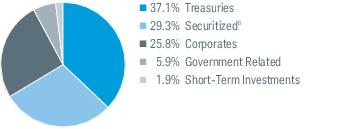
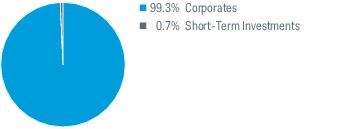
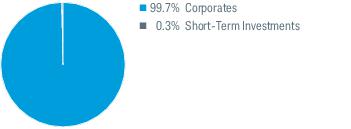
2. Significant Accounting Policies (continued):
(j) Indemnification:
Under the funds’ organizational documents, the officers and trustees are indemnified against certain liabilities arising out of the performance of their duties to the funds. In addition, in the normal course of business the funds enter into contracts with their vendors and others that provide general indemnifications. The funds’ maximum exposure under these arrangements is unknown as this would involve future claims that may be made against the funds. However, based on experience, the funds expect the risk of loss attributable to these arrangements to be remote.
(k) Recent Accounting Standards:
In March 2020, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update “Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform on Financial Reporting (Topic 848)” (ASU 2020-04), which provides optional temporary financial reporting relief from the effect of certain types of contract modifications due to the planned discontinuation of the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) and other interbank-offered based reference rates at the end of 2021. The temporary relief provided is effective for certain reference rate-related contract modifications that occur during the period March 12, 2020 through December 31, 2022. At this time, management believes the adoption of ASU 2020-04 will not have a material impact to the financial statements.
3. Risk Factors:
Investing in the funds may involve certain risks, as discussed in the funds’ prospectus, including, but not limited to, those described below. Any of these risks could cause an investor to lose money.
Market Risk. Financial markets rise and fall in response to a variety of factors, sometimes rapidly and unpredictably. Markets may be impacted by economic, political, regulatory and other conditions, including economic sanctions and other government actions. In addition, the occurrence of global events, such as war, terrorism, environmental disasters, natural disasters, and epidemics may also negatively affect the financial markets. As with any investment whose performance is tied to these markets, the value of an investment in a fund will fluctuate, which means that an investor could lose money over short or long periods.
Investment Style Risk. The funds are index funds. Therefore, the funds follow the securities included in an index during upturns as well as downturns. Because of their indexing strategy, the funds do not take steps to reduce market exposure or to lessen the effects of a declining market. In addition, because of each fund’s expenses, each fund’s performance may be below that of its respective index. Errors relating to the index may occur from time to time and may not be identified by the index provider for a period of time. In addition, market disruptions could cause delays in the index’s rebalancing schedule. Such errors and/or market disruptions may result in losses for the fund.
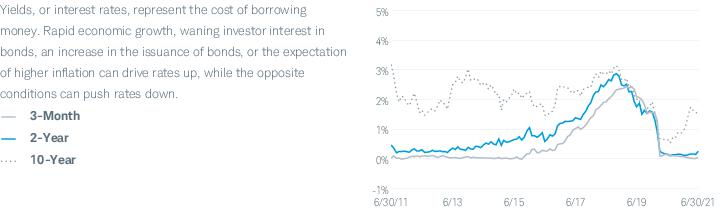
Interest Rate Risk. Interest rates rise and fall over time. As with any investment whose yield reflects current interest rates, a fund’s yield will change over time. During periods when interest rates are low, a fund’s yield (and total return) also may be low. Changes in interest rates also may affect a fund’s share price: a rise in interest rates generally causes a fund’s share price to fall. The longer a fund’s portfolio duration, the more sensitive to interest rate movements its share price is likely to be. Also, a change in a central bank’s monetary policy or economic conditions, among other things, may result in a change in interest rates, which could have sudden and unpredictable effects on the markets and significantly impact the value of fixed-income securities in which a fund invests. A sudden or unpredictable rise in interest rates may cause volatility.
Credit Risk. The funds are subject to the risk that a decline in the credit quality of an issuer, guarantor or liquidity provider of a portfolio investment or a counterparty could cause the funds to lose money or underperform. The funds could lose money if, due to a decline in credit quality, the issuer, guarantor or liquidity provider of a portfolio investment or a counterparty fails to make, or is perceived as being unable or unwilling to make, timely principal or interest payments or otherwise honor its obligations.
Inflation-Protected Security Risk. The value of inflation-protected securities, including TIPS, generally will fluctuate in response to changes in “real” interest rates, generally decreasing when real interest rates rise and increasing when real interest rates fall. Real interest rates represent nominal (or stated) interest rates reduced by the expected impact of inflation. In addition, interest payments on inflation-indexed securities will generally vary up or down along with the rate of inflation.
Sampling Index Tracking Risk. To the extent a fund uses sampling techniques, the fund may not fully replicate the index and may hold securities not included in the index. As a result, a fund is subject to the risk that the investment adviser’s investment management strategy, the implementation of which is subject to a number of constraints, may not produce the intended results. If a fund uses a sampling approach, it may not track the return of the index as well as it would if a fund purchased all of the securities in its index.