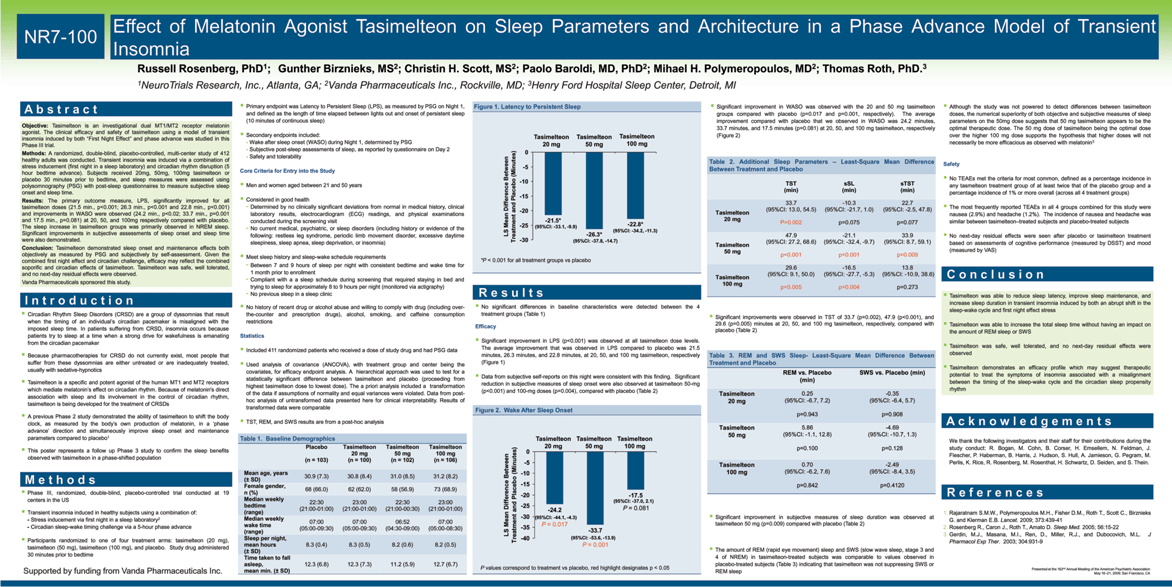
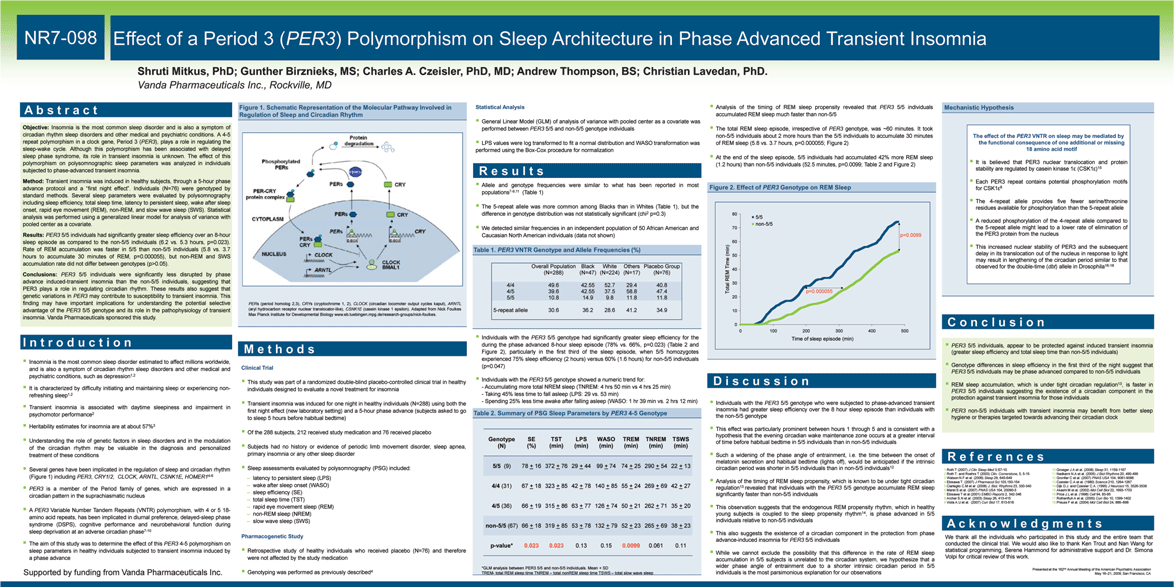
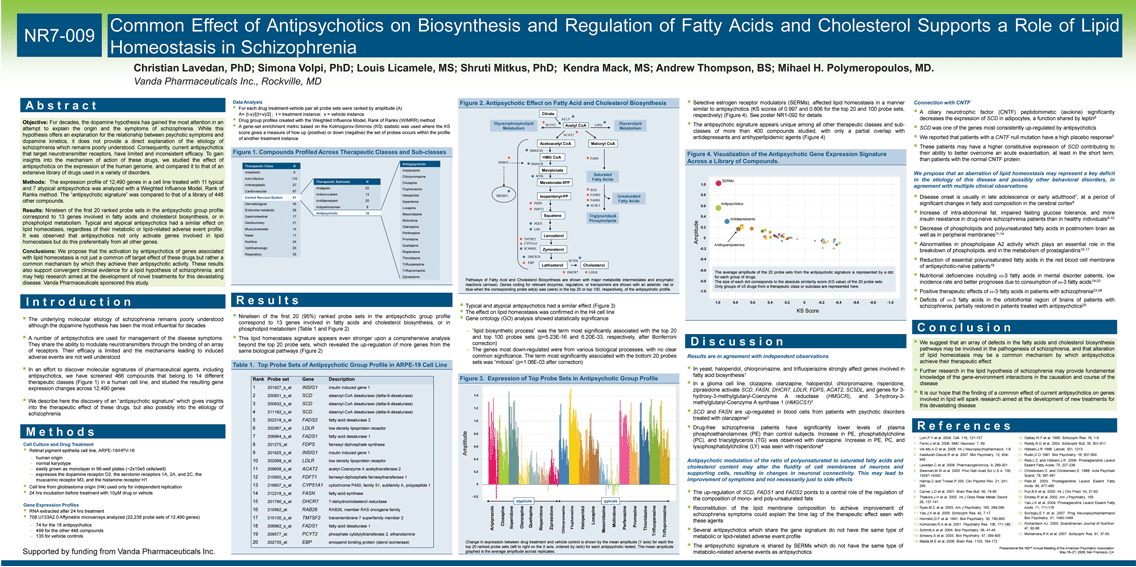
| Table 1. Top Probe Sets of Antipsychotic Group Profile in ARPE-19 Cell Line A b s t r a c t I n t r o d u c t i o n NR7-009 Objective: For decades, the dopamine hypothesis has gained the most attention in an attempt to explain the origin and the symptoms of schizophrenia. While this hypothesis offers an explanation for the relationship between psychotic symptoms and dopamine kinetics, it does not provide a direct explanation of the etiology of schizophrenia which remains poorly understood. Consequently, current antipsychotics that target neurotransmitter receptors, have limited and inconsistent efficacy. To gain insights into the mechanism of action of these drugs, we studied the effect of antipsychotics on the expression of the human genome, and compared it to that of an extensive library of drugs used in a variety of disorders. Methods: The expression profile of 12,490 genes in a cell line treated with 11 typical and 7 atypical antipsychotics was analyzed with a Weighted Influence Model, Rank of Ranks method. The "antipsychotic signature" was compared to that of a library of 448 other compounds. Results: Nineteen of the first 20 ranked probe sets in the antipsychotic group profile correspond to 13 genes involved in fatty acids and cholesterol biosynthesis, or in phospholipid metabolism. Typical and atypical antipsychotics had a similar effect on lipid homeostasis, regardless of their metabolic or lipid-related adverse event profile. It was observed that antipsychotics not only activate genes involved in lipid homeostasis but do this preferentially from all other genes. Conclusions: We propose that the activation by antipsychotics of genes associated with lipid homeostasis is not just a common off target effect of these drugs but rather a common mechanism by which they achieve their antipsychotic activity. These results also support convergent clinical evidence for a lipid hypothesis of schizophrenia, and may help research aimed at the development of novel treatments for this devastating disease. Vanda Pharmaceuticals sponsored this study. Nineteen of the first 20 (95%) ranked probe sets in the antipsychotic group profile correspond to 13 genes involved in fatty acids and cholesterol biosynthesis, or in phospholipid metabolism (Table 1 and Figure 2) This lipid homeostasis signature appears even stronger upon a comprehensive analysis beyond the top 20 probe sets, which revealed the up-regulation of more genes from the same biological pathways (Figure 2) Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), affected lipid homeostasis in a manner similar to antipsychotics (KS scores of 0.997 and 0.806 for the top 20 and 100 probe sets, respectively) (Figure 4). See poster NR1-092 for details The antipsychotic signature appears unique among all other therapeutic classes and sub- classes of more than 400 compounds studied, with only a partial overlap with antidepressants and antihyperlipidemic agents (Figure 4) The underlying molecular etiology of schizophrenia remains poorly understood although the dopamine hypothesis has been the most influential for decades A number of antipsychotics are used for management of the disease symptoms. They share the ability to modulate neurotransmitters through the binding of an array of receptors. Their efficacy is limited and the mechanisms leading to induced adverse events are not well understood In an effort to discover molecular signatures of pharmaceutical agents, including antipsychotics, we have screened 466 compounds that belong to 14 different therapeutic classes (Figure 1) in a human cell line, and studied the resulting gene expression changes across 12,490 genes We describe here the discovery of an "antipsychotic signature" which gives insights into the therapeutic effect of these drugs, but also possibly into the etiology of schizophrenia Typical and atypical antipsychotics had a similar effect (Figure 3) The effect on lipid homeostasis was confirmed in the H4 cell line Gene ontology (GO) analysis showed statistically significance Results are in agreement with independent observations In yeast, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, and trifluoperazine strongly affect genes involved in fatty acid biosynthesis1 In a glioma cell line, clozapine, olanzapine, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, risperidone, ziprasidone activate SCD, FASN, DHCR7, LDLR, FDPS, ACAT2, SC5DL, and genes for 3- hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR), and 3-hydroxy-3- methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A synthase 1 (HMGCS1)2 SCD and FASN are up-regulated in blood cells from patients with psychotic disorders treated with olanzapine3 Drug-free schizophrenia patients have significantly lower levels of plasma phosphoethanolamines (PE) than control subjects. Increase in PE, phosphatidylcholine (PC), and triacylglycerols (TG) was observed with olanzapine. Increase in PE, PC, and lysophosphatidylcholine (LY) was seen with risperidone4 Disease onset is usually in late adolescence or early adulthood7, at a period of significant changes in fatty acid composition in the cerebral cortex8 Increase of intra-abdominal fat, impaired fasting glucose tolerance, and more insulin resistance in drug-naive schizophrenia patients than in healthy individuals9-10 Decrease of phospholipids and polyunsaturated fatty acids in postmortem brain as well as in peripheral membranes11-14 Abnormalities in phospholipase A2 activity which plays an essential role in the breakdown of phospholipids, and in the metabolism of prostaglandins15-17 Reduction of essential polyunsaturated fatty acids in the red blood cell membrane of antipsychotic-naive patients18 Nutritional deficiencies including ?-3 fatty acids in mental disorder patients, low incidence rate and better prognoses due to consumption of ?-3 fatty acids19-22 Positive therapeutic effects of ?-3 fatty acids in patients with schizophrenia23-28 Deficits of ?-3 fatty acids in the orbitofrontal region of brains of patients with schizophrenia; partially restored in patients treated with antipsychotics29 We suggest that an array of defects in the fatty acids and cholesterol biosynthesis pathways may be involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia, and that alteration of lipid homeostasis may be a common mechanism by which antipsychotics achieve their therapeutic effect Further research in the lipid hypothesis of schizophrenia may provide fundamental knowledge of the gene-environment interactions in the causation and course of the disease It is our hope that the finding of a common effect of current antipsychotics on genes involved in lipid will spark research aimed at the development of new treatments for this devastating disease M e t h o d s R e s u l t s D i s c u s s i o n R e f e r e n c e s C o n c l u s i o n Connection with CNTF A ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) peptidomimetic (axokine) significantly decreases the expression of SCD in adipocytes, a function shared by leptin6 SCD was one of the genes most consistently up-regulated by antipsychotics We reported that patients with a CNTF null mutation have a high placebo response5 These patients may have a higher constitutive expression of SCD contributing to their ability to better overcome an acute exacerbation, at least in the short term, than patients with the normal CNTF protein Figure 1. Compounds Profiled Across Therapeutic Classes and Sub-classes Figure 2. Antipsychotic Effect on Fatty Acid and Cholesterol Biosynthesis Figure 3. Expression of Top Probe Sets in Antipsychotic Group Profile We propose that an aberration of lipid homeostasis may represent a key deficit in the etiology of this disease and possibly other behavioral disorders, in agreement with multiple clinical observations Figure 4. Visualization of the Antipsychotic Gene Expression Signature Across a Library of Compounds. Antipsychotic modulation of the ratio of polyunsaturated to saturated fatty acids and cholesterol content may alter the fluidity of cell membranes of neurons and supporting cells, resulting in changes in neuronal connectivity. This may lead to improvement of symptoms and not necessarily just to side effects The following information concerns a use that has not been approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration The average amplitude of the 20 probe sets from the antipsychotic signature is represented by a dot for each group of drugs. The size of each dot corresponds to the absolute similarity score (KS value) of the 20 probe sets. Only groups of ^5 drugs from a therapeutic class or subclass are represented here. Pathways of Fatty Acid and Cholesterol Biosynthesis are shown with major metabolite intermediates and enzymatic reactions (arrows). Genes coding for relevant enzymes, regulators, or transporters are shown with an asterisk: red or blue when the corresponding probe set(s) was (were) in the top 20 or top 100, respectively, of the antipsychotic profile. Change in expression between drug treatment and vehicle control is shown by the mean amplitude (Y axis) for each the top 20 ranked probe sets (left to right on the X axis, ordered by rank) for each antipsychotic tested. The mean amplitude graphed is the average amplitude across replicates. Lum,P.Y et al. 2004. Cell. 116, 121-137 Ferno,J et al. 2006. BMC Neurosci. 7, 69 Vik-Mo,A.O et al. 2008. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 1-6 Kaddurah-Daouk,R et al. 2007. Mol Psychiatry. 12, 934- 945 Lavedan,C et al. 2008. Pharmacogenomics. 9, 289-301 Sleeman,M.W et al. 2003. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100, 14297-14302 Harrop,C and Trower,P 200. Clin Psychol Rev. 21, 241- 265 Carver,J.D et al. 2001. Brain Res Bull. 56, 79-85 Thakore,J.H et al. 2002. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 26, 137-141 Ryan,M.C et al. 2003. Am J Psychiatry. 160, 284-289 Yao,J.K et al. 2000. Schizophr Res. 42, 7-17 Horrobin,D.F et al. 1991. Biol Psychiatry. 30, 795-805 Komoroski,R.A et al. 2001. Psychiatry Res. 106, 171-180 Schmitt,A et al. 2004. Biol Psychiatry. 56, 41-45 Smesny,S et al. 2005. Biol Psychiatry. 57, 399-405 Maida,M.E et al. 2006. Brain Res. 1103, 164-172 Gattaz,W.F et al. 1995. Schizophr Res. 16, 1-6 Reddy,R.D et al. 2004. Schizophr Bull. 30, 901-911 Hibbeln,J.R 1998. Lancet. 351, 1213 Rudin,D.O 1981. Biol Psychiatry. 16, 837-850 Reis,L.C and Hibbeln,J.R. 2006. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 75, 227-236 Christensen,O. and Christensen,E. 1988. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 78, 587-591 Peet,M. 2003. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 69, 477-485 Puri,B.K et al. 2000. Int J Clin Pract. 54, 57-63 Emsley,R et al. 2002. Am J Psychiatry. 159 Yao,J.K et al. 2004. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 71, 171-176 Sivrioglu,E.Y et al. 2007. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 31, 1493-1499 Richardson AJ. 2003. Scandinavian Journal of Nutrition. 47, 92-98 McNamara,R.K et al. 2007. Schizophr Res. 91, 37-50 Cell Culture and Drug Treatment Retinal pigment epithelia cell line, ARPE-19/HPV-16 Cell line from glioblastoma origin (H4) used only for independent replication 24 hrs incubation before treatment with 10^M drug or vehicle Gene Expression Profiles RNA extracted after 24 hrs treatment 708 U133A2.0 Affymetrix microarrays analyzed (22,238 probe sets of 12,490 genes) human origin normal karyotype easily grown as monolayer in 96-well plates (~2x10e5 cells/well) expresses the dopamine receptor D2, the serotonin receptors 1A, 2A, and 2C, the muscarinic receptor M3, and the histamine receptor H1 74 for the 18 antipsychotics 499 for the other 448 compounds 135 for vehicle controls Data Analysis For each drug treatment-vehicle pair all probe sets were ranked by amplitude (A) A= (t-v)/[(t+v)/2] ; t = treatment instance; v = vehicle instance Drug group profiles created with the Weighted Influence Model, Rank of Ranks (WIMRR) method A gene-set enrichment metric based on the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) statistic was used where the KS score gives a measure of how up (positive) or down (negative) the set of probes occurs within the profile of another treatment instance "lipid biosynthetic process" was the term most significantly associated with the top 20 and top 100 probes sets (p=5.23E-16 and 6.20E-33, respectively, after Bonferroni correction) The genes most down-regulated were from various biological processes, with no clear common significance. The term most significantly associated with the bottom 20 probes sets was "mitosis" (p=1.06E-03 after correction) Presented at the 162nd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association May 16-21, 2009; San Francisco, CA Supported by funding from Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc. The up-regulation of SCD, FADS1 and FADS2 points to a central role of the regulation of the composition of mono- and poly-unsaturated fats Reconstitution of the lipid membrane composition to achieve improvement of schizophrenia symptoms could explain the time lag of the therapeutic effect seen with these agents Several antipsychotics which share the gene signature do not have the same type of metabolic or lipid-related adverse event profile The antipsychotic signature is shared by SERMs which do not have the same type of metabolic-related adverse events as antipsychotics |