
RXi Pharmaceuticals NASDAQ: RXII Targeting Immune Checkpoints Using Self-Delivering RNAi (sd-rxRNA®) Technology Alexey Eliseev, PhD 2nd Annual Oligonucleotide and Peptide Therapeutics Conference, Cambridge, MA March 29, 2017 Exhibit 99.1

Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Words such as “believes,” “anticipates,” “plans,” “expects,” “indicates,” “will,” “intends,” “potential,” “suggests” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. These statements are based on RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation’s (the “Company”) current beliefs and expectations. Such statements include, but are not limited to, statements about the future development of the Company’s products (including timing of clinical trials and related matters associated therewith), the expected timing of certain developmental milestones, the reporting of unblinded data, potential partnership opportunities, the Company’s competition and market opportunity and pro forma estimates. The inclusion of forward-looking statements should not be regarded as a representation by the Company that any of its plans will be achieved. Actual results may differ from those set forth in this presentation due to risks and uncertainties in the Company’s business, including those identified under “Risk Factors” in the Company’s most recently filed Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q and in other filings the Company periodically makes with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The Company does not undertake to update any of these forward-looking statements to reflect a change in its views or events or circumstances that occur after the date of this presentation.
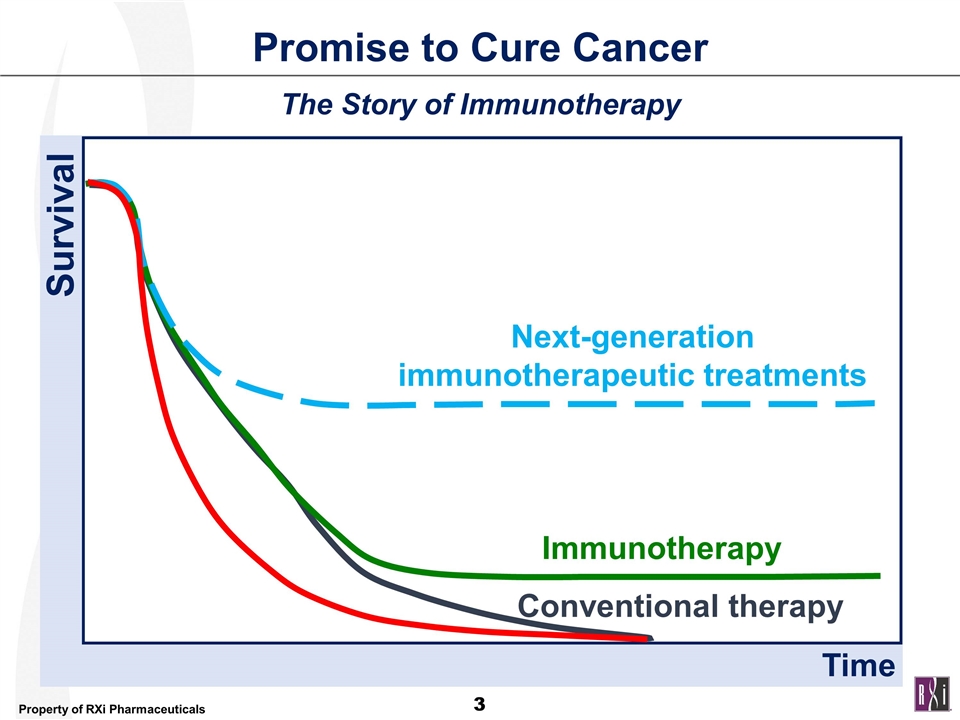
Promise to Cure Cancer The Story of Immunotherapy Survival Conventional therapy Immunotherapy Time Next-generation immunotherapeutic treatments
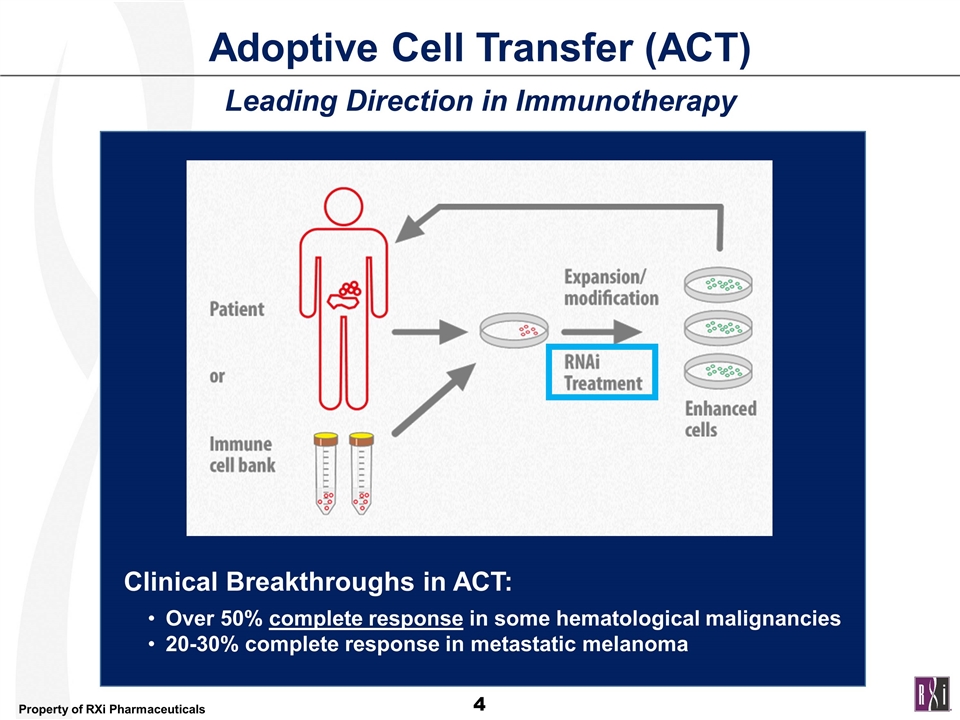
Adoptive Cell Transfer (ACT) Leading Direction in Immunotherapy Clinical Breakthroughs in ACT: Over 50% complete response in some hematological malignancies 20-30% complete response in metastatic melanoma
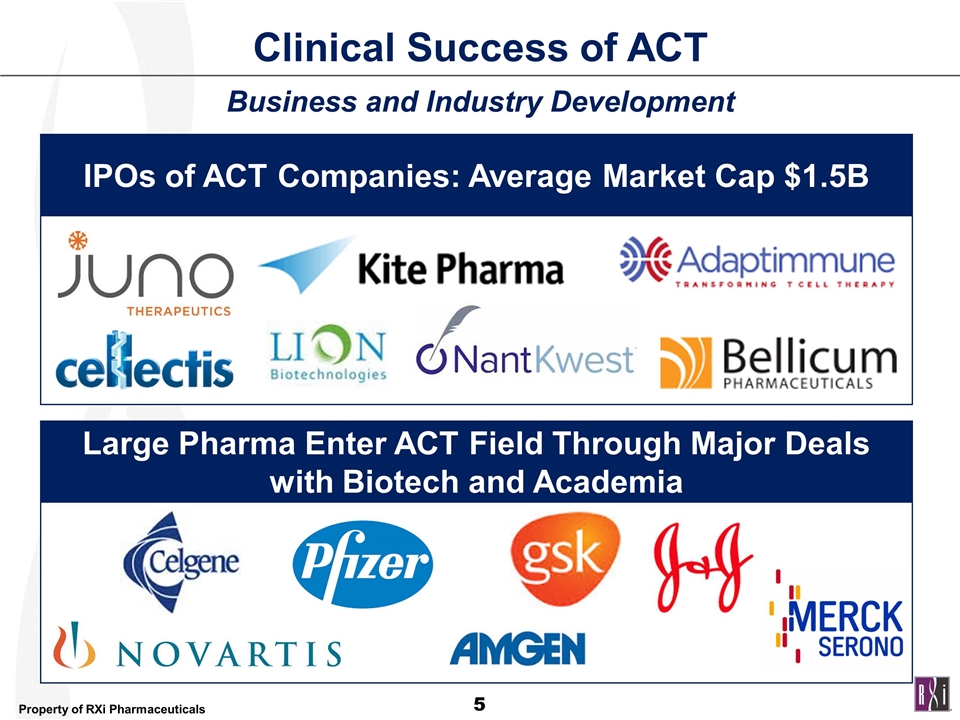
Clinical Success of ACT Business and Industry Development Large Pharma Enter ACT Field Through Major Deals with Biotech and Academia IPOs of ACT Companies: Average Market Cap $1.5B
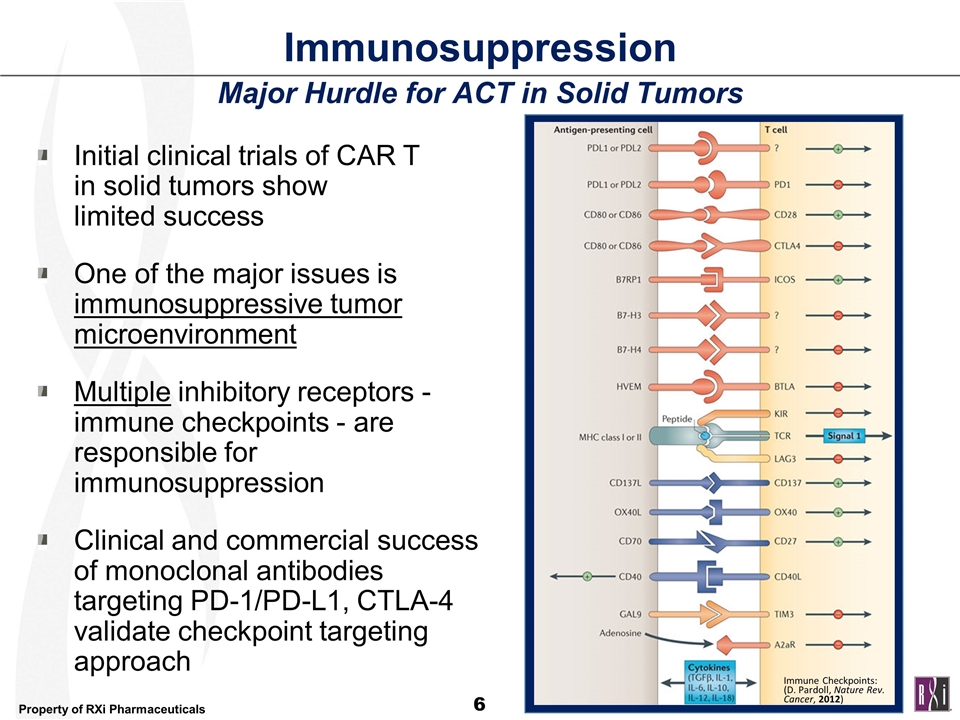
Immunosuppression Major Hurdle for ACT in Solid Tumors Initial clinical trials of CAR T in solid tumors show limited success One of the major issues is immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment Multiple inhibitory receptors - immune checkpoints - are responsible for immunosuppression Clinical and commercial success of monoclonal antibodies targeting PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4 validate checkpoint targeting approach Immune Checkpoints: (D. Pardoll, Nature Rev. Cancer, 2012)
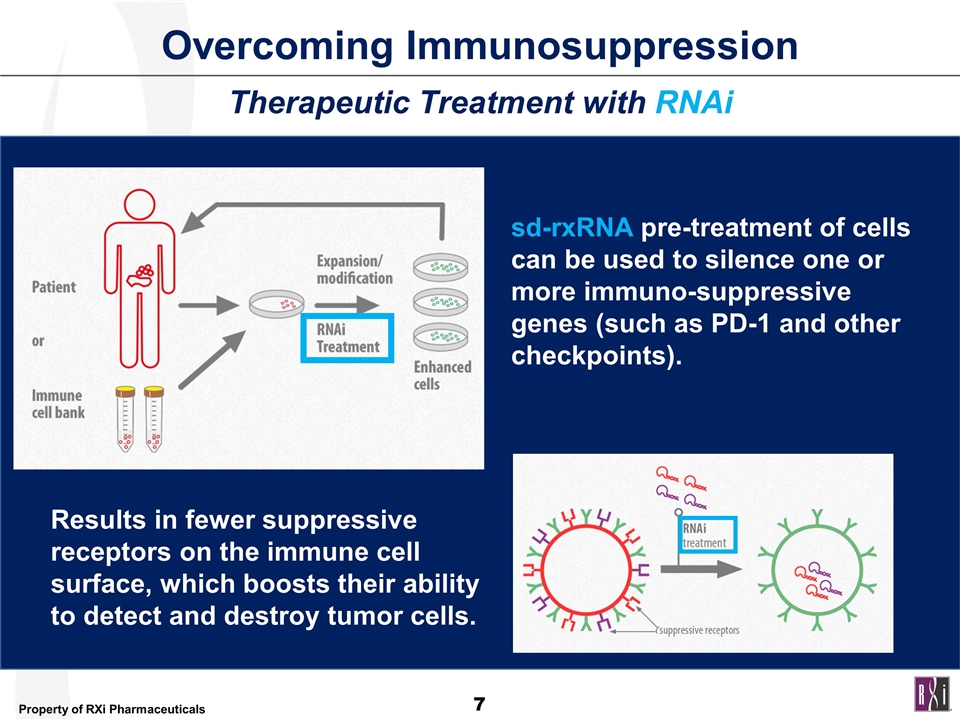
Overcoming Immunosuppression sd-rxRNA pre-treatment of cells can be used to silence one or more immuno-suppressive genes (such as PD-1 and other checkpoints). Results in fewer suppressive receptors on the immune cell surface, which boosts their ability to detect and destroy tumor cells. Therapeutic Treatment with RNAi
RXi’s sd-rxRNA: Best RNAi Technology for Adoptive Cell Transfer One of the main challenges of RNAi technologies is the delivery of hydrophilic siRNA molecules to target cells Commonly used delivery techniques (lipid formulations, electroporation) are not optimal for ex-vivo treatment of therapeutic cells RXi’s proprietary self-delivering RNAi technology provides simple and effective RNAi delivery for ex-vivo applications

sd-rxRNA Technology Provides Simple and Effective RNAi Delivery for ex-vivo Applications No delivery formulation required for local therapeutic applications Delivery not limited to a specific cell type Single chemically-modified RNA compound with improved drug-like properties Potent, stable, specific Efficient cellular uptake and gene silencing Rapid lead identification and optimization Robust, long lasting in vivo efficacy in multiple tissues Demonstrated safety and efficacy in human clinical trials
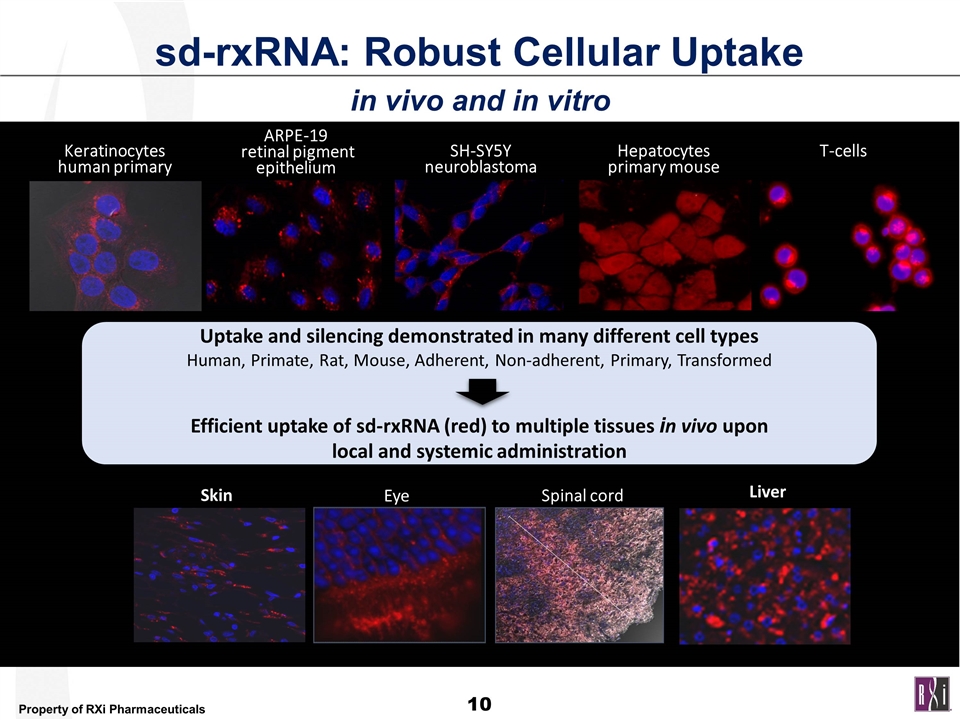
sd-rxRNA: Robust Cellular Uptake in vivo and in vitro T-cells ARPE-19 retinal pigment epithelium Hepatocytes primary mouse Keratinocytes human primary SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma Skin Eye Spinal cord Uptake and silencing demonstrated in many different cell types Human, Primate, Rat, Mouse, Adherent, Non-adherent, Primary, Transformed Efficient uptake of sd-rxRNA (red) to multiple tissues in vivo upon local and systemic administration Liver

Immuno-oncology Program with sd-rxRNA Selection of lead sd-rxRNA compounds against six different extracellular and intracellular immune check points Demonstrated silencing of all tested checkpoint targets in vitro, singly and in combinations Efficient and long-lasting silencing of immune checkpoints in vivo Applicability of sd-rxRNA transfection in cell therapy to solid tumors Filing of intellectual property that covers the use of RNAi compounds for use in cell therapy
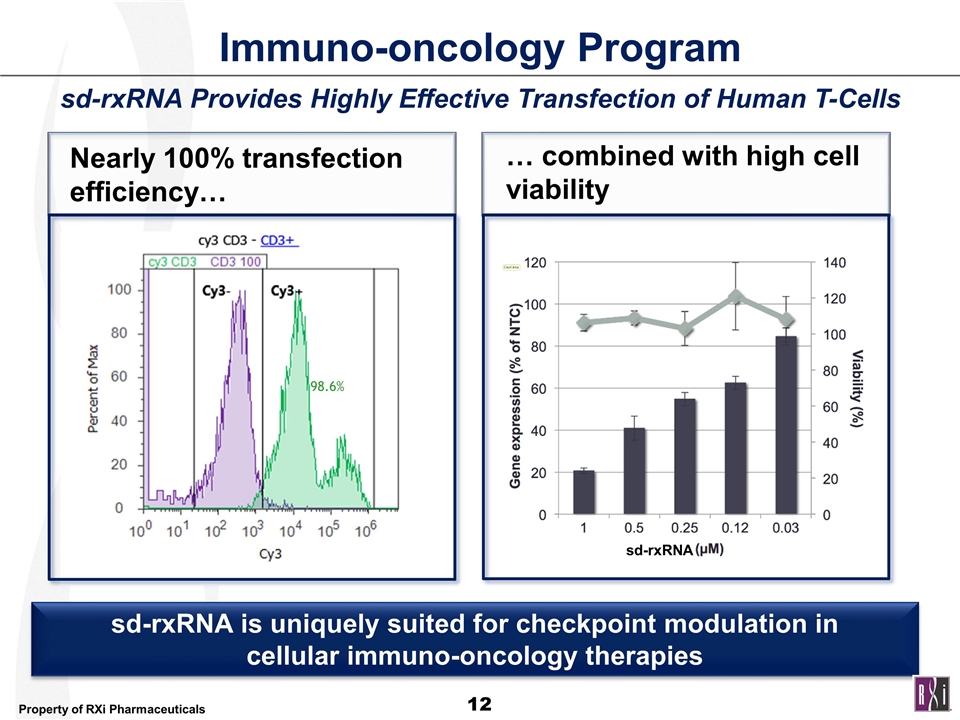
Immuno-oncology Program Nearly 100% transfection efficiency… sd-rxRNA is uniquely suited for checkpoint modulation in cellular immuno-oncology therapies 98.6% … combined with high cell viability sd-rxRNA sd-rxRNA Provides Highly Effective Transfection of Human T-Cells
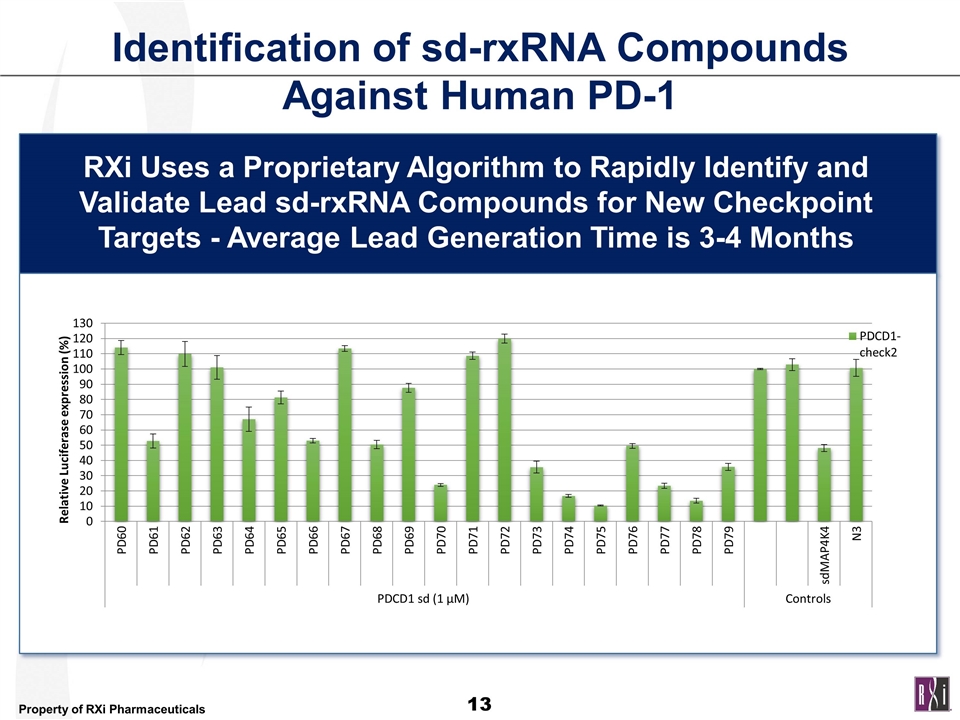
Identification of sd-rxRNA Compounds Against Human PD-1 RXi Uses a Proprietary Algorithm to Rapidly Identify and Validate Lead sd-rxRNA Compounds for New Checkpoint Targets - Average Lead Generation Time is 3-4 Months
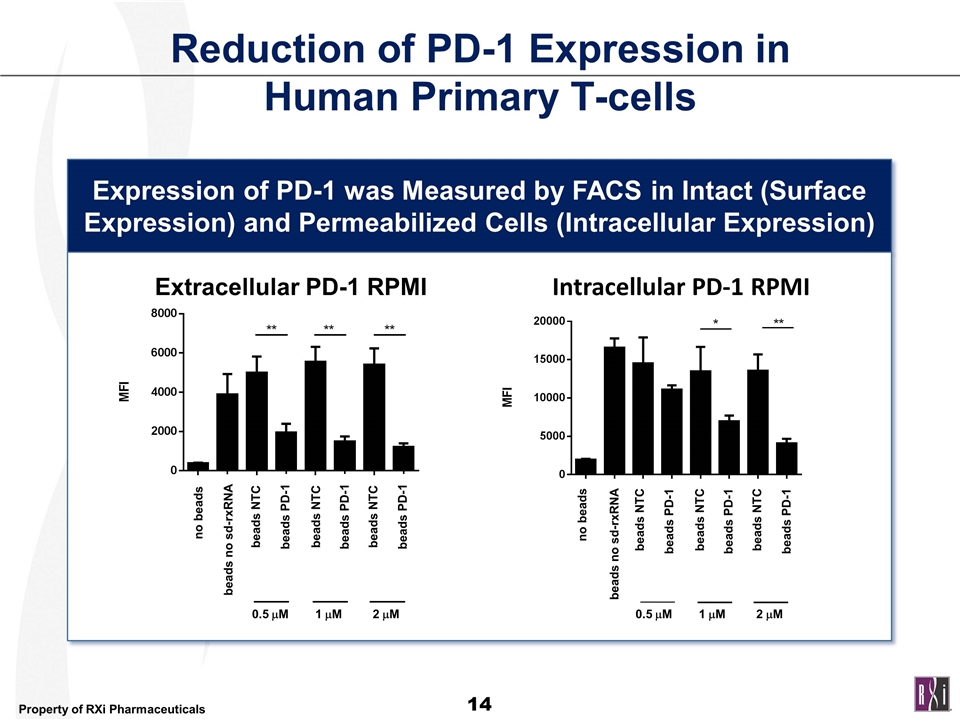
Reduction of PD-1 Expression in Human Primary T-cells Expression of PD-1 was Measured by FACS in Intact (Surface Expression) and Permeabilized Cells (Intracellular Expression) sd-rxRNA beads NTC beads PD-1 beads no sd-rxRNA no beads beads NTC beads NTC beads PD-1 beads PD-1 beads NTC beads PD-1 beads no sd-rxRNA no beads beads NTC beads NTC beads PD-1 beads PD-1 Extracellular PD-1 RPMI Intracellular PD-1 RPMI 0.5 mM 0.5 mM 1 mM 2 mM 0.5 mM 0.5 mM 1 mM 2 mM
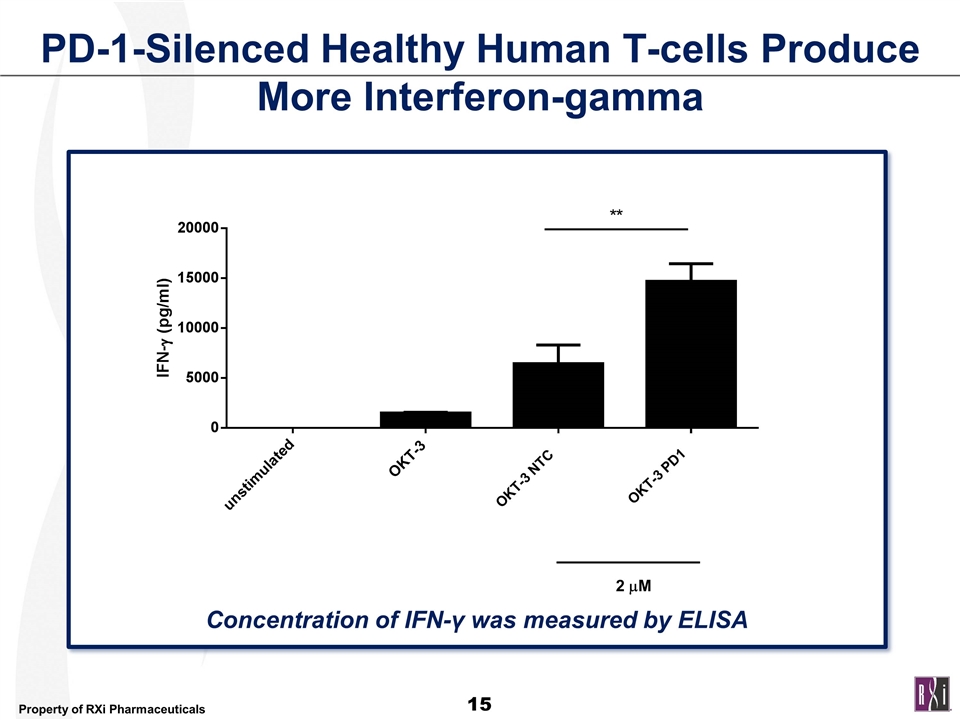
PD-1-Silenced Healthy Human T-cells Produce More Interferon-gamma Concentration of IFN-γ was measured by ELISA OKT-3 NTC OKT-3 PD1 2 mM
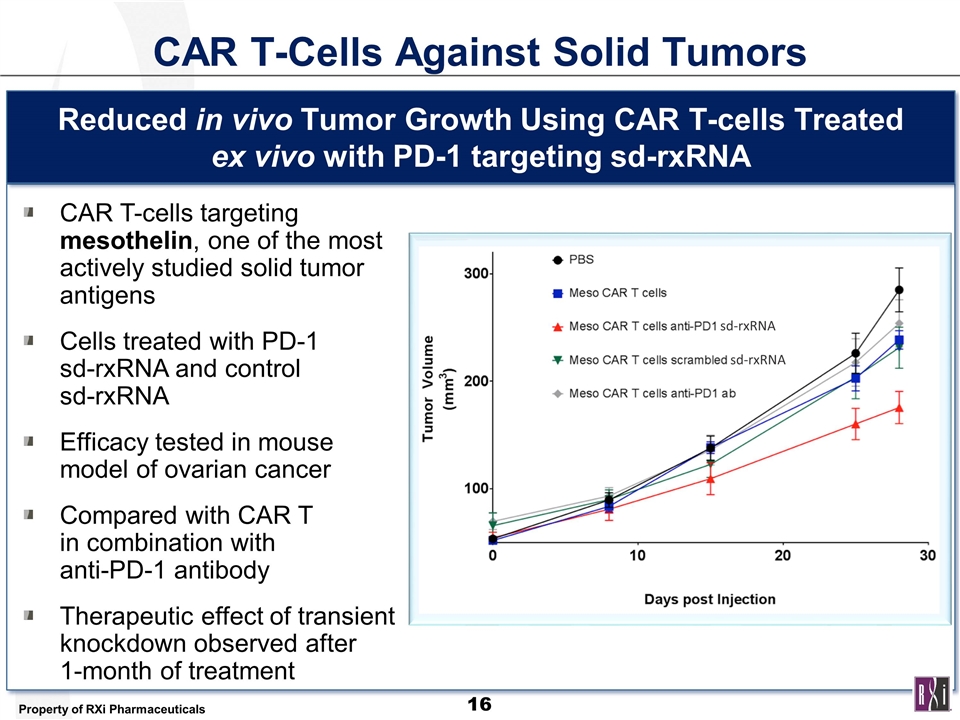
CAR T-Cells Against Solid Tumors CAR T-cells targeting mesothelin, one of the most actively studied solid tumor antigens Cells treated with PD-1 sd-rxRNA and control sd-rxRNA Efficacy tested in mouse model of ovarian cancer Compared with CAR T in combination with anti-PD-1 antibody Therapeutic effect of transient knockdown observed after 1-month of treatment Reduced in vivo Tumor Growth Using CAR T-cells Treated ex vivo with PD-1 targeting sd-rxRNA sd-rxRNA sd-rxRNA
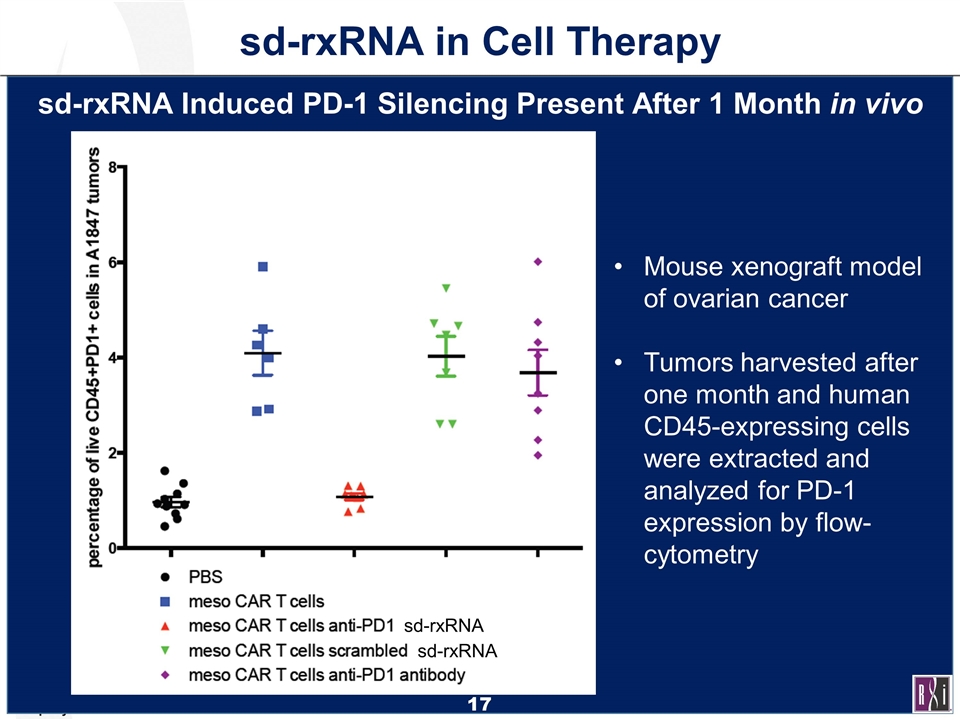
sd-rxRNA sd-rxRNA sd-rxRNA in Cell Therapy sd-rxRNA Induced PD-1 Silencing Present After 1 Month in vivo Mouse xenograft model of ovarian cancer Tumors harvested after one month and human CD45-expressing cells were extracted and analyzed for PD-1 expression by flow-cytometry
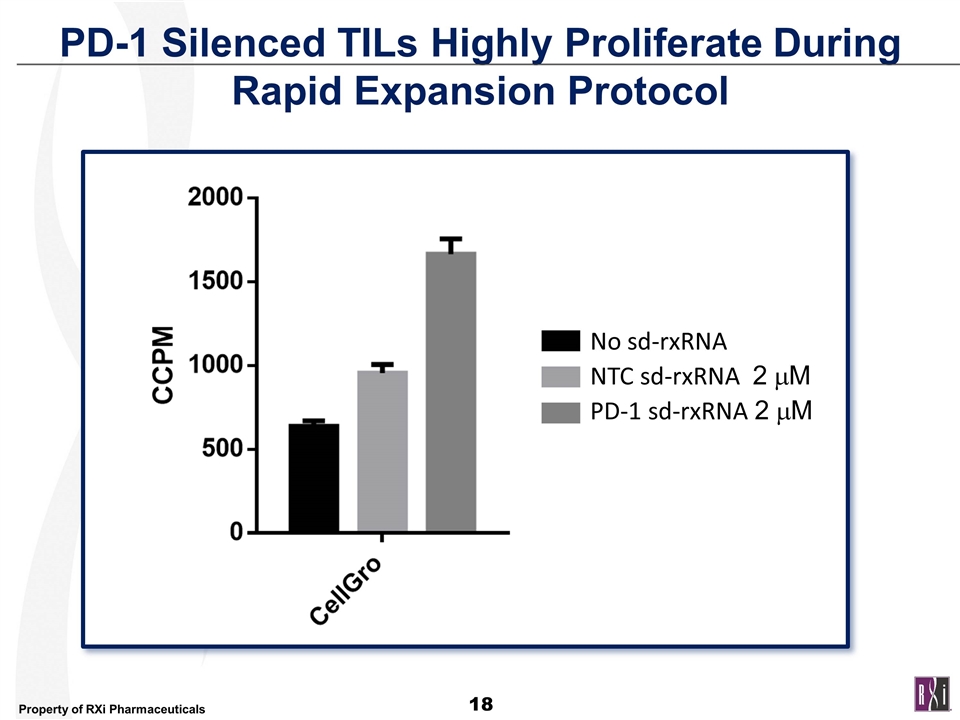
PD-1 Silenced TILs Highly Proliferate During Rapid Expansion Protocol No sd-rxRNA NTC sd-rxRNA 2 mM PD-1 sd-rxRNA 2 mM
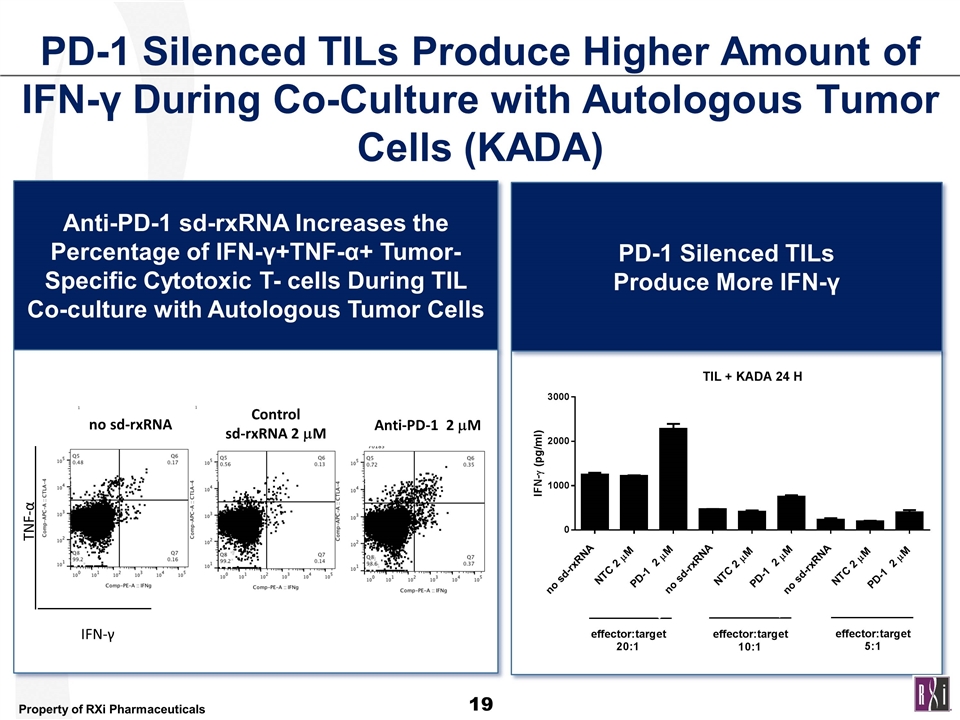
PD-1 Silenced TILs Produce Higher Amount of IFN-γ During Co-Culture with Autologous Tumor Cells (KADA) Anti-PD-1 sd-rxRNA Increases the Percentage of IFN-γ+TNF-α+ Tumor-Specific Cytotoxic T- cells During TIL Co-culture with Autologous Tumor Cells no sd-rxRNA Anti-PD-1 2 mM Control sd-rxRNA 2 mM TNF-α IFN-γ PD-1 Silenced TILs Produce More IFN-γ no sd-rxRNA no sd-rxRNA no sd-rxRNA no sd-rxRNA NTC 2 mM PD-1 2 mM no sd-rxRNA NTC 2 mM PD-1 2 mM no sd-rxRNA NTC 2 mM PD-1 2 mM
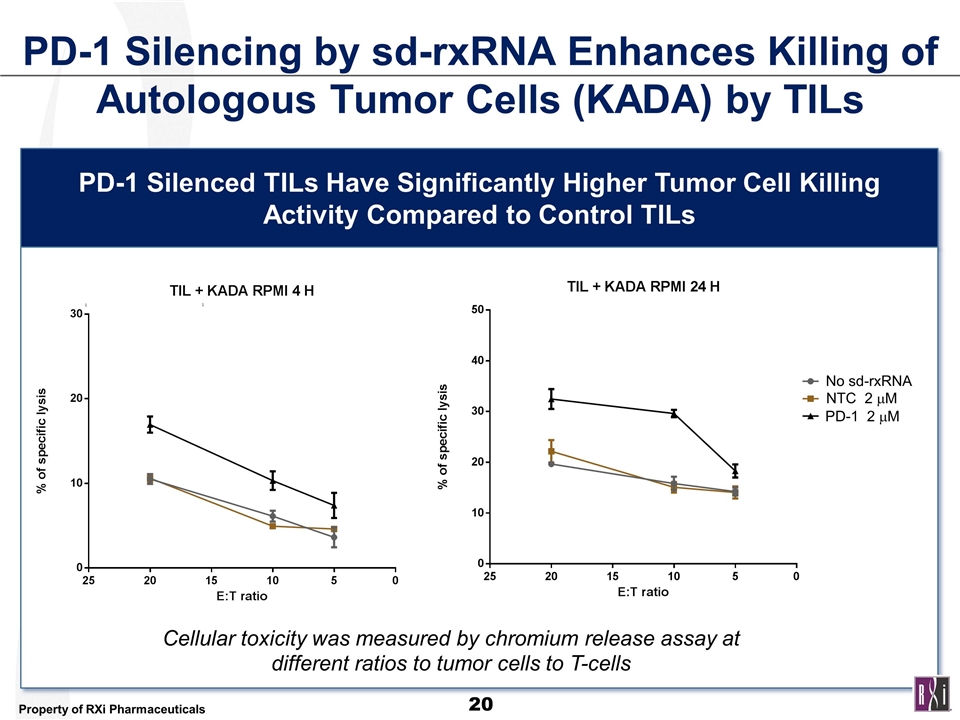
PD-1 Silencing by sd-rxRNA Enhances Killing of Autologous Tumor Cells (KADA) by TILs PD-1 Silenced TILs Have Significantly Higher Tumor Cell Killing Activity Compared to Control TILs Cellular toxicity was measured by chromium release assay at different ratios to tumor cells to T-cells No sd-rxRNA No sd-rxRNA NTC 2 mM PD-1 2 mM
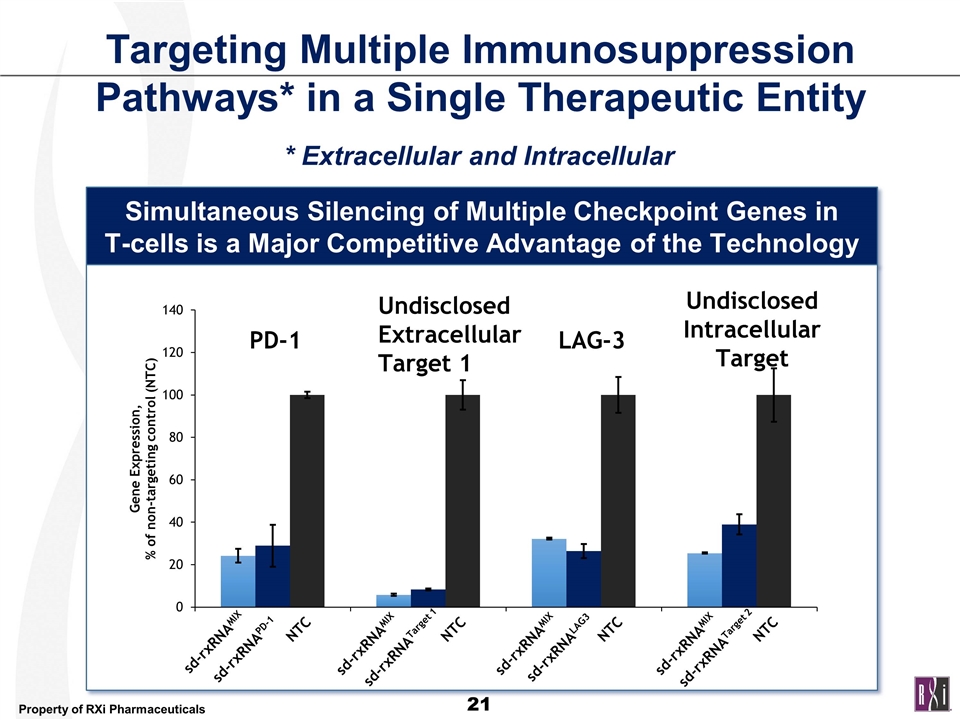
Targeting Multiple Immunosuppression Pathways* in a Single Therapeutic Entity * Extracellular and Intracellular Simultaneous Silencing of Multiple Checkpoint Genes in T-cells is a Major Competitive Advantage of the Technology sd-rxRNAMIX sd-rxRNAPD-1 sd-rxRNATarget 1 sd-rxRNALAG3 sd-rxRNATarget 2 NTC NTC NTC NTC PD-1 Undisclosed Extracellular Target 1 LAG-3 UndisclosedIntracellular Target sd-rxRNAMIX sd-rxRNAMIX sd-rxRNAMIX

Potential Advantages of RXi’s Approach to Immunotherapy Single therapeutic agent with one or multiple immune checkpoints attenuated Streamlined regulatory path No multiple combination trials required Newly discovered checkpoint targets can be rapidly tackled Therapeutic efficacy without persisting “rogue” cells in the body Transient silencing effect No permanent genome modification No RNA-related toxicity concerns Ex vivo application of sd-rxRNA Clinically proven safety of sd-rxRNA Lack of side effects related to checkpoint inhibitor toxicity Only small alterations needed in cell manufacturing process Facilitates adaptation of existing cell technologies
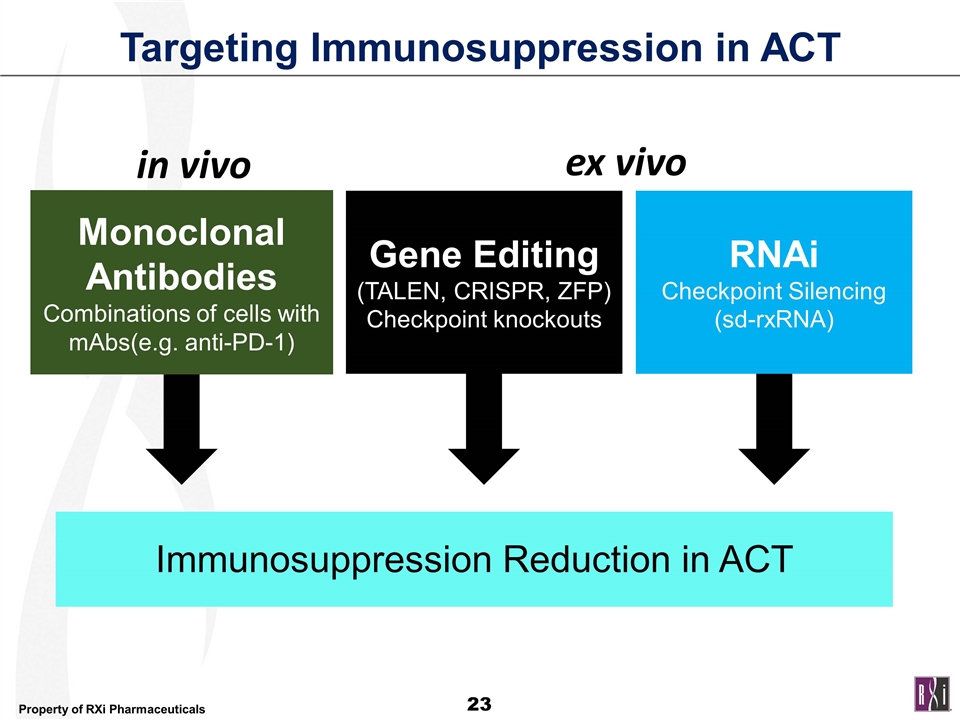
Targeting Immunosuppression in ACT Immunosuppression Reduction in ACT Monoclonal Antibodies Combinations of cells with mAbs(e.g. anti-PD-1) Gene Editing (TALEN, CRISPR, ZFP) Checkpoint knockouts RNAi Checkpoint Silencing (sd-rxRNA) ex vivo in vivo
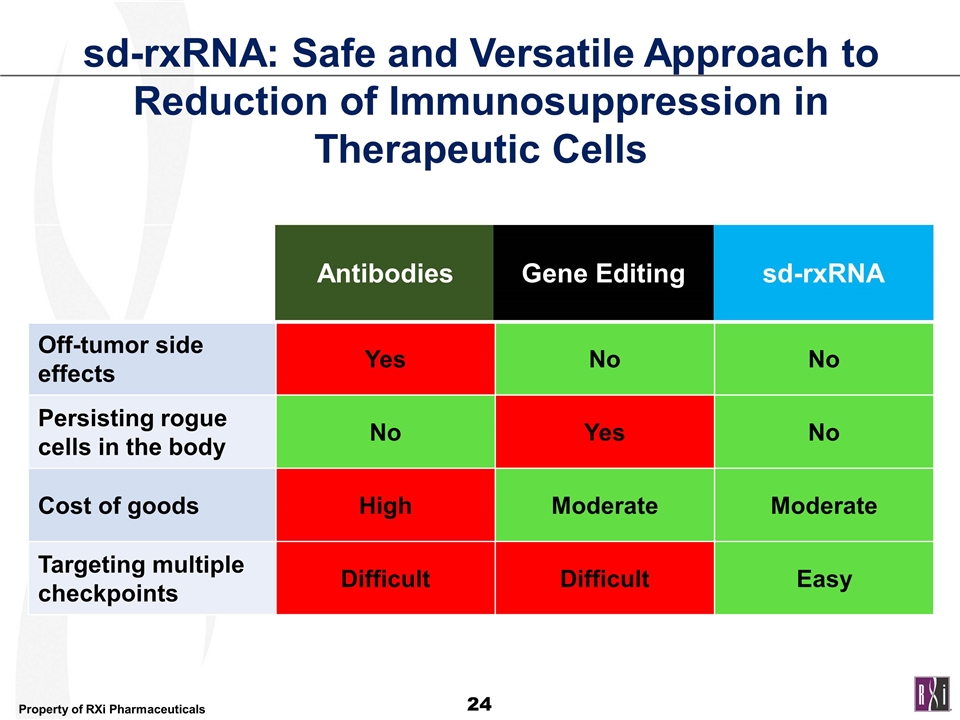
Off-tumor side effects Yes No No Persisting rogue cells in the body No Yes No Cost of goods High Moderate Moderate Targeting multiple checkpoints Difficult Difficult Easy sd-rxRNA: Safe and Versatile Approach to Reduction of Immunosuppression in Therapeutic Cells Antibodies Gene Editing sd-rxRNA

RXi Appoints Leading Oncology Experts to SAB Dr. James Griffin Chairman, Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Professor, Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Director, Medical Oncology, Brigham and Women's Hospital Scientific Advisory Boards: Lombardi Cancer Center at Georgetown University; Johns Hopkins Cancer Center; and Case Western Cancer Center. Dr. Rolf Kiessling Professor in Experimental Oncology at the Karolinska Institutet and Senior Chief Physician of Radiumhemmet at Karolinska Hospital Accredited with the discovery of Natural Killer cells (NK cells) during the mid-70’s Broad scientific expertise in the field of experimental and clinical immunology Expanding Team of Accomplished Scientific Advisors

RXi Pharmaceuticals Overview Innovation RXi harnesses the naturally occurring RNAi process which has the ability to “silence” or down-regulate the expression of a specific gene that may be overexpressed in a disease condition Proprietary Technology RXi has developed a robust RNAi therapeutic platform including self-delivering RNA (sd-rxRNA®) compounds, that has many advantages over its competitors in the RNAi space sd-rxRNA compounds have the ability to selectively block the expression of any target in the genome providing applicability to a broad spectrum of therapeutic areas Freedom to Operate Extensive patent estate provides coverage for the development and commercialization of advanced RNAi therapeutics across all therapeutic areas Developing Innovative RNAi Therapeutics - For a Better Life

Acknowledgements Advirna, Inc. Alexey Wolfson Taisia Shmushkovich Monica Betancur-Boissel SRI International Nathalie Scholler ProMab Biotechnologies Part of the presented results were obtained in collaboration with the following people and organizations Karolinska Institutet Rolf Kiessling Maarten Ligtenberg Yago Pico de Coana Iva Truxova Yuya Yoshimoto


























