UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014
OR
o TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from to .
Commission file number 1-33332
WABCO Holdings Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 20-8481962 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
Chaussee de Wavre, 1789 1160 Brussels, Belgium | ||
2770 Research Drive, Rochester Hills, MI | 48309-3511 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code +32 2 663 98 00
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common stock, par value $0.01 per share | New York Stock Exchange | |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
| Title of each class | ||
| None | ||
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. x Yes o No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. o Yes x No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. x Yes o No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this
chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). x Yes o No
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (Section 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act (Check one).
| Large Accelerated Filer | x | Accelerated Filer | o | |||
| Non-Accelerated Filer | o | Smaller Reporting Company | o | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). o Yes x No
The aggregate market value of the voting stock (Common Stock) held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of the close of business on June 30, 2014, the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter, was approximately $6.4 billion based on the closing sale price of the common stock on the New York Stock Exchange on that date. The registrant does not have any non-voting common equity.
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the issuer’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date.
| Common stock, $.01 par value, outstanding at | ||||
| February 6, 2015 | 58,459,597 | shares | ||
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III incorporates information from certain portions of the registrant's definitive proxy statement to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the fiscal year end of December 31, 2014.
WABCO HOLDINGS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
FORM 10-K
Year ended December 31, 2014
| TABLE OF CONTENTS | ||
| Page | ||
| Item 1. | ||
| Item 1A. | ||
| Item 1B. | ||
| Item 2. | ||
| Item 3. | ||
| Item 4. | ||
| Item 4A. | ||
| Item 5. | ||
| Item 6. | ||
| Item 7. | ||
| Item 7A. | ||
| Item 8. | ||
| Item 9. | ||
| Item 9A. | ||
| Item 9B. | ||
| Item 10. | ||
| Item 11. | ||
| Item 12. | ||
| Item 13. | ||
| Item 14. | ||
| Item 15. | ||
2
Information Concerning Forward Looking Statements
Certain of the statements contained in this report (other than the historical financial data and other statements of historical fact), including, without limitation, statements as to management's expectations and beliefs, are forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements were based on various facts and were derived utilizing numerous important assumptions and other important factors, and changes in such facts, assumptions or factors could cause actual results to differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements include the information concerning our future financial performance, financial condition, liquidity, business strategy, projected plans and objectives. Statements preceded by, followed by or that otherwise include the words “believes”, “expects”, “anticipates”, “strategies”, “prospects”, “intends”, “projects”, “estimates”, "continues", "evaluates", “forecasts”, “seeks”, “plans”, "goals", "potential", “may increase”, “may fluctuate”, and similar expressions or future or conditional verbs such as “will,” “should,” “would,” “may” and “could” are generally forward looking in nature and not historical facts. This report includes important information as to risk factors in “Item 1. Business”, “Item 1A. Risk Factors”, and “Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” Many important factors could cause actual results to differ materially from management's expectations, including:
| • | the actual level of commercial vehicle production in our end-markets; |
| • | adverse developments in the business of our key customers; |
| • | periodic changes to contingent liabilities; |
| • | adverse developments in general business, economic and political conditions or any outbreak or escalation of hostilities on a national, regional or international basis; |
| • | changes in international or U.S. economic conditions, such as inflation, interest rate fluctuations, foreign exchange rate fluctuations or recessions in our markets; |
| • | unpredictable difficulties or delays in the development of new product technology; |
| • | pricing changes to our products or those of our competitors, and other competitive pressures on pricing and sales; |
| • | our ability to receive components and parts from our suppliers or to obtain them at reasonable price levels due to fluctuations in the costs of the underlying raw materials; |
| • | our ability to access credit markets or capital markets on a favorable basis or at all; |
| • | our ability to service our debt obligations; |
| • | changes in the environmental regulations that affect our current and future products; |
| • | competition in our existing and future lines of business and the financial resources of competitors; |
| • | our failure to comply with regulations and any changes in regulations; |
| • | our failure to complete potential future acquisitions or to realize benefits from completed acquisitions; |
| • | our inability to implement our growth plan; |
| • | our ability to service our pension obligations; |
| • | our ability to remediate the material weakness in the controls relating to our accounting for our German pension plan obligations; |
| • | the loss of any of our senior management; |
| • | difficulties in obtaining or retaining the management and other human resource competencies that we need to achieve our business objectives; |
| • | labor relations; and |
| • | risks inherent in operating in foreign countries, including exposure to local economic conditions, government regulation, currency restrictions and other restraints, changes in tax laws and rulings, expropriation, political instability and diminished ability to legally enforce our contractual rights. |
We undertake no obligation to release publicly any revisions to any forward-looking statements, to report events or to report the occurrence of unanticipated events unless we are required to do so by law.
3
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Overview
Except as otherwise indicated or unless context otherwise requires “WABCO”, “WABCO Holdings Inc.,” “we,” “us,” “our,” and “the Company” refer to WABCO Holdings Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries.
WABCO is a leading global supplier of electronic, mechanical and mechatronic products for the world's major manufacturers of commercial trucks, buses, trailers and passenger cars. We develop, manufacture and sell control systems - including advanced braking, stability, suspension, transmission automation, as well as air compression and processing - that improve vehicle safety, efficiency and performance while reducing overall vehicle operating costs. We estimate that approximately two out of every three commercial vehicles with advanced vehicle control systems worldwide are equipped with our products. We also supply products for sophisticated, niche applications in passenger cars and sports utility vehicles (SUVs). We continue to grow in more parts of the world as we increasingly provide additional components and systems throughout the life of a vehicle, from design and development to the aftermarket.
History of Our Company
WABCO was founded in the United States in 1869 as Westinghouse Air Brake Company. We were purchased by American Standard Companies Inc. (American Standard) in 1968 and operated as the Vehicle Control Systems business division within American Standard until we were spun off from American Standard on July 31, 2007. Subsequent to our spin-off, American Standard changed its name to Trane Inc., which we herein refer to as “Trane.” On June 5, 2008, Trane was acquired in a merger with Ingersoll-Rand Company Limited (Ingersoll Rand) and exists today as a wholly owned subsidiary of Ingersoll Rand.
Products and Services
We develop, manufacture and sell advanced braking, stability, suspension and transmission automation and air management systems primarily for commercial vehicles. Our largest-selling products are pneumatic anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic braking systems (EBS), electronic stability control (ESC), automated manual transmission systems, air disc brakes, and a large variety of conventional mechanical products such as actuators, air compressors and air control valves for heavy and medium-sized trucks, buses and trailers. We also supply advanced electronic suspension controls and vacuum pumps to the passenger car and SUV markets in Europe, North America and Asia. In addition, we supply commercial vehicle aftermarket distributors and service partners as well as fleet operators with replacement parts, fleet management solutions, diagnostic tools, training and other expert services. We also provide remanufacturing services globally.
In February 2014, WABCO acquired Transics International, a leading provider of fleet management solutions in Europe. This acquisition aligns with a WABCO strategic objective to expand business relationships with fleets around the world. In September 2014, WABCO introduced its next-generation TX-TRAILERGUARD™ fleet management solution, marking the first production integration after WABCO acquired Transics. It combines the functionalities of WABCO's award-winning TrailerGuard™ telematics technology with Transics' back-office software platform TX-CONNECT™, helping fleet operators to improve vehicle safety and efficiency while reducing costs.
In 2014, we announced mBSP™, our industry-first modular braking system platform. It enables commercial vehicle manufacturers worldwide to interchangeably equip their diverse global truck and bus platforms with ABS or EBS systems based on regional market or regulatory requirements. WABCO's mBSP features the industry's highest standardization across both components and software of its ABS and EBS systems, offering vehicle makers a high degree of flexibility and scalability globally. With WABCO's unique mBSP system, truck and bus builders can achieve significant savings in development time and production costs. They can also bring new vehicles to market faster in every region of the world.
Also in 2014, we introduced OptiPace™, our breakthrough predictive economic cruise-control technology for trucks and buses. OptiPace uses on-board digital map technology and proprietary algorithms to anticipate and adapt the vehicle's most economic speed based on the road topography ahead, which enables fuel economy. OptiPace further expands WABCO's industry-leading portfolio of advanced driver assistance technologies.
In addition, we unveiled in 2014 our innovative OptiFlow™ Tail solution, an aerodynamic product that helps to improve fuel economy and operational efficiency of trailers in Europe. OptiFlow Tail continues WABCO's technology leadership to improve
4
trailer efficiency for manufacturers, fleet operators and transport companies. It also builds on experience gained through WABCO's OptiFlow SideWings, which reduce air resistance. OptiFlow products are the result of WABCO's acquisition in 2012 of Ephicas, a pioneering company in the field of aerodynamic solutions for commercial vehicles.
WABCO became the first supplier of advanced emergency braking systems (AEBS) homologated in Europe in accordance with European Union regulations. WABCO's OnGuardPLUS™ AEBS for trucks and buses that complies with European Union regulations that came into effect in 2013. It detects moving, decelerating and stationary vehicles ahead. It alerts the driver via acoustic, visual and haptic signals. OnGuardPLUS autonomously applies the brakes and can bring the vehicle to a complete stop, helping to prevent or mitigate rear-end collisions.
WABCO offers the industry's first hydraulic ABS integrated with ESCsmart™ electronic stability control. We uniquely deliver hydraulic as well as pneumatic ABS with ESC systems for manufacturers of commercial vehicles of all sizes from Class 5 to Class 8, representing the industry’s most comprehensive portfolio of stability control solutions.
Our key product groups and functions are described below.
| WABCO KEY PRODUCT GROUPS | ||
| SYSTEM / PRODUCT | FUNCTION | |
| Actuator | Converts energy stored in compressed air into mechanical force applied to foundation brake to slow or stop commercial vehicles | |
| Air Compressor and Air Processing/Air Management System | Provides compressed, dried air for braking, suspension and other pneumatic systems on trucks, buses and trailers | |
| Foundation Brake | Transmits braking force to a disc or drum (connected to the wheel) to slow, stop or hold vehicles | |
| Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) | Prevents wheel locking during braking to ensure steerability and stability | |
| Conventional Braking System | Mechanical and pneumatic devices for control of braking systems in commercial vehicles | |
| Electronic Braking System (EBS) | Electronic controls of braking systems for commercial vehicles | |
| Electronic and Conventional Air Suspension Systems | Level control of air springs in trucks, buses, trailers and cars | |
| Transmission Automation | Automates transmission gear shifting for trucks and buses | |
| Vehicle Electronic Architecture (VEA) | Central electronic modules integrating multiple vehicle control functions | |
| Vehicle Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Roll Stability Support (RSS) | Enhances driving stability | |
Key Markets and Trends
Electronically controlled products and systems are important for the growth of our business. Our markets are driven primarily by the electronics content of control systems in commercial vehicles, which has been increasing steadily with each successive vehicle platform introduction, as original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) seek to improve vehicle safety, efficiency and performance through added functionalities, and to meet evolving regulatory standards. Overall, engineering trends in commercial vehicle design show a shift in demand toward increased electronics content. Although its pace varies by region, the trend toward more and complex vehicle electronics is similar in all major geographies.
In particular, braking systems are part of this broader shift from conventional to advanced electronic systems. In addition to increasing safety, improving stopping distances, and reducing installation complexity, advanced EBSs also allow for new functionalities to be introduced more cost effectively. New functionalities include stability control, adaptive cruise control, transmission automation, brake performance warning, vehicle diagnostics, driver assistance systems as well as engine braking and engine speed controls, among others. For example, our industry-leading automated transmission controls optimize gear shifting, resulting in better fuel efficiency, less component wear and fewer parts. This technology further enhances driver safety and comfort through less physical effort.
The global commercial vehicle industry is also trending toward environmental sustainability. WABCO's technology leadership continues to deliver products and systems that increase fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, decrease vehicle weight and
5
optimize energy recovery, among other advancements that enhance environmental friendliness of trucks, buses and trailers over the lifetime of the vehicle. For example, a truck equipped with all of WABCO's green technologies can improve fuel efficiency by more than 10%. These include advanced transmission automation systems, innovative aerodynamic solutions, sophisticated driver assistance systems, and breakthrough air compression technologies, among others. We reduce vehicle weight and recuperate energy through industry-leading engineering and lighter materials, resulting in higher fuel efficiency and reduction in emissions.
A fundamental driver of demand for our products is commercial truck and bus production, which generally follows a multi-year cyclical pattern. The number of new commercial vehicles built fluctuates from year to year in different regions of the world. Nonetheless, over the last five years, we have demonstrated our ability to outperform the market by increasing the amount of WABCO content on each vehicle. During the five year period through 2014, WABCO's European sales to truck and bus (T&B) OEM customers, excluding the impact of foreign currency exchange rates, outperformed the rate of European T&B production by an average of 4% per year.
| Year to Year Change | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Sales to European T&B OEMs (at a constant FX rate) | 60 | % | 34 | % | (10 | )% | 13 | % | (7 | )% | |||||
| European T&B Production | 52 | % | 31 | % | (9 | )% | 5 | % | (9 | )% | |||||
Customers
We sell our products primarily to four groups of customers around the world: truck and bus OEMs, trailer OEMs, commercial vehicle aftermarket distributors for replacement parts and services, and major car manufacturers. Our largest customer is Daimler, which accounted for approximately 11% and 12% of our sales in 2014 and 2013, respectively. Volvo, our next largest customer, accounted for approximately 10% of our sales in both 2014 and 2013. Other key customers include Ashok Leyland, BMW, China National Heavy Truck Corporation (CNHTC), Cummins, Fiat (Iveco), Hino, Hyundai, Krone, MAN Nutzfahrzeuge AG (MAN), Meritor, Meritor WABCO (a joint venture), Paccar (DAF Trucks N.V. (DAF), Kenworth, Leyland and Peterbilt), First Automobile Works, Otto Sauer Achsenfabrik (SAF), Scania, Schmitz Cargobull AG, TATA Motors and ZF Friedrichshafen AG (ZF). For the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, our top 10 customers accounted for approximately 54% and 52% of our sales, respectively.
The largest group of our customers, representing approximately 60% of sales (62% in 2013), consists of truck and bus OEMs who are large, increasingly global and few in numbers due to industry consolidation, as well as a smaller number of off-highway (agricultural and construction) OEMs. As truck and bus OEMs grow globally, they expect suppliers to expand with them beyond their traditional markets and become reliable partners, especially in the development of new technologies. WABCO has a strong reputation for technological innovation and collaborates closely with major OEM customers to design and develop technologies used in their products. Our products play an important role in enabling further vehicle safety and efficiency. At the same time, there are few other suppliers who compete across the breadth of products that we supply globally.
The second largest group, representing approximately 26% of sales (25% in 2013), consists of the aftermarket distributor network that provides commercial vehicle operators with replacement parts as well as a range of services. This distributor network is a fragmented and diverse group of customers, covering a broad spectrum from large OEM-affiliated or OEM-owned distributors to small independent local distributors. The increasing number of trucks, buses and trailers on the road worldwide that are equipped with our products continuously increases market demand for replacement parts and services, thus generating a growing stream of recurring aftermarket sales. In addition, we continue to develop an array of service offerings - such as diagnostics, training and fleet management solutions - for repair shops and fleet operators that further enhance our presence and growth in the commercial vehicle aftermarket.
The next largest group, representing approximately 10% of sales (9% in 2013), consists of trailer manufacturers, a particularly fragmented group of local or regional players that are widely diverse in business size, focus and operation. Smaller trailer manufacturers are highly dependent on suppliers such as WABCO to provide technical expertise and product knowledge. Similar to truck and bus OEMs, trailer manufacturers rely significantly on WABCO products for safety and efficiency functions through superior technologies and customized applications of such technologies.
The smallest group, representing approximately 4% of sales (4% in 2013), consists of passenger car and SUV manufacturers that purchase our electronic air suspension systems and vacuum pumps. Electronic air suspension is a luxury feature with increasing penetration that exceeds market growth. Vacuum pumps are used with diesel and gasoline direct injection (GDI) engines; as a result, WABCO's vacuum pumps have above-average growth rates due to increasing diesel and GDI applications in Europe, Asia
6
and North America. These customers are typically large, global and sophisticated; they demand high quality in products and services.
We address our customers through a global sales force. It is organized around key accounts and customer groups and it interfaces with product marketing and management to identify opportunities and meet customer needs across our product portfolio and throughout different regions of the world.
Europe represented approximately 59% of our sales in 2014 (61% in 2013), the remainder coming primarily from Asia and the Americas. Our products are also manufactured in Europe, Asia and the Americas. WABCO's growth in Asia is enhanced by our strong roots in China and India where we have achieved leading market positions through close connectivity to customers. We are further strengthened in Asia by an outstanding network of suppliers, manufacturing sites and engineering hubs.
| WABCO SALES | ||||||||||
| By Geography | FY 2014 % of Sales | FY 2013 % of Sales | By Major End-Market | FY 2014 % of Sales | FY 2013 % of Sales | |||||
| Europe | 59 | % | 61 | % | Truck & Bus Products (OEMs) | 60 | % | 62 | % | |
| Asia | 19 | % | 18 | % | Aftermarket | 26 | % | 25 | % | |
| North America | 13 | % | 11 | % | Trailer Products | 10 | % | 9 | % | |
| South America | 6 | % | 7 | % | Car Products | 4 | % | 4 | % | |
| Other | 3 | % | 3 | % | ||||||
Additional information on the geographic distribution of our sales and our long-lived assets for the past three years may be found in Note 19 ("Geographic Information") in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Backlog
Information on our backlog is set forth under Item 7. “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Backlog” of this annual report.
Cyclical and Seasonal Nature of Business
Information on the cyclical and seasonal nature of our business is set forth under Item 7 “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Cyclical and Seasonal Nature of Business” of this annual report.
Growth Strategy
Our growth strategy is focused on four platforms, which help to further differentiate WABCO within the global commercial vehicle industry: technology innovation, geographic expansion, aftermarket growth and opportunistic automotive application of our products and systems. Drivers of growth for both our aftermarket and advanced car systems are discussed in “Customers” above.
Technology
WABCO remains focused on global technology trends that are relevant to our customers. Our technology strategy has two pillars to create value for manufacturers of commercial vehicles and fleet customers in every region of the world. One pillar is advanced vehicle and driver safety to reduce the number of accidents involving commercial vehicles. The other pillar is vehicle efficiency to improve the environmental sustainability of trucks, buses and trailers.
We continue to drive market outperformance by leveraging our industry-leading expertise in developing electronically controlled systems, including braking, stability, suspension, transmission automation and air management. We have a strong track record of innovation and we are responsible for many of the commercial vehicle industry's most important innovations including:
| • | First heavy-duty truck ABS |
| • | First electronically controlled air suspension (ECAS) system for commercial vehicles |
| • | First commercial vehicle automated manual transmission (AMT) controls system |
7
| • | First ESC system for heavy-duty commercial vehicles |
| • | First collision safety system with active braking developed for the North American market based on Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) technology |
| • | First hydraulic ABS integrated with ESC |
| • | First modular braking system platform (mBSP) that enables vehicle makers to interchangeably equip their truck and bus platforms with either ABS or EBS systems anywhere in the world |
| • | First technology (TX-TRAILERGUARD) that provides comprehensive operating data on the performance of the truck, trailer and driver in a single integrated real-time view |
| • | First technology (OptiLink™) that provides a single user interface via a mobile device, such as a smartphone, to monitor and control multiple functions on both the truck and trailer |
We continue to expand our technology portfolio by introducing new products and functionalities, and by improving the market penetration of our existing technologies. Advanced products and functionalities are typically developed and adopted first in Europe and then migrated to North America and Asia. Examples include the adoption of ABS and automated transmission systems. These technologies were first widely adopted in European markets before starting to penetrate North America and Asia. In terms of commitment to innovation, WABCO expended approximately $145.0 million in 2014, $119.4 million in 2013 and $104.3 million in 2012 for product engineering, including research activities and product development.
We are also focused on long-term opportunities as WABCO continues to anticipate and fulfill our industry's constant search for technology that advances vehicle safety and efficiency in mature and emerging markets on a cost-competitive basis.
WABCO safety technologies encompass braking systems, stability control, collision mitigation as well as accident mitigation and prevention. In 2014, we further strengthened our market leadership in collision mitigation and advanced emergency braking through OnGuard™ and OnGuardPLUS™ systems respectively. We introduced driver drowsiness alert in 2014 for OnLane™, our innovative lane departure warning system (LDWS). Also in 2014, we introduced our latest generation of hydraulic ABS - another industry first - as this system integrates seamlessly with ESCsmart electronic stability control for light- and medium-duty commercial vehicle platforms worldwide. As announced in 2014, our mBSP, the industry's first modular braking system platform, is at the heart of a commercial vehicle's braking system. It enables commercial vehicle makers to interchangeably equip their diverse global truck and bus platforms with ABS or EBS systems anywhere in the world. WABCO's mBSP uniquely features commonality of components and electronics, enabling truck and bus builders to save development time and production costs, and to bring new vehicles to market faster in every region of the world.
WABCO efficiency technologies deliver fuel economy, emissions reduction, energy recovery, weight reduction, lower maintenance costs and increased driver capability. As of 2014, more than 2.5 million WABCO automated manual transmission (AMT) systems are on the road, including our industry award-winning OptiDrive™ system. In 2014, we introduced OptiPace predictive economic cruise control that optimizes fuel consumption based on road topography ahead. Also in 2014, we presented OptiTire™, the industry’s first tire pressure monitoring system that offers external or internal wheel sensors. OptiFlow Tail for the rear-end of a trailer was added in 2014 to expand our OptiFlow aerodynamic solutions. WABCO’s Wheel End solution was also launched in 2014. A fully integrated system, Wheel End includes MAXX™22, the industry’s lightest and highest performing single-piston air disc brake; industry-leading WABCO actuator technology, brake disc and hub - a simplified blend of safety and efficiency, leading to weight savings up to 10%. 2014 also marked our latest generations of superior air supply solutions, compressors for hybrid and full electric vehicles as well as high-output lightweight compressors. For example, our latest h-comp™ compressor in full aluminum weighs 50% less than similar conventional compressors.
Geographic Expansion
Americas
WABCO’s regional headquarters for the Americas is located in Rochester Hills, Michigan. It further anchors WABCO as a global technology leader and tier-one supplier to the commercial vehicle and automotive industries. It also further demonstrates WABCO’s commitment to serving original equipment manufacturers and fleet operators in North and South America by leveraging our local capabilities and distribution channels for our vehicle safety and efficiency products and services.
North America remains a long-term growth market for WABCO, particularly in the United States, due to its expected volume of truck and bus production and the increasing adoption of vehicle safety and efficiency technologies. We participate in this market through a dual approach. Our North American joint venture, Meritor WABCO, is focused on the application and delivery of
8
WABCO’s braking and active safety systems, electronic suspension control and air management products. At the same time, WABCO North America, which in 2014 marked its second full year, provides further focus on business expansion and enhancement of WABCO’s positioning in the market. For example, in 2014, major global truck makers increased their adoption of WABCO’s automated manual transmission technologies in North America. Also in 2014, WABCO North America continued to enhance its engineering and new product development center for local applications. During 2014, WABCO’s OnGuard™ collision mitigation system, the first with active braking in North America, continued to expand its market leadership through increased adoption among major commercial vehicle makers and national fleets.
South America remains a long-term growth market for WABCO, particularly in Brazil, due to its expected volume of truck and bus production and the increasing adoption of vehicle safety and efficiency technologies. WABCO continued in 2014 as market leader for ABS and a range of our other technologies. WABCO has more than 30 years of ABS experience in Brazil and a leading position to help vehicle manufacturers comply with Brazilian legislation that mandates ABS on all new trucks, buses and trailers as of 2014. WABCO's South American headquarters near São Paulo serves as a regional hub in the manufacturing and sales network of WABCO products and systems. It also has a world-class production facility and a distribution center in the Campinas region. WABCO South America’s enhanced capabilities include product and applications engineering, aftermarket service, supply chain management and manufacturing. WABCO respects the specific needs of customers in South America through specially developed and locally adapted systems and products for emerging markets.
China
China remains a long-term growth market for WABCO due to its expected volume of truck and bus production and the increasing adoption of vehicle safety and efficiency technologies. In 2014, WABCO continued its position as market leader and supplier of choice for control systems for trucks, buses and trailers in China, the world’s largest market for commercial vehicles. As the leading provider of ABS in China, WABCO is well positioned for growth driven by the continued local enforcement of existing regulations making ABS mandatory on trucks, buses and trailers, as well as additional future regulations to cover more classes of vehicles. During 2014, we continued to expand our local capabilities while also investing in research, development, sourcing and manufacturing resources that include three wholly-owned factories in China. WABCO’s fourth factory in China is a majority-owned joint venture with FUWA, the world's largest manufacturer of commercial trailer axles. WABCO in China is recognized by major customers and industry organizations for its excellence in innovation and manufacturing. Customers value WABCO’s local capabilities for product application development and engineering as our strategy is to “design for China.” This strategy delivers optimal localized solutions to improve vehicle safety and efficiency, enhance driver effectiveness and sustain environmental friendliness. In 2014, WABCO was named “most popular remanufacturer” in China by a national industry association. WABCO Reman Solutions offers a global remanufacturing capability that spans China, Europe and North America. WABCO is the first supplier in China authorized to conduct its type of remanufacturing activity, providing further value for end-of-life product management while also enabling environmental sustainability.
India
India remains a long-term growth market for WABCO due to its expected volume of truck and bus production and the increasing adoption of vehicle safety and efficiency technologies. We participate in this market through our subsidiary WABCO INDIA, which has a 51-year track record of local market leadership in conventional braking products, advanced braking systems, air-assisted products, and automated manual transmission systems. In 2014, we inaugurated a factory in Lucknow near a factory of Tata Motors. WABCO INDIA now has five world-class manufacturing sites located in Ambattur, Jamshedpur, Mahindra World City, Pantnagar and Lucknow. WABCO INDIA serves global original equipment manufacturers based both in India and in other regions of the world. For example, WABCO’s factory in Chennai manufactures leading technologies and cost-effective products to supply commercial vehicle manufacturers in Japan, Europe and the United States, among other markets internationally. We promote increasingly advanced technologies such as ABS and ESC, which can significantly reduce the number of accidents involving commercial vehicles on India’s roads. WABCO INDIA is also a market leader in its domestic aftermarket through an extensive national distribution network and is recognized by major customers and numerous industry organizations for its excellence in engineering and manufacturing. It also leads the adaptation of WABCO’s global technology portfolio to meet the technical and economic needs of customers in emerging markets around the world. Also in 2014, we opened an application engineering center in Pune, WABCO’s second of its kind in India, enabling our engineers to further collaborate with global customers based in India.
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is another long-term growth market for the Company. Truck and bus production there is mainly in the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), which includes Russia as its major market. Headquartered in Moscow, WABCO Russia has five sales offices and more than 110 Service Partners across the country. From our recently opened distribution center in Moscow, WABCO supplies local manufacturers of trucks, trailers and buses, as well as aftermarket customers in the CIS.
9
WABCO also has a factory in Miass, Russia, which produces braking components and parts. In 2014, WABCO continued as market leader in Russia. Customers include GAZ Group, Russia's largest manufacturer of commercial vehicles, and KAMAZ, another major manufacturer of commercial vehicles. WABCO has been serving markets within the CIS for more than 40 years.
Competition
Given the importance of technological leadership, vehicle life-cycle expertise, reputation for quality and reliability, and the growing joint collaboration between OEMs and suppliers to drive new product development, the space in which we mostly operate has not historically had a large number of competitors. Our principal competitors are Knorr-Bremse (Knorr's U.S. subsidiary is Bendix Commercial Vehicle Systems) and, in certain categories, Haldex. In the advanced electronics categories, automotive players such as Bosch (automotive) and Continental have recently been present in some commercial vehicle applications. In the mechanical product categories, several Asian competitors are emerging, primarily in China, who are focused on such products. In each of our product categories, we compete on the basis of product design, manufacturing and distribution capabilities, product quality and reliability, price, delivery and service.
Manufacturing and Operations
Most of our manufacturing sites and distribution centers produce and/or house a broad range of products and serve different types of customers. Currently, approximately 69% of our manufacturing workforce is located in best cost countries such as China, India, Brazil and Poland up from approximately 45% in 2007. Facilities in best cost countries have historically helped reduce costs on more labor-intensive products, while the facilities in Western Europe are focused on producing more technologically advanced products. However, the increasing need for more advanced products and systems in emerging markets leads us to expand local supply chain capabilities to progressively cover more complex manufacturing. All facilities globally are deploying Six Sigma Lean initiatives to continuously generate productivity and improve service levels. By applying the Six Sigma philosophy and tools, we seek to improve quality and predictability of our processes. Lean is geared toward eliminating waste in our supply chain, manufacturing and administrative processes. Methodologies are customer driven and data based. In addition, our global supply chain team makes decisions on where to manufacture which products taking into account such factors as local and export demand, customer approvals, cost, key supplier locations and factory capabilities.
Our global sourcing organization purchases a wide variety of components - including electrical, electro-mechanical, cast aluminum products and steel, as well as copper, rubber and plastic containing parts - that represent a substantial portion of manufacturing costs. We source products on a global basis from three key regions: Western Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, and Asia. To support WABCO's continuing shift of manufacturing to best cost countries, we also continue to shift more of our sourcing to best cost regions. Under the leadership of the global sourcing organization, which is organized around commodity and product groups, we identify and develop key suppliers and seek to integrate them as partners into our extended enterprise. Many of our Western European suppliers are accompanying us on our move to best cost countries. Since 2007, the share of our sourcing from best cost regions has increased from 36% to approximately 44%.
We have developed a strong position in the design, development, engineering and testing of products, components and systems. We are generally regarded within our global industry as a systems expert, having in-depth technical knowledge and capabilities to support the development of advanced technology applications. Key customers depend on us and will typically involve us very early in the development process as they begin designing next generation platforms. We have approximately 1,874 employees dedicated to developing new products, components and systems as well as supporting and enhancing current applications and manufacturing processes. Our sales organization hosts application engineers that are based near customers in different regions around the world and are partially resident at some customer locations. We also have significant resources in best cost countries where we perform functions such as drawings, testing and software component development. We operate test tracks in Germany and India as well as in Finland for extreme weather test conditions.
Joint Ventures
We use joint ventures globally to expand and enhance our access to customers. Our important joint ventures are:
| • | A majority-owned joint venture (90%) in Japan with Sanwa-Seiki (WABCO Japan, Inc.) that distributes WABCO's products in the local market. |
| • | A majority-owned (70%) partnership in the United States with Cummins Engine Co. (WABCO Compressor Manufacturing Co.), a manufacturing partnership formed to produce air compressors designed by WABCO. |
10
| • | A majority-owned joint venture (70%) with Guangdong FUWA Heavy Industry Co., Ltd., (FUWA) to produce air disc brakes for commercial trailers in China. FUWA is the largest manufacturer of commercial trailer axles in China and in the world. |
| • | A 50% owned joint venture in Germany with Wurth Group (WABCOWURTH Workshop Services GmbH) that supplies commercial vehicle workshops, fleet owners and operators and end users internationally with multi-brand technology diagnostic systems. |
| • | A 50% owned partnership in North America with Meritor, Inc. (Meritor WABCO) that markets ABS and other vehicle control products. |
| • | A 49% owned partnership in South Africa with Sturrock & Robson Ltd (WABCO Automotive South Africa), a distributor of braking systems products. |
Employees
We have 11,409 employees. Approximately 50% of our employees are salaried and 50% are hourly. Approximately 52% of our workforce is in Europe, 42% is in Asia, and the remaining 6% is in the Americas.
Employees located in our sites in Europe, Asia and South America are subject to collective bargaining, with internal company agreements or external agreements or laws at the region or country level. Currently 50% of our workforce is covered by collective bargaining agreements. The employees' right to strike is typically protected by law and union membership is confidential information which does not have to be provided to the employer. The collective bargaining agreements are typically renegotiated on an annual basis. Our U.S. facilities are non-union. We have maintained good relationships with our employees around the world and historically have experienced very few work stoppages.
Intellectual Property
Patents and other proprietary rights are important to our business. We also rely upon trade secrets, manufacturing know-how, continuing technological innovations, and licensing opportunities to maintain and improve our competitive position. We review third-party proprietary rights, including patents and patent applications, as available, in an effort to develop an effective intellectual property strategy, avoid infringement of third-party proprietary rights, identify licensing opportunities, and monitor the intellectual property claims of others.
We own a large portfolio of patents that principally relate to our products and technologies, and we have, from time to time, licensed some of our patents. Patents for individual products and processes extend for varying periods according to the date of patent filing or grant and the legal term of patents in various countries where patent protection is obtained.
We protect our brands by trademark registrations in key markets in which our products are sold. Such trademark protections apply to our generic brands like the WABCO brand as well as many of our product names.
While we consider our patents and trademarks to be valuable assets, we do not believe that our competitive position is materially dependent upon any single patent or group of related patents. At the same time, we recognize that technical leadership is an ongoing pillar of success and our intellectual property portfolio will continue to grow in importance for the company as a whole as a result. The risks associated with successful patent prosecution and defense, trademark protection and the exploitation and protection of other intellectual property rights accordingly is something that we continue to focus on.
Environmental Regulation
Our operations are subject to local, state, federal and foreign environmental laws and regulations that govern activities or operations that may have adverse environmental effects and which impose liability for clean-up costs resulting from past spills, disposals or other releases of hazardous wastes and environmental compliance. Generally, the international requirements that impact the majority of our operations tend to be no more restrictive than those in effect in the United States.
Throughout the world, we have been dedicated to being an environmentally responsible manufacturer, neighbor and employer. We have a number of proactive programs under way to minimize our impact on the environment and believe that we are in substantial compliance with environmental laws and regulations. Manufacturing facilities are audited on a regular basis. Seventeen of our manufacturing sites have Environmental Management Systems (EMS), which have been certified as ISO 14001 compliant. These sites are those located in:
11
| Campinas, Brazil | Gronau, Germany | Stanowice, Poland |
| Jinan, China (2 plants) | Mannheim, Germany | Wroclaw, Poland |
| Qingdao, China | Ambattur, India | Charleston, United States |
| Taishan, China | Jamshedpur, India | Rochester Hills, United States |
| Claye-Souilly, France | Mahindra World City, India | Pyungtaek, Korea |
| Hanover, Germany | Meppel, Netherlands | |
A number of our facilities are undertaking responsive actions to address groundwater and soil issues. Expenditures in 2014 to evaluate and remediate these sites were not material.
Additional sites may be identified for environmental remediation in the future, including properties previously transferred and with respect to which the Company may have contractual indemnification obligations.
Available Information
Our web site is located at www.wabco-auto.com. Our periodic reports and all amendments to those reports required to be filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 are available free of charge through the web site. During the period covered by this report, we posted our periodic reports on Form 10-Q and our current reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to those documents to our web site as soon as such reports were filed or furnished electronically with the Securities Exchange Commission (SEC). We will continue to post to our web site such reports and amendments as soon as reasonably practicable after such reports are filed with or furnished to the SEC.
The Separation of WABCO from Trane
The spin-off by Trane of its Vehicle Control Systems business became effective on July 31, 2007, through a distribution of 100% of the common stock of WABCO to Trane's shareholders (the Distribution). The Distribution was effected through a separation and distribution agreement pursuant to which Trane distributed all of the shares of WABCO common stock as a dividend on Trane common stock, in the amount of one share of WABCO common stock for every three shares of outstanding Trane common stock to each shareholder on the record date. Trane received a private letter ruling from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and an opinion from tax counsel indicating that the spin-off was tax free to the shareholders of Trane and WABCO.
Code of Conduct and Ethics
Our Code of Conduct and Ethics, which applies to all employees, including all executive officers and senior financial officers and directors, is posted on our web site www.wabco-auto.com. The Code of Conduct and Ethics is compliant with Item 406 of SEC Regulation S-K and the NYSE corporate governance listing standards. Any changes to the Code of Conduct and Ethics that affect the provisions required by Item 406 of Regulation S-K will also be disclosed on the web site.
Any waivers of the Code of Conduct and Ethics for our executive officers, directors or senior financial officers must be approved by our Audit Committee and those waivers, if any are ever granted, would be disclosed on our web site under the caption “Exemptions to the Code of Conduct and Ethics.” There have been no waivers to the Code of Conduct and Ethics.
12
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
Any of the following factors could have a material adverse effect on our future operating results as well as other factors included in “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Information Concerning Forward Looking Statements.”
Risks Relating to Our Business
Our sales could decline due to macro-economic factors, cyclicality of the industry, regulatory changes and other factors outside of our control.
Changes in economic conditions, cyclical downturns in our industry, regulatory changes impacting the purchasing patterns of commercial vehicles, and changes in the local economies of the countries or regions in which we sell our products, such as changes in consumer confidence, increases in interest rates, inflation and increases in unemployment, could affect demand for our products, which could negatively affect our business and results of operations.
Demand for new trucks and buses in the markets in which we operate has a significant impact on our sales. In 2014, heavy truck and bus production declined year on year in Europe, our largest market which accounted for approximately 59% of our total sales. Adverse economic conditions in our markets, particularly in Europe, and other factors may cause our customers to reduce truck and bus production, which could have an adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
A global recession would negatively impact our customers and result in reduced demand for our products, which would therefore have a significant negative impact on our business.
During the 2008-2009 recession, the credit markets experienced a period of unprecedented turmoil and upheaval characterized by significantly reduced availability of credit and increased borrowing costs. The disruptions in the credit markets and impacts of the global recession negatively impacted consumer spending patterns and caused our customers to reduce truck and bus production. During 2012, the commercial vehicle industry experienced an abrupt slowdown to the significant recovery seen in 2010 and 2011 in our more developed markets, in addition to double digit declines in some of our emerging markets, namely Brazil and China. A further or "double dip" global recession could cause our customers to again reduce truck and bus production, which would have a negative impact on our business and results of operations, our operating cash flows and our financial condition.
Our exposure to exchange rate fluctuations on cross border transactions and the translation of local currency results into U.S. Dollars could negatively impact our results of operations.
We conduct business through subsidiaries in many different countries, including most of the major countries of Western Europe, Brazil, Poland, Russia, China, South Korea, India and Japan, and fluctuations in currency exchange rates have a significant impact on the reported results of our operations, which are presented in U.S. Dollars. In 2014, approximately 87% of our combined sales occurred outside of the United States. A significant and growing portion of our products are manufactured in best-cost countries and sold in various countries. Cross border transactions, both with external parties and intercompany relationships, result in exposure to foreign currency exchange effects. Accordingly, fluctuations in the currency exchange rates could negatively impact our results of operations, especially fluctuations in the exchange rates of the currencies for the countries referred to above. Additionally, our results of operations are translated into U.S. Dollars for reporting purposes. The strengthening or weakening of the U.S. Dollar results in unfavorable or favorable translation effects as the results of foreign locations are translated into U.S. Dollars.
Our future annual effective tax rate could vary significantly as a result of changes in the mix of earnings or losses and other factors.
Our overall effective tax rate is equal to our total tax expense as a percentage of our total profit or loss before tax. However, tax expenses and benefits are determined separately for each tax paying entity or group of entities that is consolidated for tax purposes in each jurisdiction. A substantial majority of our profits are earned in jurisdictions with a lower rate than the U.S. statutory rate. Losses in certain jurisdictions may provide no current financial statement tax benefit. As a result, changes in the mix of profits and losses between jurisdictions, as well as changes in U.S. or foreign tax laws or rulings, among other factors, could have a significant impact on our overall effective tax rate.
13
The value of our deferred tax assets could become impaired, which could materially and adversely affect our operating results.
As of December 31, 2014, we had approximately $160.3 million in net deferred tax assets. These deferred tax assets include net operating loss carryovers that can be used to offset taxable income in future periods and reduce income taxes payable in those future periods. Each quarter, we determine the probability of the realization of deferred tax assets, using significant judgments and estimates with respect to, among other things, historical operating results and expectations of future earnings and tax planning strategies. If we determine in the future that there is insufficient evidence to support the valuation of these assets, due to the risk factors described herein or other factors, we may be required to record or further adjust a valuation allowance to revalue our deferred tax assets. Such a revaluation could result in material non-cash expense in the period in which the valuation allowance is adjusted and could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We are subject to general risks associated with our foreign operations.
In addition to the currency exchange risks inherent in operating in many different foreign countries, there are other risks inherent in our international operations.
The risks related to our foreign operations that we more often face in the normal course of business include:
| • | changes in non-U.S. tax laws, increases in non-U.S. tax rates and the amount of non-U.S. earnings relative to total combined earnings could change and impact our combined tax rate; |
| • | foreign earnings may be subject to withholding requirements or the imposition of tariffs, price or exchange controls, or other restrictions; |
| • | general economic and political conditions in countries where we operate may have an adverse effect on our operations in those countries; |
| • | we may have difficulty complying with a variety of foreign laws and regulations, some of which may conflict with United States law, and the uncertainty created by this legal environment could limit our ability to effectively enforce our rights in certain markets; and |
| • | in several of the countries in which we do business, we rely upon the ongoing performance of our joint venture partners who bear risks similar to our risks and also may include obligations they have under related shareholders' agreements and risk of being denied access to the capital markets which could lead to resource demands on the Company in order to maintain or advance its strategy. |
The ability to manage these risks could be difficult and may limit our operations and make the manufacture and distribution of our products internationally more difficult, which could negatively affect our business and results of operations.
Increasing our financial leverage could affect our operations and profitability.
As of December 31, 2014, our total debt increased to $315.2 million, compared to $87.1 million as of our prior fiscal year end. Of this amount, $306.0 million consisted of drawings on our senior revolving credit facilities which bear interest at variable interest rates, depending on the currency in which a particular loan is denominated. Our indebtedness could affect our business and financial condition in various ways, including:
| • | increasing our interest expense if interest rates were to rise; and |
| • | potentially limiting our ability to borrow additional funds on favorable terms, or at all. |
While we believe we will have the ability to service our debt, respect all of the covenants contained in the facilities and obtain additional capital in the future if and when needed, that will depend upon our results of operations and financial position at the time, the then-current state of the credit and financial markets, and other factors that may be beyond our control. If we are unable to service our debt or obtain additional capital in the future on favorable terms, our financial condition and results of operation would be adversely affected.
Changes in factors that impact the determination of our non-U.S. pension liabilities may adversely affect us.
Certain of our non-U.S. subsidiaries sponsor defined benefit pension plans, which generally provide benefits based on negotiated amounts for each year of service. The Company’s pension expense and its required contributions to its pension plans
14
are directly affected by the value of plan assets, the projected and actual rates of return on plan assets and the actuarial assumptions the Company uses to measure its defined benefit pension plan obligations, including the discount rate at which future projected and accumulated pension obligations are discounted to a present value and the inflation rate. The Company could experience increased pension expense due to a combination of factors, including the decreased investment performance of its pension plan assets, decreases in the discount rate and changes in its assumptions relating to the expected return on plan assets. The Company could also experience increased other post-retirement expense due to decreases in the discount rate, increases in the health care trend rate and changes in demographics. If the actual trends in these factors are less favorable than our assumptions, this could have an adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
If we are unable to remediate the material weakness in the controls relating to our accounting for our German pension plan obligations, there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement in our financial statements may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
As discussed below in Item 9A (“Controls and Procedures”), our management has concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures and our internal controls over financial reporting were not effective as of December 31, 2014 due to a material weakness in the controls relating to our accounting for our German pension plan obligations. Specifically, the Company did not have effective controls in operation over the application of its actuarial assumptions on mortality or effective controls designed and in operation over the review of detailed calculations in the actuary’s model. With regards to the mortality assumptions, the controls that were in place did not operate effectively as designed to ensure the use of appropriate mortality assumptions in calculating the pension plan obligations. This control deficiency did not result in misstatements in prior period consolidated financial statements. During this year's financial statement closing process, management corrected the errors by applying the appropriate mortality assumptions in the calculation of pension plan obligations as of December 31, 2014 prior to the issuance of consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2014. With regards to the detailed calculations in our actuary’s model, the Company did not have controls designed to determine that the assumptions within our actuary’s model agreed to those determined by management. This control deficiency did not result in any material misstatements to the consolidated financial statements in any of the years presented. As discussed in Item 9A, management has taken immediate action to remediate the material weakness discussed above. However, if we are unable to remediate the material weakness in the controls relating to our accounting for our German pension plan obligations, there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement in our financial statements may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
We purchase components and parts containing base metals and other commodities. If we are unable to obtain such components and parts or obtain them at reasonable price levels due to fluctuations in the costs of the underlying raw materials, our ability to maintain existing sales margins may be affected.
We purchase a broad range of materials and components and parts throughout the world in connection with our manufacturing activities. Major items include electronic components and parts containing aluminum, steel, copper, zinc, rubber and plastics. The cost of components and parts, which reflect the cost of the raw materials used therein, represents a significant portion of our total costs. Price increases of the underlying commodities may adversely affect our results of operations. Although we maintain alternative sources for components and parts, our business is subject to the risk of price fluctuations and periodic delays in the delivery of certain raw materials to our suppliers. The sudden inability of a supplier to deliver components or to do so at reasonable prices could have a temporary adverse effect on our production of certain products or the cost at which we can produce those products. In addition, any change in the supply or price of raw materials could materially adversely affect our future business and results of operations.
If we are not able to maintain good relations with our employees, we could suffer work stoppages that could negatively affect our business and results of operations.
Employees located in our sites in Europe, Asia and South America are subject to collective bargaining, with internal company agreements or external agreements at the region or country level. Currently 50% of our workforce is covered by collective bargaining agreements. These employees' right to strike is typically protected by law and union membership is confidential information which does not have to be provided to the employer. Our U.S. facilities are non-union. Any disputes with our employee base could result in work stoppages or labor protests, which could disrupt our operations. Any such labor disputes could negatively affect our business and results of operations.
We are dependent on key customers.
We rely on several key customers. For the fiscal year ending December 31, 2014, sales to our top three customers accounted for approximately 11% (Daimler), 10% (Volvo) and 8% (Meritor WABCO, our 50%-owned joint venture in North America), respectively, of our sales, and sales to our top ten customers accounted for approximately 54% of our sales. Many of our customers
15
place orders for products on an as-needed basis and operate in cyclical industries and, as a result, their order levels have varied from period to period in the past and may vary significantly in the future. Such customer orders are dependent upon their markets and customers and may be subject to delays or cancellations. As a result of dependence on our key customers, we have experienced and could experience in the future a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations if any of the following were to occur:
| • | the loss of any key customer, in whole or in part; |
| • | a declining market in which customers reduce orders or demand reduced prices; or |
| • | a strike or work stoppage at a key customer facility, which could affect both its suppliers and customers. |
We are subject to price reduction demands from our OEM customers. These price reductions could adversely affect the results of our operations
Downward pricing pressure is a characteristic of the automotive industry, and as with other suppliers to commercial vehicle OEMs, we continue to experience price reduction demands from our customers. In the face of lower prices to customers, we must reduce our operating costs in order to maintain profitability. Whilst we have successfully implemented cost reduction initiatives, we anticipate our customers will continue to pursue aggressive pricing strategies. Customers may also request that we pay for design, engineering and tooling costs that are incurred prior to the start of production and recover these costs through amortization in the piece price of the applicable component. If the Company is unable to offset customer price reductions through improved operating efficiencies, new manufacturing processes, sourcing alternatives, technology enhancements and other initiatives, if a given program is not launched or is launched with significantly lower volumes than planned, or if we are unable to avoid price reductions from our customers, the results of our operations could be adversely affected.
If there are changes in the environmental or other regulations that affect one or more of our current or future products, it could have a negative impact on our business and results of operations.
We are currently subject to various environmental and other regulations in the United States and internationally. A risk of environmental liability is inherent in our current and former manufacturing activities. Under certain environmental laws, we could be held jointly and severally responsible for the remediation of any hazardous substance contamination at our past and present facilities and at third party waste disposal sites and could also be held liable for damages to natural resources and any consequences arising out of human exposure to such substances or other environmental damage. While we have a number of proactive programs underway to minimize the impact of the production and use of our products on the environment and believe that we are in substantial compliance with environmental laws and regulations, we cannot predict whether there will be changes in the environmental regulations affecting our products.
Any changes in the environmental and other regulations which affect our current or future products could have a negative impact on our business if we are unable to adjust our product offering to comply with such regulatory changes. In addition, it is possible that we will incur increased costs as a result of complying with environmental regulations, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We may be subject to product liability, warranty and recall claims, which may increase the costs of doing business and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to a risk of product liability or warranty claims if our products actually or allegedly fail to perform as expected or the use of our products results, or are alleged to result, in bodily injury and/or property damage. While we maintain reasonable limits of insurance coverage to appropriately respond to such exposures, large product liability claims, if made, could exceed our insurance coverage limits and insurance may not continue to be available on commercially acceptable terms, if at all. We cannot assure you that we will not incur significant costs to defend these claims or that we will not experience any product liability losses in the future. In addition, if any of our designed products are or are alleged to be defective, we may be required to participate in recalls and exchanges of such products. In the past five years, our warranty expense has fluctuated between approximately 0.8% and 1.5% of sales on an annual basis. Individual quarters were above or below the annual averages. The future cost associated with providing product warranties and/or bearing the cost of repair or replacement of our products could exceed our historical experience and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are required to plan our capacity well in advance of production and our success depends on having available capacity and effectively using it.
16
We principally compete for new business at the beginning of the development of our customers' new products. Our customers' new product development generally begins significantly prior to the marketing and production of their new products and our supply of our products generally lasts for the life of our customers' products. Nevertheless, our customers may move business to other suppliers or request price reductions during the life cycle of a product. The long development and sales cycle of our new products, combined with the specialized nature of many of our facilities and the resulting difficulty in shifting work from one facility to another, could result in variances in capacity utilization. In order to meet our customers' requirements, we may be required to supply our customers regardless of the actual cost to us and consequently we may suffer an adverse impact on our operating profit margins and results of operations.
We must continue to make technological advances, or we may not be able to successfully compete in our industry.
We operate in an industry in which technological advancements are necessary to remain competitive. Accordingly, we devote substantial resources to improve already technologically complex products and to remain a leader in technological innovation. However, if we fail to continue to make technological improvements or our competitors develop technologically superior products, it could have an adverse effect on our operating results or financial condition.
The Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, or PCAOB, is currently unable to inspect the audit work and practices of auditors operating in Belgium, including our auditor.
Our auditors, Ernst & Young Bedrijfsrevisoren BCVBA/Reviseurs d'Entreprises SCCRL, are registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB). Our auditors, like any other independent registered public accounting firms operating in Belgium, are not yet permitted, because of Belgian regulation impediments, to be subject to inspections by the PCAOB that assess their compliance with U.S. law and professional standards in connection with performance of audits of financial statements filed with the SEC. As a result, our investors may not realize the potential benefits of such inspections.
Risks Relating to the Separation
We are responsible for certain of Trane's contingent and other corporate liabilities.
Under the Indemnification and Cooperation Agreement, the Separation and Distribution Agreement and the Tax Sharing Agreement, our wholly-owned subsidiary WABCO Europe BVBA has assumed and is responsible for certain contingent liabilities related to Trane's business (including certain associated costs and expenses, whether arising prior to, at or after the Distribution) and will indemnify Trane for these liabilities. Among the contingent liabilities against which we will indemnify Trane and the other indemnities, are liabilities associated with certain non-U.S. tax liabilities and certain U.S. and non-U.S. environmental liabilities associated with certain Trane entities.
Risks Relating to Our Common Stock
Your percentage ownership in WABCO may be diluted in the future.
Your percentage ownership in WABCO may be diluted in the future because of equity awards that have already been granted and that we expect will be granted to our directors and officers in the future under our Omnibus Incentive Plan. In addition, we may in the future issue additional equity securities in order to fund working capital needs, capital expenditures and product development, or to make acquisitions and other investments, which may dilute your ownership interest.
We cannot assure you that we will pay any dividends or repurchase shares.
While we have historically returned value to shareholders in the form of share repurchases and/or dividends, our ability to repurchase shares and pay dividends is limited by available cash, contingent liabilities and surplus. Moreover, all decisions regarding the declaration and payment of dividends and share repurchases will be at the sole discretion of our Board and will be evaluated from time to time in light of our financial condition, earnings, capital requirements of our business, covenants associated with certain debt obligations, legal requirements, regulatory constraints, industry practice and other factors that our Board deems relevant.
Our shareholder rights plan and provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated by-laws, and of Delaware law may prevent or delay an acquisition of our company, which could decrease the trading price of our common stock.
17
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, amended and restated by-laws and Delaware law contain provisions that are intended to deter coercive takeover practices and inadequate takeover bids by making such practices or bids unacceptably expensive to the raider and to encourage prospective acquirers to negotiate with our Board of Directors rather than to attempt a hostile takeover. These provisions include, among others:
| • | a Board of Directors that is divided into three classes with staggered terms; |
| • | elimination of the right of our shareholders to act by written consent; |
| • | rules regarding how shareholders may present proposals or nominate directors for election at shareholder meetings; |
| • | the right of our Board to issue preferred stock without shareholder approval; and |
| • | limitations on the right of shareholders to remove directors. |
Delaware law also imposes some restrictions on mergers and other business combinations between us and any holder of 15% or more of our outstanding common stock.
On July 13, 2007, our Board adopted a shareholder rights plan, which provides, among other things, that when specified events occur, our shareholders will be entitled to purchase from us a newly created series of junior preferred stock. The preferred stock purchase rights are triggered by the earlier to occur of (i) ten business days (or a later date determined by our Board of Directors before the rights are separated from our common stock) after the public announcement that a person or group has become an “acquiring person” by acquiring beneficial ownership of 15% or more of our outstanding common stock or (ii) ten business days (or a later date determined by our Board before the rights are separated from our common stock) after a person or group begins a tender or exchange offer that, if completed, would result in that person or group becoming an acquiring person. The issuance of preferred stock pursuant to the shareholder rights plan would cause substantial dilution to a person or group that attempts to acquire us on terms not approved by our Board of Directors. The shareholder rights plan expires on July 16, 2017.
We believe these provisions protect our shareholders from coercive or otherwise unfair takeover tactics by requiring potential acquirers to negotiate with our Board and by providing our Board with more time to assess any acquisition proposal. These provisions are not intended to make our company immune from takeovers. However, these provisions apply even if the offer may be considered beneficial by some shareholders and could delay or prevent an acquisition that our Board determines is not in the best interests of our shareholders and our company.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
As of February 19, 2015, our manufacturing activities are located at 21 sites in 11 countries.
18
| Site Location | Major Products Manufactured at Location | |
| Campinas, Brazil | Vehicle control systems | |
| Jinan, China (2 plants) | Braking systems and Compressors | |
| Qingdao, China | Braking systems | |
| Taishan, China | Foundation brakes | |
| Claye-Souilly, France | Vehicle control systems | |
| Hanover, Germany | Vehicle control systems | |
| Gronau, Germany | Compressors and hydraulics | |
| Mannheim, Germany | Foundation brakes | |
| Ambattur, India | Vehicle control systems | |
| Jamshedpur, India | Vehicle control systems | |
| Mahindra World City, India | Vehicle control systems | |
| Pantnagar, India | Vehicle control systems | |
| Lucknow, India | Vehicle control systems | |
| Pyungtaek, Korea | Braking systems | |
| Meppel, Netherlands | Actuators | |
| Stanowice, Poland | Remanufactured products | |
| Wroclaw, Poland | Vehicle control systems | |
| Miass, Russia | Actuators and foundation brakes | |
| Rayong, Thailand | Actuators and foundation brakes | |
| Charleston, United States | Compressors | |
| Rochester Hills, United States | Remanufactured products | |
We own all of the plants described above, except for Jinan, China; Taishan, China; Stanowice, Poland; Miass, Russia; Rayong, Thailand; Rochester Hills, U.S. and Charleston, U.S., which are leased. Our properties are generally in good condition, are well maintained, and are generally suitable and adequate to carry out our business. In 2014, the manufacturing plants, taken as a whole, met our capacity needs.
We also own or lease warehouse and office space for administrative and sales staff. Our headquarters, located in Brussels, Belgium, is leased and our executive offices, located in Rochester Hills, Michigan, are owned.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
We may be party to a variety of legal proceedings with respect to environmental related, employee related, product related, and general liability and automotive litigation related matters that arise in the normal course of our business. While the results of these legal proceedings cannot be predicted with certainty, management believes that the final outcome of these proceedings will not have a material adverse effect on our combined results of operations or financial position. For more information on current legal proceedings, refer to Note 15 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
None.
19
ITEM 4A. EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
The following sets forth certain information as of February 19, 2015 with respect to each person who is an executive officer of the Company:
| Name | Age | Position(s) |
| Jacques Esculier | 55 | Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer |
| Prashanth Mahendra-Rajah | 45 | Chief Financial Officer |
| Robert de Vaucorbeil | 57 | Chief Human Resources Officer |
| Daniel Sebillaut | 53 | Chief Supply Chain Officer |
| Vincent Pickering | 46 | Chief Legal Officer and Secretary |
| Nikhil M. Varty | 50 | President, Americas and Vice President, Mergers & Acquisitions |
| Leon Liu | 53 | President, Truck, Bus & Car OEMs |
| Nick Rens | 50 | President, Trailer Systems, Aftermarket & Off-Highway |
| Robert Farrell | 67 | Interim Corporate Controller |
Each officer of the Company is appointed by the Board of Directors to a term of office expiring on the date of the first Board meeting after the Annual Meeting of Shareholders next succeeding his or her appointment or such officer's earlier resignation or removal.
Jacques Esculier has served as our Chief Executive Officer and director since July 2007. In May 2009, he was appointed Chairman of our Board of Directors. Prior to July 2007, Mr. Esculier served as Vice President of Trane and President of its Vehicle Control Systems business, a position he had held since January 2004. Prior to holding that position, Mr. Esculier served in the capacity of Business Leader for the Trane Commercial Systems' Europe, Middle East, Africa, India & Asia Region from 2002 through January 2004. Prior to joining Trane in 2002, Mr. Esculier spent more than six years in leadership positions at AlliedSignal/Honeywell. He was Vice President and General Manager of Environmental Control and Power Systems Enterprise based in Los Angeles, and Vice President of Aftermarket Services-Asia Pacific based in Singapore.
Prashanth Mahendra-Rajah has served as our Chief Financial Officer since June 2014. Prior to joining WABCO, Mr. Mahendra-Rajah served as Corporate Vice President and Segment CFO for the Silicon Systems Group, a division of Applied Materials, from April 2012. Prior to this, Mr. Mahendra-Rajah served as Vice President Finance, Head of Global Planning & Reporting for Visa for two years. Before then, Mr. Mahendra-Rajah spent 12 years at United Technologies where he served as Vice President, Finance, Planning and Analysis, UTC Fire and Security and Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, Building Systems and Services, Carrier Corporation.
Robert de Vaucorbeil has served as our Chief Human Resources Officer since November 2013. Prior to that, Mr. de Vaucorbeil served as our Manufacturing, Logistic and Quality HR Director, a position he had held since July 2011. Prior to joining WABCO, Mr. de Vaucorbeil was the HR and Industrial Excellence Director at Saint Gobain Packaging from October 2007. Before holding that position, Mr. de Vaucorbeil held management positions of increasing responsibilities at Delphi, ultimately serving as the HR Director of Delphi Powertrain worldwide and their Chassis Europe business.
Daniel Sebillaut has served as our Chief Supply Chain Officer since September 2013, adding to his existing role as Vice President, Manufacturing & Logistics, a position he has held since January 2011. Prior to joining WABCO, Mr. Sebillaut served as Director of Global Operations and Production Control at Delphi Corporation from September 2000. Before holding that position, Mr. Sebillaut served as Vice President for Quality and Continuous Improvement at Lear Corporation from May 1999.
Vincent Pickering has served as our Chief Legal Officer and Secretary since September 2010. Prior to joining WABCO, Mr. Pickering served as the Associate General Counsel for the Worldwide Licensing and Pricing Division of Microsoft Corp. for eight years. Prior to working at Microsoft, Mr. Pickering worked both in-house and in private practice, representing companies across a diverse range of industries that include the telecommunications and energy sectors.
Nikhil M. Varty has served as our President, Americas and Vice President, Mergers & Acquisitions since February 2012. Prior to this, Mr. Varty served as Vice President, Compression & Braking since July 2007. Prior to July 2007, Mr. Varty served as Vice President, Compression and Braking of Trane's Vehicle Control Systems business, a position he has held since January 2005. Prior to holding that position, Mr. Varty served in the capacity of Chief Financial Officer of Trane's Vehicle Control Systems
20
business. Prior to joining Trane in June 2001, Mr. Varty had more than 10 years of national and international senior level finance roles with Great Lakes Chemical Corp., AlliedSignal/Honeywell and Coopers & Lybrand.
Leon Liu has served as our President, Truck, Bus & Car OEMs since July 2014. Prior to this, Mr. Liu served as our President, Asia since January 2005. Prior to joining WABCO in 2005, Mr. Liu served as the Director of Business Planning and Strategy for Asia operations at Visteon Corporation. Before joining Visteon, he held management positions of increasing responsibilities in product development, product launches, program management, corporate strategy and business development at Ford Motor Company and several Japanese Tier-1 suppliers.
Nick Rens has served as our President, Trailer Systems, Aftermarket & Off-Highway since July 2014. Prior to this, Mr. Rens served as our Vice President, Aftermarket since November 2008. This was in addition to his role as Vice President, Trailer Systems, a role which he had held since 2005. He also assumed the role of Vice President, Driveline Controls, from January 2013 to September 2013. Previously, Mr. Rens worked for three years as our regional trailer sales leader for southern and western Europe based in Claye Souilly, France. Since 1999, Mr. Rens has also been Managing Director of WABCO Belgium where he held several sales leadership roles both in the Aftermarket and Original Equipment sales organizations. Mr. Rens has worked at the Company for almost his entire career, having joined the Company in 1989 as a product line specialist.
Robert Farrell has served as our Interim Corporate Controller since December 2014. Prior to this, Mr. Farrell served as our Vice President of Finance, Americas and M&A from March 2013 until his retirement from the Company on August 28, 2014. Prior to holding that position, Mr. Farrell served as the Company’s Vice President and General Auditor from July 2007.
21
PART II
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR THE REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Our common stock is listed on NYSE under the symbol “WBC”. Our Certificate of Incorporation, as amended, authorizes the Company to issue up to 400,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $.01 per share, and 4,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $.01 per share, all of which have been designated by our Board of Directors as a series of Junior Participating Cumulative Preferred Stock. We also have a rights agreement. Pursuant to the rights agreement, when triggered in certain takeover situations, one preferred stock purchase right will be issued for each outstanding share of our common stock.
We estimate that there are approximately 440 holders of record of the Company's common stock. A significant number of the outstanding shares of common stock which are beneficially owned by individuals or entities are registered in the name of a nominee of The Depository Trust Company, a securities depository for banks and brokerage firms. As of February 5, 2015, there were 35,824 beneficial owners of our common stock.
We have not declared or paid any cash dividends in 2014 or 2013. Our last cash dividend was paid ($0.07 per share) in the first quarter of 2009. We continuously consider ways to return capital to our stockholders, either through our open market repurchase program and/or through the payment of cash dividends.
Set forth below are the high and low sales prices for shares of our common stock for each quarterly period of 2014 and 2013.
| 2014 | High | Low | ||||
| First quarter | $ | 106.72 | $ | 83.92 | ||
| Second quarter | $ | 111.65 | $ | 100.31 | ||
| Third quarter | $ | 110.93 | $ | 90.73 | ||
| Fourth quarter | $ | 108.10 | $ | 85.22 | ||
| 2013 | ||||||
| First quarter | $ | 72.98 | $ | 62.30 | ||
| Second quarter | $ | 78.62 | $ | 64.01 | ||
| Third quarter | $ | 86.76 | $ | 73.95 | ||
| Fourth quarter | $ | 93.80 | $ | 80.81 | ||
ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Our Board of Directors has approved an open market stock repurchase program. On May 26, 2011, the Board of Directors approved the purchase of shares in an amount not to exceed $400 million, which expired on May 31, 2013. On October 26, 2012, the Board of Directors authorized the Company to enter into an additional share repurchase program for $400 million of common shares. A repurchase program for $200 million of common shares was further authorized on October 29, 2013. Both of these authorizations expired on December 31, 2014.
On December 5, 2014, the Board of Directors approved a repurchase program for an additional $500 million of common shares. This authorization expires on December 31, 2016.
The total unexpended balance under this repurchase program was $500.0 million as of December 31, 2014.
A summary of the repurchase activity for 2014 follows.
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased (a) | Average price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs (a) | Maximum Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs (a) | |||||||||
| Total through December 31, 2013 | 10,155,343 | $ | 61.08 | 10,155,343 | $ | 379,722,420 | |||||||
| January 1 - January 31 | 93,164 | $ | 91.12 | 93,164 | $ | 371,233,509 | |||||||
| February 1 - February 28 | 33,272 | $ | 99.14 | 33,272 | $ | 367,934,862 | |||||||
| March 1 - March 31 | 851,771 | $ | 103.86 | 851,771 | $ | 279,469,217 | |||||||
| Total first quarter | 978,207 | $ | 102.49 | 978,207 | |||||||||
| April 1 - April 30 | 62,715 | $ | 103.87 | 62,715 | $ | 272,955,018 | |||||||
| May 1 - May 31 | 431,656 | $ | 106.34 | 431,656 | $ | 227,052,032 | |||||||
| June 1 - June 30 | 439,968 | $ | 108.79 | 439,968 | $ | 179,135,862 | |||||||
| Total second quarter | 934,339 | $ | 107.33 | 934,339 | |||||||||
| July 1 - July 31 | 334,672 | $ | 104.42 | 334,672 | $ | 144,190,892 | |||||||
| August 1 - August 31 | 266,100 | $ | 101.19 | 266,100 | $ | 117,264,995 | |||||||
| September 1 - September 30 | 397,600 | $ | 98.08 | 397,600 | $ | 78,292,671 | |||||||
| Total third quarter | 998,372 | $ | 101.01 | 998,372 | |||||||||
| October 1 - October 31 | 205,200 | $ | 91.00 | 205,200 | $ | 59,618,782 | |||||||
| November 1 - November 30 | 184,500 | $ | 101.88 | 184,500 | $ | 40,822,299 | |||||||
| December 1 - December 31 | 122,400 | $ | 103.28 | 122,400 | $ | 500,000,000 | |||||||
| Total fourth quarter | 512,100 | $ | 97.86 | 512,100 | |||||||||
| Total through December 31, 2014 | 13,578,361 | $ | 71.57 | 13,578,361 | $ | 500,000,000 | |||||||
(a) Relates to the share repurchase programs approved in May 2011, October 2012, October 2013 and December 2014 as previously discussed.
All share repurchases were effected in accordance with the safe harbor provisions of Rule 10b-18 of the Exchange Act.
PERFORMANCE GRAPH
The following graph and table compare the cumulative total shareholder's return on our common stock from December 31, 2009 through December 31, 2014, with the Standard & Poor's 500 Index and the Standard & Poor's Auto Parts & Equipment Index. The table and graph use data supplied by S&P Capital IQ.
The comparisons reflected in the graph and table are not intended to forecast the future performance of the common stock and may not be indicative of such future performance.
Total Shareholder Returns
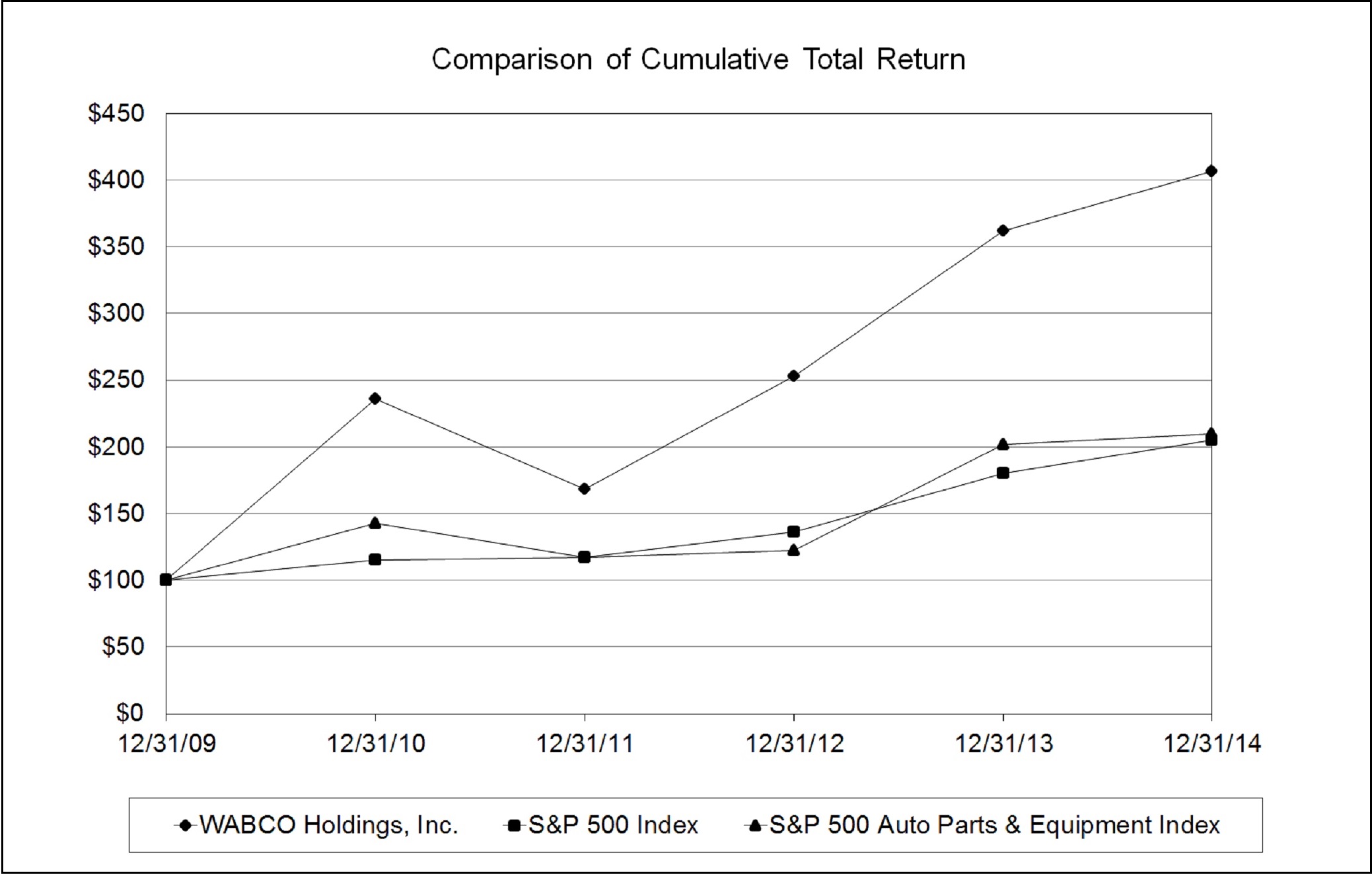
| 12/31/2009 | 12/31/2010 | 12/31/2011 | 12/31/2012 | 12/31/2013 | 12/31/2014 | |
| WABCO Holdings, Inc. | 100 | 236.25 | 168.28 | 252.77 | 362.19 | 406.28 |
| S&P 500 Index | 100 | 115.06 | 117.49 | 136.30 | 180.44 | 205.14 |
| S&P 500 Auto Parts & Equipment Index | 100 | 142.78 | 117.46 | 122.68 | 202.13 | 209.56 |
22
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
| (Amounts in millions, except share and per share data) | Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| Income Statement Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 2,851.0 | $ | 2,720.5 | $ | 2,477.4 | $ | 2,794.1 | $ | 2,175.7 | ||||||||||
| Cost of sales | 1,968.3 | 1,906.2 | 1,732.0 | 1,984.6 | 1,556.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Streamlining expenses | 11.0 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 1.5 | 4.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross profit | 871.7 | 809.1 | 740.2 | 808.0 | 615.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Selling and administrative expenses | 370.8 | 345.1 | 300.5 | 326.6 | 307.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Product engineering expenses | 145.0 | 119.4 | 104.3 | 105.1 | 85.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Streamlining expenses | 16.0 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 0.6 | (0.8 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Other operating expense, net | 8.9 | 5.0 | 3.2 | 5.8 | 5.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating income | 331.0 | 331.9 | 324.5 | 369.9 | 217.6 | |||||||||||||||
| European Commission fine reimbursement/(indemnification) | — | 279.5 | — | — | (400.4 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Equity income of unconsolidated joint ventures | 23.8 | 17.7 | 18.1 | 16.5 | 9.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Other non-operating income/(expense), net | 1.8 | 6.9 | (5.0 | ) | 20.2 | (2.2 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Interest income/(expense), net | 0.2 | 4.9 | (1.5 | ) | (1.7 | ) | (2.2 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Income/(loss) before income taxes | 356.8 | 640.9 | 336.1 | 404.9 | (177.3 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense/(benefit) (a) | 55.6 | (21.0 | ) | 23.6 | 36.7 | 36.9 | ||||||||||||||
| Net income/(loss) including noncontrolling interests | 301.2 | 661.9 | 312.5 | 368.2 | (214.2 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Less: net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 9.7 | 8.7 | 10.5 | 11.2 | 11.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income/(loss) | $ | 291.5 | $ | 653.2 | $ | 302.0 | $ | 357.0 | $ | (226.1 | ) | |||||||||
| Per share: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 4.87 | $ | 10.46 | $ | 4.73 | $ | 5.35 | $ | (3.50 | ) | |||||||||
| Diluted | $ | 4.81 | $ | 10.31 | $ | 4.62 | $ | 5.19 | $ | (3.50 | ) | |||||||||
| Average number of outstanding common shares: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | 59,907,763 | 62,474,493 | 63,906,992 | 66,693,064 | 64,562,222 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted | 60,546,454 | 63,382,564 | 65,323,389 | 68,829,440 | 64,562,222 | |||||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data (at end of period): | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 2,432.7 | $ | 2,392.8 | $ | 1,747.0 | $ | 1,623.2 | $ | 1,524.9 | ||||||||||
| Total debt | $ | 315.2 | $ | 87.1 | $ | 76.2 | $ | 78.8 | $ | 113.5 | ||||||||||
| Total shareholders' equity | $ | 841.6 | $ | 1,152.8 | $ | 676.4 | $ | 587.2 | $ | 412.3 | ||||||||||
| Cash dividends per common share | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
(a) The income tax provision for 2014 was $55.6 million on $356.8 million of pre-tax income before adjusting for noncontrolling interest, compared with an income tax benefit of $21.0 million on pre-tax income of $640.9 million before adjusting for noncontrolling interest in 2013. The income tax benefit for 2014 includes the net result of taxes on the mix of earnings in multiple tax jurisdictions, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions, and certain foreign tax planning.
The income tax benefit for 2013 includes taxes on earnings in profitable jurisdictions, income offset by fully valued net operating losses, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions, and a tax provision on unremitted foreign earnings of $300.0 million in a Belgian affiliate for which amount the Company does not assert permanent reinvestment outside the United States. This assertion is resulting from the Company recognizing earnings in the fourth quarter of 2013 from the receipt of an exceptional refund including interest from the European Commission related to the Company’s appeal of the EC fine as further discussed in Note 15 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. Additionally, the Company recorded a tax benefit for a release at the end of the year of a valuation allowance related to management’s determination that it is more likely than not that the Company will realize its deferred tax asset in a foreign jurisdiction. Management has also determined that it is more likely than not that it
23
will not realize $9.0 million of its deferred tax assets in other foreign jurisdictions and has recorded a valuation allowance against such deferred tax assets.
The income tax provision for 2012 included taxes on earnings in profitable jurisdictions, income offset by fully valued net operating losses, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions, and certain foreign tax planning. Additionally, the income tax provision is offset by the release of tax accruals for uncertain tax positions due to certain government filings submitted in January 2012 of approximately $24.8 million. Additionally, a tax benefit of $4.1 million related to the Company's filing of its 2011 U.S. Federal Income Tax Return in September 2012 was recorded during the third quarter of 2012.
The income tax provision for 2011 included taxes on earnings in profitable jurisdictions offset by benefits related to ongoing foreign tax planning activities, a decrease in a valuation allowance, and the release of certain tax accruals as a consequence of the settlement of foreign tax audits and the expiration of a statute of limitation. Additionally, the Company provided a tax provision of $12.7 million during the fourth quarter of 2011 due to the Company's decision to repatriate earnings from a foreign affiliate of approximately $299 million.
The income tax provision for 2010 included taxes on earnings in profitable jurisdictions and benefits related to ongoing foreign tax planning activities. In addition, the tax provision for 2010 excluded any benefit related to the indemnification payment of approximately $400 million for a European Commission fine as previously disclosed in the Company's 2010 Form 10-K. During the third quarter of 2010, an uncertain tax position of approximately $135.8 million was recorded for the tax deduction related to the EC fine.
For a comparative analysis of certain line items in the Income Statement Data section of this table, see Item 7. “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” which follows.
24
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
This discussion summarizes the significant factors affecting the results of operations and financial condition of WABCO during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto included elsewhere herein. Certain information in this discussion and analysis regarding industry outlook, our expectations regarding the future performance of our business and other non-historical statements are forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, the risks and uncertainties described in “Risk Factors” above. Our actual results may differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements. You should read the following discussion together with the sections entitled “Risk Factors”, “Information Concerning Forward-Looking Statements”, “Selected Financial Information”, “Liquidity and Capital Resources” and consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto included elsewhere herein.
Executive Overview
In 2014, global production of trucks and buses greater than six tons decreased in most markets. We estimate the reduction to be approximately 2% globally. WABCO's sales during the full year 2014 increased by 4.8% (6.0% excluding foreign currency translation effects) compared with the same period a year ago. Of this increase, 2.4% comes from the consolidated results in local currencies of Transics International, WABCO's newly acquired subsidiary. Overall, WABCO continued in 2014 to outperform the rate of production of trucks and buses in each region.
In 2014, WABCO's global aftermarket sales increased by 11.0% (12.7% excluding foreign currency translation effects), compared with the same period a year ago, resulting in record aftermarket revenues on a currency adjusted basis. This performance includes the benefits from the recently acquired Transics business and demonstrates the continued success of the Company's aftermarket strategies initiated several years ago.
During 2014, we continued to expand our local capabilities while also investing in research, development, sourcing and manufacturing resources. We announced in 2014 that WABCO in China has been recertified as a high technology enterprise by the government authorities. WABCO obtained such certification originally in 2010, making WABCO one of the first global suppliers in the automotive and commercial vehicle industry to qualify for this special recognition in China, the world’s largest market for production of trucks and buses. WABCO remains one of the few in its field with this official status. It also reaffirms WABCO’s well-anchored local capabilities and the Company’s continued investments in resources in China.
In 2014, we inaugurated our fifth world-class manufacturing facility in India. Our new factory in Lucknow is located near a manufacturing site of TATA Motors. WABCO INDIA’s other world-class manufacturing sites are located in Ambattur, Jamshedpur, Mahindra World City and Pantnagar. WABCO India is a major hub in our global engineering, sourcing and manufacturing network. WABCO’s extended network in India helps both local and global commercial vehicle manufacturers to further grow their domestic and export business. WABCO INDIA also supplies customers based in Japan, Europe, and the United States, among other markets internationally.
In North America in 2014, major global truck makers increased their adoption of WABCO’s automated manual transmission technologies. WABCO North America also continued to enhance its engineering and new product development center for local applications. WABCO’s OnGuard™ collision mitigation system, the first with active braking in North America, continued to expand its market leadership through increased adoption among major commercial vehicle makers and national fleets.
Throughout 2014 and despite variations in volumes of new truck and bus production across markets, WABCO continued to deliver strong profitability. Also during 2014, WABCO's Operating System continued to provide fast and flexible responses to major market changes, delivering $76.5 million of materials and conversion productivity. Gross materials productivity in 2014 represented 5.4% of total materials cost but, as expected, the impact of commodity inflation reduced net materials productivity to 5.1%. Conversion productivity in 2014 represented 6.4%, a new annual record for WABCO.
Our Markets and Our Customers
Our sales are affected by changes in truck and bus (T&B) production. Europe is our largest geographic market and sales to T&B OEMs represent our largest customer group. The table below shows the relationship between our sales to European T&B OEMs, which account for approximately 59% of our global sales to T&B OEMs, and European T&B production for the last five years. Sales data is shown at a constant Euro to U.S. Dollar exchange rate for year to year comparability and to make comparisons
25
to unit production meaningful. Over the past five years, our sales have outperformed the rate of European T&B production by an average of 4% per year.
| Year to Year Change | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Sales to European T&B OEMs (at constant FX rates) | 60 | % | 34 | % | (10 | )% | 13 | % | (7 | )% | |||||
| European T&B Production | 52 | % | 31 | % | (9 | )% | 5 | % | (9 | )% | |||||
In general, our sales track directionally with truck and bus builds. However, individual year to year sales changes are also influenced by other factors such as timing of orders and deliveries to T&B OEM customers, application content, new product introduction, price and introduction of new customer platforms. The level of truck build activity is influenced by general economic conditions, including interest rate levels and inflation.
Our aftermarket sales account for approximately 26% of total sales and are affected by a variety of factors: content on specific vehicles and breadth of our product range, number of commercial trucks in active operation, truck age, type of vehicles built, miles driven, demand for transported goods and overall economic activity. On average, our aftermarket sales (on a constant exchange to the U.S. Dollar rate) have grown by 11% annually for the last five years as shown in the table below.
Year to Year Change | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | Average Change | ||||||
| Aftermarket Sales (at constant FX rates) | 22 | % | 8 | % | 5 | % | 7 | % | 13 | % | 11 | % |
Distribution of WABCO's Sales by Major End-Markets, Product Types and Geography
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
| Major End-Markets | ||||||||
| OE Manufacturers: | ||||||||
| Truck & Bus products | 60 | % | 62 | % | 62 | % | ||
| Trailer products | 10 | % | 9 | % | 9 | % | ||
| Car products | 4 | % | 4 | % | 4 | % | ||
| Aftermarket | 26 | % | 25 | % | 25 | % | ||
| 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||
| Geography: | ||||||||
| Europe | 59 | % | 61 | % | 60 | % | ||
| North America | 13 | % | 11 | % | 11 | % | ||
| South America | 6 | % | 7 | % | 6 | % | ||
| Asia | 19 | % | 18 | % | 20 | % | ||
| Other | 3 | % | 3 | % | 3 | % | ||
| 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||
Our largest customer is Daimler, which accounts for approximately 11% of our sales. Volvo accounted for 10% of our sales in 2014. Other key customers include Ashok Leyland, BMW, China National Heavy Truck Corporation (CNHTC), Cummins, Fiat (Iveco), Hino, Hyundai, Krone, MAN Nutzfahrzeuge AG (MAN), Meritor, Meritor WABCO (a joint venture), Paccar (DAF Trucks N.V. (DAF), Kenworth, Leyland and Peterbilt), First Automobile Works, Otto Sauer Achsenfabrik (SAF), Scania, Schmitz Cargobull AG, TATA Motors and ZF Friedrichshafen AG (ZF). For the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, our top 10 customers accounted for approximately 54% and 52%, respectively, of our sales.
26
Results of Operations
Approximately 87% of our sales are outside the United States and therefore, changes in exchange rates can have a significant impact on the reported results of our operations, which are presented in U.S. Dollars. Year-over-year changes in sales and expenses for 2014 compared with 2013 and 2013 compared with 2012 are presented both with and without the effects of foreign currency translation. Changes in sales and expenses excluding foreign exchange effects are calculated using current year sales and expenses translated at prior year exchange rates. Presenting changes in sales and expenses excluding the effects of foreign currency translation is not in conformity with U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (U.S. GAAP), but we analyze this data because it is useful to us in understanding the operating performance of our business. We believe this data is also useful to shareholders for the same reason. The changes in sales and expenses excluding the effects of foreign exchange translation are not meant to be a substitute for measurements prepared in conformity with U.S. GAAP, nor to be considered in isolation. Management believes that presenting these non-U.S. GAAP financial measures is useful to shareholders because it enhances their understanding of how management assesses the operating performance of the Company's business.
Results of Operations for 2014 Compared with 2013
The following table is a summary of sales, cost of sales , gross profit, operating expenses and other selected results of operations for the periods indicated.
Year ended December 31, | Excluding Foreign Exchange Translation ** | ||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | % change reported | 2014 adjusted amount | % change adjusted | ||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 2,851.0 | $ | 2,720.5 | 4.8 | % | $ | 2,884.5 | 6.0 | % | |||||||
| Cost of sales | 1,979.3 | 1,911.4 | 3.6 | % | 2,006.1 | 5.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Gross profit | 871.7 | 809.1 | 7.7 | % | 878.4 | 8.6 | % | ||||||||||
| Operating expenses | 540.7 | 477.2 | 13.3 | % | 544.0 | 14.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Equity in net income of unconsolidated joint ventures | 23.8 | 17.7 | 34.5 | % | 23.8 | 34.5 | % | ||||||||||
| Other non-operating income, net | 1.8 | 286.4 | * | 2.5 | * | ||||||||||||
| Interest income, net | 0.2 | 4.9 | (95.9 | )% | 0.3 | (93.9 | )% | ||||||||||
| Income tax expense/(benefit) | 55.6 | (21.0 | ) | * | 61.1 | * | |||||||||||
* Percentage change not considered meaningful
** Amounts translated using 2013 average exchange rates for comparability
Sales
Our sales for 2014 were $2,851.0 million, an increase of 4.8% (6.0% excluding foreign currency translation effects) from $2,720.5 million in 2013. The increase, excluding foreign currency translation effects, includes 2.4% coming from the recently acquired Transics business and was also driven by increased WABCO content per vehicle partially offset by a 2% decline in the global production of new trucks and buses greater than six tons. Total sales in Europe, our largest market, showed a slight increase of 0.1% (0.4% excluding foreign currency translation effects) for the full year 2014, driven mainly by the recently acquired Transics business and increased WABCO content per vehicle, offset by lower levels of truck, bus and trailer production. Total sales increased 29.3% in North America due to increased WABCO content per vehicle and increased production of new trucks and buses. Total sales in Asia increased 13.3% (16.0% excluding foreign currency translation effects) driven primarily by increases in all key markets: India of 19.8% (26.3% excluding foreign currency translation effects), Japan of 4.8% (13.3% excluding foreign currency translation effects), China of 15.2% (15.5% excluding foreign currency translation effects) and South Korea of 9.8% (6.3% excluding foreign currency translation effects). Total sales in South America decreased 12.0% (4.5% excluding foreign currency translation effects) driven by an estimated 23% decline in the production of new trucks and buses in Brazil, partially offset by increased WABCO content per vehicle. WABCO's global aftermarket sales, included in the geographic numbers provided above, increased 11.0% (12.7% excluding foreign currency translation effects). This increase, which includes the benefits from the recently acquired Transics business, demonstrates the continued success of the Company's aftermarket strategies initiated several years ago.
27
Cost of Sales and Gross Profit
Our cost of sales for the year 2014 was $1,979.3 million, an increase of $67.9 million ($94.7 million excluding foreign currency translation effects) from $1,911.4 million in 2013. Within cost of sales, our largest expense is material costs, which mainly represents the purchase of components and parts. Our continued focus on productivity generated 5.4% of material savings before the impact of commodity inflation, which had a negative impact of 0.3%, bringing net materials productivity to 5.1% for the year. This productivity achievement resulted in $49.3 million of material cost savings. Our second largest expense within the cost of sales is for labor and other costs associated with converting our purchased components and parts into finished goods. Labor and other cost escalations increased conversion costs by approximately $13.7 million, while our productivity efforts generated $27.2 million of savings, or 6.4% of the conversion costs. Warranty expenses excluding volume effects were higher compared to prior year by $2.3 million in part due to a cost recovery from a supplier in 2013. Streamlining expenses increased costs by $4.1 million. Absorption of overhead costs and other indirect costs were unfavorable by $2.0 million versus the prior year primarily as a result of higher inflation on overhead costs. Volume and mix increased cost of sales by $144.7 million, and together with the increase in sales contributed $53.6 million to an increase in gross profit. Sales price reductions had a negative impact of $35.3 million on gross profit, or 1.2% of sales. Foreign currency translational effects decreased cost of sales by $26.8 million and combined with the translational effects on sales they negatively impacted gross profit in the amount of $6.7 million. Foreign currency transactional impacts also increased cost of sales by $4.4 million and negatively affected gross profit in the amount of $3.4 million. The net result of all these changes was an increase in gross profit of $62.6 million (or $69.3 million excluding foreign currency translation effects).
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses, which include selling and administrative expenses, product engineering expenses and other operating expenses, increased by $63.5 million ($66.8 million excluding foreign currency translation effects). The increase, excluding foreign currency translation effects, comprised increases in research and development investments of $9.3 million, Transics operating costs of $34.8 million, amortization of acquired intangibles in Transics of $8.9 million, labor inflation and other people-related costs of $16.7 million, and increases in streamlining and separation costs of $7.3 million. These increases were partially offset by reductions in incentive compensation of $8.2 million and other operating expenses of $2.0 million.
Equity in Net Income of Unconsolidated Joint Ventures
Equity in net income of unconsolidated joint ventures increased $6.1 million to $23.8 million in 2014 as compared to $17.7 million in 2013. This increase was primarily driven by higher income from our North American joint venture, partially offset by a decrease in income from our South African joint venture.
Other Non-Operating Income, net
Non-operating income amounted to $1.8 million in 2014 versus $286.4 million for 2013. The decrease relates primarily to the reimbursement of $279.5 million received in 2013 on a fine previously assessed in 2010 by the European Commission (the EC Fine) as further discussed in Note 15 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Interest Income, net
Net interest income decreased by $4.7 million to $0.2 million in 2014 compared to $4.9 million in 2013. This was mainly a result of interest income received in 2013 on the EC fine reimbursement amounting to approximately $5.4 million.
Income Taxes
The income tax provision for 2014 was $55.6 million on $356.8 million of pre-tax income before adjusting for noncontrolling interest, compared with an income tax benefit of $21.0 million on pre-tax income of $640.9 million before adjusting for noncontrolling interest in 2013. The income tax provision for 2014 includes the net result of taxes on the mix of earnings in multiple tax jurisdictions, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions, and certain foreign tax planning.
As previously disclosed in the Company's 2013 Form 10K, we continue to expect our effective tax rate to increase in subsequent periods following the 2013 release of a valuation allowance of $178.4 million. Our net income and effective tax rate will be negatively affected in periods following this release. However, the valuation allowance release will not affect the amount of cash paid for income taxes. Management has also determined that it is more likely than not that it will not realize $9.0 million of its deferred tax assets in other foreign jurisdictions since evidence such as historical operating profits resulted in a cumulative
28
loss position during the most recent three-year period ending on December 31, 2014 and lack of projected earnings provided sufficient negative evidence to record a valuation allowance against such deferred tax assets.
Furthermore, in 2014, the Company recorded a tax charge of $3.6 million primarily related to various income tax filings and changes in the Company's recorded tax liabilities with respect to undistributed foreign earnings due to the Company’s decision to repatriate on a non-recurring basis $15.1 million of accumulated foreign earnings of its Korean affiliate. The Company continues to assert permanent reinvestment outside the U.S. with respect to the remainder of its foreign earnings and at this time, does not have any plans or needs to repatriate additional earnings from its foreign subsidiaries except for Brazil.
Backlog
Backlog, which represents valid sales orders that have not yet been filled as of the end of the reporting period, was $1.3 billion at the end of 2014, an increase of 1.7% (15.5% excluding foreign currency translation effects) from the end of 2013. Backlog is not necessarily predictive of future business as it relates only to some of our products, and customers may still change orders and future delivery dates.
Results of Operations for 2013 Compared with 2012
The following table is a summary of sales, cost of sales , gross profit, operating expenses and other selected results of operations for the periods indicated.
Year ended December 31, | Excluding Foreign Exchange Translation ** | ||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2013 | 2012 | % change reported | 2013 adjusted amount | % change adjusted | ||||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 2,720.5 | $ | 2,477.4 | 9.8 | % | $ | 2,708.8 | 9.3 | % | |||||||
| Cost of sales | 1,911.4 | 1,737.2 | 10.0 | % | 1,910.8 | 10.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Gross profit | 809.1 | 740.2 | 9.3 | % | 798.0 | 7.8 | % | ||||||||||
| Operating expenses | 477.2 | 415.7 | 14.8 | % | 469.4 | 12.9 | % | ||||||||||
| Equity in net income of unconsolidated joint ventures | 17.7 | 18.1 | (2.2 | )% | 17.7 | (2.2 | )% | ||||||||||
| Other non-operating income/(expense), net | 286.4 | (5.0 | ) | * | 272.5 | * | |||||||||||
| Interest income/(expense), net | 4.9 | (1.5 | ) | * | 4.7 | * | |||||||||||
| Income tax (benefit)/expense | (21.0 | ) | 23.6 | * | (13.0 | ) | * | ||||||||||
* Percentage change not considered meaningful
** Amounts translated using 2012 average exchange rates for comparability
Sales
Our sales for 2013 were $2,720.5 million, an increase of 9.8% (9.3% excluding foreign currency translation effects) from $2,477.4 million in 2012. The increase, excluding foreign currency translation effects, was predominately driven by increased WABCO content per vehicle and a 3% improvement in the global production of new trucks and buses greater than six tons. Total sales in Europe, our largest market, increased approximately 11.3% (8.0% excluding foreign currency translation effects) for the full year 2013, driven mainly by increased WABCO content per vehicle and higher levels of truck, bus and trailer production. Total sales increased 7.8% in North America due to increased WABCO content per vehicle despite reduced commercial vehicle production. Total sales in Asia decreased 1.6% (increased 4.6% excluding foreign currency translation effects). The sales drop in Asia was driven primarily by reductions in total sales in India of 27.8% (21.4% excluding foreign currency translation effects) and in Japan of 13.4% (increase of 5.6% excluding foreign currency translation effects), where the markets experienced significant declines. These decreases were partially offset by an increase in sales in China of 26.5% (23.2% excluding foreign currency translation effects) and South Korea of 6.3% (3.1% excluding foreign currency translation effects). Total sales in South America increased 30.4% (43.2% excluding foreign currency translation effects) driven by increased WABCO content per vehicle in addition to the recovery in production of new trucks and buses in Brazil. The global aftermarket sales performance, included in the geographic numbers provided above, was an increase of 7.4% (7.1% excluding foreign currency translation effects), as we continued to benefit from the Company's aftermarket strategies initiated several years ago.
29
Cost of Sales and Gross Profit
Our cost of sales for the year 2013 was $1,911.4 million, an increase of $174.2 million ($173.6 million excluding foreign currency translation effects) from $1,737.2 million in 2012. Within cost of sales, our largest expense is material costs, which mainly represents the purchase of components and parts. Our continued focus on productivity generated 5.3% of material savings before the impact of commodity inflation, which had a negative impact of 0.3%, bringing net materials productivity to 5.0% for the year. This productivity achievement resulted in $58.5 million of material cost savings. Our second largest expense within the cost of sales is for labor and other costs associated with converting our purchased components and parts into finished goods. Labor and other cost escalations increased conversion costs by approximately $14.7 million, while our productivity efforts generated $25.7 million of savings, or 6.3% of the conversion costs. Better claims experience decreased warranty expenses by $9.1 million compared to last year. Streamlining expenses increased costs by $1.6 million. Absorption of overhead costs and other indirect costs were favorable by $45.0 million versus the prior year. Volume and mix increased cost of sales by $251.6 million, and together with the increase in sales contributed $10.9 million to an increase in gross profit. Sales price reductions had a negative impact of $34.2 million on gross profit, or 1.2% of sales. Foreign currency translational effects increased cost of sales by $0.6 million and combined with the translational effects on sales they positively impacted gross profit in the amount of $11.1 million. Foreign currency transactional impacts increased cost of sales by $44.0 million and negatively affected gross profit in the amount of $40.9 million. The net result of all these changes was an increase in gross profit of $68.9 million (or $57.8 million excluding foreign currency translation effects).
Operating Expenses
Operating expenses, which include selling and administrative expenses, product engineering expenses and other operating expenses, increased by $61.5 million ($53.7 million excluding foreign currency translation effects). The increase, excluding foreign currency translation effects, comprised increases in labor and other cost inflation of $11.2 million, incentive compensation of $13.6 million, research and development investments of $13.0 million, pension costs of $4.3 million due to a 2012 reduction in our UK pension obligation and streamlining and separation costs of $6.0 million. In addition, we also saw an increase in investments in global expansion of $5.6 million.
Equity in Net Income of Unconsolidated Joint Ventures
Equity in net income of unconsolidated joint ventures decreased $0.4 million to $17.7 million in 2013 as compared to $18.1 million in 2012. This decrease was primarily driven by lower income from our South African joint venture, which decreased by $0.9 million.
Other Non-Operating Income/(Expense), net
In 2013 we received a reimbursement of $279.5 million on the EC Fine as further discussed in Note 15 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. Excluding this gain in 2013, non-operating income amounted to $6.9 million versus an expense of $5.0 million for 2012, primarily a result of the release of an accrual for tax indemnification liabilities due to the settlement of a foreign tax audit.
Interest Expense, net
Net interest income increased by $6.4 million to $4.9 million in 2013 compared to an expense of $1.5 million in 2012. This was mainly a result of interest income received on the EC Fine reimbursement amounting to €4.0 million or approximately $5.4 million.
Income Taxes
The income tax benefit for 2013 was $21.0 million on $640.9 million of pre-tax income before adjusting for noncontrolling interest. The income tax benefit for 2013 includes taxes on earnings in profitable jurisdictions, income offset by fully valued net operating losses, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions, and a tax provision on unremitted foreign earnings of $300.0 million in a Belgian affiliate for which amount the Company does not assert permanent reinvestment outside the United States. This assertion is resulting from the Company recognizing earnings in the fourth quarter of 2013 from the receipt of an exceptional refund including interest from the European Commission related to the Company’s appeal of the EC Fine as further discussed in Note 16 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. Additionally, the Company recorded a tax benefit for a release at the end of the year of a valuation allowance related to management’s determination that it is more likely than not that the Company will realize its deferred tax asset in a foreign jurisdiction. Management has also determined that it is more likely than not that it
30
will not realize $10.1 million of its deferred tax assets in other foreign jurisdictions and has recorded a valuation allowance against such deferred tax assets.
The income tax provision for 2012 included taxes on earnings in profitable jurisdictions, income offset by fully valued net operating losses, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions, and certain foreign tax planning. Additionally, the income tax provision is offset by the release of tax accruals for uncertain tax positions due to certain government filings submitted in January 2012 of approximately $24.8 million. Additionally, a tax benefit of $4.1 million related to the Company's filing of its 2011 U.S. Federal Income Tax Return in September 2012 was recorded during the third quarter of 2012.
Backlog
Backlog, which represents valid sales orders that have not yet been filled as of the end of the reporting period, was $1.3 billion at the end of 2013, an increase of 19.6% (18.1% excluding foreign currency translation effects) from the end of 2012. Backlog is not necessarily predictive of future business as it relates only to some of our products, and customers may still change orders and future delivery dates.
31
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We employ several means to manage our liquidity, and we are not dependent upon any one source of funding. Our sources of financing include cash flows from operations, cash and cash equivalents, our revolving credit facilities, the use of operating leases and our former Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, which expired on September 26, 2014 as discussed in Note 11 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
We believe the combination of expected cash flows and the revolving credit facilities being committed until 2018 and 2019 will provide us with adequate liquidity to support the Company's operations. The Company also has the ability to access a wide range of additional external financing instruments.
Specifically for 2015, we expect a decrease in our capital spending primarily due to the anticipated completion of construction of a new plant in Poland. Outside of our capital expenditures and acquisition-related cash flows, our overall cash flow is expected to be in line with the Company's 2014 cash flow profile, and there are no known trends or uncertainties that are reasonably expected to have a material effect on the separate sources and uses of cash.
As of December 31, 2014, $382.0 million of the $411.7 million of cash and cash equivalents on the consolidated balance sheets was held by foreign subsidiaries. The Company considers the earnings of substantially all of its foreign subsidiaries to be permanently reinvested outside the United States and as such no additional U.S. tax cost has been provided. The Company has provided for tax at the U.S. tax rate for its Brazilian affiliate's current year earnings in 2014. During 2014, the Company also decided to repatriate on a non-recurring basis $15.1 million of accumulated foreign earnings of its Korean affiliate. The Company continues to assert permanent reinvestment outside the U.S. with respect to the remainder of its foreign earnings and at this time, does not have any plans or needs to repatriate additional earnings from its foreign subsidiaries except for Brazil. In addition, a tax provision was also provided on unremitted foreign earnings of $300.0 million in a Belgian affiliate for which the Company does not assert permanent reinvestment outside the United States. This assertion is resulting from the Company recognizing earnings in the fourth quarter of 2013 from the receipt of an exceptional refund including interest from the European Commission related to the Company’s appeal of the EC Fine as further discussed in Note 15 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. The Company estimates the amount of its unremitted foreign earnings permanently reinvested outside the United States to be approximately $800 million as of December 31, 2014; however, it is not practicable to estimate the tax liability that would arise if the earnings that are considered permanently reinvested were remitted to the United States.
Cash Flows for 2014 Compared with 2013
Net cash provided by operating activities was $314.4 million for 2014. This is in comparison with net cash provided by operating activities of $665.8 million for 2013, of which $283.7 million related to the EC Fine reimbursement as previously discussed.
We recorded net income including noncontrolling interests of $301.2 million for 2014 compared with net income including noncontrolling interests of $661.9 million for 2013. Net income for 2014 included noncash elements such as depreciation and amortization of $101.6 million. Our working capital increased by $144.7 million, primarily due to the expiration of our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program whereupon we repurchased $111.7 million of accounts receivable and, to a lesser extent, a decrease in our accounts payable.
The change in other accrued liabilities and taxes was an increase of $16.0 million for 2014 compared to $38.5 million for 2013. The major drivers of this increase were accruals for payroll, streamlining and tax-related items, partially offset by lower accruals for our incentive compensation. Other current and long-term assets for 2014 decreased $27.5 million compared to an increase of $28.8 million for 2013. This decrease was primarily due to the release of $38.2 million of restricted cash upon the expiration of our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, partially offset by increases in notes receivable from our Chinese operations. The change in other long-term liabilities for 2014 was a decrease of $0.8 million compared to $9.8 million for 2013, mainly driven by a release of accruals for tax indemnification liabilities related to a foreign tax audit, partially offset by accruals for our long-term incentive compensation and other tax-related items.
The net cash used in investing activities amounted to $211.1 million in 2014 compared to $176.7 million in 2013. This included $125.9 million of net cash paid during 2014 related to the acquisition of Tavares as discussed in Note 21 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. The net cash usage for 2014 also includes capital expenditures of $45.0 million of investments in tooling, $78.8 million on plant and equipment and $12.1 million in software to support the Company's long-term growth strategies, including the construction of a new plant in Poland. This compared with $47.0 million of investments in tooling, $61.1 million on plant and equipment and $13.4 million in computer software in 2013. We also received proceeds from the sale of $50.7 million of short-term investments during 2014.
32
The net cash used by financing activities during 2014 amounted to $121.4 million compared to net cash used by financing activities of $193.4 million during 2013.
Our total third-party debt increased $226.4 million for 2014 compared to $10.3 million for 2013. This increase was primarily driven by additional borrowings of $259.0 million under our two revolving credit facilities, a large portion of which funds our share repurchase program, partially offset by the repayment of short-term debt from the Company's access to cash collections on sold receivables under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program.
We received $15.0 million of stock option proceeds during 2014 compared with $49.7 million in 2013. The number of stock options exercised in 2014 and 2013 were 396,643 and 1,602,068, respectively.
We paid $5.7 million during 2014 for the acquisition of the remaining ownership interest in Transics as discussed in Note 21 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. We also paid $4.6 million during 2013 for the acquisition of the remaining ownership interest in our Chinese joint venture, Shandong Weiming Automotive Products (SWAP).
During 2014, we repurchased shares for a total amount of $351.5 million. As of December 31, 2014, the Company had repurchased shares for a total amount of $971.8 million under the authorized repurchase programs as discussed in Note 6 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements, and had the authority to make an additional $500.0 million of share repurchases.
Cash Flows for 2013 Compared with 2012
Net cash provided by operating activities was $665.8 million for 2013 compared with net cash provided by operating activities of $358.3 million for 2012.
We recorded net income including noncontrolling interests of $661.9 million for 2013 compared with net income including noncontrolling interests of $312.5 million for 2012. Net income for 2013 included $279.5 million related to the EC Fine reimbursement, as well as noncash elements such as depreciation and amortization of $85.2 million. Our working capital increased by $27.2 million, primarily driven by higher accounts receivable and to a lesser extent inventory. The decrease of receivables in the fourth quarter, mainly due to significant collections at year-end, was not sufficient to offset the increase in the first three quarters, a result of an increase in business activity. This also resulted in a higher level of payables which only partially offset the above.
The change in other accrued liabilities and taxes was an increase of $38.5 million for 2013 compared to a decrease of $37.9 million for 2012. The major drivers of this change were increases in accruals for payroll and incentive compensation, as well as accruals for uninvoiced goods and services. The change in other current and long-term assets for 2013 was an increase of $28.8 million compared to a decrease of $23.0 million for 2012. The main drivers of this change were increases in tax related items, notes receivables from our Chinese operations and restricted cash related to the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. The change in other long-term liabilities for 2013 was a decrease of $9.8 million compared to an increase of $2.1 million for 2012, mainly a result of the payment and release of the remaining accrual for tax indemnification liabilities due to the settlement of a foreign tax audit.
The net cash used in investing activities amounted to $176.7 million in 2013 compared to net cash used in investing activities of $105.6 million in 2012. The net cash usage for 2013 includes capital expenditures of $47.0 million of investments in tooling, $61.1 million on plant and equipment and $13.4 million in computer software, which supported our market growth and new programs during the year. This compared with $43.2 million of investments in tooling, $48.5 million on plant and equipment and $8.8 million in computer software in 2012, as well as $5.1 million for acquisitions. We also purchased $55.2 million of short-term investments in 2013.
The net cash used by financing activities during 2013 amounted to $193.4 million compared to net cash used by financing activities of $182.6 million during 2012.
As of December 31, 2013, our total third party debt was $87.1 million, consisting primarily of $47.0 million of long-term debt borrowed under our $400 million five-year revolving credit facility. During 2013, we had net borrowings of approximately $1.1 million on our revolving credit facility. Also, subsidiaries in other countries had borrowings from banks totaling $40.1 million classified as short-term debt. The increase in net borrowings of short-term debt from the prior year of $9.2 million is driven by a $36.4 million loan under a short-term borrowing with Société Générale Bank Nederland N.V. related to our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program.
33
We received $49.7 million of stock option proceeds during 2013 compared with $28.6 million in 2012. The number of stock options exercised in 2013 and 2012 were 1,602,068 and 1,312,288, respectively.
We paid $4.6 million during 2013 for the acquisition of the remaining shares in our Chinese joint venture, SWAP.
During 2013, we also paid $243.2 million for share repurchases.
Credit Facility
In July 2011, the Company entered into a $400 million multi-currency senior unsecured revolving credit facility (the 2011 Facility) that currently expires on September 1, 2018. In December 2014, we entered into another multi-currency senior unsecured revolving credit facility (the 2014 Facility) for $100 million which expires on December 17, 2019.
Under the revolving credit facilities, we may borrow, on a revolving basis, loans in an aggregate principal amount at any one time outstanding not in excess of $500 million. Up to $50 million under the 2011 Facility may be used for issuing letters of credit, of which $49.1 million was unused as of December 31, 2014, and up to $50 million is available in the form of swing line loans, all $50 million of which was available for use as of December 31, 2014.
Interest on loans under the revolving credit facilities are calculated at a rate per annum equal to an applicable margin - which can vary from 0.80% to 1.55% for the 2011 Facility and 0.45% to 1.00% for the 2014 Facility based on the Company's leverage ratio - plus LIBOR for loans denominated in U.S. Dollars, EURIBOR for loans denominated in Euros, HIBOR for loans denominated in Hong Kong Dollars and SIBOR for loans denominated in Singapore Dollars, plus mandatory costs, if any. The revolving credit facilities contain customary terms and provisions, including representations, covenants and conditions. The proceeds of the borrowings under the revolving credit facilities are largely used to fund our share repurchase program, but may also be used to finance acquisitions, refinance existing indebtedness and meet general financing requirements.
As of December 31, 2014, we had total borrowings of $306.0 million on the revolving credit facilities compared to $47.0 million as of December 31, 2013, and we were in compliance with all the covenants. See Note 14 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further details.
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program & Financing Receivables
As discussed above, our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program expired on September 26, 2014 and was not renewed.
During the year ended December 31, 2014 and prior to the expiration of the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, we sold all of our eligible receivables into the program. The receivables were removed from the balance sheet in accordance with the guidance under ASC 860, Transfers and Servicing. The total amount of receivables sold under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program for the year ended December 31, 2014 was €545.7 million ($739.9 million at weighted average exchange rates for the 2014 period through program expiration) compared to €790.8 million ($1,050.6 million at weighted average 2013 exchange rates) for the year ended December 31, 2013 and €731.7 million ($941.1 million at weighted average 2012 exchange rates) for the year ended December 31, 2012.
In connection with the expiration of the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, we entered into a separate agreement with Société Générale to repurchase accounts receivable amounting to €88.1 million ($111.7 million based on exchange rates at time of repurchase). A subordinated deposit of $38.2 million was also released to the Company, resulting in a net decrease in cash and cash equivalents of $73.5 million.
We also have financing receivables which include sales to reputable state owned and public enterprises in China that are settled through notes receivable which are registered and endorsed to the Company. These notes receivable are fully secured and generally have contractual maturities of six months or less. The notes are also available to be discounted with banking institutions in China or transferred to suppliers to settle liabilities. We discounted or transferred notes amounting to $63.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to $42.8 million in 2013 and $33.3 million in 2012. As of December 31, 2014, we had $52.8 million of guaranteed notes receivable included in "other current assets" on the consolidated balance sheets. See also Note 11 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion.
Factoring Program
On April 15, 2009, we entered into a €35 million factoring program, which has a term of five years, in respect to accounts receivable from one of our customers. We did not utilize this program, which expired on April 14, 2014.
34
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
We also use foreign exchange contracts to offset the earnings impact relating to the variability in exchange rates on certain monetary assets and liabilities denominated in non-functional currencies. These contracts have not been designated as relationship hedges. As of December 31, 2014, forward contracts for an aggregate notional amount of €77.8 million ($94.5 million at December 31, 2014 exchange rates) were outstanding with an average duration of one month. These foreign exchange contracts have offset the revaluation of assets and liabilities and resulted in a net non-operating loss of $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The majority of these exchange contracts were entered into on December 30, 2014 and had a fair value of zero as of December 31, 2014.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Please see the disclosure above in “Accounts Receivable Securitization Program & Financing Receivables”.
Contractual Obligations
Following is a summary of contractual obligations as of December 31, 2014.
Aggregate Contractual Obligations
As of December 31, 2014
(in millions)
Payments due by period (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Contractual Obligation | Total | 2015 | 2016 and 2017 | 2018 and 2019 | Beyond 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| Debt obligations (2) | $ | 315.2 | $ | 8.1 | $ | 1.1 | $ | 306.0 | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations (3) | 73.2 | 18.9 | 24.7 | 17.4 | 12.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Tax indemnifications (4) | 4.5 | 3.9 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Purchase obligations (5) | 210.0 | 210.0 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Unfunded pension and post-retirement benefits (6) | 276.0 | 28.5 | 56.3 | 55.3 | 135.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Tax liabilities (7) | 48.5 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 927.4 | $ | 269.4 | $ | 82.1 | $ | 378.7 | $ | 148.1 | ||||||||||
| (1) | The amounts and timing of such obligations, as shown in the table may vary substantially from amounts that will actually be paid in future years. For example, the actual amount to be paid under debt obligations under our revolving credit facilities will depend on the amount of debt outstanding under the agreements in each year. |
| (2) | Amounts shown for debt obligations include an immaterial amount of associated interest based on the December 31, 2014 rates applicable to each type of debt. |
| (3) | Amounts include future rental commitments under all non-cancelable operating leases in effect at December 31, 2014. |
| (4) | Amounts are probable and estimable costs that the Company is responsible for under a Tax Sharing Agreement between Trane and WABCO. Of the total $4.5 million liability, $3.9 million is classified as short-term and the Company is expecting to either pay or reverse this amount within the next 12 months. The remaining $0.6 million is classified as long-term and the Company is currently unable to estimate the timing of the potential amounts to be paid. |
| (5) | In the normal course of business we expect to purchase approximately $1.8 billion in 2015 of materials and services, and estimate that on average no more than approximately $210 million is outstanding at any one time in the form of legally binding commitments. We spent approximately $1.7 billion, $1.6 billion and $1.5 billion on materials and services in 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. |
| (6) | Amounts represent undiscounted projected benefit payments to WABCO's unfunded plans over the next ten years, as well as expected contributions to funded pension plans for 2015. The expected benefit payments are estimated based on the same assumptions used to measure our accumulated benefit obligation at the end of 2014 and include benefits attributable to estimated future employee service of current employees. |
35
| (7) | Amounts represent the Company's unrecognized tax provisions potentially owed to tax authorities as described in Note 16 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. The total liability of $48.5 million is classified as long-term and includes interest of $7.0 million. The Company is currently unable to estimate the timing of potential amounts to be paid. |
Capital Expenditures
We believe our capital spending in recent years has been sufficient to maintain efficient production capacity, to implement important product and process redesigns and to expand capacity to meet increased demand. Productivity projects have freed up capacity in our manufacturing facilities and are expected to continue to do so. We expect to continue investing to expand and modernize our existing facilities and invest in our facilities to create capacity for new product development. Specifically for 2015, however, we expect a decrease in our capital spending primarily due to the anticipated completion of our new plant in Poland as previously discussed.
Pending Adoptions of Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which is a new comprehensive revenue recognition standard on the financial reporting requirements for revenue from contracts entered into with customers. ASU 2014-09 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016. We are currently assessing the potential impact of the adoption of this guidance on the consolidated financial statements.
We do not expect the pending adoption of other recently issued accounting standards to have an impact on the consolidated financial statements.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based upon our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with those accounting principles requires us to make judgments and estimates that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Those judgments and estimates have a significant effect on the consolidated financial statements because they result primarily from the need to make estimates about the effects of matters that are inherently uncertain. Actual results could differ from those estimates. We frequently re-evaluate our judgments and estimates that are based upon historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances.
We believe that of our significant accounting policies, the ones that may involve a higher degree of uncertainty, judgment and complexity pertain to revenue recognition for multiple-element arrangements, allowance for doubtful accounts, inventory reserves, goodwill, stock-based compensation, post-retirement benefits, warranties, business combinations, income taxes, and contingencies. See Note 2 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional discussion of our accounting policies.
Revenue Recognition - The Company recognizes revenue when title and risk of loss have transferred, persuasive evidence of arrangement exists, the sales price is fixed or determinable and collectibility is reasonably assured. Certain of the Company's product offerings contain multiple deliverables including hardware with embedded firmware, back office hosting services, unspecified software upgrades and enhancements related to the software embedded in these products through service contracts, which are considered separate units of accounting. For products under these arrangements, the software and non-software components function together to deliver the tangible product’s essential functionality.
The Company allocates revenue to each element in these multiple-element arrangements based upon the relative selling prices of each deliverable. In applying the relative selling price method, the Company determines the selling price for each deliverable using vendor specific objective evidence (VSOE), if it exists, or third-party evidence (TPE) of selling price. If neither VSOE nor TPE of selling price exist for a deliverable, the best estimate of selling price (BESP) is then used for that element. BESP represents the price at which the Company would transact a sale if the element were sold on a standalone basis. The Company determines BESP for an element by considering multiple factors including, but not limited to, the Company's go-to-market strategy, pricing practices, internal costs, gross margin, market conditions and geographies. Revenue allocated to each element is then recognized when the other revenue recognition criteria are met for that element.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts - The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers. In determining the allowance for doubtful accounts, on a monthly basis, the Company analyzes the aging of accounts receivable, historical bad debts, customer creditworthiness, availability of credit insurance and current economic trends. Though management considers the valuation of the allowances proper and adequate, changes in the economy and/or deterioration of the financial condition of
36
the Company's customers could affect the reserve balances required. Historically, this valuation has proved to be a reasonable estimate of the Company's experience with doubtful debts.
Inventory Reserves - On a quarterly basis, the Company tests its inventory for slow moving and obsolete stock by considering both the historical and expected sales and the Company will record a provision, if needed. Historically, this policy has given a close approximation of the Company's experience with slow moving and obsolete inventory. From time to time unusual buying patterns or shifts in demand may cause large movements in the reserve.
Goodwill - The Company has a significant amount of goodwill on its balance sheet that is not amortized, but subject to impairment tests each fiscal year on October 1 or more often when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of goodwill may not be recoverable. The Company's impairment tests utilize the two-step approach. The first step of the goodwill impairment test compares fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying amount, including goodwill. If the fair value of a reporting unit exceeds its carrying amount, goodwill of the reporting unit is not considered impaired and thus the second step of the impairment test is unnecessary. If the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value, the second step of the goodwill impairment test shall be performed to measure the amount of impairment loss, if any. The second step of the goodwill impairment test compares the implied fair value of reporting unit goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. If the carrying amount of reporting unit goodwill exceeds the implied fair value of that goodwill, an impairment loss shall be recognized in an amount equal to that excess.
The recoverability of goodwill is measured based on one reporting unit for the total Company. WABCO's plants, engineering, technical support, distribution centers and other support functions are shared among various product families and serve all distribution channels with many customers. Based on the organizational structure, as well as the nature of financial information available and reviewed by the Company's chief operating decision maker to assess performance and make decisions about resource allocations, the Company has concluded that its total WABCO operations represent one reportable unit and that WABCO's performance and future net cash flow perspectives are best understood and assessed as such. In order to approximate the fair value of the reporting unit for purposes of testing recoverability, we use the total market capitalization of the Company, a market approach, which is then compared to the total book value of the Company. In the event the Company's fair value has fallen below book value, the Company will compare the estimated fair value of goodwill to its book value. If the book value of goodwill exceeds the estimated fair value of goodwill, the Company will recognize the difference as an impairment loss in operating income. There has been no impairment of goodwill during 2014, and the Company's goodwill was not at risk for failing the first step of its impairment test.
Stock-Based Compensation - The Company measures and recognizes in its consolidated statements of operations the expense associated with all share-based payment awards made to employees and directors including stock options, restricted stock units, performance stock units and restricted stock grants based on estimated fair values.
Commencing in 2013, the Company replaced stock options with performance stock units (PSUs), the vesting of which would occur at levels ranging from none to 200% of the number of granted PSUs depending upon the achievement of three-year cumulative earnings per share goals approved by the Compensation, Nominating and Governance Committee of the Board of Directors. See also Note 7 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion.
For stock options granted prior to 2013, the Company utilized the Black-Scholes option valuation model to measure the amount of compensation expense to be recognized for each option award. There are several assumptions that must be made when using the Black-Scholes model such as the expected term of each option, the expected volatility of the stock price during the expected term of the option, the expected dividends to be paid and the risk free interest rate expected during the option term. The risk free interest rate is based on the yield of U.S. Treasury securities that correspond to the expected holding period of the options. WABCO reviewed the historic volatility of its common stock over a four year period, the common stock of its peer group over a five year period, and the implied volatility for at the money options to purchase shares of its common stock. The five-year historical volatility period was selected since that period corresponds with the expected holding period. Based on this data, the Company chose to use a weighted average of the implied volatility of WABCO, the most recent four year historical volatility of WABCO and the median most recent one year historical volatility of WABCO's peer group prior to the spin-off date. The expected holding period was calculated by reviewing the historical exercise pattern of all holders that were granted options and the exercise behavior of officers versus non-officers. The results of the analysis support one expected holding period for all groups of employees. The expected forfeiture rate was determined based on the historical stock option forfeiture data of the Company. The dividend yield was based on an expected future dividend rate for the period at the time of grant. Of these assumptions, the expected term of the option and expected volatility of WABCO's common stock were the most difficult to estimate since they were based on the exercise behavior of employees and expected performance of WABCO's stock. An increase in the volatility of WABCO's stock would increase the amount of compensation expense on new awards. An increase in the holding period of options would also increase in compensation expense. Dividend yields and risk-free interest rates were less difficult to estimate. An increase
37
in the dividend yield would cause a decrease in expense and an increase in the risk-free interest rate would increase compensation expense.
Post-Retirement Benefits - The Company has significant pension and post-retirement benefit costs and liabilities that are developed from actuarial valuations. Inherent in these valuations are key assumptions including discount rates, expected return on plan assets, mortality rates, merit and promotion increases and the health care cost trend rate. The Company is required to consider current market conditions, including changes in interest rates and health care costs, in making its assumptions. Changes in the related pension and post-retirement benefit costs or liabilities may occur in the future due to changes in the assumptions. The assumptions as to the expected long-term rates of return on plan assets are based upon the composition of plan assets, historical long-term rates of return on similar assets and current and expected market conditions. The discount rate used for U.S. plans reflects the market rate for high-quality fixed-income investments on the Company's annual measurement date (December 31) and is subject to change each year. The discount rate was determined by matching, on an approximate basis, the coupons and maturities for a portfolio of corporate bonds (rated AA or better by Moody's Investor Services) to the expected plan benefit payments defined by the projected benefit obligation. The discount rates used for plans outside the United States are based on a combination of relevant indices regarding corporate and government securities, the duration of the liability and appropriate judgment. The impact of Health Care Reform legislation in the United States is immaterial to the Company. See the disclosures about pension and post-retirement obligations, the composition of plan assets, assumptions and other matters in Note 13 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Warranties - Products sold by WABCO are covered by a basic limited warranty with terms and conditions that vary depending upon the product and country in which it was sold. The limited warranty covers the equipment, parts and labor (in certain cases) necessary to satisfy the warranty obligation generally for a period of two years. Estimated product warranty expenses are accrued in cost of goods sold at the time the related sale is recognized. Estimates of warranty expenses are based primarily on warranty claims experience and specific customer contracts. Warranty expenses include accruals for basic warranties for product sold, as well as accruals for product recalls, service campaigns and other related events when they are known and estimable.
To the extent we experience changes in warranty claim activity or costs associated with servicing those claims, our warranty accrual is adjusted accordingly. Warranty accrual estimates are updated based upon the most current warranty claims information available. The Company's warranty costs as a percentage of net sales totaled 0.9% in 2014, 0.8% in 2013 and 1.1% in 2012. We do not expect this percentage to change materially in the near future. See Note 15 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a three-year summary of warranty costs.
Business Combinations - We allocate the fair value of purchase consideration to the assets acquired, liabilities assumed, and non-controlling interests in the acquiree generally based on their fair values at the acquisition date. The excess of the fair value of purchase consideration over the fair value of these assets acquired, liabilities assumed and non-controlling interests in the acquiree is recorded as goodwill. When determining the fair values of assets acquired, liabilities assumed, and non-controlling interests in the acquiree, management makes significant estimates and assumptions, especially with respect to intangible assets. Critical estimates in valuing intangible assets include, but are not limited to, expected future cash flows, which includes consideration of future growth rates and margins, attrition rates, future changes in technology and brand awareness, loyalty and position, and discount rates. Fair value estimates are based on the assumptions management believes a market participant would use in pricing the asset or liability. Amounts recorded in a business combination may change during the measurement period, which is a period not to exceed one year from the date of acquisition, as additional information about conditions existing at the acquisition date becomes available.
Income Taxes - We record a valuation allowance to reduce our deferred tax assets to the amount that we believe is more likely than not to be realized. While we have considered future taxable income and ongoing prudent and feasible tax planning strategies in assessing the need for the valuation allowance, in the event we were to determine that we would not be able to realize all or part of our net deferred tax assets in the future, an adjustment to decrease the net deferred tax assets would be charged to income in the period such determination was made. Likewise, should we determine that we would be able to realize our deferred tax assets in the future in excess of our net recorded amount, an adjustment to increase the net deferred tax assets would increase income in the period such determination was made. We calculate a valuation allowance in accordance with the provisions of ASC 740, Income Taxes, which requires an assessment of both positive and negative evidence regarding the realizability of these deferred tax assets, when measuring the need for a valuation allowance. We record a valuation allowance to reduce our deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized. In determining net deferred tax assets and valuation allowances, management is required to make judgments and estimates related to projections of profitability, the timing and extent of the utilization of net operating loss carry-forwards, applicable tax rates and tax planning strategies. We review the valuation allowance quarterly and maintain it until sufficient positive evidence exists to support a reversal.
38
Management has determined that it is more likely than not that it will not realize $9.0 million of its deferred tax assets in other foreign jurisdictions since evidence such as historical operating profits resulted in a cumulative loss position during the most recent three-year period ending on December 31, 2014 and lack of projected earnings provided sufficient negative evidence to record a valuation allowance against such deferred tax assets related to carryforwards for net operating losses and notional interest deductions.
As previously disclosed in the Company's 2013 Form 10K, we expect our effective tax rate to increase in subsequent periods following the 2013 release of a valuation allowance of $178.4 million. Our net income and effective tax rate will be negatively affected in periods following this release. However, the valuation allowance release will not affect the amount of cash paid for income taxes.
We also estimate our effective income tax rate quarterly, considering all known factors and the estimated effects of future events or tax planning strategies that can cause that rate to vary from the statutory rate. Estimating the outcome of future events is inherently uncertain and final resolution of those events can cause the effective tax rate to vary significantly. In addition, changes in U.S. or foreign tax laws or rulings may have a significant impact on our effective tax rate.
A tax position is a position in a previously filed tax return or a position expected to be taken in a future tax filing that is reflected in measuring current or deferred income tax assets and liabilities. Tax positions shall be recognized only when it is more likely than not (likelihood of greater than 50%), based on technical merits, that the position will be sustained. Tax positions that meet the more likely than not threshold should be measured using a probability weighted approach as the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized upon settlement. Whether the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold is met for a tax position, is a matter of judgment based on the individual facts and circumstances of that position evaluated in light of all available evidence. Tax positions are not permitted to be recognized, derecognized, or remeasured due to changes subsequent to the balance sheet date, but prior to the issuance of the financial statements. Rather, these changes are recorded in the period the change occurs with appropriate disclosure of such subsequent events, if significant. The Company accrues interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
In situations where the Company has tax deductions that would otherwise increase a deferred tax asset related to net operating losses, a tax deduction which is treated as an uncertain tax position is recorded as a reduction of the deferred tax asset on the balance sheet. In this regard, although the uncertain tax position is not reflected as an unrecognized tax benefit in the balance sheet as a recorded liability, it is disclosed in the tabular rollforward for unrecognized tax benefits in Note 16 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Contingencies - We are subject to proceedings, lawsuits and other claims related to products and other matters. We are required to assess the likelihood of any adverse judgments or outcomes to these matters as well as potential ranges of probable and reasonably possible losses. A determination of the amount of liability to be recorded, if any, for these contingencies is made after careful analysis of each individual issue. It is reasonably possible that the Company could incur losses in excess of the amounts accrued. Although this amount cannot be estimated, we believe that any additional losses would not have a material adverse impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In conjunction with the Tax Sharing Agreement, as further discussed in Note 17 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements, WABCO is responsible for certain tax and indemnification liabilities. These liabilities include indemnification liabilities to Trane of $4.5 million.
Cyclical and Seasonal Nature of Business
The industry in which we operate is cyclical. Approximately 70% of our sales are for newly manufactured trucks, buses and trailers, the production of which follows long investment cycles and are impacted by macro economic factors and legislation. Global commercial vehicle production grew consistently from 2001 through the fourth quarter of 2008, when the global commercial vehicle markets started to experience a significant decline that was unprecedented in its breadth, depth and speed which continued through 2009. All markets experienced favorable growth in 2010 while our most developed markets again experienced favorable growth in 2011. 2012 saw most markets decline with only our markets in North America and Japan experiencing growth. In 2013 we saw mixed performances across the various markets with some geographies up double digit while others were down double digit. This mixed trend continued through 2014 with a slight decline in the overall market. Our markets are difficult to predict; however, in 2015 we are again anticipating mixed markets where most are expected to be flat to down versus 2014 with the exception of the North America market which is expected to grow. The continued adoption of new technologies by truck and bus manufacturers helps our business outperform the rate of truck and bus production over the longer term. The commercial vehicle industry is not subject to material seasonal impacts.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to financial risk resulting from volatility in foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates and commodity prices. All of those risks are closely monitored.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rates
We conduct operations through controlled subsidiaries in most of the major countries of Western Europe, Brazil, Poland, China, South Korea, India and Japan as well as the United States. In addition, we conduct business in many countries through cross border sales and purchases, affiliated companies and partnerships in which we own 50% or less of the stock or partnership interest. As our financial statements are presented in U.S. Dollars, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can have a significant impact on the reported results of our operations, especially for the countries and currencies referred to above. Applying a Value-At-Risk (VAR) methodology to our foreign currency exchange rate exposure, across the translational and transactional exposures for the year 2014, the potential maximum loss in earnings is estimated to be $36 million which is based on a one-year horizon and a 95% confidence level. The VAR model is a risk analysis tool and does not purport to represent actual losses in fair value that could be incurred by us, nor does it consider the potential effect of favorable changes in market factors or our ability to pass on foreign exchange effects to commercial counterparties. See also Note 19 of Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
As of December 31, 2014, we had an aggregate $306.0 million outstanding under our revolving credit facilities. Interest on loans under the revolving credit facilities is calculated at a rate per annum equal to an applicable margin which can vary from 0.80% to 1.55% for the 2011 Facility and 0.45% to 1.00% for the 2014 Facility, based on the Company's leverage ratio - plus LIBOR for loans denominated in U.S. Dollars, EURIBOR for loans denominated in Euros, HIBOR for loans denominated in Hong Kong Dollars and SIBOR for loans denominated in Singapore Dollars, plus mandatory costs, if any. Assuming no additional borrowings or payments on the debt, a 1% change in the interest rate for our variable rate debt would have the effect of increasing or decreasing interest expense by approximately $3 million.
Commodity Exposures
We are also exposed to fluctuations in commodity prices through the purchase of base metals and steel, mainly through contractual agreements with component suppliers.
Applying a VAR methodology to our 2014 commodity exposure, the potential maximum loss in earnings is estimated to be $21 million which is based on a one-year horizon and a 95% confidence level. The VAR model is a risk analysis tool and does not purport to represent actual losses in fair value that could be incurred by us, nor does it consider the potential effect of favorable changes in market factors or our ability to pass on effects to commercial counterparties.
39
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of WABCO Holdings Inc. and Subsidiaries
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of WABCO Holdings Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, cash flows and shareholders' equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014. Our audit also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15(a). These financial statements and schedule are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of WABCO Holdings Inc. and subsidiaries at December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the consolidated results of their operations and their cash flows for each the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also, in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly in all material respects the information set forth therein.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), WABCO Holdings Inc. and subsidiaries' internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in the Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 Framework) and our report dated February 19, 2015 expressed an adverse opinion thereon.
Ernst & Young Bedrijfsrevisoren BCVBA/Reviseurs d'Entreprises SCCRL
Represented by:
/s/ Piet Hemschoote, Partner
Brussels, Belgium
February 19, 2015
40
WABCO HOLDINGS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions, except share and per share data) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Sales | $ | 2,851.0 | $ | 2,720.5 | $ | 2,477.4 | |||||
| Cost of sales | 1,979.3 | 1,911.4 | 1,737.2 | ||||||||
| Gross Profit | 871.7 | 809.1 | 740.2 | ||||||||
| Costs and expenses: | |||||||||||
| Selling and administrative expenses | 386.8 | 352.8 | 308.2 | ||||||||
| Product engineering expenses | 145.0 | 119.4 | 104.3 | ||||||||
| Other operating expense, net | 8.9 | 5.0 | 3.2 | ||||||||
| Operating income | 331.0 | 331.9 | 324.5 | ||||||||
| European Commission fine reimbursement | — | 279.5 | — | ||||||||
| Equity income of unconsolidated joint ventures, net | 23.8 | 17.7 | 18.1 | ||||||||
| Other non-operating income/(expense), net | 1.8 | 6.9 | (5.0 | ) | |||||||
| Interest income/(expense), net | 0.2 | 4.9 | (1.5 | ) | |||||||
| Income before income taxes | 356.8 | 640.9 | 336.1 | ||||||||
| Income tax expense/(benefit) | 55.6 | (21.0 | ) | 23.6 | |||||||
| Net income including noncontrolling interests | 301.2 | 661.9 | 312.5 | ||||||||
| Less: net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 9.7 | 8.7 | 10.5 | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to Company | $ | 291.5 | $ | 653.2 | $ | 302.0 | |||||
| Net income attributable to Company per common share | |||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 4.87 | $ | 10.46 | $ | 4.73 | |||||
| Diluted | $ | 4.81 | $ | 10.31 | $ | 4.62 | |||||
| Cash dividends per share of common stock | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding | |||||||||||
| Basic | 59,907,763 | 62,474,493 | 63,906,992 | ||||||||
| Diluted | 60,546,454 | 63,382,564 | 65,323,389 | ||||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
41
WABCO HOLDINGS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Net income including noncontrolling interests | $ | 301.2 | $ | 661.9 | $ | 312.5 | |||||
| Foreign currency translation effects | (144.9 | ) | (4.1 | ) | (0.8 | ) | |||||
| Unrealized losses on benefit plans, net of tax | (135.9 | ) | (1.8 | ) | (56.6 | ) | |||||
| Unrealized gains on investment | 0.2 | — | — | ||||||||
| Comprehensive income | $ | 20.6 | $ | 656.0 | $ | 255.1 | |||||
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 8.4 | 3.6 | 9.1 | ||||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to Company | $ | 12.2 | $ | 652.4 | $ | 246.0 | |||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
42
WABCO HOLDINGS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | ||||||
| (Amounts in millions, except share data) | |||||||
| ASSETS | |||||||
| Current assets: | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 411.7 | $ | 472.8 | |||
| Short-term investments | — | 55.2 | |||||
| Accounts receivable, less allowance for doubtful accounts of $4.1 in 2014 and $5.0 in 2013 | 445.6 | 346.2 | |||||
| Inventories | 189.6 | 207.2 | |||||
| Taxes receivable on income | 4.1 | — | |||||
| Future income tax benefits | 20.8 | 10.4 | |||||
| Restricted cash | — | 34.6 | |||||
| Guaranteed notes receivable | 52.8 | 51.4 | |||||
| Other current assets | 57.9 | 56.8 | |||||
| Total current assets | 1,182.5 | 1,234.6 | |||||
| Property, plant and equipment, less accumulated depreciation | 424.9 | 422.5 | |||||
| Goodwill | 421.0 | 381.2 | |||||
| Long-term future income tax benefits | 268.7 | 248.9 | |||||
| Investments in unconsolidated joint ventures | 19.6 | 19.9 | |||||
| Intangible assets, net | 78.4 | 44.3 | |||||
| Other assets | 37.6 | 41.4 | |||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 2,432.7 | $ | 2,392.8 | |||
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | |||||||
| Current liabilities: | |||||||
| Loans payable to banks | $ | 8.1 | $ | 40.1 | |||
| Accounts payable | 121.2 | 149.3 | |||||
| Accrued payroll | 103.9 | 118.8 | |||||
| Current portion of warranties | 25.8 | 29.8 | |||||
| Taxes payable | 0.1 | 3.8 | |||||
| Accrued expenses | 58.5 | 58.7 | |||||
| Other accrued liabilities | 100.1 | 84.9 | |||||
| Total current liabilities | 417.7 | 485.4 | |||||
| Long-term debt | 307.1 | 47.0 | |||||
| Post-retirement benefits | 595.0 | 438.6 | |||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | 129.2 | 120.1 | |||||
| Long-term income tax liabilities | 48.5 | 45.3 | |||||
| Other liabilities | 46.2 | 59.0 | |||||
| Total liabilities | 1,543.7 | 1,195.4 | |||||
| Shareholders’ equity: | |||||||
| Preferred stock, 4,000,000 shares authorized; none issued and outstanding | — | — | |||||
| Common stock, $.01 par value, 400,000,000 shares authorized; shares issued: 77,961,040 in 2014; 77,471,174 in 2013; and shares outstanding: 58,425,873 in 2014; 61,359,025 in 2013 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |||||
| Capital surplus | 828.3 | 800.2 | |||||
| Treasury stock, at cost: 19,535,167 shares in 2014; 16,112,149 shares in 2013 | (1,248.1 | ) | (896.6 | ) | |||
| Retained earnings | 1,663.3 | 1,371.8 | |||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income: | |||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | (158.0 | ) | (14.4 | ) | |||
| Unrealized losses on benefit plans, net of tax | (244.9 | ) | (109.0 | ) | |||
| Unrealized gains on investments | 0.2 | — | |||||
| Total shareholders’ equity | 841.6 | 1,152.8 | |||||
| Noncontrolling interests | 47.4 | 44.6 | |||||
| Total equity | 889.0 | 1,197.4 | |||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | $ | 2,432.7 | $ | 2,392.8 | |||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
43
WABCO HOLDINGS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASHFLOWS
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Operating activities: | |||||||||||
| Net income including noncontrolling interests | $ | 301.2 | $ | 661.9 | $ | 312.5 | |||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided/(used) by operating activities: | |||||||||||
| Depreciation | 81.7 | 74.6 | 65.6 | ||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles | 19.9 | 10.6 | 11.3 | ||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated joint ventures, net of dividends received | (0.2 | ) | 0.6 | (3.0 | ) | ||||||
| Non-cash stock compensation | 15.5 | 13.6 | 14.3 | ||||||||
| Deferred income tax benefit | 4.5 | (64.6 | ) | (2.9 | ) | ||||||
| Loss/(gain) on sale or disposal of property, plant and equipment | 1.4 | (0.2 | ) | 0.3 | |||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net | (123.9 | ) | (44.3 | ) | (6.2 | ) | |||||
| Inventories | (2.5 | ) | (16.0 | ) | 5.7 | ||||||
| Accounts payable | (18.3 | ) | 33.1 | (23.0 | ) | ||||||
| Other accrued liabilities and taxes | 16.0 | 38.5 | (37.9 | ) | |||||||
| Post-retirement benefits | (7.6 | ) | (3.4 | ) | (3.5 | ) | |||||
| Other current and long-term assets | 27.5 | (28.8 | ) | 23.0 | |||||||
| Other long-term liabilities | (0.8 | ) | (9.8 | ) | 2.1 | ||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 314.4 | 665.8 | 358.3 | ||||||||
| Investing activities: | |||||||||||
| Purchases of property, plant and equipment | (123.8 | ) | (108.1 | ) | (91.7 | ) | |||||
| Investments in capitalized software | (12.1 | ) | (13.4 | ) | (8.8 | ) | |||||
| Sales/(purchases) of short-term investments | 50.7 | (55.2 | ) | — | |||||||
| Acquisitions, net | (125.9 | ) | — | (5.1 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (211.1 | ) | (176.7 | ) | (105.6 | ) | |||||
| Financing activities: | |||||||||||
| Net borrowings/(repayments) of short-term revolving credit facilities | — | 1.1 | (11.6 | ) | |||||||
| Borrowings of long-term revolving credit facilities | 259.0 | — | — | ||||||||
| Net (repayments)/borrowings of short-term debt | (32.6 | ) | 9.2 | 4.2 | |||||||
| Purchases of treasury stock | (351.5 | ) | (243.2 | ) | (198.3 | ) | |||||
| Purchase of subsidiary shares from noncontrolling interest | (5.7 | ) | (4.6 | ) | — | ||||||
| Dividends to noncontrolling interest holders | (5.6 | ) | (5.6 | ) | (5.5 | ) | |||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 15.0 | 49.7 | 28.6 | ||||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities | (121.4 | ) | (193.4 | ) | (182.6 | ) | |||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (43.0 | ) | 2.1 | 2.5 | |||||||
| Net (decrease)/increase in cash and cash equivalents | (61.1 | ) | 297.8 | 72.6 | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 472.8 | 175.0 | 102.4 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 411.7 | $ | 472.8 | $ | 175.0 | |||||
| Cash paid during the period for: | |||||||||||
| Interest | $ | 2.0 | $ | 0.3 | 1.1 | ||||||
| Income taxes | $ | 48.4 | $ | 45.2 | 30.3 | ||||||
| Non cash items for the period: | |||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchase accrual | $ | — | $ | — | 2.5 | ||||||
| Unrealized gains on investments | $ | 0.2 | $ | — | — | ||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
44
WABCO HOLDINGS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
| Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Common Stock | Capital Surplus | Treasury Stock | Retained Earnings | Foreign Currency Translation | Unrealized Losses on Benefit Plans | Unrealized Gains on Investment | Non Controlling Interests | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2011 | $ | 0.7 | $ | 693.4 | $ | (456.8 | ) | $ | 416.6 | $ | (16.1 | ) | $ | (50.6 | ) | $ | — | $ | 48.6 | ||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 302.0 | — | — | — | 10.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | 0.7 | — | — | (1.4 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | — | (56.6 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchased | — | — | (199.0 | ) | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised | — | 28.5 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | — | 13.6 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (5.4 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2012 | $ | 0.7 | $ | 735.5 | $ | (655.8 | ) | $ | 718.6 | $ | (15.4 | ) | $ | (107.2 | ) | $ | — | $ | 52.3 | ||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 653.2 | — | — | — | 8.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | 1.0 | — | — | (5.1 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | — | (1.8 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchased | — | — | (240.8 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised | 0.1 | 49.7 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | — | 13.9 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in noncontrolling interest | — | 1.1 | — | — | — | — | — | (5.7 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | — | — | — | (5.6 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2013 | $ | 0.8 | $ | 800.2 | $ | (896.6 | ) | $ | 1,371.8 | $ | (14.4 | ) | $ | (109.0 | ) | $ | — | $ | 44.6 | ||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 291.5 | — | — | — | 9.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | (143.6 | ) | — | — | (1.3 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | — | (135.9 | ) | 0.2 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock purchased | — | — | (351.5 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options exercised | — | 14.9 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | — | 13.2 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in noncontrolling interest | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (5.6 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2014 | $ | 0.8 | $ | 828.3 | $ | (1,248.1 | ) | $ | 1,663.3 | $ | (158.0 | ) | $ | (244.9 | ) | $ | 0.2 | $ | 47.4 | ||||||||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
45
WABCO HOLDINGS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2014
| NOTE 1. | Description of Company |
WABCO Holdings Inc. and its subsidiaries (collectively WABCO or the Company) develops, manufactures and sells advanced braking, stability, suspension and transmission automation and air management control systems primarily for commercial vehicles. WABCO’s largest selling products are pneumatic ABS, EBS, ESC, automated manual transmission systems, air disc brakes and a large variety of conventional mechanical products such as actuators, air compressors and air control valves for heavy- and medium-sized trucks, buses and trailers. We supply advanced electronic suspension controls and vacuum pumps to the passenger car and SUV markets in Europe, North America and Asia. In addition, we supply commercial vehicle aftermarket distributors and service partners as well as fleet operators with replacement parts, fleet management solutions, diagnostic tools, training and other expert services. WABCO sells its products to four groups of customers around the world: truck and bus OEMs, trailer OEMs, commercial vehicle aftermarket distributors of replacement parts and services, and automotive OEMs. We also provide remanufacturing services globally.
WABCO was founded in the United States in 1869 as Westinghouse Air Brake Company. The Company was purchased by American Standard Companies Inc. (American Standard) in 1968 and operated as the Vehicle Control Systems business division within American Standard until the Company was spun off from American Standard on July 31, 2007. Subsequent to the spin-off, American Standard changed its name to Trane Inc., which is herein referred to as “Trane.” On June 5, 2008, Trane was acquired in a merger with Ingersoll-Rand Company Limited (Ingersoll Rand) and exists today as a wholly owned subsidiary of Ingersoll Rand.
The spin-off by Trane of its Vehicle Control Systems business became effective on July 31, 2007, through a distribution of 100% of the common stock of WABCO to Trane's shareholders (the Distribution). The Distribution was effected through a separation and distribution agreement pursuant to which Trane distributed all of the shares of WABCO common stock as a dividend on Trane common stock, in the amount of one share of WABCO common stock for every three shares of outstanding Trane common stock to each shareholder on the record date. Trane received a private letter ruling from the Internal Revenue Service and an opinion from tax counsel indicating that the spin-off was tax free to the shareholders of Trane and WABCO.
Based on the organizational structure, as well as the nature of financial information available and reviewed by the Company’s chief operating decision maker to assess performance and make decisions about resource allocations, the Company has concluded that its total WABCO operations represent one reportable segment and that WABCO’s performance and future net cash flow perspectives are best understood and assessed as such. For purposes of cash flow presentation, the Company has presented the cash flow activities for the short-term revolving credit facility and short-term debt on a net presentation basis as these items represent cash flow activities with high turnover and large amounts.
| NOTE 2. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Use of Estimates - The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Management believes the most complex and sensitive judgments, because of their significance to the condensed consolidated financial statements, result primarily from the need to make estimates about the effects of matters that are inherently uncertain. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Some of the most significant estimates included in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements are related to allowance for doubtful accounts, inventory reserves, goodwill, warranties, post-retirement benefits, income taxes and stock-based compensation. Allocation methods are described in the notes to these consolidated financial statements where appropriate.
Principles of Consolidation and Presentation - All majority owned or controlled subsidiaries of WABCO are included in the consolidated financial statements and intercompany transactions are eliminated upon consolidation. WABCO investments in unconsolidated joint ventures are included at cost plus its equity in undistributed earnings in accordance with the equity method of accounting and reflected as investments in unconsolidated joint ventures in the consolidated balance sheets. Certain amounts in the prior years' consolidated financial statements have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
Foreign Currency Translation - Adjustments resulting from translating foreign functional currency assets and liabilities into U.S. Dollars at exchange rates in effect as of the balance sheet date, and income and expense accounts at the average exchange
46
rates in effect during the period, are recorded in a separate component of shareholders' equity as accumulated other comprehensive income. Gains or losses resulting from transactions in other than the functional currency are reflected in the consolidated statements of operations as part of other non-operating income or expense, except for intercompany transactions of a long-term investment nature where the foreign exchange gains or losses from the remeasurement of such intercompany transactions is recorded within accumulated other comprehensive income.
Revenue Recognition - Sales of products are recorded when (i) title and risk of loss have transferred to the customer, (ii) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists with the customer, (iii) the sales price is fixed and determinable, and (iv) the collectability of the sales price is reasonably assured. Amounts billed to customers for shipping and handling costs are included in sales.
Certain of the Company's product offerings contain multiple deliverables including hardware with embedded firmware, back office hosting services, unspecified software upgrades and enhancements related to these products through service contracts, which are considered separate units of accounting. For products under these arrangements, the software and non-software components function together to deliver the tangible product’s essential functionality. The Company allocates revenue to each element in these multiple-element arrangements based upon the relative selling prices of each deliverable.
In evaluating the revenue recognition for the Company's multiple-element arrangements, the Company determined that in certain cases, vendor specific objective evidence (VSOE) of selling price could not be established for some or all deliverables in the arrangement as the Company infrequently sold each element on a standalone basis, did not price products within a narrow range, or had a limited sales history. When VSOE cannot be established for an element, the Company attempts to establish the selling price of the element using third-party evidence (TPE) based on competitor prices for similar deliverables sold separately. However, the Company is typically not able to establish TPE as we are unable to reliably determine the standalone selling prices of similar competitor products.
When neither VSOE nor TPE can be established for an element, the Company uses its best estimate of selling price (BESP) in the allocation of arrangement consideration. BESP represents the price at which the Company would transact a sale if the element were sold on a standalone basis. The Company determines BESP for an element by considering multiple factors including, but not limited to, the Company's go-to-market strategy, pricing practices, internal costs, gross margin, market conditions and geographies. Revenue allocated to each element is then recognized when the other revenue recognition criteria are met for that element.
The Company typically records cooperative advertising allowances, rebates and other forms of sales incentives as a reduction of sales at the later of the date of the sale or the date the incentive is offered. For these costs, the Company recorded $43.0 million, $42.4 million and $36.6 million in 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, in the accompanying consolidated statements of income.
In most countries where WABCO operates, sales are subject to VAT taxes. Sales are presented net of VAT in the consolidated statements of income.
Shipping and Handling Costs - Shipping, handling, receiving, inspecting, warehousing, internal transfer, procurement and other costs of distribution are included in cost of sales in the consolidated statements of operations.
Cash and Cash Equivalents - Cash equivalents include all highly liquid investments with maturity of three months or less when purchased. The Company classifies cash and cash equivalents that are restricted from operating use for the next twelve months as restricted cash. Amounts restricted for longer than twelve months are classified as other assets. When restrictions are no longer in place, the amounts are reclassified to cash and cash equivalents.
Investments - Investments may consist of mutual funds or deposit funds holding primarily term deposits, certificates of deposit and short-term bonds. The investments are classified as available-for-sale and are recorded in the consolidated financial statements at market value with changes in market value included in other comprehensive income. The Company classifies its investments as either short-term or long-term based on the nature of the investments, its availability of use in current operations and the Company's holding intention. The fair value of the investments is determined based on readily available pricing sources for identical instruments in less active markets (Level 2). In the event the investments experience an other-than-temporary impairment in value, such impairment is recognized as a loss in the consolidated statements of operations. As of December 31, 2014, the Company had $3.1 million of long-term investments included in "other assets" on the consolidated balance sheets.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts - The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations on its customers. In determining the allowance for doubtful accounts, on a monthly basis, WABCO analyzes the aging of accounts receivable, historical bad debts, customer creditworthiness, availability of credit insurance and current economic trends.
47
Transfers of Financial Instruments - The Company accounts for sales and transfers of financial instruments under ASC 860, Transfers and Servicing. ASC 860 states that a transfer of financial assets (either all or a portion of a financial asset) in which the transferor surrenders control over those financial assets shall be accounted for as a sale to the extent that consideration other than beneficial interests in the transferred assets is received in exchange. The Company sold receivables to the bank which qualified as financial assets since they were associated with the sale of products by the subsidiaries of the Company and accepted by the Company's customers in the ordinary course of business. For all receivables sold to the bank, the risks of collection of such receivables resided with the bank. Therefore, upon sale of the receivables to the bank, the appropriate reversal of any applicable accounts receivable allowances was recorded by the Company.
Inventory Reserves - Inventory costs are determined by the use of the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method, and are stated at the lower of such cost or market. The LIFO method is used as it provides a better matching of the costs to the sales. Inventories are categorized as finished products, products-in-process and raw materials. On a quarterly basis, the Company tests its inventory for slow moving and obsolete stock by considering both the historical and expected sales and the Company will record a provision, if needed.
Property, Plant & Equipment - Property, plant and equipment balances, including tooling, are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. WABCO capitalizes costs, including interest during construction of fixed asset additions, improvements, and betterments that add to productive capacity or extend the asset life. WABCO assesses facilities for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of these assets may not be recoverable. Maintenance and repair expenditures are expensed as incurred. Depreciation and amortization are computed on the straight-line method based on the estimated useful life of the asset or asset group, which are 40 years for buildings, 3 to 5 years for tooling and 5 to 15 years for machinery and equipment.
Computer Software Costs - WABCO capitalizes the costs of obtaining or developing internal-use computer software, including directly related payroll costs. The Company amortizes those costs on a straight-line basis over periods of up to seven years, beginning when the software is ready for its intended use. The Company assesses capitalized software costs for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of these assets may not be recoverable.
Goodwill - The Company has a significant amount of goodwill on its balance sheet that is not amortized, but subject to impairment tests each fiscal year on October 1 or more often when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of goodwill may not be recoverable. The Company's impairment tests utilize the two-step approach. The first step of the goodwill impairment test compares fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying amount, including goodwill. If the fair value of a reporting unit exceeds its carrying amount, goodwill of the reporting unit is not considered impaired and thus the second step of the impairment test is unnecessary. If the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value, the second step of the goodwill impairment test shall be performed to measure the amount of impairment loss, if any. The second step of the goodwill impairment test compares the implied fair value of reporting unit goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. If the carrying amount of reporting unit goodwill exceeds the implied fair value of that goodwill, an impairment loss shall be recognized in an amount equal to that excess.
The recoverability of goodwill is measured based on one reporting unit for the total Company. Our plants, engineering, technical support, distribution centers and other support functions are shared among various product families and serve all distribution channels with many customers. Based on the organizational structure, as well as the nature of financial information available and reviewed by the Company's chief operating decision maker to assess performance and make decisions about resource allocations, the Company has concluded that its total WABCO operations represent one reportable segment and that WABCO's performance and future net cash flow perspectives are best understood and assessed as such. In order to approximate the fair value of the reporting unit for purposes of testing recoverability, we use the total market capitalization of the Company, a market approach, which is then compared to the total book value of the Company. In the event the Company's fair value has fallen below book value, the Company will compare the estimated fair value of goodwill to its book value. If the book value of goodwill exceeds the estimated fair value of goodwill, the Company will recognize the difference as an impairment loss in operating income. There has been no impairment of goodwill during 2014.
Other Intangible Assets with Determinable Lives - Other intangible assets with determinable lives consist of customer and distribution relationships, patented and unpatented technology, in-process research and development, and other intangibles and are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives, ranging from 1 to 15 years. WABCO assesses intangible assets for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of these assets may not be recoverable.
Warranties - Products sold by WABCO are covered by a basic limited warranty with terms and conditions that vary depending upon the product and country in which it was sold. The limited warranty covers the equipment, parts and labor (in certain cases) necessary to satisfy the warranty obligation generally for a period of two years. Estimated product warranty expenses are accrued
48
in cost of sales at the time the related sale is recognized. Estimates of warranty expenses are based primarily on warranty claims experience and specific customer contracts. Warranty expenses include accruals for basic warranties for product sold, as well as accruals for product recalls, service campaigns and other related events when they are known and estimable. To the extent WABCO experiences changes in warranty claim activity or costs associated with servicing those claims, its warranty accrual is adjusted accordingly. Warranty accrual estimates are updated based upon the most current warranty claims information available. The Company's warranty costs as a percentage of sales totaled 0.9% in 2014, 0.8% in 2013 and 1.1% in 2012. See Note 15 for a summary of warranties.
Post-retirement Benefits - All post-retirement benefits are accounted for on an accrual basis using actuarial assumptions. Post-retirement pension benefits are provided for substantially all employees of WABCO, both in the United States and abroad through plans specific to each of WABCO's legal entities. In addition, in the United States, certain employees receive post-retirement health care and life insurance benefits. The impact of Health Care Reform legislation in the United States is immaterial to the Company. The costs of the benefits provided through plans of WABCO are included in the accompanying consolidated financial statements and summarized in detail along with other information pertaining to these plans in Note 13. Plans are primarily concentrated in the United Kingdom, Austria, Germany, and Switzerland.
WABCO is also required to measure a defined benefit post-retirement plan's assets and obligations that determine its funded status as of the end of the employer's fiscal year, and recognize changes in the funded status of a defined benefit post-retirement plan in comprehensive income in the year in which the changes occur.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments - Financial instruments consist mainly of cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable and loans payable to banks. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the carrying amounts of these instruments approximated their fair values. Long-term debt also approximated fair value as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities - The Company recognizes all derivative financial instruments in the consolidated financial statements at fair value. Changes in the fair value of derivative financial instruments which qualify for hedge accounting are recorded as an offset to the changes in fair value of the underlying hedged item and are included in the account other non-operating expense, net or other operating expense, net. See Note 20 for further details on derivative instruments.
Research, Development and Engineering Expenses - Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. WABCO expended approximately $145.0 million in 2014, $119.4 million in 2013 and $104.3 million in 2012 for research activities, product development and for product engineering.
Business Combinations - We allocate the fair value of purchase consideration to the assets acquired, liabilities assumed, and non-controlling interests in the acquiree generally based on their fair values at the acquisition date. The excess of the fair value of purchase consideration over the fair value of these assets acquired, liabilities assumed and non-controlling interests in the acquiree is recorded as goodwill. When determining the fair values of assets acquired, liabilities assumed, and non-controlling interests in the acquiree, management makes significant estimates and assumptions, especially with respect to intangible assets. Critical estimates in valuing intangible assets include, but are not limited to, expected future cash flows, which includes consideration of future growth rates and margins, attrition rates, future changes in technology and brand awareness, loyalty and position, and discount rates. Fair value estimates are based on the assumptions management believes a market participant would use in pricing the asset or liability. Amounts recorded in a business combination may change during the measurement period, which is a period not to exceed one year from the date of acquisition, as additional information about conditions existing at the acquisition date becomes available.
Income Taxes - Deferred income taxes are determined on the liability method, and are recognized for all temporary differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements. No provision is made for U.S. income taxes applicable to undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries that are permanently reinvested, except for Brazil's current year earnings and $300.0 million of unremitted foreign earnings related to a Belgian affiliate resulting from the receipt of an exceptional refund including interest from the European Commission related to the Company’s appeal of the EC fine.
A tax position is a position in a previously filed tax return or a position expected to be taken in a future tax filing that is reflected in measuring current or deferred income tax assets and liabilities. Tax positions are recognized only when it is more likely than not (likelihood of greater than 50%) based on technical merits, that the position will be sustained upon examination. Tax positions that meet the more likely than not threshold are measured using a probability weighted approach as the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized upon settlement. Tax positions are not permitted to be recognized, derecognized, or remeasured due to changes subsequent to the balance sheet date, but prior to the issuance of the
49
financial statements. Rather, these changes are recorded in the period the change occurs with appropriate disclosure of such subsequent events, if significant.
We record a valuation allowance to reduce our deferred tax assets to the amount that we believe is more likely than not to be realized. We calculate this valuation allowance in accordance with the provisions of ASC 740, Income Taxes which requires an assessment of both positive and negative evidence regarding the realizability of these deferred tax assets, when measuring the need for a valuation allowance. While we have considered future taxable income and ongoing prudent and feasible tax planning strategies in assessing the need for the valuation allowance, in the event we were to determine that we would not be able to realize all or part of our net deferred tax assets in the future, an adjustment to decrease the net deferred tax assets would be charged to income in the period such determination was made. Likewise, should we determine that we would be able to realize our deferred tax assets in the future in excess of our net recorded amount, an adjustment to increase the net deferred tax assets would increase income in the period such determination was made.
Earnings Per Share - Basic net income per share has been computed using the weighted average number of WABCO common shares outstanding. The average number of outstanding shares of common stock used in computing diluted net income per share includes weighted average incremental shares when the impact is not anti-dilutive. The weighted average incremental shares represent the net amount of shares the Company would issue upon the assumed exercise of in-the-money stock options and vesting of restricted stock units (RSUs) and deferred stock units (DSUs) after assuming that the Company would use the proceeds from the exercises to repurchase stock. The weighted average incremental shares also includes the net amount of shares issuable for performance stock units (PSUs) at the end of the reporting period, if any at all, based on the number of shares issuable if the end of the period were the end of the vesting period.
Anti-dilutive shares, if applicable, are excluded and represent those options, RSUs, PSUs and DSUs whose assumed proceeds were greater than the average price of the Company's common stock.
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||
| Weighted average incremental shares included | 638,691 | 908,071 | 1,416,397 | |||
| Shares excluded due to anti-dilutive effect | — | 3,000 | 480,756 | |||
Comprehensive Income/(Loss) - Comprehensive income/(loss) consists of net income, foreign currency translation adjustments (including that on intercompany transactions of a long-term investment nature), pension liability adjustments, unrecognized gains or losses on post-retirement benefit plans and unrecognized gains or losses on investments, and is presented in the accompanying consolidated statements of shareholders' equity and comprehensive income.
Stock-Based Compensation - WABCO measures and recognizes in its consolidated statements of operations the expense associated with all share-based payment awards made to employees and directors including stock options, RSUs, PSUs, DSUs and restricted stock grants based on estimated fair values.
All options granted prior to 2007 were adjusted upon the Distribution into two separate options, one relating to the Company's common stock and one relating to Trane common stock. This adjustment was made such that immediately following the Distribution (i) the number of shares relating to the Company options were equal to the number of shares of Company common stock that the option holder would have received in the Distribution had Trane options represented outstanding shares of Trane common stock, and (ii) the per share option exercise price of the original Trane stock option was proportionally allocated between the two types of stock options based upon the relative per share trading prices of the Company and Trane immediately following the Distribution. Thus, upon the Distribution, WABCO options are being held by both WABCO and Trane employees and Trane options continued to be held by WABCO employees. Options granted to WABCO employees in 2007 were equitably adjusted upon Distribution so as to relate solely to shares of the Company's common stock. These adjustments preserved the economic value of the awards immediately prior to the Distribution. All Company options issued as part of this adjustment and the Trane options are fully vested at this time. Further, for purposes of vesting and the post-termination exercise periods applicable to such stock options, the Trane Inc. Management Development and Compensation Committee determined that continued employment with the Company will be viewed as continued employment with the issuer of the options.
Outstanding WABCO options held by non-WABCO employees or directors that arose as a result of the Distribution are not reflected in compensation expense recognized by the Company. Consequently, these stock options do not result in any tax benefits to the Company at any time. The WABCO options held by non-employees or directors are considered in the Company's diluted EPS calculation.
50
| NOTE 3. | Recently Issued Accounting Standards |
The adoption of recently issued accounting standards did not have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements, nor do we expect the pending adoption of recently issued accounting standards to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In August 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update 2014-15 (ASU 2014-15) Presentation of Financial Statements - Going Concern, which provide guidance about management's responsibility in evaluating whether there is substantial doubt relating to an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern and to provide related footnote disclosures as applicable. ASU 2014-15 is effective for the interim and annual periods ending after December 15, 2016. The Company does not expect any material impact from adoption of this guidance on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which is a new comprehensive revenue recognition standard on the financial reporting requirements for revenue from contracts entered into with customers. ASU 2014-09 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016. The Company is currently assessing the potential impact of the adoption of this guidance on its consolidated financial statements.
In July 2013, the FASB issued ASU 2013-11, Presentation of an Unrecognized Tax Benefit When a Net Operating Loss Carryforward, a Similar Tax Loss, or a Tax Credit Carryforward Exists, which provides guidance on the presentation of unrecognized tax benefits when a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward exists. ASU 2013-11 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2013. The Company adopted the provisions of ASU 2013-11 as of March 31, 2014, which did not affect the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In February 2013, the FASB issued ASU 2013-02, Reporting of Amounts Reclassified out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income. ASU 2013-02 aims to improve the reporting of reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income. The entities are required to report the effect of significant reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income on the respective line items in net income. We adopted the provisions of ASU 2013-02 as of March 31, 2013.
| NOTE 4. | Other Comprehensive Income |
The table below presents the changes in accumulated other comprehensive loss for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012:
51
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| (Amount in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments: | |||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period | (5.5 | ) | (9.5 | ) | (12.9 | ) | |||||
| Adjustment for the period | (142.6 | ) | 4.0 | 3.4 | |||||||
| Balance at end of period | (148.1 | ) | (5.5 | ) | (9.5 | ) | |||||
Losses on intra-entity transactions (1): | |||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period | (8.9 | ) | (5.9 | ) | (3.2 | ) | |||||
| Adjustment for the period | (1.0 | ) | (3.0 | ) | (2.7 | ) | |||||
| Balance at end of period | (9.9 | ) | (8.9 | ) | (5.9 | ) | |||||
| Unrealized gains on investments: | |||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period | — | — | — | ||||||||
| Adjustment for the period | 0.4 | — | — | ||||||||
| Amounts reclassified to earnings, net | (0.2 | ) | — | — | |||||||
| Balance at end of period | 0.2 | — | — | ||||||||
| Pension and Post-retirement Plans: | |||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period | (109.0 | ) | (107.2 | ) | (50.6 | ) | |||||
| Other comprehensive income before reclassifications | (140.1 | ) | (6.6 | ) | (58.2 | ) | |||||
Amounts reclassified to earnings, net (2) | 4.2 | 4.8 | 1.6 | ||||||||
| Balance at end of period | $ | (244.9 | ) | $ | (109.0 | ) | $ | (107.2 | ) | ||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss at end of period | $ | (402.7 | ) | $ | (123.4 | ) | $ | (122.6 | ) | ||
(1) Relates to intra-entity foreign currency transactions that are of a long term investment nature, when the entities to the transaction are consolidated, combined or accounted for by the equity method in the Company's financial statements.
(2) This accumulated other comprehensive income component, net of taxes of $1.6 million, $2.0 million and $0.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, is included in the computation of net periodic pension cost. See Note 13 for additional details.
| NOTE 5. | Streamlining Expenses |
The Company classifies employee-related streamlining charges as either a one-time benefit arrangement or an ongoing benefit arrangement as appropriate. The Company accounts for employee related terminations as streamlining when the position is not being replaced. From time to time the Company also has streamlining charges that are not related to employees, such as facility exit costs.
Based on market declines occurring in the fourth quarter of 2008, we commenced a streamlining program on October 28, 2008 (the 2008/2009 Program), which began with a consultative process with works councils and employee representatives globally. The 2008/2009 Program reduced our global workforce by approximately 1,800 employees. This level of reduction in workforce brought our capacity in line with market demand, while still allowing us to continue our focus on core strategies, including technology, new products, globalization, and quality and productivity initiatives. We believe the completion of these actions created sufficient flexibility in production and helped us to cope with anticipated demand volatility. The Company does not expect to incur any further charges on the 2008/2009 Program.
Based on the Company’s efforts to maintain our global footprint, the Company may periodically enter into other streamlining programs as deemed necessary (Other Programs).
52
The following is a summary of changes in the Company’s streamlining program liabilities for the year ended December 31, 2014 (amounts in millions). Activity for the period consisted primarily of termination payments and employee-related charges.
| 2008 / 2009 Program | |||
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | $ | 5.9 | |
| Charges during 2014 | — | ||
| Payments during 2014 | (2.6 | ) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2014 | $ | 3.3 | |
| Other Programs | |||
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | $ | 19.0 | |
| Charges during 2014 | 27.0 | ||
| Payments during 2014 | (15.4 | ) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2014 | $ | 30.6 | |
| Total foreign exchange translation effects | $ | (1.9 | ) |
| Total streamlining liability as of December 31, 2014 | $ | 32.0 | |
A balance of $12.8 million is included in other liabilities (non-current) and $19.2 million is included in other accrued liabilities (current) as of December 31, 2014.
The following is a summary of current and cumulative streamlining costs:
Charges for Year Ended December 31, 2014 | Cumulative Charges as of December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2008/2009 Program | Other Programs | 2008/2009 Program | Other Programs | ||||||||||||
| Employee-related charges – cost of sales | $ | — | $ | 9.9 | $ | 45.7 | $ | 26.5 | ||||||||
| Employee-related charges – selling and administrative | — | 16.0 | 45.8 | 36.0 | ||||||||||||
| Total employee related charges | — | 25.9 | 91.5 | 62.5 | ||||||||||||
| Other non-employee related charges | — | 1.1 | — | 2.9 | ||||||||||||
| Total program costs | $ | — | $ | 27.0 | $ | 91.5 | $ | 65.4 | ||||||||
| NOTE 6. | Capital Stock |
The following is a summary of net shares outstanding and shares issued or reacquired during the years ending December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
53
| Number of Shares of Common Stock | ||||||||
| Total Shares | Treasury Shares | Net Shares Outstanding | ||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2011 | 74,242,930 | (9,477,275 | ) | 64,765,655 | ||||
| Shares issued upon exercise of stock options | 1,312,288 | — | 1,312,288 | |||||
| Shares issued upon vesting of RSUs | 194,247 | — | 194,247 | |||||
| Shares issued for DSUs | 5,041 | — | 5,041 | |||||
| Shares issued for stock awards | 800 | — | 800 | |||||
| Shares purchased for treasury | — | (3,530,880 | ) | (3,530,880 | ) | |||
| Balance, December 31, 2012 | 75,755,306 | (13,008,155 | ) | 62,747,151 | ||||
| Shares issued upon exercise of stock options | 1,600,850 | — | 1,600,850 | |||||
| Shares issued upon vesting of RSUs | 106,768 | — | 106,768 | |||||
| Shares issued for DSUs | 7,350 | — | 7,350 | |||||
| Shares issued for stock awards | 900 | — | 900 | |||||
| Shares purchased for treasury | — | (3,103,994 | ) | (3,103,994 | ) | |||
| Balance, December 31, 2013 | 77,471,174 | (16,112,149 | ) | 61,359,025 | ||||
| Shares issued upon exercise of stock options | 394,899 | — | 394,899 | |||||
| Shares issued upon vesting of RSUs | 91,235 | — | 91,235 | |||||
| Shares issued for DSUs | 2,932 | — | 2,932 | |||||
| Shares issued for stock awards | 800 | — | 800 | |||||
| Shares purchased for treasury | — | (3,423,018 | ) | (3,423,018 | ) | |||
| Balance, December 31, 2014 | 77,961,040 | (19,535,167 | ) | 58,425,873 | ||||
The Company accounts for purchases of treasury stock under the cost method with the costs of such share purchases reflected in treasury stock in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. When treasury shares are reissued, they are recorded at the average cost of the treasury shares acquired since the inception of the share buy back programs, net of shares previously reissued and the Company reflects the difference between the average cost paid and the amount received for the reissued shares in capital surplus. As of December 31, 2014, no shares have been reissued.
On May 26, 2011, the Board of Directors approved a program to repurchase shares of the Company's common stock in an amount not to exceed $400 million, which expired on May 31, 2013. On October 26, 2012, the Board of Directors authorized the Company to enter into an additional share repurchase program for $400 million of common shares. A repurchase program for $200 million of common shares was further authorized on October 29, 2013 as a result of the receipt of an exceptional refund including interest from the European Commission related to the Company's appeal of the EC Fine. Both of these authorizations expired on December 31, 2014.
On December 5, 2014, the Board of Directors approved a repurchase program for an additional $500 million of common shares. This authorization expires on December 31, 2016.
As of December 31, 2014, the Company had repurchased a total of $971.8 million of shares under these four repurchase programs, leaving an unexpended balance of $500.0 million available to repurchase shares in the future. Between January 1, 2015 and February 19, 2015, the Company repurchased an additional 311,046 shares for a total of $30.8 million. The Company plans to continue to repurchase shares at prevailing market prices. The timing and amount of share repurchases, if any, will depend on a variety of factors including, among other things, share price, market conditions and applicable regulatory requirements.
| NOTE 7. | Stock-Based Compensation |
The Company's Certificate of Incorporation authorizes the Company to issue up to 400,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share and 4,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.01 per share.
The Company paid no dividends on our common stock in 2014, 2013 and 2012.
The WABCO Holdings Inc. 2007 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the 2007 Omnibus Plan), was formally adopted by our Board of Directors prior to the Distribution. The 2007 Omnibus Plan was replaced in May 2009 by the WABCO Holdings Inc. 2009
54
Omnibus Incentive Plan (the 2009 Omnibus Plan), and further amended in May 2013 (the 2009 Restated Omnibus Plan) as approved by the shareholders at the Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
The 2009 Restated Omnibus plan is intended to promote our long-term financial success and increase shareholder value by providing us with greater flexibility to implement the optimal mix of annual and long-term cash, equity and equity-based incentives. It is also intended to align the interests of our employees with the interests of our shareholders by affording them certain opportunities to acquire an interest in our stock. We believe that these incentives and opportunities will encourage our executives and other key employees to continue in our employment, by providing them with a competitive level of compensation that varies based on our performance.
Under the 2009 Omnibus Plan and 2009 Restated Omnibus Plan, the Company may issue the following types of awards: stock options, stock appreciation rights (sometimes referred to as SARs), RSUs, PSUs, DSUs, restricted shares, annual incentive awards and long-term incentive awards. The maximum number of shares or units that may be issued under the 2009 Restated Omnibus Plan is 5,100,000. No participant shall be granted stock options, stock appreciation rights, or both with respect to more than 750,000 shares during any calendar year. No individual shall be granted restricted shares or restricted stock units, with respect to 200,000 shares or units as the case may be during any calendar year. If an award under either the 2007 Omnibus Plan, the 2009 Omnibus Plan or the 2009 Restated Omnibus Plan expires or becomes unexercisable without having been exercised in full, or, with respect to full-value incentive awards, is forfeited to or repurchased by the Company, the unpurchased shares will become available for future grant or sale under the 2009 Restated Omnibus Plan.
As of December 31, 2014, a total of 1,214,604 stock options, RSUs, PSUs and DSUs were outstanding and there were 3,599,569 shares remaining available for grant under the 2009 Restated Omnibus Plan.
Commencing in 2013, the Company replaced the stock options component of the equity incentive awards with PSUs, the vesting of which would occur at levels ranging from none to 200% of the number of granted PSUs depending upon the achievement of three-year cumulative earnings per share goals approved by the Compensation, Nominating and Governance Committee of the Board of Directors. The Company assesses the expected achievement levels at the end of each reporting period. As of December 31, 2014, the Company believes it is probable that the performance conditions will be met and has accrued for the compensation expense accordingly.
The DSUs are granted to our non-management directors as part of the equity portion of their annual retainer and are fully vested at grant. Each DSU provides the right to the issuance of a share of our common stock, within ten days after the earlier of the director's death or disability, the 13-month anniversary of the grant date or the director's separation from service. Each director may also elect within a month after the grant date to defer the receipt of shares for five or more years. No election can be made to accelerate the issuance of stock from a DSU.
The Company records stock-based compensation based on the estimated fair value of the award at the grant date and is recognized as an expense in the consolidated statements of income over the requisite service period. Total stock-based compensation cost recognized during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 were as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | $ | 15.5 | $ | 13.6 | $ | 14.3 | |||||
The following tables summarize the stock options, RSUs, PSUs, DSUs and stock awards activity for each of the periods presented:
55
| Underlying Shares | Weighted - Average Exercise Price | Weighted - Average Grant Date Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
| WABCO employees | Trane employees | Total | ||||||||||||||
| Options Outstanding December 31, 2011 | 3,090,240 | 852,437 | 3,942,677 | $ | 29.61 | |||||||||||
| Options Granted | 284,691 | — | 284,691 | $ | 58.71 | $ | 23.10 | |||||||||
| Options Exercised | (1,037,538 | ) | (279,205 | ) | (1,316,743 | ) | $ | 21.9 | ||||||||
| Options Forfeited | (37,260 | ) | (5,173 | ) | (42,433 | ) | $ | 40.74 | ||||||||
| Options Outstanding December 31, 2012 | 2,300,133 | 568,059 | 2,868,192 | $ | 35.82 | |||||||||||
| Options Granted | — | — | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
| Options Exercised | (1,359,825 | ) | (242,243 | ) | (1,602,068 | ) | $ | 31.08 | ||||||||
| Options Forfeited | (53,391 | ) | (200 | ) | (53,591 | ) | $ | 52.71 | ||||||||
| Options Outstanding December 31, 2013 | 886,917 | 325,616 | 1,212,533 | $ | 41.2 | |||||||||||
| Options Granted | — | — | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
| Options Exercised | (298,032 | ) | (98,611 | ) | (396,643 | ) | $ | 38.01 | ||||||||
| Options Forfeited | (8,036 | ) | (200 | ) | (8,236 | ) | $ | 58.54 | ||||||||
| Options Outstanding December 31, 2014 | 580,849 | 226,805 | 807,654 | $ | 42.60 | |||||||||||
| Exercisable at December 31, 2014 | 493,912 | 226,805 | 720,717 | $ | 40.63 | |||||||||||
| Underlying Shares | Weighted - Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
| RSUs Outstanding December 31, 2011 | 476,264 | $ | 38.47 | |||
| RSUs Granted | 123,777 | $ | 58.86 | |||
| RSUs Vested | (227,139 | ) | $ | 22.09 | ||
| RSUs Forfeited | (19,937 | ) | $ | 53.63 | ||
| RSUs Outstanding December 31, 2012 | 352,965 | $ | 55.30 | |||
| RSUs Granted | 112,964 | $ | 68.37 | |||
| RSUs Vested | (129,755 | ) | $ | 43.70 | ||
| RSUs Forfeited | (47,707 | ) | $ | 60.86 | ||
| RSUs Outstanding December 31, 2013 | 288,467 | $ | 64.72 | |||
| RSUs Granted | 93,070 | $ | 100.78 | |||
| RSUs Vested | (114,485 | ) | $ | 64.39 | ||
| RSUs Forfeited | (14,584 | ) | $ | 75.08 | ||
| RSUs Outstanding December 31, 2014 | 252,468 | $ | 77.56 | |||
| Underlying Shares | Weighted - Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
| PSUs Outstanding December 31, 2012 | — | $ | — | |||
| PSUs Granted | 94,364 | $ | 68.10 | |||
| PSUs Forfeited | (9,954 | ) | $ | 68.10 | ||
| PSUs Outstanding December 31, 2013 | 84,410 | $ | 68.10 | |||
| PSUs Granted | 65,508 | $ | 103.41 | |||
| PSUs Forfeited | (10,940 | ) | $ | 77.38 | ||
| PSUs Outstanding December 31, 2014 | 138,978 | $ | 84.01 | |||
56
| Underlying Shares | Weighted - Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
| DSUs Outstanding December 31, 2011 | 8,580 | $ | 57.14 | |||
| DSUs Granted | 9,227 | $ | 53.12 | |||
| DSUs Issued | (5,041 | ) | $ | 64.51 | ||
| DSUs Outstanding December 31, 2012 | 12,766 | $ | 51.32 | |||
| DSUs Granted | 5,864 | $ | 75.12 | |||
| DSUs Issued | (7,350 | ) | $ | 52.39 | ||
| DSUs Outstanding December 31, 2013 | 11,280 | $ | 63.00 | |||
| DSUs Granted | 7,156 | $ | 107.70 | |||
| DSUs Issued | (2,932 | ) | $ | 75.12 | ||
| DSUs Outstanding December 31, 2014 | 15,504 | $ | 78.11 | |||
| Shares | Weighted - Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
| Stock Awards granted: | ||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2012 | 800 | $ | 60.02 | |||
| Year ended December 31, 2013 | 900 | $ | 70.53 | |||
| Year ended December 31, 2014 | 800 | $ | 96.37 | |||
There were no stock options granted in 2014 and 2013. In 2012, a total of 284,691 options were granted, all of which are exercisable in equal installments over a period of three years.
The table below shows the vesting schedule of the RSUs granted for each of the periods presented:
| Vesting Schedule | |||||||||||
| Equal installments over 3 years | After 2 years | After 3 years | After 4 years | Total | |||||||
| RSUs granted in 2012 | 103,581 | 6,454 | 12,746 | 996 | 123,777 | ||||||
| RSUs granted in 2013 | 109,254 | — | 3,710 | — | 112,964 | ||||||
| RSUs granted in 2014 | 78,966 | 1,934 | 12,170 | — | 93,070 | ||||||
As discussed above, the PSUs granted in each of the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 vest, if at all, and at levels depending upon, the achievement of certain three-year cumulative earnings per share goals. The DSUs granted in each of the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 vest immediately upon grant.
As of December 31, 2014, the total aggregate intrinsic value of stock option awards outstanding was $48.0 million. The total aggregate intrinsic value of options exercisable and options outstanding, less expected forfeitures, as of the same date was $44.3 million and $48.0 million, respectively. Aggregate intrinsic value is calculated by subtracting the exercise price of the option from the closing price of the Company's common stock on December 31, 2014, multiplied by the number of shares per each option.
The total intrinsic value of options exercised was $24.9 million, $69.9 million and $49.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Total fair value of shares vested was $11.8 million, $9.5 million and $14.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 respectively. The 493,887 of unvested options, RSUs and PSUs as of December 31, 2014 will result in the recognition of $20.4 million of compensation cost to be recognized over a weighted average period of 1.8 years.
The contractual life of all options is 10.0 years. The weighted average remaining contractual life of options outstanding as of December 31, 2014 was 3.9 years, while that of the vested options was 3.6 years. The tax benefit from stock options exercised during the period was $0.4 million and $1.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, and was immaterial for the year ended December 31, 2012.
57
The weighted average grant date fair value was calculated under the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The following table summarizes the significant assumptions used for the grants during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||
| Assumption | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||
| Risk-free interest rate | N/A | N/A | 0.81 | % | ||
| Expected volatility | N/A | N/A | 44.48 | % | ||
| Expected holding period | N/A | N/A | 5 years | |||
| Expected dividend yield | N/A | N/A | — | % | ||
The risk free interest rate is based on the yield of U.S. Treasury securities that correspond to the expected holding period of the options. WABCO reviewed the historic volatility of its common stock over a four-year period, the common stock of its peer group over a five-year period, and the implied volatility for at the money options to purchase shares of its common stock. The five-year historical volatility period was selected since that period corresponds with the expected holding period. Based on this data, the Company chose to use a weighted average of the implied volatility of WABCO, the most recent four-year historical volatility of WABCO and the median most recent three-year historical volatility of WABCO’s peer group prior to the spin-off date. The expected holding period was calculated by reviewing the historical exercise pattern of all holders that were granted options and the exercise behavior of officers versus non-officers. The results of the analysis support one expected holding period for all groups of employees. The dividend yield was based on an expected future dividend amount for the period at the time of grant.
| NOTE 8. | Other Operating and Non-Operating Expense / (Income), Net |
Other expense/(income) was as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Operating expense: | |||||||||||
| Bank charges | $ | 2.2 | $ | 2.0 | $ | 1.5 | |||||
| Miscellaneous taxes | 5.7 | 2.9 | 2.4 | ||||||||
| Other expense/(income), net | 1.0 | 0.1 | (0.7 | ) | |||||||
| $ | 8.9 | $ | 5.0 | $ | 3.2 | ||||||
| Non-operating (income)/expense: | |||||||||||
| Indemnification settlements, net | $ | (4.3 | ) | $ | (8.8 | ) | $ | 3.4 | |||
| Securitization and receivable discount fees | 0.9 | 1.0 | 1.1 | ||||||||
| Foreign exchange (gain)/loss | (0.9 | ) | (2.3 | ) | 0.8 | ||||||
| Other expense/(income), net | 2.5 | 3.2 | (0.3 | ) | |||||||
| $ | (1.8 | ) | $ | (6.9 | ) | $ | 5.0 | ||||
| NOTE 9. | Inventories |
The components of inventories, which are carried on a last-in, first-out (LIFO) basis, are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Finished products | $ | 87.3 | $ | 93.9 | |||||
| Products in process | 7.5 | 7.2 | |||||||
| Raw materials | 94.8 | 106.1 | |||||||
| Inventories at cost | $ | 189.6 | $ | 207.2 | |||||
58
Inventory costs are primarily comprised of direct material and labor costs, as well as material overhead such as inbound freight and custom and excise duties. The current replacement cost approximated the LIFO carrying cost for 2014 and 2013.
Inventory reserves amounted to $13.0 million and $17.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, respectively.
| NOTE 10. | Property, Plant and Equipment |
The components of property, plant and equipment, at cost, are as follow:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | |||||
| Land | $ | 23.4 | $ | 23.8 | |||
| Buildings | 193.2 | 178.7 | |||||
| Machinery and equipment | 615.9 | 659.0 | |||||
| Improvements in progress | 49.1 | 39.2 | |||||
| Gross property, plant and equipment | 881.6 | 900.7 | |||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | 456.7 | 478.2 | |||||
| Net property, plant and equipment | $ | 424.9 | $ | 422.5 | |||
Depreciation expense for owned assets, including those under capital leases, for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $81.7 million, $74.6 million and $65.6 million, respectively.
Net property, plant and equipment includes tooling investments of $75.8 million and $80.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 respectively.
| NOTE 11. | Accounts Receivable Securitization Program & Financing Receivables |
On September 23, 2009, the Company established an accounts receivable securitization program (the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program) with Société Générale Bank Nederland N.V. The maximum funding from receivables that may be sold into the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program and outstanding at any point in time is €80 million, following the voluntary reduction in January 2013 of the program from €100 million to €80 million. The Accounts Receivable Securitization Program expired on September 26, 2014, and was not renewed.
During the year ended December 31, 2014 and prior to the expiration of the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, the Company sold all of its eligible receivables into the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. The receivables were removed from the balance sheet in accordance with the guidance under ASC 860, Transfers and Servicing. The total amount of receivables sold under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program for the year ended December 31, 2014 was €545.7 million ($739.9 million at weighted average exchange rates for the 2014 period through program expiration), compared to €790.8 million ($1,050.6 million at weighted average 2013 exchange rates) for the year ended December 31, 2013 and €731.7 million ($941.1 million at weighted average 2012 exchange rates) for the year ended December 31, 2012. There were no eligible receivables sold and outstanding as of December 31, 2014 compared to €75.0 million ($103.6 million at December 31, 2013 exchange rates) as of December 31, 2013.
The fair value of the receivables sold equaled the carrying cost at time of sale, and no gain or loss was recorded as a result of the sale. The Company estimates the fair value of sold receivables using Level 3 inputs based on historical and anticipated performance of similar receivables, including historical and anticipated credit losses (if any). As part and through the expiration of the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, the Company continued to service the receivables. The Company sold the receivables at face value, but received actual funding net of a subordinated deposit account with Société Générale until collections were received from customers for the receivables sold. The Company was exposed to the credit losses of sold receivables up to the amount of its subordinated deposit account at each settlement date. Credit losses for receivables sold and past due as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 were both immaterial. Servicing fees paid for the program were $0.6 million, $0.8 million and $0.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 respectively.
59
In connection with the expiration of the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, the Company entered into a separate agreement with Société Générale to repurchase accounts receivable amounting to €88.1 million ($111.7 million based on exchange rates at time of repurchase). A subordinated deposit of $38.2 million was also released to the Company, resulting in a net decrease in cash and cash equivalents of $73.5 million.
On April 15, 2009, the Company entered into a €35 million factoring program, which has a term of five years, with respect to accounts receivable from one of our customers. We did not utilize this program which expired on April 14, 2014.
Other receivables available for financing include sales to reputable state owned and public enterprises in China that are settled through bankers acceptance drafts which are registered and endorsed to the Company. These notes receivable are fully guaranteed by banks and generally have contractual maturities of six months or less, but the ultimate recourse remains against the trade debtor. These guaranteed notes are available for discounting with banking institutions in China or transferring to suppliers to settle liabilities. The total amount of notes receivable discounted or transferred for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $63.8 million, $42.8 million and $33.3 million, respectively. Expenses related to discounting these notes amounted to $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, which are included in “other non-operating expense, net.” There were no expenses for the year ended December 31, 2013 and $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2012. The fair value of these guaranteed notes receivable is determined based on Level 2 inputs including credit ratings and other criteria observable in the market. The fair value of these notes equal their carrying amounts of $52.8 million and $51.4 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and are included in “other current assets” on the consolidated balance sheets.
The Company monitors the credit quality of both the drawers of the draft and guarantors on a monthly basis by reviewing various factors such as payment history, level of state involvement in the institution, size, national importance as well as current economic conditions in China. Since the Company has not experienced any historical losses nor is the Company expecting future credit losses based on a review of the various credit quality indicators described above, we have not established a loss provision against these receivables as of December 31, 2014 or 2013.
| NOTE 12. | Goodwill and Intangible Assets |
The following table summarizes the changes in the carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | |||||
| Balance of goodwill, beginning of year | $ | 381.2 | $ | 371.7 | |||
| Acquisitions | 91.6 | — | |||||
| Foreign exchange translation | (51.8 | ) | 9.5 | ||||
| Balance of goodwill, end of year | $ | 421.0 | $ | 381.2 | |||
The changes in the carrying value of intangible assets for the years ended December 31 are as follow:
60
| Capitalized Software | Other Intangible Assets | Total | ||||||||||
| Gross intangible assets as of: | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2011 | $ | 90.9 | $ | 22.8 | $ | 113.7 | ||||||
| Additions | 8.7 | 4.6 | 13.3 | |||||||||
| Disposals | (4.5 | ) | — | (4.5 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign exchange translation | 0.4 | (0.4 | ) | — | ||||||||
| December 31, 2012 | 95.5 | 27.0 | 122.5 | |||||||||
| Additions | 13.5 | 2.2 | 15.7 | |||||||||
| Disposals | (1.9 | ) | (0.5 | ) | (2.4 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign exchange translation | 4.3 | (0.2 | ) | 4.1 | ||||||||
| December 31, 2013 | 111.4 | 28.5 | 139.9 | |||||||||
| Additions | 12.7 | 53.7 | 66.4 | |||||||||
| Disposals | (17.7 | ) | — | (17.7 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign exchange translation | (14.5 | ) | (11.6 | ) | (26.1 | ) | ||||||
| December 31, 2014 | $ | 91.9 | $ | 70.6 | $ | 162.5 | ||||||
| Accumulated amortization as of: | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2011 | $ | (70.5 | ) | $ | (7.5 | ) | $ | (78.0 | ) | |||
| Amortization expense | (6.6 | ) | (2.9 | ) | (9.5 | ) | ||||||
| Disposals | 4.3 | — | 4.3 | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange translation | — | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||||||||
| December 31, 2012 | (72.8 | ) | (10.3 | ) | (83.1 | ) | ||||||
| Amortization expense | $ | (7.5 | ) | $ | (3.1 | ) | $ | (10.6 | ) | |||
| Disposals | 1.9 | 0.4 | 2.3 | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange translation | (3.4 | ) | (0.8 | ) | (4.2 | ) | ||||||
| December 31, 2013 | (81.8 | ) | (13.8 | ) | (95.6 | ) | ||||||
| Amortization expense | (9.1 | ) | (12.7 | ) | (21.8 | ) | ||||||
| Disposals | 17.7 | — | 17.7 | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange translation | 10.7 | 4.9 | 15.6 | |||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | $ | (62.5 | ) | $ | (21.6 | ) | $ | (84.1 | ) | |||
| Net intangible assets as of: | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | $ | 29.4 | $ | 49.0 | $ | 78.4 | ||||||
The Company expects to incur approximately $21 million to $23 million of amortization expense for each of the next five fiscal years.
| NOTE 13. | Post-retirement Benefits |
WABCO employees participate in a number of benefit plans. The plans include a 401(k) savings plan for the Company's U.S. salaried and hourly employees, which is an individual-account defined contribution plan. WABCO employees in certain countries including Germany, the United Kingdom, France and Switzerland, participate in defined benefit plans or retiree medical plans sponsored by local WABCO legal entities.
Further, WABCO has assumed responsibility for certain retiree medical plans in the United States and a pension plan in Germany relating to former employees of Trane's Bath & Kitchen division.
61
Benefits under defined benefit pension plans on a worldwide basis are generally based on years of service and either employee compensation during the last years of employment or negotiated benefit levels.
WABCO recognizes in its consolidated balance sheets an asset for a defined benefit post-retirement plan's overfunded status or a liability for a plan's underfunded status. The long-term liability of $595.0 million on the consolidated balance sheets is primarily due to the underfunded plan in Germany, where the majority of the Company's prior and current employees are based.
The following table provides a reconciliation of the changes in pension and retirement health and life insurance benefit obligations and fair value of assets for the years ending December 31, 2014 and 2013, and a statement of the funded status as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
| 2014 | 2014 | 2013 | 2013 | ||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Health & Life Ins. Benefits | Pension Benefits | Health & Life Ins. Benefits | Pension Benefits | |||||||||||
| Reconciliation of benefit obligation: | |||||||||||||||
| Obligation at beginning of year | $ | 14.0 | $ | 606.2 | $ | 15.0 | $ | 585.4 | |||||||
| Service cost | 0.1 | 12.4 | 0.1 | 12.7 | |||||||||||
| Interest cost | 0.5 | 21.7 | 0.5 | 20.8 | |||||||||||
| Participant contributions | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |||||||||||
| Actuarial loss / (gain) | 2.6 | 248.6 | — | (7.7 | ) | ||||||||||
| Benefit payments | (4.2 | ) | (31.0 | ) | (2.0 | ) | (28.4 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign exchange effects | — | (83.9 | ) | — | 22.3 | ||||||||||
| Other | — | 3.6 | — | 0.9 | |||||||||||
| Obligation at end of year | $ | 13.3 | $ | 777.8 | $ | 14.0 | $ | 606.2 | |||||||
| 2014 | 2014 | 2013 | 2013 | ||||||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | Health & Life Ins. Benefits | Pension Benefits | Health & Life Ins. Benefits | Pension Benefits | |||||||||||
| Reconciliation of fair value of plan assets: | |||||||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | $ | — | $ | 178.1 | $ | — | $ | 172.1 | |||||||
| Actual return on assets | — | 24.7 | — | 3.7 | |||||||||||
| Employer contributions | 3.9 | 29.1 | 1.6 | 27.4 | |||||||||||
| Participant contributions | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |||||||||||
| Benefit payments | (4.2 | ) | (31.0 | ) | (2.0 | ) | (28.4 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign exchange effects | — | (11.9 | ) | — | 4.0 | ||||||||||
| Other expenses | — | (1.1 | ) | — | (0.9 | ) | |||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | — | $ | 188.1 | $ | — | $ | 178.1 | |||||||
| Funded Status at December 31 | $ | (13.3 | ) | $ | (589.7 | ) | $ | (14.0 | ) | $ | (428.1 | ) | |||
| Amounts recognized in the balance sheet: | |||||||||||||||
| Noncurrent assets | $ | — | $ | 13.7 | $ | — | $ | 20.1 | |||||||
| Current liabilities | (1.6 | ) | (20.1 | ) | (1.7 | ) | (21.9 | ) | |||||||
| Noncurrent liabilities | (11.7 | ) | (583.3 | ) | (12.3 | ) | (426.3 | ) | |||||||
| Net amounts recognized in balance sheet: | $ | (13.3 | ) | $ | (589.7 | ) | $ | (14.0 | ) | $ | (428.1 | ) | |||
| Cumulative amounts recognized in other comprehensive income consist of: | |||||||||||||||
| Prior service cost | $ | 0.1 | $ | 1.9 | $ | 0.2 | $ | — | |||||||
| Net actuarial loss | 9.5 | 340.5 | 7.2 | 147.0 | |||||||||||
| Total (before tax effects) | $ | 9.6 | $ | 342.4 | $ | 7.4 | $ | 147.0 | |||||||
62
$17.4 million of the amount in other comprehensive income as of December 31, 2014 is expected to be recognized as post-retirement costs in 2015.
The following table provides a summary of pension plans with accumulated benefit obligations in excess of assets as of December 31:
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||
(Amounts in millions) | Foreign Pension Plans | Foreign Pension Plans | ||||
| For all plans: | ||||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 692.4 | $ | 545.8 | ||
| For pension plans with accumulated benefit obligations in excess of plan assets: | ||||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 547.7 | $ | 390.9 | ||
Total post-retirement costs are shown below:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Foreign pensions | $ | 31.6 | $ | 30.9 | $ | 20.2 | |||||
| Health & Life insurance benefits | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ||||||||
| Total post-retirement costs, including accretion expense | $ | 32.6 | $ | 31.9 | $ | 21.2 | |||||
Components of post-retirement costs are broken out in the tables below:
Pension Benefit Costs
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Service cost-benefits earned during period | $ | 12.3 | $ | 12.7 | $ | 9.2 | |||||
| Interest cost on projected benefit obligation | 21.6 | 20.8 | 22.3 | ||||||||
| Less: assumed return on plan assets | (8.1 | ) | (8.8 | ) | (8.6 | ) | |||||
| Amortization of prior service cost | (0.1 | ) | 0.1 | (0.1 | ) | ||||||
| Amortization of net loss | 5.9 | 6.1 | 1.7 | ||||||||
| Plan amendments | — | — | (4.3 | ) | |||||||
| Net defined benefit plan cost after amendments | $ | 31.6 | $ | 30.9 | $ | 20.2 | |||||
Other Post-Retirement Benefit Costs
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Interest and service cost on projected benefit obligation | $ | 0.6 | $ | 0.6 | $ | 0.6 | |||||
| Amortization of net loss | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | ||||||||
| Defined benefit plan cost | $ | 1.0 | $ | 1.0 | $ | 1.0 | |||||
For plans where the total unrecognized net gain or loss exceeds the greater of 10% of the projected benefit obligation or 10% of the plan assets, the excess is amortized on a straight-line basis over the average expected future working lifetime of the active participants of that plan. For plans without active participants, the amortization period is the average life expectancy of plan participants.
Major assumptions used in determining the benefit obligation and net cost for post-retirement plans are presented below as weighted averages:
63
| Benefit Obligation at December 31 | 2014 Health & Life Ins. Benefits | 2014 Foreign Pension Plans | 2013 Health & Life Ins. Benefits | 2013 Foreign Pension Plans | |||||||
| Discount rate | 3.50 | % | 2.43 | % | 4.00 | % | 3.70 | % | |||
| Salary growth | N/A | 3.03 | % | N/A | 3.18 | % | |||||
| Net Periodic Pension Cost for the year | |||||||||||
| Discount rate | 4.00 | % | 3.71 | % | 3.25 | % | 3.63 | % | |||
| Salary growth | N/A | 3.18 | % | N/A | 3.22 | % | |||||
| Expected return on plan assets | N/A | 4.27 | % | N/A | 5.38 | % | |||||
The discount rate assumption in this chart changed from 2013 to 2014, resulting in a change in the pension benefit obligation. In the chart above that reconciles the change in benefit obligations for the year, the impact of the discount rate change is included in the actuarial loss/(gain) line item. The discount rate noted for foreign pension plans is a weighted average rate based on each of the applicable country's rates.
The assumed rate of return is a long-term investment return that takes into account the classes of assets held by the plan and expected returns for each class of assets. Return expectations reflect forward-looking analysis as well as historical experience.
During 2014, the Company, in consultation with its actuaries, revised certain demographic assumptions, in particular mortality, related to its pension plan in Germany to provide an improved reflection of the Company's current employee workforce there. The effect of this change in actuarial assumption is included in the actuarial loss for the year ended December 31, 2014 as shown above.
WABCO's asset management strategy focuses on maintaining a diversified portfolio using various classes of assets to generate attractive returns while managing risk. The Company periodically reviews its target asset allocations for a given plan to ensure it aligns with the asset management strategy. In determining the target asset allocation for a given plan, consideration is given to the nature of its liabilities, and portfolios are periodically rebalanced with reference to the target level.
Asset Allocation | 2014 | 2013 | 2014 Target | 2013 Target | |||||||
| Equity securities | 28 | % | 22 | % | 28 | % | 24 | % | |||
| Debt securities | 11 | % | 24 | % | 11 | % | 71 | % | |||
| Insurance contracts | 46 | % | 46 | % | 46 | % | — | % | |||
| Investments in collective foundations | 14 | % | — | % | 14 | % | — | % | |||
| Other * | 1 | % | 8 | % | 1 | % | 5 | % | |||
* Included in "other" above are mutual funds held in real estate.
In July 2013, the Company purchased a buy-in contract from an insurance company related to a group of existing retirees covered under our United Kingdom pension plan as of that date. The buy-in did not trigger settlement accounting, and resulted in a shift in the 2013 asset allocation versus target.
All assets are measured at the current fair value. The fair values of the insurance contract and investments in collective foundations are determined based on applicable discount rates and other observable inputs (Level 2). For all other assets, the Company determines fair value for each class of assets in its entirety using quoted prices in active markets for identical assets (Level 1). The Company has not changed the valuation techniques and inputs used during the periods presented. The fair values for each class of assets are presented below:
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | |||||
| Equity securities | $ | 52.7 | $ | 40.0 | |||
| Debt securities | 20.7 | 42.5 | |||||
| Insurance contracts | 87.0 | 82.2 | |||||
| Investments in collective foundations | 25.6 | — | |||||
| Other * | 2.1 | 13.4 | |||||
| Total fair value of plan assets | $ | 188.1 | $ | 178.1 | |||
64
* Included in "other" above are mutual funds held in real estate.
WABCO makes contributions to funded pension plans that at a minimum, meet all statutory funding requirements. Contributions in 2014, including payment of benefits incurred by unfunded plans, totaled $29.1 million. Contributions in 2015 are expected to be in line with the contributions made during 2014.
Expected future benefit payments are shown in the table below:
(Amounts in millions) | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020-2024 | ||||||||||||
| Domestic plans without subsidy | $ | 1.7 | $ | 1.5 | $ | 1.4 | $ | 1.3 | $ | 1.2 | $ | 4.5 | ||||||
| Foreign pension plans | $ | 26.8 | $ | 26.9 | $ | 26.5 | $ | 26.6 | $ | 26.2 | $ | 131.4 | ||||||
The weighted average annual assumed rate of increase in the health care cost trend rate was 7.0% for 2013, 6.8% for 2014 and is assumed to lower to 6.5% in 2015 and then gradually decline to 4.75% by 2022. The health care cost trend rate assumption has the following effect:
(Amounts in millions) | 1% Increase | 1% Decrease | ||||
| Effect on the health care component of accumulated post-retirement obligation | $ | 0.8 | $ | (0.7 | ) | |
| Effect on total of service and interest cost components of net periodic post-retirement health care benefit costs | $ | — | $ | — | ||
| NOTE 14. | Debt |
On July 8, 2011, the Company entered into a $400 million multi-currency five-year senior unsecured revolving credit facility (the 2011 Facility) with the lenders and agent banks party thereto, including Banc of America Securities Limited as agent, issuing bank and swingline lender, and Banc of America Securities Limited, Citigroup Global Markets Limited, Fortis Bank S.A./N.V., ING Belgium SA/NV, Société Générale Corporate & Investment Banking, The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ, Ltd and The Royal Bank of Scotland NV, (Belgium) Branch, as mandated lead arrangers and bookrunners and Credit Lyonnais and Unicredit Bank AG as lead arrangers. As of December 31, 2014, this is our principal bank credit facility and it expires on September 1, 2018 pursuant to an amendment agreement to extend the original expiry date.
On December 17, 2014, the Company entered into a new $100 million multi-currency five-year senior unsecured revolving credit facility (the 2014 Facility) with the lenders and agent banks party thereto, including Citibank International Limited as Agent, and Bank of America N.A., London Branch, Citigroup Global Markets Limited, BNP Paribas Fortis Bank S.A./N.V., the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ Ltd. and Unicredit Bank AG as lead arrangers. This facility will expire on December 17, 2019.
Under the revolving credit facilities, the Company may borrow, on a revolving basis, loans in an aggregate principal amount at any one time outstanding not in excess of $500 million. Up to $50 million under the 2011 Facility may be used for issuing letters of credit, of which $49.1 million was unused as of December 31, 2014, and up to $50 million is available in the form of swing line loans, all $50 million of which was available for use as of December 31, 2014.
The following table summarizes the balance outstanding on these facilities:
| As of December 31, 2014 | As of December 31, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | Outstanding borrowings | Letters of credit | Aggregate interest rate | Outstanding borrowings | Letters of credit | Aggregate interest rate | |||||||||||||||
| 2011 Facility | $ | 206.0 | $ | 0.9 | 0.97 | % | $ | 47.0 | $ | 1.2 | 1.04 | % | |||||||||
| 2014 Facility | 100.0 | $ | — | 0.81 | % | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
| $ | 306.0 | $ | 0.9 | $ | 47.0 | $ | 1.2 | ||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the carrying amounts of the facilities approximated fair value based upon Level 2 inputs.
Interest on loans under the revolving credit facilities will be calculated at a rate per annum equal to an applicable margin - which can vary from 0.80% to 1.55% for the 2011 Facility and 0.45% to 1.00% for the 2014 Facility based on the Company's
65
leverage ratio - plus LIBOR for loans denominated in U.S. Dollars, EURIBOR for loans denominated in Euros, HIBOR for loans denominated in Hong Kong Dollars and SIBOR for loans denominated in Singapore Dollars, plus mandatory costs, if any.
The applicable margins used to determine the LIBOR loan rate are determined based upon the Company's leverage ratio, which represents the ratio of our consolidated net indebtedness on the last day of any fiscal quarter to consolidated adjusted EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization adjusted for certain items) for the period of four consecutive fiscal quarters ending on such day. The revolving credit facilities also provide for certain of the borrowers to pay various fees including a participation fee on the amount of the lenders' commitments thereunder.
The revolving credit facilities contain terms and provisions (including representations, covenants and conditions) customary for credit agreements of this type. Our primary financial covenant is a leverage test which requires net indebtedness not to exceed three times adjusted four quarter trailing EBITDA. Additional financial covenants include an interest coverage test and a maximum subsidiary indebtedness test. The interest coverage test requires three times interest expense not to exceed adjusted four quarter trailing EBITDA. The maximum subsidiary indebtedness test limits the total aggregate amount of indebtedness of WABCO's subsidiaries, excluding indebtedness under the facilities, to $500 million , of which not more than $150 million may be secured. Financial covenants are not subject to any future changes in U.S. GAAP accounting standards and all cash on the balance sheet can be deducted for net indebtedness purposes. In addition, expenses and payments related to any streamlining of WABCO’s operations are excluded when calculating the four quarter trailing adjusted EBITDA. Other covenants include delivery of financial reports and other information, compliance with laws including environmental laws and permits, ERISA and U.S. regulations, limitations on liens, mergers and sales of assets and change of business. We were in compliance with all the covenants.
As of December 31, 2014 the Company had the ability to borrow an incremental $193.1 million under the revolving credit facilities, compared to $351.8 million as of December 31, 2013.
As of December 31, 2014, the Company's various subsidiaries had borrowings from banks totaling $9.2 million, of which $1.1 million was classified as long-term debt. The remaining $8.1 million supports local working requirements. This is in comparison to $40.1 million as of December 31, 2013, of which $36.4 million related to our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program referred to in Note 11 above.
| NOTE 15. | Warranties, Guarantees, Commitments and Contingencies |
Warranties
Products sold by WABCO are covered by a basic limited warranty with terms and conditions that vary depending upon the product and country in which it was sold. The limited warranty covers the equipment, parts and labor (in certain cases) necessary to satisfy the warranty obligation generally for a period of two years. Estimated product warranty expenses are accrued in cost of goods sold at the time the related sale is recognized. Estimates of warranty expenses are based primarily on warranty claims experience and specific customer contracts. Warranty expenses include accruals for basic warranties for product sold, as well as accruals for product recalls, service campaigns and other related events when they are known and estimable. To the extent WABCO experiences changes in warranty claim activity or costs associated with servicing those claims, its warranty accrual is adjusted accordingly. Warranty accrual estimates and the allocation of warranty between short and long term are updated based upon the most current warranty claims information available.
The following is a summary of changes in the Company’s product warranty liability for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
66
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Balance of warranty costs accrued, beginning of period | $ | 51.6 | $ | 55.2 | $ | 52.6 | |||||
| Warranty costs accrued | 27.1 | 25.4 | 30.2 | ||||||||
| Warranty claims settled | (28.0 | ) | (30.5 | ) | (28.4 | ) | |||||
| Foreign exchange translation effects | (5.5 | ) | 1.5 | 0.8 | |||||||
| Balance of warranty costs accrued, end of period | $ | 45.2 | $ | 51.6 | $ | 55.2 | |||||
| Current liability, included in current portion of warranties | $ | 25.8 | $ | 29.8 | $ | 33.8 | |||||
| Long-term liability, included in other liabilities | $ | 19.4 | $ | 21.8 | $ | 21.4 | |||||
| Warranty costs net of recoveries | $ | 24.9 | $ | 21.4 | $ | 27.1 | |||||
Guarantees and Commitments
Future minimum rental commitments under all non-cancelable operating leases with original terms in excess of one year in effect as of December 31, 2014, are: $18.9 million in 2015; $13.4 million in 2016; $11.3 million in 2017; $8.9 million in 2018; $8.5 million in 2019 and $12.2 million thereafter, amounting to a total of $73.2 million. Net rental expense for all operating leases was $20.4 million, $18.9 million and $19.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
The Company has bank guarantees for $49.9 million which is comprised of uncollateralized bank guarantees, of which $43.9 million is related to tax and other litigation, $0.9 million is related to letters of credit, $0.7 million is related to performance bonds and $4.4 million is related to other items.
Right of Recourse
In the ordinary course of business, the Company may receive banker's acceptance drafts from customers in China in payment of outstanding accounts receivable. These banker's acceptance drafts are non-interest bearing obligations of the issuing bank and generally have contractual maturities of six months or less. The Company may use these banker's acceptance drafts prior to the scheduled maturity date to settle outstanding accounts payable with vendors. Banker's acceptance drafts transferred to vendors are subject to customary right of recourse provisions prior to their scheduled maturity date. As of December 31, 2014, the Company had approximately $15.1 million of banker's acceptance drafts subject to customary right of recourse provisions, which were transferred to vendors and had not reached their scheduled maturity date. Historically, the banker's acceptance drafts have settled upon maturity without any claim of recourse against the Company.
Contingencies
General
We are subject to proceedings, lawsuits and other claims related to products and other matters. We are required to assess the likelihood of any adverse judgments or outcomes to these matters as well as potential ranges of probable and reasonably possible losses. A determination of the amount of liability to be recorded, if any, for these contingencies is made after careful analysis of each individual issue.
Litigation
On June 23, 2010, the European Commission (the Commission) issued a decision imposing a total of €326.1 million in fines, or approximately $400 million on the date of assessment (the EC Fine), on the former American Standard Companies Inc. (now Trane Inc., hereinafter referred to as American Standard or Trane), and certain of its European subsidiaries engaged in the Bath and Kitchen business and successor entities for infringements of European Union competition rules relating to the distribution of bathroom fixtures and fittings in a number of European countries. Pursuant to our Indemnification and Cooperation Agreement with Trane, WABCO Europe BVBA (an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of WABCO) is responsible for, and is liable to indemnify Trane Inc. and Ideal Standard International (representing the successor to the Bath and Kitchen business, and owner of certain of the former American Standard subsidiaries) and their owners against the EC Fine.
As required by the Indemnification and Cooperation Agreement, WABCO paid the fine amount into escrow on August 30, 2010, using €230.0 million of cash on hand and €96.1 million of additional borrowings under a revolving credit facility. The funds
67
were subsequently released from escrow and paid to the Commission. After reviewing all of the elements of the case, WABCO decided to appeal the decision in order to try to have the fine reduced.
On September 16, 2013, the General Court of the European Union delivered its judgment and reversed in part the decision of the Commission, reducing the original fine of €326.1 million by €205.8 million to €120.3 million. Since WABCO had paid the full amount of the EC Fine (as described above), WABCO received the full amount of the reimbursement from the Commission during the fourth quarter of 2013. The Commission did not appeal the judgment of the General Court within the mandatory time limit. The judgment of the General Court was thus deemed final.
Other
In conjunction with the Tax Sharing Agreement, as further discussed in Note 17, WABCO is responsible for certain tax and indemnification liabilities. These liabilities include probable indemnification liabilities to Trane of $4.5 million as of December 31, 2014. It is reasonably possible that the Company could incur losses in excess of the amounts accrued. Although this amount cannot be estimated, we believe that any additional losses would not have a material adverse impact on the consolidated financial statements.
| NOTE 16. | Income Taxes |
Income before income taxes and the applicable provision for income taxes were :
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Income before income taxes: | |||||||||||
| Domestic | $ | 49.8 | $ | 94.4 | $ | 77.2 | |||||
| Foreign | 307.0 | 546.5 | 258.9 | ||||||||
| $ | 356.8 | $ | 640.9 | $ | 336.1 | ||||||
| Provision/(benefit) for income taxes: | |||||||||||
| Current: | |||||||||||
| Domestic | $ | 18.0 | $ | 11.4 | $ | (6.2 | ) | ||||
| Foreign | 33.1 | 32.2 | 32.7 | ||||||||
| $ | 51.1 | $ | 43.6 | $ | 26.5 | ||||||
| Deferred: | |||||||||||
| Domestic | $ | 3.0 | $ | 101.7 | $ | 0.1 | |||||
| Foreign | 1.5 | (166.3 | ) | (3.0 | ) | ||||||
| $ | 4.5 | $ | (64.6 | ) | $ | (2.9 | ) | ||||
| Total provision/(benefit) | $ | 55.6 | $ | (21.0 | ) | $ | 23.6 | ||||
A reconciliation between the actual income tax expense provided and the income taxes computed by applying the statutory federal income tax rate of 35.0% in 2014, 2013 and 2012 to the income before income taxes is as follows:
68
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Tax provision at statutory rate | $ | 124.9 | $ | 224.3 | $ | 117.4 | |||||
| State income taxes | 0.7 | — | — | ||||||||
| Separation related taxes and contingencies | — | — | 2.2 | ||||||||
| Foreign earnings taxed at other than 35% | (82.0 | ) | (93.9 | ) | (71.9 | ) | |||||
| (Decrease)/increase in valuation allowance | (1.1 | ) | (261.9 | ) | 109.8 | ||||||
| Unremitted foreign earnings | (3.6 | ) | 107.4 | — | |||||||
| EC Fine indemnity | — | — | (116.3 | ) | |||||||
| Tax contingencies/(reversals) | 3.3 | (0.4 | ) | (21.9 | ) | ||||||
| Equity compensation | 4.8 | 4.4 | 5.0 | ||||||||
| Other, net | 8.6 | (0.9 | ) | (0.7 | ) | ||||||
| Total provision/(benefit) | $ | 55.6 | $ | (21.0 | ) | $ | 23.6 | ||||
The effective income tax rates for 2014 and 2013 were 15.6% and (3.3)%, respectively. The income tax provision for 2014 includes the net result of taxes on the mix of earnings in multiple tax jurisdictions, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions, and certain foreign tax planning. Furthermore, in 2014, the Company recorded a tax charge of $3.6 million primarily related to various income tax filings and changes in the Company's recorded tax liabilities with respect to undistributed foreign earnings due to the Company’s decision to repatriate on a non-recurring basis $15.1 million of accumulated foreign earnings of its Korean affiliate. The Company continues to assert permanent reinvestment outside the U.S. with respect to the remainder of its foreign earnings and at this time, does not have any plans or needs to repatriate additional earnings from its foreign subsidiaries except for Brazil.
The nature of the reconciling item "Foreign earnings taxed at other than 35%" is net of permanent differences including non-taxable income in foreign jurisdictions, foreign tax credits and rulings, resulting in a net tax benefit.
As previously disclosed in the Company's 2013 Form 10K, we continue to expect our effective tax rate to increase in subsequent periods following the 2013 release of a valuation allowance of $178.4 million. Our net income and effective tax rate will be negatively affected in periods following this release. However, the valuation allowance release will not affect the amount of cash paid for income taxes. Management has also determined that it is more likely than not that it will not realize $9.0 million of its deferred tax assets in other foreign jurisdictions since evidence such as historical operating profits resulted in a lack of taxable earnings during the most recent three-year period ended December 31, 2014 and lack of projected earnings provided sufficient negative evidence to record a valuation allowance against such deferred tax assets related to carryforwards for net operating losses and notional interest deductions.
In 2013, the income tax benefit includes taxes on earnings in profitable jurisdictions, income offset by fully valued net operating losses, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions, and a tax provision on unremitted foreign earnings of $300.0 million in a Belgian affiliate for which the Company does not assert permanent reinvestment outside the United States as discussed further below. Additionally, the tax provision is offset by the release of a valuation allowance related to management’s determination that it is more likely than not that the Company will realize its deferred tax asset in a foreign jurisdiction as also discussed below. Furthermore, the Company also recognized a tax benefit of $2.4 million due to the impact of U.S. tax legislation enacted in January 2013 and a tax benefit of $2.4 million related to the Company's filing of its 2012 U.S. Federal Income Tax Return in September 2013. Additionally in 2013, the Company recorded a tax provision related to unremitted foreign earnings of $300.0 million in a Belgian affiliate for which the Company does not assert permanent reinvestment outside the United States. This assertion is resulting from the Company recognizing earnings in the fourth quarter of €209.8 million from the receipt of an exceptional refund including interest from the European Commission related to the Company’s appeal of the EC Fine.
In 2012, the income tax provision was offset by the release of tax accruals for uncertain tax positions due to certain government filings submitted in January 2012 of approximately $24.8 million, as adjusted from an amount of $18.8 million as previously disclosed in the Company's 2011 Form 10-K. As a result of a settlement of a foreign tax audit in the fourth quarter of 2012, a portion of the EC fine deduction claimed in 2010 was accepted and added to existing net operating losses. The tax effect of this settlement was $116.3 million, the benefit for which was fully offset by an increase to a valuation allowance and thus had no impact on the Company's effective tax rate.
The approximate dollar and diluted earnings per share amounts of tax reductions related to tax holidays and incentive tax credits in various countries in which the Company does business were $15.6 million and $0.26 in 2014, $7.8 million and $0.12
69
in 2013 and $6.5 million and $0.10 in 2012, respectively. The tax holidays and incentive tax credits expire at various dates through 2026.
The following table details the gross deferred tax liabilities and assets and the related valuation allowances:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | |||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: | |||||||
| Basis difference in noncontrolling interest | $ | 10.5 | $ | 11.9 | |||
| Facilities (accelerated depreciation, capitalized interest and purchase accounting differences) | 19.0 | 21.0 | |||||
| Unremitted foreign earnings | 103.3 | 107.8 | |||||
| Intangibles | 16.8 | 3.4 | |||||
| $ | 149.6 | $ | 144.1 | ||||
| Deferred tax assets: | |||||||
| Foreign net operating losses and tax credits | $ | 170.1 | $ | 195.7 | |||
| Post-retirement and other employee benefits | 105.4 | 43.2 | |||||
| Intangibles | 34.0 | 35.7 | |||||
| Inventory | 1.1 | 0.8 | |||||
| Warranties | 1.6 | 1.4 | |||||
| Other | 6.7 | 16.5 | |||||
| $ | 318.9 | $ | 293.3 | ||||
| Valuation allowances | (9.0 | ) | (10.1 | ) | |||
| Net deferred tax assets | $ | 160.3 | $ | 139.1 | |||
As of December 31, 2014, the Company has $491.0 million of net operating loss carry forwards (NOLs) available for utilization in future years. Approximately $455.6 million of such NOLs have an unlimited life and the remainder is available for periods of up to 7 years. The NOLs primarily consist of NOLs inherited by WABCO upon separation from Trane and losses incurred in post-spin years. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has provided a valuation allowance of $9.0 million representing the value of the associated deferred tax asset with regard to $27.9 million of NOLs and tax credits available for up to 6 years. Management has determined that it is more likely than not that it will not realize $9.0 million of its deferred tax assets in other foreign jurisdictions and has recorded a valuation allowance against such deferred tax assets as discussed above.
Unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2014 amounted to $48.5 million primarily related to the WABCO business which is classified as a long-term liability and the Company is currently unable to estimate the timing of potential amounts to be paid.
There are no material unrecognized tax benefits related to WABCO obligations directly to tax authorities for Trane’s Bath & Kitchen business as further discussed in Note 17. Interest related to unrecognized tax benefits recorded in the 2014, 2013 and 2012 consolidated statements of income were $1.0 million, $0.3 million and $1.1 million, respectively. Total accrued interest as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was approximately $7.0 million, $6.0 million and $5.7 million, respectively. The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows (exclusive of interest):
70
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
| Beginning balance, January 1 | $ | 39.3 | $ | 41.9 | $ | 209.6 | ||||
| Additions for tax positions related to current year | 2.2 | — | — | |||||||
| Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 25.8 | 1.2 | 7.5 | |||||||
| Reductions for tax positions related to prior years | — | — | (172.4 | ) | ||||||
| Cash settlements | — | (2.0 | ) | (1.5 | ) | |||||
| Expirations of statute of limitations | (25.8 | ) | (2.0 | ) | (2.6 | ) | ||||
| Foreign exchange | — | 0.2 | 1.3 | |||||||
| Ending balance, December 31 | $ | 41.5 | $ | 39.3 | $ | 41.9 | ||||
During 2014, the Company reversed $25.8 million of unrecognized tax benefits due to the expiration of a statute of limitation. This expiration also had a correlative impact on other unrecognized tax benefits which resulted in the Company recording an unrecognized tax benefit of $25.8 million (excluding penalties and interest) during 2014.
In 2013, the reversal of $4.0 million during the year relates to the settlement of certain US state tax exposures and the expiration of statutes of limitations in certain foreign jurisdictions
In 2012, as a result of the settlement of a foreign tax audit, $342.3 million, at December 31, 2012 foreign exchange rates, of the EC Fine tax deduction claimed in 2010 was accepted. Thus, the 2010 reserve for this uncertain tax position has been reversed which added $116.3 million to existing net operating losses in a foreign jurisdiction that had a full valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset for such NOLs. The remaining amount of $29.0 million was also removed from the tabular rollforward for unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2012, due to the settlement. The reversal of $172.4 million during 2012 relates to the settlement of a foreign tax audit as described above, certain government filings submitted in January 2012, and the expiration of statutes of limitation.
As of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, there were $41.5 million, $39.3 million and $41.9 million of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would impact the annual effective tax rate.
We conduct business globally and, as a result, WABCO or one or more of our subsidiaries file income tax returns in the U.S. federal, state and local, and foreign jurisdictions. In the normal course of business, we are subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world, including such major jurisdictions as Belgium, Brazil, China, France, Germany, India, the Netherlands, Poland, the United Kingdom and the United States. With no material exceptions, the Company is no longer subject to examinations by tax authorities for years before 2009. The Company is currently under examination in the United States for tax years 2010, 2011 and 2012.
As a result of the allocation of purchase accounting (principally goodwill) to foreign subsidiaries, the book basis in the net assets of the foreign subsidiaries exceeds the related U.S. tax basis in the subsidiaries' stock. Such investments are considered permanent in duration and accordingly, no deferred taxes have been provided on such differences, which are significant. The Company considers the earnings of substantially all of its foreign subsidiaries to be permanently reinvested outside the United States due to operational, strategic and other needs to support the growth of the Company and as such, no deferred tax liability has been provided. However, the Company has provided for tax at the U.S. tax rate for its Brazilian affiliate's current year earnings in 2014 and also decided to repatriate $15.1 million of excess foreign earnings of its Korean affiliate. The Company continues to assert permanent reinvestment outside the U.S. with respect to the remainder of its foreign earnings and at this time, does not have any plans or needs to repatriate additional earnings from its foreign subsidiaries except for Brazil.
In addition, as discussed above, due to the receipt in the fourth quarter of 2013 of an exceptional refund including interest from the European Commission that increased earnings beyond these operational, strategic and other needs outside the United States, the Company recorded a tax provision for $300.0 million of its Belgian affiliate’s earnings for which the Company does not assert permanent reinvestment outside the United States. The Company estimates the amount of its permanently reinvested unremitted foreign earnings to be approximately $800 million as of December 31, 2014, however, it is not practicable to estimate the tax liability that would arise if the earnings that are considered permanently reinvested were remitted to the United States.
| NOTE 17. | Tax and Indemnification Liabilities Transferred from Trane to WABCO |
Pursuant to the Tax Sharing Agreement between Trane and WABCO, entered into on July 16, 2007, and other agreements with Trane as filed in WABCO’s Form 10 prior to its spin-off from Trane, WABCO is responsible for certain tax contingencies
71
and indemnification liabilities. As noted in Note 16, the liabilities as of December 31, 2014 included no material amounts related to non-U.S. entities of Trane’s former Bath and Kitchen business but for which WABCO entities have obligations directly to non-U.S. tax authorities. In addition, as of December 31, 2014, the Company had probable indemnification liabilities of $4.5 million, compared to $9.2 million as of December 31, 2013, of which $3.9 million were classified within short-term liabilities and $0.6 million within long-term liabilities on the balance sheet. It is reasonably possible that the Company could incur losses in excess of the amounts accrued. Although this amount cannot be estimated, we believe that any additional losses would not have a material adverse impact on the consolidated financial statements.
For the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, approximately $4.3 million, $8.8 million and $1.2 million of indemnification liabilities were reversed, respectively, due to the settlement of foreign tax audits and expiration of statutes of limitations. We also paid indemnification liabilities of $0.7 million during 2014 in relation to the above.
Under an indemnification agreement, WABCO Brazil is responsible for certain claims related to its business for periods prior to the spin-off of WABCO from American Standard. In particular, there are tax claims pending in various stages of the Brazilian legal process related to income, social contribution and/or value added taxes for which a contingency exists and which may or may not ultimately be incurred by the Company. The estimated total amount of the claims as of December 31, 2014 was $42.8 million including interest. However, based on management’s assessment and advice of our external legal counsel, the Company believes that it has valid arguments in all of these cases and the likelihood of loss is not probable and thus no accrual is required at this time.
NOTE 18. Related Party Transactions
Investments in and Advances to Unconsolidated Joint Ventures
WABCO has three investments in affiliates that are accounted for under the equity method. The first of these investments is in Meritor WABCO. Meritor WABCO, in which WABCO has a 50% equity ownership, markets braking systems products and sells the majority of WABCO products in the United States. The second of these investments is in WABCO Automotive South Africa (WABCO SA). WABCO SA, in which WABCO has a 49% equity ownership, is a distributor of breaking systems products and sells WABCO products primarily in South Africa. The third investment is in WABCOWURTH Workshop Services GmbH (WABCOWURTH). WABCOWURTH, in which WABCO has a 50% equity ownership, supplies commercial vehicle workshops, fleet owners and operators and end users internationally with its multi-brand technology diagnostic system.
As of December 31, 2014, WABCO has net investments in and advances to Meritor WABCO of $15.9 million, WABCO SA of $3.3 million and WABCOWURTH of $0.4 million. WABCO received dividends from the joint ventures of $23.4 million, $18.3 million and $15.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
| (Amounts in millions) | WABCO Sales to | WABCO Purchases from | |||||||||||||||||||||
Joint Venture | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||||
| Meritor WABCO | $ | 218.7 | $ | 176.0 | $ | 180.7 | $ | 0.7 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| WABCO SA | 4.5 | 5.7 | 6.7 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| WABCOWURTH | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | WABCO Receivables from | WABCO Payables to | |||||||||||||
| Joint Venture | 2014 | 2013 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||
| Meritor WABCO | $ | 32.0 | $ | 28.3 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
| WABCO SA | 1.1 | 1.1 | — | — | |||||||||||
| WABCOWURTH | — | 0.2 | — | 0.6 | |||||||||||
Consolidated Joint Ventures
WABCO has three fully consolidated joint ventures as of December 31, 2014. The first of these joint ventures is in Japan with Sanwa-Seiki where Sanwa-Seiki distributes WABCO's products in the local market. WABCO's ownership interest in the joint venture with Sanwa-Seiki is 90%.
The second joint venture is in the United States with Cummins Engine Co. (Cummins), a manufacturing partnership formed to produce air compressors designed by WABCO. WABCO's ownership interest in the joint venture with Cummins is 70%.
The third joint venture is with Guangdong FUWA Heavy Industry Co., Ltd., (FUWA) to produce air disc brakes for commercial trailers in China. FUWA is the largest manufacturer of commercial trailer axles in China and in the world. WABCO's ownership interest in the joint venture with FUWA is 70%.
A fourth joint venture with Mingshui Automotive Fitting Factory (MAFF) to produce conventional mechanical products to the local market was ended in 2013 when the Company acquired the remaining shares in the joint venture, SWAP. Prior to this acquisition, WABCO's ownership interest in this joint venture with MAFF was 70%. Sales to and purchases from MAFF were immaterial in the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012. See Note 21 for further information.
| (Amounts in millions) | WABCO Sales to | WABCO Purchases from | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Joint Venture | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||||
| Sanwa-Seiki | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.2 | $ | 31.3 | $ | 33.7 | $ | 42.9 | |||||||||||
| Cummins | 86.0 | 72.9 | 75.8 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| FUWA | 6.3 | 3.0 | 1.0 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
NOTE 19. Geographic Information
WABCO is a fully integrated global business with management structures established in a variety of ways, including around products, distribution channels and key customers. Our largest customer is Daimler, which accounted for 11%, 12% and 11% of our sales in 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Volvo, our next largest customer, accounted for 10% of our sales in all three years 2014, 2013 and 2012. WABCO's plants, engineering, technical support, distribution centers and other support functions are shared among various product families and serve all distribution channels with many customers. Based on the organizational structure, as well as the nature of financial information available and reviewed by the Company's chief operating decision maker to assess performance and make decisions about resource allocations, the Company has concluded that its total WABCO operations represent one reportable segment and that WABCO's performance and future net cash flow perspectives are best understood and assessed as such.
European sales for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 accounted for 59%, 61% and 60% of total sales, respectively. Asian sales for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 accounted for 19%, 18% and 20% of total sales, respectively. We are strongly rooted in China and India and have achieved a leading position in the marketplace through increasingly close connectivity to customers. We continue to be strengthened in Asia by an outstanding network of suppliers, manufacturing sites and engineering hubs.
Geographic Data
72
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Product Sales: | |||||||||||
| OEM | $ | 2,099.4 | $ | 2,043.5 | $ | 1,847.4 | |||||
| Aftermarket | 751.6 | 677.0 | 630.0 | ||||||||
| Sales-Geographic distribution (a): | |||||||||||
| United States | $ | 383.5 | $ | 296.2 | $ | 274.5 | |||||
Europe (countries below are included in this total) | 1,668.5 | 1,666.3 | 1,496.7 | ||||||||
| Germany | 698.7 | 731.3 | 657.6 | ||||||||
| France | 89.8 | 99.5 | 89.0 | ||||||||
| Sweden | 206.8 | 215.4 | 201.7 | ||||||||
Other (countries below are included in this total) | 799.0 | 758.0 | 706.2 | ||||||||
| Japan | 105.4 | 100.5 | 116.1 | ||||||||
| China | 221.8 | 192.6 | 152.3 | ||||||||
| Brazil | 156.7 | 180.9 | 135.3 | ||||||||
| India | 127.1 | 106.1 | 147.0 | ||||||||
| Total sales | $ | 2,851.0 | $ | 2,720.5 | $ | 2,477.4 | |||||
| (a) | Sales to external customers are classified by country of destination. |
| As of December 31, | |||||||||||
(Amounts in millions) | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||
| Long-lived Assets (b) | |||||||||||
| Geographic distribution: | |||||||||||
| United States | $ | 22.0 | $ | 20.2 | $ | 14.1 | |||||
Europe (countries below are included in this total) | 727.4 | 655.7 | 607.8 | ||||||||
| Germany | 284.9 | 323.7 | 303.2 | ||||||||
| Poland | 127.6 | 110.8 | 93.7 | ||||||||
Other (countries below are included in this total) | 212.5 | 213.5 | 220.5 | ||||||||
| India | 97.2 | 97.7 | 104.1 | ||||||||
| Total long-lived assets | $ | 961.9 | $ | 889.4 | $ | 842.4 | |||||
| (b) | Amounts are presented on a net basis |
NOTE 20. Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging, requires a company to recognize all of its derivative instruments as either assets or liabilities on the balance sheet at fair value. The accounting for changes in the fair value of a derivative instrument depends on whether it qualifies and has been designated as a relationship hedge. For those derivative instruments that are designated and qualify as hedging instruments, a company must designate the hedging instrument, based upon the exposure being hedged, as a fair value hedge, cash flow hedge, or a hedge of a net investment in a foreign operation.
The Company recognizes all derivative financial instruments in the consolidated balance sheets at fair value using Level 2 inputs and these are classified as “other current assets,” “other assets,” “other accrued liabilities” or “other liabilities” on the consolidated balance sheets. Level 2 inputs used by the Company in valuing its derivative instruments include model-based valuation techniques for which all significant assumptions are observable in the market. The earnings impact resulting from changes in the fair value of derivative instruments is recorded in the same line item in the consolidated statements of operations as the underlying exposure being hedged or in accumulated other comprehensive income (AOCI) for derivatives that qualify and have been designated as cash flow hedges or hedges of a net investment in a foreign operation. Any ineffective portion of a financial instrument's change in fair value is recognized in earnings together with changes in the fair value of any derivatives not designated as relationship hedges.
73
Foreign exchange contracts are used by the Company to offset the earnings impact relating to the variability in exchange rates on certain assets and liabilities denominated in non-functional currencies and have not been designated as relationship hedges. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, forward contracts for an aggregate notional amount of €77.8 million ($94.5 million at December 31, 2014 exchange rates) and €61.8 million ($85.3 million at December 31, 2013 exchange rates) were outstanding with an average duration of one month. These foreign exchange contracts have offset the revaluation of assets and liabilities. The majority of these exchange contracts were entered into on December 30, 2014. The fair value of the derivatives was immaterial as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
For the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company recognized net gains on its derivative instruments of $2.2 million and net losses of $2.2 million, respectively, in "other non-operating income/expense, net" within the consolidated statements of operations.
NOTE 21. Business Combinations
2014 Acquisitions
On February 12, 2014, WABCO Europe BVBA (WABCO Europe), a Belgian subsidiary of the Company, entered into a stock purchase agreement (the Agreement) to purchase all of the outstanding shares of Tavares NV (Tavares), a limited liability company incorporated under the laws of Belgium, for a cash purchase price of €111.1 million ($151.0 million based on exchange rates on the acquisition date). This included the acquisition of €15.3 million of net cash held by its subsidiary Transics International NV (Transics), resulting in net consideration of €95.8 million ($130.2 million based on exchange rates on the acquisition date).
At the date of acquisition, Tavares held 96.84% of the outstanding shares of Transics, a limited liability company incorporated under the laws of Belgium listed on NYSE Euronext Brussels. Transics develops and markets fleet management solutions to help commercial vehicle manufacturers and fleet operators to more efficiently and safely manage their trucks and trailers. The suite of innovative solutions offered by Transics helps to improve fuel efficiency and productivity while lowering operating costs.
The allocation of the total purchase price to the assets and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date is final as of December 31, 2014 and is summarized as follows:
| (Amounts in millions) | |||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 25.3 | |
| Trade receivables | 15.6 | ||
| Trade payables | (5.4 | ) | |
| Debt | (4.5 | ) | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | (13.9 | ) | |
| Property, plant and equipment | 3.5 | ||
| Intangible assets | 51.1 | ||
| Other assets purchased and liabilities assumed, net | (6.6 | ) | |
| Identifiable net assets acquired | $ | 65.1 | |
| Goodwill | 91.6 | ||
| Noncontrolling interest | (5.7 | ) | |
| Total purchase price allocation | $ | 151.0 | |
The intangible assets include amounts recognized for the fair value of trade name and customer-based and technology-related assets. The fair values of the intangible assets and noncontrolling interest were determined based on an income and cost approach. The intangible assets are being amortized over a weighted-average useful life of approximately 6 years, the majority of which is not deductible for tax purposes. The goodwill generated is primarily attributable to expected synergies and is not deductible for tax purposes. The transaction-related costs were expensed as incurred and are recorded within other non-operating expense.
On April 10, 2014, in connection with the acquisition of Tavares, WABCO Europe launched a mandatory public takeover bid on all remaining shares and warrants issued by Transics in accordance with applicable Belgian takeover rules. Immediately following the initial acceptance period of the public bid, WABCO Europe launched a squeeze-out procedure that closed on May 16, 2014 for an additional payment of €4.2 million ($5.7 million based on exchange rates on the acquisition date), resulting in
74
WABCO Europe directly and indirectly owning all shares and warrants in Transics for a total net consideration of €99.9 million ($135.9 million based on exchange rates on the acquisition date).
The pro forma effects of this acquisition would not materially impact the Company's reported results for any period presented and as a result, no pro forma financial statements have been presented.
2012 Acquisitions
On September 13, 2012, the Company completed its acquisition of Ephicas, based in the Netherlands, a pioneering company in the field of innovative aerodynamic solutions for commercial vehicles. The Company acquired all of the equity interests in Ephicas and also assumed certain liabilities. Leveraging Ephicas’ expertise and patented technologies, the Company is developing a range of aerodynamic products – branded OptiFlow™ – that are designed to increase vehicle efficiency and reduce fuel consumption for trucks, trailers and buses.
The acquisition was recorded in accordance with ASC 805, Business Combinations. ASC 805 requires that all identifiable intangible assets be recognized as an asset apart from goodwill if the asset arises from contractual or other legal rights, or is separable from the acquired entity. The fair value of the Ephicas business identified intangible assets was $2.1 million and goodwill was $3.6 million.
NOTE 22. Noncontrolling Interests
On April 10, 2014, in connection with the acquisition of Tavares, WABCO Europe launched a mandatory public takeover bid on all remaining shares and warrants issued by Transics in accordance with applicable Belgian takeover rules. Immediately following the initial acceptance period of the public bid, WABCO Europe launched a squeeze-out procedure that closed on May 16, 2014. Net consideration paid as a result of the squeeze-out amounted to $5.7 million. See Note 21 for further discussion of the acquisition.
On August 30, 2013, the Company acquired the remaining shares in its Chinese joint venture, SWAP, for cash consideration of $4.6 million thus increasing its ownership from 70% to 100%. The acquisition resulted in the elimination of the noncontrolling interest.
NOTE 23. Quarterly Data (Unaudited)
| Year 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | First | Second | Third | Fourth | |||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 729.5 | $ | 735.0 | $ | 707.3 | $ | 679.1 | |||||||
| Cost of sales | 511.6 | 505.3 | 487.3 | 474.9 | |||||||||||
| Gross profit | 217.9 | 229.7 | 220.0 | 204.2 | |||||||||||
| Income before income taxes | 87.7 | 95.8 | 94.0 | 79.3 | |||||||||||
| Income tax expense | 15.8 | 17.9 | 9.5 | 12.4 | |||||||||||
| Net income attributable to Company | $ | 69.4 | $ | 75.0 | $ | 82.0 | $ | 65.1 | |||||||
| Net income per common share | |||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 1.13 | $ | 1.24 | $ | 1.38 | $ | 1.11 | |||||||
| Diluted | $ | 1.12 | $ | 1.23 | $ | 1.37 | $ | 1.10 | |||||||
75
| Year 2013 | |||||||||||||||
| (Amounts in millions) | First | Second | Third | Fourth | |||||||||||
| Sales | $ | 644.7 | $ | 678.2 | $ | 677.1 | $ | 720.5 | |||||||
| Cost of sales | 447.0 | 471.6 | 477.6 | 515.2 | |||||||||||
| Gross profit | 197.7 | 206.6 | 199.5 | 205.3 | |||||||||||
| Income before income taxes | 84.2 | 95.5 | 90.5 | 370.8 | |||||||||||
| Income tax expense / (benefit) | 8.2 | 9.7 | 8.0 | (46.8 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net income attributable to Company | $ | 73.7 | $ | 83.2 | $ | 80.0 | $ | 416.3 | |||||||
| Net income per common share | |||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 1.17 | $ | 1.33 | $ | 1.28 | $ | 6.73 | |||||||
| Diluted | $ | 1.15 | $ | 1.31 | $ | 1.26 | $ | 6.65 | |||||||
The sum of each value line for the four quarters does not necessarily equal the amount reported for the full year because of rounding.
The income tax benefit for 2013 includes taxes on earnings in profitable jurisdictions, income offset by fully valued net operating losses, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions, and a tax provision on unremitted foreign earnings of $300.0 million in a Belgian affiliate for which amount the Company does not assert permanent reinvestment outside the United States. This assertion is resulting from the Company recognizing earnings in the fourth quarter from the receipt of an exceptional refund including interest from the European Commission related to the Company’s appeal of the EC fine as further discussed in Note 15. Additionally, the Company recorded a tax benefit for a release at the end of the year of a valuation allowance related to management’s determination that it is more likely than not that the Company will realize its deferred tax asset in a foreign jurisdiction. Management has also determined that it is more likely than not that it will not realize $9.0 million of its deferred tax assets in other foreign jurisdictions and has recorded a valuation allowance against such deferred tax assets.
The income tax benefit recorded in the third quarter of 2012 is the net result of the release of tax accruals for uncertain tax positions due to certain government filings submitted in January 2012, a tax benefit related to the Company's filing of its 2011 U.S. Federal Income Tax Return in September 2012, taxes on earnings in profitable jurisdictions, income offset by fully valued net operating losses, the accrual of interest on uncertain tax positions and benefits from certain foreign tax planning.
76
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
The Company has established a Disclosure Controls Committee that assists the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer in their evaluation of the Company's disclosure controls and procedures. Our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded, based on their evaluation as of the end of the period covered by this report, that our disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, Rule 13a-15(e), were not effective as of December 31, 2014 due to the material weakness in internal control over financial reporting on pension accounting described in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting below. Notwithstanding the material weakness discussed below, our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has concluded that the consolidated financial statements for the periods covered by and included in this Form 10-K are fairly presented in all material respects in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (GAAP).
Management's Report On Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for the Company. The Company's internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of consolidated financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. The Company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
| (i) | pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company, |
| (ii) | provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company, and |
| (iii) | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company's assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements. |
Due to its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies and procedures included in such controls may deteriorate.
The Company conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting based upon the 1992 framework in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The scope of our efforts included all of our operations other than those that we acquired in the February 12, 2014 acquisition of Transics. In accordance with the SEC's published guidance, because we acquired these operations during our fiscal year, we excluded these operations from our assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. Total assets as of December 31, 2014 and total revenues for the year ended December 31, 2014 related to the Transics operations were $176.1 million and $64.1 million, respectively. SEC rules require that we complete our assessment of the internal controls over financial reporting of the Transics operations within one year after the date of the acquisition. Based upon such evaluation, our management concluded that the Company's internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of December 31, 2014 due to the material weakness described below.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. In connection with the above assessment, management identified the following control deficiency as of December 31, 2014 that constituted a material weakness:
Calculation of German Pension Plan Obligations - Management has concluded that there is a material weakness in the Company’s accounting for pension plan obligations. Specifically, the Company did not have effective controls in operation over the application of its actuarial assumptions on mortality or effective controls designed and in operation over the review of the detailed calculations in the actuary’s model in calculating pension plan obligations relating to its defined benefit plan in Germany.
77
With regards to mortality assumptions, the controls that were in place did not operate effectively as designed to ensure the use of appropriate mortality assumptions in calculating the pension plan obligations. This control deficiency did not result in misstatements in prior period consolidated financial statements. During this year's financial statement closing process, management corrected the error by applying the appropriate mortality assumptions in the calculation of pension plan obligations as of December 31, 2014 prior to the issuance of consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2014.
With regards to the detailed calculations in our actuary’s model, the Company did not have controls designed to determine that the assumptions within our actuary's model agreed to those determined by management. This control deficiency did not result in any material misstatements to the consolidated financial statements in any of the years presented.
Management concluded that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement to our annual or interim consolidated financial statements could have occurred and not been detected or prevented. Accordingly, the Company has determined that this control deficiency constituted a material weakness.
The Company's effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, has been audited by Ernst & Young Bedrijfsrevisoren BCVBA/Reviseurs d'Entreprises SCCRL, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their attestation report which is included immediately below.
Plan for Remediation
Management has taken immediate action to remediate the material weakness discussed above. We have implemented or plan to implement remedial measures including improvements in the review of mortality assumptions used in the valuation of our pension obligation and strengthening our review controls over the actuarial model through the use of a secondary external actuarial firm. The material weakness will not be considered remediated until the applicable remedial controls operate for a sufficient period of time and management has concluded, through testing, that these controls are operating effectively.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in internal control over financial reporting during the most recent fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
WABCO Holdings Inc.
February 19, 2015
78
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of WABCO Holdings Inc. and Subsidiaries
We have audited WABCO Holdings Inc. and subsidiaries' internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in the Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 Framework) (the COSO criteria). WABCO Holdings Inc. and subsidiaries' management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
As indicated in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, management’s assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting did not include the internal controls of Transics International NV, which is included in the 2014 consolidated financial statements of WABCO Holdings Inc., and constituted $176.1 million of total assets as of December 31, 2014 and $64.1 million of revenues for the year then ended. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting of WABCO Holdings Inc., also did not include an evaluation of the internal control over financial reporting of Transics International NV.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The following material weakness has been identified and included in management’s assessment: management’s review of actuarial assumptions on mortality and review of detailed calculations in the actuary's model in calculating the defined pension benefit plan obligation in Germany.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of WABCO Holdings Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, cash flows and shareholders' equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014. This material weakness was considered in determining the nature, timing and extent of audit tests applied in our audit of the 2014 financial statements, and this report does not affect our report dated February 19, 2015, which expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
In our opinion, because of the effect of the material weakness described above on the achievement of the objectives of the control criteria, WABCO Holdings Inc. and subsidiaries has not maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on the COSO criteria.
79
Ernst & Young Bedrijfsrevisoren BCVBA/Reviseurs d'Entreprises SCCRL
Represented by:
/s/ Piet Hemschoote, Partner
Brussels, Belgium
February 19, 2015
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
80
PART III
| ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
Pursuant to instruction G(3) to Form 10-K, the information required by Item 10 with respect to the Directors of the Company set forth under the heading “Proposal 1 - Election of Directors” and “Directors” in the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year covered by this report is incorporated herein by reference.
The information required by Item 10 with respect to the executive officers of the Company has been included in Part I of this Form 10-K (as Item 4A) under the heading “Executive Officers of the Registrant” in reliance on Instruction G(3) of Form 10-K and Instruction 3 to Item 401(b) of Regulation S-K.
Pursuant to instruction G(3) to Form 10-K, information concerning the Audit Committee and audit committee financial expert disclosure set forth under the headings “Governance - Board Matters and Committee Membership” and “- Committees of the Board - Audit Committee” in the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year covered by this report is incorporated herein by reference.
Pursuant to instruction G(3) to Form 10-K, information concerning compliance with Section 16(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 by officers and directors of the Company set forth under the heading “Certain Relationships or Related Person Transactions and Section 16 Reporting Compliance - Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year covered by this report is incorporated herein by reference.
Information regarding our Code of Conduct and Ethics set forth under the caption “Code of Conduct and Ethics” in Item 1 of Part I of this Form 10-K is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
Pursuant to Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K, information concerning director and officer executive compensation and related matters set forth under the headings “Report of the Compensation, Nominating and Governance Committee,” “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” “Executive Compensation” and “Director Compensation” in the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year covered by this report is incorporated herein by reference.
Pursuant to instruction G(3) to Form 10-K, information concerning compensation committee interlocks and insider participation set forth under the headings “Governance - Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” in the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year covered by this report is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
Pursuant to Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K, information concerning shares of common stock of the Company beneficially owned by management set forth under the heading “Common Stock Ownership of Officers, Directors and Significant Shareholders” in the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year covered by this report is incorporated herein by reference.
Pursuant to Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K, information concerning securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans set forth under the heading “Equity Compensation Plans” in the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year covered by this report is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND, DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
Pursuant to Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K, information concerning certain relationships and related party transactions and director independence set forth under the headings “Certain Relationships or Related Person Transactions and Section 16 Reporting Compliance - Certain Relationships and Related Person Transactions,” and “Governance - Independence Standards for Board
81
Service” and “Availability of Corporate Governance Materials” in the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year covered by this report is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
Pursuant to Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K, information concerning principal accounting fees and services set forth under the heading “Audit Committee Matters - Audit Committee's Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures” and “Audit and Non-Audit Fees” in the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year covered by this report is incorporated herein by reference.
82
PART IV
| ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
| (a) | 1. and 2. Financial statements and financial statement schedules |
The financial statements and financial statement schedule listed in the Index to Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedule on the following page are incorporated herein by reference.
(b) The exhibits to this Report are listed on the accompanying Index to Exhibits and are incorporated herein by reference or are file as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
83
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULE
| Page No. | ||
| 1 | Financial Statements: | |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | ||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations for years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 | ||
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 | ||
| Consolidated Balance Sheets at December 31, 2014 and 2013 | ||
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 | ||
| Consolidated Statements of Shareholders' Equity for years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 | ||
| Notes to Financial Statements | ||
| 2 | Financial statement schedule, years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 | |
| Schedule II - Valuation and Qualifying Accounts | ||
All other schedules have been omitted because the information is not applicable or is not material or because the information required is included in the financial statements or the notes thereto.
84
SCHEDULE II - VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
Years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012
(Amounts in thousands)
| Description | Balance Beginning of Period | Additions | Deductions | Foreign Currency Translation Effects | Balance End of Period | ||||||||||
| 2014: | |||||||||||||||
| Reserve deducted from assets: | |||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts receivable | 4,999 | 384 | (817 | ) | (505 | ) | 4,061 | ||||||||
| 2013: | |||||||||||||||
| Reserve deducted from assets: | |||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts receivable | 3,581 | 1,346 | (66 | ) | 138 | 4,999 | |||||||||
| 2012: | |||||||||||||||
| Reserve deducted from assets: | |||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts receivable | 3,425 | 418 | (314 | ) | 52 | 3,581 | |||||||||
85
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
WABCO HOLDINGS INC.
By: /s/ Jacques Esculier
Jacques Esculier
Chief Executive Officer and Director
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signatures | Title | Date |
| /s/ Jacques Esculier | Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors | February 19, 2015 |
| Jacques Esculier | (Principal Executive Officer) | |
| /s/ Prashanth Mahendra-Rajah | Chief Financial Officer | February 19, 2015 |
| Prashanth Mahendra-Rajah | ||
| /s/ Robert Farrell | Vice President and Interim Controller | February 19, 2015 |
| Robert Farrell | ||
| * | Director | February 19, 2015 |
| Jean-Paul L. Montupet | ||
| * | Director | February 19, 2015 |
| G. Peter D'Aloia | ||
| * | Director | February 19, 2015 |
| John F. Fiedler | ||
| * | Director | February 19, 2015 |
| Dr. Juergen Gromer | ||
| * | Director | February 19, 2015 |
| Mary Petrovich | ||
| * | Director | February 19, 2015 |
| Kenneth J. Martin | ||
| * | Director | February 19, 2015 |
| Michael T. Smith | ||
| * | Director | February 19, 2015 |
| Donald J. Stebbins | ||
| * | Director | February 19, 2015 |
| David N. ("Nick") Reilly | ||
* Signed by Attorney-in-fact
| /s/ Vincent Pickering |
Vincent Pickering Attorney-in-fact |
86
WABCO HOLDINGS INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
INDEX TO EXHIBITS
(The File Number of the Registrant, WABCO Holdings Inc., is 1-33332)
Certain of the following exhibits, designated with an asterisk (*) are filed herewith. The exhibits not so designated have been previously filed by the registrant with the Commission and are incorporated herein by reference to the documents indicated in parentheses, following the descriptions of such exhibits.
| Exhibit No. | Description |
| 2.1 | Separation and Distribution Agreement, dated as of July 16, 2007, by and between Trane Inc. and WABCO Holdings Inc. (previously filed as Exhibit 2.1 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 20, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 3.1 | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (previously filed as Exhibit 3.1 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 18, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 3.2 | Amended and Restated By-Laws of WABCO Holdings Inc. (previously filed as Exhibit 3.2 to the Company’s Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 15, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 4.1 | Rights Agreement, dated as of July 16, 2007, by and between WABCO Holdings Inc. and The Bank of New York (previously filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 18, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 4.2 | Certificate of Designation of Junior Participating Cumulative Preferred Stock (previously filed as Exhibit 4.2 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 18, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 4.3 | Right Certificate (attached as an exhibit to the Rights Agreement, dated as of July 16, 2007, by and between WABCO Holdings Inc. and the Bank of New York (previously filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 18, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 4.4 | Form of Specimen Common Stock Certificate (previously filed as Exhibit 4.4 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on November 8, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.1 | Tax Sharing Agreement, entered into as of July 16, 2007, by and among Trane Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries and WABCO Holdings Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 20, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.2 | Employee Matters Agreement, dated as of July 16, 2007, by and between Trane Inc. and WABCO Holdings Inc. (previously filed as Exhibit 10.3 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 20, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.3 | Indemnification and Cooperation Agreement, made and entered into as of July 16, 2007, by and among Trane Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries and WABCO Holdings Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries (previously filed as Exhibit 10.4 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 20, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.4 | WABCO Holdings Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form S-8 (File No. 333-144906), filed on July 27, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.5 | Amendment to WABCO Holdings Inc. Omnibus Incentive Plan (previously filed as Exhibit 10.5 to the Company's Form 10-K, as amended (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 17, 2012 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.6 | Amended and Restated WABCO Holdings Inc.2009 Omnibus Incentive Plan (previously filed as Appendix C to the Company's Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A (File No. 001-33332), filed on April 19, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
87
| 10.7 | Form of Indemnification Agreement for executive officers and members of the Board of Directors (previously filed as Exhibit 10.6 to the Company's Form 10-12B, as amended (File No. 001-33332), filed on May 23, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.8 | Form of WABCO Holdings Inc. Stock Option Grant Agreement for U.S. Employees (previously filed as Exhibit 10.7 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on November 8, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.9 | Form of WABCO Holdings Inc. Stock Option Grant Agreement for Non-U.S. Employees (previously filed as Exhibit 10.8 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on November 8, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.10 | Form of WABCO Holdings Inc. Restricted Unit Grant Agreement for U.S. Employees (previously filed as Exhibit 10.9 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on November 8, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.11 | Form of WABCO Holdings Inc. Restricted Unit Grant Agreement for Non-U.S. Employees (previously filed as Exhibit 10.10 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on November 8, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.12 | Form of WABCO Holdings Inc 2009 Omnibus Incentive Plan Performance-Based Restricted Unit Grant Agreement (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 28, 2011 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.13 | Form of Director Deferred Stock Unit Award Agreement under the WABCO Holdings Inc 2009 Omnibus Incentive Plan (previously filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 26, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.14 | WABCO Holdings Inc. Change of Control Severance Plan (previously filed as Exhibit 10.11 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on November 8, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.15 | Amendment No. 1 to WABCO Holdings Inc. Change of Control Severance Plan, (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 14, 2008 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.16 | Amendment No. 2 to WABCO Holdings Inc. Change of Control Severance Plan, effective as of December 31, 2008 (previously filed as Exhibit 10.14 to the Company's Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 24, 2009 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.17 | Amendment No. 3 to WABCO Holdings Inc. Change of Control Severance Plan, effective as of January 1, 2012 (previously filed as Exhibit 10.17 to the Company's Form 10-K, as amended (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 17, 2012 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.18 | Amendment No. 4 to WABCO Holdings Inc. Change of Control Severance Plan, effective as of November 30, 2012 (previously filed as Exhibit 10.18 to the Company’s Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 15, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.19 | WABCO Holdings Inc. Deferred Compensation Plan (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form S-8 (File No. 333-148972), filed on January 31, 2008 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.20 | Amendment to WABCO Holdings Inc. Deferred Compensation Plan, effective as of December 31, 2008 (previously filed as Exhibit 10.16 to the Company's Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 24, 2009 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.21 | WABCO Holdings Inc. Supplemental Savings Plan (previously filed as Exhibit 10.20 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on November 8, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.22 | Amendment to WABCO Holdings Inc. Supplemental Savings Plan, effective as of December 31, 2008 (previously filed as Exhibit 10.18 to the Company's Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 24, 2009 and herein incorporated by reference). |
88
| 10.23 | Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation Program for Belgian Executives (Summary of French Language Program Document) (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on May 7, 2009 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.24 | Partnership Agreement, dated January 9, 1990, as amended by Amendment No. 1 thereto, dated May 29, 1990, and Amendment No. 2 thereto, entered into as of May 10, 2006, of Meritor WABCO Vehicle Control Systems (formerly known as Rockwell WABCO Vehicle Control Systems), by and between WABCO Automotive Control Systems, Inc. and ArvinMeritor Brake Holdings, Inc. (successor-in-interest to Rockwell Brake Systems, Inc.) (previously filed as Exhibit 10.5 to the Company's Form 10-12B (File No. 001-33332), filed on May 23, 2007 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.25 | $400,000,000 Facility Agreement, dated July 8, 2011, for WABCO Holdings Inc. arranged by Banc of America Securities Limited, Citigroup Global Markets Limited, Fortis Bank S.A./N.V., ING Belgium SA/NV, Société Générale Corporate & Investment Banking, The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ, LTD., The Royal Bank of Scotland NV, (Belgium) Branch, and Credit Lyonnais and Unicredit Bank AG, with Banc of America Securities Limited acting as agent (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 11, 2011 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.26 | Amendment Letter, dated August 23, 2013, to the $400,000,000 Facility Agreement, dated July 8, 2011, for WABCO Holdings Inc. arranged by Banc of America Securities Limited, Citigroup Global Markets Limited, Fortis Bank S.A./N.V., ING Belgium SA/NV, Société Générale Corporate & Investment Banking, The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ, LTD., The Royal Bank of Scotland NV, (Belgium) Branch, and Credit Lyonnais and Unicredit Bank AG, with Banc of America Securities Limited acting as agent (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on August 26, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.27 | $100,000,000 Facility Agreement dated December 17, 2014, for WABCO Holdings Inc. arranged by Bank of America N.A., London Branch, Citigroup Global Markets Limited, BNP Paribas Fortis Bank S.A./N.V., The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ, Ltd. and Unicredit Bank AG with Citigroup Global Markets Limited acting as coordinator and Citibank International Limited acting as agent (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on December 19, 2014 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.28 | Management Agreement, effective as of January 1, 2012 between WABCO Europe SPRL/BVBA and Jacques Esculier (previously filed as Exhibit 10.31 to the Company’s Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 15, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.29 | Management Agreement, effective as of January 1, 2012 between WABCO Europe SPRL/BVBA and Nikhil Varty (previously filed as Exhibit 10.32 to the Company’s Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 15, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.30 | Letter from the Company to Nikhil Varty, dated November 12, 2012 (previously filed as Exhibit 10.36 to the Company’s Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 15, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.31 | First Amendment to Management Agreement for Nikhil Varty, executed as of December 30, 2012 between WABCO Europe SPRL/BVBA and Nikhil Varty (previously filed as Exhibit 10.37 to the Company’s Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 15, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.32 | First Amendment to Offer Letter for Nikhil Varty dated November 12, 2012 from the Company to Nikhil Varty (previously filed as Exhibit 10.39 to the Company’s Form 10-K (File No. 001-33332), filed on February 15, 2013 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.33 | Offer letter from the Company to Prashanth Mahendra-Rajah, dated March 20, 2014 (previously filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on April 25, 2014 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 10.34 | Offer letter from the Company to Leon Liu, dated June 5, 2014 (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on July 25, 2014 and herein incorporated by reference). |
89
| 10.35 | Stock Purchase Agreement, made on February 12, 2014, among Creafund Transics Shares Stille Maatschap, Ludwig Lemenu, Walter Mastelinck, Cassel BVBA, Uniholding SA and WABCO Europe BVBA (previously filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 10-Q (File No. 001-33332), filed on April 25, 2014 and herein incorporated by reference). |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of the Company.* |
| 23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young Bedrijfsrevisoren BCVBA/Réviseurs d'Entreprises SCCRL.* |
| 24.1 | Powers of Attorney (G. Peter D'Aloia, John F. Fiedler, Dr. Juergen Gromer, Kenneth J. Martin, Mary Petrovich, Michael T. Smith, Donald J. Stebbins, Jean-Paul L. Montupet and David N. ("Nick") Reilly.* |
| 31.1 | Certification of the Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.* |
| 31.2 | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.* |
| 32.1 | Certification of the Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.* |
| 32.2 | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.* |
| 101 | The following financial information from WABCO Holdings Inc.'s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2014, filed with the SEC on February 19, 2015, formatted in Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL): (i) the Consolidated Statements of Operations, (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income, (iii) the Consolidated Balance Sheets, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, (v) the Consolidated Statements of Shareholders' Equity, and (vi) Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
90