The Australian dollar is the national currency of Australia and the currency of the accounts of the Reserve Bank of Australia, the Australian central bank. The official currency code for the Australian dollar is “AUD.” The Australian dollar is referred to in Australia as “dollar.” As with U.S. currency, 100 Australian cents are equal to one Australian dollar. In Australia, unlike most other countries, cash transactions are rounded to the nearest five cents. The most commonly used symbol used to represent the Australian dollar is “A$.”
In 1913, the Commonwealth Bank of Australia issued the first Australian currency notes. In 1915, the Commonwealth Bank of Australia became the exclusive issuer of currency in Australia. From 1930 through the 1960s, the Australian banking system underwent substantial transformation. In 1960, the Reserve Bank of Australia was established. In 1966, a new decimalized currency was introduced. At various times throughout the 1900s, the value of Australian currency was based on a fixed quantity of gold; at other times, the Australian dollar was pegged to foreign currencies, including the U.S. dollar. Beginning in 1983, the Australian dollar’s value was allowed to float, with the result that its value now depends almost entirely on market forces. The foregoing information is compiled from the Reserve Bank of Australia’s website (www.rba.gov.au).
Euro
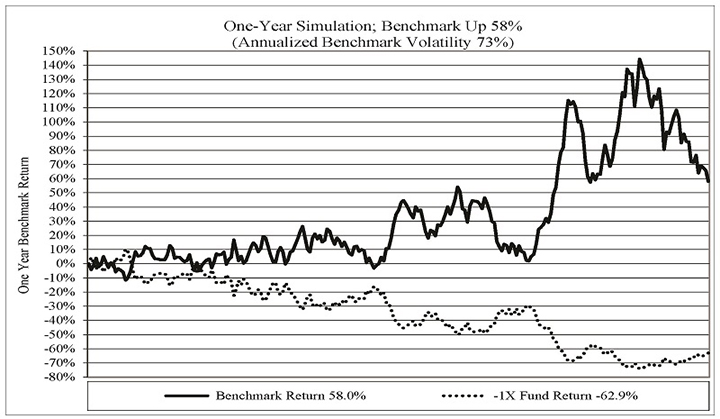
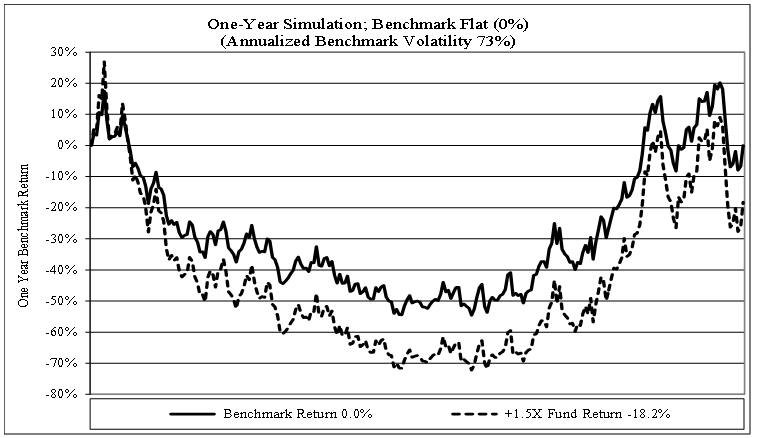
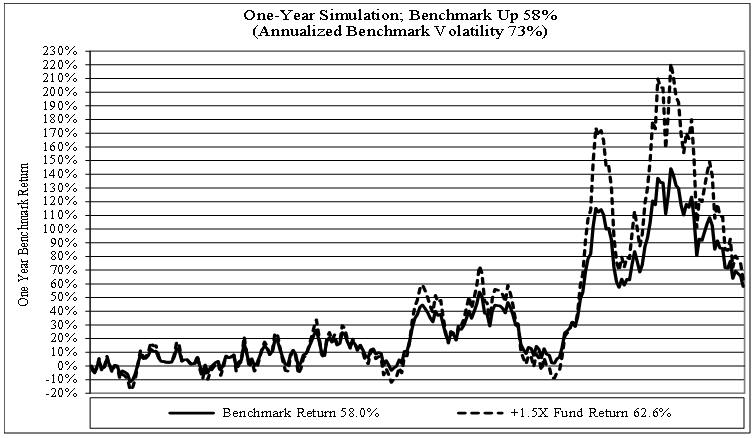
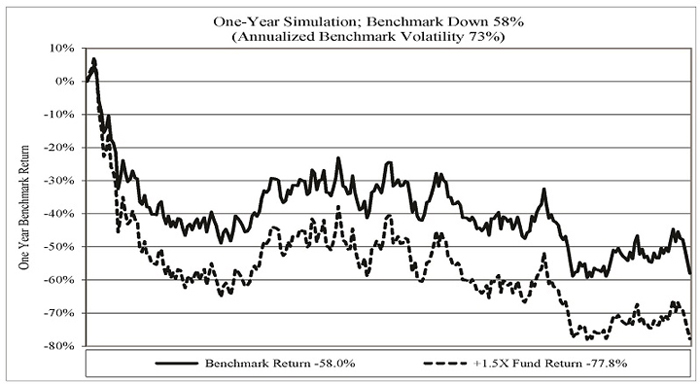
ProShares Short Euro, ProShares UltraShort Euro and ProShares Ultra Euro are designed to correspond, before fees and expenses, to the inverse(-1), two times the inverse(-2x), or two times (2x) of the daily performance of the euro spot price versus the U.S. dollar, respectively. These Funds use the 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) euro/U.S. dollar exchange rate as provided by Bloomberg, expressed in terms of U.S. dollars per unit of foreign currency, as the basis for the underlying benchmark.
In 1998, the European Central Bank in Frankfurt was organized by Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal and Spain in order to establish a commoncurrency-the euro. Unlike the U.S. Federal Reserve System, the Bank of Japan and other comparable central banks, the European Central Bank is a central authority that conducts monetary policy for an economic area consisting of many otherwise largely autonomous states.
At its inception on January 1, 1999, the euro was launched as an electronic currency used by banks, foreign exchange dealers and stock markets. In 2002, the euro became cash currency for approximately 300 million citizens of twelve European countries (the eleven countries mentioned above, in addition to Greece). As of December 31, 2018, 23 countries used the euro, including Andorra, Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Monaco, the Netherlands, Portugal, San Marino, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain and the Vatican City.
Although the European countries that have adopted the euro are members of the European Union (“EU”), the United Kingdom, Denmark and Sweden are EU members that have not adopted the euro as their national currency.
Japanese Yen
ProShares UltraShort Yen and ProShares Ultra Yen are designed to correspond, before fees and expenses, to two times the inverse(-2x) or two times (2x), respectively, of the daily performance of the Japanese yen spot price versus the U.S. dollar. These Funds use the 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) Japanese yen/U.S. dollar exchange rate as provided by Bloomberg, expressed in terms of U.S. dollars per unit of foreign currency, as the basis for the underlying benchmark.
The Japanese yen has been the official currency of Japan since 1871. The Bank of Japan has been operating as the central bank of Japan since 1882.
Description of the VIX Futures Indexes
The VIX Funds seek to offer exposure to forward equity market volatility by obtaining exposure to the VIX Futures Indexes, which are based on publicly traded VIX futures contracts. The VIX Futures Indexes are intended to reflect the returns that are potentially available through an unleveraged investment in the VIX futures contracts comprising each VIX Futures Index. The VIX, which is not the index underlying the VIX Funds, is calculated based on the prices of put and call options on the S&P 500. The VIX Funds can be expected to perform very differently from the VIX.
The Short-Term VIX Index employs rules for selecting VIX futures contracts comprising the Short-Term VIX Index and a formula to calculate a level for that index from the prices of these VIX futures contracts. Specifically, the VIX futures contracts comprising the Short-Term VIX Index represent the prices of two near-term VIX futures contracts, replicating a position that rolls the nearest month VIX futures to the next month VIX futures on a daily basis in equal fractional amounts. This results in a constant weighted average maturity ofone-month. The roll period begins on the Tuesday prior to the monthly CBOE VIX futures settlement and runs through the Tuesday prior to the subsequent month’s CBOE VIX futures settlement date.
16