Exhibit 99.4

May 2019 Investor Presentation Copyright Akari Therapeutics, Plc - 2019

2 Disclaimers Certain statements in this presentation constitute contains “forward - looking” statements within the meaning of Section 27A of th e Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. These forward - looking statements reflect our current views about our plans, intentio ns, expectations, strategies and prospects, which are based on the information currently available to us and on assumptions we have made. Although we believe tha t our plans, intentions, expectations, strategies and prospects as reflected in or suggested by those forward - looking statements are reasonable, we can g ive no assurance that the plans, intentions, expectations or strategies will be attained or achieved. Furthermore, actual results may differ materially from t hos e described in the forward - looking statements and will be affected by a variety of risks and factors that are beyond our control. Such risks and uncertainties f or our company include, but are not limited to: needs for additional capital to fund our operations, our ability to continue as a going concern; uncertainties of ca sh flows and inability to meet working capital needs; an inability or delay in obtaining required regulatory approvals for nomacopan (Coversin) and any other produc t c andidates, which may result in unexpected cost expenditures; our ability to obtain orphan drug designation in additional indications; risks inherent in drug de velopment in general; uncertainties in obtaining successful clinical results for nomacopan and any other product candidates and unexpected costs that may result the ref rom; difficulties enrolling patients in our clinical trials; failure to realize any value of nomacopan and any other product candidates developed and being develo ped in light of inherent risks and difficulties involved in successfully bringing product candidates to market; inability to develop new product candidates and sup port existing product candidates; the approval by the FDA and EMA and any other similar foreign regulatory authorities of other competing or superior products brou ght to market; risks resulting from unforeseen side effects; risk that the market for nomacopan may not be as large as expected; risks associated with the depart ure of our former Chief Executive Officers and other executive officers; risks associated with the SEC investigation; inability to obtain, maintain and enforce pa tents and other intellectual property rights or the unexpected costs associated with such enforcement or litigation; inability to obtain and maintain commercial ma nuf acturing arrangements with third party manufacturers or establish commercial scale manufacturing capabilities; the inability to timely source adequate supply of our active pharmaceutical ingredients from third party manufacturers on whom the company depends; unexpected cost increases and pricing pressures and r isk s and other risk factors detailed in our public filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, including our most recently filed Annual Rep ort on Form 20 - F filed with the SEC on April 23, 2019. The statements made in this presentation speak only as of the date stated herein, and subsequent events and developments may cau se our expectations and beliefs to change. Unless otherwise required by applicable securities laws, we do not intend, nor do we undertake any obligation, to upd ate or revise any forward - looking statements contained in this presentation to reflect subsequent information, events, results or circumstances or otherwise. W hil e we may elect to update these forward - looking statements publicly at some point in the future, we specifically disclaim any obligation to do so, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. The trademarks included herein are the property of the owners thereof and are used for reference purposes only. Such use shou ld not be construed as an endorsement of such products. This presentation shall not constitute an offer to sell or the solicitation of an offer to buy, nor shall there be any sale o f t hese securities in any state or other jurisdiction in which such offer, solicitation or sale would be unlawful prior to registration or qualification under the sec uri ties laws of any such state or other jurisdiction.
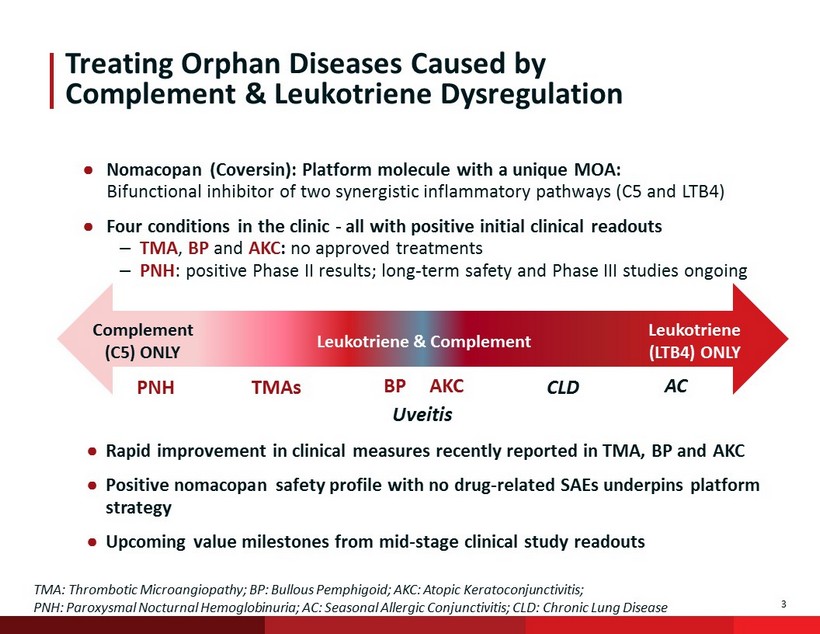
3 Treating Orphan Diseases Caused by Complement & Leukotriene Dysregulation ● Nomacopan (Coversin): Platform molecule with a unique MOA: Bifunctional inhibitor of two synergistic inflammatory pathways (C5 and LTB4) ● Four conditions in the clinic - all with positive initial clinical readouts – TMA , BP and AKC : no approved treatments – PNH : positive Phase II results; long - term safety and Phase III studies ongoing Complement (C5) ONLY Leukotriene & Complement Leukotriene (LTB4) ONLY PNH TMAs CLD AC Uveitis BP AKC TMA: Thrombotic Microangiopathy; BP: Bullous Pemphigoid; AKC: Atopic Keratoconjunctivitis; PNH: Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria; AC: Seasonal Allergic Conjunctivitis; CLD: Chronic Lung Disease ● Rapid improvement in clinical measures recently reported in TMA, BP and AKC ● Positive nomacopan safety profile with no drug - related SAEs underpins platform strategy ● Upcoming value milestones from mid - stage clinical study readouts
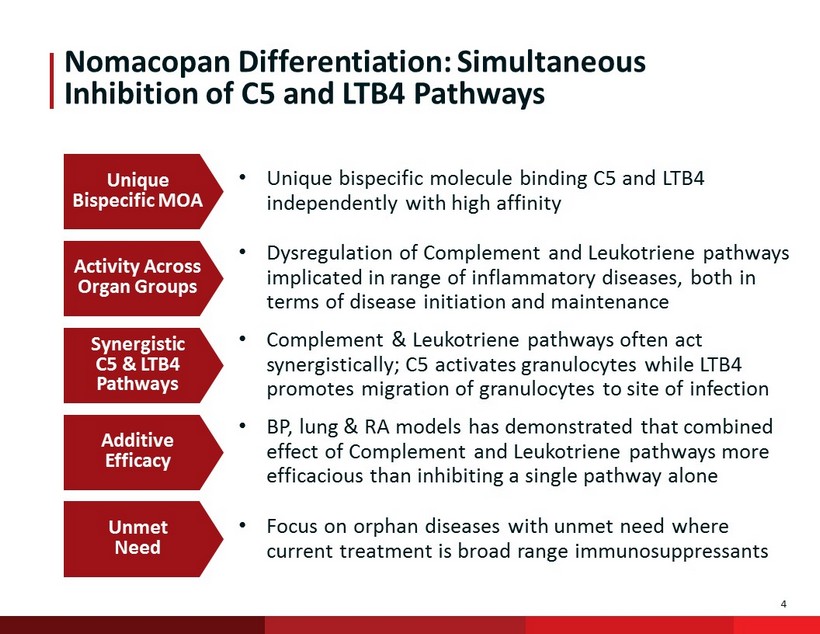
4 Nomacopan Differentiation: Simultaneous Inhibition of C5 and LTB4 Pathways Unique Bispecific MOA Activity Across Organ Groups Synergistic C5 & LTB4 Pathways Additive Efficacy Unmet Need • Unique bispecific molecule binding C5 and LTB4 independently with high affinity • Dysregulation of Complement and Leukotriene pathways implicated in range of inflammatory diseases, both in terms of disease initiation and maintenance • Complement & Leukotriene pathways often act synergistically; C5 activates granulocytes while LTB4 promotes migration of granulocytes to site of infection • BP, lung & RA models has demonstrated that combined effect of Complement and Leukotriene pathways more efficacious than inhibiting a single pathway alone • Focus on orphan diseases with unmet need where current treatment is broad range immunosuppressants

5 Clinical Programs
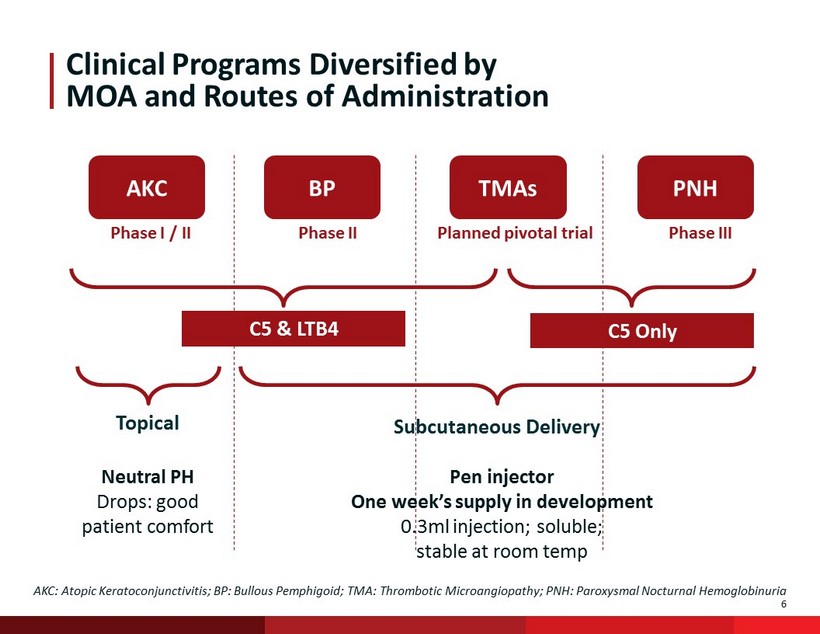
6 Phase I / II Phase II Planned pivotal trial Phase III Clinical Programs Diversified by MOA and Routes of Administration BP AKC PNH TMAs C5 Only C5 & LTB4 Subcutaneous Delivery Topical AKC: Atopic Keratoconjunctivitis; BP: Bullous Pemphigoid; TMA: Thrombotic Microangiopathy; PNH: Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglob inu ria Pen injector One week’s supply in development 0.3ml injection; soluble; stable at room temp Neutral PH Drops: good patient comfort

7 Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA) After Transplant Significant Unmet Need • Orphan condition in which there is evidence that both terminal complement activation and possibly LTB4 have a role in driving disease • Complications following bone marrow transplantation (BMT) in ≤30% patients. In target patients, paediatric mortality in excess of 80% • Nomacopan used on a named patient basis for Pediatric HSCT - TMA • Positive FDA meeting, trial designed around multiple responder endpoints • Pivotal trial anticipated to commence Q4; primary endpoint TMA response HSCT - TMA Adult TMA - HSCT Other TMA/Vasculitis aHUS Rosenthal(2016) Journal of Blood Medicine 7: 181 - 186 Potential expedited approval with a single pivotal study Gateway condition into other TMAs Could be potential first indication for nomacopan approval
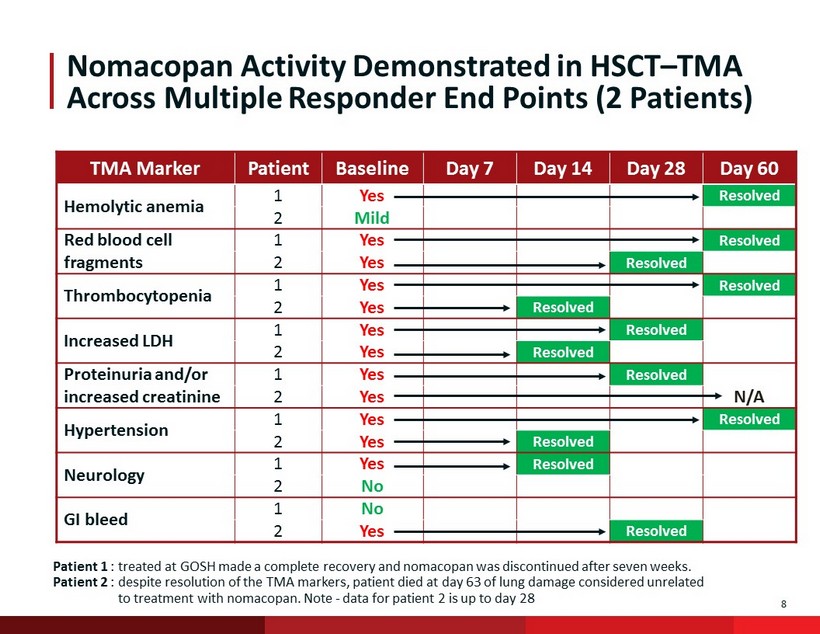
8 Nomacopan Activity Demonstrated in HSCT – TMA Across Multiple Responder End Points (2 Patients) TMA Marker Patient Baseline Day 7 Day 14 Day 28 Day 60 Hemolytic anemia 1 Yes Resolved 2 Mild Red blood cell fragments 1 Yes Resolved 2 Yes Resolved Thrombocytopenia 1 Yes Resolved 2 Yes Resolved Increased LDH 1 Yes Resolved 2 Yes Resolved Proteinuria and/or increased creatinine 1 Yes Resolved 2 Yes N/A Hypertension 1 Yes Resolved 2 Yes Resolved Neurology 1 Yes Resolved 2 No GI bleed 1 No 2 Yes Resolved Patient 1 : treated at GOSH made a complete recovery and nomacopan was discontinued after seven weeks. Patient 2 : despite resolution of the TMA markers, patient died at day 63 of lung damage considered unrelated to treatment with nomacopan . Note - d ata for patient 2 is up to day 28
9 • Orphan condition in which there is evidence that both terminal complement activation (C5) and LTB4 have a role in driving disease • Preclinical studies showed a dose response and combined C5 & LTB4 more effective than LTB4 alone • Elevated C5/LTB4 in ex - vivo study of BP patients • Existing treatment primarily steroids • Clinical objective is steroid sparing and rapid reduction symptoms • Ongoing Phase IIa study Bullous Pemphigoid (BP) Bullous Pemphigoid Pemphigus Vulgaris SJS Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita BP expected to provide POC validity of combined C5 & LTB4 inhibition Significant market with expansion potential into related conditions
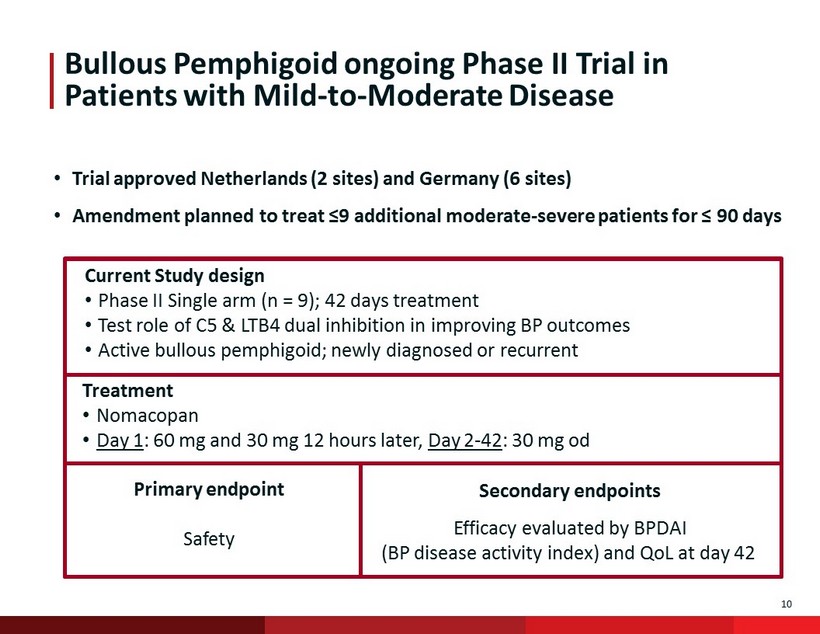
10 Bullous Pemphigoid ongoing Phase II Trial in Patients with Mild - to - Moderate Disease Current Study design • Phase II Single arm (n = 9); 42 days treatment • Test role of C5 & LTB4 dual inhibition in improving BP outcomes • Active bullous pemphigoid; newly diagnosed or recurrent Treatment • Nomacopan • Day 1 : 60 mg and 30 mg 12 hours later, Day 2 - 42 : 30 mg od Primary endpoint Safety Secondary endpoints Efficacy evaluated by BPDAI (BP disease activity index) and QoL at day 42 • Trial approved Netherlands (2 sites) and Germany (6 sites) • Amendment planned to treat ≤9 additional moderate - severe patients for ≤ 90 days

11 Prior to treatment, two of three patients were on topical corticosteroids (mometasone), while the third patient was naïve to steroid treatment & received no steroid while on nomacopan. There was no planned tapering of topical steroid dose, but patients did use less than th e 30g permitted to day 21. After day 21, any use of mometasone was regarded as rescue therapy, and both patients were only treated with nomacopan. In the 7 - 11 - day period prior to initiation on nomacopan , the two patients showed either no or minor improvement in BPDAI score (between 0 and 5%), and no improvement in blisters while being treated with topical steroids alone. 0 20 40 0 20 40 60 Day C l i n i c a l S c o r e BPDAI Blisters/Erosions Mean BPDAI and Blister Score First three Patients Phase 2 BP trial Mean BPDAI and Blister Score BPDAI Blisters/Erosions • By Day 7, 21 and day 42 of treatment, the BPDAI global score fell by a mean of 31%, 45% and 52% • By Day 7, 21 and day 42 of treatment, blisters/erosions dropped by a mean of 45%, 75% and 87% Planned amendment to extend into severe patients Daily SQ nomacopan well tolerated no drug - related adverse events Bullous Pemphigoid Initial Study Data* Three Patients: Global and Blisters BPDAI *

12 Potential Application in Both Surface and Back of Eye Indications • AKC • Severe dry eye disease • Other keratopathies • MMP Surface of the Eye Back of the Eye Key Indications Development Stage • Uveitis • AMD • Proliferative retinopathies • Clinical – AKC Phase I/II • Preclinical Administration • Topical • Topical – nomacopan • Intravitreal - PASylated Mode of action • C5 and LTB4 • LTB4 – 20X elevated • C5 and LTB4 • Down regulation of Th17 • M2 macrophage – VEGF* * Sasaki F et al. JCI Insight, Sept. 2018

13 Indications of C5 & LTB4 Activity in Front and Back of the Eye Indications 18.61 9.97 24.37 464.04 0 100 200 300 400 500 pg/mL Tear fluid LTB4 Normal Tolerant Intolerant Allergic * Eskandarpour M et al. Poster 797 (B0275) ARVO 2019 • Wide range of surface of the eye inflammatory conditions with overlap between dry eye disease and allergic conjunctivitis • Tear fluid LTB4 levels in contact lens tolerant & intolerant subjects, & allergic conjunctivitis patients • LTB4 levels – 20X in allergic conjunctivitis LTB4 receptor C5a receptor Front of the Eye Back of the Eye Autoimmune Uveitis (EAU) Model • Intravitreal nomacopan reported significant improvement in uveitis model versus control • Significant down - regulation of Th1/Th17 cells and IL - 17A production • Effect approx. equal to intravitreal dexamethasone • C5 & LTB4 receptors both identified in retina* • Uveitis treatment currently primarily steroids
14 Atopic Keratoconjunctivitis (AKC) AKC VKC PKC SAC SJS MMP • AKC: severe eye surface inflammation causing infiltration of immune cells (neutrophils & T cells) – a major cause of blindness • Topical drugs, such as steroids or cyclosporine treatments complicated by issues with comfort and side effects of chronic usage • Pre - clinical model demonstrated equivalence to cyclosporine • Ongoing Phase I/II study Potential to be first surface of eye biological treatment Different formulation allows potential pricing & licensing flexibility Expansion potential into other poorly - treated surface of the eye diseases

15 AKC Phase I/II Proof - of - Principle Trial Design Study design • Phase I/II randomized, double masked , placebo - controlled, safety and dose finding study • Part A : 3 patients open label - safety • Part B : 16 randomized patients • All patients on maximum cyclosporine Treatment • Nomacopan topical eye drops twice daily for 2 months • Placebo eye drops Primary endpoint • Safety, comfort Secondary endpoints • Composite score, comprised of six (6) clinical signs & five (5) symptoms
16 • No serious drug - related adverse effects • Post - instillation comfort reported as comfortable at all time points – By Day 14, >35% decrease in composite disease scores in both patients – Patient 1 had a disease flare at Day 42 • Marked improvement in symptoms of discomfort from a mean of 2.5 at baseline on cyclosporine to 0.25 by Day 14 (where 0 is no discomfort and 3 is intolerable discomfort) • Next stage of trial (part B) – 16 patients randomized, double masked – To support recruitment, trial expanded to additional clinical centres Initial AKC Clinical Data: First Two Patients Rapid Improvement in Composite Clinical Scores

17 Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) • PNH: ultra - rare, life threatening, clonal disorder of red blood cells • Phase III clinical trial: (CAPSTONE) ongoing ‒ Naïve patients randomized to nomacopan plus SOC* vs. SOC ‒ Six month treatment / ~30 patients ‒ End points: transfusion independence & hemoglobin • Resistant treatment program: ‒ Treatment of two resistant patients ongoing in Holland & USA Focus on patient convenience: SQ, highly soluble, stable at room temp, New formulation in development for auto injector pen with 1 week dosing * SOC = Standard of Care
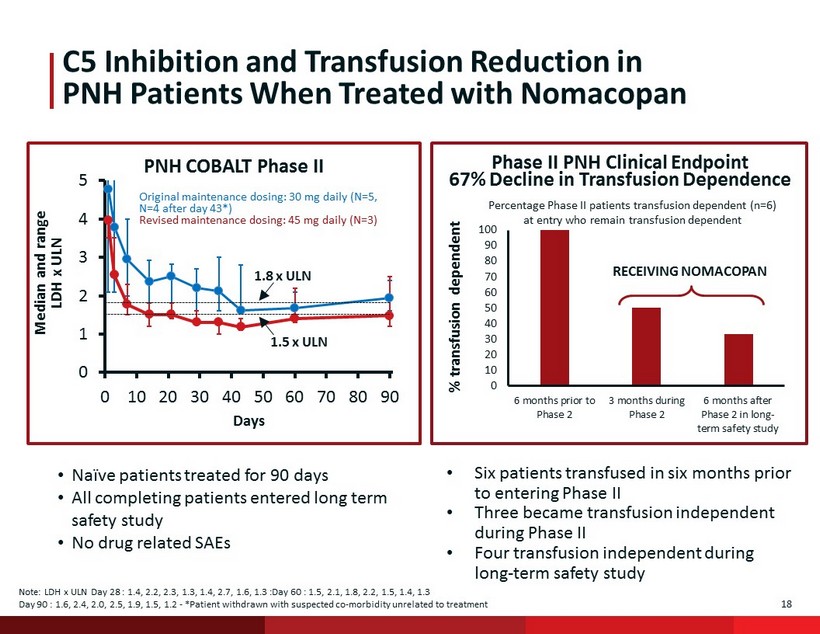
18 C5 Inhibition and Transfusion Reduction in PNH Patients When Treated with N omacopan 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Days PNH COBALT Phase II Median and range LDH x ULN Original maintenance dosing: 30 mg daily (N=5, N=4 after day 43*) Revised maintenance dosing: 45 mg daily (N=3) 1.8 x ULN 1.5 x ULN • Naïve patients treated for 90 days • All completing patients entered long term safety study • No drug related SAEs Note: LDH x ULN Day 28 : 1.4, 2.2, 2.3, 1.3, 1.4, 2.7, 1.6, 1.3 :Day 60 : 1.5, 2.1, 1.8, 2.2, 1.5, 1.4, 1.3 Day 90 : 1.6, 2.4, 2.0, 2.5, 1.9, 1.5, 1.2 - *Patient withdrawn with suspected co - morbidity unrelated to treatment • Six patients transfused in six months prior to entering Phase II • Three became transfusion independent during Phase II • Four transfusion independent during long - term safety study Percentage Phase II patients transfusion dependent (n=6) at entry who remain transfusion dependent RECEIVING NOMACOPAN % transfusion dependent 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 6 months prior to Phase 2 3 months during Phase 2 6 months after Phase 2 in long- term safety study Phase II PNH Clinical Endpoint 67% Decline in Transfusion Dependence
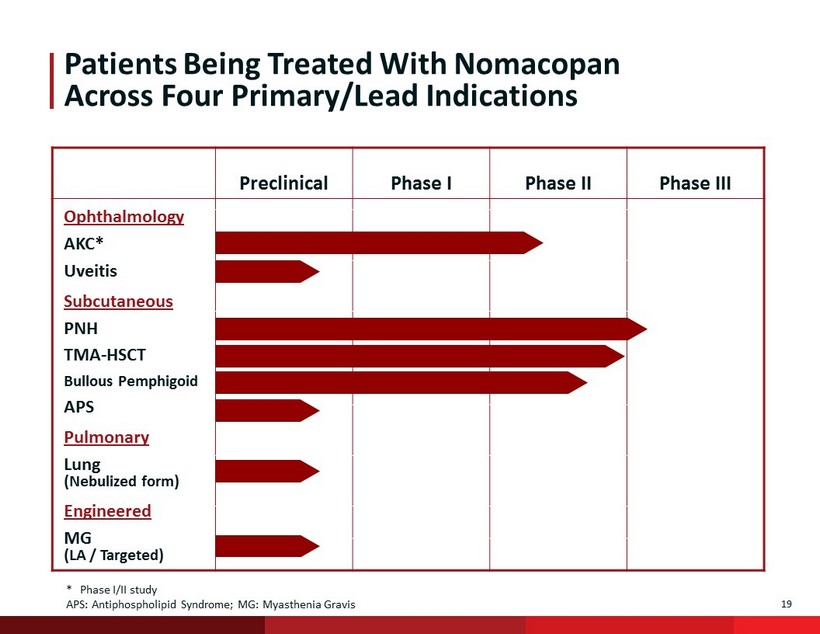
19 Patients Being Treated With N omacopan Across Four Primary/Lead Indications Preclinical Phase I Phase II Phase III * Phase I/II study APS: Antiphospholipid Syndrome; MG: Myasthenia Gravis Ophthalmology AKC* Subcutaneous PNH TMA - HSCT Bullous Pemphigoid Pulmonary Lung (Nebulized form) Engineered MG (LA / Targeted) Uveitis APS

20 ● $20 million financing facility* with Aspire Capital ● ~1.6 billion ordinary shares outstanding / equivalent to 16 million ADSs ● Multiple expected short - to mid - term clinical readouts: – BP : complete mild to moderate patients Q4 2019 – BP : expansion to severe 2H 2019 – TMA : Q4 2019 - pivotal trial approval/open – AKC: complete Part A mid 2019, Part B Q4 2019 – PNH: staged readouts – Auto - injector pen formulation : Phase I study initiation 2H 2019 Financial and Clinical Wrapup Meaningful Upcoming Clinical Milestones * Less than $1 million drawn down to date

APPENDIX
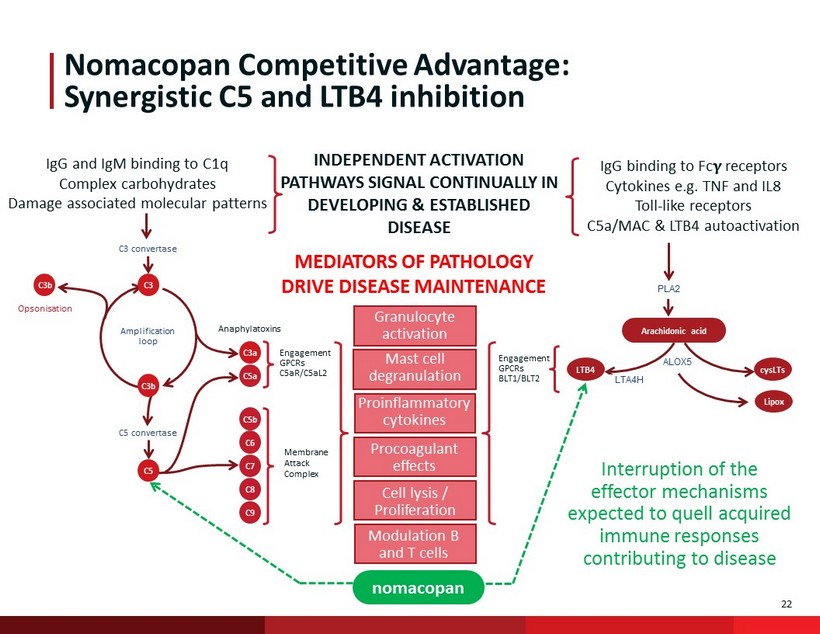
22 ALOX5 Engagement GPCRs BLT1/BLT2 Nomacopan Competitive Advantage: Synergistic C5 and LTB4 inhibition PLA2 Arachidonic acid C3 C3b C3 convertase Opsonisation Amplification loop C5 convertase C3a C5b C6 C7 C9 C8 C5 Engagement GPCRs C5aR/C5aL2 C3b Anaphylatoxins C5a LTB4 Membrane Attack Complex nomacopan LTA4H cysLTs IgG binding to Fc receptors Cytokines e.g. TNF and IL8 Toll - like receptors C5a/MAC & LTB4 autoactivation IgG and IgM binding to C1q Complex carbohydrates Damage associated molecular patterns INDEPENDENT ACTIVATION PATHWAYS SIGNAL CONTINUALLY IN DEVELOPING & ESTABLISHED DISEASE MEDIATORS OF PATHOLOGY DRIVE DISEASE MAINTENANCE Granulocyte activation Proinflammatory cytokines Procoagulant effects Cell lysis / Proliferation Modulation B and T cells Mast cell degranulation Lipox Interruption of the effector mechanisms expected to quell acquired immune responses contributing to disease
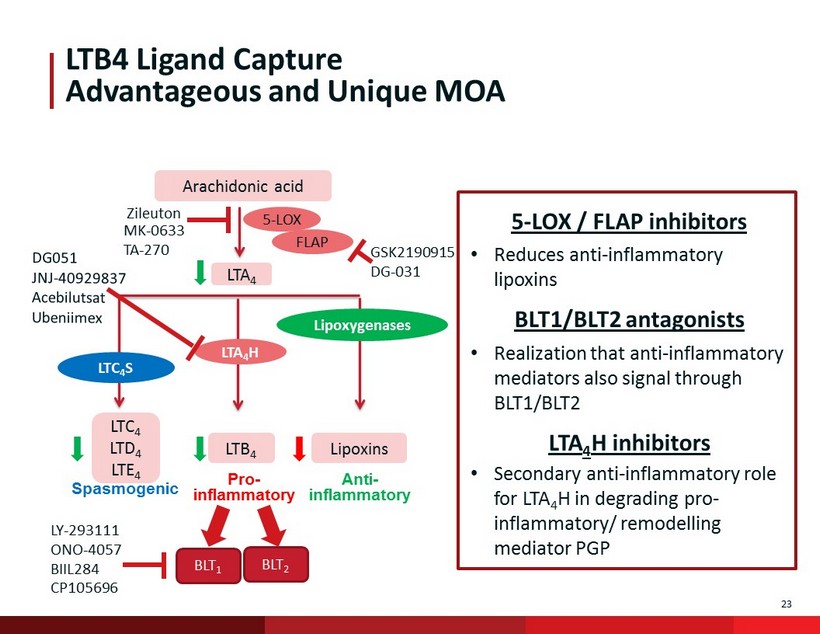
23 LTB4 Ligand Capture Advantageous and Unique MOA Arachidonic acid LTA 4 Lipoxins LTB 4 LTC 4 LTD 4 LTE 4 5 - LOX FLAP LTA 4 H LTC 4 S Lipoxygenases Pro - inflammatory Anti - inflammatory Spasmogenic Zileuton GSK2190915 DG - 031 MK - 0633 TA - 270 5 - LOX / FLAP inhibitors • Reduces anti - inflammatory lipoxins BLT1/BLT2 antagonists • Realization that anti - inflammatory mediators also signal through BLT1/BLT2 LTA 4 H inhibitors • Secondary anti - inflammatory role for LTA 4 H in degrading pro - inflammatory/ remodelling mediator PGP BLT 1 BLT 2 LY - 293111 ONO - 4057 BIIL284 CP105696
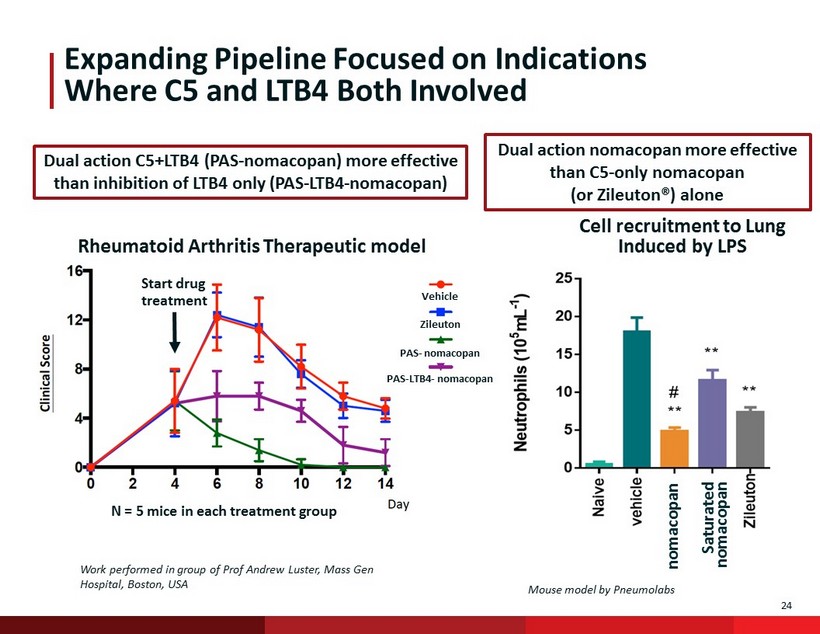
24 N = 5 mice in each treatment group Start drug treatment Expanding Pipeline Focused on Indications Where C5 and LTB4 Both Involved Zileuton PAS - nomacopan PAS - LTB4 - nomacopan Cell recruitment to Lung Induced by LPS Dual action nomacopan more effective than C5 - only nomacopan (or Zileuton®) alone Dual action C5+LTB4 (PAS - nomacopan ) more effective than inhibition of LTB4 only (PAS - LTB4 - nomacopan ) Work performed in group of Prof Andrew Luster, Mass Gen Hospital, Boston, USA Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapeutic model Vehicle nomacopan Mouse model by Pneumolabs Saturated nomacopan 24

May 2019 Investor Presentation
























