| Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figures
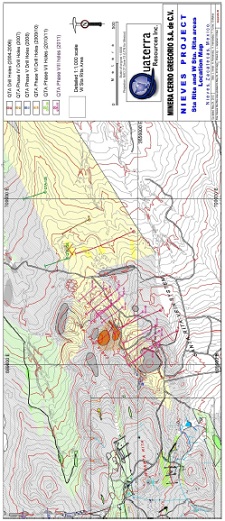
Figure 4-1 Location of the Nieves Property
Figure 4-2 Location of the Nieves Property showing major roads and waterways
Figure 4-3 Concessions on the Nieves Property
Figure 5-1 Dirt road accessing Nieves Property (Photo from Doris Fox)
Figure 5-2 Major geological and physiographical regions and mining districts in Mexico (after Stone 2010)
Figure 5-3 Typical landscape on the Nieves Property looking north (photo from Doris Fox)
Figure 5-4 (left) Power lines crossing property, (right) Santa Rita Mill (photos from Doris Fox)
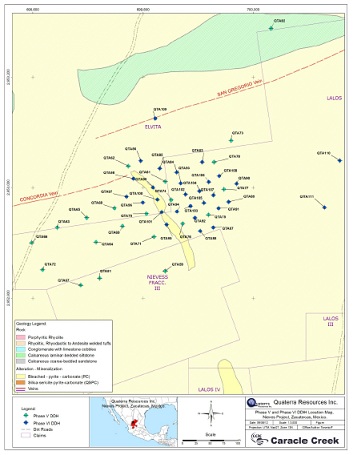
Figure 6-1 Location of old mines on the Nieves Property
Figure 6-2 Location of holes drilled by Kennecott, Western and Quaterra between 1994 and 2000
Figure 6-3 Location of drill holes in Phase I, II and III drill programs
Figure 6-4 Location of drill holes in Phase IV drill program
Figure 6-5 Location of drill holes in Phase V and VI drill programs
Figure 7-1 Sedimentary layers in argillite (photo from Doris Fox)
Figure 7-2 Surface expression of clastic sediments on the property (photo by Doris Fox)
Figure 7-3 Geology map of the Nieves Property
Figure 7-4 Carbonate- quartz-sulphide mineralized veins
Figure 7-5 Mineralized oxide-breccia in core (photo by Doris Fox)
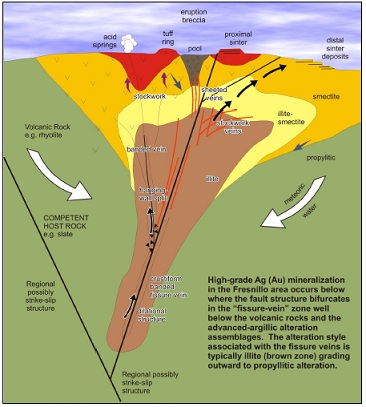
Figure 8-1 Schematic cross section of a typical rift related epithermal low-sulphidation system (after Corbett 2004)
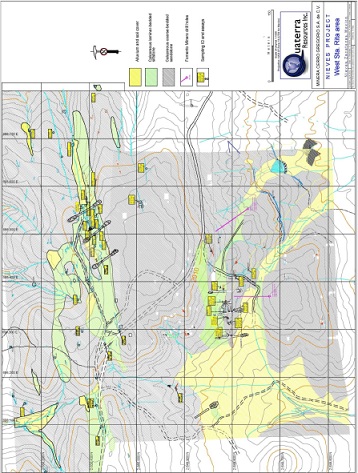
Figure 9-1 Geology and location of drill holes and geophysical survey lines (red lines) in the Santa Rita area
Figure 9-2 Geology and location of channels, samples and geophysical survey lines in the West Santa Rita area
Figure 9-3 Pole-Dipole Resistivity/IP data along Line 6800 in the West Santa Rita area
Figure 9-4 Pole-Dipole Resistivity/IP data along Line 7200 in the West Santa Rita area
Figure 10-1 Typical Drill Hole Cap and Marker (photo by Doris Fox)
Figure 10-2 Areas of mineralization on the Nieves Property
Figure 10-3 Location of drill holes in Phase VII and VIII drill programs
Figure 10-4 A) Core tray marked with hole ID, depth to-from of core and box number. B) typical sample ID
marking in core box. C) Locked core storage 1 of 5. D) Core storage
Figure 11-1 Core Cutting and sample prep area at core logging / core storage facilty (Photo by Doris Fox)
Figure 12-1 Core storage and logging compound
Figure 12-2 Core storage by hole and depth
Figure 12-3 Water well at logging compound
Figure 12-4 Federal survey claim marker monument
Figure 12-5 Federal survey claim marker with datum peg showing date, datum and federal identification number
Figure 12-6 Dolores vein looking down the shaft
Figure 12-7 Concordia shaft
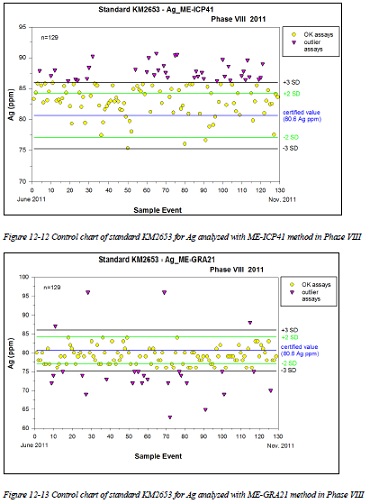
Figure 12-8 Control chart of standard KM2653 for Ag analyzed with ME-ICP41 method in Phase VII
Figure 12-9 Control chart of standard KM2653 for Ag analyzed with ME-GRA21 method in Phase VII
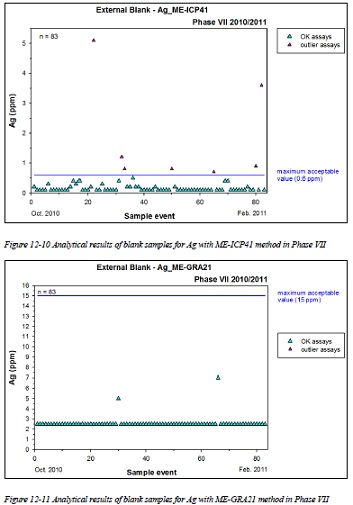
Figure 12-10 Analytical results of blank samples for Ag with ME-ICP41 method in Phase VII
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 12-11 Analytical results of blank samples for Ag with ME-GRA21 method in Phase VII
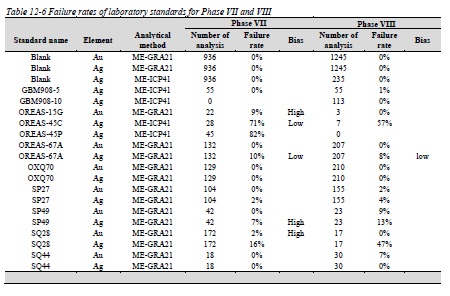
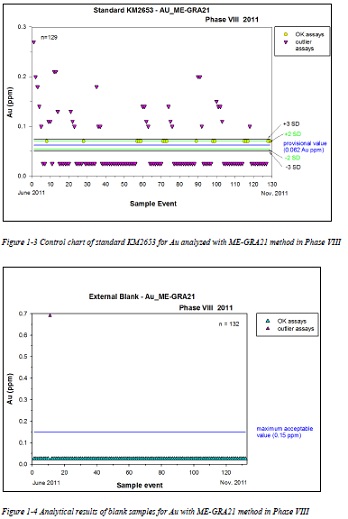
Figure 12-12 Control chart of standard KM2653 for Ag analyzed with ME-ICP41 method in Phase VIII
Figure 12-13 Control chart of standard KM2653 for Ag analyzed with ME-GRA21 method in Phase VIII
Figure 12-14 Analytical results of blank samples for Ag with ME-ICP41 method in Phase VIII
Figure 12-15 Analytical results of blank samples for Ag with ME-GRA21 method in Phase VIII
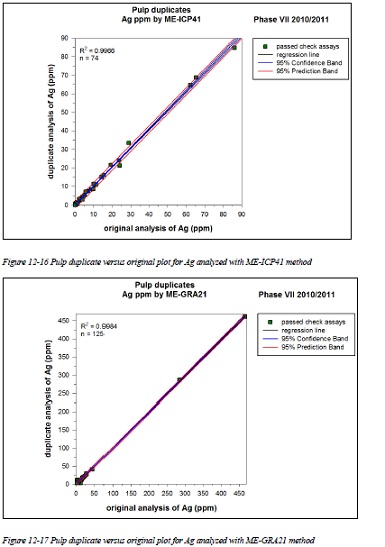
Figure 12-16 Pulp duplicate versus original plot for Ag analyzed with ME-ICP41 method
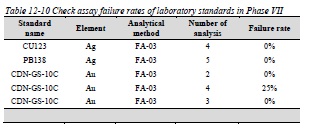
Figure 12-17 Pulp duplicate versus original plot for Ag analyzed with ME-GRA21 method
Figure 12-18 Pulp duplicate versus original plot for Ag analyzed with ME-ICP41 method
Figure 12-19 Pulp duplicate versus original plot for Ag analyzed with ME-GRA21 method
Figure 12-20 Core duplicate versus original plot for Ag analyzed with ME-ICP41 method
Figure 12-21 Core duplicate versus original plot for Ag analyzed with ME-GRA21 method
Figure 12-22 Plot of check assays versus original assays for Ag analyzed with ICP
Figure 12-23 Plot of check assays versus original assays for Ag analyzed with gravimetric method
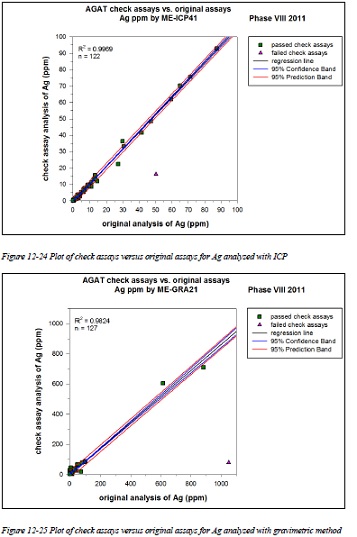
Figure 12-24 Plot of check assays versus original assays for Ag analyzed with ICP
Figure 12-25 Plot of check assays versus original assays for Ag analyzed with gravimetric method
Figure 14-1 Drill Hole Distribution of all holes at Nieves
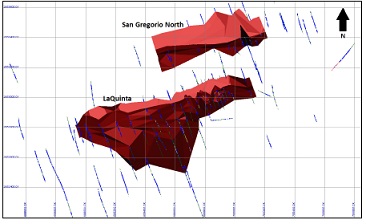
Figure 14-2 View of Topo & Mineralized Domain Looking NW
Figure 14-3 Sectional view of mineralized domain showing Ag assays (looking NE)
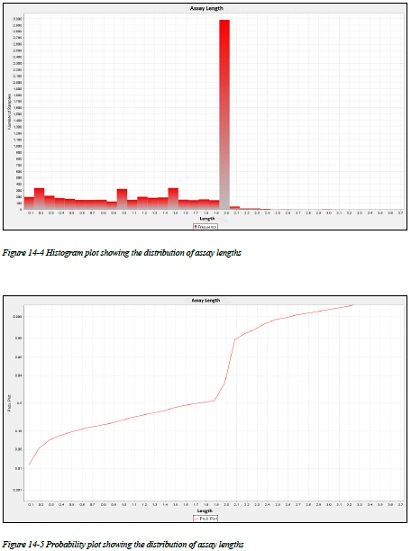
Figure 14-4 Histogram plot showing the distribution of assay lengths
Figure 14-5 Probability plot showing the distribution of assay lengths
Figure 14-6 Histogram showing Ag composite grade distribution for the La Quinta area
Figure 14-7 Plan view showing block model
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Tables
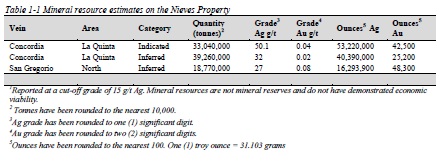
Table 1-1 Mineral resource estimates on the Nieves Property
Table 4-1 List of concessions on the Nieves Property
Table 4-2 Details of tax payments to the Mexican government on the Nieves Property
Table 4-3 Details of NSR on the Nieves Property
Table 6-1 Summary of exploration activities between 1994 and 2010
Table 6-2 Drill programs completed by Kennecott, Western and Quaterra
Table 6-3 Significant drilling results completed by Quaterra in 1999 and 2000
Table 6-4 Drilling summary on the Nieves Property between 2004 and 2010
Table 6-5 Drill highlights on the Nieves Property between 2004 and 2010
Table 6-6 Historic Santa Rita resources calculated by CRM (Cavey, 1999)
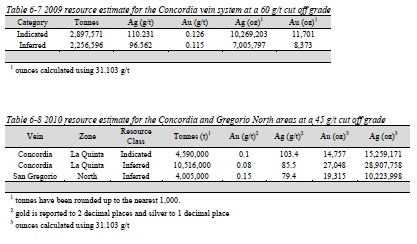
Table 6-7 2009 resource estimate for the Concordia vein system at a 60 g/t cut off grade
Table 6-8 2010 resource estimate for the Concordia and Gregorio North areas at a 45 g/t cut off grade
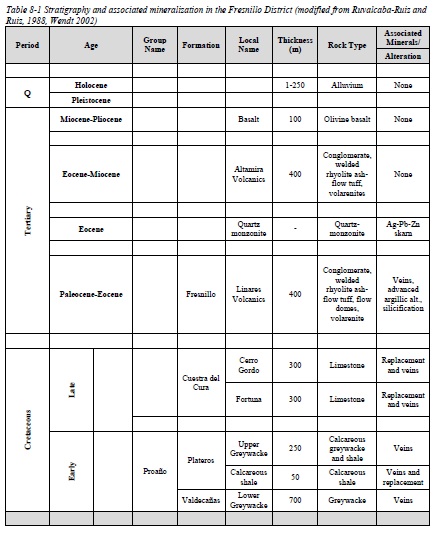
Table 8-1 Stratigraphy and associated mineralization in the Fresnillo District (modified from Ruvalcaba-Ruiz and
Ruiz, 1988, Wendt 2002)
Table 8-2 Major Altiplano ore deposits (after Wendt 2002)
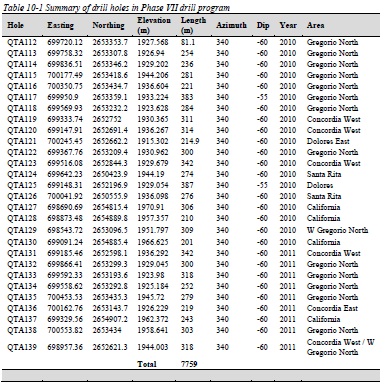
Table 10-1 Summary of drill holes in Phase VII drill program
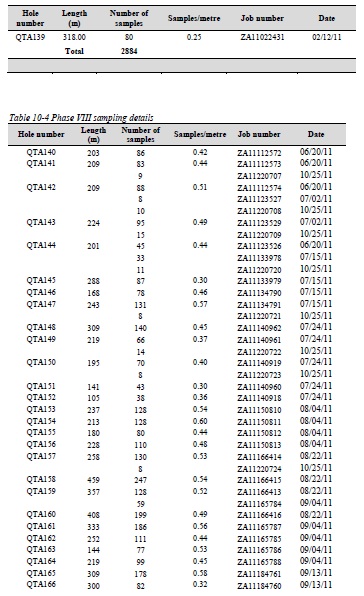
Table 10-2 Summary of drill holes in Phase VIII drill program
Table 10-3 Phase VII sampling details
Table 10-4 Phase VIII sampling details
Table 10-5 Drill highlights of Phase VII exploration program
Table 10-6 Drill highlights of Phase VIII exploration program from hole QTA140 to QTA169
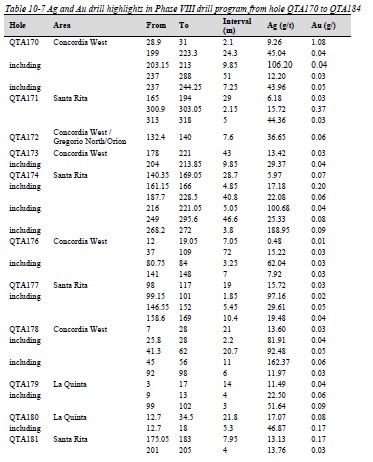
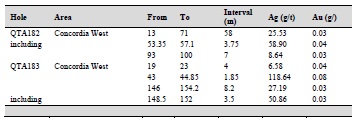
Table 10-7 Ag and Au drill highlights in Phase VIII drill program from hole QTA170 to QTA184
Table 11-1 Frequency of QC samples in Phase VII drill program
Table 11-2 Frequency of QC samples in Phase VIII drill program
Table 11-3 Characteristics of customized standard inserted in Phase VII and VIII drill programs
Table 11-4 Description of analytical methods for Ag and Au
Table 11-5 List of internal lab standards inserted by ALS Minerals
Table 11-6 Analytical methods of check assays at Skyline
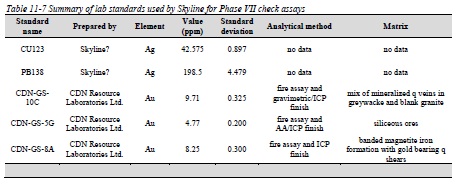
Table 11-7 Summary of lab standards used by Skyline for Phase VII check assays
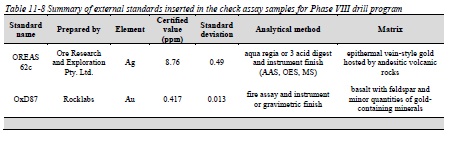
Table 11-8 Summary of external standards inserted in the check assay samples for Phase VIII drill program
Table 11-9 Analytical methods of check assays for Ag and Au at AGAT Laboratories
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Table 12-1 Verification of drill hole locations
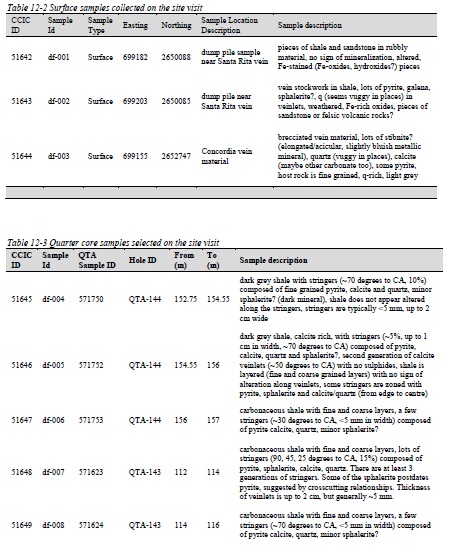
Table 12-2 Surface samples collected on the site visit
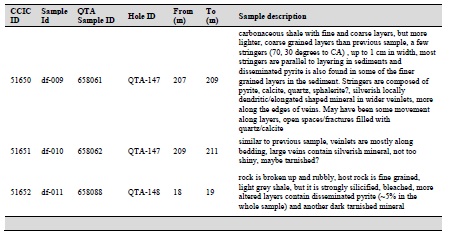
Table 12-3 Quarter core samples selected on the site visit
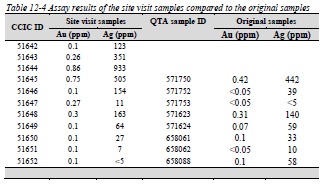
Table 12-4 Assay results of the site visit samples compared to the original samples
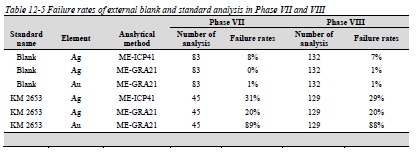
Table 12-5 Failure rates of external blank and standard analysis in Phase VII and VIII
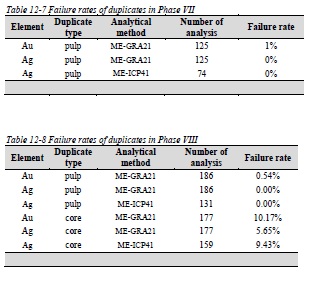
Table 12-6 Failure rates of laboratory standards for Phase VII and VIII
Table 12-7 Failure rates of duplicates in Phase VII
Table 12-8 Failure rates of duplicates in Phase VIII
Table 12-9 Check assay failure rates of external blanks and standards in Phase VII drill program
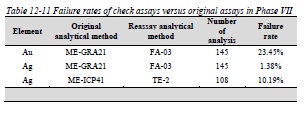
Table 12-10 Check assay failure rates of laboratory standards in Phase VII
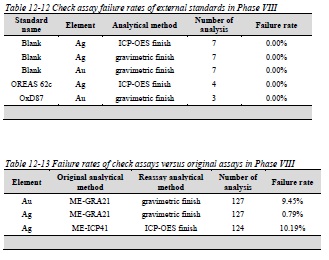
Table 12-11 Failure rates of check assays versus original assays in Phase VII
Table 12-12 Check assay failure rates of external standards in Phase VIII
Table 12-13 Failure rates of check assays versus original assays in Phase VIII
Table 14-1 Mineral resource statement1 (Caracle Creek, June 22nd, 2012)
Table 14-2 Data used in estimating the mineral resources at Nieves
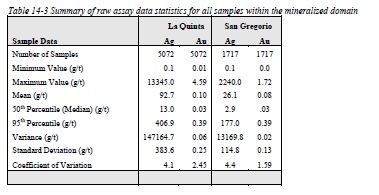
Table 14-3 Summary of raw assay data statistics for all samples within the mineralized domain
Table 14-4 Summary of 2m composite data statistics for all samples within the mineralized domain
Table 14-5 Block model definitions for Nieves 134
Table 14-6 Nieves Block Model Parameters 134
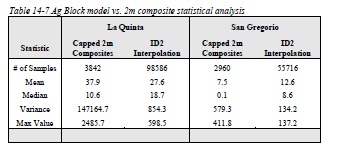
Table 14-7 Ag Block model vs. 2m composite statistical analysis
Table 14-8 Mineral resource statement1 (Caracle Creek, June 22nd, 2012)
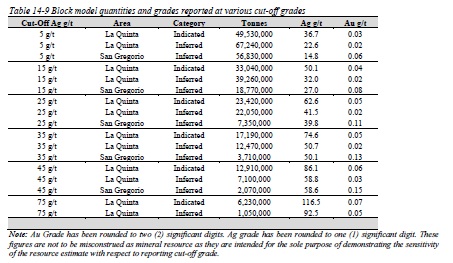
Table 14-9 Block model quantities and grades reported at various cut-off grades
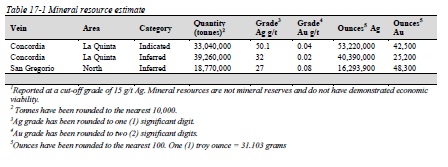
Table 17-1 Mineral resource estimate
Table 18-1 Recommended exploration budget on the Nieves Property
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Appendices
Appendix 1 - Certificates of Authors
Appendix 2 - Surface sampling in the West Santa Rita area
Appendix 3 - QA/QC plots for Au and QA/QC summary of previous drilling phases
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
1.0 Summary
Caracle Creek International Consulting Inc. ("Caracle Creek") of Toronto, Ontario, Canada was contracted by Quaterra Resources Inc. ("Quaterra") of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, to prepare an Independent Technical Report (the "Report"), compliant with National Instrument 43-101 ("NI43-101"), companion policy NI43-101CP and Form 43-101F1 on the Nieves Property (the "Property"). The Report summarizes the details and results of the 2010 and 2011 exploration program and includes an updated resource estimate for the Property.
The Nieves Property is located in the Francisco R. Murguia Municipality of the Zacatecas Mining District near the southeastern boundary of the Sierra Madre Occidental Physiographic Province in central Mexico.
The Property is centered approximately at 694856E, 2651009N (NAD27 Mexico, Zone13N), approximately 150 km northwest of the state capital of Zacatecas and 90 km north of the mining community of Fresnillo.
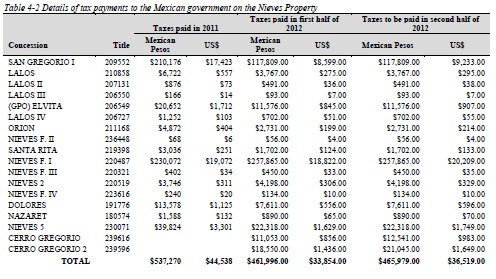
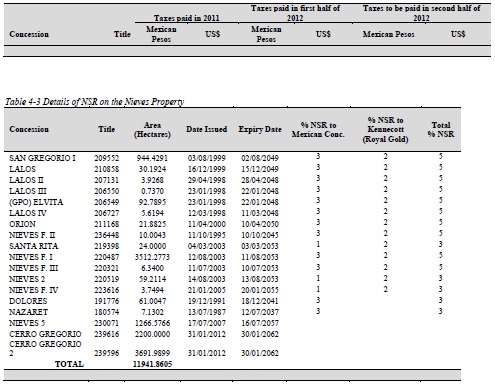
The Nieves Property consists of 18 concessions covering approximately 12,064.0725 ha. The concessions are registered in the name Minera Cerro Gregorio, as of August 5, 2011, a Mexican company wholly owned by Quaterra. The Nieves Property is jointly owned by Quaterra and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC. ("Blackberry"). In 2011, Quaterra and Blackberry (through Minera Cerro Gregorio) paid US $44,538 in taxes to maintain the concessions. In 2012, Quaterra and Blackberry paid US $33,854 and are required to pay an additional US $36,519 to maintain the Nieves Property. Taxes are payable every six months to the Mexican government. Net smelter return royalties remain outstanding on each of the concessions acquired from Kennecott (recently purchased by Royal Gold Inc.) and the Mexican concessionaires (Abelardo Garza Hernandez, Noel McAnulty and Bill Shafer) (Table 4-3).
The Nieves Property is located on the western flank of the Central Altiplano in Mexico, just east of the Sierra Madre Occidental ranges. The Nieves Property is underlain by Mesozoic "argillite" of the Caracol Formation, which is overlain by Tertiary rhyolitic volcanoclastic rocks. The two units are separated by a Tertiary age basal conglomerate and conglomeratic sandstone sequence. The Caracol Formation is isoclinally folded with an axial plane cleavage. Later brittle deformation, faulting and vein structures, affected all the rocks in the area.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Silver mineralization on the Nieves Property is classified as low-sulfidation epithermal mineralization and it is the primary exploration target. Epithermal silver veins are the dominant deposit type in the region with world class examples such as Pachuca, Fresnillo and Guanajuato.
On the Nieves Property there are three major east to northeast trending silver vein systems: California, Concordia- San Gregorio -Dolores-Nino and Santa Rita vein systems. There is also an east-northeast to east-southeast striking breccia system, containing manganese mineralization, on the east side of the Property. All these areas have been worked on by local miners.
Silver mineralization is hosted in veins that are less than 10 cm wide and contain pyrite, stibnite, sphalerite, galena, chalcopyrite and silver sulphosalts such as proustite, pyrargirite, freibergite, acanthite, jamesonite and tetrahedrite.
Between March 2010 and June 2012, Quaterra and Blackberry completed an exploration program on the Nieves Property consisting of a geophysical survey, mapping and sampling and drilling.
The geophysical survey consists of six lines, a total of 28.4 line-kilometers, of vector controlled source audio-magnetotellurics and induced polarization (CSAMT/CSIP) and nine follow-up lines of pole/dipole induced polarization (IP) totaling 16.5 line-kilometers. Nine anomalous zones were detected and validated with IP lines using 50 meter dipole spacings. Most of the anomalies appear to be westward extensions of mineralized veins previously drilled, including the Dolores, Santa Rita, Nino and Orion veins. The most interesting area identified to date is West Santa Rita, located 1000 to 1200 meters west of the main Santa Rita mine and over 500 meters from Quaterra's nearest drill hole.
Mapping and sampling was completed to follow up the geophysical anomalies. The most interesting area was identified in the West Santa Rita, where mapping identified two groups of narrow, sub-parallel 2 to 30 centimeter wide calcite-quartz veinlets, some of which contain strong gold and silver mineralization. Gold values are up to 8.11 g/t over 0.2 m and silver values are up to 253 g/t over 0.4 m.
Quaterra and Blackberry completed two phases of drill programs (VII and VIII) between March 2010 and October 2011, consisting of 73 drill holes and totaling 18,547.25 m. Most of the drilling concentrated on the Concordia-Dolores-San Gregorio vein system, but significant amount of drilling is located in the California and Santa Rita vein systems as well.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
The drill program was very successful at increasing the size of known mineralized zones along all the major vein systems. Mineralization along the Concordia vein system was extended an additional 400 m, to a total of approximately 1,300 m. The length of known mineralization along the California vein system was increased to a total of approximately 550 m and it remains open to the east. Phase VII and VIII drill programs were successful in doubling the strike length of the Gregorio North mineralized zone loated north of the San Gregorio vein, extending the strike length of the mineralized zone to approximately 1200 m. A total of 15 drill holes systematically tested the Santa Rita vein system over 500 m along strike, and the total length of mineralization was extended to approximately 750 m and remains open to the west.
The best intersections include 149 g/t Ag and 0.11 g/t Au over 31.25 m, which includes 6320 g/t Ag and 1.82 g/t Au over 0.25 m in drill hole QTA123 along the Concordia West vein, 104 g/t Ag over 19 m, including 6410 g/t Ag over 0.1 m and 5960 g/t over 0.1 m in drill hole QTA137 along the California vein, and 152.2 g/t Ag and 0.12 g/t Au over 57 m in drill hole QTA144 in the Concordia West area.
Metallurgical testing concluded that 86% of the feed silver can be recovered into a final concentrate of 2.3 kg/tonne silver with open circuit flotation. Minor element assays conducted on the concentrate indicated elevated levels of antimony, arsenic and fluorine, which may result in smelter penalties.
Independent, NI 43-101 compliant resources at the Quaterra Resources Nieves property were estimated by Jason Baker P.Eng. (APENS#9627), a Geological Engineer with Caracle Creek and an independent qualified person as defined by NI 43-101. The mineral resources are reported in accordance with National Instrument 43-101 and have been estimated in compliance with generally accepted CIM "Estimation of Mineral Resource and Mineral Reserves Best Practices" guidelines. Block model quantities and grade estimates for the Nieves property were classified according to the latest CIM Definition Standards for Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves. The results of the updated mineral resource estimate are summarized in Table 1-1.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
The QP's opinion is that the Nieves Property is an excellent exploration project, the size of the silver resource has grown substantially with the last two phases of drilling and silver mineralization on the Nieves Property is comparable to other world class silver deposits in the area, such as Pachuca, Fresnillo and Guanajuato.
Caracle Creek recommends a exploration program of approximately CDN $ 1,761,440, consisting of the collection of more specific gravity data in the Gregorio North area to increase the confidence level of the tonnage estimate, more infill drilling in both La Quinta and Gregorio North areas where there is significant inferred resource present, exploration drilling in the West Santa Rita area to test the geophysical anomaly and the down dip extent of the mineralization identified on the surface, and drill testing of the new geophysical targets in the other areas.
2.0 Introduction
2.1 Introduction
Caracle Creek International Consulting Inc. ("Caracle Creek") of Toronto, Ontario, Canada was contracted by Quaterra Resources Inc. ("Quaterra") of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, to prepare an Independent Technical Report (the "Report"), compliant with National Instrument 43-101 ("NI43-101"), companion policy NI43-101CP and Form 43-101F1 on the Nieves Property (the "Property"). The purpose of the Report is to summarize the 2010 and 2011 exploration program and provide an update to material changes to the property since the last property visit in May, 2010 and the last Technical Report dated September 15, 2010 (Stone, 2010), including an updated resource estimate.
The information, conclusions and recommendations contained herein are based on a review of digital and hard copy data and information supplied to Caracle Creek by the Company, as well as various published geological reports, and discussions with representatives from the Company who are familiar with the Property and the area in general. Some of the information on the Property are from previous NI 43-101 reports written by Stephen Wetherup in 2006 (Wetherup, 2006) and Michelle Stone in 2009 and 2010 (Stone, 2009 and 2010), both of Caracle Creek. Additional references are listed in the Reference section (19.0).
Doris Fox (P.Geo., Associate of Caracle Creek) visited the Property on March 11th and 12th, 2012 where she was shown the Property by Hector Fernandez, a company employee. Significant intersections from 10 diamond drill holes were reviewed and 11 samples were selected for independent analysis.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
2.2 Terminology
Definitions are from Long (2008) and Smee (2008), except where indicated. Accuracy: the closeness of measurements to a "true" value.
Aqua Regia: Mixture of Hydrochloric Acid (HCl), Nitric Acid (HNO3) and de-mineralized water (2:2:2). It is a strong acid digestion capable of decomposing metal salts, carbonates, sulphides, most sulphates and some oxides and silicates. Aqua Regia will digest precious metals including Au, Ag, Pt and Pd (Acme website: www.acmelab.com). This is also known as a partial digestion, as not all of the rock is dissolved.
Blank: a sample of uncrushed rock or drill core that is known to contain very low or non-detectable concentration of the element being sought. A blank is used to monitor contamination of samples during preparation and analysis.
Certified Reference Materials ("CRM"): standard pulp (powdered) samples that have been subjected to rigorous international testing and have a certificate of analysis with a certified "accepted mean" and standard deviation. Ideally, a cut-off grade, mean grade and high grade CRM is analyzed with samples. CRMs are used to monitor accuracy and precision of analyses.
Duplicates: A split of the original sample analyzed by the same laboratory under the same analytical conditions as the original sample. There are three types of duplicates: field duplicates (split of the drill core), reject or preparation duplicate (split of coarse material) and pulp duplicate (split of powdered material). Field duplicates monitor errors in sampling, preparation and analysis of samples. Reject duplicates monitor errors in preparation and analysis of samples. Pulp duplicates monitor errors in analysis of samples.
Fusion: Method for total to near total decomposition of samples. A portion of sample pulp is mixed with flux such as lithium metaborate (LiBO2) or sodium peroxide (Na2O2) that lowers the melting point. The mixture is then heated in a muffle furnace until molten. After cooling the fused mass is digested in 5% HNO3 (nitric acid) (Acme website: www.acmelab.com). Fusion method is suitable for many refractory, difficult to dissolve minerals (such as chromite, ilmenite, spinel, cassiterite and Ta-W minerals).
ICP-MS: Inductively Coupled Plasma - Mass Spectrometer: An instrument capable of determining the concentrations of 70+ elements simultaneously by measuring the mass of ions generated by an argon gas plasma heated to 10,000°K and passing through a magnetic quadrupole to the detector. Capable of ultra low detection limits (ppb to ppt) with very wide linear ranges (up to 7 orders of magnitude) (Acme Analytical Laboratories Ltd: www.acmelab.com).
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
ISO: International Standards Organization.
ISO 9001:2008 Quality Management Systems - Requirements: is intended for use in any organization regardless of size, type or product (including service). It provides a number of requirements which an organization needs to fulfill if it is to achieve customer satisfaction through consistent products and services which meet customer expectations. It includes a requirement for the continual (i.e. planned) improvement of the Quality Management System. Certification to an ISO 9001 standard does not guarantee any quality of end products and services; rather, it certifies that formalized business processes are being applied (wikipedia.org and http://isotc.iso.org).
ISO/IEC 17025: is the main standard used by testing and calibration laboratories. There are many commonalities with the ISO 9000 standard, but ISO/IEC 17025 adds in the concept of competence to the equation and it applies directly to those organizations that produce testing and calibration results. There are two main sections in ISO/IEC 17025 - Management Requirements and Technical Requirements. Management requirements are primarily related to the operation and effectiveness of the quality management system within the laboratory. Technical requirements address the competence of staff, methodology and test/calibration equipment (wikipedia.org and http://isotc.iso.org).
QA/QC: Quality Assurance/ Quality Control
Quality Assurance (QA): information collected to demonstrate and quantify the reliability of assay data. Quality Assurance provides a measurement of the uncertainty in the underlying data.
Quality Control (QC): procedures used to maintain a desired level of quality in the assay database. Quality Control leads to corrections of errors or changes in procedures that improve overall data quality.
Pulps: the portion of a sample reduced to a finer size fraction after crushing, pulverizing or sieving and will be used in an analytical test (Acme website: www.acmelab.com).
Precision: the ability to consistently reproduce a measurement. Precise data tightly groups around an average value.
Rejects: the portion of a sample after preparation that is not part of the pulps fraction (Acme website: www.acmelab.com).
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
2.3 Units
The Metric System is the primary system of measure and length used in this Report and is generally expressed in kilometres (km), metres (m) and centimetres (cm); volume is expressed as cubic metres (m3), mass expressed as metric tonnes (t), area as hectares (ha), and gold and silver concentrations as grams per tonne (g/t). Conversions from the Metric System to the Imperial System are provided below and quoted where practical. Many of the geologic publications and more recent documents now use the Metric System but older documents almost exclusively refer to the Imperial System. Metals and minerals acronyms in this report conform to mineral industry accepted usage and the reader is directed to www.maden.hacettepe.edu.tr/dmmrt/index.html for a glossary.
Conversion factors utilized in this report include:
• 1 troy ounce/ton = 34.285714 grams/tonne
• 1 gram/tonne = 0.029167 troy ounces/ton
• 1 troy ounce = 31.103477 grams
• 1 gram = 0.032151 troy ounces
The term gram/tonne or g/t is expressed as "gram per tonne" where 1 gram/tonne = 1 ppm (part per million) = 1000 ppb (part per billion). The mineral industry accepted terms Au g/t and g/t Au are substituted for "grams gold per metric tonne" or "g Au/t". Other abbreviations include ppb = parts per billion; ppm = parts per million; oz/t = troy ounce per short ton; Moz = million ounces; Mt = million tonne; t = tonne (1000 kilograms); SG = specific gravity; lb/t = pound/ton; and, st = short ton (2000 pounds).
Dollars are expressed in Canadian currency (CAD$) unless otherwise noted. Zinc (Zn), copper (Cu) and lead (Pb) are reported in US$ per pound (US$/lb) or US$ per metric tonne (US$/t). Gold (Au) and silver (Ag) are stated in US$ per troy ounce (US$/oz). Where quoted, Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinates are provided in NAD27, Zone 13Q, Mexico.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
2.4 Caracle Creek Qualifications
Caracle Creek International Consulting Inc. is an international consulting company with the head office of Canadian operations based in Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. Caracle Creek provides a wide range of geological and geophysical services to the mineral industry. With offices in Canada (Sudbury and Toronto, Ontario and Vancouver, British Columbia) and South Africa (Johannesburg), Caracle Creek is well positioned to service its international client base.
Caracle Creek's mandate is to provide professional geological and geophysical services to the mineral exploration and development industry at competitive rates and without compromise. Caracle Creek's professionals have international experience in a variety of disciplines with services that include:
• Exploration Project Generation, Design and Management
• Data Compilation and Exploration Target Generation
• Property Evaluation and Due Diligence Studies
• Independent Technical Reports (43-101)/Competent Person Reports
• Mineral Resource/Reserve Modelling, Estimation, Audit; Conditional Simulation
• 3D Geological Modelling, Visualization and Database Management
In addition, Caracle Creek has access to the most current software for data management, interpretation and viewing, manipulation and target generation.
The Qualified Person and co-author of this Report is Zsuzsanna Magyarosi, Ph.D., P.Geo. Ms. Magyarosi is a Senior Geologist for Caracle Creek International Consulting and a geologist in good standing with the Association of Professional Geoscientists of Ontario (APGO #2031). Ms. Magyarosi has 10 years of experience in the mineral exploration industry and in academia and has authored/co-authored several Independent Technical Reports (NI43-101). Ms. Magyarosi did not visit the property. Ms. Magyarosi is responsible for the entire report, except for the Mineral Resource Estimates section (14.0) and the Caracle Creek Site Visit section (12.1).
Another Qualified Person and co-author of this Report is Jason Baker, B.Eng., P.Eng. Mr. Baker is a Geological Engineer with CCIC and an engineer in good standing with the Association of Professional Engineers of Nova Scotia (APENS#9627). Mr. Baker has over 10 years of experience in geological modelling and resource calculations in both exploration (Gold, Lead & Zinc) and operations (Coal, Gypsum, Lead and Zinc). Mr. Baker is responsible for the Mineral Resource Estimates section (14.0) of the report. Mr. Baker did not visit the property.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Another Qualified Person and co-author of this report is Doris Fox, M.Sc., P.Geo. Ms. Fox is an associate senior geologist for Caracle Creek International Consulting and a geologist in good standing with the Association of Professional Geoscientists of Ontario (APGO #1430). Ms. Fox has 10 years of experience in the mineral exploration industry and in academia and has authored/co-authored several Independent Technical Reports (NI43-101). Ms. Fox visited the property and is responsible for the Caracle Creek Site Visit section (12.1) and jointly responsible for the Accessibility, Climate, Local Resources, Infrastructure, and Physiography section (5.0), Geological Setting and Mineralization section (7.0), Deposit Types section (8.0), Sampling Procedures section (10.2) and Sample Security section (11.1).
Certificates of Qualifications are provided in Appendix 1.
3.0 Reliance on Other Experts
Caracle Creek has completed this Report in accordance with the methodology and format outlined in National Instrument 43-101, companion policy NI43-101CP and Form 43-101F1. This Report was prepared by competent and professional individuals from Caracle Creek on behalf of the Company and is directed solely for the development and presentation of data with recommendations to allow the Company and current or potential partners to reach informed decisions.
The information, conclusions and recommendations contained herein are based on a review of digital and hard copy data and information supplied to Caracle Creek by the Company, as well as various published geological reports, and discussions with representatives from the Company who are familiar with the Property and the area in general. Caracle Creek has assumed that the reports and other data listed in the "References" section of this report are substantially accurate and complete.
Caracle Creek has relied exclusively on information provided by the Company regarding land tenure and underlying agreements, and all of these sources appear to be of sound quality. Caracle Creek is unaware of any technical data other than that presented by the Company or its agents. Caracle Creek did not conduct an in-depth review of mineral title and ownership and the title ownership and status of claims as outlined in this Report was obtained from Quaterra. While title documents and option/purchase agreements were reviewed for this study as provided by Quaterra, it does not constitute, nor is it intended to represent, a legal, or any other opinion as to title.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Legal documents provided by Quaterra include:
1. Agreement between Quaterra and Blackberry to option a 50% interest in the Nieves Project, dated April 10, 2003
2. Joint venture agreement between Quaterra and Blackberry, dated January, 2006
The dates, titles and authors of all reports that were used as a source of information for this Technical Report are listed in the "References" section of this report. The dates and authors of these reports also appear in the text of this Report where relevant, indicating the extent of the reliance on these reports.
4.0 Property Description and Location
4.1 Location
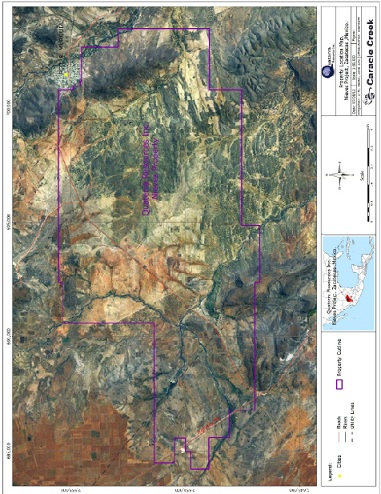
The Nieves Property is located in the Francisco R. Murguia Municipality of the Zacatecas Mining District near the southeastern boundary of the Sierra Madre Occidental Physiographic Province in central Mexico (Figure 4-1 and Figure 4-2). The Property is centered approximately at 694856E, 2651009N (NAD27 Mexico, Zone13), approximately 150 km northwest of the state capital of Zacatecas and 90 km north of the mining community of Fresnillo.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 4-1 Location of the Nieves Property
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 4-2 Location of the Nieves Property showing major roads and waterways
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
4.2 Description and Ownership
The Nieves Property consists of 18 concessions, issued for 50 years, covering approximately 12,064.0725 ha (Table 4-1 and Figure 4-3). These concessions are registered in the name Minera Cerro Gregorio, as of August 5, 2011, a Mexican company wholly owned by Quaterra. Minera Cerro Gregorio does not own the surface rights on the concessions. The location of a concession is determined from the position of a single claim monument ("mojonera"). The corners are all located based on surveyed distances and bearings from that monument by a registered Mexican Mineral Concession Surveyor.
The Nieves Property is jointly owned by Quaterra and Blackberry. In 2011, Quaterra and Blackberry (through Minera Cerro Gregorio) paid US $44,538 to the Mexican government in taxes to maintain the concessions (Table 4-2). In 2012, Quaterra and Blackberry paid US $33,854 and are required to pay an additional US $36,519 to maintain the Nieves Property. The taxes are payable every six months. Net smelter return royalties remain outstanding on each of the concessions acquired from Kennecott (recently purchased by Royal Gold Inc.) and the Mexican concessionaires (Abelardo Garza Hernandez, Noel McAnulty and Bill Shafer) (Table 4-3).
On January 16th, 1995, Kennecott entered into an option agreement with Mexican concessionaires that allowed Kennecott to explore and acquire the Nieves Property by making specified option payments over five years, and advance minimum royalty payments.
On March 13th, 1998, Kennecott transferred its rights under the Nieves option to Western in consideration for an uncapped 2% NSR on certain core concessions and a 1% NSR on others.
Western subsequently assigned its rights to the Nieves Project as specified in the "Underlying Agreement" to Quaterra on March 26th, 1999, in consideration for 1,444,460 common shares of the Company at a deemed price of CDN$0.20 per share (CDN$288,892). In addition, the Company issued 360,000 common shares at a deemed price of CDN$0.20 per share (CDN$72,000) to the concessionaires in lieu of the US$50,000 option payment otherwise due under the terms of the Underlying Agreement.
The payment schedule in the Underlying Agreement was amended on November 22nd, 1999, February 11th, 2000 and May 2002, such that US$30,000 was paid in January 2000, US$15,000 in May 2002 and US$25,000 in January 2003, for a total of US$70,000. In addition, to acquire the interest in the claim fractions the Company paid US$40,000 to the concessionaires. Advanced minimum royalty (AMR) payments of US$75,000 are due on or before the 26th of January each year from 2004 until the commencement of commercial production. The Nieves concessions are subject to a maximum 3% NSR to the original concession holders, which the Company may purchase at any time for US$2 million (Table 4-3).
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
On April 10th, 2003, Quaterra completed a US$1.5 million limited partnership financing with Blackberry, whereby Blackberry could earn a 50% interest in the Property by funding two exploration programs of US$750,000 each. The initial payment of US$750,000 received in the 2003 Fiscal Year was expended on a 5,300-metre drill program on the Nieves Property. During the 2004 Fiscal Year, Blackberry elected to continue by advancing a further US$750,000 towards a follow-up drill program completed in May 2005, thereby earning a 50% interest in the Property. The partners signed a joint venture agreement in 2006 and have jointly contributed to all exploration costs subsequently incurred.
On January 24th, 2007, Kennecott's royalty was purchased by Royal Gold Inc.
On August 5, 2011, the Nieves asset was transferred into a single purpose company, Minera Cerro Gregorio.
The author is not aware of any significant environmental liabilities related to the current exploration of the Nieves Property. The areas of primary mineral exploration are generally flat-lying, sparsely populated with a few cultivated areas and the remaining land area used for the periodic grazing of livestock. Minimal rehabilitation measures such as stabilizing slopes and planting local flora (Buffell grass) in areas of disturbance is usually sufficient to satisfy the ecological authorities, the Instituto de Investigaciones Forestales, Agricolas y Pecuarias ("INIFAP"), a government office based in Calera, Zacatecas. There is little to no surface water for exploration or mining activities but an abundance of ground water exists and the ownership of mineral rights generally allows access to ground water as needed.
Dispersed tailings from historic operations are present and a number of the historic workings have old waste dumps associated with them. It is recommended that Quaterra locate and document all of the historic dumps (ore and tailings), mark and fence off or otherwise make secure all open holes and workings, and initiate baseline environmental studies.
To the extent known to the author, no permits are required to conduct exploration work on the property, there are no significant factors and risks that may affect access, title, or the right or ability to perform work on the property.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 4-3 Concessions on the Nieves Property
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| Table 4-1 List of concessions on the Nieves Property |
| | Concession | Title | Area (ha) | Date Issued | Expiry Date |
| 1 | SAN GREGORIO I | 209552 | 944.4291 | 03/08/1999 | 02/08/2049 |
| 2 | LALOS | 210858 | 30.1924 | 16/12/1999 | 15/12/2049 |
| 3 | LALOS II | 207131 | 3.9268 | 29/04/1998 | 28/04/2048 |
| 4 | LALOS Ill | 206550 | 0.7370 | 23/01/1998 | 22/01/2048 |
| 5 | (GPO) ELVITA | 206549 | 92.7895 | 23/01/1998 | 22/01/2048 |
| 6 | LALOS IV | 206727 | 5.6194 | 12/03/1998 | 11/03/2048 |
| 7 | ORION | 211168 | 21.8825 | 11/04/2000 | 10/04/2050 |
| 8 | nieves f. ii | 236448 | 6.4577 | 11/10/1995 | 10/10/2045 |
| 9 | SANTA RITA | 219398 | 24.0000 | 04/03/2003 | 03/03/2053 |
| 10 | nieves f. i | 220487 | 3638.0359 | 12/08/2003 | 11/08/2053 |
| 11 | nieves f. iii | 220321 | 6.3400 | 11/07/2003 | 10/07/2053 |
| 12 | NIEVES 2 | 220519 | 59.2114 | 14/08/2003 | 13/08/2053 |
| 13 | nieves f. iv | 223616 | 3.7494 | 21/01/2005 | 20/01/2055 |
| 14 | DOLORES | 191776 | 61.0047 | 19/12/1991 | 18/12/2041 |
| 15 | nazaret | 180574 | 7.1302 | 13/07/1987 | 12/07/2037 |
| 16 | NIEVES 5 | 230071 | 1266.5766 | 17/07/2007 | 16/07/2057 |
| 17 | cerro gregorio | 239616 | 2200.0000 | 31/01/2012 | 30/01/2062 |
| 18 | cerro gregorio 2 | 239596 | 3691.9899 | 31/01/2012 | 30/01/2062 |
| | total | | 12064.0725 | | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| | 5.0 Accessibility, Climate, Local Resources, Infrastructure, and Physiography |
5.1 Access
Quaterra/Blackberry exploration activities are co-ordinated from the small town of Nieves (now re-named Francisco R. Murguia) where they maintain an office and a house. The town of Nieves is accessed via Highway 49, a paved, two-lane toll highway approximately 200km north of the city of Zacatecas.
Figure 5-1 Dirt road accessing Nieves Property (Photo from Doris Fox)
Thetown of Nieves is accessed via a 17 km paved road from Highway 49. The nearest major population and service centre to Nieves is the mining town of Fresnillo located ~90 km to the south. Fresnillo has a population of approximately 75,000 and services the Fresnillo Mine run by Penoles. Fresnillo offers a substantial professional work force experienced in mining and related activities in addition to most other supplies and services. International airports are located within approximately a three hour drive of the Property in the city of Zacatecas to the south, and in Torreon (Coahuila state) to the north. Road access to the Property is excellent with the main paved highway to Nieves running along the northern portion of the Property (Figure 4-1 and Figure 4-2). A network of dirt roads and trails provide access to the historical mining operations and extend southward to all areas of the Property. Drill and access roads can be easily built as most of the Nieves Property is flat-lying with only a few dry creek beds (Figure 5-3).
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
5.2 Physiography, Climate and Vegetation
The Nieves Property lies within the Mexican Altiplano or Mesa Central region. This region is flanked to the west by the Sierra Madre Occidental and to the east by the Sierra Madre Oriental mountain ranges (Figure 5-2). The Altiplano in this region is dominated by broad alluvium filled plains between rolling to rugged mountain ranges and hills reaching up to 3,000m above mean sea level ("AMSL") and average elevations in valleys of approximately 1,700m. Elevations on the Nieves Property range from 1,900m to 2,000m AMSL. The terrain is generally flat-lying with a prominent north-south trending ridge along the eastern portion of the Property with moderate to vertical slopes (Figure 5-3). There is very little human habitation on the Property, with only a few widely scattered farm houses, although the town of Nieves directly borders the Property to the northeast.
The climate in the region is continental, warm and arid with temperatures ranging from 0oC to 41oC, averaging ~21oC and less than 1,000 mm of annual precipitation. Due to the limited precipitation, vegetation is sparse and hardy consisting mainly of grasses, low thorny shrubs (including mesquite) and various cacti, with scattered oak forests at higher elevations. Surface water is rare but ground water is readily available. Drilling is feasible year round. Rain in the wet season, May to October, can make drilling conditions difficult due to muddy ground conditions, but not impossible.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 5-2 Major geological and physiographical regions and mining districts in Mexico (after Stone 2010)
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 5-3 Typical landscape on the Nieves Property looking north (photo from Doris Fox)
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
5.3 Infrastructure and Local Resources
Core logging, cutting and storage facilities are located on the Nieves Property in addition to their La Quinta field office. Other infrastructure in the area includes: (1) a power line adequate to support a small mill (eg. 100 tonnes per day), (2) an existing mill structure on the Property at the Santa Rita vein area which could be refurbished, (3) a spur of the main Zacatecas rail line that connects the city of Rio Grande, located 18 km to the south, and (4) operating smelters in San Luis Potosi (copper and zinc, approximately 350 km to the south) and in Torreon, Coahuila state (Penoles lead-zinc smelter, approximately 200 km north). As there are existing mines in the area and historic mining operations on the Property, the people living in the area of the Nieves Property are knowledgeable about mining and exploration and are generally supportive of possible increased employment opportunities.
Figure 5-4 (left) Power lines crossing property, (right) Santa Rita Mill (photos from Doris Fox)
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
The Nieves Property is in exploration stage, therefore discussions on potential tailings storage areas, potential waste disposal areas, heap leach pad areas and potential processing tailings storage area for mining operations is not currently relevant.
6.0 HISTORY
6.1 Exploration activities between 1560 and 1994
The first discovery on the area covered by the Nieves Property was the Santa Rita Vein in 1560 by Spanish explorers (Turner, 1999; Cavey, 1999). Soon after in 1574 the Concordia vein was discovered. The Santa Rita and Concordia- San Gregorio-Dolores veins were the focus of mining by the Spanish and Mexican miners until 1880.
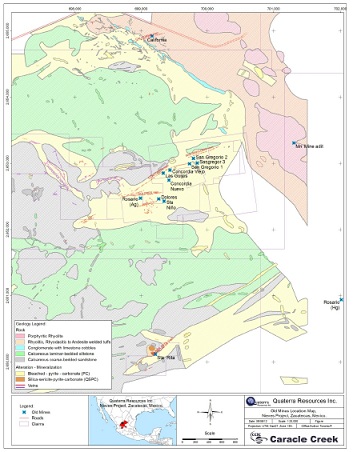
Most of the activity in the Nieves District occurred between 1880 and 1910, when an English company, the Mexican Rosario Mining Company, and two Californian companies, the Almaden Mining Company and the Concordia M. and M. Company, worked in the area. These companies worked on the Concordia vein primarily while a small independent miner Gonzales Pinera worked concurrently on the San Gregorio vein (Turner, 1999; Cavey, 1999). The location of the old mines are shown in Figure 6-1.
Prior to the 1910 revolution, which halted all production in the Nieves District, total ore production in the District was estimated at 50,000 tonnes (Turner, 1999). The only production reported is from the Concordia Mine where 5,414 tonnes at a grade of 4,065 g/t silver were produced (Figure 6-1). This production data cannot be relied upon and has not been verified by the qualified person. The qualified person has not done sufficient work to classify the historical production as current mineral resource and is not treating the historical estimate as current mineral resource.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Between 1910 and 1978 several companies (including Fresnillo Mining: 1936; Scurry-Rainbow: mid-1960's to 1978) attempted to de-water, sample, and re-open the historical workings in the Concordia and Santa Rita mines, and were largely unsuccessful (Figure 6-1). However, underground drilling from this period intersected and confirmed the presence of the Santa Rita Vein 100 m below the 8th level. Included in this time period, is a site visit by D.B. Dill for Penoles Mining, in 1954, who compiled and preserved much of the historical data for the Nieves District. Dill (1954) reported 21,500 tonnes of probable ore at a width of 0.92 m and a grade of 0.92 g/t Au, 1131 g/t Ag, and 2-4% Sb, still remained in the Concordia Vein and a prospective 120,000 additional tonnes. This resource estimate cannot be relied upon, has not been verified by the qualified person, nor is it NI43-101 compliant resource estimate. The qualified person has not done sufficient work to classify the historical estimate as current mineral resource and is not treating the historical estimate as current mineral resource.
The Santa Rita vein and refurbished mill and flotation plant were purchased by Fomento Minero in 1978, who operated the mine until 1987. Fomento Minero also sank three shafts and deepened a historic shaft along the Concordia- San Gregorio vein system during the 1970's (Figure 6-1). The flotation mill was capable of running 100 tonnes/day during this time and was fed 50% tailings and 50% ore with an average head grade of 130 g/t silver, 2% lead, 2.4% zinc and 2.5% antimony, according to Consejo Recursos Minerales (CRM) (Cavey, 1999). Today, all that remains are the building foundations, abandoned shafts and power lines.
Figure 6-1 Location of old mines on the Nieves Property
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
6.2 Exploration activities between 1994 and 2010
Exploration activities between 1994 and 2010 included mapping, rock and soil sampling, several geophysical surveys and a total of 9 drill programs (Table 6-1). The companies performing the work included Kennecott, Western Copper, Quaterra and the joint venture of Quaterra and Blackberry.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
6.2.1 Kennecott exploration between 1994 and 1996
In the early 1990's, a group of Mexican concessionaires (Abelardo Garza Hernandez, Noel McAnulty and Bill Shafer) assembled a land position in the area and presented it to Kennecott who signed the option agreement on January 16th, 1995. Exploration work completed by Kennecott included geologic mapping, surface sampling (535 rock samples and 131 rock chip samples), three soil surveys, geophysical surveying (airborne and ground magnetic surveys, IPR survey, controlled source audio-frequency magneto-telluric survey) and reverse circulation (RC) drilling of the San Gregorio, California and Orion West veins (Figure 6-2 and Table 6-2).
In 1995 and 1996, 8 drill holes (NV01 to NV08) were drilled totaling 1532.5 m. The drilling intersected several zones of significant silver mineralization hosted by two distinct styles of mineralization. Drill hole NV08 in the California area intercepted two separate 2m intervals of high grade silver vein mineralization that returned assay values of 367 g/t and 795 g/t of silver at depths of 108m and 116m, respectively. In contrast, drill hole NV03 intersected a large low grade zone of silver mineralization at a depth of 180 m depth that averaged 82 g/t silver over 28 m. Drill hole NV03 also encountered a high grade silver vein at 148 m depth that returned 254 g/t silver over 2 m. Drill hole NV06 also encountered a large zone of low-grade silver mineralization that returned 67 g/t silver over 68 m.
Kennecott conducted several geophysical surveys including airborne and ground magnetic surveys, a single dipole-dipole induced polarization and resistivity (IPR) line and seven controlled source audiofrequency magneto-telluric (CSAMT) lines. No results were available to the author.
6.2.2 Western Copper exploration in 1997 and 1998
On March 13th, 1998, Kennecott transferred its rights under the Nieves option to Western in consideration for an uncapped 2% NSR on certain core concessions and a 1% NSR royalty on others. Before assigning its rights to the Nieves Project to Quaterra on March 26th, 1999, Western drilled 5 RC holes testing the California vein system (Figure 6-2 and Table 6-2). The holes were drilled in the area around hole NV08. Western also twinned hole NV08 and reproduced similar assay values for the intercepts reported by Kennecott including 890 g/t Silver over 1.0m in drill hole WCNV01. Holes drilled to intercept mineralization below drill hole NV08 returned assay values of 841 g/t silver over 0.45m, 109 g/t silver over 0.8m, and 1,081 g/t silver over 0.35m in drill hole WCNV04.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
6.2.3 Quaterra exploration in 1999 and 2000
Western Copper transferred its rights to the Nieves Property to Quaterra on March 26, 1999. In 1999 and 2000 Quaterra completed an exploration program consisting of geological mapping, sampling and drilling (Figure 6-2 and Table 6-1). Quaterra completed 10 drill holes on the Concordia and Gregorio North veins in conjunction with surface mapping and sampling programs during 1999 and 2000 and deepened four holes (Table 6-1 and Table 6-2). Table 6-3 shows significant drill results.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 6-2 Location of holes drilled by Kennecott, Western and Quaterra between 1994 and 2000.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
6.2.4 Quaterra and Blackberry 2003-2010
On April 10th, 2003, Quaterra completed a US$1.5 million limited partnership financing with Blackberry, whereby Blackberry could earn a 50% interest in the Property by funding two exploration programs of US$750,000 each, which was fulfilled. In 2006 Quaterra and Blackberry signed a joint venture agreement and have jointly contributed to all exploration costs subsequently incurred.
Exploration between 2003 and 2010 by Quaterra and Blackberry included air photograph interpretation, surface sampling, field work, two geophysical surveys, six drill programs and three 43-101 independent technical reports, two of which include 43-101 compliant resource estimations.
Drilling
Drilling by Quaterra and Blackberry started in 2004 and included six drill programs consisting of 72 drill holes, totaling 34,048.43 m (Figure 6-3 to Figure 6-5 and Table 6-4). Holes were drilled on every vein system on the property, but most of the veins concentrated on the Concordia vein system, where the resource was estimated.
Most of the drill holes were planned to target geophysical anomalies, to extend the known mineralized zones in length and depth and for in-fill drilling to increase the confidence in the resource estimation.
The drill programs were very successful and extended the known mineralized zones in several areas. The Concordia vein system was extended to at least 1,100 m along strike and 400 m down dip. Drill highlights are summarized in Table 6-5.
Table 6-4 Drilling summary on the Nieves Property between 2004 and 2010
| Year | Phase | Area | | Number of holes | Total drilled (m) | Hole(s) | | | |
| | | Total Drilled | | 11 | | 5,170.92 | | | | |
| 2006 | III | Concordia/Dolores | 4 | | 3,329.69 | QTA35, QTA36, QTA40, QT41 |
| | | Majada East | | 1 | | 651.05 | QTA42 | | | |
| | | Manto 4 | | 1 | | 459.03 | QTA39 | | | |
| | | Concordia/Gregorio North/Orion 1 | | 650.54 | QTA38 | | | |
| | | Santa Rita | | 1 | | 803.76 | QTA37 | | | |
| | | Total Drilled | | 8 | | 5,894.07 | | | | |
| 2007 | IV | Concordia/Dolores | 14 | | 4,611.80 | QTA43-QTA55, QTA57 | |
| | | Santa Rita | | 1 | | 402.00 | QTA56 | | | |
| | | Jasperiode Grande | 1 | | 376.00 | QTA58 | | | |
| | | Total Drilled | | 16 | | 5,389.80 | | | | |
| 2008 | V | Concordia | | 23 | | 5,744.00 | QTA59-QTA81 | | |
| | | Gregorio North | | 1 | | 429.00 | QTA82 | | | |
| | | Total Drilled | | 24 | | 6,173.00 | | | | |
| 2009 | VI | Concordia | | 13 | | 2,902.70 | QTA83-QTA95 | | |
| | | Total Drilled | | 13 | | 2,902.70 | | | | |
| 2010 | VI | Concordia | | 16 | | 2,778.00 | QTA95-QTA111 | | |
| | | Total Drilled | | 16 | | 3,216.00 | | | | |
| | | Total | | 72 | | 34,048.43 | QTA11-QTA111 | | |
| |
| Table 6-5 Drill highlights on the Nieves Property between 2004 and 2010 |
| Vein system | Hole | From | To | Interval (m) | Au (g/tonne) | Ag (g/tonne) | Pb (%) | Zn (%) | Phas |
| Concordia | QTA-13 | 202.3 | 203.3 | 1 | 0.28 | 545 | 0.61 | 0.5 | I |
| | | including | 203.1 | 203.3 | 0.2 | 0.66 | 2590 | 3.02 | 2.41 | I |
| | | QTA-19 | 207.6 | 209.1 | 1.5 | 1.39 | 4020 | 3.42 | 2.8 | I |
| | | | 425.2 | 426 | 0.8 | 0.49 | 915 | 0.92 | 0.31 | I |
| | | QTA-20 | 198.2 | 199.2 | 1 | 0.43 | 463 | 0.41 | 0.3 | I |
| | | QTA-21 | 281.41 | 283.85 | 2.44 | 0.47 | 224 | 0.63 | 0.39 | I |
| | | including | 283 | 283.85 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 471 | 1.29 | 0.75 | I |
| | | QTA-22 | 85.61 | 89.57 | 3.96 | <0.05 | 203 | 0.25 | 0.29 | I |
| | | | 129.5 | 131.65 | 2.15 | 0.09 | 201 | 0.07 | 0.16 | I |
| | | QTA-27 | 161.3 | 161.5 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 928 | 1.79 | 2.58 | II |
| | | | 172 | 174 | 2 | <0.05 | 173 | 0.27 | 0.33 | II |
| | | | 174 | 174.73 | 0.73 | 0.07 | 337 | 0.37 | 0.33 | II |
| | | | 182.3 | 182.6 | 0.3 | 0.32 | 488 | 1.58 | 1.72 | II |
| | | | 191.79 | 192.5 | 0.71 | 0.61 | 932 | 0.64 | 0.57 | II |
| | | | 197.57 | 197.77 | 0.2 | 0.58 | 1105 | 1.17 | 2.57 | II |
| | | | 208 | 208.9 | 0.9 | <0.05 | 260 | 0.21 | 0.22 | II |
| | | QTA-28 | 243.15 | 243.25 | 0.1 | <0.05 | 1835 | 2.11 | 2.25 | II |
| | | | 243.8 | 243.9 | 0.1 | 0.07 | 894 | 1.45 | 1.17 | II |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 6-3 Location of drill holes in Phase I, II and III drill programs
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 6-4 Location of drill holes in Phase IV drill program
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 6-5 Location of drill holes in Phase V and VI drill programs
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Geophysical surveys
Geophysical survey 2003
In November and December 2003, Quaterra and Blackberry completed a geophysical survey consisting of 10 lines (6.6 km in length) of CSAMT and Controlled Source Induced Polarization (CSIP) for a total of 66 line-km. In addition, a Ground Magnetometer survey was completed consisting of 12 lines including the 10 lines surveyed with CSAMT for total of 76 line-km of magnetic surveying. The work was performed by Zonge Engineering and Research Organization of Tucson, Arizona (Job No. 0319). The CSAMT survey greatly extended coverage of the survey completed in 1995 and 1996 by Zonge Engineering on behalf of Kennecott. The survey identified several prospective anomalies, a number of which correspond to areas of known mineralization, but extend far beyond the limits of previous drilling (Quaterra News Release February 3, 2004).
The CSAMT survey identified six conductive features, three of which correspond to the areas of known mineralization along the Santa Rita, San Gregorio and Majada veins, the rest were previously unknown. These conductive zones coincide with some of the IP anomalies. The anomalies are interpreted to represent mineralization, have a southwest-northeast trend extending for distances up to 3.5 km and spaced at intervals of approximately 1000 m from north to south across the Nieves property.
The survey also identified a large undrilled IP anomaly west of San Gregorio and several smaller untested anomalies in the adjacent areas.
Geophysical survey 2010
Between May and August 2010, Quaterra and Blackberry conducted a geophysical survey performed by Zonge Engineering (Job No. 10094). The survey consists of 25 lines utilizing dipole-dipole or pole-dipole IPR (Induced Polarization and Resistivity) arrays, covering the Concordia-San Gregorio-Dolores vein system (14 lines); east extension of Santa Rita vein system (4 lines); the California vein system (4 lines); Manto-1 CSAMT target (1 line); and the El Rosario mercury occurrence (2 lines).
The results of the survey indicate the Concordia and San Gregorio are two separate veins and not fault offsets of the same vein, and identified strong anomalies along strike to the east and west of both veins that have not been drilled. The San Gregorio vein appears to be the eastern extension of the Orion vein, which is generally unexplored and under-explored for a distance of over 2500 meters.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
The results of the survey east of the historic mine at Santa Rita vein indicate a zone of anomalies extending eastward a distance of 1000 m. The results from the two lines surveyed at the El Rosario mercury occurrence identified narrow zones of weak IP anomalies.
Metallurgical testing
In May, 2010, G&T Metallurgical Services Ltd. completed a metallurgical assessment on behalf of Quaterra and Blackberry. The test used crushed ore that was approximately 100 kg in weight. The main objective of the test was to determine the chemical and mineral content of the composite, assess the ore hardness and develop an outline of a treatment process to recover silver using conventional mineral processing techniques.
The sample contained 79 g/t Ag with minor amounts of Cu (0.08%), Pb (0.14%) and Zn (0.1%). The minerals included quartz, micas, feldspar, pyrite, goethite, sphalerite, galena, silver sulphides (0.07%) and chalcopyrite, in decreasing order of abundance. The silver minerals were polybasite, freibergite and stromeyerite. The ore hardness was determined to be 10.8 kWh/tonne (moderately soft) using a Bond ball mill work index test procedure.
Open circuit flotation testing indicated that about 86% of the feed silver can be recovered into a final concentrate containing 2.3 kg/tonne silver. It was recommended that future test work should investigate coarser primary grind sizes.
The test also suggested that regrinding the rougher concentrate to a nominal 20 (im K80 had no significant benefit on silver metallurgy. Increasing the pH level of the cleaner circuit to 10 significantly improved the grade of silver in the final concentrate.
6.3 Historical Mineral Resource and Mineral Reserve Estimates
6.3.1 CRM 1992
In 1992, CRM estimated the resources and reserves remaining in the Santa Rita Vein system (Table 6-6). These resource estimates cannot be relied upon, have not been verified by the qualified person, nor are they NI43-101 compliant resource estimates. The qualified person has not done sufficient work to classify the historical estimates as current mineral resource and is not treating the historical estimates as current mineral resources.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
6.3.2 Quaterra/Blackberry 2009 and 2010 resource estimates
Quaterra and Blackberry contracted Caracle Creek to complete 43-101 compliant resources on the Nieves Property (Stone, 2009, 2010). The results are summarized in Table 6-7 and Table 6-8. Caracle Creek is not treating these resources as current; the resource within this report is the current resource on the Nieves Property.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
7.0 Geological Setting and Mineralization
7.1 Regional Geology
The Nieves Property lies on the western flank of the Central Altiplano in Mexico, just east of the Sierra Madre Occidental ranges (Figure 4-1). Basement rocks underlying the western Altiplano are a Mesozoic assemblage of marine sedimentary and submarine volcanic rocks belonging to the Guerrero Terrane (Simmons, 1991) that sit unconformably on Precambrian continental rocks. In the Nieves area, the boundary between the Guerrero Terrane rocks and younger Jurassic-Cretaceous sedimentary sequences (interpreted to be the Caracol Formation on the Property) is unclear.
The late Cretaceous to early Tertiary Laramide Orogeny folded and thrust faulted the basement rocks throughout the area and preceded the emplacement of mid-Tertiary plutons and related dykes and stocks (Ruvalcaba-Ruiz and Thompson, 1988). Mesozoic marine rocks are host to the San Nicolas VMS deposit
(Wendt, 2002).
Unconformably overlying the Mesozoic basement rocks in the western Altiplano are units from the late Cretaceous to Tertiary, Sierra Madre Occidental magmatic arc (Figure 7-3). These rocks consist of a lower assemblage of late Cretaceous to Tertiary volcanic, volcaniclastic, conglomerate and locally limestone rocks, the "lower volcanic complex" and a Tertiary (approximately 25-45 Ma) "upper volcanic supergroup" of caldera related, rhyolite ash-flow tuffs and flows. Eocene to Oligocene intrusions occur throughout the Altiplano and are related to the later felsic volcanic event. Locally, these two units are separated by an unconformity (Ruvalcaba-Ruiz and Thompson, 1988).
A late NE-SW extensional tectonic event accompanied by major strike-slip fault movement affected the Altiplano starting approximately 35 Ma ago. This extension was most intense during the Miocene and developed much of the basin and range topography currently exhibited in the area. Subsequent erosion of the ranges has covered most of the valleys.
7.2 Property Geology
Rocks underlying the Nieves Property are of two distinct ages: (1) Mesozoic "argillite" (interpreted to represent a calcareous finely bedded turbidite flysch) as belonging to the Caracol Formation overlain by (2) Tertiary rhyolitic volcaniclastic rocks separated by a presumably Tertiary age basal conglomerate and conglomeratic sandstone sequence. At Nieves, the Caracol Formation is isoclinally folded with an axial plane cleavage. Nieves veins parallel the cleavage.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
7.2.1 Mesozoic Rocks
The most common rock types underlying the Nieves Property form a thick sequence of fine laminar grey to dark green argillite beds up to 1m thick that hosts the silver mineralization (Figure 7-1. These rocks have been assigned to the Caracol Formation of the late Cretaceous age. Argillite beds are more abundant to the south in the Santa Rita area and to the west in the Concordia area. The Caracol Formation is isoclinally folded with an axial plane cleavage, fold axes strike east-northeast to east and beds strike east-west and dip steeply south to near vertical.
Figure 7-1 Sedimentary layers in agrillite (photo from Doris Fox)
7.2.2 Tertiary Clastic Rocks
On the east side of the Nieves Property the Caracol Formation is overlain unconformably by a 1 to 10m thick conglomerate composed of rounded to sub-rounded limestone boulders 2 to 20 cm in diameter in a grey to brown sandstone groundmass. Above the limestone conglomerate there is up to 130m of conglomeratic sandstone with thin bands of calcareous conglomerate which was intersected in drill hole QTA-18 (Figure 7-2). These units dip shallowly.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 7-2 Surface expression of clastic sediments on the property (photo by Doris Fox)
7.2.1 Tertiary Volcanic Rocks
In drill hole QTA-18 (Phase I) 46m of rhyodacitic to andesitic welded tuff occur above the conglomerate and conglomeratic sandstone. A thin 1.5 to 2m unit of grey to dark grey basalt occurs above the tuff and is in turn overlain by at least 56m of porphyritic rhyolite flows striking north-northwest and dipping northeast. These porphyritic rhyolite flows underlie a prominent north trending ridge on the east side of the Property and are the host rock for manganese-calcite veins and breccia mineralization previously exploited by local miners (Figure 5-3 shows the ridge).
7.2.2 Structural Geology
The oldest structures on the Nieves Property are the folds which affect the Mesozoic argillite beds. These structures are likely related to compression during the Laramide Orogeny in the Cretaceous. Thrust faults are also common features of structures attributed to the Laramide Orogeny and several have been suspected to occur on the Nieves Property.
Post-Laramide structures are in all cases brittle in nature and affect both the Mesozoic Caracol Formation sedimentary rocks and the Tertiary volcanic and sedimentary rocks. These structures include: (1) faults that strike 330o to 000o and dip moderately northeast to east with east plunging slicken-sides, (2) faults that strike 170o to 180o and dip steeply to the west, and (3) major vein structures that strike 240o to 270o and dip 60o to 90o to the south. A late vertical fault structure striking 020o to 030o offsets the major mineralized structures and offsets the Concordia from the San Gregorio vein systems.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 7-3 Geology map of the Nieves Property
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
7.3 Mineralization
7.3.1 Alteration and Styles of Mineralization
Generally, Mesozoic Caracol Formation rocks proximal to mineralized zones exhibit a weak bleaching halo that results from the oxidation of 2% to 5% disseminated pyrite throughout these rocks. Pyrite and thin calcite veinlets occur adjacent to mineralized zones in a pyrite-carbonate alteration assemblage called P-C type (pyrite-carbonate).
A local, more intense alteration assemblage includes weak to moderate sericite replacing thin calcite veinlets and weak to advanced fine-grained quartz replacing calcite, associated with an increase in fine grained pyrite. This alteration type, described as QSPC (quartz-sericite-pyrite-carbonate) is present in close proximity to the mineralized structures in some drill holes. Stibnite rosettes are commonly associated with the sericite veinlets.
Silicification, mainly of sandstone beds, occurs in a few zones on the Nieves Property as in the hill located north of the Santa Rita vein. Weak chlorite alteration of tuffs and conglomeratic sandstone occurs in drill hole QTA-18 in the manganese mine area within the Tertiary rhyolitic rocks on the east side of the Property (Figure 7-3).
Four types of mineralization have been identified on the Nieves Property and are described below.
Jasperoid Structures
Jasperoid structures located to the northwest of the Concordia-Dolores vein system are characterized by silicified tan to black coloured rocks with abundant thin jasper, fine grained quartz micro-breccia and veinlets with up to 5% disseminated pyrite. These jasperoid structures are 1 to 12m wide, strike northwest and dip southwest. Locally, jasperoid bodies are anomalous in gold, arsenic and antimony with erratic silver, lead and zinc values.
Possibly a related mineralization style to the jasperoid structures are silica breccia veins that are typically composed of small silicified rock fragments in a saccaroidal quartz groundmass.
Iron carbonate veins
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Iron carbonate veins include mostly calcite and scarce rhodochrosite with hairline to 10 cm wide pyrite veinlets which are abundant up to hundreds of meters away from partially to totally replaced quartz veins. Some veinlets contain stibnite and silver sulphosalts and are abundant in surface alteration halos as well as above and below ore intercepts in drill core. Low grade silver often is associated with this type of veinlet.
Carbonate-quartz-sulphide veins
Carbonate-quartz-sulphide veins are the most economically important veins and consist of calcite that is partially to totally replaced by grey to white, chalcedonic, fine-grained quartz veins and veinlets (Figure 7-4). These veins are from centimetres to 1.5m wide with up to 50% sulphide minerals. Sulphides include pyrite, stibnite, sphalerite, galena, chalcopyrite and the silver sulphosalts: proustite, pyrargyrite, jamesonite and scarce tetrahedrite. The best grades of silver, gold, lead and zinc occur in these veins and past production has come primarily from this vein type.
Figure 7-4 Carbonite-quartz-sulphide mineralized veins
Calcite-manganese-oxide breccias and veins
These mineralized structures which may be 5 to 10m wide and up to 150m long include breccias formed by sub-angular volcanic fragments in a clay-altered sandy groundmass (Figure 7-5). Thin veinlets of ferro-manganese oxides form stockwork zones of clay-altered volcanic rocks and occur along the borders of the breccia bodies in the Manganese mine area (Figure 7-3).
Figure 7-5 Mineralized oxide-breccia in core (photo by Doris Fox)
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
7.3.2 Mineralized Zones
On the Nieves Property there are three major east to east-northeast striking silver vein systems, the California, Concordia- San Gregorio-Dolores, and Santa Rita veins systems (Figure 7-3). In addition to these silver mineralized systems there is an east-northeast to east-southeast striking manganese breccia system hosted by rhyolitic rocks on the east side of the Property. Local miners have worked on all of these areas, previously.
California Vein System
The California vein is marked by a shaft and series of small open cuts aligned 250° to 255° over a distance of 300m. Only thin and discontinuous quartz-oxide veinlets outcrop near the workings. The California vein system shows a large 150-600m wide alteration zone extending about 2,700m along strike. Local stockwork zones contain thin calcite veinlets in part weakly replaced by quartz-oxide veinlets. The California vein was intercepted in Kennecott hole NV08 in two intervals at depths of 108m and 116.0m that returned assays of 367 g/t silver over 2m and 795 g/t silver over 2m respectively. Recent drilling increased the length of known mineralization along the California vein system to approximately 550 m and mineralization remains open to the east.
Concordia- San Gregorio-Dolores Vein System
The Concordia- San Gregorio -Dolores vein system has a known strike length, in mine workings of nearly 1.8 km in two system of veins, (1) the 240°-260° striking Concordia-San Gregorio vein and (2) the 260°-270° striking Dolores splay. Both veins dip from 60° southward to near vertical.
The Concordia- San Gregorio -Dolores system is composed of carbonate to quartz-sulphide veins and varies in width from tens of centimetres up to 1.5m. The most recent drill program extended the total length of the known mineralized zone along the Concordia vein to approximately 1300 meters.
The San Gregorio vein appears to be the continuation of the Concordia structure, assuming approximately 50m of left lateral offset from a north trending fault that presumably follows the San Gregorio arroyo. The San Gregorio vein structure can be traced in some small open cuts for about 500m to the northeast at an azimuth of 250° to 260°. Surface samples from 10 to 40 cm wide calcite to quartz veins with oxides returned silver assays of up to 954 g/t.
The Dolores vein is interpreted to be a splay of the Concordia vein, strikes at 260° to 270° and is traced for nearly 500m on surface by numerous small open cuts and at least five shafts. A stockwork zone of thin calcite to quartz and oxides veinlets in the hanging wall extends on surface for up to 250m across strike from the main vein and along strike for an additional 350m from the last workings on the vein. Surface samples of some of the thin stockwork veinlets from this zone returned silver assays of up to 553 g/t.
The Concordia and Dolores veins appear to intersect to the west of the Rosario Shaft in an area of abundant calcite and lesser quartz veinlets. This area was evaluated on the surface by two long trenches separated by 85m, with 2m wide channel samples collected 10 to 20 cm below the surface. No results were available to the author.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
A total of 15 drill holes systematically tested the Santa Rita vein system over 500 along strike, the total length of mineralization was extended to approximately 750 m and remains open to the west. Drilling suggests the presence of several parallel vein systems.
The Gregorio North area is located north of the San Gregorio vein, in the Gregorio Hill area and it is probably part of the Concodia-San Gegorio-Dolores vein system. The recent drill program was successful in extending the length of the mineralized zone to approximately 1200 m.
Santa Rita Vein System
The Santa Rita vein system, located in southern portion of the Property, strikes 230° to 260° and can be recognized in shafts and in short drifts for over 500m. Last production during 1970-1985 came from the lower levels of the mine which was deepening to 9 levels reaching a depth of 282m. The Santa Rita vein contains a series of veinlets in the footwall that form a wide stockwork zone in an area of 100 x 100m centered on a small silica altered hill north of the main Santa Rita drift. A sub-parallel vein also occurs about 100m southwest of the main Santa Rita vein.
Quaterra hole QTA-16 tested the Santa Rita vein at a depth of 350m and intercepted a 3.1m interval that averages 71.44 g/t silver, 0.56% lead and 0.91% zinc. QTA-37 also appears to have cut the Santa Rita vein system at 416m depth where it encountered a 5.90m zone that averaged 104 g/t silver, 0.23% lead, and 0.55% zinc.
In the phase VII and VIII drill program, a total of 15 drill holes systematically tested the Santa Rita vein system over 500 along strike, the total length of mineralization was extended to approximately 750 m and remains open to the west. Drilling suggests the presence of several parallel vein systems.
Recent mapping on the West Santa Rita area identified two groups of narrow, sub-parallel 2 to 30 centimeter wide calcite-quartz veinlets, some of which contain strong gold and silver mineralization. The first group of veinlets has an east-northeasterly trend and extends 120 to 200 meters along strike with a width of 100 meters. The best results include 8.11 ppm gold over 0.2 meters, 253 ppm silver over 0.4 meters, 4,460 ppm lead and 2,690 ppm zinc over 0.4 meters.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
7.3.3 Manganese Mineralization
Various small pits and drifts sunk on calcite-manganese-oxides breccias and stockwork veinlets hosted in volcanic rocks occur 1 km east of the Concordia-Dolores- San Gregorio vein system on the eastern side of the Nieves Property (Figure 7-3)
The stockwork zone is flanked to the north and south by two breccia structures formed by sub-angular volcanic fragments in clay altered sandy groundmass with irregular ferroan calcite and manganese oxides of possible hydrothermal origin. The north breccia structure is 150m long by 5 to 10m wide, trends 290 to 300 and dips 75° to south. The southern breccia is 115m long by 7m wide, trends 070 and dips 75o to the north.
A second zone of calcite-manganese-oxide breccia occurs 230m south of those described above. It is 150m long by 5m wide, trends 075 and dips 67o north. Surface and underground rock samples from this area were anomalous in silver, arsenic, antimony, tungsten, molybdenum and cobalt. Drill hole QTA-18 tested the depth extent of these structures but intersected no significant mineralization.
8.0 Deposit Types
Silver mineralization on the Nieves Property is best classified as low-sulphidation epithermal mineralization and is the primary exploration target. Several other styles of mineralization are found within the ages of rocks observed on the Nieves Property and are potential secondary exploration targets.
8.1 Epithermal High-Grade Silver Veins
Within the Altiplano Region of Mexico, epithermal silver veins are the dominant deposit type with world-class examples such as Pachuca, Zacatecas, Fresnillo, and Guanajuato. The closest of these world class examples is the Fresnillo Deposit owned and operated by Penoles, located 90 km to the south of the Nieves Property. Several styles of silver mineralization occur in the Fresnillo Deposit including (1) mantos and chimneys, (2) stockworks (Cerro Proano area), (3) disseminated ores in areas of propylitic alteration, and (4) veins that show vertical mineralogical zonation (e.g. the Santo Nino vein). The veins are currently being mined by Penoles and they are actively exploring for more of these mineralized structures (Garcia et al. 1991).
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
In the Santo Nino Vein the high-grade silver mineralization averaging 769 g/t silver, 0.56 g/t gold, 0.99% zinc, 0.5% lead, 0.03% copper; (Gemmel et al. 1988) is hosted in a single fault structure that locally bifurcates or is separated into en-echelon offset structures. It is between 0.5 to 4m wide, averaging 2.5m wide, and extends for over 2.5 km. Typically in these veins, the high-grade silver (gold) zone is constrained in elevation within the vein structure to up to 500m vertically, or between 180 to 750m depths (Garcia et al. 1991), below which the veins becomes dominated by base-metal sulphides and progressively lower in precious metal content (Garcia et al. 1991). A model for the formation of the Fresnillo fissure veins was proposed by authors such as Buchanan (1981) and modified and incorporated into the low-sulphidation epithermal model over the last 20 years (e.g. Corbett 2002; Corbett and Leach 1998; Hedenquist et al. 1996, Simmons et al. 1988). The low-sulphidation epithermal model predicts that the Fresnillo epithermal veins: (1) formed in rifting or tensional environments; (2) formed along normal or strike-slip fault structures; (3) are mineralogically zoned vertically; (4) have the highest precious metal zones within boiling horizons (likely related to paleo-water tables); and, (5) are in faults that diffuse as they near the surface and are accompanied with intense acid-sulphate alteration (advanced argillic and silicification) that cap the systems (Figure 8-1).
The geology of the Fresnillo District (Table 8-1) has been well studied and appears to be very similar to the geology observed on the Nieves Property. The Nieves Property and the Fresnillo District are underlain by a Jurassic-Cretaceous turbidite flysch sequence (Nieves; appears to be an argillite) and greywacke (Fresnillo) units that have been overlain by Tertiary volcanic rocks. Tertiary volcanism in this region is attributed to have occurred in conjunction with extensional tectonics associated with major strike-slip motion on north to northwest trending faults. In the Fresnillo District, epithermal fluids ascended along steeply dipping extensional fault structures generally oriented east-west (Simmons et al. 1988). On the Nieves Property, there are several north to north-northwest trending mapped faults as well as the main vein orientations which have a roughly east-west orientation, very similar to the mineralized veins and structures in the Fresnillo District.
8.2 Other Deposit types in the District
The Altiplano Region contains several other deposit types such as Carbonate Replacement Deposits (e.g. San Martin, Charcas), Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide deposits (San Nicolas), Sedex (Francisco I. Madero) and Stockwork deposits (Real de Angeles) (Wendt 2002) (Table 8-2). These other deposit types are generally hosted within the Mesozoic rock units that underlie the Tertiary volcanic rocks and as the Mesozoic rocks are the dominant rock type underlying the Nieves Property, these other deposit types are possible secondary exploration targets.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 8-1 Schematic cross section of a typical rift released epithermal low-sulphidation system (after Corbett 2004)
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
*CRD = Carbonate Replacement Deposit
**E-Vein = Epithermal Vein
***VMS = Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide
****Tonnages reportedin historic, are not current, have not been verified or re-calculcated to NI 43-101 standards. These data should not be relied upon.
9.1 Geophysical work
9.1.1 2011
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
In April 2011, Quaterra contracted Mira Geoscience AGIC (Advanced Geophysical Interpretation Centre) to invert ground magnetic data from the Nieves Property. The purpose of the project was to advance geological understanding of the magnetic characteristics of the low magnetic anomaly identified in the ground geophysical survey completed by Zonge in 2003 (see section 6.2.4). The results of this data inversion indicated that the geophysics model was poorly constrained due to insufficient data particularly along the western edge of the magnetic low anomaly. In December, 2011, Zonge International was contracted to conduct additional ground magnetometer surveying along 14 N-S lines with a spacing of 200m between lines (Job No. 11191). The data from this survey indicates the magnetic low extends an additional 1200 meters west for a total E-W length of 2200m. Zonge was then retained to model the magnetic low and they concluded the magnetic low is best explained by a reversely polarized source body at a depth of 800m (1150 m elevation) below ground surface with spatial dimensions of 2600m NE-SW and 1800m NW-SE.
In June and July 2011, Quaterra contracted Zonge International to conduct IPR surveys along 9 lines (Job No. 11112) consisting of 6 lines over the Santa Rita vein and its western extension; 2 lines to evaluation the eastern extension of the California vein and 1 line to evaluate the area beneath Tertiary volcanic rocks further east. The results of this survey indicate the Santa Rita vein extends 700m west of the historic workings, appears to become two veins rather than a single vein, and the strike of the veins change from NE-SW to nearly E-W. The two lines on the California vein also suggest the vein extends only a very short distance to the east. The line over the Tertiary volcanic rocks was able to penetrate the volcanic rocks but did not detect anomalous IP response.
9.1.2 2012
At the end of 2011 realization that the geophysical response of several of the vein systems including the Santa Rita, Dolores, Nino and Orion veins extended to the western edge of the existing survey coverage, a decision was made to conduct additional geophysical surveying to better define the extend and character of these vein systems. In the first quarter of 2012 Quaterra retained Zonge International (Job No. 11190) to conduct a survey consisting of six lines, a total of 28.4 line-kilometers, of vector CSAMT and CSIP and nine follow-up lines of pole-dipole IPR totaling 16.5 line-kilometers (Figure 9-1). The six lines of vector CSAMT/CSIP were spaced 400 meters apart and covered 1,000 hectares west of the main veins in the area of the enigmatic magnetic low.
Nine anomalous zones were detected and validated with IP lines using 50 meter dipole spacings. Most of the anomalies appear to be westward extensions of mineralized veins previously drilled, including the Dolores, Santa Rita, Nino and Orion veins.
The anomalies were followed up by mapping and sampling (see section 9.2). The most interesting area identified to date is West Santa Rita, located 1000 to 1200 meters west of the central portion of the main
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Santa Rita mine and over 500 meters from Quaterra's nearest drill hole on line 7700E. The IP and resistivity results are shown along lines 6800E and 7200E ( Figure 9-2, Figure 9-3 and Figure 9-4).
In addition the data also indicates the Nino vein extends well to the west from its previously known geophysical extent a strike length of 1500m along which no drilling has been done. Outcrop in the area is sparse but at least one sample from a fault zone coinciding with the anomalous IP zone defining the Nino vein is anomalous in gold and silver.
Figure 9-1 Geology and location of drill holes and geophysical survey lines (red lines) in the Santa Rita area
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 9-2 Geology and location of channels, samples and geophysical survey lines in the West Santa Rita area
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 9-3 Pole-Dipole Resistivity/IP data along Line 6800 in the West Santa Rita area
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 9-4 Pole-Dipole Resistivity/IP data along Line 7200 in the West Santa Rita area
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
9.2 Mapping and sampling
Mapping and sampling was completed to follow up the geophysical anomalies. The most interesting area was identified in West Santa Rita in the southern part of the Nieves Property (Figure 9-1 and Figure 9-2). Mapping identified two groups of narrow, sub-parallel 2 to 30 centimeter wide calcite-quartz veinlets, some of which contain strong gold and silver mineralization. The first group of veinlets has an east-northeasterly trend and extends 120 to 200 meters along strike with a width of 100 meters.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
The second group of veinlets is located approximately 200 m north of the first group, has an easterly trend and 60 to 80° dip to the south and extends 300 meters along strike with an 80 meter width.
A total of 39 rock chip samples contain gold values ranging from <0.05 ppm to 8.11 ppm (over 0.2 meters), with six of the samples above 2 ppm gold (Appendix 2). Silver values range from <0.02 ppm to 253 ppm (over 0.4 meters), with seven samples at or above 29 ppm silver. Lead and zinc range from 2 ppm and 7 ppm to 4,460 ppm lead and 2,690 ppm zinc over 0.4 meters, respectively.
Pathfinder elements like mercury and antimony report assays up to 32 ppm and 2280 ppm, respectively, suggesting that the veinlets may represent high level leakage, an idea supported by the presence of geophysical anomalies (chargeability highs and resistivity lows) starting at a depth of 50 to 100 meters below surface (see section 9.1).
10.0 Drilling
10.1 Drilling progress
Between March 2010 and October 2011, Quaterra completed Phase VII and Phase VIII drill programs. B.D.W. International Drilling of Mexico S.A. de C.V. was contracted to perform the drilling.
Drill holes were located using a RTK Trimble (model R8), double frequency GPS with precision to 1 cm. Down hole survey readings were recorded on average approximately every 50 m using an Eastman Single Shot instrument. Survey results have been corrected for magnetic declination (+9°).
When completed, drill holes are capped with an approximately 45 cm square concrete slab with the drill hole number etched into it for permanent identification (Figure 10-1).
Figure 10-1 Typical Drill Hole Cap and Marker (photo by Doris Fox)
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
10.1.1 Phase VII
Phase VII diamond drill program on the Nieves Property in Zacatecas, Mexico commenced on March 2010 and was completed at the end of February 2011. Twenty-eight NQ holes were drilled comprising 7759 m (Figure 10-3 and Table 10-1).
The phase VII drill program was designed to test numerous IP anomalies on several separate vein systems that appeared similar to other anomalies associated with known mineralization.
Fourteen drill holes were drilled on the Gregorio North area, two holes were drilled on the Dolores area, six holes were drilled on the Concordia area, four holes were drilled on the California area and two holes were drilled on the Santa Rita area (Table 10-1 and Figure 10-2).
All drill holes in Phase VII drill program were drilled with a 340° azimuth and -60° or -55° dip. True thicknesses are approximately 80% of intercept width.
The average overburden depth is 4.34 m with a maximum overburden depth of 20.5 m in drill holeQTA115.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 10-2 Areas of mineralization on the Nieves Property
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
10.1.2 Phase VIII
Phase VIII drill program commenced in June, 2011 and was completed in October, 2011. Forty-five NQ holes were drilled comprising 10,788.25 m (Figure 10-3 and Table 10-2). Phase VIII drill program was designed to test extensions and shallower parts of the La Quinta-Concordia and Gregorio North vein systems.
Five drill holes were drilled on the Gregorio North area, 2 holes were drilled on the Concordia East area, 12 holes were drilled on the Concordia West area, 5 holes were drilled on the La Quinta area, 3 holes were drilled on the Concordia West/Gregorio North/Orion area, 2 holes were drilled on the Disquito Orion East area, located south of Orion East and northwest of the Concordia vein, 2 holes were drilled on the California area, 13 holes were drilled on the Santa Rita area and 1 hole was drilled on the Mariana vein, located southwest of the Jasperoide Grande vein (Figure 10-2).
All drill holes in Phase VII drill program were drilled with an azimuth between 320° and 340° and a dip between -60° or -50°. True thicknesses are approximately 80% of intercept width.
The average overburden depth is 2.09 m with a maximum overburden depth of 6.25 m in drill hole QTA181.
Table 10-2 Summary of drill holes in Phase VIII drill program
| Hole | Easting | Northing | Elevation (m) | Length (m) | Azimuth | Dip | Year | Area |
| QTA154 | 699286.99 | 2652862.97 | 1932.00 | 213.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West |
| QTA155 | 699432.02 | 2654911.44 | 1965.33 | 180.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | California |
| QTA156 | 698965.19 | 2654753.10 | 1959.09 | 228.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | California |
| QTA157 | 699125.20 | 2652745.03 | 1935.38 | 258.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West |
| QTA158 | 699235.86 | 2649896.45 | 1970.28 | 459.00 | 320 | -60 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA159 | 699319.96 | 2649969.11 | 1965.00 | 357.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA160 | 699202.63 | 2649874.95 | 1975.94 | 408.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA161 | 699124.64 | 2649887.81 | 1982.16 | 333.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA162 | 699345.81 | 2650090.86 | 1955.02 | 252.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA163 | 699347.47 | 2650173.36 | 1961.65 | 144.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA164 | 699102.80 | 2649918.28 | 1986.84 | 219.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA165 | 699421.93 | 2650157.06 | 1957.72 | 309.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita Concordia West / Gregorio |
| QTA166 | 698919.55 | 2652714.62 | 1942.58 | 300.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | North/Orion |
| QTA167 | 698585.54 | 2652721.11 | 1953.82 | 282.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Disquito Orion East |
| QTA168 | 699033.47 | 2652715.39 | 1938.03 | 270.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West |
| QTA169 | 699470.94 | 2650253.03 | 1956.51 | 210.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA170 | 699051.92 | 2652668.43 | 1939.21 | 327.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West |
| QTA171 | 699455.19 | 2650120.90 | 1951.72 | 381.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA172 | 699015.67 | 2652762.84 | 1937.83 | 237.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West / Gregorio North/Orion |
| QTA173 | 698986.70 | 2652698.14 | 1940.64 | 288.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West |
| QTA174 | 699383.87 | 2650124.39 | 1955.57 | 318.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA175 | 698957.81 | 2652768.33 | 1939.26 | 201.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West / Gregorio North/Orion |
| QTA176 | 699414.43 | 2652898.07 | 1931.56 | 228.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West |
| QTA177 | 699458.47 | 2650189.87 | 1960.24 | 227.75 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA178 | 699476.14 | 2652947.48 | 1929.10 | 144.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West |
| QTA179 | 699561.90 | 2652995.22 | 1924.95 | 111.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | La Quinta |
| QTA180 | 699669.62 | 2653009.59 | 1922.70 | 141.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | La Quinta |
| QTA181 | 699416.01 | 2650090.31 | 1952.94 | 282.00 | 320 | -50 | 2011 | Santa Rita |
| QTA182 | 699404.98 | 2652921.32 | 1930.83 | 147.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia West |
| QTA183 | 700181.03 | 2653097.25 | 1924.47 | 195.00 | 340 | -60 | 2011 | Concordia East |
| QTA184 | 697303.26 | 2652466.07 | 1964.40 Total | 187.50 10788.25 | 350 | -50 | 2011 | Mariana vein |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 10-3 Location of drill holes in Phase VII and VIII drill programs
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
10.2 Sampling procedures
Core boxes were collected from the drill site and brought to the core storage facility on the Nieves Property for logging and sampling by the project or assistant geologists on a daily basis. The drill core was washed, photographed and core recovery estimated. Rock types, alteration minerals, textural and structural features, veining, and mineralized zones documented. Sample intervals were selected and measured, marked with permanent marker and given a sample number and sample tag by the geologists (Figure 10-4). From this point, technicians were given the core to split, using a core saw, into halves where one half of each interval was placed with the sample tag into a sample bag and marked with the sample number. The other half was placed back into the core box in its original position and the core boxes were then stacked on racks and stored in order and by hole number in their core storage facility.
The geologists visually selected sample intervals based on the presence of quartz-carbonate veins, silicification or the presence of sulphide minerals. The rock surrounding any significant mineralized zones was also sampled for several metres above and below the mineralization. Samples were placed into individual plastic bags marked with a unique sample identification number and with a sample tag placed into the bag. Sample ID numbers and meterages were also written on the core trays. Samples were then packaged into sealed sacks and taken by ALS employees to ALS Minerals Laboratories in Guadalajara, Mexico for preparation.
A total of 2884 samples were analyzed in Phase VII drill program, not including standards and blanks (Table 10-3). The length of samples in Phase VII ranges from 0.05 to 3 m; the average length is 1.51 m. 83 blanks and 45 standards were also sent for analysis. No core duplicates were included.
A total of 4876 samples were analyzed in Phase VIII drill program, not including QC samples (standards, blanks and core duplicates) (Table 10-4). The length of samples in Phase VIII ranges from 0.05 to 2.25 m; the average sample length is 1.69 m.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 10-4 A) Core tray marked with hold ID, depth to-from of core and box number. B) typical sample ID marking in core box. C) Locked core storage 1 of 5. D) Core storage.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
10.3 Drill Data and Drilling Results
Phase VII and Phase VIII drill programs were very successful at increasing the size of the known mineralized zones along most of the major vein systems on the Nieves Property. Drill highlights are summarized in Table 10-5, Table 10-6 and Table 10-7.
The best intersections include 149 g/t Ag and 0.11 g/t Au over 31.25 m, which includes 6320 g/t Ag and 1.82 g/t Au over 0.25 m in drill hole QTA123 along the Concordia West vein, 104 g/t Ag over 19 m, including 6410 g/t Ag over 0.1 m and 5960 g/t over 0.1 m in drill hole QTA137 along the California vein, and 152.2 g/t Ag and 0.12 g/t Au over 57 m in drill hole QTA144 in the Concordia West area (Table 10-5, Table 10-6 and Table 10-7).
10.3.1 Concordia
A total of 28 drill holes were drilled along the Concordia vein system, which includes the Concordia East, La Quinta and the Concordia West areas.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Twenty drill holes were drilled in the Concordia West area, extending the mineralized zone approximately 200 m to the west. Most of the drill holes (QTA119, QTA120, QTA123, QTA131, QTA139, QTA143, QTA144, QTA153, QTA157, QTA168, QTA170 and QTA172) intersected significant mineralization, but holes QTA131, QTA139, QTA166 and QTA167 did not intersect significant mineralization (Table 10-5, Table 10-6 and Table 10-7). Mineralization remains open to the west.
The Concordia East area was tested with three drill holes (QTA136, QTA151 and QTA183), two of which intersected high grade mineralization extending the mineralized zone 200 m east of the La Quinta area.
The total length of the known mineralized zone along the Concordia vein system was extended to approximately 1300 meters. Stockwork style mineralization, typical of Concordia vein, has now been intersected on a minimum spacing of 100 m over a total strike length of 1000 m. Holes QTA140, QTA141, QTA142, QTA152, QTA154, QTA176, QTA178, QTA179, QTA180 and QTA182 intersected low to moderate grade Ag mineralization at shallow depth, suggesting the presence of mineralization up-dip, near surface (Table 10-6 and Table 10-7).
10.3.2 California
A total of 6 drill holes (QTA127, QTA128, QTA130, QTA137, QTA155 and QTA156) were drilled along the California vein system. QTA130 intersected several shallow, stockwork style mineralization (Table 10-5). Holes QTA137 and QTA155 were drilled near the east end of previously known mineralization and intersected high grade mineralization (Table 10-5 and Table 10-6). QTA127, drilled to the west of the known mineralized zone, did not intersect significant mineralization.
Recent drilling increased the length of known mineralization along the California vein system to approximately 550 m and mineralization remains open to the east.
10.3.3 Gregorio North
A total of 18 holes were drilled along the Gregorio North vein system. Holes QTA112 to QTA118, QTA122, QTA132, QTA133 and QTA134 traced the Gregorio North vein for an additional 500 m to the west (Table 10-5). The grade and thickness of the vein decreases to the west, indicated by drill holes QTA122, QTA133 and QTA134. The two best holes (QTA115 and QTA116) are located on the east end of the Gregorio North vein. Holes QTA135 and QTA138 intersected weak mineralization in the vein 100 and 200 m further to the east.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Phase VII and VIII drill programs were successful in doubling the strike length of the Gregorio North vein, extending the strike length of the vein to approximately 1200 m.
10.3.4 Santa Rita
A total of 15 drill holes systematically tested the Santa Rita vein system over 500 along strike, the total length of mineralization was extended to approximately 750 m and remains open to the west. Drilling suggests the presence of several parallel vein systems.
Most of the drill holes intersected significant mineralization (Table 10-6 and Table 10-7). Low grade Ag mineralization was intersected in holes QTA161 and QTA169. Holes QTA124 and QTA126, drilled east of the known mineralization on the Santa Rita vein, intersected weak mineralization.
10.3.5 Other areas
Two holes (QTA121 and QTA125) intersected weak mineralization on the Dolores vein (Table 10-5). QTA129 drilled at Orion failed to return any mineralization (Table 10-5). Hole QTA184 was drilled along the Mariana vein, but failed to intersect significant mineralization.
Table 10-5 Drill highlights of Phase VII exploration program
| Hole | Area | From | To | Interval | Au | Ag | Ag | Pb | Zn | |
| (m) | (g/tonne) | (g/tonne) | (oz/ton) | (%) | (%) | |
| | | 148.85 | 187.5 | 38.65 | 0.1 | 23 | 0.7 | 0.02 | 0.03 | |
| includes | | 180.7 | 183.15 | 2.45 | 0.25 | 120 | 3.5 | 0.07 | 0.16 | |
| QTA117 | Gregorio N | 70.75 | 85 | 14.25 | 0.13 | 14 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.01 | |
| | | 132 | 140 | 8 | 0.16 | 56 | 1.6 | 0.03 | 0.06 | |
| QTA118 | Gregorio N | 85.5 | 87.75 | 2.25 | 0.03 | 24 | 0.7 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| | | 99.5 | 101.05 | 1.55 | 0.03 | 27 | 0.8 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| | | 146.1 | 148.3 | 2.2 | 0.27 | 34 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| | | 154.5 | 157.85 | 3.35 | 0.1 | 31 | 0.9 | 0.03 | 0.12 | |
| | | 181.95 | 182.2 | 0.25 | 1.2 | 1175 | 34.3 | 0.85 | 1.6 | |
| | | 205 | 210.05 | 5.05 | 0.03 | 21 | 0.6 | 0.02 | 0.06 | |
| | | 221.1 | 224.3 | 3.2 | 0.03 | 57 | 1.7 | 0.14 | 0.21 | |
| QTA119 | Concordia W | 106.7 | 108.5 | 1.8 | 0.52 | 88 | 2.6 | 0.18 | 0.33 | |
| | | 136.55 | 142.1 | 5.55 | 0.04 | 30 | 0.9 | 0.02 | 0.04 | |
| | | 158.1 | 218.05 | 59.95 | 0.04 | 17 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.07 | |
| QTA120 | Concordia W | 48.1 | 52.5 | 4.4 | 0.33 | 15 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| | | 51.85 | 52.5 | 0.65 | 1.8 | 71 | 2.1 | 0.01 | 0.07 | |
| | | 170.6 | 182.3 | 11.7 | 0.06 | 36 | 1.1 | 0.04 | 0.27 | |
| QTA121 | Dolores E | 109.3 | 109.85 | 0.55 | 0.61 | 16 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.12 | |
| QTA122 | Gregorio N | 60.2 | 67.1 | 6.9 | 0.08 | 14 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.01 | |
| QTA123 | Concordia W | 103.6 | 181.7 | 78.1 | 0.06 | 69 | 2 | 0.07 | 0.08 | |
| | | 103.6 | 134.85 | 31.25 | 0.11 | 149 | 4.4 | 0.12 | 0.14 | |
| includes | | 114.4 | 128.25 | 13.85 | 0.12 | 290 | 8.5 | 0.2 | 0.24 | |
| includes | | 117.2 | 117.45 | 0.25 | 1.82 | 6320 | 184.5 | 2.96 | 2.94 | |
| QTA124 | Santa Rita | 118 | 124.6 | 6.6 | 0.03 | 30 | 0.9 | 0.06 | 0.09 | |
| QTA125 | Dolores | 84 | 87.7 | 3.7 | 0.23 | 11 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| | | 210 | 225 | 15 | 0.05 | 23 | 0.7 | 0.02 | 0.04 | |
| QTA128 | California | 128 | 131 | 3 | 0.07 | 13 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| QTA130 | California | 22 | 30 | 8 | 0.05 | 79 | 2.3 | 0.03 | 0.1 | |
| includes | | 26 | 28 | 2 | 0.07 | 215 | 6.3 | 0.08 | 0.17 | |
| | | 80.1 | 83 | 2.9 | 0.03 | 108 | 3.2 | 0.04 | 0.24 | |
| | | 99 | 105 | 6 | 0.03 | 89 | 2.6 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| includes | | 103 | 105 | 2 | 0.03 | 235 | 6.9 | 0.09 | 0.05 | |
| | | 157 | 158.9 | 1.9 | 0.05 | 119 | 3.5 | 0.04 | 0.1 | |
| QTA131 | Concordia West | 279.95 | 280.1 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 181 | 5.3 | 3.71 | 1.49 | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| Hole | Area | From | To | Interval (m) | Au (g/tonne) | Ag (g/tonne) | Ag (oz/ton) | Pb (%) | Zn (%) |
| QTA132 | Gregorio North | 138 | 192.1 | 54.1 | 0.13 | 37.4 | 1.1 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| | | 204.95 | 212 | 7.05 | 0.03 | 20.4 | 0.6 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| QTA133 | Gregorio North | 207.6 | 207.7 | 0.1 | 0.92 | 1380 | 40.3 | 1.69 | 10.5 |
| | | 222.5 | 222.65 | 0.15 | 1.18 | 1810 | 52.9 | 1.41 | 3.64 |
| QTA134 | Gregorio North | 47.7 | 51 | 3.3 | 0.05 | 42.7 | 1.2 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| | | 110 | 111.85 | 1.85 | 0.11 | 66.2 | 1.9 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| | | 133 | 139.6 | 6.6 | 0.04 | 30.9 | 0.9 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| QTA135 | Gregorio North | 159 | 196.65 | 37.65 | 0.12 | 18.1 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| includes | | 160.1 | 162 | 1.9 | 0.21 | 121 | 3.5 | 0.02 | 0.13 |
| includes | | 172.9 | 173.2 | 0.3 | 1.03 | 62.3 | 1.8 | 0.08 | 0.27 |
| QTA136 | Concordia East | 84 | 90.7 | 6.7 | 0.23 | 92.9 | 2.7 | 0.03 | 0.11 |
| includes | | 89.45 | 89.8 | 0.35 | 1.15 | 1510 | 44.1 | 0.51 | 1.81 |
| QTA137 | California | 77 | 96 | 19 | 0.03 | 104 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| includes | | 80.55 | 85.4 | 4.85 | 0.03 | 342.5 | 10 | 0.12 | 0.15 |
| includes | | 83.7 | 83.8 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 6410 | 187.2 | 2.06 | 3.28 |
| includes | | 85.3 | 85.4 | 0.1 | 0.06 | 5960 | 174 | 2.53 | 0.44 |
| QTA138 | Gregorio North | 187 | 195 | 8 | 0.14 | 24.8 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.05 |
| includes | | 192.6 | 193 | 0.4 | 1.79 | 290 | 0.5 | 0.03 | 0.78 |
| QTA139 | Concordia West | 291 | 293 | 2 | 0.03 | 15.5 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| Hole | Area | From | To | Interval (m) | Au (g/tonne) | Ag (g/tonne) | Ag (oz/ton) | Pb (%) | Zn (%) | |
| | | 155.1 | 158.3 | 3.2 | 0.03 | 52.4 | 1.5 | 0.05 | 0.06 | |
| QTA143 | Concordia West | 68.1 | 76 | 7.9 | 0.17 | 15.3 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.01 | |
| | | 98 | 148 | 50 | 0.08 | 66.9 | 2 | 0.05 | 0.08 | |
| includes | | 108 | 146 | 38 | 0.08 | 81.5 | 2.4 | 0.07 | 0.1 | |
| includes | | 108 | 110 | 2 | 0.46 | 353 | 10.3 | 0.24 | 0.29 | |
| QTA144 | Concordia West | 32 | 38.5 | 6.5 | 0.29 | 12.6 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| | | 107 | 164 | 57 | 0.12 | 152.5 | 4.5 | 0.12 | 0.17 | |
| includes | | 109 | 125.65 | 16.65 | 0.23 | 290.9 | 8.5 | 0.23 | 0.3 | |
| includes | | 110.85 | 115.6 | 4.75 | 0.41 | 447.4 | 13.1 | 0.35 | 0.51 | |
| QTA145 | Disquito Orion East | 192.5 | 192.6 | 0.1 | 0.13 | 115 | 3.4 | 0.07 | 0.16 | |
| QTA146 | Gregorio North | 20 | 28.35 | 8.35 | 0.17 | 7.5 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.01 | |
| QTA147 | Gregorio North | 145.55 | 180 | 34.45 | 0.15 | 16.5 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| QTA148 | Gregorio North | 0.25 | 87 | 86.75 | 0.13 | 13.3 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| | | 155 | 186 | 31 | 0.09 | 30.3 | 0.9 | 0.02 | 0.04 | |
| QTA150 | Gregorio North | 17 | 29.85 | 12.85 | 0.11 | 6.5 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| QTA152 | La Quinta | 13 | 17 | 4 | 0.23 | 23.9 | 0.7 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| | | 50.3 | 53 | 2.7 | 0.61 | 20.7 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| QTA153 | Concordia West | 50.3 | 53 | 2.7 | 0.61 | 20.7 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| | | 107 | 187 | 80 | 0.1 | 37.5 | 1.1 | 0.05 | 0.07 | |
| includes | | 117.4 | 125.75 | 8.35 | 0.56 | 134.5 | 3.9 | 0.09 | 0.11 | |
| includes | | 120 | 121.5 | 1.5 | 2.71 | 317.2 | 9.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |
| includes | | 168.5 | 172.05 | 3.55 | 0.13 | 228.7 | 6.7 | 0.4 | 0.52 | |
| QTA154 | Concordia West | 34 | 114 | 80 | 0.03 | 18.1 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| QTA155 | California | 111.25 | 111.45 | 0.2 | 0.03 | 64 | 1.9 | 0.02 | 0.15 | |
| QTA156 | California | 90 | 98 | 8 | 0.08 | 31 | 0.9 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| QTA157 | Concordia West | 103 | 219 | 116 | 0.04 | 20 | 0.6 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| includes | | 106 | 116.05 | 10.05 | 0.06 | 59 | 1.7 | 0.02 | 0.07 | |
| includes | | 173.95 | 174.2 | 0.25 | 2.18 | 2140 | 62.5 | 1.54 | 2.48 | |
| includes | | 192.65 | 200.25 | 7.6 | 0.07 | 47 | 1.4 | 0.21 | 0.1 | |
| QTA167 | Disquito | 219.95 | 220.4 | 0.45 | 2.9 | 11 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.02 | |
| QTA168 | Concordia West | 15 | 20.6 | 5.6 | 1.22 | 5 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.01 | |
| | | 170.2 | 213 | 42.8 | 0.09 | 46 | 1.3 | 0.04 | 0.08 | |
| | | 172.1 | 183.2 | 11.1 | 0.14 | 93 | 2.7 | 0.07 | 0.12 | |
| | | 173.35 | 181.25 | 7.9 | 0.16 | 107 | 3.1 | 0.08 | 0.13 | |
| QTA158 | Santa Rita | 98 | 137.1 | 39.1 | 0.05 | 19 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.12 | |
| | | 241 | 259.7 | 18.7 | 0.03 | 18 | 0.5 | 0.07 | 0.25 | |
| QTA159 | Santa Rita | 61 | 82.8 | 21.8 | 0.03 | 25 | 0.7 | 0.09 | 0.19 | |
| includes | | 62.9 | 69.05 | 6.15 | 0.03 | 79 | 2.3 | 0.27 | 0.49 | |
| includes | | 68.6 | 69.05 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 556 | 16.2 | 2.07 | 4.83 | |
| | | 273 | 288 | 15 | 0.05 | 60 | 1.8 | 0.12 | 0.21 | |
| QTA160 | Santa Rita | 130 | 150 | 20 | 0.04 | 34 | 1 | 0.19 | 0.16 | |
| | | 200.45 | 244 | 43.55 | 0.08 | 15 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.08 | |
| | | 294 | 306 | 12 | 0.21 | 19 | 0.5 | 0.02 | 0.07 | |
| QTA161 | Santa Rita | 36 | 66 | 30 | 0.04 | 24 | 0.7 | 0.13 | 0.2 | |
| | | 124.75 | 265.6 | 140.85 | 0.06 | 20 | 0.6 | 0.03 | 0.06 | |
| includes | | 183.45 | 205 | 21.55 | 0.03 | 44 | 1.3 | 0.06 | 0.09 | |
| QTA162 | Santa Rita | 149.5 | 149.9 | 0.4 | 0.39 | 55 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 2.88 | |
| QTA163 | Santa Rita | 120.35 | 124.1 | 3.75 | 0.08 | 11 | 0.3 | 0.03 | 0.05 | |
| QTA164 | Santa Rita | 118 | 121.95 | 3.95 | 0.05 | 58 | 1.7 | 0.03 | 0.14 | |
| Hole | Area | From | To | Interval (m) | Au (g/tonne) | Ag (g/tonne) | Ag (oz/ton) | Pb (%) | Zn (%) |
| | | 142 | 153 | 11 | 0.03 | 77 | 2.3 | 0.15 | 0.21 |
| QTA165 | Santa Rita | 117 | 163 | 46 | 0.03 | 19 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| | | 221.7 | 250 | 28.3 | 0.03 | 18 | 0.5 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| QTA169 | Santa Rita | 34 | 113 | 79 | 0.03 | 32 | 0.9 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| includes | | 68.1 | 70 | 1.9 | 0.03 | 210 | 6.1 | 0.15 | 0.08 |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
11.0 Sample Preparation, Analyses and Security
11.1 Sample Security
Core boxes are delivered to the core logging facility from the drill twice per day. The core is logged onsite and core samples are selected and marked by the logging geologist. No minimum or maximum sample lengths are used; the sample length is determined by the geologist based on presence and intensity of mineralization. The start and end of a sample and the sample ID are marked by the geologist on the side of the core box using a red permanent marker. The end of the box with the hole number is also marked with a red "X" for easy visual recognition in core storage. The marked core boxes are taken to the onsite core cutting area and the core is split into two halves using a water-cooled circular diamond saw (Figure 11-1). One half of the core is taken for analysis and the remaining half is left in the box for future reference and stored in the locked core storage facility. After a sample is cut, each sample is placed immediately in a plastic sample bag with a pre-printed sample tag supplied by the lab in booklets of 50 sequential, numerical tags. The depth to and from of the core sample are marked in the sample tag booklet. The sample bags are stapled shut and set aside. Once a significant number of samples have been bagged, the samples are placed in rice bags with predetermined standards, duplicates and blanks. Blank and duplicate sample tag id's are recorded in the core box following the core sample.
Two to three times per month during the drill program, the samples were picked-up at the core logging facility in Nieves by an ALS Minerals operated transport truck. The truck transported the samples directly to the ALS prep lab in Guadalajara, Mexico. While waiting for the ALS truck to arrive, samples in rice bags are stored inside the locked core storage facility.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 11-1 Core Cutting and sample prep area at core logging/core storage facility (Photo by Doris Fox)
11.2 QA/QC procedures
11.2.1 Frequency of QC samples
In Phase VII, the 3069 samples sent for analysis included 83 blanks (3% of samples) and 45 standards (1% of samples) (Table 11-1). No core duplicates were included. Out of 44 jobs sent to the lab, no external standards were inserted into 9 of the jobs and no external blanks and standards were inserted into 13 jobs.
The frequency of insertion of the quality control samples in Phase VII drill program is adequate for this stage of the project, but the number of quality control samples and the frequency of their insertion should be higher in the future for a systematic monitoring of assay quality. According to Sketchley (1998), 10% to 15% of quality control samples should be included with every sample batch. Every 20 sample should include 1 standard, 1 blank and 1 duplicate.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
In Phase VIII, the 5315 samples sent for analysis included 132 external blanks (2% of samples), 130 external standards (2% of samples) and 177 core duplicates (3%) (Table 11-2). The frequency of QC samples improved in Phase VIII drill program, compared to Phase VII drill program, following recommendations given by Caracle Creek in August, 2011.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
11.2.2 Blanks and standards
The source of blank material is a gravel (consisting of barren rocks) quarry located approximately 15 km to the west of the Nieves property and it is supplied by a local farmer by pick-up truck in bulk. The blank samples are prepared by Quaterra geotechs. The blank material is purposely put in plastic sample bags in weights heavier than most samples so that the sample weight can be used to help identify blanks when data is returned from the lab. Blank material is stored outside the core storage facility in sample bags within watertight plastic 45gallon drums.
Standard material is stored in the field office in 2L plastic jugs. The only external standard used is a custom made standard (KM 2653) prepared by Smee & Associates Consulting Ltd. Table 11-3 summarizes the standard information for Ag and Au.
The standard is characterized as a Provisional (not certified) standard for Au with a relative standard deviation between 5% and 15% and caution must be exercised when assessing the accuracy of data (Smee, 2010).
Standards are used to check the accuracy of the analysis. The rules for the standards and blank samples include:
The analytical method used in the round robin of standard KM 2653 for Ag is 4 acid digestion followed by instrument finish and for Au is fire assay and instrument finish.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
1.The standard is considered a failure when it returns a value that falls outside ±3 standard deviation.
2. The standard is marked as a "warning" when it returns a value between ±2 and ±3 standard deviation. If three or more adjacent standards are on the same side of the Au mean value and fall between ±2 and ±3 standard deviation, then all standards are classified as failure. This may indicate a bias in the laboratory.
3. A blank sample greater than the maximum acceptable value, which is typically three times the detection limit, is a failure. A failure in the blanks indicates a contamination during sample preparation in the laboratory.
11.2.3 Duplicates
Core duplicates were inserted only in Phase VIII drill program. Lab duplicates were inserted in the laboratory.
Core and laboratory duplicates are used to check the precision of the analysis: analytical errors, sample preparation errors and nugget effect. The original values versus the duplicate values are plotted and compared. If the R2 value of the correlation line is greater than 0.95%, all the duplicates pass. A duplicate
11.3 Sample Preparation
Samples were shipped to ALS Minerals Lab in Guadalajara, Mexico for preparation, then to ALS Minerals Vancouver, B.C. for analysis (Quaterra Resources Inc. webpage: www.quaterra.com). All ALS laboratories in North America are registered to ISO 9001:2008, and have received ISO 17025 accreditations for specific procedures (ALS Minerals website: www.alsglobal.com).
The samples were weighed, logged into the ALS Minerals system, fine crushed to 70%-2 mm or better, split using a riffle splitter and pulverized to 85% passing 75 microns or better.
11.4 Analytical methods
Silver was analyzed with two methods including aqua regia digest and a combination of ICP-AES (Inductively Coupled Plasma - Atomic Emission Spectroscopy) finish and fire assay and gravimetric finish. Gold was analyzed with fire assay and gravimetric finish (Table 11-4). The rest of the elements were analyzed with aqua regia digestion and ICP-AES finish.
In the aqua regia digest and ICP-AES finish, the samples are digested in aqua regia in a graphite heating block (ALS Minerals website: www.alsglobal.com). After cooling, the solution is diluted to 12.5 ml with deionized water, mixed and analyzed by ICP-AES. The results are corrected for inter-element spectral interferences.
In the fire assay and gravimetric finish, the samples are decomposed with fire assay fusion, during which the sample is fused with a mixture of lead oxide, sodium carbonate, borax, silica and other reagents to produce a lead button, which is cupelled to remove the lead (ALS Minerals website: www.alsglobal.com). The remaining gold and silver bead is separated in dilute nitric acid, annealed and weighed as gold. Silver is determined by the difference in weights.
Table 11-4 Description of analytical methods for AG and Au
| Analytical method | Element | Analyte range (ppm) | Sample weight | Description |
| ME-ICP41 | Ag | 0.2-100 | > 1 g | Aqua regia digestion and ICP-AES finish |
| ME-GRA21 | Au | 0.05-1,000 | 30 g | Fire assay and fravimetric finish |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| Analytical method | Element | Analyte range (ppm) | Sample weight | Description |
| ME-GRA21 | Ag | 5-10,000 | 30 g | Fire assay and gravimetric finish |
| Ag-OG46 | Ag | 1-1,000 | | Aqua regia digestion and ICP-AES finish |
11.5 QA/QC procedures in ALS Minerals Labs
ALS Minerals inserted internal standards (Table 11-5), blanks and duplicates in every job at regular intervals.
For every 50 samples prepared, ALS Minerals inserts an additional split from the coarse crushed material to create a pulverizing duplicate, which is processed and analyzed in a similar manner to the other samples in the submission (ALS Minerals website: www.alsglobal.com).
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
11.6 Check assays
11.6.1 Phase VII
A total of 158 samples from Phase VII were sent for check assays to Skyline Assayers and Laboratories of Tucson, Arizona. The samples included 145 rejects from ALS Minerals, 3 % core duplicates and their rejects from ALS Minerals, 4 blanks and 3 standards. The standard was the same customized standard inserted with the original assays (KM2653) (Table 11-3).
The analytical methods of check assay samples are summarized in Table 11-6. All Skyline laboratories have received ISO 17025 accreditations for the analytical methods used for the check assays (Skyline website: http://www2.skylinelab.com). Table 11-7 summarizes the properties of lab standards inserted by Skyline.
| Table 11-6 Analytical methods of check assays at Skyline |
| Element | Analytical method | Description | Detection limit |
| Au | FA-3 | Fire Assay - Gravimetric | 0.03-1,000 ppm |
| Ag | FA-3 | Fire Assay - Gravimetric | 0.03-1,000 ppm |
| Ag | TE-2 | Trace Elements by Aqua Regia leach analyzed by ICP/OES (32 elements) | 0.2 ppm |
11.6.2Phase VIII
A total of 127 samples from Phase VIII drill program were sent to AGAT Laboratories of Sudbury, Canada for preparation and sent to AGAT Laboratories of Mississauga, Ontario for analysis. The samples included 127 pulp rejects from ALS, 7 blanks, 4 silver standards and 3 gold standards. AGAT Laboratories is accredited and certified for ISO 9001 and ISO/IEC 17025 accreditations.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Analytical methods of check assays for Ag and Au at AGAT are the same as the analytical methods of the original samples (Table 11-9).
The names of the laboratory standards were not provided by AGAT, but the laboratory QC data indicates that internal standards were inserted for both Ag and Au. Five types of silver standards were inserted ranging from 116 and 811 g/t Ag in value. Two types of gold standards were inserted with values 0.922 and 5.865 g/t Au.
12.1 Caracle Creek Site Visit
A property site visit was conducted by D. Fox of Caracle Creek on March 11th and 12th, 2012. Several drill sites, artisanal pits, the core storage facility, geological logging area, sample cutting area and field office were all visited while onsite.
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
The property was accessed by toll highway from Zacatecas to Nieves. From Nieves, the property and core logging facility were accessed by dirt road. A network or narrow dirt roads and trails criss-cross the property from the logging facility to the drill sites and abandoned artisanal pits and shafts.
The compound containing the core logging and core storage facility contained within a chain link fence with locked gate preventing vehicle access (Figure 12-1 and Figure 12-2). Once inside the gated compound, the individual storage rooms are locked and prevent access to the core logging and core cutting areas. The onsite geology office is a separate building within the compound and is also kept locked. The main working office is located in the town of Nieves within a locked house compound and also serves as a field house for the geologists. Paper and digital maps, cross-sections and long sections are stored in the Nieves field house office.
Figure 12-1 Core storage and logging compound
| August 9th, 2012 | CARACLE CREEK INTERNATIONAL COSULTING INC. | |
| | Toronto - Vancouver - Sudbury - Johannesburg | |
 | Independent Technical Report: Nieves Property Quaterra Resources Inc. and Blackberry Ventures 1, LLC |
Figure 12-2 Core storage by hole and depth
Several drill sites from the Phase VII and VIII drill programs were visited. The drill programs were completed before the site visit so it was not possible to see a drill in operation on the property. The drill sites are marked with a cement slab with the drill hole ID marked on the top (Figure 10-1). Using a handheld GPS the coordinates of three drill hole markers were recorded to compare with Quaterra's coordinates. The coordinates matched to within the error of the handheld GPS.
One drill hole, QTA-144, was reviewed in its entirety to compare logging descriptions and listed lithologies with actual core. The logging descriptions, lithologies and to-from depths were consistent with observations from the core. The sample intervals were marked on the sample boxes. During logging, the geologist photographs the core to maintain a complete record in the event core is destroyed. The core photos are digitally stored in the Nieves geology office by hole number and depth.
The results of the external blank and standard for Phase VII and VIII are summarized in Table 12-5. The control charts for standard and blank for Ag analyzed with both methods are shown on Figure 12-8 to Figure 12-15. The control charts for Au are in Appendix 3 of the report.
Silver assays analyzed with the ME-ICP41 method are biased high (Figure 12-8 and Figure 12-12) and Ag assays analyzed with the ME-GRA21 method are biased low (Figure 12-9 and Figure 12-13). These biases show no correlation with time suggesting a systematic, not a temporary problem.
The failure rates of customized standard KM 2653 is high for Ag analyzed with both methods and very high for Au in both phases of drilling.
There are several reasons for the high failure rate of the standard for Au. One of them is the difference in methodology. The standard was analyzed for certification with fire assay and instrument finish and Au in the Nieves project was analyzed with fire assay and gravimetric finish.
The other reason for the high failure rate of the standard for Au is that the standard is classified as a provisional (not certified) standard for Au with an RSD (relative standard deviation) between 5 and 15%, therefore it should be used with caution when assessing the accuracy of data (Smee, 2010).
Also, the detection limit for Au is 0.05 ppm and the Au grade of standard is 0.062 ppm, which is very close to the detection limit, within the acceptable interval for a blank sample (3 times the detection limit).
The failure rates of the blank are acceptable for both Ag and Au in both phases of drilling.
The performance of the laboratory standards were also checked due to the high failure rates of external standards. The failure rates of the laboratory standards are summarized in Table 12-6.
Internal standards OREAS-45C and OREAS-45P have very high failure rates probably due to the matrix of these standards, which is ferruginous soil which does not match the matrix of the drill core samples (Table 11-5).
The slightly high failure rate of standard OREAS-67A for Ag is probably caused by a difference in analytical methods. OREAS-67A is certified for 4 acid digestion and AAS, OES or MS finish (Table 11-5) and the samples were analyzed with fire assay and gravimetric finish.
The reason of the high failure rate of standard SQ28 for Ag (16% and 47.06%) is probably also due to different analytical methods. Standard SQ28 is certified for instrument finish (AAS or ICP-ES), but the samples were analyzed with gravimetric finish (Table 11-5).
Overall, the results of internal standards are acceptable. There is at least one standard for every analytical method used for Ag and Au that performed adequately.
The failure rates of pulp duplicates in Phase VII are summarized in Table 12-7. The failure rates of pulp and core duplicates in Phase VIII are summarized in Table 12-8. Duplicate plots for silver are shown in Figure 12-16 to Figure 12-21. Duplicate plots for Au are shown in Appendix 3.
The failure rates of all duplicates are within acceptable limits. The failure rates of core duplicates are slightly high, which may be indicative of the style of mineralization characterized by narrow veinlets.
The failure rates of the external blank and standard for Ag and Au are summarized in Table 12-9. The failure rates of blanks are acceptable for Au and Ag analyzed with the FA-03 method and too high for Ag analyzed with the TE-2 method (Table 11-6).
The failure rates of the external standard are too high for Au and Ag analyzed with both methods, similar to the original assays by ALS. The reasons for the high failure rates are the same as the reasons for high failure rates in the original analysis (see section 12.2.1).
The failure rates of laboratory standards are summarized in Table 12-10. The failure rates for Ag are within the acceptable limits for both methods (Table 11-7). The failure rate of Au is too high.