
Exhibit 99.2 January 2019 Corporate Overview

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation includes forward-looking statements that reflect our current views with respect to, among other things, our plans to develop and commercialize our product candidates, including our interpretation of preclinical and clinical studies and the success and timing of our product development activities and clinical trials, our intention to advance the development of SB206 for molluscum, which is subject to our ability to obtain additional financing or enter into strategic relationships to enable such development, the future prospects of our business and financial condition and our needs for additional financing. These forward- looking statements are included throughout this presentation. We have used the words “anticipate,” “assume,” “believe,” “continue,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “potential,” “predict,” “project,” “future,” “will,” “seek,” “foreseeable”, “targeted” and similar terms and phrases to identify forward-looking statements in this presentation. The forward-looking statements contained in this presentation are based on management’s current expectations and are subject to substantial risks, uncertainty and changes in circumstances. Actual results may differ materially from these expectations due to risks and uncertainties including, but not limited to: risks and uncertainties in the clinical development process, including, among others, length, expense, ability to enroll patients, reliance on third parties, and that results of earlier research and preclinical or clinical trials may not be predictive of results, conclusions or interpretations of later research or trials; risks related to the regulatory approval process, which is lengthy, time- consuming and inherently unpredictable; our ability to obtain substantial additional funding for the further advancement and development of our product candidates; our ability to identify and enter into strategic relationships for the further development and potential commercialization of our product candidates; and other risks and uncertainties described in our annual report filed with the SEC on Form 10-K for the twelve months ended Dec. 31, 2017, and in any subsequent filings with the SEC. Any forward-looking statement made by us in this presentation speaks only as of the date of this presentation. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or review any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise, except as may be required by any applicable securities laws. 2

Core Technology Platform Based on Nitric Oxide ▪ Naturally produced nitric oxide has diverse biological activity within the body − Immunology (bacterial, viral and inflammatory responses) − Cardiology/pulmonology (vasodilation/hemostasis, anti-coagulation, and respiration) − Neurology (neurotransmitter) ▪ Physiological effects are controlled by the dose of nitric oxide − Depending on dose and release kinetics, nitric oxide has positive or negative effects on the human body (e.g. anti- or pro-inflammatory) − Necessary to tune nitric oxide dose over time (e.g. release rates) to selectively target therapeutic indications and maximize desired effects − Our bodies naturally manage the complexity via multiple nitric oxide-donors/carriers to help ensure nitric oxide is in the right place at the right time ▪ Robustly studied in the literature − In general, the role and mechanisms of nitric oxide have been well researched − Prior to Novan, nitric oxide therapies have been limited by the ability to store and deliver tunable amounts of nitric oxide 3
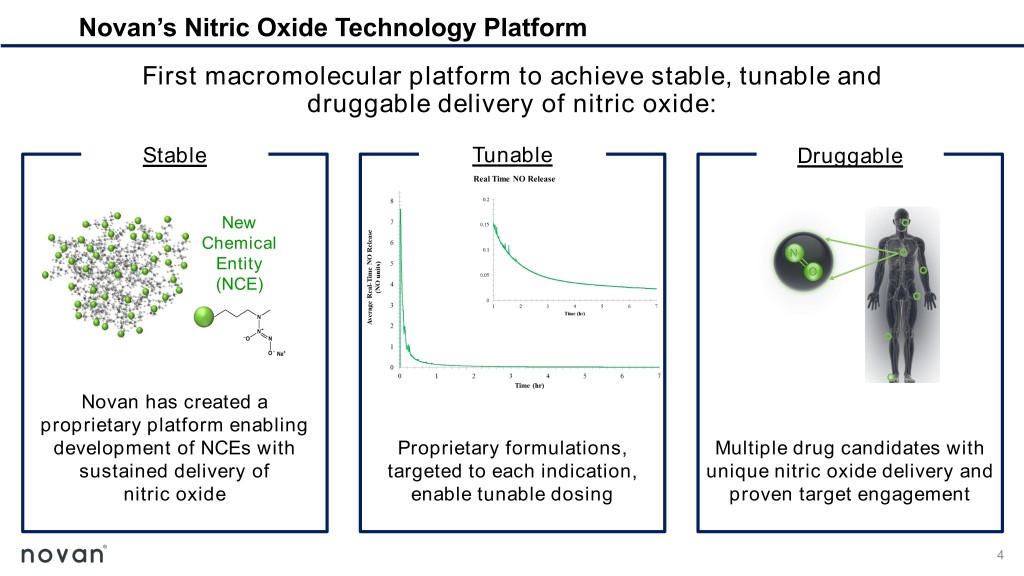
Novan’s Nitric Oxide Technology Platform First macromolecular platform to achieve stable, tunable and druggable delivery of nitric oxide: Stable Tunable Druggable New Chemical Entity (NCE) Novan has created a proprietary platform enabling development of NCEs with Proprietary formulations, Multiple drug candidates with sustained delivery of targeted to each indication, unique nitric oxide delivery and nitric oxide enable tunable dosing proven target engagement 4

Experienced Leadership Team Alignment of significant scientific and drug development expertise to Novan’s short, intermediate and longer-term opportunities Robert A. Ingram G. Kelly Martin Executive Chairman Chief Executive Officer Paula Brown Stafford Carri Geer, PhD President and Chief Operating Officer SVP, Chief Technology Officer Elizabeth Messersmith, PhD Jeff Hunter SVP, Chief Development Officer EVP, Chief Business Officer Andrew Novak Tomoko Maeda-Chubachi, MD VP, Chief Accounting Officer VP, Medical Dermatology 5
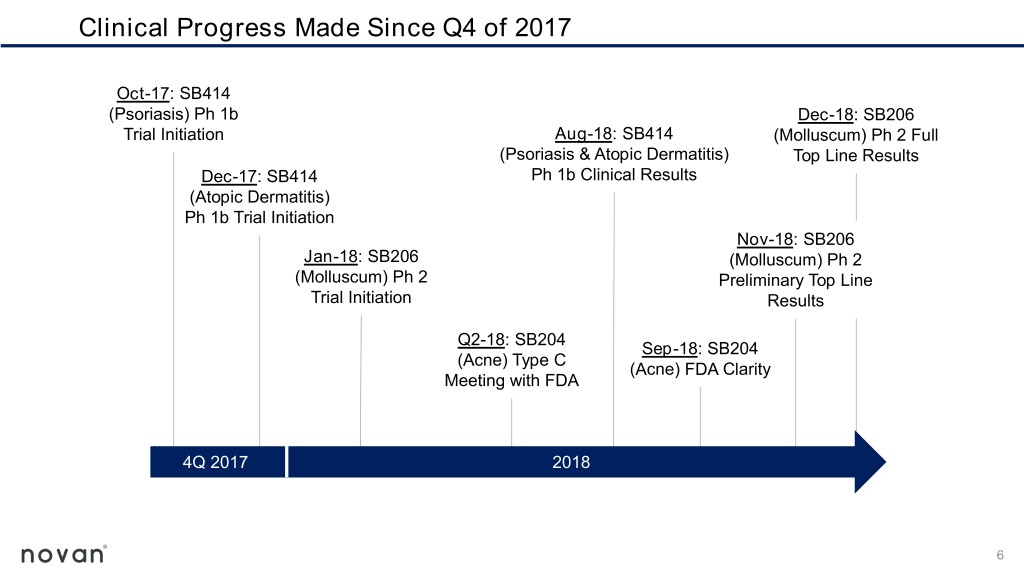
Clinical Progress Made Since Q4 of 2017 Oct-17: SB414 (Psoriasis) Ph 1b Dec-18: SB206 Trial Initiation Aug-18: SB414 (Molluscum) Ph 2 Full (Psoriasis & Atopic Dermatitis) Top Line Results Dec-17: SB414 Ph 1b Clinical Results (Atopic Dermatitis) Ph 1b Trial Initiation Nov-18: SB206 Jan-18: SB206 (Molluscum) Ph 2 (Molluscum) Ph 2 Preliminary Top Line Trial Initiation Results Q2-18: SB204 Sep-18: SB204 (Acne) Type C (Acne) FDA Clarity Meeting with FDA 4Q 2017 2018 6
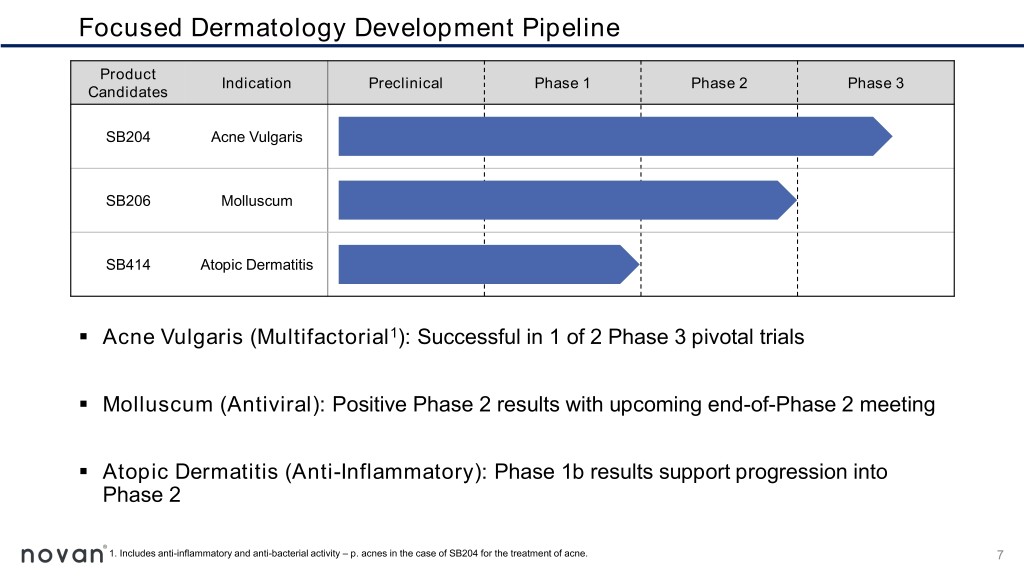
Focused Dermatology Development Pipeline Product Indication Preclinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Candidates SB204 Acne Vulgaris SB206 Molluscum SB414 Atopic Dermatitis ▪ Acne Vulgaris (Multifactorial1): Successful in 1 of 2 Phase 3 pivotal trials ▪ Molluscum (Antiviral): Positive Phase 2 results with upcoming end-of-Phase 2 meeting ▪ Atopic Dermatitis (Anti-Inflammatory): Phase 1b results support progression into Phase 2 1. Includes anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial activity – p. acnes in the case of SB204 for the treatment of acne. 7
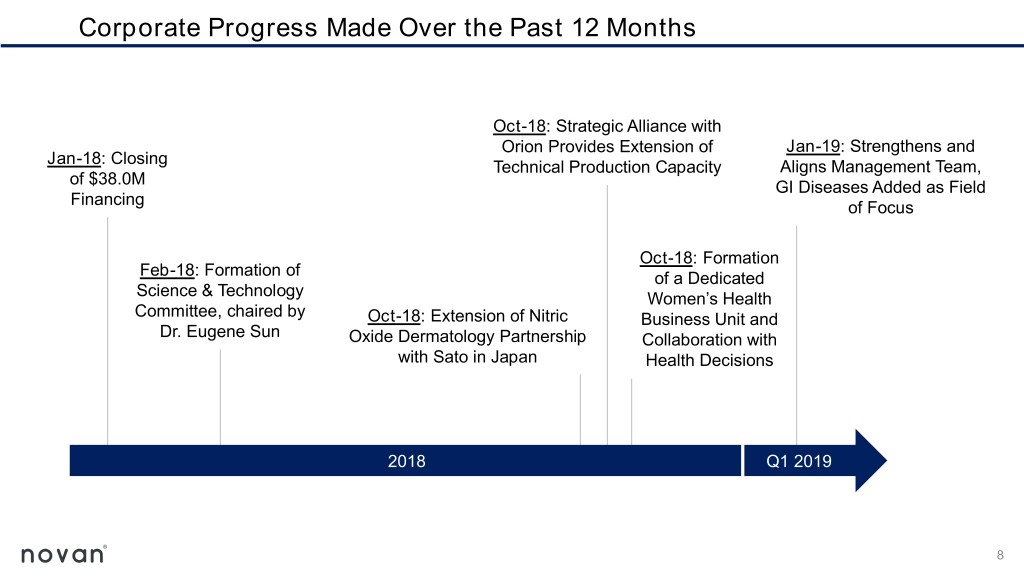
Corporate Progress Made Over the Past 12 Months Oct-18: Strategic Alliance with Orion Provides Extension of Jan-19: Strengthens and Jan-18: Closing Technical Production Capacity Aligns Management Team, of $38.0M GI Diseases Added as Field Financing of Focus Oct-18: Formation Feb-18: Formation of of a Dedicated Science & Technology Women’s Health Committee, chaired by Oct-18: Extension of Nitric Business Unit and Dr. Eugene Sun Oxide Dermatology Partnership Collaboration with with Sato in Japan Health Decisions 2018 Q1 2019 8

Value Creation Opportunities Over the Past 12 Months ▪ Sato/Japan amendment to include SB206: EGW and molluscum1 − ~$11M of upfront non-dilutive cash inflows; payable in installments through 3Q 2019 − Further potential milestone and royalty payments ▪ Multiple geographic business development discussions ongoing ▪ Women’s Health business unit established; HPV academic research collaboration with University of Alabama-Birmingham and clinical research collaboration with Health Decisions2 ▪ Expansion of technical production capacity with Orion/Finland enables business leveragability3 ▪ Addition of gastrointestinal (GI) diseases as a therapeutic focus area as part of overall science and business strategy 1. Novan Expands Nitric Oxide Dermatology Business Partnership with Sato in Japan 2. Novan Creates Dedicated Women’s Health Business Unit 3. Novan Extends Technical Production Capacity and 9 Reaches Agreement with Orion Corporation
Nitric Oxide Platform Expansion: Women’s Health & Gastroenterology Women’s Health Gastroenterology ▪ Novan’s nitric oxide technology has demonstrated the ▪ Inherent connection between the multi-factorial ability to inhibit HPV amplification and replication in pathologies of GI diseases and the demonstrable nonclinical models anti-microbial, anti-viral and anti-inflammatory properties of Novan’s nitric oxide technology ▪ Targeting high-risk HPV infections and associated cancers affecting women ▪ Nitric oxide produced in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract regulates many of its functions1-3 ▪ Clinical research collaboration established with Health Decisions, a specialist women’s health CRO ▪ Nitric oxide supplied from nitric oxide donors are ▪ protective against gastric damage in a dose- Existing multi-year research collaboration with dependent manner1-3 University of Alabama-Birmingham extended ▪ ▪ NO-releasing variants of NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti- Pipeline: inflammatory drugs) have enhanced therapeutic − Previously announced Phase 2 data for the benefit versus NSAID alone2,3 treatment of external genital warts (EGW) provide a specific late stage clinical asset that targets HPV-associated diseases “The future of this field with respect to drug development will require patented molecules that will − IND enabling preclinical studies ongoing targeting high-risk HPV release the gaseous mediator at a rate appropriate for promoting health, and at the specific locations where the effects of the mediator are most needed”3 1. MacNaughton WK, et al. (1989). Endothelium-derived relaxing factor (nitric oxide) has protective actions in the stomach. Life Sci 45: 1869–1876 2. Wallace JL (2019). Nitric oxide in the gastrointestinal tract: opportunities 10 for drug development. Br. J. Pharmacol. 176: 147–154 3. Wallace JL et al. (2017) Gaseous Mediators in Gastrointestinal Mucosal Defense and Injury. Dig. Dis. Sci. 62: 2223-2230
Molluscum Contagiosum Overview Molluscum is a contagious skin infection caused by the ▪ Prevalence of ~6 million in the US1,2 molluscipoxvirus, a double- − ~1 million diagnosed annually stranded DNA virus − ~90% of patients below the age of 18 ▪ Typically present with 10-30 lesions, up to 100 in severe cases − Avg. time to resolution is 13 months2 ▪ No FDA-approved treatments indicated for molluscum 1. QuintilesIMS. Market Opportunity Assessment EGW, Common Warts and Molluscum, March 2017 (Jul’14-Jun’16 Study Period). 2. Olsen JR et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:190-5. 3. Ormerod AD et al. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141(6):1051-1053 11
Anti-Viral Mechanism of Action ▪ Multiple publications show nitric oxide inhibits viral replication via S-nitrosylation in the following viruses: − Human papillomavirus (HPV): double-stranded DNA virus − Herpes simplex virus (HSV): double-stranded DNA virus − Coxsackievirus: single-stranded RNA virus − Dengue virus: single-stranded RNA virus ▪ Novan’s nitric oxide technology has demonstrated the ability to inhibit HPV amplification and replication in nonclinical models, as well as efficacy in a Phase 2 clinical trial against external genital warts ▪ The inhibition of viral replication demonstrated in HPV is hypothesized to be translatable to other double stranded DNA virus families: − Adenoviridae − Polymoviridae − Poxviridae (e.g. molluscipoxvirus, a double-stranded DNA virus) ▪ Mechanism of action supported by in vitro data against vaccinia, a double-stranded DNA pox virus ▪ And now, Novan has demonstrated efficacy against the molluscipoxvirus in a Phase 2 clinical trial Sources: Colasanti, M. et al. S-Nitrosylation of Viral Proteins: Molecular Bases for Antiviral Effect of Nitric Oxide IUBMB Life; 1999 (48) 25-31. Kroen, KD. J Clin Invest. 1993;91(6):2446-2452.; Karupiah, G; et al. Science. 1993;261(5127):1445-1448. Saura, M; et al. Immunity. 1999;10:21-28. Takhampunya, R; et al. J Gen Virol. 2006;87:3003-3011. McHale, K et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Efficacy of Nitric Oxide-Releasing Antiviral Therapeutic Agents 12 Society for Investigative Dermatology Annual Meeting 2016 .
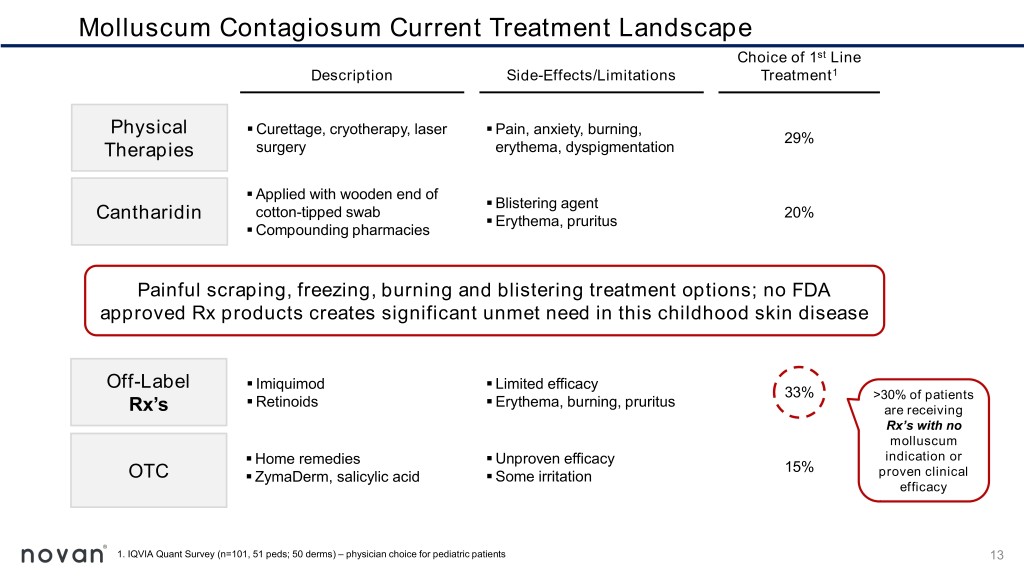
Molluscum Contagiosum Current Treatment Landscape Choice of 1st Line Description Side-Effects/Limitations Treatment1 Physical ▪ Curettage, cryotherapy, laser ▪ Pain, anxiety, burning, 29% Therapies surgery erythema, dyspigmentation ▪ Applied with wooden end of ▪ Blistering agent cotton-tipped swab 20% Cantharidin ▪ Erythema, pruritus ▪ Compounding pharmacies Painful scraping, freezing, burning and blistering treatment options; no FDA approved Rx products creates significant unmet need in this childhood skin disease Off-Label ▪ Imiquimod ▪ Limited efficacy 33% ▪ Retinoids ▪ Erythema, burning, pruritus >30% of patients Rx’s are receiving Rx’s with no molluscum ▪ Home remedies ▪ Unproven efficacy indication or 15% OTC ▪ ZymaDerm, salicylic acid ▪ Some irritation proven clinical efficacy 1. IQVIA Quant Survey (n=101, 51 peds; 50 derms) – physician choice for pediatric patients 13
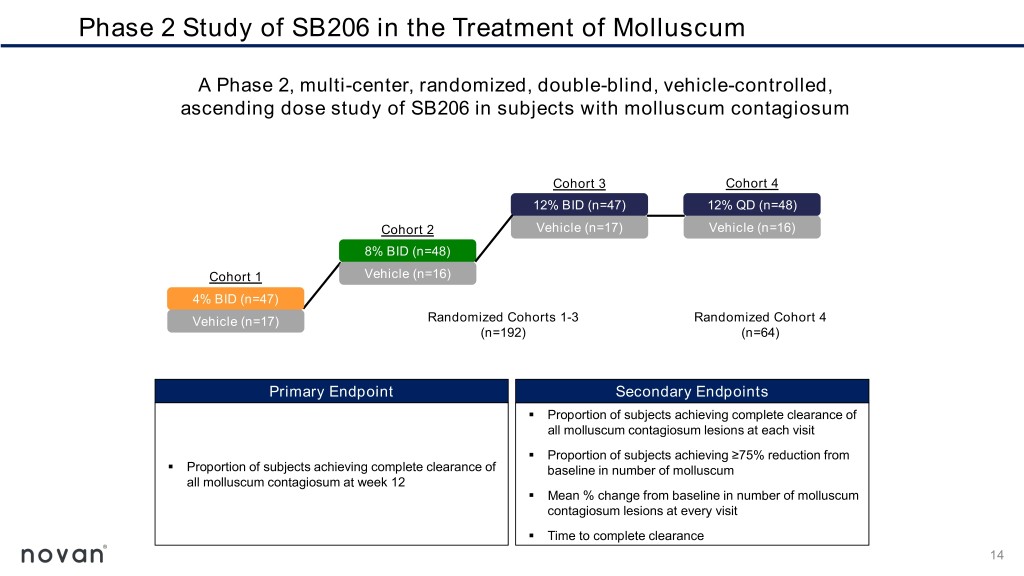
Phase 2 Study of SB206 in the Treatment of Molluscum A Phase 2, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled, ascending dose study of SB206 in subjects with molluscum contagiosum Cohort 3 Cohort 4 12% BID (n=47) 12% QD (n=48) Cohort 2 Vehicle (n=17) Vehicle (n=16) 8% BID (n=48) Cohort 1 Vehicle (n=16) 4% BID (n=47) Vehicle (n=17) Randomized Cohorts 1-3 Randomized Cohort 4 (n=192) (n=64) Primary Endpoint Secondary Endpoints ▪ Proportion of subjects achieving complete clearance of all molluscum contagiosum lesions at each visit ▪ Proportion of subjects achieving ≥75% reduction from ▪ Proportion of subjects achieving complete clearance of baseline in number of molluscum all molluscum contagiosum at week 12 ▪ Mean % change from baseline in number of molluscum contagiosum lesions at every visit ▪ Time to complete clearance 14
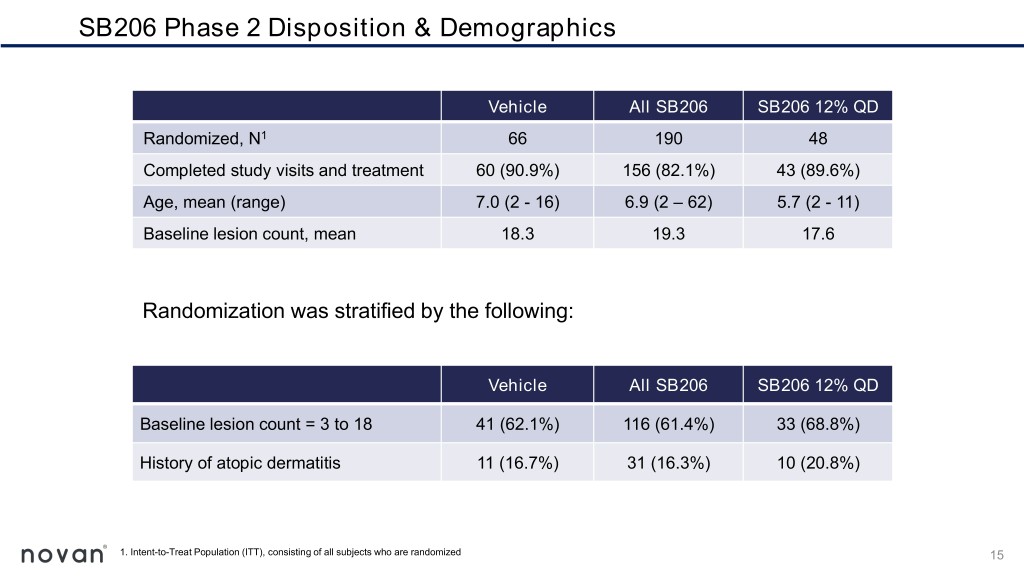
SB206 Phase 2 Disposition & Demographics Vehicle All SB206 SB206 12% QD Randomized, N1 66 190 48 Completed study visits and treatment 60 (90.9%) 156 (82.1%) 43 (89.6%) Age, mean (range) 7.0 (2 - 16) 6.9 (2 – 62) 5.7 (2 - 11) Baseline lesion count, mean 18.3 19.3 17.6 Randomization was stratified by the following: Vehicle All SB206 SB206 12% QD Baseline lesion count = 3 to 18 41 (62.1%) 116 (61.4%) 33 (68.8%) History of atopic dermatitis 11 (16.7%) 31 (16.3%) 10 (20.8%) 1. Intent-to-Treat Population (ITT), consisting of all subjects who are randomized 15
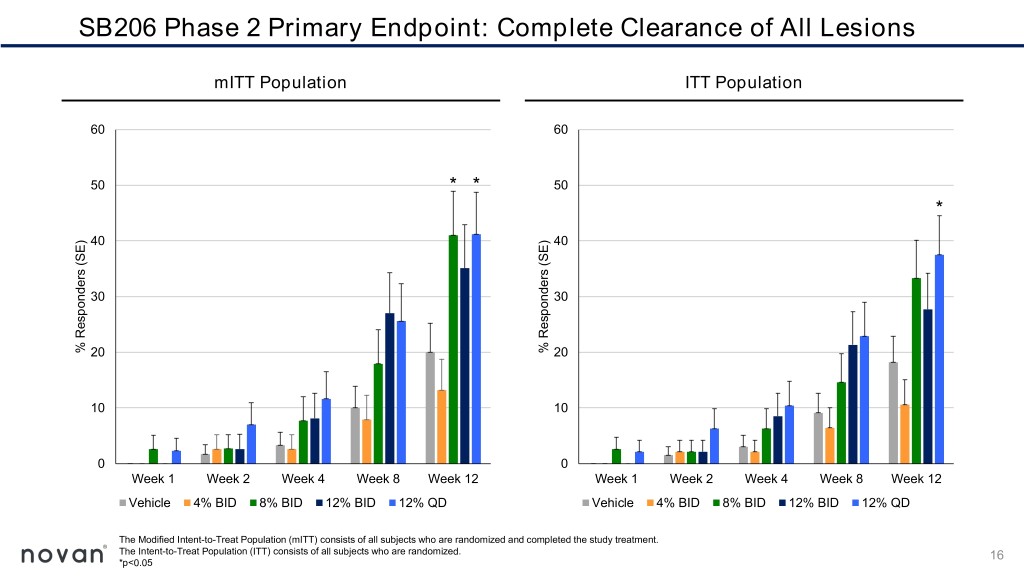
SB206 Phase 2 Primary Endpoint: Complete Clearance of All Lesions mITT Population ITT Population 60 60 50 * * 50 * 40 40 30 30 % Responders (SE) Responders % 20 (SE) Responders % 20 10 10 0 0 Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 8 Week 12 Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 8 Week 12 Vehicle 4% BID 8% BID 12% BID 12% QD Vehicle 4% BID 8% BID 12% BID 12% QD The Modified Intent-to-Treat Population (mITT) consists of all subjects who are randomized and completed the study treatment. The Intent-to-Treat Population (ITT) consists of all subjects who are randomized. 16 *p<0.05
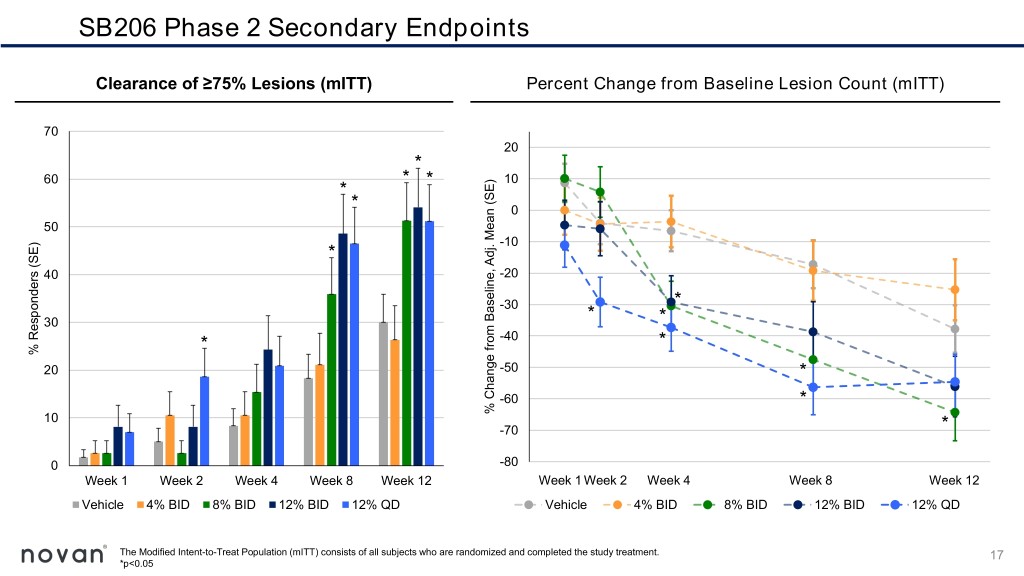
SB206 Phase 2 Secondary Endpoints Clearance of ≥75% Lesions (mITT) Percent Change from Baseline Lesion Count (mITT) 70 20 * 60 * * 10 * * 0 50 -10 * 40 -20 -30 * 30 * * * -40 * % Responders (SE) Responders % 20 -50 * -60 * 10 Adj.Mean(SE) % ChangefromBaseline, -70 * 0 -80 Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 8 Week 12 Week 1 Week 2 Week 4 Week 8 Week 12 Vehicle 4% BID 8% BID 12% BID 12% QD Vehicle 4% BID 8% BID 12% BID 12% QD The Modified Intent-to-Treat Population (mITT) consists of all subjects who are randomized and completed the study treatment. 17 *p<0.05
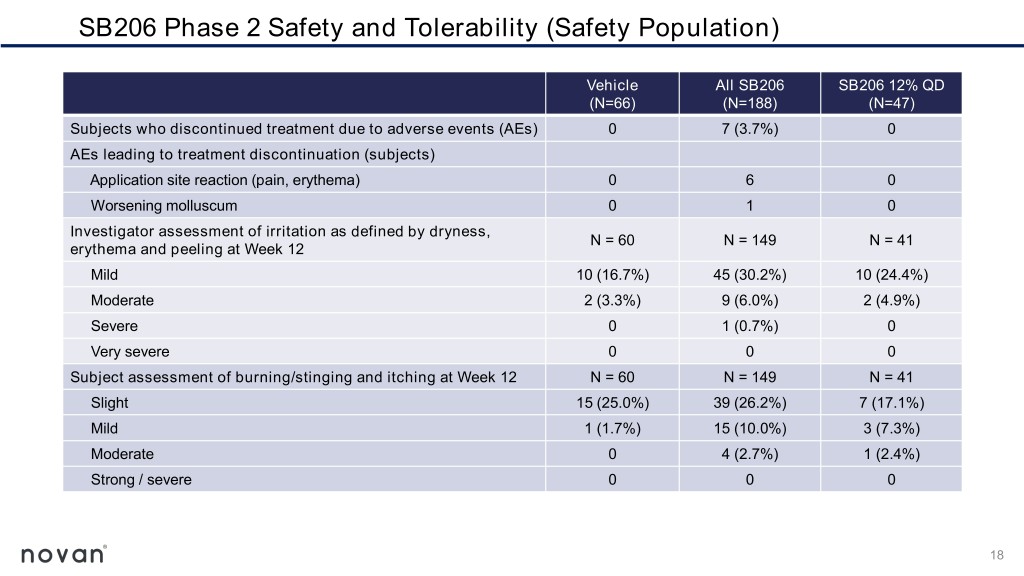
SB206 Phase 2 Safety and Tolerability (Safety Population) Vehicle All SB206 SB206 12% QD (N=66) (N=188) (N=47) Subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse events (AEs) 0 7 (3.7%) 0 AEs leading to treatment discontinuation (subjects) Application site reaction (pain, erythema) 0 6 0 Worsening molluscum 0 1 0 Investigator assessment of irritation as defined by dryness, N = 60 N = 149 N = 41 erythema and peeling at Week 12 Mild 10 (16.7%) 45 (30.2%) 10 (24.4%) Moderate 2 (3.3%) 9 (6.0%) 2 (4.9%) Severe 0 1 (0.7%) 0 Very severe 0 0 0 Subject assessment of burning/stinging and itching at Week 12 N = 60 N = 149 N = 41 Slight 15 (25.0%) 39 (26.2%) 7 (17.1%) Mild 1 (1.7%) 15 (10.0%) 3 (7.3%) Moderate 0 4 (2.7%) 1 (2.4%) Strong / severe 0 0 0 18

Summary of SB206 Phase 2 Top Line Results ▪ Higher rates of complete clearance of all molluscum lesions at Week 12 for the three highest doses, 8% twice-daily, 12% twice-daily and 12% once- daily, more than double the rate observed in the vehicle group ▪ Statistically significant reductions in molluscum lesions as early as Week 2 with 12% once-daily ▪ Attractive safety and tolerability profile, a critical and highly appealing feature for a predominantly childhood disease ▪ No quantifiable levels of systemic exposure detected for SB206 12% twice or once-daily at Week 12 ▪ SB206 as a once-daily, at-home, caregiver-applied topical therapy with a rapid treatment benefit, if approved, would satisfy an important patient- care need for the treatment of molluscum 19

SB206 for the Treatment of Molluscum Path Forward ▪ Novan has requested an end-of-Phase 2 meeting with the FDA − This meeting would enable Novan and the FDA to agree on a Phase 3 development plan for molluscum with SB206 12% once-daily as the active treatment arm ▪ Following a successful end-of-Phase 2 meeting with the FDA, the Company plans to initiate a Phase 3 program of SB206 for molluscum in 1H 20191 ▪ Top line results from Phase 3 program possible by the end of 2019 or early in 2020 1. Subject to obtaining additional financing or strategic partnering 20

SB204 as a Potential Treatment for Acne Vulgaris ▪ In 2Q 2018, conducted a Type C meeting; focus was on the severe patient population ▪ In 3Q 2018, the FDA provided feedback in their minutes on two paths forward: − One additional pivotal trial for moderate-to-severe acne patients, or − Additional preliminary trials for a severe-only patient population ▪ We believe one additional pivotal Phase 3 trial in moderate-to-severe acne patients is most pragmatic path forward for Novan ▪ Recent positive Phase 3 acne clinical trial results from Cassiopea and Foamix, follow disappointing results from Dermira 21

Confirmatory SB204 Phase 3 Clinical Trial Optimizations ▪ We have executed a business arrangement with a specialized- dermatology Contract Research Organization (CRO) for trial start-up activities ▪ Trial Optimizations: − Increased patient density per clinical site relative to NI-AC301 or NI- AC302 − Fewer sites relative to NI-AC301 or NI-AC302 − Enrich patient selection – increase inflammatory lesion count at baseline relative to NI-AC301 or NI-AC302 − Train IGA Assessors, before and during trial; ensure consistency in assessing IGA scores − Photograph patients’ acne to support training and illustrate IGA scoring system 22

Atopic Dermatitis Overview ▪ ~22M Americans suffer from mild-to- moderate AD1 − ~80% of disease burden ▪ Typically patients are treated first line with topical therapies − Corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors and PDE4 inhibitors ▪ Nitric oxide targets the NLRP3 inflammasome and has the ability to impact multiple mechanisms of the disease2 1. https://nationaleczema.org/research/eczema-facts/ 2. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018 Aug;17(8):588-606. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2018.97. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Bruchard, M. et al. 2015. Nat. Immunol. 16(8):859-870.; Ting, J. et al. 2015 Nat. Immunol. 16(8):794-796.; Mishra B et al. Nat. Immunol. 2013; 14(1):52-60; Hollenbach, S. Effects of SB414 Cream on S. aureus and Tissue Cytokines in an Atopic Dermatitis Mouse Model. Presented at 2018 23 IID..
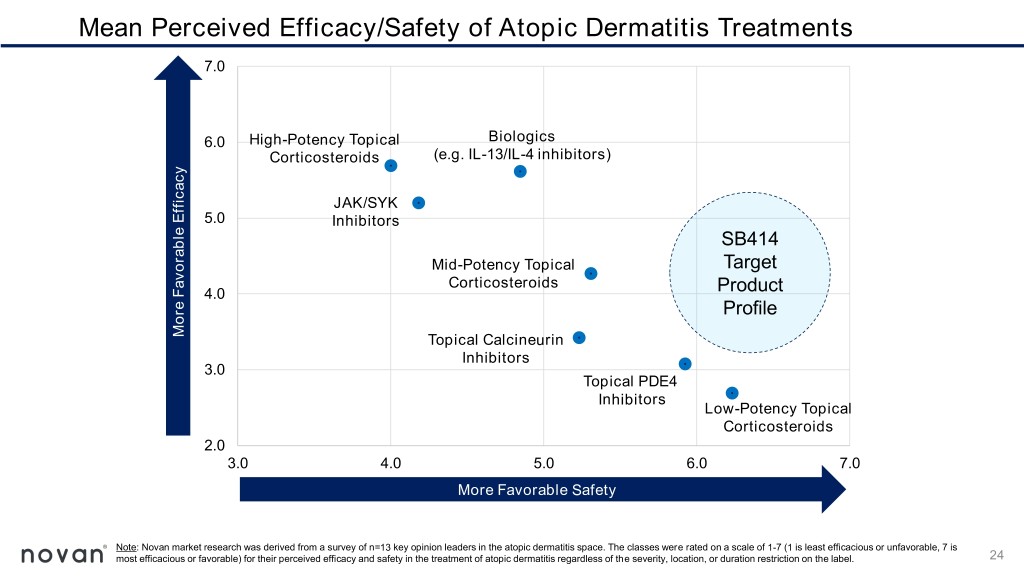
Mean Perceived Efficacy/Safety of Atopic Dermatitis Treatments 7.0 6.0 High-Potency Topical Biologics Corticosteroids (e.g. IL-13/IL-4 inhibitors) JAK/SYK 5.0 Inhibitors SB414 Mid-Potency Topical Target Corticosteroids 4.0 Product Profile Perceived Efficacy Perceived More Favorable Efficacy Favorable More Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors 3.0 Topical PDE4 Inhibitors Low-Potency Topical Corticosteroids 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 MorePerceived Favorable Safety Safety Note: Novan market research was derived from a survey of n=13 key opinion leaders in the atopic dermatitis space. The classes were rated on a scale of 1-7 (1 is least efficacious or unfavorable, 7 is most efficacious or favorable) for their perceived efficacy and safety in the treatment of atopic dermatitis regardless of the severity, location, or duration restriction on the label. 24
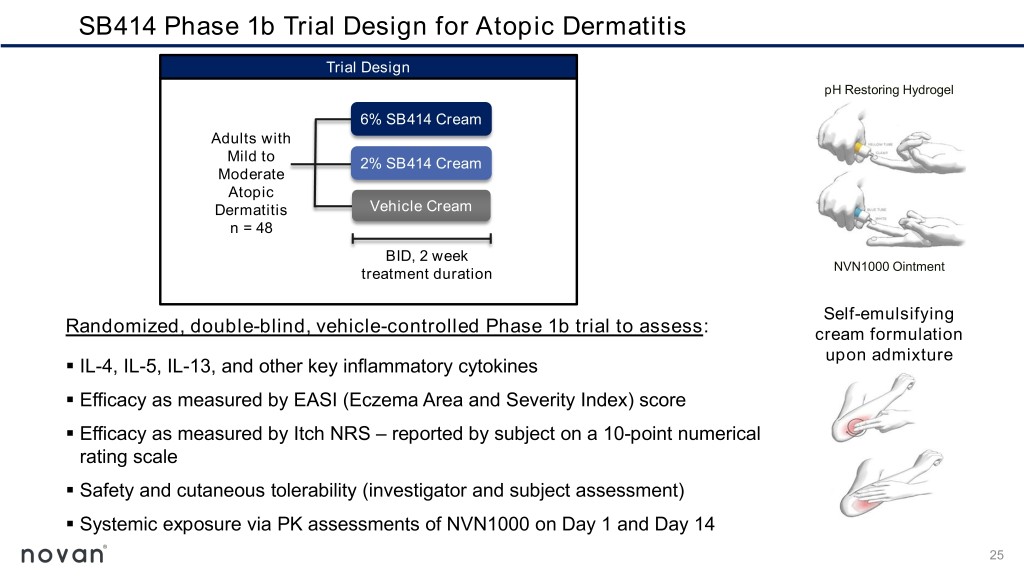
SB414 Phase 1b Trial Design for Atopic Dermatitis Trial Design pH Restoring Hydrogel 6% SB414 Cream Adults with Mild to 2% SB414 Cream Moderate Atopic Dermatitis Vehicle Cream n = 48 BID, 2 week treatment duration NVN1000 Ointment Self-emulsifying Randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled Phase 1b trial to assess: cream formulation upon admixture ▪ IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and other key inflammatory cytokines ▪ Efficacy as measured by EASI (Eczema Area and Severity Index) score ▪ Efficacy as measured by Itch NRS – reported by subject on a 10-point numerical rating scale ▪ Safety and cutaneous tolerability (investigator and subject assessment) ▪ Systemic exposure via PK assessments of NVN1000 on Day 1 and Day 14 25
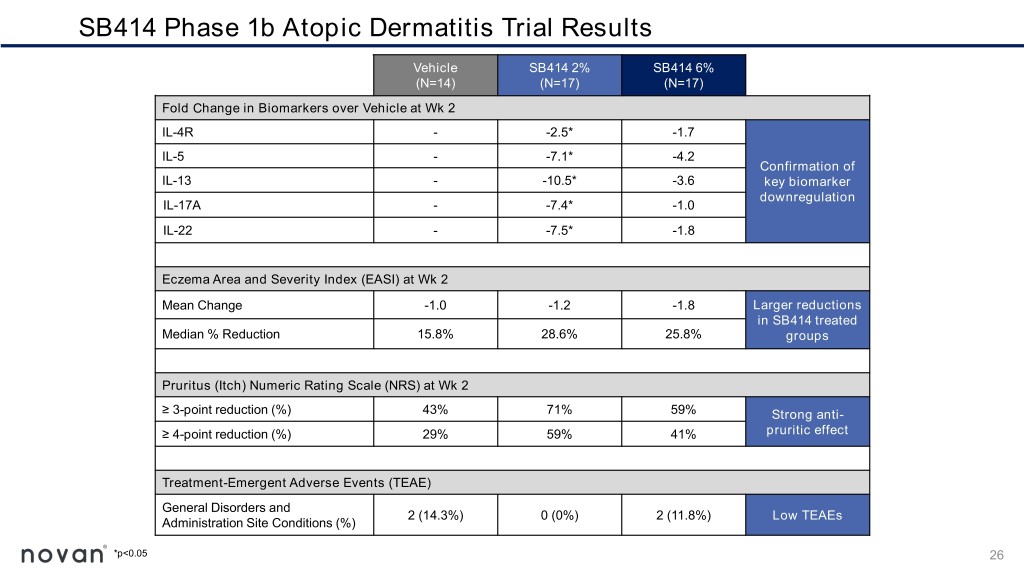
SB414 Phase 1b Atopic Dermatitis Trial Results Vehicle SB414 2% SB414 6% (N=14) (N=17) (N=17) Fold Change in Biomarkers over Vehicle at Wk 2 IL-4R - -2.5* -1.7 IL-5 - -7.1* -4.2 Confirmation of IL-13 - -10.5* -3.6 key biomarker downregulation IL-17A - -7.4* -1.0 IL-22 - -7.5* -1.8 Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) at Wk 2 Mean Change -1.0 -1.2 -1.8 Larger reductions in SB414 treated Median % Reduction 15.8% 28.6% 25.8% groups Pruritus (Itch) Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) at Wk 2 ≥ 3-point reduction (%) 43% 71% 59% Strong anti- ≥ 4-point reduction (%) 29% 59% 41% pruritic effect Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events (TEAE) General Disorders and 2 (14.3%) 0 (0%) 2 (11.8%) Low TEAEs Administration Site Conditions (%) *p<0.05 26
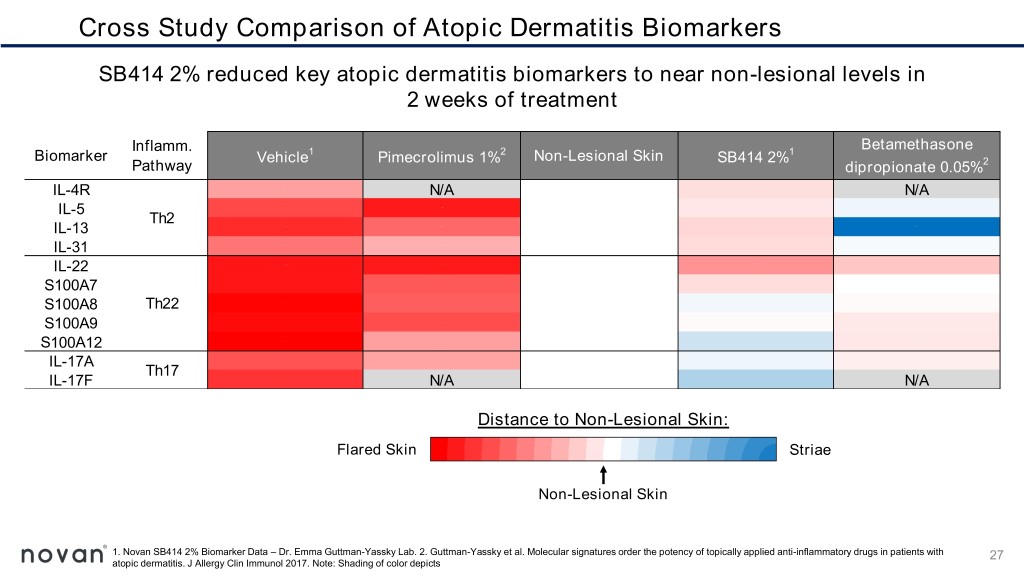
Cross Study Comparison of Atopic Dermatitis Biomarkers SB414 2% reduced key atopic dermatitis biomarkers to near non-lesional levels in 2 weeks of treatment Inflamm. Betamethasone Biomarker Vehicle1 Pimecrolimus 1%2 Non-Lesional Skin SB414 2%1 Pathway dipropionate 0.05%2 IL-4R N/A N/A IL-5 Th2 IL-13 IL-31 IL-22 S100A7 S100A8 Th22 S100A9 S100A12 IL-17A Th17 IL-17F N/A N/A Distance to Non-Lesional Skin: Flared Skin Striae Non-Lesional Skin 1. Novan SB414 2% Biomarker Data – Dr. Emma Guttman-Yassky Lab. 2. Guttman-Yassky et al. Molecular signatures order the potency of topically applied anti-inflammatory drugs in patients with 27 atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2017. Note: Shading of color depicts

Financial Update ▪ Cash balance at September 30, 2018 was $12.2 million ▪ Cash on hand along with the upfront payments expected from the Sato Amendment anticipated to provide a cash runway into late 2Q 2019 ▪ Operating model adjustments from fixed infrastructure to variable activities and costs, including: − Established strategic alliance with Orion Corporation in October 2018, enabling technology transfer and manufacture of our product candidates; − Realigned internal resources and reduced overall headcount in November 2018; − Evaluating current drug manufacturing capabilities and alternative structures that align with our operating strategy and the needs of current and potential future partners. ▪ Focused on pursuing relevant financing alternatives, with a particular emphasis on non-dilutive options, to strengthen the Company’s capital position and advance the business platform ▪ Established long-term performance-based bonus awards for all Tangible Stockholder Return Plan participants to align compensation incentives with interests of our shareholders 28
Previous 12 Months Objectives and Results Corporate Clinical o Further strengthened o Finalize SB204 (acne) business management team and board construct and clinical/regulatory o Execute on business pathway development interest around o SB206 (molluscum) Phase 2 platform and across trial top line results and clinical geographies path forward o De-risk the platform in order to o SB414 (psoriasis & atopic maximize shareholder value dermatitis) Phase 1b trial top o $35M Capital raise in January line results and clinical path forward 2018 29




























