Use these links to rapidly review the document
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Filed Pursuant to Rule 424(B)(3)
Registration File No. 333-168796
PROSPECTUS

TRIUMPH GROUP, INC.
Offer to Exchange
8.625% Senior Notes due 2018
Registered under the Securities Act
For
A Like Principal Amount of Outstanding 8.625% Senior Notes due 2018
We are offering, upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in this prospectus and the accompanying letter of transmittal, to exchange up to $350,000,000 aggregate principal amount of our 8.625% Senior Notes due July 15, 2018, registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the "Securities Act," and referred to in this prospectus as the new notes, for an equal principal amount of our outstanding 8.625% Senior Notes due July 15, 2018, which are referred to in this prospectus as the old notes. The new notes will represent the same debt as the old notes and will be issued under the same indenture as the old notes.
The exchange offer expires at 5:00 p.m., New York City time,
on September 22, 2010, unless extended.
Terms of the Exchange Offer
- •
- We will exchange new notes for all old notes that are validly tendered and not withdrawn prior to the expiration of the exchange offer.
- •
- You may withdraw tenders of old notes at any time prior to the expiration of the exchange offer.
- •
- The terms of the new notes will be identical in all material respects to the terms of the old notes, except that the new notes will be registered under the Securities Act and will generally not be subject to transfer restrictions, will not be entitled to registration rights and will not have the right to earn additional interest under circumstances relating to our registration obligations.
- •
- The new notes will be guaranteed on a full, joint and several basis by each of our domestic restricted subsidiaries that is a borrower under any of our credit facilities or that guarantees any of our debt or that of any of our restricted subsidiaries under our credit facilities and in the future by any domestic restricted subsidiaries that are borrowers under any credit facility or that guarantee any of our debt or that of any of our restricted subsidiaries incurred under any credit facility.
- •
- We will not receive any cash proceeds from the exchange offer.
- •
- The exchange of old notes for new notes pursuant to this exchange offer generally should not be a taxable event for U.S. federal income tax purposes. See the discussion under the caption "Certain U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations."
- •
- There is no existing market for the new notes to be issued, and we do not intend to apply for listing or quotation on any securities exchange or market.
See "Risk Factors" on page 23 of this prospectus for a discussion of factors you should consider before participating in this exchange offer.
NEITHER THE SEC NOR ANY STATE SECURITIES COMMISSION HAS APPROVED OR DISAPPROVED OF THE NEW NOTES OR DETERMINED IF THIS PROSPECTUS IS TRUTHFUL OR COMPLETE. ANY REPRESENTATION TO THE CONTRARY IS A CRIMINAL OFFENSE.
Each broker-dealer that receives new notes for its own account pursuant to this exchange offer must acknowledge that it will deliver a prospectus in connection with any resale of such new notes. The letter of transmittal states that by so acknowledging and by delivering a prospectus, a broker-dealer will not be deemed to admit that it is an "underwriter" within the meaning of the Securities Act. This prospectus, as it may be amended or supplemented from time to time, may be used by a broker-dealer in connection with resales of new notes received in exchange for old notes where such old notes were acquired by such broker-dealer as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities. We have agreed that we will make this prospectus available to any broker-dealer for use in connection with any such resale until the earlier of 180 days after the date the exchange offer registration statement becomes effective and the date on which a broker-dealer is no longer required to deliver a prospectus in connection with market-making or other trading activities. See "Plan of Distribution."
The date of this prospectus is August 23, 2010
Incorporation of Certain Documents by Reference | 3 | |
Where You Can Find More Information | 3 | |
Industry and Market Data | 4 | |
Disclosure Regarding Forward-Looking Statements | 5 | |
Summary | 7 | |
Risk Factors | 23 | |
The Exchange Offer | 39 | |
Use of Proceeds | 48 | |
Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges | 48 | |
Capitalization | 49 | |
The Vought Acquisition | 50 | |
Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Information | 52 | |
Notes to the Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Statements | 56 | |
Triumph Selected Historical Financial Data | 63 | |
Vought Selected Historical Financial Data | 64 | |
Triumph Management's Discussion and Analysis of Triumph's Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 65 | |
Vought Management's Discussion and Analysis of Vought's Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 90 | |
Business | 113 | |
Description of Certain Indebtedness | 136 | |
Description of New Notes | 140 | |
Plan of Distribution | 187 | |
Certain U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations | 188 | |
Legal Matters | 189 | |
Experts | 189 |
You should rely only on the information in this prospectus. We have not authorized any other person to provide you with different information. If anyone provides you with different or inconsistent information, you should not rely on it. We are not making an offer to exchange and issue the new notes in any jurisdiction where the offer or exchange is not permitted. You should assume that the information appearing in this prospectus is accurate only as of the date on the front cover of this prospectus. Our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects may have changed since that date.
Unless otherwise indicated or required by context, the terms "Triumph," the "Company," "we," "us," and "our" as used in this prospectus refer to Triumph Group, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries. The term "Vought Acquisition" refers to our acquisition of Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc. on June 16, 2010 and the term "Vought" as used in this prospectus refers to Vought Aircraft Industries Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries or, with respect to the time period after the Vought Acquisition, Triumph Aerostructures, LLC (as successor to Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.) and its consolidated subsidiaries.
Our fiscal year begins on April 1 and ends on March 31 of the following year. In the context of any discussion of our financial information in this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein, any reference to a year or to any quarter of that year relates to the fiscal year ended on March 31 of that year. Prior to the Vought Acquisition, Vought's fiscal year began on January 1 and ended on December 31 of that year. In the context of any discussion of Vought's historical financial information in this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein, any reference to a year or to any quarter of that year relates to the fiscal year ended on December 31 of that year. Following the Vought Acquisition, Vought's fiscal year is the same as our fiscal year.
2
INCORPORATION OF CERTAIN DOCUMENTS BY REFERENCE
The SEC allows us to "incorporate by reference" in this prospectus the information in other documents that we file with it. This means that we are disclosing important information by referring to another document separately filed with the SEC. This information incorporated by reference is deemed to be part of this prospectus, except for any information superseded by information in this prospectus. Information in documents that we file later with the SEC will automatically update and supersede information contained in documents filed earlier with the SEC or contained in this prospectus. We incorporate by reference the documents set forth below:
- •
- our Annual Report on Form 10-K and Form 10-K/A for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010;
- •
- our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2010; and
- •
- our Current Reports on Form 8-K filed on April 30, 2010, May 24, 2010, May 26, 2010, May 28, 2010, June 9, 2010, June 22, 2010 and June 25, 2010 (excluding information furnished under Item 2.02, 7.01 or 9.01).
We also incorporate by reference into this prospectus any future filings made by us with the SEC under Sections 13(a), 13(c), 14 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act (other than those made pursuant to Item 2.02 or Item 7.01 of Form 8-K or any other information "furnished" to the SEC, unless specifically stated otherwise) after the date of this prospectus and prior to the later of (i) the termination or completion of the exchange offer and (ii) the termination of the period of time described under "Plan of Distribution" during which we have agreed to make available this prospectus to broker-dealers in connection with certain resales of the new notes.
You may obtain any of the documents incorporated by reference in this prospectus from the SEC through the SEC's website at the address provided above and on our website atwww.triumphgroup.com. Information contained or linked to or from our website is not a part of this prospectus. You also may request a copy of any document incorporated by reference in this prospectus, at no cost, by writing or calling us at the following address: Triumph Group, Inc., 1550 Liberty Ridge Drive, Suite 100, Wayne, PA 19087, (610) 251-1000, Attention: Investor Relations.
To obtain timely delivery, you must request the information no later than September 15, 2010, which is five business days prior to the expiration of this exchange offer. In the event that we extend the exchange offer, you must submit your request at least five business days before the expiration of the exchange offer, as extended. We may extend the exchange offer in our sole discretion. See "The Exchange Offer" for more detailed information.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-4 under the Securities Act with respect to the new notes. The registration statement, including the attached exhibits and schedules, contains additional relevant information about us and the new notes. The rules and regulations of the SEC allow us to omit from this prospectus certain information included in the registration statement.
We file reports and other information with the SEC under the Exchange Act. You may read and copy any of this information at the SEC's public reference room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. Please call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information on the operation of the SEC's public reference room. Our SEC filings also are available on the SEC's website athttp://www.sec.gov.
3
In this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein, we refer to information and statistics regarding our industry, the size of certain markets and our position within the sectors in which we compete. Some of the market and industry data contained in this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein is based on independent industry and trade publications or other publicly available information, or information published by original equipment manufacturers, or "OEMs," while other information is based on our good faith estimates, which are derived from our review of internal surveys, as well as independent sources listed in this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein and the knowledge and experience of our management in the markets in which we operate. The estimates contained in this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein have also been based on information obtained from our customers, suppliers and other contacts in the markets in which we operate. Although we believe that these independent sources and internal data are reliable as of their respective dates, the information contained in them has not been independently verified, and we cannot assure you as to the accuracy or completeness of this information. As a result, you should be aware that the market and industry data and the market share estimates set forth in this prospectus, and beliefs and estimates based thereon, may not be reliable. We have made rounding adjustments to reach some of the figures included in this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein. As a result, amounts shown as totals in some tables may not be arithmetic aggregations of the amounts that precede them.
4
DISCLOSURE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus contains or incorporates by reference statements that are forward-looking statements within the meaning of the federal securities laws, including statements about our expectations, beliefs, intentions and strategies for the future. We have identified some of these forward-looking statements with words such as "anticipates," "believes," "expects," "estimates," "may," "will," "should" and "intends" and the negative of these words or other comparable terminology. These forward-looking statements include, without limitation, our expectations with respect to the costs and changes, capitalization and anticipated financial impact of the acquisition of Vought as well as risks resulting from economic and market conditions, the regulatory environment in which we operate, competitive activities and other business conditions.
These forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties that could cause the our actual results to differ materially from results anticipated in these forward-looking statements. Because of these uncertainties, you should not rely on these forward-looking statements. Most of these factors are outside of our control and are difficult to predict. Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements include but are not limited to:
- •
- our ability to successfully integrate the Vought business and other acquired businesses and realize the anticipated benefits of such acquisitions;
- •
- availability of required capital;
- •
- product liabilities in excess of insurance;
- •
- technological developments;
- •
- dependence of certain of our businesses on certain key customers;
- •
- limited availability of raw materials;
- •
- limited availability of skilled personnel;
- •
- costs and expenses and any liabilities associated with pending or threatened litigation;
- •
- the effects of customers canceling or modifying orders;
- •
- actions taken or conditions imposed by the United States and foreign governments;
- •
- the effect on our net sales of defense budget reductions by government customers;
- •
- the impact of volatile fuel prices on the airline industry;
- •
- our ability to attract and retain qualified professionals;
- •
- long-term trends in passenger and cargo traffic in the airline industry;
- •
- changes in governmental regulation;
- •
- the impact of work stoppages or labor disruptions at our locations or at our customers or suppliers;
- •
- international hostilities and terrorism;
- •
- general economic conditions or cyclical factors affecting the aerospace industry or our business;
- •
- returns on pension assets and impacts of future discount rate changes on pension obligations; and
- •
- environmental liabilities arising out of past or present operations.
5
We base our forward-looking statements on information currently available to us, and, except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update these statements, whether as a result of changes in underlying factors, new information, future events or other developments except as required by law. We do not, nor does any other person, assume responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of those statements. All of the forward-looking statements are qualified in their entirety by reference to the factors discussed above as well as those discussed under "Risk Factors."
6
This summary contains basic information about our company and the exchange offer. It may not contain all the information that may be important to you. Investors should carefully read this entire prospectus, including the information set forth under "Risk Factors" and in our consolidated financial statements and the related notes thereto. Unless otherwise indicated or required by the context, the terms "Triumph," the "Company," "we," "us," and "our," refer to Triumph Group, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries. The term "Vought Acquisition" refers to our acquisition of Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc. on June 16, 2010 and the term "Vought" as used in this prospectus refers to Vought Aircraft Industries Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries or, with respect to the time period after the Vought Acquisition, Triumph Aerostructures, LLC (as successor to Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.) and its consolidated subsidiaries. Our fiscal year begins on April 1 and ends on March 31 of the following year. In the context of any discussion of our financial information in this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein, any reference to a year or to any quarter of that year relates to the fiscal year ended on March 31 of that year. Prior to the Vought Acquisition, Vought's fiscal year began on January 1 and ended on December 31 of that year. In the context of any discussion of Vought's historical financial information in this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein, any reference to a year or to any quarter of that year relates to the fiscal year ended on December 31 of that year. Following the Vought Acquisition, Vought's fiscal year is the same as our fiscal year.
We are a leading manufacturer of and provider of repair and maintenance services for aerospace systems and components, serving a broad spectrum of companies within the aerospace industry. We design, engineer, manufacture, repair and overhaul aircraft components and aerostructures. Our customers consist of original equipment manufacturers, or "OEMs," of commercial, military, regional and business aircraft and components, the U.S. military, commercial airlines and air cargo carriers, and include:
• Boeing | • Honeywell | |
• Airbus (a division of EADS NV) | • Lockheed Martin | |
• Bell Helicopter (a division of Textron) | • Northrop Grumman | |
• Cessna (a division of Textron) | • Raytheon | |
• Gulfstream (a division of General Dynamics) | • Rolls-Royce | |
• General Electric | • Sikorsky (a division of United Technologies) |
Our diversification across OEMs and platforms, coupled with our ever-broadening product offerings, enables us to respond to the evolving needs of our customers. In addition, we are well positioned in a highly fragmented industry, as one of a limited number of companies worldwide that can offer a broad range of products, systems and services to the largest aerospace companies. For the year ended March 31, 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, we generated net sales of $1.3 billion and $406.4 million, respectively. On a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition, for the year ended March 31, 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, we generated net sales of $3.2 billion and $763.4 million, respectively. As of June 30, 2010, we had a current backlog of approximately $3.3 billion. See "—Summary Consolidated Historical and Pro Forma Financial Data of Triumph."
We operate through a decentralized structure of 44 aerospace companies with 64 locations in the United States, Europe, Mexico and Thailand, while maintaining an integrated marketing and sales force for all of our operating companies. Through our decentralized structure, we are able to preserve specialized skills and distinct customer bases for many of our group companies, which enhances our diversification and increases our operating flexibility to better serve our customers. Our sales and marketing team serves as a single point of customer contact for our extensive range of products. The
7
team consists of customer-focused sales professionals as well as specialists at individual operating companies who assist them with expertise and depth of knowledge in particular products.
Aerospace End Markets and Platforms
Our customer base includes nearly all of the world's major OEMs, the U.S. military and a number of commercial airlines and air cargo carriers. The chart below presents our net sales by end market for the twelve months ended March 31, 2010 on a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition. Amounts have been rounded where necessary.
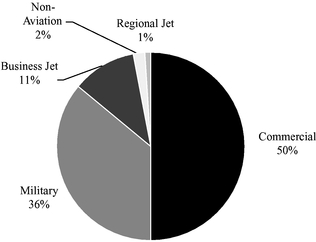
We provide products and services to the following platforms used in the commercial, military, business and regional aircraft end markets:
- •
- Large wide-body aircraft with twin aisles (more than 200 seats). Wide-body aircraft for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Boeing 747-8, 767, 777 and 787 and the Airbus A330/340, A350 and A380, as well as the A350XWB, planned for entry into service in 2013.
- •
- Smaller narrow-body aircraft with single aisles (excluding regional aircraft) (100 to 200 seats). Narrow-body aircraft for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Boeing 737, the Airbus A320 family and the Bombardier C series.
- •
- Fighter and Attack Aircraft—Fighter aircraft are used to engage in air-to-air combat and to control the airspace over the battlefield, thereby enabling other allied forces to carry out their missions. Attack aircraft support ground troops in close air support roles and penetrating attacks. Fighter and attack aircraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the F/A-18 Hornet, the F-15 Eagle, the F-16 Fighting Falcon, the F-35 Lightning II and the E-2C Hawkeye.
- •
- Transport Aircraft or Cargo Aircraft—Aircraft in this category are used to transport troops, equipment and humanitarian aid, and are able to operate from short and roughly prepared airfields and to perform airdrops of troops and equipment when landing is not an option. Transport and cargo aircraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Boeing C-17 Globemaster III, and the Lockheed Martin C-130 Hercules.
Commercial Aircraft Market.
Military Aircraft Market.
8
- •
- Rotorcraft—Rotorcraft have broad and varied uses including intra-theater cargo delivery, troop transport and rapid insertion, observation and patrol, ground attack and search and rescue and special operations. Rotorcraft have been critical to the U.S. military's efforts in Iraq and Afghanistan and their heavy usage has led to continued demand for new rotorcraft and repairs and refurbishments of existing military rotorcraft. Rotorcraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the UH-60 Black Hawk, V-22 Osprey, CH-47 Chinook and the AH-64 Apache.
- •
- Unmanned Air Vehicles ("UAVs")—UAVs have generally been used for observation and command and control. This class of aircraft plays an important role in U.S. military strategy, and is also being increasingly used for weapons delivery and air combat. UAV platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Global Hawk, the Predator and the Hunter.
- •
- Aerial Tanker Aircraft—Tankers are used to deliver fuel to other aircraft while airborne and are essential to the effective use of combat and support aircraft. Tanker aircraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the KC-10 and KC-135. In addition, the U.S. Air Force recently issued a request for proposal ("RFP") for designs for the KC-X tanker, which will replace the KC-135. We provide parts, assemblies and services for the planned proposals of both Boeing (a modified version of its 767 commercial airframe) and EADS (the A330 Tanker).
In addition, we provide parts, assemblies and services to Space Vehicles, such as the Delta Launch Space Vehicle and International Space Station.
Business Jet Aircraft Market. The business jet market includes personal and business jet aircraft with a worldwide fleet today exceeding 14,000 aircraft. There are currently more than 40 different models of business jets in production or development, ranging from very light jets (VLJ) seating four passengers to transcontinental business jets that carry up to 19 passengers. The business jet market is generally classified into three major segments: light (which include VLJ, entry and light jets with sale prices ranging from approximately $1 million to $10 million per aircraft), medium (which include light-mid, medium and super-mid jets with sale prices ranging from approximately $10 million to $20 million per aircraft), and heavy (which include heavy, long range and ultra long range jets with sale prices ranging from approximately $20 million to $45 million per aircraft). Purchasers of business jets include U.S. and foreign corporations, fractional leasing companies, wealthy individuals and U.S. and foreign governments. Our business jet customers include Bombardier, Cessna, Dassault Aviation, Embraer, Gulfstream, Hawker Beechcraft and Learjet. We typically provide parts, assemblies and services to our business jet customers across all of their business jet platforms.
Regional Jet Aircraft Market. The regional jet market includes smaller commercial jet aircraft ranging in size from approximately 40 to 110 seats. Regional jet aircraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Embraer EM145, the Bombardier/Canadair CRJ700, CRJ1000 and CRJ200, the Bombardier/DeHavilland DHC 8 series and the British Aerospace BAE146/AVRO RJ.
We currently offer our products and services through two operating segments: Aerospace Systems and Aftermarket Services.
Aerospace Systems
Aerospace Systems engages in the design, development, manufacture, repair, sales and lifecycle support of complete metallic structural assemblies, as well as mechanical, electromechanical, hydraulic and hydromechanical control systems. Aerospace Systems serves as a single point of customer contact for this extensive range of products, which we believe gives us a significant competitive advantage over
9
many of our competitors. Aerospace System's products range from highly integrated systems and assemblies to kits of components to individual components and satisfy customer requirements at various stages of the manufacturing process. Aerospace Systems also performs complex machining processes, offers machining capabilities and structural component forming, and provides customers with the full range of structural components, as well as complete assemblies and subassemblies. Aerospace Systems' customers include aerospace OEMs and other tier one manufacturers who supply them, airlines, air cargo carriers, and domestic and foreign militaries. For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, Aerospace Systems generated net sales before inter-segment eliminations of $1,073.5 million and $346.9 million, respectively.
The principal products and services of our Aerospace Systems segment prior to the Vought Acquisition are set forth below.
| • | Acoustic insulation systems | • | Exhaust nozzles and ducting | • | Main engine gear box assemblies | ||||||
| • | Aircraft and engine mounted | • | Floor beams | • | Primary and secondary flight | ||||||
| accessory drive | • | Heat exchangers | control systems | ||||||||
| • | Cockpit control levers | • | High-lift actuation | • | Stretch-formed leading edges and | ||||||
| • | Composite and metal bonding | • | Landing gear actuation systems | fuselage skins | |||||||
| • | Composite ducts and floor panels | • | Landing gear components and | • | Windows and window assemblies | ||||||
| • | Control system valve bodies | assemblies | • | Wing spars and stringers |
Acquisition of Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.
On June 16, 2010, we completed our acquisition of Vought. The results of Vought are included in the Aerospace Systems segment from June 16, 2010 through June 30, 2010. Vought is a leading global manufacturer of aerostructure products for commercial, military and business jet aircraft. For the twelve months ended March 28, 2010, the commercial, military and business jet aircraft end markets accounted for $1,008.1 million, $691.0 million and $258.9 million, respectively, of Vought's revenue, or 52%, 35%, and 13%, respectively, of Vought's total revenue. Vought develops and manufactures a wide range of complex aerostructures such as aircraft fuselages, wing and tail assemblies, engine nacelles, flight control surfaces as well as helicopter cabins. Vought's diverse and long-standing customer base consists of the leading aerospace OEMs, including Airbus, Boeing, Cessna, Gulfstream, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman and Sikorsky, as well as the U.S. military. We believe that Vought's new product and program development expertise, engineering and composite capabilities, the importance of its aerostructure products to its OEM customer base and Vought's advanced manufacturing capabilities make Vought an important partner to its customers. Vought collaborates with its customers and provides the latest technologies to address their needs for complex, highly engineered aerostructures. Vought's products are used on many of the largest and longest running programs in the aerospace industry, including the Boeing 737, 747-8, 767 and 777, C-17 Globemaster III, CH-47 Chinook, the Airbus 330/340, Lockheed Martin C-130, Sikorsky H-60 and Gulfstream G350, G450, G500 and G550. Vought is also a key supplier to its customers on programs that it believes have high growth potential, such as the Northrop Grumman Global Hawk unmanned aerial vehicle, Boeing 787 and V-22 Osprey. For the twelve months ended March 28, 2010, Vought generated total revenue of approximately $2.0 billion. See "—Vought Summary Historical Consolidated Financial Data."
Aftermarket Services
Aftermarket Services performs maintenance, repair and overhaul services ("MRO") for commercial and military markets on components and assemblies manufactured by third parties. Aftermarket Services also designs, engineers, manufactures, repairs and overhauls aftermarket aerospace engine components. It offers comprehensive MRO solutions, and FAA-approved repairs and parts manufacturing options in addition to providing aftermarket parts and services to airlines, air cargo carriers and third-party overhaul facilities. Aftermarket Services offers repair capability for
10
FAA-approved assemblies which range from detailed components to complex subsystems, including APUs, thrust reversers, flight controls, engine accessories and avionics. Aftermarket Services also performs repair and overhaul services and supplies spare parts for various types of cockpit instruments and gauges for a broad range of commercial airlines on a worldwide basis. For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, Aftermarket Services generated net sales before inter-segment eliminations of $225.0 million and $59.8 million, respectively.
The principal products and services of our Aftermarket Services segment are set forth below.
Repairs and Overhauls: | Fabricates, Repairs and Overhauls: | Refurbishes and Airline Interior Products: | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| • | Air cycle machines | • | Blades and vanes | • | Light assemblies | |||||
| • | APUs | • | Cabin interior panes, shades, light | • | Overhead bins | |||||
| • | Cockpit instrumentation | sensors and other plastic | • | Sidewalls | ||||||
| • | Constant speed drives | components | ||||||||
| • | Engine and airframe accessories | • | Combustors | |||||||
| • | Flight control surfaces | • | Stators | |||||||
| • | Integrated drive generators | • | Transition ducts | |||||||
| • | Nacelles | |||||||||
| • | Remote sensors | |||||||||
| • | Thrust reversers | |||||||||
Segment Reporting
In anticipation of the acquisition of Vought in early fiscal 2011, management began to consider certain organizational changes in an effort to align the operations reporting units. Management is currently evaluating the impact of the reorganization on the Company's externally reported segments in accordance with ASC Topic 280,Segment Reporting.
We believe that we will benefit from the following competitive strengths:
Diverse Business Mix. Through organic growth and disciplined acquisitions, we have diversified the end markets we serve in order to minimize the impact that any single segment, platform or product of the aerospace industry could have on our results. The Vought Acquisition will further diversify our product and customer base, by expanding our capabilities into complex aerostructure products and allowing us to leverage Vought's strong existing customer relationships which complement our own.
Broad Array of Products and Services. We provide aerospace customers a single point of purchase for a diverse array of technically complex products and services for a wide range of aerospace platforms and programs, which we believe gives us a competitive advantage in developing strategic partnerships with OEMs. We design, engineer and manufacture aircraft components to meet our customers' particular requirements. In some cases, we own the proprietary rights to these designs and, accordingly, our customers generally rely on us to regularly repair, overhaul or replace these components, which provides us with a recurring source of cash flow. For our customers, we also perform repair and overhaul services on various aviation components manufactured by third parties. Our acquisition of Vought will expand our presence in many of today's most important commercial platforms and in important fixed-wing and rotorcraft military aircraft. The success of these and other legacy programs provides a strong foundation for us and positions us for future growth on new commercial programs.
Advanced Manufacturing and Technical Capabilities. We are leading global manufacturers of some of the largest and most technologically advanced parts and assemblies for a diverse range of aircraft. Vought adds capabilities in aerostructures, precision assembly techniques, automated assembly processes
11
and large-bed machining and fabrication of large composite fiber reinforced parts to our own capabilities, which include highly proprietary actuation products, geared products, structural components, thermal products and controls. We employ over 250 engineers supporting design programs and over 800 manufacturing engineers. Our manufacturing facilities have achieved ISO 9001 certification, a certification of internationally recognized quality standards for manufacturing.
Significant Customer Relationships and Industry Presence. We believe that our strong customer relationships and market-leading industry positions are the result of our dedication to meeting our customers' complex specifications, our focus on quality control and our delivery of high quality products and services. Our customer base includes nearly all of the world's major OEMs (Boeing, Airbus, Bell Helicopter, Cessna, General Electric, Gulfstream, Honeywell, Lockheed Martin, Raytheon and Sikorsky), commercial airlines, the U.S. military and air cargo carriers, including Federal Express and United Parcel Service. We are an important supplier to many long-lived commercial and military platforms, including, Airbus 330/340, Boeing 737, 747-8, 767 and 777, C-17 Globemaster III and V-22 Osprey, Lockheed Martin C-130, Sikorsky H-60, Gulfstream G350, G450, G500 and G550, and are well positioned to capitalize on future growth in these established programs and other new program launches.
Robust Backlog. As of June 30, 2010, our backlog was approximately $3.3 billion. Backlog is generally comprised of actual purchase orders with firm delivery dates or contract requirements generally within the next 24 months. The majority of our sales are from orders issued under long-term contracts, generally of a three to five-year duration. Our backlog increases our management's visibility on future business activity levels.
Strong Free Cash Flow Generation. Despite the economic challenges faced by the commercial airline industry over the last several years and the worldwide economic recession, we have been able to achieve strong and consistent cash flow generation over that time period. Legacy aircraft programs, such as the C-17, CH-47 Chinook, V-22, UH-60 Black Hawk, Global Hawk, 737, 767, 777 and A330/340 which require only moderate capital expenditures to support current delivery rates, provide us with a source of strong, recurring cash flow. We have generated this growth and consistency in our cash flow through a combination of improved expense management, prudent management of capital expenditures to meet changing industry conditions and effective management of working capital.
Conservative Balance Sheet and Financial Strategy. As of June 30, 2010, our total net debt to capitalization was 48.6%. In addition, as of June 30, 2010 we had $35.7 million of cash and cash equivalents and $403.1 million of availability under our revolving credit facility.
High Barriers to Entry. The FAA certification process and the prevalence of long-term sole source or preferred supplier contracts serve as significant barriers to entry in the aerospace component and aerostructures markets. Certification by the FAA and foreign regulatory authorities is rigorous and requires significant time and capital expenditures in order to develop the capabilities to design, manufacture, test and certify aerospace component and aerostructure parts and assemblies. To obtain the approvals necessary to compete for contracts, companies make substantial up-front investments as well as develop and demonstrate sophisticated manufacturing expertise and experienced-based industry and aircraft knowledge. In addition, OEMs frequently award long-term sole source or preferred supplier contracts for the provision of particular parts for a particular platform. As a result, with respect to many of the platforms we supply, we are the only currently qualified FAA-certified supplier of such parts. We have achieved this position by implementing the technology to enable us to meet these stringent regulatory requirements and the exacting standards of our customers.
Experienced Leadership. Our senior management team and directors are highly experienced in the aviation parts and services industry, operationally focused and maintain extensive business relationships from which we as a whole benefit. Our senior executives and directors have extensive experience in the
12
aviation industry and have successfully managed our businesses through various industry cycles. The acquisition of Vought has provided us with additional management and directors with extensive industry experience and expertise. We believe our management has the vision, focus and experience to position us for success in the future.
Our business strategy is to sustain our high level of growth through internal product development and capability expansion, as well as through acquisitions. We are committed to pursuing the strategies established during our formation in 1993 in becoming the "vendor of choice" in the worldwide aviation industry. These five core strategies are as follows:
Develop Additional Products and Services. We offer integrated solutions for complex systems by integrating the capabilities of our operating companies, thereby adding greater value for our customers and their products. In addition, we place a high priority on the ongoing technological development and application of our products and services. We intend to continue to introduce new aviation products and services and to acquire select products and services to take advantage of opportunities in the aerospace industry and to respond to our customers' increasing demands. We plan to further expand our position as a consolidated point of purchase to our customers by capitalizing on the ongoing trend toward outsourcing and the reduction of approved suppliers and vendors by OEMs and airlines and air cargo carriers.
Market Complete Capabilities. As we continue to expand our product and service offerings, we plan to leverage our network of companies to cross-sell their capabilities to our existing customers and attract new customers. We strive to be our customers' most valued partner through excellence in product and process technologies and by providing modern and efficient production facilities. In addition, we strive to build on our reputation for quality and performance and to introduce best operating practices across our operations. Our network of companies will continue to share group marketing representatives and jointly bid on projects where appropriate, while still maintaining their individual identities. We believe that the breadth of our customer relationships, capabilities and experience, and our quality of service and support will enable us to win additional customer business.
Expand Operating Capacity. We plan to continue to increase our operating capacity to meet our expected internal growth and to meet expected growth in the aerospace industry. We intend to continue to prudently invest in state-of-the-art plants and equipment to improve our operating efficiencies and increase our operating margins.
Increase Our International Presence. We intend to continue to take advantage of the expanding international market for aviation products and services as worldwide air travel increases and foreign nations purchase used aircraft that require more frequent repair and maintenance. We currently supply products and services to substantially all major commercial passenger and air cargo airlines worldwide, have manufacturing and service facilities in France, Germany, Mexico, Thailand and the United Kingdom and retain independent sales representatives in a number of foreign countries. Furthermore, we intend to globalize our production processes through initiatives such as global sourcing. We believe that our initiatives will allow us to reduce costs, expand our capabilities and provide strategic benefits to our customers. We intend to build on our existing international presence through continued market penetration and, as appropriate opportunities arise, foreign acquisitions.
Pursue Complementary Acquisitions. We expect to continue to grow through acquisitions of other companies, assets or product lines that add to, complement, enhance or diversify our existing aviation products and services and program portfolio. We have successfully completed 34 acquisitions since 1996. We believe the fragmented nature of a large portion of the market for aircraft products and services will provide us with additional attractive acquisition opportunities. Through selective
13
acquisitions, we aim to broaden our product offerings, add new specialized technologies, expand capacity for high-demand products and services, build on existing customer relationships and enter new markets.
On June 16, 2010, we completed our previously announced acquisition of Vought pursuant to an Agreement and Plan of Merger dated March 23, 2010, by and among Triumph, Vought, Spitfire Merger Corporation, our wholly owned subsidiary ("Merger Sub") and TC Group, L.L.C. ("Carlyle"), as the Holder Representative (the "Merger Agreement"). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, (i) Merger Sub was merged with and into Vought and (ii) then Vought was merged with and into Triumph Aerostructures, LLC, our direct wholly owned limited liability company subsidiary, with Triumph Aerostructures, LLC as the surviving entity in the mergers. The consideration for the Vought Acquisition consisted of $547.9 million in cash and 7,496,165 shares of our common stock. On June 16, 2010, we also discharged, repaid or otherwise retired approximately $603.1 million of Vought's indebtedness, which represented substantially all of Vought's outstanding indebtedness. We refer to transactions described in this paragraph as the "Vought Acquisition."
As a result of the Vought Acquisition, certain equity funds managed by TC Group, L.L.C. (which we refer to in this prospectus as Carlyle) that were stockholders of Vought, hold approximately 31% of our outstanding shares of common stock. We refer to these equity funds in this prospectus as the Carlyle equity funds. On June 16, 2010, pursuant to a stockholders agreement, dated March 23, 2010, by and among Triumph, the Carlyle equity funds and Carlyle, we expanded the size of our board of directors and appointed Adam Palmer, Elmer Doty and Ralph Eberhart to our board of directors. The Carlyle equity funds, Carlyle and investment funds managed by each of them are prohibited from acquiring additional shares of our common stock and taking certain other actions to seek to gain control of Triumph without our prior written consent.
We funded the Vought Acquisition through cash on hand and the following activities (the "Financing Transactions" and together with the Vought Acquisition, the "Transactions"):
- •
- the issuance of 7,496,165 shares of our common stock to the Vought stockholders;
- •
- the issuance by the Company of $350,000,000 aggregate principal amount of old notes at a price equal to 99.27% of the face value;
- •
- the borrowing by the Company of $350,000,000 principal amount under a new senior secured term loan credit facility (the "Term Loan Facility") at a price equal to 99.5% of the face value; and
- •
- the borrowing by the Company of $128,300,000, drawn under the Company's $535,000,000 revolving credit facility (the "Revolving Credit Facility" and together with the Term Loan Facility, the "Credit Facilities").
14
Summary of the Terms of the Exchange Offer
The following is a brief summary of the terms of the exchange offer. Please see "The Exchange Offer" for a more complete description of the exchange offer.
Old Notes | $350.0 million aggregate principal amount of 8.625% Senior Notes due 2018. | |
New Notes | Up to $350.0 million aggregate principal amount of 8.625% Senior Notes due 2018, which have been registered under the Securities Act. The terms of the new notes are identical in all material respects to the terms of the old notes, except that the new notes are registered under the Securities Act and are generally not subject to transfer restrictions, are not entitled to registration rights and do not have the right to earn additional interest under circumstances relating to our registration obligations. | |
Exchange Offer | We are offering to exchange the new notes for a like principal amount of old notes. Currently, there is $350.0 million in aggregate principal amount of old notes outstanding. | |
Old notes may be exchanged only in minimum denominations of $2,000 and integral multiples of $1,000 in excess of $2,000. New notes will be issued only in minimum denominations of $2,000 and integral multiples of $1,000 in excess of $2,000. | ||
Subject to the terms of this exchange offer, we will exchange new notes for all of the old notes that are validly tendered and not withdrawn prior to the expiration of this exchange offer. The new notes will be issued in exchange for corresponding old notes in this exchange offer, if consummated, as soon as practicable after the expiration of this exchange offer. | ||
Expiration Date | This exchange offer will expire at 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on September 22, 2010, unless we extend it. We do not currently intend to extend the expiration date. | |
Withdrawal of Tenders | You may withdraw the tender of your old notes at any time prior to the expiration date. | |
Certain U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations | The exchange by a U.S. Holder (as defined in "Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences") of old notes for new notes in this exchange offer generally should not constitute a taxable exchange for U.S. federal income tax purposes. See "Certain U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations." | |
Conditions to this Exchange Offer | This exchange offer is subject to customary conditions, which we may waive. See "The Exchange Offer—Conditions." |
15
Procedures for Tendering | If you wish to accept this exchange offer and your old notes are held by a custodial entity such as a bank, broker, dealer, trust company or other nominee, you must instruct this custodial entity to tender your old notes on your behalf pursuant to the procedures of the custodial entity. If your old notes are registered in your name, you must complete, sign and date the accompanying letter of transmittal, or a facsimile of the letter of transmittal, according to the instructions contained in this prospectus and the letter of transmittal. You must also mail or otherwise deliver the letter of transmittal, or a facsimile of the letter of transmittal, together with the old notes and any other required documents, to the exchange agent at the address set forth on the cover page of the letter of transmittal. | |
Custodial entities that are participants in The Depository Trust Company, or "DTC," may tender old notes through DTC's Automated Tender Offer Program, or "ATOP," which enables a custodial entity, and the beneficial owner on whose behalf the custodial entity is acting, to electronically agree to be bound by the letter of transmittal.A letter of transmittal need not accompany tenders effected through ATOP. | ||
By signing, or agree to be bound by, the letter of transmittal, you will represent to us that, among other things: | ||
• you are acquiring the new notes in the ordinary course of your business; | ||
• you have no arrangement or understanding with any person to participate in a distribution (within the meaning of the Securities Act) of the new notes; | ||
• you are not an affiliate of the issuer (within the meaning of Rule 405 under the Securities Act); and | ||
• if you are a broker-dealer registered under the Exchange Act, you are participating in the exchange offer for your own account and are exchanging old notes acquired as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities and you will deliver a prospectus in connection with any resale of the new notes. | ||
See "The Exchange Offer—Eligibility; Transferability." | ||
Transferability | Under existing interpretations of the Securities Act by the staff of the SEC contained in several no-action letters to third parties, and subject to the immediately following sentence, we believe that the new notes will generally be freely transferable by holders after the exchange offer without further compliance with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act (subject to representations required to be made by each holder of old notes, as set forth above). However any holder of old notes who: | |
• is one of our "affiliates" (as defined in Rule 405 under the Securities Act), |
16
• does not acquire the new notes in the ordinary course of business, | ||
• distributes, intends to distribute, or has an arrangement or understanding with any person to distribute the new notes as part of the exchange offer, or | ||
• is a broker-dealer who purchased old notes directly from us | ||
will not be able to rely on the interpretations of the staff of the SEC, will not be permitted to tender old notes in the exchange offer and, in the absence of any exemption, must comply with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act in connection with any resale of the new notes. | ||
Our belief that transfers of new notes would be permitted without registration or prospectus delivery under the conditions described above is based on SEC interpretations given to other, unrelated issuers in similar exchange offers. We cannot assure you that the SEC would make a similar interpretation with respect to our exchange offer. We will not be responsible for or indemnify you against any liability you may incur under the Securities Act. | ||
Each broker-dealer that receives new notes for its own account under the exchange offer in exchange for old notes that were acquired by the broker-dealer as a result of market-making or other trading activity must acknowledge that it will deliver a prospectus in connection with any resale of the new notes. See "Plan of Distribution." | ||
Consequences of Failure to Exchange | Any old notes that are not tendered in the exchange offer, or that are not accepted in the exchange, will remain subject to the restrictions on transfer. Since the old notes have not been registered under the U.S. federal securities laws, you will not be able to offer or sell the old notes except under an exemption from the requirements of the Securities Act or unless the old notes are registered under the Securities Act. Upon the completion of the exchange offer, we will have no further obligations, except under limited circumstances, to provide for registration of the old notes under the U.S. federal securities laws. See "The Exchange Offer—Consequences of Failure to Tender." | |
Use of Proceeds | We will not receive any proceeds from the exchange of notes pursuant to the exchange offer. We will pay all expenses incident to the exchange offer. | |
Exchange Agent | U.S. Bank National Association, the trustee under the indenture, is serving as the exchange agent for this exchange offer. See "The Exchange Offer—Exchange Agent" for the address and telephone number of the exchange agent. |
17
Summary of the Terms of the New Notes
The terms of the new notes are identical in all material respects to the terms of the old notes, except that the new notes are registered under the Securities Act and are generally not subject to transfer restrictions, are not entitled to registration rights and do not have the right to earn additional interest under circumstances relating to our registration obligations. The new notes will evidence the same debt as the old notes. The new notes will be governed by the same indenture under which the old notes were issued.
The summary below describes the principal terms of the new notes. Please see "Description of the New Notes" for further information regarding the new notes.
Issuer | Triumph Group, Inc. | |
Notes Offered | $350,000,000 aggregate principal amount of 8.625% senior notes due July 15, 2018. | |
Maturity Date | July 15, 2018. | |
Interest | Interest on the new notes will accrue at a rate of 8.625% per annum, payable semi-annually in cash in arrears on January 15 and July 15 of each year, commencing January 15, 2011. | |
Guarantees | The new notes will be guaranteed on the date of issuance on a full, joint and several basis by each of our domestic restricted subsidiaries that is a borrower under the Credit Facilities or that guarantees any of our debt or that of any of our restricted subsidiaries under the Credit Facilities and in the future by any of our domestic restricted subsidiaries that are borrowers under any credit facility or that guarantee any of our debt or that of any of our domestic restricted subsidiaries incurred under any credit facility. Under certain circumstances, the guarantees may be released without action by, or the consent of, the holders of the new notes. | |
Ranking | The new notes and the guarantees will be our and our subsidiary guarantors' senior unsecured obligations and they will rank: | |
• equal in right of payment to our and our subsidiary guarantors' existing and future senior indebtedness, including our and our subsidiary guarantors' obligations under our Credit Facilities; | ||
• senior in right of payment to our and our subsidiary guarantors' existing and future subordinated indebtedness; | ||
• effectively subordinated to all of our and our subsidiary guarantors' existing and future secured debt (including under our Credit Facilities) to the extent of the value of the assets securing such debt; and | ||
• structurally subordinated in right of payment to all indebtedness and other liabilities of our existing and future subsidiaries that do not guarantee the new notes. | ||
As of June 30, 2010, we had $1,335.3 million million in consolidated indebtedness outstanding, including $644.0 million of secured indebtedness. See "Description of the New Notes—Ranking." |
18
For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2010, on a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition, the Company's non-guarantor subsidiaries would have generated net sales of $79.0 million, or 2.5% of our consolidated net sales, and as of June 30, 2010, our non-guarantor subsidiaries had total assets of $277.8 million, total liabilities of $211.7 million and stockholders' equity of $66.1 million. | ||
Optional Redemption | We may redeem the new notes, in whole or in part, at any time on or after July 15, 2014 at the applicable redemption prices described under "Description of New Notes—Optional Redemption," plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the redemption date. At any time before July 15, 2014, we may redeem the new notes, in whole or in part, at a redemption price equal to 100% of their principal amount plus a make whole premium, together with accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the redemption date. In addition, we may redeem up to 35% of the new notes before July 15, 2013 with the net cash proceeds from certain equity offerings at the redemption price described under "Description of New Notes—Optional Redemption." | |
Change of Control | If we experience specific kinds of changes of control, we will be required to offer to purchase all of the new notes at a purchase price of 101% of their principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the date of purchase. For more details, see "Description of New Notes—Change of Control." | |
Certain Covenants | We will issue the new notes under an indenture with U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (the "Trustee"). The indenture, among other things, will limit our and our restricted subsidiaries' ability to: | |
• incur additional indebtedness; | ||
• pay dividends or make other distributions; | ||
• make other restricted payments and investments; | ||
• create liens; | ||
• incur restrictions on the ability of restricted subsidiaries to pay dividends or make certain other payments; | ||
• sell assets, including capital stock of restricted subsidiaries; | ||
• enter into sale and leaseback transactions; | ||
• merge or consolidate with other entities; and | ||
• enter into transactions with affiliates. | ||
These covenants are subject to a number of important qualifications and limitations. See "Description of New Notes—Certain Covenants." |
19
Absence of a Public Market | The new notes will be a new issue of securities for which there will not initially be a market. Accordingly, there can be no assurance as to the development or liquidity of any market for the new notes. We do not intend to apply for a listing of the new notes on any securities exchange or maintain a trading market for them. |
Risk Factors
Prospective purchasers of the notes should carefully consider all of the information set forth in this prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference herein and, in particular, should evaluate the specific factors under the section "Risk Factors" for considerations relevant to an investment in the new notes.
Triumph Summary Historical and Pro Forma Consolidated Financial Data
The following table sets forth our summary historical consolidated financial information for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2008, 2009 and 2010, the three months ended June 30, 2009 and 2010 and our unaudited pro forma consolidated results of operations for the twelve months ended March 31, 2010 and for the three months ended June 30, 2010. The summary historical financial data for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2008, 2009 and 2010 have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements and related notes which are incorporated by reference in this prospectus. The summary historical financial date for the three months ended June 30, 2009 and 2010 have been derived from our unaudited consolidated financial statements and related notes which are incorporated by reference in this prospectus. The results of operations for the interim periods are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year or for any future period. The historical results included below and elsewhere in this prospectus are not necessarily indicative of our future performance, and you should read the following information together with our audited and unaudited consolidated financial statements and notes incorporated by reference in this prospectus as well as the information under the caption "Triumph Management's Discussion and Analysis" in this prospectus.
The unaudited pro forma consolidated financial data for the twelve months ended March 31, 2010 have been derived by giving pro forma effect to the consummation of the Vought Acquisition as if it had occurred on April 1, 2009, in the case of the summary unaudited pro forma consolidated statement of income data and other financial data. The unaudited pro forma consolidated financial data for the three months ended June 30, 2010 have been derived by giving pro forma effect to the consummation of the Vought Acquisition as if it had occurred on April 1, 2010, in the case of the summary unaudited pro forma consolidated statement of income data and other financial data. These unaudited pro forma combined financial data assume that the Vought Acquisition is accounted for using the acquisition method of accounting with Triumph treated as the acquiring entity and represents a current estimate of the combined financial information based on historical financial information of Triumph and Vought. In addition, the unaudited combined pro forma financial data include adjustments, which are preliminary and may be revised. There can be no assurance that such revisions will not result in material changes. The unaudited pro forma consolidated financial data have been presented for informational purposes only. The unaudited pro forma combined financial data are not necessarily indicative of what our financial position or results of operations actually would have been had the Vought Acquisition been completed as of the dates indicated. In addition, the unaudited pro forma condensed consolidated financial information does not purport to project our future financial position or operating results. The information presented below should be read in conjunction with the historical consolidated financial statements of Triumph and Vought, including related notes, and with the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements of Triumph and Vought, including the related notes, appearing elsewhere in this prospectus. See "Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Information," "Triumph Management's Discussion and Analysis of Triumph's Financial Condition and
20
Results of Operations" and "Vought Management's Discussion and Analysis of Vought's Financial Condition and Results of Operations."
| | Historical | Pro forma | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | As of and for the Fiscal Years Ended March 31, | As of and for the Three Months Ended June 30, | As of and for the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, | As of and for the Three Months Ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||||||
| | 2008(1) | 2009(2) | 2010(3) | 2009 | 2010 | 2010(4)(5) | 2010(6) | ||||||||||||||||
| | (U.S. dollars in millions, except percentages and ratios) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Statement of income data: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 1,151.1 | $ | 1,240.4 | $ | 1,294.8 | $ | 316.1 | $ | 406.4 | $ | 3,218.3 | $ | 763.4 | |||||||||
Operating costs and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Cost of sales (excluding depreciation) | 822.3 | 877.8 | 927.2 | 224.3 | 297.9 | 2,476.5 | 615.1 | ||||||||||||||||
Gross profit | 328.8 | 362.6 | 367.6 | 91.8 | 108.5 | 741.8 | 148.3 | ||||||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense | 159.3 | 162.1 | 157.9 | 39.8 | 43.4 | 280.8 | 79.6 | ||||||||||||||||
Acquisition-related costs | — | — | — | — | 17.4 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 43.2 | 48.6 | 54.4 | 14.1 | 14.8 | 118.4 | 24.3 | ||||||||||||||||
Operating income | 126.3 | 151.9 | 155.3 | 37.9 | 32.9 | 342.6 | 44.4 | ||||||||||||||||
Interest expense and other(4) | 19.9 | 17.0 | 28.8 | 5.4 | 11.8 | 84.8 | 22.3 | ||||||||||||||||
Gain on early extinguishment of debt | — | (0.9 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations, before income taxes | 106.4 | 135.8 | 126.5 | 32.5 | 21.1 | 257.9 | 22.1 | ||||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 34.7 | 43.1 | 41.2 | 11.0 | 9.5 | 90.2 | 7.8 | ||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations(5) | $ | 71.7 | $ | 92.7 | $ | 85.3 | 21.5 | 11.6 | $ | 167.6 | 14.3 | ||||||||||||
Balance sheet data (end of period): | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash | $ | 13.7 | $ | 14.5 | $ | 157.2 | 30.9 | $ | 35.7 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
Working capital | 416.8 | 372.2 | 487.8 | 466.8 | 503.1 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Property and equipment, net | 311.4 | 332.5 | 327.6 | 329.9 | 716.8 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Total assets | 1,412.8 | 1,591.2 | 1,712.7 | 1,587.9 | 4,496.4 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Total debt | 396.0 | 459.4 | 505.8 | 453.4 | 1,335.3 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Total stockholders' equity | 706.4 | 788.6 | 860.7 | 818.4 | 1,372.6 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Statement of cash flows data: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net cash flows provided by operating activities | $ | 45.7 | $ | 135.0 | $ | 169.6 | $ | 32.5 | $ | 22.7 | — | — | |||||||||||
Net cash flows used in investing activities | (119.8 | ) | (185.6 | ) | (62.5 | ) | (8.0 | ) | (350.0 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
Net cash flows provided by financing activities | 79.8 | 52.1 | 35.3 | (8.5 | ) | 206.3 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 43.2 | 48.6 | 54.4 | 14.1 | 14.8 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | (57.0 | ) | (45.4 | ) | (31.7 | ) | (7.1 | ) | (16.9 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
Other financial data: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Backlog | $ | 1,278 | $ | 1,323 | $ | 1,309 | $ | 1,278 | $ | 3,338 | $ | 3,412 | $ | 3,338 | |||||||||
Ratio of earnings to fixed charges(4)(7) | 4.8x | 6.2x | 4.6x | 5.7x | 2.6x | 3.5x | 1.9x | ||||||||||||||||
- (1)
- Includes the acquisition of the assets and business of B. & R. Machine & Tool Corp. from the date of acquisition (February 2008).
- (2)
- Includes the acquisitions of Merritt Tool Company, Inc., Saygrove Defence and Aerospace Group Limited, and The Mexmil Company, LLC and the acquisition of the aviation segment of Kongsberg Automotive Holdings ASA from the date of each respective acquisition (March 2009).
- (3)
- Includes the acquisition of DCL Avionics, Inc. (January 2010) and Fabritech, Inc. (March 2010) from the date of each respective acquisition.
- (4)
- Pro forma interest expense excludes incremental interest expense attributable to our 8% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2017, issued in November 2009, the remaining proceeds of which were used to partially finance the Vought Acquisition. If this debt had been outstanding as of April 1, 2009, we would have incurred additional interest expense, including amortization of discount and finance fees of approximately $9.2 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010.
- (5)
- The pro forma income from continuing operations in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of income includes adjustments of (1) $34.2 million for the elimination of Vought's amortization of prior service costs and amortization of actuarial losses on pension and other post-retirement benefits, (2) $11.0 million of estimated amortization of off market contract fair value margin adjustment and (3) $2.0 million for the elimination of management fees to The Carlyle Group. See Note 7 to "Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Information."
- (6)
- The pro forma income from continuing operations in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of income includes adjustments of (1) $8.6 million for the elimination of Vought's amortization of prior service costs and amortization of actuarial losses on pension and other post-retirement benefits, (2) $3.8 million of estimated amortization of off market contract fair value margin adjustment, (3) $0.4 million for the elimination of management fees to The Carlyle Group, and (4) $43.5 million for the elimination of both Triumph's and Vought's acquisition-related costs. See Note 7 to "Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Financial Information."
- (7)
- For purposes of calculating this ratio, "earnings" consists of income from continuing operations before income taxes and income from equity affiliates plus (a) fixed charges minus interest capitalized during the period, (b) distributed income from equity affiliates and (c) amortization of previously capitalized interest. "Fixed charges" consists of interest expense, capitalized interest, amortization of discount on indebtedness and an appropriate portion of rental expense representative of the interest factor. Estimated interest expense on the new debt issuances is based on an assumed blended average interest rate of 6.25%. A 1/8% change in the interest rate would cause a corresponding increase or decrease to annual interest expense of approximately $1.3 million ($0.3 million per quarter).
21
Vought Summary Historical Consolidated Financial Data
The following table sets forth the summary historical consolidated financial information of Vought for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, the three months ended March 29, 2009 and March 28, 2010, and the twelve months ended March 28, 2010. The summary historical financial data for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 have been derived from Vought's audited consolidated financial statements and related notes incorporated by reference in this prospectus. The summary historical financial data for the three months ended March 29, 2009 and March 28, 2010 have been derived from Vought's unaudited historical consolidated financial statements and related notes incorporated by reference in this prospectus. The unaudited consolidated financial data for the twelve months ended March 28, 2010 have been derived by adding the financial data from Vought's audited historical consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2009 to the financial data from Vought's unaudited historical consolidated financial data for the three months ended March 28, 2010 and subtracting the financial data from Vought's unaudited historical consolidated financial data for the three months ended March 29, 2009 (each included elsewhere in this prospectus). In the opinion of management, such unaudited financial data reflect all adjustments, consisting only of normal and recurring adjustments, necessary for a fair statement of the results of those periods. The results of operations for the interim periods are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year or for any future period. The information set forth below is only a summary and is not necessarily indicative of the results of future operations of Vought or Triumph, and you should read the following information together with Vought's audited and unaudited consolidated financial statements and notes incorporated by reference in this prospectus and the section of this prospectus entitled "Vought Management's Discussion and Analysis of Vought's Financial Condition and Results of Operations."
| | As of and for Fiscal Years Ended December 31, | As of and for Three Months Ended | As of and for Twelve Months Ended | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | March 29, 2009 | March 28, 2010 | March 28, 2010 | |||||||||||||||
| | (U.S. dollars in millions, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 1,613.1 | $ | 1,775.0 | $ | 1,877.8 | $ | 390.3 | $ | 470.5 | $ | 1,958.0 | |||||||||
Costs and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Cost of sales | 1,284.8 | 1,492.9 | 1,594.8 | 324.8 | 391.5 | 1,661.5 | |||||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense | 133.3 | 135.3 | 122.6 | 28.5 | 39.7 | 133.8 | |||||||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 1,418.1 | 1,628.2 | 1,717.4 | 353.3 | 431.2 | 1,795.3 | |||||||||||||||
Operating income | 195.0 | 146.8 | 160.4 | 37.0 | 39.3 | 162.7 | |||||||||||||||
Other income (expense) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest income | 3.6 | 4.4 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.6 | |||||||||||||||
Other gain (loss) | (0.1 | ) | 48.7 | 1.3 | — | — | 1.3 | ||||||||||||||
Equity in loss of joint venture | (4.0 | ) | (0.6 | ) | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
Interest expense | (62.6 | ) | (67.2 | ) | (57.0 | ) | (15.0 | ) | (12.6 | ) | (54.6 | ) | |||||||||
Income before income taxes | 131.9 | 132.1 | 105.4 | 22.2 | 26.8 | 110.0 | |||||||||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | 0.1 | 0.2 | (9.3 | ) | — | — | (9.3 | ) | |||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations(1) | $ | 131.8 | $ | 131.9 | $ | 114.7 | $ | 22.2 | $ | 26.8 | $ | 119.3 | |||||||||
Balance sheet data (end of period): | |||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 75.6 | $ | 86.7 | $ | 116.0 | $ | 165.4 | $ | 149.7 | $ | 149.7 | |||||||||
Trade and other receivables | 81.4 | 138.5 | 127.9 | 147.8 | 159.5 | 159.5 | |||||||||||||||
Inventories | 362.8 | 311.8 | 511.3 | 351.3 | 453.4 | 453.4 | |||||||||||||||
Property and equipment, net | 295.2 | 279.2 | 275.9 | 275.6 | 273.1 | 273.1 | |||||||||||||||
Total assets | 1,620.9 | 1,727.6 | 1,509.9 | 1,876.8 | 1,513.5 | 1,513.5 | |||||||||||||||
Total debt(2) | 683.0 | 869.9 | 589.8 | 1,030.6 | 590.4 | 590.4 | |||||||||||||||
Total stockholders' equity (deficit) | (665.8 | ) | (934.1 | ) | (503.5 | ) | (877.3 | ) | (466.0 | ) | (466.0 | ) | |||||||||
Statement of cash flows data: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 34.2 | $ | (154.5 | ) | $ | 111.8 | $ | (73.0 | ) | $ | 40.0 | $ | 224.8 | |||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | (49.6 | ) | (14.2 | ) | 247.2 | (8.3 | ) | (6.7 | ) | 248.8 | |||||||||||
Net cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities | (2.4 | ) | 179.8 | (329.7 | ) | 160.0 | 0.4 | (489.3 | ) | ||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | (57.4 | ) | (69.3 | ) | (42.0 | ) | (8.3 | ) | (6.7 | ) | (40.4 | ) | |||||||||
Other financial data: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total funded backlog | $ | 2,288.1 | $ | 2,451.0 | $ | 2,067.3 | $ | 2,736.2 | $ | 2,102.5 | $ | 2,102.5 | |||||||||
- (1)
- Income from continuing operations is calculated before other comprehensive income (loss) relating to the following: (1) pension and OPEB related adjustments of $100.0 million and $(365.1) million in 2009 and 2008, respectively and (2) minimum pension liability adjustments and adoption of provisions of theCompensation—Retirement Benefits topic of the ASC adjustments of $(22.4) million in 2007.
- (2)
- As of December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, capital leases represented less than $0.1 million of Vought's total debt balance. Total debt as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 includes $2.4 million and $8.2 million, respectively, of unamortized discount related to Vought's long-term debt.
22
An investment in the new notes involves risks that could cause you to lose all or part of your original investment, including the risks described below. Please be aware that other risks may prove to be important in the future and that new risks may emerge at any time, and we cannot predict such risks or estimate the extent to which they may affect our financial performance. Prior to making a decision to tender your old notes, you should carefully consider the following discussion of risks and the other information in this prospectus, and carefully read the risks described in the documents incorporated by reference in this prospectus, including those set forth under the caption "Risk Factors" in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2010. If there is any inconsistency between the information set forth in this section and any documents incorporated by reference which discuss risk factors applicable to the businesses of Triumph prior to the Vought Acquisition, you should rely on the information set forth in this section.
Risks Relating to Our Business and Our Industry
Factors that have an adverse impact on the aerospace industry may adversely affect our results of operations and liquidity.
A substantial percentage of our gross profit and operating income on a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition was derived from commercial aviation for fiscal year 2010. Our operations have been focused on designing, engineering, manufacturing, repairing and overhauling a broad portfolio of aerostructures, aircraft components, accessories, subassemblies and systems. Therefore, our business is directly affected by economic factors and other trends that affect our customers in the aerospace industry, including a possible decrease in outsourcing by OEMs and aircraft operators or projected market growth that may not materialize or be sustainable. We are also significantly dependent on sales to the commercial aerospace market, which has been cyclical in nature with significant downturns in the past. When these economic and other factors adversely affect the aerospace industry, they tend to reduce the overall customer demand for our products and services, which decreases our operating income. Economic and other factors that might affect the aerospace industry may have an adverse impact on our results of operations and liquidity. We have credit exposure to a number of commercial airlines, some of which have encountered financial difficulties. In addition, an increase in energy costs and the price of fuel to the airlines, similar to that which occurred in 2008, could result in additional pressure on the operating costs of airlines. The market for jet fuel is inherently volatile and is subject to, among other things, changes in government policy on jet fuel production, fluctuations in the global supply of crude oil and disruptions in oil production or delivery caused by sudden hostility in oil producing areas. Often airlines are unable to pass on increases in fuel prices to customers by increasing fares due to the competitive nature of the airline industry, and this compounds the pressure on operating costs. Other events of general impact such as terrorist attacks against the industry or pandemic health crises may lead to declines in the worldwide aerospace industry that could adversely affect our business and financial condition.
In addition, demand for our maintenance, repair and overhaul services is strongly correlated with worldwide flying activity. A significant portion of the maintenance, repair and overhaul ("MRO") activity required on commercial aircraft is mandated by government regulations that limit the total time or number of flights that may elapse between scheduled MRO events. As a result, although short-term deferrals are possible, MRO activity is ultimately required to continue to operate the aircraft in revenue-producing service. Therefore, over the intermediate and long term, trends in the MRO market are closely related to the size and utilization level of the worldwide aircraft fleet, as reflected by the number of available seat miles, commonly referred to as ASMs, and cargo miles flown. Consequently, conditions or events which contribute to declines in worldwide ASMs and cargo miles flown, such as those mentioned above, could negatively impact our MRO business.
23
Cancellations, reductions or delays in customer orders may adversely affect our results of operations.
Our overall operating results are affected by many factors, including the timing of orders from large customers and the timing of expenditures to manufacture parts and purchase inventory in anticipation of future sales of products and services. A large portion of our operating expenses are relatively fixed. Because several of our operating locations typically do not obtain long-term purchase orders or commitments from our customers, they must anticipate the future volume of orders based upon the historic purchasing patterns of customers and upon our discussions with customers as to their anticipated future requirements. These historic patterns may be disrupted by many factors, including changing economic conditions, inventory adjustments, or work stoppages or labor disruptions at our customers. Cancellations, reductions or delays in orders by a customer or group of customers could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may fail to realize all of the expected benefits of the Vought Acquisition.
On June 16, 2010, we completed the Vought Acquisition. Vought was a company with revenues almost twice our revenues prior to the acquisition and approximately as many employees. The Vought Acquisition is by far the largest acquisition we have made. The success of the Vought Acquisition will depend, in part, on our ability to realize the anticipated benefits from combining the businesses of Triumph and Vought. However, to realize these anticipated benefits, we must successfully combine the businesses. If we are not able to achieve these objectives, or do not do so in a timely manner, the anticipated benefits of the Vought Acquisition may not be realized fully or at all or may take longer to realize than expected.
In addition, it is possible that the integration process could result in the loss of key employees, the disruption of each company's ongoing businesses or inconsistencies in standards, controls, procedures and policies that adversely affect our ability to maintain relationships with customers, suppliers and employees or to achieve the anticipated benefits of the Vought Acquisition. Integration efforts between the two companies will also divert management attention and resources and could have an adverse effect on us during the transition period.
Our acquisition strategy exposes us to risks, including the risk that we may not be able to successfully integrate acquired businesses.
We have a consistent strategy to grow, in part, through the acquisition of additional businesses in the aerospace industry and are continuously evaluating various acquisition opportunities, including those outside the United States and those that may have a material impact on our business. Our ability to grow by acquisition is dependent upon, among other factors, the availability of suitable acquisition candidates. Growth by acquisition involves risks that could adversely affect our operating results, including difficulties in integrating the operations and personnel of acquired companies, the risk of diverting the attention of senior management from our existing operations, the potential amortization of acquired intangible assets, the potential impairment of goodwill and the potential loss of key employees of acquired companies. We may not be able to consummate acquisitions on satisfactory terms or, if any acquisitions are consummated, successfully integrate these acquired businesses.
A significant decline in business with a key customer could have a material adverse effect on us.
The Boeing Company, or Boeing Commercial, Military & Space, represented approximately 52% of our net sales on a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition, and on a stand-alone basis, 30% of Triumph's net sales and 66% of Vought's net sales, in each case for the twelve months ended March 31, 2010, covering virtually every Boeing plant and product. As a result, a significant reduction in purchases by Boeing could have a material adverse impact on our financial
24
position, results of operations, and cash flows. In addition, some of our other group companies rely significantly on particular customers, the loss of which could have an adverse effect on those businesses.
Demand for military and defense products is dependent upon government spending.
The military and defense market is largely dependent upon government budgets, particularly the U.S. defense budget, and even an increase in defense spending may not be allocated to programs that would benefit our business. Moreover, the new military aircraft programs in which we participate may not enter full-scale production as expected. A change in the levels of defense spending or levels of military flight operations could curtail or enhance our prospects in the military and defense market depending upon the programs affected.
For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, approximately 36% of our sales on a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition and 37% of Triumph sales on a stand-alone basis were derived from the military and defense market, which includes primarily indirect sales to the U.S. Government. Approximately 35% of Vought's revenue for fiscal year 2009 was derived from the military and defense market, which includes primarily indirect sales to the U.S. Government. As a result, our exposure to the military and defense market is significant.
We also face the risk that the C-17 program could be completed upon fulfillment of currently outstanding production orders. We currently have a contract with Boeing to support C-17 production through April 2011. The President's proposed 2010 budget does not include funding for the procurement of new C-17 aircraft, although Congress has proposed adding funding for additional aircraft. Boeing currently has confirmed orders with the U.S. Air Force and various foreign militaries to produce C-17 through 2012 at a rate of approximately 10 aircraft per year. In addition there are additional orders for 2013 that have been confirmed and Boeing has reported that there is strong interest from India for 10 aircraft as well as interest from Qatar, Saudi Arabia, South Africa and Japan. These additional orders would allow production to be continued through 2014 at today's current rate. However, there can be no assurance that these additional orders will materialize. Our business could be adversely impacted if the U.S. Government does not fund additional C-17 aircraft or if additional orders from Foreign Militaries do not materialize and Boeing decides not to fund beyond their current commitment. As a result, the loss of the C-17 program and the failure to win additional work to replace the C-17 program could materially reduce our cash flow and results of operations.
Future volatility in the financial markets may impede our ability to successfully access capital markets and ensure adequate liquidity and may adversely affect our customers and suppliers.
Future turmoil in the capital markets may impede our ability to access the capital markets when we would like, or need, to raise capital or restrict our ability to borrow money on favorable terms. Such market conditions could have an adverse impact on our flexibility to react to changing economic and business conditions and on our ability to fund our operations and capital expenditures in the future. In addition, interest rate fluctuations, financial market volatility or credit market disruptions may also negatively affect our customers' and our suppliers' ability to obtain credit to finance their businesses on acceptable terms. As a result, our customers' need for and ability to purchase our products or services may decrease, and our suppliers may increase their prices, reduce their output or change their terms of sale. If our customers' or suppliers' operating and financial performance deteriorates, or if they are unable to make scheduled payments or obtain credit, our customers may not be able to pay, or may delay payment of, accounts receivable owed to us, and our suppliers may restrict credit or impose different payment terms. Any inability of customers to pay us for our products and services or any demands by suppliers for different payment terms, may adversely affect our earnings and cash flow.
25
Our international sales and operations are subject to applicable laws relating to trade, export controls and foreign corrupt practices, the violation of which could adversely affect our operations.
We must comply with all applicable export control laws and regulations of the United States and other countries. United States laws and regulations applicable to us include the Arms Export Control Act, the International Traffic in Arms Regulations ("ITAR"), the Export Administration Regulations ("EAR") and the trade sanctions laws and regulations administered by the United States Department of the Treasury's Office of Foreign Assets Control ("OFAC"). EAR restricts the export of dual-use products and technical data to certain countries, while ITAR restricts the export of defense products, technical data and defense services. The U.S. Government agencies responsible for administering EAR and ITAR have significant discretion in the interpretation and enforcement of these regulations. We cannot provide services to certain countries subject to United States trade sanctions unless we first obtain the necessary authorizations from OFAC. In addition, we are subject to the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act ("FCPA") which generally bars bribes or unreasonable gifts to foreign governments or officials.
Violations of these laws or regulations could result in significant additional sanctions including fines, more onerous compliance requirements, more extensive debarments from export privileges, loss of authorizations needed to conduct aspects of our international business and criminal penalties and may harm our ability to enter into contracts with the U.S. government. A future violation of ITAR or the other regulations enumerated above could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our expansion into international markets may increase credit, currency and other risks, and our current operations in international markets expose us to such risks.
As we pursue customers in Asia, South America and other less developed aerospace markets throughout the world, our inability to ensure the creditworthiness of our customers in these areas could adversely impact our overall profitability. In addition, with operations in China, Germany, Mexico, Thailand and the United Kingdom, and customers throughout world, we will be subject to the legal, political, social and regulatory requirements and economic conditions of other jurisdictions. In the future, we may also make additional international capital investments, including further acquisitions of companies outside the United States or companies having operations outside the United States. Risks inherent to international operations include, but are not limited to, the following:
- •
- difficulty in enforcing agreements in some legal systems outside the United States;
- •
- imposition of additional withholding taxes or other taxes on our foreign income, tariffs or other restrictions on foreign trade and investment, including currency exchange controls;
- •
- fluctuations in exchange rates which may affect demand for our products and services and may adversely affect our profitability in U.S. dollars;
- •
- inability to obtain, maintain or enforce intellectual property rights;
- •
- changes in general economic and political conditions in the countries in which we operate;
- •
- unexpected adverse changes in the laws or regulatory requirements outside the United States, including those with respect to environmental protection, export duties and quotas;
- •
- failure by our employees or agents to comply with U.S. laws affecting the activities of U.S. companies abroad;
- •
- difficulty with staffing and managing widespread operations; and
- •
- difficulty of and costs relating to compliance with the different commercial and legal requirements of the countries in which we operate.
26
We may need additional financing for acquisitions and capital expenditures and additional financing may not be available on terms acceptable to us.
A key element of our strategy has been, and continues to be, internal growth supplemented by growth through the acquisition of additional aerospace companies and product lines. In order to grow internally, we may need to make significant capital expenditures, such as investing in facilities in low cost countries, and may need additional capital to do so. Our ability to grow is dependent upon, and may be limited by, among other things, access to markets and conditions of markets, availability under the Revolving Credit Facility and Securitization Facility and by particular restrictions contained in the Revolving Credit Facility and our other financing arrangements. In that case, additional funding sources may be needed, and we may not be able to obtain the additional capital necessary to pursue our internal growth and acquisition strategy or, if we can obtain additional financing, the additional financing may not be on financial terms that are satisfactory to us.
Competitive pressures may adversely affect us.
We have numerous competitors in the aerospace industry. We compete primarily with the top-tier systems integrators and the manufacturers that supply them, some of which are divisions or subsidiaries of OEMs and other large companies that manufacture aircraft components and subassemblies. Our OEM competitors, which include Boeing, Airbus, Bell Helicopter, Cessna, Gulfstream, Honeywell, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon, Rolls Royce and Sikorsky may choose not to outsource production of aerostructures or other components due to, among other things, their own direct labor and overhead considerations, capacity utilization at their own facilities and desire to retain critical or core skills. Consequently, traditional factors affecting competition, such as price and quality of service, may not be significant determinants when OEMs decide whether to produce a part in-house or to outsource. We also face competition from non-OEM component manufacturers including, Alenia Aeronautica, Fuji Heavy Industries, GKN Westland Aerospace (U.K.), Goodrich Corp., Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Spirit AeroSystems and Stork Aerospace. Competition for the repair and overhaul of aviation components comes from three primary sources: OEMs, major commercial airlines and other independent repair and overhaul companies.
We may need to expend significant capital to keep pace with technological developments in our industry.
The aerospace industry is constantly undergoing development and change and it is likely that new products, equipment and methods of repair and overhaul service will be introduced in the future. In order to keep pace with any new developments, we may need to expend significant capital to purchase new equipment and machines or to train our employees in the new methods of production and service.
The construction of aircraft is heavily regulated and failure to comply with applicable laws could reduce our sales or require us to incur additional costs to achieve compliance, and we may incur significant expenses to comply with new or more stringent governmental regulation.
The aerospace industry is highly regulated in the United States by the FAA and in other countries by similar agencies. We must be certified by the FAA and, in some cases, by individual OEMs in order to engineer and service parts, components and aerostructures used in specific aircraft models. If any of our material authorizations or approvals were revoked or suspended, our operations would be adversely affected. New or more stringent governmental regulations may be adopted, or industry oversight heightened in the future, and we may incur significant expenses to comply with any new regulations or any heightened industry oversight.
27
Some contractual arrangements with customers may cause us to bear significant up-front costs that we may not be able to recover.
Many new aircraft programs require that major suppliers bear the cost of design, development and engineering work associated with the development of the aircraft usually in exchange for a long-term agreement to supply critical parts once the aircraft is in production. If the aircraft fails to reach the full production stage or we fail to win the long-term contract, the outlays we have made in research and development and other start-up costs may not generate our anticipated return on investment.
We may not realize our anticipated return on capital commitments made to expand our capabilities.
We continually make significant capital expenditures to implement new processes and to increase both efficiency and capacity. Some of these projects require additional training for our employees and not all projects may be implemented as anticipated. If any of these projects do not achieve the anticipated increase in efficiency or capacity, our returns on these capital expenditures may be lower than expected.
Any product liability claims in excess of insurance may adversely affect our financial condition.
Our operations expose us to potential liability for personal injury or death as a result of the failure of an aircraft component that has been serviced by us or the failure of an aircraft component designed or manufactured by us. While we believe that our liability insurance is adequate to protect us from these liabilities, our insurance may not cover all liabilities. Additionally, as the number of insurance companies providing general aviation product liability insurance coverage has decreased in recent years, insurance coverage may not be available in the future at a cost acceptable to us. Any material liability not covered by insurance or for which third-party indemnification is not available could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition.
The lack of available skilled personnel may have an adverse effect on our operations.
From time to time, some of our operating locations have experienced difficulties in attracting and retaining skilled personnel to design, engineer, manufacture, repair and overhaul sophisticated aircraft components. Our ability to operate successfully could be jeopardized if we are unable to attract and retain a sufficient number of skilled personnel to conduct our business. Additionally, the service of key members of the Vought management team and other personnel are expected to be critical to ensure the smooth and timely integration of Vought's business into Triumph.
Any exposure to environmental liabilities may adversely affect us.
Our business, operations and facilities are subject to numerous stringent federal, state, local and foreign environmental laws and regulations, and we are subject to potentially significant fines or penalties, including criminal sanctions, if we fail to comply with these requirements. Pursuant to certain environmental laws, a current or previous owner or operator of a contaminated site may be held liable for the entire cost of investigation, removal or remediation of hazardous materials at such property, whether or not the owner or operator knew of, or was responsible for, the presence of any hazardous materials. Although management believes that our operations and facilities are in material compliance with such laws and regulations, future changes in such laws, regulations or interpretations thereof or the nature of our operations or regulatory enforcement actions which may arise, may require us to make significant additional capital expenditures to ensure compliance in the future. Certain of our facilities, including facilities acquired and operated by us or one of our subsidiaries have at one time or another been under active investigation for environmental contamination by federal or state agencies when acquired and, at least in some cases, continue to be under investigation or subject to remediation for potential or identified environmental contamination. Lawsuits, claims and costs involving
28
environmental matters are likely to continue to arise in the future. Individual facilities of ours have also been subject to investigation on occasion for possible past waste disposal practices which might have contributed to contamination at or from remote third-party waste disposal sites. In some instances, we are indemnified by prior owners or operators and/or present owners of the facilities for liabilities which we incur as a result of these investigations and the environmental contamination found which pre-dates our acquisition of these facilities, subject to certain limitations, including but not limited to specified exclusions, deductibles and limitations on the survival period of the indemnity. We also maintain a pollution liability policy that provides coverage, subject to specified limitations, for specified material liabilities associated with the clean-up of certain on-site pollution conditions, as well as defense and indemnity for certain third-party suits (including Superfund liabilities at third-party sites), in each case, to the extent not otherwise indemnified. However, if we were required to pay the expenses related to environmental liabilities for which neither indemnification nor insurance coverage is available, these expenses could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
We are currently involved in intellectual property litigation, which could have a material and adverse impact on our profitability, and we could become so involved again in the future.
We and other companies in our industry possess certain proprietary rights relating to designs, engineering, manufacturing processes and repair and overhaul procedures. In the event that we believe that a third party is infringing upon our proprietary rights, we may bring an action to enforce such rights. In addition, third parties may claim infringement by us with respect to their proprietary rights and may initiate legal proceedings against us in the future. The expense and time of bringing an action to enforce such rights or defending against infringement claims can be significant, as in the case of the litigation arising out of the claims of Eaton Corporation discussed in "Business—Legal Proceedings." Intellectual property litigation involves complex legal and factual questions which makes the outcome of any such proceedings subject to considerable uncertainty. Not only can such litigation divert management's attention, but it can also expose the Company to damages and potential injunctive relief which, if granted, may preclude the company from making, using or selling particular products or technology. The expense and time associated with such litigation may have a material and adverse impact on our profitability.
We do not own certain intellectual property and tooling that is important to our business.
In our overhaul and repair businesses, OEMs of equipment that we maintain for our customers increasingly include language in repair manuals relating to their equipment asserting broad claims of proprietary rights to the contents of the manuals used in our operations. Although we believe that our use of manufacture and repair manuals is lawful, there can be no assurance that OEMs will not try to enforce such claims, including through the possible use of legal proceedings, or that any such actions will be unsuccessful.
Our business also depends on using certain intellectual property and tooling that we have rights to use pursuant to license grants under our contracts with our OEM customers. These contracts contain restrictions on our use of the intellectual property and tooling and may be terminated if we violate certain of these restrictions. Our loss of a contract with an OEM customer and the related license rights to use an OEM's intellectual property or tooling would materially adversely affect our business.
Our fixed-price contracts may commit us to unfavorable terms.
For the year fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, a significant portion of our net sales on a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition were derived from fixed-price contracts under which we have agreed to provide components or aerostructures for a price determined on the date we entered into the contract. Several factors may cause the costs we incur in fulfilling these contracts to
29
vary substantially from our original estimates, and we bear the risk that increased or unexpected costs may reduce our profit or cause us to sustain losses on these contracts. In a fixed-price contract, we must fully absorb cost overruns, notwithstanding the difficulty of estimating all of the costs we will incur in performing these contracts. Because our ability to terminate contracts is generally limited, we may not be able to terminate our performance requirements under these contracts at all or without substantial liability and, therefore, in the event we are sustaining reduced profits or losses, we could continue to sustain these reduced profits or losses for the duration of the contract term. Our failure to anticipate technical problems, estimate delivery reductions, estimate costs accurately or control costs during performance of a fixed-price contract may reduce the profitability of a fixed-price contract or cause significant losses.
Any significant disruption from key suppliers of raw materials and key components could delay production and decrease revenue.
We are highly dependent on the availability of essential raw materials such as carbon fiber, aluminum and titanium, and purchased engineered component parts from our suppliers, many of which are available only from single customer-approved sources. Moreover, we are dependent upon the ability of our suppliers to provide raw materials and components that meet our specifications, quality standards and delivery schedules. Our suppliers' failure to provide expected raw materials or component parts could require us to identify and enter into contracts with alternate suppliers that are acceptable to both us and our customers, which could result in significant delays, expenses, increased costs and management distraction and adversely affect production schedules and contract profitability.
We have from time to time experienced limited interruptions of supply, and we may experience a significant interruption in the future. Our continued supply of raw materials and component parts are subject to a number of risks including:
- •
- availability of capital to our suppliers;
- •
- the destruction of our suppliers' facilities or their distribution infrastructure;
- •
- a work stoppage or strike by our suppliers' employees;
- •
- the failure of our suppliers to provide raw materials or component parts of the requisite quality;
- •
- the failure of essential equipment at our suppliers' plants;
- •
- the failure or shortage of supply of raw materials to our suppliers;
- •
- contractual amendments and disputes with our suppliers; and
- •
- geopolitical conditions in the global supply base.
In addition, some contracts with our suppliers for raw materials, component parts and other goods are short-term contracts, which are subject to termination on a relatively short-term basis. The prices of our raw materials and component parts fluctuate depending on market conditions, and substantial increases in prices could increase our operating costs, which, as a result of our fixed price contracts, we may not be able to recoup through increases in the prices of our products.
Due to economic difficulty, we may face pressure to renegotiate agreements resulting in lower margins. Our suppliers may discontinue provision of products to us at attractive prices or at all, and we may not be able to obtain such products in the future from these or other providers on the scale and within the time periods we require. Furthermore, substitute raw materials or component parts may not meet the strict specifications and quality standards we and our customers demand, or that the U.S. Government requires. If we are not able to obtain key products on a timely basis and at an affordable cost, or we experience significant delays or interruptions of their supply, revenues from sales of products that use these supplies will decrease.
30
Our operations depend on our manufacturing facilities, which are subject to physical and other risks that could disrupt production.
Our manufacturing facilities could be damaged or disrupted by a natural disaster, war, or terrorist activity. We maintain property damage and business interruption insurance at the levels typical in our industry, however, a major catastrophe, such as an earthquake, hurricane, flood, tornado or other natural disaster at any of our sites, or war or terrorist activities in any of the areas where we conduct operations could result in a prolonged interruption of our business. Any disruption resulting from these events could cause significant delays in shipments of products and the loss of sales and customers and we may not have insurance to adequately compensate us for any of these events.
Significant consolidation by aerospace industry suppliers could adversely affect our business.
The aerospace industry has recently experienced consolidation among suppliers. Suppliers have consolidated and formed alliances to broaden their product and integrated system offerings and achieve critical mass. This supplier consolidation is in part attributable to aircraft manufacturers more frequently awarding long-term sole-source or preferred supplier contracts to the most capable suppliers, thus reducing the total number of suppliers. This consolidation could cause us to compete against certain competitors with greater financial resources, market penetration and purchasing power. When we purchase component parts and services from suppliers to manufacture our products, consolidation reduces price competition between our suppliers, which could diminish incentives for our suppliers to reduce prices. If this consolidation continues, our operating costs could increase and it may become more difficult for us to be successful in obtaining new customers.
Due to the size and long-term nature of many of our contracts, we are required by GAAP to estimate sales and expenses relating to these contracts in our financial statements, which may cause actual results to differ materially from those estimated under different assumptions or conditions.
Our financial statements are prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. These principles require our management to make estimates and assumptions regarding our contracts that affect the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Contract accounting requires judgment relative to assessing risks, estimating contract sales and costs, and making assumptions for schedule and technical issues. Due to the size and nature of many of our contracts, the estimation of total sales and cost at completion is complicated and subject to many variables. While we base our estimates on historical experience and on various assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances at the time made, actual results may differ materially from those estimated.
We may be subject to work stoppages at our facilities or those of our principal customers and suppliers, which could seriously impact the profitability of our business.
At March 31, 2010, we employed 12,508 people on a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition, of which 26.7% belonged to unions. Our unionized workforces and those of our customers and suppliers may experience work stoppages. For example, the International Association of Machinists-represented employees at Vought's Nashville, Tennessee, plant engaged in a strike that continued for approximately 16 weeks during 2008 and 2009. A contingency plan was implemented that allowed production to continue in Nashville during the course of that strike. Additionally, our union contract with Local 848 of UAW with employees at our Dallas and Grand Prairie, Texas, facilities expires on October 3, 2010. If we are unable to negotiate a new contract with that workforce, our operations may be disrupted and we may be prevented from completing production and delivery of products from those facilities, which would negatively impact our results of operations.
31
Many aircraft manufacturers, airlines and aerospace suppliers have unionized workforces. Strikes, work stoppages or slowdowns experienced by aircraft manufacturers, airlines or aerospace suppliers, such as the recent strike at Boeing's C-17 facilities, could reduce our customers' demand for our products or prevent us from completing production. In turn, this may have a material adverse affect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Financial market conditions may adversely affect the benefit plan assets we have inherited from Vought, increase funding requirements and materially impact our statement of financial position.
The benefit plan assets we have inherited from Vought as a result of the Vought Acquisition are invested in a diversified portfolio of investments in both the equity and debt categories, as well as limited investments in real estate and other alternative investments. The current market values of all of these investments, as well as the related benefit plan liabilities are impacted by the movements and volatility in the financial markets. In accordance with theCompensation—Retirement Benefits topic of the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC), we have recognized the over-funded or under-funded status of a defined benefit postretirement plan as an asset or liability in our balance sheet, and will recognize changes in that funded status in the year in which the changes occur. The funded status is measured as the difference between the fair value of the plan's assets and the projected benefit obligation. A decrease in the fair value of these plan assets or an increase in interest rates resulting from movements in the financial markets will increase the under-funded status of the plans recorded in our statement of financial position and result in additional cash funding requirements to meet the minimum required funding levels.
The U.S. Government is a significant customer of our largest customers, and we and they are subject to specific U.S. Government contracting rules and regulations.
As a result of the Vought Acquisition, we have become a more significant provider of aerostructures to military aircraft manufacturers. The military aircraft manufacturers' business, and by extension, our business, is affected by the U.S. Government's continued commitment to programs under contract with our customers. The terms of defense contracts with the U.S. Government generally permit the government to terminate contracts partially or completely, either for its convenience or if we default by failing to perform under the contract. Termination for convenience provisions provide only for our recovery of unrecovered costs incurred or committed, settlement expenses and profit on the work completed prior to termination. Termination for default provisions provide for the contractor to be liable for excess costs incurred by the U.S. Government in procuring undelivered items from another source. On contracts where the price is based on cost, the U.S. Government may review our costs and performance, as well as our accounting and general business practices. Based on the results of such audits, the U.S. Government may adjust our contract-related costs and fees, including allocated indirect costs. In addition, under U.S. Government purchasing regulations, some of our costs, including most financing costs, portions of research and development costs, and certain marketing expenses may not be subject to reimbursement.
We bear the potential risk that the U.S. Government may unilaterally suspend our customers or us from new contracts pending the resolution of alleged violations of procurement laws or regulations. Sales to the U.S. Government are also subject to changes in the government's procurement policies in advance of design completion. An unexpected termination of, or suspension from, a significant government contract, a reduction in expenditures by the U.S. Government for aircraft using our products, lower margins resulting from increasingly competitive procurement policies, a reduction in the volume of contracts awarded to us, or substantial cost overruns could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
32
We are subject to the requirements of the National Industrial Security Program Operating Manual for facility security clearance, which is a prerequisite for our ability to perform on classified contracts for the U.S. Government.
A Department of Defense, or DoD, facility security clearance is required in order to be awarded and perform on classified contracts for the DoD and certain other agencies of the U.S. Government, which is a significant part of our business. We have obtained clearance at appropriate levels that require stringent qualifications, and it may be required to seek higher level clearances in the future. We cannot assure you that we will be able to maintain our security clearance. If for some reason our security clearance is invalidated or terminated, we may not be able to continue to perform our present classified contracts or be able to enter into new classified contracts, which could affect our ability to compete for and capture new business.
We may be unable to effectively implement the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system at Vought.
In 2009, Vought began the planning and design phase of an ERP system which is scheduled for completion in 2011. If this implementation is not managed effectively it may delay our ability to obtain accurate financial information with respect to the Vought business or obtain the information necessary to effectively manage the Vought business, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Risks Relating to the Exchange Offer and the New Notes
If you fail to exchange your old notes for new notes, they may be difficult to resell.
If you do not exchange your old notes for new notes in this exchange offer, the old notes you hold will continue to be subject to the existing transfer restrictions described in the legend on the global security representing the outstanding old notes. These restrictions on transfer exist because we issued the old notes pursuant to an exemption from the registration requirements of the Securities Act and applicable state securities laws. The old notes that are not exchanged for new notes will remain restricted securities. Accordingly, those old notes may not be offered or sold, unless registered under the Securities Act and applicable state securities laws, except pursuant to an exemption from, or in a transaction not subject to, the Securities Act and applicable state securities laws. Because we anticipate that most holders of old notes will elect to participate in this exchange offer, we expect that the liquidity of the market for the old notes after the completion of this exchange offer may be substantially limited. Any old notes tendered and exchanged in the exchange offer will reduce the aggregate principal amount at maturity of the old notes not exchanged.
You may not receive the new notes in the exchange offer if the exchange offer procedures are not properly followed.
We will issue the new notes in exchange for your old notes only if you properly tender the old notes before expiration of the exchange offer. Neither we nor the exchange agent are under any duty to give notification of defects or irregularities with respect to the tenders of the old notes for exchange. If you are the beneficial holder of old notes that are held through your broker, dealer, commercial bank, trust company or other nominee, and you wish to tender such notes in the exchange offer, you should promptly contact the person through whom your old notes are held and instruct that person to tender on your behalf.
33
Broker-dealers may become subject to the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act and any profit on the resale of the new notes may be deemed to be underwriting compensation under the Securities Act.
Any broker-dealer that acquires new notes in the exchange offer for its own account in exchange for old notes which it acquired through market-making or other trading activities must acknowledge that it will comply with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act in connection with any resale transaction by that broker-dealer. Any profit on the resale of the new notes and any commission or concessions received by a broker-dealer may be deemed to be underwriting compensation under the Securities Act.
If an active trading market does not develop for the new notes, you may be unable to sell the new notes or to sell them at a price you deem sufficient.
The new notes will be securities for which there is no established trading market. We do not intend to list the new notes on any exchange or maintain a trading market for them. We give no assurance as to:
- •
- the liquidity of any trading market that may develop;
- •
- the ability of holders to sell their new notes; or
- •
- the price at which holders would be able to sell their new notes.
Even if a trading market develops, the new notes may trade at higher or lower prices than their principal amount or purchase price, depending on many factors, including:
- •
- prevailing interest rates;
- •
- the number of holders of the new notes;
- •
- the interest of securities dealers in making a market for the new notes;
- •
- the market for similar debt securities; and
- •
- our financial performance.
Our substantial indebtedness could adversely affect our financial health and our ability to fulfill our obligations under the new notes.
After completing the Vought Acquisition, we have a substantial amount of indebtedness. As of June 30, 2010, our total indebtedness is $1,335.3 million and we had an additional $403.1 million available for borrowing under our Revolving Credit Facility. Our indebtedness could have important consequences to you, including:
- •
- making it more difficult for us to satisfy our obligations with respect to the new notes;
- •
- increasing our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions;
- •
- requiring that a portion of our cash flow from operations be used for the payment of interest on our debt, thereby reducing our ability to use our cash flow to fund working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions and general corporate requirements;
- •
- limiting our ability to obtain additional financing to fund future working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions and general corporate requirements;
- •
- limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and the aerospace and defense industry; and
- •
- placing us at a competitive disadvantage to our competitors that have less indebtedness.
34
We and our subsidiaries may be able to incur additional indebtedness in the future, including senior indebtedness and secured indebtedness. Our existing debt agreements do not fully prohibit us or our subsidiaries from doing so. If new indebtedness is added to our and our subsidiaries' current indebtedness levels, the related risks that we and they now face could intensify.
If we are unable to generate sufficient cash flow or otherwise obtain funds necessary to make required payments on our indebtedness we would be in default. Our ability to meet our obligations will depend upon our future performance, which will be subject to prevailing economic conditions, and to financial, business and other factors, including factors beyond our control.
Some of our indebtedness is subject to floating interest rates, which would result in our interest expense increasing if interest rates rise.
As of June 30, 2010, we had $557.2 million of indebtedness subject to floating interest rates, including $350.0 million of indebtedness under our Term Loan Facility. On a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition, our cash interest expense for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, would have been approximately $77.2 million and $22.3 million, respectively. A 1% increase in floating interest rates would have increased such annual interest expense by approximately $5.3 million. Accordingly, our interest expense may increase as a result of interest rate fluctuations. The actual impact of a 1% increase would depend on the amount of floating rate debt outstanding, which fluctuates from time to time. In addition, pro forma interest expense excludes incremental interest expense attributable to our 8% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2017, issued in November 2009, the remaining proceeds of which were used to partially finance the Vought Acquisition. If this debt had been outstanding as of April 1, 2009, we would have incurred additional interest expense, including amortization of discount and finance fees of approximately $9.2 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010. Increased interest expense would reduce our funds available for operations or other purposes.
Our debt agreements contain restrictions that limit our flexibility in operating our business.
Our Revolving Credit Facility and the indentures governing our existing notes contain, and our Term Loan Facility and the indenture governing the new notes contain, various covenants that limit our ability to engage in specified types of transactions. These covenants limit our, and certain of our subsidiaries' ability to, among other things:
- •
- incur additional indebtedness;
- •
- pay dividends or make other distributions;
- •
- make investments;
- •
- create liens;
- •
- incur restrictions on the ability of restricted subsidiaries to pay dividends or make certain other payments;
- •
- sell assets, including capital stock of subsidiaries;
- •
- enter into sale and leaseback transactions;
- •
- merge or consolidate with other entities; and
- •
- enter into transactions with affiliates.
Complying with these covenants may cause us to take actions that are not favorable to holders of the notes and may make it more difficult for us to successfully execute our business strategy and compete against companies who are not subject to such restrictions.
35
In addition, a breach of any of these covenants could result in a default under the Credit Facilities or our indentures. Upon the occurrence of an event of default under the Credit Facilities, the lenders could elect to declare all amounts outstanding under the Credit Facilities to be immediately due and payable and terminate all commitments to extend further credit. If we were unable to repay those amounts, the lenders under the Credit Facilities could proceed against the collateral granted to them to secure that indebtedness. The acceleration of our indebtedness under one agreement may permit acceleration of indebtedness under other agreements that contain cross-default or cross-acceleration provisions. If our indebtedness is accelerated, we may not have sufficient assets to repay our indebtedness under the Credit Facilities as well as our unsecured indebtedness, including the new notes, and we may not be able to borrow sufficient funds to refinance it. Even if we are able to obtain new financing, it may not be on commercially reasonable terms or on terms that are acceptable to us. See "Description of Other Indebtedness."
We may not be able to generate sufficient cash to service all of our indebtedness, including the new notes, and we may not be able to refinance our indebtedness on commercially reasonable terms.
Our ability to make payment on and to refinance our debt and fund planned expenditures depends on our ability to generate cash flow in the future, which is subject to general economic, financial, competitive, legislative and regulatory factors and other factors that are beyond our control. We cannot assure you that our business will generate cash flow from operations or that future borrowings will be available to us under our credit facilities, including our Revolving Credit Facility and our receivables financing facility, in an amount sufficient to enable us to pay our debt or to fund our other liquidity needs. We cannot assure you that we will be able to refinance our borrowing arrangements or any other outstanding debt on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Refinancing our borrowing arrangements could cause us to:
- •
- pay interest at a higher rate or increased fees; or
- •
- be subject to additional or more restrictive covenants than those outlined in this prospectus.
Our inability to generate sufficient cash flow to service our debt or refinance our indebtedness on commercially reasonable terms would have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
We are dependent on dividends and other distributions from our subsidiaries.
The Company has no operations of its own and derives substantially all of its net sales and cash flows from its subsidiaries. Our principal assets are the equity interests that we hold in our operating subsidiaries. As a result, we are dependent on dividends and other distributions from our subsidiaries to generate the funds necessary to meet our financial obligations, including the payment of principal and interest on our outstanding debt. Our subsidiaries are legally distinct from us and have no obligation to make funds available to us for such payment.
The new notes will not be secured, and therefore will be effectively subordinated to all of our and the subsidiary guarantors' existing and future secured indebtedness.
The new notes will not be secured by any of our assets or any assets of our subsidiaries. In the event of a bankruptcy or similar proceeding involving us or our subsidiaries, our assets which serve as collateral under our secured indebtedness would be made available to satisfy our obligations under any secured indebtedness we may have, including obligations under the Credit Facilities, before any payments are made on the notes. As of June 30, 2010, we had $644.0 million of secured indebtedness outstanding. Moreover, the indenture governing the new notes permits us to incur additional indebtedness that is secured.
36
Claims of holders of new notes will be structurally subordinate to claims of creditors of any of our subsidiaries that do not guarantee the new notes.
The new notes will not be guaranteed by our present and future foreign subsidiaries, domestic unrestricted subsidiaries and future subsidiaries that do not guarantee our Credit Facilities. Accordingly, claims of holders of the new notes will be structurally subordinate to the claims of creditors of these non-guarantor subsidiaries, including trade creditors. All obligations of our non-guarantor subsidiaries will have to be satisfied before any of the assets of such subsidiaries would be available for distribution, upon a liquidation or otherwise, to us or a guarantor of the notes.
For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, on apro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition, the non-guarantor subsidiaries of the Company generated 2.5% of the Company's net sales. In addition, as of June 30, 2010, the non-guarantor subsidiaries of the Company held 6.2% of the Company's assets and 19.2% of the Company's liabilities.
The lenders under the Credit Facilities will have the discretion to release the guarantors under the Credit Facilities in a variety of circumstances, which will cause those guarantors to be released from their guarantees of the notes.
While any obligations under the Credit Facilities remain outstanding, a guarantee of the new notes may be released without action by, or consent of, any holder of the new notes or the trustee under the indenture, if the applicable guarantor is no longer a borrower or a guarantor of obligations under the Credit Facilities or any other indebtedness. See "Description of Notes." The lenders under the Credit Facilities will have the discretion to release certain guarantees under the Credit Facilities in a variety of circumstances. You will not have a claim as a creditor against any subsidiary that is no longer a guarantor of the new notes, and the indebtedness and other liabilities, including trade payables, whether secured or unsecured, of non-guarantor subsidiaries will effectively be senior to claims of holders of the new notes.
Fraudulent conveyance laws may permit courts to void the guarantors' guarantees of the new notes in specific circumstances, which would interfere with the payment under the guarantors' guarantees.
Federal and state statutes may allow courts, under certain circumstances described generally below, to void the guarantors' guarantees of the new notes. If such avoidance occurs, the applicable guarantors would no longer be liable in respect of the new notes and holders of the new notes might be required to return payments received from our guarantors in the event of bankruptcy or other financial difficulty of such guarantors. Under United States federal bankruptcy law and comparable provisions of state fraudulent conveyance laws, a guarantee could be set aside if, among other things, a subsidiary guarantor, at the time it incurred the debt evidenced by its guarantee:
- •
- incurred the guarantee with the intent of hindering, delaying or defrauding current or future creditors; or
- •
- received less than reasonably equivalent value or fair consideration for incurring the guarantee; and
- •
- was insolvent or was rendered insolvent by reason of the incurrence;
- •
- was engaged, or about to engage, in a business or transaction for which the assets remaining with it constituted unreasonably small capital to carry on such business; or
- •
- intended to incur, or believed that it would incur, debts beyond its ability to pay as those debts mature.
37
The tests for fraudulent conveyance, including the criteria for insolvency, will vary depending upon the law of the jurisdiction that is being applied. Generally, however, a debtor would be considered insolvent if:
- •
- the sum of the debtor's debts and liabilities, including contingent liabilities, was greater than the debtor's assets at fair valuation;
- •
- the present fair saleable value of the debtor's assets was less than the amount required to pay the probable liability on the debtor's total existing debts and liabilities, including contingent liabilities, as they became absolute and matured; or
- •
- it could not pay its debts as they became due.
In addition, each guarantee will contain a provision intended to limit the guarantor's liability to the maximum amount that it could incur without causing the incurrence of obligations under its guarantee to be a fraudulent conveyance. This provision may not be effective to protect the guarantees from being voided under fraudulent conveyance laws, or may eliminate the guarantor's obligations or reduce the guarantor's obligations to an amount that effectively makes the guarantee worthless. At least one bankruptcy court has found this kind of provision to be ineffective to protect the guarantees. If a court voids a guarantee or holds it unenforceable, you will cease to be a creditor of the applicable subsidiary guarantor.
We may be unable to repurchase the new notes if we experience a change of control.
If we were to experience a change of control, as that term is defined in the indenture governing the new notes, we will be required to offer to purchase all of the existing new notes at 101% of their principal amount plus accrued and unpaid interest to the repurchase date. Our failure to repay holders tendering new notes upon a change of control will result in an event of default under the new notes. In certain circumstances, the Credit Facilities will prohibit repayment of the new notes without the consent of the required lenders thereunder, which consent we may not be able to obtain. In addition, the events that constitute a change of control, or an event of default, under the new notes may also require us to repay (or otherwise permit acceleration of) other indebtedness immediately. If a change of control were to occur, we cannot assure you that we would have sufficient funds to repay all such outstanding indebtedness or to purchase the new notes. We expect that we would require additional financing from third parties to fund any such purchases, and we cannot assure you that we would be able to obtain financing on satisfactory terms or at all.
Changes in our credit rating could adversely affect the market price or liquidity of the notes.
Credit rating agencies continually revise their ratings for the companies that they follow, including us. The credit rating agencies also evaluate our industry as a whole and may change their credit ratings for us based on their overall view of our industry. We cannot be sure that credit rating agencies will maintain their initial ratings on the new notes. A negative change in our ratings could have an adverse effect on the market price of the new notes.
38
In connection with the issuance of the old notes on June 16, 2010, we entered into a registration rights agreement with the initial purchasers, which provides for the exchange offer. The exchange offer will permit eligible holders of notes to exchange the old notes for the new notes that are identical in all material respects with the old notes, except that:
- •
- the new notes have been registered under the U.S. federal securities laws and will not bear any legend restricting their transfer;
- •
- the new notes bear a different CUSIP number from the old notes;
- •
- the new notes generally will not be subject to transfer restrictions and will not be entitled to registration rights; and
- •
- the holders of the new notes will not be entitled to earn additional interest under circumstances relating to our registration obligations under the registration rights agreement.
The new notes will evidence the same debt as the old notes. Holders of new notes will be entitled to the benefits of the indenture.
The following summary of certain provisions of the registration rights agreement does not purport to be complete and is subject to, and is qualified in its entirety by reference to, all the provisions of the registration rights agreement. You should refer to the exhibits that are a part of the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part for a copy of the registration rights agreement. See "Where You Can Find More Information."
General
We are making the exchange offer to comply with our contractual obligations under the registration rights agreement. Except under limited circumstances, upon completion of the exchange offer, our obligations with respect to the registration of the old notes will terminate.
We agreed, pursuant to the registration rights agreement, to:
- •
- cause to be filed within 180 days after June 16, 2010 an exchange offer registration statement with the SEC,
- •
- use our reasonable best efforts to cause the exchange offer registration statement to become effective as soon as practicable, but in no event later than 270 days after June 16, 2010, and
- •
- have the exchange offer registration statement remain effective for use by one or more participating broker-dealers until the earlier of 180 days after the date the exchange offer registration statement becomes effective and the date on which a broker-dealer is no longer required to deliver a prospectus in connection with market-making or other trading activities.
We will commence the exchange offer promptly after the exchange offer registration statement is declared effective by the SEC. We will keep the exchange offer open for not less than 30 calendar days (or longer if required by applicable law) after the date notice of the exchange offer is mailed to the holders of the old notes.
For each old note surrendered to us pursuant to the exchange offer, the holder of such old note will receive a new note having a principal amount equal to that of the surrendered old note. Old notes may be exchanged only in minimum denominations of $2,000 and integral multiples of $1,000 in excess of $2,000. New notes will be issued only in minimum denominations of $2,000 and integral multiples of $1,000 in excess of $2,000. Interest on each new note will accrue from the last interest payment date on which interest was paid on the old note surrendered in exchange thereof or, if no interest has been paid on the old note, from the date of its original issue.
39
In connection with the issuance of the old notes, we arranged for the old notes to be issued in the form of global notes through the facilities of DTC acting as depositary. The new notes will also be issued in the form of global notes registered in the name of DTC or its nominee and each beneficial owner's interest in it will be transferable in book-entry form through DTC.
Holders of old notes do not have any appraisal or dissenters' rights in connection with the exchange offer. Old notes which are not tendered for exchange or are tendered but not accepted in connection with the exchange offer will remain outstanding and be entitled to the benefits of the indenture under which they were issued, including accrual of interest, but, subject to a limited exception, will not be entitled to any registration rights under the applicable registration rights agreement. See "—Consequences of Failure to Tender."
We will be deemed to have accepted validly tendered old notes when and if we have given oral or written notice to the exchange agent of our acceptance. Subject to the terms and conditions of this exchange offer, delivery of new notes will be made by the exchange agent on the settlement date upon receipt of such notice. The exchange agent will act as agent for the tendering holders for the purpose of receiving the new notes from us. If any tendered old notes are not accepted for exchange because of an invalid tender, the occurrence of other events described in this prospectus or otherwise, we will return the certificates for any unaccepted old notes, at our expense, to the tendering holder as promptly as practicable after the expiration of the exchange offer.
The exchange offer is not being made to, nor will we accept tenders for exchange from, holders of the old notes in any jurisdiction in which the exchange offer or the acceptance of it would not be in compliance with the securities or blue sky laws of that jurisdiction.
Eligibility; Transferability
We are making this exchange offer in reliance on interpretations of the staff of the SEC set forth in several no-action letters. However, we have not sought our own no-action letter. Based upon these interpretations, we believe that you, or any other person receiving new notes, may offer for resale, resell or otherwise transfer such new notes without complying with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the U.S. federal securities laws, if:
- •
- you are, or the person or entity receiving such new notes is, acquiring such new notes in the ordinary course of business;
- •
- you do not, nor does any such person or entity, have an arrangement or understanding with any person or entity to participate in any distribution of the new notes (within the meaning of the Securities Act);
- •
- you are not, nor is any such person or entity, our affiliate as such term is defined under Rule 405 under the Securities Act; and
- •
- you are not acting on behalf of any person or entity who could not truthfully make these statements.
To participate in the exchange offer, you must represent as the holder of old notes that each of these statements is true.
In addition, each broker-dealer registered under the Exchange Act must also (i) represent that it is participating in the exchange offer for its own account and is exchanging old notes acquired as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities, (ii) confirm that it has not entered into any arrangement or understanding with the Issuer or any affiliate of the Issuer to distribute the new notes and (iii) must acknowledge that it will deliver a prospectus in connection with any resale of the new notes. The letter of transmittal states that by acknowledging that it will deliver, and by delivering, a prospectus, a broker-dealer will not be deemed to admit that it is an underwriter within the meaning of
40
the Securities Act. This prospectus, as it may be amended or supplemented from time to time, may be used by a broker-dealer in connection with resale of the new notes received in exchange for the old notes where such old notes were acquired by such broker-dealer as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities. We have agreed that, for a period of 180 days after the date the exchange offer registration statement becomes effective, we will amend or supplement this prospectus in order to expedite or facilitate the disposition of any new notes by such broker-dealers.
Any holder of old notes who is our affiliate, who does not acquire the new notes in the ordinary course of business, who intends to participate in the exchange offer for the purpose of distributing the new notes or is a broker-dealer who purchased the old notes directly from us:
- •
- will not be able to rely on the interpretation of the staff of the SEC set forth in the no-action letters described above; and
- •
- must comply with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act in connection with any sale or transfer of the new notes, unless the sale or transfer is made pursuant to an exemption from those requirements.
Expiration of the Exchange Offer; Extensions; Amendments
The exchange offer will expire at 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on September 22, 2010, or the expiration date, unless we extend the exchange offer. To extend the exchange offer, we will notify the exchange agent and each registered holder of any extension before 9:00 a.m., New York City time, on the next business day after the previously scheduled expiration date. We reserve the right to extend the exchange offer, delay accepting any tendered old notes or, if any of the conditions described below under the heading "—Conditions" have not been satisfied, to terminate the exchange offer. We also reserve the right to amend the terms of the exchange offer in any manner. We will give oral or written notice of such delay, extension, termination or amendment to the exchange agent.
If we amend the exchange offer in a manner that we consider material, we will disclose such amendment by means of a prospectus supplement, and we will extend the exchange offer so that at least five business days remain in the exchange offer following notice of the material change.
If we determine to make a public announcement of any delay, extension, amendment or termination of the exchange offer, we will do so by making a timely release through an appropriate news agency.
If we delay accepting any old notes or terminate the exchange offer, we promptly will pay the consideration offered, or return any old notes deposited, pursuant to the exchange offer as required by Rule 14e-1(c) under the Exchange Act.
Conditions
Notwithstanding any other term of the exchange offer, we will not be required to accept for exchange, or issue any new notes for, any old notes, and may terminate or amend the exchange offer before the acceptance of the old notes, if:
- •
- we determine that the exchange offer violates any law, statute, rule, regulation or interpretation by the staff of the SEC or any order of any governmental agency or court of competent jurisdiction; or
- •
- any action or proceeding is instituted or threatened in any court or by or before any governmental agency relating to the exchange offer which, in our judgment, could reasonably be expected to impair our ability to proceed with the exchange offer.
41
The conditions listed above are for our sole benefit and may be asserted by us regardless of the circumstances giving rise to any of these conditions. We may waive these conditions in our reasonable discretion in whole or in part at any time and from time to time prior to the expiration date. The failure by us at any time to exercise any of the above rights shall not be considered a waiver of such right, and such right shall be considered an ongoing right which may be asserted at any time and from time to time.
In addition, we will not accept for exchange any old notes tendered, and no new notes will be issued in exchange for those old notes, if at any time any stop order is threatened or issued with respect to the registration statement for the exchange offer and the new notes or the qualification of the indenture under the Trust Indenture Act of 1939. In any such event, we must use reasonable best efforts to obtain the withdrawal of any stop order as soon as practicable.
In addition, we will not be obligated to accept for exchange the old notes of any holder that has not made to us the representations described under "—Eligibility; Transferability" and "Plan of Distribution."
Procedures for Tendering
A holder of old notes who wishes to accept this exchange offer, and whose old notes are held by a custodial entity such as a bank, broker, dealer, trust company or other nominee, must instruct the custodial entity to tender and consent with respect to that holder's old notes on the holder's behalf pursuant to the procedures of the custodial entity.
To tender in this exchange offer, a holder of old notes must either:
(i) complete, sign and date the letter of transmittal (or a facsimile thereof) in accordance with its instructions, including guaranteeing the signature(s) to the letter of transmittal, if required, and mail or otherwise deliver such letter of transmittal or such facsimile, together with the certificates representing the old notes specified therein, to the exchange agent at the address set forth in the letter of transmittal for receipt on or prior to the expiration date; or
(ii) comply with the DTC's Automated Tender Offer Program, or ATOP, procedures for book-entry transfer described below on or prior to the expiration date.
The exchange agent and DTC have confirmed that the exchange offer is eligible for ATOP. The letter of transmittal (or facsimile thereof), with any required signature guarantees, or (in the case of book-entry transfer) an agent's message in lieu of the letter of transmittal, and any other required documents, must be transmitted to and received by the exchange agent on or prior to the expiration date of the exchange offer at one of its addresses set forth under "—Exchange Agent" in this prospectus or as set forth in the letter of transmittal. Old notes will not be deemed surrendered until the letter of transmittal and signature guarantees, if any, or agent's message, are received by the exchange agent.
The method of delivery of old notes, the letter of transmittal, and all other required documents to the exchange agent is at the election and risk of the holder. Instead of delivery by mail, holders should use an overnight or hand delivery service, properly insured. In all cases, sufficient time should be allowed to assure delivery to and receipt by the exchange agent on or before the expiration date. Do not send the letter of transmittal or any old notes to anyone other than the exchange agent.
All new notes will be delivered only in book-entry form through DTC. Accordingly, if you anticipate tendering other than through DTC, you are urged to contact promptly a bank, broker or other intermediary (that has the capability to hold securities custodially through DTC) to arrange for receipt of any new notes to be delivered to you pursuant to the exchange offer and to obtain the
42
information necessary to provide the required DTC participant with account information for the letter of transmittal.
Book-Entry Delivery Procedures for Tendering Old Notes Held with DTC
If you wish to tender old notes held on your behalf by a custodial entity with DTC, you must:
(i) inform your custodial entity of your interest in tendering your old notes pursuant to the exchange offer; and
(ii) instruct your custodial entity to tender all old notes you wish to be tendered in the exchange offer into the exchange agent's account at DTC on or prior to the expiration date. Any financial institution that is a nominee in DTC, including Euroclear and Clearstream, must tender old notes by effecting a book-entry transfer of the old notes to be tendered in the exchange offer into the account of the exchange agent at DTC by electronically transmitting its acceptance of the exchange offer through the ATOP procedures for transfer. DTC will then verify the acceptance, execute a book-entry delivery to the exchange agent's account at DTC, and send an agent's message to the exchange agent. An "agent's message" is a message, transmitted by DTC to and received by the exchange agent and forming part of a book-entry confirmation, which states that DTC has received an express acknowledgement from an organization that participates in DTC (a "participant") tendering old notes that the participant has received and agrees to be bound by the terms of the letter of transmittal and that we may enforce the agreement against the participant. A letter of transmittal need not accompany tenders effected through ATOP.
Proper Execution and Delivery of Letter of Transmittal
Signatures on a letter of transmittal or notice of withdrawal described below (see "—Withdrawal of Tenders"), as the case may be, must be guaranteed by an eligible institution unless the old notes tendered pursuant to the letter of transmittal are tendered (i) by a holder who has not completed the box entitled "Special Delivery Instructions" or "Special Issuance and Payment Instructions" on the letter of transmittal or (ii) for the account of an eligible institution. If signatures on a letter of transmittal or notice of withdrawal are required to be guaranteed, such guarantee must be made by an eligible guarantor institution within the meaning of Rule 17Ad-15 under the Exchange Act.
If the letter of transmittal is signed by the holder(s) of old notes tendered thereby, the signature(s) must correspond with the name(s) as written on the face of the old notes without alteration, enlargement or any change whatsoever. If any of the old notes tendered thereby are held by two or more holders, all such holders must sign the letter of transmittal. If any of the old notes tendered thereby are registered in different names on different old notes, it will be necessary to complete, sign and submit as many separate letters of transmittal, and any accompanying documents, as there are different registrations of certificates.
If old notes that are not tendered for exchange pursuant to the exchange offer are to be returned to a person other than the holder thereof, certificates for such old notes must be endorsed or accompanied by an appropriate instrument of transfer, signed exactly as the name of the registered owner appears on the certificates, with the signatures on the certificates or instruments of transfer guaranteed by an eligible institution.
If the letter of transmittal is signed by a person other than the holder of any old notes listed therein, such old notes must be properly endorsed or accompanied by a properly completed bond power, signed by such holder exactly as such holder's name appears on such old notes. If the letter of transmittal or any old notes, bond powers or other instruments of transfer are signed by trustees, executors, administrators, guardians, attorneys-in-fact, officers of corporations or others acting in a fiduciary or representative capacity, such persons should so indicate when signing, and, unless waived
43
by us, evidence satisfactory to us of their authority to so act must be submitted with the letter of transmittal.
No alternative, conditional, irregular or contingent tenders will be accepted. By executing the letter of transmittal (or facsimile thereof), the tendering holders of old notes waive any right to receive any notice of the acceptance for exchange of their old notes. Tendering holders should indicate in the applicable box in the letter of transmittal the name and address to which payments and/or substitute certificates evidencing old notes for amounts not tendered or not exchanged are to be issued or sent, if different from the name and address of the person signing the letter of transmittal. If no such instructions are given, old notes not tendered or exchanged will be returned to such tendering holder.
�� All questions as to the validity, form, eligibility (including time of receipt), and acceptance and withdrawal of tendered old notes will be determined by us in our absolute discretion, which determination will be final and binding. We reserve the absolute right to reject any and all tendered old notes determined by us not to be in proper form or not to be properly tendered or any tendered old notes our acceptance of which would, in the opinion of our counsel, be unlawful. We also reserve the right to waive, in our absolute discretion, any defects, irregularities or conditions of tender as to particular old notes, whether or not waived in the case of other old notes. Our interpretation of the terms and conditions of the exchange offer (including the instructions in the letter of transmittal) will be final and binding on all parties. Unless waived, any defects or irregularities in connection with tenders of old notes must be cured within such time as we shall determine. Although we intend to notify holders of defects or irregularities with respect to tenders of old notes, neither we, the exchange agent nor any other person will be under any duty to give such notification or shall incur any liability for failure to give any such notification. Tenders of old notes will not be deemed to have been made until such defects or irregularities have been cured or waived.
Any holder whose old notes have been mutilated, lost, stolen or destroyed will be responsible for obtaining replacement securities or for arranging for indemnification with the trustee of the old notes. Holders may contact the exchange agent for assistance with such matters.
Withdrawal of Tenders
You may withdraw tenders of old notes at any time prior to the expiration date.
For a withdrawal of a tender to be effective, a written or facsimile transmission notice of withdrawal must be received by the exchange agent prior to the deadline described above at its address set forth under "—Exchange Agent" in this prospectus. The withdrawal notice must:
- •
- specify the name of the person who tendered the old notes to be withdrawn;
- •
- must contain a description of the old notes to be withdrawn, the certificate numbers shown on the particular certificates evidencing such old notes and the aggregate principal amount represented by such old notes; and
- •
- must be signed by the holder of those old notes in the same manner as the original signature on the letter of transmittal, including any required signature guarantees, or be accompanied by evidence satisfactory to us that the person withdrawing the tender has succeeded to the beneficial ownership of the old notes. In addition, the notice of withdrawal must specify, in the case of old notes tendered by delivery of certificates for such old notes, the name of the registered holder, if different from that of the tendering holder or, in the case of old notes tendered by book-entry transfer, the name and number of the account at DTC to be credited with the withdrawn old notes. The signature on the notice of withdrawal must be guaranteed by an eligible institution unless the old notes have been tendered for the account of an eligible institution.
44
Withdrawal of tenders of old notes may not be rescinded, and any old notes properly withdrawn will be deemed not validly tendered for purposes of this exchange offer. Properly withdrawn old notes may, however, be retendered by again following one of the procedures described in "—Procedures for Tendering" prior to the expiration date.
Exchange Agent
U.S. Bank National Association has been appointed the exchange agent for this exchange offer. Letters of transmittal and all correspondence in connection with this exchange offer should be sent or delivered by each holder of old notes, or a beneficial owner's commercial bank, broker, dealer, trust company or other nominee, to the exchange agent as follows:
| By Mail or Hand Delivery: | U.S. Bank National Association 60 Livingston Avenue Mail Station—EP-MN-WS2N St. Paul, Minnesota 55107-2292 | |
| Attention: | Specialized Finance | |
| Telephone: | (800) 934-6802 |
We will pay the exchange agent reasonable and customary fees for its services and will reimburse it for its reasonable, out-of-pocket expenses in connection with this exchange offer.
Fees and Expenses
We will bear the expenses of soliciting tenders. The principal solicitation is being made by mail. However, we may make additional solicitations by telegraph, telephone or in person by our officers and regular employees and those of our affiliates.
We have not retained any dealer-manager in connection with the exchange offer and will not make any payments to broker-dealers or others soliciting acceptances of the exchange offer. We may, however, pay the exchange agent reasonable and customary fees for its services and reimburse it for its related reasonable out-of-pocket expenses. We will pay the other cash expenses incurred in connection with the exchange offer.
Transfer Taxes
We will pay all transfer taxes, if any, applicable to the exchange of old notes under the exchange offer. The tendering holder, however, will be required to pay any transfer taxes, whether imposed on the registered holder or any other person, if:
- •
- new notes are to be delivered to, or issued in the name of, any person other than the registered holder of the old notes so exchanged,
- •
- tendered old notes are registered in the name of any person other than the person signing the letter of transmittal, or
- •
- a transfer tax is imposed for any reason other than the exchange of old notes under the exchange offer.
If satisfactory evidence of payment of transfer taxes is not submitted with the letter of transmittal, the amount of any transfer taxes will be billed to the tendering holder.
45
Accounting Treatment
We will record the new notes at the same carrying value as the old notes as reflected in our accounting records on the date of the exchange. Accordingly, we will not recognize any gain or loss for accounting purposes upon completion of the exchange offer.
Consequences of Failure to Tender
All untendered old notes will remain subject to the restrictions on transfer provided for in the old notes and in the indenture. The old notes that are not exchanged for new notes pursuant to the exchange offer will remain restricted securities. Accordingly, such old notes may be resold only:
- •
- to us (upon redemption thereof or otherwise),
- •
- pursuant to a registration statement which has been declared effective under the Securities Act,
- •
- for so long as the old notes are eligible for resale pursuant to Rule l44A, to a person the holder of the old notes and any person acting on its behalf reasonably believes is a "qualified institutional buyer" as defined in Rule l44A, that purchases for its own account or for the account of another qualified institutional buyer, in each case to whom notice is given that the transfer is being made in reliance on Rule l44A, or
- •
- pursuant to any other available exemption from the registration requirements of the Securities Act (in which case we and the trustee shall have the right to require the delivery of an opinion of counsel, certifications and/or other information satisfactory to us and the trustee),
in each case subject to compliance with any applicable foreign, state or other securities laws.
Upon completion of the exchange offer, due to the restrictions on transfer of the old notes and the absence of such restrictions applicable to the new notes, it is likely that the market, if any, for old notes will be relatively less liquid than the market for new notes. Consequently, holders of old notes who do not participate in the exchange offer could experience significant diminution in the value of their old notes, compared to the value of the new notes. The holders of old notes not tendered will have no further registration rights, except that, under limited circumstances, we may be required to file a shelf registration statement for a continuous offer of old notes.
Information Regarding the Registration Rights Agreement
As noted above, we are effecting the exchange offer to comply with the registration rights agreement. The registration rights agreement requires us to:
- •
- cause to be filed within 180 days after June 16, 2010 an exchange offer registration statement with the SEC,
- •
- use our reasonable best efforts to cause the exchange offer registration statement to become effective as soon as practicable, but in no event later than 270 days after June 16, 2010;
- •
- use our reasonable best efforts to consummate the exchange offer not later than 30 days after the 270th day after June 16, 2010; and
- •
- cause to be filed a shelf registration statement for the resale of the old notes under certain circumstances and to use our reasonable best efforts to cause such registration statement to become effective under the Securities Act.
The requirements described in the first three bullets above under the registration rights agreement will be satisfied when we complete the exchange offer.
46
In the event that:
- •
- the registration statement is not filed with the SEC on or prior to the 180th day after June 16, 2010,
- •
- the registration statement has not been declared effective by the SEC on or prior to the 270th day after June 16, 2010, or
- •
- the exchange offer is not completed or the shelf registration statement, if required, has not become effective on or prior to the 300th day after June 16, 2010 (or, under certain circumstances, within 90 days of a request to file a shelf registration statement),
the interest rate on the old notes will be increased by a rate of 0.25% per annum during the 90-day period following such registration default and shall increase by 0.25% per annum at the end of each subsequent 90-day period, but in no event shall such increase exceed 1.00% per annum. Following the cure of all such registration defaults, the accrual of additional interest shall cease and the interest rate will be reduced to the original interest rate borne by the old notes.
Under the registration rights agreement, we have also agreed to keep the registration statement for the exchange offer effective for not less than 30 calendar days (or longer, if required by applicable law) after the date on which notice of the exchange offer is mailed to holders.
Our obligations to register the new notes will terminate upon the completion of the exchange offer. However, under certain circumstances specified in the registration rights agreement, we may be required to file a shelf registration statement for a continuous offer in connection with the old notes.
This summary includes only the material terms of the registration rights agreement. For a full description, you should refer to the complete copy of the registration rights agreement, which has been filed as an exhibit to the registration statement relating to the exchange offer and the new notes. See "Where You Can Find More Information."
47
This exchange offer is intended to satisfy our obligations under the registration rights agreement into which we entered when we issued the old notes. We will not receive any cash proceeds from this exchange offer. In exchange for the old notes that you tender pursuant to this exchange offer, you will receive new notes in like principal amount. The old notes that are surrendered in exchange for the new notes will be retired and cancelled by us upon receipt and cannot be reissued. The issuance of the new notes under this exchange offer will not result in any increase in our outstanding indebtedness. We will pay all expenses incident to the exchange offer.
RATIO OF EARNINGS TO FIXED CHARGES
Our ratio of earnings to fixed charges for each of the fiscal years ended 2006 through 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010 was as follows:
| | Year Ended March 31, | Three Months Ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2010 | |||||||||||||
Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges(1) | 4.0x | 4.3x | 4.8x | 6.2x | 4.6x | 2.6x | |||||||||||||
- (1)
- For purposes of calculating this ratio, "earnings" consists of income from continuing operations before income taxes and income from equity affiliates plus (a) fixed charges minus interest capitalized during the period, (b) distributed income from equity affiliates and (c) amortization of previously capitalized interest. "Fixed charges" consists of interest expense, capitalized interest, amortization of discount on indebtedness and an appropriate portion of rental expense representative of the interest factor.
48
The following table sets forth our cash and capitalization as of June 30, 2010.
You should read the data set forth in the table below in conjunction with "The Vought Acquisition," "Unaudited Pro Forma Financial Information," "Triumph Summary Historical Consolidated Financial Data," "Vought Summary Historical Consolidated Financial Data," "Triumph Management's Discussion and Analysis of Triumph's Financial Condition and Results of Operations," "Vought Management's Discussion and Analysis of Vought's Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and our and Vought's consolidated audited and unaudited financial statements and the accompanying notes incorporated by reference in this prospectus.
| | As of June 30, 2010 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | (unaudited) (in millions) | ||||
Cash | $ | 35.7 | |||
Revolving Credit Facility(1) | $ | 85.0 | |||
Securitization Facility(2) | 120.0 | ||||
Equipment leasing facility and other capital leases(3) | 71.7 | ||||
Other debt | 7.9 | ||||
Term Loan Facility(4) | 348.3 | ||||
Senior promissory notes | 11.1 | ||||
Old Notes(5) | 347.5 | ||||
8% senior subordinated notes due 2017 | 172.6 | ||||
2.625% convertible senior subordinated notes due 2026(6) | 171.2 | ||||
Total debt | $ | 1,335.3 | |||
Stockholders' equity | 1,372.6 | ||||
Total capitalization | $ | 2,707.9 | |||
- (1)
- The total commitment available for borrowing under the Revolving Credit Facility is $535.0 million. In connection with the Vought Acquisition, we borrowed $148.6 million under the Revolving Credit Facility. As of June 30, 2010 approximately $403.1 million was available for borrowing under the Revolving Credit Facility and we had approximately $46.9 million in letters of credit outstanding. See "Description of Certain Indebtedness."
- (2)
- In connection with the Vought Acquisition, we amended the Securitization Facility to increase availability from $125.0 million to $175.0 million. As of June 30, 2010, we had $120.0 million outstanding under the Securitization Facility.
- (3)
- The equipment leasing facility is a seven-year Master Leasing Facility of certain existing property and equipment. The equipment leasing facility bears interest at a weighted average fixed rate of 6.2% per annum.
- (4)
- Consists of a $350.0 million senior secured term loan with a six-year maturity entered into concurrently with the closing of the Vought Acquisition, net of discount, arrangement fees and expenses.
- (5)
- Consists of the $350.0 million aggregate principal amount of old notes, net of discount.
- (6)
- The convertible notes bear interest at a fixed rate of 2.625% per annum and are recorded at a discount and are being accreted to their face value of $179.1 million through September 2011.
49
On June 16, 2010, we completed our previously announced acquisition of Vought pursuant to the Merger Agreement. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, (i) Merger Sub was merged with and into Vought and (ii) then Vought was merged with and into Triumph Aerostructures, LLC, our direct wholly owned limited liability company subsidiary, with Triumph Aerostructures, LLC as the surviving entity in the mergers. The consideration for the Vought Acquisition consisted of $547.9 million in cash and 7,496,165 shares of our common stock. We also discharged, repaid or otherwise retired approximately $603.1 million of Vought's existing indebtedness, which represented substantially all of Vought's outstanding indebtedness.
As a result of the Vought Acquisition, the Carlyle equity funds own approximately 31% of our outstanding common stock. In connection with the merger, we also entered into a stockholders agreement with the Carlyle equity funds and Carlyle, pursuant to which, on June 16, 2010, we increased the size of our board of directors from six directors to nine and appointed Adam Palmer, Elmer Doty and Ralph Eberhart to our board of directors. The Carlyle equity funds are entitled to designate three persons to our board of directors until they no longer hold 66.67% of the shares that they received in the merger; they are entitled to designate two persons to our board of directors until they no longer hold 33.33% of the shares that they received in the merger; and they are entitled to designate one person to our board of directors as long as they own at least 5% of our outstanding common stock. The Carlyle equity funds may not transfer or hedge any shares of our common stock that they received in the merger for one year following the closing, and after this period the Carlyle equity funds will be prohibited from making transfers to certain large holders of our common stock. The Carlyle equity funds, Carlyle and investment funds managed by each of them have also agreed to customary standstill restrictions which prohibit them from acquiring additional shares of our common stock and taking certain other actions to seek to gain control of Triumph without our prior written consent. These restrictions survive until the later of (i) the date on which there are no Carlyle-designated directors on our board and (ii) the date on which the Carlyle equity funds and their affiliates own less than 10% of our outstanding common stock. In addition, for two years following the closing, Carlyle has agreed to certain non-competition restrictions with respect to business activities conducted by Vought. From the closing until December 31, 2011, Carlyle has agreed that it will not solicit for employment or employ specified members of Vought's senior management team. We have also granted the Carlyle equity funds demand and piggy-back registration rights, which commence after the one-year transfer restriction period expires.
We funded the Vought Acquisition through cash on hand and the following activities:
- •
- the issuance of 7,496,165 shares of our common stock to the Vought stockholders;
- •
- the issuance by the Company of $350,000,000 aggregate principal amount of old notes at a price equal to 99.27% of the face value;
- •
- the borrowing by the Company of $350,000,000 principal amount under the Term Loan Facility at a price equal to 99.5% of the face value; and
- •
- the borrowing by the Company of $128,300,000, drawn under the Revolving Credit Facility.
Term Loan Facility
Simultaneously with the closing of the Vought Acquisition, we entered into the Term Loan Facility, which is a six-year term loan facility in an aggregate principal amount equal to $350.0 million at a price equal to 99.5% of the face value, with principal repayable in quarterly installments at a rate of 1.00% per year, with the balance payable on the final maturity date. Borrowings under the new senior secured term loan facility bear interest, at our option, at either the base rate (the highest of the prime rate announced by Royal Bank of Canada, the administrative agent to the facility, the federal funds effective
50
rate plus 0.50%, or the Eurodollar Rate (adjusted for certain reserve requirements) for a Eurodollar loan with a one-month interest period plus 1.00%) plus an applicable margin or at the rate which Eurodollar deposits for one, two, three or six months appear on the Reuters Screen LIBOR01 Page (adjusted for certain reserve requirements), which is referred to as the "Eurodollar Rate," plus an applicable margin. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the minimum base rate is 2.5% and the minimum Eurodollar Rate (before giving effect to any adjustment for reserve requirements) is 1.5%. See "Description of Certain Indebtedness."
Revolving Credit Facility
On May 10, 2010, we entered into the Revolving Credit Facility, a revolving credit facility in the aggregate principal amount of $535.0 million, to expire and be repaid in full by the fourth anniversary of the closing date of the Vought Acquisition. Borrowings under the Revolving Credit Facility bear interest, at our option, at either the base rate plus an applicable margin or the Eurodollar Rate plus an applicable margin. The Revolving Credit Facility replaced and refinanced our 2009 Credit Facility. See "Description of Certain Indebtedness."
51
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information of Triumph is presented to show how Triumph might have looked if the Vought Acquisition had occurred on the dates and for the periods indicated below. The following unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been derived by applying pro forma adjustments to the historical consolidated financial statements of Triumph and Vought. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of income for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 gives effect to the Vought Acquisition as if it had occurred on April 1, 2009 and combines Triumph's audited consolidated statement of income for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 with Vought's unaudited consolidated statement of income for the twelve-month period ended March 28, 2010. Vought's unaudited consolidated statement of income for the twelve-month period ended March 28, 2010 has been prepared by adding the financial data from Vought's unaudited consolidated income statement for the three months ended March 28, 2010 to the results from Vought's audited consolidated income statement for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009 and deducting the financial data from Vought's unaudited consolidated income statement from the three months ended March 29, 2009.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of income for the three months ended June 30, 2010 assumes that the acquisition took place on April 1, 2010. Triumph's unaudited statement of income for the three months ended June 30, 2010 has been combined with Vought's unaudited statement of income for the period from April 1, 2010 through June 15, 2010. Triumph's unaudited statement of income for the three months ended June 30, 2010, includes the results of Vought from June 16, 2010.
The historical consolidated financial information of Triumph and Vought has been adjusted in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements to give effect to pro forma events that are (1) directly attributable to the Vought Acquisition, (2) factually supportable and (3) with respect to the statements of income, expected to have a continuing impact on the combined results. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information should be read in conjunction with the accompanying notes to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements. All pro forma adjustments and their underlying assumptions are described more fully in the notes to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements. In addition, the unaudited condensed combined financial information should be read in conjunction with the following historical consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes of Triumph and Vought for the applicable periods:
- •
- Separate historical financial statements of Triumph as of and for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 and the related notes included in the Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on May 14, 2010;
- •
- Separate historical financials statements of Vought as of and for the year ended December 31, 2009 and the related notes thereto, included in Exhibit 99.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 22, 2010;
- •
- Separate historical unaudited interim consolidated balance sheet of Vought as of March 28, 2010, and the unaudited consolidated statement of operations for the three months ended March 28, 2010, and March 28, 2009, and the notes related thereto, included in Exhibit 99.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 22, 2010; and
- •
- Separate historical financial statements of Triumph as of and for the three months ended June 30, 2010 and the related note includes in Triumph's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2010.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been presented for informational purposes only. The pro forma information is not necessarily indicative of what Triumph's financial position or results of operations actually would have been had the Vought Acquisition been completed as of the dates indicated. In addition, the unaudited pro forma condensed combined
52
financial information does not purport to project the future financial position or operating results of Triumph. All material accounts and transactions between Triumph and Vought have been eliminated from the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements do not include pro forma adjustments for Triumph's February 2010 acquisition of Fabritech, Inc.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information has been prepared using the acquisition method of accounting under existing GAAP. Triumph has been treated as the acquirer in the Vought Acquisition for accounting purposes, and the total purchase price of the Vought Acquisition, including related fees and expenses, has been allocated to Triumph's net assets based upon Triumph's preliminary estimates of fair value. The pro forma information presented, including allocations of purchase price, has been prepared based on preliminary estimates using information available as of the date of this filing. The final allocation of the total purchase price to Vought's net assets will be based on a formal valuation of the fair value of Vought's net assets that existed as of the closing date of the Vought Acquisition. Differences between Triumph's preliminary estimates (for example, estimates as to fair value of acquired property, plant and equipment as well as intangible assets) presented in the accompanying unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements and the final acquisition accounting for such items will occur and these differences could be material and could have a material impact on Triumph's future results of operations and financial position.
The unaudited pro forma combined financial information does not reflect any cost savings, operating synergies or revenue enhancements that Triumph may achieve as a result of the Vought Acquisition or the costs to combine the operations of Triumph and Vought or the costs necessary to achieve these cost savings, operating synergies and revenue enhancements.
53
Triumph Group, Inc. and Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.
Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statements of Income
Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2010
(in millions, except per share data) | Triumph | Vought | Reclassification Adjustments | | Pro Forma Adjustments | | Pro Forma Combined | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Net sales | $ | 1,294.8 | $ | 1,958.0 | $ | — | $ | (34.5 | ) | (A | ) | $ | 3,218.3 | ||||||||||
Operating costs and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Cost of sales | 927.2 | 1,661.5 | (37.5 | ) | (1 | ) | (74.7 | ) | (B | ) | 2,476.5 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 157.9 | 133.8 | (8.9 | ) | (1 | ) | (2.0 | ) | (C | ) | 280.8 | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 54.4 | — | 46.4 | (1 | ) | 17.6 | (E | ) | 118.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 1,139.5 | 1,795.3 | — | (59.1 | ) | 2,875.7 | ||||||||||||||||||
Operating income | 155.3 | 162.7 | — | 24.6 | 342.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense and other | 28.8 | 52.7 | — | 3.3 | (F | ) | 84.8 | ||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations, before income taxes | 126.5 | 110.0 | — | 21.3 | 257.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
Income tax provision (benefit) | 41.2 | (9.3 | ) | — | 58.3 | (G | ) | 90.2 | |||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 85.3 | $ | 119.3 | $ | — | $ | (37.0 | ) | $ | 167.6 | ||||||||||||
Earnings per share—basic: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 5.18 | $ | 7.00 | |||||||||||||||||||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding—basic | 16.5 | 24.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Earnings per share—diluted: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 5.12 | $ | 6.94 | |||||||||||||||||||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding—diluted | 16.7 | 24.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
See the accompanying notes to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements which are an integral part of these statements. The pro forma reclassifications and adjustments are explained in Note 6 and Note 7, respectively.
54
Triumph Group, Inc. and Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.
Unaudited Pro Forma Condensed Combined Statements of Income
Three Months Ended June 30, 2010
(in millions, except per share data) | Triumph | Vought | Reclassification Adjustments | | Pro Forma Adjustments | | Pro Forma Combined | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Net sales | $ | 406.4 | $ | 362.3 | $ | — | $ | (5.3 | ) | (A | ) | $ | 763.4 | ||||||||||
Operating costs and expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Cost of sales | 297.9 | 352.4 | (8.0 | ) | (1 | ) | (27.2 | ) | (B | ) | 615.1 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 43.4 | 38.4 | (1.8 | ) | (1 | ) | (0.4 | ) | (C | ) | 79.6 | ||||||||||||
Acquisition-related costs | 17.4 | 26.1 | — | (43.5 | ) | (D | ) | — | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 14.8 | — | 9.8 | (1 | ) | (0.3 | ) | (E | ) | 24.3 | |||||||||||||
| 373.5 | 416.9 | — | (71.4 | ) | 719.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
Operating income | 32.9 | (54.6 | ) | — | 66.1 | 44.4 | |||||||||||||||||
Interest expense and other | 11.8 | 9.8 | — | 0.7 | (F | ) | 22.3 | ||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations, before income taxes | 21.1 | (64.4 | ) | — | 65.4 | 22.1 | |||||||||||||||||
Income tax provision (benefit) | 9.5 | — | — | (1.7 | ) | (G | ) | 7.8 | |||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 11.6 | $ | (64.4 | ) | $ | — | $ | 67.1 | $ | 14.3 | ||||||||||||
Earnings per share—basic: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 0.65 | $ | 0.60 | |||||||||||||||||||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding—basic | 17.8 | 24.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Earnings per share—diluted: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 0.62 | $ | 0.57 | |||||||||||||||||||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding—diluted | 18.7 | 25.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
See the accompanying notes to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements which are an integral part of these statements. The pro forma reclassifications and adjustments are explained in Note 6 and Note 7, respectively.
55
NOTES TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED
COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. DESCRIPTION OF TRANSACTION
On June 16, 2010, Triumph Group, Inc. ("Triumph") completed its previously-announced acquisition of Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc. ("Vought"), pursuant to an Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated March 23, 2010 (the "Merger Agreement"). Upon completion of the transactions contemplated by the Merger Agreement, Vought became a wholly owned subsidiary of Triumph (the "Vought Acquisition"). Upon completion of the Vought Acquisition, holders of Vought common stock and equity awards received, in the aggregate, $547.9 million in cash and 7,496,165 shares of Triumph common stock.
At the effective time of the Vought Acquisition, each outstanding option to purchase shares of Vought common stock and each stock appreciation right in respect of Vought common stock granted under the 2001 Vought Stock Option Plan and the 2006 Vought Incentive Award Plan, whether or not exercisable, vested in full and was cancelled, and holders of such options and stock appreciation rights received an amount in cash equal to the excess, if any, of approximately $34.847 over the per share exercise price for each share subject to the option or stock appreciation right, less required withholding taxes.
At the effective time of the Vought Acquisition, each Vought restricted stock unit granted under the 2006 Vought Incentive Award Plan became fully vested and was converted into the right to receive an amount in cash equal to approximately $34.847 per share, less required withholding taxes.
2. BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND ORGANIZATION
The accompanying unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information was prepared using the acquisition method of accounting and was based on the historical financial statements of Triumph and Vought. For ease of reference, all pro forma statements use Triumph's period end dates and Vought's reported information has been recast accordingly to correspond to Triumph's period end dates by adding Vought's comparable quarterly periods as necessary.
The acquisition method of accounting is based on Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 805,Business Combinations, which Triumph adopted on April 1, 2009 and used the fair value concepts defined in ASC Topic 820,Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, which Triumph has adopted as required.
ASC Topic 805, requires, among other things, that most assets acquired and liabilities assumed be recognized at their fair values as of the acquisition date. Financial statements of Triumph issued after completion of the Vought Acquisition will reflect such fair values, measured as of the acquisition date, which may be different than the estimated fair values included in these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements. The financial statements of Triumph issued after the completion of the Vought Acquisition will not be retroactively restated to reflect the historical financial position or results of operations of Vought. In addition, ASC Topic 805 establishes that the consideration transferred be measured at the closing date of the Vought Acquisition at the then-current market price, which has been reflected in these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements.
ASC Topic 820, defines the term "fair value" and sets forth the valuation requirements for any asset or liability measured at fair value, expands related disclosure requirements and specifies a hierarchy of valuation techniques based on the nature of the inputs used to develop the fair value measures. Fair value is defined as "the price that would be received to sell and asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date." This is an
56
NOTES TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED
COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND ORGANIZATION (Continued)
exit price concept for valuation of the asset or liability. In addition, market participants are assumed to be unrelated (to Triumph) buyers and sellers in the principal (or the most advantageous) market for the asset or liability. Fair value measurements for an asset assume the highest and best use by these market participants. As a result of these standards, Triumph may be required to record assets which are not intended to be used or sold and/or to value assets at fair value measures that do not reflect Triumph's intended use of those assets. Many of these fair value measurements can be highly subjective and it is also possible that other professionals, applying reasonable judgment to the same facts and circumstances, could develop and support a range of alternative estimated amounts.
Under ASC Topic 805, acquisition-related transaction costs (i.e., advisory, legal, other professional fees, etc.) and certain acquisition-related restructuring charges impacting the target company are not included as a component of consideration transferred, but are accounted for as expenses in the periods in which the costs are incurred. Total advisory, legal, regulatory and valuation costs incurred by Triumph were approximately $40.5 million, of which $1.1 million was expensed during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, $17.4 million was expensed during the three months ended June 30, 2010 and the remainder is being capitalized as deferred financing costs. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements do not reflect restructuring charges expected to be incurred in connection with the Vought Acquisition.
3. ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Triumph has identified certain differences in accounting policies between Triumph and Vought, including financial statement classification and inventory capitalization policies and has made pro forma adjustments, as presented herein, for these policies. At this time, Triumph is not aware of any differences in accounting policies that would have a material impact on the combined financial statements, and the unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements do not assume any other differences in accounting policies. Now that the Vought Acquisition has been completed, Triumph will perform a detailed review of Vought's accounting policies. As a result of that review, Triumph may identify additional differences between the accounting policies of the two companies that, when conformed, could have a material impact on the combined financial statements.
4. CONSIDERATION TRANSFERRED
The following is a preliminary estimate of consideration transferred to effect the acquisition of Vought:
(in millions, except per share amounts) | Shares | Estimated Fair Value | Form of Consideration | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Number of Triumph shares to be issued to Vought shareholders(1) | 7.5 | |||||||
Multiplied by Triumph's share price as of June 15, 2010 | $ | 67.35 | $ | 504.9 | Triumph common stock | |||
Cash consideration transferred to Vought shareholders | 547.9 | Cash | ||||||
Estimate of consideration transferred | $ | 1,052.8 | ||||||
- (1)
- Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, Triumph issued 7,496,165 shares of common stock as part of the consideration to Vought shareholders.
57
NOTES TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED
COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
4. CONSIDERATION TRANSFERRED (Continued)
The price of Triumph common stock used to measure consideration transferred was $67.35, the closing stock price of Triumph on June 15, 2010.
5. ESTIMATES OF THE ASSETS ACQUIRED AND LIABILITIES ASSUMED
The following is a preliminary estimate of the assets acquired and the liabilities assumed by Triumph in the Vought Acquisition, reconciled to the estimate of consideration transferred:
| | (in millions) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Book value of net assets acquired March 31, 2010 | $ | (466.0 | ) | ||
Less: Vought historical goodwill | (404.8 | ) | |||
Less: Vought historical intangible assets | (18.6 | ) | |||
Plus: Vought expected accrued transaction costs at closing | (26.8 | ) | |||
Adjusted book value of net assets acquired | (916.2 | ) | |||
Adjustments to: | |||||
Other current assets | (4.0 | ) | |||
Inventory | (22.4 | ) | |||
Property & equipment, net | 100.0 | ||||
Deferred taxes | 116.1 | ||||
Intangible assets, net | 864.0 | ||||
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | (29.6 | ) | |||
Debt | (1.8 | ) | |||
Goodwill | 946.7 | ||||
Total adjustments | 1,969.0 | ||||
Estimate of consideration transferred | $ | 1,052.8 | |||
The purchase price allocation for purposes of these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements was primarily limited to the identification and valuation of intangible assets. Triumph believes this was an appropriate approach based on review of similar type acquisitions, which appeared to indicate that the most significant and material portion of the purchase price would be allocated to intangible assets.
The following is a discussion of the adjustments made to Vought's assets and liabilities in connection with the preparation of these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements:
Property & equipment: As of the effective time of the Vought Acquisition, property & equipment is required to be measured at fair value, unless those assets are classified as held-for-sale on the acquisition date. The acquired assets can include assets that are not intended to be used or sold, or that are intended to be used in a manner other than their highest and best use. Triumph does not have sufficient information at this time as to the specific types, nature, age, condition or location of these assets. In addition, more information is needed regarding the nature and types of machinery and equipment, which is the majority of Vought's property & equipment balance, in order to assess these assets against current technology products, costs and values. All of these elements can cause differences between fair value and net book value. For purposes of these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements, Triumph considered other comparable acquisition transactions and
58
NOTES TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED
COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
5. ESTIMATES OF THE ASSETS ACQUIRED AND LIABILITIES ASSUMED (Continued)
estimated that the fair value adjustment to increase property and equipment would approximate $100 million. The estimate of fair value is preliminary and subject to change and could vary materially from the actual adjustment on the closing date. The estimated remaining weighted average useful life of the underlying assets is estimated to be 10 years. A 20% change in the valuation of property and equipment would cause an increase or decrease to annual depreciation expense of approximately $5.5 million ($1.4 million per quarter), assuming a weighted average useful life of 10 years.
Intangibles assets: As of the effective time of the Vought Acquisition, intangible assets are required to be measured at fair value and these acquired assets could include assets that are not intended to be used or sold or that are intended to be used in a manner other than their highest and best use. For purposes of these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements, it is assumed that all assets will be used and be used in a manner that represents their highest and best use. Based on internal assessments as well as discussions with Vought and external third-party valuation advisors, Triumph has identified the following significant intangible assets: customer relationships/contracts, and the Vought tradename.
The fair value of these intangible assets is normally determined primarily through the use of the "income approach," which requires an estimate or forecast of all the expected future cash flows either through the use of either the multi-period excess earnings method or relief-from-royalty method.
At this time, Triumph does not have sufficient information as to the amount, timing and risk of the estimated cash flows needed to value the customer relationship/contracts and the Vought tradename. Some of the more significant assumptions inherent in the development of estimated cash flows, from the perspective of a market participant, include: the amount and timing of projected future cash flows (including net sales, costs of sales, selling, general and administrative expenses and working capital/contributory asset charges) and the discount rate selected to measure the risk inherent in the future cash flows. However, for purposes of these unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements, using currently available information, such as Vought's historical and projected revenues, customer attrition rates, cost structure, and certain other high-level assumptions, the fair value of the customer relationship/contracts and the Vought tradename were estimated by external third party valuation advisors and reviewed by Triumph management and were as follows: Customer relationship/contracts—$230.0 million with a weighted average useful life of 15.8 years; and the Vought tradename—$634.0 million with an indefinite life.
These preliminary estimates of fair value and weighted-average useful life will likely be different from the final acquisition accounting, and the difference could have a material impact on the accompanying unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements. Once Triumph and its third-party valuation advisors have full access to the specifics of the Vought intangible assets, additional insight will be gained that could impact: (i) the estimated total value assigned to intangible assets, (ii) the estimated allocation of value between finite-lived and indefinite-lived intangible assets and/or (iii) the estimated weighted-average useful life of each category of intangible assets. The estimated intangible asset values and their useful lives could be impacted by a variety of factors that may become known to us only upon access to additional information and/or by changes in such factors that may occur prior to the effective time of the Vought Acquisition. A 20% change in the valuation of definite lived intangible assets would cause a corresponding increase or decrease to annual amortization expense of approximately $4.6 million ($1.2 million per quarter), assuming a weighted-average useful
59
NOTES TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED
COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
5. ESTIMATES OF THE ASSETS ACQUIRED AND LIABILITIES ASSUMED (Continued)
life of 10 years. The estimated intangible asset values and their useful lives could be impacted by a variety of factors that may become known to Triumph only upon access to additional information.
Goodwill: Goodwill is calculated as the difference between the acquisition date fair value of the estimated consideration transferred and the values assigned to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed. Goodwill is not amortized but rather subject to an annual impairment test.
6. RECLASSIFICATIONS
Certain reclassification adjustments have been made to the historical financial statements of Vought to conform to Triumph's presentation as follows:
- (1)
- Certain selling, general and administrative costs that Triumph classifies as selling, general and administrative expenses; and depreciation and amortization expenses that Triumph classifies separately are included in Cost of Sales on Vought's statements of income. This adjustment reclassifies Vought's historical Cost of Sales and Selling, General & Administrative to the respective captions presented in Triumph's historical statements of income.
7. ADJUSTMENTS TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
- (A)
- Reflects adjustments for the following (in millions):
| | Year Ended March 31, 2010 | Three Months Ended June 30, 2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Reduction in revenue for sales from Triumph to Vought which eliminate in combination | $ | (34.5 | ) | $ | (5.3 | ) | |
- (B)
- Reflects adjustments for the following (in millions):
| | Year Ended March 31, 2010 | Three Months Ended June 30, 2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Reduction in cost of sales for sales from Triumph to Vought which eliminate in combination | $ | (34.5 | ) | $ | (5.3 | ) | |
Adjustment to eliminate profit on net sales by Triumph that are in Inventory of Vought | 1.9 | (0.7 | ) | ||||
Reverse Vought's amortization of prior service costs and amortization of actuarial (gains) losses on pension and other post-retirement benefits | (34.2 | ) | (8.6 | ) | |||
Impact of the elimination of general and administrative costs from inventory per Triumph's policy(1) | 3.1 | (8.8 | ) | ||||
Amortization of off market contract fair value margin adjustment | (11.0 | ) | (3.8 | ) | |||
| $ | (74.7 | ) | $ | (27.2 | ) | ||
- (1)
- See footnote 8, Note (C) below.
60
NOTES TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED
COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
7. ADJUSTMENTS TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF INCOME (Continued)
- (C)
- Reflects adjustments for the following (in millions):
| | Year Ended March 31, 2010 | Three Months Ended June 30, 2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Elimination of management fees to The Carlyle Group | $ | (2.0 | ) | $ | (0.4 | ) | |
- (D)
- Reflects the elimination of nonrecurring charges for advisory, legal, regulatory and valuation costs directly attributable to the transaction.
- (E)
- Reflects adjustments for the following (in millions):
| | Year Ended March 31, 2010 | Three Months Ended June 30, 2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
New intangible asset amortization | $ | 14.5 | $ | 3.0 | |||
Depreciation on property and equipment fair value adjustment | 10.0 | (1.8 | ) | ||||
Eliminate Vought's historical intangible asset amortization expense | (6.9 | ) | (1.5 | ) | |||
| $ | 17.6 | $ | (0.3 | ) | |||
- (F)
- Reflects adjustments for the following (in millions):
| | Year Ended March 31, 2010 | Three Months Ended June 30, 2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Interest expense on new debt issuances used to partially finance the Vought Acquisition(1) | $ | 55.1 | $ | 11.8 | |||
Amortization of deferred financing fees related to new debt issuances | 2.8 | 0.6 | |||||
Vought's historical interest expense on debt to be repaid(2) | (54.6 | ) | (11.4 | ) | |||
| $ | 3.3 | $ | 1.0 | ||||
- (1)
- Estimated interest expense on the new debt issuances is based on an assumed blended average interest rate of 6.25%. A 1/8% change in the interest rate would cause a corresponding increase or decrease to annual interest expense of approximately $1.3 million ($0.3 million per quarter).
- (2)
- This included amortization of debt origination costs and debt discount for each period.
This pro forma adjustment excludes incremental interest expense attributable to Triumph's 8% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2017, issued in November 2009, the remaining proceeds of which were used to partially finance the Vought Acquisition. If this debt had been in place as of April 1, 2009, Triumph would have incurred additional interest expense, including amortization of discount and finance fees of approximately $9.2 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010.
- (G)
- This represents the tax effect of adjustments to income from continuing operations, before income taxes primarily related to expense associated with incremental debt to partially finance the Vought Acquisition and increased amortization resulting from estimated fair value adjustments for acquired intangibles. In addition, Vought's historical income tax provision included the reversal of a valuation allowance against deferred income taxes, which Triumph would have reversed through
61
NOTES TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED
COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
7. ADJUSTMENTS TO THE UNAUDITED PRO FORMA CONDENSED COMBINED STATEMENTS OF INCOME (Continued)
purchase accounting, thus resulting in a significant increase in the pro forma income tax provision applicable to Vought's operations. Triumph has assumed a 35.0% and 36.0% blended tax rate for fiscal 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, respectively, representing the estimated combined effective global tax rates. This estimated blended tax rate recognizes that Vought is predominately a U.S. based entity and that the debt incurred by Triumph to effect the Vought Acquisition is an obligation of a U.S. entity. However, the effective tax rate of the combined entity could be significantly different (either higher or lower) depending on post-acquisition activities.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined basic and diluted earnings per share calculations are based on the combined basic and diluted weighted-average shares. The historical basic and diluted weighted-average shares of Vought are assumed to be replaced by the shares issued by Triumph to effect the Vought Acquisition.
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements do not reflect revenue synergies or the expected cost savings. Although Triumph management expects that cost savings will result from the Vought Acquisition, there can be no assurance that these cost savings will be achieved. The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial statements also do not reflect estimated restructuring charges associated with the expected cost savings, which will be expensed as incurred.
62
TRIUMPH SELECTED HISTORICAL FINANCIAL DATA
The selected historical financial data of Triumph for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008, 2009 and 2010 and as of March 31, 2008, 2009 and 2010 are derived from Triumph's audited consolidated financial statements and related notes incorporated by reference in this prospectus. The selected historical financial data of Triumph for the three months ended June 30, 2010 and 2009 are derived from Triumph's unaudited consolidated financial statements and related notes incorporated by reference in this prospectus. The information set forth below is only a summary and is not necessarily indicative of the results of future operations of Triumph, and you should read the following information together with Triumph's audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto and Triumph's unaudited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto, each incorporated by reference in this prospectus and the section of this prospectus entitled "Triumph's Management's Discussion and Analysis of Triumph's Financial Condition and Results of Operations."
| | Historical | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | As of and for the Fiscal Years Ended March 31, | As of and for the Three Months Ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| (U.S. dollars in millions, except ratios) | 2008(1) | 2009(2) | 2010(3) | 2009 | 2010(4) | ||||||||||||
Operating Data: | |||||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 1,151.1 | $ | 1,240.4 | $ | 1,294.8 | $ | 316.1 | $ | 406.4 | |||||||
Cost of sales | 822.3 | 877.8 | 927.2 | 224.3 | 297.9 | ||||||||||||
| 328.8 | 362.6 | 367.6 | 91.8 | 108.5 | |||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense | 159.3 | 162.1 | 157.9 | 39.8 | 43.4 | ||||||||||||
Acquisition-related costs | — | — | — | — | 17.4 | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 43.2 | 48.6 | 54.4 | 14.1 | 14.8 | ||||||||||||
Operating income | 126.3 | 151.9 | 155.3 | 37.9 | 32.9 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense and other | 19.9 | 17.0 | 28.8 | 5.4 | 11.8 | ||||||||||||
Gain on early extinguishment of debt | — | (0.9 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Income from continuing operations, before income taxes | 106.4 | 135.8 | 126.5 | 32.5 | 21.1 | ||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 34.7 | 43.1 | 41.2 | 11.0 | 9.5 | ||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 71.7 | $ | 92.7 | $ | 85.3 | $ | 21.5 | $ | 11.6 | |||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | |||||||||||||||||
Working capital | $ | 416.8 | $ | 372.2 | $ | 487.8 | $ | 466.8 | $ | 503.1 | |||||||
Total assets | 1,412.8 | 1,591.2 | 1,712.7 | 1,587.9 | 4,496.4 | ||||||||||||
Long-term debt, including current portion | 396.0 | 459.4 | 505.8 | 453.4 | 1,335.3 | ||||||||||||
Total stockholders' equity | 706.4 | 788.6 | 860.7 | 818.4 | 1,372.6 | ||||||||||||
- (1)
- Includes the acquisition of the assets and business of B. & R. Machine & Tool Corp. from the date of acquisition (February 2008).
- (2)
- Includes the acquisitions of Merritt Tool Company, Inc., Saygrove Defence and Aerospace Group Limited, and The Mexmil Company, LLC and the acquisition of the aviation segment of Kongsberg Automotive Holdings ASA from the date of each respective acquisition (March 2009).
- (3)
- Includes the acquisition of DCL Avionics, Inc. (January 2010) and Fabritech, Inc. (March 2010) from the date of each respective acquisition.
- (4)
- Includes the Vought Acquisition from the date of acquisition (June 16, 2010).
63
VOUGHT SELECTED HISTORICAL FINANCIAL DATA
The selected historical financial data of Vought for each of the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 and as of December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 are derived from Vought's audited consolidated financial statements and related notes incorporated in this prospectus. The selected financial data as of and for the three months ended March 29, 2009 and March 28, 2010 are derived from Vought's unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto incorporated in this prospectus. The information set forth below is only a summary and is not necessarily indicative of the results of future operations of Vought or us, and you should read the following information together with Vought's audited and unaudited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto incorporated in this prospectus and the section of this prospectus entitled "Vought Management's Discussion and Analysis of Vought's Financial Condition and Results of Operations."
| | As of and for the Years Ended December 31, | As of and for the Three Months Ended | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (U.S. dollars in millions) | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | March 29, 2009 | March 28, 2010 | ||||||||||||
Operating Data: | |||||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 1,613.1 | $ | 1,775.0 | $ | 1,877.8 | $ | 390.3 | $ | 470.5 | |||||||
Cost of sales | 1,284.8 | 1,492.9 | 1,594.8 | 324.8 | 391.5 | ||||||||||||
| 328.3 | 282.1 | 283.0 | 65.5 | 79.0 | |||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense | 133.3 | 135.3 | 122.6 | 28.5 | 39.7 | ||||||||||||
Operating income | 195.0 | 146.8 | 160.4 | 37.0 | 39.3 | ||||||||||||
Other income (expense) | |||||||||||||||||
Interest income | 3.6 | 4.4 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.1 | ||||||||||||
Other (income) loss | (0.1 | ) | 48.7 | 1.3 | — | — | |||||||||||
Equity in loss of joint venture | (4.0 | ) | (0.6 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Interest expense | (62.6 | ) | (67.2 | ) | (57.0 | ) | (15.0 | ) | (12.6 | ) | |||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes | 131.9 | 132.1 | 105.4 | 22.2 | 26.8 | ||||||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | 0.1 | 0.2 | (9.3 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
Income from continuing operations(1) | $ | 131.8 | $ | 131.9 | $ | 114.7 | $ | 22.2 | $ | 26.8 | |||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | |||||||||||||||||
Working capital | $ | 88.0 | $ | 406.8 | $ | 116.5 | $ | 451.2 | $ | 139.5 | |||||||
Total assets | 1,620.9 | 1,727.6 | 1,509.9 | 1,876.8 | 1,513.5 | ||||||||||||
Long-term debt, including current portion(2) | 683.0 | 869.9 | 589.8 | 1,030.6 | 590.4 | ||||||||||||
Total stockholders' equity (deficit) | (665.8 | ) | (934.1 | ) | (503.5 | ) | (877.3 | ) | (466.0 | ) | |||||||
- (1)
- Income from continuing operations is calculated before other comprehensive income (loss) relating to the following: (1) pension and OPEB related adjustments of $100.0 million and $(365.1) million in 2009 and 2008, respectively and (2) minimum pension liability adjustments and adoption of provisions of theCompensation—Retirement Benefits topic of the ASC adjustments of $(22.4) million in 2007.
- (2)
- As of December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, capital leases represented less than $0.1 million of Vought's total debt balance. Total debt as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 includes $2.4 million and $8.2 million, respectively, of unamortized discount related to Vought's long-term debt.
64
TRIUMPH MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
TRIUMPH'S FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion contains Triumph management's discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations for Triumph and should be read in conjunction with Triumph's consolidated financial statements and the related notes.
Overview
We are a major supplier to the aerospace industry and have two operating segments: (i) Triumph Aerospace Systems Group, whose companies design, engineer, manufacture and sell a wide range of proprietary and build-to-print components, assemblies and systems for the global aerospace OEM market; and (ii) Triumph Aftermarket Services Group, whose companies serve aircraft fleets, notably commercial airlines, the U.S. military and cargo carriers, through the maintenance, repair and overhaul of aircraft components and accessories manufactured by third parties.
On June 16, 2010, we announced the completion of the Vought Acquisition. The acquired business is operating as Triumph Aerostructures-Vought Commercial Division and Triumph Aerostructures-Vought Integrated Programs Division.
Financial highlights for the first quarter of the fiscal year ending March 31, 2011 include:
- •
- Net sales for the first quarter of the fiscal year ending March 31, 2011 increased 28.5% to $406.4 million, including 2.1% increase due to organic growth.
- •
- Operating income in the first quarter of fiscal 2011 decreased 13.3% to $32.9 million, which included $17.4 million of acquisition-related expenses associated with the Vought Acquisition.
- •
- Income from continuing operations for the first quarter of fiscal 2011 decreased 46.2% to $11.6 million, due to the acquisition-related expenses associated with the Vought Acquisition.
- •
- Backlog increased to $3.3 billion due to the Vought Acquisition, having an organic increase of 1% from the prior year, but an organic decrease of 1% sequentially from the prior quarter.
- •
- Income from continuing operations was $0.62 per diluted common share, which included the effect of $0.71 per diluted share for acquisition-related expenses associated with the Vought Acquisition.
- •
- We generated $22.7 million of cash flow from operating activities.
Financial highlights for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 include:
- •
- Net sales for fiscal 2010 increased 4.4% to $1.29 billion.
- •
- Operating income in fiscal 2010 increased 2.2% to $155.3 million.
- •
- Net income for fiscal 2010 decreased 23.0% to $67.8 million.
- •
- Backlog decreased 1.0% over the prior year to $1.3 billion.
For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, net sales totaled $1.29 billion, a 4.4% increase from fiscal year 2009 net sales of $1.24 billion. Net income for fiscal year 2010 decreased 23.0% to $67.8 million, or $4.07 per diluted common share, versus $88.0 million, or $5.30 per diluted common share, for fiscal year 2009. As discussed in further detail below under "Results of Operations," the decrease in net income is attributable to the write-down of the carrying value of our discontinued operation to estimated fair value less cost to sell, as well as the additional interest expense associated with the issuance of our 8% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2017 in November 2009, offset by the contribution from recent acquisitions.
65
Our working capital needs are generally funded through cash flows from operations and borrowings under our credit arrangements. For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, we generated approximately $169.6 million of cash flows from operating activities, used approximately $62.5 million in investing activities and generated approximately $35.3 million in financing activities.
We continue to remain focused on growing our core businesses as well as growing through strategic acquisitions. Our organic sales declined in fiscal 2010 due to major program delays, the dramatic decline in the regional and business jet markets due to the overall economy, lower passenger and freight traffic and airline inventory de-stocking. Our Company has an aggressive but selective acquisition approach that adds capabilities and increases our capacity for strong and consistent internal growth.
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010, we acquired Fabritech, Inc. (now Triumph Fabrications—St. Louis) and DCL Avionics, Inc. (now part of Triumph Instruments—Burbank), collectively, the "fiscal 2010 acquisitions." The results of Triumph Fabrications—St. Louis are included in the Company's Aftermarket Services Segment from the date of acquisition.
In March 2009, we acquired Merritt Tool Company, Inc. (now Triumph Structures—East Texas), Saygrove Defence & Aerospace Group Limited (now Triumph Actuation & Motion Control Systems—UK), the aviation segment of Kongsberg Automotive Holdings ASA (now Triumph Controls—U.K and Triumph Controls—Germany) and The Mexmil Company, LLC (now Triumph Insulation Systems), collectively, the "fiscal 2009 acquisitions." The results for the fiscal 2009 acquisitions are included in the Company's Aerospace Systems Segment.
Results of Operations
The following includes a discussion of our consolidated and business segment results of operations. The Company's diverse structure and customer base do not provide for precise comparisons of the impact of price and volume changes to our results. However, we have disclosed the significant variances between the respective periods.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
We prepare and publicly release quarterly unaudited financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. In accordance with recent SEC guidance on Compliance and Disclosure Interpretations, we also disclose and discuss certain non-GAAP financial measures in our public releases. Currently, the non-GAAP financial measures that we disclose are EBITDA, which is our income from continuing operations before interest, income taxes, depreciation and amortization, and Adjusted EBITDA, which is EBITDA adjusted for acquisition related costs associated with the Vought Acquisition. We disclose EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA on a consolidated and an operating segment basis in our earnings releases, investor conference calls and filings with the SEC. The non-GAAP financial measures that we use may not be comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies. Also, in the future, we may disclose different non-GAAP financial measures in order to help our investors more meaningfully evaluate and compare our future results of operations to our previously reported results of operations.
We view EBITDA as an operating performance measure and as such we believe that the GAAP financial measure most directly comparable to it is income from continuing operations. In calculating EBITDA, we exclude from income from continuing operations the financial items that we believe should be separately identified to provide additional analysis of the financial components of the day-to-day operation of our business. We have outlined below the type and scope of these exclusions and the material limitations on the use of these non-GAAP financial measures as a result of these exclusions. EBITDA is not a measurement of financial performance under GAAP and should not be considered as a measure of liquidity, as an alternative to net income (loss), income from continuing operations, or as
66
an indicator of any other measure of performance derived in accordance with GAAP. Investors and potential investors in our securities should not rely on EBITDA as a substitute for any GAAP financial measure, including net income (loss) or income from continuing operations. In addition, we urge investors and potential investors in our securities to carefully review the reconciliation of EBITDA to income from continuing operations set forth below, in our earnings releases and in other filings with the SEC and to carefully review the GAAP financial information included as part of our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q and our Annual Reports on Form 10-K that are filed with the SEC, as well as our quarterly earnings releases, and compare the GAAP financial information with our EBITDA.
EBITDA is used by management to internally measure our operating and management performance and by investors as a supplemental financial measure to evaluate the performance of our business that, when viewed with our GAAP results and the accompanying reconciliation, we believe provides additional information that is useful to gain an understanding of the factors and trends affecting our business. We have spent more than 15 years expanding our product and service capabilities partially through acquisitions of complementary businesses. Due to the expansion of our operations, which included acquisitions, our income from continuing operations has included significant charges for depreciation and amortization. EBITDA excludes these charges and provides meaningful information about the operating performance of our business, apart from charges for depreciation and amortization. We believe the disclosure of EBITDA helps investors meaningfully evaluate and compare our performance from quarter to quarter and from year to year. We also believe EBITDA is a measure of our ongoing operating performance because the isolation of non-cash charges, such as depreciation and amortization, and non-operating items, such as interest and income taxes, provides additional information about our cost structure, and, over time, helps track our operating progress. In addition, investors, securities analysts and others have regularly relied on EBITDA to provide a financial measure by which to compare our operating performance against that of other companies in our industry.
Set forth below are descriptions of the financial items that have been excluded from our income from continuing operations to calculate EBITDA and the material limitations associated with using this non-GAAP financial measure as compared to income from continuing operations:
- •
- Amortization expense may be useful for investors to consider because it represents the estimated attrition of our acquired customer base and the diminishing value of product rights and licenses. We do not believe these charges necessarily reflect the current and ongoing cash charges related to our operating cost structure.
- •
- Depreciation may be useful for investors to consider because it generally represents the wear and tear on our property and equipment used in our operations. We do not believe these charges necessarily reflect the current and ongoing cash charges related to our operating cost structure.
- •
- The amount of interest expense and other we incur may be useful for investors to consider and may result in current cash inflows or outflows. However, we do not consider the amount of interest expense and other to be a representative component of the day-to-day operating performance of our business.
- •
- Income tax expense may be useful for investors to consider because it generally represents the taxes which may be payable for the period and the change in deferred income taxes during the period and may reduce the amount of funds otherwise available for use in our business. However, we do not consider the amount of income tax expense to be a representative component of the day-to-day operating performance of our business.
67
Management compensates for the above-described limitations of using non-GAAP measures by using a non-GAAP measure only to supplement our GAAP results and to provide additional information that is useful to gain an understanding of the factors and trends affecting our business.
The following table shows our EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA reconciled to our income from continuing operations for the indicated periods (in thousands):
| | Three months ended June 30, | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | |||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 11,580 | $ | 21,521 | |||
Depreciation and amortization | 14,797 | 14,076 | |||||
Interest expense and other | 11,791 | 5,326 | |||||
Income tax expense | 9,479 | 11,023 | |||||
EBITDA | 47,647 | 51,946 | |||||
Acquisition-related expenses | 17,367 | — | |||||
Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 65,014 | $ | 51,946 | |||
The following table shows our EBITDA reconciled to our income from continuing operations for the indicated periods (in thousands):
| | Fiscal Year Ended March 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 85,288 | $ | 92,741 | $ | 71,635 | ||||
Depreciation and amortization | 54,418 | 48,611 | 43,215 | |||||||
Interest expense and other | 28,865 | 16,929 | 19,942 | |||||||
Gain on early extinguishment of debt | (39 | ) | (880 | ) | — | |||||
Income tax expense | 41,167 | 43,124 | 34,748 | |||||||
EBITDA | $ | 209,699 | $ | 200,525 | $ | 169,540 | ||||
The fluctuations from period to period within the amounts of the components of the reconciliations above are discussed further below within Results of Operations.
Quarter ended June 30, 2010 compared to quarter ended June 30, 2009
| | Quarter Ended June 30, | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | ||||||
| | (in thousands) | |||||||
Net sales | $ | 460,350 | $ | 316,130 | ||||
Segment operating income | $ | 58,536 | $ | 44,268 | ||||
Corporate expenses | (25,686 | ) | (6,398 | ) | ||||
Total operating income | 32,850 | 37,870 | ||||||
Interest expense and other | 11,791 | 5,326 | ||||||
Income tax expense | 9,479 | 11,023 | ||||||
Income from continuing operations | 11,580 | 21,521 | ||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net | (208 | ) | (3,482 | ) | ||||
Net income | $ | 11,372 | $ | 18,039 | ||||
68
Net sales increased by $90.3 million, or 28.5%, to $406.4 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 from $316.1 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2009. The Vought Acquisition along with the fiscal 2010 acquisitions contributed $83.5 million of the net sales increase. Excluding the effects of the Vought acquisition and the fiscal 2010 acquisitions, organic sales increased $6.7 million, or 2.1%.
Cost of sales increased by $73.5 million, or 32.8%, to $297.8 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 from $224.3 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2009. This increase includes the impact of the Vought Acquisition and the fiscal 2010 acquisitions noted above, which contributed $69.9 million. Excluding the effects of these acquisitions, gross margin was 29.4% for the quarter ended June 30, 2010, compared with 29.0% for the quarter ended June 30, 2009.
Segment operating income increased by $14.3 million, or 32.2%, to $58.5 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 from $44.3 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2009. The segment operating income increase was a direct result of contributions from the Vought Acquisition and the fiscal 2010 acquisitions ($8.7 million), as well as improvement in organic gross margin ($3.0 million), decreased legal expenses ($2.0 million) including the net recovery of $0.8 million of prior legal costs and a favorable settlement of a retroactive pricing agreement, offset by costs related to the signing of a collective bargaining agreement.
Corporate expenses increased by $19.3 million, or 301.5%, to $25.7 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 from $6.4 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2009. Corporate expenses included $17.4 million of non-recurring acquisition-related transaction and integration costs associated with the Vought Acquisition. The remaining corporate expense increase was impacted by higher salaries and bonus ($3.4 million) due to increased corporate head count as compared to the prior year period and an increase of $0.2 million of start up costs related to the Mexican facility compared to the prior year period.
Interest expense and other increased by $6.5 million, or 121.4%, to $11.8 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 compared to $5.3 million for the prior year period. This increase was due to higher average debt outstanding during the quarter ended June 30, 2010 as compared to the quarter ended June 30, 2009, including the Senior Subordinated Notes due 2017 (the "2017 Notes"), the Senior Notes due 2018 (the "2018 Notes") and the Term Loan Facility, along with higher interest rates on our Revolving Credit Facility.
The effective income tax rate for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 was 45.0% compared to 33.9% for the quarter ended June 30, 2009. The effective income tax rate is impacted by the $17.4 million in acquisition-related expenses, which were only partially deductible for tax purposes. For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2011, the Company expects its effective tax rate to be approximately 36%.
Loss from discontinued operations before income taxes was $0.3 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 compared with a loss from discontinued operations before income taxes of $5.4 million, for the quarter ended June 30, 2009, which includes an impairment charge of $2.5 million. The benefit for income taxes was $0.1 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 compared to a benefit of $1.9 million in the prior year period.
69
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 compared to fiscal year ended March 31, 2009
| | Year Ended March 31, | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | ||||||
| | (in thousands) | |||||||
Net sales | $ | 1,294,780 | $ | 1,240,378 | ||||
Segment operating income | 181,566 | 178,882 | ||||||
Corporate general and administrative expenses | (26,285 | ) | (26,968 | ) | ||||
Total operating income | 155,281 | 151,914 | ||||||
Interest expense and other | 28,865 | 16,929 | ||||||
Gain on early extinguishment of debt | (39 | ) | (880 | ) | ||||
Income tax expense | 41,167 | 43,124 | ||||||
Income from continuing operations | 85,288 | 92,741 | ||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net | (17,526 | ) | (4,745 | ) | ||||
Net income | $ | 67,762 | $ | 87,996 | ||||
Net sales increased by $54.4 million, or 4.4%, to $1.29 billion for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 from $1.24 billion for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. The fiscal 2010 acquisitions and fiscal 2009 acquisitions contributed $123.3 million in net sales. Organic sales declined $68.9 million, or 5.6%, which was negatively impacted by major program delays, the decline in the regional jet market due to the overall economy, lower passenger and freight traffic and airline inventory de-stocking. Prior year sales were negatively impacted by the Boeing strike.
Cost of sales increased by $49.5 million, or 5.6%, to $927.2 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 from $877.7 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. This increase includes the acquisitions noted above, which contributed $92.0 million. Excluding the effects of these acquisitions, gross margin was 28.7% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, compared with 29.2% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009.
Segment operating income increased by $2.7 million, or 1.5%, to $181.6 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 from $178.9 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. Operating income growth was a direct result of margins attained on increased sales as described above, and decreases in litigation costs ($0.9 million) and bad debt expense ($1.6 million), partially offset by increases in depreciation and amortization ($5.8 million) primarily from the fiscal 2009 acquisitions.
Corporate expenses decreased by $0.7 million, or 2.5%, to $26.3 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 from $27.0 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009, primarily due to decreased healthcare and workers' compensation costs ($0.8 million), consulting expenses ($1.6 million) and computer services costs ($1.0 million), partially offset by increases in acquisition-related costs ($1.6 million). In addition, we have recognized expenses of approximately $4.1 million start-up costs related to the Mexican facility, predominately recorded within corporate expenses.
Interest expense and other increased by $11.9 million, or 70.5%, to $28.9 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 compared to $16.9 million for the prior year. During fiscal 2010, the Company issued $175.0 million in principal amount of the 2017 Notes, resulting in additional interest expense of approximately $5.3 million. The initial interest payment on this debt is due May 15, 2010. Fiscal 2010 also included full-year interest expense on our equipment leasing facility representing an additional $4.0 million from fiscal 2009. During fiscal 2009, the Company entered into certain foreign currency derivative instruments that did not meet hedge accounting criteria and primarily were intended to protect against exposure related to fiscal 2009 acquisitions. These instruments resulted in a gain of $1.4 million in fiscal 2009, which is included in interest expense and other. Also during fiscal 2009, the Company paid $15.4 million to purchase $18.0 million of principal on the convertible senior
70
subordinated notes, resulting in a gain on early extinguishment of $0.9 million. Included in interest expense and other is noncash interest expense of $8.1 million and $7.9 million for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively, of which $6.1 million and $5.8 million, respectively, reflect accretion of interest recognized in accordance with the convertible debt accounting standard.
The effective tax rate was 32.6% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 and 31.8% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. The increase in the tax rate was primarily due to the lapse of the research and experimentation tax credit as of January 1, 2010.
Loss from discontinued operations before income taxes was $26.9 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, which included impairment charges of $19.9 million, compared with a loss from discontinued operations before income taxes of $7.3 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. Due to failed negotiations with certain potential buyers of the business occurring during the quarter ended December 31, 2009, the Company reassessed its estimated fair value of the business based on current viable offers to purchase the business, recent performance results and overall market conditions, resulting in a write-down, which was applied to accounts receivable, inventory and property, plant and equipment. The Company recognized a pre-tax loss of $17.4 million in the third quarter of fiscal 2010, based on the write-down of the carrying value of the business to estimated fair value less cost to sell. Included in the loss from discontinued operations for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 is an additional impairment charge of $2.5 million recorded during the first quarter of fiscal 2010. The income tax benefit for discontinued operations was $9.4 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 compared to a benefit of $2.6 million for the prior year.
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 compared to fiscal year ended March 31, 2008
| | Year Ended March 31, | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| | (in thousands) | |||||||
Net sales | $ | 1,240,378 | $ | 1,151,090 | ||||
Segment operating income | 178,882 | 148,292 | ||||||
Corporate general and administrative expenses | (26,968 | ) | (21,967 | ) | ||||
Total operating income | 151,914 | 126,325 | ||||||
Interest expense and other | 16,929 | 19,942 | ||||||
Gain on early extinguishment of debt | (880 | ) | — | |||||
Income tax expense | 43,124 | 34,748 | ||||||
Income from continuing operations | 92,741 | 71,635 | ||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net | (4,745 | ) | (8,468 | ) | ||||
Net income | $ | 87,996 | $ | 63,167 | ||||
Net sales increased by $89.3 million, or 7.8%, to $1.24 billion for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 from $1.15 billion for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008. The fiscal 2009 acquisitions and the fiscal 2008 acquisition of B. & R. Machine & Tool Corp. (now Triumph Structures—Long Island) together contributed $37.0 million. Excluding the effects of this acquisition, organic sales growth was $52.3 million, or 4.5%, which was negatively impacted by the Boeing strike and major program delays (particularly in the 787 and 747-8 programs), partially offset by a favorable settlement of a retroactive pricing agreement.
The Aerospace Systems segment benefited primarily from increased sales to our OEM customers driven by increased military aircraft build rates, while the increase in sales for our Aftermarket Services segment was the result of increased demand for our services due to growth in global air traffic.
71
Cost of sales increased by $55.4 million, or 6.7%, to $877.7 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 from $822.3 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008. This increase includes the acquisitions noted above, which contributed $17.9 million. Excluding the effects of these acquisitions, gross margin was 28.6% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009, compared with 28.4% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008. Despite having consistent consolidated gross margin, the gross margin for our Aerospace Systems segment was favorably impacted by contribution from the acquisition of B. & R. Machine & Tool Company and the favorable settlement of a retroactive pricing agreement, whereas the gross margin for our Aftermarket Services segment was negatively impacted by charges due to contract terminations ($1.3 million) and changes in estimate under power-by-the-hour contracts ($1.1 million) as well as losses at our Phoenix APU facility due to cost overruns and excess overhead ($4.8 million) and higher than expected warranty expenses ($0.6 million).
Segment operating income increased by $30.5 million, or 20.6%, to $178.9 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 from $148.3 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008. Operating income growth was a direct result of margins attained on increased sales as described above, the contribution of $13.8 million from the above-mentioned acquisitions, and decreases in litigation costs ($3.7 million) and incentive compensation ($1.3 million), partially offset by increases in payroll ($2.4 million) and depreciation and amortization expenses ($1.1 million) associated with our acquisitions.
Corporate expenses increased by $5.0 million, or 22.8%, to $27.0 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 from $22.0 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008, primarily due to increased healthcare ($3.0 million), stock compensation costs ($0.6 million) and the write-off of acquisition costs on a potential acquisition that was not consummated ($0.5 million), partially offset by decreases in litigation costs ($1.8 million).
Interest expense and other decreased by $3.0 million, or 15.1%, to $16.9 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 compared to $19.9 million for the prior year. During fiscal 2009, the Company entered into certain foreign currency derivative instruments that did not meet hedge accounting criteria and primarily were intended to protect against exposure related to fiscal 2009 acquisitions. These instruments resulted in a gain of $1.4 million in fiscal 2009, which is included in interest expense and other. In addition to this gain, the decrease in interest expense was impacted by declining interest rates. Also during fiscal 2009, the Company paid $15.4 million to purchase $18.0 million of principal on the convertible senior subordinated notes, resulting in a gain on early extinguishment of $0.9 million. Included in interest expense and other is non-cash interest expense of $7.9 million and $8.1 million for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively, of which $5.8 million and $6.5 million, respectively, reflect accretion of interest recognized in accordance with the convertible debt accounting standard.
The effective tax rate was 31.8% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 and 32.9% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008. The decrease in the tax rate was primarily due to the retroactive reinstatement of the research and experimentation tax credit back to January 1, 2008.
Loss from discontinued operations before income taxes was $7.3 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009, compared with a loss from discontinued operations before income taxes of $13.0 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008, which included an impairment charge of $4.0 million. The income tax benefit for discontinued operations was $2.6 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 compared to a benefit of $4.6 million for the prior year.
Business Segment Performance
The Aerospace Systems segment consists of the Company's operations that manufacture products primarily for the aerospace OEM market. The Aerospace Systems segment's operations design and engineer mechanical and electromechanical controls, such as hydraulic systems and components, main engine gearbox assemblies, accumulators and mechanical control cables. The Aerospace Systems
72
segment's revenues are also derived from stretch forming, die forming, milling, bonding, machining, welding and assembly and fabrication of complex aerostructures and various structural components used in aircraft wings, fuselages tail assemblies, engine nacelles, flight control surfaces as well as helicopter cabins. Further, the segment's operations also design and manufacture composite assemblies for floor panels, environmental control system ducts and non-structural cockpit components. These products are sold to various aerospace OEMs on a global basis.
The Aftermarket Services segment consists of the Company's operations that provide maintenance, repair and overhaul services to both commercial and military markets on components and accessories manufactured by third parties. Maintenance, repair and overhaul revenues are derived from services on auxiliary power units, airframe and engine accessories, including constant-speed drives, cabin compressors, starters and generators, and pneumatic drive units. In addition, the Aftermarket Services segment's operations repair and overhaul thrust reversers, nacelle components and flight control surfaces. The Aftermarket Services operations also perform repair and overhaul services, and supply spare parts for various types of cockpit instruments and gauges for a broad range of commercial airlines on a worldwide basis.
We currently generate a majority of our revenue from clients in the commercial aerospace industry, the military, and the business jet industry. Our growth and financial results are largely dependent on continued demand for our products and services from clients in these industries. If any of these industries experiences a downturn, our clients in these sectors may conduct less business with us. The following table summarizes our net sales by end market by business segment. The loss of one or more of our major customers or an economic downturn in the commercial airline or the military and defense markets could have a material adverse effect on our business.
| | Three months ended June 30, | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | ||||||
Aerospace Systems | ||||||||
Commercial aerospace | 38.3 | % | 33.6 | % | ||||
Military | 34.0 | % | 34.8 | % | ||||
Regional | 2.0 | % | 3.7 | % | ||||
Business Jets | 7.1 | % | 4.7 | % | ||||
Non-aviation | 3.9 | % | 4.9 | % | ||||
Total Aerospace Systems net sales | 85.3 | % | 81.7 | % | ||||
Aftermarket Systems | ||||||||
Commercial aerospace | 11.0 | % | 13.4 | % | ||||
Military | 1.8 | % | 2.9 | % | ||||
Regional | 0.4 | % | 0.6 | % | ||||
Business Jets | 0.7 | % | 0.7 | % | ||||
Non-aviation | 0.8 | % | 0.7 | % | ||||
Total Aftermarket Services net sales | 14.7 | % | 18.3 | % | ||||
Total Consolidated net sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||
The increase in our percentage of net sales of commercial aerospace and business jets for the quarter ended June 30, 2010, was attributable to the Vought Acquisition, while the regional jet end-market continues to decline in the current economy. We continue to experience an increase in the mix
73
of the commercial aerospace end-market. We also continue to experience growth in the military end-market.
| | Year Ended March 31, | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||
Aerospace Systems | |||||||||||
Commercial aerospace | 35.4 | % | 28.3 | % | 30.7 | % | |||||
Military | 34.8 | % | 33.0 | % | 29.5 | % | |||||
Regional | 3.1 | % | 5.3 | % | 4.2 | % | |||||
Business Jets | 4.6 | % | 7.9 | % | 8.1 | % | |||||
Non-aviation | 4.7 | % | 5.1 | % | 6.2 | % | |||||
Total Aerospace Systems net sales | 82.6 | % | 79.6 | % | 78.7 | % | |||||
Aftermarket Systems | |||||||||||
Commercial aerospace | 13.0 | % | 14.4 | % | 13.7 | % | |||||
Military | 2.5 | % | 3.3 | % | 3.3 | % | |||||
Regional | 0.5 | % | 0.6 | % | 0.9 | % | |||||
Business Jets | 0.7 | % | 0.9 | % | 0.7 | % | |||||
Non-aviation | 0.7 | % | 1.2 | % | 2.7 | % | |||||
Total Aftermarket Services net sales | 17.4 | % | 20.4 | % | 21.3 | % | |||||
Total Consolidated net sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | |||||
The decline in our percentage of net sales to the Business jet and Regional jet markets for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, was due to the overall economic conditions and the Commercial aerospace end market was impacted by major program delays in fiscal 2010, as well as continued growth in the Military end market. Sales to the Commercial aerospace end market were negatively impacted in fiscal 2009 by the Boeing strike.
Business Segment Performance—Quarter ended June 30, 2010 compared to quarter ended June 30, 2009
| | Quarter Ended June 30, | | % of Total Sales | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | % Change | 2010 | 2009 | |||||||||||
| | (in thousands) | | | | ||||||||||||
NET SALES | ||||||||||||||||
Aerospace Systems | $ | 346,856 | $ | 259,973 | 33.4 | % | 85.4 | % | 82.2 | % | ||||||
Aftermarket Services | 59,797 | 57,784 | 3.5 | % | 14.7 | % | 18.3 | % | ||||||||
Elimination of inter-segment sales | (303 | ) | (1,627 | ) | (81.4 | )% | (0.1 | )% | (0.5 | )% | ||||||
Total net sales | $ | 406,350 | $ | 316,130 | 28.5 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
| | Quarter Ended June 30, | | % of Segment Sales | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | % Change | 2010 | 2009 | |||||||||||
| | (in thousands) | | | | ||||||||||||
SEGMENT OPERATING INCOME | ||||||||||||||||
Aerospace Systems | $ | 54,414 | $ | 41,845 | 30.0 | % | 15.7 | % | 16.1 | % | ||||||
Aftermarket Services | 4,122 | 2,423 | 70.1 | % | 6.9 | % | 4.2 | % | ||||||||
Corporate | (25,686 | ) | (6,398 | ) | 301.5 | % | N/A | N/A | ||||||||
Total segment operating income | $ | 32,850 | $ | 37,870 | (13.3 | )% | 8.1 | % | 12.0 | % | ||||||
74
Aerospace Systems: The Aerospace Systems segment net sales increased by $86.9 million, or 33.4%, to $346.9 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 from $260.0 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2009. The increase was primarily due to the additional sales associated with the Vought Acquisition and fiscal 2010 acquisitions of $83.5 million, in addition to organic sales growth of $3.4 million.
Aerospace Systems segment operating income increased by $12.6 million, or 30.0%, to $54.4 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 from $41.8 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2009. Operating income increased due to contributions from the Vought Acquisition and the fiscal 2010 acquisitions ($8.7 million), as well as decreases in litigation ($2.0 million) and a favorable settlement of a retroactive pricing agreement, offset by costs related to the signing of a collective bargaining agreement.
Aerospace Systems segment operating income as a percentage of segment sales decreased to 15.7% for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 as compared to 16.1% for the quarter ended June 30, 2009, due to the lower margins contributed by the Vought Acquisition and the fiscal 2010 acquisitions, offset by the reduction in expenses discussed above.
Aftermarket Services: The Aftermarket Services segment net sales increased by $2.0 million, or 3.5%, to $59.8 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 from $57.8 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2009.
Aftermarket Services segment operating income increased by $1.7 million, or 70.1%, to $4.1 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 from $2.4 million for the quarter ended June 30, 2009. Operating income increased primarily due to increased sales volume as described above, as well as an increase in gross margin of approximately 1% as a result of increased efficiencies in production associated with the higher volume of work and decreased salaries ($0.7 million) due to lower headcounts. In addition, the prior year period included $0.3 million in expenses incurred to shut down a service facility in Austin, Texas. The results of our Phoenix, Arizona APU operations were accretive to the segment's results.
Aftermarket Services segment operating income as a percentage of segment sales increased to 6.9% for the quarter ended June 30, 2010 as compared with 4.2% for the quarter ended June 30, 2009, due to an increase in gross margin, as well as the continued improvements in production and operations at the Phoenix APU operations.
Business Segment Performance—Fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 compared to fiscal year ended March 31, 2009
| | Year Ended March 31, | | % of Total Sales | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | % Change | 2010 | 2009 | |||||||||||
| | (in thousands) | | | | ||||||||||||
NET SALES | ||||||||||||||||
Aerospace Systems | $ | 1,073,494 | $ | 988,359 | 8.6 | % | 82.9 | % | 79.7 | % | ||||||
Aftermarket Services | 224,991 | 254,638 | (11.6 | )% | 17.4 | % | 20.5 | % | ||||||||
Elimination of inter-segment sales | (3,705 | ) | (2,619 | ) | 41.5 | % | (0.3 | )% | (0.2 | )% | ||||||
Total net sales | $ | 1,294,780 | $ | 1,240,378 | 4.4 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
75
| | Year Ended March 31, | | % of Segment Sales | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2010 | 2009 | % Change | 2010 | 2009 | |||||||||||
| | (in thousands) | | | | ||||||||||||
SEGMENT OPERATING INCOME | ||||||||||||||||
Aerospace Systems | $ | 170,457 | $ | 168,006 | 1.5 | % | 15.9 | % | 17.0 | % | ||||||
Aftermarket Services | 11,109 | 10,876 | 2.1 | % | 4.9 | % | 4.3 | % | ||||||||
Corporate | (26,285 | ) | (26,968 | ) | (2.5 | )% | N/A | N/A | ||||||||
Total segment operating income | $ | 155,281 | $ | 151,914 | 2.2 | % | 12.0 | % | 12.2 | % | ||||||
Aerospace Systems: The Aerospace Systems segment net sales increased by $85.1 million, or 8.6%, to $1.07 billion for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 from $988.4 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. The fiscal 2009 acquisitions contributed $123.0 million of increased net sales. Organic sales decreased by $37.8 million due to declines in the business jet and regional jet markets due to the overall economic conditions and major program delays, however, the prior year period sales were negatively impacted by the Boeing strike.
Aerospace Systems segment operating income increased by $2.5 million, or 1.5%, to $170.5 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 from $168.0 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. Operating income increased primarily due to margins attained on increased sales, including the contribution from the above-mentioned acquisitions, as well as decreases in litigation expenses ($0.9 million) and bad debt expenses ($2.3 million), partially offset by increases in depreciation and amortization ($6.0 million) primarily associated with the fiscal 2009 acquisitions.
Aerospace Systems segment operating income as a percentage of segment sales decreased to 15.9% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 as compared with 17.0% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009, due to the decrease in gross margin.
Aftermarket Services: The Aftermarket Services segment net sales decreased by $29.6 million, or 11.6%, to $225.0 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 from $254.6 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. This decrease was due to a decline in global commercial air traffic and airline inventory de-stocking resulting in lower demand for the repair and overhaul of auxiliary power units and the brokering of similar units.
Aftermarket Services segment operating income increased by $0.2 million, or 2.1%, to $11.1 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 from $10.9 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. Despite decreased sales volume as described above, operating income increased primarily due to charges recorded in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 for cost overruns and excess overhead at our Phoenix APU operations, contract terminations and changes in estimate under power-by-the hour ("PBH") contracts, offset by $0.3 million in expenses incurred to shut down a service facility in Austin, Texas in fiscal 2010. While the results of our Phoenix APU operations continue to improve, operating margins continued to be dilutive to the segment's results.
Aftermarket Services segment operating income as a percentage of segment sales increased to 4.9% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 as compared with 4.3% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009, due to a decline in sales volume offset by improved results at the Phoenix APU operations.
76
Business Segment Performance—Fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 compared to fiscal year ended March 31, 2008
| | Year Ended March 31, | | % of Total Sales | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2009 | 2008 | % Change | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| | (in thousands) | | | | ||||||||||||
NET SALES | ||||||||||||||||
Aerospace Systems | $ | 988,359 | $ | 907,376 | 8.9 | % | 79.7 | % | 78.8 | % | ||||||
Aftermarket Services | 254,638 | 246,609 | 3.3 | % | 20.5 | % | 21.4 | % | ||||||||
Elimination of inter-segment sales | (2,619 | ) | (2,895 | ) | (9.5 | )% | (0.2 | )% | (0.2 | )% | ||||||
Total net sales | $ | 1,240,378 | $ | 1,151,090 | 7.8 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
| | Year Ended March 31, | | % of Segment Sales | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2009 | 2008 | % Change | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| | (in thousands) | | | | ||||||||||||
SEGMENT OPERATING INCOME | ||||||||||||||||
Aerospace Systems | $ | 168,006 | $ | 124,812 | 34.6 | % | 17.0 | % | 13.8 | % | ||||||
Aftermarket Services | 10,876 | 23,480 | (53.7 | )% | 4.3 | % | 9.5 | % | ||||||||
Corporate | (26,968 | ) | (21,967 | ) | 22.8 | % | N/A | N/A | ||||||||
Total segment operating income | $ | 151,914 | $ | 126,325 | 20.3 | % | 12.2 | % | 11.0 | % | ||||||
Aerospace Systems: The Aerospace Systems segment net sales increased by $81.0 million, or 8.9%, to $988.4 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 from $907.4 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008. The increase was primarily due to organic sales growth to our OEM customers of $44.0 million driven by increased aircraft build rates and by a favorable settlement of a retroactive pricing agreement, negatively impacted by the Boeing strike and major program delays (particularly in the 787 and 747-8 programs). The net sales contributed from the fiscal 2009 acquisitions and the fiscal 2008 acquisition of B. & R. Machine & Tool Corp. (now Triumph Structures—Long Island) of $37.0 million accounted for the remaining increase.
Aerospace Systems segment operating income increased by $43.2 million, or 34.6%, to $168.0 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 from $124.8 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008. Operating income increased primarily due to margins attained on increased sales, including the contribution of $13.8 million from the above-mentioned acquisitions, as well as decreases in litigation expenses ($3.8 million) and incentive compensation ($1.1 million), partially offset by increases in payroll ($2.9 million) and healthcare costs ($2.0 million).
Aerospace Systems segment operating income as a percentage of segment sales increased to 17.0% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 as compared with 13.8% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008, due to the contribution of the acquisition of B. & R. Machine & Tool Corp., the reduction in expenses discussed above, and the favorable settlement of a retroactive pricing agreement.
Aftermarket Services: The Aftermarket Services segment net sales increased by $8.0 million, or 3.3%, to $254.6 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 from $246.6 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008. This increase was due to increased market penetration in the repair and overhaul of auxiliary power units and thrust reversers primarily at our Thailand repair and maintenance facility. These increases were offset by decreased fleet utilization by customers under PBH contracts impacting revenue by approximately $3.1 million.
77
Aftermarket Services segment operating income decreased by $12.6 million, or 53.7%, to $10.9 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 from $23.5 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008. Operating income decreased primarily due to losses at the Phoenix APU operations due to cost overruns and excess overhead ($4.8 million), higher than expected warranty expenses ($0.6 million), lower than expected PBH revenue ($3.1 million), PBH contract charges ($1.1 million) and additional charges for the early termination of a maintenance contract ($1.3 million), partially offset by higher margins attained on increased sales as described above, as well as decreases in payroll ($0.8 million) and incentive compensation expenses ($1.1 million).
Aftermarket Services segment operating income as a percentage of segment sales decreased to 4.3% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 as compared with 9.5% for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008, due to the $5.5 million in charges due to contract terminations and changes in estimate under PBH contracts as well as the production and operation losses at the Phoenix APU operations.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our working capital needs are generally funded through cash flow from operations and borrowings under our credit arrangements and leasing arrangements. During the three months ended June 30, 2010, we generated approximately $22.7 million of cash flows in operating activities, used approximately $350.0 million in investing activities and received approximately $206.3 million in financing activities. During the year ended March 31, 2010, we generated approximately $169.6 million of cash flow from operating activities, used approximately $62.5 million in investing activities and generated approximately $35.3 million in financing activities.
Cash flows from operations for the three months ended June 30, 2010 decreased $9.8 million, or 30.2% from the three months ended June 30, 2009. Our cash flows from operations decreased due to a decrease of $6.7 million in net income, which included $17.4 million in acquisition-related expenses for the Vought Acquisition. The decrease in cash flows was driven by an inventory cash usage of $11.7 million, and $12.4 million of interest paid at closing on assumed debt from the Vought Acquisition, offset by continued improvements in cash collection efforts resulting in a $17.8 million improvement as compared to the three months ended June 30, 2009.
Cash flows from operations for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 increased $34.7 million, or 25.7%, from the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009. Our cash flows from operations increased despite a decrease of $20.2 million in net income, which included $5.8 million in additional non-cash charges for depreciation and amortization due to the fiscal 2009 acquisitions and $19.9 million in impairment charges within discontinued operations during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010. The increase in cash flows resulted from continued improvements in our inventory management resulting in a source of cash of $30.2 million as compared to the use of cash of $7.7 million in the prior year period.
As of June 30, 2010, $403.1 million was available under our Revolving Credit Facility. On June 30, 2010, an aggregate amount of approximately $85.0 million was outstanding under the Revolving Credit Facility, all of which was accruing interest at LIBOR plus applicable basis points totaling 3.35% per annum. Amounts repaid under the Revolving Credit Facility may be reborrowed. At March 31, 2010, there were no borrowings and $6.1 million in letters of credit outstanding under the 2009 Credit Facility. At March 31, 2009, there were $127.7 million in borrowings and $5.6 million in letters of credit outstanding under the 2009 Credit Facility. The level of unused borrowing capacity under the Company's Revolving Credit Facility varies from time to time depending in part upon its compliance with financial and other covenants set forth in the related agreement. The Revolving Credit Facility contains certain affirmative and negative covenants including limitations on specified levels of indebtedness to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, and interest coverage
78
requirements, and includes limitations on, among other things, liens, mergers, consolidations, sales of assets, and incurrence of debt. The Company is currently in compliance with all such covenants.
At June 30, 2010, there was $120.0 million outstanding under the Securitization Facility. In June 2010, the Company entered into an amended receivable securitization facility, increasing the purchase limit from $125,000 to $175,000. In connection with the Securitization Facility, the Company sells on a revolving basis certain accounts receivable to Triumph Receivables, LLC, a wholly-owned special-purpose entity, which in turn sells a percentage ownership interest in the receivables to commercial paper conduits sponsored by financial institutions. The Company is the servicer of the accounts receivable under the Securitization Facility. As of June 30, 2010, the maximum amount available under the Securitization Facility was $118,600. The Securitization Facility is due to expire in June 2011 and is subject to annual renewal through August 2013. Interest rates are based on prevailing market rates for short-term commercial paper plus a program fee and a commitment fee. The program fee is 0.50% on the amount outstanding under the Securitization Facility. Additionally, the commitment fee is 0.65% on 102% of the maximum amount available under the Securitization Facility. In connection with amending the Securitization Facility, the Company incurred approximately $461,000 of financing costs. These costs, along with the $540,000 of unamortized financing costs prior to the amendment, are being amortized over the life of the Securitization Facility. The Company securitizes its accounts receivable, which are generally non-interest bearing, in transactions that are accounted for as borrowings pursuant to theTransfers and Servicing topic of the ASC. The agreement governing the Securitization Facility contains restrictions and covenants which include limitations on the making of certain restricted payments, creation of certain liens, and certain corporate acts such as mergers, consolidations and the sale of substantially all assets.
In June 2010, the Company issued the 2018 Notes for $350.0 million in principal amount. The 2018 Notes were sold at 99.270% of principal amount for net proceeds of $347.5 million, and have an effective interest yield of 8.75%. Interest on the 2018 Notes is payable semi-annually in cash in arrears on January 15 and May 15 of each year. We used the net proceeds as partial consideration of the Vought Acquisition. In connection with the issuance of the 2018 Notes, the Company incurred approximately $7.1 million of costs, which were deferred and are being amortized on the effective interest method over the term of the notes.
Also in June 2010, the Company entered into a six-year Term Loan Facility for $350.0 million in principal amount. The proceeds of the loans under the Term Loan Facility, which were 99.500% of the principal amount, were used to consummate the Vought Acquisition. Borrowings under the Term Loan Facility bear interest, at the Company's option, at either the base rate (subject to a 2.50% floor), plus a margin between 1.750% and 2.000%, or at the Eurodollar Rate (subject to a 1.50% floor), plus a margin driven by net leverage between 2.750% and 3.000%. In connection with the closing on the Term Loan Facility, the Company incurred approximately $7.5 million of costs, which were deferred and are being amortized into expense over the term of Term Loan Facility.
In November 2009, the Company issued the 2017 Notes for $175.0 million principal amount. The 2017 Notes were sold at 98.558% of principal amount for net proceeds of $172.5 million, and have an effective interest yield of 8.25%. Interest on the 2017 Notes is payable semi-annually in cash in arrears on May 15 and November 15 of each year. We intend to use the net proceeds for general corporate purposes, which includes debt reduction, including repayment of amounts outstanding under the Revolving Credit Facility, without any permanent reduction of the commitments thereunder. In connection with the issuance of the 2017 Notes, the Company incurred approximately $4.4 million of costs, which were deferred and are being amortized on the effective interest method over the term of the notes.
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010, we completed fiscal 2010 acquisitions. The total cash paid at closing for the fiscal 2010 acquisitions of $23.2 million was funded by cash from operations. The fiscal
79
2010 acquisitions provide for deferred and contingent payments of $0.1 million and $16.0 million, respectively. The fair value of the contingent payments is $10.6 million as of March 31, 2010.
During the year ended March 31, 2009, we generated approximately $135.0 million of cash flow from operating activities, used approximately $185.6 million in investing activities and generated approximately $52.1 million in financing activities. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009, our increased cash flow from operations was attributable to higher net income and an improved performance on working capital due to increased cash collections efforts, offset by timing of cash disbursements and utilization of inventory.
As of March 31, 2010, the maximum amount available under the Securitization Facility was $123.5 million. At March 31, 2010, there was $75.0 million outstanding under the Securitization Facility included in the current portion of long-term debt on the consolidated balance sheet, representing the minimum borrowing requirement.
In March 2009, we acquired Merritt Tool Company, Inc. (now Triumph Structures—East Texas), Saygrove Defence & Aerospace Group Limited (now Triumph Actuation & Motion Control Systems—UK), the aviation segment of Kongsberg Automotive Holdings ASA (now Triumph Controls—UK and Triumph Controls—Germany) and The Mexmil Company, LLC (now Triumph Insulation Systems), collectively the "fiscal 2009 acquisitions". No in-process research and development was attributed to the fiscal 2009 acquisitions. The total cash paid at closing for the fiscal 2009 acquisitions of $143.6 million was funded by borrowings under our 2009 Credit Facility. The fiscal 2009 acquisitions further provide for deferred payments of $3.5 million, of which $2.1 million and $1.4 million are payable in March 2010 and September 2010, respectively. The fiscal 2009 acquisitions also provide for contingent payments of $24.9 million, certain of which are contingent upon the achievement of specified earnings levels during the earnout period and another $10.0 million that is contingent upon entering into a specific customer contract. The maximum earnout amounts payable in respect of fiscal 2010, 2011, 2012 and 2013 are $2.3 million, $4.6 million, $5.4 million and $2.6 million, respectively. The contingent amounts have not been recorded as the contingencies have not been resolved and the consideration has not been paid.
Also in March 2009, we entered into a 7-year Master Lease Agreement (the "Leasing Facility") creating a capital lease of certain existing property and equipment, resulting in net proceeds of $58.5 million after deducting debt issuance costs of approximately $0.2 million. In June 2009, the Company added additional capital leases resulting in proceeds of $6.7 million. The net proceeds from the Leasing Facility were used to repay a portion of the outstanding indebtedness under the Company's Revolving Credit Facility. The debt issuance costs have been recorded as other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and are being amortized over the term of the Leasing Facility. The Leasing Facility bears interest at a weighted average fixed rate of 6.2% per annum.
Cash provided by operations for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008 was $45.7 million, compared to cash provided by operations of $41.3 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2007. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008, our increased cash flow from operations was attributable to higher net income offset by a decline in performance on working capital, due to timing of cash collections and utilization of inventory offset by timing of cash disbursements.
In February 2008, we acquired the assets and business of B. & R. Machine & Tool Corp. (now Triumph Structures—Long Island), located in Westbury, New York. The total cash paid at closing for the acquisition of $67.0 million was funded by borrowings under our 2009 Credit Facility. The purchase agreement provides for an earnout note for $13.0 million. Payments under the earnout note are contingent upon the achievement of certain earnings levels during the earnout period. The maximum amounts payable in respect of fiscal 2009, 2010 and 2011, are $3.5 million, $4.5 million and $5.0 million, respectively.
80
During February 2008, we exercised existing authority to make stock repurchases and repurchased 220,000 shares of our outstanding shares under the program for an aggregate consideration of $12.3 million, funded by borrowings under our 2009 Credit Facility. In February 2008, the Company's Board of Directors then authorized an increase in our existing stock repurchase program by up to an additional 500,000 shares of our common stock. As a result, as of May 15, 2009, we remain able to purchase an additional 500,800 shares. Repurchases may be made from time to time in open market transactions, block purchases, privately negotiated transactions or otherwise at prevailing prices. No time limit has been set for completion of the program.
On September 18, 2006, we issued $201.3 million in convertible senior subordinated notes (the "Convertible Notes"). The Convertible Notes are direct, unsecured, senior subordinated obligations of the Company, and rank (i) junior in right of payment to all of our existing and future senior indebtedness, (ii) equal in right of payment with any other future senior subordinated indebtedness, and (iii) senior in right of payment to all subordinated indebtedness.
The Company received net proceeds from the sale of the Convertible Notes of approximately $195.0 million after deducting offering expenses of approximately $6.3 million. The use of the net proceeds from the sale was for prepayment of our outstanding senior notes, including a "make whole" premium, fees and expenses in connection with the prepayment, and to repay a portion of the outstanding indebtedness under our 2009 Credit Facility. Approximately $6.3 million in debt issuance costs have been recorded as other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Debt issuance costs are being amortized over a period of five years.
Effective April 1, 2009, we adopted the convertible debt accounting standard, which requires retrospective application. The convertible debt accounting standard requires separately accounting for the liability and equity components of the Convertible Notes in a manner that reflects our nonconvertible debt borrowing rate when interest and amortization expense is recognized in subsequent periods. The excess of the principal amount of the liability component over its carrying amount has been recognized as debt discount and amortized using the effective interest method. This change in accounting for the Convertible Notes has been applied to our consolidated financial statements on a retrospective basis, as required by the standard. For more details on the impact of this change on our consolidated financial statements, see Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements. As of March 31, 2009, the remaining discount of $15.9 million will be amortized on the effective interest method through October 1, 2011.
The Convertible Notes bear interest at a fixed rate of 2.625% per annum, payable in cash semi-annually in arrears on each April 1 and October 1 beginning April 1, 2007. During the period commencing on October 6, 2011 and ending on, but excluding, April 1, 2012 and each six-month period from October 1 to March 31 or from April 1 to September 30 thereafter, the Company will pay contingent interest during the applicable interest period if the average trading price of a Note for the five consecutive trading days ending on the third trading day immediately preceding the first day of the relevant six-month period equals or exceeds 120% of the principal amount of the Convertible Notes. The contingent interest payable per Note in respect of any six-month period will equal 0.25% per annum calculated on the average trading price of a Note for the relevant five trading day period. This contingent interest feature represents an embedded derivative. Since it is in the control of the Company to call the Convertible Notes at any time after October 6, 2011, the value of the derivative was determined to be de minimis. Accordingly, no value has been assigned at issuance or at March 31, 2009.
The Convertible Notes mature on October 1, 2026 unless earlier redeemed, repurchased or converted. The Company may redeem the Convertible Notes for cash, either in whole or in part, anytime on or after October 6, 2011 at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the Convertible Notes to be redeemed plus accrued and unpaid interest, including contingent interest
81
and additional amounts, if any, up to but not including the date of redemption. In addition, holders of the Convertible Notes will have the right to require the Company to repurchase for cash all or a portion of their Convertible Notes on October 1, 2011, 2016 and 2021, at a repurchase price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the Convertible Notes to be repurchased plus accrued and unpaid interest, including contingent interest and additional amounts, if any, up to, but not including, the date of repurchase. The Convertible Notes are convertible into the Company's common stock at a rate equal to 18.3655 shares per $1,000 principal amount of the Convertible Notes (equal to an initial conversion price of approximately $54.45 per share), subject to adjustment as described in the Indenture. Upon conversion, the Company will deliver to the holder surrendering the Convertible Notes for conversion, for each $1,000 principal amount of Convertible Notes, an amount consisting of cash equal to the lesser of $1,000 and the Company's total conversion obligation and, to the extent that the Company's total conversion obligation exceeds $1,000, at the Company's election, cash or shares of the Company's common stock in respect of the remainder.
The Convertible Notes are eligible for conversion upon meeting certain conditions as provided in the indenture agreement. For the periods from October 1, 2007 through December 31, 2007 and January 1, 2008 through March 31, 2008, the Convertible Notes were eligible for conversion; however, during this period, none of the Convertible Notes were converted.
To be included in the calculation of diluted earnings per share, the average price of the Company's common stock for the fiscal year must exceed the conversion price per share of $54.45. The average price of the Company's stock for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2010 and March 31, 2009 was $46.68 and $46.49, respectively. Therefore, no additional shares were included in the diluted earnings per share calculations for those fiscal years. The average price of the Company's stock for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2008 was $68.95. Accordingly, 777,059 additional shares were included in the diluted earnings per share calculation.
If the Company undergoes a fundamental change, holders of the Convertible Notes will have the right, subject to certain conditions, to require the Company to repurchase for cash all or a portion of their Convertible Notes at a repurchase price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the Convertible Notes to be repurchased plus accrued and unpaid interest, including contingent interest and additional amounts, if any.
During fiscal 2010, the Company paid $4.0 million to purchase $4.2 million in principal on the Convertible Notes, resulting in a reduction in the carrying amount of the Convertible Notes of $3.8 million and a gain on extinguishment of less than $0.1 million. During fiscal 2009, we paid $15.4 million to purchase $18.0 million of principal on the convertible senior subordinated notes, resulting in a reduction in the carrying amount of the Convertible Notes of $16.3 million and a gain on early extinguishment of $0.9 million.
The indentures under the Company's debt agreements and the Revolving Credit Facility contain restrictions and covenants which include limitations on the Company's ability to incur additional indebtedness, issue stock options or warrants, make certain restricted payments and acquisitions, create liens, enter into transactions with affiliates, sell substantial portions of its assets and pay cash dividends. Additional covenants require compliance with financial tests, including leverage and interest coverage ratio.
On April 18, 2008, the Company entered into a financing agreement amendment with the City of Shelbyville, Indiana related to the City of Shelbyville, Indiana Economic Development Revenue Bonds, Series 2005 (the "2005 Bonds"). The amendment divides the original $6.3 million bond, of which $5.8 million was drawn as of April 18, 2008, into two separate bonds, a floating rate bond and a fixed rate bond that replace the original bond in its entirety. Both bonds are due to mature on October 1, 2020. The floating rate bond, Series 2005A, is authorized to be issued in the aggregate principal amount of $0.5 million, and bears interest at a variable rate equal to approximately ninety percent of the
82
three-month LIBOR rate (the effective rate was 2.00% at June 30, 2010). The proceeds of the Series 2005A Bonds of up to $0.5 million were used to fund the expansion of one of the Company's subsidiary's facility. The fixed rate bond, Series 2005B, is authorized to be issued in the aggregate principal amount of $5.8 million, and bears interest at a fixed rate equal to 4.45%.
On April 18, 2008, the Company entered into a loan agreement with the Montgomery County Industrial Development Authority related to the Economic Development Revenue Bond, Series 2008 (the "2008 Bonds"). The proceeds of the 2008 Bonds of up to $5.0 million were used to fund improvements to property and equipment at one of the Company's subsidiaries. The 2008 Bonds are due to mature on April 18, 2023 and bear interest at a variable rate equal to approximately ninety percent of the three-month LIBOR rate (the effective rate was 2.50% at June 30, 2010). As of June 30, 2010, $2.1 million was drawn against the 2008 Bonds.
Capital expenditures were approximately $31.7 million for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 and $16.9 million for the three months ended June 30, 2010, primarily for manufacturing machinery and equipment. For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, we funded these expenditures through borrowings under our 2009 Credit Facility and for the three months ended June 30, 2010, we funded these expenditures through cash generated from operations. We expect capital expenditures to be approximately $80.0 to 90.0 million for our fiscal year ending March 31, 2011. The expenditures are expected to be used mainly to expand capacity or replace old equipment at several facilities.
The expected future cash flows for the next five years for long term debt, leases and other obligations are as follows:
| | Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Contractual Obligations | Total | Less than 1 Year | 1 - 3 Years | 3 - 5 Years | After 5 Years | |||||||||||
| | (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||
Debt principal(1) | $ | 1,349,820 | $ | 139,664 | $ | 213,345 | $ | 114,534 | $ | 882,277 | ||||||
Debt-interest(2) | 375,140 | 53,532 | 102,324 | 92,475 | 126,809 | |||||||||||
Operating leases | 90,772 | 28,830 | 30,277 | 17,976 | 13,689 | |||||||||||
Contingent payments(3) | 48,775 | 12,500 | 18,449 | 17,826 | — | |||||||||||
Purchase obligations | 901,470 | 562,145 | 338,168 | 1,108 | 49 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 2,765,977 | $ | 796,671 | $ | 702,563 | $ | 243,919 | $ | 1,022,824 | ||||||
- (1)
- Included in the Company's consolidated balance sheet at June 30, 2010, plus discounts on the Convertible Notes, Term Loan Facility, the 2017 Notes and 2018 Notes of $7.9 million and $1.7 million, $2.4 million and $2.5 million, respectively, being amortized to expense through September 2011, July 2016, November 2017 and July 2018, respectively.
- (2)
- Includes fixed-rate interest only.
- (3)
- Includes unrecorded contingent payments in connection with the fiscal 2009 acquisitions.
The above table excludes unrecognized tax benefits of $6.7 million as of June 30, 2010 since we cannot predict with reasonable certainty the timing of cash settlements with the respective taxing authorities.
The table also excludes our pension benefit obligations. We made contributions to our union pension plans of $1.5 million and $0.3 million in fiscal 2010 and 2009, respectively. As a result of the Vought Acquisition, we expect to make total pension and post-retirement plan contributions of $165.0 million to our defined benefit plans during fiscal 2011. The Company is required to make minimum contributions to its defined benefit pension plans under the minimum funding requirements of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act, the Pension Funding Equity Act of 2004 and the Pension
83
Protection Act of 2006. On June 25, 2010, the Preservation of Access to Care for Medical Beneficiaries and Pension Relief Act of 2010 (the "Relief Act"), was signed into law. The Relief Act provides for temporary, targeted funding relief (subject to certain terms and conditions) for single employer and multiemployer pension plans that suffered significant losses in asset value due to the steep market slide in 2008. The Relief Act could have a significant impact on plan contributions beyond fiscal 2011.
We believe that cash generated by operations and borrowings under the Revolving Credit Facility will be sufficient to meet anticipated cash requirements for our current operations for the foreseeable future. However, we have a stated policy to grow through acquisitions and are continuously evaluating various acquisition opportunities. As a result, we currently are pursuing the potential purchase of a number of candidates. In the event that more than one of these transactions are successfully consummated, the availability under the Revolving Credit Facility might be fully utilized and additional funding sources may be needed. There can be no assurance that such funding sources will be available to us on terms favorable to us, if at all.
Critical Accounting Policies
Critical accounting policies are those accounting policies that can have a significant impact on the presentation of our financial condition and results of operations, and that require the use of complex and subjective estimates based upon past experience and management's judgment. Because of the uncertainty inherent in such estimates, actual results may differ from these estimates. Below are those policies applied in preparing our financial statements that management believes are the most dependent on the application of estimates and assumptions. For additional accounting policies, see Note 2 of "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements."
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Trade receivables are presented net of an allowance for doubtful accounts. In determining the appropriate allowance, we consider a combination of factors, such as industry trends, our customers' financial strength and credit standing, and payment and default history. The calculation of the required allowance requires a judgment as to the impact of these and other factors on the ultimate realization of our trade receivables. We believe that these estimates are reasonable and historically have not resulted in material adjustments in subsequent periods when the estimates are adjusted to actual amounts.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market using the average cost or specific identification methods. We write down our inventory for estimated obsolescence or unmarketable inventory equal to the difference between the cost of inventory and estimated market value based upon assumptions about future demand and market conditions. If actual market conditions are less favorable than those anticipated, inventory adjustments may be required. We believe that these estimates are reasonable and historically have not resulted in material adjustments in subsequent periods when the estimates are adjusted to actual amounts.
Revenue and Profit Recognition
Revenues are recognized in accordance with the contract terms when products are shipped, delivery has occurred or services have been rendered, pricing is fixed or determinable, and collection is reasonably assured.
A significant portion of our contracts are within the scope of theRevenue—Construction-Type and Production-Type Contracts topic of the ASC and revenue and costs on contracts are recognized using percentage-of-completion methods of accounting. Accounting for the revenue and profit on a contract requires estimates of (1) the contract value or total contract revenue, (2) the total costs at completion,
84
which is equal to the sum of the actual incurred costs to date on the contract and the estimated costs to complete the contract's scope of work and (3) the measurement of progress towards completion. Depending on the contract, we measure progress toward completion using either the cost-to-cost method or the units-of-delivery method.
- •
- Under the cost-to-cost method, progress toward completion is measured as the ratio of total costs incurred to our estimate of total costs at completion. We recognize costs as incurred. Profit is determined based on our estimated profit margin on the contract multiplied by our progress toward completion. Revenue represents the sum of our costs and profit on the contract for the period.
- •
- Under the units-of-delivery method, revenue on a contract is recorded as the units are delivered and accepted during the period at an amount equal to the contractual selling price of those units. The costs recorded on a contract under the units-of-delivery method are equal to the total costs at completion divided by the total units to be delivered. As our contracts can span multiple years, we often segment the contracts into production lots for the purposes of accumulating and allocating cost. Profit is recognized as the difference between revenue for the units delivered and the estimated costs for the units delivered.
Adjustments to original estimates for a contract's revenues, estimated costs at completion and estimated total profit are often required as work progresses under a contract, as experience is gained and as more information is obtained, even though the scope of work required under the contract may not change, or if contract modifications occur. These estimates are also sensitive to the assumed rate of production. Generally, the longer it takes to complete the contract quantity, the more relative overhead that contract will absorb. The impact of revisions in cost estimates is recognized on a cumulative catch-up basis in the period in which the revisions are made. Provisions for anticipated losses on contracts are recorded in the period in which they become evident ("forward losses") and are first offset against costs that are included in inventory, with any remaining amount reflected in accrued contract liabilities in accordance with theRevenue—Construction-Type and Production-Type Contracts topic. Revisions in contract estimates, if significant, can materially affect our results of operations and cash flows, as well as our valuation of inventory. Furthermore, certain contracts are combined or segmented for revenue recognition in accordance with theRevenue—Construction-Type and Production-Type Contracts topic.
Advance payments and progress payments received on contracts-in-process are first offset against related contract costs that are included in inventory, with any remaining amount reflected in current liabilities.
Amounts representing contract change orders or claims are only included in revenue when such change orders or claims have been settled with our customer and to the extent that units have been delivered. Additionally, some contracts may contain provisions for revenue sharing, price re-determination, requests for equitable adjustments, change orders or cost and/or performance incentives. Such amounts or incentives are included in contract value when the amounts can be reliably estimated and their realization is reasonably assured.
Although fixed-price contracts, which extend several years into the future, generally permit us to keep unexpected profits if costs are less than projected, we also bear the risk that increased or unexpected costs may reduce our profit or cause the Company to sustain losses on the contract. In a fixed-price contract, we must fully absorb cost overruns, not withstanding the difficulty of estimating all of the costs we will incur in performing these contracts and in projecting the ultimate level of revenue that may otherwise be achieved.
Our failure to anticipate technical problems, estimate delivery reductions, estimate costs accurately or control costs during performance of a fixed price contract may reduce the profitability of a fixed price contract or cause a loss. We believe we have recorded adequate provisions in the financial
85
statements for losses on fixed-price contracts, but we cannot be certain that the contract loss provisions will be adequate to cover all actual future losses.
The Aftermarket Services Segment provides repair and overhaul services, certain of which services are provided under long term power-by-the-hour contracts. The Company applies the proportional performance method to recognize revenue under these contracts. Revenue is recognized over the contract period as units are delivered based on the relative fair value in proportion to the total estimated contract consideration. In estimating the total contract consideration, we evaluate the projected utilization of our customer's fleet over the term of the contract, in connection with the related estimated repair and overhaul servicing requirements to the fleet based on such utilization. Changes in utilization of the fleet by our customers, among other factors, may have an impact on these estimates and require adjustments to our estimates of revenue to be realized.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives are not amortized; rather, they are tested for impairment on at least an annual basis. Additionally, intangible assets with finite lives continue to be amortized over their useful lives.
The Company's operating segments of Aerospace Systems and Aftermarket Services are also the reporting units under ASC 350,Intangibles—Goodwill and Other. The Chief Executive Officer, President and Chief Operating Officer and the Chief Financial Officer comprise the Company's Chief Operating Decision Maker ("CODM"). The Company's CODM evaluates performance and allocates resources based upon review of segment information. Each of the operating segments is comprised of a number of operating units which are considered to be components under ASC 350. The operating units, for which discrete financial information exists, are aggregated for purposes of goodwill impairment testing. The Company's acquisition strategy is to acquire companies that complement and enhance the capabilities of the operating segments of the Company. Each acquisition is assigned to either the Aerospace Systems reporting unit or the Aftermarket Services reporting unit. The goodwill that results from each acquisition is also assigned to the reporting unit to which the acquisition is allocated, because it is that reporting unit which is intended to benefit from the synergies of the acquisition.
ASC 350 requires a two-step impairment test for goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives. The first step is to compare the carrying amount of the reporting unit's assets to the fair value of the reporting unit. If the fair value exceeds the carrying value, no further work is required and no impairment loss is recognized. If the carrying amount exceeds the fair value, then the second step is required to be completed, which involves allocating the fair value of the reporting unit to each asset and liability, with the excess being implied goodwill. An impairment loss occurs if the amount of the recorded goodwill exceeds the implied goodwill. The determination of the fair value of our reporting units is based, among other things, on estimates of future operating performance of the reporting unit being valued. We are required to complete an impairment test for goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives and record any resulting impairment losses at least annually. Changes in market conditions, among other factors, may have an impact on these estimates and require interim impairment assessments.
We completed our required annual impairment test in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010 and determined that there was no impairment. Our methodology for determining the fair value of a reporting unit includes the use of an income approach which discounts future net cash flows to their present value at a rate that reflects the Company's cost of capital, otherwise known as the discounted cash flow method ("DCF"). These estimated fair values are based on estimates of future cash flows of the businesses. Factors affecting these future cash flows include the continued market acceptance of the products and services offered by the businesses, the development of new products and services by the businesses and the underlying cost of development, the future cost structure of the businesses, and
86
future technological changes. The Company also incorporated market multiples for comparable companies in determining the fair value of our reporting units. Any such impairment would be recognized in full in the reporting period in which it has been identified.
In fiscal 2010, we conducted additional sensitivity analysis to assess the risk for potential impairment based upon changes in the key assumptions in our goodwill valuation test. We reviewed the Aftermarket Services reporting unit since it had significant changes in its economic indicators and adjusted for select changes in the risk adjusted discount rate to consider both the current return requirements of the market and the risks inherent in the reporting unit, expected long-term growth rate and cash flow projections to determine if any decline in the estimated fair value of a reporting unit could result in a goodwill impairment. Based upon our additional analysis, it was determined that there was no impairment to be recognized, however, the fair value of our Aftermarket Services reporting unit was not substantially in excess of its carrying amount, as the fair value exceeded the carrying value by approximately 5%. The amount of goodwill for our Aftermarket Services reporting unit amounted to $74.1 million at March 31, 2010. Going forward, we will continue to monitor the performance of this reporting unit in relation to the key assumptions in our analysis. If management determines that impairment exists, the impairment will be recognized in the period in which it is identified.
In the event that market multiples for stock price to EBITDA in the aerospace and defense markets decrease, or the expected EBITDA for our reporting units decreases, a goodwill impairment charge may be required, which would adversely affect our operating results and financial condition. No impairment charges have been incurred during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2010, 2009 or 2008.
Finite-lived intangible assets are amortized over their useful lives ranging from 5 to 30 years. We continually evaluate whether events or circumstances have occurred that would indicate that the remaining estimated useful lives of our long-lived assets, including intangible assets, may warrant revision or that the remaining balance may not be recoverable. Intangible assets are evaluated for indicators of impairment. When factors indicate that long-lived assets, including intangible assets, should be evaluated for possible impairment, an estimate of the related undiscounted cash flows over the remaining life of the long-lived assets, including intangible assets, is used to measure recoverability. Some of the more important factors we consider include our financial performance relative to our expected and historical performance, significant changes in the way we manage our operations, negative events that have occurred, and negative industry and economic trends. If any impairment is indicated, measurement of the impairment will be based on the difference between the carrying value and fair value of the asset, generally determined based on the present value of expected future cash flows associated with the use of the asset. For the fiscal years ended March 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008, there were no reductions to the remaining useful lives and no write-downs of long-lived assets, including intangible assets, were required.
Post-retirement Plans
The liabilities and net periodic cost of our pension and other post-retirement plans are determined using methodologies that involve several actuarial assumptions, the most significant of which are the discount rate, the expected long-term rate of asset return, the assumed average rate of compensation increase and rate of growth for medical costs. The actuarial assumptions used to calculate these costs are reviewed annually or when a remeasurement is necessary. Assumptions are based upon management's best estimates, after consulting with outside investment advisors and actuaries, as of the measurement date.
The assumed discount rate utilized is based on a point in time estimate as of our annual measurement date or as of remeasurement dates as needed. This rate is determined based upon on a review of yield rates associated with long-term, high quality corporate bonds as of the measurement
87
date and use of models that discount projected benefit payments using the spot rates developed from the yields on selected long-term, high quality corporate bonds.
The assumed expected long-term rate of return on assets is the weighted average rate of earnings expected on the funds invested or to be invested to provide for the benefits included in the Projected Benefit Obligation ("PBO"). The expected average long-term rate of return on assets is based principally on the counsel of our outside investment advisors. This rate is based on actual historical returns and anticipated long-term performance of individual asset classes with consideration given to the related investment strategy. This rate is utilized principally in calculating the expected return on plan assets component of the annual pension expense. To the extent the actual rate of return on assets realized over the course of a year differs from the assumed rate, that year's annual pension expense is not affected. The gain or loss reduces or increases future pension expense over the average remaining service period of active plan participants expected to receive benefits.
The assumed average rate of compensation increase represents the average annual compensation increase expected over the remaining employment periods for the participating employees. This rate is utilized principally in calculating the PBO and annual pension expense.
In addition to our defined benefit pension plans, we provide certain healthcare and life insurance benefits for some retired employees. Such benefits are unfunded as of June 30, 2010. Employees achieve eligibility to participate in these contributory plans upon retirement from active service if they meet specified age and years of service requirements. Election to participate for eligible employees must be made at the date of retirement. Qualifying dependents at the date of retirement are also eligible for medical coverage. Current plan documents reserve our right to amend or terminate the plans at any time, subject to applicable collective bargaining requirements for represented employees. From time to time, we have made changes to the benefits provided to various groups of plan participants. Premiums charged to most retirees for medical coverage prior to age 65 are based on years of service and are adjusted annually for changes in the cost of the plans as determined by an independent actuary. In addition to this medical inflation cost-sharing feature, the plans also have provisions for deductibles, co-payments, coinsurance percentages, out-of-pocket limits, schedules of reasonable fees, preferred provider networks, coordination of benefits with other plans, and a Medicare carve-out.
In accordance with theCompensation—Retirement Benefits topic of the ASC we recognized the funded status of our benefit obligation in our statement of financial position as of December 31, 2008. This funded status is remeasured as of our annual remeasurement date. The funded status is measured as the difference between the fair value of the plan's assets and the PBO or accumulated postretirement benefit obligation of the plan. In order to recognize the funded status, we determined the fair value of the plan assets. The majority of our plan assets are publicly traded investments which were valued based on the market price as of the date of remeasurement. Investments that are not publicly traded were valued based on the estimated fair value of those investments as of the remeasurement date based on our evaluation of data from fund managers and comparable market data.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2008, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued FASB Staff Position ("FSP") No. 157-1, which amends Statement of Financial Accounting Standards ("SFAS") No. 157,Fair Value Measurements ("SFAS 157") to exclude SFAS No. 13,Accounting for Leases, and other accounting pronouncements that address fair value measurements for lease transactions, and FSP No. 157-2, which primarily were codified into ASC 820,Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures ("ASC 820") and delayed the effective date of SFAS 157 as it relates to nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities until April 1, 2009 for the Company, except for items that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the Company's financial statements on a recurring basis. The nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial
88
liabilities for which the Company had previously not applied the fair value provisions of SFAS 157 include: goodwill; intangible and other long-lived asset impairment testing; asset retirement obligations; liabilities for exit or disposal activities; and business combinations. The adoption had no impact on the Company's financial position, results of operations and cash flows as the Company did not have any non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities that were recognized or disclosed at fair value on a recurring basis at March 31, 2009.
In April 2009, the FASB issued FSP No. 157-4,Determining Fair Value When the Volume and Level of Activity for the Asset or Liability Have Significantly Decreased and Identifying Transactions That Are Not Orderly, which primarily was codified into ASC 820. The FSP requires entities to evaluate the significance and relevance of market factors for fair value inputs to determine if, due to reduced volume and market activity, the factors are still relevant and substantive measures of fair value. The FSP is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after June 15, 2009, and the adoption did not have any effect on our financial position or results of operations.
In December 2008, the FASB issued FSP FAS 132(R)-1,Employers' Disclosures about Postretirement Benefit Plan Assets, which primarily was codified into ASC 715,Compensation and Benefits. This FSP amends SFAS No. 132 (revised 2003),Employers' Disclosures about Pensions and Other Postretirement Benefits, to provide guidance on an employer's disclosures about plan assets of a defined benefit pension or other postretirement plan on investment policies and strategies, major categories of plan assets, inputs and valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of plan assets and significant concentrations of risk within plan assets. This FSP was effective for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2009, with earlier application permitted. Upon initial application, the provisions of this FSP are not required for earlier periods that are presented for comparative purposes. The required disclosures under the FSP have been included in Note 14 of "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements."
In April 2009, the FASB issued FSP FAS 107-1 and APB 28-1, which was primarily codified into ASC 825,Financial Instruments. This FSP amends SFAS No. 107,Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments, to require disclosures about fair value of financial instruments not measured on the balance sheet at fair value in interim financial statements as well as in annual financial statements. Prior to this FSP, fair values for these assets and liabilities were only disclosed annually. This FSP applies to all financial instruments within the scope of SFAS 107 and requires all entities to disclose the method(s) and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value of financial instruments. This FSP was effective for interim periods ending after June 15, 2009, with early adoption permitted for periods ending after March 15, 2009. The Company adopted this FSP in the quarter ended December 31, 2009 and the adoption of this FSP did not have a material effect on its disclosures.
Effective April 1, 2009, the Company adopted SFAS No. 141(R),Business Combinations ("SFAS 141(R)") which was primarily codified into ASC 805,Business Combinations, and SFAS No. 160,Accounting and Reporting of Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements, an amendment of ARB No. 51 ("SFAS 160"), which was primarily codified into ASC 810,Consolidations. SFAS 141(R) and SFAS 160 significantly change the accounting for and reporting of business combination transactions and noncontrolling (minority) interests. The adoption of SFAS 141(R) and SFAS 160 did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
89
VOUGHT MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF VOUGHT'S
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The information contained in the following section does not reflect the consummation of the Vought Acquisition which occurred on June 16, 2010 and is substantially reproduced from Vought's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010 and Vought's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2010. The following discussion contains Vought management's discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations for Vought and should be read in conjunction with Vought's consolidated financial statements and the related notes and interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements and the related notes which are incorporated by reference into this prospectus.
Overview
Vought is a leading global manufacturer and developer of aerostructures serving commercial, military and business jet aircraft. Its products are used on many of the largest and longest running programs in the aerospace industry. Vought is also a key supplier on newer platforms that Vought believes have high growth potential. Vought generates approximately 50% of its revenues from the commercial aircraft market but is also diversified across the military and business jet markets, which provide the balance of its revenues.
Vought's customer base consists of leading aerospace original equipment manufacturers or OEMs, including Airbus, Boeing, Cessna, Gulfstream, Hawker Beechcraft, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman and Sikorsky, as well as the U.S. Air Force. Vought generates over 80% of its revenues from its three largest customers, Airbus, Boeing and Gulfstream.
Although the majority of its revenues are generated by sales in the U.S. market, Vought generates approximately 10% of its revenue from sales outside of the United States.
Most of Vought's revenues are generated under long-term contracts. Its customers typically place orders well in advance of required deliveries, which gives Vought considerable visibility with respect to its future revenues. These advance orders also generally create a significant backlog for Vought, which was approximately $2.1 billion at December 31, 2009 and March 28, 2010. Vought's calculation of backlog includes only firm orders for commercial and business jet programs and funded orders for government programs, which causes its backlog to be substantially lower than the estimated aggregate dollar value of its contracts and may not be comparable to others in the industry.
For Vought's commercial and business jet programs, changes in the economic environment and the financial condition of airlines may cause its customers to increase or decrease deliveries, adjusting firm orders that would affect Vought's backlog. Also, volatility in the financial markets may impact the overall demand for Vought's commercial and business aircraft products. To the extent financial market conditions worsen, Vought could experience decline in the future on demand for its commercial and business aircraft products. For its military aircraft programs, the Department of Defense and other government agencies have the right to terminate both Vought's contracts and/or Vought's customers' contracts either for default or, if the government deems it to be in its best interest, for convenience.
The market for Vought's commercial, military and business jet programs has historically been cyclical. While the commercial, military and business jet markets experienced a period of increased production in recent years, the unprecedented global market and economic conditions along with tighter credit conditions resulted in reduced aircraft demand in 2009. These factors have led to a decrease in spending by businesses and consumers alike, and could continue to have an adverse effect on the demand for Vought's aerostructures by both Vought's commercial customers and the U.S. government for the next few years. Additionally, future volatility in the U.S. and international markets and economies and delayed recovery of business and consumer spending could adversely affect
90
Vought's liquidity and financial condition, including its ability to refinance maturing liabilities and access the capital markets to meet liquidity needs and the liquidity and financial condition of its customers.
Commercial Aircraft. Sales to the commercial aircraft market are affected by the financial health of the commercial airline industry, passenger and cargo air traffic, the introduction of new aircraft models, and the availability and profile of used aircraft. Production rates slowed on many of Vought's commercial aircraft in 2009 and Vought expects those lower rates to continue through 2010 with a slow recovery thereafter.
Military Aircraft. U.S. national defense spending and procurement funding decisions, global geopolitical conditions, and current operational use of the existing military aircraft fleet drive sales in the military aircraft market. Vought believes that the demand for its rotorcraft programs, which are some of the key equipment being used in military operations, will experience some pressure during the next several years. Historically, the majority of Vought's military revenues and a significant portion of its total revenue have been generated from its C-17 program. The U.S. government has funded aircraft that would support C-17 production through mid-2012. However, Vought's business could be adversely impacted if the Government does not fund additional C-17 aircraft.
Business Jet Aircraft. Sales to the business jet aircraft market are driven by long-term economic expansion, the increasing inconvenience of commercial airline travel, growing international acceptance and demand for business jet travel, fractional ownership of business jets and the introduction of new business jet models. Reflecting the pressures in the financial and business markets in 2009, Vought experienced reduced production rates on several of its programs and was notified of the suspension of the Cessna Citation Columbus—Model 850 program. Vought expects those reduced delivery rates to continue through the end of 2010 with slow recovery thereafter. In spite of these pressures, as a major supplier to the top-selling G350, G450, G500 and G550 and Citation X programs, Vought still believes it is well positioned to operate in key segments of the business jet market as macro-economic conditions continue to improve.
On July 30, 2009, Vought sold the assets and operations of its 787 business conducted at North Charleston, South Carolina to a wholly owned subsidiary of The Boeing Company. Concurrent with the closing of the transaction, Vought entered into an agreement terminating and resolving rights and obligations under the existing 787 supply agreement. Under a newly negotiated contract, Vought still manufactures certain components for the 787 program as well as provides engineering services to Boeing pursuant to an engineering services agreement. Vought is providing certain transition services to Boeing pursuant to a transition services agreement and performing new work scope on the Boeing 737 and 777 aircraft pursuant to a long-term supply agreement.
Under the terms of the senior credit facility, Vought is required to prepay or refinance any amounts outstanding of its $270.0 million Senior Notes by the last business day of 2010 or it must repay the aggregate amount of loans outstanding at that time under the senior credit facility unless a lender waives such prepayment (so long as a majority of its lenders (voting on a class basis) agree to such waiver). Because of the requirement to refinance the Senior Notes, the amounts outstanding under Vought's senior credit facility have been classified as a current liability as of March 28, 2010.
On March 23, 2010, Vought entered into a merger agreement with Triumph Group, Inc. pursuant to which Vought will be acquired by Triumph. It is anticipated that in connection with that transaction all of Vought's currently outstanding material indebtedness will be repaid in full. The consummation of the acquisition is subject to, among other things, approval of Triumph's stockholders and other customary closing conditions, which may not be satisfied. In the event that the anticipated acquisition is not completed and such indebtedness remains outstanding, Vought plans to refinance its senior credit facility or the Senior Notes prior to the last business day of 2010. There are no assurances that Vought
91
will be able to refinance on commercially reasonable terms or at all. This creates an uncertainty about Vought's ability to continue as a going concern. Notwithstanding this, the consolidated financial statements and related notes have been prepared assuming that Vought will continue as a going concern.
Basis of Presentation
The following provides a brief description of some of the items that appear in Vought's financial statements and general factors that impact these items. It is Vought's practice to close its books and records based on a thirteen-week quarter, which can lead to different period end dates for comparative purposes. The interim financial statements and tables of financial information included herein are labeled based on that convention. This practice only affects interim periods, as Vought's fiscal years end on December 31.
Revenue and Profit Recognition. Vought records revenue and profit for its long-term contracts using a percentage of completion method with, depending on the contract, either cost-to-cost or units-of-delivery as its basis to measure progress toward completing the contract.
- •
- Under the cost-to-cost method, progress toward completion is measured as the ratio of total costs incurred to Vought's estimate of total costs at completion. Vought recognizes costs as incurred. Profit is determined based on Vought's estimated profit margin on the contract multiplied by its progress toward completion. Revenue represents the sum of Vought's costs and profit on the contract for the period.
- •
- Under the units-of-delivery method, revenue on a contract is recorded as the units are delivered and accepted during the period at an amount equal to the contractual selling price of those units. The costs recorded on a contract under the units-of-delivery method are equal to the total costs at completion divided by the total units to be delivered. As Vought's contracts can span multiple years, it often segments the contracts into production lots for the purposes of accumulating and allocating cost. Profit is recognized as the difference between revenue for the units delivered and the estimated costs for the units delivered.
Amounts representing contract change orders or claims are only included in revenue when such change orders or claims have been settled with Vought's customer and to the extent that units have been delivered. Additionally, some of Vought's contracts may contain terms or provisions, such as price re-determination, requests for equitable adjustments or price escalation, which are included in its estimate of contract value when the amounts can be reliably estimated and their realization is reasonably assured.
The impact of revisions in estimates is recognized on the cumulative catch-up basis in the period in which such revisions are made. Changes in Vought's estimates of contract value or profit can impact revenue and/or cost of sales. For example, in the case of a customer settlement of a pending change order or claim, Vought may recognize additional revenue and/or margin depending on the production lot's stage of completion. Provisions for anticipated losses on contracts are recorded in the period in which they become evident ("forward losses").
For a further discussion of Vought's revenue recognition policy, see "—Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates—Revenue and Profit Recognition."
Cost of sales. Cost of sales includes direct production costs such as labor (including fringe benefits), material costs, manufacturing and engineering overhead and production tooling costs. Examples of costs included in overhead are costs related to quality assurance, information technology, indirect labor and fringe benefits, depreciation and amortization and other support costs such as supplies and utilities.
92
Selling, general and administrative expenses. Selling, general and administrative expenses include expenses for executive management, program management, business management, human resources, accounting, treasury, and legal. The major cost elements of selling, general and administrative expenses include salary and wages, fringe benefits, stock compensation expense, travel and supplies. In addition, these expenses include period expenses for non-recurring program development, such as research and development and other non-recurring activities, as well as costs that are not reimbursed under U.S. Government contract terms.
Interest expense, net. Interest expense, net reflects interest income and expense, and includes the amortization of capitalized debt origination costs and the amortization of the original issue discount on an additional $200.0 million of term loans Vought borrowed pursuant to its existing senior credit facilities ("Incremental Facility").
Other income (loss). Other income (loss) represents miscellaneous items unrelated to Vought's core operations.
Equity in loss of joint venture. Equity in loss of joint venture reflected Vought's share of the loss from Global Aeronautica, a joint venture in which Vought formerly participated. As a result of the sale of its equity interest in Global Aeronautica in 2008, Vought's results of operations are no longer impacted by this joint venture.
Income tax benefit (expense). Income tax benefit (expense) represents federal income tax provided on Vought's net book income from continuing operations. For a further discussion of Vought's income tax provision, please see Note 15—Income Taxes in the notes to Vought's consolidated financial statements and Note 10—Income Taxes in the notes to Vought's interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax. Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax represents the revenue and expenses associated with Vought's 787 business conducted at North Charleston, South Carolina that was sold to Boeing Commercial Airplanes Charleston South Carolina, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of The Boeing Company on July 30, 2009 ("Sale of the Charleston 787 business"). Vought's gain on the sale of this business is also reflected as income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax. See Note 3—Discontinued Operations in the notes to Vought's consolidated financial statements and in the notes to Vought's interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
93
Results of Operations
Quarter Ended March 28, 2010 Compared to Quarter ended March 29, 2009
| | Three Months Ended March 28, 2010 | Three Months Ended March 29, 2009 | $ Change | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | (in millions) | ||||||||||
Revenue: | |||||||||||
Commercial | $ | 229.9 | $ | 168.5 | $ | 61.4 | |||||
Military | 172.9 | 146.2 | 26.7 | ||||||||
Business jets | 67.7 | 75.6 | (7.9 | ) | |||||||
Total revenue | $ | 470.5 | $ | 390.3 | $ | 80.2 | |||||
Costs and expenses: | |||||||||||
Cost of sales | 391.5 | 324.8 | 66.7 | ||||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 39.7 | 28.5 | 11.2 | ||||||||
Total costs and expenses | $ | 431.2 | $ | 353.3 | $ | 77.9 | |||||
Operating income | 39.3 | 37.0 | 2.3 | ||||||||
Interest expense, net | (12.5 | ) | (14.8 | ) | 2.3 | ||||||
Income tax expense | — | — | — | ||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 26.8 | $ | 22.2 | $ | 4.6 | |||||
Income from discontinued operations, net of tax | — | (4.3 | ) | 4.3 | |||||||
Net Income | $ | 26.8 | $ | 17.9 | $ | 8.9 | |||||
Revenues. Revenue for the three months ended March 28, 2010 was $470.5 million, an increase of $80.2 million, or 21%, compared with the same period in the prior year. When comparing the first quarter of 2010 with the same period in the prior year:
- •
- Commercial revenue increased $61.4 million, or 36%, primarily due to increased sales for the 747-8 program.
- •
- Military revenue increased $26.7 million, or 18% mainly due to increased deliveries for the V-22 and C-130 programs as well as higher spares deliveries for the C-17 program.
- •
- Business Jet revenue decreased $7.9 million, or 10%, primarily due to the absence in 2010 of non-recurring sales for the Cessna Citation Columbus 850.
Operating income. Operating income from continuing operations for the three months ended March 28, 2010 was $39.3 million, an increase of $2.3 million, or 6%, compared with $37.0 million for the comparable period in the prior year. This increase was largely due to increased deliveries on 747-8 program and the absence in 2010 of a pension and other post-employment benefits curtailment charge recognized in 2009 that resulted from the IAM collective bargaining agreement in Nashville partially offset by lower margins on military programs.
Interest expense, net. Interest expense, net for the three-month period ended March 28, 2010 was $12.5 million, a decrease of $2.3 million, or 16%, compared with $14.8 million for the same period in the prior year. Interest expense decreased due to lower outstanding debt balances in 2010 as compared to 2009.
Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax. Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax for the three-month period ended March 29, 2009 was $4.3 million reflecting the loss recognized on the operations of the 787 business during that period.
94
Year Ended December 31, 2009 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2008
Revenue. Revenue for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $1,877.8 million, an increase of $102.8 million, or 6%, compared with 2008. When comparing the current and the prior year:
- •
- Commercial revenue increased $98.6 million, or 12%. Revenue for Vought's Boeing programs increased $157.5 million primarily for the 747 program and the initial sales for the engineering and transition services agreements for the 787 program. Partially offsetting these increases was a $58.9 million decrease in revenue for Vought's Airbus programs primarily due to the completion of an Airbus program in the second quarter of 2009.
- •
- Military revenue increased $56.9 million, or 9%, primarily due to increased deliveries on the V-22 and, C-130 programs as well as increased spare part deliveries for the C-17 program.
- •
- Business Jet revenue decreased $52.7 million, or 16%, primarily due to reduced delivery rates directed by Vought's customers.
Operating income (loss). Operating income (loss) for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $160.4 million, an increase of $13.6 million, or 9% compared to $146.8 million in 2008. There were several unusual items in 2008 contributing to the 2009 increase in operating income as compared to 2008. Vought's operating income for 2009 excluded two specific items that affected 2008. Those items were the $38.3 million of costs associated with the strike at Vought's Nashville facility and the $17.3 million of higher future projected pension expenses applied to programs. These factors contributed to a reduction in operating income in 2008 as compared to 2009 and were partially offset by the release of $22.6 million of purchase accounting reserves in 2008 reflecting the completion of the 747-400 model deliveries and non-recurring costs of $9.6 million in 2009 reflecting the impact of the pension and other post-retirement benefits curtailment resulting from the 2009 collective bargaining agreement with the International Association of Machinists at Vought's Nashville, Tennessee facility.
Interest expense, net. Interest expense, net for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $56.3 million, a decrease of $6.5 million compared with 2008. Interest expense decreased primarily due to the adjustment during 2009 to capitalize approximately $5.6 million of interest costs to appropriately reflect the book value of Property, Plant and Equipment included in Vought's assets-under-construction balance in fiscal periods prior to 2009. The remainder of the decrease resulted from a reduction in the weighted average outstanding balance during 2009 partially offset by the acceleration of $7.1 million of debt origination costs from the pay down of $355.0 million of term loans outstanding.
Other income (loss). Other income for the year ended December 31, 2008 primarily reflected the $47.1 million gain from the sale of Vought's equity interest in its Global Aeronautica joint venture. Vought did not have a similar transaction during 2009.
Income tax benefit (expense). Income tax benefit for the year ended December 31, 2009 primarily reflects a reversal of $9.1 million of income tax expense due to a change in tax legislation. During the fourth quarter, the President signed into law the Workers, Homeownership and Business Assistance Act of 2009. The Law provides for a suspension of certain limitations on Alternative Minimum Tax net operating losses. Prior to the Law being enacted, Vought had estimated a $9.1 million federal AMT liability incurred in connection with the sale of the Charleston 787 business, and had allocated that expense to discontinued operations. The Law has enabled the Company to fully utilize net operating losses and therefore Vought will not owe AMT for the year. TheIncome Taxes topic of the ASC requires that tax law changes be allocated to continuing operations; therefore Vought recorded a $9.1 million benefit to offset the related expense in discontinued operations. Vought was also able to carryback its 2008 AMT net operating loss to recover $0.4 million of previously paid AMT taxes and recorded a tax benefit in the tax provision.
95
Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax. Income from discontinued operations, net of tax for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $213.6 million primarily due to the sale of the Charleston 787 business recorded during the period. This transaction included $275.0 million of income recognized for the resolution of 787 contractual matters as well as a $38.3 million loss on the sale of the Charleston 787 business.
Year Ended December 31, 2008 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2007
Revenue. Revenue for the year ended December 31, 2008 was $1,775.0 million, an increase of $161.9 million, or 10%, compared with the same period in the prior year. When comparing the current and the prior year:
- •
- Commercial revenue increased $66.0 million, or 8%. Revenue for Vought's Boeing programs increased $49.9 million primarily due to increased non-recurring sales for the 747-8 program and initial deliveries on the 787 program. In addition, revenue for Vought's Airbus programs increased $16.1 million primarily due to higher deliveries.
- •
- Military revenue increased $77.4 million, or 15%, primarily due to higher delivery rates on the H-60 and the V-22 programs.
- •
- Business Jet revenue increased $18.5 million, or 6%, primarily due to increased deliveries to Gulfstream and the initial non-recurring revenue on the Cessna Columbus—Model 850 program.
Operating income (loss). Operating income (loss) for the year ended December 31, 2008 was $146.8 million, a decrease of $48.2 million or 25% compared to 2007. During 2008, overall program margins were lower than the prior year primarily due to a $38.3 million impact from costs associated with the strike at Vought's Nashville facility and a $17.3 million impact related to higher future projected pension expenses applied to programs. The remaining difference in program margins was primarily due to the absence of favorable contract changes recorded in 2007, partially offset by the release of $22.6 million of purchase accounting reserves reflecting the completion of the 747-400 model deliveries.
Interest expense, net. Interest expense, net for the year ended December 31, 2008 was $62.8 million, an increase of $3.8 million compared with the same period in the prior year. Interest expense increased primarily due to higher borrowings and related costs under the Incremental Facility partially offset by a reduction in the effective interest rate on Vought's other variable rate indebtedness.
Other income (loss). Other income (loss) for the year ended December 31, 2008 primarily reflects Vought's $47.1 million gain from the sale of its entire equity interest in Global Aeronautica.
Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax. Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax for the year ended December 31, 2008 was $38.2 million, a decrease of $47.3 million compared with 2007. The decrease was due to a reduction in non-recurring 787 program expenses as the start-up phase of that program ended.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As noted above, the following discussion contains Vought management's discussion and analysis of Vought's liquidity and capital resources on a stand-alone basis for the three months ended March 28, 2010 and the year ended December 31, 2009. In connection with the Vought Acquisition, Triumph retired substantially all of Vought's debt. Following the consummation of the Vought Acquisition on June 16, 2010, Triumph's Securitization Facility and the Revolving Credit Facility are available to finance Vought's liquidity requirements.
96
Liquidity is an important factor in determining Vought's financial stability. Vought is committed to maintaining adequate liquidity. The primary sources of Vought's liquidity include cash flow from operations, borrowing capacity through its credit facility and the long-term capital markets and negotiated advances and progress payments from its customers. Vought's liquidity requirements and working capital needs depend on a number of factors, including the level of delivery rates under its contracts, the level of developmental expenditures related to new programs, growth and contractions in the business cycle, contributions to its pension plans as well as interest and debt payments. Vought's liquidity requirements fluctuate from period to period as a result of changes in the rate and amount of its investments in its programs, changes in delivery rates under existing contracts and production associated with new contracts.
For certain aircraft programs, milestone or advance payments from customers' finance working capital, which helps to improve Vought's liquidity. In addition, Vought may, in the ordinary course of business, settle outstanding claims or other contractual matters with customers or suppliers or Vought may receive payments for change orders not previously negotiated. Settlement of such matters can have a significant impact on its results of operations and cash flows.
Vought believes that cash flow from operations, cash and cash equivalents on hand and funds that will be raised as part of a refinancing or restructuring of its senior credit facility and Senior Notes will provide adequate funding for its ongoing working capital expenditures, pension contributions and capital investments required to meet its current contractual and legal commitments for at least the next twelve months. However, there is no assurance that Vought can refinance the Senior Notes or the senior credit facility prior to the last business day of 2010.
Vought's pension plan funding obligations also impact its liquidity and capital resources. In Vought's annual report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009, Vought provided estimates of its pension plan contributions for 2010 - 2014. Vought's future pension contributions are primarily driven by the funded level of its plans as of December 31 of each fiscal year. Two of the factors used in determining Vought's liability under its plan are the discount rate and the market value of the plan assets.
Macro-economic conditions, the corporate bond rates and the fluctuations in the fair value of Vought's plan assets as a result of the volatility in global financial markets will continue to impact its required contributions in future periods.
Vought's ability to refinance its indebtedness or obtain additional sources of financing will be affected by economic conditions and financial, business and other factors, some of which are beyond its control.
As of March 28, 2010, Vought's total outstanding debt was approximately $590.4 million. This amount includes $270.0 million of 8% Senior Notes due 2011 ("Senior Notes") and $320.4 million of term loans outstanding under its senior credit facilities. Additionally, as of March 28, 2010, Vought had $41.3 million in outstanding letters of credit with $43.4 million of restricted cash as collateral for them. As of December 31, 2009, Vought's total outstanding indebtedness was approximately $589.8 million. This amount included $270.0 million of Senior Notes and $322.2 million of term loans outstanding under its senior credit facility. Additionally, at December 31, 2009, Vought had $41.3 million in outstanding letters of credit.
On July 30, 2009 Vought entered into an Amendment to its Credit Agreement ("Amendment") which modified the Credit Agreement to allow the sale of the Charleston 787 business (discussed in Note 3—Discontinued Operations in the notes to Vought's consolidated financial statements) and provided for use of cash proceeds from the transaction to (i) pay down $355.0 million of term loans outstanding and (ii) repay outstanding amounts on its revolver of $135.0 million and to permanently reduce revolving commitments under the Credit Agreement to $100.0 million. The Amendment
97
converted the synthetic letter of credit facility under the Credit Agreement into additional term loan of $50.0 million, a portion of which is used as cash collateral for letters of credit previously issued under the synthetic letter of credit facility. This term loan is repayable on December 22, 2010. As of December 31, 2009, the cash restricted as collateral for outstanding letters of credit was $43.8 million. The Amendment increased the interest rate on all loans to London Interbank Offering Rate (LIBOR) plus a margin of 4.00%, with a minimum LIBOR floor of 3.50%.
Vought's outstanding term loans, including amounts under the Incremental Facility, are repayable in equal quarterly installments of approximately $1.5 million with the balance due on December 22, 2011. Vought's revolving commitments are scheduled to expire on December 22, 2010. However, Vought has an extension provision that allows it to extend its revolving commitments with lenders who agree to such extension to a date to be agreed. Vought is also obligated to pay an annual commitment fee on the unused portion of its revolver of 0.5% or less, based on its leverage ratio.
Under the terms of the senior credit facility, Vought is required to prepay or refinance any amounts outstanding of its $270.0 million Senior Notes by the last business day of 2010 or Vought must repay the aggregate amount of loans outstanding at that time under the senior credit facility unless a lender waives such prepayment (so long as a majority of Vought's lenders (voting on a class basis) agree to such waiver). Because of the requirement to refinance the Senior Notes, the amounts outstanding under Vought's senior credit facility have been classified as a current liability as of March 28, 2010.
On March 23, 2010, Vought entered into a merger agreement with Triumph Group, Inc. pursuant to which Vought will be acquired by Triumph. It is anticipated that in connection with that transaction all of Vought's currently outstanding material indebtedness will be repaid in full. The consummation of the acquisition is subject to, among other things, approval of Triumph's stockholders and other customary closing conditions, which may not be satisfied. In the event that the anticipated acquisition is not completed and such indebtedness remains outstanding, Vought plans to refinance its senior credit facility or the Senior Notes prior to the last business day of 2010. There are no assurances that Vought will be able to refinance on commercially reasonable terms or at all. This creates an uncertainty about Vought's ability to continue as a going concern. Notwithstanding this, the consolidated financial statements and related notes have been prepared assuming that Vought will continue as a going concern.
Credit Agreements and Debt Covenants. The indenture governing Vought's Senior Notes and its credit agreement contain customary affirmative and negative covenants for facilities of this type, including limitations on its indebtedness, liens, investments, distributions, mergers and acquisitions, dispositions of assets, subordinated debt and transactions with affiliates. The credit agreement also requires that Vought maintains certain financial covenants including a leverage ratio, the requirement to maintain minimum interest coverage ratios, as defined in the agreement, and a limitation on its capital spending levels. The indenture governing Vought's Senior Notes also contains various restrictive covenants, including the incurrence of additional indebtedness unless the debt is otherwise permitted under the indenture. As of March 28, 2010, Vought was in compliance with the covenants in the indenture and its credit agreement.
Vought's senior credit facilities (including its Incremental Facility) are material to its financial condition and results of operations because those facilities are its primary source of liquidity for working capital. The indenture governing Vought's outstanding Senior Notes is material to its financial condition because it governs a significant portion of Vought's long-term capitalization while restricting Vought's ability to conduct its business.
Vought's senior credit facilities use Credit Agreement EBITDA to determine its compliance with two financial maintenance covenants. See "Non-GAAP Financial Measures" below for a discussion of Credit Agreement EBITDA and reconciliation of that non-GAAP financial measure to net cash
98
provided by (used in) operating activities. Vought is required not to permit its consolidated total leverage ratio, or the ratio of funded indebtedness (net of cash) at the end of each quarter to Credit Agreement EBITDA for the twelve months ending on the last day of that quarter, to exceed 4.00:1.00 for fiscal periods ending during 2009, 3.75:1.00 for fiscal periods during 2010 and 3.50:1.00 for fiscal periods thereafter. Vought also is required not to permit its consolidated net interest coverage ratio, or the ratio of Credit Agreement EBITDA for the twelve months ending on the last day of a quarter to Vought's consolidated net interest expense for the twelve months ending on the same day, to be less than 3.50:1.00 for fiscal periods ending during 2009 and for fiscal periods thereafter. Each of these covenants is tested quarterly, and Vought's failure to comply could result in a default and, potentially, an event of default under Vought's senior credit facilities. If not cured or waived, an event of default could result in acceleration of this indebtedness. Vought's credit facilities also use Credit Agreement EBITDA to determine the interest rates on Vought's borrowings, which are based on the consolidated total leverage ratio described above. Changes in Vought's leverage ratio may result in increases or decreases in the interest rate margin applicable to loans under Vought's senior credit facilities. Accordingly, a change in Vought's Credit Agreement EBITDA could increase or decrease its cost of funds. The actual results of the total leverage ratio and net interest coverage ratio for the three-month period ended March 28, 2010 were 1.61:1.00 and 5.39:1.00, respectively. The actual results of the total leverage ratio and net interest coverage ratio for the year ended December 31, 2009 were 1.69:1.00 and 5.28:1.00, respectively.
The indenture governing Vought's outstanding Senior Notes contains a covenant that restricts its ability to incur additional indebtedness unless, among other things, Vought can comply with a fixed charge coverage ratio. Vought may incur additional indebtedness only if, after giving pro forma effect to that incurrence, its ratio of Credit Agreement EBITDA to total consolidated debt less cash on hand for the four fiscal quarters ending as of the most recent date for which internal financial statements are available meets certain levels or Vought has availability to incur such indebtedness under certain baskets in the indenture. Accordingly, Credit Agreement EBITDA is a key factor in determining how much additional indebtedness Vought may be able to incur from time to time to operate its business.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures. Vought has historically disclosed to investors Credit Agreement EBITDA, which is a non-GAAP financial measure that Vought's management uses to assess its compliance with the covenants in its senior credit agreement and its ongoing ability to meet its obligations and manage its levels of indebtedness. Credit Agreement EBITDA is calculated in accordance with Vought's senior credit agreement and includes adjustments that are material to Vought's operations but that its management does not consider reflective of its ongoing core operations. Pursuant to Vought's senior credit agreement, Credit Agreement EBITDA is calculated by making adjustments to Vought's net income (loss) to eliminate the effect of Vought's (1) income tax expense, (2) net interest expense, (3) any amortization or write-off of debt discount and debt issuance costs and commissions, discounts and other fees and charges associated with indebtedness, (4) depreciation and amortization expense, (5) any extraordinary, unusual or non-recurring expenses or gains/losses (including gains/losses on sales of assets outside of the ordinary course of business, non-recurring expenses associated with the 787 program and certain expenses associated with Vought's facilities consolidation efforts) net of any extraordinary, unusual or non-recurring income or gains, (6) any other non-cash charges, expenses or losses, restructuring and integration costs, (7) stock-option based compensation expenses and (8) all fees and expenses paid pursuant to Vought's Management Agreement with Carlyle. See Note 15—Related Party Transactions in the notes to Vought's interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements. Credit Agreement EBITDA is not calculated on the same basis as EBITDA, which is used elsewhere in the section of this prospectus entitled "Triumph Management's Discussion and Analysis of Triumph's Financial Condition and Results of Operations."
99
Adjusted EBITDA for the three-month period ended March 28, 2010 was $60.7 million, a decrease of $7.5 million from the same period in the prior year. The following table is a reconciliation of the non-GAAP measure from Vought's cash flows from operations:
Reconciliation of Non-GAAP Measure—Credit Agreement EBITDA
| | For the Three Months Ended | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | March 28, 2010 | March 29, 2009 | ||||||
| | (in millions) | |||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 40.0 | $ | (73.0 | ) | |||
Interest expense, net | 12.5 | 14.8 | ||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | — | — | ||||||
Stock compensation expense | (2.7 | ) | (0.5 | ) | ||||
Non-cash interest expense | (1.6 | ) | (1.8 | ) | ||||
787 tooling amortization | — | 0.5 | ||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities | 2.4 | 107.3 | ||||||
EBITDA | $ | 50.6 | $ | 47.3 | ||||
Non-recurring investment in Boeing 787(1) | — | 3.1 | ||||||
Unusual charges & other non-recurring program costs(2) | 6.9 | 7.2 | ||||||
Pension & OPEB curtailment and non-cash expense(3) | — | 9.6 | ||||||
Other(4) | 3.2 | 1.0 | ||||||
Credit Agreement EBITDA | $ | 60.7 | $ | 68.2 | ||||
- (1)
- Investment in Boeing 787—The Boeing 787 program, described elsewhere in this quarterly report, required substantial start-up costs in prior periods as Vought built a new facility in South Carolina and invested in new manufacturing technologies dedicated to the program. These start-up investment costs were expensed in Vought's financial statements over several periods due to their magnitude and timing. Vought's credit agreement excludes its significant start-up investment in the Boeing 787 program because it represented an unusual significant investment in a major new program that was not indicative of ongoing core operations. Accordingly, the impact of the investment that was expensed during the period was excluded from the calculation of Credit Agreement EBITDA.
- (2)
- Unusual charges and other non-recurring program costs—Vought's senior credit agreement excludes its expenses for unusual events in its operations and non-recurring costs that are not indicative of ongoing core operating performance, and accordingly the charges that have been expensed during the period are added back to Credit Agreement EBITDA.
For the three-month periods ended March 28, 2010 and March 29, 2009, Vought incurred $3.9 million and $3.1 million, respectively, of non-recurring costs primarily related to a facilities rationalization initiative and $3.0 million and $0.3 million of non-recurring costs related to Information Systems implementation initiatives. Additionally, for the three-month period ended March 29, 2009, Vought recognized an additional $3.8 million in non-recurring program costs related to the strike at Vought's Nashville facility.
- (3)
- Pension and other post-retirement benefits curtailment and non-cash expense related to the Compensation—Retirement Benefits topic of the ASC—The credit agreement allows Vought to remove non-cash benefit expenses, so to the extent that the recorded expense
100
exceeds the cash contributions to the plan it is reflected as an adjustment in calculating Adjusted EBITDA. During the three-month period ended March 29, 2009, Vought recognized $9.6 million curtailment resulting from the new IAM collective bargaining agreement. For more information, please refer to Note 6—Pension and Other Post-Retirement Benefits to Vought's interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
- (4)
- Other—Includes non-cash stock expense and related party management fees. Vought's credit agreement provides that these expenses are reflected as an adjustment in calculating Credit Agreement EBITDA.
Credit Agreement EBITDA for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 was $254.7 million, $263.9 million and $277.4 million, respectively. The following table is a reconciliation of the non-GAAP measure from Vought's cash flows from operations:
| | For the Years Ended | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | December 31, 2007 | |||||||||
| | (in millions) | |||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 111.8 | $ | (154.5 | ) | $ | 34.2 | |||||
Interest expense, net | 56.3 | 62.8 | 59.0 | |||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | (9.3 | ) | 0.2 | 0.1 | ||||||||
Stock compensation expense | (2.5 | ) | (1.1 | ) | (5.2 | ) | ||||||
Equity in losses of joint venture | — | (0.6 | ) | (4.0 | ) | |||||||
Gain (loss) from asset sales and other losses | (41.2 | ) | 49.8 | (1.8 | ) | |||||||
Non-cash interest expense | (13.1 | ) | (5.8 | ) | (3.1 | ) | ||||||
787 tooling amortization | 1.1 | 0.8 | — | |||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities | 328.3 | 266.1 | 86.9 | |||||||||
EBITDA | $ | 431.4 | $ | 217.7 | $ | 166.1 | ||||||
Investment in Boeing 787 and sale of the Charleston 787 business(1) | (213.6 | ) | 33.3 | 95.9 | ||||||||
Unusual charges & other non-recurring program costs(2) | 19.3 | 56.7 | 6.1 | |||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment and other assets(3) | 2.9 | (48.2 | ) | 1.9 | ||||||||
Pension & OPEB curtailment and non-cash expense(4) | 10.3 | — | — | |||||||||
Other(5) | 4.4 | 4.4 | 7.4 | |||||||||
Credit Agreement EBITDA | $ | 254.7 | $ | 263.9 | $ | 277.4 | ||||||
- (1)
- Investment in Boeing 787 and sale of the Charleston 787 business—The Boeing 787 program, described elsewhere in Vought's periodic reports, required substantial start-up costs in prior periods as Vought built a new facility in South Carolina and invested in new manufacturing technologies dedicated to the program. These start-up investment costs were expensed in Vought's financial statements over several periods due to their magnitude and timing. As a result of the sale of the Charleston 787 business to Boeing, Vought settled outstanding contractual matters with Boeing and recognized a loss on the sale of the related assets and liabilities of the business. Vought's credit agreement excludes all gains or losses recognized on the sale of assets and it excludes Vought's
101
significant start-up investment in the Boeing 787 program because it represented an unusual significant investment in a major new program that was not indicative of ongoing core operations. Accordingly, the impact of the settlement of contractual matters, loss on the sale of the assets and liabilities and the investment that was expensed during the period was excluded from the calculation of Credit Agreement EBITDA. Also included in this adjustment is Vought's loss in its joint venture with Global Aeronautica. Vought's net loss was $0.6 million and $4.0 million for the fiscal years 2008 and 2007, respectively. On June 10, 2008, Vought sold its entire equity interest in Global Aeronautica to Boeing and as a result, in subsequent periods, Vought's Credit Agreement EBITDA calculation will not be impacted by this joint venture. For more information, please refer to Note 8—Investment in Joint Venture in Vought's consolidated financial statements.
- (2)
- Unusual charges and other non-recurring program costs—Vought's senior credit agreement excludes Vought's expenses for unusual events in its operations and non-recurring costs that are not indicative of ongoing core operating performance, and accordingly the charges that have been expensed during the period are added back to Credit Agreement EBITDA. For the year ended December 31, 2008, Vought recognized an additional $38.3 million in non-recurring program costs related to the strike at its Nashville facility and $1.8 million in non-recurring program costs related to the Boeing strike. However, during the year ended December 31, 2009, Vought reversed $(0.5) million in non-recurring program costs related to the strike at its Nashville facility because the actual strike-related costs incurred on those programs were lower than the original estimates. Vought incurred $10.0 million, $8.4 million and $6.1 million of non-recurring costs related to a facilities rationalization initiative for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, which have been added back to Credit Agreement EBITDA. Also, during the year ended December 31, 2009, Vought recognized $1.8 million of non-recurring costs related to the suspension of the Cessna Citation Columbus—Model 850 business jet program and $8.0 million of non-recurring costs related to Information Systems implementation initiatives. Vought did not incur similar costs in 2008 and 2007. During the year ended December 31, 2008, Vought recorded $8.2 million of non-recurring specific warranty costs. Vought did not incur similar costs in 2009 and 2007.
- (3)
- (Gain) loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment ("PP&E") and other assets—On occasion, where the asset is no longer needed for Vought's business and ceases to offer sufficient value or utility to justify its retention of the asset, Vought chooses to sell the asset at a gain or loss. Typically, these assets are PP&E. However, in 2008, Vought sold its entire equity interest in Global Aeronautica to Boeing and as a result, recorded a $47.1 million gain on the sale. Gains and losses resulting from the disposal of assets impact Vought's results of operations for the period in which the asset was sold. Vought's credit agreement provides that those gains and losses are reflected as an adjustment in calculating Credit Agreement EBITDA.
- (4)
- Pension and other post-retirement benefits curtailment and non-cash expense related to theCompensation—Retirement Benefits topic of the ASC—The credit agreement allows Vought to remove non-cash benefit expenses, so to the extent that the recorded expense exceeds the cash contributions to the plan it is reflected as an adjustment in calculating Credit Agreement EBITDA. During the year ended December 31, 2009, Vought recognized $9.6 million curtailment resulting from the new IAM collective bargaining agreement. For more information, please refer to Note 14—Pension and Other Post-Retirement Benefits in Vought's consolidated financial statements.
102
- (5)
- Other—includes non-cash stock expense, related party management fees and costs associated with the preparation of documents in connection with a planned initial public equity offering. Vought's credit agreement provides that these expenses are reflected as an adjustment in calculating Credit Agreement EBITDA.
Vought believes that each of the adjustments made in order to calculate Credit Agreement EBITDA is meaningful to investors because it gives them the ability to assess Vought's compliance with the covenants in its senior credit agreement and its ongoing ability to meet its obligations and manage its levels of indebtedness.
The use of Credit Agreement EBITDA as an analytical tool has limitations and you should not consider it in isolation, or as a substitute for analysis of Vought's results of operations as reported in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Some of these limitations are:
- •
- it does not reflect Vought's cash expenditures, or future requirements, for all contractual commitments;
- •
- it does not reflect Vought's significant interest expense, or the cash requirements necessary to service its indebtedness;
- •
- it does not reflect cash requirements for the payment of income taxes when due;
- •
- it does not reflect working capital requirements;
- •
- although depreciation and amortization are non-cash charges, the assets being depreciated and amortized will often have to be replaced in the future and Adjusted EBITDA does not reflect any cash requirements for such replacements; and
- •
- it does not reflect the impact of earnings or charges resulting from matters Vought considers not to be indicative of its ongoing operations, but may nonetheless have a material impact on Vought's results of operations.
Because of these limitations, Credit Agreement EBITDA should not be considered as a measure of discretionary cash available to Vought to invest in the growth of Vought's business or as an alternative to net income or cash flow from operations determined in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Management compensates for these limitations by not viewing Credit Agreement EBITDA in isolation, and specifically by using other U.S. GAAP measures, such as cash flow provided by (used in) operating activities and capital expenditures, to measure Vought's liquidity. Vought's calculation of Credit Agreement EBITDA may not be comparable to the calculation of similarly titled measures reported by other companies and differs from the measure entitled "Adjusted EBITDA" presented elsewhere in this prospectus. See "Non-GAAP Financial Measures," "Summary—Triumph Summary Historical and Pro Forma Consolidated Financial Data" and "Summary—Vought Summary Historical Consolidated Financial Data."
103
Cash Flow Summary
| | For the Three Months Ended | | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | March 28, 2010 | March 29, 2009 | Change | |||||||
| | (in millions) | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 26.8 | $ | 17.9 | $ | 8.9 | ||||
Non-cash items | 15.6 | 16.4 | (0.8 | ) | ||||||
Changes in working capital | (2.4 | ) | (107.3 | ) | 104.9 | |||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 40.0 | (73.0 | ) | 113.0 | ||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (6.7 | ) | (8.3 | ) | 1.6 | |||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 0.4 | 160.0 | (159.6 | ) | ||||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 33.7 | 78.7 | (45.0 | ) | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 116.0 | 86.7 | 29.3 | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 149.7 | $ | 165.4 | $ | (15.7 | ) | |||
Net cash provided by operating activities for the three-month period ended March 28, 2010 was $40.0 million, an increase of $113.0 million compared to cash used of $73.0 million for the same period in 2009. This change primarily resulted from the timing of customer payments for the 747-8 program and the timing of milestone payments for the C-17 program.
Net cash used in investing activities for the three months ended March 28, 2010 was $6.7 million, a decrease of $1.6 million compared to net cash used in investing activities of $8.3 million for the same period in 2009. The change is due to fewer capital expenditures in 2010.
Net cash provided by financing activities for the three months ended March 28, 2010 was $0.4 million, a change of $159.6 million compared to cash provided of $160.0 million for the same period in 2009. This change primarily resulted from the absence in 2010 of the $135.0 million in revolver borrowings and the $25.0 million conversion of the synthetic letter of credit facility to a term loan that occurred in 2009.
Cash Flow Summary
| | Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||
| | (in millions) | |||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 328.3 | $ | 93.7 | $ | 46.3 | ||||
Non-cash items | 111.8 | 17.9 | 74.8 | |||||||
Changes in working capital | (328.3 | ) | (266.1 | ) | (86.9 | ) | ||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 111.8 | (154.5 | ) | 34.2 | ||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | 247.2 | (14.2 | ) | (49.6 | ) | |||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | (329.7 | ) | 179.8 | (2.4 | ) | |||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 29.3 | 11.1 | (17.8 | ) | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 86.7 | 75.6 | 93.4 | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 116.0 | $ | 86.7 | $ | 75.6 | ||||
104
Year Ended December 31, 2009 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2008
Net cash provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $111.8 million, an increase of $266.3 million compared to net cash used in operating activities of $154.5 million for the prior year. This change primarily resulted from the settlement of contractual matters related to the 787 program partially offset by increased cash requirements for the 747-8 program.
Net cash provided by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $247.2 million, an increase of $261.4 million compared to net cash used in investing activities of $14.2 million for the same period in 2008. The change was primarily due to the $289.2 million, net of fees, of proceeds received for the sale of the Charleston 787 business and a $27.3 million decrease in capital expenditures in 2009 offset by the $55.1 million of proceeds from the sale of assets in 2008 including the sale to Boeing of Vought's equity interest in Global Aeronautica.
Net cash used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2009 was $329.7 million, a change of $509.5 million compared with cash provided of $179.8 million for 2008. This change primarily resulted from the $184.6 million in net proceeds from the Incremental Facility in 2008, the use of $355.0 million of proceeds from the sale of the Charleston 787 business to pay down outstanding term loans in 2009 and the restriction of $43.8 million as collateral for outstanding letters of credit in 2009, partially offset by the conversion of the $75.0 million of the synthetic letter of credit facility to a term loan in 2009.
Year Ended December 31, 2008 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2007
Net cash used in operating activities for year ended December 31, 2008 was $154.5 million, a change of $188.7 million compared to cash provided by operating activities of $34.2 million for the prior year. The change primarily resulted from the following items: increased cash funding requirements of $59.7 million for Vought's defined benefit pension plans; lower cash from the timing of milestone and advance payments from customers of approximately $67.0 million; as well as $62.0 million of higher working capital requirements in 2008 related to the ramp-up of the 787 program.
Net cash used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2008 was $14.2 million, a decrease of $35.4 million compared to net cash used in investing activities of $49.6 million for the prior year. This improvement is due to a $30.8 million increase in proceeds provided by the sale of assets and a $16.5 million decrease in contributions to Global Aeronautica partially offset by an $11.9 million increase in capital expenditures.
Net cash provided by financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2008 was $179.8 million, a change of $182.2 million compared to net cash used in financing activities of $2.4 million for the prior year. The change primarily resulted from the $184.6 million in net proceeds provided by borrowings under the Incremental Facility.
105
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes the scheduled maturities of financial obligations and expiration dates of commitments as of December 31, 2009:
| | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | Thereafter | Total | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior credit facilities | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Term loans | $ | 236.6 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 236.6 | |||||||||
Incremental facility | 85.6 | — | — | — | — | — | 85.6 | ||||||||||||||||
Total senior credit facilities(1) | $ | 322.2 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 322.2 | |||||||||
Operating leases | 21.7 | 13.7 | 9.3 | 4.9 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 57.1 | ||||||||||||||||
Senior notes | — | 270.0 | — | — | — | — | 270.0 | ||||||||||||||||
Purchase Obligations(2) | 459.3 | 143.7 | 18.0 | 12.0 | — | — | 633.0 | ||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 803.2 | $ | 427.4 | $ | 27.3 | $ | 16.9 | $ | 4.0 | $ | 3.5 | $ | 1,282.3 | |||||||||
- (1)
- In addition to the obligations in the table, at December 31, 2008, Vought had contractual interest payment obligations as follows: (a) variable interest rate payments on $322.2 million outstanding under Vought's senior credit facilities based upon LIBOR plus a margin of 4.00%, which correlated to an interest rate of 7.50% at December 31, 2009 and (b) $21.6 million per year on the Senior Notes.
- (2)
- Includes contractual obligations for which Vought is committed to purchase goods and services as of December 31, 2009. The most significant of these obligations relate to raw material and parts supply contracts for Vought's manufacturing programs and these amounts are primarily comprised of open purchase order commitments to vendors and subcontractors. Many of these agreements provide Vought the ability to alter or cancel orders and require its suppliers to mitigate the impact from any changes. Even where purchase orders specify determinable prices, quantities and delivery time frames, generally the purchase obligations remain subject to frequent modification and therefore are highly variable. As a result, Vought regularly experiences significant fluctuations in the aggregate amount of purchase obligations, and the amount reflected in the table above may not be indicative of its purchase obligations over time. The ultimate liability for these obligations may be reduced based upon modification or termination provisions included in some of Vought's purchase contracts, the costs incurred to date by vendors under these contracts or by recourse under normal termination clauses in firm contracts with Vought's customers.
In addition to the financial obligations detailed in the table above, Vought also had obligations related to its benefit plans at December 31, 2009 as detailed in the following table. Vought's other
106
post-retirement benefits are not required to be funded in advance, so benefit payments are paid as they are incurred. Vought's expected net contributions and payments are included in the table below:
| | Pension Benefits | Other Post-retirement Benefits | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | (in millions) | ||||||||
Benefit obligation at December 31, 2009 | $ | 1,958.3 | $ | 402.3 | |||||
Plan assets at December 31, 2009 | 1,342.6 | — | |||||||
Projected contributions | |||||||||
2010 | 102.7 | 38.4 | |||||||
2011 | 176.8 | 38.9 | |||||||
2012 | 142.1 | 38.5 | |||||||
2013 | 123.0 | 37.9 | |||||||
2014 | 108.3 | 37.5 | |||||||
Total 2010 - 2014 | $ | 652.9 | $ | 191.2 | |||||
Current plan documents reserve Vought's right to amend or terminate the plans at any time, subject to applicable collective bargaining requirements for represented employees.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
None.
Inflation
A majority of Vought's sales are conducted pursuant to long-term contracts that set fixed unit prices and some of which provide for price adjustment through escalation clauses. The effect of inflation on Vought's sales and earnings is minimal because the selling prices of those contracts, established for deliveries in the future, generally reflect estimated costs to be incurred in these future periods. Vought's estimated costs take into account a projected rate of inflation for the duration of the relevant contract.
Vought's supply base contracts are conducted on a fixed price basis in U.S. dollars. In some cases Vought's supplier arrangements contain escalation adjustment provisions based on accepted industry indices, with appropriate forecasting incorporated in program financial estimates. Raw materials price escalation has been mitigated through existing long-term agreements, which remain in place for several more years. Vought's expectations are that in the long-term, the demand for these materials will continue to put additional pressures on pricing. Strategic cost reduction plans will continue to focus on mitigating the effects of this demand curve on Vought's operations.
Critical Accounting Policies
Vought's discussion and analysis of its financial position and results of operations are based upon its consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported for assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses. Although Vought evaluates its estimates, which are based on the most current and best available information and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, on an ongoing basis, actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. Vought believes the following items are the critical accounting policies and most significant estimates and assumptions used
107
in the preparation of its financial statements. These accounting policies conform to the accounting policies contained in the consolidated financial statements included in this annual report.
Accounting Estimates. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes and, in particular, estimates of contract costs and revenues used in the earnings recognition process. Vought has recorded all estimated contract losses that are reasonably estimable and probable. To enhance reliability in its estimates, Vought employs a rigorous estimating process that is reviewed and updated at least on a quarterly basis. However, actual results could differ from those estimates.
Revenue and Profit Recognition. The majority of Vought's sales are made pursuant to written contractual arrangements or "contracts" to design, develop and manufacture aerostructures to the specifications of the customer under firm fixed price contracts. These contracts are within the scope of theRevenue—Construction-Type and Production-Type Contracts topic of the ASC and revenue and costs on contracts are recognized using percentage-of-completion methods of accounting. Accounting for the revenue and profit on a contract requires estimates of (1) the contract value or total contract revenue, (2) the total costs at completion, which is equal to the sum of the actual incurred costs to date on the contract and the estimated costs to complete the contract's scope of work and (3) the measurement of progress towards completion. Depending on the contract, Vought measures progress toward completion using either the cost-to-cost method or the units-of-delivery method.
- •
- Under the cost-to-cost method, progress toward completion is measured as the ratio of total costs incurred to Vought's estimate of total costs at completion. Vought recognizes costs as incurred. Profit is determined based on its estimated profit margin on the contract multiplied by its progress toward completion. Revenue represents the sum of Vought's costs and profit on the contract for the period.
- •
- Under the units-of-delivery method, revenue on a contract is recorded as the units are delivered and accepted during the period at an amount equal to the contractual selling price of those units. The costs recorded on a contract under the units-of-delivery method are equal to the total costs at completion divided by the total units to be delivered. As its contracts can span multiple years, Vought often segments the contracts into production lots for the purposes of accumulating and allocating cost. Profit is recognized as the difference between revenue for the units delivered and the estimated costs for the units delivered.
Adjustments to original estimates for a contract's revenues, estimated costs at completion and estimated total profit are often required as work progresses under a contract, as experience is gained and as more information is obtained, even though the scope of work required under the contract may not change, or if contract modifications occur. These estimates are also sensitive to the assumed rate of production. Generally, the longer it takes to complete the contract quantity, the more relative overhead that contract will absorb. The impact of revisions in cost estimates is recognized on a cumulative catch-up basis in the period in which the revisions are made. Provisions for anticipated losses on contracts are recorded in the period in which they become evident ("forward losses") and are first offset against costs that are included in inventory, with any remaining amount reflected in accrued contract liabilities in accordance with the Construction and Production-Type Contracts topic. Revisions in contract estimates, if significant, can materially affect Vought's results of operations and cash flows, as well as Vought's valuation of inventory. Furthermore, certain contracts are combined or segmented for revenue recognition in accordance with the Construction and Production-Type Contracts topic.
Advance payments and progress payments received on contracts-in-process are first offset against related contract costs that are included in inventory, with any remaining amount reflected in current liabilities.
108
Accrued contract liabilities consisted of the following:
| | March 28, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | (in millions) | ||||||||||
Advances and progress billings | $ | 34.2 | $ | 59.4 | $ | 126.8 | |||||
Forward loss | — | 1.7 | 6.4 | ||||||||
Other | 5.8 | 13.1 | 7.9 | ||||||||
Total accrued contract liabilities | $ | 40.0 | $ | 74.2 | $ | 141.1 | |||||
Amounts representing contract change orders or claims are only included in revenue when such change orders or claims have been settled with Vought's customer and to the extent that units have been delivered. Additionally, some contracts may contain provisions for revenue sharing, price re-determination, requests for equitable adjustments, change orders or cost and/or performance incentives. Such amounts or incentives are included in contract value when the amounts can be reliably estimated and their realization is reasonably assured.
Although fixed-price contracts, which extend several years into the future, generally permit Vought to keep unexpected profits if costs are less than projected, Vought also bears the risk that increased or unexpected costs may reduce its profit or cause the Company to sustain losses on the contract. In a fixed-price contract, Vought must fully absorb cost overruns, notwithstanding the difficulty of estimating all of the costs it will incur in performing these contracts and in projecting the ultimate level of revenue that may otherwise be achieved. Vought's failure to anticipate technical problems, estimate delivery reductions, estimate costs accurately or control costs during performance of a fixed-price contract may reduce the profitability of a fixed-price contract or cause a loss. Vought believes it has recorded adequate provisions in the financial statements for losses on fixed-price contracts, but it cannot be certain that the contract loss provisions will be adequate to cover all actual future losses.
As mentioned above, the vast majority of Vought's revenue is related to the sale of manufactured end item products and spare parts. Any revenue related to the provision of services is accounted for separately and is not material to Vought's results of operations.
Inventories. Inventoried costs primarily relate to work in process and represent accumulated contract costs less the portion of such costs allocated to delivered items. Accumulated contract costs include direct production costs, manufacturing and engineering overhead, production tooling costs, and certain general and administration expenses.
In accordance with industry practice, inventoried costs are classified as a current asset and include amounts related to contracts having production cycles longer than one year; therefore, a portion thereof will not be realized within one year. See Note 5 to Vought's consolidated financial statements.
Goodwill. Goodwill is tested for impairment, at least annually, in accordance with the provisions of theIntangibles—Goodwill and Other topic of the ASC. Under this topic, the first step of the goodwill impairment test used to identify potential impairment compares the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying value. Vought has concluded that it is a single reporting unit. Accordingly, all assets and liabilities are used to determine Vought's carrying value. Based on review of its annual impairment tests, Vought did not recognize impairment charges in 2009, 2008 or 2007.
Additionally, in connection with the sale of the Charleston 787 business on July 30, 2009 (discussed in Note 3—Discontinued Operations in the notes to Vought's consolidated financial statements), $122.9 million of Vought's goodwill balance was allocated to that business based on the relative fair value of its assets compared to the total value of the consolidated company. Subsequently, Vought performed an interim impairment test of its remaining Goodwill balance and determined the balance was not impaired.
109
For this testing Vought uses an independent valuation firm to assist in the estimation of enterprise fair value using standard valuation techniques such as discounted cash flow, market multiples and comparable transactions. The discounted cash flow fair value estimates are based on management's projected future cash flows and the estimated weighted average cost of capital. The estimated weighted average cost of capital is based on a risk-free interest rate and other factors such as equity risk premiums and the ratio of total debt and equity capital.
Vought must make assumptions regarding estimated future cash flows and other factors used by the independent valuation firm to determine the fair value. If these estimates or the related assumptions change, Vought may be required to record non-cash impairment charges for goodwill in the future.
Post-Retirement Plans. The liabilities and net periodic cost of Vought's pension and other post-retirement plans are determined using methodologies that involve several actuarial assumptions, the most significant of which are the discount rate, the expected long-term rate of asset return, the assumed average rate of compensation increase and rate of growth for medical costs. The actuarial assumptions used to calculate these costs are reviewed annually or when a remeasurement is necessary. Assumptions are based upon management's best estimates, after consulting with outside investment advisors and actuaries, as of the measurement date.
The assumed discount rate utilized is based on a point in time estimate as of Vought's December 31 annual measurement date or as of remeasurement dates as needed. This rate is determined based upon on a review of yield rates associated with long-term, high quality corporate bonds as of the measurement date and use of models that discount projected benefit payments using the spot rates developed from the yields on selected long-term, high quality corporate bonds.
The assumed expected long-term rate of return on assets is the weighted average rate of earnings expected on the funds invested or to be invested to provide for the benefits included in the Projected Benefit Obligation ("PBO"). The expected average long-term rate of return on assets is based principally on the counsel of Vought's outside investment advisors and was projected at 8.5% in 2009, 2008 and 2007. This rate is based on actual historical returns and anticipated long-term performance of individual asset classes with consideration given to the related investment strategy. This rate is utilized principally in calculating the expected return on the plan assets component of the annual pension expense. To the extent the actual rate of return on assets realized over the course of a year differs from the assumed rate, that year's annual pension expense is not affected. The gain or loss reduces or increases future pension expense over the average remaining service period of active plan participants expected to receive benefits.
The assumed average rate of compensation increase represents the average annual compensation increase expected over the remaining employment periods for the participating employees. This rate is estimated to be 4% and is utilized principally in calculating the PBO and annual pension expense.
In addition to its defined benefit pension plans, Vought provides certain healthcare and life insurance benefits for certain eligible retired employees. Such benefits were unfunded as of December 31, 2009 and March 28, 2010. Employees achieve eligibility to participate in these contributory plans upon retirement from active service if they meet specified age and years of service requirements. Election to participate for some employees must be made at the date of retirement. Qualifying dependents at the date of retirement are also eligible for medical coverage. Current plan documents reserve Vought's right to amend or terminate the plans at any time, subject to applicable collective bargaining requirements for represented employees. From time to time, Vought has made changes to the benefits provided to various groups of plan participants. Premiums charged to most retirees for medical coverage prior to age 65 are based on years of service and are adjusted annually for changes in the cost of the plans as determined by an independent actuary. In addition to this medical inflation cost-sharing feature, the plans also have provisions for deductibles, co-payments,
110
coinsurance percentages, out-of-pocket limits, schedules of reasonable fees, preferred provider networks, coordination of benefits with other plans, and a Medicare carve-out. A one-percentage-point shift in the medical trend rate would have the effect shown in Note 14 to Vought's consolidated financial statements.
In accordance with theCompensation—Retirement Benefits topic of the ASC Vought recognized the funded status of its benefit obligation in its statement of financial position as of December 31, 2008. This funded status was remeasured for some plans as of January 31, 2009 and September 27, 2009 due to plan amendments and for all plans as of December 31, 2009, Vought's annual remeasurement date. The funded status is measured as the difference between the fair value of the plan's assets and the PBO or accumulated postretirement benefit obligation of the plan. In order to recognize the funded status, Vought determined the fair value of the plan assets. The majority of Vought's plan assets are publicly traded investments which were valued based on the market price as of the date of remeasurement. Investments that are not publicly traded were valued based on the estimated fair value of those investments as of December 31, 2009 based on Vought's evaluation of data from fund managers and comparable market data.
Accounting Changes and Pronouncements
In December 2007, the FASB issued an accounting standard that provides revised guidance on how acquirors recognize and measure the consideration transferred, identifiable assets acquired, liabilities assumed, noncontrolling interests, and goodwill acquired in a business combination. This standard also expands required disclosures surrounding the nature and financial effects of business combinations. Vought adopted the guidance of this accounting standard, currently included in theBusiness Combinations Topic of the ASC on January 1, 2009. Vought considered the provisions of this accounting standard with respect to the sale of the Charleston 787 business (as discussed in Note 3—Discontinued Operations in the notes to Vought's consolidated financial statements).
FASB issued an accounting standard that requires enhanced disclosures about the plan assets of a company's defined benefit pension and other postretirement plans. The enhanced disclosures are intended to provide users of financial statements with a greater understanding of: (1) how investment allocation decisions are made, including the factors that are pertinent to an understanding of investment policies and strategies; (2) the major categories of plan assets; (3) the inputs and valuation techniques used to measure the fair value of plan assets; (4) the effect of fair value measurements using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) on changes in plan assets for the period; and (5) significant concentrations of risk within plan assets. Vought adopted the provisions of this accounting standard on January 1, 2009 and provided the required enhanced disclosures for its pension plan assets in Note 14—Pension and Other Post Retirement Benefits in the notes to Vought's consolidated financial statements.
In May 2009, the FASB issued an accounting standard that requires an entity to recognize in the financial statements the effects of all subsequent events that provide additional evidence about conditions that existed at the date of the balance sheet. For nonrecognized subsequent events that must be disclosed to keep the financial statements from being misleading, an entity is required to disclose the nature of the event as well as an estimate of its financial effect, or a statement that such an estimate cannot be made. Vought adopted this accounting standard for its fiscal period ending June 28, 2009 and it has not had a material effect on its consolidated financial statements.
In June 2009, the FASB issued an accounting standard that establishes the FASB Accounting Standards Codification (the Codification) as the source of authoritative U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (U.S. GAAP). Vought adopted this accounting standard for Vought's fiscal period ending September 27, 2009.
111
Following the Codification, the FASB will not issue new standards in the form of Statements, FASB Staff Positions or Emerging Issues Task Force Abstracts. Instead, it will issue Accounting Standards Updates (ASUs), which will serve to update the Codification, provide background information about the accounting guidance and provide the basis for conclusions on the changes to the Codification. GAAP is not intended to be changed as a result of the Codification, but it will change the way the accounting guidance is organized and presented. As a result, these changes have a significant impact on how Vought references GAAP in its financial statements and in its accounting policies for financial statements issued for interim and annual periods ending after September 15, 2009.
In Vought's annual report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009, it began the process of implementing the statement by removing references to FASB statement numbers in the footnotes that follow and explaining the adherence to authoritative accounting guidance in plain English, where appropriate.
In December 2009, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2009-17, "Consolidations (Topic 810)—Improvements to Financial Reporting by Enterprises Involved with Variable Interest Entities" ("ASU 2009-17"). ASU 2009-17 changes how a reporting entity determines when an entity that is insufficiently capitalized or is not controlled through voting (or similar rights) should be consolidated. The determination of whether a reporting entity is required to consolidate another entity is based on, among other things, the other entity's purpose and design and the reporting entity's ability to direct the activities of the other entity that most significantly impact the other entity's economic performance. ASU 2009-17 requires a reporting entity to provide additional disclosures about its involvement with variable interest entities and any significant changes in risk exposure due to that involvement. A reporting entity is required to disclose how its involvement with a variable interest entity affects the reporting entity's financial statements. ASU 2009-17 is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2009, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Vought adopted ASU 2009-17 as of January 1, 2010, and its application had no impact on Vought's interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
In January 2010, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2010-06, "Improving Disclosures about Fair Value Measurements" ("ASU 2010-06"), which provides amendments toFair Value Measurements and Disclosures—Overall subtopic of the ASC. ASU 2010-06 requires additional disclosures and clarifications of existing disclosures for recurring and nonrecurring fair value measurements. Vought adopted this update for its fiscal year beginning January 1, 2010. ASU 2010-06 did not have a material impact on Vought's interim unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements.
112
Our Company
We are a leading manufacturer of and provider of repair and maintenance services for aerospace systems and components, serving a broad spectrum of companies within the aerospace industry. We design, engineer, manufacture, repair and overhaul aircraft components and aerostructures. Our customers consist of original equipment manufacturers, or "OEMs," of commercial, military, regional and business aircraft and components, the U.S. military, commercial airlines and air cargo carriers, and include:
• Boeing | • Honeywell | |
• Airbus (a division of EADS NV) | • Lockheed Martin | |
• Bell Helicopter (a division of Textron) | • Northrop Grumman | |
• Cessna (a division of Textron) | • Raytheon | |
• Gulfstream (a division of General Dynamics) | • Rolls-Royce | |
• General Electric | • Sikorsky (a division of United Technologies) |
Our diversification across OEMs and platforms, coupled with our ever-broadening product offerings, enables us to respond to the evolving needs of our customers. In addition, we are well positioned in a highly fragmented industry, as one of a limited number of companies worldwide that can offer a broad range of products, systems and services to the largest aerospace companies. For the year ended March 31, 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, we generated net sales of $1.3 billion and $406.4 million, respectively. On a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition, for the year ended March 31, 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, we generated net sales of $3.2 billion and $763.4 million, respectively. As of June 30, 2010, we had a current backlog of approximately $3.3 billion. See "—Summary Consolidated Historical and Pro Forma Financial Data of Triumph."
We operate through a decentralized structure of 44 aerospace companies with 64 locations in the United States, Europe, Mexico and Thailand, while maintaining an integrated marketing and sales force for all of our operating companies. Through our decentralized structure, we are able to preserve specialized skills and distinct customer bases for many of our group companies, which enhances our diversification and increases our operating flexibility to better serve our customers. Our sales and marketing team serves as a single point of customer contact for our extensive range of products. The team consists of customer-focused sales professionals as well as specialists at individual operating companies who assist them with expertise and depth of knowledge in particular products.
113
Aerospace End Markets and Platforms
Our customer base includes nearly all of the world's major OEMs, the U.S. military and a number of commercial airlines and air cargo carriers. The chart below presents our net sales by end market for the twelve months ended March 31, 2010 on a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Vought Acquisition. Amounts have been rounded where necessary.

We provide products and services to the following platforms used in the commercial, military, business and regional aircraft end markets:
- •
- Large wide-body aircraft with twin aisles (more than 200 seats). Wide-body aircraft for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Boeing 747-8, 767, 777 and 787 and the Airbus A330/340, A350 and A380, as well as the A350XWB, planned for entry into service in 2013.
- •
- Smaller narrow-body aircraft with single aisles (excluding regional aircraft) (100 to 200 seats). Narrow-body aircraft for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Boeing 737, the Airbus A320 family and the Bombardier C series.
Commercial Aircraft Market.
- •
- Fighter and Attack Aircraft—Fighter aircraft are used to engage in air-to-air combat and to control the airspace over the battlefield, thereby enabling other allied forces to carry out their missions. Attack aircraft support ground troops in close air support roles and penetrating attacks. Fighter and attack aircraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the F/A-18 Hornet, the F-15 Eagle, the F-16 Fighting Falcon, the F-35 Lightning II and the E-2C Hawkeye.
- •
- Transport Aircraft or Cargo Aircraft—Aircraft in this category are used to transport troops, equipment and humanitarian aid, and are able to operate from short and roughly prepared airfields and to perform airdrops of troops and equipment when landing is not an option. Transport and cargo aircraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Boeing C-17 Globemaster III, and the Lockheed Martin C-130 Hercules.
- •
- Rotorcraft—Rotorcraft have broad and varied uses including intra-theater cargo delivery, troop transport and rapid insertion, observation and patrol, ground attack and search and rescue and special operations. Rotorcraft have been critical to the U.S. military's efforts in Iraq and
Military Aircraft Market.
114
- •
- Unmanned Air Vehicles ("UAVs")—UAVs have generally been used for observation and command and control. This class of aircraft plays an important role in U.S. military strategy, and is also being increasingly used for weapons delivery and air combat. UAV platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Global Hawk, the Predator and the Hunter.
- •
- Aerial Tanker Aircraft—Tankers are used to deliver fuel to other aircraft while airborne and are essential to the effective use of combat and support aircraft. Tanker aircraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the KC-10 and KC-135. In addition, the U.S. Air Force recently issued a request for proposal ("RFP") for designs for the KC-X tanker, which will replace the KC-135. We provide parts, assemblies and services for the planned proposals of both Boeing (a modified version of its 767 commercial airframe) and EADS (the A330 Tanker).
Afghanistan and their heavy usage has led to continued demand for new rotorcraft and repairs and refurbishments of existing military rotorcraft. Rotorcraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the UH-60 Black Hawk, V-22 Osprey, CH-47 Chinook and the AH-64 Apache.
In addition, we provide parts, assemblies and services to Space Vehicles, such as the Delta Launch Space Vehicle and International Space Station.
Business Jet Aircraft Market. The business jet market includes personal and business jet aircraft with a worldwide fleet today exceeding 14,000 aircraft. There are currently more than 40 different models of business jets in production or development, ranging from very light jets (VLJ) seating four passengers to transcontinental business jets that carry up to 19 passengers. The business jet market is generally classified into three major segments: light (which include VLJ, entry and light jets with sale prices ranging from approximately $1 million to $10 million per aircraft), medium (which include light-mid, medium and super-mid jets with sale prices ranging from approximately $10 million to $20 million per aircraft), and heavy (which include heavy, long range and ultra long range jets with sale prices ranging from approximately $20 million to $45 million per aircraft). Purchasers of business jets include U.S. and foreign corporations, fractional leasing companies, wealthy individuals and U.S. and foreign governments. Our business jet customers include Bombardier, Cessna, Dassault Aviation, Embraer, Gulfstream, Hawker Beechcraft and Learjet. We typically provide parts, assemblies and services to our business jet customers across all of their business jet platforms.
Regional Jet Aircraft Market. The regional jet market includes smaller commercial jet aircraft ranging in size from approximately 40 to 110 seats. Regional jet aircraft platforms for which we provide parts, assemblies and services include the Embraer EM145, the Bombardier/Canadair CRJ700, CRJ1000 and CRJ200, the Bombardier/DeHavilland DHC 8 series and the British Aerospace BAE146/AVRO RJ.
Our Business Segments
We currently offer our products and services through two operating segments: Aerospace Systems and Aftermarket Services.
Aerospace Systems
Aerospace Systems engages in the design, development, manufacture, repair, sales and lifecycle support of complete metallic structural assemblies, as well as mechanical, electromechanical, hydraulic and hydromechanical control systems. Aerospace Systems serves as a single point of customer contact for this extensive range of products, which we believe gives us a significant competitive advantage over many of our competitors. Aerospace System's products range from highly integrated systems and assemblies to kits of components to individual components and satisfy customer requirements at various stages of the manufacturing process. Aerospace Systems also performs complex machining processes,
115
offers machining capabilities and structural component forming, and provides customers with the full range of structural components, as well as complete assemblies and subassemblies. Aerospace Systems' customers include aerospace OEMs and other tier one manufacturers who supply them, airlines, air cargo carriers, and domestic and foreign militaries. For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, Aerospace Systems generated net sales before inter-segment eliminations of $1,073.5 million and $346.8 million, respectively.
The principal products and services of our Aerospace Systems segment prior to the Vought Acquisition are set forth below.
| • | Acoustic insulation systems | • | Exhaust nozzles and ducting | • | Main engine gear box assemblies | ||||||
| • | Aircraft and engine mounted | • | Floor beams | • | Primary and secondary flight | ||||||
| accessory drive | • | Heat exchangers | control systems | ||||||||
| • | Cockpit control levers | • | High-lift actuation | • | Stretch-formed leading edges and | ||||||
| • | Composite and metal bonding | • | Landing gear actuation systems | fuselage skins | |||||||
| • | Composite ducts and floor panels | • | Landing gear components and | • | Windows and window assemblies | ||||||
| • | Control system valve bodies | assemblies | • | Wing spars and stringers |
Acquisition of Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.
On June 16, 2010, we completed our acquisition of Vought. The results of Vought are included in the Aerospace Systems segment from June 16, 2010 through June 30, 2010. Vought is a leading global manufacturer of aerostructure products for commercial, military and business jet aircraft. For the twelve months ended March 28, 2010, the commercial, military and business jet aircraft end markets accounted for $1,008.1 million, $691.0 million and $258.9 million, respectively, of Vought's revenue, or 52%, 35%, and 13%, respectively, of Vought's total revenue. Vought develops and manufactures a wide range of complex aerostructures such as aircraft fuselages, wing and tail assemblies, engine nacelles, flight control surfaces as well as helicopter cabins. Vought's diverse and long-standing customer base consists of the leading aerospace OEMs, including Airbus, Boeing, Cessna, Gulfstream, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman and Sikorsky, as well as the U.S. military. We believe that Vought's new product and program development expertise, engineering and composite capabilities, the importance of its aerostructure products to its OEM customer base and Vought's advanced manufacturing capabilities make Vought an important partner to its customers. Vought collaborates with its customers and provides the latest technologies to address their needs for complex, highly engineered aerostructures. Vought's products are used on many of the largest and longest running programs in the aerospace industry, including the Boeing 737, 747-8, 767 and 777, C-17 Globemaster III, CH-47 Chinook, the Airbus 330/340, Lockheed Martin C-130, Sikorsky H-60 and Gulfstream G350, G450, G500 and G550. Vought is also a key supplier to its customers on programs that it believes have high growth potential, such as the Northrop Grumman Global Hawk unmanned aerial vehicle, Boeing 787 and V-22 Osprey. For the twelve months ended March 28, 2010, Vought generated total revenue of approximately $2.0 billion. See "—Vought Summary Historical Consolidated Financial Data."
Vought designs, manufactures and supplies both metal and composite aerospace structural assemblies including the following:
- •
- fuselage sections (including upper and lower ramp assemblies, skin panels, aft sections, and pressure bulkheads);
- •
- wings and wing assemblies (including skin panels, spars, and leading edges);
- •
- empennages (tail assemblies, including horizontal and vertical stabilizers, horizontal and vertical leading edge assemblies, elevators and rudders);
- •
- nacelles and nacelle components (the structures around engines, including fan cowls, inlet cowls, pylons and exhaust nozzles);
116
- •
- rotorcraft cabins and substructures;
- •
- detail parts (metallic and composite); and
- •
- control surfaces (including flaps, ailerons, rudders, spoilers and elevators).
The tables in the following three end markets summarize the major programs that Vought currently has under long-term contract by customer and product, indicating in each case whether Vought is a sole-source provider and the year of commencement of the program. For the purposes of the tables, Vought is considered a sole-source provider if it is currently the only provider of the structures it supplies for that program. The year of commencement of a program is the year a contract was signed with the OEM.
Commercial Aircraft Products. Vought produces a wide range of commercial aircraft products and participates in a number of major commercial programs for a variety of customers.
Vought is one of the largest independent manufacturers of aerostructures for Boeing Commercial Airplanes ("Boeing Commercial"). Vought is also one of the largest U.S. manufacturers of aerostructures for Airbus and has more than 20 years of commercial aircraft experience with the various Airbus entities. Vought's major commercial programs are summarized as follows:
Commercial Aircraft Customer/Platform | Product | Sole-Source | Year Program Commenced | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airbus | |||||||
| A330/340 | Upper skin panel assemblies, center spar and midrear spar, mid and outboard leading edge assemblies | ü | 1988 | ||||
| A340-500/600 | Upper skin panel, stringers, center spar and midrear spar, mid and outboard leading edge assemblies | ü | 1998 | ||||
| Boeing | |||||||
| 737 | Inboard flaps | 2009 | |||||
| 747 | Fuselage panels and empennage (vertical stabilizer, horizontal stabilizer and aft body section) | ü | 1966 | ||||
| 767 | Wing center section, horizontal stabilizer and aft fuselage section | ü | 1980 | ||||
| 777 | 1993—Inboard flaps, spoilers and spare requirements 2009—outboard flaps and ailerons | ü | 1993, 2009 | ||||
| 787 | Detail parts and frame assembly | ü | 2005 | ||||
117
Military Aircraft Products. Vought produces a broad array of products for military organizations both in the United States and around the world. In the United States, Vought provides aerostructures for a variety of military platforms, including transport, rotorcraft and unmanned aircraft utilized by all four branches of the U.S. military. Vought's major military programs are summarized as follows:
Military Aircraft Customer/Platform | Product | Sole-Source | Year Program Commenced | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bell/Boeing | |||||||||
| V-22 Osprey | Fuselage skin panels, empennage (sole-source) and ramp door assemblies | 1993 | |||||||
| Boeing | |||||||||
| C-17 Globemaster III | Empennage and nacelle components | ü | 1983 | ||||||
| Lockheed Martin | |||||||||
| C-130J Hercules | Empennage | ü | 1953 | ||||||
| Northrop Grumman | |||||||||
| Global Hawk | Integrated composite wing | ü | 1999 | ||||||
| Sikorsky | |||||||||
| H-60 | Cabin structure | 2004 | |||||||
| U.S. Air Force | |||||||||
| C-5 Galaxy | Flaps, slats, elevators, wing tips and panels | 2002 | |||||||
Business Jet Aircraft Products. Vought's customers in this market include primary business jet aircraft manufacturers such as Cessna, Gulfstream, and Hawker Beechcraft. We believe that Vought is the largest aerostructures supplier to Gulfstream for its G350, G450, G500, and G550 models. Vought's major business jet programs are summarized as follows:
Business Jet Aircraft Customer/Platform | Product | Sole-Source | Year Program Commenced | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cessna | |||||||||
| Citation X | Upper and lower wing skin assemblies | ü | 1992 | ||||||
| Gulfstream | |||||||||
| G350 and G450 | Nacelle components and wing boxes | ü | 1983 | ||||||
| G500 and G550 | Integrated wings | ü | 1993 | ||||||
| Hawker Beechcraft | |||||||||
| Hawker 800 | Nacelle components | ü | 1981 | ||||||
Aftermarket Services
Aftermarket Services performs maintenance, repair and overhaul services ("MRO") for commercial and military markets on components and assemblies manufactured by third parties. Aftermarket Services also designs, engineers, manufactures, repairs and overhauls aftermarket aerospace engine components. It offers comprehensive MRO solutions, and FAA-approved repairs and parts manufacturing options in addition to providing aftermarket parts and services to airlines, air cargo carriers and third-party overhaul facilities. In connection with its repair and overhaul activities, Aftermarket Services also provides leasing packages and exchange programs pursuant to which customers may lease replacement parts temporarily while their original equipment is repaired, or exchange them permanently. Aftermarket Services offers repair capability for FAA-approved assemblies which range from detailed components to complex subsystems, including APUs, thrust reversers, flight controls, engine accessories and avionics. Aftermarket Services also performs repair and overhaul services and supplies spare parts for various types of cockpit instruments and gauges for a broad range of commercial airlines on a worldwide basis. For the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010 and the three months ended June 30, 2010, Aftermarket Services generated net sales before inter-segment eliminations of $225.0 million and $59.8 million, respectively.
118
The principal products and services of our Aftermarket Services segment are set forth below.
Repairs and Overhauls: | Fabricates, Repairs and Overhauls: | Refurbishes and Airline Interior Products: | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
• Air cycle machines • APUs • Cockpit instrumentation • Constant speed drives • Engine and airframe accessories • Flight control surfaces • Integrated drive generators • Nacelles • Remote sensors • Thrust reversers | • Blades and vanes • Cabin interior panes, shades, light sensors and other plastic components • Combustors • Stators • Transition ducts | • Light assemblies • Overhead bins • Sidewalls |
Segment Reporting
In anticipation of the acquisition of Vought in early fiscal 2011, management began to consider certain organizational changes in an effort to align the operations reporting units. Management is currently evaluating the impact of the reorganization on the Company's externally reported segments in accordance with ASC Topic 280,Segment Reporting.
Competitive Strengths
We believe that we will benefit from the following competitive strengths:
Diverse Business Mix. Through organic growth and disciplined acquisitions, we have diversified the end markets we serve in order to minimize the impact that any single segment, platform or product of the aerospace industry could have on our results. The Vought Acquisition will further diversify our product and customer base, by expanding our capabilities into complex aerostructure products and allowing us to leverage Vought's strong existing customer relationships which complement our own.
Broad Array of Products and Services. We provide aerospace customers a single point of purchase for a diverse array of technically complex products and services for a wide range of aerospace platforms and programs, which we believe gives us a competitive advantage in developing strategic partnerships with OEMs. We design, engineer and manufacture aircraft components to meet our customers' particular requirements. In some cases, we own the proprietary rights to these designs and, accordingly, our customers generally rely on us to regularly repair, overhaul or replace these components, which provides us with a recurring source of cash flow. For our customers, we also perform repair and overhaul services on various aviation components manufactured by third parties. Our acquisition of Vought will expand our presence in many of today's most important commercial platforms and in important fixed-wing and rotorcraft military aircraft. The success of these and other legacy programs provides a strong foundation for us and positions us for future growth on new commercial programs.
Advanced Manufacturing and Technical Capabilities. We are leading global manufacturers of some of the largest and most technologically advanced parts and assemblies for a diverse range of aircraft. Vought adds capabilities in aerostructures, precision assembly techniques, automated assembly processes and large-bed machining and fabrication of large composite fiber reinforced parts to our own capabilities, which include highly proprietary actuation products, geared products, structural components, thermal products and controls. We employ over 250 engineers supporting design programs and over 800 manufacturing engineers. Our manufacturing facilities have achieved ISO 9001 certification, a certification of internationally recognized quality standards for manufacturing.
119
Significant Customer Relationships and Industry Presence. We believe that our strong customer relationships and market-leading industry positions are the result of our dedication to meeting our customers' complex specifications, our focus on quality control and our delivery of high quality products and services. Our customer base includes nearly all of the world's major OEMs (Boeing, Airbus, Bell Helicopter, Cessna, Gulfstream, General Electric, Honeywell, Lockheed Martin, Raytheon and Sikorsky), commercial airlines, the U.S. military and air cargo carriers, including Federal Express and United Parcel Service. We are an important supplier to many long-lived commercial and military platforms, including, Airbus 330/340, Boeing 737, 747-8, 767 and 777, C-17 Globemaster III and V-22 Osprey, Lockheed Martin C-130, Sikorsky H-60, Gulfstream G350, G450, G500 and G550, and are well positioned to capitalize on future growth in these established programs and other new program launches.
Robust Backlog. As of June 30, 2010, our backlog was approximately $3.3 billion. Backlog is generally comprised of actual purchase orders with firm delivery dates or contract requirements generally within the next 24 months. The majority of our sales are from orders issued under long-term contracts, generally of a three to five-year duration. Our backlog increases our management's visibility on future business activity levels.
Strong Free Cash Flow Generation. Despite the economic challenges faced by the commercial airline industry over the last several years and the worldwide economic recession, we have been able to achieve strong and consistent cash flow generation over that time period. Legacy aircraft programs, such as the C-17, CH-47 Chinook, V-22, UH-60 Black Hawk, Global Hawk, 737, 767, 777 and A330/340 which require only moderate capital expenditures to support current delivery rates, provide us with a source of strong, recurring cash flow. We have generated this growth and consistency in our cash flow through a combination of improved expense management, prudent management of capital expenditures to meet changing industry conditions and effective management of working capital.
Conservative Balance Sheet and Financial Strategy. As of June 30, 2010, our total net debt to capitalization was 48.6%. In addition, as of June 30, 2010 we had $35.7 million of cash and cash equivalents and $403.1 million of availability under our revolving credit facility.
High Barriers to Entry. The FAA certification process and the prevalence of long-term sole source or preferred supplier contracts serve as significant barriers to entry in the aerospace component and aerostructures markets. Certification by the FAA and foreign regulatory authorities is rigorous and requires significant time and capital expenditures in order to develop the capabilities to design, manufacture, test and certify aerospace component and aerostructure parts and assemblies. To obtain the approvals necessary to compete for contracts, companies make substantial up-front investments as well as develop and demonstrate sophisticated manufacturing expertise and experienced-based industry and aircraft knowledge. In addition, OEMs frequently award long-term sole source or preferred supplier contracts for the provision of particular parts for a particular platform. As a result, with respect to many of the platforms we supply, we are the only currently qualified FAA-certified supplier of such parts. We have achieved this position by implementing the technology to enable us to meet these stringent regulatory requirements and the exacting standards of our customers.
Experienced Leadership. Our senior management team and directors are highly experienced in the aviation parts and services industry, operationally focused and maintain extensive business relationships from which we as a whole benefit. Our senior executives and directors have extensive experience in the aviation industry and have successfully managed our businesses through various industry cycles. The acquisition of Vought has provided us with additional management and directors with extensive industry experience and expertise. We believe our management has the vision, focus and experience to position us for success in the future.
120
Business Strategy
Our business strategy is to sustain our high level of growth through internal product development and capability expansion, as well as through acquisitions. We are committed to pursuing the strategies established during our formation in 1993 in becoming the "vendor of choice" in the worldwide aviation industry. These five core strategies are as follows:
Develop Additional Products and Services. We offer integrated solutions for complex systems by integrating the capabilities of our operating companies, thereby adding greater value for our customers and their products. In addition, we place a high priority on the ongoing technological development and application of our products and services. We intend to continue to introduce new aviation products and services and to acquire select products and services to take advantage of opportunities in the aerospace industry and to respond to our customers' increasing demands. We plan to further expand our position as a consolidated point of purchase to our customers by capitalizing on the ongoing trend toward outsourcing and the reduction of approved suppliers and vendors by OEMs and airlines and air cargo carriers.
Market Complete Capabilities. As we continue to expand our product and service offerings, we plan to leverage our network of companies to cross-sell their capabilities to our existing customers and attract new customers. We strive to be our customers' most valued partner through excellence in product and process technologies and by providing modern and efficient production facilities. In addition, we strive to build on our reputation for quality and performance and to introduce best operating practices across our operations. Our network of companies will continue to share group marketing representatives and jointly bid on projects where appropriate, while still maintaining their individual identities. We believe that the breadth of our customer relationships, capabilities and experience, and our quality of service and support will enable us to win additional customer business.
Expand Operating Capacity. We plan to continue to increase our operating capacity to meet our expected internal growth and to meet expected growth in the aerospace industry. We intend to continue to prudently invest in state-of-the-art plants and equipment to improve our operating efficiencies and increase our operating margins.
Increase Our International Presence. We intend to continue to take advantage of the expanding international market for aviation products and services as worldwide air travel increases and foreign nations purchase used aircraft that require more frequent repair and maintenance. We currently supply products and services to substantially all major commercial passenger and air cargo airlines worldwide, have manufacturing and service facilities in France, Germany, Mexico, Thailand and the United Kingdom and retain independent sales representatives in a number of foreign countries. Furthermore, we intend to globalize our production processes through initiatives such as global sourcing. We believe that our initiatives will allow us to reduce costs, expand our capabilities and provide strategic benefits to our customers. We intend to build on our existing international presence through continued market penetration and, as appropriate opportunities arise, foreign acquisitions.
Pursue Complementary Acquisitions. We expect to continue to grow through acquisitions of other companies, assets or product lines that add to, complement, enhance or diversify our existing aviation products and services and program portfolio. We have successfully completed 33 acquisitions since 1996. We believe the fragmented nature of a large portion of the market for aircraft products and services will provide us with additional attractive acquisition opportunities. Through selective acquisitions, we aim to broaden our product offerings, add new specialized technologies, expand capacity for high-demand products and services, build on existing customer relationships and enter new markets.
121
Sales, Marketing and Engineering
While each of our operating companies maintains responsibility for selling and marketing its specific products, we have developed two group marketing teams focused on cross-selling our broad capabilities. The focus of these two marketing organizations, one for the Aerospace Systems Group and one for the Aftermarket Services Group, is to sell systems, integrated assemblies and repair and overhaul services, reaching across our operating companies, to our OEM, military, airline and air cargo customers. We also conduct sales activities in the Wichita, Kansas area through Triumph Wichita Support Center, a third-party sales organization dedicated solely to a sales effort on behalf of Triumph Group companies, which is staffed by sales professionals focused on Boeing IDS, Spirit AeroSystems, Cessna, Bombardier/Learjet and Raytheon. In certain limited cases, we use independent, commission-based representatives to facilitate responsiveness to each customer's changing needs and current trends in each market/geographic region in which we operate.
All three of these marketing organizations operate as the front-end of the selling process, establishing or maintaining relationships, identifying opportunities to leverage our brand, and providing service for our customers. Each individual operating company is responsible for its own engineering and technical support, pricing, manufacturing and product support. Also, within the Aerospace Systems Group, we have created a group engineering function to provide integrated solutions to meet our customer needs by designing systems that integrate the capabilities of our companies.
A significant portion of our government and defense contracts are awarded on a competitive bidding basis. We generally do not bid or act as the primary government contractor, but will typically bid and act as a subcontractor on contracts on a fixed-fee basis. We generally sell to our other customers on a fixed-fee, negotiated-contract or purchase-order basis.
As a result of our integrated sales and marketing organization, a significant portion of our net sales are derived from sales where two or more Triumph companies work together to achieve a result neither could accomplish on its own. We offer our customers the ability to satisfy a broad range of requirements from a single source.
Customers
For the year ended March 31, 2010, the Boeing Company, or Boeing, represented approximately 30% of our net sales. Sales to Boeing are diversified, as we provide a variety of products and services to more than 10 major programs spread among Boeing's commercial airline, military and space businesses. No other customer accounted for more than 10% of our net sales. Our customer base includes nearly all of the world's major OEMs and commercial airlines, the U.S. military and a number of air cargo carriers. Our customer base includes companies that, among them, produce or operate the full range of aerospace platforms and other markets, including:
- •
- Large Commercial Jets, such as Boeing 737, 747, 767, 777, 787 and Airbus 319, 320, 321, 330, 350, 380;
- •
- Military Aircraft, such as Boeing C-17 Globemaster III, F/A-18 Hornet, V-22 Osprey, CH-47 Chinook, Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk, Lockheed Martin F-16 Fighting Falcon and F-35 Lightning II, Northrop Grumman E-2C Hawkeye 2000, and Space Vehicles, such as Delta Launch Space Vehicle and International Space Station;
- •
- Business Jets, such as Bombardier, Cessna, Challenger, Gulfstream, and Learjet; and
- •
- Regional Commercial Jets, such as Bombardier CRJ100/200, CRJ700 and Embraer ERJ 135/145, ERJ 170/190.
122
On June 16, 2010, we completed the Vought acquisition. The Vought business generates a large proportion of its revenues from three large customers. The following table reports the total revenue from these customers relative to Vought's total revenue.
| | Year Ended December 31, 2009 | Year Ended December 31, 2008 | Year Ended December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Customers | Revenue | Percent of Total Revenue | Revenue | Percent of Total Revenue | Revenue | Percent of Total Revenue | |||||||||||||
| | ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||
Airbus | $ | 163.4 | 9 | % | $ | 222.3 | 13 | % | $ | 206.2 | 13 | % | |||||||
Boeing | 1,188.8 | 63 | % | 976.4 | 55 | % | 919.0 | 57 | % | ||||||||||
Gulfstream | 244.0 | 13 | % | 275.7 | 15 | % | 259.1 | 16 | % | ||||||||||
Total revenue to large customers | 1,596.2 | 85 | % | 1,474.4 | 83 | % | 1,384.3 | 86 | % | ||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 1,877.8 | 100 | % | $ | 1,775.0 | 100 | % | $ | 1,613.1 | 100 | % | |||||||
Backlog
We have a number of long-term agreements with several of our customers. These agreements generally describe the terms under which the customer may issue purchase orders to buy our products and services during the term of the agreement. These terms typically include a list of the products or repair services customers may purchase, initial pricing, anticipated quantities and, to the extent known, delivery dates. In tracking and reporting our backlog, however, we only include amounts for which we have actual purchase orders with firm delivery dates, contract requirements generally within the next 24 months or funded orders for government programs, which primarily relates to sales to our OEM customer base. Purchase orders issued by our aftermarket customers are usually completed within a short period of time. As a result, our backlog data relates primarily to the OEM customers. The backlog information set forth below does not include the sales that we expect to generate from long-term agreements for which we do not have actual purchase orders with firm delivery dates. As a result, our backlog may fluctuate at any given time depending on whether we have received significant new firm orders, funded orders or authorizations to proceed before the date of measurement. For example, our military funded orders or authorizations to proceed generally are awarded when the Department of Defense budget for the relevant year has been approved, resulting in a significant increase in backlog at that time.
As of June 30, 2010, our continuing operations had outstanding purchase orders representing an aggregate invoice price of approximately $3,338 million, of which $3,305 million and $33 million relate to the Aerospace Systems Group and the Aftermarket Services Group, respectively. As of June 30 2009, our continuing operations had outstanding purchase orders representing an aggregated invoice price of approximately $1,279 million, of which $1,245 million and $34 million relate to the Aerospace Systems Group and the Aftermarket Services Group, respectively. Of the backlog of $3,338 million as of June 30, 2010, approximately $389 million will not be shipped by June 30, 2011.
Proprietary Rights and Intellectual Property
We benefit from our proprietary rights relating to designs, engineering and manufacturing processes and repair and overhaul procedures. For some products, our particular manufacturing capabilities are required by the customer's specifications or designs, thereby necessitating reliance on us for the production of such specially designed products. We also hold two SFAR 36 certifications that permit us to develop proprietary repair procedures to be used in some repair and overhaul processes.
We view our name and mark as significant to our business as a whole. Our products are protected by a portfolio of patents, trademarks, licenses or other forms of intellectual property that expire at
123
various dates in the future. We develop and acquire new intellectual property on an ongoing basis and consider all of our intellectual property to be valuable. However, based on the broad scope of our product lines, management believes that the loss or expiration of any single intellectual property right would not have a material effect on our results of operations, our financial position or our business segments. Our policy is to file applications and obtain patents for our new products as appropriate, including product modifications and improvements. While patents generally expire 20 years after the patent application filing date, new patents are issued to us on a regular basis.
In our overhaul and repair businesses, OEMs of equipment that we maintain for our customers increasingly include language in repair manuals that relate to their equipment asserting broad claims of proprietary rights to the contents of the manuals used in our operations. There can be no assurance that OEMs will not try to enforce such claims including the possible use of legal proceedings. In the event of such legal proceedings, there can be no assurance that such actions against the Company will be unsuccessful. However, we believe that our use of manufacture and repair manuals is lawful.
Operating Locations
We conduct our business through operating companies and divisions. The following chart describes the operations, customer base and certain other information with respect to our principal operating locations at June 30, 2010:
Operation | Subsidiary | Operating Location | Business | Type of Customers | Number of Employees | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRIUMPH AEROSPACE SYSTEMS GROUP | ||||||||||||
| Construction Brevetees d'Alfortville | Construction Brevetees d'Alfortville SAS | Alfortville, France | Manufactures mechanical ball bearing control assemblies for the aerospace, ground transportation, defense and marine industries. | Commercial and Military OEMs, Ground Transportation and Marine OEMs. | 66 | |||||||
Triumph Actuation & Motion Control Systems | Triumph Actuation & Motion Control Systems—UK, Ltd. | Buckley, UK | Designs and builds proprietary advanced control products for flight actuation and motor control applications in all electrical aircraft and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles ("UAVs"). | Commercial, General Aviation, and Military OEMs. | 48 | |||||||
Triumph Actuation Systems—Clemmons(1) Triumph Actuation Systems—Freeport | Triumph Actuation Systems, LLC | Clemmons, NC Freeport, NY | Designs, manufactures and repairs complex hydraulic and hydromechanical aircraft components and systems, such as variable displacement pumps and motors, linear actuators and valves, and cargo door actuation systems. | Commercial, General Aviation, and Military OEMs; Commercial Airlines, General Aviation and Military Aftermarket. | 245 | |||||||
Triumph Actuation Systems—Connecticut | Triumph Actuation Systems—Connecticut, LLC | Bloomfield, CT East Lyme, CT Bethel, CT | Designs, manufactures and repairs complex hydraulic, hydromechanical and mechanical components and systems, such as nose wheel steering motors, helicopter blade lag dampers, mechanical hold open rods, coupling and latching devices, as well as mechanical and electromechanical actuation products. | Commercial, General Aviation, and Military OEMs; Military Aftermarket. | 154 | |||||||
Triumph Actuation Systems—Valencia(1) | Triumph Actuation Systems—Valencia, Inc. | Valencia, CA | Designs, manufactures and repairs complex hydraulic and hydromechanical aircraft components and systems, such as accumulators, actuators, complex valve packages, and landing gear retract actuators. | Commercial, General Aviation, and Military OEMs. | 197 | |||||||
124
Operation | Subsidiary | Operating Location | Business | Type of Customers | Number of Employees | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triumph Aerospace Systems—Newport News | Triumph Aerospace Systems—Newport News, Inc. | Newport News, VA San Diego, CA Huntsville, AL New Haven, CT | Offers a fully integrated range of capabilities, including systems engineering, conceptual engineering, mechanical design and analysis, prototype and limited-rate production, and instrumentation assembly and testing services and complex structural composite design and manufacturing. | Commercial and Military OEMs; Commercial and Military Aftermarket. | 132 | |||||||
Triumph Aerospace Systems—Seattle | Triumph Actuation Systems—Connecticut, LLC | Redmond, WA Rochester, NY | System engineering and integration for landing gear, hydraulic, deployment, cargo door and electro-mechanical type systems. Capabilities include design, analysis and testing to support these types of systems and components. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs. | 73 | |||||||
Triumph Aerospace Systems—Wichita(1) | Triumph Aerospace Systems—Wichita, Inc. | Wichita, KS | Designs and manufactures aircraft windows, sheet metal assemblies (wing spars and leading edges), pilot/co-pilot control wheels, cockpit sun visors, and structural composite parts for the aerospace industry. | Commercial and General Aviation OEMs; General Aviation Aftermarket. | 161 | |||||||
Triumph Aerostructures—Vought Division(2) Triumph Aerostructures—Vought Commercial Division Triumph Aerostructures—Vought Integrated Programs Division | Triumph Aerostructures, LLC | Dallas, TX Grand Prairie, TX Hawthorne, CA Nashville, TN Stuart, FL(1) Milledgeville, GA | Designs and manufactures major airframe structures such as fuselage assemblies, wings, empennages, nacelles and other components for prime manufacturers of aircraft. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs. | 5,715 | |||||||
Triumph Composite Systems | Triumph Composite Systems, Inc. | Spokane, WA | Manufactures interior non-structural composites for the aviation industry, including environmental control system ducting, floor panels, aisle stands and glare shields. | Commercial, General Aviation, and Military OEMs; Commercial Aftermarket. | 457 | |||||||
Triumph Controls(1) | Triumph Controls, LLC | North Wales, PA Shelbyville, IN | Designs and manufactures mechanical and electromechanical control systems. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs and Aftermarket. | 131 | |||||||
Triumph Controls—Germany Triumph Controls—UK | Triumph Controls—Germany, GmbH Triumph Controls—UK, Ltd. | Heiligenhaus, Germany Basildon, UK | Produces and repairs cable control systems for ground, flight, engine management and cabin comfort features in aircraft. | Commercial and Military OEMs. | 37 | |||||||
Triumph Fabrications—Fort Worth(1) | Triumph Fabrication—Fort Worth, Inc. | Fort Worth, TX | Manufactures metallic/composite bonded components and assemblies. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs and Aftermarket. | 111 | |||||||
Triumph Fabrications—Hot Springs | Triumph Fabrications—Hot Springs, Inc. | Hot Springs, AR | Produces complex sheet metal parts and assemblies, titanium hot forming, and performs chem-milling and other metal finishing processes. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs and Aftermarket. | 355 | |||||||
125
Operation | Subsidiary | Operating Location | Business | Type of Customers | Number of Employees | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Triumph Fabrications—St. Louis | Triumph Fabrications—St. Louis, Inc. (formerly Fabritech, Inc.) Triumph Fabrications—Orangeburg, Inc. | East Alton, IL Orangeburg, SC | Provides maintenance and manufactured solutions for aviation drive train, mechanical, hydraulic and electrical hardware items including gearboxes, cargo hooks and vibration absorbers. Also, produces fabricated textile items such as seat cushions and sound insulation blankets for military rotary-wing platforms. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military Aftermarket. | 62 | |||||||
Triumph Fabrications—Shelbyville | The Triumph Group Operations, Inc. | Shelbyville, IN | Produces aircraft fuselage skins, leading edges and web assemblies through the stretch forming of sheet, extrusion, rolled shape and light plate metals. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs. | 88 | |||||||
Triumph Fabrications—San Diego(1) Triumph Fabrications—Phoenix | Triumph Fabrications—San Diego, Inc. Triumph Engineered Solutions, Inc. | El Cajon, CA Chandler, AZ | Produces complex welded and riveted sheet metal assemblies for aerospace applications. Components include exhaust systems, ducting, doors, panels, control surfaces and engine components. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs. | 198 | |||||||
Triumph Gear Systems—Park City(1) Triumph Gear Systems—Macomb(1) | Triumph Gear Systems, Inc. Triumph Gear Systems—Macomb, Inc. | Park City, UT Macomb, MI | Specializes in the design, development, manufacture, sale and repair of gearboxes, high-lift flight control actuators, gear-driven actuators and gears for the aerospace industry. | Commercial and Military OEMs and Aftermarket. | 437 | |||||||
Triumph Insulation Systems | Triumph Insulation Systems, LLC | Santa Ana, CA Mexicali, Mexico Beijing, China(3) | Designs, manufactures and repairs thermal-acoustic insulation systems for commercial aerospace applications. | Commercial and Military OEMs. | 848 | |||||||
Triumph Group—Mexico | Triumph Group—Mexico, S. de R.L. de C.V. | Zacatecas, Mexico | Provides rough machining of gears, actuations and structure components, as well as assembly, fabrications, engineering and composites to Triumph companies and certain customers. Facility scheduled to open Summer of 2010. | Commercial and General Aviation OEMs. | 8 | |||||||
Triumph Northwest | The Triumph Group Operations, Inc. | Albany, OR | Machines and fabricates refractory, reactive, heat and corrosion-resistant precision products. | Military, Medical and Electronic OEMs. | 23 | |||||||
Triumph Processing | Triumph Processing, Inc. | Lynwood, CA | Provides high-quality finishing services to the aerospace, military and commercial industries. | Commercial, General Aviation, and Military OEMs. | 87 | |||||||
Triumph Structures—East Texas | Triumph Structures—East Texas, Inc. | Kilgore, TX | Manufactures structural components specializing in complex precision machining primarily for commercial and military aerospace programs. | Commercial and Military OEMs. | 88 | |||||||
Triumph Structures—Everett Triumph Structures—Brea | Triumph Structures—Everett, Inc. | Everett, WA Brea, CA | Produces airframe structures, such as skins, stringers, ribs, spars, straps and monolithic structures ranging in size from a few inches to 120 feet long. Specialized machining for complex structural components | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs. | 207 | |||||||
Triumph Structures—Kansas City | Triumph Structures—Kansas City, Inc. | Grandview, MO | Manufactures precision machined parts and mechanical assemblies for the aviation, aerospace and defense industries. | Commercial and Military OEMs. | 124 | |||||||
Triumph Structures—Long Island | Triumph Structures—Long Island, LLC | Westbury, NY | Manufactures high quality structural and dynamic parts and assemblies for commercial and military aerospace programs. | Commercial and Military OEMs. | 116 | |||||||
126
Operation | Subsidiary | Operating Location | Business | Type of Customers | Number of Employees | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triumph Structures—Los Angeles | Triumph Structures—Los Angeles, Inc. | Chatsworth, CA City of Industry, CA Walnut, CA | Manufactures long structural components, such as stringers, cords, floor beams and spars for the aviation industry. Machines, welds and assembles large complex precision structural components. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs. | 286 | |||||||
Triumph Structures—Wichita | Triumph Structures—Wichita, Inc. | Wichita, KS | Specializes in complex, high speed monolithic precision machining, turning, subassemblies, and sheet metal fabrication, serving domestic and international aerospace customers. | Commercial and Military OEMs. | 160 | |||||||
Triumph Thermal Systems(1) | Triumph Thermal Systems, Inc. | Forest, OH | Designs, manufactures and repairs aircraft thermal transfer components and systems. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military OEMs. | 176 | |||||||
TRIUMPH AFTERMARKET SERVICES GROUP | ||||||||||||
| Triumph Accessory Services—Wellington(1) | The Triumph Group Operations, Inc. | Wellington, KS Milwaukee, WI | Provides maintenance services for aircraft heavy accessories and airborne electrical power generation devices, including constant speed drives, integrated drive generators, air cycle machines and electrical generators. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military Aftermarket. | 114 | |||||||
Triumph Accessory Services—Grand Prairie(1) | Triumph Accessory Services—Grand Prairie, Inc. | Grand Prairie, TX | Provides maintenance services for engine and air frame accessories including a variety of engine gearboxes, pneumatic starters, valves and drive units, hydraulic actuators, lube system pumps, fuel nozzles, fuel pumps and fuel controls. | Commercial and Military Aftermarket. | 112 | |||||||
Triumph Air Repair(1) | The Triumph Group Operations, Inc. | Phoenix, AZ | Repairs and overhauls auxiliary power units (APUs) and related accessories; sells, leases and exchanges APUs, related components and other aircraft material. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military Aftermarket. | 103 | |||||||
Triumph Airborne Structures(1) | Triumph Airborne Structures, Inc. | Hot Springs, AR | Repairs and overhauls fan reversers, nacelle components, flight control surfaces and other aerostructures. | Commercial Aftermarket. | 125 | |||||||
Triumph Aviation Services—Asia(1) | Triumph Aviation Services Asia Ltd. | Chonburi, Thailand | Repairs and overhauls complex aircraft operational components, such as auxiliary power units (APUs), nacelles, constant speed drives, fan reversers and related accessories. | Commercial Aftermarket. | 108 | |||||||
Triumph Engines—Tempe(1) | Triumph Engineered Solutions, Inc. | Tempe, AZ | Designs, engineers, manufactures, repairs and overhauls aftermarket aerospace gas turbine engine components and provides repair services and aftermarket parts and services to aircraft operators, maintenance providers, and third-party overhaul facilities. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military Aftermarket. | 112 | |||||||
Triumph Instruments—Burbank(1) | Triumph Instruments—Burbank, Inc. | Burbank, CA Van Nuys, CA | Repairs and overhauls aircraft instrumentation, power systems and avionics. Distributes and repairs aircraft smoke detectors and industrial instrumentation. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military Aftermarket. | 62 | |||||||
Triumph Instruments—Ft. Lauderdale(1) | Triumph Instruments, Inc. | Ft. Lauderdale, FL | Specializes in the repair, overhaul and exchange of electromechanical and pneumatic aircraft instruments. | Commercial, General Aviation and Military Aftermarket. | 40 | |||||||
127
Operation | Subsidiary | Operating Location | Business | Type of Customers | Number of Employees | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triumph Interiors | Triumph Interiors, LLC | Oakdale, PA(1), Grand Prairie, TX(1) | Refurbishes and repairs aircraft interiors such as sidewalls, ceiling panels, galleys and overhead storage bins and manufactures a full line of PMA interior lighting and plastic components. | Commercial Aftermarket. | 104 | |||||||
Triumph San Antonio Support Center | The Triumph Group Operations, Inc. | San Antonio, TX | Provides maintenance services for aircraft ground support equipment. | Military Aftermarket. | 30 | |||||||
DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS | ||||||||||||
| Triumph Precision Castings | Triumph Precision Castings Co. | Chandler, AZ | Applies advanced directionally solidified (polycrystal or single crystal) and Equiax investment casting processes to produce products for the commercial and defense gas turbine market. | Commercial and Military Aftermarket. | 70 | |||||||
- (1)
- Designates FAA-certified repair station.
- (2)
- Triumph Aerostructures, LLC is the successor entity to Vought.
- (3)
- Through an affiliate, Triumph Insulation Systems, LLC manages a 50% interest in a joint venture operating in Beijing China, with Beijing Kailan Aviation Technology Co., Ltd., an unrelated party based in China. Our interest in the joint venture is accounted for in our consolidated financial statements on the equity method.
United States and International Operations
Our revenues from our continuing operations to customers in the United States for fiscal years 2010, 2009 and 2008 were approximately $1,039.0 million, $974.0 million and $914.0 million, respectively. Our revenues from our continuing operations to customers in all other countries for fiscal years 2010, 2009 and 2008 were approximately $256.0 million, $267.0 million, and $237.0 million, respectively.
As of March 31, 2010 and 2009, our long-lived assets for our continuing operations located in the United States were approximately $855.0 million and $851.0 million, respectively. As of March 31, 2010 and 2009, our long-lived assets for our continuing operations located in all other countries were approximately $74.0 million and $63.0 million, respectively.
On June 16, 2010, we completed the Vought acquisition. Although the majority of the revenues of the Vought business are generated by sales into the U.S. market, as shown on the following table, a significant portion of the revenues of the Vought business are generated by sales to OEMs located outside of the United States.
| | Year Ended December 31, 2009 | Year Ended December 31, 2008 | Year Ended December 31, 2007 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Revenue Source | Revenue | Percent of Total Revenue | Revenue | Percent of Total Revenue | Revenue | Percent of Total Revenue | ||||||||||||||
| | ($ in millions) | |||||||||||||||||||
United States | $ | 1,713.9 | 91 | % | $ | 1,552.7 | 87 | % | $ | 1,406.9 | 87 | % | ||||||||
International(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||
England | 149.4 | 8 | % | 153.3 | 9 | % | 143.0 | 9 | % | |||||||||||
Other | 14.5 | 1 | % | 69.0 | 4 | % | 63.2 | 4 | % | |||||||||||
Total International | 163.9 | 9 | % | 222.3 | 13 | % | 206.2 | 13 | % | |||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 1,877.8 | 100 | % | $ | 1,775.0 | 100 | % | $ | 1,613.1 | 100 | % | ||||||||
128
Raw Materials and Replacement Parts
We purchase raw materials, primarily consisting of extrusions, forgings, castings, aluminum and titanium sheets and shapes, from various vendors. We also purchase replacement parts which are utilized in our various repair and overhaul operations. We believe that the availability of raw materials to us is adequate to support our operations.
Competition
We compete primarily with the top-tier systems integrators and manufacturers that supply them, some of which are divisions or subsidiaries of other large companies, in the manufacture of aircraft systems components and subassemblies. OEMs are increasingly focusing on assembly activities while outsourcing more manufacturing and repair to third parties, and therefore are less of a competitive force than in previous years.
Participants in the aerospace industry compete primarily on the basis of breadth of technical capabilities, quality, turnaround time, capacity and price. However, traditional factors affecting competition, such as price and quality of service, may not be significant determinants when OEMs decide whether to produce a part in-house or to outsource. OEMs may choose not to outsource production of parts and assemblies due to, among other things, their own direct labor and overhead considerations, capacity utilization at their own facilities and desire to retain critical or core skills.
When OEMs choose to outsource, they typically do so for one or more of the following reasons: lower cost; capacity limitations; a business need or desire to utilize others' unique engineering and design capabilities; a desire to share the required up-front investment; risk sharing; and strategic reasons in support of sales. Our ability to compete for large contracts depends upon: our underlying cost structure and ability to price competitively; the readiness and availability of our facilities, equipment and personnel to undertake and nimbly implement the programs; our engineering and design capabilities; our ability to manufacture or rapidly procure both metal and composite structures; our ability to support its customer's needs for strategic work placement; and our ability to finance the upfront costs of new contracts.
We compete with numerous U.S. and international companies on a worldwide basis. Primary competition comes from internal work completed by the operating units of OEMs including Airbus, Boeing, Gulfstream, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman Raytheon and Sikorsky and independent aerostructures suppliers in the United States and overseas who, like us, provide services and products to the OEMs. Our principal competitors among independent aerostructures suppliers include: Alenia Aeronautica, Fuji Heavy Industries, GKN Westland Aerospace (U.K.), Goodrich Corp., Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Spirit AeroSystems and Stork Aerospace.
With respect to our repair and overhaul of aviation components, competition comes from three primary sources, some with greater financial and other resources than we have: OEMs, major commercial airlines and other independent repair and overhaul companies. Some major commercial airlines continue to own and operate their own service centers, while others have begun to sell or outsource their repair and overhaul services to other aircraft operators or third parties. Large domestic and foreign airlines that provide repair and overhaul services typically provide these services not only for their own aircraft but for other airlines as well. OEMs also maintain service centers which provide repair and overhaul services for the components they manufacture. Other independent service organizations also compete for the repair and overhaul business of other users of aircraft components.
Government Regulation and Industry Oversight
The aerospace industry is highly regulated in the United States by the FAA and in other countries by similar agencies. We must be certified by the FAA and, in some cases, by individual OEMs, in order to engineer and service parts and components used in specific aircraft models. If material
129
authorizations or approvals were revoked or suspended, our operations would be adversely affected. New and more stringent government regulations may be adopted, or industry oversight heightened, in the future and these new regulations, if enacted, or any industry oversight, if heightened, may have an adverse impact on us. See "Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Industry and Our Business—Our international sales and operations are subject to applicable laws relating to trade, export controls and foreign corrupt practices, the violation of which could adversely affect our operations."
We must also satisfy the requirements of our customers, including OEMs, that are subject to FAA regulations, and provide these customers with products and repair services that comply with the government regulations applicable to aircraft components used in commercial flight operations. The FAA regulates commercial flight operations and requires that aircraft components meet its stringent standards. In addition, the FAA requires that various maintenance routines be performed on aircraft components, and we currently satisfy these maintenance standards in our repair and overhaul services. Several of our operating locations are FAA-approved repair stations.
Generally, the FAA only grants licenses for the manufacture or repair of a specific aircraft component, rather than the broader licenses that have been granted in the past. The FAA licensing process may be costly and time-consuming. In order to obtain an FAA license, an applicant must satisfy all applicable regulations of the FAA governing repair stations. These regulations require that an applicant have experienced personnel, inspection systems, suitable facilities and equipment. In addition, the applicant must demonstrate a need for the license. Because an applicant must procure manufacturing and repair manuals from third parties relating to each particular aircraft component in order to obtain a license with respect to that component, the application process may involve substantial cost.
The license approval processes for the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA was formed in 2002 and is handling most of the responsibilities of the national aviation authorities in Europe, such as the United Kingdom Civil Aviation Authority), which regulates this industry in the European Union, the Civil Aviation Administration of China, and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities are similarly stringent, involving potentially lengthy audits. In addition, use of foreign suppliers and sale to foreign customers, such as Airbus, and foreign governments may subject us and Vought to the requirements of the U.S. Export Administration Regulations and the International Trafficking in Arms Regulations.
The military aerospace industry is highly regulated by the U.S. Department of Defense. The Defense Contract Management Agency has certified certain of our companies to provide products to the U.S. military. These companies are subject to review by the Defense Contract Management Agency whether they contract directly with the U.S. Government or provide products to an OEM that contracts directly with the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government contracts held by us and our customers are subject to unique procurement and administrative rules based on laws and regulations. U.S. Government contracts are, by their terms, subject to termination by the U.S. Government either for its convenience or default by the contractor. In addition, U.S. Government contracts are conditioned upon the continuing availability of Congressional appropriations. Congress usually appropriates funds for a given program on a yearly basis, even though contract performance may take many years. Consequently, at the outset of a major program, the contract is usually partially funded, and additional monies are normally committed to the contract by the procuring agency only as appropriations are made by Congress for future years. Our operations are also subject to a variety of worker and community safety laws. For example, the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970, or "OSHA," mandates general requirements for safe workplaces for all employees. In addition, OSHA provides special procedures and measures for the handling of hazardous and toxic substances. Specific safety standards have been promulgated for workplaces engaged in the treatment, disposal or storage of hazardous waste. We believe that our operations are in material compliance with OSHA's health and safety requirements.
130
Environmental Matters
Our businesses, operations and facilities are subject to numerous stringent federal, state, local and foreign environmental laws and regulation by government agencies, including the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, or the "EPA." Among other matters, these regulatory authorities impose requirements that regulate the emission, discharge, generation, management, transportation and disposal of hazardous materials, pollutants and contaminants, govern public and private response actions to hazardous or regulated substances which may be or have been released to the environment, and require us to obtain and maintain licenses and permits in connection with our operations. This extensive regulatory framework imposes significant compliance burdens and risks on us. Although our management believes that our operations and facilities are in material compliance with such laws and regulations, future changes in these laws, regulations or interpretations thereof or the nature of our operations or regulatory enforcement actions which may arise, may require us to make significant additional capital expenditures to ensure compliance in the future.
Certain of our facilities, including facilities acquired and operated by us or one of our subsidiaries, have at one time or another been under active investigation for environmental contamination by federal or state agencies when acquired, and at least in some cases, continue to be under investigation or subject to remediation for potential or identified environmental contamination. We are frequently indemnified by prior owners or operators and/or present owners of the facilities for liabilities which we incur as a result of these investigations and the environmental contamination found which pre-dates our acquisition of these facilities, subject to certain limitations. We also maintain a pollution liability policy that provides coverage, subject to specified limitations, for specified material liabilities associated with the clean-up of certain on-site pollution conditions, as well as defense and indemnity for certain third party suits (including Superfund liabilities at third party sites), in each case, to the extent not otherwise indemnified. However, if we were required to pay the expenses related to environmental liabilities for which neither indemnification nor insurance coverage is available, these expenses could have a material adverse effect on us.
The facilities acquired by us from Vought as a result of the completion of the Vought acquisition have been previously owned and operated by other entities and remediation is currently taking place at several facilities in connection with contamination that occurred prior to Vought's ownership. In particular, Vought acquired several of its facilities from Northrop Grumman in July of 2000, including the Hawthorne, California facility, the Stuart, Florida facility, the Milledgeville, Georgia facility and three Texas facilities, at which remediation projects are underway.
The acquisition agreement between Northrop Grumman Corporation and Vought transferred certain pre-existing (as of July 24, 2000) environmental liabilities to Vought, which are now our liabilities as a result of the Vought Acquisition. We are liable for the first $7.5 million and 20% of the amount between $7.5 million and $30 million for environmental costs incurred relating to pre-existing matters as of July 24, 2000. Pre-existing environmental liabilities at the formerly Northrop Grumman Corporation sites exceeding our $12 million liability limit remain the responsibility of Northrop Grumman Corporation under the terms of the acquisition agreement, to the extent they are identified within 10 years from the acquisition date. Thereafter, to the extent environmental remediation is required for hazardous materials including asbestos, urea formaldehyde foam insulation or lead-based paints, used as construction materials in, on, or otherwise affixed to structures or improvements on property acquired from Northrop Grumman Corporation, we would be responsible. We do not believe that we have material outstanding or unasserted liabilities for hazardous materials on facilities we acquired from Vought.
As of June 30, 2010, our balance sheet included an accrued liability of $2.1 million million for accrued environmental liabilities.
131
Employees
As of March 31, 2010, for our continuing operations we employed 5,991 persons, of whom 647 were management employees, 90 were sales and marketing personnel, 697 were technical personnel, 789 were administrative personnel and 3,768 were production workers. As of March 31, 2010, for our discontinued operations, we employed 30 persons, of whom 1 was a management employee, 1 was a sales and marketing employee, 4 were technical personnel, 3 were administrative personnel and 21 were production workers.
Several of our subsidiaries are parties to collective bargaining agreements with labor unions. Under those agreements, we currently employ approximately 590 full-time employees. As of March 31, 2010, approximately 9.8% of our permanent employees were represented by labor unions and approximately 20.0% of net sales were derived from the facilities at which at least some employees are unionized. We have not experienced any material labor-related work stoppage and consider our relations with our employees to be good.
Following completion of the Vought Acquisition on June 16, 2010, we also employ all of Vought's employees. As of December 31, 2009, Vought employed approximately 5,900 people. Of those employed at year-end, approximately 2,800, or 47%, were represented by four separate unions. Local 848 of the United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America represents approximately 2,100 of the employees located in Dallas and Grand Prairie, Texas. This union contract, which covers the majority of Vought's production and maintenance employees at its Dallas and Grand Prairie, Texas facilities, is in effect through October 3, 2010. Aero Lodge 735 of the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers represents approximately 650 of the employees located in Nashville, Tennessee. This union contract is in effect through January 15, 2012.
We believe that Vought had constructive working relationships with its unions prior to the completion of the Vought Acquisition and Vought had generally been successful in negotiating collective bargaining agreements in the past. Before the 2008 strike at its Nashville facility by the employees represented by Local 735 of the IAM, Vought had not suffered an interruption of business as a result of a labor dispute since 1989.
Our inability to negotiate an acceptable contract with any of these labor unions could result in strikes by the affected workers and increased operating costs as a result of higher wages or benefits paid to union members. If the unionized workers were to engage in a strike or other work stoppage, or other employees were to become unionized, we could experience a significant disruption of our operations and higher ongoing labor costs, which could have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Properties
Our executive offices are located in Wayne, Pennsylvania, where we lease 11,700 square feet of space. In addition, as of June 30, 2010, we owned or leased the following operating facilities.
Location | Description | Square Footage | Owned/ Leased | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
TRIUMPH AEROSPACE SYSTEMS GROUP | |||||||
Hot Springs, AR | Manufacturing facility/office | 217,300 | Owned | ||||
Chandler, AZ | Manufacturing facility/office | 34,300 | Leased | ||||
Brea, CA | Manufacturing facility | 90,000 | Leased | ||||
Chatsworth, CA | Manufacturing facility/office | 101,900 | Owned | ||||
Chatsworth, CA | Manufacturing facility | 21,600 | Leased | ||||
City of Industry, CA | Manufacturing facility/office | 75,000 | Leased | ||||
El Cajon, CA | Manufacturing facility/office | 122,400 | Leased | ||||
132
Location | Description | Square Footage | Owned/ Leased | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Hawthorne, CA | Manufacturing facility | 1,348,659 | Leased | ||||
Lynwood, CA | Processing and finishing facility/office | 59,700 | Leased | ||||
Lynwood, CA | Office/warehouse/aerospace metal processing | 105,000 | Leased | ||||
San Diego, CA | Force measurement systems facility | 7,000 | Leased | ||||
Santa Ana, CA | Office | 15,300 | Leased | ||||
Torrance, CA | Processing facility. | 84,654 | Leased | ||||
Valencia, CA | Manufacturing facility/office | 87,000 | Leased | ||||
Walnut, CA | Manufacturing facility/office | 105,000 | Leased | ||||
Bethel, CT | Office | 1,700 | Leased | ||||
Bloomfield, CT | Manufacturing facility/office | 29,800 | Leased | ||||
East Lyme, CT | Manufacturing facility/office | 59,600 | Owned | ||||
New Haven, CT | Engineering/manufacturing | 2,400 | Leased | ||||
Stuart, FL | Manufacturing facility | 519,690 | Leased | ||||
Alfortville, France | Manufacturing facility/office | 7,500 | Leased | ||||
Milledgeville, GA | Manufacturing facility/assembly facility | 566,168 | Owned | ||||
Heiligenhaus, Germany | Manufacturing facility/office | 2,200 | Leased | ||||
East Alton, IL | Machine shop/office | 25,000 | Leased | ||||
Shelbyville, IN | Manufacturing facility/office | 193,900 | Owned | ||||
Shelbyville, IN | Manufacturing facility/office | 100,000 | Owned | ||||
Wichita, KS | Manufacturing facility/office | 145,200 | Leased | ||||
Wichita, KS | Manufacturing facility/office | 130,300 | Leased | ||||
Macomb, MI | Manufacturing facility/office | 86,000 | Leased | ||||
Mexicali, Mexico | Manufacturing facility/office | 261,000 | Leased | ||||
Zacatecas, Mexico | Manufacturing facility/office | 270,000 | Leased | ||||
Grandview, MO | Manufacturing facility/office | 78,000 | Owned | ||||
Freeport, NY | Manufacturing facility/office/warehouse | 29,000 | Owned | ||||
Rochester, NY | Engineering Office | 5,000 | Leased | ||||
Westbury, NY | Manufacturing facility/office | 93,500 | Leased | ||||
Westbury, NY | Aerospace Metal Processing | 12,500 | Leased | ||||
Clemmons, NC | Manufacturing facility/repair/office | 110,000 | Owned | ||||
Forest, OH | Manufacturing facility/office | 125,000 | Owned | ||||
Albany, OR | Machine shop/office | 25,000 | Owned | ||||
North Wales, PA | Manufacturing facility/office | 111,400 | Owned | ||||
Orangeburg, SC | Machine shop | 52,000 | Owned | ||||
Nashville, TN | Manufacturing facility/assembly facility/office | 2,198,740 | Owned | ||||
Dallas, TX | High speed wind tunnel | 28,878 | Owned | ||||
Dallas, TX | Manufacturing facility/office | 4,855,293 | Leased | ||||
Grand Prairie, TX | Manufacturing facility | 804,456 | Leased | ||||
Fort Worth, TX | Manufacturing facility/office | 114,100 | Owned | ||||
Irving, TX | Office | 16,168 | Leased | ||||
Kilgore, TX | Manufacturing facility/office | 83,000 | Owned | ||||
Basildon, UK. | Manufacturing facility/office | 1,900 | Leased | ||||
Buckley, UK. | Manufacturing facility/office | 8,000 | Leased | ||||
Park City, UT | Manufacturing facility/office | 180,000 | Owned | ||||
Newport News, VA | Engineering/Manufacturing/office | 93,000 | Leased | ||||
Everett, WA | Manufacturing facility | 153,000 | Leased | ||||
Redmond, WA | Manufacturing facility/office | 19,400 | Leased | ||||
Spokane, WA | Manufacturing facility/office | 392,000 | Owned | ||||
133
Location | Description | Square Footage | Owned/ Leased | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
TRIUMPH AFTERMARKET SERVICES GROUP | |||||||
Hot Springs, AR | Machine shop/office | 219,700 | Owned | ||||
Chandler, AZ | Thermal processing facility/office | 15,000 | Leased | ||||
Phoenix, AZ | Repair and overhaul shop/office | 50,000 | Leased | ||||
Phoenix, AZ | Repair and overhaul/office | 24,800 | Leased | ||||
Tempe, AZ | Manufacturing facility/office | 13,500 | Owned | ||||
Tempe, AZ | Machine shop | 9,300 | Owned | ||||
Tempe, AZ | Machine shop | 32,000 | Owned | ||||
Burbank, CA | Instrument shop/warehouse/office | 23,000 | Leased | ||||
Ft. Lauderdale, FL | Instrument shop/warehouse/office | 11,700 | Leased | ||||
Wellington, KS | Repair and overhaul/office | 65,000 | Leased | ||||
Oakdale, PA | Production/warehouse/office | 68,000 | Leased | ||||
Dallas, TX | Production/office | 28,600 | Leased | ||||
Grand Prairie, TX | Repair and overhaul shop/office | 60,000 | Leased | ||||
San Antonio, TX | Repair and overhaul/office | 30,000 | Leased | ||||
Chonburi, Thailand | Repair and overhaul shop/office | 85,000 | Owned | ||||
Milwaukee, WI | Office | 2,600 | Leased | ||||
DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS | |||||||
Chandler, AZ | Casting facility/office | 31,000 | Leased | ||||
We believe that our properties are adequate to support our operations for the foreseeable future.
Legal Proceedings
On July 9, 2004, Eaton Corporation and several Eaton subsidiaries filed a complaint against us, our subsidiary, Frisby Aerospace, LLC (now named Triumph Actuation Systems, LLC), certain related subsidiaries and certain employees of ours and our subsidiaries. The complaint was filed in the Circuit Court of the First Judicial District of Hinds County, Mississippi and alleged nineteen causes of action under Mississippi law. In particular, the complaint alleged the misappropriation of trade secrets and intellectual property allegedly belonging to Eaton relating to hydraulic pumps and motors used in military and commercial aviation. Triumph Actuation Systems and the individual defendants filed separate responses to Eaton's claims. Triumph Actuation Systems filed counterclaims against Eaton alleging common law unfair competition, interference with existing and prospective contracts, abuse of process, defamation, violation of North Carolina's Unfair and Deceptive Trade Practices Act, and violation of the false advertising provisions of the Lanham Act. We and defendant Jeff Frisby, President of Triumph Actuation Systems at the time the engineer defendants were hired, moved to dismiss the complaint for lack of personal jurisdiction.
The above allegations also relate to alleged conduct that has been the subject of an investigation by the office of the U.S. Attorney in Jackson, Mississippi. On January 22, 2004, a search warrant was executed on the offices of Triumph Actuation Systems in connection with this investigation. Triumph Actuation Systems cooperated with the investigation. On December 20, 2006, five engineers of Triumph Actuation Systems who are former employees of Eaton Aerospace, LLC, were indicted by a grand jury sitting in the Southern District of Mississippi on five counts of trade secret misappropriation, conspiracy to misappropriate trade secrets, and mail and wire fraud. On June 15, 2007, all counts other than part of one count were dismissed by the court, leaving a charge of conspiracy to misappropriate trade secrets.
On October 11, 2007, the government obtained a new indictment against the same five engineer defendants raising new charges arising out of the same investigation, which were essentially reiterated in a second superseding indictment obtained on November 7, 2007. The defendant engineers
134
subsequently filed pretrial motions, including motions to dismiss. On April 25, 2008, the court granted some of those motions and dismissed seven of the twelve counts of the second superseding indictment. The government appealed the dismissal with respect to three of the seven counts dismissed. On January 21, 2009, while the appeal was still pending, the government obtained a new indictment against the five engineers containing three counts stating essentially the same charges as those covered by the government's appeal. On February 9, 2009, the United States Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit unanimously affirmed the dismissal of one of the counts covered by the government's appeal and reversed as to the other two counts. (The government thereafter dismissed the two counts of the most recent indictment similar to the two counts restored by the appellate court.) On September 10, 2009, upon agreement of the government and the defendant engineers, the trial court entered an order continuing the case until after the trial in the civil case filed by Eaton and staying all proceedings except the issuance of orders related to previously filed motions and the parties' compliance with ongoing discovery obligations. The trial court has since disposed of all pending motions.
No charges have been brought against Triumph Actuation Systems or us, and we understand that neither Triumph Actuation Systems nor the Company is currently the subject of the criminal investigation.
In the civil case, following stays of most discovery while the parties litigated a motion to dismiss and a motion to protect the defendant engineers' Fifth Amendment rights, discovery recommenced in late August 2007. However, on January 4, 2008, the judge in the civil case, Judge Bobby DeLaughter, recused himself on his own motion. The case was reassigned to Chief Judge W. Swan Yerger.
On January 24, 2008, Triumph Actuation Systems filed a motion to stay all discovery in order to review and reconsider Judge DeLaughter's prior orders based on the ongoing federal investigation of an alleged ex parte and inappropriate relationship between Judge DeLaughter and Ed Peters, a lawyer representing Eaton for whom Judge DeLaughter had worked prior to his appointment to the bench. Judge DeLaughter was thereafter suspended from the bench and indicted by a federal grand jury sitting in the Northern District of Mississippi. On July 30, 2009, Judge DeLaughter pled guilty to a count of obstruction of justice contained in the indictment and, on November 13, 2009, was sentenced to 18 months in federal prison.
Triumph Actuation Systems filed other motions relating to this alleged inappropriate relationship with Mr. Peters, including a motion for sanctions. Judge Yerger ordered that this conduct be examined and has undertaken, along with a newly appointed Special Master, to review Judge DeLaughter's rulings in the case from the time Mr. Peters became involved. That review is ongoing. The court has stayed all other proceedings while conducting its review of the conduct of Mr. Peters, with the exception of the period between October 30, 2008 and March 4, 2009 when discovery on the merits was briefly reopened. The case has been removed from the court's trial calendar for the date previously set, and no alternative date has been assigned.
It is too early to determine what, if any, exposure to liability Triumph Actuation Systems or the Company might face as a result of the civil suit. We intend to continue to vigorously defend the allegations contained in Eaton's complaint and to vigorously prosecute the counterclaims brought by Triumph Actuation Systems.
In the ordinary course of our business, we are also involved in disputes, claims, lawsuits, and governmental and regulatory inquiries that we deem to be immaterial. Some may involve claims or potential claims of substantial damages, fines or penalties. While we cannot predict the outcome of any pending or future litigation or proceeding, we do not believe that any pending matter will have a material effect, individually or in the aggregate, on our financial position or results of operations, although no assurances can be given to that effect.
135
DESCRIPTION OF CERTAIN INDEBTEDNESS
We summarize below the principal terms of certain agreements to which we are a party. This summary is not a complete description of all of the terms of the relevant agreements and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the actual terms of the respective documents.
Revolving Credit Facility
On May 10, 2010, the Company entered into a Credit Agreement among the Company, the lenders party thereto and PNC Bank, National Association, as administrative agent (the "Revolving Credit Agreement"). Borrowings under the Revolving Credit Agreement became available on June 16, 2010 in connection with the consummation of the Vought Acquisition. Simultaneously with the consummation of the Vought Acquisition, substantially all of the Company's domestic subsidiaries became parties to the Revolving Credit Agreement as borrowers and are jointly and severally liable for the obligations thereunder. The obligations under the Revolving Credit Agreement and related documents are secured by liens on substantially all assets of the Company and its domestic subsidiaries pursuant to a Guarantee and Collateral Agreement, dated as of June 16, 2010, among the Company, the subsidiaries of the Company party thereto and PNC Bank, National Association, as administrative agent under the Revolving Credit Agreement (the "Revolver Guarantee and Collateral Agreement"), and certain other collateral documents. Such liens are pari passu to the liens securing the Company's obligations under the Term Loan Facility described below pursuant to an intercreditor agreement dated June 16, 2010 among the agents under the Revolving Credit Agreement and the Term Loan Facility, the Company and its domestic subsidiaries that are borrowers and/or guarantors under the Revolving Credit Agreement and the Term Loan Facility (the "Intercreditor Agreement").
The Revolving Credit Agreement replaced and refinanced the Company's Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of August 14, 2009 (the "2009 Credit Facility"), which agreement was terminated and all obligations thereunder paid in full upon the consummation of the Vought Acquisition.
Pursuant to the Revolving Credit Agreement, the Company and its subsidiary borrowers can borrow, repay and re-borrow revolving credit loans, and cause to be issued letters of credit, in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $535.0 million outstanding at any time. The comparable limit under the 2009 Credit Facility was $485.0 million. Approximately $148.6 million in loans were drawn under the Revolving Credit Agreement in connection with the consummation of the Vought Acquisition.
Loans under the Revolving Credit Agreement bear interest, at the Company's option, by reference to a base rate or a rate based on LIBOR, in either case plus an applicable margin determined quarterly based on the Company's Total Leverage Ratio (as defined below) as of the last day of each fiscal quarter. The Company is also required to pay a quarterly commitment fee on the average daily unused portion of the Revolving Credit Agreement for each fiscal quarter and fees in connection with the issuance of letters of credit. All outstanding principal and interest under the Revolving Credit Agreement will be due and payable on the fourth anniversary of the Vought Acquisition.
The Revolving Credit Agreement contains representations, warranties, events of default and covenants customary for financings of this type including, without limitation, financial covenants under which the Company is obligated to maintain on a consolidated basis, as of the end of each fiscal quarter, a certain minimum Interest Coverage Ratio, maximum Total Leverage Ratio and maximum Senior Leverage Ratio (in each case as defined in the Revolving Credit Agreement).
In addition, on June 16, 2010, the Company entered into a First Amendment to the Revolving Credit Agreement (the "First Amendment") which, among other things, amended certain provisions of the Revolving Credit Agreement to permit collateral to be shared between the administrative agent for
136
the benefit of the lenders under the Revolving Credit Agreement and certain other parties for the benefit of the holders of certain industrial revenue bond obligations of the Company and its subsidiaries.
At June 30, 2010, there were $85.0 million in borrowings and $46.9 million in letters of credit outstanding under the Revolving Credit Agreement. As of June 30, 2010, the Company had borrowing capacity under this facility of $401.3 million, after reductions for borrowings and letters of credit outstanding under the facility.
Term Loan Facility
Simultaneously with the closing of the Vought Acquisition, the Company entered into a Credit Agreement dated as of June 16, 2010 with Royal Bank of Canada, as administrative agent, and the other parties thereto (the "Term Loan Facility"). The Term Loan Facility provides for a six-year term loan in a principal amount of $350.0 million, repayable in equal quarterly installments at a rate of 1.00% of the original principal amount per year, with the balance payable on the final maturity date. The proceeds of the loans under the Term Loan Facility were used to consummate the Vought Acquisition.
The obligations under the Term Loan Facility are guaranteed by substantially all of the Company's domestic subsidiaries and secured by liens on substantially all of the Company's and the guarantors' assets pursuant to a Guarantee and Collateral Agreement, dated as of June 16, 2010, among the Company, the subsidiaries of the party thereto and Royal Bank of Canada, as administrative agent (the "Term Loan Guarantee and Collateral Agreement") and certain other collateral agreements, in each case subject to the Intercreditor Agreement. Borrowings under the Term Loan Facility bear interest, at the Company's option, at either the base rate (subject to a floor), plus an applicable margin, or at the Eurodollar Rate (subject to a floor), plus an applicable margin.
The Term Loan Facility contains certain covenants, restrictions and events of default, in each case substantially similar to those under the Revolving Credit Agreement including, but not limited to, a maximum total leverage ratio, a maximum Senior Leverage Ratio, and a minimum Interest Coverage Ratio. In addition, the Term Loan Facility provides for mandatory principal prepayments on the term loans outstanding thereunder under certain circumstances.
Senior Subordinated Notes Due 2017
On November 16, 2009, Triumph issued $175.0 million principal amount of 8% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2017 (the "2017 Notes"). The 2017 Notes were sold at 98.558% of principal amount and have an effective interest yield of 8.25%. Interest on the 2017 Notes is payable semi-annually in cash in arrears on May 15 and November 15 of each year. In connection with the issuance of the 2017 Notes, Triumph incurred approximately $4.4 million of costs, which were deferred and are being amortized on the effective interest method over the term of the 2017 Notes.
The 2017 Notes are senior subordinated unsecured obligations of Triumph and rank subordinated to all of the existing and future senior indebtedness of Triumph and the Existing Note Guarantors (defined below), including the notes and borrowings under the Credit Facilities, and pari passu with Triumph's and the Existing Note Guarantors' existing and future senior subordinated indebtedness. The 2017 Notes are guaranteed, on a full, joint and several basis, by each of our domestic restricted subsidiaries that guarantees any of our debt or that of any of our restricted subsidiaries under our revolving credit facility, and in the future by any domestic restricted subsidiaries that guarantee any of our debt or that of any of our domestic restricted subsidiaries incurred under our Revolving Credit Facility and any facility that replaces or refinances it (collectively, the "Existing Note Guarantors"), in each case on a senior subordinated basis.
137
Triumph has the option to redeem all or a portion of the 2017 Notes at any time prior to November 15, 2013 at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 2017 Notes redeemed plus an applicable premium set forth in the indenture governing the 2017 Notes (the "2017 Indenture") and accrued and unpaid interest, if any. The 2017 Notes are also subject to redemption, in whole or in part, at any time on or after November 15, 2013, at redemption prices equal to (i) 104% of the principal amount of the 2017 Notes redeemed, if redeemed prior to November 15, 2014, (ii) 102% of the principal amount of the 2017 Notes redeemed, if redeemed prior to November 15, 2015 and (iii) 100% of the principal amount of the Notes redeemed, if redeemed thereafter, plus accrued and unpaid interest. In addition, at any time prior to November 15, 2012, Triumph may redeem up to 35% of the principal amount of the 2017 Notes with the net cash proceeds of qualified equity offerings at a redemption price equal to 108% of the aggregate principal amount plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, subject to certain limitations set forth in the 2017 Indenture.
Upon the occurrence of a change of control, Triumph must offer to purchase the 2017 Notes from holders at 101% of their principal amount plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the date of purchase.
The 2017 Indenture contains covenants that, among other things, limit Triumph's ability and the ability of certain of Triumph's subsidiaries to (i) grant liens on their assets, (ii) make dividend payments, other distributions or other restricted payments, (iii) incur restrictions on the ability of the certain subsidiaries to pay dividends or make other payments, (iv) enter into sale and leaseback transactions, (v) merge, consolidate, transfer or dispose of substantially all of their assets, (vi) incur additional indebtedness, (vii) use the proceeds from sales of assets, including capital stock of restricted subsidiaries, and (viii) enter into transactions with affiliates.
Convertible Senior Subordinated Notes
On September 18, 2006, Triumph issued $201.3 million in convertible senior subordinated notes (the "Convertible Notes"). The Convertible Notes are direct, unsecured, senior subordinated obligations of Triumph, and rank (i) junior in right of payment to all of Triumph's existing and future senior indebtedness and (ii) equal in right of payment with any other future senior subordinated indebtedness. As a result of repurchases of the Convertible Notes since the issue date, approximately $179.1 million of Convertible Notes remain outstanding.
The Convertible Notes bear interest at a fixed rate of 2.625% per annum, payable in cash semi-annually in arrears on each April 1 and October 1. During the period commencing on October 6, 2011 and ending on, but excluding, April 1, 2012 and each nine-month period from October 1 to March 31 or from April 1 to December 31 thereafter, Triumph will pay contingent interest during the applicable interest period if the average trading price of a Convertible Note for the five consecutive trading days ending on the third trading day immediately preceding the first day of the relevant nine-month period equals or exceeds 120% of the principal amount of the Convertible Notes. The contingent interest payable per Convertible Note in respect of any nine-month period will equal 0.25% per annum calculated on the average trading price of a Convertible Note for the relevant five trading day period.
The Convertible Notes mature on October 1, 2026 unless earlier redeemed, repurchased or converted. Triumph may redeem the Convertible Notes for cash, either in whole or in part, anytime on or after October 6, 2011 at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the Convertible Notes to be redeemed plus accrued and unpaid interest, including contingent interest and additional amounts, if any, up to but not including the date of redemption. In addition, holders of the Convertible Notes will have the right to require Triumph to repurchase for cash all or a portion of their Convertible Notes on October 1, 2011, 2016 and 2021, at a repurchase price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the Convertible Notes to be repurchased plus accrued and unpaid interest, including contingent interest and additional amounts, if any, up to, but not including, the date of
138
repurchase. The Convertible Notes are convertible into Triumph's common stock at a rate equal to 18.3655 shares per $1,000 principal amount of the Convertible Notes (equal to an initial conversion price of approximately $54.45 per share), subject to adjustment as described in the indenture governing the Convertible Notes. Upon conversion, Triumph will deliver to the holder surrendering the Convertible Notes for conversion, for each $1,000 principal amount of Convertible Notes, an amount consisting of cash equal to the lesser of $1,000 and Triumph's total conversion obligation and, to the extent that Triumph's total conversion obligation exceeds $1,000, at Triumph's election, cash or shares of Triumph's common stock in respect of the remainder.
The Convertible Notes are eligible for conversion upon meeting certain conditions as provided in the indenture governing the Convertible Notes. For the fiscal quarter ended March 31, 2010, the Convertible Notes were not eligible for conversion. Accordingly, Triumph has classified the Convertible Notes as long-term as of March 31, 2010.
Receivables Securitization Program
In June 2010, the Company entered into an amended receivable securitization facility (the "Securitization Facility"), increasing the purchase limit from $125.0 million to $175.0 million. In connection with the Securitization Facility, the Company sells on a revolving basis certain accounts receivable to Triumph Receivables, LLC, a wholly-owned special-purpose entity, which in turn sells a percentage ownership interest in the receivables to commercial paper conduits sponsored by financial institutions. The Company is the servicer of the accounts receivable under the Securitization Facility. As of June 30, 2010, the maximum amount available under the Securitization Facility was $118.6 million. The Securitization Facility is due to expire in June 2011 and is subject to annual renewal through August 2013. Interest rates are based on prevailing market rates for short-term commercial paper plus a program fee and a commitment fee. The program fee is 0.50% on the amount outstanding under the Securitization Facility. Additionally, the commitment fee is 0.65% on 102% of the maximum amount available under the Securitization Facility. At June 30, 2010, there was $120.0 million outstanding under the Securitization Facility. In connection with amending the Securitization Facility, the Company incurred approximately $461,000 of financing costs. These costs, along with the $540,000 of unamortized financing costs prior to the amendment, are being amortized over the life of the Securitization Facility. The Company securitizes its accounts receivable, which are generally non-interest bearing, in transactions that are accounted for as borrowings pursuant to theTransfers and Servicing topic of the ASC.
The agreement governing the Securitization Facility contains restrictions and covenants which include limitations on the making of certain restricted payments, creation of certain liens, and certain corporate acts such as mergers, consolidations and the sale of substantially all assets.
Equipment Leasing Facility
During March 2009, Triumph entered into a Master Leasing Facility, creating a seven-year capital lease of certain property and equipment of Triumph and its subsidiaries and resulting in net proceeds of $58.5 million. The net proceeds from the facility were used to repay a portion of the outstanding indebtedness under the 2009 Credit Facility. The facility bears interest at a weighted-average fixed rate of 6.1% per annum.
139
On June 16, 2010 we issued in a private placement $350,000,000 aggregate principal amount of 8.625% senior notes due 2018. The old notes were not registered under the Securities Act and were issued, and the new notes will be issued, under an Indenture, dated as of June 16, 2010, among the Company, each Guarantor and U.S. Bank National Association, as Trustee (the "Indenture"). For purposes of this section of this prospectus, references to the "Company," "we," "us," "our" or similar terms refer solely to Triumph Group, Inc., and not its Subsidiaries. The term "notes" refers collectively to the new notes and the old notes.
The terms of the new notes are identical in all material respects with the old notes, except that:
- •
- the new notes have been registered under the U.S. federal securities laws and will not bear any legend restricting their transfer;
- •
- the new notes bear a different CUSIP number from the old notes;
- •
- the new notes generally will not be subject to transfer restrictions and will not be entitled to registration rights; and
- •
- the holders of the new notes will not be entitled to earn additional interest under circumstances relating to our registration obligations under the registration rights agreement.
The new notes will evidence the same debt as the old notes.
The terms of the new notes include those stated in the Indenture and those made part of the Indenture by reference to the Trust Indenture Act of 1939 (as amended, the "Trust Indenture Act"). The following description is only a summary of the material provisions of the Indenture and the new notes. We urge you to read the Indenture and the new notes because those documents, not this description, define your rights as holders of the new notes. You may request copies of the Indenture at our address set forth under the heading "Where you can find more information." Certain defined terms used in this description but not defined below under "—Certain Definitions" have the meanings assigned to them in the Indenture.
General
The exchange offer for the new notes will be for $350.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 8.625% senior notes due 2018. The Company may issue additional notes (the "Additional Notes") under the Indenture, subject to the limitations described below under the covenant "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt." The new notes, together with any old notes that remain outstanding after the exchange offer and any Additional Notes subsequently issued under the Indenture will be treated as a single class for all purposes of the Indenture, including, without limitation, waivers, consents, amendments, redemptions and offers to purchase. Unless the context otherwise requires, for all purposes of the Indenture and this "Description of New Notes," references to the new notes include any Additional Notes actually issued.
Principal, Maturity and Interest
Interest on the new notes will be accrue at 8.625% per annum. Interest on the new notes will be payable semi-annually in cash in arrears on January 15 and July 15, commencing on January 15, 2011. The Company will make each interest payment to the Holders of record of the new notes on the immediately preceding January 1 and July 1. Interest on the new notes will accrue from the most recent date to which interest has been paid or, if no interest has been paid, from and including the
140
Issue Date. Interest will be computed on the basis of a 360-day year comprised of twelve 30-day months.
Principal of and premium, if any, and interest on the new notes will be payable, and the new notes will be exchangeable and transferable, at the office or agency of the Company maintained for such purposes, which, initially, will be the corporate trust office of the Trustee located at Two Liberty Place, 50 South 16th Street, Suite 2000, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19102;provided, however, that payment of interest may be made at the option of the Company by check mailed to the Person entitled thereto as shown on the security register. The new notes will be issued only in fully registered form without coupons, in denominations of $2,000 and any integral multiple of $1,000 in excess thereof. No service charge will be made for any registration of transfer, exchange or redemption of the new notes, except in certain circumstances for any tax or other governmental charge that may be imposed in connection therewith.
Additional Interest may accrue and be payable under the circumstances set forth therein. See "Exchange Offer; Registration Rights." References herein to "interest" shall be deemed to include any such Additional Interest.
Guarantees
The new notes will be Guaranteed, on a full, joint and several basis, by the Guarantors pursuant to the Indenture (the "Note Guarantees"). On the Issue Date, each of our domestic Restricted Subsidiaries that (1) is a borrower under our Credit Agreement or (2) Guarantees any Debt of the Company or any of its domestic Restricted Subsidiaries, in each case incurred under our Credit Agreement, will Guarantee the new notes on a senior basis. After the Issue Date, the new notes will be guaranteed by any of our domestic Restricted Subsidiaries (other than any domestic Restricted Subsidiary that is a Receivables Subsidiary) that (1) becomes a borrower under any of our Credit Facilities or (2) Guarantees any of our Debt or any Debt of our domestic Restricted Subsidiaries, in each case incurred under any of our Credit Facilities. See "—Additional Note Guarantees."
The Indenture provides that the Obligations of a Guarantor under its Note Guarantee will be limited to the maximum amount as will result in the Obligations of such Guarantor under the Note Guarantee not to be deemed to constitute a fraudulent conveyance or fraudulent transfer under federal or state law. See "Risk Factors—Fraudulent conveyance laws may permit courts to void the guarantors' guarantees of the new notes in specific circumstances, which would interfere with the payment under the guarantors' guarantees." As of the Issue Date, all of our Subsidiaries will be "Restricted Subsidiaries" other than Triumph Receivables, LLC, Triumph Group Charitable Foundation, Triumph Interiors, Ltd, Saygrove Actuation & Motion Control Limited and Airframe Spares & Logistics GmbH, each of which will be Unrestricted Subsidiaries on the Issue Date. Under the circumstances described below under the subheading "—Certain Covenants—Limitation on Creation of Unrestricted Subsidiaries," other of our Subsidiaries in the future may be designated as "Unrestricted Subsidiaries." Unrestricted Subsidiaries will not be subject to many of the restrictive covenants in the Indenture and will not Guarantee the new notes.
The Indenture provides that in the event of a sale or other transfer or disposition of all of the Capital Interests in any Guarantor to any Person that is not an Affiliate of the Company in compliance with the terms of the Indenture, the occurrence of any other transaction permissible under the Indenture pursuant to which such Guarantor ceases to be a Subsidiary, the sale or other transfer of all or substantially all the assets of a Guarantor (including by way of merger or consolidation) to a Person that is not an Affiliate of the Company in compliance with the terms of the Indenture, or the release of a Guarantor of all of its Guarantee obligations in respect of the Credit Facilities, then such Guarantor shall be deemed automatically and unconditionally released and discharged of any obligations under its
141
Note Guarantee. At the request of the Company, the Company, such Guarantor and the Trustee will execute a supplemental indenture evidencing such release and discharge; provided that the Company delivers an Officer's Certificate to the Trustee certifying that the conditions to such release have been satisfied.
Not all of our Subsidiaries will Guarantee the new notes. For the fiscal year ending March 31, 2010, on a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Transactions, the Company's non-Guarantor Subsidiaries would have generated net sales of $79.0 million, or 2.5% of our consolidated net sales, and $11.9 million, and as of June 30, 2010 such non-Guarantor Subsidiaries had total assets of $277.8 million. As of June 30, 2010 such non-Guarantor Subsidiaries had $134.9 million of indebtedness and other liabilities. In the event of a bankruptcy, liquidation or reorganization of such non-Guarantor Subsidiaries, claims of creditors of such non-Guarantor Subsidiaries, including trade creditors, secured creditors and creditors holding Debt and Guarantees issued by those non-Guarantor Subsidiaries, and claims of preferred stockholders (if any) of those non-Guarantor Subsidiaries generally will have priority with respect to the assets of those non-Guarantor Subsidiaries over the claims of creditors of the Company, including Holders of the new notes.
Ranking
Ranking of the New Notes
The new notes will be senior unsecured obligations of the Company, and will rank:
- •
- equal in right of payment to any existing and future senior Debt of the Company, including Debt under the Credit Agreement;
- •
- senior in right of payment to all existing and future Subordinated Obligations of the Company;
- •
- effectively subordinated to the Company's secured Debt to the extent of the value of the assets securing such Debt, including Debt under the Credit Agreement to the extent of the value of the collateral therefor; and
- •
- structurally subordinated to all Debt and other liabilities of the Company's existing and future Subsidiaries that do not Guarantee the notes.
Ranking of the Note Guarantees
Each Note Guarantee will be a senior unsecured obligation of each Guarantor, and will rank:
- •
- equal in right of payment to any existing and future senior Debt of that Guarantor;
- •
- senior in right of payment to all existing and future Subordinated Obligations of that Guarantor; and
- •
- effectively subordinated to that Guarantor's secured Debt to the extent of the value of the assets securing such Debt, including the guarantee obligations of such Guarantor in respect of the Credit Agreement to the extent of the value of the collateral therefor.
Offers to Purchase; Open Market Purchases
We are not required to make any mandatory redemption or sinking fund payments with respect to the notes. However, under certain circumstances, we may be required to offer to purchase notes as described under the captions "���Change of Control" and "Certain Covenants—Limitation on Sales of
142
Assets and Subsidiary Stock." We may at any time and from time to time purchase notes in the open market or otherwise.
Optional Redemption
The notes may be redeemed, in whole or in part, at any time prior to July 15, 2014, at the option of the Company upon not less than 30 nor more than 60 days' prior notice mailed by first class mail (and/or, to the extent permitted by applicable procedures or regulations, electronically) to each Holder's registered address, at a Redemption Price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the notes to be redeemed plus the Applicable Premium, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the applicable redemption date (subject to the right of registered Holders of the notes on a relevant record date to receive interest due on a relevant interest payment date). In addition, the notes are subject to redemption, at the option of the Company, in whole or in part, at any time on or after July 15, 2014, upon not less than 30 nor more than 60 days' notice at the following Redemption Prices (expressed as percentages of the principal amount to be redeemed) set forth below, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the redemption date (subject to the right of registered Holders of the notes on a relevant record date to receive interest due on a relevant interest payment date), if redeemed during the 12-month period beginning on July 15 of the years indicated:
Year | Redemption Price | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
2014 | 104.313 | % | ||
2015 | 102.156 | % | ||
2016 and thereafter | 100.000 | % | ||
In addition to the optional redemption provisions of the notes in accordance with the provisions of the preceding paragraphs, prior to July 15, 2013, the Company may at its option, with the net proceeds of one or more Qualified Equity Offerings, redeem up to 35% of the aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes (including Additional Notes) at a Redemption Price equal to 108.625% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon, if any, to, but not including, the date of redemption (subject to the right of registered Holders of the notes on a relevant record date to receive interest due on a relevant interest payment date); provided that at least 65% of the principal amount of notes (including Additional Notes) issued under the Indenture remains outstanding immediately after the occurrence of any such redemption (excluding notes held by the Company or its Subsidiaries) and that any such redemption occurs within 90 days following the closing of any such Qualified Equity Offering.
Selection
If less than all of the notes are to be redeemed, the Trustee will select the notes or portions thereof to be redeemed by lot, pro rata or by any other method the Trustee shall deem fair and appropriate (subject to the Depository Trust Company procedures).
No notes of $2,000 or less shall be redeemed in part. Notices of redemption shall be mailed by first class mail (and/or, to the extent permitted by applicable procedures or regulations, electronically) at least 30 but no more than 60 days before the redemption date to each Holder of notes to be redeemed at its registered address. If any note is to be redeemed in part only, the notice of redemption that relates to that note shall state the portion of the principal amount thereof to be redeemed. A new note in principal amount equal to the unredeemed portion of the original note, if any, will be issued in the name of the Holder thereof upon cancellation of the original note. New notes called for redemption become due on the date fixed for redemption. On and after the redemption date, interest ceases to accrue on notes or portions of them called for redemption.
143
Change of Control
Upon the occurrence of a Change of Control, the Company will make an Offer to Purchase all of the outstanding notes at a Purchase Price in cash equal to 101% of the principal amount tendered, together with accrued interest, if any, to but not including the Purchase Date;provided that if the Company has exercised its right to redeem all of the notes as described above under the caption "—Optional Redemption" prior to the time the Company would be required to make an Offer to Purchase, the Company shall not be required to make such Offer to Purchase. For purposes of the foregoing, an Offer to Purchase shall be deemed to have been made if (i) within 60 days following the date of the consummation of a transaction or series of transactions that constitutes a Change of Control, the Company commences an Offer to Purchase for all outstanding notes at the Purchase Price and (ii) all notes properly tendered pursuant to the Offer to Purchase are purchased on the terms of such Offer to Purchase.
Although there is a limited body of case law interpreting the phrase "all or substantially all," as used in the definition of "Change of Control," there is no precise established definition of the phrase under applicable law. As a consequence, in certain circumstances, there may be a degree of uncertainty as to whether a particular transaction would involve a disposition of "all or substantially all" of the assets of the Company. It may be unclear as to whether a Change of Control has occurred and whether a Holder of notes may require the Company to make an Offer to Purchase the notes as described above.
Subject to the limitations discussed below, the Company could, in the future, enter into a highly leveraged transaction, reorganization, restructuring, merger or similar transaction, that would not constitute a Change of Control under the Indenture, but that could increase the amount of Debt outstanding at such time or otherwise affect the Company's capital structure or credit ratings. The definition of Change of Control may be amended or modified with the written consent of a majority in aggregate principal amount of outstanding notes. See "—Amendment, Supplement and Waiver." The Company will be required to comply with the requirements of Rule 14e-1 under the Exchange Act and any other applicable securities laws or regulations in connection with any repurchase of the notes as described above. To the extent that the provisions of any securities laws or regulations conflict with the Change of Control provisions of the Indenture, the Company will comply with the applicable securities laws and regulations and will be deemed to have complied with its obligations under the Change of Control provisions of the Indenture by virtue of such compliance.
The Company will not be required to make an Offer to Purchase upon a Change of Control if (i) a third party makes such Offer to Purchase contemporaneously with or upon a Change of Control in the manner, at the times and otherwise in compliance with the requirements of the Indenture and purchases all notes validly tendered and not withdrawn under such Offer to Purchase or (ii) a notice of redemption has been given pursuant to the Indenture as described above under the caption "—Optional Redemption."
Holders of the notes may not be entitled to require the Company to purchase their notes in certain circumstances involving a significant change in the composition of the Board of Directors of the Company, including in connection with a proxy contest, where the Company's Board of Directors initially publicly opposes the election of a dissident slate of directors, but subsequently approves such directors for the purposes of the Indenture. This may result in a change in the composition of the Board of Directors of the Company that, but for such subsequent approval, would have otherwise constituted a Change of Control requiring a repurchase offer under the terms of the Indenture.
The Company's ability to repurchase notes pursuant to an Offer to Purchase may be limited by a number of factors. The occurrence of certain of the events that constitute a Change of Control would constitute a default under the Credit Agreement. In addition, certain events that may constitute a change of control under the Credit Agreement and cause a default under those agreements may not
144
constitute a Change of Control under the Indenture. Future Debt of the Company and its Subsidiaries may also contain prohibitions of certain events that would constitute a Change of Control or require such Debt to be repurchased upon a Change of Control. Moreover, the exercise by the holders of their right to require the Company to repurchase the notes could cause a default under such Debt, even if the Change of Control itself does not, due to the financial effect of such repurchase on the Company. Finally, the Company's ability to pay cash to the holders upon a repurchase may be limited by the Company's then existing financial resources. There can be no assurance that sufficient funds will be available when necessary to make any required repurchases.
In the event that at the time of a Change of Control the terms of the Credit Agreement restrict or prohibit the repurchase of notes as contemplated in the Indenture, then prior to the electronic delivery or mailing of the Offer to Purchase required in connection with a Change of Control but in any event within 30 days following any Change of Control, the Company shall (i) repay in full all Debt under the applicable Credit Agreement or, if doing so will allow the purchase of notes, offer to repay in full all such Debt and repay such Debt of each lender who has accepted such offer, or (ii) obtain the requisite consent under the Credit Agreement to permit the repurchase of the notes as provided in the Indenture.
In addition, an Offer to Purchase may be made in advance of a Change of Control, conditional upon the occurrence of such Change of Control, if a definitive agreement is in place for the Change of Control at the time of launching the Offer to Purchase.
Certain Covenants
Set forth below are certain covenants contained in the Indenture:
Limitation on Incurrence of Debt
The Company will not, and will not permit any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to, Incur any Debt (including Acquired Debt);provided that the Company and any of its Restricted Subsidiaries may Incur Debt (including Acquired Debt) if, immediately after giving effect to the Incurrence of such Debt and the receipt and application of the proceeds therefrom, (a) the Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio of the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries, determined on a pro forma basis as if any such Debt (including any other Debt being Incurred contemporaneously), and any other Debt Incurred since the beginning of the Four Quarter Period (as defined below) had been Incurred and the proceeds thereof had been applied at the beginning of the Four Quarter Period, and any other Debt repaid since the beginning of the Four Quarter Period had been repaid at the beginning of the Four Quarter Period, would be greater than 2.25:1 and (b) no Default or Event of Default shall have occurred and be continuing at the time or as a consequence of the Incurrence of such Debt;provided further, that Restricted Subsidiaries that are not Guarantors may not Incur any Debt pursuant to this paragraph if the Secured Leverage Ratio of the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries, determined on a pro forma basis as if any such Debt (including any other Debt being Incurred contemporaneously), and any other Debt Incurred since the beginning of the Four Quarter Period (as defined below) had been Incurred and the proceeds thereof had been applied at the beginning of the Four Quarter Period, and any other Debt repaid since the beginning of the Four Quarter Period had been repaid at the beginning of the Four Quarter Period, would be greater than 3.0:1.
Notwithstanding the immediately preceding paragraph, the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries may Incur Permitted Debt.
For purposes of determining any particular amount of Debt under this "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" covenant, Guarantees or obligations with respect to letters of credit supporting Debt otherwise included in the determination of such particular amount shall not be included. For purposes of determining compliance with this "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" covenant, in the event that an
145
item of Debt meets the criteria of more than one of the types of Debt described above, including categories of Permitted Debt and under part (a) in the first paragraph of this "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" covenant, the Company, in its sole discretion, shall classify, and from time to time may reclassify, all or any portion of such item of Debt,provided that Debt Incurred under the Credit Facilities on the Issue Date shall at all times be treated as Incurred pursuant to clause (i) of the definition of "Permitted Debt". The accrual of interest, the accretion or amortization of original issue discount and the payment of interest on Debt in the form of additional Debt or payment of dividends on Capital Interests in the forms of additional shares of Capital Interests with the same terms will not be deemed to be an Incurrence of Debt or issuance of Capital Interests for purposes of this covenant.
Limitation on Restricted Payments
The Company will not, and will not permit any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to, directly or indirectly, make any Restricted Payment unless, at the time of and after giving effect to the proposed Restricted Payment:
(a) no Default or Event of Default shall have occurred and be continuing or will occur as a consequence thereof;
(b) after giving effect to such Restricted Payment on a pro forma basis, the Company would be permitted to Incur at least $1.00 of additional Debt pursuant to the provisions described in the first paragraph under the "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" covenant; and
(c) after giving effect to such Restricted Payment on a pro forma basis, the aggregate amount expended or declared for all Restricted Payments made on or after the Reference Date (excluding Restricted Payments permitted by clauses (ii), (iii), (iv), (v), (vi) (vii), (viii), (ix), (xi), (xii) and (xiii) of the next succeeding paragraph) shall not exceed the sum (without duplication) of:
(1) 50% of the Consolidated Net Income (or, if Consolidated Net Income shall be a deficit, minus 100% of such deficit) of the Company accrued on a cumulative basis during the period (taken as one accounting period) from the Reference Date and ending on the last day of the fiscal quarter immediately preceding the date of such proposed Restricted Payment, plus
(2) 100% of the aggregate net proceeds (including the Fair Market Value of property other than cash) received by the Company subsequent to the Reference Date either (i) as a contribution to its common equity capital or (ii) from the issuance and sale (other than to a Subsidiary) of its Qualified Capital Interests (excluding any Qualified Capital Interests issued in connection with the Company's acquisition of Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.), including Qualified Capital Interests issued upon the conversion or exchange of Debt or Redeemable Capital Interests of the Company, and from the exercise of options, warrants or other rights to purchase such Qualified Capital Interests (other than, in each case, Capital Interests or Debt sold to a Subsidiary of the Company), plus
(3) 100% of the net reduction in Investments (other than Permitted Investments), made by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary subsequent to the Reference Date, in any Person, resulting from (i) payments of interest on Debt, dividends, repayments of loans or advances, or any sale or disposition of such Investments (but only to the extent such items are not included in the calculation of Consolidated Net Income), or (ii) the redesignation of an Unrestricted Subsidiary as a Restricted Subsidiary (or the causing of a Person that is not a Subsidiary to become a Restricted Subsidiary), not to exceed in the case of any Person the amount of Investments previously made by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary in such Person subsequent to the Reference Date.
146
Notwithstanding the foregoing provisions, the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries may take the following actions,provided that, at the time of and after giving effect to the proposed Restricted Payment, no Default or Event of Default shall have occurred and be continuing or will occur as a consequence thereof:
(i) the payment of any dividend on Capital Interests in the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary or the consummation of any irrevocable redemption within 60 days after declaration thereof or the giving of such irrevocable notice, as applicable, if, at the declaration date or notice thereof, such payment was permitted by the foregoing provisions of this covenant;
(ii) the purchase, repurchase, redemption, defeasance or other acquisition or retirement of any Capital Interests of the Company by conversion into, or by or in exchange for, Qualified Capital Interests, or out of Net Cash Proceeds of the substantially concurrent sale (other than to a Subsidiary of the Company) of Qualified Capital Interests of the Company;provided, however, that the Net Cash Proceeds from such sale of Qualifying Capital Interests will be excluded from clause (c)(2) of the preceding paragraph to the extent applied to any such purchase, repurchase, redemption, defeasance or other acquisition or retirement;
(iii) the redemption, defeasance, repurchase or acquisition or retirement for value of any Debt of the Company or a Guarantor that is subordinate in right of payment to the notes or the applicable Note Guarantee out of the Net Cash Proceeds of a substantially concurrent issue and sale (other than to a Subsidiary of the Company) of (x) new Refinancing Debt of the Company or such Guarantor, as the case may be, Incurred in accordance with the Indenture or (y) Qualified Capital Interests of the Company;
(iv) the purchase, redemption, retirement or other acquisition for value of Capital Interests in the Company or any direct or indirect parent of the Company (or any payments to a direct or indirect parent company of the Company for the purposes of permitting any such repurchase) held by directors, employees, former directors or former employees of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary (or their estates or beneficiaries under their estates) upon death, disability, retirement or termination of employment or alteration of employment status or pursuant to the terms of any agreement under which such Capital Interests were issued;provided that the aggregate cash consideration paid for such purchase, redemption, retirement or other acquisition of such Capital Interests does not exceed $2.5 million in any calendar year;provided,further, that any unused amounts in any calendar year may be carried forward to one or more future periods subject to a maximum aggregate amount of repurchases made pursuant to this clause (iv) not to exceed $5.0 million in any calendar year;provided, however, that such amount in any calendar year may be increased by an amount not to exceed (A) the cash proceeds received by the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries from the sale of Qualified Capital Interests of the Company or any direct or indirect parent company of the Company (to the extent contributed to the Company) to employees of the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries that occurs after the Issue Date;provided, however, that the amount of such cash proceeds utilized for any such repurchase, retirement, other acquisition or dividend will not increase the amount available for Restricted Payments under clause (c) of the first paragraph of this covenant; plus (B) the cash proceeds of key man life insurance policies received by the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries after the Issue Date (provided, however, that the Company may elect to apply all or any portion of the aggregate increase contemplated by the proviso of this clause (iv) in any calendar year and, to the extent any payment described under this clause (iv) is made by delivery of Debt and not in cash, such payment shall be deemed to occur only when, and to the extent, the obligor on such Debt makes payments with respect to such Debt);
(v) repurchase of Capital Interests deemed to occur upon the exercise of stock options, warrants or other convertible or exchangeable securities or the vesting of restricted stock units;
147
(vi) the extension of credit that constitutes intercompany Debt, the Incurrence of which was permitted pursuant to the covenant described under "—Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" pursuant to clauses (v) and (xii) of the definition of "Permitted Debt";
(vii) cash payment, in lieu of issuance of fractional shares in connection with the exercise of warrants, options or other securities convertible into or exchangeable for the Capital Interests of the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary;
(viii) the declaration and payment of dividends to holders of any class or series of Redeemable Capital Interests of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary issued or Incurred in compliance with the covenant described above under "—Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" to the extent such dividends are included in the definition of Consolidated Fixed Charges;
(ix) the purchase, repurchase, redemption, defeasance or other acquisition or retirement for value of any Subordinated Obligation (i) at a purchase price not greater than 101% of the principal amount of such Subordinated Obligation in the event of a change of control in accordance with provisions similar to the "Change of Control" covenant or (ii) at a purchase price not greater than 100% of the principal amount thereof in accordance with provisions similar to the "Limitation on Asset Sales" covenant;provided that, prior to or simultaneously with such purchase, repurchase, redemption, defeasance or other acquisition or retirement, the Company has made the Offer to Purchase upon a Change of Control or Offer to Purchase to the extent provided in the Indenture with respect to the notes and has completed the repurchase or redemption of all notes validly tendered for payment in connection with such Offer to Purchase;
(x) the payment of regular cash quarterly dividends on the Company's common stock not to exceed $10.0 million in any calendar year;
(xi) other Restricted Payments not in excess of $50.0 million in the aggregate since the Reference Date;
(xii) any refinancing, redemption, repayment, defeasance or purchase of the Convertible notes; and
(xiii) any payments made in connection with the Transactions pursuant to any agreements or documents related to the Transactions described in the Offering Memorandum (without giving effect to subsequent amendments, waivers or other modifications to such agreements or documents).
If the Company makes a Restricted Payment which, at the time of the making of such Restricted Payment, in the good faith determination of the Company, would be permitted under the requirements of the Indenture, such Restricted Payment shall be deemed to have been made in compliance with the Indenture notwithstanding any subsequent adjustment made in good faith to the Company's financial statements affecting Consolidated Net Income.
As of June 30, 2010, the Company would have been able to make Restricted Payments in the amount of $25.5 million pursuant to clause (c) of the first paragraph of this covenant.
Limitation on Liens
The Company will not, and will not permit any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to create, incur, assume or otherwise cause or suffer to exist or become effective any Lien of any kind securing Debt (other than Permitted Liens) upon any of their property or assets, now owned or hereafter acquired, unless all payments due under the Indenture and the notes are secured on an equal and ratable basis with the obligations so secured (or in the case of Subordinated Obligations, prior or senior thereto, with the same relative priority as the notes shall have with respect to such Subordinated Obligations) until such time as such obligations are no longer secured by a Lien. For purposes of this covenant, the
148
Receivables Transaction Amount relating to any Qualified Receivables Transaction shall be deemed to be Debt secured by a Lien on the applicable accounts receivable and related assets and such accounts receivable and related assets shall be deemed to be assets of the originator thereof.
Limitation on Dividend and Other Payment Restrictions Affecting Restricted Subsidiaries
The Company will not, and will not permit any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to, directly or indirectly, cause or suffer to exist or become effective or enter into any encumbrance or restriction (other than pursuant to the Indenture or any law, rule, regulation or order) on the ability of any Restricted Subsidiary to (i) pay dividends or make any other distributions on its Capital Interests to the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary or pay any Debt owed to the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary, (ii) make loans or advances to the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary or (iii) transfer any of its property or assets to the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary.
However, the preceding restrictions will not apply to the following encumbrances or restrictions existing under or by reason of:
(a) any encumbrance or restriction in existence on the Issue Date, including those under the Credit Agreement, the Existing Receivables Facility or the Leasing Facility and any amendments, modifications, restatements, renewals, increases, supplements, refundings, replacements, refinancings thereof;provided that the amendments, modifications, restatements, renewals, increases, supplements, refundings, replacement or refinancings, in the good faith judgment of the Company, are no more restrictive in any material respect, taken as a whole, with respect to such dividend or other payment restrictions than those contained in these agreements on the Issue Date or refinancings thereof;
(b) any encumbrance or restriction which exists with respect to an acquired property in existence at the time of such acquisition pursuant to an agreement, so long as the encumbrances or restrictions in any such agreement relate solely to the property so acquired (and are not or were not created in anticipation of or in connection with the acquisition thereof);
(c) any encumbrance or restriction which exists with respect to a Person that becomes a Restricted Subsidiary or merges with or into a Restricted Subsidiary of the Company on or after the Issue Date, which is in existence at the time such Person becomes a Restricted Subsidiary, but not created in connection with or in anticipation of such Person becoming a Restricted Subsidiary, and which is not applicable to any Person or the property or assets of any Person other than such Person or the property or assets of such Person becoming a Restricted Subsidiary;
(d) any encumbrance or restriction pursuant to an agreement effecting a permitted renewal, refunding, replacement, refinancing or extension of Debt Incurred pursuant to an agreement containing any encumbrance or restriction referred to in the foregoing clauses (a) through (c), so long as the encumbrances and restrictions contained in any such refinancing agreement are no less favorable in any material respect to the Holders than the encumbrances and restrictions contained in the agreements governing the Debt being renewed, refunded, replaced, refinanced or extended in the good faith judgment of the Company;
(e) customary provisions restricting subletting or assignment of any lease, contract, or license of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary or provisions in agreements that restrict the assignment of such agreement or any rights thereunder;
(f) any encumbrance or restriction by reason of applicable law, rule, regulation or order;
(g) any encumbrance or restriction under the Indenture, the notes and the Note Guarantees;
(h) any encumbrance or restriction under a contract for the sale or other disposition of assets or Capital Interests, including, without limitation, any agreement for the sale or other disposition of a Subsidiary, that restricts distributions of the applicable assets or Capital Interests to be sold, or of any assets of a Subsidiary to be sold, pending such sale or other disposition;
149
(i) restrictions on cash and other deposits or net worth imposed by customers under contracts entered into in the ordinary course of business;
(j) customary provisions with respect to the disposition or distribution of assets or property in joint venture agreements, asset sale agreements, stock sale agreements, sale leaseback agreements and other similar agreements;
(k) any restriction with respect to the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary (or any of its property or assets) imposed by customary provisions in Hedging Obligations or Swap Contracts, in each case, not entered into for speculative purposes;
(l) Purchase Money Debt and Capital Lease Obligations permitted under the Indenture for property acquired in the ordinary course of business that impose restrictions on that property so acquired of the nature described in clause (iii) of the first paragraph hereof;
(m) Liens securing Debt otherwise permitted to be incurred under the Indenture, including the provisions of the covenant described above under the caption "—Limitation on Liens" that limit the right of the debtor to dispose of the assets subject to such Liens;
(n) any Non-Recourse Receivable Subsidiary Indebtedness or other contractual requirements of a Receivable Subsidiary that is a Restricted Subsidiary in connection with a Qualified Receivables Transaction;provided that such restrictions apply only to such Receivable Subsidiary or the receivables and related assets described in the definition of Qualified Receivables Transaction which are subject to such Qualified Receivables Transaction; and
(o) any other agreement governing Debt entered into after the Issue Date that contains encumbrances and restrictions that are not materially more restrictive with respect to any Restricted Subsidiary than those in effect on the Issue Date with respect to that Restricted Subsidiary pursuant to agreements in effect on the Issue Date.
Nothing contained in this "Limitation on Dividends and Other Payments Affecting Restricted Subsidiaries" covenant shall prevent the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary from (i) creating, incurring, assuming or suffering to exist any Liens otherwise permitted in the "Limitation on Liens" covenant or (ii) restricting the sale or other disposition of property or assets of the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries that secure Debt of the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries Incurred in accordance with the "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" and "Limitation on Liens" covenants in the Indenture.
Limitation on Asset Sales
The Company will not, and will not permit any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to, consummate an Asset Sale unless:
(1) the Company (or the Restricted Subsidiary, as the case may be) receives consideration at the time of the Asset Sale at least equal to the Fair Market Value (such Fair Market Value to be determined at the time of contractually agreeing to such Asset Sale) of the assets or Capital Interests issued or sold or otherwise disposed of;
(2) at least 75% of the consideration received in the Asset Sale by the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary is in the form of cash or Eligible Cash Equivalents. For purposes of this provision, each of the following will be deemed to be cash:
(a) any liabilities, as shown on the most recent consolidated balance sheet of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary (other than contingent liabilities and liabilities that are by their terms subordinated to the notes or any Note Guarantee) that are assumed by the
150
transferee of any such assets pursuant to a customary assignment and assumption agreement that releases the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary from further liability; and
(b) any securities, notes or other obligations received by the Company or any such Restricted Subsidiary from such transferee that are converted by the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary into cash within 180 days of their receipt to the extent of the cash received in that conversion.
Within 360 days after the receipt of any Net Cash Proceeds from an Asset Sale, the Company (or the applicable Restricted Subsidiary, as the case may be) may apply such Net Cash Proceeds at its option:
(1) to prepay, repay, redeem or purchase any secured Debt (other than Subordinated Obligations) of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary and cause such Debt to be permanently retired and the related commitment (if any) to be permanently reduced in an amount equal to the principal amount so prepaid, repaid, redeemed or repurchased;
(2) to prepay, repay, redeem or purchase any unsecured Debt (other than Subordinated Obligations) of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary and cause such Debt to be permanently retired and the related commitment (if any) to be permanently reduced in an amount equal to the principal amount so prepaid, repaid, redeemed or repurchased; provided that to the extent the Company repays any such Debt, the Company shall equally and ratably repay the notes as provided under the caption "—Optional Redemption," through open-market purchases (to the extent such purchases are at or above 100% of the principal amount thereof) or by making an Offer to Purchase (in accordance with the procedures set forth below relating to Asset Sales) to all Holders of notes to purchase their notes at 100% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued but unpaid interest to the date of purchase;
(3) to acquire all or substantially all of the assets of, or any Capital Interests of, another Permitted Business, if, after giving effect to any such acquisition of Capital Interests, the Permitted Business is or becomes a Restricted Subsidiary of the Company;
(4) to make a capital expenditure in or that is used or useful (as determined in the good faith judgment of the Company) in a Permitted Business or to make expenditures for maintenance, repair or improvement of existing properties and assets in accordance with the provisions of the Indenture;
(5) to acquire other assets that are not classified as current assets under GAAP and that are used or useful (as determined in the good faith judgment of the Company) in a Permitted Business; or
(6) any combination of the foregoing.
Any Net Cash Proceeds from Asset Sales that are not applied or invested as provided in the preceding paragraph of this covenant will constitute "Excess Proceeds." When the aggregate amount of Excess Proceeds exceeds $10.0 million, the Company will, within 30 days, make an Offer to Purchase to all Holders of notes (on apro rata basis to each series of notes), and to all holders of other Debt rankingpari passu with the notes containing provisions similar to those set forth in the Indenture with respect to assets sales, in an amount equal to the Excess Proceeds. The offer price in any Offer to Purchase will be equal to 100% of the principal amount plus accrued and unpaid interest to the date of purchase, and will be payable in cash. If any Excess Proceeds remain after consummation of an Offer to Purchase; the Company may use those funds for any purpose not otherwise prohibited by the Indenture and they will no longer constitute Excess Proceeds. If the aggregate principal amount of notes and otherpari passu debt tendered into such Offer to Purchase exceeds the amount of Excess
151
Proceeds, the Trustee will select the notes to be purchased on a pro rata basis among each series. Upon completion of each Offer to Purchase, the amount of Excess Proceeds will be reset at zero.
Pending the final application of any Net Cash Proceeds pursuant to this covenant, such Net Cash Proceeds may be applied temporarily to reduce Indebtedness outstanding under a revolving credit facility or may otherwise be invested in any manner not prohibited by the Indenture.
The Company will comply with the requirements of Rule 14e-1 under the Exchange Act and any other applicable securities laws and regulations thereunder to the extent those laws and regulations are applicable in connection with each repurchase of notes pursuant to an Offer to Purchase. To the extent that the provisions of any securities laws or regulations conflict with the Asset Sale provisions of the Indenture, the Company will comply with the applicable securities laws and regulations and will be deemed to have complied with its obligations under the Asset Sale provisions of the Indenture by virtue of such compliance.
The agreements governing our other Debt contain, and future agreements may contain, restrictions on the conduct of our business, including restrictions on our ability to conduct Asset Sales and on our ability to apply the proceeds of any permitted Asset Sale to payment of the notes.
Limitation on Transactions with Affiliates
The Company will not, and will not permit any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to, directly or indirectly, make any payment to, or sell, lease, transfer or otherwise dispose of any of its properties or assets to, or purchase any property or assets from, or enter into or make or amend any transaction or series of related transactions, contract, agreement, loan, advance or Guarantee with, or for the benefit of, any Affiliate of the Company (each of the foregoing, an "Affiliate Transaction"), unless:
(i) such Affiliate Transaction is on terms that are not materially less favorable to the Company or the relevant Subsidiary than those that could reasonably have been obtained in a comparable arm's length transaction by the Company or such Subsidiary with a Person who is not an Affiliate;
(ii) with respect to any Affiliate Transaction or series of related Affiliate Transactions involving aggregate consideration in excess of $5.0 million, the Company delivers to the Trustee a resolution adopted in good faith by the majority of the Board of Directors of the Company approving such Affiliate Transaction and set forth in an Officer's Certificate certifying that such Affiliate Transaction complies with clause (i) above; and
(iii) with respect to any Affiliate Transaction or series of related Affiliate Transactions involving aggregate consideration in excess of $15.0 million, the Company must obtain and deliver to the Trustee a written opinion of a nationally recognized investment banking, accounting or appraisal firm (an "Independent Financial Advisor") stating that the transaction is fair to the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary, as the case may be, from a financial point of view.
The foregoing limitation does not limit, and shall not apply to:
(1) Restricted Payments that are permitted by the provisions of the Indenture described above under "—Limitation on Restricted Payments" and Investments permitted pursuant to the definition of Permitted Investments (other than pursuant to clause (f) of such definition);
(2) the payment of reasonable and customary fees and indemnities and other benefits to members of the Board of Directors of the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary who are outside directors;
(3) the payment of reasonable and customary compensation and other benefits (including retirement, health, option, deferred compensation and other benefit plans) and indemnities to
152
officers and employees of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary as determined by the Board of Directors thereof in good faith;
(4) transactions between or among the Company and/or its Restricted Subsidiaries;
(5) any agreement or arrangement as in effect on the Issue Date and any amendment or modification thereto so long as such amendment or modification is not more disadvantageous to the Holders of the notes in any material respect, including, without limitation, (i) transactions with Triumph Receivables, LLC in connection with the Existing Receivables Facility and (ii) transactions with Carlyle as set forth in Note 15 to the Interim Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements of Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc. for the quarter ended March 28, 2010 incorporated by reference in this Offering Memorandum from Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.'s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 28, 2010;
(6) any contribution of capital to the Company;
(7) transactions permitted by, and complying with, the provisions of the Indenture described below under "—Consolidation, Merger, Conveyance, Transfer or Lease";
(8) any transaction with a joint venture, partnership, limited liability company or other entity (other than an Unrestricted Subsidiary) that would constitute an Affiliate Transaction solely because the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary owns an equity interest in such joint venture, partnership, limited liability company or other entity;
(9) transactions with customers, clients, suppliers or purchasers or sellers of goods or services, in each case, in the ordinary course of business and consistent with past practice and on terms that are not materially less favorable to the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary, as the case may be, as determined in good faith by the Company, than those that could be obtained in a comparable arm's length transaction with a Person that is not an Affiliate of the Company; and
(10) transactions effected as part of a Qualified Receivables Transaction.
Limitation on Sale and Leaseback Transactions
The Company will not, and will not permit any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to, enter into any Sale and Leaseback Transaction unless:
(i) the consideration received in such Sale and Leaseback Transaction is at least equal to the Fair Market Value of the property sold,
(ii) prior to and after giving effect to the Attributable Debt in respect of such Sale and Leaseback Transaction, the Company and such Restricted Subsidiary comply with the "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" covenant contained herein, and
(iii) at or after such time the Company and such Restricted Subsidiary also comply with the "Limitation on Asset Sales" covenant contained herein.
Provision of Financial Information
Whether or not required by the Commission, so long as any notes are outstanding, the Company will furnish to the Holders of notes, or file electronically with the Commission through the Commission's Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis and Retrieval System (or any successor system), within the time periods specified in the Commission's rules and regulations:
(1) all quarterly and annual financial information that would be required to be contained in a filing with the Commission on Forms 10-Q and 10-K if the Company were required to file such Forms, including a "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
153
Operations" and, with respect to the annual information only, a report on the annual financial statements by the Company's certified independent accountants; and
(2) all current reports that would be required to be filed with the Commission on Form 8-K if the Company were required to file such reports.
In addition, whether or not required by the Commission, the Company will file a copy of all of the information and reports referred to in clauses (1) and (2) above with the Commission for public availability within the time periods specified in the Commission's rules and regulations (unless the Commission will not accept such a filing) and make such information available to prospective investors. If the Commission will not accept the Company's filings for any reason, the Company will post the reports referred to in the preceding paragraph on our website within the time periods that would apply if the Company were required to file those reports with the Commission.
In addition, the Company and the Subsidiary Guarantors have agreed that, for so long as any notes remain outstanding, they will furnish to the Holders and to prospective investors, upon their request, the information required to be delivered pursuant to Rule 144A(d)(4) under the Securities Act.
If the Company has designated any of its Subsidiaries as Unrestricted Subsidiaries, then the quarterly and annual financial information required by the preceding paragraph shall include a reasonably detailed presentation, either on the face of the financial statements or in the footnotes thereto, and in "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," of the financial condition and results of operations of the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries separate from the financial condition and results of operations of the Unrestricted Subsidiaries of the Company.
Additional Note Guarantees
On the Issue Date, each of the Guarantors will Guarantee the notes in the manner and on the terms set forth in the Indenture.
After the Issue Date, the Company will cause each of its domestic Restricted Subsidiaries (other than any domestic Restricted Subsidiary that is a Receivables Subsidiary) that (1) is a borrower under any Credit Facility or (2) Guarantees any Debt of the Company or any of its domestic Restricted Subsidiaries incurred under any Credit Facility to Guarantee the notes.
Each Note Guarantee will state that it will be limited to an amount not to exceed the maximum amount that can be Guaranteed by that Restricted Subsidiary without rendering the Guarantee, as it relates to such Restricted Subsidiary, voidable under applicable law relating to fraudulent conveyance or fraudulent transfer or similar laws affecting the rights of creditors generally.
Each Guarantee will be released in accordance with the provisions of the indenture described under "—Guarantees" above.
Limitation on Creation of Unrestricted Subsidiaries
Triumph Receivables, LLC, Triumph Group Charitable Foundation, Triumph Interiors, Ltd, Saygrove Actuation & Motion Control Limited and Airframe Spares & Logistics GmbH will be Unrestricted Subsidiaries on the Issue Date. After the Issue Date, the Company may designate any other Subsidiary of the Company to be an "Unrestricted Subsidiary" as provided below, in which event such Subsidiary and each other Person that is then or thereafter becomes a Subsidiary of such Subsidiary will be deemed to be an Unrestricted Subsidiary.
154
"Unrestricted Subsidiary" means:
(1) any Subsidiary designated as such in the Indenture or, after the Issue Date, by the Board of Directors of the Company in an Officer's Certificate in the manner set forth below; and
(2) any Subsidiary of an Unrestricted Subsidiary.
The Company may designate any Subsidiary (including any newly acquired or newly formed Subsidiary or a Person becoming a Subsidiary through merger or consolidation or Investment therein) to be an Unrestricted Subsidiary after the Issue Date only if:
(i) neither the Company nor any of its Restricted Subsidiaries:
(A) provides credit support for, or Guarantee of, any Debt of such Subsidiary or any Subsidiary of such Subsidiary (including any undertaking, agreement or instrument evidencing such Debt, but excluding, in the case of a Receivable Subsidiary, any Standard Securitization Undertakings);
(B) is directly or indirectly liable for any Debt of such Subsidiary or any Subsidiary of such Subsidiary (except, in the case of a Receivable Subsidiary any Standard Securitization Undertakings); or
(C) has any direct or indirect obligation to maintain or preserve such Person's financial condition or to cause such Person to achieve any specified levels of operating results, including by way of subscription for additional Capital Interests of such Person;
(ii) such Subsidiary does not own any Capital Interests of, or own or hold any Lien on any property of, any Restricted Subsidiary of the Company; and
(iii) either:
(A) the Subsidiary to be so designated has total assets of $1,000 or less; or
(B) the Company could make a Restricted Payment at the time of designation in an amount equal to the greater of the Fair Market Value or net book value of such Subsidiary pursuant to the "Limitation on Restricted Payments" covenant (and such amount is thereafter treated as a Restricted Payment for the purpose of calculating the amount available for Restricted Payments thereunder).
An Unrestricted Subsidiary may be designated as a Restricted Subsidiary if (i) all the Debt of such Unrestricted Subsidiary could be Incurred under the "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" covenant and (ii) all the Liens on the property and assets of such Unrestricted Subsidiary could be incurred pursuant to the "Limitation on Liens" covenant.
Consolidation, Merger, Conveyance, Transfer or Lease
The Company will not in any transaction or series of transactions, consolidate with or merge into any other Person (other than a merger of a Restricted Subsidiary into the Company in which the Company is the continuing Person), or sell, assign, convey, transfer, lease or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of the assets of the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries (determined on a consolidated basis), taken as a whole, to any other Person, unless:
(i) either: (a) the Company shall be the continuing Person or (b) the Person (if other than the Company) formed by such consolidation or into which the Company is merged, or the Person that acquires, by sale, assignment, conveyance, transfer, lease or other disposition, all or substantially all of the property and assets of the Company (such Person, the "Surviving Entity"), (1) shall be a corporation, partnership, limited liability company or similar entity organized and validly existing under the laws of the United States, any political subdivision thereof or any state
155
thereof or the District of Columbia and (2) shall expressly assume, by a supplemental indenture, the due and punctual payment of all amounts due in respect of the principal of (and premium, if any) and interest on all the notes and the performance of the covenants and obligations of the Company under the Indenture and the Registration Rights Agreement;provided that at any time the Company or its Successor Entity is not a corporation, there shall be a co-issuer of the notes that is a corporation;
(ii) immediately after giving effect to such transaction or series of transactions on a pro forma basis (including, without limitation, any Debt Incurred in connection with or in respect of such transaction or series of transactions), no Default or Event of Default shall have occurred and be continuing or would result therefrom;
(iii) immediately after giving effect to any such transaction or series of transactions on a pro forma basis (including, without limitation, any Debt Incurred in connection with or in respect of such transaction or series of transactions) as if such transaction or series of transactions had occurred on the first day of the determination period, the Company (or the Surviving Entity if the Company is not continuing) could Incur $1.00 of additional Debt under the provisions described in the first paragraph of "—Limitation on Incurrence of Debt"; and
(iv) the Company delivers, or causes to be delivered, to the Trustee, in form satisfactory to the Trustee, an Officer's Certificate and an opinion of counsel, each stating that such consolidation, merger, sale, conveyance, assignment, transfer, lease or other disposition complies with the requirements of the Indenture.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, failure to satisfy the requirements of the preceding clauses (ii) and (iii) will not prohibit:
(a) a merger between the Company and a Restricted Subsidiary that is a wholly owned Subsidiary of the Company; or
(b) a merger between the Company and an Affiliate incorporated solely for the purpose of converting the Company into a Person organized under the laws of the United States or any political subdivision or state thereof (other than its then-current state of organization) or for the purpose of changing its form of organization; so long as, in each case, the amount of Debt of the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries is not increased thereby.
For all purposes of the Indenture and the notes, Subsidiaries of any Surviving Entity will, upon such transaction or series of transactions, become Restricted Subsidiaries or Unrestricted Subsidiaries as provided pursuant to the Indenture and all Debt, and all Liens on property or assets, of the Surviving Entity and its Subsidiaries that was not Debt, or were not Liens on property or assets, of the Company and its Subsidiaries immediately prior to such transaction or series of transactions shall be deemed to have been Incurred upon such transaction or series of transactions.
Upon any transaction or series of transactions that are of the type described in, and are effected in accordance with, the conditions described in the immediately preceding paragraphs, the Surviving Entity (if other than the Company) shall succeed to, and be substituted for, and may exercise every right and power of, the Company, under the Indenture with the same effect as if such Surviving Entity had been named as the Company therein; and when a Surviving Entity duly assumes all of the obligations and covenants of the Company pursuant to the Indenture and the notes, except in the case of a lease of all or substantially all of the Company's assets, the predecessor Person shall be relieved of all such obligations.
156
Limitation on Business Activities
The Company will not, and will not permit any Restricted Subsidiary to, engage in any business other than a Permitted Business.
Payments for Consent
The Company will not, and will not permit any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to, directly or indirectly, pay or cause to be paid any consideration to or for the benefit of any Holder of notes for or as an inducement to any consent, waiver or amendment of any of the terms or provisions of the Indenture or the notes unless such consideration is offered to be paid and is paid to all Holders of the notes that consent, waive or agree to amend in the time frame set forth in the solicitation documents relating to such consent, waiver or agreement.
Events of Default
Each of the following is an "Event of Default" under the Indenture:
(1) default in the payment in respect of the principal of (or premium, if any, on) any Note when due and payable (whether at Stated Maturity or upon repurchase, acceleration, optional redemption or otherwise);
(2) default in the payment of any interest upon any Note when it becomes due and payable, and continuance of such default for a period of 30 days;
(3) except as permitted by the Indenture, any Note Guarantee of any Significant Subsidiary required to be a Guarantor pursuant to the Indenture (or any group of Restricted Subsidiaries required to be Guarantors pursuant to the Indenture that, taken together, would constitute a Significant Subsidiary), shall for any reason cease to be, or it shall be asserted by any Guarantor or the Company not to be, in full force and effect and enforceable in accordance with its terms;
(4) default in the performance, or breach, of any covenant or agreement (including the Company's obligations described under "—Change of Control" above) of the Company or any Guarantor in the Indenture (other than a covenant or agreement a default in whose performance or whose breach is specifically addressed in clauses (1), (2) or (3) above), and continuance of such default or breach for a period of 60 days after written notice thereof has been given to the Company by the Trustee or to the Company and the Trustee by the Holders of at least 25% in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes;
(5) a default or defaults under any bonds, debentures, notes or other evidences of Debt (other than the notes) by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary having, individually or in the aggregate, a principal or similar amount outstanding of at least $25.0 million, whether such Debt now exists or shall hereafter be created, which default or defaults (A) shall have resulted in the acceleration of the maturity of such Debt prior to its express maturity or (B) shall constitute a failure to pay principal of at least $25.0 million on such Debt when due and payable after the expiration of any applicable grace period with respect thereto;
(6) the entry against the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary that is a Significant Subsidiary of a final judgment or final judgments for the payment of money in an aggregate amount in excess of $25.0 million, by a court or courts of competent jurisdiction, which judgments remain undischarged, unwaived, unstayed, unbonded or unsatisfied for a period of 60 consecutive days; or
(7) certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization of the Company or any Significant Subsidiary (or any group of Restricted Subsidiaries that, taken together, would constitute a Significant Subsidiary).
157
If an Event of Default (other than an Event of Default specified in clause (7) above with respect to the Company) occurs and is continuing, then and in every such case the Trustee or the Holders of not less than 25% in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes may declare the principal of the notes and any accrued interest on the notes to be due and payable immediately by a notice in writing to the Company (and to the Trustee if given by Holders);provided, however, that after such acceleration, but before a judgment or decree based on acceleration, the Holders of a majority in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes may, under certain circumstances, rescind and annul such acceleration if all Events of Default (other than the nonpayment of accelerated principal of, premium, if any, or interest on the notes) have been cured or waived as provided in the Indenture.
In the event of a declaration of acceleration of the notes solely because an Event of Default described in clause (5) above has occurred and is continuing, the declaration of acceleration of the notes shall be automatically rescinded and annulled if the event of default or payment default triggering such Event of Default pursuant to clause (5) shall be remedied or cured by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary of the Company or waived by the holders of the relevant Debt within 20 business days after the declaration of acceleration with respect thereto and if the rescission and annulment of the acceleration of the notes would not conflict with any judgment or decree of a court of competent jurisdiction obtained by the Trustee for the payment of amounts due on the notes.
If an Event of Default specified in clause (7) above occurs with respect to the Company, the principal of and any accrued interest on the notes then outstanding shall ipso facto become immediately due and payable without any declaration or other act on the part of the Trustee or any Holder. For further information as to waiver of defaults, see "—Amendment, Supplement and Waiver." The Trustee may withhold from Holders notice of any Default (except Default in payment of principal of, premium, if any, and interest) if the Trustee determines that withholding notice is in the best interests of the Holders.
No Holder of any Note will have any right to institute any proceeding with respect to the Indenture or for any remedy thereunder, unless such Holder shall have previously given to the Trustee written notice of a continuing Event of Default and unless also the Holders of at least 25% in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes shall have made written request to the Trustee, and provided indemnity reasonably satisfactory to the Trustee, to institute such proceeding as Trustee, and the Trustee shall not have received from the Holders of a majority in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes a direction inconsistent with such request and shall have failed to institute such proceeding within 60 days. Such limitations do not apply, however, to a suit instituted by a Holder of a Note directly (as opposed to through the Trustee) for enforcement of payment of the principal of (and premium, if any) or interest on such Note on or after the respective due dates expressed in such Note.
The Company will be required to furnish to the Trustee annually a statement as to the performance of certain obligations under the Indenture and as to any default in such performance. The Company also is required to notify the Trustee within five Business Days after it becomes aware of the occurrence of any Default or Event of Default.
Amendment, Supplement and Waiver
Without the consent of any Holders, the Company, the Guarantors and the Trustee, at any time and from time to time, may enter into one or more indentures supplemental to the Indenture for any of the following purposes:
(1) to evidence the succession of another Person to the Company and the assumption by any such Successor Entity of the covenants of the Company in the Indenture, the Note Guarantees and the new notes;
158
(2) to add to the covenants of the Company for the benefit of the Holders, or to surrender any right or power herein conferred upon the Company;
(3) to add additional Events of Default;
(4) to provide for uncertificated notes in addition to or in place of the certificated notes;
(5) to evidence and provide for the acceptance of appointment under the Indenture by a successor Trustee;
(6) to provide for or confirm the issuance of Additional notes in accordance with the terms of the Indenture;
(7) to add a Guarantor or to release a Guarantor in accordance with the terms of the Indenture;
(8) to cure any ambiguity, defect, omission, mistake or inconsistency;
(9) to make any other provisions with respect to matters or questions arising under the Indenture;provided that such actions pursuant to this clause (9) shall not adversely affect the interests of the Holders in any material respect, as determined in good faith by the Board of Directors of the Company;
(10) to conform the text of the Indenture or the notes to any provision of this "Description of New Notes" to the extent that the Trustee has received an Officer's Certificate stating that such text constitutes an unintended conflict with the description of the corresponding provision in this "Description of New Notes";
(11) to effect or maintain the qualification of the Indenture under the Trust Indenture Act;
(12) to secure the notes; or
(13) to provide for the issuance of exchange securities which shall have terms substantially identical in all respects to the notes (except that the transfer restrictions contained in the notes shall be modified or eliminated as appropriate) and which shall be treated, together with any outstanding notes, as a single class of securities.
With the consent of the Holders of not less than a majority in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes (including consents obtained in connection with a purchase of, or tender offer or exchange offer for, notes), the Company, the Guarantors and the Trustee may enter into an indenture or indentures supplemental to the Indenture for the purpose of adding any provisions to or changing in any manner or eliminating any of the provisions of the Indenture or the notes or of modifying in any manner the rights of the Holders of the notes under the Indenture, including the definitions therein; provided, however, that no such supplemental indenture shall, without the consent of the Holder of each outstanding Note affected thereby:
(1) change the Stated Maturity of any Note or of any installment of interest on any Note, or reduce the amount payable in respect of the principal thereof or the rate of interest thereon or any premium payable thereon, or reduce the amount that would be due and payable on acceleration of the maturity thereof, or change the place of payment where, or the coin or currency in which, any Note or any premium or interest thereon is payable, or impair the right to institute suit for the enforcement of any such payment on or after the Stated Maturity thereof, or change the date on which any notes may be subject to redemption or reduce the Redemption Price therefor;
(2) reduce the percentage in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes, the consent of whose Holders is required for any such supplemental indenture, or the consent of
159
whose Holders is required for any waiver (of compliance with certain provisions of the Indenture or certain defaults thereunder and their consequences) provided for in the Indenture;
(3) modify the obligations of the Company to make Offers to Purchase upon a Change of Control or from the Excess Proceeds of Asset Sales if such modification is made after the time that the Company is required to make an Offer to Purchase in connection with a Change of Control or Asset Sale;
(4) modify or change any provision of the Indenture affecting the ranking of the notes or any Note Guarantee in a manner adverse to the Holders of the notes;
(5) modify any of the provisions of this paragraph or provisions relating to waiver of defaults or certain covenants, except to increase any such percentage required for such actions or to provide that certain other provisions of the Indenture cannot be modified or waived without the consent of the Holder of each outstanding Note affected thereby; or
(6) release any Note Guarantees required to be maintained under the Indenture (other than in accordance with the terms of the Indenture).
The Holders of not less than a majority in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes may on behalf of the Holders of all the notes waive any past default under the Indenture and its consequences, except a default:
(1) in any payment in respect of the principal of (or premium, if any) or interest on any notes (including any Note which is required to have been purchased pursuant to an Offer to Purchase which has been made by the Company), or
(2) in respect of a covenant or provision hereof which under the Indenture cannot be modified or amended without the consent of the Holder of each outstanding Note affected, each of which, for the avoidance of doubt, shall require the consent of all the Holders of the notes outstanding.
Satisfaction and Discharge of the Indenture; Defeasance
The Company and the Guarantors may terminate their respective obligations under the Indenture (a "Discharge") when:
(1) either: (A) all notes that have been authenticated and delivered have been delivered to the Trustee for cancellation, or (B) all such notes not theretofore delivered to the Trustee for cancellation (i) have become due and payable or (ii) will become due and payable within one year or are to be called for redemption within one year under irrevocable arrangements satisfactory to the Trustee for the giving of notice of redemption by the Trustee in the name, and at the expense, of the Company, and the Company has irrevocably deposited or caused to be deposited with the Trustee immediately available funds or U.S. Government Obligations in an amount sufficient to pay and discharge the entire indebtedness on the notes, not theretofore delivered to the Trustee for cancellation, for principal of, premium, if any, and interest to the Stated Maturity or date of redemption;
(2) the Company has paid or caused to be paid all other sums then due and payable under the Indenture by the Company;
(3) the deposit will not result in a breach or violation of, or constitute a default under, any other instrument to which the Company or any Guarantor is a party or by which the Company or any Guarantor is bound;
160
(4) the Company has delivered irrevocable instructions to the Trustee under the Indenture to apply the deposited money toward the payment of the notes at maturity or on the redemption date, as the case may be; and
(5) the Company has delivered to the Trustee an Officer's Certificate and an opinion of counsel, each stating that all conditions precedent under the Indenture relating to the Discharge have been complied with.
The Company may elect, at its option, to have its obligations discharged with respect to the outstanding notes ("legal defeasance"). Such defeasance means that the Company will be deemed to have paid and discharged the entire indebtedness represented by the outstanding notes, except for:
(1) the rights of Holders of such notes to receive payments in respect of the principal of and any premium and interest on such notes when payments are due;
(2) the Company's obligations with respect to such notes concerning issuing temporary notes, registration of notes, mutilated, destroyed, lost or stolen notes and the maintenance of an office or agency for payment and money for security payments held in trust;
(3) the rights, powers, trusts, duties and immunities of the Trustee;
(4) the Company's right of optional redemption; and
(5) the legal defeasance provisions of the Indenture.
If the Company exercises its legal defeasance option, the Subsidiary Guarantees in effect at such time will terminate.
In addition, the Company may elect, at its option, to have its obligations released with respect to certain covenants contained in the Indenture ("covenant defeasance"), including, without limitation, its obligation to make Offers to Purchase in connection with Asset Sales and any Change of Control and any omission to comply with such obligation shall not constitute a Default or an Event of Default with respect to the notes. In the event covenant defeasance occurs, certain events (not including non-payment, bankruptcy and insolvency events) described under "Events of Default" will no longer constitute an Event of Default with respect to the notes.
In order to exercise either legal defeasance or covenant defeasance with respect to outstanding notes:
(1) the Company must irrevocably have deposited or caused to be deposited with the Trustee as trust funds in trust for the purpose of making the following payments, specifically pledged as security for, and dedicated solely to the benefits of the Holders of such notes: (A) money in an amount, or (B) U.S. government obligations, which through the scheduled payment of principal and interest in respect thereof in accordance with their terms will provide, not later than the due date of any payment, money in an amount or (C) a combination thereof, in each case sufficient without reinvestment, in the opinion of a nationally recognized firm of independent public accountants expressed in a written certification thereof delivered to the Trustee, to pay and discharge, and which shall be applied by the Trustee to pay and discharge, the entire indebtedness in respect of the principal of and premium, if any, and interest on such notes on the Stated Maturity thereof or (if the Company has made irrevocable arrangements satisfactory to the Trustee for the giving of notice of redemption by the Trustee in the name and at the expense of the Company) the redemption date thereof, as the case may be, in accordance with the terms of the Indenture and such notes;
(2) in the case of legal defeasance, the Company shall have delivered to the Trustee an opinion of counsel stating that (A) the Company has received from, or there has been published by, the Internal Revenue Service a ruling or (B) since the date of the Indenture, there has been a
161
change in the applicable United States federal income tax law, in either case (A) or (B) to the effect that, and based thereon such opinion shall confirm that, the Holders of such notes will not recognize gain or loss for United States federal income tax purposes as a result of the deposit, defeasance and discharge to be effected with respect to such notes and will be subject to United States federal income tax on the same amount, in the same manner and at the same times as would be the case if such deposit, defeasance and discharge were not to occur;
(3) in the case of covenant defeasance, the Company shall have delivered to the Trustee an opinion of counsel to the effect that the Holders of such outstanding notes will not recognize gain or loss for United States federal income tax purposes as a result of the deposit and covenant defeasance to be effected with respect to such notes and will be subject to United States federal income tax on the same amount, in the same manner and at the same times as would be the case if such deposit and covenant defeasance were not to occur;
(4) no Default or Event of Default with respect to the outstanding notes shall have occurred and be continuing at the time of such deposit after giving effect thereto (other than a Default or Event of Default resulting from the borrowing of funds to be applied to such deposit and the grant of any Lien to secure such borrowing);
(5) such legal defeasance or covenant defeasance shall not cause the Trustee to have a conflicting interest within the meaning of the Trust Indenture Act (assuming all notes are in default within the meaning of such Act);
(6) such legal defeasance or covenant defeasance shall not result in a breach or violation of, or constitute a default under, any material agreement or material instrument (other than the Indenture) to which the Company is a party or by which the Company is bound; and
(7) the Company shall have delivered to the Trustee an Officer's Certificate and an opinion of counsel, each stating that all conditions precedent with respect to such legal defeasance or covenant defeasance have been complied with.
In connection with a Discharge, in the event the Company becomes insolvent within the applicable preference period after the date of deposit, monies held for the payment of the notes may be part of the bankruptcy estate of the Company, disbursement of such monies may be subject to the automatic stay of the bankruptcy code and monies disbursed to Holders may be subject to disgorgement in favor of the Company's estate. Similar results may apply upon the insolvency of the Company during the applicable preference period following the deposit of monies in connection with defeasance.
The Trustee
U.S. Bank National Association will act as the Trustee under the Indenture and as the initial paying agent and registrar for the notes. The Trustee from time to time may extend credit to the Company in the normal course of business. Except during the continuance of an Event of Default, the Trustee will perform only such duties as are specifically set forth in the Indenture. During the continuance of an Event of Default that has not been cured or waived, the Trustee will exercise such of the rights and powers vested in it by the Indenture and use the same degree of care and skill in their exercise, as a prudent person would exercise or use under the circumstances in the conduct of such person's own affairs.
The Indenture and the Trust Indenture Act contain certain limitations on the rights of the Trustee, should it become a creditor of the Company, to obtain payment of claims in certain cases or to realize on certain property received in respect of any such claim as security or otherwise. The Trustee will be permitted to engage in other transactions; however, if it acquires any "conflicting interest" (as defined in the Trust Indenture Act) it must eliminate such conflict within 90 days, apply to the Commission for permission to continue or resign.
162
The Holders of a majority in principal amount of the outstanding notes will have the right to direct the time, method and place of conducting any proceeding for any remedy available to the Trustee or exercising any trust or power conferred on the Trustee, subject to certain exceptions. The Indenture provides that in case an Event of Default has occurred and is continuing, the Trustee shall exercise such of the rights and powers vested in it by the Indenture, and use the same degree of care and skill in their exercise, as a prudent person would exercise or use under the circumstances in the conduct of such person's own affairs. Subject to such provisions, the Trustee shall be under no obligation to exercise any of the rights or powers vested in it by the Indenture at the request or direction of any of the Holders pursuant to the Indenture, unless such Holders shall have provided to the Trustee security or indemnity reasonably satisfactory to the Trustee against the costs, expenses and liabilities which might be incurred by it in compliance with such request or direction.
No recourse may, to the full extent permitted by applicable law, be taken, directly or indirectly, with respect to the obligations of the Company or the Guarantors on the notes or under the Indenture or any related documents, any certificate or other writing delivered in connection therewith, against (i) the Trustee in its individual capacity, or (ii) any partner, owner, beneficiary, agent, officer, director, employee, agent, successor or assign of the Trustee, each in its individual capacity, or (iii) any holder of equity in the Trustee.
No Personal Liability of Stockholders, Partners, Officers or Directors
No director, officer, employee, stockholder, general or limited partner or incorporator, past, present or future, of the Company or any of its Subsidiaries, as such or in such capacity, shall have any personal liability for any obligations of the Company under the notes, any Note Guarantee or the Indenture by reason of his, her or its status as such director, officer, employee, stockholder, general or limited partner or incorporator. Each Holder of notes by accepting a Note waives and releases all such liability. The waiver and release are part of the consideration for the issuance of the notes. Such waiver may not be effective to waive liabilities under the federal securities laws and it is the view of the Commission that such a waiver is against public policy.
Governing Law
The Indenture and the notes are governed by, and will be construed in accordance with, the laws of the State of New York.
Certain Definitions
Set forth below is a summary of certain of the defined terms used in the Indenture. Reference is made to the Indenture for the full definition of all such terms, as well as any capitalized term used herein for which no definition is provided.
"Acquired Debt" means Debt (1) of a Person or any of its Subsidiaries existing at the time such Person becomes a Restricted Subsidiary or (2) assumed in connection with the acquisition of assets from such Person. Acquired Debt shall be deemed to have been Incurred, with respect to clause (1) of the preceding sentence, on the date such Person becomes a Restricted Subsidiary and, with respect to clause (2) of the preceding sentence, on the date of consummation of such acquisition of assets.
"Additional Interest" means all additional interest owing on the notes pursuant to the Registration Rights Agreement.
"Affiliate" of any Person means any other Person directly or indirectly controlling or controlled by or under direct or indirect common control with such Person. For the purposes of this definition, "control" when used with respect to any Person means the power to direct the management and policies of such Person, directly or indirectly, whether through the ownership of voting securities, by
163
contract or otherwise; and the terms "controlling" and "controlled" have meanings that correspond to the foregoing. For purposes of the "Limitation on Transactions with Affiliates" covenant, any Person directly or indirectly owning 15% or more of the outstanding Capital Interests of the Company will be deemed an Affiliate.
"Applicable Premium" means, with respect to any Note on any applicable redemption date, the greater of:
(1) 1% of the then outstanding principal amount of the Note; and
(2) the excess of:
(a) the present value at such redemption date of (i) the Redemption Price of the Note at July 15, 2014 (such Redemption Price being set forth in the table appearing above under the caption "—Optional Redemption") plus (ii) all required interest payments due on the Note through July 15, 2014 (excluding accrued but unpaid interest), computed using a discount rate equal to the Treasury Rate as of such redemption date plus 50 basis points; over
(b) the then outstanding principal amount of the Note.
"Asset Acquisition" means:
(a) an Investment by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary in any other Person pursuant to which such Person shall become a Restricted Subsidiary, or shall be merged with or into the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary; or
(b) the acquisition by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary of the assets of any Person which constitute all or substantially all of the assets of such Person, any division or line of business of such Person or any other properties or assets of such Person other than in the ordinary course of business and consistent with past practices.
"Asset Sale" means any transfer, conveyance, sale, lease or other disposition (including, without limitation, dispositions pursuant to any consolidation or merger) by the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to any Person (other than to the Company or one or more of its Restricted Subsidiaries) in any single transaction or series of transactions of:
(i) Capital Interests in another Person (other than directors' qualifying shares or shares or interests required to be held by foreign nationals pursuant to local law); or
(ii) any other property or assets (other than in the normal course of business, including, as applicable, inventory sales and any sale or other disposition of obsolete or permanently retired equipment);
provided, however, that the term "Asset Sale" shall exclude:
(a) any asset disposition permitted by the provisions described under "—Consolidation, Merger, Conveyance, Lease or Transfer" that constitutes a disposition of all or substantially all of the assets of the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries taken as a whole;
(b) any transfer, conveyance, sale, lease or other disposition of property or assets, the gross proceeds of which (exclusive of indemnities) do not exceed in any one or related series of transactions $5.0 million;
(c) sales or other dispositions of cash or Eligible Cash Equivalents;
(d) sales of interests in Unrestricted Subsidiaries;
(e) the sale and leaseback of any assets within 90 days of the acquisition thereof;
164
(f) the disposition of assets that, in the good faith judgment of the Company, are no longer used or useful in the business of such entity;
(g) a Restricted Payment or Permitted Investment that is otherwise permitted by the Indenture;
(h) any trade-in of equipment in exchange for other equipment;provided that in the good faith judgment of the Company, the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary receives equipment having a fair market value equal to or greater than the equipment being traded in;
(i) the concurrent purchase and sale or exchange of Related Business Assets or a combination of Related Business Assets between the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries and another person to the extent that the Related Business Assets received by the Company or its Restricted Subsidiaries are of equivalent or better market value than the Related Business Assets transferred;
(j) the creation of a Lien (but not the sale or other disposition of the property subject to such Lien);
(k) leases or subleases in the ordinary course of business to third persons not interfering in any material respect with the business of the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries and otherwise in accordance with the provisions of the Indenture;
(l) any disposition by a Subsidiary to the Company or by the Company or a Subsidiary to a Restricted Subsidiary;
(m) dispositions of accounts receivable in connection with the collection or compromise thereof in the ordinary course of business and consistent with past practice, including, without limitation, those under the GE/Citi Sales Arrangements or similar arrangements;
(n) licensing or sublicensing of intellectual property or other general intangibles in accordance with industry practice in the ordinary course of business;
(o) any transfer of accounts receivable, or a fractional undivided interest therein, by a Receivable Subsidiary in a Qualified Receivables Transaction;
(p) sales of accounts receivable to a Receivable Subsidiary pursuant to a Qualified Receivables Transaction for the Fair Market Value thereof, including cash in an amount at least equal to 75% of the Fair Market Value thereof (for the purposes of this clause (p), Purchase Money notes will be deemed to be cash);
(q) foreclosures on assets to the extent it would not otherwise result in a Default or Event of Default; or
(r) sales or transfers of equipment under the Leasing Facility.
For purposes of this definition, any series of related transactions that, if effected as a single transaction, would constitute an Asset Sale, shall be deemed to be a single Asset Sale effected when the last such transaction which is a part thereof is effected.
"Attributable Debt" in respect of a Sale and Leaseback Transaction means, at the time of determination, the present value (discounted at the rate of interest implicit in such transaction) of the total obligations of the lessee for rental payments during the remaining term of the lease included in such Sale and Leaseback Transaction (including any period for which such lease has been or may be extended).
"Average Life" means, as of any date of determination, with respect to any Debt, the quotient obtained by dividing (i) the sum of the products of (x) the number of years from the date of
165
determination to the dates of each successive scheduled principal payment (including any sinking fund or mandatory redemption payment requirements) of such Debt multiplied by (y) the amount of such principal payment by (ii) the sum of all such principal payments.
"Board of Directors" means (i) with respect to the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary, its board of directors or any duly authorized committee thereof; (ii) with respect to a corporation, the board of directors of such corporation or any duly authorized committee thereof; and (iii) with respect to any other entity, the board of directors or similar body of the general partner or managers of such entity or any duly authorized committee thereof.
"Capital Interests" in any Person means any and all shares, interests (including Preferred Interests), participations or other equivalents in the equity interest (however designated) in such Person and any rights (other than Debt securities convertible into an equity interest), warrants or options to acquire an equity interest in such Person.
"Capital Lease Obligations" means any obligation under a lease that is required to be capitalized for financial reporting purposes in accordance with GAAP; and the amount of Debt represented by such obligation shall be the capitalized amount of such obligations determined in accordance with GAAP; and the Stated Maturity thereof shall be the date of the last payment of rent or any other amount due under such lease prior to the first date upon which such lease may be terminated by the lessee without payment of a penalty.
"Carlyle" means The Carlyle Group and if applicable, each of its respective Affiliates and funds or partnerships managed by it or its respective Affiliates but not including, however, any portfolio companies of any of the foregoing.
"Change of Control" means:
(1) the Company becomes aware of (by way of a report or any other filing pursuant to Section 13(d) of the Exchange Act, proxy, vote, written notice or otherwise) the acquisition by any "person" or "group" (as such terms are used in Sections 13(d) and 14(d) of the Exchange Act), that is or becomes the ultimate "beneficial owner" (as such term is used in Rules 13d-3 and 13d-5 under the Exchange Act, except that for purposes of this clause (1) such person or group shall be deemed to have "beneficial ownership" of all shares that any such person or group has the right to acquire, whether such right is exercisable immediately or only after the passage of time), directly or indirectly, of more than 50% of the Voting Interests in the Company,
(2) during any period of two consecutive years, individuals who at the beginning of such period constituted the Board of Directors of the Company (together with any new directors whose election by the Board of Directors or whose nomination for election by the equityholders of the Company was approved by a vote of a majority of the directors of the Company then still in office who were either directors at the beginning of such period or whose election or nomination for election was previously so approved) cease for any reason to constitute a majority of the Company's Board of Directors then in office, or
(3) the Company sells, conveys, transfers or leases (either in one transaction or a series of related transactions) all or substantially all of its assets to a Person other than a Restricted Subsidiary of the Company.
"Code" means the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended from time to time, and the regulations promulgated thereunder.
"Common Interests" of any Person means Capital Interests in such Person that do not rank prior, as to the payment of dividends or as to the distribution of assets upon any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of such Person, to Capital Interests of any other class in such Person.
166
"Company" means Triumph Group, Inc. and any Successor Entity.
"Consolidated Cash Flow Available for Fixed Charges" means, with respect to any Person for any period:
(i) the sum of, without duplication, the amounts for such period, taken as a single accounting period, of:
(a) Consolidated Net Income;
(b) Consolidated Non-cash Charges;
(c) Consolidated Interest Expense to the extent the same was deducted in computing Consolidated Net Income;
(d) Consolidated Income Tax Expense; and
(e) any expenses or charges related to any equity offering, Permitted Investment, recapitalization or Debt Incurrence permitted to be made under the Indenture (whether or not successful) or related to this offering of the notes; less
(ii) the amount of extraordinary, non-recurring or unusual gains.
"Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio" means, with respect to any Person, the ratio of the aggregate amount of Consolidated Cash Flow Available for Fixed Charges of such Person for the four full fiscal quarters, treated as one period, for which financial information in respect thereof is available immediately preceding the date of the transaction (the "Transaction Date") giving rise to the need to calculate the Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (such four full fiscal quarter period being referred to herein as the "Four Quarter Period") to the aggregate amount of Consolidated Fixed Charges of such Person for the Four Quarter Period. In addition to and without limitation of the foregoing, for purposes of this definition, "Consolidated Cash Flow Available for Fixed Charges" and "Consolidated Fixed Charges" shall be calculated after giving effect, on a pro forma basis for the period of such calculation, to any Asset Sales or other dispositions or Asset Acquisitions, investments, mergers, consolidations and discontinued operations (as determined in accordance with GAAP) and designations of any Restricted Subsidiary to be an Unrestricted Subsidiary or any Unrestricted Subsidiary to be a Restricted Subsidiary occurring during the Four Quarter Period or any time subsequent to the last day of the Four Quarter Period and on or prior to the Transaction Date, as if such Asset Sale or other disposition or Asset Acquisition (including the incurrence or assumption of any such Acquired Debt), investment, merger, consolidation, disposed operation or designation occurred on the first day of the Four Quarter Period. For purposes of this definition, pro forma calculations shall be made in accordance with Article 11 of Regulation S-X promulgated under the Securities Act.
If the Debt which is the subject of a determination of the Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio is Acquired Debt, or Debt Incurred in connection with the simultaneous acquisition of any Person, business, property or assets, or Debt of an Unrestricted Subsidiary being designated as a Restricted Subsidiary, then such ratio shall be determined by giving effect (on a pro forma basis, as if the transaction had occurred at the beginning of the Four Quarter Period) to (x) the Incurrence of such Acquired Debt or such other Debt by the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries and (y) the inclusion, in Consolidated Cash Flow Available for Fixed Charges, of the Consolidated Cash Flow Available for Fixed Charges of the acquired Person, business, property or assets or redesignated Subsidiary.
Furthermore, in calculating "Consolidated Fixed Charges" for purposes of determining the denominator (but not the numerator) of this "Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio":
(i) interest on outstanding Debt determined on a fluctuating basis as of the Transaction Date and which will continue to be so determined thereafter shall be deemed to have accrued at a fixed
167
rate per annum equal to the rate of interest on such Debt in effect (taking into account any Hedging Obligations or Swap Contract applicable to such Debt) on the Transaction Date; and
(ii) if interest on any Debt actually incurred on the Transaction Date may optionally be determined at an interest rate based upon a factor of a prime or similar rate, a eurocurrency interbank offered rate, or other rates, then the interest rate in effect (taking into account any Hedging Obligations applicable to such Debt) on the Transaction Date will be deemed to have been in effect during the Four Quarter Period.
If such Person or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries directly or indirectly Guarantees Debt of a third Person, the above clause shall give effect to the incurrence of such Guaranteed Debt as if such Person or such Subsidiary had directly incurred or otherwise assumed such Guaranteed Debt.
"Consolidated Fixed Charges" means, with respect to any Person for any period, the sum of, without duplication, the amounts for such period of:
(i) Consolidated Interest Expense; and
(ii) the product of (a) all dividends and other distributions paid or accrued during such period in respect of Redeemable Capital Interests of such Person and its Restricted Subsidiaries (other than dividends paid in Qualified Capital Interests), times (b) a fraction, the numerator of which is one and the denominator of which is one minus the then current combined federal, state and local statutory tax rate of such Person, expressed as a decimal.
"Consolidated Income Tax Expense" means, with respect to any Person for any period, the provision for federal, state, local and foreign income taxes of such Person and its Restricted Subsidiaries for such period as determined on a consolidated basis in accordance with GAAP paid or accrued during such period, including any penalties and interest related to such taxes or arising from any tax examinations, to the extent the same were deducted in computing Consolidated Net Income.
"Consolidated Interest Expense" means, with respect to any Person for any period, without duplication, the sum of:
(i) the total interest expense of such Person and its Restricted Subsidiaries for such period as determined on a consolidated basis in accordance with GAAP, including, without limitation:
(a) any amortization of Debt discount;
(b) the net cost under any Hedging Obligation or Swap Contract in respect of interest rate protection (including any amortization of discounts);
(c) the interest portion of any deferred payment obligation;
(d) all commissions, discounts and other fees and charges owed with respect to letters of credit, bankers' acceptances, financing activities or similar activities; and
(e) all accrued interest;
(ii) the interest component of Capital Lease Obligations paid, accrued and/or scheduled to be paid or accrued by such Person and its Restricted Subsidiaries during such period determined on a consolidated basis in accordance with GAAP; and
(iii) all capitalized interest of such Person and its Restricted Subsidiaries for such period;
less interest income of such Person and its Restricted Subsidiaries for such period;provided, however, that Consolidated Interest Expense will exclude (I) the amortization or write-off of debt issuance costs and deferred financing fees, commissions, fees and expenses, (II) any expensing of interim loan commitment and other financing fees and (III) any interest on the Convertible notes to the extent not paid in cash.
168
"Consolidated Net Income" means, with respect to any specified Person for any period, the aggregate of the Net Income of such Person and its Subsidiaries for such period, on a consolidated basis, determined in accordance with GAAP;provided that:
(1) the Net Income (but not loss) of any Person that is not a Restricted Subsidiary or that is accounted for by the equity method of accounting shall be included only to the extent of the amount of dividends or distributions paid in cash to the specified Person or a Restricted Subsidiary thereof;
(2) the Net Income of any Restricted Subsidiary shall be excluded to the extent that the declaration or payment of dividends or similar distributions by that Restricted Subsidiary of that Net Income is not at the date of determination permitted without any prior governmental approval (that has not been obtained) or, directly or indirectly, by operation of the terms of its charter or any agreement, instrument, judgment, decree, order, statute, rule or governmental regulation applicable to that Restricted Subsidiary or its equity holders;
(3) the Net Income of any Person acquired during the specified period for any period prior to the date of such acquisition shall be excluded;
(4) gains or losses on Asset Sales shall be excluded;
(5) the cumulative effect of a change in accounting principles shall be excluded;
(6) non-recurring expenses and charges related to the Transaction shall be excluded in an amount not to exceed $40,000,000; and
(7) notwithstanding clause (1) above, (x) the Net Income (but not loss) of any Unrestricted Subsidiary shall be excluded, whether or not distributed to the specified Person or one of its Subsidiaries and (y) the Net Income (or loss) attributable to any discontinued operations shall be excluded.
"Consolidated Non-cash Charges" means, with respect to any Person for any period, the aggregate depreciation, amortization (including amortization of goodwill, other intangibles, deferred financing fees, debt issuance costs, commissions, fees and expenses) and non-cash charges and non-cash expenses of such Person and its Restricted Subsidiaries, including, without limitation, non-cash charges and non-cash expenses related to stock-based compensation, asset impairments or writedowns, reducing Consolidated Net Income of such Person and its Restricted Subsidiaries for such period, determined on a consolidated basis in accordance with GAAP (excluding any such charges constituting an extraordinary item or loss or any charge which requires an accrual of or a reserve for cash charges for any future period).
"Convertible Notes" means the 2.625% convertible senior subordinated notes due 2026 issued by the Company on September 18, 2006 and governed by the indenture dated as of September 18, 2006 between the Company and The Bank of New York Trust Company, N.A. as trustee.
"Credit Agreement" means collectively, (1) the Company's senior secured term loan credit facility, dated the Issue Date, by and among the Company, the guarantors named therein and Royal Bank of Canada, as administrative agent, and the other agents and lenders named therein, providing for term loan borrowings and (2) the Company's Revolving Credit Agreement, dated May 10, 2010, by and among the Company, the guarantors named therein and PNC Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, and the other agents and lenders named therein, providing for revolving credit borrowings, including, in each of case (1) and (2), all related notes, letters of credit, collateral documents, Guarantees, and any other related agreements and instruments executed and delivered in connection therewith, in each case as further amended, modified, supplemented, restated, refinanced, refunded or replaced in whole or in part from time to time including by or pursuant to any agreement or instrument that extends the maturity of any Debt thereunder, or increases the amount of available
169
borrowings thereunder (provided that such increase in borrowings is permitted under clause (i) or (xiv) of the definition of the term "Permitted Debt"), or adds Subsidiaries of the Company as additional borrowers or guarantors thereunder, in each case with respect to such agreements or any successor or replacement agreements and whether by the same or any other agent, lender, group of lenders, purchasers or debt holders.
"Credit Facilities" means (i) the Credit Agreement, as amended, restated, supplemented, waived, replaced (whether or not upon termination, and whether with the original lenders or otherwise), restructured, repaid, refunded, refinanced or otherwise modified from time to time, including any agreement or indenture extending the maturity thereof, refinancing, replacing or otherwise restructuring all or any portion of the Debt under such agreements or any successor or replacement agreement or agreements or increasing the amount loaned or issued thereunder or altering the maturity thereof, (ii) any Qualified Receivables Transaction and (iii) whether or not the agreements referred to in clauses (i) and (ii) remain outstanding, one or more debt facilities, commercial paper facilities or Debt Issuances with banks, investment banks, insurance companies, mutual funds, other institutional lenders, institutional investors or any of the foregoing providing for revolving credit loans, term loans, notes, bonds, indentures, debentures, receivables financing (including through the sale of receivables to such lenders, other financiers or to special purpose entities formed to borrow from (or sell such receivables to) such lenders or other financiers against such receivables), letters of credit, bankers' acceptances, other borrowings or Debt Issuances, in each case, as amended, restated, modified, renewed, extended, refunded, replaced or refinanced (in each case, without limitation as to amount), in whole or in part, from time to time (including through one or more Debt Issuances) and any agreements and related documents governing Debt or Obligations incurred to refinance amounts then outstanding or permitted to be outstanding, whether or not with the original administrative agent, lenders, investment banks, insurance companies, mutual funds, other institutional lenders, institutional investors or any of the foregoing and whether provided under the original agreement, indenture or other documentation relating thereto.
"Debt" means at any time (without duplication), with respect to any Person, whether recourse is to all or a portion of the assets of such Person, or non-recourse, the following: (i) all indebtedness of such Person for money borrowed or for the deferred purchase price of property, excluding any trade payables or other current liabilities incurred in the normal course of business; (ii) all obligations of such Person evidenced by bonds, debentures, notes, or other similar instruments; (iii) all reimbursement obligations of such Person with respect to letters of credit, bankers' acceptances or similar facilities (excluding obligations in respect of letters of credit or bankers' acceptances issued in respect of trade payables) issued for the account of such Person;provided that such obligations shall not constitute Debt except to the extent drawn and not repaid within five business days; (iv) all indebtedness created or arising under any conditional sale or other title retention agreement with respect to property or assets acquired by such Person; (v) all Capital Lease Obligations of such Person; (vi) the maximum fixed redemption or repurchase price of Redeemable Capital Interests in such Person at the time of determination; (vii) the liquidation amount or liquidation preference of any Preferred Interests issued by a Restricted Subsidiary that is not a Subsidiary Guarantor; (viii) any Swap Contracts and Hedging Obligations of such Person at the time of determination; (ix) Attributable Debt with respect to any Sale and Leaseback Transaction to which such Person is a party; and (x) all obligations of the types referred to in clauses (i) through (ix) of this definition of another Person, the payment of which, in either case, (A) such Person has Guaranteed or (B) is secured by (or the holder of such Debt or the recipient of such dividends or other distributions has an existing right, whether contingent or otherwise, to be secured by) any Lien upon the property or other assets of such Person, even though such Person has not assumed or become liable for the payment of such Debt. For purposes of the foregoing: (a) the maximum fixed repurchase price of any Redeemable Capital Interests that do not have a fixed repurchase price shall be calculated in accordance with the terms of such Redeemable Capital Interests as if such Redeemable Capital Interests were repurchased on any date on which Debt shall be required
170
to be determined pursuant to the Indenture;provided, however, that, if such Redeemable Capital Interests are not then permitted to be repurchased, the repurchase price shall be the book value of such Redeemable Capital Interests; (b) the amount outstanding at any time of any Debt issued with original issue discount is the principal amount of such Debt less the remaining unamortized portion of the original issue discount of such Debt at such time as determined in conformity with GAAP, but such Debt shall be deemed Incurred only as of the date of original issuance thereof; (c) the amount of any Debt described in clause (viii) is the net amount payable (after giving effect to permitted set-off) if such Swap Contracts or Hedging Obligations are terminated at that time due to default of such Person; (d) the amount of any Debt described in clause (x)(A) above shall be the maximum liability under any such Guarantee; (e) the amount of any Debt described in clause (x)(B) above shall be the lesser of (I) the maximum amount of the obligations so secured and (II) the Fair Market Value of such property or other assets; (f) interest, fees, premium, and expenses and additional payments, if any, will not constitute Debt; and (g) to the extent not otherwise included in this definition, the Receivables Transaction Amount outstanding relating to any Qualified Receivables Transaction shall be deemed to constitute Debt and, in any Qualified Receivables Transaction structured as a transfer of accounts receivable and related assets, such Debt shall be deemed to constitute Debt of the originator of such accounts receivable and related assets.
The amount of Debt of any Person at any date shall be the outstanding balance at such date of all unconditional obligations as described above and the maximum liability, only upon the occurrence of the contingency giving rise to the obligations, of any contingent obligations at such date;provided, however, that in the case of Debt sold at a discount, the amount of such Debt at any time will be the accreted value thereof at such time.
"Debt Issuances" means, with respect to the Company or any Subsidiary Guarantor, one or more issuances after the Issue Date of Debt evidenced by notes, debentures, bonds or other similar securities or instruments.
"Default" means any event that is, or after notice or passage of time, or both, would be, an Event of Default.
"Eligible Bank" means a bank or trust company (i) that is organized and existing under the laws of the United States of America or Canada, or any state, territory, province or possession thereof, (ii) that, as of the time of the making or acquisition of an Investment in such bank or trust company, has combined capital and surplus in excess of $500 million and (iii) the senior Debt of which is rated at least "A-2" by Moody's or at least "A" by S&P.
"Eligible Cash Equivalents" means any of the following Investments: (i) securities issued or directly and fully guaranteed or insured by the United States or any agency or instrumentality thereof (provided that the full faith and credit of the United States is pledged in support thereof) maturing not more than one year after the date of acquisition; (ii) time deposits in and certificates of deposit of any Eligible Bank,provided that such Investments have a maturity date not more than two years after date of acquisition and that the Average Life of all such Investments is one year or less from the respective dates of acquisition; (iii) repurchase obligations with a term of not more than 180 days for underlying securities of the types described in clause (i) above entered into with any Eligible Bank; (iv) direct obligations issued by any state of the United States or any political subdivision or public instrumentality thereof,provided that such Investments mature, or are subject to tender at the option of the holder thereof, within 365 days after the date of acquisition and, at the time of acquisition, have a rating of at least A from S&P or A-2 from Moody's (or an equivalent rating by any other nationally recognized rating agency); (v) commercial paper of any Person other than an Affiliate of the Company and other than structured investment vehicles,provided that such Investments have one of the two highest ratings obtainable from either S&P or Moody's and mature within 180 days after the date of acquisition; (vi) overnight and demand deposits in and bankers' acceptances of any Eligible Bank and demand
171
deposits in any bank or trust company to the extent insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation against the Bank Insurance Fund; (vii) money market funds substantially all of the assets of which comprise Investments of the types described in clauses (i) through (vi); and (viii) instruments equivalent to those referred to in clauses (i) through (vi) above or funds equivalent to those referred to in clause (vii) above denominated in Euros or any other foreign currency comparable in credit quality and tender to those referred to in such clauses and customarily used by corporations for cash management purposes in jurisdictions outside the United States to the extent reasonably required in connection with any business conducted by any Restricted Subsidiary organized in such jurisdiction, all as determined in good faith by the Company.
"Exchange Act" means the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
"Existing Receivables Facility" means the receivables purchase agreement dated as of August 7, 2008, as amended from time to time, among Triumph Receivables, LLC, as seller, the Company, as servicer, the various purchaser groups from time to time party thereto, and PNC Bank, National Association as administrator, together with all related notes, letters of credit, collateral documents, Guarantees, and any other related agreements and instruments executed and delivered in connection therewith (including without limitation the purchase and sale agreement dated August 7, 2008, as amended from time to time, among the Company, individually and as servicer, Triumph Receivables, LLC and the other Subsidiaries party thereto), in each case as further amended, modified, supplemented, restated, refinanced, refunded or replaced in whole or in part from time to time including by or pursuant to any agreement or instrument that extends the maturity of any Debt thereunder, or increases the amount of available borrowings thereunder (provided that such increase in borrowings is permitted under clause (i) or (xiv) of the definition of the term "Permitted Debt"), or adds Subsidiaries of the Company as additional sellers, originators, borrowers or guarantors thereunder, in each case with respect to such agreement or any successor or replacement agreement and whether by the same or any other agent, lender, group of lenders, purchasers or debt holders.
"Expiration Date" has the meaning set forth in the definition of "Offer to Purchase."
"Fair Market Value" means, with respect to the consideration received or paid in any transaction or series of transactions, the fair market value thereof as determined in good faith by the Company.
"Financing Transactions" has the meaning given such term in the Offering Memorandum.
"Four Quarter Period" has the meaning set forth in the definition of "Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio."
"GAAP" means generally accepted accounting principles in the United States consistently applied as set forth in (i) the opinions and pronouncements of the Accounting Principles Board of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, (ii) statements and pronouncements of the Financial Accounting Standards Board, and (iii) such other statements by such other entity as may be approved by a significant segment of the accounting profession of the United States, as they are in effect as of the Reference Date.
"GE/Citi Sales Arrangements" means the several receivables sales agreements between certain Subsidiaries of the Company and Citibank, N.A. or General Electric Capital Corporation, dated between June 2004 and December 2006.
"Guarantee" means, as applied to any Debt of another Person, (i) a guarantee (other than by endorsement of negotiable instruments for collection in the normal course of business), direct or indirect, in any manner, of any part or all of such Debt, (ii) any direct or indirect obligation, contingent or otherwise, of a Person guaranteeing or having the effect of guaranteeing the Debt of any other Person in any manner and (iii) an agreement of a Person, direct or indirect, contingent or otherwise, the practical effect of which is to assure in any way the payment (or payment of damages in the event
172
of non-payment) of all or any part of such Debt of another Person (and "Guaranteed" and "Guaranteeing" shall have meanings that correspond to the foregoing).
"Guarantor" means any Person that Guarantees the notes in accordance with the provisions of the Indenture and their respective successors and assigns.
"Hedging Obligations" of any Person means the obligations of such Person pursuant to any interest rate agreement, currency agreement or commodity agreement entered into in the ordinary course of the Company's business.
"Holder" means a Person in whose name a Note is registered in the security register.
"Incur" means, with respect to any Debt or other obligation of any Person, to create, issue, incur (by conversion, exchange or otherwise), assume, Guarantee or otherwise become liable in respect of such Debt or other obligation or the recording, as required pursuant to GAAP or otherwise, of any such Debt or other obligation on the balance sheet of such Person;provided, however, that a change in GAAP or an interpretation thereunder that results in an obligation of such Person that exists at such time becoming Debt shall not be deemed an Incurrence of such Debt. Debt otherwise Incurred by a Person before it becomes a Subsidiary of the Company shall be deemed to be Incurred at the time at which such Person becomes a Subsidiary of the Company. "Incurrence," "Incurred," "Incurrable" and "Incurring" shall have meanings that correspond to the foregoing. A Guarantee by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary of Debt Incurred by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary, as applicable, shall not be a separate Incurrence of Debt. In addition, the following shall not be deemed a separate Incurrence of Debt:
(1) amortization of Debt discount or accretion of principal with respect to a non-interest bearing or other discount security;
(2) the payment of regularly scheduled interest in the form of additional Debt of the same instrument or the payment of regularly scheduled dividends on Capital Interests in the form of additional Capital Interests of the same class and with the same terms;
(3) the obligation to pay a premium in respect of Debt arising in connection with the issuance of a notice of redemption or making of a mandatory offer to purchase such Debt; and
(4) unrealized losses or charges in respect of Hedging Obligations and Swap Contracts, in each case, not entered into for speculative purposes.
"Initial Purchasers" means RBC Capital Markets Corporation and such other initial purchasers party to the purchase agreement entered into in connection with the sale of the notes dated June 8, 2010.
"Investment" by any Person means any direct or indirect loan, advance (or other extension of credit) or capital contribution to (by means of any transfer of cash or other property or assets to another Person or any other payments for property or services for the account or use of another Person) another Person, including, without limitation, the following: (i) the purchase or acquisition of any Capital Interest or other evidence of beneficial ownership in another Person; (ii) the purchase, acquisition or Guarantee of the Debt of another Person; and (iii) the purchase or acquisition of the business or assets of another Person substantially as an entirety but shall exclude: (a) accounts receivable and other extensions of trade credit in accordance with the Company's customary practices; (b) the acquisition of property and assets from suppliers and other vendors in the normal course of business; and (c) prepaid expenses and workers' compensation, utility, lease and similar deposits, in the normal course of business.
"Issue Date" means June 16, 2010, the date of original issuance of the notes.
173
"Leasing Facility" means the master lease agreement dated as of March 18, 2009 by and between Triumph Structures—Los Angeles, Inc., as lessee, and Banc of America Leasing & Capital, LLC, as lessor, together with all related notes, letters of credit, collateral documents, Guarantees, and any other related agreements and instruments executed and delivered in connection therewith, in each case as further amended, modified, supplemented, restated, refinanced, refunded or replaced in whole or in part from time to time including by or pursuant to any agreement or instrument that extends the maturity of any Debt thereunder, or increases the amount of available borrowings thereunder (provided that such increase in borrowings is permitted under clause (i), (x) or (xiv) of the definition of the term "Permitted Debt"), or adds Subsidiaries of the Company as additional borrowers or guarantors thereunder, in each case with respect to such agreement or any successor or replacement agreement and whether by the same or any other agent, lender, group of lenders, purchasers or debt holders.
"Lien" means, with respect to any property or other asset, any mortgage, deed of trust, deed to secure debt, pledge, hypothecation, assignment, deposit arrangement, security interest, lien (statutory or otherwise), charge, easement, encumbrance, preference, priority or other security agreement or preferential arrangement of any kind or nature whatsoever on or with respect to such property or other asset (including, without limitation, any conditional sale or other title retention agreement having substantially the same economic effect as any of the foregoing).
"Moody's" means Moody's Investors Service, Inc. and any successor to its rating agency business.
"Net Cash Proceeds" means, with respect to Asset Sales of any Person, cash and Eligible Cash Equivalents received, net of: (i) all reasonable out-of-pocket costs and expenses of such Person incurred in connection with such a sale, including, without limitation, all legal, accounting, title and recording tax expenses, commissions and other fees and expenses incurred and all federal, state, foreign and local taxes arising in connection with such an Asset Sale that are paid or required to be accrued as a liability under GAAP by such Person; (ii) all payments made by such Person on any Debt that is secured by such properties or other assets in accordance with the terms of any Lien upon or with respect to such properties or other assets or that must, by the terms of such Lien or such Debt or in order to obtain a necessary consent to such transaction or by applicable law, be repaid to any other Person (other than the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary thereof) in connection with such Asset Sale; and (iii) all contractually required distributions and other payments made to minority interest holders in Restricted Subsidiaries of such Person as a result of such transaction;provided, however, that: (a) in the event that any consideration for an Asset Sale (which would otherwise constitute Net Cash Proceeds) is required by (I) contract to be held in escrow pending determination of whether a purchase price adjustment will be made or (II) GAAP to be reserved against other liabilities in connection with such Asset Sale, such consideration (or any portion thereof) shall become Net Cash Proceeds only at such time as it is released to such Person from escrow or otherwise; and (b) any non-cash consideration received in connection with any transaction, which is subsequently converted to cash, shall become Net Cash Proceeds only at such time as it is so converted.
"Non-Recourse Receivable Subsidiary Indebtedness" has the meaning set forth in the definition of "Receivable Subsidiary" and shall, for the avoidance of doubt, include Debt under the Existing Receivables Facility.
"Note Guarantee" means the Guarantee of each Guarantor of the notes.
"Obligations" means, with respect to any Debt, any principal, premium, interest (including any interest accruing subsequent to the filing of a petition in bankruptcy, reorganization or similar proceeding at the rate provided for in the documentation with respect thereto, whether or not such interest is an allowed claim under applicable state, federal or foreign law), penalties, fees, indemnifications, reimbursements (including reimbursement obligations with respect to letters of credit and banker's acceptances), damages and other liabilities, and Guarantees of payment of such principal,
174
interest, penalties, fees, indemnifications, reimbursements, damages and other liabilities, payable under the documentation governing such Debt.
"Offer" has the meaning set forth in the definition of "Offer to Purchase."
"Offer to Purchase" means a written offer (the "Offer") sent by the Company electronically or by first-class mail, postage prepaid, to each Holder at his address appearing in the security register on the date of the Offer, offering to purchase up to the aggregate principal amount of notes set forth in such Offer at the purchase price set forth in such Offer (as determined pursuant to the Indenture). Unless otherwise required by applicable law, the offer shall specify an expiration date (the "Expiration Date") of the Offer to Purchase which shall be, subject to any contrary requirements of applicable law, not less than 30 days or more than 60 days after the date of mailing of such Offer and a settlement date (the "Purchase Date") for purchase of notes within five business days after the Expiration Date. The Company shall notify the Trustee at least 15 days (or such shorter period as is acceptable to the Trustee) prior to the mailing of the Offer of the Company's obligation to make an Offer to Purchase, and the Offer shall be mailed by the Company or, at the Company's request, by the Trustee in the name and at the expense of the Company. The Offer shall contain all instructions and materials necessary to enable such Holders to tender notes pursuant to the Offer to Purchase. The Offer shall also state:
(1) the Section of the Indenture pursuant to which the Offer to Purchase is being made;
(2) the Expiration Date and the Purchase Date;
(3) the aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes offered to be purchased pursuant to the Offer to Purchase (including, if less than 100%, the manner by which such amount has been determined pursuant to Indenture covenants requiring the Offer to Purchase) (the "Purchase Amount");
(4) the purchase price to be paid by the Company for each Note accepted for payment (as specified pursuant to the Indenture) (the "Purchase Price");
(5) that the Holder may tender all or any portion of the notes registered in the name of such Holder and that any portion of a Note tendered must be tendered in a minimum amount of $2,000 principal amount (and integral multiples of $1,000 in excess thereof);
(6) the place or places where notes are to be surrendered for tender pursuant to the Offer to Purchase, if applicable;
(7) that, unless the Company defaults in making such purchase, any Note accepted for purchase pursuant to the Offer to Purchase will cease to accrue interest on and after the Purchase Date, but that any Note not tendered or tendered but not purchased by the Company pursuant to the Offer to Purchase will continue to accrue interest at the same rate;
(8) that, on the Purchase Date, the Purchase Price will become due and payable upon each Note accepted for payment pursuant to the Offer to Purchase;
(9) that each Holder electing to tender a Note pursuant to the Offer to Purchase will be required to surrender such Note or cause such Note to be surrendered at the place or places set forth in the Offer prior to the close of business on the Expiration Date (such Note being, if the Company or the Trustee so requires, duly endorsed by, or accompanied by a written instrument of transfer in form satisfactory to the Company and the Trustee duly executed by, the Holder thereof or his attorney duly authorized in writing);
(10) that Holders will be entitled to withdraw all or any portion of notes tendered if the Company (or its paying agent) receives, not later than the close of business on the Expiration Date, a facsimile transmission or letter setting forth the name of the Holder, the aggregate
175
principal amount of the notes the Holder tendered, the certificate number of the Note the Holder tendered and a statement that such Holder is withdrawing all or a portion of his tender;
(11) that that if less than all of such holder's notes are tendered for purchase, such Holder will be issued new notes, such new notes will be equal in principal amount to the unpurchased portion of the notes surrendered and the unpurchased portion of the Notes must be equal to $2,000 or an integral multiple of $1,000 in excess of $2,000; and
(12) if applicable, that, in the case of any Holder whose note is purchased only in part, the Company shall execute, and the Trustee shall authenticate and deliver to the Holder of such note without service charge, a new note or notes, of any authorized denomination as requested by such Holder, in the aggregate principal amount equal to and in exchange for the unpurchased portion of the aggregate principal amount of the notes so tendered.
"Offering Memorandum" means the offering memorandum dated June 8, 2010 relating to the offer and sale of the notes.
"Officer's Certificate" means a certificate signed by the principal executive officer, the principal financial officer or the principal accounting officer of the Company or such Guarantor, as applicable.
"Performance Guaranty" means the performance guaranty dated as of August 7, 2008, as amended from time to time, by the Company, as performance guarantor, in favor of PNC Bank, National Association for the benefit of the various purchaser groups pursuant to the Existing Receivables Facility.
"Permitted Business" means any business similar in nature to any business conducted by the Company and the Restricted Subsidiaries on the Issue Date and any business reasonably ancillary, incidental, complementary or related to, or a reasonable extension, development or expansion of, the business conducted by the Company and the Restricted Subsidiaries on the Issue Date, in each case, as determined in good faith by the Company.
"Permitted Debt" means:
(i) Debt Incurred pursuant to any Credit Facilities in an aggregate principal amount at any one time outstanding not to exceed $1,175.0 million minus any amount used to permanently repay such Obligations (or permanently reduce commitments with respect thereto),provided that such repayment is made pursuant to the "Limitation on Asset Sales" covenant;
(ii) Debt under the notes and contribution, indemnification and reimbursement obligations owed by the Company or any Guarantor to any of the other of them in respect of amounts paid or payable on such Notes;
(iii) Guarantees of the notes;
(iv) Debt of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary outstanding on the Issue Date (other than Debt described in clauses (i), (ii) or (iii) above), including without limitation Debt under the Leasing Facility, the Company's 8% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2017, the Convertible Notes and the Performance Guaranty under the Existing Receivables Facility;
(v) intercompany Debt between the Company and a Restricted Subsidiary or between Restricted Subsidiaries,provided that if for any reason such Debt ceases to be held by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary, as applicable, such Debt shall cease to be Permitted Debt under this clause (v) and shall be deemed Incurred as Debt of the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary, as applicable, for purposes of the Indenture;
(vi) Guarantees Incurred by the Company of Debt of a Restricted Subsidiary otherwise permitted to be incurred under the Indenture;provided that such Guarantees are subordinated to
176
the notes to the same extent as the Debt being Guaranteed if such Debt is a Subordinated Obligation;
(vii) Guarantees by any Restricted Subsidiary of Debt of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary, including Guarantees by any Restricted Subsidiary of Debt under the Credit Facilities otherwise permitted to be incurred under the Indenture;provided that such Guarantees are subordinated to the notes to the same extent as the Debt being Guaranteed if such Debt is a Subordinated Obligation;
(viii) Debt incurred in respect of workers' compensation claims and self-insurance obligations, and, for the avoidance of doubt, indemnity, bid, performance, warranty, release, appeal, surety and similar bonds, letters of credit for operating purposes and completion Guarantees provided or incurred (including Guarantees thereof) by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary in the ordinary course of business;
(ix) Debt under Swap Contracts and Hedging Obligations, in each case, not entered into for speculative purposes;
(x) Debt of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary pursuant to Capital Lease Obligations and Purchase Money Debt,provided that the aggregate principal amount of such Debt outstanding at any time may not exceed $100.0 million in the aggregate;
(xi) Debt arising from agreements of the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary providing for indemnification, contribution, earnout, adjustment of purchase price or similar obligations, in each case, incurred or assumed in connection with the acquisition or disposition of any business, assets or Capital Interests of a Restricted Subsidiary otherwise permitted under the Indenture;
(xii) the issuance by any of the Company's Restricted Subsidiaries to the Company or to any of its Restricted Subsidiaries of shares of Preferred Interests;provided, however, that:
(a) any subsequent issuance or transfer of Capital Interests that results in any such Preferred Interests being held by a Person other than the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary; and
(b) any sale or other transfer of any such Preferred Interests to a Person that is not either the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary;
shall be deemed, in each case, to constitute an issuance of such Preferred Interests by such Restricted Subsidiary that was not permitted by this clause (xiii);
(xiii) Debt arising from the honoring by a bank or other financial institution of a check, draft or similar instrument drawn against insufficient funds in the ordinary course of business;provided, however, that such Debt is extinguished within five business days of Incurrence;
(xiv) Debt of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary not otherwise permitted pursuant to this definition, in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $25.0 million at any time outstanding;
(xv) promissory notes, other than those issued to evidence Debt otherwise permitted hereunder, in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $6.0 million;
(xvi) Debt arising under the GE/Citi Sales Arrangements;
(xvii) Purchase Money Notes Incurred by any Receivable Subsidiary that is a Restricted Subsidiary in a Qualified Receivables Transaction and Non-Recourse Receivable Subsidiary Indebtedness;
177
(xviii) Refinancing Debt in respect of Debt Incurred pursuant to the first paragraph of "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" covenant or pursuant to clauses (ii), (iii) or (iv) above
(xviii) Debt which (A) is contemplated by clause (x)(B) of the definition of "Debt" and (B) could be secured with a Lien pursuant to clause (17) of the definition of "Permitted Liens"; and
(xix) Standard Securitization Undertakings.
"Permitted Investments" means:
(a) Investments in existence on the Issue Date;
(b) Investments required pursuant to any agreement or obligation of the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary, in effect on the Issue Date, to make such Investments;
(c) Investments in cash and Eligible Cash Equivalents;
(d) Investments in property and other assets, owned or used by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary in the normal course of business;
(e) Investments by the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries in the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary;
(f) Investments by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary in a Person, if as a result of such Investment (A) such Person becomes a Restricted Subsidiary or (B) such Person is merged, consolidated or amalgamated with or into, or transfers or conveys substantially all of its assets to, or is liquidated or wound up into, the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary;
(g) Swap Contracts and Hedging Obligations, in each case, not entered into for speculative purposes;
(h) receivables owing to the Company or any of its subsidiaries and advances to suppliers, in each case if created, acquired or made in the ordinary course of business and payable or dischargeable in accordance with customary trade terms;
(i) Investments received in settlement of obligations owed to the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary and as a result of bankruptcy or insolvency proceedings or upon the foreclosure or enforcement of any Lien in favor of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary;
(j) Investments in joint ventures not in excess of $20.0 million in the aggregate at any one time outstanding;
(k) Investments by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary not otherwise permitted under this definition, in an aggregate amount not to exceed $50.0 million at any one time outstanding;
(l) loans and advances (including for travel and relocation) to employees in an amount not to exceed $2.5 million in the aggregate at any one time outstanding;
(m) Investments the payment for which consists solely of Capital Interests (excluding Redeemable Capital Interests) of the Company;
(n) any Investment in any Person to the extent such Investment represents the non-cash portion of the consideration received in connection with an Asset Sale consummated in compliance with the covenant described under "—Certain Covenants—Limitation on Asset Sales" or any other disposition of Property not constituting an Asset Sale;
(o) payroll, travel and similar advances to cover matters that are expected at the time of such advances ultimately to be treated as expenses for accounting purposes and that are made in the ordinary course of business and consistent with past practice;
178
(p) Guarantees by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary of Debt of the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary (other than a Receivable Subsidiary) otherwise permitted by the covenant described hereunder "—Certain Covenants—Limitation on Incurrence of Debt"; and
(q) any Investment by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary in a Receivable Subsidiary or any Investment by a Receivable Subsidiary in any other Person in connection with a Qualified Receivables Transaction, so long as any Investment in a Receivable Subsidiary is in consideration of a Purchase Money Note or an Investment in Capital Interests.
"Permitted Liens" means:
(1) Liens on the assets of the Company, any Guarantor or any Receivables Subsidiary which secure Obligations incurred under Credit Facilities in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed the greater of (i) $1,175.0 million and (ii) the Secured Debt Cap;
(2) Liens in favor of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary;
(3) Liens on property of a Person existing at the time such Person is merged with or into or consolidated with the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary of the Company,provided that such Liens were not incurred in contemplation of or in connection with such merger or consolidation and do not extend to any assets other than those of the Person merged into or consolidated with the Company or the Restricted Subsidiary;
(4) Liens on property existing at the time of acquisition thereof by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary of the Company,provided that such Liens were not incurred in contemplation of or in connection with such acquisition and do not extend to any property other than the property so acquired by the Company or the Restricted Subsidiary;
(5) Liens existing on the Issue Date;
(6) pledges or deposits by such Person under workmen's compensation laws, unemployment insurance laws or similar legislation, or good faith deposits in connection with bids, tenders, contracts (other than for the payment of Debt) or leases to which such Person is a party, or deposits to secure public or statutory obligations of such Person or deposits of cash or United States government bonds to secure surety or appeal bonds to which such Person is a party, or deposits as security for contested taxes or import or customs duties or for the payment of rent, in each case Incurred in the ordinary course of business;
(7) Liens imposed by law, including carriers', warehousemen's and mechanics' materialmen's and repairmen's Liens, in each case for sums not yet due or being contested in good faith by appropriate proceedings if a reserve or other appropriate provisions, if any, as shall be required by GAAP shall have been made in respect thereof;
(8) Liens for taxes, assessments or other governmental charges not yet subject to penalties for non-payment or which are being contested in good faith by appropriate proceedings provided that appropriate reserves required pursuant to GAAP have been made in respect thereof;
(9) Liens in favor of issuers of surety or performance bonds or letters of credit or bankers' acceptances issued pursuant to the request of and for the account of such Person in the ordinary course of its business; provided, however, that such letters of credit do not secure Debt;
(10) Liens securing Swap Contracts and Hedging Obligations, in each case, not entered into for speculative purposes;
179
(11) Liens relating to banker's liens, rights of set-off or similar rights and remedies as to deposit accounts or other funds maintained with a depositary institution; provided that:
(a) such deposit account is not a dedicated cash collateral account and is not subject to restrictions against access by the Company in excess of those set forth by regulations promulgated by the Federal Reserve Board; and
(b) such deposit account is not established by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary for the purpose of providing collateral to the depository institution;
(12) any Lien resulting from the deposit of money or other cash equivalents or other evidence of indebtedness in trust for the purpose of defeasing Debt of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary;provided that the incurrence of Debt and such defeasance or satisfaction and discharge are not prohibited by the Indenture;
(13) Liens securing Obligations in respect of Debt (including Capital Lease Obligations and Purchase Money Debt) permitted by clause (x) of the definition of "Permitted Debt" covering only the assets acquired, constructed, improved or developed with, or secured by, such Debt;
(14) Liens incurred in the ordinary course of business of the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary of the Company with respect to obligations that do not exceed $10.0 million at any one time outstanding;
(15) Liens securing Obligations in respect of (a) Debt permitted by clause (xiv) of the definition of "Permitted Debt" (and any Guarantee thereof) and (b) Debt of Subsidiaries other than Subsidiary Guarantors; provided, in the case of clause (b), that such Liens attach only to assets of Restricted Subsidiaries other than Subsidiary Guarantors;
(16) Liens securing Debt permitted by clause (xv) of the definition of "Permitted Debt";
(17) Liens on Capital Interests of an Unrestricted Subsidiary that secure Debt or other obligations of such Unrestricted Subsidiary;
(18) Liens securing Obligations in respect of Refinancing Debt;provided that any such Lien covers only the assets that secure the Debt being refinanced;
(19) leases, subleases, survey exceptions, encumbrances, easements or reservations of, or rights of others for, licenses, rights-of-way, sewers, electric lines, telegraph and telephone lines and other similar purposes, or zoning or other restrictions as to the use of real properties or Liens incidental to the conduct of the business of such Person or to the ownership of its properties which were not Incurred in connection with Indebtedness and which do not in the aggregate materially impair the use of such properties in the operation of the business of the Company and its Subsidiaries;
(20) Liens on assets transferred to a Receivable Subsidiary or on assets of a Receivable Subsidiary, in either case incurred in connection with a Qualified Receivables Transaction;
(21) Liens arising under the GE/Citi Sales Arrangements;
(22) Liens arising from Uniform Commercial Code financing statement filings regarding operating leases entered into by the Company and the Restricted Subsidiaries in the ordinary course of business; and
(23) judgment and attachment Liens not giving rise to an Event of Default and notices of lis pendens and associated rights related to litigation being contested in good faith by appropriate proceedings and for which adequate reserves have been made.
"Person" means any individual, corporation, limited liability company, partnership, joint venture, trust, unincorporated organization or government or any agency or political subdivision thereof.
180
"Preferred Interests," as applied to the Capital Interests in any Person, means Capital Interests in such Person of any class or classes (however designated) that rank prior, as to the payment of dividends or as to the distribution of assets upon any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of such Person, to shares of Common Interests in such Person.
"Purchase Amount" has the meaning set forth in the definition of "Offer to Purchase."
"Purchase Date" has the meaning set forth in the definition of "Offer to Purchase."
"Purchase Money Debt" means Debt
(i) Incurred to finance the purchase or construction (including additions and improvements thereto) of any assets (other than Capital Interests) of such Person or any Restricted Subsidiary; and
(ii) that is secured by a Lien on such assets where the lender's sole security is to the assets so purchased or constructed; and in either case that does not exceed 100% of the cost and to the extent the purchase or construction prices for such assets are or should be included in "addition to property, plant or equipment" in accordance with GAAP.
"Purchase Money Note" means a promissory note of a Receivable Subsidiary to the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary, which note must be repaid from cash available to the Receivable Subsidiary, other than amounts required to be established as reserves pursuant to agreements, amounts paid to investors in respect of interest, principal and other amounts owing to such investors and amounts paid in connection with the purchase of newly generated receivables. The repayment of a Purchase Money Note may be subordinated to the repayment of other liabilities of the Receivable Subsidiary on terms determined in good faith by the Company to be substantially consistent with market practice in connection with Qualified Receivables Transactions.
"Purchase Price" has the meaning set forth in the definition of "Offer to Purchase."
"Qualified Capital Interests" in any Person means a class of Capital Interests other than Redeemable Capital Interests.
"Qualified Equity Offering" means (i) an underwritten public equity offering of Qualified Capital Interests pursuant to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act yielding gross proceeds to either of the Company, or any direct or indirect parent company of the Company, of at least $50.0 million or (ii) a private equity offering of Qualified Capital Interests of the Company, or any direct or indirect parent company of the Company, other than (x) any such public or private sale to an entity that is an Affiliate of the Company and (y) any public offerings registered on Form S-8;provided that, in the case of an offering or sale by a direct or indirect parent company of the Company, such parent company contributes to the capital of the Company the portion of the Net Cash Proceeds of such offering or sale necessary to pay the aggregate Redemption Price (plus accrued interest to the redemption date) of the notes to be redeemed pursuant to the provisions described under the third paragraph of "—Optional Redemption."
"Qualified Receivables Transaction" means any transaction or series of transactions entered into by the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries pursuant to which the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary transfers to (a) a Receivable Subsidiary (in the case of a transfer by the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries) or (b) any other Person (in the case of a transfer by a Receivable Subsidiary), or grants a security interest in, any accounts receivable (whether now existing or arising in the future) of the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries, and any assets related thereto, including, without limitation, all collateral securing such accounts receivable, all contracts and all Guarantees or other obligations in respect of such accounts receivable, proceeds of such accounts receivable and other assets which are customarily transferred or in respect of which security interests are customarily granted in connection with an accounts receivable financing transaction;provided such
181
transaction is on market terms as determined in good faith by the Company at the time the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary enters into such transaction. For the avoidance of doubt, on the Issue Date, the Existing Receivables Facility shall qualify as a Qualified Receivables Transaction.
"Receivable Subsidiary" means a Subsidiary of the Company:
(1) that is formed solely for the purpose of, and that engages in no activities other than activities in connection with, financing accounts receivable of the Company and/or its Restricted Subsidiaries;
(2) that is designated by the Board of Directors as a Receivable Subsidiary pursuant to an Officer's Certificate that is delivered to the Trustee;
(3) that is either (a) a Restricted Subsidiary or (b) an Unrestricted Subsidiary designated in accordance with the covenant described under "—Certain Covenants—Limitation on Creation of Unrestricted Subsidiaries";
(4) no portion of the Debt or any other obligation (contingent or otherwise) of which (a) is at any time Guaranteed by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary (excluding Guarantees of obligations (other than any Guarantee of Debt) pursuant to Standard Securitization Undertakings), (b) is at any time recourse to or obligates the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary in any way, other than pursuant to Standard Securitization Undertakings or (c) subjects any asset of the Company or any other Restricted Subsidiary of the Company, directly or indirectly, contingently or otherwise, to the satisfaction thereof, other than pursuant to Standard Securitization Undertakings (such Debt, "Non-Recourse Receivable Subsidiary Indebtedness");
(5) with which neither the Company nor any Restricted Subsidiary has any material contract, agreement, arrangement or understanding other than (a) contracts, agreements, arrangements and understandings entered into in the ordinary course of business on terms no less favorable to the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary than those that might be obtained at the time from Persons that are not Affiliates of the Company in connection with a Qualified Receivables Transaction as determined in good faith by the Board of Directors of the Company, (b) fees payable in the ordinary course of business in connection with servicing accounts receivable in connection with such a Qualified Receivables Transaction as determined in good faith by the Board of Directors of the Company and (c) any Purchase Money Note issued by such Receivable Subsidiary to the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary; and
(6) with respect to which neither the Company nor any other Restricted Subsidiary has any obligation (a) to subscribe for additional shares of Capital Interests therein or make any additional capital contribution or similar payment or transfer thereto except in connection with a Qualified Receivables Transaction or (b) to maintain or preserve the solvency or any balance sheet term, financial condition, level of income or results of operations thereof.
For the avoidance of doubt, on the Issue Date, Triumph Receivables, LLC shall qualify as a Receivable Subsidiary.
"Receivables Transaction Amount" means, (a) with respect to any Qualified Receivables Transaction entered into by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary and structured as a sale of receivables and related assets by the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary rather than a secured loan to the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary, the amount of obligations outstanding under the legal documents entered into as part of such Qualified Receivables Transaction on any date of determination that would be characterized as principal if such Qualified Receivables Transaction were structured as a secured lending transaction rather than as a sale and (b) with respect to any Qualified Receivables Transaction entered into by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary and structured as a secured loan to the Company or such Restricted Subsidiary, the principal amount of such loan.
182
"Redeemable Capital Interests" in any Person means any equity security of such Person that by its terms (or by terms of any security into which it is convertible or for which it is exchangeable), or otherwise (including the passage of time or the happening of an event), is required to be redeemed (other than in exchange for Qualified Capital Interests), is redeemable (other than in exchange for Qualified Capital Interests) at the option of the holder thereof in whole or in part (including by operation of a sinking fund), or is convertible or exchangeable for Debt of such Person at the option of the holder thereof, in whole or in part, at any time prior to the Stated Maturity of the notes;provided that only the portion of such equity security which is required to be redeemed, is so convertible or exchangeable or is so redeemable at the option of the holder thereof before such date will be deemed to be Redeemable Capital Interests. Notwithstanding the preceding sentence, any equity security that would constitute Redeemable Capital Interests solely because the holders of the equity security have the right to require the Company to repurchase such equity security upon the occurrence of a change of control or an asset sale will not constitute Redeemable Capital Interests if the terms of such equity security provide that the Company may not repurchase or redeem any such equity security pursuant to such provisions unless such repurchase or redemption complies with the covenant described above under the caption "—Certain Covenants—Limitation on Restricted Payments." The amount of Redeemable Capital Interests deemed to be outstanding at any time for purposes of the Indenture will be the maximum amount that the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries may become obligated to pay upon the maturity of, or pursuant to any mandatory redemption provisions of, such Redeemable Capital Interests or portion thereof, exclusive of accrued dividends.
"Redemption Price," when used with respect to any Note to be redeemed, means the price at which it is to be redeemed pursuant to the Indenture.
"Reference Date" means October 1, 2009.
"Refinancing Debt" means Debt that refunds, refinances, renews, replaces or extends any Debt permitted to be Incurred by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary pursuant to the terms of the Indenture, whether involving the same or any other lender or creditor or group of lenders or creditors, but only to the extent that
(i) the Refinancing Debt is subordinated to the notes or the Note Guarantees, as applicable, to at least the same extent as the Debt being refunded, refinanced or extended, if such Debt was subordinated to the notes,
(ii) the Refinancing Debt is scheduled to mature either (a) no earlier than the Debt being refunded, refinanced or extended or (b) at least 91 days after the maturity date of the notes,
(iii) the Refinancing Debt has an Average Life at the time such Refinancing Debt is Incurred that is equal to or greater than the Average Life of the Debt being refunded, refinanced, renewed, replaced or extended,
(iv) such Refinancing Debt is in an aggregate principal amount that is less than or equal to the sum of (a) the aggregate principal or accreted amount (in the case of any Debt issued with original issue discount, as such) then outstanding under the Debt being refunded, refinanced, renewed, replaced or extended, (b) the amount of accrued and unpaid interest, if any, on such Debt being refinanced and any reasonably determined premium necessary to accomplish any such refinancing and (c) the amount of reasonable and customary fees, expenses and costs related to the Incurrence of such Refinancing Debt, and
(v) such Refinancing Debt is Incurred by the same Person (or its successor) that initially Incurred the Debt being refunded, refinanced, renewed, replaced or extended, except that the Company may Incur Refinancing Debt to refund, refinance, renew, replace or extend Debt of any Restricted Subsidiary of the Company.
183
"Registration Rights Agreement" means the Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of the Issue Date, among the Company, the Guarantors and the Initial Purchasers.
"Related Business Assets" means assets (other than cash or Eligible Cash Equivalents) used or useful in a Permitted Business,provided that any assets received by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary in exchange for assets transferred by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary shall not be deemed to be Related Business Assets if they consist of securities of a Person, unless upon receipt of the securities of such Person, such Person would become a Restricted Subsidiary.
"Restricted Payment" is defined to mean any of the following:
(a) any dividend or other distribution declared and paid on the Capital Interests in the Company or on the Capital Interests in any Restricted Subsidiary of the Company that are held by, or declared and paid to, any Person other than the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary of the Company, other than:
(i) dividends, distributions or payments made solely in Qualified Capital Interests in the Company and
(ii) dividends or distributions payable to the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary of the Company or to other holders of Capital Interests of a Restricted Subsidiary on a pro rata basis;
(b) any payment made by the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries to purchase, redeem, acquire or retire any Capital Interests in the Company (including the conversion into, or exchange for, Debt, of any Capital Interests) other than any such Capital Interests owned by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary (other than a payment made solely in Qualified Capital Interests in the Company);
(c) any payment made by the Company or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries (other than a payment made solely in Qualified Capital Interests in the Company) to redeem, repurchase, defease (including an in substance or legal defeasance) or otherwise acquire or retire for value (including pursuant to mandatory repurchase covenants), prior to any scheduled maturity, scheduled sinking fund or mandatory redemption payment, Debt of the Company or any Guarantor that is subordinated in right of payment to the notes or Note Guarantees (excluding any Debt owed to the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary), except payments of principal and interest in anticipation of satisfying a sinking fund obligation, principal installment or final maturity, in each case, within one year of the due date thereof;
(d) any Investment by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary in any Person, other than a Permitted Investment; and
(e) any designation of a Restricted Subsidiary as an Unrestricted Subsidiary.
"Restricted Subsidiary" means any Subsidiary that has not been designated as an "Unrestricted Subsidiary" in accordance with the Indenture. For the avoidance of doubt, Triumph Receivables, LLC, Triumph Group Charitable Foundation, Triumph Interiors, Ltd, Saygrove Actuation & Motion Control Limited and Airframe Spares & Logistics GmbH will be Unrestricted Subsidiaries on the Issue Date.
"S&P" means Standard & Poor's, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., and any successor to its rating agency business.
"Sale and Leaseback Transaction" means any direct or indirect arrangement pursuant to which property is sold or transferred by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary and is thereafter leased back as a capital lease by the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary.
184
"Secured Debt" means, without duplication, (i) any Debt secured by a Lien and (ii) any Debt of a Restricted Subsidiary that is not a Guarantor Incurred pursuant to the first paragraph of the "Limitation on Incurrence of Debt" covenant.
"Secured Debt Cap" means, as of any date of determination, an amount of Secured Debt (including the outstanding Receivables Transaction Amount relating to Qualified Receivables Transactions) equal to the greatest principal amount of Secured Debt that could have been Incurred on such date so long as the Company's Secured Leverage Ratio for its most recently ended Four Quarter Period would not have been in excess of 3.0 to 1.0.
"Secured Leverage Ratio" means, as of any date of determination (the "Determination Date"), the ratio of (a) the aggregate principal amount of Secured Debt of the Company and its Restricted Subsidiaries on the Determination Date (excluding any Hedging Obligations or Swap Contracts, in each case, not entered into for speculative purposes but including the outstanding Receivables Transaction Amount relating to Qualified Receivables Transactions) to (b) Consolidated Cash Flow Available for Fixed Charges for the most recently ended Four Quarter Period for which internal financial statements are available prior to the Determination Date (the "Reference Period"). For purposes of making the computation referred to above, the Secured Leverage Ratio shall be calculated, if applicable, on a pro forma basis in respect of clauses (a) and (b) thereof as are appropriate and consistent with the pro forma adjustments set forth in the definition of Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio.
"Significant Subsidiary" has the meaning set forth in Rule 1-02 of Regulation S-X under the Securities Act and Exchange Act, but shall not include any Unrestricted Subsidiary.
"Standard Securitization Undertakings" means representations, warranties, covenants and indemnities entered into by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary which are reasonably customary in an accounts receivable securitization transaction as determined in good faith by the Company, including Guarantees by the Company or any Restricted Subsidiary of any of the foregoing obligations of the Company or a Restricted Subsidiary.
"Stated Maturity," when used with respect to (i) any Note or any installment of interest thereon, means the date specified in such Note as the fixed date on which the principal amount of such Note or such installment of interest is due and payable and (ii) any other Debt or any installment of interest thereon, means the date specified in the instrument governing such Debt as the fixed date on which the principal of such Debt or such installment of interest is due and payable.
"Subordinated Obligations" means any Debt of the Company or any Guarantor that is subordinate or junior in right of payment to the notes or the Note Guarantees pursuant to a written agreement to that effect.
"Subsidiary" means, with respect to any Person, any corporation, limited or general partnership, trust, association or other business entity of which more than 50% of the total voting power of shares of the Voting Interests is at the time owned, directly or indirectly, by:
(1) such Person;
(2) such Person and one or more Subsidiaries of such Person; or
(3) one or more Subsidiaries of such Person.
"Subsidiary Guarantor" means each Subsidiary of the Company that is a Guarantor.
"Successor Entity" means a corporation or other entity that succeeds to and continues the business of Triumph Group, Inc.
"Swap Contract" means (a) any and all rate swap transactions, basis swaps, credit derivative transactions, forward rate transactions, commodity swaps, commodity options, forward commodity
185
contracts, equity or equity index swaps or options, bond or bond price or bond index swaps or options or forward bond or forward bond price or forward bond index transactions, interest rate options, forward foreign exchange transactions, cap transactions, floor transactions, collar transactions, currency swap transactions, cross- currency rate swap transactions, currency options, spot contracts, or any other similar transactions or any combination of any of the foregoing (including, without limitation, any fuel price caps and fuel price collar or floor agreements and similar agreements or arrangements designed to protect against or manage fluctuations in fuel prices and any options to enter into any of the foregoing), whether or not any such transaction is governed by or subject to any master agreement, and (b) any and all transactions of any kind, and the related confirmations, which are subject to the terms and conditions of, or governed by, any form of master agreement published by the International Swaps and Derivatives Association, Inc., any International Foreign Exchange Master Agreement, or any other master agreement (any such master agreement, together with any related schedules, a "Master Agreement"), including any such obligations or liabilities under any Master Agreement.
"Transactions" has the meaning given such term in the Offering Memorandum.
"Treasury Rate" means the yield to maturity at the time of computation of United States Treasury securities with a constant maturity (as compiled and published in the most recent Federal Reserve Statistical Release H.15 (519) which has become publicly available at least two Business Days prior to the date fixed for prepayment (or, if such Statistical Release is no longer published, any publicly available source for similar market data)) most nearly equal to the then remaining term of the notes to July 15, 2014;provided, however, that if the then remaining term of the notes to July 15, 2014 is not equal to the constant maturity of a United States Treasury security for which a weekly average yield is given, the Treasury Rate shall be obtained by linear interpolation (calculated to the nearest one-twelfth of a year) from the weekly average yields of United States Treasury securities for which such yields are given, except that, if the then remaining term of the notes to July 15, 2014 is less than one year, the weekly average yield on actually traded United States Treasury securities adjusted to a constant maturity of one year shall be used.
"U.S. Government Obligations" means securities that are (a) direct obligations of the United States of America for the timely payment of which its full faith and credit is pledged or (b) obligations of a Person controlled or supervised by and acting as an agency or instrumentality of the United States of America the timely payment of which is unconditionally guaranteed as a full faith and credit obligation of the United States of America, which, in either case, are not callable or redeemable at the option of the issuer thereof, and shall also include a depositary receipt issued by a bank (as defined in Section 3(a)(2) of the Securities Act), as custodian with respect to any such U.S. Government Obligations or a specific payment of principal of or interest on any such U.S. Government Obligations held by such custodian for the account of the holder of such depositary receipt; provided that (except as required by law) such custodian is not authorized to make any deduction from the amount payable to the holder of such depositary receipt from any amount received by the custodian in respect of the U.S. Government Obligations or the specific payment of principal of or interest on the U.S. Government Obligations evidenced by such depositary receipt.
"Voting Interests" means, with respect to any Person, securities of any class or classes of Capital Interests in such Person entitling the holders thereof generally to vote on the election of members of the Board of Directors or comparable body of such Person.
186
Each broker-dealer that receives new notes for its own account pursuant to this exchange offer must acknowledge that it will deliver a prospectus meeting the requirements of the Securities Act in connection with any resale of such new notes. This prospectus, as it may be amended or supplemented from time to time, may be used by a broker-dealer in connection with resales of new notes received in exchange for old notes where such old notes were acquired as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities. We have agreed that we will make this prospectus, as amended or supplemented, available to any broker-dealer for use in connection with any such resale until the earlier of 180 days after the date the exchange offer registration statement becomes effective and the date on which a broker-dealer is no longer required to deliver a prospectus in connection with market-making or other trading activities.
We will not receive any proceeds from any sale of new notes by broker-dealers. New notes received by broker-dealers for their own account pursuant to the exchange offer may be sold from time to time in one or more transactions in the over-the-counter market, in negotiated transactions, through the writing of options on the new notes or a combination of such methods of resale, at market prices prevailing at the time of resale, at prices related to such prevailing market prices or negotiated prices. Any such resale may be made directly to purchasers or to or through brokers or dealers who may receive compensation in the form of commissions or concessions from any such broker-dealer and/or the purchasers of any new notes. Any broker-dealer that resells new notes that were received by it for its own account pursuant to this exchange offer and any broker or dealer that participates in a distribution of such new notes may be deemed to be an "underwriter" within the meaning of the Securities Act and any profit on any such resale of new notes and any commission or concessions received by any such persons may be deemed to be underwriting compensation under the Securities Act. The letter of transmittal states that, by acknowledging that it will deliver and by delivering a prospectus, a broker-dealer will not be deemed to admit that it is an "underwriter" within the meaning of the Securities Act.
Until the earlier of 180 days after the date the exchange offer registration statement becomes effective and the date on which a broker-dealer is no longer required to deliver a prospectus in connection with market-making or other trading activities, we will promptly send additional copies of this prospectus and any amendment or supplement to this prospectus to any broker-dealer that requests such documents in the letter of transmittal. Pursuant to the registration rights agreement, we have agreed to pay all expenses incident to this exchange offer (including the expenses of one counsel for the holders of the notes) and will indemnify the holders of the notes (including any broker-dealers) against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act.
187
CERTAIN U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS
The following is a summary of certain material U.S. federal income tax consequences relating to the exchange of the old notes for new notes in the exchange offer by U.S. Holders (defined below), but does not purport to be a complete analysis of all the potential tax considerations to holders of old notes or new notes. This summary is based upon the Code, Treasury Regulations, Internal Revenue Service, which we refer to as the IRS, rulings and pronouncements, and judicial decisions now in effect, all of which are subject to change at any time by legislative, administrative, or judicial action, possibly with retroactive effect. We have not sought and will not seek any rulings from the IRS with respect to the statements made and the conclusions reached in the following summary, and accordingly, there can be no assurance that the IRS will not successfully challenge the tax consequences described below.
This summary only applies to U.S. Holders that exchange old notes for new notes in the exchange offer. This summary is limited to tax consequences to U.S. Holders that are original beneficial owners of the old notes, that purchased old notes at their original issue price for cash and that hold such old notes as capital assets within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code. This summary does not address the tax consequences to subsequent purchasers of the old notes or the new notes. This summary also does not discuss the effect of any state, local, foreign or other tax laws or any U.S. federal estate, gift or alternative minimum tax considerations. In addition, this summary does not describe every aspect of U.S. federal income taxation that may be relevant to holders. It does not discuss tax rules that may apply in light of a holder's particular circumstances and it does not discuss special tax rules that may apply, including, without limitation, rules that may apply if a holder is:
- •
- a bank;
- •
- a financial institution;
- •
- a broker or dealer in securities or currencies;
- •
- a trader in securities that elects to use a mark-to-market method of accounting for securities holdings;
- •
- an insurance company;
- •
- a person whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar;
- •
- a tax-exempt organization;
- •
- an investor in a pass-through entity holding the notes;
- •
- an S-corporation, a partnership or other entity treated as a partnership for tax purposes;
- •
- a U.S. expatriate;
- •
- a person holding notes as a part of a hedging, conversion or other risk-reduction transaction or a straddle for tax purposes; or
- •
- a foreign person or entity.
YOU ARE ADVISED TO CONSULT YOUR TAX ADVISOR WITH RESPECT TO THE APPLICATION OF THE U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX LAWS TO YOUR PARTICULAR SITUATION AS WELL AS ANY TAX CONSEQUENCES ARISING UNDER THE U.S. FEDERAL ESTATE, GIFT OR ALTERNATIVE MINIMUM TAX RULES OR UNDER THE LAWS OF ANY STATE, LOCAL, FOREIGN OR OTHER TAXING JURISDICTION OR UNDER ANY APPLICABLE TAX TREATY.
For purposes of the following summary, a "U.S. Holder" is a beneficial owner of notes that is, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, (i) a citizen or individual resident of the United States; (ii) a corporation or other entity taxable as a corporation created or organized under the laws of the
188
United States, any state thereof, or the District of Columbia; (iii) an estate, the income of which is includible in income for U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source; or (iv) a trust, if a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over the trust's administration and one or more U.S. persons have the authority to control all its substantial decisions or if a valid election to be treated as a U.S. person is in effect with respect to such trust.
Exchange Offer
The exchange of the old notes for the new notes in the exchange offer should not constitute a taxable exchange for U.S. Holders, because the new notes should not be considered to differ materially in kind or extent from the old notes. As a result, for U.S. federal income tax purposes (i) a U.S. Holder should not recognize any income, gain or loss as a result of exchanging the old notes for the new notes; (ii) the holding period of the new notes should include the holding period of the old notes exchanged therefor; and (iii) the aggregate adjusted tax basis of the new notes should be equal to the aggregate adjusted tax basis of the old notes exchanged therefor immediately before such exchange.
Certain legal matters in connection with this offering will be passed upon for us by Ballard Spahr LLP.
The consolidated financial statements and schedule of Triumph Group, Inc. as of March 31, 2010 and 2009, and for each of the three years in the period ended March 31, 2010, appearing in Triumph Group, Inc.'s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2010, and the effectiveness of Triumph Group, Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2010, included therein, have been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their reports thereon, included therein, and incorporated herein by reference. Such consolidated financial statements and schedule are incorporated herein by reference in reliance upon such reports given on the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
The consolidated financial statements of Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc. as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 and for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009, incorporated by reference in Triumph Group, Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K dated June 22, 2010, and the effectiveness of Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, have been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in its reports thereon dated March 25, 2010 (which contains an explanatory paragraph describing conditions that raised substantial doubt about Vought Aircraft Industries, Inc.'s ability to continue as a going concern as described in Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements), incorporated by reference therein, and incorporated herein by reference. Such consolidated financial statements have been incorporated herein by reference in reliance upon such reports given on the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
189
TRIUMPH GROUP, INC.
Offer to Exchange
8.625% Senior Notes due 2018
Registered under the Securities Act
For
A Like Principal Amount of Outstanding 8.625% Senior Notes due 2018
PROSPECTUS
August 23, 2010