As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 26, 2008
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 20-F
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d)
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended: December 31, 2007
Commission file number: 000-51490
CONTAX PARTICIPAÇÕES S.A.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter)
| | | |
| Contax Holding Company | | The Federative Republic of Brazil |
| (Translation of Registrant’s Name into English) | | (Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) |
Rua do Passeio 56, 16º andar (parte)
20021-290 Rio de Janeiro – RJ – Brazil
(Address of principal executive offices)
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None
Securities registered or to be registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
| | | |
| Title of Each Class | | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
| | | |
| Preferred Shares, without par value (“preferred shares”) | | Bovespa |
| Common Shares, without par value (“common shares”) | | Bovespa |
Securities for which there is a reporting obligation pursuant to Section 15(d) of the Act:None
The number of outstanding shares of each of the Issuer’s classes of capital, common or preferred stock, as of the close of the period covered by the annual report was:
10,031,914 preferred shares
5,824,772 common shares
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yeso Noþ
If this report is an annual or transition report, indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Yeso Noþ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yesþ Noo
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, or a non-accelerated filer. See definition of “accelerated filer and large accelerated filer” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large accelerated filero Non-accelerated filero Accelerated filerþ
Indicate by check mark which basis of accounting the registrant has used to prepare the financial statements included in this filing:
| | | | | |
| | | International Financial Reporting Standards as | | |
| | | issued by the International Accounting | | |
| U.S. GAAPo | | Standards Boardo | | Otherþ |
If “Other” has been checked in response to the previous question, indicate by check mark which financial statement item the registrant has elected to follow. Item 17o Item 18þ
If this is an annual report, indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell Company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yeso Noþ
PRESENTATION OF INFORMATION
Contax Participações S.A is a corporation (sociedade por ações) incorporated under Brazilian corporate law. We operate pursuant to our by-laws, other legislation and regulations in Brazil and, where applicable, local legislation. Our principal executive office is located at Rua do Passeio, 56, 16º andar (parte), 20021-290 Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, and the telephone number at that office is +55 21 3131-0274.
In this annual report on Form 20-F, except where otherwise specified, the “Company,” “we,” “us,” “our” and “Contax” refer to Contax Participações S.A. and its operational subsidiary, TNL Contax S.A. References to Contax Holding refer only to Contax Participações S.A., and do not include TNL Contax S.A. References to TNL Contax refer only to TNL Contax S.A., and do not include Contax Holding. References to the Company’s businesses and operations are references to the businesses and operations of its subsidiary TNL Contax S.A.
Our previous majority shareholder, Telemar Participações S.A., is referred to as Telemar Participações. On April 25, 2008, negotiations relating to the restructuring of the ownership structure of Telemar Participações were concluded. One of the results was the approval of the partial spin-off of Telemar Participações, with the transfer of its shareholders’ equity related to the shares issued by Contax to a new company created especially for this purpose denominated CTX Participações S.A. (“CTX Participações”).
Our two main clients are Telemar Norte Leste S.A., or Tmar, and its subsidiary TNL PCS S.A., or Oi, both of which are indirectly under common control with us and are jointly referred to as “Telemar.” Recently, Telemar adopted the commercial name “Oi” for its fixed line terminals, long-distance services, mobile services, as well as broadband and corporated voice and data service operations. The parent company of Tmar is Tele Norte Leste Participações S.A., or TNL, which was our majority shareholder before our spin-off to the shareholders of TNL. See “Item 4. Information on the Company – Corporate Reorganization.”
References to “U.S. dollars,” “U.S.$” or “$” are to the lawful currency of the United States, and references to “real,” “reais” or “R$” are to the lawful currency of Brazil. Any discrepancies in tables between totals and sums of the amounts listed are due to rounding.
This annual report is presented inreais. On December 31, 2007, the commercial selling rate forreaiswas R$1.7713 to U.S.$1.00. However, for the convenience of the reader and given the dates of the financial statements, some real amounts presented throughout this document have been translated into U.S.$ at the commercial market rate forreaisin effect as of June 16, 2008, which was at R$1.6277 to U.S.$1.00.
References in this annual report to “preferred shares” and “common shares” are to the preferred shares and common shares, respectively, of Contax Holding and collectively referred to as the “shares.” References to “American Depositary Shares” or “ADSs” are to American Depositary Shares, each representing one preferred share. The ADSs are evidenced by American Depositary Receipts, or ADRs.
References to “Consolidated Financial Statements” are to the consolidated financial statements of Contax as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 and for the three years in the period ended December 31, 2007.
Contax Holding became the parent company of TNL Contax in November 2004. This transaction has been accounted for, at historical cost, as a merger of entities under common control. In order to present the financial statements in a format that is comparable from year to year and represents the business of Contax Holding and its subsidiary going forward, the financial information of these companies was combined for all periods presented. See “Item 4. Information on the Company – Corporate Reorganization”.
We have prepared our Consolidated Financial Statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States, or U.S. GAAP.
3
We publish financial statements in Brazil in accordance with Brazilian corporate law, specifically Law no. 6,404, as amended, and the rules and regulations of theComissão de Valores Mobiliários, or the CVM, the Brazilian Securities Commission, and, referred to herein as “Brazilian GAAP.” Brazilian GAAP when applied to us differs in certain significant respects from U.S. GAAP.
We are subject to the informational requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or the Exchange Act, as amended, and we file reports and other information with the SEC. However, as a foreign private issuer, we are exempt from the proxy rules of Section 14 and the short-swing profit rules of Section 16 under the Exchange Act.
Certain terms are defined the first time they are used in this annual report.
4
FORWARD-LOOKING INFORMATION
This annual report contains forward-looking statements. We may also make forward-looking statements in press releases and oral statements. Statements that are not statements of historical fact, including statements about our management’s beliefs and expectations are forward-looking statements. All forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties. Many of the forward-looking statements contained in this annual report are identified by the use of forward-looking words such as “anticipate,” “forecast,” “believe,” “could,” “expect,” “should,” “plan,” “estimate,” “intend,” “predict,” “target,” and “potential,” among others. These statements appear in a number of places in this annual report and include statements regarding our intent, belief or current expectations with respect to, among other things:
| | • | | the growth in the Brazilian outsourcing contact center sector; and |
| |
| | • | | the performance of the Brazilian economy in general. |
Accordingly, our actual results of operations may be different from our current expectations, and the reader should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements speak only as of the date they are made. Factors that might affect such forward-looking statements include, among other things:
| | • | | our future operations performance; |
| |
| | • | | the demand for our services; |
| |
| | • | | competitive factors in the sector in which we compete; |
| |
| | • | | changes in the regulatory framework for our clients in the telecommunications, utilities and financial sectors in Brazil; |
| |
| | • | | changes in labor law and tax requirements; |
| |
| | • | | economic, business and political conditions in Brazil and in the international markets, including governmental changes and restrictions on the ability to transfer capital across borders; and |
| |
| | • | | the impact of fluctuations in the price of our shares. |
PART I
Item 1. Identity of Directors, Senior Management and Advisers
Not applicable.
Item 2. Offer Statistics and Expected Timetable
Not applicable.
5
Item 3. Key Information
Selected Financial Data
The following table presents our selected financial data as of the dates and for each of the periods indicated, presented inreaisand prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. The selected financial information as of December 31, 2005, 2004, and 2003 and for each of the years ended December 31, 2004 and 2003 has been derived from our audited financial statements, not included in this annual report, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP and presented inreaisin a manner consistent with the information set forth in our Consolidated and Combined Financial Statements. The data as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 and for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2007 have been derived from our audited Consolidated Financial Statements. You should read this information together with such financial statements, including the notes thereto and “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects.” The financial statements and information appear in Item 18 of this annual report, together with the audit report of PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, our independent registered public accounting firm.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | | | 2004 | | | 2003 | |
| | | (in thousands of reais, except per share data) | |
Statement of Operations Data | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net operating revenue from services rendered | | | 1,365,815 | | | | 1,218,583 | | | | 1,044,787 | | | | 654,616 | | | | 410,690 | |
| Cost of services rendered | | | (1,174,035 | ) | | | (1,037,353 | ) | | | (855,907 | ) | | | (574,071 | ) | | | (334,751 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross profit | | | 191,780 | | | | 181,230 | | | | 188,880 | | | | 80,545 | | | | 75,939 | |
| Operating expenses | | | (104,763 | ) | | | (83,800 | ) | | | (71,840 | ) | | | (47,845 | ) | | | (31,234 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income | | | 87,017 | | | | 97,430 | | | | 117,040 | | | | 32,700 | | | | 44,705 | |
| Financial income (expenses) net | | | (3,548 | ) | | | 18,405 | | | | 14,352 | | | | (4,662 | ) | | | (2,141 | ) |
| Income from continuing operations* | | | 55,451 | | | | 77,681 | | | | 81,240 | | | | 16,470 | | | | 61,240 | |
| Loss from discontinued operations* | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (9,667 | ) | | | (59,336 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) and comprehensive income (loss) for the year | | | 55,451 | | | | 77,681 | | | | 81,240 | | | | 6,803 | | | | 1,904 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Earnings (Loss) per Share
(inreais)** | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income from continuing operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common shares — basic | | | 3.37 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.25 | | | | 0.86 | | | | 0.86 | |
| Common shares — diluted | | | 3.23 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.25 | | | | 0.86 | | | | 0.86 | |
| Preferred shares — basic and diluted | | | 3.40 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.25 | | | | 0.86 | | | | 0.86 | |
| Net income (loss) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common shares — basic (i)(ii) | | | 3.37 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.25 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Common shares — diluted (i)(ii) | | | 3.23 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.25 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Preferred shares — basic and diluted (i)(ii) | | | 3.40 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.25 | | | | 0.36 | | | | 0.10 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding — basic (i)(iii) | | | 5,747,315 | | | | 6,264,303 | | | | 6,368,696 | | | | 6,368,696 | | | | 6,368,696 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding — diluted (i)(iii) | | | 6,005,323 | | | | 6,264,303 | | | | 6,368,696 | | | | 6,368,696 | | | | 6,368,696 | |
| Weighted average preferred shares outstanding — basic and diluted (i)(iii) | | | 10,704,436 | | | | 12,532,231 | | | | 12,737,390 | | | | 12,737,390 | | | | 12,737,390 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance Sheet Data | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 240,310 | | | | 231,299 | | | | 229,488 | | | | 85,152 | | | | 33,268 | |
| Property and equipment, net | | | 342,535 | | | | 309,727 | | | | 265,379 | | | | 182,936 | | | | 105,492 | |
| Total assets | | | 764,711 | | | | 683,275 | | | | 620,466 | | | | 406,052 | | | | 326,333 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | 291,799 | | | | 234,458 | | | | 203,080 | | | | 111,289 | | | | 197,047 | |
| Long-term liabilities | | | 178,031 | | | | 77,295 | | | | 56,831 | | | | 14,089 | | | | 3,093 | |
| Shareholders’ equity | | | 294,881 | | | | 371,522 | | | | 360,555 | | | | 280,674 | | | | 126,193 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | | | 764,711 | | | | 683,275 | | | | 620,466 | | | | 406,052 | | | | 326,333 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash Flow Data | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities (continuing operations*) | | | 203,119 | | | | 143,411 | | | | 221,410 | | | | 71,387 | | | | 88,272 | |
| Operating activities (discontinued operations*) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (30,945 | ) | | | (26,449 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | (51,409 | ) | | | (70,544 | ) | | | (5,297 | ) | | | 109,336 | | | | 4,406 | |
| Investing activities (continuing operations*) | | | (142,699 | ) | | | (71,056 | ) | | | (88,988 | ) | | | (97,894 | ) | | | (42,224 | ) |
| Investing activities (discontinued operations*) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 17,211 | | | | — | | | | 4,895 | |
6
| | | |
| (i) | | Due to numerous expansion plans dating back to the Telemar days, Contax inherited several million “inactive” shareholders. In an effort to reduce unnecessary administration and operating costs and to provide a low cost form of liquidity for these small shareholders, Contax decided to do a reverse stock split on November 17, 2007 with the outcome being a significant reduction of shareholders base in Brazil. Since ADR holders are mainly concentrated in the hands of institutional investors in large quantities, the reverse stock split was not needed and therefore was not done for the ADRs. |
| |
| (ii) | | Due to the reverse stock split carried out on November 17, 2007, earnings per share are shown based on groups of 20 shares for comparison amongst periods. In this case, the numbers of ADRs was considered grouped, for comparison, even though the grouping of ADRs did not occur. |
| |
| (iii) | | Due to the reverse stock split carried out on November 17, 2007, the number of shares excluding treasury was divided by 20 for comparison amongst periods. In this case, the numbers of ADRs was considered grouped, for comparison, even though the grouping of ADRs did not occur. |
| |
| * | | Discontinued operations relate to data center activities. |
| |
| ** | | The computation of earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2005, 2004 and 2003 is based on the number of shares outstanding of Contax Holding on the date of the spin-off. |
Exchange Rates
We will pay any cash dividends or interest on capital and make any other cash distributions with respect to our shares inreais. Accordingly, exchange rate fluctuations will affect the U.S. dollar amounts received or to be received by the holders of ADSs on conversion by The Bank of New York, as depositary, or the Depositary, of dividends and distributions inreaison the preferred shares represented by the ADSs. Fluctuations in the exchange rate between therealand the U.S. dollar will also affect the U.S. dollar equivalent of the price of the preferred shares on the Brazilian stock exchanges. Foreign currencies may only be purchased through a Brazilian bank authorized to operate in these markets.
Until March 4, 2005, there were two legal foreign exchange markets in Brazil, the commercial rate exchange market, or the Commercial Market, and the floating rate exchange market, or the Floating Market. On January 25, 1999, the Brazilian government announced the unification of the exchange positions of the Brazilian financial institution in the Commercial Market and in the Floating Market, leading to a convergence in the pricing and liquidity of both markets. The Commercial Market was reserved primarily for foreign trade transactions and transactions that generally required prior approval from Brazilian monetary authorities, such as the purchase and sale of registered investments by foreign persons and related remittances of funds abroad (including the payment of principal of and interest on loans, notes, bonds and other debt instruments denominated in foreign currencies and duly registered with the Brazilian Central Bank (Banco Central do Brasil), or Central Bank of Brazil, or Central Bank. The Floating Market rate generally applied to specific transactions for which approval by the Brazilian Central Bank was not required. Both the Commercial Market rate and the Floating Market rate were reported by the Central Bank on a daily basis.
On March 4, 2005, the Brazilian Central Bank issued Resolution no. 3,265, introduced several changes in the Brazilian foreign exchange regime, including: (i) the unification of the foreign exchange markets into a single exchange market, the Foreign Exchange Market; (ii) the easing of several rules for the acquisition of foreign currency by Brazilian residents; and (iii) the extension of the term for converting foreign currency derived from Brazilian exports. On March 8, 2006, the Brazilian government issued Provisional Measure no. 315, enacted on August 24, 2006 (“PM 315”), which has been approved by the Law no. 11,371, enacted on November 28, 2006. Together with the underlying regulations issued by the National Monetary Council (Conselho Monetário Nacional – “CMN”), this Law no. 11,371 made the currency exchange rules more flexible, making it possible to maintain export revenues (from merchandise or services) abroad, in the exporter’s account or in a Brazilian bank authorized to operate in the exchange market. On March 18, 2008, the Central Bank issued Circular No. 3,379, allowing Brazilian exporters of goods and services to maintain the totality of their revenues obtained with exports offshore. Furthermore, the PM 315, now Law number 11,371/06, permits registration with the Central Bank, in local currency, of the foreign capital invested in legal entities located in Brazil which had not been previously registered and was not eligible for another form of registration by the Central Bank (so-called “contaminated capital”). This set of recent measures represents a step towards a more flexible Brazilian system. It is expected that the Central Bank will issue further regulations in relation to foreign exchange transactions, as well as on payments and transfers of Brazilian currency between Brazilian residents and non-residents, including those made through the so-called non-resident accounts (also known as CC5 accounts).
7
The following table sets forth the Commercial Market/Foreign Exchange Market selling rates published by the Central Bank expressed inreaisper U.S. dollar for the periods indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Average | | | | | | | |
| Period | | Period-end | | | for period* | | | High | | | Low | |
| 2003 | | | 2.8882 | | | | 3.0715 | | | | 3.6623 | | | | 2.8219 | |
| 2004 | | | 2.6544 | | | | 2.9259 | | | | 3.2051 | | | | 2.6544 | |
| 2005 | | | 2.3407 | | | | 2.4125 | | | | 2.7621 | | | | 2.1633 | |
| 2006 | | | 2.1380 | | | | 2.1771 | | | | 2.3711 | | | | 2.0586 | |
| 2007 | | | 1.7713 | | | | 1.9483 | | | | 2.1556 | | | | 1.7325 | |
| January 2008 | | | 1.7603 | | | | 1.7743 | | | | 1.8301 | | | | 1.7414 | |
| February 2008 | | | 1.6833 | | | | 1.7277 | | | | 1.7681 | | | | 1.6715 | |
| March 2008 | | | 1.7491 | | | | 1.7373 | | | | 1.8301 | | | | 1.6700 | |
| April 2008 | | | 1.6872 | | | | 1.6889 | | | | 1.7534 | | | | 1.6575 | |
| April 2008 | | | 1.6872 | | | | 1.6889 | | | | 1.7534 | | | | 1.6575 | |
| May 2008 | | | 1.6294 | | | | 1.6605 | | | | 1.6949 | | | | 1.6294 | |
| June 2008 (through 16) | | | 1.6277 | | | | 1.6319 | | | | 1.6428 | | | | 1.6215 | |
| | | |
| * | | Average of the rates on each day in the period. |
Source: Brazilian Central Bank
On December 31, 2007, the commercial selling rate forreaiswas R$1.7713 to U.S.$1.00. On June 16, 2008, the Foreign Exchange Market selling rate was R$1.6277 to U.S.$1.00.
Risk Factors
The following factors should be carefully considered in addition to the other information presented in this annual report.
Risks Relating to Our Business
A large portion of our revenues originates from a limited number of clients, and the loss of one or more of these clients could significantly impact our financial condition.
We strategically focus our marketing efforts on developing long-term relationships with large companies in targeted sectors. As a result, we rely on a limited number of significant clients for a large percentage of our revenues. Our contracts with our two largest clients, Telemar and Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais Ltda., or Orbitall, accounted for 50.7% and 15.0%, respectively, of our revenues for the year ended December 31, 2007. The final term of our agreement with the Telemar entities (our main client encompassing Tmar and its wholly owned subsidiary Oi, both of which are indirectly under common control with us) is between December 2009 and December 2011. The final term of our agreement with Orbitall, our second largest client, is April 2009.
We have observed in recent years a trend toward corporate consolidation and change of control of companies in our targeted sectors, such as financial services, utilities and internet. Such events may cause the termination of existing contracts, and the loss of the revenues associated with such contracts.
The loss of any key client or the failure to retain a significant amount of business with our key clients would have a negative impact on our total revenues and our financial condition as a whole.
8
If the trend toward outsourcing of contact center services were reversed, the growth rate of our business could be reduced.
The outsourced contact center industry has expanded considerably in the past years as a result of an outsourcing trend observed in contact center services. One of the premises upon which the growth of our business and operations is based is that this outsourcing trend will continue.
However, external factors, such as increases in taxes on revenues that could significantly impact the cost of services rendered by contact center companies, could cause our current and prospective clients to maintain or return to the use of their in-house functions and thus reduce the trend towards outsourcing of contact center services. As the Brazilian government has historically increased taxes on revenues or on income, we may see ourselves forced into adjusting our pricing in order to maintain our profit margins, which could unfavorably impact the decision of our clients to retain us.
Additionally, our clients may be subject to restrictions on their ability to outsource contact center services. For example, a lower court ruling has been issued against one of our clients, alleging that under Brazilian law it was not permitted for this client to outsource certain specific contact center activities that may be protected by Brazilian bank secrecy rules. If this and similar rulings continue narrowing the scope of the services we are allowed to render, we could lose a part of our revenues as our current and prospective clients become restricted from outsourcing certain of their contact center operations.
Exhibit II to Regulation No. 17 (Anexo II da Norma Regulamentadora nº 17), approved by Rule No. 9, issued by the Brazilian Labor Department as of March 30, 2007 (Portaria nº 09), sets forth rules related to contact center operators’ safety and health conditions and establishes sanctions for the breach of such rules. Compliance with Regulation No. 17, as amended, may result in the increase of costs incurred by both in-house and outsourced contact centers in connection with the safety and health conditions of employees. The cost of compliance to our Company could reach 5.5% and we cannot guarantee that this cost increase will be passed to all our contractors.
Moreover, if the government adopts laws that restrict or dictate costly specifications regarding contact center operations and procedures, it could affect current and future clients’ decisions to outsource certain activities, since such laws could unfavorably impact our profit margins and cause us to adjust the pricing of our contracts.
Increases in the use of automated customer services could reduce the demand for our services.
A major part of our services is provided by our contact center attendants. Over time, services provided by live attendants may have to compete against an increase in the use of automated channels which allow customers of our clients to directly access self-service assistance systems (e.g., internet sites and automated phone services, such as voice recognition and Interactive Voice Response, a device that automates retrieval and processing of information by phone using touch tone signaling or voice recognition so as to access information residing on a server and reply with a pre-recorded response, such as in “bank-by-phone” transactions), which could mitigate the necessity of personal contact with a contact center attendant. If automated services were to become more technically viable and thus more widely used, the demand for our services could be reduced.
Our ability to recruit, motivate and retain qualified management and operators could affect the quality of our services, which could impact our ability to attract new clients and retain existing ones.
Since our business is labor intensive, our ability to attract and retain personnel is key to our continued success. We place significant importance on our ability to recruit, train, and retain qualified personnel. We employed 61,397 employees as of December 31, 2007. On average, we experienced a monthly turnover of approximately 5.0% of our personnel, requiring us to continuously recruit and train replacement personnel as a result of a changing and expanding workforce. In addition, demand for qualified technical professionals conversant with certain technologies may exceed supply, as new and additional skills are required to keep pace with evolving technology. In the event that we are unable to recruit, motivate and retain qualified personnel, the quality of our services could be affected, which could impact our ability to attract new clients and retain existing ones. Additionally, we may experience an increase in personnel costs as a result of: (i) a decrease in the productivity of our employees resulting from the loss of qualified, experienced personnel, and (ii) an increase in recruiting, training and severance costs related to a higher employee turnover.
9
Our inability to pass through cost increases could seriously harm our profit margins.
In Brazil, it is common for agreements to be renegotiated annually so that their prices are readjusted to account for inflationary variations in costs. Labor collective bargaining agreements in the contact center industry are also renegotiated on an annual basis to adjust for inflationary pressures, which results in an increase in our personnel costs. Hence, to protect against increases in costs of, among other things, telecommunications, energy, facilities lease and especially personnel, most of our contact center services contracts also have annual rate adjustment clauses that provide for price increases in an effort to cover such cost escalations. Nevertheless, we may decide not to exercise the right to adjust our prices fully in view of competitive conditions or other client relationship issues. In this case, we will not be able to pass through all of our cost increases. In the past, for example, we have had to adjust some of our customer prices at rates below their respective inflationary adjustment indexes. If any of our costs increase and we are not able to negotiate a commensurate rate adjustment with our clients, our profit margins would be adversely affected.
Our operating results may be harmed if we are unable to maximize our contact center capacity utilization.
Our profitability depends largely on how effectively we utilize our contact center capacity. In order to create the additional capacity necessary to accommodate new or expanded outsourcing contracts, as well as face significantly higher utilization during peak periods, we must consider opening new facilities or expanding current ones. The opening or expansion of a contact center may result, at least in the short term, in idle capacity. If we lose one or more significant clients, if the volume of calls from our clients’ customers decline or if a significant contract is not implemented in the anticipated time frame, our capacity utilization will be affected.
In addition, our profitability is significantly influenced by our ability to accurately forecast incoming calls. An excess of operators, based on an overestimated forecast, may cause us to lose profitability due to unused capacity. In contrast, if there are more incoming calls than forecasted, we may not be able to handle the call volume, and we may lose revenues or fail to meet performance requirements under our contracts. For the failure to meet such requirements, we may be subject to penalties and indemnities under certain clauses of our contracts.
Despite our ongoing efforts to maximize capacity utilization, we are subject to experiencing periods of idle capacity. This might occur mainly on the commencement of new operations or the termination of an existing contract.
There can be no assurance that we will be able to achieve or maintain optimal utilization of our contact center capacity.
If our clients are not successful, the amount of business they outsource may be diminished and could result in lower revenues for us.
Our revenues are dependent on the success of our clients. If our clients are not successful, the amount of business they outsource may be reduced. Furthermore, due to the inbound nature of most of our services (e.g., customer care), the amount of revenue generated from any particular service contract is dependent upon consumers’ interest in, and use of, our clients’ products and services.
If our clients are not successful or their customers reduce their use of our contact center services, our revenues and the expansion of our business would be adversely affected.
The failure to keep our technology up to date may prevent us from remaining competitive.
Our business is dependent on our servers, desktops, telecommunications and network equipment, software applications and IT processes and procedures. The failure to maintain our technology capabilities or to respond effectively to technology changes could adversely affect our competitiveness. Our continued growth and future profitability depends, among other factors, on the introduction of new services that effectively leverage and respond to technological developments.
10
There can be no assurance that (i) our IT and telecommunications systems will be adequate to meet our clients’ future needs; (ii) we will be able to incorporate new technology to enhance and develop our existing services; and (iii) technologies or services developed by our competitors will not render our services uncompetitive or obsolete.
Interruption of our contact center services could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our ability to provide our contact center services is dependent upon our ability to protect our facilities and operations against damage that may be caused by fire, natural disasters, power and telecommunications failures, computer viruses, labor strikes, acts of sabotage or terror and other emergencies. We currently have backup systems for our most critical power and data storage and business interruption insurance to offset, in part, certain losses we may incur if our facilities or operations are adversely affected by events outside our control. Despite the implementation of these systems and contingency plans, as well as network security measures, we may still experience interruption at one or more of our facilities, and we may be unable to provide the services we are contractually obligated to deliver.
As a result of any such interruption: (i) our revenues could be reduced as a result of reduced activity, as most of our contractual compensation is calculated based on speaking time or number of available workstations; (ii) we may be required to pay non-compensatory contractual penalties, since we may be unable to meet certain agreed-upon quality targets (service level agreements) as a result of such interruption; (iii) we may be required to pay indemnities to our clients for lost profits and damages, if we breach or are unable to deliver our services; and (iv) if we continue to fail to meet our obligations, our clients may be entitled to terminate their contracts with us.
Depending on the amount of penalties and indemnifications we may have to pay as a result of the interruption of our services, our financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Breaches of our contact center service contracts could expose us to significant monetary penalties.
We are exposed to different types of contractual penalties as a result of material breaches of our contractual service obligations. A fair number of our contracts contain provisions setting penalties for breaches at different degrees, determined based on formulas that take into consideration: (i) the nature and extent of the breach, (ii) the amount of revenues raised or due under the relevant contract in a given year, or (iii) the point in time during the life of the contract in which the breach occurs. We also have entered into contracts that require us to indemnify our clients for their losses resulting from breach of our obligations under such agreements. As a general matter, we are unable to quantify our potential exposure under these provisions, as the penalty amounts are based on future variables relating to the nature of the breach, the amount of revenues actually earned or the amount of time during which the contract has been outstanding.
Our exposure for discretionary early termination in connection with our contact center service agreement with Telemar shall be in the amount equivalent to the revenue we obtain in connection with such agreement during three months prior to the date Telemar sends us a notice of termination of the agreement. Our exposure to penalties related to damages caused by the termination of our agreement with Telemar as a result of a contractual breach by us shall be limited to 5.0% of our annual revenue in connection with such agreement. Based upon the level of revenue generated in 2007 as a result of such agreement, the early termination penalty would have been in the amount of approximately R$173 million (U.S.$89 million), while our exposure to penalties related to damages for the year could have been up to an amount of approximately R$35 million (U.S.$18 million).
11
Our exposure for discretionary early termination in connection with our contact center service agreement with Orbitall is equivalent to one-sixth of the estimated revenue for the period within the early termination date and the final term of the Agreement. The estimated revenue shall be calculated based on the average monthly revenue of the 3 months prior to the early termination, the minimum amount of such penalty being equivalent to 1 month’s revenue. In case of a material breach of the agreement by us, we may be subject to the payment of the amount of the actual damages incurred by Orbitall, up to 30.0% of the amount of the monthly invoice sent to Orbitall in connection with such agreement during the month when the breach occurs. Nevertheless, the amount of any such damages would be fact specific and is not determinable at this time. Based upon the level of revenue generated in 2007 as a result of such agreement, if we had breached this agreement we would have been subject to penalties in the amount of approximately R$5.1 million (U.S.$2.4 million).
As a result, our exposure for breach under these contracts, though currently indeterminable, may have a significant negative impact on our results.
We may be unable to achieve the same performance levels we have been experiencing with our performance-based compensation contracts.
We derived approximately 29.0% of our net revenues in the fiscal year of 2007 from operations with performance-based compensation, consisting mostly of telemarketing and debt collection services. These services depend not only on our success in selling a product, locating a debtor or negotiating a debt settlement, but also on other factors that are beyond our control. For telemarketing activities, for example, our compensation is measured according to the amount of our clients’ products that we are able to sell in a given period of time or on a sales target which we are required to meet. Consequently, our performance-based compensation for telemarketing can be affected by, among other things, the attractiveness of the products and services we will be selling for our clients. In addition, prevailing macroeconomic conditions in Brazil, such as GDP growth, unemployment and availability of disposable income, also affect our performance-based compensation more acutely than they affect enterprises that rely solely on fixed-based compensation, since such macroeconomic conditions directly affect consumer spending and default rates. Consequently, there can be no assurance that we will be able to maintain the same level of our past performance in the future or that we will not incur losses with our performance-based compensation contracts.
We may be responsible for labor liabilities which could have an adverse effect on our profitability.
We were involved in 4,024 labor claims as of December 31, 2007. Although the total amount of all labor claims filed against us is approximately R$260,715 thousand (U.S.$147,189 thousand) as of December 31, 2007, we record provisions for any contingent liabilities in proportion to our historical losses, which, on that date, amounted to approximately R$38,954 thousand (U.S.$21,992 thousand). We also are subject to potential administrative proceedings brought by the Brazilian Labor Department.
If all of the labor claims filed against us or a greater portion of such claims than we have provisioned for were resolved against us, our profitability would be adversely affected. In addition, although we have contractual arrangements with both Orbitall and Telemar according to which they shall reimburse us for the costs we may incur in connection with the claims referred above, if those entities fail to comply with such reimbursement arrangements our margins could be adversely affected. There can be no assurance that additional labor claims and proceedings will not be brought against us in the future, or if they are, that an adverse ruling regarding such claims and proceedings would not have a negative impact on the cost of services rendered by us, or result in the impositions of penalties or other negative consequences.
Our business is highly competitive and our failure to effectively compete could result in the loss of clients or decreased profitability.
We face significant competition and believe that this competition will intensify. There are numerous providers of our services, including other contact center service companies, niche players, consulting companies and many small companies that offer low-end services (primarily outbound services). Aside from those competitors, our clients and potential clients may also decide to utilize in-house personnel to perform contact center services they currently outsource, or maintain their in-house customer service and product support activities. We also face competition from automated customer services, through the use of Internet, Interactive Voice Response, voice recognition and other technologies.
12
Our competitors’ services and pricing practices, as well as the timing and circumstances of the entry of additional competitors into our market may harm our business. The trend towards international expansion by foreign competitors and continuous technology changes may bring new competitors into our market and may increase pricing pressures. Our failure to compete successfully could result in loss of clients and specific service contracts or could result in decreased profitability.
CTX Participações holds the majority of our voting shares and there may be circumstances in which its interests differ from or conflict with the interests of our other shareholders.
We are controlled by CTX Participações, which spun-off from Telemar Participações in April 2008 and holds 58.8% of our common stock. As controlling shareholder, CTX Participações is entitled to appoint the majority of the members of our board of directors and has the power to, among other things, modify our business plan, determine the date of dividend payments, approve corporate restructurings and sell our material assets. We cannot assure that our controlling shareholder will not take actions that might differ from or conflict with the interests of our other shareholders.
We may be liable for fraudulent activities or misappropriation of our clients’ information by our employees or third parties.
Our contact center business puts us in possession of sensitive client information. Despite our internal controls and our efforts to protect our clients’ information, we may be held liable for fraudulent activities by our employees or by third parties. For example, unauthorized persons may be able to breach our physical or network security systems. Meanwhile, authorized employees may misuse their authorization rights or the information to which they have access. Our failure to prevent these occurrences could: (i) damage our reputation with our clients and the market; (ii) allow them to terminate their contracts with us; (iii) expose us to potential liability; and (iv) subject us to the previously discussed contractual penalties and indemnities, all of which may substantially harm our business and results of operations.
Risks Relating to Brazil
The Brazilian government has exercised, and continues to exercise, significant influence over the Brazilian economy. This involvement, as well as Brazilian political and economic conditions, could adversely impact our business, operations and the market price of our shares and ADSs.
The Brazilian government frequently intervenes in the Brazilian economy and occasionally makes drastic changes in policy and regulations. The Brazilian government’s actions to control inflation and implement macroeconomic policies have often involved wage and price controls, currency devaluations, capital controls and limits on imports, among other things. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and the market price of our shares and ADSs may be adversely affected by changes in policies or regulations, or by other factors such as:
| | • | | devaluations and other currency fluctuations; |
| |
| | • | | inflation rates; |
| |
| | • | | interest rates; |
| |
| | • | | liquidity of domestic capital and lending markets; |
| |
| | • | | energy shortages; |
| |
| | • | | exchange controls and restrictions on remittances abroad (such as those that were briefly imposed in 1989 and early 1990); |
| |
| | • | | monetary policy; |
13
| | • | | tax policy; and |
| |
| | • | | other political, diplomatic, social and economic developments in or affecting Brazil. |
Uncertainty over whether possible changes in policies or rules affecting these or other factors may contribute to economic uncertainties in Brazil and to heightened volatility in the Brazilian securities markets and securities issued abroad by Brazilian issuers. These uncertainties could adversely affect our activities. Historically, members of the executive and legislative branches of the Brazilian government, as well as other related persons, have been investigated on the grounds of alleged illicit or unethical behavior. It is not possible to predict the outcome of such investigations and whether the outcome will adversely affect the Brazilian economy. As a consequence of their impact on the Brazilian economy, these uncertainties and allegations of unethical or illegal conduct may have a material adverse effect on us and may also adversely affect the trading price of our common shares.
Inflation and certain government measures to curb inflation may have adverse effects on the Brazilian economy, the Brazilian securities market, our business and operations and the market price of the shares.
Brazil has historically experienced extremely high rates of inflation. Inflation and some of the Brazilian government’s measures taken in an attempt to curb inflation have had significant negative effects on the Brazilian economy. While inflation has been kept largely under control since the introduction of therealin 1994, inflationary pressures persist. Actions taken in an effort to curb inflation, coupled with speculation about possible future governmental actions, have contributed to economic uncertainty in Brazil and heightened volatility in the Brazilian securities market. According to theÍndice Geral de Preços-Mercado, or IGP-M, a general price inflation index published byFundação Getúlio Vargas, or FGV, the Brazilian general price inflation rates were 1.2%, 3.8% and 7.7% in 2005, 2006 and 2007, respectively. According to theÍndice Geral de Preços - - Disponibilidade Interna, or IGP-DI, another general price inflation index published by FGV, the Brazilian general price inflation rates were 1.2%, 3.8% and 7.9% in 2005, 2006 and 2007, respectively. According to theÍndice Nacional de Preços ao Consumidor Ampliado, or IPCA, published by theInstituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística, or IBGE, the Brazilian consumer price inflation rates were 5.7%, 3.1% and 4.5% in 2005, 2006 and 2007, respectively. In the first quarter of 2008, inflation measured by the IGP-M, IGP-DI and IPCA, was approximately 2.36%, 2.07% and 1.51%, respectively, or 9.44%, 8.28% and 6.04% on an annualized basis, respectively.
Brazil may experience high levels of inflation in the future. Inflationary pressures may lead to further government intervention in the economy, including the introduction of government policies that could adversely affect the economy overall and our business in particular.
Changes in Brazilian labor law may negatively affect us.
Brazilian companies are subject not only to the Federal Constitution and ordinary legislation concerning labor relations (mainly theConsolidação das Leis do Trabalho, or CLT), but also to collective bargaining agreements between employers’ associations and employee unions or between individual employers and employee unions, in addition to administrative orders, technical notes and instructions issued by the Brazilian Labor Department. In addition, the tendency of Brazilian labor laws and regulators to protect employees from dismissal has created barriers to the loosening of labor standards. Furthermore, due to the volume of cases and insufficient personnel, the labor courts are typically slow in deciding the labor claims and disputes that are submitted to them for resolution.
The Brazilian Labor Department continuously issues and revises current labor regulations regarding specific practices in different business sectors. In April 2007, the Brazilian Labor Department published a technical note setting forth new guidelines concerning labor practices and regulations regarding contact center activities. These rules include, among other things, employees’ directives regarding work environment, working hours and breaks, ergonomic equipment design standards and guidance on labor related diseases (Exhibit II to Regulation No. 17 (Anexo II da Norma Regulamentadora nº 17), approved by Rule No. 9, issued by the Brazilian Labor Department as of March 30, 2007 (Portaria nº 09) — See “Item 3 – Risk Factors — If the trend toward outsourcing of contact center services were reversed, the growth rate of our business could be reduced”). Labor inspectors have been paying greater attention to these factors and, as a result, have been requiring strict compliance by companies with workplace health and safety rules. Enforcement of these new regulations may lead to increased costs, which we may not be able to pass through to our clients or, in some cases, administrative fines, which would adversely affect our financial condition.
14
Regulatory proposals, such as the creation of a “do not call list”, could restrict our contact center services.
A series of bills have been presented to Congress and to local legislative branches of certain states and municipalities proposing to regulate several aspects of the outbound telemarketing services we provide, such as: (i) the days and hours in which outbound calls are allowed; and (ii) the creation of a national “do not call list.” Following several discussions and public hearings, the Commission of Science, Technology, Innovation, Communication and Information Technology of the Brazilian Senate (Comissão de Ciência, Tecnologia, Inovação, Comunicação e Informática) approved an amendment to Bill No. 243/04, which sets forth the creation of the “do not call list”, limiting the outbound telemarketing services to the hours between 9:00 am to 9:00 pm on business days and between 10:00 am to 4:00 pm on Saturdays, as well as prohibiting outbound telemarketing services on Sundays and holidays. Such amendment to Bill No. 243/04 still needs to be approved by the majority of the members of the Senate. The proposal is currently being discussed by the Commission for Constitution, Justice and Citizenship (Comissão de Constituição, Justiça e Cidadania), which is expected to issue a conclusive decision and submit the bill to the Plenary of the Senate and to the President of Brazil for final examination and approval. If approved, such amended bill will enter into effect after a grace period of one year.
If these bills are passed, our ability to make outbound calls may be significantly restricted, which would adversely impact our current revenue and growth opportunities.
Exchange rate instability may adversely affect our financial condition.
The Brazilian currency has been devalued frequently over the past four decades. Throughout this period, the Brazilian government has implemented various economic plans and used various exchange rate policies, including sudden devaluations, periodic mini-devaluations (such as daily adjustments), exchange controls, dual exchange rate markets and a floating exchange rate system. From time to time, there have been significant fluctuations in the exchange rate between the Brazilian currency and the U.S. dollar and other currencies. Based on the real/U.S. dollar exchange rate, therealappreciated against the U.S. dollar by 8.8%, 13.4%, 9.5% and 20.7% in 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2007, respectively. In the first quarter of 2008, therealappreciated against the U.S. dollar by 1.25% based on thereal/U.S. dollar commercial exchange rate as of the close of business on March 31, 2008.
Devaluation of therealrelative to the U.S. dollar could create additional inflationary pressures in Brazil by generally increasing the price of imported products and requiring recessionary government policies including tighter monetary policy. On the other hand, appreciation of therealagainst the U.S. dollar may lead to a deterioration of the country’s current account and the balance of payments, as well as to a dampening of export-driven growth. Devaluations also reduce the U.S. dollar value of distributions and dividends on the ADRs and the U.S. dollar equivalent of the market price of our shares and, as a result, the ADRs.
We may be unable to convertreaisinto U.S. dollars to make dividend distributions to our ADS holders.
In the past, Brazil’s economy has experienced balance of payment deficits and shortages in foreign exchange reserves, and the government has responded by restricting the ability of persons or entities, Brazilian or foreign, to convertreaisinto any foreign currency. The government may institute a restrictive exchange control policy in the future. Any restrictive exchange control policy could prevent or restrict our access to U.S. dollars to meet our dividend payment obligations.
15
Economic and market conditions in other emerging market countries may adversely affect the Brazilian economy and, therefore, the market value of our common shares and ADSs and our ability to access the capital markets.
The market for securities issued by Brazilian companies is influenced by economic and market conditions in Brazil, and, to varying degrees, market conditions in other Latin American and emerging market economies. Although economic conditions are different in each country, the reaction of investors to developments in one emerging market country may cause the capital markets in other countries to fluctuate. Developments or conditions in other emerging market countries have at times significantly affected the availability of credit in the Brazilian economy and resulted in considerable outflows of funds and declines in the amount of foreign currency invested in Brazil, as well as limited access to international capital markets, which may adversely affect our ability to borrow funds at an acceptable interest rate or to raise equity capital when and if there should be a need for us to do so. Such developments have included the devaluation of the Mexican peso in December 1994, the Asian economic crisis of 1997, the Russian currency crisis of 1998 and the 2001 economic and political crisis in Argentina. The continuing political crisis in Venezuela and the socialist-oriented government of Bolivia may also influence investors’ perceptions of risk in Brazil. Although market concerns that similar crises would occur in Brazil have not become a reality, the volatility in market prices for Brazilian securities has varied from time to time as a result of such crises.
Risks Relating to the ADSs and the Preferred Shares
You may not be able to sell the ADSs or preferred shares at the price or time you desire because an active or liquid market for the ADSs or the preferred shares will not likely develop.
There has not been a public market for either our ADSs or our preferred shares. We have obtained approval for the listing of our preferred shares on the Bovespa (the stock exchange of the State of São Paulo, Brazil, the main Brazilian stock exchange), but we do not intend to list the ADSs in any organized market or stock exchange. As a result, active trading in the ADSs will not likely develop. Similarly, active trading in the preferred shares in the United States will not likely develop. Active, liquid trading markets generally result in lower price volatility and more efficient execution of buy and sell orders for investors.
The relative volatility and illiquidity of the Brazilian securities markets may substantially limit your ability to sell the preferred shares underlying the ADSs at the price and time you desire.
Investing in securities that trade in emerging markets, such as Brazil, often involves greater risk than investing in securities of issuers in the United States, and such investments are generally considered to be more speculative in nature. The Brazilian securities market is substantially smaller, less liquid and more concentrated than major securities markets in the United States. As a result, the price for the preferred shares may be subject to substantial volatility, and it may be difficult to find a buyer or a seller at certain times. Accordingly, although you are entitled to withdraw the preferred shares underlying the ADSs from the Depositary at any time, your ability to sell the preferred shares underlying the ADSs at a price and time of your choosing may be substantially limited. There is also significantly greater concentration in the Brazilian securities market than in the United States. As of December 31, 2007, the aggregate market capitalization of the 10 largest companies listed on the Bovespa was approximately U.S.$708.97 billion, representing almost 50.7% of the aggregate market capitalization of that market. The top 10 stocks in terms of trading volume accounted for approximately 51.3%, 46.1% and 45.8% of all shares traded on the Bovespa in 2005, 2006 and in 2007, respectively.
Holders of preferred shares and ADSs have limited voting rights.
Of our two classes of capital shares outstanding, only our common shares have full voting rights. Except in certain limited circumstances, our preferred shares will be entitled to full voting rights only in the event that we fail to pay the minimum dividends for a period of three consecutive years. As a result of these limited voting rights and the fact that CTX Participações holds 58.8% of our common stock, holders of our preferred shares and, therefore, of our ADSs, generally will not be able to influence any corporate decision requiring a shareholder vote, including the declaration of dividends.
16
Holders of ADSs are not entitled to attend shareholders’ meetings and may only vote through the Depositary.
Under Brazilian law, only shareholders registered as such in our corporate books may attend shareholders’ meetings. All preferred shares underlying the ADSs are registered in the name of the Depositary. A holder of ADSs, accordingly, is not entitled to attend shareholders’ meetings. A holder of ADSs is entitled to instruct the Depositary as to how to vote the preferred shares represented by ADSs, in accordance with procedures provided for in the Deposit Agreement, but a holder of ADSs will not be able to vote the underlying preferred shares directly at a shareholders’ meeting or to appoint a proxy to do so.
Holders of ADSs may have fewer and less well-defined shareholders’ rights than shareholders of U.S. public companies.
Our corporate affairs are governed by our by-laws and Brazilian corporate law, which may differ from the legal principles that would apply if we were incorporated in a jurisdiction in the United States. Under Brazilian corporate law, the holders of our preferred shares and our ADSs may have fewer and less well-defined rights to protect their interests relative to actions taken by our Board of Directors or the holders of our common shares than under the laws of other jurisdictions outside Brazil.
When compared to Delaware corporation law, Brazilian corporate law and practice have less detailed and well-established rules, and judicial precedents relating to protections afforded to non-controlling security holders and the review of management decisions involving duty of care and duty of loyalty standards in the context of corporate restructurings, transactions with related parties, and sale-of-business transactions. In addition, shareholders in Brazilian companies must hold at least 5.0% of the outstanding share capital of a corporation in order to have standing to bring a shareholder derivative suit, and shareholders in Brazilian companies ordinarily do not have standing to bring class action suits.
Although Brazilian law imposes restrictions on insider trading and price manipulation, the Brazilian securities markets may not be as highly regulated and supervised as the U.S. securities markets or markets in other jurisdictions. In addition, rules and policies against self-dealing and regarding the preservation of shareholder interests may be less well-defined and enforced in Brazil than in the United States, potentially causing disadvantages to holders of the preferred shares and/or ADSs. Corporate disclosures may be less complete or informative than what may be expected of a U.S. public company.
Holders of ADSs or preferred shares may not receive any dividends.
According to Brazilian corporate law and our by-laws, we must pay dividends to our shareholders totaling at least 25.0% of our annual net income, as determined and adjusted under Brazilian GAAP, except that we may use current net income (as per Brazilian corporate law): (i) to offset accumulated losses; (ii) to constitute a reserve for unrealized profits; (iii) to constitute a reserve for contingencies (if such contingencies are not already provisioned for); and (iv) to constitute a legal reserve (up to 5.0% of current net income, limited to 20.0% of the share capital).
In extreme circumstances, we may not pay dividends to our shareholders in a particular fiscal year if, at a shareholders’ meeting, our Board of Directors advises our shareholders that such distributions would not be advisable in view of our financial condition.
Exchange controls and restrictions on remittances abroad may adversely affect holders of ADSs.
Brazilian law provides that whenever there is a significant imbalance in Brazil’s balance of payments or a significant possibility that such imbalance will exist, the Brazilian government may impose temporary restrictions on the remittance to foreign investors of the proceeds of their investment in Brazil (as it did for approximately six months in 1989 and early 1990) and on the conversion of Brazilian currency into foreign currencies. These restrictions could hinder or prevent the Brazilian custodian of our shares underlying the ADSs or holders who have exchanged the ADSs for our underlying shares from converting dividends, distributions or the proceeds from any sale of such shares into U.S. dollars and remitting such U.S. dollars abroad. In such an event, the Brazilian custodian for our shares will hold thereaisthat it cannot convert for the account of holders of the ADSs who have not been paid. Neither the custodian nor the Depositary will be required to invest thereais or be liable for any interest.
17
Dividends received by United States individuals will not be “qualified dividend income” eligible for a 15.0% tax rate.
For United States federal income tax purposes, U.S. shareholders within the meaning of section 7701(a)(30) of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986 generally will recognize, to the extent of our current and accumulated earnings and profits, ordinary income on the receipt of cash dividends on shares. Unless the class of shares with respect to which distributions are made is readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States, any dividend income will not be treated as “qualified dividend income” eligible for a 15.0% tax rate in the case of U.S. shareholders who are individuals. We do not intend to list the ADSs on an established securities market in the United States. As a result, any dividends received by United States individuals will not be “qualified dividend income” eligible for a 15.0% tax rate.
If you surrender your ADSs and withdraw preferred shares, you risk losing the ability to remit foreign currency abroad and certain Brazilian tax advantages.
As an ADS holder, you will benefit from the electronic certificate of foreign capital registration to be obtained by the Custodian for our preferred shares underlying the ADSs in Brazil, which permits the Custodian to convert dividends and other distributions with respect to the preferred shares into foreign currency and remit the proceeds abroad. If you surrender your ADSs and withdraw preferred shares, you will be entitled to continue to rely on the Custodian’s electronic certificate of foreign capital registration for only five business days from the date of withdrawal. Thereafter, upon the disposition of or distributions relating to such preferred shares, you will not be able to remit foreign currency abroad unless you obtain your own electronic certificate of foreign capital registration or you qualify under Brazilian foreign investment regulations that entitle some foreign investors to buy and sell shares on Brazilian stock exchanges without obtaining separate electronic certificates of foreign capital registration. If you do not qualify under the foreign investment regulations you will generally be subject to less favorable tax treatment of dividends and distributions on, and the proceeds from any sale of, such preferred shares.
If you attempt to obtain your own electronic certificate of foreign capital registration, you may incur expenses or suffer delays in the application process, which could delay your ability to receive dividends or distributions relating to our shares or the return of your capital in a timely manner. The Depositary’s electronic certificate of foreign capital registration may also be adversely affected by future regulatory changes.
Changes in Brazilian tax laws may have an adverse impact on the taxes applicable to the disposition of the ADSs or preferred shares.
According to Law no. 10,833, enacted on December 29, 2003, the disposition or sale of assets located in Brazil by a non-resident to either a Brazilian resident or non-resident is subject to taxation in Brazil, regardless of the domicile of the purchaser or whether the disposition occurs outside Brazil. If the disposition or sale of assets located in Brazil is interpreted to include a disposition or sale of our ADSs, this provision could result in the imposition of income tax on the gains from such a sale or disposition of our ADSs by a non-resident of Brazil to another non-resident of Brazil. However, considering the general and unclear scope of Law no. 10,833 and the absence of jurisprudence in respect thereof, we are unable to predict whether an interpretation applying such tax laws to dispositions of the ADSs solely between non-residents could ultimately prevail in Brazilian courts.
Holders of ADSs may be unable to exercise preemptive rights with respect to our shares.
Under Brazilian law, if we issue new shares for cash as part of a capital increase, we generally must grant our shareholders the right to purchase a sufficient number of shares to maintain their existing ownership percentage. Rights to purchase shares in these circumstances are known as preemptive rights. We may not be able to offer our preferred shares to U.S. holders of ADSs pursuant to preemptive rights granted to holders of our shares in connection with any future issuance of our preferred shares unless a registration statement under the Securities Act of 1933, or the Securities Act, is effective with respect to such preferred shares and preemptive rights, or an exemption from the registration requirements of the Securities Act is available. We are not obligated to file a registration statement relating to preemptive rights with respect to our preferred shares, and we cannot assure you that we will file any such registration statement. If such a registration statement is not filed and an exemption from registration does not exist, The Bank of New York, as depositary, will attempt to sell the preemptive rights, and you will be entitled to receive the proceeds of such sale. However, these preemptive rights will expire if the Depositary does not sell them, and U.S. holders of ADSs will not realize any value from the granting of such preemptive rights.
18
Holders of ADSs may face difficulties in serving process on or enforcing judgments against us and other persons.
Contax Holding and TNL Contax are corporations organized under the laws of Brazil, and all the members of our Board of Directors and all of our Executive Officers and our independent public accountants reside or are based in Brazil. All of our assets and those of these other persons are located in Brazil. As a result, it may not be possible for you to effect service of process upon us or these other persons within the United States or other jurisdictions outside Brazil or to enforce against us or these other persons judgments obtained in the United States or other jurisdictions outside Brazil. Because judgments of U.S. courts for civil liabilities based upon the U.S. federal securities laws may only be enforced in Brazil if certain conditions are met, you may face greater difficulties in protecting your interests in the case of actions by us or our Board of Directors or Executive Officers than would shareholders of a U.S. company. Although, subject to certain conditions, investors generally would be permitted to bring an original action in Brazilian courts under the U.S. federal securities laws, pursuing such an action in a Brazilian court could prove difficult given the relative inexperience of such courts in these matters.
Item 4. Information on the Company
History and Organizational Structure
Contax Participações S.A. was incorporated in Brazil on July 31, 2000 as a corporation, orsociedade por ações, under the name Caroaci Participações S.A. Its primary functions were those of a typical holding company. Contax Holding’s registered address is: Rua do Passeio 56, 16º andar (parte), 20021-290, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil. Its telephone number is +55 21 3131-0274.
Contax Holding is the sole parent company of TNL Contax S.A., a corporation incorporated in Brazil on April 3, 2000 as asociedade por açõesunder the name Contax S.A. TNL Contax is the only significant subsidiary of Contax Holding and is an operational entity that conducts contact center service activities.
On December 29, 2004, the shareholders of TNL approved a proposal from its Board of Directors to spin off Contax Holding to TNL’s shareholders for two primary reasons: (i) to realize the full value of the Company as a separate entity and (ii) to allow the management of TNL to focus on its telecommunications operations. The referred spin-off was consummated in August 2005 with the delivery of our shares to the shareholders of TNL.
In June 2006, the Company approved its first share buyback program, which was concluded in November 2006 and resulted in the repurchase of 5,887 thousand common shares (corresponding to 294 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split referred to below) and 11,774 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 589 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split), representing 100% of the number of shares authorized to be repurchased under that program.
In November 2006, the Company implemented its second buyback program, which was concluded in July 2007 and resulted in the repurchase of 5,298 thousand common shares (corresponding to 265 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 24,058 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 1,203 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split).
The Company’s third share buyback program was implemented in July 2007 and was concluded in October 2007, with the repurchase of 3,193 thousand common shares (corresponding to 160 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 18,277 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 914 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split).
19
A total of 14,378 thousand common shares (corresponding to 719 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 54,109 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 2,705 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) were repurchased as part of these three buyback programs, of which 10,878 thousand common shares (corresponding to 544 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 54,109 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 2,705 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split ) were cancelled and 3,500 thousand common shares (corresponding to 175 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) were held in treasury without reducing the Company’s capital stock.
On October 17, 2007, our shareholders approved the Reverse Stock Split of all shares representing the Company’s capital stock at the ratio of twenty (20) shares for one (1) share of same type. See “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects — Key Events in 2007 — Reverse Stock Split.”
On October 18, 2007, 179,660 common shares (corresponding to 9 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) were sold to the Company’s officers, pursuant to the Stock Option Plan, approved by the general shareholders’ meeting held on April 16, 2007, while 3,320 thousand common shares (corresponding to 166 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split ) were held in treasury. See “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects — Key Events in 2007 — Stock Option Plan.”
Altogether, the Company invested R$161 million in the three buyback programs, of which R$41 million were invested in 2006 and R$120 million in 2007.
Our shareholders approved, at a general shareholders’ meeting held on October 17, 2007, the reverse split of all shares representing the Company’s capital stock at the ratio of twenty (20) shares for one (1) share of same type, which, beginning on November 17, 2007, have been traded on a reverse split basis (the “Reverse Stock Split”). No Reverse Stock Split took place in relation to the ADRs, the current ratio being 20 ADRs for one (1) preferred share. See “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects — Key Events in 2007 — Reverse Stock Split.”
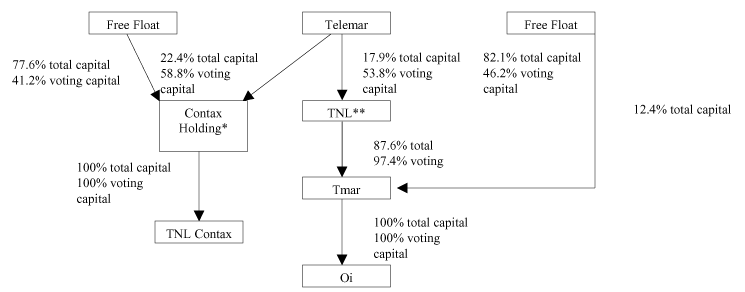
The following organizational chart illustrates the business structure of Telemar Participações, Contax’s previous controlling shareholder, and its subsidiaries on December 31, 2007:
| | | |
| * | | Shareholdings as of December 31, 2007. |
| |
| ** | | Shareholdings as of December 31, 2007. |
| |
| *** | | Held indirectly through a wholly owned subsidiary. |
20
On April 25, 2008, negotiations relating to the restructuring of the ownership structure of Telemar Participações were concluded. One of the results was the approval of the partial spin-off of Telemar Participações, with the transfer of its shareholders’ equity related to the shares issued by Contax to a new company created especially for this purpose denominated CTX Participações S.A.. See Item 5: Recent Developments.
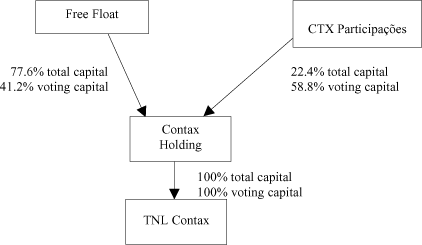
The following organizational chart illustrates the business structure of CTX Participações, Contax’s controlling shareholder, and its subsidiaries following the partial spin-off:
Overview
The Company has experienced overall growth of its businesses since its inception. Based on information provided by Call Center Inf and available in the most recent financial statements published by Brazilian contact center companies, in 2007 it confirmed its position as the largest contact center service provider in Brazil based on 2006 revenues, which was maintained in 2008 based on 2007 revenues. We specialize in the design, implementation, and operation of complex contact centers, in order to help our clients improve their customer relationships and maximize the value they provide to their customers. Our clients include many of Brazil’s largest companies in the telecommunications, financial services, utilities and Internet sectors.
TNL Contax began operations at the end of 2000 in response to opportunities in the Brazilian contact center outsourcing market. TNL Contax initially provided outsourced services previously rendered by Telemar in order to reduce costs and increase the quality of Telemar’s in-house activities. In addition, TNL Contax provided integrated services with Telemar to their large corporate customers.
During 2007 we kept a constant client base in comparison to the previous year, providing quality service to over 50 clients. Our business strategy is focused on developing long-term relationships with large companies in targeted sectors. We offer a variety of channels of communications to interact with customers, including voice, Internet, e-mail, mail and fax services. As of December 31, 2007, we had 61,397 employees (49,132 in 2006) and operated 28,043 workstations (22,407 in 2006) distributed throughout 22 contact centers (18 in 2006) in Brazil.
Our services are designed to enhance the quality of customer interaction at all stages of the customer lifecycle, from identifying and acquiring new customers through providing information and customer services, rendering technical support, customer retention, and debt collection.
21
Industry Overview
The scope of customer interaction by contact centers generally has expanded from single purpose (generally, basic support or marketing) to integrated service offerings (combining services such as customer care, telemarketing, technical support, customer retention, and debt collection) through various communication channels. As a consequence, the outsourced contact center sector has evolved from primarily single-facility, low technology environments to large, full-service organizations with multi-channel, large-volume contact centers that use sophisticated technology platforms to support such activities.
Companies traditionally relied on in-house personnel and infrastructure to perform sales, direct marketing and customer care. However, driven by increasing competition and higher customer sophistication, companies began to outsource their contact center activities in order to focus on their core businesses and to reduce costs. Because such activities face significant fluctuations in demand, many companies have found that it is not cost-effective to maintain excess capacity, particularly during peak traffic periods. Moreover, many companies have recognized that they were not appropriately equipped to conduct contact center activities and could not keep pace with the rapid changes in technology.
Outsourced contact center providers are able to render services at lower overall costs as a result of their ability to amortize fixed costs over a large number of customers, resulting in economies of scale in operations and technology. For example, by turning to an outsourcer, a company can obtain access to sophisticated technology platforms, such as call management software, Interactive Voice Response systems, predictive dialers (devices used to automate the method of making outbound calls and direct them to an operator when a live person answers, thereby screening out answering machines, busy signals or other operator intercepts) and automatic call distributors, without the cash outlay or maintenance costs that would be required to implement these features in-house. Because of their specialization and experience, outsourced contact center providers are also able to achieve higher quality and productivity, allowing their clients to focus on their core businesses while retaining and enhancing customer relationships.
Today, companies face the challenge of delivering consistent levels of customer service, regardless of the channel of communications utilized or their customers’ locations. This trend has been fueled by the continued growth in Internet and e-mail use, and the increasingly remote nature of customer interactions. Moreover, companies are increasingly focused on better, differentiated customer services and on increasing the value of their customer relationships through the cross-selling of additional products or services. By working in partnership with an outsourcer, a company can focus on its strategy for acquisition, retention and growth of its customer base without being overburdened with the complexities of day-to-day contact center operations.
Contact center activities are becoming central to the way companies choose to enhance customer loyalty and retention. According to IDC (a market intelligence and consulting company specializing in the IT and telecommunication industries), the outsourced contact center market worldwide had gross revenues of approximately U.S.$66.12 billion in 2007, with the Brazilian market contributing with U.S.$3.48 billion. The IDC estimates that five key sectors constitute approximately 80.0% of this market: telecommunications, technology/consumer, financial services, health care and transportation/leisure. The two biggest companies of the Brazilian contact center market (Contax and Atento) together had gross revenues of approximately U.S.$1,076 million in 2006 and U.S.$1,625 million in 2007.
Factors that influence companies worldwide to outsource their contact center needs include the following:
| | • | | Increasing importance for companies to retain and enhance customer relationships; |
| |
| | • | | Increasing need for companies to focus on core competencies rather than non-revenue producing activities; |
| |
| | • | | Rapid changes in technology requiring personnel with specialized technical expertise and continued investment in new contact center equipment and services; |
22
| | • | | Increasing need to integrate and manage complex systems incorporating a variety of hardware and software systems spanning a number of technology generations; and |
| |
| | • | | Extensive and ongoing training requirements. |
Brazilian contact center outsourcers have enjoyed significant growth over the past several years. Several factors contributed to this growth:
| | • | | Increase in telephony penetration.Prior to Brazil’s privatization of state-owned telecommunications companies in 1998, telephony penetration in Brazil was very low, limiting the use of contact centers as an effective way to deliver customer service on a broad basis. Today, a larger portion of the Brazilian population can access customer services in general through different communication channels, including both mobile and fixed-line terminals. According to the Brazilian telecommunications regulatory agency (Agência Nacional de Telecomunicações), or Anatel, total wireline and wireless penetration grew from 42.8 million in 1999 to 160 million in 2007. |
| | • | | Expansion of contact center-intensive service sectors due to economic stabilization and privatization.In the mid-1990s, Brazil implemented successful economic reforms which created a stable macro-economic environment, spurring the growth of financial services and, consequently, the consumer base of these companies. Brazil concurrently privatized large state-owned service providers in the telecommunications, electric, water and gas sectors, which brought about large investments and a rapid growth in customers. |
| | • | | Pressure to reduce costs.Pricing pressures from competition and shareholder demands for higher returns have forced Brazilian companies to streamline personnel, through restructuring and outsourcing, and make other cost reductions, including reducing face-to-face customer services. |
There are still a number of companies in Brazil that maintain contact center operations in-house. We believe that such companies still elect to keep such activities in-house because of a lack of confidence in the quality of outsourced services, even though in-house contact centers may be more expensive to maintain. A key factor for the success of any contact center outsourcer is the ability to provide high quality service at a cost lower than in-house operations.
According to the most recent data provided by IDC, the total number of outsourced workstations in Brazil grew from 90,809 workstations in 2005, to roughly 101,124 in 2006 and 127,670 in 2007, which represents growth of approximately 13.8% and 26.3% in 2006 and 2007, respectively. It is our belief that this increase in outsourced contact center workstations is an indication of substantial growth opportunities for outsourcers of contact center services in the next few years.
In our quest for improving the services we provide to our customers, we launched, on November 12, 2007, a project to voluntarily join the Seal of Ethics of PROBARE — Brazilian Program for Self-Regulation of the Client Relations Market. PROBARE is an initiative of three entities active in the client, consumers and companies relations market in Brazil: ABEMD —Associação Brasileira de Marketing Direto(Brazilian Association of Direct Marketing), ABRAREC —Associação Brasileira das Relações Empresa Cliente(Brazilian Association of Client Relations) and ABT -Associação Brasileira de Telesserviços(Brazilian Association of TeleServices). These entities identified the need for definition of standards of self-regulation in the client, consumers and companies relations sector, in order to improve services provided to consumers and customers contractors.
In order to achieve this prestigious emblem of excellence in service, our Company underwent a rigorous auditing program according to which it had to meet strict requirements. On December 19, 2007, our Antártica site, in São Paulo was officially certified and we are working to fulfill the same requirements in other operational sites.
23
Our Strategy
During the last few years, Contax has been able to achieve and maintain its leadership of Brazil’s contact center market share. According to IDC, we have been able to capture approximately 30.0% of the market growth experienced over the last five years. In 2005, a strategy entitled “Leadership in Execution”, aiming the evolution of our core business, was launched, looking to strengthen our focus on innovation and programs that offer excellent services for our customers.
The strategy was built mainly on two pillars: the improvement of main products (services, sales and credit recovery) and the pursuit of excellence in our support areas and our operational model. With this in mind, our approach to refining our principal product offerings focused on:
Customer care:We feel that one of the reasons many clients are resistant to outsourcing their customer service function is fear of lowering quality and thus jeopardizing the relationships they have with their customers. Being able to assure quality and personalized service in keeping with our clients’ expectations will permit us to win more clients. We expect that by enhancing the customer service model currently in use in the market, implementing actions that make each contact more profitable, raising quality in a consistent way and increasing contact efficiency, we will be able to deliver the high standards expected by the market.
Debt collection:We see potential for development in the debt collection market. Each industry segment and each client has different requests concerning the way a collection should be processed. We believe the successful model used with some of our clients can be successfully implemented in other operations, depending on the needs of other clients. Through developing pilot tests to try new methods of debt collection, integrating management information systems with customers’ needs, providing debt collection operators with proper training, as well as implementing customized forms of variable earnings, we believe that we will be able to continue to grow our customer base.
Telemarketing:The quality of our services in telemarketing has been improving each year. The model we developed along with our oldest client, Telemar, has brought very positive results, proving to be successful both for Telemar and for us. We believe that by customizing this model to specific clients’ needs, we believe that we will be able to fulfill our other clients’ requirements.
The development of our support areas and operational model included the following principal elements:
Human resources:We believe our employees are the key to our success. We focus on attracting and retaining new employees, monitoring their performance and using diverse training methods to meet each client’s needs. By developing a structured career plan and providing various performance initiatives, we are able to achieve employee excellence and instill Contax values in our workforce.
Operational model:By providing our clients with services during the entire customer lifecycle and developing a successful value proposal in Contax’s main product classes, we believe we can continue to enhance our operational model.
IT systems:We believe that infrastructure and technology are important elements in providing superior services and attracting new clients. We seek to sustain a competitive advantage and to distinguish our services by maintaining advanced IT systems and by retaining strong partnerships with leading technology providers.
Commercial model:We have recently added specialized members to our sales force and created a product management marketing function in order to expand our range of clients and services. We are developing new product offerings that focus on specific segments of our clients’ businesses and are continually identifying clients that are not currently “key accounts” to whom we seek to provide a broader range of call center services.
In addition, in 2006, the Company adopted a vision known as “WE MAKE CUSTOMERS FOR LIFE”, which translates into the concept of creating long-term relationships with customers and focusing on business development. Within this context, several actions have occurred throughout the last several years allowing for the implementation of the strategy such as the creation of the Operations Offices, which specializes in customer care, debt collection and telemarketing, as well as the creation of a Department of Products, which has been developing and helping to implement a set of product offers in the three main product lines.
24
Competition
The outsourced contact center sector in Brazil is competitive and fragmented. Our top five largest competitors are listed below. We also compete with a variety of companies, including niche providers, consulting companies, IT providers, and numerous small companies that offer low value-added services (primarily outbound telemarketing services). In addition, we compete with in-house contact centers, which continue to represent the largest segment of contact center activities. In addition, some of our outbound services also compete with other forms of direct marketing, such as mail and e-mail messages, and with traditional media, such as television and radio.
We believe offshore outsourcing, where the contact center provider is not located in the same country as its customers, is neither a threat nor a significant opportunity for us at this time. Because Brazil is a low-cost country and the national language is Portuguese, it is unlikely that contact center service providers in other countries, usually referred to as “offshore” facilities, could provide Portuguese-speaking customer service at a lower cost than providers in Brazil. Although Brazil has competitive labor costs when compared to those of other countries and a large qualified workforce, we do not believe that significant opportunities exist to provide services for other countries at this time. We monitor these opportunities on a regular basis.
We also face competition from automated customer services, through the use of Internet, Interactive Voice Response, voice recognition and other technologies. We provide automated customer services as a part of our contact services and continue to develop our technology in this area. However, an increase in the use of automated services could prevent us from effectively passing through our costs to our clients, and may also shorten the speaking time of our calls.
As a result of intense competition, contact center services are frequently subject to pricing pressures. Competition for contracts for many of our services takes the form of competitive bidding on proposals, which take into account quality, technical and cost factors.
Exhibit II to Regulation No. 17 (Anexo II da Norma Regulamentadora nº 17), approved by Rule No. 9, issued by the Brazilian Labor Department as of March 30, 2007 (Portaria nº 09), sets forth rules related to telemarketing/telephone operators safety and health conditions and establishes sanctions for the breach of such rules. Although compliance with Regulation No. 17, as amended, may result in the increase of costs incurred by both in- house and outsourced contact centers in connection with the safety and health conditions of our employees, complying with such rules provides us a chance of enhancing competitive advantage over smaller players, which face entry barriers into the industry, as well as stimulating outsourcing as a whole.
In 2005 we became, and remained in 2006 and 2007, the leading contact center service provider in terms of revenues (based on information in the most recent financial statements published by Brazilian contact center companies). Our major competitors in Brazil are:
| | • | | Atento. Atento is a part of the Spanish group Telefonica, which in Brazil controls a large fixed-line operator (Telesp), an Internet provider (Terra) and, together with Portugal Telecom, Brazil’s leading mobile operator (Vivo). Atento has operated in the Brazilian market since 1999. After acquiring several companies in the sector, they became one of the largest contact center services providers in Brazil. Two of Atento’s major clients are Telefônica and Unibanco. |
| | • | | Tivit. Controlled by one of the largest private economic conglomerates in Brazil, called the Votorantim Group, that invests in various segments such as cement, financial services and infrastructure. Tivit has increased in Brazil buying two contact center companies: Softway and Telefutura. Following those acquisitions, Tivit has become one of the fifth largest contact center providers in Brazil. Two of Tivit’s major clients are Santander and Telefonica. |
| | • | | Dedic.Dedic is part of the Portuguese group Portugal Telecom, which controls, jointly with Telefonica, Brazil’s largest mobile operator Vivo. Dedic renders services, directly or indirectly, primarily to Portugal Telecom’s subsidiaries in Brazil. |
25
| | • | | ACS.Controlled by Algar Group, a diversified Brazilian conglomerate, ACS was founded in 1999 with headquarters located in Uberlândia, in the state of Minas Gerais. We believe ACS’s two main clients are CTBC (a telecom operator in Uberlândia that is part of the Algar Group) and American Express Brazil. |
| | • | | Teleperformance. Teleperformance is a French company that operates in approximately 45 countries. In 2004, Teleperformance increased its Brazilian operations by merging with Companhia Brasileira de Contact Center, after which Teleperformance became one of the largest contact center service providers in Brazil. Two of Teleperformance’s major clients are UOL (one of the major Brazilian Internet providers) and Sky/Direct (a Pay-TV provider). On August 14, 2007, Brasil Telecom, which was its largest client in Brazil and represented approximately 70.0% of their revenue, terminated its service agreement with Teleperformance. |
Our Business
We offer a variety of integrated customer-interactive products and services covering all stages of the customer lifecycle through multiple communications channels. Each of our main service offerings (customer care, telemarketing, technical support, retention, and debt collection, as described below) showcases our ability to add value to our clients’ Customer Relationship Management (CRM) strategies, while anticipating their needs. CRM refers to our strategy of identifying customer needs, improving customer interactions, and customizing contacts, sales approaches, and automation to provide optimum service to each type of customer to maximize the bottom line benefits to the organization.
We believe we operate in a flexible environment that can accommodate dynamic shifts in volume, workload and staffing requirements. We seek to build upon and strengthen our end-customer relationships on behalf of our clients. Our operators are thoroughly trained in the applicable products and services they are supporting and, as a result, they can act as a seamless extension of our clients’ efforts to acquire and service their end-customers.
Our business approach is geared toward creating unique products and services that are developed jointly with our clients, leveraging our experience and best practices for each new client we serve. Building on these tailored products and services, we have developed particular strengths (e.g., customer retention, debt collection) that we can leverage by servicing other clients across diverse sectors.
The main services rendered by us are the following:
| | • | | Customer Care. Our customer care solutions focus on the assurance of the excellence of customer care operations and on understanding the reasons why customers contact the Company, which are followed by specific recommendations for improving customer care service. Contax also develops cross-selling and up-selling strategies associated with customer service efforts and identifies opportunities for automation. Our customer service solutions are segmented into interactive voice response (IVR), personal services (B2C and B2B), technical support, field support and back-office. |
| | • | | Telemarketing. This service is focused on providing efficient solutions for attracting new clients (whether through active, receptive or blended approaches) and improving returns from the existing portfolio, always focusing on the specific characteristics of each client and its target market. The main pillars for achieving and exceeding these targets are (i) efficient contact, through dialers and enhancement of contact lists, and (ii) the quality of the salespeople, achieved through recruiting focused on the appropriate profile of potential employees, regular training and motivation. |
| | • | | Technical Support. We provide comprehensive technical product support for our clients’ customers. For example, we handle troubleshooting calls of consumer products, respond to software and hardware problems, provide support for ISPs’ dial-up and broadband customers, and manage corporate IT help desks. For such services, we employ qualified personnel with specialized technical training in dedicated teams. |
26
| | • | | Retention. We provide our clients with customer retention services, whether by persuading their end-customers not to cancel a service or by observing customer behavior and taking preventive measures to avoid cancellation requests. We collaborate with our clients by mapping final customers’ opinions, in order to ensure the adoption of adequate strategies for reversing intentions to cancel services. |
| | • | | Debt Collection. We design debt collection strategies together with our clients to maximize results, while emphasizing customer retention. We participate from the early stages of developing our clients’ collection strategy to the actual execution of the strategy, using database filters (systems that prioritize contacts and determine the type of service each customer will receive), predictive dialers and other automatic contact tools, such as voice mail and text messages typically sent to wireless handheld devices, in order to maximize the likelihood of customer contact and behavior models that enable us to categorize customers’ risk and identify the most efficient techniques of interacting with customers. In order to enhance our performance, we launch pilot programs to test the statistical efficiency of specific tools and strategies. |
The percentages of revenues, derived from each of the services listed above, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| Services | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
| Customer Care | | | 53.0 | % | | | 54.0 | % | | | 57.7 | % |
| Telemarketing | | | 13.7 | % | | | 12.3 | % | | | 11.9 | % |
| Technical Support | | | 2.5 | % | | | 2.3 | % | | | 2.7 | % |
| Retention | | | 5.0 | % | | | 3.9 | % | | | 3.6 | % |
| Debt Collection | | | 17.1 | % | | | 15.3 | % | | | 13.2 | % |
| Other | | | 8.7 | % | | | 12.3 | % | | | 10.9 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | |
We also offer other services such as dispatch, back-office support, and surveys, among others. Furthermore, we continuously work with our clients to develop new products.
On a monthly basis, we handle approximately 160 million customer contacts over the telephone at our 22 contact center sites. Our technology infrastructure provides for the effective distribution of calls to one or more of our sites.
Markets and Clients
We provide contact center services primarily across the following sectors:
| | • | | Telecommunications. We provide a full range of contact center services to Telemar, our largest client. Telemar’s operations include fixed line terminals, long-distance services, mobile services, as well as broadband and corporate voice and data services. In addition to traditional customer care services, we deliver extensive client retention and debt collection services for /Telemar’s retail and corporate customers. Because we have a strong relationship with Telemar and because other telecom groups control their own contact center companies, we have not actively pursued other opportunities in this sector. |
| | • | | Financial Services.New financial products and service offerings have expanded our opportunities in this sector. We provide a broad range of services to the credit card, retail bank and insurance segments, as well as to consumer credit companies. This sector continues to grow in importance for us since many financial institutions have in-house operations that fit into our strategy of focusing on clients with high volume and highly complex services. |
| | • | | Utilities.There are several large companies in Brazil in the power, water and sewage, and gas distribution segments. Currently, we provide services to a few power distribution companies in the Southeast and Northeast regions of Brazil. We intend to continue to expand our activities in this sector and our success could be enhanced if there is further privatization in the water and sewage segment. |
27
| | • | | Internet. We have developed specific end-to-end services for Internet service providers, or ISPs, by servicing iG, Brazil’s largest ISP, and, more recently, Telemar’s new ISP subsidiary. We are particularly interested in providing customer acquisition, retention and technical support services to the growing number of broadband Internet access providers. |
Other key sectors include pay TV, travel and transportation, among other service providers. We conduct all of our business in Brazil and all of it in Portuguese.
The percentages of revenues, with respect to each sector listed above, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| Sector | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
| Telecommunications | | | 50.8 | % | | | 57.6 | % | | | 64.5 | % |
| Financial Services | | | 33.5 | % | | | 31.5 | % | | | 27.4 | % |
| Utilities | | | 2.0 | % | | | 1.9 | % | | | 1.5 | % |
| Internet | | | 1.3 | % | | | 1.2 | % | | | 1.1 | % |
| Other | | | 12.4 | % | | | 7.9 | % | | | 5.6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Client Contracts
Most of our relevant contact center services agreements range from three to six year terms and allow clients to terminate services after an initial lock-in period, which varies from 18 to 60 months. Most of these contracts establish penalties calculated as a percentage of the estimated value due for the remaining term of the agreement. We have historically established long-term relationships with our clients based on the continuous renewal of our contracts and expansion of the services we provide.
Pricing models have evolved over the last few years. In the past, most of our contracts were based on capacity rental, where the client defined the number of workstations to be employed for a fixed price. Most of our inbound service contracts are now billed based on speaking time, where the client pays for each minute of conversation of our operators with customers. Other services are mostly priced on a pay-for-performance basis, where we either receive a combination of a fixed-rate fee plus a success fee or payments that are wholly performance-based. Typically, performance-based compensation is used in debt collection and telemarketing services.
Our services can be rendered on a fully-outsourced or partially-outsourced basis. Partially-outsourced services may include providing our contact center infrastructure when clients desire to use their own employees or providing our human resources when clients have already invested in their own facilities.
Nearly all of our contracts include Service Level Agreements (SLAs) that define performance requirements and minimum quality thresholds. Service Level Agreements are agreements between service providers and their customers that define, among other things, the services provided, the metrics associated with these services, acceptable and unacceptable service levels (e.g., speed of answer goals), liabilities on the part of the service provider and the customer in the case of non-performance, and actions to be taken in specific performance. The most common Service Level Agreement provision on inbound services is related to the time a customer should wait to be serviced. This is typically measured as the minimum percentage of phone calls that should be answered in a maximum time frame (e.g., an “80/20” Service Level Agreement provision requires that at least 80.0% of the calls will be answered in no longer than 20 seconds). With the increased complexity of outsourced services, more Service Level Agreement provisions are required by clients, such as service interruption, adherence to defined scripts, and even operator turnover. If we do not meet a Service Level Agreement provision, we may be liable for penalties or a price reduction of our services.
28
Our clients are entitled to receive penalties and indemnifications from us when they face operational problems or damages resulting from an act of imprudence, negligence, gross negligence or willful misconduct by us in connection with the delivery of our services. These penalties, and consequently the respective amounts due thereunder, vary depending on the type and level of each failure. Hence, we cannot quantify an amount for these penalties in advance, since it is only possible to determine the nature and extent of those failures when a specific event occurs. Regarding our indemnification obligations, we have other contracts pursuant to which we may be required to pay the total amount of the damages incurred by a client, as calculated by the client, an arbitrator or a judge in a legal proceeding. As a result, we are unable to estimate the amount of these indemnifications, since such amount would be directly related to the nature and extent of the damages incurred by our clients and caused by us, our Directors, Officers, employees or subcontractors. Our exposure in any of these circumstances could be significant.
Although still significantly dependent on our contracts with our two largest clients, Telemar and Orbitall, we have seen a steady decrease in their contribution to our total revenues in the past few years. For the years of 2005, 2006 and 2007, the contract with Telemar represented 64.5%, 57.6% and 50.7% of our revenues. The revenue derived from Orbitall’s operation represented 17.4% of our total revenues in 2005, and a stable 15.0% for both 2006 and 2007 fiscal years. The reduction in participation over our revenue is explained by (a) our continued commercial efforts to further our relationship with other existing clients as well as to attract new clients, (b) our performance maximization through productivity gains, changes in the assistance processes in several operations, which resulted in less overall volume of businesses and total revenue from these two clients, and (c) the improvement that these clients, mainly Telemar have made in their internal processes, the automation of some services and the requirement of reduction of some SLAs.
Result Variance and Seasonality
We experience variations in our results of operations primarily due to the timing of our clients’ Customer Relationship Management initiatives, such as customer acquisition and sales campaigns. For example, we experience higher activity in December, which is typically a month of higher volume of promotional activities and sales for our clients.
Our periodic results may also be impacted by the start of significant operations under a new contract or the termination of an existing one. The start of a contract may adversely affect our results, since we incur start-up costs that are recovered throughout the course of the contract, such as hiring and training personnel and IT implementation. The termination of our existing contracts may also adversely impact our results, as we would incur increases in costs relating to the severance of our employees and the reallocation of our assets, as well as suffer lower utilization rates of our facilities.
Another relevant factor that may impact our results is the practice of annual rate adjustments, usually related to past inflation. This practice is very common in Brazil and some of our contracts allow for rate adjustments on an annual basis while some of our costs (e.g., telecommunications, leased facilities) have periodic rate adjustments according to past inflation. If any significant client contract has its rate adjusted, our monthly results may be positively impacted in relation to the previous month. We are currently in negotiations with the labor union and any increase in our employees’ wages or benefits that may result from the conclusion of these negotiations may have an impact on our business until the contractual rate adjustments with our clients become effective. Our annual labor union negotiation typically results in compensation increases, which could take the form of a percentage salary increase and/or one-time payment. In the event of the latter, our cash flow in a given period would be more acutely affected.
Human Resource Management
We believe human resources are the key to the success of our business. In December 31, 2007, our headcount totaled 61,397 employees. Accordingly, we continuously refine our approach to hiring, training and managing qualified personnel at all levels of our organization, which we believe to be one of our core strengths. We offer classroom, online and on-the-job training programs for our employees, ranging from training regarding information about our clients and the products and services they offer to techniques of telephone-based sales and customer service. Once hired, each new operator receives on-site training, the duration of which depends upon the complexity of the services to be provided.
29
In order to guarantee productivity and quality of our employee’s performance, we have developed specific training programs related to customer care, telemarketing and debt collection techniques. For activities with performance-based compensation services, we have specific training programs to guarantee constant results.
We also focus on employee retention. This effort is important since initial training, particularly for inexperienced and young recruits, is costly and time consuming. Moreover, better-qualified and more experienced operators generally achieve higher productivity levels and greater revenue per workstation.
We have an aggressive internal employee promotion program. Our systems and tools allow us to track each operator’s performance using predefined indicators, such as punctuality, absence and productivity. These systems allow us to reward our best employees, and provide specific training for underachievers, resulting in greater productivity and reducing total human resources costs. We have variable compensation programs for activities that are linked to the achievement of performance-based goals.
Facilities
Our principal executive office, known as Passeio, is located in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. This facility currently serves as the headquarters for senior management and the financial, information technology, human resources and administrative departments. Passeio also houses some contact center operations, with 3,199 workstations, and it is currently our largest facility with 24,924 square meters. We currently operate a total of 22 contact centers in seven different states, plus Brazil’s Federal District.
We believe our existing facilities are adequate to meet current requirements and to accommodate minor expansions. Instead of maintaining extra capacity for future demands, we have opted for a strategy of high capacity utilization. In order to meet aggressive implementation requirements of new clients, we have developed a group of suppliers with standardized products and services, capable of quickly responding to our need for additional workstations or facility expansion. Furthermore, in locations such as São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, where there is a higher likelihood of future growth from client demand, we seek to lease premises that allow for significant expansion, if necessary.
We seek new locations where there are favorable workforce demographics, ample telecommunication and electricity services and easy access to transportation for employees. We also perform a cost-benefit analysis of every potential location in light of rental costs, setup/retrofit costs, local tax incentives, safety features, and the cost of future expansion. This has led us to achieve competitive advantages in connection with the location of our facilities: (a) our operations are geographically spread, covering a substantial part of the main economic areas of Brazil; and (b) we have important operations in places like the Northeast of Brazil which allow us to render services at lower general costs, mainly as a result of local tax incentives and high performance of our personnel at lower labor costs.
30
The following table sets forth additional information concerning our facilities at December 31, 2007:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | # Work | | | # | | | Sq. | | | |
| Sites | | | | State | | Stations | | | Employees | | | Meters | | | Expiration |
| Passeio1 | | | | RJ | | | 3,199 | | | | 6,857 | | | | 24,924 | | | Oct. 1, 2010 |
| Niterói | | | | RJ | | | 1,617 | | | | 4,139 | | | | 13,624 | | | Dec. 30, 2009 |
| Makenzie | | | | RJ | | | 1,808 | | | | 4,233 | | | | 10,077 | | | Dec. 30, 2009 |
| Mauá | | | | RJ | | | 1,558 | | | | 2,967 | | | | 9,702 | | | Feb. 28, 2013 |
| São Cristóvão2 | | | | RJ | | | 491 | | | | 2 | | | | 5,632 | | | Not Applicable |
| Antártica | | | | SP | | | 2,926 | | | | 6,091 | | | | 27,723 | | | June 13, 2009 |
| Paulista | | | | SP | | | 2,417 | | | | 6,105 | | | | 17,574 | | | Dec. 31, 2011 |
| Rubens Meireles | | | | SP | | | 284 | | | | 625 | | | | 2,752 | | | July 2, 2011 |
| Augusta | | | | SP | | | 279 | | | | 705 | | | | 2,863 | | | May 31, 2011 |
| Inhaúma3 | | | | SP | | | 472 | | | | 52 | | | | 3,350 | | | June 30, 2011 |
| Oliveira Coutinho4 | | | | SP | | | 569 | | | | 9 | | | | 7,500 | | | Not Applicable |
| Lapa5 | | | | SP | | | 1,255 | | | | 2,947 | | | | 17,000 | | | April 2, 2012 |
| Prado | | | | MG | | | 2,725 | | | | 6,223 | | | | 11,998 | | | Dec. 31, 2009 |
| Nova Lima | | | | MG | | | 237 | | | | 541 | | | | 977 | | | Oct. 31, 2011 |
| C. da Pólvora | | | | BA | | | 1,337 | | | | 3,413 | | | | 7,757 | | | Dec. 30, 2009 |
| Comércio | | | | BA | | | 1,317 | | | | 3,086 | | | | 11,000 | | | April 01, 2009 |
| Borges de Mello | | | | CE | | | 2,547 | | | | 6,282 | | | | 15,246 | | | Dec. 31, 2009 |
| Pr—ncipe | | | | PE | | | 661 | | | | 1,511 | | | | 3,805 | | | Dec. 30, 2009 |
| Conquista | | | | PE | | | 860 | | | | 1,966 | | | | 9,256 | | | June 24, 2011 |
| Porto Alegre | | | | RS | | | 382 | | | | 1,004 | | | | 1,290 | | | Undefined term |
| Distrito Federal | | | | DF | | | 54 | | | | 91 | | | | 320 | | | June 30, 2008 |
| Contorno | | | | MG | | | 1,048 | | | | 2,548 | | | | 9,546 | | | July 30, 2010 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | | | | | 28,043 | | | | 61,397 | | | | 213,916 | | | |
| | | |
| 1 | | Includes both contact center operations and our headquarters. |
| |
| 2 | | We acquired this real property on December 20, 2007. We own the title deed, but it has not yet been registered at the Notary Public. The price of the building and land acquired by Contax on December 2007 was R$3,459 thousands. This site was launched to house operations for financial clients, where we manage the technological park and infrastructure of the clients’ contact center, while the client is in charge of personnel. |
| |
| 3 | | This site was also launched to house operations for a financial institution, where we manage the technological park and infrastructure of the client’s contact center, while the client is in charge of personnel. |
| |
| 4 | | Since March 3, 2007, we have been rendering our services to a financial institution from this site, on which such financial institution is the lessor and is in charge of personnel in this site. |
| |
| 5 | | Launched in September 2007, the Lapa site was created to accommodate the increase in the volume of our operations. |
Information Technology
Our growth and business success, among other factors, depends on highly effective technology and therefore, in 2007, Contax created a New Technologies Department to oversee our use of new technology, with a focus on:
| | • | | Research of new technologies and benchmarks to allow permanent business growth; |
| | • | | Identify promising partners or technologies adhering to our strategy; and |
| | • | | Evaluate infrastructure alternative solutions and products, in order to reduce operational costs and enhance business effectiveness to continuous increase customer’s satisfaction. |
31
Significant investments in telecommunications and IT infrastructure have continuously been made with the purpose of meeting our and our clients’ requirements. It is vital that we continue to invest in the development of new and innovative systems on a timely basis in order to maintain our competitiveness.
We use industry-standard software and hardware from IBM, Lenovo, Microsoft, Oracle and Cisco, EMC, Avaya, Nortel, SAP, Novell, Genesys, Dell, Altitude, Intervoice, Nice, CA, Symantec and others for operations and administrative functions, in addition to our own internally developed software and applications. For the purposes of interacting with our clients’ databases, we have implemented highly customized services. In some services, we also utilize systems and software developed by our clients.
We have developed the internal capability to design software services applicable to our business requirements. Our in-house software development team is comprised of approximately forty systems programmers and analysts. We have successfully developed in-house systems that have resulted in a competitive advantage by allowing us to tailor our services as well as control and reduce our operational costs, particularly those related to employee productivity. See “– Our Strategy.”
We utilize sophisticated technology for our business, from our telephony platforms (Avaya and Nortel) to our workstations, computer equipment (Dell, IBM, Lenovo and others) and professional recorders, as well as productivity tools, such as predictive dialers, Interactive Voice Response Units, automated call distributors and workforce management software. Our customer service professionals have the tools to initiate and efficiently handle millions of service interactions on a daily basis. Our telephony infrastructure, partnered with Tmar’s as well as other carriers’ data and telephony networks, provide several options when routing voice and data contacts throughout our different sites. These platforms support such features as voice over IP, or VoIP, best services routing, skills-based routing and schedule adherence.
During the last fiscal year some new technologies have been deployed:
| | • | | Digital voice recording: captures and stores service calls. |
| | • | | Blade server: compact servers which fit in a unique chassis sharing energy, cooling system, drivers, ports and other blade servers. These servers combine energy efficiency, consolidation and mobility, reducing costs and increasing productivity. |
| | • | | Multiuser solution (CPU share): allows up to 10 users to share a unique CPU (computer processing unit). |
| | • | | Service monitoring software: monitoring service that prevents activity interruption problems in the network. Able to issue reports and manage network services. |
| | • | | Thin clients: we have plans to implement this solution in a large scale, aiming to reduce desktop size computers, running few or no installed applications, with strong server dependency to process tasks. The main benefits are low energy consumption, decrease of technical support needs and increase warranty usage. |
Our IT infrastructure has also been improved due to the selection of ISACA’s CobiT 4.0 as our IT framework, providing more transparency, better quality and lower costs per transaction. Our business partners – software developers, professional services, service desk and others – are encouraged to comply with well-known and accepted best practices, such as:
| | • | | the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, or ITIL, a framework of best practice approaches intended to facilitate the delivery of high quality IT services. ITIL outlines an extensive set of management procedures intended to support businesses in achieving both quality and value, in a financial sense, in IT operations. These procedures are supplier independent and have been developed to provide guidance across the IT infrastructure, development, and operations; |
32
| | • | | the Project Management Book Of Knowledge, or PMBOK, published by the Project Management Institute, or PMI, and widely accepted to be the standard in project management. The PMBOK documents information and practices applicable to any type of project, not just IT related projects; and |
| | • | | the Capability Maturity Model, or CMM, a process improvement approach based on a process model that can assess organizations against a scale of five process maturity levels. Each level ranks the organization according to its standardization of processes in the subject area being assessed, and the subject areas can be as diverse as software engineering, systems engineering, project management, risk management, system acquisition, IT services and personnel management. |
Our Wide Area Network (computer network which covers a wide geographic area), or WAN, infrastructure is based on high-speed links that use the latest technology in connectivity. This enables good performance and provides security to the networking environment of our clients. The entire Local Area Network, or LAN (computer network which covers a restricted/limited geographic area), and WAN environments are tailored to support VoIP communication using standardized questions and answers, with focus on segregation of information to guarantee availability and reliability in data and voice communication.
Capital Expenditures
The following table sets forth our capital expenditures for the periods indicated below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
| | | (in thousands ofreais) | |
| |
| Telecommunications and IT systems | | | 76,665 | | | | 64,035 | | | | 75,564 | |
| Leasehold improvements | | | 33,287 | | | | 36,549 | | | | 37,392 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | | 12,249 | | | | 5,510 | | | | 8,552 | |
| Other | | | 11,217 | | | | 2,764 | | | | 7,188 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Total capital expenditures | | | 133,418 | | | | 108,858 | | | | 128,696 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Our capital expenditure is mostly linked to our rate of growth, with a small part (approximately 20.0%) being applied towards general upgrades and quality improvements of our existing systems.
Sales and Marketing
Our commercial efforts are focused on the largest Brazilian economic conglomerates, which we believe have the potential need for a significant number of outsourced services. As a result of this strategy, we channel virtually all of our sales efforts through our direct corporate sales force, consisting of twelve key account managers, led by three commercial managers and supported by a team of seven internal sales representatives who are responsible for supporting the key account managers in designing commercial proposals. The key account managers are classified into three groups: the “Hunter” group focuses on acquiring new clients, the “Farmer” group focuses on expanding business with existing clients, and the “Farmer Itaucard/Citibank/Orbitall” group focuses on expanding our service to a specific client in the credit card processing business.
According to our “Leadership in Execution” strategy, in 2005, we structured the Products Solutions Development team in order to enable us to deliver customized products to our clients. Based on our understanding of our customers’ needs and specific requirements, this team generates customized solutions using in-house knowledge and experience. Furthermore, this division is responsible for managing the entire service delivery process, interfacing with various other areas of Contax.
33
Moreover, we also organize sales, products and marketing teams with two main guidelines: (1) structuring and developing Contax’s service offerings, focused on three lines of services: Customer Service, Sales and Debt Collection; and (2) assisting our operational divisions in implementing best practices.
In 2006, we launched a strategy known by the slogan “WE MAKE CUSTOMERS FOR LIFE”, which illustrates our deep commitment to, and alignment with, our clients’ long-term satisfaction. This new vision stimulates us to organize and present ourselves as a strategic partner, focused on the final customer of our clients, thus creating an interdependent relationship with our direct clients. We intend to be a relationship company rather than a simple service company.
Insurance
Our assets and liabilities of material value and high risk are currently covered by insurance policies maintained by Contax Holding and TNL Contax, which guarantee coverage for material damage and loss of revenue arising from such damage. In May 2008, TNL Contax obtained its own insurance policies, all renewed until May 2009, in the amounts listed below, which it believes will be adequate for the nature and risks of its activities and sufficient to ensure the protection of its net worth and operational continuity.
Our insurance policies comprise the following coverage, measured by the risks and nature of our assets:
| | | | | | | | | |
| Coverage Type | | Amount Covered in 2007 | | Amount Covered in 2008 |
| Property damage | | R$ | 70,211 thousand | | R$ | 61,400 thousand |
| Business interruption | | R$ | 51,305 thousand | | R$ | 42,654 thousand |
| General liability | | R$ | 5,000 thousand | | R$ | 10,000 thousand |
| Directors and Officers’ liability | | U.S.$ | 60,000 thousand | | U.S.$ | 100,000 thousand |
Intellectual Property
We do not have any trademarks filed or registered under our name in Brazil. However, we use all of the “Contax” trademarks which were filed by TNL. TNL holds 17 trademarks containing the word “Contax” filed with the Brazilian Institute for Intellectual Property (Instituto Nacional de Propriedade Intelectual), or INPI, which will be assigned to us by TNL at no cost, upon authorization granted by INPI. Of these trademarks, eight were already registered and nine trademark requests are still pending for registration with INPI. Four of these nine trademarks are currently being opposed by third parties. However, these opposed trademarks are not linked to our core business or widely recognized in the Brazilian market as part of our identity. Hence, we are not significantly dependent on them and, as a result, even if such oppositions would cause us to lose the opposed trademarks, this would not have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
There are currently seven domain names registered with the “Contax” name at the Center of Information and Coordination of Dot BR – NIC.BR (Núcleo de Informação e Coordenação do Ponto BR – NIC.br), the Brazilian institution responsible for registering domain names. Among them, there are four (www.contax-net.com.br,www.contaxt.com.br,www.contaxtelemar.com.br,www.telemarcontaxt.com.br) registered under the name of Contax Holding, one (www.contax.com.br) registered under the name of TNL Contax, and two (www.contax.net.br,www.contaxt.net.br) registered under the name of TNL. The domains registered by TNL will be assigned to us at no cost, upon authorization of NIC.BR.
Item 4A. Unresolved Staff Comments
Not applicable.
Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects
The following discussion and analysis of our results of operations, financial condition and liquidity should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this annual report.
34
Executive Overview
We provide contact center services, such as customer care, telemarketing, technical support, customer retention, and debt collection. Continuing a leadership plan initiated in 2005, our net revenues of R$1,365,815 thousand in 2007 makes us the largest contact center provider of Brazil in terms of revenues and represented an increase of 12.1% as compared to 2006, based on information provided by IDC and available in the most recent financial statements published by Brazilian contact center companies.
Our services vary based on the nature of the contact interaction (i.e., whether the contact is inbound or outbound), and are generally rendered from our 28,043 workstations (in 2007) through various communication channels, such as by telephone, web, mail, e-mail and fax. Our revenues are calculated based on a number of indicators, including the number of workstations, speaking time and performance targets, which vary in accordance with the type of service and contractual arrangements we have with our clients.
Our results are significantly impacted by the following factors, among others:
| | • | | the acquisition or loss of a major client; |
| | • | | fluctuations in demand for our services; |
| | • | | our ability to pass through to our clients increases in costs; |
| | • | | our ability to efficiently manage our workforce productivity; and |
| | • | | success or failure with respect to our performance-based services. |
Acquisition or Loss of a Major Client
The acquisition or loss of a major client may have a significant effect on our results. Beginning operations under a new contract may adversely impact our results, since we have start-up costs that are recovered throughout the course of the contract, such as hiring and training personnel and IT implementation. The termination of our existing contracts may also adversely affect our results, as we would incur costs to terminate employees and re-allocate assets, as well as suffer lower utilization rates of our facilities.
Fluctuations in Demand for Our Services
The increase and decrease of services required by our major clients has a significant impact on our results, particularly as such fluctuations affect capacity utilization rates. The growth of our clients’ customer bases can increase the overall need for contact center services, such as customer service, telemarketing, collection and retention. If our clients’ customer bases erode or other events occur, such as increased automated customer service, a decrease in call volume and/or speaking time and, consequently, a decrease in our revenues could result.
Our Ability to Pass Through to Our Clients Increases in Total Costs
Our ability to obtain rate adjustments to compensate for increased costs is a significant factor in our results. Our business is very labor intensive and personnel costs are among the key factors impacting our costs. These costs include wages, costs of employee benefits and payroll taxes. For 2007, personnel costs accounted for 73.5% of our total costs, while the remaining 26.5% represented costs associated with third-party services, depreciation and our facilities.
Our annual collective labor negotiations involve the discussion of compensation and benefits. To protect against cost increases related to telecommunications, energy and our leased facilities as well as the impact of inflation, most of our contracts have annual rate adjustment clauses that allow for price increases to cover any such cost escalation. We may decide not to exercise the right to adjust prices fully in view of competitive conditions and/or other client relationship issues.
35
Our Ability to Efficiently Manage Our Workforce Productivity
Our profitability depends largely on the productivity of our workforce. Workforce productivity involves both traffic planning, which consists of designing facilities and resources to meet user requirements, and corresponding workforce management.
Inbound services based on speaking time represented 45.0% of our net revenues in 2007. Efficient traffic planning is key to the profitability of our services, by bringing the number of operators as close as possible to the levels required to deal with incoming call volume. An excess number of operators, based on an overestimated forecast, may cause us to lose profitability due to idle capacity. In contrast, if there are more incoming calls than originally forecasted, we may not have enough operators to deal with the additional call volume and we may be subject to Service Level Agreements’ penalties.
Workforce management involves team scheduling that requires the use of sophisticated planning tools to determine the number of employees scheduled at each shift for each type of service, according to our forecast of call volume and speaking time per call, as well as complying with all labor regulations related to our services. We employ advanced planning and control software packages and have developed several systems that contribute to increased employee productivity. These systems include proprietary software that links payroll to employee login time and a company-wide intranet that measures individual and team performance indicators. A significant deviation in these performance indicators could have a material impact on our results.
Success or Failure with Respect to Our Performance-Based Services
Approximately 29.0% of our net revenues in 2007 were derived from operations with performance-based revenues, which involve telemarketing and debt collection services. Performance targets include successful sales and collection percentages on bad debt, among other performance indicators. For example, if we are able to collect more money in a given month, our revenue for such debt collection services rendered can be significantly higher and thus more profitable. Our success or failure on such performance-based services can significantly impact our results in any given period.
Key Events in 2007
Volume of Operations:
During the past fiscal year, we experienced an expansion in our volume of operations, primarily in the second half of 2007. In addition to contracts with new clients, our growth resulted from the expansion of services provided to our existing clients (especially in the financial sector). This growth in new services required an increase of 25.2% in workstations, from 22,407 workstations in December 2006 to 28,043 workstations in December 2007. Our headcount also increased 25.0%, from 49,132 employees in December 2006 to 61,397 employees in December 2007.
The increase in size and also the ability to readjust contracts with clients to reflect cost increase translated into a net revenue increase of 12.1%, so that in 2007 net revenue came to a total of R$1,365.8 million as compared to R$1,218.6 million in 2006 (an increase of R$147.2 million).
In 2007, Contax’s growth resulted mainly from the increase of revenues derived from our other customers besides Telemar, which increased 32.3% from 2006 to 2007. From the product point of view, customer care continued to account for the biggest portion of net revenue, representing 53.0% of the total. Debt collection and telemarketing accounted for 17.1% and 13.7%, respectively, and we firmly believe that they have significant growth potential in the coming years.
36
Internal Controls:
During the last few years, Contax has been working to improve its corporate governance, giving special attention to implementing and periodically evaluating all of the internal controls mechanisms and their alignment with the best managerial practices.
Various areas of the Company, including billing, treasury, accounting and human resources, were involved in this project that started in 2006, when our internal audit area was created, and facilitated our adherence to Sarbanes-Oxley, or SOX, legislation. The outcome of the project was the improvement in the Company’s internal controls and procedures.
For the year ended on December 31, 2007, Contax, as an accelerated filer, is required to obtain from its outside auditors an attestation report on management’s assessment of the issuer’s control over financial reporting pursuant to requirements established by SOX. See Item 15 – Controls and Procedures.
Stock Option Plan:
Our Stock Option Plan was approved at our general shareholders’ meeting held on April 16, 2007. The purpose of our Stock Option Plan, established pursuant to article 168, paragraph 3, of Law no. 6,404/76, is to attract executives to the Company, as well as to retain and ensure a closer alignment between the interests of the management of the Company and the interests of the shareholders, sharing the risks of the capital market.
Reverse Stock Split:
Due to numerous expansion plans dating back to the Telemar days, Contax inherited several million “inactive” shareholders. In an effort to reduce unnecessary administration and operating costs and to provide a low cost form of liquidity for these small shareholders, Contax decided to do a reverse stock split with the outcome being a significant reduction of shareholders base in Brazil. On October 17, 2007, our shareholders approved the Reverse Stock Split of all shares representing the Company’s capital stock at the ratio of twenty (20) shares for one (1) share of same type. Since ADR holders are mainly concentrated in the hands of institutional investors in large quantities, no Reverse Stock Split took place in relation to the ADRs, so that currently the ratio is 20 ADRs for one (1) preferred share.
Since November 19, 2007, the shares representing the Company’s capital stock have been traded in the new ratio of 20:1.
After we decided to conduct a reverse stock split in the proportion of 20 shares to 1, our shareholders were given a month to either acquire new stock in order to hold at least one share according to the new ratio or to sell their shares free of transaction costs. After the stipulated timeframe, however, there were still some shareholders that had not taken any action and therefore, were left with fractions of shares. The Company sold part of these fractions in auctions at the Bovespa, however, there are still remaining fractions of shares. A new auction date will be disclosed in the near future.
Share Buyback Program:
On March, 2007, our second buyback program, which had been approved on November, 30, 2006, ended. The Company bought back 5,298 thousand common shares (corresponding to 265 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 24,058 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 1,203 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split).
On July 26, 2007, the Company approved its third share buyback program, amounting to the acquisition of 3,193 thousand common shares (corresponding to 160 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 18,277 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 914 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split).
37
With the three programs over 2006 and 2007, the Company bought back 14,378 thousand common shares (corresponding to 719 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 54,109 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 2,705 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) repurchased. From these total, 10,878 thousand common shares (corresponding to 544 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 54,109 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 2,705 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) were cancelled and 3,500 thousand common shares (corresponding to 175 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) were held in treasury, without reducing the Company’s capital stock.
Altogether, the Company invested R$161 million in the three buyback programs, of which R$41 million in 2006 and R$120 million in 2007.
BNDES Loan Agreement:
On August 23, 2007, the Company’s Board of Directors signed a loan agreement of R$216.5 million from BNDES (Brazilian Development Bank) for the subsidiary TNL Contax S.A., as approved by the Executive Board of BNDES on May 22, 2007. Repayment will occur within a six-year settlement term, including a two year grace period, with an annual cost of TJLP (the Brazilian long-term interest rate) plus 2.0%.
The funds are for increasing installed capacity, upgrading current facilities, training programs, improving service quality and productivity and investments in marketing activities, within the PROSOFT- Corporate (Software Industry and Correlated Services Development Program).
In October 2007, the first tranche of the BNDES loan was provided in the amount of R$100 million, followed by additional tranches on the January 28, January 30 and June 12, 2008, in the amounts of R$40 million, R$10 million and R$61.8 million, respectively. The funds received so far from BNDES amount to a total of R$211.8 million.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
In preparing our financial statements, we have relied on estimates and assumptions derived from historical experience and various other factors that we deemed reasonable and relevant. “Critical accounting policies” are those that are important to the portrayal of our financial condition and results and require management’s most difficult, subjective or complex judgments, estimates and assumptions.
The application of these critical accounting policies often requires judgments made by management regarding the effects of matters that are inherently uncertain. Our estimates, including but not limited to the provisions for accounts receivable and contingent liabilities, may differ from the actual value of such assets or liabilities. The following is a discussion of our critical accounting policies, including some of the variables, assumptions and sensitivities underlying the estimates relating to:
| | • | | depreciation of property and equipment; |
| | • | | payroll and related accruals; |
| | • | | deferred and recoverable income tax and social contribution. |
38
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenues on an accrual basis at the time services are rendered, except with respect to some of our performance-based services, which we recognize upon their measurement and acceptance by our client. Most service contract revenues are calculated based on indicators such as quantity of workstations, speaking time and on performance targets. Revenues are calculated based on information available in our IT systems that relate to the volume of data services rendered to each client. Revenues related to our performance-based services are calculated based on data available in our and our clients’ IT systems. In addition, we usually allocate operation managers to review, reconcile and discuss such indicators with clients. Some revenue adjustments are recorded after discussions with such clients.
Depreciation of Property and Equipment
We depreciate property and equipment using the straight-line method at rates we judge compatible with the useful lives of the underlying assets. The useful lives of IT equipment and Furniture and fixtures were reviewed due to the reduction of the estimated economic useful life of assets acquired before December 31, 2006. The evaluation and determination of the new economic useful life of these assets was performed in accordance with the rules of A.B.N.T – Brazilian Association of Technical Rules. Given the complex nature of our telecommunications and IT systems, the estimates of useful lives require considerable judgment and are inherently uncertain, due to rapidly changing technology and practices in our business sector, which could cause early obsolescence of such systems.
Management periodically reviews our long-lived assets, primarily buildings and equipment to be held and used in the business, for the purpose of determining and measuring their impairment on a recurring basis or when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of an asset or group of assets may not be recoverable. Write-down of the carrying value of assets or groups of assets is recorded if and when appropriate.
Payroll and Related Accruals
Payroll and related accruals are the most significant costs of our operations, and are calculated and recorded on an accrual basis by our payroll system. Payroll and related accruals include wages and salaries, paid vacation, Christmas bonus (décimo terceiro salárioor thirteenth salary), social security charges, executive profit sharing plan and employees’ payroll tax withholdings, most of which are defined by Brazilian labor law.
For paid vacation provision, each employee is entitled to a 30-day calendar paid annual vacation, corresponding to 133.3% of a monthly salary. We record a monthly provision for paid vacations, until such benefit is paid (when employees effectively take their vacations). For the thirteenth salary payment provision, we record a monthly provision equal to 1/12 of each employee’s monthly salary until such benefit is paid. Fringe benefits, such as paid transportation and meal vouchers, are recognized as expenses on a monthly basis when provided to employees.
Management’s executive profit sharing plan is performance-based on the achievement of several financial and quality targets of the Company as well as individual employees’ targets, determined on an annual basis. This provision is recorded on a monthly basis and is recalculated at year-end based on our best estimate of targets attained, as set in the annual budget process, but the actual total amount is only final after being reviewed and approved by our Board of Directors.
Contingencies
The preparation of our financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions regarding contingencies that affect our overall financial condition or relate to the changes in the real value of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and accounting revenues and expenses during the reported period. Such contingencies include those related to the legal proceedings discussed in Note 15 to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Under U.S. GAAP, provisions for contingencies are recognized for the amounts of probable losses based on legal advice from our in-house and external legal counsel and management’s opinion of the outstanding contingent matters. We continuously evaluate the provisions for contingencies based on changes in relevant facts, circumstances and events, such as judicial decisions, that may impact our estimates, which in turn could have a material impact on our results of operations and shareholders’ equity. While management believes that the current provisions for contingencies are adequate, there can be no assurance that these factors will not change in the future.
39
Labor Claims. Labor claim provisions in the total amount of R$38,955 thousand (U.S.$21,992 thousand), as of December 31, 2007, relate mainly to salary equalization claims (R$22,954 thousand (U.S.$12,959 thousand)), unpaid overtime salary (R$4,500 thousand (U.S.$2,540 thousand)), and the remaining R$11,501 thousand (U.S.$6,493 thousand) to various other factors (e.g., accidents and benefits, among others).
Tax Claims. Our total provisions for tax contingencies amount to R$7,776 thousand (U.S.$4,390 thousand) and relate mainly to social security taxes (R$5,196 thousand (U.S.$2,933 thousand)), as of December 31, 2007 owed to the National Institute of Social Security (Instituto Nacional de Seguridade Social — INSS). Other provisions regarding tax claims are related to the mandatory contribution (R$1,098 thousand (U.S.$620 thousand)), as of December 31, 2007 to the Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo Municipalities regarding services tax, or ISS, and another provision of R$1,482 thousand (U.S.$837 thousand) for PIS/COFINS.
We do not believe that the proceedings recorded as probable losses, if decided in a manner that is adverse to us, will have a material adverse effect on our financial condition. It is possible, however, that future results of operations could be materially affected by changes in our assumption, and the effectiveness of our strategies with respect to legal proceedings.
Deferred and Recoverable Income Tax and Social Contribution
We record deferred tax credits arising from timing differences and tax loss carryforwards. These projections include several assumptions related to the performance of the Company, exchange rates, service volumes, tax rates and other factors that could differ from current estimates.
There is no time limit for the use of tax loss carryforwards according to current Brazilian tax regulations. However, accumulated tax losses may offset no more than 30.0% of the taxable profit in any year.
Results of Operations
Results of Operations for the Year ended December 31, 2007
compared with the Year ended December 31, 2006
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Period over | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Period over | | | period | | | Results as a | |
| | | | | | | | | | | period | | | percentage | | | percentage of net | |
| | | Year | | | change | | | change | | | sales for the year | |
| | | ended December 31, | | | Favorable | | | Favorable | | | ended December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | (unfavorable) | | | (unfavorable) | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | (in thousands ofreais) | |
| Net operating revenues of services rendered | | | 1,365,815 | | | | 1,218,583 | | | | 147,232 | | | | 12 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % |
| Cost of services rendered | | | (1,174,035 | ) | | | (1,037,353 | ) | | | (136,682 | ) | | | -13 | % | | | -86 | % | | | -85 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | (89,117 | ) | | | (72,379 | ) | | | (16,738 | ) | | | -23 | % | | | -7 | % | | | -6 | % |
| Other operating expenses, net | | | (15,646 | ) | | | (11,421 | ) | | | (4,225 | ) | | | -37 | % | | | -1 | % | | | -1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 87,017 | | | | 97,430 | | | | (10,413 | ) | | | -11 | % | | | 6 | % | | | 8 | % |
| Net financial income (expenses) | | | (3,548 | ) | | | 18,405 | | | | (21,953 | ) | | | -119 | % | | | 0 | % | | | 2 | % |
| Non-operating income (expenses), net | | | 67 | | | | — | | | | 67 | | | | — | | | | 0 | % | | | 0 | % |
| Income tax and social contribution benefit | | | (28,085 | ) | | | (38,154 | ) | | | 10,069 | | | | 26 | % | | | -2 | % | | | -3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | 55,451 | | | | 77,681 | | | | (22,230 | ) | | | -29 | % | | | 4 | % | | | 6 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net Operating Revenues of Services Rendered
For the year ended December 31, 2007, net revenue increased by R$147,232 thousand compared to 2006, representing an increase of 12.1%, from R$1,218,583 thousand in 2006 to R$1,365,815 thousand in 2007. This growth was achieved through: (i) the expansion of the volume of operations with our existing clients, especially in the financial sector; (ii) the adjustment of fees in connection with existing contracts to reflect increase in costs of services rendered and (iii) new businesses, such as new infrastructure management operations launched in 2007. Although one of our main clients – Telemar – is a telecommunications carrier, our growth in rendering services to companies in sectors other than telecommunications was 32.3% in 2007. Our ability to add-on new business to our clients’ portfolios shows strong alignment with our customer relationship strategy and the perception of the quality of our services by the client.
40
As in the previous year, there was a reduction in the rendering of certain services to Telemar, mainly due to improvements carried out in the revision of processes, automation, and revision of SLAs (service level agreements), which along with the increase in revenues obtained from services to other clients-sectors, caused the share of the annual revenue derived from the agreement with Telemar to be reduced from 57.6% in 2006 to 50.7% in 2007. Nevertheless, we understand that we constantly need to pursue optimization of operations in order to improve the cost-benefit ratio for our customers, even if this causes a reduction in the volume of businesses, as it builds a long term relationship with our clients.
From the product point of view, customer care continued to account for the biggest portion of net revenue, representing 53.0% of the total. Telemarketing and debt collection accounted for 13.7% and 17.1%, respectively, which we believe have a greater growth potential.
Cost of Services Rendered
Total cost of services increased by R$136,682 thousand in 2007, representing an increase of 13.2% from R$1,037,353 thousand in 2006 to R$1,174,035 thousand in 2007. Of the total costs of services rendered in 2007, 73.5% are related to personnel expenses (75.8% in 2006), mainly with payroll, charges, benefits and training, among others. The remaining 26.5% (24.2% in 2006) are expenditures in connection with third-party services, maintenance of equipment, rental of properties and data circuits, expenditures related to facilities, general expenses and depreciation. The cost variation in 2007, when compared to 2006, occurred mainly due to the growth of services rendered upon demand by our customers, which significantly impacted costs but also increased our revenues, since 90.0% of the costs are variable and so directly related to the growth of business volume.
Personnel expenses have been affected by an increase of 25.0% in headcount (from 49,132 employees in December 2006 to 61,397 employees in December 2007), and were also affected by the R$13,000 thousand for the collective bargaining agreement and by R$18,000 thousand in training costs due to the growth in volume of services rendered. These increases were partially offset by the benefit of productivity gain realized by the Company in the amount of R$10 million.
Costs incurred in connection with third-party services increased 18.7%, and mainly reflect expenses to send collection correspondence, telephony costs for new collections and telesales operations and costs related to facilities for new sites. Rental and insurance costs increased 7.8%, mainly in connection with new businesses, but also due to rental of certain operational infrastructure until our owned sites become operational.
In 2007, depreciation increased by R$34,319 thousand, or 57.7%, chiefly due to: (i) the adoption of new depreciation criteria (R$27,191 thousand),which led the monthly depreciation rates in the areas of information technology equipment and furniture and fixtures to be reviewed due to the reduction of the economic useful life estimate of assets acquired in these lines up to December 31, 2006. The evaluation and determination studies of the new economic useful life of these assets were prepared in accordance with the rules of A.B.N.T. – the Brazilian Association of Technical Rules — by a specialized consultant qualified for this activity, whose newly determined technical report was issued on May 7, 2007; and (ii) investments to support business growth.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses of R$89,117 thousand in 2007 grew by 23.1% as compared to 2006, corresponding to a R$16,738 thousand increase. This difference includes an increase of R$15,949 thousand, resulting from the increase of expenditures for administrative personnel, specialized services, marketing and general expenses to sustain business growth, supporting areas, allowance for doubtful accounts in the amount of R$4,033 thousand and is offset by a decrease in costs incurred by commercial and administrative areas with property lease in the amount of R$3,244 thousand.
41
Other Net Operating Expenses
Other operating expenses increased by R$4,225 thousand, from R$11,421 thousand in 2006 to R$15,646 thousand in 2007. The increase was due primarily to: (i) a R$1,695 thousand increase in the provision for contingencies due to an increase in labor lawsuits; and (ii) a R$2,530 thousand increase related to court and lawsuit expenses, urban property tax and other taxes and fees.
Net Financial Income (Expenses)
In 2007, net financial result was a loss of R$3,548 thousand, as compared to an income of R$18,405 thousand in 2006. The R$21,953 thousand decline was due to: (i) a lower revenue from financial investments resulting from the lower average cash availability as a result of the share buyback programs and the fall in the Brazilian interest rates -SELIC — (R$12,004); (ii) an increase in expenses with the leasing of equipments due to the agreements entered into 2006 (R$2,800); (iii) higher expenses from the monetary restatement of contingencies (R$1,976); (iv) higher amount of provisory contribution over financial movements (CPMF) due to the expansion of operations (R$1,571); and (v) other expenses mainly related to taxes on financial operations (R$3,602).
Net Non-operating Income (Expenses)
During 2007, we had a non-operating income of R$67 thousand, resulting from the sale of certain unused assets.
Income Tax and Social Contribution Benefit
In 2007, the Income and Social Contribution taxes (at a rate of 34.0%) were in line with the amounts determined by prevailing laws, resulting in a total amount of R$28,085 thousand being paid. When compared to last year’s payment of R$38,154 thousand, the reduction occurred mainly due to the adoption of new depreciation criteria, which impact in the income tax and social contribution was R$9,245 thousand.
Net Income
Despite a higher gross income derived from the expansion of our operations, we had a net income of R$55,451 thousand in 2007, a R$22,230 thousand decrease when compared to 2006. The decline in net income despite the increase in gross income was due to the adoption of new depreciation criteria of certain fixed assets, causing a higher depreciation in the period, combined with a lower net financial result, as mentioned above.
42
Results of Operations for the Year ended December 31, 2006
compared with the Year ended December 31, 2005
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Period over | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Period over | | | period | | | Results as a | |
| | | | | | | | | | | period | | | percentage | | | percentage of net | |
| | | Year | | | change | | | change | | | sales for the year | |
| | | ended December 31, | | | Favorable | | | Favorable | | | ended December 31, | |
| | | 2006 | | | 2005 | | | (unfavorable) | | | (unfavorable) | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
| | | (in thousands of reais) | |
| Net operating revenues of services rendered | | | 1,218,583 | | | | 1,044,787 | | | | 173,796 | | | | 17 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % |
| Cost of services rendered | | | (1,037,353 | ) | | | (855,907 | ) | | | (181,446 | ) | | | -21 | % | | | -85 | % | | | -82 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | (72,379 | ) | | | (59,742 | ) | | | (12,637 | ) | | | -21 | % | | | -6 | % | | | -6 | % |
| Other operating expenses, net | | | (11,421 | ) | | | (12,098 | ) | | | 677 | | | | 6 | % | | | -1 | % | | | -1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 97,430 | | | | 117,040 | | | | (19,610 | ) | | | -17 | % | | | 8 | % | | | 11 | % |
| Net financial income (expenses) | | | 18,405 | | | | 14,352 | | | | 4,053 | | | | 28 | % | | | 2 | % | | | 1 | % |
| Non-operating income (expenses), net | | | 0 | | | | 235 | | | | (235 | ) | | | — | | | | 0 | % | | | 0 | % |
| Income tax and social contribution benefit | | | (38,154 | ) | | | (50,387 | ) | | | 12,233 | | | | 24 | % | | | -3 | % | | | -5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | 77,681 | | | | 81,240 | | | | (3,559 | ) | | | -4 | % | | | 6 | % | | | 8 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net Operating Revenues of Services Rendered
For the year ended December 31, 2006, net revenue increased by R$173,796 thousand compared to 2005, representing an increase of 16.6%, from R$1,044,787 thousand in 2005 to R$1,218,583 thousand in 2006. Most of the growth was a result of the existing client portfolio. The provision of services with excellence, the continued delivery of results and the constant concern with quality and innovation have enabled Contax to evolve in the relationship with its clients, resulting in the rendering of new services.
Despite the continued growth in overall operations and an increase in revenues in 2006, Contax experienced, mainly in the second half of that year, a reduction in its volume of operations with certain clients, especially with Telemar. This reduction was partially caused by Contax’s performance maximization by means of productivity gains, as well as changes in the assistance processes in several operations. Consequently, these actions reduced the volume of businesses, decreasing the total cost for its clients. Another relevant part of this reduction was caused by the improvement that these clients have made to their internal processes, by the automation of some services and by the reduction in service levels provided by some SLAs (service level agreements), all of which caused a decrease in the volume of operations carried out by Contax, affecting its revenue.
On a general note, during 2006, although Contax increased net revenues by R$204,613 thousand due to the acquisition of new services and new clients, it also experienced a reduction of R$30,817 thousand in the second half of 2006 due to the efficiency gains previously mentioned, resulting in a net increase of R$174 million. The Company understands that to build a long-term relationship with its clients it needs to constantly pursue optimization of operations in order to improve clients’ benefit-cost relation, even if at certain times this causes a reduction in the volume of business.
We operated 74 fewer workstations in 2006 than in 2005, representing a decrease of 0.3%, from 22,481 workstations in 2005 to 22,407 in 2006. The average monthly revenue per workstation increased by 0.5% in 2006, from R$4,477 in 2005 to R$4,501 in 2006.
Cost of Services Rendered
Total cost of services increased by R$181,446 thousand in 2006, representing an increase of 21.2%, from R$855,907 thousand in 2005 to R$1,037,353 thousand in 2006. Out of costs of services provided in 2006, 75.8% are related to personnel expenses, comprised of salaries, social charges, benefits, training, among others (versus 78.4% in 2005). The remaining 24.2% (versus approximately 21.6% in 2005) are expenditures for third-party services, equipment maintenance, rental, expenditures with facilities, general expenses and depreciation. Approximately 90.0% of the costs of services continue to be variable, that is, directly related to the growth of business volume.
43
The increase of costs in 2006 was mainly due to the volume growth of services demanded by our clients, which also increased revenue. Personnel costs were also affected by the 2005 collective bargaining agreement, which increased salaries by 5.0% from January 2006, with an aggregate annual increase of R$23,364 thousand. Gains with productivity and improvement in the internal processes of contracting clients also produced R$3,981 thousand in personnel dismissal costs, given the reduction in the volume of some operations, as with our customer Telemar, especially in the second half of 2006, as discussed previously.
Costs for third-party services mainly reflect expenses to send collection notices, telephony costs for new collections and telesales operations, costs for facilities for new sites and also some operations where infrastructure was rented from third parties until our own sites were operating.
Aiming at being more efficient in the implementation of our strategy, we carried out a restructuring plan in some departments. This restructuring contributed, mainly as from the second half of 2006, to the improvement in the performance and productivity of our operations, as well as to improved cost management in supporting areas.
Depreciation increased by R$17,622 thousand in 2006, from R$41,907 thousand in 2005 to R$59,529 thousand in 2006, representing an increase of 42.1%. This depreciation is attributable to investments made in 2005 and 2006 in the amount of R$128,696 thousand and R$108,858 thousand, respectively, to support business growth.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses of R$72,379 thousand in 2006 grew by 21.2% as compared to 2005, which corresponded to a R$12,637 thousand increase. Of this increase, R$9,356 thousand came from the increase of expenditures with personnel, specialized services, marketing and other general expenses to support the business growth.
Other Net Operating Expenses
Other operating expenses decreased by R$677 thousand, from R$12,098 thousand in 2005 to R$11,421 thousand in 2006. This decrease was due to: (i) a R$2,495 thousand decrease in the provision for contingencies, mainly by a reduction of the amount of contingent liability per lawsuit, based on a reduction in the risk in labor lawsuits filed against us during 2006; (ii) a R$758 thousand increase in the Municipal Real Estate Taxes (IPTU) assessed on our leased facilities; and (iii) a R$1,059 thousand increase in other operating expenses, such as fines, other taxes and judicial and procedural costs.
Net Financial Income (Expenses)
Net financial income totaled R$18,405 thousand in 2006 compared to income of R$14,352 thousand in 2005. This increase was due to a R$4,864 thousand increase in financial income from interest on marketable securities, partially offset by an increase in expense of R$811 thousand resulting mostly from taxes and contributions on financial transactions (IOF and CPMF, respectively).
Net Non-operating Income (Expenses)
During 2006, we did not have any non-operating income (as compared to R$235 thousand in non-operating income in 2005).
44
Income Tax and Social Contribution Benefit
In 2006, we recorded income tax provisions of R$38,154 thousand (as opposed to R$50,387 thousand in 2005), which represented (i) 34.0% of earnings before income tax, in the amount of R$39,384 thousand (as opposed to R$44,753 thousand in 2005), and (ii) tax effects in the amount of R$1,230 thousand.
Net Income
Net income decreased by 4.4% in 2006, from R$81,240 thousand in 2005 to R$77,681 thousand in 2006. This result was negatively affected mainly by the operating margin loss caused by the events mentioned above, partially offset by the increase in our financial results, less the effect of Income Tax and Social Contribution on the events previously described (including productivity improvement and net financial income).
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Cash and cash equivalents as of the end of 2007 and 2006 were equal to R$240,310 thousand and R$231,299 thousand, respectively. Following is a summary of the principal changes in cash flows during the past two years.
Net cash flows from operating activities increased R$59,708 thousand, representing an increase of 41.6%, from R$143,411 thousand in 2006 to R$203,119 thousand in 2007. Even with the decrease of net income for the year of R$22,230 thousand, as compared to 2006, a combination of factors influenced positively the results of the net cash provided by operating activities, such as: (i) increase in depreciation of R$ 36,194 thousand, due to, primarily, the adoption of a new method of calculating the useful life of equipment and machinery, which specifically resulted in an increase in the amount of R$ 27,191 thousand; (ii) R$ 25,361 gained from net increase of accounts receivable (including deferred tax assets) minus accounts payable (including payroll); (iii) R$ 12,981 from increase in the provision for contingencies of new labor claims; and (iv) R$ 2,494 provisioned to adjust the market value of the shares in connection with the stock option plan.Net cash flows used in investing activities increased R$71,643 thousand, representing a duplication of 2006 figures (a 100.8% increase), from R$71,056 thousand to R$142,699 thousand in 2007. A significant part of the total variation (R$41,894 thousand) happened because the Company entered into equipment leasing operations during 2006, ceasing such practice in 2007. The remainder of the variation relates to business expansion of our operations during the year, which caused an organic growth in property and equipment expenditure. The increase in capital expenditure for property and equipment is positively correlated with the growth of our business.
Net cash flows from financing activities increased R$19,135 thousand, representing an increase of 27.1% from R$(70,544) thousand in 2006 to R$(51,409) thousand in 2007. The main reasons for the increase in our net cash flow derived from financing activities is explained by four factors: (i) in 2007, our Company obtained a long-term facility from BNDES, having raised, initially, R$100,060 thousand; (ii) also, there was a difference of 10.8% in the payment of dividends, representing a reduction of approximately R$1,397 thousand when comparing to 2006 figures; (iii) the share buyback program increased by 188.2%, consuming an extra R$77,923 thousand in 2007, when compared to 2006 figures; and (iv) there was an increase of 30.0% in lease payments, from R$16,220 thousand in 2006 to R$21,091 thousand in 2007, representing an extra of R$4,871 thousand in payments made;
As long as the Company continues to present a natural growth of business and results, we believe that our current cash and cash equivalents and cash flows from operations will be adequate to meet anticipated working capital needs, continued expansion objectives and anticipated levels of capital expenditures for the foreseeable future.
45
Contractual Obligations at December 31, 2007
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Payments due by period | |
| | | | | | | Less than | | | | | | | | | | | More than | |
| Contractual obligations | | Total | | | 1 year | | | 1-3 years | | | 3-5 years | | | 5 years | |
| | | (in thousands ofreais) | |
| Capital (finance) lease | | | 44,188 | | | | 18,219 | | | | 23,159 | | | | 2,812 | | | | — | |
| Operating lease (facilities)* | | | 82,210 | | | | 28,591 | | | | 44,509 | | | | 8,943 | | | | 166 | |
| Financings (BNDES)** | | | 129,841 | | | | 7,863 | | | | 45,546 | | | | 57,067 | | | | 19,365 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 256,239 | | | | 54,672 | | | | 113,214 | | | | 68,821 | | | | 19,531 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| * | | Most of our facilities’ lease agreements can be terminated before their expiration, with one to six months’ prior notice, subject to a penalty equivalent to three times the monthly rent. |
| |
| ** | | Includes estimated interest payments. |
At December 31, 2007, we had not incurred any additional contractual obligations.
Recent Developments
Telemar Participações S.A. restructuring process concluded on April 2008
On April 25, 2008, negotiations relating to the restructuring of the ownership structure of Telemar Participações (Contax’s previous controlling shareholder) were concluded. This restructuring included the replacement of certain shareholders in order to expand the financing and investment capacity of Telemar Participações and its subsidiaries.
The restructuring included the followings phases: (i) an increase in the capital of Telemar Participações; (ii) the repurchase by Telemar Participações of outstanding shares; (iii) the purchase and sale of shares among Telemar Participações’ shareholders; and (iv) the restructuring of Fiago Participações S.A. (one of Telemar Participações’ shareholders).
On the same date, an Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting of Telemar Participações unanimously approved the partial spin-off of Telemar Participações, with the transfer of that portion of its shareholders’ equity related to the shares issued by Contax held by Telemar Participações to a new company created especially for this purpose called CTX Participações.
The partial spin-off is one of the phases of the restructuring and was necessary in order to separate Telemar Participações’interests into two different companies that will operate in the contact center and telecommunications industries, respectively.
46
The tables below show the capital structure after the restructuring of the controlling group:
• Before the partial spin-off:
| | | | | | | | | |
| TELEMAR PARTICIPAÇÕES S.A. | | COMMON (ON) STOCK | | | % | |
| BNDES Participações S.A. – BNDESPar | | | 858,225,280 | | | | 25.00 | % |
| Fiago Participações S.A. | | | 683,147,324 | | | | 19.90 | % |
| Lexpart Participações S.A. | | | 352,730,590 | | | | 10.27 | % |
| LF Tel S.A. | | | 352,730,590 | | | | 10.27 | % |
| Asseca Participações S.A. | | | 352,730,590 | | | | 10.27 | % |
| AG Telecom Participações | | | 352,730,590 | | | | 10.27 | % |
| Alutrens Participações | | | 343,290,112 | | | | 10.00 | % |
| Fundação Atlântico de Seguridade Social | | | 137,316,044 | | | | 4.00 | % |
TOTAL | | | 3,432,901,120 | | | | 100 | % |
• After the partial spin-off:
| | | | | | | | | |
| CTX PARTICIPAÇÕES S.A. | | COMMON (ON) STOCK | | | % | |
| AG Telecom Participações S.A. | | | 705,461,180 | | | | 22.83 | % |
| LF TEL S.A. | | | 705,461,180 | | | | 22.83 | % |
| Fundação Atlântico de Seguridade Social | | | 314,592,775 | | | | 10.18 | % |
SUBTOTAL | | | 1,725,515,135 | | | | 55.84 | % |
| BNDES Participações S.A. – BNDESPar | | | 463,234,643 | | | | 15.00 | % |
| PREVI | | | 354,485,146 | | | | 11.47 | % |
| PETROS | | | 273,671,814 | | | | 8.85 | % |
| FUNCEF | | | 273,704,271 | | | | 8.85 | % |
TOTAL | | | 3,090,611,008 | | | | 100 | % |
Acquisition by Telemar of Brasil Telecom
On April 25, 2008, Telemar, our major client, entered into a Share Purchase Agreement with the controlling shareholders of Brasil Telecom S.A., or BrT, for the acquisition of 81,092,986 common shares of Brasil Telecom Participações S.A., or BrT Part, representing 60.5% of its voting capital stock and 22.3% of its total share capital, including 247,317,180 common shares and 120,911,021 preferred shares of BrT held by BrT Part, representing 99.1% of the outstanding voting capital stock and 65.6% of the total share capital of BrT. Total purchase price is R$5.9 billion, adjusted by the variation of the interbank rate and any dividends declared up to the closing date. The acquisition is contingent upon a number of regulatory measures and approvals by Anatel, the Brazilian Securities Commission (“CVM”), the Brazilian Antitrust Authority (“CADE”), the Bovespa and the SEC.
Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees
We are managed by a Board of Directors (Conselho de Administração) and a Board of Executive Officers (Diretoria). According to our by-laws, members of the Board of Directors are appointed by our shareholders, which in turn, nominate the Executive Officers.
47
Board of Directors
The Board of Directors is currently composed of twelve regular members and eleven alternates, each serving a three-year term. The Board of Directors holds regular meetings once every three months, with special meetings called upon by any member of the Board of Directors anytime.
In regard to the appointment of Directors, Brazilian corporate law and the CVM regulations provide the following:
| | (i) | | holders of preferred shares representing at least 10.0% of the total capital stock of a company may appoint one member to the Board of Directors and its respective alternate; |
| | (ii) | | holders of common shares representing at least 15.0% of the total common shares with voting rights may appoint one member to the Board of Directors and its respective alternate; and |
| | (iii) | | if items (i) and (ii) above do not occur, holders of common shares and holders of preferred shares representing together more than 10.0% of the total capital of a company may jointly appoint one member to the Board of Directors and its respective alternate. |
Those rights may only be exercised by shareholders that prove their continuous share ownership during the last three months prior to our shareholders’ meeting.
Brazilian corporate law determines that shareholders holding more than 5.0% of common shares are entitled to exercise cumulative voting rights (voto múltiplo) so as to increase their chances of electing at least one member to the Board of Directors. Under the cumulative voting process, each voting share is entitled to a number of votes equal to the number of Board seats being filled at the relevant shareholders’ meeting, such votes which can be cast to a single or more candidates. As a result of cumulative voting, controlling shareholders may be prevented from controlling all seats of the Board, while minority shareholders may be allowed to appoint at least one member of that body. Common shares participating in the cumulative voting process will not be counted for the purposes of appointing Board members in the circumstances described in (ii) and (iii) of the preceding paragraph.
None of our Directors have service contracts with Contax Holding or with TNL Contax providing for benefits upon termination of their employment.
The members of the Company’s Board of Directors were appointed for a three-year term beginning at our Annual Shareholders’ Meeting held on April 18, 2006 until our Annual Shareholders’ Meeting in 2009. Nonetheless, at the Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting held on June 17, 2008, the composition of our Board of Directors was modified pursuant to Article 141, Paragraph 3, of Law no. 6,404/76, and new board members were elected to complete the term until the Annual Shareholders’ Meeting of 2009.
48
The following are the current members of our Board of Directors and their respective positions:
| | | |
| Name | | Position |
| Fernando Antonio Pimentel Melo | | Chairman |
| Pedro Jereissati | | Director |
| Carlos Jereissati | | Director |
| Cristina Anne Betts | | Director |
| Lúcio Otávio Ferreira | | Director |
| Flavio Eduardo Sznajder | | Director |
| Rafael Andrade da Cunha Pereira | | Director |
| Antonio Adriano Silva | | Director |
| Erik Persson | | Director |
| Sérgio Francisco da Silva | | Director |
| Leonardo Vital Brazil Teixeira | | Director |
| Isabel S. Ramos Kemmelmeier | | Director |
The following are brief biographies of the members of our Board of Directors, all of whom have served as members of the Board since June 17, 2008, unless otherwise noted:
Fernando Antonio Pimentel Melo. Born on August 29, 1953, Mr. Melo holds a Law degree from Universidade Federal de Pernambuco. He was elected a member of CTX Participações S.A. on April 25, 2008 and has been the CEO of Fundação Atlântico de Seguridade Social since March, 2005. He was also a lawyer for Fundação Telebrás de Seguridade Social – SISTEL from 1996 to 2004 and CEO of ABRAPP from 2001 to 2007.
Pedro Jereissati. Born on May 24, 1978, Mr. Pedro Jereissati obtained a degree in Business Administration from Fundação Armando Álvares Penteado — FAAP in 2000, and a MBA from Kellogg School of Management of the Northwestern University, in Chicago, US, in 2005. Mr. Jereissati joined the La Fonte group in 1995, firstly at the group’s operational area at the Iguatemi shopping mall in São Paulo. Since 1998, following the acquisition of Tele Norte Leste Participações S.A.’s control by La Fonte Telecom S.A., he engages in the group’s telecommunications business. In 2001, he became Director of New Business with La Fonte Participações S.A., and since 2005, he has been the Vice President of Finance with Iguatemi Empresa de Shopping Centers S.A., a company listed at Bolsa de Valores de São Paulo S.A. – BVSP (São Paulo Stock Exchange). He is a member of the Boards of Directors of Iguatemi Empresa de Shopping Centers S.A., Telemar Participações S.A. and Tele Norte Leste Participações S.A., and an alternate member of the Board of Directors of Telemar Norte Leste S.A.. In 2003, he was appointed by President Luis Inácio Lula da Silva as a member of the President’s Economic and Social Development Board.
Carlos Jereissati. Born on September 4, 1971, Mr. Carlos Jereissati obtained a degree in Business Administration from Fundação Getúlio Vargas -FGV – SP in 1994, and took a number of specialization courses abroad, including: Management for Success (University of Michigan Business School, 2002), Spring Convention (International Council of Shopping Centers, 1998, 1999, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005 and 2006, Real State Finance & Investment (Euromoney Training, 1998). Since 1996, he has been a member of the executive board of Iguatemi Empresa de Shopping Centers – IESC, of which he is the current chairman. He was President and Vice President of ABRASCE — Associação Brasileira de Shopping Centers S/A (Brazilian Association of Shopping Malls) from 2002 to 2004 and from 2005 to 2006, and is currently a member of this entity’s Advisory Board. He was a member of the President’s Economic and Social Development Board and is a member of IBRAVO — Associação Brasil Voluntário (Association of Brazilian Volunteers) since 1995 and a member of ICSC — International Council of Shopping Centers, since 1994.
Cristina Anne Betts. Born on October 20, 1969, Ms. Betts holds a degree in Business Administration from Fundação Getúlio Vargas – FGV (1991), with MBA from INSEAD, France. She has been the Vice President of Finance at Iguatemi Empresa de Shopping Centers S.A since April 2008. Previously, she worked at PriceWaterhouse (1992 – 1995), Banco Credit Suisse First Boston Garantia (1995 – 1999), Bain & Company (1999 – 2004) and Tam Linhas Aéreas S/A, where she held the position of Chief Strategic Planning and Controllership Officer, as well as being in charge of the Investor Relations area (2004 to 2008).
49
Lúcio Otávio Ferreira. Born on August 26, 1967, Mr. Ferreira holds a degree in Business Administration from FUMEC MG, in addition to an Executive MBA in Finance from IBMEC-MG, obtained in 1994. Mr. Ferreira has been the Chief Financial Officer of the Andrade Gutierrez group holding company since 2005. He is also Chief Investor Relations Officer of Andrade Gutierrez Participações S.A., a position he was elected to on September 29, 2006. He was Project Finance and Project Structuring Manager of Andrade Gutierrez Concessões from 1997 to 2001 and Financial Manager of the company until 2005. He was the Financial Manager of the SINDI group -Kit Eletro from 1994 to 1996, and of the Belgo Mineira group from 1991 to 1994. Also, he worked at Caixa Econômica Federal as a clerk from 1989 to 1991 and, at Banco Nacional, as Financial Transaction Desk Manager from 1986 to 1989.
Flavio Eduardo Sznajder. Born on March 15, 1971, Mr. Sznajder holds a Masters degree in Administration Sciences (MSc.) from Coppead-UFRJ and a degree in Engineering from PUC-RJ. He is a partner at Bogari Capital and a member of Fundo AG-Angra Investment Committee since 2005. He was also a Director of Andrade Gutierrez Telecomunicações from 2001 to 2007, a member of the Finance Committee of Telemar Participações from 2003 to 2007, a member of the Board of Directors of TG Agro alcohol plant in 2006 and 2007, a member of the Board of Directors of Pegasus Telecom S.A. in 2001 and 2002, a senior associate with Booz-Allen & Hamilton’s telecommunications group from 1997 to 1999 and in 2001. He also worked at Gradus Management Consultancy as a senior associate and at Banco BBM as a trainee.
Rafael Andrade da Cunha Pereira. Born on May 17, 1975, Mr. Pereira obtained a degree in Mechanical Engineering from Universidade Estadual de Minas Gerais / PUC — MG in 1997, and an MBA-Full Time from Esade Business School in 2005. Mr. Pereira has been working for the Andrade Gutierrez group since 2001, in the Heavy Construction and Concession areas, where he held the positions of Trainee Engineer, Civil Work Engineer, Commercial and Project Development Manager. He is also an alternate member of the board of directors of the Andrade Gutierrez group holding company since January 2008. He is also a partner in Trópica Ltda. since July 2007, and, since 1995, managing partner and CEO of Lagamar Empreendimentos Ltda., a company engaged in planning, implementing and running hotels and real estate developments. He was managing partner and CEO of Bela Empreendimentos Ltda. from 1998 to 2001.
Antonio Adriano Silva.Born on March 2, 1944, Mr. Silva is the Chief of Staff for the Vice President of Brazil. Previously, he worked at Coteminas – Cia. de Tecidos Norte de Minas from 1979 to 2002, and was Technical Advisor to Brazilian Senator José Alencar for 4 years (1989/2002). He has also been a member of the Board of Directors of CEMIG – Companhia Energética de Minas Gerais since 1999.
Erik Persson. Mr. Persson was born on March 11, 1954. He obtained a degree in Economics from UFRGS – Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul in 1999, and a post-graduate degree in Business Management from IBMEC – Rio de Janeiro in 2006. He was Planning and Social Security Director of PREVI – Caixa de Previdência dos Funcionários da PREVI from 2000 to 2006. Previously, he was a member of the Boards of Directors of VALE – Cia. Vale do Rio Doce S.A. from 2001 to 2007 and Fiago S.A. from 2007 to May 2008.
Sergio Francisco da Silva.Born on January 3, 1962, Mr. Silva holds a degree in Psychology from Universidade Paulista – São Paulo, and post-graduate degrees in Project (2004) and Planning, Budgeting and Public Management (2005), both from Fundação Getúlio Vargas. At present, Mr. Silva takes a Finance MBA course at IBMEC. He holds the position of Director of Administration and Information Technology of Fundação dos Economiários Federais since August 2007. Previously, he was Executive Director of APCEF/SP from 1992 to 1994, a member of Caixa Econômica Federal (CEF) Labor Relations Committee from 1996 to 1997, a member of the National Executive Board of CEF’s Employees from 1996 to 1998, a member of the São Paulo State Health Board from 1998 to 1999, Health Secretary for the Bank Workers Union of São Paulo, Osasco and Region from 1997 to 2000, a member of the Board of Directors of “SÃO PAULO CONFIA” from 2000 to 2002, Finance Secretary for the Bank Workers Union of São Paulo, Osasco and Region from 2000 to 2002, a member of the Boards of Directors of Fiago Participações S.A. and Telenorte Celular Participações, and Director of Benefits and Administration with Fundação dos Economiários Federais from 2003 to 2007. He is currently a member of the Audit Committee of Brasil Telecom Participações S.A.
50
Leonardo Vital Brazil Teixeira. Born on March 5, 1972, Mr. Teixeira holds a degree in Economics from Faculdade Candido Mendes, Rio de Janeiro. He has been Executive Manager of Market Transactions at Fundação Petrobras de Seguridade Social — PETROS since March 2008. Previously, he held the position of Executive Manager of Finance Management at Fundação Petros, from July 2003 to March 2008. He also worked as Variable Income Asset Manager at Bradesco Asset Management – BRAM, from June 2001 to July 2003. Additionally, he worked at Banco Boavista InterAtlantico as Senior Trader at the bank’s Treasury and Asset areas from May 1997 to June 2001.
Isabel S. Ramos Kemmelmeier.Mrs. Kemmelmeier, born on December 3, 1974, was elected a member of the Board of Directors on April 18, 2006. She graduated from Pontifícia Universidade Católica — Rio de Janeiro in Civil Engineering, where she specialized in Production Engineering. She holds an MBA in Finance from Instituto Brasileiro de Mercado de Capitais — IBMEC. She worked at Opportunity Asset Management from July 1996 until March 2006, where she headed the Equity Research Department from 2003 until 2006. Previously, she served as member of the Fiscal Council of Lojas Renner, Iochpe Maxion, AES Tietê, Eletrobrás, Eletropaulo, Usiminas, COMGAS, Telemig Celular, Telesp and CRT Celular. She was also a member of the Board of Directors of Eletrobrás.
Executive Officers
Our by-laws provide that the Board of Executive Officers shall consist of one President (CEO), one Chief Financial Officer (CFO), and up to three other officers. The Executive Officers are to be elected by the Board of Directors for a term of three years and may be removed from office at any time. The current Executive Officers were last appointed at our Board of Directors Meetings held on April 26, 2006 and July 27, 2006, and will serve until the first Board of Directors Meeting following the Annual Shareholders Meeting of 2009.
The following are the Executive Officers and their respective positions:
| | | |
| Name | | Position |
| Francis James Leahy Meaney | | President (CEO) |
| Michel Neves Sarkis | | Chief Financial Officer (CFO)/Investor Relations Officer |
| José Luiz Cardoso Albano | | Officer |
| Rosangela Maria de Oliveira Lutti | | Officer |
Francis James Leahy Meaney. Mr. Meaney, born on November 4, 1964, is our founder and has been our CEO since our inception in 2000. He is active in various contact center industry organizations, including ABT (Brazilian Association of Telemarketing Companies) of which he is a Vice-President. Previously, he was a Vice President at Global Crossing Latin America in Miami from 1999 to 2000, General Manager for Conectel, the leading paging company in Brazil, from 1997 to 1999 and management consultant for various consumer products companies in Latin America between 1990 and 1997. He began his career at Credit Suisse First Boston in New York, where he worked from 1986 to 1988. He holds a B.A. in Economics from the University of Notre Dame and an MBA from Harvard Business School. He also completed the Advanced Management Program at INSEAD.
Michel Neves Sarkis. Mr. Sarkis, born on February 28, 1969, has acted as our CFO since April 2001 and was designated Investor Relations Officer in December 2004 of our Company. Prior to joining us, he worked for five years as an auditor of PricewaterhouseCoopers from June 1990 to August 1995. He also acted as Divisional Controller of Pepsi in Minas Gerais and Rio de Janeiro for more than two years, from August 1995 to November 1997, where he was responsible for the financial department. In November 1997, he was appointed General Manager of the Rio de Janeiro Division of Conectel Paging Company. In 1999, he went to Prosegur Brazil as General Manager of the Bahia and Espírito Santo Division. He holds a B.A. in Management from UFES – Universidade Federal do Espírito Santo and an Accounting degree from Faculdade Costa Braga — São Paulo and an MBA from Pontifícia Universidade Católica — São Paulo.
51
José Luiz Cardoso Albano. Mr. Albano, born on January 6, 1962, has acted as our Executive Officer since May 2002. Prior to becoming our Operating Officer, he acted as General Manager of Telemar in Rio Grande do Norte. Prior to that, he was responsible for the management of Telemar contact center in Fortaleza, which centralized its operations in seven states of the northeast region of Brazil. Previously, he worked as a contact center manager for TIM / Maxitel, a mobile telephony carrier in Belo Horizonte (from 1999 to 2000). He acted as an Operational Manager of Minas Gerais and Brasília branch offices of Quatro A, a contact center company (from 1996 to 1999). Also, he worked at Cimentos Mauá (from 1987 to 1994). He holds a B.A. in Management from Faculdade Cândido Mendes and a B.A. in Marketing from Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais and in Human Resources from FGV Minas Gerais. He also holds a BA in Business Administration from Fundação Dom Cabral (2005).
Rosangela Maria de Oliveira Lutti. Ms. Lutti, born on March 1, 1954, was appointed as our Executive Officer on July 27, 2006. Ms. Lutti has worked at Contax as Human Resources Officer since October 2005. Previously, she worked four years at Bunge Fertilizantes as Human Resources Officer, between March 2001 and March 2005, and at Camargo Correa S.A. holding as Organizational Development Officer from August 2000 to March 2001. She also worked at Pirelli Cabos S.A. as Human Resources Officer from July 1998 to August 2000. She has a degree in Social Service from Faculdade Paulista de Serviço Social and a post degree in Human Resources from FGV.
Fiscal Council (Conselho Fiscal)
According to Brazilian corporate law, the Fiscal Council (conselho fiscal) of a company does not need to operate on a permanent basis. It shall only be installed, and its members elected, if so required by shareholders representing 10.0% of our common or 5.0% of our preferred shares outstanding. In such occasion, it shall consist of three to five effective members and respective alternates, elected at a shareholders’ meeting for a term ending on the Annual Shareholders Meeting following their election. At our Annual Shareholders Meeting held on April 4, 2008, our shareholders required the installation of our Fiscal Council and five members and respective alternates were elected to compose this body. At our Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting held on June 17, 2008, our controlling shareholders elected one sitting member and one alternate member to integrate the Company’s Fiscal Council, in complementation to the term of office in 2009, due to the resignation of the previous occupants.
The Fiscal Council operates in accordance with the relevant provisions set forth under Brazilian corporate law and in the Company’s by-laws. Under such provisions, the Fiscal Council is a corporate body, independent from the Company’s Board of Directors and Board of Executive Officers and from its independent registered public accounting firm. The Fiscal Council’s primary responsibility under Brazilian law is to monitor management’s activities, review the financial statements, and report its findings to the shareholders.
Brazilian corporate law further establishes that the Fiscal Council may not contain members that are: (i) on the Board of Directors, (ii) on the Board of Executive Officers, (iii) employed by us or a controlled Company, and (iv) spouses or relatives of our management, up to and including the third degree of relationship. Under Brazilian corporate law, holders of preferred shares have the right to elect separately one member of the Fiscal Council. Also, under the Brazilian corporate law, minority groups of shareholders that hold at least 10.0% of the voting shares also have the right to elect separately one member of the Fiscal Council.
Despite some apparent similarities to the U.S. audit committee as provided for under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, a Fiscal Council established under Brazilian corporate law has not typically been considered equivalent or comparable to a U.S. audit committee formed according to the provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and the New York Stock Exchange, or NYSE, listing standards. The listing standards of the São Paulo Stock Exchange, where our shares are listed, do not require that companies listed with it form or maintain a permanent Fiscal Council or a comparable U.S. audit committee-type body. As a result, our Fiscal Council will not be upgraded to discharge the same responsibilities of a U.S. audit committee formed according to the provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and the NYSE listing standards.
52
The following table indicates the persons elected to our Fiscal Council at our Annual Shareholders Meeting held on April 4, 2008 and at our Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting held on June 17, 2008, which shall serve as members of that body until the Annual Shareholders Meeting of 2009.
| | | |
| Name | | Position |
| Allan Kardec de Melo Ferreira | | Chairman |
| Aparecido Carlos Correia Galdino | | Regular Member |
| Sergio Bernstein | | Regular Member |
| Luiz Felix de Freitas | | Regular Member |
| Marcio Luciano Mancini | | Regular Member |
Allan Kardec de Melo Ferreira.Mr. Ferreira, born on November 19, 1945, holds a degree in law from the Pontifícia Universidade Católica de Minas Gerais (1970). He is also a member of the Fiscal Council of TNL and has been a member of the Fiscal Council of Tmar since May 2002. From 1972 to 1978, he was responsible for the bidding processes department of the Andrade Gutierrez Group, and from 1979 to 1993 he was head of the international legal department. Currently, he is a consultant for corporate matters and matters related to bidding processes and concessions.
Aparecido Carlos Correia Galdino.Mr. Galdino, born on April 4, 1941, holds a degree in Business Administration from Faculdades Integradas Princesa Isabel (1978). He started his career at the Jereisatti group in 1971 and has been part of the group’s development and growth path. He is CFO of La Fonte Participações S.A., and a member of the Boards of Directors of Iguatemi Empresa de Shopping Centers S.A. and La Fonte Telecom S.A.
Sergio Bernstein. Mr. Bernstein, born on April 16, 1937, holds a Civil Engineering degree from the Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (1959) and took a number of finance and administration courses in Brazil and abroad. From 1990 to 2007, Mr. Bernstein worked at the Jereissati group as a Vice President. Since then, he has been an advisor and member of the Board of Directors of the Jereissati Group. Previously, among other activities, he worked for 27 years at General Electric do Brasil, where he was Controller Director for 6 years and Vice President of Finance for 4 years.
Luiz Felix de Freitas. Mr. Freitas, born on February 26, 1959, holds a bachelor’s degree in business administration and a post-degree in Strategic Management of Information Technology. He has worked in Banco do Brasil since 1974, and was a consultant to BB — DTVM from 1988 until 1998. Since 2004, he is the manager of internal controls and conformity of PREVI — Caixa de Previdência dos Funcionários do Banco do Brasil. He was the coordinator to the Commissions of Corporate Management and Internal Controls of ABRAPP — Associação Brasileira de Entidades Fechadas de Previdência Complementar. Also, he is the professor of the MBA courses in Process and Control Management of IDEAS – Instituto de Desenvolvimento de Estudos Aplicados à Seguridade, a partnership with UFRJ-COPPE and PUC-MG.
Marcio Luciano Mancini. Mr. Mancini, born on March 27, 1973, is a certified analyst and fund manager by CVM and was invited to the Fiscal Council of our Company in 2006. He holds a bachelor’s degree in business from EAESP/FGV (June/1997). He is also a member of the Fiscal Councils of Duratex, Eletropaulo, Copel, Sanepar and Dixie-Toga. Mr. Mancini was a member of the Fiscal Councils of Unipar, Renner Participações S.A., Lojas Renner S.A., Comgás, Fosfértil — Fertilizantes Fosfatados S.A., Lojas Americanas S.A., ACESITA S.A., AES Tiête S.A. and AES Sul Distribuidora Gaúcha de Energia. He worked at Hedging-Griffo Asset Management as a buy-side analyst from February 1997 to April 2002, covering the utilities’ industry, and at BMS PARTNERS Serviços Financeiros as a junior financial analyst of investment projects.
Compensation of Directors, Executive Officers and Fiscal Council Members
For the year ended December 31, 2007, the aggregate amount of compensation, including cash and benefits in kind, paid by Contax to all of its Directors, Executive Officers and Fiscal Council members was approximately R$4,189 thousand. Contax is not required under Brazilian law to disclose, and has not otherwise disclosed, the compensation of its Directors, Officers or Fiscal Council members on an individual basis.
53
Share Ownership
The members of Contax Holdings’ Board of Directors and Fiscal Council together own less than 0.10% of Contax Holding’s common shares or total capital stock. On April 16, 2007, the General Shareholders’ Meeting approved the Stock Option Plan, pursuant to article 168, paragraph 3, of Law no. 6,404/76. Our Executive Officers are limited to purchasing up to 5.0% of the Company’s total capital stock.
Employees
On December 31, 2007, we had a total of 61,397 employees and 244 trainees distributed among the following locations:
| | | | | | | | | |
| City/State | | Employees | | | Trainees | |
| Rio de Janeiro/RJ | | | 14,059 | | | | 74 | |
| Niterói/RJ | | | 4,139 | | | | 6 | |
| São Paulo/SP | | | 16,534 | | | | 62 | |
| Salvador/BA | | | 6,499 | | | | 31 | |
| Recife/PE | | | 3,477 | | | | 41 | |
| Fortaleza/CE | | | 6,282 | | | | 9 | |
| Belo Horizonte/MG | | | 9,312 | | | | 20 | |
| Porto Alegre/RS | | | 1,004 | | | | 1 | |
| Brasília/DF | | | 91 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 61,397 | | | | 244 | |
| | | | | | | |
The employees are distributed between our administrative (5.0%) and operational (95.0%) areas.
Approximately 28.4% of our employees are members of the telecommunications company workers and switchboard operators unions. These unions represent the employees’ professional category and are affiliated with the Interstate Federation of Telecommunications Workers (Federação Interestadual dos Trabalhadores em Telecomunicações – Fittel) or National Federation of Telecommunications (Federação Nacional de Telecomunicações – Fenatel). The base date for the collective labor bargaining agreement for the category is May, at which time salary adjustments are negotiated. The conditions of the collective labor bargaining agreement are negotiated annually and in a centralized manner with Fittel and the unions of the states where we have operations. These negotiations are carried out between union representatives and a team of experienced negotiators from TNL Contax.
We maintain a courteous and professional relationship with the union representatives and invite them to visit our sites on a regular basis to show the labor condition improvements that we continue to make for our employees.
Employee Benefits
We provide the following benefits to our employees: (i) medical plan; (ii) dental plan; (iii) life insurance; (iv) food program for employees who work six hours per day; (v) meal program for employees who work eight hours per day; (vi) transportation; (vii) discount plan with certain pharmacies; (viii) funeral expenses plan; and (ix) daycare assistance. Officers, managers and coordinators are also entitled to mobile telephones with monthly credits varying from R$60 to R$120.
Career and Salary Plan
In order to remain competitive in the market and maintain our remuneration structure in line with our goals of employee satisfaction and rewarding individual performance, we revised our Career Plan in the second half of 2006. Although there were no major changes, the Career Plan is designed to provide additional opportunity for internal employees, such as promotions.
54
Employees assigned to some of our operations, such as telemarketing, retention, debt collection units and Orbitall operations are eligible for variable remuneration, linked to the achievement of individual as well as collective goals.
All employees are eligible for our profit sharing plan which is linked both our performance and to individual goals set annually.
Outsourcing
We also engage service companies to provide services related to our secondary activities, such as janitorial services, security, office assistants and helpdesk. At December 31, 2007, we used the services of approximately 1,281 outsourced workers.
Workplace Health and Safety
As required by law, we maintain two workplace health and safety programs: the occupational health program (Programa de Controle Médico de Saúde Ocupacional), or PCMSO, and the workplace risk prevention program (Programa de Prevenção de Riscos Ambientais), or PPRA. In addition, we maintain a safety-at-work program, called Internal Commission for the Prevention of Accidents (Comissão Interna de Prevenção de Acidentes), or CIPA. We also carry out ergonomic and noise level studies and have a workplace exercise program to help prevent work-related injuries.
Item 7. Major Shareholders and Related Party Transactions
Major Shareholders
We have two classes of share capital outstanding, common shares and preferred shares. Only the common shares have full voting rights. The preferred shares have limited voting rights in connection with certain matters. See “Item 10. Additional Information — Memorandum and Articles of Association — Voting Rights.”
The following table sets forth the information concerning the ownership of our common shares by CTX Participações and by other shareholders holding five percent or more of our common shares, as of April 25, 2008. Except for the shareholders listed below, we are not aware of any other shareholder owning more than five percent of common shares. None of the major shareholders listed below have any different or special voting rights attached to their shares.
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Number of | | | Percentage of | |
| | | common | | | outstanding | |
| Shareholders | | shares owned | | | common shares | |
| CTX Participações S.A. | | | 3,425,209 | | | | 58.80 | |
| Caixa de Previdência dos Funcionários do Banco do Brasil — PREVI | | | 308,510 | | | | 5.30 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 3,733,719 | | | | 64.10 | |
| | | | | | | |
55
The following table sets forth, as of May, 2008, information concerning the ownership of the common voting stock of CTX Participações.
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Number of | | | Percentage of | |
| | | common | | | outstanding | |
| CTX Participações shareholder | | shares owned | | | common shares | |
| AG Telecom Participações S.A. | | | 705,461,180 | | | | 22.83 | |
| L.F. Tel S.A. | | | 705,461,180 | | | | 22.83 | |
| Fundação Atlântico de Seguridade Social | | | 314,592,775 | | | | 10.18 | |
| BNDES Participações S.A. — BNDESPar | | | 463,234,643 | | | | 15.00 | |
| PREVI | | | 354,485,146 | | | | 11.47 | |
| PETROS | | | 273,671,814 | | | | 8.85 | |
| FUNCEF | | | 273,704,271 | | | | 8.85 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 3,090,611,008 | | | | 100.000 | |
| | | | | | | |
CTX Participações’ Shareholders’ Agreements
Certain CTX Participações’ shareholders are parties to two shareholders’ agreements with respect to their interests in CTX Participações S.A.. AG Telecom Participações S.A., Andrade Gutierrez Investimentos em Telecomunicações S.A., L.F. Tel S.A., Asseca Participações S.A., BNDES Participações S.A., Fiago Participações S.A. and Fundação Atlântico de Seguridade Social are parties to a Shareholders’ agreement, dated April 25, 2008, which governs: (1) special procedures and quorum requirements for the approval of certain corporate resolutions by the management; (2) rules for the election of the members of the board of directors, fiscal council and executive officers; (3) rules in regard to voting rights during the general shareholders’ meetings of CTX Participações; (4) conditions which would constitute a lien on the shares or subscription rights; (5) requirements in regard to the exercise of the right of first refusal and the preemptive rights of the shareholders in the case of a disposal and subscription of shares of CTX Participações; (6) tag along rights in which the direct or indirect transfer of control of CTX Participações can only be effected; and (7) appraisal rights in the case of a disposal of shares of CTX Participações in the event of a transfer of control of the shareholder.
Pursuant to the first Shareholders’ agreement, CTX Participações’ controlling shareholders have also agreed to exercise their voting rights in the shareholders’ meetings of CTX Participações in order to: (1) maintain their investment in Contax Participações S.A. (2) have CTX Participações properly manage Contax Participações S.A. and its subsidiaries and assure decisions and actions by the companies’ management are taken in the companies’ best interests and according to market conditions. Under the first Shareholders’ agreement, CTX Participações’s shareholders must meet prior to any general shareholders’ or board of directors’ meeting of CTX Participações or any of their affiliates, to vote on the matters to be subsequently submitted at those meetings (the “Prior Meetings”). Each controlling shareholder is entitled to one vote at the Prior Meeting and all the decisions taken in this meeting bind all the controlling shareholders’ votes in the general shareholders’ meetings, including votes of shareholders who have not participated in the Prior Meeting. The controlling shareholders are also bound to assure that directors appointed by them vote at meetings of the board of directors in accordance with decisions taken in the Prior Meetings and that such decisions are implemented. Except as otherwise provided in the shareholders’ agreements, resolutions at the Prior Meetings are passed by the vote of holders of a simple majority of shares. However, certain matters, such as matters relating to related party transactions, approval of the name for the position of chief executive officer of Contax Participações require the approval of 66.7% of the shares affected by such Shareholders’ agreement; changes in preferences and capital increase require the approval of 70.0% of the shares affected by such Shareholders’ agreement; and changes in the corporate purpose and any decision resulting in the change of control of CTX Participações requires the approval of 84.0% of the shares affected by such Shareholders’ agreement.
AG Telecom Participações S.A., L.F. Tel S.A., Fundação Atlântico de Seguridade Social and Asseca Participações S.A. (CTX Participações’s controlling shareholders) are parties to a second Shareholders’ agreement, also dated April 25, 2008. This second instrument outlines (1) rules in regard to voting rights during the general shareholders’ meetings of CTX Participações; (2) holding of Prior Meetings; and (3) transfer of CTX Participações’ shares owned by its controlling shareholders.
56
Holders of ADSs
In the United States, the preferred shares trade in the form of American Depositary Shares, ADSs, each representing 20 ADRs of the same type, issued by The Bank of New York, as depositary, pursuant to a Deposit Agreement among us, the Depositary and the registered holders and beneficial owners of ADSs from time to time. Our ADSs are not listed on any stock exchange in the United States.
Due to numerous expansion plans dating back to the Telemar days, Contax inherited several million “inactive” shareholders. In an effort to reduce unnecessary administration and operating costs and to provide a low cost form of liquidity for these small shareholders, Contax announced a reverse stock split on October 17, 2007 with the outcome being a significant reduction of shareholders base in Brazil. On November 19, 2007 all the shares started being traded exclusively in groups of twenty. Since ADR holders are mainly concentrated in the hands of institutional investors in large quantities, the reverse stock split was not needed and the Reverse Stock Split did not affect the ADSs, which are not being traded in groups of twenty.
Related Party Transactions
Set forth below is a description of the related party transactions that are material to us. Related party transactions refer to any loans receivable, accounts receivable from services rendered and any other debts with our shareholders, subsidiaries, unconsolidated affiliates or shareholders. For further information about transactions with related parties see Note 17 to our Consolidated and Combined Financial Statements as well as to our interim consolidated financial statements.
Telemar/Contax Contracts
We are a party to two main related party agreements with the Telemar entities (our main client encompassing Tmar and its wholly owned subsidiary Oi, both of which are indirectly under common control with us): (i) an agreement related to contact center services provided by us to Telemar, on a fully outsourced basis, and (ii) an agreement related to telecommunications services provided by Telemar to us. Such agreements were executed on November 30, 2004 and duly approved at Tmar’s Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting on December 17, 2004.
Prior to such contracts, we performed all contact center activities for Telemar, under various contracts, both on a fully outsourced as well as on a partially outsourced basis. Such partial outsourcing services were usually performed in facilities and with equipment owned by Telemar. Telemar was also responsible for all facilities costs such as general maintenance and electricity.
The total amount of our operating revenues derived from Telemar was R$744.2 million in 2007 and R$765.7 million in 2006, representing respectively, 50.4% and 58.0% of our total revenues in those years. Our relationship with Telemar is currently represented by several distinct and independent services, such as customer services for Telemar’s fixed line business, outbound telemarketing to attract additional mobile customers, customer support for prepaid and postpaid mobile users, technical support for broadband subscribers, and debt collection services.
Telemar, in turn, is our main telecommunications services provider (fixed-switched telecommunication service, mobile services, long distance/toll-free, data, and other services) and, most importantly, provides such services, directly or through us, to some of our clients, at their option. The total amount paid to Telemar and its subsidiaries for these services was equal to R$24,706 in 2007, R$20,087 thousand in 2006, and R$8,486 thousand in 2005, or 2.1%, 1.9%, and 1.0% of the total costs of our services rendered and operation expenses in 2007, 2006, and 2005, respectively. While Telemar currently provides most of our telecommunications services, if it were to become unable or unwilling to provide these services, we believe that we would be able to obtain such services from another provider with a minimum of disruption to our business.
57
We also have contracts to provide contact center services to Brasil Cap and Brasil Veículos, both shareholders of Telemar Participações (our previous controlling shareholder), which provided annual revenues of R$3,584 thousand and R$6,664 thousand, respectively, as of December 31, 2007. Following the restructuring of Telemar Participações and the creation of CTX Participações on April 25, 2008, both Brasil Cap and Brasil Veículos – through Alutrens Participações – are no longer shareholders of either CTX Participações or Telemar Participações.
BNDES/Contax Contracts
In 2007, we entered into a loan agreement with BNDES for the total amount of R$216,514, with the purpose of financing the expansion of our installed capacity, upgrading current facilities, training programs, improving service quality and productivity and investments in marketing activities, within the PROSOFT- Corporate (Software Industry and Correlated Services Development Program).
In October 2007, the first tranche of the BNDES loan was provided in the amount of R$100 million, followed by additional tranches on the January 28, January 30 and June 12, 2008, in the amounts of R$40 million, R$10 million and R$61.8 million, respectively. The funds received so far from BNDES amount to a total of R$211.8 million.
Facilities Lease Agreements
Some of our facilities are located on real estate that is leased from related parties. Most of these related party lease agreements are with Telemar. Lease expense for all related party lease agreements totaled R$6,219 thousand, R$3,590 thousand, and R$396 thousand in 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively. During the first period under the full outsourcing contract entered into in 2005 with Telemar, Contax occupied Telemar’s real estate in order to fulfill its contract, and given that Contax, at its expense, had to pursue several infrastructure investments in the real properties, Contax was contractually exempted from the corresponding lease payments. In 2006, the exemption expired and Contax started to pay to Telemar the monthly leases of the occupied real estate.
Transactions with our Board of Directors or Executive Officers
None of the members of our Board of Directors or Executive Officers, or any close member of their respective families, has or has had any direct interest in any transaction effected with us which is or was unusual in its nature or conditions, or significant to our business.
As of December 31, 2007, no outstanding loans or guarantees have been made to the members of the Boards of Directors or Executive Officers or the Fiscal Council, or any close member of their respective families.
Item 8. Financial Information
Consolidated Statements and Other Financial Information
See “Item 18. Financial Statements.”
58
Legal Proceedings
General
We are party to a number of legal actions arising from our regular course of business. Although the amount of the global liability that could arise with respect to these actions cannot be accurately predicted, in our opinion, such actions, if decided adversely to us, would not, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. We are subject to contingencies with respect to tax, labor and other claims. The composition of our contingency provisions is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | At December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
| | | (in thousands of reais) | |
Nature | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Labor | | | 38,955 | ** | | | 22,989 | * | | | 24,001 | |
| Tax | | | 7,776 | | | | 5,793 | | | | 4,852 | |
| Civil | | | 129 | | | | 117 | | | | 64 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 46,860 | | | | 28,899 | | | | 28,917 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| * | | The amounts as of December 31, 2006 and 2005 include R$6,067 thousand of provisions related to former Tmar ‘s employees made during the year 2005 and the amount as of December 31, 2006 also includes part of R$6,575 thousand of provisions related to former Tmar ‘s employees. |
| |
| ** | | Pursuant to the service agreement executed by Telemar and TNL Contax, it was defined that labor claims arising from the transfer of labor agreements from Telemar to the Company shall be incumbent upon Telemar, which amount has been recorded as a counter entry to “Receivable Credits”. The amount of labor claims under Telemar’s responsibility as of December 31, 2007, was R$11,550 thousand, with the other R$27,405 thousand being labor claims filed against TNL Contax by employees and former employees. |
Labor
Judicial
As a part of our ongoing operations, we have been the defendant in a number of lawsuits brought by our employees, labor unions and the Labor Public Prosecution Office (Ministério Público do Trabalho). We have established what we believe to be an adequate reserve to cover these claims.
As at December 31, 2007, we were involved in approximately 4,024 employment-related legal proceedings, as opposed to 2,022 in 2006. The total estimated amount involved in these proceedings is R$260,715 thousand (U.S.$147,188 thousand), as compared to R$131,387 thousand (U.S.$74,176 thousand) in 2006. We record provisions for any contingent liabilities in proportion to our historical losses, which, on that date, amounted to approximately R$38,954 thousand (U.S.$21,992 thousand), as compared to R$22,990 thousand (U.S.$12,979 thousand) in 2006:
| | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | |
| | | (in thousands of reais) | |
Types of risk* | | | | |
| Probable | | | 38,955 | |
| Possible/Remote | | | 221,761 | |
| | | | |
| Total | | | 260,716 | |
| | | | |
| | | |
| * | | The types of risk have been determined by our management, based on the opinion of external legal counsel and existing legal precedents. |
Most of these proceedings relate to claims for: (i) overtime; (ii) salary equalization; (iii) continuity of service; and (iv) damages, pain and suffering. The increase in the number of labor law suits, from 2,022 in 2006 to 4,024; in 2007 is directly related to the significant increase in the number of employees since 2004.
59
There was a lawsuit filed by the São Paulo State Labor Prosecution Office in 2005 against contact center service providers, including TNL Contax, and their clients, principally financial institutions, alleging that such clients are not allowed to outsource their contact center services, since this is allegedly an activity strictly related to those clients’ core business. This lawsuit, still not finally decided, argues that activities directly related to the core business of a company cannot be outsourced. There is some jurisprudence consolidated by the Superior Labor Court a few years ago regarding this matter. However, due to the fact that this jurisprudence is not uncontroversial, the market cannot ascertain with confidence what are the activities that are (or not) directly related to a company’s core business and which cannot, therefore, be outsourced.
Administrative Proceedings
As at December 31, 2007, approximately 45 notices of alleged violations of labor laws were pending against us. The amounts involved in such notices of infraction depend on the type of violation, the number of employees involved, and whether the alleged violation is a first time offense. Until December 31, 2007, in order to file administrative appeals, we performed administrative deposits, as required by law, in the approximate amount of R$43,245 thousand (U.S.$24,414 thousand), in connection with fines regarding five administrative proceedings; and R$47,625 thousand (U.S.$26,887 thousand), concerning 20 other administrative proceedings that we lost at the lower administrative level.
We have disputed all these notices of infraction before the administrative authority and are awaiting a final decision in these administrative proceedings. Nevertheless, if such decisions are not favorable to us in administrative courts, we are allowed and intend to seek the judicial courts in order to request not only annulment of any and all debts assigned to us by the administrative courts, but also reimbursement for administrative appeals filed on the contingency of payment.
Since we classify the risk of loss of these notices of infractions as being “possible,” we have not included them, nor the amounts deposited in connection with fines, as part of our contingent liability.
The alleged labor violations relate mainly to the following infractions: (i) failure to present documents to the labor inspectors; (ii) failure to grant holidays; (iii) noncompliance with workplace health and safety rules; (iv) failure to grant intraday and weekly rest breaks; (v) late payment of the wages (after the fifth business day of the month); (vi) failure to pay the FGTS on the remuneration failure to pay administrative fines; (vii) payment in cash of the transport-tickets; and (viii) noncompliance with the determined quota for hiring juvenile interns (menores aprendizes).
Under Brazilian law, if a company has more than 100 employees, two to five percent of its employees must be rehabilitated social security beneficiaries or qualified persons with disabilities. Because of our inability to meet this quota, in September 2002 we entered into a Conduct Adjustment Term (Termo de Ajuste de Conduta), or the Commitment, with the Attorney General for Labor, under which we were granted a period of three years to meet the hiring quota. However, even though we implemented a program aimed at hiring rehabilitated social security beneficiaries and persons with disabilities, the positions available could not be filled. Pursuant to the terms of the Commitment, therefore, we have been sending reports at every six months to the Office of the Attorney General for Labor and the Regional Labor Office to show that positions have been made available to meet the quota.
Tax
We are party to 17 tax claims (being defendants in 4 claims) mainly related to social security taxes owed to the National Institute of Social Security (Instituto Nacional de Seguridade Social — INSS), to the mandatory contribution, services tax (ISS) and PIS/COFINS. See also “Item 5 – Critical Accounting Policies And Estimates – Contingencies – Tax Claims.”
Civil
We are subject to 45 civil claims. There are only six claims in an amount greater than R$50,000, mostly arising from accidents suffered by employees at work or diseases alleged to be derived from work.
The two highest claims filed against us are for R$233 thousand (U.S.$132 thousand) and R$165 thousand (U.S.$93 thousand), respectively. These claims relate to two distinct lawsuits brought by former employees. In the first lawsuit the plaintiff claims health related as a result of having contracted a labor-related disease allegedly while working for us. The plaintiff charges us with omission in fulfilling certain precautions related to the workplace safety rules. Our external legal counsel believes that the chances of an unfavorable outcome to us in the civil lawsuit are “possible”. The second lawsuit is brought by a former employee seeking indemnification for health-related damages as a result of having contracted a labor-related disease allegedly while working for us. This second plaintiff claims that, apart from working for us, he/she also pursued artistic activities, which allegedly could not be continued in light of the disease.
60
On December 8, 2004, Constitutional Amendment (C.A.) 45 was published. This C.A. became known as the “Reform of Judiciary Power” and expanded the competence of the Brazilian Labor Courts. Before its publication, such competence was restricted to conflicts between employers and employees. Now, the Labor Courts are competent to settle disputes arising not only from employment relationships, but also from labor relationships (in a broad sense), including, for example, disputes stemming from services provided by independent workers and indemnifications related to work activities. This rule could affect the outcome of the two current Civil Claims mentioned above - - as they are derived from labor relationships — which can be sent to the Labor Courts, for final judgment.
Policy on Dividend Distribution
The preferred shares are entitled under our by-laws to receive, to the extent of available distributable profits and reserves, a non-cumulative preferred dividend in an amount equal to the greater of (i) six percent per year on the amount resulting from the division of the subscribed capital by the total amount of our shares, and (ii) three percent of the equity value of the share, or the Preferred Dividend. To the extent there are additional distributable profits, we are also required to distribute to all shareholders an amount equal to at least 25.0% of the adjusted net income, or the General Dividend, determined in accordance with Brazilian corporate law. Our obligation to pay General Dividends to holders of preferred shares will be met inasmuch as a Preferred Dividend is paid. Payment of General Dividends may be limited to the net realized income for the year, provided that the difference is recorded as unrealized reserve. Net income recorded in unrealized income reserve, when realized and as long as not offset by losses for subsequent years, should be added to the first dividend declared after realization. We may also make additional distributions to the extent of available distributable profits and reserves. All of the aforementioned distributions may be made as dividends or as tax-deductible interest on capital. See “Item 10. Additional Information — Memorandum and Articles of Association — Allocation of Net Income and Distribution of Dividends.”
Significant Changes
See “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects.”
Item 9. The Offer and Listing
Information Regarding the Price History of the Stock to Be Offered or Listed
The principal trading market for the preferred shares is the Bovespa. As of December 31, 2007, we had approximately 83 thousand shareholders.
The preferred shares commenced trading separately on the Bovespa on August 2005. The following table sets forth the reported high and low closing sale prices for preferred shares on the Bovespa for the periods indicated, adjusted for dividends and interest on capital.
62
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Reais per | |
| | | Preferred Shares * | |
| | | High | | | Low | |
2007 | | | | | | | | |
| 3rd Quarter | | | 55.73 | | | | 47.80 | |
| 4th Quarter | | | 54.80 | | | | 48.45 | |
2008 | | | | | | | | |
| 1st Quarter | | | 51.66 | | | | 43.37 | |
| January | | | 52.99 | | | | 45.00 | |
| February | | | 51.99 | | | | 47.50 | |
| March | | | 49.99 | | | | 37.60 | |
| April | | | 40.88 | | | | 35.00 | |
| May | | | 51.00 | | | | 37.50 | |
| June (through 16, 2008) | | | 51.00 | | | | 47.00 | |
| | | |
| * | | Prices per share after the Reverse Stock Split. |
Source:Bloomberg
In the United States, the preferred shares trade in the form of ADSs, each representing one-twentieth of a preferred share, issued by the Depositary pursuant to a Depositary Agreement among the Company, the Depositary and the registered holders and beneficial owners from time to time of ADSs. As of June 13, 2008, there were 34,211 thousand ADSs outstanding. The following table sets forth the reported high and low closing sales prices for ADSs for the period indicated.
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | U.S. dollars per ADS | |
| | | High | | | Low | |
2007 | | | | | | | | |
| 3rd Quarter | | | 1.41 | | | | 1.05 | |
| 4th Quarter | | | 1.50 | | | | 1.20 | |
2008 | | | | | | | | |
| 1st Quarter | | | 1.37 | | | | 1.02 | |
| January | | | 1.32 | | | | 1.20 | |
| February | | | 1.35 | | | | 1.22 | |
| March | | | 1.37 | | | | 1.02 | |
| April | | | 1.09 | | | | 1.01 | |
| May | | | 1.45 | | | | 1.09 | |
| June (through 16, 2008) | | | 1.52 | | | | 1.30 | |
Source:The Bank of New York ADR Inform
Trading on the Brazilian Stock Exchanges
In May 2000, the main Brazilian stock exchanges merged into the Bovespa. Since the merger, private equity and debt have been traded in Brazil only on the Bovespa. Brazilian federal, state and municipal public debt have been traded exclusively on, and privatization auctions have been carried out exclusively at, the Rio de Janeiro Stock Exchange.
There are no specialists or market makers for Contax Holdings’ shares on the Bovespa.
63
The Bovespa is a non-profit entity owned by its member brokerage firms. Trading on the Bovespa is limited to member brokerage firms and a limited number of authorized non-members. The Bovespa has two open outcry trading sessions each day from 11:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m., São Paulo time, for all securities traded on all markets, except during daylight savings time in the United States. During daylight savings time in the United States, the sessions are normally from 10:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m., São Paulo time, to closely mirror the NYSE trading hours.
Trading is also conducted between 11:00 a.m. and 6:00 p.m., or between 10:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m. during daylight savings time in the United States, on an automated system known as the Computer Assisted Trading System (Sistema de Negociação Assistida por Computador) on the Bovespa and on the National Electronic Trading System (Sistema Electrônico de Negociação Nacional). This system is a computerized system that links electronically with the seven smaller regional exchanges.
On September 20, 1999, the Bovespa launched the so-called “After Market”, with the objective of expanding business opportunities and offering investors a more flexible trading schedule. Trading in the After Market takes place from 6:45 p.m. to 7:30 p.m. on an online system connected to traditional and internet brokers. All stocks traded during the regular trading session of the day may be traded on the After Market. However, only cash market trading via the Bovespa’s electronic trading system is allowed. Trading on the After Market is subject to regulatory limits on price volatility and on the volume of shares transacted through internet brokers. The maximum variation allowed for stock prices on the After Market, whether positive or negative, corresponds to 2.0% in relation to the closing price at the regular trading session.
In order to better control volatility, the Bovespa adopted a “circuit breaker” system pursuant to which trading sessions may be suspended for a period of 30 minutes or one hour whenever the indices of the Bovespa fall below the limits of 10.0% or 15.0%, respectively, in relation to the index registered in the previous trading session.
Settlement of transactions on the Bovespa is effected three business days after the trade date without adjustment of the purchase price for inflation. Payment for shares is made through the facilities of a separate clearinghouse, which maintains accounts for member brokerage firms. The seller is ordinarily required to deliver the shares to the exchange on the second business day following the trade date. The clearinghouse for the Bovespa is the Brazilian Settlement and Custody Company (Companhia Brasileira de Liquidação e Custódia S.A.), or CBLC, which is controlled mainly by member brokerage firms and banks that are not members of that exchange.
Trading in securities listed on the Bovespa may be executed off the exchanges in certain circumstances, although such trading is very limited.
The Bovespa is significantly less liquid than the NYSE or other major exchanges around the world. As of December 2007, the aggregate market capitalization of the 404 companies listed on the Bovespa was equivalent to R$2,478 trillion and the 10 largest companies listed on that exchange represented approximately 50.7% of the total market capitalization of all listed companies. In contrast, as of December 2007, the aggregate market capitalization of the nearly 2,296 companies listed on the NYSE was U.S.$27.1 trillion and the 10 largest companies listed on the NYSE represented approximately 34.0% of the total market capitalization of all listed companies. The average daily trading volume of Bovespa and NYSE for December 2007 was approximately R$6.3 million and U.S.$119.2 billion, respectively. Although any of the outstanding shares of a listed company may trade on the Bovespa, in most cases fewer than half of the listed shares are actually available for trading by the public, the remainder being held by small groups of controlling persons, by government entities or by one principal shareholder. For this reason, data showing the total market capitalization of Brazilian stock exchanges tend to overstate the liquidity of the Brazilian equity market.
The Brazilian equity market is relatively small and illiquid compared to major world markets. In 2007, the monthly trading volume on the Bovespa averaged approximately U.S.$44.3 billion.
Trading on Brazilian stock exchanges by nonresidents of Brazil is subject to certain limitations under Brazilian foreign investment legislation. See “Item 10. Additional Information-Exchange Controls and Other Limitations Affecting Security Holders.”
64
Regulation of the Brazilian Securities Market
The Brazilian securities markets are regulated by the CVM, which has authority over the stock exchanges and the securities markets generally, and by the Brazilian Central Bank, which has, among other powers, licensing authority over brokerage firms and regulates foreign investment and foreign exchange transactions. The Brazilian securities markets are governed by (i) Law no. 6,385, as amended and supplemented, which is the principal law governing the Brazilian securities markets; (ii) the Brazilian corporate law (Law No. 6.404/76), as amended and supplemented; and (iii) the regulations issued by the CVM, the CMN, and the Brazilian Central Bank (collectively, the Securities Laws).
Under Brazilian corporate law, a company is either public, acompanhia aberta, such as Contax, or private, acompanhia fechada. All public companies are registered with the CVM and are subject to reporting requirements. A company registered with CVM may have its securities traded either on the Bovespa or in the Brazilian over-the-counter market. Shares of companies listed on the Bovespa may not simultaneously trade on the Brazilian over-the-counter market. The shares of a public company may also be traded privately, subject to certain limitations. To be listed on the Bovespa, a company must apply for registration with the CVM and the Bovespa. Once the Bovespa has admitted a company to listing and the CVM has accepted its registration as a public company, its securities may be traded on the Bovespa.
The trading of securities on the Bovespa may be suspended at the request of a company in anticipation of the announcement of a material event. Trading may also be suspended at the initiative of the Bovespa or the CVM, based on or due to a belief that, among other reasons, a company has provided inadequate information regarding a material event or has provided inadequate responses to inquiries by the CVM or the Bovespa.
The trading of shares is prohibited under certain circumstances as follows: (i) trading by the company of its own shares except for cancellation or maintenance in treasury for further disposal, according to Rule 10/80, issued by the Brazilian Securities Exchange Commission; (ii) trading by the company’s controlling shareholders, Officers, Directors or members of any technical or advisory body established pursuant to its by-laws; (iii) trading by persons who, as a result of their position, title or relationship with the company, have knowledge of the impending disclosure of a material event; and (iv) trading by the persons listed under item (iii) above during the 15-day period before the disclosure of the company’s quarterly and annual financial statements.
The Brazilian securities markets are principally governed by the Securities Laws, as well as by regulations issued by the CVM and the CMN. These laws and regulations, among others, provide for disclosure requirements, restrictions on insider trading and price manipulation, and protection of minority shareholders. However, the Brazilian securities markets are not as highly regulated and supervised as the United States securities markets or markets in certain other jurisdictions.
Recent changes to Brazilian corporate laws and regulations increased the rights of minority shareholders, including holders of preferred shares, by granting them restricted voting rights. The amended Brazilian corporate law also granted more regulatory power to the CVM. On December 28, 2007, Law No. 11.638 was enacted, implementing changes in the accounting standards adopted by the Brazilian corporate law with respect to the preparation and reporting by Brazilian companies of financial statements in accordance with Brazilian GAAP.
Disclosure Requirements
Through its Instruction no. 358, the CVM revised and consolidated the requirements regarding the disclosure and use of information related to material facts and acts of publicly held companies, including the disclosure of information in the trading and acquisition of securities issued by publicly held companies.
Such requirements include provisions that:
| | • | | establish the concept of a material fact that gives rise to reporting requirements. Material facts include decisions made by the controlling shareholders, resolutions of the general shareholders’ meeting of shareholders and of management of the company, or any other facts related to the company’s business (whether occurring within the company or otherwise somehow related thereto) that may influence the price of its publicly traded securities, or the decision of investors to trade such securities or to exercise any of such securities’ underlying rights; |
65
| | | | |
| | • | | specify examples of facts that are considered to be material, which include, among others, the execution of shareholders’ agreements providing for the transfer of control, the entry or withdrawal of shareholders that maintain any managing, financial, technological or administrative function with or contribution to the company, and any corporate restructuring undertaken among related companies; |
| |
| | • | | require the Officer of Investor Relations, to publish and inform the CVM and also the stock exchange and entities of the organized over-the-counter market where the securities issued by the company are traded, as the case may be, any material events occurred or related to their business; |
| |
| | • | | require the controlling shareholders, directors, members of the administrative council, of the Fiscal Council and of any technical and consultative bodies, according to the by-laws, to report any material event they are aware of to the Officer of Investor Relations, who will provide for its disclosure. In the event those people referred above have personal knowledge about material events and verify omission by the Officer of Investor Relations towards investors in the fulfilling of his communication and disclosing duties, they will only be exempt from responsibility if they communicate the material events to the CVM immediately; |
| |
| | • | | require simultaneous disclosure of material facts to all markets in which the corporation’s securities are admitted for trading; |
| |
| | • | | require the acquirer of a controlling stake in a corporation to publish material facts, including its intentions to promote, or not, within a year, the cancellation of the registration of publicly-held companies; |
| |
| | • | | establish rules regarding disclosure requirements in the acquisition and disposal of a material stockholding stake; and |
| |
| �� | • | | forbid the use of insider information. |
Item 10. Additional Information
Memorandum and Articles of Association
In addition to the description in this Item 10, you should also review the copy of our by-laws incorporated by reference as an exhibit to this annual report. Under Brazilian corporate law, no memorandum or articles of association are required. Our only constitutive documents are the by-laws and the minutes of the General Shareholders’ Meeting that provided for our incorporation.
Organization
We are a listed Company duly registered with the CVM under no. 01910-0 and our by-laws are filed under no. 33.3.0027541-0 with the Board of Trade (Junta Comercial) of the State of Rio de Janeiro. According to Article 3 of our by-laws, our business purpose is to participate, directly or indirectly, in other companies as partner, shareholder or quotaholder, in Brazil or abroad. We have no present intention of listing our shares on any organized market or stock exchange in the United States.
Except as described in this section, our by-laws do not contain provisions addressing the duties, authority, or liabilities of Directors and senior management, which are instead established by Brazilian corporate law.
66
Qualification of Directors
Brazilian corporate law provides that only shareholders of a company may be appointed to its Board of Directors. There is no minimum share ownership or residency requirement for qualification as a Director. If a Director is a non-Brazilian resident, he or she must appoint an attorney-in-fact to receive service of process.
According to Brazilian corporate law, persons disqualified by special law, or sentenced for a bankruptcy offense, fraud, bribery or corruption, misappropriation of public funds or embezzlement, crimes against the national economy or decency or public property, or to any criminal sanction which precludes, even temporarily, access to public office are disqualified for election to an administrative office in the corporation. A person who has been declared by the CVM to be incapacitated is also ineligible to an administrative office in a publicly held corporation.
The officers shall have unblemished reputations and are ineligible, except if a waiver is granted by the general meeting, in the following cases: (i) holding of a position in a competing company, specially in management board or advisory or finance committees; and (ii) conflicting interests with the company.
Allocation of Net Income and Distribution of Dividends
Our by-laws require the Board of Directors to recommend, at each annual shareholders’ meeting, the allocation of net income from the preceding fiscal year as follows:
| | • | | 5.0% to a legal reserve, not to exceed 20.0% of the paid-in capital of Contax; |
| |
| | • | | at least 25.0% of adjusted net income against payment of dividends. As required by Brazilian corporate law, such amount will be increased if required to satisfy payment of dividends of preferred shares; and |
| |
| | • | | respecting the entry in the reserve for profits to be realized, the remaining net income should be allocated in the reserve for expansion for working capital purposes. The total amount registered in the reserve for expansion together with the amount enrolled in profit reserves is limited to the total amount recorded as paid-in capital. |
Whenever we accumulate or reserve profits, the Board of Directors can authorize the allocation of interim dividends, as provided under Brazilian corporate law. In general, we have to pay dividends first to holders of preferred shares and then, to holders of common shares. The remaining balance will be distributed equally among all of the shares of our capital stock. Dividends not claimed within three years of the date on which they were made available for distribution will revert to us. See “Item 8. Financial Information — Policy on Dividend Distribution.”
In lieu of the payment of dividends as stated above, we may elect to make payments to shareholders characterized as interest on our capital. See “— Taxation — Brazilian Tax Considerations — Distribution of Interest on Capital.”
Shareholders’ Meetings
The annual shareholders’ meetings are held once a year, generally during the first four months following the end of the fiscal year. Extraordinary meetings can be called at any time.
Our shareholders have the power to decide any matters related to our corporate purpose and to pass any resolutions they deem necessary for our protection and development through a shareholders’ vote at a shareholders’ meeting.
We convene the shareholders’ meetings by publishing a notice in the national edition ofValor Econômico, a Brazilian newspaper, and also in the Official Gazette of the State of Rio de Janeiro (Diário Oficial do Estado do Rio de Janeiro). The notice must be published no fewer than three times, the first of which must be at least 15 calendar days prior to the scheduled meeting date.
67
The notice must always contain the meeting’s place, date, time and agenda and, in case of a proposed amendment to the by-laws, an indication of the subject matter affected by such proposal.
The Board of Directors, or, in some specific situations set forth in Brazilian corporate law, the shareholders or the Fiscal Council, if in operation, has the power to call shareholders’ meetings. A shareholder may be represented at a shareholders’ meeting by its attorney-in-fact so long as that attorney-in-fact was appointed within one year of such meeting. The attorney-in-fact must be another shareholder, a member of our management, a lawyer, or a financial institution. The power of attorney granted to the attorney-in-fact must comply with certain formalities set forth by Brazilian law.
In order to be legally convened after a first call, a shareholders’ meeting must obtain a quorum representing at least one-quarter of the issued and outstanding voting capital. If this quorum is not met, a shareholders’ meeting can be held with any quorum after a second call has been published. However, if the purpose of a shareholders’ meeting is to amend our by-laws, shareholders representing at least two-thirds of the issued and outstanding voting capital must be present. If this quorum is not met, the Board of Directors may call a second meeting with notice given at least eight calendar days prior to the scheduled meeting, in accordance with the rules of publication described above. No minimum quorum requirements apply to a second meeting, except that certain voting requirements may still apply as described below.
Voting Rights
Each common share entitles its holder to one vote at our shareholders’ meetings. Except as otherwise provided by law, resolutions of a shareholders’ meeting are passed by the vote of holders of our common shares. Abstentions are not taken into account.
Holders of preferred shares may acquire full voting rights if we fail to pay dividends for three consecutive years. They will continue to have voting rights until dividends are duly paid.
Pursuant to Brazilian corporate law, the approval of the following matters requires: (i) a separate vote of shareholders representing the majority of each class of the outstanding, adversely affected preferred shares; and (ii) a vote of shareholders representing the majority of the issued and outstanding common shares:
| | • | | the creation of preferred shares or the increase of an existing class of shares without preserving their proportion with other classes of shares, except as already authorized by our by-laws; |
| |
| | • | | a change of a preference, privilege or redemption or amortization provision of any class of preferred shares; and |
| |
| | • | | the creation of a new class of preferred shares that has a preference, privilege or redemption or amortization provision which is superior to those of existing preferred shares. |
Preferred shareholders do not have a vote on any other matter in addition to the ones previously mentioned, except that they can elect one member and respective alternate to sit on our Fiscal Council, if in operation, and, if they come to hold more than 10.0% of our capital stock, they can elect one member and respective alternate to sit on our Board of Directors. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees.”
Notwithstanding the actions described above, the approval of a majority of the holders of the issued and outstanding common shares is required to approve the following matters:
| | • | | a reduction of the mandatory dividend set forth in our by-laws; |
| |
| | • | | the approval of a merger, spin-off or consolidation; |
| |
| | • | | our participation in a group of companies, orgrupo de sociedades, the management of which is coordinated through contractual relationships and equity ownership, as defined under Brazilian corporate law; |
68
| | • | | a change in our business purpose; |
| |
| | • | | the creation of founders’ shares(partes beneficiárias); |
| |
| | • | | the cessation of our liquidation process; and |
| |
| | • | | approval of our dissolution. |
Pursuant to Brazilian corporate law, holders of common shares, voting at a shareholders’ meeting, have the exclusive power to:
| | • | | amend the by-laws, including changing the rights of holders of common shares; |
| |
| | • | | elect or dismiss members of the Board of Directors or Fiscal Council, if in operation; |
| |
| | • | | review the yearly accounts prepared by management and accept or reject management’s financial statements, and decide on the allocation of: (i) net profits for payment of the mandatory dividend, and (ii) funds to the various reserve accounts; |
| |
| | • | | authorize the issuance of debentures and founders’ shares(partes beneficiárias), except that the Board of Directors is empowered to approve the issuance of simple debentures that are not convertible into shares and have no real guarantee; |
| |
| | • | | suspend the rights of shareholders who have not fulfilled their obligations as imposed by law or by the by-laws; |
| |
| | • | | accept or reject the valuation of assets contributed by a shareholder in consideration for issuance of capital stock; |
| |
| | • | | pass resolutions authorizing: (i) the reorganization of our legal form; (ii) our merger, spin-off, dissolution or liquidation; and (iii) the election or dismissal of liquidators and the inspection of their accounts; and |
| |
| | • | | authorize our management to file for bankruptcy or requestconcordata(a reorganization process similar to Chapter 11 proceedings under U.S. bankruptcy law). |
Related Party Transactions
According to Brazilian corporate law, a shareholder may not vote on resolutions to approve the following matters: (i) an evaluation report of property transferred by such shareholder as capital contribution to a company; (ii) the accounts of such shareholder while serving as an officer of a company; or (iii) any other resolution that may benefit such shareholder personally or in which such shareholder and the company may have a conflicting interest. Resolutions passed with a vote of a conflicted shareholder may be voided and such shareholder held liable for damages and required to disgorge any benefits incurred.
Brazilian corporate law also provides that a Director or Officer shall not take part in any (i) corporate transaction in which they have an interest that conflicts with those of the company, or (ii) decision made by other Directors or Officers regarding such conflicting transaction. The conflicted Director or Officer shall disclose their impediment to the other Directors or Officers and request that the nature and extent of their interests be recorded in the minutes of the meeting of the Board of Directors or of the Board of Executive Officers. In addition, a Director or Officer may only execute contracts with a company under reasonable and fair terms in line with prevailing market standards or in accordance with the same guidelines that the company would observe when executing contracts with unrelated third parties. Any business executed by such Director or Officer and the company in disagreement with these rules may be voided and the Director or Officer required to return to the company any benefits incurred.
69
Withdrawal Rights
Brazilian corporate law provides that under certain circumstances a shareholder has the right to require that its equity interests in a company be redeemed for payment. Such payment shall not be lower than the company’s pro-rata net worth (as per its most recently approved balance sheet) unless an independent valuation were to determine a lower economic value for the company’s equity value.
Withdrawal rights may be exercised:
| | (i) | | by the dissenting or nonvoting holders of the adversely affected class of shares (including any holder of preferred shares of an adversely affected class) in the event that the holders of a majority of all outstanding common shares authorize: |
| | • | | the creation of preferred shares or an increase of an existing class of shares without preserving their proportion with other classes of shares, except as already authorized in our by-laws; |
| |
| | • | | a change in the preferences, privileges, or redemption or amortization provisions of any class of preferred shares; or |
| |
| | • | | the creation of a new class of preferred shares that has a preference, privilege, or redemption or amortization provision that is superior to those of existing preferred shares. |
| | (ii) | | by all dissenting or nonvoting shareholders, in the event that the holders of a majority of all outstanding common shares authorize: |
| | • | | a reduction of the mandatory dividend set forth in our by-laws; |
| |
| | • | | the approval of our consolidation or merger into another company; |
| |
| | • | | our participation in agrupo de sociedades; |
| |
| | • | | a change in our business purpose; |
| |
| | • | | our spin-off, if such spin-off implies (a) a change in our business purpose (except if the spun-off assets revert to a company whose main purpose is the same as ours), (b) a reduction of the mandatory dividend set forth in our by-laws, or (c) our participation in agrupo de sociedades; or |
| |
| | • | | the acquisition of control of another company at a price which exceeds certain limits set forth in Brazilian corporate law. |
Notwithstanding the above, in the event that we are consolidated or merged with another company, become part of agrupo de sociedades, or acquire the control of another company for a price in excess of certain limits imposed by Brazilian corporate law, holders of any type or class of shares that are marketable and dispersed in the market will not have the right to withdraw. Shares are considered marketable when that type or class of shares is part of a general stock exchange index, as defined by the CVM, in Brazil or abroad. Shares are considered dispersed in the market when the controlling shareholder, the parent company or other companies under its control hold less than half the total amount of that share type or class.
Dissenting or nonvoting shareholders are also entitled to withdrawal rights in the event that the entity resulting from a merger or spin-off does not have its shares listed in an exchange or traded in the secondary market within 120 days from the shareholders’ meeting that approved the relevant merger or spin-off.
70
Dissenting or nonvoting shareholders are only entitled to withdrawal rights when they are shareholders of record at the time of the first notice calling for a shareholders’ meeting to vote on this matter is published or at the time when a material fact (fato relevante) was announced, whichever occurs earlier.
Withdrawal rights lapse 30 days after publication of the minutes of the shareholders’ meeting that gave rise to such withdrawal rights, except when the resolution is approved pending confirmation by the holders of preferred shares (such confirmation to be given at special meeting to be held within one year). In this event, such 30-day period for dissenting shareholders begins at the date of publication of the minutes of the shareholders’ meeting. Within 10 days after expiration of the exercise period of withdrawal rights, we are entitled to reconsider any resolution or decision that gave rise to such withdrawal rights, in the event that the reimbursement of shares held by dissenting shareholders is deemed to have a negative impact on our financial stability.
In any one of the situations explained above, shares would be redeemable at their net book value, based on the most recent balance sheet approved by shareholders. The reimbursement amount can only be lower than the net book value amount if it is based on the economic value of the enterprise, as determined by an appraisal process in accordance with Brazilian corporate law. If the shareholders’ meeting that gave rise to such withdrawal rights is held more than 60 days after the date of the most recently approved balance sheet, shareholders may require that the reimbursement value of their shares be calculated based on a new balance sheet dated up to 60 days prior to that shareholders’ meeting.
Liquidation Procedures
In the event of our liquidation, the holders of preferred shares would be entitled to priority in relation to holders of common shares in the reimbursement of capital, with no premium. The reimbursement amount to which they would be entitled is based on the portion of the capital stock represented by the preferred shares, as adjusted from time to time to reflect any capital increases or reductions. First, after all our creditors have been paid, the residual assets, if any, would be applied towards the amount of capital represented by preferred shares to its respective holders. Once holders of preferred shares have been fully reimbursed, the holders of the common shares will be reimbursed, to the extent of remaining assets, if any, on the portion of the capital stock represented by common shares. All our shareholders will participate equally and ratably in any remaining residual assets.
Form and Transfer of Securities
Our shares are maintained in book-entry form with a transfer agent, Banco do Brasil S.A., or the Registrar, that serves as the registrar for those of our shares that will be freely traded on the Bovespa. To make a transfer of shares, the Registrar makes an entry in the register by debiting the share account of the transferor and crediting the share account of the transferee.
Transfers of shares by a foreign investor are made in the same way and executed by the investor’s local Custodian on the investor’s behalf.
The Bovespa and clearing systems, such as member brokerage firms and banks, control Brazil’s clearing house for equity of Brazilian listed companies, CBLC. Shareholders may choose, at their discretion, to hold their shares through CBLC. Shares are added to the CBLC system through Brazilian institutions that have clearing accounts with the CBLC. Our shareholder registry indicates which shares are kept at the CBLC system.
Transfer of Control
The sale of a controlling block of shares of a publicly held Company, such as Contax, can only be effected if the acquirer undertakes to make a public offering to purchase the remaining common shares at a price equal to at least 80.0% of the amount paid for each voting share in such controlling block. Such public offering must comply with the rules issued by the CVM. In addition, the acquirer may grant the option to the minority shareholders to keep their shares upon receipt of a premium equal to the difference between the market value of the shares and the amount paid for the shares comprising the controlling block.
71
The concept of sale of control is defined by Brazilian corporate law and regulations as the direct or indirect: (i) transfer of (A) shares included in the controlling block or subject to a shareholders’ agreement, or (B) securities convertible into voting shares; or (ii) assignment of shares and other securities subscription rights, or rights attached to securities convertible into shares, that may result in the disposal of control of a company.
Amendments
Our by-laws were amended on October 17, 2007 to reflect the cancellation of 1,443,472 common shares and 18,277,422 preferred shares held in treasury, without reduction of our capital stock (3,500,000 common shares still being held in treasury), as approved at our Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting held on such date. It also approved the reverse-split, pursuant to article 12 of Law 6,404/76, of all shares representing our capital stock (following the cancellation of the shares in treasury) at the ratio of 20 (twenty) shares to 1 (one) share of the same type. In consequence, the caption of article 5 of our by-laws will now have the following wording:"Article 5 — The Company’s Capital Stock comprises R$223,873,116.10 (two hundred and twenty three million, eight hundred and seventy three thousand, one hundred and sixteenreaisand tencentavos), divided into 317,133,733 shares, of which 116,495,445 are common and 200,638,288 are preferred shares, all registered book-entry shares with no par value.”
After the operations related to the reverse-split, our capital stock will be R$223,873,116.10 (two hundred twenty three million, eight hundred and seventy three thousand, one hundred and sixteenreaisand tencentavos), divided into 15,856,686 shares, of which 5,824,772 are common shares and 10,031,914 are preferred shares. A General Meeting shall be called to adjust Article 5 of our by-laws related to the capital stock.
Article 13 of our by-laws was last amended after our Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting held on June 17, 2008 to increase the maximum number of members of the Company’s Board of Directors, from 11 to 13 members.
Disclosure of Shareholder Ownership
Brazilian regulations establish that the controlling shareholders, directly or indirectly, and those shareholders who elected the members of the Board of Directors or Fiscal Council, if in operation, as well as any other person or group of persons acting together or representing the same interest and who directly or indirectly hold 5.0% or more of any type or class of shares in a publicly held company, disclose their respective shareholdings to the company. In the event that an acquisition results in a change of control of a company or of its administrative structure, as well as when the acquisition results in the obligation to tender a public offer, the acquirer of the control of such company shall publish a press release regarding the shareholdings, as required by Brazilian regulations. The officer of investor relations is responsible for transmitting the information to the CVM and the stock exchanges. Every 5.0% increment or disposal in shareholding must be similarly disclosed. See “Item 9. The Offer and Listing-Disclosure Requirements.”
Material Contracts
We are a party to a material contract with Telemar related to contact center services rendered by us to both Tmar and Oi, which was executed on November 30, 2004 and duly approved at Tmar’s Extraordinary Shareholders’ Meeting on December 17, 2004.
The total amount of our net operating revenues derived from Telemar was R$692 million in 2007 and R$703.4 million in 2006, representing 50.7% and 57.6%, respectively, of our total revenues in those years. Our relationship with Telemar is currently comprised of several distinct and independent services, such as customer services for Telemar fixed line business, outbound telemarketing to attract additional mobile customers, customer service for prepaid and postpaid mobile users, technical support for broadband subscribers, and debt collection services.
On April 1, 2004, Orbitall, one of Brazil’s main credit card processing companies, executed an agreement with us, or the Orbitall Agreement, according to which we agreed to provide contact center services to the customers of Orbitall’s clients, such as Citibank, Credicard, Itaucard, Banespa, Sodexo, VR Vales and Medial Saúde. So far, the Orbitall Agreement has accounted for a significant portion of our revenues (second only to the Telemar service agreement) and we expect it to be one of our main service agreements in the foreseeable future. The term of the Orbitall Agreement is three years. On December 2006 this contract was extended until April 2009; it is currently renewable at the option of the parties.
72
See the reference to such material contracts as well as to their amendments in “Item 19. Exhibits.”
BNDES Loan Agreement
On June 20, 2007, the Company’s Board of Directors approved the loan agreement of R$216.5 million from BNDES (the Brazilian Development Bank) to the subsidiary TNL Contax S.A., as approved by the Executive Board of BNDES on May 22, 2007. Repayment will occur within a six-year settlement term, including a two year grace period, with an annual cost of TJLP (the Brazilian long-term interest rate) plus 2.0%.
The funds are for increasing installed capacity, upgrading current facilities, training programs, improving service quality and productivity and investments in marketing activities, within the PROSOFT- Corporate (Software Industry and Correlated Services Development Program).
In October 2007, the first tranche of the BNDES loan was provided in the amount of R$100 million, followed by additional tranches on the January 28, January 30 and June 12, 2008, in the amounts of R$40 million, R$10 million and R$61.8 million, respectively. The total funds received so far from BNDES amount to R$211.8 million.
Exchange Controls and Other Limitations Affecting Shareholders
There are no restrictions on ownership of our capital stock by individuals or legal entities domiciled outside Brazil. However, the right to convert dividend payments and proceeds from the sale of preferred shares into foreign currency and to remit such amounts outside Brazil is subject to restrictions under foreign investment legislation and foreign exchange regulations, which generally requires, among other things, that the relevant investments be registered with the Brazilian Central Bank. Such restrictions on the remittance of foreign capital abroad could hinder or prevent the acting as custodian for the Depositary of the preferred shares underlying the ADSs, or holders who have exchanged ADSs for preferred shares from converting dividends, distributions or the proceeds from any sale of such preferred shares into U.S. dollars, as the case may be, and remitting such U.S. dollars abroad. Holders of ADSs could be adversely affected by delays in, or refusal to grant any, required government approval for conversions of Brazilian currency payments and remittances abroad of amounts owed to holders of ADSs. See “Item 3. Key Information-Risk Factors-Risks Relating to the ADSs and the Preferred Shares.”
Foreign investors may register their investments under Law no. 4,131 or Resolution no. 2,689 of the CMN. Registration under Law no. 4,131 or under Resolution no. 2,689 generally enables foreign investors to convert into foreign currency dividends, other distributions and sales proceeds received in connection with registered investments and to remit such amounts abroad. Resolution no. 2,689 affords favorable tax treatment to foreign investors who are not resident in a tax haven jurisdiction, which is defined under Brazilian tax laws as a country that does not impose taxes or where the maximum income tax rate is lower than 20.0% or that restricts the disclosure of shareholder composition or ownership of investments (“Tax Haven”).
All investments made by a foreign investor under Resolution no. 2,689 will be subject to an electronic registration with the Brazilian Central Bank.
Under Resolution no. 2,689, foreign investors may invest in almost all financial assets and engage in almost all transactions available to local investors in the Brazilian financial and capital markets, provided that certain requirements are fulfilled. In accordance with Resolution no. 2,689, the definition of foreign investor includes individuals, legal entities, mutual funds and other collective investment entities, domiciled or headquartered abroad.
Resolution no. 2,689 prohibits the offshore transfer or assignment of title to Brazilian securities, except in the cases of (i) corporate reorganization effected abroad by a foreign investor, or (ii) inheritance.
73
Pursuant to Resolution no. 2,689, foreign investors must:
| | • | | appoint at least one representative in Brazil with powers to take action relating to the foreign investment; |
| |
| | • | | complete the appropriate foreign investor registration forms; |
| |
| | • | | obtain registration as a foreign investor with the CVM; and |
| |
| | • | | register their foreign investment with the Brazilian Central Bank. |
Securities and other financial assets held by the foreign investor pursuant to Resolution no. 2,689 must be registered or maintained in deposit accounts or under the custody of an entity duly licensed by the Brazilian Central Bank or the CVM or in registry, clearing and custody systems authorized by the Brazilian Central Bank or the CVM. In addition, the trading of securities is restricted to transactions carried out in exchanges or in organized over-the-counter markets recognized by the CVM.
Resolution no. 1,927 of the CMN provides for the issuance of depositary receipts in foreign markets in respect of shares of Brazilian issuers.
Under the mechanics of an ADS program, the custodian for the Depositary holds those shares that correspond to the ADSs issued abroad so that such shares are blocked from trading on the Bovespa. The Depositary will keep a record of the ADS holders and record the transfers of ADSs made by such ADS holders. Distributions made by us will be paid to the custodian, who will remit such distribution outside Brazil to the Depositary, so that it can in turn distribute these proceeds to the ADS holders of record.
To allow that dividends paid inreaisbe legally converted into U.S. dollars and remitted outside Brazil to holders of ADSs, the Brazilian Central Bank has issued an electronic certificate of foreign capital registration in the name of the Depositary, which is kept by the custodian on the Depositary’s behalf. Pursuant to the electronic certificate of foreign capital registration, the custodian is allowed to convert, into foreign currency, dividends and other distributions denominated inreaiswith respect to the preferred shares represented by ADSs and remit the proceeds of such distributions outside Brazil to the Depositary, so that it can in turn forward such proceeds to the ADS holders of record.
In the event that a holder of ADSs exchanges such ADSs for preferred shares, the holder will be entitled to continue to rely on the Depositary’s electronic certificate of foreign capital registration for five business days after the exchange, after which the holder must seek to obtain its own electronic certificate of foreign capital registration with the Brazilian Central Bank. Thereafter, unless the preferred shares are held by a duly registered investor pursuant to Resolution no. 2,689 or unless a holder of preferred shares applies for and obtains a new certificate of registration, such holder may not be able to convert into foreign currency and remit outside Brazil the proceeds from the disposition of, or distributions with respect to, the preferred shares. Also, if not registered under Resolution no. 2,689, such holder will be subject to less favorable Brazilian tax treatment than a holder of ADSs. In addition, if the foreign investor resides in a Tax Haven, the investor will also be subject to less favorable tax treatment. See “Item 3. Key Information. Risk factors — Risks relating to the ADSs and preferred shares — If you surrender your ADSs and withdraw preferred shares, you risk losing the ability to remit foreign currency abroad and certain Brazilian tax advantages.” and “— Material tax considerations-Material Brazilian tax considerations.”
Under current Brazilian legislation, the federal government may impose temporary restrictions on remittances of foreign capital abroad in the event of a serious imbalance or an anticipated serious imbalance of Brazil’s balance of payments. For approximately six months in 1989 and early 1990, the Brazilian government froze all dividend and capital repatriations held by the Brazilian Central Bank that were owed to foreign equity investors, in order to preserve Brazil’s foreign currency reserves. These amounts were subsequently released in accordance with federal government directives. There can be no assurance that the Brazilian government will not impose similar restrictions on foreign repatriations in the future. See “Item 3. Key Information. Risk factors — Risks relating to Brazil.”
74
Registered Capital
Investments in preferred shares by (i) a holder not deemed to be domiciled in Brazil for Brazilian tax purposes, (ii) a non-Brazilian holder, who is registered with the CVM under Resolution no. 2,689, or (iii) the Depositary, are eligible for registration with the Brazilian Central Bank. Such registration (the amount so registered being referred to as Registered Capital) allows the remittance outside Brazil of foreign currency, converted at the commercial market rate, acquired with the proceeds of distributions on and amounts realized through dispositions of such preferred shares. The Registered Capital per preferred shares purchased in the form of an ADS, or purchased in Brazil and deposited with the Depositary in exchange for an ADS, will be equal to its purchase price (stated in U.S. dollars). The Registered Capital per preferred shares withdrawn upon cancellation of an ADS will be the U.S. dollar equivalent of (i) the average price of a preferred shares on the Bovespa on the day of withdrawal; or (ii) if no preferred shares were traded on that day, the average price on the Bovespa during the 15 trading sessions immediately preceding such withdrawal. The U.S. dollar equivalent will be determined on the basis of the average commercial market rates quoted by the Brazilian Central Bank on such date or dates.
A non-Brazilian holder of preferred shares may experience delays in effecting Brazilian Central Bank registration, which may consequently delay remittances of currencies abroad. Such a delay may adversely affect the amount in U.S. dollars received by the non-Brazilian holder.
Taxation
The following summary contains a description of the principal Brazilian and U.S. federal income tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership and disposition of shares or ADSs. Such summary does not, however, purport to be a comprehensive description of all the tax considerations that may be relevant to a decision to purchase shares or ADSs. The summary is based upon the tax laws of Brazil and the United States and regulations under these tax laws as currently in effect, which are subject to change. Although there is at present no income tax treaty between Brazil and the United States, the tax authorities of the two countries have had discussions that may culminate in such a treaty. No assurance can be given, however, as to whether or when a treaty will enter into force or how it will affect the U.S. holders of shares or ADSs. Prospective holders of preferred shares or ADSs should consult their own tax advisors as to the tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership and disposition of shares or ADSs in their particular circumstances.
Brazilian Tax Considerations
The following discussion summarizes the principal Brazilian tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership and disposition of shares or ADSs by a non-Brazilian holder. The following is a general discussion only, and therefore does not specifically address all of the Brazilian tax considerations applicable to any particular Non-Resident Holder. It is based upon the tax laws of Brazil as in effect on the date of this filing, which are subject to change, possibly with retroactive effect, and to differing interpretations, which may result in different tax consequences from those described below.
The tax consequences described below do not take into account the effects of any tax treaties or reciprocity of tax treatment entered into by Brazil and other countries. Please note that Brazil has not entered into any tax treaty with the United States. Also, the discussion does not address any tax consequences under the tax laws of any state or municipality of Brazil either. Each prospective investor is urged to consult its own tax advisor about the Brazilian tax consequences of an investment in our shares or the ADSs.
Taxation of Dividends
Dividends paid by us in cash or in kind from profits of periods beginning on or after January 1, 1996 (i) to the Depositary in respect of shares underlying ADSs or (ii) to a non-Brazilian holder in respect of shares, will generally not be subject to Brazilian withholding tax. Dividends paid from profits generated before January 1, 1996 may be subject to Brazilian withholding tax at varying rates, according to the tax legislation applicable to each corresponding year.
75
Distribution of Interest on Capital
Brazilian corporations may make payments to shareholders characterized as interest on capital of the Company as an alternative form of making dividend distributions. The rate of interest may not be higher than the Brazilian long-term interest rate, or TJLP, as determined by the Central Bank from time to time. The total amount distributed as interest on capital may not exceed the greater of (i) 50.0% of net income (after social contribution on profits and before the provision for corporate income tax and the amounts attributable to shareholders as shareholders’ interest on equity) for the year in respect of which the payment or credit is made or (ii) 50.0% of retained earnings for the year prior to the year in respect of which the payment or credit is made. Payments of interest on capital are decided by the shareholders on the basis of recommendations of a Company’s Board of Directors.
Distribution of interest on capital paid to Brazilian and non-Brazilian holders of shares, including payments to the Depositary in respect of shares underlying ADSs, are deductible by us for Brazilian corporate income tax purposes. Such payments are subject to Brazilian withholding tax at the rate of 15.0%, except for payments to persons who are exempt from tax in Brazil, which payments are free of Brazilian tax, and except for payments to persons situated in Tax Havens (that is, a country or location that does not impose income tax or where the income tax rate is lower than 20.0% or where the local legislation imposes restrictions on disclosing the shareholding composition or the ownership of the investment), which payments are subject to tax at a 25.0% rate.
No assurance can be given that our Board of Directors will not recommend that future distributions of profits will be made by means of interest on capital instead of by means of dividends.
Amounts paid as interest on capital (net of applicable withholding tax) may be treated as payments in respect of the dividends we are obligated to distribute to our shareholders in accordance with our by-laws and Brazilian corporate law. Distributions of interest on capital in respect of the shares, including distributions to the Depositary in respect of shares underlying ADSs, may be converted into U.S. dollars and remitted outside of Brazil, subject to applicable exchange controls.
Taxation of Gains Outside Brazil
Until January 31, 2004, the sale or other disposition of ADSs or shares entered into by and between non-Brazilian holders outside Brazil was not subject to Brazilian income tax, as such a transaction did not involve payments by a person located in Brazil. Brazilian Law no. 10,833 provides that, commencing on February 1, 2004, “the acquirer, individual or legal entity resident or domiciled in Brazil, or the acquirer’s attorney-in-fact, when such acquirer is resident or domiciled abroad, shall be responsible for the retention and payment of the income tax applicable to capital gains under Article 18 of Law no. 9,249 of December 26, 1995 earned by the individual or legal entity resident or domiciled abroad who disposes of property located in Brazil.”
The Brazilian tax authorities have issued a normative instruction confirming that, pursuant to Law no. 10,833, these tax authorities intend to assess income tax on capital gains earned by non-Brazilian residents who earn a capital gain in the disposition of assets located in Brazil, regardless of whether the Buyer is a Brazilian resident or not. Holders of ADSs outside Brazil may have grounds to assert that Brazilian Law no. 10,833 does not apply to sales or other dispositions of ADSs, as ADSs are not assets located in Brazil. However, except in the situations described below in the section Taxation of Gains in Brazil, the sale or other disposition of shares abroad would be subject to the provisions of Brazilian Law no. 10,833. Considering the general and unclear scope of such provisions and the lack of a final judicial court ruling in respect thereof, we are unable to predict whether such understanding will ultimately prevail in of Brazil. Any capital gains arising from sales or other dispositions outside Brazil would be subject to Brazilian income tax at the rate of 15.0% or, if the investor is located in a Tax Haven, 25.0%. Brazilian Law no. 10,833 requires the purchaser of our shares outside Brazil or its attorney-in-fact in Brazil to withhold the income tax. A disposition of shares can only occur abroad if an investor decides to cancel its investment in ADSs and register the underlying shares as a direct foreign investment under Law no. 4,131.
76
Taxation of Gains in Brazil
The deposit of shares in exchange for ADSs may be subject to Brazilian tax on capital gains at the rate of 15.0%, or 25.0% in the case of Tax-Haven residents, if the acquisition cost of the shares is lower than (a) the average price per share on a Brazilian stock exchange on which the greatest number of such shares were sold on the day of deposit; or (b) if no shares were sold on that day, the average price on the Brazilian stock exchange on which the greatest number of shares were sold in the 15 trading sessions immediately preceding such deposit. In such case, the difference between the acquisition cost and the average price of the shares calculated as above will be considered to be a capital gain subject to taxation. Such taxation is not applicable in case of Non-Resident Holders registered under Resolution no. 2,689 (other than Tax-Haven residents), which are currently not subject to income tax in such a transaction.
The withdrawal of ADSs in exchange for shares is not subject to Brazilian tax. Any exercise of preemptive rights relating to the ADSs will not be subject to Brazilian taxation. Any gain on the sale or assignment of preemptive rights relating to shares by the depositary on behalf of holders of ADSs will be subject to Brazilian income taxation according to the same rules applicable to the sale or disposition of shares.
Under Brazilian law, the tax consequences of an investment in Brazil will depend on the type of the investment and the domicile of the investor. Generally, a Non-Brazilian Holder may invest in Brazil in accordance with CMN Resolution no. 2,689 (a “2689 Investment”) or with Law no. 4,131 (a “4131 Investment”). In order for a Brazilian investment by a Non-Brazilian Holder to qualify as a 2689 Investment, the Non-Brazilian Holder must appoint a Brazilian custodian for its investment, register its investment with the Central Bank, and satisfy certain other requirements. An investment in shares by a Non-Brazilian Holder that is registered with the Central Bank but that is not a 2689 Investment may be classified as a 4131 Investment.
Gain realized by a Non-Brazilian Holder on the disposition of shares held as a 2689 Investment on the Bovespa (which includes the transactions carried out on the organized over-the-counter market) is not subject to Brazilian income tax, unless the Non-Brazilian Holder is organized under the laws or a resident of a Tax Haven, in which case such gain is subject to income tax at a rate of 15.0%. Gain realized by a Non-Brazilian Holder on the disposition of shares held as a 2689 Investment that is not carried out on the Bovespa is subject to Brazilian income tax at a rate of 15.0%.
In all cases other than a 2689 Investment (including a 4131 Investment), gain realized by a Non-Brazilian Holder on the disposition of shares to a Brazilian resident, whether or not carried out on the Bovespa, is subject to Brazilian income tax at the rate of 15.0%, except for dispositions that are not carried out on the Bovespa by a Non-Brazilian Holder organized under the laws or a resident of a Tax Haven, which are subject to tax at a rate of 25.0%.
In addition, a withholding tax of 0.005% will also be assessed on the sales price or other disposition value of shares sold or disposed of in transactions carried out on a Brazilian stock exchange, except in the case of a 2689 Investment by a Non-Brazilian Holder who is not organized under the laws or a resident of a Tax Haven. Such tax must be withheld by one of the following entities: (i) the agent receiving the sale or disposition order from the client; (ii) the stock exchange responsible for registering the transactions; or (iii) the entity responsible for the settlement and payment of the transactions. This 0.005% withholding income tax is not levied in day trade transactions.
The current preferential treatment for non-Brazilian holders of ADSs and non-Brazilian holders of shares under Resolution no. 2,689 may not continue in the future.
In the case of a redemption of shares or a capital reduction by a Brazilian corporation, with subsequent withdraw of the ADSs, the positive difference between the amount received by the non-resident and the acquisition cost of the shares redeemed is treated as capital gain derived from the sale or exchange of shares not carried out on a Brazilian stock exchange market and is therefore subject to income tax at the rate of 15.0%, or 25.0%, as the case may be.
77
Any exercise of preemptive rights relating to our shares will not be subject to Brazilian taxation. Gains on the sale or assignment of preemptive rights relating to our shares by the Depositary may be subject to Brazilian taxation, according to the same rules applicable to the sale or disposition of shares. Tax authorities may attempt to tax such gains even when the sale or assignment of such rights takes place outside Brazil, based on the provisions of Law no. 10,833, as described above.
As a Non-Resident holder of ADSs, you may cancel your ADSs and exchange them for shares and no income tax may be levied on such exchange, as long as the appropriate rules are complied with in connection with the registration of the investment with the Central Bank.
Tax on Foreign Exchange and Financial Transactions
Foreign Exchange Transactions. Brazilian law imposes a Tax on Foreign Exchange Transactions, or “IOF/Exchange Tax,” on the conversion ofreaisinto foreign currency and on the conversion of foreign currency intoreais. As from January 2008, IOF/Exchange Tax rates applicable to almost all foreign currency exchange transactions were increased. As a general rule, the IOF/Exchange Tax rate is 0.38% and, in the hypotheses below, the following specific rates are applicable:
| | • | | In the case of (i) inflow and outflow related to transactions entered in the Brazilian stock exchange by 2,689 Holders; (ii) outflow related to transactions that are not carried out on the Brazilian stock exchange by 2,689 Holders; (iii) inflow related to acquisition of shares in a public offering, provided the public offer is registered with the CVM and the issuer of the securities is listed in Brazilian stock exchange; and (iv) payment of dividends and interests on capital, zero; |
| |
| | • | | In case of inflow related to transactions that are not carried out on the Brazilian stock exchange by 2,689 Holders, 1.5%. |
The Ministry of Finance is permitted to increase the rate at any time up to 25.0% on the foreign exchange transaction amount. However, any increase in rates is only authorized to apply to future transactions.
Tax on Transactions Involving Bonds and Securities.Brazilian law imposes a Tax on Transactions involving Bonds and Securities, or “IOF/Bonds Tax,” due on transactions involving bonds and securities, including those carried out on a Brazilian stock exchange. The rate of IOF/Bonds Tax applicable to transactions involving shares is currently zero, although the Minister of Finance is permitted to increase such rate at any time up to 1.5% of the transaction amount per day, but only in respect of future transactions.
Other Brazilian Taxes
There are no Brazilian inheritance, gift or succession taxes applicable to the ownership, transfer or disposition of shares or ADSs by a non-Brazilian holder except for gift and inheritance taxes levied by some states in Brazil on gifts made or inheritances bestowed by individuals or entities not resident or domiciled in Brazil or in the relevant state to individuals or entities that are resident or domiciled within such state in Brazil. There are no Brazilian stamp, issue, registration, or similar taxes or duties payable by holders of shares or ADSs.
As a general rule, until December 31, 2007, any transaction carried out in Brazil that resulted in the transfer of currencies (reais) from an account maintained with a Brazilian financial institution was subject to the Temporary Contribution on Financial Transactions, or “CPMF,” at the rate of 0.38%. Therefore, transactions carried out by the depositary of ADSs or by a holder of shares which involved the transfer of Brazilian currency through Brazilian financial institutions could be subject to the CPMF.
Funds transferred for the acquisition and sale of shares on the Brazilian stock exchange by Brazilian or non-Brazilian residents or the flow of funds transferred abroad (or from abroad) by non-Brazilian residents through a special banking account related to transactions involving the acquisition and sale of shares on the Brazilian stock exchange were exempt from CPMF.
78
In addition, according to Article 4th of Law no. 11,312, of June 27, 2006, the CPMF rate was reduced to zero on withdrawals from bank accounts of Brazilian or non-Brazilian residents used to buy shares in a public offering, provided the public offering was registered with the CVM and that the issuer of the securities was listed in the Brazilian stock exchange.
On December 31, 2007, the CPMF tax expired. Therefore, since January 1, 2008, financial transactions do not incur in the taxation at the rate of 0.38%.
The Brazilian Congress is currently analyzing a legislative bill which purpose is the creation of a new tax to replace the CPMF tax (named as the Social Contribution to the Health System Tax — “CSS Tax”). If approved, according to the current text of the bill, the CSS Tax would have some similarities to the extinguished CPMF Tax (i.e. it would be levied on transactions carried out in Brazil that result in the transfer of local currency (Real) from an account maintained with a Brazilian financial institution. However, before the CSS becomes effective, this bill must be approved by both Legislative and Executive Powers, what may or may not occur.
Material United States Federal Income Tax Considerations
The following summarizes the material U.S. federal income tax consequences applicable to the ownership and disposition of preferred shares or ADSs. The discussion that follows is based upon laws, regulations, rulings and decisions now in effect, all of which are subject to change (possibly with retroactive effect) or differing interpretations. We have not sought, and will not seek, any ruling from the U.S. Internal Revenue Service, or the IRS, with respect to the tax consequences discussed herein. Consequently, the IRS may disagree with or challenge any of such tax consequences.
This discussion deals only with preferred shares or ADSs held as capital assets and does not purport to deal with persons in special tax situations, such as financial institutions, insurance companies, tax-exempt organizations, regulated investment companies, real estate investment trusts, dealers in securities or currencies, persons holding shares as a position in a “straddle” or as part of a “hedging” or “conversion” transaction for tax purposes, U.S. Holders (as defined below) whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar, partnerships or other entities treated as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes, or persons liable for alternative minimum tax. Furthermore, this discussion does not purport to deal with persons who own, directly or indirectly, 10.0% or more of the total combined voting power of all classes of our stock entitled to vote or 10.0% or more in value of our outstanding stock. Holders should consult their own tax advisors concerning the application of U.S. federal income tax laws to their particular situations as well as any consequences of the ownership and disposition of preferred shares or ADSs arising under the laws of any other taxing jurisdiction.
This summary assumes that we are not a passive foreign investment company (“PFIC”) for U.S. federal income tax purposes. See the discussion under “— U.S. Holders — Passive Foreign Investment Company (“PFIC”) Rules” below.
U.S. Holders
A U.S. Holder is a beneficial owner of preferred shares or ADSs that is, for U.S. federal income tax purposes: a citizen or resident of the United States, a corporation, or any other entity taxable as a corporation, created or organized in or under the laws of the United States or any state thereof or the District of Columbia, an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source, or a trust if (i) a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over the trust’s administration and one or more United States persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust or (ii) the trust has in effect a valid election to be subject to tax as a U.S. person.
If a partnership (or an entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes) holds or disposes of preferred shares or ADSs, the tax treatment of a partner in that partnership will generally depend on the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. Partners in partnerships holding preferred shares or ADSs should consult their own tax advisors about the U.S. federal income tax consequences to them of holding or disposing of preferred shares or ADSs.
79
Treatment of ADS
For U.S. federal income tax purposes, a U.S. Holder of an ADS is considered the owner of the preferred shares represented by the ADS. Accordingly, the conversion of ADSs to preferred shares or the conversion of preferred shares to ADSs will not be a taxable transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and, except as otherwise noted, references in this discussion to the ownership of preferred shares include ownership of the preferred shares underlying the corresponding ADSs.
Receipt of Distributions
For U.S. federal income tax purposes, a U.S. Holder generally will recognize, to the extent of our current and accumulated earnings and profits, dividend income on the receipt of cash dividends on preferred shares equal to the U.S. dollar value of such dividends on the date of receipt (with the value of the dividends computed before reduction for any withholding tax or other applicable Brazilian tax paid). Amounts distributed in excess of our earnings and profits will decrease (but not below zero) a U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the preferred shares, and any remaining amount of the distribution will be taxed as gain from the sale or exchange of the preferred shares.
Subject to certain exceptions for short-term positions, the amount of dividends received by certain U.S. Holders (including individuals but not corporations) prior to January 1, 2011 with respect to our ADSs or preferred shares will be subject to taxation at a maximum rate of 15.0% if the dividends represent “qualified dividend income.” Dividends paid on our ADSs or preferred shares will be treated as qualified dividend income if the ADSs or preferred shares are readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States and we are not a PFIC (as discussed below). Under current guidance issued by the IRS, our ADSs should qualify as readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States as long as they are listed on the NYSE, but no assurances can be given that our ADSs will be or will remain readily tradable under future guidance. Currently, dividends paid with respect to ADSs, but not to preferred shares held directly by U.S. Holders, should constitute “qualified dividend income.”
Dividends paid on preferred shares will not be eligible for the dividends received deduction available to U.S. corporations under certain circumstances.
If we distribute foreign currency with respect to our preferred shares, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, the amount of the distribution will generally equal the fair market value in U.S. dollars of such foreign currency on the date of receipt. A U.S. Holder will have a tax basis in the foreign currency equal to its U.S. dollar value on the date of receipt, and will generally recognize gain or loss when it sells or exchanges the foreign currency. Such gain or loss will be taxable as ordinary income or loss from U.S. sources. The amount of any property other than money that we distribute with respect to our preferred shares will equal its fair market value on the date of distribution.
Distributions to U.S. Holders that are treated as dividends generally will be treated as income from sources outside the United States, and generally will be foreign source “passive” income for foreign tax credit purposes. Subject to the requirements and limitations imposed by the Code and the Treasury Regulations thereunder, a U.S. Holder may elect to claim any Brazilian tax withheld or paid with respect to any dividends distributed on shares as a foreign tax credit against the U.S. federal income tax liability of the U.S. Holder. In addition, subject to certain limitations, U.S. Holders who do not elect to claim the foreign tax credit may claim a deduction for any Brazilian tax withheld or paid with respect to shares. Complex rules determine the availability of the foreign tax credit, and U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors to determine whether and to what extent U.S. Holders may claim foreign tax credits.
Section 305 of the Code provides special rules for the tax treatment of preferred stock. According to the Treasury Regulations under that section, the term preferred stock generally refers to stock which enjoys certain limited rights and privileges (generally associated with specified dividend and liquidation priorities) but does not participate in corporate growth to any significant extent. While our preferred shares have some preferences over our common shares, the preferred shares are not fixed as to dividend payments or liquidation value; thus, although the matter is not entirely clear, we believe and have taken and intend to continue to take the position, that the preferred shares should be treated as “common stock” within the meaning of Section 305 of the Code. If the preferred shares are treated as “common stock” for purposes of Section 305 of the Code, distributions to U.S. Holders of additional
80
shares of such “common stock” or preemptive rights relating to such “common stock” with respect to their preferred shares or ADSs that are made as part of a pro rata distribution to all shareholders in most instances will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax. On the other hand, if the preferred shares are treated as “preferred stock” within the meaning of Section 305 of the Code, and if a U.S. Holder receives a distribution of additional shares or preemptive rights as described in the preceding sentence, such distributions (including amounts withheld in respect of any Brazilian taxes) will be treated as dividends that can be included in the U.S. Holder’s gross income to the same extent and in the same manner as distributions payable in cash. In that event, the amount of such distribution (and the basis of the new shares or preemptive rights so received) will equal the fair market value of the shares or preemptive rights on the date of distribution.
Sale, Exchange or Other Taxable Disposition of Preferred Shares
Upon a sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of preferred shares, a U.S. Holder will generally recognize gain or loss in an amount equal to the difference between the amount realized on the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition and the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the preferred shares so sold, exchanged or otherwise subject to disposition. Any gain or loss recognized will generally be capital gain or loss, and the capital gain or loss will generally be long-term capital gain or loss if the U.S. Holder has held or is treated as having held the preferred shares for more than one year at the time of such sale, exchange or other taxable disposition. Long-term capital gains recognized by individuals are currently subject to reduced rates of taxation. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations. The gain or loss from the sale or other disposition of shares will generally be treated as income from sources within the United States for foreign tax credit purposes. Consequently, in the case of a sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of preferred shares, a U.S. Holder may not be able to claim a foreign tax credit for Brazilian tax imposed on the gain unless it has other income from foreign sources against which it can appropriately apply the credit.
Passive Foreign Investment Company (“PFIC”) rules
Based upon the nature of our current and projected income, assets and activities, we do not believe that we are, and we do not expect the preferred shares to be considered shares of, a PFIC for U.S. Federal income tax purposes. In general, a foreign corporation is a PFIC if, for any taxable year in which the U.S. Holder holds stock in the foreign corporation, at least 75.0% of such corporation’s gross income is passive income or at least 50.0% of the value of such corporation’s assets (determined on the basis of a quarterly average) produce passive income or are held for the production of passive income. The determination of whether the preferred shares constitute shares of a PFIC is a factual determination made annually and thus may be subject to change. Subject to certain exceptions, once a U.S. Holder’s preferred shares are treated as shares in a PFIC, they remain shares in a PFIC. Dividends received by a U.S. Holder from a PFIC will not constitute qualified dividend income.
If, contrary to our belief, we were treated as a PFIC, a U.S. Holder would be subject to special rules with respect to (i) gain realized on the sale or other disposition of preferred shares and (ii) any “excess distribution” by us to the U.S. Holder (generally, any distribution during a taxable year that exceed 125.0% of the average annual taxable distribution the U.S. Holder received on the preferred shares during the preceding three taxable years or, if shorter, the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the preferred shares). Under those rules (i) the gain or excess distribution would be allocated ratably over the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the preferred shares, (ii) the amount allocated to the taxable year in which the gain or excess distribution is realized and to taxable years before the first day we became a PFIC would be taxable as ordinary income, and (iii) the amount allocated to each other year (with certain exceptions) would be subject to tax at the highest U.S. federal income tax rate in effect for that year, and an additional amount equal to the interest charge generally applicable to underpayments of tax would be imposed in respect of the tax attributable to each such year.
A U.S. Holder that owns preferred shares during any year we are a PFIC must file IRS Form 8621. In general, if we are treated as a PFIC, the rules described in the second paragraph of this section can be avoided by a U.S. Holder that elects to be subject to a mark-to-market regime for stock in a PFIC. A U.S. Holder may elect mark-to-market treatment for its preferred shares, provided that the preferred shares constitute “marketable stock” as defined in Treasury Regulations. A U.S. Holder electing the mark-to-market regime generally would treat any gain recognized under mark-to-market treatment or on an actual sale as ordinary income and would be allowed an ordinary deduction for any decrease in the value of preferred shares in any taxable year and for any loss recognized on an actual sale, but only to the extent, in each case, of previously included mark-to-market income not offset by previously deducted decreases in value. A U.S. Holder’s basis in preferred shares would increase or decrease by gain or loss taken into account under the mark-to-market regime. A mark-to-market election is generally irrevocable. Another election to treat us as a qualified electing fund would not be available because we do not currently plan to provide U.S. Holders with information sufficient to permit U.S. Holders to make such election.
81
Non-U.S. Holders
A Non-U.S. Holder is a holder of our preferred shares or ADSs who is neither a U.S. Holder nor an entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
Non-U.S. Holders will generally not be subject to U.S. federal income or withholding tax on dividends received from us with respect to preferred shares, unless such income is considered effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holder’s conduct of a trade or business in the U.S. (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, the income is attributable to a permanent establishment or, in the case of an individual Non-U.S. Holder, a fixed base maintained in the United States).
Non-U.S. Holders will generally not be subject to U.S. federal income tax on any gain recognized upon the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of preferred shares unless the gain is effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holder’s conduct of a trade or business in the U.S. (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, the income is attributable to a permanent establishment or, in the case of an individual Non-U.S. Holder, a fixed base maintained in the United States) or such Non-U.S. Shareholder is an individual who is present in the United States for 183 days or more during the taxable year of such sale, exchange or other taxable disposition and certain other conditions are met. If the first exception applies, the Non-U.S. Holder will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition as if such Non-U.S. Holder were a U.S. Holder, as described above. If the second exception applies, then the Non-U.S. Holder will generally be subject to U.S. federal income tax at a rate of 30.0% on the amount by which such Non-U.S. Holder’s U.S. source capital gains exceed such Non-U.S. Holder’s U.S. source capital losses.
In addition, any effectively connected dividends or gains realized by a Non-U.S. Holder that is a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes may also be subject to an additional branch profits tax at a rate of 30.0% (or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty).
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
In general, information reporting requirements will apply to dividends paid in respect of shares to non-corporate U.S. Holders or the proceeds received on the sale, exchange or redemption of shares by non-corporate U.S. Holders, and such amounts may be subject to U.S. backup withholding tax (currently at a rate of 28.0%). Backup withholding will not apply, however, to a U.S. Holder that (i) is a corporation or comes within certain enumerated categories of persons and, when required, demonstrates this fact or (ii) furnishes a correct taxpayer identification number and makes certain other required certifications. Generally, a U.S. Holder will provide such certifications on IRS Form W-9 (Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification) or other substitute form. A U.S. Holder that is required to but does not furnish us with its correct taxpayer identification number may also be subject to penalties imposed by the Internal Revenue Service. Non-U.S. Holders will generally not be subject to United States information reporting or backup withholding. However, Non-U.S. Holders may be required to provide certification of their non-U.S. status in connection with payments received in the United States or through certain U.S.-related financial intermediaries. Backup withholding is not an additional tax and may be claimed as a credit against the U.S. federal income tax liability of a U.S. Holder, provided that the required information is timely furnished to the IRS.
HOLDERS OF PREFERRED SHARES OR ADSS SHOULD CONSULT THEIR OWN TAX ADVISORS CONCERNING THE APPLICATION OF U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX LAWS TO THEIR PARTICULAR SITUATIONS, AS WELL AS ANY CONSEQUENCES OF THE OWNERSHIP AND DISPOSITION OF PREFERRED SHARES OR ADSS ARISING UNDER THE LAWS OF ANY OTHER TAXING JURISDICTION.
82
Documents On Display
You may read and copy the reports and other information we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including this annual report and the exhibits thereto, at the Commission’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549 and at the Commission’s regional offices at 175 W. Jackson Boulevard, Suite 900, Chicago, Illinois 60604, and 3 World Financial Center, Room 4300, New York, New York 10281. You may also obtain copies of these materials by mail from the Public Reference Room of the Commission at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549, at prescribed rates. You may obtain information on the operation of the Commission’s Public Reference Room by calling the Commission in the United States at 1-800-SEC-0330. You may also access our annual reports and some of the other information we file with or submit to the Commission electronically through the Commission’s website atwww.sec.gov.
Item 11. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Virtually none of our revenues or costs are exposed to foreign currency fluctuations since they are not directly or indirectly pegged to the U.S. dollar or any other foreign currency. We have some exposure to foreign exchange risk as a portion of our capital expenditures is comprised of investments in technology equipment which, while not denominated in foreign currencies, are indirectly impacted by the changes in exchanges rates as they contain imported parts. In 2007, approximately 54.3% of our capital expenditures included such equipment.
The interest rates risk arises from the possibility of the Company incurring in losses derived from interest rate variations that increase the financial expenses related to financings raised in the market. The Company continuously monitors the market interest rates with the purpose of evaluating the possible need of hiring operations to protect itself against the volatility risk of these rates. If interest rates increased by 1% the additional amount of annual interest expense would be R$1,442 thousand.
Item 12. Description of Securities Other Than Equity Securities
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 13. Defaults, Dividend Arrearages and Delinquencies
Not applicable.
Item 14. Material Modifications to the Rights of Security Holders and Use of Proceeds
Pursuant to the Reverse Stock Split, our shareholders approved the reverse split of all shares representing the Company’s capital stock at the ratio of twenty (20) shares for one (1) share of the same type. See “Item 5 — Operating and Financial Review and Prospects — Key Events in 2007 — Reverse Stock Split.”
Item 15. Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As of the end of the period covered by this report, the Company carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures. There are inherent limitations to the effectiveness of any system of disclosure controls and procedures, including the possibility of human error and the circumvention or overriding of the controls and procedures. Accordingly, even effective disclosure controls and procedures can only provide reasonable assurance of achieving their control objectives. Based upon and as of the date of the Company’s evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the disclosure controls and procedures are effective, at the reasonable assurance level, to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports the Company files and submits under the Exchange Act is (i) recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and (ii) accumulated and communicated to management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
83
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for the Company. Internal control over financial reporting is a process to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of our financial reporting for external purposes in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Internal control over financial reporting includes maintaining records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect our transactions; providing reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary for preparation of our financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles; providing reasonable assurance that receipts and expenditures of Company assets are made only in accordance with management and directors’ authorization; and providing reasonable assurance that unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of Company assets that could have a material effect on our financial statements would be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this evaluation, management concluded that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2007.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2007 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes, the Company’s registered independent accounting firm, which opinion is stated in their report, included herein.
Changes in Internal Controls
There has been no change in the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting during the Company’s fiscal year ended December 31, 2007 that has materially affected or is reasonably likely to materially affect the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
See report of PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes, an Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm included under “Item 18. Financial Statements”, on page F-2.
Item 16A. Audit Committee Financial Expert
We are not subject to any listing standards that require us to form an audit committee pursuant to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act or a board of auditors formed pursuant to local laws that could substantially discharge the duties of an audit committee formed pursuant to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. See “Item 6. Directors, Senior Management and Employees — Fiscal Council (Conselho Fiscal).” As a result, we have not identified a member to our Board of Directors who would qualify as an audit committee financial expert.
Item 16B. Code of Ethics
The Company has adopted a Code of Ethics that applies to its Directors, Officers, managers, controlling shareholders and members of the Fiscal Council in accordance with CVM rules satisfying the requirements of Brazilian Law. A copy of this Code of Ethics is incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 11.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005. The Company’s Code of Ethics does not address all of the principles set forth by the SEC in Section 406 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. However, it does contain many of the principles set forth in the SEC’s definition of a Code of Ethics, including standards that are (i) reasonably designed to promote full, fair, accurate and timely disclosure in reports and documents that the Company files with, or submits to, the SEC, and (ii) reasonably designed to deter certain wrongdoing, principally the prohibition against trading on inside information. Since the adoption of its Code of Ethics, Contax has not granted any implicit or explicit waivers from any provision thereof to the officers described above.
84
Item 16C. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
Fees for professional services provided by PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm in each of the last two fiscal years in each of the following categories are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Total Fees | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | (in thousands of reais) | |
| Audit Fees(1) | | | 601 | | | | 385 | |
| Audit-Related Fees(2) | | | — | | | | 810 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 601 | | | | 1,195 | |
| | | |
| (1) | | Audit Fees for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006 consist of fees billed for professional services rendered for the audits and reviews of the consolidated financial statements of the Company and other services normally provided in connection with statutory and regulatory filings. The audit fees include expenses related to compliance with SOX. |
| |
| (2) | | Audit-Related Fees for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006 consist of fees billed for assurance and related services that are traditionally performed by independent accountants that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of the Company’s financial statements. These services include consulting in connection with accounting and reporting standards and services related to internal control reviews. |
Pre-approval of policies and procedures
Our Board of Directors is currently responsible for the oversight of our independent auditor’s work. Our Board of Directors’ policy is to pre-approve all audit and non-audit services provided by BDO Trevisan Auditores Independentes and, with respect to U.S. GAAP, PricewaterhouseCoopers. These services may include audit services, audit-related services, tax services and other services, as described above. In such an event, the Board of Directors sets forth its pre-approval in detail, listing the particular services or categories of services which are pre-approved, and setting forth a budget for such services. The Board of Directors has designated its chairman, currently Mr. Ronaldo Iabrudi dos Santos Pereira, to issue such pre-approval in certain circumstances.
Item 16D. Exemptions from the Listing Standards for Audit Committees
Not applicable.
Item 16E. Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers
In July 2006, the Company implemented its first share buyback program, which was concluded in October 2006 and resulted in the repurchase of 5,887 thousand common shares (corresponding to 294 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split referred to below) and 11,774 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 589 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split), representing 100.0% of the number of shares authorized to be repurchased under that program.
In November 2006, the Company implemented its second buyback program, which was concluded in July 2007 and resulted in the repurchase of 5,298 thousand common shares (corresponding to 265 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 24,058 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 1,203 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split).
85
The Company’s third share buyback program was implemented in July 2007 and concluded in October 2007, with the repurchase of 3,193 thousand common shares (corresponding to 160 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 18,277 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 914 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split).
A total of 14,378 thousand common shares (corresponding to 719 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 54,109 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 2,705 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) were repurchased as part of these three buyback programs, of which 10,878 thousand common shares (corresponding to 544 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) and 54,109 thousand preferred shares (corresponding to 2,705 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) were cancelled and 3,500 thousand common shares (corresponding to 175 thousand shares after the Reverse Stock Split) were held in treasury without reducing the Company’s capital stock.
Altogether, the Company invested R$161 million in the three buyback programs, of which R$41 million were invested in 2006 and R$120 million in 2007. The chart below shows how each such share buyback program evolved on a monthly basis. The numbers show the repurchase programs have been basically completed. The cancellation of the repurchased common and preferred shares (now held in treasury) depends upon the deliberation of the Shareholders’ Meeting when such is conveyed for this purpose.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Total Number of Shares | | | Maximum Number of | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Purchased as Part of | | | Shares That May Yet Be | |
| | | Total Number of Shares | | | Average Price | | | Publicly Announced | | | Purchased Under the | |
| | | Purchased | | | Paid Per Share | | | Programs | | | Programs | |
| Periods in 2007 | | Preferred | | | Common | | | Preferred | | | Common | | | Preferred | | | Common | | | Preferred | | | Common | |
| January 1 to 31 | | | 196,575 | | | | 230,445 | | | | 37.80 | | | | 61.00 | | | | 196,575 | | | | 230,445 | | | | 997,575 | | | | 27,405 | |
| February 1 to 28 | | | 318,150 | | | | 27,405 | | | | 40.00 | | | | 59.60 | | | | 318,150 | | | | 27,405 | | | | 679,425 | | | | 0 | |
| March 1 to 31 | | | 679,425 | | | | — | | | | 37.80 | | | | — | | | | 679,425 | | | | — | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | |
| April 1 to 30 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | |
| May 1 to 31 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | |
| June 1 to 30 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | |
| July 1 to 31 | | | 4,000 | | | | 1,560 | | | | 52.40 | | | | 71.60 | | | | 4,000 | | | | 1,560 | | | | 1,078,619 | | | | 158,114 | |
| August 1 to 31 | | | 909,710 | | | | 158,114 | | | | 50.80 | | | | 70.60 | | | | 909,710 | | | | 158,114 | | | | 168,909 | | | | 0 | |
| September 1 to 30 | | | 161 | | | | — | | | | 52.00 | | | | — | | | | 161 | | | | — | | | | 168,748 | | | | 0 | |
| October 1 to 31 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (168,748 | ) | | | — | |
| November 1 to 30 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| December 1 to 31 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 2,108,021 | | | | 417,524 | | | | 45.30 | | | | 65.90 | | | | 2,108,021 | | | | 417,524 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | |
Note: Numbers are shown in the grouped (ratio 20:1) format for comparison purposes.
PART III
Item 17. Financial Statements
We have responded to Item 18 in lieu of responding to this item.
Item 18. Financial Statements
See pages F-1 through F-36.
86
Item 19. Exhibits
| | | |
| No. | | Description |
| | | |
| 1.1 | | By-laws of Contax Holding as of June 17, 2008. |
| | | |
| 2.1 | | Deposit Agreement, dated as of August 12, 2005 among Contax Holding, The Bank of New York, as Depositary, and Owners and Beneficial Owners of American Depositary Receipts issued thereunder. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2006.) |
| | | |
| 4.1 | | Services Agreement, dated November 30, 2004, among Telemar Norte Leste S.A, TNL PCS S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 4.2 | | First Amendment, dated December 29, 2004, to the Services Agreement between Telemar Norte Leste S.A., TNL PCS S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. dated November 30, 2004.(Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2006.) |
| | | |
| 4.3 | | Second Amendment, dated October 18, 2005, to the Services Agreement between Telemar Norte Leste S.A., TNL PCS S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. dated November 30, 2004. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.7 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2006.) |
| | | |
| 4.4 | | Third Amendment, dated May 1, 2007, to the Services Agreement between Telemar Norte Leste S.A., TNL PCS S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. dated November 30, 2004. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| 4.5 | | Contact Center Services Agreement, dated April 1, 2004, between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and Inovação Contact Center Serviços de Contatos Telefônicos Ltda. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 4.6 | | Amendment to Services Agreement, dated May 28, 2004, between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and Inovação Contact Center Serviços de Contatos Telefônicos Ltda. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 4.7 | | Amendment to the Contact Center Service Agreement, dated September 27, 2004, between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 4.8 | | Amendment to Temporary Service Agreement and Other Matters, dated September 27, 2004, between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
87
| | | |
| No. | | Description |
| | | |
| 4.9 | | Amendment, dated October 1, 2004, to the Contact Center Service Agreement between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| 4.10 | | Amendment, dated April 1, 2005, to the Contact Center Service Agreement between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.10 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| 4.11 | | Amendment, dated May 10, 2006, to the Contact Center Service Agreement between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.11 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| 4.12 | | Amendment, dated December 29, 2006, to the Contact Center Service Agreement between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.12 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| 8.1 | | List of Subsidiaries. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 8.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2006.) |
| | | |
| 11.1 | | Code of Ethics of Contax Holding. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 11.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 12.1 | | Certification of the Chief Executive Officer of the Company, pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. (Filed herewith.) |
| | | |
| 12.2 | | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer of the Company, pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. (Filed herewith.) |
| | | |
| 13.1 | | Certifications of the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer of the Company, pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. (Furnished herewith.) |
88
SIGNATURES
Contax Participações S.A. hereby certifies that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form 20-F and that it has duly caused and authorized the undersigned to sign this annual report on its behalf.
| | | | | |
| | CONTAX PARTICIPAÇÕES S.A.
| |
| | By: | /s/ Francis James Leahy Meaney | |
| | | Name: Francis James Leahy Meaney | |
| | | Title: Chief Executive Officer | |
Dated: June 26, 2008
89
Contax Participações S.A.
Consolidated and Combined Financial Statements at December 31, 2007 and 2006 and for the three years in the period ended December 31, 2005 and Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.
Table of contents:
| | | |
| | F-2 |
| |
| | F-3 |
| |
| | F-4 |
| |
| | F-5 |
| |
| | F-6 |
| |
| Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements | | F-7 |
90
Contax Participações S.A.
Consolidated and Combined Financial Statements
at December 31, 2007 and 2006 and for the three years in the
period
ended December 31, 2007
and Report of Independent Registered
Public Accounting Firm
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders Contax Participações S.A.
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and the related consolidated statements of operations, of cash flows, and of changes in stockholders’ equity present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Contax Participações S.A. and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2007 and 2006, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2007 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2007, based on criteria established inInternal Control — Integrated Frameworkissued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 15. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits (which was an integrated audit in 2007). We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers Auditores Independentes
Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
June 23, 2008
F-2
Contax Participações S.A.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
December 31, 2007 and 2006
(Expressed in thousands of Brazilian Reais)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Current assets | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 240,310 | | | | 231,299 | |
| Trade accounts receivable, net | | | | | | | | |
| Related parties | | | 17,847 | | | | 8,244 | |
| Unrelated parties | | | 67,016 | | | | 45,624 | |
| Deferred taxes | | | 17,187 | | | | 12,176 | |
| Recoverable taxes | | | 25,818 | | | | 33,887 | |
| Prepaid expenses | | | 2,807 | | | | 2,248 | |
| Others | | | 3,263 | | | | 2,167 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total current assets | | | 374,248 | | | | 335,645 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Property and equipment, net | | | 274,559 | | | | 265,593 | |
| Intagible | | | 67,976 | | | | 44,134 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | 342,535 | | | | 309,727 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Other assets | | | | | | | | |
| Deferred taxes | | | 12,006 | | | | 19,903 | |
| Recoverable taxes | | | 5,568 | | | | | |
| Judicial deposits | | | 17,787 | | | | 7,938 | |
| Receivable from Telemar | | | 11,550 | | | | 6,570 | |
| Receivable from Other | | | 128 | | | | 2,751 | |
| Other non-current assets | | | 889 | | | | 741 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total other assets | | | 47,928 | | | | 37,903 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | | 764,711 | | | | 683,275 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Current liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Borrowings | | | 300 | | | | | |
| Suppliers | | | 72,466 | | | | 47,761 | |
| Payroll and related accruals | | | 143,349 | | | | 112,382 | |
| Taxes other than on income | | | 14,163 | | | | 10,471 | |
| Taxes on income | | | 24,827 | | | | 29,088 | |
| Dividends payable | | | 14,271 | | | | 12,390 | |
| Current-portion of capital lease obligations | | | 18,218 | | | | 21,091 | |
| Stock options plan | | | 1,862 | | | | — | |
| Other current liabilities | | | 2,343 | | | | 1,275 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 291,799 | | | | 234,458 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Long-term liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Borrowings | | | 100,060 | | | | | |
| Provisions for contingencies | | | 46,860 | | | | 28,899 | |
| Capital lease obligations | | | 25,970 | | | | 44,122 | |
| Deferred tax | | | 2,285 | | | | 1,529 | |
| Taxes other than on income | | | 2,391 | | | | 2,745 | |
| Stock options plan | | | 465 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total long-term liabilities | | | 178,031 | | | | 77,295 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Shareholders’ equity | | | | | | | | |
| Preferred shares — 10,031,914 issued, non-par-value shares (2006* - 242,973,900) | | | 149,249 | | | | 149,249 | |
| Common shares — 5,824,772 issued, non-par-value shares (2006* - 121,487,217) | | | 74,624 | | | | 74,624 | |
| Treasury stock — 166,017 shares (2006* 316,500) | | | (10,913 | ) | | | (780 | ) |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | 9,421 | | | | 9,386 | |
| Appropriated retained earnings | | | 68,066 | | | | 136,076 | |
| Unappropriated retained earnings | | | 4,434 | | | | 2,967 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total shareholders’ equity | | | 294,881 | | | | 371,522 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | | | 764,711 | | | | 683,275 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | |
| (*) | | See Note 3 – Reverse split of shares. The number of shares does not include treasury stock. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-3
Contax Participações S.A.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
Years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005
(Expressed in thousands of Brazilian Reais, unless otherwise stated)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years ended December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net operating revenue from services rendered | | | 1,365,815 | | | | 1,218,583 | | | | 1,044,787 | |
| Cost of services rendered | | | (1,174,035 | ) | | | (1,037,353 | ) | | | (855,907 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross profit | | | 191,780 | | | | 181,230 | | | | 188,880 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (expenses) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative | | | (89,117 | ) | | | (72,379 | ) | | | (59,742 | ) |
| Other operating expenses, net | | | (15,646 | ) | | | (11,421 | ) | | | (12,098 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income | | | 87,017 | | | | 97,430 | | | | 117,040 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial income (expenses), net | | | (3,548 | ) | | | 18,405 | | | | 14,352 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-operating income, net | | | 67 | | | | — | | | | 235 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income from operations before income tax and social contribution | | | 83,536 | | | | 115,835 | | | | 131,627 | |
| Income tax and social contribution provision | | | (28,085 | ) | | | (38,154 | ) | | | (50,387 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income and comprehensive income for the year | | | 55,451 | | | | 77,681 | | | | 81,240 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Earnings per shares (in reais) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common shares — Basic | | | 3.37 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.96 | |
| Common shares — Diluted | | | 3.23 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.96 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Preferred shares — Basic | | | 3.37 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 3.90 | |
| Preferred shares — Diluted | | | 3.37 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 3.90 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-4
Contax Participações S.A.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005
(Expressed in thousands of Brazilian Reais, unless otherwise stated)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
Operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income for the year | | | 55,451 | | | | 77,681 | | | | 81,240 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 100,642 | | | | 64,448 | | | | 45,846 | |
| Provision for doubtful accounts | | | 4,033 | | | | — | | | | | |
| Contingencies and other provisions | | | 13,278 | | | | (2,625 | ) | | | 18,061 | |
| Loss on permanent asset disposal | | | (67 | ) | | | — | | | | (235 | ) |
| Deferred tax asset, net | | | (2,682 | ) | | | 7,537 | | | | 23,155 | |
| (Increase) decrease in accounts receivable | | | (35,028 | ) | | | (21,025 | ) | | | 6,196 | |
| (Increase) decrease in other current assets | | | 6,629 | | | | (2,160 | ) | | | (25,496 | ) |
| (Increase) in other non-current assets | | | (2,228 | ) | | | 3,152 | | | | (7,180 | ) |
| Increase in payroll and related accruals | | | 30,967 | | | | 11,115 | | | | 36,484 | |
| Increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses | | | 24,705 | | | | (5,026 | ) | | | 2,642 | |
| Increase (decrease) in other current liabilities | | | 3,230 | | | | 553 | | | | 18,302 | |
| Increase (decrease) in accrued interest | | | 3,891 | | | | 2,607 | | | | (343 | ) |
| Increase (decrease) in recoverable taxes | | | (167 | ) | | | 7,154 | | | | 22,738 | |
| Increase (Decrease) in other non-current liabilities | | | 465 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 203,119 | | | | 143,411 | | | | 221,410 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Investing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital expenditure for property and equipment | | | (132,950 | ) | | | (66,964 | ) | | | (88,109 | ) |
| Capital expenditure for discontinued operation Judicial deposits | | | (9,849 | ) | | | (4,154 | ) | | | (1,521 | ) |
| Proceeds of disposal of property and equipment | | | 100 | | | | 62 | | | | 642 | |
| Proceeds of disposal of property and equipment discontinued operation | | | | | | | | | | | 17,211 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash used in investing activities | | | (142,699 | ) | | | (71,056 | ) | | | (71,777 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Treasury stock purchases | | | (119,317 | ) | | | (41,394 | ) | | | | |
| Proceeds from sale of treasury stock | | | 472 | | | | | | | | | |
| Payments of long-term obligation (leases) | | | (21,091 | ) | | | (16,220 | ) | | | (3,938 | ) |
| Proceeds from long-term borrowings | | | 100,060 | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of dividends | | | (11,533 | ) | | | (12,930 | ) | | | (1,359 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | | (51,409 | ) | | | (70,544 | ) | | | (5,297 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | 9,011 | | | | 1,811 | | | | 144,336 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | | | 231,299 | | | | 229,488 | | | | 85,152 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | | | 240,310 | | | | 231,299 | | | | 229,488 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income tax and social contribution paid | | | 26,085 | | | | 27,999 | | | | 27,230 | |
| Interest paid | | | 2,023 | | | | 296 | | | | 389 | |
Non-cash transations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property and equipament purchased with capital leases | | | — | | | | 41,894 | | | | 40,587 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
Contax Participações S.A.
Consolidated Statement
of Changes in Shareholder’s Equity,
Years ended December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005
(Expressed in thousands of Brazilian Reais, unless otherwise stated)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Paid-in Capital | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Additional | | | Treasury | | | Appropriated | | | | | | | |
| | | Number of shares outstanding | | | Preffered | | | Common | | | Paid-in | | | Shares | | | Retained | | | Retained | | | | |
| | | Preferred | | | Common | | | Total | | | Shares | | | Shares | | | Capital | | | Purchases | | | Earnings | | | Earnings | | | Total | |
At December 31, 2004 | | | 253,202,318 | | | | 126,601,159 | | | | 379,803,477 | | | | 149,249 | | | | 74,624 | | | | 50,000 | | | | — | | | | 6,013 | | | | 788 | | | | 280,674 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Split of shares | | | 1,545,482 | | | | 772,758 | | | | 2,318,240 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 81,240 | | | | 81,240 | |
| Statutory reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 57,477 | | | | (57,477 | ) | | | | |
| Appropriation of net income to: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends approved | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (1,359 | ) | | | (1,359 | ) |
| Legal reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,033 | | | | (4,033 | ) | | | | |
| Unrealized earnings reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 5,727 | | | | (5,727 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2005 | | | 254,747,800 | | | | 127,373,917 | | | | 382,121,717 | | | | 149,249 | | | | 74,624 | | | | 50,000 | | | | — | | | | 73,250 | | | | 13,432 | | | | 360,555 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Split of shares | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Treasury shares purchases | | | (11,949,100 | ) | | | (6,028,000 | ) | | | (17,977,100 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (41,394 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (41,394 | ) |
| Cancellation of shares | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (40,614 | ) | | | 40,614 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends approved | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | �� | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (13,432 | ) | | | (13,432 | ) |
Dividends proposed from Unrealized
Earnings Reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (7,050 | ) | | | | | | | (7,050 | ) |
| Net income for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 77,681 | | | | 77,681 | |
| Statutory reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 53,234 | | | | (53,234 | ) | | | | |
| Appropriation of net income to: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends proposed | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (4,838 | ) | | | (4,838 | ) |
| Legal reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,736 | | | | (3,736 | ) | | | | |
| Unrealized earnings reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 12,906 | | | | (12,906 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2006 | | | 242,798,700 | | | | 121,345,917 | | | | 364,144,617 | | | | 149,249 | | | | 74,624 | | | | 9,386 | | | | (780 | ) | | | 136,076 | | | | 2,967 | | | | 371,522 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Treasury shares purchases | | | (42,160,412 | ) | | | (8,350,472 | ) | | | (50,510,884 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (119,317 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (119,317 | ) |
| Cancellation of shares | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 108,580 | | | | (108,580 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Sale of treasury stocks | | | | | | | 179,660 | | | | 179,660 | | | | | | | | | | | | 35 | | | | 604 | | | | | | | | | | | | 639 | |
| Reverse Split of shares | | | (190,606,374 | ) | | | (107,516,350 | ) | | | (298,122,724 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends approved | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends proposed from Unrealized Earnings Reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (12,637 | ) | | | | | | | (12,637 | ) |
| Net income for the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 55,451 | | | | 55,451 | |
| Statutory reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 38,464 | | | | (38,464 | ) | | | | |
| Appropriation of net income to: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends proposed | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (777 | ) | | | (777 | ) |
| Legal reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,699 | | | | (2,699 | ) | | | | |
| Unrealized earnings reserve | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 12,044 | | | | (12,044 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2007 | | | 10,031,914 | | | | 5,658,755 | | | | 15,690,669 | | | | 149,249 | | | | 74,624 | | | | 9,421 | | | | (10,913 | ) | | | 68,066 | | | | 4,434 | | | | 294,881 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-6
| 1 | | Description of Business |
| |
| (a) | | Operations |
| |
| | | Contax Participações S.A. (“Contax Holding”), established on July 31, 2000, is a publicly-held Company whose registered corporate purpose is to hold interests in other commercial enterprises and civil societies as a partner, shareholder or quota holder in Brazil or abroad. Its only subsidiary, TNL Contax S.A. (“TNL Contax”) (together with Contax Holding, the “Company”), is a contact center service provider, which corporate purpose is providing telephonic customer assistance services in general. |
| |
| | | The Company obtained its registration in BOVESPA and SEC and started the negotiations of shares and ADRs on August 29, 2005 in BOVESPA and on August 31, 2005 in the USA over-the-counter market. |
| |
| (b) | | TNL Contax |
| |
| | | TNL Contax S.A., established in August, 1988, privately-held company, which corporate purpose is to provide telephonic customer assistance services in general, offering a variety of integrated customer interaction solutions between its clients and their consumers, including telemarketing operations, customer services, customer retention, technical support and bill collection through a variety of communication channels, including telephone contacts, internet access, e-mail, fax, development of technological solutions related to the telephonic customer assistance services offer, among others. |
| |
| 2 | | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
| |
| (a) | | Basis of presentation |
| |
| | | The Consolidated Financial Statements were prepared in accordance with accounting practices generally accepted in the United States of America (“US GAAP”), which differ in certain respects from the accounting practices adopted in Brazil that are used to prepare the Company’s statutory financial statements. |
| |
| | | The consolidation and combination process for the balance sheet and the statements of operations, cash flows and shareholders’ equity reflects the aggregate of the balances and changes in assets, liabilities, shareholders’ equity and income and expense accounts, according to their nature, together with the elimination of inter-company transactions and unrealized profits. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-7
| (b) | | Fair value of financial instruments |
| |
| | | The carrying amounts reported in the balance sheet for cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, and other receivables and accrued expenses approximate their fair values due to the short-term nature of these financial instruments. |
| |
| (c) | | Concentration of credit risks |
| |
| | | Financial instruments which expose the Company to concentration of credit risk consist primarily of cash equivalents and accounts receivable. All cash equivalents are maintained in Brazil with prime financial institutions. Management believes its credit policies are prudent and reflect normal business terms and risk. The Company does not anticipate nonperformance by the counterparties and, accordingly, does not require collateral. |
| |
| (d) | | Use of estimates |
| |
| | | The Consolidated Financial Statements include estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingencies and the amounts of revenues and expenses. The application of this significant accounting policy often requires judgments made by management regarding the effects of matters that are inherently uncertain. Our estimates, including but not limited to the provisions of accounts receivables and contingent liabilities, may differ from the actual value of such assets or liabilities. |
| |
| (e) | | Cash and cash equivalents |
| |
| | | Cash and cash equivalents are considered to be all highly liquid investments with an original maturity to the Company of three months or less. |
| |
| (f) | | Revenue recognition |
| |
| | | We recognize revenues on an accrual basis at the time the services are rendered, except with respect to some of our performance-based services, which we recognize upon measurement and acceptance by our client. The service contract revenues are calculated based on indicators like quantity of workstations, speaking time and on performance targets. Revenues are calculated based on information available in our IT systems that relate to the volume of data services rendered to each client. Revenues related to our performance-based services are calculated based on data available in our clients’ IT systems. In addition, we usually allocate operations managers to review, reconcile and discuss such indicators with clients. Some revenue adjustments are recorded after discussions with such clients. |
| |
| (g) | | Costs and expenses |
| |
| | | The operating costs and expenses are recorded on an accrual basis and pertain mainly to personnel expenses. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-8
| (h) | | Financial income and expenses |
| |
| | | Financial income and expenses pertain mainly to interest and monetary variations resulting from financial investments loan contracts signed with a subsidiary and leasing contracts, all recorded on an accrual basis. |
| |
| (i) | | Provision for doubtful accounts |
| |
| | | This provision is recorded to recognize probable losses in relation to accounts receivable, whose calculation is based on estimates considering the situation of each customer and the guarantees provided by them. The basis for measurement of the provision considers the position of each overdue client individually. |
| |
| (j) | | Judicial deposits |
| |
| | | The Company questions, in some situations, whether certain liabilities or lawsuits filed against the company are fair or not. Pursuant to these questionings, by court order or by strategy of the management, the referred amounts may be deposited in court and the liabilities will not be considered as settled. In these situations, if it is not possible to redeem the deposit, except for a court decision favorable to the entity. These deposits may be monetarily updated. |
| |
| (k) | | Property and equipment |
| |
| | | The investment in property and equipment is stated at original cost. Property and equipment is depreciated using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives. The principal depreciation rates are detailed in Note 12. |
| |
| | | Management reviews long-lived assets, primarily buildings and equipment to be held and used in the business, for the purpose of determining and measuring impairment on a recurring basis or when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of an asset or group of assets may not be recoverable. Write-down of the carrying value of assets or groups of assets is recorded if and when appropriate. |
| |
| (l) | | Provisions for contingencies |
| |
| | | The recognition, measurement and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities and legal obligations are carried out according to the criteria set forth in FAS 5. |
| |
| | | Contingent Assets – are not recognized on an accounting basis, except when the management is in total control of the situation or when there are real guarantees or favorable decisions, on which it is no longer possible to file appeals, characterizing the gain as practically certain. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-9
| | | Contingent liabilities – constituted by means of individual analysis, by complaints, based on the opinion of management and in-house counsel, as well as outside legal advisers. The bases, amounts involved and types of main contingencies are described in Note 16. |
| |
| | | Legal obligations – arise from tax obligations whose purpose of claim is its lawfulness or constitutionality. |
| |
| (m) | | Income tax and social contribution |
| |
| | | Provisions for deferred and payable income tax and social contribution and tax credit on temporary differences are established at the base rate of 34%, comprised of a 25% federal income tax rate plus a 9% social contribution rate. In accordance with SFAS 109 — “Accounting for Income Taxes,” the deferred tax effects of tax loss carry forwards and temporary differences and adjustments to US GAAP have been recognized in the Consolidated Financial Statements. A valuation allowance is made when it is more likely than not that tax assets will not be fully recoverable in the future. |
| |
| | | Prepaid income tax and social contribution are recorded as “Recoverable taxes.” |
| |
| (n) | | Payroll and related accruals |
| |
| | | The amounts related to vacation pay owed to the employees are covered by provisions established in proportion to the acquisition period thereof. |
| |
| | | The subsidiary TNL Contax has a profit sharing program, for all its employees, pursuant to the agreement entered into with FITTEL – Interstate Federation of Employees of Telecommunications Companies. This profit sharing program is based on increasing operating gains and individual performance, in which all the employees take part. |
| |
| (o) | | Loans |
| |
| | | Loans taken are recognized initially in the funds receivables, net of transaction costs. Subsequently, loans taken are presented by the cost amortized, which includes charges and interest proportional to the period incurred. |
| |
| (p) | | Leasings |
| |
| | | Leasing contracts are treated as finance leases when any of the following conditions is met: (i) the contract transfer the leased asset at the end of the lease term (ii) the contract contains a bargain purchase option (iii) the present value of the future lease payments equals or exceeds 90% of the fair value of the leased asset and, (iv) the lease term equals or exceeds 75% of the useful life of the leased asset. |
| |
| | | Leasing contracts treated as finance leases are recognized as both an asset (equipment) and a liability (short and long-term debt). |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-10
| (q) | | Other current liabilities |
| |
| | | These are stated at known or estimated amounts, including, when applicable, accrued charges and monetary variations incurred on a pro rata basis. |
| |
| (r) | | Statements of cash flows |
| |
| | | The statement of cash flows is presented in accordance with FAS 95, “Statement of Cash Flows,” which establishes specific presentation requirements and requires certain disclosures, such as the amount of interest and income taxes paid and non-cash transactions such as acquisition of property, plant and equipment through capital leases, utilization of escrow deposits in settlement of liabilities and debt for equity conversions, among others. |
| |
| (s) | | Segment Information |
| |
| | | As the company operates in only one segment and one geographic area, no segment information is disclosed. |
| |
| 3 | | Earnings per share |
| |
| | | For the purpose of these financial statements, the computation of earnings per share for 2006 and 2005 is based on the number of shares with the effect of the reverse split of shares in the proportion of 20 shares for 1 share of the same type. Since preferred and common shareholders have different dividend, voting and liquidation rights, basic and diluted earnings per share have been calculated using the “two-class” method. The “two-class” method is an earnings allocation formula that determines earnings per share for preferred and common stock according to the dividends to be paid as required by the Company’s by-laws and participation rights in undistributed earnings. Basic earnings per common share is computed by reducing net income by distributable and undistributable net income available to preferred shareholders and dividing net income available to common shareholders by the average number of common shares outstanding. Net income available to preferred shareholders is the sum of the preferred stock dividends and the preferred shareholders’ portion of undistributed net income. Undistributed net income is computed by deducting total dividends (the sum of preferred and common stock dividends) from net income. Undistributed net income is shared equally by the preferred and common shareholders on a “pro rata” basis. |
| |
| | | On August 17, 2005, Contax Holding’s Shareholders approved a split of its shares, to equalize its number of shares to the number of TNL for share distribution purpose that occurred shortly after. The split ratio was 1.006.103 for each 1 Contax Holding’s share. |
| |
| | | First share buyback program. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-11
| | | At the Extraordinary Meeting of the Board of Directors held on June 29, 2006, the share buyback proposal was approved, with funds registered in the Capital Reserve and Statutory Reserve, totaling the buyback of 5,886,700 common shares and 11,773,900 preferred shares, fully cancelled as per resolution of the Extraordinary General Meeting held on November 28, 2006. |
| |
| | | Second share buyback program.
At the Extraordinary Meeting held on November 30, 2006, the Board of Directors approved the launch proposal of the share buyback program, with funds registered in the Capital Reserve and Statutory Reserve, which amounted to the buyback of 5,298,300 common shares and 24,058,190 preferred shares, cancelled on July 31, 2007, thus maintaining 1,750,000 common shares in treasury, as per resolution at the Extraordinary General Meeting held on July 27, 2007. |
| |
| | | Third share buyback program.
At the Extraordinary Meeting, held on July 26, 2007, the Board of Directors approved the new share buyback program with funds registered in the Capital Reserve and Statutory Reserve, totaling the buyback of 18,277,422 preferred shares and 3,193,472 common shares, cancelled on October 17, 2007, of which 1,750,000 common shares are kept in treasury, pursuant to the resolutions of the General Extraordinary Meeting, totaling 3,500,000 common shares in treasury. |
| |
| | | Sale of shares
On October 18, 2007 179,660 common shares were sold to the Company’s executives, in conformity with the Stock Option Plan approved at the Extraordinary General Meeting held on April 16, 2007. |
| |
| | | Reverse split of shares.
At the Extraordinary General Meeting held on October 17, 2007, the reverse split of all shares representing the Company’s capital stock was approved, in the proportion of 20 shares for 1 share of the same type. As per the call to the shareholders, a term of until November 16, 2007 was granted for the execution of the adjustments in the share positions. The information disclosed regarding the amount of shares prior to this date does not include a retroactive effect of the reverse split of shares. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-12
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
| Net income for the year | | | 55,451 | | | | 77,681 | | | | 81,240 | |
| Less preferred shares dividends | | | (777 | ) | | | (4,838 | ) | | | (8,955 | ) |
| Less common shares dividends | | | | | | | | | | | (4,478 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Remaining net income equally allocated to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| preferred shares | | | 35,302 | | | | 46,954 | | | | 40,727 | |
| common shares | | | 19,371 | | | | 25,889 | | | | 27,080 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Total net income allocated to: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| preferred shares | | | 36,079 | | | | 51,792 | | | | 49,682 | |
| common shares | | | 19,371 | | | | 25,889 | | | | 31,558 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares outstanding — Basic: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common | | | 5,747,315 | | | | 6,264,303 | | | | 6,368,696 | |
| Preferred | | | 10,704,436 | | | | 12,532,231 | | | | 12,737,390 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of shares outstanding — Diluted: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common | | | 6,005,323 | | | | 6,264,303 | | | | 6,368,696 | |
| Preferred | | | 10,704,436 | | | | 12,532,231 | | | | 12,737,390 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted earnings per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common | | | 3.37 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.96 | |
| Preferred | | | 3.37 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 3.90 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted earnings per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common | | | 3.23 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 4.96 | |
| Preferred | | | 3.37 | | | | 4.13 | | | | 3.90 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-13
| 4 | | Recently issued accounting pronouncements |
| |
| (i) | | SFAS 141 (Revised) |
| |
| | | In December 2007, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued FAS 141R – Business Combinations. This statement applies to all transactions or events in which an entity obtains control of one or more businesses, except for joint ventures, assets that do not constitute a business, combination of businesses under common control and not-for-profit organizations. This Statement shall be applied prospectively to business combinations for which the acquisition date is on or after the beginning of the first annual reporting period beginning on or after December 15, 2008. Earlier application is prohibited. The objective of this statement is to improve the relevance, representational faithfulness and comparability of the information that a reporting entity provides in its financial reports about a business combination and its effects. The Company is currently studying the impact of this standard and will apply it as of the fiscal year beginning January 1, 2009. |
| |
| (ii) | | SFAS 160 |
| |
| | | In December 2007, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issuedFAS 160 – Non-controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements, which applies to all entities that prepare consolidated financial statements, except not-for-profit organizations. |
| |
| | | This Statement amends ARB 51 to establish accounting and reporting standards for the non-controlling interest in a subsidiary and for the deconsolidation of a subsidiary. |
| |
| | | This Statement shall be effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning on or after December 15, 2008. Earlier adoption is prohibited. This Statement shall be applied prospectively as of the beginning of the fiscal year in which this Statement is initially adopted, except for the presentation and disclosure requirements. The objective of this statement is to improve the relevance, comparability and transparency of the financial information that a reporting entity provides in its consolidated financial statements by establishing accounting and reporting standards that require more extensive disclosure that clearly identifies and distinguishes between the interests of the Parent Company and the interests of the non-controlling owners. The Company is currently studying the impact of this standard and will apply it as of the fiscal year beginning January 1, 2009. |
| |
| (iii) | | SFAS 161 |
| |
| | | In March 2008, the (FASB) issued SFAS 161, “Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities”, The new standard is intended to improve financial reporting about instruments and hedging activities by requiring enhanced disclosures to enable investors to better understand their effects on an entity’s financial position, financial performance, and cash flows. It is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after November 15, 2008 with early application encouraged. We are currently studying the possible effects which may arise upon adoption of this standard. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-14
| (iv) | | SFAS 159 |
| |
| | | In February 2007, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued SFAS No. 159, “The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities”. SFAS No. 159 permits entities to choose to measure many financial instruments and certain other items at fair value. The objective is to improve financial reporting by providing entities with the opportunity to mitigate volatility in reported earnings caused by measuring related assets and liabilities differently without having to apply complex hedge accounting provisions. This Statement is expected to expand the use of fair value measurement, which is consistent with the Board’s long-term measurement objectives for accounting for financial instruments. The fair value option established by this Statement permits all entities to choose to measure eligible items at fair value at specified election dates. This standard is effective for fiscal years ending on or after November 15, 2007. The Company is currently studying the impact of this standard and will apply it as of the fiscal year beginning on January 1, 2008 |
| |
| (v) | | SFAS 157 |
| |
| | | In September 2006, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued SFAS No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements”. SFAS No. 157 defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in generally accepted accounting principles, and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. This statement applies under other accounting pronouncements that require or permit fair value measurements, the Board having previously concluded in those accounting pronouncements that fair value is relevant measurement attribute. Accordingly, this Statement does not require any new fair value measurements. Accordingly to the Board, a single definition of fair value, together with a framework for measuring fair value, should result in increased consistency and comparability in fair value measurements. This standard is effective for fiscal years ending on or after November 15, 2007. The Company is currently studying the impact of this standard and will apply this standard as of the fiscal year beginning on January 1, 2008. |
| |
| (vi) | | SFAS 157-2 |
| |
| | | In February 2008, the Financial Accounting Standard (FASB) issued FSP FAS 157-2, “Effective Date of FASB Statement No. 157”. The objective of this FSP is to delay the effective date of FASB Statement No. 157, Fair Value Measurements, for nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities, except for items that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a recurring basis. The delay is intended to allow the Board and constituents additional time to consider the effect of various implementation issues that have arisen, or that may arise, from the application of Statement 157. This FSP shall be effective upon issuance. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-15
| 5 | | Cost of Services Rendered and Operating Expenses |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, 2007 | |
| | | | | | | Selling, | | | | |
| | | | | | | general | | | | |
| | | Cost of | | | and | | | | |
| | | services | | | adminis- | | | | |
| | | rendered | | | trative | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Personnel (i) | | | 863,257 | | | | 45,112 | | | | 908,369 | |
| Third-party services (ii) | | | 158,276 | | | | 31,127 | | | | 189,403 | |
| Depreciation (iii) | | | 93,848 | | | | 6,794 | | | | 100,642 | |
| Facilities (iv) | | | 49,134 | | | | 1,724 | | | | 50,858 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts (v) | | | | | | | 4,033 | | | | 4,033 | |
| Other | | | 9,520 | | | | 327 | | | | 9,847 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 1,174,035 | | | | 89,117 | | | | 1,263,152 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, 2006 | |
| | | | | | | Selling, | | | | |
| | | | | | | general | | | | |
| | | Cost of | | | and | | | | |
| | | services | | | adminis- | | | | |
| | | rendered | | | trative | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Personnel (i) | | | 786,712 | | | | 34,799 | | | | 821,511 | |
| Third party services (ii) | | | 133,384 | | | | 27,366 | | | | 160,750 | |
| Depreciation (iii) | | | 59,529 | | | | 4,919 | | | | 64,448 | |
| Facilities (iv) | | | 45,579 | | | | 3,513 | | | | 49,092 | |
| Other costs and expenses | | | 12,149 | | | | 1,782 | | | | 13,931 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 1,037,353 | | | | 72,379 | | | | 1,109,732 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-16
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, 2005 | |
| | | | | | | Selling, | | | | |
| | | | | | | general | | | | |
| | | Cost of | | | and | | | | |
| | | services | | | adminis- | | | | |
| | | rendered | | | trative | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Personnel (i) | | | 670,998 | | | | 28,771 | | | | 699,769 | |
| Third party services (ii) | | | 93,055 | | | | 24,038 | | | | 117,093 | |
| Depreciation (iii) | | | 41,907 | | | | 3,939 | | | | 45,846 | |
| Facilities (iv) | | | 39,385 | | | | 1,354 | | | | 40,739 | |
| Other costs and expenses | | | 10,562 | | | | 1,640 | | | | 12,202 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 855,907 | | | | 59,742 | | | | 915,649 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| (i) | | Personnel cost has presented an increase due to the growth of the business volume. The Company provisioned for its 2007 profit sharing program the amount of R$15,483 due to the fact that the negotiations regarding said program are not concluded with FITTEL. The management carried out the provision taking into account its best estimate to conclude the negotiations, verifying the background of previous negotiations, technical analysis and the current status of this negotiation. |
| |
| (ii) | | Third party services considered as “Costs of services rendered” refer mainly to data processing and workstation maintenance, while third-party services considered “Selling, general and administrative” refer to expenses with consulting, traveling, legal counsel and others. |
| |
| (iii) | | The increase arises from the reduction of the useful life expected for the assets recorded in the items regarding IT equipment, and furniture and fixtures (Note 12), and from the investments carried out due to the increase in business volume |
| |
| (iv) | | Facilities expenses include mainly amounts which are being paid for the rental of properties and contact center operating infrastructure. |
| |
| (v) | | Allowance for doubtful accounts related to past due receivables. |
| 6 | | Other operating income (expenses), net |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years ended December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for contingencies (Note 16) | | | (10,108 | ) | | | (8,413 | ) | | | (10,908 | ) |
| Other, net (i) | | | (5,538 | ) | | | (3,008 | ) | | | (1,190 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | (15,646 | ) | | | (11,421 | ) | | | (12,098 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| (i) | | “Other, net” refers, mainly, to IPTU – Municipal Real Estate Tax from the leased buildings. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-17
| 7 | | Financial income (expenses), net |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years ended December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
Financial income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest on securities | | | 15,681 | | | | 25,523 | | | | 21,569 | |
| Other | | | 966 | | | | 1,018 | | | | 108 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 16,647 | | | | 26,541 | | | | 21,677 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Financial expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Bank charges, including CPMF (i) | | | (6,903 | ) | | | (5,332 | ) | | | (5,341 | ) |
| Interest and monetary restatement of contingencies | | | (4,683 | ) | | | (2,707 | ) | | | (1,000 | ) |
| Interest on BNDES financing | | | (1,873 | ) | | | | | | | | |
| Other (ii) | | | (6,736 | ) | | | (97 | ) | | | (984 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | (20,195 | ) | | | (8,136 | ) | | | (7,325 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | (3,548 | ) | | | 18,405 | | | | 14,352 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| (i) | | CPMF, or “Provisory Contribution over Financial Movements” is a contribution paid by individuals and companies over withdrawals from bank and financial investment accounts. |
| |
| (ii) | | “Other expenses” refers mainly to taxes on financial operations interest on short-term liabilities and leasing obligations. |
| 8 | | Income tax and social contribution |
| |
| | | Income taxes in Brazil comprise federal income tax and social contribution, which is an additional federal tax. The statutory composite enacted tax rate applicable in the periods presented is 34%, represented by a 25% federal income tax rate plus a 9% social contribution rate. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-18
| | | The amount reported as income tax expense in our Consolidated Financial Statements information is reconciled to the statutory rates as follows: |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years ended December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
| Income from continuing operations before tax and social contribution | | | 83,537 | | | | 115,836 | | | | 131,627 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Federal income tax and social contribution expense at statutory enacted rates | | | (28,402 | ) | | | (39,384 | ) | | | (44,753 | ) |
| Adjustments to derive effective tax rate: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Tax effects on permanent differences | | | 317 | | | | 1,230 | | | | (5,634 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income tax and social contribution tax provision | | | (28,085 | ) | | | (38,154 | ) | | | (50,387 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | (28,085 | ) | | | (38,154 | ) | | | (50,387 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
The Company recorded credits from income tax and social contribution on tax loss carryforwards negative basis for social contribution and temporary differences. A valuation allowance is made when it is more likely than not that tax assets will not be fully recoverable.
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| Deferred taxes: | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for contingencies | | | 12,006 | | | | 7,592 | |
| Profit sharing | | | 6,631 | | | | 3,060 | |
| Tax loss carryforwards | | | 10,556 | | | | 21,427 | |
| | | | | | | |
| |
| | | | 29,193 | | | | 32,079 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Current deferred tax assets | | | 17,187 | | | | 12,176 | |
| Long-term deferred tax assets | | | 12,006 | | | | 19,903 | |
The Company adopted the provisions of FASB Interpretation No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes, on January 1, 2007. There was no impact to the Company’s financial position and results of operation as a result of the implementation of Interpretation 48. The Company records the financial statement effects of an income tax position when it is more likely than not, based on the technical merits, that it will be sustained upon examination. A tax position that meets the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold is measured and recorded as the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50 percent likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement with a taxing authority. Previously recognized tax positions are derecognized in the first period in which it is no longer more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained. The benefit associated with previously unrecognized tax positions are generally recognized in the first period in which the more-likely-than-not threshold is met at the reporting date, the tax matter is ultimately settled through negotiation or litigation or when the related statute of limitations for the relevant taxing authority to examine and challenge the tax position has expired. The recognition, derecognition and measurement of tax positions are based on management’s best judgment given the facts, circumstance and information available at the reporting date.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-19
Differences between a tax position taken or expected to be taken in the Company’s tax returns and the amount of benefit recognized and measured in the financial statements result in unrecognized tax benefits, which are recorded ‘in the balance sheet as a either a liability for unrecognized tax benefits or reductions to recorded tax assets, as applicable. The liability for unrecognized tax benefits expected to be realized within one year is classified as current in the balance sheet.
Interest and penalties are accrued with respect to unrecognized tax benefits in accordance with the legislation of the respective taxing jurisdictions. The Company recognizes interest and penalties accrued on unrecognized tax benefits as a component of interest expense.
The Company’s income tax returns are subject to review for a period of five years.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-20
| 9 | | Cash and cash equivalents |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and banks accounts (i) | | | 114,440 | | | | 65,235 | |
| Certificate of deposits (ii) | | | 125,870 | | | | 166,064 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 240,310 | | | | 231,299 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | |
| (i) | | The amounts are kept in a current account, as the Company has accounts payable due on the first days of each month, relating to the payment of suppliers, taxes and payroll. |
| |
| (ii) | | In general, these financial investments are indexed by the Brazilian Interbank Certificate of Deposit (“CDI”) rate, with daily liquidity and maturity after one month from the date of issuance. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | Short | | | Long | | | Short | | | Long | |
| | | term | | | term | | | term | | | term | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income tax on temporary differences | | | 4,876 | | | | 8,828 | | | | 2,257 | | | | 5,582 | |
| Social Contribution on temporary differences | | | 1,755 | | | | 3,178 | | | | 810 | | | | 2,010 | |
| Income tax on tax loss carryfowards | | | 7,753 | | | | | | | | 6,327 | | | | 9,414 | |
| Social Contribution on tax loss carryfowards | | | 2,803 | | | | | | | | 2,782 | | | | 2,897 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 17,187 | | | | 12,006 | | | | 12,176 | | | | 19,903 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | Short | | | Long | | | Short | |
| | | term | | | term | | | term | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income tax recoverable (i) | | | 17,269 | | | | | | | | 19,546 | |
| Social contribution recoverable (i) | | | 6,379 | | | | | | | | 7,210 | |
| Withholding taxes | | | 1,740 | | | | 3,688 | | | | 5,634 | |
| ISS recoverable (ii) | | | | | | | 1,880 | | | | 931 | |
| Other | | | 430 | | | | | | | | 566 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 25,818 | | | | 5,568 | | | | 33,887 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| (i) | | Recoverable income tax and social contribution relate to advance payments made throughout the year to be compensated with income tax and social contribution payable upon filling of the Company’s tax return. |
| |
| (ii) | | Recoverable ISS is classified as Long Term due to the repayment terms with Municipal bodies. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-21
| 12 | | Property and equipment and intangible assets, net |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Annual | |
| | | | | | | Accumulated | | | | | | | | | | depreciation | |
| | | Cost | | | depreciation | | | Net | | | Net | | | rate (%) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Telecom and IT systems (i) | | | 261,544 | | | | (160,226 | ) | | | 101,318 | | | | 126,311 | | | | 33,3 to 20 | |
| Improvements on third party assets | | | 157,707 | | | | (36,771 | ) | | | 120,936 | | | | 100,221 | | | | 10 | |
| Furniture and fixtures (i) | | | 47,104 | | | | (14,692 | ) | | | 32,412 | | | | 25,168 | | | | 12,5 to 10 | |
| Construction in progress | | | 1,530 | | | | | | | | 1,530 | | | | 877 | | | | | |
| Buildings | | | 2,628 | | | | | | | | 2,628 | | | | | | | | 4 | |
| Land | | | 831 | | | | | | | | 831 | | | | | | | | | |
| Other | | | 20,199 | | | | (5,295 | ) | | | 14,904 | | | | 13,016 | | | | 10 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Intangible Software | | | 112,081 | | | | (44,105 | ) | | | 67,976 | | | | 44,134 | | | | 20 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 603,624 | | | | (261,089 | ) | | | 342,535 | | | | 309,727 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| (i) | | The leasing contracts related to these assets vary from 5 to 8 years and the Company has the ability, at its option, to extend these contracts by the same periods (see note 16 (b)). |
The increases are related to the increase in the amount of customer workstations in the São Paulo, Pernambuco and Rio de Janeiro sites, associated with the expansion of the Company’s activities.
For the year ended December 31, 2007 depreciation related to Telecom and IT Systems and Furnitures acquired through finance leases amounted to R$ 16,373 (R$ 12,738 and R$ 2,646 for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively)
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-22
The useful lives of IT equipment and Furniture and fixtures were reviewed due to the reduction of the estimated economic useful life of assets acquired up to December 31, 2006. The evaluation and determination of the new economic useful life of these assets was performed in accordance with the rules of A.B.N.T – Brazilian Association of Technical Rules in 2007, the increase in depreciation that affected net income due to the new useful life, net of the corresponding tax effects, was R$17,496. Without considering the effects of this change, earnings per share for the year ended December 31, 2007 would be as follows:
| | | | | |
| Basic earnings per share: | | | | |
| Common | | | 4.43 | |
| Preferred | | | 4.43 | |
| | | | | |
| Diluted earnings per share: | | | | |
| Common | | | 4.24 | |
| Preferred | | | 4.43 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | |
| | | | | | | Final | | | Financial | | | | |
| Purpose | | Funding | | | maturity | | | charges | | | Amount | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Nacional currency | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
BNDES(Operation expansion and update) | | | 10.5.2007 | | | | 9.15.2013 | | | TJLP+ 2% p.y. (i) | | | 100,360 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Current | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 300 | |
Noncurrent | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 100,060 | |
On August 23, 2007, the subsidiary TNL Contax entered into a financing agreement with BNDES in the amount of R$216,514 with the purpose of financing the expansion of its installed capacity, improving current facilities, qualifying human resources, improving the quality of services and productivity, and investing in marketing actions.
The financing was obtained within the scope of the Program for the Development of the Software Industry and Correlated Services – PROSOFT-Company.
On October 5, 2007, the first installment, in the amount of R$100,002, was received. The release of the remaining installments is linked to the verification of the application of the investments.
The maturity date of the financial charges shall be quarterly up to September 15, 2009, becoming monthly for the period between October 15, 2009 until the final maturity date or termination date of the contract. The principal shall mature monthly as from October 15, 2009.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-23
The Company, as per the agreement’s determination, presented guarantees through sureties from prime financial institutions:
| | | | | |
| | | Limit by | |
| Surety | | Debt (%) | |
| | | | | |
| - Banco Safra S/A | | | 12.04 | % |
| - Banco Votorantim S/A | | | 55.56 | % |
| - Banco Alfa S/A | | | 32.40 | % |
| | | | |
| | | | 100.00 | % |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-24
Movement of the financing in the year ended on December 31, 2007.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Interest | | | Financial | | | | |
| Purpose | | Funding | | | amortization | | | charges | | | 2007 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BNDES | | | 100,002 | | | | (1,574 | ) | | | 1,932 | | | | 100,360 | |
Schedule of annual disbursement until the expiration of the agreement.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BNDES | | Principal | | | Interest | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2008 | | | | | | | 7,863 | | | | 7,863 | |
| 2009 | | | 6,254 | | | | 7,831 | | | | 14,085 | |
| 2010 | | | 25,015 | | | | 6,446 | | | | 31,461 | |
| 2011 | | | 25,015 | | | | 4,489 | | | | 29,504 | |
| 2012 | | | 25,015 | | | | 2,548 | | | | 27,563 | |
| 2013 | | | 18,761 | | | | 604 | | | | 19,365 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 100,060 | | | | 29,781 | | | | 129,841 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| 14 | | Taxes other than on income |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Consolidated | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | Short | | | Long | | | Short | | | Long | |
| | | term | | | term | | | term | | | term | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Services Tax — ISS | | | 8,296 | | | | | | | | 5,523 | | | | | |
| Social Security Financing (COFINS) | | | 5,089 | | | | | | | | 4,170 | | | | | |
| INSS — Installments | | | 768 | | | | 2,391 | | | | 768 | | | | 2,745 | |
| Other | | | 10 | | | | | | | | 10 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 14,163 | | | | 2,391 | | | | 10,471 | | | | 2,745 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Income tax payable | | | 18,018 | | | | 21,249 | |
| Social contribuition payable | | | 6,809 | | | | 7,839 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 24,827 | | | | 29,088 | |
| | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-25
| 16 | | Commitments and Contingencies |
| |
| (a) | | Contingencies |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31 | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Tax | | | | | | | | |
| Services Tax — ISS | | | 1,098 | | | | 671 | |
| Contributions to the National Social Security Institute — INSS (i) | | | 5,196 | | | | 5,122 | |
| PIS/COFINS | | | 1,482 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | 7,776 | | | | 5,793 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Labor(ii) | | | 38,955 | | | | 22,989 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | 38,955 | | | | 22,989 | |
| | | | | | | |
Civil | | | 129 | | | | 117 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total | | | 46,860 | | | | 28,899 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | The provisions for contingencies reflect management’s best estimates for the amounts deemed sufficient to cover probable losses from pending claims on the balance sheet date and are based on the expert opinions of legal advisors. The Company and its subsidiary maintain judicial deposits to ensure the right of recourse in lawsuits of tax and labor nature. |
| | (i) | | Provision to regulate contributions to SENAC and SEBRAE entities, in the payments made to INSS (National Institute of Social Security), accordingly to the FPAS (Pension and Social Assistance Fund) table. |
| |
| | (ii) | | Pursuant to the services agreement executed by Telemar and TNL Contax, it was defined that labor claims, arising from the migration of work agreements shall be incumbent upon Telemar, which amount has been recorded as a counter entry to “Receivable Credits”. The amount of labor claims under Telemar’s responsibility amounts to R$ 11,550 thousand. The labor claims filed against TNL CONTAX by employees and former employees amount to R$ 27,405 thousand. |
| | | In the third quarter of 2006, TNL Contax was imposed an official notification regarding contributions to INSS in the amount of R$ 21.9 million. Of this amount, R$ 3.5 million was recognized as a contingency provision and R$ 3.7 million refer to third parties liabilities that are being totally assumed by these third parties and did not affect the results for the period as its was recorded in the “Taxes paid in installments” account (see Note 14) as a counter entry to the “Other assets” account. For the remaining R$ 14.7 million, the Company has argued a defense appeal, since it does not agree with the position adopted by the fiscal authorities. Based on the opinion of its external legal advisors, the Company’s position is that there are good possibilities of success, therefore, it has not recognized any provision for this amount. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-26
| | | As a part of our ongoing operations, we have been the defendant in a number of lawsuits brought by our employees, labor unions and the Labor Public Prosecution Office (Ministério Público do Trabalho). We have established what we believe to be an adequate reserve to cover these claims. |
| |
| (b) | | Commitments |
| |
| | | Leasing |
| |
| | | The Company maintains several commercial leasing agreements for IT equipment that are being treated as finance leases and have been recorded as both an asset (equipment) and a liability (long-term debt) at their inception: |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Liability balances | |
| | | Inception | | Maturity | | Number of | | | Assets balance | | | Current part of long-term | | | Long-term | |
| Lessor | | date | | date | | installments | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| HP Financial | | 20/12/2004
a 29/09/2005 | | 20/11/2007
a 29/08/2008 | | | 36 | | | | 4,588 | | | | 6,553 | | | | 970 | | | | 3,724 | | | | — | | | | 970 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| IBM Leasing | | 01/07/2005
a 29/07/2005 | | 01/06/2008
a 29/06/2008 | | | 36 | | | | 329 | | | | 460 | | | | 118 | | | | 237 | | | | — | | | | 118 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| HP Financial | | 29/10/2005
a 27/04/2006 | | 29/09/2009
a 27/03/2010 | | | 48 | | | | 11,453 | | | | 15,233 | | | | 4,744 | | | | 4,744 | | | | 4,881 | | | | 9,625 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| CIT | | 27/11/2005 | | 27/10/2009 | | | 48 | | | | 8,532 | | | | 11,144 | | | | 3,272 | | | | 3,272 | | | | 4,143 | | | | 7,416 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| DIBENS (UBB) | | 23/09/2005 | | 03/11/2010 | | | 48 | | | | 9,041 | | | | 11,275 | | | | 3,490 | | | | 3,490 | | | | 3,121 | | | | 6,611 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| IBM Leasing | | 25/01/2006 | | 25/12/2009 | | | 48 | | | | 454 | | | | 606 | | | | 189 | | | | 189 | | | | 189 | | | | 378 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| HP Financial | | 1/12/2006
a 24/9/2006 | | 5/11/2011
a 23/9/2011 | | | 60 | | | | 12,736 | | | | 16,398 | | | | 3,663 | | | | 3,663 | | | | 9,140 | | | | 12,736 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| IBM Leasing | | 28/06/2006 | | 24/10/2011 | | | 60 | | | | 6,268 | | | | 8,040 | | | | 1,772 | | | | 1,772 | | | | 4,496 | | | | 6,268 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 53,401 | | | | 69,709 | | | | 18,218 | | | | 21,091 | | | | 25,970 | | | | 44,122 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-27
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Inception | | Maturity | | Number of | | | Payments for the year | | | Expenses for the year | |
| Lessor | | date | | date | | installments | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| HP Financial | | 20/12/2004 | | 20/11/2007 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | a 29/09/2005 | | a 29/08/2008 | | | 36 | | | | 3,724 | | | | 3,890 | | | | 2,030 | | | | 2,030 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| IBM Leasing | | 01/07/2005 | | 01/06/2008 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | a 29/07/2005 | | a 29/06/2008 | | | 36 | | | | 237 | | | | 237 | | | | 131 | | | | 131 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| HP Financial | | 29/10/2005 | | 29/09/2009 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | a 27/04/2006 | | a 27/03/2010 | | | 48 | | | | 4,744 | | | | 4,246 | | | | 3,780 | | | | 3,382 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| CIT | | 11/27/2005 | | 10/27/2009 | | | 48 | | | | 3,272 | | | | 2,245 | | | | 2,612 | | | | 1,790 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| DIBENS (UBB) | | 9/23/2005 | | 11/3/2010 | | | 48 | | | | 3,490 | | | | 3,330 | | | | 2,234 | | | | 2,157 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| IBM Leasing | | 1/25/2006 | | 25/12/2009 | | | 48 | | | | 189 | | | | 189 | | | | 151 | | | | 151 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| HP Financial | | 1/12/2006
a 24/9/2006 | | 5/11/2011
a 23/9/2011 | | | 60 | | | | 3,663 | | | | 1,915 | | | | 3,663 | | | | 1,915 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| IBM Leasing | | 6/28/2006 | | 10/24/2011 | | | 60 | | | | 1,772 | | | | 822 | | | | 1,772 | | | | 822 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 21,091 | | | | 16,874 | | | | 16,373 | | | | 12,378 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Payments due by period | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | More | |
| | | | | | | Less than | | | | | | | | | | | than | |
| Contractual obligations | | Total | | | 1 year | | | 1-3 years | | | 3-5 years | | | 5 years | |
| | | | (in thousands ofreais) | |
| Capital (finance) lease | | | 44,188 | | | | 18,219 | | | | 23,159 | | | | 2,812 | | | | | |
| Operating lease (facilities) | | | 82,210 | | | | 28,591 | | | | 44,509 | | | | 8,943 | | | | 166 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 126,398 | | | | 46,810 | | | | 67,668 | | | | 11,755 | | | | 166 | |
| 17 | | Shareholders’ equity |
| |
| (a) | | Share capital |
| |
| | | Contax Participações capital of R$ 223,873 as of December 31, 2007, is comprised of 15,856,686 (2006* — 364,461,117) registered shares, with no par value, of which 5,824,772 (2006* — 121,487,217) are common shares and 10,031,914 (2006* — 242,973,900) are preferred shares. |
| |
| | | The Company started a share buyback programs on June 29 and November 30, 2006 (see Note 3) under which 6,028,000 common shares and 11,949,100 preferred shares were acquired and 5,886,700 common shares and 11,773,900 preferred shares were subsequently cancelled up to December 31, 2006. |
| |
| | | Each common share is entitled to one vote in the Shareholder’s General Meeting. |
| | | |
| (*) | | See Note 3 – Reverse split of shares. The number of shares does not include treasury stock. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-28
| | | The preferred shares issued by the Company do not have voting rights, but are granted refund priority in the event of liquidation of the Company, without goodwill, and in the payment of non-cumulative minimum dividends, on the basis of: (a) 6% per year over the amount resulting from the division of the subscribed capital by the number of shares of the Company or, (b) 3% pear year over the share net equity value, prevailing the higher amount between (a) and (b). |
| |
| | | The preferred shares may represent up to 2/3 (two thirds) of the total shares issued by the Company, with the possibility of changing the previous existing proportion between common and preferred shares. |
| |
| | | On August 17, 2005, an Extraordinary General Meeting of Contax Participações approved the split of the total of its outstanding shares, resulting in the issue of 2,318,240 new shares (772,758 common shares and 1,545,482 preferred shares), which have been fully allocated to TNL to be distributed, according to the aforementioned Extraordinary General Meeting held on December, 29, 2004, to TNL’s shareholders, in a ratio 1:1, thus satisfying the capital share reduction mentioned above. |
| |
| (b) | | Additional paid-in capital |
| |
| | | The capital reserve constituted in November 2004, in the amount of R$ 50,000, destined to the repurchase of shares, as per resolution of the board of directors on June 29, 2006, amounts to R$ 9,421 as of December 31, 2007 (2006 – R$ 9,386) . |
| |
| (c) | | Dividends |
| |
| | | According to the Company’s by-laws, Contax Holding has to distribute dividends for each fiscal year in the amount of not less than 25% of the net profit adjusted in accordance with clause 202 of Law No. 6404/76. The Company may also distribute quarterly dividends, as long as the total amount of paid dividends does not exceed the capital reserve. In accordance with Brazilian Corporate Law, on December 31, 2007, management proposed the payment of R$ 13,414 as the minimum mandatory dividends, prescribed by Law No. 6404/76 and was recognized as dividends payable. |
| |
| | | At the Annual General Meeting held on April 16, 2007, was approved the distribution of R$ 11,888 as dividends proposed in the year ended December 31, 2006, to the Company’s shareholders owning shares on April 16, 2007. Dividends were paid as from April 27, 2007, remunerated through the application of the Referential Rate – TR, since January 01, 2007. |
| |
| | | On April 18, 2006, the distribution of R$ 13,432 as dividends, proposed by management on December 31, 2005, was deliberated and approved by the annual shareholders meeting. On June 5, 2006 the dividends were paid to Contax Holding’s shareholders. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-29
| | | The annual dividend distributed to holders of preferred shares (the “Preferred Dividend”) has priority in the allocation of Adjusted Net Income when determining the Preferred Dividend in relation to the general dividend. Remaining amounts to be distributed, if any, are allocated first to the payment of a dividend to holders of common shares in an amount equal to the Preferred Dividend and the remainder, if any, is distributed equally among holders of preferred shares and common shares. |
| |
| | | The Preferred Dividends corresponds to a non-cumulative preferred dividend equal to 6% of share capital determined in according to accounting practices adopted in Brazil, in proportion of preferred shares to total capital, or 3% of shareholders’ equity book value per share, whichever is greater. |
| |
| (d) | | Appropriated retained earnings |
| |
| | | Brazilian laws require that certain appropriations be made from retained earnings to reserve accounts on an annual basis, all determined in accordance with amounts stated in the statutory accounting records, as detailed below: |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Unrealized | | | Statutory | | | Legal | | | | |
| | | Earnings Reserve | | | Reserve | | | Reserve | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2005 | | | 11,363 | | | | 57,477 | | | | 4,410 | | | | 73,250 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proposed dividends from retained earnings | | | (7,050 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (7,050 | ) |
| Appropriation from retained earnings | | | 12,906 | | | | 53,234 | | | | 3,736 | | | | 69,876 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2006 | | | 17,219 | | | | 110,711 | | | | 8,146 | | | | 136,076 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Used to cancellation of shares | | | | | | | (108,580 | ) | | | | | | | (108,580 | ) |
| Proposed dividends from retained earnings | | | (12,637 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (12,637 | ) |
| Appropriation from retained earnings | | | 12,044 | | | | 38,464 | | | | 2,699 | | | | 53,207 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2007 | | | 16,626 | | | | 40,595 | | | | 10,845 | | | | 68,066 | |
| | | The purpose and basis of appropriation to such reserves is described below: |
| | • | | Unrealized earnings reserve — this represents principally our share of earnings of controlled entity, not yet received in the form of cash dividends. |
| |
| | • | | Legal reserve — this reserve is a requirement for all Brazilian corporations and represents the appropriation of 5% of annual net income under accounting practices adopted in Brazil up to a limit of 20% of the Company capital. |
| |
| | • | | Statutory reserve — this reserve is an investment reserve that is constituted to insure future investments and to reinforce the Company’s working capital. Any statutory reserve, together with all Appropriated retained earnings, is limited to the Company’s capital. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-30
| (e) | | Stock option plan |
| |
| | | At the Extraordinary General Stockholders’ Meeting, held on April 16, 2007, approval was given for a stock option plan. The Board of Directors is responsible for administering the plan, and will introduce stock purchase programs from time to time. |
| |
| | | The Stock Option Program initiated in 2007 includes 3 beneficiaries, who are entitled to a total corresponding to up to 1.9% of the subscribed and paid in share capital, representing 350,000 thousand common shares granted under the program of April 2007. The options may be exercised as from October 1, 2007, in four equal annual blocks. |
| |
| | | The exercise price that has been set was based on the weighted average Bovespa quotation over the 30 days immediately preceding the concession date, and will be monetarily adjusted according to “Ìndice Geral de Preços – Mercado—IGP-M” (general market inflation index). |
| |
| | | The market value of the shares on the last business day of the year 2007 was R$ 68.99 per share. |
| |
| | | The following table shows the position of the options in effect as at December 31, 2007: |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Stock options outstanding | |
| | | Weighted | | | | |
| Stock | | average | | | Weighted | |
| (in thousand | | remaining life | | | average | |
| of shares) | | (months) | | | exercise price | |
| |
| 341,017 | | | 40 | | | | 54.4 | |
| | | The Company’s stock-options qualify for liability treatment under SFAS No. 123R, “Share-Based Payment”. Compensation expense of R$ 2,494 was recognized, based on the fair value of the options outstanding at December 31, 2007. |
| |
| | | During the year 8,983 shares were exercised and the related amount was R$ 167. |
| |
| | | At December 31, 2007, the number of exercisable options was 127,604 and the unrecognized compensation expense was R$ 5,215. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-31
| | | The fair value of the options was calculated using the Black & Scholes option pricing model based on the following assumptions: |
| | | | | |
| Strike price | | | 54.4 | |
| Market price | | | 68.9 | |
| Strike (%) | | 21.15 | %(ITM) |
| Volatility | | | 34.3 | % |
| Market rate | | | 12.72 | % |
| Dividend yield | | | 1.4 | % |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-32
| 3 | | Transactions with related parties |
| |
| | | The main transactions between the Company and other related parties can be summarized as follows: |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Brasil | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Brasil CAP | | | Veículos | | | | | | | Paggo | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Capitali- | | | Companhia | | | | | | | Adminstradora | | | Paggo | | | | | | | |
| | | Oi Fixa | | | Oi móvel | | | zações S.A. | | | de Seguros | | | OI Internet | | | de cartões | | | Acquirer | | | BNDES | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | | | 12,279 | | | | 4626 | | | | 285 | | | | 595 | | | | | | | | 62 | | | | | | | | | | | | 17,847 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Suppliers | | | 2,699 | | | | 236 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,935 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Borrowings | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 100,359 | | | | 100,359 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues from services rendered | | | 573,003 | | | | 161,055 | | | | 3,584 | | | | 6,644 | | | | 10,092 | | | | 418 | | | | 84 | | | | | | | | 754,880 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Costs and expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Costs of services rendered | | | (24,225 | ) | | | (6,700 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (30,925 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest financing | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (1,873 | ) | | | (1,873 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2006 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Brasil | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Brasil CAP | | | Veículos | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Capitali- | | | Companhia | | | | | | | |
| | | OI Fixa | | | Oi móvel | | | zações S.A. | | | de Seguros | | | OI Internet | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | | | 7,430 | | | | | | | | 274 | | | | 540 | | | | | | | | 8,244 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Suppliers | | | 1,807 | | | | 131 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,938 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues from services rendered | | | 605,750 | | | | 152,284 | | | | 3,241 | | | | 5,805 | | | | 7,657 | | | | 774,737 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Costs and expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Costs of services rendered | | | (26,547 | ) | | | (2,344 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (28,891 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-33
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2005 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Brasil | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Brasil CAP | | | Veículos | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Capitali- | | | Companhia | | | | | | | |
| | | OI fixa | | | OI móvel | | | zações S.A. | | | de Seguros | | | OI Internet | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | | | 426 | | | | | | | | 243 | | | | 548 | | | | | | | | 1,217 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Suppliers | | | 1,647 | | | | 132 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,779 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues from services rendered | | | 572,378 | | | | 96,276 | | | | 2,699 | | | | 4,481 | | | | 5,331 | | | | 681,165 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Costs and expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Costs of services rendered | | | (7,016 | ) | | | (1,866 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (8,882 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | The transactions with related parties are carried out at terms, rates and conditions similar to those for third parties. |
| |
| 19 | | Risk management |
| |
| (a) | | Estimates |
| |
| | | The Company has evaluated its assets and liabilities relating to the market/realization values, through available information and evaluation methodologies established by management. However, the market data interpretation, as well as the selection of evaluation methods require a reasonable judgment and estimate to produce the most adequate market value. Therefore, actual amounts may differ from the estimates. The use of different market hypothesis and/or methodologies for estimates, approximates, the estimated realization values. |
| |
| (b) | | Financial instruments |
| |
| | | As of December 31, 2007 and 2006, the Company had no transactions involving derivatives. |
| |
| (c) | | Cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivables, other assets and accounts payable |
| |
| | | The recorded values approximate the market values. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-34
| (d) | | Financings |
| |
| | | On August 23, 2007, the subsidiary TNL Contax S.A. signed a financing agreement with BNDES in the amount of R$216,514 with the purpose of financing the expansion of installed capacity, improving current facilities, qualifying human resources, improving the quality of services and productivity, and investing in marketing shares. On October 5, 2007, the first tranche in the amount of R$100,002 was received (Note 13). |
| |
| (e) | | Credit risk |
| |
| | | The credit risk associated with trade accounts receivable is not relevant, due to the financial size of the companies to which the Company provides services. |
| |
| | | The provision for doubtful accounts is recorded to recognize probable losses in relation to accounts receivable, whose calculation is based on estimates considering the situation of each customer and the guarantees provided by them. The basis for measurement of the provision considers the position of each overdue client individually. |
| |
| | | Concentration of Credit Risk |
| |
| | | The credit risk associated with the trade accounts receivable is not relevant, comparing to the size of the financial volume of the companies which the Company provides services. The credits of bad debt provision are adequately covered to make face the eventual losses in its accomplishments. |
| |
| | | In the year ended December 31, 2007 one client accounted for 50,7%of the Company’s revenues (2006 – 57,5%) |
| |
| (f) | | Interest rates risk |
| |
| | | The associated risk arises from the possibility of the Company incurring in losses derived from interest rate variations that increase the financial expenses related to financings raised in the market. The Company continuously monitors the market interest rates with the purpose of evaluating the possible need of hiring operations to protect itself against the volatility risk of these rates. |
| |
| 20 | | Insurance |
| |
| | | The Company has a corporative program for risk management to obtain minimum risks, searching at the market compatibles covers with its size and operations. Management understands that the amounts of the policies to cover any possible future material damages and loss of revenues arising from such damages (loss of profits) are sufficient to guarantee the integrity of its assets and full protection of the continuity of its operations. |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-35
| | | At December 31, 2007, The Company had the following main insurance policies contracted with third parties: |
| | | | | |
| | | Amounts | |
| Insurance lines | | insured | |
| | | | | |
| D&O Management Civil Liability | | | 106,230 | |
| Fire — Permanent assets | | | 70,211 | |
| Loss of income | | | 51,305 | |
| Comprehensive general liability | | | 5,000 | |
| 21 | | Subsequent event |
| |
| (a) | | BNDES fund raising |
| |
| | | According to the financing agreement entered into on August 23, 2007, with the subsidiary TNL Contax S.A., on January 28, 2008 and January 30, 2008 the second and third releases were carried out, in the amount of R$40,001 and R$10,000, respectively. Up to this date the amount released totals R$150,003. |
| |
| (b) | | Corporate Restructuring of Telemar Participações S.A. |
| |
| | | On April 25, 2008, the Extraordinary General Meeting approved the partial spin-off of Telemar Participações S.A. (“TmarPart”), with the version of a portion of its shareholders’ equity related to the shares issued by the Company held by TmarPart, to the new company, incorporated for this purposes under the corporate name CTX Participações S.A. (“CTX”), as published in the Material Fact on this same date. |
| |
| | | The Partial Spin-off is one of the restructuring stages, and is justified by the need to segregate into distinct companies the interest in the contact center activities from the other telecommunications activities, corresponding to the investment of TmarPart in Tele Norte Leste Participações S.A. |
| |
| | | CTX was incorporated with a capital stock of R$70,000, divided into 3,090,611,008 common shares which will be attributed to the shareholders of TmarPart, at the ratio of one share of CTX to each share of TmarPart. CTX will be responsible only for the investment related to the shares issued by Contax Participações S.A, without any solidarity with TmarPart, pursuant to article 233, sole paragraph, of Law no. 6,404/76. |
* * *
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-36
EXHIBIT INDEX
| | | |
| No. | | Description |
| | | |
| 1.1 | | By-laws of Contax Holding as of June 17, 2008. |
| | | |
| 2.1 | | Deposit Agreement, dated as of August 12, 2005 among Contax Holding, The Bank of New York, as Depositary, and Owners and Beneficial Owners of American Depositary Receipts issued thereunder. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2006.) |
| | | |
| 4.1 | | Services Agreement, dated November 30, 2004, among Telemar Norte Leste S.A, TNL PCS S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 4.2 | | First Amendment, dated December 29, 2004, to the Services Agreement between Telemar Norte Leste S.A., TNL PCS S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. dated November 30, 2004.(Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2006.) |
| | | |
| 4.3 | | Second Amendment, dated October 18, 2005, to the Services Agreement between Telemar Norte Leste S.A., TNL PCS S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. dated November 30, 2004. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.7 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2006.) |
| | | |
| 4.4 | | Third Amendment, dated May 1, 2007, to the Services Agreement between Telemar Norte Leste S.A., TNL PCS S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. dated November 30, 2004. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| 4.5 | | Contact Center Services Agreement, dated April 1, 2004, between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and Inovação Contact Center Serviços de Contatos Telefônicos Ltda. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 4.6 | | Amendment to Services Agreement, dated May 28, 2004, between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and Inovação Contact Center Serviços de Contatos Telefônicos Ltda. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 4.7 | | Amendment to the Contact Center Service Agreement, dated September 27, 2004, between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 4.8 | | Amendment to Temporary Service Agreement and Other Matters, dated September 27, 2004, between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 4.9 | | Amendment, dated October 1, 2004, to the Contact Center Service Agreement between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| No. | | Description |
| | | |
| 4.10 | | Amendment, dated April 1, 2005, to the Contact Center Service Agreement between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais LTDA. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.10 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| 4.11 | | Amendment, dated May 10, 2006, to the Contact Center Service Agreement between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.11 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| 4.12 | | Amendment, dated December 29, 2006, to the Contact Center Service Agreement between Orbitall Serviços e Processamento de Informações Comerciais S.A. and TNL Contax S.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.12 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2007.) |
| | | |
| 8.1 | | List of Subsidiaries. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 8.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on June 29, 2006.) |
| | | |
| 11.1 | | Code of Ethics of Contax Holding. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 11.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form 20-F filed on August 10, 2005.) |
| | | |
| 12.1 | | Certification of the Chief Executive Officer of the Company, pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. (Filed herewith.) |
| | | |
| 12.2 | | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer of the Company, pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. (Filed herewith.) |
| | | |
| 13.1 | | Certifications of the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer of the Company, pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. (Furnished herewith.) |