UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D. C. 20549
[x]ANNUALREPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For thefiscal yearendedDecember 31,2014
or
[ ] TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from ________ to _________
Commission File Number 001-35032

PARK STERLING CORPORATION |
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) |
NORTH CAROLINA | 27-4107242 |
(State or other jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer |
incorporation or organization) | Identification No.) |
1043 E. Morehead Street, Suite 201 | | |
Charlotte, North Carolina | 28204 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
(704) 716-2134 (Registrant’s telephone number, including area code) ___________________________ Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: |
| | Name of each exchange |
Title of each class | | on which registered |
Common Stock, $1.00 par value | | NASDAQ Global Select Market |
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☑
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes☐ No☑
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer ☐ | | Accelerated filer ☑ |
| | |
Non-accelerated filer ☐ | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company ☐ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☑
As of June 30, 2014, the aggregate market value of the common stock of the registrant held by non-affiliates was approximately $269,605,107 (based on the closing price of $6.55 per share on June 30, 2014). For purposes of the foregoing calculation only, all directors and executive officers of the registrant have been deemed affiliates.
The number of shares of common stock of the registrant outstanding as of February 28, 2015 was 44,865,791.
Documents Incorporated by Reference
Portions of the registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement for its 2015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders scheduled to be held on May 20, 2015 are incorporated by reference into Part III, Items 10-14.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
Table of Contents
| | | Page No. |
| | | | |
Part I | | | |
| | | | |
Item 1. | Business | 2 | |
| | | | |
Item 1A. | Risk Factors | 12 | |
| | | | |
Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments | 24 | |
| | | | |
Item 2. | Properties | 24 | |
| | | | |
Item 3. | Legal Proceedings | 24 | |
| | | | |
Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | 24 | |
| | | | |
Part II | | | |
| | | | |
Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters andIssuer Purchases of Equity Securities | 25 | |
| | | | |
Item 6. | Selected Financial Data | 28 | |
| | | | |
Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition andResults of Operations | 29 | |
| | | | |
Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk | 60 | |
| | | | |
Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | 60 | |
| | | | |
Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accountingand Financial Disclosure | 126 | |
| | | | |
Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures | 126 | |
| | | | |
Item 9B. | Other Information | 127 | |
| | | | |
Part III | | | |
| | | | |
Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | 128 | |
| | | | |
Item 11. | Executive Compensation | 130 | |
| | | | |
Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Managementand Related Stockholder Matters | 130 | |
| | | | |
Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | 130 | |
| | | | |
Item 14. | Principal Accounting Fees and Services | 131 | |
| | | | |
Part IV | | | |
| | | | |
Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules | 131 | |
| | | | |
| | Signatures | 132 | |
| | | | |
| | Exhibit Index | 134 | |
PART I
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Information set forth in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including information incorporated by reference in this document, may constitute “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements can be identified by the fact that they do not relate strictly to historical or current facts and often use words such as “may,” “plan,” “contemplate,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “intend,” “continue,” “expect,” “project,” “predict,” “estimate,” “could,” “should,” “would,” “will,” “goal,” “target” and similar expressions. The forward-looking statements express management’s current expectations or forecasts of future events, results and conditions, the general business strategy of engaging in bank mergers, organic growth, branch openings and closings, expansion in new markets, hiring of additional personnel, expansion or addition of product capabilities, expected footprint of the banking franchise and anticipated asset size; anticipated loan growth; changes in loan mix and deposit mix; capital and liquidity levels; net interest income; provision expense; noninterest income and noninterest expenses; realization of deferred tax asset; credit trends and conditions, including loan losses, allowance for loan loss, charge-offs, delinquency trends and nonperforming asset levels; the amount, timing and prices of share repurchases; the payment of common stock dividends; and other similar matters. These forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future results or performance and by their nature involve certain risks and uncertainties that are based on management’s beliefs and assumptions and on the information available to management at the time that these disclosures were prepared. Actual outcomes and results may differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, any of these forward-looking statements.
You should not place undue reliance on any forward-looking statement and should consider all of the following uncertainties and risks, as well as those more fully discussed elsewhere in this report, including Item 1A. “Risk Factors,” and in any of the Company’s subsequent filings with the SEC: failure to realize synergies and other financial benefits from the Provident Community merger within expected time frames; increases in expected costs or decreases in expected savings or difficulties related to merger integration matters; inability to identify and successfully negotiate and complete additional combinations with other potential merger partners or to successfully integrate such businesses into the Company, including the Company’s ability to adequately estimate or to realize the benefits and cost savings from and limit any unexpected liabilities acquired as a result of any such business combination; failure to generate an adequate return on investment related to new branches or other hiring initiatives; inability to generate future organic growth in loan balances, retail banking, wealth management, capital markets or mortgage banking through the hiring of new personnel, development of new products, opening of de novo branches or otherwise; variability in the performance of covered loans and associated loss share related expenses; the effects of negative or soft economic conditions, including stress in the commercial real estate markets or failure of continued recovery in the residential real estate markets; changes in consumer and investor confidence and the related impact on financial markets and institutions; changes in interest rates; failure of assumptions underlying the establishment of allowances for loan losses; deterioration in the credit quality of the loan portfolio or in the value of the collateral securing those loans; deterioration in the value of securities held in the investment securities portfolio; the possibility of recognizing other than temporary impairments on holdings of collateralized loan obligation securities as a result of the Volcker Rule; the impacts on the Company of a potential increasing rate environment; the potential impacts of any government shutdown or ceiling impasse, including the risk of a United States credit rating downgrade or default, or continued global economic instability, which could cause disruptions in the financial markets, impact interest rates and cause other potential unforeseen consequences; fluctuations in the market price of the common stock, regulatory, legal and contractual requirements, other uses of capital, the Company’s financial performance, market conditions generally, and future actions by the board of directors, in each case impacting repurchases of common stock or declaration of dividends; legal and regulatory developments including changes in the federal risk-based capital rules; increased competition from both banks and nonbanks; changes in accounting standards, rules and interpretations, inaccurate estimates or assumptions in accounting, including acquisition accounting fair market value assumptions and accounting for purchased credit-impaired loans, and the impact on the Company’s financial statements; and management’s ability to effectively manage credit risk, market risk, operational risk, legal risk, and regulatory and compliance risk.
Forward-looking statements speak only as of the date they are made, and the Company undertakes no obligation to update any forward-looking statement to reflect the impact of circumstances or events that arise after the date the forward-looking statement was made.
Item 1. Business
General
Park Sterling Corporation (the “Company”) was formed in 2010 to serve as the holding company for Park Sterling Bank (the “Bank”) pursuant to a bank holding company reorganization effective January 1, 2011, and is registered with the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (the “Federal Reserve Board”) under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended (the “BHC Act”). The Bank is a North Carolina-chartered commercial nonmember bank that was incorporated in September 2006 and opened for business at 1043 E. Morehead Street, Suite 201, Charlotte, North Carolina on October 25, 2006. At December 31, 2014, the Company’s primary operations and business were that of owning the Bank. Prior to January 1, 2011, the Company conducted no operations other than obtaining regulatory approval for the holding company reorganization. The main office of both the Company and the Bank is located at 1043 E. Morehead Street, Suite 201, Charlotte, North Carolina, 28204, and its phone number is (704) 716-2134.
In August 2010, the Bank raised gross proceeds of $150 million in an equity offering (the “Public Offering”), to facilitate a change in the Bank’s business plan from primarily organic growth at a moderate pace to creating a regional community bank through a combination of mergers and acquisitions and accelerated organic growth. Consistent with this growth strategy, over the past several years the Bank has opened additional branches in North Carolina and South Carolina and in 2014 expanded into the Virginia market through the opening of a loan production office, followed by the opening of a full-service branch in Richmond, Virginia. The Bank has received approval to open a second full-service branch in Richmond, Virginia, which it intends to open in 2015. In addition, since the Public Offering, the Company has completed the following acquisitions of community banks in its existing or targeted markets:
| | ● | In May 2014, the Company acquired Provident Community Bancshares, Inc. (“Provident Community”), the parent company of Provident Community Bank, N.A., which operated nine branches in South Carolina. |
| | ● | In October 2012, the Company acquired Citizens South Banking Corporation (“Citizens South”), the parent company of Citizens South Bank, which operated 21 branches in North Carolina, South Carolina and North Georgia. |
| | ● | In November 2011, the Company acquired Community Capital Corporation (“Community Capital”), the parent company of CapitalBank, which operated 18 branches in the Upstate and Midlands area of South Carolina. |
Each of these banks has merged into the Bank.
The Company remains focused on its intention to create a regional community bank with locations in North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia and North Georgia, through selective acquisitions of banks or branches and organic growth through the opening of additional branches and selective investment in additional bankers and enhanced products and services.
Banking Services
Our objective since inception has been to provide the strength and product diversity of a larger bank and the service and relationship attention that characterizes a community bank. We strive to develop a personal relationship with our customers so that we are positioned to anticipate and address their financial needs.
Through our branches and offices, we provide banking services to small and mid-sized businesses, owner-occupied and income-producing real estate owners, residential builders, institutions, professionals and consumers doing business or residing within our target markets. We provide a wide range of banking products, including personal, business and non-profit checking accounts, IOLTA accounts, individual retirement accounts, business and personal money market accounts, time deposits, overdraft protection, safe deposit boxes and online and mobile banking. Our lending activities include a range of short- to medium-term commercial (including asset-based lending), real estate, construction, residential mortgage and home equity and consumer loans, as well as long-term residential mortgages. Our wealth management activities include investment management, private banking, personal trust and investment brokerage services. Our cash management activities include remote deposit capture, lockbox services, sweep accounts, purchasing cards, ACH and wire payments. Our capital markets activities include interest rate and currency risk management products, loan syndications and debt placements. We are committed to providing“Answers You Can Bank OnSM” to our customers. We prides ourselves on being large enough to help customers achieve their financial aspirations, yet small enough to care that they do. We are focused on building a banking franchise that is noted for sound risk management, broad product capabilities, strong community focus and exceptional customer service.
Market Area
The Bank serves its customers through eighteen full-service branches in North Carolina, twenty-eight full-service branches and one drive-through facility in South Carolina, five full-service branches in North Georgia and one full-service branch in Richmond, Virginia. The Bank has received approval to open a second full-service branch in Richmond, Virginia, which it intends to open in 2015.
The Bank maintains nineteen branches in the Charlotte-Concord-Gastonia Metropolitan Statistical Area (“MSA”) in North Carolina and eleven branches in the Greenville-Anderson-Mauldin MSA in South Carolina. Additionally, we serve our communities through six branches in the Greenwood, South Carolina MSA, four in the Spartanburg, South Carolina MSA, two each in the Newberry, South Carolina MSA and Columbia, South Carolina MSA, and one each in the Raleigh, North Carolina MSA, the Wilmington, North Carolina MSA, the Charleston-North Charleston, South Carolina MSA, and the Richmond, Virginia MSA. Our five North Georgia branches are not located in an identified MSA.
With the Bank’s operations stretching from Virginia, throughout the Carolinas and down into North Georgia, we have a diverse economic and customer base. We do not believe we are dependent on any one or any several customers or types of business whose loss would have a material adverse effect on us.
Competition
Commercial banking and other financial activities in all of our market areas are highly competitive, and there are numerous branches of national, regional and local institutions in each of these markets. We compete for deposits in our banking markets with other commercial banks, savings banks and other thrift institutions, credit unions, agencies issuing United States government securities, and all other organizations and institutions engaged in money market transactions. In our lending activities, we compete with all other financial institutions as well as consumer finance companies, mortgage companies and other lenders. In our wealth management activities, we compete with commercial and investment banking firms, investment advisory firms and brokerage firms.
Interest rates, both on loans and deposits, and prices of fee-based services are significant competitive factors among financial institutions generally. Other important competitive factors include office location, office hours, the quality of customer service, community reputation, continuity of personnel and services, and, in the case of larger commercial customers, relative lending limits and the ability to offer sophisticated cash management and other commercial banking services. Many of our competitors have greater resources, broader geographic markets and higher lending limits than we do, and they can offer more products and services and can better afford and make more effective use of media advertising, support services and electronic technology than we can. To counter these competitive disadvantages, we depend on our reputation as a community bank in our local markets, our direct customer contact, our ability to make credit and other business decisions locally, our wide range of banking products and our personalized service.
In recent years, federal and state legislation has heightened the competitive environment in which all financial institutions conduct their business, and the potential for competition among financial institutions of all types has increased significantly. Additionally, with the elimination of restrictions on interstate banking, commercial banks operating in our market areas may be required to compete not only with other financial institutions based in the states in which we operate, but also with out-of-state financial institutions which may acquire institutions, or establish or acquire branch offices in these states, or otherwise offer financial services across state lines, thereby adding to the competitive atmosphere of the industry in general.
Employees
As of February 28, 2015, we employed 534 people and had 514 full time equivalent employees. Each of these individuals is an employee of the Bank. There are no employees at the bank holding company level. We are not a party to a collective bargaining agreement, and we consider our relations with employees to be good.
Subsidiaries
The Company’s primary subsidiary is the Bank. In addition, the Company has four wholly owned non-consolidated subsidiaries, Community Capital Corporation Statutory Trust I, CSBC Statutory Trust I, Provident Community Bancshares Capital Trust I, and Provident Community Bancshares Capital Trust II, which were used to issue $10.3 million, $15.5 million, $4.1 million, and $8.2 million (before related acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments), respectively, of trust preferred securities (“TruPS”) by these predecessor companies. The Company has fully and unconditionally guaranteed each trust’s obligations under the preferred securities. Proceeds from these securities were used by the predecessor companies to purchase junior subordinated notes in Community Capital, Citizens South, and Provident Community, respectively, which constitute Tier I capital of the Company.
The Bank has two subsidiaries, Park Sterling Financial Services, Inc., and Citizens Properties, LLC. Park Sterling Financial Services, Inc., originally Citizens South Financial Services, Inc., primarily owns stock in a title insurance company which was used by Citizens South Bank for certain real estate transactions and continues to operate as such. Citizens Properties, LLC was formed in January 2012 for the purpose of holding, managing and resolving certain real estate that was acquired through foreclosure, or other nonperforming and substandard assets, and continues to operate as such.
Supervision and Regulation
Bank holding companies and state commercial banks are subject to extensive supervision and regulation by federal and state agencies. Regulation of bank holding companies and banks is intended primarily for the protection of consumers, depositors, borrowers, the Federal Deposit Insurance Fund (the “DIF”) and the banking system as a whole and not for the protection of shareholders or creditors. The following is a brief summary of certain material statutory and regulatory provisions applicable to the Company and the Bankbut is not intended to be an exhaustive description of all statutes and regulations applicable to our business. To the extent such provisions are described, this description is qualified in its entirety by reference to the applicable laws and regulations.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”), enacted in July 2010, has had and will continue to have a broad impact on the financial services industry, including significant regulatory and compliance changes including, among other things: (i) enhanced resolution authority of troubled and failing banks and their holding companies; (ii) increased capital and liquidity requirements; (iii) increased regulatory examination fees; (iv) changes to assessments to be paid to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) for federal deposit insurance; (v) enhanced corporate governance and executive compensation requirements and disclosures; and (vi) numerous other provisions designed to improve supervision and oversight of, and strengthening safety and soundness for, the financial services sector. Additionally, the Dodd-Frank Act established a new framework for systemic risk oversight within the financial system to be distributed among new and existing federal regulatory agencies, including the Financial Stability Oversight Council, the Federal Reserve Board, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, and the FDIC. Many of the requirements called for in the Dodd-Frank Act continue to be implemented, and/or are subject to implementing regulations over the course of several years. Given the uncertainty associated with the manner in which the provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act will be implemented by the various regulatory agencies and through regulations, the full extent of the impact such requirements will have on financial institutions’ operations is unclear. The changes resulting from the Dodd-Frank Act may impact the profitability of our business activities, require changes to certain of our business practices, or otherwise adversely affect our business. These changes may also require us to invest significant management attention and resources to evaluate and make necessary changes in order to comply with new statutory and regulatory requirements.
In addition, from time to time, various other legislative and regulatory initiatives are introduced in Congress and state legislatives, as well as regulatory agencies, that may impact the Company or the Bank. Such initiatives may include proposals to expand or contract the powers of bank holding companies and depository institutions or proposals to substantially change the financial institution regulatory system. Such legislation could change bank statutes and the operating environment of the Company in substantial and unpredictable ways. If enacted, such legislation could increase or decrease the cost of doing business, limit or expand permissible activities or affect the competitive balance among banks, savings associations, credit unions and other financial institutions. We cannot predict whether any such legislation or regulatory policies will be enacted or, if enacted, the effect that such would have on our financial condition or results of operations, which could be material.
General.As a registered bank holding company, the Company is subject to regulation under the BHC Act and to inspection, examination and supervision by the Federal Reserve Board. In general, the Federal Reserve Board may initiate enforcement actions for violations of laws and regulations and unsafe or unsound practices. The Federal Reserve Board may assess civil money penalties, issue cease and desist or removal orders and require that a bank holding company divest subsidiaries, including subsidiary banks. The Company is also required to file reports and other information with the Federal Reserve Board regarding its business operations and those of the Bank.
The Bank is a North Carolina-chartered commercial nonmember bank subject to regulation, supervision and examination by its chartering regulator, the North Carolina Commissioner of Banks (the “NC Commissioner”), and by the FDIC, as deposit insurer and primary federal regulator. As an insured depository institution, numerous federal and state laws, as well as regulations promulgated by the FDIC and the NC Commissioner, govern many aspects of the Bank’s operations. The NC Commissioner and the FDIC regulate and monitor compliance with these state and federal laws and regulations, as well as the Bank’s operations and activities, including, but not limited to, loan and lease loss reserves, lending and mortgage operations, interest rates paid on deposits and received on loans, the payment of dividends to the Company, loans to officers and directors, record-keeping, mergers of state-chartered banks, capital requirements, and the establishment of branches. The Bank is a member of the Federal Home Loan Bank of Atlanta, which is one of the 12 regional banks comprising the Federal Home Loan Bank (“FHLB”) system.
In addition to state and federal banking laws, regulations and regulatory agencies, the Company and the Bank are subject to various other laws, regulations and supervision and examination by other regulatory agencies, including, with respect to the Company, the SEC and the NASDAQ Global Select Market (“NASDAQ”).
Bank Holding Companies. The Federal Reserve Board is authorized to adopt regulations affecting various aspects of bank holding companies.In general, the BHC Act limits the business of bank holding companies and its subsidiaries to banking, managing or controlling banks and other activities that the Federal Reserve Board has determined to be so closely related to banking as to be a proper incident thereto. The Federal Reserve Board has the power to order a bank holding company or its subsidiaries to terminate any activity or control of any nonbank subsidiary when the continuation of the activity or control constitutes a serious risk to the financial safety, soundness or stability of any bank subsidiary of that bank holding company.
The BHC Act requires prior Federal Reserve Board approval for, among other things, the acquisition by a bank holding company of direct or indirect ownership or control of more than 5% of the voting shares or substantially all the assets of any bank, or for a merger or consolidation of a bank holding company with another bank holding company. The BHC Act also prohibits a bank holding company from acquiring direct or indirect control of more than 5% of the outstanding voting stock of any company engaged in a non-banking business unless such business is determined by the Federal Reserve Board to be so closely related to banking as to be a proper incident thereto.
The Company also is subject to the North Carolina Bank Holding Company Act of 1984. This state legislation requires the Company, by virtue of its ownership of the Bank, to register as a bank holding company with the NC Commissioner.
Under the BHC Act, a bank holding company may elect to become a “financial holding company,” provided certain conditions are met. A financial holding company, and the companies it controls, are permitted to engage in activities considered “financial in nature,” (including, without limitation, insurance and securities activities), and therefore may engage in a broader range of activities than permitted by bank holding companies and their subsidiaries. The Company remains a bank holding company, but may at some time in the future elect to become a financial holding company. If the Company were to do so, the Bank would have to be well capitalized, well managed and have at least a satisfactory rating under the Community Reinvestment Act (“CRA”), which is discussed below.
Acquisitions.As an acquirer, we must comply with numerous laws related to our acquisition activity. As noted above, under the BHC Act, a bank holding company may not directly or indirectly acquire ownership or control of more than 5% of the voting shares or substantially all of the assets of any bank or merge or consolidate with another bank holding company without the prior approval of the Federal Reserve Board. In addition, the Bank Merger Act requires prior approval from the applicable federal regulatory agency (the FDIC, in the case of the Bank) before any bank may merge or consolidate with, acquire the assets of or assume the deposit liabilities of another bank. Current federal law authorizes interstate acquisitions of banks by well-capitalized and well-managed bank holding companies, and allows a bank headquartered in one state to merge with or acquire a bank headquartered in another state (where the resulting institution is well-capitalized and well-managed) as long as neither of the states has opted out of such interstate bank merger authority, in each case subject to any state requirement that the target bank shall have been in existence and operating for a minimum period of time, not to exceed five years, and to certain deposit market-share limitations.
Branching.With appropriate regulatory approvals, North Carolina commercial banks are authorized to establish branches both in North Carolina as well as in other states, where the laws of the state where thede novo branch is to be opened would permit a bank chartered by that state to open ade novo branch. A bank that establishes a branch in another state may conduct any activity at that branch office that is permitted by the law of that state to the extent that the activity is permitted either for a state bank chartered by that state or for a branch in the state of an out-of-state national bank.
Minimum Capital Requirements.The various federal bank regulators, including the Federal Reserve Board and the FDIC, have adopted substantially similar minimum risk-based and leverage capital guidelines applicable to United States banking organizations, including bank holding companies and banks. In addition, these regulatory agencies may from time to time require that a banking organization maintain capital above the minimum prescribed levels, whether because of its financial condition or actual or anticipated growth.
In July 2013, the regulatory agencies approved final regulatory capital rules that replace the existing general risk-based capital and related rules, broadly revising the basic definitions and elements of regulatory capital and making substantial changes to the credit risk weightings for banking and trading book assets. The new regulatory capital rules establish the benchmark capital rules and capital floors that are generally applicable to United States banks under the Dodd-Frank Act and make the capital rules consistent with heightened international capital standards known as Basel III. These new capital standards apply to all banks, regardless of size, and to all bank holding companies with consolidated assets greater than $500 million.
Under the new capital guidelines, applicable regulatory capital components consist of (1) common equity Tier 1 capital (common stock, including related surplus, and retained earnings, plus limited amounts of minority interest in the form of common stock, net of goodwill and other intangibles (other than mortgage servicing assets), deferred tax assets arising from net operating loss and tax credit carry forwards above certain levels, mortgage servicing rights above certain levels, gain on sale of securitization exposures and certain investments in the capital of unconsolidated financial institutions, and adjusted by unrealized gains or losses on cash flow hedges and accumulated other comprehensive income items (subject to the ability of a non-advanced approaches institution to make a one-time irrevocable election to exclude from regulatory capital most components of AOCI)), (2) additional Tier 1 capital (qualifying non-cumulative perpetual preferred stock, including related surplus, plus qualifying Tier 1 minority interest and, in the case of holding companies with less than $15 billion in consolidated assets at December 31, 2009, certain grandfathered trust preferred securities and cumulative perpetual preferred stock in limited amounts, net of mortgage servicing rights, deferred tax assets related to temporary timing differences, and certain investments in financial institutions) and (3) Tier 2 capital (the allowance for loan and lease losses in an amount not exceeding 1.25% of standardized risk-weighted assets, plus qualifying preferred stock, qualifying subordinated debt and qualifying total capital minority interest, net of Tier 2 investments in financial institutions). Total Tier 1 capital, plus Tier 2 capital, constitutes total risk-based capital. The required minimum ratios are as follows:
| | ● | common equity Tier 1 capital ratio (common equity Tier 1 capital to standardized total risk-weighted assets) of 4.5%; |
| | ● | Tier 1 capital ratio (Tier 1 capital to standardized total risk-weighted assets) of 6%; |
| | ● | total capital ratio (total capital to standardized total risk-weighted assets) of 8%; and |
| | ● | leverage ratio (Tier 1 capital to average total consolidated assets) of 4%. |
Advanced approaches banking organizations (those organizations with either total assets of $250 billion or more, or with foreign exposure of $10 billion or more) also are subject to a supplementary leverage ratio that incorporates a broader set of exposures in the denominator. The new capital guidelines also provide that all covered banking organizations must maintain a new capital conservation buffer of common equity Tier 1 capital in an amount greater than 2.5% of total risk-weighted assets to avoid being subject to limitations on capital distributions and discretionary bonus payments to executive officers. Advanced approaches organizations also are subject to a countercyclical capital buffer. Failure to satisfy the capital buffer requirements will result in increasingly stringent limitations on various types of capital distributions, including dividends, share buybacks and discretionary payments on Tier 1 instruments, and discretionary bonus payments.
Non-advanced approaches banking organizations, including the Company and the Bank, must begin compliance with the new minimum capital ratios and the standardized approach for risk-weighted assets as of January 1, 2015, and the revised definitions of regulatory capital and the revised regulatory capital deductions and adjustments are being phased in over time for such organizations beginning as of that date. The capital conservation buffer will be phased in for all banking organizations beginning January 1, 2016.
The new capital guidelines reflect changes from the June 2012 proposals that minimize the impact of the revised capital regulations on community banks. In particular, banking organizations with less than $15 billion in total assets (including the Company and the Bank) are not subject to the phase-out of non-qualifying Tier 1 capital instruments, such as TruPS, that were issued and outstanding prior to May 19, 2010. In addition, non-advanced approaches banking organizations have a one-time option to exclude certain components of accumulated other comprehensive income from inclusion in regulatory capital, comparable to treatment under the current capital rules. The Company currently plans to continue to exclude certain components of accumulated other comprehensive income from inclusion in regulatory capital. The regulations also retain the existing treatment for residential mortgage exposures in the current risk-based capital rules, rather than adopt the proposed changes that would have required banking organizations to determine the risk weights based on a complex categorization and loan-to-value assessment.
Although the new capital guidelines alleviate some of the concerns of community banks with the capital standards as originally proposed, the new capital standards impose significant changes on the definition of capital, including the inability to include instruments such as TruPS in Tier 1 capital going forward and new constraints on the inclusion of minority interests, mortgage servicing assets, deferred tax assets and certain investments in the capital of unconsolidated financial institutions. In addition, the new guidelines increase the risk-weights of various assets, including certain high volatility commercial real estate and past due asset exposures.
The risk-based guidelines in effect prior to January 1, 2015 defined a three-Tier capital framework. Tier 1 capital generally was defined to include the sum of common shareholders’ equity, qualifying non-cumulative perpetual preferred stock (including any related surplus), a limited amount of trust preferred securities and qualifying minority interests in consolidated subsidiaries, minus goodwill, other intangible assets (other than certain servicing assets), certain credit-enhancing interest-only strips, deferred tax assets in excess of certain thresholds and certain other items. Tier 2 capital generally included qualifying subordinated debt, certain hybrid capital instruments, qualifying preferred stock and a limited amount of the allowance for loan losses. Tier 3 capital included primarily qualifying unsecured subordinated debt. The sum of Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital less investments in unconsolidated subsidiaries equaled qualifying total capital. Under these risk-based guidelines, the Company and the Bank were required to maintain a minimum ratio of Tier 1 capital to total risk-weighted assets of 4% and a minimum ratio of total capital to risk-weighted assets of 8%. The leverage capital requirements in effect prior to January 1, 2015 required banking organizations that met certain criteria, including excellent asset quality, high liquidity, low interest rate exposure and good earnings, and that had received the highest regulatory rating, to maintain a ratio of Tier 1 capital to total adjusted average assets of at least 3%. All other institutions were required to maintain a minimum leverage capital ratio of not less than 4%, unless a higher leverage capital ratio was warranted by the particular circumstances or risk profile of the institution. The Company and the Bank were in compliance with all such capital requirements as of December 31, 2014.
To assess a bank’s capital adequacy, federal banking agencies, including the FDIC, have also adopted regulations to require an assessment of exposure to declines in the economic value of a bank’s capital due to changes in interest rates. Under such a risk assessment, examiners will evaluate a bank’s capital for interest rate risk on a case-by-case basis, with consideration of both quantitative and qualitative factors. Applicable considerations include the quality of the bank’s interest rate risk management process, the overall financial condition of the bank and the level of other risks at the bank for which capital is needed. Institutions with significant interest rate risk may be required to hold additional capital. The agencies also issued a joint policy statement providing guidance on interest rate risk management, including a discussion of the critical factors affecting the agencies’ evaluation of interest rate risk in connection with capital adequacy.
Prompt Corrective Action.The Federal Deposit Insurance Act (the “FDI Act”), as amended by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation Improvement Act of 1991 (“FDICIA”), among other things, identifies five capital categories for insured depository institutions (well capitalized, adequately capitalized, undercapitalized, significantly undercapitalized and critically undercapitalized) and requires the respective federal regulatory agencies to implement systems for “prompt corrective action” for insured depository institutions that do not meet minimum capital requirements within such categories. An institution is subject to progressively more restrictive constraints on operations, management and capital distributions, depending on the category in which it is classified. Failure to meet the capital guidelines could also subject a banking institution to capital raising requirements. In addition, pursuant to the FDICIA, the various federal regulatory agencies have prescribed certain non-capital standards for safety and soundness relating generally to operations and management, asset quality and executive compensation, and such agencies may take action against a financial institution that does not meet the applicable standards.
The various federal regulatory agencies have adopted substantially similar regulations that define the five capital categories identified under the FDICIA, using the capital ratios as the relevant capital measures. The new capital requirement guidelines incorporate the revised changes in regulatory capital into the prompt corrective action framework, using the total risk-based capital ratio, the Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio, the common equity Tier 1 ratio, the leverage ratio (including, for certain large institutions, beginning January 1, 2018, the supplementary leverage ratio), as well as a tangible equity to total assets ratio, under which an institution’s capital adequacy will be measured for purposes of the “prompt corrective action” framework. Effective January 1, 2015, generally an insured depository institution will be treated as:
| | ● | “well capitalized” if its total risk-based capital ratio is at least 10%, its Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio is at least 8%, its common equity Tier 1 capital ratio is at least 6.5%, its leverage ratio is at least 5% and, if applicable, its supplementary leverage ratio is at least 6%; |
| | ● | “adequately capitalized” if its total risk-based capital ratio is at least 8%, its Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio is at least 6%, its common equity Tier 1 capital ratio is at least 4.5%, its leverage ratio is at least 4% and, if applicable, its supplementary leverage ratio is at least 3%, and it is not considered a well-capitalized institution; |
| | ● | “undercapitalized” if its total risk-based capital ratio is less than 8%, its Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio is less than 6%, its common equity Tier 1 capital ratio is less than 4.5%, its leverage ratio is less than 4% or, if applicable, its supplementary leverage ratio is less than 3%; |
| | ● | “significantly undercapitalized” if its total risk-based capital ratio is less than 6%, its Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio is less than 4%, its common equity Tier 1 capital ratio is less than 3%, or its leverage ratio is less than 3%; and |
| | ● | “critically undercapitalized” if it has a ratio of tangible equity (Tier 1 capital plus non-Tier 1 perpetual preferred stock) to total assets equal to or less than 2%. |
Under regulations effective as of December 31, 2014, generally an institution was treated as “well capitalized” if its ratio of total capital to risk-weighted assets was at least 10%, its ratio of Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets was at least 6%, its ratio of Tier 1 capital to total assets was at least 5%, and it was not subject to any order or directive by any such regulatory authority to meet a specific capital level. Under these guidelines, the Company and the Bank were considered “well capitalized” as of December 31, 2014. Under the new regulations, in effect on January 1, 2015, management currently estimates that both the Company and the Bank remained “well capitalized”.
OtherSafety and Soundness Regulations. The Federal Reserve Board has enforcement powers over bank holding companies and has authority to prohibit activities that represent unsafe or unsound practices or constitute violations of law, rule, regulation, administrative order or written agreement with a federal regulator. These powers may be exercised through the issuance of cease and desist orders, civil monetary penalties or other actions.
There also are a number of obligations and restrictions imposed on bank holding companies and their depositary institution subsidiaries by federal law and regulatory policy that are designed to reduce potential loss exposure to the depositors of such depository institutions and to the DIF in the event the depository institution is insolvent or is in danger of becoming insolvent. For example, a bank holding company is expected to act as a source of financial strength to each subsidiary bank and to commit resources to support each such subsidiary bank. Under this policy, the Federal Reserve Board may require a holding company to contribute additional capital to an undercapitalized subsidiary bank and may disapprove of the payment of dividends to the holding company’s shareholders if the Federal Reserve Board believes the payment of such dividends would be an unsafe or unsound practice.
In addition, the “cross guarantee” provisions of federal law require insured depository institutions under common control to reimburse the FDIC for any loss suffered or reasonably anticipated by the DIF as a result of the insolvency of commonly controlled insured depository institutions or for any assistance provided by the FDIC to commonly controlled insured depository institutions in danger of failure. The FDIC may decline to enforce the cross-guarantee provisions if it determines that a waiver is in the best interests of the DIF. The FDIC’s claim for reimbursement under the cross-guarantee provisions is superior to claims of shareholders of the insured depository institution or its holding company but is subordinate to claims of depositors, secured creditors and nonaffiliated holders of subordinated debt of the commonly controlled depository institution.
Federal and state banking regulators also have broad enforcement powers over the Bank, including the power to impose fines and other civil and criminal penalties, and to appoint a conservator (with the approval of the Governor in the case of a North Carolina state bank) in order to conserve the assets of any such institution for the benefit of depositors and other creditors. The NC Commissioner also has the authority to take possession of a North Carolina state bank in certain circumstances, including, among other things, when it appears that such bank has violated its charter or any applicable laws, is conducting its business in an unauthorized or unsafe manner, is in an unsafe or unsound condition to transact its business or has an impairment of its capital stock.
In June 2010, the federal bank regulatory agencies issued comprehensive final guidance on incentive compensation policies intended to ensure that the incentive compensation policies of banking organizations do not undermine the safety and soundness of such organizations by encouraging excessive risk taking. The guidance, which covers senior executives and other employees who have the ability to expose an institution to material amounts of risk (either individually or as part of a group), is based upon the key principles that a banking organization’s incentive compensation arrangements should (i) provide incentives that appropriately balance risk and financial results in a manner that does not encourage employees to expose their organizations to imprudent risks, (ii) be compatible with effective internal controls and risk management and (iii) be supported by strong corporate governance, including active and effective oversight by the organization’s board of directors. The applicable federal regulator will review, as part of the regular, risk-focused examination process, the incentive compensation arrangements of banking organizations, such as the Company, that are not “large, complex banking organizations,” based on the scope and complexity of the organization’s activities and the prevalence of incentive compensation arrangements. These supervisory findings will be included in reports of examination and will be incorporated into the organization’s supervisory ratings, which can affect the organization’s ability to make acquisitions and take other actions. The applicable federal regulator can take enforcement action against an institution if its incentive compensation arrangements, or related risk-management control or governance processes, pose a risk to the organization’s safety and soundness and the organization is not taking prompt and effective measures to correct the deficiencies.
Deposit Insurance and Assessments.The Bank’s deposits are insured by the DIF as administered by the FDIC, up to the applicable limits set by law (currently $250,000 for accounts under the same name and title), and are subject to the deposit insurance premium assessments of the DIF. The DIF imposes a risk-based deposit insurance premium system under which the assessment rates for an insured depository institution vary according to the level of risk incurred in its activities. To arrive at an assessment rate for a small banking institution (an institution with assets of less than $10 billion), the FDIC places it in one of four risk categories determined by reference to its capital levels and supervisory ratings. In addition, in the case of those institutions in the lowest risk category, the FDIC further determines its assessment rate based on certain specified financial ratios or, if applicable, its long-term debt ratings. The assessment rate schedule can change from time to time, at the discretion of the FDIC, subject to certain limits. Under the current system, premiums are assessed quarterly. Assessments are calculated as a percentage of average consolidated total assets less average tangible equity during the assessment period. The Dodd-Frank Act also increased the minimum designated reserve ratio of the DIF from 1.15% to 1.35% (subsequently set at 2% by the FDIC) of the estimated amount of total insured deposits.
In addition to deposit insurance assessments, insured depository institutions have been required to pay a pro rata portion of the interest due on the obligations issued by the Financing Corporation to fund the closing and disposal of failed thrift institutions by the Resolution Trust Corporation.
The FDIC may terminate the deposit insurance of any insured depository institution if it determines after a hearing that the institution has engaged in unsafe or unsound practices, is in an unsafe or unsound condition to continue operations or has violated any applicable law, regulation, rule, order or condition imposed by the FDIC or the Federal Reserve Board. It also may suspend deposit insurance temporarily during the hearing process for the permanent termination of insurance, if the institution has no tangible capital. If insurance of accounts is terminated, the accounts at the institution at the time of the termination, less subsequent withdrawals, shall continue to be insured for a period of six months to two years, as determined by the FDIC. We are not aware of any practice, condition or violation that might lead to termination of the Bank’s deposit insurance.
Dividends and Repurchase Limitations.The payment of dividends and repurchase of stock by the Company are subject to certain requirements and limitations of North Carolina corporate law. In addition, the Federal Reserve Board has issued a policy statement regarding payment of cash dividends by a bank holding company, indicating that a bank holding company generally should pay cash dividends only to the extent that the holding company’s net income for the past year is sufficient to cover the cash dividends, the holding company’s prospective rate of earnings retention is consistent with the holding company’s capital needs and overall financial condition, and the holding company is not in danger of not meeting its minimum regulatory capital adequacy ratios. As a bank holding company, the Company also must obtain Federal Reserve Board approval prior to repurchasing its Common Stock in excess of 10% of its consolidated net worth during any twelve-month period unless the Company (i) both before and after the repurchase satisfies capital requirements for "well capitalized" bank holding companies; (ii) is well managed; and (iii) is not the subject of any unresolved supervisory issues.
The Company is a legal entity separate and apart from the Bank. The primary source of funds for distributions paid by the Company, as well as funds used to pay principal and interest on the Company’s indebtedness, is dividends from the Bank, and the Bank is subject to laws and regulations that limit the amount of dividends it can pay. North Carolina law provides that, subject to certain capital requirements, the Bank generally may declare a dividend out of undivided profits as the board of directors deems expedient.
In addition to the foregoing, the ability of either the Company or the Bank to pay dividends may be affected by the various minimum capital requirements and the capital and non-capital standards established under the FDICIA, as described above. For instance, as an insured depository institution, the Bank is prohibited from making capital distributions, including the payment of dividends, if after such distribution the institution would be “undercapitalized” (as defined). Furthermore, if in the opinion of a federal regulatory agency, a bank under its jurisdiction is engaged in or is about to engage in an unsafe or unsound practice (which, depending on the financial condition of the bank, could include the payment of dividends), such agency may require, after notice and hearing, that such bank cease and desist from such practice. The right of the Company, its shareholders and its creditors to participate in any distribution of assets or earnings of the Bank is further subject to the prior claims of creditors against the Bank.
Volcker Rule. The Dodd-Frank Act amended the BHC Act to require the federal banking regulatory agencies to adopt rules that prohibit banks and their affiliates from engaging in proprietary trading and investing in and sponsoring a covered fund (such as a hedge fund and or private equity fund), commonly referred to as the “Volcker Rule.” In December 2013, the federal banking regulatory agencies adopted a final rule construing the Volcker Rule, which was effective April 1, 2014. Banking entities will have until July 21, 2016 (expected to be extended until July 21, 2017 by the Federal Reserve Board) to conform their activities to the requirements of the rule.
Interchange Fees.The Dodd-Frank Act also amended the Electronic Fund Transfer Act to require that the amount of any interchange fee charged for electronic debit transactions by debit card issuers having assets over $10 billion must be reasonable and proportional to the actual cost of a transaction to the issuer, commonly referred to as the “Durbin Amendment”. The Federal Reserve Board has adopted final rules which limit the maximum permissible interchange fees that such issuers can receive for an electronic debit transaction. Although the restrictions on interchange fees do not apply to institutions with less than $10 billion in assets, the price controls could negatively impact bankcard services income for smaller banks if the reductions that are required of larger banks cause industry-wide reduction of swipe fees.
Transactions with Affiliates of the Bank.Transactions between an insured bank and any of its affiliates are governed by Sections 23A and 23B of the Federal Reserve Act. An affiliate of a bank is any company or entity that controls or is under common control with the bank. Sections 23A and 23B, as implemented by the Federal Reserve Board’s Regulation W, (i) limit the extent to which a bank or its subsidiaries may engage in covered transactions (including extensions of credit) with any one affiliate to an amount equal to 10% of such bank’s capital stock and retained earnings, and limit such transactions with all affiliates to an amount equal to 20% of capital stock and retained earnings; (ii) require collateralization of between 100% and 130% for extensions of credit to an affiliate; and (iii) require that all affiliated transactions be on terms that are consistent with safe and sound banking practices. The term “covered transaction” includes the making of loans, purchasing of assets, issuing of guarantees and other similar types of transactions and, pursuant to the Dodd-Frank Act, includes securities lending, repurchase agreements and derivative activities. In addition, any covered transaction by a bank with an affiliate and any purchase of assets or services by a bank from an affiliate must be on terms that are substantially the same, or at least as favorable to the bank, as those that prevailing at the time for similar transactions with non-affiliates.
Community Reinvestment Act.Under the CRA, any insured depository institution has a continuing and affirmative obligation, consistent with its safe and sound operation, to help meet the credit needs of its entire community, including low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. The CRA neither establishes specific lending requirements or programs for institutions nor limits an institution’s discretion to develop the types of products and services that it believes are best suited to its particular community. The CRA requires the FDIC, in connection with its examination of a bank, to assess the institution’s record of meeting the credit needs of its community and to take such record into account in its evaluation of certain bank applications, including applications for additional branches and acquisitions. In addition, in connection with an application by a bank holding company to acquire a bank or other bank holding company, the Federal Reserve Board is required to assess the record of each subsidiary bank of the bank holding company. Failure to adequately meet the credit needs of the community it serves could impose additional requirements or limitations on a bank or delay action on an application. The Bank received a “satisfactory” rating in its most recent CRA examination, dated April 11, 2014.
Loans to Insiders.Federal law also constrains the types and amounts of loans that the Bank may make to its executive officers, directors and principal shareholders. Among other things, these loans are limited in amount, must be approved by the Bank’s board of directors in advance, and must be on terms and conditions as favorable to the Bank as those available to an unrelated person. The Dodd-Frank Act strengthened restrictions on loans to insiders and expanded the types of transactions subject to the various limits, including derivative transactions, repurchase agreements, reverse repurchase agreements and securities lending or borrowing transactions. The Dodd-Frank Act also places restrictions on certain asset sales to and from an insider to an institution, including requirements that such sales be on market terms and, in certain circumstances, approved by the institution’s board of directors.
Bank Secrecy Act; Anti-Money Laundering.We are subject to the Bank Secrecy Act, as amended by the USA PATRIOT Act (the “BSA”). The BSA gives the federal government powers to address terrorist threats through enhanced domestic security measures, expanded surveillance powers, increased information sharing, and broadened anti-money laundering requirements. The BSA takes measures intended to encourage information sharing among institutions, bank regulatory agencies and law enforcement bodies and imposes affirmative obligations on a broad range of financial institutions, including the Company. The following obligations are among those imposed by the BSA:
• Financial institutions must establish anti-money laundering programs that include, at minimum: (i) internal policies, procedures and controls; (ii) specific designation of an anti-money laundering compliance officer; (iii) ongoing employee training programs; and (iv) an independent audit function to test the anti-money laundering program.
• Financial institutions must satisfy minimum standards with respect to customer identification and verification, including adoption of a written customer identification program appropriate for the institution’s size, location and business.
• Financial institutions that establish, maintain, administer or manage private banking accounts or correspondent accounts in the United States for non-United States persons or their representatives (including foreign individuals visiting the United States) must establish appropriate, specific and where necessary, enhanced due diligence policies, procedures and controls designed to detect and report money laundering through these accounts.
• Financial institutions may not establish, maintain, administer or manage correspondent accounts for foreign shell banks (foreign banks that do not have a physical presence in any country).
• Bank regulators are directed to consider a bank’s effectiveness in combating money laundering when ruling on certain applications.
Commercial Real Estate (“CRE”) andConstruction and Development (“C&D”) Concentration Guidance.In 2006 and again in 2008, federal banking agencies, including the FDIC, issued guidance designed to emphasize risk management for institutions with significant CRE and C&D loan concentrations. The guidance reinforces and enhances the FDIC’s existing regulations and guidelines for real estate lending and loan portfolio management and emphasizes the importance of strong capital and loan loss allowance levels and robust credit risk-management practices for institutions with significant CRE and C&D exposure. While the defined thresholds past which a bank is deemed to have a concentration in CRE loans prompt enhanced risk management protocols, the guidance does not establish specific lending limits. Rather, the guidance seeks to promote sound risk management practices that will enable banks to continue to pursue CRE and C&D lending in a safe and sound manner. In addition, a bank should perform periodic market analyses for the various property types and geographic markets represented in its portfolio and perform portfolio level stress tests or sensitivity analyses to quantify the impact of changing economic conditions on asset quality, earnings and capital.
Consumer Laws and Regulations.Banks are also subject to certain laws and regulations that are designed to protect consumers. Among the more prominent of such laws and regulations are the Truth in Lending Act, the Truth in Savings Act, the Electronic Fund Transfer Act, the Expedited Funds Availability Act, the Equal Credit Opportunity Act, the Fair Credit Reporting Act, the Fair Housing Act, the Home Mortgage Disclosure Act, the Real Estate Settlement Procedures Act and consumer privacy protection provisions of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and comparable state laws. These laws and regulations mandate certain disclosure requirements and regulate the manner in which financial institutions deal with consumers. With respect to consumer privacy, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act generally prohibits disclosure of customer information to non-affiliated third parties unless the customer has been given the opportunity to object and has not objected to such disclosure. Financial institutions are further required to disclose their privacy policies to customers annually.
The Dodd-Frank Act created the Bureau of Consumer Financial Protection (the “Bureau”) within the Federal Reserve System. The Bureau is tasked with establishing and implementing rules and regulations under certain federal consumer protection laws with respect to the conduct of providers of certain consumer financial products and services. The Bureau has rulemaking authority over many of the statutes governing products and services offered to bank consumers. In addition, the Dodd-Frank Act permits states to adopt consumer protection laws and regulations that are more stringent than those regulations promulgated by the Bureau and state attorneys general are permitted to enforce consumer protection rules adopted by the Bureau against state-chartered institutions. The Bureau has examination and primary enforcement authority with respect to depository institutions with $10 billion or more in assets. Depository institutions with less than $10 billion in assets are subject to rules promulgated by the Bureau, but continue to be examined and supervised by federal banking regulatory agencies for consumer compliance purposes.
During 2013, the Bureau issued a series of proposed and final rules related to mortgage loan origination and mortgage loan servicing. In particular, in January 2013, the Bureau issued its final rule, which was effective January 10, 2014, on ability to repay and qualified mortgage standards to implement various requirements of the Dodd-Frank Act amending the Truth in Lending Act. The final rule requires mortgage lenders to make a reasonable and good faith determination, based on verified and documented information, that a borrower will have the ability to repay a mortgage loan according to its terms before making the loan. The final rule also includes a definition of a “qualified mortgage,” which provides the lender with a presumption that the ability to repay requirements has been met. This presumption is conclusive (i.e. a safe harbor) if the loan is a “prime” loan and rebuttable if the loan is a higher-priced, or subprime, loan. The ability-to-repay rule has the potential to significantly affect our business, as a borrower can challenge a loan’s status as a qualified mortgage or that the lender otherwise established the borrower’s ability to repay in a direct cause of action for three years from the origination date, or as a defense to foreclosure at any time. In addition, the value and marketability of non-qualified mortgages may be adversely affected.
Anti-Tying Restrictions.Under amendments to the BHC Act and Federal Reserve Board regulations, a bank is prohibited from engaging in certain tying or reciprocity arrangements with its customers. In general, a bank may not extend credit, lease or sell property, or furnish any services or fix or vary the consideration for these on the condition that (i) the customer obtain or provide some additional credit, property or services from or to the bank, its bank holding company or any subsidiary of the bank holding company or (ii) the customer may not obtain some other credit, property or services from a competitor of the bank, except to the extent reasonable conditions are imposed to assure the soundness of the credit extended. Certain arrangements are permissible: a bank may offer combined-balance products and may otherwise offer more favorable terms if a customer obtains two or more traditional bank products; and certain foreign transactions are exempt from the general rule. A bank holding company or any bank affiliate also is subject to anti-tying requirements in connection with electronic benefit transfer services.
Annual Disclosure Statement
This Annual Report on Form 10-K also serves as the annual disclosure statement of the Bank pursuant to Part 350 of the FDIC’s rules and regulations. This statement has not been reviewed or confirmed for accuracy or relevance by the FDIC.
Website Access to the Company’s SEC Filings
The Company maintains an Internet website at www.parksterlingbank.com (this uniform resource locator, or URL, is an inactive textual reference only and is not intended to incorporate the Company’s website into this Annual Report on Form 10-K). The Company makes available, free of charge on or through this website, its annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, as soon as reasonably practicable after the Company electronically files each such report or amendment with, or furnishes it to, the SEC.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
In addition to the other information included and incorporated by reference in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, you should carefully consider the risk factors and uncertainties described below in evaluating an investment in the Company’s Common Stock. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to the Company, or which the Company currently deems not material, also may adversely impact the Company’s business operations. The value or market price of the Company’s Common Stock could decline due to any of these identified or other risks, and you could lose all or part of your investment.
Risks Associated With Our Growth Strategy
We may not beable to implement aspects of our growth strategy.
Our growth strategy contemplates the continued expansion of our business and operations both organically and by selective acquisitions such as through the establishment or acquisition of banks and banking offices in our market areas and other markets. Implementing these aspects of our growth strategy depends, in part, on our ability to successfully identify acquisition opportunities and strategic partners that will complement our operating philosophy and to successfully integrate their operations with ours, as well as generate loans and deposits of acceptable risk and expense. To successfully acquire or establish banks or banking offices, we must be able to correctly identify profitable or growing markets, as well as attract the necessary relationships and high caliber banking personnel to make these new banking offices profitable. In addition, we may not be able to identify suitable opportunities for further growth and expansion or, if we do, we may not be able to successfully integrate these new operations into our business. As consolidation of the financial services industry continues, the competition for suitable acquisition candidates may increase. We will compete with other financial services companies for acquisition opportunities, and many of these competitors have greater financial resources than we do and may be able to pay more for an acquisition than we are able or willing to pay. We can offer no assurance that we will have opportunities to acquire other financial institutions or acquire or establish any new branches or loan production offices, or that we will be able to negotiate, finance and complete any opportunities available to us. If we are unable to effectively implement our growth strategies, our business, results of operations and stock price may be materially and adversely affected.
Future expansion involves risks.
The acquisition by us of other financial institutions or parts of those institutions, or the establishment ofde novo branch offices and loan production offices, involves a number of risks, including the risk that:
| | ● | we may incur substantial costs in identifying and evaluating potential acquisitions and merger partners, or in evaluating new markets, hiring experienced local managers, and opening new offices; |
| | ● | our estimates and judgments used to evaluate credit, operations, management and market risks relating to target institutions may not be accurate; |
| | ● | the institutions we acquire may have distressed assets and there can be no assurance that we will be able to realize the value we predict from those assets or that we will make sufficient provisions or have sufficient capital for future losses; |
| | ● | we may be required to take write-downs or write-offs, restructuring and impairment, or other charges related to the institutions we acquire that could have a significant negative effect on our financial condition and results of operations; |
| | ● | there may be substantial lag-time between completing an acquisition or opening a new office and generating sufficient assets and deposits to support costs of the expansion; |
| | ● | we may not be able to finance an acquisition, or the financing we obtain may have an adverse effect on our results of operations or result in dilution to our existing shareholders; |
| | ● | our management’s attention in negotiating a transaction and integrating the operations and personnel of the combining businesses may be diverted from our existing business and we may not be able to successfully integrate such operations and personnel; |
| | ● | our announcement of another transaction prior to completion of a merger could result in a delay in obtaining regulatory or shareholder approval for a merger, which could have the effect of limiting our ability to fully realize the expected financial benefits from the transaction; |
| | ● | we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for an acquisition; |
| | ● | we may enter new markets where we lack local experience or that introduce new risks to our operations, or that otherwise result in adverse effects on our results of operations; |
| | ● | we may introduce new products and services we are not equipped to manage or that introduce new risks to our operations, or that otherwise result in adverse effects on our results of operations; |
| | ● | we may incur intangible assets in connection with an acquisition, or the intangible assets we incur may become impaired, which results in adverse short-term effects on our results of operations; |
| | ● | we may assume liabilities in connection with an acquisition, including unrecorded liabilities that are not discovered at the time of the transaction, and the repayment of those liabilities may have an adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and stock price; or |
| | ● | we may lose key employees and customers. |
We cannot assure you that we will be able to successfully integrate any banking offices that we acquire into our operations or retain the customers of those offices. If any of these risks occur in connection with our expansion efforts, it may have a material and adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
We may not be able tomaintain our rate of growth, which may adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
We have grown rapidly since we commenced operations in October 2006, and our business strategy contemplates continued growth, both organically and through acquisitions. We can provide no assurance that we will continue to be successful in increasing the volume of loans and deposits or in introducing new products and services at acceptable risk levels and upon acceptable terms while managing the costs and implementation risks associated with our historical or modified organic growth strategy. We may be unable to continue to increase our volume of loans and deposits or to introduce new products and services at acceptable risk levels for a variety of reasons, including an inability to maintain capital and liquidity sufficient to support continued growth. If we are successful in continuing our growth, we cannot assure you that further growth would offer the same levels of potential profitability or that we would be successful in controlling costs and maintaining asset quality. Accordingly, an inability to maintain growth, or an inability to effectively manage growth, could adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition and stock price.
New bank office facilities and other facilities may not be profitable.
We may not be able to organically expand into new markets that are profitable for our franchise. The costs to start up new bank branches and loan production offices in new markets, other than through acquisitions, and the additional costs to operate these facilities would increase our noninterest expense and may decrease our earnings. It may be difficult to adequately and profitably manage our growth through the establishment of bank branches or loan production offices in new markets. In addition, we can provide no assurance that our expansion into any such new markets will successfully attract enough new business to offset the expenses of their operation. If we are not able to do so, our earnings and stock price may be negatively impacted.
Acquisition of assets and assumption of liabilities may expose us to intangible asset risk, which could impact our results of operations and financial condition.
In connection with any acquisitions, as required by United States generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”), we will record assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their fair value, and, as such, acquisitions may result in us recording intangible assets, including deposit intangibles and goodwill. We will perform a goodwill valuation at least annually to test for goodwill impairment. Impairment testing is a two-step process that first compares the fair value of goodwill with its carrying amount, and second measures impairment loss by comparing the implied fair value of goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. Adverse conditions in our business climate, including a significant decline in future operating cash flows, a significant change in our stock price or market capitalization, or a deviation from our expected growth rate and performance, may significantly affect the fair value of any goodwill and may trigger impairment losses, which could be materially adverse to our results of operations, financial condition and stock price.
Thecontinuedsuccess of our growth strategy depends on our ability to identify and retain individuals with experience and relationships in the markets in which we intend to expand.
Our growth strategy contemplates that we will continue to expand our business and operations to other markets in the Carolinas and Virginia. We intend to primarily target market areas that we believe possess attractive demographic, economic or competitive characteristics. To expand into new markets successfully, we must identify and retain experienced key management members with local expertise and relationships in these markets. Competition for qualified personnel in the markets in which we may expand may be intense, and there may be a limited number of qualified persons with knowledge of and experience in the commercial banking industry in these markets. Even if we identify individuals that we believe could assist us in establishing a presence in a new market, we may be unable to recruit these individuals away from other banks or be unable to do so at a reasonable cost. In addition, the process of identifying and recruiting individuals with the combination of skills and attributes required to carry out our strategy is often lengthy. Our inability to identify, recruit and retain talented personnel to manage new offices effectively would limit our growth and could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and stock price.
We may need additional access to capital, which we may be unable to obtain on attractive terms or at all.
We may need to incur additional debt or equity financing in the future to make strategic acquisitions or investments, for future growth or to fund losses or additional provision for loan losses in the future. Our ability to raise additional capital, if needed, will depend in part on conditions in the capital markets at that time, which are outside our control, and on our financial performance. Accordingly, we may be unable to raise additional capital, if and when needed, on terms acceptable to us, or at all. If we cannot raise additional capital when needed, our ability to further expand our operations through internal growth and acquisitions could be materially impaired and our stock price negatively affected.
Risks Associated With Our Business
Our business may be adversely affected by conditions in the financial markets and economic conditions generally.
The domestic and international capital and credit markets have been experiencing volatility and disruption for over five years, resulting in uncertainty in the financial markets in general. During this time, the financial markets and economic conditions generally have been materially and adversely affected by significant declines in the values of nearly all asset classes and by a serious lack of liquidity. Global securities markets, and bank holding company stock prices in particular, have been negatively affected, as has in general the ability of banks and bank holding companies to raise capital or borrow in the debt markets.
From December 2007 through June 2009, the U.S. economy was in recession, and business activity across a wide range of industries and regions in the U.S. was greatly reduced.
Although there has been recent improvement in general economic conditions in our market, with evidence of stabilizing home prices and a reduction in unemployment levels, there can be no assurance that the environment will continue to improve in the near term. Unemployment levels remain elevated, housing prices remain depressed, and demand for housing remains weak due to distressed sales and tightened lending standards. Consequently, there can be no assurance that the economic conditions will continue to improve in the near term. A return of recessionary conditions and/or continued negative developments in the domestic and international credit markets may significantly affect the markets in which we do business, the value of our loans and investments and our ongoing operations, costs and profitability.
In addition, an extended deterioration in local economic conditions in our markets and target markets could drive losses beyond those that are or will be provided for in our allowance for loan losses and result in the following consequences:
| | ● | increases in loan delinquencies; |
| | ● | increases in nonperforming loans and foreclosures; |
| | ● | decreases in demand for our products and services, which could adversely affect our liquidity position; |
| | ● | decreases in the value of the collateral securing our loans, especially real estate, which could reduce customers’ borrowing power; and |
| | ● | decreases in our ability to raise additional capital on terms acceptable to us, or at all. |
Until conditions improve, we expect our business, financial condition and results of operations to continue to be challenged, which could negatively impact our stock price.
Our estimated allowance for loan losses may not be sufficient to cover actual loan losses, which could adversely affect our earnings.
We maintain an allowance for loan losses in an attempt to cover loan losses inherent in our loan portfolio. The determination of the allowance for loan losses, which represents management’s estimate of probable losses inherent in our credit portfolio, involves a high degree of judgment and complexity. Our policy is to establish reserves for estimated losses on delinquent and other problem loans when it is determined that losses are expected to be incurred on such loans. At December 31, 2014, our allowance for loan losses totaled approximately $8.3 million, which represented 0.52% of total loans and 92.79% of total nonperforming loans. Management’s determination of the adequacy of the allowance is based on various factors, including an evaluation of the portfolio, current economic conditions, the volume and type of lending conducted by us, composition of the portfolio, the amount of our classified assets, seasoning of the loan portfolio, the status of past due principal and interest payments and other relevant factors. Changes in such estimates may have a significant impact on our financial statements. If our assumptions and judgments prove to be incorrect, our current allowance may not be sufficient and adjustments may be necessary to allow for different economic conditions or adverse developments in our loan portfolio. In addition, we may be required to increase the allowance due to the conditions of loans acquired as result of our acquisitions of financial institutions should the remaining acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments for such loans be judged inadequate relative to their estimated future performance. Federal and state regulators also periodically review our allowance for loan losses and may require us to increase our provision for loan losses or recognize further loan charge-offs, based on judgments different from those of management. Our allowance for loan losses decreased as a percentage of total loans throughout 2014 as our asset quality continued to improve and previously recognized impairment on our purchased credit-impaired (“PCI”) loans was reversed in part. However, no assurance can be given that the allowance will be adequate to cover loan losses inherent in our loan portfolio, and we may experience losses in our loan portfolio or perceive adverse conditions and trends that may require us to significantly increase our allowance for loan losses in the future. Any increase in our allowance for loan losses would have an adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition, which could impact our stock price.
If our nonperforming assets increase, our earnings will suffer.
At December 31, 2014, our nonperforming assets totaled approximately $20.9 million, or 0.89% of total assets. Our nonperforming assets adversely affect our earnings in various ways. We do not record interest income on nonaccrual loans or other real estate owned (“OREO”). We must reserve for probable losses, which is established through a current period charge to the provision for loan losses as well write-downs from time to time, as appropriate, of the value of properties in our OREO portfolio to reflect changing market values. Additionally, there are legal fees associated with the resolution of problem assets as well as carrying costs such as taxes, insurance and maintenance related to our OREO. Further, the resolution of nonperforming assets requires the active involvement of management, which can distract them from more profitable activity. Finally, if our estimate for the recorded allowance for loan losses proves to be incorrect and our allowance is inadequate, we will have to increase the allowance accordingly and as a result our earnings may be adversely affected, which could impact our stock price.
Failure to comply with the terms oftheFDIC loss-share agreementsacquired from Citizens Southmay result in significant losses.
As a result of our merger with Citizens South, we assumed certain FDIC loss-share agreements. These loss-share agreements cover approximately $45.4 million (net of related fair value marks) in assets, and provide that the FDIC will reimburse us for between 80 and 95 percent of net losses on covered assets. We must comply with the specific, detailed and cumbersome compliance, servicing, notification and reporting requirements provided in the agreements. Our failure to comply with the terms of the agreements or to properly service the loans and OREO under the requirements of the loss-share agreements may cause individual loans or large pools of loans to lose eligibility for loss-share payments from the FDIC. This could result in material losses that are currently not anticipated.
Our concentration in loans secured by real estate, particularly commercial real estate and construction and development, may increase our loan losses.
We offer a variety of secured loans, including commercial lines of credit, commercial term loans, real estate, construction, home equity, consumer and other loans. Many of our loans are secured by real estate (both residential and commercial) in our market areas. Consequently, declines in economic conditions in these market areas may have a greater effect on our earnings and capital than on the earnings and capital of larger financial institutions whose real estate loan portfolios are more geographically diverse.
At December 31, 2014, approximately 87% of our loans had real estate as a primary or secondary component of collateral, with 15% of those loans secured by construction and development collateral. The real estate collateral in each case provides an alternate source of repayment in the event of default by the borrower and may deteriorate in value during the time the credit is extended. If we are required to liquidate the collateral securing a loan to satisfy the debt during a period of reduced real estate values, our earnings and capital could be adversely affected. Real estate values have declined significantly during the recent economic crisis. Although real estate prices in most of our markets have stabilized or are improving, a renewed decline in real estate values would expose us to further deterioration in the value of the collateral for all loans secured by real estate and may adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Commercial real estate loans are generally viewed as having more risk of default than residential real estate loans, particularly when there is a downturn in the business cycle. They are also typically larger than residential real estate loans and consumer loans and depend on cash flows from the owner’s business or the property to service the debt. Cash flows may be affected significantly by general economic conditions and a downturn in the local economy or in occupancy rates in the local economy where the property is located, each of which could increase the likelihood of default on the loan. Because our loan portfolio contains a number of commercial real estate loans with relatively large balances, the deterioration of one or a few of these loans could cause a significant increase in the percentage of nonperforming loans. An increase in nonperforming loans could result in a loss of earnings from these loans, an increase in the provision for loan losses and an increase in charge-offs, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition, which could negatively affect our stock price.
Banking regulators are examining commercial real estate lending activity with heightened scrutiny and may require banks with higher levels of commercial real estate loans to implement improved underwriting, internal controls, risk management policies and portfolio stress testing, as well as possibly higher levels of allowances for losses and capital levels as a result of commercial real estate lending growth and exposures, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, which in turn could negatively affect our stock price.
Since we engage in lending secured by real estate and may be forced to foreclose on the collateral property and own the underlying real estate, we may be subject to the increased costs associated with the ownership of real property, which could adversely impact our results of operations and stock price.
Since we originate loans secured by real estate, we may have to foreclose on the collateral property to protect our investment and may thereafter own and operate such property, in which case we are exposed to the risks inherent in the ownership of real estate. The amount that we, as a mortgagee, may realize after a default is dependent upon factors outside of our control, including, but not limited to: general or local economic conditions; environmental cleanup liability; neighborhood values; interest rates; real estate tax rates; operating expenses of the mortgaged properties; supply of and demand for rental units or properties; ability to obtain and maintain adequate occupancy of the properties; zoning laws; governmental rules, regulations and fiscal policies; and acts of God. Certain expenditures associated with the ownership of real estate, principally real estate taxes and maintenance costs, may adversely affect the income from the real estate. Therefore, the cost of operating income-producing real property may exceed the rental income earned from such property, and we may have to advance funds in order to protect our investment or we may be required to dispose of the real property at a loss.
We maintain a number of large lending relationships, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations if our borrowers were not toperform according to the terms of these loans.
Our ten largest lending relationships (including aggregate exposure to guarantors) at December 31, 2014, range from $7.3 million to $20.8 million and averaged $10.3 million. None of these lending relationships was included in nonperforming loans at December 31, 2014. The deterioration of one or more large relationship loans could result in a significant increase in our nonperforming loans and our provision for loan losses, which would negatively impact our results of operations.
The FDIC deposit insurance assessments that we are required to pay may increase in the future, which would have an adverse effect on our earnings.
As an insured depository institution, we are required to pay quarterly deposit insurance premium assessments to the FDIC to maintain the level of the FDIC deposit insurance reserve ratio. The recent failures of many financial institutions have significantly increased the loss provisions of the DIF, resulting in a decline in the reserve ratio. As a result of recent economic conditions and the enactment of the Dodd-Frank Act, the FDIC revised its assessment rates which raised deposit premiums for certain insured depository institutions. If these increases are insufficient for the DIF to meet its funding requirements, further special assessments or increases in deposit insurance premiums may be required. The Company is generally unable to control the amount of premiums that it is required to pay for FDIC insurance. If there are additional bank or financial institution failures, the FDIC may increase the deposit insurance assessment rates. Any future assessments, increases or required prepayments in FDIC insurance premiums may materially adversely affect our earnings and could negatively affect our stock price.
The downgrade ofUnited States government securities by the credit rating agencies and Europe’s debt crisis could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The continuing debates in Congress regarding the national debt ceiling, federal budget deficit concerns, and overall weakness in the economy have resulted in actual and threatened downgrades of United States government securities by the various major credit ratings agencies in recent years. A further downgrade could create uncertainty in the United States and global financial markets and economies. Any such adverse impact could cause other events which, directly or indirectly, could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, the possibility that certain European Union (“EU”) member states will default on their debt obligations has negatively impacted economic conditions and global markets. The continued uncertainty over the outcome of international and the EU’s financial support programs and the possibility that other EU member states may experience similar financial troubles could further disrupt global markets. The negative impact on economic conditions and global markets could also have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our net interest income could be negatively affected by further interest rate adjustments by the Federal Reserve Board.
As a financial institution, our earnings are dependent upon our net interest income, which is the difference between the interest income that we earn on interest-earning assets, such as investment securities and loans, and the interest expense that we pay on interest-bearing liabilities, such as deposits and borrowings. Therefore, any change in general market interest rates, including changes resulting from changes in the Federal Reserve Board’s policies, affects us more than non-financial institutions and can have a significant effect on our net interest income and total income. Our assets and liabilities may react differently to changes in overall market rates or conditions because there may be mismatches between the repricing or maturity characteristics of our assets and liabilities. As a result, an increase or decrease in market interest rates could have a material adverse effect on our net interest margin and results of operations. Actions by monetary and fiscal authorities, including the Federal Reserve Board, could have an adverse effect on our deposit levels, loan demand, business and results of operations.
The Federal Reserve Board has held interest rates at almost zero over recent years. Unemployment, gross domestic product and inflation continue to lead the Board in its decision-making surrounding interest rate movement. The consistent low rate environment has negatively impacted our net interest margin, notwithstanding decreases in nonperforming loans and improvements in deposit mix. Any reduction in net interest income will negatively affect our business, financial condition, liquidity, results of operations, cash flows and/or the price of our securities.
The primary tool that management uses to measure short-term interest rate risk is a net interest income simulation model prepared by an independent correspondent bank.As of December 31, 2014, the Company is considered to be in a liability-sensitive position, meaning income and capital are generally expected to decrease with an increase in short-term interest rates and, conversely, to increase with a decrease in short-term interest rates. However, based on the results of this simulation model, which assumed a static environment with no contemplated asset growth or changes in our balance sheet management strategies, if short-term interest rates immediately decreased by 200 basis points, we could expect net income and capital to decrease by approximately $815 thousand over a 12-month period. This result is primarily due to the current low interest rate environment, under which interest rates on the Company’s average interest-bearing liabilities cannot benefit fully from a 200 basis point rate reduction, without turning negative, while yields on our average interest-earning assets could decline by 200 basis points. Furthermore, if short-term interest rates increase by 300 basis points, simulation modeling predicts net interest income will also decline by approximately $6.6 million over a 12-month period as a result of our liability-sensitive position. The actual amount of any increase or decrease may be higher or lower than predicted by our simulation model.
We are subject to extensive regulation that could limit or restrict our activities.
We operate in a highly regulated industry and currently are subject to examination, supervision and comprehensive regulation by the NC Commissioner, the FDIC and the Federal Reserve Board. Our compliance with these regulations is costly and restricts certain of our activities, including payment of dividends, mergers and acquisitions, investments, loans and interest rates charged, locations of offices, and the ability to accept brokered deposits. We must also meet regulatory capital requirements. If we fail to meet these capital and other regulatory requirements, our financial condition, liquidity, deposit funding strategy and results of operations would be materially and adversely affected. Our failure to remain well capitalized and well managed for regulatory purposes could affect customer confidence, the ability to execute our business strategies, the ability to grow our assets or establish new branches, the ability to obtain or renew brokered deposits, our cost of funds and FDIC insurance, the ability to pay dividends on our Common Stock and the ability to make acquisitions.
The laws and regulations applicable to the banking industry could change at any time, and we cannot predict the effects of these changes on our business and profitability. For example, new legislation or regulation could limit the manner in which we may conduct our business, including our ability to obtain financing, attract deposits and make loans. Many of these regulations are intended to protect depositors, the public and the FDIC, not shareholders. In addition, the burden imposed by these regulations may place us at a competitive disadvantage compared to competitors who are less regulated. The laws, regulations, interpretations and enforcement policies that apply to us have been subject to significant change in recent years, sometimes retroactively applied, and may change significantly in the future.
The Dodd-Frank Act represents a significant overhaul of many aspects of the regulation of the financial-services industry, including new or revised regulation of such things as systemic risk, capital adequacy, deposit insurance assessments and consumer financial protection. The federal banking regulators have adopted new regulatory capital rules applicable to United States banking organizations. Complying with these and other new legislative or regulatory requirements, and any programs established thereunder, could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we have to record an other-than-temporary-impairment in connection with ourcollateralized loan obligations (“CLOs”) as a result of the Volcker Rule, it could have a negative impact on our profitability.
The Volcker Rule generally prohibits banking entities from engaging in proprietary trading and investing in and sponsoring a covered fund (such as a hedge fund and or private equity fund). At December 31, 2014, we held two investments in senior tranches of CLOs totaling $14.8 million, with a net unrealized loss of $232,000 which currently would be prohibited under the Volcker Rule. Unless the CLO documentation is amended to avoid inclusion within the rule’s prohibitions, we would have to recognize write-downs of these securities, by recognizing an other-than-temporary impairment (“OTTI”) in conformity with GAAP rules, and sell these securities before July 2017. As we approach July 2017, the price of these securities could be negatively impacted as many holders of these and similar instruments will be forced to liquidate their positions. Any OTTI charges could significantly impact our earnings.
Our success depends significantly on economic conditions in our market areas.
Unlike larger organizations that are more geographically diversified, our banking offices are currently concentrated in North Carolina, South Carolina, North Georgia, and Richmond, Virginia, and we expect that our banking offices will remain primarily concentrated in North Carolina, South Carolina, North Georgia and Virginia. As a result of this geographic concentration, our financial results will depend largely upon economic conditions in these market areas. If the communities in which we operate do not grow or if prevailing economic conditions, locally or nationally, deteriorate, this may have a significant impact on the amount of loans that we originate, the ability of our borrowers to repay these loans and the value of the collateral securing these loans. A return to economic downturn conditions caused by inflation, recession, unemployment, government action or other factors beyond our control would likely contribute to the deterioration of the quality of our loan portfolio and reduce our level of deposits, which in turn would have an adverse effect on our business.
In addition, some portions of our target market are in coastal areas, which are susceptible to hurricanes and tropical storms. Such weather events can disrupt our operations, result in damage to our properties, decrease the value of real estate collateral for our loans and negatively affect the local economies in which we operate. We cannot predict whether or to what extent damage that may be caused by future hurricanes or other weather events will affect our operations or the economies in our market areas, but such weather events could result in a decline in loan originations, a decline in the value or destruction of properties securing our loans and an increase in delinquencies, foreclosures and loan losses. Our business or results of operations may be adversely affected by these and other negative effects of hurricanes or other significant weather events.
If we lose key employees, our business may suffer.
Our operating results and ability to adequately manage our growth and minimize loan losses is highly dependent on the services, managerial abilities and performance of our current executive officers and other key personnel, many of whom have significant local experience and contacts within our market areas. If we lose key employees temporarily or permanently, this could disrupt our business and adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and liquidity.
To be profitable, we must compete successfully with other financial institutions that have greater resources and capabilities than we do.
The banking business in our target markets is highly competitive. Many of our existing and potential competitors are larger and have greater resources than we do and have been in existence a longer period of time. We compete with these institutions in both attracting deposits and originating loans. We may not be able to attract customers away from our competition. We compete for loans and deposits with other commercial banks; savings banks; thrifts; trust companies; credit unions; securities brokerage firms; mortgage brokers; insurance companies; mutual funds; and industrial loan companies.
Competitors that are not depository institutions are generally not regulated as extensively as we are and, therefore, may have greater flexibility in competing for business. Other competitors are subject to similar regulation but have the advantages of larger established customer bases, higher lending limits, extensive branch networks, greater advertising and marketing budgets or other factors.
Our legal lending limit is determined by law and is calculated as a percentage of our capital and unimpaired surplus. The size of the loans that we are able to offer to our customers is less than the size of the loans that larger competitors are able to offer. This limit may affect our success in establishing relationships with the larger businesses in our market. We may not be able to successfully compete with the larger banks in our target markets.
Our liquidity needs could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Our primary sources of funds are deposits and loan repayments. While scheduled loan repayments are a relatively stable source of funds, they are subject to the ability of borrowers to repay the loans. The ability of borrowers to repay loans can be adversely affected by a number of factors, including, but not limited to, changes in economic conditions, adverse trends or events affecting business industry groups, reductions in real estate values or markets, availability of, and/or access to, sources of refinancing, business closings or lay-offs, inclement weather, natural disasters and international instability. Additionally, deposit levels may be affected by a number of factors, including, but not limited to, rates paid by competitors, general interest rate levels, regulatory capital requirements, returns available to customers on alternative investments and general economic conditions. Accordingly, we may be required from time to time to rely on secondary sources of liquidity to meet withdrawal demands or otherwise fund operations. Such sources include FHLB advances, sales of securities and loans, federal funds lines of credit from correspondent banks and borrowings from the Federal Reserve Discount Window, as well as additional out-of-market time deposits and brokered deposits. While we believe that these sources are currently adequate, there can be no assurance they will be sufficient to meet future liquidity demands, particularly if we continue to grow and experience increasing loan demand. We may be required to slow or discontinue loan growth, capital expenditures or other investments or liquidate assets should such sources not be adequate.
We depend on the accuracy and completeness of information about customers and counterparties, which, if incorrect or incomplete, could harm our earnings.
In deciding whether to extend credit or enter into other transactions with customers and counterparties, we rely on information furnished to us by or on behalf of customers and counterparties, including financial statements and other financial information. We also may rely on representations of customers, counterparties or other third parties as to the accuracy and completeness of that information and, with respect to financial statements, on reports of independent auditors. For example, in deciding whether to extend credit to customers, we may assume that a customer’s audited financial statements conform to GAAP and present fairly, in all material respects, the financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of the customer. Our earnings are significantly affected by our ability to properly originate, underwrite and service loans. Our financial condition and results of operations could be negatively impacted to the extent we incorrectly assess the creditworthiness of our borrowers, fail to detect or respond to deterioration in asset quality in a timely manner, or rely on information provided to us, such as financial statements that do not comply with GAAP and may be materially misleading.
The soundness of other financial institutions could adversely affect us.
Our ability to engage in routine funding transactions could be adversely affected by the actions and commercial soundness of other financial institutions. Financial services institutions are interrelated as a result of trading, clearing, counterparty or other relationships. We have exposure to many different industries and counterparties and we routinely execute transactions with counterparties in the financial industry. As a result, defaults by, or even rumors or questions about, one or more financial services institutions, or the financial services industry generally, have led to market-wide liquidity problems and could lead to losses or defaults by us or other institutions. Many of these transactions expose us to credit risk in the event of default of our counterparty or customer. In addition, our credit risk may be exacerbated when the collateral held by us cannot be realized upon or is liquidated at prices not sufficient to recover the full amount of the financial instrument exposure due to us. There can be no assurance that any such losses would not materially and adversely affect our results of operations.
Negative public opinion could damage our reputation and adversely impact our earnings.
Reputation risk, or the risk to our business, earnings and capital from negative public opinion, is inherent in our operations. Negative public opinion can result from our actual or alleged conduct in any number of activities, including lending practices, corporate governance and acquisitions, and from actions taken by government regulators and community organizations in response to those activities. Negative public opinion can adversely affect our ability to keep and attract customers and employees and can expose us to litigation and regulatory action and adversely impact our results of operations. Although we take steps to minimize reputation risk in dealing with our customers and communities, this risk will always be present given the nature of our business.
We are subject to security and operational risks including risks relating to our use of technology that, if not managed properly, could disrupt our business, result in the disclosure or misuse of confidential or proprietary information, damage our reputation, increase our costs and cause losses. Any such failure also could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
To conduct our business, we rely heavily on technology-driven products and services and on communications and information systems. Our future success will depend, in part, on our ability to address our customers’ needs by using technology to provide products and services that will satisfy customer demands for convenience as well as to create additional efficiencies in operations. We have taken measures to implement backup systems and other safeguards with respect to the physical infrastructure and systems that support our operations, but our ability to conduct business may be adversely affected by any significant and widespread disruption to our infrastructure or systems. Our financial, accounting, data processing, check processing, electronic funds transfer, loan processing, online banking, mobile banking, automated teller machines (“ATMs”) backup or other operating systems and facilities may fail to operate properly or become disabled or damaged as a result of a number of factors including events that are wholly or partially beyond our control and adversely affect our ability to process these transactions or provide these services. There could be sudden increases in customer transaction volume, electrical or telecommunications outages, natural disasters, events arising from local or larger scale political or social matters, including terrorist acts, and cyber attacks. We continuously update these systems to support our operations and growth. This updating entails significant costs and creates risks associated with implementing new systems and integrating them with existing ones.
Information security risks for financial institutions have significantly increased in recent years in part because of the proliferation of new technologies, the use of the Internet and telecommunications technologies to conduct financial transactions, and the increased sophistication and activities of organized crime, hackers and other external parties. Our operations rely on the secure processing, transmission and storage of confidential, proprietary and other information in our computer systems and networks. We rely on our digital technologies, computer and email systems, software, and networks to conduct our operations, as well as on the honesty and integrity of our employees and vendors with access to those elements. In addition, to access our products and services, our customers may use computers, personal smartphones, tablet PCs, and other mobile devices that are beyond our control systems. Our technologies, systems, networks, and our customers’ devices may be subject to, or the target of, cyber attacks, computer viruses, malicious code, phishing attacks or information security breaches that could result in the unauthorized release, gathering, monitoring, misuse, loss or destruction of our or our customers’ confidential, proprietary and other information, or otherwise disrupt our or our customers’ or other third parties’ business operations.
We also face the risk of unauthorized activity, fraud or theft by our employees and/or vendors that could result in disclosure or misuse of our customers’ confidential, proprietary or other information. In addition, we face the risk of operational failure, termination or capacity constraints of any of the third parties with which we do business or that facilitate our business activities, including financial intermediaries that we use to facilitate transactions. Any such failure, termination or constraint could adversely affect our ability to effect transactions, service our customers, manage our exposure to risk or expand our business and could have a significant adverse impact on our liquidity, financial condition and results of operations.
There can be no assurance that we will not experience material losses related to cyber attacks or other information security breaches. Cyber security and the continued development and enhancement of our controls, processes and practices designed to protect our systems, computers, software, data and networks from attack, damage or unauthorized access remain a priority for us and we may be required to expend significant additional resources to continue to modify or enhance our protective measures or to investigate and remediate any information security vulnerabilities.
Risks Related to our Common Stock
We may issue additional shares of stock or equity derivative securities, including awards to current and future executive officers, directors and employees, which could result in the dilution of shareholders’ investment.
Our authorized capital includes 200,000,000 shares of Common Stock and 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock. As of December 31, 2014, we had 44,859,798 shares of Common Stock outstanding, including 921,095 shares of unvested and performance-based restricted stock which have voting rights but no economic interest prior to vesting, and had reserved or otherwise set aside for issuance 2,171,357 shares underlying outstanding options and 839,287 shares that are available for future grants of stock options, restricted stock or other equity-based awards pursuant to our equity incentive plans. Subject to NASDAQ rules, our board of directors generally has the authority to issue all or part of any authorized but unissued shares of Common Stock or preferred stock for any corporate purpose. We anticipate that we will issue additional equity in connection with the acquisition of other strategic partners and that in the future we likely will seek additional equity capital as we develop our business and expand our operations, depending on the timing and magnitude of any particular future acquisition. These issuances would dilute the ownership interests of existing shareholders and may dilute the per share book value of the Common Stock. New investors also may have rights, preferences and privileges that are senior to, and that adversely affect, our then existing shareholders.
In addition, the issuance of shares under our equity compensation plans will result in dilution of our shareholders’ ownership of our Common Stock. The exercise price of stock options could also adversely affect the terms on which we can obtain additional capital. Option holders are most likely to exercise their options when the exercise price is less than the market price for our Common Stock. They may profit from any increase in the stock price without assuming the risks of ownership of the underlying shares of Common Stock by exercising their options and selling the stock immediately.
Our stock price may be volatile, which could result in losses to our investors and litigation against us.
Our stock price has been volatile in the past and several factors could cause the price to fluctuate in the future. These factors include, but are not limited to actual or anticipated variations in earnings, changes in analysts’ recommendations or projections, our announcement of developments related to our businesses, operations and stock performance of other companies deemed to be peers, new technology used or services offered by traditional and nontraditional competitors, news reports of trends and concerns and other issues related to the financial services industry. Fluctuations in our stock price may be unrelated to our performance. General market declines or market volatility in the future, especially in the financial institutions sector, could adversely affect the price of our Common Stock, and the current market price may not be indicative of future market prices.
Stock price volatility may make it more difficult for you to resell our Common Stock when you want and at prices you find attractive. Moreover, in the past, securities class action lawsuits have been instituted against some companies following periods of fluctuation in the market price of their securities. We could in the future be the target of similar litigation. Securities litigation could result in substantial costs and divert management’s attention and resources from our normal business, which could result in losses to investors.
Future sales of our Common Stock by shareholders or the perception that those sales could occur may cause our Common Stock price to decline.
Although our Common Stock is listed for trading on NASDAQ, the trading volume in the Common Stock may be lower than that of other larger financial services companies. A public trading market having the desired characteristics of depth, liquidity and orderliness depends on the presence in the marketplace of willing buyers and sellers of the Common Stock at any given time. This presence depends on the individual decisions of investors and general economic and market conditions over which we have no control. Given the potential for lower relative trading volume in the Common Stock, significant sales of the Common Stock in the public market, or the perception that those sales may occur, could cause the trading price of our Common Stock to decline or to be lower than it otherwise might be in the absence of those sales or perceptions.
State laws and provisions in our articles of incorporation or bylaws could make it more difficult for another company to purchase us, even though such a purchase may increase shareholder value.
In many cases, shareholders may receive a premium for their shares if we were purchased by another company. State law and our articles of incorporation and bylaws could make it difficult for anyone to purchase us without approval of our board of directors. For example, our articles of incorporation divide our board of directors into three classes of directors serving staggered three-year terms with approximately one-third of the board of directors elected at each annual meeting of shareholders. This classification of directors makes it difficult for shareholders to change the composition of our board of directors. As a result, at least two annual meetings of shareholders would be required for the shareholders to change a majority of directors, whether or not a change in the board of directors would be beneficial and whether or not a majority of shareholders believe that such a change would be desirable.
Our ability to pay dividends is limited and we may be unable to pay future dividends.
Our board of directors initiated payment of cash dividends in 2013. However, any future declaration of dividends will be made at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on a number of factors, including our future earnings, capital requirements, financial condition, future prospects, regulatory restrictions, and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant. We make no assurances that we will pay any dividends in the future. The holders of our Common Stock are entitled to receive dividends only when and if declared by our board of directors out of funds legally available for that purpose. As part of our consideration to pay cash dividends, we intend to retain adequate funds from future earnings to support the development and growth of our business.
Moreover, we are a bank holding company that is a separate and distinct legal entity from the Bank. As a result, our ability to make dividend payments, if any, on our Common Stock depends primarily upon receipt of dividends and other distributions received from the Bank. Various federal and state regulations limit the amount of dividends that the Bank may pay to us and that we may pay to our shareholders. It is the policy of the Federal Reserve Board that bank holding companies should pay cash dividends on common stock only out of net income available over the past year and only if prospective earnings retention is consistent with the organization’s expected future needs and financial condition. In addition, our right to participate in any distribution of assets of the Bank or any other subsidiary we may have from time to time upon the subsidiary’s liquidation or otherwise, and thus the ability of our shareholders to benefit indirectly from such distribution, will be subject to the prior claims of creditors of the subsidiary, except to the extent any of our claims as a creditor of the subsidiary may be recognized. As a result, our Common Stock effectively will be subordinated to all existing and future liabilities and obligations of the Bank and any other subsidiaries we may have.
Your right to receive liquidation and dividend payments on our Common Stock is junior to our existing and future indebtedness and to any other senior securities we may issue in the future.
Shares of our Common Stock are equity interests in the Company and do not constitute indebtedness. This means that shares of our Common Stock will rank junior to all of our indebtedness and to other nonequity claims against us and our assets available to satisfy claims against us, including in our liquidation. As of December 31, 2014, we had outstanding approximately $23.6 million (excluding acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments) aggregate principal amount of junior subordinated debt which, in addition to our other liabilities, would be senior in right of payment to our Common Stock. We also may incur additional indebtedness from time to time without the approval of the holders of our Common Stock.
Our common shareholders also are subject to the prior dividend and liquidation rights of any preferred stock outstanding from time to time. Our board of directors is authorized to issue classes or series of preferred stock in the future without any action on the part of our common shareholders.
Our Common Stock is not insured by the FDIC.
Our Common Stock is not a savings or deposit account, and is not insured by the FDIC or any other governmental agency and is subject to risk, including the possible loss of all or some principal.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 2. Properties
The Company leases a building located at 1043 E. Morehead Street, Charlotte, North Carolina that serves as its corporate headquarters and the Bank’s main branch office location. The Company also leases space in a building adjacent to the Morehead Street location to accommodate the Company’s expanded operations. Both of the buildings are owned by an entity with respect to which a former director is president.
At December 31, 2014, the Bank operated 52 full service branches and one drive through facility located in North Carolina, South Carolina, North Georgia and Virginia. The Bank leases eleven of these branches and the remaining properties are owned. Management believes the terms of the various leases are consistent with market standards and were arrived at through arm’s length bargaining. Additional information relating to premise, equipment and lease commitments is set forth in Note 8 – Premises and Equipment or Note 15 – Leases to the Company’s audited financial statements as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 and for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and the notes thereto, included in Part II, Item 8 of this report (the “Consolidated Financial Statements”).
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
In the ordinary course of business, the Company may be a party to various legal proceedings from time to time. There are no material pending legal proceedings to which the Company is a party or of which any of its property is subject. In addition, the Company is not aware of any threatened litigation, unasserted claims or assessments that could have a material adverse effect on its business, operating results or financial condition.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, RelatedStockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases ofEquity Securities
Common Stock Market Prices; Dividends
The Company’s Common Stock is traded publicly on NASDAQ under the symbol “PSTB”. The following table summarizes and sets forth the high and low closing sales prices of the Common Stock on NASDAQ and dividends declared per share for the periods indicated:
Year | Quarter | | High | | | Low | | | Dividend | |
2014 | Fourth | | $ | 7.77 | | | $ | 6.58 | | | $ | 0.02 | |
| | Third | | | 7.06 | | | | 6.58 | | | | 0.02 | |
| | Second | | | 6.98 | | | | 6.27 | | | | 0.02 | |
| | First | | | 7.21 | | | | 6.51 | | | | 0.02 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2013 | Fourth | | $ | 7.28 | | | $ | 6.00 | | | $ | 0.02 | |
| | Third | | | 6.81 | | | | 5.74 | | | | 0.02 | |
| | Second | | | 6.02 | | | | 5.16 | | | | n/a | |
| | First | | | 6.06 | | | | 5.20 | | | | n/a | |
As of February 28, 2015, there were 44,865,791 shares of our Common Stock outstanding held by approximately 2,100 shareholders of record.
Under North Carolina law, we are authorized to pay dividends as declared by our board of directors, provided that no such distribution results in our insolvency on a going concern or balance sheet basis. On July 26, 2013, our board of directors approved the initiation of a quarterly cash dividend to our common shareholders. Future dividends will be subject to board approval. As we are a legal entity separate and distinct from the Bank, our principal source of funds with which we can pay dividends to our shareholders is dividends we receive from the Bank. For that reason, our ability to pay dividends is subject to the limitations that apply to the Bank. For more information on applicable restrictions on the payment of dividends, see Note 13 – Regulatory Matters to the Consolidated Financial Statements and the section captioned “Supervision and Regulation- Dividend and Repurchase Limitations” under Part I, Item 1, “Business” of this report.
UnregisteredSales ofEquitySecurities
We did not sell any of our equity securities during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014 that were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”).
Repurchase ofEquitySecurities
The following table provides information regarding the purchase of equity securities by the Company during the three months ended December 31, 2014:
Period | | (a) Total Number of Shares Purchased(1) | | | (b) Average Price Paid per Share | | | (c) Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | | | (d) Maximum Number of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs (2) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Repurchases from October 1, 2014through October 31, 2014 | | | 505 | | | $ | 7.00 | | | | - | | | | 2,200,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Repurchases from November 1, 2014through November 30, 2014 | | | 1,065 | | | | 7.67 | | | | - | | | | 2,200,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Repurchases from December 1, 2014through December 31, 2014 | | | 489 | | | | 6.88 | | | | - | | | | 2,200,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | 2,059 | | | $ | 7.32 | | | | - | | | | 2,200,000 | |
| | (1) | Represents shares of the Company’s Common Stock acquired by the Company in connection with satisfaction of tax withholding obligations on vested restricted stock. |
| | (2) | On October 29, 2014, the board of directors approved a new share repurchase program, which will expire on November 1, 2016, to repurchase up to 2,200,000 of our common shares from time to time, depending on market conditions and other factors. The new share repurchase program replaces the prior share repurchase program which expired on November 1, 2014. |
Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative total shareholder return (“CTSR”) of our Common Stock during the previous five years with the CTSR over the same measurement period of the S&P 500 Index, the Keefe Bruyette & Woods (“KBW”) Bank Index and the KBW Regional Bank Index. Each trend line assumes that $100 was invested on December 31, 2009 and that all dividends were reinvested. The information in the graph below for all periods prior to January 1, 2011 is that of the Bank on a stand-alone basis.
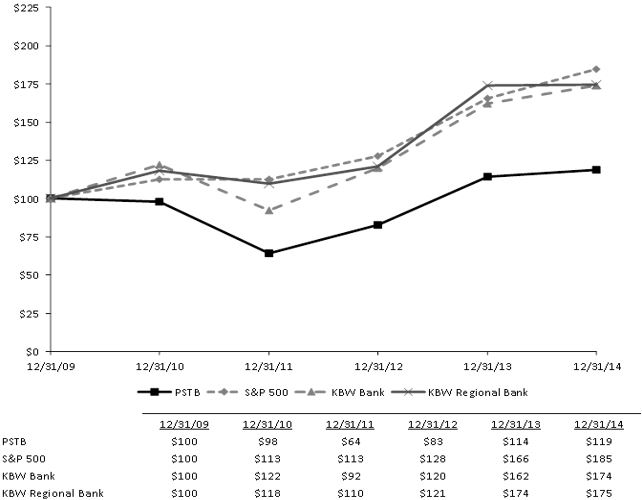
The foregoing performance graph and related information shall not be deemed to be “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC or subject to Regulation 14A or 14C or to the liabilities of Section 18 under the Exchange Act, nor shall it be incorporated by reference into any future filing under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, except to the extent that we specifically incorporate it by reference into any such filing.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The following selected consolidated financial data for the five years ended December 31, 2014 are derived from our consolidated financial statements and other data. The selected consolidated financial data should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Financial Statements. The information in the selected financial data for all periods prior to January 1, 2011 is that of the Bank on a stand-alone basis. Year-to-year financial information comparability is affected by the transaction expenses and the accounting treatment of our mergers as described in Part I, Item 1. “Business” and in Note 3 - Business Combinations to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
| | | At or for the Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 (1) | | | 2012 (1) | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands, except per share data) | |
Income Statement Data | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total interest income | | $ | 85,297 | | | $ | 78,805 | | | $ | 57,946 | | | $ | 25,564 | | | $ | 22,642 | |
Total interest expense | | | 7,655 | | | | 6,382 | | | | 6,570 | | | | 6,169 | | | | 7,607 | |
Net interest income | | | 77,642 | | | | 72,423 | | | | 51,376 | | | | 19,395 | | | | 15,035 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | (1,286 | ) | | | 746 | | | | 2,023 | | | | 9,385 | | | | 17,005 | |
Net interest income (loss) after provision | | | 78,928 | | | | 71,677 | | | | 49,353 | | | | 10,010 | | | | (1,970 | ) |
Noninterest income | | | 13,953 | | | | 15,086 | | | | 11,372 | | | | 1,647 | | | | 126 | |
Noninterest expense | | | 73,934 | | | | 64,099 | | | | 54,076 | | | | 24,960 | | | | 11,053 | |
Income (loss) before taxes | | | 18,947 | | | | 22,664 | | | | 6,649 | | | | (13,303 | ) | | | (12,897 | ) |
Income tax expense (benefit) | | | 6,058 | | | | 7,359 | | | | 2,306 | | | | (4,944 | ) | | | (5,038 | ) |
Net income (loss) | | | 12,889 | | | | 15,305 | | | | 4,343 | | | | (8,359 | ) | | | (7,859 | ) |
Preferred dividends | | | - | | | | 353 | | | | 51 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Net income (loss) to common shareholders | | $ | 12,889 | | | $ | 14,952 | | | $ | 4,292 | | | $ | (8,359 | ) | | $ | (7,859 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Per Share Data | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic earnings (loss) per common share | | $ | 0.29 | | | $ | 0.34 | | | $ | 0.12 | | | $ | (0.29 | ) | | $ | (0.58 | ) |
Diluted earnings (loss) per common share | | $ | 0.29 | | | $ | 0.34 | | | $ | 0.12 | | | $ | (0.29 | ) | | $ | (0.58 | ) |
Cash dividends (2) | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 0.04 | | | | n/a | | | | n/a | | | | n/a | |
Weighted-average common shares outstanding: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | 43,924,457 | | | | 43,965,408 | | | | 35,101,407 | | | | 28,723,647 | | | | 13,558,221 | |
Diluted | | | 44,247,000 | | | | 44,053,253 | | | | 35,108,229 | | | | 28,723,647 | | | | 13,558,221 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance Sheet Data | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 51,390 | | | $ | 55,067 | | | $ | 184,142 | | | $ | 28,543 | | | $ | 65,378 | |
Investment securities | | | 491,424 | | | | 401,463 | | | | 245,571 | | | | 210,146 | | | | 140,590 | |
Loans | | | 1,572,431 | | | | 1,286,977 | | | | 1,346,116 | | | | 748,668 | | | | 399,829 | |
Allowance for loan losses | | | (8,262 | ) | | | (8,831 | ) | | | (10,591 | ) | | | (10,154 | ) | | | (12,424 | ) |
Total assets | | | 2,359,230 | | | | 1,960,827 | | | | 2,032,831 | | | | 1,113,222 | | | | 616,108 | |
Deposits | | | 1,851,354 | | | | 1,599,885 | | | | 1,632,004 | | | | 846,637 | | | | 407,820 | |
Borrowings | | | 180,000 | | | | 55,996 | | | | 80,143 | | | | 49,765 | | | | 20,874 | |
Subordinated debt | | | 23,583 | | | | 22,052 | | | | 21,573 | | | | 12,296 | | | | 6,895 | |
Shareholders’ equity | | $ | 275,105 | | | $ | 262,120 | | | $ | 275,739 | | | $ | 190,054 | | | $ | 177,101 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Profitability Ratios | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Return on average total assets | | | 0.59 | % | | | 0.76 | % | | | 0.32 | % | | | -1.20 | % | | | -1.46 | % |
Return on average stockholders’ equity | | | 4.78 | % | | | 5.42 | % | | | 1.99 | % | | | -4.69 | % | | | -8.00 | % |
Net interest margin (3) | | | 3.96 | % | | | 4.20 | % | | | 4.29 | % | | | 3.06 | % | | | 2.95 | % |
Efficiency ratio (4) | | | 80.88 | % | | | 73.33 | % | | | 88.29 | % | | | 119.76 | % | | | 71.39 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Asset Quality Ratios | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net charge-offs to total loans | | | -0.06 | % | | | 0.23 | % | | | 0.12 | % | | | 1.54 | % | | | 3.00 | % |
Allowance for loan losses to total loans | | | 0.52 | % | | | 0.68 | % | | | 0.78 | % | | | 1.34 | % | | | 3.11 | % |
Nonperforming loans to total loans and OREO | | | 0.56 | % | | | 0.94 | % | | | 1.29 | % | | | 2.61 | % | | | 10.53 | % |
Nonperforming assets to total assets | | | 0.89 | % | | | 1.37 | % | | | 2.11 | % | | | 3.25 | % | | | 7.04 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liquidity Ratios | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loans to total deposits | | | 84.93 | % | | | 80.44 | % | | | 82.49 | % | | | 82.49 | % | | | 94.99 | % |
Liquidity ratio (5) | | | 19.55 | % | | | 20.92 | % | | | 21.96 | % | | | 28.80 | % | | | 50.50 | % |
Equity to total assets | | | 11.66 | % | | | 13.37 | % | | | 13.56 | % | | | 17.07 | % | | | 28.75 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Capital Ratios | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tangible common equity to tangible assets (6) | | | 11.66 | % | | | 13.37 | % | | | 12.14 | % | | | 16.73 | % | | | 28.75 | % |
Tier 1 leverage | | | 10.17 | % | | | 11.63 | % | | | 11.25 | % | | | 17.77 | % | | | 27.39 | % |
Tier 1 risk-based capital | | | 13.46 | % | | | 15.34 | % | | | 15.09 | % | | | 19.53 | % | | | 40.20 | % |
Total risk-based capital | | | 13.95 | % | | | 16.46 | % | | | 16.30 | % | | | 21.61 | % | | | 43.06 | % |
(1) | Revised to reflect measurement period adjustments to goodwill. |
(2) | On July 26, 2013, our board of directors approved the initiation of a quarterly cash dividend to our common shareholders. |
| Future dividends are subject to board approval. |
(3) | Net interest margin is presented on a tax equivalent basis. |
(4) | Calculated by dividing noninterest expense by the sum of net interest income and noninterest income. |
| Gains and losses on sales of securities and OREO are excluded from the calculation. |
(5) | Calculated by dividing total liquid assets by net deposits and short-term liabilities. |
(6) | Non-GAAP Financial Measure. See "Non-GAAP Financial Measures" in Item 7. "Management's Discussion and Analysis ofFinancial Condition and Results of Operations" in this report for a reconciliation of this non-GAAP measure to the mostdirectly comparable GAAP measure. |
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following is a discussion of our financial position and results of operations and should be read in conjunction with the information set forth in Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors” and the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Executive Overview
The Company experienced strong financial performance in 2014 and continued growth. On May 1, 2014, we completed our merger with Provident Community and we merged Provident Community Bank, N.A. with and into the Bank. In addition, immediately prior to completion of the merger, the Company purchased from the United States Department of the Treasury (“Treasury”) the issued and outstanding shares of Provident Community’s Fixed Rate Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock, Series A (the “Provident Community Series A Preferred Stock”) and all of the related warrants to purchase shares of Provident Community’s common stock, for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $5.1 million (representing a 45% discount from face value). Thereafter, pursuant to the Agreement and Plan of Merger, the Provident Community Series A Preferred Stock and related warrants were cancelled in connection with the completion of the merger. We also entered the Richmond, Virginia market by opening a loan production office, followed by the opening of a full-service branch and hiring three experienced bankers.
We reported net income available to common shareholders of $12.9 million, or $0.29 per share, for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to net income available to common shareholders of $15.0 million, or $0.34 per share, for the year ended December 31, 2013. Excluding merger-related expenses and gain on sale of securities, we reported adjusted net income available to common shareholders of $15.2 million, or $0.34 per share, for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to adjusted net income available to common shareholders of $16.3 million, or $0.37 per share, for the year ended December 31, 2013. Merger-related expenses totaled $3.6 million in 2014 compared to $2.2 million in 2013. Gain on sale of securities totaled $180 thousand in 2014 compared to $98 thousand in 2013. Results for 2014 include eight months of operating results from Provident Community.
Net interest income increased $5.2 million, or 7%, for the year ended December 31, 2014 to $77.6 million, compared to $72.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. Provision expense decreased $2.0 million, or 272%, for the year ended December 31, 2014 to a release of $1.3 million, compared to provision expense of $746 thousand for the year ended December 31, 2013, reflecting improved asset quality. Noninterest income decreased $1.1 million, or 8%, for the year ended December 31, 2014 to $14.0 million, compared to $15.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. Included in noninterest income for 2014 are bank-owned life insurance death benefits of $651 thousand as well a $4.0 million increase in expenses related to FDIC loss share agreements. Noninterest expenses increased $9.8 million, or 15%, for the year ended December 31, 2014 to $73.9 million, compared to $64.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, due to the inclusion of eight months of expense from the Provident Community merger as well as hiring initiatives designed to drive future organic growth opportunities.
Asset quality continued to improve during 2014 and remains a point of strength for the Company. Nonperforming loans decreased $3.4 million, or 28%, from $12.3 million, or 0.95% of total loans, at December 31, 2013 to $8.9 million, or 0.56% of total loans, at December 31, 2014, due to the continued resolution of problem loans. Nonperforming assets decreased by $5.9 million, or 22%, from $26.8 million at December 31, 2013 to $20.9 million at December 31, 2014 due to successful disposition of numerous OREO properties and the continued resolution of problem assets. Nonperforming assets decreased to 0.89% of total assets at December 31, 2014 from 1.37% at December 31, 2013.
The allowance for loan losses was $8.3 million, or 0.52% of total loans, at December 31, 2014, compared to $8.8 million, or 0.68% of total loans, at December 31, 2013. Net charge-offs decreased $4.0 million, or 133%, from $3.0 million, or 0.23% of total loans, for the year ended December 31, 2013 to a net recovery of $1.0 million, or 0.06% of total loans, for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Total assets increased $398.4 million, or 20%, to $2.4 billion at December 31, 2014. Loans and loans held for sale increased $284.9 million, or 22% from December 31, 2013, to $1.6 billion. The investment securities portfolio, including nonmarketable equity securities, increased $95.6 million, or 23% from December 31, 2013, to $503.0 million. All other asset categories increased $11.9 million, or 6% from December 31, 2013. Cash and cash equivalents decreased $3.7 million, or 7%.
Total deposits increased $251.5 million, or 16%, from December 31, 2013, to $1.9 billion at December 31, 2014 due primarily to the merger with Provident Community. Total borrowings increased $125.5 million, or 161%, to $203.6 million at December 31, 2014 compared to $78.0 million at December 31, 2013, due to $125 million in short-term Federal Home Loan Bank advances used to fund organic loan growth.
Total shareholders’ equity increased $13.0 million, or 5%, to $275.1 million at December 31, 2014 compared to $262.1 million at December 31, 2013, driven by net income of $12.9 million.We remained well capitalized at December 31, 2014. Tangible common equity as a percentage of tangible assets was at 10.13% and Tier 1 leverage ratio was 10.17%.
Adjusted net income and related per share measures, as well as tangible common equity and tangible assets, and related ratios, are non-GAAP financial measures. For reconciliations to the most comparable GAAP measures, see “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” below.
Business Overview
The Company, a North Carolina corporation, was formed in October 2010 to serve as the holding company for the Bank and is a bank holding company registered with the Federal Reserve Board. The Bank was incorporated in September 2006 as a North Carolina-chartered commercial nonmember bank. On January 1, 2011, the Company acquired all of the outstanding common stock of the Bank in exchange for shares of the Company’s Common Stock, on a one-for-one basis, in a statutory share exchange transaction effected under North Carolina law pursuant to which the Company became the bank holding company for the Bank.
As discussed previously and throughout the document, as part of our growth strategy, the Company has consummated several acquisitions. The Company acquired Community Capital in November 2011, Citizens South in October 2012 and Provident Community in May 2014. Additionally, from an organic standpoint, over the past several years the Company has opened additional branches in North and South Carolina, and during 2014, the Bank opened a loan production office in Richmond, Virginia followed by the opening of a full service branch.The Bank has also received approval to open a second full-service branch in Richmond, Virginia, which it intends to open in 2015. The Bank currently anticipates that it will open additional branch offices and/or loan production offices in its target markets in the future.
The Company provides a full array of retail and commercial banking services, including wealth management and capital market activities, through its offices located in North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia and Virginia. Our objective since inception has been to provide the strength and product diversity of a larger bank and the service and relationship attention that characterizes a community bank.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2 – Summary of Significant Accounting Policies to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a description of recent accounting pronouncements including the respective expected dates of adoption and effects on results of operations and financial condition.
Critical Accounting Policiesand Estimates
In the preparation of our financial statements, we have adopted various accounting policies that govern the application of accounting principles generally accepted in the United States and in accordance with general practices within the banking industry. Our significant accounting policies are described in Note 2 – Summary of Significant Accounting Policies to the Consolidated Financial Statements. While all of these policies are important to understanding the Consolidated Financial Statements, certain accounting policies described below involve significant judgment and assumptions by management that have a material impact on the carrying value of certain assets and liabilities. We consider these accounting policies to be critical accounting policies. The judgment and assumptions we use are based on historical experience and other factors, which we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Because of the nature of the judgment and assumptions we make, actual results could differ from these judgments and assumptions that could have a material impact on the carrying values of our assets and liabilities and our results of operations.
PCI Loans.Loans purchased with evidence of credit deterioration since origination and for which it is probable that all contractually required payments will not be collected are considered credit impaired. Evidence of credit quality deterioration as of the purchase date may include statistics such as internal risk grade, past due and nonaccrual status, recent borrower credit scores and recent loan-to-value (“LTV”) percentages. PCI loans are initially measured at fair value, which includes estimated future credit losses expected to be incurred over the life of the loan. Accordingly, the associated allowance for credit losses related to these loans is not carried over at the acquisition date. We estimate the cash flows expected to be collected at acquisition using specific credit review of certain loans, quantitative credit risk, interest rate risk and prepayment risk models, and qualitative economic and environmental assessments, each of which incorporate our best estimate of current key relevant factors, such as property values, default rates, loss severity and prepayment speeds.
Under the accounting guidance for PCI loans, the excess of cash flows expected to be collected over the estimated fair value is referred to as the accretable yield and is recognized in interest income over the remaining life of the loan, or pool of loans, in situations where there is a reasonable expectation about the timing and amount of cash flows to be collected. The difference between the contractually required payments and the cash flows expected to be collected at acquisition, considering the impact of prepayments, is referred to as the nonaccretable difference and is available to absorb future charge-offs.
In addition, subsequent to acquisition, we periodically evaluate our estimate of cash flows expected to be collected. These evaluations, performed quarterly, require the continued usage of key assumptions and estimates, similar to the initial estimate of fair value. In the current economic environment, estimates of cash flows for PCI loans require significant judgment given the impact of home price and property value changes, changing loss severities, prepayment speeds and other relevant factors. Decreases in the expected cash flows will generally result in a charge to the provision for credit losses resulting in an increase to the allowance for loan losses. Significant increases in the expected cash flows will generally result in an increase in interest income over the remaining life of the loan, or pool of loans. Disposals of loans, which may include sales of loans to third parties, receipt of payments in full or part from the borrower or foreclosure of the collateral, result in removal of the loan from the PCI loan portfolio at its carrying amount. Trends are reviewed in terms of traditional credit metrics such as accrual status, past due status, and weighted-average grade of the loans within each of the accounting pools. In addition, the relationship between the change in the unpaid principal balance and change in the fair value mark is assessed to correlate the directional consistency of the expected loss for each pool.
PCI loans currently represent loans acquired in connection with the acquisitions of Community Capital, Citizens South and Provident Community that were deemed credit impaired. PCI loans that were classified as nonperforming loans by the acquired institutions are no longer classified as nonperforming so long as, at acquisition and quarterly re-estimation periods, we believe we will fully collect the new carrying value of these loans. It is important to note that judgment regarding the timing and amount of cash flows to be collected is required to classify PCI loans as performing, even if the loan is contractually past due.
Allowance for Loan Losses.The allowance for loan losses is based upon management's ongoing evaluation of the loan portfolio and reflects an amount considered by management to be its best estimate of known and inherent losses in the portfolio as of the balance sheet date. The determination of the allowance for loan losses involves a high degree of judgment and complexity. In making the evaluation of the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses, management considers current economic and market conditions, independent loan reviews performed periodically by third parties, portfolio trends and concentrations, delinquency information, management's internal review of the loan portfolio, internal historical loss rates and other relevant factors. While management uses the best information available to make evaluations, future adjustments to the allowance may be necessary if conditions differ substantially from the assumptions used in making the evaluations. In addition, regulatory examiners may require us to recognize changes to the allowance for loan losses based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examination. Although provisions have been established by loan segments based upon management's assessment of their differing inherent loss characteristics, the entire allowance for losses on loans, other than the portion related to PCI loans and specific reserves on impaired loans, is available to absorb further loan losses in any segment.Further information regarding our policies and methodology used to estimate the allowance for possible loan losses is presented in Note 5 – Loans to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
OREO.OREO, consisting of real estate acquired through, or in lieu of, loan foreclosures is recorded at the lower of cost or fair value less estimated selling costs when acquired. Fair value is determined based on independent market prices, appraised values of the collateral or management’s estimation of the value of the collateral. Management also considers other factors, including changes in absorption rates, length of time the property has been on the market and anticipated sales values, which have resulted in adjustments to the collateral value estimates indicated in certain appraisals. At the time of foreclosure or initial possession of collateral, any excess of the loan balance over the fair value of the real estate held as collateral is treated as a charge against the allowance for loan losses.
Subsequent declines in the fair value of OREO below the new cost basis are recorded through valuation adjustments. Significant judgments and complex estimates are required in estimating the fair value of other real estate, and the period of time within which such estimates can be considered current is significantly shortened during periods of market volatility. In response to market conditions and other economic factors, management may utilize liquidation sales as part of its problem asset disposition strategy. As a result of the significant judgments required in estimating fair value and the variables involved in different methods of disposition, the net proceeds realized from sales transactions could differ significantly from appraisals, comparable sales, and other estimates used to determine the fair value of other real estate. Management reviews the value of other real estate periodically and adjusts the values as appropriate. Revenue and expenses from OREO operations as well as gains or losses on sales and any subsequent adjustments to the value are recorded as net cost (earnings) of operation of other real estate owned, a component of non-interest expense.
FDIC Indemnification Asset.In accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 805, the FDIC indemnification asset was initially recorded at its fair value, and is measured separately from the related covered assets because the indemnification asset is not contractually embedded in the covered assets or transferrable with them in the event of disposal. The FDIC indemnification asset is measured at carrying value subsequent to initial measurement. Improved cash flows of the underlying covered assets will result in impairment of the FDIC indemnification asset and thus amortization through non-interest income. Impairment of the underlying covered assets will increase the cash flows of the FDIC indemnification asset and result in a credit to the provision for loan losses for acquired loans. Impairment and, when applicable, its subsequent reversal are included in the provision for loan losses in the consolidated statements of income.
The purchase and assumption agreements between the Bank and the FDIC, as discussed in Note 6 – FDIC Loss Share Agreements to the Consolidated Financial Statements, each contain a provision that obligates the Bank to make a true-up payment to the FDIC if the realized losses of each of the applicable acquired banks are less than expected. Any such true-up payment that is materially higher than current estimates could have a negative effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. These amounts are recorded in other liabilities on the balance sheet. The actual payment will be determined at the end of the term of the loss sharing agreements and is based on the negative bid, expected losses, intrinsic loss estimate, and assets covered under the loss share agreements.
Income Taxes. Income taxes are provided based on the asset-liability method of accounting, which includes the recognition of deferred tax assets (“DTAs”) and liabilities for the temporary differences between carrying amounts and tax bases of assets and liabilities, computed using enacted tax rates. In general, we record a DTA when the event giving rise to the tax benefit has been recognized in the Consolidated Financial Statements.
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, we had a net DTA in the amount of approximately $35.6 million and $36.3 million, respectively. The decrease is primarily the result of earnings of $12.9 million during 2014, offset by fair market value adjustments related to the merger with Provident Community and a $1.6 million DTA acquired through that merger. We evaluate the carrying amount of our DTA quarterly in accordance with the guidance provided in FASB ASC Topic 740 (“ASC 740”), in particular, applying the criteria set forth therein to determine whether it is more likely than not (i.e., a likelihood of more than 50%) that some portion, or all, of the DTA will not be realized within its life cycle, based on the weight of available evidence. In most cases, the realization of the DTA is dependent upon the Company generating a sufficient level of taxable income in future periods, which can be difficult to predict. If our forecast of taxable income within the carry forward periods available under applicable law is not sufficient to cover the amount of net deferred assets, such assets may be impaired. Based on the weight of available evidence, we have determined that it is more likely than not that we will be able to fully realize the existing DTA. Accordingly, we considered it appropriate not to establish a DTA valuation allowance at either December 31, 2014 or 2013.
Further information regarding our income taxes is presented in Note 12 —Income Taxes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
In addition to traditional measures, management uses tangible assets, tangible common equity, tangible book value, adjusted allowance for loan losses to loans, adjusted net income, adjusted noninterest income, adjusted noninterest expenses and adjusted net interest margin, and related ratios and per-share measures, each of which is a non-GAAP financial measure. Management uses (i) tangible assets, tangible common equity and tangible book value (which exclude goodwill and other intangibles from equity and assets) and related ratios to evaluate the adequacy of shareholders' equity and to facilitate comparisons with peers; (ii) adjusted allowance for loan losses (which includes net fair market value adjustments related to acquired loans) to evaluate both its asset quality and asset quality trends, and to facilitate comparisons with peers; and (iii) adjusted net income, adjusted noninterest income and adjusted noninterest expense (which exclude merger-related expenses and gain or loss on sale of securities, as applicable) and adjusted net interest margin (which excludes accelerated accretion of net acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments) to evaluate its core earnings and to facilitate comparisons with peers.
The following table presents these non-GAAP financial measures and provides a reconciliation of these non-GAAP measures to the most directly comparable GAAP measure reported in the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements at December 31:
| Reconciliation of Non-GAAP Financial Measures | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | (dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) | |
| Tangible assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 2,359,230 | | | $ | 1,960,827 | | | | | |
Less: intangible assets | | | 40,200 | | | | 35,086 | | | | | |
Tangible assets | | $ | 2,319,030 | | | $ | 1,925,741 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tangible common equity: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total common equity | | $ | 275,105 | | | $ | 262,120 | | | | | |
Less: intangible assets | | | 40,200 | | | | 35,086 | | | | | |
Tangible common equity | | $ | 234,905 | | | $ | 227,034 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tangible common equity to tangible assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tangible common equity | | $ | 234,905 | | | $ | 227,034 | | | | | |
Divided by: tangible assets | | | 2,319,030 | | | | 1,925,741 | | | | | |
Tangible common equity to tangible assets | | | 10.13 | % | | | 11.79 | % | | | | |
Total equity to total assets | | | 11.66 | % | | | 13.37 | % | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tangible book value per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issued and outstanding shares | | | 44,859,798 | | | | 44,730,669 | | | | | |
Less: nondilutive restricted stock awards | | | (921,095 | ) | | | (770,399 | ) | | | | |
Period end dilutive shares (1) | | | 43,938,703 | | | | 43,960,270 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tangible common equity | | $ | 234,905 | | | $ | 227,034 | | | | | |
Divided by: period end dilutive common shares (2) | | | 43,938,703 | | | | 43,960,270 | | | | | |
Tangible common book value per share | | $ | 5.35 | | | $ | 5.16 | | | | | |
Total common book value per share | | $ | 6.26 | | | $ | 5.96 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjusted allowance for loan losses (3): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for loan losses | | $ | 8,262 | | | $ | 8,831 | | | | | |
Plus: acquisition accounting net FMV adjustments to acquired loans | | | 35,419 | | | | 37,783 | | | | | |
Adjusted allowance for loan losses | | $ | 43,681 | | | $ | 46,614 | | | | | |
Divided by: total loans (excluding LHFS) | | | 1,580,693 | | | | 1,295,808 | | | | | |
Adjusted allowance for loan losses to total loans | | | 2.76 | % | | | 3.60 | % | | | | |
Allowance for loan losses to total loans | | | 0.52 | % | | | 0.68 | % | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjusted net income: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Pretax income (as reported) | | $ | 18,947 | | | $ | 22,664 | | | $ | 6,649 | |
Plus: merger-related expenses | | | 3,616 | | | | 2,211 | | | | 5,895 | |
Less: gain on sale of securities | | | (180 | ) | | | (98 | ) | | | (1,478 | ) |
Pretax income | | | 22,383 | | | | 24,777 | | | | 11,066 | |
Tax expense | | | 7,163 | | | | 8,089 | | | | 3,558 | |
Adjusted net income | | | 15,220 | | | | 16,688 | | | | 7,508 | |
Preferred dividends | | | - | | | | 353 | | | | 51 | |
Adjusted net income available to common shareholders | | $ | 15,220 | | | $ | 16,335 | | | $ | 7,457 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Divided by: weighted average diluted shares | | | 44,247,000 | | | | 44,053,253 | | | | 35,108,229 | |
Adjusted net income available to common shareholders per share | | $ | 0.34 | | | $ | 0.37 | | | $ | 0.21 | |
Estimated tax rate | | | 31.97 | % | | | 32.65 | % | | | 32.15 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjusted net interest margin: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net interest income (as reported) | | $ | 77,642 | | | $ | 72,423 | | | $ | 51,376 | |
Plus: tax-equivalent adjustments | | | 421 | | | | 431 | | | | 140 | |
Less: accelerated mark accretion | | | (411 | ) | | | (1,454 | ) | | | (2,650 | ) |
Less: other accelerated accretion | | | - | | | | - | | | | (121 | ) |
Adjusted net interest income | | | 77,652 | | | | 71,400 | | | | 48,745 | |
Divided by: average earning assets | | | 1,970,221 | | | | 1,736,276 | | | | 1,202,990 | |
Adjusted net interest margin | | | 3.94 | % | | | 4.11 | % | | | 4.05 | % |
Net interest margin (fully tax-equivalent) | | | 3.96 | % | | | 4.20 | % | | | 4.28 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjusted noninterest income: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest income (as reported) | | $ | 13,953 | | | $ | 15,086 | | | $ | 11,372 | |
Less: gain on sale of securities | | | (180 | ) | | | (98 | ) | | | (1,478 | ) |
Adjusted noninterest income | | $ | 13,773 | | | $ | 14,988 | | | $ | 9,894 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjusted noninterest expense: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest expense (as reported) | | $ | 73,934 | | | $ | 64,099 | | | $ | 54,076 | |
Less: merger-related expenses | | | (3,616 | ) | | | (2,211 | ) | | | (5,895 | ) |
Adjusted noninterest expense | | $ | 70,318 | | | $ | 61,888 | | | $ | 48,181 | |
(1) | Revised to reflect measurement period adjustments to goodwill. |
(2) | There were 921,095 and 770,399 nonvested restricted shares outstanding at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, including certain stock price performance-based restricted shares granted to officers and directors following the holding company reorganization. These stock price performance-based restricted shares vest one-third each when the Company’s stock price per share reaches the following performance thresholds for 30 consecutive trading days: (i) 125% of offer price ($8.13); (ii) 140% of offer price ($9.10); and (iii) 160% of offer price ($10.40). These anti-dilutive restricted shares are issued (and thereby have voting rights), but are not included in earnings per share or tangible book value per share calculations until they vest (and thereby have economic rights). |
(3) | Provided merely as supplemental information for comparing the combined allowance and fair market value adjustments to the combined acquired and non-acquired loan portfolios; fair market value adjustments are available only for losses on acquired loans. |
Results of Operations
Summary. The Company recorded net income available to common shareholders of $12.9 million, or $0.29 per diluted common share, for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to a net income available to common shareholders of $15.0 million, or $0.34 per diluted common share, for the year ended December 31, 2013 and net income of $4.3 million, or $0.12 per diluted common share, for the year ended December 31, 2012. Excluding merger-related expenses and gain on sale of securities, the Company reported adjusted net income available to common shareholders of $15.2 million, or $0.34 per share, for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to adjusted net income of $16.3 million, or $0.37 per share, for the year ended December 31, 2013 and adjusted net income of $7.5 million, or $0.21 per share, for the year ended December 31, 2012.
Merger-related expenses totaled $3.6 million in 2014 compared to $2.2 million in 2013 and $5.9 million in 2012. Gains on sale of securities totaled $180 thousand in 2014 compared to $98 thousand in 2013 and $1.5 million in 2012. Results for 2014 include eight months of operations from the merger with Provident Community. Results for 2013 include a full year of operations from the merger with Citizens South, and results for 2012 include three months of operations from the merger with Citizens South. Adjusted net income available to common shareholders is a non-GAAP financial measure. For a reconciliation to the most comparable GAAP measure, see “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” above.
The following table presents selected ratios for the Company for the years ended December 31:
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
Return on Average Assets | | 0.59 | % | | | 0.76 | % | | | 0.32 | % | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Return on Average Equity | | 4.78 | % | | | 5.42 | % | | | 1.99 | % | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Period End Equity to Total Assets | | 11.66 | % | | | 13.37 | % | | | 13.56 | % | |
Net Income. The following table summarizes components of net income and the changes in those components for the years ended December 31:
| | | Components of Net Income | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | Change 2014 vs. 2013 | | | Change 2013 vs. 2012 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Interest income | | $ | 85,297 | | | $ | 78,805 | | | $ | 57,946 | | | $ | 6,492 | | | | 8 | % | | $ | 20,859 | | | | 36 | % |
Interest expense | | | 7,655 | | | | 6,382 | | | | 6,570 | | | | 1,273 | | | | 20 | % | | | (188 | ) | | | -3 | % |
Net interest income | | | 77,642 | | | | 72,423 | | | | 51,376 | | | | 5,219 | | | | 7 | % | | | 21,047 | | | | 41 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Provision for loan losses | | | (1,286 | ) | | | 746 | | | | 2,023 | | | | (2,032 | ) | | | -272 | % | | | (1,277 | ) | | | -63 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest income | | | 13,953 | | | | 15,086 | | | | 11,372 | | | | (1,133 | ) | | | -8 | % | | | 3,714 | | | | 33 | % |
Noninterest expense | | | 73,934 | | | | 64,099 | | | | 54,076 | | | | 9,835 | | | | 15 | % | | | 10,023 | | | | 19 | % |
Net income before taxes | | | 18,947 | | | | 22,664 | | | | 6,649 | | | | (3,717 | ) | | | -16 | % | | | 16,015 | | | | 241 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income tax expense | | | 6,058 | | | | 7,359 | | | | 2,306 | | | | (1,301 | ) | | | -18 | % | | | 5,053 | | | | 219 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | 12,889 | | | | 15,305 | | | | 4,343 | | | | (2,416 | ) | | | -16 | % | | | 10,962 | | | | 252 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Preferred dividends | | | - | | | | 353 | | | | 51 | | | | (353 | ) | | | -100 | % | | | 302 | | | | 592 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income to common shareholders | | $ | 12,889 | | | $ | 14,952 | | | $ | 4,292 | | | $ | (2,063 | ) | | | -14 | % | | $ | 10,660 | | | | 248 | % |
For the year ended December 31, 2014, we generated net income available to common shareholders of $12.9 million, compared to net income available to common shareholders of $15.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2013. The change in our results of operations in 2014 includes an increase of $5.2 million in net interest income and a decrease of $2.0 million in the provision for loan losses, offset by a $1.1 million decrease in noninterest income and an increase of $9.8 million in noninterest expense. We also recorded tax expense of $6.1 million in 2014 compared to $7.4 million in 2013. Results for 2014 include eight months of operations from the merger with Provident Community.
The Company generated net income available to common shareholders of $15.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, compared to net income available to common shareholders of $4.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2012. The change in our results of operations in 2013 includes an increase of $21.0 million in net interest income, a decrease of $1.3 million in the provision for loan losses and a $3.7 million increase in noninterest income, partially offset by an increase of $10.0 million in noninterest expense. We also recorded tax expense of $7.4 million in 2013 compared to $2.3 million in 2012. Results for 2013 include a full year of operations from the merger with Citizens South.
Details of the changes in the various components of net income are further discussed below.
Net Interest Income.Our largest source of earnings is net interest income, which is the difference between interest income on interest-earning assets and interest expense paid on deposits and other interest-bearing liabilities. The primary factors that affect net interest income are changes in volume and yields of earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities, which are affected in part by management’s responses to changes in interest rates through asset/liability management.
Net interest income increased $5.2 million, or 7%, to $77.6 million in 2014 compared to $72.4 million in 2013, and increased $21.0 million, or 41%, to $72.4 million in 2013 compared to $51.4 million in 2012. Average earning assets increased in both 2014 and 2013, which was primarily driven by organic loan growth, the addition of Provident Community assets following the merger on May 1, 2014 and the addition of Citizens South assets following the merger on October 1, 2012.
Net interest income for the years ended December 31, 2014, December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012 included $411 thousand, $1.5 million and $2.8 million, respectively, of accelerated accretion of net acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments for purchased performing loans, as accounted for under the contractual cash flow method of accounting. This accelerated accretion, which was not anticipated at the time of acquisition, resulted from a combination of (i) borrowers repaying performing acquired loans faster than required by their contractual terms; and/or (ii) restructuring loans in such a way as to effectively result in a new loan under the contractual cash flow method of accounting, both of which result in the associated remaining credit and interest rate marks being fully accreted into interest income.
The following table summarizes the average volume of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities and average yields and rates for the years ended December 31:
| | | Net Interest Margin | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | Average | | | Income/ | | | Yield/ | | | Average | | | Income/ | | | Yield/ | | | Average | | | Income/ | | | Yield/ | |
| | | Balance | | | Expense | | | Rate | | | Balance | | | Expense | | | Rate | | | Balance | | | Expense | | | Rate | |
| | (dollars in thousands) | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest-earning assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loans with fees (1)(2)(3) | | $ | 1,445,691 | | | $ | 75,045 | | | | 5.19 | % | | $ | 1,328,210 | | | $ | 72,809 | | | | 5.48 | % | | $ | 896,769 | | | $ | 53,334 | | | | 5.95 | % |
Federal funds sold | | | 564 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.18 | % | | | 14,737 | | | | 24 | | | | 0.16 | % | | | 22,731 | | | | 49 | | | | 0.22 | % |
Investment securities - taxable | | | 430,557 | | | | 9,318 | | | | 2.16 | % | | | 299,641 | | | | 5,029 | | | | 1.68 | % | | | 216,055 | | | | 3,606 | | | | 1.67 | % |
Investment securities - tax-exempt (2)(3) | | | 20,887 | | | | 874 | | | | 4.19 | % | | | 17,166 | | | | 1,047 | | | | 6.10 | % | | | 18,044 | | | | 750 | | | | 4.16 | % |
Nonmarketable equity securities | | | 7,619 | | | | 362 | | | | 4.75 | % | | | 6,163 | | | | 150 | | | | 2.43 | % | | | 7,092 | | | | 194 | | | | 2.74 | % |
Other interest-earning assets | | | 64,903 | | | | 118 | | | | 0.18 | % | | | 70,359 | | | | 177 | | | | 0.25 | % | | | 42,299 | | | | 153 | | | | 0.36 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total interest-earning assets | | | 1,970,221 | | | | 85,718 | | | | 4.35 | % | | | 1,736,276 | | | | 79,236 | | | | 4.56 | % | | | 1,202,990 | | | | 58,086 | | | | 4.83 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for loan losses | | | (9,535 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (10,797 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (9,788 | ) | | | | | | | | |
Cash and due from banks | | | 18,187 | | | | | | | | | | | | 17,392 | | | | | | | | | | | | 20,657 | | | | | | | | | |
Premises and equipment | | | 58,330 | | | | | | | | | | | | 57,015 | | | | | | | | | | | | 32,886 | | | | | | | | | |
Other assets | | | 162,124 | | | | | | | | | | | | 162,628 | | | | | | | | | | | | 102,445 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 2,199,327 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,962,514 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,349,190 | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and shareholders' equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest-bearing liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest-bearing demand | | $ | 348,314 | | | $ | 294 | | | | 0.08 | % | | $ | 292,698 | | | $ | 272 | | | | 0.09 | % | | $ | 135,255 | | | $ | 313 | | | | 0.23 | % |
Savings and money market | | | 509,640 | | | | 1,934 | | | | 0.38 | % | | | 447,421 | | | | 1,293 | | | | 0.29 | % | | | 293,175 | | | | 1,175 | | | | 0.40 | % |
Time deposits - core | | | 473,509 | | | | 2,620 | | | | 0.55 | % | | | 481,435 | | | | 1,696 | | | | 0.35 | % | | | 298,144 | | | | 1,475 | | | | 0.49 | % |
Brokered deposits | | | 150,497 | | | | 577 | | | | 0.36 | % | | | 103,630 | | | | 847 | | | | 0.81 | % | | | 137,737 | | | | 1,476 | | | | 1.07 | % |
Total interest-bearing deposits | | | 1,481,960 | | | | 5,425 | | | | 0.37 | % | | | 1,325,184 | | | | 4,108 | | | | 0.31 | % | | | 864,311 | | | | 4,439 | | | | 0.51 | % |
Federal Home Loan Bank advances | | | 94,973 | | | | 596 | | | | 0.63 | % | | | 56,685 | | | | 550 | | | | 0.97 | % | | | 55,861 | | | | 600 | | | | 1.07 | % |
Subordinated debt and other borrowings | | | 26,724 | | | | 1,634 | | | | 6.11 | % | | | 25,606 | | | | 1,724 | | | | 6.73 | % | | | 17,666 | | | | 1,531 | | | | 8.67 | % |
Total borrowed funds | | | 121,697 | | | | 2,230 | | | | 1.83 | % | | | 82,291 | | | | 2,274 | | | | 2.76 | % | | | 73,527 | | | | 2,131 | | | | 2.90 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total interest-bearing liabilities | | | 1,603,657 | | | | 7,655 | | | | 0.48 | % | | | 1,407,475 | | | | 6,382 | | | | 0.45 | % | | | 937,838 | | | | 6,570 | | | | 0.70 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net interest rate spread | | | | | | | 78,063 | | | | 3.87 | % | | | | | | | 72,854 | | | | 4.11 | % | | | | | | | 51,516 | | | | 4.13 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest-bearing demand deposits | | | 301,127 | | | | | | | | | | | | 255,149 | | | | | | | | | | | | 182,702 | | | | | | | | | |
Other liabilities | | | 25,039 | | | | | | | | | | | | 22,521 | | | | | | | | | | | | 13,383 | | | | | | | | | |
Shareholders' equity | | | 269,504 | | | | | | | | | | | | 275,742 | | | | | | | | | | | | 215,267 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and shareholders' equity | | $ | 2,199,327 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,960,887 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,349,190 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net interest margin | | | | | | | | | | | 3.96 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 4.20 | % | | | | | | | | | | | 4.28 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(1) Nonaccrual loans are included in the average loan balances.
(2) Interest income and yields are presented on a fully tax-equivalent basis.
(3) Fully tax-equivalent basis at 38.55% tax rate for nontaxable securities and loans.
The following table details the calculation of fully tax-equivalent net interest income for the years ended December 31:
Tax Equivalent Adjustments | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Net interest income, as reported | | $ | 77,642 | | | $ | 72,423 | | | $ | 51,376 | |
Tax equivalent adjustments | | | 421 | | | | 431 | | | | 140 | |
Fully tax-equivalent net interest income | | $ | 78,063 | | | $ | 72,854 | | | $ | 51,516 | |
Changes in interest income and interest expense can result from variances in both volume and rates. The following table presents the relative impact on tax-equivalent net interest income to changes in the average outstanding balances of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities and the rates earned and paid on such assets and liabilities:
Volume and Rate Variance Analysis
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 vs. 2013 | | | 2013 vs. 2012 | |
| | | Increase/(Decrease) Due to | |
| | | Volume | | | Rate | | | Total | | | Volume | | | Rate | | | Total | |
| | (dollars in thousands) | |
| Interest-earning assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loans with fees (1) | | $ | 6,269 | | | $ | (4,033 | ) | | $ | 2,236 | | | $ | 24,655 | | | $ | (5,180 | ) | | $ | 19,475 | |
Federal funds sold | | | (24 | ) | | | 1 | | | | (23 | ) | | | (15 | ) | | | (10 | ) | | | (25 | ) |
Investment securities - taxable | | | 2,515 | | | | 1,774 | | | | 4,289 | | | | 1,399 | | | | 24 | | | | 1,423 | |
Investment securities - tax-exempt | | | 191 | | | | (364 | ) | | | (173 | ) | | | (45 | ) | | | 342 | | | | 297 | |
Nonmarketable equity securities | | | 52 | | | | 160 | | | | 212 | | | | (24 | ) | | | (20 | ) | | | (44 | ) |
Other interest-earning assets | | | (12 | ) | | | (47 | ) | | | (59 | ) | | | 86 | | | | (62 | ) | | | 24 | |
Total earning assets | | | 8,991 | | | | (2,509 | ) | | | 6,482 | | | | 26,056 | | | | (4,907 | ) | | | 21,150 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest-bearing liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest bearing demand | | | 49 | | | | (27 | ) | | | 22 | | | | 255 | | | | (296 | ) | | | (41 | ) |
Savings and money market | | | 208 | | | | 433 | | | | 641 | | | | 532 | | | | (414 | ) | | | 118 | |
Time deposits - core | | | (36 | ) | | | 960 | | | | 924 | | | | 776 | | | | (555 | ) | | | 221 | |
Brokered deposits | | | 275 | | | | (545 | ) | | | (270 | ) | | | (321 | ) | | | (296 | ) | | | (629 | ) |
Total interest bearing deposits | | | 496 | | | | 821 | | | | 1,317 | | | | 1,243 | | | | (1,561 | ) | | | (331 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal Home Loan Bank advances | | | 306 | | | | (260 | ) | | | 46 | | | | 8 | | | | (58 | ) | | | (50 | ) |
Other borrowings | | | 72 | | | | (162 | ) | | | (90 | ) | | | 611 | | | | (418 | ) | | | 193 | |
Total borrowed funds | | | 378 | | | | (422 | ) | | | (44 | ) | | | 620 | | | | (477 | ) | | | 143 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total interest-bearing liabilities | | | 874 | | | | 399 | | | | 1,273 | | | | 1,863 | | | | (2,038 | ) | | | (188 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Increase in net interest income | | $ | 8,117 | | | $ | (2,908 | ) | | $ | 5,209 | | | $ | 24,193 | | | $ | (2,869 | ) | | $ | 21,338 | |
(1) Nonaccrual loans are included in the average loan balances.
Net interest income on a tax-equivalent basis totaled $78.1 million in 2014 as compared to $72.9 million in 2013. The interest rate spread, which represents the rate earned on interest-earning assets less the rate paid on interest-bearing liabilities, was 3.87% in 2014 and represented a decrease from the 2013 net interest rate spread of 4.11%. The net interest margin decreased 24 basis points in 2014 to 3.96% from 4.20% in 2013. The decrease in net interest margin was primarily due to decreased yields on loans and decreased accelerated accretion of net acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments on purchased performing loans.
Adjusted net interest margin, which excludes accelerated accretion of net acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments, was 3.94% in 2014 and represented a 17 basis point decrease from the 2013 adjusted net interest margin of 4.11%. This change is the result of lower yields on interest earning assets as discussed above. Adjusted net interest margin is a non-GAAP financial measure. For a reconciliation to the most comparable GAAP measure, see “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” above.
Tax-equivalent interest income increased $6.5 million, or 8%, to $85.7 million in 2014 compared to $79.2 million in 2013 as a result of higher average earning assets. Average earning assets increased $233.9 million, or 13%, to $2.0 billion for 2014 from $1.7 billion in 2013. Average loans increased $117.5 million, or 9%, as a result of organic loan growth and the merger with Provident Community. Average investments, including nonmarketable equity securities, increased $136.1 million, or 42%, to $459.1 million. Average federal funds sold decreased $14.2 million, or 96%, to $564 thousand, and average other interest-earning assets decreased $5.5 million, or 6%, to $64.9 million. Other interest-earning assets include interest-earning balances at correspondent banks. The yield on earning assets decreased to 4.35% in 2014 from 4.56% in 2013. This decrease included a 29 basis point decrease in loan yields.
Interest expense increased by $1.3 million, or 20%, to $7.7 million in 2014 compared to $6.4 million in 2013, primarily due to an increase in the average interest-bearing liabilities and an increase in the average rate paid on interest-bearing liabilities, which increased 3 basis points to 0.48% from 0.45% in 2013. Average interest-bearing liabilities increased $196.2 million, or 14%, to $1.6 billion from $1.4 billion in 2013, primarily due to the addition of Provident Community liabilities, as well as additional borrowings. Average interest-bearing demand deposits increased $55.6 million, or 19%, to $348.3 million in 2014 compared to $292.7 million in 2013. Average savings and money market accounts increased $62.2 million, or 14%, to $509.6 million in 2014, compared to $447.4 million in 2013. Average core time deposits decreased $7.9 million, or 2%, to $473.5 million in 2014 from $481.4 million in 2013. Average brokered deposits, which consist of brokered interest-bearing deposits, brokered money market accounts, and brokered certificates of deposits, increased $46.9 million during 2014, to help fund organic loan growth.
Net interest income on a tax-equivalent basis totaled $72.9 million in 2013 as compared to $51.7 million in 2012. The interest rate spread, was 4.11% in 2013 and represented a slight decrease from the 2012 net interest rate spread of 4.13%. The net interest margin decreased 8 basis points in 2013 to 4.20% from 4.28% in 2012. The decrease in net interest margin was primarily due to the expiration of amortization of fair market value adjustments on acquired deposits and decreased accelerated accretion of net acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments on purchased performing loans.
Adjusted net interest margin, which excludes accelerated accretion of net acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments, was 4.11% in 2013 and represented an increase from the 2012 adjusted net interest margin of 4.05%. This change is the result of the inclusion of a full year of results from the merger with Citizens South. Adjusted net interest margin is a non-GAAP financial measure. For a reconciliation to the most comparable GAAP measure, see “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” above.
Tax-equivalent interest income increased $21.1 million, or 36%, to $79.2 million in 2013 compared to $58.1 million in 2012 as a result of higher average earning assets. Average earning assets increased $533.3 million, or 44%, to $1.7 billion for 2013 from $1.2 billion in 2012. Average loans increased $431.4 million, or 48%, as a result of the inclusion of a full year of results from Citizens South. Average investments increased $82.7 million, or 35%, to $316.8 million. Average federal funds sold decreased $8.0 million, or 35%, to $14.7 million, and average other interest-earning assets increased $28.1 million, or 66%, to $70.4 million. Other interest-earning assets include interest-earning balances at correspondent banks. The yield on earning assets decreased to 4.56% in 2013 from 4.83% in 2012. This decrease included a 47 basis point decrease in loan yields resulting from the decrease in accelerated accretion of net acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments on purchased performing loans.
Interest expense decreased nominally by $188 thousand, or 3%, to $6.4 million in 2013 compared to $6.6 million in 2012, primarily due to a decrease in the average rate paid on interest-bearing liabilities, which declined 25 basis points to 0.45% from 0.70% in 2012. The decrease in average rate paid resulted from management re-pricing actions on deposit rates. Average interest-bearing liabilities increased $469.6 million, or 50%, to $1.4 billion from $937.8 million in 2012, primarily as a result of the merger with Citizens South. Average interest-bearing demand deposits increased $157.4 million, or 116%, to $292.7 million in 2013 compared to $135.3 million in 2012. Average savings and money market accounts increased $154.2 million, or 53%, to $447.4 million in 2013, compared to $293.2 million in 2012. Average core time deposits increased $183.3 million, or 61%, to $481.4 million in 2013 from $298.1 million in 2012. Average brokered deposits, which consist of brokered interest-bearing deposits, brokered money market accounts, and brokered certificates of deposits, decreased $34.1 million during 2013, which is primarily a function of management electing not to renew maturing time deposits. As a result of the brokered money market deposit program initiated in December 2013 in connection with our $50 million investment strategy, our brokered deposits now include money market and interest-bearing deposits.
The Company’s hedging policies permit the use of various derivative financial instruments to manage exposure to changes in interest rates. Details of derivatives and hedging activities are set forth in Note 17 – Derivative Financial Instruments and Hedging Activities to the Consolidated Financial Statements. Information regarding the impact of fluctuations in interest rates on the Company’s derivative financial instruments is set forth below in the section entitled “Market Risk and Interest Rate Sensitivity”.
Provision for Loan Losses. The provision for loan losses decreased $2.0 million to a release of $1.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to a provision of $746 thousand and $2.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The decrease in provision for 2014 is a result of improvement in the quality of our loans and net recoveries of $1.0 million in 2014. We also recorded a $209 net impairment reversal associated with PCI loan pools and a $278 thousand reversal of a previous charge attributable to the FDIC loss share agreements assumed from Citizens South. Generally, these additional expected losses are reflected as a provision for loan losses, and offset with an expected benefit through the FDIC indemnification asset for those acquired loans covered by the FDIC loss share agreements.
The decrease in the provision for 2013 compared to 2012 is primarily a result of a decrease in outstanding loans and improved asset quality. We also recorded a $501 thousand benefit in 2013 attributable to the FDIC loss share agreements assumed from Citizens South caused by an increase in expected loss in those acquired loans. Also included in the provision expense for 2013 was net impairment reversal of $607 thousand associated with PCI loan pools, compared to a net impairment charge related to PCI loan pools of $967 thousand in 2012.
Noninterest Income.The following table summarizes components of noninterest income for the years ended December 31:
| Noninterest Income | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | Change 2014 vs. 2013 | | | Change 2013 vs. 2012 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Service charges on deposit accounts | | $ | 3,881 | | | $ | 2,646 | | | $ | 1,814 | | | $ | 1,235 | | | | 47 | % | | $ | 832 | | | | 46 | % |
Income from fiduciary activities | | | 2,748 | | | | 2,779 | | | | 2,332 | | | | (31 | ) | | | -1 | % | | | 447 | | | | 19 | % |
Commissions and fees from investment brokerage | | | 452 | | | | 419 | | | | 287 | | | | 33 | | | | 8 | % | | | 132 | | | | 46 | % |
Gain on sale of securities available-for-sale | | | 180 | | | | 98 | | | | 1,478 | | | | 82 | | | | 84 | % | | | (1,380 | ) | | | -93 | % |
Bankcard services income | | | 2,632 | | | | 2,373 | | | | 1,085 | | | | 259 | | | | 11 | % | | | 1,288 | | | | 119 | % |
Mortgage banking income | | | 2,641 | | | | 3,123 | | | | 2,478 | | | | (482 | ) | | | -15 | % | | | 645 | | | | 26 | % |
Income from bank-owned life insurance | | | 2,688 | | | | 1,863 | | | | 1,264 | | | | 825 | | | | 44 | % | | | 599 | | | | 47 | % |
Amortization of indemnification asset | | | (3,203 | ) | | | (189 | ) | | | - | | | | (3,014 | ) | | | 1595 | % | | | (189 | ) | | | 100 | % |
Loss share true-up liability expense | | | (587 | ) | | | (59 | ) | | | - | | | | (528 | ) | | | 895 | % | | | (59 | ) | | | 100 | % |
Other noninterest income | | | 2,521 | | | | 2,033 | | | | 634 | | | | 488 | | | | 24 | % | | | 1,399 | | | | 221 | % |
Total noninterest income | | $ | 13,953 | | | $ | 15,086 | | | $ | 11,372 | | | $ | (1,133 | ) | | | -8 | % | | $ | 3,714 | | | | 33 | % |
As a result of our merger and acquisition activity over the past several years, noninterest income has become a key component of our earnings. Noninterest income decreased $1.1 million, or 8%, to $14.0 million in 2014 from $15.1 million in 2013. Impacting noninterest income in 2014 was a $3.0 million increase in the amortization of the FDIC indemnification asset and a $528 thousand increase in true-up expenses related to our FDIC loss share agreements. The increase in FDIC loss-share related expenses reflects reductions in the Company’s loss share reimbursement expectations given better than originally forecast performance of the underlying covered loans. The commercial components of the Bank of Hiawassee and New Horizons Bank loss share agreements, which account for approximately 63% of covered loans, expire in March 2015 and April 2016, respectively. The Company expects expenses related to loss share agreements to taper as the expiration of the Bank of Hiawassee commercial agreement approaches in the first quarter of 2015.
Service charges on deposit accounts increased $1.2 million, or 47%, to $3.9 million in 2014 from $2.6 million in 2013. This increase is due to the addition of deposit accounts resulting from the Provident Community merger as well as an increase in deposit accounts resulting from our expanded retail and commercial banking activities. Commissions and fees from investment brokerage activity increased 8% to $452 thousand in 2014, from $419 thousand in 2013. Income from bankcard services increased $259 thousand, or 11%, to $2.6 million in 2014 from $2.4 million in 2013. Income from bank-owned life insurance increased $825 thousand, or 44%, to $2.7 million in 2014 from $1.9 million in 2013, which is a result of $651 thousand in death benefits received in 2014 and $8.5 million of bank-owned life insurance acquired in connection with the Provident Community merger. We also reported gains on the sale of securities of $180 thousand in 2014, compared to $98 thousand in 2013. Income from fiduciary activities associated with asset management, investment brokerage, and trust services decreased $31 thousand from 2013 to 2014. Following a review of wealth management activities, in 2013 we determined to exit the custody business in 2014 and resources previously focused on the custody business were redirected to our core asset management business. Mortgage banking income also decreased $482 thousand, or 15%, to $2.6 million in 2014, from $3.1 million in 2013. Other noninterest income increased $488 thousand, or 24%, to $2.5 million in 2014 from $1.8 million in 2013. Other noninterest income includes $646 thousand in income generated from our capital markets activities, including increased customer hedging activities.
In 2013, noninterest income increased $3.7 million, or 33%, to $15.1 million from $11.4 million in 2012. Service charges on deposit accounts increased $832 thousand, or 46%, to $2.6 million in 2013 from $1.8 million in 2012. This increase was due to an increase in deposit accounts that resulted from our expanded retail and commercial banking activities. Income from fiduciary activities associated with asset management, investment brokerage, and trust services increased $447 thousand from 2012 to 2013. Commissions and fees from investment brokerage activity increased 45% to $419 thousand in 2013, from $287 thousand in 2012. We reported gains on the sale of securities of $98 thousand in 2013, compared to $1.5 million in 2012. Income from bankcard services increased $1.3 million, or 119%, to $2.4 million in 2013 from $1.1 million in 2012. Mortgage banking income increased $645 thousand, or 26%, to $3.1 million in 2013, from $2.5 million in 2012. Income from bank-owned life insurance increased $599 thousand, or 47%, to $1.9 million in 2013 from $1.3 million in 2012, which was a result of $18.8 million of bank-owned life insurance acquired in connection with the Citizens South merger. Other noninterest income increased $1.2 million, or 182%, to $2.0 million in 2013 from $634 thousand in 2012. Included in the 2013 results was a nontaxable $1.1 million gain generated from settling, at a discount, the contingent underwriting fee liability remaining from the Public Offering.
Excluding gain on sale of securities of $180 thousand in 2014, $98 thousand in 2013 and $1.5 million in 2012, respectively, adjusted noninterest income decreased $1.2 million in 2014, and increased $5.1 million in 2013. Adjusted noninterest income is a non-GAAP financial measure. For a reconciliation to the most comparable GAAP measure, see “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” above.
Noninterest Expense. The following table summarizes components of noninterest expense for the years ended December 31:
| Noninterest Expense | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | Change 2014 vs. 2013 | | | Change 2013 vs. 2012 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Salaries and employee benefits | | $ | 39,538 | | | $ | 34,570 | | | $ | 29,396 | | | $ | 4,968 | | | | 14 | % | | $ | 5,174 | | | | 18 | % |
Occupancy and equipment | | | 10,409 | | | | 7,691 | | | | 4,654 | | | | 2,718 | | | | 35 | % | | | 3,037 | | | | 65 | % |
Advertising and promotion | | | 1,494 | | | | 839 | | | | 781 | | | | 655 | | | | 78 | % | | | 58 | | | | 7 | % |
Legal and professional fees | | | 3,486 | | | | 3,142 | | | | 3,190 | | | | 344 | | | | 11 | % | | | (48 | ) | | | -2 | % |
Deposit charges and FDIC insurance | | | 1,491 | | | | 1,647 | | | | 1,250 | | | | (156 | ) | | | -9 | % | | | 397 | | | | 32 | % |
Data processing and outside service fees | | | 6,449 | | | | 5,950 | | | | 4,371 | | | | 499 | | | | 8 | % | | | 1,579 | | | | 36 | % |
Communication fees | | | 1,974 | | | | 1,737 | | | | 945 | | | | 237 | | | | 14 | % | | | 792 | | | | 84 | % |
Core deposit intangible amortization | | | 1,269 | | | | 1,029 | | | | 564 | | | | 240 | | | | 23 | % | | | 465 | | | | 82 | % |
Net cost (earnings) of operation of OREO | | | 817 | | | | (371 | ) | | | 3,462 | | | | 1,188 | | | | -320 | % | | | (3,833 | ) | | | -111 | % |
Loan and collection expense | | | 1,350 | | | | 1,972 | | | | 1,221 | | | | (622 | ) | | | -32 | % | | | 751 | | | | 62 | % |
Postage and supplies | | | 667 | | | | 1,009 | | | | 791 | | | | (342 | ) | | | -34 | % | | | 218 | | | | 28 | % |
Other noninterest expense | | | 4,990 | | | | 4,884 | | | | 3,451 | | | | 106 | | | | 2 | % | | | 1,433 | | | | 42 | % |
Total noninterest expense | | $ | 73,934 | | | $ | 64,099 | | | $ | 54,076 | | | $ | 9,835 | | | | 15 | % | | $ | 10,023 | | | | 19 | % |
The level of noninterest expense substantially affects our profitability. Total noninterest expense was $73.9 million in 2014, an increase of $9.8 million, or 15%, from $64.1 million in 2013. The increase is primarily due to the inclusion of eight months of expense from the Provident Community merger, as well as hiring initiatives designed to drive future organic growth opportunities. Total noninterest expense was $64.1 million in 2013, an increase of $10.0 million, or 18%, from $54.1 million in 2012. The increase was primarily due to the inclusion of a full year of expense from the Citizens South merger.
In 2014, we incurred approximately $3.6 million in expenses related to the Provident Community merger resulting from core system conversion and employee benefit plans conversions. Excluding merger-related expenses of $3.6 million, $2.2 million and $5.9 million in 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, adjusted noninterest expense increased $8.4 million, or 14%, to $70.3 million in 2014 from $61.9 million in 2013; and $13.7 million, or 28%, to $61.9 million in 2013 from $48.4 million in 2012, primarily as a result of the aforementioned mergers and organic growth initiatives. Adjusted noninterest expense is a non-GAAP financial measure. For a reconciliation to the most comparable GAAP measure, see “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” above.
The largest component of noninterest expense is salaries and employee benefits, which increased $5.0 million, or 14%, to $39.5 million in 2014 from $34.6 million in 2013. This increase is primarily due to the increase in the number of employees resulting from the Provident Community merger, as well as hiring initiatives designed to drive future organic growth opportunities. Occupancy and equipment expense increased 35% from $7.7 million in 2013 to $10.4 million in 2014, primarily due to the acquisition of property with the Provident Community merger as well as the opening of the office in Richmond, Virginia. Advertising and promotion expense increased $655 thousand, or 78% from 2013 to 2014 as the Company embarked on a new marketing campaign in 2014 to promote a new corporate brand, “Answers You Can Bank OnSM.” Data processing and outside service fees increased $499 thousand or 8% to $6.4 million in 2014, from $6.0 million in 2013. The increase in these fees is due to fees associated with merger integration and core processing integration from the merger with Provident Community. Communication fees increased 14% to $2.0 million in 2014 from $1.7 million in 2013, which is due to the expanded branch network resulting from the merger with Provident Community. We realized a net cost of operation of other real estate during 2014 of $817 thousand, compared to a net gain of $371 thousand in 2013. During 2014, we sold 279 properties for a net gain of $436 thousand, compared to 282 properties sold during 2013 for a net gain of $2.1 million. Loan collection expense decreased $622 thousand, or 32%, to $1.4 million in 2014 from $2.0 million in 2013 as loan quality continues to improve. Other noninterest expense increased $106 thousand, or 2%, to $5.0 million in 2014 from $4.9 million in 2013.
Salaries and employee benefits increased $5.2 million, or 18%, to $34.6 million in 2013 from $29.4 million in 2012. This increase was primarily due to the increase in the number of employees resulting from the Citizens South merger, as well as the continued expansion of our management team. Additionally, in 2012, we incurred merger-related salary and employee benefit expenses of $2.0 million primarily associated with certain contractual payments to executives of the acquired companies.
Occupancy and equipment expense increased 65% from $4.7 million in 2012 to $7.7 million in 2013, primarily due to the acquisition of property with the Citizens South merger. Data processing and outside service fees increased $1.6 million or 36% to $6.0 million in 2013, from $4.4 million in 2012. The increase in these fees was due to one-time processing fees related both to exiting the custody business and to installation of a new allowance management system, as well as fees associated with merger integration and core processing integration from the mergers with Citizens South and Community Capital. Communication fees increased 84% to $1.7 million in 2013 from $945 thousand in 2012, which was due to the expanded branch network resulting from the merger with Citizens South. We realized a net gain on operation of other real estate during 2013 of $371 thousand, compared to a net cost of $3.5 million in 2012. During 2013, we sold 282 properties for a net gain of $2.1 million, compared to 144 properties sold during 2012 for a net gain of $253 thousand. Loan collection expense increased $751 thousand, or 62%, to $2.0 million in 2013 from $1.2 million in 2012. Other noninterest expense increased $1.2 million, or 37%, to $4.3 million in 2013 from $3.2 million in 2012. Included in the 2013 increase was a loss on disposal of fixed assets of $432 thousand, due primarily to the write-off of a former branch, which had contained a now-relocated ATM that has been shuttered and moved into other real estate owned.
Income Taxes.We generate non-taxable income from tax-exempt investment securities and loans as well as bank-owned life insurance. Accordingly, the level of such income in relation to income before taxes affects our effective tax rate. We recognized income tax expense of $6.1 million for 2014, $7.4 million for 2013 and $2.3 million for 2012. The effective tax rate for the year ended December 31, 2014 was 32.0%, compared to 32.5% for the year ended December 31, 2012 and 34.7% for the year ended December 31, 2012.
We reported net DTAs of $35.6 million and $36.3 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The decrease is primarily the result of earnings of $12.9 million during 2014, offset by fair market value adjustments related to the merger with Provident Community and a $1.6 million DTA acquired through that merger. We evaluate the carrying amount of our DTA quarterly in accordance with the guidance provided in ASC 740, in particular applying the criteria set forth therein to determine whether it is more likely than not (i.e., a likelihood of more than 50%) that some portion, or all, of the DTA will not be realized within its life cycle, based on the weight of available evidence. In most cases, the realization of the DTA is dependent upon generating a sufficient level of taxable income in future periods, which can be difficult to predict. In addition to projected earnings, we also consider projected asset quality, liquidity, and our strong capital position, which could be leveraged to increase earning assets and generate taxable income, our growth plans and other relevant factors. Based on the weight of available evidence, we determined that as of both December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 that it is more likely than not that we will be able to fully realize the existing DTA and therefore considered it appropriate not to establish a DTA valuation allowance at either December 31, 2014 or December 31, 2013. See Note 12 – Income Taxes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Financial Condition
Summary. Total assets increased $398.4 million, or 20%, to $2.4 billion as of December 31, 2014. This increase is primarily the result of the addition of Provident Community assets as a result of the merger, as well as organic growth. Other increases were in investment securities available-for-sale of $26.2 million, or 7%; investment securities held-to-maturity of $63.8 million, or 123%; nonmarketable equity securities of $5.6 million, or 95%; loans held for sale of $9.2 million, or 377%; net loans of $285.5 million, or 22%; Federal funds sold of $185 thousand, or 62%; premises and equipment of $3.3 million, or 6%; bank-owned life insurance of $9.9 million, or 21%; goodwill of $2.8 million, or 11%; core deposit intangible of $2.3 million, or 27%; and other assets including accrued interest payable of $2.8 million, or 50%. Offsetting the increases were decreases in cash and interest bearing balances of $3.9 million, or 7%; OREO of $2.5 million, or 17%; FDIC indemnification asset of $6.1 million, or 60%; and deferred tax assets of $695 thousand, or 2%.
Total liabilities at December 31, 2014 were $2.1 billion, an increase of $385.4 million, or 23%, from total liabilities of $1.7 billion at December 31, 2013. Total deposits increased $251.5 million, or 16%, and total borrowings increased $125.5 million, or 161%. Total borrowings included $23.6 million and $15.2 million of Tier 1 eligible junior subordinated debt, net of acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments, at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Also included in borrowings at December 31, 2013 was $6.9 million in Tier 2 eligible subordinated debt which the Bank redeemed in full on June 30, 2014. Total shareholders’ equity increased $13.0 million, or 5%, during the year to $275.1 million at December 31, 2014.
Investment Securities and Other Earning Assets.We use investment securities to generate interest income through the employment of excess funds, to provide liquidity, to fund loan demand or deposit liquidation, and to pledge as collateral, where required. The composition of our investment portfolio, as presented in the table below, changes from time to time as we consider our liquidity needs, interest rate expectations, asset/liability management strategies, and capital requirements.
Securities available-for-sale are carried at fair market value, with unrealized holding gains and losses reported in accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax. Securities held-to-maturity are carried at amortized cost. At December 31, 2014, the market value of investment securities totaled $493.3 million, compared to $400.8 million at December 31, 2013. The increase in investment securities during 2014 is due to securities acquired from Provident Community that were reinvested during 2014. Investment securities with a fair market value of $58.5 million were transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity during 2014.
Included in our investment securities portfolio are two investments in senior tranches of CLOs totaling $14.8 million at December 31, 2014, which could be impacted by the new bank investment criteria of Volcker Rule. Our investments in the two CLOs, which had a net unrealized loss of $232,000 at December 31, 2014, currently would be prohibited under the Volcker Rule. The Company will determine any disposition plans for these securities as the documentation is, or is not, amended. Under current federal regulations, banks have until July 21, 2016 (expected to be extended to July 21, 2017) to conform their CLO interests to avoid the trading restrictions under the Volcker Rule. Unless the documentation is amended to avoid inclusion within the rule’s prohibitions, we would have to recognize OTTI with respect to these securities in conformity with GAAP rules. We held no other security types potentially affected by the Volcker Rule at December 31, 2014.
The following table presents a summary of the fair value of investment securities at December 31:
| Fair Value of Investment Portfolio | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | % | | | | | | | % | | | | | | | % | |
| | | 2014 | | | of Total | | | 2013 | | | of Total | | | 2012 | | | of Total | |
Securities available-for-sale: | | (dollars in thousands) | |
U.S. Government agencies | | $ | 537 | | | | 0 | % | | $ | 558 | | | | 0 | % | | $ | 583 | | | | 0 | % |
Municipal securities | | | 12,851 | | | | 3 | % | | | 16,506 | | | | 5 | % | | | 17,958 | | | | 7 | % |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | | 147,015 | | | | 39 | % | | | 90,248 | | | | 26 | % | | | 138,205 | | | | 56 | % |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | 144,080 | | | | 38 | % | | | 103,349 | | | | 30 | % | | | 56,752 | | | | 23 | % |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | 4,868 | | | | 1 | % | | | 61,402 | | | | 18 | % | | | 20,936 | | | | 9 | % |
Asset-backed securities | | | 61,050 | | | | 16 | % | | | 71,077 | | | | 20 | % | | | 10,722 | | | | 5 | % |
Corporate and other securities | | | 3,570 | | | | 1 | % | | | 4,445 | | | | 1 | % | | | 415 | | | | 0 | % |
Equity securities | | | 1,712 | | | | 0 | % | | | 1,906 | | | | 1 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
Total investment securities | | $ | 375,683 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 349,491 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 245,571 | | | | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities held-to-maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | $ | 44,454 | | | | 38 | % | | $ | 40,733 | | | | 79 | % | | $ | - | | | | 0 | % |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | 8,564 | | | | 7 | % | | | 4,908 | | | | 10 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations (CMBS) | | | 58,742 | | | | 50 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
Asset-backed securities | | | 5,867 | | | | 5 | % | | | 5,693 | | | | 11 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
Total investment securities | | $ | 117,627 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 51,334 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | - | | | | 0 | % |
The following table summarizes the maturity distribution schedule of the amortized cost of securities available-for-sale and held-to-maturity with corresponding weighted-average yields at December 31, 2014. Weighted-average yields for securities exempt from both Federal and state income taxes and Federal income taxes only have been computed on a fully taxable-equivalent basis using a statutory tax rate of 38.55%. The amount of tax-equivalent adjustment is $243 thousand and relates exclusively to municipal securities for the periods presented. Mortgage-backed securities are included in maturity categories based on their stated maturity date. Expected maturities may differ from contractual maturities for a variety of reasons, including the ability of issuers to call or prepay obligations and the ability of borrowers to prepay underlying mortgage collateral. Equity securities are reported with maturities over 10 years, as these securities have no maturity dates.
| Contractual Maturities of Investment Portfolio - Amortized Cost | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 1-5 years | | | 5-10 years | | | Over 10 years | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | Weighted | | | | | | | Weighted | | | | | | | Weighted | | | | | | | Weighted | |
| | | | | | | Average | | | | | | | Average | | | | | | | Average | | | | | | | Average | |
December 31, 2014 | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | | | Amount | | | Yield | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Securities available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Government agencies | | $ | 508 | | | | 4.05 | % | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | 508 | | | | 4.05 | % |
Municipal securities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 11,955 | | | | 4.60 | % | | | 11,955 | | | | 4.60 | % |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | | - | | | | - | | | | 11,354 | | | | 2.09 | % | | | 133,601 | | | | 2.45 | % | | | 144,955 | | | | 2.42 | % |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | - | | | | - | | | | 8,194 | | | | 2.04 | % | | | 136,579 | | | | 2.21 | % | | | 144,773 | | | | 2.20 | % |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,974 | | | | 1.63 | % | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,974 | | | | 1.63 | % |
Asset-backed securities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 61,833 | | | | 1.98 | % | | | 61,833 | | | | 1.98 | % |
Corporate and other securities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,328 | | | | 5.98 | % | | | 3,328 | | | | 5.98 | % |
Equity securities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,250 | | | | 14.41 | % | | | 1,250 | | | | 14.41 | % |
Total investment securities | | $ | 508 | | | | 4.05 | % | | $ | 24,522 | | | | 1.98 | % | | $ | 348,546 | | | | 2.24 | % | | $ | 373,576 | | | | 2.35 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities held-to-maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | 43,331 | | | | 2.89 | % | | $ | 43,331 | | | | 2.98 | % |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 8,440 | | | | 2.87 | % | | | 8,440 | | | | 2.87 | % |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | - | | | | - | | | | 60,783 | | | | 2.80 | % | | | - | | | | - | | | | 60,783 | | | | 2.80 | % |
Asset-backed securities | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,978 | | | | 2.87 | % | | | 5,978 | | | | 2.87 | % |
Total investment securities | | $ | - | | | | - | | | $ | 60,783 | | | | 2.80 | % | | $ | 57,749 | | | | 2.88 | % | | $ | 118,532 | | | | 2.84 | % |
At December 31, 2014, there were no holdings of any one issuer, other than the United States government and its agencies, in an amount greater than 10% of our total consolidated shareholders’ equity.
At December 31, 2014, we had $485 thousand in Federal funds and $34.4 million in interest-bearing deposits with other FDIC-insured financial institutions. This compares with $41.7 million in interest-bearing deposits with other FDIC-insured financial institutions and $300 thousand in Federal funds at December 31, 2013.
Loans.We consider asset quality to be of primary importance, and employ seasoned credit professionals and documented processes to ensure effective oversight of credit approvals and asset quality monitoring. Our internal loan policy is reviewed by our board of directors’ Loan and Risk Committee on an annual basis and our underwriting guidelines are reviewed and updated on a periodic basis. A formal loan review process is maintained both to ensure adherence to lending policies and to ensure accurate loan grading and is reviewed by our board of directors. Since inception, we have promoted the separation of loan underwriting from the loan production staff through our credit department. Currently, credit administration analysts or portfolio managers are responsible for underwriting and assigning proper risk grades for all commercial loans with exposure in excess of $500 thousand. Underwriting is completed on standardized forms including a loan approval form and supporting documents which outline the loan's structure and a detailed analysis of loan purpose, borrower strength (including individual and global cash flow worksheets), repayment sources and, when applicable, collateral positions and guarantor strength. The credit memorandum further identifies exceptions to policy and/or regulatory limits, total exposure, internal risk grades and other relevant credit information. Loans are approved or denied by varying levels of signature authority based on total customer relationship exposure. A management-level loan committee reviews all loans greater than $3 million and is responsible for approving all credits in excess of the chief credit officer and senior credit officers’ lending authority, which was increased in October 2014 from $3 million to $5 million.
Our loan underwriting policy contains LTV limits that are at or below levels required under regulatory guidance, when such guidance is available, including limitations for non-real estate collateral, such as accounts receivable, inventory and marketable securities. When applicable, we compare LTV with loan-to-cost guidelines and usually limit loan amounts to the lower of the two ratios. We also consider FICO scores and strive to uphold a high standard when extending loans to individuals. We have not underwritten any subprime, hybrid, no-documentation or low-documentation products.
All acquisition, construction and development (“AC&D”) loans, whether related to commercial or consumer borrowers, are subject to policies, guidelines and procedures specifically designed to properly identify, monitor and mitigate the risk associated with these loans. Loan officers receive and review a cost budget from the borrower at the time an AC&D loan is originated. Loan draws are monitored against the budgeted line items during the development period in order to identify potential cost overruns. Individual draw requests are verified through review of supporting invoices as well as site inspections performed by an external inspector. Additional periodic site inspections are performed by loan officers at times that do not coincide with draw requests in order to keep abreast of ongoing project conditions. Our exposure to AC&D loans has declined significantly since the Public Offering and current loan origination is focused on 1 – 4 family residential construction for retail customers and 1-4 family residential home construction to selected well-qualified builders, as well as owner-occupied commercial and pre-leased commercial build-to-suit properties. Concentrations as a percent of capital are reported to the board of directors on a quarterly basis. Market conditions for AC&D loans continued to improve in 2014 due to increasing new home sales in our primary markets. As of December 31, 2014, approximately 2% of our AC&D loan portfolio, commercial and consumer, falls under the watch list.
Our second mortgage exposure is primarily attributable to our home equity lines of credit (“HELOC”) portfolio, which totaled approximately $155 million as of December 31, 2014. HELOCs typically have a draw period of 10 years followed by a 10- or 15- year repayment period. During the draw period, a borrower is only required to make interest payments. Once the draw period has concluded, the line is typically placed on a 1% repayment schedule or is renewed. Management closely monitors HELOCs for end-of-draw periods and works with customers as the end-of-draw approaches. Reviews of all outstanding HELOCs are performed on at least a semi-annual basis.
All loans are assigned an internal risk grade and are reviewed continuously for payment performance and updated through annual portfolio reviews. Loans on the Bank’s watch list are monitored through periodic watch meetings and monthly impairment meetings. Classified loans are generally managed by a dedicated special asset team who is experienced in various loan rehabilitation and work out practices. Special asset loans are generally managed with a least-loss strategy.
At December 31, 2014, total loans, net of deferred fees, increased $284.9 million, or 22%, to $1.6 billion, compared to $1.3 billion at December 31, 2013, due to organic loan growth and the Provident Community merger. The Company’s metropolitan markets, which include Charlotte, Raleigh and Wilmington, North Carolina, Greenville and Charleston, South Carolina and Richmond, Virginia, reported organic growth of $152.0 million due to continued success in origination efforts. The composition of the portfolio shifted slightly, with commercial loans representing 72% of the total loan portfolio at December 31, 2014, compared to 71% at December 31, 2013, and consumer loans representing 28% of the total loan portfolio at December 31, 2014, compared to 29% at December 31, 2013. The primary changes in commercial loans were commercial and industrial which increased to 11% of the total loan portfolio at December 31, 2014 from 9% at December 31, 2013; AC&D- commercial real estate which increased to 5% of the total loan portfolio at December 31, 2014 from 4% at December 31, 2013 and AC&D- lots, land, and development which decreased to 3% of the total loan portfolio at December 31, 2014 from 5% at December 31, 2013. The primary changes in consumer loans were HELOCs which decreased to 10% of the total loan portfolio from 11% at December 31, 2013; and other loans to individuals which decreased to 1% of the total loan portfolio at December 31, 2014 from 2% at December 31, 2013.
The following table presents a summary of the loan portfolio at December 31:
Summary of Loans By Segment and Class | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | % | | | 2013 | | | % | | | 2012 | | | % | | | 2011 | | | % | | | 2010 | | | % | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 173,786 | | | | 11 | % | | $ | 122,400 | | | | 9 | % | | $ | 119,132 | | | | 9 | % | | $ | 80,746 | | | | 11 | % | | $ | 48,401 | | | | 12 | % |
Commercial real estate (CRE) -owner occupied | | | 333,782 | | | | 21 | % | | | 267,581 | | | | 21 | % | | | 299,416 | | | | 22 | % | | | 169,663 | | | | 22 | % | | | 55,089 | | | | 14 | % |
CRE - investor incomeproducing | | | 470,647 | | | | 30 | % | | | 382,187 | | | | 30 | % | | | 371,957 | | | | 27 | % | | | 194,235 | | | | 26 | % | | | 110,407 | | | | 28 | % |
Acquisition, constructionand development (AC&D) | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | 140,661 | | | | 10 | % | | | 92,349 | | | | 12 | % | | | 87,846 | | | | 22 | % |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | 29,401 | | | | 2 | % | | | 19,959 | | | | 2 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 55,443 | | | | 3 | % | | | 65,589 | | | | 5 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
AC&D - CRE | | | 71,590 | | | | 5 | % | | | 56,759 | | | | 4 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
Other commercial | | | 5,045 | | | | 0 | % | | | 3,849 | | | | 0 | % | | | 5,628 | | | | 1 | % | | | 15,658 | | | | 2 | % | | | 3,225 | | | | 1 | % |
Total commercial loans | | | 1,139,694 | | | | 72 | % | | | 918,324 | | | | 71 | % | | | 936,794 | | | | 69 | % | | | 552,651 | | | | 73 | % | | | 304,968 | | | | 77 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 205,150 | | | | 13 | % | | | 173,376 | | | | 13 | % | | | 188,532 | | | | 14 | % | | | 79,512 | | | | 10 | % | | | 21,716 | | | | 5 | % |
Home equity lines of credit(HELOC) | | | 155,297 | | | | 10 | % | | | 143,754 | | | | 11 | % | | | 163,625 | | | | 12 | % | | | 90,408 | | | | 12 | % | | | 56,968 | | | | 14 | % |
Residential construction | | | 55,882 | | | | 4 | % | | | 40,821 | | | | 3 | % | | | 52,812 | | | | 4 | % | | | 25,126 | | | | 3 | % | | | 9,051 | | | | 2 | % |
Other loans to individuals | | | 22,586 | | | | 1 | % | | | 18,795 | | | | 2 | % | | | 15,553 | | | | 1 | % | | | 11,496 | | | | 2 | % | | | 7,245 | | | | 2 | % |
Total consumer loans | | | 438,915 | | | | 28 | % | | | 376,746 | | | | 29 | % | | | 420,522 | | | | 31 | % | | | 206,542 | | | | 27 | % | | | 94,980 | | | | 23 | % |
Total loans | | | 1,578,609 | | | | 100 | % | | | 1,295,070 | | | | 100 | % | | | 1,357,316 | | | | 100 | % | | | 759,193 | | | | 100 | % | | | 399,948 | | | | 100 | % |
Deferred fees | | | 2,084 | | | | 0 | % | | | 738 | | | | 0 | % | | | (609 | ) | | | 0 | % | | | (371 | ) | | | 0 | % | | | (119 | ) | | | 0 | % |
Total loans, net ofdeferred fees | | $ | 1,580,693 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 1,295,808 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 1,356,707 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 758,822 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 399,829 | | | | 100 | % |
The following table details loan maturities by loan class and interest rate type at December 31, 2014:
Loan Portfolio Maturities by Loan Class and Rate Type | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Within | | | One | | | | | | | | | |
| | | One | | | Year to | | | After Five | | | | | |
December 31, 2014 | | Year | | | Five Years | | | Years | | | Total | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 52,123 | | | $ | 104,472 | | | $ | 17,191 | | | $ | 173,786 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 20,362 | | | | 225,307 | | | | 88,113 | | | | 333,782 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 42,819 | | | | 319,097 | | | | 108,731 | | | | 470,647 | |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | 29,094 | | | | 307 | | | | - | | | | 29,401 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 16,207 | | | | 34,452 | | | | 4,784 | | | | 55,443 | |
AC&D - CRE | | | 17,895 | | | | 40,897 | | | | 12,798 | | | | 71,590 | |
Other commercial | | | 2,110 | | | | 2,544 | | | | 391 | | | | 5,045 | |
Residential mortgages | | | 8,850 | | | | 23,330 | | | | 172,970 | | | | 205,150 | |
HELOC | | | 9,216 | | | | 33,574 | | | | 112,507 | | | | 155,297 | |
Residential construction | | | 21,548 | | | | 14,278 | | | | 20,056 | | | | 55,882 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 11,502 | | | | 8,446 | | | | 2,638 | | | | 22,586 | |
Total loans | | $ | 231,726 | | | $ | 806,704 | | | $ | 540,179 | | | $ | 1,578,609 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fixed interest rate | | $ | 84,639 | | | $ | 609,953 | | | $ | 221,249 | | | $ | 915,841 | |
Variable interest rate | | | 147,087 | | | | 196,751 | | | | 318,930 | | | | 662,768 | |
Total loans | | $ | 231,726 | | | $ | 806,704 | | | $ | 540,179 | | | $ | 1,578,609 | |
Variable interest rate loans are included in all of our loan types. We had a total of $662.8 million in variable rate loans as of December 31, 2014, of which $165.9 million included an interest rate floor. Variable rate loans are indexed to several indices, including (i) the prime rate as published inThe Wall Street Journal; (ii) the London InterBank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”); (iii) the 1-year Treasury rate; and (iv) our internal Main Street Prime rate. In addition, we inherited several variable rate indices through our mergers with Citizens South and Community Capital that are no longer used on originated or renewed loans. During the underwriting process, analysts perform their analysis at the fully-indexed rate as well as a “stressed” rate to identify payment capacity in a rising rate environment.
Allowance for Loan Losses.The allowance for loan losses is based upon management's ongoing evaluation of the loan portfolio and reflects an amount considered by management to be its best estimate of known and inherent losses in the portfolio as of the balance sheet date. The determination of the allowance for loan losses involves a high degree of judgment and complexity. In making the evaluation of the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses, management considers current economic and market conditions, independent loan reviews performed periodically by third parties, portfolio trends and concentrations, delinquency information, management's internal review of the loan portfolio, internal historical loss rates and other relevant factors. While management uses the best information available to make evaluations, future adjustments to the allowance may be necessary if conditions differ substantially from the assumptions used in making the evaluations. In addition, regulatory examiners may require us to recognize changes to the allowance for loan losses based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examination. Although provisions have been established by loan segments based upon management's assessment of their differing inherent loss characteristics, the entire allowance for losses on loans, other than the portions related to PCI loans and specific reserves on impaired loans, is available to absorb further loan losses in any segment.
Our Allowance for Loan Losses Committee is responsible for overseeing our allowance and works with our chief executive officer, senior financial officers, senior risk management officers and the Audit Committee of the board of directors in developing and achieving our allowance methodology and practices. Our allowance for loan loss methodology includes four components – specific reserves, quantitative reserves, qualitative reserves and reserves on PCI loans.
Since the fourth quarter of 2011, we have introduced certain enhancements to our allowance methodology that, in management’s opinion, provide a better estimate and an allowance for loan losses which better reflects the inherent loss within each loan product. Quantitatively, since the fourth quarter of 2011, we have shifted from historical loss experience of peers to our own actual loss experience and have segregated our loans by product. In the third quarter of 2013, we further segregated the AC&D portfolio by collateral type. These enhancements strengthen the granularity of the allowance methodology and better align with our present origination activities, which are focused on construction rather than development activities. Additionally, we regularly review the look back periods being used for each of our loan products to continue to present an estimated risk and loss consistent with expectations.
Qualitatively, during the second quarter of 2012, we eliminated the use of traditional risk grade factors as a single forward-looking qualitative indicator and instead shifted our focus to five specific environmental factors- portfolio trends, portfolio concentrations, economic and market conditions, changes in lending practices and other factors. During the third quarter of 2013, we applied the qualitative other factors against CRE – investor income producing loans and residential mortgage loans to adjust for inherent risks that, in our judgment, are not adequately reflected in historical loss rates. In 2014, the Company introduced two new environmental factors – changes in loan review system and geographical considerations- into the qualitative reserve component. Management believes these additional categories provide more clarity in the determination of the allowance. Additionally, we regularly review the look back periods being used for each of our loan products to continue to present an estimated risk and loss consistent with expectations. As a result of this review, we have extended the look back periods for several loan products in 2014.
In addition to the enhancements noted above, the Company reclassified the minimum reserve amounts previously utilized in its quantitative component to the qualitative component. A minimum reserve is utilized when the Company has insufficient internal loss history or when internal loss history falls below the minimum reserve percentage. Minimums are determined by analyzing Federal Reserve Bank charge-off data for all insured federal- and state-chartered commercial banks. This change represented a reclassification between components of the allowance and had no impact on the calculation in total.
The changes and refinements discussed above, in aggregate, did not have a material impact on the estimated allowance at December 31, 2014. These changes, in management’s judgment, produce a non-PCI allowance for loan losses that best reflects the estimate of inherent losses in the loan portfolio at December 31, 2014.
The following table presents a breakdown of our allowance for loan losses, by component and by loan product type as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. Details of the seven environmental factors for inclusion in the qualitative component of the allowance methodology as well as additional information about the four components and our policies and methodology used to estimate the allowance for loan losses are presented in Note 5 – Loans and Allowance for Loan Losses to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
| | | December 31, 2014 | |
| | | Specific Reserve | | | Quantitative Reserve | | | Qualitative Reserve | | | Reserve on PCI Loans | |
(dollars in thousands) | | $ | | | % of Total Allowance | | | $ | | | % of Total Allowance | | | $ | | | % of Total Allowance | | | $ | | | % of Total Allowance | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 44 | | | | 0.53 | % | | $ | 737 | | | | 8.92 | % | | $ | 764 | | | | 9.47 | % | | $ | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 18 | | | | 0.22 | % | | | 160 | | | | 1.94 | % | | | 539 | | | | 6.57 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 57 | | | | 0.69 | % | | | 800 | | | | 8.80 | % | | | 952 | | | | 11.72 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 222 | | | | 2.69 | % | | | 229 | | | | 2.84 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 11 | | | | 0.13 | % | | | 281 | | | | 3.40 | % | | | 292 | | | | 3.62 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
AC&D - CRE | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 36 | | | | 0.43 | % | | | 358 | | | | 4.34 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
Other commercial | | | 19 | | | | 0.23 | % | | | 4 | | | | 0.05 | % | | | 9 | | | | 0.11 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 138 | | | | 1.67 | % | | | 101 | | | | 1.22 | % | | | 202 | | | | 2.47 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
HELOC | | | 382 | | | | 4.62 | % | | | 472 | | | | 5.71 | % | | | 785 | | | | 9.66 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
Residential construction | | | 4 | | | | 0.05 | % | | | 261 | | | | 3.16 | % | | | 270 | | | | 3.35 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
Other loans to individuals | | | 12 | | | | 0.15 | % | | | 8 | | | | 0.10 | % | | | 95 | | | | 1.14 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 685 | | | | 8.29 | % | | $ | 3,082 | | | | 36.42 | % | | $ | 4,495 | | | | 55.29 | % | | $ | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
| | | December 31, 2013 | |
| | | Specific Reserve | | | Quantitative Reserve | | | Qualitative Reserve | | | Reserve on PCI Loans | |
(dollars in thousands) | | $ | | | % of Total Allowance | | | $ | | | % of Total Allowance | | | $ | | | % of Total Allowance | | | $ | | | % of Total Allowance | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 14 | | | | 0.16 | % | | $ | 1,304 | | | | 14.77 | % | | $ | 173 | | | | 1.96 | % | | $ | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 14 | | | | 0.16 | % | | | 319 | | | | 3.61 | % | | | 66 | | | | 0.75 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 527 | | | | 5.97 | % | | | 1,111 | | | | 12.58 | % | | | 159 | | | | 1.80 | % | | | 360 | | | | 4.08 | % |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 755 | | | | 8.55 | % | | | 84 | | | | 0.95 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 1,496 | | | | 16.94 | % | | | 255 | | | | 2.89 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
AC&D - CRE | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 267 | | | | 3.02 | % | | | 32 | | | | 0.36 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
Other commercial | | | 18 | | | | 0.20 | % | | | 5 | | | | 0.06 | % | | | 1 | | | | 0.01 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 167 | | | | 1.89 | % | | | 135 | | | | 1.53 | % | | | 56 | | | | 0.63 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
HELOC | | | 137 | | | | 1.55 | % | | | 699 | | | | 7.92 | % | | | 214 | | | | 2.42 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
Residential construction | | | 7 | | | | 0.08 | % | | | 336 | | | | 3.80 | % | | | 48 | | | | 0.55 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
Other loans to individuals | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 64 | | | | 0.72 | % | | | 8 | | | | 0.09 | % | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 884 | | | | 10.01 | % | | $ | 6,491 | | | | 73.50 | % | | $ | 1,096 | | | | 12.41 | % | | $ | 360 | | | | 4.08 | % |
The allowance for loan losses was $8.3 million, or 0.52% of total loans, at December 31, 2014 compared to $8.8 million, or 0.68% of total loans, at December 31, 2013. The allowance for loan losses is increased by provisions charged to operations and reduced by loans charged off, net of recoveries. The decrease in the allowance for loan losses was a function of (i) a decrease of $3.5 million in the quantitative component of the allowance due to a decrease in historic loss rates which resulted in a decrease in charge-offs over the look-back period, as well as the reclassification of minimum reserve amounts as discussed above, (ii) an increase of $3.4 million in the qualitative component of the allowance due to significant organic loan growth in 2014 and the reclassification of the minimum reserve amount, (iii) a decrease of $360 thousand in the reserve on PCI loans driven by the reversal of $209 thousand of previously recognized impairments offset by current year net recovery of impairments of $278 thousand and (iv) a decrease of $199 thousand in specific reserves which change periodically as loans move through or out of the impairment process.
Net charge-offs decreased $4.0 million, or 133%, from net charge-off of $3.0 million, or 0.23% of total loans, for the year ended December 31, 2013 to net recoveries of $1.0 million, or 0.06% of total loans, for the year ended December 31, 2014. The decrease in net charge-offs is the result of significant recoveries received on previously charged-off loans.
In accordance with GAAP, acquired loans were adjusted to reflect estimated fair market value at consummation and the associated allowance for loan losses was eliminated. At December 31, 2014, acquired loans comprised 32% of our total loans, compared to 44% at December 31, 2013. The ratio of the allowance for loan losses to total loans was 0.52% at December 31, 2014 and 0.68% at December 31, 2013. The ratio of the adjusted allowance for loan losses to total loans, which includes the remaining acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments for acquired loans, was 2.76% at December 31, 2014 and 3.60% at December 31, 2013. Adjusted allowance for loan losses to loans is a non-GAAP financial measure which is provided as supplemental information for comparing the combined allowance and fair market value adjustments to the combined acquired and non-acquired loan portfolios. Fair market value adjustments are available only for losses on acquired loans. For a reconciliation to the most comparable GAAP measure, see “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” above.
While management believes that it uses the best information available to determine the allowance for loan losses, and that the Company’s allowance for loan losses is maintained at a level appropriate in light of the risk inherent in our loan portfolio based on an assessment of various factors affecting the loan portfolio, unforeseen market conditions could result in adjustments to the allowance for loan losses, and net income could be significantly affected, if circumstances differ substantially from the assumptions used in making the final determination. The allowance for loan losses to total loans may increase if our loan portfolio deteriorates due to economic conditions or other factors.
The following table presents a summary of changes in the allowance for loan losses, including the reserve for PCI loans, and includes information regarding charge-offs and selected coverage ratios, for the years ended December 31:
Allowance for Loan Losses | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Balance, beginning of period | | $ | 8,831 | | | $ | 10,591 | | | $ | 10,154 | | | $ | 12,424 | | | $ | 7,402 | |
Provision for loan losses charged to operations | | | (1,286 | ) | | | 746 | | | | 2,023 | | | | 9,385 | | | | 17,005 | |
Provision for loan losses recorded throughFDIC loss share receivable | | | (278 | ) | | | 501 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Charge-offs: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | (161 | ) | | $ | (1,454 | ) | | $ | (565 | ) | | $ | (778 | ) | | $ | (1,338 | ) |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | (193 | ) | | | (52 | ) | | | (204 | ) | | | (194 | ) | | | (105 | ) |
CRE - investor income producing | | | (298 | ) | | | (734 | ) | | | (1,132 | ) | | | (136 | ) | | | (840 | ) |
AC&D | | | - | | | | (177 | ) | | | (652 | ) | | | (9,865 | ) | | | (7,752 | ) |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | (15 | ) | | | (87 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | (16 | ) | | | (6 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Other commercial | | | - | | | | (386 | ) | | | (94 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | (162 | ) | | | (1,142 | ) | | | (129 | ) | | | (128 | ) | | | (154 | ) |
HELOC | | | (996 | ) | | | (838 | ) | | | (406 | ) | | | (1,762 | ) | | | (1,496 | ) |
Residential construction | | | (201 | ) | | | (277 | ) | | | (328 | ) | | | (222 | ) | | | (347 | ) |
Other loans to individuals | | | (50 | ) | | | (100 | ) | | | (12 | ) | | | - | | | | (10 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Charge-offs | | | (2,092 | ) | | | (5,253 | ) | | | (3,522 | ) | | | (13,085 | ) | | | (12,042 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Recoveries: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 487 | | | $ | 187 | | | $ | 79 | | | $ | 236 | | | $ | 2 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 263 | | | | 7 | | | | - | | | | 3 | | | | 16 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 123 | | | | 480 | | | | 57 | | | | 3 | | | | 1 | |
AC&D | | | - | | | | 25 | | | | 1,602 | | | | 1,157 | | | | 35 | |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | 98 | | | | 221 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 1,727 | | | | 726 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Other commercial | | | 1 | | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 198 | | | | 416 | | | | 12 | | | | - | | | | 4 | |
HELOC | | | 69 | | | | 66 | | | | 33 | | | | 17 | | | | 1 | |
Residential construction | | | 57 | | | | 61 | | | | 124 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 64 | | | | 56 | | | | 29 | | | | 14.00 | | | | - | |
Total Recoveries | | | 3,087 | | | | 2,246 | | | | 1,936 | | | | 1,430 | | | | 59 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net charge-offs (recoveries) | | | 995 | | | | (3,007 | ) | | | (1,586 | ) | | | (11,655 | ) | | | (11,983 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, end of period | | $ | 8,262 | | | $ | 8,831 | | | $ | 10,591 | | | $ | 10,154 | | | $ | 12,424 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net charge-offs to total loans | | | -0.06 | % | | | 0.23 | % | | | 0.12 | % | | | 1.54 | % | | | 3.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | . | | | | | |
Allowance for loan losses to total loans | | | 0.52 | % | | | 0.68 | % | | | 0.78 | % | | | 1.34 | % | | | 3.11 | % |
The following table presents the allocation of the allowance for loan losses, including the reserve for PCI loans, by category for the years ended December 31:
Allocation of the Allowance for Loan Losses | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
(dollars in thousands) | | Amount | | | % of Loans to Total Loans | | | Amount | | | % of Loans to Total Loans | | | Amount | | | | % of Loans to Total Loans | | | Amount | | | % of Loans to Total Loans | | | Amount | | | % of Loans to Total Loans | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 1,563 | | | | 11 | % | | $ | 1,491 | | | | 9 | % | | $ | 1,074 | | | | | 9 | % | | $ | 703 | | | | 11 | % | | $ | 896 | | | | 12 | % |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 721 | | | | 21 | % | | | 399 | | | | 21 | % | | | 496 | | | | | 22 | % | | | 740 | | | | 22 | % | | | 1,061 | | | | 14 | % |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 1,751 | | | | 30 | % | | | 2,157 | | | | 30 | % | | | 1,102 | | | | | 27 | % | | | 2,106 | | | | 26 | % | | | 2,105 | | | | 28 | % |
AC&D | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | 4,699 | | | | | 10 | % | | | 3,883 | | | | 12 | % | | | 4,695 | | | | 22 | % |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | 458 | | | | 2 | % | | | 839 | | | | 2 | % | | | - | | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 591 | | | | 3 | % | | | 1,751 | | | | 5 | % | | | - | | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
AC&D - CRE | | | 395 | | | | 5 | % | | | 299 | | | | 4 | % | | | - | | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % |
Other commercial | | | 32 | | | | 0 | % | | | 25 | | | | 0 | % | | | 8 | | | | | 1 | % | | | 17 | | | | 2 | % | | | 408 | | | | 1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 443 | | | | 13 | % | | | 358 | | | | 13 | % | | | 654 | | | | | 14 | % | | | 309 | | | | 10 | % | | | 320 | | | | 5 | % |
HELOC | | | 1,651 | | | | 10 | % | | | 1,050 | | | | 11 | % | | | 1,463 | | | | | 12 | % | | | 1,898 | | | | 12 | % | | | 871 | | | | 14 | % |
Residential construction | | | 542 | | | | 4 | % | | | 390 | | | | 3 | % | | | 1,046 | | | | | 4 | % | | | 455 | | | | 3 | % | | | 98 | | | | 2 | % |
Other loans to individuals | | | 115 | | | | 1 | % | | | 72 | | | | 2 | % | | | 49 | | | | | 1 | % | | | 43 | | | | 2 | % | | | 86 | | | | 2 | % |
Unallocated | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | | 0 | % | | | - | | | | 0 | % | | | 1,884 | | | | 0 | % |
| | | $ | 8,262 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 8,831 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 10,591 | | | | | 101 | % | | $ | 10,154 | | | | 100 | % | | $ | 12,424 | | | | 100 | % |
We evaluate and estimate off-balance sheet credit exposure at the same time we estimate credit losses for loans by a similar process, including an estimate of commitment usage levels. These estimated credit losses are not recorded as part of the allowance for loan losses, but are recorded to a separate liability account by a charge to income, if material. Loan commitments, unused lines of credit and standby letters of credit make up the off-balance sheet items reviewed for potential credit losses. At both December 31, 2014 and 2013, $125 thousand was recorded as an other liability for off-balance sheet credit exposure.
Nonperforming Assets.Nonperforming assets, which consist of nonaccrual loans, accruing troubled debt restructurings (“TDRs”), accruing loans for which payments are 90 days or more past due, and OREO, totaled $20.9 million at December 31, 2014 compared to $26.8 million at December 31, 2013. Nonperforming loans, which consist of nonaccrual loans, accruing TDRs and accruing loans for which payments are 90 days or more past due, decreased $3.4 million, or 28%, to $8.9 million, or 0.56% of total loans and OREO at December 31, 2014, compared to $12.3 million, or 0.94% of total loans and OREO at December 31, 2013. The decreases in nonperforming assets from 2013 are due to the successful disposition of numerous OREO properties and the continued resolution of problem loans.
It is our general policy to place a loan on nonaccrual status when it is over 90 days past due and there is reasonable doubt that all principal and interest will be collected.Nonaccrual loans decreased $2.8 million, or 34%, in 2014 to $5.6 million from $8.4 million at December 31, 2013. Nonaccrual TDRs are included in the nonaccrual loan amounts noted. At December 31, 2014, nonaccrual TDR loans were $841 thousand and had a recorded allowance of $1 thousand. At December 31, 2013, nonaccrual TDR loans were $4.4 million and had no recorded allowance. Accruing TDRs totaled $3.3 million at December 31, 2014 and $3.9 million at December 31, 2013.
Interest that would have been recorded on nonaccrual loans for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, had they performed in accordance with their original terms, totaled $1.1 million, $3.0 million and $540 thousand, respectively. Interest income included in the results of operations for 2014, 2013 and 2012, with respect to loans that subsequently went to non-accrual, totaled $158 thousand, $310 thousand and $157 thousand, respectively.
We grade loans with an internal risk grade scale of 10 through 90, with grades 10 through 50 representing “pass” loans, grade 60 representing “special mention” and grades 70 and higher representing “classified” credit grades, respectively. Loans are reviewed on a regular basis internally, and at least annually by an external loan review group, to ensure loans are graded appropriately. Credits are reviewed for past due trends, declining cash flows, significant decline in collateral value, weakened guarantor financial strength, management concerns, market conditions and other factors that could jeopardize the repayment performance of the loan. Documentation deficiencies including collateral perfection and outdated or inadequate financial information are also considered in grading loans.
All loans graded 60 or worse are included on our list of “watch loans,” which represent potential problem loans, and are updated periodically and reported to both management and the Loan and Risk Committee of the board of directors quarterly. Impairment analyses are performed on all classified loans (risk grade of 70 or worse) and generally greater than $150 thousand as well as selected other loans as deemed appropriate.At December 31, 2014, we maintained “watch loans” totaling $18.9 million compared to $35.2 million at December 31, 2013. Approximately $4 million of the watch loans at December 31, 2014 were acquired loans. The future level of watch loans cannot be predicted, but rather will be determined by several factors, including overall economic conditions in the markets served.
We employ one of three potential methods to determine the fair value of impaired loans:
1) Fair value of collateral method. This is the most common method and is used when the loan is collateral dependent. In most cases, we will obtain an “as is” appraisal from a third-party appraisal group. The fair value from that appraisal may be adjusted downward for liquidation discounts for foreclosure or quick sale scenarios, as well as any applicable selling costs.
2) Cash flow method. This method is used when we believe that we will collect the loan primarily from cash flows generated by the borrower.
3) Observable market value method. This is the method used least often by us. Fair value is based on the offering price from a note buyer, in either the local community or a national loan sale advisor.
With respect to nonaccrual commercial and nonaccrual AC&D loans made to consumers, we typically utilize an “as-is,” or “discounted,” value to determine an appropriate fair value. When appraising projects with an expected cash flow to be received over a period of time, such as acquisition and development/land development loans, fair value is determined using a discounted cash flow methodology. We also account for expected selling and holding costs when determining an appropriate property value.
As of December 31, 2014, there were $49.9 million of AC&D - CRE loans kept current with bank-funded reserves of approximately $2.6 million. As of December 31, 2013, there were $37.0 million of AC&D loans kept current with bank-funded reserves of approximately $1.6 million. In both periods, these loans were still in the construction period of their lending arrangement.
At December 31, 2014, OREO totaled $12.0 million, all of which is recorded at values based on our most recent appraisals. Included in the total is $3.0 million of OREO covered under the FDIC loss share agreements as of December 31, 2014. At December 31, 2013, OREO totaled $14.5 million, all of which was recorded at values based on the most recent appraisals then available. Included in that total is $5.1 million of OREO covered under the FDIC loss share agreements. The decrease in OREO from 2013 is primarily due to successful dispositions.
The following table summarizes nonperforming assets at December 31:
Nonperforming Assets | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | | 2011 | | | 2010 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Nonaccrual loans | | $ | 5,585 | | | $ | 8,428 | | | $ | 10,374 | | | $ | 16,256 | | | $ | 40,911 | |
Past due 90 days or more and accruing | | | 30 | | | | 17 | | | | 77 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Troubled debt restructuring | | | 3,289 | | | | 3,854 | | | | 7,367 | | | | 3,972 | | | | 1,198 | |
Total nonperforming loans | | | 8,904 | | | | 12,299 | | | | 17,818 | | | | 20,228 | | | | 42,109 | |
OREO | | | 11,990 | | | | 14,492 | | | | 25,073 | | | | 14,403 | | | | 1,246 | |
Loans held for sale | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,560 | | | | - | |
Total nonperforming assets | | $ | 20,894 | | | $ | 26,791 | | | $ | 42,891 | | | $ | 36,191 | | | $ | 43,355 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PCI loans: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding customer balance | | $ | 165,686 | | | $ | 197,040 | | | $ | 278,200 | | | $ | 106,688 | | | $ | - | |
Carrying amount | | | 133,241 | | | | 163,787 | | | | 234,282 | | | | 63,818 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Nonperforming loans to total loans and OREO | | | 0.56 | % | | | 0.94 | % | | | 1.29 | % | | | 2.61 | % | | | 10.53 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Nonperforming assets to total assets | | | 0.89 | % | | | 1.37 | % | | | 2.11 | % | | | 3.25 | % | | | 7.04 | % |
Deposits.We offer a broad range of deposit instruments, including personal and business checking accounts, individual retirement accounts, business and personal money market accounts and time deposits, at competitive interest rates. Deposit account terms vary according to the minimum balance required, the time periods the funds must remain on deposit, and the interest rate, among other factors. We regularly evaluate the internal cost of funds, survey rates offered by competing institutions, review cash flow requirements for lending and liquidity and execute rate changes when deemed appropriate.
Total deposits at December 31, 2014 were $1.9 billion, increasing $251.5 million, or 16%, from December 31, 2013, net of acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments. Average deposits for 2014 were $1.8 billion, an increase of $202.8 million, or 13%, from 2013. The majority of the increase in average deposits during 2014 is attributed to the acquisition of Provident Community. Brokered deposits remain attractive given their relatively lower interest costs and flexible term structures, and will continue to be selectively utilized in our normal funding and interest rate risk management practices. Brokered deposits consist of brokered interest-bearing deposits, brokered money market accounts, and brokered certificates of deposits. Brokered money market and interest-bearing deposits are the result of the brokered money market deposit program initiated in December 2013.
The following table sets forth our average balance of deposit accounts and the average cost for each category of deposit for the years ended December 31:
Average Deposits and Costs | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | Average | | | % of | | | Average | | | Average | | | % of | | | Average | |
(dollars in thousands) | | Balance | | | Total | | | Cost | | | Balance | | | Total | | | Cost | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Demand deposits | | $ | 649,441 | | | | 36 | % | | | 0.05 | % | | $ | 547,847 | | | | 35 | % | | | 0.05 | % |
Savings and money market | | | 509,640 | | | | 29 | % | | | 0.38 | % | | | 447,421 | | | | 28 | % | | | 0.29 | % |
Time deposits - core | | | 473,509 | | | | 27 | % | | | 0.55 | % | | | 481,435 | | | | 30 | % | | | 0.35 | % |
Brokered deposits | | | 150,497 | | | | 8 | % | | | 0.36 | % | | | 103,630 | | | | 7 | % | | | 0.81 | % |
Total deposits | | $ | 1,783,087 | | | | 100 | % | | | 0.30 | % | | $ | 1,580,333 | | | | 100 | % | | | 0.26 | % |
The aggregate amounts of time deposits in denominations of $100,000 or more at December 31, 2014, and 2013, were $198.1 million and $284.7 million, respectively. In July 2010, the Dodd-Frank Act permanently increased the insurance limit on deposit accounts from $100,000 to $250,000. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, we had $50.9 million and $37.7 million in time deposits greater than $250,000, respectively.
The following table indicates the amount of our time deposits by time remaining until maturity as of December 31, 2014:
Maturities of Time Deposits | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Within | | | 3-6 | | | 6-12 | | | 1-5 | | | >5 | | | | | |
December 31, 2014 | | 3 Months | | | Months | | | Months | | | Years | | | Years | | | Total | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Time deposits of $100,000 or more | | $ | 32,809 | | | $ | 24,216 | | | $ | 55,330 | | | $ | 86,798 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 199,153 | |
Other time deposits | | | 66,996 | | | | 48,794 | | | | 97,039 | | | | 129,399 | | | | - | | | | 342,228 | |
Total time deposits | | $ | 99,805 | | | $ | 73,010 | | | $ | 152,369 | | | $ | 216,197 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 541,381 | |
Borrowings.Borrowings totaled $203.6 million at December 31, 2014 compared to $78.0 million at December 31, 2013, net of acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments. The increase in borrowings was due an additional $125 million in short-term advances from the FHLB during 2014 to help fund significant loan growth. On June 30, 2014, the Bank redeemed in full $6.9 million of its 11% Subordinated Notes, due June 30, 2019 at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the subordinated notes redeemed plus accrued but unpaid interest.
As a result of its mergers, the Company’s capital structure includes trust preferred securities previously issued by the predecessor companies through specially formed trusts. The combined total amount outstanding of the acquired trusts as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 was $38.1 million ($23.6 million, net of mark to market) and $25.8 million ($15.2 million, net of mark to market), respectively.
The following table details subordinated debt as of December 31, 2014 and 2013:
| | | Originally | | | Fair MarketValue | | | Carrying | | Maturity | | Current | |
| | | Issued | | | Adjustment | | | Amount | | Date | | Rate | |
| | (dollars in thousands) | |
| 2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Junior Subordinated Debt: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Community Capital I | | $ | 10,310 | | | $ | (4,131 | ) | | $ | 6,179 | | 06/15/36 | | | 1.79060 | % |
Citizens South I | | | 15,464 | | | | (6,008 | ) | | | 9,456 | | 12/15/35 | | | 1.81060 | % |
Provident Community I | | | 4,125 | | | | (1,467 | ) | | | 2,658 | | 10/01/36 | | | 1.97510 | % |
Provident Community II | | | 8,247 | | | | (2,957 | ) | | | 5,290 | | 03/01/37 | | | 1.97560 | % |
Total Subordinated Debt | | $ | 38,146 | | | $ | (14,563 | ) | | $ | 23,583 | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Subordinated Debt | | $ | 6,895 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 6,895 | | 06/30/19 | | | 11.00000 | % |
Junior Subordinated Debt: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Community Capital I | | | 10,310 | | | | (4,323 | ) | | | 5,987 | | 06/15/36 | | | 1.79290 | % |
Citizens South I | | | 15,464 | | | | (6,294 | ) | | | 9,170 | | 12/15/35 | | | 1.81290 | % |
Total Junior Subordinated Debt | | | 25,774 | | | | (10,617 | ) | | | 15,157 | | | | | | |
Total Subordinated Debt | | $ | 32,669 | | | $ | (10,617 | ) | | $ | 22,052 | | | | | | |
The following table details short and long-term borrowings at December 31:
Schedule of Borrowed Funds | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | % Change | | | | | | | % Change | | | | | |
| | | | | | | From Prior | | | | | | | From Prior | | | | | |
| | | 2014 | | | Year | | | 2013 | | | Year | | | 2012 | |
| | (dollars in thousands) | |
| Short-term: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Repurchase agreements | | $ | - | | | | -100.0 | % | | $ | 996 | | | | -90.2 | % | | $ | 10,143 | |
FHLB advances | | | 125,000 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 35,000 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | 15,000 | |
Total short-term | | | 125,000 | | | | 247.3 | % | | | 35,996 | | | | 43.2 | % | | | 25,143 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Long-term: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
FHLB advances | | | 55,000 | | | | 175.0 | % | | | 20,000 | | | | -63.6 | % | | | 55,000 | |
Subordinated debt | | | 23,583 | | | | 6.9 | % | | | 22,052 | | | | 2.2 | % | | | 21,573 | |
Total long-term | | | 78,583 | | | | 86.9 | % | | | 42,052 | | | | -45.1 | % | | | 76,573 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total borrowed funds | | $ | 203,583 | | | | 160.8 | % | | $ | 78,048 | | | | -23.3 | % | | $ | 101,716 | |
The following table details balances outstanding related to short-term borrowings at December 31 and annual information for the years presented:
Short-Term Borrowings | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Weighted | | | Maximum | | | Average | | | Average | |
| | | | | | | Average | | | Amount | | | Daily Balance | | | Annual | |
| | | Balance at | | | Interest Rate | | | Outstanding | | | Outstanding | | | Interest | |
| | | Year End | | | at Year End | | | During Year | | | During Year | | | Rate Paid | |
| | (dollars in thousands) | |
| 2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Repurchase agreements | | $ | - | | | | 0.00 | % | | $ | 8,692 | | | $ | 2,698 | | | | 0.10 | % |
Federal funds purchased | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 100 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.37 | % |
FHLB advances | | | 125,000 | | | | 0.23 | % | | | 125,000 | | | | 40,027 | | | | 0.21 | % |
Total | | $ | 125,000 | | | | 0.23 | % | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Repurchase agreements | | $ | 996 | | | | 0.10 | % | | $ | 10,955 | | | $ | 3,805 | | | | 0.04 | % |
Federal funds purchased | | | - | | | | 0.00 | % | | | 435 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.61 | % |
FHLB advances | | | 35,000 | | | | 0.33 | % | | | 35,000 | | | | 35,000 | | | | 0.33 | % |
Total | | $ | 35,996 | | | | 0.32 | % | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, two FHLB Fixed Rate Credit one month borrowing agreements in the amounts of $60.0 million and $65.0 million, respectively, matured. These borrowings were replaced with three FHLB Fixed Rate Credit one month borrowing agreements totaling $165 million at an average rate of 0.20%. Management currently expects to continue replacing the one month FHLB Fixed Rate Credit borrowings with similar short-term agreements for the near term. At December 31, 2014, the Company had an additional $196.8 million of credit available from the FHLB, $183.6 million of credit available from the Federal Reserve Discount Window, and $70.0 million of credit available from correspondent banks.
Contractual Obligations, Commitments and Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
In the ordinary course of operations, we may enter into certain contractual obligations that could include the funding of operations through debt issuances as well as leases for premises and equipment.
The following table summarizes our significant fixed and determinable contractual obligations at December 31, 2014:
Contractual Obligations | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Less Than | | | | | | | | | | | More Than | | | | | |
December 31, 2014 | | 1 Year | | | 1-3 Years | | | 3-5 Years | | | 5 Years | | | Total | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Time deposits | | $ | 325,184 | | | $ | 188,426 | | | $ | 27,771 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 541,381 | |
Deposits without a stated maturity | | | 1,245,773 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,245,773 | |
FHLB advances | | | 125,426 | | | | 55,304 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 180,731 | |
Subordinated debt | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 23,583 | | | | 23,583 | |
Operating lease obligations | | | 2,133 | | | | 3,112 | | | | 2,000 | | | | 4,699 | | | | 11,944 | |
FDIC loss share agreement - estimated true-up (1) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,552 | | | | 5,552 | |
Total | | $ | 1,698,517 | | | $ | 246,842 | | | $ | 29,771 | | | $ | 33,834 | | | $ | 2,008,963 | |
(1) Amount is included in other liabilities on the balance sheet.
Information about our off-balance sheet risk exposure is presented in Note 16 – Off-Balance Sheet Risk to the Consolidated Financial Statements. At December 31, 2014, we had $328.3 million of pre-approved but unused lines of credit, $5.4 million of standby letters of credit and $717 thousand of commercial letters of credit. As part of ongoing business, we currently do not participate in transactions that generate relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as entities often referred to as special purpose entities, which generally are established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or other contractually narrow or limited purposes. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company maintained a reserve of $125 thousand, which is in other liabilities, for off-balance sheet credit exposure.
As part of Citizens South’s Plan of Conversion and Reorganization in May 2002, Citizens South established a memo liquidation account in an amount equal to its equity at the time of the conversion of approximately $44 million for the benefit of eligible account holders and supplemental eligible account holders who continue to maintain their accounts at Citizens South Bank after the conversion. In accordance with the memo liquidation account, in the event of a complete liquidation of Citizens South Bank, each eligible account holder and supplemental eligible account holder would be entitled to receive a distribution from the liquidation account in an amount proportionate to the current adjusted qualifying balances for accounts then held. In connection with the Citizens South merger and the subsequent merger of Citizens South Bank into the Bank, the Bank assumed this memo liquidation account. This liquidation account is reviewed and adjusted annually. The value of the liquidation account was $7.6 million at both December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Liquidity refers to the ability to manage future cash flows to meet the needs of depositors and borrowers and to fund operations. We strive to maintain sufficient liquidity to fund future loan demand and to satisfy fluctuations in deposit levels. This is achieved primarily in the form of available lines of credit from various correspondent banks, the FHLB, the Federal Reserve Discount Window and through our investment portfolio. In addition, we may have short-term investments at our primary correspondent bank in the form of Federal funds sold. Liquidity is governed by an asset/liability policy approved by the board of directors and administered by an internal Asset-Liability Management Committee (the “ALCO”). The ALCO reports monthly asset/liability-related matters to the Loan and Risk Committee of the board of directors.
Our internal liquidity ratio (total liquid assets, or cash and cash equivalents, divided by deposits and short-term liabilities) at December 31, 2014 was 19.55% compared to 20.92% at December 31, 2013. Both ratios exceeded our minimum internal target of 10%. The slight decline in liquidity is due to the deployment of cash into loans and the reclassification of $58 million in available-for-sale investments to the held-to-maturity classification. Both ratios exceeded our minimum internal target of 10%. If we continue to see rapid loan growth as we have seen over the past year, we may utilize additional sources of liquidity through the use of available credit lines, additional borrowing capacity through unpledged securities, and brokered deposits.In addition, at December 31, 2014, we had $196.8 million of credit available from the FHLB, $183.6 million of credit available from the Federal Reserve Discount Window, and available lines totaling $70.0 million from correspondent banks.
At December 31, 2014, we had $328.3 million of pre-approved but unused lines of credit, $5.4 million of standby letters of credit and $717 thousand of commercial letters of credit. In management's opinion, these commitments represent no more than normal lending risk to us and will be funded from normal sources of liquidity.
Our capital position is reflected in our shareholders’ equity, subject to certain adjustments for regulatory purposes. Shareholders’ equity, or capital, is a measure of our net worth, soundness and viability. We continue to remain in a well capitalized position. Shareholders’ equity on December 31, 2014 was $275.1 million, compared to $262.1 million at December 31, 2013. The $13.0 million increase was primarily the result of net income of $12.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, a $3.3 million increase in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) from unrealized securities gains, $1.1 million of net share based compensation and $250 thousand in proceeds from the exercise of stock options. These increases were partially offset by the repurchase of 136,743 shares of Common Stock in open market transactions and the acquisition of 19,942 shares in connection with satisfaction of tax withholding obligations on vested restricted stock.
Risk-based capital regulations adopted by the Federal Reserve Board and the FDIC require bank holding companies and banks to achieve and maintain specified ratios of capital to risk-weighted assets. The risk-based capital rules are designed to measure different components of capital in relation to the credit risk of both on- and off-balance sheet items. Under the guidelines, one of four risk weights is applied to the different on-balance sheet items. Off-balance sheet items, such as loan commitments, are also subject to risk weighting after conversion to balance sheet equivalent amounts. These guidelines also specify that banks that are experiencing internal growth or making acquisitions will be expected to maintain capital positions substantially above the minimum supervisory levels. Under regulations in effect at December 31, 2014, the relevant components of capital consisted of Tier 1 capital (generally common shareholders’ equity, a limited amount of qualifying perpetual preferred stock and trust preferred securities, and minority interests in consolidated subsidiaries, net of goodwill and other intangible assets, deferred tax assets in excess of certain thresholds and certain other items), Tier 2 capital (generally certain preferred stock, mandatorily convertible debt securities and term subordinated debt) and total capital (consisting of Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital). Under these regulations, at December 31, 2014, banks were required to maintain a minimum total capital to total risk-weighted assets ratio of 8.00%, at least half of which was required to be in the form of Tier 1 capital. At December 31, 2014, the Company and the Bank both satisfied their minimum regulatory capital requirements and each was “well capitalized” within the meaning of federal regulatory requirements.
Actual and required capital levels at December 31 for each of the past two years are presented below:
Capital Ratios | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Regulatory Minimums | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | To Be Well | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Capitalized | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Under | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Prompt | |
| | | | | | | | | | | For Capital | | | Corrective | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Adequacy | | | Actions | |
| | | December 31 | | | Purposes | | | Provisions | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(dollars in thousands) | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | Ratio | | | Ratio | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Park Sterling Corporation | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 capital | | $ | 231,088 | | | $ | 218,552 | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 2 capital | | | 8,469 | | | | 15,956 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total capital | | $ | 239,557 | | | $ | 234,508 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Risk-adjusted average assets | | $ | 1,717,003 | | | $ | 1,424,574 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Average assets | | $ | 2,273,275 | | | $ | 1,879,283 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Risk-based capital ratios | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 capital | | | 13.46 | % | | | 15.34 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 6.00 | % |
Total capital | | | 13.95 | % | | | 16.46 | % | | | 8.00 | % | | | 10.00 | % |
Tier 1 leverage ratio | | | 10.17 | % | | | 11.63 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 5.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Park Sterling Bank | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 capital | | $ | 216,110 | | | $ | 193,830 | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 2 capital | | | 8,469 | | | | 15,956 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total capital | | $ | 224,579 | | | $ | 209,786 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Risk-adjusted average assets | | $ | 1,713,612 | | | $ | 1,420,331 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Average assets | | $ | 2,259,856 | | | $ | 1,861,925 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Risk-based capital ratios | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 capital | | | 12.61 | % | | | 13.65 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 6.00 | % |
Total capital | | | 13.11 | % | | | 14.77 | % | | | 8.00 | % | | | 10.00 | % |
Tier 1 leverage ratio | | | 9.56 | % | | | 10.41 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 5.00 | % |
In connection with the Bank’s Public Offering in August 2010, the Bank had committed to its regulators to maintain a Tier 1 leverage ratio, calculated as Tier 1 capital to average assets, of at least 10.00% for three years. This commitment expired on August 18, 2013.
In July 2013, the federal banking regulatory agencies approved final regulatory capital rules that replace the existing general risk-based capital and related rules, broadly revising the basic definitions and elements of regulatory capital and making substantial changes to the credit risk weightings for banking and trading book assets. The new regulatory capital rules establish the benchmark capital rules and capital floors that are generally applicable to United States banks under the Dodd-Frank Act and make the capital rules consistent with heightened international capital standards known as Basel III. These new capital standards apply to all banks, regardless of size, and to all bank holding companies with consolidated assets greater than $500 million.
Under the new capital guidelines, applicable regulatory capital components consist of (1) common equity Tier 1 capital (common stock, including related surplus, and retained earnings, plus limited amounts of minority interest in the form of common stock, net of goodwill and other intangibles (other than mortgage servicing assets), deferred tax assets arising from net operating loss and tax credit carry forwards above certain levels, mortgage servicing rights above certain levels, gain on sale of securitization exposures and certain investments in the capital of unconsolidated financial institutions, and adjusted by unrealized gains or losses on cash flow hedges and accumulated other comprehensive income items (subject to the ability of a non-advanced approaches institution to make a one-time irrevocable election to exclude from regulatory capital most components of AOCI)), (2) additional Tier 1 capital (qualifying non-cumulative perpetual preferred stock, including related surplus, plus qualifying Tier 1 minority interest and, in the case of holding companies with less than $15 billion in consolidated assets at December 31, 2009, certain grandfathered trust preferred securities and cumulative perpetual preferred stock in limited amounts, net of mortgage servicing rights, deferred tax assets related to temporary timing differences, and certain investments in financial institutions) and (3) Tier 2 capital (the allowance for loan and lease losses in an amount not exceeding 1.25% of standardized risk-weighted assets, plus qualifying preferred stock, qualifying subordinated debt and qualifying total capital minority interest, net of Tier 2 investments in financial institutions). Total Tier 1 capital, plus Tier 2 capital, constitutes total risk-based capital. The required minimum ratios are as follows:
| | ● | common equity Tier 1 capital ratio (common equity Tier 1 capital to standardized total risk-weighted assets) of 4.5%; |
| | ● | Tier 1 capital ratio (Tier 1 capital to standardized total risk-weighted assets) of 6%; |
| | ● | total capital ratio (total capital to standardized total risk-weighted assets) of 8%; and |
| | ● | leverage ratio (Tier 1 capital to average total consolidated assets) of 4%. |
Advanced approaches banking organizations (those organizations with either total assets of $250 billion or more, or with foreign exposure of $10 billion or more) also are subject to a supplementary leverage ratio that incorporates a broader set of exposures in the denominator. The new capital guidelines also provide that all covered banking organizations must maintain a new capital conservation buffer of common equity Tier 1 capital in an amount greater than 2.5% of total risk-weighted assets to avoid being subject to limitations on capital distributions and discretionary bonus payments to executive officers. Advanced approaches organizations also are subject to a countercyclical capital buffer. Failure to satisfy the capital buffer requirements will result in increasingly stringent limitations on various types of capital distributions, including dividends, share buybacks and discretionary payments on Tier 1 instruments, and discretionary bonus payments.
Non-advanced approaches banking organizations, including the Company and the Bank, must begin compliance with the new minimum capital ratios and the standardized approach for risk-weighted assets as of January 1, 2015, and the revised definitions of regulatory capital and the revised regulatory capital deductions and adjustments are being phased in over time for such organizations beginning as of that date. The capital conservation buffer will be phased in for all banking organizations beginning January 1, 2016.
The final regulatory capital rules also incorporate these changes in regulatory capital into the prompt corrective action framework, under which the thresholds for “adequately capitalized” banking organizations will be equal to the new minimum capital requirements. Under this framework, in order to be considered “well capitalized”, insured depository institutions will be required to maintain a Tier 1 leverage ratio of 5%, a common equity Tier 1 risk-based capital measure of 6.5%, a Tier 1 risked-based capital ratio of 8% and a total risk-based capital ratio of 10%. Under the new regulations, in effect on January 1, 2015, management currently estimates that both the Company and the Bank would be considered “well capitalized”.
The new capital guidelines reflect changes from the June 2012 proposals that minimize the impact of the revised capital regulations on community banks. In particular, banking organizations with less than $15 billion in total assets (including the Company and the Bank) are not be subject to the phase-out of non-qualifying Tier 1 capital instruments, such as TruPS, that were issued and outstanding prior to May 19, 2010. In addition, non-advanced approaches banking organizations have a one-time option to exclude certain components of accumulated other comprehensive income from inclusion in regulatory capital, comparable to treatment under the current capital rules. The Company currently plans to continue to exclude certain components of AOCI from inclusion in regulatory capital. The regulations also retain the existing treatment for residential mortgage exposures in the current risk-based capital rules, rather than adopt the proposed changes that would have required banking organizations to determine the risk weights based on a complex categorization and loan-to-value assessment.
Although the new capital guidelines alleviate some of the concerns of community banks with the capital standards as originally proposed, the new capital standards will impose significant changes on the definition of capital, including the inability to include instruments such as TruPS in Tier 1 capital going forward and new constraints on the inclusion of minority interests, mortgage servicing assets, deferred tax assets and certain investments in the capital of unconsolidated financial institutions. In addition, the new guidelines increase the risk-weights of various assets, including certain high volatility commercial real estate and past due asset exposures.
Market Risk andInterest RateSensitivity
As a financial institution, and based on the nature of our operations, we are exposed to market risk, the primary source of which is interest rate risk. Interest rate risk results from timing differences in the repricing of assets and liabilities, changes in relationships between rate indices, and the potential exercise of explicit or embedded options. Effective management of interest rate risk is intended to protect the Company’s capital and profitability through various interest rate environments. Such risk is inherent to the business of banking given the inability to fully match the time horizons and interest rate characteristics of all customer related cash flows, as generated in the Company’s financial activities.The ALCO actively evaluates and manages interest rate risk using a process developed by the Company. The ALCO is also responsible for approving our asset/liability management policies, overseeing the formulation and implementation of strategies to improve balance sheet positioning and earnings, and reviewing our interest rate sensitivity position.
The primary measures that management uses to evaluate short-term interest rate risk include (i) net interest income at risk, which projects the impact of different interest rate scenarios on net interest income over one-year and two-year time horizons; and (ii) economic value of equity at risk, which measures potential long-term risk in the balance sheet by valuing our assets and liabilities at “market” under different interest rate scenarios. In addition, management considers cumulative gap summary, which measures potential changes in cash flows should interest rates rise or fall.
These measures have historically been calculated under a simulation model prepared by an independent vendor assuming incremental 100 basis point shocks (or immediate shifts) in interest rates up to a total increase or decrease of 400 basis points, as well as non-parallel interest rate shifts. These simulations estimate the impact that various changes in the overall level of interest rates over a one- and two-year time horizon have on net interest income and economic value of equity. The results help us develop strategies for managing exposure to interest rate risk. Like any forecasting technique, interest rate simulation modeling is based on a large number of assumptions. In this case, the assumptions relate primarily asset and liability prepayments, deposit decay rates and interest rates. We believe that the assumptions are reasonable, both individually and in the aggregate. Nevertheless, the simulation modeling process produces only a sophisticated estimate, not a precise calculation of exposure. The overall interest rate risk management process is subject to annual review by an outside professional services firm to ascertain its effectiveness as required by Federal regulations.
Our current guidelines for net interest income at risk call for preventive measures if over the next twelve months (i) a 400 basis point shock, or immediate increase or decrease, would affect net interest income by more than 30.00% over the next twelve months; (ii) a 300 basis point shock would affect net interest income by more than 22.50%; (iii) a 200 basis point shock would affect net interest income by more than 15.00%; or, (iv) a 100 basis point shock would affect net interest income by more than 7.50%. We currently operate well within these guidelines. As of December 31, 2014, based on the results of this simulation model, which assumed a static environment with no contemplated asset growth or changes in our balance sheet management strategies, we could, for example, expect net interest income to decrease by approximately 5.3% over twelve months if short-term interest rates immediately increased by 200 basis points, given that we are currently in a liability-sensitive position. Similarly, if short-term interest rates decreased by 200 basis points, net interest income could be expected to decrease by approximately 1.0% over twelve months, as the cost of interest-bearing liabilities would be unable to fully benefit from a 200 basis point decline in rate while our yield on interest-earning assets could suffer materially from the decline. As of December 31, 2013, based on the results of this simulation model, which assumed a static environment with no contemplated asset growth or changes in our balance sheet management strategies, we could expect net interest income to decrease by approximately 3.8% over twelve months if short-term interest rates immediately decreased by 200 basis points. Similarly, if short-term interest rates increased by 200 basis points, net interest income could be expected to decrease by approximately 5.4% over twelve months given that we are currently in a liability-sensitive position.
Our current guidelines for economic value of equity call for preventive measures if (i) a 400 basis point shock, or immediate increase or decrease, would affect economic value of equity by more than 40.00% over the next twelve months; (ii) a 300 basis point shock would affect economic value of equity by more than 30.00%; (iii) a 200 basis point shock would affect economic value of equity by more than 22.50%; or, (iv) a 100 basis point shock would affect economic value of equity by more than 11.25%. We currently operate well within these guidelines. As of December 31, 2014, based on the results of this simulation model, which assumed a static environment with no contemplated asset growth or changes in our balance sheet management strategies, we could, for example, expect economic value of equity to decrease by approximately 11.9% over twelve months if short-term interest rates immediately increased by 200 basis points, given that we are currently in a liability-sensitive position. Conversely, if short-term interest rates decreased by 200 basis points, economic value of equity could be expected to increase by approximately 2.3% over twelve months. As of December 31, 2013, based on the results of this simulation model, which assumed a static environment with no contemplated asset growth or changes in our balance sheet management strategies, we could expect economic value of equity to increase by approximately 12.4% over twelve months if short-term interest rates immediately decreased by 200 basis points. Conversely, if short-term interest rates increased by 200 basis points, economic value of equity could be expected to decrease by approximately 13.5% over twelve months.
Financial institutions are subject to interest rate risk to the degree that their interest-bearing liabilities, primarily deposits, mature or reprice more or less frequently, or on a different basis, than their interest-earning assets, primarily loans and investment securities. The match between the scheduled repricing and maturities of our interest-earning assets and liabilities within defined periods is referred to as “gap” analysis. The following table reflects our rate sensitive assets and liabilities by maturity as of December 31, 2014. Variable rate loans are shown in the category of due “within three months” because they reprice with changes in the prime lending rate. Fixed rate loans are presented assuming the entire loan matures on the final due date, although payments are actually made at regular intervals and are not reflected in this schedule.
Interest Rate Gap Sensitivity | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Within | | | Three | | | One Year | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Three | | | Months to | | | to Five | | | After | | | | | |
At December 31, 2014 | | Months | | | One Year | | | Years | | | Five Years | | | Total | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Interest-earning assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest-bearing deposits | | $ | 34,356 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 34,356 | |
Federal funds sold | | | 485 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 485 | |
Securities | | | 57,882 | | | | 60,479 | | | | 188,877 | | | | 195,718 | | | | 502,956 | |
Loans | | | 594,402 | | | | 221,059 | | | | 692,647 | | | | 84,187 | | | | 1,592,295 | |
Total interest-earning assets | | | 687,125 | | | | 281,538 | | | | 881,524 | | | | 279,905 | | | | 2,130,092 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest-bearing liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Demand deposits | | | 405,012 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 405,012 | |
MMDA and savings | | | 583,942 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 583,942 | |
Time deposits | | | 100,206 | | | | 224,921 | | | | 216,197 | | | | 57 | | | | 541,381 | |
Short term borrowings | | | 125,000 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 125,000 | |
Long term borrowings | | | 73,146 | | | | - | | | | 20,000 | | | | (14,563 | ) | | | 78,583 | |
Total interest-bearing liabilities | | | 1,287,306 | | | | 224,921 | | | | 236,197 | | | | (14,506 | ) | | | 1,733,918 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Derivatives | | | 120,370 | | | | - | | | | 45,000 | | | | (165,370 | ) | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest sensitivity gap | | $ | (479,811 | ) | | $ | 56,617 | | | $ | 690,327 | | | $ | 129,041 | | | $ | 396,174 | |
Cumulative interest sensitivity gap | | $ | (479,811 | ) | | $ | (423,194 | ) | | $ | 267,133 | | | $ | 396,174 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Percentage of total assets | | | | | | | -17.94 | % | | | | | | | | | | | | |
We use certain derivative instruments to help manage economic and interest rate risk related to commercial loans, long-term debt and other funding sources. We also use derivatives to facilitate transactions on behalf of our customers. At December 31, 2014, the Company had derivative financial instruments with a total notional amount of $165.4 million, with a net fair value loss of $761 thousand. At times, we will be required to post collateral to certain counterparties when our loss positions exceed certain negotiated limits. As a result of the unfavorable position of the instruments at December 31, 2014, the Company posted collateral of approximately $2.4 million with counterparties. See Note 17 – Derivative Financial Instruments and Hedging Activities to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of our derivative financial instruments and hedging activities.
Impact of Inflation and Changing Prices
As a financial institution, we have an asset and liability make-up that is distinctly different from that of an entity with substantial investments in plant and inventory, because the major portions of a commercial bank’s assets are monetary in nature. As a result, our performance may be significantly influenced by changes in interest rates. Although we, and the banking industry, are more affected by changes in interest rates than by inflation in the prices of goods and services, inflation is a factor that may influence interest rates. However, the frequency and magnitude of interest rate fluctuations do not necessarily coincide with changes in the general inflation rate. Inflation does affect operating expenses in that personnel expenses and the cost of supplies and outside services tend to increase more during periods of high inflation.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
The section captioned “Market Risk and Interest Rate Sensitivity” under Part II, Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” of this report is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data

Report of Independent Registered public accounting firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors
Park Sterling Corporation
Charlotte, North Carolina
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Park Sterling Corporation (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in shareholders’ equity, and cash flows, for each of the years in the three year period ended December 31, 2014. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Park Sterling Corporation as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three year period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established inInternal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated March 6, 2015, expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ DIXON HUGHES GOODMAN LLP
Charlotte, North Carolina
March 6, 2015
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2014 and 2013
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands, except per share data) | |
| | | | | | | | | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Cash and due from banks | | $ | 16,549 | | | $ | 13,087 | |
Interest-earning balances at banks | | | 34,356 | | | | 41,680 | |
Federal funds sold | | | 485 | | | | 300 | |
Investment securities available-for-sale, at fair value | | | 375,683 | | | | 349,491 | |
Investment securities held-to-maturity(fair value of $117,627 and $51,334 at December 31, 2014and 2013, respectively) | | | 115,741 | | | | 51,972 | |
Nonmarketable equity securities | | | 11,532 | | | | 5,905 | |
Loans held for sale | | | 11,602 | | | | 2,430 | |
Loans: | | | | | | | | |
Non-covered | | | 1,538,354 | | | | 1,224,674 | |
Covered | | | 42,339 | | | | 71,134 | |
Less allowance for loan losses | | | (8,262 | ) | | | (8,831 | ) |
Net loans | | | 1,572,431 | | | | 1,286,977 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Premises and equipment, net | | | 59,247 | | | | 55,923 | |
Bank-owned life insurance | | | 57,712 | | | | 47,832 | |
Deferred tax asset | | | 35,623 | | | | 36,318 | |
Other real estate owned - noncovered | | | 8,979 | | | | 9,404 | |
Other real estate owned - covered | | | 3,011 | | | | 5,088 | |
Goodwill | | | 29,240 | | | | 26,457 | |
FDIC indemnification asset | | | 3,964 | | | | 10,025 | |
Core deposit intangible | | | 10,960 | | | | 8,629 | |
Accrued interest receivable | | | 4,467 | | | | 4,222 | |
Other assets | | | 7,648 | | | | 5,087 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 2,359,230 | | | $ | 1,960,827 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Deposits: | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest-bearing | | $ | 321,019 | | | $ | 255,861 | |
Interest-bearing | | | 1,530,335 | | | | 1,344,024 | |
Total deposits | | | 1,851,354 | | | | 1,599,885 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Short-term borrowings | | | 125,000 | | | | 35,996 | |
Long-term borrowings | | | 55,000 | | | | 20,000 | |
Subordinated debt | | | 23,583 | | | | 22,052 | |
Accrued interest payable | | | 398 | | | | 412 | |
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | | | 28,790 | | | | 20,362 | |
Total liabilities | | | 2,084,125 | | | | 1,698,707 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Commitments (Notes 15 and 16) | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Shareholders' equity: | | | | | | | | |
Preferred stock, no par value5,000,000 shares authorized; 0 issued and outstandingat December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively | | | - | | | | - | |
Common stock, $1.00 par value200,000,000 shares authorized; 44,859,798and 44,730,669 shares issued and outstanding atDecember 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively | | | 44,860 | | | | 44,731 | |
Additional paid-in capital | | | 222,819 | | | | 222,596 | |
Accumulated earnings (deficit) | | | 8,901 | | | | (405 | ) |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | | | (1,475 | ) | | | (4,802 | ) |
Total shareholders' equity | | | 275,105 | | | | 262,120 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and shareholders' equity | | $ | 2,359,230 | | | $ | 1,960,827 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Years Ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands, except per share data) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loans, including fees | | $ | 74,867 | | | $ | 72,669 | | | $ | 53,194 | |
Federal funds sold | | | 1 | | | | 24 | | | | 49 | |
Taxable investment securities | | | 9,318 | | | | 5,029 | | | | 3,606 | |
Tax-exempt investment securities | | | 631 | | | | 756 | | | | 750 | |
Nonmarketable equity securities | | | 362 | | | | 150 | | | | 194 | |
Interest on deposits at banks | | | 118 | | | | 177 | | | | 153 | |
Total interest income | | | 85,297 | | | | 78,805 | | | | 57,946 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Money market, NOW and savings deposits | | | 2,270 | | | | 1,570 | | | | 1,488 | |
Time deposits | | | 3,155 | | | | 2,538 | | | | 2,951 | |
Short-term borrowings | | | 86 | | | | 7 | | | | 11 | |
Long-term borrowings | | | 513 | | | | 550 | | | | 600 | |
Subordinated debt | | | 1,631 | | | | 1,717 | | | | 1,520 | |
Total interest expense | | | 7,655 | | | | 6,382 | | | | 6,570 | |
Net interest income | | | 77,642 | | | | 72,423 | | | | 51,376 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Provision for loan losses | | | (1,286 | ) | | | 746 | | | | 2,023 | |
Net interest income after provision for loan losses | | | 78,928 | | | | 71,677 | | | | 49,353 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Service charges on deposit accounts | | | 3,881 | | | | 2,646 | | | | 1,814 | |
Income from fiduciary activities | | | 2,748 | | | | 2,779 | | | | 2,332 | |
Commissions and fees from investment brokerage | | | 452 | | | | 419 | | | | 287 | |
Gain on sale of securities available-for-sale | | | 180 | | | | 98 | | | | 1,478 | |
Bankcard services income | | | 2,632 | | | | 2,373 | | | | 1,085 | |
Mortgage banking income | | | 2,641 | | | | 3,123 | | | | 2,478 | |
Income from bank-owned life insurance | | | 2,688 | | | | 1,863 | | | | 1,264 | |
Amortization of indemnification asset | | | (3,203 | ) | | | (189 | ) | | | - | |
Loss share true-up liability expense | | | (587 | ) | | | (59 | ) | | | - | |
Other noninterest income | | | 2,521 | | | | 2,033 | | | | 634 | |
Total noninterest income | | | 13,953 | | | | 15,086 | | | | 11,372 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Noninterest expense | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Salaries and employee benefits | | | 39,538 | | | | 34,570 | | | | 29,396 | |
Occupancy and equipment | | | 10,409 | | | | 7,691 | | | | 4,654 | |
Advertising and promotion | | | 1,494 | | | | 839 | | | | 781 | |
Legal and professional fees | | | 3,486 | | | | 3,142 | | | | 3,190 | |
Deposit charges and FDIC insurance | | | 1,491 | | | | 1,647 | | | | 1,250 | |
Data processing and outside service fees | | | 6,449 | | | | 5,950 | | | | 4,371 | |
Communication fees | | | 1,974 | | | | 1,737 | | | | 945 | |
Core deposit intangible amortization | | | 1,269 | | | | 1,029 | | | | 564 | |
Net cost (earnings) of operation of other real estate owned | | | 817 | | | | (371 | ) | | | 3,462 | |
Loan and collection expense | | | 1,350 | | | | 1,972 | | | | 1,221 | |
Postage and supplies | | | 667 | | | | 1,009 | | | | 791 | |
Other noninterest expense | | | 4,990 | | | | 4,884 | | | | 3,451 | |
Total noninterest expense | | | 73,934 | | | | 64,099 | | | | 54,076 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income taxes | | | 18,947 | | | | 22,664 | | | | 6,649 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income tax expense | | | 6,058 | | | | 7,359 | | | | 2,306 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | 12,889 | | | | 15,305 | | | | 4,343 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Preferred dividends | | | - | | | | 353 | | | | 51 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income to common shareholders | | $ | 12,889 | | | $ | 14,952 | | | $ | 4,292 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic earnings per common share | | $ | 0.29 | | | $ | 0.34 | | | $ | 0.12 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted earnings per common share | | $ | 0.29 | | | $ | 0.34 | | | $ | 0.12 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average common shares outstanding | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | 43,924,457 | | | | 43,965,408 | | | | 35,101,407 | |
Diluted | | | 44,247,000 | | | | 44,053,253 | | | | 35,108,229 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Years Ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012
| | | For the Years Ended December 31 | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 12,889 | | | $ | 15,305 | | | $ | 4,343 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities available for sale and transferred securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Change in net unrealized gains (losses) during the period | | | 10,464 | | | | (13,200 | ) | | | 1,908 | |
Change in net unrealized loss on securities transferred to held to maturity | | | (2,055 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
Reclassification adjustment for net gains recognized in net income | | | (180 | ) | | | (98 | ) | | | (1,478 | ) |
Total securities available for sale and transferred securities | | | 8,229 | | | | (13,298 | ) | | | 430 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Derivatives: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Change in the accumulated gain (loss) on effective cash flow hedge derivatives | | | (3,381 | ) | | | 545 | | | | - | |
Reclassification adjustment for interest payments | | | 422 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Total derivatives | | | (2,959 | ) | | | 545 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive income (loss), before tax | | | 5,270 | | | | (12,753 | ) | | | 430 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deferred tax expense (benefit) related to other comprehensive income | | | 1,943 | | | | (4,753 | ) | | | 112 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | | | 3,327 | | | | (8,000 | ) | | | 318 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total comprehensive income | | $ | 16,216 | | | $ | 7,305 | | | $ | 4,661 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTSOF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Years Ended December 31,2014,2013 and 2012
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Accumulated | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Additional | | | Accumulated | | | Other | | | Total | |
| | | Preferred Stock | | | Common Stock | | | Paid-In | | | Earnings | | | Comprehensive | | | Shareholders' | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Shares | | | Amount | | | Capital | | | (Deficit) | | | Income (Loss) | | | Equity | |
| | | (dollars in thousands, except share amounts) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2011 | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | 32,643,627 | | | $ | 32,644 | | | $ | 172,390 | | | $ | (17,860 | ) | | $ | 2,880 | | | $ | 190,054 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Shares of preferred stock issued | | | 20,500 | | | | 20,500 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 20,500 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issuance of restricted stock grants | | | - | | | | - | | | | 78,000 | | | | 78 | | | | (78 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Share-based compensation expense | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,012 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,012 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Shares issued for Citizens South merger | | | - | | | | - | | | | 11,857,226 | | | | 11,857 | | | | 46,721 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 58,578 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock repurchased | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,000 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (12 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (15 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Dividends on preferred stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (51 | ) | | | - | | | | (51 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,343 | | | | - | | | | 4,343 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 318 | | | | 318 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2012 | | | 20,500 | | | | 20,500 | | | | 44,575,853 | | | | 44,576 | | | | 221,033 | | | | (13,568 | ) | | | 3,198 | | | | 275,739 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Redemption of preferred stock | | | (20,500 | ) | | | (20,500 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (20,500 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issuance of restricted stock grants | | | - | | | | - | | | | 174,000 | | | | 174 | | | | (174 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Forfeitures of restricted stock grants | | | - | | | | - | | | | (23,860 | ) | | | (23 | ) | | | 23 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercise of stock options | | | - | | | | - | | | | 60,943 | | | | 60 | | | | 248 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 308 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Share-based compensation expense | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,776 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,776 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock repurchased | | | - | | | | - | | | | (56,267 | ) | | | (56 | ) | | | (310 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (366 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Dividends on preferred stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (353 | ) | | | - | | | | (353 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Dividends on common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,789 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,789 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 15,305 | | | | - | | | | 15,305 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (8,000 | ) | | | (8,000 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2013 | | | - | | | | - | | | | 44,730,669 | | | | 44,731 | | | | 222,596 | | | | (405 | ) | | | (4,802 | ) | | | 262,120 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Shares issued | | | - | | | | - | | | | 252 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issuance of restricted stock grants | | | - | | | | - | | | | 238,613 | | | | 239 | | | | (239 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Forfeitures of restricted stock grants | | | - | | | | - | | | | (7,250 | ) | | | (7 | ) | | | 7 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercise of stock options | | | - | | | | - | | | | 54,199 | | | | 54 | | | | 196 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 250 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Share-based compensation expense | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,129 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,129 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock repurchased | | | - | | | | - | | | | (156,685 | ) | | | (157 | ) | | | (870 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1,027 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Dividends on common stock | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,583 | ) | | | - | | | | (3,583 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 12,889 | | | | - | | | | 12,889 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,327 | | | | 3,327 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2014 | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | 44,859,798 | | | $ | 44,860 | | | $ | 222,819 | | | $ | 8,901 | | | $ | (1,475 | ) | | $ | 275,105 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTSOF CASH FLOWS
Years Ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and2012
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 12,889 | | | $ | 15,305 | | | $ | 4,343 | |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to netcash provided (used) by operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accretion on acquired loans | | | (9,323 | ) | | | (8,513 | ) | | | (7,462 | ) |
Net amortization (accretion) on investments | | | 2,190 | | | | 564 | | | | (2,425 | ) |
Other depreciation and amortization, net | | | 9,983 | | | | 4,928 | | | | 3,403 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | (1,286 | ) | | | 746 | | | | 2,023 | |
Share-based compensation expense | | | 1,129 | | | | 1,776 | | | | 2,012 | |
Deferred income taxes | | | 5,208 | | | | 8,460 | | | | 2,255 | |
Amortization (accretion) of FDIC indemnification asset | | | 3,203 | | | | 189 | | | | - | |
Net gains on sales of investment securities available-for-sale | | | (180 | ) | | | (98 | ) | | | (1,478 | ) |
Net gains on sales of loans held for sale | | | (1,134 | ) | | | (1,835 | ) | | | (1,182 | ) |
Net (gains) losses on disposals of premises and equipment | | | 400 | | | | 412 | | | | (94 | ) |
Net gains on sales of other real estate owned | | | (532 | ) | | | (2,061 | ) | | | (253 | ) |
Writedowns of other real estate owned | | | 604 | | | | 1,394 | | | | 2,421 | |
Income from bank owned life insurance | | | (2,688 | ) | | | (1,863 | ) | | | (1,264 | ) |
Proceeds of loans held for sale | | | 58,761 | | | | 110,118 | | | | 71,855 | |
Disbursements for loans held for sale | | | (66,409 | ) | | | (96,566 | ) | | | (78,053 | ) |
Change in assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Increase in FDIC indemnification asset | | | (793 | ) | | | (1,444 | ) | | | (926 | ) |
(Increase) decrease in accrued interest receivable | | | 500 | | | | (401 | ) | | | 1,381 | |
(Increase) decrease in other assets | | | (1,623 | ) | | | 4,176 | | | | (5,258 | ) |
Decrease in accrued interest payable | | | (1,575 | ) | | | (104 | ) | | | (1,433 | ) |
Increase (decrease) in accrued expenses and other liabilities | | | 4,548 | | | | (2,424 | ) | | | 6,055 | |
Net cash provided (used) by operating activities | | | 13,872 | | | | 32,759 | | | | (4,080 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net (increase) decrease in loans | | | (182,401 | ) | | | 53,294 | | | | 78,196 | |
Purchases of premises and equipment | | | (4,591 | ) | | | (2,625 | ) | | | (4,845 | ) |
Proceeds from disposals of premises and equipment | | | 138 | | | | 1,650 | | | | 221 | |
Purchases of investment securities available-for-sale | | | (165,027 | ) | | | (191,521 | ) | | | (31,115 | ) |
Purchases of investment securities held-to-maturity | | | (10,447 | ) | | | (52,178 | ) | | | - | |
Proceeds from sales of investment securities available-for-sale | | | 161,434 | | | | 28,128 | | | | 46,367 | |
Proceeds from maturities and call of investment securities available-for-sale | | | 49,206 | | | | 45,412 | | | | 43,998 | |
Proceeds from maturities and call of investment securities held-to-maturity | | | 5,127 | | | | 503 | | | | - | |
Proceeds from life insurance death benefit | | | 1,081 | | | | - | | | | - | |
FDIC reimbursement of recoverable covered asset losses | | | 3,651 | | | | 9,720 | | | | 3,698 | |
Proceeds from sale of other real estate owned | | | 14,200 | | | | 21,455 | | | | 13,096 | |
Net (purchases) redemptions of nonmarketable equity securities | | | (2,679 | ) | | | 1,517 | | | | 6,079 | |
Acquisitions, net of cash paid | | | 59,045 | | | | - | | | | 24,283 | |
Net cash provided (used) by investing activities | | | (71,263 | ) | | | (84,645 | ) | | | 179,978 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net decrease in deposits | | | (12,860 | ) | | | (30,342 | ) | | | (42,933 | ) |
Advances (repayments) of short-term borrowings | | | 84,244 | | | | (9,147 | ) | | | (7,300 | ) |
Advances (repayments) of long-term borrowings | | | (13,310 | ) | | | (15,000 | ) | | | 30,000 | |
Redemption of preferred stock | | | - | | | | (20,500 | ) | | | - | |
Exercise of stock options | | | 250 | | | | 308 | | | | - | |
Repurchase of common stock | | | (1,027 | ) | | | (366 | ) | | | (15 | ) |
Dividends on common stock | | | (3,583 | ) | | | (1,789 | ) | | | - | |
Dividends on preferred stock | | | - | | | | (353 | ) | | | (51 | ) |
Net cash provided (used) by financing activities | | | 53,714 | | | | (77,189 | ) | | | (20,299 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | (3,677 | ) | | | (129,075 | ) | | | 155,599 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning | | | 55,067 | | | | 184,142 | | | | 28,543 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents, ending | | $ | 51,390 | | | $ | 55,067 | | | $ | 184,142 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash paid for interest | | $ | 7,669 | | | $ | 6,486 | | | $ | 7,615 | |
Cash paid for income taxes | | | 701 | | | | 240 | | | | 94 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing and financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Change in unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale securities, net of tax | | $ | 5,176 | | | $ | (8,343 | ) | | $ | 318 | |
Change in unrealized gain (loss) on cash flow hedge, net of tax | | | (1,849 | ) | | | 343 | | | | - | |
Transfer from other assets to investment securities available-for-sale | | | - | | | | 1,393 | | | | - | |
Loans transferred to other real estate owned | | | 8,806 | | | | 10,207 | | | | 11,896 | |
Transfer from securities available-for-sale to held-to-maturity | | | 58,972 | | | | - | | | | - | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 1 – ORGANIZATION AND OPERATIONS
Park Sterling Corporation (the “Company”) was formed in 2010 to serve as the holding company for Park Sterling Bank (the “Bank”) pursuant to a bank holding company reorganization effective January 1, 2011, and is registered with the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (the “Federal Reserve Board”) under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended (the “BHC Act”). The Bank is a North Carolina-chartered commercial nonmember bank that was incorporated in September 2006 and opened for business at 1043 E. Morehead Street, Suite 201, Charlotte, North Carolina on October 25, 2006. At December 31, 2014, the Company’s primary operations and business were that of owning the Bank. Prior to January 1, 2011, the Company conducted no operations other than obtaining regulatory approval for the holding company reorganization. The main office of both the Company and the Bank is located at 1043 E. Morehead Street, Suite 201, Charlotte, North Carolina, 28204, and its phone number is (704) 716-2134.
In August 2010, the Bank raised gross proceeds of $150 million in an equity offering (the “Public Offering”), to facilitate a change in the Bank’s business plan from primarily organic growth at a moderate pace to creating a regional community bank through a combination of mergers and acquisitions and accelerated organic growth. Consistent with this growth strategy, over the past several years the Bank has opened additional branches in North Carolina and South Carolina and in 2014 expanded into the Virginia market through the opening of a loan production office, followed by the opening of a full-service branch, in Richmond, Virginia. In addition, since the Public Offering, the Company has completed the following acquisitions of community banks in its existing or targeted markets:
| | ● | In May 2014, the Company acquired Provident Community Bancshares, Inc. (“Provident Community”), the parent company of Provident Community Bank, N.A., which operated nine branches in South Carolina. |
| | ● | In October 2012, the Company acquired Citizens South Banking Corporation (“Citizens South”), the parent company of Citizens South Bank, which operated 21 branches in North Carolina, South Carolina and North Georgia. |
| | ● | In November 2011, the Company acquired Community Capital Corporation (“Community Capital”), the parent company of CapitalBank, which operated 18 branches in the Upstate and Midlands area of South Carolina. |
Each of these banks has merged into the Bank.
NOTE 2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation-The accounting and reporting policies of the Company conform with United States generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") and prevailing practices within the banking industry. The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Bank and the Company. The Company evaluates subsequent events through the date of filing of the consolidated financial statements with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
Use of Estimates-The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Material estimates that are particularly susceptible to significant change relate to the determination of the allowance for loan losses, nonaccretable discounts, purchase accounting accretion adjustments, realization of deferred tax assets and the fair value of financial instruments and other accounts.
Segments -The Company, through the Bank, provides a broad range of financial services to individuals and companies. These services include personal, business and non-profit checking accounts, IOLTA accounts, individual retirement accounts, business and personal money market accounts, time deposits, overdraft protection, safe deposit boxes and online and mobile banking. Lending activities include a range of short-to medium-term commercial (including asset-based lending), real estate, construction, residential mortgage and home equity and consumer loans, as well as long-term residential mortgages. Wealth management activities include investment management, personal trust services, and investment brokerage services. Cash management activities include remote deposit capture, lockbox services, sweep accounts, purchasing cards, ACH and wire payments. Capital markets activities include interest rate and currency risk management products, loan syndications and debt placements. While the Company's decision makers monitor the revenue streams of the various financial products and services, operations are managed and financial performance is evaluated on an organization-wide basis. Accordingly, the Company's banking and finance operations are not considered by management to constitute more than one reportable operating segment.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Reclassifications -Certain noninterest income reported in the prior year financial statements have been reclassified to conform to the 2014 presentation. Reclassifications include amortization of indemnification asset and loss share true-up liability expense previously disclosed in other noninterest income which are now reported as separate line items. The reclassification had no effect on net income, comprehensive income or shareholders’ equity as previously reported.
Business Combinations, Method of Accounting for Loans Acquired, andFederal Deposit Insurance Corporation (the “FDIC”)Indemnification Asset–Generally, acquisitions are accounted for under the acquisition method of accounting in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 805,Business Combinations. A business combination occurs when the Company acquires net assets that constitute a business, or acquires equity interests in one or more other entities that are businesses and obtains control over those entities. Business combinations are effected through the transfer of consideration consisting of cash and/or common stock and are accounted for using the acquisition method. Accordingly, the assets and liabilities of the acquired entity are recorded at their respective fair values as of the closing date of the acquisition. Determining the fair value of assets and liabilities, especially the loan portfolio, is a complicated process involving significant judgment regarding methods and assumptions used to calculate estimated fair values.Fair values are preliminary and subject to refinement for up to one year after the closing date of the acquisition as information relative to closing date fair values becomes available. The results of operations of an acquired entity are included in our consolidated results from the closing date of the merger, and prior periods are not restated. No allowance for loan losses related to the acquired loans is recorded on the acquisition date because the fair value of the loans acquired incorporates assumptions regarding future credit losses. Loans acquired are recorded at fair value exclusive of any loss share agreements with the FDIC. The fair value estimates associated with the acquired loans include estimates related to expected prepayments and the amount and timing of expected principal, interest and other cash flows.
In connection with an acquisition the Company may assume purchase and assumption agreements that the acquired institution entered into with the FDIC, providing for loss share agreements related to the covered assets. The Bank records an estimated receivable from the FDIC in connection with such loss share agreements. The FDIC indemnification asset is measured separately from the related covered assets as it is not contractually embedded in the assets and is not transferable with the assets, without approval of the FDIC, should the Company choose to dispose of them. Fair value is estimated at the acquisition date using projected cash flows related to the loss sharing agreements based on the expected reimbursements for losses and the applicable loss sharing percentages. These expected reimbursements do not include reimbursable amounts related to future covered expenditures. These cash flows are discounted to reflect the uncertainty of the timing and receipt of the loss sharing reimbursement from the FDIC. The Company will offset any recorded provision for loan losses related to acquired loans by recording an increase in the FDIC indemnification asset in an amount equal to the increase in expected cash flow, which is the result of a decrease in expected cash flow of acquired loans. An increase in expected cash flows on acquired loans results in a decrease in cash flows on the FDIC indemnification asset, which is recognized in the future as amortization through non-interest income over the lesser of the term of the loss share agreement or the life of the loan.
The Company incurs expenses related to the assets indemnified by the FDIC, and pursuant to the loss share agreements certain costs are reimbursable by the FDIC and are included in quarterly claims made by the Company. The estimates of reimbursements are netted against these covered expenses in the income statement.
Cash and Cash Equivalents-For the purpose of presentation in the statement of cash flows, cash and cash equivalents include cash and due from banks, interest-earning balances at banks and Federal funds sold. Generally, Federal funds sold are repurchased the following day.
Investment Securities - Investment securities available-for-sale are reported at fair value and consist of debt instruments that are not classified as trading securities or as held to maturity securities. Investment securities held-to-maturity are reported at amortized cost. Unrealized holding gains and losses, net of applicable taxes, on available-for-sale securities are reported as a net amount in other comprehensive income. Gains and losses on the sale of available-for-sale securities are determined using the specific-identification method and are recorded on a trade date basis. Declines in the fair value of individual available-for-sale securities below their amortized cost that are other than temporary impairments would result in write-downs of the individual securities to their fair value and would be included in earnings as realized losses. Premiums and discounts are recognized in interest income using the interest method over the period to maturity.
Nonmarketable Equity Securities –Nonmarketable equity securities include the costs of the Company’s investments in the stock of the Federal Home Loan Bank of Atlanta (“FHLB”). As a condition of membership, the Bank is required to hold stock in the FHLB. These securities do not have a readily determinable fair value as their ownership is restricted and there is no market for these securities. The Bank carries these nonmarketable equity securities at cost and periodically evaluates them for impairment. Management considers these nonmarketable equity securities to be long-term investments. Accordingly, when evaluating these securities for impairment, management considers the ultimate recoverability of the par value rather than recognizing temporary declines in value. The primary factor supporting the carrying value of these securities is the commitment of the FHLB to perform its obligations, which includes providing credit and other services to the Bank. Upon request, the stock may be sold back to the FHLB, at cost.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The Company has invested in the stock of several unaffiliated financial institutions. The Company owns less than five percent of the outstanding shares of each institution, and the stocks either have no quoted market value or are not readily marketable. Also included in nonmarketable equity securities is the investment in CSBC Statutory Trust I, Community Capital Corporation Statutory Trust I, Provident Community Bancshares Capital Trust I and Provident Community Bancshares Capital Trust II. See Note 4 – Investments and Note 11 – Borrowings.
Loans Held for Sale –Loans intended for sale are carried at the lower of cost or estimated fair value in the aggregate. This includes, but may not be limited to, loans originated through the Company’s mortgage activities. Residential mortgage loans originated and intended for sale are comprised of accepting residential mortgage loan applications, qualifying borrowers to standards established by investors, funding residential mortgages and selling mortgages to investors under pre-existing commitments.
Loans –Loans originated by the Company and which management has the intent and ability to hold for the foreseeable future or until maturity are reported at their outstanding principal balances adjusted for any direct principal charge-offs, the allowance for loan losses and any deferred fees or costs on originated loans. Interest on originated loans is calculated by using the simple interest method on daily balances of the principal amount outstanding. Loan origination fees are capitalized and recognized as an adjustment of the yield of the related loan. See Note 5 – Loans.
Purchased Credit-Impaired (“PCI”) Loans - Purchased loans acquired in a business combination are recorded at estimated fair value on the date of acquisition without the carryover of the related allowance for loan losses. PCI loans are accounted for under the “Receivables” topic of the ASC when the loans have evidence of credit deterioration since origination and it is probable at the date of acquisition that the Company will not collect all contractually required principal and interest payments. Evidence of credit quality deterioration as of the date of acquisition may include statistics such as internal risk grades and past due and nonaccrual status. Purchased impaired loans generally meet the Company’s definition for nonaccrual status. Any excess of cash flows expected at acquisition over the estimated fair value is referred to as the accretable yield and is recognized into interest income over the remaining life of the loan when there is a reasonable expectation about the amount and timing of such cash flows. The difference between contractually required payments at acquisition and the cash flows expected to be collected at acquisition is referred to as the nonaccretable difference, and is available to absorb credit losses on those loans. Subsequent decreases to the expected cash flows will generally result in a provision for loan losses. Subsequent significant increases in cash flows result in a reversal of the provision for loan losses to the extent of prior charges, or a reclassification of the nonaccretable difference with a positive impact on future interest income. For acquired loans subject to a loss sharing agreement with the FDIC, the FDIC indemnification asset will be adjusted prospectively in a similar, consistent manner with increases and decreases in expected cash flows limited to the term of the loss share agreements.
Purchased Performing Loans – The Company accounts for performing loans acquired in business combinations using the contractual cash flows method of recognizing discount accretion based on the acquired loans’ contractual cash flows. Purchased performing loans are recorded at fair value, including a credit discount. The fair value discount is accreted as an adjustment to yield over the estimated lives of the loans. There is no allowance for loan losses established at the acquisition date for purchased performing loans. A provision for loan losses is recorded for any further deterioration in these loans subsequent to the acquisition.
Nonperforming Loans – For all classes of loans, except PCI loans, loans are placed on non-accrual status upon becoming contractually past due 90 days or more as to principal or interest (unless they are adequately secured by collateral, are in the process of collection and are reasonably expected to result in repayment), when terms are renegotiated below market levels in response to a financially distressed borrower or guarantor, or where substantial doubt about full repayment of principal or interest is evident.
When a loan is placed on non-accrual status, the accrued and unpaid interest receivable is reversed and the loan is accounted for on the cash or cost recovery method until qualifying for return to accrual status. All payments received on non-accrual loans are applied against the principal balance of the loan. A loan may be returned to accrual status when all delinquent interest and principal become current in accordance with the terms of the loan agreement and when doubt about repayment is resolved. Generally, for all classes of loans, a charge-off is recorded when it is probable that a loss has been incurred and when it is possible to determine a reasonable estimate of the loss.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Impaired Loans – For all classes of loans, except PCI loans, loans are considered impaired when, based on current information and events, it is probable the Company will be unable to collect all amounts due in accordance with the original contractual terms of the loan agreement, including scheduled principal and interest payments. Impaired loans may include all classes of nonaccrual loans and loans modified in a troubled debt restructuring ("TDR"). If a loan is impaired, a specific valuation allowance is allocated, if necessary, so that the loan is reported net, at the present value of estimated future cash flows using the interest rate implicit in the original agreement or at the fair value of collateral if repayment is expected solely from the collateral. Interest payments on impaired loans are typically applied to principal unless collectability of the principal amount is probable, in which case interest is recognized on a cash basis. Impaired loans, or portions thereof, are charged off when deemed uncollectible.
Loans Modified in a TDR - Loans are considered to be a TDR if, for economic or legal reasons related to the borrower's financial condition, the Company makes certain concessions to the original contract terms related to amount, interest rate, amortization or maturity that it would not otherwise consider. Generally, a nonaccrual loan that has been modified in a TDR remains on nonaccrual status for a period of at least six months to demonstrate that the borrower is able to meet the terms of the modified loan. However, performance prior to the modification, or significant events that coincide with the modification, are included in assessing whether the borrower can meet the new terms and may result in the loan being returned to accrual status at the time of loan modification or after a shorter performance period. If the borrower's ability to meet the revised payment schedule is uncertain, the loan remains on nonaccrual status.
Allowance for Loan Losses – The allowance for loan losses is based upon management's ongoing evaluation of the loan portfolio and reflects an amount considered by management to be its best estimate of known and inherent losses in the portfolio as of the balance sheet date. The determination of the allowance for loan losses involves a high degree of judgment and complexity. In making the evaluation of the adequacy of the allowance for loan losses, management considers current economic and market conditions, independent loan reviews performed periodically by third parties, portfolio trends and concentrations, delinquency information, management's internal review of the loan portfolio, internal historical loss rates and other relevant factors. While management uses the best information available to make evaluations, future adjustments to the allowance may be necessary if conditions differ substantially from the assumptions used in making the evaluations. In addition, regulatory examiners may require the Company to recognize changes to the allowance for loan losses based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examination. Although provisions have been established by loan segments based upon management's assessment of their differing inherent loss characteristics, the entire allowance for losses on loans, other than the portions related to PCI loans and specific reserves on impaired loans, is available to absorb further loan losses in any segment. Further information regarding the Company’s policies and methodology used to estimate the allowance for loan losses is presented in Note 5 – Loans.
Other Real Estate Owned (“OREO”) - Real estate acquired through, or in lieu of, loan foreclosure is held for sale and is recorded at fair value less estimated selling costs when acquired, establishing a new cost basis. Subsequent to foreclosure, valuations are periodically performed by management and further write-downs are made based on these valuations. Revenue and expenses from operations are included in other expense.
Premises and Equipment- Company premises and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is calculated on the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, which are generally 39.5 years for buildings and 3 to 7 years for furniture and equipment. Leasehold improvements are depreciated over the lesser of the term of the respective lease or the estimated useful lives of the improvements. Repairs and maintenance costs are charged to operations as incurred and additions and improvements to premises and equipment are capitalized. Upon sale or retirement, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and any gains or losses are reflected in current operations.
Goodwill and IntangibleAssets-Intangible assets consist primarily of goodwill and core deposit intangibles that result from the acquisition of other banks. Core deposit intangibles represent the value of long-term deposit relationships acquired in these transactions. Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the sum of the estimated fair values of the tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired less the estimated fair value of the liabilities assumed. Goodwill has an indefinite useful life and is evaluated for impairment annually or more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. An impairment loss is recognized to the extent that the carrying amount exceeds the asset’s fair value.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The goodwill impairment analysis is a two-step test. The first step, used to identify potential impairment, involves comparing the reporting unit’s estimated fair value to its carrying value, including goodwill. If the estimated fair value of a reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, there is an indication of potential impairment and the second step is performed to measure the amount of impairment of goodwill assigned to that reporting unit.
If required, the second step involves calculating an implied fair value of goodwill for each reporting unit for which the first step indicated impairment. The implied fair value of goodwill is determined in a manner similar to the amount of goodwill calculated in a business combination, by measuring the excess of the estimated fair value of the reporting unit, as determined in the first step, over the aggregate estimated fair values of the individual assets, liabilities and identifiable intangibles as if the reporting unit was being acquired in a business combination. If the implied fair value of goodwill exceeds the carrying value of the goodwill assigned to the reporting unit, there is no impairment. If the carrying value of goodwill assigned to a reporting unit exceeds the implied fair value of the goodwill, an impairment charge is recorded for the excess. An impairment loss cannot exceed the carrying value of goodwill assigned to a reporting unit, and the loss establishes a new basis of goodwill.
In September 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-08, which gives entities the option of first performing a qualitative assessment to test goodwill for impairment on a reporting-unit-by-reporting-unit basis. If, after performing the qualitative assessment, an entity concludes that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, the entity would perform the two-step goodwill impairment test described in ASC 350. However, if, after applying the qualitative assessment, the entity concludes that it is not more likely than not that the fair value is less than the carrying amount, the two-step goodwill impairment test is not required.
The Company performed the qualitative assessment as outlined in ASU 2011-08 in assessing the carrying value of goodwill related to its acquisitions as of October 1, 2014, its annual test date, and determined that it was unlikely that the fair value was less than the carrying amount and that no further testing or impairment charge was necessary. Should the Company’s future earnings and cash flows decline and/or discount rates increase, an impairment charge to goodwill and other intangible assets may be required. There have been no events subsequent to the October 1, 2014 evaluation that caused the Company to perform an interim review of the carrying value of goodwill related to any of its acquisitions.
Core deposit intangibles are amortized over the estimated useful lives of the deposit accounts acquired (generally ten years on a straight line basis).
Investment in a Qualified Affordable Housing Project - The Company currently invests in the Community Affordable Housing Equity Corporation (“CAHEC”), a qualified affordable housing project. CAHEC assists in providing low-income housing and historic preservation in the United States. The Company assumed this investment in connection with the acquisition of Provident Community. As of December 31, 2014, the Company holds an investment of $508 thousand which is recorded in other assets on the balance sheet. There are no commitments or contingent commitments to provide additional capital. In connection with the investment in CAHEC, the Company recognized a net income tax benefit of approximately $10 thousand in income tax expense in the Consolidated Statement of Income for the year ended December 31, 2014. No impairment was recognized or identified for this investment at December 31, 2014.
Securities Sold Under Agreements to Repurchase – The Company sells certain securities under agreements to repurchase. The agreements are treated as collateralized financing transactions and the obligations to repurchase securities sold are reflected as a liability in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The dollar amount of the securities underlying the agreements remains in the asset accounts.
Advertising Costs- Advertising costs are expensed as incurred and advertising communication costs the first time the advertising takes place. The Company may establish accruals for anticipated advertising expenses within the course of a fiscal year.
Income Taxes - Income tax expense is the total of the current year income tax due or refundable and the change in deferred tax assets and liabilities (excluding deferred tax assets and liabilities related to components of other comprehensive income). Deferred tax assets and liabilities are the expected future tax amounts for the temporary differences between carrying amounts and tax bases of assets and liabilities, computed using enacted tax rates. A valuation allowance, if needed, reduces deferred tax assets to the expected amount most likely to be realized. Realization of deferred tax assets generally is dependent upon the generation of a sufficient level of future taxable income and recoverable taxes paid in prior years. Although realization is not assured, management believes it is more likely than not that all of the deferred tax assets will be realized. The Company is subject to U.S. Federal income tax as well as state and local income tax in several jurisdictions. Tax years 2011 through 2014 remain open to examination by the Federal taxing authority. Interest and penalties on income tax assessments or income tax refunds are recognized in the Consolidated Statements of Income as a component of noninterest expense.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Per Share Results - Basic and diluted earnings per common share are computed based on the weighted-average number of shares outstanding during each period. Diluted earnings per common share reflects the potential dilution that could occur if all dilutive stock options were exercised.
In 2012, the Company issued 78,000 restricted stock awards, and repurchased 3,000 shares of common stock in open market transactions pursuant to the stock repurchase program approved by the board of directors in November 2012. Also in 2012, the Company issued 11,857,226 shares of Common Stock in connection with the merger with Citizens South. In 2013, the Company issued 174,000 restricted stock awards, issued 60,943 shares pursuant to the exercise of stock options and repurchased 56,267 shares in open market transactions. In 2014, the Company issued 238,613 restricted stock awards, issued 54,199 shares pursuant to the exercise of stock options, repurchased 136,743 shares of Common Stock in open market transactions and acquired 19,942 shares in connection with satisfaction of tax withholding obligations on vested restricted stock.
Basic and diluted earnings per common share have been computed based upon net income as presented in the accompanying consolidated statements of income divided by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding or assumed to be outstanding as summarized below in each case as of December 31,:
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average number of commonshares outstanding excludingunvested restricted shares | | | 43,924,457 | | | | 43,965,408 | | | | 35,101,407 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Effect of dilutive stock options andunvested shares | | | 322,543 | | | | 87,845 | | | | 6,822 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average number of commonshares and dilutive potential commonshares outstanding | | | 44,247,000 | | | | 44,053,253 | | | | 35,108,229 | |
There were 1,927,740 outstanding stock options and 842,170 outstanding restricted shares that were anti-dilutive for the year ended December 31, 2014. There were 243,617 dilutive stock options and 78,925 dilutive restricted shares outstanding for the year ended December 31, 2014. There were 2,177,592 outstanding stock options and 730,514 outstanding restricted shares outstanding that were anti-dilutive for the year ended December 31, 2013. There were 47,959 dilutive stock options and 39,885 dilutive restricted shares outstanding for the year ended December 31, 2013. There were 3,118,891 outstanding stock options and 640,239 outstanding restricted shares outstanding that were anti-dilutive for the year ended December 31, 2012. There were 801 dilutive stock options and 6,021 dilutive restricted shares outstanding for the year ended December 31, 2012. See Note 20 – Employee and Director Benefit Plans for more information.
Share-Based Compensation -The Company may grant share-based compensation to employees, non-employee directors and other eligible parties in the form of stock options, restricted stock or other instruments. Share-based compensation expense is measured based on the fair value of the award at the date of grant and is charged to earnings on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, which is currently up to seven years. The fair value of stock options is estimated at the date of grant using a Black-Scholes option pricing model and related assumptions. The amortization of share-based compensation is adjusted for actual forfeiture experience. The fair value of restricted stock awards, subject to share price performance vesting requirements, is estimated using a Monte Carlo simulation and related estimated assumptions for volatility and a risk free interest rate.
The compensation expense for share-based compensation plans was $1.1 million, $1.8 million and $2.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Derivative Financial Instruments and Hedging Activities - The Company utilizes interest rate swap agreements, considered to be cash flow hedges, as part of the management of interest rate risk to modify the repricing characteristics of certain portions of its portfolios of interest-bearing liabilities. Under the guidelines of ASC 815-10, “Derivatives and Hedging,” all derivative instruments are required to be carried at fair value on the balance sheet.
Cash flow hedges are accounted for by recording the fair value of the derivative instrument on the balance sheet as either a freestanding asset or liability, with a corresponding offset recorded in other comprehensive income within shareholders’ equity, net of tax. Amounts are reclassified from other comprehensive income to the income statement in the period or periods the hedged forecasted transaction affects earnings. Cash flows from cash flow hedges are classified in the same category as the cash flows from the items being hedged. Derivative gains and losses not effective in hedging the expected cash flows of the hedged item are recognized immediately in the income statement. At the hedge’s inception and at least quarterly thereafter, a formal assessment is performed to determine the effectiveness of the cash flow hedge. If it is determined that a derivative instrument has not been or will not continue to be highly effective as a hedge, hedge accounting is discontinued. See Note 17 – Derivative Financial Instruments and Hedging Activities.
Fair value hedges are accounted for under ASC Topic 815 which requires that the method selected for assessing hedge effectiveness must be reasonable, be defined at the inception of the hedging relationship and be applied consistently throughout the hedging relationship. The Company uses the dollar-offset method for assessing effectiveness using the cumulative approach. The dollar-offset method compares the fair value of the hedging derivative with the fair value of the hedged exposure. The cumulative approach involves comparing the cumulative changes in the hedging derivative’s fair value to the cumulative changes in the hedged exposure’s fair value. The calculation of dollar offset is the change in clean fair value of the hedging derivative, divided by the change in fair value of the hedged exposure attributable to changes in the London InterBank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) curve. To the extent that the cumulative change in fair value of the hedging derivative offsets from 80% to 125% of the cumulative change in fair value of the hedged exposure, the hedge will be deemed effective. The change in fair value of the hedging derivative and the change in fair value of the hedged exposure are recorded in earnings. Any hedge ineffectiveness is also reflected in current earnings. Cash flows from fair value hedges are classified in the same category as the cash flows from the items being hedged.
If a derivative instrument designated as a fair value hedge is terminated or the hedge designation removed, the difference between a hedged item’s then carrying amount and its face amount is recognized into income over the original hedge period. Likewise, if a derivative instrument designated as a cash flow hedge is terminated or the hedge designation removed, related amounts accumulated in other accumulated comprehensive income are reclassified into earnings over the original hedge period during which the hedged item affects income.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements –The following is a summary of recent authoritative pronouncements:
In January 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2014-01, "Investments --Equity Method and Joint Ventures (Topic 323): Accounting for Investments in Qualified Affordable Housing Projects". This update revises the criteria required to elect the measurement and presentation alternative under ASC 323-740 and simplifies the method of amortization of the investment for entities investing in flow-through limited liability entities that manage or invest in affordable housing projects qualifying for the low-income housing tax credit. The update allows entities that meet the required criteria to qualify to present the investment performance net of income tax expense to better represent the economics of the investment (rather than traditional investment accounting under the equity or cost method). If the entity qualifies for the measurement and presentation alternative, it may amortize the initial cost of the investment in proportion to the related tax credits received (the proportional allocation method). The amendments must be retrospectively applied for all periods presented. For public business entities this update is effective for annual periods, and interim reporting periods within those annual periods, beginning after December 15, 2014. Early adoption is permitted.The Company adopted this guidance as of December 31, 2014. The related disclosures can be found in Note 2- Summary of Significant Accounting Policies of these financial statements.
In January 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-04, “Receivables—Troubled Debt Restructurings by Creditors (Subtopic 310-40): Reclassification of Residential Real Estate Collateralized Consumer Mortgage Loans upon Foreclosure (a consensus of the FASB Emerging Issues Task Force)” (“ASU 2014-04”). ASU 2014-04 amended the Receivables—Troubled Debt Restructurings by Creditors subtopic of the ASC to address the reclassification of consumer mortgage loans collateralized by residential real estate upon foreclosure. The amendments clarify the criteria for concluding that an in-substance repossession or foreclosure has occurred, and a creditor is considered to have received physical possession of residential real estate property collateralizing a consumer mortgage loan. The amendments also outline interim and annual disclosure requirements. The amendments will be effective for the Company for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2014. Companies are allowed to use either a modified retrospective transition method or a prospective transition method when adopting this update. Early adoption is permitted. The Company does not expect these amendments to have a material effect on its financial statements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers” (“ASU 2014-09”). ASU 2014-09 changes the recognition of revenue from contracts with customers. The core principle of the new guidance is that an entity should recognize revenue to reflect the transfer of goods and services to customers in an amount equal to the consideration the entity receives or expects to receive. The guidance will be effective for the Company for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance but does not expect these amendments to have a material effect on its financial statements.
In June 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-11, “Repurchase-to-Maturity Transactions, Repurchase Financings, and Disclosures” (“ASU 2014-11”). ASU 2014-11 makes limited amendments to the guidance on accounting for certain repurchase agreements. The new guidance (1) requires entities to account for repurchase-to-maturity transactions as secured borrowings (rather than as sales with forward repurchase agreements), (2) eliminates accounting guidance on linked repurchase financing transactions, and (3) expands disclosure requirements related to certain transfers of financial assets that are accounted for as sales and certain transfers (specifically, repos, securities lending transactions, and repurchase-to-maturity transactions) accounted for as secured borrowings. The amendments will be effective for the Company for the first interim or annual period beginning after December 15, 2014. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance but does not expect these amendments to have a material effect on its financial statements.
In June 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-12, “Accounting for Share-Based Payments When the Terms of an Award Provide That a Performance Target Could Be Achieved after the Requisite Service Period—a consensus of the FASB Emerging Issues Task Force” (“ASU 2014-12”). ASU 2014-12 clarifies that performance targets associated with stock compensation should be treated as a performance condition and should not be reflected in the grant date fair value of the stock award. The amendments will be effective for the Company for fiscal years that begin after December 15, 2015. The Company will apply the guidance to all stock awards granted or modified after the amendments are effective. The Company does not expect these amendments to have a material effect on its financial statements.
In August 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-14, "Receivables - Troubled Debt Restructurings by Creditors: Classification of Certain Government-Guaranteed Mortgage Loans upon Foreclosure" (“ASU 2014-19”). This update addresses the diversity in practice regarding the classification and measurement of foreclosed loans which were part of a government-sponsored loan guarantee program. If certain criteria are met, the loan should be derecognized and a separate other receivable should be recorded upon foreclosure at the amount of the loan balance (principal and interest) expected to be recovered from the guarantor. This update is effective for public business entities for annual periods, and interim periods within those annual periods, beginning after December 15, 2014. The update may be adopted either prospectively or on a modified retrospective basis. Early adoption is permitted, provided the entity has adopted ASU 2014-04. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance but does not expect these updates to have a material effect on its financial statements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 3 – BUSINESS COMBINATIONS
Provident Community Bancshares, Inc.
On May 1, 2014, Provident Community was merged with and into the Company, with the Company as the surviving entity, pursuant to the Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of March 4, 2014. Under the terms of the Agreement and Plan of Merger, each share of Provident Community common stock was cancelled and converted into the right to receive a cash payment from the Company equal to $0.78 per share, or approximately $1.4 million in the aggregate. In addition, immediately prior to completion of the merger, the Company purchased from the United States Department of the Treasury (“Treasury”) the issued and outstanding shares of Provident Community’s Fixed Rate Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock, Series A (the “Provident Community Series A Preferred Stock”) and all of the related warrants to purchase shares of Provident Community’s common stock, for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $5.1 million (representing a 45% discount from face value). Thereafter, pursuant to the Agreement and Plan of Merger, the Provident Community Series A Preferred Stock and related warrants were cancelled in connection with the completion of the merger. Simultaneously with completion of the merger, Provident Community Bank, N.A. was merged into the Bank.
The assets acquired and liabilities assumed from Provident Community were recorded at their fair value as of the closing date of the merger. Fair values are preliminary and subject to refinement for up to one year after the closing date of the acquisition as additional information regarding the closing date fair values becomes available.Goodwill of $3.4 million was initially recorded at the time of the acquisition. As a result of refinements to the fair value mark on loans, OREO, other assets and other liabilities, goodwill as indicated below is $2.8 million. The following table summarizes the consideration paid by the Company in the merger with Provident Community and the amounts of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed recognized at the acquisition date:
| | | As Recordedby | | | Fair Value and Other | | | | | |
| | | Provident | | | Merger Related | | | As Recorded | |
| | | Community | | | Adjustments | | | by the Company | |
Consideration Paid | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash | | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,397 | |
Fair value of non-controlling interest | | | | | | | | | | | 5,096 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fair Value of Total Consideration Transferred | | | | | | | | | | $ | 6,493 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Recognized amounts of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 65,538 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 65,538 | |
Securities | | | 124,035 | | | | - | | | | 124,035 | |
Nonmarketable equity securities | | | 2,948 | | | | - | | | | 2,948 | |
Loans held for sale | | | 390 | | | | - | | | | 390 | |
Loans, net of allowance | | | 112,412 | | | | (6,797 | ) | | | 105,615 | |
Premises and equipment | | | 3,150 | | | | 32 | | | | 3,182 | |
Core deposit intangibles | | | - | | | | 3,600 | | | | 3,600 | |
Interest receivable | | | 748 | | | | (3 | ) | | | 745 | |
Other real estate owned | | | 3,666 | | | | (702 | ) | | | 2,964 | |
Bank owned life insurance | | | 8,536 | | | | - | | | | 8,536 | |
Deferred tax asset | | | 1,628 | | | | 4,828 | | | | 6,456 | |
Other assets | | | 1,438 | | | | (218 | ) | | | 1,220 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets acquired | | $ | 324,489 | | | $ | 740 | | | $ | 325,229 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deposits | | $ | 264,281 | | | $ | 177 | | | $ | 264,458 | |
Federal Home Loan Bank advances | | | 37,500 | | | | 3,915 | | | | 41,415 | |
Junior Subordinated Debt | | | 12,372 | | | | (4,558 | ) | | | 7,814 | |
Short term borrowings | | | 4,760 | | | | - | | | | 4,760 | |
Other liabilities | | | 2,087 | | | | 985 | | | | 3,072 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities assumed | | $ | 321,000 | | | $ | 519 | | | $ | 321,519 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total identifiable assets | | $ | 3,489 | | | $ | 221 | | | $ | 3,710 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Goodwill resulting from acquisition | | | | | | | | | | $ | 2,783 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The following table discloses certain pro forma information as if Provident Community had been acquired on January 1, 2014 and January 1, 2013, respectively. These results combine the historical results of Provident Community in the Company’s consolidated statement of income and, while certain adjustments were made for the estimated impact of certain fair value adjustments and other acquisition-related activity, they are not indicative of what would have occurred had the acquisition taken place on January 1, 2014, and January 1, 2013. In particular, no adjustments have been made to eliminate the amount of Provident Community provision for loan losses of $500 thousand in 2013 or the impact of OREO write-downs recognized by Provident Community in 2014 that may not have been necessary had the acquired loans and OREO been recorded at fair value as of the beginning of 2014 or 2013.Acquisition-related costs of $3.6 million included in the Company’s consolidated statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2014 are not included in the proforma information below.
| | | Pro Forma | |
| | | Years Ended | |
| | | December 31, 2014 | | | December 31, 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues(net interest income plus other income) | | $ | 93,139 | | | $ | 97,709 | |
Net income | | $ | 9,549 | | | $ | 12,434 | |
Citizens South Banking Corporation
On October 1, 2012, Citizens South was merged with and into the Company, with the Company as the surviving legal entity, in accordance with an Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of May 13, 2012. Under the terms of the Citizens South merger agreement, Citizens South stockholders received either $7.00 in cash or 1.4799 shares of the Company’s Common Stock for each Citizens South share they owned immediately prior to the merger, subject to the limitation that the total consideration paid in the merger would consist of 30% in cash and 70% in Common Stock. The Citizens South merger was structured to be tax-free to Citizens South stockholders with respect to the shares of Common Stock received in the merger and taxable with respect to the cash received in the merger. Cash was paid in lieu of fractional shares. The aggregate merger consideration consisted of 11,857,226 shares of Common Stock and $24.3 million in cash. Based on the $4.94 per share closing price of the Common Stock on September 28, 2012, the last trading date prior to consummation of the merger, the transaction value was $82.9 million. In addition, in connection with the merger, the preferred stock previously issued by Citizens South to the Treasury in connection with Citizens South’s participation in the Small Business Lending Fund (the “SBLF”) program was converted to 20,500 shares of a substantially identical newly created series of the Company’s preferred stock. See Note 14 – Preferred Stock for further discussion. Also in connection with the merger, the Company assumed certain loss share agreements with the FDIC related to prior acquisitions by Citizens South. See Note 6 – FDIC Loss Share Agreements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 4 – INVESTMENTS
The amortized cost and fair value of investment securities available-for-sale and securities held-to-maturity, with gross unrealized gains and losses, at December 31 follows:
Amortized Cost and Fair Value of Investment Portfolio
| | | | | | | Gross | | | Gross | | | | | |
| | | Amortized | | | Unrealized | | | Unrealized | | | Fair | |
| | | Cost | | | Gains | | | Losses | | | Value | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Government agencies | | $ | 508 | | | $ | 29 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 537 | |
Municipal securities | | | 11,955 | | | | 896 | | | | - | | | | 12,851 | |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | | 144,955 | | | | 2,156 | | | | (96 | ) | | | 147,015 | |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | 144,773 | | | | 625 | | | | (1,318 | ) | | | 144,080 | |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | 4,974 | | | | - | | | | (106 | ) | | | 4,868 | |
Asset-backed securities | | | 61,833 | | | | - | | | | (783 | ) | | | 61,050 | |
Corporate and other securities | | | 3,328 | | | | 242 | | | | - | | | | 3,570 | |
Equity securities | | | 1,250 | | | | 462 | | | | - | | | | 1,712 | |
Total securities available-for-sale | | $ | 373,576 | | | $ | 4,410 | | | $ | (2,303 | ) | | $ | 375,683 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities held-to-maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | $ | 43,331 | | | $ | 1,123 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 44,454 | |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | 8,440 | | | | 124 | | | | - | | | | 8,564 | |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | 60,783 | | | | - | | | | (2,041 | ) | | | 58,742 | |
Asset-backed securities | | | 5,978 | | | | - | | | | (111 | ) | | | 5,867 | |
Total securities held-to-maturity | | $ | 118,532 | | | $ | 1,247 | | | $ | (2,152 | ) | | $ | 117,627 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2013 | | | | | | | | | | | 1,202 | | | | | |
Securities available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Government agencies | | $ | 513 | | | $ | 45 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 558 | |
Municipal securities | | | 15,826 | | | | 680 | | | | - | | | | 16,506 | |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | | 90,043 | | | | 741 | | | | (536 | ) | | | 90,248 | |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | 105,667 | | | | 51 | | | | (2,369 | ) | | | 103,349 | |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | 66,396 | | | | - | | | | (4,994 | ) | | | 61,402 | |
Asset-backed securities | | | 73,369 | | | | 1 | | | | (2,293 | ) | | | 71,077 | |
Corporate and other securities | | | 4,461 | | | | - | | | | (16 | ) | | | 4,445 | |
Equity securities | | | 1,393 | | | | 513 | | | | - | | | | 1,906 | |
Total securities available-for-sale | | $ | 357,668 | | | $ | 2,031 | | | $ | (10,208 | ) | | $ | 349,491 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities held-to-maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | $ | 41,125 | | | $ | - | | | $ | (392 | ) | | $ | 40,733 | |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | 4,982 | | | | - | | | | (74 | ) | | | 4,908 | |
Asset-backed securities | | | 5,865 | | | | - | | | | (172 | ) | | | 5,693 | |
Total securities held-to-maturity | | $ | 51,972 | | | $ | - | | | $ | (638 | ) | | $ | 51,334 | |
In 2014, commercial mortgage-backed securities (“MBS”) with a fair market value of $58.5 million were transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity. These securities had an aggregate unrealized loss of $2.2 million ($1.5 million, net of tax) on the date of transfer. The net unamortized, unrealized loss on the transferred securities included in accumulated other comprehensive income in the accompanying balance sheet as of December 31, 2014 totaled $2.1 million. This amount will be amortized out of accumulated other comprehensive income over the remaining life of the underlying securities as an adjustment of the yield on those securities. As a result, the amortized cost of these investments of $60.8 million is higher than the $58.0 million carrying value of the securities as of December 31, 2014. There were no transfers of securities during the year ended December 31, 2013.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
At December 31, 2014 and 2013, investment securities with a fair market value of $162.8 million and $99.5 million, respectively, were pledged to secure repurchase agreements, to secure public and trust deposits, to secure interest rate swaps, and for other purposes as required and permitted by law.
At December 31, 2014 and 2013, commercial mortgage-backed obligations include $56.8 million and $55.7 million, respectively, of delegated underwriting and servicing (“DUS”) bonds collateralized by multi-family properties and backed by an agency of the United States government, and $6.0 million and $5.7 million, respectively, of private-label securities collateralized by commercial properties.
At December 31, 2014 and 2013, asset-backed securities include a $6.0 million and $5.7 million, respectively, security that is equally collateralized by the Federal family education loan program and private student loan program.
The amortized cost and fair value of investment securities available-for-sale and held-to-maturity at December 31, 2014 and 2013 are shown below. Expected maturities will differ from contractual maturities because borrowers may have the right to call or prepay obligations with or without call or prepayment penalties. All of the Company’s residential agency-pass through securities and residential collateralized mortgage obligations are backed by an agency of the United States government. None of our residential agency-pass through securities and residential collateralized mortgage obligations are private-label securities.
| Maturities of Investment Portfolio | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2014 | |
| | | Amortized | | | Fair | |
| | | Cost | | | Value | |
Securities available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Government agencies | | | | | | | | |
Due after one year through five years | | $ | 508 | | | $ | 537 | |
| Municipal securities | | | | | | | | |
Due after ten years | | | 11,955 | | | | 12,851 | |
| Residential agency pass-through securities | | | | | | | | |
Due after five years through ten years | | | 11,354 | | | | 11,532 | |
Due after ten years | | | 133,601 | | | | 135,483 | |
| Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | | | | | | |
Due after five years through ten years | | | 8,194 | | | | 8,087 | |
Due after ten years | | | 136,579 | | | | 135,993 | |
| Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | | | | | | |
Due after five years through ten years | | | 4,974 | | | | 4,868 | |
| Asset-backed securities | | | | | | | | |
Due after ten years | | | 61,833 | | | | 61,050 | |
| Corporate and other securities | | | | | | | | |
Due after ten years | | | 3,328 | | | | 3,570 | |
| Equity securities | | | | | | | | |
Due after ten years | | | 1,250 | | | | 1,712 | |
Total securities available-for-sale | | $ | 373,576 | | | $ | 375,683 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Securities held-to-maturity: | | | | | | | | |
| Residential agency pass-through securities | | | | | | | | |
Due after ten years | | $ | 43,331 | | | $ | 44,454 | |
| Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | | | | | | |
Due after ten years | | | 8,440 | | | | 8,564 | |
| Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | | | | | | |
Due after five years through ten years | | | 60,783 | | | | 58,742 | |
| Asset-backed securities | | | | | | | | |
Due after ten years | | | 5,978 | | | | 5,867 | |
Total securities held-to-maturity | | $ | 118,532 | | | $ | 117,627 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Sales of investment securities available-for-sale for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 are as follows:
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
Proceeds from sales | | $ | 161,434 | | | $ | 28,128 | | | $ | 46,367 | |
Gross realized gains | | | 427 | | | | 343 | | | | 1,478 | |
Gross realized losses | | | (247 | ) | | | (245 | ) | | | - | |
Management evaluates its investments quarterly for other than temporary impairment, relying primarily on industry analyst reports, observation of market conditions and interest rate fluctuations. The following table shows gross unrealized losses and fair value, aggregated by investment category and length of time that the individual securities have been in a continuous unrealized loss position for securities with unrealized losses at December 31, 2014 and 2013. None of the securities are deemed to be other than temporarily impaired since none of the unrealized losses relate to the marketability of the securities or the issuer’s ability to honor redemption obligations, as all but one of the bonds are issued by United States government agencies with the remaining bond being partially guaranteed by a government agency, and it is more likely than not that the Company will not have to sell the investments before recovery of their amortized cost basis. At December 31, 2014, there are 23 securities in a loss position for twelve months or more. At December 31, 2013, five securities were in a loss position for twelve months or more.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”) amended the Bank Holding Company Act (the “BHC Act”) to require the federal banking regulatory agencies to adopt rules that prohibit banks and their affiliates from engaging in proprietary trading and investing in and sponsoring a covered fund (such as a hedge fund and or private equity fund), commonly referred to as the “Volcker Rule.” In December 2013, the federal banking regulatory agencies adopted a final rule construing the Volcker Rule, effective April 1, 2014. Banking entities have until July 21, 2016 (expected to be extended to July 21, 2017) to conform their activities to the requirements of the rule. At December 31, 2013, the Company held four investments in senior tranches of collateralized loan obligations with a fair value of $23.6 million which were included in asset-backed securities. The collateral eligibility language in one of the securities, with a fair value of $5.0 million, was amended during the fourth quarter of 2013 to comply with the new bank investment criteria under the Volcker Rule. The Company also sold one of the securities for a loss of $33 thousand. The Company’s investments in the remaining two securities, which had a net unrealized loss of $232,000 at December 31, 2014, currently would be prohibited under the Volcker Rule. The Company will determine any disposition plans for these securities as the documentation is, or is not, amended. Unless the documentation is amended to avoid inclusion within the rule’s prohibitions, the Company would have to recognize other-than-temporary-impairment with respect to these securities in conformity with GAAP rules. The Company held no other security types potentially affected by the Volcker Rule at December 31, 2014.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
| Investment Portfolio Gross Unrealized Losses and Fair Value | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Less Than 12 Months | | | 12 Months or More | | | Total | |
| | | Fair | | | Unrealized | | | Fair | | | Unrealized | | | Fair | | | Unrealized | |
| | | Value | | | Losses | | | Value | | | Losses | | | Value | | | Losses | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential agency mortgage-backed securities | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 3,857 | | | $ | (96 | ) | | $ | 3,857 | | | $ | (96 | ) |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | 29,122 | | | | (142 | ) | | | 48,824 | | | | (1,176 | ) | | | 77,946 | | | | (1,318 | ) |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,868 | | | | (106 | ) | | | 4,868 | | | | (106 | ) |
Asset-backed securities | | | 38,528 | | | | (296 | ) | | | 22,522 | | | | (487 | ) | | | 61,050 | | | | (783 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total temporarily impairedavailable-for-sale securities | | $ | 67,650 | | | $ | (438 | ) | | $ | 80,071 | | | $ | (1,865 | ) | | $ | 147,721 | | | $ | (2,303 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities held-to-maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 58,743 | | | $ | (2,041 | ) | | $ | 58,743 | | | $ | (2,041 | ) |
Asset-backed securities | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,867 | | | | (111 | ) | | | 5,867 | | | | (111 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total temporarily impairedheld-to-maturity securities | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 64,610 | | | $ | (2,152 | ) | | $ | 64,610 | | | $ | (2,152 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential agency mortgage-backed securities | | $ | 32,674 | | | $ | (536 | ) | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 32,674 | | | $ | (536 | ) |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | 55,856 | | | | (1,687 | ) | | | 18,167 | | | | (682 | ) | | | 74,023 | | | | (2,369 | ) |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | 42,391 | | | | (3,247 | ) | | | 19,011 | | | | (1,747 | ) | | | 61,402 | | | | (4,994 | ) |
Asset-backed securities | | | 56,106 | | | | (2,236 | ) | | | 4,986 | | | | (57 | ) | | | 61,092 | | | | (2,293 | ) |
Corporate and other securities | | | 3,945 | | | | (16 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,945 | | | | (16 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total temporarily impairedavailable-for-sale securities | | $ | 190,972 | | | $ | (7,722 | ) | | $ | 42,164 | | | $ | (2,486 | ) | | $ | 233,136 | | | $ | (10,208 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securities held-to-maturity: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential agency mortgage-backed securities | | $ | 40,733 | | | $ | (392 | ) | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 40,733 | | | $ | (392 | ) |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | 4,908 | | | | (74 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,908 | | | | (74 | ) |
Asset-backed securities | | | 5,693 | | | | (172 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,693 | | | | (172 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total temporarily impairedheld-to-maturity securities | | $ | 51,334 | | | $ | (638 | ) | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 51,334 | | | $ | (638 | ) |
The Company has nonmarketable equity securities consisting of investments in several unaffiliated financial institutions, as well as the investments in four statutory trusts. These investments totaled $11.5 million and $5.9 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Included in these amounts was $10.1 million and $4.9 million of FHLB stock at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. All nonmarketable equity securities were evaluated for impairment as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. The following factors have been considered in determining the carrying amount of FHLB stock: (1) management’s current belief that the Company has sufficient liquidity to meet all operational needs in the foreseeable future and would not need to dispose of the stock below recorded amounts, (2) management’s belief that the FHLB has the ability to absorb economic losses given the expectation that the FHLB has a high degree of government support and (3) redemptions and purchases of the stock are at the discretion of the FHLB. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company estimated that the fair values of nonmarketable equity securities equaled or exceeded the cost of each of these investments and, therefore, the investments were not impaired.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 5 – LOANS AND ALLOWANCE FOR LOAN LOSSES
The Company’s loan portfolio was comprised of the following at December 31:
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | PCI loans | | | All other loans | | | Total | | | PCI loans | | | All other loans | | | Total | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 5,552 | | | $ | 168,234 | | | $ | 173,786 | | | $ | 5,737 | | | $ | 116,663 | | | $ | 122,400 | |
Commercial real estate (CRE) - owner-occupied | | | 30,554 | | | | 303,228 | | | | 333,782 | | | | 35,760 | | | | 231,821 | | | | 267,581 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 43,866 | | | | 426,781 | | | | 470,647 | | | | 56,996 | | | | 325,191 | | | | 382,187 | |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | 514 | | | | 28,887 | | | | 29,401 | | | | - | | | | 19,959 | | | | 19,959 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 13,660 | | | | 41,783 | | | | 55,443 | | | | 22,699 | | | | 42,890 | | | | 65,589 | |
AC&D - CRE | | | 112 | | | | 71,478 | | | | 71,590 | | | | 121 | | | | 56,638 | | | | 56,759 | |
Other commercial | | | 1,187 | | | | 3,858 | | | | 5,045 | | | | 137 | | | | 3,712 | | | | 3,849 | |
Total commercial loans | | | 95,445 | | | | 1,044,249 | | | | 1,139,694 | | | | 121,450 | | | | 796,874 | | | | 918,324 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 28,730 | | | | 176,420 | | | | 205,150 | | | | 32,826 | | | | 140,550 | | | | 173,376 | |
Home equity lines of credit (HELOC) | | | 1,734 | | | | 153,563 | | | | 155,297 | | | | 1,402 | | | | 142,352 | | | | 143,754 | |
Residential construction | | | 6,574 | | | | 49,308 | | | | 55,882 | | | | 6,920 | | | | 33,901 | | | | 40,821 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 758 | | | | 21,828 | | | | 22,586 | | | | 1,189 | | | | 17,606 | | | | 18,795 | |
Total consumer loans | | | 37,796 | | | | 401,119 | | | | 438,915 | | | | 42,337 | | | | 334,409 | | | | 376,746 | |
Total loans | | | 133,241 | | | | 1,445,368 | | | | 1,578,609 | | | | 163,787 | | | | 1,131,283 | | | | 1,295,070 | |
Deferred fees | | | - | | | | 2,084 | | | | 2,084 | | | | - | | | | 738 | | | | 738 | |
Total loans, net of deferred fees | | $ | 133,241 | | | $ | 1,447,452 | | | $ | 1,580,693 | | | $ | 163,787 | | | $ | 1,132,021 | | | $ | 1,295,808 | |
Included in the loan totals at December 31, 2014 and 2013 is $42.3 million and $71.1 million, respectively, of covered loans pursuant to the FDIC loss share agreements. Of these amounts, at December 31, 2014 and 2013, $39.8 million and $68.0 million, respectively, is included in PCI loans and $2.5 million and $3.2 million, respectively, is included in all other loans.
At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company had sold participations in loans aggregating $6.5 million and $3.3 million, respectively, to other financial institutions on a nonrecourse basis. Collections on loan participations and remittances to participating institutions conform to customary banking practices.
The Bank accepts residential mortgage loan applications and funds loans of qualified borrowers. Funded loans are sold with limited recourse to investors under the terms of pre-existing commitments. The Bank executes all of its loan sales agreements under best efforts contracts with investors. From time to time, the Company may choose to hold certain mortgage loans on balance sheet. In addition, as part of the Provident Community merger, the Company serviced $3.7 million residential mortgage loans for the benefit of others as of December 31, 2014. The Company did not service residential mortgage loans for the benefit of others as of December 31, 2013.
Loans sold with limited recourse are 1-4 family residential mortgages originated by the Bank and sold to various other financial institutions. Various recourse agreements exist, ranging from thirty days to twelve months. The Company’s exposure to credit loss in the event of nonperformance by the other party to the loan is represented by the contractual notional amount of the loan. Since none of the loans have ever been returned to the Company, the amount of total loans sold with limited recourse does not necessarily represent future cash requirements. Total loans sold with limited recourse in 2014 and 2013 was $58.8 million and $110.1 million, respectively.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The outstanding principal balance and the carrying amount of acquired loans that were recorded at fair value at the acquisition date that are included in the consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2014 and 2013 were as follows:
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | PCI loans | | | Purchased Performing loans | | | Total | | | PCI loans | | | Purchased Performing loans | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding principal balance | | $ | 165,686 | | | $ | 367,768 | | | $ | 533,454 | | | $ | 197,040 | | | $ | 408,970 | | | $ | 606,010 | |
Carrying amount: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | | 5,552 | | | | 11,032 | | | | 16,584 | | | | 5,737 | | | | 18,377 | | | | 24,114 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 30,554 | | | | 101,071 | | | | 131,625 | | | | 35,760 | | | | 103,834 | | | | 139,594 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 43,866 | | | | 62,493 | | | | 106,359 | | | | 56,996 | | | | 69,368 | | | | 126,364 | |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | 514 | | | | - | | | | 514 | | | | - | | | | 97 | | | | 97 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 13,660 | | | | 8,052 | | | | 21,712 | | | | 22,699 | | | | 13,509 | | | | 36,208 | |
AC&D - CRE | | | 112 | | | | - | | | | 112 | | | | 121 | | | | 3,218 | | | | 3,339 | |
Other commercial | | | 1,187 | | | | 734 | | | | 1,921 | | | | 137 | | | | 1,889 | | | | 2,026 | |
Residential mortgage | | | 28,730 | | | | 91,291 | | | | 120,021 | | | | 32,826 | | | | 98,104 | | | | 130,930 | |
HELOC | | | 1,734 | | | | 83,573 | | | | 85,307 | | | | 1,402 | | | | 86,512 | | | | 87,914 | |
Residential construction | | | 6,574 | | | | 3,928 | | | | 10,502 | | | | 6,920 | | | | 7,155 | | | | 14,075 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 758 | | | | 2,615 | | | | 3,373 | | | | 1,189 | | | | 2,377 | | | | 3,566 | |
| | | $ | 133,241 | | | $ | 364,789 | | | $ | 498,030 | | | $ | 163,787 | | | $ | 404,440 | | | $ | 568,227 | |
Concentrations of Credit-Loans are primarily made within the Company’s operating footprint of North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia and Virginia. Real estate loans can be affected by the condition of the local real estate market. Commercial and industrial loans can be affected by the local economic conditions. The commercial loan portfolio has concentrations in business loans secured by real estate including construction loans and real estate development loans. Primary concentrations in the consumer loan portfolio include home equity lines of credit and residential mortgages. At December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, the Company had no loans outstanding with non-United States entities.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Allowance for Loan Losses-The following table presents, by portfolio segment, the activity in the allowance for loan losses for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
| | | Commercial and industrial | | | CRE - owner-occupied | | | CRE - investor income producing | | | AC&D | | | AC&D-1-4 family construction | | | AC&D- lots, land, & development | | | AC&D- CRE | | | Other commercial | | | Residential mortgage | | | HELOC | | | Residential construction | | | Other loans to individuals | | | Total | |
For the year ended December 31, 2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for Loan Losses, excluding PCI: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, beginning of year | | $ | 1,491 | | | $ | 399 | | | $ | 1,797 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 839 | | | $ | 1,751 | | | $ | 299 | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 358 | | | $ | 1,050 | | | $ | 390 | | | $ | 72 | | | $ | 8,471 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | (254 | ) | | | 252 | | | | 123 | | | | | | | | (464 | ) | | | (2,871 | ) | | | 96 | | | | 6 | | | | 48 | | | | 1,384 | | | | 296 | | | | 29 | | | | (1,355 | ) |
Charge-offs | | | (161 | ) | | | (193 | ) | | | (292 | ) | | | - | | | | (15 | ) | | | (16 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (161 | ) | | | (852 | ) | | | (201 | ) | | | (50 | ) | | | (1,941 | ) |
Recoveries | | | 487 | | | | 263 | | | | 123 | | | | - | | | | 98 | | | | 1,727 | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 198 | | | | 69 | | | | 57 | | | | 64 | | | | 3,087 | |
Net (charge-offs) recoveries | | | 326 | | | | 70 | | | | (169 | ) | | | - | | | | 83 | | | | 1,711 | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 37 | | | | (783 | ) | | | (144 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 1,146 | |
Ending balance | | $ | 1,563 | | | $ | 721 | | | $ | 1,751 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 458 | | | $ | 591 | | | $ | 395 | | | $ | 32 | | | $ | 443 | | | $ | 1,651 | | | $ | 542 | | | $ | 115 | | | $ | 8,262 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PCI Impairment Allowance for Loan Losses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, beginning of year | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 360 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 360 | |
PCI impairment charge-offs | | | - | | | | - | | | | (6 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1 | ) | | | (144 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (151 | ) |
PCI impairment recoveries | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Net PCI impairment charge-offs | | | - | | | | - | | | | (6 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (1 | ) | | | (144 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (151 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Reversal of PCI impairment | | | - | | | | - | | | | (354 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 144 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (209 | ) |
Benefit attributable to FDIC loss shareagreements | | | - | | | | - | | | | 278 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 278 | |
Total provision for loan losses charged to operations | | | - | | | | - | | | | (76 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 144 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 69 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Provision for loan losses recorded through FDIC loss share receivable | | | - | | | | - | | | | (278 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (278 | ) |
Ending balance | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Allowance for Loan Losses | | $ | 1,563 | | | $ | 721 | | | $ | 1,751 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 458 | | | $ | 591 | | | $ | 395 | | | $ | 32 | | | $ | 443 | | | $ | 1,651 | | | $ | 542 | | | $ | 115 | | | $ | 8,262 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
For the year ended December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for Loan Losses, excluding PCI: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, beginning of year | | $ | 849 | | | $ | 496 | | | $ | 1,102 | | | $ | 4,157 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 454 | | | $ | 1,463 | | | $ | 1,046 | | | $ | 49 | | | $ | 9,624 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 1,693 | | | | (52 | ) | | | 933 | | | | (4,157 | ) | | | 705 | | | | 1,031 | | | | 299 | | | | 16 | | | | 319 | | | | 359 | | | | (673 | ) | | | 31 | | | | 504 | |
Charge-offs | | | (1,238 | ) | | | (52 | ) | | | (718 | ) | | | - | | | | (87 | ) | | | (6 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (831 | ) | | | (838 | ) | | | (44 | ) | | | (64 | ) | | | (3,878 | ) |
Recoveries | | | 187 | | | | 7 | | | | 480 | | | | - | | | | 221 | | | | 726 | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 416 | | | | 66 | | | | 61 | | | | 56 | | | | 2,221 | |
Net (charge-offs) recoveries | | | (1,051 | ) | | | (45 | ) | | | (238 | ) | | | - | | | | 134 | | | | 720 | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | (415 | ) | | | (772 | ) | | | 17 | | | | (8 | ) | | | (1,657 | ) |
Ending balance | | $ | 1,491 | | | $ | 399 | | | $ | 1,797 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 839 | | | $ | 1,751 | | | $ | 299 | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 358 | | | $ | 1,050 | | | $ | 390 | | | $ | 72 | | | $ | 8,471 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PCI Impairment Allowance for Loan Losses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, beginning of year | | $ | 225 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 542 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 200 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 967 | |
PCI impairment charge-offs | | | (216 | ) | | | - | | | | (16 | ) | | | (177 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (386 | ) | | | (311 | ) | | | - | | | | (233 | ) | | | (36 | ) | | | (1,375 | ) |
PCI impairment recoveries | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 25 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 25 | |
Net PCI impairment charge-offs | | | (216 | ) | | | - | | | | (16 | ) | | | (152 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (386 | ) | | | (311 | ) | | | - | | | | (233 | ) | | | (36 | ) | | | (1,350 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PCI provision for loan losses | | | (9 | ) | | | - | | | | 376 | | | | (390 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 386 | | | | 111 | | | | - | | | | 233 | | | | 36 | | | | 743 | |
Benefit attributable to FDIC loss shareagreements | | | (104 | ) | | | - | | | | (205 | ) | | | (192 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (501 | ) |
Total provision for loan losses charged to operations | | | (113 | ) | | | - | | | | 171 | | | | (582 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 386 | | | | 111 | | | | - | | | | 233 | | | | 36 | | | | 242 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Provision for loan losses recorded through FDIC loss share receivable | | | 104 | | | | - | | | | 205 | | | | 192 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 501 | |
Ending balance | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 360 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 360 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Allowance for Loan Losses | | $ | 1,491 | | | $ | 399 | | | $ | 2,157 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 839 | | | $ | 1,751 | | | $ | 299 | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 358 | | | $ | 1,050 | | | $ | 390 | | | $ | 72 | | | $ | 8,831 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
| | | Commercial and industrial | | | CRE - owner-occupied | | | CRE - investor income producing | | | AC&D | | | Other commercial | | | Residential mortgage | | | HELOC | | | Residential construction | | | Other loans to individuals | | | Total | |
For the year ended December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for Loan Losses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, beginning of year | | $ | 703 | | | $ | 740 | | | $ | 2,106 | | | $ | 3,883 | | | $ | 17 | | | $ | 309 | | | $ | 1,898 | | | $ | 455 | | | $ | 43 | | | $ | 10,154 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 632 | | | | (40 | ) | | | 71 | | | | (676 | ) | | | 85 | | | | 262 | | | | (62 | ) | | | 795 | | | | (11 | ) | | | 1,056 | |
PCI provision for loan losses | | | 225 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 542 | | | | - | | | | 200 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 967 | |
Charge-offs | | | (565 | ) | | | (204 | ) | | | (1,132 | ) | | | (652 | ) | | | (94 | ) | | | (129 | ) | | | (406 | ) | | | (328 | ) | | | (12 | ) | | | (3,522 | ) |
Recoveries | | | 79 | | | | - | | | | 57 | | | | 1,602 | | | | - | | | | 12 | | | | 33 | | | | 124 | | | | 29 | | | | 1,936 | |
Net (charge-offs) recoveries | | | (486 | ) | | | (204 | ) | | | (1,075 | ) | | | 950 | | | | (94 | ) | | | (117 | ) | | | (373 | ) | | | (204 | ) | | | 17 | | | | (1,586 | ) |
Ending balance | | $ | 1,074 | | | $ | 496 | | | $ | 1,102 | | | $ | 4,699 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 654 | | | $ | 1,463 | | | $ | 1,046 | | | $ | 49 | | | $ | 10,591 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The following table presents, by portfolio segment, the balance in the allowance for loan losses disaggregated on the basis of the Company’s impairment measurement method and the related recorded investment in loans at December 31, 2014 and 2013.
| | | Commercial and industrial | | | CRE - owner-occupied | | | CRE - investor income producing | | | AC&D-1-4 family construction | | | AC&D- lots, land, & development | | | AC&D- CRE | | | Other commercial | | | Residential mortgage | | | HELOC | | | Residential construction | | | Other loans to individuals | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for Loan Losses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Individually evaluated for impairment | | $ | 44 | | | $ | 18 | | | $ | 57 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 11 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 19 | | | $ | 138 | | | $ | 382 | | | $ | 4 | | | $ | 12 | | | $ | 685 | |
Collectively evaluated for impairment | | | 1,519 | | | | 703 | | | | 1,694 | | | | 458 | | | | 580 | | | | 395 | | | | 13 | | | | 305 | | | | 1,269 | | | | 538 | | | | 103 | | | | 7,577 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 1,563 | | | | 721 | | | | 1,751 | | | | 458 | | | | 591 | | | | 395 | | | | 32 | | | | 443 | | | | 1,651 | | | | 542 | | | | 115 | | | | 8,262 | |
Purchased credit-impaired | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 1,563 | | | $ | 721 | | | $ | 1,751 | | | $ | 458 | | | $ | 591 | | | $ | 395 | | | $ | 32 | | | $ | 443 | | | $ | 1,651 | | | $ | 542 | | | $ | 115 | | | $ | 8,262 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Recorded Investment in Loans: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Individually evaluated for impairment | | $ | 376 | | | $ | 2,889 | | | $ | 1,271 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 1,073 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 143 | | | $ | 2,525 | | | $ | 2,481 | | | $ | 369 | | | $ | 90 | | | $ | 11,217 | |
Collectively evaluated for impairment | | | 167,858 | | | | 300,339 | | | | 425,510 | | | | 28,887 | | | | 40,710 | | | | 71,478 | | | | 3,715 | | | | 173,895 | | | | 151,082 | | | | 48,939 | | | | 21,738 | | | | 1,434,151 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 168,234 | | | | 303,228 | | | | 426,781 | | | | 28,887 | | | | 41,783 | | | | 71,478 | | | | 3,858 | | | | 176,420 | | | | 153,563 | | | | 49,308 | | | | 21,828 | | | | 1,445,368 | |
Purchased credit-impaired | | | 5,552 | | | | 30,554 | | | | 43,866 | | | | 514 | | | | 13,660 | | | | 112 | | | | 1,187 | | | | 28,730 | | | | 1,734 | | | | 6,574 | | | | 758 | | | | 133,241 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 173,786 | | | $ | 333,782 | | | $ | 470,647 | | | $ | 29,401 | | | $ | 55,443 | | | $ | 71,590 | | | $ | 5,045 | | | $ | 205,150 | | | $ | 155,297 | | | $ | 55,882 | | | $ | 22,586 | | | $ | 1,578,609 | |
| | | Commercial and industrial | | | CRE - owner-occupied | | | CRE - investor income producing | | | AC&D-1-4 family construction | | | AC&D- lots, land, & development | | | AC&D- CRE | | | Other commercial | | | Residential mortgage | | | HELOC | | | Residential construction | | | Other loans to individuals | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | �� | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for Loan Losses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Individually evaluated for impairment | | $ | 14 | | | $ | 14 | | | $ | 527 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 18 | | | $ | 167 | | | $ | 137 | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 884 | |
Collectively evaluated for impairment | | | 1,477 | | | | 385 | | | | 1,270 | | | | 839 | | | | 1,751 | | | | 299 | | | | 7 | | | | 191 | | | | 913 | | | | 383 | | | | 72 | | | | 7,587 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 1,491 | | | | 399 | | | | 1,797 | | | | 839 | | | | 1,751 | | | | 299 | | | | 25 | | | | 358 | | | | 1,050 | | | | 390 | | | | 72 | | | | 8,471 | |
Purchased credit-impaired | | | - | | | | - | | | | 360 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 360 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 1,491 | | | $ | 399 | | | $ | 2,157 | | | $ | 839 | | | $ | 1,751 | | | $ | 299 | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 358 | | | $ | 1,050 | | | $ | 390 | | | $ | 72 | | | $ | 8,831 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Recorded Investment in Loans: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Individually evaluated for impairment | | $ | 265 | | | $ | 1,902 | | | $ | 3,216 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 1,888 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 262 | | | $ | 4,513 | | | $ | 3,014 | | | $ | 66 | | | $ | 60 | | | $ | 15,186 | |
Collectively evaluated for impairment | | | 116,398 | | | | 229,919 | | | | 321,975 | | | | 19,959 | | | | 41,002 | | | | 56,638 | | | | 3,450 | | | | 136,037 | | | | 139,338 | | | | 33,835 | | | | 17,546 | | | | 1,116,097 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 116,663 | | | | 231,821 | | | | 325,191 | | | | 19,959 | | | | 42,890 | | | | 56,638 | | | | 3,712 | | | | 140,550 | | | | 142,352 | | | | 33,901 | | | | 17,606 | | | | 1,131,283 | |
Purchased credit-impaired | | | 5,737 | | | | 35,760 | | | | 56,996 | | | | - | | | | 22,699 | | | | 121 | | | | 137 | | | | 32,826 | | | | 1,402 | | | | 6,920 | | | | 1,189 | | | | 163,787 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 122,400 | | | $ | 267,581 | | | $ | 382,187 | | | $ | 19,959 | | | $ | 65,589 | | | $ | 56,759 | | | $ | 3,849 | | | $ | 173,376 | | | $ | 143,754 | | | $ | 40,821 | | | $ | 18,795 | | | $ | 1,295,070 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The Company’s loan loss allowance methodology includes four components, as described below:
1) Specific Reserve Component. Specific reserves represent the current impairment estimate on specific loans, for which it is probable that the Company will be unable to collect all amounts due according to contractual terms based on current information and events. Impairment measurement reflects only a deterioration of credit quality and not changes in market rates that may cause a change in the fair value of the impaired loan. The amount of impairment may be measured in one of three ways, including (i) calculating the present value of expected future cash flows, discounted at the loan’s interest rate implicit in the original document and deducting estimated selling costs, if any; (ii) observing quoted market prices for identical or similar instruments traded in active markets, or employing model-based valuation techniques for which all significant assumptions are observable in the market; and (iii) determining the fair value of collateral, which is utilized for both collateral-dependent loans and for loans when foreclosure is probable.
Impaired loans with a balance less than or equal to $150 thousand are viewed in two groups: those which have experienced charge-offs and those recorded at legal balance. Those loans which have experienced charge-offs have no additional reserve applied unless specifically calculated at a point in time when the loan balance exceeded $150 thousand. Those loans recorded at their legal balance are reserved for based on a pooled probability of default and loss given default calculation.
2) Quantitative Reserve Component. Quantitative reserves represent the current loss contingency estimate on pools of loans, which is an estimate of the amount for which it is probable that the Company will be unable to collect all amounts due on homogeneous groups of loans according to contractual terms should one or more events occur, excluding those loans specifically identified above.
The historical loss experience of the Company is collected quarterly by evaluating internal loss data. The estimated historical loss rates are grouped by loan product type. The Company utilizes average historical losses to represent management’s estimate of losses inherent in a particular portfolio. The historical look back period is estimated by loan type, and the Company applies the appropriate historical loss period which best reflects the inherent loss in the applicable portfolio considering prevailing market conditions.
In the past, the Company has recorded a minimum reserve as part of the quantitative component. A minimum reserve is utilized when the Company has insufficient internal loss history or when internal loss history falls below the minimum reserve percentage. Minimums are determined by analyzing Federal Reserve Bank charge-off data for all insured federal- and state-chartered commercial banks. During 2014, the Company determined that it would use the calculated average historical loss rates and adjust to the minimum reserve amounts in its qualitative component. This change represented a reclassification between components of the allowance and had no impact on the calculation in total.
During 2013, the Company segregated the AC&D portfolio into three collateral types: (i) 1-4 family construction, (ii) lots, land and development and (iii) CRE construction. These enhancements strengthen the granularity of the allowance methodology and are reflective of the distinctions in credit quality indicators for the three collateral types as well as the Company’s present origination activities.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The following look back periods were utilized by management in determining the quantitative reserve component at December 31, 2014 and 2013:
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
Look back periods (in calendar quarters) | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | | 15 | | | | 15 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 15 | | | | Minimum | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 15 | | | | 15 | |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | 15 | | | | 15 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 15 | | | | 15 | |
AC&D - CRE | | | 15 | | | | Minimum | |
Other commercial | | | 15 | | | | Minimum | |
Residential mortgage | | | 15 | | | | 12 | |
HELOC | | | 15 | | | | 12 | |
Residential construction | | | 15 | | | | 12 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 15 | | | | Minimum | |
The changes in the look back periods noted above were made to provide a better estimate of the loss inherent in the portfolio for each loan category and to reflect the availability of loss history. The Company also performs a quantitative calculation on the acquired purchased performing loan portfolio. There is no allowance for loan losses established at the acquisition date for purchased performing loans. The historical loss experience discussed above is applied to the acquired purchased performing loan portfolio and the result is compared to the remaining fair value mark on this portfolio. A provision for loan losses is recorded for any further deterioration in these loans subsequent to the acquisition. At December 31, 2014, this analysis indicated a need for a $117 thousand provision for loan losses for the acquired purchased performing portfolio. There was no additional provision for loan losses for the acquired purchased performing portfolio as of December 31, 2013. The remaining mark on the acquired purchased performing loan portfolio was $3.0 million and $4.5 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
3) Qualitative Reserve Component. Qualitative reserves represent an estimate of the amount for which it is probable that environmental or other relevant factors will cause the aforementioned loss contingency estimate to differ from the Company’s historical loss experience or other assumptions. These factors include portfolio trends, portfolio concentrations, economic and market conditions, changes in lending practices and other factors. In 2014, the Company introduced two new factors: changes in loan review systems and geographic considerations. Management believes these refinements simplify application of the qualitative component of the allowance methodology. Each of the factors, except other factors, can range from 0.00% (not applicable) to 0.15% (very high). Other factors are reviewed on a situational basis and are adjusted in 5 basis point increments, up or down, with a maximum of 0.50%. Details of the seven environmental factors for inclusion in the allowance methodology are as follows:
| | i. | Portfolio trends, which may relate to such factors as type or level of loan origination activity, changes in asset quality (i.e., past due, special mention, non-performing) and/or changes in collateral values; |
| | ii. | Portfolio concentrations, which may relate to individual borrowers and/or guarantors, geographic regions, industry sectors, loan types and/or other factors; |
| | iii. | Economic and market trends, which may relate to trends and/or levels of gross domestic production, unemployment, bankruptcies, foreclosures, housing starts, housing prices, equity prices, competitor activities and/or other factors; |
| | iv. | Changes in lending practices, which may relate to changes in credit policies, procedures, systems or staff; |
| | v. | Changes in loan review system, which may introduce variation in loan grading, collateral adequacy and valuation and impairment classification; |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
| | vi. | Geographical considerations, which may relate to economic and/or environmental issues unique to a geographical area including but not limited to elimination of a major employer, natural disaster, or long-term states of emergency; and |
| | vii. | Other factors, which is intended to capture the incremental adjustment, by loan type, to internally calculated minimum reserves (as discussed above) as well as environmental factors not specifically identified above. |
In addition, qualitative reserves on purchased performing loans are based on the Company’s judgment around the timing difference expected to occur between accretion of the fair market value credit adjustment and realization of actual loans losses.
4) Reserve on PCI Loans.In determining the acquisition date fair value of PCI loans, and in subsequent accounting, the Company generally aggregates purchased loans into pools of loans with common risk characteristics. Expected cash flows at the acquisition date in excess of the fair value of loans are recorded as interest income over the life of the loans using a level yield method if the timing and amount of the future cash flows of the pool is reasonably estimable. Subsequent to the acquisition date, significant increases in cash flows over those expected at the acquisition date are recognized as interest income prospectively. Decreases in expected cash flows after the acquisition date are recognized by recording an allowance for loan losses. In pools where impairment has already been recognized, an increase in cash flows will result in a reversal of prior impairment. Management analyzes these acquired loan pools using various assessments of risk to determine and calculate an expected loss. The expected loss is derived using an estimate of a loss given default based upon the collateral type and/or specific review by loan officers of loans generally greater than $1.0 million, and the probability of default that was determined based upon management’s review of the loan portfolio. Trends are reviewed in terms of traditional credit metrics such as accrual status, past due status, and weighted average risk grade of the loans within each of the accounting pools. In addition, the relationship between the change in the unpaid principal balance and change in the fair value mark is assessed to correlate the directional consistency of the expected loss for each pool.
This analysis resulted in net recovery of impairment for the year ended December 31, 2014 of $209 thousand. Additionally, approximately $(278) thousand was attributable to covered loans under FDIC loss share agreements. These covered loan impairments were a function of an increase in expected losses and as a result, the FDIC indemnification asset was increased. See Note 6 – FDIC Loss Share Agreements for further discussion. These impairments are in a single covered PCI loan pool and are in the CRE – investor income producing loan segment.
The allowance for loan losses is increased by provisions charged to operations and reduced by loans charged off, net of recoveries. The decrease in the allowance for loan losses from December 31, 2013 to December 31, 2014 was a function of the following:
| | (1) | a decrease of $3.5 million in the quantitative component of the allowance due to a decrease in historical loss rates applied to the portfolio as significant charge-offs from 2010 are replaced with low loss or recovery periods in 2014. In addition, changes in look-back periods in the residential construction loan type, which better reflect the inherent loss in the portfolio, and the reclassification of the minimum reserve amounts to the qualitative component contributed to the decrease. |
| | (2) | An increase of $3.4 million in the qualitative component of the allowance primarily due to the reclassification of minimum reserve amounts noted in item (1) above as well as management’s decision to increase certain factors based on rapid loan growth, entrance into new markets, and caution surrounding the economic recovery. |
| | (3) | A decrease of $360 thousand in the reserve on PCI loans due to the reversal of previously recognized impairments. |
| | (4) | A decrease of $199 thousand in specific reserves which change periodically as loans move through or out of the impairment process. |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The Company evaluates and estimates off-balance sheet credit exposure at the same time it estimates credit losses for loans by a similar process. These estimated credit losses are not recorded as part of the allowance for loan losses, but are recorded to a separate liability account by a charge to income, if material. Loan commitments, unused lines of credit and standby letters of credit make up the off-balance sheet items reviewed for potential credit losses. At both December 31, 2014 and 2013, $125 thousand was recorded as an other liability for off-balance sheet credit exposure.
Credit Quality Indicators-The Company uses several credit quality indicators to manage credit risk in an ongoing manner. The Company's primary credit quality indicator is an internal credit risk rating system that categorizes loans into pass, special mention, or classified categories. Credit risk ratings are applied individually to those classes of loans that have significant or unique credit characteristics that benefit from a case-by-case evaluation. These are typically loans to businesses or individuals in the classes that comprise the commercial portfolio segment. Groups of loans that are underwritten and structured using standardized criteria and characteristics, such as statistical models (e.g., credit scoring or payment performance), are typically risk rated and monitored collectively. These are typically loans to individuals in the classes that comprise the consumer portfolio segment.
The following are the definitions of the Company's credit quality indicators:
| | Pass: | | Loans in classes that comprise the commercial and consumer portfolio segments that are not adversely rated, are contractually current as to principal and interest, and are otherwise in compliance with the contractual terms of the loan agreement. PCI loans that were recorded at estimated fair value on the acquisition date are generally assigned a “pass” loan grade because their net financial statement value is based on the present value of expected cash flows. Management believes there is a low likelihood of loss related to those loans that are considered pass. |
|
Special Mention:
|
|
Loans in classes that comprise the commercial and consumer portfolio segments that have potential weaknesses that deserve management's close attention. If not addressed, these potential weaknesses may result in deterioration of the repayment prospects for the loan. Management believes there is a moderate likelihood of some loss related to those loans that are considered special mention.
|
|
Classified:
|
|
Loans in the classes that comprise the commercial and consumer portfolio segments that are inadequately protected by the sound worth and paying capacity of the borrower or of the collateral pledged, if any. Management believes that there is a distinct possibility that the Company will sustain some loss if the deficiencies related to classified loans are not corrected in a timely manner.
|
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The Company's credit quality indicators are periodically updated on a case-by-case basis. The following tables present the recorded investment in the Company's loans as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, by loan class and by credit quality indicator.
| | | As of December 31, 2014 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Commercial | | | | | | | CRE-Investor | | | AC&D- | | | AC&D- lots, | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | and | | | CRE-Owner | | | Income | | | 1-4 family | | | land, & | | | | | | | Other | | | Total | |
| | | Industrial | | | Occupied | | | Producing | | | construction | | | development | | | AC&D- CRE | | | Commercial | | | Commercial | |
Pass | | $ | 172,638 | | | $ | 328,712 | | | $ | 461,955 | | | $ | 29,401 | | | $ | 52,568 | | | $ | 71,590 | | | $ | 4,902 | | | $ | 1,121,766 | |
Special mention | | | 493 | | | | 1,925 | | | | 6,934 | | | | - | | | | 1,335 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,687 | |
Classified | | | 655 | | | | 3,145 | | | | 1,758 | | | | - | | | | 1,540 | | | | - | | | | 143 | | | | 7,241 | |
Total | | $ | 173,786 | | | $ | 333,782 | | | $ | 470,647 | | | $ | 29,401 | | | $ | 55,443 | | | $ | 71,590 | | | $ | 5,045 | | | $ | 1,139,694 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | |
| | | Residential | | | | | | | Residential | | | Other Loans to | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Total | |
| | | Mortgage | | | HELOC | | | Construction | | | Individuals | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Consumer | |
Pass | | $ | 202,214 | | | $ | 147,893 | | | $ | 55,290 | | | $ | 22,445 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 427,842 | |
Special mention | | | 1,802 | | | | 6,122 | | | | 227 | | | | 99 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 8,250 | |
Classified | | | 1,134 | | | | 1,282 | | | | 365 | | | | 42 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,823 | |
Total | | $ | 205,150 | | | $ | 155,297 | | | $ | 55,882 | | | $ | 22,586 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 438,915 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,578,609 | |
| | | As of December 31, 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Commercial | | | | | | | CRE-Investor | | | AC&D- | | | AC&D- lots, | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | and | | | CRE-Owner | | | Income | | | 1-4 family | | | land, & | | | | | | | Other | | | Total | |
| | | Industrial | | | Occupied | | | Producing | | | construction | | | development | | | AC&D- CRE | | | Commercial | | | Commercial | |
Pass | | $ | 120,037 | | | $ | 260,472 | | | $ | 373,464 | | | $ | 19,959 | | | $ | 60,332 | | | $ | 56,759 | | | $ | 3,587 | | | $ | 894,610 | |
Special mention | | | 1,692 | | | | 6,126 | | | | 3,628 | | | | - | | | | 2,802 | | | | - | | | | 150 | | | | 14,398 | |
Classified | | | 671 | | | | 983 | | | | 5,095 | | | | - | | | | 2,455 | | | | - | | | | 112 | | | | 9,316 | |
Total | | $ | 122,400 | | | $ | 267,581 | | | $ | 382,187 | | | $ | 19,959 | | | $ | 65,589 | | | $ | 56,759 | | | $ | 3,849 | | | $ | 918,324 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | - | |
| | | Residential | | | | | | | Residential | | | Other Loans to | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Total | |
| | | Mortgage | | | HELOC | | | Construction | | | Individuals | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Consumer | |
Pass | | $ | 169,519 | | | $ | 137,626 | | | $ | 39,824 | | | $ | 18,301 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 365,270 | |
Special mention | | | 1,864 | | | | 2,893 | | | | 766 | | | | 488 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 6,011 | |
Classified | | | 1,993 | | | | 3,235 | | | | 231 | | | | 6 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 5,465 | |
Total | | $ | 173,376 | | | $ | 143,754 | | | $ | 40,821 | | | $ | 18,795 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 376,746 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,295,070 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Aging Analysis of Accruing and Non-Accruing Loans -The Company considers a loan to be past due or delinquent when the terms of the contractual obligation are not met by the borrower. PCI loans are included as a single category in the table below as management believes, regardless of their age, there is a lower likelihood of aggregate loss related to these loan pools. Additionally, PCI loans are discounted to allow for the accretion of income on a level yield basis over the life of the loan based on expected cash flows. Regardless of accruing status, the associated discount on these loan pools results in income recognition. The following presents, by class, an aging analysis of the Company’s accruing and non-accruing loans as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
| | | 30-59 | | | 60-89 | | | Past Due | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Days | | | Days | | | 90 Days | | | PCI | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Past Due | | | Past Due | | | or More | | | Loans | | | Current | | | Total Loans | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 123 | | | $ | 18 | | | $ | 73 | | | $ | 5,552 | | | $ | 168,020 | | | $ | 173,786 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,616 | | | | 30,554 | | | | 301,612 | | | | 333,782 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | - | | | | - | | | | 571 | | | | 43,866 | | | | 426,210 | | | | 470,647 | |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 514 | | | | 28,887 | | | | 29,401 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 13,660 | | | | 41,783 | | | | 55,443 | |
AC&D - CRE | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 112 | | | | 71,478 | | | | 71,590 | |
Other commercial | | | 40 | | | | 143 | | | | - | | | | 1,187 | | | | 3,675 | | | | 5,045 | |
Total commercial loans | | | 163 | | | | 161 | | | | 2,260 | | | | 95,445 | | | | 1,041,665 | | | | 1,139,694 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 57 | | | | 68 | | | | 1,058 | | | | 28,730 | | | | 175,237 | | | | 205,150 | |
HELOC | | | 343 | | | | 60 | | | | 228 | | | | 1,734 | | | | 152,932 | | | | 155,297 | |
Residential construction | | | 157 | | | | - | | | | 341 | | | | 6,574 | | | | 48,810 | | | | 55,882 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 29 | | | | 1 | | | | 41 | | | | 758 | | | | 21,757 | | | | 22,586 | |
Total consumer loans | | | 586 | | | | 129 | | | | 1,668 | | | | 37,796 | | | | 398,736 | | | | 438,915 | |
Total loans | | $ | 749 | | | $ | 290 | | | $ | 3,928 | | | $ | 133,241 | | | $ | 1,440,401 | | | $ | 1,578,609 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 96 | | | $ | 52 | | | $ | 149 | | | $ | 5,737 | | | $ | 116,366 | | | $ | 122,400 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 418 | | | | - | | | | 209 | | | | 35,760 | | | | 231,194 | | | | 267,581 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 655 | | | | - | | | | 3,161 | | | | 56,996 | | | | 321,375 | | | | 382,187 | |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 19,959 | | | | 19,959 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 48 | | | | - | | | | 292 | | | | 22,699 | | | | 42,550 | | | | 65,589 | |
AC&D - CRE | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 121 | | | | 56,638 | | | | 56,759 | |
Other commercial | | | - | | | | 112 | | | | - | | | | 137 | | | | 3,600 | | | | 3,849 | |
Total commercial loans | | | 1,217 | | | | 164 | | | | 3,811 | | | | 121,450 | | | | 791,682 | | | | 918,324 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | - | | | | 32 | | | | 1,340 | | | | 32,826 | | | | 139,178 | | | | 173,376 | |
HELOC | | | 248 | | | | 160 | | | | 698 | | | | 1,402 | | | | 141,246 | | | | 143,754 | |
Residential construction | | | 25 | | | | - | | | | 66 | | | | 6,920 | | | | 33,810 | | | | 40,821 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 14 | | | | 11 | | | | - | | | | 1,189 | | | | 17,581 | | | | 18,795 | |
Total consumer loans | | | 287 | | | | 203 | | | | 2,104 | | | | 42,337 | | | | 331,815 | | | | 376,746 | |
Total loans | | $ | 1,504 | | | $ | 367 | | | $ | 5,915 | | | $ | 163,787 | | | $ | 1,123,497 | | | $ | 1,295,070 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Impaired Loans - All classes of loans are considered impaired when, based on current information and events, it is probable the Company will be unable to collect all amounts due in accordance with the original contractual terms of the loan agreement, including scheduled principal and interest payments. Impaired loans may include all classes of nonaccrual loans and loans modified in a TDR. If a loan is impaired, a specific valuation allowance is allocated, if necessary, so that the loan is reported net, at the present value of estimated future cash flows using the rate implicit in the original loan agreement or at the fair value of collateral if repayment is expected solely from the collateral. Additionally, a portion of the Company’s qualitative factors accounts for potential impairment on loans generally less than $150 thousand. Interest payments on impaired loans are typically applied to principal unless collectability of the principal amount is reasonably assured, in which case interest is recognized on a cash basis. Impaired loans, or portions thereof, are charged off when deemed uncollectible.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company’s quarterly cash flow analyses on PCI loan pools indicated net recovery of impairment of $209 thousand. These impairments are in a single covered PCI loan pool and are in the CRE – investor income producing loan segment. During the year ended December 31, 2013, the Company’s quarterly cash flow analyses indicated net recovery of impairment of $607 thousand. These impairments are in a single covered PCI loan pool and are in the CRE – investor income producing loan segment. These amounts are not included in the tables below.
| | | December 31, 2014 | | | December 31, 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Unpaid | | | Related | | | | | | | Unpaid | | | Related | |
| | | Recorded | | | Principal | | | Allowance For | | | Recorded | | | Principal | | | Allowance For | |
| | | Investment | | | Balance | | | Loan Losses | | | Investment | | | Balance | | | Loan Losses | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Impaired Loans with No Related Allowance Recorded: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 47 | | | $ | 126 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 183 | | | $ | 473 | | | $ | - | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,815 | | | | 1,955 | | | | - | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 30 | | | | 47 | | | | - | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,888 | | | | 4,475 | | | | - | |
Other commercial | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 150 | | | | 167 | | | | - | |
Total commercial loans | | | 47 | | | | 126 | | | | - | | | | 4,066 | | | | 7,117 | | | | - | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 322 | | | | 420 | | | | - | | | | 3,080 | | | | 3,926 | | | | - | |
HELOC | | | 363 | | | | 499 | | | | - | | | | 2,478 | | | | 2,855 | | | | - | |
Residential construction | | | 322 | | | | 376 | | | | - | | | | 26 | | | | 39 | | | | - | |
Other loans to individuals | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 58 | | | | 62 | | | | - | |
Total consumer loans | | | 1,007 | | | | 1,295 | | | | - | | | | 5,642 | | | | 6,882 | | | | - | |
Total impaired loans with no relatedallowance recorded | | $ | 1,054 | | | $ | 1,421 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 9,708 | | | $ | 13,999 | | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Impaired Loans with an Allowance Recorded: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 329 | | | $ | 348 | | | $ | 44 | | | $ | 82 | | | $ | 90 | | | $ | 14 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 2,889 | | | | 2,982 | | | | 18 | | | | 87 | | | | 88 | | | | 14 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 1,271 | | | | 1,357 | | | | 57 | | | | 3,186 | | | | 3,673 | | | | 527 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 1,073 | | | | 1,187 | | | | 11 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Other commercial | | | 143 | | | | 159 | | | | 19 | | | | 112 | | | | 112 | | | | 18 | |
Total commercial loans | | | 5,705 | | | | 6,033 | | | | 149 | | | | 3,467 | | | | 3,963 | | | | 573 | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 2,203 | | | | 2,241 | | | | 138 | | | | 1,433 | | | | 1,485 | | | | 167 | |
HELOC | | | 2,118 | | | | 2,534 | | | | 382 | | | | 536 | | | | 587 | | | | 137 | |
Residential construction | | | 47 | | | | 72 | | | | 4 | | | | 40 | | | | 42 | | | | 7 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 90 | | | | 90 | | | | 12 | | | | 2 | | | | 4 | | | | - | |
Total consumer loans | | | 4,458 | | | | 4,937 | | | | 536 | | | | 2,011 | | | | 2,118 | | | | 311 | |
Total impaired loans with anallowance recorded | | $ | 10,163 | | | $ | 10,970 | | | $ | 685 | | | $ | 5,478 | | | $ | 6,081 | | | $ | 884 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Impaired Loans: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 376 | | | $ | 474 | | | $ | 44 | | | $ | 265 | | | $ | 563 | | | $ | 14 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 2,889 | | | | 2,982 | | | | 18 | | | | 1,902 | | | | 2,043 | | | | 14 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 1,271 | | | | 1,357 | | | | 57 | | | | 3,216 | | | | 3,720 | | | | 527 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 1,073 | | | | 1,187 | | | | 11 | | | | 1,888 | | | | 4,475 | | | | - | |
Other commercial | | | 143 | | | | 159 | | | | 19 | | | | 262 | | | | 279 | | | | 18 | |
Total commercial loans | | | 5,752 | | | | 6,159 | | | | 149 | | | | 7,533 | | | | 11,080 | | | | 573 | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 2,525 | | | | 2,661 | | | | 138 | | | | 4,513 | | | | 5,411 | | | | 167 | |
HELOC | | | 2,481 | | | | 3,033 | | | | 382 | | | | 3,014 | | | | 3,442 | | | | 137 | |
Residential construction | | | 369 | | | | 448 | | | | 4 | | | | 66 | | | | 81 | | | | 7 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 90 | | | | 90 | | | | 12 | | | | 60 | | | | 66 | | | | - | |
Total consumer loans | | | 5,465 | | | | 6,232 | | | | 536 | | | | 7,653 | | | | 9,000 | | | | 311 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total impaired loans | | $ | 11,217 | | | $ | 12,391 | | | $ | 685 | | | $ | 15,186 | | | $ | 20,080 | | | $ | 884 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The average recorded investment and interest income recognized on impaired loans, by class, for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 is shown in the table below.
| | | December 31, 2014 | | | December 31, 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Average | | | Interest | | | Average | | | Interest | |
| | | Recorded | | | Income | | | Recorded | | | Income | |
| | | Investment | | | Recognized | | | Investment | | | Recognized | |
Impaired Loans with No Related | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance Recorded: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 382 | | | $ | 19 | | | $ | 276 | | | $ | 5 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 2,090 | | | | 54 | | | | 2,108 | | | | 106 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 620 | | | | 24 | | | | 980 | | | | - | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 1,034 | | | | 98 | | | | 2,978 | | | | 202 | |
Other commercial | | | 60 | | | | 4 | | | | 158 | | | | 9 | |
Total commercial loans | | | 4,186 | | | | 199 | | | | 6,500 | | | | 322 | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 1,689 | | | | 31 | | | | 2,688 | | | | 57 | |
HELOC | | | 1,390 | | | | 19 | | | | 1,513 | | | | 20 | |
Residential construction | | | 80 | | | | - | | | | 20 | | | | - | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 23 | | | | 1 | | | | 64 | | | | 4 | |
Total consumer loans | | | 3,182 | | | | 51 | | | | 4,285 | | | | 81 | |
Total impaired loans with no relatedallowance recorded | | $ | 7,368 | | | $ | 250 | | | $ | 10,785 | | | $ | 403 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Impaired Loans with anAllowance Recorded: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 224 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 487 | | | $ | 2 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 695 | | | | 20 | | | | 47 | | | | 12 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 1,052 | | | | 9 | | | | 2,829 | | | | 2 | |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | 19 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 243 | | | | 16 | | | | 50 | | | | - | |
Other commercial | | | 176 | | | | 8 | | | | 22 | | | | - | |
Total commercial loans | | | 2,409 | | | | 53 | | | | 3,435 | | | | 16 | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 1,825 | | | | 42 | | | | 1,282 | | | | 33 | |
HELOC | | | 1,597 | | | | 29 | | | | 920 | | | | 1 | |
Residential construction | | | 267 | | | | 1 | | | | 24 | | | | - | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 42 | | | | 4 | | | | 1 | | | | - | |
Total consumer loans | | | 3,731 | | | | 76 | | | | 2,227 | | | | 34 | |
Total impaired loans with anallowance recorded | | $ | 6,140 | | | $ | 129 | | | $ | 5,662 | | | $ | 50 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Impaired Loans: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 606 | | | $ | 19 | | | $ | 763 | | | $ | 7 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 2,785 | | | | 74 | | | | 2,155 | | | | 118 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 1,672 | | | | 33 | | | | 3,809 | | | | 2 | |
AC&D - 1-4 family construction | | | 19 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 1,277 | | | | 114 | | | | 3,028 | | | | 202 | |
Other commercial | | | 236 | | | | 12 | | | | 180 | | | | 9 | |
Total commercial loans | | | 6,595 | | | | 252 | | | | 9,935 | | | | 338 | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 3,514 | | | | 73 | | | | 3,970 | | | | 90 | |
HELOC | | | 2,987 | | | | 48 | | | | 2,433 | | | | 21 | |
Residential construction | | | 347 | | | | 1 | | | | 44 | | | | - | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 65 | | | | 5 | | | | 65 | | | | 4 | |
Total consumer loans | | | 6,913 | | | | 127 | | | | 6,512 | | | | 115 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total impaired loans | | $ | 13,508 | | | $ | 379 | | | $ | 16,447 | | | $ | 453 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company recognized $379 thousand of interest income with respect to impaired loans, specifically accruing TDRs, within the period the loans were impaired. During the year ended December 31, 2013, the Company recognized $453 thousand of interest income with respect to impaired loans, specifically accruing TDRs, within the period the loans were impaired. During the year ended December 31, 2012, the Company recognized $150 thousand of interest income with respect to impaired loans, specifically accruing TDRs, within the period the loans were impaired.
Nonaccrual and Past Due Loans -It is the general policy of the Company to place a loan on nonaccrual status when there is probable loss or when there is reasonable doubt that all principal will be collected, or when it is over 90 days past due. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, there were $30 thousand and $17 thousand, respectively, in loans past due 90 days or more and accruing interest. These loans are secured and considered fully collectible at December 31, 2014 and 2013. The recorded investment in nonaccrual loans at December 31, 2014 and 2013 follows:
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
Commercial: | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | $ | 329 | | | $ | 200 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | 1,616 | | | | 209 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | 680 | | | | 3,192 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | 7 | | | | 292 | |
Other commercial | | | - | | | | 112 | |
Total commercial loans | | | 2,632 | | | | 4,005 | |
Consumer: | | | | | | | | |
Residential mortgage | | | 1,549 | | | | 2,007 | |
HELOC | | | 1,022 | | | | 2,348 | |
Residential construction | | | 341 | | | | 66 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | 41 | | | | 2 | |
Total consumer loans | | | 2,953 | | | | 4,423 | |
Total nonaccrual loans | | $ | 5,585 | | | $ | 8,428 | |
Interest income included in the results of operations for 2014, 2013 and 2012, with respect to loans that subsequently went to nonaccrual, totaled $158 thousand, $310 thousand and $157 thousand, respectively. If interest on these loans had been accrued in accordance with their original terms, interest income would have increased by $1.1 million, $3.0 million and $540 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Purchased Credit-Impaired Loans–PCI loans had an unpaid principal balance of $165.7 million and a carrying value of $133.2 million at December 31, 2014. PCI loans had an unpaid principal balance of $197.0 million and a carrying value of $163.8 million at December 31, 2013. PCI loans represented 5.6% and 8.4% of total assets at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Determining the fair value of the PCI loans required the Company to estimate cash flows expected to result from those loans and to discount those cash flows at appropriate rates of interest and taking into account prepayment assumptions. For such loans, the excess of cash flows expected at acquisition over the estimated fair value is recognized as interest income over the remaining lives of the loans and is called the accretable yield. The difference between contractually required payments at acquisition and the cash flows expected to be collected at acquisition reflects the impact of estimated credit losses and is called the nonaccretable difference. In accordance with GAAP, there was no carry-over of previously established allowance for loan losses from acquired companies.
In conjunction with the Provident Community acquisition, the PCI loan portfolio was accounted for at fair value as follows:
| | | May 1, 2014 | |
| | | | | |
Contractual principal and interest at acquisition | | $ | 46,177 | |
Nonaccretable difference | | | (10,153 | ) |
Expected cash flows at acquisition | | | 36,024 | |
Accretable yield | | | (5,589 | ) |
| | | | | |
Basis in PCI loans at acquisition - estimated fair value | | $ | 30,435 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
In conjunction with the Citizens South acquisition, the PCI loan portfolio was accounted for at fair value as follows:
| | | October 1, 2012 | |
| | | | | |
Contractual principal and interest at acquisition | | $ | 294,283 | |
Nonaccretable difference | | | (47,941 | ) |
Expected cash flows at acquisition | | | 246,342 | |
Accretable yield | | | (37,724 | ) |
| | | | | |
Basis in PCI loans at acquisition - estimated fair value | | $ | 208,618 | |
A summary of changes in the accretable yield for PCI loans for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 follows.
Accretable yield table | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accretable yield, beginning of year | | $ | 39,249 | | | $ | 42,734 | | | $ | 14,264 | |
Addition from the Citizens South acquisition | | | - | | | | - | | | | 37,724 | |
Addition from the Provident Community acquisition | | | 5,589 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Interest income | | | (15,766 | ) | | | (14,903 | ) | | | (7,462 | ) |
Reclassification of nonaccretable difference due toimprovement in expected cash flows | | | 9,886 | | | | 12,143 | | | | 479 | |
Other changes, net | | | 1,582 | | | | (725 | ) | | | (2,271 | ) |
Accretable yield, end of year | | $ | 40,540 | | | $ | 39,249 | | | $ | 42,734 | |
Troubled Debt Restructuring -In situations where, for economic or legal reasons related to a borrower's financial difficulties, management may grant a concession for other than an insignificant period of time to the borrower that would not otherwise be considered, the related loan is classified as a TDR. Management strives to identify borrowers in financial difficulty early and work with them to modify to more affordable terms. These modified terms may include rate reductions, principal forgiveness, payment forbearance and other actions intended to minimize the economic loss and to avoid foreclosure or repossession of the collateral. All loan modifications are made on a case-by-case basis.
The Company allocated $373 thousand and $565 thousand, respectively, of specific reserves to customers whose loan terms have been modified in a TDR as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013. As of December 31, 2014, the Company had 18 TDR loans totaling $4.1 million, of which $841 thousand are nonaccrual loans. As of December 31, 2013, the Company had 11 TDR loans totaling $8.2 million, of which $4.4 million are nonaccrual loans.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The following table presents a breakdown of the types of concessions made by loan class during the twelve-month period ended December 31, 2014 and 2013:
| | | Year ended December 31, 2014 | | | Year ended December 31, 2013 | |
| | | Number of loans | | | Pre-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment | | | Post-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment | | | Number of loans | | | Pre-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment | | | Post-Modification Outstanding Recorded Investment | |
Below market interest rate: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
AC&D- lots, land & development | | | 1 | | | $ | 184 | | | $ | 184 | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
Residential mortgage | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 43 | | | | 43 | |
Total | | | 1 | | | | 184 | | | | 184 | | | | 1 | | | | 43 | | | | 43 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Extended payment terms: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | | 1 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 10 | | | | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 962 | | | | 962 | |
Other commercial | | | 1 | | | | 143 | | | | 143 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Residential mortgage | | | 1 | | | | 657 | | | | 657 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
HELOC | | | 1 | | | | 174 | | | | 174 | | | | 1 | | | | 1,250 | | | | 1,250 | |
Residential construction | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Total | | | 4 | | | | 984 | | | | 984 | | | | 2 | | | | 2,212 | | | | 2,212 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | 5 | | | $ | 1,168 | | | $ | 1,168 | | | | 3 | | | $ | 2,255 | | | $ | 2,255 | |
Commercial TDRs - Commercial TDRs (including commercial and industrial, commercial real estate, AC&D and other commercial loans) often result from a workout where an existing commercial loan is restructured and a concession is given. These workouts may involve lengthening the amortization period of the amortized principal beyond market terms, or reducing the interest rate below market terms for the original remaining life of the loan. In the case of extended amortization, this concession reduces the minimum monthly payment and increases the balloon payment at the end of the term of the loan. Other concessions can potentially involve forgiveness of principal, collateral concessions, or reduction of accrued interest. The impact of the TDR on the allowance for loan losses is based on the changes in borrower payment performance rather than just the TDR classification. All TDRs are designated as impaired loans. TDRs, like other impaired loans, are measured based on discounted cash flows, comparing the modified loan to pre-modified terms or, if the loan is deemed to be collateral dependent, collateral value less anticipated selling costs. TDRs having a book balance of less than $150,000, along with other impaired loans of similar size, are measured in a pooled approach utilizing loss given default and probability of default parameters. TDRs may remain in accruing status if the borrower remains less than 90 days past due per the restructured loan terms and no loss is expected. A borrower may be considered for removal from TDR status if it is no longer experiencing financial difficulties and can qualify for new loan terms which do not represent a concession, subject to the normal underwriting standards and processes for similar extensions of credit. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has one commercial TDR with a reduced interest rate and two commercial TDRs where an extension of maturities was granted. All commercial TDRs are paying according to the terms of the modification as of December 31, 2014.
Consumer TDRs - Consumer TDRs (including residential mortgage, HELOC, residential construction and other consumer loans) often result from a workout where an existing loan is modified and a concession is given. These workouts typically lengthen the amortization period of the amortized principal beyond market terms or reduce the interest rate below market terms. The impact of the TDR on the allowance for loan losses is based on the changes in borrower payment performance rather than the TDR classification. TDRs like other impaired loans are measured based on discounted cash flows or collateral value, less anticipated selling costs, of the modified loan using pre-modified interest rates. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has two consumer TDRs where an extension of maturities was granted. All consumer TDRs are paying according to the terms of the modification as of December 31, 2014.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The following table presents loans modified as TDRs within the twelve months ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, and for which there was a payment default during the twelve months ended December 31, 2014 and 2013:
| | | Twelve months ended December 31, 2014 | | | Twelve months ended December 31, 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Numberof loans | | | Recorded Investment | | | Numberof loans | | | Recorded Investment | |
Below market interest rate: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | 1 | | | $ | 3,610 | |
| | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 3,610 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Extended payment terms: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential construction | | | 1 | | | $ | 173 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | 1 | | | | 173 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | 1 | | | $ | 173 | | | | 1 | | | $ | 3,610 | |
The Company does not deem a TDR to be successful until it has been re-established as an accruing loan. The following table presents the successes and failures of the types of modifications indicated within the 12 months ended December 31, 2014 and 2013:
| | | Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2014 | |
| | | Paid in full | | | Paying as restructured | | | Foreclosure/Default | |
| | | Number of loans | | | Recorded Investment | | | Number of loans | | | Recorded Investment | | | Number of loans | | | Recorded Investment | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Below market interest rate | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | 1 | | | $ | 222 | | | | - | | | $ | - | |
Extended payment terms | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3 | | | | 970 | | | | 2 | | | | 338 | |
Total | | | - | | | $ | - | | | | 4 | | | $ | 1,192 | | | | 2 | | | $ | 338 | |
| | | Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2013 | |
| | | Paid in full | | | Paying as restructured | | | Foreclosure/Default | |
| | | Number of loans | | | Recorded Investment | | | Number of loans | | | Recorded Investment | | | Number of loans | | | Recorded Investment | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Below market interest rate | | | 2 | | | $ | 164 | | | | 4 | | | $ | 2,108 | | | | 1 | | | $ | 3,116 | |
Extended payment terms | | | 2 | | | | 438 | | | | 6 | | | | 2,993 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Total | | | 4 | | | $ | 602 | | | | 10 | | | $ | 5,101 | | | | 1 | | | $ | 3,116 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Related Party Loans–From time to time, the Company engages in loan transactions with its directors, executive officers and their related interests (collectively referred to as “related parties”). Such loans are made in the ordinary course of business and on substantially the same terms and collateral as those for comparable transactions prevailing at the time and do not involve more than the normal risk of collectability or present other unfavorable features. A summary of activity in loans to related parties is as follows:
Loans to Directors, Executive Officers and Their Related Interests
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
Balance, beginning of year | | $ | 17,247 | | | $ | 4,184 | |
Disbursements | | | 2,369 | | | | 16,037 | |
Repayments | | | (5,576 | ) | | | (2,974 | ) |
Balance, end of year | | $ | 14,040 | | | $ | 17,247 | |
At December 31, 2014, the Company had pre-approved but unused lines of credit totaling $3.2 million to related parties.
NOTE 6 –FDIC LOSS SHARE AGREEMENTS
In connection with the Citizens South acquisition, the Bank assumed two purchase and assumption agreements with the FDIC that cover approximately $42.3 million and $71.1 million of covered loans as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and $3.0 million and $5.1 million of covered OREO as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Citizens South acquired these assets in prior transactions with the FDIC.
Within the first purchase and assumption agreement are two loss share agreements that originated in March 2010, related to Citizen South’s acquisition of Bank of Hiawassee, a Georgia state-chartered bank headquartered in Hiawassee, Georgia. Under these loss-share agreements, the FDIC will cover 80% of net loan losses up to $102 million and 95% of net loan losses that exceed $102 million. The term of the loss-share agreements is ten years for losses and recoveries on residential real estate loans, five years for losses on all other loans and eight years for recoveries on all other loans. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Bank recorded an estimated receivable from the FDIC in the amount of $3.0 million and $6.6 million, respectively, related to these loss share agreements.
Within the second purchase and assumption agreement are two loss share agreements that originated in April 2011, related to Citizens South’s acquisition of New Horizons Bank, a Georgia state-chartered bank headquartered in East Ellijay, Georgia. The first loss share agreement covers certain residential loans and OREO for a period of ten years. The other loss-share agreement covers all remaining covered assets for a period of five years. Pursuant to the terms of these loss-share agreements, the FDIC is obligated to reimburse the Bank for 80% of all eligible losses, which begins with the first dollar of loss occurred, and certain collection and disposition expenses with respect to covered assets. The Bank has a corresponding obligation to reimburse the FDIC for 80% of eligible recoveries with respect to covered assets for a period of ten years for residential properties and eight years for all other covered assets. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Bank recorded an estimated receivable from the FDIC in the amount of $1.0 million and $3.4 million, respectively, related to these loss share agreements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The following table provides changes in the estimated receivable from the FDIC during 2014 and 2013:
FDIC Loss Share Receivable | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Balance, beginning of period | | $ | 10,025 | | | $ | 18,697 | |
Increase (decrease) in expected losses on loans | | | (278 | ) | | | 501 | |
Additional losses to OREO | | | 96 | | | | 817 | |
Reimbursable expenses (income) | | | 974 | | | | (394 | ) |
Amortization discounts and premiums, net | | | (3,203 | ) | | | (189 | ) |
Reimbursements from the FDIC | | | (3,650 | ) | | | (9,720 | ) |
Other changes, net | | | - | | | | 313 | |
Balance, end of period | | $ | 3,964 | | | $ | 10,025 | |
The estimated receivable from the FDIC is measured separately from the related covered assets and is recorded at carrying value. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the projected cash flows related to the FDIC receivable for losses on covered loans and assets were approximately $3.8 million and $11.5 million, respectively. Included in the estimated receivable above is a component of amortization which will be recognized over the life of the agreement, with increases or decreases based on estimated performance of the underlying loans.
In relation to the FDIC indemnification asset is an expected "true-up" with the FDIC related to the loss share agreements described above. The loss share agreements between the Bank and the FDIC with respect to New Horizons Bank and Bank of Hiawassee each contain a provision that obligates the Company to make a "true-up" payment to the FDIC if the realized losses of each of these acquired banks are less than expected. An estimate of this amount is determined each reporting period. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the “true-up” amount was estimated to be approximately $5.4 million and $5.0 million, respectively, at the end of the loss share agreements. These amounts are recorded in other liabilities on the balance sheet. The actual payment will be determined at the end of the term of the loss sharing agreements and is based on the negative bid, expected losses, intrinsic loss estimate, and assets covered under the loss share agreements.
NOTE 7 - OTHER REAL ESTATE OWNED
The Company owned $12.0 million and $14.5 million in total OREO at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The portion of OREO covered under the loss share agreements with the FDIC at December 31, 2014 and 2013 totaled $3.0 million and $5.1 million, respectively.
Transactions in OREO for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 are summarized below:
Non-Covered OREO | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Beginning balance | | $ | 9,404 | | | $ | 18,427 | |
Additions | | | 2,821 | | | | 3,945 | |
Acquired through merger | | | 2,964 | | | | - | |
Sales | | | (5,774 | ) | | | (12,324 | ) |
Writedowns | | | (436 | ) | | | (644 | ) |
Ending balance | | $ | 8,979 | | | $ | 9,404 | |
Covered OREO | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Beginning balance | | $ | 5,088 | | | $ | 6,646 | |
Additions | | | 5,985 | | | | 6,262 | |
Sales | | | (7,894 | ) | | | (7,070 | ) |
Writedowns | | | (168 | ) | | | (750 | ) |
Ending balance | | $ | 3,011 | | | $ | 5,088 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 8 – PREMISES AND EQUIPMENT
The following is a summary of premises and equipment at December 31:
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
Buildings | | $ | 37,098 | | | $ | 34,871 | |
Land | | | 17,154 | | | | 16,431 | |
Furniture and equipment | | | 9,315 | | | | 8,677 | |
Leasehold improvements | | | 1,448 | | | | 1,057 | |
Fixed assets in process | | | 815 | | | | 389 | |
Premises and equipment | | | 65,830 | | | | 61,425 | |
Accumulated depreciation | | | (6,583 | ) | | | (5,502 | ) |
Premises and equipment, net | | $ | 59,247 | | | $ | 55,923 | |
Depreciation and amortization expense for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 amounted to $3.9 million, $3.4 million and $1.8 million, respectively. These amounts are included in the occupancy and equipment line item in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
NOTE 9 – GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
In accordance with GAAP, the Company does not amortize goodwill. However, core deposit intangible assets are amortized over the estimated life of the asset. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, intangible assets consisted of core deposit premiums, net of accumulated amortization, and amounted to $11.0 million and $8.6 million, respectively. Amortization expense related to the core deposit premium was $1.3 million, $1.0 million, and $564 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Amortization of core deposit intangible assets is computed using the straight-line method over an amortization period of ten years. Estimated amortization expense for the years ending December 31 is as follows (dollars in thousand):
2015 | | $ | 1,389 | |
2016 | | | 1,389 | |
2017 | | | 1,389 | |
2018 | | | 1,389 | |
2019 | | | 1,389 | |
2020 and thereafter | | | 4,015 | |
| | | $ | 10,960 | |
Goodwill represents the excess of the acquisition cost over the fair value of the net assets acquired. The Company evaluated the carrying value of goodwill as of October 1, 2014, its annual test date, and determined that no impairment charge was necessary. Should the Company’s future earnings and cash flows decline and/or discount rates increase, an impairment charge to goodwill and other intangible assets may be required. There have been no events subsequent to the October 1, 2014 evaluation that caused the Company to perform an interim review of the carrying value of goodwill. The following table presents a rollforward of goodwill by acquired bank:
| | | Community | | | Citizens | | | Provident | | | | | |
| | | Capital | | | South | | | Community | | | Total | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Goodwill balance, December 31, 2012 | | $ | 622 | | | $ | 22,529 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 23,151 | |
Additions | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Adjustments | | | - | | | | 3,306 | | | | - | | | | 3,306 | |
Goodwill balance, December 31, 2013 | | | 622 | | | | 25,835 | | | | - | | | | 26,457 | |
Additions | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,783 | | | | 2,783 | |
Adjustments | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Goodwill balance, December 31, 2014 | | $ | 622 | | | $ | 25,835 | | | $ | 2,783 | | | $ | 29,240 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 10 – DEPOSITS
The following is a summary of deposits at December 31:
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
Noninterest bearing demand deposits | | $ | 321,019 | | | $ | 255,861 | |
Interest-bearing demand deposits | | | 405,012 | | | | 296,995 | |
Money market deposits | | | 435,922 | | | | 390,059 | |
Savings | | | 83,820 | | | | 48,701 | |
Brokered deposits | | | 141,771 | | | | 166,280 | |
Certificates of deposit and other time deposits | | | 463,810 | | | | 441,989 | |
Total deposits | | $ | 1,851,354 | | | $ | 1,599,885 | |
The aggregate amounts of time deposits in denominations of $100,000 or more at December 31, 2014, and 2013, were $198.1 million and $284.7 million, respectively. In July 2010, the Dodd-Frank Act permanently increased the insurance limit on deposit accounts from $100,000 to $250,000. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company had $50.9 million and $37.7 million in time deposits greater than $250,000, respectively.
At December 31, 2014, the scheduled maturities of time deposits, which include brokered certificates of deposit, certificates of deposit and other time deposits are as follows:
| | | Total | |
| | | | | |
2015 | | $ | 325,184 | |
2016 | | | 160,359 | |
2017 | | | 28,067 | |
2018 | | | 24,748 | |
2019 and greater | | | 3,023 | |
Total time deposits | | $ | 541,381 | |
Interest expense on time deposits totaled $3.1 million, $2.5 million and $3.0 million in the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 11 – BORROWINGS
Borrowings outstanding at December 31, 2014 and 2013 consist of the following:
��
| | | | | | | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Weighted | | | | | | | Weighted | |
| | | | Interest | | | | | | | Average | | | | | | | Average | |
| | Maturity | | Rate | | | Balance | | | Interest Rate | | | Balance | | | Interest Rate | |
Short-term borrowings: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Repurchase agreements | various | | | 0.0000 | % | | $ | - | | | | | | | $ | 996 | | | | | |
FHLB Fixed Rate Credit | 01/13/15 | | | 0.2100 | % | | | 60,000 | | | | | | | | - | | | | | |
FHLB Fixed Rate Credit | 01/21/15 | | | 0.2400 | % | | | 65,000 | | | | | | | | - | | | | | |
FHLB Adjustable Rate Credit(1) | 1/6/2014 | | | 0.3529 | % | | | - | | | | | | | | 10,000 | | | | | |
FHLB Adjustable Rate Credit(1) | 1/6/2014 | | | 0.3529 | % | | | - | | | | | | | | 10,000 | | | | | |
FHLB Adjustable Rate Credit(2) | 1/21/2014 | | | 0.2945 | % | | | - | | | | | | | | 15,000 | | | | | |
Total short-term borrowings | | | | | | | 125,000 | | | | 0.2256 | % | | | 35,996 | | | | 0.40 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | �� |
Long-term borrowings: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
FHLB Adjustable Rate Credit(3) | 01/07/16 | | | 0.2616 | % | | | 10,000 | | | | | | | | - | | | | | |
FHLB Adjustable Rate Credit(3) | 01/07/16 | | | 0.2616 | % | | | 10,000 | | | | | | | | - | | | | | |
FHLB Fixed Rate Hybrid | 09/26/16 | | | 1.9050 | % | | | 5,000 | | | | | | | | 5,000 | | | | | |
FHLB Fixed Rate Hybrid | 09/26/16 | | | 2.0675 | % | | | 5,000 | | | | | | | | 5,000 | | | | | |
FHLB Fixed Rate Hybrid | 09/26/16 | | | 2.2588 | % | | | 5,000 | | | | | | | | 5,000 | | | | | |
FHLB Fixed Rate Hybrid | 09/26/16 | | | 2.0250 | % | | | 5,000 | | | | | | | | 5,000 | | | | | |
FHLB Adjustable Rate Credit(4) | 01/21/16 | | | 0.2714 | % | | | 15,000 | | | | | | | | - | | | | | |
Total Federal Home Loan Bank | | | | | | | 55,000 | | | | 0.9197 | % | | | 20,000 | | | | 2.06 | % |
Subordinated debt | 06/30/19 | | | 11.000 | % | | | - | | | | | | | | 6,895 | | | | | |
Junior subordinated debt | 06/15/36 | | | 1.7906 | % | | | 6,179 | | | | | | | | 5,986 | | | | | |
Junior subordinated debt | 12/15/35 | | | 1.8106 | % | | | 9,456 | | | | | | | | 9,171 | | | | | |
Junior subordinated debt | 10/01/36 | | | 1.9751 | % | | | 2,658 | | | | | | | | - | | | | | |
Junior subordinated debt | 03/01/37 | | | 1.9756 | % | | | 5,290 | | | | | | | | - | | | | | |
Total long-term borrowings | | | | | | | 78,583 | | | | 1.2022 | % | | | 42,052 | | | | 3.44 | % |
| Total borrowings | | | | | | $ | 203,583 | | | | | | | $ | 78,048 | | | | | |
(1) Adjustable rate based on three-month LIBOR plus 11 basis points.
(2) Adjustable rate based on one-month LIBOR plus 13 basis points.
(3) Adjustable rate based on three-month LIBOR plus 3 basis points.
(4) Adjustable rate based on three-month LIBOR plus 4 basis points.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, two FHLB Fixed Rate Credit one month borrowing agreements in the amounts of $60.0 million and $65.0 million, respectively, matured. These borrowings were replaced with three FHLB Fixed Rate Credit one month borrowing agreements totaling $165 million at an average rate of 0.20%. At December 31, 2014, the Company had an additional $196.8 million of credit available from the FHLB, $183.6 million of credit available from the Federal Reserve Discount Window, and $70.0 million of credit available from correspondent banks.
FHLB borrowing agreements provide for lines of credit up to 20% of the Bank’s assets. The FHLB borrowings are collateralized by a blanket pledge arrangement on all residential first mortgage loans, HELOCs and loans secured by multi-family real estate that the Bank owns. At December 31, 2014, the carrying value of loans pledged as collateral to the FHLB and the Federal Reserve totaled $560.4 million.
In September 2009, the Bank issued $6.9 million in aggregate principal amount of its 11% Subordinated Notes, due June 30, 2019 (the “Notes”). On June 30, 2014, the Bank redeemed these Notes in full at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the Notes redeemed plus accrued but unpaid interest.
As a result of its mergers, the Company’s capital structure includes trust preferred securities previously issued by the predecessor companies through specially formed trusts. The combined total amount outstanding of the acquired trusts as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 was $38.1 million ($23.6 million, net of mark to market) and $25.8 million ($15.2 million, net of mark to market), respectively.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Community Capital previously had formed Community Capital Corporation Statutory Trust I, an unconsolidated statutory business trust, which issued $10.3 million ($6.1 million, net of mark to market) of trust preferred securities that were sold to third parties. The rate on the trust preferred securities acquired through the Community Capital merger adjusts quarterly to three-month LIBOR plus 1.55%. Citizens South previously had formed CSBC Statutory Trust I, an unconsolidated statutory business trust, which issued $15.5 million ($9.4 million, net of mark to market) of trust preferred securities that were sold to third parties. The rate on the trust preferred securities acquired through the Citizens South merger adjusts quarterly to three-month LIBOR plus 1.57%. Provident Community previously had formed Provident Community Bancshares Capital Trust I and Provident Community Bancshares Capital Trust II. Each trust is an unconsolidated statutory business trust, which issued $4.1 million ($2.6 million, net of mark to market) and $8.2 million ($5.3 million, net of mark to market), respectively, of trust preferred securities that were sold to third parties. The rate on each of the trust preferred securities acquired through the Provident Community merger adjusts quarterly to three-month LIBOR plus 1.74%. The Company has fully and unconditionally guaranteed each trust’s obligations under the preferred securities.
The amounts presented are after related acquisition accounting fair market value adjustments. The proceeds of the sales of the trust preferred securities were used to purchase junior subordinated debt from the predecessor companies, which are presented as junior subordinated debt in the condensed consolidated balance sheets of the Company and qualify for inclusion in Tier 1 Capital for regulatory capital purposes, subject to certain limitations.
NOTE 12 – INCOME TAXES
Income taxes are provided based on the asset-liability method of accounting, which includes the recognition of DTAs and liabilities for the temporary differences between carrying amounts and tax bases of assets and liabilities, computed using enacted tax rates. In general, the Company records a DTA when the event giving rise to the tax benefit has been recognized in the consolidated financial statements.
The significant components of the provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31 are as follows:
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
Current tax provision: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 655 | | | $ | (1,248 | ) | | $ | - | |
State | | | 195 | | | | 147 | | | | 51 | |
Total current tax provision | | | 850 | | | | (1,101 | ) | | | 51 | |
Deferred tax provision: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | | 4,646 | | | | 7,468 | | | | 1,859 | |
State | | | 562 | | | | 992 | | | | 396 | |
Total deferred tax provision | | | 5,208 | | | | 8,460 | | | | 2,255 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net provision for income taxes | | $ | 6,058 | | | $ | 7,359 | | | $ | 2,306 | |
The difference between the provision for income taxes and the amounts computed by applying the statutory federal income tax rate of 35% to income before income taxes for the years ended December 31 are summarized below:
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tax at the statutory federal rate | | $ | 6,631 | | | $ | 7,706 | | | $ | 2,261 | |
Increase (decrease) resulting from: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
State income taxes, net of federal tax effect | | | 493 | | | | 751 | | | | 295 | |
Nondeductible merger expenses | | | 72 | | | | 6 | | | | 318 | |
Tax exempt income | | | (1,299 | ) | | | (1,008 | ) | | | (722 | ) |
Other permanent differences | | | 161 | | | | (96 | ) | | | 154 | |
Provision for income taxes | | $ | 6,058 | | | $ | 7,359 | | | $ | 2,306 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. Significant components of deferred taxes at December 31 are as follows:
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Deferred tax assets relating to: | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for loan losses | | $ | 2,990 | | | $ | 3,089 | |
Net unrealized losses on securities | | | - | | | | 3,034 | |
Unrealized loss on transferred securities | | | 766 | | | | - | |
Net unrealized losses on cash flow hedges | | | 909 | | | | - | |
Fair market value adjustments related to mergers | | | 10,362 | | | | 12,018 | |
Stock option expense | | | 2,754 | | | | 2,524 | |
Pre-opening costs and expenses | | | 242 | | | | 276 | |
Other real estate writedowns | | | 4,270 | | | | 4,456 | |
Deferred compensation | | | 3,730 | | | | 3,560 | |
AMT credit carry forward | | | 1,728 | | | | 1,397 | |
Net operating loss carry forwards | | | 11,539 | | | | 12,032 | |
Nonaccrual interest | | | - | | | | 1,258 | |
FDIC acquisitions | | | 3,261 | | | | - | |
Accrued incentive compensation | | | 795 | | | | 706 | |
Other | | | 2,934 | | | | 1,088 | |
Total deferred tax assets | | | 46,280 | | �� | | 45,438 | |
Deferred tax liabilities relating to: | | | | | | | | |
Core deposit intangible | | | (4,086 | ) | | | (3,206 | ) |
Net unrealized gains on securities | | | (786 | ) | | | - | |
Net unrealized gains on cash flow hedges | | | - | | | | (202 | ) |
Property and equipment | | | (2,644 | ) | | | (3,381 | ) |
FDIC acquisitions | | | - | | | | (437 | ) |
Deferred loan costs | | | (2,127 | ) | | | (1,131 | ) |
Prepaid expenses | | | (446 | ) | | | (442 | ) |
Other | | | (568 | ) | | | (321 | ) |
Total deferred tax liabilities | | | (10,657 | ) | | | (9,120 | ) |
Net recorded deferred tax asset | | $ | 35,623 | | | $ | 36,318 | |
As of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, the Company had a net DTA in the amount of approximately $35.6 million and $36.3 million, respectively. The decrease is primarily the result of $12.9 million in earnings during 2014. The Company adjusted its net deferred tax asset as a result of reductions in the North Carolina corporate income tax rate that were enacted July 23, 2013 and will become effective January 1, 2015. The lower corporate income tax rate resulted in a reduction in the deferred tax asset in 2014 and a decrease in current period income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2014.
The Company evaluates the carrying amount of the DTA quarterly in accordance with the guidance provided in ASC 740, in particular applying the criteria set forth therein to determine whether it is more likely than not (i.e., a likelihood of more than 50%) that some portion, or all, of the DTA will not be realized within its life cycle, based on the weight of available evidence. In most cases, the realization of the DTA is dependent upon generating a sufficient level of taxable income in future periods, which can be difficult to predict. In addition to projected earnings, the Company also considers projected asset quality, liquidity, its strong capital position, which could be leveraged to increase earning assets and generate taxable income, its growth plans and other relevant factors. Based on the weight of available evidence, the Company determined that as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 that it is more likely than not that it will be able to fully realize the existing DTA and therefore considered it appropriate not to establish a DTA valuation allowance at either December 31, 2014 or December 31, 2013.
The Company had a federal net operating loss carryforward of $28.5 million and $28.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, which expire in varying amounts through 2031. As a result of several acquisitions since 2011, Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code (“Section 382”) places an annual limitation on the amount of federal net operating loss carryforwards the Company may utilize. Additionally, Section 382 limits the Company’s ability to utilize certain tax deductions such as realized built in losses (“RBIL”) due to the existence of net unrealized built-in losses (“NUBIL”) at the time of the change in control. The Company is allowed to carryforward any such RBIL under terms similar to those related to net operating losses. The Company expects all Section 382 limited carryforwards to be realized within the acceptable carryforward period.
The Company had state net operating loss carryforwards of $41.6 million and $46.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, which expire in varying amounts through 2026.
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company had no material unrecognized tax benefits or accrued interest and penalties. It is the Company’s policy to account for interest and penalties accrued relative to unrecognized tax benefits as a component of income tax expense.
Federal and state tax returns for 2011 and subsequent tax years remain subject to examination by taxing authorities as of December 31, 2014.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 13 – REGULATORY MATTERS
The Company and Bank are subject to various regulatory capital requirements administered by the federal banking agencies. Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can initiate certain mandatory and possibly additional discretionary actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could have a direct material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Under capital adequacy guidelines and the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action, the Company and the Bank must meet specific capital guidelines that involve quantitative measures of the assets, liabilities, and certain off-balance-sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting practices. The capital amounts and classifications are also subject to qualitative judgments by the regulators about components, risk weightings, and other factors. Prompt corrective action provisions are not applicable to bank holding companies.
The Bank’s mortgage banking division qualifies as a HUD-approved Title II Supervised Mortgagee and issues mortgages insured by the US Department of Housing and Urban Development (“HUD”). A Title II supervised mortgagee must maintain an adjusted net worth equal to a minimum of $1 million, plus 1% of FHA originations in excess of $25 million, up to a maximum of $2.5 million. Possible penalties related to noncompliance with this minimum net worth requirement include the revocation of the Bank’s license to issue HUD-insured mortgages, which may have a material adverse affect on the Company’s financial condition and results of operations. For the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Bank satisfied the requirement of maintaining $1 million in adjusted net worth.
Quantitative measures established by regulation to ensure capital adequacy require the Bank and the Company to maintain minimum amounts and ratios of different components of capital to risk-weighted assets and average assets. The Company’s capital position is reflected in its shareholders’ equity, subject to certain adjustments for regulatory purposes. In particular, deferred tax assets that are dependent on future taxable income do not qualify for inclusion as core capital based on the capital guidelines of the primary federal supervisory agencies for the Bank and the Company. Based on the capital guidelines in effect on December 31, 2014, the disallowed portion of deferred tax assets at December 31, 2014 was $27.7 million for the Company and $30.2 million for the Bank. The disallowed portion of deferred tax assets at December 31, 2013 was $27.7 million for the Company and $30.4 million for the Bank.
Risk-based capital regulations adopted by the Federal Reserve Board and the FDIC require bank holding companies and banks to achieve and maintain specified ratios of capital to risk-weighted assets. The risk-based capital rules are designed to measure different components of capital in relation to the credit risk of both on- and off-balance sheet items. Under the guidelines, one of four risk weights is applied to the different on-balance sheet items. Off-balance sheet items, such as loan commitments, are also subject to risk weighting after conversion to balance sheet equivalent amounts. These guidelines also specify that banks that are experiencing internal growth or making acquisitions will be expected to maintain capital positions substantially above the minimum supervisory levels. Under regulations in effect at December 31, 2014, the relevant components of capital consisted of Tier 1 capital (generally common shareholders’ equity, a limited amount of qualifying perpetual preferred stock and trust preferred securities, and minority interests in consolidated subsidiaries, net of goodwill and other intangible assets, deferred tax assets in excess of certain thresholds and certain other items), Tier 2 capital (generally certain preferred stock, mandatorily convertible debt securities and term subordinated debt) and total capital (consisting of Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital). Under these regulations, at December 31, 2014, banks were required to maintain a minimum total capital to total risk-weighted assets ratio of 8.00%, at least half of which was required to be in the form of Tier 1 capital. At December 31, 2014, the Company and the Bank both satisfied their minimum regulatory capital requirements and each was “well capitalized” within the meaning of federal regulatory requirements.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Management believes that, as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company and the Bank meet all capital adequacy requirements to which they are subject, as set forth below:
Capital Ratios | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | To Be Well | |
| | | | | | | | | | | For Capital | | | Capitalized Under | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Adequacy | | | Prompt Corrective | |
| | | Actual | | | Purposes | | | Actions Provisions | |
| | | Amount | | | Ratio | | | Amount | | | Ratio | | | Amount | | | Ratio | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Park Sterling Corporation | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Risk-Based Capital Ratio | | $ | 239,557 | | | | 13.95 | % | | $ | 137,360 | | | | 8.00 | % | | $ | 171,700 | | | | 10.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Capital Ratio | | | 231,088 | | | | 13.46 | % | | | 68,680 | | | | 4.00 | % | | | 103,020 | | | | 6.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Leverage Ratio | | | 231,088 | | | | 10.17 | % | | | 90,931 | | | | 4.00 | % | | | 113,664 | | | | 5.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Risk-Based Capital Ratio | | $ | 234,508 | | | | 16.46 | % | | $ | 113,966 | | | | 8.00 | % | | $ | 142,457 | | | | 10.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Capital Ratio | | | 218,552 | | | | 15.34 | % | | | 56,983 | | | | 4.00 | % | | | 85,474 | | | | 6.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Leverage Ratio | | | 218,552 | | | | 11.63 | % | | | 75,171 | | | | 4.00 | % | | | 93,964 | | | | 5.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Park Sterling Bank | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Risk-Based Capital Ratio | | $ | 224,579 | | | | 13.11 | % | | $ | 137,089 | | | | 8.00 | % | | $ | 171,361 | | | | 10.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Capital Ratio | | | 216,110 | | | | 12.61 | % | | | 68,544 | | | | 4.00 | % | | | 102,817 | | | | 6.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Leverage Ratio | | | 216,110 | | | | 9.56 | % | | | 90,394 | | | | 4.00 | % | | | 112,993 | | | | 5.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Risk-Based Capital Ratio | | $ | 209,786 | | | | 14.77 | % | | $ | 113,626 | | | | 8.00 | % | | $ | 142,033 | | | | 10.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Capital Ratio | | | 193,830 | | | | 13.65 | % | | | 56,813 | | | | 4.00 | % | | | 85,220 | | | | 6.00 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Tier 1 Leverage Ratio | | | 193,830 | | | | 10.41 | % | | | 74,477 | | | | 4.00 | % | | | 93,096 | | | | 5.00 | % |
In July 2013, the regulatory agencies approved final regulatory capital rules that replace the existing general risk-based capital and related rules, broadly revising the basic definitions and elements of regulatory capital and making substantial changes to the credit risk weightings for banking and trading book assets. Under the new capital guidelines, applicable regulatory capital components consist of (1) common equity Tier 1 capital (common stock, including related surplus, and retained earnings, plus limited amounts of minority interest in the form of common stock, net of goodwill and other intangibles (other than mortgage servicing assets), deferred tax assets arising from net operating loss and tax credit carry forwards above certain levels, mortgage servicing rights above certain levels, gain on sale of securitization exposures and certain investments in the capital of unconsolidated financial institutions, and adjusted by unrealized gains or losses on cash flow hedges and accumulated other comprehensive income items (subject to the ability of a non-advanced approaches institution to make a one-time irrevocable election to exclude from regulatory capital most components of AOCI)), (2) additional Tier 1 capital (qualifying non-cumulative perpetual preferred stock, including related surplus, plus qualifying Tier 1 minority interest and, in the case of holding companies with less than $15 billion in consolidated assets at December 31, 2009, certain grandfathered trust preferred securities and cumulative perpetual preferred stock in limited amounts, net of mortgage servicing rights, deferred tax assets related to temporary timing differences, and certain investments in financial institutions) and (3) Tier 2 capital (the allowance for loan and lease losses in an amount not exceeding 1.25% of standardized risk-weighted assets, plus qualifying preferred stock, qualifying subordinated debt and qualifying total capital minority interest, net of tier 2 investments in financial institutions). Total Tier 1 capital, plus Tier 2 capital, constitutes total risk-based capital. The required minimum ratios are as follows:
| | ● | common equity Tier 1 capital ratio (common equity Tier 1 capital to standardized total risk-weighted assets) of 4.5%; |
| | ● | Tier 1 capital ratio (Tier 1 capital to standardized total risk-weighted assets) of 6%; |
| | ● | total capital ratio (total capital to standardized total risk-weighted assets) of 8%; and |
| | ● | leverage ratio (Tier 1 capital to average total consolidated assets) of 4%. |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Advanced approaches banking organizations (those organizations with either total assets of $250 billion or more, or with foreign exposure of $10 billion or more) also are subject to a supplementary leverage ratio that incorporates a broader set of exposures in the denominator. The new capital guidelines also provide that all covered banking organizations must maintain a new capital conservation buffer of common equity Tier 1 capital in an amount greater than 2.5% of total risk-weighted assets to avoid being subject to limitations on capital distributions and discretionary bonus payments to executive officers. Advanced approaches organizations also are subject to a countercyclical capital buffer. Failure to satisfy the capital buffer requirements would result in increasingly stringent limitations on various types of capital distributions, including dividends, share buybacks and discretionary payments on Tier 1 instruments, and discretionary bonus payments.
Non-advanced approaches banking organizations, including the Company and the Bank, must begin compliance with the new minimum capital ratios and the standardized approach for risk-weighted assets as of January 1, 2015, and the revised definitions of regulatory capital and the revised regulatory capital deductions and adjustments are being phased in over time for such organizations beginning as of that date. The capital conservation buffer will be phased in for all banking organizations beginning January 1, 2016.
Federal regulations require institutions to set aside specified amounts of cash as reserves against transaction and time deposits. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the required cash reserves were satisfied by vault cash on hand and amounts due from correspondent banks.
On November 2, 2012, the Company announced a common stock repurchase program for up to 2.2 million shares. The original repurchase plan was in effect until November 1, 2014. On October 29, 2014, the Company’s board of directors approved a new share repurchase program. This plan is in effect for two years and permits the Company to effect the repurchases from time to time through a combination of open market repurchases, privately negotiated transactions, accelerated share repurchase transactions, and other derivative transactions. The specific timing and amount of repurchases depend on general market conditions, the trading of stock, regulatory, legal, and contractual requirements and the Company’s financial performance. During 2014, the Company repurchased 136,743 shares of Common Stock in open market transactions under the repurchase program at an average price of $6.56 and acquired 19,942 shares at an average price of $6.69 in connection with satisfaction of tax withholding obligations on vested restricted stock, and during 2013, the Company repurchased 56,267 common shares, at an average price of $6.46 per share in open market transactions under the repurchase program.
The Company must obtain Federal Reserve Board approval prior to repurchasing its Common Stock in excess of 10% of its net worth during any twelve-month period unless the Company (i) both before and after the redemption satisfies capital requirements for "well capitalized" state member banks; (ii) received a one or two rating in its last examination; and (iii) is not the subject of any unresolved supervisory issues. Although the payment of dividends and repurchase of stock by the Company are subject to certain requirements and limitations of North Carolina corporate law, except as set forth in this paragraph, neither the NC Commissioner nor the FDIC have promulgated any regulations specifically limiting the right of the Company to pay dividends or repurchase shares. However, the ability of the Company to pay dividends or repurchase shares may be dependent upon the Company's receipt of dividends from the Bank.
Under the laws of the State of North Carolina, provided the Bank does not make distributions that reduce its capital below its applicable required capital, the board of directors of the Bank may declare such distributions as the directors deem proper.As noted above, the Bank would also be prohibited from declaring any dividend the payment of which would result in the Bank becoming undercapitalized. Finally, an undercapitalized institution is generally prohibited from paying dividends to its shareholders.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
As part of Citizens South’s Plan of Conversion and Reorganization in May 2002, it established a memo liquidation account in an amount equal to its equity at the time of the conversion of approximately $44 million for the benefit of eligible account holders and supplemental eligible account holders who continue to maintain their accounts at Citizens South Bank after the conversion. In accordance with the memo liquidation account, in the event of a complete liquidation of Citizens South Bank, each eligible account holder and supplemental eligible account holder would be entitled to receive a distribution from the liquidation account in an amount proportionate to the current adjusted qualifying balances for accounts then held. In connection with the Citizens South merger and the subsequent merger of Citizens South Bank into the Bank, the Bank assumed this memo liquidation account. This liquidation account is reviewed and adjusted annually. The value of the liquidation account was $7.6 million at both December 31, 2014 and 2013.
NOTE 14 – PREFERRED STOCK
In connection with the Citizens South acquisition, the Company issued 20,500 shares of its Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock, Series C (the “Series C Preferred Stock”) upon conversion of Citizens South’s preferred stock that previously was issued to the Treasury pursuant to a Securities Purchase Agreement between Citizens South and the Treasury in connection with Citizens South’s participation in the SBLF program. On September 30, 2013, the Company fully redeemed the 20,500 shares of the Series C Preferred Stock and exited the SBLF program. The Series C Preferred Stock, which had a liquidation value of $1,000 per share, was entitled to receive non-cumulative dividends, payable quarterly, at a rate determined by reference to the level of “Qualified Small Business Lending”.
NOTE 15 – LEASES
The Company has noncancelable operating leases extending to the year 2026 pertaining to bank premises. Some of these leases provide for the payment of property taxes and insurance and contain various renewal options. These renewal options are at substantially the same basis as current rental terms. The exercise of these options is dependent on future events. Accordingly, the following summary does not reflect possible additional payments due if renewal options are not exercised.
Future minimum lease payments, by year and in the aggregate, under noncancelable operating leases with initial or remaining terms in excess of one year are as follows:
2015 | | $ | 2,133 | |
2016 | | | 1,869 | |
2017 | | | 1,243 | |
2018 | | | 1,073 | |
2019 | | | 926 | |
Thereafter | | | 4,699 | |
Total | | $ | 11,944 | |
Rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $2.8 million, $1.3 million and $1.1 million, respectively.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 16 – OFF-BALANCE SHEET RISK
In the normal course of business, the Company is party to financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk necessary to meet the financing needs of customers. These financial instruments include commitments to extend credit, undisbursed lines of credit and letters of credit. The instruments involve, to varying degrees, elements of credit risk in excess of the amount recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The contract amounts of these instruments express the extent of involvement the Company has in these financial instruments.
Commitments to extend credit and undisbursed lines of credit are agreements to lend to a customer as long as there is no violation of conditions established in the contract. Commitments generally have fixed expiration dates or other termination clauses and may require payment of a fee.
Standby letters of credit are conditional commitments issued by the Company to guarantee the performance of a customer to a third party. Commercial letters of credit are issued specifically to facilitate commerce and typically result in the commitment being drawn on when the underlying transaction is consummated between the customer and a third party. The credit risk involved in issuing letters of credit is essentially the same as that involved in extending loan facilities to customers. The fair value of these commitments is immaterial at December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Since some of the commitments are expected to expire without being drawn upon, the total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent future cash requirements. The Company evaluates each customer’s creditworthiness on a case-by-case basis. The amount of collateral obtained, if deemed necessary by the Company, upon extension of credit is based on management’s credit evaluation of the borrower. Collateral obtained varies but may include real estate, stocks, bonds, and certificates of deposit. In management’s opinion, these commitments represent no more than normal lending risk to the Company and will be funded from normal sources of liquidity.
A summary of the contract amount of the Company’s exposure to off-balance sheet risk as of December 31, 2014 is as follows:
| | | Contractual | |
| | | Amount | |
Financial instruments whose contract amounts represent credit risk: | | | | |
Undisbursed lines of credit | | $ | 328,293 | |
Standby letters of credit | | | 5,402 | |
Commercial letters of credit | | | 717 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 17 – DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES
The Company uses certain derivative instruments, including interest rate floors and swaps, to meet the needs of its customers while managing the interest rate risk associated with certain transactions. The following table summarizes the derivative financial instruments utilized by the Company:
| | | | | December 31, 2014 | | | December 31, 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Estimated Fair Value | | | | | | | Estimated Fair Value | |
| | | Balance Sheet | | Notional | | | | | | | | | | | Notional | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Location | | Amount | | | Gain | | | Loss | | | Amount | | | Gain | | | Loss | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flow hedges: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate contracts: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Pay fixed swaps | | Other assets and other liabilities | | $ | 70,000 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 2,414 | | | $ | 70,000 | | | $ | 545 | | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fair value hedges: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate contracts: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Pay fixed rate swaps with counterparty | | Other liablities | | $ | 24,792 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 440 | | | $ | 5,626 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 258 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Not designated as hedges: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Customer-related interest rate contracts: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Matched interest rate swaps with borrower | | Other assets | | $ | 35,289 | | | $ | 1,154 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
Matched interest rate swaps with counterparty | | Other liabilities | | | 35,289 | | | | - | | | | 1,154 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | $ | 70,578 | | | $ | 1,154 | | | $ | 1,154 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total derviatives | | $ | 165,370 | | | $ | 1,154 | | | $ | 4,008 | | | $ | 75,626 | | | $ | 545 | | | $ | 258 | |
The Company entered into an interest rate swap agreement during October 2013 with a notional amount of $20.0 million. This derivative instrument is used to protect the Company from future interest rate risk on a portion of its floating rate FHLB borrowings. This derivative instrument is a $20.0 million three-year forward starting, five-year interest rate swap with an effective date of October 21, 2016. The instrument carries a fixed rate of 3.439% with quarterly payments commencing in January 2017. This derivative instrument is accounted for as a cash flow hedge with effective changes in fair market value recorded in other comprehensive income net of tax. This derivative instrument is carried at a fair market value of $(939) thousand and $298 thousand at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and is included in other liabilities at December 31, 2014 and other assets at December 31, 2013. As a result of the unfavorable position of the instrument at December 31, 2014, the Company posted collateral of approximately $939 thousand with the counterparty.
The Company entered into three interest rate swap agreements during December 2013 with an aggregate notional amount of $50.0 million. These derivative instruments are used to protect the Company from future interest rate risk related to a seven-year commitment of floating rate broker-dealer sweep accounts through a brokered deposit program. These derivative instruments are a combination of a $12.5 million forward starting, five-year interest rate swap; a $12.5 million forward starting, seven-year interest rate swap; and a $25.0 million two-year forward starting swap. Effective dates for these derivative instruments are January 2, 2014, January 2, 2014 and January 4, 2016, respectively. These instruments carry a fixed rate of 1.688% with monthly payments commencing February 3, 2014, a fixed rate of 2.341% with monthly payments commencing February 3, 2014, and a fixed rate of 3.104% with monthly payments commencing February 1, 2016, respectively. These derivative instruments are accounted for as cash flow hedges with effective changes in fair market value recorded in other comprehensive income net of tax. These derivative instruments are carried at a fair market value of $(1.5) million and $247 thousand at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and are included in other liabilities at December 31, 2014 and other assets at December 31, 2013. As a result of the unfavorable position of the instruments at December 31, 2014, the Company posted collateral of approximately $1.5 million with the counterparty.
At December 31, 2014, the Company had seven loan swaps accounted for as fair value hedges in accordance with ASC 815,Derivatives and Hedging. The aggregate original notional amount of these loan swaps was $26.1 million. These derivative instruments are used to protect the Company from interest rate risk caused by changes in the LIBOR curve in relation to certain designated fixed rate loans. The derivative instruments are used to convert these fixed rate loans to an effective floating rate. If the LIBOR rate is below the stated fixed rate of the loan for a given period, the Company will owe the floating rate payer the notional amount times the difference between LIBOR and the stated fixed rate. If LIBOR is above the stated rate for any given period during the term of the contract, the Company will receive payments based on the notional amount times the difference between LIBOR and the stated fixed rate.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
To meet the needs of the Company’s customers, the Company has entered into seven interest rate swap agreements to convert certain fixed-rate receivables to floating rates and certain fixed-rate obligations to floating rates. To offset this interest rate risk, the Company has entered into substantially identical agreements with a third party to swap these fixed rate agreements into variable rates. The interest rate swaps are used to provide fixed rate financing while managing interest rate risk and were not designated as hedges. The interest rate swaps pay and receive interest based on a floating rate based on one month LIBOR, with payments being calculated on the notional amount. The interest rate swaps are settled monthly, with varying maturities. There were no interest rate swap agreements to cover certain fixed-rate receivable to floating rates and certain fixed-rate obligations to floating rates at December 31, 2013.
The interest rate swaps had a notional amount of $35.3 million at December 31, 2014, representing the amount of fixed-rate receivables outstanding and liabilities outstanding, and are included in other assets and other liabilities at their fair values of $1.2 million. All changes in fair value are recorded as other income within non-interest income. Fair values for interest rate swap agreements are based upon the amounts required to settle the contracts. At December 31, 2014, there was no impact to earnings as the changes in the fair value of both the fixed and variable legs of the swap completely offset each other.
The following table details the location and amounts recognized in the Consolidated Statements of Income and Statement of Comprehensive Income:
| | | Effective Portion | |
| | | Pre-tax Gain (Loss) | | | | Pre-tax Gain (Loss) Reclassified | |
| | | Recognized in OCI | | Location of Amounts Reclassified | | from AOCI into Income | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | from AOCI into Income | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flow hedges: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate contracts | | $ | (3,381 | ) | | $ | 545 | | Total interest expense | | $ | 422 | | | $ | - | |
| | | Pre-tax Gain (Loss) | | | | Pre-tax Gain (Loss) | |
| | | Recognized in OCI | | Location of Amounts | | Recognized in Income | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | Recognized in Income | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
Fair value hedges: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate contracts | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Pay fixed rate swaps with counterparty | | | - | | | | - | | Total interest income | | $ | (261 | ) | | $ | (175 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Not designated as hedges: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Client-related interest rate contracts | | | - | | | | - | | Other income | | $ | (78 | ) | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | $ | (339 | ) | | $ | (175 | ) |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 18 – ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
The before and after tax amounts allocated to each component of other comprehensive income (loss) are presented in the following table. Reclassification adjustments related to securities available for sale are included in gain (loss) on sale of securities available-for-sale in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. Amortization of net unrealized losses on securities transferred to held-to-maturity are included in interest income on taxable investment securities in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Income.
| | | December 31, 2014 | | | December 31, 2013 | |
| | | Before Tax Amount | | | Tax Expense (Benefit) | | | Net of Tax Amount | | | Before Tax Amount | | | Tax Expense (Benefit) | | | Net of Tax Amount | |
Securities available for sale and transferred securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Change in net unrealized gains (losses) during the period | | $ | 10,464 | | | $ | 3,893 | | | $ | 6,571 | | | $ | (13,200 | ) | | $ | (4,919 | ) | | $ | (8,281 | ) |
Change in net unrealized loss on securities transferred to held to maturity | | | (2,055 | ) | | | (773 | ) | | | (1,282 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Reclassification adjustment for net gains recognized in net income | | | (180 | ) | | | (67 | ) | | | (113 | ) | | | (98 | ) | | | (36 | ) | | | (62 | ) |
Total securities available for sale and transferred securities | | | 8,229 | | | | 3,053 | | | | 5,176 | | | | (13,298 | ) | | | (4,955 | ) | | | (8,343 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Derivatives: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Change in the accumulated loss on effective cash flow hedge derivatives | | | (3,381 | ) | | | (1,269 | ) | | | (2,112 | ) | | | 545 | | | | 202 | | | | 343 | |
Reclassification adjustment for interest payments | | | 422 | | | | 159 | | | | 263 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Total derivatives | | | (2,959 | ) | | | (1,110 | ) | | | (1,849 | ) | | | 545 | | | | 202 | | | | 343 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total other comprehensive income (loss) | | $ | 5,270 | | | $ | 1,943 | | | $ | 3,327 | | | $ | (12,753 | ) | | $ | (4,753 | ) | | $ | (8,000 | ) |
The following table presents activity in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax, by component for the periods indicated.
| | | Securities Available for Sale | | | Securities Transferred from Available for Sale to Held to Maturity | | | Derivatives | | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | |
Balance, January 1, 2014 | | $ | (5,145 | ) | | $ | - | | | $ | 343 | | | $ | (4,802 | ) |
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | | | 5,289 | | | | - | | | | (2,112 | ) | | | 3,177 | |
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | (113 | ) | | | - | | | | 263 | | | | 150 | |
Transfer of securities from available for sale to held to maturity | | | 1,282 | | | | (1,282 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
Net other comprehensive income (loss) during the period | | | 6,458 | | | | (1,282 | ) | | | (1,849 | ) | | | 3,327 | |
Balance, December 31, 2014 | | $ | 1,313 | | | $ | (1,282 | ) | | $ | (1,506 | ) | | $ | (1,475 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, January 1, 2013 | | $ | 3,198 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 3,198 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | | | (8,281 | ) | | | - | | | | 343 | | | | (7,938 | ) |
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | (62 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (62 | ) |
Net other comprehensive income (loss) during the period | | | (8,343 | ) | | | - | | | | 343 | | | | (8,000 | ) |
Balance, December 31, 2013 | | $ | (5,145 | ) | | $ | - | | | $ | 343 | | | $ | (4,802 | ) |
NOTE 19 – FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
The Company is required to disclose the estimated fair value of financial instruments, both assets and liabilities on and off the balance sheet, for which it is practicable to estimate fair value. These fair value estimates are made at each balance sheet date, based on relevant market information and information about the financial instruments. Fair value estimates are intended to represent the price at which an asset could be sold or the price for which a liability could be settled in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. However, given there is no active market or observable market transactions for many of the Company’s financial instruments, the Company has made estimates of many of these fair values which are subjective in nature, involve uncertainties and matters of significant judgment and therefore cannot be determined with precision. Changes in assumptions could significantly affect the estimated values. The methodologies used for estimating the fair value of financial assets and financial liabilities are discussed below:
Cash and Cash Equivalents–Cash and cash equivalents, which are comprised of cash and due from banks, interest-earning balances at banks and Federal funds sold, approximate their fair value.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Investment Securities Available-for-Saleand Investment Securities Held-to-Maturity-Fair value for investment securities is based on the quoted market price if such information is available. If a quoted market price is not available, fair values are based on quoted market prices of comparable instruments.
Nonmarketable Equity Securities–Cost is a reasonable estimate of fair value for nonmarketable equity securities because no quoted market prices are available and the securities are not readily marketable. The carrying amount is adjusted for any other than temporary declines in value.
Loans Held for Sale-For certain homogenous categories of loans, such as residential mortgages, fair value is estimated using the quoted market prices for securities backed by similar loans, adjusted for differences in loan characteristics.
Loans, net of allowance -The fair value of other types of loans is estimated by discounting the future cash flows using the current rates at which similar loans would be made to borrowers with similar credit ratings and for the same remaining maturities. Further adjustments are made to reflect current market conditions. There is no discount for liquidity included in the expected cash flow assumptions.
FDIC Indemnification Asset –The fair values for the FDIC indemnification asset are estimated based on discounted future cash flows using current discount rates.
Accrued Interest Receivable-The carrying amount is a reasonable estimate of fair value.
Deposits-The fair value of deposits with no stated maturities, including demand deposits, savings, money market and NOW accounts, is the amount payable on demand at the reporting date. The fair value of deposits that have stated maturities, primarily time deposits, is estimated by discounting expected cash flows using the rates currently offered for instruments of similar remaining maturities.
Borrowings-The fair values of short-term and long-term borrowings are based on discounting expected cash flows at the interest rate for debt with the same or similar remaining maturities and collateral requirements.
Subordinated Debentures –The fair value of fixed rate subordinated debentures is estimated using a discounted cash flow calculation that applies the Company’s current borrowing rate. The carrying amounts of variable rate borrowings are reasonable estimates of fair value because they can reprice frequently.
Accrued Interest Payable-The carrying amount is a reasonable estimate of fair value.
Derivative Instruments – Derivative instruments, including interest rate swaps and swap fair value hedges, are recorded at fair value on a recurring basis. Fair value measurement is based on discounted cash flow models. All future floating cash flows are projected and both floating and fixed cash flows are discounted to the valuation date.
Financial Instruments with Off-Balance Sheet Risk-With regard to financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk discussed in Note 16 – Off-Balance Sheet Risk, it is not practicable to estimate the fair value of future financing commitments.
The Company utilizes fair value measurements to record fair value adjustments to certain assets and liabilities and to determine fair value disclosures. Securities available-for-sale and derivative instruments are recorded at fair value on a recurring basis. Additionally, from time to time, the Company may be required to record other assets at fair value on a nonrecurring basis. These nonrecurring fair value adjustments typically involve application of lower of cost or market accounting or write-downs of individual assets.
The Company groups assets and liabilities at fair value in three levels, based on the markets in which the assets and liabilities are traded and the reliability of the assumptions used to determine fair value.
| | Level 1 | Valuation is based upon quoted prices for identical instruments traded in active markets. |
| | | |
| | Level 2 | Valuation is based upon quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar instruments in markets that are not active and model-based valuation techniques for which all significant assumptions are observable in the market. |
| | Level 3 | Valuation is generated from model-based techniques that use at least one significant assumption not observable in the market. These unobservable assumptions reflect estimates of assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability. Valuation techniques may include the use of option pricing models, discounted cash flow models and similar techniques. |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The carrying amounts and estimated fair values of the Company’s financial instruments, none of which are held for trading purposes, are as follows at December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | Fair Value Measurements | |
| | | Carrying | | | Estimated | | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets or Liabilities | | | Significant Other Observable Inputs | | | Significant Unobservable Inputs | |
| | | Amount | | | Fair Value | | | (Level 1) | | | (Level 2) | | | (Level 3) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2014: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 51,390 | | | $ | 51,390 | | | $ | 51,390 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
Investment securities available-for-sale | | | 375,683 | | | | 375,683 | | | | 1,712 | | | | 372,401 | | | | 1,570 | |
Investment securities held-to-maturity | | | 115,741 | | | | 117,627 | | | | - | | | | 117,627 | | | | - | |
Nonmarketable equity securities | | | 11,532 | | | | 11,532 | | | | - | | | | 11,532 | | | | - | |
Loans held for sale | | | 11,602 | | | | 11,602 | | | | - | | | | 11,602 | | | | - | |
Loans, net of allowance | | | 1,572,431 | | | | 1,514,294 | | | | - | | | | 28,800 | | | | 1,485,494 | |
FDIC indemnification asset | | | 3,964 | | | | 3,802 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,802 | |
Accrued interest receivable | | | 4,467 | | | | 4,467 | | | | - | | | | 4,467 | | | | - | |
Derivative instruments | | | 1,154 | | | | 1,154 | | | | - | | | | 1,154 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deposits with no stated maturity | | | 1,309,973 | | | | 1,309,973 | | | | - | | | | 1,309,973 | | | | - | |
Deposits with stated maturities | | | 541,381 | | | | 543,728 | | | | - | | | | 543,728 | | | | - | |
Borrowings | | | 203,583 | | | | 203,207 | | | | - | | | | 203,207 | | | | - | |
Accrued interest payable | | | 398 | | | | 398 | | | | - | | | | 398 | | | | - | |
Derivative instruments | | | 4,008 | | | | 4,008 | | | | - | | | | 4,008 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2013: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Financial assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 55,067 | | | $ | 55,067 | | | $ | 55,067 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
Investment securities available-for-sale | | | 349,491 | | | | 349,491 | | | | 1,906 | | | | 347,585 | | | | - | |
Investment securities held-to-maturity | | | 51,972 | | | | 51,334 | | | | - | | | | 51,334 | | | | - | |
Nonmarketable equity securities | | | 5,905 | | | | 5,905 | | | | - | | | | 5,905 | | | | - | |
Loans held for sale | | | 2,430 | | | | 2,430 | | | | - | | | | 2,430 | | | | - | |
Loans, net of allowance | | | 1,286,977 | | | | 1,267,349 | | | | - | | | | 5,884 | | | | 1,261,465 | |
FDIC indemnification asset | | | 10,025 | | | | 10,025 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,025 | |
Accrued interest receivable | | | 4,222 | | | | 4,222 | | | | - | | | | 4,222 | | | | - | |
Derivative instruments | | | 545 | | | | 545 | | | | - | | | | 545 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deposits with no stated maturity | | | 1,055,457 | | | | 1,055,457 | | | | - | | | | 1,055,457 | | | | - | |
Deposits with stated maturities | | | 544,428 | | | | 545,111 | | | | - | | | | 545,111 | | | | - | |
Borrowings | | | 78,048 | | | | 77,899 | | | | - | | | | 77,899 | | | | - | |
Accrued interest payable | | | 412 | | | | 412 | | | | - | | | | 412 | | | | - | |
Derivative instruments | | | 258 | | | | 258 | | | | - | | | | 258 | | | | - | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The following is a description of valuation methodologies used for assets and liabilities recorded at fair value:
Investment Securities-Investment securities available-for-sale are recorded at fair value on a recurring basis. Investment securities held-to-maturity are valued at quoted market prices or dealer quotes similar to securities available for sale. Fair value measurement is based upon quoted prices, if available. If quoted prices are not available, fair values are measured using independent pricing models or other model-based valuation techniques such as present value of future cash flows, adjusted for the security’s credit rating, prepayment assumptions and other factors such as credit loss assumptions. Level 1 securities include those traded on an active exchange, such as the New York Stock Exchange, United States Treasury securities that are traded by dealers or brokers in active over-the-counter markets and money market funds. Level 2 securities include MBS issued by government-sponsored entities or private label entities, municipal bonds and corporate debt securities that are valued using quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets. Securities classified as Level 3 include a corporate debt security in a less liquid market whose value is determined by reference to the going rate of a similar debt security if it were to enter the market at period end. The derived market value requires significant management judgment and is further substantiated by discounted cash flow methodologies.
Derivative Instruments-Derivative instruments held or issued by the Company for risk management purposes are traded in over-the-counter markets where quoted market prices are not readily available. For those derivatives, the Company uses a third party to measure the fair value on a recurring basis. The Company classifies derivative instruments held or issued for risk management purposes as Level 2. As of December 31, 2014, the Company’s derivative instruments consist of interest rate swaps and swap fair value hedges, and as of December 31, 2013, the Company’s derivative instruments consist of swap fair value hedges.
Loans -Loans for which it is probable that payment of interest and principal will not be made in accordance with the contractual terms of the loan agreement are considered impaired. Once a loan is identified as individually impaired, management measures it for the estimated impairment. The fair value of impaired loans is estimated using one of several methods, including collateral value, discounted cash flows or a pooled probability of default and loss given default calculation. Those impaired loans not requiring a specific allowance represent loans for which the fair value exceeds the recorded investments in such loans. Impaired loans where a specific allowance is established based on the fair value of collateral require classification in the fair value hierarchy. The Company records such impaired loans as nonrecurring Level 3.
The Company recorded the seven loans involved in fair value hedges at fair market value on a recurring basis. The Company does not record other loans at fair value on a recurring basis.
Loans held for sale –Loans held for sale are adjusted to lower of cost or market upon transfer from the loan portfolio to loans held for sale. Subsequently, loans held for sale are carried at the lower of carrying value or fair value. Fair value is based upon independent market prices, appraised values of the collateral, management’s estimation of the value of the collateral or commitments on hand from investors within the secondary market for loans with similar characteristics. The fair value adjustments for loans held for sale are recorded as nonrecurring Level 2.
Other real estate owned -OREO is adjusted to fair value upon transfer of the loans to OREO. Subsequently, OREO is carried at the lower of carrying value or fair value less costs to sell. Fair value is based upon independent market prices, appraised values of the collateral or management’s estimation of the value of the collateral. When the fair value of the collateral is measured due to further deterioration in the value of the OREO since initial recognition, the Company records the foreclosed asset as nonrecurring Level 3.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Assets and Liabilities Recorded at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
The following table sets forth by level, within the fair value hierarchy, the Company’s assets and liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis at December 31, 2014 and 2013:
| | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for | | | Significant Other | | | Significant | | | | |
| | | Identical | | | Observable | | | Unobservable | | | Assets/ | |
| | | Assets | | | Inputs | | | Inputs | | | Liabilities | |
Description | | (Level 1) | | | (Level 2) | | | (Level 3) | | | at Fair Value | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2014 recurring | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Government agencies | | $ | - | | | $ | 537 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 537 | |
Municipal securities | | | - | | | | 12,851 | | | | - | | | | 12,851 | |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | | - | | | | 147,015 | | | | - | | | | 147,015 | |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | - | | | | 144,080 | | | | - | | | | 144,080 | |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | - | | | | 4,868 | | | | - | | | | 4,868 | |
Asset-backed securities | | | - | | | | 61,050 | | | | - | | | | 61,050 | |
Corporate and other securities | | | - | | | | 2,000 | | | | 1,570 | | | | 3,570 | |
All other equity securities | | | 1,712 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,712 | |
Fair value loans | | | - | | | | 28,800 | | | | - | | | | 28,800 | |
Derivative instruments | | | - | | | | (2,854 | ) | | | - | | | | (2,854 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2013 recurring | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Government agencies | | $ | - | | | $ | 558 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 558 | |
Municipal securities | | | - | | | | 16,506 | | | | - | | | | 16,506 | |
Residential agency pass-through securities | | | - | | | | 90,248 | | | | - | | | | 90,248 | |
Residential collateralized mortgage obligations | | | - | | | | 103,349 | | | | - | | | | 103,349 | |
Commercial mortgage-backed obligations | | | - | | | | 61,402 | | | | - | | | | 61,402 | |
Asset-backed securities | | | - | | | | 71,077 | | | | - | | | | 71,077 | |
Corporate and other securities | | | - | | | | 4,445 | | | | - | | | | 4,445 | |
All other equity securities | | | 1,906 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,906 | |
Fair value loans | | | - | | | | 5,884 | | | | - | | | | 5,884 | |
Derivative instruments | | | - | | | | 287 | | | | - | | | | 287 | |
Securities measured on a Level 3 recurring basis at December 31, 2014 include a corporate debt security whose value is determined by the going rate of a similar debt security if it were to enter the market at period end with additional liquidity discounts applied due to a smaller available market.
At December 31, 2013, the Company transferred a corporate debt security investment from Level 3 to Level 2. In December 2013, the Company received notice that this corporate debt security would be satisfied at its book value in January 2014. The full book value of this security was received on January 31, 2014. Valuation techniques are consistent with techniques used in prior periods. Other than the corporate debt security discussed above, there were no transfers between valuation levels for any accounts for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. If different valuation techniques are deemed necessary, the transfers will be considered to occur at the end of the period that the accounts are valued.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The following is a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances for assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
| | | Securities | |
| | | Available | |
| | | For Sale | |
| | | | | |
Fair value, January 1, 2013 | | $ | 415 | |
Transfer out of level 3 | | | (415 | ) |
Fair value, December 31, 2013 | | $ | - | |
Security acquired from Provident Community | | | 1,435 | |
Change in unrealized gain recognized in other comprehensive income | | | 135 | |
Fair value, December 31, 2014 | | $ | 1,570 | |
Assets Recorded at Fair Value on a Nonrecurring Basis
The Company may be required, from time to time, to measure certain other financial assets at fair value on a nonrecurring basis in accordance with GAAP. These adjustments to fair value usually result from application of lower of cost or market accounting or impairment charges of individual assets. Processes are in place for overseeing the valuation procedures for Level 3 measurements of OREO and impaired loans. The assets are reviewed on a quarterly basis to determine the accuracy of the observable inputs, generally third party appraisals, auction values, values derived from trade publications and data submitted by the borrower, and the appropriateness of the unobservable inputs, generally discounts due to current market conditions and collection issues. Discounts are based on asset type and valuation source; deviations from the standard are documented. The discounts are periodically reviewed to determine whether they remain appropriate. Consideration is given to current trends in market values for the asset categories and gain and losses on sales of similar assets.
Discounts range from 0% to 100% depending on the nature of the assets and source of value. Real estate is valued based on appraisals or evaluations, discounted by 8% at a minimum with higher discounts for property in poor condition or property with characteristics that may make it more difficult to market. Commercial loans secured by receivables or non-real estate collateral are generally valued using the discounted cash flow method. Inputs are determined on a borrower-by-borrower basis.
Impaired loans and related write-downs are based on the fair value of the underlying collateral if repayment is expected solely from the collateral or using a pooled probability of default and loss given default calculation. Collateral values are reviewed quarterly and estimated using customized discounting criteria and appraisals.
Other real estate owned is based on the lower of the cost or fair value of the underlying collateral less expected selling costs. Collateral values are estimated primarily using appraisals and reflect a market value approach. Fair values are reviewed quarterly and new appraisals are generally obtained annually.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The following table sets forth by level, within the fair value hierarchy, the Company’s assets at fair value on a nonrecurring basis at December 31, 2014 and 2013:
Fair Value on a Nonrecurring Basis | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Quoted Prices | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | in Active | | | Significant | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Markets for | | | Other | | | Significant | | | | | |
| | | Identical | | | Observable | | | Unobservable | | | Assets/ | |
| | | Assets | | | Inputs | | | Inputs | | | (Liabilities) | |
Description | | (Level 1) | | | (Level 2) | | | (Level 3) | | | at Fair Value | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
OREO | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 7,408 | | | $ | 7,408 | |
Impaired loans: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | | - | | | | - | | | | 208 | | | | 208 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | - | | | | - | | | | 56 | | | | 56 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | - | | | | - | | | | 353 | | | | 353 | |
AC&D - lots, land, & development | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Other commercial | | | - | | | | - | | | | 148 | | | | 148 | |
Residential mortgage | | | - | | | | - | | | | 954 | | | | 954 | |
HELOC | | | - | | | | - | | | | 570 | | | | 570 | |
Residential construction | | | - | | | | - | | | | 357 | | | | 357 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | - | | | | - | | | | 78 | | | | 78 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
OREO | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 9,085 | | | $ | 9,085 | |
Impaired loans: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Commercial and industrial | | | - | | | | - | | | | 69 | | | | 69 | |
CRE - owner-occupied | | | - | | | | - | | | | 73 | | | | 73 | |
CRE - investor income producing | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,659 | | | | 2,659 | |
Other commercial | | | - | | | | - | | | | 93 | | | | 93 | |
Residential mortgage | | | - | | | | - | | | | 510 | | | | 510 | |
HELOC | | | - | | | | - | | | | 184 | | | | 184 | |
Residential construction | | | - | | | | - | | | | 34 | | | | 34 | |
Other loans to individuals | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | |
The following table presents the decrease in value of OREO, which is measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis, for which a fair value adjustment has been included in the income statement. These items represent write-downs of OREO based on the appraised value of collateral.
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
OREO | | $ | (604 | ) | | $ | (1,394 | ) |
In accordance with accounting for foreclosed property, the carrying value of OREO is periodically reviewed and written down to fair value and any loss is incurred in earnings. During the year ended December 31, 2014, OREO with a carrying value of $8.1 million was written down by $604 thousand to $7.4 million. During the year ended December 31, 2013, OREO with a carrying value of $5.6 million was written down by $1.4 million to $4.2 million.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
The table below presents the valuation methodology and unobservable inputs for Level 3 assets measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis at December 31, 2014.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | Weighted | |
| | | Fair Value | | Valuation Methodology | | Unobservable Inputs | | Range of Inputs | | | Average Discount | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
OREO | | $ | 7,408 | | Appraisals | | Discount to reflect current | | | 0% - 59 | % | | | 3.68 | % |
| | | | | | | | market conditions | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Impaired loans | | | 1,744 | | Probability of default | | Discount to reflect probability | | | 0% - 100 | % | | | 12.99 | % |
| | | | | | model | | and loss given default | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 980 | | Collateral based | | Discount to reflect current | | | 0% - 100 | % | | | 38.32 | % |
| | | | | | measurements | | market conditions and | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | ultimate collectability | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 10,132 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
NOTE 20 – EMPLOYEE AND DIRECTOR BENEFIT PLANS
Employment Contracts-Employment agreements are used from time to time to ensure a stable and competent management base. The Company’s Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, President, and Chief Risk Officer are each subject to an employment agreement. Each executive’s agreement is for an initial term of three years and is subject to automatic one-year renewals on the third anniversary of its initial effective date and each successive anniversary unless either party provides timely notice of non-renewal.The agreements provide for benefits as spelled out in the contracts and cannot be terminated by the Board of Directors, except for cause, without prejudicing the officers’ rights to receive certain vested rights, including compensation. In the event of a change in control of the Company and in certain other events, as defined in the agreements, the Company or any successor to the Company will be bound to the terms of the contracts.
The Company has inherited from its mergers a number of individual deferred compensation and supplemental retirement agreements with certain employees, former employees and former directors who were previously officers or directors of the predecessor company that provide for salary continuation benefits upon retirement. These individual agreements also provide for benefits in the event of early retirement, death or substantial change in control of the Company. The expense associated with these plans was $431 thousand, $460 thousand and $57 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The total liability associated with these assumed supplemental retirement plans was $8.3 million and $8.4 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
To assist funding the above liabilities, the acquired entities had insured the lives of certain current and former directors and officers. Earnings on those policies are used to offset employee benefit expenses. The Company also purchased and owns Bank-Owned Life Insurance (“BOLI”) policies on certain key officers of the Company, including the Chief Executive Officer, the Chief Financial Officer, the President and the Chief Risk Officer. The Company is the current owner and beneficiary of the policies and has the right to exercise all incidents of ownership. Cash surrender values of BOLI policies, including BOLI policies acquired in mergers, at December 31, 2014 and 2013 were $57.7 million and $47.8 million, respectively. In 2014, the Company received $1.1 million in death proceeds from two policies, resulting in $651 thousand of additional noninterest income. There were no death proceeds received in 2013 or 2012.
Certain BOLI policies acquired through mergers are subject to split dollar arrangements, wherein under separate agreement with the insured party, the insured party has the right to designate a beneficiary for an amount equal to 50 percent of the difference between the total policy death proceeds and the policy cash surrender value at the date of the employee’s death up to $100,000. For these split dollar arrangements, once vested in the benefit, the insured party has the right to continue to designate a beneficiary after retirement from the Company. As a result, the Company has recognized a liability as the split dollar arrangement effectively provides a post-employment retirement benefit after separation of service from the Company. The liability accrued for split dollar agreements that provide a post-retirement benefit at December 31, 2014 and 2013 was $2.0 million and $1.7 million, respectively. The expense associated with these split dollar arrangements was $304 thousand and $61 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The expense for the year ended December 31, 2012 was immaterial.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
During 2013, the Company implemented a deferred compensation plan whereby certain employees and directors are given the option to defer compensation until retirement or separation of employment. Interest is accrued on the balances at a rate of 3.25%. The expense associated with this plan was $23 thousand and $5 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The total liability accrued for the deferred compensation plan was $871 thousand and $328 thousand at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Retirement Savings -The Company has a profit sharing and 401(k) plan for the benefit of substantially all employees subject to certain minimum age and service requirements. Under this plan, the Company matches 100% of employee contributions to a maximum of 3% of annual compensation and 50% of employee contributions greater than 3% to a maximum of 6% of annual compensation, up to an annual compensation generally equal to the Internal Revenue Service’s compensation threshold in effect from time to time. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company’s profit sharing and 401(k) plan owned 88,411, and 141,760 shares, respectively, of the Company’s Common Stock as a result of an investment election allowed under the Community Capital 401(k) savings plan, which has been merged into the Company’s plan. The Company no longer offers the Company’s Common Stock as an investment option in its 401(k) plan and effective February 3, 2015, all Company stock will be liquidated in the Company’s 401(k) plan. The estimated value of the shares held at December 31, 2014 and 2013 was $650 thousand and $1.0 million, respectively.
The Company’s contribution expense under the profit sharing and 401(k) plan was $1.1 million, $912 thousand and $685 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Share Based Plans-The Company maintains share-based plans for directors and employees. During 2010, the Board of Directors of the Bank adopted and shareholders approved, the Park Sterling Bank 2010 Stock Option Plan for Directors and the Park Sterling Bank 2010 Employee Stock Option Plan (the “2010 Plans”), which provided for an aggregate of 1,859,550 shares of Common Stock reserved for the granting of options. The 2010 Plans were substantially similar to the 2006 option plans for directors and employees, which provided for an aggregate of 990,000 of shares of Common Stock reserved for options. Upon effectiveness of the holding company reorganization, the Company assumed all outstanding options under the 2010 Plans and the 2006 plans, and the Company’s Common Stock was substituted as the stock issuable upon the exercise of options under these plans. As a result, there will be no further awards under the 2010 Plans. At December 31, 2014, there were options to purchase 1,890,397 shares of Common Stock outstanding under these plans.
Also during 2010, the Board of Directors of the Company adopted and shareholders approved the Park Sterling Corporation 2010 Long-Term Incentive Plan for directors and employees ( the “2010 LTIP”), which was effective upon the holding company reorganization and replaced the 2010 Plans. The 2010 LTIP provided for an aggregate of 1,016,400 of shares of Common Stock reserved for issuance to employees and directors in connection with stock options, restricted stock awards, and other stock-based awards. At December 31, 2014, there were options to purchase 115,007 shares of Common Stock and 761,132 unvested restricted stock awards outstanding under the 2010 LTIP. The 2010 LTIP was frozen upon effectiveness of the Company’s 2014 Long Term Incentive Plan (described below), and no future awards may be made thereunder.
In March 2014, the Board of Directors of the Company adopted and in May 2014 shareholders approved the Park Sterling Corporation 2014 Long-Term Incentive Plan for directors and employees (the “2014 LTIP”), which replaced the 2010 LTIP. An aggregate of 1,000,000 of shares of Common Stock, plus any shares subject to an award granted under the 2010 LTIP that was outstanding on March 26, 2014 that may expire, be forfeited or otherwise terminate unexercised, have been reserved for issuance to employees and directors under the 2014 LTIP in connection with stock options, restricted stock awards, and other stock-based awards. The 2014 LTIP will expire on May 23, 2024 and no awards may be made after that date. At December 31, 2014, there were 159,963 unvested restricted stock awards outstanding under the 2014 LTIP.
As a result of the Citizens South merger, at the effective date of the merger, the Company assumed the awards outstanding under the Citizens South Bank 1999 Stock Option Plan (the “1999 Citizens South Plan”), the Citizens South Banking Corporation 2003 Stock Option Plan (the “2003 Citizens South Plan”) and the Citizens South Banking Corporation 2008 Equity Incentive Plan ( the “2008 Citizens South Plan”), each of which has been renamed as a Park Sterling Corporation plan.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
In addition, under the 2003 Citizens South Plan and the 2008 Citizens South Plan, the Company retained the right to grant future non-qualified stock options and, in the case of the 2008 Citizens South Plan, stock appreciation rights (“SARs”) to eligible employees and directors of, or in the case of the 2008 Citizens South Plan service providers to, the Company or the Bank who were not employees or directors of or service providers to the Company or the Bank at the effective time of the merger. Stock options and SARS are evidenced by an award agreement that specifies, as applicable, the number of shares, date of grant, exercise price, vesting period and expiration date, and other information. Awards under the these plans have an exercise price at least equal to the fair market value of the Common Stock on the grant date, cannot be exercised more than 10 years after the grant date and generally expire or are forfeited upon termination of employment prior to the end of the award term, except in limited circumstances such as death, disability, retirement or change in control. At December 31, 2014, there were options to purchase 12,431 shares of Common Stock outstanding under the 2003 Citizens South Plan and options to purchase 152,892 shares of Common Stock outstanding under the 2008 Citizens South Plan. The 2003 Citizens South Plan expired by its terms in May 2013, and the 2008 Citizens South Plan was frozen in May 2014 upon effectiveness of the 2014 LTIP. As a result, no future awards may be made under these plans.
The 1999 Citizens South Plan was frozen at the time of merger, and no future awards could be granted under this plan thereafter. At December 31, 2014, there were options to purchase 630 shares of Common Stock outstanding under the 1999 Citizens South Plan.
The exercise price of each option under these plans is not less than the market price of the Company’s Common Stock on the date of the grant. The exercise price of all options outstanding at December 31, 2014 under these plans ranges from $3.04 to $15.45 and the average exercise price was $7.40. The Company funds the option shares from authorized but unissued shares. The Company does not typically purchase shares to fulfill the obligations of the stock benefit plans. Options granted become exercisable in accordance with the plans’ vesting schedules which are generally three years. All unexercised options expire ten years after the date of the grant.
As contemplated during the Public Offering, in 2011 the Company awarded certain stock price performance-based restricted shares under the 2010 LTIP to officers and directors following the holding company reorganization. During 2013, 13,860 of these restricted shares were forfeited, and there were no forfeitures of these restricted shares during 2014. At December 31, 2014, there were 554,400 stock price performance-based restricted shares outstanding, which will vest one-third each when the Company’s stock price per share reaches the following performance thresholds for 30 consecutive trading days: (i) 125% of offer price ($8.13); (ii) 140% of offer price ($9.10); and (iii) 160% of offer price ($10.40). These anti-dilutive restricted shares are issued (and thereby have voting rights), but are not included in earnings per share calculations until they vest (and thereby have economic rights).
Activity in the Company’s share-based plans is summarized in the following tables:
| | | Outstanding Options | |
| | | | | | | Weighted | | | | | | | Weighted | | | Weighted | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Average | | | | | | | Average | | | Average | | | | | |
| | | Number | | | Exercise | | | Non-Vested | | | Exercise | | | Contractual | | | Intrinsic | |
| | | Outstanding | | | Price | | | Options | | | Price | | | Term (Years) | | | Value | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2011 | | | 2,145,189 | | | $ | 7.62 | | | | 1,037,771 | | | $ | 2.59 | | | | 7.67 | | | $ | 7,045 | |
Options acquired through merger | | | 990,278 | | | | 8.33 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | | |
Options granted | | | 15,000 | | | | 4.65 | | | | 15,000 | | | | 4.65 | | | | | | | | | |
Exercised | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | | |
Expired and forfeited | | | (30,775 | ) | | | 7.94 | | | | (30,775 | ) | | | 7.94 | | | | | | | | | |
Options vested | | | - | | | | - | | | | (471,804 | ) | | | 1.03 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2012 | | | 3,119,692 | | | $ | 7.84 | | | | 550,192 | | | $ | 6.28 | | | | 5.27 | | | $ | 102,762 | |
Options granted | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | | |
Options exercised | | | (60,942 | ) | | | 5.09 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | | |
Expired and forfeited | | | (833,199 | ) | | | 9.34 | | | | (1,667 | ) | | | 4.99 | | | | | | | | | |
Options vested | | | - | | | | - | | | | (499,079 | ) | | | 6.39 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2013 | | | 2,225,551 | | | $ | 7.35 | | | | 49,446 | | | $ | 5.19 | | | | 5.65 | | | $ | 1,471,095 | |
Options granted | | | 17,500 | | | | 6.70 | | | | 17,500 | | | | 6.70 | | | | | | | | | |
Options exercised | | | (54,199 | ) | | | 4.67 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | | | | |
Expired and forfeited | | | (17,495 | ) | | | 9.07 | | | | (3,333 | ) | | | 4.46 | | | | | | | | | |
Options vested | | | - | | | | - | | | | (42,780 | ) | | | 5.28 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2014 | | | 2,171,357 | | | $ | 7.40 | | | | 20,833 | | | $ | 6.39 | | | | 4.69 | | | $ | 1,668,621 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercisable at December 31, 2014 | | | 2,150,523 | | | $ | 7.41 | | | | | | | | | | | | 4.65 | | | | | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
| | | Nonvested Restricted Shares | |
| | | | | | | Weighted | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Average | | | Aggregate | |
| | | Number | | | Grant Date | | | Intrinsic | |
| | | Outstanding | | | Fair Value | | | Value | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2011 | | | 568,260 | | | $ | 3.91 | | | $ | 2,318,501 | |
Restricted shares granted | | | 78,000 | | | | 4.75 | | | | 407,940 | |
Change in intrinsic value of stockprice based performance grants | | | - | | | | - | | | | 653,499 | |
At December 31, 2012 | | | 646,260 | | | $ | 4.01 | | | | 3,379,940 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Restricted shares granted | | | 174,000 | | | | 5.70 | | | | 1,242,360 | |
Expired and forfeited | | | (23,860 | ) | | | 4.59 | | | | (170,360 | ) |
Restricted shares vested | | | (26,001 | ) | | | 4.75 | | | | (185,644 | ) |
Change in intrinsic value of stockprice based performance grants | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,048,712 | |
At December 31, 2013 | | | 770,399 | | | $ | 4.35 | | | | 5,315,008 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Restricted shares granted | | | 238,613 | | | | 6.53 | | | | 1,753,806 | |
Expired and forfeited | | | (7,250 | ) | | | 5.67 | | | | (53,287 | ) |
Restricted shares vested | | | (80,667 | ) | | | 5.40 | �� | | | (592,906 | ) |
Change in intrinsic value of stockprice based performance grants | | | - | | | | - | | | | 347,428 | |
At December 31, 2014 | | | 921,095 | | | $ | 4.81 | | | | 6,770,049 | |
There were 17,500 stock options granted during 2014. The fair value of each option award is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The average grant date fair value per share of options granted in 2014 and 2012 was $6.70 and $1.60, respectively. There were no stock options granted during 2013. Assumptions used for grants in 2014 and 2012 were as follows:
Assumptions in Estimating Option Values | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2012 | |
Weighted-average volatility | | | 38.6% - 39.0 | % | | | 35.58 | % |
Expected dividend yield | | | 1 | % | | | 0 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | | 2.22 | % | | | 0.63 | % |
Expected life (years) | | | 7 | | | | 0-7 | |
The fair value of options vested was $100 thousand, $1.3 million and $1.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
There were 238,613, 174,000 and 78,000 shares of restricted stock granted during 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The average grant date fair value of restricted shares granted in 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $6.53, $5.70 and $4.75, respectively.
The Company recognized compensation expense for share based compensation plans of $1.1 million, $1.8 million and $2.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. At December 31, 2014, unrecognized compensation expense related to non-vested stock options of $41 thousand was expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.07 years and unrecognized compensation expense related to restricted shares of $1.7 million was expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 0.87 years. At December 31, 2013, unrecognized compensation expense related to non-vested stock options of $35 thousand was expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 0.46 years and unrecognized compensation expense related to restricted shares of $1.2 million was expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 0.87 years.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
NOTE 21 – SUMMARIZED QUARTERLY INFORMATION (UNAUDITED)
A summary of selected quarterly financial information for 2014 and 2013 follows:
| | | 2014 Quarter Ended (unaudited) | | | 2013 Quarter Ended (unaudited) | |
| | | 4th | | | 3rd | | | 2nd | | | 1st | | | 4th | | | 3rd | | | 2nd | | | 1st | |
| | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total interest income | | $ | 22,348 | | | $ | 22,586 | | | $ | 21,157 | | | $ | 19,206 | | | $ | 19,602 | | | $ | 19,736 | | | $ | 20,144 | | | $ | 19,323 | |
Total interest expense | | | 1,792 | | | | 1,854 | | | | 2,078 | | | | 1,931 | | | | 1,900 | | | | 1,422 | | | | 1,473 | | | | 1,587 | |
Net interest income | | | 20,556 | | | | 20,732 | | | | 19,079 | | | | 17,275 | | | | 17,702 | | | | 18,314 | | | | 18,671 | | | | 17,736 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | (420 | ) | | | (484 | ) | | | (365 | ) | | | (17 | ) | | | 781 | | | | (419 | ) | | | 75 | | | | 309 | |
Net interest income after provision | | | 20,976 | | | | 21,216 | | | | 19,444 | | | | 17,292 | | | | 16,921 | | | | 18,733 | | | | 18,596 | | | | 17,427 | |
Noninterest income | | | 3,351 | | | | 3,138 | | | | 3,978 | | | | 3,486 | | | | 4,155 | | | | 3,257 | | | | 4,106 | | | | 3,568 | |
Noninterest expense | | | 19,307 | | | | 20,648 | | | | 18,236 | | | | 15,743 | | | | 15,476 | | | | 15,670 | | | | 16,922 | | | | 16,031 | |
Income before taxes | | | 5,020 | | | | 3,706 | | | | 5,186 | | | | 5,035 | | | | 5,600 | | | | 6,320 | | | | 5,780 | | | | 4,964 | |
Income tax expense | | | 1,564 | | | | 1,254 | | | | 1,760 | | | | 1,480 | | | | 1,561 | | | | 2,106 | | | | 1,968 | | | | 1,724 | |
Preferred dividends | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 302 | | | | 51 | |
Net income | | $ | 3,456 | | | $ | 2,452 | | | $ | 3,426 | | | $ | 3,555 | | | $ | 4,039 | | | $ | 4,214 | | | $ | 3,510 | | | $ | 3,189 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic earnings per common share | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 0.06 | | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 0.09 | | | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 0.07 | |
Diluted earnings per common share | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 0.06 | | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 0.09 | | | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | 0.08 | | | $ | 0.07 | |
NOTE 22 – PARK STERLING CORPORATION (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
Condensed financial statements for Park Sterling Corporation (Parent Company Only) follow:
Condensed Balance Sheets | |
| | | December 31, | | | December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Cash and due from banks | | $ | 3,203 | | | $ | 8,417 | |
Investment securities available-for-sale, at fair value | | | 12,851 | | | | 16,354 | |
Investment in banking subsidiary | | | 284,473 | | | | 254,073 | |
Nonmarketable equity securities | | | 1,146 | | | | 774 | |
Premises and equipment, net | | | - | | | | 13 | |
Other assets | | | 208 | | | | 454 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 301,881 | | | $ | 280,085 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Subordinated debt | | $ | 23,583 | | | $ | 15,157 | |
Accrued interest payable | | | 75 | | | | 39 | |
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | | | 3,118 | | | | 2,769 | |
Total liabilities | | | 26,776 | | | | 17,965 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Shareholders' equity: | | | | | | | | |
Common Stock | | | 44,860 | | | | 44,731 | |
Additional paid-in capital | | | 222,819 | | | | 222,596 | |
Accumulated earnings (deficit) | | | 8,901 | | | | (405 | ) |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | | | (1,475 | ) | | | (4,802 | ) |
Total shareholders' equity | | | 275,105 | | | | 262,120 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and shareholders' equity | | $ | 301,881 | | | $ | 280,085 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Condensed Statements of Income | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2014 | | | December 31, 2013 | | | December 31, 2012 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Other interest income | | $ | 688 | | | $ | 756 | | | $ | 1,432 | |
Gain (loss) on sale of securities available-for-sale | | | 276 | | | | (41 | ) | | $ | 989 | |
Other income | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | 100 | |
Total income | | | 965 | | | | 715 | | | | 2,521 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expense | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | | 1,252 | | | | 958 | | | | 761 | |
Other operating expense | | | 1,209 | | | | 557 | | | | 1,030 | |
Total expense | | | 2,461 | | | | 1,515 | | | | 1,791 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss before income taxes and equity in undistributedearnings of subsidiary | | | (1,496 | ) | | | (800 | ) | | | 730 | |
Income tax expense | | | (679 | ) | | | (528 | ) | | | 114 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss before equity in undistributed earnings ofsubsidiary | | | (817 | ) | | | (272 | ) | | | 616 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Preferred dividends | | | - | | | | 353 | | | | 51 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity in undistributed earnings of subsidiary | | | 13,706 | | | | 15,577 | | | | 3,727 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income to common shareholders | | $ | 12,889 | | | $ | 14,952 | | | $ | 4,292 | |
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(table amounts in thousands, except share data and per share amounts)
Condensed Statements of Cash Flow | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2014 | | | December 31, 2013 | | | December 31, 2012 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 12,889 | | | $ | 15,305 | | | $ | 4,343 | |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to netcash provided by (used for) operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity in undistributed earnings in banking subsidiary | | | (14,385 | ) | | | (16,105 | ) | | | (3,613 | ) |
Amortization (accretion) of investment securities available-for-sale | | | (34 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 499 | |
Other depreciation and amortization, net | | | 614 | | | | 482 | | | | 444 | |
Loss on disposal of premises and equipment | | | 11 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Net (gains) losses on sales of investment securities available-for-sale | | | (276 | ) | | | 41 | | | | (989 | ) |
Change in assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Increase) decrease in other assets | | | 246 | | | | (118 | ) | | | 669 | |
Increase in accrued interest payable | | | (1,324 | ) | | | - | | | | (1,272 | ) |
Increase (decrease) in other liabilities | | | 264 | | | | (22 | ) | | | (19 | ) |
Net cash used for operating activities | | | (1,995 | ) | | | (403 | ) | | | 62 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from maturities and call of investment securities available-for-sale | | | 1,625 | | | | - | | | | 30,607 | |
Proceeds from sales of investment securities available-for-sale | | | 2,405 | | | | 8 | | | | 17 | |
Acquisition of Provident Community | | | (6,493 | ) | | | - | | | | (24,283 | ) |
Net cash provided by (used for) investing activities | | | (2,463 | ) | | | 8 | | | | 6,341 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Purchase of common stock | | | (1,027 | ) | | | (366 | ) | | | (15 | ) |
Proceeds from exercise of stock options | | | 250 | | | | 308 | | | | - | |
Investment in banking subsidiary | | | 21 | | | | 245 | | | | (5,000 | ) |
Dividends on preferred stock | | | - | | | | (353 | ) | | | (51 | ) |
Dividends on common stock | | | (3,583 | ) | | | (1,789 | ) | | | - | |
Redemption of preferred stock | | | - | | | | (20,500 | ) | | | - | |
Dividend from banking subsidiary | | | 3,583 | | | | 22,289 | | | | - | |
Net cash used for financing activities | | | (756 | ) | | | (166 | ) | | | (5,066 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents | | | (5,214 | ) | | | (561 | ) | | | 1,337 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning | | | 8,417 | | | | 8,978 | | | | 7,641 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents, ending | | $ | 3,203 | | | $ | 8,417 | | | $ | 8,978 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing and financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Change in unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale securities, net of tax | | $ | 5,175 | | | $ | (8,343 | ) | | $ | 318 | |
Change in unrealized gain (loss) on cash flow hedge, net of tax | | | (1,848 | ) | | | 343 | | | | - | |
Transfer from investment securities to investment in subsidiary | | | - | | | | - | | | | 6,541 | |
NOTE 23 –SUBSEQUENT EVENT
On January 29, 2015, the Company announced that its board of directors has declared a regular quarterly cash dividend to its common shareholders of $0.03 per common share, payable on February 24, 2015 to all shareholders of record as of the close of business on February 10, 2015.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosures
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the management of the Company, under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) of the Exchange Act.
Based upon that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective (1) to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports filed or submitted by it under the Exchange Act was recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and (2) to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by the Company in such reports is accumulated and communicated to the Company’s management, including its Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act). The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance to management and the board of directors regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of the Company’s financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
The Company’s management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. In making this assessment, it used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) inInternal Control—Integrated Framework (2013). Based on its assessment, management believes that, as of December 31, 2014, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria.
The Company’s internal control over financial reporting has been audited by Dixon Hughes Goodman LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm. Their report, which appears below, expresses an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There was no change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the fourth fiscal quarter of 2014 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders
Park Sterling Corporation
We have audited Park Sterling Corporation’s (the “Company”) internal control overfinancial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013)issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control overfinancial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control overfinancial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control overfinancial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, Park Sterling Corporation maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established inInternal Control—Integrated Framework (2013)issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements of Park Sterling Corporation as of and for the year ended December 31, 2014, and our report dated March 6, 2015, expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
/s/ DIXON HUGHES GOODMAN LLP
Charlotte, North Carolina
March 6, 2015
Item 9B. Other Information
None.
Part III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Board of Directors
The following persons currently serve as members of the Company’s Board of Directors:
Walter C. Ayers,Sr.
Retired President and Chief Executive Officer, Virginia Bankers Association.
Leslie M. Baker, Jr.
Chairman of the Board, Park Sterling Corporation and Park Sterling Bank.
Retired Chairman of the Board, Wachovia Corporation.
Larry W. Carroll
President, Carroll Financial Associates, Inc.
James. C. Cherry
Chief Executive Officer, Park Sterling Corporation and Park Sterling Bank.
Jean E. Davis
Retired head of Operations, Technology and e-Commerce, Wachovia Corporation.
Patricia C. Hartung
Executive Director, Upper Savannah Council of Governments.
Thomas B. Henson
President and Chief Executive Officer, Henson-Tomlin Interests, LLC.
Senior Managing Partner, Southeastern Private Investment Fund.
Jeffrey S. Kane
Retired Senior Vice President in charge of Charlotte office, Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond.
Kim S. Price
Vice-Chairman of the Board, Park Sterling Corporation and Park Sterling Bank.
Former President and CEO of Citizens South Banking Corporation.
Ben R. Rudisill, II
President, Rudisill Enterprises, Inc.
Biographical information for each member of the Board of Directors can be found in the Company’s Proxy Statement for its 2015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders scheduled to be held on May 20, 2015 (the “2015 Proxy Statement”) under the caption “Election of Directors,” which section is incorporated herein by reference.
Executive Officers
The following persons have beendesignated as the Company’s executive officers:
James C. Cherry. Mr. Cherry, age 64, has served as Chief Executive Officer of the Company since its formation and of the Bank since its Public Offering. He retired as the Chief Executive Officer for the Mid-Atlantic Banking Region at Wachovia Corporation in 2006, and previously served as President of Virginia Banking, Head of Trust and Investment Management, and in various positions in North Carolina banking including Regional Executive, Area Executive, City Executive, Corporation Banking and Loan Administration Manager, and Retail Banking Branch Manager for Wachovia. Mr. Cherry was formerly Chairman of the Virginia Bankers Association. He is currently a director of Armada Hoffler Properties, Inc., a Virginia-based real estate company. Mr. Cherry has over 30 years of banking experience.
Bryan F. Kennedy III.Mr. Kennedy, age 57, has been President of the Company since its formation and President of the Bank since its Public Offering. Prior to the Bank’s Public Offering, he served as President and Chief Executive Officer of the Bank since its formation in October 2006. Prior to helping organize the Bank in 2006, he served in various roles at Regions Bank, including President-North Carolina from November 2004 to January 2006, President-Charlotte from January 2003 to November 2004, and Executive Vice President from November 2001 to January 2003. From June 1991 to November 2001 he served initially as Senior Vice President and then as Executive Vice President of Park Meridian Bank, which was acquired by Regions Financial Corporation in November 2001. Mr. Kennedy serves on the Board of Directors of Cato Corporation, a publicly traded company. Mr. Kennedy has over 30 years of banking experience.
David L. Gaines. Mr. Gaines, age 55, has been Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of the Company since its formation and Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of the Bank since its Public Offering. He was the deputy and then Chief Risk Officer for Corporate and Investment Banking at Wachovia Corporation from September 2001 to November 2006. Prior to that, he was Senior Vice President and Comptroller of Wachovia Corporation from July 2000 to September 2001. Other Wachovia experiences include the coordination of the Merger Integration Project Office for the Wachovia-First Union merger, leadership of Risk Management for Wachovia Capital Markets and United States Corporate Banking and various geographically-based relationship management positions. Mr. Gaines has over 25 years of banking experience.
Nancy J. Foster. Ms. Foster, age 53, has been Executive Vice President and Chief Risk Officer of the Company and the Bank since November 2010. Prior to joining the Bank, she was first Executive Vice President and Chief Credit Officer and then Executive Vice President and Chief Risk & Credit Officer of CIT Group from January 2007 to December 2009. She was Group Senior Vice President, Specialized Lending at LaSalle Bank/ABNAmro from March 2005 to January 2007, Group Senior Vice President, Credit Policy and Portfolio Management from August 2001 to March 2005, Group Senior Vice President and Chief Credit Officer, Asset Based Lending and Metropolitan Commercial Banking from 1999 to 2001, and Executive Vice President and Chief Credit Officer, Community Banks from 1993 to 1999. Ms. Foster previously held various lending and managerial roles in Middle Market Banking at LaSalle Bank. Ms. Foster has over 25 years of banking experience.
MarkS. Ladnier. Mr. Ladnier, age 56, has been Group Senior Vice President and Head of Operations and Information Technology since January 2014. Prior to joining the Bank, he was Senior Vice President and Southeast Market Leader for Premier Alliance, a professional services practice, from November 2012 to December 2013. Mr. Ladnier previously served as Executive Vice President and Chief Information Officer for Real Estate Lending at Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., from January 2009 to September 2011 and in a number of leadership roles at its predecessor company, Wachovia Bank, N.A., including Senior Vice President and Chief Information Officer for Lending Technology, Senior Vice President and Basel Program Director, and Senior Vice President and eCommerce Program Director, from January 1987 to December 2008. Mr. Ladnier has over 25 years of banking experience.
Code of Ethics
The Company has adopted a written Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers (the “Senior Code of Ethics”) that applies to the Company’s Chief Executive Officer (the principal executive officer), Chief Financial Officer (the principal financial officer), Chief Accounting Officer (the principal accounting officer), and Controller. The Company has also adopted a Code of Ethics (the “Code of Ethics”) that applies to all employees, officers and directors of the Company as well as any subsidiary company officers that are executive officers of the Company. The Senior Code of Ethics and Code of Ethics are available on the Company’s website atwww.parksterlingbank.com and print copies are available to any shareholder that requests a copy. Any amendments to the Senior Code of Ethics or Code of Ethics, or waivers of these policies, to the extent applicable to the Chief Executive Officer, the Chief Financial Officer and the Chief Accounting Officer, will be disclosed on the Company’s website promptly following the date of such amendment or waiver, as applicable.
Additional Information
The additional information required by this Item 10 appears under the captions “Election of Directors – Committees of the Board of Directors – Audit Committee,” “Corporate Governance Matters – Audit Committee Financial Expert”, “—Process for Nominating Potential Director Candidates” and “—Code of Ethics,” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in the 2015 Proxy Statement, which sections are incorporated herein by reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this Item 11 appears under the captions “Election of Directors – Compensation of Directors”, “Compensation Discussion and Analysis”, “Compensation of Executive Officers”, “Compensation and Development Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” and “Compensation and Development Committee Report on Executive Compensation” in the 2015 Proxy Statement, which sections are incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this Item 12 regarding the security ownership of certain beneficial owners and management appears under the caption “Beneficial Ownership of Common Stock” in the 2015 Proxy Statement, which section is incorporated herein by reference. The following table sets forth summary information regarding the Company’s equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2014:
Equity Compensation Plan Information | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | (a) | | | (b) | | | (c) | |
Plan category (1) | | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options | | | Weighted -average exercise price of outstanding options | | | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) | |
Equity compensation plans approved by our shareholders | | | 2,005,404 | | | $ | 7.56 | | | | 839,287 | (3) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity compensation plans not approved by our shareholders (2) | | | 165,953 | | | | 5.46 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | 2,171,357 | | | $ | 7.84 | | | | 839,287 | |
(1) This table does not include outstanding options to purchase 630 shares of the Company’s common stock that were assumed by the Company in connection with the Citizens South acquisition, which were originally issued under the Citizens South Bank 1999 Stock Option Plan (renamed the Park Sterling Bank 1999 Stock Option Plan). The weighted-average option price of these assumed options was $3.22 at December 31, 2014. No additional awards may be granted under this plan.
(2) In connection with the Citizens South acquisition, the Company assumed and retained the ability to issue awards in accordance with applicable NASDAQ listing standards under the following plans, which were not approved by the Company’s shareholders but were previously approved by Citizens South’s stockholders prior to the acquisition: the Citizens South Banking Corporation 2003 Stock Option Plan (renamed the Park Sterling Corporation 2003 Stock Option Plan (“2003 Citizens South Plan”)) and the Citizens South Banking Corporation 2008 Equity Incentive Plan (renamed the Park Sterling Corporation 2008 Equity Incentive Plan (“2008 Citizens South Plan”)). The 2003 Citizens South Plan expired by its terms in May 2013, and the 2008 Citizens South Plan was frozen in May 2014 upon the effectiveness of the Company’s 2014 Long-term Incentive Plan (“2014 LTIP”). As a result, no additional awards may be granted under these plans.
(3) Represents shares available for issuance in connection with stock options, restricted stock awards and other stock-based awards under the 2014 LTIP.
A description of the Company’s equity compensation plans, including the material features of the 2008 Citizens South Plan and the 2003 Citizens South Plan, is presented in Note 20 – Employee and Director Benefit Plans to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this Item 13 appears under the captions “Election of Directors – Committees of the Board of Directors”, “Corporate Governance – Director Independence” and “Transactions with Related Persons and Certain Control Persons” in the 2015 Proxy Statement, which sections are incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal AccountingFees and Services
The information required by this Item 14 appears under the captions “Ratification of the Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm—Fees” and “—Policy on Audit Committee Pre-Approval of Audit and Permissible Non-Audit Services by the Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in the 2015 Proxy Statement, which sections are incorporated herein by reference.
With the exception of the information expressly incorporated herein by reference, the 2015 Proxy Statement shall not be deemed filed as part of this report.
Part IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
The following documents are filed as part of this report:
| | (a) | Financial statements, included in Part II, Item 8. “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data”: |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Balance Sheets
Consolidated Statements of Income
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| | (c) | Exhibits: The exhibits listed on the Exhibit Index of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are filed herewith or have been previously filed and are incorporated herein by reference to other filings. |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this Annual Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
PARK STERLING CORPORATION
March 6, 2015 | | | | By: | | /s/ JAMES C. CHERRY | |
| | | | | | | James C. Cherry | |
| | | | | | | Chief Executive Officer | |
| | | | |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons, on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on March 6, 2015.
/S/ JAMES C. CHERRY March 6, 2015
James C. Cherry
Chief Executive Officer and Director
(Principal Executive Officer)
/S/ DAVID L. GAINES March 6, 2015
David L. Gaines
Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial Officer)
/S/ SUSAN D. SABO March 6, 2015
Susan D. Sabo
Chief Accounting Officer
(Principal Accounting Officer)
/S/ WALTER C. AYERS March 6, 2015
Walter C. Ayers
Director
/S/ LESLIE M. BAKER JR. March 6, 2015
Leslie M. Baker Jr.
Chairman of the Board
/S / LARRY W. CARROLL March 6, 2015
Larry W. Carroll
Director
/S / JEAN E. DAVIS March 6, 2015
Jean E. Davis
Director
/S / PATRICIA C. HARTUNG March 6, 2015
Patricia C. Hartung
Director
/S/ THOMAS B. HENSON March 6, 2015
Thomas B. Henson
Director
/S / JEFFREY S. KANE March 6, 2015
Jeffrey S. Kane
Director
/S/ KIM S. PRICE March 6, 2015
Kim S. Price
Director
/S /BEN R. RUDISILL, II March 6, 2015
Ben R. Rudisill, II
Director
Exhibit Index
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibits |
| | |
2.1 | Agreement and Plan of Merger dated May 13, 2012 by and between Park Sterling Corporation and Citizens South Banking Corporation, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed May 17, 2012 |
| | |
3.1 | Articles of Incorporation of the Company, as amended, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-35032) filed May 9, 2014 |
| | |
3.2 | Bylaws of the Company, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed January 13, 2011 |
| | |
4.1 | Specimen Stock Certificate of the Company, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed January 13, 2011 |
| | |
| | The Company has certain long-term debt but has not filed the instruments evidencing such debt as part of Exhibit 4 as none of such instruments authorize the issuance of debt exceeding 10 percent of the total consolidated assets of the Company. The Company agrees to furnish a copy of each such agreement to the Securities and Exchange Commission upon request. |
| | |
10.1 | Employment Agreement by and between James C. Cherry and the Bank effective August 18, 2010, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed January 13, 2011* |
| | |
10.2 | Employment Agreement by and between Bryan F. Kennedy III and the Bank effective August 18, 2010, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed January 13, 2011* |
| | |
10.3 | Employment Agreement by and between David L. Gaines and the Bank effective August 18, 2010, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed January 13, 2011* |
| | |
10.4 | Employment Agreement by and between Nancy J. Foster and the Bank effective November 15, 2010, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35032) filed March 31, 2011* |
| | |
10.5 | Park Sterling Bank 2006 Employee Stock Option Plan and related form of award agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed January 13, 2011* |
| | |
10.6 | Park Sterling Bank 2006 Stock Option Plan for Directors and related form of award agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed January 13, 2011* |
| | |
10.7 | Park Sterling Bank 2010 Employee Stock Option Plan and related form of award agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 of the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (Registration No. 333-172016) filed February 2, 2011* |
| | |
10.8 | Park Sterling Bank 2010 Stock Option Plan for Directors and related form of award agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 of the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (Registration No. 333-172016) filed February 2, 2011* |
| | |
10.9 | Park Sterling Corporation 2010 Long-Term Incentive Plan and related form of award agreements, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed January 13, 2011* |
| | |
10.10 | Form of Non-Employee Director Nonqualified Stock Option Award pursuant to the Park Sterling Corporation 2010 Long-Term Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35032) filed March 31, 2011* |
10.11 | Form of Employee Restricted Stock Award Agreement pursuant to the Park Sterling Corporation 2010 Long-Term Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35032) filed March 31, 2011* |
| | |
10.12 | Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Award Agreement pursuant to the Park Sterling Corporation 2010 Long-Term Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35032) filed March 31, 2011* |
| | |
10.13 | Consulting Agreement between Kim S. Price and the Company, effective October 1, 2012, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35032) filed March 15, 2013* |
| | |
10.14 | Noncompetition Agreement by and between Kim S. Price and the Company, dated as of May 13, 2012, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35032) filed March 15, 2013* |
| | |
10.15 | Waiver and Settlement Agreement by and between Kim S. Price and the Company, dated as of May 13, 2012, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35032) filed March 15, 2013* |
| | |
10.16 | Amended Deferred Compensation and Income Continuation Agreement between Citizens South Bank and Ben R. Rudisill, II dated March 15, 2004, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 of Citizen South Banking Corporation’s (“Citizens South”) Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 0-23971) filed March 16, 2005, as amended by the First Amendment thereto, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of Citizens South’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 0-23971) filed November 8, 2008* |
| | |
10.17 | Amended Director Retirement Agreement between Citizens South Bank and Ben R. Rudisill, II dated March 15, 2004, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.27 of Citizens South’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 0-23971) filed March 16, 2005, as amended by the First Amendment thereto, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 of Citizens South’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 0-23971) filed November 8, 2008* |
| | |
10.18 | Purchase and Assumption Agreement – Whole Bank – All Deposits, dated as of April 15, 2011 among Citizens South Bank, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation as receiver of New Horizons Bank, East Ellijay, Georgia, and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of Citizens South’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 0-23971) filed April 19, 2011 |
| | |
10.19 | Purchase and Assumption Agreement – Whole Bank – All Deposits, dated as of March 19, 2010 among Citizens South Bank, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation as receiver of Bank of Hiawassee, Hiawassee, Georgia, and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of Citizens South’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 0-23971) filed March 23, 2010 |
| | |
10.20 | Park Sterling Bank Deferred Compensation Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-35032) filed May 10, 2013* |
| | |
10.21 | Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Time-Vesting) pursuant to the Park Sterling Corporation 2010 Long-Term Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-35032) filed May 10, 2013* |
| | |
10.22 | Form of Employee Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Time-Vesting) pursuant to the Park Sterling Corporation 2010 Long-Term Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-35032) filed May 10, 2013* |
| | |
10.23 | Park Sterling Corporation 2014 Long-Term Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (File No. 333-196173) filed May 22, 2014* |
| | |
10.24 | Form of Employee Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Time-Vesting) pursuant to the Park Sterling Corporation 2014 Long-Term Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed May 22, 2014* |
10.25 | Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Time-Vesting) pursuant to the Park Sterling Corporation 2014 Long-Term Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed May 22, 2014* |
| | |
10.26 | Form of Nonqualified Stock Option Award Agreement pursuant to the Park Sterling Corporation 2014 Long-Term Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35032) filed May 22, 2014* |
| | |
21.1 | Subsidiaries of the Company |
| | |
23.1 | Consent of Dixon Hughes Goodman LLP |
| | |
31.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| | |
31.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| | |
32.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| | |
32.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 |
| | |
101 | Interactive data files pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T: (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013; (ii) Consolidated Statements of Income for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012; (iii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012; (iv) Condensed Consolidated Statements of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012; (v) Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012; and (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
| | |
| | * Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement |
136


