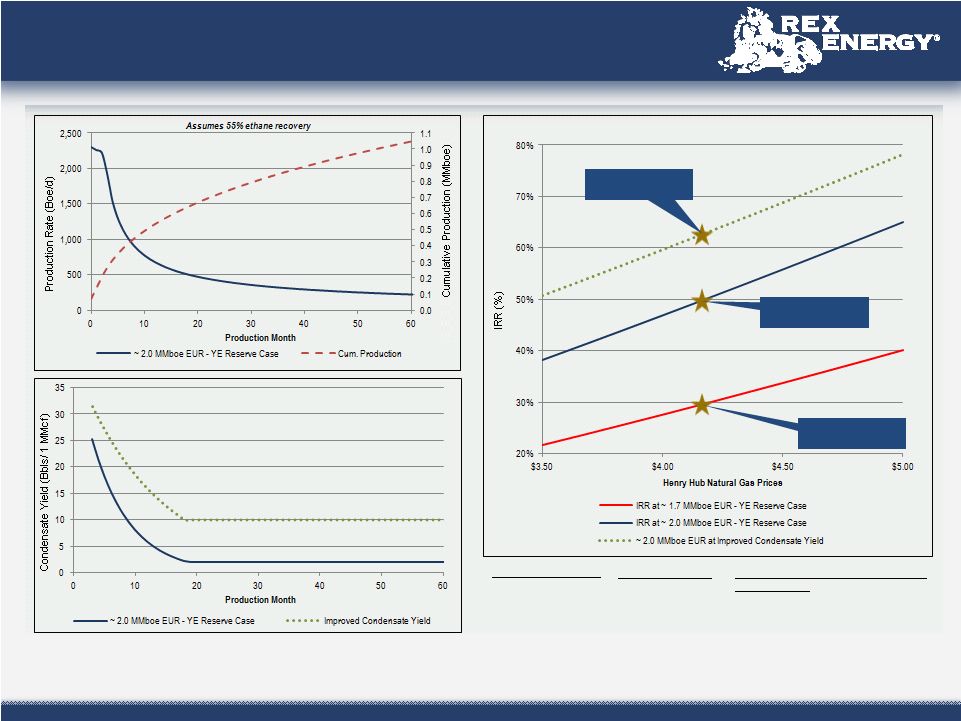
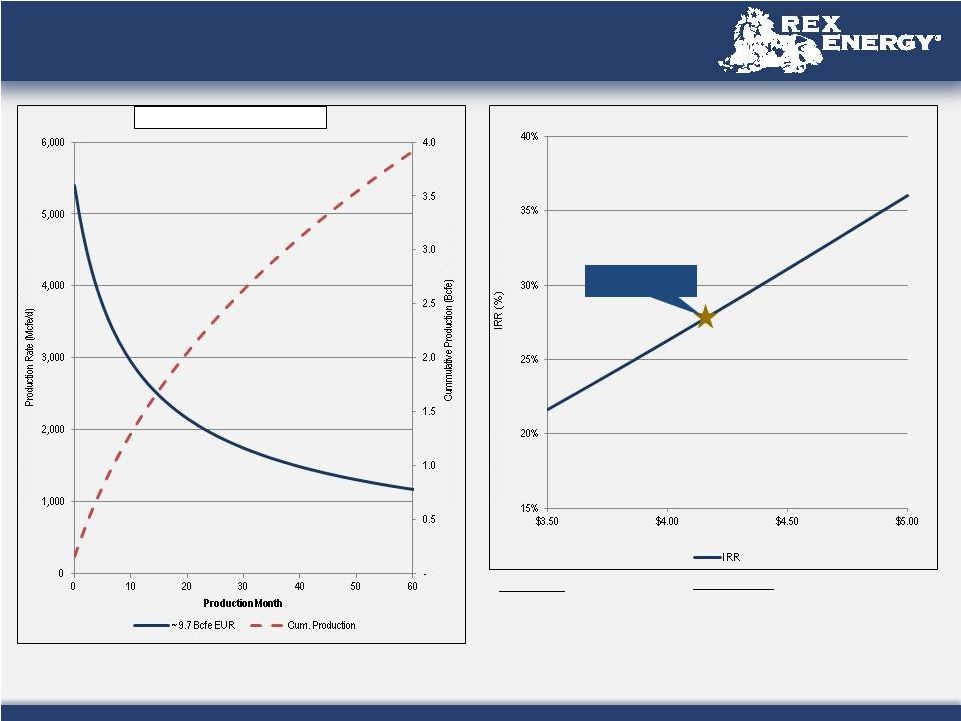
Estimates Used in This Presentation 3 Hydrocarbon Volumes The SEC permits publicly-reporting oil and gas companies to disclose “proved reserves” in their filings with the SEC. “Proved reserves” are estimates that geological and engineering data demonstrate with reasonable certainty to be recoverable in future years from known reservoirs under existing economic and operating conditions. SEC rules also permit the disclosure of “probable” and possible” reserves. Rex Energy discloses proved reserves but does not disclose probable or possible reserves. We may use certain broader terms such as “resource potential,” “EUR” (estimated ultimate recovery of resources, defined below) and other descriptions of volumes of potentially recoverable hydrocarbons throughout this presentation. These broader classifications do not constitute “reserves” as defined by the SEC and we do not attempt to distinguish these classifications from probable or possible reserves as defined by SEC guidelines. In addition, we are prohibited from disclosing hydrocarbon quantities that do not constitute reserves in documents filed with the SEC. The company defines EUR as the cumulative oil and gas production expected to be economically recovered from a reservoir or individual well from initial production until the end of its useful life. Our estimates of EURs and resource potential have been prepared internally by our engineers and management without review by independent engineers. These estimates are by their nature more speculative than estimates of proved, probable, and possible reserves and accordingly are subject to substantially greater risk of being actually realized. We include these estimates to demonstrate what we believe to be the potential for future drilling and production by the company. Ultimate recoveries will be dependent upon numerous factors including actual encountered geological conditions, the impact of future oil and gas pricing, exploration and development costs, and our future drilling decisions and budgets based upon our future evaluation of risk, returns and the availability of capital and, in many areas, the outcome of negotiation of drilling arrangements with holders of adjacent or fractional interest leases. Estimates of resource potential and other figures may change significantly as development of our resource plays provide additional data and therefore actual quantities that may ultimately be recovered will likely differ materially from these estimates. Potential Drilling Locations Our estimates of potential drilling locations are prepared internally by our engineers and management and are based upon a number of assumptions inherent in the estimate process. Management, with the assistance of engineers and other professionals, as necessary, conducts a topographical analysis of our unproved prospective acreage to identify potential well pad locations using operationally approved designs and considering several factors, which may include but are not limited to access roads, terrain, well azimuths, and well pad sizes. For our operations in Pennsylvania, we then calculate the number of horizontal well bores for which the company appears to control sufficient acreage to drill the lateral wells from each potential well pad location to arrive at an estimated number of net potential drilling locations. For our operations in Ohio, we calculate the number of horizontal well bores that may be drilled from the potential well pad and multiply this by the company’s net working interest percentage of the proposed unit to arrive at an estimated number of net potential drilling locations. In both cases, we then divide the unproved prospective acreage by the number of net potential drilling locations to arrive at an average well spacing. Management uses these estimates to, among other things, evaluate our acreage holdings and to formulate plans for drilling. Any number of factors could cause the number of wells we actually drill to vary significantly from these estimates, including: the availability of capital, drilling and production costs, commodity prices, availability of drilling services and equipment, lease expirations, regulatory approvals and other factors. |