UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
| | | |
þ | | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | | For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2006. |
OR |
o | | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | | For the transition period from to . |
Commission File Number 001-33284
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | | |
| Massachusetts | | 04-3412465 |
(State or other jurisdiction of
incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer
Identification No.) |
| | | |
| 160 Second Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts | | 02142 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
(617) 492-5554
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | |
Title of Each Class | | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
| |
Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | | The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 ofRegulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of thisForm 10-K or any amendment to thisForm 10-K. þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer or a non-accelerated filer. See definitions of “accelerated filer and large accelerated filer” inRule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
o Large accelerated filer o Accelerated filer þ Non-accelerated filer
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined inRule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes o No þ
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant, computed by reference to the last sale price of the common stock reported on the NASDAQ Global Market as of March 15, 2007, was approximately $320,102,561. The registrant has elected to use March 15, 2007 as the calculation date because on June 30, 2006 (the last business date of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter), the registrant was a privately held concern.
As of March 15, 2007, there were 24,744,284 shares of the registrant’s Common Stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE:
Portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for the 2007 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A not later than 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this annual report onForm 10-K, are incorporated herein by reference into Part III of this annual report onForm 10-K.
Forward-Looking Statements
Statements in this annual report onForm 10-K that are not strictly historical in nature are forward-looking statements. These statements include, but are not limited to, statements about: the timing of the commencement, enrollment, and completion of our clinical trials for our product candidates; the progress or success of our product development programs; the status of regulatory approvals for our product candidates; the timing of product launches; our ability to protect our intellectual property and operate our business without infringing upon the intellectual property rights of others; and our estimates for future performance, anticipated operating losses, future revenues, capital requirements, and our needs for additional financing. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “anticipates,” “believes,” “could,” “estimates,” “expects,” “intends,” “may,” “plans,” “potential,” “predicts,” “projects,” “should,” “will,” “would,” “goal,” and similar expressions intended to identify forward-looking statements. These statements are only predictions based on current information and expectations and involve a number of risks and uncertainties. The underlying information and expectations are likely to change over time. Actual events or results may differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements due to various factors, including, but not limited to, those set forth in “ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS” and elsewhere in this annual report onForm 10-K. Except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
PART I
In this annual report onForm 10-K, unless the context indicates otherwise, references to “Molecular Insight,” “the Company,” “our company,” “we,” “us,” and similar references, refer to Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals, Inc. All references to years in thisForm 10-K, unless otherwise noted, refer to our fiscal years, which end on December 31. For example, a reference to “2006” or “fiscal 2006” means the12-month period that ended December 31, 2006.
Overview
We are a biopharmaceutical company specializing in the emerging field of molecular medicine, applying innovations in the identification and targeting of disease at the molecular level to improve patient healthcare by addressing significant unmet medical needs. We are focused on discovering, developing and commercializing innovative and targeted radiotherapeutics and molecular imaging pharmaceuticals with initial applications in the areas of oncology and cardiology. Radiotherapeutics are radioactive drugs, or radiopharmaceuticals, that are systemically administered and selectively target cancer cells to deliver radiation for therapeutic benefit. This ability to selectively target cancer cells allows therapeutic radiation to be delivered to tumors while minimizing radiation exposure to normal tissues. Molecular imaging pharmaceuticals are radiopharmaceuticals that enable early detection of disease through the visualization of subtle changes in biochemical and biological processes.
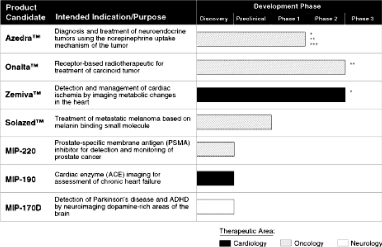
We currently have two clinical-stage radiotherapeutic product candidates, Azedra, which has Orphan Drug status and a Fast Track designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, and Onalta, which has Orphan Drug status. We have one clinical-stage molecular imaging pharmaceutical product candidate, Zemiva. We are also developing additional product candidates by leveraging our expertise in radiochemistry and radiolabeling founded on our core proprietary technologies, including our Ultratrace technology and Single Amino Acid Chelate, or SAAC, technology. Using our proprietary technologies, we have identified potential candidates that may be useful in the detection or treatment of prostate cancer, heart failure and neurodegenerative disease, which is a disease characterized by the gradual and progressive loss of nerve cells. Additionally, several other indications relating to the future development for Zemiva have been identified, such as diabetes, chronic kidney disease and heart failure.
2
The following table summarizes our current product candidates:
| | |
| * | | Known molecule commercialized outside the United States |
| |
| ** | | Orphan Drug status |
| |
| *** | | Fast Track designation |
Our Radiotherapeutic Oncology Product Candidates: Azedra and Onalta for Neuroendocrine Tumors
Our radiotherapeutic product candidates, Azedra and Onalta, are being developed as treatments for various neuroendocrine tumors. Azedra is designated as a Fast Track drug, and both product candidates are designated as Orphan Drugs by the FDA and are being developed to serve a patient population where currently there are no approved therapies for reducing tumor size. Orphan Drug status is designed to facilitate the development of new therapies for rare diseases or conditions, those which generally affect fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States. Additional criteria include the ability of a product to address a medical need where there are no other treatment options or to provide a significant benefit over other therapies.
The initial target market for Azedra is for the treatment of metastatic neuroendocrine tumors, such as pheochromocytoma, carcinoid and neuroblastoma that are not amenable to treatment with surgery or conventional chemotherapy. Metastatic tumors are tumors that spread to other organs or parts of the body. We intend to develop Azedra for the treatment of pheochromocytoma and carcinoid in adults, and for neuroblastoma in children. The initial target market for Onalta is for the treatment of metastatic carcinoid and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in patients whose symptoms are not controlled by somatostatin analog therapy. Somatostatin is a hormone distributed throughout the body that acts as a regulator of endocrine and nervous system function by inhibiting the secretion of several other hormones such as growth hormones, insulin and gastrin. Somatostatin analog therapy (or octreotide or sandostatin) is used to alleviate the symptoms associated with carcinoid syndrome. Conventional somatostatin analogs, such as Sandostatin, are indicated for the alleviation of symptoms of carcinoid syndrome. However, patients become refractory to the treatment after an average duration of effect of six months and once refractory, there currently are no approved treatment options available to alleviate carcinoid syndrome symptoms.
Azedra
Azedra is one of our two lead radiotherapeutic product candidates under development for the treatment of cancer. Formerly known as Ultratrace MIBG, or I-131-metaiodobenzylguanidine, Azedra consists of the MIBG molecule chemically bound to a radioactive iodine isotope through our proprietary Ultratrace technology. Azedra has received Orphan Drug status and a Fast Track designation by the FDA. The iodine isotope, depending on the particular isotope selected, acts either diagnostically for imaging disease or therapeutically to
3
deliver targeted radiation to the tumor site. Azedra incorporates an iodine isotope, targets specific tumor cells and does not contain unwanted carrier molecules, or cold contaminants.
Azedra Mechanism of Action
MIBG is a synthetic hormone analog of the biogenic amine norepinephrine, which was first described by researchers at the University of Michigan. Norepinephrine is a chemical made by nerve cells that is released from the adrenal gland in response to stress and low blood pressure. The mechanism by which MIBG molecules accumulate in tumors is very selective and controlled by the protein called the norepinephrine transporter, which is expressed on the cell surface. A norepinephrine transporter, or NET, enables the direct movement of norepinephrine into, out of, within or between cells. Like the hormone norepinephrine, MIBG is concentrated by NET and stored within specific types of neuronal tissue and tumor cells. The uptake and prolonged retention of MIBG within tumor cells potentially constitutes a superior molecular targeting mechanism. However, the number of MIBG molecules taken up by a tumor cell is limited. To maximize the accumulation of radioactive MIBG molecules in tumors so that they can be optimally treated by radiotherapy, the amount of non-radioactive MIBG molecules present in the drug must be minimized. By doing so we also minimize potential chemical toxicity associated with administration of MIBG containing cold contaminants. Our proprietary Ultratrace technology reduces the amount of cold contaminants by several orders of magnitude and thereby enhances accumulation of MIBG in the tumor.
Azedra Clinical Programs
Azedra has received Orphan Drug status and a Fast Track designation by the FDA. We are conducting initial clinical trials with Azedra in adults with either pheochromocytoma or carcinoid, and depending on the trial results and with input from the FDA, we plan to then move into clinical trials with children with neuroblastoma. We are currently conducting a Phase 1 clinical trial with Azedra in adults at Duke University, with data from nine of an anticipated twelve patients received. The Phase 1 dosimetry trial is designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability and distribution of Azedra in adult patients with one of two forms of neuroendocrine cancer — either carcinoid or pheochromocytoma. The data from this Phase 1 trial will be used to calculate the radiation dose of Azedra as well. Upon input from the FDA, we expect to begin a Phase 1/2 safety, dose ranging and efficacy clinical trial with Azedra in adults, with an estimated twelve patients at four to six U.S. centers. We have recently submitted a Phase 1/2 clinical trial protocol to the FDA for review.
Onalta
Onalta is our other lead radiotherapeutic product candidate under development for the treatment of cancer. Formerly known as OctreoTher, Onalta is our brand name for edotreotide, an yttrium-90 radiolabeled somatostatin peptide analog that we recently in-licensed from Novartis Pharma AG, or Novartis. Onalta is a radiolabeled somastatin analog that binds to somastatin receptors which are present on neuroendocrine tumors such as carcinoid and neuroendocrine pancreatic tumors. Somatostatin and its analogs bind to somatostatin receptors found on neuroendocrine tumor cells. We are developing Onalta for the radiotherapeutic treatment of metastatic carcinoid and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in patients whose symptoms are not controlled by conventional somatostatin analog therapy.
Onalta Mechanism of Action
Onalta attaches to tumor cells that have receptors for the peptide hormone somatostatin. These receptors become overexpressed in cancers such as carcinoid and other select neuroendocrine tumors. Such tumors are referred to as somatostatin receptor positive tumors, or SSRTs. The octreotide portion of the Onalta molecule binds specifically to somatostatin receptors and serves as a carrier for targeted delivery of the therapeutic radioisotope yttrium-90 to the tumor.
4
Onalta Clinical Programs
We recently acquired Onalta from Novartis which conducted three Phase 1 and three Phase 2 clinical trials involving more than 300 patients. We will build upon the extensive experience Novartis has had with the drug in order to inform protocol design. We intend to pursue an indication for Onalta for the treatment of somatostatin positive pancreatic neuroendocrine and carcinoid tumors, whose symptoms are not controlled by conventional somatostatin analog therapy.
Our Lead Molecular Imaging Pharmaceutical Product Candidate: Zemiva
Zemiva is our lead molecular imaging pharmaceutical product candidate under development for the diagnosis of cardiac ischemia, or insufficient blood flow to the heart. Zemiva is our brand name forI-123-BMIPP or iodofiltic acid I-123, which has been commercially available in Japan and used in the non-acute setting under the name Cardiodine for over ten years. To our knowledge, no significant safety events have been reported. Cardiodine has been the subject of over 200 peer-review articles and we understand it has been used in over 500,000 patients. The initial target market for our lead molecular imaging pharmaceutical product candidate, Zemiva, is for the diagnosis of cardiac ischemia in the emergency department setting. A second target market for Zemiva is for the diagnosis of coronary disease in the non-acute setting.
Zemiva Mechanism of Action
Zemiva is a fatty acid analog that is trapped in healthy heart cells that have appropriate blood supply. In contrast, retention of Zemiva is reduced in ischemic heart cells. Because of its high uptake and long retention in healthy heart cells, Zemiva provides high quality images of the heart. Uptake of Zemiva in the heart most likely reflects normal fatty acid metabolism. In the setting of cardiac ischemia, reduction in fatty acid metabolism is mirrored by decreased cardiac uptake of Zemiva.
Zemiva Clinical Programs
We have completed three clinical trials, including two multi-center Phase 2 clinical trials and a Phase 1 clinical trial at Massachusetts General Hospital. Data from these trials have been presented at leading scientific forums, including the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology and the American Heart Association annual scientific meetings. Results from our Phase 2a trial were published in the peer-reviewed journalCirculationand cited at the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology meeting. A Phase 2a clinical trial is a stage of drug development for an experimental drug designed to assess short-term safety and efficacy in a moderate number of patients. Taken in the aggregate, we believe that our clinical results provide preliminary indications of the safety and efficacy of Zemiva. More detailed information with respect to these trials is as follows:
| | |
| | • | Multi-Center Phase 2b Clinical Trial. In March 2005, we completed enrollment of 105 patients in our multi-center Phase 2b clinical trial of Zemiva. A Phase 2b clinical trial is a stage of drug development for an experimental drug designed to assess short-term safety and efficacy as well as therapeutic value. This trial was designed to evaluate the safety and feasibility of Zemiva for the detection of cardiac ischemia in patients with suspected ACS whose symptoms occurred within 30 hours prior to Zemiva injection. The objectives of the study were to evaluate: 1) the performance characteristics (accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value which tell us how likely it is that a patient does not have ACS, given that their Zemiva imaging test result was negative for detection/exclusion of ACS); and 2) the safety of a single injection of Zemiva in patients suspected of ACS. The study was designed as an open-label Phase 2 study that recruited high-likelihood and intermediate- to low-likelihood ACS patients. Patients were imaged with Zemiva for the presence or absence of altered fatty acid metabolism due to cardiac ischemia. Preliminary findings of this study suggested that Zemiva demonstrates the ability to detect areas of cardiac ischemia with results generally consistent with traditional diagnostic techniques, including those requiring substantially greater time to complete. Preliminary analysis also suggested that there is a high negative predictive value when Zemiva is administered to these patients at rest. |
5
| | |
| | • | Multi-Center Phase 2a Clinical Trial. We enrolled 32 patients in our multi-center Phase 2a clinical trial of Zemiva, a clinical trial for an experimental drug designed to assess safety and efficacy in a moderate number of patients. This trial evaluated the safety and feasibility of Zemiva for the detection of ischemia subsequent to a documented ischemic event. The multi-center Phase 2a study was designed to characterize the cardiac uptake of Zemiva in the hearts of patients who had experienced an ischemic event (induced during the exercise portion of clinically indicated stress/rest cardiac perfusion imaging test) within 30 hours prior to study drug administration. The results of the Zemiva cardiac images were also compared with the results of the cardiac perfusion study. We believe that the data suggest that Zemiva administered to resting patients with ischemia safely detects an ischemic event up to 30 hours after the event occurred, without the use of a stress test. Currently marketed perfusion agents must be used within two hours after the cessation of symptoms as recommended by the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology’s position paper on diagnosing suspected ischemia in the emergency department setting. |
| |
| | • | Phase 1 Clinical Trial. We enrolled six volunteers in our single-center Phase 1 clinical trial for Zemiva, which is a trial in which the product candidate is first researched in a small number of human subjects. This trial evaluated the safety, radiation dosimetry, organ distribution and effects of fasting on cardiac uptake. Each volunteer was studied twice: once while fasting and once after a predetermined meal. Results from this study suggest that Zemiva is safe and that it provides high quality cardiac images with a five- to six-fold reduction in radiation dose compared to current perfusion agents. |
| |
| | • | Use of BMIPP in Japan. In Japan, I-123-BMIPP (or Zemiva) is marketed as Cardiodine by Nihon Medi-Physics, which is a joint venture between Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. and a subsidiary of General Electric Company (the maker of Myoview). Cardiodine has an established safety profile and has demonstrated clinical utility through use, we understand, in more than 500,000 patients in Japan. It has been the subject of over 400 peer-reviewed articles. From this clinical experience in Japan, to our knowledge no serious adverse events or safety concerns related to I-123-BMIPP have been reported. We have an agreement with Nihon Medi-Physics that allows us to read and reference data from their Japanese regulatory filings and Phase 4 study in Japan in connection with our submissions to the FDA. To our knowledge, Nihon Medi-Physics does not have I-123-BMIPP patent rights in or outside of Japan. |
We believe that the data from completed trials and the use of I-123-BMIPP in Japan support our decision to advance Zemiva into pivotal registration trials. As part of our U.S. regulatory strategy for Zemiva, we have initiated a normative clinical trial as follows:
| | |
| | • | Phase 2 Normals Database Clinical Trial. We have a Phase 2 clinical trial underway to develop our own reference database of normal images for myocardial SPECT imaging, or a Normals database. A Normals database is a valuable tool for the physician interpreting the cardiac image, regardless of whether the study is read by a nuclear cardiologist, nuclear medicine physician or radiologist. Such a database enables the interpreting physician to compare a patient’s cardiac image against that of a “normal” image as defined by computer-compiled data. Consistent with this standard practice, we are conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial to develop our own Normals database that will be used as part of our pivotal registration clinical trials and in the commercialization of Zemiva, if approved by the FDA or comparable regulatory bodies outside the United States. This trial is designed to include approximately 120 patients. |
Our Other Pipeline Product Candidates
In addition to Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva, we are developing a portfolio of product candidates for oncological molecular imaging and targeted radiotherapy as well as cardiovascular molecular imaging using our proprietary technologies. Applied independently and in combination, these technologies enable the development of innovative and targeted radiotherapeutics and molecular imaging pharmaceuticals that use both small molecules and peptides.
6
Solazed
Solazed is a targeted radiotherapeutic that we intend to develop for the treatment of malignant metastatic melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer. We recently in-licensed the compound from Bayer Schering Pharma Aktiengesellschaft, or Schering. Solazed is a small molecule compound that targets melanin, a naturally occurring pigment responsible for the color of the skin and the dark color of the melanoma tumor.
MIP-220
We are developing a non-invasive method for visualization of prostate cancer through molecular imaging. We are engaged in discovery studies of a molecular imaging pharmaceutical for detection of prostate-specific membrane antigen, or PSMA, expression which would enable the detection and monitoring of prostate cancer, with the intention to be able to detect subtle manifestation of metastatic disease in men with elevated serum prostate specific antigen, or PSA, but no other obvious symptoms. Metastatic disease is a disease that can result in the transmission of cancerous cells from an original site to one or more sites elsewhere in the body. We currently have identified a series of compounds that bind PSMA and localize in human prostate tumors. Our next step will be to select the lead compound to carry into preclinical development for human use.
MIP-190
We are developing a non-invasive way to assess the progression of heart failure through the monitoring of angiotensin converting enzyme, or ACE, in human hearts. In conjunction with scientists at the University of Maryland Medical Center, we have engaged in NIH-sponsored development of cardiovascular compounds to target ACE as a marker for the assessment of heart failure patients. Such compounds would be novel in that they would enable the evaluation of ACE in human hearts with chronic ischemia and heart failure using external imaging. The level of ACE has been shown to increase in the heart muscle as heart failure progresses. A means of non-invasively monitoring ACE levels may allow doctors to better manage heart failure to slow down clinical progression. We currently have identified a lead compound that is radiolabeled using our SAAC technology, which displays strong binding to ACE both in isolated enzymes and in animal studies.
MIP-170D
We are developing a potential aid in the objective diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, or ADHD. Our neurology preclinical discovery program,MIP-170D, represents a class of compounds that bind to specific molecular targets in the brain. As molecular imaging pharmaceuticals, these compounds have the potential of aiding doctors in the diagnosis of disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and ADHD. Our next steps will be to select the lead compound to carry into preclinical development for human use.
Our Proprietary Technology Platforms
We have developed platform technologies that allow radiochemistry to be integrated into the medicinal chemistry stage of discovery. As such, compounds can be made which allow the screening of compounds which are chemically equivalent to the ultimately radiolabeled compound. This integration allows both the rapid synthesis and screening of large numbers of compounds, and ensures the radiolabeling platform can be used for manufacturing.
Our core proprietary technologies include our Ultratrace technology and SAAC technology. These technologies drive development of our current portfolio and should enable the research and development of future molecular imaging pharmaceuticals and targeted radiotherapeutic candidates. Our core proprietary technologies, applied independently and together, include:
| | |
| | • | Ultratrace Technology. Our Ultratrace technology is a proprietary solid-phase radiolabeling technology that enables the development of ultrapure radiopharmaceuticals which are devoid of unnecessary cold contaminants, thereby enhancing safety, specificity and potency. Cold contaminants are nonradioactive, or unlabeled targeting molecules, which may potentially induce unnecessary side effects and |
7
| | |
| | | suboptimize efficacy by competing with radiolabeled targeting molecules for binding to limited numbers of receptor target sites. |
| | |
| | • | SAAC Technology. The ability to reliably and robustly incorporate medically useful radioactive metals into biologically relevant targeting molecules is critical to the design of successful radiopharmaceuticals for molecular imaging and targeted radiotherapy. Single Amino Acid Chelate, or SAAC, is our unique metal binding chemistry platform technology. It represents a new family of compounds with superior metal binding properties for leading radionuclides used for imaging and therapy, namely technetium-99m and rhenium-186 and rhenium-188. This technology incorporates a metal binding, or chelating, group that can rapidly and efficiently bind to technetium or rhenium for diagnostic and therapeutic uses with an amino acid portion that allows it to be incorporated into any peptide sequence through the use of conventional peptide chemistry. |
| |
| | • | SAACQ Technology. Two widely employed techniques for visualizing specific biological processes are fluorescence microscopy and radioisotope imaging. Different from current technologies, our new fluorescence-based technology called SAACQ enables the visualization of radiopharmaceuticals interacting with cellular structures. This advance promises to accelerate the development of targeted radiotherapeutics and molecular imaging pharmaceuticals by allowing live cell activity to be viewed by fluorescent microscopy. |
| |
| | • | Nanotrace Discovery. Our Nanotrace Discovery targeting platform technology allows for the rapid creation and screening of new leads for molecular targeting of disease. We believe that we can utilize this technology to create libraries of radiolabeled compounds in a relatively short period of time. Nanotrace Discovery appears to be applicable to major disease categories such as cardiovascular disease, oncology and neurology. |
Sales, Marketing and Manufacturing
We intend to market Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva through our own specialty sales and marketing team. Considering the concentrated nature of our initial target markets, we believe that approximately five to 10 highly specialized sales representatives will be sufficient to support the market for Azedra and Onalta in the first year. We believe that a dedicated sales force of approximately 50 to 100 individuals upon commercial launch of Zemiva will be sufficient to support the market for Zemiva in the first year. To support medical education efforts for the product, we plan to hire a group of five to 10 medical liaisons with emergency department or nuclear medicine expertise to provide technical training and education.
Our initial marketing focus for Azedra and Onalta will be on large cancer centers specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of neuroendocrine tumors with an established capability for targeted radiotherapy delivery. There are approximately 25 such centers in the United States. Our initial marketing focus for Zemiva will be on large hospitals with over 200 beds that have nuclear medicine capabilities available 24 hours a day. There are approximately 1,800 hospitals in the United States with emergency departments and over 200 beds. Of these, 80% have nuclear medicine capabilities available 24 hours a day. Thus, our target hospital focus will be on approximately 1,400 hospitals that tend to be clustered in concentrated areas of large populations. Approximately 76% of emergency department visits occur at hospitals with over 200 beds.
We currently manufacture in our laboratories the quantities of Azedra that we are using for our existing clinical trials. We are exploring additional manufacturing options for Onalta.
Zemiva is currently manufactured for our preclinical and clinical trials at a manufacturing facility owned by MDS Nordion located in Vancouver, Canada which is, to our knowledge, compliant with current Good Manufacturing Practices, or cGMP. We believe that the MDS Nordion facility is sufficient to produce Zemiva required for use through our clinical trials. We do not, however, have any experience in commercial-scale manufacturing. Therefore, if we receive FDA approval of Zemiva, we may need to rely on contractual relationships with third-party manufacturers for commercial scale production. We anticipate that the manufacture of the other products in our development pipeline will be outsourced to experienced cGMP-compliant medical manufacturing companies.
8
Competition
We will compete for market share against large pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, smaller companies that are collaborating with larger pharmaceutical companies, new companies, academic institutions, government agencies and other public and private research organizations. Many of these competitors, either alone or together with their partners, may develop new product candidates that will compete with ours, and these competitors may, and in certain cases do, operate larger research and development programs or have substantially greater financial resources than we do.
If Azedra or Onalta are approved, their competition will be the current standard of care and companies that are engaged in the development and commercialization of targeted radiotherapeutics for treatment of cancer.
If Zemiva is approved, its competition in the emergency department setting will be the current standard of care in the assessment of chest pain patients who present to emergency departments. This standard involves several diagnostic products and procedures, in some cases involving the use of perfusion imaging agents, which in the aggregate may require several hours or days of hospitalization to reach an ultimate diagnosis.
Perfusion imaging agents such as Cardiolite (from Bristol-Myers Squibb Imaging), Myoview (from Amersham, a subsidiary of General Electric Company) and thallium, are considered unable to reliably detect cardiac ischemia more than two hours after the cessation of chest pains, thereby making them of limited value in the emergency department setting. Many patients who present with chest pain in the emergency department are beyond the perfusion agents’two-hour window of active symptoms when they arrive or their symptoms subside while waiting in the emergency department. Additionally, as their hearts may be unstable, stress testing with these agents is contraindicated in patients with suspected ACS in the emergency department setting. Sales of perfusion agents in the acute setting account for, to our knowledge, less than 5% of the overall sales for these agents.
Perfusion agents would be, however, Zemiva’s main competition in the non-acute market if regulatory approval is obtained. We estimate that worldwide sales of Cardiolite, Myoview and thallium were approximately $1.0 billion in 2004. Currently, these perfusion agents are used almost exclusively in nonacute settings in connection with stress testing where the patient’s stress is induced (either by exercise or a pharmacological stress agent) as they are generally required to be used within two hours after the cessation of chest pain.
Patents and Proprietary Rights
Our success depends in part on our ability to obtain and maintain a competitive position in the marketplace. This includes obtaining proprietary protection for our product candidates, technology, and know-how; preventing others from infringing our proprietary rights; and operating without infringing the proprietary rights of others. Our policy is to seek to protect our proprietary position by, among other methods, applying for and obtaining U.S. and foreign patents relating to our proprietary technologies, inventions, and improvements that are important to our business. This includes obtaining patent term extensions or restorations when possible. In addition, we rely on trade secrets, know-how, continuing technological innovation and in-licensing opportunities to develop and maintain our proprietary positions. Furthermore, we intend to build brand identity in our company, our technologies and our product candidates, and for this purpose have applied for certain trademarks, as described below.
As of December 31, 2006, we had seven issued U.S. patents and 10 issued foreign patents which are counterparts to the U.S. filings. We had eight pending U.S. patent applications, and 33 pending foreign patent applications that have been nationalized in various countries. Additionally, we have obtained licenses from third parties for the patent rights to U.S. and foreign patents and patent applications to make, use, sell and import certain proprietary technologies and compounds. Patent rights for in-licensed technologies are not included in the above totals. While we believe our patents and patent applications may be important for certain aspects of our business, such as those related to specific product candidates such as BMIPP derivatives whose patents and applications expire between 2016 and 2023, we also believe that our success also depends upon innovation, technical expertise, and responsiveness to the medical needs of an aging patient population. While
9
our patented technology may delay or deter a competitor in offering a competing product, we believe our technical capability should also allow us to obtain limited market exclusivity in the United States under the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, or the Hatch-Waxman Act, and abroad through similar legislation.
The original patent protecting the composition of BMIPP expired in 2003. However, we believe that Zemiva, or I-123-BMIPP, is a new chemical entity in the United States and Europe and, therefore, should be eligible for market exclusivity under the FDCA as amended by the Hatch-Waxman Act. We are also pursuing three additional patent families (in the United States and internationally) to provide up to 18 years of new patent-based exclusivity for certain aspects of BMIPP and BMIPP-derivative compositions and their uses, with the patent and patent applications expiring generally in 2023.
The Hatch-Waxman Act provides a five-year period of non-patent marketing exclusivity to the first applicant to gain approval of an NDA for a new chemical entity. A drug can be classified as a new chemical entity if the FDA has not previously approved any other new drug containing the same active agent. During the exclusivity period, the FDA may not accept for review an abbreviated new drug application, or ANDA, or a 505(b)(2) NDA submitted by another company for another version of such drug, where the applicant does not own or have a legal right of reference to all the data required for approval. Protection under the Hatch-Waxman Act will not prevent the filing or approval of another full NDA, but the applicant would be required to conduct its own adequate and well-controlled clinical trials to demonstrate safety and effectiveness. The Hatch-Waxman Act also provides three years of marketing exclusivity for an NDA, 505(b)(2) NDA or supplements to existing NDAs if new clinical investigations are essential to the approval of the applications, for example, for new indications, dosages, or strengths of an existing drug. This three-year exclusivity covers only the conditions associated with the new clinical investigations and does not prohibit the FDA from approving ANDAs for drugs containing the original active agent.
The Hatch-Waxman Act also permits a patent restoration term of up to five years as compensation for patent term lost during product development and the FDA regulatory review process. However, patent term restoration cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years. The patent term restoration period is generally one-half the time between the effective date of an investigational new drug exemption, or IND, and the submission date of an NDA, plus the time between the submission date of an NDA and the approval of that application. Only one patent applicable to an approved drug is eligible for the extension and it must be applied for prior to expiration of the patent. The United States Patent and Trademark Office, in consultation with the FDA, reviews and approves the application for any patent term extension or restoration. In the future, we may consider applying for restorations of patent term for some of our currently owned or licensed patents to add patent life beyond the current expiration date, depending on the expected length of clinical trials and other factors involved in the filing of the relevant NDA.
The patent positions of companies like ours are generally uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions. Our ability to maintain and solidify our proprietary position for our technology will depend on our success in obtaining effective claims and enforcing those claims once granted. We do not know with certainty whether any of our patent applications or those patent applications that we license will result in the issuance of any new patents. Our issued patents and those that may issue in the future, or those licensed to us, may be challenged, invalidated, or circumvented, which could limit our ability to stop competitors from marketing related products, or could affect the length of term of patent protection that we may have for our products. In addition, the rights granted under any issued patents may not provide us with sufficient proprietary protection or competitive advantages against competitors with similar technology. Furthermore, our competitors may independently develop similar technologies or duplicate any technology developed by us and, to the extent they seek to protect these technologies through patents and such technologies are determined to contain valid and enforceable claims, they could achieve a legal determination that our products or technologies are infringing these third-party patents. Because of the extensive time required for development, testing and regulatory review of a potential product, it is possible that before any of our products can be commercialized, any related patent may expire, or that such patent may remain in force for only a short period following commercialization of a product candidate, thereby reducing any advantage of the patent with respect to that product candidate. While patent term restoration is available under theHatch-Waxman Act and similar laws,
10
we cannot predict whether such patent term restoration will be granted to us as to any particular patent covering such product candidate.
We rely in some circumstances on trade secrets to protect our technology, particularly with respect to certain aspects of our Zemiva manufacturing process. Trade secrets, however, can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors, contract manufacturers and other entities with whom we do business. However, these agreements may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors. To the extent that our employees, consultants or contractors use intellectual property owned by others in their work for us, disputes may arise as to the proprietary rights or resulting know-how generated in related inventions.
We currently use Molecular Insighttm and the Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals logo as trademarks in the United States and other countries. We have sought trademark registration for the Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals logo, Azedratm, Ultratracetm, Nanotracetm, Zemivatm, SAACtm and SAACQtm in the United States and in countries outside the United States. We have sought trademark registration for Molecular Insighttm, Onaltatm, Solazedtm, Rintaratm, Unectratm and Velepintm in the United States. We cannot guarantee any of these marks will be approved in the United States or in foreign jurisdictions. In addition, we have obtained rights to the following Internet domain names: www.molecularinsight.com, www.zemiva.com, www.zemiva.org, www.zemiva.net, www.velepin.com, www.velepin.org, www.velepin.net, www.ultratrace.org, www.ultratrace.net., www.azedra.com, www.azedra.net, www.solazed.com, www.solazed.org, and www.solazed.net.
Government Regulation
Government authorities in the United States and foreign countries extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, labeling, promotion, advertising, distribution, sampling, marketing and import and export of pharmaceutical products. Our targeted radiotherapeutics and molecular imaging pharmaceuticals in the United States will be subject to FDA regulation as drugs under the FDCA, and require FDA approval prior to commercial distribution. The process of obtaining governmental approvals and complying with ongoing regulatory requirements requires the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources. In addition, statutes, rules, regulations and policies may change and new legislation or regulations may be issued that could delay such approvals. If we fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements at any time during the product development process, approval process, or after approval, we may become subject to administrative or judicial sanctions. These sanctions could include the FDA’s refusal to approve pending applications, withdrawals of approvals, clinical holds, warning letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of our operations, injunctions, fines, civil penalties or criminal prosecution. Any agency enforcement action could have a material adverse effect on us.
The U.S. regulatory scheme for the development and commercialization of new pharmaceutical products can be divided into three distinct phases: an investigational phase including both preclinical and clinical investigations leading up to the submission of an NDA; a period of FDA review culminating in the approval or refusal to approve the NDA; and the post-marketing period. Each of these phases is described below.
Preclinical Phase
The preclinical phase involves the characterization, product formulation and animal testing necessary to prepare an IND for submission to the FDA. The IND must be reviewed and authorized by the FDA before the drug can be tested in humans. Once a new pharmaceutical agent has been identified and selected for further development, preclinical testing is conducted to confirm pharmacological activity, to generate safety data, to evaluate prototype dosage forms for appropriate release and activity characteristics, and to confirm the integrity and quality of the material to be used in clinical trials. A bulk supply of the active ingredient to support the necessary dosing in initial clinical trials must be secured. Data from the preclinical investigations and detailed information on proposed clinical investigations are compiled in an IND submission and submitted
11
for FDA before human clinical trials may begin. If the FDA does not formally communicate an objection to the IND within 30 days, the specific clinical trials outlined in the IND may go forward.
Clinical Phase
The clinical phase of drug development follows a successful IND submission and involves the activities necessary to demonstrate the safety, tolerability, efficacy, and dosage of the substance in humans, as well as the ability to produce the substance in accordance with the FDA’s cGMP requirements. Data from these activities are compiled in an NDA requesting approval to market the drug for a given use, or indication. Clinical trials must be conducted under the supervision of qualified investigators in accordance with good clinical practice, and according to IND-approved protocols detailing, among other things, the study objectives and the parameters, or endpoints, to be used in assessing safety and efficacy. Each trial must be reviewed, approved and conducted under the auspices of an independent Institutional Review Board, or IRB, and each trial, with limited exceptions, must include all subjects’ informed consent. The clinical evaluation phase typically involves the following sequential process:
Phase 1 clinical trials are conducted in a limited number of healthy subjects to determine the drug’s safety, tolerability, and biological performance. The total number of subjects in Phase 1 clinical trials varies, but is generally in the range of 20 to 80 people (or less in some cases, such as drugs with significant human experience).
Phase 2 clinical trials involve administering the drug to subjects suffering from the target disease or condition to evaluate the drug’s potential efficacy and appropriate dose. The number of subjects in Phase 2 trials is typically several hundred subjects or less.
Phase 3 clinical trials are performed after preliminary evidence suggesting effectiveness has been obtained and safety, tolerability, and appropriate dosing have been established. Phase 3 clinical trials are intended to gather additional data needed to evaluate the drug’s overall benefit-risk relationship of the drug and to provide adequate instructions for its use. Phase 3 trials usually include from several hundred to several thousand subjects.
Throughout the clinical testing phase, samples of the product made in different batches are tested for stability to establish shelf life constraints. In addition, increasingly large-scale production protocols and written standard operating procedures must be developed for each aspect of commercial manufacture and testing.
The clinical trial phase is both costly and time-consuming, and may not be completed successfully within any specified time period, if at all. The FDA closely monitors the progress of each of the three phases of clinical trials that are conducted under an IND and may, at its discretion, reevaluate, alter, suspend, or terminate the testing at any time for various reasons, including a finding that the subjects or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. The FDA can also request additional clinical testing as a condition to product approval. Additionally, new government requirements may be established that could delay or prevent regulatory approval of our products under development. Furthermore, institutional review boards, which are independent entities constituted to protect human subjects in the institutions in which clinical trials are being conducted, have the authority to suspend clinical trials in their respective institutions at any time for a variety of reasons, including safety issues.
New Drug Application and Review
After the successful completion of Phase 3 clinical trials, the sponsor of the new drug submits an NDA to the FDA requesting approval to market the product for one or more indications. An NDA is a comprehensive, multi-volume application that includes, among other things, the results of all preclinical and clinical studies, information about the drug’s composition, and the sponsor’s plans for producing, packaging, and labeling the drug. In most cases, the NDA must be accompanied by a substantial user fee. FDA has 60 days after submission to review the completeness and organization of the application, and may refuse to accept it for continued review, or refuse to file, if the application is found deficient. After filing, the FDA reviews an NDA to determine, among other things, whether a product is safe and effective for its intended use. Drugs that
12
successfully complete NDA review may be marketed in the United States, subject to all conditions imposed by the FDA.
Prior to granting approval, the FDA generally conducts an inspection of the facilities, including outsourced facilities that will be involved in the manufacture, production, packaging, testing and control of the drug product for cGMP compliance. The FDA will not approve the application unless cGMP compliance is satisfactory. If the FDA determines that the marketing application, manufacturing process, or manufacturing facilities are not acceptable, it will outline the deficiencies in the submission and will often request additional testing or information. Notwithstanding the submission of any requested additional information, the FDA ultimately may decide that the marketing application does not satisfy the regulatory criteria for approval and refuse to approve the application by issuing a “not approvable” letter.
The length of the FDA’s review can range from a few months to several years or more. Once an NDA is in effect, significant changes such as the addition of one or more new indications for use generally require prior approval of an sNDA including additional clinical trials or other data required to demonstrate that the product as modified remains safe and effective.
Fast Track Review
The Food and Drug Administration Modernization Act of 1997, or the Modernization Act, establishes a statutory program for relatively streamlined approval of “Fast Track” products, which are defined under the Modernization Act as new drugs or biologics intended for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening condition that demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for this condition. Fast Track status requires an official designation by the FDA.
Abbreviated New Drug Application and Review
An ANDA is a type of NDA that is used for the review and approval of a generic drug product. A generic drug product is one that is the same as a previously approved innovator drug product, which means it has the same active ingredient, dosage form, strength, route of administration, quality, performance characteristics, and intended use. An ANDA is generally not required to include preclinical and clinical data to establish safety and effectiveness. Instead, generic applicants must scientifically demonstrate that their product is bioequivalent to the previously approved drug, which means that it performs in the same manner. None of the products currently under development by Molecular Insight will be eligible for ANDA approval, although it is possible that competing products based on our product could be approved by this route at some future time.
Section 505(b)(2) Applications
If a proposed drug product represents only a limited change from a product that has already been approved by the FDA, yet differs in more ways than those permitted under the ANDA requirements, then the applicant may be able to submit a type of NDA referred to as a 505(b)(2) application. This route of approval is potentially applicable to the development of Azedra, which has previously been approved as an imaging agent for pheochromocytoma and neuroblastoma, each a specific type of neuroendocrine tumor. In effect, a 505(b)(2) applicant is permitted to rely on information in the scientific literature, or previous safety and efficacy determinations by the FDA, rather than submitting the full complement of clinical or other data that would otherwise be required for NDA approval. However, the 505(b)(2) sponsor must provide any additional clinical or other data needed to supplementand/or establish the relevance and applicability of prior findings for the new product formulation.
Orphan Drug Status
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant Orphan Drug designation to drugs intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States. We have received Orphan Drug designation for Azedra and Onalta and may file for Orphan Drug designation for the use of other potential product candidates. However, obtaining FDA approval to market a product with Orphan Drug exclusivity may not provide us with a material commercial advantage.
13
Orphan Drug designation must be requested before submitting an NDA. After the FDA grants Orphan Drug designation, the identity of the therapeutic agent and its potential orphan use are disclosed publicly by the FDA. Although Orphan Drug designation does not shorten or otherwise convey any advantage in the regulatory approval process, approved Orphan Drugs are granted a seven year period of market exclusivity during which the FDA may not approve any other application to market the same drug for the same disease except in very limited circumstances. These circumstances are an inability to supply the drug in sufficient quantities, or a situation in which a subsequent product has shown superior safety or efficacy. This exclusivity, however, could also block the approval of our product for seven years if a competitor obtains earlier approval of the same drug for the same indication.
Post-Approval Phase
Once the FDA has approved a new drug for marketing, the product becomes available for physicians to prescribe in the United States. After approval, we must comply with post-approval requirements, including ongoing compliance with cGMP regulations, delivering periodic reports to the FDA, submitting descriptions of any adverse reactions reported, and complying with drug sampling and distribution requirements. We are required to maintain and provide updated safety and efficacy information to the FDA. We are also required to comply with requirements concerning advertising and promotional labeling.
Compliance with post-approval requirements will require us to expend time, money, and effort on an ongoing basis. We use, and will continue to use, third-party manufacturers, including MDS Nordion, to produce certain of our products in clinical and commercial quantities. Future FDA inspections may identify compliance issues at our facilities or at the facilities of our contract manufacturers that may disrupt production or distribution, or require substantial resources to correct.
In addition, discovery of problems with a product or the failure to comply with requirements may result in restrictions including withdrawal or recall of the product from the market or other voluntary or FDA-initiated action that could delay further marketing. Newly discovered or developed safety or efficacy data may require changes to a product’s approved labeling, including the addition of new warnings and contraindications. Also, the FDA may require post-market testing and surveillance to monitor the product’s safety or efficacy, including additional clinical studies, known as Phase 4 trials, to evaluate long-term effects.
Other Regulation in the United States
Healthcare Reimbursement
Government and private sector initiatives to limit the growth of healthcare costs, including price regulation, competitive pricing, coverage and payment policies, and managed-care arrangements, are continuing in many countries where we do business, including the United States. These changes are causing the marketplace to put increased emphasis on the delivery of more cost-effective medical products. Government programs, including Medicare and Medicaid, private healthcare insurance and managed-care plans have attempted to control costs by limiting the amount of reimbursement they will pay for particular procedures or treatments. This has created an increasing level of price sensitivity among customers for our products. Some third-party payers must also approve coverage for new or innovative devices or therapies before they will reimburse healthcare providers who use the medical devices or therapies. Even though a new medical product may have been cleared for commercial distribution, we may find limited demand for the product until reimbursement approval has been obtained from governmental and private third-party payers.
Environmental Regulation
We are also subject to various environmental laws and regulations both within and outside the United States. Like many other pharmaceutical and medical device companies, our operations involve the use of substances, including hazardous wastes, which are regulated under environmental laws, primarily manufacturing and sterilization processes. We do not expect that compliance with environmental protection laws will have a material impact on our consolidated results of operations, financial position or cash flow. These laws and
14
regulations are all subject to change, however, and we cannot predict what impact, if any, such changes might have on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our research is also dependent on our maintenance of a Radioactive Materials license from the Massachusetts Department of Public Health which allows us to acquire, use and store quantities of radioactive isotopes that are critical for the manufacture and testing of research products.
Foreign Regulation
Whether or not we obtain FDA approval for a product, we must obtain approval from the comparable regulatory authorities of foreign countries before we can commence clinical trials or marketing of the product in those countries. The approval process varies from country to country, and the time may be longer or shorter than that required for FDA approval. The requirements governing the conduct of clinical trials, product licensing, pricing and reimbursement also vary greatly from country to country. Although governed by the applicable jurisdiction, clinical trials conducted outside of the United States typically are administered under a three-phase sequential process similar to that discussed above for pharmaceutical products.
Under European Union regulatory systems, we may submit marketing authorization applications either under a centralized or decentralized procedure. The centralized procedure, which is available for medicines produced by biotechnology or which are highly innovative, provides for the grant of a single marketing authorization that is valid for all European Union member states. This authorization is a marketing authorization approval, or MAA. The decentralized procedure provides for mutual recognition of national approval decisions. Under this procedure, the holder of a national marketing authorization may submit an application to the remaining member states. Within 90 days of receiving the applications and assessment report, each member state must decide whether to recognize approval. This procedure is referred to as the mutual recognition procedure, or MRP.
In addition, regulatory approval of prices is required in most countries other than the United States. We face the risk that the prices which result from the regulatory approval process would be insufficient to generate an acceptable return to us or our collaborators.
Employees
As of March 15, 2007, we had 41 full-time employees, 30 of whom have M.D.s, Ph.D.s or other advanced degrees, and one part-time employee. Thirty of our employees are engaged in research and development, clinical development and regulatory affairs and quality assurance of our product candidates. Eleven of our employees plus one part-time employee are classified in general and administrative, which includes operations, business development, finance, accounting, human resources, external communications, facilities management and general administration.
Available Information
We were incorporated in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts in 1997 under the name Imaging Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. and subsequently changed our name to Biostream, Inc. in 1998, and subsequently changed our name again to Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals, Inc. in 2003. Our principal executive offices are located at 160 Second Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 02142, and our telephone number is(617) 492-5554. Our Internet site address iswww.molecularinsight.com. Information found on, or that can be accessed through, our website is not incorporated by reference into this annual report onForm 10-K. We make available free of charge on or through our website our filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, including this annual report onForm 10-K, quarterly reports onForm 10-Q, current reports onForm 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”) as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. Further, a copy of this annual report is located at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, D.C. 20549. Information on the operation of the Public Reference Room can be obtained by calling the SEC at1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains an Internet website that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding our filings atwww.sec.gov.
15
You should consider carefully the following information about the risks described below, together with the other information contained in this Annual Report and in our other public filings before making any investment decisions regarding our stock. If any of the following risks actually occurs, our business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth prospects would likely be materially and adversely affected. In these circumstances, the market price of our common stock would likely decline, and you may lose all or part of the money you paid to buy our common stock.
This report contains forward-looking statements (within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995) that are based on management’s current expectations, estimates, forecasts, and projections about the Company and its business. In addition, other written or oral statements which constitute forward-looking statements may be made from time to time by or on behalf of Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Any statement in this report that is not a statement of historical fact is a forward-looking statement, and in some cases, words such as “believe,” “estimate,” “project,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “anticipate,” “plans,” “seeks,” and similar expressions identify forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual outcomes and results to differ materially from the anticipated outcomes or result. These statements are not guarantees of future performance, and undue reliance should not be placed on these statements. Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals, Inc. undertakes no obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from what is expressed or forecasted in our forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, the following:
Risks Related to Our Product Candidates and Operations
We are largely dependent on the success of our lead product candidates, Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva, and we may not be able to successfully commercialize these potential products.
We have incurred and will continue to incur significant costs relating to the development and marketing of our lead product candidates, Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva. We have not obtained approval to market these potential products in any jurisdiction and we may never be able to obtain approval or, if approvals are obtained, to commercialize these products successfully. If we fail to successfully commercialize these products, we may be unable to generate sufficient revenue to sustain and grow our business, and our business, financial condition and results of operations will be adversely affected.
We have recently begun to direct significant efforts toward the expansion of our scientific staff and research capabilities to identify and develop product candidates in addition to Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva. We do not know whether our planned preclinical development or clinical trials for these other product candidates will begin on time or be completed on schedule, if at all. In addition, we do not know whether any of our clinical trials will result in marketable products. We do not anticipate that any additional product candidates will reach the market for at least several years, if at all.
If we fail to obtain U.S. regulatory approval of Azedra, Onalta or Zemiva, or any of our other current or future product candidates, we will be unable to commercialize these potential products in the United States.
The development, testing, manufacturing and marketing of our product candidates are subject to extensive regulation by governmental authorities in the United States. In particular, the process of obtaining FDA approval is costly and time consuming, and the time required for such approval is uncertain. Our product candidates must undergo rigorous preclinical and clinical testing and an extensive regulatory approval process mandated by the FDA. Such regulatory review includes the determination of manufacturing capability and product performance. Generally, only a small percentage of pharmaceutical products are ultimately approved for commercial sale.
16
We can give no assurance that our current or future product candidates will be approved by the FDA or any other governmental body. In addition, there can be no assurance that all necessary approvals will be granted for future product candidates or that FDA review or actions will not involve delays caused by requests for additional information or testing that could adversely affect the time to market for and sale of our product candidates. Further failure to comply with applicable regulatory requirements can, among other things, result in the suspension of regulatory approval as well as possible civil and criminal sanctions.
Failure to enroll patients in our clinical trials may cause delays in developing Azedra, Onalta or Zemiva or any of our other current or future product candidates.
We may encounter delays in the development and commercialization, or fail to obtain marketing approval, of Azedra, Onalta or Zemiva or any other future product candidate if we are unable to enroll enough patients to complete clinical trials. Our ability to enroll sufficient numbers of patients in our clinical trials depends on many factors, including the severity of illness of the population, the size of the patient population, the nature of the clinical protocol, the proximity of patients to clinical sites, the eligibility criteria for the trial and competing clinical trials. Delays in planned patient enrollment may result in increased costs and harm our ability to complete our clinical trials and obtain regulatory approval.
Delays in clinical testing could result in increased costs to us and delay our ability to generate revenue.
Significant delays in clinical testing could materially impact our product development costs. We do not know whether planned clinical trials will begin on time, will need to be restructured or will be completed on schedule, if at all. Clinical trials can be delayed for a variety of reasons, including delays in obtaining regulatory approval to commence and continue a study, delays in reaching agreement on acceptable clinical study terms with prospective sites, delays in obtaining institutional review board approval to conduct a study at a prospective site, and delays in recruiting patients to participate in a study.
In addition, we typically rely on third-party clinical investigators to conduct our clinical trials and other third-party organizations to oversee the operations of these clinical trials and to perform data collection and analysis. As a result, we may face additional delays outside of our control if these parties do not perform their obligations in a timely fashion. Significant delays in testing or regulatory approvals for any of our current or future product candidates, including Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva, could prevent or cause delays in the commercialization of such product candidates, reduce potential revenues from the sale of such product candidates and cause our costs to increase.
Our clinical trials for any of our current or future product candidates may produce negative or inconclusive results and we may decide, or regulators may require us, to conduct additional clinicaland/or preclinical testing for these product candidates or cease our trials.
We will only receive regulatory approval to commercialize a product candidate if we can demonstrate to the satisfaction of the FDA, or the applicable foreign regulatory agency, that the product candidate is safe and effective. In April 2005, we completed a Phase 2b clinical trial for Zemiva and are currently planning a pivotal Phase 2 clinical trial for Zemiva. In addition, we commenced a Phase 1 clinical trial for Azedra in 2006, which is ongoing. Although Novartis has conducted clinical trials for Onalta, we have not. We intend to start discussions with the FDA regarding the clinical investigation plan, which may include a radiation dosimetry component in addition to safety and efficacy studies. We do not know whether our existing or future clinical trials will demonstrate safety and efficacy sufficiently to result in marketable products. Because our clinical trials for Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva and our other product candidates may produce negative or inconclusive results, we may decide, or regulators may require us, to conduct additional clinicaland/or preclinical testing for these product candidates or cease our clinical trials. If this occurs, we may not be able to obtain approval for these product candidates or our anticipated time to market for these product candidates may be substantially delayed and we may also experience significant additional development costs. We may also be required to undertake additional clinical testing if we change or expand the indications for our product candidates.
17
If approved, the commercialization of our product candidates, including Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva, may not be profitable due to the need to develop sales, marketing and distribution capabilities, or make arrangements with a third party to perform these functions.
In order for the commercialization of our potential products to be profitable, our products must be cost-effective and economical to manufacture on a commercial scale. Subject to regulatory approval, we expect to incur significant sales, marketing, distribution and, to the extent we do not outsource manufacturing, manufacturing expenses in connection with the commercialization of Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva and our other potential products as we do not currently have a dedicated sales force, we do not have manufacturing capability, and we have no experience in the sales, marketing and distribution of pharmaceutical products. In order to commercialize Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva or any of our other potential products that we develop, we must develop sales, marketing and distribution capabilities or make arrangements with a third party to perform these functions. Developing a sales force is expensive and time-consuming, and we may not be able to develop this capacity. If we are unable to establish adequate sales, marketing and distribution capabilities, independently or with others, we may not be able to generate significant revenue and may not become profitable. Our future profitability will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to:
| | |
| | • | the costs and timing of developing a commercial scale manufacturing facility or the costs of outsourcing the manufacturing of Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva; |
| |
| | • | receipt of FDA approval of Azedra, Onalta, Zemiva and our other product candidates, as applicable; |
| |
| | • | the terms of any marketing restrictions or post-marketing commitments imposed as a condition of approval by the FDA or foreign regulatory authorities; |
| |
| | • | the costs of filing, prosecuting, defending and enforcing any patent claims and other intellectual property rights; |
| |
| | • | costs of establishing sales, marketing and distribution capabilities; |
| |
| | • | the effect of competing technological and market developments; and |
| |
| | • | the terms and timing of any collaborative, licensing and other arrangements that we may establish. |
Even if we receive regulatory approval for Azedra, Onalta, Zemiva or any of our other product candidates, we may never receive significant revenues from any of them. To the extent that we are not successful in commercializing our potential products, we will incur significant additional losses and the price of our common stock will be negatively affected.
We do not have patent rights to the composition of Zemiva, and if we cannot gain and exploit a period of marketing exclusivity under the Food, Drug & Cosmetic Act, as amended, we may not be able to successfully commercialize Zemiva or our other product candidates.
We do not have patent rights to the composition of Zemiva. The original patent protecting BMIPP, the underlying active molecule in Zemiva, expired in 2003. We believe that Zemiva is a new chemical entity in the United States and should be eligible for market exclusivity under the Food, Drug & Cosmetic Act, or FDCA, as amended by the Hatch-Waxman Act of 1984. A drug can be classified as a new chemical entity if the FDA has not previously approved any other new drug containing the same active agent. Under sections 505(c)(3)(D)(ii) and 505(j)(5)(D)(ii) of the FDCA, as amended by the Hatch-Waxman Act of 1984, a new chemical entity that is granted regulatory approvals may, in the absence of patent protections, be eligible for five years of marketing exclusivity in the United States following regulatory approval. This marketing exclusivity will protect us from any other applicant utilizing the materials in support of our new drug application, or NDA, during the exclusivity period. However, there is no assurance that Zemiva will be considered a new chemical entity for these purposes or be entitled to the period of marketing exclusivity. If we are not able to gain or exploit the period of marketing exclusivity, we may not be able to successfully commercialize Zemiva or may face significant competitive threats to such commercialization from other manufacturers, including the manufacturers of generic alternatives. Further, even if Zemiva is considered a new chemical entity and we are able to gain five years of marketing exclusivity, another company could also
18
gain such marketing exclusivity under the provisions of the FDCA, as amended by the Hatch-Waxman Act, if such company can complete a full NDA with a complete human clinical trial process and obtain regulatory approval of its product.
Our proprietary rights may not adequately protect our intellectual property and product candidates and if we cannot obtain adequate protection of our intellectual property and product candidates, we may not be able to successfully market our product candidates.
Our commercial success will depend in part on obtaining and maintaining intellectual property protection for our technologies and product candidates. We will only be able to protect our technologies and product candidates from unauthorized use by third parties to the extent that valid and enforceable patents cover them, or that other market exclusionary rights apply. Our lead cardiovascular molecular imaging candidate, Zemiva, is not covered by patent rights. We hold the patent rights to our second generation cardiac candidate, a derivative of Zemiva. Because Zemiva itself is not patented, we depend on obtaining the five year period of marketing exclusivity under the FDCA for Zemiva as a new chemical entity. Failure to obtain this marketing exclusivity right would permit competitors to gain access to the market for Zemiva.
While we have issued enforceable patents covering our oncology product candidateMIP-220, our neurology product candidateMIP-170 and our Ultratrace radiolabeling technology platform, some of our patent rights for these compounds and technologies are still pending patent applications. We cannot guarantee these patent applications will issue as patents. The patent positions of life sciences companies, like ours, can be highly uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions for which important legal principles remain unresolved. No consistent policy regarding the breadth of claims allowed in such companies’ patents has emerged to date in the United States. The general patent environment outside the United States also involves significant uncertainty. Accordingly, we cannot predict the breadth of claims that may be allowed or that the scope of these patent rights would provide a sufficient degree of future protection that would permit us to gain or keep our competitive advantage with respect to these products and technology. Additionally, life science companies like ours are dependent on creating a pipeline of products. We may not be able to develop additional proprietary technologies or product candidates that produce commercially viable products, or that are themselves patentable.
Our issued patents may be subject to challenge and possibly invalidated by third parties. Changes in either the patent laws or in the interpretations of patent laws in the United States or other countries may diminish the market exclusionary ability of our intellectual property.
In addition, others may independently develop similar or alternative compounds and technologies that may be outside the scope of our intellectual property. Should third parties obtain patent rights to similar compounds or radiolabeling technology, this may have an adverse effect on our business.
We also rely on trade secrets to protect our technology, especially where we do not believe patent protection is appropriate or obtainable. In particular, we rely on trade secrets to protect certain manufacturing aspects of our compound Zemiva. Trade secrets, however, are difficult to protect. While we believe that we use reasonable efforts to protect our trade secrets, our own or our strategic partners’ employees, consultants, contractors or advisors may unintentionally or willfully disclose our information to competitors. We seek to protect this information, in part, through the use of non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with employees, consultants, advisors and others. These agreements may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for a breach. In addition, we cannot ensure that those agreements will provide adequate protection for our trade secrets, know-how or other proprietary information and prevent their unauthorized use or disclosure.
To the extent that consultants or key employees apply technological information independently developed by them or by others to our product candidates, disputes may arise as to the proprietary rights of the information, which may not be resolved in our favor. Consultants and key employees that work with our confidential and proprietary technologies are required to assign all intellectual property rights in their discoveries to us. However, these consultants or key employees may terminate their relationship with us, and we cannot preclude them indefinitely from dealing with our competitors. If our trade secrets become known to
19
competitors with greater experience and financial resources, the competitors may copy or use our trade secrets and other proprietary information in the advancement of their products, methods or technologies. If we were to prosecute a claim that a third party had illegally obtained and was using our trade secrets, it would be expensive and time consuming and the outcome would be unpredictable. In addition, courts outside the United States are sometimes less willing to protect trade secrets than courts in the United States. Moreover, if our competitors independently develop equivalent knowledge, we would lack any contractual claim to this information, and our business could be harmed.
Our ability to commercialize our product candidates will depend on our ability to sell such products without infringing the patent or proprietary rights of third parties. If we are sued for infringing intellectual property rights of third parties, such litigation will be costly and time consuming and an unfavorable outcome would have a significant adverse effect on our business.
Our ability to commercialize our product candidates will depend on our ability to sell such products without infringing the patents or other proprietary rights of third parties. Third-party intellectual property in the fields of cardiology, oncology, neurology, and radiopharmaceutical technologies are complicated, and third-party intellectual property rights in these fields are continuously evolving. We have not performed searches for third-party intellectual property rights that may raisefreedom-to-operate issues, and we have not obtained legal opinions regarding commercialization of our product candidates. As such, there may be existing patents that may affect our ability to commercialize our product candidates.
In addition, because patent applications are published 18 months after their filing, and because applications can take several years to issue, there may be currently pending third-party patent applications that are unknown to us, which may later result in issued patents. If a third-party claims that we infringe on its patents or other proprietary rights, we could face a number of issues that could seriously harm our competitive position, including:
| | |
| | • | infringement claims that, with or without merit, can be costly and time consuming to litigate, can delay the regulatory approval process and can divert management’s attention from our core business strategy; |
| |
| | • | substantial damages for past infringement which we may have to pay if a court determines that our products or technologies infringe upon a competitor’s patent or other proprietary rights; |
| |
| | • | a court order prohibiting us from commercializing our products or technologies unless the holder licenses the patent or other proprietary rights to us, which such holder is not required to do; |
| |
| | • | if a license is available from a holder, we may have to pay substantial royalties or grant cross licenses to our patents or other proprietary rights; and |
| |
| | • | redesigning our process so that it does not infringe the third-party intellectual property, which may not be possible, or which may require substantial time and expense including delays in bringing our own products to market. |
Such actions could harm our competitive position and our ability to generate revenue and could result in increased costs.
We may be unable to obtain Orphan Drug marketing exclusivity for certain of our product candidates and if another party obtains Orphan Drug exclusivity instead, approval of our product for the same indication could be prevented for seven years.
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant Orphan Drug designation to drugs intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is defined by the FDA as a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States. Orphan Drug designation does not shorten the development or regulatory review time of a drug, but does provide limited advantages in the regulatory review and approval process. The company that obtains the first FDA approval for a designated Orphan Drug indication receives marketing exclusivity for use of that drug for that indication for a period of seven years. Moreover, even if we obtain Orphan Drug exclusivity for one or more indications, our exclusivity may be lost if the FDA later
20
determines that the request for designation was materially defective, or if we are unable to assure sufficient quantity of the drug. Orphan Drug exclusivity for Azedra and Onalta also would not prevent a competitor from obtaining approval of a different drug to treat the same Orphan Drug indications.
If our product candidates, including Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva, do not gain market acceptance among physicians, patients and the medical community, we will be unable to generate significant revenue, if any.
The products that we develop may not achieve market acceptance among physicians, patients, third-party payers and others in the medical community. If we receive the regulatory approvals necessary for commercialization, the degree of market acceptance will depend upon a number of factors, including:
| | |
| | • | limited indications of regulatory approvals; |
| |
| | • | the establishment and demonstration in the medical community of the clinical efficacy and safety of our product candidates and their potential advantages over existing diagnostic compounds; |
| |
| | • | the prevalence and severity of any side effects; |
| |
| | • | our ability to offer our product candidates at an acceptable price; |
| |
| | • | the relative convenience and ease of administration of our products; |
| |
| | • | the strength of marketing and distribution support; and |
| |
| | • | sufficient third-party coverage or reimbursement. |
The market may not accept Azedra, Onalta or Zemiva based on any number of the above factors. If Zemiva is approved, its primary competition in the emergency department setting will be the then current standard of care, which involves several diagnostic products, and its primary competition in the non-acute setting will be existing perfusion agents such as Cardiolite and Myoview. As of the time that Azedra and Onalta are approved, there may be other therapies available which directly compete for the same indications. The market may choose to continue utilizing the existing products for any number of reasons, including familiarity with or pricing of these existing products. The failure of any of our product candidates to gain market acceptance could impair our ability to generate revenue, which could have a material adverse effect on our future business, financial condition and results of operations.
We have no commercial manufacturing facility for Azedra, Onalta, Zemiva or any of our other product candidates and no experience in manufacturing products for commercial purposes and the failure to find manufacturing partners or create a manufacturing facility ourselves could have an adverse impact on our ability to grow our business.
We have no commercial manufacturing facility for Azedra, Onalta, Zemiva or our other product candidates and no experience in manufacturing commercial quantities of our product candidates. As such, we are dependent on third parties to supply our product candidates according to our specifications, in sufficient quantities, on time, in compliance with appropriate regulatory standards and at competitive prices. We cannot be sure that we will be able to obtain an adequate supply of our product candidates on acceptable terms, or at all.
Zemiva is BMIPP that has been radiolabeled with I-123. We are currently aware of only one commercial provider of BMIPP, MDS Nordion, in the United States. There is no assurance that we will be able to obtain sufficient amounts of BMIPP from this provider to produce adequate quantities of Zemiva. If this provider is unable to meet our demand, we would be required to find alternative sources of BMIPP, including producing BMIPP ourselves or contracting with third parties to produce BMIPP. We are not aware of any proprietary or technical reasons prohibiting the manufacture of BMIPP by us or a third party. However finding an alternative source for Zemiva would likely result in unforeseen costs and delays to the commercialization of Zemiva.
We have contracted with a Canadian company, MDS Nordion, to construct a manufacturing facility to radiolabel BMIPP and supply Zemiva. There can be no assurance that there will not be delays in the construction or completion of this facility. Such delays may adversely affect our ability to meet demand for
21
Zemiva. In addition, we may be required to use a portion of the proceeds from our initial public offering to assist in the funding of the manufacture of Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva and our other product candidates.
Manufacturers supplying biopharmaceutical products must comply with FDA regulations which require, among other things, compliance with the FDA’s evolving regulations on cGMPs, which are enforced by the FDA through its facilities inspection program. The manufacture of products at any facility will be subject to strict quality control, testing and record keeping requirements, and continuing obligations regarding the submission of safety reports and other post-market information. Since the commercial manufacturing facility for Zemiva has not been constructed, the FDA has not certified the cGMP compliant manufacture of Zemiva. We cannot guarantee that the resultant facility will pass FDA inspection, or that future changes to cGMP manufacturing standards will not also affect the cGMP compliant manufacture of Zemiva.
Azedra is in a Phase 1 clinical trial andMIP-220,MIP-190 andMIP-170 are in preclinical or discovery stages. We have no commercial cGMP manufacturing capability for these candidates, and currently no third-party manufacturer for them. As such, we may not be able to obtain sufficient quantities of these product candidates as we develop our pre-clinical or clinical programs for these compounds. We will need to enter into additional manufacturing arrangements for the manufacturing needs for all other product candidates. We have not yet determined if we will construct our own manufacturing facility for these product candidates, or if MDS Nordion will be contracted to fulfill this role, or if another manufacturer will be sought. We cannot guarantee that a suitable manufacturer for these product candidates will be found, or that we will be able to secure manufacturing agreements on acceptable terms with any of these manufacturers. We also cannot guarantee that such manufacturer will be able to supply sufficient quantities of our product candidates, or that they will meet the requirements for clinical testing and cGMP manufacturing.
If we fail to attract and retain senior management, consultants, advisors and scientific and technical personnel, our product development and commercialization efforts could be impaired.
Our performance is substantially dependent on the performance of our senior management and key scientific and technical personnel, particularly David Barlow, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, and John Babich, our President and Chief Scientific Officer. Although we have entered into employment agreements with five members of our senior management, David Barlow, John Babich, John McCray, Nicholas Borys and Bob Gallahue, there is no assurance that they will remain in our employ for the entire term of such employment agreements. The loss of the services of any member of our senior management or our scientific or technical staff may significantly delay or prevent the development of our product candidates and other business objectives by diverting management’s attention to transition matters and identification of suitable replacements, if any, and could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition. We maintain key man life insurance on David Barlow and John Babich.
We also rely on consultants and advisors to assist us in formulating our research and development strategy. All of our consultants and advisors are either self-employed or employed by other organizations, and they may have conflicts of interest or other commitments, such as consulting or advisory contracts with other organizations, that may affect their ability to contribute to us.
In addition, we believe that we will need to recruit additional executive management and scientific and technical personnel. There is currently intense competition for skilled executives and employees with relevant scientific and technical expertise, and this competition is likely to continue. The inability to attract and retain sufficient scientific, technical and managerial personnel could limit or delay our product development efforts, which would adversely affect the development of our product candidates and commercialization of our potential products and growth of our business.
We expect to expand our research, development, clinical research and marketing capabilities and, as a result, we may encounter difficulties in managing our growth, which could disrupt our operations.
We expect to have significant growth in expenditures, the number of our employees and the scope of our operations, in particular with respect to those potential products that we elect to commercialize independently or together with others. To manage our anticipated future growth, we must continue to implement and improve
22
our managerial, operational and financial systems, expand our facilities and continue to train qualified personnel. Due to our limited resources, we may not be able to effectively manage the expansion of our operations or train additional qualified personnel. The physical expansion of our operations may lead to significant costs and may divert our management and business development resources. Any inability to manage growth could delay the execution of our business plan or disrupt our operations.
We will need to raise additional funds in order to finance the anticipated commercialization of our product candidates by incurring indebtedness, through collaboration and licensing arrangements, or by issuing securities which may cause dilution to existing stockholders or require us to relinquish rights to our technologies and our product candidates.
Developing our product candidates, conducting clinical trials, establishing manufacturing facilities and developing marketing and distribution capabilities is expensive. We will need to finance future cash needs through additional public or private equity offerings, debt financings or corporate collaboration and licensing arrangements. We cannot be certain that additional funding will be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. If adequate funds are not available, we may be required to delay, reduce the scope of or eliminate one or more of our research or development programs or our commercialization efforts. To the extent that we raise additional funds by issuing equity securities, our stockholders may experience additional dilution. Debt financing, if available, may involve restrictive covenants. To the extent that we raise additional funds through collaboration and licensing arrangements, it may be necessary to relinquish some rights to our technologies or our product candidates or grant licenses on terms that are not favorable to us.
We have a history of losses and expect to continue to incur losses and may not achieve or maintain profitability.
We have incurred net losses every year since our inception in 1997 and have generated no revenue during the development stage from product sales or licenses to date. As of December 31, 2006, we had a deficit accumulated during the development stage of approximately $85.3 million. We expect to incur additional losses for at least the next several years and cannot be certain that we will ever achieve profitability. As a result, our business is subject to all of the risks inherent in the development of a new business enterprise, such as the risks that we may not obtain substantial additional capital needed to support the expenses of developing our technology and commercializing our potential products; develop a market for our potential products; successfully transition from a company with a research focus to a company capable of either manufacturing and selling potential products or profitably licensing our potential products to others;and/or attract and retain qualified management, technical and scientific staff.
We currently have no significant source of revenue and may never become profitable.
To date, we have not generated any revenue for product sales and we do not know when or if any of our product candidates will generate revenue. Our ability to generate revenue depends on a number of factors, including our ability to successfully complete clinical trials for Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva and obtain regulatory approval to commercialize these potential products. Even then, we will need to establish and maintain sales, marketing, distribution and to the extent we do not outsource manufacturing, manufacturing capabilities. We plan to rely on one or more strategic collaborators to help generate revenues in markets outside of the United States, and we cannot be sure that our collaborators, if any, will be successful. Our ability to generate revenue will also be impacted by certain challenges, risks and uncertainties frequently encountered in the establishment of new technologies and products in emerging markets and evolving industries. These challenges include our ability to:
| | |
| | • | execute our business model; |
| |
| | • | create brand recognition; |
| |
| | • | manage growth in our operations; |
| |
| | • | create a customer base cost-effectively; |
23
| | |
| | • | retain customers; |
| |
| | • | access additional capital when required; and |
| |
| | • | attract and retain key personnel. |
We cannot be certain that our business model will be successful or that it will successfully address these and other challenges, risks and uncertainties. If we are unable to generate significant revenue, we may not become profitable, and we may be unable to continue our operations. Even if we are able to commercialize Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva, we may not achieve profitability for at least several years, if at all, after generating material revenue.
We license patent rights from third-party owners. If such owners do not properly maintain or enforce the patents underlying such licenses, our competitive position and business prospects will be harmed.
We are party to a number of licenses that give us rights to third-party intellectual property that is necessary or useful for our business. In particular, we have obtained the nonexclusive rights from Novartis Pharma AG, or Novartis, for certain radiolabeled somatostatin analogs and the exclusive rights to the particular somatostatin analog compound edotreotide, along with know how related to the manufacture and use of this compound. We may enter into additional licenses to third-party intellectual property in the future. Our success will depend in part on the ability of our licensors to obtain, maintain and enforce patent protection for their intellectual property, in particular, those patents to which we have secured exclusive rights. Our licensors may not successfully prosecute the patent applications to which we are licensed. Even if patents issue with respect to these patent applications, our licensors may fail to maintain these patents, may determine not to pursue litigation against other companies that are infringing these patents, or may pursue such litigation less aggressively than we would. In addition, our licensors may terminate their agreements with us in the event we breach the applicable license agreement and fail to cure the breach within a specified period of time. Without protection for the intellectual property we license, other companies might be able to offer substantially identical products for sale, which could adversely affect our competitive business position and harm our business prospects.
Under the license agreement with Novartis Pharma AG, Novartis has retained an option to reacquire rights in the compound if annual sales exceed a certain threshold level. If Novartis does exercise this call back option, we will be required to sell to Novartis the rights in the compound which may have a negative affect on our operating results.
We currently have an existing material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting. If we are unable to improve and maintain the quality of our system of internal control over financial reporting, any deficiencies could materially and adversely affect our ability to report timely and accurate financial information about us.
In connection with the audit of our consolidated financial statements, as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006, management identified a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting. This was a matter that, in our judgment, could adversely affect our ability to record, process, summarize and report financial information consistent with the assertions of management in our financial statements. A material weakness is defined as a significant deficiency, or combination of significant deficiencies, that results in more than a remote likelihood that a material misstatement of the financial statements will not be prevented or detected. Specifically, our controls over the application of generally accepted accounting principles were ineffective because the company (1) did not maintain a sufficient complement of personnel with an appropriate level of accounting knowledge, experience, and training in the application of generally accepted accounting principals commensurate with the Company’s financial accounting and reporting requirements; and (2) the period-end financial close and reporting process was not operating effectively. In an effort to remediate this material weakness, the Company intends to hire additional accounting and financial personnel, and to enhance its financial reporting procedures and systems. This resulted in a number of post-close adjustments and corrections. We cannot be certain that the measures we have taken or plan to take will ensure that we will maintain adequate controls over our financial processes and reporting in
24
the future. Any failure to maintain adequate controls or to adequately implement required new or improved controls could harm our operating results or cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations. Inadequate internal controls could also cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information.
Beginning no later than with our Annual Report onForm 10-K for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2007, we will be required to furnish a report by our management on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. This report will contain, among other matters, an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of the end of our 2007 fiscal year, including a statement as to whether or not our internal control over financial reporting is operating effectively. This assessment must include disclosure of any material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting identified by management. Beginning in 2008, assuming we meet the definition of an accelerated filer, this report should also contain a statement that our independent registered public accounting firm has issued an attestation report on management’s assessment of such internal control. If we are unable to assert that our internal control over financial reporting is effective as of December 31, 2007, we could lose investor confidence in the accuracy and completeness of our financial reports, which could have an adverse effect on our stock price.
We have relied on government funding, which could require us to take action with respect to our technology or patents that may not be in our best interest and which, if lost or reduced, could have an adverse effect on our research and development.
We have relied on government research grants for a portion of our funding, including grants awarded by the National Institutes of Health under the Small Business Innovation Research program and the Small Business Technology Transfer program. Most of our government grants have been awarded as Phase 1 grants and we expect to file Phase 2 grant applications where appropriate, but we cannot be assured that these grants or any new Phase 1 grant applications will be awarded to us, nor can we be sure that we will continue to be eligible to receive such grants now that our initial public offering is completed.
Under the terms of our government grants, we have all right, title and interest in our patents, copyrights and data pertaining to our product development, subject to certain rights of the government. Under existing regulations, the government receives a royalty-free license for federal government use for all patents developed under a government grant. In addition, under certain circumstances the government may require us to license technology resulting from the government funded projects to third parties and may require that we manufacture our product in the United States, even if we determine that such actions are not in our best interest.
Funding of government grants is subject to government appropriation and all of our government contracts contain provisions which make them terminable at the convenience of the government. The government could terminate, reduce or delay the funding under any of our grants at any time. Accordingly, there is no assurance that we will receive funding of any grants that we may be awarded, including the approximately $984,200 remaining portion of grants that we had been awarded as of December 31, 2006. In the event we are not successful in obtaining any new government grants or extensions to existing grants, our research and development efforts could be adversely affected.
Risks Related to Our Industry
Our competitors may develop products that are less expensive, safer or more effective, which may diminish or eliminate the commercial success of any potential products that we may commercialize.
If our competitors market products that are less expensive, safer or more effective than our future products developed from our product candidates, or that reach the market before our product candidates, we may not achieve commercial success. For example, if approved, Zemiva will compete in the emergency department setting with the current standard of care in the assessment of chest pain patients who present to emergency departments. This standard involves several diagnostic products and procedures, in some cases involving the use of perfusion imaging agents, which in the aggregate may require several hours or days of hospitalization to reach an ultimate diagnosis. If approved, Zemiva’s primary competition in the non-acute setting will be perfusion imaging agents such as Cardiolite produced by Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging, Myoview produced by GE Healthcare, and generic thallium, the primary U.S. supplier being Tyco
25
Healthcare/Mallinckrodt. The market may choose to continue utilizing the existing products for any number of reasons, including familiarity with or pricing of these existing products. The failure of Zemiva or any of our product candidates to compete with products marketed by our competitors would impair our ability to generate revenue, which would have a material adverse effect on our future business, financial condition and results of operations.
We expect to compete with several pharmaceutical companies including Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging, GE Healthcare and Tyco Healthcare/Mallinckrodt, and our competitors may:
| | |
| | • | develop and market products that are less expensive or more effective than our future products; |
| |
| | • | commercialize competing products before we or our partners can launch any products developed from our product candidates; |
| |
| | • | operate larger research and development programs or have substantially greater financial resources than we do; |
| |
| | • | initiate or withstand substantial price competition more successfully than we can; |
| |
| | • | have greater success in recruiting skilled technical and scientific workers from the limited pool of available talent; |
| |
| | • | more effectively negotiate third-party licenses and strategic relationships; and |
| |
| | • | take advantage of acquisition or other opportunities more readily than we can. |
We expect to compete for market share against large pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, smaller companies that are collaborating with larger pharmaceutical companies, new companies, academic institutions, government agencies and other public and private research organizations.
In addition, the life sciences industry is characterized by rapid technological change. Because our research approach integrates many technologies, it may be difficult for us to stay abreast of the rapid changes in each technology. If we fail to stay at the forefront of technological change, we may be unable to compete effectively. Our competitors may render our technologies obsolete by advances in existing technological approaches or the development of new or different approaches, potentially eliminating the advantages in our product discovery process that we believe we derive from our research approach and proprietary technologies.
The use of hazardous materials in our operations may subject us to environmental claims or liabilities.
Our research and development activities involve the use of hazardous materials, including chemicals and biological and radioactive materials. Injury or contamination from these materials may occur and we could be held liable for any damages, which could exceed our available financial resources. This liability could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to federal, state and local laws and regulations governing the use, manufacture, storage, handling and disposal of hazardous materials and waste products. We may be required to incur significant costs to comply with environmental laws and regulations in the future that could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we fail to comply with extensive regulations enforced by the FDA and other agencies with respect to pharmaceutical products, the commercialization of our product candidates could be prevented, delayed or halted.
Research, preclinical development, clinical trials, manufacturing and marketing of our product candidates are subject to extensive regulation by various government authorities. We have not received marketing approval for Azedra, Onalta, Zemiva or our other product candidates. The process of obtaining FDA and other required regulatory approvals is lengthy and expensive, and the time required for such approvals is uncertain. The approval process is affected by such factors as:
| | |
| | • | the severity of the disease; |
26
| | |
| | • | the quality of submission relating to the product candidate; |
| |
| | • | the product candidate’s clinical efficacy and safety; |
| |
| | • | the strength of the chemistry and manufacturing control of the process; |
| |
| | • | the manufacturing facility compliance; |
| |
| | • | the availability of alternative treatments; |
| |
| | • | the risks and benefits demonstrated in clinical trials; and |
| |
| | • | the patent status and marketing exclusivity rights of certain innovative products. |
Any regulatory approvals that we or our partners receive for our product candidates may also be subject to limitations on the indicated uses for which the product candidate may be marketed or contain requirements for potentially costly post-marketingfollow-up studies. The subsequent discovery of previously unknown problems with the product candidate, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, may result in restrictions on the marketing of the product candidate and withdrawal of the product candidate from the market.
U.S. manufacturing, labeling, storage and distribution activities also are subject to strict regulating and licensing by the FDA. The manufacturing facilities for our biopharmaceutical products are subject to periodic inspection by the FDA and other regulatory authorities and from time to time, these agencies may send notice of deficiencies as a result of such inspections. Our failure, or the failure of our biopharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, to continue to meet regulatory standards or to remedy any deficiencies could result in corrective action by the FDA or these other authorities, including the interruption or prevention of marketing, closure of our biopharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, and fines or penalties.
Regulatory authorities also will require post-marketing surveillance to monitor and report to the FDA potential adverse effects of our product candidates. Congress or the FDA in specific situations can modify the regulatory process. If approved, any of our product candidates’ subsequent failure to comply with applicable regulatory requirements could, among other things, result in warning letters, fines, suspension or revocation of regulatory approvals, product recalls or seizures, operating restrictions, injunctions and criminal prosecutions.
The FDA’s policies may change and additional government regulations may be enacted that could prevent or delay regulatory approval of our product candidates. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of adverse government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action. If we are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we might not be permitted to market our product candidates and our business could suffer.
In the future, we intend to distribute and sell our potential products outside of the United States, which will subject us to further regulatory risk.
In addition to seeking approval from the FDA for Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva in the United States, we intend to seek the governmental approval required to market Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva and our other potential products in European Union countries such as the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Belgium, Holland and Italy through third parties. We may in the future also seek approvals for additional countries. The regulatory review process varies from country to country, and approval by foreign government authorities is unpredictable, uncertain and generally expensive. Our ability to market our potential products could be substantially limited due to delays in receipt of, or failure to receive, the necessary approvals or clearances. We anticipate commencing the applications required in some or all of these countries following approval by the FDA; however, we may decide to file applications in advance of the FDA approval if we determine such filings to be both time and cost effective. If we export any of our potential products that have not yet been cleared for domestic commercial distribution, such products may be subject to FDA export restrictions. Marketing of our potential products in these countries, and in most other countries, is not permitted until we have obtained required approvals or exemptions in each individual country. Failure to obtain necessary regulatory approvals could impair our ability to generate revenue from international sources.
27
Market acceptance of our potential products will be limited if users are unable to obtain adequate reimbursement from third-party payers.
Government health administration authorities, private health insurers and other organizations generally provide reimbursement for products like our product candidates, and our commercial success will depend in part on these third-party payers agreeing to reimburse patients for the costs of our potential products. Even if we succeed in bringing any of our product candidates to market, we cannot assure you that third-party payers will consider our potential products cost effective or provide reimbursement in whole or in part for their use.
Significant uncertainty exists as to the reimbursement status of newly approved health care products. Each of our product candidates is intended to replace or alter existing therapies or procedures. These third-party payers may conclude that our product candidates are less safe, effective or cost-effective than these existing therapies or procedures. Therefore, third-party payers may not approve our products candidates for reimbursement.
If third-party payers do not approve our product candidates for reimbursement or fail to reimburse for them adequately, sales will suffer as some physicians or their patients will opt for a competing product that is approved for reimbursement or is adequately reimbursed. Even if third-party payers make reimbursement available, these payers’ reimbursement policies may adversely affect our ability and the ability of our potential collaborators to sell our potential products on a profitable basis.
The trend toward managed healthcare in the United States, the growth of organizations such as health maintenance organizations and legislative proposals to reform healthcare and government insurance programs could significantly influence the purchase of healthcare services and products, resulting in lower prices and reduced demand for our products which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, legislation and regulations affecting the pricing of our product candidates may change in ways adverse to us before or after the FDA or other regulatory agencies approve any of our product candidates for marketing. While we cannot predict the likelihood of any of these legislative or regulatory proposals, if any government or regulatory agencies adopt these proposals, they could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Product liability claims may damage our reputation and, if insurance proves inadequate, the product liability claims may harm our business.
We may be exposed to the risk of product liability claims that is inherent in the biopharmaceutical industry. A product liability claim may damage our reputation by raising questions about our product’s safety and efficacy and could limit our ability to sell one or more products by preventing or interfering with commercialization of our potential products.
In addition, product liability insurance for the biopharmaceutical industry is generally expensive to the extent it is available at all. There can be no assurance that we will be able to obtain and maintain such insurance on acceptable terms or that we will be able to secure increased coverage if the commercialization of our potential products progresses, or that future claims against us will be covered by our product liability insurance. Moreover, there can be no assurance that the existing coverage of our insurance policyand/or any rights of indemnification and contribution that we may have will offset any future claims. We currently maintain product liability insurance of $10 million per occurrence and in the aggregate for clinical trial related occurrences only. We believe that this coverage is currently adequate based on current and projected business activities and the associated risk exposure, although we expect to increase this coverage as our business activities and associated risks grow. A successful claim against us with respect to uninsured liabilities or in excess of insurance coverage and not subject to any indemnification or contribution could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
28
We could be negatively impacted by the application or enforcement of federal and state fraud and abuse laws, including anti-kickback laws and other federal and state anti-referral laws.
We are not aware of any current business practice which is in violation of any federal or state fraud and abuse law. However, continued vigilance to assure compliance with all potentially applicable laws will be a necessary expense associated with product development. For example, all product marketing efforts must be strictly scrutinized to assure that they are not associated with improper remunerations to referral sources in violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute and similar state statutes. Remunerations may include potential future activities for our product candidates, including discounts, rebates and bundled sales, which must be appropriately structured to take advantage of statutory and regulatory “safe harbors.” From time to time we engage physicians in consulting activities. In addition, we may decide to sponsor continuing medical education activities for physicians or other medical personnel. We also may award or sponsor study grants to physicians from time to time. All relationships with physicians, including consulting arrangements, continuing medical education and study grants, must be similarly reviewed for compliance with the Anti-Kickback Statute to assure that remuneration is not provided in return for referrals. Patient inducements may also be unlawful. Inaccurate reports of product pricing, or a failure to provide product at an appropriate price to various governmental entities, could also serve as a basis for an enforcement action under various theories.
Claims which are “tainted” by virtue of kickbacks or a violation of self-referral rules may be alleged as false claims if other elements of a violation are established. The federal False Claims Act, which includes a provision allowing whistleblowers to bring actions on behalf of the federal government and receive a portion of the recovery, applies to those who submit a false claim and those who cause a false claim to be submitted. Because our potential customers may seek payments from the federal healthcare programs for our product candidates, even during the clinical trial stages, we must assure that we take no actions which could result in the submission of false claims. For example, free product samples which are knowingly or with reckless disregard billed to the federal healthcare programs could constitute false claims. If the practice was facilitated or fostered by us, we could be liable. Moreover, inadequate accounting for or a misuse of federal grant funds used for product research and development could be alleged as a violation of the False Claims Act or other relevant statutes.
The risk of our being found in violation of these laws is increased by the fact that many of them have not been fully interpreted by the regulatory authorities or the courts, and their provisions are open to a variety of interpretations, and additional legal or regulatory change.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
Our stock price may be volatile, and your investment in our stock could decline in value.
The market prices for securities of biotechnology companies in general have been highly volatile and may continue to be highly volatile in the future. The following factors, in addition to other risk factors described in this section, may have a significant impact on the market price of our common stock:
| | |
| | • | results from and any delays in the clinical trials programs; |
| |
| | • | failure or delays in entering additional product candidates into clinical trials; |
| |
| | • | failure or discontinuation of any of our research programs; |
| |
| | • | delays in establishing new strategic relationships; |
| |
| | • | delays in the development of our product candidates and commercialization of our potential products; |
| |
| | • | market conditions in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors and issuance of new or changed securities analysts’ reports or recommendations; |
| |
| | • | actual and anticipated fluctuations in our quarterly financial and operating results; |
| |
| | • | developments or disputes concerning our intellectual property or other proprietary rights; |
| |
| | • | introduction of technological innovations or new commercial products by us or our competitors; |
29
| | |
| | • | issues in manufacturing our product candidates or products; |
| |
| | • | market acceptance of our products; |
| |
| | • | third-party healthcare reimbursement policies; |
| |
| | • | FDA or other United States or foreign regulatory actions affecting us or our industry; |
| |
| | • | litigation or public concern about the safety of our product candidates or products; and |
| |
| | • | additions or departures of key personnel. |
These and other external factors may cause the market price and demand for our common stock to fluctuate substantially, which may limit or prevent investors from readily selling their shares of common stock and may otherwise negatively affect the liquidity of our common stock. In addition, in the past, when the market price of a stock has been volatile, holders of that stock have instituted securities class action litigation against the company that issued the stock. If any of our stockholders brought a lawsuit against us, we could incur substantial costs defending the lawsuit. Such a lawsuit could also divert the time and attention of our management.
If the ownership of our common stock continues to be highly concentrated, it may prevent you and other stockholders from influencing significant corporate decisions and may result in entrenchment of management or conflicts of interest that could cause our stock price to decline.
As of March 15, 2007, our executive officers, directors, and their affiliates beneficially own or control approximately 15.62% of the outstanding shares of our common stock. Accordingly, these executive officers, directors and their affiliates, acting as a group, will have substantial influence over the outcome of corporate actions requiring stockholder approval, including the election of directors, any merger, consolidation or sale of all or substantially all of our assets, or any other significant corporate transactions. These stockholders may also delay or prevent a change of control of our company, even if such a change of control would benefit our other stockholders. The significant concentration of stock ownership may adversely affect the trading price of our common stock due to investors’ perception that entrenchment of management or conflicts of interest may exist or arise.
A significant portion of our total outstanding shares are restricted from immediate resale but may be sold into the market in the near future. This could cause the market price of our common stock to drop significantly, even if our business is doing well.
Sales of a substantial number of shares of our common stock in the public market could occur at any time. These sales, or the perception in the market that the holders of a large number of shares intend to sell shares, could reduce the market price of our common stock. We had outstanding 24,744,284 shares of common stock as of March 15, 2007. The shares that were sold in our IPO may be resold in the public market immediately, and 19,744,284 shares that are currently restricted as a result of securities laws orlock-up agreements will be able to be sold in the near future as set forth below.
| | | |
Number of Shares and % of Total Outstanding | | Date Available for Sale into Public Market |
| |
| 18,801,857 shares, or 75.98% | | On August 1, 2007, which is 181 days, subject to extension in certain cases, after the date of our initial public offering due to thelock-up agreements between the holders of these shares and the underwriters or the Company, respectively. However, the underwriters or the Company, as applicable, can waive the provisions of theselock-up agreements and allow these stockholders to sell their shares at any time. Sales of these shares by ‘‘affiliates” and sales of these shares by non-“affiliates” who have held such shares for less than two years are subject to the volume limitations, manner of sale provisions, and public information requirements of Rule 144. |
30
We intend to register the shares of common stock issuable or reserved for issuance under our equity plans prior to August 1, 2007, which is 181 days after the date of our initial public offering. In addition to the foregoing, there were options to purchase 871,636 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase 394,877 shares of common stock outstanding and exercisable as of March 15, 2007.
Evolving regulation of corporate governance and public disclosure may result in additional expenses and continuing uncertainty.
Changing laws, regulations and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, new SEC regulations, and Nasdaq National Market rules are creating uncertainty for public companies. As a result of these new rules, we will incur additional costs associated with our public company reporting requirements. In addition, these new rules could make it more difficult or more costly for us to obtain certain types of insurance, including director and officer liability insurance, and this could make it difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our board of directors.
We are presently evaluating and monitoring developments with respect to new and proposed rules and cannot predict or estimate the amount of the additional costs we may incur or the timing of such costs. These new or changed laws, regulations, and standards are subject to varying interpretations, in many cases due to their lack of specificity, and as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies. This could result in continuing uncertainty regarding compliance matters and higher costs necessitated by ongoing revisions to disclosure and governance practices.
We are committed to maintaining high standards of corporate governance and public disclosure. As a result, we intend to invest resources to comply with evolving laws, regulations, and standards, and this investment may result in increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management time and attention from revenue-generating activities to compliance activities. If our efforts to comply with new or changed laws, regulations, and standards differ from the activities intended by regulatory or governing bodies due to ambiguities related to practice, regulatory authorities may initiate legal proceedings against us and we may be harmed.
We have limited experience attempting to comply with public company obligations, including Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
As directed by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, the SEC has adopted rules requiring public companies to include a report of management on the company’s internal controls over financial reporting in their annual reports onForm 10-K. In addition, the independent registered public accounting firm auditing a public company’s financial statements must attest to and report on management’s assessment of the effectiveness of the company’s internal controls over financial reporting of all companies deemed an accelerated filer under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. The requirement to include a report of management on the company’s internal controls over financial reporting will first apply to our annual report onForm 10-K for our fiscal year ending December 31, 2007. If we are unable to conclude that we have effective internal controls over financial reporting as of December 31, 2007, as required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, investors could lose confidence in the reliability of our financial statements, which could result in a decrease in the value of our securities.
We have never paid dividends on our common stock, and except for payment of accrued dividends to certain preferred holders, we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
We have not paid cash dividends on our common stock to date. We currently intend to retain our future earnings, if any, to fund the development and growth of our business, and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our capital stock for the foreseeable future. In addition, the terms of existing or any future debt facilities may preclude us from paying dividends on our stock. As a result, capital appreciation, if any, of our common stock will be your sole source of gain for the foreseeable future.
31
Some provisions of our Restated Articles of Organization and Amended and Restated Bylaws may inhibit potential acquisition bids that you may consider favorable.
Our Restated Articles of Organization and Amended and Restated Bylaws contain provisions that may enable our Board of Directors to resist a change in control of our company even if a change in control were to be considered favorable by stockholders. These provisions include:
| | |
| | • | the authorization of undesignated preferred stock, the terms of which may be established and shares of which may be issued without stockholder approval; |
| |
| | • | advance notice procedures required for stockholders to nominate candidates for election as directors or to bring matters before an annual meeting of stockholders; |
| |
| | • | limitations on persons authorized to call a meeting of stockholders; |
| |
| | • | a staggered Board of Directors; and |
| |
| | • | supermajority voting requirements to remove directors from office. |
These and other provisions contained in our charter and bylaws could delay or discourage transactions involving an actual or potential change in control of us or our management, including transactions which our stockholders might otherwise receive a premium for their shares over then current prices, and may limit the ability of stockholders to remove our current management or approve transactions that our stockholders may deem to be in their best interest and, therefore, could adversely affect the price of our common stock.
| |
| ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
Facilities
Our principal executive and administrative office is a leased facility located in Cambridge, Massachusetts that consists of approximately 8,783 square feet of office space and 4,084 square feet of laboratory space. These facilities are occupied pursuant to a lease agreement that expires on June 30, 2008. We believe that our current facilities will meet our anticipated needs for the remainder of the lease term. We are currently assessing our facilities needs after the expiration of our lease term and reviewing options that are available to us.
| |
| ITEM 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
We are not a party to any material legal proceedings.
| |
| ITEM 4. | SUBMISSION OF MATTERS TO A VOTE OF SECURITY HOLDERS |
During the three-month period ended December 31, 2006, there were no matters submitted to a vote of our stockholders.
PART II
| |
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Market for Registrant’s Common Stock
Our initial public offering of our common stock was registered on the Registration Statement onForm S-1, as amended (RegistrationNo. 333-129570), which was declared effective by the SEC on February 1, 2007.
32
Our common stock is listed on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “MIPI” and started trading on February 2, 2007. Prior to such date there was no public market for our common stock.
Number of Stockholders
As of March 15, 2007, there were approximately 230 stockholders of record of our common stock.
Dividends
We have never declared or paid any dividends on our common stock. We currently intend to retain any future earnings to fund the development and expansion of our business, and therefore we do not anticipate paying cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. Any future determination to pay dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on our financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements, restrictions contained in future financing instruments, and other factors our board of directors deems relevant.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table summarizes our outstanding securities and securities available for future issuance under our equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2006 (our last completed fiscal year end).
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Number of Securities
| |
| | | Number of Securities
| | | | | | Remaining Available for
| |
| | | to be Issued Upon
| | | Weighted-Average
| | | Future Issuance Under
| |
| | | Exercise of
| | | Price of
| | | Equity Compensation Plans
| |
| | | Outstanding Options,
| | | Outstanding Options,
| | | (Excluding Securities Reflected
| |
| | | Warrants, and Rights
| | | Warrants, and Rights
| | | in Column [a])
| |
Plan Category | | [a] | | | [b] | | | [c] | |
| |
| Equity compensation plans approved by stockholders | | | 1,870,840 | (1) | | $ | 2.46 | | | | 2,622,190 | (2) |
| Equity compensation plans not approved by stockholders | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 1,870,840 | (1) | | $ | 2.46 | | | | 2,622,190 | (2) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| (1) | | Options issued under the 1997 Stock Option Plan, which terminated on January 9, 2007. |
| |
| (2) | | Includes 2,300,000 shares reserved and available for issuance under the Amended and Restated 2006 Equity Incentive Plan, which was approved by the stockholders on August 31, 2006. The 2006 Plan allows for awards to be granted after February 1, 2007, the effective date of the Company’s initial public offering. No option was granted under the 2006 Plan as of December 31, 2006. |
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2006, we issued the following securities that were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”):
In September 2006 and October 2006, we issued an aggregate principal amount of $15.4 million of convertible promissory notes to certain qualified institutional buyers. Upon the consummation of our initial public offering, the notes converted into a total of 2,029,159 shares of our common stock, reflecting a conversion price of $7.80 per share. In connection with these notes, we issued to each noteholder warrants with a five-year term to purchase 394,877 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $7.80 per share. We claimed exemption from registration under the Securities Act for the sales and issuances of these securities by virtue of Section 4(2) of the Securities Act and by virtue of Rule 506 of Regulation D. Such sales and issuances did not involve any public offering, were made without general solicitation or advertising and each purchaser was an accredited investor with access to all relevant information necessary to evaluate the
33
investment and represented to us that the shares were being acquired for investment. The recipients of securities in each of these transactions represented their intention to acquire the securities for investment only and not with a view to or for sale in connection with any distribution thereof. Appropriate legends were affixed to the share certificates and instruments issued in all such transactions.
In November 2006 and as a condition to its agreement to consent to the issuance of the securities disclosed above, we issued a warrant to Ritchie Debt Acquisition Fund, Ltd., which was assigned to BlueCrest Venture Finance Master Fund Limited, to purchase up to 61,538 shares of our common stock at a price of $7.80 per share. This warrant expires on the earlier of i) seven years, ii) 180 days after the effectiveness of our initial public offering, or iii) the sale of our company. We claimed exemption from registration under the Securities Act for the sale and issuance of this warrant by virtue of Section 4(2) of the Securities Act. Such sale and issuance did not involve any public offering, was made without general solicitation or advertising and the purchaser was an accredited investor with access to all relevant information necessary to evaluate the investment and represented to us that the shares were being acquired, or the shares issuable pursuant to warrant exercise would be acquired, for investment purposes only and not with a view to or for sale in connection with any distribution thereof.
Since January 1, 2004, we granted stock options to certain employees, directors and consultants under our 1997 Stock Option Plan covering an aggregate of 1,565,799 shares of common stock, at exercise prices ranging from $0.60 to $14.00 per share. Of these, options covering an aggregate of 43,985 shares were canceled without being exercised. We claimed exemption from registration under the Securities Act for the sales and issuances of such options by virtue of Rule 701 promulgated under the Securities Act, in that they were offered and sold either pursuant to written compensatory plans or pursuant to a written contract relating to compensation, as provided by Rule 701. The recipients of securities in each of these transactions represented their intention to acquire the securities for investment only and not with a view to or for sale in connection with any distribution thereof and appropriate legends were affixed to the share certificates and instruments issued in such transactions. All recipients had adequate access, through their relationships with us, to information about us.
No underwriters were employed in any of the above transactions.
Use of Proceeds
On February 1, 2007, the Company’s initial public offering of 5,000,000 shares of its common stock registered on the registration statement ofForm S-1, as amended (RegistrationNo. 333-129570) was declared effective by the SEC. The offering closed on February 7, 2007. The underwriters of the offering were RBC Capital Markets Corporation, Jefferies & Company, Inc., A.G. Edwards & Sons, Inc. and Oppenheimer & Co., Inc.
All 5,000,000 shares of our common stock registered in the offering were sold at the initial public offering price per share of $14.00. Warrants automatically convertible upon the initial public offering were also exercised at this time. Net proceeds to the Company were approximately $63.3 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses totaling approximately $8.1 million. No payments for such expenses were made directly or indirectly to (i) any of our directors, officers or their associates, (ii) any person(s) owning 10% or more of any class of our equity securities, or (iii) any of our affiliates.
As of December 31, 2006, we had not completed our initial public offering and, therefore, none of the proceeds of that offering had been received or used as of the fiscal period covered by this annual report.
There has been no material change in our planned use of proceeds from our initial public offering as described in our final prospectus filed with the SEC pursuant to Rule 424(b).
34
| |
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
SELECTED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL DATA
The selected consolidated financial data set forth below should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this filing. The selected consolidated financial data as of December 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006 and for the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006 are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this filing. The selected financial data as of December 31, 2002 and 2003 and for the years ended December 31, 2002 and 2003 are derived from audited consolidated financial statements not included in this annual report onForm 10-K.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | Period from
| |
| | | | | | January 10, 1997
| |
| | | | | | (Date of Inception)
| |
| | | | | | through
| |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | | December 30, | |
| | | 2002 | | | 2003 | | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | |
| | | (In thousands, except per share data) | |
| |
Consolidated Statements of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue-research and development grants | | $ | 624 | | | $ | 723 | | | $ | 569 | | | $ | 1,232 | | | $ | 325 | | | $ | 4,416 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development | | | 2,317 | | | | 2,775 | | | | 5,381 | | | | 8,855 | | | | 16,635 | | | | 45,285 | |
| General and administrative | | | 1,562 | | | | 1,266 | | | | 3,520 | | | | 11,025 | | | | 10,211 | | | | 34,618 | |
| Amortization of licensed patent rights(2) | | | 3,798 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 9,767 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total operating expenses | | | 7,677 | | | | 4,041 | | | | 8,901 | | | | 19,880 | | | | 26,846 | | | | 89,670 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss from operations | | | (7,053 | ) | | | (3,317 | ) | | | (8,332 | ) | | | (18,648 | ) | | | (26,521 | ) | | | (85,254 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other (expense) income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | | 3 | | | | 1 | | | | 20 | | | | 488 | | | | 469 | | | | 1,126 | |
| Interest expense | | | (6 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (141 | ) | | | (1,214 | ) | | | (1,376 | ) |
| Interest expense — related parties | | | (28 | ) | | | (29 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (57 | ) |
| Management fee income — related party | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 233 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total other (expense) income, net | | | (30 | ) | | | (30 | ) | | | 17 | | | | 347 | | | | (745 | ) | | | (74 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | (7,084 | ) | | | (3,348 | ) | | | (8,315 | ) | | | (18,301 | ) | | | (27,266 | ) | | | (85,328 | ) |
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock dividends and accretion of issuance costs | | | — | | | | (613 | ) | | | (1,312 | ) | | | (4,046 | ) | | | (4,958 | ) | | | (10,930 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders | | $ | (7,084 | ) | | $ | (3,961 | ) | | $ | (9,628 | ) | | $ | (22,347 | ) | | $ | (32,224 | ) | | $ | (96,258 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders | | $ | (3.77 | ) | | $ | (1.13 | ) | | $ | (2.55 | ) | | $ | (5.30 | ) | | $ | (7.18 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average shares used to compute basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders | | | 1,879 | | | | 3,515 | | | | 3,773 | | | | 4,213 | | | | 4,490 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
35
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2002 | | | 2003 | | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents(1) | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 1,711 | | | $ | 846 | | | $ | 5,811 | | | $ | 8,916 | |
| Working capital (deficit)(1) | | | (2,128 | ) | | | (1,709 | ) | | | (2,566 | ) | | | 12,977 | | | | 598 | |
| Total assets(2) | | | 212 | | | | 2,232 | | | | 1,573 | | | | 19,654 | | | | 12,934 | |
| Long term obligations, net of current portion | | | 5 | | | | 158 | | | | 113 | | | | 3,429 | | | | 16,382 | |
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock(1) | | | — | | | | 7,552 | | | | 15,538 | | | | 45,236 | | | | 48,090 | |
| Total stockholders’ (deficit) equity | | | (5,238 | ) | | | (9,023 | ) | | | (17,831 | ) | | | (35,135 | ) | | | (61,864 | ) |
| | |
| (1) | | The significant changes in cash and cash equivalents, working capital (deficit) and redeemable convertible preferred stock as of December 31, 2003, 2004, 2005 and 2006 from the previous periods presented result from cash received from the issuance of redeemable convertible preferred stock (prior to accrual of dividends) and a convertible note payable during the periods then ended. |
| |
| (2) | | The decrease in amortization expense related to licensed patent rights in periods subsequent to 2002 results from the amortization of licensed patent rights, which was fully amortized through December 31, 2002. The significant increase in total assets from December 31, 2004 to December 31, 2005 is a result of cash received for the issuance of Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock in March and April of 2005. |
| |
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
When you read this section of thisForm 10-K, it is important that you also read the financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in thisForm 10-K. This section of this annual report contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties, such as statements of our plans, objectives, expectations, and intentions. We use words such as “anticipate,” “estimate,” “plan,” “project,” “continuing,” “ongoing,” “expect,” “believe,” “intend,” “may,” “will,” “should,” “could,” and similar expressions to identify forward-looking statements. Our actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements for many reasons, including the factors described below and in the “Risk Factors” section of thisForm 10-K.
Overview
We are a development stage biopharmaceutical company that commenced operations in 1997. We specialize in the emerging field of molecular medicine, applying advancements in the identification and targeting of disease at the molecular level to advance patient healthcare by addressing significant unmet needs. We focus on discovering, developing and commercializing innovative and targeted radiotherapeutics and molecular imaging pharmaceuticals with initial applications in the areas of oncology and cardiology. We have devoted substantially all of our efforts towards the research and development of our product candidates. We have had no revenue from product sales and have funded our operations through the private placement of equity securities, debt financings and government grant funding. We have never been profitable and have incurred an accumulated deficit during the development stage of $85.3 million from inception through December 31, 2006.
We expect to incur significant operating losses for the next several years. Research and development expenses relating to our clinical and pre-clinical product candidates will continue to increase. In particular, we expect to incur increased development costs in connection with our ongoing and expected clinical trials for Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva. We expect general and administrative expense to increase as we prepare for the commercialization of our product candidates and as we begin to operate as a public company.
36
On February 1, 2007, the Company’s initial public offering of 5,000,000 shares of its common stock registered on the registration statement ofForm S-1, as amended (RegistrationNo. 333-129570) was declared effective by the SEC. All registered shares were sold at the initial public offering price of $14.00 per share. Warrants automatically convertible upon the initial public offering were also exercised at this time. Net proceeds to the Company were approximately $63.3 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses totaling approximately $8.1 million. We intend to use our cash to fund research and development activities for our product candidates and general corporate purposes, including capital expenditures and working capital.
Financial Operations Overview
Revenue — Research and Development Grants. Our revenue to date has been derived from National Institutes of Health, or NIH, grants. We have not had any product sales and do not expect product sales in the near future. In the future, we expect our revenue to consist of product sales and payments from collaborative or strategic relationships, as well as from additional grants. Funding of government grants is subject to government appropriation and all of our government contracts contain provisions which make them terminable at the convenience of the government. The government could terminate, reduce or delay the funding under any of our grants at any time. Accordingly, there is no assurance that we will receive funding of any grants that we may be awarded, including the approximately $984,200 remaining portion of grants that we had been awarded as of December 31, 2006. In the event we are not successful in obtaining any new government grants or extensions to existing grants, our research and development efforts could be adversely affected.
Research and Development Expense. Research and development expense consists of expenses incurred in developing and testing product candidates. These expenses consist primarily of salaries and related expenses for employees, as well as fees for consultants engaged in research and development activities, fees paid to professional service providers for monitoring our clinical trials and for acquiring and evaluating clinical trial data, costs of contract manufacturing services and materials used in clinical trials, depreciation of capital resources used to develop our product candidates and facilities costs. We expense research and development costs as incurred. Certain research and development activities are partially funded by NIH grants described above. All costs related to such grants are included in research and development costs. We believe that significant investment in product development is necessary and plan to continue these investments as we seek to develop our product candidates and proprietary technologies.
For the periods indicated, research and development expenses for our programs in the development of Azedra, Zemiva and our other platform and general R&D programs were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ending December 31, | |
Program | | 2003 | | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Azedra and Ultratrace platform | | $ | 539 | | | $ | 170 | | | $ | 485 | | | $ | 3,958 | |
| Zemiva | | | 916 | | | | 3,352 | | | | 5,309 | | | | 5,625 | |
| Other Platform and general R&D | | | 1,320 | | | | 1,859 | | | | 3,061 | | | | 7,052 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | $ | 2,775 | | | $ | 5,381 | | | $ | 8,855 | | | $ | 16,635 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
We in-licensed Onalta and Solazed in November 2006 and January 2007, respectively. For the periods indicated above, we had no research and development expenses for the development of Onalta and Solazed.
We do not know if we will be successful in developing our drug candidates. While we expect that expenses associated with the completion of our current clinical programs would be substantial, we believe that such expenses are not reasonably certain. The timing and amount of these expenses will depend upon the costs associated with potential future clinical trials of our drug candidates, and the related expansion of our research and development organization, regulatory requirements, advancement of our preclinical programs and product manufacturing costs, many of which cannot be determined with accuracy at this time based on our stage of development. This is due to the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with the duration and cost of
37
clinical trials, which vary significantly over the life of a project as a result of unanticipated events arising during clinical development, including with respect to:
| | |
| | • | the number of clinical sites included in the trial; |
| |
| | • | the length of time required to enroll suitable subjects; |
| |
| | • | the number of subjects that ultimately participate in the trials; and |
| |
| | • | the efficacy and safety results of our clinical trials and the number of additional required clinical trials. |
Our expenditures are subject to additional uncertainties, including the terms and timing of regulatory approvals and the expense of filing, prosecuting, defending or enforcing any patent claims or other intellectual property rights. In addition, we may obtain unexpected or unfavorable results from our clinical trials. We may elect to discontinue, delay or modify clinical trials of some drug candidates or focus on others. A change in the outcome of any of the foregoing variables in the development of a drug candidate could mean a significant change in the costs and timing associated with the development of that drug candidate. For example, if the FDA or other regulatory authority were to require us to conduct clinical trials beyond those that we currently anticipate, or if we experience significant delays in any of our clinical trials, we would be required to expend significant additional financial resources and time on the completion of clinical development. Additionally, future commercial and regulatory factors beyond our control will evolve and therefore impact our clinical development programs and plans over time.
Beyond our three lead drug candidates, we anticipate that we will select drug candidates and research projects for further development on an ongoing basis in response to the preclinical and clinical success, as well as the commercial potential of such drug candidates.
General and Administrative Expense. General and administrative expense consists primarily of salaries and other related costs for personnel in executive, finance, accounting, information technology and human resource functions. Other costs include facility costs not otherwise included in research and development expense, legal fees relating to patent and corporate matters and fees for accounting services.
Costs Related to Delays in Initial Public Offering. We expensed the costs associated with the initial filing of our registration statement onForm S-1. Our initial public offering, which was effective on February 1, 2007, was delayed for a period in excess of 90 days, and as a result it was deemed an aborted offering in accordance with Staff Accounting Bulletin Topic 5A. These costs which total $2.2 million and $720,000 are included in general and administrative expenses in the Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2005 and December 31, 2006, respectively. We have capitalized costs associated with our subsequent offering process as of December 31, 2006.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense. Operating expenses include stock-based compensation expense. Stock-based compensation expense results from the issuance of stock-based awards, such as options and restricted stock to employees, members of our Board of Directors and consultants in lieu of cash consideration for services received. Prior to the adoption of Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 123(R)Share-Based Payment,we used the intrinsic value method of accounting for awards to employees and members of our Board of Directors and the fair value method for nonemployees in accordance with SFAS No. 123Accounting for Stock-Based Compensationand Emerging Issues Task Force “EITF” IssueNo. 96-18,Accounting for Equity Instruments That are Issued to Other Than Employees for Acquiring, or in Conjunction with Selling, Goods or Services. On January 1, 2006 we adopted SFAS No. 123(R) to account for stock-based awards. We use the fair value method of accounting for all other awards. Compensation expense for options and restricted stock granted to employees and nonemployees is classified either as research and development expense or general and administrative expense based on the job function of the individual receiving the grant. These costs which total $2.8 million and $1.9 million are included in the Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2005 and December 31, 2006, respectively. See discussion under “Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates — Stock-Based Compensation.”
38
Other (Expense) Income, Net. Other (expense) income, net includes interest income and interest expense. Interest income consists of interest earned on our cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments. Interest expense consists of interest incurred on equipment leases and on debt instruments.
Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Dividends and Accretion of Issuance Costs. Redeemable convertible preferred stock dividends and accretion of issuance costs consists of cumulative, undeclared dividends payable on the securities and accretion of the issuance costs and costs allocated to issued warrants to purchase common stock. The issuance costs on these shares and warrants were recorded as a reduction to the carrying value of the redeemable convertible preferred stock when issued, and are accreted to redeemable convertible preferred stock using the interest method through the earliest redemption dates of each series of redeemable convertible preferred stock (A, B and C) by a charge to additional paid-in capital and net loss attributable to common stockholders. Upon the consummation of the initial public offering of the Company which was declared effective by the SEC on February 1, 2007, the redeemable convertible preferred stock automatically converted into common stock on a33-for-1 basis and the cumulative but unpaid dividends (with limited exception) converted into common stock based upon formulas established at each issuance date of the securities. Accordingly, we no longer record dividends and accretion on the redeemable convertible preferred stock.
Critical Accounting Policies
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based upon our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, or GAAP. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities and expenses and disclosures of contingent obligations. On an on-going basis, we evaluate our estimates and judgments, including those related to accrued expenses, fair valuation of stock and income taxes. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
We believe the following critical accounting policies affect our more significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements.
Accrued Expenses. As part of the process of preparing consolidated financial statements, we are required to estimate accrued expenses. This process involves identifying services that have been performed on our behalf and estimating the level of services performed and the associated cost incurred for such services as of each balance sheet date in our consolidated financial statements. Examples of estimated expenses for which we accrue include: professional service fees, such as legal and accounting fees; contract service fees, such as fees paid to clinical monitors, data management organizations and investigators in conjunction with clinical trials; fees paid to contract manufacturers in conjunction with the production of clinical materials; and employee bonuses. In connection with such service fees, our estimates are most affected by our understanding of the status and timing of services provided relative to the actual levels of services incurred by such service providers. The majority of our service providers invoice us monthly in arrears for services performed. In the event that we do not identify certain costs which have begun to be incurred, or we under- or over-estimate the level of services performed or the costs of such services, our reported expenses for such period would be too low or too high. Determining the date on which certain services commence, the level of services performed on or before a given date and the cost of such services often involves judgment. We make these judgments in accordance with GAAP based upon the facts and circumstances known to us.
We attempt to mitigate the risk of inaccurate estimates, in part, by communicating with our service providers when other evidence of costs incurred is unavailable.
Stock-Based Compensation. We issue stock awards such as options and restricted stock to employees, members of our Board of Directors and consultants for incentive purposes and in lieu of cash consideration for services received. Prior to the adoption of SFAS No. 123(R), we used the intrinsic value method of accounting
39
for awards to employees and members of our Board of Directors. Under the intrinsic value method, all terms are fixed, the measurement date is the date of grant. Stock-based compensation to the extent the fair value of our common stock exceeds the exercise price of stock options granted to employees on the measurement date is recorded as deferred stock-based compensation in the equity section of the consolidated balance sheets and is amortized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the awards, typically four years, in the consolidated statement of operations. In the notes to our consolidated financial statements, we provide pro forma disclosures in accordance with SFAS No. 123 and related pronouncements and SFAS No. 148,Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation-Transition and Disclosure.
On January 1, 2006 we adopted SFAS No. 123(R) to account for stock-based awards. We historically have not recorded stock-based compensation expense for stock awards issued to employees with fixed terms and with exercise prices at least equal to the fair value of the underlying common stock on the measurement date. Effective January 1, 2006, we began recording compensation costs over the vesting period for the unvested portion of the other awards issued after being considered a public company, which would include awards granted after November 8, 2005, using the grant date fair value. We will continue to record compensation cost on awards issued prior to this date following the provisions of APB Opinion No. 25, i.e. the prospective transition method under SFAS No. 123(R) for the awards granted while not a public company. Compensation cost for awards granted after January 1, 2006 will be accounted for under the fair value method and recognized over the requisite service period.
We use the fair value method of accounting for all other awards. For stock options granted to nonemployees, the fair value of the stock options is estimated using the Black-Scholes valuation model. This model utilizes the estimated fair value of the common stock and requires that, at the measurement date of the award, which is usually the date services are completed, we make assumptions with respect to the expected life of the option, the volatility of the fair value of the common stock, risk free interest rates and expected dividend yields of our common stock. Higher estimates of volatility and expected life of the option increase the value of an option and the resulting expense. Stock-based compensation computed on awards to nonemployees is recognized over the period of expected service by the nonemployee (which is generally the vesting period). As the service is performed, we are required to update these assumptions and periodically revalue unvested options and make adjustments to the stock-based compensation expense using the new valuation. These adjustments have resulted in stock-based compensation expense in addition to the amount originally estimated or recorded as the deemed fair value of our stock has increased over the last two years, with a corresponding increase in compensation expense in the consolidated statements of operations in the periods of re-measurement. Ultimately, the final compensation charge for each option grant to nonemployees is unknown until the performance of services is completed. We account for transactions in which services are received in exchange for equity instruments based either on the fair value of such services received from nonemployees or of the equity instruments issued, whichever is more reliably measured. The two factors which most effect charges or credits to operations related to stock-based compensation for nonemployee awards are the fair value of the common stock underlying stock options for which such stock-based compensation is recorded and the volatility of such fair value.
Income Taxes. As part of the process of preparing our consolidated financial statements, we are required to estimate our income tax expense in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. This process involves estimating our current tax expense together with assessing temporary differences resulting from differing treatments of items for tax and financial reporting purposes. These differences result in deferred tax assets and liabilities. As a result of our historical operating losses, as of December 31, 2006, we had federal tax net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $56.9 million and research and development tax credits of $1.4 million, which expire at various dates through 2026. As of December 31, 2006 we had a deferred tax asset aggregating $27.3 million. We have recorded a full valuation allowance of these otherwise recognizable deferred tax assets due to the uncertainty surrounding the timing of the realization of the tax benefit. In the event that we determine in the future that we will be able to realize all or a portion of the deferred tax asset, a reduction in the deferred tax valuation allowance would increase net income or reduce the net loss in the period in which such a determination is made. The Tax Reform Act of 1986 contains provisions that limit the utilization of net operating loss carryforwards and credits available to be used in any given year in the event
40
of significant changes in ownership interest, as defined. The amount of the net operating loss carryforwards that may be utilized to offset future taxable income, when earned, may be subject to certain limitations, based upon changes in the ownership of our stock that haveand/or may occur. We have not conducted an evaluation as to whether any portion of our tax loss carryforwards have been limited, and therefore, based upon the changes in ownership, a limitation may have occurred.
Results of Operations
Years Ended December 31, 2006 and 2005
Revenue — Research and Development Grants. Revenue decreased by $907,000, or 74%, to $325,000 for the year ended December 31, 2006 from $1,232,000 for the year ended December 31, 2005. During 2006 and 2005 we received funding under eight grants with the majority of effort and reimbursable expenses incurred in 2005.
Research and Development Expense. Research and development expense increased $7.7 million, or 87%, to $16.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 from $8.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. 2006 included $2.4 million of costs for the Zemiva Normals and Azedra dosimetry clinical trials as well as $1.6 million of costs for manufacturingset-up for future Zemiva and Azedra clinical trials, while 2005 included Phase 2b Zemiva clinical trial costs in the first half of 2005. Also contributing to the increase was $1.4 million in additional compensation related expense in the 2006 compared to the 2005 period due to growth in personnel hired in the second half of 2005 and employed for the full year in 2006. Stock-based compensation expense decreased by $11,000 to $219,000 in 2006 from $230,000 in 2005, due primarily to a decrease in the estimated fair value of our stock price in 2006. During 2005, we experienced an increase in the deemed face value in our common stock which increased compensation expense associated with certain awards subject to variable accounting treatment.
As clinical sites are initiated and patients are enrolled in our clinical programs, we anticipate incurring increased costs from professional service firms helping to support the clinical program by performing independent clinical monitoring, data acquisition and data evaluation. We also anticipate incurring increased costs related to hiring of additional research and development and clinical personnel and increased costs associated with production and distribution of clinical trial material. We also expect that our research and development expense will increase as we pursue the identification and development of other product candidates, which we plan to fund through our own resources or through strategic collaborations.
General and Administrative Expense. General and administrative expense decreased $800,000, or 7.3%, to $10.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 from $11.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. The decrease was primarily attributed to lower costs in 2006 associated with our postponed initial public offering. In 2005 costs associated with our postponed initial public offering totaled $2.2 million compared to $720,000 in 2006. Costs associated with our initial public offering beginning in the second half of 2006 were capitalized. Partly offsetting the decreases was an increase in compensation expense related to our growth in administrative headcount from 5 in the beginning of 2005 to 10 at the end of 2006. Stock-based compensation decreased $900,000 to $1.7 million in 2006 compared to $2.6 million in the 2005, due primarily to a decrease in the estimated fair value of our stock price in 2006. During 2005, we experienced an increase in the deemed face value in our common stock which increased compensation expense associated with certain awards subject to variable accounting treatment. The 2006 decrease in stock-based compensation was offset in part by adoption of SFAS No. 123(R), which resulted in charges of $127,000.
After completing the initial public offering, we anticipate greater general and administrative expenses, such as additional costs for investor relations, increased costs for Sarbanes-Oxley compliance and other activities associated with operating as a publicly-traded company. These increases will also include the hiring of additional finance and administrative personnel. In addition, we expect to continue to incur greater internal and external business development costs to support our various product development efforts, which can vary from period to period.
41
Other (Expense) Income, Net. Other (expense) income, net decreased $1.1 million to $(745,000) for the year ended December 31, 2006 from net other income of $348,000 for the year ended December 31, 2005. During 2006 and 2005, interest income was $469,000 and $489,000, respectively, and interest expense was $1.2 million and $141,000, respectively. The increase in interest expense for the 2006 compared to 2005 was primarily due to interest expense on a note payable issued in September 2005 and fully outstanding for all of 2006 as well as additional interest expense resulting from convertible notes issued in September 2006.
Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Dividends and Accretion of Issuance Costs. Redeemable convertible preferred stock dividends and accretion of issuance costs increased $900,000 to $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 from $4.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. This increase was attributable to Series C outstanding for the entire twelve months in 2006 compared to only six months in the 2005 period. A 2005 period special dividend related to the year ending December 31, 2005 was accrued and largely contributed to the 2005 dividend amount. Upon completion of the initial public offering no redeemable convertible preferred stock is outstanding, and, accordingly, there will be no further accrual of dividends or accretion of issuance costs on these shares after completion of the initial public offering and the required conversion.
Years Ended December 31, 2005 and 2004
Revenue — Research and Development Grants. Revenue increased $631,000, or 111%, to $1.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 from $569,000 for the year ended December 31, 2004. During 2005 and 2004, we received funding under eight grants, however, the majority of effort and reimbursable expenses were incurred in 2005.
Research and Development Expense. Research and development expense increased $3.5 million, or 65%, to $8.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 from $5.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2004. The year ended December 31, 2004 included the Phase 2a Zemiva clinical trial costs, while the year ended December 31, 2005 included costs for the Phase 2b Zemiva clinical trial which began in the second half of 2004 and continued through the first half of 2005. The Phase 2b Zemiva clinical trial enrolled a greater number of patients, resulting in an increase of approximately $745,000 from the 2004 to the 2005 period. Also contributing to the increase was the growth in the number of research and development personnel, which resulted in $1.8 million of additional compensation expense in the 2005 period relative to the 2004 period. Stock-based compensation contributed to a lesser extent to the increase, increasing by $182,000 to $230,000 in the 2005 period from $48,000 in the 2004 period.
General and Administrative Expense. General and administrative expense increased $7.5 million, or 214%, to $11 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 from $3.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2004. Costs associated with our postponed initial public offering totaled $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. Also contributing to the increase was growth in administrative headcount from 5 to 10 personnel, which amounted to $900,000 of additional expense from 2004 to 2005. A $593,000 increase in legal costs resulted primarily from legal fees associated with stockholder litigation, patent applications, patent management and general corporate representation. Marketing costs increased $549,000 during 2005 over 2004 for costs associated primarily with market research for the Zemiva program. Stock-based compensation increased $2.3 million to $2.6 million in 2005 increasing from $311,000 in 2004, due primarily to the effect of an increase in the fair value of our common stock on awards subject to variable accounting treatment.
Other (Expense) Income, Net. Other income, net increased $332,000 to $348,000 for the year ended December 31, 2005 from $16,000 for the year ended December 31, 2004. During the year ended December 31, 2005 and 2004, interest income was $489,000 and $20,000, respectively, and other interest expense was $141,000 and $3,000, respectively. The increase in interest income for the year ended December 31, 2005 compared to the twelve months ended December 31, 2004 was primarily due to increased yields on investments resulting from greater average cash balances available for investment as a result of the sales of Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock in March and April of 2005 and the Ritchie Note at September 30, 2005. The increase in interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2005 compared to the year ended December 31, 2004 was primarily due to interest expense on the Ritchie Note.
42
Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Dividends and Accretion of Issuance Cost. Redeemable convertible preferred stock dividends and accretion of issuance costs increased to $4.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 from $1.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2004. This increase was attributable to Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock outstanding for 2005 plus the Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock outstanding after the first quarter of 2005. Also contributing to the increase in 2005 was a special dividend accrued related to the Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock in February 2005. Following consummation of our initial public offering, no redeemable convertible preferred stock is outstanding, and, accordingly, there will be no further accrual of dividends or accretion of issuance costs on these shares.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
On February 1, 2007, the Company’s initial public offering of 5,000,000 shares of its common stock registered on the registration statement ofForm S-1, as amended (RegistrationNo. 333-129570) was declared effective by the SEC. All registered shares were sold at the initial public offering price of $14.00 per share. Warrants automatically convertible upon the initial public offering were also exercised at this time. Net proceeds to the Company were approximately $63.3 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses totaling approximately $8.1 million. We intend to use our cash to fund Zemiva and Azedra clinical trials and research and development activities for our pre-clinical new product candidates, debt repayment as debt becomes due, and general corporate purposes, including capital expenditures and working capital. To date, we have used a portion of the net proceeds of the initial public offering consistent with our intent discussed immediately above.
Prior to our IPO, we have financed our business primarily through the issuance of equity securities, revenues from government grants, debt financings and equipment leases. Through December 31, 2006, we had received net cash proceeds of $49.3 million from the issuance of shares of preferred and common stock, $15.2 million from issuance of convertible notes payable, $5.0 million from a note payable, and $4.3 million from government grants. At December 31, 2006, we had $8.9 million in cash and cash equivalents available to finance future operations. Our cash and cash equivalents are held at two financial institutions to reduce our concentration risk. Management believes that the financial institutions it uses are of high credit quality. Since our inception, we have generated significant operating losses in developing our product candidates. Accordingly, we have historically used cash in our operating activities, and for the year ending December 31, 2006 we used approximately $22.1 million to fund these activities. As we continue to develop our product candidates and begin to incur increased sales and marketing costs related to commercialization of our future products, we expect to incur additional operating losses until such time, if any, as our efforts result in commercially viable products.
Based on our operating plans, including our contractual obligations as outlined below, we believe that the proceeds from our initial public offering, together with our existing cash resources and government grant funding as of December 31, 2006, will be sufficient to finance our planned operations through the second half of 2008. However, over the next several years, we will require significant additional funds to conduct clinical and non-clinical trials, achieve regulatory approvals and, subject to such approvals, commercially launch Azedra, Onalta and Zemiva. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including the scope of progress made in our research and development activities and our clinical trials. We may also need additional funds for possible future strategic acquisitions of businesses, products or technologies complementary to our business. If additional funds are required, we may raise such funds from time to time through public or private sales of equity or from borrowings. Financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all, and our failure to raise capital when needed could materially adversely impact our growth plans and our financial condition and results of operations. If available, additional equity financing may be dilutive to holders of our common stock and debt financing may involve significant cash payment obligations and covenants that restrict our ability to operate our business.
43
Annual Cash Flows
Years Ended December 31, 2006 and 2005
Net cash used in operating activities increased by $7.9 million to $22.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $14.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2005. The increase in cash used was due primarily to an increase in the net loss of $8.8 million primarily related to expenditures on Zemiva and Azedra clinical trials and manufacturing. Net cash provided by investing activities increased by $24.7 million to $11.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $12.8 million used in 2005. This increase was due to the maturity of investments during the year ended December 31, 2006. Net cash provided by the financing activities decreased by $18.7 million to $13.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2006 compared to $32.0 million in 2005. The primarily reason for the decrease was due to proceeds from Series C redeemable preferred stock included in 2005. In 2006 we received proceeds of $15.4 million from the issuance of convertible notes, and made payments of $1.7 million on notes payable.
Years Ended December 31, 2005 and 2004
Net cash used in operating activities increased by $8.0 million to $14.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 compared to $6.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2004. The increase in cash used was due primarily to an increase in the net loss of $10.0 million primarily related to expenditures on the Phase 2b clinical trial for Zemiva. Net cash used by investing activities increased $12.6 million to $12.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 compared to $203,000 for the same period in 2004. This increase was due to the purchase of investments from funds raised in financing activities. Net cash provided by financing activities increased by $26.5 million to $32.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2005 compared to $5.5 million for the same period in 2004. In the year ended December 31, 2005, we raised $26.4 million from the issuance of Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock, and in 2004, we raised $4.7 million from the issuance of Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock, all net of expenses incurred. Also during the year ended December 31, 2005, we received $5.4 million from the issuance of notes payable.
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes our outstanding contractual obligations as of December 31, 2006:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Payments Due by Period | |
Contractual Obligations | | Total | | | 2007 | | | 2008-2009 | | | 2010-2011 | | | 2012-beyond | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Operating Leases | | $ | 583 | | | $ | 392 | | | $ | 191 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Development and manufacturing purchase obligations(1) | | | 2,807 | | | | 2,807 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Notes Payable(2) | | | 19,021 | | | | 1,775 | | | | 17,246 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Interest on notes payable | | | 1,174 | | | | 221 | | | | 953 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 23,585 | | | $ | 5,195 | | | $ | 18,390 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| (1) | | We are party to a number of licenses that give us rights to third-party intellectual property that is necessary or useful for our business. Under those licenses, we are obligated to pay to the third parties various fees, royalties or milestone payments. The above amounts represents contractual obligations. Additional amounts may be due upon completion of milestones. |
| |
| (2) | | See Note 6 to the Financial Statements “Notes Payable”. |
Operating Leases
Our commitments under operating leases consist of payments relating to our real estate leases in Cambridge, Massachusetts, expiring in 2008. The commitments are $392,000 and $191,000 for the years 2007 and 2008, respectively.
44
Capital Leases
We had no capital leases as of December 31, 2006.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Other than the operating leases for our office, we do not engage in off-balance sheet financing arrangements.
Future Funding Requirements
We expect to devote substantial resources to further our commercialization efforts. Our future funding requirements and our ability to raise additional capital will depend on factors that include:
| | |
| | • | the timing and amount of expense incurred to complete our clinical trials; |
| |
| | • | the costs and timing of the regulatory process as we seek approval of our products in development; |
| |
| | • | the advancement of our pipeline products into development; |
| |
| | • | the timing, receipt and amounts of milestone payments to our existing development partners; |
| |
| | • | our ability to generate new relationships with industry partners whose business plans seek long-term commercialization opportunities which allow for up-front deposits or advance payments in exchange for license agreements; |
| |
| | • | the timing, receipt and amount of sales, if any, from our products in development; |
| |
| | • | the cost of manufacturing (paid to third parties) of our licensed products, and the cost of marketing and sales activities of those products; |
| |
| | • | the continued willingness of our vendors to provide trade credit on historical terms; |
| |
| | • | the costs of prosecuting, maintaining, and enforcing patent claims, if any claims are made; |
| |
| | • | our ability to maintain existing collaborative relationships and establish new relationships as we advance our products in development; and |
| |
| | • | the receptivity of the financial market to biopharmaceutical companies. |
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2006, the FASB issued FASB Interpretation No. 48,Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes, an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109(“FIN 48”). FIN 48 clarifies the accounting for uncertainties in income taxes recognized in an enterprise’s financial statements. FIN 48 requires that we determine whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination by the appropriate taxing authority. If a tax position meets the “more likely than not” recognition criteria, FIN 48 requires the tax position be measured at the largest amount of benefit greater than 50 percent likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement. This accounting standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2006. We do not believe the effect, if any, of adopting FIN 48 will have a material impact on our financial position and results of operations.
In September 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 157,Fair Value Measurements(“SFAS 157”), which establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about the use of fair value measurements and liabilities in interim and annual reporting periods subsequent to initial recognition. Prior to the issuance of SFAS 157, which emphasizes that fair value is a market-based measurement and not an entity-specific measurement, there were different definitions of fair value and limited definitions for applying those definitions in GAAP. SFAS 157 is effective for us on a prospective basis for the reporting period beginning January 1, 2008. We do not believe the effect, if any, of adopting SFAS 157 will have a material impact on our financial position and results of operations.
In February 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 159,Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities (“SFAS 159”),which expands the standards under SFAS 157,Fair Value Measurementsto provide
45
entities the one-time election (Fair Value Option or FVO) to measure financial instruments and certain other items at fair value. SFAS 159 also amends Statement No. 115 (SFAS 115) to require the presentation of investments inavailable-for-sale securities and trading securities:
a) in the aggregate of those fair value and non-fair-value amounts in the same line item and parenthetically disclose the amount of fair value included in the aggregate amount or
b) in two separate line items to display the fair value and non-fair-value carrying amounts.
This Statement is effective as of the beginning of an entity’s first fiscal year that begins after November 15, 2007, provided the entity also elects to apply the provisions of FASB Statement No. 157,Fair Value Measurements. The Company does not believe the effect, if any, of adopting SFAS 159 will have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations.
In September 2006, the Securities and Exchange Commission released Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 108, or SAB 108, to address diversity in practice regarding consideration of the effects of prior year errors when quantifying misstatements in current year financial statements. The staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission concluded that registrants should quantify financial statement errors using both a balance sheet approach and an income statement approach and evaluate whether either approach results in quantifying a misstatement that, when all relevant quantitative and qualitative factors are considered, is material. SAB 108 states that if correcting an error in the current year materially affects the current year’s income statement, the prior period financial statements must be restated. SAB 108 is effective for fiscal years ending after November 15,2006. The adoption of SAB 108 did not significantly affect our financial condition or results of operations.
| |
| ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURE ABOUT MARKET RISK |
We invest our available funds in accordance with our investment policy to preserve principal, maintain proper liquidity to meet operating needs and maximize yields. We invest cash balances in excess of operating requirements first in short-term, highly liquid securities, with original maturities of 90 days or less, and money market accounts. Depending on our level of available funds and our expected cash requirements, we may invest a portion of our funds in corporate debt, commercial paper and U.S. government securities with maturities of more than three months and less than a year. These securities are classified asavailable-for-sale and are recorded on the balance sheet at fair market value with any unrealized gains or losses reported as a separate component of stockholders’ deficit (accumulated other comprehensive loss). Our investments are sensitive to interest rate risk. We believe, however, that the effect, if any, of reasonable possible near-term changes in interest rates on our financial position, results of operations and cash flows generally would not be material due to the short-term nature of these investments. In particular, as of December 31, 2006, because our available funds are invested solely in cash equivalents, our risk of loss due to changes in interest rates is not material, even if market interest rates were to increase or decrease immediately and uniformly by 10% from levels at December 31, 2006.
Effects of Inflation
Our assets are primarily monetary, consisting largely of cash, cash equivalents and investments in debt securities with short-term maturities. Because of their liquidity, these assets are not directly affected by inflation. Due to the nature of our intellectual property, inflation is not a significant factor. Because we intend to retain and continue to use our existing equipment, furniture and fixtures and leasehold improvements, we believe that the incremental inflation related to replacement costs of such items will not materially affect our operations or cash flows. However, the effects of inflation on our expenditures, the most significant of which are for personnel (existing and new) and contract services, could increase our level of expenses and impact the rate at which we use our resources.
| |
| ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTAL DATA |
The financial statements required by this item are located beginning on F-1 of this report.
46
| |
| ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer performed an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined inRules 13a-l5(e) andl5d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934) as of the end of the period covered by this annual report. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of December 31, 2006 in providing them with material information related to the Company in a timely manner, as required to be disclosed in the reports the Company files under the Exchange Act.
A “material weakness”, as defined under the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) was identified. A material weakness is a control deficiency, or a combination of control deficiencies, that result in more than a remote likelihood that a material misstatement of the annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected. As of December 31, 2006, the Company did not maintain effective internal control over financial reporting because the Company: (1) did not maintain a sufficient complement of personnel with an appropriate level of accounting knowledge, experience, and training in the application of generally accepted accounting principals commensurate with the Company’s financial accounting and reporting requirements; and (2) the period-end financial close and reporting process was not operating effectively. In an effort to remediate this material weakness, the Company intends to hire additional accounting and financial personnel, and to enhance its financial reporting procedures and systems.
Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
As directed by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, the SEC has adopted rules requiring public companies to include a report of management on the company’s internal controls over financial reporting in their annual reports onForm 10-K. In addition, the public accounting firm auditing a public company’s financial statements must attest to and report on management’s assessment of the effectiveness of the company’s internal controls over financial reporting.
This annual report does not include a report of the Company’s management’s assessment regarding internal control over financial reporting or an attestation report of the Company’s registered public accounting firm due to a transition period established by rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission for newly public companies. The requirement of management assessment on the company’s internal control over financial reporting will first apply to our annual report onForm 10-K for our fiscal year ending December 31, 2007.
| |
| ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
PART III
Certain information required by Part III ofForm 10-K is omitted from this report because we expect to file a definitive proxy statement for our 2007 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “Proxy Statement”) within 120 days after the end of our fiscal year pursuant to Regulation 14A promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and the information included in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference to the extent provided below.
47
| |
| ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
The information in response to this item is hereby incorporated by reference to the information under the headings “Election of Directors,” “Directors and Executive Officers,” “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” and “Corporate Governance and Board Matters” in our Proxy Statement.
We have adopted a Code of Conduct and Business Ethics, which applies to all our directors, officers and employees, including our Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and all other executive officers. The Code of Conduct and Business Ethics is posted on our website,http://www.molecularinsight.com in connection with “Investor Relations” materials. In addition, we will provide to any person without charge, upon request, address to Chief Operating Officer at Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 160 Second Street, Cambridge, MA 02142 a copy of our Code of Conduct and Business Ethics. We intend to satisfy the disclosure requirement regarding any amendment to, or waiver of, a provision of the Code of Conduct and Business Ethics for our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer or persons performing similar functions, by posting such information on our website.
| |
| ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information in response to this item is hereby incorporated by reference to the information under the heading “Compensation of Executive Officers and Directors” in the Company’s Proxy Statement.
| |
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information in response to this item is hereby incorporated by reference to the information under the heading “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” in the Company’s Proxy Statement.
| |
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information in response to this item is hereby incorporated by reference to the information under the headings “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” and “Corporate Governance and Board Matters” in the Company’s Proxy Statement.
| |
| ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANTS FEES AND SERVICES |
The information in response to this item is hereby incorporated by reference to the information under the heading “Independent Public Accountants Fees and Services” in the Company’s Proxy Statement.
PART IV
| |
| ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
(a) The following documents are filed as part of this Report:
(1) Financial Statements
See Index to Financial Statements onpage F-1.
(2) Supplemental Schedules
All other schedules have been omitted because the required information is not present in amounts sufficient to require submission of the schedule, or because the required information is included in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
(3) Exhibits
See Item 15(b) below.
48
(b) The following exhibits are filed as part of, or incorporated by reference into, this annual report onForm 10-K:
| | | | | |
Number | | Description of Document |
| |
| | 3 | .1** | | Restated Articles of Organization, filed May 30, 2006, as amended by Articles of Amendment, filed September 7, 2006. |
| | 3 | .2** | | Amended and Restated Bylaws. |
| | 4 | .1** | | Reference is made to Exhibits 3.1 and 3.2. |
| | 4 | .2** | | Form of Common Stock Certificate. |
| | 10 | .1** | | Unit Purchase Agreement for the Purchase of Shares of Series B Preferred Stock of the Company dated as of February 23, 2004. |
| | 10 | .2** | | Stock Purchase Agreement for the Purchase of Series C Preferred Stock of the Company dated as of March 29, 2005. |
| | 10 | .3** | | Amended and Restated Voting Agreement by and among the Company and certain holders of Common Stock and Series A Preferred Stock, the holders of Series B Preferred Stock and the holders of Series C Preferred Stock dated as of March 29, 2005. |
| | 10 | .4** | | Investors Rights Agreement by and between the Company and the holders of Series C Preferred Stock dated as of March 29, 2005. |
| | 10 | .5** | | Registration Rights Agreement by and among the Company and certain holders of Common Stock and Series A Preferred Stock, the holders of Series B Preferred Stock and the holders of Series C Preferred Stock dated as of March 29, 2005. |
| | 10 | .6** | | Lease Agreement dated as of June 19, 2003 by and between the Company and RayJoe Limited Partnership. |
| | 10 | .7** | | Employment Agreement dated as of January 1, 2003 by and between the Company and John Babich. |
| | 10 | .8** | | Employment Agreement dated as of February 7, 2003 by and between the Company and David Barlow. |
| | 10 | .9** | | Employment Agreement dated as of March 3, 2003 by and between the Company and John McCray. |
| | 10 | .10** | | Employment Agreement dated as of May 1, 2004 by and between the Company and Nicholas Borys. |
| | 10 | .11** | | Employment Agreement dated as of July 1, 2005 by and between the Company and Bob Gallahue. |
| | 10 | .12†** | | License Agreement, dated as of October 25, 1999, between the Company and Nihon Medi-Physics Co. Ltd. |
| | 10 | .13†** | | Development, Manufacturing and Supply Agreement, dated June 14, 2004, as amended by Amendment No. 1, between the Company and MDS Nordion, a division of MDS (Canada) Inc. |
| | 10 | .14†** | | Exclusive License Agreement, dated as of December 29, 1997, between the Company and Georgetown University. |
| | 10 | .15†** | | Exclusive License Agreement, dated as of March 1, 2000, between the Company and Georgetown University. |
| | 10 | .16†** | | License Agreement, dated as of December 15, 2000, between the Company and The Board of Governors of the University of Western Ontario. |
| | 10 | .17†** | | License Agreement, dated as of September 5, 2003, between the Company and The Board of Governors of the University of Western Ontario. |
| | 10 | .18** | | 1997 Stock Option Plan. |
| | 10 | .19** | | Amended and Restated 2006 Equity Incentive Plan. |
| | 10 | .20** | | Consulting Agreement dated as of January 1, 2005 by and between the Company and William Eckelman. |
| | 10 | .21†** | | Exclusive License Agreement, dated as of December 28, 2005, between the Company, Georgetown University and Johns Hopkins University. |
49
| | | | | |
Number | | Description of Document |
| |
| | 10 | .22** | | Employment Agreement dated June 23, 2005 by and between the Company and James A. Wachholz. |
| | 10 | .23†** | | BMIPP Supply Agreement, dated as of January 12, 2006, between the Company and MDS Nordion, a division of MDS (Canada) Inc. |
| | 10 | .24†** | | Agreement, dated as of March 22, 2006, as amended, between the Company and MDS Nordion, a division of MDS (Canada) Inc. |
| | 10 | .25†** | | Amendment No. 2, dated May 9, 2006, between the Company and MDS Nordion to Development, Manufacturing and Supply Agreement, dated June 14, 2004, and Amendment No. 1, dated May 9, 2006, between the Company and MDS Nordion to BMIPP Supply Agreement, dated January 12, 2006. |
| | 10 | .26** | | Amendment No. 3, dated November 26, 2006, between the Company and MDS Nordion to Development, Manufacturing and Supply Agreement, dated June 14, 2004. |
| | 10 | .27†** | | License Agreement, dated as of November 3, 2006, between the Company and Novartis Pharma AG. |
| | 10 | .28†** | | License Agreement, dated as of December 6, 2006, between the Company and McMaster University. |
| | 10 | .29†** | | First Amendment, dated January 4, 2007, between the Company and Novartis Pharma AG to the License Agreement dated November 3, 2006. |
| | 10 | .30†** | | Technology Transfer Agreement, dated December 20, 2006, between the Company and Mallinckrodt Inc. |
| | 10 | .31†** | | License, Development and Commercialization Agreement, dated January 15, 2007, between the Company and Bayer Schering Pharma Aktiengesellschaft. |
| | 10 | .32** | | Securities Purchase Agreement, dated September 28, 2006, among the Company and the Purchasers of Convertible Notes and Common Stock Warrants. |
| | 10 | .33** | | Amendment No. 1 to Registration Rights Agreement, dated September 28, 2006, among the Company and certain holders of Common Stock and Series A Preferred Stock, the holders of Series B Preferred Stock, the holders of Series C Preferred Stock, and the holders of Convertible Notes. |
| | 10 | .34** | | Amendment No. 1 to Employment Agreement between the Company and John Babich, dated November 14, 2005. |
| | 10 | .35** | | Amendment No. 1 to Employment Agreement between the Company and David Barlow, dated November 14, 2005. |
| | 10 | .36** | | Amendment No. 1 to Employment Agreement between the Company and John McCray, dated November 14, 2005. |
| | 10 | .37** | | Amendment No. 1 to Employment Agreement between the Company and Nicholas Borys, dated November 14, 2005. |
| | 10 | .38** | | Amendment No. 1 to Employment Agreement between the Company and Bob Gallahue, dated November 14, 2005. |
| | 10 | .39 | | Employment Agreement between the Company and Norman D. LaFrance, dated as of April 18, 2007. |
| | 14 | .1 | | Code of Ethics |
| | 21 | .1** | | Subsidiaries of the Registrant. |
| | 31 | .1 | | Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certifications by the Registrant’s Chief Executive Officer |
| | 31 | .2 | | Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certifications by the Registrant’s Chief Financial Officer |
| | 32 | .1 | | Section 1350 Certifications by the Registrant’s Chief Executive Officer |
| | 32 | .2 | | Section 1350 Certifications by the Registrant’s Chief Financial Officer |
| | |
| ** | | Incorporated herein by reference to the exhibits under the same exhibit numbers previously filed with the Registrant’s Registration Statement onForm S-1 filed with the Commission, as amended (Registration No. 333-129570), as declared effective on February 1, 2007. |
50
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
(A Development Stage Company)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | | | | |
| | | F-2 | |
| Consolidated Financial Statements: | | | | |
| | | F-3 | |
| | | F-4 | |
| | | F-5 | |
| | | F-7 | |
| | | F-8 | |
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Cambridge, Massachusetts
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and subsidiaries (a development stage company) (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2006 and 2005, and the related consolidated statements of operations, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ deficit, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2006, and for the period from January 10, 1997 (date of inception) through December 31, 2006. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2006 and 2005, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2006, and for the period from January 10, 1997 (date of inception) through December 31, 2006, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
March 30, 2007
F-2
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Current assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 5,810,540 | | | $ | 8,915,857 | |
| Investments | | | 12,562,814 | | | | — | |
| Accounts receivable — research and development grants | | | 330,593 | | | | 127,924 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | 398,350 | | | | 1,563,314 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total current assets | | | 19,102,297 | | | | 10,607,095 | |
| Property and equipment — net | | | 493,079 | | | | 886,783 | |
| Deferred stock offering costs | | | — | | | | 982,195 | |
| Other assets | | | 58,931 | | | | 458,102 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 19,654,307 | | | $ | 12,934,175 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
| Notes payable, current portion | | $ | 1,588,275 | | | $ | 1,734,672 | |
| Accounts payable | | | 1,669,847 | | | | 1,499,830 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | 1,976,797 | | | | 5,812,055 | |
| Accrued expenses — related parties | | | 748,334 | | | | 684,243 | |
| Success fee derivative liability | | | 142,400 | | | | 278,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 6,125,653 | | | | 10,008,800 | |
| Notes payable — less current portion | | | 3,360,125 | | | | 1,832,384 | |
| Convertible notes payable | | | — | | | | 5,093,884 | |
| Convertible notes payable — related party | | | — | | | | 9,433,119 | |
| Convertible notes payable — accrued interest | | | — | | | | 111,255 | |
| Convertible notes payable — accrued interest related party | | | — | | | | 206,028 | |
| Deferred rent | | | 67,707 | | | | 22,568 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 10) | | | | | | | | |
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock, $0.01 par value — at carrying value, including accrued dividends; authorized 359,515 shares at December 31, 2005 and 2006; 315,570 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2005 and 2006 (liquidation preference and redemption value of approximately $55,880,000 and $46,879,000 at December 31, 2005, and $63,000 and $49,000 at December 31, 2006) | | | 45,235,745 | | | | 48,089,941 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Stockholders’ deficit | | | | | | | | |
| Common stock, $0.01 par value; authorized, 19,166,667 shares at December 31, 2005 and 100,000,000 at December 31, 2006; issued and outstanding, 4,452,693 and 4,637,493 shares at December 31, 2005 and December 31, 2006, respectively | | | 44,527 | | | | 46,375 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | 24,212,687 | | | | 23,770,599 | |
| Deferred stock-based compensation | | | (1,319,970 | ) | | | (352,224 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | | | (10,351 | ) | | | (520 | ) |
| Deficit accumulated during the development stage | | | (58,061,816 | ) | | | (85,328,034 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total stockholders’ deficit | | | (35,134,923 | ) | | | (61,863,804 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ deficit | | $ | 19,654,307 | | | $ | 12,934,175 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-3
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Period from
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | January 10, 1997
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (Date of Inception)
| |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | | through December 31,
| |
| | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Revenue — research and development grants | | $ | 569,273 | | | $ | 1,232,084 | | | $ | 325,068 | | | $ | 4,415,593 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development | | | 5,298,317 | | | | 8,652,801 | | | | 16,383,307 | | | | 44,177,224 | |
| Research and development — related parties | | | 83,156 | | | | 202,539 | | | | 251,899 | | | | 1,107,301 | |
| General and administrative | | | 3,108,640 | | | | 9,991,013 | | | | 8,381,662 | | | | 31,006,189 | |
| General and administrative — related parties | | | 411,060 | | | | 1,034,069 | | | | 1,829,502 | | | | 3,611,328 | |
| Amortization of licensed patent rights | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 9,767,130 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total operating expenses | | | 8,901,173 | | | | 19,880,422 | | | | 26,846,370 | | | | 89,669,172 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss from operations | | | (8,331,900 | ) | | | (18,648,338 | ) | | | (26,521,302 | ) | | | (85,253,579 | ) |
| Other (expense) income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | | 19,601 | | | | 488,506 | | | | 468,882 | | | | 1,125,673 | |
| Interest expense | | | (3,104 | ) | | | (140,988 | ) | | | (1,213,798 | ) | | | (1,376,262 | ) |
| Interest expense-related parties | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (57,200 | ) |
| Management fee income-related party | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 233,334 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total other (expense) income, net | | | 16,497 | | | | 347,518 | | | | (744,916 | ) | | | (74,455 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | (8,315,403 | ) | | | (18,300,820 | ) | | | (27,266,218 | ) | | | (85,328,034 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock dividends and accretion of issuance costs | | | (1,312,132 | ) | | | (4,046,637 | ) | | | (4,957,900 | ) | | | (10,929,564 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders | | $ | (9,627,535 | ) | | $ | (22,347,457 | ) | | $ | (32,224,118 | ) | | $ | (96,257,598 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders | | $ | (2.55 | ) | | $ | (5.30 | ) | | $ | (7.18 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average shares used to compute basic and diluted loss per share attributable to common stockholders | | | 3,773,439 | | | | 4,213,484 | | | | 4,489,661 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-4
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Redeemable
| | | Stockholders’ Deficit | |
| | | Convertible
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Deficit
| | | | | | | |
| | | Preferred Stock,
| | | Common Stock
| | | | | | | | | | | | Note
| | | Deferred
| | | Accumulated
| | | Accumulated
| | | | | | | |
| | | $0.01 Par Value | | | $0.01 Par Value | | | Additional
| | | Treasury Stock | | | Receivable
| | | Stock-
| | | Other
| | | During the
| | | Total
| | | Total
| |
| | | Number of
| | | Carrying
| | | Number of
| | | Par
| | | Paid-In
| | | Number of
| | | | | | from
| | | Based
| | | Comprehensive
| | | Development
| | | Stockholders’
| | | Comprehensive
| |
| | | Shares | | | Value | | | Shares | | | Value | | | Capital | | | Shares | | | Cost | | | Stockholder | | | Compensation | | | Loss | | | Stage | | | Deficit | | | Loss | |
| |
Balance, January 1, 2004 | | | 120,317 | | | | 7,552,080 | | | | 3,963,241 | | | | 39,632 | | | | 22,678,767 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (295,650 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (31,445,593 | ) | | | (9,022,844 | ) | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options | | | — | | | | — | | | | 329,332 | | | | 3,293 | | | | 191,456 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 194,749 | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of warrants | | | — | | | | — | | | | 33,951 | | | | 340 | | | | 54,660 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 55,000 | | | | | |
| Issuance of Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock and common stock warrants, net of $198,514 of issuance costs | | | 52,670 | | | | 6,542,786 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 211,000 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 211,000 | | | | | |
| Conversion of accounts payable into Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock | | | 993 | | | | 131,076 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation for nonemployee awards | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 45,509 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 45,509 | | | | | |
| Preferred stock dividends | | | — | | | | 1,016,920 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,016,920 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,016,920 | ) | | | | |
| Accretion of issuance costs and warrants | | | — | | | | 295,212 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (295,212 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (295,212 | ) | | | | |
| Deferred stock-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 728,550 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (728,550 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | |
| Amortization of deferred stock-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 312,892 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 312,892 | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (8,315,403 | ) | | | (8,315,403 | ) | | $ | (8,315,403 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total comprehensive loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | (8,315,403 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2004 | | | 173,980 | | | | 15,538,074 | | | | 4,326,524 | | | | 43,265 | | | | 22,597,810 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (295,650 | ) | | | (415,658 | ) | | | — | | | | (39,760,996 | ) | | | (17,831,229 | ) | | | | |
| Exercise of common stock options | | | — | | | | — | | | | 126,169 | | | | 1,262 | | | | 74,439 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 75,701 | | | | | |
| Collection of note receivable from stockholder | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 295,650 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 295,650 | | | | | |
| Issuance of Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of $1,106,800 of issuance costs | | | 141,590 | | | | 27,470,581 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 24,000 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 24,000 | | | | | |
| Series B warrant modification | | | — | | | | (560,000 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 560,000 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 560,000 | | | | | |
| Preferred stock dividends | | | — | | | | 2,416,820 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,416,820 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,416,820 | ) | | | | |
| Accretion of issuance costs and warrants | | | — | | | | 370,270 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (370,270 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (370,270 | ) | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation for nonemployee awards | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 166,728 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 166,728 | | | | | |
| Deferred stock-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,576,800 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3,576,800 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | | |
(continued)
F-5
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Redeemable
| | | Stockholders’ Deficit | |
| | | Convertible
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Deficit
| | | | | | | |
| | | Preferred Stock,
| | | Common Stock
| | | | | | | | | | | | Note
| | | Deferred
| | | Accumulated
| | | Accumulated
| | | | | | | |
| | | $0.01 Par Value | | | $0.01 Par Value | | | Additional
| | | Treasury Stock | | | Receivable
| | | Stock-
| | | Other
| | | During the
| | | Total
| | | Total
| |
| | | Number of
| | | Carrying
| | | Number of
| | | Par
| | | Paid-In
| | | Number of
| | | | | | from
| | | Based
| | | Comprehensive
| | | Development
| | | Stockholders’
| | | Comprehensive
| |
| | | Shares | | | Value | | | Shares | | | Value | | | Capital | | | Shares | | | Cost | | | Stockholder | | | Compensation | | | Loss | | | Stage | | | Deficit | | | Loss | |
| |
| Amortization of deferred stock-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,672,488 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,672,488 | | | | | |
Unrealized holding loss onavailable-for-sale investments | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (10,351 | ) | | | — | | | | (10,351 | ) | | $ | (10,351 | ) |
| Net loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (18,300,820 | ) | | | (18,300,820 | ) | | $ | (18,300,820 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total comprehensive loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | (18,311,171 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2005 | | | 315,570 | | | | 45,235,745 | | | | 4,452,693 | | | | 44,527 | | | | 24,212,687 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,319,970 | ) | | | (10,351 | ) | | | (58,061,816 | ) | | | (35,134,923 | ) | | | | |
| Adoption of SFAS 123(R) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (798,146 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 798,146 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0 | | | | | |
| Exercise of common stock options | | | — | | | | — | | | | 184,800 | | | | 1,848 | | | | 126,272 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 128,120 | | | | | |
| Warrants issued in conjunction with convertible notes payable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 954,758 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 954,758 | | | | | |
| Preferred stock dividends | | | — | | | | 2,540,010 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,540,010 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,540,010 | ) | | | | |
| Accretion of issuance costs | | | — | | | | 314,186 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (314,186 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (314,186 | ) | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation for nonemployee awards | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,023,079 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,023,079 | | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation for employee awards | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 733,539 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 733,539 | | | | | |
| Warrants issued in connection with Ritchie notes payable | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 201,606 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 201,606 | | | | | |
| Amortization of deferred stock-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 169,600 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 169,600 | | | | | |
Unrealized holding gain onavailable-for-sale investments | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 9,831 | | | | — | | | | 9,831 | | | $ | 9,831 | |
| Beneficial conversion in connection with convertible notes payable | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 171,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 171,000 | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (27,266,218 | ) | | | (27,266,218 | ) | | $ | (27,266,218 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total comprehensive loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | (27,256,387 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2006 | | | 315,570 | | | $ | 48,089,941 | | | | 4,637,493 | | | $ | 46,375 | | | $ | 23,770,599 | | | | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (352,224 | ) | | $ | (520 | ) | | $ | (85,328,034 | ) | | $ | (61,863,804 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-6
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Period from
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | January 10, 1997
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (Date of Inception)
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | through
| |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | | December 31,
| |
| | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | $ | (8,315,403 | ) | | $ | (18,300,820 | ) | | $ | (27,266,218 | ) | | $ | (85,328,034 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to cash used in operating activities, net of acquisition: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Noncash interest expense on promissory notes payable to stockholders | | | — | | | | 22,814 | | | | 854,439 | | | | 906,953 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 106,206 | | | | 139,276 | | | | 307,030 | | | | 10,982,125 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | | 358,403 | | | | 2,839,216 | | | | 1,926,218 | | | | 10,393,705 | |
| Deferred rent | | | (45,140 | ) | | | (45,140 | ) | | | (45,139 | ) | | | (135,419 | ) |
| Other | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 4,787 | |
| Changes in assets and liabilities, net of the acquisition of Zebra Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Accounts receivable | | | (37,087 | ) | | | (244,128 | ) | | | 202,669 | | | | (65,777 | ) |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | (50,371 | ) | | | (44,594 | ) | | | (1,095,546 | ) | | | (1,216,224 | ) |
| Accounts payable | | | 992,914 | | | | 31,848 | | | | (741,194 | ) | | | 754,024 | |
| Accrued expenses and other | | | 951,180 | | | | 836,628 | | | | 3,827,259 | | | | 5,821,859 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses-related parties | | | (142,270 | ) | | | 570,338 | | | | (64,091 | ) | | | 790,910 | |
| Deferred revenue — government grants | | | 14,233 | | | | (14,233 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | | (6,167,335 | ) | | | (14,208,795 | ) | | | (22,094,573 | ) | | | (57,091,091 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of investments | | | — | | | | (14,573,165 | ) | | | — | | | | (14,573,165 | ) |
| Proceeds from matured investments | | | | | | | 2,000,000 | | | | 12,572,645 | | | | 14,572,645 | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | (202,542 | ) | | | (226,945 | ) | | | (716,605 | ) | | | (1,720,053 | ) |
| Collection of advance and note receivable for stockholder | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 135,500 | |
| Net cash received on acquisition of Zebra Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 171,560 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | | | (202,542 | ) | | | (12,800,110 | ) | | | 11,856,040 | | | | (1,413,513 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Offering costs | | | — | | | | — | | | | (387,148 | ) | | | (387,148 | ) |
| Advances received for stock subscription — net | | | — | | | | | | | | — | | | | 5,314,619 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of notes payable — net of issuance costs | | | — | | | | 4,992,500 | | | | 15,490,428 | | | | 20,482,928 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of notes payable to stockholders and issuance of warrants | | | 700,000 | | | | 375,000 | | | | — | | | | 1,645,000 | |
| Payment on notes payable | | | (120,392 | ) | | | (185,141 | ) | | | (1,887,549 | ) | | | (2,193,082 | ) |
| Proceeds from sale of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock — net of issuance costs | | | — | | | | 295,650 | | | | — | | | | 2,958,857 | |
| Proceeds from sale of Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock — net of issuance costs | | | 4,681,275 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 4,681,275 | |
| Proceeds from sale of Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock — net of issuance costs | | | — | | | | 26,419,581 | | | | — | | | | 26,419,581 | |
| Payments on capital lease obligations | | | (5,101 | ) | | | | | | | — | | | | (74,999 | ) |
| Proceeds from exercise of common stock options and warrants | | | 249,749 | | | | | | | | 128,120 | | | | 453,570 | |
| Proceeds from sale of common stock and warrants, net of issuance costs | | | — | | | | 75,701 | | | | — | | | | 8,168,215 | |
| Proceeds from sale of restricted stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 32,850 | |
| Repurchase of common stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (50,400 | ) |
| Repayment of loan payable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (20,000 | ) |
| Repayment of installment note payable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (10,804 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | | 5,505,531 | | | | 31,973,291 | | | | 13,343,851 | | | | 67,420,462 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | (864,346 | ) | | | 4,964,386 | | | | 3,105,317 | | | | 8,915,857 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents — beginning of period | | | 1,710,500 | | | | 846,154 | | | | 5,810,540 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents — end of period | | $ | 846,154 | | | $ | 5,810,540 | | | $ | 8,915,857 | | | $ | 8,915,857 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flows information: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash paid for interest | | $ | 3,104 | | | $ | 67,184 | | | $ | 250,572 | | | $ | 376,896 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Noncash investing and financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Notes payable to stockholders including accrued interest of $55,000 converted into Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 605,000 | |
| Accrued expenses and accounts payable converted into redeemable convertible preferred stock | | | 131,076 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 210,243 | |
| Leasehold improvements paid by landlord | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 203,127 | |
| Issuance of notes payable for prepaid insurance and conversion of accrued expenses | | | 274,000 | | | | 67,986 | | | | — | | | | 341,986 | |
| Property and equipment included in accounts payable | | | 21,169 | | | | 47,778 | | | | 31,907 | | | | 31,907 | |
| Issuance of 349,525 shares of common stock and 354,200 stock options on acquisition of Zebra Pharmaceuticals, Inc., net of cash received | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 10,041,257 | |
| Acquisition of equipment under capital lease obligations | | | — | | | | | | | | — | | | | 74,999 | |
| Deferred stock offering costs included in accounts payable and accrued expenses | | | — | | | | — | | | | 595,047 | | | | 595,047 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-7
| |
| 1. | NATURE OF BUSINESS AND OPERATIONS |
Nature of Business — Molecular Insight Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (the “Company”) was incorporated in January 1997 and is a biopharmaceutical company focused on the research, development and commercialization of innovative molecular imaging pharmaceuticals and targeted radiotherapeutics designed to improve patient diagnosis, treatment and management. The Company is based in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Development Stage Company — Revenue generating activities have been limited to research and development services pursuant to certain governmental research and development grants, and no revenues have been recorded from the sale of products from its planned principal business activity. Accordingly, the Company is classified as a development stage company.
Operations — The Company has incurred significant net losses and negative operating cash flows since inception. As December 31, 2006, the Company had an accumulated deficit of $85.3 million, and a stockholders’ deficit of $61.9 million. The Company incurred net losses of approximately $18.3 million, and approximately $27.3 million, and used $14.2 million and $22.1 million in cash flows from operating activities during the years ended December 31, 2005, and December 31, 2006, respectively. As of December 31, 2006, the Company had $8.9 million of cash and cash equivalents and working capital of approximately $598,000. The Company will require significant additional funds to conduct clinical and non-clinical trials, achieve regulatory approvals, and, subject to such approvals, commercially launch its products. The Company has funded its operations through December 31, 2006, through the issuance of redeemable convertible preferred stock, the issuance of common stock, the issuance of convertible and other notes payable to certain stockholders and financial institutions, and revenues earned from government research and development grants. The Company’s long-term success is dependant on obtaining sufficient capital to fund the research and development of its products, to bring about their successful commercial release, to generate revenue and, ultimately, attain profitable operations. On February 7, 2007, the Company completed an initial public offering, raising $63.3 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses totaling approximately $8.1 million. In connection with the initial public offering, all outstanding shares of Series A, B, and C Preferred Stock were converted into common shares of 4,010,539, 1,788,758, and 4,719,652, respectively. An additional 1,340,624, 258,851, and 448,184 shares of common stock were issued in satisfaction of the then accrued but unpaid dividends on the Series A, B, and C Preferred Stock, respectively. Warrants to purchase common stock were automatically converted into 403,779 shares of the Company’s common stock at an average price of $3.45 per share. In addition, the Convertible Notes and accrued interest (see Note 6), approximately $15.7 million at December 31, 2006, converted into 2,029,159 shares of common stock. As a result of the initial public offering, the Company believes it has enough cash to fund operations into the second half of 2008.
Other Risks and Uncertainties — The Company is also subject to other risks common to companies in the biopharmaceutical industry including, but not limited to, new technological innovations, dependence on key personnel, protection of proprietary technology, compliance with government regulations and approval requirements, commercialization of its potential products, uncertainty of market acceptance of products, competition from larger companies, ability to reach commercial production of its product candidates, and the need to obtain additional financing.
F-8
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| |
| 2. | SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
Principles of Consolidation — The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company, its wholly owned subsidiary, Biostream Therapeutics, Inc. (“BTI”) from the date of acquisition, February 29, 2000, and its subsidiary, ATP Therapeutics, Inc. (“ATP”), from the date of its incorporation on March 4, 1999 through its dissolution on October 26, 2005. ATP was formed as a joint venture by the Company and an independent physician to pursue pre-clinical development of certain patents held by the physician. The physician contributed a license on the patents to the joint venture for a 40.0% interest, and the Company received a 60.0% interest for its commitment to fund development. In September 2000, the Company purchased an additional 200,000 shares of unissued common stock of ATP for $1,000,000 thereby increasing its ownership interest to 63.6%. In October 2005, the Company acquired the remaining 36.4% of ATP in exchange for all rights to ATP’s intellectual property and written records. ATP was dissolved due to its inactive status on October 26, 2005. The Company recognized all of ATP’s losses as the Company has been ATP’s sole source of funding and the Company’s equity absorbed all losses. The minority interest in this investment was not material. Intercompany accounts and transactions for all subsidiaries have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates — The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and use assumptions that affect reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the balance sheet dates and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from these estimates. Significant estimates reflected in these financial statements include the estimated fair values of the Company’s common and redeemable convertible preferred stock, warrants, certain accruals and reserves, stock-based compensation and the valuation allowance recognized on the deferred tax assets.
Revenue Recognition — The Company recognizes revenue from government grants for research and development as services are performed provided contractual agreements exist, the fees are fixed or determinable and the collection is probable. Amounts recognized are limited to amounts due from the grantor based upon the contract or grant terms. The Company has been awarded government grants from the National Institutes of Health (“NIH”) to provide research services related to certain areas of the Company’s research. Such grants are generally on a cost sharing basis with the Company also contributing to the costs of research. Payments received in advance of costs being incurred are recorded as deferred revenue.
Under the terms of the NIH grants, the Company has all right, title and interest in its patents, copyrights and data pertaining to its product development, subject to certain rights of the government. Under existing regulations, the government receives a royalty-free license for federal government use for all patents developed under a government grant. In addition, under certain circumstances the government may require the Company to license technology resulting from the government-funded projects to third parties and may require that the Company manufacture its product in the United States. However, ownership in such technology remains with the Company.
Funding of government grants is subject to government appropriation and all of these grants contain provisions which allow for termination at the convenience of the government. These grants require the Company to comply with certain government regulations. Management believes that the Company has complied with all regulations that, if not met, could have a material adverse impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements or the Company’s eligibility for future grant awards.
Research and Development — Research and development expense consists of expenses incurred in developing and testing product candidates. These expenses consist primarily of salaries and related expenses for personnel, fees paid to professional service providers in conjunction with independently monitoring clinical
F-9
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
trials and acquiring and evaluating data in conjunction with clinical trials, costs of contract manufacturing services, costs of materials used in clinical trials and research and development, depreciation of capital assets used to develop products and costs of facilities. Research and development costs, including those incurred and supported with government grants, are expensed as incurred and included under such caption in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Certain research and development activities are partially funded with government grants, which are recognized as revenue.
Cash and Cash Equivalents — Cash and cash equivalents include cash and highly liquid investments (primarily money market funds) purchased within three months of the maturity date.
Investments — Investments consist of marketable securities which have a maturity date greater than three months when purchased and are available for operating purposes. These investments are recorded at fair value and accounted for asavailable-for-sale securities with any unrealized gains or losses reported as a separate component of stockholders’ deficit. As of December 31, 2005, short-term investments consist of corporate bonds and commercial paper. The fair value approximates the carrying value as of December 31, 2005, due to the short-term nature of these investments, with the adjustment from amortized cost included in accumulated other comprehensive loss. There are no investments at December 31, 2006.
Deferred Stock Offering Costs — Costs directly associated with the Company’s filing of amendment No. 2 to itsForm S-1 related to its initial public offering (“Offering”) of securities have been capitalized and recorded as deferred stock offering costs. The Company filed its initialForm S-1 with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 8, 2005; with amendment No. 1 filed on January 19, 2006. Subsequent to the filing of amendment No. 1, the Company decided to postpone the offering, and expensed approximately $2.2 million and approximately $720,000 of offering costs during the years ended December 31, 2005 and 2006, respectively, related to the initial filing and amendment No. 1. The Company filed an additional amendment in 2006 and completed its initial public offering on February 7, 2007. Deferred offering costs relating to amendment No. 2 were approximately $982,000 as of December 31, 2006. Upon completion of the February 7, 2007 initial public offering, such costs were recorded as a reduction of the proceeds received in arriving at the amount to be recorded in stockholders’ deficit.
Property and Equipment — Property and equipment are recorded at cost. Depreciation and amortization is provided using the straight-line method over the estimated lives of the related assets or over the term of the lease (for leasehold improvements and leased equipment), if shorter as follows: lab and other equipment — 3 years; furniture and fixtures — 5 years; leasehold improvements — 2.5 years.
Other Assets — Other assets include $434,106 of debt issuance costs incurred in connection with the Loan and Security Agreement with Ritchie Multi-Strategy Global, LLC (see Note 6) which have been capitalized and are being amortized as a component of interest expense over the term of the debt. As of December 31, 2005 and December 31, 2006, the carrying amount for these costs was $49,540 and $332,698, respectively, $5,306 and $27,276 having been amortized as a component of interest expense through these respective dates.
Licensed Patent Rights — On February 29, 2000, the Company acquired all of the outstanding stock of BTI, which was accounted for under the purchase method of accounting. The acquired licensed patent rights of $9.8 million were assigned a three year useful life and were fully amortized as of December 31, 2002.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets — The Company reviews its long-lived assets for possible impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of a long-lived asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is evaluated by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying
F-10
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. No impairment losses have been recognized through December 31, 2006.
Income Taxes — Deferred tax assets and liabilities relate to temporary differences between financial reporting and income tax bases of assets and liabilities and are measured using enacted tax rates and laws expected to be in effect at the time of their reversal. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce the net deferred tax asset to the amount more likely than not to be realized.
Stock-Based Compensation — On January 1, 2006, the Company adopted Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 123(R),Share-Based Payment, (“SFAS 123(R)”) to account for stock-based awards. SFAS 123(R) addresses accounting for share-based awards, including shares issued under employee stock purchase plans, stock options, and share-based awards with compensation cost measured using the fair value of the awards issued. In accordance with SFAS 123(R), the Company recognizes compensation cost for granted but unvested awards, new awards, and awards modified, repurchased or cancelled after the required effective date.
Prior to January 1, 2006, the Company accounted for stock-based awards to employees using the intrinsic value method as prescribed by Accounting Principles Board (“APB”) Opinion No. 25,Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees, and related interpretations. Accordingly, no compensation expense was recorded for options issued to employees in fixed amounts and with fixed exercise prices at least equal to the fair value of the Company’s common stock at the date of grant. Prior to the adoption of SFAS 123(R), all stock-based awards to non-employees were accounted for at their fair value in accordance with SFAS No. 123,Accounting for Stock-Based Compensationand Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”)No. 96-18,Accounting for Equity Instruments That Are Issued to Other Than Employees for Acquiring, or in Conjunction with Selling, Goods or Services.
The Company has recorded stock-based compensation under SFAS 123(R) using the modified prospective method for the unvested portion of stock-based awards granted after being considered a public company (November 8, 2005). However, the Company will continue to record compensation cost on awards granted prior to November 8, 2005 following the provisions of APB Opinion No. 25, using the prospective method of SFAS 123(R) for awards granted while not considered a public company. For awards issued after January 1, 2006, the Company has elected to recognize compensation cost for awards with service conditions on a straight line basis over the requisite service period. Prior to the adoption of SFAS 123(R), the Company used the straight-line method of recognition for all awards. As a result of adoption of SFAS 123(R), the Company has recognized additional compensation cost and increase in net loss in the year ended December 31, 2006 of $199,447 (or $0.04 per basic and diluted share) over what would have been recognized using the intrinsic value method under APB Opinion No. 25. There was no impact on the presentation in the consolidated statements of cash flows as no excess tax benefits have been realized subsequent to adoption. The company has adopted the simplified method for determining of the APIC pool as provided by FSP 123(R)-3.
Prior to adopting SFAS 123(R), the Company followed the disclosure provisions of SFAS No. 123, for all employee stock-based awards. For purposes of the pro forma disclosure, the fair value of each employee option grant was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. Prior to filing the Company’s initial registration statement, the Company used the minimum value method, which includes the use of a zero volatility factor. Subsequent to the initial filing of the registration statement, the Company used an estimated
F-11
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
volatility factor based upon comparable companies. The assumptions used for all grants during the applicable periods presented are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Risk-free interest rate | | | 2.84 | % | | | 3.85 | % | | | 4.8 | % |
| Expected dividend yield | | | 0.0 | % | | | 0.0 | % | | | 0.0 | % |
| Expected option life | | | 4 years | | | | 4 years | | | | 6.25 years | |
| Expected stock volatility (minimum value method) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0.0 | % |
| Expected stock volatility (fair value method) | | | — | | | | 65 | % | | | 65.9 | % |
The pro forma impact on reported net loss attributable to common stockholders using the minimum value method provided by SFAS No. 123 was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2004 | | | 2005 | |
| |
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders, as reported | | $ | (9,627,535 | ) | | $ | (22,347,457 | ) |
| Add back: stock-based employee compensation expense included in reported net loss | | | 312,892 | | | | 2,839,216 | |
| Deduct: stock-based employee compensation expense determined under fair value method | | | (70,407 | ) | | | (2,854,531 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Pro forma net loss attributable to common stockholders | | $ | (9,385,050 | ) | | $ | (22,362,772 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders: | | | | | | | | |
| As reported | | $ | (2.55 | ) | | $ | (5.30 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Pro forma | | $ | (2.49 | ) | | $ | (5.31 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
Net Loss Per Share — Basic and diluted net loss per common share is calculated by dividing the net loss applicable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of unrestricted common shares outstanding during the periods. Diluted net loss per share is the same as basic net loss per share, since the effects of potentially dilutive securities are anti-dilutive for all periods presented. Anti-dilutive securities, which consist of redeemable convertible preferred stock, common stock issuable upon conversion of accrued cumulative dividends on preferred stock, stock options, warrants and convertible debt that are not included in the diluted net loss per share calculation, aggregated 7,982,073, 13,852,403, and 17,296,690 potential common shares as of December 31, 2004, 2005, and 2006, respectively. In addition, unvested common stock pursuant to restricted stock awards are excluded from the calculation of basic loss per share until such shares vest but are included in diluted net loss per share if inclusion is not antidilutive.
The Company’s redeemable convertible preferred stock accrues dividends (see Note 8) that may either be paid in cash or in common stock at the election of the holder. If conversion is elected, the number of shares into which the dividends may be converted is based upon the conversion ratio for the redeemable convertible preferred stock and may result in the holders of the redeemable convertible preferred stock receiving common stock with a fair value that is greater than the recorded amount of accrued dividends. If the conversion feature of the accrued dividends has an intrinsic value greater than the dividend earned, the beneficial conversion feature is recognized and treated as a distribution to preferred stockholders for purposes of net loss per share calculations.
F-12
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Redeemable convertible preferred stock dividends and accretion of issuance costs, and any beneficial conversion feature for each period presented in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations are as follow:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Period from
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | January 10, 1997
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (Date of Inception)
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | through
| |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | | December 31,
| |
| | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Preferred stock dividends | | $ | 1,016,920 | | | $ | 2,416,820 | | | $ | 2,540,010 | | | $ | 6,534,799 | |
| Accretion of issuance costs | | | 126,412 | | | | 288,033 | | | | 314,186 | | | | 780,601 | |
| Accretion of warrants | | | 168,800 | | | | 82,237 | | | | — | | | | 251,037 | |
| Beneficial conversion stock dividend | | | — | | | | 1,259,547 | | | | 2,103,704 | | | | 3,363,127 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock dividends and accretion of issuance costs | | $ | 1,312,132 | | | $ | 4,046,637 | | | $ | 4,957,900 | | | $ | 10,929,564 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Concentration of Credit Risk and Significant Customers — Financial instruments which potentially expose the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments. The Company’s cash and cash equivalents were held at two financial institutions at December 31, 2005 and December 31, 2006. The investments were held at one financial institution at December 31, 2005. Management believes that the financial institutions are of high credit quality. All of the Company’s research and development revenue is from a single United States government agency.
Guarantees: Indemnified Obligations — The Company leases office space under a non-cancelable operating lease (see Note 10). The Company has indemnification arrangements under this lease that require the Company to indemnify the landlord against claims, actions or damages incurred in connection with the premises covered by the Company’s lease and the Company’s use of the premises.
The Company had not experienced any losses related to these indemnification obligations, and no claims with respect thereto were outstanding through December 31, 2006. The Company does not expect significant claims related to these indemnification obligations, and consequently concluded that the fair value of these obligations is negligible and no related reserves were established in any period presented in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments — The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial instruments, which include cash equivalents, investments, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued expenses approximate their fair values due to their short-term nature. The fair value of the Company’s notes payable approximates $18,411,000 as of December 31, 2006.
Segments — The Company conducts its operations and manages its business as one operating segment.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements — In June 2006, the FASB issued FASB Interpretation No. 48,Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes, an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109(“FIN 48”). FIN 48 clarifies the accounting for uncertainties in income taxes recognized in an enterprise’s financial statements. FIN 48 requires that the Company determine whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination by the appropriate taxing authority. If a tax position meets the “more likely than not” recognition criteria, FIN 48 requires the tax position be measured at the largest amount of benefit greater than 50 percent likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement. This accounting standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2006. The Company does not believe the effect, if any, of adopting FIN 48 will have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations.
F-13
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
In September 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 157,Fair Value Measurements(“SFAS 157”), which establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about the use of fair value measurements and liabilities in interim and annual reporting periods subsequent to initial recognition. Prior to the issuance of SFAS 157, which emphasizes that fair value is a market-based measurement and not an entity-specific measurement, there were different definitions of fair value and limited definitions for applying those definitions in GAAP. SFAS 157 is effective for the Company on a prospective basis for the reporting period beginning January 1, 2008. The Company does not believe the effect, if any, of adopting SFAS 157 will have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations.
In February 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 159,Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities (“SFAS 159”),which expands the standards under SFAS 157,Fair Value Measurementsto provide entities the one-time election (Fair Value Option or FVO) to measure financial instruments and certain other items at fair value. SFAS 159 also amends Statement No. 115 (SFAS 115) to require the presentation of investments inavailable-for-sale securities and trading securities:
a) in the aggregate of those fair value and non-fair-value amounts in the same line item and parenthetically disclose the amount of fair value included in the aggregate amount or
b) in two separate line items to display the fair value and non-fair-value carrying amounts.
This Statement is effective as of the beginning of an entity’s first fiscal year that begins after November 15, 2007, provided the entity also elects to apply the provisions of FASB Statement No. 157,Fair Value Measurements.The Company does not believe the effect, if any, of adopting SFAS 159 will have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations.
In September 2006, the Securities and Exchange Commission released Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 108, or SAB 108, to address diversity in practice regarding consideration of the effects of prior year errors when quantifying misstatements in current year financial statements. The staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission concluded that registrants should quantify financial statement errors using both a balance sheet approach and an income statement approach and evaluate whether either approach results in quantifying a misstatement that, when all relevant quantitative and qualitative factors are considered, is material. SAB 108 states that if correcting an error in the current year materially affects the current year’s income statement, the prior period financial statements must be restated. SAB 108 is. effective for fiscal years ending after November 15, 2006. The adoption of SAB 108 did not significantly affect our financial condition or results of operations.
| |
| 3. | STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION |
Stock Option Plan — The Company’s stock-based awards include common stock options, common stock warrants and restricted common stock. In 1997, the Company’s stockholders and Board of Directors approved the 1997 Stock Option Plan (the “1997 Plan”). Under the 1997 Plan, the Board of Directors may grant incentive stock options and nonqualified stock options to officers, directors, and other key employees of the Company, its subsidiaries and non-employees and consultants. The 1997 Plan permits the Board of Directors to determine the number of options, the exercise price, the vesting schedule and the expiration date of stock options. The 1997 Plan provides that the exercise price of each incentive stock option must be at least equal to 100% of the estimated fair market value of the common stock on the grant date (110% of fair market value in the case of stockholders who, at the time the option is granted, own more than 10% of the total outstanding common stock), and requires that all such options have an expiration date before the tenth anniversary of the grant date of such options (or the fifth anniversary of the date of grant in the case of 10% stockholders). Options typically expire 10 years from the date of grant and generally vest over a period of four years from the date of grant. In May 2006, the Board of Directors voted to amend the 1997 Plan by increasing the
F-14
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
reserved shares by 666,667, which was subsequently approved by stockholders in August 2006 to allow for a total of 2,833,333 shares issuable under the 1997 Plan. As of December 31, 2006, the Company had 322,190 shares of common stock available for future grant under the 1997 Plan. The Company satisfies share option exercises and issuance of share awards through the issuance of new shares.
SFAS 123(R) — On January 1, 2006, the Company adopted the provisions of SFAS 123(R). The Company has computed stock-based compensation under SFAS 123(R) for options granted using the Black-Scholes option pricing model for the year ended December 31, 2006. In using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, the Company makes certain assumptions with respect to the estimated lives of the awards, expected volatility of the common stock during the expected option life, risk free interest rates, and dividend rates.
The assumptions used are as follows:
| | | |
| | | Year Ended
|
| | | December 31,
|
| | | 2006 |
| |
| Risk free interest rates | | 4.33% to 5.01% |
| Expected dividend yield | | 0% |
| Expected forfeiture rate | | 1.45% |
| Expected life | | 6.25 years |
| Expected volatility | | 65.02% to 68.60% |
The weighted average expected volatility is was 65.80% for the year ended December 31, 2006. The weighted average expected option term for the year ended December 31, 2006 reflects the application of the simplified method set forth in the Securities and Exchange Commission Staff Accounting Bulletin, or SAB, No. 107, which was issued in March 2005. The simplified method defines the life as the average of the contractual term of the options and the weighted average vesting period for all option tranches.
The Company based its estimate of expected volatility using volatility data from comparable public companies in similar industries and markets because there was no public market for the Company’s common stock as of December 31, 2006, and therefore a lack of market based company-specific historical and implied volatility information. The Company intends to continue to consistently apply this process using the same or similar entities until a sufficient amount of historical information regarding the volatility of its own share price becomes available, or unless circumstances change such that the identified entities are no longer similar to the Company.
Stock-based compensation expense for each period presented in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations are as follows (no amounts have been capitalized in any period):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Period from
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | January 10, 1997
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | (Date of Inception)
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | through
| |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | | December 31,
| |
| | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Stock-based compensation charged to: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development | | $ | 24,705 | | | $ | 146,176 | | | $ | 156,690 | | | $ | 2,170,698 | |
| Research and development — related parties | | | 23,156 | | | | 83,406 | | | | 62,599 | | | | 179,618 | |
| General and administrative | | | 310,542 | | | | 2,609,634 | | | | 1,706,929 | | | | 8,043,389 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 358,403 | | | $ | 2,839,216 | | | $ | 1,926,218 | | | $ | 10,393,705 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
F-15
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
2003 Awards — In May of 2003, certain employees and nonemployees cancelled their stock option agreements with exercise prices ranging from $1.20 to $15.00 per share with a weighted-average exercise price of $6.54 per share. A total of 371,757 options were cancelled for employees and 61,733 for nonemployees. Unamortized deferred stock-based compensation as of May 2003, of $68,450 was expensed upon cancellation. The Company granted, 181 days after cancellation, options having the same terms and with an exercise price equal to the then fair value of the Company’s common stock on such date. Accordingly, in December 2003, the Company issued to these same employees and nonemployees options to purchase 371,757 and 61,733 shares of common stock, respectively with an exercise price of $0.60 per share, the then estimated fair value per share on the date of grant. The vesting and exercise periods for these newly issued options were consistent with the vesting and exercise period on the cancelled shares, with the exception of the employees’ options, which have an exercise period of 10 years. Also in 2003, the Company granted stock options for the purchase of 130,129 shares of common stock to nonemployees, all with an exercise price of $0.60 per share. Vesting for these options were either immediate or for terms up to four years. No incremental stock-based compensation resulted from the cancellation and re-grant of employee options.
In 2003, the Company also issued 6,476 shares of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock in lieu of cash compensation to certain officers and employees. The fair value of the stock of $349,704 was recorded as stock-based compensation expense in the year ended December 31, 2003.
During 2003, the Company issued to the Chief Executive Officer 547,500 shares of restricted common stock in exchange for $32,850 in cash and the issuance of a partial recourse (50%), non interest bearing note receivable for $295,650. These shares are subject to Stock Restriction and Stock Pledge Agreements. Under the original terms of these Agreements, the shares vest through February 7, 2007 and if the Chief Executive Officer were to terminate employment for any reason prior to February 7, 2007, any unvested shares are repurchasable by the Company at the original issuance price or a price determined based upon a formula that changes upon the termination circumstances. The agreements were amended on December 12, 2005 to set the repurchase price to be paid to the officer upon termination at $0.60 per share (the original purchase price per share). All other terms remained unchanged. As of December 31, 2005, 410,625 of these shares are vested. Every quarter another 27,375 shares are scheduled to vest. The underlying shares issued to the Chief Executive Officer were subject to variable accounting treatment until a measurement date occurred that fixed the terms, which occurred on December 12, 2005 upon the repayment of the related officer loan. There was no compensation expense in 2003 relating to these shares because the fair value of the shares on the issuance date and December 31, 2003 was the same. However, due to an increase in the fair value of the shares, the Company recorded deferred stock-based compensation of $591,300 and $3,022,200, respectively and $325,215 and $2,490,138, respectively of compensation expense (included in general and administrative expense) for this award for the years ended December 31, 2004 and 2005, respectively. The amendment fixed the amount of compensation to be an aggregate of $3,613,500, with the remaining deferred amount of $798,146 at December 31, 2005. On January 1, 2006, upon adoption of SFAS 123(R), the grant date fair value of non-vested shares using the Black-Scholes model was $907,123, which will be charged to compensation expense on a straight line basis through the final vesting date of February 7, 2007. The stock based compensation expense related to the option award for the year ended December 31, 2006 was $823,632.
2004 and 2005 Awards — During 2004 and 2005, the Company granted stock options to purchase 14,268 and 27,500 shares, respectively, of common stock to nonemployees at an exercise price of $0.60 and $1.20 per share, respectively. The Company recorded stock-based compensation expense relating to these awards of $12,770 and $66,094 in 2004 and 2005, respectively, using the fair value method and based on the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following assumptions: estimated useful life of 10 years, average risk-free interest rate of 4.23%, volatility of 66% and no expected dividends.
F-16
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The Company also granted stock options during 2004 and 2005 to purchase 127,083 and 628,750 shares, respectively, of common stock to employees at an exercise price of $0.60 and between $1.20 and $7.20 per share, respectively. The stated exercise prices were determined to be below the fair value of the common stock on the measurement dates for awards from January 1, 2004 through July 1, 2005. As a result, the Company recorded deferred stock-based compensation of $137,250 in 2004 and $554,598 in 2005 for the difference between the exercise price per share and the fair value per share at the respective grant dates. Compensation expense related to stock options granted to the employees was $17,243, $152,781, and $369,047 for the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006, respectively. As of December 31, 2005 and 2006, the Company had an aggregate of $517,124, and $352,224, respectively of unamortized stock-based compensation remaining to be amortized related to these awards. As of December 31, 2006, the remainder of compensation expense is expected to be recognized over the next three years.
During 2005, the Company granted to three executive officers options providing for the purchase of 213,333 shares of common stock at $1.20 per share. Options for the purchase of 106,667 shares vest ratably over a four year period and the remaining 106,666 shares vest upon the earlier of the fourth anniversary of the grant date or the achievement of performance milestones (including an initial public offering of the Company’s common stock, regulatory approvals and other performance objectives).
Additional options to purchase 443,250 common shares between $1.20 and $7.20 per share were issued during 2005 to other employees and consultants and vest over four years.
2006 Awards — In March of 2006, the Company granted fully vested options for the purchase of 123,200 common shares at $0.60 per share in connection with a litigation matter (see Note 10). The estimated fair value of the options was determined to be approximately $517,000. In May of 2006, the Company granted to three executive officers options for the purchase of 275,000 common shares at $4.80 per share that vest over four years. Options to purchase 65,000 common shares at $4.80 per share were also issued to other employees and members of the Board of Directors and vest over four years and two years, respectively. In September of 2006, options to purchase 101,667 common shares at $5.22 per share were issued to employees and nonemployees and vest over four years.
Certain of the Company’s option agreements provide that in the event of a change in control of the Company, as defined, any unvested options will become immediately vested and exercisable. The total shares of common stock pursuant to such unvested options as of December 31, 2005 and December 31, 2006 were approximately 508,100 and 1,018,230, respectively.
F-17
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Information concerning all stock option activity for the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005, and 2006 is summarized as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| | | | | | Weighted
| | | | | | Weighted
| | | | | | Weighted
| |
| | | | | | Average
| | | | | | Average
| | | | | | Average
| |
| | | | | | Exercise
| | | | | | Exercise
| | | | | | Exercise
| |
| | | Number of
| | | Price per
| | | Number of
| | | Price per
| | | Number of
| | | Price per
| |
| | | Shares | | | Share | | | Shares | | | Share | | | Shares | | | Share | |
| |
| Options outstanding beginning of period | | | 1,192,323 | | | $ | 0.78 | | | | 1,002,675 | | | $ | 0.84 | | | | 1,517,006 | | | $ | 1.74 | |
| Granted | | | 141,351 | | | | 0.60 | | | | 656,583 | | | | 2.82 | | | | 564,867 | | | | 3.96 | |
| Exercised | | | (329,332 | ) | | | 0.60 | | | | (126,169 | ) | | | 0.60 | | | | (184,800 | ) | | | 0.66 | |
| Forfeited | | | (1,667 | ) | | | 0.60 | | | | (16,083 | ) | | | 1.20 | | | | (6,667 | ) | | | 0.60 | |
| Cancelled | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,500 | ) | | | 6.90 | |
| Expired | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (17,067 | ) | | | 0.60 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options outstanding end of period | | | 1,002,675 | | | $ | 0.84 | | | | 1,517,006 | | | $ | 1.74 | | | | 1,870,839 | | | $ | 2.46 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options exercisable | | | 578,507 | | | $ | 0.96 | | | | 636,158 | | | $ | 0.92 | | | | 852,609 | | | $ | 1.25 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options available for grant | | | 834,660 | | | | | | | | 194,160 | | | | | | | | 322,190 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average fair value of options granted during the period | | | | | | $ | 1.20 | | | | | | | $ | 2.49 | | | | | | | $ | 4.88 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The total intrinsic value of outstanding options as of December 31, 2006 was $17,847,622. The total intrinsic value of options exercised for the years ended December 31, 2004 was $358,351, December 31, 2005 was $832,729 and December 31, 2006 was $2,089,469.
Information concerning restricted stock activity for the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006 is summarized as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| | | | | | Weighted
| | | | | | Weighted
| | | | | | Weighted
| |
| | | | | | Average
| | | | | | Average
| | | | | | Average
| |
| | | Number of
| | | Grant Date
| | | Number of
| | | Grant Date
| | | Number of
| | | Grant Date
| |
| | | Shares | | | Fair Value | | | Shares | | | Fair Value | | | Shares | | | Fair Value | |
| |
| Nonvested shares at beginning of period | | | 355,875 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | | 246,375 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | | 136,875 | | | $ | 0.60 | |
| Granted | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Vested | | | (109,500 | ) | | | 0.60 | | | | (109,500 | ) | | | 0.60 | | | | (109,500 | ) | | | 0.60 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Nonvested shares at end of period | | | 246,375 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | | 136,875 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | | 27,375 | | | $ | 0.60 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The total fair value of shares vested during the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006 was $183,960, $538,740, and $823,632, respectively. The weighted average remaining contractual term of the restricted stock is five months. The total compensation cost related to the unvested awards is $83,491, which will be recognized over the remaining term of two months.
F-18
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The following table summarizes additional information about stock options outstanding at December 31, 2006:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Weighted
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Average
| | | Weighted
| | | | | | Weighted
| |
| | | | Number of
| | | Remaining
| | | Average
| | | Number of
| | | Average
| |
| | | | Options
| | | Contractual
| | | Exercise
| | | Options
| | | Exercise
| |
Exercise Price | | | Outstanding | | | Life (Years) | | | Price | | | Exercisable | | | Price | |
| |
| $ | 0.06 | | | | 51,964 | | | | 1.98 | | | | | | | | 51,964 | | | | | |
| | 0.60 | | | | 722,093 | | | | 5.31 | | | | | | | | 623,202 | | | | | |
| | 1.20 | | | | 257,500 | | | | 8.14 | | | | | | | | 60,214 | | | | | |
| | 3.00 | | | | 282,083 | | | | 8.50 | | | | | | | | 70,526 | | | | | |
| | 4.80 | | | | 339,999 | | | | 8.86 | | | | | | | | 1,667 | | | | | |
| | 5.22 | | | | 99,667 | | | | 9.75 | | | | | | | | 0 | | | | | |
| | 6.00 | | | | 63,334 | | | | 8.70 | | | | | | | | 15,835 | | | | | |
| | 7.20 | | | | 33,334 | | | | 8.88 | | | | | | | | 8,335 | | | | | |
| | 9.78 | | | | 333 | | | | 3.22 | | | | | | | | 333 | | | | | |
| | 11.46 | | | | 20,532 | | | | 2.91 | | | | | | | | 20,533 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| $ | 0.06-$11.46 | | | | 1,870,839 | | | | 7.12 | | | $ | 2.46 | | | | 852,609 | | | $ | 1.25 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The following table summarizes certain information pertaining to options granted from January 1, 2004 through December 31, 2006:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Intrinsic
|
| | | | | | | | | Value of
|
| | | Common Shares
| | Exercise Price
| | Fair Value of Common Stock
| | Awards at
|
Grant Date | | Under Option | | per Share | | on Grant Date | | Grant Date |
| |
| 05/13/04 | | | 126,351 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 1.68 | | | $ | 136,459 | |
| 09/21/04 | | | 9,167 | | | | 0.60 | | | | 1.68 | | | | 9,900 | |
| 12/14/04 | | | 5,833 | | | | 0.60 | | | | 1.68 | | | | 6,300 | |
| 02/18/05 | | | 244,167 | | | | 1.20 | | | | 3.24 | | | | 498,100 | |
| 04/07/05 | | | 26,667 | | | | 1.20 | | | | 3.24 | | | | 54,400 | |
| 07/01/05 | | | 282,083 | | | | 3.00 | | | | 3.24 | | | | 67,700 | |
| 09/13/05 | | | 65,000 | | | | 6.00 | | | | 6.00 | | | | — | |
| 11/16/05 | | | 38,333 | | | | 7.20 | | | | 7.20 | | | | — | |
| 03/16/06 | | | 123,200 | | | | 0.60 | | | | 4.80 | | | | 517,440 | |
| 05/09/06 | | | 340,000 | | | | 4.80 | | | | 4.80 | | | | — | |
| 09/30/06 | | | 101,667 | | | | 5.22 | | | | 5.22 | | | | — | |
Exercise Prices — In determining the exercise prices for stock-based awards, the Company’s Board of Directors considers the estimated fair value of the common stock as of each grant date. The determination of the deemed fair value of the Company’s common stock involves significant assumptions, estimates and complexities that impact the amount of stock-based compensation. The estimated fair value of the Company’s common stock has been determined by the Board of Directors after considering a broad range of factors including, but not limited to, the illiquid nature of an investment in common stock, the Company’s historical financial performance and financial position, the Company’s significant accomplishments and future prospects, opportunity for liquidity events and, recent sale and offer prices of the common and redeemable convertible preferred stock in private transactions negotiated at arm’s length.
F-19
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
In September 2005, the Board of Directors concluded, on a retrospective basis, that the fair value of the common stock on each measurement date in 2004 and through July 1, 2005 for measuring stock-based compensation was $1.68 and $3.24, respectively.
For the awards granted on September 13, 2005 and November 16, 2005, the Board of Directors determined, on a contemporaneous basis, the estimated fair value of the common stock to be $6.00 and $7.20 per share, respectively, and options granted on these dates had exercise prices equal to $6.00 and $7.20 per share, respectively. These exercise prices were in excess of the retrospectively determined fair values on the relevant dates.
For awards granted on May 9, 2006 and September 30, 2006, the Board of Directors determined on a contemporaneous basis the estimated fair value of the common stock to be $4.80 and $5.22 per share, respectively.
| |
| 4. | PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT |
Property and equipment consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Lab and other equipment | | $ | 534,085 | | | $ | 1,094,499 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | | | 72,034 | | | | 113,552 | |
| Leasehold improvements | | | 433,690 | | | | 532,492 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total property and equipment, at cost | | | 1,039,809 | | | | 1,740,543 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | | (546,730 | ) | | | (853,760 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Property and equipment, net | | $ | 493,079 | | | $ | 886,783 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
In 2003, the Company entered into a new lease for its current facility (see Note 10). The agreement provided for the landlord to pay approximately 67% or up to a maximum of approximately $205,000 ofagreed-upon leasehold improvements. The improvements were completed in December 2003 and the space was placed into service in January 2004. The Company’s portion of leasehold improvements was $121,364 and the landlord’s portion was $203,127. The Company and landlord paid improvements are included in leasehold improvements. The landlord’s portion has been recorded with a corresponding liability recorded for deferred rent. The deferred rent is being amortized as an offset to rent expense over the remaining term of the lease. The current portion of the deferred rent is included in accrued expenses in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and is shown in Note 5. The long-term portion of deferred rent is presented separately in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Depreciation and amortization expense was $106,206, $139,276, and $307,030 for the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005, and 2006, respectively.
F-20
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Accrued expenses consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Accrued bonuses | | $ | 927,918 | | | $ | 1,488,310 | |
| Clinical trials | | | 106,547 | | | | 1,129,697 | |
| Professional fees | | | 328,250 | | | | 1,081,632 | |
| Accrued vacation | | | 139,279 | | | | 88,380 | |
| Deferred rent — current portion | | | 45,140 | | | | 45,140 | |
| Clinical trials materials | | | 36,110 | | | | 207,005 | |
| Commercial manufacturing | | | — | | | | 1,265,497 | |
| Accrued grant costs | | | 173,041 | | | | — | |
| Accrued marketing costs | | | 100,000 | | | | — | |
| Accrued loan interest | | | 33,041 | | | | — | |
| Accrued purchases | | | 27,980 | | | | 268,166 | |
| Other | | | 59,491 | | | | 238,183 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | $ | 1,976,797 | | | $ | 5,812,055 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Stockholder Notes Payable — In 2002, the Company issued unsecured notes payable (“Notes”) to two members of its Board of Directors (who are also officers and stockholders) totaling $550,000, bearing annual interest at 10%, all payable within one year. In addition, the Notes included detached warrants to purchase 33,951 shares of the Company’s common stock at $1.62 per share. The principal and accrued interest of $55,000 was converted in 2003 into 11,203 shares of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock at $54.00 per share, the price at which that tranche of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock had been issued. The fair value of the warrants on the date of grant was determined to be $2,200 using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model (and the following assumptions: life of two years (full term), volatility of 72% and a risk-free rate of interest of 1.45%). Accordingly, $2,200 was allocated to the warrants and recorded as a discount to the Notes and this debt discount was amortized to interest expense through 2003. The warrants were exercised in 2004 (see Note 9).
Commercial Notes Payable — In February 2004, the Company issued an unsecured note payable to its former legal counsel for approximately $103,000, representing the then outstanding balance of invoices for professional services. The note, bearing no interest, was payable in monthly installments of $5,000 beginning in March 2004, until paid in full in November, 2005.
In 2004, the Company entered into two commercial financing agreements with a vendor to finance the payment of approximately $168,000 in insurance premiums for up to 12 months. Finance charges of approximately $3,000 (annual weighted average percentage rate of approximately 3.82%) was added to the principal.
In 2005, the Company entered into a financing agreement for the payment of approximately $102,000 of insurance premiums for up to 10 months until paid in full in May, 2006. A finance charge of approximately $2,800 (annual percentage rate of approximately 6.5%) was added to the principal. At December 31, 2006, all amounts have been repaid.
F-21
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
In October 2006, the Company entered into a financing agreement for the payment of approximately $105,000 of insurance premiums for up to seven months at an annual interest rate of 6.74%. At December 31, 2006, the outstanding balance of $70,000 has been included in the current portion of notes payable in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Convertible Notes Payable — In December of 2004, the Company issued an unsecured convertible note payable to a new investor for $700,000, due one year from the date of issuance, at an annual interest rate of 3%. The full outstanding principal amount of the note, plus accrued interest, had a mandatory conversion feature into either (i) preferred stock at a price per share at which a qualified financing, as defined, was completed subsequent to the issuance of the note but prior to maturity, or (ii) into shares of Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock at the rate of $132 per share, in the event the Company was unable to complete a qualified financing prior to maturity. In April, 2005, the principal and accrued interest of $5,586 were converted into 3,493 shares of Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock (“Series C”) at $202 per share, the price at which Series C had been issued (see Note 8).
In March of 2005, the Company issued unsecured convertible promissory notes to three existing stockholders (one being a member of the Board of Directors) for a total principal of approximately $375,000, due one year from the date of issuance, at an annual interest rate of 3%. The full outstanding principal amount of the notes, plus accrued interest, carried a mandatory conversion feature into either (i) preferred stock at a price per share at which a qualified financing, as defined, was completed subsequent to the issuance of the notes but prior to maturity, or (ii) into shares of Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock at the rate of $132 per share, in the event the Company was unable to complete a qualified financing prior to maturity. In April, 2005, the principal amount was converted into 1,983 shares of Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock at $202 per share, the price at which Series C had been issued (see Note 8).
Senior Note Payable — On September 30, 2005, the Company issued a $5.0 million note payable to Ritchie Multi-Strategy Global, LLC (“Ritchie”) pursuant to a Loan and Security Agreement (“Ritchie Note”), to be used for working capital and general corporate activities, which was ultimately assigned to BlueCrest Venture Master Fund Limited ( “Ritchie”). The Ritchie Note is secured by a first priority security interest in the Company’s assets, excluding intellectual property and contains non-financial covenants. The Company was required to pay interest only through December 31, 2005, and thereafter, the principal and interest is payable in equal monthly amounts over 35 months. The interest rate of the debt is 7.93%. In addition, as a condition to Ritchie extending the credit, the Company agreed to pay a fee to Ritchie in the amount of $250,000 should a liquidation event (as defined) occur prior to June 30, 2006 or $300,000 should a liquidation event occur subsequent to that date. A liquidation event is defined in the agreement as including, among other things, a change in control of the Company, a sale of all or substantially all of the Company’s assets or an initial public offering of the Company’s common stock. This fee was determined to be an embedded derivative which requires separate accounting and is presented separately in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet as “success fee derivative liability”. The estimated fair value of the success fee was determined to be $142,400 and $278,000 at December 31, 2005 and December 31, 2006, respectively. The derivative will be revalued at each reporting period with the charges recognized in earnings until settled. The initial embedded derivative value was recorded as a debt discount and is being amortized over the life of the loan.
On September 28, 2006, the company paid $175,000 and on November 6, 2006, the Company issued a warrant to purchase 61,538 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $7.80 per share to the holder of Ritchie Note issued on September 30, 2005. The cash and warrant were issued in consideration of the note holder waiving certain covenants that prohibited certain additional indebtedness. The warrant is exercisable, in whole or in part, anytime from the issue date to the earliest of (i) the seventh anniversary of the issue date, (ii) 180 days after the date on which the Securities and Exchange Commission declares effective a registration statement onForm S-1 for the initial public offering of common stock by the Company, or (iii) the date on
F-22
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
which the Company consummates the sale of all or substantially all of its assets or consummates a merger, consolidation or similar transaction or series of related transactions pursuant to which the Company is not the surviving entity. The fair value of the warrant at the date of grant was determined to be approximately $200,000 using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model (including the following assumptions: expected life of seven years, volatility of 69% and risk-free rate of 4.9%). The aggregate fair value of approximately $375,000 was recorded as a debt issuance cost and is being amortized over the life of the note.
Convertible Notes Payable — On September 28, 2006 and October 4, 2006 the Company executed agreements to issue convertible notes (the “Convertible Notes”) in the amount of $15.0 million and $0.4 million, respectively with detachable warrants with existing shareholders and new third parties (the “Holders”). The Convertible Notes are due three years from the date of issuance (the “Maturity Date”), and bear an interest rate of 8% per annum and are unsecured. The interest is compounded quarterly and calculated on the basis of actual days elapsed based upon a365-day year. Interest is payable on the Maturity Date. A beneficial conversion charge was not recorded as the effective conversion price exceeded the current stock value at the date the Convertible Notes were issued. As the interest accrued is convertible into common stock at the conversion rate effective upon issuance, the Company evaluates whether interest earned has a beneficial conversion feature as it accrues. The beneficial conversion feature is computed based upon the difference between the conversion price and the fair value of the Company’s common stock as such interest is accrued. For the period ended December 31, 2006, a beneficial conversion value of $171,000 was recognized in the fourth quarter of 2006 as additional debt discount (interest expense) and paid-in capital. The detachable warrants issued with the Convertible Notes were valued under a Black-Scholes model using a volatility factor of 64.92% which resulted in a debt discount of approximately $954,758. The discount was recorded as an increase to paid-in capital and is being amortized over the life of the Convertible Notes as additional interest expense.
Conversion: In the event that a Qualified Public Offering, as defined, is completed on or prior to the Maturity Date or at any time such Convertible Notes are outstanding at the election of the holders, the full outstanding principal amount of these Convertible Notes plus accrued but unpaid interest will automatically be converted into that number of fully paid, validly issued and non-assessable shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, of the Company (the “Common Stock”) obtained by dividing (i) the Principal and all accrued interest at Maturity Date by (ii) $7.80. This number is subject to equitable adjustment in the event of a stock split, subdivision, reclassification or other similar transaction. No fractional shares of common stock shall be issued upon conversion of these Convertible Notes but a cash payment will be made with respect to any fraction of a share which would otherwise be issued upon the surrender of these Convertible Notes, or portion thereof, for conversion. As discussed in Note 12, upon the effectiveness of the Company’s initial public offering on February 1, 2007, the Convertible Notes and accrued interest converted into 2,029,159 shares of common shares.
Reservation of Stock: The Company is required to reserve and keep available out of its authorized common stock, solely for the purpose of issuance upon the conversion of these Convertible Notes, such number of shares of common stock as shall be issuable upon conversion.
Covenants: The Company was subject to various non financial covenants related to the Convertible Notes.
Debt consisted of the following as of December 31, 2006:
| | | | | |
Description | | Principal Balance | |
| |
| Convertible Note Debt | | $ | 15,400,000 | |
| Ritchie Note | | | 3,550,887 | |
| Insurance Financing Note | | | 69,911 | |
| | | | | |
| Total | | $ | 19,020,798 | |
| | | | | |
F-23
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
As of December 31, 2006, future payments of principal on all existing notes were due as follows:
| | | | | |
| | | Principal Payments
| |
| | | as of December 31,
| |
Fiscal Year Ending December 31, | | 2006 | |
| |
| 2007 | | $ | 1,775,227 | |
| 2008 | | | 1,845,571 | |
| 2009 | | | 15,400,000 | |
| | | | | |
| Total principal payments | | | 19,020,798 | |
| Less: current portion | | | 1,775,227 | |
| Less: debt discount | | | 926,740 | |
| | | | | |
| Total noncurrent notes payable | | $ | 16,318,831 | |
| | | | | |
The Company has recorded no provision or benefit for income taxes for any period presented due to its net operating losses and doubt as to the realizability of the resulting carryforwards of those losses and other deferred tax assets. Deferred tax assets consisted of the following as of December 31:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Net operating loss carryforwards | | $ | 12,104,000 | | | $ | 22,384,000 | |
| Deferred research and development costs | | | 1,477,000 | | | | 1,301,000 | |
| Research and development tax credits | | | 1,374,000 | | | | 2,067,000 | |
| Property and equipment | | | 129,000 | | | | 69,000 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | 1,408,000 | | | | 1,486,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 16,492,000 | | | | 27,307,000 | |
| Valuation allowance | | | 16,492,000 | | | | 27,307,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net deferred tax asset | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2006, the Company had net operating loss carryforwards totaling approximately $56.9 million (federal) and $48.6 million (state), which expire at various dates from 2011 through 2026 (federal) and from 2007 through 2011 (state). The amount of the net operating loss carryforwards that may be utilized to offset future taxable income, when earned, may be subject to certain limitations, based upon changes in the ownership of the Company’s stock that have or may occur. The Company has not conducted an evaluation as to whether any portion of its tax loss carryforwards has been limited, and therefore, based upon the changes in ownership, a limitation may have occurred. As of December 31, 2006, the Company had research and development tax credits totaling approximately $1,350,000 (federal) and $717,000 (state), which are available to offset future tax liabilities when incurred, which begin to expire in 2011 for federal and state and fully expire in 2026 (federal) and 2021 (state).
The Company has recorded a full valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets since the Company believes it is more likely than not, that it will not be able to realize the assets. During the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006, the valuation allowance increased by approximately $3,463,000, $5,236,000 and $10,815,000, respectively. The change in the valuation allowance in each period is due to the net increase in deferred tax assets each period (primarily from the net operating loss carryforwards and research and development tax credits) and the Company providing a full valuation against the asset for the reason stated above.
F-24
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| |
| 8. | REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK |
The Company has authorized 359,515 shares of preferred stock for issuance, of which certain shares are designated as Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock (“Series A”), Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock (“Series B”) and Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock (“Series C”). The Company first issued redeemable convertible preferred stock in 2003. The following table summarizes the activity and other information for the redeemable convertible preferred stock:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Series A | | | Series B | | | Series C | | | Total | |
| | | Number of
| | | Carrying
| | | Number of
| | | Carrying
| | | Number of
| | | Carrying
| | | Number of
| | | Carrying
| |
| | | Shares | | | Value | | | Shares | | | Value | | | Shares | | | Value | | | Shares | | | Value | |
| |
| Shares designated at: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2004 | | | 150,000 | | | | — | | | | 61,000 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 211,000 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2005 | | | 150,000 | | | | — | | | | 61,000 | | | | — | | | | 148,515 | | | | — | | | | 359,515 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2006 | | | 150,000 | | | | | | | | 61,000 | | | | | | | | 148,515 | | | | | | | | 359,515 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, January 1, 2004 | | | 120,317 | | | | 7,552,080 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 120,317 | | | | 7,552,080 | |
| Issuance of Series B, net of $198,514 of issuance costs | | | — | | | | — | | | | 52,670 | | | | 6,542,786 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 52,670 | | | | 6,542,786 | |
| Conversion of accrued expenses into Series B | | | — | | | | — | | | | 993 | | | | 131,076 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 993 | | | | 131,076 | |
| Accretion of issuance costs and warrants | | | — | | | | 51,969 | | | | — | | | | 243,243 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 295,212 | |
| Preferred stock dividends | | | — | | | | 673,792 | | | | — | | | | 343,128 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,016,920 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2004 | | | 120,317 | | | | 8,277,841 | | | | 53,663 | | | | 7,260,233 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 173,980 | | | | 15,538,074 | |
| Issuance of Series C, net of $1,106,800 of issuance costs | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 141,590 | | | | 27,470,581 | | | | 141,590 | | | | 27,470,581 | |
| Accretion of issuance costs and warrants | | | — | | | | 50,997 | | | | — | | | | 142,296 | | | | — | | | | 176,977 | | | | — | | | | 370,270 | |
| Series B warrant modification | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (560,000 | ) | | | — | | | | (560,000 | ) |
| Preferred stock dividends | | | — | | | | 981,777 | | | | — | | | | 354,176 | | | | — | | | | 1,080,867 | | | | — | | | | 2,416,820 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2005 | | | 120,317 | | | | 9,310,615 | | | | 53,663 | | | | 7,756,705 | | | | 141,590 | | | | 28,168,425 | | | | 315,570 | | | | 45,235,745 | |
| Accretion of issuance costs and warrants | | | — | | | | 52,430 | | | | — | | | | 23,976 | | | | — | | | | 237,780 | | | | — | | | | 314,186 | |
| Preferred stock dividends | | | — | | | | 673,790 | | | | — | | | | 354,176 | | | | — | | | | 1,512,044 | | | | — | | | | 2,540,010 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance December 31, 2006 | | | 120,317 | | | $ | 10,036,835 | | | | 53,663 | | | $ | 8,134,857 | | | | 141,590 | | | $ | 29,918,249 | | | | 315,570 | | | $ | 48,089,941 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Liquidation preference at: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2004 | | | | | | $ | 13,979,000 | | | | | | | $ | 7,427,000 | | | | | | | $ | — | | | | | | | $ | 21,406,000 | |
| December 31, 2005 | | | | | | | 18,417,000 | | | | | | | | 7,781,000 | | | | | | | | 29,682,000 | | | | | | | | 55,880,000 | |
| December 31, 2006 | | | | | | | 23,584,000 | | | | | | | | 8,135,000 | | | | | | | | 31,194,000 | | | | | | | | 62,913,000 | |
| Redemption value at | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2004 | | | | | | $ | 8,434,000 | | | | | | | $ | 7,427,000 | | | | | | | $ | — | | | | | | | $ | 15,861,000 | |
| December 31, 2005 | | | | | | | 9,416,000 | | | | | | | | 7,781,000 | | | | | | | | 29,682,000 | | | | | | | | 46,879,000 | |
| December 31, 2006 | | | | | | | 10,089,000 | | | | | | | | 8,135,000 | | | | | | | | 31,194,000 | | | | | | | | 49,148,000 | |
In 2001, the Company collected approximately $2,820,000 in subscriptions for a proposed issuance of Series A at $70 per share from new and existing investors. An additional $250,000 in subscriptions was received in the beginning of 2002 from new and existing investors, also at $70 per share. Subsequent to the initial subscriptions, the Company began to experience pressure on the price being asked from new prospective investors. The Company continued to pursue raising equity by reducing the price per share of the proposed Series A to $54 per share for new subscriptions, and subsequently received approximately $380,000 in 2002 and $2,363,000 in 2003 from new and existing investors. The Company settled these advances by issuing a total of 94,697 shares of Series A in 2003 at the previously described purchase prices of $70 and $54 per
F-25
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
share. Both existing and new investors participated in purchasing Series A. New investors purchased 15% and 15% of the Series A at the $70 and $54 per share price, respectively. The Company incurred $259,843 in costs associated with the issuance of the Series A and such costs were recorded as a reduction in the carrying value of the Series A.
Also in 2003, the Company issued a total of 19,144 shares of Series A at a price of $54 per share made up of (1) conversion of two notes payable with principal of $550,000 and accrued interest of $55,000 to two members of its Board of Directors (who are also officers and stockholders) for 11,203 shares of Series A (see Note 6), (2) Stock-based compensation for officers and employees in the amount of $118,900 represented by 2,201 shares of Series A (see Note 3), and (3) conversion of accounts payable and accrued expenses in the amount of $310,000 for 5,740 shares of Series A. The Company also issued an additional 6,476 shares of Series A to officers and employees for stock-based compensation during 2003. These issuances were based upon the $54 per share price.
In the fourth quarter of 2003, subsequent to the above 2003 transactions, the Company received additional advanced stock subscriptions aggregating $2,118,800 for a planned sale of Series B. During 2004, the Company issued 52,670 shares of Series B at $132 per share in exchange for the $2,118,800 of net stock subscription proceeds received in 2003, as well as for the additional cash proceeds of $4,833,500 received in 2004. The Company incurred $198,514 in costs associated with the issuance of the Series B; such costs were recorded as a reduction in the carrying value of the Series B. Also in 2004, the Company issued 993 shares of Series B at a price of $132 per share in settlement of $131,000 of accrued liabilities.
In connection with the issuance of the Series B, the holders of Series B received warrants to purchase 357,753 shares of common stock at $3.96 per share (“Series B Warrants”). The Series B warrants expire on the earlier of the consummation of a qualified financing (as defined) or five years from date of issuance (see Note 9).
In March and April of 2005, the Company issued a total of 136,115 shares of Series C at $202 per share for net cash proceeds of $27.5 million. The Company incurred $1,106,800 in costs associated with the issuance of the Series C; such costs were recorded as a reduction in the carrying value of the Series C.
In addition, in March 2005, the Company issued (1) 3,493 shares of Series C at $202 per share upon conversion of a note payable with principal of $700,000 and accrued interest of $5,586 (see Note 6) and (2) 1,983 shares of Series C at $202 per share upon conversion of three notes payable with a total principal of approximately $400,000 (see Note 6).
In connection with the issuance of the Series C, the Company issued a warrant to purchase 16,501 shares of the Company’s common stock to its placement agent. The warrant expires five years from the date of grant and has an exercise price of $6.06 per share (see Note 9).
The rights, preferences and privileges of the Series A, Series B and Series C (collectively “Preferred Stock”) are detailed below:
Voting Rights — Generally, Series A, Series B and Series C preferred stockholders vote together with all other classes and series of stock as a single class on all actions to be taken by the stockholders. The Company’s Articles of Organization does provide that each of Series A, B and C shall vote separately for approval of certain transactions, including, without limitation, the amendment of the Company’s Certificate of Organization in a manner that would adversely affect each such series of Preferred Stock, the liquidation or dissolution of the Company, the acquisition of another entity, changing the Company’s line of business, declaring dividends and similar matters. Series A, B and C shares entitle each holder to such number of votes per share as is equal to the number of whole shares into which the stock is convertible, subject to certain restrictions as defined. In accordance with an agreement signed in
F-26
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
2005 among certain holders of common stock, Series A, Series B and Series C, such holders will cause and maintain election to the Board of Directors of one Series A director, as designated by the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, who shall initially be the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, one Series B director, as designated by Cerberus Partners, L.P., the largest holder of Series B, one Series C director, as defined, one management director, who shall initially be the Company’s President, and three additional directors with appropriate industry experience and qualified outside directors, as defined.
Dividends — Dividends are cumulative whether or not declared by the Board of Directors and accrue at a quarterly rate per share of $1.40 for Series A, $1.65 for Series B and at an annual rate of 5% for Series C. Dividends on Series C compound quarterly. Upon the occurrence of a liquidation event or mandatory conversion, as defined, of the Series A, Series B or Series C, the dividends accrued but unpaid, are payable by the Company and, at the option of the holder, may be payable in shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price equal to $0.35 and $0.66 with respect to Series A and B, respectively and with respect to Series C, the lesser of $1.01 or the fair value of the Company’s common stock at time of conversion. The Preferred Stock is senior to all common stock with respect to dividends, and Series C is senior to Series B with respect to dividends, and Series B is senior to Series A with respect to dividends. No dividends shall be paid or declared on common shares or any other class of stock which are junior to the Preferred Stock. At December 31, 2005 and 2006, accrued and unpaid dividends were as follows: for Series A — $2,216,495 and $2,890,275, respectively; for Series B — $697,304 and $1,051,479, respectively: for Series C — $1,080,867 and $2,593,038, respectively.
As the dividends are convertible into common stock at fixed conversion prices, if the fair value of the common stock exceeds the conversion price when the dividends are earned, a beneficial conversion feature exists for the potential common shares issued for these dividends. The Company measures the value of the beneficial conversion feature as the difference between the common share fair value and the conversion price and recognizes such amount as incremental preferred dividends. The Company did not recognize any beneficial conversion feature related to convertible dividends during 2004. During the years ended December 31, 2005 and December 31, 2006, dividends that accrued on Series A, Series B, and Series C included beneficial conversion features, which resulted in the recognition of a beneficial conversion amount of $1,259,547 and $2,103,704, respectively, as an increase to the redeemable convertible preferred stock dividends in the computation of net loss attributable to common stockholders.
As described above, certain Series A stockholders made payments in 2001 and 2002 in advance of the Series A closing which did not occur until January 2003. For many of these stockholders, the date between their advance and issuance of stock was much greater than was expected. In 2005, upon a review of the Series A documents by the Company’s newly hired legal counsel, it was brought to management’s attention that the extended period between certain advances and the Series A closing was not typical. Management brought this to the attention of the Company’s Board of Directors at a meeting in February, 2005 and, after considering the matters, the Board of Directors approved $308,000 to be added to the cumulative dividends accrued on the Series A held by these investors. The original subscription agreements entered into by these stockholders did not require a payment of interest or dividends. The amount has been added to the carrying value of the Series A in February 2005. This amount has not been declared and is not to be paid in cash. However, all dividends are payable in cash or convertible into common stock upon any conversion of the redeemable preferred stock. On the date the special dividend was approved, the special dividend (if converted) would be convertible into approximately 146,667 shares of common stock which had a fair value of approximately $475,000. The beneficial conversion feature of $167,000 has been included in redeemable convertible preferred stock dividends and accretion of issuance costs in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations for 2005. Several Company officers, including the Chief Executive Officer, were recipients of the special dividend as they held Series A.
F-27
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Liquidation — In the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution orwinding-up of the Company, or in the event of insolvency, as defined, the holders of Series C are entitled to receive before any distribution or payment is made to any holders of common stock or any other class or series of capital stock, an amount for Series C equal to $202 per share plus any accrued but unpaid dividends. Upon the availability of funds after Series C payments, Series A and B are entitled to receive, before any distribution or payment is made to any holders of common stock or any other class or series of capital stock, an amount for Series A equal to $70 per share plus a 30% compounded annual return on the original purchase price, plus any accrued but unpaid dividends, and an amount for Series B equal to $132 per share plus any accrued but unpaid dividends. If such amount per share of Series A or Series B would have been higher if each share had converted to common stock immediately prior to such liquidating event, as defined, then that higher amount would be paid in liquidation. After the liquidation preference payments to all preferred stockholders, the remaining assets of the Company available for distribution shall be distributed ratably among the holders of common stock.
If, upon any such liquidation, dissolution orwinding-up of the Company, as defined, the remaining assets of the Company available for distribution to its stockholders are insufficient to pay the holders of Series C the full amounts to which they are entitled, the holders of Series C shall share ratably in any distribution of the remaining assets and funds of the Company pursuant to the terms of the respective agreements. The same terms are applicable for the Series A and Series B stockholders.
Conversion — The Series A, Series B and Series C are convertible at any time at the option of the holder into common stock on a33.33-to-1 ratio. This ratio is subject to adjustment upon certain events such as a stock split, subdivision of the Company’s common stock, recapitalization of the Company’s capital stock or similar event. Additionally, the Series C is subject to adjustment for any equity issued at a lower price per share pursuant to a weighted average anti-dilution provision. Certain issuance, such as issuances pursuant to the Company’s option plan, upon the conversion of preferred stock or as approved by the stockholders, are excluded for this anti-dilution protection and, therefore, no adjustment to the conversion ratio will be made upon those stock issuances. Through February 1, 2007, the date of conversion of such shares, no adjustment to the conversion price occurred.
The Series A mandatorily converts into common stock (i) immediately prior to the closing of an initial public offering where the gross proceeds to the Company equal or exceed $15 million and the price per share in the offering is 200% of the then current conversion price of the Series A, (ii) upon the sale of all or substantially all of the Company’s common stock for a price that is at least 200% of the Series A conversion price then in effect or (iii) upon the consent of a majority of the Series A to conversion. The Series B mandatorily converts into common stock (i) immediately prior to the closing of an initial public offering where the gross proceeds to the Companyand/or the stockholders equals or exceeds $10 million, (ii) upon the consent of a majority of the Company’s stockholders to effect the sale of all or substantially all of its capital stock to a third party or (iii) upon the consent of a majority of the Company’s stockholders to effect the merger or consolidation of the Company with a third-party pursuant to which the Company is not the surviving entity or there is a change in voting control of the Company. The Series C mandatorily converts into common stock (i) immediately prior to the closing of an initial public offering where the gross proceeds to the Company equal or exceed $30 million and the price per share in the offering equals or exceeds $5 per common share, or (ii) upon the consent of a majority of the Series C to such conversion. On February 1, 2007, the initial public offering was declared effective by the SEC, and all outstanding shares of Series A, B and C Convertible Preferred Stock were converted into common stock shares of 4,010,539, 1,788,758 and 4,719,652, respectively. An additional 1,340,624, 258,851 and 448,184 shares of common stock were issued in satisfaction of the then accrued but unpaid dividends on the Series A, B and C Convertible Preferred Stock, respectively. Warrants to purchase
F-28
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
common stock were automatically converted into 403,779 shares of the Company’s common stock at an average price of $3.45 per share.
Redemption — At the written election of any holder of Series A made not less than 30 days prior to defined anniversaries of the date the stock was first issued, the Company is required to redeem shares as follows: on the fifth (5th) anniversary in 2008, up to 331/3% of the shares then held, on the sixth (6th) anniversary in 2009, up to 662/3%, and on the seventh (7th) anniversary in 2010, up to 100% of shares then held. These redemption rights of Series A shall terminate, if not otherwise exercised, in 2011 on the eighth anniversary date of the first issue date of the shares. The redemption price is equal to the Series A purchase price ($54 or $70 per share) plus all accrued but unpaid dividends.
At the written election of any holder of Series B at least 10 days prior to the date of the consummation of the completion of a qualified financing, the Company shall redeem up to331/3% of the shares then held. A qualified financing with respect to the Series B is defined as one in which the Company raises an aggregate net proceeds of at least $10 million through the sale of stock in one or more related transactions. Although considered a Qualified Financing, the Series C was excluded from this definition by amendment to the Company’s charter for Series B prior to the Series C issuance in 2005. Prior to that time, however, the Company chose 2005 as a first date of redemption for the Series B.
In addition, the Series B holder may redeem up to 662/3% of the shares then held on the first anniversary of the issue date, and up to 100% of the shares then held on the second anniversary of the issue date. The redemption price is equal to the Series B purchase price of $132 per share plus all accrued but unpaid dividends.
By written notice to the Company by a majority of the holders of Series C given at any time on or after the seventh (7th) anniversary in 2012, subject to certain restrictions, as defined, the Company shall redeem all, but not less than all, of the outstanding shares of Series C. The redemption price is equal to the Series C purchase price of $202 per share plus all accrued but unpaid dividends.
Registration Rights — The holders of Series A, Series B and Series C and certain other stockholders have certain rights to register their shares of common stock received upon conversion under the Securities Act of 1933 pursuant to a registration rights agreement. The holders may require the Company to register such shares upon the closing of an initial public offering. If such registration statement is not filed by the Company within the filing deadlines, as defined, the holders are entitled to liquidated damages equal to 1.5% of the aggregate market price of such securities to be registered. The investors will also be entitled to unlimited piggyback registration rights on registration of the Company, subject to certain limitation.
Participation Rights — The holders of Series C have certain participation rights in additional issuances of common stock.
F-29
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The following is a schedule of redemption values(1):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of
| | | As of
| | | |
| | | December 31,
| | | December 31,
| | | First Date of Scheduled
|
Issuance | | 2005 | | | 2006 | | | Redemption |
| |
| Series A(2) | | $ | 9,416,000 | | | $ | 10,089,000 | | | January, 2008 |
| Series B(3) | | | 7,781,000 | | | | 8,135,000 | | | Upon notice of a qualified financing (as defined) |
| Series C(4) | | | 29,682,000 | | | | 31,194,000 | | | March, 2012 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 46,879,000 | | | $ | 49,418,000 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| (1) | | Amounts shown include the original purchase price plus dividends accrued through dates shown. Amounts change due to the accrual of dividends; therefore the actual redemption amounts, if ever redeemed, will be different. |
| |
| (2) | | Based on the redemption period described above, shares of Series A may be redeemed as follows: up to 40,107, 80,213 and 120,317 in 2008, 2009 and 2010, respectively. The redemption value of these shares will increase annually due to the accrual of dividends at a quarterly dividend rate per share of $1.40. |
| |
| (3) | | Based on the redemption criteria described above, shares of Series B may be redeemed as follows: up to 17,888, 35,775 and 53,663 beginning on the date of a qualified financing (as defined) followed by the first and second anniversary thereafter, respectively. The redemption value of these shares will increase annually due to the accrual of dividends at a quarterly dividend rate per share of $1.65. |
| |
| (4) | | Based on the redemption period described above, all shares of Series C may be redeemed in 2012. The redemption value of these shares will increase annually due to the accrual of dividends at a quarterly dividend rate per share of 5%. |
The aggregate amount of redeemable preferred stock that is redeemable at fixed or determinable dates upon the redemption terms noted above as of December 31, 2006 is as follows:
| | | | | |
| 2008 | | $ | 3,307,000 | |
| 2009 | | | 3,307,000 | |
| 2010 | | | 3,307,000 | |
| Thereafter | | | 31,451,000 | |
| Amount subject to contingent redemption | | | 8,046,000 | |
| | | | | |
| | | $ | 49,418,000 | |
| | | | | |
Preferred Stock Issuance Costs — The Company is accreting the stock issuance costs of each series of redeemable convertible preferred stock from the original issuance date to the earliest date of redemption using the effective interest method. These direct costs generally consist of fees paid to placement agents, the fair value of warrants issued to placement agents, legal fees, statutory fees and other direct costs. For the Series A, B and C, the total costs of issuance are $259,843, $198,514 and $1,106,800, respectively. The accretion increases the carrying value of the redeemable convertible preferred stock and reduces additional paid-in capital. Accretion amounts are shown in the first table of this Note.
F-30
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
On January 10, 1997, the Company issued 499,467 shares of common stock to its founders pursuant to restricted stock arrangements for $12,254 in cash and deferred stock-based compensation of $546,000.
In 1997, the Company issued 307,800 shares of common stock to employees and nonemployees for $18,250 in cash and deferred stock-based compensation of $1,673,200.
In 1998, the Company issued 132,115 shares of common stock to existing and new stockholders for $1,288,121 in cash.
In 1999, the Company issued 108,333 shares of common stock to existing and new stockholders for $1,625,000 in cash.
In 1999, the Company purchased 35,000 shares of common stock from an employee who left the Company pursuant to a restricted stock agreement for $50,400 (the common stock being retired in 2000).
In 2000, the Company issued 376,367 shares of its common stock for $15.00 per share, resulting in total proceeds of $5,645,500. The Company incurred cash costs of $392,406 in connection with the sale and committed to issue a warrant with a fair value of $271,000. Total issuance costs were therefore $663,406, which were charged to additional paid-in capital.
During 2000, the Company issued 850 shares of its common stock for an ascribed value of $15.00 per share in exchange for services. The ascribed amount was determined to be fair value at the date of the transaction.
In April 2006, the Board of Directors and the stockholders, respectively, approved the restatement of the Company’s articles of organization and bylaws, and effected a 1-for-6 reverse common stock split.
On April 18, 2006, the stockholders also approved the expansion of the Board of Directors to nine directors that will be effective upon the closing of an Offering. Additionally, on April 3, 2006 and April 18, 2006, the Board of Directors and the stockholders, respectively, approved upon the closing of an Offering, the 2006 Equity Incentive Plan and the reservation of 2,300,000 shares of common stock for issuance thereunder.
Common Stock Warrants — As mentioned above, in 2000, the Company committed to issue a warrant to purchase 32,090 shares of common stock for $15.00 per share with a fair value of $271,000. The fair value was determined using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model (including the following assumptions: life of six years (full term), volatility of 50% and a risk-free rate of interest of 6.5%). Accordingly, approximately $271,000 was included as an issuance cost of common stock in 2000 and was included in additional paid-in capital.
During 2002, the Company issued $1.62 per share warrants with a two-year exercise period to purchase 33,951 shares of the Company’s common stock to two officers who are also members of the Board of Directors in connection with two notes payable due to these individuals (see Note 6).
In connection with the issuance of the Series B, the holders of Series B received warrants to purchase 357,743 shares of common stock at $3.96 per share (“Series B Warrants”). The Series B Warrants were to expire on the earlier of the consummation of a qualified financing (as defined) or five years from date of issuance. The fair value of the Series B Warrants at the date of grant was determined to be approximately $211,000 using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model (including the following assumptions: life of five years (full term), volatility of 70% and a risk-free rate of interest of 3.07%). Accordingly, approximately $211,000 of the net proceeds from the sale of the Series B was subtracted from the carrying value of the Series B and recorded as an increase to additional paid-in capital.
In connection with the issuance of Series C in 2005, the Series B Warrants were modified so as to not allow the Series B Warrants to expire pursuant to the original terms. The amendment also irrevocably waived the termination provision for any future financings so that the warrants will expire upon the earlier or five years from the date of issuance in 2004 or upon an initial public offering of the Company’s common stock. As
F-31
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
a result of this modification, the Company determined the fair value of the warrants immediately before and after the modification using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model (including the following assumptions: life of zero and four years (remaining terms), respectively, volatility of 68% and a risk-free rate of interest of 2.99%) and the incremental value of $560,000 was subtracted from the carrying value of the Series C as an issuance cost and recorded as an increase to additional paid-in capital.
In 2005, the Company issued a warrant to purchase 16,501 shares of the Company’s common stock to its placement agent in connection with the issuance of the Series C. The warrant is exercisable for five years at an exercise price of $6.06 per share. The fair value of the warrants at the date of grant was determined to be approximately $24,000 using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model (including the following assumptions: life of five years, volatility of 67% and a risk-free rate of interest of 4.17%). Accordingly, approximately $24,000 was included as an issuance cost of the Series C in 2005 and was included in additional paid-in capital.
In 2006, the Company issued warrants to purchase 394,877 shares of the Company’s common stock in connection with the Convertible Notes issued in September 2006 (see Note 6). The warrants are exercisable for five years at an exercise price of $7.80 per share. The fair value of the warrants of $954,758 was recorded as a debt discount and is being amortized over the life of the Convertible Notes as additional interest expense.
On November 6, 2006, the Company issued a warrant to Ritchie Debt Acquisition Fund, Ltd., which was assigned to BlueCrest Venture Finance Master Fund Limited (see Note 6), to purchase 61,538 shares of common stock with an exercise price of $7.80 and the earlier of a seven year life or 180 days after the date on which the SEC declares effective a registration statement onForm S-1 or certain other events. The fair value of the warrant of approximately $201,606 was recorded as a debt issuance cost and is being amortized over the life of the Note.
As of December 31, 2006, the Company had the following warrants outstanding to purchase shares of our common stock (which are fully vested and exercisable):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | Exercise
| | | | |
| | | Shares | | | Price | | | Term | |
| |
| Issued in 2000 | | | 32,090 | | | $ | 15.00 | | | | 6 | (a) |
| Issued in 2003 in connection with Series B | | | 357,743 | | | | 3.96 | | | | 5 | (a) |
| Issued in 2005 to placement agent in connection with Series C | | | 16,501 | | | | 6.06 | | | | 5 | (a) |
| Issued in 2006 in connection with convertible note payable | | | 394,877 | | | | 7.80 | | | | 5 | (b) |
| Issued in 2006 in connection with other notes payable | | | 61,538 | | | | 7.80 | | | | 7 | (c) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 862,749 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| (a) | | expire on the earlier of listed years or the consummation of a qualified financing event. |
| |
| (b) | | expire on the earlier of the consummation of a qualified financing event or three years from the date of issuance |
| |
| (c) | | expire on the earliest of (1) the seventh anniversary of the warrant issue date, (2)180 days after the date on which the SEC declares effective a registration statement onForm S-1 for the initial public offering of Common Stock by the Company, or (3) the date on which the Company consummates the sale of all or substantially all of its assets or consummates a merger, consolidation or similar transaction or series of related transactions pursuant to which the Company is not the surviving entity. |
Common Stock Anti-Dilution Rights — The sale of common stock in 2000 included certain stockholder rights. Pursuant to the agreement with these stockholders, in the next offering in which the cumulative amount raised by the Company equaled at least $10 million (the “Qualified Financing”), if (i) the average per-share
F-32
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
purchase price of the common stock sold in such Qualified Financing was less than $15.00 or (ii) the average per-share purchase price of the preferred stock sold in such Qualified Financing divided by the number of shares of common stock into which each share of preferred stock may be converted was less than $15.00, then those investors purchasing the common stock in 2000 had a right to receive the number of shares of common stock necessary to reduce their average per share purchase price to the average per-share purchase price in the Qualified Financing. In 2002, to settle its obligations pursuant to this agreement, the Company issued 1,676,283 shares of common stock to these stockholders and recorded par value of the stock as an increase in common stock and a reduction in additional paid-in capital.
Registration Rights. In 1997, the Company entered into a Principal Stockholders Agreement with each of the six founding stockholders (at December 31, 2006, only one was employed by the Company). These agreements provided, in part, that if at any time during the succeeding 10 year period, the Company registered any of its common stock in a public offering either for the Company’s account or for the account of selling stockholders, the Company will use its best efforts to include in such registration all or any part of the capital stock such individual requests to be registered, subject to certain limitations. At December 31, 2006, total shares of common stock subject to these rights equal 818,747. Additionally, the employment agreements for several executive officers of the Company provide that they shall each have piggyback registration rights for shares held by them equal to the most favorable piggyback registration rights granted by the Company to its stockholders. Accordingly, these executive officers have the same piggyback registration rights. The shares of common stock subject to these rights at December 31, 2006 were 3,024,450.
Reserved Shares — The following is a summary of common stock reserved for the following identified purposes at December 31, 2006:
| | | | | |
| | | December 31,
| |
| | | 2006 | |
| |
| Conversion of Series A | | | 5,386,888 | |
| Conversion of Series B | | | 2,054,292 | |
| Conversion of Series C | | | 5,147,560 | |
| Warrants on common stock | | | 862,749 | |
| Common stock options | | | 2,193,030 | |
| Convertible note payable | | | 2,015,468 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | 17,659,986 | |
| | | | | |
| |
| 10. | COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
Manufacturing Agreement with MDS Nordion. On June 4, 2004, the Company entered into a process development and manufacturing agreement with MDS Nordion, a division of MDS (Canada) for the development of a facility for the cGMP manufacture of Zemiva, and to supply our requirements for Zemiva during the clinical trial process (the “Manufacturing Agreement”). Pursuant to the Manufacturing Agreement, Nordion will provide access to a manufacturing facility at their premises in Vancouver, British Columbia, a portion of which will be solely dedicated for the production and supply of Zemiva during our clinical trials. The facility utilized under this agreement is owned by Nordion, and used for the production and supply of Zemiva on a priority basis. The Company was obligated to pay a facility fee upon execution of the Manufacturing Agreement. The Company also made milestone payments related to various phases of the process development. A percentage of each milestone was paid upon execution of the agreement, another percentage was paid upon commencement of the milestone, and the remainder of each milestone payment was paid upon completion of the milestone. As of December 31, 2006, the company had made all payments
F-33
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
required under this agreement aggregating to approximately $2.1 million. The term of the Manufacturing Agreement initially was through 2005, but the agreement has been extended through December 31, 2007.
Commercial Manufacture and Supply Agreement with MDS Nordion. On January 12, 2006, the Company entered into a six-year, renewable agreement with MDS Nordion for the commercial manufacture and supply of Zemiva (the “Supply Agreement”). Under the Supply Agreement, the Company paid $725,000 as an up-front payment and is obligated to make additional payments totaling $1.4 million upon MDS Nordion reaching certain manufacturing preparation milestones. A percentage of each milestone payment is due upon commencement of various phases of construction and process validation, and the remainder of each milestone payment is due upon facility commissioning and demonstration of production capability. As of December 31, 2006, the Company paid $1.2 million under this Supply Agreement. For the year ended December 31, 2006, the Company has recorded approximately $1,7 million of research and development expenses relating to the Supply Agreement in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations. One month subsequent to obtaining manufacturing preparedness, the Company is obligated to pay a monthly facility reservation fee of $24,000 which can be offset against monthly supply purchases by the Company. The Supply Agreement establishes cost of batch and cost per dose maximums.
Azedra Technology Transfer with MDS Nordion. On March 22, 2006, the Company has entered into an agreement with MDS Nordion to scale up MDS Nordion for the production of Azedra clinical material (the “Azedra Agreement”). Under the Azedra Agreement, the Company was originally obligated to make payments to MDS for upfront milestones amounting to $750,000 in 2006. This was amended in July 2006, by a Phase IIb amendment of $110,000, and an additional amendment of $270,000 in October 2006. The milestone payments are for various phases of the process development. A percentage of each milestone is due upon execution of the agreement, another percentage is due upon commencement of the milestone, and the remainder of each milestone payment is due upon completion of the milestone. As of December 31, 2006, the Company has made payments of approximately $995,000. Since these costs are non-refundable and for R&D purposes, all charges are recognized as expenses occurred. For the year ended December 31, 2006, the Company has recorded approximately $1.0 million of research and development expenses relating to the Azedra Agreement in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
Licensing Agreements — The Company has exclusively licensed certain of its patent rights from third-parties, as well as related parties, including certain members of the Board of Directors and the Company’s Advisory Board, who are also stockholders of the Company. In exchange for the exclusive rights, the Company is obligated to pay the licensor patent expenses and a royalty on net sales of future products ranging from 1% to 4% of net sales, depending on the license agreement. There have been no sales of products subject to such license agreements through December 31, 2006. In addition, some of the license agreements require the Company to pay certain lump sum payments upon attainment of certain clinical milestones, none of which has been achieved through December 31, 2006. In addition, in exchange for access to non-patent, confidential clinical information from one of the third-parties on one of its potential products, the Company has entered into an agreement with this third-party which requires the Company to pay the third-party a royalty which ranges from 2% to 7% on net sales of a defined future product for the first indication, depending on the extent to which the third-party’s clinical data expedites U.S. regulatory approval of the defined product. There have been no sales of product through December 31, 2006.
Three of the Company’s license agreements are with Georgetown University. In addition to royalty obligations which are included in the above, the agreements provide for the Company to pay up to $2.5 million in milestone payments upon the attainment of certain approvals in the regulatory process and other clinical milestones. Certain milestone payments may be reduced by up to 50% for subsequent new drug applications submitted for new uses of the same compound. If paid, these milestone payments would be creditable against future royalty payments. As of December 31, 2006, the Company has paid approximately $28,000 under these
F-34
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
agreements. For the year ended December 31, 2006, $18,000 was charged to Research and Development for these agreements.
In November 2006, the Company executed an agreement with Novartis Pharma AG (Novartis), for the nonexclusive license of technology under a general patent, as well as the exclusive license of technology under a Novartis specific patent. This agreement relates to certain aspects of the Company’s oncology product candidate Onalta. The agreement allows the Company to use this technology for the worldwide development and commercialization of OctreoTher. The Company is obligated to pay royalties based on net sales of the product, for the life of the patents, or alternatively, for a term following first commercial sale, whichever is longer. There have been no sales of products subject to such license agreements through December 31, 2006. The Company is also obligated to pay milestone payments totaling $4.0 million upon the attainment of certain approvals in the regulatory process. None have been achieved as of December 31, 2006. Milestone payments are partially creditable against future royalty payments. The Company expects to pay a license fee of $1.0 million in the second quarter of 2007.
In December 2006, the Company executed an addendum to the Novartis agreement allowing for an exclusive license of the technology under the general patent. The addendum calls for additional license fees, milestone payments totaling $600,000, and royalty payments to a third-party, Dr. Eric P. Krenning. There have been no sales of products subject to such license agreements and none of the relevant milestones have been achieved through December 31, 2006. The Company paid a license fee of $600,000 under this addendum in January of 2007.
Both the Novartis License and subsequent addendum were not effective until a third-party, Mallinckrodt (see below), terminated a separate license with Novartis. The Company received notice from Novartis that it had terminated its license agreement with Mallinckrodt on January 12, 2007.
In December 2006, the Company executed an agreement with Tyco Inc. / Mallinckrodt Medical, Inc (Mallinckrodt), whereby Mallinckrodt will transfer the technology and materials necessary for the manufacture of OctreoTher. This agreement relates to the Company’s oncology product candidate Onalta, and it complements the rights obtained in the agreement with Novartis Pharma, AG., by providing manufacturing rights and production know-how for Onalta. Under this agreement, the Company is obligated to make an upfront payment, and various payments for phases in the technology transfer process. The Company is also obligated to make a one-time purchase of certain existing quantities of production supplies from Mallinckrodt. The term of this agreement is for as long as the Company manufactures and sells Onalta, on acountry-by-country basis. The Company paid $700,000 under this agreement in January of 2007. The Mallinckrodt Agreement was not effective until the Company executed its license agreement with Novartis in December 2006, and Novartis terminated its separate license with Mallinckrodt on January 12, 2007.
In December 2006, the Company entered into an exclusive license agreement with McMaster University for worldwide rights to certain platform technology used for radiolabeling compounds. This technology platform is not currently used with any of the Company’s existing product candidates, but the Company is exploring the applicability of radiolabeling to its oncology product candidates. The Company has the right to sublicense these rights and also has an obligation to maintain the related patent rights. In exchange for this exclusive license, the Company is obligated to pay an upfront, nonrefundable licensing fee, future royalties on any products that are radiolabeled using the licensed technology for the term of the patent rights, minimum annual royalties (that are creditable against royalties) and future milestone payments totaling $575,000 relative to clinical trials for particular indications and certain stages of the regulatory process. The term of this agreement is through the last to expire of the patent rights and the Company has the right to terminate the agreement upon providing ninety days written notice. There have been no sales of products subject to such license agreements and none of the relevant milestones have been achieved through December 31, 2006. The Company paid the initial license fee of $10,000 in the first quarter of 2007.
F-35
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Operating Leases — The Company rents laboratory and office space located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, under a noncancelable operating lease. The lease terminates in June 2008, and does not contain an option to renew. The lease agreement provides that the Company pay fixed monthly rental payments of $31,322. Total rent expense, including amortization of a deferred rent liability, under these arrangements was $126,873, $205,754, and $336,691 in 2004, 2005 and 2006, respectively.
The Company leases an apartment for an officer at a cost of approximately $2,000 per month pursuant to a renewable1-year lease (expiring in May 2007, as amended).
At December 31, 2006, minimum annual rental payments were as follows:
| | | | | |
Year | | Amount | |
| |
| 2007 | | $ | 395,831 | |
| 2008 | | | 190,916 | |
| | | | | |
| | | $ | 586,747 | |
| | | | | |
In addition to the minimum payments, the Company pays the landlord for allocated taxes and common area usage. These contingent rental payments fluctuate during the term of the lease and are immaterial.
Employment Agreements — The Company has employment agreements with its officers that continue until terminated in accordance with the provisions of the agreements. Pursuant to the terms, the officers will receive annual base salaries. The base salaries are adjusted annually and, as adjusted, aggregate approximately $2.4 million per all agreements, for calendar years after December 31, 2006. The officers are also eligible to earn bonuses based on the discretionary accomplishment of goals set by the Board of Directors. Either the Company or the officer may terminate their employment agreement at any time, with or without cause. In the event the Company terminates the employment agreement without cause or the officer terminates his employment for good reason, as defined, the officer may be entitled to receive severance pay up to one year’s base salary. In addition, each agreement provides that in the event of a change in control of the Company, as defined, any unvested options that the officer may hold will become immediately vested and exercisable. The total of such unvested options as of December 31, 2006 was 816,332.
Litigation — On June 30, 2004 a small group of stockholders comprised of David Elmaleh, Havacom, N.V., IBS Turnaround Fund, L.P., John Pattillo and Greg Shoukimas commenced a civil suit in Massachusetts Superior Court against the Company and certain of our present and former officers. The complaint alleged that the officers breached fiduciary duties to the Company and to the plaintiffs by approving and benefiting from stock transactions in 2001 and 2002. The plaintiffs alleged that these transactions resulted in the Company receiving less money in connection with the sale of stock and in an improper dilution of certain stockholders. In March 2005, the individual defendants moved for a dismissal of the claims asserted directly against them. On July 1, 2005, the Court found, as a matter of law, that the individual defendants did not breach their fiduciary duties to the plaintiffs and dismissed those claims, leaving only the derivative claims purportedly asserted on behalf of the Company pending. On October 11, 2005, the plaintiffs served a Motion for Reconsideration of the Court’s dismissal of their direct claims. By order dated June 20, 2006, the Court denied plaintiffs’ Motion for Reconsideration of this dismissal.
Promptly after receiving notice of the service of the complaint, the disinterested members of our Board of Directors appointed a Special Litigation Committee (“SLC”), comprised of disinterested directors to investigate the allegations. The SLC retained independent counsel to assist it in its investigation. On July 14, 2005, the SLC unanimously determined that the transactions in question were proper and submitted a report to the remaining disinterested members of the Board of Directors with its conclusions and the recommendation that the Company seek to terminate the remaining claims. On July 24, 2005, the remaining disinterested members of the Board of Directors adopted the report and its recommendations. On August 9, 2005, the
F-36
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Company’s counsel served a motion to dismiss the remaining derivative claims on plaintiffs. By Order dated April 12, 2006, the Court granted the Motion to Dismiss, and dismissed all derivative claims. Final judgment dismissing the Complaint was entered on July 20, 2006. On October 27, 2006, a Stipulation of Dismissal of Plaintiffs’ Appeal was filed, which was docketed by the Court, completely disposing of the matter without payment of any consideration by the Company to the plaintiffs.
Pursuant to indemnification agreements between the Company and its officers and directors, legal fees for the present and former officers against which the Action has been asserted, were paid by the Company.
By letter dated September 9, 2005, counsel for Mr. Keith Greenfield, a shareholder and former director, threatened to sue the Company if it did not confirm that Mr. Greenfield held a valid option to purchase 123,200 shares of common stock that was originally granted to him on February 15, 1999, pursuant to the Zebra Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 1998 Incentive and Non-Qualified Stock Option Plan. This option was considered terminated in May 2003. However, pursuant to Board action dated December 9, 2003, a new option grant was purportedly approved but never executed in 2003. As Mr. Greenfield left the Company shortly thereafter, the books and records never reflected the purportedly approved option because the option was never issued. Until Mr. Greenfield presented a signed amendment to his original 1999 option agreement in 2006, the Company vigorously disputed Mr. Greenfield’s claim that he was entitled to receive a new option for the terminated option.
On February 20, 2006, Mr. Greenfield sued in Massachusetts Superior Court with regard to those claims and in connection therewith, provided to the Company a copy of a July 1, 2001 amendment to his original grant, which purportedly established his entitlement to the option as purportedly approved in December 2003. On the basis of this purported amendment to his original grant, the Company reflected on its books and records, and Mr. Greenfield signed an option agreement for, a fully vested option for 123,200 shares at an exercise price of $0.60 per share, which was issued on March 16, 2006. On March 20, 2006, a Notice of Dismissal in the action was filed. Mr. Greenfield exercised the option on March 20, 2006. Because a measurement date was not established in 2003, as the Company and the recipient did not reach mutual understanding of the terms of the award, the Company has accounted for the Greenfield option as granted in March 2006, when an executed option agreement was put in place, which was immediately exercised. Stock based-compensation expense of $517,000 was recognized for this award.
Subsequent to March 20, 2006, Mr. Greenfield claimed that he is entitled to attorneys’ fees and to amounts for certain tax ramifications allegedly arising from the previously-described dispute regarding his option. On April 6, 2006, Mr. Keith Greenfield, sued the Company, Mr. John Babich, the President of the Company, and the Company’s legal counsel, Foley & Lardner, LLP, in the United States District Court in Boston. In the complaint, Mr. Greenfield alleged that the Company and Mr. Babich, the Company’s legal counsel, engaged in fraud and negligent misrepresentations arising out of communications between Foley & Lardner, LLP and Mr. Greenfield’s counsel concerning Mr. Greenfield’s option rights. The Complaint sought damages in excess of $500,000. On July 31, 2006, the District Court dismissed the complaint. Mr. Greenfield appealed that ruling. All parties subsequently entered into a Confidential Settlement and General Release Agreement (the “Agreement”) having a closing date of December 1, 2006. This Agreement settled the litigation and released the parties from all claims. No amounts were paid to Mr. Greenfield. On December 1, 2006, the First Circuit Court of Appeals docketed a joint Agreement of Dismissal, with prejudice, which terminated all further proceedings in this matter without payment of any consideration by the Company to the plaintiff.
The Company has not accrued for any loss related to these claims at December 31, 2006 as management believes they were not considered probable.
F-37
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| |
| 11. | OTHER RELATED-PARTY TRANSACTIONS AND RELATIONSHIPS |
Certain related party transactions are described in Notes 3, 6, 8, 9 and 10. The following are other related party transactions.
During 2004, 2005 and 2006, the Company expensed $126,000, $271,500, and $284,500, respectively for remuneration to members of the Board of Directors for service on the Board, as well as a consulting arrangement with a member of the Board. In 2004, approximately $111,000 of the amounts owed to one of these directors was converted into 1,841 shares of Series B based on $132 per share, the last price paid for the securities by investors (see Note 8).
Mr. David Barlow became Chairman of the Company’s Board of Directors in 2000 and Chief Executive Officer in 2003. During this period and continuing, Mr. Barlow’s brother has been a partner in the law firm representing the Company as legal counsel. Mr. Barlow’s brother has not provided any direct service to the Company. During the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006, fees billed by such firm (including costs related to the issuances of capital stock) were$410,867, $1,907,734, and $2,193,194, respectively.
On September 28, 2006, the Company issued a convertible note with detachable warrants in the amount of $10 million to a principal stockholder in conjunction with six other notes for $15.0 million (see Note 6). The warrants held by the principal stockholder were valued at $619,978 and resulted in a debt discount. Interest expense of $53,092 was recorded as of December 31, 2006, relating to the amortization of the discount.
Combining the above mentioned consulting arrangements and legal fees paid to related parties with the stock-based compensation to related parties as described in Note 3, the total charges to expense for related parties is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2004 | | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Research and development — related parties | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock — based compensation | | $ | 23,156 | | | $ | 83,406 | | | $ | 62,599 | |
| Consulting fees | | | 60,000 | | | | 119,133 | | | | 189,300 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 83,156 | | | $ | 202,539 | | | $ | 251,899 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| General and administrative — related parties | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Consulting fees | | $ | 66,000 | | | $ | 121,000 | | | $ | 284,500 | |
| Legal fees | | | 345,060 | | | | 913,069 | | | | 1,545,002 | |
| Interest expense | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 411,060 | | | $ | 1,034,069 | | | $ | 1,829,502 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Included in accrued expense — related parties in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets is the following:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2005 | | | 2006 | |
| |
| Legal | | $ | 691,834 | | | $ | 317,294 | |
| Consulting | | | 56,500 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 748,334 | | | $ | 317,294 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
F-38
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
On January 15, 2007, the Company executed an agreement with Schering Aktiengesellschaft for an exclusive, worldwide, royalty-bearing license under the Schering Patents and Schering Know-How to develop and commercialize specific products within a field and territory as defined in the agreement. This agreement relates to the Company’s oncology product candidate Solazed. Under the agreement, the Company paid a license fee of $1 million in the first quarter of 2007. Additionally, the Company is obligated to pay a royalty on net sales of the product, for a term defined as the longer of the life of the patents, or ten years following first commercial sale. The Company is also obligated to pay milestone payments, totaling $9.0 million, upon the commencement of clinical trials and the attainment of certain approvals in the regulatory process. The Company has made no additional payments under this agreement.
On February 7, 2007, the Company completed an initial public offering of 5,000,000 shares of its common stock at a public offering price of $14.00 per share. Warrants automatically convertible upon the initial public offering were also exercised at this time. Net proceeds to the Company were approximately $63.3 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses totaling approximately $8.1 million.
In connection with the initial public offering discussed above, all outstanding shares of Series A, B and C Preferred Stock were converted into common stock shares of 4,010,539, 1,788,758 and 4,719,652, respectively. An additional 1,340,624, 258,851 and 448,184 shares of common stock were issued in satisfaction of the then accrued but unpaid dividends on the Series A, B and C Preferred Stock, respectively. Warrants to purchase common stock were automatically converted into 403,779 shares of the Company’s common stock at an average price of $3.45 per share. In addition, the Convertible Notes and accrued interest (see Note 6), $15,717,283 at December 31, 2006, converted into 2,029,159 shares of common shares.
On February 21, 2007 Ritchie exercised its warrant to purchase 61,538 shares of the Company’s common stock. Ritchie elected a net share settlement whereby they received 24,671 shares of common stock in exchange for the warrant held.
| |
| 13. | EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLAN |
Effective January 1, 2001, the Company adopted an employee savings and retirement plan, or 401(k) plan (the “Plan”), that covers all employees of the Company who meet certain defined requirements. Under the terms of the Plan, employees may elect to make tax-deferred contributions through payroll deductions within statutory and plan limits. The Company may elect to make discretionary matching contributions to the Plan, but has not made any since plan inception through December 31, 2006.
F-39
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(A Development Stage Company)
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| |
| 14. | UNAUDITED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA |
The following table presents unaudited quarterly financial data of the Company. The Company’s quarterly results of operations for these periods are not necessarily indicative of future results of operations.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Basic and
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Diluted Net
| |
| | | | | | | | | Net Loss
| | | Loss per Share
| |
| | | Revenue Under
| | | | | | Attributable to
| | | Attributable to
| |
| | | Research and
| | | | | | Common
| | | Common
| |
| | | Development Grants | | | Net Loss | | | Stockholders | | | Stockholders | |
| |
Year Ended December 31, 2005 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| First Quarter | | $ | 267,846 | | | $ | (3,250,119 | ) | | $ | (4,159,350 | ) | | $ | (1.01 | ) |
| Second Quarter | | | 159,116 | | | | (3,228,435 | ) | | | (4,013,595 | ) | | | (0.96 | ) |
| Third Quarter | | | 254,180 | | | | (4,914,160 | ) | | | (5,991,569 | ) | | | (1.42 | ) |
| Fourth Quarter | | | 550,942 | | | | (6,908,106 | ) | | | (8,182,943 | ) | | | (1.91 | ) |
Year Ending December 31, 2006 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| First Quarter | | $ | 81,518 | | | $ | (6,842,194 | ) | | $ | (7,796,808 | ) | | $ | (1.79 | ) |
| Second Quarter | | | 82,391 | | | | (5,548,469 | ) | | | (6,487,889 | ) | | | (1.44 | ) |
| Third Quarter | | | 42,550 | | | | (6,594,515 | ) | | | (7,586,010 | ) | | | (1.67 | ) |
| Fourth Quarter | | | 118,609 | | | | (8,281,040 | ) | | | (10,353,411 | ) | | | (2.28 | ) |
F-40
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Company has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
David S. Barlow
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
Date: April 2, 2007
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Company and in the capacities and as of the date indicated:
| | | | | | | |
Signature | | Title | | Date |
| |
| By: | | /s/ David S. Barlow David S. Barlow | | Chief Executive Officer; Chairman
of the Board
| | April 2, 2007 |
| | | | | | | |
| By: | | /s/ John W. Babich John W. Babich, Ph.D. | | President; Director | | April 2, 2007 |
| | | | | | | |
| By: | | /s/ Robert Gallahue Robert Gallahue | | Chief Financial Officer
(principal accounting officer) | | April 2, 2007 |
| | | | | | | |
| By: | | /s/ Daniel Frank Daniel Frank | | Director | | April 2, 2007 |
| | | | | | | |
| By: | | /s/ Kim D. Lamon Kim D. Lamon, M.D., Ph.D. | | Director | | April 2, 2007 |
| | | | | | | |
| By: | | /s/ David M. Stack David M. Stack | | Director | | April 2, 2007 |
| | | | | | | |
| By: | | /s/ Lionel Sterling Lionel Sterling | | Director | | April 2, 2007 |
| | | | | | | |
| By: | | /s/ Harry Stylli Harry Stylli, Ph.D. | | Director | | April 2, 2007 |