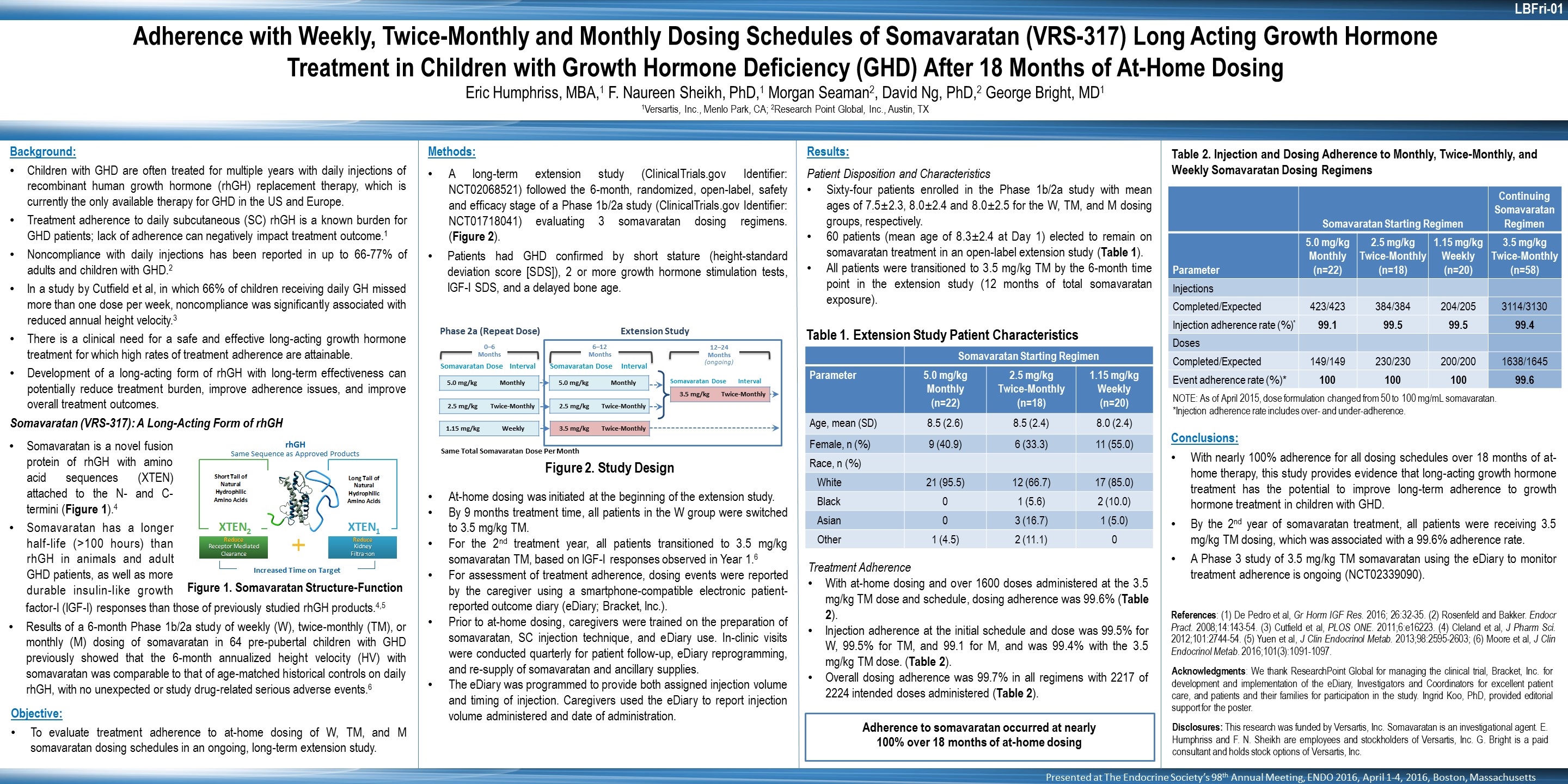
Background: Children with GHD are often treated for multiple years with daily injections of recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) replacement therapy, which is currently the only available therapy for GHD in the US and Europe. Treatment adherence to daily subcutaneous (SC) rhGH is a known burden for GHD patients; lack of adherence can negatively impact treatment outcome.1 Noncompliance with daily injections has been reported in up to 66-77% of adults and children with GHD.2 In a study by Cutfield et al, in which 66% of children receiving daily GH missed more than one dose per week, noncompliance was significantly associated with reduced annual height velocity.3 There is a clinical need for a safe and effective long-acting growth hormone treatment for which high rates of treatment adherence are attainable. Development of a long-acting form of rhGH with long-term effectiveness can potentially reduce treatment burden, improve adherence issues, and improve overall treatment outcomes. Somavaratan (VRS-317): A Long-Acting Form of rhGH Methods: A long-term extension study (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02068521) followed the 6-month, randomized, open-label, safety and efficacy stage of a Phase 1b/2a study (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01718041) evaluating 3 somavaratan dosing regimens. (Figure 2). Patients had GHD confirmed by short stature (height-standard deviation score [SDS]), 2 or more growth hormone stimulation tests, IGF-I SDS, and a delayed bone age. At-home dosing was initiated at the beginning of the extension study. By 9 months treatment time, all patients in the W group were switched to 3.5 mg/kg TM. For the 2nd treatment year, all patients transitioned to 3.5 mg/kg somavaratan TM, based on IGF-I responses observed in Year 1.6 For assessment of treatment adherence, dosing events were reported by the caregiver using a smartphone-compatible electronic patient-reported outcome diary (eDiary; Bracket, Inc.). Prior to at-home dosing, caregivers were trained on the preparation of somavaratan, SC injection technique, and eDiary use. In-clinic visits were conducted quarterly for patient follow-up, eDiary reprogramming, and re-supply of somavaratan and ancillary supplies. The eDiary was programmed to provide both assigned injection volume and timing of injection. Caregivers used the eDiary to report injection volume administered and date of administration. Figure 1. Somavaratan Structure-Function Adherence to somavaratan occurred at nearly 100% over 18 months of at-home dosing Adherence with Weekly, Twice-Monthly and Monthly Dosing Schedules of Somavaratan (VRS-317) Long Acting Growth Hormone Treatment in Children with Growth Hormone Deficiency (GHD) After 18 Months of At-Home Dosing Eric Humphriss, MBA,1 F. Naureen Sheikh, PhD,1 Morgan Seaman2, David Ng, PhD,2 George Bright, MD1 1Versartis, Inc., Menlo Park, CA; 2Research Point Global, Inc., Austin, TX Disclosures: This research was funded by Versartis, Inc. Somavaratan is an investigational agent. E. Humphriss and F. N. Sheikh are employees and stockholders of Versartis, Inc. G. Bright is a paid consultant and holds stock options of Versartis, Inc. Somavaratan is a novel fusion protein of rhGH with amino acid sequences (XTEN) attached to the N- and C-termini (Figure 1).4 Somavaratan has a longer half-life (>100 hours) than rhGH in animals and adult GHD patients, as well as more durable insulin-like growth Objective: To evaluate treatment adherence to at-home dosing of W, TM, and M somavaratan dosing schedules in an ongoing, long-term extension study. Results: Patient Disposition and Characteristics Sixty-four patients enrolled in the Phase 1b/2a study with mean ages of 7.5±2.3, 8.0±2.4 and 8.0±2.5 for the W, TM, and M dosing groups, respectively. 60 patients (mean age of 8.3±2.4 at Day 1) elected to remain on somavaratan treatment in an open-label extension study (Table 1). All patients were transitioned to 3.5 mg/kg TM by the 6-month time point in the extension study (12 months of total somavaratan exposure). Treatment Adherence With at-home dosing and over 1600 doses administered at the 3.5 mg/kg TM dose and schedule, dosing adherence was 99.6% (Table 2). Injection adherence at the initial schedule and dose was 99.5% for W, 99.5% for TM, and 99.1 for M, and was 99.4% with the 3.5 mg/kg TM dose. (Table 2). Overall dosing adherence was 99.7% in all regimens with 2217 of 2224 intended doses administered (Table 2). LBFri-01 Presented at The Endocrine Society’s 98th Annual Meeting, ENDO 2016, April 1-4, 2016, Boston, Massachusetts Conclusions: With nearly 100% adherence for all dosing schedules over 18 months of at-home therapy, this study provides evidence that long-acting growth hormone treatment has the potential to improve long-term adherence to growth hormone treatment in children with GHD. By the 2nd year of somavaratan treatment, all patients were receiving 3.5 mg/kg TM dosing, which was associated with a 99.6% adherence rate. A Phase 3 study of 3.5 mg/kg TM somavaratan using the eDiary to monitor treatment adherence is ongoing (NCT02339090). References: (1) De Pedro et al, Gr Horm IGF Res. 2016; 26:32-35. (2) Rosenfeld and Bakker. Endocr Pract. 2008;14:143-54. (3) Cutfield et al, PLOS ONE. 2011;6:e16223. (4) Cleland et al, J Pharm Sci. 2012;101:2744-54. (5) Yuen et al, J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:2595-2603; (6) Moore et al, J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(3):1091-1097. Acknowledgments: We thank ResearchPoint Global for managing the clinical trial, Bracket, Inc. for development and implementation of the eDiary, Investigators and Coordinators for excellent patient care, and patients and their families for participation in the study. Ingrid Koo, PhD, provided editorial support for the poster. Somavaratan Starting Regimen Parameter 5.0 mg/kg Monthly (n=22) 2.5 mg/kg Twice-Monthly (n=18) 1.15 mg/kg Weekly (n=20) Age, mean (SD) 8.5 (2.6) 8.5 (2.4) 8.0 (2.4) Female, n (%) 9 (40.9) 6 (33.3) 11 (55.0) Race, n (%) White 21 (95.5) 12 (66.7) 17 (85.0) Black 0 1 (5.6) 2 (10.0) Asian 0 3 (16.7) 1 (5.0) Other 1 (4.5) 2 (11.1) 0 Table 1. Extension Study Patient Characteristics factor-I (IGF-I) responses than those of previously studied rhGH products.4,5 Results of a 6-month Phase 1b/2a study of weekly (W), twice-monthly (TM), or monthly (M) dosing of somavaratan in 64 pre-pubertal children with GHD previously showed that the 6-month annualized height velocity (HV) with somavaratan was comparable to that of age-matched historical controls on daily rhGH, with no unexpected or study drug-related serious adverse events.6 Somavaratan Starting Regimen Continuing Somavaratan Regimen Parameter 5.0 mg/kg Monthly (n=22) 2.5 mg/kg Twice-Monthly (n=18) 1.15 mg/kg Weekly (n=20) 3.5 mg/kg Twice-Monthly (n=58) Injections Completed/Expected 423/423 384/384 204/205 3114/3130 Injection adherence rate (%)* 99.1 99.5 99.5 99.4 Doses Completed/Expected 149/149 230/230 200/200 1638/1645 Event adherence rate (%)* 100 100 100 99.6 Table 2. Injection and Dosing Adherence to Monthly, Twice-Monthly, and Weekly Somavaratan Dosing Regimens NOTE: As of April 2015, dose formulation changed from 50 to 100 mg/mL somavaratan. *Injection adherence rate includes over- and under-adherence. Figure 2. Study Design 5.0 mg/kg Monthly 6–12 Months 12–24 Months (ongoing) 0–6 Months Somavaratan Dose Interval Phase 2a (Repeat Dose) Extension Study 2.5 mg/kg Twice-Monthly 1.15 mg/kg Weekly 5.0 mg/kg Monthly 2.5 mg/kg Twice-Monthly 3.5 mg/kg Twice-Monthly Somavaratan Dose Interval Somavaratan Dose Interval Same Total Somavaratan Dose Per Month 3.5 mg/kg Twice-Monthly
