; (d) key management personnel and close members of such individuals' families; or (e) enterprises in which a substantial interest in the voting power is owned, directly or indirectly by any person described in (c) or (d) or over which such a person is able to exercise significant influence.
| (a) | Loan from Hodgkinson Equity Corporation (“HEC”) |
HEC loan to the Company
On June 22, 2009, as amended on September 30, 2009 and December 31, 2009, the Company entered into an agreement with HEC in regard to the outstanding debt of $1,800,000 assumed from DEAL by the Company. Pursuant to the agreements, $450,000 of the debt was converted into 1,363,636 units consisting of 1,363,636 common shares and 681,818 common share purchase warrants exercisable at a price of $0.55 for a period of 5 years. The fair value of the units was estimated to be $450,000. The remaining $1,350,000 was converted into a 12% note due on January 1, 2011 and the Company was required to pay 3% fee on the outstanding balance of the loan as at December 31, 2009. As a result of the sale of 5% working interest in the Drake/Woodrush area to HEC in December 2009 (effective June 1, 2009), both parties agreed to reduce the loan balance by the purchase price of $911,722 including taxes and adjustments. In addition, the loan balance was further reduced by a payment of $50,351. As at December 31, 2009, a balance of $387,927 remained outstanding. As at December 31, 2010, a balance of $250,000 remained outstanding. In January 2011, the remaining balance of loan from HEC was repaid in full in cash (see Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements for details).
| (b) | Loan from Brownstone Ventures Inc. (“Brownstone”) |
On June 22, 2009, as amended on September 30, 2009 and December 31, 2009, the Company entered into an agreement with Brownstone in regard to the outstanding debt of $4,604,040 (US$3,780,000). Pursuant to the agreement, $2,200,000 (US$2,000,000) of the debt was converted into 6,666,667 units consisting of 6,666,667 common shares and 3,333,333 common share purchase warrants exercisable at a price of $0.55 for a period of 5 years. The fair value of the units was estimated to be US$2,000,000. The remaining $2,070,140 (US$1,780,000) of the debt was converted into a Canadian dollar denominated 12% note due on January 1, 2011.
As a part of the debt settlement on June 22, 2009, the Company also issued Brownstone 2,000,000 common share purchase warrants exercisable at $0.50 for a period of 2 years, with an option to force the exercise of the warrants if the Company’s common shares trade at a price of $0.80 or greater for 30 consecutive calendar days.
As at December 31, 2009, a balance of $1,957,474 remained outstanding comprised of the loan balance of $2,070,140 minus unamortized portion of finance fees of $112,666. In December 2010, the loan was paid off in full in cash.
| (c) | During 2011, compensation awarded to key management included a total of salaries and consulting fees of $1,771,981 (2010 - $1,215,191 and 2009 - $1,470,947) and non-cash stock-based compensation of $451,071 (2010 - $486,018 and 2009 - $188,668). Key management includes the Company’s officers and directors. The salaries and consulting fees are included in general and administrative expenses. Included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities at December 31, 2011 is $396,618 (December 31, 2010 - $12,000 and December 31, 2009 - $Nil) owing to a company controlled by an officer of the Company. |
| (d) | In 2011, the Company incurred a total of $2,301 (2010 - $268,440 and 2009 - $382,748) in interest expense and finance costs to a company controlled by an officer of the Company and Brownstone. |
| (e) | Included in interest and other income, in 2011, is $30,000 (2010 - $30,000 and 2009 - $30,000) received from the companies controlled by officers of the Company for rental income. |
| (f) | In July 2008, Brownstone Ventures Inc. (“Brownstone”) became a 28.53% working interest partner in the US properties. Previously, Brownstone controlled more than 10% of outstanding common shares of the Company. Effective September 28, 2011, Brownstone ceased to control more than 10% of outstanding common shares of the Company. Included in accounts receivable at December 31, 2011 is $Nil (2010 - $168,771 and 2009 - $72,752) owing from Brownstone. |
| (g) | In December 2009, a company controlled by the CEO of the Company (“HEC”) became a 5% working interest partner in the Woodrush property. Included in accounts receivable at December 31, 2011 is $Nil (2010 - $967 and 2009 - $Nil) owing from HEC. Included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities at December 31, 2011 is $53,668 (2010 - $166,139 and 2009 - $63,679) owing to HEC. |
| (h) | In 2011, we completed a private placement of 11,010,000 units issued at US$0.30 per unit. Certain directors and officers of the Company purchased 2,000,000 units of this offering (see Note 13 to the consolidated financial statements for details). |
| (i) | In December 2011, HEC exercised 250,000 warrants with an exercise price of US$0.35 each that were issued in February 2011. |
| (j) | Included in the total salaries and consulting fees incurred during 2009 was $107,000 paid to a former officer of the Company to terminate the consulting agreement. |
C. Interests of Experts and Counsel
Not Applicable.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL INFORMATION.
| A. | Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information |
Financial Statements
| Description | | Page |
| | | |
| Consolidated Financial Statements for the Years Ended December 31, 2011 and 2010 | | F-1 - F54 |
Supplementary Oil and Gas Reserve Estimation and Disclosures - Unaudited
Legal Proceedings
The Directors and the management of the Company do not know of any material, active or pending, legal proceedings against them; nor is the Company involved as a plaintiff in any material proceeding or pending litigation.
The Directors and the management of the Company know of no active or pending proceedings against anyone that might materially adversely affect an interest of the Company.
Dividend Policy
The Company has not paid any dividends on its common shares. The Company may pay dividends on its common shares in the future if it generates profits. Any decision to pay dividends on common shares in the future will be made by the board of directors on the basis of the earnings, financial requirements and other conditions existing at such time.
None.
ITEM 9. THE OFFER AND LISTING
| A. | Offering and Listing Details |
The Company’s common shares are traded on the Toronto Stock Exchange and on the NYSE Amex, in both cases under the symbol “DEJ.” The following tables set forth for the periods indicated, the high and low closing prices in Canadian dollars of our common shares traded on the Toronto Stock Exchange and in United States dollars on the NYSE Amex. The Company traded on the Toronto Stock Exchange Venture Exchange in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, until November 20, 2008 when it began trading on the Toronto Stock Exchange. The Company changed its symbol to “DEJ” after a one for three share consolidation effective October 1, 2003. The Company changed its Toronto Stock Exchange trading symbol on May 23, 2007 to “DEJ” to coincide with its listing on the American Stock Exchange (now NYSE Amex) on the same day under the symbol “DEJ”.
The following table contains the annual high and low market prices for the five most recent fiscal years:
| Toronto Stock Exchange (Cdn$) | | | | | | |
| | | High | | | Low | |
| 2011 | | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.24 | |
| 2010 | | $ | 0.48 | | | $ | 0.29 | |
| 2009 | | $ | 0.76 | | | $ | 0.23 | |
| 2008(1) | | $ | 2.17 | | | $ | 0.23 | |
| 2007 | | $ | 3.28 | | | $ | 1.02 | |
(1) Common shares listed on Toronto Stock Exchange on November 20, 2008.
| NYSE Amex (US$) | | | | | | |
| | | High | | | Low | |
| 2011 | | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.21 | |
| 2010 | | $ | 0.50 | | | $ | 0.26 | |
| 2009 | | $ | 0.67 | | | $ | 0.12 | |
| 2008 | | $ | 2.17 | | | $ | 0.25 | |
| 2007(1) | | $ | 2.95 | | | $ | 1.29 | |
(1) Shares listed for trading on NYSE Amex on May 7, 2007
The following table contains the high and low market prices for our common shares on the Toronto Stock Exchange and the NYSE Amex for each fiscal quarter for the two most recent fiscal years and any subsequent period:
| Toronto Stock Exchange (Cdn$) | | | | | | |
| | | High | | | Low | |
| 2012 | | | | | | | | |
| Q1 | | $ | 0.46 | | | $ | 0.35 | |
| 2011 | | | | | | | | |
| Q4 | | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.24 | |
| Q3 | | $ | 0.34 | | | $ | 0.24 | |
| Q2 | | $ | 0.44 | | | $ | 0.30 | |
| Q1 | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.30 | |
| 2010 | | | | | | | | |
| Q4 | | $ | 0.38 | | | $ | 0.29 | |
| Q3 | | $ | 0.41 | | | $ | 0.30 | |
| Q2 | | $ | 0.45 | | | $ | 0.29 | |
| Q1 | | $ | 0.48 | | | $ | 0.29 | |
(1) Common shares listed on Toronto Stock Exchange on November 20, 2008.
| NYSE Amex (US$) | | | | | | |
| | | High | | | Low | |
| 2012 | | | | | | | | |
| Q1 | | $ | 0.57 | | | $ | 0.34 | |
| 2011 | | | | | | | | |
| Q4 | | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.21 | |
| Q3 | | $ | 0.40 | | | $ | 0.23 | |
| Q2 | | $ | 0.45 | | | $ | 0.31 | |
| Q1 | | $ | 0.53 | | | $ | 0.30 | |
| 2010 | | | | | | | | |
| Q4 | | $ | 0.38 | | | $ | 0.29 | |
| Q3 | | $ | 0.44 | | | $ | 0.28 | |
| Q2 | | $ | 0.50 | | | $ | 0.28 | |
| Q1 | | $ | 0.47 | | | $ | 0.26 | |
(1) Shares listed for trading on NYSE Amex on May 7, 2007
The following table contains the high and low market prices for our common shares on the Toronto Stock Exchange and the NYSE Amex for each of the most recent six months:
| Toronto Stock Exchange (Cdn$) | | | | | | |
| | | High | | | Low | |
| October, 2011 | | $ | 0.40 | | | $ | 0.24 | |
| November, 2011 | | $ | 0.44 | | | $ | 0.33 | |
| December, 2011 | | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.29 | |
| January, 2012 | | $ | 0.55 | | | $ | 0.38 | |
| February, 2012 | | $ | 0.50 | | | $ | 0.41 | |
| March, 2012 | | $ | 0.46 | | | $ | 0.35 | |
| NYSE Amex (US$) | | | | | | |
| | | High | | | Low | |
| October, 2011 | | $ | 0.39 | | | $ | 0.21 | |
| November, 2011 | | $ | 0.44 | | | $ | 0.32 | |
| December, 2011 | | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.29 | |
| January, 2012 | | $ | 0.57 | | | $ | 0.38 | |
| February, 2012 | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.41 | |
| March, 2012 | | $ | 0.49 | | | $ | 0.34 | |
On April 20, 2012, the closing price of our common shares on the TSX was Cdn $0.29 per common share and on the NYSE Amex was US $0.30 per common share.
Not Applicable.
Our common shares, no par value, are traded on the TSX under the symbol “DEJ” and are traded on the NYSE Amex under the symbol "DEJ".
Not Applicable.
Not Applicable.
Not Applicable.
ITEM 10. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Not Applicable.
| B. | Memorandum and Articles of Association |
Dejour Energy Inc. (formerly Dejour Enterprises Ltd.) is incorporated under the laws of British Columbia, Canada. The Company was originally incorporated as “Dejour Mines Limited” on March 29, 1968 under the laws of the Province of Ontario. By articles of amendment dated October 30, 2001, the issued shares were consolidated on the basis of one (1) new for every fifteen (15) old shares and the name of the Company was changed to Dejour Enterprises Ltd. On June 6, 2003, the shareholders approved a resolution to complete a one-for-three-share consolidation, which became effective on October 1, 2003. In 2005, the Company was continued in British Columbia under the Business Corporations Act (British Columbia) (the “Act”). Effective March 9, 2011, the Company changed its name from Dejour Enterprises Ltd. to Dejour Energy Inc.
There are no restrictions on what business the Company may carry on in the Articles of Incorporation.
Under Article 17 of the Company’s Articles and under Part 5, Division 3 of the Act, a director must declare its interest in any existing or proposed contract or transaction with the Company and is not allowed to vote on any transaction or contract with the Company in which has a disclosable interest, unless all directors have a disclosable interest in that contract or transaction, in which case any or all of those directors may vote on such resolution. A director may hold any office or place of profit with the Company in conjunction with the office of director, and no director shall be disqualified by his office from contracting with the Company. A director or his firm may act in a professional capacity for the Company and he or his firm shall be entitled to remuneration for professional services. A director may become a director or other officer or employee of, or otherwise interested in, any corporation or firm in whom the Company may be interested as a shareholder or otherwise. The director shall not be accountable to the Company for any remuneration or other benefits received by him from such other corporation or firm subject to the provisions of the Act.
Article 16 of the Company’s Articles addresses the powers and duties of the directors. Directors must, subject to the Act, manage or supervise the management of the business and affairs of the Company and have the authority to exercise all such powers which are not required to be exercised by the shareholders as governed by the Act. Article 19 of the Company’s Articles addresses Committees of the Board of Directors. Directors may, by resolution, create and appoint an executive committee consisting of the director or directors that they deem appropriate. This executive committee has, during the intervals between meetings of the Board, all of the directors’ powers, except the power to fill vacancies in the Board, the power to remove a Director, the power to change the membership of, or fill vacancies in, any committee of the Board and any such other powers as may be set out in the resolution or any subsequent directors’ resolution. Directors may also by resolution appoint one or more committees other than the executive committee.
These committees may be delegated any of the directors’ powers except the power to fill vacancies on the board of directors, the power to remove a director, the power to change the membership or fill vacancies on any committee of the directors, and the power to appoint or remove officers appointed by the directors. Article 18 of the Company’s Articles details the proceedings of directors. A director may, and the Secretary or Assistant Secretary, if any, on the request of a director must call a meeting of the directors at any time. The quorum necessary for the transaction of the business of the directors may be fixed by the directors and if not so fixed shall be deemed to a majority of the directors. If the number of directors is set at one, it quorum is deemed to be one director.
Article 8 of the Company’s Articles details the borrowing powers of the directors. They may, on behalf of the Company:
| · | Borrow money in a manner and amount, on any security, from any source and upon any terms and conditions as they deem appropriate; |
| · | Issue bonds, debentures, and other debt obligations either outright or as security for any liability or obligation of the Company or any other person at such discounts or premiums and on such other terms as they consider appropriate; |
| · | Guarantee the repayment of money by any other person or the performance of any obligation of any other person; and |
| · | Mortgage, charge, or grant a security in or give other security on, the whole or any part of the present or future assets and undertaking of the Company. |
A director need not be a shareholder of the Company, and there are no age limit requirements pertaining to the retirement or non-retirement of directors. The directors are entitled to the remuneration for acting as directors, if any, as the directors may from time to time determine. If the directors so decide, the remuneration of directors, if any, will be determined by the shareholders. The remuneration may be in addition to any salary or other remuneration paid to any officer or employee of the Company as such who is also a director. The Company must reimburse each director for the reasonable expenses that he or she may incur in and about the business of the Company. If any director performs any professional or other services for the Company that in the opinion of the directors are outside the ordinary duties of a director, or if any director is otherwise specially occupied in or about the Company’s business, he or she may be paid remuneration fixed by the directors, or, at the option of that director, fixed by ordinary resolution and such remuneration may be either in addition to, or in substitution for, any other remuneration that he or she may be entitled to receive. Unless other determined by ordinary resolution, the directors on behalf of the Company may pay a gratuity or pension or allowance on retirement to any director who has held any salaried office or place of profit with the Company or to his or her spouse or dependents and may make contributions to any fund and pay premiums for the purchase or provision of any such gratuity, pension or allowance.
Article 21 of the Company’s Articles provides for the mandatory indemnification of directors, former directors, and alternate directors, as well as his or hers heirs and legal personal representatives, or any other person, to the greatest extent permitted by the Act. The indemnification includes the mandatory payment of expenses actually and reasonably incurred by such person in respect of that proceeding. The failure of a director, alternate director, or officer of the Company to comply with the Act or the Company’s Articles does not invalidate any indemnity to which he or she is entitled. The directors may cause the Company to purchase and maintain insurance for the benefit of eligible parties who:
| (a) | is or was a director, alternate director, officer, employee or agent of the Company; |
| (b) | is or was a director, alternate director, officer employee or agent of a corporation at a time when the corporation is or was an affiliate of the Company; |
| (c) | at the request of the Company, is or was a director, alternate director, officer, employee or agent of a corporation or of a partnership, trust, joint venture or other unincorporated entity; |
| (d) | at the request of the Company, holds or held a position equivalent to that of a director, alternate director or officer of a partnership, trust, joint venture or other unincorporated entity; |
against any liability incurred by him or her as such director, alternate director, officer, employee or agent or person who holds or held such equivalent position
Under Article 9 of the Company’s Articles and subject to the Act, the Company may alter its authorized share structure by directors’ resolution or ordinary resolution, in each case determined by the directors, to:
| (a) | create one or more classes or series of shares or, if none of the shares of a series of a class or series of shares are allotted or issued, eliminate that class or series of shares; |
| (b) | increase, reduce or eliminate the maximum number of shares that the Company is authorized to issue out of any class or series of shares or establish a maximum number of shares that the company is authorized to issue out of any class or series of shares for which no maximum is established; |
| (c) | subdivide or consolidate all or any of its unissued, or fully paid issued, shares; |
| (d) | if the Company is authorized to issue shares of a class or shares with par value; |
| (i) | decrease the par value of those shares; or |
| (ii) | if none of the shares of that class of shares are allotted or issued, increase the par value of those shares; |
| (e) | change all or any of its unissued, or fully paid issued, shares with par value into shares without par value or any of its unissued shares without par value into shares with par value; |
| (f) | alter the identifying name of any of its shares; or |
by ordinary resolution otherwise alter its share or authorized share structure.
Subject to Section9.2 of the Company’s Articles and the Act, the Company may:
| (1) | by directors’ resolution or ordinary resolution, in each case determined by the directors, create special rights or restrictions for, and attach those special rights or restrictions to, the shares of any class or series of shares, if none of those shares have been issued, or vary or delete any special rights or restrictions attached to the shares of any class or series of shares, if none of those shares have been issued; and |
| (2) | by special resolution of the shareholders of the class or series affected, do any of the acts in Section 9.1 of the Company’s Articles if any of the shares of the class or series of shares has been issued. |
The Company may by resolution of its directors or by ordinary resolution, in each case as determined by the directors, authorize an alteration of its Notice of Articles in order to change its name.
The directors may, whenever they think fit, call a meeting of shareholders. An annual general meeting shall be held once every calendar year at such time (not being more than 15 months after holding the last preceding annual meeting) and place as may be determined by the Directors.
There are no limitations upon the rights to own securities.
There are no provisions that would have the effect of delaying, deferring, or preventing a change in control of the Company.
There is no special ownership threshold above which an ownership position must be disclosed. However, any ownership level above 10% must be disclosed to the TSX and all applicable Canadian Securities Commission.
Description of Share Capital
The Company is authorized to issue an unlimited number of common shares, preferred shares and series 1 preferred shares of which, as of April 26, 2012, 130,786,069 common shares, are issued and outstanding.The rights, preferences and restrictions attaching to each class of the Company’s shares are as follows:
Common Shares
All the common shares of the Company are of the same class and, once issued, rank equally as to dividends, voting powers, and participation in assets. All common shareholders are entitled to receive notice of, attend and be heard at any meeting of shareholders of the Company, excepting a meeting of the holders of shares of another class, as such, and excepting a meeting of the holders of a particular series, as such. Holders of shares of common stock are entitled to one vote for each share held of record on all matters to be acted upon by the shareholders, including the election of directors.Except as otherwise required by law the holders of the Company’s common shares will possess all voting power. Generally, all matters to be voted on by shareholders must be approved by a majority (or, in the case of election of directors, by a plurality) of the votes entitled to be cast by all common shares that are present in person or represented by proxy. Subject to the special rights and restrictions attached to the shares of any class or series of classes, one holder of common shares issued, outstanding and entitled to vote, represented in person or by proxy, is necessary to constitute a quorum at any meeting of our shareholders.
Upon liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, whether voluntary or involuntary, or other disposition of the property or assets of the Company, holders of shares of common stock are entitled to receive pro rata the assets of Company, if any, remaining after payments of all debts and liabilities to the holders of preferred shares or any other shares ranking senior to shares of common stock. No shares have been issued subject to call or assessment. There are no pre-emptive or conversion rights and no provisions for redemption or purchase for cancellation, surrender, or sinking or purchase funds.
The holders of the Company’s common shares will be entitled to such cash dividends as may be declared from time to time by our Board of Directors but such dividend will rank junior to the holders of preferred shares and series 1 preferred shares.
In the event of any merger or consolidation with or into another company in connection with which the Company’s common shares are converted into or exchangeable for shares, other securities or property (including cash), all holders of the Company’s common shares will be entitled to receive the same kind and amount of shares and other securities and property (including cash).
There are no indentures or agreements limiting the payment of dividends on the Company’s common shares and there are no special liquidation rights or subscription rights attaching to the Company’s common shares.
Preferred Shares
Preferred shares may, at any time and from time to time, be issued in one or more series and the Company may, by directors’ resolution or ordinary resolution, do one or more of the following:
| · | determine the maximum number of shares of any of those series of preferred shares that the Company is authorized to issue, determine that there is no maximum number or alter any determination made or otherwise, in relation to a maximum number of those shares, and authorize the alteration of the Notice of Articles accordingly; |
| · | alter the Articles of the Company, and authorize the alteration of the Notice of Articles, to create an identifying name by which the shares of any of those series of preferred shares may be identified or to alter any identifying name created for those shares; and |
| · | alter the Articles of the Company, and authorize the alteration of the Notice of Articles, to attach special rights or restrictions to the shares of any of those series of preferred shares or to alter any special rights or restrictions attached to those shares, subject to the special rights and restrictions attached to the preferred shares. |
If the alterations, determinations or authorizations contemplated above are to be made in relation to a series of shares of which there are issued shares, those alterations, determinations or authorizations may be made by ordinary resolution. However, no special rights or restrictions attached to a series of preferred shares shall confer on the series of preferred shares priority over another series of preferred shares respecting (i) dividends or (ii) return of capital on the dissolution of the Company or on the occurrence of any event that entitles the shareholders holding the shares of all series of preferred shares to a return of capital.
All holders of preferred shares shall not be entitled to receive notice of, attend and be heard at any meeting of or vote at any meeting of shareholders of the Company, except any specific meeting of the holders of preferred shares.
The holders of the Company’s preferred shares will be entitled to such cash dividends as may be declared from time to time by our Board of Directors and shall rank senior to the holders of our common shares and any other shares of the Company ranking junior to the preferred shares.
Upon liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, whether voluntary or involuntary, or other disposition of the property or assets of the Company, holders of the holders of the Preferred Shares, including the Series 1 Preferred Shares, shall be entitled to receive, for each preferred share held, from the property and assets of the Company, a sum equivalent to the amount paid up thereon together with the premium (if any) thereon and any dividends declared thereon before any amount shall be paid or any property or asset of the Company is distributed to the holders of the common shares or any other shares ranking junior to the preferred shares with respect to repayment of capital. After payment to the holders of the preferred shares of the amount so payable to them, the holders of the preferred shares shall not be entitled to share in any further distribution of the property or assets of the Company except as specifically provided in special rights and restrictions attached to any particular series of preferred shares
Series 1 Preferred Shares
The Company may, at any time and from time to time, issue series 1 preferred shares. The Company may, by directors’ resolution or ordinary resolution passed before the issue of any series 1 preferred shares, in each case as determined by the directors or, if there are issued series 1 preferred shares, by ordinary resolution, do one or more of the following:
| · | determine the maximum number of the series 1 preferred shares that the Company is authorized to issue, determine that there is no maximum number or alter any determination made in relation to a maximum number of those shares, and authorize the alteration of the Notice of Articles accordingly; |
| · | alter the Articles of the Company, and authorize the alteration of the Notice of Articles, to alter the name of the series 1 preferred shares; and |
| · | alter the Articles of the Company, and authorize the alteration of the Notice of Articles, to attach special rights or restrictions to the series 1 preferred shares or to alter any special rights or restrictions attached to those shares, subject to the special rights and restrictions attached to the preferred shares. |
The special rights and restrictions that may be attached to the series 1 preferred shares may include, without in any way limiting or restricting the generality of such paragraph, rights and restrictions respecting the following:
| · | the rate or amount of dividends, whether cumulative, non-cumulative or partially cumulative and the dates, places and currencies of payment thereof; |
| · | the consideration for, and the terms and conditions of, any purchase for cancellation or redemption thereof, including redemption after a fixed term or at a premium, conversion or exchange rights; |
| · | the terms and conditions of any share purchase plan or sinking fund; |
| · | the restrictions respecting the payment of dividends on, or the repayment of capital in respect of, any other shares of the Company; |
| · | the issuance of any shares of any other class or series of shares of the Company or any evidences of indebtedness or any other securities convertible into or exchangeable for such shares |
No special rights or restrictions attached to the series 1 preferred shares confers on the series 1 preferred shares priority over another series of preferred shares respecting (i) dividends or (ii) return of capital on the dissolution of the Company or on the occurrence of any event that entitles the shareholders holding the shares of all series of preferred shares to a return of capital.
All holders of series 1 preferred shares are not entitled to receive notice of, attend and be heard at any meeting of or vote at any meeting of shareholders of the Company, except any specific meeting of the holders of series 1 preferred shares.
The holders of the Company’s series 1 preferred shares will be entitled to such cash dividends as may be declared from time to time by the Company’s Board of Directors and will rank senior to the holders of the Company’s common shares and any other shares of the Company ranking junior to the preferred shares.
Dividend Record
The Company has not paid any dividends on its common shares and has no policy with respect to the payment of dividends.
Ownership of Securities and Change of Control
There are no limitations on the rights to own securities, including the rights of non-resident or foreign shareholders to hold or exercise voting rights on the securities imposed by foreign law or by the constituent documents of the Company.
Any person who beneficially owns, directly or indirectly, or exercises control or direction over more than 10% of the Company’s voting shares is considered an insider, and must file an insider report with the Canadian regulatory commissions within ten days of becoming an insider, disclosing any direct or indirect beneficial ownership of, or control or direction over securities of the Company. In addition, if the Company itself holds any of its own securities, the Company must disclose such ownership.
There are no provisions in the Company’s Articles or Notice of Articles that would have an effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change in control of the Company operating only with respect to a merger, acquisition or corporate restructuring involving the Company or its subsidiaries.
Differences from Requirements in the United States
Except for the Company’s quorum requirements, certain requirements related to related party transactions and the requirement for notice of shareholder meetings, discussed above, there are no significant differences in the law applicable to the Company, in the areas outlined above, in Canada versus the United States. In most states in the United States, a quorum must consist of a majority of the shares entitled to vote. Some states allow for a reduction of the quorum requirements to less than a majority of the shares entitled to vote. Having a lower quorum threshold may allow a minority of the shareholders to make decisions about the Company, its management and operations. In addition, most states in the United States require that a notice of meeting be mailed to shareholders prior to the meeting date. Additionally, in the United States, a director may not be able to vote on the approval of any transaction in which the director has an interest.
The following are material contracts to which the Company is a party:
Bank Line of Credit and Bridge Loan
In March 2010, the Company negotiated a credit facility for a bridge loan of up to $5,000,000 with a due date of September 22, 2010. This facility was secured by a first floating charge over all the assets of DEAL, and bore interest at 12% per annum. At December 31, 2011, the Canadian oil and natural gas interests and properties with a carrying amount of $nil (December 31, 2010 - $12,418,812) were held as collateral for the loan. By agreement, the due date of the loan was extended to October 31, 2011. Pursuant to the agreement, outstanding advances were due to be fully repaid no later than October 31, 2011 or, upon the earlier of non-core asset sales of DEAL. During the year ended December 31, 2011, the Company made total monthly principal payments of $700,000 and repaid the outstanding balance of $4,100,000 in full. This facility was used to support the development of the Company’s oil and gas properties in the Drake/Woodrush area.
In September 2011, the Company obtained a $7 million revolving operating demand loan (“line of credit”), including a letter of credit facility to a maximum of $700,000 for a maximum one year term, from a Canadian Bank to refinance the bridge loan and to provide operating funds. The line of credit is at an interest rate of Prime + 1% (total 4% p.a. currently) and collateralized by a $10,000,000 debenture over all assets of DEAL and a $10,000,000 guarantee from Dejour Energy Inc. In December 2011, the Company renewed the line of credit with the Canadian Bank. The next review date is scheduled on or before May 1, 2012, but subject to change at the discretion of the bank. As at December 31, 2011, a total of $5,545,457 of this facility was utilized.
According to the terms of the facility, DEAL is required to maintain a working capital ratio of greater than 1:1 at all times. The working capital ratio is defined as the ratio of (i) current assets (including any undrawn and authorized availability under the facility) less unrealized hedging gains to (ii) current liabilities (excluding current portion of outstanding balances of the facility) less unrealized hedging losses. As at December 31, 2011, the Company is in compliance with the working capital ratio requirement.
HEC loan to DEAL
On May 15, 2008, DEAL issued a promissory note for up to $2,000,000 to HEC, a private company controlled by the CEO of the Company.The promissory note is secured by the assets, equipment, fixtures, inventory and accounts receivable of DEAL, bears interest at the Royal Bank of Canada Prime Rate per annum, and has a loan fee of 1% of the outstanding amount per month. The principal, interest and loan fee were payable on demand after August 15, 2008. Upon securing the bank line of credit in August 2008, HEC signed a subordination and postponement agreement which restricted the principal repayment of the promissory note subject to the bank’s prior approval and DEAL meeting certain loan covenants. As at December 31, 2008, $1,950,000 had been advanced on the promissory note. Repayments of $90,642 and $59,358 were made on March 5, 2009 and on April 3, 2009 respectively. As at June 22, 2009, the Company assumed from DEAL the remaining outstanding balance of $1,800,000.
HEC loan to the Company
On August 11, 2008, the Company borrowed $600,000 from HEC. The loan was secured by all assets of the Company, repayable on demand, bore interest at the Canadian prime rate per annum, and had a loan fee of 1% of the outstanding amount per month. At December 31, 2008 $600,000 had been advanced to the Company.On March 19, 2009, a repayment of $600,000 was made and as at December 31, 2009, no balance remained outstanding.
On September 12, 2008, as consideration for HEC agreeing to postpone the $2,000,000 promissory note and providing the additional loan of $600,000, HEC was granted an option to become a working interest partner with DEAL. Upon electing to become a working interest partner, HEC must pay DEAL an amount equal to 10% of the actual price paid for the acquisition of the Montney (Buick Creek) property in northeastern British Columbia. HEC is also required to pay its pro-rata share of the operating costs. On February 26, 2009, HEC exercised its option and elected to become a 10% working interest partner in DEAL’s Montney (Buick Creek) property. The option price was $90,642.
On June 22, 2009, as amended on September 30, 2009 and December 31, 2009, the Company entered into an agreement with HEC in regard to the outstanding debt of $1,800,000 assumed from DEAL by the Company. Pursuant to the agreements, $450,000 of the debt was converted into 1,363,636 units consisting of 1,363,636 common shares and 681,818 common share purchase warrants exercisable at a price of $0.55 for a period of 5 years. The fair value of the units was estimated to be $450,000. The remaining $1,350,000 was converted into a 12% note due on January 1, 2011 and the Company was required to pay 3% fee on the outstanding balance of the loan as at December 31, 2009. As a result of the sale of 5% working interest in the Drake/Woodrush area to HEC in December 2009 (effective June 1, 2009), both parties agreed to reduce the loan balance by the purchase price of $911,722 including taxes and adjustments. In addition, the loan balance was further reduced by a payment of $50,351. As at December 31, 2009, a balance of $387,927 remained outstanding. In December 2010, a repayment of $137,927 was made to HEC by the Company. As at December 31, 2010, a balance of $250,000 remained outstanding. Subsequent to December 31, 2010, the loan was repaid in full in cash.
Brownstone loan to the Company
On June 18, 2008, a promissory note with a face value of $4,078,800 (US $4,000,000) was issued to Brownstone. Brownstone owned more than 10% of outstanding common shares of the Company and one of Brownstone’s directors also serves on the board of directors of the Company.The promissory note was securedby a general security agreement issued by the Company in favour of Brownstone,and bore interest at 5% per annum. The principal and interest were repayable by the earlier of the completion of an equity and/or debt financing, and July 1, 2009. During the year ended December 31, 2008, a repayment of $222,948 (US$220,000) was made and at December 31, 2008 a balance of $4,604,040 (US$3,780,000) owed.
On June 22, 2009, as amended on September 30, 2009 and December 31, 2009, the Company entered into an agreement with Brownstone in regard to the outstanding debt of $4,604,040 (US$3,780,000). Pursuant to the agreement, $2,200,000 (US$2,000,000) of the debt was converted into 6,666,667 units consisting of 6,666,667 common shares and 3,333,333 common share purchase warrants exercisable at a price of $0.55 for a period of 5 years. The fair value of the units was estimated to be US$2,000,000. The remaining $2,070,140 (US$1,780,000) of the debt was converted into a Canadian dollar denominated 12% note due on January 1, 2011. As at December 31, 2009, a balance of $1,957,474 remained outstanding comprised of the loan balance of $2,070,140 minus unamortized portion of finance fees of $112,666. In December 2010, the loan was paid off in full in cash.
As a part of the debt settlement on June 22, 2009, the Company also issued Brownstone 2,000,000 common share purchase warrants exercisable at $0.50 for a period of 2 years, with an option to force the exercise of the warrants if the Company’s common shares trade at a price of $0.80 or greater for 30 consecutive calendar days.
Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and Pengrowth Corporation dated April 17, 2009
In April 2009, the Company’s Canadian subsidiary, DEAL, entered into a purchase and sale agreement with Pengrowth Corporation. Under the agreement, DEAL agreed to sell 100% of its working interest in the Carson Creek area to Pengrowth for gross proceeds of $2,100,000.
In 2009, the Company’s Canadian subsidiary, DEAL, entered into the following purchase and sale Agreements in regard to the disposition of a total 25% working interest in the Drake/Woodrush area for total gross proceeds of $4,500,000:
| Date of agreement | | Transferee | | Working interest % | | | Gross Proceeds | |
| June 10, 2009 | | John James Robinson | | | 3 | % | | $ | 540,000 | |
| June 15, 2009 | | C.U. YourOilRig Corp. | | | 10 | % | | $ | 1,800,000 | |
| July 8, 2009 | | Woodrush Energy Partners LLC | | | 6 | % | | $ | 1,080,000 | |
| July 31, 2009 | | RockBridge Energy Inc. | | | 1 | % | | $ | 180,000 | |
| December 31, 2009 | | HEC | | | 5 | % | | $ | 900,000 | |
There are no governmental laws, decrees, or regulations in Canada relating to restrictions on the export or import of capital, or affecting the remittance of interest, dividends, or other payments to non-resident holders of the Company’s common stock. Any remittances of dividends to United States residents are, however, subject to a 15% withholding tax (10% if the shareholder is a corporation owning at least 10% of the outstanding Common Stock of the Company) pursuant to Article X of the reciprocal tax treaty between Canada and the United States.
Except as provided in the Investment Canada Act (the “ICA”), there are no limitations specific to the rights of non-Canadians to hold or vote the common shares of the Company under the laws of Canada or the Province of British Columbia or in the charter documents of the Company.
Management of the Company considers that the following general summary is materially complete and fairly describes those provisions of the ICA pertinent to an investment by an American investor in the Company.
The ICA requires a non-Canadian making an investment which would result in the acquisition of control of a Canadian business, the gross value of the assets of which exceed certain threshold levels or the business activity of which is related to Canada’s cultural heritage or national identity, to either notify, or file an application for review with, Investment Canada, the federal agency created by the ICA.
The notification procedure involves a brief statement of information about the investment of a prescribed form which is required to be filed with Investment Canada by the investor at any time up to 30 days following implementation of the investment. It is intended that investments requiring only notification will proceed without government intervention unless the investment is in a specific type of business activity related to Canada’s cultural heritage and national identity.
If an investment is reviewable under the ICA, an application for review in the form prescribed is normally required to be filed with Investment Canada prior to the investment taking place and the investment may not be implemented until the review has been completed and the Minister responsible for Investment Canada is satisfied that the investment is likely to be of net benefit to Canada. If the Minister is not satisfied that the investment is likely to be of net benefit to Canada, the non-Canadian must not implement the investment or, if the investment has been implemented, may be required to divest himself of control of the business that is the subject of the investment.
The following investments by non-Canadians are subject to notification under the ICA:
| (a) | an investment to establish a new Canadian business; and |
| (b) | an investment to acquire control of a Canadian business that is not reviewable pursuant to the ICA. |
An investment is reviewable under the ICA if there is an acquisition by a non-Canadian of a Canadian business and the asset value of the Canadian business being acquired equals or exceeds the following thresholds:
| (a) | for non-WTO Investors, the threshold is $5,000,000 for a direct acquisition and over $50,000,000 for an indirect acquisition. The $5,000,000 threshold will apply however for an indirect acquisition if the asset value of the Canadian business being acquired exceeds 50% of the asset value of the global transaction; |
| (b) | except as specified in paragraph (c) below, a threshold is calculated annually for reviewable direct acquisitions by or from WTO Investors. The threshold for 2012 is $330,000,000. Pursuant to Canada’s international commitments, indirect acquisitions by or from WTO Investors are not reviewable; and |
| (c) | the limits set out in paragraph (a) apply to all investors for acquisitions of a Canadian business that is a cultural business.: |
WTO Investor as defined in the ICA means:
(a) an individual, other than a Canadian, who is a national of a WTO Member or who has the right of permanent residence in relation to that WTO Member;
| (b) | a government of a WTO Member, whether federal, state or local, or an agency thereof; |
| | an entity that is not a Canadian-controlled entity, and that is a WTO investor-controlled entity, as determined in accordance with the ICA; |
| (c) | a corporation or limited partnership: |
| (i) | that is not a Canadian-controlled entity, as determined pursuant to the ICA; |
| (ii) | that is not a WTO investor within the meaning of the ICA; |
| (iii) | of which less than a majority of its voting interests are owned by WTO investors; |
| (iv) | that is not controlled in fact through the ownership of its voting interests; and |
| (v) | of which two thirds of the members of its board of directors, or of which two thirds of its general partners, as the case may be, are any combination of Canadians and WTO investors; |
| (i) | that is not a Canadian-controlled entity, as determined pursuant to the ICA; |
| (ii) | that is not a WTO investor within the meaning of the ICA; |
| (iii) | that is not controlled in fact through the ownership of its voting interests, and |
| (iv) | of which two thirds of its trustees are any combination of Canadians and WTO investors, or |
| (e) | any other form of business organization specified by the regulations that is controlled by a WTO investor. |
WTO Member as defined in the ICA means a member of the World Trade Organization.
Generally, an acquisition is direct if it involves the acquisition of control of the Canadian business or of its Canadian parent or grandparent and an acquisition is indirect if it involves the acquisition of control of a non-Canadian parent or grandparent of an entity carrying on the Canadian business. Control may be acquired through the acquisition of actual or de jure voting control of a Canadian corporation or through the acquisition of substantially all of the assets of the Canadian business. No change of voting control will be deemed to have occurred if less than one-third of the voting control of a Canadian corporation is acquired by an investor.
The ICA specifically exempts certain transactions from either notification or review. Included among the category of transactions is the acquisition of voting shares or other voting interests by any person in the ordinary course of that person’s business as a trader or dealer in securities.
CANADIAN FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS
The following summary describes the principal Canadian federal income tax considerations generally applicable to a holder who is the beneficial holder of common shares of the Company and who, at all relevant times, for the purposes of the application of the Income Tax Act(Canada) and the Income Tax Regulations (collectively, the “Canada Tax Act”) (i) deals at arm’s length with the Company, (ii) is not affiliated with the Company, (iii) holds the common shares as capital property, and (iv) who, for the purposes of the Canada Tax Act and the Canada – United States Income Tax Convention (the “Treaty”), is at all relevant times resident in and only in the United States, is a qualifying person entitled to all of the benefits of the Treaty, and (v) does not use or hold and is not deemed to use or hold the shares in carrying on a business in Canada (a “U.S. Holder”). Special rules, which are not discussed below, may apply to a U.S. Holder that is an insurer or authorized foreign bank that carries on business in Canada and elsewhere.
This summary is based on the current provisions of the Canada Tax Act and the current published administrative policies and assessing practices of the Canada Revenue Agency (“CRA”) published in writing prior to the date hereof. This summary also takes into account all specific proposals to amend the Canada Tax Act and Regulations publicly announced by the Minister of Finance (Canada) prior to the date hereof (collectively, the “Tax Proposals”) and assumes all Tax Proposals will be enacted in the form proposed. There is no certainty that the Tax Proposals will be enacted in the form proposed, if at all. This summary does not otherwise take into account or anticipate any changes in laws or administrative policy or assessing practice whether by judicial, regulatory, administrative or legislative decision or action nor does it take into account provincial, territorial or foreign income tax legislation or considerations.
This summary is of a general nature only and is not, and is not intended to be, nor should it be construed to be, legal or tax advice to any particular purchaser of Units. This summary is not exhaustive of all Canadian federal income tax considerations. Accordingly, purchasers should consult their own tax advisors regarding the income tax consequences of purchasing Units based on their particular circumstances.
Dividends
Dividends paid or credited or deemed to be paid or credited to a U.S. Holder by the Company will be subject to Canadian withholding tax at the rate of 25% under the Canada Tax Act, subject to any reduction in the rate of withholding to which the U.S. Holder is entitled under the Treaty. For example, if the U.S. Holder is entitled to benefits under the Treaty and is the beneficial owner of the dividends, the applicable rate of Canadian withholding tax is generally reduced to 15%. The rate of Canadian withholding tax for such U.S. Holder will generally be further reduced under the Treaty to 5% if such holder is a corporation that beneficially owns at least 10% of the voting shares of the Company, and may be further reduced to nil if such holder is a qualifying pension fund or charity.
Dispositions
A U.S. Holder will not be subject to tax under the Canada Tax Act on any capital gain realized on a disposition of a common share (including a deemed disposition on death), unless the common share is or is deemed to be “taxable Canadian property” to the U.S. Holder for the purposes of the Canada Tax Act and the U.S. Holder is not entitled to relief under the Treaty.
Generally, provided the Shares are listed on a “designated stock exchange” as defined in the Canada Tax Act (which includes the TSX) at the time of disposition, the Shares will not constitute taxable Canadian property of a U.S. Holder, unless at any time during the 60-month period immediately preceding the disposition, the U.S. Holder, persons with whom the U.S. Holder did not deal at arm’s length, or the U.S. Holder together with all such persons, owned 25% or more of the issued shares of any class of shares of the Company and more than 50% of the fair market value of those shares was derived directly or indirectly from any one or combination of (i) real or immovable property situated in Canada,(ii) Canadian resource properties, (iii) timber resource properties, and (iv) options in respect of, or interests in, or for civil rights law rights in, property described in any of (i) to (iii), whether or not that property exists.
U.S. Holders whose common shares may constitute taxable Canadian property should consult with their own tax advisors.
CERTAIN UNITED STATES FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS
The following is a general summary of certain material U.S. federal income tax considerations applicable to a U.S. Holder (as defined below) arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares of the Company.
This summary is for general information purposes only and does not purport to be a complete analysis or listing of all potential U.S. federal income tax considerations that may apply to a U.S. Holder arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares. In addition, this summary does not take into account the individual facts and circumstances of any particular U.S. Holder that may affect the U.S. federal income tax consequences to such U.S. Holder, including specific tax consequences to a U.S. Holder under an applicable tax treaty. Accordingly, this summary is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, legal or U.S. federal income tax advice with respect to any U.S. Holder. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal, U.S. federal alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and foreign tax consequences relating to the acquisition, ownership and disposition of common shares.
No legal opinion from U.S. legal counsel or ruling from the Internal Revenue Service (the “IRS”) has been requested, or will be obtained, regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares. This summary is not binding on the IRS, and the IRS is not precluded from taking a position that is different from, and contrary to, the positions taken in this summary. In addition, because the authorities on which this summary is based are subject to various interpretations, the IRS and the U.S. courts could disagree with one or more of the positions taken in this summary.
Scope of this Summary
Authorities
This summary is based on the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), Treasury Regulations (whether final, temporary, or proposed), published rulings of the IRS, published administrative positions of the IRS, U.S. court decisions, the Convention Between Canada and the United States of America with Respect to Taxes on Income and on Capital, signed September 26, 1980, as amended (the “Treaty”), and U.S. court decisions that are applicable and, in each case, as in effect and available, as of the date of this document. Any of the authorities on which this summary is based could be changed in a material and adverse manner at any time, and any such change could be applied on a retroactive or prospective basis which could affect the U.S. federal income tax considerations described in this summary. This summary does not discuss the potential effects, whether adverse or beneficial, of any proposed legislation that, if enacted, could be applied on a retroactive or prospective basis.
U.S. Holders
For purposes of this summary, the term "U.S. Holder" means a beneficial owner of common shares that is for U.S. federal income tax purposes:
| · | an individual who is a citizen or resident of the U.S.; |
| · | a corporation (or other entity taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes) organized under the laws of the U.S., any state thereof or the District of Columbia; |
| · | an estate whose income is subject to U.S. federal income taxation regardless of its source; or |
| · | a trust that (a) is subject to the primary supervision of a court within the U.S. and the control of one or more U.S. persons for all substantial decisions or (b) has a valid election in effect under applicable Treasury regulations to be treated as a U.S. person. |
Non-U.S. Holders
For purposes of this summary, a “non-U.S. Holder” is a beneficial owner of common shares that is not a U.S. Holder. This summary does not address the U.S. federal income tax consequences to non-U.S. Holders arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares. Accordingly, a non-U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal, U.S. federal alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and foreign tax consequences (including the potential application of and operation of any income tax treaties) relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares.
U.S. Holders Subject to Special U.S. Federal Income Tax Rules Not Addressed
This summary does not address the U.S. federal income tax considerations applicable to U.S. Holders that are subject to special provisions under the Code, including the following U.S. Holders: (a) U.S. Holders that are tax-exempt organizations, qualified retirement plans, individual retirement accounts, or other tax-deferred accounts; (b) U.S. Holders that are financial institutions, underwriters, insurance companies, real estate investment trusts, or regulated investment companies; (c) U.S. Holders that are dealers in securities or currencies or U.S. Holders that are traders in securities that elect to apply a mark-to-market accounting method; (d) U.S. Holders that have a “functional currency” other than the U.S. dollar; (e) U.S. Holders that own common shares as part of a straddle, hedging transaction, conversion transaction, constructive sale, or other arrangement involving more than one position; (f) U.S. Holders that acquired common shares in connection with the exercise of employee stock options or otherwise as compensation for services; (g) U.S. Holders that hold common shares other than as a capital asset within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code (generally, property held for investment purposes); (h) partnerships and other pass-through entities (and investors in such partnerships and entities); or (i) U.S. Holders that own or have owned (directly, indirectly, or by attribution) 10% or more of the total combined voting power of the outstanding shares of the Company. This summary also does not address the U.S. federal income tax considerations applicable to U.S. Holders who are: (a) U.S. expatriates or former long-term residents of the U.S. subject to Section 877 of the Code; (b) persons that have been, are, or will be a resident or deemed to be a resident in Canada for purposes of the Act; (c) persons that use or hold, will use or hold, or that are or will be deemed to use or hold common shares in connection with carrying on a business in Canada; (d) persons whose common shares constitute “taxable Canadian property” under the Act; or (e) persons that have a permanent establishment in Canada for the purposes of the Treaty. U.S. Holders that are subject to special provisions under the Code, including U.S. Holders described immediately above, should consult their own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal, U.S. federal alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and foreign tax consequences relating to the acquisition, ownership and disposition of common shares.
If an entity that is classified as a partnership (or pass-through entity) for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds common shares, the U.S. federal income tax consequences to such partnership and the partners of such partnership generally will depend on the activities of the partnership and the status of such partners. Partners of entities that are classified as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes should consult their own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares.
Tax Consequences Not Addressed
This summary does not address the U.S. federal, U.S. federal alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and foreign tax consequences to U.S. Holders of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal, U.S. federal alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and foreign tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of common shares.
U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences of the Acquisition, Ownership, and Disposition of Common Shares
If the Company is not considered a “passive foreign investment company” (a “PFIC”, as defined below) at any time during a U.S. Holder’s holding period, the following sections will generally describe the U.S. federal income tax consequences to U.S. Holders of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of the Company’s common shares.
Distributions on Common Shares
A U.S. Holder that receives a distribution, including a constructive distribution, with respect to a common share will be required to include the amount of such distribution in gross income as a dividend (without reduction for any Canadian income tax withheld from such distribution) to the extent of the current or accumulated “earnings and profits” of the Company, as computed for U.S. federal income tax purposes. A dividend generally will be taxed to a U.S. Holder at ordinary income tax rates. To the extent that a distribution exceeds the current and accumulated “earnings and profits” of the Company, such distribution will be treated first as a tax-free return of capital to the extent of a U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the common shares and thereafter as gain from the sale or exchange of such common shares (see “Sale or Other Taxable Disposition of Common Shares” below). However, the Company does not intend to maintain the calculations of earnings and profits in accordance with U.S. federal income tax principles, and each U.S. Holder should therefore assume that any distribution by the Company with respect to the common shares will constitute ordinary dividend income. Dividends received on common shares generally will not be eligible for the “dividends received deduction.”
For taxable years beginning before January 1, 2013, a dividend paid by the Company generally will be taxed at the preferential tax rates applicable to long-term capital gains if (a) the Company is a “qualified foreign corporation” (as defined below), (b) the U.S. Holder receiving such dividend is an individual, estate, or trust, and (c) certain holding period requirements are met. The Company generally will be a “qualified foreign corporation” under Section 1(h)(11) of the Code (a “QFC”) if (a) the Company is eligible for the benefits of the Treaty, or (b) common shares of the Company are readily tradable on an established securities market in the U.S. However, even if the Company satisfies one or more of such requirements, the Company will not be treated as a QFC if the Company is a PFIC for the taxable year during which the Company pays a dividend or for the preceding taxable year. (See the section below under the heading "Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules").
If the Company is a QFC, but a U.S. Holder otherwise fails to qualify for the preferential tax rate applicable to dividends discussed above, a dividend paid by the Company to a U.S. Holder, including a U.S. Holder that is an individual, estate, or trust, generally will be taxed at ordinary income tax rates (and not at the preferential tax rates applicable to long-term capital gains). The dividend rules are complex, and each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the dividend rules.
Sale or Other Taxable Disposition of Common Shares
A U.S. Holder will recognize gain or loss on the sale or other taxable disposition of common shares in an amount equal to the difference, if any, between (a) the amount of cash plus the fair market value of any property received and (b) such U.S. Holder’s tax basis in such common shares sold or otherwise disposed of. Subject to the PFIC rules discussed below, any such gain or loss generally will be capital gain or loss, which will be long-term capital gain or loss if, at the time of the sale or other disposition, such common shares are held for more than one year.
Gain or loss recognized by a U.S. Holder on the sale or other taxable disposition of common shares generally will be treated as “U.S. source” for purposes of applying the U.S. foreign tax credit rules unless the gain is subject to tax in Canada and is sourced as “foreign source” under the Treaty and such U.S. Holder elects to treat such gain or loss as “foreign source.”
Preferential tax rates apply to long-term capital gains of a U.S. Holder that is an individual, estate, or trust. There are currently no preferential tax rates for long-term capital gains of a U.S. Holder that is a corporation. Deductions for capital losses are subject to significant limitations under the Code.
Receipt of Foreign Currency
The amount of any distribution paid in foreign currency to a U.S. Holder in connection with the ownership of common shares, or on the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of common shares, generally will be equal to the U.S. dollar value of such foreign currency based on the exchange rate applicable on the date of receipt (regardless of whether such foreign currency is converted into U.S. dollars at that time). A U.S. Holder that receives foreign currency and converts such foreign currency into U.S. dollars at a conversion rate other than the rate in effect on the date of receipt may have a foreign currency exchange gain or loss, which generally would be treated as U.S. source ordinary income or loss. If the foreign currency received is not converted into U.S. dollars on the date of receipt, a U.S. Holder will have a basis in the foreign currency equal to its U.S. dollar value on the date of receipt. Any U.S. Holder who receives payment in foreign currency and engages in a subsequent conversion or other disposition of the foreign currency may have a foreign currency exchange gain or loss that would be treated as ordinary income or loss, and generally will be U.S. source income or loss for foreign tax credit purposes. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own U.S. tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences of receiving, owning, and disposing of foreign currency.
Foreign Tax Credit
A U.S. Holder who pays (whether directly or through withholding) Canadian income tax with respect to dividends paid on common shares generally will be entitled, at the election of such U.S. Holder, to receive either a deduction or a credit for such Canadian income tax paid. Generally, a credit will reduce a U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability on a dollar-for-dollar basis, whereas a deduction will reduce a U.S. Holder’s income subject to U.S. federal income tax. This election is made on a year-by-year basis and applies to all foreign taxes paid (whether directly or through withholding) by a U.S. Holder during a year.
Complex limitations apply to the foreign tax credit, including the general limitation that the credit cannot exceed the proportionate share of a U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability that such U.S. Holder’s “foreign source” taxable income bears to such U.S. Holder’s worldwide taxable income. In applying this limitation, a U.S. Holder’s various items of income and deduction must be classified, under complex rules, as either “foreign source” or “U.S. source.” Generally, dividends paid by a foreign corporation should be treated as foreign source for this purpose, and gains recognized on the sale of stock of a foreign corporation by a U.S. Holder should be treated as U.S. source for this purpose, except as otherwise provided in an applicable income tax treaty, and if an election is properly made under the Code. However, the amount of a distribution with respect to the common shares that is treated as a “dividend” may be lower for U.S. federal income tax purposes than it is for Canadian federal income tax purposes, resulting in a reduced foreign tax credit allowance to a U.S. Holder. In addition, this limitation is calculated separately with respect to specific categories of income. Dividends paid by the Company generally will constitute “foreign source” income and generally will be categorized as “passive income.”
The foreign tax credit rules are complex, and each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the foreign tax credit rules.
Additional Tax on Passive Income
| | For tax years beginning after December 31, 2012, certain individuals, estates and trusts whose income exceeds certain thresholds will be required to pay a 3.8% Medicare surtax on “net investment income” including, among other things, dividends and net gain from disposition of property (other than property held in a trade or business). U.S. Holders should consult with their own tax advisors regarding the effect, if any, of this tax on their ownership and disposition of common shares. |
Information Reporting; Backup Withholding Tax For Certain Payments
Under U.S. federal income tax law and regulations, certain categories of U.S. Holders must file information returns with respect to their investment in, or involvement in, a foreign corporation. For example, recently enacted legislation generally imposes new U.S. return disclosure obligations (and related penalties) on U.S. Holders that hold certain specified foreign financial assets in excess of $50,000. The definition of specified foreign financial assets includes not only financial accounts maintained in foreign financial institutions, but also, unless held in accounts maintained by a financial institution, any stock or security issued by a non-U.S. person, any financial instrument or contract held for investment that has an issuer or counterparty other than a U.S. person and any interest in a foreign entity. U. S. Holders may be subject to these reporting requirements unless their common shares are held in an account at a domestic financial institution. Penalties for failure to file certain of these information returns are substantial. U.S. Holders of common shares should consult with their own tax advisors regarding the requirements of filing information returns, these rules, including the requirement to file an IRS Form 8938.
Payments made within the U.S., or by a U.S. payor or U.S. middleman, of dividends on, and proceeds arising from the sale or other taxable disposition of, common shares generally will be subject to information reporting and backup withholding tax, at the rate of 28% (and increasing to 31% for payments made after December 31, 2012), if a U.S. Holder (a) fails to furnish such U.S. Holder’s correct U.S. taxpayer identification number (generally on Form W-9), (b) furnishes an incorrect U.S. taxpayer identification number, (c) is notified by the IRS that such U.S. Holder has previously failed to properly report items subject to backup withholding tax, or (d) fails to certify, under penalty of perjury, that such U.S. Holder has furnished its correct U.S. taxpayer identification number and that the IRS has not notified such U.S. Holder that it is subject to backup withholding tax. However, certain exempt persons, such as corporations, generally are excluded from these information reporting and backup withholding tax rules. Any amounts withheld under the U.S. backup withholding tax rules will be allowed as a credit against a U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability, if any, or will be refunded, if such U.S. Holder furnishes required information to the IRS in a timely manner. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the information reporting and backup withholding rules.
Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules
If the Company were to constitute a PFIC (as defined below) for any year during a U.S. Holder’s holding period, then certain different and potentially adverse tax consequences would apply to such U.S. Holder’s acquisition, ownership and disposition of common shares.
The Company generally will be a PFIC under Section 1297 of the Code if, for a tax year, (a) 75% or more of the gross income of the Company for such tax year is passive income (the “income test”) or (b) 50% or more of the value of its average quarterly assets held by the Company either produce passive income or are held for the production of passive income, based on the fair market value of such assets (the “asset test”). “Gross income” generally includes all revenues less the cost of goods sold, plus income from investments and from incidental or outside operations or sources, and “passive income” includes, for example, dividends, interest, certain rents and royalties, certain gains from the sale of stock and securities, and certain gains from commodities transactions. Active business gains arising from the sale of commodities generally are excluded from passive income if substantially all (85% or more) of a foreign corporation’s commodities are (a) stock in trade of such foreign corporation or other property of a kind which would properly be included in inventory of such foreign corporation, or property held by such foreign corporation primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business, (b) property used in the trade or business of such foreign corporation that would be subject to the allowance for depreciation under Section 167 of the Code, or (c) supplies of a type regularly used or consumed by such foreign corporation in the ordinary course of its trade or business, and certain other requirements are satisfied.
In addition, for purposes of the PFIC income test and asset test described above, if the Company owns, directly or indirectly, 25% or more of the total value of the outstanding shares of another foreign corporation, the Company will be treated as if it (a) held a proportionate share of the assets of such other foreign corporation and (b) received directly a proportionate share of the income of such other foreign corporation. In addition, for purposes of the PFIC income test and asset test described above, “passive income” does not include any interest, dividends, rents, or royalties that are received or accrued by the Company from a “related person” (as defined in Section 954(d)(3) of the Code), to the extent such items are properly allocable to the income of such related person that is not passive income.
Under certain attribution rules, if the Company is a PFIC, U.S. Holders will be deemed to own their proportionate share of any subsidiary of the Company which is also a PFIC (a ‘‘Subsidiary PFIC’’), and will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on (i) a distribution on the shares of a Subsidiary PFIC or (ii) a disposition of shares of a Subsidiary PFIC, both as if the holder directly held the shares of such Subsidiary PFIC.
The Company does not believe that it was a PFIC during the tax year ending December 31, 2011. However, PFIC classification is fundamentally factual in nature, generally cannot be determined until the close of the tax year in question, and is determined annually. Additionally, the analysis depends, in part, on the application of complex U.S. federal income tax rules, which are subject to differing interpretations. Furthermore, if for any given year the Company reaches either of the test standards (i.e., “income test” and “asset test”), it remains a PFIC forever, no matter how active it becomes in the future. Consequently, there can be no assurance that the Company has never been and will not become a PFIC for any tax year during which U.S. Holders hold common shares.
If the Company were a PFIC in any tax year and a U.S. Holder held common shares, such holder generally would be subject to special rules with respect to “excess distributions” made by the Company on the common shares and with respect to gain from the disposition of common shares. An “excess distribution” generally is defined as the excess of distributions with respect to the common shares received by a U.S Holder in any tax year over 125% of the average annual distributions such U.S. Holder has received from the Company during the shorter of the three preceding tax years, or such U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares. Generally, a U.S. Holder would be required to allocate any excess distribution or gain from the disposition of the common shares ratably over its holding period for the common shares. Such amounts allocated to the year of the disposition or excess distribution would be taxed as ordinary income, and amounts allocated to prior tax years would be taxed as ordinary income at the highest tax rate in effect for each such year and an interest charge at a rate applicable to underpayments of tax would apply.
While there are U.S. federal income tax elections that sometimes can be made to mitigate these adverse tax consequences (including, without limitation, the “QEF Election” and the “Mark-to-Market Election”), such elections are available in limited circumstances and must be made in a timely manner. U.S. Holders should be aware that, for each tax year, if any, that the Company is a PFIC, the Company can provide no assurances that it will satisfy the record keeping requirements of a PFIC, or that it will make available to U.S. Holders the information such U.S. Holders require to make a QEF Election under Section 1295 of the Code with respect of the Company or any Subsidiary PFIC. U.S. Holders are urged to consult their own tax advisers regarding the potential application of the PFIC rules to the ownership and disposition of common shares, and the availability of certain U.S. tax elections under the PFIC rules.
F. Dividends and Paying Agents
Not Applicable.
G. Statements by Experts
Not Applicable.
H. Documents on Display
We are subject to the informational requirements of the Exchange Act and file reports and other information with the SEC. You may read and copy any of our reports and other information at, and obtain copies upon payment of prescribed fees from, the Public Reference Room maintained by the SEC at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. In addition, the SEC maintains a Website that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding registrants that file electronically with the SEC at http://www.sec.gov. The public may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330.
We are required to file reports and other information with the securities commissions in Canada. You are invited to read and copy any reports, statements or other information, other than confidential filings, that we file with the provincial securities commissions. These filings are also electronically available from the Canadian System for Electronic Document Analysis and Retrieval (“SEDAR”) (http://www.sedar.com), the Canadian equivalent of the SEC’s electronic document gathering and retrieval system.
We “incorporate by reference” information that we file with the SEC, which means that we can disclose important information to you by referring you to those documents. The information incorporated by reference is an important part of this Form 20-F and more recent information automatically updates and supersedes more dated information contained or incorporated by reference in this Form 20-F.
As a foreign private issuer, we are exempt from the rules under the Exchange Act prescribing the furnishing and content of proxy statements to shareholders.
We will provide without charge to each person, including any beneficial owner, to whom a copy of this annual report has been delivered, on the written or oral request of such person, a copy of any or all documents referred to above which have been or may be incorporated by reference in this annual report (not including exhibits to such incorporated information that are not specifically incorporated by reference into such information). Requests for such copies should be directed to us at the following address:598 – 999 Canada Place, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada V6C 3E1, Telephone: (604) 638-5050, Facsimile: (604) 638-5051.
Not applicable.
ITEM 11. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
The Company is engaged primarily in mineral and oil and gas exploration and production and manages related industry risk issues directly. The Company may be at risk for environmental issues and fluctuations in commodity pricing. Management is not aware of and does not anticipate any significant environmental remediation costs or liabilities in respect of its current operations.
The Company’s functional currency is the Canadian dollar. The Company operates in foreign jurisdictions, giving rise to significant exposure to market risks from changes in foreign currency rates. The financial risk is the risk to the Company’s operations that arises from fluctuations in foreign exchange rates and the degree of volatility of these rates. Currently, the Company does not use derivative instruments to reduce its exposure to foreign currency risk.
The Company also has exposure to a number of risks from its use of financial instruments including: credit risk, liquidity risk, and market risk. This note presents information about the Company’s exposure to each of these risks and the Company’s objectives, policies and processes for measuring and managing risk, and the Company’s management of capital.
The Board of Directors has overall responsibility for the establishment and oversight of the Company’s risk management framework. The Board has implemented and monitors compliance with risk management policies. The Company’s risk management policies are established to identify and analyze the risks faced by the Company, to set appropriate risk limits and controls, and to monitor risks and adherence to market conditions and the Company’s activities.
Credit risk arises from credit exposure to receivables due from joint venture partners and marketers included in accounts receivable. The maximum exposure to credit risk is equal to the carrying value of the financial assets.
The Company is exposed to third party credit risk through its contractual arrangements with its current or future joint venture partners, marketers of its petroleum and natural gas production and other parties. In the event such entities fail to meet their contractual obligations to the Company, such failures may have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
The objective of managing the third party credit risk is to minimize losses in financial assets. The Company assesses the credit quality of the partners, taking into account their financial position, past experience, and other factors. The Company mitigates the risk of non-collection of certain amounts by obtaining the joint venture partners’ share of capital expenditures in advance of a project and by monitoring accounts receivable on a regular basis. As at December 31, 2011 and 2010, no accounts receivable has been deemed uncollectible or written off during the year.
As at December 31, 2011, the Company’s receivables consist of $64,583 (2010 - $195,514) from joint interest partners, $774,100 (2010 - $408,700) from oil and natural gas marketers and $48,498 (2010 - $84,412) from other trade receivables.
The Company considers all amounts outstanding for more than 90 days as past due. Currently, there is no indication that amounts are non-collectable; thus an allowance for doubtful accounts has not been set up. As at December 31, 2011, $5,787 (2010 - $152,056) of accounts receivable are past due, all of which are considered to be collectable.
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will not be able to meet its financial obligations as they become due. The Company’s approach to managing liquidity is to ensure, as far as possible, that it will have sufficient liquidity to meet its liabilities when due, under both normal and stressed conditions without incurring unacceptable losses or risking harm to the Company’s reputation.
As the industry in which the Company operates is very capital intensive, the majority of the Company’s spending is related to its capital programs. The Company prepares annual capital expenditure budgets, which are regularly monitored and updated as considered necessary. Further, the Company utilizes authorizations for expenditures on both operated and non-operated projects to further manage capital expenditures. To facilitate the capital expenditure program, the Company has a bank line of credit facility (note 8). The Company also attempts to match its payment cycle with collection of oil and natural gas revenues on the 25th of each month.
Accounts payable are considered due to suppliers in one year or less while the bridge loan was repaid in full during the year ended December 31, 2011. The bank line of credit, which is scheduled to be reviewed on or before May 1, 2012, is repayable upon demand.
Market risk is the risk that changes in market prices, such as foreign exchange rates, commodity prices, and interest rates will affect the Company’s net earnings. The objective of market risk management is to manage and control market risk exposures within acceptable limits, while maximizing returns. The Company utilizes financial derivatives to manage certain market risks. All such transactions are conducted in accordance with the risk management policy that has been approved by the Board of Directors.
| (d) | Foreign Currency Exchange Risk |
Foreign currency exchange rate risk is the risk that the fair value of financial instruments or future cash flows will fluctuate as a result of changes in foreign exchange rates. Although substantially all of the Company’s oil and natural gas sales are denominated in Canadian dollars, the underlying market prices in Canada for oil and natural gas are impacted by changes in the exchange rate between the Canadian and United States dollars. Given that changes in exchange rate have an indirect influence, the impact of changing exchange rates cannot be accurately quantified. The Company had no forward exchange rate contracts in place as at or during the year ended December 31, 2011 and 2010.
The Company was exposed to the following foreign currency risk at December 31, 2011:
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| Expressed in foreign currencies | | CND$ | | | CND$ | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 1,772,982 | | | | 601,519 | |
| Accounts receivable | | | 69,667 | | | | 168,770 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | | (1,346,564 | ) | | | (227,531 | ) |
| Balance sheet exposure | | | 496,085 | | | | 542,758 | |
The following foreign exchange rates applied for the year ended and as at December 31:
| | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| YTD average USD to CAD | | | 1.0170 | | | | 0.9946 | |
| December 31, 2011 | | | 0.9893 | | | | 1.0305 | |
The Company has performed a sensitivity analysis on its foreign currency denominated financial instruments. Based on the Company’s foreign currency exposure noted above and assuming that all other variables remain constant, a 10% appreciation of the US dollar against the Canadian dollar would result in the decrease of net loss of $49,609 at December 31, 2011 (2010 - $54,276). For a 10% depreciation of the above foreign currencies against the Canadian dollar, assuming all other variables remain constant, there would be an equal and opposite impact on net loss.
Interest rate risk is the risk that future cash flows will fluctuate as a result of changes in market interest rates. During the year ended December 31, 2011, interest rate fluctuations on the Company’s credit facility have no significant impact on its net loss because the Company had no floating rate debt in place at or during the year ended December 31, 2011. The Company had no interest rate swaps or financial contracts in place at or during the year ended December 31, 2011 and 2010.
Commodity price risk is the risk that the fair value of financial instruments or future cash flows will fluctuate as a result of changes in commodity prices. Commodity prices for oil and natural gas are impacted by world economic events that dictate the levels of supply and demand. The Company has attempted to mitigate commodity price risk on its future sales of crude oil through the use of financial derivative sales contracts.
With respect to the commodity contracts in place at December 31, 2011, an increase of US$10/barrel in the price of oil, assuming all other variables remain constant, would have positively impacted income before taxes by approximately $120,000 (2010 - $Nil). A similar decline in commodity prices would be an equal and opposite impact on income before taxes. The Company had no commodity contracts in place at December 31, 2010.
| (g) | Capital Management Strategy |
The Company’s policy on capital management is to maintain a prudent capital structure so as to maintain financial flexibility, preserve access to capital markets, maintain investor, creditor and market confidence, and to allow the Company to fund future developments. The Company considers its capital structure to include share capital, cash and cash equivalents, bank line of credit, and working capital. In order to maintain or adjust capital structure, the Company may from time to time issue shares or enter into debt agreements and adjust its capital spending to manage current and projected operating cash flows and debt levels.
The Company’s current borrowing capacity is based on the lender’s review of the Company’s oil and gas reserves. The Company is also subject to various covenants. Compliance with these covenants is monitored on a regular basis and at December 31, 2011, the Company is in compliance with all covenants.
The Company’s share capital is not subject to any external restrictions. The Company has not paid or declared any dividends, nor are any contemplated in the foreseeable future. There have been no changes to the Company’s capital management strategy during the year ended December 31, 2011.
ITEM 12. DESCRIPTION OF SECURITIES OTHER THAN EQUITY SECURITIES
A.-C.
Not applicable.
D. American Depositary Receipts
The Company does not have securities registered as American Depositary Receipts.
PART II
ITEM 13. DEFAULTS, DIVIDEND ARREARAGES AND DELINQUENCIES
None.
ITEM 14. MATERIAL MODIFICATIONS TO THE RIGHTS OF SECURITY HOLDERS AND USE OF PROCEEDS
A. – D.
None.
Not Applicable.
ITEM 15. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
| A. | Disclosure Controls and Procedures |
As of the end of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s “disclosure controls and procedures” (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), was performed by the Company’s management, under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer. Based on that evaluation, the Company’s CEO and CFO have concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were not effective to give reasonable assurance that the information required to be disclosed by the Company in reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is (i) recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and (ii) accumulated and communicated to management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
The reason that our management concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective is because a few submissions required to be furnished on Form 6-K were inadvertently filed late. The applicable information was filed on a timely basis with the Canadian securities regulators on SEDAR and was publicly accessible onwww.SEDAR.com and on the Company’s website, but was not timely furnished on Edgar on Form 6-K. We have taken steps designed to ensure that future information required to be furnished on Form 6-K will be so furnished on a timely basis.
| B. | Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting |
The Company’s management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over the Company’s internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards. It should be noted that a control system, no matter how well conceived or operated, can only provide reasonable assurance, not absolute assurance, that the objectives of the control system are met. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with policies and procedures may deteriorate.
The Company’s management, (with the participation of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and the Company’s Chief Financial Officer), conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2011. This evaluation was based on the criteria set forth in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on its assessment, management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2011, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective and management’s assessment did not identify material weaknesses.
| C. | Attestation Report of the Registered Public Accounting Firm |
Because the Company is not an “accelerated filer” or “large accelerated filer” within the meaning of such terms under the Exchange Act, this Annual Report is not required to include an attestation report of the Company’s independent auditors regarding the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
| D. | Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting |
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, the Company improved staff training and the review of financial statement close process and used 3rd party consulting assistance to address certain weaknesses in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that were identified in 2010.
ITEM 16. [RESERVED]
ITEM 16A. AUDIT COMMITTEE FINANCIAL EXPERT
The Company does not have any audit committee financial expert that serves on the Company’s audit committee. In 2011, the Company adopted the International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”), previously we prepared our financial statements in accordance with Canadian generally accepted accounting principles. The audit committee members do not yet have sufficient experience and in-depth of understanding of IFRS such that they meet the SEC definition of audit committee financial expert.
ITEM 16B. CODE OF ETHICS
The Board of Directors of the Company has adopted a Code of Conduct and Ethics that outlines the Company’s values and its commitment to ethical business practices in every business transaction. This code applies to all directors, officers, and employees of the Company and its subsidiaries and affiliates. A copy of the Company’s Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available on the Company’s website atwww.dejour.com.
Reporting Unethical and Illegal Conduct/Ethics Questions
The Company is committed to taking prompt action against violations of the Code of Conduct and Ethics and it is the responsibility of all directors, officers and employees to comply with the Code and to report violations or suspected violations to the Company’s Compliance Officer. Employees may also discuss their concerns with their supervisor who will then report suspected violations to the Compliance Officer.
The Compliance Officer is appointed by the Board of Directors and is responsible for investigating and resolving all reported complaints and allegations and shall advise the President and CEO, the CFO and/or the Audit Committee.
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, the Company did not substantially amend, waive, or implicitly waive any provision of the Code with respect to any of the directors, executive officers or employees subject to it.
ITEM 16C. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The following table sets out the fees billed to the Company by BDO Canada LLP for professional services rendered during fiscal years ended December 31, 2011 and December 31, 2010. During these years, BDO Canada LLP was our external auditors.
| | | Year ended
December 31, 2011 | | | Year ended
December 31, 2010 | |
| Audit Fees (1) | | $ | 152,639 | | | $ | 145,900 | |
| Audit Related Services(2) | | $ | 251,853 | | | $ | 49,680 | |
| Tax Fees(3) | | | Nil | | | | Nil | |
| All Other Fees(4) | | | 24,691 | | | | 5,534 | |
Notes:
| (1) | Audit fees consist of fees for the audit of the Company’s annual financial statements and review of the Company’s quarterly financial statements, or services that are normally provided in connection with statutory and regulatory filings or engagements. |
| (2) | Audit-related fees consist of fees for assurance and related services that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of the Company’s financial statements and are not reported as Audit fees. During fiscal 2011 and 2010, the services provided in this category included reviews on IFRS conversion, consultation on accounting and audit-related matters, and review of reserves disclosure. |
| (3) | Tax fees consist of fees for tax compliance services, tax advice and tax planning. During fiscal 2011 and 2010, the services provided in this category included assistance and advice in relation to the preparation of corporate income tax returns. |
| (4) | The services provided in this category included all other services fees that are not reported as other categories and consist of Canadian Public Accountability Board,, US gatekeeper review and administration fees. |
Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures
Generally, in the past, prior to engaging the Company’s auditors to perform a particular service, the Company’s audit committee has, when possible, obtained an estimate for the services to be performed. The audit committee in accordance with procedures for the Company approved all of the services described above.
In relation to the pre-approval of all audit and audit-related services and fees the Company’s audit committee charter provides that the audit committee shall:
Review and pre-approve all audit and audit-related services and the fees and other compensation related thereto, and any non-audit services, provided by the Company’s external auditors. The pre-approval requirement is waived with respect to the provision of non-audit services if:
| i. | the aggregate amount of all such non-audit services provided to the Company constitutes not more than five percent of the total amount of revenues paid by the Company to its external auditors during the fiscal year in which the non-audit services are provided; |
| ii. | such services were not recognized by the Company at the time of the engagement to be non-audit services; and |
| iii. | such services are promptly brought to the attention of the Committee by the Company and approved prior to the completion of the audit by the Committee or by one or more members of the Committee who are members of the Board to whom authority to grant such approvals has been delegated by the Committee. |
Provided the pre-approval of the non-audit services is presented to the Committee’s first scheduled meeting following such approval such authority may be delegated by the Committee to one or more independent members of the Committee.
We did not rely on the de minimus exemption provided by Section (c)(7)(i)(C) of Rule 2-01 of SEC Regulation S-X in 2011.
ITEM 16D. EXEMPTIONS FROM THE LISTING STANDARDS FOR AUDIT COMMITTEES
None.
ITEM 16E. PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES BY THE ISSUER AND AFFILIATED PERSONS
The Company did not repurchase any common shares in the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011.
ITEM 16F. CHANGE IN REGISTRANT’S CERTIFYING ACCOUNTANT
Effective on August 20, 2010, we terminated the services of our principal registered independent public accountant, Dale Matheson Carr-Hilton Labonte LLP (“DMCL”).
In DMCL’s principal accountant reports on our financial statements for each of the fiscal years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, no adverse opinion was issued and no opinion of DMCL was modified as to audit scope or accounting principles. No audit reports of DMCL in each of the past two fiscal years contained any adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion, or was qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope, or accounting principles.
The change in auditor was recommended and approved by our audit committee.
In the two most recent fiscal years and any interim period preceding the dismissal of DMCL, we are not aware of any disagreements with DMCL on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedure, which disagreement(s), if not resolved to the satisfaction of DMCL, would have caused it to make references to the subject matter of the disagreement(s) in connection with its report.
We are not aware of any reportable events (as set forth in Item 16F(a)(1)(v) of Form 20-F) that have occurred during the two most recent fiscal years and the interim period preceding the dismissal of DMCL.
On August 20, 2010, we engaged BDO Canada LLP (“BDO”) as its new principal registered independent accountant effective on August 20, 2010, to audit our financial records. BDO is registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board. During the two most recent fiscal years and the interim period preceding the appointment of BDO, we did not consult BDO regarding the application of accounting principles to a specified transaction, either completed or proposed; or the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on our financial statements, and neither a written report nor oral advice was provided to us that it considered an important factor in reaching a decision as to any accounting, auditing or financial reporting issue; or any matter that was either the subject of a disagreement (as defined in Item 16F(a)(1)(iv) of Form 20-F) or a reportable event (as described in Item 16F(a)(1)(v) of Form 20-F).
ITEM 16G. CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The Company’s common shares are listed on the NYSE Amex. Section 110 of the NYSE Amex Company Guide permits the NYSE Amex to consider the laws, customs and practices of foreign issuers in relaxing certain NYSE Amex listing criteria, and to grant exemptions from NYSE Amex listing criteria based on these considerations. A company seeking relief under these provisions is required to provide written certification from independent local counsel that the non-complying practice is not prohibited by home country law. A description of the significant ways in which the Company’s governance practices differ from those followed by domestic companies pursuant to NYSE Amex standards is as follows:
Shareholder Meeting Quorum Requirement: The NYSE Amex minimum quorum requirement for a shareholder meeting is one-third of the outstanding shares of common stock. In addition, a company listed on NYSE Amex is required to state its quorum requirement in its bylaws. The Company’s quorum requirement is set forth in its Articles and bylaws. A quorum for a meeting of members of the Company is one holder of common shares issued, outstanding and entitled to vote, represented in person or by proxy.
Proxy Delivery Requirement: NYSE Amex requires the solicitation of proxies and delivery of proxy statements for all shareholder meetings, and requires that these proxies shall be solicited pursuant to a proxy statement that conforms to SEC proxy rules. The Company is a “foreign private issuer” as defined in Rule 3b-4 under the Exchange Act, and the equity securities of the Company are accordingly exempt from the proxy rules set forth in Sections 14(a), 14(b), 14(c) and 14(f) of the Exchange Act. The Company solicits proxies in accordance with applicable rules and regulations in Canada.
Shareholder Approval Requirement:The Company will follow Toronto Stock Exchange rules for shareholder approval of new issuances of its common shares. Following Toronto Stock Exchange rules, shareholder approval is required for certain issuances of shares that: (i) materially affect control of the Company; or (ii) provide consideration to insiders in aggregate of 10% or greater of the market capitalization of the listed issuer and have not been negotiated at arm’s length. Shareholder approval is also required, pursuant to TSX rules, in the case of private placements: (x) for an aggregate number of listed securities issuable greater than 25% of the number of securities of the listed issuer which are outstanding, on a non-diluted basis, prior to the date of closing of the transaction if the price per security is less than the market price; or (y) that during any six month period are to insiders for listed securities or options, rights or other entitlements to listed securities greater than 10% of the number of securities of the listed issuer which are outstanding, on a non-diluted basis, prior to the date of the closing of the first private placement to an insider during the six month period.
The foregoing is consistent with the laws, customs and practices in Canada.
In addition, the Company may from time-to-time seek relief from NYSE Amex corporate governance requirements on specific transactions under Section 110 of the NYSE Amex Company Guide by providing written certification from independent local counsel that the non-complying practice is not prohibited by our home country law, in which case, the Company shall make the disclosure of such transactions available on the Company’s website at www.dejour.com. Information contained on its website is not part of this annual report.
ITEM 16H – MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE
Not Applicable.
PART III
ITEM 17. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Company has elected to provide financial statements pursuant to Item 18.
ITEM 18. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
On January 1, 2011, the Company adopted International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) for financial reporting purposes, using a transition date of January 1, 2010. The Company’s annual audited Consolidated Financial Statements for the year ended December 31, 2011, including 2010 required comparative information, have been prepared in accordance with IFRS, as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”) and interpretations of the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (“IFRIC”). Financial statements prior to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010 were prepared in accordance with Canadian generally accepted accounting principles (“Canadian GAAP”).
Our consolidated financial statements are included in this Annual Report beginning on page F-1.
ITEM 19. EXHIBITS
Financial Statements
| Description | | Page |
| | | |
| Consolidated Financial Statements for the Years Ended December 31, 2011 and 2010. | | F-1 - F-56 |
Supplementary Oil and Gas Reserve Estimation and Disclosures - Unaudited
Exhibit
Number | | Description |
| | | |
| 1.1 | | Articles (1) |
| 1.2 | | Notice of Articles (1) |
| 1.3 | | Certificate of Continuation (1) |
| 1.4 | | Notice of Alteration (1) |
| 1.5 | | Certificate of Name Change (1) |
| 1.6 | | Amendment to Articles to Include Special Rights (1) |
| 4.1 | | Participation Agreement between the Registrant, Retamco Operating, Inc. and Brownstone Ventures (US) dated July 14, 2006(3) |
| 4.2 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant, Retamco Operating, Inc., and Brownstone Ventures (US) Inc. dated June 17, 2008 (4) |
| 4.3 | | Loan Agreement between DEAL and HEC dated May 15, 2008 (5) |
| 4.4 | | Loan Agreement between the Company and HEC dated August 11, 2008 (5) |
| 4.5 | | Loan Agreement between the Company and HEC dated June 22, 2009 (5) |
| 4.6 | | Loan Agreement between the Company and Brownstone Ventures (US) Inc. dated June 22, 2009 (5) |
| 4.7 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and Pengrowth Corporation dated April 17, 2009 (5) |
| 4.8 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and John James Robinson dated June 10, 2009 (5) |
| 4.9 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and C.U. YourOilRig Corp. dated June 15, 2009 (5) |
| 4.10 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and Woodrush Energy Partners LLC dated July 8, 2009 (5) |
| 4.11 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and RockBridge Energy Inc. dated July 31, 2009 (5) |
| 4.12 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and HEC dated December 31, 2009 (5) |
| 4.13 | | Loan Agreement between the Registrant and Toscana Capital Corporation dated February 19, 2010 (6) |
| 4.14 | | Amended Loan Agreement between the Registrant and Toscana Capital Corporation dated September 1, 2010 (6) |
| 4.15 | | Credit Facility Agreement between DEAL and Canadian Western Bank dated August 3, 2011 (7) |
| 4.16 | | Credit Facility Renewal Letter between DEAL and Canadian Western Bank dated December 29, 2011 (7) |
Exhibit
Number | | Description |
| | | |
| 4.17 | | Option Plan (1) |
| 4.18 | | Option Plan (Sub-Plan) (1) |
| 8.1 | | List of Subsidiaries (7) |
| 12.1 | | Certification of CEO Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)* |
| 12.2 | | Certification of CFO Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)* |
| 13.1 | | Certification of CEO Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350* |
| 13.2 | | Certification of CFO Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350* |
| 15.1 | | Consent of BDO Canada LLP* |
| 15.2 | | Letter from Dale Matheson Carr-Hilton Labonte LLP (7) |
| 15.3 | | Consent Letter from AJM Deloitte, LLP* |
| 15.4 | | Consent Letter from Gustavson Associates* |
| 15.5 | | Consent Letter from GLJ Petroleum Consultants Ltd. (7) |
| 99.1 | | Reserve Estimation and Economic Evaluation of Dejour’s Canadian Oil and Gas Properties Prepared by AJM Deloitte, Effective December 31, 2011* |
| 99.2 | | Reserve Estimate and Financial Forecast as to Dejour’s Interests in the Kokopelli Field Area, Garfield County, Colorado, and the South Rangely Field Area, Rio Blanco County, Colorado Prepared by Gustavson Associates, Effective January 1, 2012* |
| 99.3 | | Reserves Assessment and Evaluation of Dejour’s Canadian Oil and Gas Properties Prepared by GLJ Petroleum Consultants Ltd., Effective December 31, 2010 (7) |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s registration statement on Form S-8, filed with the commission on February 16, 2012. |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F, filed July 14, 2006. |
| (3) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F/A amendment no. 2, filed December 7, 2007. |
| (4) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F, filed on June 30, 2009. |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F, filed on June 30, 2010. |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F, filed on June 30, 2011. |


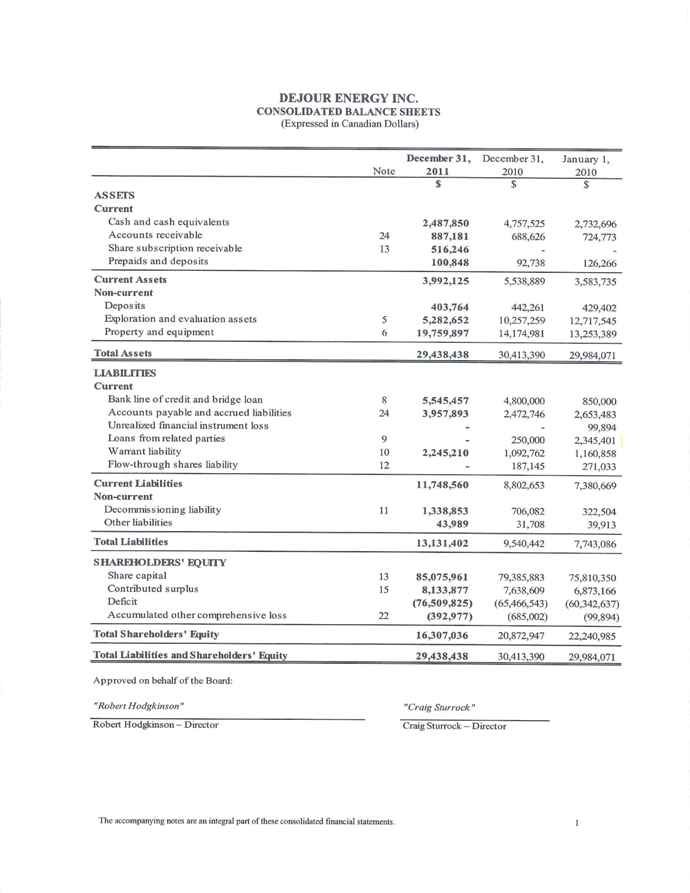


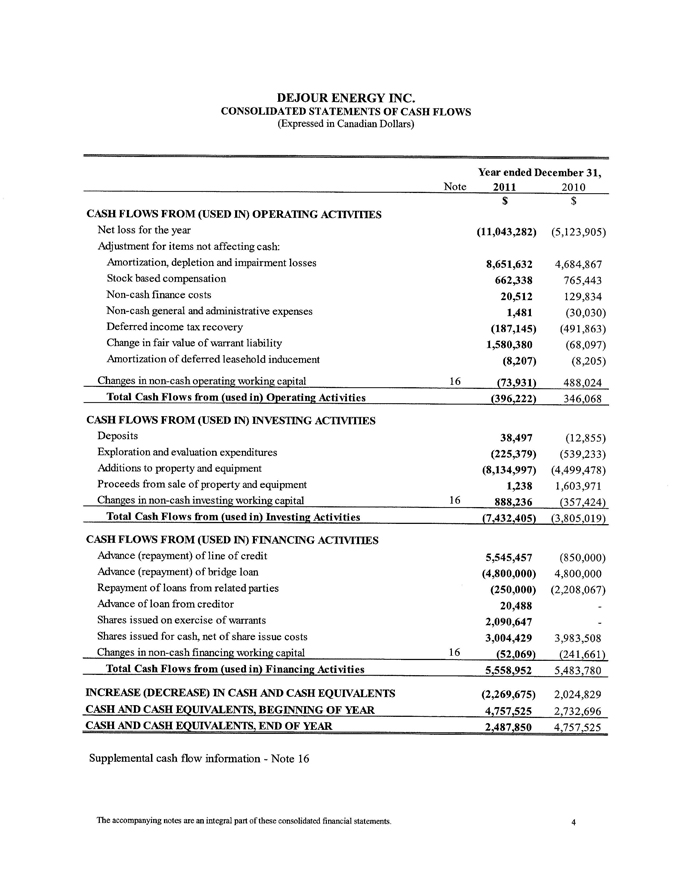

















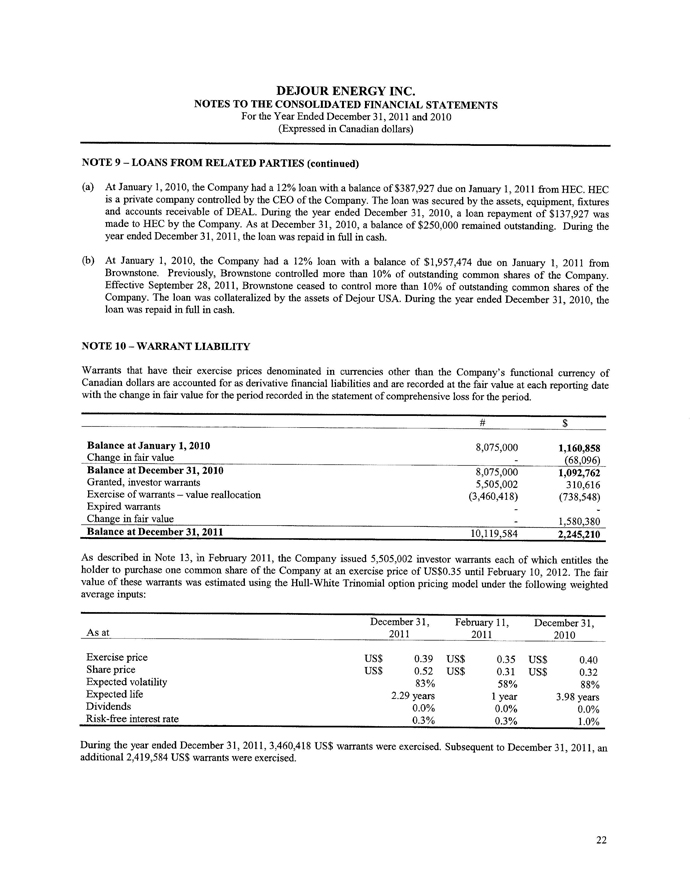
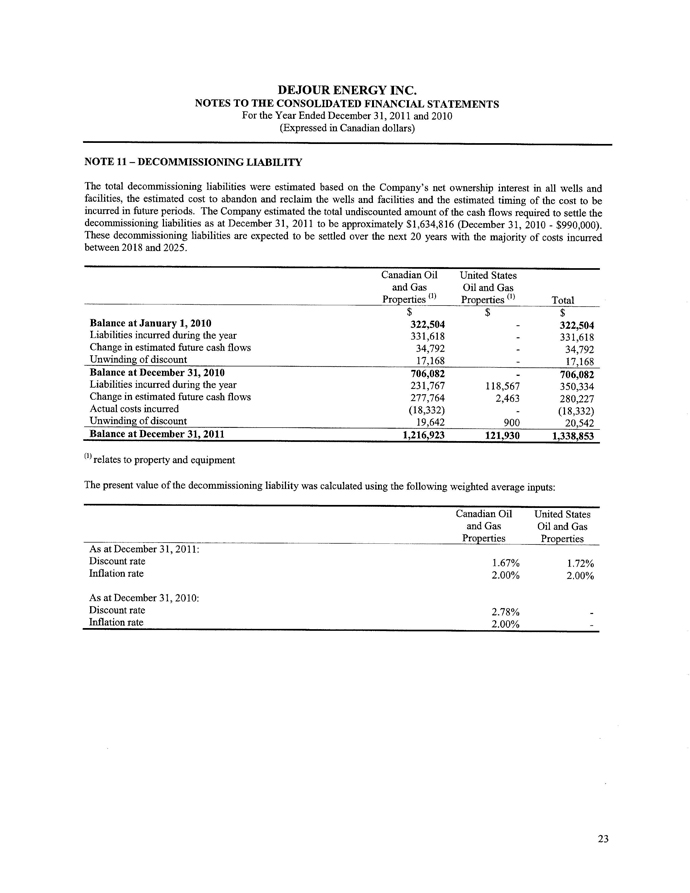
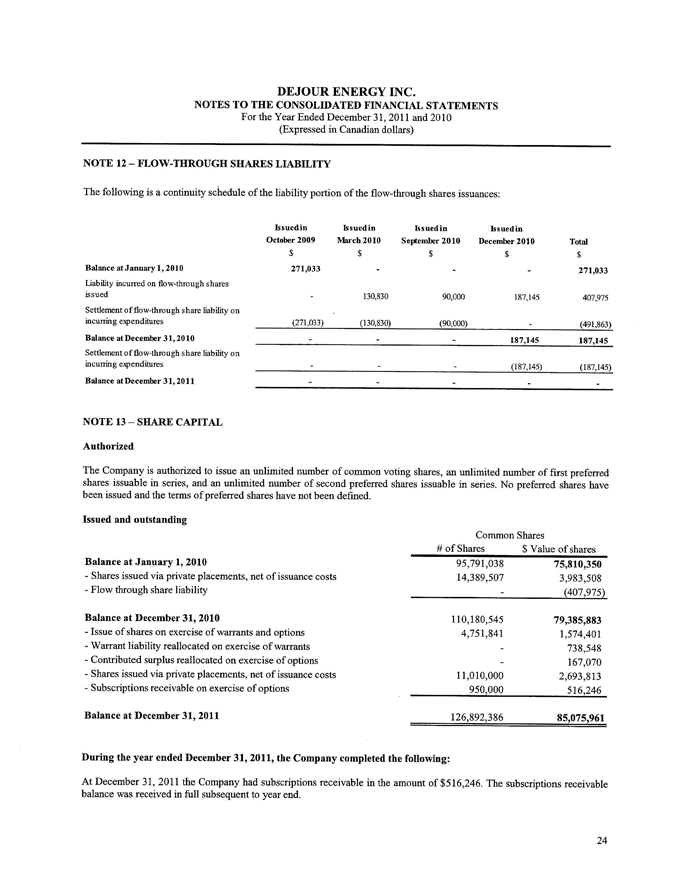


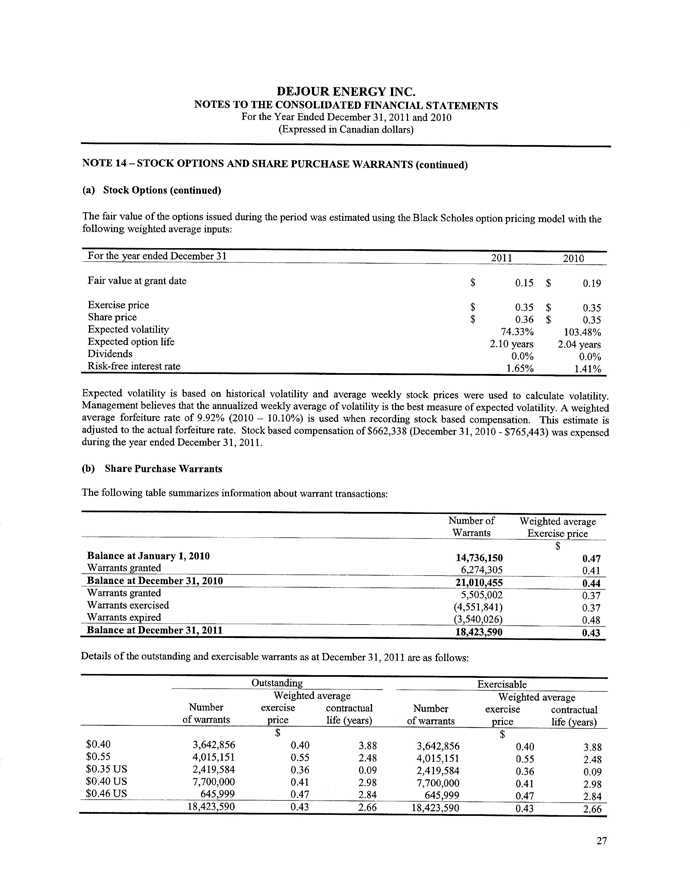
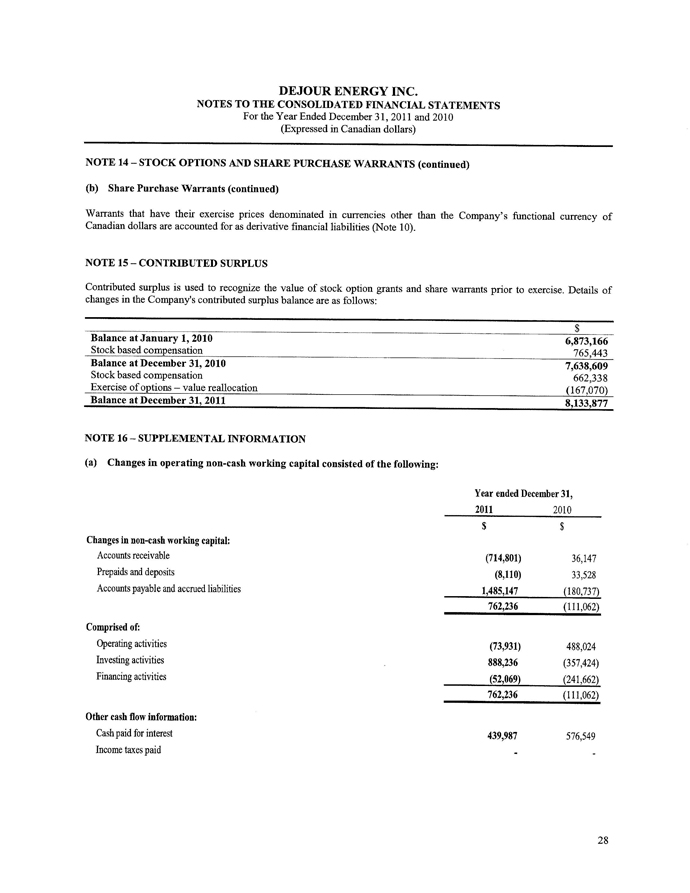


















SUPPLEMENTARY OIL AND GAS RESERVE ESTIMATION AND DISCLOSURES – ASC 932 (UNAUDITED)
Select supplementary oil and gas reserve estimation and disclosure are provided in accordance with U.S. disclosure requirements. The standards of the SEC require that proved reserves be estimated using existing economic conditions (constant pricing). Based on this methodology, the Company’s results have been calculated utilizing the 12-month average price for each of the years presented within this supplementary disclosure.
The Company’s 2011 and 2010 financial results were prepared in accordance with IFRS. As the Company’s IFRS transition date was January 1, 2010, 2009 results were prepared in accordance with Canadian GAAP.
The Company reports in Canadian currency and therefore the Reserves Data pertaining to the Company’s reserves in the United States set forth in the tables below has been converted to Canadian dollars at the prevailing conversion rate at December 31, 2011. The conversion rate used per Bank of Canada is 1.0170.
| (a) | Net proved oil and gas reserves |
As at December 31, 2011, the Company’s oil and gas reserves are located in both Canada and the United States.
In 2011, Deloitte & Touche LLP (“AJM Deloitte” or “AJM”) of Calgary, Alberta, independent petroleum engineering consultants based in Calgary, Alberta were retained by the Company to evaluate the Canadian properties of the Company. Their report, titled “Reserve Estimation and Economic Evaluation, Dejour Energy (Alberta) Ltd.”, is dated March 23, 2012 and has an effective date of December 31, 2011. In 2010, the Company engaged independent qualified reserve evaluators, GLJ Petroleum Consultants Ltd. (“GLJ”) to review the Company’s proved developed and undeveloped oil and gas reserves in Canada.
Gustavson Associates (“Gustavson”), an independent petroleum engineering consultants based in Denver, Colorado were retained by the Company to evaluate the US properties of the Company. Their report, titled “Reserve and Resources Evaluation Report, Dejour Energy (USA) Corp., Leasehold Uintah, Grand, and Emery Counties, Utah and Moffat, Rio Blanco, Garfield, Mesa, Delta, and Gunnison Counties, Colorado, USA” is dated February 15, 2012 and has an effective date of January 1, 2012.
In accordance with applicable securities laws, AJM Deloitte, and Gustavson Associates (“Gustavson”), have used both constant and forecast prices and costs in estimating the reserves and future net cash flows contained in their reports. Actual future net cash flows will be affected by other factors, such as actual production levels, supply and demand for oil and natural gas, curtailments or increases in consumption by oil and natural gas purchasers, changes in governmental regulation or taxation and the impact of inflation on costs.
The tables in this section set forth oil and gas information prepared by the Company in accordance with U.S. disclosure standards, including Accounting Standards Codification 932 (“ASC 932”). Reserves have been estimated in accordance with the US Securities and Exchange Commission’s (“SEC”) definitions and guidelines. The changes in our net proved reserve quantities are outlined below.
Net reserves are Dejour royalty and working interest remaining reserves, less all Crown, freehold, and overriding royalties and interests that are not owned by Dejour.
Proved reserves are those estimated quantities of crude oil, natural gas and natural gas liquids that can be estimated with a high degree of certainty to be economically recoverable under existing economic and operating conditions. It is likely that the actual remaining quantities recovered will exceed the estimated proved reserves.
Proved developed reserves are those reserves that are expected to be recovered from existing wells and installed facilities or, if facilities have not been installed, that would involve a low expenditure (e.g. when compared to the cost of drilling a well) to put the reserves on production. Developed reserves may be subdivided into producing and non-producing.
Proved undeveloped reserves are those reserves that are expected to be recovered from known accumulations where a significant expenditure (e.g. when compared to the cost of drilling a well) is required to render them capable of production.
The Company cautions users of this information as the process of estimating crude oil and natural gas reserves is subject to a level of uncertainty. The reserves are based on economic and operating conditions; therefore, changes can be made to future assessments as a result of a number of factors, which can include new technology, changing economic conditions and development activity.
| (a) | CONSTANT PRICES AND COSTS - YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2011 |
Net Proved Developed and
Proved Undeveloped Reserves
| | | Canada | | | United States | | | Total | |
| | | Light and | | | Natural Gas | | | | | | Barrels of Oil | | | | | | Natural Gas | | | | | | Barrels of Oil | | | Light and | | | | | | Natural Gas | | | | | | Barrels of Oil | |
| | | Medium Oil | | | Liquids | | | Natural Gas | | | Equivalent | | | Condensate | | | Liquids | | | Natural Gas | | | Equivalent | | | Medium Oil | | | Condensate | | | Liquids | | | Natural Gas | | | Equivalent | |
| | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (MMcf) | | | (Mboe) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (MMcf) | | | (Mboe) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (MMcf) | | | (Mboe) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2010 | | | 167 | | | | 4 | | | | 936 | | | | 327 | | | | 326 | | | | - | | | | 45,308 | | | | 7,877 | | | | 167 | | | | 326 | | | | 4 | | | | 46,244 | | | | 8,204 | |
| Discoveries | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 93 | | | | 1,078 | | | | 273 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 93 | | | | 1,078 | | | | 273 | |
| Extensions * | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Infill Drilling * | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Improved Recovery* | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Technical Revisions | | | 190 | | | | - | | | | (24 | ) | | | 186 | | | | (39 | ) | | | 3,770 | | | | (5,072 | ) | | | 2,885 | | | | 190 | | | | (39 | ) | | | 3,770 | | | | (5,096 | ) | | | 3,071 | |
| Dispositions | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Economic Factors | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Production | | | (40 | ) | | | - | | | | (160 | ) | | | (67 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (40 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (160 | ) | | | (67 | ) |
| December 31, 2011 | | | 317 | | | | 4 | | | | 752 | | | | 446 | | | | 287 | | | | 3,863 | | | | 41,314 | | | | 11,035 | | | | 317 | | | | 287 | | | | 3,867 | | | | 42,066 | | | | 11,481 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Developed | | | 317 | | | | 4 | | | | 752 | | | | 446 | | | | - | | | | 14 | | | | 158 | | | | 40 | | | | 317 | | | | - | | | | 18 | | | | 910 | | | | 486 | |
| Undeveloped | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 287 | | | | 3,849 | | | | 41,156 | | | | 10,995 | | | | - | | | | 287 | | | | 3,849 | | | | 41,156 | | | | 10,995 | |
| Total | | | 317 | | | | 4 | | | | 752 | | | | 446 | | | | 287 | | | | 3,863 | | | | 41,314 | | | | 11,035 | | | | 317 | | | | 287 | | | | 3,867 | | | | 42,066 | | | | 11,481 | |
| * | The above change categories correspond to standards set out in the Canadian Oil and Gas Evaluation Handbook. For reporting under NI 51-101, reserves additions under Infill Drilling, reserves additions under Infill Drilling, Improved Recovery and Extensions should be combined and reported as "Extensions and Improved Recovery" |
During 2011, proved undeveloped reserves for natural gas were decreased by 4,152 Mmcf, mainly due to decrease in natural gas in the Kokopelli (formerly Gibson Gulch) property from technical revision.
Also, in 2011, proved undeveloped reserves for natural gas liquids were increased by 3,849 Mbbl, mostly due to increase in natural gas liquids in the Kokopelli (formerly Gibson Gulch) property from technical revision.
In addition, the Company incurred approximately $7 million in expenditures mainly for development of undeveloped reserves to convert 92 Mbbl proved undeveloped reserves for oil into 243 Mbbl developed reserves in the Woodrush property.
CONSTANT PRICES AND COSTS - YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2010
Net Proved Developed and
Proved Undeveloped Reserves
| | | Canada | | | United States | | | Total | |
| | | Light and | | | Natural Gas | | | | | | Barrels of Oil | | | | | | | | | Barrels of Oil | | | Light and | | | | | | Natural Gas | | | | | | Barrels of Oil | |
| | | Medium Oil | | | Liquids | | | Natural Gas | | | Equivalent | | | Condensate | | | Natural Gas | | | Equivalent | | | Medium Oil | | | Condensate | | | Liquids | | | Natural Gas | | | Equivalent | |
| | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (MMcf) | | | (Mboe) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (MMcf) | | | (Mboe) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (Mbbl) | | | (MMcf) | | | (Mboe) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2009 | | | 98 | | | | 4 | | | | 753 | | | | 227 | | | | 397 | | | | 60,197 | | | | 10,430 | | | | 98 | | | | 397 | | | | 4 | | | | 60,950 | | | | 10,657 | |
| Discoveries | | | - | | | | - | | | | 195 | | | | 33 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 195 | | | | 33 | |
| Improved Recovery* | | | 66 | | | | - | | | | (19 | ) | | | 63 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 66 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (19 | ) | | | 63 | |
| Technical Revisions | | | 70 | | | | 2 | | | | 654 | | | | 181 | | | | (71 | ) | | | (14,889 | ) | | | (2,553 | ) | | | 70 | | | | (71 | ) | | | 2 | | | | (14,235 | ) | | | (2,372 | ) |
| Dispositions | | | - | | | | - | | | | (59 | ) | | | (10 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (59 | ) | | | (10 | ) |
| Economic Factors | | | - | | | | - | | | | (69 | ) | | | (12 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (69 | ) | | | (12 | ) |
| Production | | | (67 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | (519 | ) | | | (155 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (67 | ) | | | - | | | | (2 | ) | | | (519 | ) | | | (155 | ) |
| December 31, 2010 | | | 167 | | | | 4 | | | | 936 | | | | 327 | | | | 326 | | | | 45,308 | | | | 7,877 | | | | 167 | | | | 326 | | | | 4 | | | | 46,244 | | | | 8,204 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Developed | | | 74 | | | | 4 | | | | 955 | | | | 238 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 74 | | | | - | | | | 4 | | | | 955 | | | | 238 | |
| Undeveloped | | | 93 | | | | - | | | | (19 | ) | | | 89 | | | | 326 | | | | 45,308 | | | | 7,877 | | | | 93 | | | | 326 | | | | - | | | | 45,289 | | | | 7,966 | |
| Total | | | 167 | | | | 4 | | | | 936 | | | | 327 | | | | 326 | | | | 45,308 | | | | 7,877 | | | | 167 | | | | 326 | | | | 4 | | | | 46,244 | | | | 8,204 | |
| * | The above change categories correspond to standards set out in the Canadian Oil and Gas Evaluation Handbook. For reporting under NI 51-101, reserves additions under Infill Drilling, reserves additions under Infill Drilling, Improved Recovery and Extensions should be combined and reported as "Extensions and Improved Recovery" |
| As at December 31, | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| | | (Per IFRS) | | | (As Restated under IFRS) | | | (Per US GAAP) | |
| Canada | | | | | | | | | |
| Proved oil and gas properties | | $ | 23,149,485 | | | $ | 16,191,797 | | | $ | 17,535,742 | |
| Unproved oil and gas properties | | | 71,552 | | | | 41,060 | | | | 9,047,242 | |
| Total capital costs | | | 23,221,037 | | | | 16,232,857 | | | | 26,582,984 | |
| Accumulated depletion and depreciation | | | (5,819,933 | ) | | | (3,453,777 | ) | | | (7,691,609 | ) |
| Impairment | | | (1,298,207 | ) | | | (360,268 | ) | | | (16,016,752 | ) |
| Net capitalized costs | | $ | 16,102,897 | | | $ | 12,418,812 | | | $ | 2,874,623 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| United States | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proved oil and gas properties | | $ | 4,075,774 | | | $ | 1,695,655 | | | $ | 266,048 | |
| Unproved oil and gas properties | | | 27,772,327 | | | | 27,500,879 | | | | 28,350,076 | |
| Total capital costs | | | 31,848,101 | | | | 29,196,534 | | | | 28,616,124 | |
| Impairment | | | (23,524,342 | ) | | | (17,807,885 | ) | | | (500,866 | ) |
| Net capitalized costs | | $ | 8,323,759 | | | $ | 11,388,649 | | | $ | 28,115,258 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proved oil and gas properties | | $ | 27,225,259 | | | $ | 17,887,452 | | | $ | 17,801,790 | |
| Unproved oil and gas properties | | | 27,843,879 | | | | 27,541,939 | | | | 37,397,318 | |
| Total capital costs | | | 55,069,138 | | | | 45,429,391 | | | | 55,199,108 | |
| Accumulated depletion and depreciation | | | (5,819,933 | ) | | | (3,453,777 | ) | | | (7,691,609 | ) |
| Impairment | | | (24,822,549 | ) | | | (18,168,153 | ) | | | (16,517,618 | ) |
| Net capitalized costs | | $ | 24,426,656 | | | $ | 23,807,461 | | | $ | 30,989,881 | |
| Note: | Capitalized costs were disclosed under US GAAP as of December 31, 2010 and 2009. Effective January 1, 2011, the Company has adopted IFRS. Therefore, 2010 figures were restated under IFRS. |
| For the years ended December 31 | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| | | (Per IFRS) | | | (As Restated under IFRS) | | | (Per US GAAP) | |
| Canada | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property acquisition costs (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proved oil and gas properties | | $ | 47,158 | | | $ | 10,659 | | | $ | 434,434 | |
| Unproved oil and gas properties | | | 8,548 | | | | 26,601 | | | | - | |
| Exploration costs (2) | | | 32,482 | | | | 60,856 | | | | 1,626,120 | |
| Development costs (3) | | | 6,410,244 | | | | 4,121,724 | | | | - | |
| Capital Expenditures | | $ | 6,498,432 | | | $ | 4,219,840 | | | $ | 2,060,554 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Unite d States | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property acquisition costs (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proved oil and gas properties | | $ | 40,143 | | | $ | 14,640 | | | $ | 32,122 | |
| Unproved oil and gas properties | | | 146,062 | | | | 220,937 | | | | 161,770 | |
| Exploration costs (2) | | | 38,287 | | | | 556,347 | | | | 19,186 | |
| Development costs (3) | | | 1,608,585 | | | | - | | | | 313,577 | |
| Capital Expenditures | | $ | 1,833,077 | | | $ | 791,924 | | | $ | 526,655 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property acquisition costs (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proved oil and gas properties | | $ | 87,301 | | | $ | 25,299 | | | $ | 466,556 | |
| Unproved oil and gas properties | | | 154,610 | | | | 247,538 | | | | 161,770 | |
| Exploration costs (2) | | | 70,769 | | | | 617,203 | | | | 1,645,306 | |
| Development costs (3) | | | 8,018,829 | | | | 4,121,724 | | | | 313,577 | |
| Capital Expenditures | | $ | 8,331,509 | | | $ | 5,011,764 | | | $ | 2,587,209 | |
| (1) | Acquisitions are not net of disposition of properties. |
| (2) | Geological and geophysical capital expenditures and drilling costs for exploraton wells drilled |
| (3) | Includes equipping and facilities capital expenditures |
| (d) | Results of Operations of Producing Activities |
| For the years ended December 31 | | 2011 | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| | | (IFRS) | | | (IFRS) | | | (US GAAP) | |
| Canada | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oil and gas sales, net of royalties and commodity contracts | | $ | 7,196,464 | | | $ | 6,773,860 | | | $ | 6,216,519 | |
| Operating costs and capital taxes | | | (1,975,294 | ) | | | (2,101,046 | ) | | | (2,503,571 | ) |
| Transportation costs | | | (507,959 | ) | | | (507,843 | ) | | | (411,432 | ) |
| Depletion, depreciation and accretion | | | (2,392,870 | ) | | | (3,485,186 | ) | | | (3,673,382 | ) |
| Income taxes (1) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Results of operations | | $ | 2,320,341 | | | $ | 679,785 | | | $ | (371,866 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| United States | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oil and gas sales, net of royalties and commodity contracts | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| Operating costs and capital taxes | | | (16,227 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Transportation costs | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Depletion, depreciation and accretion | | | (10,483 | ) | | | (7,518 | ) | | | (9,099 | ) |
| Income taxes (1) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Results of operations | | $ | (26,710 | ) | | $ | (7,518 | ) | | $ | (9,099 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Oil and gas sales, net of royalties and commodity contracts | | $ | 7,196,464 | | | $ | 6,773,860 | | | $ | 6,216,519 | |
| Lease operating costs and capital taxes | | | (1,991,521 | ) | | | (2,101,046 | ) | | | (2,503,571 | ) |
| Transportation costs | | | (507,959 | ) | | | (507,843 | ) | | | (411,432 | ) |
| Depletion, depreciation and accretion | | | (2,403,353 | ) | | | (3,492,704 | ) | | | (3,682,481 | ) |
| Income taxes (1) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Results of operations | | $ | 2,293,631 | | | $ | 672,267 | | | $ | (380,965 | ) |
(1) Dejour is currently not taxable.
| (e) | Standardized Measure of Discounted Future Net Cash Flows and Changes Therein |
The standardized measure of discounted future net cash flows is based on estimates made by AJM Deloitte (2010 by GLJ) and Gustavson of net proved reserves. Future cash inflows are computed based on the average of the first day constant prices in each of the 12 months for the year ended December 31, 2011 and cost assumptions applied against annual future production from proved crude oil and natural gas reserves. Future development and production costs are computed based on the average of the first day constant prices in each of the 12 months for the year ended December 31, 2011 and assume the continuation of existing economic conditions. Future income taxes are calculated by applying statutory income tax rates. The Company is currently not taxable. The standardized measure of discounted future net cash flows is computed using a 10 percent discount factor.
The Company cautions users of this information that the discounted future net cash flows relating to proved oil and gas reserves are neither an indication of the fair market value of our oil and gas properties, nor of the future net cash flows expected to be generated from such properties. The discounted future cash flows do not include the fair market value of exploratory properties and probable or possible oil and gas reserves, nor is consideration given to the effect of anticipated future changes in crude oil and natural gas prices, development, asset retirement and production costs and possible changes to tax and royalty regulations. The prescribed discount rate of 10 percent is arbitrary and may not appropriately reflect future interest rates.
Standardized Measure of Discounted Future Net Cash Flows
| As at December 31, 2011 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands of Canadian dollars) | | Canada | | | USA | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Future cash from revenues after royalties | | $ | 32,005 | | | $ | 298,776 | | | $ | 330,781 | |
| Future production costs | | | (10,900 | ) | | | (72,833 | ) | | | (83,733 | ) |
| Future development costs | | | (150 | ) | | | (88,377 | ) | | | (88,527 | ) |
| Future income taxes | | | (931 | ) | | | - | | | | (931 | ) |
| Future net cash flows | | | 20,024 | | | | 137,566 | | | | 157,590 | |
| Less: 10% annual discount factor | | | (1,565 | ) | | | (104,104 | ) | | | (105,669 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Standardized measure of discounted future net cash flow | | $ | 18,459 | | | $ | 33,462 | | | $ | 51,921 | |
| As at December 31, 2010 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands of Canadian dollars) | | Canada | | | USA | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Future cash from revenues after royalties | | $ | 15,777 | | | $ | 228,318 | | | $ | 244,095 | |
| Future production costs | | | (8,833 | ) | | | (44,116 | ) | | | (52,949 | ) |
| Future development costs | | | (3,172 | ) | | | (79,711 | ) | | | (82,883 | ) |
| Future income taxes | | | - | | | | (15,982 | ) | | | (15,982 | ) |
| Future net cash flows | | | 3,772 | | | | 88,509 | | | | 92,281 | |
| Less: 10% annual discount factor | | | (841 | ) | | | (62,561 | ) | | | (63,402 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Standardized measure of discounted future net cash flow | | $ | 2,931 | | | $ | 25,948 | | | $ | 28,879 | |
| (f) | Changes in Standardized Measure of Discounted Future Net Cash Flows |
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2011 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands of Canadian dollars) | | Canada | | | USA | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Present Value At 10% , January 1, 2011 | | $ | 2,931 | | | $ | 25,948 | | | $ | 28,879 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and transfers of oil and gas produced, net of production costs | | | (4,713 | ) | | | - | | | | (4,713 | ) |
| Net changes in prices, production costs and royalties | | | 3,143 | | | | (25,191 | ) | | | (22,048 | ) |
| Extensions, discovery, less related costs | | | - | | | | 840 | | | | 840 | |
| Development costs incurred during the period | | | 6,410 | | | | - | | | | 6,410 | |
| Revisions of previous quantity estimates | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Accretion of discount | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Net change in income taxes | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Changes resuling from technical revisions and others | | | 10,688 | | | | 31,865 | | | | 42,553 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Present Value At 10%, December 31, 2011 | | $ | 18,459 | | | $ | 33,462 | | | $ | 51,921 | |
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2010 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands of Canadian dollars) | | Canada | | | USA | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Present Value At 10% , January 1, 2010 | | $ | 2,113 | | | $ | 14,272 | | | $ | 16,385 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and transfers of oil and gas produced, net of production costs | | | (4,169 | ) | | | - | | | | (4,169 | ) |
| Net changes in prices, production costs and royalties | | | 1,259 | | | | 13,548 | | | | 14,807 | |
| Extensions, discovery, less related costs | | | 700 | | | | - | | | | 700 | |
| Development costs incurred during the period | | | 3,179 | | | | - | | | | 3,179 | |
| Revisions of previous quantity estimates | | | 1,565 | | | | (1,106 | ) | | | 459 | |
| Accretion of discount | | | 211 | | | | - | | | | 211 | |
| Net change in income taxes | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Other | | | (1,927 | ) | | | (766 | ) | | | (2,693 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Present Value At 10% , December 31, 2010 | | $ | 2,931 | | | $ | 25,948 | | | $ | 28,879 | |
SIGNATURES
The registrant hereby certifies that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form 20-F and that it has duly caused and authorized the undersigned to sign this annual report on its behalf.
| | | | DEJOUR Energy Inc. |
| | | | |
| Dated: | 2013 | | |
| | | | Robert L. Hodgkinson |
| | | | Chairman & CEO |
EXHIBIT INDEX
Exhibit
Number | | Description |
| 1.1 | | Articles (1) |
| 1.2 | | Notice of Articles (1) |
| 1.3 | | Certificate of Continuation (1) |
| 1.4 | | Notice of Alteration (1) |
| 1.5 | | Certificate of Name Change (1) |
| 1.6 | | Amendment to Articles to Include Special Rights (1) |
| 4.1 | | Participation Agreement between the Registrant, Retamco Operating, Inc. and Brownstone Ventures (US) dated July 14, 2006(3) |
| 4.2 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant, Retamco Operating, Inc., and Brownstone Ventures (US) Inc. dated June 17, 2008 (4) |
| 4.3 | | Loan Agreement between DEAL and HEC dated May 15, 2008 (5) |
| 4.4 | | Loan Agreement between the Company and HEC dated August 11, 2008 (5) |
| 4.5 | | Loan Agreement between the Company and HEC dated June 22, 2009 (5) |
| 4.6 | | Loan Agreement between the Company and Brownstone Ventures (US) Inc. dated June 22, 2009 (5) |
| 4.7 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and Pengrowth Corporation dated April 17, 2009 (5) |
| 4.8 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and John James Robinson dated June 10, 2009 (5) |
| 4.9 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and C.U. YourOilRig Corp. dated June 15, 2009 (5) |
| 4.10 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and Woodrush Energy Partners LLC dated July 8, 2009 (5) |
| 4.11 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and RockBridge Energy Inc. dated July 31, 2009 (5) |
| 4.12 | | Purchase and Sale Agreement between the Registrant and HEC dated December 31, 2009 (5) |
| 4.13 | | Loan Agreement between the Registrant and Toscana Capital Corporation dated February 19, 2010 (6) |
| 4.14 | | Amended Loan Agreement between the Registrant and Toscana Capital Corporation dated September 1, 2010 (6) |
| 4.15 | | Credit Facility Agreement between DEAL and Canadian Western Bank dated August 3, 2011 (7) |
| 4.16 | | Credit Facility Renewal Letter between DEAL and Canadian Western Bank dated December 29, 2011 (7) |
| 4.17 | | Option Plan (1) |
| 4.18 | | Option Plan (Sub-Plan) (1) |
| 8.1 | | List of Subsidiaries (7) |
| 12.1 | | Certification of CEO Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)* |
| 12.2 | | Certification of CFO Pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)* |
| 13.1 | | Certification of CEO Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350* |
Exhibit
Number | | Description |
| | | |
| 13.2 | | Certification of CFO Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350* |
| 15.1 | | Consent of BDO Canada LLP* |
| 15.2 | | Letter from Dale Matheson Carr-Hilton Labonte LLP (7) |
| 15.3 | | Consent Letter from AJM Deloitte, LLP* |
| 15.4 | | Consent Letter from Gustavson Associates* |
| 15.5 | | Consent Letter from GLJ Petroleum Consultants Ltd. (7) |
| 99.1 | | Reserve Estimation and Economic Evaluation of Dejour’s Canadian Oil and Gas Properties Prepared by AJM Deloitte, Effective December 31, 2011* |
| 99.2 | | Reserve Estimate and Financial Forecast as to Dejour’s Interests in the Kokopelli Field Area, Garfield County, Colorado, and the South Rangely Field Area, Rio Blanco County, Colorado Prepared by Gustavson Associates, Effective January 1, 2012* |
| 99.3 | | Reserves Assessment and Evaluation of Dejour’s Canadian Oil and Gas Properties Prepared by GLJ Petroleum Consultants Ltd., Effective December 31, 2010 (7) |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s registration statement on Form S-8, filed with the commission on February 16, 2012. |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F, filed July 14, 2006. |
| (3) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F/A amendment no. 2, filed December 7, 2007. |
| (4) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F, filed on June 30, 2009. |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F, filed on June 30, 2010. |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s annual report on Form 20-F, filed on June 30, 2011. |
Exhibit 12.1
CERTIFICATION
I, Robert L. Hodgkinson, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on Form 20-F of Dejour Energy Inc.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the company as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The company’s other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the company and have:
(a) Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the company, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards;
(c) Evaluated the effectiveness of the company’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed in this report any change in the company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the company’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5. The company’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the company’s auditors and the audit committee of the company’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the company’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the company’s internal control over financial reporting.
| Date: __________, 2013 | | |
| | | Robert L. Hodgkinson |
| | | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
| | | Principal Executive Officer |
Exhibit 12.2
CERTIFICATION
I, Mathew Wong, certify that:
1. I have reviewed this annual report on Form 20-F of Dejour Energy Inc.;
2. Based on my knowledge, this report does not contain any untrue statement of a material fact or omit to state a material fact necessary to make the statements made, in light of the circumstances under which such statements were made, not misleading with respect to the period covered by this report;
3. Based on my knowledge, the financial statements, and other financial information included in this report, fairly present in all material respects the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the company as of, and for, the periods presented in this report;
4. The company’s other certifying officer(s) and I are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) and internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) for the company and have:
(a) Designed such disclosure controls and procedures, or caused such disclosure controls and procedures to be designed under our supervision, to ensure that material information relating to the company, including its consolidated subsidiaries, is made known to us by others within those entities, particularly during the period in which this report is being prepared;
(b) Designed such internal control over financial reporting, or caused such internal control over financial reporting to be designed under our supervision, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards;
(c) Evaluated the effectiveness of the company’s disclosure controls and procedures and presented in this report our conclusions about the effectiveness of the disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this report based on such evaluation; and
(d) Disclosed in this report any change in the company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by the annual report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the company’s internal control over financial reporting; and
5. The company’s other certifying officer(s) and I have disclosed, based on our most recent evaluation of internal control over financial reporting, to the company’s auditors and the audit committee of the company’s board of directors (or persons performing the equivalent functions):
(a) All significant deficiencies and material weaknesses in the design or operation of internal control over financial reporting which are reasonably likely to adversely affect the company’s ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information; and
(b) Any fraud, whether or not material, that involves management or other employees who have a significant role in the company’s internal control over financial reporting.
| Date: ___________, 2013 | | |
| | | |
| | | Mathew Wong |
| | | Chief Financial Officer |
| | | Principal Accounting and Financial Officer |
Exhibit 13.1
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO
18 U.S.C. §1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the annual report of Dejour Energy Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 20-F for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Robert Hodgkinson, Chief Executive Officer of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. §1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to the best of my knowledge:
(1) The Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2) The information contained in this Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
| | |
| | |
| | Robert Hodgkinson |
| | Chief Executive Officer |
| | Principal Executive Officer |
| | _____________, 2013 |
A signed original of this written statement required by Section 906 has been provided to the Company and will be retained by the Company and furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission or its staff upon request. The foregoing certification is being furnished solely pursuant to 18 U.S.C. §1350 and is not being filed as part of the annual report or as a separate disclosure document.
Exhibit 13.2
CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO
18 U.S.C. §1350,
AS ADOPTED PURSUANT TO
SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002
In connection with the annual report of Dejour Energy Inc. (the “Company”) on Form 20-F for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on the date hereof (the “Report”), I, Mathew Wong, Chief Financial Officer of the Company, certify, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. §1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, that to the best of my knowledge:
(1) The Report fully complies with the requirements of Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934; and
(2) The information contained in this Report fairly presents, in all material respects, the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
| | |
| | |
| | Mathew Wong |
| | Chief Financial Officer |
| | Principal Accounting and Financial Officer |
| | _____________, 2013 |
A signed original of this written statement required by Section 906 has been provided to the Company and will be retained by the Company and furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission or its staff upon request. The foregoing certification is being furnished solely pursuant to 18 U.S.C. §1350 and is not being filed as part of the annual report or as a separate disclosure document.