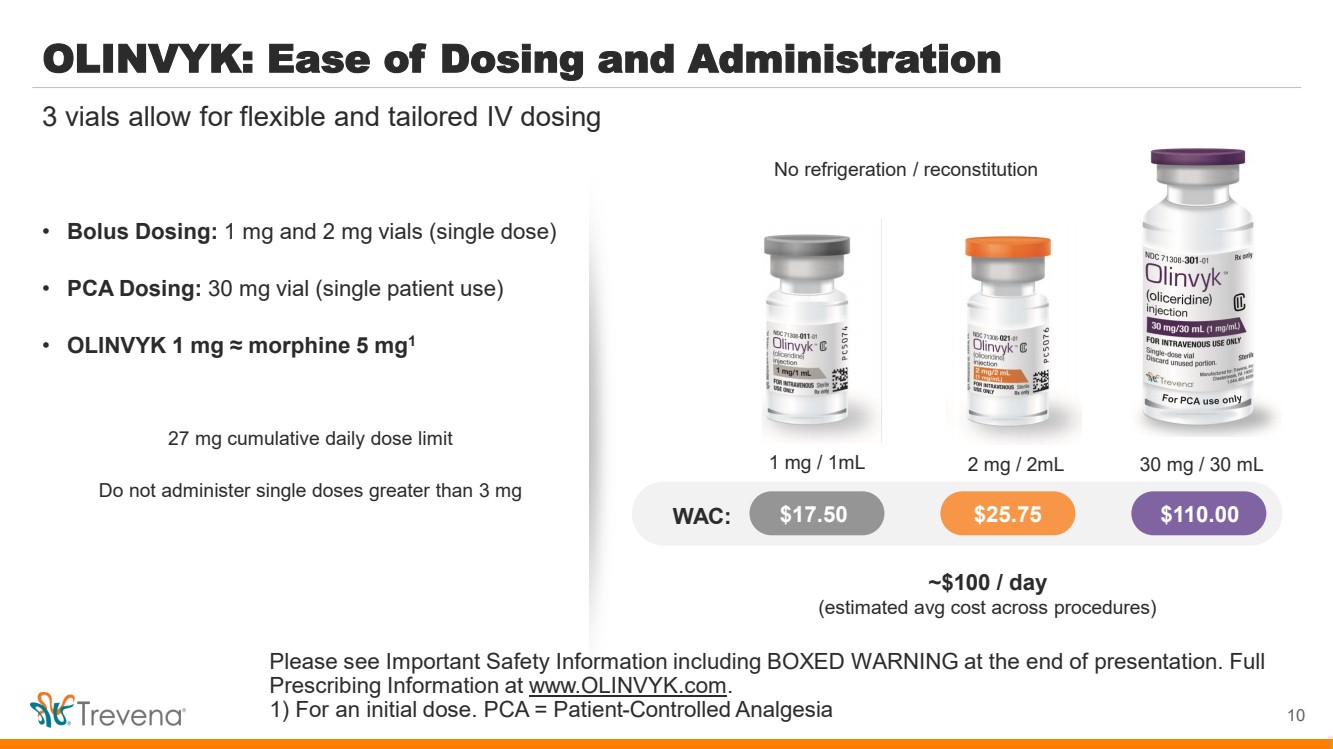
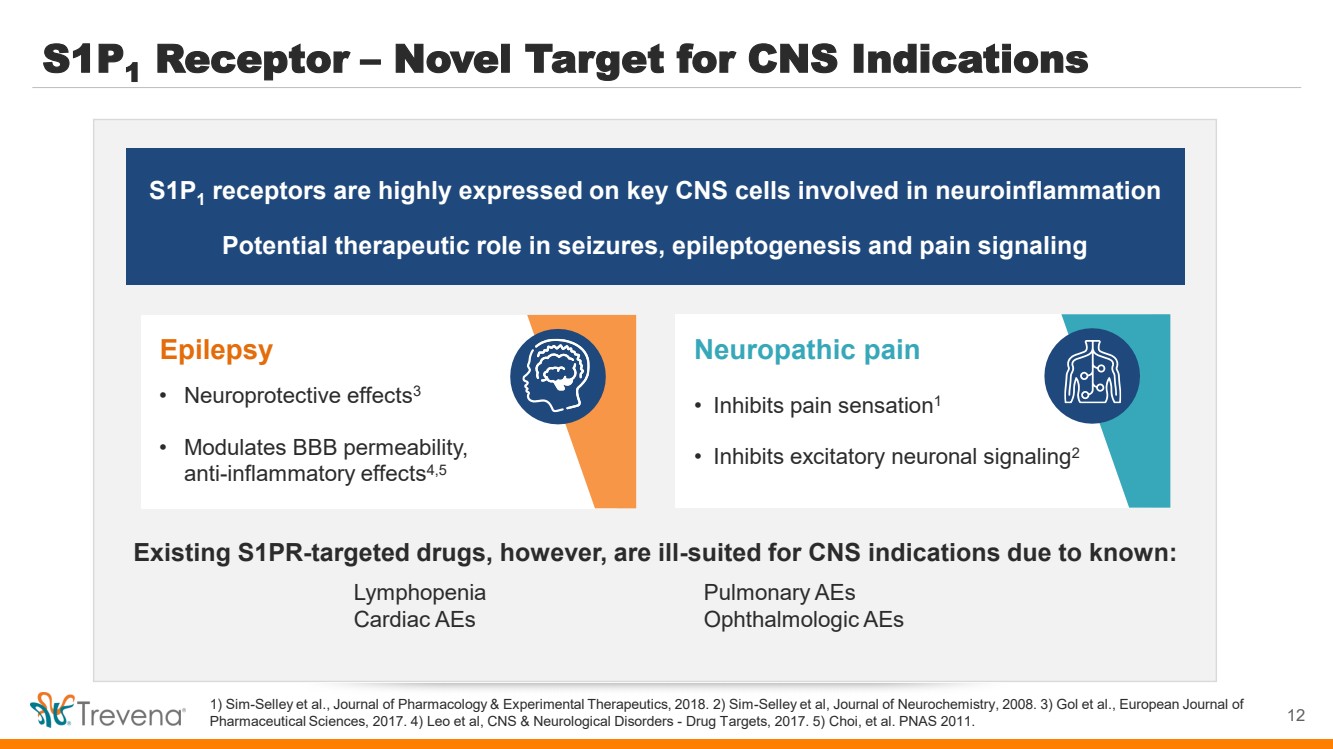
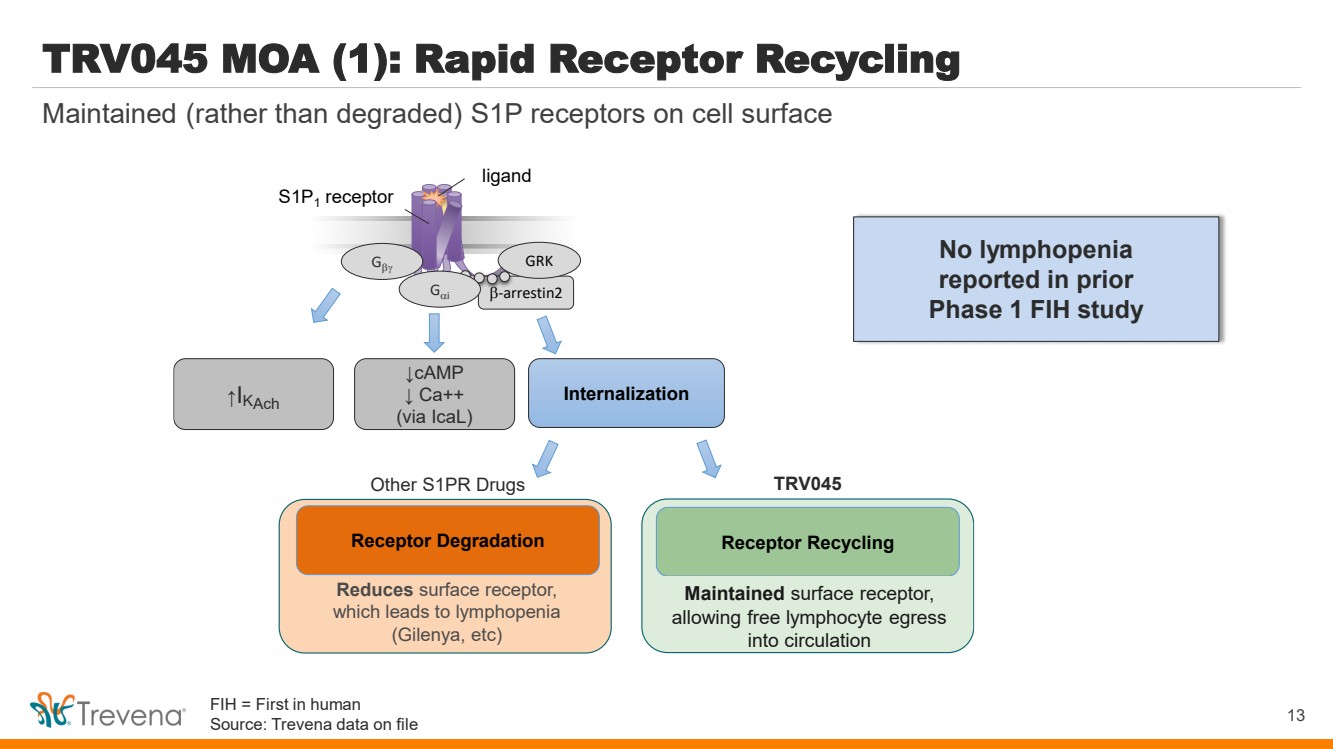
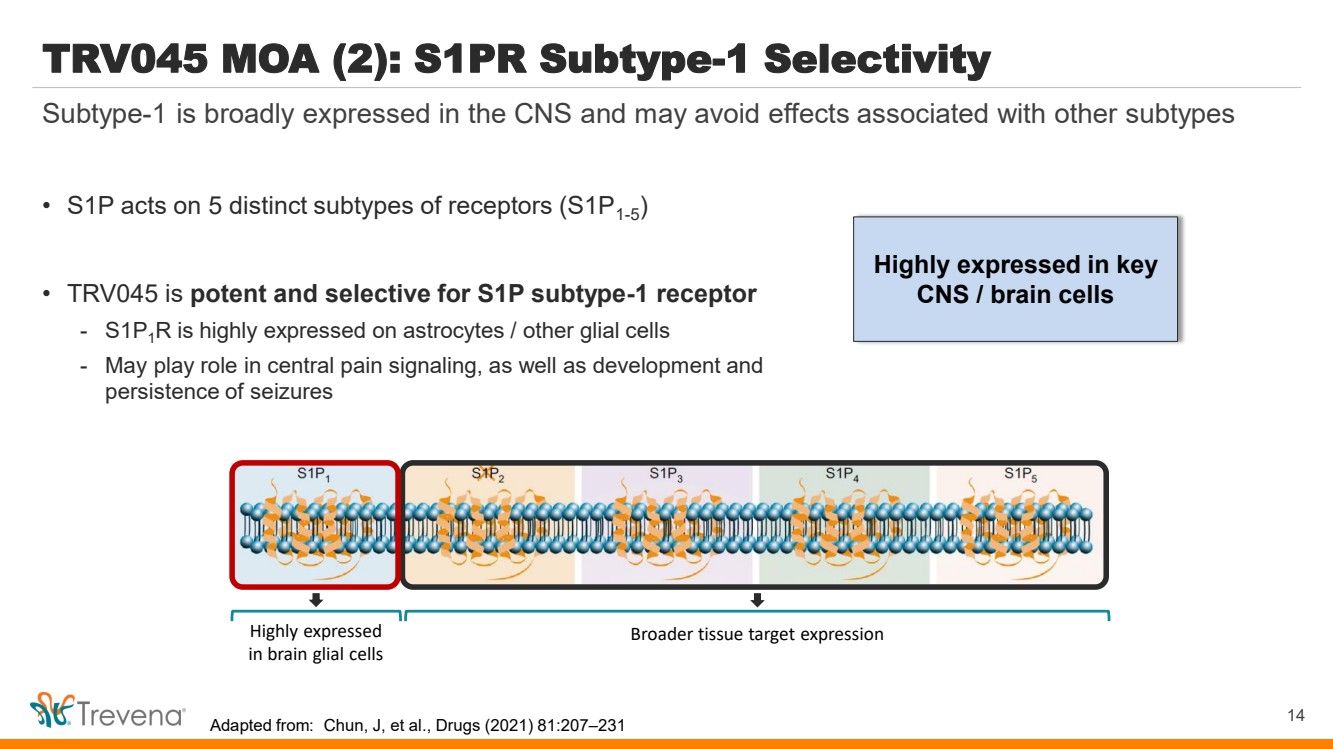
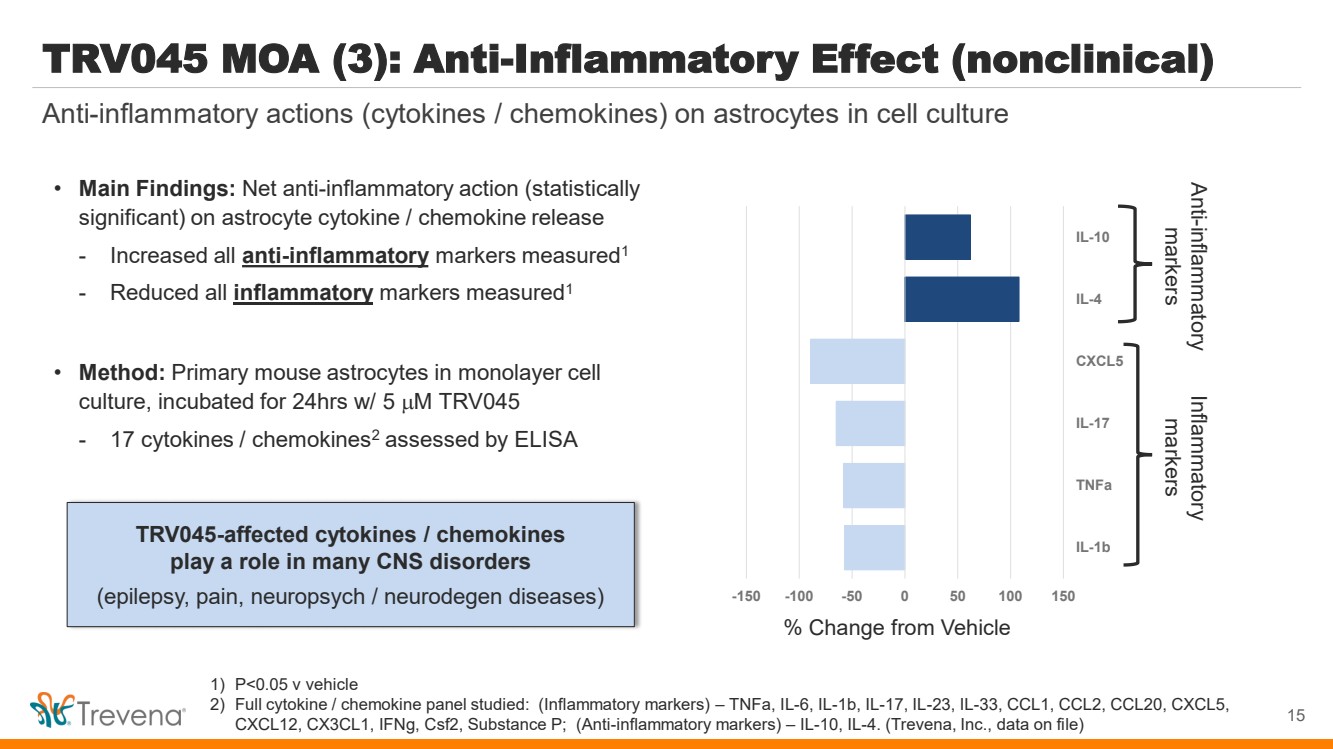
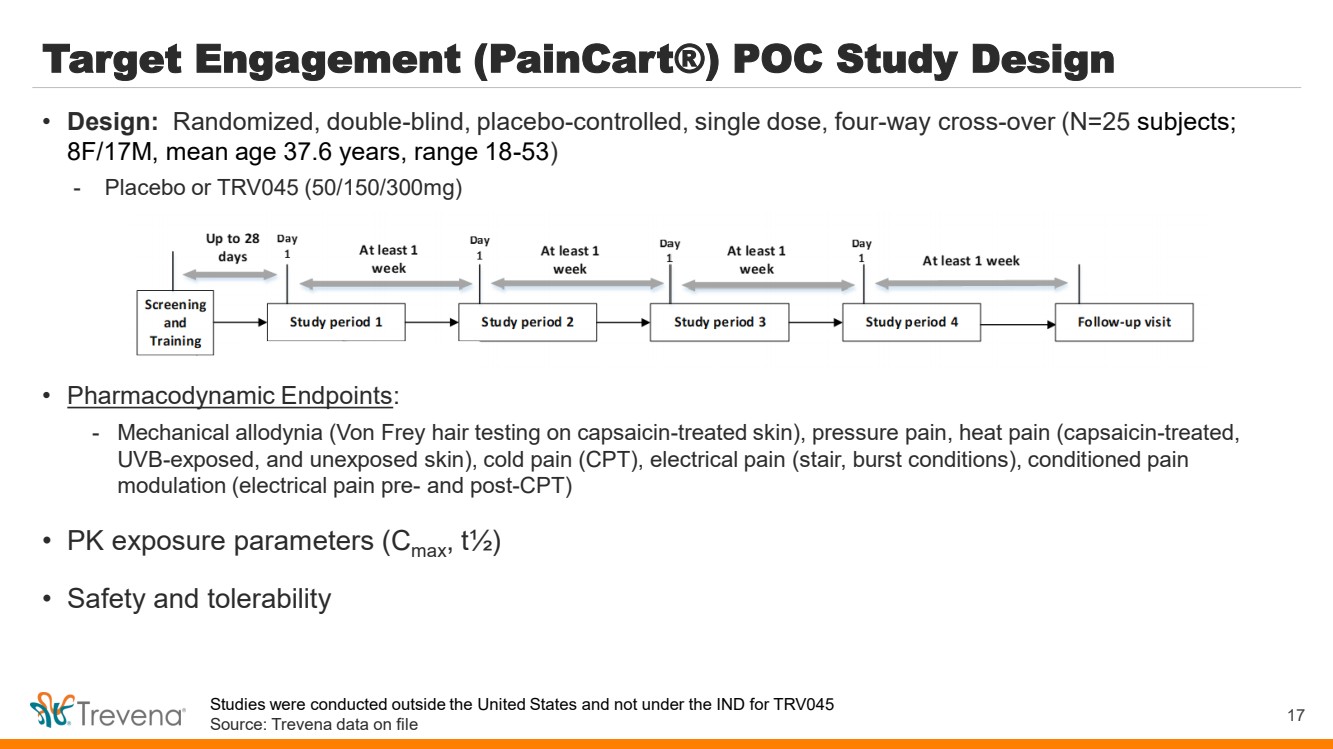
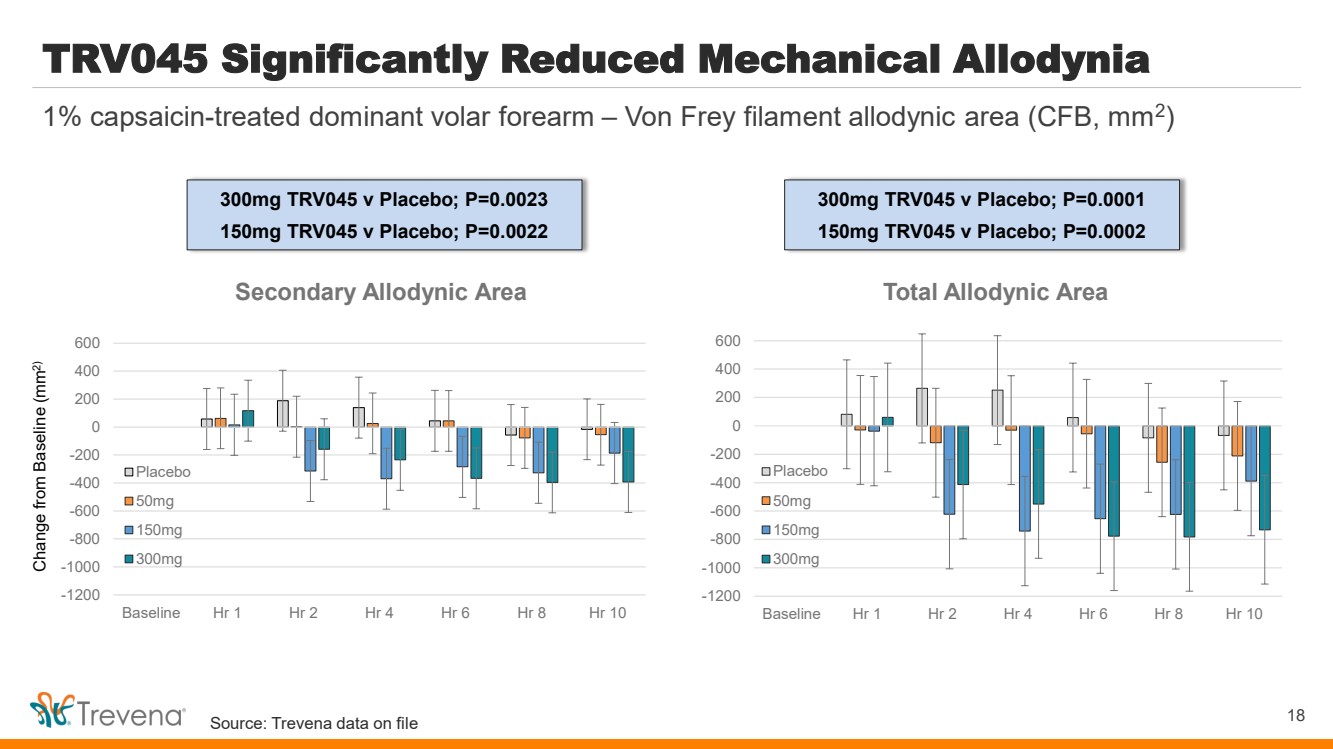
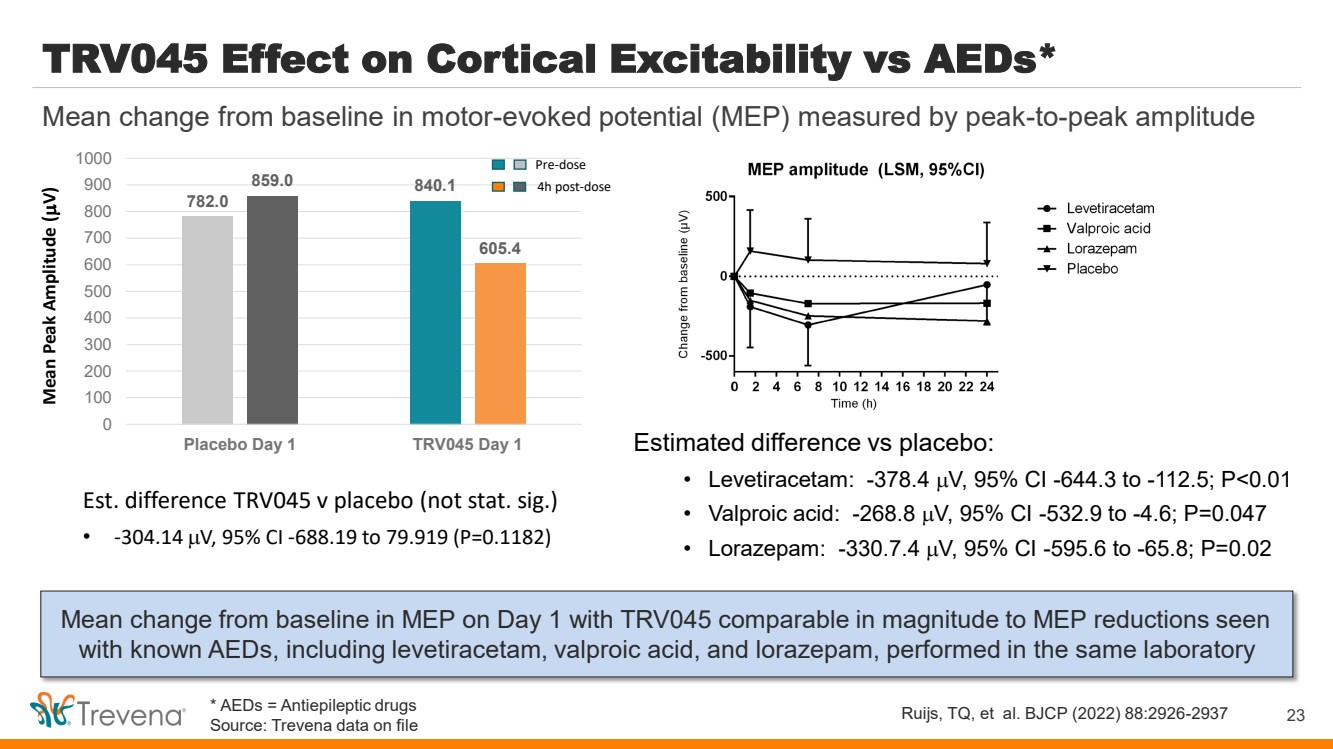
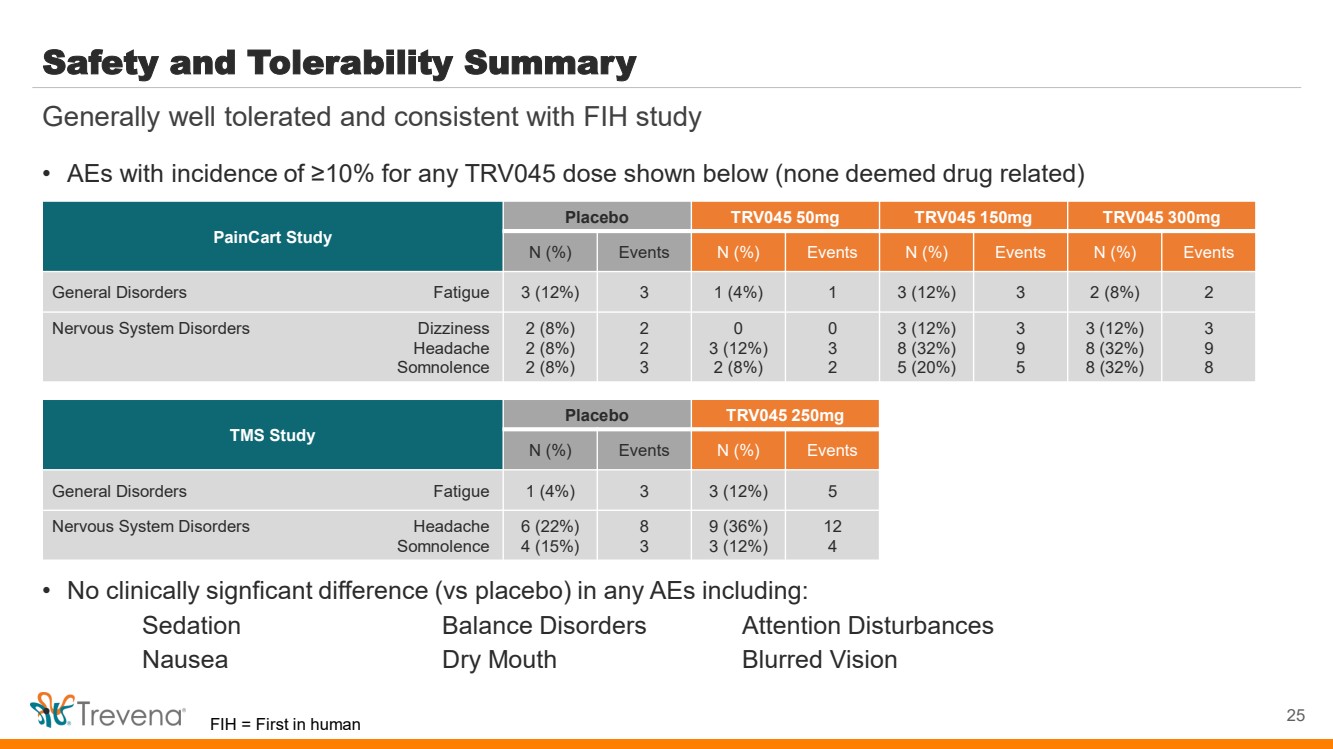
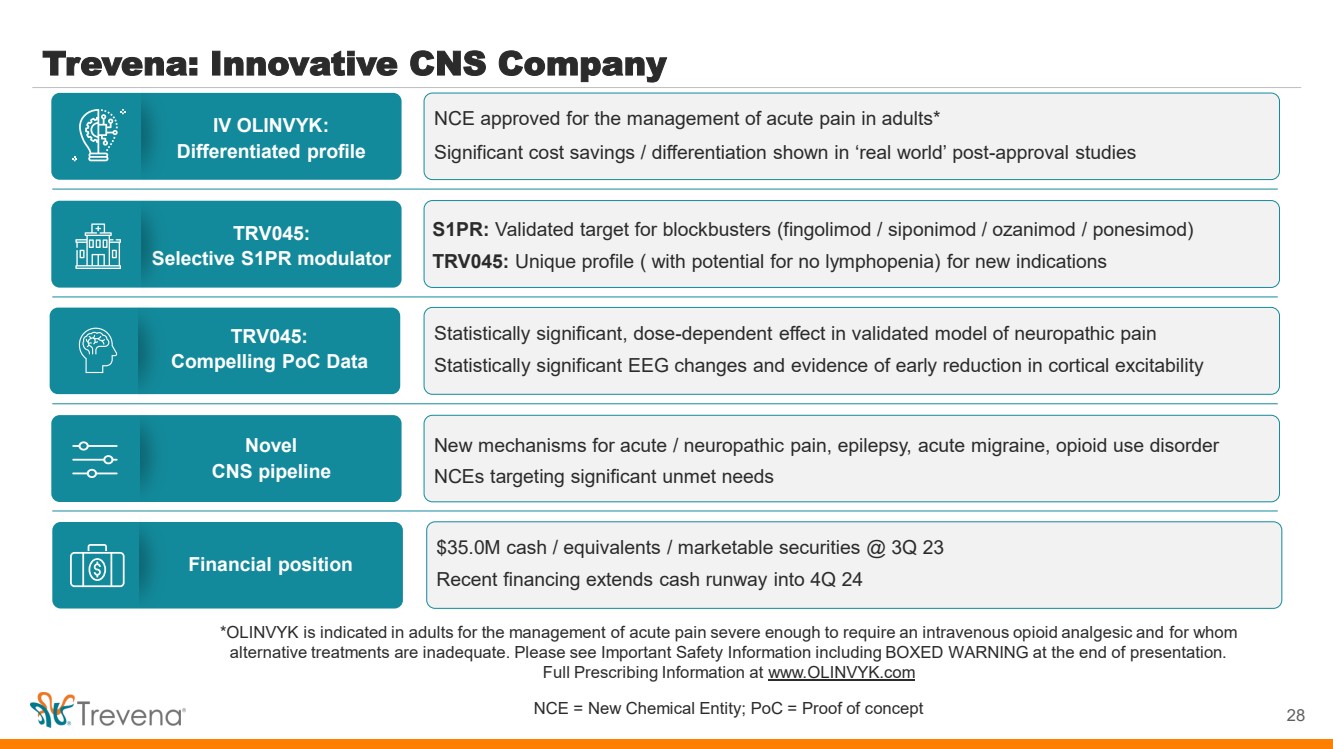
| WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS • Prolonged use of opioids during pregnancy can result in withdrawal in the neonate that may be life-threatening. Observe newborns for signs of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly. Advise pregnant women using OLINVYK for a prolonged period of the risk of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and ensure that appropriate treatment will be available. • Profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result from the concomitant use of OLINVYK with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants (e.g., non-benzodiazepine sedatives/hypnotics, anxiolytics, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, antipsychotics, other opioids, or alcohol). Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for use in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate, prescribe the lowest effective dose, and minimize the duration. • OLINVYK was shown to have mild QTc interval prolongation in thorough QT studies where patients were dosed up to 27 mg. Total cumulative daily doses exceeding 27 mg per day were not studied and may increase the risk for QTc interval prolongation. Therefore, the cumulative total daily dose of OLINVYK should not exceed 27 mg. • Increased plasma concentrations of OLINVYK may occur in patients with decreased Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 function or normal metabolizers taking moderate or strong CYP2D6 inhibitors; also in patients taking a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, in patients with decreased CYP2D6 function who are also receiving a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, or with discontinuation of a CYP3A4 inducer. These patients may require less frequent dosing and should be closely monitored for respiratory depression and sedation at frequent intervals. Concomitant use of OLINVYK with CYP3A4 inducers or discontinuation of a moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor can lower the expected concentration, which may decrease efficacy, and may require supplemental doses. • Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use (usually greater than one month). Presentation and symptoms may be nonspecific and include nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. If confirmed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids and wean patient from the opioid. • OLINVYK may cause severe hypotension, including orthostatic hypotension and syncope in ambulatory patients. • There is increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administrationof certain CNS depressant drugs (e.g., phenothiazines or general anesthetics). Monitor these patientsfor signs of hypotension. In patients with circulatory shock, avoid the use of OLINVYK as it may cause vasodilation that can further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. • Avoid the use of OLINVYK in patients with impaired consciousness or coma. OLINVYK should be used with caution in patients who may be susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention,such as those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure or brain tumors, as a reduction in respiratory drive and the resultantCO2 retention can further increase intracranial pressure. Monitor such patientsfor signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularlywhen initiating therapy. • As with all opioids, OLINVYK may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi, and may cause increases in serum amylase. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis,for worsening symptoms. • There is increased risk in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has already been compromised by a reduced blood volume or concurrent administrationof certain CNS depressant drugs (e.g., phenothiazines or general anesthetics). Monitor these patientsfor signs of hypotension. In patients with circulatory shock, avoid the use of OLINVYK as it may cause vasodilation that can further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure. • Avoid the use of OLINVYK in patients with impaired consciousness or coma. OLINVYK should be used with caution in patients who may be susceptible to the intracranial effects of CO2 retention,such as those with evidence of increased intracranial pressure or brain tumors, as a reduction in respiratory drive and the resultantCO2 retention can further increase intracranial pressure. Monitor such patientsfor signs of sedation and respiratory depression, particularlywhen initiating therapy. • As with all opioids, OLINVYK may cause spasm of the sphincter of Oddi, and may cause increases in serum amylase. Monitor patients with biliary tract disease, including acute pancreatitis,for worsening symptoms. • OLINVYK may increase the frequency of seizures in patients with seizure disorders and may increase the risk of seizuresin vulnerable patients. Monitor patients with a history of seizure disorders for worsened seizure control. • Do not abruptly discontinue OLINVYK in a patient physically dependent on opioids. Gradually taper the dosage to avoid a withdrawal syndrome and return of pain. Avoid the use of mixed agonist/antagonist (e.g., pentazocine, nalbuphine, and butorphanol) or partial agonist (e.g., buprenorphine) analgesics in patients who are receiving OLINVYK, as they may reduce the analgesic effect and/or precipitate withdrawal symptoms. • OLINVYK may impair the mental or physical abilities needed to perform potentially hazardous activities such as driving a car or operating machinery. • Although self-administration of opioids by patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) may allow each patient to individually titrate to an acceptable level of analgesia, PCA administration has resulted in adverse outcomes and episodes of respiratory depression. Health care providers and family members monitoring patients receiving PCA analgesia should be instructed in the need for appropriate monitoring for excessive sedation, respiratory depression, or other adverse effects of opioid medications. ADVERSE REACTIONS Adverse reactions are described in greater detail in the Prescribing Information. The most common (incidence ≥10%) adverse reactions in Phase 3 controlled clinical trials were nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, constipation, pruritus, and hypoxia. PLEASE see www.OLNVYK.com for full prescribing information including BOXED warning and important safety information 31 |