UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D. C. 20549
FORM 10-Q
[X] QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d)
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the Quarterly Period ended June 30, 2019
OR
[ ] TRANSITION REPORT UNDER SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE EXCHANGE ACT
For the transition period from
__________to __________
Commission File No.: 333-177532
KAYA HOLDINGS, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)

| Delaware | | 90-0898007 |
| (Stateorother jurisdiction ofincorporation ororganization) | | (I.R.S.Employer Identification Number) |
888 S. Andrews Avenue
Suite 302
Ft. Lauderdale, Florida 33316
(Address of principal executive offices)
(954)-892-6911
(Issuer's telephone number)
Indicatebycheck mark whether the registrant (1) hasfiled all reportsrequired to befiled bySection 13 or 15(d) ofthe Exchange Actduring the past 12months (or forsuch shorter period that theregistrant wasrequired to file such reports), and (2) hasbeen subject to such filing requirements forthe past 90days.Yes[X] No [ ]
Indicatebycheck mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to besubmittedpursuant toRule 405 ofRegulation ST (§232.405 ofthis chapter) during the preceding 12months(or for suchshorter period that theregistrantwasrequired to submit suchfiles).Yes [X ] No [ ]
Indicatebycheck mark whether the registrant is alarge acceleratedfiler,anacceleratedfiler,anonacceleratedfiler,or asmaller reporting companyoremerging growthcompany.Seethe definitions of“large acceleratedfiler,”“accelerated filer” and “smaller reportingcompany” and“emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of theExchange Act. (Check one):
| Large Accelerated Filer [ ] | Accelerated Filer [ ] |
| Non-accelerated Filer [ ] | Smaller reporting company [X] |
| | Emerging growth company [X] |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. [ ]
Indicatebycheckmark whether the registrantis ashell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 ofthe Exchange Act.)Yes [ ] No [X]
As of August 19, 2019, theIssuer had 173,598,080sharesof itscommon stock outstanding.
KAYAHOLDINGS, INC.
INDEXTOQUARTERLYREPORTON FORM 10 Q
Part I –Financial Information Page
| Item1.Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements | Page |
| CondensedConsolidated Balance Sheet | 3 |
| CondensedConsolidated Statements ofOperation | 4 |
| CondensedConsolidated Statements ofCash Flows | 5 |
| StatementofStockholder’s equity forsix months ended June 30, 2019 and 2018 | 6 |
| Notes toCondensedConsolidated Financial Statements | 7 |
| Item2.Management’s Discussion andAnalysis ofFinancial Condition and Results ofOperations | 32 |
| Item3.QuantitativeandQualitative Disclosures AboutMarket Risk | 71 |
| Item4.ControlsandProcedures | 71 |
| | |
| PartIIOther Information | |
| | |
| Item1.Legal Proceedings | 72 |
| Item1A. RiskFactors | 72 |
| Item2.Unregistered Sales ofEquity Securities and Use ofProceeds | 72 |
| Item3.DefaultsUponSenior Securities | 73 |
| Item4.Mine Safety Disclosures | 73 |
| Item5.Other Information | 73 |
| Item6.Exhibits | 73 |
| Signatures | 74 |
Kaya Holdings, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets
June 30, 2019 (Unaudited) and December 31, 2018
| ASSETS | | | | |
| | | (Unaudited) | | (Audited) |
| | | June 30, 2019 | | December 31, 2018 |
| CURRENT ASSETS: | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and equivalents | | $ | 120,083 | | | $ | 111,512 | |
| Inventory-net of allowance | | | 123,954 | | | | 131,542 | |
| Prepaid expenses | | | 12,774 | | | | 20,541 | |
| Total current assets | | | 256,811 | | | | 263,595 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| NON-CURRENT ASSETS: | | | | | | | | |
| Right-of-use asset - operating lease | | | 525,451 | | | | — | |
| Property and equipment, net | | | 2,252,858 | | | | 2,348,780 | |
| Deposits | | | 31,523 | | | | 31,523 | |
| Total other assets | | | 2,809,832 | | | | 2,380,303 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 3,066,643 | | | $ | 2,643,898 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY (DEFICIENCY) | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| CURRENT LIABILITIES: | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expense | | $ | 651,958 | | | $ | 562,016 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expense-related parties | | | 7,737 | | | | 7,737 | |
| Accrued interest | | | 883,814 | | | | 659,169 | |
| Right-of-use liabiliy - operating lease | | | 146,040 | | | | — | |
| Convertible notes payable-net of discount | | | 334,052 | | | | 2,894,294 | |
| Notes payable | | | 9,312 | | | | 9,312 | |
| Derivative liabilities | | | 10,644,017 | | | | 19,783,034 | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 12,676,930 | | | | 23,915,562 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| LONG TERM LIABILITIES: | | | | | | | | |
| Convertible notes payable-related party-net of discount | | | 500,000 | | | | 500,000 | |
| Convertible notes payable-net of discount | | | 4,557,583 | | | | 1,283,557 | |
| Notes payable-related party | | | 250,000 | | | | 250,000 | |
| Rights-of-use liability-operating lease | | | 383,938 | | | | — | |
| Total long term liabilities | | | 5,691,521 | | | | 2,033,557 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities | | | 18,368,451 | | | | 25,949,119 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY (DEFICIT): | | | | | | | | |
| Convertible preferred stock, Series C, par value $.001; 10,000,000 shares authorized; | | | | | | | | |
| 49,900 and 49,900 issued and outstanding at June 30, 2019 and December 31, 2018 | | | 50 | | | | 50 | |
| , respectively | | | | | | | | |
| Common stock , par value $.001; 500,000,000 shares authorized; | | | | | | | | |
| 173,598,080 shares issued as of June 30, 2019 and | | | | | | | | |
| 165,812,128 shares issued as of December 31, 2018 | | | 173,598 | | | | 165,812 | |
| Subscriptions payable | | | 163,630 | | | | 397,209 | |
| Additional paid in capital | | | 17,384,679 | | | | 17,100,137 | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (31,811,640 | ) | | | (39,924,912 | ) |
| Non-controlling interest | | | (1,212,125 | ) | | | (1,043,517 | ) |
| Net stockholders' equity/(deficit) | | | (15,301,808 | ) | | | (23,305,221 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity/(deficit) | | $ | 3,066,643 | | | $ | 2,643,898 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Kaya Holdings, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations
(Unudited)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the three | | For the three | | For the six | | For the six |
| | | months ended | | months ended | | months ended | | months ended |
| | | June 30, 2019 | | June 30, 2018 | | June 30, 2019 | | June 30, 2018 |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales | | $ | 249,121 | | | $ | 291,133 | | | $ | 512,879 | | | $ | 546,498 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of sales | | | 92,719 | | | | 118,420 | | | | 238,231 | | | | 221,011 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross profit | | | 156,402 | | | | 172,713 | | | | 274,648 | | | | 325,487 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Professional fees | | | 145,119 | | | | 172,331 | | | | 190,969 | | | | 1,358,059 | |
| Salaries and wages | | | 114,415 | | | | 102,192 | | | | 260,870 | | | | 235,632 | |
| General and administrative | | | 217,197 | | | | 175,158 | | | | 460,220 | | | | 339,246 | |
| Total operating expenses | | | 476,731 | | | | 449,681 | | | | 912,059 | | | | 1,932,937 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating loss | | | (320,329 | ) | | | (276,968 | ) | | | (637,411 | ) | | | (1,607,450 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other income(expense): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | | (132,193 | ) | | | (137,784 | ) | | | (258,395 | ) | | | (283,808 | ) |
| Amortization of debt discount | | | (366,177 | ) | | | (544,357 | ) | | | (713,786 | ) | | | (1,124,122 | ) |
| Derivative liabilities expense | | | (115,253 | ) | | | (356,394 | ) | | | (562,148 | ) | | | (1,913,591 | ) |
| Gain (loss) on extinguishment of debt | | | — | | | | — | | | | (25,000 | ) | | | — | |
| Change in derivative liabilities expense | | | 4,736,220 | | | | (256,374 | ) | | | 10,141,165 | | | | 16,105,145 | |
| Other income (expense) | | | 14 | | | | — | | | | 238 | | | | — | |
| Total other income (expense) | | | 4,122,620 | | | | (1,294,909 | ) | | | 8,582,075 | | | | 12,783,624 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | | 3,802,291 | | | | (1,571,877 | ) | | | 7,944,664 | | | | 11,176,174 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) attributed to non-controlling interest | | | (61,449 | ) | | | (37,909 | ) | | | (168,608 | ) | | | (74,554 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) attributed to Kaya Holdings, Inc. | | | 3,863,740 | | | | (1,533,968 | ) | | | 8,113,272 | | | | 11,250,728 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic net income (loss) per common share | | $ | 0.02 | | | $ | (0.01 | ) | | $ | 0.05 | | | $ | 0.08 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of common shares outstanding - Basic | | | 173,598,080 | | | | 139,409,719 | | | | 170,872,997 | | | | 139,251,765 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted net income (loss) per common share | | $ | 0.01 | | | $ | (0.01 | ) | | $ | 0.02 | | | $ | 0.08 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of common shares outstanding - Diluted | | | 423,656,593 | | | | 139,409,719 | | | | 420,931,510 | | | | 139,251,765 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Kaya Holdings, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statement of Cashflows
(Unaudited)
| | | For the six | | For the six |
| | | months ended | | months ended |
| | | June 30, 2019 | | June 30, 2018 |
| OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | |
| Net income/(loss) | | $ | 8,113,272 | | | $ | 11,250,728 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | | | | | | | | |
| Net income/(loss) attributable to non-controlling interest | | | (168,608 | ) | | | (74,554 | ) |
| Depreciation | | | 115,590 | | | | 43,149 | |
| Imputed interest | | | 33,749 | | | | 15,000 | |
| Loss (Gain) on Extinguishment of Debt | | | 25,000 | | | | — | |
| Derivative expense | | | 562,148 | | | | 1,913,591 | |
| Change in derivative liabilities | | | (10,141,165 | ) | | | (16,105,145 | ) |
| Amortization of debt discount | | | 713,786 | | | | 1,124,122 | |
| Stock issued for interest | | | — | | | | — | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
| Prepaid expense | | | 7,767 | | | | (12,904 | ) |
| Inventory | | | 7,588 | | | | (27,809 | ) |
| Right-of-use asset | | | 113,142 | | | | — | |
| Deposits | | | — | | | | 66,974 | |
| Accrued interest | | | 224,645 | | | | 238,881 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | | | 89,940 | | | | 974,251 | |
| Right-of-use liabilities | | | (108,615 | ) | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | | (411,761 | ) | | | (593,716 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of property and equipment | | | (19,668 | ) | | | (114,655 | ) |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | | (19,668 | ) | | | (114,655 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from Common stock subscription | | | — | | | | 50,000 | |
| Proceeds from convertible debt | | | 440,000 | | | | 570,000 | |
| Payments on notes payable | | | — | | | | (51,274 | ) |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | | 440,000 | | | | 568,726 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| NET INCREASE IN CASH | | | 8,571 | | | | (139,645 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| CASH BEGINNING BALANCE | | | 111,512 | | | | 318,462 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| CASH ENDING BALANCE | | $ | 120,083 | | | $ | 178,817 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION: | | | | | | | | |
| Taxes paid | | | — | | | | — | |
| Interest paid | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| NON-CASH TRANSACTIONS AFFECTING OPERATING, INVESTING | | | | | | | | |
| AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | | | | |
| Reclassification of derivative liability to additional paid in capital | | | — | | | | — | |
| Value of accrued interest payable reclassified as principal | | | — | | | | 7,133 | |
| Adoption of lease standard ASC 842 | | | 638,593 | | | | — | |
| Derivative liability on convertible note payable | | | 440,000 | | | | — | |
| Value of common shares issued for conversion of convertible | | | 233,579 | | | | — | |
| notes payable issued from stock payable | | | | | | | | |
| Value of common shares issued as payment of interest | | | — | | | | 12,499 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Kaya Holdings, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity
For the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2018
(Unaudited)
| | | Preferred Stock | | | | Common Stock | | | | Subscription Payable | | Additional Paid-in Capital | | Accumulated Deficit | | Noncontrolling Interest | | Total Stockholders' Equity |
| | | Shares | | Amount | | Shares | | Amount | | Amount | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, December 31, 2017 | | | 49,900 | | | $ | 50 | | | | 138,993,087 | | | $ | 138,992 | | | $ | 152,796 | | | $ | 12,811,671 | | | $ | (44,672,209 | ) | | $ | (833,710 | ) | | $ | (32,402,410 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Imputed interest | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7,500 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7,500 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common stock issued for debt conversion and interest | | | — | | | | — | | | | 416,632 | | | | 417 | | | | — | | | | 12,082 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 12,499 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Imputed interest | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 57,450 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 57,450 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment on subscriptions payable | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 50 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 50 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (11,250,728 | ) | | | (74,554 | ) | | | (11,176,174 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, June 30, 2018 | | | 49,900 | | | $ | 50 | | | | 139,409,719 | | | $ | 139,409 | | | $ | 152,846 | | | $ | 12,888,703 | | | $ | (33,421,481 | ) | | $ | (908,264 | ) | | $ | (21,148,737 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | | | 49,900 | | | $ | 50 | | | | 165,812,128 | | | $ | 165,812 | | | $ | 397,209 | | | $ | 17,100,137 | | | $ | (39,924,912 | ) | | $ | (1,043,517 | ) | | $ | (23,305,222 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Imputed interest | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 33,749 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 33,750 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss on debt extinguishment | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 25,000 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 25,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common stock issued for debt conversion and interest | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7,785,952 | | | | 7,786 | | | | (233,579 | ) | | | 225,793 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 8,113,272 | | | | (168,608 | ) | | | 7,944,664 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, June 30, 2019 | | | 49,900 | | | $ | 50 | | | | 173,598,080 | | | $ | 173,598 | | | $ | 163,630 | | | $ | 17,384,679 | | | $ | (31,811,640 | ) | | $ | (1,212,125 | ) | | $ | (15,301,808 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 1 – ORGANIZATION AND NATURE OF THE BUSINESS
Organization
Kaya Holdings, Inc. FKA (Alternative Fuels Americas, Inc.) is a holding company. The Company was incorporated in 1993 and has engaged in a number of businesses. Its name was changed on May 11, 2007 to NetSpace International Holdings, Inc. (a Delaware corporation) (“NetSpace”). NetSpace acquired 100% of Alternative Fuels Americas, Inc. (a Florida corporation) in January 2010 in a stock-for-member interest transaction and issued 6,567,247 shares of common stock and 100,000 shares of Series C convertible preferred stock to existing shareholders. Certificate of Amendment to the Certificate of Incorporation was filed in October 2010 changing the Company’s name from NetSpace International Holdings, Inc. to Alternative Fuels Americas, Inc. (a Delaware corporation). Certificate of Amendment to the Certificate of Incorporation was filed in March 2015 changing the Company’s name from Alternative Fuels Americas, Inc. (a Delaware corporation) to Kaya Holdings, Inc.
The Company has three subsidiaries, Alternative Fuels Americas, Inc, a Florida corporation, which is wholly-owned, Marijuana Holdings Americas, Inc., a Florida corporation (“MJAI”), which is majority-owned and 34225 Kowitz Road, LLC, a wholly-owned Oregon limited liability company which holds the Company’s recently acquired 26 acre property in Lebanon, Oregon on which it plans to develop a legal cannabis cultivation and manufacturing facility. MJAI develops and operates the Company’s legal cannabis retail operations in Oregon through controlling ownership interests in five Oregon limited liability companies: MJAI Oregon 1 LLC, MJAI Oregon 2 LLC, MJAI Oregon 3 LLC, MJAI Oregon 4 LLC and MJAI Oregon 5 LLC (Inactive).
Nature of the Business
In January 2014, KAYS incorporated MJAI, a wholly-owned subsidiary, to focus on opportunities in the legal recreational and medical marijuana in the United States. MJAI has concentrated its efforts in Oregon, where through controlled Oregon limited liability companies, it initially secured licenses to operate a medical marijuana dispensary (an “MMD”) and following legalization of recreational cannabis use in Oregon, has secured licenses to operate four retail outlets and purchased 26 acres for development as a legal cannabis cultivation and manufacturing facility. The Company has developed the Kaya Shack™ brand for its retail operations.
On July 3, 2014 opened its first Kaya Shack™ MMD in Portland, Oregon. In April 2015, KAYS commenced its own medical marijuana grow operations for the cultivation and harvesting of legal marijuana thereby becoming the first publicly traded U.S. company to own a majority interest in a vertically integrated legal marijuana enterprise in the United States. In October 2015, concurrent with Oregon commencing legal sales of recreational marijuana through MMDs, KAYS opened its second retail outlet in Salem, Oregon, the Kaya Shack™ Marijuana Superstore. During 2015, the Company also consolidated its grow operations and manufacturing operations into a single facility in Portland, Oregon.
In 2016, Oregon began the process to transition legal marijuana sales from Oregon Health Authority (“OHA”) licensed MMDs and grow operations to Oregon Liquor Control Commission (“OLCC”) licensed recreational marijuana retailers and producer and processing facilities. Effective January 1, 2017, all retailers of recreational marijuana were required to have a recreational marijuana sales license issued by the OLLC for each retail outlet operated.
In 2016 the Company applied for OLLC licenses for its two initial Kaya Shack™ retail outlets (Portland, Oregon and South Salem, Oregon), and also submitted license applications for its two new locations under construction and development at that time.
In late December 2016, we received our OLCC recreational license for the South Salem Kaya Shack™ Marijuana Superstore (Kaya Shack™ OLCC Marijuana Retailer License #1) and recreational and medical sales continued without interruption from 2016 through the present at that location.
On March 21, 2017, we received our North Salem Kaya Shack™ outlet (Kaya Shack™ OLCC Marijuana Retailer License #2) a 2,600-square foot Kaya Shack™ Marijuana Superstore in North Salem, Oregon, whereupon the location opened for business with both recreational and medical sales.
On May 2, 2017, we received our OLCC recreational license for our Portland Kaya Shack™ outlet (Kaya Shack™ OLCC Marijuana Retailer License #3) after a delay of approximately four months. During that period, we were limited to solely medical sales at the Portland location. Upon receipt of Kaya Shack™ OLCC Marijuana Retailer License #3, recreational sales recommenced at that location. Our OLCC License for the Central Salem Kaya Shack™ Marijuana Superstore (Kaya Shack™ OLCC Marijuana Retailer License #4) has been filed and is pending completion, inspection and final licensing.
During August of 2017, we purchased 26 acres in Lebanon, Oregon, for development as a legal cannabis cultivation and manufacturing facility. The company is in the process of planning and permitting.
On February 15, 2018, we received our OLCC recreational, medical and home delivery license for the Central Salem Kaya ShackTMoutlet (Kaya ShackTM OLCC Marijuana Retailer License #4) a 3,100-square foot Kaya ShackTM Marijuana Superstore in Central Salem, Oregon. After various construction and permitting delays, On April 12, 2018, the location opened for business with both recreational and medical sales.
On August 18, 2018, the Company had concluded the purchase of the Eugene, Oregon based Sunstone Farms manufacturing facility, which is licensed by the OLCC for both the production of medical and recreational marijuana flower and the processing of cannabis concentrates/extracts/edibles. The purchase includes a 12,000 square foot building housing and indoor grow facility, as well as equipment for growing and extraction activity. The facility can produce in excess of 800 pounds cannabis flower annually as currently outfitted.
As part of planned expansion and renovations for the facility, the Company has begun the site improvements and is ramping up production to feed the existing four OLCC licensed cannabis retail stores in Oregon.
NOTE 2 – LIQUIDITY AND GOING CONCERN
The Company’s consolidated financial statements as of June 30, 2019 have been prepared on a going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and the settlement of liabilities and commitments in the normal course of business. The Company incurred a net income of $8,113,272 for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and a net income of $11,250,728 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. The decrease in net income is due to the changes in derivative liabilities and the company continues to have operating losses. At June 30, 2019 the Company has a working capital deficiency of $12,420,119 and is totally dependent on its ability to raise capital. The Company has a plan of operations and acknowledges that its plans of operations may not result in generating positive working capital in the near future. Even though management believes that it will be able to successfully execute its business plan, which includes third-party financing and capital issuance, and meet the Company’s future liquidity needs, there can be no assurances in that regard. These matters raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this material uncertainty. Management recognizes that the Company must generate additional funds to successfully develop its operations and activities. Management plans include:
| • | | the sale of additional equity and debt securities, |
| • | | alliances and/or partnerships with entities interested in and having the resources to support the further development of the Company’s business plan, |
| • | | business transactions to assure continuation of the Company’s development and operations, |
| • | | development of a unified brand and the pursuit of licenses to operate recreational and medical marijuana facilities under the branded name. |
NOTE 3 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (U.S. GAAP) under the accrual basis of accounting.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes.
Such estimates and assumptions impact both assets and liabilities, including but not limited to: net realizable value of accounts receivable and inventory, estimated useful lives and potential impairment of property and equipment, the valuation of intangible assets, estimate of fair value of share based payments and derivative liabilities, estimates of fair value of warrants issued and recorded as debt discount, estimates of tax liabilities and estimates of the probability and potential magnitude of contingent liabilities.
Making estimates requires management to exercise significant judgment. It is at least reasonably possible that the estimate of the effect of a condition, situation or set of circumstances that existed at the date of the financial statements, which management considered in formulating its estimate could change in the near term due to one or more future non-conforming events. Accordingly, actual results could differ significantly from estimates.
Risks and Uncertainties
The Company’s operations are subject to risk and uncertainties including financial, operational, regulatory and other risks including the potential risk of business failure.
The Company has experienced, and in the future expects to continue to experience, variability in its sales and earnings. The factors expected to contribute to this variability include, among others, (i) the uncertainty associated with the commercialization and ultimate success of the product, (ii) competition inherent at other locations where product is expected to be sold (iii) general economic conditions and (iv) the related volatility of prices pertaining to the cost of sales.
Fiscal Year
The Company’s fiscal year-end is December 31.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Kaya Holdings, Inc. and all wholly and majority-owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany balances have been eliminated.
Wholly-owned subsidiaries:
| | · | Alternative Fuels Americas, Inc. (a Florida corporation) |
| | · | 34225 Kowitz Road, LLC (an Oregon LLC) |
Majority-owned subsidiaries:
| | · | Marijuana Holdings Americas, Inc. (a Florida corporation) |
Non-Controlling Interest
The company owns 55% of Marijuana Holdings Americas, Inc.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are carried at cost and represent cash on hand, demand deposits placed with banks or other financial institutions and all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less. The Company had no cash equivalents.
Inventory
Inventory consists of finished goods purchased, which are valued at the lower of cost or market value, with cost being determined on the first-in, first-out method. The Company periodically reviews historical sales activity to determine potentially obsolete items and also evaluates the impact of any anticipated changes in future demand. Total Value of Finished goods inventory as of June 30, 2019 is $123,954 and $131,542 as of December 31, 2018. No allowance as necessary as of June 30, 2019 and December 31, 2018.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation and is reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
Depreciation of property and equipment is provided utilizing the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives, ranging from 5-30 years of the respective assets. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred.
Upon sale or retirement of property and equipment, the related cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and any gain or loss is reflected in the statements of operations.
Long-lived assets
The Company reviews long-lived assets and certain identifiable intangibles held and used for possible impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. In evaluating the fair value and future benefits of its intangible assets, management performs an analysis of the anticipated undiscounted future net cash flow of the individual assets over the remaining amortization period. The Company recognizes an impairment loss if the carrying value of the asset exceeds the expected future cash flows.
Operating Leases
We lease our retail stores under non-cancellable operating leases. Most store leases include tenant allowances from landlords, rent escalation clauses and/or contingent rent provisions. We recognize rent expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term, excluding contingent rent, and record the difference between the amount charged to expense and the rent paid as a deferred rent liability.
Deferred Rent and Tenant Allowances
Deferred rent is recognized when a lease contains fixed rent escalations. We recognize the related rent expense on a straight-line basis starting from the date of possession and record the difference between the recognized rental expense and cash rent payable as deferred rent. Deferred rent also includes tenant allowances received from landlords in accordance with negotiated lease terms. The tenant allowances are amortized as a reduction to rent expense on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease starting at the date of possession.
Earnings Per Share
In accordance with ASC 260, Earnings per Share, the Company calculates basic earnings per share by dividing net income (loss) by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share are computed if the Company has net income; otherwise it would be anti-dilutive, and would result from the conversion of a convertible note.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with ASC 740, Accounting for Income Taxes, as clarified by ASC 740-10, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes. Under this method, deferred income taxes are determined based on the estimated future tax effects of differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities given the provisions of enacted tax laws. Deferred income tax provisions and benefits are based on changes to the assets or liabilities from year to year. In providing for deferred taxes, the Company considers tax regulations of the jurisdictions in which the Company operates, estimates of future taxable income, and available tax planning strategies. If tax regulations, operating results or the ability to implement tax-planning strategies vary, adjustments to the carrying value of deferred tax assets and liabilities may be required. Valuation allowances are recorded related to deferred tax assets based on the “more likely than not” criteria of ASC 740.
ASC 740-10 requires that the Company recognize the financial statement benefit of a tax position only after determining that the relevant tax authority would more likely than not sustain the position following an audit. For tax positions meeting the “more-likely-than-not” threshold, the amount recognized in the financial statements is the largest benefit that has a greater than 50 percent likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement with the relevant tax authority.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company measures assets and liabilities at fair value based on an expected exit price as defined by the authoritative guidance on fair value measurements, which represents the amount that would be received on the sale of an asset or paid to transfer a liability, as the case may be, in an orderly transaction between market participants. As such, fair value may be based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. The authoritative guidance on fair value measurements establishes a consistent framework for measuring fair value on either a recurring or nonrecurring basis whereby inputs, used in valuation techniques, are assigned a hierarchical level.
The following are the hierarchical levels of inputs to measure fair value:
| • | | Level 1 – Observable inputs that reflect quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| • | | Level 2 - Inputs reflect quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in markets that are not active; quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the assets or liabilities; or inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means. |
| • | | Level 3 – Unobservable inputs reflecting the Company’s assumptions incorporated in valuation techniques used to determine fair value. These assumptions are required to be consistent with market participant assumptions that are reasonably available. |
| | Fair Value Measurements at June 30, 2019 |
| | | Level 1 | | | | Level 2 | | | | Level 3 | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash | $ | 120,083 | | | $ | | | | $ | | |
| Total assets | | 120,083 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Convertible debentures, net of discounts of $917,478 | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,391,635 | |
| Short term debt, net of discounts of $-0- | | - | | | | 259,312 | | | | - | |
| Derivative liability | | - | | | | - | | | | 10,644,017 | |
| Total liabilities | | - | | | | 259,312 | | | | 16,035,652 | |
| | $ | 120,083 | | | $ | (259,312) | | | $ | (16,035,652) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2018 |
| | | Level 1 | | | | Level 2 | | | | Level 3 | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash | $ | 111,512 | | | $ | | | | $ | | |
| Total assets | | 111,512 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Convertible debentures, net of discounts of $1,191,264 | | - | | | | - | | | | 4,677,851 | |
| Short term debt, net of discounts of $-0- | | - | | | | 259,312 | | | | - | |
| Derivative liability | | - | | | | - | | | | 19,783,034 | |
| Total liabilities | | - | | | | 259,312 | | | | 24,460,885 | |
| | $ | 111,512 | | | $ | (259,312) | | | $ | (24,460,885) | |
The carrying amounts of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities, such as cash, prepaid expenses, other current assets, accounts payable & accrued expenses, certain notes payable and notes payable – related party, approximate their fair values because of the short maturity of these instruments.
The Company accounts for its derivative liabilities, at fair value, on a recurring basis under level 3. See Note 7.
Embedded Conversion Features
The Company evaluates embedded conversion features within convertible debt under ASC 815 “Derivatives and Hedging” to determine whether the embedded conversion feature(s) should be bifurcated from the host instrument and accounted for as a derivative at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in earnings. If the conversion feature does not require derivative treatment under ASC 815, the instrument is evaluated under ASC 470-20 “Debt with Conversion and Other Options” for consideration of any beneficial conversion feature.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company does not use derivative instruments to hedge exposures to cash flow, market, or foreign currency risks. The Company evaluates all of it financial instruments, including stock purchase warrants, to determine if such instruments are derivatives or contain features that qualify as embedded derivatives.
For derivative financial instruments that are accounted for as liabilities, the derivative instrument is initially recorded at its fair value and is then re-valued at each reporting date, with changes in the fair value reported as charges or credits to income. For option-based simple derivative financial instruments, the Company uses the Binomial option-pricing model to value the derivative instruments at inception and subsequent valuation dates. The classification of derivative instruments, including whether such instruments should be recorded as liabilities or as equity, is re-assessed at the end of each reporting period.
In July 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-11Earnings Per Share (Topic 260); Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (Topic 480); Derivative and Hedging (Topic 815). The amendments in Part I of this Update change the classification analysis of certain equity-linked financial instruments (or embedded features) with down round features. When determining whether certain financial instruments should be classified as liabilities or equity instruments, a down round feature no longer precludes equity classification when assessing whether the instrument is indexed to an entity’s own stock. The amendment also clarify existing disclosure requirements for equity-classified instruments. As a result, a freestanding equity-linked financial instrument (or embedded conversion option) no longer would be accounted for as a derivative liability at fair value as a result of the existence of a down round feature. For freestanding equity classified financial instruments, the amendments require entities that present earnings per share (“EPS”) in accordance with Topic 260 to recognize the effect of the down round feature when it is triggered. That effect is treated as a dividend and as a reduction of income available to common shareholders in basic EPS. Convertible instruments with embedded conversion options that have down round features are now subject to the specialized guidance for contingent beneficial conversion features (in Subtopic 470-20, Debt-Debt with Conversion and Other Options), including related EPS guidance (in Topic 260). The amendments in Part II of this Update recharacterize the indefinite deferral of certain provisions of Topic 480 that now are presented as pending content in the Codification, to a scope exception. Those amendments do not have an accounting effect.
Prior to this Update, an equity-linked financial instrument with a down round feature that otherwise is not required to be classified as a liability under the guidance in Topic 480 is evaluated under the guidance in Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging, to determine whether it meets the definition of a derivative. If it meets that definition, the instrument (or embedded feature) is evaluated to determine whether it is indexed to an entity’s own stock as part of the analysis of whether it qualifies for a scope exception from derivative accounting. Generally, for warrants and conversion options embedded in financial instruments that are deemed to have a debt host (assuming the underlying shares are readily convertible to cash or the contract provides for net settlement such that the embedded conversion option meets the definition of a derivative), the existence of a down round feature results in an instrument not being considered indexed to an entity’s own stock. This results in a reporting entity being required to classify the freestanding financial instrument or the bifurcated conversion option as a liability, which the entity must measure at fair value initially and at each subsequent reporting date.
The amendments in this Update revise the guidance for instruments with down round features in Subtopic 815-40, Derivatives and Hedging—Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity, which is considered in determining whether an equity-linked financial instrument qualifies for a scope exception from derivative accounting. An entity still is required to determine whether instruments would be classified in equity under the guidance in Subtopic 815-40 in determining whether they qualify for that scope exception. If they do qualify, freestanding instruments with down round features are no longer classified as liabilities and embedded conversion options with down round features are no longer bifurcated.
For entities that present EPS in accordance with Topic 260, and when the down round feature is included in an equity-classified freestanding financial instrument, the value of the effect of the down round feature is treated as a dividend when it is triggered and as a numerator adjustment in the basic EPS calculation. This reflects the occurrence of an economic transfer of value to the holder of the instrument, while alleviating the complexity and income statement volatility associated with fair value measurement on an ongoing basis. Convertible instruments are unaffected by the Topic 260 amendments in this Update.
The amendments in Part 1 of this Update are a cost savings relative to former accounting. This is because, assuming the required criteria for equity classification in Subtopic 815-40 are met, an entity that issued such an instrument no longer measures the instrument at fair value at each reporting period (in the case of warrants) or separately accounts for a bifurcated derivative (in the case of convertible instruments) on the basis of the existence of a down round feature. For convertible instruments with embedded conversion options that have down round features, applying specialized guidance such as the model for contingent beneficial conversion features rather than bifurcating an embedded derivative also reduces cost and complexity. Under that specialized guidance, the issuer recognizes the intrinsic value of the feature only when the feature becomes beneficial instead of bifurcating the conversion option and measuring it at fair value each reporting period.
The amendments in Part II of this Update replace the indefinite deferral of certain guidance in Topic 480 with a scope exception. This has the benefit of improving the readability of the Codification and reducing the complexity associated with navigating the guidance in Topic 480.
The Company adopted this new standard on January 1, 2019; however, the Company needs to continue the derivative liabilities due to variable conversion price on some of the convertible instruments. As such, it did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Beneficial Conversion Feature
For conventional convertible debt where the rate of conversion is below market value, the Company records a "beneficial conversion feature" ("BCF") and related debt discount.
When the Company records a BCF, the relative fair value of the BCF is recorded as a debt discount against the face amount of the respective debt instrument (offset to additional paid in capital) and amortized to interest expense over the life of the debt.
Debt Issue Costs and Debt Discount
The Company may record debt issue costs and/or debt discounts in connection with raising funds through the issuance of debt. These costs may be paid in the form of cash, or equity (such as warrants). These costs are amortized to interest expense over the life of the debt. If a conversion of the underlying debt occurs, a proportionate share of the unamortized amounts is immediately expensed.
Original Issue Discount
For certain convertible debt issued, the Company may provide the debt holder with an original issue discount. The original issue discount would be recorded to debt discount, reducing the face amount of the note and is amortized to interest expense over the life of the debt.
Extinguishments of Liabilities
The Company accounts for extinguishments of liabilities in accordance with ASC 860-10 (formerly SFAS 140) “Accounting for Transfers and Servicing of Financial Assets and Extinguishment of Liabilities”. When the conditions are met for extinguishment accounting, the liabilities are derecognized and the gain or loss on the sale is recognized.
Stock-Based Compensation - Employees
The Company accounts for its stock-based compensation in which the Company obtains employee services in share-based payment transactions under the recognition and measurement principles of the fair value recognition provisions of section 718-10-30 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification. Pursuant to paragraph 718-10-30-6 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification, all transactions in which goods or services are the consideration received for the issuance of equity instruments are accounted for based on the fair value of the consideration received or the fair value of the equity instrument issued, whichever is more reliably measurable.
The measurement date used to determine the fair value of the equity instrument issued is the earlier of the date on which the performance is complete or the date on which it is probable that performance will occur.
If the Company is a newly formed corporation or shares of the Company are thinly traded, the use of share prices established in the Company’s most recent private placement memorandum (based on sales to third parties) (“PPM”), or weekly or monthly price observations would generally be more appropriate than the use of daily price observations as such shares could be artificially inflated due to a larger spread between the bid and asked quotes and lack of consistent trading in the market.
The fair value of share options and similar instruments is estimated on the date of grant using a Binomial Option Model option-pricing valuation model. The ranges of assumptions for inputs are as follows:
| • | | Expected term of share options and similar instruments: The expected life of options and similar instruments represents the period of time the option and/or warrant are expected to be outstanding. Pursuant to Paragraph 718-10-50-2(f)(2)(i) of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification the expected term of share options and similar instruments represents the period of time the options and similar instruments are expected to be outstanding taking into consideration of the contractual term of the instruments and employees’ expected exercise and post-vesting employment termination behavior into the fair value (or calculated value) of the instruments. Pursuant to paragraph 718-10-S99-1, it may be appropriate to use the simplified method, i.e., expected term = ((vesting term + original contractual term) / 2), if (i) A company does not have sufficient historical exercise data to provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate expected term due to the limited period of time its equity shares have been publicly traded; (ii) A company significantly changes the terms of its share option grants or the types of employees that receive share option grants such that its historical exercise data may no longer provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate expected term; or (iii) A company has or expects to have significant structural changes in its business such that its historical exercise data may no longer provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate expected term. The Company uses the simplified method to calculate expected term of share options and similar instruments as the company does not have sufficient historical exercise data to provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate expected term. |
| • | | Expected volatility of the entity’s shares and the method used to estimate it. Pursuant to ASC Paragraph 718-10-50-2(f)(2)(ii) a thinly-traded or nonpublic entity that uses the calculated value method shall disclose the reasons why it is not practicable for the Company to estimate the expected volatility of its share price, the appropriate industry sector index that it has selected, the reasons for selecting that particular index, and how it has calculated historical volatility using that index. The Company uses the average historical volatility of the comparable companies over the expected contractual life of the share options or similar instruments as its expected volatility. If shares of a company are thinly traded the use of weekly or monthly price observations would generally be more appropriate than the use of daily price observations as the volatility calculation using daily observations for such shares could be artificially inflated due to a larger spread between the bid and asked quotes and lack of consistent trading in the market. |
| • | | Expected annual rate of quarterly dividends. An entity that uses a method that employs different dividend rates during the contractual term shall disclose the range of expected dividends used and the weighted-average expected dividends. The expected dividend yield is based on the Company’s current dividend yield as the best estimate of projected dividend yield for periods within the expected term of the share options and similar instruments. |
| • | | Risk-free rate(s). An entity that uses a method that employs different risk-free rates shall disclose the range of risk-free rates used. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for periods within the expected term of the share options and similar instruments. |
Generally, all forms of share-based payments, including stock option grants, warrants and restricted stock grants and stock appreciation rights are measured at their fair value on the awards’ grant date, based on estimated number of awards that are ultimately expected to vest.
The expense resulting from share-based payments is recorded in general and administrative expense in the statements of operations.
Stock-Based Compensation – Non Employees
Equity Instruments Issued to Parties Other Than Employees for Acquiring Goods or Services
The Company accounts for equity instruments issued to parties other than employees for acquiring goods or services under guidance of Sub-topic 505-50 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification (“Sub-topic 505-50”).
Pursuant to ASC Section 505-50-30, all transactions in which goods or services are the consideration received for the issuance of equity instruments are accounted for based on the fair value of the consideration received or the fair value of the equity instrument issued, whichever is more reliably measurable. The measurement date used to determine the fair value of the equity instrument issued is the earlier of the date on which the performance is complete or the date on which it is probable that performance will occur. If the Company is a newly formed corporation or shares of the Company are thinly traded the use of share prices established in the Company’s most recent private placement memorandum (“PPM”), or weekly or monthly price observations would generally be more appropriate than the use of daily price observations as such shares could be artificially inflated due to a larger spread between the bid and asked quotes and lack of consistent trading in the market.
The fair value of share options and similar instruments is estimated on the date of grant using a Binomial option-pricing valuation model. The ranges of assumptions for inputs are as follows:
| • | | Expected term of share options and similar instruments: Pursuant to Paragraph 718-10-50-2(f)(2)(i) of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification the expected term of share options and similar instruments represents the period of time the options and similar instruments are expected to be outstanding taking into consideration of the contractual term of the instruments and holder’s expected exercise behavior into the fair value (or calculated value) of the instruments. The Company uses historical data to estimate holder’s expected exercise behavior. If the Company is a newly formed corporation or shares of the Company are thinly traded the contractual term of the share options and similar instruments is used as the expected term of share options and similar instruments as the Company does not have sufficient historical exercise data to provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate expected term. |
| • | | Expected volatility of the entity’s shares and the method used to estimate it. Pursuant to ASC Paragraph 718-10-50-2(f)(2)(ii) a thinly-traded or nonpublic entity that uses the calculated value method shall disclose the reasons why it is not practicable for the Company to estimate the expected volatility of its share price, the appropriate industry sector index that it has selected, the reasons for selecting that particular index, and how it has calculated historical volatility using that index. The Company uses the average historical volatility of the comparable companies over the expected contractual life of the share options or similar instruments as its expected volatility. If shares of a company are thinly traded the use of weekly or monthly price observations would generally be more appropriate than the use of daily price observations as the volatility calculation using daily observations for such shares could be artificially inflated due to a larger spread between the bid and asked quotes and lack of consistent trading in the market. |
| • | | Expected annual rate of quarterly dividends. An entity that uses a method that employs different dividend rates during the contractual term shall disclose the range of expected dividends used and the weighted-average expected dividends. The expected dividend yield is based on the Company’s current dividend yield as the best estimate of projected dividend yield for periods within the expected term of the share options and similar instruments. |
| • | | Risk-free rate(s). An entity that uses a method that employs different risk-free rates shall disclose the range of risk-free rates used. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for periods within the expected term of the share options and similar instruments. |
Pursuant to ASC paragraph 505-50-25-7, if fully vested, non-forfeitable equity instruments are issued at the date the grantor and grantee enter into an agreement for goods or services (no specific performance is required by the grantee to retain those equity instruments), then, because of the elimination of any obligation on the part of the counterparty to earn the equity instruments, a measurement date has been reached. A grantor shall recognize the equity instruments when they are issued (in most cases, when the agreement is entered into). Whether the corresponding cost is an immediate expense or a prepaid asset (or whether the debit should be characterized as contra-equity under the requirements of paragraph 505-50-45-1) depends on the specific facts and circumstances.
Pursuant to ASC paragraph 505-50-45-1, a grantor may conclude that an asset (other than a note or a receivable) has been received in return for fully vested, non-forfeitable equity instruments that are issued at the date the grantor and grantee enter into an agreement for goods or services (and no specific performance is required by the grantee in order to retain those equity instruments). Such an asset shall not be displayed as contra-equity by the grantor of the equity instruments. The transferability (or lack thereof) of the equity instruments shall not affect the balance sheet display of the asset. This guidance is limited to transactions in which equity instruments are transferred to other than employees in exchange for goods or services. Section 505-50-30 provides guidance on the determination of the measurement date for transactions that are within the scope of this Subtopic.
Pursuant to Paragraphs 505-50-25-8 and 505-50-25-9, an entity may grant fully vested, non-forfeitable equity instruments that are exercisable by the grantee only after a specified period of time if the terms of the agreement provide for earlier exercisability if the grantee achieves specified performance conditions. Any measured cost of the transaction shall be recognized in the same period(s) and in the same manner as if the entity had paid cash for the goods or services or used cash rebates as a sales discount instead of paying with, or using, the equity instruments. A recognized asset, expense, or sales discount shall not be reversed if a share option and similar instrument that the counterparty has the right to exercise expires unexercised.
Pursuant to ASC paragraph 505-50-30-S99-1, if the Company receives a right to receive future services in exchange for unvested, forfeitable equity instruments, those equity instruments are treated as unissued for accounting purposes until the future services are received (that is, the instruments are not considered issued until they vest). Consequently, there would be no recognition at the measurement date and no entry should be recorded.
Revenue Recognition
Effective January 1, 2018, the Company adopted ASC 606 – Revenue from Contracts with Customers. Under ASC 606, the Company recognizes revenue from the commercial sales of products, licensing agreements and contracts to perform pilot studies by applying the following steps: (1) identifying the contract with a customer; (2) identify the performance obligations in the contract; (3) determine the transaction price; (4) allocate the transaction price to each performance obligation in the contract; and (5) recognize revenue when each performance obligation is satisfied. For the comparative periods, revenue has not been adjusted and continues to be reported under ASC 605 – Revenue Recognition. Under ASC 605, revenue is recognized when the following criteria are met: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) the performance of service has been rendered to a customer or delivery has occurred; (3) the amount of fee to be paid by a customer is fixed and determinable; and (4) the collectability of the fee is reasonably assured.
To confirm, all of our OLCC licensed cannabis retail sales operations are conducted and operated on a “cash and carry” basis- product(s) from our inventory accounts are sold to the customer(s) and the customer settles the account at time of receipt of product via cash payment at our retail store; the transaction is recorded at the time of sale in our point of sale software system. Revenue is only reported after product has been delivered to the customer and the customer has paid for the product with cash.
To date the only other revenue we have received is for ATM transactions and revenue from this activity is only reported after we receive payment via check from the ATM service provider company.
Cost of Sales
Cost of sales represents costs directly related to the purchase of goods and third party testing of the Company’s products.
Related Parties
The Company follows subtopic 850-10 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification for the identification of related parties and disclosure of related party transactions.
Pursuant to Section 850-10-20 the related parties include a. affiliates of the Company; b. Entities for which investments in their equity securities would be required, absent the election of the fair value option under the Fair Value Option Subsection of Section 825–10–15, to be accounted for by the equity method by the investing entity; c. trusts for the benefit of employees, such as pension and profit-sharing trusts that are managed by or under the trusteeship of management; d. principal owners of the Company; e. management of the Company; f. other parties with which the Company may deal if one party controls or can significantly influence the management or operating policies of the other to an extent that one of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests; and g. Other parties that can significantly influence the management or operating policies of the transacting parties or that have an ownership interest in one of the transacting parties and can significantly influence the other to an extent that one or more of the transacting parties might be prevented from fully pursuing its own separate interests.
The consolidated financial statements shall include disclosures of material related party transactions, other than compensation arrangements, expense allowances, and other similar items in the ordinary course of business. However, disclosure of transactions that are eliminated in the preparation of consolidated or combined financial statements is not required in those statements.
The disclosures shall include: a. the nature of the relationship(s) involved; b. a description of the transactions, including transactions to which no amounts or nominal amounts were ascribed, for each of the periods for which income statements are presented, and such other information deemed necessary to an understanding of the effects of the transactions on the financial statements; c. the dollar amounts of transactions for each of the periods for which income statements are presented and the effects of any change in the method of establishing the terms from that used in the preceding period; and d. amounts due from or to related parties as of the date of each balance sheet presented and, if not otherwise apparent, the terms and manner of settlement.
Contingencies
The Company follows subtopic 450-20 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification to report accounting for contingencies. Certain conditions may exist as of the date the consolidated financial statements are issued, which may result in a loss to the Company but which will only be resolved when one or more future events occur or fail to occur. The Company assesses such contingent liabilities, and such assessment inherently involves an exercise of judgment. In assessing loss contingencies related to legal proceedings that are pending against the Company or unasserted claims that may result in such proceedings, the Company evaluates the perceived merits of any legal proceedings or unasserted claims as well as the perceived merits of the amount of relief sought or expected to be sought therein.
If the assessment of a contingency indicates that it is probable that a material loss has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be estimated, then the estimated liability would be accrued in the Company’s financial statements. If the assessment indicates that a potentially material loss contingency is not probable but is reasonably possible, or is probable but cannot be estimated, then the nature of the contingent liability, and an estimate of the range of possible losses, if determinable and material, would be disclosed.
Loss contingencies considered remote are generally not disclosed unless they involve guarantees, in which case the guarantees would be disclosed. However, there is no assurance that such matters will not materially and adversely affect the Company’s business, consolidated financial position, and consolidated results of operations or consolidated cash flows.
Uncertain Tax Positions
The Company did not take any uncertain tax positions and had no adjustments to its income tax liabilities or benefits pursuant to the provisions of Section 740-10-25 for the reporting period ended June 30, 2019.
Subsequent Events
The Company follows the guidance in Section 855-10-50 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification for the disclosure of subsequent events. The Company will evaluate subsequent events through the date when the financial statements are issued.
Pursuant to ASU 2010-09 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification, the Company as an SEC filer considers its financial statements issued when they are widely distributed to users, such as through filing them on EDGAR.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the FASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by the Company as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, the Company believes that the effect of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material effect on its consolidated financial position or results of operations upon adoption.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02,Leases (Topic 842) (ASU 2016-02).Under ASU No. 2016-2, an entity is required to recognize right-of-use assets and lease liabilities on its balance sheet and disclose key information about leasing arrangements. ASU No. 2016-02 offers specific accounting guidance for a lessee, a lessor and sale and leaseback transactions. Lessees and lessors are required to disclose qualitative and quantitative information about leasing arrangements to enable a user of the financial statements to assess the amount, timing and uncertainty of cash flows arising from leases. For public companies, the Company adopted this standard on January 1, 2019 using the modified retrospective method. The new standard provides a number of optional practical expedients in transition. The Company elected the package of practical expedients’, which permitted the Company not to reassess under the new standard its prior conclusions about lease identification, lease classification and initial direct costs; and all of the new standard’s available transition practical expedients.
On adoption, the Company recognized a right of use asset of $638,593, operating lease liabilities of $638,593, based on the present value of the remaining minimum rental payments under current leasing standards for its existing operating lease.
The new standard also provides practical expedients for a company’s ongoing accounting. The Company elected the short-term lease recognition exemption for its leases. For those leases with a lease term of 12 months or less, the Company will not recognize ROU assets or lease liabilities.
In July 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-11,Earnings Per Share (Topic 260); Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (Topic 480); Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): (Part I) Accounting for Certain Financial Instruments with Down Round Features, (Part II) Replacement of the Indefinite Deferral for Mandatorily Redeemable Financial Instruments of Certain Nonpublic Entities and Certain Mandatorily Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests with a Scope Exception” to simply the accounting for certain instruments with down round features. The amendments require companies to disregard the down round feature when assessing whether the instrument is indexed to its own stock, for purposes of determining liability or equity classification. Further, companies that provide earnings per share (“EPS”) data will adjust the basic EPS calculation for the effect of the feature when triggered and will also recognize the effect of the trigger within equity. The standard is effective for public companies for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2018. Early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted this new standard on January 1, 2019 and did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 4 – PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
Property, plant and equipment consisted of the following at June 30, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
| | | June 30, 2019 | | December 31, 2018 |
| (Unaudited) | (Audited) |
| ATM Machine | | $ | 11,000 | | | $ | 11,000 | |
| Computer | | | 22,736 | | | | 22,736 | |
| Furniture & Fixtures | | | 49,408 | | | | 49,408 | |
| HVAC | | | 41,768 | | | | 25,000 | |
| Land | | | 697,420 | | | | 697,420 | |
| Leasehold Improvements | | | 333,529 | | | | 333,529 | |
| Machinery and Equipment | | | 408,133 | | | | 405,233 | |
| Sign | | | 43,594 | | | | 43,594 | |
| Structural | | | 1,017,359 | | | | 1,017,359 | |
| Vehicle | | | 79,744 | | | | 79,744 | |
| Total | | | 2,704,691 | | | | 2,685,023 | |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation | | | (451,833) | | | | (336,243) | |
| Property, Plant and Equipment - net | | $ | 2,252,858 | | | $ | 2,348,780 | |
Depreciation expense totaled of $115,590 and $43,149 for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
NOTE 5 – NON-CURRENT ASSETS
Other assets consisted of the following at June 30, 2019 and December 31, 2018:
| | | June 30, 2019 (Unaudited) | | December 31, 2018 (Audited) |
| Construction Deposits | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Rent Deposits | | | 22,032 | | | | 22,032 | |
| Security Deposits | | $ | 9,491 | | | $ | 9,491 | |
| Non-Current Assets | | $ | 31,523 | | | $ | 31,523 | |
NOTE 6 – CONVERTIBLE DEBT
These debts have a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation are initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts have been amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.05% to 2.63%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 243.37%, trading prices ranging from $0.045 per share to $0.41 per share and a conversion price ranging from $0.03 per share to $0.10 per share. The total derivative liabilities associated with these notes were $10,644,017 at June 30, 2019 and $19,783,034 at December 31, 2018.
See Below Summary Table
| Convertible Debt Summary |
| | Debt Type | Debt Classification | Interest Rate | Due Date | Ending |
| CT | LT | 6.30.19 | 12.31.18 |
| | | | | | | | |
| A | Convertible | X | | 10.0% | 1-Jan-17 | 25,000 | $ 25,000 |
| B | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 65,700 | 65,700 |
| C | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 32,850 | 32,850 |
| D | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 209,047 | 209,047 |
| O | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 109,167 | 109,167 |
| P | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 52,767 | 52,767 |
| Q | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 52,050 | 52,050 |
| S | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 50,400 | 50,400 |
| T | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 250,000 | 250,000 |
| X | Convertible | X | | 8.0% | 1-Jan-19 | 66,800 | 66,800 |
| BB | Convertible | X | | 10.0% | 1-Jan-19 | 50,000 | 50,000 |
| CC | Convertible | X | | 10.0% | 1-Jan-19 | 100,000 | 100,000 |
| EE | Convertible | | X | 0.0% | 31-Dec-21 | 500,000 | 500,000 |
| KK | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 150,000 | 150,000 |
| LL | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 600,000 | 600,000 |
| MM | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 100,000 | 100,000 |
| NN | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 500,000 | 500,000 |
| OO | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 500,000 | 500,000 |
| PP | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 500,000 | 500,000 |
| QQ | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 150,000 | 150,000 |
| RR | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 500,000 | 500,000 |
| SS | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 150,000 | 150,000 |
| TT | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 300,000 | 300,000 |
| UU | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 150,000 | 150,000 |
| VV | Convertible | | X | 5.0% | 31-Jan-20 | 100,333 | 100,333 |
| XX | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 100,000 | 100,000 |
| YY | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 155,000 | 155,000 |
| ZZ | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 150,000 | 150,000 |
| AAA | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 95,000 | 95,000 |
| BBB | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 80,000 | 80,000 |
| CCC | Convertible | X | | 8.0% | 1-Jan-20 | 25,000 | 25,000 |
| DDD | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 70,000 | - |
| EEE | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 150,000 | - |
| FFF | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 15,000 | - |
| GGG | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 75,000 | - |
| HHH | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 35,000 | - |
| III | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 25,000 | - |
| JJJ | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 50,000 | - |
| KKK | Convertible | | X | 8.0% | 1-Jan-21 | 20,000 | - |
| Total Convertible Debt | | | | | 6,309,114 | 5,869,114 |
| Less: Discount | | | | | (917,479) | (1,191,263) |
| Convertible Debt, Net of Discounts | | | | $ 5,391,635 | $ 4,677,851 |
| Convertible Debt, Net of Discounts, Current | | | $ 334,052 | $ 2,894,294 |
| Convertible Debt, Net of Discounts, Long-term | | | $ 5,057,583 | $ 1,783,557 |
FOOTNOTES FOR CONVERTIBLE DEBT SUMMARY TABLE
(A)
At the option of the holder the convertible note may be converted into shares of the Company’s common stock at the lesser of $0.40 or 20% discount to the market price, as defined, of the Company’s common stock. The Company is currently in discussions with the lender on a payment schedule. The outstanding balance of this note is convertible into a variable number of the Company’s common stock. Therefore the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation are initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts have being amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.18% to 2.63%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 243.37%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.45 per share and a conversion price ranging from $0.05 per share to $0.41 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $50,576.
A recap of the balance of outstanding convertible debt at June 30, 2019 is as follows:
| Principal balance | | $ | 25,000 | |
| Accrued interest | | | 25,576 | |
| Balance maturing for the period ending: | | | | |
| June 30, 2019 | | $ | 50,576 | |
The Company valued the derivative liabilities at June 30, 2019 at $23,468. The Company recognized a change in the fair value of derivative liabilities for the six months ended June 30, 2019 of $1,606 which were charged (credited) to operations. In determining the indicated values at June 30, 2019, since the debt is in default, the company used the maximum value these embedded options represent, with a trading price of $0.09, and conversion prices of $0.07 per share.
(B), (C), (D)
All these amended debts have a price adjustment provision. Therefore the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts have been amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.05% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 243.23%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.14 per share and a conversion price ranging from $0.03 per share to $0.04 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $550,015.
(O)
On March 31, 2016 the Company received $100,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 12%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.41% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 157.47%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share and a conversion price of $0.03 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $131,091. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $195,201.
(P)
On July 13, 2016 the Company received $50,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 12%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.41% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 157.47%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share and a conversion price of $0.03 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $63,364. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $94,352.
(Q)
On August 30, 2016 the Company received $50,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 12%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.41% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 154.71%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share a conversion price of $0.03 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $62,503. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $93,071.
(S)
On December 1, 2016 the Company received $50,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 12%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.85% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 154.71%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share and a conversion price of $0.03 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $60,522. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $90,120.
(T)
On December 30, 2016 the Company received $250,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 1.08% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 154.71%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share and a conversion price of $0.03 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $300,320. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $447,192.
(X)
On November 18, 2016 the Company received $60,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 10%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.85% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 154.71%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share and a conversion price of $0.03 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $76,797. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $96,465.
(BB)
On September 23, 2015 the Company received a total of $50,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $50,000 with interest accruing at 10%. The note is convertible after September 23, 2015 and is convertible into the Company’s common stock at a conversion rate of $0.03 per share. The market value of the stock at the date when the debt becomes convertible was $0.078. The debt issued is a result of a financing transaction and contain a beneficial conversion feature. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $57,482. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $72,204.
(CC)
On September 23, 2015 the Company received a total of $100,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $100,000 with interest accruing at 10%. The note is convertible after September 23, 2015 and is convertible into the Company’s common stock at a conversion rate of $0.03 per share. The market value of the stock at the date when the debt becomes convertible was $0.078. The debt issued is a result of a financing transaction and contain a beneficial conversion feature. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $114,965. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $144,409.
(EE)
At December 31, 2013 the Company was indebted to an affiliated shareholder of the Company for $840,955, which consisted of $737,100 principal and $103,895 accrued interest, with interest accruing at 10%. On January 2, 2014 the Company entered into a Debt Modification Agreement whereby the total amount of the debt was reduced to $750,000 and there is no accrued interest or principal due until December 31, 2017. $500,000 of the debt is convertible into 50,000 Series C Convertible Preferred Shares of Kaya Holdings Inc., which if converted are subject to resale restrictions through December 31, 2015. The two-year note in the aggregate amount of $500,000 is convertible into the Company’s preferred stock at a conversion rate of $10.00 per share of preferred. At a conversion rate of 433.9297 common shares to 1 preferred share, this would result in a total of 21,696,485 common shares issued if all debt was converted. The market value of the stock at the date of issuance of the debt was $0.04. The debt issued is a result of a financing transaction and contain a beneficial conversion feature valued at $500,000 to be amortized over the life of the debt. As of June 30, 2019, the debt discount was amortized in full.
On January 1, 2018 the holder of the note extended the due date until December 31, 2021.
As of June 30, 2019, the balance of the debt was $500,000. The remaining $250,000 is not convertible. The company has imputed interest on both the convertible debt and the non-convertible debt. The company used an interest rate of 9% for calculation purposes. The net balance of $250,000 of the non-convertible portion is reflected on the balance sheet.
The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 was $812,519.
(KK)
On January 4, 2017, the Company received $150,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.04 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.85% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 154.71%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share and a conversion price of $0.03 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $180,025. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $268,066.
(LL)
On January 20, 2017, the Company received $600,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8% The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.07 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.85% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 154.71%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.31 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $717,967. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $1,069,091.
(MM)
On January 31, 2017, the Company received $100,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8% The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.07 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.87% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 154.71%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.31 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $119,417. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $177,818.
(NN)
On February 7, 2017, the Company received $500,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8% The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.10 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.87% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 154.71%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.31 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $596,306. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $887,931.
(OO)
On February 21, 2017, the Company received $500,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8% The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.10 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.87% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to154.71%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.30 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest and net of the discount amounted to $594,750. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $885,615.
(PP)
On May 11, 2017, the Company received $500,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8% The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.05 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.87% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 139.70%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $504,321, net of the discount of $81,652. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $872,544.
(QQ)
On July 17, 2017, the Company received $150,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8% The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.05 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.87% to 2.63%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 139.70%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $144,063, net of the discount of $29,395. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $258,289.
(RR)
On November 1, 2017, the Company received $500,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8% The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 1.49% to 2.63%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 138.23%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $446,883, net of the discount of $119,756. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $843,756.
(SS)
On December 21, 2017, the Company received $150,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8% The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 1.49% to 2.63%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 131.81%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.27 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $130,765, net of the discount of $37,560. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $250,645.
(TT)
On February 5, 2018, the Company received $300,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8% The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 1.49% to 2.63%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 132.27%, trading prices ranging from $.05 per share to $0.49 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $266,628, net of the discount of $66,906. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $496,650.
(UU)
On March 23, 2018, the Company received $150,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 1.49% to 2.63%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 132.27%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.14 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $140,062, net of the discount of $25,193. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $246,073.
(VV)
On December 21, 2017 the Company received a total of $80,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $80,000 with interest accruing at 10% per year. The note is due January 1, 2019 with monthly payments of principal and interest. On January 30, 2018, the accredited investor advanced an additional $20,000. The total $100,000 including $333 of unpaid interest was exchanged for a convertible note (Note VV). Interest is stated at 5%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.10 per share. Note is Due in January of 2020. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 1.49% to 2.59%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 132.27%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.14 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $81,392, net of the discount of $26,033. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $140,030.
(XX)
On May 29, 2018, the Company received $100,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 1.82% to 2.63%, volatility from 84.63% to 127.07%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.16 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $86,192, net of the discount of $22,509. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $161,862.
(YY)
On July 18, 2018, the Company received $155,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.48% to 2.81%, volatility from 84.63% to 126.88%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.13 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $116,675, net of the discount of $50,113. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $248,357.
(ZZ)
On August 13, 2018, the Company received $150,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.48% to 2.81%, volatility from 84.63% to 126.90%, trading prices ranging from $0.065 per share to $0.13 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $117,272, net of the discount of $43,281. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $239,072.
(AAA)
On September 24, 2018, the Company received $95,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.83%, volatility from 84.63% to 126.38%, trading price at $0.065 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $79,516, net of the discount of $21,293. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $150,110.
(BBB)
On November 23, 2018, the Company received $80,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. In January 2019, the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.81%, volatility from 84.63% to 118.96%, trading price at $0.065 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $57,305, net of the discount of $26,535. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $124,842.
(CCC)
On December 21, 2018, the Company received $25,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.05 per share. On January 22, 2019, the ratchet provision was activated due to issuance of another convertible note. As such, the conversion price was decreased from $0.05 per share to $0.03 per share. As the change is greater than 10%, the discount of $25,000 was recorded as a loss on extinguishment. the maturity date of the notes had been extended to January 1, 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.63%, volatility from 84.63% to 100.81%, trading price of ranging from $0.065 to $0.11 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $18,999, net of the discount of $7,048. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $33,996.
(DDD)
On January 22, 2019, the Company received $70,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. Note is due in January of 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.59%, volatility from 84.63% to 100.81%, trading price of ranging from $0.065 to $0.11 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $31,854, net of the discount of $40,585. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $107,866.
(EEE)
On February 11, 2019, the Company received $150,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. Note is due in January of 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.48%, volatility from 84.63% to 100.81%, trading price of ranging from $0.065 to $0.11 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $32,468, net of the discount of $122,102. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $230,163.
(FFF)
On March 20, 2019, the Company received $15,000 from the issuance of convertible debt. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. Note is due in January of 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.40%, volatility from 82.70% to 100.81%, trading price of ranging from $0.065 to $0.11 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $2,377, net of the discount of $12,958. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $22,835.
(GGG)
On April 6, 2019 the Company received $75,000 from the issuance of convertible debt to the Cayman Venture Capital Fund pursuant to the May 2017 Financing Agreement, as amended. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. The Note is Due in January of 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.40%, volatility from 82.70% to 100.81%, trading price of ranging from $0.065 to $0.11 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $11,421, net of the discount of $64,976. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $113,760.
(HHH)
On April 22, 2019 the Company received $35,000 from the issuance of convertible debt to the High Net Worth Investor pursuant to the January 2018 Financing Agreement, as amended. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. The Note is Due in January of 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.40%, volatility from 82.70% to 100.81%, trading price of ranging from $0.065 to $0.11 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $4,424, net of the discount of $31,105. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $52,905.
(III)
On May 6, 2019 the Company received $25,000 from the issuance of convertible debt to the High Net Worth Investor pursuant to the January 2018 Financing Agreement, as amended. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. The Note is Due in January of 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.40%, volatility from 82.70% to 100.81%, trading price of ranging from $0.065 to $0.11 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $2,570, net of the discount of $22,731. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $37,675.
(JJJ)
On May 21, 2019 the Company received $50,000 from the issuance of convertible debt to the Cayman Venture Capital Fund pursuant to the January 2018 Financing Agreement, as amended. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. The Note is Due in January of 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.40%, volatility from 82.70% to 100.81%, trading price of ranging from $0.065 to $0.11 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $3,822, net of the discount of $46,616. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $75,105.
(KKK)
On June 5, 2019 the Company received $20,000 from the issuance of convertible debt to the High Net Worth Investor pursuant to the January 2018 Financing Agreement, as amended. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 per share. The Note is Due in January of 2021. This note has a price adjustment provision. Therefore, the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 2.27% to 2.40%, volatility from 82.70% to 100.81%, trading price of ranging from $0.065 to $0.11 per share. The balance of the convertible note at June 30, 2019 including accrued interest amounted to $978, net of the discount of $19,132. The derivative liability associated with this note as of June 30, 2019 were $29,944.
NOTE 7 – NON-CONVERTIBLE DEBT
A-Non Related Party
| | | June 30,
2019 | | December 31, 2018 |
| Note 3 | | | -0- | | | | -0- | |
| Note 4 | | | -0- | | | | -0- | |
| Note 5 | | | 9,312 | | | | 9,312 | |
| Note 6 | | | -0- | | | | -0- | |
| Total Non-Convertible Debt | | | 9,312 | | | | 9,312 | |
(3) On May 17, 2016 the Company received a total of $75,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $75,000 with interest accruing at 10%. The note holder is entitled to subscribe for and purchase from the company 2,371,187 paid and non-assessable shares of the Common Stock at the price of $0.0316297 per share (the “Warrant Exercise Price”) for a period of five (5) years commencing from the earlier of such time as that certain $75,000, 10% promissory note due May 17, 2018 has been fully repaid or the start of the Acceleration Period as defined in “The Note” or May 17, 2018.
(4) On May 9, 2016 the Company received a total of $75,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $75,000 with interest accruing at 10%. The note holder is entitled to subscribe for and purchase from the company 2,371,187 paid and non-assessable shares of the Common Stock at the price of $0.0316297 per share (the “Warrant Exercise Price”) for a period of five (5) years commencing from the earlier of such time as that certain $75,000, 10% promissory note due May 9, 2018 has been fully repaid or the start of the Acceleration Period as defined in “The Note” or May 9, 2018
(5) On September 16, 2016 the Company received a total of $31,661 to be used for equipment in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $31,661 with interest accruing at 18% per year and a 10% loan fee. The note is default as of June 30, 2019.
(6) On December 21, 2017 the Company received a total of $80,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $80,000 with interest accruing at 10% per year The note is due January 1, 2019 with monthly payments of principal and interest. On January 30, 2018 the accredited investor advanced an additional $20,000. The total $100,000 including $333 of unpaid interest was exchanged for a convertible note (Note VV) due January 1, 2020
| Loan payable - Stockholder, 0%, Due December 31, 2021 (1) | | $ | 250,000 | | | $ | 250,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 250,000 | | | $ | 250,000 | |
| (1) | | At December 31, 2013 the Company was indebted to an affiliated shareholder of the Company for $840,955, which consisted of $737,100 principal and $103,895 accrued interest, with interest accruing at 10%. On January 2, 2014 the Company entered into a Debt Modification Agreement whereby the total amount of the debt was reduced to $750,000 and there is no accrued interest or principal due until December 31, 2017. $500,000 of the debt is convertible into 50,000 Series C Convertible Preferred Shares of Kaya Holdings Inc., which if converted are subject to resale restrictions through December 31, 2015. The two-year note in the aggregate amount of $500,000 is convertible into the Company’s preferred stock at a conversion rate of $10.00 per share of preferred. At a conversion rate of 433.9297 common shares to 1 preferred share, this would result in a total of 21,696,485 common shares issued if all debt was converted. The market value of the stock at the date of issuance of the debt was $0.04. The debt issued is a result of a financing transaction and contain a beneficial conversion feature valued at $500,000 to be amortized over the life of the debt. Total amortization for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $201,092. On January 1, 2018 the holder of the note extended the due date until January 1, 2021. As of June 30, 2019, the balance of the debt was $500,000. The remaining $250,000 is not convertible. The company has imputed interest on both the convertible debt and the non-convertible debt. The company used an interest rate of 4% for calculation purposes. The net balance of $250,000 of the non-convertible portion is reflected on the balance sheet. |
Summary Notes Payable Schedule-All Debt
| Balance December 31, 2018 | | $ | 6,128,424 | |
| New Notes Payable | | | 440,000 | |
| Addition due to amendment | | | -0- | |
| Repaid Notes Payable | | | -0- | |
| Conversions | | | -0- | |
| Balance June 30, 2019 | | $ | 6,568,424 | |
NOTE 8 – STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
The Company has 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock authorized with a par value of $0.001, of which 100,000 shares have been designated as Series C convertible preferred stock (“Series C” or “Series C preferred stock”). The Board has the authority to issue the shares in one or more series and to fix the designations, preferences, powers and other rights, as it deems appropriate.
Each share of Series C has 433.9297 votes on any matters submitted to a vote of the stockholders of the Company and is entitled to dividends equal to the dividends of 433.9297 shares of common stock. Each share of Series C preferred stock is convertible at any time at the option of the holder into 433.9297 shares of common stock.
The Company has 500,000,000 shares of common stock authorized with a par value of $0.001. Each share of common stock has one vote per share for the election of directors and all other items submitted to a vote of stockholders. The common stock does not have cumulative voting rights, preemptive, redemption or conversion rights.
In February of 2018 the Company authorized the issuance of 6,200,000 shares of common shares of Kaya Holdings Inc. for employee compensation and consulting fees. The shares were valued at $942,400. As of December 31, 2018, all 6,200,000 shares were issued on July 6, 2018.
In February of 2018, the Company authorized the issuance of 138,866 restricted common shares of Kaya Holdings, Inc. stock to an accredited investor that is a current shareholder of the company. The restricted common shares were issued as payment of interest of $4,166.
In February of 2018, the Company authorized the issuance of 277,766 restricted common shares of Kaya Holdings, Inc. stock to an accredited investor that is a current shareholder of the company. The restricted common shares were issued as payment of interest of $8,333.
In February of 2018, the Company authorized the issuance of 633,288 restricted common shares of Kaya Holdings, Inc. stock to an accredited investor that is a current shareholder of the company. This was a conversion of a Note Payable and Interest with a total value of $28,498, the Note Payable was due January 1, 2019.
In February of 2018, the Company authorized the issuance of 563,566 restricted common shares of Kaya Holdings, Inc. stock to an accredited investor that is a current shareholder of the company. This was a conversion of a Notes Payable and Interest with a total value of $16,907 the Note Payable was due January 1, 2019.
In June of 2018, the Company sold 500,000 shares of common stock for gross proceeds of $50,000.
In May of 2018 the company filed a form S-8 this Registration Statement covers an additional 10,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share of Kaya Holdings, Inc. (the “Company”), which may be offered pursuant to the Company’s 2011 Stock Incentive Plan (the “Plan”), as amended on November 24, 2014, September 22, 2016 and May 1, 2018.
In June of 2018, the Company authorized the issuance of 1,000,000 shares of common shares of Kaya Holdings Inc. for legal service. The shares were valued at $138,500. As of December 31, 2018, all shares were issued on July 6, 2018.
On July 6, 2018, the Company issued 1,805,555 shares of common shares of Kaya Holdings Inc. that previously recorded as stock payable in 2017 in satisfaction of promissory note due November 30, 2017 in the amount of $54,166, for principal and accrued but unpaid interest, which is convertible at $0.03 per share. In addition, the Company authorized 3,200,000 shares of Kaya Holdings Inc. for services at value of $301,510. As of December 31, 2018, 1,000,000 shares were unissued and valued at $65,000.
In August of 2018, the Company sold 2,500,000 shares of common stock for gross proceeds of $250,000. As of September 30, 2018, all shares were issued on August 24, 2018.
In August of 2018, the Company issued total of 12,000,000 shares to acquire the OLCC licensed marijuana production and processing facility, consisting of the building and equipment. The shares were valued at $1,417,200 (See Note 11).
In September of 2018, the Company authorized the issuance of 7,785,952 restricted common shares of Kaya Holdings, Inc. stock to an accredited investor of the company. This was a conversion of a Notes Payable and Interest with a total value of $233,579, the Note Payable was due January 1, 2019.
In September of 2018 the Company authorized the issuance of 100,000 shares of common shares of Kaya Holdings Inc. for professional service. The shares were valued at $11,200 and the shares were issued on November 27, 2018.
On March 5, 2019, total of 7,785,952 shares of common stock had been issued from stock payable to settle the conversion dated on September 16, 2018.
NOTE 9 DERIVATIVE LIABILITIES
Effective January 1, 2019, an equity-linked financial instrument with a down round feature that otherwise is not required to be classified as a liability under the guidance in Topic 480 is evaluated under the guidance in Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging, to determine whether it meets the definition of a derivative. If it meets that definition, the instrument (or embedded feature) is evaluated to determine whether it is indexed to an entity’s own stock as part of the analysis of whether it qualifies for a scope exception from derivative accounting. Generally, for warrants and conversion options embedded in financial instruments that are deemed to have a debt host (assuming the underlying shares are readily convertible to cash or the contract provides for net settlement such that the embedded conversion option meets the definition of a derivative), the existence of a down round feature results in an instrument not being considered indexed to an entity’s own stock. This results in a reporting entity being required to classify the freestanding financial instrument or the bifurcated conversion option as a liability, which the entity must measure at fair value initially and at each subsequent reporting date.
However,, due to a recognition of tainting, due to variable conversion price on some of the convertible notes, all convertible notes are considered to have a derivative liability, therefore the Company accounted for these Notes under ASC Topic 815-15 “Embedded Derivative.” The derivative component of the obligation is initially valued and classified as a derivative liability with an offset to discounts on convertible debt. Discounts are amortized to interest expense over the respective term of the related note. In determining the indicated value of the convertible note issued, the Company used the Binomial Options Pricing Model with a risk-free interest rate of ranging from 0.05% to 2.63%, volatility ranging from 84.63% to 243.22%, trading prices ranging from $0.045 per share to $0.41 per share and a conversion price ranging from $0.03 per share to $0.10 per share.
As a result of the application of ASC No. 815, the fair value of the ratchet feature related to convertible debt and warrants is summarized as follow:
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 | | $ | 19,783,034 | |
| Initial | | | 1,002,148 | |
| Change in Derivative Values | | | (10,141,165 | ) |
| Conversion of debt-reclass to APIC | | | -0- | |
| Balance as of June 30, 2019 | | $ | 10,644,017 | |
The Company recorded the debt discount to the extent of the gross proceeds raised, and expensed immediately the remaining fair value of the derivative liability, as it exceeded the gross proceeds of the note.
The Company recorded the amortization of debt discount of $366,177 and $713,786 for the three and six months ended June 30, 2019, respectively.
The Company recorded derivative liability expense of $115,254 and $562,148 for the three and six months ended June 30, 2019, respectively.
The Company recorded a change in the value of embedded derivative liabilities income of $4,736,229 and $10,141,165 for the three and six months ended June 30, 2019, respectively.
NOTE 10 – DEBT DISCOUNT
The Company recorded the debt discount to the extent of the gross proceeds raised, and expensed immediately the remaining fair value of the derivative liability, as it exceeded the gross proceeds of the note.
Debt discount amounted to $917,479 as of June 30, 2019.
The Company recorded the amortization of debt discount of $366,177 and $713,786 for the three and six months ended June 30, 2019, respectively.
NOTE 11 – RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
At December 31, 2014, the Company was indebted to an affiliated shareholder of the Company for $840,955, which consisted of $737,100 principal and $103, 895 accrued interest, with interest accruing at 10%. On January 2, 2014, the Company entered into a Debt Modification Agreement whereby the total amount of the debt was reduced to $750,000 and no interest accrued until December 31, 2015. $500,000 of the debt is convertible into 50,000 Series C Convertible Preferred Shares of KAYS. The remaining $250,000 is not convertible.
On December 31, 2015, the Company entered into an agreement to extend the debt until December 31, 2017 with no additional interest for the extension period. On January 1, 2018 the Company entered into an agreement to further extend the debt until December 31, 2021 with no additional interest for the extension period.
At December 2017, the company was indebted to Craig Frank, Chairman, CEO and Acting CFO for KAYS, in the amount of $7,737.00 for travel and miscellaneous expenses incurred by Mr. Frank from travel and related activities in Oregon.
In each of 2017 and 2018, the Company issued stock grants to Jordi Arimany and Carrie Schwarz for 100,000 shares of KAYS stock for their service as board members. The stock was issued from Treasury as restricted stock and carries a one-year restriction before it can be registered for resale pursuant to Rule 144.
In 2017 and 2018, the Company issued stock grants to Craig Frank for 2,000,000 and 3,000,00 shares of KAYS stock respectively, pursuant to his employment agreement via board resolution. Jordi Arimany and Carrie Schwarz for 100,000 shares of KAYS stock. The stock was issued from Treasury as restricted stock and carries a one year restriction before it can be registered for resale pursuant to Rule 144.
In August, 2018 KAYS entered into an agreement with Bruce Burwick, (who subsequently joined the Board of Directors and became an affiliate of the Company) to purchase the Eugene, Oregon based Sunstone Farms grow and manufacturing facility, which is licensed by the OLCC for both the production (growing) of medical and recreational marijuana flower and the processing of cannabis concentrates/extracts/edibles. The purchase includes a 12,000 square foot building housing an indoor grow facility, as well as equipment for growing and extraction activity. KAYS paid Bruce Burwick $1,300,000.00 for the real property and schedule of equipment that was and is used to operate the facility.
Bruce Burwick acquired the property for satisfaction of a promissory note due him for $1,433,000.00. The purchase price of $1.3 million for the OLCC licensed marijuana production and processing facility, consisting of the building and equipment was paid for by the issuance of 12 million shares of KAYS restricted stock to the seller at closing. The shares carry a lock-up-restriction that allows for their staged eligibility for resale over a 61-month period from the date of the purchase of the facility by KAYS. Additionally, the seller purchased 2.5 million restricted shares for $250,000 in cash in a private transaction with the Company. The proceeds from the sale of those shares were and are being used for acquisition related expenses, transitional operating costs and facility capital improvements with respect to the production and processing facility we purchased.
NOTE 12 – STOCK OPTION PLAN
In 2011 the Alternative Fuels America, Inc. 2011 Incentive Stock Plan (the “Plan”), which provides for equity incentives to be granted to the Company’s employees, executive officers or directors or to key advisers or consultants. Equity incentives may be in the form of stock options with an exercise price not less than the fair market value of the underlying shares as determined pursuant to the 2011 Incentive Stock Plan, restricted stock awards, other stock based awards, or any combination of the foregoing. The 2011 Incentive Stock Plan is administered by the board of directors.
NOTE 13 – WARRANTS
On September 8, 2015 the Company received a total of $100,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $100,000 with interest accruing at 10%. The note holder is entitled to subscribe for and purchase from the company 3,161,583 paid and non-assessable shares of the Common Stock at the price of $0.0316297 per share (the “Warrant Exercise Price”) for a period of five (5) years commencing from the earlier of such time as that certain $100,000, 10% promissory note due September 9, 2017 has been fully repaid or the start of the Acceleration Period as defined in “The Note” or September 9, 2017. As of June 30, 2019, the note was paid in full.
On September 9, 2015 the Company received a total of $100,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $100,000 with interest accruing at 10%. The note holder is entitled to subscribe for and purchase from the company 3,161,583 paid and non-assessable shares of the Common Stock at the price of $0.0316297 per share (the “Warrant Exercise Price”) for a period of five (5) years commencing from the earlier of such time as that certain $100,000, 10% promissory note due September 9, 2017 has been fully repaid or the start of the Acceleration Period as defined in “The Note” or September 9, 2017. As of June 30, 2019, the note was paid in full.
On May 9, 2016 the Company received a total of $75,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $75,000 with interest accruing at 10%. The note holder is entitled to subscribe for and purchase from the company 2,371,187 paid and non-assessable shares of the Common Stock at the price of $0.0316297 per share (the “Warrant Exercise Price”) for a period of five (5) years commencing from the earlier of such time as that certain $75,000, 10% promissory note due May 9, 2018 has been fully repaid or the start of the Acceleration Period as defined in “The Note” or May 9, 2018. As of June 30, 2019, the note was paid in full.
On May 17, 2016 the Company received a total of $75,000 from an accredited investor in exchange for a two year note in the aggregate amount of $75,000 with interest accruing at 10%. The note holder is entitled to subscribe for and purchase from the company 2,371,187 paid and non-assessable shares of the Common Stock at the price of $0.0316297 per share (the “Warrant Exercise Price”) for a period of five (5) years commencing from the earlier of such time as that certain $75,000, 10% promissory note due May 17, 2018 has been fully repaid or the start of the Acceleration Period as defined in “The Note” or May 17, 2018. As of June 30, 2019, the note was paid in full.
| Warrants issued to Non-Employees | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | Weighted | Weighted |
| | | | | Average | Average |
| | | | Warrants | Exercise | Contract |
| | | | Issued | Price | Terms Years |
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 | 11,065,540 | 0.0316297 | 3.8 |
| Granted | | | -0- | -0- | -0- |
| Exercised | | | -0- | - | - |
| Expired | | | -0- | - | - |
| Balance as of June 30, 2019 | 11,065,540 | 0.0316297 | 3.55 |
NOTE 14 – COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Operating Leases
The Company has several operating leases for an office and store lease in Fort Lauderdale, Florida and several locations in Oregon under arrangements classified as leases under ASC 842.
Effective June 12, 2017, the Company leased the office space in Fort Lauderdale, Florida under a 5-year operating lease expiring June 30, 2022. The lease provides for increases in future minimum annual rental payments based on defined annual increase beginning with monthly payments of $4,017 and culminating in a monthly payment of $4,839. The total amount of rental payments due over the lease term is being charged to rent expense according to the straight-line method over the term of the lease. The lease was terminated on July 3, 2019 and the Company agreed to issue landlord 500,000 shares of common stock as penalty for early termination.
Effective June 1, 2019, the Company leased the office space in Fort Lauderdale, Florida under a 2-year operating lease expiring May 31, 2021. The rental payment is $1,802 per month. The total amount of rental payments due over the lease term is being charged to rent expense according to the straight-line method over the term of the lease.
Effective May 15, 2014, the Company leased an unit in Portland, Oregon under a 5-year operating lease expiring May 15, 2019. In May 2019, the lease had been extended to May 15, 2024. The lease provides for increases in future minimum annual rental payments based on defined annual increase beginning with monthly payments of $2,250 and culminating in a monthly payment of $2,632. The total amount of rental payments due over the lease term is being charged to rent expense according to the straight-line method over the term of the lease. The lease is now on a month-to-month basis.
Effective June 1, 2015, the Company leased an unit in Salem, Oregon under a 5-year operating lease expiring May 31, 2020. The lease provides for increases in future minimum annual rental payments based on defined annual increase beginning with monthly payments of $3,584 and culminating in a monthly payment of $4,034. The total amount of rental payments due over the lease term is being charged to rent expense according to the straight-line method over the term of the lease. The lease is now on a month-to-month basis.
Effective April 15, 2016, the Company leased an unit in Salem, Oregon under a 5-year operating lease expiring April 15, 2021. The lease provides for increases in future minimum annual rental payments based on defined annual increase beginning with monthly payments of $4,367 and culminating in a monthly payment of $4,915. The total amount of rental payments due over the lease term is being charged to rent expense according to the straight-line method over the term of the lease. The lease is now on a month-to-month basis.
Effective April 15, 2016, the Company leased an unit in Salem, Oregon under a 5-year operating lease expiring April 15, 2021. The lease provides for increases in future minimum annual rental payments based on defined annual increase beginning with monthly payments of $4,617 and culminating in a monthly payment of $5,196. The total amount of rental payments due over the lease term is being charged to rent expense according to the straight-line method over the term of the lease. The lease is now on a month-to-month basis.
The Company utilizes the incremental borrowing rate in determining the present value of lease payments unless the implicit rate is readily determinable. The Company used an estimated incremental borrowing rate of 9.32% to estimate the present value of the right of use liability.
The Company has right-of-use assets of $525,451 and operating lease liabilities of $529,978 as of June 30, 2019. Operating lease expense for the three and six months ended June 30, 2019 was $75,789 and $139,325, respectively. The Company had cash used in operating activities related to leases of $45,830 and $101,878 during the three and six months ended June 30, 2019, respectively.
| Maturity of Lease Liabilities at June 30, 2019 | | Amount |
| | 2019 (excluding the six months ended June 30, 2019) | | | $ | 146,040 | |
| | 2020 | | | | 237,635 | |
| | 2021 | | | | 154,856 | |
| | 2022 | | | | 54,688 | |
| | Later years | | | | — | |
| | Total lease payments | | | | 593,219 | |
| | Less: Imputed interest | | | | (63,241 | ) |
| | Present value of lease liabilities | | | $ | 529,978 | |
NOTE 15 – SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On July 2, 2019 the Company received $75,000.00 from the issuance of convertible debt to the Cayman Venture Capital Fund pursuant to the May 2017 Finance Agreement, as amended. Interest is stated at 8%. The Note and Interest is convertible at $0.03 per share. The Note is Due in January of 2021.
On July 30, 2019 the Company announced that they had signed an Agreement with The Franchise Academy, a Leading Canadian Franchise Development and Sales Group, to establish and implement the Kaya Shack™ Retail Cannabis Store Franchise Program in Canada Targeting 75-100 Kaya Shack™ retail cannabis stores in Canada by 2024, subject to regulatory approval and market acceptance.
Inthis Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q,the terms“KayaHoldings,”“KAYS,”“theCompany,”“we,”“us” and“our” refer to Kaya Holdings, Inc.and its subsidiaries, unless the context indicates otherwise.
CautionaryNoteRegarding Forward LookingStatements
Information contained in this QuarterlyReport on Form 10-Qcontains “forward-looking statements” within themeaningofSection27A ofthe Securities Actof 1933, asamended(the“Securities Act”) andSection21E of theSecurities Exchange Act of 1934, asamended (the ‘Exchange Act”). These forward-looking statements are generally identifiable by use ofthewords“may,”“will,” “should,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “believe,” “intend”or“project”or thenegativeofthese words orother variations onthese words orcomparableterminology.
The forward-looking statements herein representourexpectations, beliefs, plans, intentions orstrategies concerning futureevents.Ourforward-looking statements arebasedonassumptions that may beincorrect,andthere canbe noassurance that any projections orother expectations included in anyforward-looking statements will come topass. Moreover, ourforward-looking statements aresubject to various known and unknownrisks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause ouractual results, performance orachievementsto bematerially differentfrom futureresults, performance orachievements expressed orimpliedby anyforward-looking statements.
Exceptasrequiredbyapplicable laws, weundertake noobligation toupdate publicly any forward-looking statements for anyreason, even if newinformation becomes available orother events occur inthe future.
AvailableInformation
Wefile annual, quarterlyandspecial reports andother information with the Securities andExchange Commission (“SEC”) thatareavailable through theSEC’sElectronic Data Gathering Analysis andRetrieval System, known asEDGAR,throughtheSEC’swebsite (www.sec.gov).
Item 2.Management’s Discussion andAnalysisofFinancial Condition andResults ofOperations.
Business Overview
PARTI
Item 1. Business.
Overview
Kaya Holdings, Inc., “KAYS” or the “Company” a Delaware corporation, is a vertically integrated legal marijuana enterprise that produces, distributes, and/or sells a full range of premium cannabis products including flower, oils, vape cartridges and cannabis infused confections, baked goods and beverages through a fully integrated group of subsidiaries and companies supporting highly distinctive brands.
Current Oregon Operations
In Oregon, all of the Company’s operations are licensed by the Oregon Liquor Control Commission (the “OLCC’), which has jurisdiction over legal medical and recreational cannabis grow, production and retail operations. The Company originally commenced operations in Oregon in July 2014, operating medical marijuana dispensaries (“MMDs”) when only medical marijuana sales had been legalized. However, this afforded the Company to be in position to rapidly move into the grow, production and retailing of recreational marijuana when legalization of recreational cannabis sales followed shortly thereafter in October 2015.
The Company currently operates a chain of three Kaya Shack™ retail outlets and has developed its own proprietary Kaya Farms™ strains of cannabis, which it grows and produces (together with edibles and other cannabis products) at its Eugene, Oregon Sunstone Farms indoor cannabis grow and production facility, which KAYS acquired in October 2018 and is presently operating under a Management Agreement pending transfer of the licenses by the OLCC to the Company, upon completion of a satisfactory compliance review.
Additionally, the Company also owns a 26-acre parcel in Lebanon, Linn County, Oregon, which it purchased in August 2017 on which it intends to construct a cannabis cultivation and manufacturing complex, which will initially consist of an 85,000-square foot Kaya Farms™ greenhouse grow and production facility. The Company maintains a genetics library of over 30 strains of cannabis it has developed and has also formulated various cannabis-infused edibles, marijuana cigarettes and other cannabis derivatives under its proprietary “Kaya” brand names.
The Company’s business strategy seeks to achieve four fundamentals objectives:
| · | maintaining direct access to customers (to own the relationship with end-users); |
| · | effecting vertical integration to control the supply chain (to control cost, selection and quality); |
| · | introducing strong brands in tradition and innovative categories (to control asset development); and |
| · | creating the capacity to expand nationally and internationally as regulations and opportunities permit. |
Domestic and International Plans for Expansion
The Company is focusing its efforts on expanding its operations both domestically and internationally by:
| · | replicating its Kaya Shack™ brand retail outlets through franchising, initially in Canada, where the production and use of marijuana for both medical and recreational purposes is legal nationwide and ultimately into U.S. states where medical and recreational marijuana production and use is legal or expected to become legal in the near term; |
| · | retaining Franchise Academy, Inc., a franchise consulting group, to assist it, together with Garfinkle Biderman LLP, a Canadian law firm specializing in the franchise arena, in the development, planning, launch and implementation of its retail franchise program in Canada; |
| · | utilizing its marijuana grow, processing, manufacturing and production facilities (which have the capability to grow and process up to 100,000 pounds of cannabis annually) to support its planned franchised outlets, in order to both maintain quality control and offer customers a consistent customer experience while reducing costs of goods to franchisees; |
| · | developing, producing and marketing, additional cannabis products, including flower, concentrates, extracts, cannabis-infused edibles, topicals, marijuana cigarettes and other specialty cannabis derivatives using its proprietary Kaya Shack™ and Kaya Farms™ brands edibles, marijuana cigarettes, extracts, and topicals; |
| · | establishing a branch in Israel, where it will seek to grow and export legal medical and recreational cannabis to European and Asian countries, as regulations permit; and |
| · | ultimately, taking advantage of anticipated regulatory changes to export cannabis and cannabis products from Oregon to other jurisdictions where medical and recreational cannabis use is legal. |
The Company has formed Kaya Brands International, Inc. (“Kaya International”), a new Florida subsidiary, to undertake its planned Canadian retail franchise operations and other planned operations outside the U.S.
CorporateInformation
Our corporate office is located at 915 Middle River Drive, Suite 316, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, 33304. Our telephone number is 954-892-6911 and our corporate website is www.kayaholdings.com. Information contained on our corporate website does not constitute part of this Memorandum.
Market Overview
According to Arcview Market Research and its research partner BDS Analytics, over the next 10 years, the legal cannabis industry will see much progress around the globe. Spending on legal cannabis worldwide is expected to hit $57 billion by 2027. The adult-use (recreational) market will cover 67% of the spending; medical marijuana will take up the remaining 33%.
The largest single market of cannabis buyers will be in North America, going from $9.2 billion in 2017 to $47.3 billion a decade later. The largest growth spread, however, is predicted within the rest-of-world markets, from $52 million spent in 2017 to a projected $2.5 billion in 2027.
While the U.S. market is expected to be dominated by recreational sales, the European market may have greater medical sales due to the inclusion of cannabis in the government subsidized healthcare systems. The European market is expected to be the single largest arena for medical marijuana.
The worldwide adult recreational cannabis market remains hampered by the United Nations and its 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. The Arcview and BDS report believes nothing will be done to change the U.N. attitude until U.S. federal laws legalize marijuana something many industry experts and pundits believes will happen after the 2020 presidential election.
Important Industry Considerations
| · | The initial decision by many U.S. states and Canada to create medical-only cannabis regulations prompted many other countries to act similarly. This increased further after California and Canada legalized adult recreational use. |
| · | South America has some of the most liberal medical cannabis programs. Led by Brazil, Argentina, Peru and Uruguay (the only country in the world in which adult recreational use is legal for all its citizens), the South American medical cannabis market may grow from $125 million in 2018 to $776 million in 2027. |
| · | Germany is poised to be the leader of the European cannabis market, and Italy is expected to be second with $1.2 billion in sales by 2027. Overall, however, the European cannabis market is not expected to grow as stridently as its potential suggests. |
| · | Australia’s legal cannabis market is forecast to grow from $52 million in 2018 to $1.2 billion in 2027, the 5th largest in the world. |
| · | Israel has a small population and a long history of legal medical marijuana use. It continues as a leader with years in the development of cannabis pharmaceuticals. |
| · | Canada is among the few countries where investors have already shown confidence in the future legality of the cannabis industry; they are betting with billions of dollars pouring into public equity investments. |
Source: www.forbes.com |Legal Cannabis Industry Poised For Big Growth, In North America And Around The World | Thomas Pellechia | March 1, 2018.
The Kaya™ Family of Brands
Kaya Holdings, Inc., “KAYS” or the “Company” a Delaware corporation, is a vertically integrated legal marijuana enterprise that produces, distributes, and/or sells a full range of premium cannabis products including flower, oils, vape cartridges and cannabis infused confections, baked goods and beverages through a fully integrated group of subsidiaries and companies supporting highly distinctive brands.
Currently Operational Brands (2014-2019)





Next Stage Traditional (2019-2021)




Next Stage Innovative (2019-2021)




Note: The “Next Stage Traditional” and “Next Stage Innovative” brands are all targeted for release over the 6-18 months. The Company is currently awaiting the status of the license transfer at the Kaya Farms Indoor Marijuana Grow, Processing & Cannaceutical Production Facility in Eugene, Oregon, and the pending license issuance of the Kaya Farms Ag Facility in Lebanon, Oregon to finalize the release dates for these brands in Oregon. In the event that the license transfer at the Eugene facility and/or the licensing approval and construction timeline of the Lebanon facility is delayed or experiences difficulties, the Company has sourced other alternatives to expedite the release of the brands and will update shareholders accordingly as to revised brand rollout dates (if any).
TheKaya Shack™Brand

KayaHoldings operates theKaya Shack™ brand oflegal medical and recreational retail marijuana retail stores.
KayaHoldings operates threerecreational marijuana retail outlets andmedical marijuana dispensaries in Oregon under the KayaShack™ brand.
Dubbed bythe mainstream press asthe “StarbucksofMarijuana” after ourfirst outlet opened in July 2014, ouroperating concept issimple:todeliver aconsistent customer experience (quality products, fair prices andsuperior customer service) to abroadanddiverse base ofcustomers. Kaya Shack™ meets the quality needs of the“marijuana enthusiast”, the comfort and atmosphere ofall including “soccer moms” and the price sensitivitiesofcasual smokers.
Additionally, Kaya Holdings maintains an active fourth OLCC Marijuana Retail License which it is seeking to move to its Eugene, Oregon Kaya Farms Indoor Production and Processing Facility so that the Company may offer a “Kaya Farm Store” and also serve as a retail delivery hub for Eugene, Oregon.
The Kaya Shack™brandcommunicates positive thinking andjoy,with signs adorning thewalls that read“It’sa Good Dayto have a GoodDay,”“Some of ourHappiest Days Haven’t Even HappenedYet,” and oursignature“BeKind.”
KayaShack™ retail outlets are open 7daysaweek- Monday through Saturday from8:00amto 10:00 pm, and Sunday8:00 AMto 9:00 PM.Operations follow an operational manual that details procedures for 18areasofoperation includingsafety,compliance, store opening,storeclosing, merchandising, handling of cash,inventory control, product intake, store appearance andemployee conduct.
Incompliance with regulations, all marijuana andmarijuana infused products sold through our storesare quality tested byindependent labs to assure adherence tostrict quality and OLCCregulations.
The Company is exploring opportunities to expand its operations beyond Oregonbyreplicating its Kaya Shack™ brandretail outlets throughfranchising in other states whererecreational cannabis useis legal orexpected tobecome legal in the near term, aswell as in Canada, where itis legal nationwide.KAYSalso is targeting opening corporate owned marijuana production andprocessing facilities to supportthe envisioned franchised outlets, and toboth maintain quality control andoffer customers aconsistent customer experience while reducing costs of goods tofranchisees.
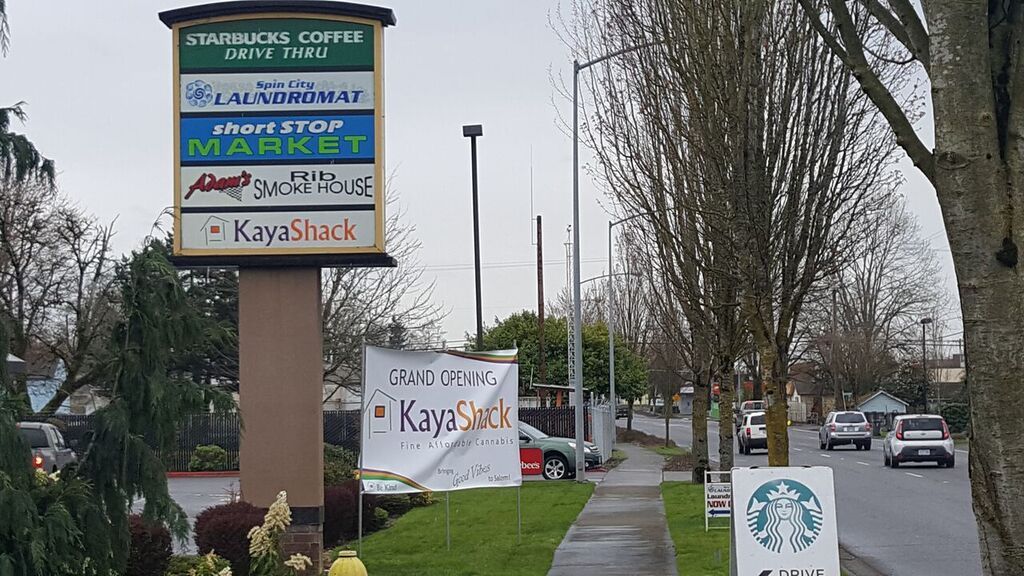

Kaya Shack™ Retail Outlets

Allstores feature acheck outstand wrapped to feature theCompany’sproprietarybrand ofpre-rolls, Kaya Buddies. TheBuddies program isan exciting andpopular pre-roll offering, featuring awide selection (15-15strainsofpre-rolls) andfeaturing ourspecial Kaya Saying in each Buddies tube. Aglass display case showcasesat least 25strainsofmarijuana flower, which the stores serveto customers “deli style”, weighing straight fromthe jartothe customer’s take-out tube. Anadditional display case with avaried selectionofoils, concentrates andtopicalsrounds out thecannabis productdisplay.

The stores also feature standing display cases with cannabis intended glasswareunder theCompany’s brandReally HappyGlass, aswell as a rack ofproprietaryt-shirtdesigns marketed under the Company brand KayaGear.Thestore also has ahospitality area that offers freewater,coffee, tea andhotcocoa. Asrequired bylaw,all products containing marijuana are either behind locked glass orbehindthecounter and out ofcustomer reach.
| I. | Kaya Shack™ , 1719 SE Hawthorne Blvd.,Portland, Oregon. |

OurfirstKayaShack™ OLCClicensed marijuana store (located in the heart ofthe trendy Hawthorne district in southeast Portland, the “GreenwichVillage” oftheWest Coast)opened forbusiness July 03, 2014. Thestore is locatednext door to acellphonerepair shop,and near toDevil’sDill restaurant and No Fun pub.There are also aMcMenamins restaurant, tattoo parlor, convenience store, hair/nail salon and asoccer sportsbar.Theareaaroundtheshopis mixed use(commercial and residential) and has afootprintofapproximately700squarefeetand is themodel for theCompany’ssmall urban shops.
| II. | Kaya Shack™Marijuana Superstore, SouthSalem, Oregon. |

Oursecond Kaya Shack™ OLCClicensed marijuana store (located in South Salem, Oregon)opened forbusinessonOctober17, 2015.The store islocated in astrip mall alongside aCaesar’s Pizza,Aaron’sfurniture, aconvenience store, atanning salon, and anail salon. Theplaza also has aSubway, asports barandalaundromat. The area aroundthe shop isprimarily commercial with residential complexes underconstructionandhas afootprint ofapproximately2,100 squarefeet and
| III. | Kaya Shack™ Marijuana Superstore, Central Salem, Oregon. |
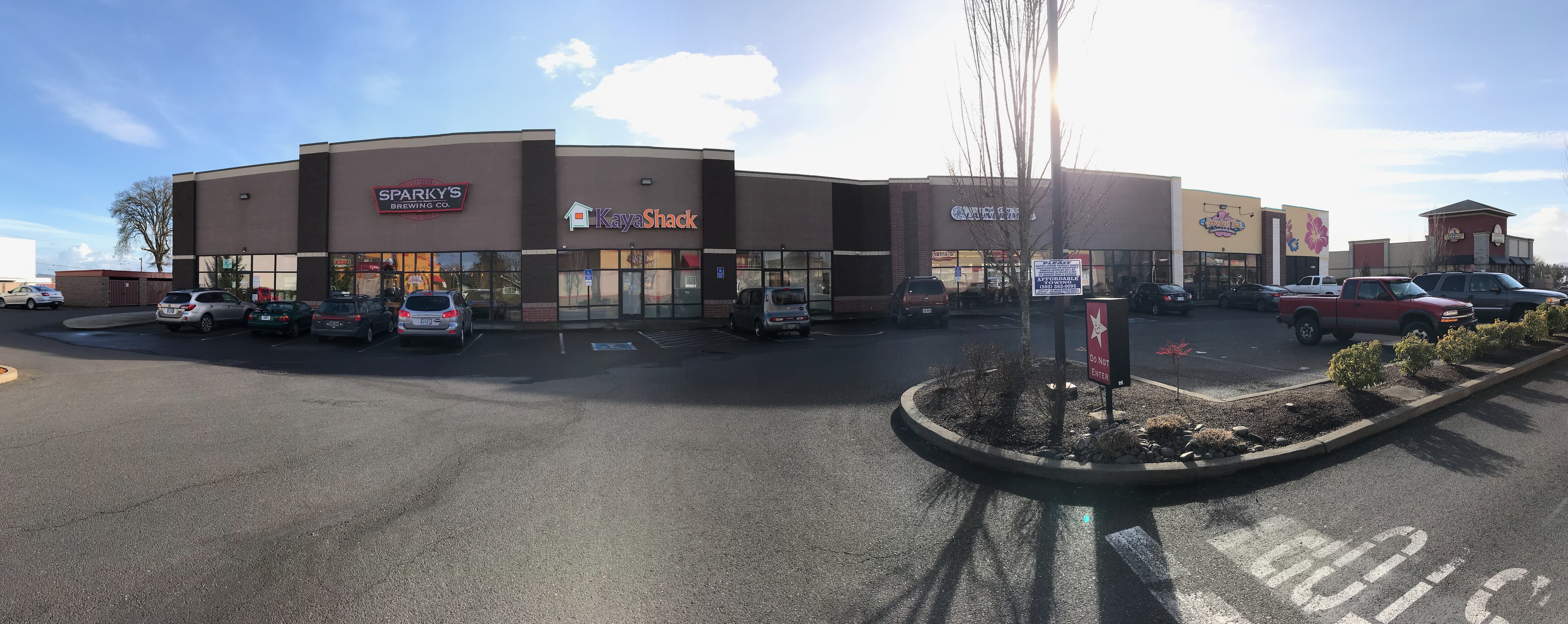

OurthirdKayaShack™ (located in Central Salem, Oregon) opened forbusiness February 15, 2018. Thestoreislocatedin astrip mall directly behind CarlJr.andPopeye’sChicken restaurants and alongside amicrobrewery sportsbar,laundromat, andHawaiian sandwich shop.The area around the shopis primarily commercial with residential complexes ready to open Summer 2018. Ithasafootprint ofapproximately 3100square feet and utilizes the Kaya Shack™ Marijuana Superstore model.
Kaya Shack™CarFleetand HomeDelivery

The Companyislicensedbythe OLCC forhome delivery forallfourstores. TheCompany is interested in developing its delivery service and has afleet of 4Kaya Cars (wrapped Fiat 500sfeaturing theCompany’sbranding logos andcolors andoutfitted with safes andsecurity) attheready,andonce the supportsoftware enabling compliant delivery is released KayaShack™ will commence with its homedelivery service.Weexpect delivery to extend ourvisibility,assist inbuilding brandawareness,andallow the Company to service abroader geographicterritory.The Company hasdeveloped the website www.kayadelivers.com to advance the growth ofits delivery service.
Tomakeuse of thecars while the Company waits to launch delivery service, the cars are currently used forpromotional purposes atcommunity fairs and rovingbillboards.
Kaya Farms™
Lebanon, Linn County, Oregon Marijuana GrowandManufacturing Complex

Inearly2015,KAYScommenced its ownmedical marijuana growoperationsforthe cultivationandharvesting oflegal marijuana thereby becoming the first publicly traded U.S.company to own amajority interest in avertically integrated legal marijuana enterprise in the United States. Since that timeKAYShas operated variousgrowfacilities to feed the KayaShack Supply Chain, andin August 2017,KAYSacquired its first propertyfor alarge scale facility- a26-acre parcel in Lebanon, LinnCounty,Oregon, where weintend to develop an 85,000-square footKaya Farms™ Farmand greenhouse facility
Management believes that the acquisitionanddevelopmentofthe property will position the Company forfuture growth and expansion, including increased Marijuana Canopy production to the maximum extent allowed bylaw through use ofboth greenhouse and outdoor grows,as well asexpansionofits production capabilities with brands inoils,vapecartridges, concentrates, aselectionofedibles, and infusedcreams and lotions. When Federal Prohibition ofmarijuanaends andnationalandinternational cannabis trade can begin, webelieve that Oregonis uniquely positioned tobecomeAmerica’s“potbasket”dueto itssuperiorclimate andstate historyinvolving generations ofOregonian CannabisGrowers;ideal weather+extensive generational knowledge =superior, lower costcannabis products forexport.
Wefiledforzoning and land use approval inearly2018, andafter numerous regulatory challenges and delays,wefinally received zoning and landuse approvalin early 2019to build ontheproperty.Wearepresently in thefinal planning stages andare awaiting theculminationofthe OLCC licensing process to begin construction. Under presentlaws the property can easily deliver 6-8,000 pounds ofcannabis each year;if future regulations permit webelieve that wecan expand that capability toapproximately 100,000 pounds ofcannabis eachyear.

Kaya FarmsIndoorMarijuanaGrow,Processing &Cannaceutical Production Facility

OnOctober23, 2018KAYSannounced that it hadconcluded the purchase ofthe Eugene, Oregon based Sunstone Farms growand manufacturingfacility,which is licensed by theOLCC forboth the production (growing) ofmedicalandrecreational marijuana flower and the processing ofcannabis concentrates/extracts/edibles. Thepurchase includes a 12,000 square footbuilding housing an indoor growfacility, aswell asequipment forgrowingandextractionactivity.The facility can producein excess of 800 poundscannabis flower annually ascurrently outfitted, aswellas asubstantial amount ofmanufactured extracts andrelated cannabis products.
The purchase priceof $1.3millionfor theOLCC licensed marijuana production andprocessingfacility,consisting ofthe building andequipment waspaid for bythe issuance of 12million shares ofKAYSrestricted stock tothe seller atclosing. The shares carry alock-up-restriction that allows fortheir staged eligibility forresaleover a61-month period from thedateofthe purchase ofthe facility byKAYS.
Additionally,theseller purchased2.5million restricted sharesfor $250,000in cash in aprivate transaction with theCompany.The proceedsfrom thesale ofthose shareswere andare being used foracquisition related expenses, transitional operating costsand facility capital improvements with respect to the production and processing facility wepurchased.
KAYSintendstoutilizetheprocessing facilities to growtheirowntop-shelf, connoisseur-grade marijuana flower, producevariousbrands ofoils, edibles, concentrates andextracts, and develop medical gradelaboratory facilities forthe production of aproprietary Kaya Cannaceuticals™ line of both CBD andCBD/THC products forthe health, skincare andmedical industries.
Pursuanttoaninterim Management Agreement entered into between theparties, the Company hasassumed operations ofthe 12,000-square footfacility pending transfer of thelicensesbythe OLCCtotheCompany,uponcompletionof asatisfactory compliancereview.Aspart ofplanned expansion andrenovationsfor thefacility,KAYSbegan site improvements and has begun supplying its three KayaShack™ retail outlets with Kaya Farms™ cannabis and cannabis products fromthe facility
Acquisitionof theEugene,Oregonfacility has enabled the Company to recommence its KayaFarms™ cannabisgrow,processing and manufacturing operations. Please see the following pages forcopies oftesting results andpictures ofvarious aspectsofproduction.

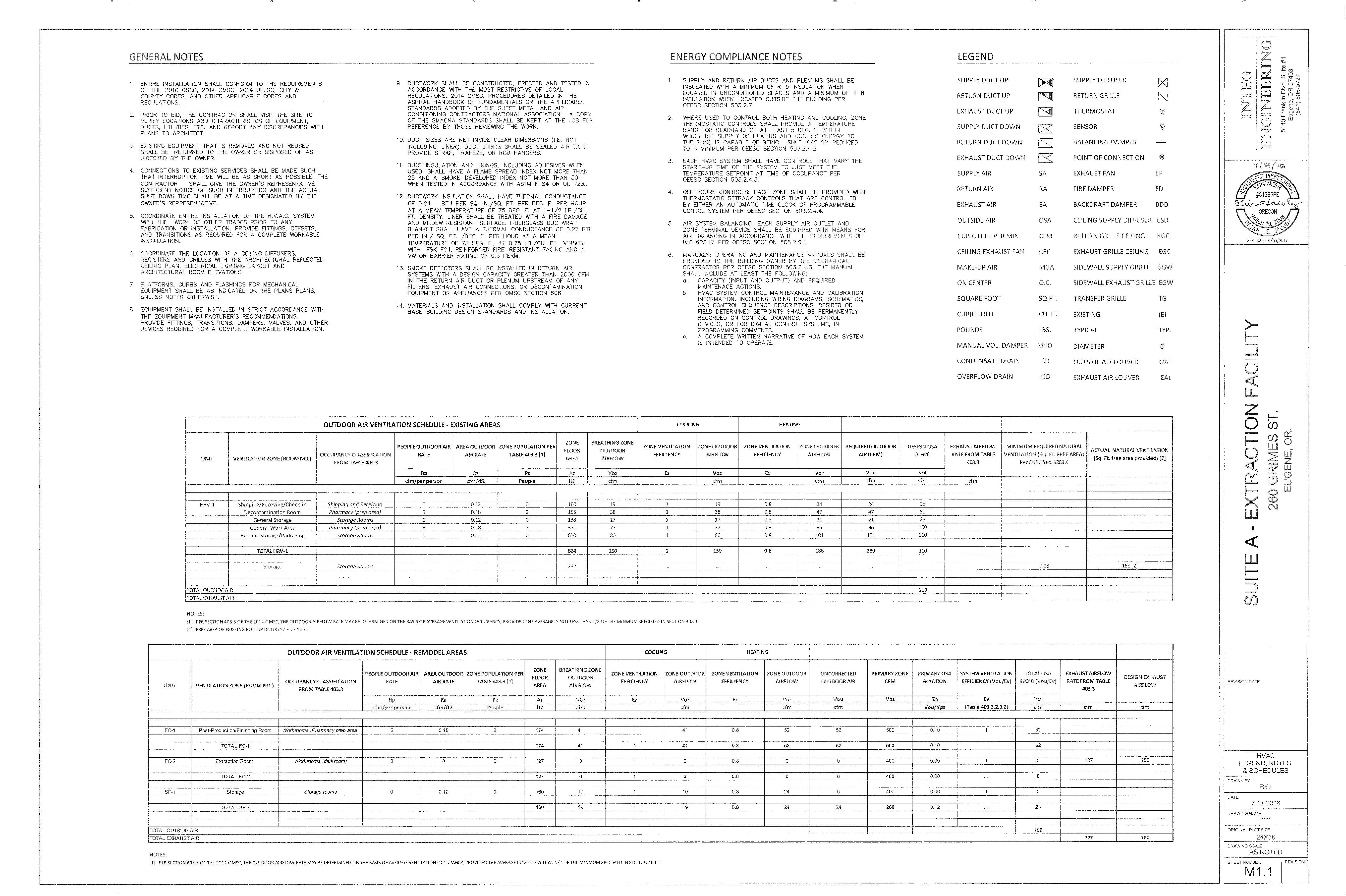
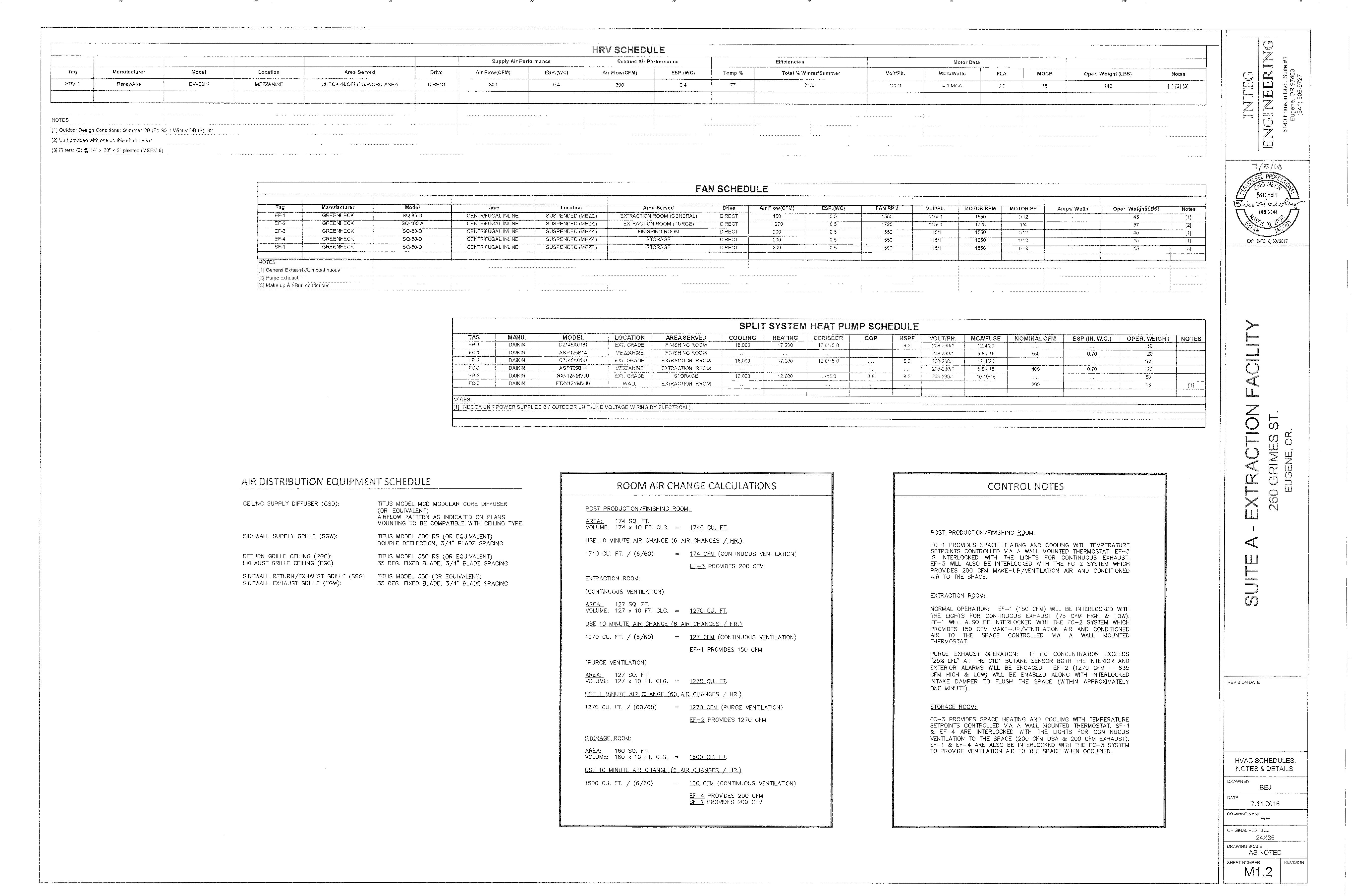








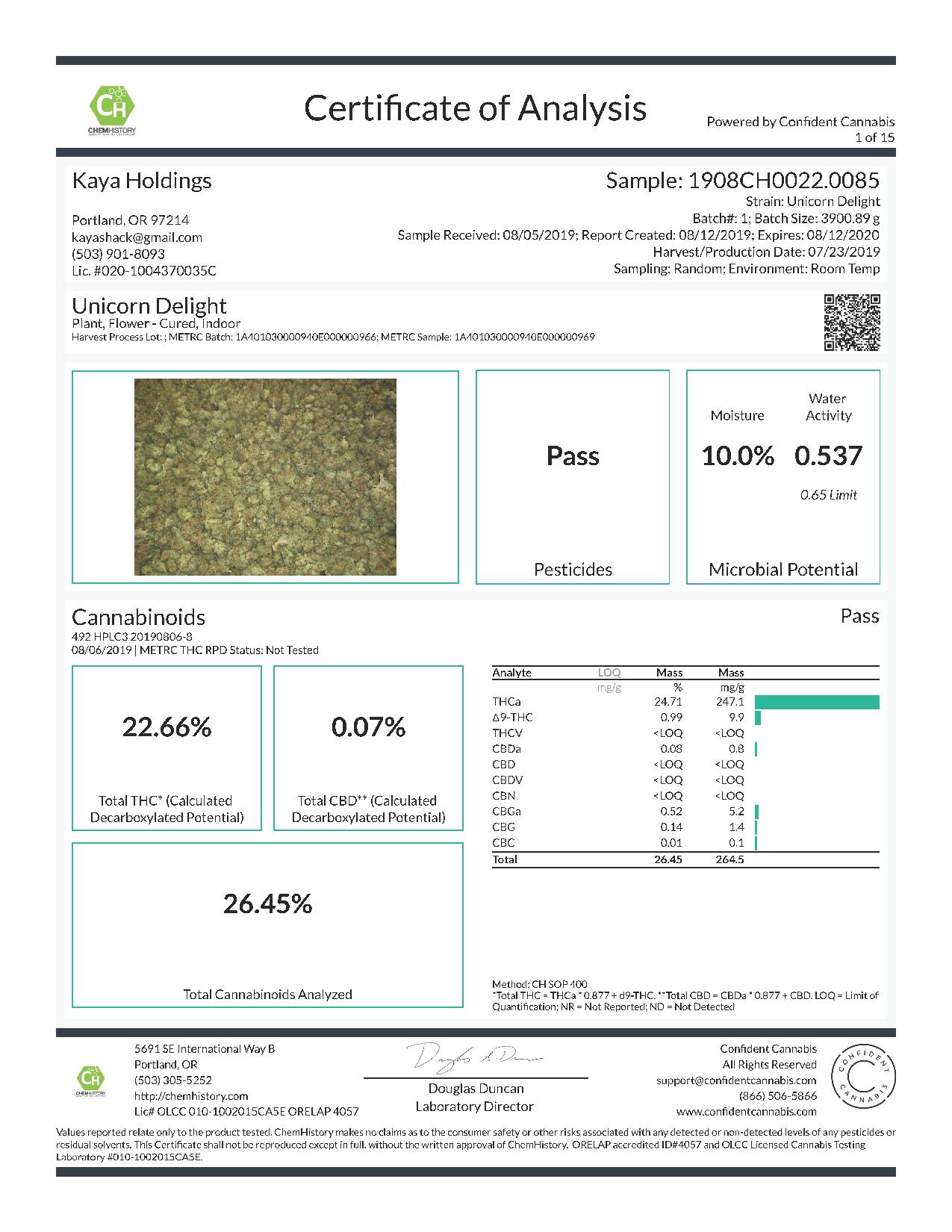


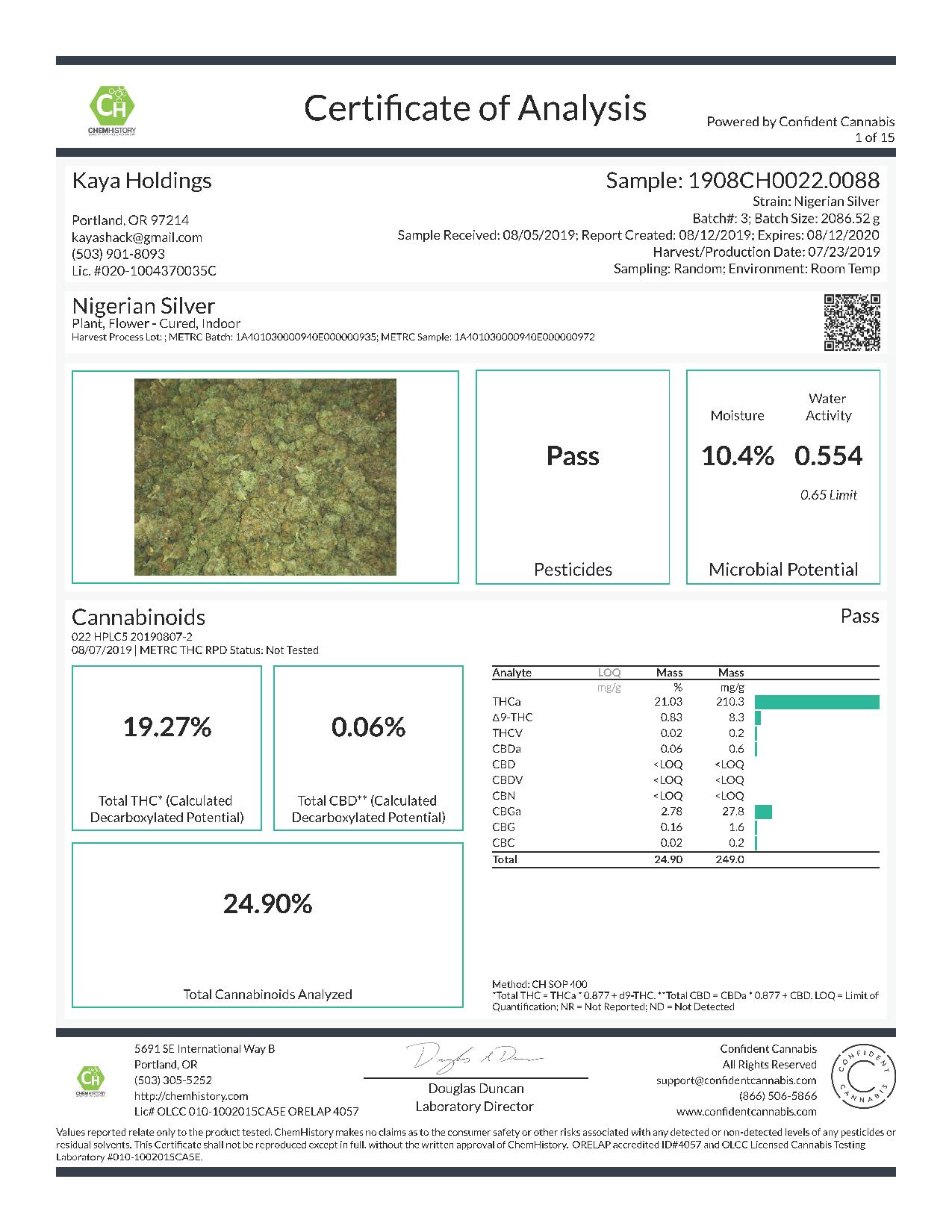


Kaya Farms™-CannabisandCannabis Products
Kaya Buddie™StrainSpecificCannabisCigarettes


In 2016the Company introduced asignature lineofstrain-specific connoisseur-grade, pre-rolled cannabis cigarettes branded as “KayaBuddies™”. KayaBuddies™ cannabis cigarettes have been verywell received bymedical patients andrecreational users, with the Companyselling over 100,000Kaya Buddies™ since launching thebrand in January 2016.The brand,marketedunderthe tagline “Buds with Benefits”, features over 50different strains ofconnoisseur-grade, highquality cannabis and proprietary specialty blends. Many cannabis retailers produce prerolls, but nonethatwe know ofoffer strain specific preroll made fromthebuds oftheflower.
PotentialExpansion
The Company is focusing its efforts on expanding its operations both domestically and internationally by:
· replicating its Kaya Shack™ brand retail outlets through franchising, initially in Canada, where the production and use of marijuana for both medical and recreational purposes is legal nationwide and ultimately into U.S. states where medical and recreational marijuana production and use is legal or expected to become legal in the near term;
· retaining Franchise Academy, Inc., a franchise consulting group, to assist it, together with Garfinkle Biderman LLP, a Canadian law firm specializing in the franchise arena, in the development, planning, launch and implementation of its retail franchise program in Canada;
· utilizing its marijuana grow, processing, manufacturing and production facilities (which have the capability to grow and process up to 100,000 pounds of cannabis annually) to support its planned franchised outlets, in order to both maintain quality control and offer customers a consistent customer experience while reducing costs of goods to franchisees;
· developing, producing and marketing, additional cannabis products, including flower, concentrates, extracts, cannabis-infused edibles, topicals, marijuana cigarettes and other specialty cannabis derivatives using its proprietary Kaya Shack™ and Kaya Farms™ brands edibles, marijuana cigarettes, extracts, and topicals;
· establishing a branch in Israel, where it will seek to grow and export legal medical and recreational cannabis to European and Asian countries, as regulations permit; and
· ultimately, taking advantage of anticipated regulatory changes to export cannabis and cannabis products from Oregon to other jurisdictions where medical and recreational cannabis use is legal.
Domestic and International Plans for Expansion
The Company has formed Kaya Brands International, Inc. (“Kaya International”), a new Florida subsidiary, to undertake its planned Canadian retail franchise operations and other planned operations outside the U.S.
GrowthStrategy
The Company has establishedawell-defined strategy forentering and maintaining astrong presence in the legal marijuanasector.The cornerstones ofthis strategy include:
| | · | All operations are tobeconducted in accordance with State and Local Laws andFederal Enforcement Policies andPriorities as itrelates to Marijuana(asoutlined in the Justice Department's Cole Memo dated August 29, 2013, USAttorney General Jeff Sessions Memo dated January 4, 2018,and subsequent commentary from USAttorneyforthe District ofOregon Billy Williams). |
| · | | The Companywill seek to operate in avertically integrated manner(grow,process andsell) wherever permitted bylaw. Instates orcountries where vertical integration is notpermitted, the Company plans to determine which ofthe permitted activities offers the mostpotential for growth andvalue creation. |
| · | | TheCompany will seek toengage, sponsor orlead local advocacy andlobbying groupsthat have asignificant impact onthe evolution andcharacter oflaws and the regulations underwhich legal marijuana operations areimplemented inselect markets. |
| · | | TheCompany shall workwith law enforcementandgovernment officials to insure compliance withall regulations. |
MarketingandSales
The Company will only market its legal marijuanaas incompliance with applicable statelaw.The Company employs amarketing campaign consistingof fourcornerstones:
| | · | Promotingandestablishing the Kaya Shack™ brand. |
| | · | Apositive and active online presence. |
| | · | Daily specialsandpromotions. |
| | · | Quirkyand funholiday specials. |
Our corestrategic marketing objectives include:
| | | EstablishingandEnhancing the Kaya Shack™ Brand –positioning theCompany’sbrand to havepositive andvalue related associations with all prospective andexisting customers. |
| | | Operating Cooperatively-cooperation,as astrategy,helps develop anetwork ofsuppliers and marketing channels able to promote KayaShack™. |
| | | DeliveringValue-customer value isachieved whenthe perceived value ofwhat wesell along with the value ofthe experience wedeliver exceeds the price wecharge. |
| | | Driving CustomerTraffic-the only two ways toincrease storeincome is tosell more to ourexisting customers andattract newcustomers. Programs are inplace to accomplish both tasks. |
Government Regulation
Wearesubjecttogeneral business regulations and laws, as well as regulations and laws directly applicable to ouroperations.As wecontinue to expandthe scope of ouroperations,theapplication ofexisting laws andregulations could include matters such as pricing, advertising, consumer protection, quality ofproducts, andintellectual property ownership. Inaddition,wewill also besubject to newlaws and regulations directly applicable to ouractivities.
Anyexistingor newlegislation applicable to uscould expose usto substantialliability,including significant expenses necessarytocomply with such laws andregulations, which could hinder orpreventthegrowthof ourbusiness.
Federal, stateandlocal laws andregulations governing legal recreational and medical marijuana use are broadin scope and aresubject to evolving interpretations, which could require usto incur substantial costs associated with compliance. Inaddition, violations ofthese laws orallegations ofsuch violations could disrupt ourplanned business andadversely affect ourfinancial condition and results ofoperations.Inaddition, it ispossible that additionalorrevised federal, state andlocal laws andregulations may beenacted in the future governing thelegal marijuanaindustry.There can be noassurance that wewill beable to comply with any suchlaws andregulations andits failure to do socould significantly harm ourbusiness, financial condition andresults ofoperations.
Competition
The legal marijuana sectorisrapidly growingandthe Company faces significant competition intheoperationofretail outlets, MMDsandgrowfacilities. Manyofthese competitors will have fargreater experience, moreextensive industry contacts andgreater financial resources than theCompany.There can be noassurance that wecan adequately compete to succeed in ourbusiness plan.
Employees
As ofthe date as ofthisReport,our Oregonoperations have atotal of 15-20part-time store employees including budtenders, trimmers, growers, and 6full-time employees, consisting of 3store managers, aVicePresident ofMarketing andBrand development, the SeniorVicePresidentofCannabis Operations and aVicePresident ofCultivation.Additionally,we engageseveral consultants to assistwith daily duties and business plan implementation and execution. Additional employees will behired and other consultants engaged inthe futureasourbusiness expands.
Results of Operations
Three months ended June 30, 2019 compared to three months ended June 30, 2018
Revenues
We had revenues of $249,121 for the three months ended June 30, 2019 as compared to revenues of $291,133 for the three months ended June 30, 2018. The slight decrease in revenue during the current period was due to the normal fluctuation in the market.
Cost of Goods Sold
Our cost of goods sold for the three months ended June 30, 2019 was $92,719 compared to cost of goods sold of $118,420 for the three months ended June 30, 2018. The slight decrease in cost of goods sold during the current period was due to normal fluctuation in the wholesale cannabis market.
Salaries and Wages
Salaries and Wages increased to $114,415 for the three months ended June 30, 2019 as compared to $102,192 for the three months ended June 30, 2018. The increase in salaries and wages during the current period was due to normal increase in labor cost.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative increased to $217,197 for the three months ended June 30, 2019 as compared to $175,158 for the three months ended June 30, 2018. This increase reflects the fact that some of the expenses associated with this category have increased over time.
Professional Fees
Professional fees were $145,119 for the three months ended June 30, 2019, as compared to $172,331 for the three months ended June 30, 2018. Our professional fees were primarily attributable to accounting, auditing and legal fees associated with maintaining our public markets listing.
Interest Expense
Interest expense and debt amortization expense decreased to $498,370 for the three months ended June 30, 2019 from $682,141 for the three months ended June 30, 2018. These decreases were due to lesser debt incurred over the past 12 months to acquire land and fund expansion of our operations.
Derivative Liabilities Expense
Derivative liabilities expense decreased to $115,253 for the three months ended June 30, 2019 from $356,394 for the three months ended June 30, 2018. These decreases were due to change in stock price as well as the volatility factors used in the derivative calculations.
Change in Fair Value of Embedded Derivative Liabilities
We had gain of $4,736,229 from change in fair value of embedded derivative liabilities for the three months ended June 30, 2019, compared to loss of $256,374 from change in fair value of embedded derivative liabilities for the three months ended June 30, 2018. These gain were due to change in stock price as well as the volatility factors used in the derivative calculations.
Net Income attributed to Kaya Holdings Inc.
We incurred net income of $3,863,740 attributed to Kaya Holdings Inc. for the three months ended June 30, 2019, as compared to a net loss of $1,533,968 for the three months ended June 30, 2018.
The majority of our net income during the three-month period ending June 30, 2019 was a result of the derivative liabilities associated with our Convertible Debt and a reduction in our stock price as well as the less volatility factors used in the derivative calculations. The net loss attributed to non-controlling interest for the three months ended June 30, 2019 and 2018 were $61,449 and $37,909, respectively.
Six months ended June 30, 2019 compared to six months ended June 30, 2018
Revenues
We had revenues of $512,879 for the six months ended June 30, 2019, as compared to revenues of $546,498 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. The slight decrease in revenue during the current period was due to the normal fluctuation in the market.
Cost of Goods Sold
Our cost of goods sold for the six months ended June 30, 2019 was $238,231 compared to cost of goods sold of $221,011 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. The slight increase in cost of goods sold during the current period was due to normal fluctuation in the wholesale cannabis market.
Salaries and Wages
Salaries and Wages increased to $260,870 for the six months ended June 30, 2019 as compared to $235,632 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. The increase in salaries and wages was due to normal increase in labor cost.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative increased to $460,220 for the six months ended June 30, 2019, as compared to $339,246 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. This increase reflects the fact that some of the expenses associated with this category have increased over time.
Professional Fees
Professional fees were $190,969 for the six months ended June 30, 2019, as compared to $1,358,059 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. The decrease in professional fees was a result of stock issuance in exchange for professional services and the shares were valued at market price on issuance date.
Interest expense
Interest expense and debt amortization expense decreased to $972,181 for the six months ended June 30, 2019 from $1,407,930 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. These decreases were due to lesser debt incurred over the past 12 months to acquire land and fund expansion of our operations.
Derivative Liabilities Expense
Derivative liabilities expense decreased to $562,148 for the six months ended June 30, 2019 from $1,913,591 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. These decreases were due to change in stock price as well as the volatility factors used in the derivative calculations.
Loss on extinguishment of debt
Loss on extinguishment of debt was $25,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2019 as compared to $-0- for the six months ended June 30, 2018. The loss was due to ratchet provision, which is change in conversion price on one of the convertible notes issued in 2018.
Change in Fair Value of Embedded Derivative Liabilities
Changes in Fair Value in Embedded Derivative Liabilities
Gain from change in fair value of embedded derivative liabilities decreased to $10,141,165 for the six months ended June 30, 2019 from $16,105,145 for the six months ended June 30, 2018. These decreases were due to change in stock price as well as the volatility factors used in the derivative calculations.
Net Income attributed to Kaya Holdings Inc.
We incurred net income of $8,113,272 attributed to Kaya Holdings Inc. for the six months ended June 30, 2019, as compared to a net income of $11,250,728 for the six months ended June 30, 2018.
The majority of our net income during the six-month period ending June 30, 2019 was a result of the derivative liabilities associated with our Convertible Debt and a reduction in our stock price as well as the less volatility factors used in the derivative calculations. The net loss attributed to non-controlling interest for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2018 were $168,608 and $74,554, respectively.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
May 2017 Financing
On May 11, 2017, we entered into a second financing agreement with Cayman Venture Capital Fund (the “Institutional Investor”) which had previously completed approximately $3.3 Million in in financing as listed in the 2018 10-K and previous filings to provide the Company with up to an additional $5.8 million in convertible note funding (the “May 2017 Notes \ ”) through July 31, 2018 (the “May 2017 Financing Agreement ”). The May 2017 Financing Agreement was amended as of July 31, 2017, to increase the amount of funding available to the Company thereunder to $6.3 million and to extend the time period for such funding to May 31, 2019 and was subsequently amended as of November 15, 2017 and as of March 31, 2018, to further increase the amount of funding available to the Company thereunder to $7.75 million and to provide for the remaining $5.8million in principal amount of May 2017 Notes to be (a) convertible into shares of the Company’s common stock at conversion prices ranging from $0.03 to $0.11 pursuant to the terms of each May 2017 Note as described below; and (b) to extend the time period for such funding to April 30, 2020.
Pursuant to an additional agreement reached as of March 31, 2018, KAYS and the Institutional Investor agreed that effective as of January 1, 2019, (a) the maturity date of all then outstanding Company promissory notes held by the Institutional Investor and its affiliate, NWP Finance LTD, will be extended from January 1, 2019 to January 1, 2020; (b) all of the $1.75 million in principal amount of May 2017 Notes currently outstanding and the remaining $5.8 million in principal amount of May 2017 Notes which may be issued under the Agreement, as amended, are to be secured by a mortgage lien on the Company’s 26-acre Lebanon, Oregon property, substantially similar in form and substance to the mortgage securing the $500,000 in principal amount of $0.03 Secured Notes purchased by the Institutional Investor, with the caveat that the property, improvements or rights to utilize them cannot be directly or indirectly leased, assigned or otherwise pledged to any entity without approval of the Institutional Investor, and in the event that there is a change in control of the Company or its subsidiaries the May 2017 Notes become immediately due and payable; and (c) the Institutional Investor was be granted piggy-back registration rights with respect to shares of the Company’s common stock it may hold or is issuable upon conversion of any Notes it or its Assigns may hold in the event the Company files a Registration Statement on Form S-1 with the Securities and Exchange Commission under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended to sell shares of its common stock or permit the resale by shareholders of previously issued shares of common stock, up to a maximum of 30% of the shares registered under such registration statement.
Moreover, effective as of January 20, 2019, the Agreement was further amended to: (a) extend the due dates for funding due under the Agreement for each of the remaining trenches (including the $420,000 remaining “$0.03” Notes that were due to expire December 31, 2018) by six (6) months; (b) agree to extend the maturity date all then outstanding Company promissory notes held by the Institutional Investor and its affiliate, NWP Finance LTD, from January 1, 2020 to January 1, 2021; and (c) pursuant to price adjustment features in the outstanding Notes held by the Institutional Investor, the Company confirmed that all outstanding Notes with a conversion price greater than $0.03 held by the Institutional Investor would be lowered to $0.03 per share at time of conversion.
As of the date of this Quarterly report, the Institutional Investor has purchased an aggregate of $2,625,000 in principal amount of May 2017 Notes from the Company under the May 2017 Financing Agreement, as amended to date, of which are (i) convertible into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price of $0.03; and (ii) secured by a mortgage lien on the Company’s 26 acre Lebanon, Oregon property (the “$0.03 Secured Notes ”).
January 2018 Financing
Effective January 22, 2018, and amended as of July 31, 2018 we entered into a financing agreement with a high net worth investor (the “HNW Investor ”) to provide the Company with up to $1.4 million in convertible note funding (the “January 2018 Notes ”) through July 31, 2018 (the “ January 2018 Financing Agreement ”). Pursuant to the January 2018 Financing Agreement, upon execution of the January 2018 Financing Agreement, the HNW Investor purchased $100,000 in principal amount of January 2018 Notes, which are convertible into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price of $0.10 per share (the“$0.10 Notes ”).
While the January 2018 Financing Agreement granted the HNW Investor the right to acquire additional January 2018 Notes by certain deadlines if additional funding was provided, no additional $0.10 Notes were purchased until the January 2018 Financing Agreement was amended in December, 2018 to allow the HNW investor the right to purchase an additional $25,000 of January 2018 Notes, which are convertible into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price of $0.05 per share (the“$0.05 Notes ”). In January 2019 the Agreement was further amended to lower the conversion price of the previously purchased $0.10 Note to $0.05, and to modify terms of the $0.10 Note to make them consistent with the May 2017 Financing Agreement executed with the Institutional Investor, and to allow for the right of the HNW Investor to acquire an additional $200,000 of January 2018 Notes, which are convertible into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price of $0.03 per share (the“$0.03 Notes ”).
In March, 2019 the agreement was further amended to lower the conversion prices of the previously issued $0.05 Notes to $0.03. As of the date of this Quarterly report, the HNW Investor has purchased an additional aggregate of $75,000 in principal amount of the $0.03 Notes and has indicated he will purchase the remaining $125,000 of the $0.03 Notes.
All the above securities were issued pursuant to the exemption from registration under the Securities Act afforded by Section 4(a)(2) thereof and Regulation D thereunder.
Use of Proceeds
The proceeds from the offer and sale of the $2.1M Notes, the May 2017 Notes and the January 2018 notes and are and will be used to fund the Company’s growth plan, including the expansion of our chain of Kaya Shack™ Marijuana Superstores in Oregon, the acquisition and development of our Lebanon, Oregon legal cannabis cultivation and manufacturing facility, the operation and development of our Eugene, Oregon 12,000 square foot indoor legal marijuana grow and manufacturing facility and the development and introduction of new Kaya Shack™ branded cannabis products.
Plan of Operations
Management believes that consummation of the proceeds received and expected to be received from the above described financings as well as any other financing transactions that it may enter into, combined with existing and anticipated revenues, has alleviated the Company’s financial difficulties to a significant extent and will allow the Company to meet its anticipated working capital needs for a period of between twelve and eighteen months from the date of this report. However, there can be no assurance that the balance of the $7.75 million financing will be completed, or that management’s belief will be correct and that the Company will not sooner require additional financing to meet its working capital needs prior to achieving profitability or positive cash flow. Moreover, we may not be successful in raising additional capital on commercially reasonable terms, if and when needed, in which case our business, financial condition, cash flows and results of operations may be materially and adversely affected.
Note Conversion
On March 5, 2019, a total of 7,785,952 shares of common stock were issued to Cayman Venture Capital Fund in consideration of settlement a total of $233,579 in principal and interest pursuant to a Note Conversion. The Note was reported as converted on September 16, 2018 when the documents were submitted but the shares were not issued until March 5, 2019. The shares have now been issued and are in electronic format in an account at the transfer agent pending delivery to the Cayman Venture Capital Fund. For more information see Footnote “R” to Convertible Debt Summary in Note 6 to the Financials.
Future Employee Stock Plan Issuances and Director and Officer Restricted Stock issuances
On December 28, 2018 KAYS informed she staff of the Kaya Shack Operations that they had been allocated a total of 2,050,000 shares of stock from the KAYS 2011 Employee Stock Plan (the “Plan”) for their service to the Company. The shares are subject to final approval of and confirmation by the Board of Directors to determine that the potential share issuances are valid according to the terms of the plan and other limitations, and will be reviewed at the next Board Meeting. Upon confirmation of eligibility and issuance from the Board of Directors, the recipients will be issued an account statement evidencing their shares along with instructions as how to effect delivery from the transfer agent.
Pursuant to consulting agreements entered into on February 19, 2018 via Board Stipulation, BMN Consultants is scheduled to receive 3,000,000 shares of KAYS stock in Q-1 from the KAYS 2011 Employee Stock Plan (the “Plan”) for W. David Jones’s service to the Company during 2019. The shares are considered to be fully paid when issued.
Pursuant to consulting agreements entered into on February 19, 2018 via Board Stipulation, Tudog Consultants is scheduled to receive 3,000,000 shares of KAYS restricted stock in Q-1 for Craig Frank’s service to the Company during 2019. The shares are considered to be fully paid when issued.
Pursuant to annual compensation schedules, each of the three (3) Board Members is scheduled to receive 100,000 shares of KAYS restricted stock in Q-1 for their service to the Company during 2019. The shares are considered to be fully paid when issued.
The above awards are all subject to final approval of and confirmation by the Board of Directors to determine that the potential share issuances are valid according to the terms of the plan and other qualifications and will be reviewed at the next Board Meeting.
Item 3.Quantitative andQualitative DisclosuresAboutMarket Risk
Notapplicable.
Item 4.Controls andProcedures
EvaluationofDisclosure ControlsandProcedures
Under thedirectionofChief Executive Officer and Acting Chief Financial Officer (ourprincipal executive, financial andaccounting officer), weevaluatedourdisclosure controls and procedures as of June 30, 2019. OurChief Executive Officer andActing Chief Financial Officer (ourprincipal executive, financial andaccounting officer) concluded that ourdisclosure controls andprocedures were noteffective as ofJune 30, 2019 for thereasonsset forthin ourAnnual Report on Form 10-K forthe year ended December 31, 2017.
Wemaintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed toensurethat the information required to bedisclosed in the reportsthatwefile under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934(the “Exchange Act”) is recorded, processed, summarizedandreported withinthetime periods specified intheSEC’srules and forms,andthat suchinformationisaccumulated and communicated to ourmanagement, including ourChief Executive Officer (ourprincipal executive, financial and accounting officer), asappropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures. Indesigningandevaluating the disclosure controls andprocedures, management recognized that anycontrols andprocedures,nomatter howwell designed andoperated, can onlyprovide reasonable assurance ofachieving the desired control objectives, and inreachingareasonable level ofassurance, management necessarily was required toapply its judgment inevaluating the costbenefit relationship ofpossible controls andprocedures.
Asrequiredby SEC Rule 13a15(b), wecarried outan evaluation, under thesupervision and with the participation of ourmanagement, including ourChief Executive Officer (ourprincipal executive, financial andaccounting officer), ofthe effectiveness ofthe design and operation of ourdisclosure controls andproceduresas ofJune 30, 2019.Based on theforegoing, ourChief Executive Officer(ourprincipal executive, financial andaccounting officer) concluded that ourdisclosure controls and procedures were noteffective.Itshouldbenoted that the design of anysystemofcontrols is basedinpart uponcertain assumptions aboutthe likelihoodoffuture events, and there can be no assurancethat any designwill succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions, regardless of howremote.
Changesin Internal Controls
There wasnochangein ourinternal controls orin other factors that could affect these controls during the quarter ended June 30, 2019,that has materially affected, or isreasonably likely to materially affect, ourinternal controls overfinancial reporting.Wedo notanticipate any changes toourinternal controls atthis time.
PARTII –OTHERINFORMATION
Item 1.Legal Proceedings
Aspreviously reported in ourperiodic reports filed under the Securities Exchange Actof 1934,inthe fourthquarterof 2018,KAYSconcluded thepurchase ofthe Eugene, Oregonbased Sunstone Farmsgrowand manufacturingfacility,which is licensedbythe Oregon Liquor ControlCommission (the “OLCC”) for boththe production (growing) ofmedical and recreational marijuana flower and the processingofcannabis concentrates/extracts/edibles. The purchaseincludeda 12,000squarefootbuilding housing an indoor growfacility,aswell as equipmentforgrowing and extractionactivity.The facility can producein excess of 800 poundscannabis flower annually as currently outfitted, aswellas asubstantial amount ofmanufactured extracts and related cannabis products.KAYSentered into amanagement agreement with the holder ofexisting OLCC licenses (“Sunstone”) tooversee operations atthe facility pendingtransfer of thelicense toKAYS,which were awarewould be anextendedandcumbersome process.
Atall times since we beganthe transaction processand on anongoing basis since thetransactionwasconcluded,wehave workedin close cooperation with the OLCC ateach stage toboth document the transaction, renew the existing licenses and transfer the licenses to usand submitted asubstantial volumeof paperwork totheOLCCwith respect tothe foregoing.Wecommunicated with the OLCC onnumerous occasionsandrequested guidance as to howto legally structure and complete thetransferofthe licenses to us.
InNovember2018, wewere notified that that theOLCC wasdoingaComplianceReview,pending the requested transfer of thelicenses (which is normal practice) and that they mayhave issueswithhowcertain aspects ofthe transactionwerestructured.
Weasked the OLCCforguidance with respect to interim operation of thefacilityandwere advised to continue operating as usual. Subsequently, in February andMarch of 2019, the OLCCissued Conditional Letters ofauthoritysothat the facility could continue operations for aperiodnot toexceedoneyear fromthe dates issued, pendingtheSunstone License renewals and processing of therequested license transfers toKAYS.
Notwithstandingtheforegoing,inmid-April 2019, we wereadvised bySunstone that it hadbeen notified that the OLCCwas proposing that Sunstone’s licenses becancelled, claiming that that Sunstone had notfiled paperwork correctly with respect to the transaction orits historical ownership.
Sunstone’s attorney has filedarequestfor ahearing which we havebeen advisedbythe OLCCcould take over ayear to occur and resolve dueto the extensive number oflicensing matters being processed. Acursory review of theresolution ofother sale-related compliance matters listed ontheOLCC’swebsite showsthat it is notatypical to for the OLCCto seek revocationof alicense, butthat often thesettlement ofthat matter includes the sale andtransfer of thelicense which,is what weare seeking. For therecord, neitherKAYS nor our Oregon OLCClicensed entities werenamed inOLCC action.
The Company notes thatin a new andemerging regulatory environment forlegal cannabis production andsale, licensing issues such asthepresent oneperiodically arise. Infact,aspreviously reported,theCompanyhasencountered suchissues in connection with its Portland, Oregon retail outlet and its planned Lebanon, Oregongrow andproduction operation, all ofwhichweresatisfactorily resolved in theCompany’s favor. Accordingly,the Company iscooperating with Sunstoneand the OLCC with respect to this matter and is optimistic that oncethe extensive recordofpaperwork submitted to and consultation with the OLCC has been reviewed, it willbeable secure transferofthe OLCClicenses.
Item 1A. RiskFactors.
See“Item 1A.Risk Factors” in our AnnualReport on Form 10-K forthe year ended December31, 2018.
Item 2.Unregistered Sales ofEquity Securitiesand Use ofProceeds
OnJanuary22, 2019 theCompany received $70,000 fromthe issuance ofconvertible debt to the CaymanVentureCapital Fund pursuantto the May 2017Financing Agreement,asamended. Interestisstated at 8%. TheNote andInterest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 pershare.TheNote is Due inJanuary of 2021.
On February11, 2019 theCompany received $150,000 fromthe issuance ofconvertible debt tothe CaymanVentureCapitalFundpursuant to the May 2017Financing Agreement, as amended. Interest isstated at 8%. TheNoteandInterest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 pershare.TheNote is Due inJanuary of 2021.
OnMarch20, 2019the Company received $15,000 fromthe issuance ofconvertible debt tothe High NetWorthInvestorpursuant tothe January 2018Financing Agreement, asamended. Interest is stated at 8%. TheNoteandInterest is convertible into common shares at $0.03per share. The Noteis Due inJanuary of 2021.
On April 16, 2019the Company received $75,000 from theissuanceofconvertible debt tothe CaymanVentureCapital Fund pursuant totheMay 2017Financing Agreement, as amended. Interest isstated at 8%. TheNote andInterest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 pershare. TheNote is Due inJanuary of 2021.
OnApril22, 2019the Company received $35,000 from theissuanceofconvertible debt to the High NetWorthInvestor pursuant to the January 2018Financing Agreement, asamended. Interest is stated at 8%. TheNoteandInterest is convertible into common shares at $0.03per share. The NoteisDue inJanuary of 2021.
On May 6, 2019the Company received $35,000 from theissuanceofconvertible debtto theHighNetWorthInvestor pursuantto the January 2018Financing Agreement, asamended. Interest is stated at 8%. TheNote andInterest is convertible into common shares at $0.03per share. The NoteisDue inJanuary of 2021.
On May 21, 2019the Company received $50,000 from theissuanceofconvertible debt tothe CaymanVentureCapital Fund pursuant totheMay 2017Financing Agreement, as amended. Interest isstated at 8%. TheNote andInterest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 pershare. TheNote is Due inJanuary of 2021.
On June 5, 2019the Company received $20,000 from theissuanceofconvertible debtto theHighNetWorthInvestor pursuantto the January 2018Financing Agreement, asamended. Interest is stated at 8%. TheNote andInterest is convertible into common shares at $0.03per share. The NoteisDue inJanuary of 2021.
On July 2, 2019the Company received $75,000 from theissuanceofconvertible debt tothe CaymanVentureCapital Fund pursuant totheMay 2017Financing Agreement, as amended. Interest isstated at 8%. TheNote andInterest is convertible into common shares at $0.03 pershare. TheNote is Due inJanuary of 2021.
All ofthe foregoing securities wereissued pursuanttotheexemption from theregistration afforded bySection 4 (a) (2) ofthe Securities act of 1933, asamended and therules and regulations thereunder.
Item 3.Defaults UponSenior Securities.
None.
Item 4.Mine SafetyDisclosures.
Notapplicable.
Item 5.Other Information.
None
Item 6.Exhibits
SIGNATURES
Inaccordance with Section 13 or 15(d) ofthe Exchange Act, the registrant caused this reportto besigned onits behalf by theundersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Dated: August 19, 2019
KAYA HOLDINGS, INC.
By:/s/ Craig Frank
Craig Frank, Chairman, President, Chief Executive Officer and Acting Chief Financial Officer (Principal Executive, Financial and Accounting Officer)













































