UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
☒ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020
OR
☐ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from __________ to __________
Commission file number: 001-34887

Net Element, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware | 90-1025599 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer |
3363 NE 163rd Street, Suite 605 | 33160 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (305) 507-8808
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share | NETE | The Nasdaq Stock Market, LLC (Nasdaq Capital Market) |
Securities registered pursuant tp Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act:
| Title of each class |
Warrants, each exercisable for one share of Common Stock |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. ☐ YES ☒ NO
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. ☐ YES ☒ NO
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ☒ YES ☐ NO
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). ☒ YES ☐ NO
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer," "smaller reporting company," and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer ☐ | Accelerated filer ☐ |
|
|
Non-accelerated filer ☒ | Smaller reporting company ☒ |
|
|
| Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. □
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). ☐ YES ☒ NO
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s common equity, other than shares held by persons who may be deemed affiliates of the registrant, as of June 30, 2020 was approximately $32.4 million.
The registrant had 5,208,236 shares of common stock outstanding as of March 23, 2021.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
None.
|
| Page |
|
| |
|
|
|
Item 1. | ||
|
|
|
Item 1A. | ||
|
|
|
Item 1B. | 35 | |
|
|
|
Item 2. | 35 | |
|
|
|
Item 3. | 36 | |
|
|
|
Item 4. | 36 | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Item 5. | 36 | |
|
|
|
Item 6. | 36 | |
|
|
|
Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations. | 37 |
|
|
|
Item 7A. | 46 | |
|
|
|
Item 8. | 46 | |
|
|
|
Item 9. | Changes In and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure. | 46 |
|
|
|
Item 9A. | 46 | |
|
|
|
Item 9B. | 47 | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Item 10. | 48 | |
|
|
|
Item 11. | 50 | |
|
|
|
Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters. | 51 |
|
|
|
Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence. | 52 |
|
|
|
Item 14. | 53 | |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Item 15. | 54 | |
|
|
|
Item 16. | 63 | |
|
|
|
| 64 | ||
NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K (this "Report") includes statements that express our opinions, expectations, beliefs, plans, objectives, assumptions or projections regarding future events or future results and therefore are, or may be deemed to be, “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the federal securities laws. All statements other than statements of historical facts contained in this Report may be forward-looking statements, including, statements regarding our business operations, economic performance and financial condition, including in particular: our business strategy and means to implement the strategy; assumptions and projections about our industry; measures of future results of operations, such as revenue, expenses, operating margins, and earnings per share; other operating metrics such as shares outstanding and capital expenditures; our success and timing in developing and introducing new products or services and expanding our business, including with respect to joint ventures; the successful integration of future acquisitions; our future responses to and the anticipated impact of novel coronavirus COVID-19 (“COVID-19”); and the potential merger between the Company and Mullen Technologies, Inc. (“Mullen”) and the related transactions. These forward-looking statements can generally be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology, including the terms “believes,” “estimates,” “continues,” “anticipates,” “expects,” “seeks,” “projects,” “intends,” “plans,” “may,” “will,” “would” or “should” or, in each case, their negative or other variations or comparable terminology.
By their nature, forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties because they relate to events and depend on circumstances that may or may not occur in the future. These factors include, but are not limited to, the following:
| • | our ability (or inability) to continue as a going concern; | |
| • | the continued outbreak of a health epidemic or pandemic, including COVID-19; | |
| • | the impact of any new or changes made to laws, regulations, card network rules or other industry standards affecting our business; | |
| • | the impact of any significant chargeback liability and liability for merchant or customer fraud, which we may not be able to accurately anticipate and/or collect; | |
| • | our ability to secure or successfully migrate merchant portfolios to new bank sponsors if current sponsorships are terminated; | |
| • | our and our bank sponsors’ ability to adhere to the standards of Visa and MasterCard payment card brand; | |
| • | our reliance on third-party processors and service providers; | |
| • | our dependence on independent sales groups (“ISGs”) that do not serve us exclusively to introduce us to new merchant accounts; | |
| • | our ability to retain clients, many of which are small- and medium-sized businesses ("SMBs"), which can be difficult and costly to retain; | |
| • | our ability to pass along increases in interchange costs and other costs to our merchants; | |
| • | our ability to protect against unauthorized disclosure of merchant and cardholder data, whether through breach of our computer systems or otherwise; | |
| • | the effect of the loss of key personnel on our relationships with ISGs, card brands, bank sponsors and our other service providers; | |
| • | the effects of increased competition, which could adversely impact our financial performance; | |
| • | the impact of any increase in attrition due to an increase in closed merchant accounts and/or a decrease in merchant charge volume that we cannot anticipate or offset with new accounts; | |
| • | the effect of adverse business conditions on our merchants; | |
| • | our ability to adopt technology to meet changing industry and customer needs or trends; | |
| • | the impact of any decline in the use of credit cards as a payment mechanism for consumers or adverse developments with respect to the credit card industry in general; | |
| • | the impact of any adverse conditions in industries in which we obtain a substantial amount of our bankcard processing volume; | |
| • | the impact of seasonality on our operating results; | |
| • | the impact of any failure in our systems due to factors beyond our control; | |
| • | the impact of any material breaches in the security of third-party processing systems we use; | |
| • | the impact of any new and potential governmental regulations designed to protect or limit access to consumer information; | |
| • | the impact on our profitability if we are required to pay federal, state or local taxes on transaction processing; | |
| • | the impact on our growth and profitability if the markets for the services that we offer fail to expand or if such markets contract; | |
| • | significant losses we have incurred and may continue to experience in the future; | |
| • | foreign laws and regulations, which are subject to change and uncertain interpretation; | |
| • | geopolitical instability, including the recent outbreak and continuing spread of COVID-19, and other conditions that may adversely affect trends in consumer, business and government spending; | |
| • | the Company’s ability (or inability) to obtain additional financing in sufficient amounts or on acceptable terms when needed; | |
| • | the impact on our operating results as a result of impairment of our goodwill and intangible assets; | |
| • | our material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting and our ability to maintain effective controls over financial reporting in the future; and | |
| • | ineffective risk management policies and procedures; | |
| • | our ability to protect our systems and data from continually evolving cybersecurity risks or other technological risks; | |
| • | the failure of the Mullen merger to be completed or a significant continued delay in the consummation of the merger, as well as business unceratinties whilc ethe merger is pending, and | |
| • | the risk factors included in Part I, Item 1A of this Annual Report on Form 10-K |
Although we base these forward-looking statements on assumptions that we believe are reasonable when made, we caution you that forward- looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and that our actual results of operations, financial condition and liquidity, and industry developments may differ materially from statements made in or suggested by the forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. If these or other risks and uncertainties (including those described in Part I, Item 1A of this Report and our subsequent filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC” or the “Commission”)) materialize, or if the assumptions underlying any of these statements prove incorrect, our actual results may be materially different from those expressed or implied by such statements. In addition, even if our results of operations, financial condition and liquidity, and industry developments are consistent with the forward-looking statements contained in this filing, those results or developments may not be indicative of results or developments in subsequent periods.
In light of these risks and uncertainties, we caution you not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. Any forward-looking statement that we make in this filing speaks only as of the date of such statement, and we undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statement or to publicly announce the results of any revision to any of those statements to reflect future events or developments, except as required by applicable law. Comparisons of results for current and any prior periods are not intended to express any future trends or indications of future performance, unless specifically expressed as such, and should only be viewed as historical data.
Net Element, Inc., (“Net Element”) a Delaware corporation, is a holding company that conducts its operations through its subsidiaries. Net Element and its subsidiaries are referred to collectively as the “Company,” “Net Element,” “we,” “us,” or “our,” unless the context requires otherwise.
Company Overview
Net Element is a global technology and value-added solutions group that supports electronic payments acceptance in a multi-channel environment including point-of-sale (POS), e-commerce and mobile devices. The Company operates two business segments as a provider of North American Transaction Solutions and International Transaction Solutions.
We offer a broad range of payment acceptance and transaction processing services that enable merchants of all sizes to accept and process over 100 different payment options in more than 120 currencies, including credit, debit, prepaid and alternative payments. We also provide merchants with value-added services and technologies including integrated payment technologies, POS solutions, fraud management, information solutions and analytical tools.
We are differentiated by our technology-centered value-added service offerings built around our payments ecosystem and our diversified business model, which enables us to provide our varied customer base with a broad range of transaction-processing services from a single source across numerous channels and geographic markets. We believe these capabilities provide several competitive advantages that will enable us to continue to penetrate our existing customer base with complementary new services, win new customers, develop new sales channels and enter new markets. We believe these competitive advantages include:
● | Our ability to provide competitive products through use of proprietary technologies; | |
● | Our ability to provide in one package a range of services that traditionally had to be sourced from different vendors; | |
● | Our ability to provide a single agnostic on-boarding and merchant management platform to our indirect non-bank sales force ("Sales Partners"); | |
● | Our ability to provide management and optimization tools to our Sales Partners amongst multiple networks and platforms; | |
● | Our ability to serve customers with disparate operations in several geographies with technology solutions that enable them to manage their business as one enterprise; and | |
● | Our ability to capture and analyze data across the transaction processing value chain and use that data to provide value-added services that are differentiated from those offered by pure-play vendors that serve only one portion of the transaction processing value chain (such as only merchant acquiring or POS). |
We have operations and offices located within the United States (“U.S.”) (domestic) and outside of the U.S. (international) where sales, customer service and/or administrative personnel are based. Through U.S. based subsidiaries, we generate revenues from transactional services, valued-added payment services and technologies that we provide to SMBs. Through wholly owned subsidiaries, we focus on transactional services, mobile payment transactions, online payment transactions, value-added payment services and technologies in selected international markets.
Our business is characterized by transaction related fees, multi-year contracts, and a diverse client base, which allows us to grow alongside our clients. Our multi-year contracts allow us to achieve a high level of recurring revenues with the same clients. While the contracts typically do not specify fixed revenues to be realized thereunder, they do provide a framework for revenues to be generated based on volume of services provided during such contracts’ term.
Products and Services Information
Our broad suite of services spans the entire transaction processing value chain of commerce enabling services and technologies and includes a range of front-end customer-facing solutions, as well as back-end support services and account reconciliation. We deliver our value-added solutions from a suite of proprietary technology products, software, cloud-based applications, processing services, fraud management offerings, and customer support programs that we configure to meet our client’s individual needs.
Many of our payment solutions are technology-enabled in that they incorporate or are incorporated into innovative, technology-driven solutions, including enterprise software solutions, designed to enable merchants to better manage their businesses.
Integrated and Vertical Markets. Our integrated and vertical market solutions provide advanced payments technology that is deeply integrated into business enterprise software solutions either owned by us or by our partners. We grow our business when new merchants implement our enterprise software solutions and when new or existing merchants enable payments services through enterprise software solutions sold by us or by our partners. Our primary technology-enabled solutions include integrated and vertical markets, ecommerce and multi-channel solutions, each as described below:
● | Unified Payments – doing business as Unified Payments, we provide businesses of all sizes and types throughout the United States with a wide range of fully-integrated payment acceptance solutions, value-added POS and business process management services;
| |
● | PayOnline – through our subsidiary, PayOnline Systems (“PayOnline”), we provide a wide range of value-added online solutions in the selected international markets utilizing our fully-integrated, agnostic electronic commerce platform that simplifies complex enterprise online transaction processing challenges from payment acceptance and processing through risk prevention and payment security via point-to-point encryption and tokenization solutions;
| |
● | Pay-Travel – integrated payment processing solutions to the travel industry, which includes integrations with various Global Distribution Systems (“GDS”) such as Amadeus®, Galileo®, Sabre®, additional geo filters and passenger name record (PNR) through Pay-Travel service offered by PayOnline;
| |
● | Aptito POS Platform – an integrated POS platform developed on Apple’s® iOS and Android® mobile operating systems for the hospitality, retail, service and on the go industries. Our goal with Aptito is to create an easy to use POS and business management solution, which incorporates everything a small business needs to help streamline every-day management, operations and payment acceptance;
| |
● | Restoactive – utilizing Aptito POS Platform architecture, we have developed and launched Restoactive, which seamlessly plugs into a current restaurant environment through integrations with some of the biggest POS and restaurant management platforms available on the market today;
| |
● | Unified m-POS – mobile POS application makes accepting payments on the go easy and secure. Mobile application is EMV-compliant, accepts traditional and contactless transactions such as Apple Pay®. Unified m-POS application is available for download in Apple’s App Store and Google Play;
| |
● | Zero Pay – zero-fee payment acceptance program for SMB merchants in the United States. Zero Pay program saves merchants costs involved in accepting credit and debit cards using mobile POS;
| |
● | Netevia – our internally developed future-ready multi-channel payments and merchant management platform. Connecting and simplifying payments across sales channels through a single integration point, Netevia delivers end-to-end payment processing through easy-to-use APIs. The Netevia platform is the core of the Company’s technology stack and includes multiple value-added modules that streamline payment processes and create additional revenue streams for our clients. | |
| ● | Blade - our internally developed, proprietary, fully automated, artificial intelligence powered underwriting solution with predictive scoring. Built for underwriting and on-boarding of new merchants, reducing potential risks and decision-making time while improving the customer experience. | |
| ● | Netevia Mastercard for SMB - The Netevia Mastercard®, powered by Aliaswire’s patented technology, is part of a unique platform that combines efficient and low-cost payment processing with the ability to save money on credit and debit card payment acceptance fees. |
Recent Developments
The outbreak and continuing spread of the COVID-19 pandemic has negatively affected businesses across the globe, in particular the service industry, which includes restaurants, a significant part of our business, as well as disrupted global supply chains and workforce participation, and created significant volatility and disruption of financial markets. Further, this has resulted in government authorities around the world implementing numerous measures to try to reduce the spread of COVID-19, such as travel bans and restrictions, quarantines, “shelter-in-place,” “stay-at-home” or similar orders, business limitations or total shutdowns. For example, many of our restaurant merchants that we service located within mainland United States, as well as hospitality and retail sector merchants, have been temporarily closed, have shortened operating hours and/or have otherwise been adversely affected by the impact and continuing spread of COVID-19. These merchants have experienced significant sales declines or no sales at all due to closure of their business. Additionally, the COVID-19 outbreak has negatively impacted our employee productivity, including affecting the availability of employees reporting for work.
Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, we took initiatives to help minimize the risks to our business and protect our shareholders. Our management team’s experience during the 2008 financial crisis proved to be very valuable in dealing with the on-going crisis. Our entire staff is fully committed and working diligently to support our merchants through these difficult times. Most of our merchants have contactless payment acceptance capabilities through their POS solutions, as well as, e-commerce and mobile contactless payment acceptance capabilities to eliminate the need for physical payments to help reduce the spread of COVID-19. The following initiatives, including an extensive business continuity plan, have been implemented:
Risk Management:
● | Enhanced risk controls and safeguards have been put in place for merchants that sell products with an extended delivery time frame, products paid in advance, catering, ticketing, transportation and travel related merchants |
● | For those employees that will be working from home, we have implemented a “remote work” policy and provided employees with the technology necessary to do so |
● | For those employees that require office attendance, we are taking significant steps to ensure seamless service delivery while safeguarding employees health |
Contactless Payments:
● | Most of our merchants have contactless payment acceptance capabilities through their POS devices from equipment manufacturers such as PAX, Poynt and Verifone which are fully integrated into Netevia and Aptito platforms |
● | We launched an initiative to deploy contactless payment acceptance equipment to merchants that don’t currently have it |
● | Mobile contactless payment acceptance is available through our Unified mPOS App which can be downloaded from Apple’s App Store and Google’s Google Play Apps |
● | Online ecommerce payments through shopping carts allow our merchants to sell their products and services to customers that prefer to shop from the convenience of their homes |
During March 2020, our Company evaluated its liquidity position, future operating plans, and its labor force, which included a reduction in the labor force and compensation to executives and other employees, in order to maintain current payment processing functions, capabilities, and continued customer service to its merchants. We are also seeking sources of capital to pay our contractual obligations as they come due, in light of these uncertain times. Management believes that its operating strategy will provide the opportunity for us to continue as a going concern as long as we are able to obtain additional financing. At this time, due to our continuing losses from operations, negative working capital, the course and possible changing conditions of the COVID-19 pandemic, including any measures to control the spread domestically and internationally, we cannot predict the impact of these conditions on our ability to obtain financing necessary for the Company to fund its future working capital requirements. Our Company has also decided to explore strategic alternatives and potential options for its business, including sale of the Company or certain assets, licensing of technology, spin-offs, or a business combination. Accordingly, on August 4, 2020, the Company entered into a merger agreement in connection with the contemplated merger (the “Merger”) with Mullen Technologies, Inc., a California corporation (“Mullen”), and certain related transactions, including a divestiture of the Company’s existing business operations. See “—Recent Developments—Mullen Merger and Related Transactions” for additional information. There can be no assurance, at this time, regarding the eventual outcome of our planned strategic alternatives, including the Merger and the related transactions. In most respects, it is still too early in the COVID-19 pandemic to be able to quantify or qualify the longer-term ramifications on our merchant processing business, our merchants, our planned strategic alternatives to enhance current shareholder value, our current investors, and/or future potential investors.
As part of our Company's plan to obtain capital to fund future operations, on March 27, 2020, our Company entered into a Master Exchange Agreement, (the “ESOUSA Agreement”) with ESOUSA Holdings, LLC ("ESOUSA"), a related party. Prior to entering into the ESOUSA Agreement, ESOUSA agreed to acquire an existing promissory note that had been previously issued by the Company, of up to $2,000,000 in principal amount outstanding and unpaid interest due to RBL Capital Group, LLC ("RBL"). Pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement, the Company had the right, at any time prior to March 27, 2021, to request ESOUSA, and ESOUSA agreed upon each such request, to exchange this promissory note in tranches on the dates when the Company instructs ESOUSA, for such number of shares of the Company’s common stock (“Common Stock”) as determined under the ESOUSA Agreement based upon the number of shares of Common Stock (already in ESOUSA’s possession) that ESOUSA sold in order to finance its purchase of such tranche of the promissory note from RBL. ESOUSA will purchase each tranche of the promissory note equal to 88% of the gross proceeds from the shares of Common Stock sold by ESOUSA to finance the purchase of such exchange amount from RBL. Each such tranche shall be $148,000 unless otherwise agreed to by the Company and ESOUSA.
On April 23, 2020 and August 3, 2020, the Company entered into certain amendments to the ESOUSA Agreement, which together increased from $2,000,000 to $15,000,000 the principal amount and unpaid interest of one or more promissory notes of the Company or its direct or indirect subsidiaries that ESOUSA either purchased in whole or has an irrevocable right to purchase in tranches from RBL in connection with the ESOUSA Agreement.
On May 7, 2020, the Company entered into a promissory note (the “Note”) evidencing an unsecured loan (the “Loan”) in the amount of $491,493 made to the Company under the Paycheck Protection Program (the “PPP”). The Note matures on May 7, 2022 and bears interest at a rate of 1% per annum. Beginning December 7, 2020, the Company is required to make 17 monthly payments of principal and interest, with the principal component of each such payment based upon the level amortization of principal over a two-year period from May 7, 2020. Pursuant to the terms of the CARES Act and the PPP, the Company may apply to the Lender for forgiveness for the amount due on the Loan. The amount eligible for forgiveness is based on the amount of Loan proceeds used by the Company (during the eight-week period after the Lender makes the first disbursement of Loan proceeds) for the payment of certain covered costs, including payroll costs (including benefits), interest on mortgage obligations, rent and utilities, subject to certain limitations and reductions in accordance with the CARES Act and the PPP. No assurance can be given, at this time, that the Company will obtain forgiveness of the Loan in whole or in part.
On May 18, 2020, the Company entered into a promissory note in the amount of $159,899 made to the Company by the U.S. Small Business Administration under the Economic Injury Disaster Loan program.
Mullen Merger and Related Transactions
On August 4, 2020, the Company entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger (the “Merger Agreement”) with Mullen and Mullen Acquisition, Inc., a California corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”). Pursuant to, and on the terms and subject to the conditions of, the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub will be merged with and into Mullen, with Mullen continuing as the surviving corporation in the Merger. The parties to the Merger Agreement intend that the number of shares of the Company’s common stock outstanding immediately after the Merger effective time on a fully diluted and fully converted basis will not exceed 75,000,000, with 15% of such common stock outstanding immediately after the Merger effective time on a fully diluted and fully converted basis to be allocated to the persons that hold shares of the Company common stock immediately prior to the Merger effective time (the “Parent Pre-Merger Stockholders”) (subject to upward adjustment described below).
The parties to the Merger Agreement intend that, subject to the Company’s stockholders’ approval, the Company will effect a private placement of the Company common stock prior to the Merger effective time (the “Private Placement”) and to loan at 14% annual interest rate compounding monthly all or a portion of the net proceeds of the Private Placement to Mullen on an unsecured basis. In connection with such financing, for every one dollar of loan funding (including all accrued interest on such loans) provided by the Company to Mullen prior to the Merger effective time, the Parent Pre-Merger Stockholders will retain an additional 0.00000067% of the shares of the Company common stock to be outstanding on a fully diluted basis immediately after the Merger effective time.
The Parties to the Merger Agreement intend that, prior to the Merger effective time but, subject to and after the Company’s stockholders’ approval, the Company will divest itself of its existing business operations to another party, and will cause such party to assume all liabilities of the Company directly related to its operations of its existing business immediately prior to the closing of such divestiture (the “Divestiture”).
As contemplated by the Merger Agreement, on August 11, 2020, our Company as lender, borrowed an additional $500,000 from RBL and entered into an unsecured Promissory Note, dated August 11, 2020 (the “Note”), with Mullen. Pursuant to the Note, Mullen borrowed from the Company $500,000. Prior to maturity of the loan, the principal amount of the loan will carry an interest rate of 14% per annum compounded monthly and payable upon demand. This loan will mature on the earlier of (i) the date that the Merger Agreement is terminated for any reason by any party thereto and (ii) the Merger Effective Time (as defined in the Merger Agreement).
On December 29, 2020, the Company entered into the First Amendment (the “Amendment”) to the Merger Agreement with Mullen and the Merger Sub.
Prior to the parties’ execution and delivery of the Amendment, Section 8.1(b) of the Merger Agreement provided that the Merger Agreement may be terminated and the merger contemplated in the Merger Agreement (the “Merger”) and other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement may be abandoned at any time prior to the merger effective time, notwithstanding any requisite approval and adoption of the Merger Agreement and the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement by the shareholders of Mullen and/or the stockholders of the Company, by either Company or Mullen if the merger effective time shall not have occurred on or before December 31, 2020 (the “Outside Date”). Pursuant to the Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub amended Section 8.01(b) of the Merger Agreement to extend the Outside Date to March 31, 2021.
In addition, pursuant to the Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub agreed that, if the registration statement on Form S-4 (with the merger proxy statement included as part of the prospectus) is not filed with the SEC on or prior January 15, 2021, then Mullen will pay the Company an agreed sum of $13,333 per day (the “Late Fee”) until the such registration statement (with the merger proxy statement included as part of the prospectus) is filed with the SEC. All accumulated Late Fees will be due and payable by Mullen on the 5th day of each calendar month commencing February 5, 2021 and on the 5th day of each month thereafter until the above-refenced filing has occurred.
On March 30, 2021, the Company entered into the Second Amendment (the “Second Amendment”) to Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of August 4, 2020, as amended by the First Amendment dated as of December 29, 2020 (the “Merger Agreement”) with Mullen Technologies, Inc., a California corporation (“Mullen”), Mullen Acquisition, Inc., a California corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”). Prior to the parties’ execution and delivery of the Second Amendment, Section 8.1(b) of the Merger Agreement, as amended, provided that the Merger Agreement may be terminated and the merger contemplated in the Merger Agreement (the “Merger”) and other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement may be abandoned at any time prior to the merger effective time, notwithstanding any requisite approval and adoption of this Agreement and the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement by the shareholders of Mullen and/or the stockholders of the Company, by either Company or Mullen if the merger effective time shall not have occurred on or before March 31, 2021 (the “Outside Date”). Pursuant to the Second Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub amended Section 8.01(b) of the Merger Agreement to extend the Outside Date to April 30, 2021.
The foregoing description of the Second Amendment does not purport to be complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by, the full text of such agreement, a copy of which is attached hereto as Exhibit 2.1 and incorporated herein by reference.
Consummation of the Merger, the Divestiture, the Private Placement and the other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement, is subject to customary conditions including, among others, the approval of the Company’s stockholders. There is no guarantee that the Merger, the Divestiture, the Private Placement or the other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement will be completed. For additional information, see the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 30, 2020, as amended.
We continue our mission to build value for our shareholders as we work through the crisis caused by the pandemic.
Outlook
Our strategy is to ensure that our business remains successful in a rapidly changing market under the current circumstances, creating sustainable value for all our stakeholders, including our clients, distribution partners and shareholders. We aim to achieve superior results for our clients by having a deep understanding of their payment acceptance needs, extensive market reach, strong product development and technology enablement.
Planned for 2021:
We will continue to focus on understanding our clients and addressing their payment acceptance needs in core market segments, in spite of the current CPVID-19 crisis, and the uncertainty in the state of the economy.
● | Continue managed growth in all key segments and expand our network of referral partners | |
● | Drive and improve client retention | |
● | Expand our client base in selected markets | |
| ● | Enable our clients with contactless payment acceptance technologies | |
● | Deliver value-added products to our clients to increase efficiencies and payment acceptance | |
● | Launch new tools to reach our clients, such as digital channels, and deepening partner relations |
We believe that new and disruptive technologies will provide us the opportunity to differentiate ourselves from our competition, continue developing and delivering innovative payment solutions in 2021, in spite of COVID-19.
● | Continue to enhance Netevia, our future-ready multi-channel payments platform, enabling intelligent routing of payments for the application development community | |
● | Continue to scale and enhance new product launches that will add value to our clients | |
● | Extend our capabilities in next-generation POS hardware and software, and deepening our partner proposition | |
● | Commence trials of advanced technologies around business intelligence and mobile based payments acceptance | |
● | Continue the further development of disruptive emerging technologies such as contactless payment technologies, payments enablement for Internet of Things (“IoT”), biometrics payment acceptance and artificial intelligence | |
● | Continue research and investments in future emerging payment technologies |
Realize the full potential of our business model.
● | Assess the current operations in light of current pandemic and the closure of businesses until the economy gears up and businesses achieve normal operations | |
● | Develop additional payment network relationships to integrate with our technologies | |
| ● | Diversify our client base to include relationships in the online sales and home delivery segments |
We continue to believe that disruptive technologies such as biometrics payments, contactless payment technologies, and artificial intelligence will play key roles in future commerce. These technologies will encourage innovation through development of value-added services and cater to both merchants and their customers.
We believe Netevia, our future-ready payments and merchant management platform will act as a framework and core for a number of value-added services that can connect merchants and consumers directly utilizing these disruptive technologies while increasing the economic efficiency of all transactions being made within the ecosystem. Specifically, Netevia delivers end-to-end payment processing through easy-to-use APIs and complements the Company’s ability to perform in a multi-channel environment, including point-of-sale (POS), e-commerce and mobile devices and will enable the Company to perform as a hub for disruptive emerging technology solutions.
Our Mission and Vision
Our mission is to power global commerce and allow our clients to conduct business globally through a centralized solution. We believe that by understanding the consumer behavior and the needs of our merchants is the most effective and, ultimately, the most profitable means to accomplish our mission and create long-term value for all stakeholders.
We drive client growth through our in-depth knowledge of global transactional services and related value-added service offerings which separate us from the competition.
Our vision is to set the standard for multi-channel payments acceptance and value-added service offerings with focus on the creation of an unified global transaction acceptance ecosystem. We believe in disruptive emerging technologies and, as such, we have developed Netevia, our future-ready multi-channel payments platform to support development of value-added solutions designed for everyday commerce. Moving forward, we believe exciting projects and disruptive technologies like biometric payments and artificial intelligence will provide us the opportunity to continue developing innovative payments solutions, which will provide value to our clients.
In order to achieve this vision, we seek to further develop single on-boarding, global transaction acceptance ecosystem. Manifesting this vision requires scaling our direct and indirect connectivity to multiple payment and mobile networks internationally. By implementing this vision, we believe that we will be able to provide centralized, global multi-channel transactional platform to our clients internationally.
Our Strategy
Subject to the potential Merger between the Company and Mullen and the related transactions, including the Divestiture, our strategy is to capitalize on consumer appetite for digital payment methods, the perceived movement towards a cashless society. To continue to grow our business, our strategy is to focus on providing merchants with the ability to process a variety of electronic transactions across multiple channels. We seek to leverage the adoption of and transition to card, electronic and digital-based payments by expanding our market share through our distribution channels and services innovations. We also seek growth through strategic acquisitions to improve our offerings, scale and geography. We intend to continue to invest in and leverage our technology infrastructure and our people to increase our penetration in existing markets.
Key elements of our business strategy include:
● | Continued investment in our core technology and new technology offerings; | |
● | Allocation of resources and expertise to grow in commerce and payments segments; | |
● | Grow and control distribution by adding new merchants and partners; | |
● | Leverage technology and operational advantages throughout our global footprint; | |
● | Expansion of our cardholder and subscriber customer base; |
● | Continue to develop seamless multinational solutions for our clients; | |
● | Increase monetization while creating value for our clients; | |
● | Focus on continued improvement and operation excellence; and | |
● | Pursue potential domestic and international acquisitions of, investments in, and alliances with companies that have high growth potential, significant market presence or key technological capabilities. |
With our existing infrastructure and supplier relationships, we believe that we can accommodate revenue growth, after adjusting for the effects of the current pandemic. We believe that our available capacity and infrastructure will allow us to take advantage of operational efficiencies and increased margin as we grow our processing volume and expand to other geographical territories.
Market Overview
The financial technology and transaction processing industry is an integral part of today’s worldwide financial structure. The industry is continually evolving, driven in large part by technological advances. The benefits of card-based payments allow merchants to access a broader universe of consumers, enjoy faster settlement times and reduce transaction errors. By using credit or debit cards, consumers are able to make purchases more conveniently, whether in person, over the Internet, or by mail, fax or telephone, while gaining the benefit of loyalty programs, such as frequent flyer miles or cash back, which are increasingly being offered by credit or debit card issuers.
In addition, consumers are also beginning to use card-based and other electronic payment methods for purchases at an earlier age in life, and increasingly for small dollar amount purchases. Given these advantages of card-based payment systems to merchants and consumers, favorable demographic trends, and the resulting proliferation of credit and debit card usage, we believe businesses will increasingly seek to accept card-based payment systems in order to remain competitive.
We believe that cash transactions are becoming progressively obsolete. The proliferation of bankcards has made the acceptance of bankcard payments a virtual necessity for many businesses, regardless of size, in order to remain competitive. In addition, the advent and growth of e-commerce and crypto-currencies have marked a significant new trend in the way business is being conducted. E-commerce is dependent upon credit and debit cards, as well as other cashless payment processing methods.
The payment processing industry continues to evolve rapidly, based on the application of new technology and changing customer needs. We intend to continue to evolve with the market to provide the necessary technological advances to meet the ever-changing needs of our market place. Traditional players in the industry must quickly adapt to the changing environment or be left behind in the competitive landscape.
The recent outbreak and continuing spread of COVID-19 is currently impacting countries, communities, supply chains and markets, global financial markets, as well as, the largest industry group serviced by our Company. The Company cannot predict, at this time, whether COVID-19 will
continue to have a material impact on our future financial condition and results of operations due to understaffing in the service sector and the decrease in revenues and profits, particularly restaurants, and any possible future government ordinances that may further restrict restaurant and other service or retail sectors operations.
Business Segments
We operate two reportable business operating segments: (i) North American Transaction Solutions and (ii) International Transaction Solutions. Our segments are designed to establish lines of businesses that support our client base and further globalize our solutions. Management determines the reportable segments based on the internal reporting used by our Chief Operating Decision Maker to evaluate performance and to assess where to allocate resources. The principal revenue stream for all segments comes from service and transaction related fees.
North American Transaction Solutions
North American Transaction Solutions is currently our largest segment, where through our subsidiary TOT Payments, LLC, doing business as Unified Payments, we provide businesses of all sizes and types with a wide range of fully-integrated payment acceptance solutions at the point of sale, including Merchant Acquiring, e-commerce, mobile commerce, POS and other business solutions. Our largest service in this segment is Merchant Acquiring, which facilitates the acceptance of cashless transactions at the POS, whether a retail transaction at a physical business location, a mobile commerce transaction through a mobile or tablet device, which includes m-POS acceptance, Android Pay™, Apple Pay™ and Samsung Pay or an electronic commerce transaction over the web. Geographical presence for this segment is North America.
International Transaction Solutions
Through our subsidiary, PayOnline, we provide a wide range of value-added online and mobile solutions utilizing our fully-integrated, platform agnostic electronic commerce offering that simplifies complex enterprise online transaction processing challenges from payment acceptance and processing through risk prevention and payment security via point-to-point encryption and tokenization solutions. Our proprietary SaaS suite of solutions for electronic and mobile commerce gateway and payment processing platform is compliant at Level 1 of PCI DSS, streamlines the order-to-cash process, improves electronic payment acceptance and reduces the scope of burden of PCI DSS compliance. PayOnline holds a potential leadership position in the Russian Federation as one of the largest independent Internet Payment Services Providers (“IPSP”).
|
| North American Transaction Solutions |
| International Transaction Solutions |
|
|
|
|
|
Clients: |
| Businesses and business owners of all types and sizes. Current focus on SMB merchants |
| Online businesses, merchants requiring cross-border payment acceptance, content providers and mobile applications of all types and sizes |
|
|
|
|
|
Goals: |
| To help business grow commerce at the retail, online and m-POS. Enable multi-channel commerce |
| To help businesses transact online with ease and security and help digital merchants monetize their content in a mobile environment |
|
|
|
|
|
Key Solutions: |
| ● Integrated payments acceptance ● Value-added services ● Aptito POS technology ● m-POS technology ● Smart payment POS terminal ● Business performance analytics ● Marketing / loyalty |
| ● Integrated online and mobile billing solutions ● Complete cross-border toolkit for online business ● Integrated GDS transaction processing ● Mobile content monetization and management ● Security / risk management ● Marketing / loyalty |
|
|
|
|
|
Segment Revenue: |
|
| ||
Dollars Volume Processed: |
Our segments are designed to establish lines of businesses that support our client base and further globalize our solutions. Management determines the reportable segments based on the internal reporting used by our Chief Operating Decision Maker to evaluate performance and to assess where to allocate resources. The principal revenue stream for all segments came from service and transaction related fees during 2020 and 2019.
Revenues from each of our operating segments as a percentage of total revenues are displayed in the below table.
Year ended December 31, | ||||||||
2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Total revenues generated: | ||||||||
North American Transaction Solutions | 95 | % | 90 | % | ||||
International Transaction Solutions | 5 | % | 10 | % | ||||
No country outside the U.S. represents greater than 10% of our total revenues.
Comparative segment revenues and related financial information pertaining to our segments for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 are presented in the tables in Note 16, Segment Information, to our consolidated financial statements (the “Consolidated Financial Statements”), which are included elsewhere in this Report.
North American Transaction Solutions Segment
Our North American Transaction Solutions segment revenues are primarily derived from processing payment acceptance transactions in a multi-channel environment for SMB merchants and includes fees for providing processing, loyalty and software services, and sales and support of POS devices. Revenues are generated from a variety of sources, including:
● | Discount fees charged to a merchant for processing of a transaction. The discount fee is typically either a percentage of the purchase amount or an interchange fee plus a fixed dollar amount or percentage; | |
● | Processing fees charged to merchants for processing of a transaction; | |
● | Processing fees charged to our Sales Partners who have outsourced their transaction processing to us; | |
● | Sales and support of POS devices; | |
● | Fees from providing reporting and other services; | |
● | Software license fees for Aptito POS platform, which includes hospitality and SMB retail point-of-sale application; | |
● | PCI compliance fees charged to a merchant for providing PCI compliance on annual basis; and | |
● | Business software license fees for merchant analytics and back office reporting. |
We typically provide our services as part of a broader payment acceptance solution to our business clients across multiple channels, including:
● | Retail Merchants – physical businesses or storefront locations, such as retailers, supermarkets, restaurants, hotels and other brink and mortar facilities, which we refer to as Retail; |
● | Mobile Merchants – physical businesses with remote or wireless storefront locations, such as small retail and service providers that use mobile devices with POS capabilities to accept electronic payments, which we refer to as Mobile; and |
● | Online – online businesses or website locations, such as retailers, digital content providers, and mobile application developers with Internet-based storefronts that can be accessed through a personal computer or a mobile device, where we refer to as e-commerce. |
North American Transaction Solutions Marketing. We employ a variety of go-to-market strategies in our North American Transaction Solutions segment. We mostly partner with indirect non-bank Sales Partners, such as independent sales agents, independent sales groups and referral partners that use our brand to market services (“ISG”), independent sales groups that we sponsor to Card Brands as registered Independent Sales Organizations (“ISO”) and which market services under their own brands, independent software vendors (“ISV”), value added resellers (“VAR”), and payment services providers (“PSP”) to sell our payment solutions to Small Business Merchants ("SMB"). We believe that this sales approach provides us with access to an experienced sales force to market our services with limited investment in sales infrastructure and management time. We believe our focus on the unique needs of SMB allows us to develop compelling offerings for our sales channels to bring to prospective merchants and provides us with a competitive advantage in our target market.
Sales & Marketing Support – Among the services and capabilities we provide are rapid application response time, merchant application acceptance by a proprietary and secure on-line sales portal, superior customer service, merchant reporting and robust analytics. In addition, by controlling the underwriting process we believe we offer the ISGs more rapid and consistent review of merchant applications than may be available from other service providers. Additionally, in certain circumstances, we offer our sales organizations tailored compensation programs and unique technology applications to assist them in the sales process. We keep an open dialogue with our Sales Partners to address their concerns as quickly as possible and work with them in investigating chargebacks or potentially suspicious activity with the aim of ensuring our merchants do not unduly suffer downtime or the unnecessary withholding of funds.
Sales & Marketing Compensation – As compensation for their referral of merchant accounts, we pay our Sales Partners an agreed-upon recurring commission, or percentage of the income we derive from the transactions we process from the merchants they refer to us. The amount of the recurring commissions we pay to our Sales Partners varies on a case-by-case basis and depends on several factors, including but not limited to the number and type of merchants each group refers to us. We provide additional incentives to our Sales Partners, including, from time to time, advances and merchant acquisition bonuses that are secured by income earned from the referred merchant and repayable from future compensation that may be earned by the groups in respect to the merchants they have referred to us. For the year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, we had provided merchant acquisition incentives to Sales Partners in an aggregate amount of approximately $604,000 and $1.8 million, respectively. Our organic growth plan calls for future incentives to be funded to our Sales Partners for referred merchants.
North American Transaction Solutions. Our solutions are designed to help SMB merchants accept cashless payments in a multi-channel payment environment, which spans across POS, e-commerce, mobile devices and smart payment terminals.
Aptito POS Platform – An integrated POS platform developed on Apple’s® iOS and Android® mobile operating systems for the hospitality, retail, service and on the go industries. Our goal with Aptito is to create an easy to use POS and business management solution, which incorporates everything a small business needs to help streamline every-day management, operations and payment acceptance as well as provide efficient ways to decrease labor and operation expenses by automating routine processes through innovative technologies.
● | Aptito Restaurant POS – proprietary, fully integrated cloud-based POS and restaurant management system developed on Apple’s® iOS and Android® mobile operating system is designed to be used as a stand-alone all digital POS or be extended to include: m-POS, self-ordering kiosk, digital menus, pay at the table EMV and NFC ready card readers, cash drawers, receipt and kitchen printers. The need for uptime in a hospitality environment is paramount and as such our Aptito Restaurant POS local server allows our merchants to remain online, even if the Internet connection to the cloud is lost. Our local server solution is automatically synchronized with the cloud, providing 99.99% uptime. |
● | Aptito Retail POS – cloud-based POS solution is available on Apple® iOS and Android® mobile operating platforms and allows retailers to focus on their business and improve the in-store experience. Retailers are able to customize Aptito Retail POS based on their environment. Peripherals for Aptito Retail POS include a fully integrated cash drawer, thermal receipt printer, barcode scanner, barcode printer and EMV-compliant point of sale acceptance terminal. This allows retailers the ability to customize their POS solution based on their unique needs. The need for uptime in a retail environment is paramount and as such our Aptito Retail POS local server allows our merchants to remain online, even if the Internet connection to the cloud is lost. Our local server solution is automatically synchronized with the cloud, providing 99.99% uptime. |
● | Aptito Kiosk – innovative self-order kiosk gives customers complete control over their restaurant experience. Our innovative solution is a stellar addition to any hotel, fine dining or quick service restaurant and increases profit and decreases labor cost. |
● | Aptito Smart Payment Terminal – Aptito & Poynt, partnered to provide restaurants with a most robust seamless POS Solution using the latest technology available. By using the Aptito POS application on Poynt’s smart payment terminal, business owners can finally accept payments anywhere and get access to Poynt value-added applications marketplace to further expand Aptito POS capabilities. |
● | Restoactive – utilizing Aptito POS Platform architecture, we have developed and launched Restoactive, which seamlessly plugs into a current restaurant environment through integrations with some of the biggest POS and restaurant management platforms such as: MICROS®, POSitouch®, Aloha® and Symphony®. By integrating into the leading POS and restaurant management platforms, Restoactive is now accessible by over 500,000 restaurants in the United States. We believe Restoactive to be the first of its kind integrated platform, which introduces an all-in-one digital menu, kiosk and m-POS application into an existing POS environment without the need to displace existing restaurant management platforms. |
● | Unified m-POS – mobile application is available on Apple® iOS and Android® mobile operating platforms and makes it easier and safer to take business on the go. Whether at the local farmer’s market or at a customer’s site, Unified m-POS accepts payments with ease and security. Mobile application is EMV-compliant, accepts traditional and contactless transactions such as Apple Pay®. Unified m-POS allows merchants to send invoices to their customers and utilize the Zero Pay program to accept credit and debit payments while saving on processing fees. Unified m-POS application is available for download in Apple’s App Store and Google Play. |
In addition to enhancing our ability to drive core merchant acquiring sales, Aptito POS Platform allows us to earn incremental revenue from business clients. Currently, revenue model is based on a SaaS fee, which we bill on a per station basis and additional services fee, which we bill for additional applications we offer.
We also believe that Aptito POS Platform can help enhance client retention because we believe it will become core to our clients’ businesses and position us as a value-added partner. For example, business owners may use our business management tools to manage their employees’ work schedules, payroll, patron reservations, operate customer loyalty and gift card programs, manage inventory, and/or provide analytics on their business.
Other POS Platforms – We act as an authorized dealer for various POS manufacturers and POS software providers and deploy these systems where our proprietary products are not the best fit. Systems we offer are fully integrated with our payment acceptance capabilities.
Netevia Payments Platform – We believe Netevia, our future-ready payments platform will act as a framework and core for a number of value-added services that can connect merchants and consumers directly utilizing disruptive technologies while increasing the economic efficiency of all transactions being made within the ecosystem. Specifically, Netevia Payments Platform delivers end-to-end payment processing through easy-to-use APIs and complements the Company’s ability to perform in a multi-channel environment, including POS, e-commerce and mobile devices and will enable the Company to perform as a hub for disruptive emerging technology solutions. Netevia Payments Platform is the core of the Company’s technology stack.
● | Netevia Payment Gateway – Netevia's online payment gateway provides a set of APIs for online sellers to integrate payment acceptance, both B2C and B2B, into their platforms. Advanced merchant hierarchy and management functions include a virtual terminal and a suite of fraud management tools. |
● | Netevia Light POS – the combination of Netevia Light POS application and PAX Technology’s Android-based interactive smart payment terminals offers a robust and flexible state-of-the-art solution to help merchants seamlessly transact across multiple touch points, providing a convenient way of doing day-by-day operations through a modern, self-explainable user interface and user experience. A variety of functions, such as gratuity adjustment, on-screen signature capture, invoicing and support of the Zero Pay program makes this solution ideal for many types of businesses. |
● | Netevia Invoicing – invoicing solution that offers an ability to track and reconcile payments while allowing customers to receive and pay invoices via a Netevia HQ. Tasks that were once manual are now streamlined and automated, providing accounts receivable teams with a clear and complete view of invoice details and statuses. |
Merchant Management Platform – We have developed Netevia, a merchant management platform. Netevia HQ is a value-added module of Netevia Payments Platform and is designed to enhance responsiveness of our Sales Partners and improve sales efficiency. The cloud-based solution provides to both Sales Partners and merchants an integrated toolkit to more effectively manage a variety of sales, operations, reporting and accounting functions. The system is designed to improve conversion rates, technology advisory functions and to reduce deployment time for merchants. It also allows troubleshooting of merchant issues in real-time with built in underwriting and risk monitoring functions. Netevia HQ is currently one of the few cloud-based systems nationwide that allows Sales Partners to onboard and monitor merchants on multiple processing platforms through a single interface.
● | Netevia HQ for Sales Partners – allows Sales Partners to onboard merchants on multiple processing platforms available in the U.S. Its merchant underwriting and boarding process is seamless and paperless. Merchant Library allows Sales Partners to safely store and retrieve any agreement, form or contract related to merchants. Sales Partners that utilize the system are equipped with flexible merchant pricing options, risk management modules and residual and sales incentive calculations, which allow easier management of most of their day-to-day operations. Sales Partners compensation and merchant profitability can be managed using multi-level, single-click, drill-down navigation to pricing, detail, and summary statement information. |
● | Netevia HQ On the Go – fully integrated, digital onboarding interface designed for Sales Partners and merchants, streamlines and automates merchant account sign-up process, delivers real-time decisions and paperless boarding approval from online and mobile devices. Mobile boarding capability facilitates API-driven, instant boarding to multiple payment processing platforms and provides new merchants with a modular approach for providing their personal and business information. The platform manages underwriting, risk assessment, merchant ID assignments and is compliant with banking standards such as Know Your Customer regulations. |
● | Netevia HQ for Merchants – integrated reporting, accounting and analytics back office solution for SMB merchants with access to value-added solutions that increase productivity. A variety of reporting tools along with easy to understand charts enables merchants to analyze sales and improve performance. The ticket system allows merchants direct communication with Company’s service and technical support designed to improve the customer service experience. |
● | Unified Insights – the integrated Unified Insights module is a business dashboard focused on “Big Data” that gives merchants a 360-degree view of their business in a more usable format. With Unified Insights, merchants can compare current revenue, online reputation, and social media activity to their past performance and to similar business in their area. |
North American Transaction Solutions Competition. Many large and small companies compete with us in providing payment processing services and related services to a wide range of merchants. Many of our current and prospective competitors have substantially greater financial, technical and marketing resources, larger customer bases, longer operating histories, more developed infrastructures, greater name recognition and/or more established relationships in the industry than we have. Because of this our competitors may be able to adopt more aggressive pricing policies than we can, develop and expand their service offerings more rapidly, adapt to new or emerging technologies and changes in customer requirements more quickly, take advantage of acquisitions and other opportunities more readily, achieve greater economies of scale, and devote greater resources to the marketing and sale of their services. There are also many smaller transaction processors that provide various services to small and medium sized merchants.
We believe that our specific focus on smaller merchants, in addition to our understanding of the needs and risks associated with providing payment processing services to small merchants and indirect non-bank sales forces, gives us a competitive advantage over larger competitors, which have a broader market perspective and priorities. We also believe that we have a competitive advantage over competitors of a similar or smaller size that may lack our extensive experience, value-added product offering and resources.
North American Transaction Solutions Industry Mix and Geography. In the United States, we have developed significant expertise in industries that we believe present relatively low risks as the customers are generally present and the products or services are generally delivered at the time the transaction is processed. These include:
● | Restaurants | |
● | Schools and educational services | |
● | Brick and mortar retailers | |
● | Convenience and liquor stores | |
● | Professional service providers | |
● | Hotel and lodging establishments |
Merchants we served in the North American Transaction Solutions segment during 2020 processed an average of $14,800 per month in cashless transactions with an average transaction value of approximately $41 per transaction. Larger payment processors have traditionally underserved these merchants. As a result, these merchants have historically paid higher transaction fees than larger merchants and have not been provided with tailored solutions and on-going services that larger merchants typically receive from larger payment processing providers.
Our card-present processing volume for the year ended December 31, 2020 represented 78% of the total North American Transaction Solution volume, and card-not-present processing volume represented 22%.
As of December 31, 2020, approximately 50.9% of our SMB merchants were restaurants, 11.2% were general merchandise, 11.9% were professional services, 9.7% were food store, and 8.5% were automotive. The high concentration in restaurants reflects the efforts of our sales team actively targeting our Aptito POS product line.
The following table reflects the percentage concentration of our merchant base by category:
2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Restaurants | 50.9 | % | 47.9 | % | ||||
General Merchandise | 11.2 | % | 13.1 | % | ||||
Professional Services | 11.9 | % | 11.5 | % | ||||
Food Stores | 9.7 | % | 9.3 | % | ||||
Automotive | 8.5 | % | 7.4 | % | ||||
Health / Beauty | 1.4 | % | 7.3 | % | ||||
Educational Services | 1.3 | % | 2.7 | % | ||||
Hotels / Motels | 1.3 | % | 0.4 | % | ||||
Other | 3.8 | % | 0.4 | % | ||||
In December 2020, SMB merchants located in the following states represented the following percentage of our SMB card processing volume: New York represented 25.9%, Florida represented 13.4% California represented 9.1%, New Jersey represented 6.1% and Texas represented 5.5%. No other state represented more than 5% of our total SMB card processing volume. Our geographic concentration tends to reflect states where we maintain a stronger sales force.
Please refer to Item 1A. Risk Factors, with respect to "Health concerns arising from the outbreak of a health epidemic or pandemic, including the coronavirus, may have an adverse effect on our business".
North American Transaction Solutions Risk Management. In the United States, we focus our sales efforts on low-risk bankcard merchants and have developed systems and procedures designed to minimize our exposure to potential merchant losses. While we also board higher risk merchants which provide a higher gross margin, these accounts are closely monitored by our risk underwriting department.
Effective risk management helps us minimize merchant losses for the mutual benefit of our merchants, Independent Sales Groups and ourselves. Our Underwriting and Risk Management Policy and procedures help to protect us from fraud perpetrated by our merchants. We believe our knowledge and experience in dealing with attempted fraud has resulted in our development and implementation of effective risk management and fraud prevention systems and procedures.
We employ the following systems and procedures to minimize our exposure to merchant and transaction fraud:
● | Merchant Application Underwriting – there are varying degrees of risk associated with different merchant types based on their industry, the nature of the merchant’s business, processing volumes and average transaction size. As such, varying levels of scrutiny are needed to evaluate a merchant application and to underwrite a prospective merchant account. These range from basic due diligence for merchants with low risk profiles to more comprehensive review for higher risk merchants. The results of this assessment serve as the basis for decisions regarding acceptance of the merchant account, criteria for establishing reserve requirements, processing limits, average transaction amounts and pricing. Once aggregated, these factors also assist the Company in monitoring transactions for those accounts when pre-determined criteria have been exceeded. |
● | Merchant Monitoring – we employ several levels of merchant account monitoring to help us identify suspicious transactions and trends. Daily merchant activity is sorted into a number of customized reports by our systems. Our risk management team reviews any unusual activity highlighted by these reports, such as larger than normal transactions or credits, and monitors other parameters that are helpful in identifying suspicious activity. We have daily windows to decide if any transactions should be held for further review and this provides us time to interview a merchant or issuing bank to determine the validity of suspicious transactions. We also place merchants who require special monitoring on alert status and have engaged a third-party web crawling solution that scans all merchant websites for content and integrity. |
● | Investigation and Loss Prevention – if a merchant exceeds any parameters established by our underwriting and/or risk management staff or violates regulations established by the applicable bankcard network or the terms of our merchant agreement, one of our investigators will identify the incident and take appropriate action to reduce our exposure to loss and the exposure of our merchant. This action may include requesting additional transaction information, withholding or diverting funds, verifying delivery of merchandise or even deactivating the merchant account. Additionally, Relationship Managers may be instructed to retrieve equipment owned by us. In addition, to protect ourselves from unexpected losses, we maintain a reserve account with our sponsoring bank, which can be used to offset any losses incurred at a given time. As of December 31, 2020, our reserve balance was approximately $781,000. The reserve is replenished as required by funding 0.03% of bankcard processing volume. In the case of our self-designated bin, this is triggered when it falls below $25,000. This reserve is included on our consolidated balance sheet under the caption “other long-term assets” and reflected as restricted cash for purposes of the statement of cash flows. |
● | Reserves – some of our merchants are required to post reserves (cash deposits) that are used to offset chargebacks incurred. Our sponsoring banks hold such reserves related to our merchant accounts as long as we are exposed to loss resulting from a merchant’s processing activity. In the event that a small company finds it difficult to post a cash reserve upon opening an account with us, we may build the reserve by retaining a percentage of each transaction the merchant performs until the reserve is established. This solution permits the merchant to fund our reserve requirements gradually as its business develops. As of December 31, 2020, total reserve deposits were approximately $13.3 million. We have no legal title to the cash accounts maintained at the sponsor bank in order to cover potential chargeback and related losses under the applicable merchant agreements. We also have no legal obligation to these merchants with respect to these reserve accounts. Accordingly, we do not include these accounts and the corresponding obligation to the merchants in our consolidated financial statements. |
North American Transaction Solutions Sponsoring Banks and Data Processors. Because we are not a “member bank” as defined by Visa, MasterCard, American Express and Discover (“Card Brands”), in order to authorize and settle payment transactions for merchants, we must be sponsored by a financial institution that holds member bank status with the Card Brands (“Sponsorship Bank” in the case of Visa and MasterCard) and various third-party vendors (“Data Processors”) to assist us with these functions. Card Brand rules restrict us from performing funds settlement or accessing merchant settlement funds and require that these funds be in the possession of a Sponsorship Bank until the merchant is funded.
Sponsoring Bank. We have agreements with several banks that sponsor us for membership in the Visa, MasterCard, American Express and Discover card brands and settle card transactions for our merchants. These agreements allow us to use the banks’ identification numbers, referred to as Bank Identification Number (“BIN”) for Visa transactions and Interbank Card Association (“ICA”) number for MasterCard transactions. The principal Sponsoring Bank through which we processed the majority of our transaction in the United States during 2020 was with Esquire Bank, N.A. In addition, we process transactions through BIN sponsorship agreements with Citizens Bank, N.A. and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. From time to time, we may enter into agreements with additional banks.
Data Processor. We have agreements with several Data Processors to provide us with, on a non-exclusive basis, transaction processing and transmittal, transaction authorization and data capture, and access to various reporting tools. Our primary processing vendor in the United States is Priority, which provides us with the processing conduit to the Total System Services, Inc., a Global Payments Company (“TSYS”) and Fiserv, Inc., formerly known as First Data Corporation (“FDC”) authorization and settlement network. We have entered into several service agreements with Priority. Each of the Priority service agreements may be terminated by Priority if, among other things, (i) certain insolvency events occur with respect to us or (ii) we fail to maintain our good standing with Card Brands. We may terminate each of the agreements if, among other things, (i) certain insolvency events occur with respect to Priority, (ii) Priority materially breaches any of the terms, covenants or conditions of the agreements and fails to cure such breach within 30 days following receipt of written notice thereof, or (iii) under certain circumstances, Priority is unable to perform services described in the agreement. In addition, we maintain direct processing agreements with TSYS and FDC.
As an example of processing an electronic payment, the below diagram illustrates the participants involved in a payment transaction. There are four main participants, the Merchant, the Service Provider (Unified Payments), the Sponsoring Bank and the Data Processor. Merchants are primarily business owners that accept credit card payment in exchange for their merchandise and services.
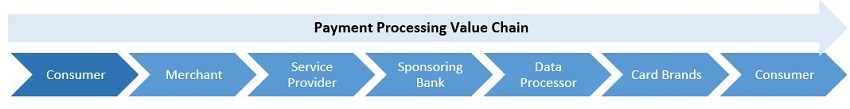
International Transaction Solutions Segment
International Transaction Solutions Operations. Through our subsidiary, PayOnline, we provide a wide range of value-added online and mobile solutions utilizing our fully-integrated, platform agnostic electronic commerce offering that simplifies complex enterprise online transaction processing challenges from payment acceptance and processing through risk prevention and payment security via point-to-point encryption and tokenization solutions. Our proprietary SaaS suite of solutions for electronic and mobile commerce gateway and payment processing platform is compliant at Level 1 of PCI DSS, streamlines the order-to-cash process, improves electronic payment acceptance and reduces the scope of burden of PCI DSS compliance. PayOnline holds a leadership position in the Russian Federation as one of the largest independent Internet Payment Services Provider (“IPSP”).
Our International Transaction Solutions segment revenues are primarily derived from processing cashless transactions for online merchants and includes fees for providing processing, loyalty and software services. Revenues are generated from a variety of sources, including:
● | Discount fees charged to a merchant for processing of a transaction. The discount fee is typically a percentage of the purchase amount; | |
● | Processing fees charged to merchants for processing of a transaction; | |
● | Processing fees charged to our sales partners who have outsourced their transaction processing to us; | |
● | Fees from providing reporting and other services; | |
● | Software license fees for white-label platform; | |
● | Payment gateway transaction fees; | |
● | Business software license fees for merchant analytics, back office reporting; and monetarization; | |
● | Big Data monetization through upsell on payment confirmation page to the end consumer. |
International Transaction Solutions Marketing. The vast majority of International Transaction Solutions sales are direct sales, through our marketing efforts and fully automated leads management system. The marketing department of International Transaction Solutions segment consists of 4 specialists, responsible for product pricing, company branding and positioning, monitoring of competitors and technological developments, public relations and web marketing activities. Our marketing mix includes, but not limited to:
● | Search Engine Optimization – PayOnline is in the top 10 results with most frequently used keywords in Google.ru and Yandex search engines. | |
● | Social Media – PayOnline social media channels include Facebook, Vkontakte, Twitter, and YouTube. | |
● | Corporate Blog – Our corporate blog featured on popular developer communities like HabraHabr and GeekTimes is consistently in the Top 10. | |
● | Industry Research – Every year PayOnline specialists prepare and publish over 120+ research papers on popular e-commerce and IT development forums. | |
● | RUNET – PayOnline is a payment processing provider for RUNET-ID (Russia’s largest Internet professionals’ social platform), Russian Internet Forum and Russian Interactive Week. | |
● | Conferences – Every year our experts participate in 30+ trade shows and professional conferences. | |
● | Education – Our senior managers are frequently invited by top international regulators, universities and business schools as lecturers and experts in the field of payments. |
Merchants we served during 2020 in the International Transaction Solutions segment processed an average of $19,620 per month in cashless transactions with an average transaction value of approximately $14.79 per transaction. Banks and traditional processors have traditionally underserved these merchants due to multi-national and cross-border requirements for these merchants.
During 2020, our sales department consisted of 18 specialists who are responsible for managing the leads, execution of the client agreements, client boarding, customization of the solutions, implementation of the payment acceptance solutions and post-sale client relationship.
International Transaction Solutions. Our solutions combine payment processing, mobile commerce, online shopping cart tools, web site design, web hosting and web related services which enable businesses to establish a presence and commercial capability on the Internet in a quick and simple fashion.
PayOnline Platform – We have developed the PayOnline Platform, a proprietary technology platform serving large and fast-growing internet-led multinationals with complex payment needs, supported by our vertical expertise. Our reliable and secure proprietary technology platform enables merchants to accept a vast array of payment types, across multiple channels, anywhere in the world. Utilizing PayOnline Platform, we have built universal flexible payment solution adapted for websites and mobile applications. The solution includes:
● | Personal Client Area: web-interface for clients to control and manage payments. |
● | Adaptive payment form with the possibility of customization. |
● | Simple payment process: binding card to account, moment payments, recurrent payments, temporary blocking of payment, reserving of payments, invoicing by e-mail. |
● | Customization of protocol 3-D Secure for client's business needs. |
● | Ability to customize the default settings of anti-fraud system. |
● | Integrations with various Global Distribution Systems (“GDS”) such as Amadeus®, Galileo®, Sabre®, additional geo filters and passenger name record (PNR). |
● | Integrations with Apple iOS, Android and Microsoft mobile platforms for mobile application. |
Payments from Start to Finish. PayOnline Platform reduces the payment integration time for merchants, banks and SaaS providers to just a few minutes with its PayOnline Application Program Interface (“API”) service. Easy, easier, easiest: PayOnline integration service simplifies complex payment integration when using APIs and makes the laborious task of adapting payment processes obsolete.
Complete Toolkit for Online Business. More than 20 integration modules for the world's most popular CMS (Content Management System) are available for clients with sites created on basis of CMS. A complete, modular system of web-based services gives our merchants the flexibility to add more options as and when required - without costly or lengthy IT projects.
International Transaction Solutions Competition. International Transaction Solutions segment primarily competes with other companies operating in the online payment processing market in emerging markets. In our key geographical market – Russian Federation, we compete primarily with the acquiring banks and payment processors (including payment aggregators). We cannot compete with acquiring banks or payment processors on pricing. Our major advantages relate to our robust, payment processor agnostic solution that simplifies complex enterprise online payment processing challenges from payment acceptance and processing through to risk prevention and payment security via tokenization solutions. Our competitive advantages include:
● | Suite of individually tailored e-commerce solutions | |
● | Payment conversion management | |
● | Seamless client payment acceptance implementation | |
● | Quick development and implementation of custom payment acceptance solutions | |
● | Multiple integrated payment acceptance methods | |
● | Wide geography of payment acceptance with a single integration | |
● | More than 120 currencies accepted worldwide | |
● | Proprietary Anti-Fraud System |
International Transaction Solutions Industry Mix. We have developed significant expertise in industries that we believe present opportunities for growth. These include:
● | Internet stores | |
● | Professional service providers | |
● | Travel services | |
● | Telecommunications | |
● | Social media networks | |
● | Financial services | |
● | Utilities and government services | |
● | Digital content providers |
The following table reflects the percentage concentration of our merchant base by class:
2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Internet Stores | 47.1 | % | 48.4 | % | ||||
Professional Service | 4.7 | % | 2.2 | % | ||||
Travel Services | 1.8 | % | 7.0 | % | ||||
Telecommunications | 13.9 | % | 14.7 | % | ||||
Social Media Networks | 6.7 | % | 0.4 | % | ||||
Financial Services | 4.1 | % | 1.5 | % | ||||
Utilities and Government Services | 3.8 | % | 4.1 | % | ||||
Digital content providers | 4.4 | % | 7.2 | % | ||||
Other | 13.5 | % | 14.5 | % | ||||
International Transaction Solutions Risk Management. In the emerging markets, we focus our sales efforts on electronic commerce merchants and have developed systems and procedures designed to minimize our exposure to potential merchant losses and provide our merchants with cross-border payment acceptance.
Effective risk management helps us minimize merchant losses for the mutual benefit of our merchants and ourselves. Our Anti-Fraud System allows us to identify and prevent up to 99.9% of potential fraud related to bankcard processing in the electronic commerce environment. Our Underwriting and Risk Management Policy and procedures help to protect us from fraud perpetrated by our merchants. 150 different fraud filters allow our clients to maintain high level or payment conversion. Our risk management is conducted in both manual and automatic modes.
Manual Risk Management involves specialists of our Underwriting and Risk Management Department, who are responsible for the following:
● | Analysis of risks and underwriting of our partners, i.e. acquiring banks, financial companies and payment processors | |
● | Analysis of potential risks and underwriting of our potential clients, i.e. merchants accepting payments over internet | |
● | Manual validation of disputed payments | |
● | Advising of our potential and current clients on how to correctly setup up fraud monitoring methods and tools | |
● | Future development of our fraud monitoring and prevention systems, based on the client needs and recent trends in e-commerce and m-commerce marketplace and regulations |
PayOnline Anti-Fraud System is our proprietary Fully Automated Risk Management system. The system is based on the latest know-how of the informational and financial security aspects of the payment processing industry, as well as rules and recommendations of Visa and MasterCard on fraud prevention in electronic commerce.
Major components of PayOnline Anti-Fraud System include but are not limited to:
● | Advance monitoring of the bank card transaction in automated mode, using 150 filters, individually tuned for each client, where each transaction is evaluated by key parameters, such as country where bank card is issued, country from where the payment is requested, amount of payment, amount of all payments by this card in the past 24 hours/month, IP address, etc. | |
● | Additional validation of the bankcard by using 3-D Secure protocol or validation by charging random amount on the card. | |
● | Monitoring of the transactions by specialists of the Underwriting and Risk Management Department. |
Online Solutions Licensing and Certifications. In order to perform services at the highest level of safety and quality of service, PayOnline holds various industry certifications and licenses.
● | PCI DSS Level 1 – PayOnline is certified to Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (“PCI DSS”) Level 1 standard version 3.2 PCI DSS. Certificate received by PayOnline March 2, 2018, allows the company to process online payment transactions. During 2018, PayOnline was certified to PCI DSS Level 1 version 3.1, as of March 8, 2018. | |
● | SDP / CISP – PayOnline has passed international certification by Visa and MasterCard and is involved in MasterCard Site Data Protection (“SDP”) program and the Visa Cardholder Information Security Program (“CISP”). | |
● | MasterCard – Since 2009, PayOnline is accredited as the official international Service Provider of MasterCard Worldwide, participates in the MasterCard SDP program and, in addition, has the status of MasterCard DataStorage Entity. | |
● | Visa –Since 2009, PayOnline is accredited as the official Service Provider of Visa International payment system, participates in the Visa CISP program and holds the status of Visa Third Party Processor (“TPP”). | |
● | Cryptographic Transport Layer Security (“TLS”) Protocol – Data exchange between the enterprise e-commerce and PayOnline is made via secure channels, using the HTTPS protocol. TLS cryptographic protocol uses asymmetric cryptography for authentication, symmetric encryption for confidentiality and authenticity of the message codes to preserve the integrity of messages. | |
● | Qualys – PayOnline regularly passes ASV-scan procedure (automated external security audit) provided by Qualys in accordance with the requirements of international payment systems to companies with certified PCI DSS. Approximately 50 companies from the Forbes Global 100 list use Qualys to secure their business. |
International Transaction Solutions Sponsoring Banks and Data Processors. Because we are not a “member bank” or a licensed financial services institution as defined by Visa, MasterCard, American Express and Discover (“Card Brands”), in order to authorize and settle payment transactions for merchants, we must be partner with a financial institution that holds member bank status with the Card Brands (“Partner Bank”) and various third-party vendors (“Data Processors”), if necessay, to assist us with these functions. Card Brand rules restrict us from performing funds settlement or accessing merchant settlement funds and require that these funds be in the possession of a Partner Bank until the merchant is funded.
Partner Banks. Since 2008, PayOnline has been working to increase the number of partnership agreements and platform integrations with different banks, financial institutions and payment processors. Our worldwide expansion requires a broader range of regions and currencies covered by such partnership agreements, enabling us to provide international payment processing.
Our key partnerships and integrations in the Russian Federation include:
● | SDM Bank | ● | QIWI Bank |
● | VTB Bank | ● | WebMoney |
● | Round Bank | ● | Absolutbank |
● | Raiffesenbank | ● | Yandex.Money |
Our key international partnerships and integrations include:
● | Latvijas Pasta Banka | ● | Kyrgyzkommertsbank |
● | Rietumu Bank | ● | Paysafe |
● | Wirecard Bank | ● | Authorize.net |
● | Kazkommertsbank | ● | Skrill |
● | Kazkommertsbank Tajikistan | ● | PayPal |
● | Poynt | ● | Paya |
● | TSYS | ● | Esquire Bank |
● | Experian | ● | Docusign |
● | Clover | ● | Cardflight |
● | HP | ● | Pax |
As an example of processing an electronic payment, the below diagram illustrates the participants involved in a payment transaction. There are four main participants, the Merchant, the Service Provider (PayOnline), the Partner Bank and the Data Processor (PayOnline). Merchants are primarily business owners that accept credit card payment in exchange for their merchandise and services.
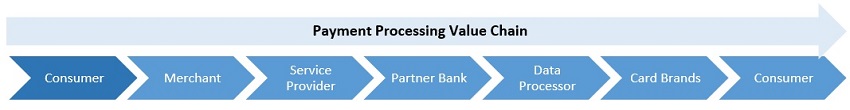
Research and Development
We recognize the importance of having access to the leading technology in order to develop advanced products for our customers, independent sales agents, consumers and for our own internal use. To this end, development of our products is conducted in-house. We are maintaining three development centers and four development teams of IT architects, quality assurance professionals and software developers. We support mobile platforms including Apple® iOS, Android®, and Windows®. We also support server-side software development for Java, ASP.NET, and PHP platforms. We also provide user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) engineering and system administration dedicated to financial services and value-added technology businesses.
Our IT development center is headquartered in North Miami Beach, Florida (U.S.), where we employ a Chief Technology Officer (“CTO”) and POS products Testing & Development Engineer.
Our Moscow (Russia) IT development center employs 7 technical directors, managing the PayOnline platform development teams.
Our representative office in Yekaterinburg (Russia) employs two team leaders managing Netevia and our value-added services development teams.
Intellectual Property
We have several trademarks and service marks, which are important to our business. The following trademarks and service marks are the subject of trademark registrations and are used in our financial services business:
● | Net Element | ● | Restoactive |
● | Unified Payments | ● | TOT |
● | PayOnline | ● | Netevia |
● | Payonline.ru | ● | Aptito |
● | Digital Provider | ● | Team Unified |
We regard our software as proprietary and attempt to protect it, where applicable, with copyrights, trade secret measures and non-disclosure agreements. Despite these protections, it may be possible for competition or users to copy aspects of our intellectual property or to obtain information that we regard as trade secrets. Existing copyright laws afford only limited practical protection for computer software. The laws of foreign countries generally do not protect our proprietary rights in our products to the same extent as the laws of the United States. In addition, we may experience more difficulty in enforcing our proprietary rights in certain foreign jurisdictions.
Employees
Our total number of staff as of December 31, 2020 was 62 full-time employees. The staff at North American Transaction Solutions segment includes 32 employees, of which 12 work for Net Element Software located in Yekaterinburg, Russia. Our International Transaction Solutions segment, located in Moscow, Russia had 18 employees.
Corporate History and Information
Our Company was formed in 2010 and incorporated as a Cayman Islands exempted company with limited liability under the name Cazador Acquisition Corporation Ltd. (“Cazador”). Cazador was a blank check company incorporated for the purpose of effecting a merger; share capital exchange; asset acquisition; share purchase; reorganization or similar business combination with one or more operating businesses or assets. In 2012, Cazador completed a merger (the “Merger”) with Net Element, Inc., a Delaware corporation, which was a company with businesses in the online media and mobile commerce payment processing markets. Immediately prior to the effectiveness of the Merger, the Company (then known as Cazador) changed its jurisdiction of incorporation by discontinuing as an exempted company in the Cayman Islands and continuing and domesticating as a corporation incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware. Effective upon consummation of the Merger, (i) Net Element, Inc. was merged with and into the Company, resulting in Net Element ceasing to exist and the Company continuing as the surviving company in the Merger, and (ii) the Company changed its name to Net Element International, Inc. In 2013, the Company divested its non-core entertainment assets. In December 2013, the Company changed its name to Net Element, Inc. We entered the mobile payments business through the launch of Tot Money (renamed Digital Provider in 2015) in Russia in 2012. We entered the financial technology and value-added transactional service business through the acquisitions of Unified Payments in April 2013 and Aptito in June 2013. We entered the online payment business with our acquisition of PayOnline in May 2015. During 2017, Digital Provider's operations were combined into PayOnline.
Our principal office is located at 3363 NE 163 rd Street, Suite 605, North Miami Beach, Florida 33160, and our main telephone number is (305) 507-8808. Our corporate website is at http:www.netelement.com.
Regulations
Various aspects of our business are subject to U.S. and non-U.S. federal, state and local regulation. The operations of PayOnline, are subject to regulation in non-U.S. markets it operates in and may become subject to the laws and regulations of additional foreign jurisdictions as and when its business expands into additional markets. Many domestic and foreign laws and regulations that affect companies conducting business on the Internet and companies transmitting user information and payments via text message or other electronic means are still evolving and the interpretation of such laws and regulations are often uncertain. Failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations may result in the suspension or revocation of licenses or registrations, the limitation, suspension or termination of services and/or the imposition of civil and criminal penalties and/or fines. The services of PayOnline to mobile phone carriers also are subject to certain of the rules and policies of such carriers and ongoing contractual covenants with such carriers, the violation of which may result in penalties and/or fines and possible termination of PayOnline's services. Certain of our services are also subject to rules set by various payment networks, such as Visa and MasterCard, as more fully described below under "Association and Network Rules".
Association and Network Rules. While not legal or governmental regulation, we are subject to the network rules of Visa, MasterCard and other payment networks. In order to provide processing services, a number of our subsidiaries are registered with Visa and/or MasterCard as service providers for member institutions. Various subsidiaries of ours are also processor level members of numerous networks or are otherwise subject to various network rules in connection with processing services and other services we provide. As such, we are subject to applicable card association, networks and national scheme rules that could subject us to fines or penalties. The payment networks routinely update and modify their requirements. On occasion, we receive notices of non-compliance and fines, which might be related to excessive chargebacks by a merchant or data security failures. Our failure to comply with the networks' requirements or to pay the fines they impose could cause the termination of our registration and require us to stop providing payment services.
Dodd-Frank Act. In July 2010, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 was signed into law in the United States. The Dodd-Frank Act has resulted in significant structural and other changes to the regulation of the financial services industry. Among other things, the Dodd-Frank Act established the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, or CFPB, to regulate consumer financial services, including many offered by our clients.
The Dodd-Frank Act provided two self-executing statutory provisions limiting the ability of payment card networks to impose certain restrictions that became effective in July 2010. The first provision allows merchants to set minimum dollar amounts (not to exceed $10) for the acceptance of a credit card (and allows federal governmental entities and institutions of higher education to set maximum amounts for the acceptance of credit cards). The second provision allows merchants to provide discounts or incentives to entice consumers to pay with cash, checks, debit cards or credit cards, as the merchant prefers.
Separately, the so-called Durbin Amendment to the Dodd-Frank Act provided that interchange fees that a card issuer or payment network receives or charges for debit transactions will now be regulated by the Federal Reserve and must be "reasonable and proportional" to the cost incurred by the card issuer in authorizing, clearing and settling the transaction. Payment network fees, such as switch fees may not be used directly or indirectly to compensate card issuers in circumvention of the interchange transaction fee restrictions. In July 2011, the Federal Reserve published the final rules governing debit interchange fees. Effective in October 2011, debit interchange rates for card issuing financial institutions with more than $10 billion of assets are capped at $0.21 per transaction with an additional component of five basis points of the transaction's value to reflect a portion of the issuer's fraud losses plus, for qualifying issuing financial institutions, an additional $0.01 per transaction in debit interchange for fraud prevention costs. The debit interchange fee would be $0.24 per transaction on a $38 debit card transaction, the average transaction size for debit card transactions. In July 2013, the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia determined that the Federal Reserve's regulations implementing the Durbin Amendment were invalid. The U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia, or D.C. Circuit, reversed this decision on March 21, 2014, generally upholding the Federal Reserve's interpretation of the Durbin Amendment and the Federal Reserve's rules implementing it. On August 18, 2014, the plaintiffs in this litigation filed a petition for a writ of certiorari asking the U.S. Supreme Court to review the D.C. Circuit's decision with respect to the interchange fee cap. We continue to monitor developments in the litigation surrounding these rules. Regardless of the outcome of the litigation, the cap on interchange fees is not expected to have a material direct impact on our results of operations.
In addition, the new rules contain prohibitions on network exclusivity and merchant routing restrictions. Beginning in October 2011, (i) a card payment network may not prohibit a card issuer from contracting with any other card payment network for the processing of electronic debit transactions involving the issuer's debit cards and (ii) card issuing financial institutions and card payment networks may not inhibit the ability of merchants to direct the routing of debit card transactions over any card payment networks that can process the transactions. Since April 2012, most debit card issuers have been required to enable at least two unaffiliated card payment networks on each debit card. We do not expect the prohibition on network exclusivity to impact our ability to pass on network fees and other costs to our clients. These regulatory changes create both opportunities and challenges for us. Increased regulation may add to the complexity of operating a payment processing business, creating an opportunity for larger competitors to differentiate themselves both in product capabilities and service delivery.
Federal Trade Commission Act and Other Laws Impacting our Customers' Business. All persons engaged in commerce, including, but not limited to, us and our merchant and financial institution customers are subject to Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act prohibiting unfair or deceptive acts or practices, or UDAP. In addition, there are other laws, rules and or regulations, including the Telemarketing Sales Act, that may directly impact the activities of our merchant customers and in some cases may subject us, as the merchant's payment processor, to investigations, fees, fines and disgorgement of funds in the event we are deemed to have aided and abetted or otherwise provided the means and instrumentalities to facilitate the illegal activities of the merchant through our payment processing services. Various federal and state regulatory enforcement agencies including the Federal Trade Commission, or FTC, and the states' attorney general have authority to take action against nonbanks that engage in UDAP or violate other laws, rules and regulations and to the extent we are processing payments for a merchant that may be in violation of laws, rules and regulations, we may be subject to enforcement actions and as a result may incur losses and liabilities that may impact our business.
Anti-Money Laundering and Counter Terrorist Regulation. We are also subject to U.S. federal anti-money laundering laws and regulations, including the Bank Secrecy Act, as amended by the USA PATRIOT Act of 2001 (collectively, the BSA). The BSA requires, among other things, that money services businesses to develop and implement risk-based anti-money laundering programs, report large cash transactions and suspicious activity and maintain transaction records
We are additionally subject to economic, export, and trade sanctions programs administered by the Treasury Department’s Office of Foreign Assets Control, or OFAC, and the U.S Department of Commerce. Furthermore, to the extent of future foreign investment or other joint ventures, we are subject to the regulations administered by the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States. These programs may prohibit or restrict transactions to or from or dealings with specified countries, their governments and, in certain circumstances, their nationals, narcotics traffickers, and terrorists or terrorist organizations. We are also subject to other countries’ laws, where applicable, regarding anti-money laundering, counter terrorist financing and proceeds of crime.
Privacy. Our financial institution clients are required to comply with privacy regulations imposed under the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act. These regulations place restrictions on the use of non-public personal information. All financial institutions must disclose detailed privacy policies to their customers and offer them the opportunity to direct the financial institution not to share information with third parties. The regulations, however, permit financial institutions to share information with non-affiliated parties who perform services for the financial institutions. We believe that our company’s present activities fall under exceptions to the consumer notice and opt-out requirements in this law for third-party service providers to financial institutions. However, the laws governing privacy generally remain unsettled. We will update our policies and procedures, where relevant, should it be determined that our activities do not fall within exceptions to Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act requirements. Our businesses operating outside of the U.S. may be subject to other legal requirements concerning the use and protection of certain customer information.
Anti-Corruption. We are subject to applicable anti-corruption laws, such as the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, in the jurisdictions in which we operate. Anti-corruption laws generally prohibit offering, promising, giving, or authorizing others to give anything of value, either directly or indirectly, to a government official or private party in order to influence official action or otherwise gain an unfair business advantage
Anti-Boycott. We are required to comply with U.S. anti-boycott regulations. U.S. law prohibits cooperation with any “illegal boycott request,” which includes a request from a third party to take certain actions against countries friendly to the U.S. These prohibited actions include, but are not limited to, refusal to do business with or in countries friendly to the U.S., or with other persons or entities that do business in or with countries friendly to the U.S.; furnishing information about business relationships with or in countries friendly to the U.S.; and executing business documents such as contracts, letters of credit, warranties that contain illegal boycott requests.
Other Laws and Regulations
Since we collect certain information from members and users on our platform, we will be subject to current and future government regulations regarding the collection, use and safeguarding of consumer information over the Internet and mobile communication devices. These regulations and laws may involve taxation, tariffs, user privacy, rights of publicity, data protection, content, intellectual property, distribution, electronic contracts and other communications, consumer protection and electronic payment services. In many cases, it may be unclear how existing laws governing issues such as property ownership, sales and other taxes, libel and personal privacy apply to the Internet or mobile communication services as the vast majority of these laws were adopted prior to the advent of these technologies and do not contemplate or address the unique issues raised by the Internet and e-commerce.
There are a number of legislative proposals that are anticipated or pending before the U.S. Congress, various state legislative bodies, and foreign governments concerning data protection which could affect us. Many states, for example, have already passed laws requiring notification to subscribers when there is a security breach of personal data. It is possible that these laws may be interpreted and applied in a manner that is inconsistent with our data practices. If so, in addition to the possibility of fines, this could result in an order requiring that we change our data practices, which could have an adverse effect on our business. In addition, some states are interpreting their own statutes differently than federal law. This may create additional compliance burdens.
We are subject to foreign laws and regulations that affect the electronic payments industry in each of the foreign countries in which we operate. Some of these countries, such as the Russian Federation and the United Kingdom, have undergone significant political, economic and social change in recent years. In these countries, there is a greater risk of new, unforeseen changes that could result from, among other things, instability or changes in a country’s or region’s economic conditions; changes in laws or regulations or in the interpretation of existing laws or regulations, whether caused by a change in government or otherwise; increased difficulty of conducting business in a country or region due to actual or potential political or military conflict; or action by the European Union or the United States, Canada or other governments that may restrict our ability to transact business in a foreign country or with certain foreign individuals or entities, such as sanctions by or against the Russian Federation.
Legislation could be passed that limits our ability to use or store information about our users. The Federal Trade Commission (the "FTC") and various states have established regulatory guidelines issued under the Federal Trade Commission Act and various state acts, respectively, that govern the collection, use and storage of consumer information, establishing principles relating to notice, consent, access and data integrity and security. Our practices are designed to comply with these guidelines. For example, we disclose that we collect a range of information about our users, such as their names, email addresses, search histories and activity on our platform. We also use and store such information primarily to personalize the experience on our platforms, provide customer support and display relevant advertising. While we do not sell or share personally identifiable information with third parties for direct marketing purposes, we do have relationships with third parties that may allow them access to user information for other purposes.
The foregoing list of laws and regulations to which we are subject is not exhaustive, and the regulatory framework governing our operations changes continuously. Enactment of new laws and regulations may affect our operations, and could potentially result in increased regulatory compliance costs, litigation expense, adverse publicity, and/or loss of revenue. We believe our policies and practices comply with the FTC privacy guidelines and other applicable laws and regulations. However, if our belief proves incorrect, or if these guidelines, laws or regulations or their interpretations change or new legislation or regulations are enacted, we may be compelled to provide additional disclosures to our users, obtain additional consents from our users before collecting or using their information or implement new safeguards to help our users manage our (or others') use of their information, among other changes.
Rules and Policies of and Contractual Covenants with Mobile Phone Carriers. While not governmental regulation, PayOnline is subject to certain of the rules and policies of mobile phone carriers to which PayOnline provides payment processing services and ongoing contractual covenants with such mobile phone carriers. The mobile phone carriers may from time to time update or otherwise modify or supplement their rules and policies. PayOnline periodically is subject to the imposition of fines or penalties as a result of failure to comply with such rules, policies and/or contractual covenants. PayOnline’s failure to comply with the mobile phone carriers’ respective requirements or to pay the fines or penalties they impose could result in the termination of PayOnline’s services.
Telematics Laws and Regulations in the Russian Federation. The relationships between PayOnline and telecommunications carriers in Russia are governed by the general rules of civil law for the provision of services (Chapter 39 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, because the “information and entertainment services” (content services) provided by PayOnline are inextricably linked with the networks of telecommunications carriers, these services are subject to the requirements of the Rules of Mobile Communications Services Provision, approved by the Decree of the Russian Federation Government dated May 25, 2005 No. 328. These Rules govern the relationship between a customer using mobile communication services and a telecommunications carrier in respect of mobile radio communications services, mobile radiotelephone services and/or mobile satellite radio services in the public network. Although PayOnline is not a telecommunications carrier, many requirements of such Rules are present in PayOnline’s contracts with telecommunications carriers, and such contracts impose responsibility and liability on PayOnline for violations.
PayOnline has a license for the provision of telematics services in Russia. PayOnline is considered an operator of telematics services in Russia because it has a direct connection to equipment of telecommunications carriers and it affects electronic communications (i.e., receiving, processing and/or transmitting electronic messages). Operators of telematics services in Russia are regulated by the Federal Law “On Communication” dated July 2, 2003 No. 126-FZ. This Federal Law provides the legal basis for activity in the field of communications in the Russian Federation and territories under the Russian Federation jurisdiction, defines the powers of public authorities in the field of communications, as well as the rights and responsibilities of persons involved in such activities or using communication services. PayOnline also is subject to the Rules of Telematics Services Provision approved by the Decree of the Russian Federation Government dated September 10, 2007 No. 575. These Rules govern the relationship between a customer or a user, on the one hand, and a telecommunications carrier providing telematics communication services, on the other hand, in the provision of telematics communication services.
The activity of PayOnline to some extent is regulated by the Federal Law “On Operational and Investigative Activities” dated August 12, 1995 No. 144-FZ. This Federal Law determines the content of the operational and investigative activities in the Russian Federation, and provides for a system of guarantees in the process of operational and investigative operations. Operational and investigative activities include activities carried out openly and secretly by operational branches of certain government bodies in order to protect life, health, rights and freedoms of the person and the citizen, property, security of the society and the state from criminal attacks.
In carrying out activities on the Internet in Russia, PayOnline is subject to the Federal Law “On Advertising” dated March 13, 2006 No. 38-FZ. The objectives of this Federal Law are the development of markets for goods and services based on the principles of fair competition, ensuring the common economic space in the Russian Federation, the realization of the rights of consumers to receive fair and accurate advertising, creating favorable conditions for the production and distribution of public service announcements, preventions of violations of the Russian Federation on advertising, as well as the suppression of improper advertising. PayOnline’s activities on the Internet in Russia also are subject to the Federal Law “On Protection of Children from Information Harmful to Health” dated December 29, 2010 No. 436-FZ. This Federal Law provides regulations protecting children from information harmful to their health and/or development.
Concerning relations with Federal communication service providers, PayOnline can be involved in regulation of personal data of subscribers. In case of transferring by Federal communication service providers’ information which includes personal data PayOnline has to take measures to protect such data as the operator of personal data must take. The list of such measures is described in Federal Law “On Personal Data” dated 27.07.2006 No 152. This Federal Law and Federal Law “On Communication” establish rules of usage of personal data of subscribers. Taking into account that this regulation is to be applied only in case of transferring information with personal data from Federal communication service providers it is important to clarify that common execution of contracts with these providers do not stipulate transferring of personal data.
Seasonality
Historically, we have experienced seasonal fluctuations in our revenues as a result of consumer spending patterns, especially in the restaurant business. Revenues have been weaker during the first quarter of the calendar year and stronger during the second, third and fourth quarters. We expect our business to continue experiencing seasonal fluctuations consistent with this historical pattern including the continued effects of the pandemic.
Available Information
We are subject to the informational requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended ('the Exchange Act") and file or furnish reports, proxy statements, and other information with the SEC. You can read our SEC filings over the Internet at the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov. Our filings with the SEC, including our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and any amendments to those reports, also are available free of charge on the investors section of our website at http://investor.netelement.com/en/ir when such reports are available on the SEC’s website. Further corporate governance information, including our certificate of incorporation, bylaws, governance guidelines, board committee charters, and code of business conduct and ethics, is also available on the investors section of our website.
The contents of the websites referred to above are not incorporated into this filing or in any other report or document we file with the SEC, and any references to these websites are intended to be inactive textual references only.
Investing in our securities involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risks and uncertainties described below, together with all of the other information in this Report, including “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes, as well as the preceding “Business” section of this Report, before engaging in any transaction in our securities. Any of the following risks could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and/or prospects, and cause the value of our securities to decline, which could cause you to lose all or part of your investment.
Risks Related to our Financial Condition
Our financial condition creates doubt as to whether we will continue as a going concern. If we do not continue as a going concern, investors may lose their entire investment.
Since our inception, we have incurred significant operating losses. We sustained a net loss of approximately $5.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 and an accumulated deficit of approximately $184.7 million at December 31, 2020. We had a negative working capital of approximately $1.7 million at December 31, 2020. Our current assets at December 31, 2020 included approximately $4.5 million in cash, $7.1 million of accounts receivable and $1.1 million in prepaid expenses. Our current liabilities included approximately $11.8 million in accounts payable and accrued expenses, $1.6 million in deferred revenue and $1.3 million in current notes payable.
As of the filing date of this Report with the SEC, management expects that our cash flows from operations will not be sufficient to fund our current operations through 2021. We will require additional capital in order to continue our existing business operations and to fund our obligations. At this time, the outbreak and continuing spread of the novel coronavirus (“COVID-19”) pandemic is continuing to impact countries, communities, supply chains and markets, global financial markets, as well as, the largest industry group serviced by our Company. To date, COVID-19 has not had a material impact on the Company's revenues as compared to the previous year. However, the Company cannot predict whether COVID-19 will have a material impact on our future financial condition and results of operations due to understaffing in the service sector and the decrease in revenues and profits, particularly restaurants, and any possible future government ordinances that may further restrict restaurant and other service or retail sectors operations, including the potential course of COVID 19, and measures instituted to control the spread domestically and internationally.
Our company is re-evaluating its operating plans in order to maintain current payment processing functions, capabilities, and continued customer service to its merchants, and is also seeking sources of capital to pay our contractual obligations as they come due, in light of these uncertain times. Management believes that upon re-evaluating its operating strategy it will provide the opportunity for us to continue as a going concern as long as we are able to obtain additional financing. At this time, due to our continuing losses from operations, negative working capital, and the COVID-19 pandemic, we cannot predict the impact of these conditions on our ability to obtain financing necessary for the Company to fund its working capital requirements. In most respects, there is still uncertainty regarding the measures in place to control the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic to be able to quantify or qualify the longer-term ramifications on our business, our merchants, and our potential investors.
At this time, we cannot determine the capital we will need to finance our continuing operations over the next 12 months, due to an inability to be able to quantify or qualify the longer-term ramifications on our business, our merchants, and our potential investors due to COVID-19. We may raise additional funds through debt financing and/or the issuance of equity securities, there being no assurance that any type of financing on terms satisfactory to us will be available or otherwise occur. Debt financing must be repaid regardless of whether we generate revenues or cash flows from operations and may be secured by substantially all of our assets. Any equity financing or debt financing that requires the issuance of equity securities or warrants to the lender would cause the percentage ownership by our current stockholders to be diluted, which dilution may be substantial. Also, any additional equity securities issued may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to those of existing stockholders. If such financings are not available when required or are not available on acceptable terms, we may be unable to continue servicing our current merchants, implement a restructured business plan, or take advantage of business opportunities, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and/or prospects and may ultimately require us to suspend or cease operations, which could cause investors to lose the entire amount of their investment.
Risks Related to Our Business and Operations
The outbreak of a health epidemic or pandemic, including the COVID-19 coronavirus, may have an adverse effect on our business.
Our business could be materially and adversely affected by the continued or possible outbreak of a widespread health epidemic or pandemic, including arising from various strains of avian flu or swine flu, such as H1N1, or the COVID-19 coronavirus, particularly if located in industry sectors from which we derive a significant amount of revenue or profit, such as restaurants. The occurrence of the continued spread of the pandemic outbreak or other adverse public health developments could materially disrupt our business and operations. Such events could also significantly impact our industry and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
For example, many of our restaurant merchants that we service located within mainland United States, as well as hospitality and retail sector merchants, have been temporarily closed, have shortened operating hours and/or have otherwise been adversely affected by the impact continuing spread of COVID-19. These merchants have experienced significant sales declines or no sales at all due to closure of their business or limiting in-dining capacity. Additionally, the COVID-19 outbreak has negatively impacted employee productivity, including affecting the availability of employees reporting for work.
Additionally, our business, financial condition and results of operations have been and may be further impacted in several ways, including, but not limited to, the following:
● | disruptions to our operations, including due to restrictions on our operations, sales and marketing efforts, product development and other important business activities; |
● | reduced processing volumes, particularly due to disruptions to the businesses and operations of our merchants; |
● | greater difficulty in collecting customer receivables; |
● | a fluctuation in foreign currency exchange rates or interest rates could result from market uncertainties; and |
● | an increase in the cost or the difficulty to obtain debt or equity financing could affect our financial condition or our ability to fund operations. |
Additionally, COVID-19 could impact our internal controls over financial reporting as a portion of our workforce is required to work from home and therefore new processes, procedures, and controls could be required to respond to changes in our business environment. Further, should any key employees become ill from COVID-19 and unable to work, the attention of the management team could be diverted.
Although we will continue to monitor the situation and take further actions, which may include further altering our operations, in order to protect the best interests of our employees, merchants and partners and to comply with government requirements, there is no certainty that such measures will be enough to mitigate the risks posed by the virus, and our ability to perform critical functions could be harmed.
We are unable to accurately predict the impact that COVID-19 will have on our results of operations, due to uncertainties including the ultimate geographic spread of the virus within and outside of the United States, the severity of the disease, the duration of the outbreak, and actions that have been taken by governmental authorities to contain COVID-19 or to treat its impact. The potential effects of COVID-19 may also impact many of our other risk factors discussed in this “Risk Factors” section. However, while it is premature to accurately predict the ultimate impact of these developments, we expect our results for the quarter ending March 31, 2021 to be impacted with potential continuing adverse impacts beyond March 31, 2021.
Global economic, political, and other conditions, including the recent COVID-19 pandemic, may adversely affect trends in consumer, business, and government spending, which may adversely impact the demand for our services and our revenue and profitability.
Financial services, payments, and technology industries in which we operate depend heavily upon the overall level of consumer, business, and government spending. A sustained deterioration in the general economic conditions (including distress in financial markets, turmoil in specific economies around the world, and additional government intervention), particularly in the United States or Europe, or increases in interest rates in key countries in which we operate may adversely affect our financial performance by reducing the number or average purchase amount of transactions involving payment cards. A reduction in the amount of consumer spending could result in a decrease of our revenue and profits. The current threats to global economic growth include geopolitical instability in Russia, Ukraine, the Middle East and other oil producing countries. Instability in these regions could affect economic conditions in Europe and the United States. In addition, in March 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of the COVID-19 a pandemic. The global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has had a negative effect on the global economy and consumer spending, disrupted the financial markets and created increased overall volatility.
Adverse economic trends may accelerate the timing, or increase the impact of, risks to our financial performance. Such trends may include, but are not limited to, the following:
● | Declining economies, foreign currency fluctuations, and the pace of economic recovery can change consumer spending behaviors on which a significant portion of our revenues are dependent. | |
● | Low levels of consumer and business confidence typically associated with recessionary environments, and those markets experiencing relatively high unemployment, may cause decreased spending by cardholders. | |
● | Budgetary concerns in the United States and other countries around the world could affect the United States and other specific sovereign credit ratings, impact consumer confidence and spending, and increase the risks of operating in those countries. | |
● | Emerging market economies tend to be more volatile than the more established markets we serve in the United States and Europe, and adverse economic trends may be more pronounced in such emerging markets. | |
● | Financial institutions may restrict credit lines to cardholders or limit the issuance of new cards to mitigate cardholder defaults. | |
● | Uncertainty and volatility in the performance of our clients' businesses may make estimates of our revenues, rebates, incentives, and realization of prepaid assets less predictable. | |
● | Our clients may decrease spending for value-added services. | |
● | Government intervention, including the effect of laws, regulations, and /or government investments in our clients, may have potential negative effects on our business and our relationships with our clients or otherwise alter their strategic direction away from our products. |
A weakening in the economy could also force some retailers to close, resulting in exposure to potential credit losses and declines in transactions, and reduced earnings on transactions due to a potential shift to large discount merchants. Additionally, credit card issuers may reduce credit limits and become more selective in their card issuance practices. Changes in economic conditions could adversely impact our future revenues and profits and result in a downgrade of our corporate capacity to borrow, which may lead to termination or modification of certain contracts and make it more difficult for us to obtain new business. Any of these developments could have a material adverse impact on our overall business and results of operations.
Our ability to anticipate and respond to changing industry trends and the needs and preferences of our clients and consumers may affect our competitiveness or demand for our products, which may adversely affect our operating results.
Financial services, payments, and technology industries are subject to rapid technological advancements, new products and services, including mobile payment applications, evolving competitive landscape, developing industry standards, and changing client and consumer needs and preferences. We expect that new services and technologies applicable to the financial services, payments, and technology industries will continue to emerge. These changes in technology may limit the competitiveness of and demand for our services. Also, our clients and their customers continue to adopt new technology for business and personal uses. We must anticipate and respond to these changes in order to remain competitive within our relative markets. For example, our ability to provide innovative POS technologies to our merchant clients could have an impact on our North American Transaction Solutions segment.
Failure to develop value-added services that meet the needs and preferences of our clients could have an adverse effect on our ability to compete effectively in our industry. Furthermore, clients' and their customers' potential negative reaction to our products and services can spread quickly through social media and damage our reputation before we have the opportunity to respond. If we are unable to anticipate or respond to technological changes or evolving industry standards on a timely basis, our ability to remain competitive could be materially adversely affected.
Substantial and increasingly intense competition worldwide in the financial services, payments, and technology industries may materially and adversely affect our overall business and operations.
Financial services, payments, and technology industries are highly competitive and our payment solutions compete against all forms of financial services and payment systems, including cash and checks, and electronic, mobile, and e-commerce payment platforms. If we are unable to differentiate ourselves from our competitors, drive value for our clients and/or effectively align our resources with our goals and objectives, we may not be able to compete effectively. Our competitors may introduce their own value-added or other services or solutions more effectively than we do, which could adversely impact our growth. We also compete against new entrants that have developed alternative payment systems, e-commerce payment systems, and payment systems for mobile devices. Failure to compete effectively against any of these competitive threats could have a material adverse effect on us. In addition, the highly competitive nature of our industry could lead to increased pricing pressure which could have a material impact on our overall business and results of operations.
Potential changes in the competitive landscape, including disintermediation from other participants in the payments value chain, could harm our business.
We expect that the competitive landscape will continue to change, including:
● | Rapid and significant changes in technology, resulting in new and innovative payment methods and programs that could place us at a competitive disadvantage and that could reduce the use of our products. | |
● | Competitors, clients, governments, and other industry participants may develop products that compete with or replace our value-added products and services. | |
● | Participants in the financial services, payments, and technology industries may merge, create joint ventures, or form other business combinations that may strengthen their existing business services or create new payment services that compete with our services. | |
● | New services and technologies that we develop may be impacted by industry-wide solutions and standards related to migration to EMV chip technology, tokenization, or other safety and security technologies. |
Failure to compete effectively against any of these competitive threats could have a material adverse effect on us.
The market for our electronic commerce services is evolving and may not continue to develop or grow rapidly enough for us to develop and increase our profitability.
If the number of electronic commerce transactions does not grow or if consumers or businesses do not continue to adopt our services, it could have a material adverse effect on the profitability of our business, financial condition, and results of operations. We believe future growth in the electronic commerce market will be driven by the cost, ease-of-use, and quality of products and services offered to consumers and businesses. In order to consistently increase and maintain our profitability, consumers and businesses must continue to adopt our services, including our merchant suite, Aptito and PayOnline solutions.
If we cannot compete effectively, we will lose business.
We believe our merchant processing business is positioned to be competitive in our target markets. We cannot guarantee that we will be able to maintain or increase revenues from our existing operations, or that our proposed future operations will be implemented successfully. Our principal competitive considerations include:
● | financial resources to allocate to proper marketing and sales efforts; | |
● | the ability to develop and maintain our operations, applications and technologies; | |
● | the ability to effectively implement our business plans and strategies; | |
● | establishing our brand name; | |
● | financial resources to support working capital needs and required capital investments; and | |
● | effects of sanctions on our business. |
We rely on third-party processors and service providers; if they fail or no longer agree to provide their services, our merchant relationships could be adversely affected and we could lose business.
We rely on agreements with several large payment processing organizations to enable us to provide card authorization, data capture, settlement and merchant accounting services and access to various reporting tools for the merchants we serve. We also outsource other services including reorganizing and accumulating daily transaction data on a merchant-by-merchant and card issuer-by-card issuer basis and forwarding the accumulated data to the relevant Payment Card Brands. Many of these organizations and service providers are our competitors, and we do not have long-term contracts with most of them. Typically, our contracts with these third parties are for one-year and are subject to cancellation upon limited notice by either party. The termination by our service providers of their arrangements with us or their failure to perform their services efficiently and effectively may adversely affect our relationships with the merchants whose accounts we serve and may cause those merchants to terminate their processing agreements with us.
We rely on bank sponsors, which have substantial discretion with respect to certain elements of our business practices, in order to process bankcard transactions. If these sponsorships are terminated and we are not able to secure or successfully migrate merchant portfolios to new bank sponsors, we will not be able to conduct our business.
Because we are not a bank, we are unable to belong to and attain direct membership to Visa and MasterCard. Visa and MasterCard operating regulations require us to be sponsored by a bank in order to process bankcard transactions. We are currently registered with Visa and MasterCard through the sponsorship from banks that are members of the card brands. The principal sponsoring bank through which we process the significant majority of our transactions is Esquire Bank, N.A.. If our sponsorships are terminated and we are not able to secure or successfully migrate merchant portfolios to new bank sponsors, we will not be able to conduct our business.
If we or our bank sponsors fail to adhere to the standards of Visa and MasterCard, our registrations with these organizations could be terminated, and we could be required to stop providing payment processing services for Visa and MasterCard.
Substantially all of the transactions we process involve Visa or MasterCard. If we or our bank sponsors fail to comply with the applicable requirements of the Visa or MasterCard payment card brands, Visa or MasterCard could suspend or terminate our registration. The termination of our registration or any changes in the Visa or MasterCard rules that would impair our registration could prevent us from providing transactional processing services.
If PayOnline fails to maintain its key partnerships with banks, financial institutions or payment processors, our financial results could be adversely affected.
PayOnline’s business relies on partnering with different banks, financial institutions and payment processors to expand globally in order to enable it to provide international payment processing. To the extent PayOnline fails to maintain key partnerships with such banks, financial institutions or payment processors, our financial results could be adversely affected. Such failure to maintain partnerships may be due to mergers and/or consolidations of banks, financial institutions and payment processors, which may result in potential changes in their business processes that could negatively affect PayOnline operations, in particular in emerging markets, such as Kazakhstan.
We periodically experience increases in interchange and other related costs, and if we cannot pass these increases along to our merchants, our profit margins will decline.
We pay interchange fees and assessments to issuing banks through the card brands for each transaction we process using their credit and debit cards. From time to time, the card brands increase the interchange fees that they charge processors and the sponsoring banks. At their sole discretion, our sponsoring banks have the right to pass any increases in interchange fees on to us. In addition, our sponsoring banks may seek to increase their Visa and MasterCard sponsorship fees to us, all of which are based upon the dollar amount of the payment transactions we process. If we are not able to pass these fee increases along to merchants through corresponding increases in merchant discount, our profit margins will decline.
To acquire and retain merchant accounts, we depend on independent non-bank sales groups that do not serve us exclusively.
We rely on the efforts of ISGs to market our services to merchants seeking to establish a credit card processing relationship. ISGs are companies that seek to introduce to us, as well as our competitors, newly established and existing small merchants, including retailers, restaurants and other service providers. Generally, our agreements with ISGs are not exclusive and they have the right to refer merchants to other providers of transaction payment processing services. Our failure to maintain our relationships with our existing ISGs and to recruit and establish new relationships with other ISGs could adversely affect our revenues and internal growth and increase our merchant attrition.
Unauthorized disclosure of data, whether through cybersecurity breaches, computer viruses or otherwise, could expose us to liability, protracted and costly litigation and could damage our reputation.
We process, store and/or transmit sensitive data, such as names, addresses, credit or debit card numbers and bank account numbers, and we may have liability if we fail to protect this data in accordance with applicable laws and our clients’ specifications. The loss of data could result in significant fines and sanctions by our clients or governmental bodies, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. These concerns about security are increased when we transmit information over the Internet. Computer viruses can be distributed and spread rapidly over the Internet and could infiltrate our systems, which might disrupt our services and make them unavailable. In addition, a significant cybersecurity breach could result in payment networks prohibiting us from processing transactions on their networks or the loss of clients. We have been in the past and could be in the future, subject to breaches of security by hackers. It is possible that our encryption of data and other protective measures may not prevent unauthorized access. Although we have not to date incurred material losses or liabilities as a result of those breaches, a future breach of our system may subject us to material losses or liability, including payment of fines and claims for unauthorized purchases with misappropriated credit or debit card or bank account information or other similar fraud claims. A misuse of such data or a cybersecurity breach could harm our reputation and deter clients from using electronic payments generally and our services specifically, increase our operating expenses in order to correct the breaches or failures, expose us to uninsured liability, increase our risk of regulatory scrutiny, subject us to lawsuits and/or result in the imposition of material penalties and fines under applicable laws or by our clients.
Our operating results are subject to seasonality, and, if our revenues are below our seasonal norms during our historically stronger quarters, our financial results could be adversely affected.
We have experienced in the past, and expect to continue to experience, seasonal fluctuations in our revenues as a result of consumer spending patterns. Historically, revenues have been weaker during the first quarter of the calendar year and stronger during the second, third and fourth quarters. If, for any reason, our revenues are below seasonal norms during the second, third or fourth quarter, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
New and potential governmental regulations designed to protect or limit access to consumer information could adversely affect our ability to provide, or impair the value of, the services we currently provide to our merchants.
Due to the increasing public concern over consumer privacy rights, governmental bodies in the United States and abroad have adopted, and are considering adopting, additional laws and regulations restricting the purchase, sale and sharing of personal information about customers. For example, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act requires non-affiliated third-party service providers to financial institutions to take certain steps to ensure the privacy and security of consumer financial information. We believe our present activities fall under exceptions to the consumer notice and opt-out requirements contained in this law for third-party service providers to financial institutions. However, the laws governing privacy generally remain unsettled. Even in areas where there has been some legislative action, such as the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and other consumer statutes, it is difficult to determine whether and how existing and proposed privacy laws or changes to existing privacy laws will apply to our business. Limitations on our ability to access and use customer information could adversely affect our ability to provide the services we currently offer to our merchants or impair the value of these services. Several states have proposed legislation that would limit the use of personal information gathered using the Internet. Some proposals would require proprietary online service providers and website owners to establish privacy policies. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act went into effect on January 1, 2020 and imposes significant requirements on covered businesses, including mandatory disclosure of customers’ data when requested, customer data erasure in some contexts, and notification that customers can object to sale of their data, among numerous other provisions. It is foreseeable that other states may follow with similar legislation. Congress has also considered privacy legislation that could further regulate the use of consumer information obtained over the Internet or in other ways. Our compliance with these privacy laws and related regulations could materially affect our operations.
Changes to existing laws or the passage of new laws could:
● | create uncertainty in the marketplace that could reduce demand for our services; | |
● | restrict or limit our ability to sell certain products and services to certain customers; | |
● | limit our ability to collect and to use merchant and cardholder data; or | |
● | increase the cost of doing business as a result of litigation costs or increased operating costs; |
Any changes to existing laws or the passage of new laws that have effects such as those described above could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we are required to pay federal, state or local taxes on transaction processing, it could negatively impact our profit margins.
Transaction processing companies may become subject to federal, state or local taxation of certain portions of their fees charged to merchants for their services. Application of these taxes is an emerging issue in our industry and taxing jurisdictions have not yet adopted uniform positions on this topic. If we are required to pay such taxes and are unable to pass this tax expense through to our merchant clients, or are unable to produce increased cash flow to offset such taxes, these taxes would negatively impact our profit margins.
We are subject to foreign laws and regulations, which are subject to change and uncertain interpretation.
We are subject to foreign laws and regulations that affect the electronic payments industry in each of the foreign countries in which we operate. Some of these countries, such as the Russian Federation, have undergone significant political, economic and social change in recent years. In these countries, there is a greater risk of new, unforeseen changes that could result from, among other things, instability or changes in a country’s or region’s economic conditions; changes in laws or regulations or in the interpretation of existing laws or regulations, whether caused by a change in government or otherwise; increased difficulty of conducting business in a country or region due to actual or potential political or military conflict; or action by the European Union, the United States or other governments that may restrict our ability to transact business in a foreign country or with certain foreign individuals or entities, such as sanctions by or against the Russian Federation.
Proposed foreign legislation and regulations could also affect our business. For example, the Russian Federal Tax Service is interested in all betting sites that render services to Russian citizens and wants to have these sites operate their business within the Russian Federation. Some believe that Russian regulators will lobby for a ban on payments for betting sites operating outside of Russia. If such a bill is adopted, then betting sites not registered in Russia could be limited in their ability to process payments, which could harm our customers and adversely affect our payment processing business.
Our management has identified continued material weaknesses in our controls and procedures as of December 31, 2020, which, if not properly remedied, could result in material misstatements in our financial statements.
As of the end of the period covered by this Report, our management conducted an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and Rule 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act). Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective because there are a limited number of personnel employed and we cannot have an adequate segregation of duties, and due to the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting as discussed in “Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting” in Part II, Item 9A of this Report. Accordingly, management cannot provide reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objective. Management works to mitigate these risks by being personally involved in all substantive transactions and attempts to obtain verification of transactions and accounting policies and treatments involving our operations, including those overseas. We are in the process of reviewing and, where necessary, modifying controls and procedures throughout the Company and we plan to address deficiencies identified as needed during 2021, pending the economic uncertainty at this time, concerning the Covid-19 pandemic and the re-allocation of current resources
Acquisition activities could result in operating difficulties, dilution to our stockholders and other harmful consequences, and we may not achieve the anticipated benefits of the acquisitions.
We have built our current business primarily through acquisitions of intellectual property and other assets in connection with acquiring businesses, such as Unified Payments, Aptito and PayOnline, and we may selectively pursue strategic acquisitions in the future. Future acquisitions could divert management’s time and focus from operating our business. In addition, integrating an acquired company, business or technology is risky and may result in unforeseen operating difficulties and expenditures. Foreign acquisitions also involve unique risks related to integration of operations across different cultures and languages, currency risks and the particular economic, political and regulatory risks associated with specific countries. We may not accurately assess the value or prospects of acquisition candidates, and the anticipated benefits from our future or even past acquisitions may not materialize. In addition, future acquisitions or dispositions could result in potentially dilutive issuances of our equity securities, including our common stock, the incurrence of significant amounts of debt, contingent liabilities or amortization expenses, or write-offs of goodwill, any of which could negatively affect our financial condition.
We are dependent upon certain key relationships. If any of our key relationships were to deteriorate, our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Our success, particularly the success of our payment processing business, is dependent, in part, upon industry relationships of our Chief Executive Officer, Oleg Firer. If we were to lose the services of Mr. Firer, or if the industry relationships of Mr. Firer on which we rely were to deteriorate, our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected. To our knowledge, Mr. Firer currently has no plans to retire or leave us in the near future, and we are not aware of any material adverse developments in his industry relationships. We do not have “key person” insurance on the life of Mr. Firer or any other member of our management team.
If we fail to adequately protect or enforce our intellectual property rights, competitors may create and market products and services similar to ours. In addition, we may be subject to intellectual property litigation and infringement claims by third parties.
Our ability to compete effectively is dependent in part upon the proprietary nature of our technologies and software platforms. We generally rely on a combination of trade secret, copyright, trademark and patent law to protect our proprietary rights in our intellectual properties. Although we attempt to protect our proprietary technologies through trade secrets, trademarks, patents and license and other agreements, these may be insufficient. In addition, if we license our software in non-U.S. countries, because of differences in foreign laws concerning proprietary rights, our intellectual properties may not receive the same degree of protection in non-U.S. countries as they would in the United States. We may not always be able to successfully protect or enforce our proprietary information and assets against competitors, which may materially adversely affect our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, there can be no assurance that our competitors will not independently utilize existing technologies to develop products that are substantially equivalent or superior to ours, which also could materially adversely affect our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
Although we do not believe that our intellectual properties infringe the rights of others, and while to date we have not been subject to such claims, we may be exposed to, or threatened with, future litigation by other parties alleging that our technologies infringe their intellectual property rights. Any intellectual property claims, regardless of their merit, could be time consuming, expensive to litigate or settle and could divert management resources and attention. An adverse determination in any intellectual property claim could require us to pay damages and/or stop using our technologies and other material found to be in violation of another party’s rights and could prevent us from licensing our technologies to others. In order to avoid these restrictions, we may have to seek a license. Such a license may not be available on reasonable terms, could require us to pay significant license fees and may significantly increase our operating expenses. A license also may not be available to us at all. As a result, we may be required to use and/or develop non-infringing alternatives, which could require significant effort and expense. If we cannot obtain a license or develop alternatives for any infringing aspects of our business, we may be forced to limit our technologies and may be unable to compete effectively. Any of these adverse consequences could have a material adverse effect on our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
Further, from time to time we may be engaged in disputes regarding the licensing of our intellectual property rights, including matters related to the terms of our licensing arrangements. These types of disputes can be asserted by our licensees or prospective licensees or by other third parties as part of negotiations with us or in private actions seeking monetary damages or injunctive relief or in regulatory actions. Requests for monetary and injunctive remedies asserted in claims like these could be material and could have a significant impact on our business prospects. Any disputes with our licensees, potential licensees or other third parties could materially adversely affect our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates could negatively affect our financial results.
We earn revenues and interest income, pay expenses, own assets and incur liabilities in countries using currencies other than the U.S. dollar. In the year ended December 31, 2020, we used one functional currency - the Russian ruble - in addition to the U.S. dollar, and derived approximately 5% of our total net revenues from operations outside the United States in Russia and CIS. As of December 31, 2020, the foreign exchange rate for the Russian ruble increased by approximately 19.9% as compared to the daily rate at December 31, 2019. Because our consolidated financial statements are presented in U.S. dollars, we must translate net revenues, interest income and expenses, as well as assets and liabilities, into U.S. dollars at exchange rates in effect during or at the end of each reporting period. Therefore, increases or decreases in the value of the U.S. dollar against other major currencies will affect the amounts of our net revenues, interest income, operating expenses and the value of balance sheet items, including intercompany assets and obligations. Because we have operations in Russia, our exchange rate risk is highly sensitive to the prevailing value of the U.S. dollar relative to the Russian ruble, which exchange rates have fluctuated significantly in recent months as a result, in part, of the continuing instability in Ukraine and Syria as well as continued sanctions against Russia. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, particularly the U.S. dollar against the Russian ruble, may materially adversely affect our financial results.
Our business is subject to complex and evolving U.S. and foreign laws and regulations regarding privacy, data protection and other matters. Many of these laws and regulations are subject to change and uncertain interpretations, and could result in claims, changes to our business practices, increased cost of operations or declines in user growth or engagement, or otherwise harm our business.
We are subject to a number of foreign and domestic laws and regulations that affect companies conducting business on the Internet and companies transmitting user information and payments via text message or other electronic means, many of which are still evolving and the interpretation of which are often uncertain. Failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations may result in the suspension or revocation of licenses or registrations, the limitation, suspension or termination of services and/or the imposition of civil and criminal penalties and/or fines. The services of PayOnline to mobile phone carriers also are subject to certain of the rules and policies of such carriers and ongoing contractual covenants with such carriers, the violation of which may result in penalties and/or fines and possible termination of PayOnline’s services. For additional information, see “Business Description - Regulation” in Part I, Item 1 of this Report.
Poor perception of our brand, business or industry could harm our reputation and adversely affect our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
The success of our business depends in part on our reputation within our industries and with our clients and consumers. We may be the subject of unflattering reports in blogs, video blogs and the media about our business and our business model. Any damage to our reputation could harm our ability to obtain and retain contracts with mobile phone carriers, content providers, advertisers and other customers, which could materially adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition and business.
Our business is subject to the risks of hurricanes, floods, fires and other natural catastrophic events and to interruption by man-made problems such as computer viruses or terrorism.
Our systems and operations are vulnerable to damage or interruption from hurricanes, floods, fires, power losses, telecommunications outages, terrorist attacks, acts of war, human errors, break-ins and similar events. Our U.S. corporate offices are located in Miami, Florida, which is an area that is at high risk of hurricane and flood damage. In addition, acts of terrorism, which may be targeted at metropolitan areas that have higher population density than rural areas, could cause disruptions in our business or the economy as a whole. The servers that we use through various third-party service providers are not located in Miami, Florida but may also be vulnerable to computer viruses, break-ins and similar disruptions from unauthorized tampering with our computer systems, which could lead to interruptions, delays, loss of critical data or the unauthorized disclosure of confidential information. Such service providers may not have sufficient protection or recovery plans in certain circumstances, and our insurance may not be sufficient to compensate us for losses that may occur. As we rely heavily on our servers, computer and communications systems and the Internet to conduct our business, such disruptions could negatively impact our ability to run our business and either directly or indirectly disrupt our customers’ respective businesses, which could have an adverse effect on our business prospects, operating results and financial condition.
Our merchants may be unable to satisfy obligations for which we may also be liable.
We are subject to the risk of our merchants being unable to satisfy obligations for which we may also be liable. For example, we and our merchant acquiring alliances may be subject to contingent liability for transactions originally acquired by us that are disputed by the cardholder and charged back to the merchants. If we or the alliance is unable to collect this amount from the merchant because of the merchant’s insolvency or other reasons, we or the alliance will bear the loss for the amount of the refund paid to the cardholder. We have an active program to manage our credit risk and often mitigate our risk by obtaining collateral. It is possible, however, that a default on such obligations by one or more of our merchants could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Fraud by merchants or others could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We may be subject to potential liability for fraudulent electronic payment transactions or credits initiated by merchants or others. Examples of merchant fraud include when a merchant or other party knowingly uses a stolen or counterfeit credit, debit or prepaid card, card number, or other credentials to record a false sales transaction, processes an invalid card, or intentionally fails to deliver the merchandise or services sold in an otherwise valid transaction. Criminals are using increasingly sophisticated methods to engage in illegal activities such as counterfeiting and fraud. It is possible that incidents of fraud could increase in the future. Failure to effectively manage risk and prevent fraud would increase our chargeback liability or other liability. Increases in chargebacks or other liability could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Risks Related to the Mullen Merger
Failure of the Merger to be completed or a significant continued delay in the consummation of the Merger could negatively impact us.
If the contemplated Merger is not completed or continues to be significantly delayed, we may be subject to a number of material risks, including, but not limited to the following:
● | the price of our common stock may decline to the extent that the relevant current market price reflects a market assumption that the Merger will be completed; |
● | costs related to the Merger, such as legal, accounting, certain financial advisory and financial printing fees, must be paid even if the Merger is not completed; |
● | we could be subject to litigation related to the Merger; |
● | we will not realize the benefit of the time and resources, financial and otherwise, committed by our management to matters relating to the Merger that could have been devoted to pursuing other beneficial opportunities; |
● | we may be unsuccessful in completing an alternative strategic transaction on terms that are as favorable as the terms of the proposed transaction with Merger, or at all; and |
● | we may be unable to continue as a going concern. |
We will be subject to business uncertainties while the Merger is pending.
Uncertainty about the effect of the contemplated Merger on employees, merchants, partners and other persons with whom we have a business relationship may have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. These uncertainties may impair our ability to attract, retain and motivate key personnel and merchants pending the consummation of the Merger, as such personnel and merchants may experience uncertainty about their future roles and relationships following the consummation of the Merger. Additionally, these uncertainties could cause our merchants, partners and others with whom we deal to seek to change, or fail to extend, existing business relationships with us. In addition, competitors may target our existing merchants by highlighting potential uncertainties that may result from or in connection with the Merger. The pursuit of the Merger may also place a burden on our management and internal resources. Any significant diversion of management attention away from ongoing business concerns could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
On March 30, 2021, the Company entered into the Second Amendment (the “Second Amendment”) to Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of August 4, 2020, as amended by the First Amendment dated as of December 29, 2020 (the “Merger Agreement”) with Mullen Technologies, Inc., a California corporation (“Mullen”), Mullen Acquisition, Inc., a California corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”). Prior to the parties’ execution and delivery of the Second Amendment, Section 8.1(b) of the Merger Agreement, as amended, provided that the Merger Agreement may be terminated and the merger contemplated in the Merger Agreement (the “Merger”) and other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement may be abandoned at any time prior to the merger effective time, notwithstanding any requisite approval and adoption of this Agreement and the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement by the shareholders of Mullen and/or the stockholders of the Company, by either Company or Mullen if the merger effective time shall not have occurred on or before March 31, 2021 (the “Outside Date”). Pursuant to the Second Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub amended Section 8.01(b) of the Merger Agreement to extend the Outside Date to April 30, 2021.
The foregoing description of the Second Amendment does not purport to be complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by, the full text of such agreement, a copy of which is attached hereto as Exhibit 2.1 and incorporated herein by reference.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
Our officers, directors and their affiliates own a large portion of our common stock. Future sales or distributions of our common stock in the public market by us or our officers, directors and their affiliates could adversely affect the trading price of our common stock.
At March 30, 2021, our officers, directors and their affiliates beneficially owned approximately 14.9% of our common stock. Sales or distributions of a substantial number of shares of our common stock by our officers, directors and their affiliates in the public market, or the perception that these sales or distributions might occur, may cause the market price of our common stock to decline.
In addition, we may sell equity securities in the future to obtain funds for general corporate, working capital, acquisitions or other purposes. We may sell these securities at a discount to the then market price. Any future sales of equity securities will dilute the holdings of existing stockholders, possibly reducing the value of their investment.
In addition, we may sell equity securities in the future to obtain funds for general corporate, working capital, acquisitions or other purposes. We may sell these securities at a discount to the then market price. Any future sales of equity securities will dilute the holdings of existing stockholders, possibly reducing the value of their investment.
The market price and trading volume of our common stock may be volatile, which could result in rapid and substantial losses for our stockholders.
You should consider an investment in our common stock to be risky, and you should invest in our common stock only if you can withstand a significant loss and wide fluctuations in the market value of your investment. Many factors could cause the market price of our common stock to rise and fall, including the following:
● | our announcements or our competitors’ announcements regarding new products or services, enhancements, significant contracts, acquisitions or strategic investments; |
● | changes in earnings estimates or recommendations by securities analysts, if any, who cover our common stock; |
● | results of operations that are below our announced guidance or below securities analysts’ or consensus estimates or expectations; |
● | fluctuations in our quarterly financial results or the quarterly financial results of companies perceived to be similar to us; |
● | changes in our capital structure, such as future issuances of securities, sales of large blocks of common stock by our stockholders or our incurrence of additional debt; |
● | investors’ general perception of us and our industry; |
● | changes in general economic and market conditions; |
● | changes in industry conditions; and |
● | changes in regulatory and other dynamics. |
In addition, if the market for stocks in our industry, or the stock market in general, experiences a loss of investor confidence, the trading price of our common stock could decline for reasons unrelated to our business, financial condition or results of operations. If any of the foregoing occurs, it could cause our stock price to fall and may expose us to lawsuits that, even if successfully defended, could be costly to defend and a distraction to management.
We are a “smaller reporting company,” and we cannot be certain if the reduced disclosure requirements applicable to smaller reporting companies will make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are a “smaller reporting company,” as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. As a smaller reporting company, we have relied on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not smaller reporting companies. These exemptions include reduced financial disclosure and reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements. We may continue to rely on such exemptions for so long as we remain a smaller reporting company under applicable SEC rules and regulations. Accordingly, we cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result of our reduced disclosures, there may be less active trading in our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
General Risk Factors
We incur increased costs as a result of being a public company.
As a public company, we currently incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses not incurred by private companies. It may be time consuming, difficult and costly for us to develop, implement and maintain the additional internal controls, processes and reporting procedures required by federal statutes, SEC rules, other government regulations affecting public companies and/or stock exchange compliance requirements. We may need to hire additional financial reporting, internal auditing and other finance staff in order to develop, implement and maintain appropriate internal controls, processes and reporting procedures, which will increase our expenses and adversely affect our operating results and financial condition.
We are the subject of various legal proceedings which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or operating results.
We are involved in various litigation matters. We may, from time to time, also be involved in or be the subject of governmental or regulatory agency inquiries or investigations. If we are unsuccessful in our defense in the litigation matters, or any other legal proceeding, we may be forced to pay damages or fines and/or change our business practices, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. For more information about our legal proceedings, see “Legal Proceedings” in Part I, Item 3 of this Report.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
Not applicable.
North American Transaction Solutions
During May 2013, we entered into a lease agreement, for approximately 4,101 square feet of office space located at 3363 N.E. 163rd Street, Suites 705 through 707, North Miami Beach, Florida 33160. The term of the lease agreement was from May 1, 2013 through December 31, 2016, with monthly rent increasing from $16,800 per month at inception to $19,448 per month (or $233,377 per year) for the period from January 1, 2016 through December 31, 2016. The lease was extended for a period of five years commencing August 1, 2017 and expiring July 31, 2022 with equal monthly base rent installments of $14,354 ($172,248 per year) plus sales tax. In September 2020, we entered into an agreement with the Landlord modifying this existing lease. In consideration of payment to Landlord of the sum of $65,600, the Company surrendered all existing premises occupied by it and entered into a new 4 year lease for a smaller premises at Unit #707 in the same building for a monthly rent of $2,954. There will be a $65,600 payment payable as follows: (1) $22,700 due upon the execution of the Modification of Lease Agreement; (2) $20,100 due on or before December 31, 2020; and (3) $22,800 due on or before March 31, 2021. Except as previously mentioned, all other terms and conditions of the initial lease agreement continues to remain in effect. The first two payments have been made and the Company is expected to make the third payment on March 31, 2021, at this time.
On September 26, 2019, we entered into a lease for additional office space in the building that our current office space is located for our North American Transactions Solutions. The space is for 5,875 square feet and the term is for 5 years commencing on September 23, 2019 and expiring on September 30, 2024. The monthly base rent is $16,156 ($193,875 per year) plus sales tax. In consideration of our Company foregoing its rights to credits from the landlord towards the cubicle installation and foregoing its rights to one (1) of the (2) month rent deposits prepaid to the landlord , the lease was amended. The amended lease requires the Company to begin paying $11,500 effective July 7, 2020, with the original monthly rent payment of $16,156 commencing on January 1, 2021. In addition, commencing on March 1, 2021, our Company will begin making up the difference between the original monthly lease payment of $16,156 and the amended monthly lease payment of $11,500, the deferred monthly rent, by paying the landlord an additional $2,000 per month until the deferred portion of the rent is fully repaid. All outstanding amounts of deferred rent shall be subject to interest at an annual the rate of 4%. The Company occupied the space in July of 2020.
Net Element Software, our subsidiary, currently leases approximately 1,654 square feet of office space in Yekaterinburg, Russia, where we develop value added services, mobile applications, smart terminals applications, sales central ERP system development and marketing activities, at an annual rent of approximately $21,000.The lease term expired on June 1, 2019 and was renewed with indefinite terms.
International Transaction Solutions
The Company occupies an office in Moscow, Russia with approximately 1600 square feet at an annual rent of $50,900, which lease expired on February 10, 2020. This lease was renewed with indefinite terms.
We believe that our current facilities are suitable and adequate for our present purposes, and we anticipate that we will be able to extend our existing leases on terms satisfactory to us or move to new facilities on acceptable terms.
For a discussion of legal proceedings, see “Litigation, Claims and Assessments” in Note 10 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, which is incorporated by reference herein.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Market Information
Our common stock began trading on The NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “NETE” on October 3, 2012.
Holders
As of December 31, 2020, our common stock was held by 211 registered shareholders of record. The number of record holders was determined from the records of our transfer agent and does not include beneficial owners of common stock whose shares are held in the names of various securities brokers, dealers and registered clearing agencies. Our transfer agent is Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company.
Dividends
We have not historically declared any dividends. We have no present intention of paying any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future, as any earnings will be used to help generate growth. The decision on the payment of dividends in the future rests within the discretion of the Board of Directors and will depend upon, among other things, our earnings, capital requirements and financial condition, as well as other relevant factors. There are no restrictions in our certificate of incorporation or bylaws that restrict us from declaring dividends.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
The information included under Item 12 of Part III of this Report is hereby incorporated by reference into this Item 5 of Part II of this Report.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
Sale of Unregistered Securities
Information required by Item 701 of Regulation S-K as to other unregistered equity securities we sold during the period covered by this Report that were not registered under the Securities Act has been previously reported in the Company’s Current Reports on Form 8-K filed with the Commission in addition to the following:
In January 2021, we issued 200,000 shares of our common stock in exchange for a tranche of $1,960,000 aggregate amount, less any fees, of certain RBL promissory notes purchased by ESOUSA pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement.
Such shares of common stock were issued to ESOUSA under an exemption from the registration requirements of the Securities Act in reliance upon Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act. See Note 8 to the condensed consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
For the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, we did not repurchase any shares of our common stock.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
Not Applicable.
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with our audited financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this Report. This discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements that involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Our actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward- looking statements as a result of many factors, including but not limited to those under the heading “Risk Factors” in Part I, Item 1A of this Report. Certain amounts in this section may not foot due to rounding.
Overview
We are a financial technology-driven group specializing in payment acceptance and value-added solutions across multiple channels in the United States and selected international markets. We are differentiated by our proprietary technology which enables us to provide a broad suite of payment products, end-to-end transaction processing services and superior client support. We are able to deliver our services across multiple points of access, or “multi-channel,” including brick and mortar locations, software integration, e-commerce, mobile operator billing, mobile and tablet-based solutions. In the United States, via our U.S. based subsidiaries, we generate revenues from transactional services and value-added payment technologies for small and medium-sized businesses. Through PayOnline, we provide transactional services, mobile payment transactions, online payment transactions and other payment technologies in selected international markets, the Russian Federation, Eurasian Economic Community (“EAEC”), Europe and Asia.
Our transactional services business enables merchants to accept credit cards as well as other forms of payment, including debit cards, checks, gift cards, loyalty programs and alternative payment methods in traditional card-present or swipe transactions, as well as card-not-present transactions, such as those conducted over the phone or through the Internet or a mobile device. We market and sell our services through both independent sales groups (“ISGs”), which are non-employee, external sales organizations and other third-party resellers of our products and services, and directly to merchants through electronic media, telemarketing and other programs, including utilizing partnerships with other companies that market products and services to local and international merchants. We have agreements with several banks that sponsor us for membership in the Visa ®, MasterCard ®, American Express ® and Discover ® card brands and settle card transactions for our merchants. These agreements allow us to use the banks’ identification numbers, referred to as Bank Identification Numbers (BIN) for Visa® transactions and Interbank Card Association (ICA) number for MasterCard® transactions. The principal sponsoring banks through which we process the majority of our transaction in the United States include Citizens Bank, Esquire Bank, N.A. and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. From time to time, we may enter into agreements with additional banks. We perform core functions for merchants such as application processing, underwriting, number account set-up, risk management, fraud detection, merchant assistance and support, equipment deployment, chargeback services and offer our own dedicated BIN and ICA for various types of specialty merchants.
Netevia, our future-ready payments and merchant management platform acts as a framework and core for a number of value-added services that connect merchants and consumers directly utilizing disruptive emerging technologies while increasing the economic efficiency of all transactions being made within the ecosystem. Specifically, Netevia delivers end-to-end payment processing through easy-to-use APIs and complements the Company’s ability to perform in a multi-channel environment, including point-of-sale (POS), e-commerce and mobile devices and will enable the Company to perform as a hub for disruptive emerging technology solutions.
Our mobile payments business, previously provided through Digital Provider, has been combined with PayOnline to provide contracts with mobile operators that give us the ability to offer our clients in-app, premium SMS (short message services, which is a text messaging service), Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)-click, one click and other carrier billing services. We have substantially reorganized this business, and currently we are not generating revenues from new mobile content. We have not yet been able to find or solidify an acceptable joint venture partner or other arrangement that provides sufficient profit potential and operating benefit for our mobile payments operations.
PayOnline provides flexible, high-tech payment solutions to companies doing business on the Internet or in the mobile environment. PayOnline specializes in integration and customization of payment solutions for websites and mobile apps. In particular, PayOnline arranges payment on the website of any commercial organization, which increases the convenience of using the website and helps maximize the number of successful transactions. In addition, PayOnline is focused on providing online and mobile payment acceptance services to the travel industry through direct integration with leading Global Distribution Systems (“GDS”), which include Amadeus® and Sabre®. Key geographic regions that PayOnline serves include Eastern Europe, Central Asia, Western Europe, North America and Asia major sub regions. PayOnline offices are located in Moscow, Russia.
Aptito is a proprietary, cloud-based payments platform for the hospitality industry, which creates an online consumer experience in offline commerce environments via tablet, mobile and all other cloud-connected devices. Aptito’s easy to use point-of-sale (“POS”) system makes things easier by providing a comprehensive solution to the hospitality industry to help streamline management and operations. Orders placed tableside by customers directly speed up the ordering process and improve overall efficiency. Aptito’s mobile POS system provides portability to the staff while performing all the same functions as a traditional POS system.
Recent Developments
The COVID-19 pandemic has and continues to affect businesses across the globe, in particular the service industry, which includes restaurants, a significant part of our business. Over the past year, we have taken initiatives to help minimize the risks to our business and protect our shareholders. Our management team’s experience during the 2008 financial crisis is proving to be very valuable in dealing with the current crisis. Our entire staff is fully committed and working diligently to support our merchants through these difficult times. Most of our merchants have contactless payment acceptance capabilities through their POS solutions, as well as, e-commerce and mobile contactless payment acceptance capabilities to eliminate the need for physical payments to help reduce the spread of the virus. The following initiatives, including an extensive business continuity plan, have been implemented:
Risk Management:
● | Enhanced risk controls and safeguards have been put in place for merchants that sell products with an extended delivery time frame, products paid in advance, catering, ticketing, limo and travel related merchants |
● | Onboarding of new merchants in the above categories has been put on hold until further notice |
● | For those employees that will be working from home, we have implemented a “remote work” policy and provided employees with the technology necessary to do so |
● | For those employees that require office attendance, we are taking significant steps to ensure seamless service delivery while safeguarding employees health |
Contactless Payments:
● | Most of our merchants have contactless payment acceptance capabilities through their POS devices from equipment manufacturers such as PAX, Poynt and Verifone which are fully integrated into Netevia and Aptito platforms |
● | We launched an initiative to deploy contactless payment acceptance equipment to merchants that don’t currently have it |
● | Mobile contactless payment acceptance is available through our Unified mPOS App which can be downloaded from Apple’s App Store and Google’s Google Play Apps |
● | Online ecommerce payments through shopping carts allow our merchants to sell their products and services to customers that prefer to shop from the convenience of their homes |
Moving forward, we will continue proactively managing the situation and providing support for our merchants. We continue our mission to build value for our shareholders as we work our way out of this crisis. We believe that given our team experience, dedicated and talented staff and our dedication to the business we will emerge stronger than ever. We wish our shareholders, partners, merchants and their loved ones good health during these difficult times.
To date, COVID-19 has not had a material impact on the Company. However, the Company cannot predict whether COVID-19 will have a material impact on our future financial condition and results of operations due to understaffing in the service sector and the decrease in revenues and profits, particularly from restaurants, which is the largest industry group serviced by our Company, any possible future government ordinances that may further restrict restaurant and other service or retail sector operations, or measures undertaken to contain and eliminate the spread domestically and internationally. The exact extent of the impact from COVID-19 will depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted. In most respects, it is still too early in the COVID-19 pandemic to be able to quantify or qualify the longer-term ramifications on our business, our merchants, and our potential investors. The Company is aware that the processing volume for the year ended 2021 may continue to be affected, primarily due to any possible complete closure or suspension of dine-in services in the restaurant industry, in particular.
Acquisitions of Recurring Cash Flow Portfolios
From time to time, the Company acquires future recurring revenue streams from sales agents in exchange for an upfront cash payment. This results in an increase in net cash flow to the Company. The acquisitions of recurring cash flows are treated as asset acquisitions, resulting in recording a recurring cash flow portfolio intangible asset, at cost, on the date of acquisition. These assets are amortized over a straight-line period of approximately four years and is included in intangible assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets (See Note 6 - item labeled “Portfolio and Clients Lists”, on the accompanying consolidated audited financial statements). During the year ended December 31, 2019 we acquired the following recurring cash flow portfolios. There were no recurring cash flow portfolios acquired during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
Universal Partners, LLC
On July 30, 2018, our subsidiary, Unified Portfolio Acquisitions, LLC (the “Purchaser”), entered into an Advance and Residual Purchase Agreement (the “Agreement”) with Universal Partners, LLC (“Universal”). Pursuant to the Agreement, the Purchaser acquired certain transactional services portfolios (“cash flow assets”) from Universal and Payment Club, LLC (together with Universal, the “Seller”) for $2,700,000 (the “Advance Amount”). The cash flow assets consist of residuals (the “Residuals”) that the Sellers are entitled to receive pursuant to certain agreements (the “Combined Marketing Agreements”) with TOT Payments, LLC (doing business as Unified Payments), our subsidiary, or any other agreements pursuant to which the Seller is entitled to residuals.
The Advance Amount is to be repaid to the Purchaser whereby each and every month, commencing from July 1, 2018 (the “Effective Date”) and for a period of 24 months thereafter, terminating on June 30, 2020 (the “Advance Period”), the Purchaser is entitled to a certain amount of the Residuals. Such Residuals due to the Purchaser are secured by certain of the Seller’s property as collateral.
At the end of the Advance Period (the “Transfer Date”), the Purchaser and the Seller have agreed to create a new static portfolio pool of mutually agreed residual income from Seller portfolios comprising merchant accounts boarded by the Seller under the Combined Marketing Agreements that on the Transfer are generating at least $120,000 per month in net cash flow income (the “Portfolio Residuals”). From and after the Transfer Date, the Purchaser and Seller will share/split the Portfolio Residuals with the Purchaser owning an 80% interest in the Portfolio Residuals and the Seller owning a 20% interest in the Portfolio Residuals.
As of December 31, 2020, the Purchaser and Seller agreed to and finalized the terms of a new static portfolio.
Argus Merchant Services, LLC
On December 26, 2018, Unified Portfolio Acquisitions, LLC (the “Purchaser”), a subsidiary of Net Element, Inc. (the “Company”), entered into an Advance and Residual Purchase Agreement (the “Agreement”) with Argus Merchant Services, LLC ("Argus") and Treasury Payments, LLC ("Treasury"); Argus and Treasury are collectively referred to herein as the (“Seller”). Pursuant to the Agreement, the Purchaser acquired certain transactional services portfolios (“cash flow assets”) from the Seller for a total purchase consideration of $1,426,000. The cash flow assets consist of residuals (the “Residuals”) that the Seller is entitled to receive pursuant to certain agreements (including any amendments of such agreements, the “Combined Marketing Agreements”) with TOT Payments, LLC (doing business as Unified Payments, a subsidiary of the Company).
On December 27, 2018, the Purchaser paid to Seller $1,150,000 (the “Advance Amount”). The Advance Amount and the balance of the purchase consideration is to be repaid to the Purchaser from Residuals due to the Seller, whereby each and every month, commencing from January 2019 (the “Effective Date”) and for a period of 24 months (the “Advance Period”), the Purchaser will be entitled to a certain amount of the Seller’s Residuals. Such Residuals due to the Purchaser are secured by certain of the Seller’s property as collateral.
At the end of the Advance Period (the “Transfer Date”), the Purchaser will receive an ownership interest in a portfolio of cash flow assets by creating with the Seller, a new static portfolio pool of mutually agreed residual income from Seller portfolios comprising merchant accounts boarded by the Seller under the Combined Marketing Agreements.
As of December 31, 2020, the Purchaser and Seller have not finalized the terms of a new static portfolio.
Operating Segments
Our reportable segments are business units that offer different products and services in different geographies. The reportable segments are each managed separately because they offer distinct products, in distinct geographic locations, with different delivery and service processes.
North American Transaction Solutions
Our North American Transaction Solutions business segment consists of the former Unified Payments business and Aptito. This segment operates primarily in North America. In March 2013, we acquired all of the business assets of Unified Payments, a provider of comprehensive turnkey, payment processing solutions to small and medium size business owners (merchants) and independent sales organizations across the United States. In April 2013, we acquired 80% of Aptito, a cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (“SaaS”) restaurant management solution, which provides integrated POS, mPOS, Kiosk, Digital Menus functionality to drive consumer engagement via Apple® iPad®-based POS, kiosk and all other cloud-connected devices.
International Transaction Solutions
Our International Transaction Solutions segment consists of PayOnline, which also now includes our mobile payments operations, primarily located in Russia. PayOnline provides a secure online payment processing system to accept bank card payments for goods and services.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our significant accounting policies are described more fully in Note 3 of the accompanying notes to our audited consolidated financial statements.
The preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires the Company to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses for the reporting period. Such estimates include, but are not limited to, the value of purchase consideration paid and identifiable assets acquired and assumed in acquisitions, goodwill and asset impairment review, valuation reserves for accounts receivable, valuation of acquired or current merchant portfolios, incurred but not reported claims, revenue recognition for multiple element arrangements, loss reserves, assumptions used in the calculation of equity-based compensation and in the calculation of income taxes, and certain tax assets and liabilities, as well as, the related valuation allowances. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Below is a summary of the Company’s critical accounting policies and estimates for which the nature of management’s assumptions are material due to the levels of subjectivity and judgment necessary to account for highly uncertain matters or the susceptibility of such matters to change, and for which the impact of the estimates and assumptions on financial condition or operating performance is material.
Revenue
We recognize revenue when all of the following criteria are met: (1) the parties to the contract have approved the contract and are committed to perform their respective obligations, (2) we can identify each party’s rights regarding the goods or services to be transferred, (3) we can identify the payment terms for the goods or services to be transferred, (4) the contract has commercial substance, and (5) it is probable that we will collect substantially all of the consideration to which we will be entitled in exchange for the goods or services that will be transferred to the customer. The Company considers persuasive evidence of a sales arrangement to be the receipt of a billable transaction from aggregators, signed contract or the processing of a credit card transaction. Collectability is assessed based on a number of factors, including transaction history with the customer and the credit worthiness of the customer. If it is determined that the collection is not reasonably assured, revenue is not recognized until collection becomes reasonably assured, which is generally upon receipt of cash. We record cash received in advance of revenue recognition as deferred revenue. Revenue consists primarily of fees generated through the electronic processing of payment transactions and related services and is recognized as revenue during the period the transactions are processed or when the related services are performed.
The majority of our revenues is derived from volume-based payment processing fees ("discount fees”) and other related fixed transaction or service fees. Discount fees represent a percentage of the dollar amount of each credit or debit transaction processed. Discount fees are recognized at the time the merchants’ transactions are processed. Generally, where we have control over merchant pricing, merchant portability, credit risk and ultimate responsibility for the merchant relationship, revenues are reported at the time of sale on a gross basis equal to the full amount of the discount charged to the merchant. This amount includes interchange fees paid to card issuing banks and assessments paid to payment card networks pursuant to which such parties receive payments based primarily on processing volume for particular groups of merchants. Revenues generated from merchant portfolios where we do not have control over merchant pricing, liability for merchant losses or credit risk or rights of portability are reported net of interchange and other fees.
Revenues are also derived from a variety of fixed transaction or service fees, including authorization fees, convenience fees, statement fees, annual fees, and fees for other miscellaneous services, such as handling chargebacks. Revenues derived from service fees are recognized at the time the services are performed and there are no further performance obligations. Revenue from the sale of equipment is recognized upon transfer of ownership and delivery to the customer, after which there are no further performance obligations.
We primarily report revenues gross as a principal versus net as an agent. Although some of our processing agreements vary with respect to specific terms, the transactional processing service fees collected from merchants generally are recognized as revenue on a gross basis as we are the principal in the delivery of the managed payments solutions to the sellers. The gross fees we collect are intended to cover the interchange, assessments and other processing and non-processing fees which are included and are part of our gross margin.
Accounts Receivable and Credit Policies
Accounts receivable consist primarily of uncollateralized credit card processing residual payments due from processing banks requiring payment within thirty days following the end of each month. Accounts receivable also include amounts due from the sales of our technology solutions to our customers. The carrying amount of accounts receivable is reduced by an allowance for doubtful accounts, if necessary, which reflects management’s best estimate of the amounts that will not be collected. The allowance is estimated based on management’s knowledge of its customers, historical loss experience and existing economic conditions. Accounts receivable and the allowance are written-off when, in management’s opinion, all collection efforts have been exhausted.
Goodwill
Our goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net identifiable assets acquired in business combinations. The goodwill generated from the business combinations is primarily related to the value placed on the employee workforce and expected synergies. Judgment is involved in determining if an indicator or change in circumstances relating to impairment has occurred. Such changes may include, among others, a significant decline in expected future cash flows, a significant adverse change in the business climate, and unforeseen competition.
We have the option of performing a qualitative assessment of impairment to determine whether any further quantitative testing for impairment is necessary. The option of whether or not to perform a qualitative assessment is made annually and may vary by reporting unit. Factors we consider in the qualitative assessment include general macroeconomic conditions, industry and market conditions, cost factors, overall financial performance of our reporting units, events or changes affecting the composition or carrying amount of the net assets of its reporting units, sustained decrease in its share price, and other relevant entity specific events. If we determine on the basis of qualitative factors that the fair value of the reporting unit is more likely than not less than the carrying value, then we perform a quantitative test for that reporting unit. The fair value of each reporting unit is compared to the reporting unit’s carrying value, including goodwill. Subsequent to the adoption on January 1, 2017 of Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2017-04, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other: Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment, if the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, we recognize an impairment equal to the excess carrying value, not to exceed the total amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit.
At December 31, 2019, our management determined that an impairment charge of approximately $1.3 million was necessary to reduce the goodwill relating to the acquisition of PayOnline which is part of our International Transaction Solutions segment . We did not recognize any impairment charge to goodwill during the year ended December 31, 2020.
How We Assess Our Business
Technology Enabling Payment Solutions
Our technology provides comprehensive payment solutions to small and medium size businesses and organizations. Our merchant services includes third-party integrated payment solutions, as well as, traditional payment services across our strategic vertical markets.
Proprietary Software and Payments
Our proprietary software and payments services, Aptito, delivers embedded payment solutions to our clients through company-owned software and we also provide the traditional merchant processing model.
Corporate Expenses and Eliminations
Our corporate expenses and eliminations category includes corporate overhead expenses, when presenting reportable segment information. For additional information on our segments, see Note 16 of our accompanying audited consolidated financial statements.
Key Operating Metrics
We evaluate our performance through key operating metrics, including:
• | the dollar volume of payments our clients process through us (“payment volume”); |
• | the portion of our payment volume that is produced by integrated transactions; and |
• | period-to-period payment volume attrition. |
Our payment volume for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 was $2.7 billion and $3.6 billion, respectively, representing a period- to-period decrease of 25%. We focus on volume, because it reflects the scale and economic activity of our client base and because a significant part of our revenue is derived as a percentage of our clients’ dollar volume receipts. Payment volume reflects the addition of new clients and same store payment volume growth of existing clients, partially offset by client attrition during the period. The COVID-19 pandemic affected businesses across the globe, in particular the service industry, which includes restaurants, a significant part of our business.
Total transactions processed during 2020 were 73.3 million compared to 106 million for 2019.
Results of Operations for the Year Ended December 31, 2020 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2019
We reported a net loss attributable to common stockholders of approximately $5.9 million or ($1.34) loss per share for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to a net loss of approximately $6.5 million or ($1.60) loss per share for the year ended December 31, 2019. This resulted in a decrease in net loss attributable to stockholders of approximately 9% primarily due to a decrease of approximately $2.3 million in selling, general, and administrative expenses, partially offset by an increase in non-cash compensation of approximately $0.7 million. There were no goodwill impairment charges during the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to an impairment charge of approximately $1.3 million recorded at December 31, 2019.
The following table sets forth our sources of revenues, cost of revenues and gross margins for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
Gross Margin Analysis:
Twelve | Twelve | |||||||||||||||||||
Months Ended | Months Ended | Increase / | ||||||||||||||||||
Source of Revenues | December 31, 2020 | Mix | December 31, 2019 | Mix | (Decrease) | |||||||||||||||
North American Transaction Solutions | $ | 62,556,698 | 95.2 | % | $ | 61,778,002 | 95.0 | % | $ | 778,696 | ||||||||||
International Transaction Solutions | 3,148,424 | 4.8 | % | 3,221,609 | 5.0 | % | (73,185 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 65,705,122 | 100.0 | % | $ | 64,999,611 | 100.0 | % | $ | 705,511 | ||||||||||
Twelve | Twelve | |||||||||||||||||||
Months Ended | % of | Months Ended | % of | Increase / | ||||||||||||||||
Cost of Revenues | December 31, 2020 | revenues | December 31, 2019 | revenues | (Decrease) | |||||||||||||||
North American Transaction Solutions | $ | 53,593,342 | 85.7 | % | $ | 52,395,752 | 84.8 | % | $ | 1,197,590 | ||||||||||
International Transaction Solutions | 2,268,061 | 72.0 | % | 2,325,958 | 72.2 | % | (57,897 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 55,861,403 | 85.0 | % | $ | 54,721,710 | 84.2 | % | $ | 1,139,693 | ||||||||||
Twelve | Twelve | |||||||||||||||||||
Months Ended | % of | Months Ended | % of | Increase / | ||||||||||||||||
Gross Margin | December 31, 2020 | revenues | December 31, 2019 | revenues | (Decrease) | |||||||||||||||
North American Transaction Solutions | $ | 8,963,356 | 14.3 | % | $ | 9,382,250 | 15.2 | % | $ | (418,894 | ) | |||||||||
International Transaction Solutions | 880,363 | 28.0 | % | 895,651 | 27.8 | % | (15,288 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 9,843,719 | 15.0 | % | $ | 10,277,901 | 15.8 | % | $ | (434,182 | ) | |||||||||
Net revenues consist primarily of service fees from transaction processing. Net revenues were approximately $65.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to approximately $65.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Cost of revenues represents direct costs of generating revenues, including commissions, mobile operator fees, interchange expense, processing and non-processing fees. Cost of revenues for the year ended December 31, 2020 were approximately $55.9 million as compared to approximately $54.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The increase in cost of revenues in 2020 as compared to 2019 of approximately $1.1 million was in line with the increase in net revenues for our North American Transaction Solutions segment.
Gross Margin for the year ended December 31, 2020 was approximately $9.8 million, or 15.0% of net revenue, as compared to approximately $10.3 million, or 15.8% of net revenue, for the year ended December 31, 2019. The primary reason for the decrease in the gross margin percentage was primarily the result of the competitive pressure in our industry, relating to costs that cannot be passed through to our merchants.
Operating Expenses Analysis:
Total operating expenses were approximately $14.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, as compared to total operating expenses of approximately $15.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Total operating expenses for the year ended December 31, 2020 consisted of selling, general and administrative expenses of approximately $7.0 million, non-cash compensation of approximately $2.7 million, bad debt expense of approximately $1.6 million, and depreciation and amortization expense of approximately $3.0 million. For the year ended December 31, 2019, total operating expenses consisted of general and administrative expenses of approximately $9.3 million, non-cash compensation of approximately $2.1 million, bad debt expense of approximately $1.4 million, and depreciation and amortization expense of approximately $3.1 million.
The components of our selling, general and administrative expenses are reflected in the table below.
Selling, general and administrative expenses for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 consisted of operating expenses not otherwise delineated in the accompanying audited consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, as follows:
Twelve months ended December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||
Category | North American Transaction Solutions | International Transaction Solutions | Corporate Expenses & Eliminations | Total | ||||||||||||
Salaries, benefits, taxes and contractor payments | $ | 1,688,782 | $ | 437,112 | $ | 1,349,831 | $ | 3,475,725 | ||||||||
Professional fees | 330,250 | 152,604 | 977,017 | 1,459,871 | ||||||||||||
Rent | 80,310 | 62,702 | 113,808 | 256,820 | ||||||||||||
Business development | 204,181 | 7,649 | 10,901 | 222,731 | ||||||||||||
Travel expense | 7,860 | 68,110 | 174,905 | 250,875 | ||||||||||||
Filing fees | - | - | 83,567 | 83,567 | ||||||||||||
Transaction gains | - | 55,320 | - | 55,320 | ||||||||||||
Office expenses | 258,414 | 23,732 | 91,996 | 374,142 | ||||||||||||
Communications expenses | 141,621 | 158,248 | 90,879 | 390,748 | ||||||||||||
Insurance expense | - | - | 169,457 | 169,457 | ||||||||||||
| Other expenses | 5,591 | 9,203 | 261,994 | 276,788 | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 2,717,009 | $ | 974,680 | $ | 3,324,355 | $ | 7,016,044 | ||||||||
Twelve months ended December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
Category | North American Transaction Solutions | International Transaction Solutions | Corporate Expenses & Eliminations | Total | ||||||||||||
Salaries, benefits, taxes and contractor payments | $ | 1,230,858 | $ | 516,737 | $ | 3,021,665 | $ | 4,769,260 | ||||||||
Professional fees | 520,019 | 259,349 | 1,607,185 | 2,386,553 | ||||||||||||
Rent | - | 80,107 | 221,987 | 302,094 | ||||||||||||
Business development | 226,633 | 1,747 | 44,452 | 272,832 | ||||||||||||
Travel expense | 133,300 | 46,403 | 105,422 | 285,125 | ||||||||||||
Filing fees | - | - | 103,760 | 103,760 | ||||||||||||
Transaction losses | - | (61,200 | ) | - | (61,200 | ) | ||||||||||
Office expenses | 302,764 | 23,981 | 64,897 | 391,642 | ||||||||||||
Communications expenses | 151,033 | 199,862 | 84,651 | 435,546 | ||||||||||||
Insurance expense | - | - | 150,408 | 150,408 | ||||||||||||
Other expenses | 22,804 | 10,308 | 272,652 | 305,764 | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 2,587,411 | $ | 1,077,294 | $ | 5,677,079 | $ | 9,341,784 | ||||||||
Variance | ||||||||||||||||
Category | North American Transaction Solutions | International Transaction Solutions | Corporate Expenses & Eliminations | Total | ||||||||||||
Salaries, benefits, taxes and contractor payments | $ | 457,924 | $ | (79,625 | ) | $ | (1,671,834 | ) | $ | (1,293,535 | ) | |||||
Professional fees | (189,769 | ) | (106,745 | ) | (630,168 | ) | (926,682 | ) | ||||||||
Rent | 80,310 | (17,405 | ) | (108,179 | ) | (45,274 | ) | |||||||||
Business development | (22,452 | ) | 5,902 | (33,551 | ) | (50,101 | ) | |||||||||
Travel expense | (125,440 | ) | 21,707 | 69,483 | (34,250 | ) | ||||||||||
Filing fees | - | - | (20,193 | ) | (20,193 | ) | ||||||||||
Transaction gains | - | 116,520 | - | 116,520 | ||||||||||||
Office expenses | (44,350 | ) | (249 | ) | 27,099 | (17,500 | ) | |||||||||
Communications expenses | (9,412 | ) | (41,614 | ) | 6,228 | (44,798 | ) | |||||||||
Insurance expense | - | - | 19,049 | 19,049 | ||||||||||||
| Other income | (17,213 | ) | (1,105 | ) | (10,658 | ) | (28,976 | ) | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 129,598 | $ | (102,614 | ) | $ | (2,352,724 | ) | $ | (2,325,740 | ) | |||||
The total decrease of approximately $2.3 million in selling, general and administrative expenses for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the prior year was primarily due to the staffing reductions necessary and the reduction of compensation of certain employees and executives of the Company, including independent consultants and other professionals, due to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on our operations.
The following table represents salaries, benefits, taxes and contractor payments by operating segment and the category corporate expenses and eliminations for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
| Segment | Salaries and benefits for the twelve months ended December 31, 2020 | Salaries and benefits for the twelve months ended December 31, 2019 | Increase / (Decrease) | |||||||||
North American Transaction Solutions | $ | 1,688,782 | $ | 1,230,858 | $ | 457,924 | ||||||
International Transaction Solutions | 437,112 | 516,737 | (79,625 | ) | ||||||||
Corporate Expenses & Eliminations | 1,349,831 | 3,021,665 | (1,671,834 | ) | ||||||||
Total | $ | 3,475,725 | $ | 4,769,260 | $ | (1,293,535 | ) | |||||
The following table represents professional fees by operating segment and the category corporate expenses and eliminations for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
Twelve months ended December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||
Professional Fees | North American Transaction Solutions | International Transaction Solutions | Corporate Expenses & Eliminations | Total | ||||||||||||
General Legal | $ | 5,041 | $ | 2,154 | $ | 21,414 | $ | 28,609 | ||||||||
SEC Compliance Legal Fees | - | - | 200,778 | 200,778 | ||||||||||||
Accounting and Auditing | - | - | 393,059 | 393,059 | ||||||||||||
Tax Compliance and Planning | - | - | 11,200 | 11,200 | ||||||||||||
| Consulting | 325,209 | 150,450 | 350,566 | 826,225 | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 330,250 | $ | 152,604 | $ | 977,017 | $ | 1,459,871 | ||||||||
Twelve months ended December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
Professional Fees | North American Transaction Solutions | International Transaction Solutions | Corporate Expenses & Eliminations | Total | ||||||||||||
General Legal | $ | 21,670 | $ | 31,980 | $ | 411,765 | $ | 465,415 | ||||||||
SEC Compliance Legal Fees | - | - | 177,826 | 177,826 | ||||||||||||
Accounting and Auditing | - | - | 391,134 | 391,134 | ||||||||||||
Tax Compliance and Planning | - | - | 19,800 | 19,800 | ||||||||||||
Consulting | 498,349 | 227,369 | 606,660 | 1,332,378 | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 520,019 | $ | 259,349 | $ | 1,607,185 | $ | 2,386,553 | ||||||||
Variance | ||||||||||||||||
Professional Fees | North American Transaction Solutions | International Transaction Solutions | Corporate Expenses & Eliminations | Increase / (Decrease) | ||||||||||||
General Legal | $ | (16,629 | ) | $ | (29,826 | ) | $ | (390,351 | ) | $ | (436,806 | ) | ||||
SEC Compliance Legal Fees | - | - | 22,952 | 22,952 | ||||||||||||
Accounting and Auditing | - | - | 1,925 | 1,925 | ||||||||||||
Tax Compliance and Planning | - | - | (8,600 | ) | (8,600 | ) | ||||||||||
| Consulting | (173,140 | ) | (76,919 | ) | (256,094 | ) | (506,153 | ) | ||||||||
| Total | $ | (189,769 | ) | $ | (106,745 | ) | $ | (630,168 | ) | $ | (926,682 | ) | ||||
Other Income and Expenses Delineated in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss:
Non-cash Compensation Analysis:
Non-cash compensation expense was $2.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to approximately $2.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. A summary of 2020 and 2019 non-cash compensation activity follows:
2020 Non-Cash Compensation Activity:
# of Shares | # of Options | |||||||||||
Amount | Issued | Issued | ||||||||||
| Board of Directors & Employee stock and Options | $ | 2,718,152 | 334,654 | - | ||||||||
Stock issued for consulting | - | - | - | |||||||||
Stock issued for acquisitions | - | - | - | |||||||||
Total for 2020 | $ | 2,718,152 | 334,654 | - | ||||||||
2019 Non-Cash Compensation Activity:
# of Shares | # of Options | |||||||||||
Amount | Issued | Issued | ||||||||||
Board of Directors & Employee stock and Options | $ | 2,050,862 | 248,063 | 80,000 | ||||||||
Stock issued for consulting | - | - | - | |||||||||
Stock issued for acquisitions | - | - | - | |||||||||
Total for 2019 | $ | 2,050,862 | 248,063 | 80,000 | ||||||||
Bad Debt Expense:
We reflected a bad debt expense on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations, which represents uncollected fees of approximately $1.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, compared to approximately $1.4 million for the year ended 2019. The increase of approximately $200,000 from the previous comparable period was primarily due to billing adjustments relating to chargebacks made by our processors due to the to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on our merchants.
Depreciation and Amortization Expense:
Depreciation and amortization expense consists primarily of the amortization of merchant portfolios in connection with residual buyout arrangements and client acquisition costs. Depreciation and amortization expense was approximately $3.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 and $3.1 million for the year ended 2019.
Interest Expense:
Interest expense was approximately $1.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to approximately $1.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, representing an increase of approximately $300,000 primarily due to the increase in debt borrowings during 2020 as compared to the prior year.
Funding Source | Twelve months ended December 31, 2020 | Twelve months ended December 31, 2019 | Increase / (Decrease) | |||||||||
RBL Notes | $ | 1,343,802 | $ | 1,063,921 | $ | 279,881 | ||||||
Other | 102,838 | 48,606 | 54,232 | |||||||||
Total | $ | 1,446,640 | $ | 1,112,527 | $ | 334,113 | ||||||
Other Income (Expenses):
Other income of approximately $1.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily due to recognizing a non-recurring charge to other income of approximately $1.1 million relating to merchant reserves recorded in a previous year deemed not to be a legal obligation by management.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Total assets at December 31, 2020 were approximately $26.2 million compared to approximately $23.0 million at December 31, 2019. The primary reasons for the net increase in total assets was the result of cash provided by operations and from ESOUSA in exchange for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement, and the increase in the operating lease right-of-use asset.
At December 31, 2020, we had total current assets of approximately $13.3 million as compared to approximately $8.7 million at December 31, 2019. The primary reason for the increase in current assets was the result of cash provided by operations and from financing activity primarily related to proceeds from indebtedness.
Our consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and the settlement of liabilities and commitments in the normal course of business. We sustained a net loss of approximately $5.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 and $6.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 and have an accumulated deficit of $184.7 million and a negative working capital of $1.7 million at December 31, 2020.
During the first quarter of 2020, our Company evaluated its liquidity position, future operating plans, and its labor force, which included a reduction in the labor force and compensation to executives and other employees, in order to maintain current payment processing functions, capabilities, and continued customer service to its merchants. We are also seeking sources of capital to pay our contractual obligations as they come due, in light of these uncertain times. Management believes that its operating strategy will provide the opportunity for us to continue as a going concern as long as we are able to obtain additional financing. At this time, due to our continuing losses from operations, negative working capital, and the COVID-19 pandemic, we cannot predict the impact of these conditions on our ability to obtain financing necessary for the Company to fund its future working capital requirements. Our Company has also decided to explore strategic alternatives and potential options for its business, including sale of the Company or certain assets, licensing of technology, spin-offs, or a business combination. There can be no assurance, at this time, regarding the eventual outcome of our planned strategic alternative. In most respects, it is still too early in the COVID-19 pandemic to be able to quantify or qualify the longer-term ramifications on our merchant processing business, our merchants, our planned strategic alternatives to enhance current shareholder value, our current investors, and/or future potential investors.
As part of our Company's plan to obtain capital to fund future operations, on March 27, 2020, our Company entered into a Master Exchange Agreement (the “ESOUSA Agreement”) with ESOUSA Holdings, LLC ("ESOUSA"), a related party. Prior to entering into the ESOUSA Agreement, ESOUSA agreed to acquire an existing promissory note that had been previously issued by the Company, of up to $2,000,000 in principal amount outstanding and unpaid interest due to RBL Capital Group, LLC ("RBL"). Pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement, the Company has the right, at any time prior to March 27, 2021, to request ESOUSA, and ESOUSA agreed upon each such request, to exchange this promissory note in tranches on the dates when the Company instructs ESOUSA, for such number of shares of the Company’s common stock (“Common Stock”) as determined under the ESOUSA Agreement based upon the number of shares of Common Stock (already in ESOUSA’s possession) that ESOUSA sold in order to finance its purchase of such tranche of the promissory note from RBL. ESOUSA will purchase each tranche of the promissory note equal to 88% of the gross proceeds from the shares of Common Stock sold by ESOUSA to finance the purchase of such exchange amount from RBL. Each such tranche shall be $148,000 unless otherwise agreed to by the Company and ESOUSA.
On April 23, 2020 and August 3, 2020, the Company entered into certain amendments to the ESOUSA Agreement, which together increased from $2,000,000 to $15,000,000 the principal amount and unpaid interest of one or more promissory notes of the Company or its direct or indirect subsidiaries that ESOUSA either purchased in whole or has an irrevocable right to purchase in tranches from RBL in connection with the ESOUSA Agreement.
On March 27, 2020, the Company received its first tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $148,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $148,000 from RBL under the Loan and Security Agreement (“Credit Facility”) with RBL. See Note 8. "Notes Payable" in the condensed consolidated unaudited financial statements contained in Part I, Item 1 of this Report for more information regarding the terms of the Credit Facility.
On April 28, 2020, the Company received its second tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $143,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 65,862 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $143,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility. \
On August 11, 2020, the Company received its third tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $707,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 66,190 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $707,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 21, 2020, the Company received its fourth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $401,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 45,654 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $401,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On September 25, 2020, the Company received its fifth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $426,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 50,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $426,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On December 30, 2020, the Company received its sixth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $1,960,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. In January 2021, the Company issued 200,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $1.960,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On May 7, 2020, the Company entered into a promissory note (the “Note”) evidencing an unsecured loan (the “Loan”) in the amount of $491,493 made to the Company under the Paycheck Protection Program (the “PPP”). The Note matures on May 7, 2022 and bears interest at a rate of 1% per annum. Beginning December 7, 2020, the Company is required to make 17 monthly payments of principal and interest, with the principal component of each such payment based upon the level amortization of principal over a two-year period from May 7, 2020. Pursuant to the terms of the CARES Act and the PPP, the Company may apply to the Lender for forgiveness for the amount due on the Loan. The amount eligible for forgiveness is based on the amount of Loan proceeds used by the Company (during the eight-week period after the Lender makes the first disbursement of Loan proceeds) for the payment of certain covered costs, including payroll costs (including benefits), interest on mortgage obligations, rent and utilities, subject to certain limitations and reductions in accordance with the CARES Act and the PPP. No assurance can be given, at this time, that the Company will obtain forgiveness of the Loan in whole or in part.
On May 18, 2020, the Company entered into a promissory note in the amount of $159,899 made to the Company by the U.S. Small Business Administration under the Economic Injury Disaster Loan program.
On August 4, 2020, our Company entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger (the “Merger Agreement”) with Mullen Technologies, Inc., a California corporation (“Mullen”), and Mullen Acquisition, Inc., a California corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”). Pursuant to, and on the terms and subject to the conditions of, the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub will be merged with and into Mullen (the “Merger”), with Mullen continuing as the surviving corporation in the Merger. After Mullen’s completion and delivery to our Company, of the audited financial statements for Mullen and its subsidiaries and affiliates required to be included in a registration statement, the Company intends to prepare and file with the Commission a registration statement on Form S-4 (together with all amendments thereto, the “Registration Statement”) in which the proxy statement will be included as a part of the prospectus, in connection with the registration under the Securities Act of the shares of Parent Shares to be issued in connection with the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement. The Merger Agreement contains termination rights for each of the Company and Mullen, including, among others, (i) in the event that the Merger has not been consummated by December 31, 2020, (ii) in the event that the requisite approval of the Company’s stockholders is not obtained upon a vote thereon, (iii) in the event that any governmental authority shall have taken action to restrain, enjoin or prohibit the consummation of the Merger, which action shall have become final and non-appealable and (iv) in the event that there is a breach by the other party of any of its representations, warranties, covenants or agreements, which breach is sufficiently material and not timely cured or curable. In addition, Mullen may terminate the Merger Agreement if, prior to receipt of the requisite approval of the Company’s stockholders, the Company’s board of directors shall have changed their recommendation in respect of the Merger. Further, the Company may terminate the Merger Agreement prior to receipt of the requisite approval of the Company’s stockholders to enter into a definitive agreement with respect to a Superior Proposal (as such term is defined in the Merger Agreement).
As contemplated by the Merger Agreement, on August 11, 2020, our Company as lender, borrowed an additional $500,000 from RBL and entered into an unsecured Promissory Note, dated August 11, 2020 (the “Note”), with Mullen. Pursuant to the Note, Mullen borrowed from the Company $500,000. Prior to maturity of the loan, the principal amount of the loan will carry an interest rate of 14% per annum compounded monthly and payable upon demand. This loan will mature on the earlier of (i) the date that the Merger Agreement is terminated for any reason by any party thereto and (ii) the Merger Effective Time (as defined in the Merger Agreement).
On December 29, 2020, the Company entered into the First Amendment (the “Amendment”) to the Merger Agreement with Mullen and the Merger Sub. Prior to the parties’ execution and delivery of the Amendment, Section 8.1(b) of the Merger Agreement provided that the Merger Agreement may be terminated and the merger contemplated in the Merger Agreement (the “Merger”) and other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement may be abandoned at any time prior to the merger effective time, notwithstanding any requisite approval and adoption of Merger Agreement and the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement by the shareholders of Mullen and/or the stockholders of the Company, by either Company or Mullen if the merger effective time shall not have occurred on or before December 31, 2020 (the “Outside Date”). Pursuant to the Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub amended Section 8.01(b) of the Merger Agreement to extend the Outside Date to March 31, 2021.
In addition, pursuant to the Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub agreed that, if the registration statement on Form S-4 (with the merger proxy statement included as part of the prospectus) is not filed with the SEC on or prior to January 15, 2021, then Mullen will pay the Company an agreed sum of $13,333 per day (the “Late Fee”) until the such registration statement (with the merger proxy statement included as part of the prospectus) is filed with the SEC. All accumulated Late Fees will be due and payable by Mullen on the 5th day of each calendar month commencing February 5, 2021 and on the 5th day of each month thereafter until the above-refenced filing has occurred.
On March 30, 2021, the Company entered into the Second Amendment (the “Second Amendment”) to Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of August 4, 2020, as amended by the First Amendment dated as of December 29, 2020 (the “Merger Agreement”) with Mullen Technologies, Inc., a California corporation (“Mullen”), Mullen Acquisition, Inc., a California corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”). Prior to the parties’ execution and delivery of the Second Amendment, Section 8.1(b) of the Merger Agreement, as amended, provided that the Merger Agreement may be terminated and the merger contemplated in the Merger Agreement (the “Merger”) and other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement may be abandoned at any time prior to the merger effective time, notwithstanding any requisite approval and adoption of this Agreement and the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement by the shareholders of Mullen and/or the stockholders of the Company, by either Company or Mullen if the merger effective time shall not have occurred on or before March 31, 2021 (the “Outside Date”). Pursuant to the Second Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub amended Section 8.01(b) of the Merger Agreement to extend the Outside Date to April 30, 2021.
The foregoing description of the Second Amendment does not purport to be complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by, the full text of such agreement, a copy of which is attached hereto as Exhibit 2.10 and incorporated herein by reference.
At March 31, 2021, the Company is also owed approximately $1 million from Mullen in connection with Late Fees, as previously discussed..
Consummation of the Merger, the Divestiture, the Private Placement and the other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement, is subject to customary conditions including, among others, the approval of the Company’s stockholders. There is no guarantee that the Merger, the Divestiture, the Private Placement or the other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement will be completed. For additional information, see the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 5, 2020, as amended.
As of the filing date of this Report with the SEC, management expects that our cash flows from operations will not be sufficient to fund our current operations through 2021. We will require additional capital in order to continue our existing business operations and to fund our obligations. The recent COVID-19 pandemic is currently impacting countries, communities, supply chains and global financial markets, as well as the largest industry group serviced by our Company, which is restaurants. To date, COVID-19 has not had a material impact on the Company. However, the Company cannot predict whether COVID-19 will have a material impact on our future financial condition and results of operations due to understaffing in the service sector particularly from restaurants, which is the largest industry group serviced by our Company, and any possible future government ordinances that may further restrict restaurant and other service or retail sector operations. The exact extent of the impact from COVID-19 will depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted. In most respects, it is too early in the COVID-19 pandemic to be able to quantify or qualify the longer-term ramifications on our business, our merchants, and our potential investors.
Our company re-evaluated its operating plans in order to maintain current payment processing functions, capabilities, and continued customer service to its merchants, and is also seeking sources of capital to pay our contractual obligations as they come due, in light of these uncertain times. Management believes that upon re-evaluating its operating strategy it will provide the opportunity for us to continue as a going concern as long as we are able to obtain additional financing. At this time, due to our continuing losses from operations, negative working capital, and the COVID-19 pandemic, we cannot predict the impact of these conditions on our ability to obtain financing necessary for the Company to fund its working capital requirements.
Further, at this time, we cannot determine the capital we will need to finance our continuing operations over the next 12 months, due to an inability to be able to quantify or qualify the longer-term ramifications on our business, our merchants, and our potential investors due to COVID-19. We may raise additional funds through debt financing and/or the issuance of equity securities, there being no assurance that any type of financing on terms satisfactory to us will be available or otherwise occur. Debt financing must be repaid regardless of whether we generate revenues or cash flows from operations and may be secured by substantially all of our assets. Any equity financing or debt financing that requires the issuance of equity securities or warrants to the lender would cause the percentage ownership by our current stockholders to be diluted, which dilution may be substantial. Also, any additional equity securities issued may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to those of existing stockholders. If such financings are not available when required or are not available on acceptable terms, we may be unable to continue servicing our current merchants, implement a restructured business plan, or take advantage of business opportunities, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and/or prospects and may ultimately require us to suspend or cease operations, which could cause investors to lose the entire amount of their investment.
These conditions raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. The accompanying consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might be necessary if the Company is unable to continue as a going concern.
We have a cash balance at December 31, 2020 of approximately $4.4 million..
Operating activities provided approximately $3.0 million of cash for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to approximately $2.2 million of cash used for the year ended December 31, 2019. Positive operating cash flow for the twelve months ended December 31, 2020 was primarily the result of cash provided by operations and an increase in the Company’s accounts payables and accrued expenses.
Investing activities used approximately $1.8 million of cash for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to approximately $2.5 million of cash used for the year ended December 31, 2019. The decrease in cash used by investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily attributable to the the Company not acquiring any recurring cash flows portfolios during the year ended 2020
Financing activities provided approximately $3.0 of cash for the year ending December 31, 2020 of which approximately $2.3 million was proceeds from borrowings, net of repayments. Financing activities provided approximately $3.5 of cash for the year ending December 31, 2019 of which approximately $3.0 million was proceeds from borrowings.
Off-balance sheet arrangements
At December 31, 2020, we did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements as defined in Item 303(a) (4) of Regulation S-K.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
The information contained in Note 3 to our Consolidated Financial Statements concerning a description of recent accounting pronouncements, including our expected dates of adoption and the estimated effects on our results of operations and financial condition, is incorporated by reference herein.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Not Applicable.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
The Consolidated Financial Statements and notes thereto and the reports of the independent registered public accounting firm set forth on pages F-2 through F-24 are filed as part of this Report and incorporated herein by reference.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As of the end of the period covered by this Report, our management conducted an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our chief executive officer and our chief financial officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and Rule 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act").
Disclosure controls and procedures are designed to provide reasonable, but not absolute, assurance that information required to be disclosed in our reports filed or submitted under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, as appropriate, to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Based on that evaluation, our chief executive officer and chief financial officer concluded that as of December 31, 2020, our disclosure controls and procedures were not deemed effective due to the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f ) and Rule 15d-15(f ) under the Exchange Act discussed below.
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable, but not absolute, assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the Company's annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
The management of the Company assessed the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020.
In making its assessment of internal control over financial reporting, management used the criteria issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013). Because of the material weaknesses described in the paragraphs below, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2020, the Company's internal control over financial reporting was not effective based on those criteria. We expect to maintain continuous monitoring and implement changes to existing controls, as deemed necessary, to mitigate or remediate the material control weaknesses, where applicable.
We identified a material weakness in our risk assessment process, which we determined was not operating adequately to identify and address the risks to our business and to establish appropriate control objectives given the environment in which we operate and the decentralized structure used to manage our operating activities in connection with our international operations. This material weakness in our risk assessment process was a factor contributing to the other material weaknesses which we have further described below.
As of December 31, 2020, the material weaknesses disclosed in our Form 10-K for the prior year ended December 31, 2019 have not yet been fully remediated; however, significant progress was made during 2019 in remediating certain material weaknesses. Several steps taken in improving and remediating internal controls over financial reporting include retaining a financial reporting manager, the formation of a disclosure committee, as well as, formal education and training of our Board members.
Remediation activities for our material weaknesses include:
● | Risk Assessment. We are continuing the process of designing and implementing an improved enterprise wide risk management process that follows the COSO 2013 framework and one aspect of this process will focus on identifying and mitigating risks to our business that could have an impact on our internal control over financial reporting. Our process includes periodic updates of the enterprise risk universe through the consideration of current and historical risks, periodic input from executive management, and our domestic and international segment local management. Each time a new risk is identified, we will evaluate if any additional controls are required to mitigate risks to our internal control over financial reporting. During the year ended December 31, 2019, management sent a consultant to Russia in an effort to fully understand, implement, train, and eventually test the internal controls relating to our International Transaction Solution's segment’s internal control over financial reporting. The local management team in our International Transaction Solution's segment is currently in the process of documenting processes, controls, and recommendations provided under the guidance and assistance of the Company's consultant. |
Due to the current COVID-19 pandemic, the Company has had to allocate resources to mitigate risks with its current merchant accounts and is in the process of evaluating its operational plans to eliminate any potential exposure to its disclosure controls and procedures. Pending the outcome of this uncertainty, including travel restrictions to Russia, we cannot determine how or when we expect to remediate the material weaknesses noted above, including the allocation of appropriate resources to department heads during 2021.
This annual report does not include an attestation report of the Company's registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management's report was not subject to attestation by the Company's registered public accounting firm pursuant to rules of the SEC that permit the Company to provide only management's report in this annual report.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Except as specifically described above in this Item 9A, there was no change in our internal control over financial reporting during our fourth fiscal quarter of 2020 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
On March 30, 2021, the Company entered into the Second Amendment (the “Second Amendment”) to Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of August 4, 2020, as amended by the First Amendment dated as of December 29, 2020 (the “Merger Agreement”) with Mullen Technologies, Inc., a California corporation (“Mullen”), Mullen Acquisition, Inc., a California corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”). Prior to the parties’ execution and delivery of the Second Amendment, Section 8.1(b) of the Merger Agreement, as amended, provided that the Merger Agreement may be terminated and the merger contemplated in the Merger Agreement (the “Merger”) and other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement may be abandoned at any time prior to the merger effective time, notwithstanding any requisite approval and adoption of this Agreement and the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement by the shareholders of Mullen and/or the stockholders of the Company, by either Company or Mullen if the merger effective time shall not have occurred on or before March 31, 2021 (the “Outside Date”). Pursuant to the Second Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub amended Section 8.01(b) of the Merger Agreement to extend the Outside Date to April 30, 2021.
The foregoing description of the Second Amendment does not purport to be complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by, the full text of such agreement, a copy of which is attached hereto as Exhibit 2.10 and incorporated herein by reference.
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
The directors and executive officers of the Company and their respective ages, and positions with the Company and certain business experience as of the date of this Report are set forth below. There are no family relationships among any of the directors or executive officers.
There are no material legal proceedings to which any director or executive officer of the Company, or any associate of any director or executive officer of the Company, is a party adverse to the Company or any of its subsidiaries or has a material interest adverse to the Company or any of its subsidiaries.
Name | Age | Position | ||
Oleg Firer | 43 | Executive Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | ||
Steven Wolberg | 61 | Chief Legal Officer and Secretary | ||
Jeffrey Ginsberg | 55 | Chief Financial Officer | ||
Jon Najarian | 63 | Director | ||
| John Roland | 79 | Director | ||
| Todd Raarup | 55 | Director | ||
Each of our directors will hold office until our next annual meeting of shareholders at which directors are elected or until his successor is duly elected and qualified. Executive officers serve at the discretion of our Board of Directors.
Oleg Firer, Executive Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. Mr. Firer has served as Executive Chairman since November 27, 2018 and Chief Executive Officer and a director of the Company since April 16, 2013. Previously, Mr. Firer served as Executive Chairman of Unified Payments, LLC from January 2011 until its acquisition by the Company’s subsidiary, TOT Group, Inc., on April 16, 2013 and has served as the Executive Chairman since November 2018. From July 2004 until December 2012, Mr. Firer served as President, Chief Executive Officer and Secretary (and from May 2006 until December 2012 as Treasurer and from May 2008 until December 2012 as Chief Financial Officer) of Acies Corporation, a provider of payment processing solutions to small and medium size merchants across the United States. Mr. Firer also served as a director of Acies Corporation from May 2005 until December 2012. Mr. Firer served as the President of GM Merchant Solution, Inc. (from August 2002) and Managing Partner of GMS Worldwide, LLC (from August 2003) until their assets were acquired by Acies Corporation in June 2004. From November 2002 to December 2003, Mr. Firer served as the Chief Operating Officer of Digital Wireless Universe, Inc. From December 2001 to November 2002, Mr. Firer served as the Managing Partner of CELLCELLCELL, LLC. From March 1998 to December 2001, Mr. Firer served as Vice President of SpeedUS Corp. Mr. Firer studied Computer Science at New York Technical College from 1993 to 1995. Mr. Firer currently serves as a member of Star Capital Management, LLC and Star Equities, LLC, Florida-based investment group. In addition, Mr. Firer serves as a Chairman of the Supervisory Board of the Eastern Caribbean Blockchain Association, a board member of Progressive Care, Inc. and Star Development Ltd as well as a member of the Advisory Board of the E2Exchange, the Institute of Entrepreneurs and several non-for-profit organizations, Advisory Board member of CoinBoost, Inc. and several other private technology companies. Mr. Firer supports the initiatives of the Firer Family Charitable Foundation, the charitable family fund focused on helping families and children in need. In addition, Mr. Firer serves on various committees of Electronic Transaction Association (ETA). Mr. Firer holds a diplomatic rank of the Extraordinary and Plenipotentiary Ambassador. The Company believes that Mr. Firer’s leadership roles in various payment processing companies make him qualified to serve as a director of the Company.
Steven Wolberg, Chief Legal Officer and Secretary. Mr. Wolberg has served as Chief Legal Officer and Secretary of the Company since April 16, 2013. Previously, Mr. Wolberg served in various capacities with Acies Corporation from approximately January 2009 until December 2012, including as a consultant from approximately January 2009 until October 2009, as a director from October 30, 2009 until December 2012 and as Chief Strategy Officer from March 1, 2010 until December 2012. Mr. Wolberg currently operates a solo law practice in Newton, Massachusetts, Attorney Steven Wolberg, which he has operated since January 1997. Mr. Wolberg served as Chief Counsel and Vice President of Corporate Development for Mascot Networks in Cambridge, Massachusetts from January 2000 to September 2001. Since September 1996, Mr. Wolberg has served as president of Oakland Properties, Inc., a real estate development company. From February 1993 to December 1994, Mr. Wolberg served as an attorney in the real estate and corporate divisions of Brown and Rudnick in Boston, Massachusetts. From March 1988 to November 1991, Mr. Wolberg was a partner with the law firm of Jordaan and Wolberg in Johannesburg, South Africa. From January 1986 to February 1988, Mr. Wolberg was employed as an attorney with Goodman and North in Johannesburg, South Africa. Mr. Wolberg also currently owns and serves as the Managing Member of Prime Portfolios, LLC, which holds a private investment portfolio of merchants, receiving payment processing services. Mr. Wolberg received his Bachelor of Arts from the University of Witwatersrand in Johannesburg, South Africa, his Bachelors of Laws from the University of Witwatersrand, in Johannesburg, South Africa, and his Juris Doctorate from the New England School of Law in Boston, Massachusetts. Mr. Wolberg is a member of the Massachusetts Bar Association.
Jeffrey Ginsberg, Chief Financial Officer. Mr. Ginsberg has served as Chief Financial Officer of the Company since July 9, 2018. Previously, Mr. Ginsberg served as the Vice President of Finance and Controller of the Company since April 16, 2013, responsible for financial operations management, maintenance of accounting records and maintenance of consolidated financial statements for the Company and its subsidiaries. Prior to his employment with the Company, Mr. Ginsberg was a Vice President of Finance and Controller of Unified Payments from June 2011 until acquisition by the Company in April 2013. Prior to Unified Payments, Mr. Ginsberg was a Partner at Strombeck Consulting CPA from December 2009 to April 2013. He is a graduate of Queens College with a Bachelors of Arts degree in Accounting. He is a member of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants.
Jon Najarian, Director. Mr. Najarian has been a director of the Company since March 8, 2018. Mr. Najarian is an accomplished financial industry veteran with more than 37 years of financial and capital markets industry experience. Mr. Najarian is also well-versed in cryptocurrency and blockchain technologies. Mr. Najarian is a professional investor, money manager and media analyst. He is a co-founder of Investitue, LLC, the industry leading options education firm, which recently launched “Crypto Basics,” a new educational course that covers the basics of cryptocurrency, blockchain technology, altcoins and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). He is also a host of the International ICO Channel, a part of CoinBoost, whose goal is to bridge the divide between blockchain and mainstream media by offering distribution to traditional financial media outlets. In 2016, Mr. Najarian and his brother Pete co-founded Najarian Advisors, a company advising institutional investors on options strategies. The brothers invest in and work with start-ups via Rebellion Partners, a venture consulting firm they launched in 2015. Mr. Najarian is a cast member of CNBC’s “Halftime Report” and the “Fast Money” show. He is also the feature of the “DRJ Report” on CBOE-TV popular webcast. Mr. Najarian was a linebacker for the Chicago Bears before he focused his attention to trading on the Chicago Board Options Exchange (“CBOE”). He became a member of the CBOE, NYSE, CME and CBOT and worked as a floor trader for 25 years. In 1990, he founded Mercury Trading, a market-making firm at the CBOE, which he sold in 2004 to Citadel, one of the world’s largest hedge funds. In 2005, Mr. Najarian co-founded optionMONSTER and tradeMONSTER and negotiated a partnership with General Atlantic Partners in 2014 resulting ultimately in a sale to E*Trade for $750 million in September of 2016. Mr. Najarian developed and patented trading applications and algorithms used to identify unusual activity in stock, options, futures and cryptocurrency markets. optionMONSTER, an options news and education site, was described by Securities Industry News as “content king of the options business.” Mr. Najarian is a graduate of Gustavus Adolphus College with a BA degree. We believe that Mr. Najarian’s experience in the financial and capital markets industry provides him with the necessary skills to be qualified to serve as a director of the Company. The Company’s Board of Directors determined that Mr. Najarian is an independent director for purposes of the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and under the applicable NASDAQ listing standards, and that he has the other qualifications required for service on the Company’s Audit, Compensation and Nominating and Corporate Governance Committees.
.
John Roland, Director. Effective July 10, 2020, the Board of Directors of the Company appointed Mr. John Roland as a Director of the Company to fill the vacancy from Mr. Wiegand’s resignation. John Roland, who is 79 years old, is an accomplished broadcast media professional, news presenter and reporter. Since January 2009, John has been an independent media and public relations consultant. Since October 2013, he has also served as a Media Consultant for John Roland Entertainment. From December 1969 to August 2002, John was a news anchor for Fox 5 (WNYW-TV New York). From July 1967 to November 1969, he was a Staff Reporter for KTTV (Los Angeles). In his early years with WNEW/WNYW, he was a political reporter and weekend presenter for The 10 O'Clock News. John earned his B.A. in Journalism degree from California State University at Long Beach in 1964. He has appeared in several films, credited as a television anchor and himself once. Roland played television anchors in Hero at Large (1980), Eyewitness (1981) and The Object of My Affection (1998). He played himself in The Scout (1994). He played himself in three documentaries produced by filmmaker Dennis Michael Lynch, King of the Hamptons (2011) and 2012: They Come to America, The Cost of Illegal Immigration and 2013: They Come to America 2: The Cost of Amnesty. The Board of Directors of the Company concluded that Mr. Roland should serve as a Director of the Company in light of his media and public relations experience and his general financial experience. Mr. Roland was also appointed to serve as a member of the Company’s Audit Committee. The Company’s Board of Directors determined that Mr. Roland is an independent director for purposes of the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and under the applicable NASDAQ listing standards, and that he has the other qualifications required for service on the Company’s Audit Committee.
Todd Raarup, Director. Effective July 23, 2020, the Board of Directors of the Company appointed Mr. Todd Raarup as a Director of the Company to fill the vacancy from Mr. Ash’s resignation. Todd Raarup, who is 55 years old, is an accomplished financial industry veteran. Mr. Raarup is currently the CEO of Najarian Advisors, a registered investment advisor he co-founded in 2017. From 2013, Mr. Raarup has been serving as President of Symmetric Systems LLC. Prior to founding Najarian Advisors, Mr. Raarup held a series of senior management roles at Citigroup Global Equities and Knight Trading Group. From 2005 to 2012 he was Global Head of Trading Analytics and Technology Strategy and Co-Head of Derivative Execution Services at Citigroup Global Equities, which provided market access products to institutional and broker-dealer customers. From 2000-2004, Mr. Raarup was Head of Knight Execution Partners and Head of Options Floor Trading at Knight Trading Group prior to that. From 1995 to 1999 he traded listed options for Arbitrade LLC, both on the CBOE trading floor and in London. He started his career as a CBOE floor trader for Mercury Trading from 1990 to 1994. Mr. Raarup graduated in 1994 from the University of Chicago Booth School of Business with an MBA in Analytical Finance and Econometrics. Mr. Raarup received his B.A. degree in Economics and Religious Studies from Gustavus Adolphus College. The Board of Directors of the Company concluded that Mr. Raarup should serve as a Director of the Company in light of his experience in the financial industry. Mr. Raarup was also appointed to serve as a member of the Company’s Audit, Compensation and Nominating and Corporate Governance Committees. The Company’s Board of Directors determined that Mr. Raarup is an independent director for purposes of the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and under the applicable NASDAQ listing standards, and that he has the other qualifications required for service on the Company’s Audit, Compensation and Nominating and Corporate Governance Committees
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a Code of Ethics and Business Conduct that applies to all of our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive officer and our principal financial and accounting officer. A copy of our Code of Ethics and Business Conduct has been posted to the "Investors—Corporate Governance" section of our Internet website at http://www.netelement.com. We will provide a copy of our Code of Ethics and Business Conduct to any person without charge, upon written request to our Secretary at 3363 NE 163rd Street, Suite 605, North Miami Beach, Florida 33160, fax number (305) 508-5497, e-mail address investors@netelement.com.
Audit Committee
Our Board of Directors has a separately-designated standing audit committee established in accordance with Section 3(a)(58)(A) of the Exchange Act, which is currently comprised of John Najarian (audit committee chairman), John Roland, and Todd Raarup.. Our Board of Directors has determined that John Najarian is financially sophisticated as described in NASDAQ Listing Rule 5605(c)(2) and qualifies as an "audit committee financial expert" as defined in Item 407(d)(5) of Regulation S-K. Each member of the audit committee meets the audit committee independence requirements of Nasdaq and the rules under the Exchange Act relating to audit committees.
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
Summary Compensation Table
The following table sets forth information for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 with respect to all compensation paid to or earned by each of our “named executive officers” (as defined by Item 402(m)(2) of the Regulation S-K).
Stock | Option | All Other | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Name and Principal Position | Year | Salary ($) | Bonus ($) | Awards ($) (1) | Awards ($) (1) | Compensation ($) | Total ($) | |||||||||||||||||||
Oleg Firer, Chairman and Chief | 2020 | $ | 210,750 | $ | - | $ | 1,156,608 | $ | - | $ | 59,410 | (3) | $ | 1,426,768 | ||||||||||||
| Executive Officer of Net Element | 2019 | 300,000 | 600,000 | 505,964 | - | 56,348 | (3) | 1,462,312 | ||||||||||||||||||
Steven Wolberg, Chief Legal Officer and | 2020 | 148,542 | - | 352,452 | - | 11,734 | 512,728 | |||||||||||||||||||
Secretary of Net Element | 2019 | 230,000 | - | 140,789 | 471,750 | 11,734 | 842,795 | |||||||||||||||||||
Jeffrey Ginsberg, Chief Financial Officer of Net Element (2) | 2020 | 106,313 | - | 117,845 | - | 15,949 | 240,106 | |||||||||||||||||||
2019 | 135,000 | - | - | 31,450 | 12,878 | 179,328 | ||||||||||||||||||||
(1) The amounts disclosed generally reflect the grant date fair value computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718. Grant date fair value for each award was determined based on the date approved by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors and by the closing stock price on such date.
(2) This amount consists primarily of his automobile reimbursement expense in connection with his employment agreement, health and other insurance expense.
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year End 2020
The following table sets forth information with respect to outstanding equity awards at the end of the Company’s fiscal year 2020 for the “named executive officers”:
OPTION AWARDS | SHARE AWARDS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Name | Number of securities underlying unexercised options(#) exercisable | Number of securities underlying unexercised options (#) unexercisable | Equity incentive plan awards: Number of securities underlying unexercised unearned options (#) | Option exercise price ($) | Option Expiration Date | Number of shares or units of stock that have not vested(#) | Market value of shares of units of stock that have not vested($) | Equity incentive plan awards: Number of unearned shares, units or other rights that have not vested (#) | Equity incentive plan awards: Market or payout value of unearned shares, units or other rights that have not vested ($) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Steven Wolberg | 2,000 | - | - | $ | 24.00 | 3-Oct-25 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
Steven Wolberg | 13,714 | - | - | $ | 21.20 | 13-Jun-26 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
Steven Wolberg | 12,000 | - | - | $ | 8.10 | 28-Feb-27 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Steven Wolberg | 75,000 | - | - | $ | 6.29 | 10-Apr-29 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
Jeffrey Ginsberg | 966 | - | - | $ | 13.40 | 10-Dec-24 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
Jeffrey Ginsberg | 1,006 | - | - | $ | 21.20 | 13-Jun-26 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Jeffrey Ginsberg | 4,000 | - | - | $ | 24.00 | 3-Dec-25 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Jeffrey Ginsberg | 5,000 | - | - | $ | 6.29 | 10-Apr-29 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||||
Employment Agreement
On February 25, 2020, as per approval of the Compensation Committee of the board of directors of the Company, the Company entered into an employment agreement (the “Wolberg Agreement”) with Steven Wolberg, the Company's Chief Legal Officer and Corporate Secretary. The Wolberg Agreement provides for continuation of the current base salary of $250,000. The term of the Wolberg Agreement is 5 years, with subsequent 1-year renewals. The Wolberg Agreement provides for a sign-on bonus of 10,000 shares of Company’s common stock, to be granted to Mr. Wolberg pursuant to the Company’s equity incentive plan, the severance in the amount of two times annual base salary of Mr. Wolberg if Mr. Wolberg’s employment is terminated by the Company without “cause” (as defined in the Wolberg Agreement) or Mr. Wolberg terminates the employment for “good reason” (as defined in the Wolberg Agreement). For each fiscal year during the term of the Wolberg Agreement, the Wolberg Agreement provides for a bonus arrangement equal to 50% of Mr. Wolberg’s base salary, payable in the Company’s shares of common stock or, at the Company’s discretion, in cash. Further, for each fiscal year during the term of the Wolberg Agreement, Mr. Wolberg will be eligible to receive long-term equity incentive awards, as determined by the Compensation Committee at the time of grant, pursuant to the Company’s equity incentive plan.
Director Compensation
The following table further summarizes the compensation paid to the Company's non-employee directors for service as a director during 2020:
Director Name | Fees earned or paid in cash ($) | Stock awards ($) | Total ($) | |||||||||
Howard Ash, former director | $ | - | $ | 7,504 | $ | 7,504 | ||||||
Jonathan Fichman, former director | 6,250 | - | 6,250 | |||||||||
Jon Najarian | 20,000 | 15,005 | 35,005 | |||||||||
| John J. Wiegand, former director | 12,479 | - | 12,479 | |||||||||
Todd Raarup | - | 7,501 | 7,501 | |||||||||
| John Roland | 2,500 | 7,501 | 10,001 | |||||||||
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The table below contains information regarding the beneficial ownership of our Common Stock as of March 21, 2021 by (i) each person who is known to us to beneficially own more than 5% of our Common Stock, (ii) each of our directors, (iii) each of our named executive officers and (iv) all of our directors and executive officers as a group. Except as otherwise noted below, each person or entity named in the following table has the sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of our Common Stock that he, she or it beneficially owns. Unless otherwise indicated, the address of each beneficial owner listed below is c/o Net Element, Inc., 3363 NE 163rd Street, Suite 605, North Miami Beach, FL 33160.
Name and address of beneficial owner | Amount and nature of beneficial ownership (number of shares of Common Stock beneficially owned) |
| Percent of class (1) |
|
Oleg Firer | 552,249 | (2) | 10.60 | % |
c/o Net Element, Inc. |
|
|
|
|
3363 NE 163rd Street, Suite 605, |
|
|
|
|
North Miami Beach, Florida 33160 |
|
|
|
|
Steven Wolberg | 180,287 | (3) | 3.39 | % |
c/o Net Element, Inc. |
|
|
|
|
3363 NE 163rd Street, Suite 605, |
|
|
|
|
North Miami Beach, Florida 33160 |
|
|
|
|
Jeffery Ginsberg | 28,179 |
| 0.54 | % |
c/o Net Element, Inc. |
|
|
|
|
3363 NE 163rd Street, Suite 605, |
|
|
|
|
North Miami Beach, Florida 33160 |
|
|
|
|
Jon Najarian |
|
|
|
|
c/o Net Element, Inc. | 18,492 |
| 0.36 | % |
3363 NE 163rd Street, Suite 605, |
|
|
|
|
North Miami Beach, Florida 33160 |
|
|
|
|
| John Roland | 686 | 0.01 | % | |
| c/o Net Element, Inc. | ||||
| 3363 NE 163rd Street, Suite 605, | ||||
| North Miami Beach, Florida 33160 | ||||
| Todd Raarup | 686 | 0.01 | % | |
| c/o Net Element, Inc. | ||||
| 3363 NE 163rd Street, Suite 605, | ||||
| North Miami Beach, Florida 33160 | ||||
| Esousa Holdings LLC | (4) | (4) | ||
| 211 East 43rd Street, Suite 402 | ||||
| New York, NY 10017 | ||||
All directors and executive officers as a group (6 persons) | 780,579 |
| 14.92 | % |
(1) | Applicable percentage ownership is based on 5,208,236 shares of Common Stock outstanding as of March 23, 2021 together with securities exercisable or convertible into shares of Common Stock within 60 days of March 23, 2021 for each stockholder. Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the Commission and generally includes voting or investment power with respect to securities. The shares issuable pursuant to the exercise or conversion of such securities are deemed outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage of ownership of the security holder, but are not treated as outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage of ownership of any other person. |
(2) | Mr. Firer is deemed to have beneficial ownership of 552,249 shares of Common Stock consisting of (1) 484,937 restricted shares of Common Stock held directly by Mr. Firer, and (2) as the sole member of Star Equities, LLC, Mr. Firer can be deemed to beneficially own 67,312 restricted shares of Common Stock and shares of Common Stock issuable upon exercise of the certain options of Common Stock beneficially owned by Star Equities, LLC. Mr. Firer has (a) sole voting power and sole dispositive power with respect to 67,312 restricted shares of Common Stock and (b) shared voting power and shared dispositive power with respect to the above-described shares beneficially owned by Star Equities. The restricted shares beneficially owned by Star Equities, LLC include 484,937 restricted shares of Common Stock issuable pursuant to amended option to pursuant to the Letter Agreement dated as of September 11, 2015, as modified by that certain Additional Letter Agreement dated as of October 7, 2015, as amended, with the Company. |
(3) | The shares held directly by Steven Wolberg include 107,286 shares of Common Stock issuable upon exercise of certain options to purchase Common Stock granted to Mr. Wolberg (i) as part of the Company’s incentive compensation awards and (ii) pursuant to the Letter Agreement dated as of September 11, 2015, as modified by that certain Additional Letter Agreement dated as of October 7, 2015, as amended, with the Company. |
| (4) | All information regarding shares that may be beneficially owned by Esousa Holdings LLC is based on information disclosed in a Schedule 13G/A filed by Esousa Holdings LLC with the Commission on February 16, 2021. As more fully described in such Schedule 13G/A, Esousa Holdings LLC beneficially owns 211,481 shares of Common Stock, 404,676 shares of Common Stock issuable upon exercise of the purchase warrants, each issued to Esousa Holdings LLC pursuant to the Unit Purchase Agreement between Esousa Holdings LLC and the Company on December 29, 2017. As described in item 4 of such Schedule 13G, the purchase warrants and the pre-funded Warrants are each subject to a 9.99% blocker, and the percentage set forth in row (11) of such Schedule 13G/A gives effect to such blockers. However, as more fully described in Item 4 of such Schedule 13G/A, the securities reported in rows (5), (7) and (9) of such Schedule 13G/A show the number of shares of Common Stock that would be issuable upon full exercise of such reported securities and do not give effect to such blockers. Therefore, the actual number of shares of Common Stock beneficially owned by Esousa Holdings LLC, after giving effect to such blockers, is less than the number of securities reported in rows (5), (7) and (9) of such Schedule 13G/A. |
Equity Compensation Plan Table
The following table summarizes our equity compensation plan information as of December 31, 2020. Information is included for equity compensation plans approved by our stockholders and equity compensation plans not approved by our stockholders
(c) | ||||||||||||
Number of securities | ||||||||||||
(a) | (b) | remaining available | ||||||||||
Number of securities | Weighted-average | for future issuance | ||||||||||
to be issued upon | exercise price per | under equity | ||||||||||
exercise of | share of | compensation plans | ||||||||||
outstanding options, | outstanding options, | (excluding securities | ||||||||||
Plan Category | warrants and rights | warrants and rights | reflected in column (a)) | |||||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by stockholders | 154,005 | $ | 10.73 | 209,693 | ||||||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by stockholders | - | $ | - | - | ||||||||
Total | 154,005 | 10.73 | 209,693 | |||||||||
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions
Since the beginning of fiscal 2019, the Company did not have any transactions to which it has been a participant that involved amounts that exceeded or will exceed the lesser of (i) $120,000 or (ii) one percent of the average of the Company’s total assets at year-end for the last two completed fiscal years, and in which any of the Company’s directors, executive officers or any other “related person” as defined in Item 404(a) of Regulation S-K had or will have a direct or indirect material interest, other than:
On March 27, 2020, our Company entered into a Master Exchange Agreement (the “ESOUSA Agreement”) with ESOUSA Holdings, LLC ("ESOUSA"), a related party. Prior to entering into the ESOUSA Agreement, ESOUSA agreed to acquire an existing promissory note that had been previously issued by the Company, of up to $2,000,000 in principal amount outstanding plus interest due to RBL Capital Group, LLC ("RBL"). Pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement, the Company has the right, at any time prior to March 27, 2021, to request ESOUSA, and ESOUSA agreed upon each such request, to exchange this promissory note in tranches on the dates when the Company instructs ESOUSA, for such number of shares of the Company’s common stock (“Common Stock”) as determined under the ESOUSA Agreement based upon the number of shares of Common Stock (already in ESOUSA’s possession) that ESOUSA sold in order to finance its purchase of such tranche of the promissory note from RBL Capital Group, LLC. ESOUSA will purchase each tranche of the promissory note equal to 88% of the gross proceeds from the shares of Common Stock sold by ESOUSA to finance the purchase of such Exchange Amount from RBL Capital Group, LLC. Each such tranche to be $148,000 unless otherwise agreed to by the Company and ESOUSA.
On April 23, 2020 and August 3, 2020, the Company entered into certain amendments to the ESOUSA Agreement, which together increased from $2,000,000 to $15,000,000 the principal amount and unpaid interest of one or more promissory notes of the Company or its direct or indirect subsidiaries that ESOUSA either purchased in whole or has an irrevocable right to purchase in tranches from RBL in connection with the ESOUSA Agreement.
On March 27, 2020, the Company received its first tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $148,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. Included in other accrued expenses at September 30, 2020 is approximately $145,000 in connection with this first tranche for which shares of Common Stock have not yet been issued. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $148,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On April 28, 2020, the Company received its second tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $143,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 65,862 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $143,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 11, 2020, the Company received its third tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $707,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 66,190 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $707,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 21, 2020, the Company received its fourth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $401,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 45,654 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $401,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On September 25, 2020, the Company received its fifth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $426,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 50,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $426,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On December 30, 2020, the Company received its sixth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $1,960,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. In January 2021, the Company issued 200,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $1,960,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
At December 31, 2020 and 2019, we had accrued expenses of approximately $122,000 and $127,000, respectively, which consisted primarily of various travel, professional fees, and other expenses paid and charged for by our CEO on his personal credit cards. This is reflected as due to related party on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Director Independence
Our Board of Directors currently includes three non-employee independent members: Jon Najarian, John Roland, and Todd Raarup. Each of Messrs. Najarian, Roland, and Raarup are an "independent director" as defined under NASDAQ Listing Rule 5605(a)(2). A majority of our Board members are independent directors, as three out of the four members of the Board qualify as independent under the NASDAQ listing standards and the rules of the Commission. No director is considered independent unless our Board of Directors affirmatively determines that the director has no relationship with us (directly, or as a partner, shareholder or officer of an organization that has a relationship with us) that would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment in carrying out the responsibilities of a director. Also, all members of our Board of Director’s audit committee, compensation committee and nominating and governance committee are independent directors under applicable NASDAQ and SEC rules and regulations. Howard Ash, Jonathan Fichman and John J. Wiegand, each of whom is a former director that previously served on our Board of Directors during 2020, were previously determined to be independent by our Board of Directors as well.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
Audit Fees. The aggregate fees, including expenses, billed by our principal accountant for the audit of our annual financial statements and review of financial statements included in our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and other services that are normally provided in connection with statutory and regulatory filings or engagements during each of the fiscal years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 were $390,000.
Audit-Related Fees. The aggregate fees, including expenses, billed by our principal accountant for assurance and related services that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of our financial statements not reported under “Audit Fees” above during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 were $ 0.
Tax Fees. The aggregate fees, including expenses, billed by our principal accountant for services rendered for tax compliance, tax advice and tax planning during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 were approximately $14,300 and $19,800, respectively.
All Other Fees. The aggregate fees, including expenses, billed for all other products and services provided by our principal accountant during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 were $0.
Audit Committee Pre-Approval Policy
Our audit committee is responsible for approving in advance the engagement of our principal accountant for all audit services and non-audit services, based on independence, qualifications and, if applicable, performance, and approving the fees and other terms of any such engagement. The audit committee may in the future establish pre-approval policies and procedures pursuant to which our principal accountant may provide certain audit and non-audit services to us without first obtaining the audit committee’s approval, provided that such policies and procedures (i) are detailed as to particular services, (ii) do not involve delegation to management of the audit committee’s responsibilities described in this paragraph and (iii) provide that, at its next scheduled meeting, the audit committee is informed as to each such service for which the principal accountant is engaged pursuant to such policies and procedures. In addition, the audit committee may in the future delegate to one or more members of the audit committee the authority to grant pre-approvals for such services, provided that the decisions of such member(s) to grant any such pre-approval must be presented to the audit committee at its next scheduled meeting.
All audit and audit-related services performed by our principal accountant during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 were pre-approved by our audit committee.
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules.
Documents filed as part of this Report.
1. | The following consolidated financial statements of Net Element, Inc. and subsidiaries and notes thereto and the reports of the independent registered public accounting firms thereon are set forth on pages F-2 through F-24 and are filed as part of this Report: |
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firms |
| Audited Consolidated Balance Sheets at December 31, 2020 and 2019 |
| Audited Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, Audited Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, and Audited Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
2. | Exhibits. |
A list of the exhibits filed as a part of this Report is set forth on the Exhibit Index that immediately precedes the signature pages to this Report and is incorporated herein by reference.
EXHIBIT INDEX
3.6 |
| |
|
|
|
3.7 |
| |
|
|
|
3.8 |
| |
|
|
|
3.9 |
| |
|
|
|
3.10 |
|
3.11 |
| |
|
|
|
3.12 |
| |
|
|
|
3.13 |
| |
|
|
|
4.1 |
| |
|
|
|
4.2 |
| |
|
|
|
4.3 |
| |
|
|
|
4.4 |
| |
|
|
|
4.5 |
| |
|
|
|
4.6 |
| |
|
|
|
4.7 |
|
4.8 |
| |
|
|
|
4.9 |
| |
|
|
|
4.10 |
| |
|
|
|
4.11 |
| |
|
|
|
4.12 |
| |
|
|
|
| 4.13 | Description of Company’s securities (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.13 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the Commission on March 30, 2020) | |
10.1 |
| |
|
|
|
10.2 |
| |
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
10.4 |
| |
|
|
|
10.5 |
| |
|
|
|
10.6 |
| |
|
|
|
10.7 |
| |
|
|
|
10.8 |
| |
|
|
|
10.9 |
|
10.10# |
| |
|
|
|
10.11 |
| |
|
|
|
10.12 |
| |
|
|
|
10.13 |
| |
|
|
|
10.14 |
| |
|
|
|
10.15 |
| |
|
|
|
10.16 |
| |
|
|
|
10.17 |
|
10.18 |
| |
|
|
|
10.19 |
| |
|
|
|
10.20 |
|
10.21 |
| |
|
|
|
10.22 |
| |
|
|
|
10.23 |
| |
|
|
|
10.24 |
| |
|
|
|
10.25 |
| |
|
|
|
10.26 |
| |
|
|
|
10.27 |
| |
|
|
|
10.28 |
| |
|
|
|
10.29 |
| |
|
|
|
10.30 |
| |
|
|
|
10.31 |
| |
|
|
|
10.32 |
|
10.33# |
| |
|
|
|
10.34# |
|
10.35# |
| |
|
|
|
10.36 |
| |
|
|
|
10.37 |
| |
|
|
|
10.38 |
| |
|
|
|
10.39 |
| |
|
|
|
10.40 |
| |
|
|
|
10.41 |
| |
|
|
|
10.42 |
| |
|
|
|
10.43 |
| |
|
|
|
10.44 |
| |
|
|
|
10.45 |
|
10.46 |
| |
|
|
|
10.47 |
| |
|
|
|
10.48 |
| |
|
|
|
10.49 |
| |
|
|
|
10.50 |
| |
|
|
|
10.51 |
|
10.52 |
| |
|
|
|
10.53 |
| |
|
|
|
10.54 |
| |
|
|
|
10.55 |
| |
|
|
|
10.56 |
| |
|
|
|
10.57 |
| |
|
|
|
10.58 |
| |
|
|
|
10.59 |
|
10.60 |
| |
|
|
|
10.61 |
| |
|
|
|
10.62 |
| |
|
|
|
10.63 |
| |
|
|
|
10.64 |
| |
|
|
|
10.65 |
| |
|
|
|
10.66 |
| |
|
|
|
10.67 |
| |
|
|
|
10.68# |
|
10.69# |
| |
|
|
|
10.70# |
| |
|
|
|
10.71 |
| |
|
|
|
10.72 |
| |
|
|
|
10.73 |
|
10.74 |
| |
|
|
|
10.75 |
| |
|
|
|
10.76 |
| |
|
|
|
10.77 |
| |
|
|
|
10.78 |
| |
|
|
|
10.79 |
| |
|
|
|
10.80 |
| |
|
|
|
10.81 |
| |
|
|
|
10.82 |
| |
|
|
|
10.83 |
| |
|
|
|
10.84 |
| |
|
|
|
10.85 |
|
10.86 |
|
# Indicates management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
* Filed herewith (furnished herewith with respect to Exhibit 32.1).
None.
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| Net Element, Inc. | ||
|
| ||
March 31, 2021 |
| By: | /s/ Oleg Firer |
|
|
| Oleg Firer |
|
|
| Executive Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| March 31, 2021 | By: | /s/ Oleg Firer |
|
| Oleg Firer |
|
|
|
| March 31, 2021 | By: | /s/ Jeffrey Ginsberg |
|
| Jeffrey Ginsberg |
|
| Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
|
|
|
| March 31, 2021 | By: | /s/ Jon Najarian |
|
| Jon Najarian |
|
| Director |
|
|
|
| March 31, 2021 | By: | /s/ John Roland |
|
| John Roland |
|
| Director |
| March 31, 2021 | By: | /s/ Todd Raarup |
| Todd Raarup | ||
| Director |
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
NET ELEMENT, INC.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Page |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 | |
|
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
Net Element, Inc.
Miami, Florida
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Net Element, Inc. (the “Company”) at December 31, 2020 and 2019, and the related consolidated statements of operations, changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended December 31, 2020, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the consolidated financial statements). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2020 and 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended December 31, 2020, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Going Concern Uncertainty
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As described in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has sustained recurring losses from operations and has working capital and accumulated deficits that raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to these matters are described in Note 2. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty. Our opinion is not modified with respect to this matter.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
Intangible Assets Impairment Assessments
As described in Notes 3 and 6 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has goodwill of $7.7 million at December 31, 2020. In most cases, no directly observable market inputs are available to measure the fair value to determine if the asset is impaired. Therefore, an estimate is derived indirectly and is based on net present value techniques utilizing post-tax cash flows and discount rates. The estimates that management used in calculating the net present values depend on assumptions specific to the nature of the management service activities with regard to the amount and timing of projected future cash flows; long-term forecasts; actions of competitors (competing services), future tax and discount rates.
The principal consideration for our determination that performing procedures relating to the intangible assets impairment assessment is a critical audit matter is the significant judgment by management when developing the net present value of the intangible assets. This, in turn, led to a high degree of auditor judgment, subjectivity, and effort in performing procedures and evaluating management’s significant assumptions related to the amount and timing of projected future cash flows and the discount rate.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statements. These procedures included testing management’s process for developing the fair value estimate; evaluating the appropriateness of the net present value techniques; testing the completeness and accuracy of underlying data used in the model; and evaluating the significant assumptions used by management, including the amount and timing of projected future cash flows and the discount rate. Evaluating management’s assumptions related to the amount and timing of projected future cash flows and the discount rate involved evaluating whether the assumptions used by management were reasonable considering the current and past performance of the intangible assets, the consistency with external market and industry data, and whether these assumptions were consistent with evidence obtained in other areas of the audit.
/s/ Daszkal Bolton LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2014.
Fort Lauderdale, Florida
March 31, 2021
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
ASSETS | ||||||||
Current assets: | ||||||||
Cash | $ | 4,541,013 | $ | 486,604 | ||||
Accounts receivable, net | 7,109,173 | 6,560,928 | ||||||
| Due from Mullen Technologies, Inc. | 480,000 | - | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | 1,837,972 | 1,621,144 | ||||||
Total current assets, net | 13,968,158 | 8,668,676 | ||||||
Intangible assets, net | 3,595,326 | 5,678,649 | ||||||
Goodwill | 7,681,186 | 7,681,186 | ||||||
| Operating lease right-of-use asset | 801,062 | 380,986 | ||||||
Other long term assets | 780,998 | 629,651 | ||||||
Total assets | $ | 26,826,730 | $ | 23,039,148 | ||||
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | ||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 7,171,376 | $ | 6,037,833 | ||||
Accrued expenses | 4,604,097 | 1,800,344 | ||||||
Deferred revenue | 1,607,329 | 1,401,117 | ||||||
Notes payable (current portion) | 1,330,018 | 909,086 | ||||||
| Operating lease liability (current portion) | 140,973 | 133,727 | ||||||
Due to related party | 216,657 | 126,662 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 15,070,450 | 10,408,769 | ||||||
Operating lease liability (net of current portion) | 660,621 | 247,259 | ||||||
| Notes payable (net of current portion) | 8,613,587 | 8,342,461 | ||||||
Total liabilities | 24,344,658 | 18,998,489 | ||||||
STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | ||||||||
Series A Convertible Preferred stock ($.0001 par value, 1,000,000 shares authorized, no shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019) | - | - | ||||||
Common stock ($.0001 par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized and 4,997,349 and 4,111,082 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively) | 499 | 410 | ||||||
Paid in capital | 189,700,103 | 185,297,069 | ||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (2,259,410 | ) | (2,274,187 | ) | ||||
Accumulated deficit | (184,692,067 | ) | (178,750,634 | ) | ||||
Non-controlling interest | (267,053 | ) | (231,999 | ) | ||||
Total stockholders' equity | 2,482,072 | 4,040,659 | ||||||
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $ | 26,826,730 | $ | 23,039,148 | ||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Net revenues | ||||||||
Service fees | $ | 65,705,122 | $ | 64,999,611 | ||||
Total Revenues | 65,705,122 | 64,999,611 | ||||||
Costs and expenses: | ||||||||
Cost of service fees | 55,861,403 | 54,721,710 | ||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 7,016,044 | 9,341,784 | ||||||
Non-cash compensation | 2,718,152 | 2,050,862 | ||||||
Bad debt expense | 1,566,804 | 1,350,177 | ||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 3,035,799 | 3,120,243 | ||||||
Total costs and operating expenses | 70,198,202 | 70,584,776 | ||||||
Loss from operations | (4,493,080 | ) | (5,585,165 | ) | ||||
Interest expense | (1,446,640 | ) | (1,112,527 | ) | ||||
Other income (expense) | (50,268 | ) | 1,459,615 | |||||
Impairment charge relating to goodwill | - | (1,326,566 | ) | |||||
Gain on disposition | 13,500 | - | ||||||
Net loss from continuing operations before income taxes | (5,976,488 | ) | (6,564,643 | ) | ||||
Income taxes | - | - | ||||||
Net loss from continuing operations | (5,976,488 | ) | (6,564,643 | ) | ||||
Net income attributable to the non-controlling interest | 35,054 | 106,261 | ||||||
Net loss attributable to Net Element, Inc. stockholders | (5,941,434 | ) | (6,458,382 | ) | ||||
Foreign currency translation | 14,777 | (42,025 | ) | |||||
Comprehensive loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (5,926,657 | ) | $ | (6,500,407 | ) | ||
Loss per share - basic and diluted | $ | (1.34 | ) | $ | (1.60 | ) | ||
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding - basic and diluted | 4,420,777 | 4,041,957 | ||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common Stock | Paid in | Accumulated Other | Non-controlling | Accumulated | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | Capital | Comprehensive Loss | interest | Deficit | Stockholder's Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance December 31, 2018 | 3,863,019 | $ | 386.30 | $ | 183,246,232 | $ | (2,232,163 | ) | $ | (125,737 | ) | $ | (172,292,252 | ) | $ | 8,596,466 | ||||||||||||
Share based compensation | 248,063 | 24.36 | 2,050,837 | - | - | - | 2,050,861 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | - | - | - | - | (106,262 | ) | (6,458,382 | ) | (6,564,644 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive loss - foreign currency translation | - | - | - | (42,024 | ) | - | - | (42,024 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance December 31, 2019 | 4,111,082 | $ | 410.66 | $ | 185,297,069 | $ | (2,274,187 | ) | $ | (231,999 | ) | $ | (178,750,633 | ) | $ | 4,040,659 | ||||||||||||
Share based compensation | 334,654 | 33.47 | 2,721,865 | - | - | - | 2,721,899 | |||||||||||||||||||||
ESOUSA transaction | 551,613 | 55.16 | 1,681,169 | - | - | - | 1,681,225 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | - | - | - | - | (35,054 | ) | (5,941,434 | ) | (5,976,488 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive loss - foreign currency translation | - | - | - | 14,777 | - | - | 14,777 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Balance December 31, 2020 | 4,997,349 | $ | 499.28 | $ | 189,700,103 | $ | (2,259,410 | ) | $ | (267,053 | ) | $ | (184,692,067 | ) | $ | 2,482,072 | ||||||||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||
Net loss attributable to Net Element, Inc. stockholders | $ | (5,941,434 | ) | $ | (6,458,382 | ) | ||
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
Non-controlling interest | (35,054 | ) | (106,261 | ) | ||||
Share based compensation | 2,718,152 | 2,050,862 | ||||||
Deferred revenue | 206,212 | (94,732 | ) | |||||
| Impairment for Goodwill | - | 1,326,566 | ||||||
Provision for bad debt | 2,968 | (9,226 | ) | |||||
Depreciation and amortization | 3,035,799 | 3,120,243 | ||||||
Non cash interest | 386,004 | 56,875 | ||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
Accounts receivable | (581,557 | ) | (263,758 | ) | ||||
| Due from Mullen Technologies, Inc. | (480,000 | ) | - | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | 198,448 | (132,218 | ) | |||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 3,512,074 | (1,642,618 | ) | |||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 3,021,612 | (2,152,649 | ) | |||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||
Purchase of portfolios and client acquisition costs | (603,533 | ) | (2,313,662 | ) | ||||
| Sale of Portfolio | 162,000 | - | ||||||
Purchase of equipment and changes in other assets | (1,376,810 | ) | (138,000 | ) | ||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (1,818,343 | ) | (2,451,662 | ) | ||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||
| Proceeds from SBA loans | 651,392 | - | ||||||
Proceeds from indebtedness | 4,666,190 | 3,034,500 | ||||||
Repayment of indebtedness | (2,971,054 | ) | (162,447 | ) | ||||
Lease liability | 420,608 | 380,986 | ||||||
| Related party advances | 255,576 | 202,471 | ||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 3,022,712 | 3,455,510 | ||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | (20,225 | ) | 15,505 | |||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash | 4,205,756 | (1,133,296 | ) | |||||
Cash and restricted cash at beginning of year | 1,116,255 | 2,249,551 | ||||||
Cash and restricted cash at end of year | $ | 5,322,011 | $ | 1,116,255 | ||||
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information | ||||||||
Cash paid during the period for: | ||||||||
Interest | $ | 1,060,636 | $ | 730,993 | ||||
Taxes | $ | 266,559 | $ | 120,544 | ||||
| Shares issued for redemption of indebtedness | $ | 3,822,290 | $ | - | ||||
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements
NET ELEMENT, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1. ORGANIZATION AND OPERATIONS
Net Element, Inc. (collectively with its subsidiaries, “Net Element”, “we”, “us”, “our” or the “Company”) is a financial technology-driven group specializing in payment acceptance and value-added solutions across multiple channels in the United States and selected international markets. We are differentiated by our proprietary technology which enables us to provide a broad suite of payment products and end-to-end transaction processing services. Our transactional services business enables merchants to accept credit cards as well as other forms of payment, including debit cards, checks, gift cards, loyalty programs and alternative payment methods in traditional card-present or swipe transactions, as well as card-not-present transactions, such as those conducted over the phone or through the Internet or a mobile device. We operate in two reportable business operating segments: (i) North American Transaction Solutions, and (ii) International Transaction Solutions.
We are able to deliver our services across multiple points of access, or “multi-channel,” including brick and mortar locations, software integration, e-commerce, mobile operator billing, mobile and tablet-based solutions. In the United States, via our U.S. based subsidiaries, we generate revenues from transactional services and other payment technologies for small and medium-sized businesses. Through PayOnline, we provide transactional services, mobile payment transactions, online payment transactions and other payment technologies in emerging countries in the Eurasian Economic Community ("EAEC"), Europe and Asia.
Our transactional services business enables merchants to accept credit cards as well as other forms of payment, including debit cards, checks, gift cards, loyalty programs and alternative payment methods in traditional card-present or swipe transactions, as well as card-not-present transactions, such as those conducted over the phone or through the Internet or a mobile device. We market and sell our services through both independent sales groups (“ISGs”), which are non-employee, external sales organizations and other third-party resellers of our products and services, and directly to merchants through electronic media, telemarketing and other programs, including utilizing partnerships with other companies that market products and services to local and international merchants. We have agreements with several banks that sponsor us for membership in the Visa ®, MasterCard ®, American Express ®, and Discover ® card associations and settle card transactions for our merchants. These sponsoring banks include Citizens Bank, Esquire Bank, N.A. and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. From time to time, we may enter into agreements with additional banks. We perform core functions for merchants such as application processing, underwriting, account set-up, risk management, fraud detection, merchant assistance and support, equipment deployment and chargeback services.
Our Mobile Solutions business, PayOnline, provides relationships and contracts with mobile operators that gives us the ability to offer our clients in-app, premium SMS (short message services, which is a text messaging service), Wireless Application Protocol (WAP)-click, one click and other carrier billing services. PayOnline provides flexible high- tech payment solutions to companies doing business on the Internet or in the mobile environment. PayOnline specializes in integration and customization of payment solutions for websites and mobile apps. In particular, PayOnline arranges payment on the website of any commercial organization, which increases the convenience of using the website and helps maximize the number of successful transactions. In addition, PayOnline is focused on providing online and mobile payment acceptance services to the travel industry through direct integration with leading Global Distribution Systems (“GDS”), which include Amadeus® and Sabre®. Key geographic regions that PayOnline serves include Eastern Europe, Central Asia, Western Europe, North America and Asia major sub regions. The PayOnline office is located in Moscow, Russia.
Also part of our transactional services business, Aptito is a proprietary, cloud-based payments platform for the hospitality industry, which creates an online consumer experience in offline commerce environments via tablet, mobile and all other cloud-connected devices. Aptito’s easy to use point-of-sale (“POS”) system makes things easier by providing a comprehensive solution to the hospitality industry to help streamline management and operations. Orders placed tableside by customers directly speed up the ordering process and improve overall efficiency. Aptito's mobile POS system provides portability to the staff while performing all the same functions as a traditional POS system.
NOTE 2. LIQUIDITY AND GOING CONCERN CONSIDERATIONS
Our consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and the settlement of liabilities and commitments in the normal course of business. We sustained a net loss of approximately $5.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 and have an accumulated deficit of $184.7 million and a negative working capital of $1.7 million at December 31, 2020.
The continuing spread of the novel coronavirus pandemic (“COVID-19”) is currently impacting countries, communities, supply chains and markets, global financial markets, as well as, the largest industry group serviced by our Company. The Company cannot predict, at this time, whether COVID-19 will continue to have a material impact on our future financial condition and results of operations due to understaffing in the service sector and the decrease in revenues and profits, particularly restaurants, and any possible future government ordinances that may further restrict restaurant and other service or retail sectors operations.
During March 2020, our Company evaluated its liquidity position, future operating plans, and its labor force, which included a reduction in the labor force and compensation to executives and other employees, in order to maintain current payment processing functions, capabilities, and continued customer service to its merchants. We are also seeking sources of capital to pay our contractual obligations as they come due, in light of these uncertain times. Management believes that its operating strategy will provide the opportunity for us to continue as a going concern as long as we are able to obtain additional financing. At this time, due to our continuing losses from operations, negative working capital, and the COVID-19 pandemic, we cannot predict the impact of these conditions on our ability to obtain financing necessary for the Company to fund its future working capital requirements. Our Company has also decided to explore strategic alternatives and potential options for its business, including sale of the Company or certain assets, licensing of technology, spin-offs, or a business combination. There can be no assurance, at this time, regarding the eventual outcome of our planned strategic alternatives. In most respects, it is still too early in the COVID-19 pandemic to be able to quantify or qualify the longer-term ramifications on our merchant processing business, our merchants, our planned strategic alternatives to enhance current shareholder value, our current investors, and/or future potential investors.
On March 27, 2020, our Company entered into a Master Exchange Agreement (the “ESOUSA Agreement”) with ESOUSA Holdings, LLC ("ESOUSA"), a related party. Prior to entering into the ESOUSA Agreement, ESOUSA agreed to acquire an existing promissory note that had been previously issued by the Company, of up to $2,000,000 in principal amount outstanding plus interest due to RBL Capital Group, LLC ("RBL"). Pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement, the Company has the right, at any time prior to March 27, 2021, to request ESOUSA, and ESOUSA agreed upon each such request, to exchange this promissory note in tranches on the dates when the Company instructs ESOUSA, for such number of shares of the Company’s common stock (“Common Stock”) as determined under the ESOUSA Agreement based upon the number of shares of Common Stock (already in ESOUSA’s possession) that ESOUSA sold in order to finance its purchase of such tranche of the promissory note from RBL Capital Group, LLC. ESOUSA will purchase each tranche of the promissory note equal to 88% of the gross proceeds from the shares of Common Stock sold by ESOUSA to finance the purchase of such Exchange Amount from RBL Capital Group, LLC. Each such tranche to be $148,000 unless otherwise agreed to by the Company and ESOUSA.
On April 23, 2020 and August 3, 2020, the Company entered into certain amendments to the ESOUSA Agreement, which together increased from $2,000,000 to $15,000,000 the principal amount and unpaid interest of one or more promissory notes of the Company or its direct or indirect subsidiaries that ESOUSA either purchased in whole or has an irrevocable right to purchase in tranches from RBL in connection with the ESOUSA Agreement.
On March 27, 2020, the Company received its first tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $148,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. Included in other accrued expenses at September 30, 2020 is approximately $145,000 in connection with this first tranche for which shares of Common Stock have not yet been issued. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $148,000 from RBL under the Loan and Security Agreement (“Credit Facility”) with RBL.
On April 28, 2020, the Company received its second tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $143,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 65,862 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $143,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 11, 2020, the Company received its third tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $707,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 66,190 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $707,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 21, 2020, the Company received its fourth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $401,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement.The Company issued 45,654 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $401,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On September 25, 2020, the Company received its fifth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $426,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement.The Company issued 50,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $426,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On December 30, 2020, the Company received its sixth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $1,960,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. In January 2021, the Company issued 200,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $1.960,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 4, 2020, our Company entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger (the “Merger Agreement”) with Mullen Technologies, Inc., a California corporation (“Mullen”), and Mullen Acquisition, Inc., a California corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”). Pursuant to, and on the terms and subject to the conditions of, the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub will be merged with and into Mullen (the “Merger”), with Mullen continuing as the surviving corporation in the Merger. After Mullen’s completion and delivery to our Company, of the audited financial statements for Mullen and its subsidiaries and affiliates required to be included in a registration statement, the Company intends to prepare and file with the Commission a registration statement on Form S-4 (together with all amendments thereto, the “Registration Statement”) in which the proxy statement will be included as a part of the prospectus, in connection with the registration under the Securities Act of the shares of Parent Shares to be issued in connection with the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement. The Merger Agreement contains termination rights for each of the Company and Mullen, including, among others, (i) in the event that the Merger has not been consummated by December 31, 2020, (ii) in the event that the requisite approval of the Company’s stockholders is not obtained upon a vote thereon, (iii) in the event that any governmental authority shall have taken action to restrain, enjoin or prohibit the consummation of the Merger, which action shall have become final and non-appealable and (iv) in the event that there is a breach by the other party of any of its representations, warranties, covenants or agreements, which breach is sufficiently material and not timely cured or curable. In addition, Mullen may terminate the Merger Agreement if, prior to receipt of the requisite approval of the Company’s stockholders, the Company’s board of directors shall have changed their recommendation in respect of the Merger. Further, the Company may terminate the Merger Agreement prior to receipt of the requisite approval of the Company’s stockholders to enter into a definitive agreement with respect to a Superior Proposal (as such term is defined in the Merger Agreement).
As contemplated by the Merger Agreement, on August 11, 2020, our Company as lender, entered into an unsecured Promissory Note, dated August 11, 2020 (the “Note”), with Mullen. Pursuant to the Note, Mullen borrowed from the Company $500,000. Prior to maturity of the loan, the principal amount of the loan will carry an interest rate of 14% per annum compounded monthly and payable upon demand. This loan will mature on the earlier of (i) the date that the Merger Agreement is terminated for any reason by any party thereto and (ii) the Merger Effective Time (as defined in the Merger Agreement).
On December 29, 2020, the Company entered into the First Amendment (the “Amendment”) to the Merger Agreement with Mullen and the Merger Sub. Prior to the parties’ execution and delivery of the Amendment, Section 8.1(b) of the Merger Agreement provided that the Merger Agreement may be terminated and the merger contemplated in the Merger Agreement (the “Merger”) and other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement may be abandoned at any time prior to the merger effective time, notwithstanding any requisite approval and adoption of Merger Agreement and the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement by the shareholders of Mullen and/or the stockholders of the Company, by either Company or Mullen if the merger effective time shall not have occurred on or before December 31, 2020 (the “Outside Date”). Pursuant to the Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub amended Section 8.01(b) of the Merger Agreement to extend the Outside Date to March 31, 2021.
In addition, pursuant to the Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub agreed that, if the registration statement on Form S-4 (with the merger proxy statement included as part of the prospectus) is not filed with U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) on or prior to January 15, 2021, then Mullen will pay the Company an agreed sum of $13,333 per day (the “Late Fee”) until the such registration statement (with the merger proxy statement included as part of the prospectus) is filed with the SEC. All accumulated Late Fees will be due and payable by Mullen on the 5th day of each calendar month commencing February 5, 2021 and on the 5th day of each month thereafter until the above-refenced filing has occurred.
On March 30, 2021, the Company entered into the Second Amendment (the “Second Amendment”) to Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of August 4, 2020, as amended by the First Amendment dated as of December 29, 2020 (the “Merger Agreement”) with Mullen Technologies, Inc., a California corporation (“Mullen”), Mullen Acquisition, Inc., a California corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Merger Sub”). Prior to the parties’ execution and delivery of the Second Amendment, Section 8.1(b) of the Merger Agreement, as amended, provided that the Merger Agreement may be terminated and the merger contemplated in the Merger Agreement (the “Merger”) and other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement may be abandoned at any time prior to the merger effective time, notwithstanding any requisite approval and adoption of this Agreement and the transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement by the shareholders of Mullen and/or the stockholders of the Company, by either Company or Mullen if the merger effective time shall not have occurred on or before March 31, 2021 (the “Outside Date”). Pursuant to the Second Amendment, the Company, Mullen and Merger Sub amended Section 8.01(b) of the Merger Agreement to extend the Outside Date to April 30, 2021.
The foregoing description of the Second Amendment does not purport to be complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by, the full text of such agreement, a copy of which is attached hereto as Exhibit 2.10 and incorporated herein by reference.
At March 31, 2021, the Company is also owed approximately $1 million from Mullen in connection with Late Fees, as previously discussed..
Consummation of the Merger, the Divestiture, the Private Placement and the other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement, is subject to customary conditions including, among others, the approval of the Company’s stockholders. There is no guarantee that the Merger, the Divestiture, the Private Placement or the other transactions contemplated in the Merger Agreement will be completed.
These conditions raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. The accompanying consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might be necessary if the Company is unable to continue as a going concern.
NOTE 3. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Significant accounting policies are defined as those that are reflective of significant judgments and uncertainties, and potentially result in materially different results under different assumptions and conditions. The Company’s significant accounting policies are described below.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) and pursuant to the reporting and disclosure rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
Principles of Consolidation
These consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Net Element, Inc and our subsidiary companies. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Reclassifications
Certain reclassifications of prior year amounts have been made to conform to the 2019 presentation. These reclassifications had no effect on net loss or loss per share as previously reported.
Cash
We maintain our U.S. dollar-denominated cash in several non-interest bearing bank deposit accounts. All U.S. non-interest bearing transaction accounts are insured up to a maximum of $250,000 at FDIC insured institutions. The bank balances exceeded FDIC limits by approximately $3.7 million and $134,000 at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively. We maintained approximately $43,000 and $30,000 in uninsured bank accounts in Russia and the Cayman Islands at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash represents funds held-on-deposit with processing banks pursuant to agreements to cover potential merchant losses. It is presented as other long-term assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets since the related agreements extend beyond the next twelve months. Following the adoption of ASU 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows: Restricted Cash (Topic 230), the Company includes restricted cash along with the cash balance for presentation in the consolidated statements of cash flows. The reconciliation between the consolidated balance sheet and the consolidated statement of cash flows is as follows:
December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
Cash on consolidated balance sheet | $ | 4,541,013 | $ | 486,604 | ||||
Restricted cash | 780,998 | 629,651 | ||||||
| Total cash and restricted cash | $ | 5,322,011 | $ | 1,116,255 | ||||
Accounts Receivable and Credit Policies
Accounts receivable consist primarily of uncollateralized credit card processing residual payments due from processing banks requiring payment within thirty days following the end of each month. Accounts receivable also include amounts due from the sales of our technology solutions to its customers. The carrying amount of accounts receivable is reduced by an allowance for doubtful accounts, if necessary, which reflects management’s best estimate of the amounts that will not be collected. The allowance is estimated based on management’s knowledge of its customers, historical loss experience and existing economic conditions. Accounts receivable and the allowance are written-off when, in management’s opinion, all collection efforts have been exhausted.
Other Current Assets
Other current assets consist of point-of-sale equipment which we use to service both merchants and independent sales agents ("ISG"). Often, we will provide the equipment as an incentive for merchants and independent sales agents to enter into a merchant contracts with us. The term of these contracts has an average length of three years and the cost of the equipment plus any setup fees will be amortized over the contract period. If the merchants terminate their contract with us early, they are obligated to either return the equipment or pay for it. The table below reflects the changes in other current assets, as it relates to point-of-sale equipment for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
Balance December 31, 2018 | $ | 525,000 | ||
Purchases during 2019 | 272,000 | |||
Amortization 2019 | (334,000 | ) | ||
Balance December 31, 2019 | $ | 463,000 | ||
| Purchases during 2020 | 248,000 | |||
| Amortization 2020 | (333,000 | ) | ||
| Balance December 31, 2020 | $ | 378,000 |
Also included in other current assets are prepaid PCI annual fees of approximately $298,000 and $345,000 as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and approximately $708,000 and $663,000 of prepaid annual fee commissions as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Amortization expense for the equipment placed in service for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 was approximately $333,000 and $334,000, respectively.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets acquired, either individually or with a group of other assets (but not those acquired in a business combination), are initially recognized and measured based on fair value. Goodwill acquired in business combinations is initially computed as the amount paid in excess of the fair value of the net assets acquired. We did not acquire any businesses during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
The cost of internally developing, maintaining and restoring intangible assets (including goodwill) that are not specifically identifiable, that have indeterminate lives, or that are inherent in a continuing business and related to an entity are recognized as an expense when incurred.
Intangible assets include acquired merchant relationships, recurring cash flow portfolios, referral agreements, trademarks, tradenames, website development costs and non-compete agreements. Merchant relationships represent the fair value of customer relationships purchased by us. Recurring cash flow portfolios give us the right to retain a greater share of the cash flow, in the form of paying less commissions to an independent sales agent, related to certain future transactions with the agent referred sales partners. Referral agreements represent the right to exclusively obtain referrals from a partner for their customers' credit card processing services.
We amortize definite lived identifiable intangible assets using a method that reflects the pattern in which the economic benefits of the intangible asset are expected to be consumed or otherwise utilized. The estimated useful lives of our customer-related intangible assets approximate the expected distribution of cash flows on a straight-line basis from each asset. The useful lives of contract-based intangible assets are equal to the terms of the agreement.
Management evaluates the remaining useful lives and carrying values of long-lived assets, including definite lived intangible assets, at least annually, or when events and circumstances warrant such a review, to determine whether significant events or changes in circumstances indicate that a change in the useful life or impairment in value may have occurred. There were no impairment charges during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 for the intangible assets.
Goodwill
In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other, we test goodwill for impairment for each reporting unit on an annual basis, or when events or circumstances indicate the fair value of a reporting unit is below its carrying value.
Our goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net identifiable assets acquired in business combinations. The goodwill generated from the business combinations is primarily related to the value placed on the employee workforce and expected synergies. Judgment is involved in determining if an indicator or change in circumstances relating to impairment has occurred. Such changes may include, among others, a significant decline in expected future cash flows, a significant adverse change in the business climate, and unforeseen competition.
We have the option of performing a qualitative assessment of impairment to determine whether any further quantitative testing for impairment is necessary. The option of whether or not to perform a qualitative assessment is made annually and may vary by reporting unit. Factors we consider in the qualitative assessment include general macroeconomic conditions, industry and market conditions, cost factors, overall financial performance of our reporting units, events or changes affecting the composition or carrying amount of the net assets of its reporting units, sustained decrease in its share price, and other relevant entity specific events. If the management determines on the basis of qualitative factors that the fair value of the reporting unit is more likely than not less than the carrying value, then we perform a quantitative test for that reporting unit. The fair value of each reporting unit is compared to the reporting unit’s carrying value, including goodwill. Subsequent to the adoption on January 1, 2017 of Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2017-04, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other: Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment, if the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, we recognize an impairment equal to the excess carrying value, not to exceed the total amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit.
At December 31, 2019, our management determined that an impairment charge of approximately $1.3 million was necessary to reduce the goodwill relating to the acquisition of PayOnline which is part of our International Transaction Solutions segment . We did not recognize any impairment charge to goodwill during the year ended December 31, 2020.
For a discussion of the estimate methodology and the significance of various inputs, please see the subheading below titled “Use of Estimates.”
Capitalized Customer Acquisition Costs, Net
Capitalized customer acquisition costs consist of up-front cash payments made to ISG’s for the establishment of new merchant relationships. Capitalized customer acquisition costs represent incremental, direct customer acquisition costs that are recoverable through gross margins associated with merchant contracts. The up-front cash payment to the ISG is based on the estimated gross margin for the first year of the merchant contract. The deferred customer acquisition cost asset is recorded at the time amounts are receivable but not yet earned and the capitalized acquisition costs are amortized on a straight-line basis over a period of approximately four years. Consideration paid for these agreements for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 was approximately $600,000 and $1.9 million, respectively. Because we pay an up-front fee to compensate the referral partner, the amount is treated as an asset acquisition in which we have acquired an intangible stream of referrals. This asset is amortized over a straight-line period of approximately four years and is included in intangible assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets (See Note 6 – item labeled “Client Acquisition Costs”).
Accrued Residual Commissions
We record commissions as a cost of revenues in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss. We pay agent commissions to ISGs and independent sales agents based on the processing volume of the merchants enrolled. The commission obligations are based on varying percentages of the volume processed by us on behalf of the merchants. Percentages vary based on the program type and transaction volume of each merchant.
Fair Value Measurements
Our financial instruments consist primarily of cash, accounts receivables, accounts payables, and a note payable. The carrying values of these financial instruments are considered to be representative of their fair values due to the short-term nature of these instruments. The carrying amount of notes payable of approximately $9.9 million and $9.3 million at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, approximates fair value because current borrowing rates do not materially differ from market rates for similar bank borrowings. The notes payable are classified as a Level 2 item within the fair value hierarchy.
We measure certain nonfinancial assets and liabilities at fair value on a nonrecurring basis. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. We use a three-level fair value hierarchy to prioritize the inputs used to measure fair value and maximizes the use of observable inputs and minimizes the use of unobservable inputs. The three levels of inputs used to measure fair value are as follows:
Level 1 — Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the reporting date
Level 2 — Observable market based inputs or unobservable inputs that are corroborated by market data
Level 3 — Unobservable inputs that are not corroborated by market data
These non-financial assets and liabilities include intangible assets and liabilities acquired in a business combination as well as impairment calculations, when necessary. The fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed in connection with the PayOnline acquisition, were measured at fair value by us at the acquisition date. The fair values of our merchant portfolios are primarily based on Level 3 inputs and are generally estimated based upon independent appraisals that include discounted cash flow analyses based on our most recent cash flow projections, and, for years beyond the projection period, estimates based on assumed growth rates. Assumptions are also made regarding appropriate discount rates, perpetual growth rates, and capital expenditures, among others. In certain circumstances, the discounted cash flow analyses are corroborated by a market-based approach that utilizes comparable company public trading values, and, where available, values observed in private market transactions. The inputs used by management for the fair value measurements include significant unobservable inputs, and therefore, the fair value measurements employed are classified as Level 3. Goodwill impairment is primarily based on observable inputs using company specific information and is classified as Level 3.
Leases
Effective January 1, 2019, we adopted Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842) which supersedes the lease accounting requirements in Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 840, Leases (Topic 840). Please refer to Recent Accounting Pronouncements below for additional information on the adoption of Topic 842 and the impact upon adoption to the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Under Topic 842, we applied a dual approach to all leases whereby we are a lessee and classify leases as either finance or operating leases based on the principle of whether or not the lease is effectively a financed purchase by the Company. Lease classification is evaluated at the inception of the lease agreement. Regardless of classification, we record a right-of-use asset and a lease liability for all leases with a term greater than 12 months. Our lease, for the premises we occupy for the North American Transaction Solutions segment's U.S. headquarters, was classified as an operating lease as of January 1, 2019. Operating lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease.
We identify leases in our contracts if the contract conveys the right to control the use of identified property or equipment for a period of time in exchange for consideration. We do not allocate lease consideration between lease and non-lease components and record a lease liability equal to the present value of the remaining fixed consideration under the lease. Any interest rate implicit in our leases are generally not readily determinable. Accordingly, we use our estimated incremental borrowing rate at the commencement date of the lease to determine the present value discount of the lease liability. We estimate the incremental borrowing rate for each lease based on an evaluation of our expected credit rating and the prevailing market rates for collateralized debt in a similar economic environment with similar payment terms and maturity dates commensurate with the term of the lease. The right-of-use asset for each lease is equal to the lease liability, adjusted for unamortized initial direct costs and lease incentives. We exclude options to extend or terminate leases from the calculation of the lease liability unless it is reasonably certain the option will be exercised.
Revenue Recognition and Deferred Revenue
We recognize revenue when all of the following criteria are met: (1) the parties to the contract have approved the contract and are committed to perform their respective obligations, (2) we can identify each party’s rights regarding the goods or services to be transferred, (3) we can identify the payment terms for the goods or services to be transferred, (4) the contract has commercial substance, and (5) it is probable that we will collect substantially all of the consideration to which we will be entitled in exchange for the goods or services that will be transferred to the customer. We consider persuasive evidence of a sales arrangement to be the receipt of a billable transaction from aggregators, signed contract or the processing of a credit card transaction. Collectability is assessed based on a number of factors, including transaction history with the customer and the credit worthiness of the customer. If it is determined that the collection is not reasonably assured, revenue is not recognized until collection becomes reasonably assured, which is generally upon receipt of cash. We record cash received in advance of revenue recognition as deferred revenue. Revenue consists primarily of fees generated through the electronic processing of payment transactions and related services and is recognized as revenue during the period the transactions are processed or when the related services are performed.
Our transactional processing fees are generated primarily from TOT Payments doing business as Unified Payments, which is our North American Transaction Solutions segment, PayOnline, which is our International Transaction Solutions segment, and Aptito, which is our point of sale solution for restaurants.
We work directly with payment card networks and banks so that our merchants do not need to manage the complex systems, rules, and requirements of the payments industry. We satisfy our performance obligations and therefore recognize the transactional processing service fees as revenue upon authorization of a transaction by the merchant’s customer’s bank.
The majority of our revenues is derived from volume-based payment processing fees ("discount fees”) and other related fixed transaction or service fees. Discount fees represent a percentage of the dollar amount of each credit or debit transaction processed. Discount fees are recognized at the time the merchants’ transactions are processed. Generally, where we have control over merchant pricing, merchant portability, credit risk and ultimate responsibility for the merchant relationship, revenues are reported at the time of sale on a gross basis equal to the full amount of the discount charged to the merchant. This amount includes interchange fees paid to card issuing banks and assessments paid to payment card networks pursuant to which such parties receive payments based primarily on processing volume for particular groups of merchants. Revenues generated from merchant portfolios where we do not have control over merchant pricing, liability for merchant losses or credit risk or rights of portability are reported net of interchange and other fees.
Revenues are also derived from a variety of fixed transaction or service fees, including authorization fees, convenience fees, statement fees, annual fees, and fees for other miscellaneous services, such as handling chargebacks. Revenues derived from service fees are recognized at the time the services are performed and there are no further performance obligations. Revenue from the sale of equipment is recognized upon transfer of ownership and delivery to the customer, after which there are no further performance obligations.
We primarily report revenues gross as a principal versus net as an agent. Although some of our processing agreements vary with respect to specific terms, the transactional processing service fees collected from merchants generally are recognized as revenue on a gross basis as we are the principal in the delivery of the managed payments solutions to the sellers. The gross fees we collect are intended to cover the interchange, assessments and other processing and non-processing fees which are included and are part of our gross margin.
We have primary responsibility for providing end-to-end payment processing services for our clients. Our clients contract us for all credit card processing services, including transaction authorization, settlement, dispute resolution, data/transmission security, risk management, reporting, technical support and other value-added services. We have concluded that we are the principal because we control the services before delivery to the merchant, and are primarily responsible for the delivery of the services, have discretion in setting prices charged to merchants, and are responsible for losses. We also have pricing latitude and can provide services using several different network options.
Net Loss per Share
Basic net loss per common share is computed by dividing net loss applicable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net loss per common share is determined using the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period, adjusted for the dilutive effect of common stock equivalents, consisting of shares issuable upon exercise of common stock options or warrants. In periods when losses are reported, the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding excludes common stock equivalents because their inclusion would have an anti-dilutive effect.
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined on the basis of the differences between the financial statements and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
We recognize net deferred tax assets to the extent that we believe these assets are more likely than not to be realized. In making such a determination, we consider all available positive and negative evidence, including future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, projected future taxable income, tax-planning strategies, and results of recent operations. If we determine that we would be able to realize our deferred tax assets in the future in excess of their net recorded amount, we would make an adjustment to the deferred tax asset valuation allowance, which would reduce the provision for income taxes.
We account for uncertainty in income taxes using a two-step approach to recognizing and measuring uncertain tax positions. The first step is to evaluate the tax position for recognition by determining if the weight of available evidence indicates that it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained on audit, including resolution of related appeals or litigation processes, if any. The second step is to measure the tax benefit as the largest amount that is more than 50% likely of being realized upon settlement. We classify the liability for unrecognized tax benefits as current to the extent we anticipate payment (or receipt) of cash within one year. Interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions are recognized and recorded as necessary in the provision for income taxes. The open United States tax years subject to examination with respect to our operations are 2017, 2018 and 2019.
Interchange, Network Fees and Other Cost of Services
Interchange and network fees consist primarily of fees that are directly related to discount fee revenue. These include interchange fees paid to issuers and assessment fees payable to card associations, which are a percentage of the processing volume we generate from Visa and Mastercard, AMEX, and Discover, as well as fees charged by card-issuing banks. Other costs of services include costs directly attributable to processing and bank sponsorship costs, which may not be based on a percentage of volume. These costs also include related costs such as residual payments to sales groups, which are based on a percentage of the net revenues generated from merchant referrals. In certain merchant processing bank relationships we are liable for chargebacks against a merchant equal to the volume of the transaction. Losses resulting from chargebacks against a merchant are included in other cost of services or as a bad debt expense, determined on the timing and nature of the specific transaction, on the accompanying consolidated statement of operations. We evaluate the risk for such transactions and our potential loss from chargebacks based primarily on historical experience and other relevant factors.
Advertising and Promotion Costs
Advertising and promotion costs are expensed as incurred. Advertising expense was approximately $223,000 and $273,000 for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and is included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
Equity-based Compensation
We account for grants of equity awards to employees in accordance with ASC 718, Compensation—Stock Compensation. This standard requires compensation expense to be measured based on the estimated fair value of the share-based awards on the date of grant and recognized as expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period.
Equity-based compensation was approximately $2.7 million and $2.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and is reflected on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
Foreign Currency Transactions
We are subject to exchange rate risk in our foreign operations in Russia, the functional currency of which is the Russian ruble, where we generate service fee revenues, interest income or expense, incur product development, engineering, website development, and selling, general and administrative costs and expenses. Our Russian subsidiaries pay a majority of their operating expenses in their local currencies, exposing us to exchange rate risk.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses for the reporting period. Such estimates include, but are not limited to, the value of purchase consideration paid and identifiable assets acquired and assumed in acquisitions, goodwill and asset impairment review, valuation reserves for accounts receivable, valuation of acquired or current merchant portfolios, incurred but not reported claims, revenue recognition for multiple element arrangements, loss reserves, assumptions used in the calculation of equity-based compensation and in the calculation of income taxes, and certain tax assets and liabilities, as well as, the related valuation allowances. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Below is a summary of the Company’s critical accounting estimates for which the nature of management’s assumptions are material due to the levels of subjectivity and judgment necessary to account for highly uncertain matters or the susceptibility of such matters to change, and for which the impact of the estimates and assumptions on financial condition or operating performance is material.
Goodwill
The Company tests goodwill for impairment using a fair value approach at least annually, absent some triggering event that would require an interim impairment assessment.
Significant estimates and assumptions are used in our goodwill impairment review and include the identification of reporting units, assigning assets and liabilities to reporting units, assigning goodwill to reporting units and determining the fair value of each reporting unit. Our assessment of qualitative factors involves significant judgments about expected future business performance, general market conditions, and regulatory changes. In a quantitative assessment, the fair value of each reporting unit is determined based largely on the present value of projected future cash flows, growth assumptions regarding discount rates, estimated growth rates and our future long-term business plans. Changes in any of these estimates or assumptions could materially affect the determination of fair value and the associated goodwill impairment charge for each reporting unit.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Adoption of ASU 2016-02, Leases
In February 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued ASU 2016-02, “Leases (Topic 842)” which, for operating leases, requires a lessee to recognize a right-of-use asset and a lease liability, initially measured at the present value of the lease payments, in its balance sheet. The standard also requires a lessee to recognize a single lease cost, calculated so that the cost of the lease is allocated over the lease term, on a generally straight-line basis. The ASU is effective for public companies for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Effective January 1, 2019, we adopted Topic 842 using the modified retrospective transition method. Under this method, we applied Topic 842 to the lease for the premises we occupy for our North American Transaction Solutions segment's U.S. headquarters. There was no cumulative impact adjustment necessary with the adoption to our accumulated deficit on January 1, 2019. Our consolidated financial statements for periods ending after January 1, 2019 are presented in accordance with the requirements of Topic 842, while comparative prior period amounts have not been adjusted and continue to be reported in accordance with Topic 840. Please refer to "Leases" above for a description of our lease accounting policies upon the adoption on Topic 842.
Adoption of ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, “Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments.” The amendments in this update changed how companies measure and recognize credit impairment for many financial assets. The new expected credit loss model will require companies to immediately recognize an estimate of credit losses expected to occur over the remaining life of the financial assets (including trade receivables) that are within the scope of the update. The update also made amendments to the current impairment model for held-to-maturity and available-for-sale debt securities and certain guarantees. The guidance was effective for us on January 1, 2020. The adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 4. DUE FROM MULLEN
As contemplated by the Merger Agreement referred to in Note 2, on August 11, 2020, our Company as lender, borrowed an additional $500,000 from RBL and entered into an unsecured Promissory Note, dated August 11, 2020 (the “Note”), with Mullen. Pursuant to the Note, Mullen borrowed from the Company $500,000. Prior to maturity of the loan, the principal amount of the loan will carry an interest rate of 14% per annum compounded monthly and payable upon demand. This loan will mature on the earlier of (i) the date that the Merger Agreement is terminated for any reason by any party thereto and (ii) the Merger Effective Time (as defined in the Merger Agreement).
At March 31, 2021, the Company is also owed approximately $1 million from Mullen in connection with Late Fees, pursuant to the Amendment to the Merger Agreement with Mullen.
NOTE 5. ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts, consist of amounts due from merchant service providers and to a lesser extent Russian mobile operator intermediaries. Net accounts receivable amounted to approximately $7.1 million and 6.6 million at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. Net accounts receivable consisted primarily of approximately $6.7 and $6.2 million for North American Transaction Solutions as of December 31, 2020 and 2019and approximately $300,000 and $400,000, attributed to International Transaction Solutions for merchant processing receivables at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Our allowance for doubtful accounts was approximately $214,000 and $214,000 as of December 31, 2020 and 2019. Actual write-offs may exceed estimated amounts.
NOTE 6. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
The Company had approximately $3.6 and $5.7 million in intangible assets, net of amortization, at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. Shown below are the details of the components that represent these balances.
Intangible assets consisted of the following as of December 31, 2020
Cost | Accumulated Amortization | Carrying Value | Amortization Life and Method | ||||||||||
IP Software | $ | 2,378,248 | $ | (2,321,843 | ) | $ | 40,185 | 3 years - straight-line | |||||
Portfolios and Client Lists | 7,714,665 | (6,776,317 | ) | 938,348 | 4 years - straight-line | ||||||||
Client Acquisition Costs | 8,841,617 | (6,224,824 | ) | 2,616,794 | 4 years - straight-line | ||||||||
PCI Certification | 449,000 | (449,000 | ) | - | 3 years - straight-line | ||||||||
Trademarks | 703,586 | (703,586 | ) | - | 3 years - straight-line | ||||||||
Domain Names | 437,810 | (437,810 | ) | - | 3 years - straight-line | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 20,524,925 | $ | (16,913,379 | ) | $ | 3,595,326 | ||||||
Intangible assets consisted of the following as of December 31, 2019
Cost | Accumulated Amortization | Carrying Value | Amortization Life and Method | ||||||||||
IP Software | $ | 2,343,888 | $ | (2,240,695 | ) | $ | 103,193 | 3 years - straight-line | |||||
Portfolios and Client Lists | 7,714,665 | (5,614,880 | ) | 2,099,785 | 4 years - straight-line | ||||||||
Client Acquisition Costs | 8,238,018 | (4,762,347 | ) | 3,475,671 | 4 years - straight-line | ||||||||
PCI Certification | 449,000 | (449,000 | ) | - | 3 years - straight-line | ||||||||
Trademarks | 703,586 | (703,586 | ) | - | 3 years - straight-line | ||||||||
Domain Names | 437,810 | (437,810 | ) | - | 3 years - straight-line | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 19,886,967 | $ | (14,208,318 | ) | $ | 5,678,649 | ||||||
Amortization expense for the intangible assets was approximately $2.6 million and $2.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
The following table presents the estimated aggregate future amortization expense of intangible assets:
2021 | $ | 866,629 | ||
2022 | 866,629 | |||
2023 | 866,629 | |||
2024 | 853,234 | |||
| 2025 | 142,205 | |||
Balance December 31, 2020 | $ | 3,595,326 |
NOTE 7. ACCRUED EXPENSES
At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, accrued expenses amounted to approximately $4.6 and $1.8 million, respectively. Accrued expenses represent expenses that are owed at the end of the period or are estimates of services provided that have not been billed by the provider or vendor. The following table reflect the balances outstanding as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019.
December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
Accrued professional fees | $ | 268,435 | $ | 276,239 | ||||
PayOnline accrual | 61,719 | 69,039 | ||||||
Accrued interest | 409,525 | 43,021 | ||||||
Accrued bonus | 1,690,556 | 1,318,060 | ||||||
Accrued foreign taxes | (12,336 | ) | 2,064 | |||||
Other accrued expenses | 2,186,197 | 91,921 | ||||||
| Total accrued expenses | $ | 4,604,097 | $ | 1,800,344 | ||||
Included in accrued bonus are non-discretionary compensation due to our Chairman and CEO approximating $1.3 million and $979,000 at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and approximately $386,000 and $339,000 at December 31, 2020 and 2019 for discretionary performance bonuses due to certain employees.
Other accrued expenses includes $2.0 million which was due to ESOUSA for the sixth tranche received on December 30, 2020, which was subsequently paid by the issuance of 200,000 shares in January of 2021.
NOTE 8. NOTES PAYABLE
Notes payable consist of the following:
December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
RBL Capital Group, LLC | $ | 9,431,157 | $ | 9,431,157 | ||||
| SBA Loan - EIDL | 159,899 | - | ||||||
| SBA Loan - PPP | 491,493 | - | ||||||
Subtotal | 10,082,549 | 9,431,157 | ||||||
Less: deferred loan costs | (138,944 | ) | (179,610 | ) | ||||
| Subtotal | 9,943,605 | 9,251,547 | ||||||
Less: current portion | (1,330,018 | ) | (909,086 | ) | ||||
Long term debt | $ | 8,613,587 | $ | 8,342,461 | ||||
RBL Capital Group, LLC
Effective June 30, 2014, TOT Group, Inc. and its subsidiaries as co-borrowers, TOT Payments, LLC, TOT BPS, LLC, TOT FBS, LLC, Process Pink, LLC, TOT HPS, LLC and TOT New Edge, LLC (collectively, the “co-borrowers”), entered into a Loan and Security Agreement (“Credit Facility”) with RBL Capital Group, LLC (“RBL”), as lender (the “RBL Loan Agreement”). The original terms provided us with an 18-month, $10 million credit facility with interest at the higher of 13.90% per annum or the prime rate plus 10.65%. On May 2, 2016, we renewed our Credit Facility with RBL, increasing the facility from $10 million to $15 million and extending the term through February 2019.
The co-borrowers’ obligations to RBL pursuant to the RBL Loan Agreement are secured by a first priority security interest in all of the co-borrowers’ tangible and intangible assets, including but not limited to their merchants, merchant contracts and proceeds thereof, and all right title and interest in co-borrowers’ processing contracts, contract rights, and portfolio cash flows with all processors of the co-borrowers.
On December 19, 2019, in connection with an addendum to those certain term notes made by TOT Group, Inc.in favor of RBL, the Credit Facility referred to above, we received funding of $1,000,000 and new terms were negotiated for the total outstanding notes payable amount of $9,431,157. This total loan amount bears interest at 14.19%. On January 20, 2020, we were required to make one (1) payment of interest only for $117,329, followed by five (5) payments of interest only in the amount of $111,523. Effective July 20, 2020, we were required to make forty-eight (48) monthly payments, which includes principal and interest for $258,620, until March 20, 2024 the date this term note matures. In the event any of the installments or other payment required to be made is not received by or on behalf of RBL in full within ten (10) days after the due date thereof, and the same subsequently is received and accepted by or on behalf of RBL, the Company shall pay on demand a late charge in the amount of five percent (5%) of the amount of the delinquent payment. In the event of the occurrence of an Event of Default (as defined in the Loan Agreement), the entire unpaid balance of principal and interest of the Loan shall become due and payable immediately, without notice or demand, at the election of the Note holder, provided that the holder shall endeavor (but is not required) to provide notice to the Company of any such acceleration. The Company waives demand, presentment for payment, protest, notice of protest and notice of nonpayment or dishonor of the Note. The Company shall not have any right to prepay this loan except as expressly provided in the Loan Agreement.
On June 20, 2020, in connection with those certain term notes made by TOT Group, Inc.in favor of RBL, the Credit Facility referred to above, the Company executed two (2) promissory term notes, totaling $9,431,157, which replaces all previous outstanding term notes with RBL The first term note is for $4,432,157 and bears interest at 14.19%. On December 20, 2021, we are required to make one (1) payment of interest only for $67,746, followed by eight (8) payments of interest only for the same amount, followed by a balloon payment for any outstanding principal and accrued interest of approximately $5,540,128.. The second term note is for $5,000,000 and bears interest at 14.19%. On June 20, 2020, we are required to make one (1) payment of interest only for $59,125 followed by six (6) payments of interest only for the same amount. Starting on January 20,2021, the Company shall make twenty (20) equal monthly payments of principal and interest of $137,109, followed by one (1) payment of principal and interest for approximately $3,290,475.In connection with this term note, the Company agreed to pay a financing fee of $894,311. Such financing fee will be due and payable as follows; $25,000 on February 20, 2021; $25,000 on June 20, 2021; $94,311 on August 20, 2022; and $750,000 on September 20, 2022. The Company waives demand, presentment for payment, protest, notice of protest and notice of nonpayment or dishonor of the Note. The Company shall not have any right to prepay this loan except as expressly provided in the Loan Agreement. The Company waives demand, presentment for payment, protest, notice of protest and notice of nonpayment or dishonor of the Note. The Company shall not have any right to prepay this loan except as expressly provided in the Loan Agreement.
On March 27, 2020, our Company entered into a Master Exchange Agreement (the “ESOUSA Agreement”) with ESOUSA Holdings, LLC ("ESOUSA"), a related party. Prior to entering into the ESOUSA Agreement, ESOUSA agreed to acquire an existing promissory note that had been previously issued by the Company, of up to $2,000,000 in principal amount outstanding plus interest due to RBL Capital Group, LLC ("RBL"). Pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement, the Company has the right, at any time prior to March 27, 2021, to request ESOUSA, and ESOUSA agreed upon each such request, to exchange this promissory note in tranches on the dates when the Company instructs ESOUSA, for such number of shares of the Company’s common stock (“Common Stock”) as determined under the ESOUSA Agreement based upon the number of shares of Common Stock (already in ESOUSA’s possession) that ESOUSA sold in order to finance its purchase of such tranche of the promissory note from RBL Capital Group, LLC. ESOUSA will purchase each tranche of the promissory note equal to 88% of the gross proceeds from the shares of Common Stock sold by ESOUSA to finance the purchase of such Exchange Amount from RBL Capital Group, LLC. Each such tranche to be $148,000 unless otherwise agreed to by the Company and ESOUSA.
On April 23, 2020 and August 3, 2020, the Company entered into certain amendments to the ESOUSA Agreement, which together increased from $2,000,000 to $15,000,000 the principal amount and unpaid interest of one or more promissory notes of the Company or its direct or indirect subsidiaries that ESOUSA either purchased in whole or has an irrevocable right to purchase in tranches from RBL in connection with the ESOUSA Agreement.
On March 27, 2020, the Company received its first tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $148,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. Included in other accrued expenses at September 30, 2020 is approximately $145,000 in connection with this first tranche for which shares of Common Stock have not yet been issued. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $148,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On April 28, 2020, the Company received its second tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $143,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 65,862 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $143,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 11, 2020, the Company received its third tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $707,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 66,190 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $707,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 21, 2020, the Company received its fourth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $401,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 45,654 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $401,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On September 25, 2020, the Company received its fifth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $426,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 50,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $426,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On December 30, 2020, the Company received its sixth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $1,960,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. In January 2021, the Company issued 200,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $1,960,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
SBA Loans
On May 7, 2020, the Company entered into a promissory note (the “Note”) evidencing an unsecured loan (the “Loan”) in the amount of $491,493 made to the Company under the Paycheck Protection Program (the “PPP”). The Note matures on May 7, 2022 and bears interest at a rate of 1% per annum. Beginning December 7, 2020, the Company is required to make 17 monthly payments of principal and interest, with the principal component of each such payment based upon the level amortization of principal over a two-year period from May 7, 2020. Pursuant to the terms of the CARES Act and the PPP, the Company may apply to the Lender for forgiveness for the amount due on the Loan. The amount eligible for forgiveness is based on the amount of Loan proceeds used by the Company (during the eight-week period after the Lender makes the first disbursement of Loan proceeds) for the payment of certain covered costs, including payroll costs (including benefits), interest on mortgage obligations, rent and utilities, subject to certain limitations and reductions in accordance with the CARES Act and the PPP. No assurance can be given, at this time, that the Company will obtain forgiveness of the Loan in whole or in part.
On May 18, 2020, the Company entered into a promissory note (the "Note") in the amount of $159,899 made to the Company by the U.S. Small Business Administration under the Economic Injury Disaster Loan program. Monthly installment payments on the Note will begin twelve months from the date of the Note, with the balance of any accrued principal and interest at 3.75% annually, payable thereafter.
Scheduled Notes Payable Principal Repayment at December 31, 2020 is as follows:
| 2021 | 1,330,018 | |||
| 2022 | 8,574,057 | |||
| 2023 | 5,514 | |||
2024 | 5,514 | |||
2025 | 167,446 | |||
Balance December 31, 2020 | $ | 10,082,549 |
NOTE 9. CONCENTRATIONS
Credit card processing revenues are from merchant customer transactions, which were processed primarily by one third-party processor (greater than 5%) and our own dedicated bank identification number ("BIN")/Interbank Card Association ("ICA") number during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, we processed 32% of our total revenue with Priority Payment Systems, and 53% from our own dedicated BIN/ICA with Esquire Bank, and 10% with First Data Corp.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, we processed 44% of our total revenue with Priority Payment Systems, and 38% from our own dedicated BIN/ICA with Esquire Bank.
NOTE 10. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Employment Agreement
On February 25, 2020, as per approval of the Compensation Committee (the “Committee”) of the board of directors of the Company, the Company entered into an employment agreement (the “Agreement”) with Steven Wolberg, the Company's Chief Legal Officer and Corporate Secretary. The Agreement provides for continuation of the current base salary of $250,000. The term of the Agreement is 5 years, with subsequent 1-year renewals. The Agreement provides for a sign-on bonus of 10,000 shares of Company’s common stock, to be granted to Mr. Wolberg pursuant to the Company’s equity incentive plan, the severance in the amount of two times annual base salary of Mr. Wolberg if Mr. Wolberg’s employment is terminated by the Company without “cause” (as defined in the Agreement) or Mr. Wolberg terminates the employment for “good reason” (as defined in the Agreement). For each fiscal year during the term of the Agreement, the Agreement provides for a bonus arrangement equal to 50% of Mr. Wolberg’s base salary, payable in the Company’s shares of common stock or, at the Company’s discretion, in cash. Further, for each fiscal year during the term of the Agreement, Mr. Wolberg will be eligible to receive long-term equity incentive awards, as determined by the Committee at the time of grant, pursuant to the Company’s equity incentive plan.
Minimum Billing Processing Fees Commitment
We have non-exclusive agreements with two of our processors to provide services related to processing. The agreements require us to submit a minimum number of billable processing fees. If we submit an amount that is lower than the minimum, we are required to pay to each processor the fees it would have received if we had submitted the required minimum number of billable processing fees. As of December 31, 2020, the aggregate minimum monthly processing fees for these processors amounts to approximately $150,000 per month.
Leases
North American Transaction Solutions
During May 2013, we entered into a lease agreement, for approximately 4,101 square feet of office space located at 3363 N.E. 163rd Street, Suites 705 through 707, North Miami Beach, Florida 33160. The term of the lease agreement was from May 1, 2013 through December 31, 2016, with monthly rent increasing from $16,800 per month at inception to $19,448 per month (or $233,377 per year) for the period from January 1, 2016 through December 31, 2016. The lease was extended for a period of five years commencing August 1, 2017 and expiring July 31, 2022 with equal monthly base rent installments of $14,354 ($172,248 per year) plus sales tax. In September 2020, we entered into an agreement with the Landlord modifying this existing lease. In consideration of payment to Landlord of the sum of $65,600, the Company surrendered all existing premises occupied by it and entered into a new 4 year lease for a smaller premises at Unit #707 in the same building for a monthly rent of $2,954. There will be a $65,600 payment payable as follows: (1) $22,700 due upon the execution of the Modification of Lease Agreement; (2) $20,100 due on or before December 31, 2020; and (3) $22,800 due on or before March 31, 2021. Except as previously mentioned, all other terms and conditions of the initial lease agreement continues to remain in effect. The first two payments have been made and the Company is expected to make the third payment on March 31, 2021, at this time.
On September 26, 2019, we entered into a lease for additional office space in the building that our current office space is located for our North American Transactions Solutions. The space is for 5,875 square feet and the term is for 5 years commencing on September 23, 2019 and expiring on September 30, 2024. The monthly base rent is $16,156 ($193,875 per year) plus sales tax. In consideration of our Company foregoing its rights to credits from the landlord towards the cubicle installation and foregoing its rights to one (1) of the (2) month rent deposits prepaid to the landlord , the lease was amended. The amended lease requires the Company to begin paying $11,500 effective July 7, 2020, with the original monthly rent payment of $16,156 commencing on January 1, 2021. In addition, commencing on March 1, 2021, our Company will begin making up the difference between the original monthly lease payment of $16,156 and the amended monthly lease payment of $11,500, the deferred monthly rent, by paying the landlord an additional $2,000 per month until the deferred portion of the rent is fully repaid. All outstanding amounts of deferred rent shall be subject to interest at an annual the rate of 4%. The Company occupied the space in July of 2020.
Net Element Software, our subsidiary, currently leases approximately 1,654 square feet of office space in Yekaterinburg, Russia, where we develop value added services, mobile applications, smart terminals applications, sales central ERP system development and marketing activities, at an annual rent of approximately $21,000.The lease term expired on June 1, 2019 and was renewed with indefinite terms.
International Transaction Solutions
The Company occupies an office in Moscow, Russia with approximately 1600 square feet at an annual rent of approximately $50,900, which lease expired on February 10, 2020. This lease was renewed with indefinite terms.
We believe that our current facilities are suitable and adequate for our present purposes, and we anticipate that we will be able to extend our existing leases on terms satisfactory to us or move to new facilities on acceptable terms.
The following table presents a reconciliation of the undiscounted future minimum lease payments, under the lease for the premises we occupy for our North American Transaction Solutions segment's U.S. headquarters, to the amounts reported as operating lease liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2020:
Total | ||||
Undiscounted future minimum lease payments: | ||||
2021 | $ | 229,589 | ||
2022 | 230,660 | |||
2023 | 231,764 | |||
| 2024 | 222,926 | |||
| 2025 | 129,250 | |||
Total | $ | 1,044,189 | ||
Amount representing imputed interest | (242,596 | ) | ||
Total operating lease liability | 801,593 | |||
Current portion of operating lease liability | (140,973 | ) | ||
Operating Lease Liability, non-current | $ | 660,621 | ||
As of December 31, 2020 | ||||
Remaining term on Leases | 4.00 | |||
Incremental borrowing rate | 12 | % | ||
As of December 31, 2020, the future minimum lease payments under other operating leases, not subject to Topic 842, approximates $21,000 on a yearly basis.
Litigation, Claims, and Assessments
With respect to all legal, regulatory and governmental proceedings, and in accordance with ASC 450-20, Contingencies—Loss Contingencies, we consider the likelihood of a negative outcome. If we determine the likelihood of a negative outcome with respect to any such matter is probable and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated, we record an accrual for the estimated amount of loss for the expected outcome of the matter. If the likelihood of a negative outcome with respect to material matters is reasonably possible and we are able to determine an estimate of the amount of possible loss or a range of loss, whether in excess of a related accrued liability or where there is no accrued liability, we disclose the estimate of the amount of possible loss or range of loss. However, management in some instances may be unable to estimate an amount of possible loss or range of loss based on the significant uncertainties involved in, or the preliminary nature of, the matter, and in these instances we will disclose the nature of the contingency and describe why we are unable to determine an estimate of possible loss or range of loss.
In addition, we are involved in ordinary course legal proceedings, which include all claims, lawsuits, investigations and proceedings, including unasserted claims, which are probable of being asserted, arising in the ordinary course of business and otherwise not described below. We have considered all such ordinary course legal proceedings in formulating our disclosures and assessments, which are not expected to have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial statements.
Aptito.com, Inc.
On August 6, 2014, our subsidiary (Aptito, LLC) filed a lawsuit against Aptito.com, Inc. and the shareholders of Aptito.com, Inc., in state court in the 11th Judicial Circuit in and for Miami-Dade County. This is an interpleader action in regards to 125,000 shares of our stock. Aptito, LLC acquired Aptito.com, Inc. in exchange for, among other things, 125,000 shares (prior to adjustment for two one-for-ten reverse stock splits) of our stock. There has been disagreements among the Aptito.com, Inc. shareholders as to proper distribution of the 125,000 shares (prior to adjustment for two one-for-ten reverse stock splits). To avoid any liability in regards to improper distribution, Aptito, LLC filed the interpleader action so as to allow the Defendants to litigate amongst themselves as to how the shares (prior to adjustment for two one- for-ten reverse stock splits) should be distributed. Aptito.com, Inc. opposed the motion to interplead and filed counterclaims relative to Aptito, LLC for non-delivery of the 125,000 shares (prior to adjustment for two one-for-ten reverse stock splits).
On July 18, 2017, the Court granted Aptito LLC’s motion to interplead and also indicated that Aptito, LLC could not be held liable for any alleged damages relative to the purported non- delivery of the 125,000 shares after the interpleader action was filed on August 6, 2014.
In March 2018, a new Judge in the case ruled that Aptito.com, Inc. was entitled to receive 125,000 newly issued shares of our common stock, but indicated that he was not ruling that we were required to issue such shares. We plan to appeal this ruling, and our legal counsel is addressing the counterclaims filed by Aptito.com, Inc. in this matter.
In July 2018, our counsel was disqualified due to a conflict of interest. We engaged a new law firm to represent our ongoing interests in this case. Since that time, there have been multiple Motions and claims brought by Aptito.com, Inc., including the request for rescission of the asset purchase agreement that gave rise to the share issuance obligation. All of these Motions and claims are being vigorously defended.
A court ordered mediation conference was held on April 24, 2019 but the parties were unable to reach a settlement. On May 1, 2019 the Court denied Aptito.com, Inc.’s Motion for Summary Judgement and further hearings on a variety of Motions were scheduled in this matter.
On August 14, 2019, the court granted final Summary Judgment in favor of the Company, removing Net Element as a party to the lawsuit and denying Aptito.com, Inc’s Motion for rehearing and reconsideration of this matter. Aptito, LLC, in which the Company has a majority ownership interest, remains a Defendant in this litigation. On September 17, 2019, the court granted the Company’s Motion for sanctions against the attorney representing Aptito.com, Inc. in this matter. The Company is pursuing collection of legal fees incurred from the Plaintiff and their attorney. This matter was pending a special set hearing to be held on March 23, 2020. That hearing was postponed and rescheduled for hearing in July 2020. On July 23, 2020, the Court entered a judgement against the attorney representing Aptito.com and awarded attorney fees to the Company. The attorney stated on the record he will be filing for bankruptcy. In August 2020, Plaintiffs attorney, filed an appeal against the Judgement. This matter is still proceeding. The Company intends pursuing recovery from the attorney.
Gene Zell
In June 2014, we, as plaintiff, commenced an action in the Miami-Dade Circuit Court, Florida against Gene Zell ("Zell") for defamation of our Company and CEO and tortious interference with our business relationships. In October 2014, the court granted a temporary injunction against Zell enjoining him from posting any information about our Company and CEO on any website and enjoining him from contacting our business partners or investors. Zell violated the Court Order and the Court granted a Motion imposing sanctions against Zell. We continue to seek enforcement of the Court Order.
In April 2015, Zell filed a Motion to set aside the Court Order alleging he was unaware of the Court Proceedings. The Court, on August 26, 2015, dismissed Zell’s Motion to dissolve the injunction. In March 2017 the Court dismissed another Motion brought by Zell to dissolve the injunction. Accordingly, the injunction order prohibiting Zell from making further defamatory posts remains in place.
In 2018, we filed a motion to enforce the injunction and contempt orders against Zell. The court upheld the injunction and we continue to vigorously protect its interests. We are pursuing an action for damages sustained as a result of the defamation.
On September 20, 2019, the Court granted a Permanent Injunction against Zell. The Company is evaluating pursuing actions against Zell for collection of legal fees and damages.
A trial was scheduled for April 2020 on the issue of Net Element’s damages. However, Zell recently filed bankruptcy, so that trial and all further legal proceedings involving Zell will be stayed as a result of the automatic bankruptcy stay.
Georgia Notes 18, LLC
On March 22, 2021, the Company was notified that one of its shareholder, Georgia Notes 18, LLC, filed an action in the Delaware Chancery Court to compel inspection of the Company’s books and records pertaining to a 2014 transaction in which the shareholder had an interest. The Company has engaged counsel to protect its interests in this matter. At this time, the Company cannot predict the eventual outcome of this matter.
NOTE 11. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
During the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, agent commissions resulting from merchant processing of approximately $105,000 and $75,000, respectively, were paid to Prime Portfolios, LLC, an entity owned by Oleg Firer, our Chairman and CEO, and Steven Wolberg, our Chief Legal Officer. In addition, key members of management owned companies received similar commissions and/or reimbursement for equipment purchased on the Company’s behalf, which amounted to approximately $865,000 and $758,000 for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
At December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, we had accrued expenses of approximately $122,000 and $127,000, respectively, which consisted primarily of various travel, professional fees, and other expenses paid and charged for by our CEO on his personal credit cards. This is reflected as due to related party on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
On March 27, 2020, our Company entered into a Master Exchange Agreement, (the “ESOUSA Agreement”) with ESOUSA Holdings, LLC ("ESOUSA"), a related party. Prior to entering into the ESOUSA Agreement, ESOUSA agreed to acquire an existing promissory note that had been previously issued by the Company, of up to $2,000,000 in principal amount outstanding plus interest due to RBL Capital Group, LLC ("RBL"). Pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement, the Company has the right, at any time prior to March 27, 2021, to request ESOUSA, and ESOUSA agreed upon each such request, to exchange this promissory note in tranches on the dates when the Company instructs ESOUSA, for such number of shares of the Company’s common stock (“Common Stock”) as determined under the ESOUSA Agreement based upon the number of shares of Common Stock (already in ESOUSA’s possession) that ESOUSA sold in order to finance its purchase of such tranche of the promissory note from RBL Capital Group, LLC. ESOUSA will purchase each tranche of the promissory note equal to 88% of the gross proceeds from the shares of Common Stock sold by ESOUSA to finance the purchase of such Exchange Amount from RBL Capital Group, LLC. Each such tranche to be $148,000 unless otherwise agreed to by the Company and ESOUSA.
On March 27, 2020, the Company received its first tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $148,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. Included in other accrued expenses at September 30, 2020 is approximately $145,000 in connection with this first tranche for which shares of Common Stock have not yet been issued. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $148,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On April 23, 2020 and August 3, 2020, the Company entered into certain amendments to the ESOUSA Agreement, which together increased from $2,000,000 to $15,000,000 the principal amount and unpaid interest of one or more promissory notes of the Company or its direct or indirect subsidiaries that ESOUSA either purchased in whole or has an irrevocable right to purchase in tranches from RBL in connection with the ESOUSA Agreement.
On April 28, 2020, the Company received its second tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $143,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 65,862 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $143,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 11, 2020, the Company received its third tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $707,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 66,190 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $707,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On August 21, 2020, the Company received its fourth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $401,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 45,654 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $401,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On September 25, 2020, the Company received its fifth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $426,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. The Company issued 50,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $426,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
On December 30, 2020, the Company received its sixth tranche of RBL promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $1,960,000, less any fees, from ESOUSA to be exchanged for Common Stock pursuant to the ESOUSA Agreement. In January 2021, the Company issued 200,000 shares of Common Stock to ESOUSA in connection with this exchange. Concurrently with this transaction, the Company received an equivalent aggregate amount of $1,960,000 from RBL under the Credit Facility.
NOTE 12. STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
On October 5, 2017, we effected an one-for-ten reverse stock split of our common stock. Our condensed consolidated financial statements and disclosures reflect these changes in capital structure for all periods presented.
On June 12, 2015 and June 13, 2016, our shareholders approved 100,000,000 increases in our authorized common stock to 300,000,000 and 400,000,000, respectively. On October 2, 2017, our shareholders approved a 300,000,000 decrease in our authorized common stock to 100,000,000.
Equity Incentive Plan Activity
On December 5, 2013, our shareholders approved the Net Element International, Inc. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (as amended to date, the “2013 Plan”). Awards under the 2013 Plan may be granted in any one or all of the following forms: (i) incentive stock options meeting the requirements of Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended; (ii) non-qualified stock options (unless otherwise indicated, references to “Options” include both Incentive Stock Options and Non-Qualified Stock Options); (iii) stock appreciation rights, which may be awarded either in tandem with Options or on a stand-alone basis; (iv) shares of common stock that are restricted; (v) units representing shares of common stock; (vi) units that do not represent shares of common stock but which may be paid in the form of common stock; and (vii) shares of common stock that are not subject to any conditions to vesting.
On November 27, 2018, our shareholders approved an amendment to the 2013 Plan to increase the number of shares of the Company’s common stock available for issuance by 178,900 shares resulting in the aggregate of 773,000 shares authorized for issuance under the 2013 Plan, which represented in the aggregate approximately 20% of our issued and outstanding stock as of December 31, 2019.
On October 23, 2019, our shareholders approved an amendment to the 2013 Plan to increase the number of shares of the Company’s common stock available for issuance by 177,000 shares resulting in the aggregate of 950,000 shares authorized for issuance under the 2013 Plan.
On December 1, 2020, our shareholders approved an amendment to the 2013 Plan to increase the number of shares of the Company’s common stock available for issuance by 219,500 shares resulting in the aggregate of 1,160,500 shares authorized for issuance under the 2013 Plan.
The maximum aggregate number of shares of common stock available for award under the 2013 Plan at December 31, 2020 and 2019 was 210,500 and 252,436, respectively. The 2013 Plan is administered by the compensation committee.
2013 Equity Incentive Plan - Unrestricted Shares and Stock Options
During the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, we issued common stock pursuant to the 2013 Plan to the members of our Board of Directors, and recorded a compensation charge of approximately $38,000 and $60,000, respectively.
At December 31, 2020 we had 200,648 incentive stock options outstanding with a weighted average exercise price of $10.73 and a weighted average remaining contract term of 7.07 years. At December 31, 2019 we had 154,005 incentive stock options outstanding with a weighted average exercise price of $10.73 and a weighted average remaining contract term of 8.08 years. All of the stock options were anti-dilutive at December 31, 2020 and 2019.
During the year ended December 31, 2020 our Board of Directors approved and authorized the issuance of 17,839 shares of our common stock pursuant to the 2013 Plan to members of our Board of Directors and we recorded compensation expense of approximately $37,500. Also during year ended December 30, 2020, our Board of Directors approved and authorized the issuance of 316,835 shares of our common stock pursuant to the 2013 Plan which were allocated to certain named executives, certain employees, and certain consultants of the Company and we recorded compensation expense of approximately $2.7 million. There were no incentive stock options issued during 2020.
During the year ended December 31, 2019 our Board of Directors approved and authorized the issuance of 80,000 incentive stock options which were allocated to certain named executives pursuant to the 2013 Plan and we recorded compensation expense of approximately $503,000. During the year ended December 31, 2019 our Board of Directors approved and authorized the issuance of 22,000 shares of our common stock pursuant to the 2013 Plan to members of our Board of Directors and we recorded compensation expense of approximately $138,000. Also during year ended December 30, 2019, our Board of Directors approved and authorized the issuance of 214,507 shares of our common stock pursuant to the 2013 Plan which were allocated to certain named executives, certain employees, and certain consultants of the Company and we recorded compensation expense of approximately $1,349,000.
NOTE 13. WARRANTS AND OPTIONS
Options
At December 31, 2020 and 2019, we had fully vested options outstanding to purchase 200,648 and 314,218, respectively, of shares of common stock at exercise prices ranging from $6.29 to $134.00 per share.
Due to the high level of volatility in the stock price of our common stock, our management determined the grant date fair value of the options granted during the year ended December 31, 2020 using the then quoted stock price at the grant date. There were no options granted during 2019
Warrants
At December 31, 2020 and 2019, we had warrants outstanding to purchase 404,676 and 728,583 shares of common stock, respectively. At December 31, 2020 the warrants had a weighted average exercise price of $11.12 per share purchased and a weighted average remaining contractual term of 2.00 years. At December 31, 2019, the warrants had a weighted average exercise price of $6.18 per share purchased and a weighted average remaining contractual term of 3.00 years.
Non-Incentive Plan Options
At December 31, 2020 and 2019, we had 46,643 and 323,498 non-incentive options outstanding with a weighted-average exercise price of $21.46 and $21.84, respectively, with a remaining contract term of 0.45 years at December 31, 2020 and with a remaining contract term of .92 years at December 31, 2019.
These options were out of the money at December 31, 2020 and 2019 and had no intrinsic value.
NOTE 14. INCOME TAXES
The components of income (loss) before income tax provision are as follows:
December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
2020 | 2019 | |||||||
United States | (5,817,126 | ) | (5,350,774 | ) | ||||
| Foreign | (102,768 | ) | 26,125 | |||||
| (5,919,894 | ) | (5,324,649 | ) | |||||
There was no current U.S. income tax or deferred income tax provision for years ended December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019. There were current foreign tax provisions of $21,538 and $69,811 for the years ended December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 respectively.
The following is a reconciliation of the effective income tax rate with the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate at:
December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
2020 | 2019 | |||||||
U. S. Federal statutory income tax rate | 21.00 | % | 21.00 | % | ||||
State income tax, net of federal tax benefit | 4.28 | % | 4.37 | % | ||||
Currency translation adjustment | -0.01 | % | 0.00 | % | ||||
Foreign income tax | -0.36 | % | -1.31 | % | ||||
Difference in foreign tax rates | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
Change in valuation allowance | (25.29 | )% | (25.39 | )% | ||||
Change in tax rates | - | - | ||||||
Effective income tax rate | (0.36 | )% | (1.31 | )% | ||||
The effective tax rate on operations of negative (0.36)% at December 31, 2020 varied from the statutory rate of 21%, primarily due to the permanent difference related to difference in foreign tax rates and the increase in our valuation allowance. The effective rate on operations of 1.70% at December 31, 2019 varied from the statutory rate of 21% primarily due to the permanent difference related to difference in foreign tax rates and the increase in our valuation allowance.The effective tax rate on operations of negative (1.31)% at December 31, 2020 varied from the statutory rate of 21%, primarily due to the permanent difference related to difference in foreign tax rates and the increase in our valuation allowance.
On December 22, 2017, President Trump signed into law the “Tax Cuts and Jobs Act” (TCJA) that significantly reformed the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended. The TCJA, among other things, reduces the corporate tax rate to 21 percent beginning with years starting January 1, 2018. Because a change in tax law is accounted for in the period of enactment, the deferred tax assets and liabilities have been adjusted to the newly enacted U.S. corporate rate, and the related impact to the tax expense has been recognized in the current year.
A new federal tax on Global Intangible Low – Taxed Income (GILTI) was enacted for the tax year beginning after December 31, 2017. The GILTI rules require US corporations to include in taxable income current year net earnings of their foreign subsidiaries that are controlled foreign corporations.
Significant components of our deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Net operating loss carry forwards | 19,006,668 | 18,234,015 | ||||||
| Stock based compensation | 231,984 | 162,199 | ||||||
| Basis difference in goodwill | 524,823 | 829,009 | ||||||
| Basis difference in fixed assets | 1,589 | 3,786 | ||||||
| Basis difference in intangible assets | 2,278,085 | 1,968,335 | ||||||
Allowance for bad debt (US) | - | - | ||||||
Stock price guarantee adjustment | - | - | ||||||
| Valuation allowance for deferred tax assets | (22,043,149 | ) | (21,197,343 | ) | ||||
Total deferred tax assets | - | - | ||||||
Deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||||
Basis difference in goodwill | - | - | ||||||
Basis difference in fixed assets | - | - | ||||||
Basis difference in intangible assets | - | - | ||||||
Total deferred tax liabilities | - | - | ||||||
Net deferred taxes | - | - | ||||||
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts of assets and liabilities used for income tax purposes. According to the GILTI rules, the income from foreign corporations reduce the net operating losses (‘NOLs”). At December 31, 2020, we had cumulative federal and state NOLs carry forwards of approximately $77.8 million. At December 31, 2019, we had cumulative federal and state NOLs carry forwards of approximately $73.8 million. We also have $2.6 million and $1.9 million in foreign NOLs as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The valuation allowance was increased by $0.8 million in fiscal year 2020. The fiscal 2020 increase was primarily related to additional operating loss incurred, and difference in tax and book basis of goodwill and other intangible assets. We have considered all the evidence, both positive and negative, that the NOLs and other deferred tax assets may not be realized and have recorded a valuation allowance for $22 million. The NOLs arising in the tax year beginning before January 1, 2019 can be carried back two years and forward twenty years. The NOLs arising in the tax year beginning after December 31, 2018 can only offset 80% of taxable income in any given tax year, but the remaining can be carried forward indefinitely.
The timing and manner in which we will be able to utilize some of its NOLs is limited by Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (IRC). IRC Section 382 imposes limitations on a corporation’s ability to use its NOLs when it undergoes an “ownership change.” Generally, an ownership change occurs if one or more shareholders, each of whom owns 5% or more in value of a corporation’s stock, increase their percentage ownership, in the aggregate, by more than 50% over the lowest percentage of stock owned by such shareholders at any time during the preceding three-year period. Because on June 10, 2014, we underwent an ownership change as defined by IRC Section 382, the limitation applies to us. The losses generated prior to the ownership change date (pre-change losses) are subject to the Section 382 limitation. The pre-change losses may only become available to be utilized by the Company at the rate of $2.4 million per year. Any unused losses can be carried forward, subject to their original carryforward limitation periods. In the year 2019, approximately $2.4 million in the pre-change losses was released from the Section 382 loss limitation. Since the ownership change, the cumulative amount of NOLs released from Section 382 was approximately 15.7 million.
The Company can still fully utilize the NOLs generated after the change of the ownership, which was approximately $38.1 million. Thus, the total of approximately $53.7 million as of December 31, 2020 is available to offset future income.
The open United States tax years subject to examination with respect to our operations are 2017, 2018 and 2019.
NOTE 15. OTHER INCOME
Include in other income, net for the year ended December 31, 2020, in the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive loss, is approximately $1.1 million relating to merchant reserves recorded in a previous year deemed not to be a legal obligation by management of the Company.
NOTE 16. SEGMENT INFORMATION
Our reportable segments are business units that offer different products and services in different geographies. The reportable segments are each managed separately because they offer distinct products, in distinct geographic locations, with different delivery and service processes.
North America Transaction Solutions
Our North American Transaction Solutions business segment consists of the former Unified Payments business and Aptito. This segment operates primarily in North America. In March 2013, we acquired all of the business assets of Unified Payments, a provider of comprehensive turnkey, payment processing solutions to small and medium size business owners (merchants) and independent sales organizations across the United States. In April 2013, we purchased 80% of Aptito, a cloud-based Software-as-a-Service (“SaaS”) restaurant management solution, which provides integrated POS, mPOS, Kiosk, Digital Menus functionality to drive consumer engagement via Apple® iPad®-based POS, kiosk and all other cloud-connected devices.
International Transaction Solutions
Our International Transaction Solutions segment consists of PayOnline, which includes our mobile payments operations, primarily located in Russia. PayOnline provides a secure online payment processing system to accept bank card payments for goods and services.
Segment Summary Information
Geographic Summary Information
2020 Revenues | 2020 Long-Lived Assets | 2019 Revenues | 2019 Long-Lived Assets | |||||||||||||
North America | $ | 62,556,698 | $ | 12,421,144 | $ | 61,778,002 | $ | 13,325,444 | ||||||||
Russia and CIS | 3,148,424 | 1,028,796 | 3,221,609 | 1,048,801 | ||||||||||||
The following tables present financial information of our reportable segments at and for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019. The “corporate and eliminations” column includes corporate expenses and intercompany eliminations for consolidated purposes.
Twelve months ended December 31, 2020 | North American Transaction Solutions | International Transaction Solutions | Corp Exp & Eliminations | Total | ||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 62,556,698 | $ | 3,148,424 | $ | - | $ | 65,705,122 | ||||||||
Cost of revenues | 53,593,342 | 2,268,061 | - | 55,861,403 | ||||||||||||
Gross Margin | 8,963,356 | 880,363 | - | 9,843,719 | ||||||||||||
Gross margin % | 14 | % | 28 | % | - | 15 | % | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 2,717,009 | 974,680 | 3,324,355 | 7,016,044 | ||||||||||||
Non-cash compensation | - | - | 2,718,152 | 2,718,152 | ||||||||||||
Provision for bad debt | 1,563,847 | 2,957 | - | 1,566,804 | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 3,013,256 | 22,543 | - | 3,035,799 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 1,398,617 | - | 48,023 | 1,446,640 | ||||||||||||
| Gain on disposition | (13,500 | ) | - | - | (13,500 | ) | ||||||||||
Other expense (income) | (18,455 | ) | 4,491 | 64,232 | 50,268 | |||||||||||
Net (loss) income for segment | $ | 302,582 | $ | (124,308 | ) | $ | (6,154,762 | ) | $ | (5,976,488 | ) | |||||
Goodwill | 6,671,750 | 1,009,436 | - | 7,681,186 | ||||||||||||
Other segment assets | 18,777,772 | 367,771 | - | 19,145,544 | ||||||||||||
Total segment assets | $ | 25,449,522 | $ | 1,377,207 | $ | - | $ | 26,826,730 | ||||||||
Twelve months ended December 31, 2019 | North American Transaction Solutions | International Transaction Solutions | Corp Exp & Eliminations | Total | ||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 61,778,002 | $ | 3,221,609 | $ | - | $ | 64,999,611 | ||||||||
Cost of revenues | 52,395,752 | 2,325,958 | - | 54,721,710 | ||||||||||||
Gross Margin | 9,382,250 | 895,651 | - | 10,277,901 | ||||||||||||
Gross margin % | 15 | % | 28 | % | - | 16 | % | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative | 2,587,411 | 1,077,294 | 5,677,079 | 9,341,784 | ||||||||||||
Non-cash compensation | 48,433 | - | 2,002,429 | 2,050,862 | ||||||||||||
Provision for bad debt | 1,369,015 | (18,838 | ) | - | 1,350,177 | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 3,084,013 | 36,230 | - | 3,120,243 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 1,069,506 | 282 | 42,739 | 1,112,527 | ||||||||||||
Impairment charge relating to goodwill | - | 1,326,566 | - | 1,326,566 | ||||||||||||
Other (income) expense | 300,225 | (1,482,196 | ) | (277,644 | ) | (1,459,615 | ) | |||||||||
Net (loss) income for segment | $ | 923,647 | $ | (43,687 | ) | $ | (7,444,603 | ) | $ | (6,564,643 | ) | |||||
Goodwill | 6,671,750 | 1,009,436 | - | 7,681,186 | ||||||||||||
Other segment assets | 14,906,737 | 451,225 | - | 15,357,962 | ||||||||||||
Total segment assets | $ | 21,578,487 | $ | 1,460,661 | $ | - | $ | 23,039,148 | ||||||||