
Targeted Immunology�CD40/CD40L Therapeutics Transplantation | Autoimmunity | ALS January 2023 Exhibit 99.2

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward‐looking statements that involves substantial risks and uncertainties. Any statements about the company’s future expectations, plans and prospects, including statements about its strategy, future operations, development of its product candidates, and other statements containing the words “believes,” “anticipates,” “plans,” “expects,” “estimates,” “intends,” “predicts,” “projects,” “targets,” “could,” “may,” and similar expressions, constitute forward‐looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, although not all forward‐looking statements include such identifying words. Forward‐looking statements include, but are not limited to statements regarding: expectations regarding the timing for the commencement and completion of product development or clinical trials; the rate and degree of market acceptance and clinical utility of the company’s products; the company’s commercialization, marketing and manufacturing capabilities and strategy; the company’s intellectual property position and strategy; the company’s ability to identify additional products or product candidates with significant commercial potential; the company’s estimates regarding expenses, future revenue, capital requirements and needs for additional financing; developments relating to the company’s competitors and industry; and the impact of government laws and regulations. Actual results may differ materially from those indicated by such forward‐looking statements as a result of various important factors, including: the ability to develop commercially viable product formulations; the sufficiency of the company’s cash resources; the ability to obtain necessary regulatory and ethics approvals to commence additional clinical trials; whether data from early clinical trials will be indicative of the data that will be obtained from future clinical trials; whether the results of clinical trials will warrant submission for regulatory approval of any investigational product; whether any such submission will receive approval from the United States Food and Drug Administration or equivalent foreign regulatory agencies and, if we are able to obtain such approval for an investigational product, whether it will be successfully distributed and marketed. These risks and uncertainties, as well as other risks and uncertainties that could cause the company’s actual results to differ significantly from the forward‐looking statements contained herein, are discussed in our annual report on Form 10‐K for the year ended December 31, 2021, and other filings with the SEC which can be found at www.sec.gov. Any forward‐looking statements contained in this presentation speak only as of the date hereof and not of any future date, and the company expressly disclaims any intent to update any forward‐looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. Photo: Gertrude “Trudy” Elion.
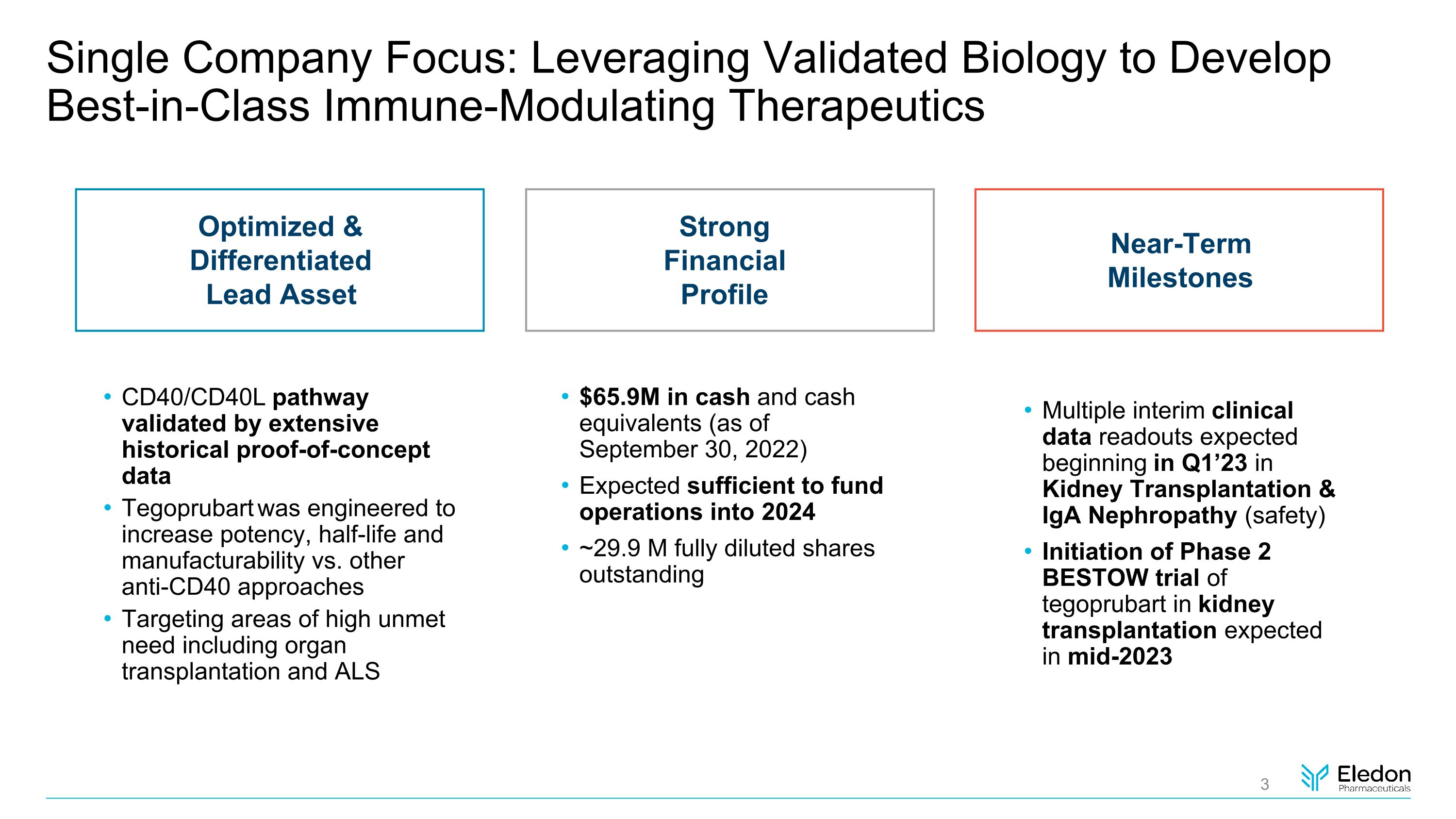
Single Company Focus: Leveraging Validated Biology to Develop Best-in-Class Immune-Modulating Therapeutics CD40/CD40L pathway validated by extensive historical proof-of-concept data Tegoprubart was engineered to increase potency, half-life and manufacturability vs. other anti-CD40 approaches Targeting areas of high unmet need including organ transplantation and ALS Optimized & Differentiated Lead Asset Near-Term Milestones Multiple interim clinical data readouts expected beginning in Q1’23 in Kidney Transplantation & IgA Nephropathy (safety) Initiation of Phase 2 BESTOW trial of tegoprubart in kidney transplantation expected in mid-2023 Strong Financial Profile $65.9M in cash and cash equivalents (as of September 30, 2022) Expected sufficient to fund operations into 2024 ~29.9 M fully diluted shares�outstanding
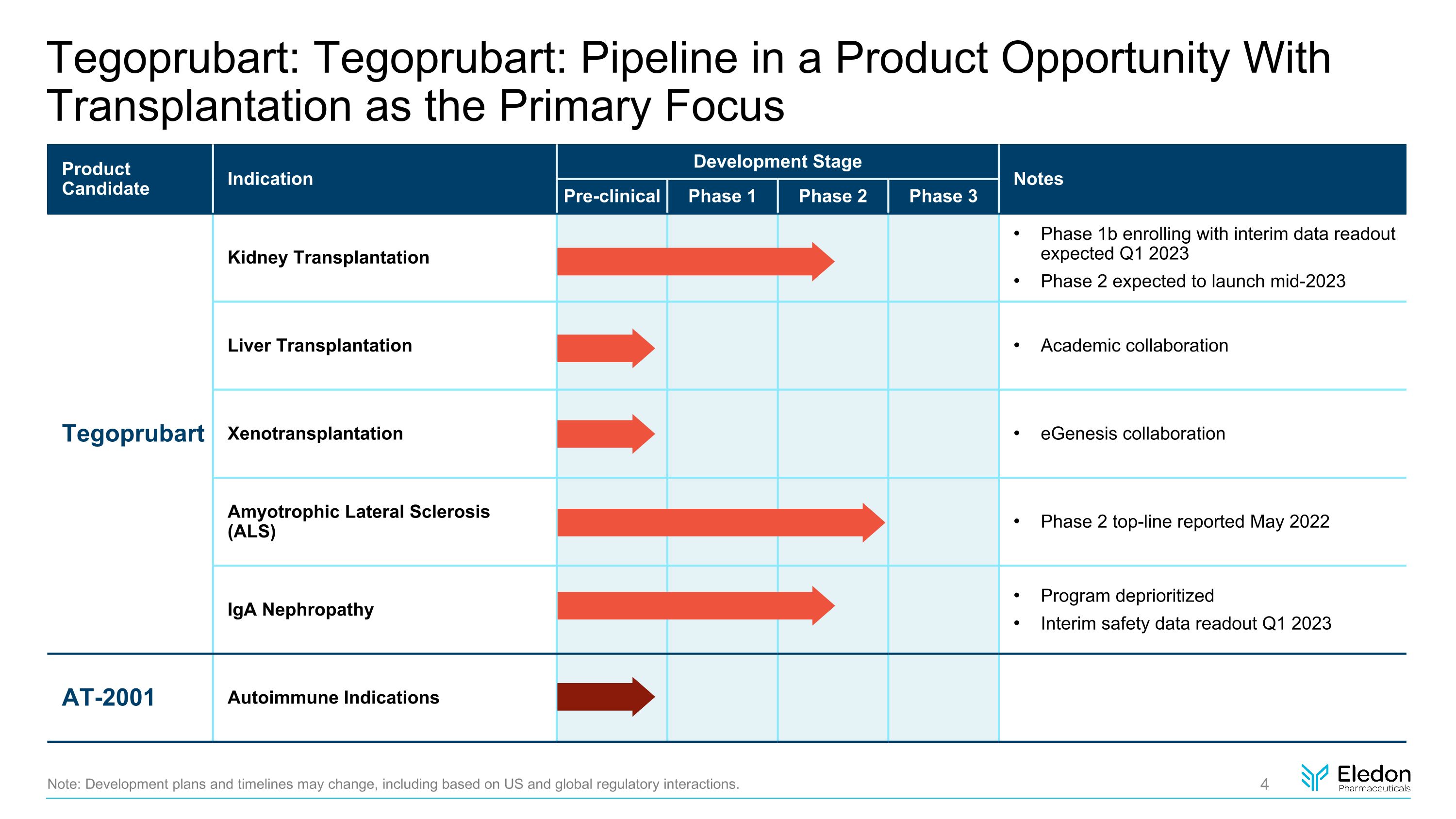
Tegoprubart: Tegoprubart: Pipeline in a Product Opportunity With Transplantation as the Primary Focus Note: Development plans and timelines may change, including based on US and global regulatory interactions. Product Candidate Indication Development Stage Notes Pre-clinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Tegoprubart Kidney Transplantation Phase 1b enrolling with interim data readout expected Q1 2023 Phase 2 expected to launch mid-2023 Liver Transplantation Academic collaboration Xenotransplantation eGenesis collaboration Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis�(ALS) Phase 2 top-line reported May 2022 IgA Nephropathy Program deprioritized Interim safety data readout Q1 2023 AT-2001 Autoimmune Indications
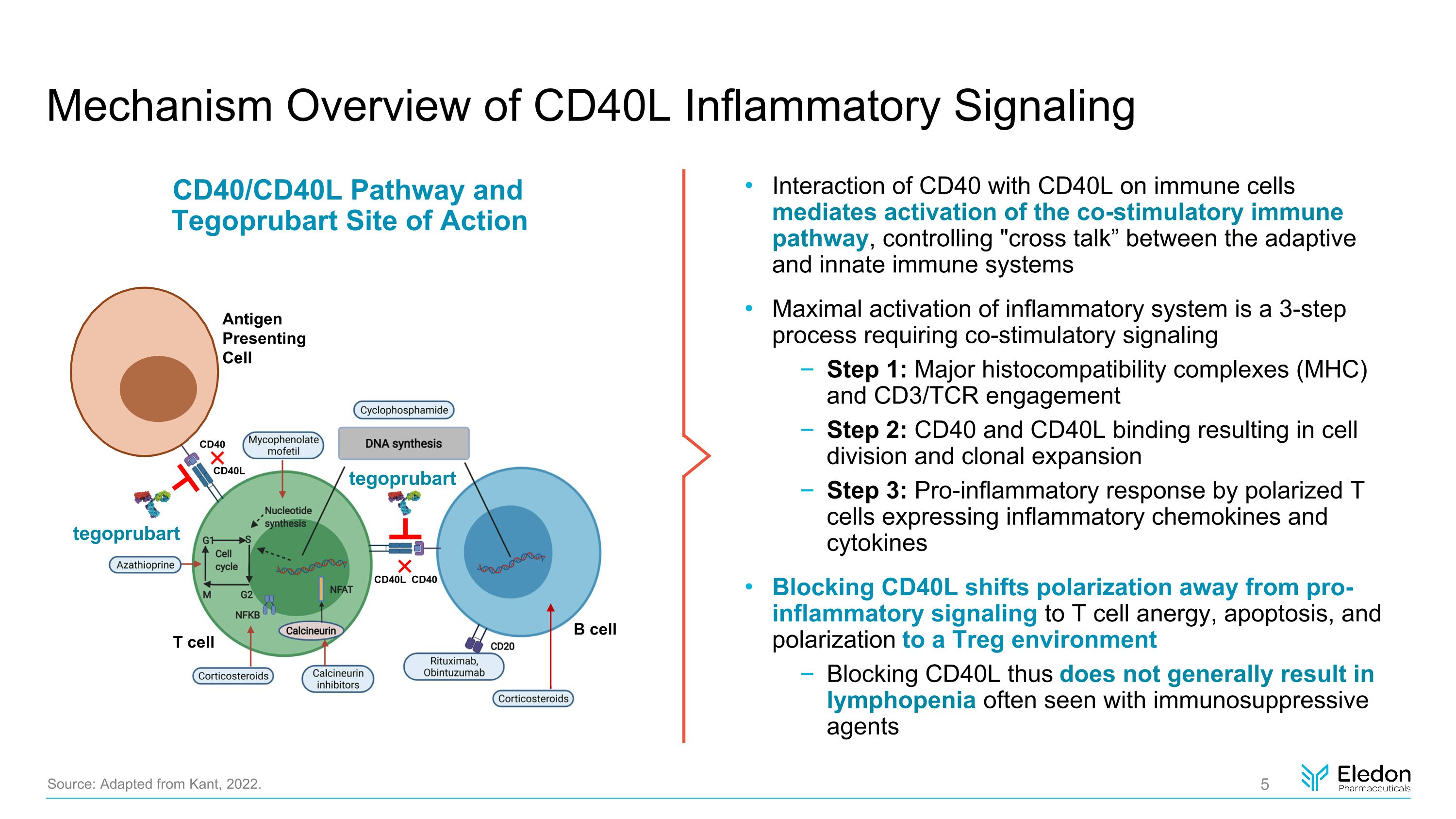
Mechanism Overview of CD40L Inflammatory Signaling Interaction of CD40 with CD40L on immune cells mediates activation of the co-stimulatory immune pathway, controlling "cross talk” between the adaptive and innate immune systems Maximal activation of inflammatory system is a 3-step process requiring co-stimulatory signaling Step 1: Major histocompatibility complexes (MHC) and CD3/TCR engagement Step 2: CD40 and CD40L binding resulting in cell division and clonal expansion Step 3: Pro-inflammatory response by polarized T cells expressing inflammatory chemokines and cytokines Blocking CD40L shifts polarization away from pro-inflammatory signaling to T cell anergy, apoptosis, and polarization to a Treg environment Blocking CD40L thus does not generally result in lymphopenia often seen with immunosuppressive agents Source: Adapted from Kant, 2022. Antigen Presenting Cell T cell B cell CD40L CD40 CD40L CD40 tegoprubart tegoprubart CD40/CD40L Pathway and Tegoprubart Site of Action
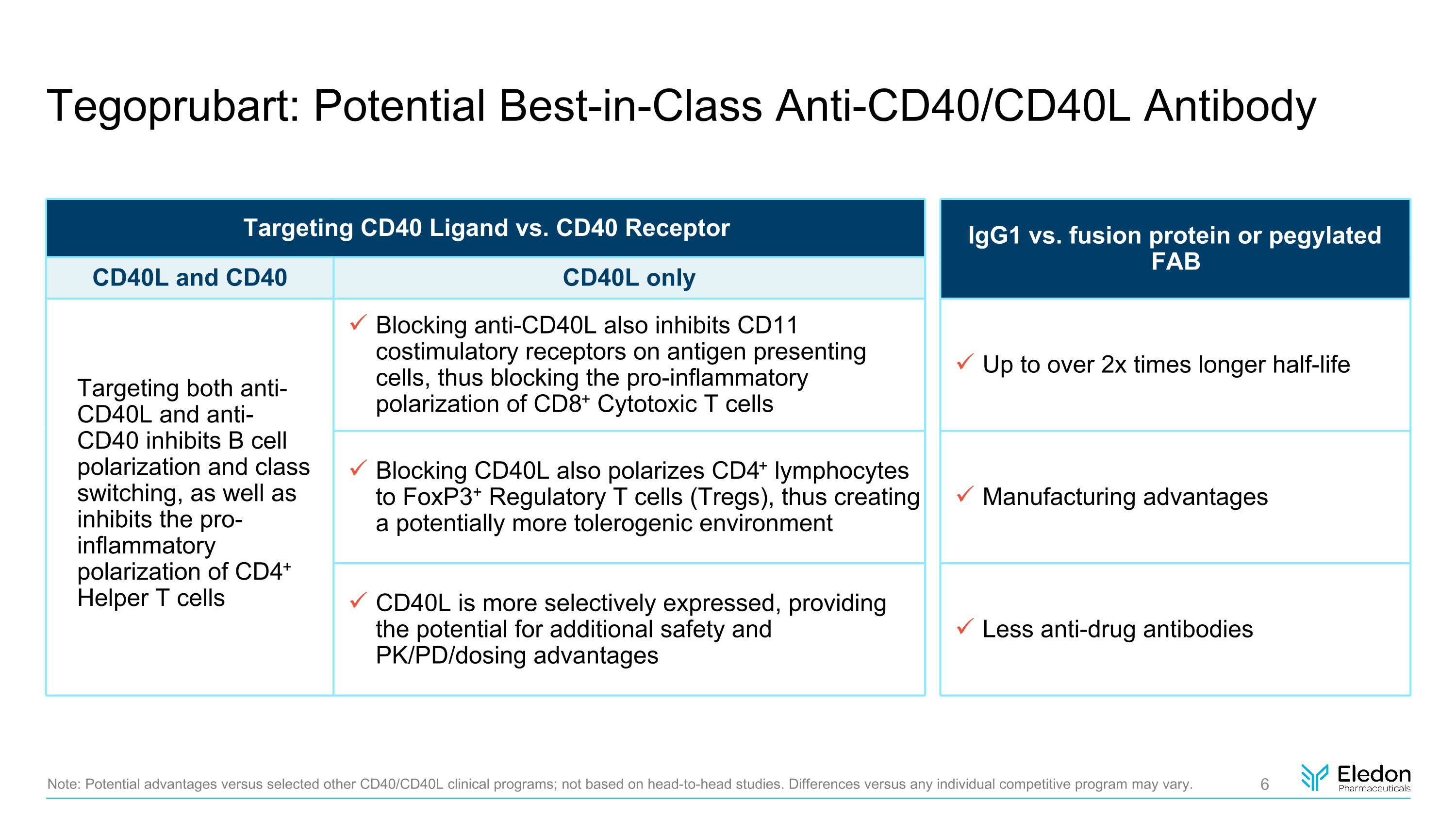
Tegoprubart: Potential Best-in-Class Anti-CD40/CD40L Antibody Targeting CD40 Ligand vs. CD40 Receptor IgG1 vs. fusion protein or pegylated FAB CD40L and CD40 CD40L only Blocking anti-CD40L also inhibits CD11 costimulatory receptors on antigen presenting cells, thus blocking the pro-inflammatory polarization of CD8+ Cytotoxic T cells Up to over 2x times longer half-life Blocking CD40L also polarizes CD4+ lymphocytes to FoxP3+ Regulatory T cells (Tregs), thus creating a potentially more tolerogenic environment Manufacturing advantages CD40L is more selectively expressed, providing the potential for additional safety and PK/PD/dosing advantages Less anti-drug antibodies Note: Potential advantages versus selected other CD40/CD40L clinical programs; not based on head-to-head studies. Differences versus any individual competitive program may vary. Targeting both anti-CD40L and anti-CD40 inhibits B cell polarization and class switching, as well as inhibits the pro-inflammatory polarization of CD4+ Helper T cells

Tegoprubart Experience
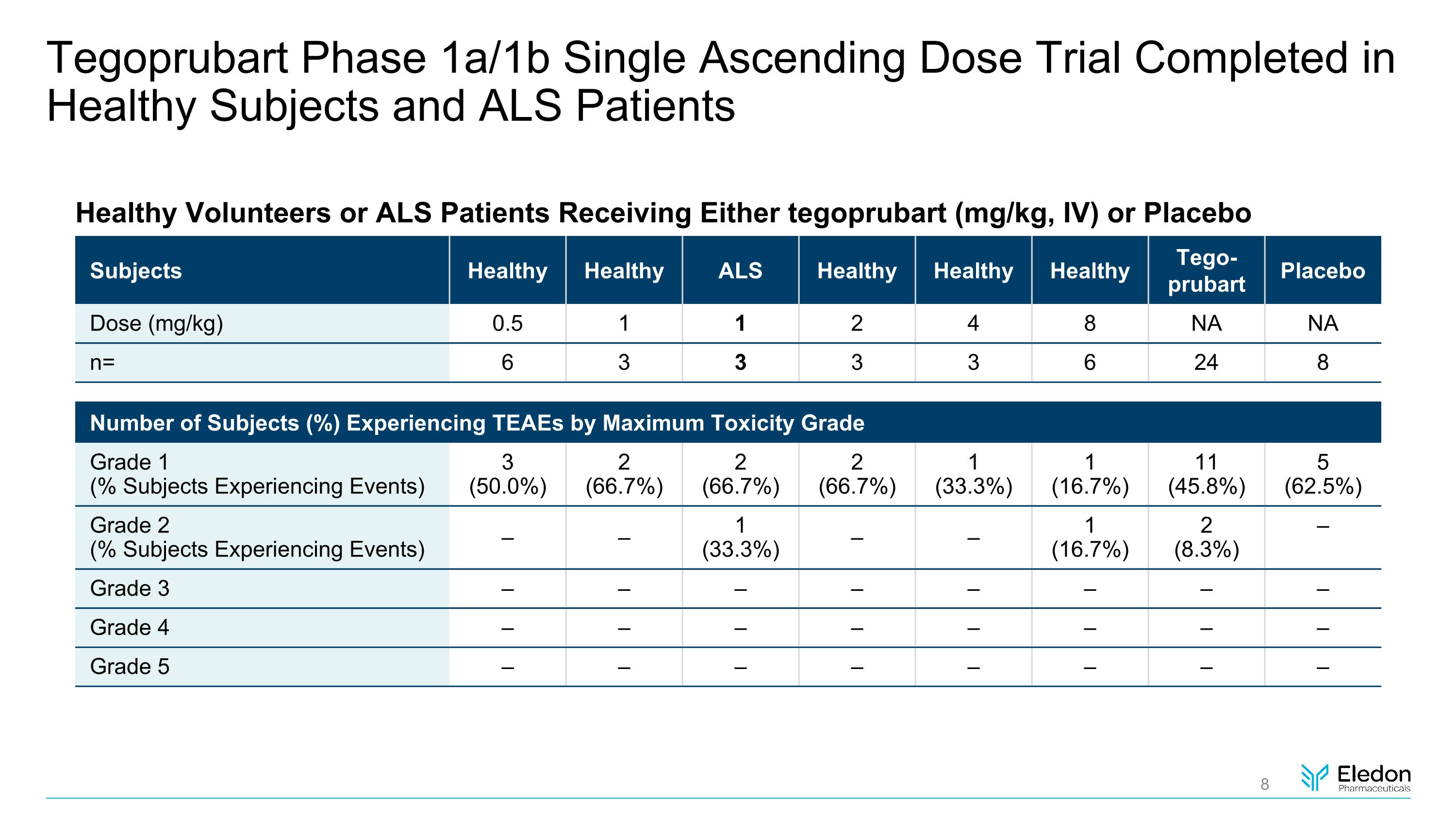
Tegoprubart Phase 1a/1b Single Ascending Dose Trial Completed in Healthy Subjects and ALS Patients Healthy Volunteers or ALS Patients Receiving Either tegoprubart (mg/kg, IV) or Placebo Subjects Healthy Healthy ALS Healthy Healthy Healthy Tego-prubart Placebo Dose (mg/kg) 0.5 1 1 2 4 8 NA NA n= 6 3 3 3 3 6 24 8 Number of Subjects (%) Experiencing TEAEs by Maximum Toxicity Grade Grade 1�(% Subjects Experiencing Events) 3�(50.0%) 2�(66.7%) 2�(66.7%) 2�(66.7%) 1�(33.3%) 1�(16.7%) 11�(45.8%) 5�(62.5%) Grade 2�(% Subjects Experiencing Events) – – 1�(33.3%) – – 1�(16.7%) 2�(8.3%) – Grade 3 – – – – – – – – Grade 4 – – – – – – – – Grade 5 – – – – – – – –
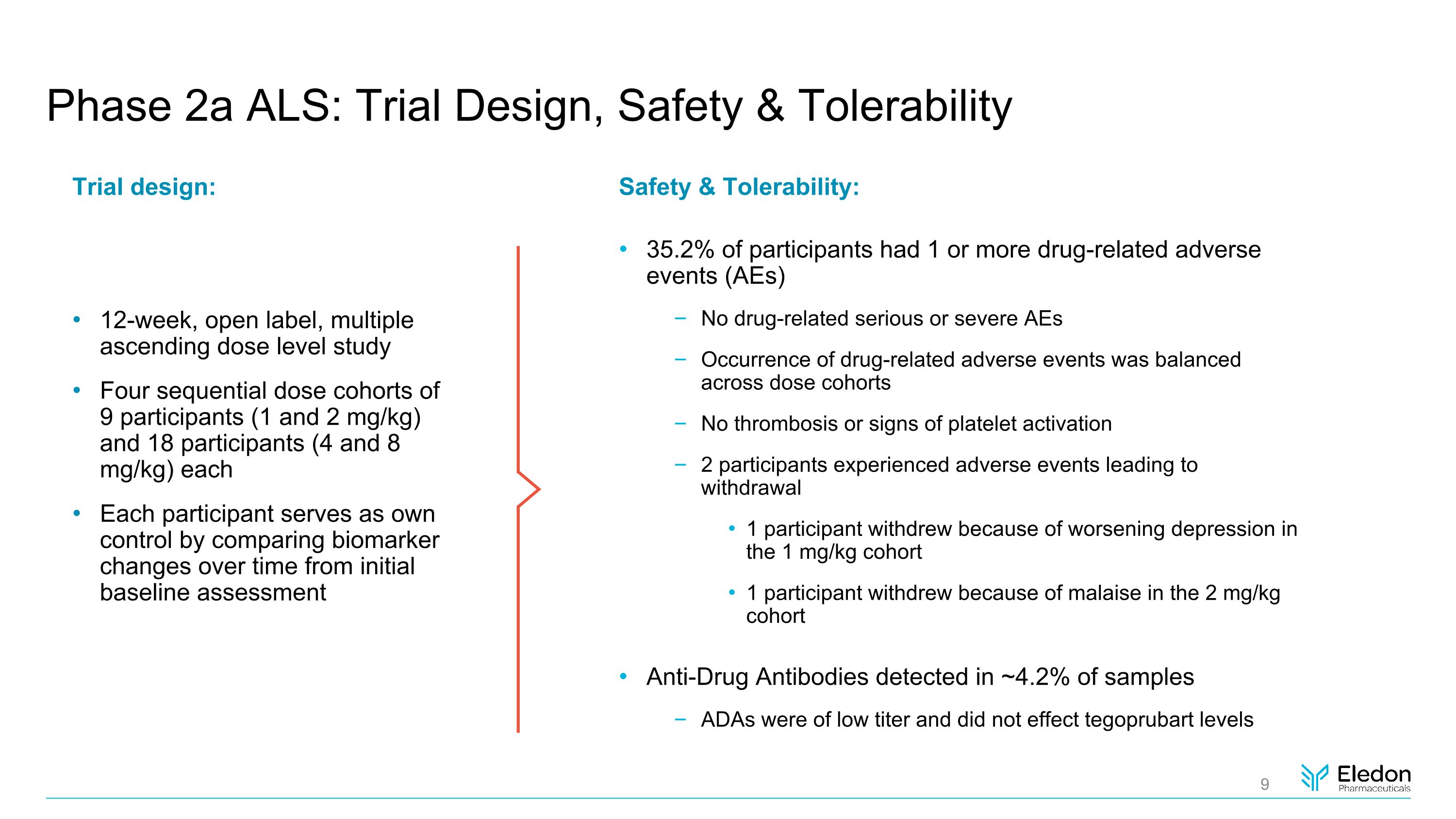
Phase 2a ALS: Trial Design, Safety & Tolerability Safety & Tolerability: 35.2% of participants had 1 or more drug-related adverse events (AEs) No drug-related serious or severe AEs Occurrence of drug-related adverse events was balanced across dose cohorts No thrombosis or signs of platelet activation 2 participants experienced adverse events leading to withdrawal 1 participant withdrew because of worsening depression in the 1 mg/kg cohort 1 participant withdrew because of malaise in the 2 mg/kg cohort Anti-Drug Antibodies detected in ~4.2% of samples ADAs were of low titer and did not effect tegoprubart levels Trial design: 12-week, open label, multiple ascending dose level study Four sequential dose cohorts of 9 participants (1 and 2 mg/kg) and 18 participants (4 and 8 mg/kg) each Each participant serves as own control by comparing biomarker changes over time from initial baseline assessment
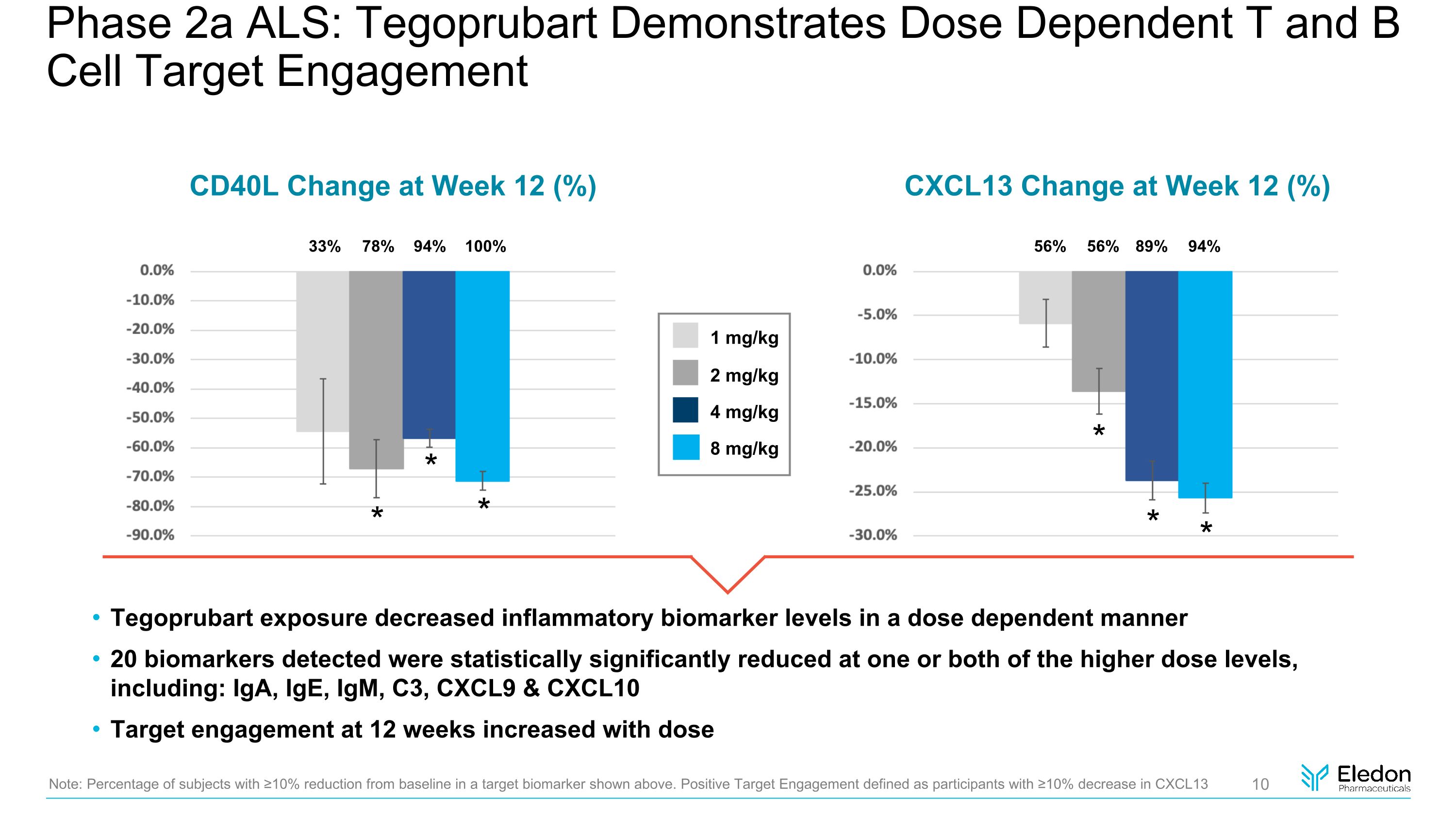
Tegoprubart exposure decreased inflammatory biomarker levels in a dose dependent manner 20 biomarkers detected were statistically significantly reduced at one or both of the higher dose levels, including: IgA, IgE, IgM, C3, CXCL9 & CXCL10 Target engagement at 12 weeks increased with dose 1 mg/kg 2 mg/kg 4 mg/kg 8 mg/kg CD40L Change at Week 12 (%) CXCL13 Change at Week 12 (%) Note: Percentage of subjects with ≥10% reduction from baseline in a target biomarker shown above. Positive Target Engagement defined as participants with ≥10% decrease in CXCL13 Phase 2a ALS: Tegoprubart Demonstrates Dose Dependent T and B Cell Target Engagement 33% 78% 94% 100% * * * 56% 56% 89% 94% * * *
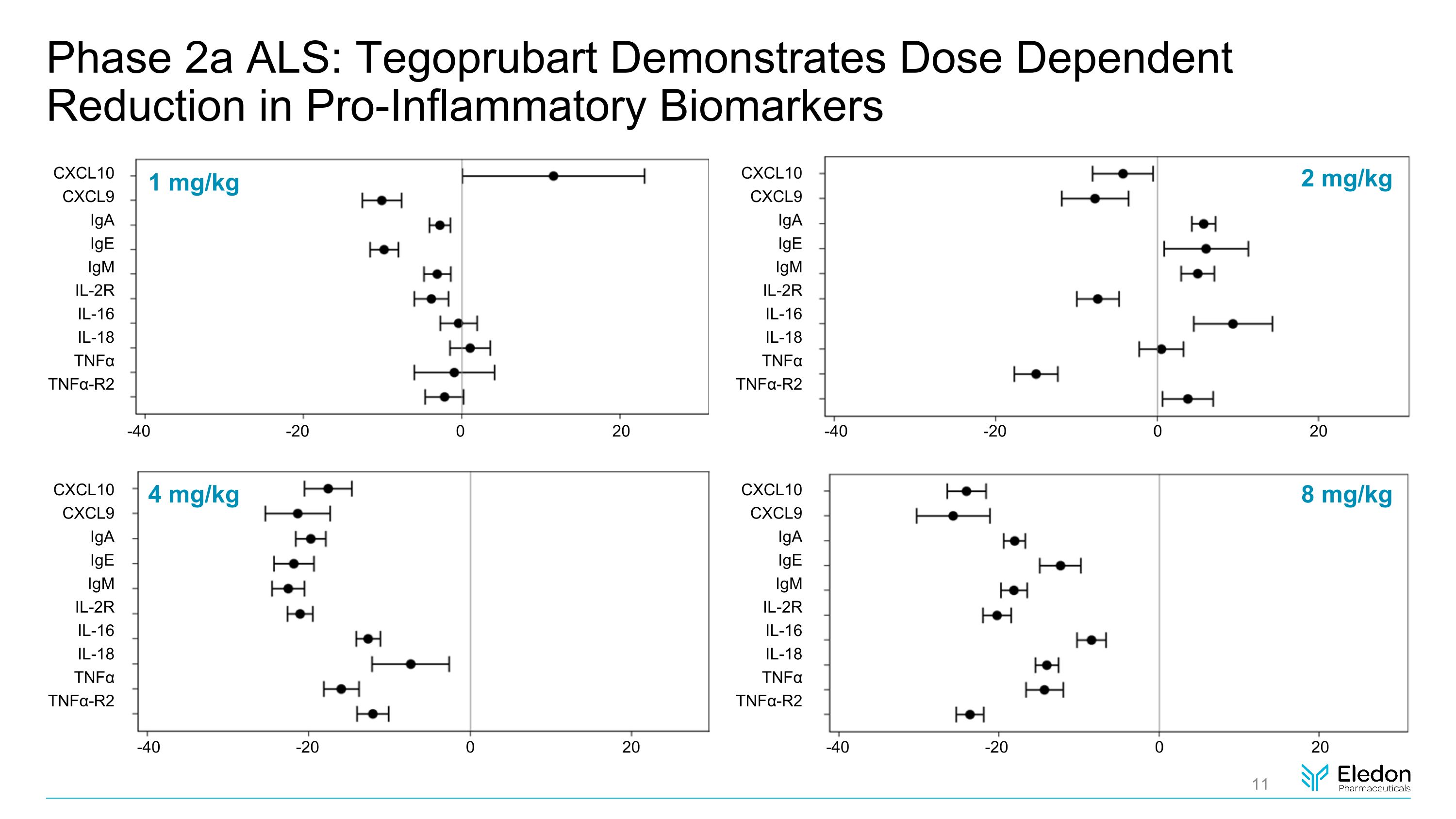
1 mg/kg 2 mg/kg 4 mg/kg 8 mg/kg CXCL10 CXCL9 IgA IgE IgM IL-2R IL-16 IL-18 TNFα TNFα-R2 CXCL10 CXCL9 IgA IgE IgM IL-2R IL-16 IL-18 TNFα TNFα-R2 -40 -20 0 20 -40 -20 0 20 -40 -20 0 20 -40 -20 0 20 CXCL10 CXCL9 IgA IgE IgM IL-2R IL-16 IL-18 TNFα TNFα-R2 CXCL10 CXCL9 IgA IgE IgM IL-2R IL-16 IL-18 TNFα TNFα-R2 Phase 2a ALS: Tegoprubart Demonstrates Dose Dependent Reduction in Pro-Inflammatory Biomarkers

Kidney Transplantation Opportunity & Clinical Development Plan
Kidney Transplantation Overview Unmet Need In the 1990s, Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) revolutionized the field of transplantation, allowing transplant medicine to grow across transplant types, and providing meaningful treatment to thousands of people CNIs provide excellent 1 year patient and graft outcomes, but: They are less effective against long term antibody mediated rejection They are nephrotoxic and slowly harm the graft over time They are associated with significant adverse effects including post-transplant new onset diabetes, tremors, and hair loss On average, transplanted kidneys from deceased donors function about 10 years Market Size 24,000+ U.S. kidney transplants per year 240,000+ Americans living with a kidney graft ~90,000 Americans face a 3-5 year wait for a kidney ~5,000 Americans per year on the transplant waiting list die without getting a transplant Pre-transplant dialysis costs over $100,000 per year Hemodialysis has a 15-20% first-year mortality rate with a 5-year survival rate of under 50% (vs. ~80% 5-year survival post kidney transplant) Annual medical cost to treat transplant patients who experience renal graft failure increase 450% Source: Donate Life America; NIDDK & Shapiro 2017; USRDS 2019; DHHS OPTN; Ghisdal 2012; Kidney.org; UCSF.
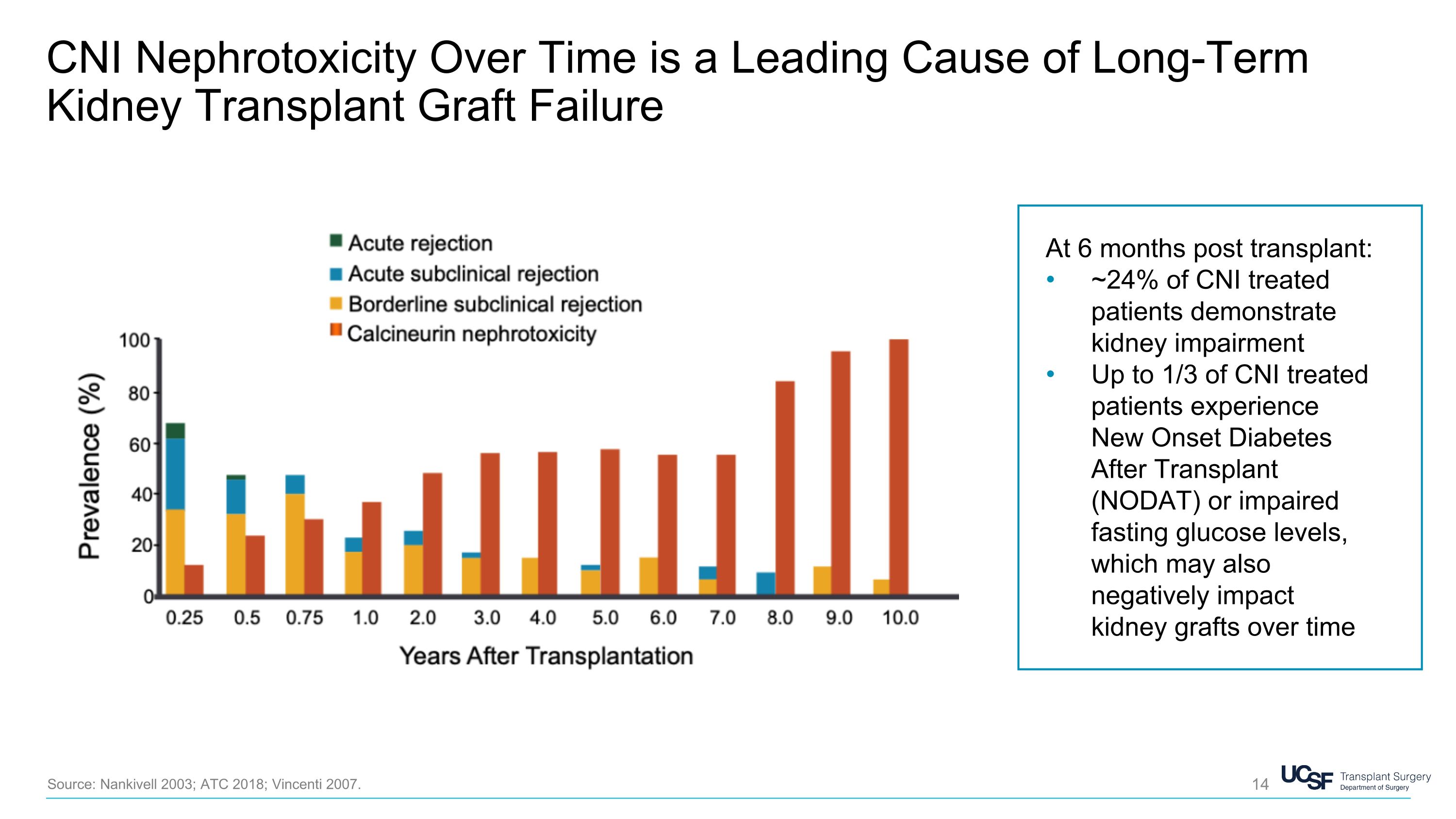
CNI Nephrotoxicity Over Time is a Leading Cause of Long-Term Kidney Transplant Graft Failure Source: Nankivell 2003; ATC 2018; Vincenti 2007. At 6 months post transplant: ~24% of CNI treated patients demonstrate kidney impairment Up to 1/3 of CNI treated patients experience New Onset Diabetes After Transplant (NODAT) or impaired fasting glucose levels, which may also negatively impact kidney grafts over time
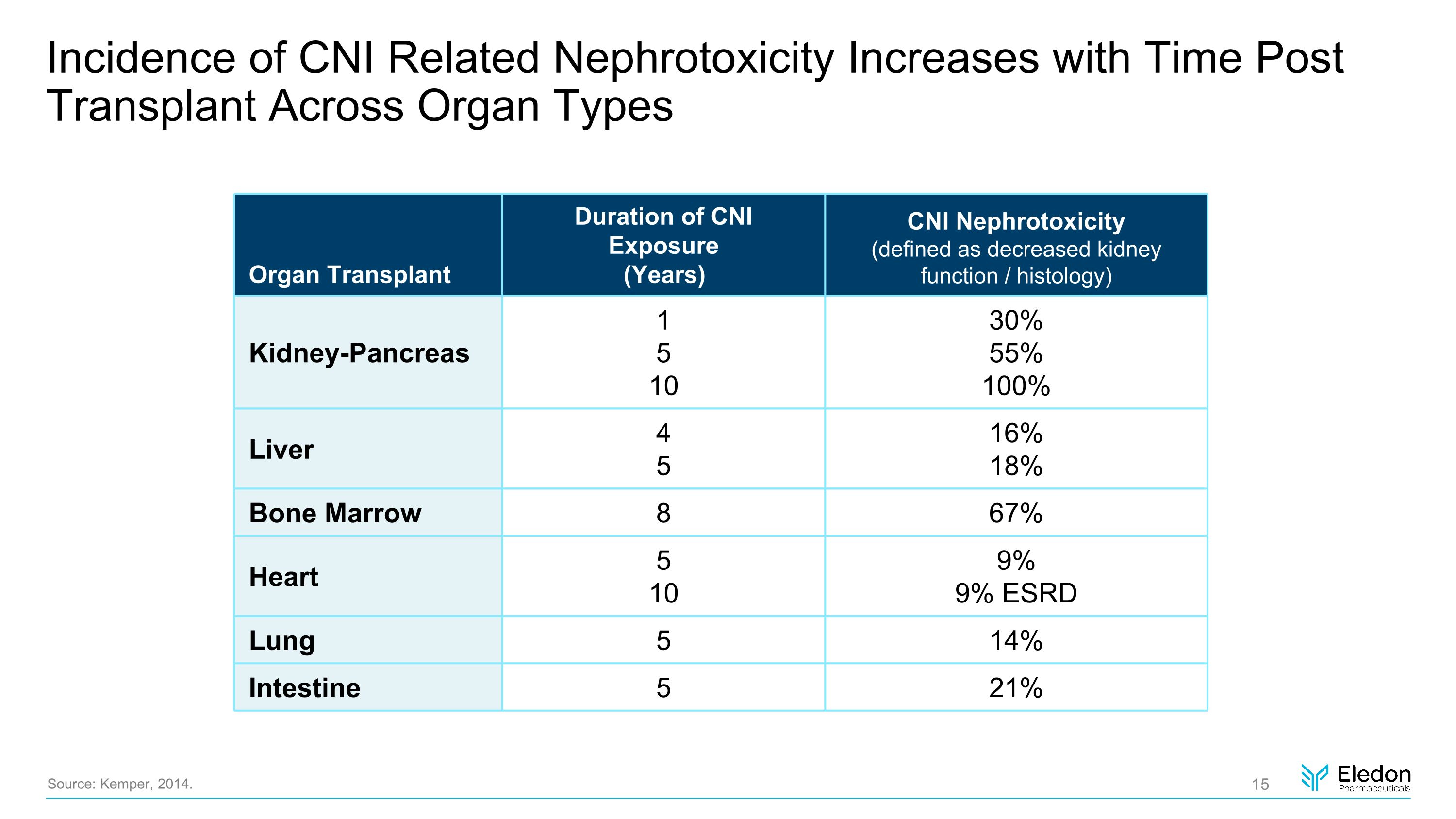
Incidence of CNI Related Nephrotoxicity Increases with Time Post Transplant Across Organ Types Source: Kemper, 2014. Organ Transplant Duration of CNI Exposure (Years) CNI Nephrotoxicity (defined as decreased kidney function / histology) Kidney-Pancreas 1 5 10 30% 55% 100% Liver 4 5 16% 18% Bone Marrow 8 67% Heart 5 10 9% 9% ESRD Lung 5 14% Intestine 5 21%
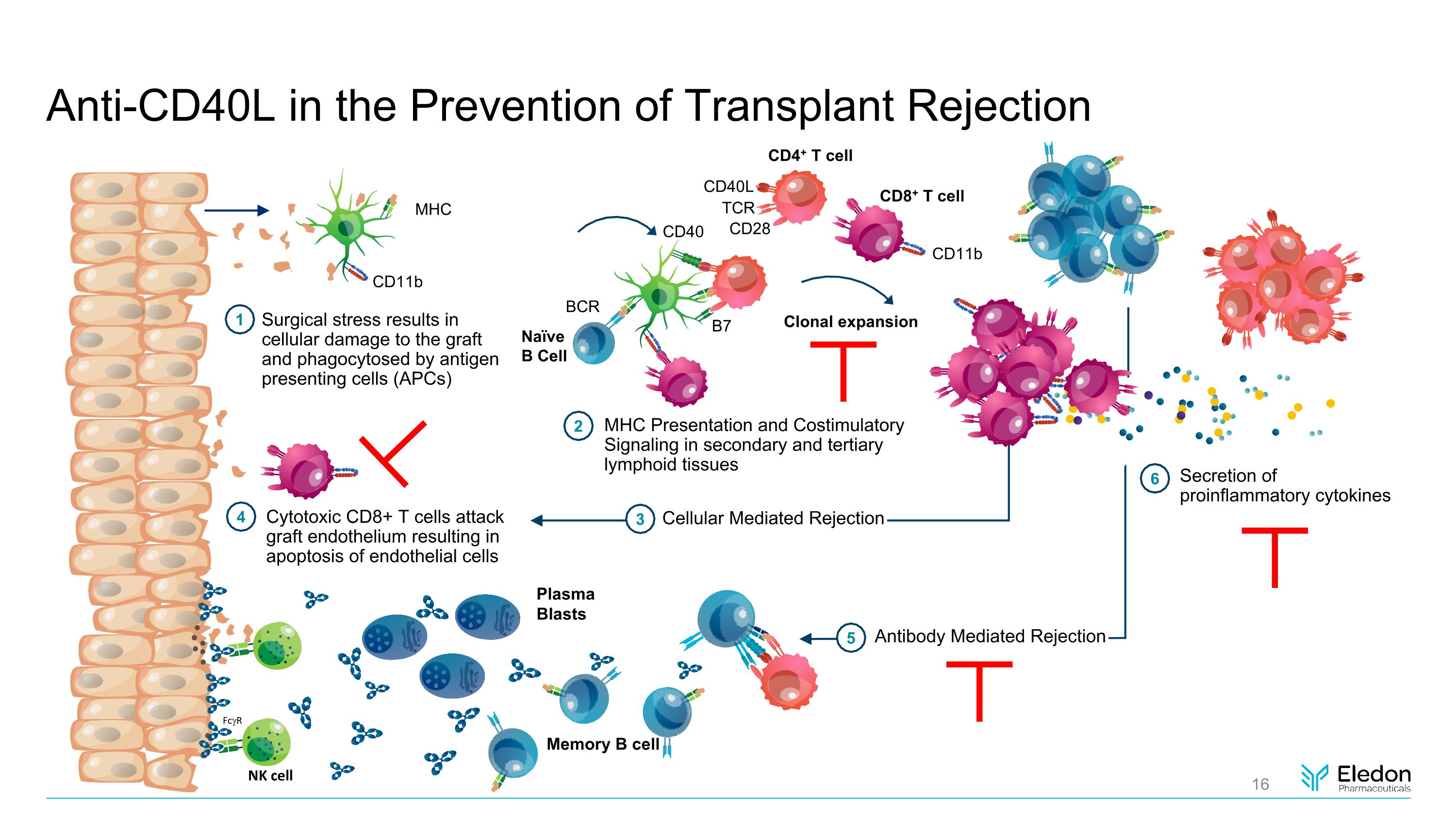
Anti-CD40L in the Prevention of Transplant Rejection Naïve B Cell B7 BCR CD40 Surgical stress results in cellular damage to the graft and phagocytosed by antigen presenting cells (APCs) MHC Presentation and Costimulatory Signaling in secondary and tertiary lymphoid tissues Clonal expansion Secretion of proinflammatory cytokines Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells attack graft endothelium resulting in apoptosis of endothelial cells Antibody Mediated Rejection Plasma Blasts Memory B cell NK cell FcgR MHC CD11b CD28 CD40L TCR CD4+ T cell 1 2 4 Cellular Mediated Rejection 3 5 6 CD11b CD8+ T cell
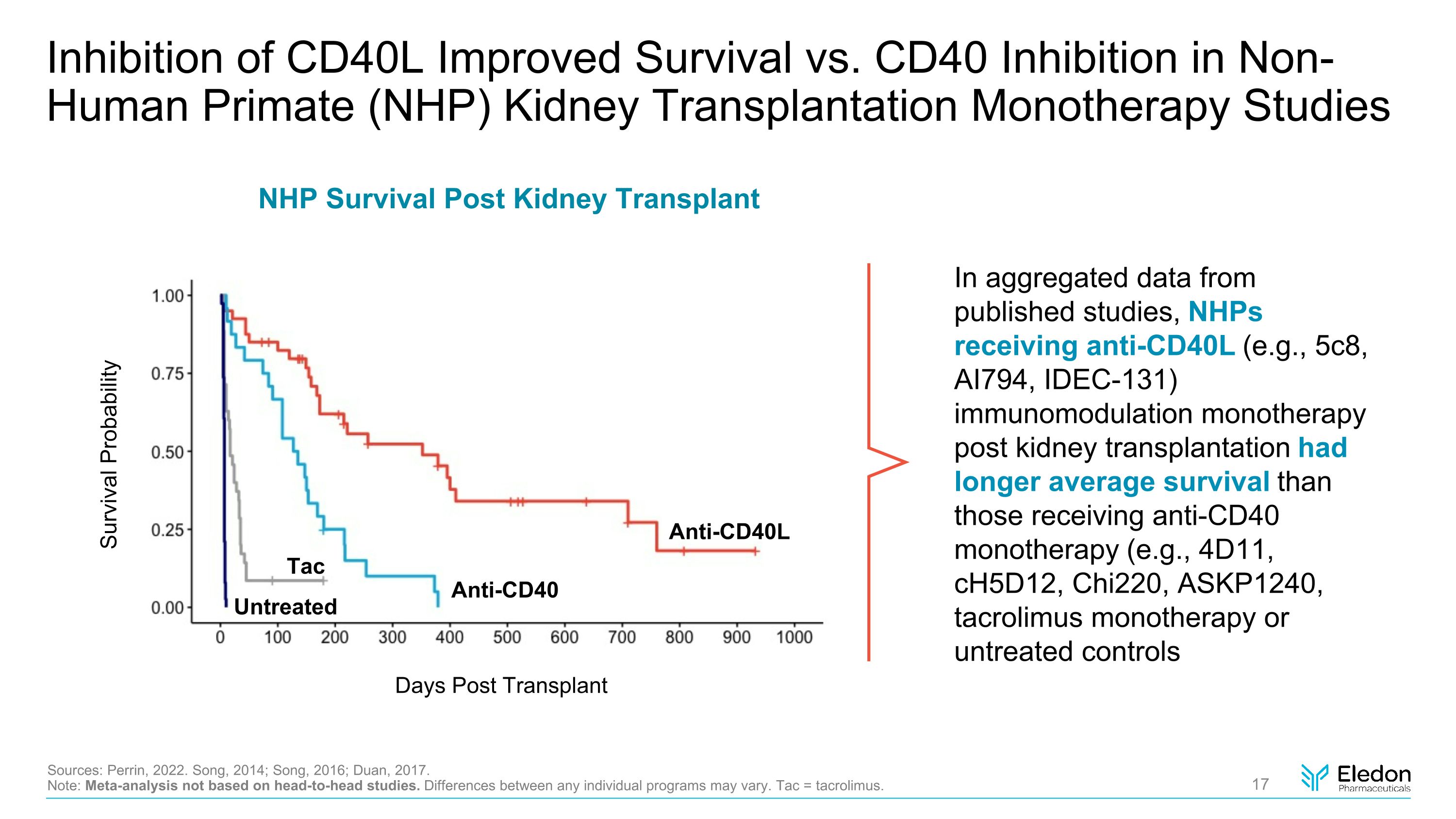
Inhibition of CD40L Improved Survival vs. CD40 Inhibition in Non-Human Primate (NHP) Kidney Transplantation Monotherapy Studies In aggregated data from published studies, NHPs receiving anti-CD40L (e.g., 5c8, AI794, IDEC-131) immunomodulation monotherapy post kidney transplantation had longer average survival than those receiving anti-CD40 monotherapy (e.g., 4D11, cH5D12, Chi220, ASKP1240, tacrolimus monotherapy or untreated controls Sources: Perrin, 2022. Song, 2014; Song, 2016; Duan, 2017. Note: Meta-analysis not based on head-to-head studies. Differences between any individual programs may vary. Tac = tacrolimus. Anti-CD40 NHP Survival Post Kidney Transplant Anti-CD40L Untreated Days Post Transplant Survival Probability Tac
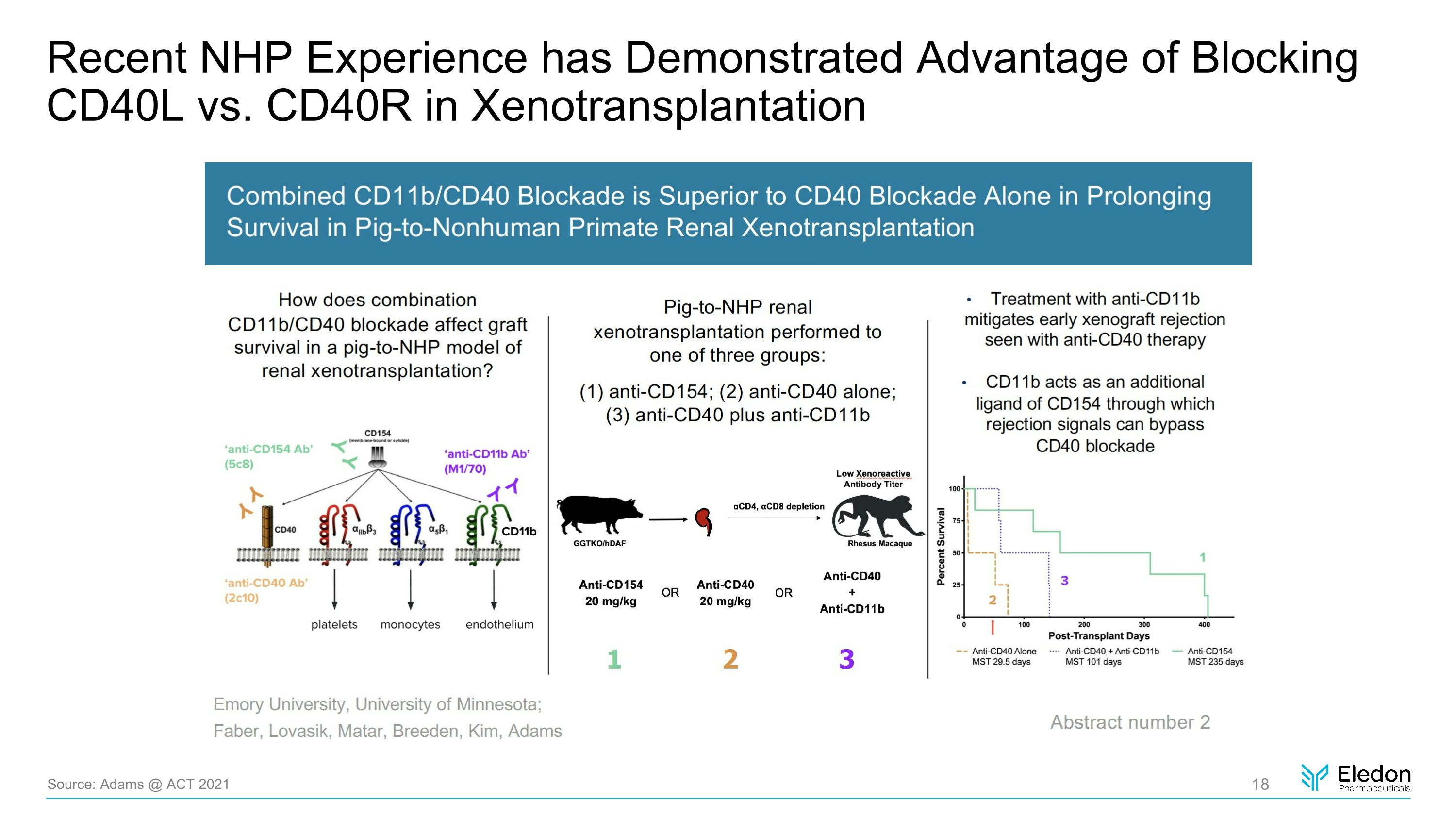
Recent NHP Experience has Demonstrated Advantage of Blocking CD40L vs. CD40R in Xenotransplantation Source: Adams @ ACT 2021
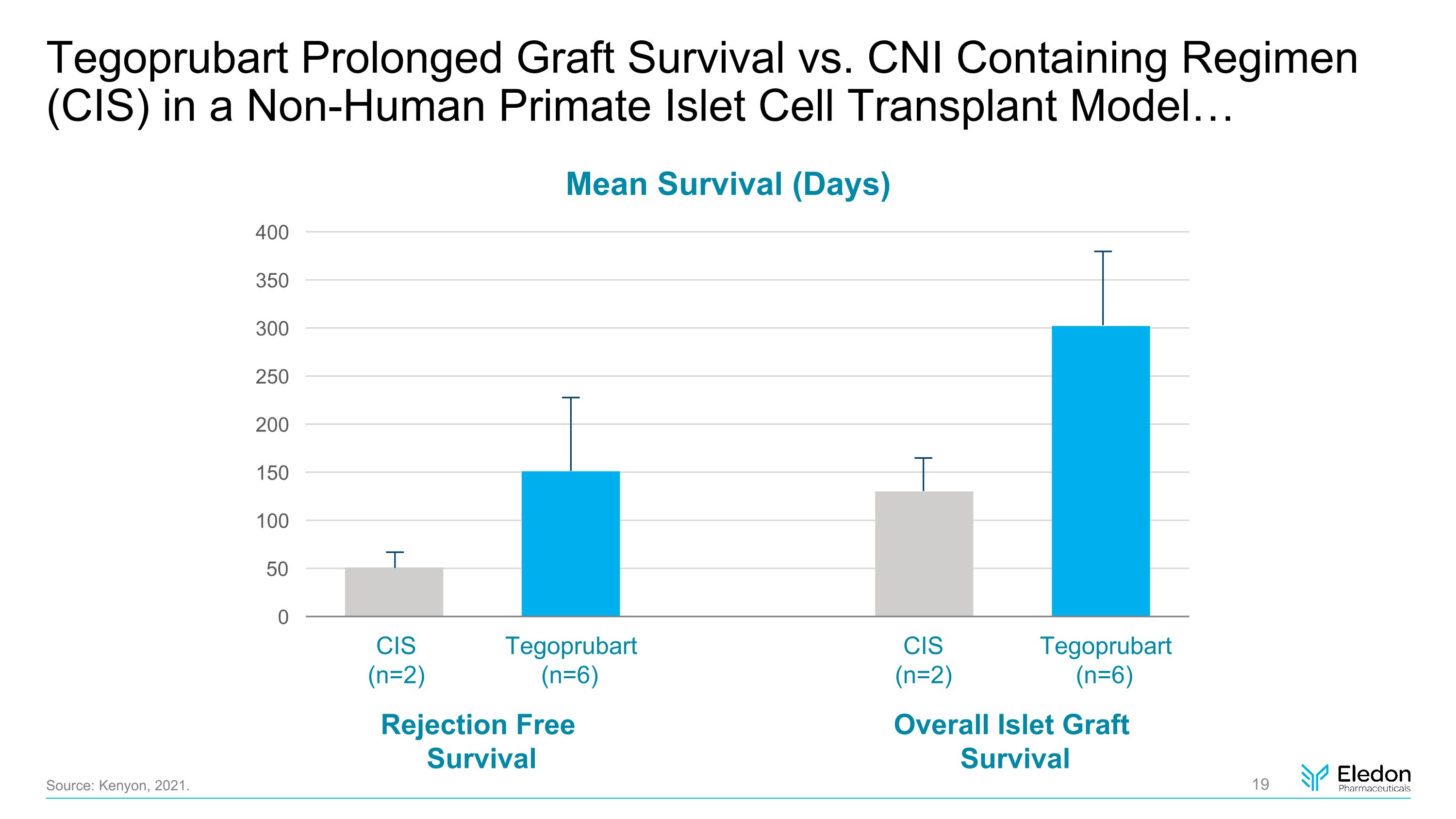
Tegoprubart Prolonged Graft Survival vs. CNI Containing Regimen (CIS) in a Non-Human Primate Islet Cell Transplant Model… Source: Kenyon, 2021. Mean Survival (Days) Rejection Free Survival Overall Islet Graft Survival CIS (n=2) CIS (n=2) Tegoprubart (n=6) Tegoprubart (n=6)
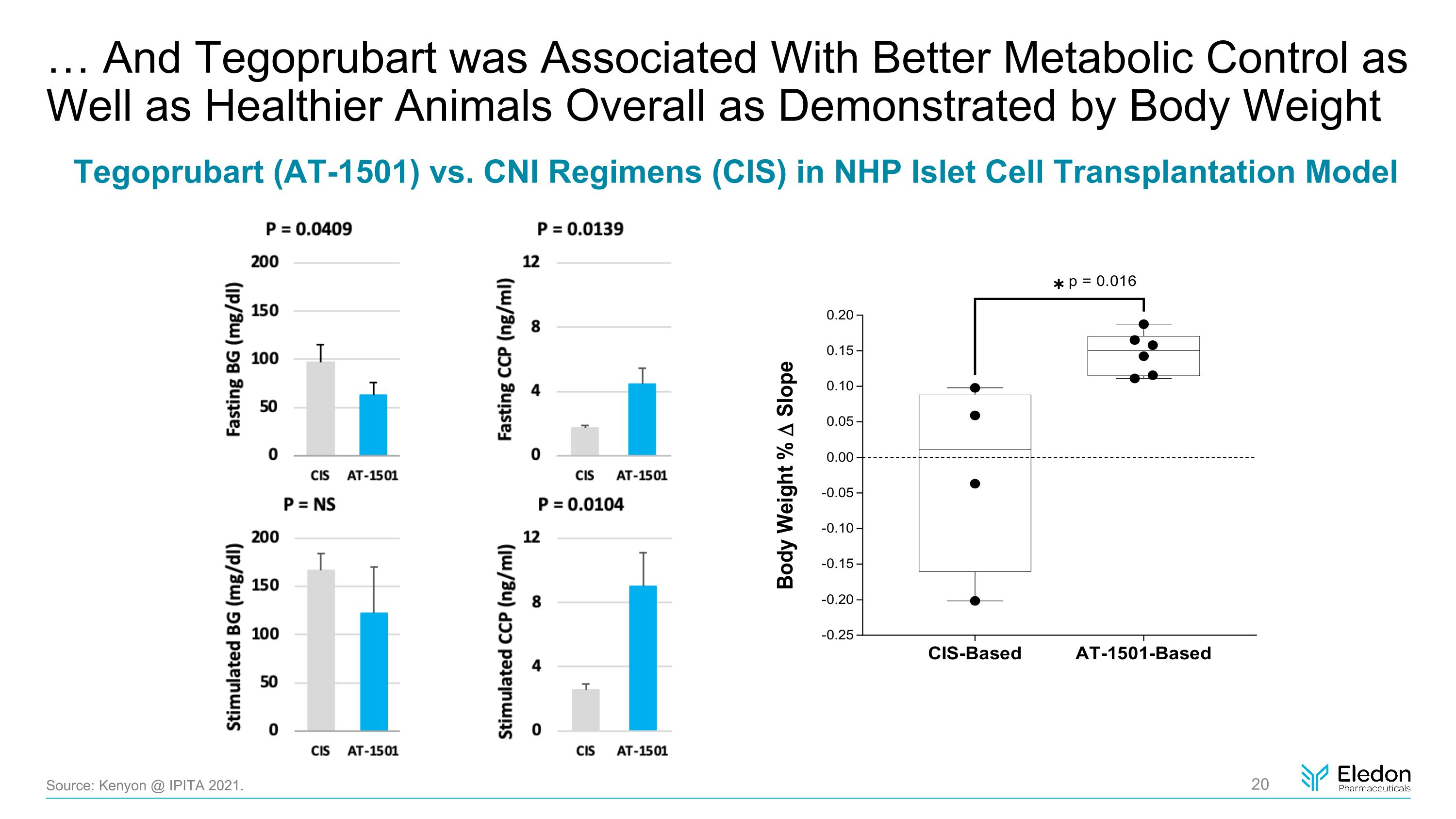
… And Tegoprubart was Associated With Better Metabolic Control as Well as Healthier Animals Overall as Demonstrated by Body Weight Tegoprubart (AT-1501) vs. CNI Regimens (CIS) in NHP Islet Cell Transplantation Model Source: Kenyon @ IPITA 2021.
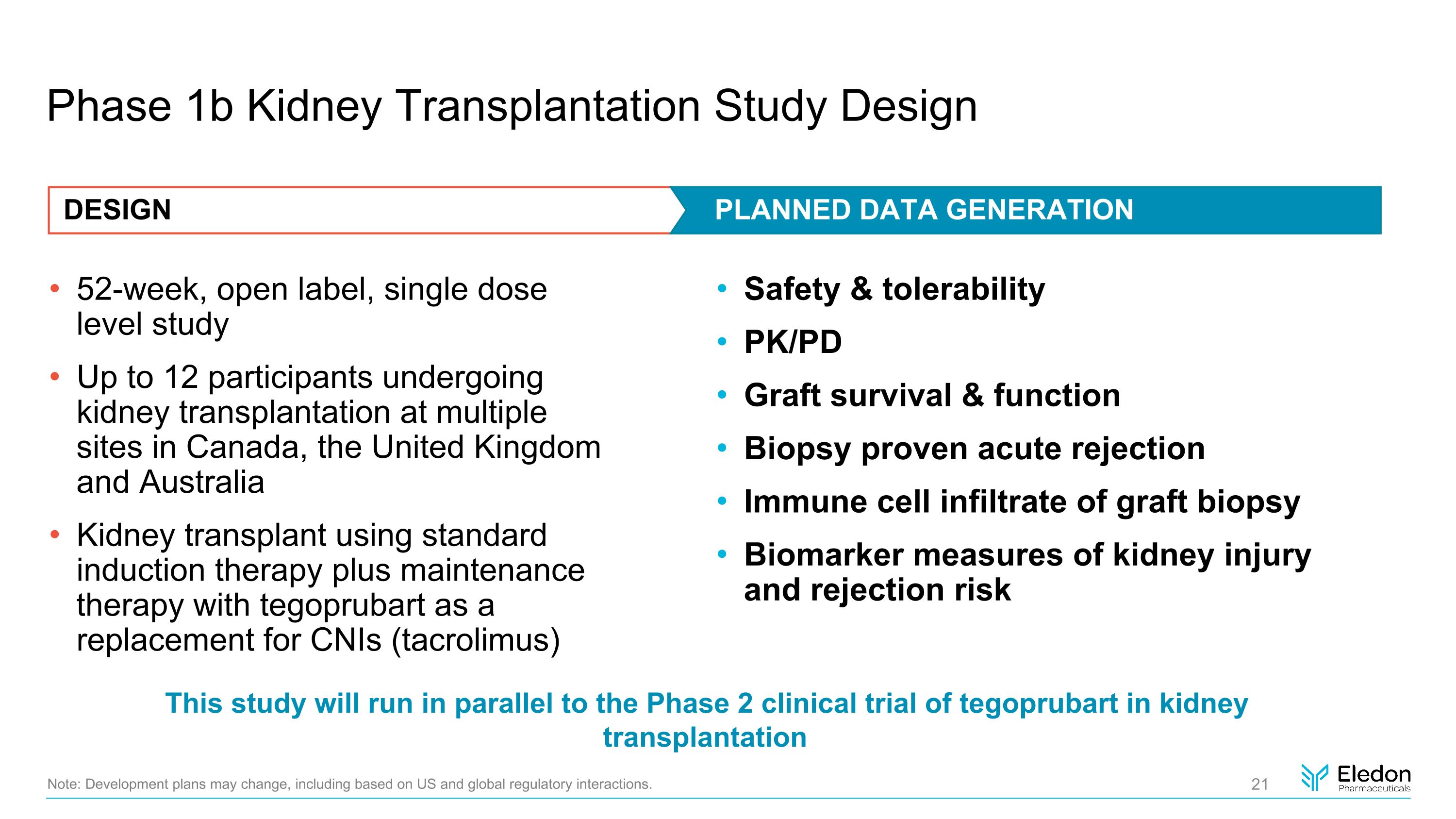
Phase 1b Kidney Transplantation Study Design 52-week, open label, single dose level study Up to 12 participants undergoing kidney transplantation at multiple sites in Canada, the United Kingdom and Australia Kidney transplant using standard induction therapy plus maintenance therapy with tegoprubart as a replacement for CNIs (tacrolimus) Safety & tolerability PK/PD Graft survival & function Biopsy proven acute rejection Immune cell infiltrate of graft biopsy Biomarker measures of kidney injury and rejection risk Note: Development plans may change, including based on US and global regulatory interactions. DESIGN PLANNED DATA GENERATION This study will run in parallel to the Phase 2 clinical trial of tegoprubart in kidney transplantation
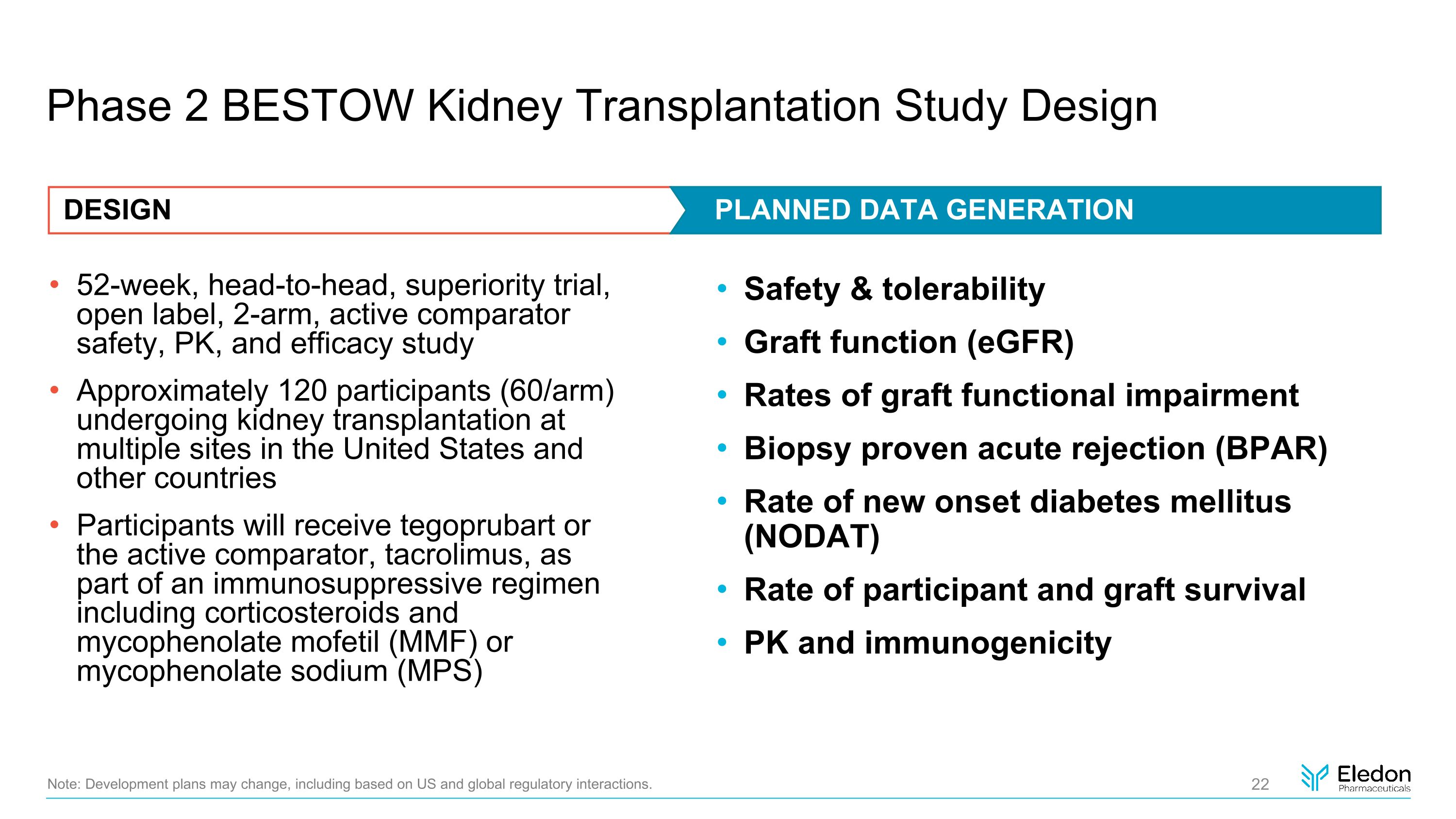
Phase 2 BESTOW Kidney Transplantation Study Design 52-week, head-to-head, superiority trial, open label, 2-arm, active comparator safety, PK, and efficacy study Approximately 120 participants (60/arm) undergoing kidney transplantation at multiple sites in the United States and other countries Participants will receive tegoprubart or the active comparator, tacrolimus, as part of an immunosuppressive regimen including corticosteroids and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or mycophenolate sodium (MPS) Safety & tolerability Graft function (eGFR) Rates of graft functional impairment Biopsy proven acute rejection (BPAR) Rate of new onset diabetes mellitus (NODAT) Rate of participant and graft survival PK and immunogenicity Note: Development plans may change, including based on US and global regulatory interactions. DESIGN PLANNED DATA GENERATION
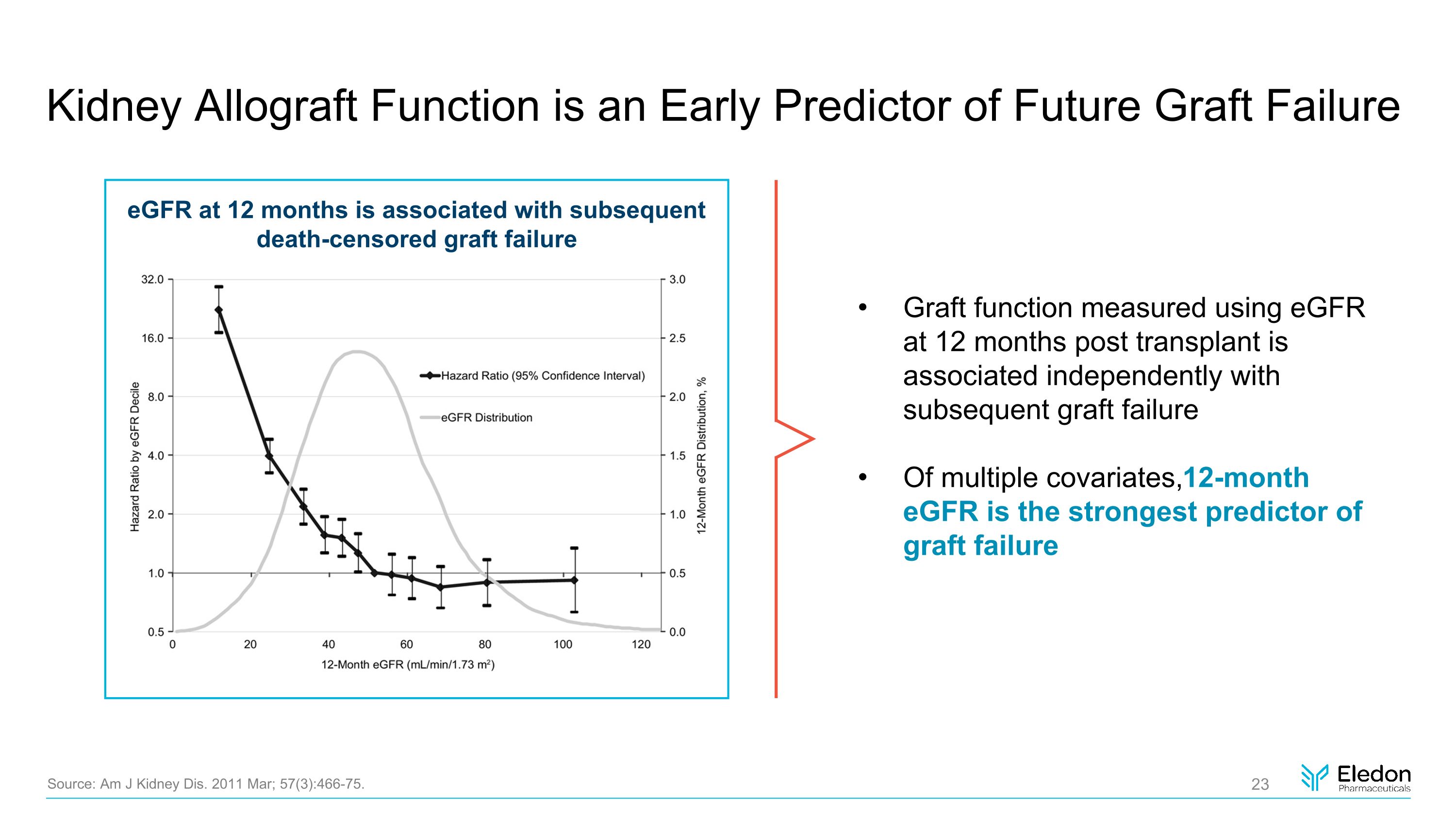
Kidney Allograft Function is an Early Predictor of Future Graft Failure eGFR at 12 months is associated with subsequent death-censored graft failure Source: Am J Kidney Dis. 2011 Mar; 57(3):466-75. Graft function measured using eGFR at 12 months post transplant is associated independently with subsequent graft failure Of multiple covariates,12-month eGFR is the strongest predictor of graft failure
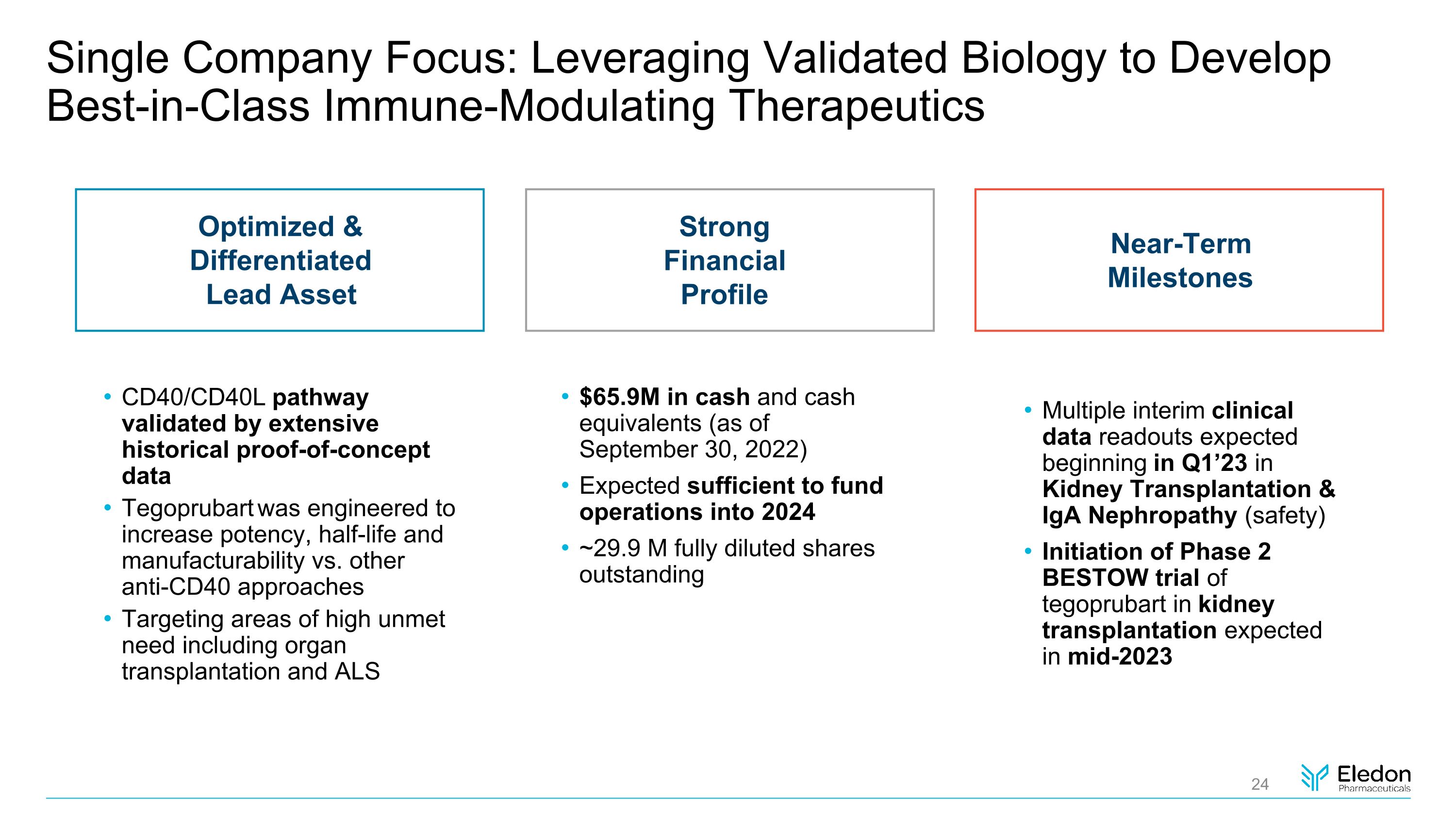
Single Company Focus: Leveraging Validated Biology to Develop Best-in-Class Immune-Modulating Therapeutics CD40/CD40L pathway validated by extensive historical proof-of-concept data Tegoprubart was engineered to increase potency, half-life and manufacturability vs. other anti-CD40 approaches Targeting areas of high unmet need including organ transplantation and ALS Optimized & Differentiated Lead Asset Near-Term Milestones Multiple interim clinical data readouts expected beginning in Q1’23 in Kidney Transplantation & IgA Nephropathy (safety) Initiation of Phase 2 BESTOW trial of tegoprubart in kidney transplantation expected in mid-2023 Strong Financial Profile $65.9M in cash and cash equivalents (as of September 30, 2022) Expected sufficient to fund operations into 2024 ~29.9 M fully diluted shares�outstanding

Eledon Pharmaceuticals 19900 MacArthur Blvd., Suite 550�Irvine, California 92612, USA�info@eledon.com�+1 949-238-8090
























