- LPCN Dashboard
- Financials
- Filings
-
Holdings
-
Transcripts
- ETFs
- Insider
- Institutional
- Shorts
-
8-K Filing
Lipocine (LPCN) 8-KOther Events
Filed: 7 Aug 18, 7:34am

Enabling oral drug delivery to improve patient compliance August 7, 2018 Corporate Presentation Exhibit 99.1

Forward - Looking Statements This presentation contains forward - looking statements about Lipocine Inc. (the “Company”). These forward - looking statements are made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward - looking statement s relate to the Company’s product candidates, the expected timing of the FDA review process related to our resubmitted NDA for TLANDO™, clini cal and regulatory processes and objectives, potential benefits of the Company’s product candidates, intellectual property and relate d m atters, all of which involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties. Actual results may differ materially from the forward - looking statemen ts discussed in this presentation . Accordingly, the Company cautions investors not to place undue reliance on the forward - looking statements contained in, or made in connection with, this presentation . Several factors may affect the initiation and completion of clinical trials, the potential advantages of the Company’s product candidates and the Company’s capital needs. Among other things, the projected commencement and completion of the Company’s clinical trials may be affected by difficulties or delays. We may encounter delays or other issues in the FDA appro val process, including that the FDA may determine there are deficiencies in our resubmitted NDA. We are also subject to risks related to t he possibility of an advisory committee meeting related to TLANDO™. In addition, the Company’s results may be affected by its ability to manage it s financial resources, difficulties or delays in developing manufacturing processes for its product candidates, preclinical and toxicolog y t esting and regulatory developments. Delays in clinical programs, whether caused by competitive developments, adverse events, patient en rol lment rates, regulatory issues or other factors, could adversely affect the Company’s financial position and prospects. Prior clin ica l trial program designs and results are not necessarily predictive of future clinical trial designs or results. If the Company’s product can did ates do not meet safety or efficacy endpoints in clinical evaluations, they will not receive regulatory approval and the Company will not be a ble to market them. The Company may not be able to enter into any strategic partnership agreements. The Company’s commercial success depends on i ts ability to manufacture, market and sell products without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. Operating expense and ca sh flow projections involve a high degree of uncertainty, including variances in future spending rates due to changes in corporate pr ior ities, the timing and outcomes of clinical trials, competitive developments and the impact on expenditures and available capital from licensing an d strategic collaboration opportunities. If the Company is unable to raise additional capital when required or on acceptable terms, it m ay have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue one or more of its drug development or discovery research programs. The Compa ny is at an early stage of development and may not ever have any products that generate significant revenue. The forward - looking statements contained in this presentation are further qualified by the detailed discussion of risks and uncertainties set forth in the Company’s a nnu al report on Form 10 - K and other periodic reports filed by the Company with the Securities and Exchange Commission, all of which can be obtai ned on the Company’s website at www.lipocine.com or on the SEC website at www.sec.gov . The forward - looking statements contained in this document represent the Company’s estimates and assumptions only as of the date of this presentation and the Company undertakes no duty or obligation to update or revise publicly any forward - looking statements contained in this presentation as a result of new information, future events or changes in the Company’s expectations. 2

Men's Health Oral Testosterone Replacement Therapy (“TRT”) Oral Androgen Therapy for Fatty Liver Disease (“NAFLD”/ “NASH”) Women's Health Oral Therapy for Prevention of Preterm Birth (“PTB”) Proprietary Drug Delivery Platform Significant Unmet Need In Both Therapeutic Areas 3 Unique Specialty Pharmaceutical Company Advanced Pipeline
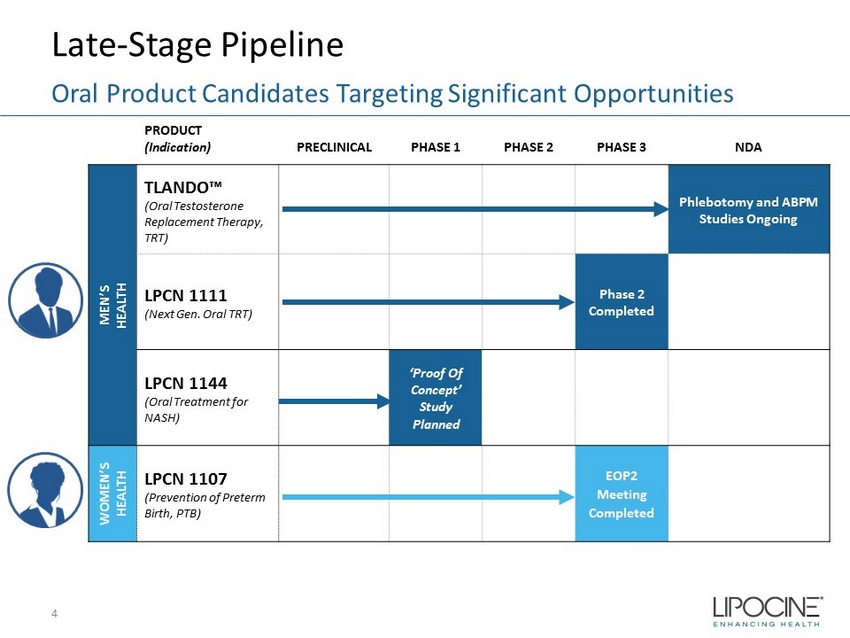
Late - Stage Pipeline 4 Oral Product Candidates Targeting Significant Opportunities PRODUCT (Indication) PRECLINICAL PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PHASE 3 NDA MEN’S HEALTH TLANDO™ (Oral Testosterone Replacement Therapy, TRT) Phlebotomy and ABPM Studies Ongoing LPCN 1111 (Next Gen. Oral TRT) Phase 2 Completed LPCN 1144 (Oral Treatment for NASH) ‘Proof Of Concept’ Study Planned WOMEN’S HEALTH LPCN 1107 (Prevention of Preterm Birth, PTB) EOP2 Meeting Completed

5

2018 2017 2016 2014 2015 350 375 400 425 450 475 500 525 550 575 600 625 650 Sep 14 Nov 14 Jan 15 Mar 15 May 15 Jul 15 Sep 15 Nov 15 Jan 16 Mar 16 May 16 Jul 16 Sep 16 Nov 16 Jan 17 Mar 17 May 17 Jul 17 Sept 17 Nov 17 Jan 18 Mar 18 May 18 Monthly TRx (000s) FDA Label Guidance Monthly TRT TRx Trend 6 TRT Market is Approaching Heights Experienced in 2013 and Growing 2017 Gross Annual Sales - $1.7B Annual estimates of 7.2 million TRx Source: IMS database TRx = Total prescriptions
Issues with Current Non - oral TRT Options • Black Box Warning – Secondary exposure to testosterone – Pulmonary oil micro embolism (POME) and anaphylaxis shock • Inconvenient application or painful injection • Poor persistence reflects need for oral – Average days on therapy is 100 days • More than 50% of patients need dosage adjustment – Burdensome for patients due to multiple doctor visits Potential Barrier To Newly Diagnosed and Existing Patients 7
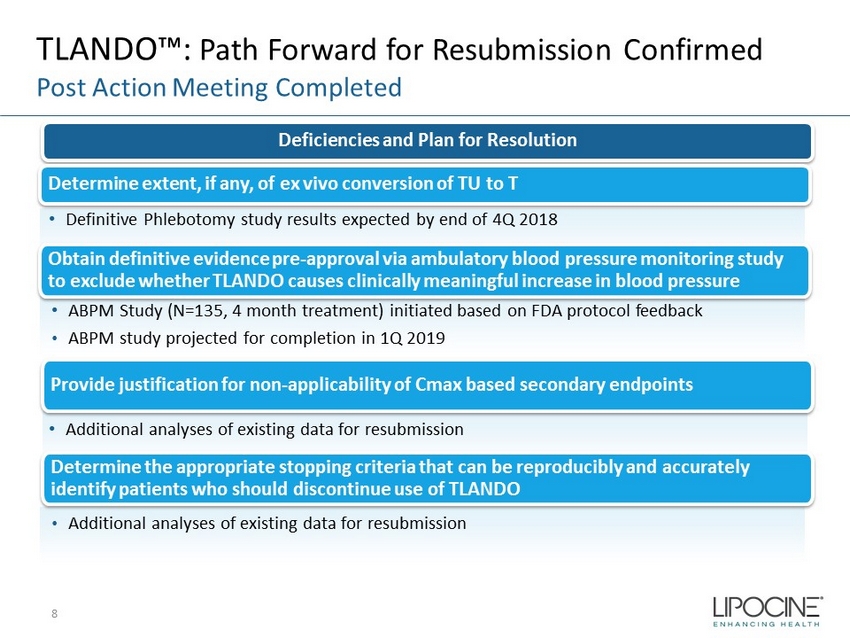
TLANDO™: Path Forward for Resubmission Confirmed Post Action Meeting Completed Deficiencies and Plan for Resolution Determine extent, if any, of ex vivo conversion of TU to T Obtain definitive evidence pre - approval via ambulatory blood pressure monitoring study to exclude whether TLANDO causes clinically meaningful increase in blood pressure 8 • Definitive Phlebotomy study results expected by end of 4Q 2018 • ABPM Study (N=135, 4 month treatment) initiated based on FDA protocol feedback • ABPM study projected for completion in 1Q 2019 Provide justification for non - applicability of Cmax based secondary endpoints Determine the appropriate stopping criteria that can be reproducibly and accurately identify patients who should discontinue use of TLANDO • Additional analyses of existing data for resubmission • Additional analyses of existing data for resubmission

9
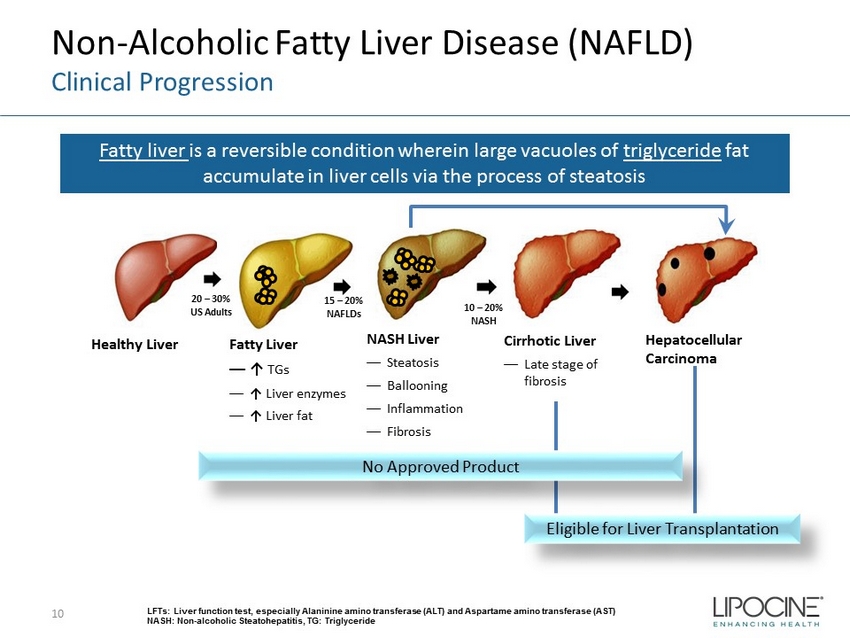
Non - Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Clinical Progression 10 Fatty liver is a reversible condition wherein large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulate in liver cells via the process of steatosis LFTs: Liver function test, especially Alaninine amino transferase (ALT) and Aspartame amino transferase (AST) NASH: Non - alcoholic Steatohepatitis, TG: Triglyceride Healthy Liver Fatty Liver — ↑ TGs — ↑ Liver enzymes — ↑ Liver fat NASH Liver — Steatosis — Ballooning — Inflammation — Fibrosis Cirrhotic Liver — Late stage of fibrosis Hepatocellular Carcinoma Eligible for Liver Transplantation 20 – 30% US Adults 15 – 20% NAFLDs 10 – 20% NASH No Approved Product
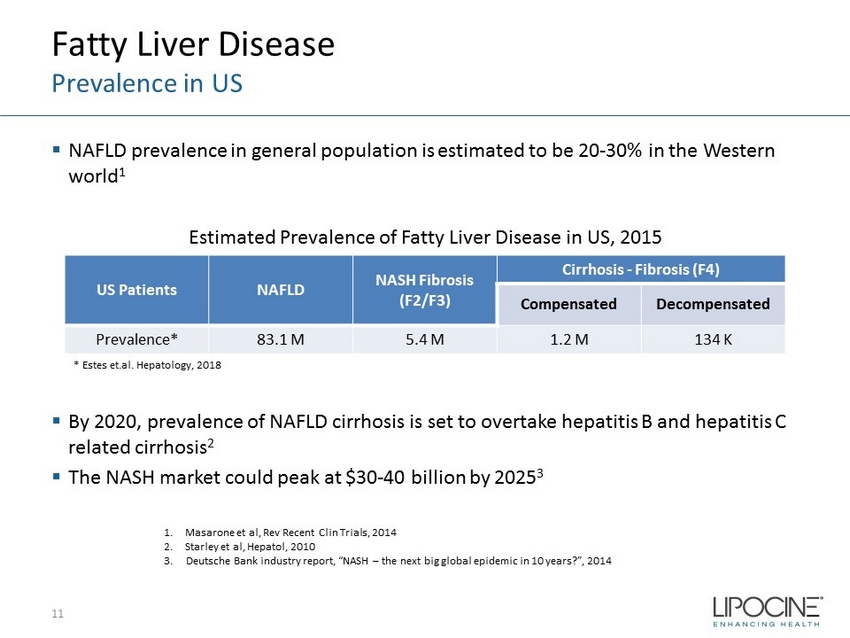
Fatty Liver Disease Prevalence in US ▪ NAFLD prevalence in general population is estimated to be 20 - 30% in the Western world 1 Estimated Prevalence of Fatty Liver Disease in US, 2015 ▪ By 2020, prevalence of NAFLD cirrhosis is set to overtake hepatitis B and hepatitis C related cirrhosis 2 ▪ The NASH market could peak at $30 - 40 billion by 2025 3 11 1. Masarone et al, Rev Recent Clin Trials, 2014 2. Starley et al, Hepatol , 2010 3. Deutsche Bank industry report, “NASH – the next big global epidemic in 10 years?”, 2014 * Estes et.al. Hepatology, 2018 US Patients NAFLD NASH Fibrosis (F2/F3) Cirrhosis - Fibrosis (F4) Compensated Decompensated Prevalence* 83.1 M 5.4 M 1.2 M 134 K
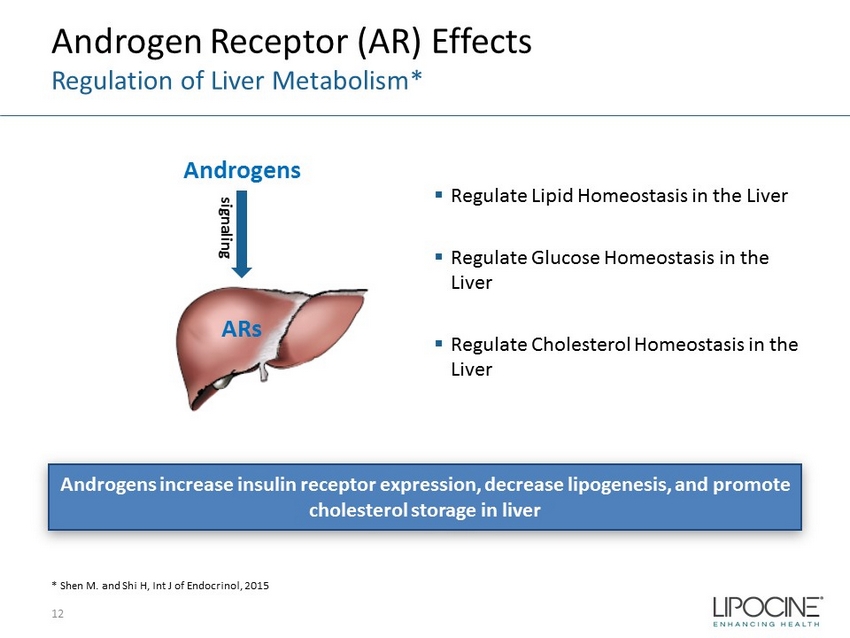
Androgen Receptor (AR) Effects Regulation of Liver Metabolism* 12 * Shen M. and Shi H, Int J of Endocrinol, 2015 Androgens increase insulin receptor expression, decrease lipogenesis, and promote cholesterol storage in liver ▪ Regulate Lipid Homeostasis in the Liver ▪ Regulate Glucose Homeostasis in the Liver ▪ Regulate Cholesterol Homeostasis in the Liver Androgens ARs signaling

Testosterone (T) Association with NAFLD and Cirrhosis 13 • NAFLD and T 1 • Cirrhosis survival and T 2 1. Kim et al., Gastroenterol: 2012 x After adjusting for age, smoking, diabetes, exercise, BMI, TG and HDL, the 1 st (lowest) T quintile (110 – 317 ng/dL) have OR of 5.12 (2.43 – 10.77) for NAFLD compared to 5 th (highest) T quintile (571 – 1343 ng/dL) x Low T (<8.3 nmol/L; 239 ng/dL) remained a significant predictor of reduced survival in in cirrhotic patients 2. Sinclair et al., Liver Trans: 2016 VAT: Visceral adipose tissue, OR: Odd Ratio,
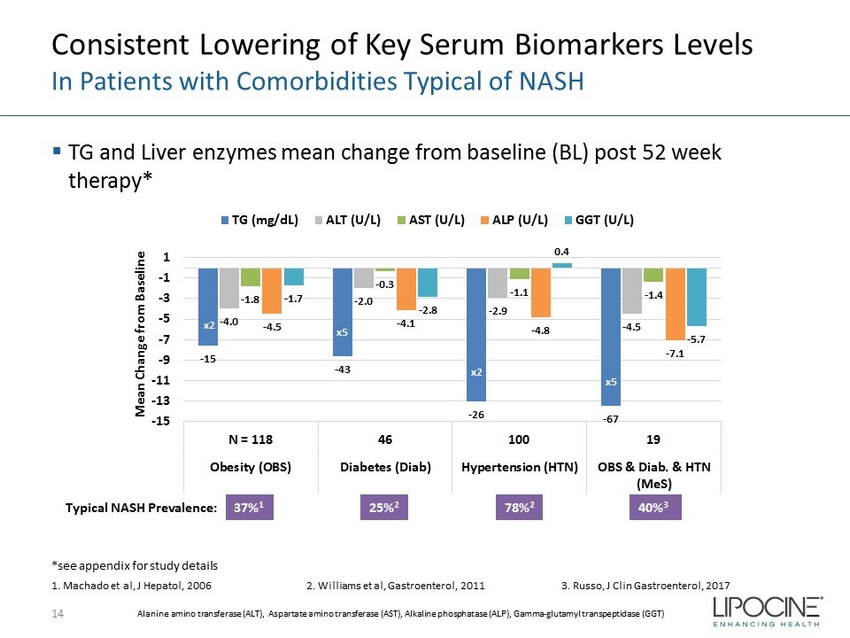
Consistent Lowering of Key Serum Biomarkers Levels In Patients with Comorbidities Typical of NASH ▪ TG and Liver enzymes mean change from baseline (BL) post 52 week therapy* 14 - 15 - 43 - 26 - 67 - 4.0 - 2.0 - 2.9 - 4.5 - 1.8 - 0.3 - 1.1 - 1.4 - 4.5 - 4.1 - 4.8 - 7.1 - 1.7 - 2.8 0.4 - 5.7 -15 -13 -11 -9 -7 -5 -3 -1 1 N = 118 46 100 19 Obesity (OBS) Diabetes (Diab) Hypertension (HTN) OBS & Diab. & HTN (MeS) Mean Change from Baseline TG (mg/dL) ALT (U/L) AST (U/L) ALP (U/L) GGT (U/L) x2 x2 x5 x5 37% 1 1. Machado et al, J Hepatol , 2006 2. Williams et al, Gastroenterol , 2011 3. Russo, J Clin Gastroenterol , 2017 Typical NASH Prevalence: 25% 2 78% 2 40% 3 *see appendix for study details Alanine amino transferase (ALT), Aspartate amino transferase (AST), Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), Gamma - glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
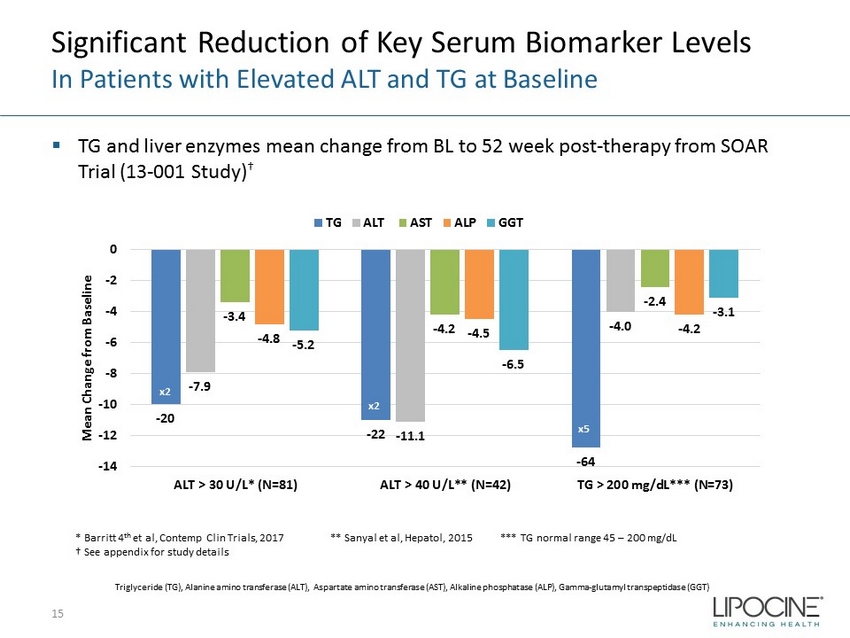
Significant Reduction of Key Serum Biomarker Levels In Patients with Elevated ALT and TG at Baseline ▪ TG and liver enzymes mean change from BL to 52 week post - therapy from SOAR Trial (13 - 001 Study) † 15 * Barritt 4 th et al, Contemp Clin Trials, 2017 ** Sanyal et al, Hepatol , 2015 *** TG normal range 45 – 200 mg/dL † See appendix for study details - 20 - 22 - 64 - 7.9 - 11.1 - 4.0 - 3.4 - 4.2 - 2.4 - 4.8 - 4.5 - 4.2 - 5.2 - 6.5 - 3.1 -14 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 ALT > 30 U/L* (N=81) ALT > 40 U/L** (N=42) TG > 200 mg/dL*** (N=73) Mean Change from Baseline TG ALT AST ALP GGT x2 x2 x5 Triglyceride (TG), Alanine amino transferase (ALT), Aspartate amino transferase (AST), Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), Gamma - glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
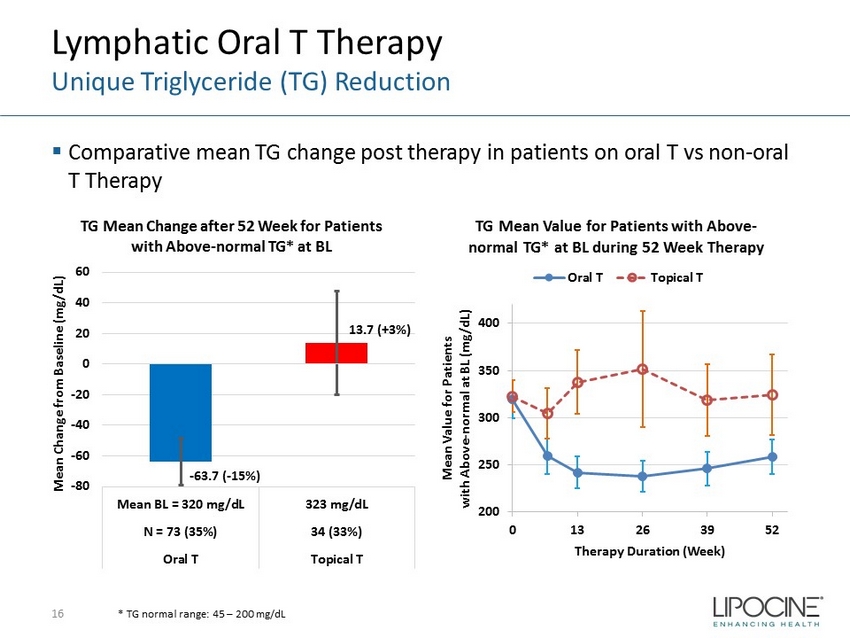
Lymphatic Oral T Therapy Unique Triglyceride (TG) Reduction ▪ Comparative mean TG change post therapy in patients on oral T vs non - oral T Therapy 16 * TG normal range: 45 – 200 mg/dL - 63.7 ( - 15%) 13.7 (+3%) -80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 Mean BL = 320 mg/dL 323 mg/dL N = 73 (35%) 34 (33%) Oral T Topical T Mean Change from Baseline (mg/dL) TG Mean Change after 52 Week for Patients with Above - normal TG* at BL 200 250 300 350 400 0 13 26 39 52 Mean Value for Patients with Above - normal at BL (mg/dL) Therapy Duration (Week) TG Mean Value for Patients with Above - normal TG* at BL during 52 Week Therapy Oral T Topical T
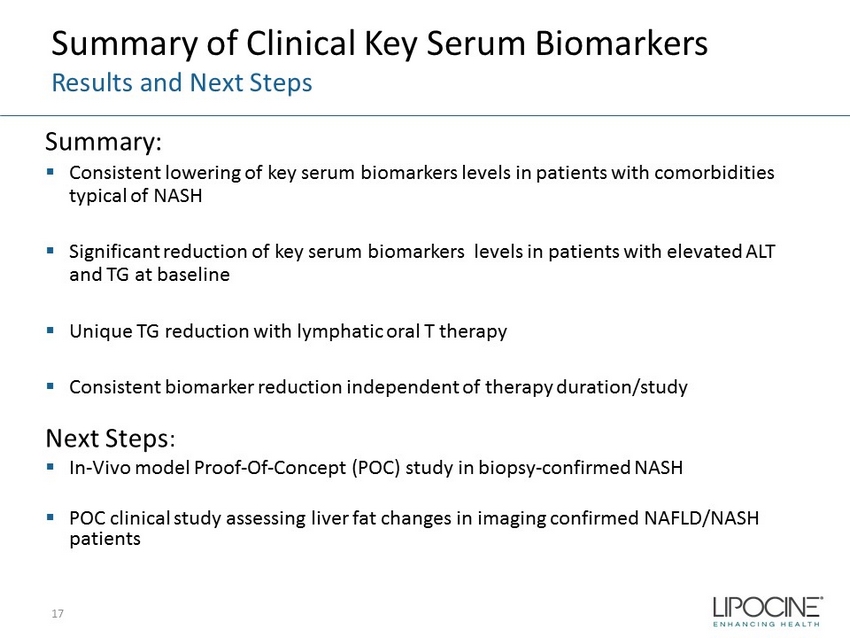
Summary of Clinical Key Serum Biomarkers Results and Next Steps Summary: ▪ Consistent lowering of key serum biomarkers levels in patients with comorbidities typical of NASH ▪ Significant reduction of key serum biomarkers levels in patients with elevated ALT and TG at baseline ▪ Unique TG reduction with lymphatic oral T therapy ▪ Consistent biomarker reduction independent of therapy duration/study Next Steps : ▪ In - Vivo model Proof - Of - Concept (POC) study in biopsy - confirmed NASH ▪ POC clinical study assessing liver fat changes in imaging confirmed NAFLD/NASH patients 17

18 LPCN 1111 QD TLANDO

LPCN 1111: Next - Generation Oral TRT ▪ Novel prodrug of testosterone for oral delivery ▪ Once - daily potential expected to sustain and improve market share of oral T franchise ▪ Once - daily feasibility established in Phase 2a and 2b clinical trials – Single - daily oral dose provides T levels in eugonadal range ▪ Development status – Phase 2 study completed – FDA Guidance meeting for Phase 3 study design completed 19 Potential Once - Daily Dosing

20
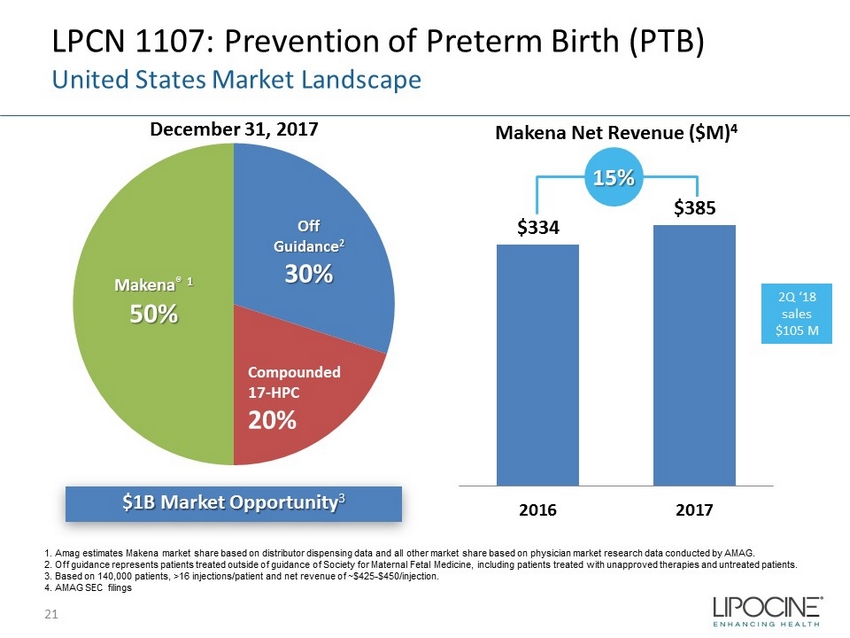
LPCN 1107: Prevention of Preterm Birth (PTB) United States Market Landscape $1B Market Opportunity 3 December 31, 2017 Makena Net Revenue ($M) 4 Makena ® 1 50% Off Guidance 2 30% Compounded 17 - HPC 20% $334 $385 2016 2017 15% 1. Amag estimates Makena market share based on distributor dispensing data and all other market share based on physician market resea rc h data conducted by AMAG. 2. Off guidance represents patients treated outside of guidance of Society for Maternal Fetal Medicine, including patients tr eat ed with unapproved therapies and untreated patients. 3. Based on 140,000 patients, >16 injections/patient and net revenue of ~$425 - $450/injection. 4. AMAG SEC filings 21 2Q ‘18 sales $105 M
LPCN 1107 - Oral HPC ▪ Potential for superior efficacy with Phase 3 target dose ▪ No patient discomfort upon administration ▪ Steady state achieved in 7 days ▪ Orphan drug designation – Major contribution to patient care ▪ Next steps: – Explore partnering opportunities LPCN 1107: First Oral PTB Candidate 22 Addresses Unmet Need

Upcoming Milestones 23 Near Term Value Drivers Event Expected Timing TLANDO™ Complete definitive phlebotomy study ABPM study results 4Q 2018 1Q 2019 LPCN 1144 Complete In - Vivo model Proof - Of - Concept study in biopsy - confirmed NASH POC clinical study results in imaging - confirmed NAFLD/NASH patients 4Q 2018 1Q 2019
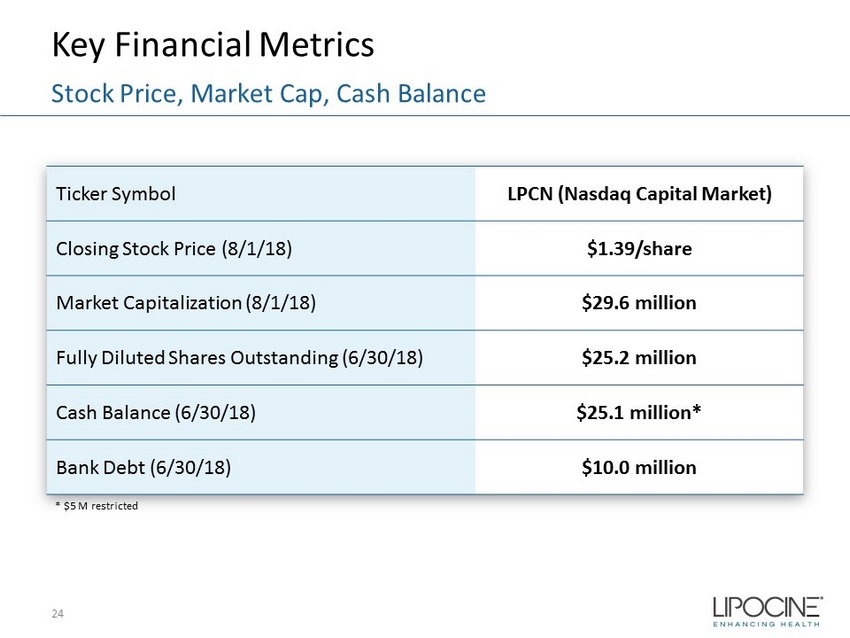
Key Financial Metrics 24 Stock Price, Market Cap, Cash Balance Ticker Symbol LPCN (Nasdaq Capital Market) Closing Stock Price (8/1/18) $1.39/share Market Capitalization (8/1/18) $29.6 million Fully Diluted Shares Outstanding (6/30/18) $25.2 million Cash Balance (6/30/18) $25.1 million* Bank Debt (6/30/18) $10.0 million * $5 M restricted
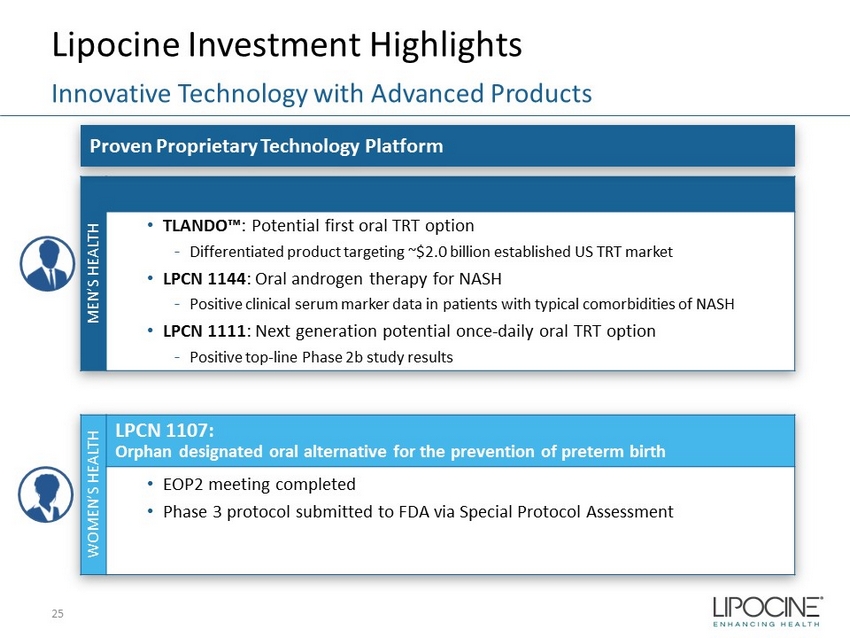
MEN’S HEALTH • TLANDO™ : Potential first oral TRT option - Differentiated product targeting ~$2.0 billion established US TRT market • LPCN 1144 : Oral androgen therapy for NASH - Positive clinical serum marker data in patients with typical comorbidities of NASH • LPCN 1111 : Next generation potential once - daily oral TRT option - Positive top - line Phase 2b study results WOMEN’S HEALTH LPCN 1107: Orphan designated oral alternative for the prevention of preterm birth • EOP2 meeting completed • Phase 3 protocol submitted to FDA via Special Protocol Assessment Lipocine Investment Highlights 25 Innovative Technology with Advanced Products Proven Proprietary Technology Platform

26
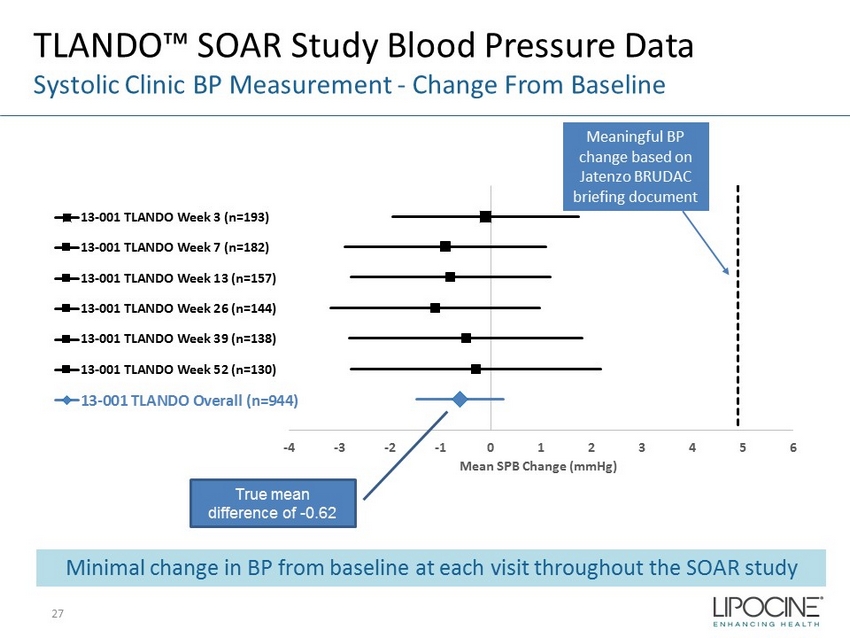
-4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Mean SPB Change (mmHg) 13-001 TLANDO Week 3 (n=193) 13-001 TLANDO Week 7 (n=182) 13-001 TLANDO Week 13 (n=157) 13-001 TLANDO Week 26 (n=144) 13-001 TLANDO Week 39 (n=138) 13-001 TLANDO Week 52 (n=130) 13-001 TLANDO Overall (n=944) TLANDO™ SOAR Study Blood Pressure Data Systolic Clinic BP Measurement - Change From Baseline True mean difference of - 0.62 Meaningful BP change based on Jatenzo BRUDAC briefing document Minimal change in BP from baseline at each visit throughout the SOAR study 27
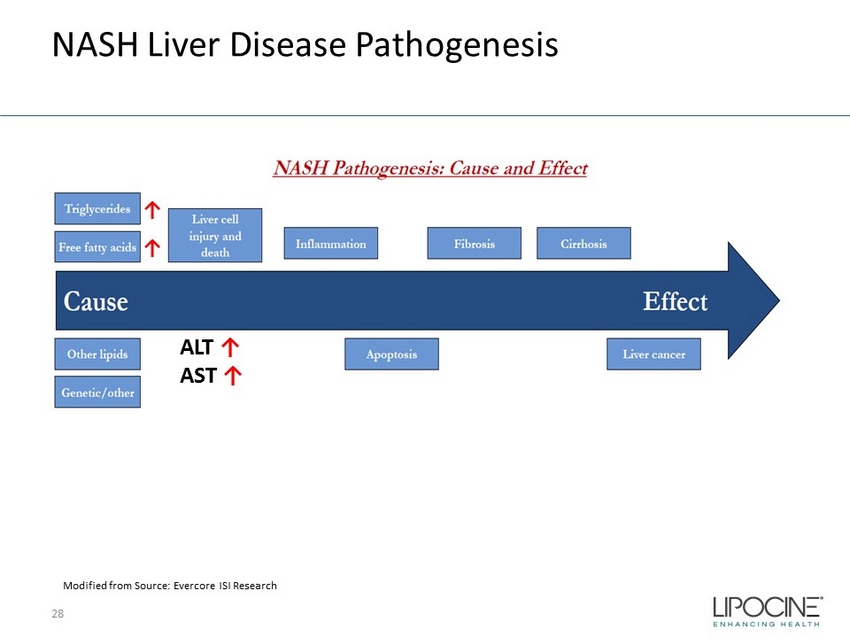
NASH Liver Disease Pathogenesis 28 ALT ↑ AST ↑ Modified from Source: Evercore ISI Research ↑ ↑
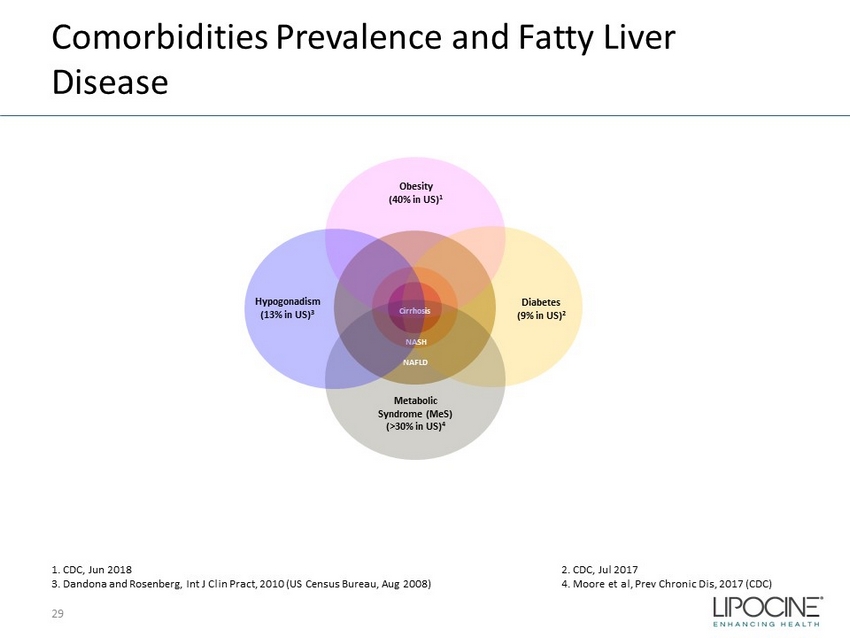
Comorbidities Prevalence and Fatty Liver Disease 29 Obesity (40% in US) 1 Diabetes (9% in US) 2 Metabolic Syndrome ( MeS ) (>30% in US) 4 NAFLD NASH Cirrhosis Hypogonadism (13% in US) 3 1. CDC, Jun 2018 2. CDC, Jul 2017 3. Dandona and Rosenberg, Int J Clin Pract , 2010 (US Census Bureau, Aug 2008) 4. Moore et al, Prev Chronic Dis, 2017 (CDC)
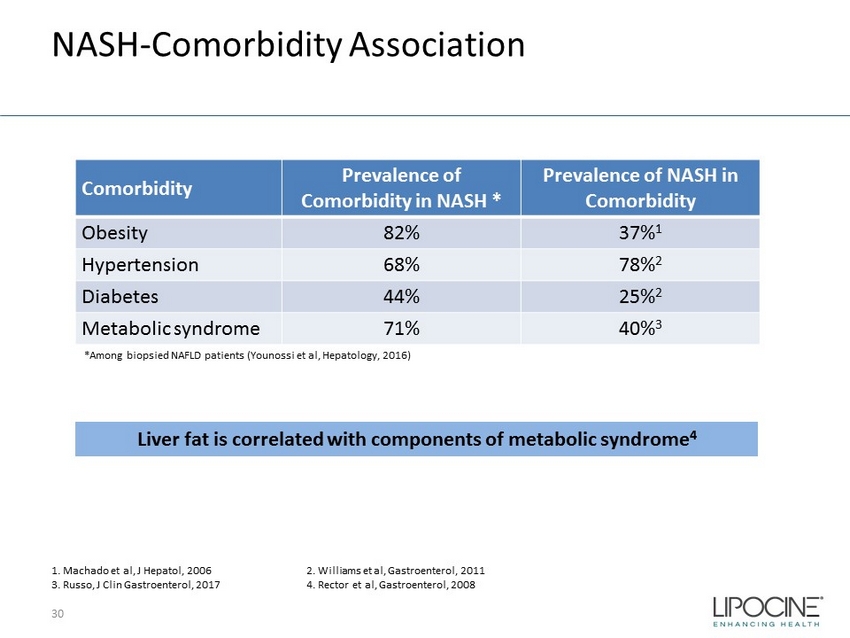
NASH - Comorbidity Association 30 Comorbidity Prevalence of Comorbidity in NASH * Prevalence of NASH in Comorbidity Obesity 82% 37% 1 Hypertension 68% 78% 2 Diabetes 44% 25% 2 Metabolic syndrome 71% 40% 3 *Among biopsied NAFLD patients ( Younossi et al, Hepatology, 2016) Liver fat is correlated with components of metabolic syndrome 4 1. Machado et al, J Hepatol , 2006 2. Williams et al, Gastroenterol , 2011 3. Russo, J Clin Gastroenterol, 2017 4. Rector et al, Gastroenterol , 2008
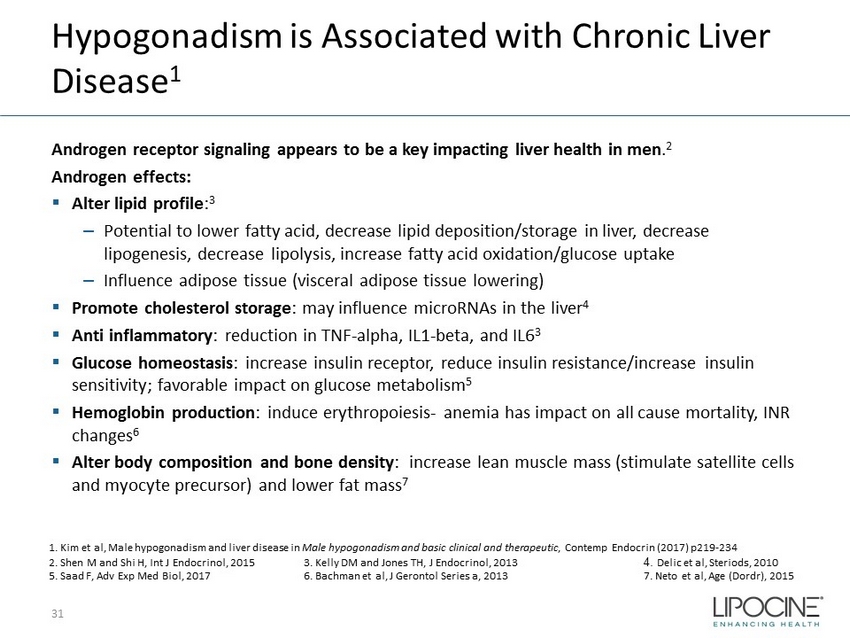
Hypogonadism is Associated with Chronic Liver Disease 1 Androgen receptor signaling appears to be a key impacting liver health in men . 2 Androgen effects: ▪ Alter lipid profile : 3 – Potential to lower fatty acid, decrease lipid deposition/storage in liver, decrease lipogenesis, decrease lipolysis, increase fatty acid oxidation/glucose uptake – Influence adipose tissue (visceral adipose tissue lowering) ▪ Promote cholesterol storage : may influence microRNAs in the liver 4 ▪ Anti inflammatory : reduction in TNF - alpha, IL1 - beta, and IL6 3 ▪ Glucose homeostasis : increase insulin receptor, reduce insulin resistance/increase insulin sensitivity; favorable impact on glucose metabolism 5 ▪ Hemoglobin production : induce erythropoiesis - anemia has impact on all cause mortality, INR changes 6 ▪ Alter body composition and bone density : increase lean muscle mass (stimulate satellite cells and myocyte precursor) and lower fat mass 7 31 1. Kim et al, Male hypogonadism and liver disease in Male hypogonadism and basic clinical and therapeutic , Contemp Endocrin (2017) p219 - 234 2. Shen M and Shi H, Int J Endocrinol, 2015 3. Kelly DM and Jones TH, J Endocrinol, 2013 4. Delic et al, Steriods , 2010 5. Saad F, Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017 6. Bachman et al, J Gerontol Series a, 2013 7. Neto et al, Age ( Dordr ), 2015
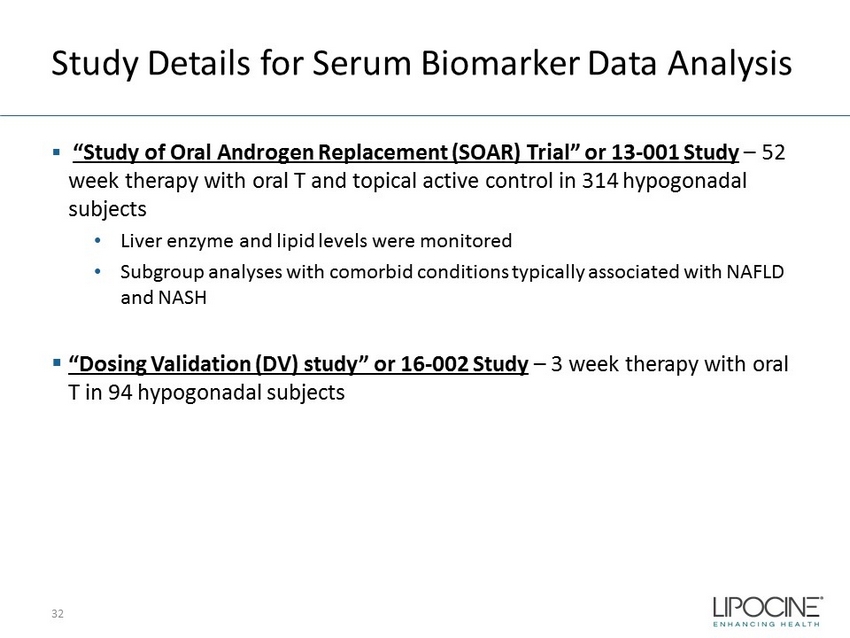
Study Details for Serum Biomarker Data Analysis ▪ “Study of Oral Androgen Replacement (SOAR) Trial” or 13 - 001 Study – 52 week therapy with oral T and topical active control in 314 hypogonadal subjects • Liver enzyme and lipid levels were monitored • Subgroup analyses with comorbid conditions typically associated with NAFLD and NASH ▪ “Dosing Validation (DV) study” or 16 - 002 Study – 3 week therapy with oral T in 94 hypogonadal subjects 32
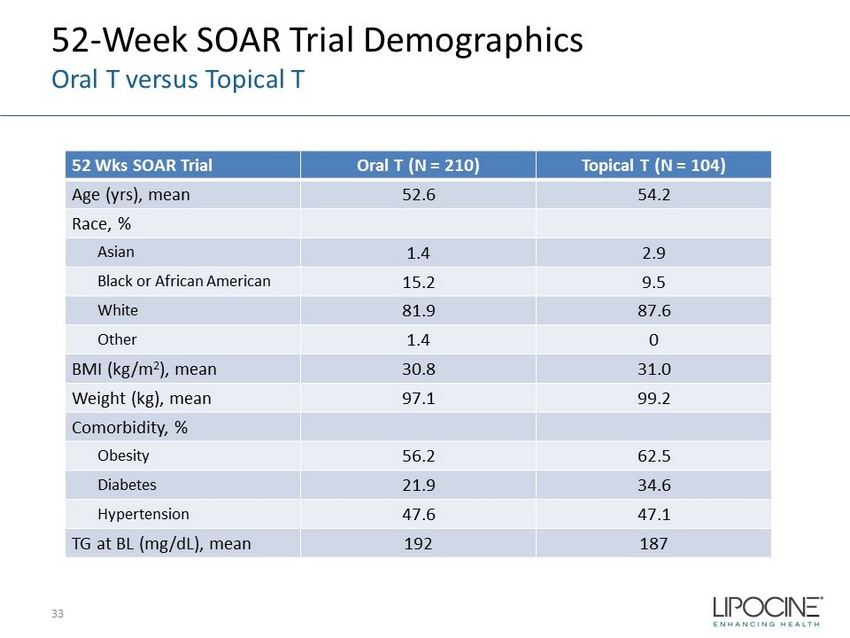
52 - Week SOAR Trial Demographics Oral T versus Topical T 52 Wks SOAR Trial Oral T (N = 210) Topical T ( N = 104) Age ( yrs ), mean 52.6 54.2 Race, % Asian 1.4 2.9 Black or African American 15.2 9.5 White 81.9 87.6 Other 1.4 0 BMI (kg/m 2 ), mean 30.8 31.0 Weight (kg), mean 97.1 99.2 Comorbidity, % Obesity 56.2 62.5 Diabetes 21.9 34.6 Hypertension 47.6 47.1 TG at BL (mg/dL), mean 192 187 33
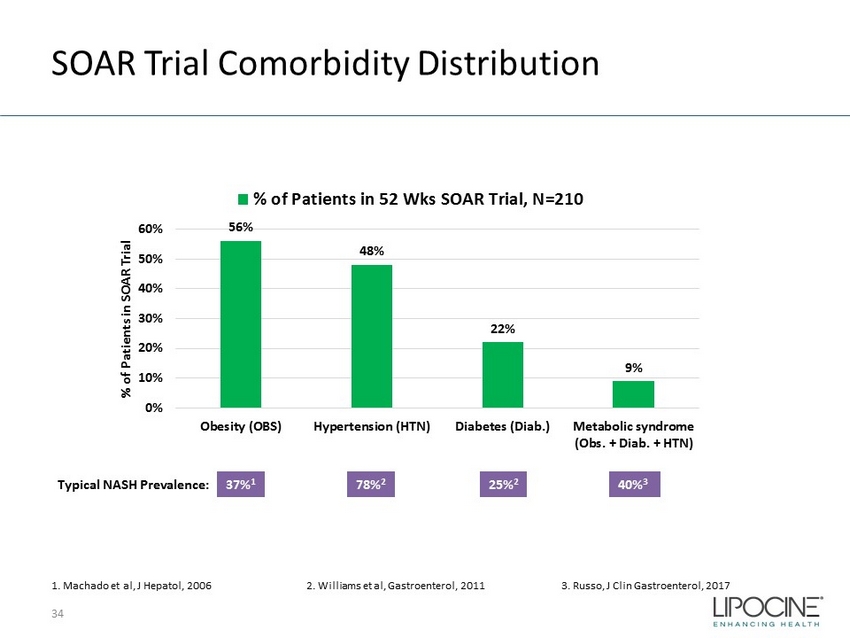
SOAR Trial Comorbidity Distribution 34 56% 48% 22% 9% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% Obesity (OBS) Hypertension (HTN) Diabetes (Diab.) Metabolic syndrome (Obs. + Diab. + HTN) % of Patients in SOAR Trial % of Patients in 52 Wks SOAR Trial, N=210 1. Machado et al, J Hepatol , 2006 2. Williams et al, Gastroenterol, 2011 3. Russo, J Clin Gastroenterol, 2017 37% 1 Typical NASH Prevalence: 78% 2 25% 2 40% 3
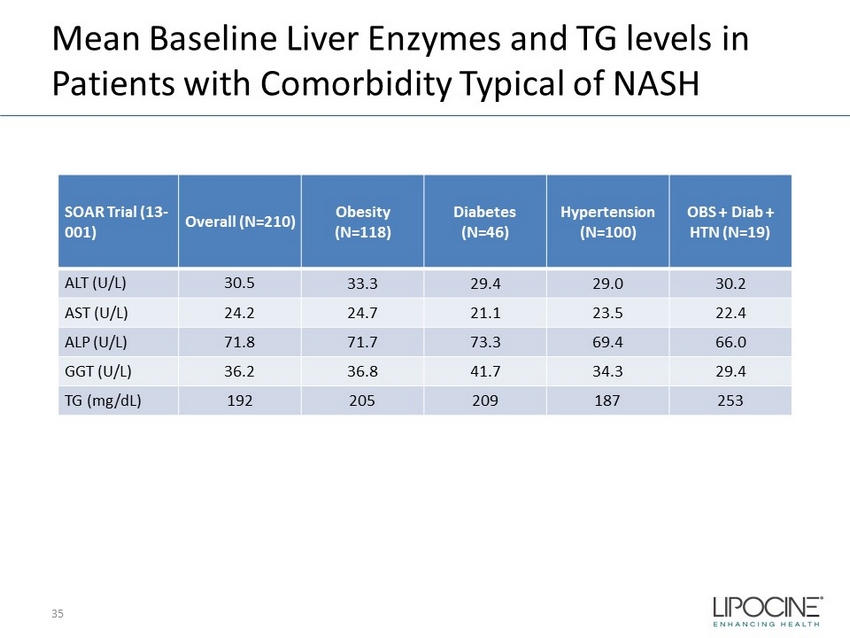
Mean Baseline Liver Enzymes and TG levels in Patients with Comorbidity Typical of NASH 35 SOAR Trial (13 - 001) Overall (N=210) Obesity (N=118) Diabetes (N=46) Hypertension (N=100) OBS + Diab + HTN (N=19) ALT (U/L) 30.5 33.3 29.4 29.0 30.2 AST (U/L) 24.2 24.7 21.1 23.5 22.4 ALP (U/L) 71.8 71.7 73.3 69.4 66.0 GGT (U/L) 36.2 36.8 41.7 34.3 29.4 TG (mg/ dL ) 192 205 209 187 253
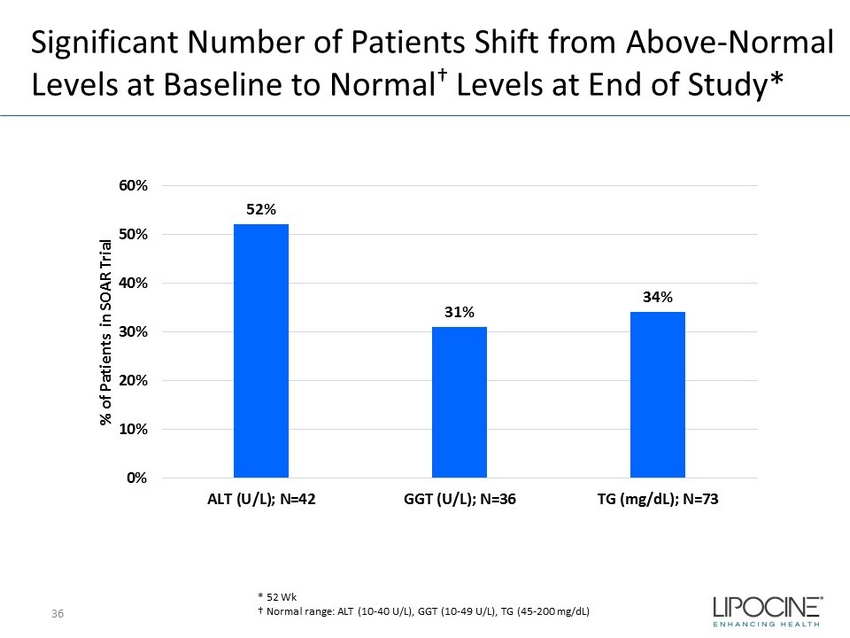
Significant Number of Patients Shift from Above - Normal Levels at Baseline to Normal † Levels at End of Study* 36 * 52 Wk N = 134 52% 31% 34% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% ALT (U/L); N=42 GGT (U/L); N=36 TG (mg/dL); N=73 % of Patients in SOAR Trial † Normal range: ALT (10 - 40 U/L), GGT (10 - 49 U/L), TG (45 - 200 mg/dL)

Consistent Marker Reduction Independent of Therapy Duration/Study ▪ TG and liver enzymes mean change post therapy in patients* with elevated serum markers in two separate studies 37 * Patients are for 4 th Quartile (above or upper normal level) of each lab at baseline. - 67 - 6.5 - 2.9 - 16.5 - 11.7 - 85 - 17 - 4.7 - 13.4 - 13.4 - 85 - 10 - 6.3 - 10.2 - 7 -20 -16 -12 -8 -4 0 TG (mg/dL), x5 ALT (U/L) AST (U/L) ALP (U/L) GGT (U/L) Mean Change from Baseline 16-002 3 Wks (N=25) 13-001 13 Wks (N=52) 13-001 52 Wks (N=52) x5 x5 x5
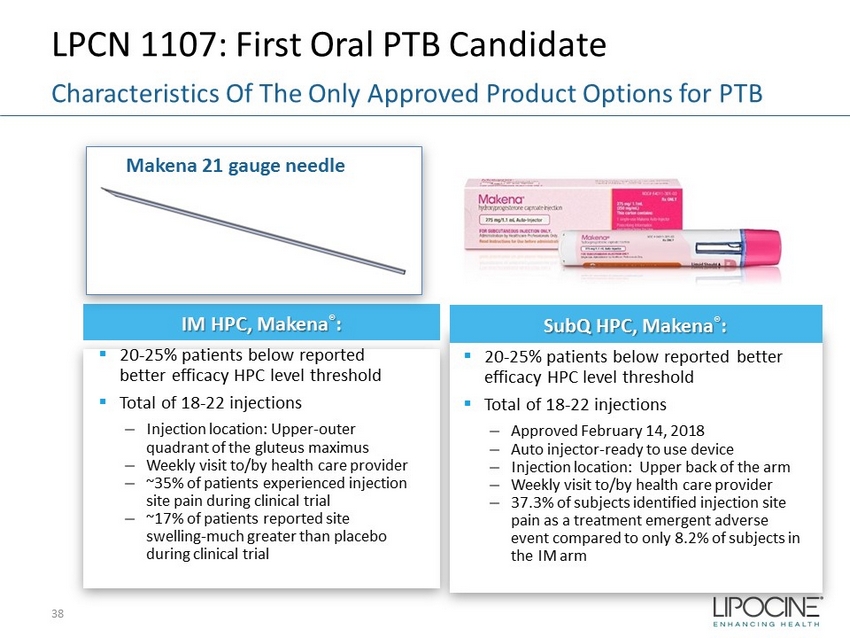
LPCN 1107: First Oral PTB Candidate 38 Characteristics Of The Only Approved Product Options for PTB IM HPC, Makena ® : ▪ 20 - 25% patients below reported better efficacy HPC level threshold ▪ Total of 18 - 22 injections – Injection location: Upper - outer quadrant of the gluteus maximus – Weekly visit to/by health care provider – ~35% of patients experienced injection site pain during clinical trial – ~17% of patients reported site swelling - much greater than placebo during clinical trial Makena 21 gauge needle SubQ HPC, Makena ® : ▪ 20 - 25% patients below reported better efficacy HPC level threshold ▪ Total of 18 - 22 injections – Approved February 14, 2018 – Auto injector - ready to use device – Injection location: Upper back of the arm – Weekly visit to/by health care provider – 37.3% of subjects identified injection site pain as a treatment emergent adverse event compared to only 8.2% of subjects in the IM arm

LPCN 1107: Advancing to Phase 3 Readiness Phase 3 Special Protocol Assessment – Progress ▪ Concurrence with FDA to date: – Study Design Elements • Single Phase 3 study • Open label, active comparator, two parallel arms (1:1 randomization) • General inclusion and exclusion criteria and treatment duration • LPCN 1107 dose of 800 mg BID – Endpoints and Analysis • Primary endpoint of proportion of PTB < 37 weeks • Non - inferiority margin of 7% • Secondary endpoint: Neonatal mortality and morbidity composite index • Interim analysis with ability to resize the study – Study size: 500 to 1000 subjects per arm ▪ Open Items – Data from food effect study to inform dosing instructions – Align on approach to fulfill infant follow up data requirement ▪ Next Steps – Continue Interactions with FDA on Phase 3 protocol via Special Protocol Assessment – Conduct Food/Fat Effect Study in preparation of Phase 3 study 39