UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023
| | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 001-36105
EMPIRE STATE REALTY TRUST, INC.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
| | | | | | | | |
| Maryland | | 37-1645259 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
111 West 33rd Street, 12th Floor
New York, New York 10120
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip Code)
(212) 687-8700
(Registrant's telephone number, including area code)
| | | | | | | | |
| Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: |
| Title of Each Class | Trading Symbol | Name of Exchange on Which Registered |
| Class A Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | ESRT | The New York Stock Exchange |
| Class B Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | N/A | N/A |
| Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: |
| None |
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☒ | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | Smaller reporting company | ☐ |
| | Emerging growth company | ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant's executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1 (b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter was $1,197,221,000 based on the June 30, 2023 closing price of the registrant's Class A common stock of $7.49 per share on the New York Stock Exchange.
As of February 22, 2024, there were 163,091,331 shares of the registrants' Class A common stock outstanding and 983,434 shares of the registrants' Class B common stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.'s Proxy Statement for its 2023 Annual Stockholders' Meeting (which is scheduled to be held on May 9, 2024 in-person and virtually via a live webcast) to be filed within 120 days after the end of the Registrant's fiscal year are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| | | | | | | | |
| EMPIRE STATE REALTY TRUST, INC. | |
| FORM 10-K | |
| TABLE OF CONTENTS | |
| | PAGE |
| PART I. | |
| 1. | Business | |
| 1A. | Risk Factors | |
| 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments | |
| 1C. | Cybersecurity | |
| 2. | Properties | |
| 3. | Legal Proceedings | |
| 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | |
| PART II. | |
| 5. | Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholders Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | |
| 6. | [Reserved] | |
| 7. | Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | |
| 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk | |
| 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | |
| 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | |
| 9A. | Controls and Procedures | |
| 9B. | Other Information | |
| 9C. | Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections | |
| PART III | |
| 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | |
| 11. | Executive Compensation | |
| 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | |
| 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | |
| 14. | Principal Accounting Fees and Services | |
| PART IV | |
| 15. | Exhibits, Financial Statements and Schedules | |
| 16. | Form 10-K Summary | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| |
| | |
DEFINITIONS
•"annualized rent" represents annualized base rent and current reimbursement for operating expenses and real estate taxes;
•"formation transactions" means a series of transactions pursuant to which we acquired, substantially concurrently with the completion of the Offering, through a series of contributions and merger transactions, our commercial portfolio of real estate assets which were held by existing entities, the ownership interests in the certain management entities of our predecessor and one development parcel;
•"fully diluted basis" means all outstanding shares of our Class A common stock at the time indicated plus shares of Class A common stock that may be issuable upon the exchange of operating partnership units on a one-for-one basis and shares of Class A common stock issuable upon the conversion of Class B common stock on a one-for-one basis, which is not the same as the meaning of “fully diluted” under generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America ("GAAP");
•"enterprise value" means all outstanding shares of our Class A common stock at the time indicated plus shares of Class A common stock that may be issuable upon the exchange of operating partnership units on a one-for-one basis and shares of Class A common stock issuable upon the conversion of Class B common stock on a one-for-one basis multiplied by the Class A common share price at December 31, 2023, plus private perpetual preferred units plus consolidated debt at December 31, 2023;
•"Malkin Group” means all of the following, as a group: Anthony E. Malkin, Peter L. Malkin and each of their spouses and lineal descendants (including spouses of such descendants), any estates of any of the foregoing, any trusts now or hereafter established for the benefit of any of the foregoing, or any corporation, partnership, limited liability company or other legal entity controlled by Anthony E. Malkin or any permitted successor in such entity for the benefit of any of the foregoing; provided, however that solely with respect to tax protection rights and parties who entered into the contribution agreements with respect to the formation transactions, the Malkin Group shall also include the lineal descendants of Lawrence A. Wien and his spouse (including spouses of such descendants), any estates of the foregoing, any trusts now or hereafter established for the benefit of any of the foregoing, or any corporation, partnership, limited liability company or other legal entity controlled by Anthony E. Malkin for the benefit of the foregoing;
•the "Offering" means the initial public offering of our Class A common stock which was completed on October 7, 2013;
•"our Company," "we," "us", "our" and "ESRT" refer to Empire State Realty Trust, Inc., a Maryland real estate investment trust, together with its consolidated subsidiaries, including Empire State Realty OP, L.P.;
•“operating partnership” refers to Empire State Realty OP, L.P., a Delaware limited partnership through which Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. conducts substantially all of its business and of which it is the general partner;
•"securityholder" means a holder of our Class A common stock or Class B common stock as well as a holder of our operating partnership's Series ES, Series 250, Series 60 and Series PR operating partnership units; and
•"traded OP units" mean our operating partnership's Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units.
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Overview
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. (NYSE: ESRT) is a NYC-focused REIT that owns and operates a portfolio of modernized, amenitized, and well-located office, retail, and multifamily assets. The Company is a recognized leader in energy efficiency and indoor environmental quality. ESRT’s flagship Empire State Building – the “World’s Most Famous Building” – includes its Observatory, the #1 attraction in the U.S. in Tripadvisor’s Travelers’ Choice Awards: Best of the Best for two consecutive years.
As of December 31, 2023, our portfolio is comprised of approximately 8.6 million rentable square feet of office space, 0.7 million rentable square feet of retail space and 727 residential units. Our office portfolio included 11 properties (including three long-term ground leasehold interests) encompassing approximately 8.6 million rentable square feet. Nine of these office properties are located in midtown Manhattan and encompass approximately 7.6 million rentable square feet, including the Empire State Building. The remaining two office properties encompass approximately 1.1 million rentable square feet and are located in Stamford, Connecticut, with immediate access to mass transportation. Additionally, we have entitled land adjacent to one of the Stamford office properties that can support the development of either office or residential per local zoning. Our multifamily portfolio included 727 residential units in New York City.
We were organized as a Maryland corporation on July 29, 2011 and commenced operations upon completion of our initial public offering and related formation transactions on October 7, 2013 (the "IPO"). Our operating partnership, Empire State Realty OP, L.P. (the "Operating Partnership"), holds substantially all of our assets and conducts substantially all of our business. As of December 31, 2023, we owned approximately 60.2% of the aggregate operating partnership units in the Operating Partnership. We, as the sole general partner in the Operating Partnership, have responsibility and discretion in the management and control of the Operating Partnership, and the limited partners in the Operating Partnership, in such capacity, have no authority to transact business for, or participate in the management activities of, the Operating Partnership. Accordingly, the Operating Partnership has been consolidated by us. We elected to be subject to tax as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2013.
Business and Growth Strategies
Our primary business objectives are to maximize cash flow and total returns to our shareholders and to increase the value of our properties through the pursuit of the following strategies:
Lease Space
We believe we benefit from the tenant flight to quality trend. Tenants seek a compelling value proposition from landlords with a strong balance sheet and low leverage that continue to invest in the improvement of their buildings, and we offer a high-quality experience in high-quality assets at our attractive price point. Our buildings are fully modernized, well-located near mass transit, well-amenitized, and feature industry leadership in energy efficiency and indoor environmental quality, which helps us to draw consistent leasing volumes through cycles. They also have character. The quality of our commercial portfolio contributed to a strong leasing year in 2023; we leased 951,000 square feet of space and made meaningful absorption progress with a 130 basis point increase in Manhattan office occupancy and a 250 basis point increase in Manhattan leased rate throughout the year. Additionally, we believe our proactive, service-intensive approach to asset and property management helps increase occupancy and rental rates.
We have a brand that we believe tenants associate with a consistently high level of quality of services, healthy buildings, amenities, maintenance, and tenant installations, with high performance design guidelines for energy efficiency and indoor environmental quality, and long-term financial stability. Through our commitment to brokers, we have developed long-term relationships with a focus to attract high quality tenants to our properties. We proactively manage and cultivate our industry relationships and make the most senior members of our management team available to our constituencies. We believe that our consistent, open dialogue with our tenants and brokers enables us to maximize our results. Our focus on performance and long-term perspective allows us to concentrate on the ongoing management of our portfolio, while we concurrently seek opportunities for growth in the future.
We do extensive diligence on our tenants' financial prospects, businesses and business models to determine if we think there is potential to establish long-term relationships in which they will both renew with us and expand over time. Since the Offering, we have completed 277 expansions with existing tenants which total 2.6 million square feet within our portfolio. Our comprehensive building management services and our strong commitment to tenant and broker relationships and satisfaction enable us to negotiate attractive leasing deals, which attracts and retains high credit-quality tenants. We proactively manage our
rent roll, foster strong tenant relationships, maintain continuous communication with our tenants, and are responsive to tenant needs. We believe the success of our long-term tenant relationships improves our operating results over time by reducing leasing, marketing and tenant improvement costs, as well as tenant turnover.
We regularly monitor our properties, perform routine preventive maintenance, and implement capital improvement programs in connection with property redevelopment and life cycle replacement of equipment and systems to protect our investments. We self-manage all of our office and retail properties, and we use a third-party property manager to manage our multifamily properties. We proactively manage our office properties and rent rolls to create efficient, modern, pre-built offices that can be rented through several lease cycles and attract high credit-quality tenants. We manage and control operating expenses at all of our properties. In addition, we have made energy efficiency retrofitting and sustainability a portfolio-wide initiative driven by economic return. We pass on cost savings achieved by such improvements to our tenants through lower utility costs and reduced operating expense escalations. We believe these initiatives make our properties more desirable to a broader tenant base than the properties of our competitors.
Sell Tickets to the Empire State Building Observatory
The Empire State Building offers panoramic views of New York and neighboring states from its world-famous 86th and 102nd floor observatories. In December 2019, we completed the Observatory’s comprehensive multi-year reimagination and redevelopment. In 2020, we reprogrammed our Observatory business to operate by reservations only, created a new focus on customer experience and reduction of crowds and lines, with an emphasis on growing revenue per visitor, and matched our hours of operation to the reservations demand to manage expenses. We enhanced health and safety protocols, improved marketing and cross-promotional activities to increase brand awareness, and managed expenses prudently.
Our efforts have resulted in strong performance from our Observatory and we experienced continued improvement in Observatory revenue and operating income throughout 2023. We had approximately 2.6 million visitors in 2023 as compared to 0.5 million in 2020, 0.8 million in 2021 and 2.2 million in 2022. Additionally, the Empire State Building Observatory was ranked the # 1 attraction in the United States in Tripadvisor's Travelers’ Choice Awards: Best of the Best for two consecutive years.
Enhance Shareholder Value
We enhance shareholder value primarily through the execution of our capital allocation strategy, maintenance of our balance sheet flexibility and enhanced transparency and disclosure. As it relates to capital allocation strategy, we (i) opportunistically recycle our capital, (ii) make selective, value-enhancing acquisitions and (iii) reinvest in our own shares through share repurchases.
We are diversified and we believe we benefit from New York City’s rebound from our office, Observatory, retail, and multifamily exposure in the city. We have a dedicated investment function to identify potential investment opportunities, which includes our Chief Investment Officer and a full acquisitions team. We believe our well-positioned balance sheet, access to capital, and expertise in redevelopment gives us significant flexibility to structure and pursue attractive investment opportunities. Since December 2021, we have completed acquisitions of three multifamily properties in Manhattan and a retail asset in the Williamsburg neighborhood of Brooklyn, NY. We have also completed the disposition of non-core assets in our greater New York metropolitan area portfolio, including office assets in Norwalk, CT, White Plains, NY and Harrison, NY, and retail assets in Westport, CT. See ITEM 2. Properties for more information.
For the foreseeable future, we intend to focus our acquisition strategy primarily on NYC office, retail and multifamily properties where we can achieve attractive returns on invested capital.
In the current financial environment, we believe our well-positioned balance sheet differentiates us in our efforts to attract brokers and new tenants, who look to partner with financially stable landlords which will invest in their customers and maintain high-quality standards at their assets. Our well-positioned balance sheet has also allowed us to be nimble and recycle capital as well as repurchase shares.
Achieve Sustainability Goals
We are recognized as a leader in the real estate industry in sustainability, and we focus on net zero emissions, energy efficiency, water use reduction, indoor environmental quality, and healthy buildings. We have pioneered certain practices to achieve emissions reduction and energy efficiency, including those described in our Empire Building Playbook, a free guide that we published in partnership with the New York Energy Research Development Authority and the Clinton Global Initiative, for existing commercial buildings to follow our lead and develop a technical and economic pathway to achieve net zero carbon reduction with a proven payback. The reduced energy consumption and emissions lower costs for us and our tenants, and we believe creates a competitive advantage for our properties. We believe that higher quality tenants prioritize sustainability, cost reduction, and lower contributions to greenhouse gas emissions.
Business Segments
Our reportable segments consist of a real estate segment and an Observatory segment. Our real estate segment includes all activities related to the ownership, management, operation, acquisition, repositioning and disposition of our commercial and multifamily real estate assets, principally office assets, located in Manhattan. Our Observatory segment operates the 86th and 102nd floor observatories at the Empire State Building. These segments are managed separately because each business requires different support infrastructure, provides different services and has dissimilar economic characteristics such as investments needed, stream of revenues and marketing strategies. We account for intersegment sales and rent as if the sales or rent were to third parties at current market prices. This intersegment rent is eliminated upon consolidation.
For more information about our segments, refer to “Financial Statements - Note 13 Segment Reporting” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Rental Revenue
We derive revenues primarily from rents, rent escalations, expense reimbursements and other income received from tenants under existing leases at each of our properties. “Escalations and expense reimbursements” consist of payments made by tenants to us under contractual lease obligations to reimburse a portion of the property operating expenses and real estate taxes incurred at each property.
We believe that the average rental rates for in-place leases at our properties are generally below the current market rates, although individual leases at particular properties presently may be leased above, at or below the current market rates within its particular submarket.
Regulation
General
The properties in our portfolio are subject to various laws, ordinances and regulations, including regulations relating to common areas. We believe each of the existing properties has the necessary permits and approvals to operate its business.
Americans with Disabilities Act
Our properties must comply with Title III of the Americans with Disabilities Act, or ("ADA"), to the extent that such properties are “public accommodations” as defined by the ADA. The ADA may require removal of structural barriers to access by persons with disabilities in certain public areas of our properties where such removal is readily achievable. We believe the existing properties are in substantial compliance with the ADA and that we will not be required to make substantial capital expenditures to address the requirements of the ADA. However, noncompliance with the ADA could result in imposition of fines or an award of damages to private litigants. The obligation to make readily achievable accommodations is an ongoing one, and we will continue to assess our properties and to make alterations as appropriate in this respect.
Environmental Matters
Under various federal, state and/or local laws, ordinances and regulations, as a current or former owner or operator of real property, we may be liable for costs and damages resulting from the presence or release of hazardous substances, waste, or petroleum products at, on, in, under or from such property, including costs for investigation or remediation, natural resource damages, or third-party liability for personal injury or property damage. These laws often impose liability without regard to whether the owner or operator knew of, or was responsible for, the presence or release of such materials, and the liability may be joint and several. Some of our properties have been or may be impacted by contamination arising from current or prior uses of the property or adjacent properties for commercial, industrial or other purposes. Such contamination may arise from spills of petroleum or hazardous substances or releases from tanks used to store such materials. We also may be liable for the costs of remediating contamination at off-site disposal or treatment facilities when we arrange for disposal or treatment of hazardous substances at such facilities, without regard to whether we comply with environmental laws in doing so. The presence of contamination or the failure to remediate contamination on our properties may adversely affect our ability to attract and/or retain tenants, and our ability to develop or sell or borrow against those properties. In addition to potential liability for cleanup costs, private plaintiffs may bring claims for personal injury, property damage or for similar reasons. Environmental laws also may create liens on contaminated sites in favor of the government for damages and costs it incurs to address such contamination. Moreover, if contamination is discovered on our properties, environmental laws may impose restrictions on the manner in which that property may be used or how businesses may be operated on that property.
Some of our properties are adjacent to or near other properties which are used for industrial or commercial purposes or have contained or currently contain underground storage tanks used to store petroleum products or other hazardous or toxic substances. Releases from these properties could impact our properties. In addition, some of our properties have previously been used by former owners or tenants for commercial or industrial activities, e.g., gas stations and dry cleaners, and a portion of the Metro Tower site is currently used for automobile parking and was formerly leased to a fueling facility that may release petroleum products or other hazardous or toxic substances at such properties or to surrounding properties. While certain properties contain or contained uses that could have or have impacted our properties, we are not aware of any liabilities related to environmental contamination that we believe will have a material adverse effect on our operations.
We have post-closing obligations related to the 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street, Westport, Connecticut properties that we sold in February 2023 to (i) close out a voluntary remediation program at 69-97 Main Street to address residual impacts of prior presence of underground storage tanks and (ii) comply with a consent order issued by the Connecticut Department of Environmental Protection to investigate soil conditions at 103-107 Main Street. We believe any expenses incurred to close out and comply with the remediation program and consent order, respectively, will be immaterial to the results of our operations.
Our property situated at 500 Mamaroneck Avenue in Harrison, New York was the subject of a voluntary remedial action work cleanup plan under an agreement with the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, but we sold this property in April 2023 and the obligations have been transferred to the buyer.
In addition, our properties are subject to various federal, state and local environmental and health and safety laws and regulations. Noncompliance with these laws and regulations could subject us or our tenants to liability. These liabilities could affect a tenant’s ability to make rental payments to us. Moreover, changes in laws could increase the potential costs of compliance with such laws and regulations or increase liability for noncompliance. This may result in significant unanticipated expenditures. We sometimes require our tenants to comply with environmental and health and safety laws and regulations and to indemnify us for any related liabilities in our leases with them. But in the event of the bankruptcy or inability of any of our tenants to satisfy such obligations, we may be required to satisfy such obligations. We are not presently aware of any instances of material non-compliance with environmental or health and safety laws or regulations at our properties, and we believe that we and/or our tenants have all material permits and approvals necessary under current laws and regulations to operate our properties.
In addition, we may become subject to new compliance requirements and/or new costs or taxes associated with natural resource or energy usage and related emissions (such as a carbon tax), which could increase our operating costs. In particular, as the owner of large commercial buildings in New York City, we are subject to Local Law 97 passed by the New York City Council in April 2019, which for each such building establishes annual limits for greenhouse gas emissions, requires yearly emissions reports beginning in May 2025, and imposes penalties for emissions above such limits. Based upon our present understanding of the law and calculations related thereto, we expect to pay no fine on any building in our commercial portfolio in the 2024-2029 first period of enforcement.
As the owner or operator of real property, we may also incur liability based on various building conditions. For example, environmental site assessments and investigations have identified asbestos or asbestos-containing material ("ACM") in certain of our properties, and it is possible that other properties that we currently own or operate or those we acquire or operate in the future contain, may contain, or may have contained ACM. Refer to “Financial Statements - Note 9 Commitments and Contingencies - Asset Retirement Obligations” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Environmental and health and safety laws require that ACM be properly managed and maintained and may impose fines or penalties on owners, operators or employers for non-compliance with those requirements. These requirements include special precautions, such as removal, abatement or air monitoring, if ACM would be disturbed during maintenance, redevelopment or demolition of a building, potentially resulting in substantial costs. In addition, we may be subject to liability for personal injury or property damage sustained as a result of releases of ACM into the environment. We are not presently aware of any material liabilities related to building conditions, including any instances of material non-compliance with asbestos requirements or any material liabilities related to asbestos.
Our properties may contain or develop harmful mold or suffer from other indoor air quality issues, which could lead to liability for adverse health effects or property damage or costs for remediation. When excessive moisture accumulates in buildings or on building materials, mold growth may occur, particularly if the moisture problem remains undiscovered or is not addressed over a period of time. Some molds may produce airborne toxins or irritants. Indoor air quality issues can also stem from inadequate ventilation, chemical contamination from indoor or outdoor sources, and other biological contaminants such as pollen, viruses and bacteria. Indoor exposure to airborne toxins or irritants above certain levels can be alleged to cause a variety of adverse health effects and symptoms, including allergic or other reactions. As a result, the presence of significant mold or
other airborne contaminants at any of our properties could require us to undertake a costly remediation program to contain or remove the mold or other airborne contaminants from the affected property or increase indoor ventilation. In addition, the presence of significant mold or other airborne contaminants could expose us to liability from our tenants, employees of our tenants or others if property damage or personal injury occurs. We are not presently aware of any material adverse indoor air quality issues at our properties.
Affordable Housing
Certain units in our multifamily properties are designated for lower income households and are therefore subject to supervision and regulation by state and federal governmental authorities which regulate affordable housing rental activities. See "Risk Factors - Government housing regulations may limit opportunities at the multifamily properties in which we invest, and failure to comply with resident qualification requirements may result in financial penalties or loss of benefits" for more information.
Insurance
We carry comprehensive liability, fire, extended coverage, earthquake, terrorism and rental loss insurance covering all of our New York City properties and our greater New York metropolitan area properties under a blanket policy. We carry additional all-risk property and business insurance, which includes terrorism insurance, on the Empire State Building through ESRT Captive Insurance Company L.L.C., or ESRT Captive Insurance, our wholly owned captive insurance company. ESRT Captive Insurance covers terrorism insurance for $1.2 billion in losses in excess of $800 million per occurrence suffered by the Empire State Building, providing us with aggregate terrorism coverage of $2 billion at that property. ESRT Captive Insurance fully reinsures the 20% coinsurance under the Terrorism Risk Insurance Program Reauthorization Act of 2015 ("TRIPRA") and the difference between the TRIPRA captive deductible and policy deductible of $100,000 for non-Nuclear, Biological, Chemical and Radiological exposures. We purchased a $50 million limit of Nuclear, Biological, Chemical and Radiological ("NBCR") insurance in excess of a $1.0 million deductible in the commercial insurance market. ESRT Captive Insurance provides NBCR insurance coverage under TRIPRA with a limit of $1.95 billion in excess of the $50 million policy. As a result, we remain only liable for the 20% coinsurance under TRIPRA for NBCR exposures within ESRT Captive Insurance, as well as a deductible equal to 20% of ESRT Captive Insurance’s prior year’s premium. As long as we own ESRT Captive Insurance, we are responsible for ESRT Captive Insurance’s liquidity and capital resources, and ESRT Captive Insurance’s accounts are part of our consolidated financial statements. If we experience a loss and ESRT Captive Insurance is required to pay under its insurance policy, we would ultimately record the loss to the extent of its required payment. The policies described above cover certified terrorism losses as defined under the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act of 2002 ("TRIA") and subsequent extensions. On December 20, 2019, the President of the United States signed into law TRIPRA act of 2019, which extended TRIA through December 31, 2027. TRIA provides for a system of shared public and private compensation for insured losses resulting from acts of terrorism. As a result, the certified terrorism coverage provided by ESRT Captive Insurance is eligible for 80% coinsurance provided by the United States Treasury in excess of a statutorily calculated deductible. ESRT Captive Insurance reinsures 100% of its 20% coinsurance for non-NBCR exposures. The 20% coinsurance on NBCR exposures is retained by ESRT Captive Insurance.
Reinsurance contracts do not relieve ESRT Captive Insurance from its primary obligations to its policyholders. Additionally, failure of the various reinsurers to honor their obligations could result in significant losses to ESRT Captive Insurance. The reinsurance has been ceded to reinsurers approved by the State of Vermont. ESRT Captive Insurance continually evaluates the reinsurers’ financial condition by considering published financial stability ratings of the reinsurers and other factors. There can be no assurance that reinsurance will continue to be available to ESRT Captive Insurance to the same extent and at the same cost. ESRT Captive Insurance may choose in the future to reevaluate the use of reinsurance to increase or decrease the amounts of risk it cedes.
In addition to insurance held through ESRT Captive Insurance described above, we carry terrorism insurance on all of our properties in an amount and with deductibles which we believe are commercially reasonable.
Our insurance policies include substantial self-insurance portions and significant deductibles and co-payments for certain events, and hurricanes in the United States have affected the availability and price of such insurance. We may discontinue certain insurance coverage on some or all of our properties in the future if the cost of premiums for any of these policies in our judgment exceeds the value of the coverage discounted for the risk of loss.
Additionally, we do not carry insurance for certain losses, including, but not limited to, losses caused by war. Furthermore, business interruption insurance due to pandemic level or other public health events may not be readily available at commercially acceptable rates.
Competition
The leasing of real estate is highly competitive in New York City and Stamford, Connecticut where we operate. We compete with numerous acquirers, developers, owners and operators of commercial real estate, many of which own or may seek to acquire or develop properties similar to ours in the same markets in which our properties are located. The principal means of competition are rent charged, location, amenities and services provided, and the nature and condition of the facility to be leased. In addition, we face competition from other real estate companies, including other REITs, private real estate funds, domestic and foreign financial institutions, life insurance companies, pension trusts, partnerships, individual investors and others, that may have greater financial resources or access to capital than we do or that are willing to acquire properties in transactions which are more highly leveraged or are less attractive from a financial viewpoint than we are willing to pursue. In addition, competition from new and existing observatories and/or broadcasting operations may have a negative impact on revenues from our Observatory operations and/or broadcasting revenues. Adverse impacts on domestic and international travel and changes in foreign currency exchange rates may also decrease demand in the future, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and ability to make distributions to our securityholders. If our competitors offer space at rental rates below current market rates, below the rental rates we currently charge our tenants, in better locations within our markets or in higher quality facilities, we may lose potential tenants and we may be pressured to reduce our rental rates below those we currently charge in order to retain tenants when our tenants’ leases expire.
Our Tax Status
We elected to be subject to tax as a REIT and have operated in a manner that we believe allows us to qualify as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2013. We believe we have been organized in conformity with the requirements for qualification and taxation as a REIT under the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, (the "Code"), and that our intended manner of operation will enable us to continue to meet the requirements for qualification and taxation as a REIT. So long as we qualify as a REIT, we generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax on our net taxable income that we distribute to our securityholders. If we fail to qualify as a REIT in any taxable year and do not qualify for certain statutory relief provisions, we will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at regular corporate rates and may be precluded from qualifying as a REIT for the subsequent four taxable years following the year during which we lost our REIT qualification. Even if we qualify as a REIT, we may be subject to certain U.S. federal, state and local taxes on our income or property.
In order to qualify as a REIT, we must distribute to our securityholders, on an annual basis, at least 90% of our REIT taxable income, determined without regard to the deduction for distributions paid and excluding net capital gains. In addition, we will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at the generally applicable corporate tax rate to the extent that we distribute less than 100% of our net taxable income (including net capital gains) and will be subject to a 4% nondeductible excise tax on the amount by which our distributions in any calendar year are less than a minimum amount specified under U.S. federal income tax laws.
In addition, to qualify as a REIT, we must ensure that we meet the REIT gross income tests annually and that at the end of each calendar quarter, at least 75% of the value of our total assets consists of cash, cash items, government securities and qualified REIT real estate assets, including certain mortgage loans and certain kinds of mortgage-backed securities. The remainder of our investment in securities (other than government securities, securities of corporations that are treated as Taxable REIT Subsidiaries ("TRSs") and qualified REIT real estate assets) generally cannot include more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of any one issuer or more than 10% of the total value of the outstanding securities of any one issuer. In addition, in general, no more than 5% of the value of our assets (other than government securities and qualified real estate assets) can consist of the securities of any one issuer, and no more than 20% of the value of our total securities can be represented by securities of one or more TRSs.
Rents from real property are generally not qualifying income for purposes of the REIT gross income tests if the rent is treated as “related party rent.” Related party rent generally includes (i) any rent paid by a corporation if the REIT (or any person who owns 10% or more of the stock of the REIT by value) directly or indirectly owns 10% or more of the stock of the corporation by vote or value and (ii) rent paid by a partnership if the REIT (or any person who owns 10% or more of the stock of the REIT by value) directly or indirectly owns an interest of 10% or more in the assets or net profits of the partnership. Under an exception to this rule, related party rent is treated as qualifying income for purposes of the REIT gross income tests if it is paid by a TRS of the REIT and (i) at least 90% of the leased space in the relevant property is rented to persons other than either TRSs or other related parties of the REIT, and (ii) the amounts paid to the REIT as rent from real property are substantially comparable to the rents paid by unrelated tenants of the REIT for comparable space.
Income from admissions to the Empire State Building Observatory, and certain other income generated by the Observatory, would not likely be qualifying income for purposes of the REIT gross income tests. We jointly elected with Observatory TRS, which is the current lessee and operator of the Observatory and which is wholly owned by our operating partnership, for Observatory TRS to be treated as a TRS of ours for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Observatory TRS leases the Empire State Building Observatory from the operating partnership pursuant to a lease that provides for fixed base rental payments and variable rental payments equal to certain percentages of Observatory TRS’s gross receipts from the operation of the Observatory. Given the unique nature of the real estate comprising the Observatory, as of the date of such lease, we did not believe that there is any space in the Empire State Building or in the same geographic area as the Empire State Building that is likely to be considered sufficiently comparable to the Observatory for the purpose of applying the exception to related party rent described above. We have received from the IRS a private letter ruling that the rent that our operating partnership receives from Observatory TRS pursuant to the lease of the Empire State Building Observatory is qualifying income for purposes of the REIT gross income tests so long as such rent reflects the fair market rental value of the Empire State Building Observatory as determined by an appraisal rendered by a qualified third-party appraiser.
In addition, our operating partnership has acquired various license agreements (i) granting certain third-party broadcasters the right to use space on the tower on the top of the Empire State Building for certain broadcasting and other communication purposes and (ii) granting certain third-party vendors the right to operate concession stands in the Observatory. We have received from the IRS a private letter ruling that the license fees that our operating partnership receives under the license agreements described above constitute qualifying income for purposes of the REIT gross income tests.
Inflation
Substantially all of our leases provide for separate real estate tax and operating expense escalations. In addition, many of the leases provide for fixed base rent increases. We believe inflationary increases may be at least partially offset by the contractual rent increases and expense escalations described above. We do not believe inflation has had a material impact on our financial position or results of operations.
Seasonality
Our Observatory business is subject to tourism trends and weather, and therefore does experience some seasonality. For the year ended December 31, 2023, approximately 17% of our annual Observatory revenue was realized in the first quarter, 26% was realized in the second quarter, 29% was realized in the third quarter, and 28% was realized in the fourth quarter. Our multifamily business experiences some seasonality based on general market trends in New York City – the winter months (November through January) are slower in terms of lease activity. We seek to mitigate this by staggering lease terms such that lease expirations are matched with seasonal demand. We do not consider the balance of our business to be subject to material seasonal fluctuations.
Leasing Trend Fluctuations
Due to the relatively small number of leases that are signed in any particular quarter, one or more larger leases may have a disproportionately positive or negative impact on average rent, tenant improvement and leasing commission costs for that period. As a result, we believe it is more appropriate when analyzing trends in average rent and tenant improvement and leasing commission costs to review activity over multiple quarters or years. Tenant improvement costs include expenditures for general improvements occurring concurrently with, but that are not directly related to, the cost of installing a new tenant. Leasing commission costs are similarly subject to significant fluctuations depending upon the length of leases being signed and the mix of tenants from quarter to quarter.
Human Capital Management
As of December 31, 2023, we employed 666 people, of whom approximately 429 are covered by collective bargaining agreements. We generally have and expect to continue to maintain good relations with our employees and workforce, including those employees covered by collective bargaining agreements. We believe that our success is realized through the attraction, retention, development, engagement and empowerment of our highly-valued and diverse employees, and we endeavor to set our policies and practices accordingly.
We offer what we believe to be generally competitive compensation and benefits. To reward and reinforce participation in the Company’s outcomes, we also make equity grants to employees. We regularly review our compensation and benefits against our peers and the industry to remain competitive.
We strive to attract, hire and retain diverse candidates who meet our high standards. Our retention strategy is based on the effective training and development of, and focus on the total wellness of, our employees. We believe continuous learning supports productivity, innovation and retention, as well as personal and professional growth for our employees. We invest in employee training, including certain programs which are mandatory for all employees, and other programs which are voluntary and self-directed on platforms provided by the Company. We also regularly assess the performance and potential of our diverse
workforce, review our succession plans and create robust developmental action plans to grow our employees and prepare them
for internal promotional opportunities. We believe our public recognition demonstrates the strength of our program. As of February 2023, we are Great Place to Work-Certified. We were also selected for inclusion in the Bloomberg Gender Equality Index in 2022 and 2023.
Offices
Our principal executive offices are located at 111 West 33rd Street, 12th floor, New York, New York 10120. We also have additional regional leasing and property management offices in Manhattan and Stamford, Connecticut. Our current facilities are adequate for our present and future operations, although we may add or eliminate regional offices, depending upon our future operations.
Available Information
Our website address is http://www.esrtreit.com. The information found on, or otherwise accessible through, our website is not incorporated by reference into, and does not form a part of, this Annual Report on Form 10-K or any other report or document we file with or furnish to the SEC. We make available, free of charge, on or through the SEC Filings section of our website, our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to such reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"), as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. We have also posted on our website the Audit Committee Charter, Compensation and Human Capital Committee Charter, Finance Committee Charter, Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee Charter, Corporate Governance Guidelines and Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, which govern our directors, officers and employees. Within the time period required by the SEC, we will post on our website any amendment to our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and any waiver applicable to our senior financial officers and our executive officers or directors. The SEC maintains an Internet site (http://www.sec.gov) that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
You should carefully consider the following risks, together with all other information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, before you decide to retain or make an investment in our securities. These are not the only risks we face. Additional risks currently unknown or deemed immaterial could have a material adverse effect on us and our REIT qualification, which could reduce our share price and cause loss of all or part of your investment. Some items below are forward-looking statements. See “Forward-Looking Statements.”
Risks Related to Our Business and Properties
Risks Relating to Portfolio Concentration
Our properties are geographically concentrated in New York and Connecticut, and adverse state or local economic or regulatory developments could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, cash flow and financial condition.
Our commercial portfolio is comprised of properties primarily in New York City as well as in Stamford, Connecticut. As a result, our business is dependent on the New York City economy in general and the market for office, retail and multifamily space in New York City in particular, which exposes us to greater economic and regulatory risks than if we owned a more geographically diverse portfolio. These risks include business layoffs, downsizing, industry slowdowns, and relocations of businesses as well as increases in real estate and other local taxes, and regulatory compliance costs. The current federal tax limits on the deductibility of state and local taxes as well as higher individual tax rate proposals may negatively impact demographic trends in high tax states like New York and Connecticut.
The threat or occurrence of a terrorist event, particularly in New York City, may materially and adversely affect the value of our properties and our ability to generate cash flow.
The threat or occurrence of a terrorist event may cause people to relocate from New York City and Stamford, Connecticut to less populated, lower-profile areas. This could trigger a decrease in the demand, occupancy and rental rates for, and materially affect the value of, our properties and our cash flow. Such negative consequences may be even more likely in a high-profile property like the Empire State Building and its Observatory. Additionally, a terrorist event could cause insurance premiums at certain of our properties to increase significantly.
We rely on three properties, in particular the Empire State Building and its Observatory, for a significant portion of our revenue.
For the year ended December 31, 2023, three of our properties together accounted for approximately 53.2% of our portfolio’s rental revenues, with the Empire State Building individually accounting for approximately 29.6%. Our revenue and cash available for distribution would be materially and adversely affected if any of these three properties were materially damaged or a significant number of their tenants experienced financial strain leading to lease default or bankruptcy filing. Additionally, for fiscal years ended December 31, 2021, 2022 and 2023, we derived revenue of approximately $41.5 million, $106.0 million and $129.4 million, respectively from the Empire State Building’s Observatory operations. Loss of revenue from the Observatory has in the past and may in the future have a material adverse impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
Our five largest tenants represented approximately 15.9% of our total commercial portfolio’s annualized rent as of December 31, 2023.
As of December 31, 2023, our five largest tenants together represented approximately 15.9% of our total commercial portfolio’s annualized rent, with our largest tenant leasing an aggregate of 0.5 million rentable square feet of office space at one of our office properties, representing approximately 5.4% of our total commercial portfolio rentable square feet and approximately 6.2% of our total commercial portfolio annualized rent. Our significant tenants have in the past, and may in the future, experience financial strain leading to lease default or bankruptcy. In such cases, we may not recover our upfront investments in tenant improvement allowances, concessions, and transaction costs like professional fees and commissions. Upon tenant default, we may experience delays and substantial costs in enforcing our rights and protecting our investment. Our business, results of operations, cash flow and financial condition could be materially adversely affected if any of our significant tenants were to suffer a downturn in their business, become insolvent, default under their leases, and/or fail to renew on favorable terms or at all.
Risks Relating to the Real Estate Market
A sustained shift away from in-person work environments to remote work could have an adverse effect on the overall demand for our office and multifamily apartment units.
Certain remote work practices implemented in reaction to the pandemic are still in place and have shifted employers and employees away from fully in-person work environments, and a more permanent shift of this type could have an adverse effect on the overall demand for our office space. Additionally, with increased employer flexibility to work from home, current and prospective residents may be less likely to live in dense urban centers or multifamily housing like the properties we own. If these trends continue, it could impair demand and value at our properties.
Adverse economic and geopolitical conditions impacting the industries of our tenants, in particular the retail industry, could cause reduced demand, rental rates and occupancy for our retail and office space.
As of December 31, 2023, approximately 18.2% of our commercial portfolio’s annualized rent was comprised of retail tenants. In recent years, the retail industry has faced reductions in sales revenues and increase in bankruptcies throughout the United States, due to a consumer shift to online shopping. This has reduced demand for physical retail space especially at street level, which typically commanded the highest rental rates per square foot in office properties.
The bankruptcy or insolvency of any tenant could result in the termination of such tenant’s lease and material losses to us.
The occurrence of a tenant bankruptcy or insolvency has in the past, and could in the future, diminish or terminate the income we receive from that tenant. We may also be unable to re-lease a terminated or rejected space on favorable terms or at all. Additionally, a large number of our tenants (measured by number of tenants as opposed to aggregate square footage) are smaller businesses that generally do not have the financial strength of larger corporate tenants. Smaller businesses generally experience a higher rate of failure than large businesses, and their insolvency could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, cash flow and financial condition.
Competition may impede our ability to attract or retain tenants or re-lease space and we may be required to make rent or other concessions and/or significant capital expenditures to improve our properties in order to retain and attract tenants.
The leasing of real estate in New York City and its surrounding metropolitan area is highly competitive in rental rates, location, services and property condition. We have seen increased competition from lessors in offering concessions, short term, amenities, indoor environmental quality and sustainability certifications. See Part I, ITEM 1, “Business – Competition” for more information. Increased competition challenges our ability to lease space and maximize our effective rents.
Upon expiration of leases at our properties and with respect to our current vacant space, we may be required to make rent or other concessions to tenants, accommodate increased requests for renovations, build-to-suit remodeling and other improvements or provide additional services to our tenants. In addition, eight of our existing properties are pre-war office properties, which may require more frequent and costly maintenance to retain existing tenants or attract new tenants than newer properties. As a result, and due to the increased competition from lessors in the greater New York City area, we have made, and may have to make, significant capital or other expenditures in order to maintain the competitiveness of our properties. There can be no assurances that any such expenditure would result in higher occupancy, higher rental rates or deter existing tenants from relocating to properties owned by our competitors. If we are unable to match the competition for lack of capital or other reasons, we may fail to attract new tenants or to renew existing tenants.
We may be unable to renew leases or re-lease vacant space on favorable terms or at all as leases expire.
As of December 31, 2023, we had approximately 0.9 million rentable square feet of vacant space in our office and retail properties. In addition, leases representing 5.4% and 6.4% of the square footage of the office and retail properties in our commercial portfolio will expire in 2024 and 2025, respectively. We cannot be assured that leases scheduled to expire will be renewed or that our properties will be re-leased at net effective rental rates at or above the current average. If the terms of the renewal or re-leasing are less favorable than current terms, or we fail to re-lease such spaces at all, our business, results of operations, cash flow and financial condition will be negatively affected.
The short-term nature of multifamily leases exposes us more quickly to the effects of declining market rents, potentially making our revenue more volatile.
Generally, our multifamily leases are for twelve months or less. If the terms of the renewal or reletting are less favorable than current terms, our business, results of operations, cash flow and financial condition will be negatively affected. Given their short-term lease structure, our multifamily rental revenues are more sensitive to market declines.
Risks Relating to Our Properties
We face various risks related to our ground leases, including those arising from breach, expiration and eminent domain proceedings, and we have no permanent economic interest in the land or improvements at such properties.
Our interests in three of our commercial office properties, 1350 Broadway, 111 West 33rd Street and 1400 Broadway, are ground leases (i.e., long-term leaseholds of the land and the improvements), rather than a fee interest in the land and the improvements. Pursuant to these ground leases, we, as tenant, perform the functions traditionally performed by owners: collect rent from our subtenants, maintain the properties and pay related expenses. We do not have a right to acquire the fee interests in these properties. The ground leases, including unilateral extension rights available to us, expire on July 31, 2050, for 1350 Broadway, December 31, 2063, for 1400 Broadway and June 10, 2077, for 111 West 33rd Street. If we are found to be in breach of any of these ground leases, the fee owner may terminate such lease, and we could lose the right to use the properties. In addition, unless we purchase the underlying fee interest in these properties or extend the terms of the ground leases on the current terms, we will lose our right to operate these properties, or continue to operate them at lower profitability. Additionally, we will not share in any increase in value of the land or improvements and will not receive any revenue from the property beyond the term of our ground leases. If the government acquires the properties under its eminent domain power, we would only be entitled to a portion of any compensation awarded. It may be more expensive for us to renew our ground leases, to the extent renewal is available at all.
We are exposed to risks associated with property development.
We have engaged, continue to engage, and may in the future engage in development activities with respect to our properties (including our Metro Tower potential development site). See Part I, ITEM 1, “Business – Overview” for more information. Development subjects us to risks beyond our control, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, including, without limitation, the availability and pricing of financing; availability and timing of zoning and other approvals; occupancy rates and rents; construction costs and delays, whether due to weather, labor conditions, material shortages or otherwise, and timely lease-up. We will fail to recover expenses and management time already incurred if we abandon any then pending development.
Significant inflation could adversely affect our business and financial results.
Increased inflation has and may in the future adversely affect us by increasing costs of properties, development and renovation. In a highly inflationary environment, we may be unable to raise rental rates at or above the rate of inflation, which could reduce our profit margins. In addition, our cost of labor and materials has and may in the future further increase. While increases in most operating expenses at our properties can be passed on to our office and retail tenants, the terms of some of our leases may limit our ability to charge our tenants for all or a portion of such increased expenses. Our inability to pass on such increased operating expenses may reduce cash flow available to service our debt and make distributions.
We may not be able to control our operating costs, or our expenses may remain constant or increase even if income from our properties decreases.
Certain costs associated with real estate investment, such as real estate taxes, insurance and maintenance costs, generally are not reduced when a property is not fully occupied, rental rates decrease or other circumstances cause a reduction in income. The terms of our leases may also limit our ability to charge our tenants for all or a portion of these expenses. Additionally, inflation has impacted and will continue to impact property operating expenses and construction costs.
We are exposed to risks from third-party property management services.
While we perform property management services for the majority of our properties, we use a third-party property management company to service our multifamily properties. If such third-party property management company does not perform in accordance with our contractual agreements and desired standards, we could be exposed to additional risks, such as costs and reputational harm.
Risks Related to Our Non-Real Estate Operations
The Observatory operations at the Empire State Building are not traditional real estate operations, and may be negatively impacted by competition, adverse weather, and changes in tourist trends.
For fiscal years ended December 31, 2021, 2022 and 2023, we derived revenues of approximately $41.5 million, $106.0 million and $129.4 million from our Observatory operations. Our revenues declined significantly in 2020, 2021 and 2022, compared to 2019, as a result of the pandemic and government mandated closures and a slow ramp-up in visitor volume after reopening in July 2020, in large part due to travel restrictions. Any future health or other economic crises, geopolitical
events (including global hostilities) or currency exchange rate fluctuations could negatively impact tourist trends and visitor demand for our Observatory, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, cash flow and financial condition. We are also susceptible to reductions in visitor demand due to adverse weather. We compete against existing observatories in New York City at the World Trade Center, Rockefeller Center, Hudson Yards, and One Vanderbilt, all of which may divert visitors and negatively impact our revenue.
The broadcasting operations at the Empire State Building are not traditional real estate operations, and competition and changes in the broadcasting of signals over air may subject us to additional risks.
We license the use of the Empire State Building broadcasting mast to third-party television and radio broadcasters. During the year ended December 31, 2023, we derived approximately $14.7 million of revenue (excluding tenant reimbursement income) from such broadcasting licenses and related leases, as compared with about $21 million at its peak. Competition from other broadcasting operations has had a negative impact on revenues from our broadcasting operations, and lease renewals have yielded reduced revenue, and higher operating expenses and capital expenditures. Our broadcast licensees also face a range of competition from advances in technologies and alternative methods of content delivery in their respective industries, as well as changes in consumer behavior, which may reduce the demand for over-the-air broadcast licenses. Recent government regulations may materially and adversely affect our broadcast revenue by reducing the demand for broadcast licenses through making more spectrum available for wireless broadband service providers.
The impairment of a significant portion of goodwill could negatively affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Our balance sheet included goodwill of approximately $491.5 million at December 31, 2023, consisting primarily of goodwill associated with our acquisition of the controlling interest in Empire State Building Company L.L.C. and 501 Seventh Avenue Associates L.L.C. On an annual basis and whenever circumstances indicate the carrying value or goodwill may be impaired, we are required to assess any such impairment and charge to operating earnings the resulting non-cash impairment. For example, during the pandemic, the closure of our Observatory caused us to perform such an assessment quarterly. See “Financial Statements – Note 4 Deferred Costs, Acquired Lease Intangibles and Goodwill” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information. An impairment could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Risks Relating to Acquisitions and Dispositions
We may be unable to identify and successfully complete acquisitions, and even if acquisitions are identified and completed, they may expose us to additional risks.
We plan to acquire new properties as we are presented with attractive opportunities, but we may face significant competition from other investors, particularly private investors who can incur more leverage. We may incur significant costs and divert management attention in connection with potential acquisitions, including ones that we are unable to complete. If we successfully identify an acquisition target and close the transaction, we may spend more than budgeted to make necessary improvements to the relevant properties and be exposed to unknown liabilities, such as environmental contamination or claims from former tenants, vendors or employees.
We may acquire properties through tax deferred contribution transactions, which could result in securityholder dilution and limit our ability to sell such assets.
In the future we may acquire properties through tax deferred contribution transactions in exchange for partnership interests in our operating partnership, which may result in dilution to securityholders, reduction of tax depreciation we could deduct over the tax life of the acquired properties (as compared with an acquisition paid in cash), and requirements to protect the contributors’ tax deferral through restrictions on our disposition of the acquired properties and/or maintenance and allocation of partnership debt to the contributors to maintain their tax bases. These restrictions could limit our ability to sell an asset at a time, or on terms, that would be favorable absent such restrictions.
If we are unable to sell, dispose of or refinance one or more properties in the future, we may be unable to realize our investment objectives.
Real estate investments are relatively difficult to sell quickly. Return of capital and realization of gains from an investment generally will occur upon disposition or refinancing. In addition, the Code imposes restrictions on the ability of a REIT to dispose of properties that are not applicable to other types of real estate companies. We may be unable to realize our investment objectives by sale, other disposition or refinancing at attractive prices within any given period of time.
We may incur taxable capital gain on the disposition of assets due to the failure of use or compliance with a Section 1031 exchange program.
From time to time we may dispose of properties in transactions that are intended to qualify as “like kind exchanges” under Section 1031 of the Code. It is possible that the qualification of a transaction as a like-kind exchange could be successfully challenged and determined to be currently taxable. In such case, our taxable income and earnings and profits would increase. In some circumstances, we may be required to pay additional dividends or, in lieu of that, corporate income tax, possibly including interest and penalties. As a result, we may be required to borrow funds to pay additional dividends or taxes, and any payment of taxes could cause us to have less cash available to distribute to our shareholders. In addition, if a like-kind exchange was later to be determined to be taxable, we may be required to amend our tax returns for the applicable year in question, including any information reports we sent our shareholders. We could also be subject to significant indemnity obligations if the applicable property was subject to a tax protection agreement.
Risks Relating to Our Indebtedness and Liquidity
Our debt, the cost of our debt and limitations in our loan documents could adversely affect us.
As of December 31, 2023, we had total debt outstanding of approximately $2.2 billion inclusive of total mortgages of approximately $877.4 million with no maturity before November 2024. See “Financial Statements – Note 5 Debt” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information. Our organizational documents do not limit the debt we may incur, and we may incur significant additional debt to finance future acquisition and development activities. Our current and potential levels of debt, and the limitations in our loan documents could have significant adverse consequences to our cash flow and our ability to service and refinance our debt. We may be forced to dispose of one or more of our properties, possibly on disadvantageous terms. We may default on our debt obligations, in which case the lenders may accelerate our debt obligations and foreclose on any mortgaged properties. Our default on one debt with cross-default provisions could result in a default on other debt. In addition, our revolving credit facility and related term loan bear interest at a variable rate. We may incur indebtedness in the future that also bears interest at a variable rate or may be required to refinance our debt at higher rates. If any one of these events were to occur, our results of operations, cash flow, financial condition, and ability to service debt and to make distributions could be adversely affected.
Our debt includes restrictions on our financial and operational flexibility and distributions.
Our debt instruments may restrict our financial and operational flexibility. For example, our lockbox and cash management agreements may require income from our properties to be deposited directly into lockbox accounts controlled by our lenders from which we receive cash after funding of defined operating and capital costs. As a result, we may be forced to borrow additional funds in order to make distributions. Additionally, many of our debt instruments contain financial covenants that impact how we run our business, including required ratios for debt-to-assets, adjusted EBITDA to consolidated fixed charges or debt service. The partnership agreement of our operating partnership may restrict our ability to pay dividends if we fail to pay the cumulative distributions on preferred units. See Part II, ITEM 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Liquidity and Capital Resources” for more information.
Mortgages expose us to foreclosure and loss of our investment in a mortgaged property.
Mortgage and other secured debt increases our risk of property losses because defaults may result in foreclosure. For tax purposes, a foreclosure generally is treated as a sale of the property for a purchase price equal to the outstanding debt. If such debt exceeds our tax basis in the property, we will recognize taxable income on foreclosure, but not receive any cash. Foreclosures could also trigger our obligations under tax protection agreements with certain legacy investors to indemnify them for certain taxes upon sale of specific properties where they had embedded phantom taxable income (or the failure to maintain certain levels of indebtedness). See “Financial Statements – Note 11 Related Party Transactions – Tax Protection Agreements” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for more information.
High mortgage rates and/or unavailability of mortgage debt may make it difficult for us to finance or refinance properties, which could reduce the number of properties we can acquire, our net income and the amount of cash distributions we can make.
If mortgage debt is unavailable at reasonable rates, we may not be able to finance the purchase of properties. If we place mortgage debt on properties, we may be unable to refinance the properties when the loans become due at comparable terms. This may result in reduced cash flows and hinder our ability to make distributions, and to raise more capital by issuing more stock or by borrowing more money. In addition, to the extent we are unable to refinance loans, we will have fewer debt guarantee opportunities available to offer under our tax protection agreements, which could trigger our related indemnification obligation.
Our growth depends on external sources of capital that are outside of our control.
Because of the distribution requirements to maintain our status as a REIT (See Part I, ITEM 1, “Business - Our Tax Status”), we may not be able to fund future capital needs, including any acquisition financing, from operating cash flow and may need to rely on third-party sources. Our access to third-party sources of capital depends, in part, on general economic and market conditions, including the cost and availability of credit, government action or inaction and its effect on the state of the capital markets, the market’s perception of our growth potential, as well as our then current financial condition. Absent needed capital, we may not be able to acquire or develop properties when opportunities exist, satisfy our debt obligations or make cash distributions to our securityholders necessary to maintain our qualification as a REIT.
Risks Related to the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic had, and any future public health crisis could have, serious adverse effects on our and our tenants’ businesses, results of operations, cash flows and financial condition, and on local, national, and global economic activity.
The COVID-19 pandemic impacted the entire U.S., including New York and Connecticut where our properties are located. Any future public health crisis could have significant impacts on how people live, work, and travel in ways that have affected and may in the future affect our properties. Recovery from pandemic travel impacts is not yet completed, our visitor volume at the Empire State Building Observatory has not yet fully returned, and we cannot predict when we may achieve visitor volume comparable to 2019 when approximately two-thirds of our visitors were international. During 2020, 2021, 2022 and 2023, visitor volume was 0.5 million, 0.8 million, 2.2 million and 2.6 million, respectively, compared to 3.5 million in 2019. Our change in operations of the Empire State Building Observatory to focus on capacity controls to maximize the customer experience, require reservations to control overcrowding and staffing costs, and our increase of per visitor pricing may cause our future Observatory results to differ from previous Observatory results.
Amongst the impacts the COVID-19 pandemic had, and any future public health crisis could have, is a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, cash flows and financial condition due to, among other factors:
•downturn in national and/or local economies that decreases prospects, demand, occupancy and rental rates for our office, multifamily and retail space, all with an adverse impact on the value or price of our assets;
•delays, cost increases and/or cancellations of planned capital projects;
•potential impairment of our ability to comply with existing debt agreements, to pay down, refinance, or extend maturing debt, and to incur new debt;
•changes in the number of domestic and international tourists to our markets;
•volatility and downward pressure on the market price of our Class A common stock and publicly traded partnership units, which may also reduce our access to capital and/or our equity currency for new acquisitions; and
•reduction of our cash flows and our ability to pay dividends, with potential impairment of REIT qualification, and business continuity.
Risks Relating to Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Natural disasters and physical climate risk could adversely impact our area and business.
Our properties are concentrated in the New York metropolitan area. Natural disasters and physical climate risk including earthquakes, storms, storm surges, tornados, floods, extreme temperatures, and hurricanes, could cause significant damage or limit access to our properties and the surrounding area. Physical climate risk, including rising sea levels, storm surges, and extreme temperature fluctuations, could adversely impact the coastal metropolitan areas in which we operate. These conditions could result in declining demand for our commercial and multifamily properties, compromise our ability to operate the buildings, make insurance less affordable or available, and increase the cost of energy and utilities at our properties. Also, certain of our properties could not be rebuilt to their existing height or size under current land use laws. In that event, we may have to upgrade such property to meet code requirements. Our disaster recovery and business continuity plans may not be adequate to address these risks.
Some of our potential losses may not be covered by insurance.
Our insurance may not be adequate to cover all losses to which we are subject. Business interruption insurance generally does not include coverage for damages from a pandemic. In addition, our insurance policies include substantial self-insurance and deductibles and co-payments for certain events. See Part I, ITEM 1, “Business – Insurance” for further information. If we experience a loss that is uninsured or exceeds our policy limits, we could incur significant costs and loss of capital or property. If the damaged property is subject to recourse debt, we would continue to be liable for the debt, regardless of the property condition. Our debt instruments contain customary covenants to maintain insurance, including terrorism insurance. While we do not believe it is likely, our lenders or ground lessors could take the position that a total or partial exclusion for losses due to terrorist acts is a breach that would accelerate debt repayment or recapture ground lease positions. In addition, if they were to prevail in requiring additional coverage, it could result in substantially higher premiums. In the future,
we may be unable to obtain insurance with insurers that satisfy the rating requirements in our agreements, which could give rise to a default under such agreements and/or impair our ability to refinance.
We may incur significant costs to comply with environmental laws, and environmental contamination may impair our ability to lease and/or sell real estate.
Under various federal, state and/or local laws, ordinances and regulations, as a current or former owner or operator of real property, we may be liable for costs and damages resulting from the presence or release of hazardous substances, waste, or petroleum products at, on, in, under or from such property, including costs for investigation or remediation, natural resource damages, or third-party liability for personal injury or property damage. These laws often impose liability without regard to whether the owner or operator knew of, or was responsible for, the presence or release of such materials, and the liability may be joint and several. Some of our properties have been or may be impacted by contamination arising from current or prior uses of the property or adjacent properties for commercial, industrial or other purposes. Such contamination may arise from spills of petroleum or hazardous substances or releases from tanks used to store such materials. For example, a portion of the Metro Tower site is currently used for automobile parking and was formerly leased to a fueling facility, and we have post-closing obligations related to our Westport properties sold in 2023 related to remediation of storage tank and soil contamination. See Part I, ITEM 1, "Business - Environmental Matters" for further information.
We also may be liable for the costs of remediating contamination at off-site disposal or treatment facilities when we arrange for disposal or treatment of hazardous substances at such facilities, without regard to whether we comply with environmental laws in doing so. The presence of contamination or the failure to remediate contamination on our properties may adversely affect our ability to attract and/or retain tenants, and our ability to develop or sell or borrow against those properties. In addition to potential liability for cleanup costs, private plaintiffs may bring claims for personal injury, property damage or for similar reasons. Environmental laws also may create liens on contaminated sites in favor of the government for damages and costs it incurs to address such contamination. Moreover, if contamination is discovered on our properties, environmental laws may impose restrictions on the manner in which that property may be used or how businesses may be operated on that property.
In addition, our properties are subject to various federal, state and local environmental and health and safety laws and regulations. Noncompliance with these laws and regulations could subject us or our tenants to liability. These liabilities could affect a tenant’s ability to make rental payments to us. Moreover, changes in laws could increase the potential costs of compliance with such laws and regulations or increase liability for noncompliance. This may result in significant unanticipated expenditures. We sometimes require our tenants to comply with environmental and health and safety laws and regulations and to indemnify us for any related liabilities in our leases with them. But in the event of the bankruptcy or inability of any of our tenants to satisfy such obligations, we may be required to satisfy such obligations.
In addition, we may become subject to new compliance requirements and/or new costs or taxes associated with natural resource or energy usage and related emissions (such as a carbon tax), which could increase our operating costs. See "We may incur significant costs to comply with environmental laws, in particular New York City’s Local Law 97" in this section.
As the owner or operator of real property, we may also incur liability based on various building conditions. For example, environmental site assessments and investigations have identified asbestos or asbestos-containing material (“ACM”) in certain of our properties, and it is possible that other properties that we currently own or operate or those we acquire or operate in the future contain, may contain, or may have contained, ACM. See “Financial Statements – Note 9 Commitments and Contingencies – Asset Retirement Obligations” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for more information. Environmental and health and safety laws require that ACM be properly managed and maintained and may impose fines or penalties on owners, operators or employers for non-compliance with those requirements. These requirements include special precautions, such as removal, abatement or air monitoring, if ACM would be disturbed during maintenance, redevelopment or demolition of a building, potentially resulting in substantial costs. In addition, we may be subject to liability for personal injury or property damage sustained as a result of releases of ACM into the environment. Additionally, our properties may contain or develop harmful mold or suffer from other indoor air quality issue, such as inadequate ventilation and contamination, which could lead to liability for adverse health effects or property damage or costs for remediation. Any liability or increased cost from the environmental risks mentioned in this section could materially and adversely affect our operations.
We acquire real estate from time to time, which carries the risk that a property we acquire may subject us to potential environmental liability as a result of the condition of the land or actions taken on the property before we acquired it. This potential environmental liability may be unknown to us at the time we acquire the property and as a result can be impossible to predict.
We may incur significant costs to comply with environmental laws, in particular New York City’s Local Law 97.
We may become subject to new compliance requirements and/or new costs or taxes associated with natural resource or energy or utility usage and related emissions (such as a “carbon tax”), which could increase our operating costs. In particular, as
the owner of large commercial and multifamily buildings in New York City, we are subject to Local Law 97 passed by the New York City Council in April 2019, which for each such building establishes annual limits for greenhouse gas emissions, requires yearly emissions reports beginning in May 2025 for full calendar year 2024, and imposes penalties for emissions above such limits. While we are actively working to reduce our carbon emissions, there can be no assurance that we will be able to operate within the limits of Local Law 97, or that the costs of compliance and/or penalties will not be material. Based upon our present understanding of the law and calculations related thereto, we expect to pay no fine on any building in our commercial portfolio in the 2024-2029 first period of enforcement.
Risks Relating to Human Capital Management
The departure of any of our key personnel could materially and adversely affect us.
Our success depends on the efforts of key personnel, particularly Anthony E. Malkin, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, whose leadership and national industry reputation benefits us in many ways. He has led the acquisition, operation and repositioning of our assets for more than two decades. Other members of our senior management team also have strong industry reputations and experience, which aid us in attracting, identifying and taking advantage of opportunities. The loss of the services of one or more members of our senior management team could materially and adversely affect us.
Our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer has outside business interests that take his time and attention away from us, which could materially and adversely affect us.
Under his employment agreement, Mr. Malkin has agreed to (a) devote a majority of his business time and attention to our business and (b) during, and for a time after, his employment with us to refrain from competition with us. Mr. Malkin is also permitted to devote time to his other investments to the extent such activities do not materially interfere with the performance of his duties to us. He owns interests in properties and businesses, including properties and businesses that were not contributed to us in the formation transactions, some of which are now supervised by our Company. As a result, Mr. Malkin and his affiliates have had, and may in the future have, management and fiduciary obligations that could conflict with his responsibilities to our Company. For example, in February 2023 we closed on the disposition of our retail assets located at 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street in Westport, Connecticut, to an entity affiliated with Mr. Malkin. See “Financial Statements – Note 11 Related Party Transactions” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information. We may choose to moderate or omit enforcement of our rights under his employment agreement to maintain our relationship with him given his knowledge of our business, relationships with our customers, and significant equity ownership in us, and this could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our failure to maintain satisfactory labor relations could materially and adversely affect us.
As of December 31, 2023, we have collective bargaining agreements that cover 429 employees, or 64% of our workforce, that service our portfolio. Our inability to negotiate acceptable renewals as existing agreements expire could result in strikes or work stoppages and disrupt our operations. In any such event for any extended period of time, we would likely engage temporary replacement workers, which would result in increased operating costs.
Risks Relating to Legal Compliance, Sustainability and Cybersecurity
We face risks associated with our tenants being designated “Prohibited Persons” by OFAC and similar requirements.
The Office of Foreign Assets Control of the U.S. Department of the Treasury (“OFAC”) maintains a list of persons designated as terrorists or who are otherwise blocked or banned (“Prohibited Persons”) from conducting business or engaging in transactions in the U.S. and thereby restricts our doing business with such persons. In addition, our leases, loans and other agreements may require us to comply with OFAC and related requirements, and any failure to do so may result in a breach of such agreements. If a tenant or other party with whom we conduct business is designated a Prohibited Person, we may be required to terminate the arrangement or face penalties. Any such termination could result in a loss of revenue or otherwise negatively affect our business.
We may incur significant costs to comply with the ADA and similar laws.
Under the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (the “ADA”), all public accommodations must meet federal requirements related to access and use by disabled persons. We have incurred and could again in the future be required to incur costs to bring any non-compliant property into compliance and to make modifications to our properties upon any renovation, any of which could involve substantial costs and material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. See Part I, ITEM 1, “Business – Americans with Disabilities Act” for more information.
We may become subject to litigation, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition.
In the past we have been, and in the future we may become, subject to litigation, including claims relating to our operations, offerings, and otherwise in the ordinary course of business. Some of these claims may result in significant defense costs and potentially significant judgments against us, some of which are not, or cannot be, insured against. We generally intend to defend ourselves vigorously; however, we cannot be certain of the ultimate outcomes of any claims that may arise in the future. Certain litigation or its resolution may affect the availability or cost of our insurance coverage, which could adversely impact our financial condition, expose us to increased uninsured risks, and/or adversely impact our ability to attract officers and directors. See “Financial Statements – Note 9 Commitments and Contingencies” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Increasing attention to sustainability matters may impact our business.
Increasing attention to sustainability matters, including those related to climate change, and increasing societal, investor and legislative pressure on companies to address sustainability matters may result in increased costs, greater litigation risks, negative impacts on our access to capital markets, and damage to our reputation. For example, policy and other responses to climate change, such as climate and energy legislation and carbon mandates, enhanced environmental reporting requirements, increasingly stringent building and energy codes, as well as technology and market changes from the transition to a low-carbon economy has and may continue to impact our business and results of operations.
In addition, organizations that provide information to investors on corporate governance and related matters have developed ratings processes for evaluating companies on their approach to sustainability matters, including climate change and transitional and physical climate-related risks. Such ratings are used by some investors to inform their investment and voting decisions. Unfavorable sustainability ratings may lead to negative investor sentiment toward us and to the diversion of investment to other industries, which could have a negative impact on our stock price and our access to and costs of capital.
We publicly announced our achievement of carbon neutrality in 2022 and our commitment to a 2030 net zero carbon emissions target for the Empire State Building and a 2035 net zero carbon emissions target for the balance of our portfolio, defined as the goal of 80% operational emissions reduction in partnership with the grid. We have implemented numerous comprehensive sustainability-focused initiatives focused on energy, emissions, water, and waste reduction along with indoor environmental quality, well-being, and healthy buildings. These aspirations, targets and objectives reflect our current plans and aspirations and are not guarantees that we will be able to achieve them. In addition, these efforts are impacted by our tenants’ willingness and ability to collaborate in reporting sustainability metrics and meeting sustainability goals. Our efforts to accomplish and accurately report on these goals and objectives present operational, regulatory, reputational, financial, legal, and other risks, any of which could have a material negative impact on us, including on our reputation and stock price.
The standards for tracking, rating, and reporting on sustainability matters are relatively new, have not been harmonized and continue to evolve rapidly at a global scale. Our selection of disclosure frameworks that seek to align with various voluntary reporting standards may change from time to time and may result in a lack of comparative data from period to period. In addition, our processes and controls may not always align with evolving voluntary standards for identifying, measuring, and reporting sustainability metrics, our interpretation of reporting standards may differ from those of others, and such standards may change over time, any of which could result in significant revisions to our goals or reported progress in achieving such goals. Our failure or perceived failure to pursue or fulfill our announced aspirations and targets or to satisfy various reporting standards within the timelines we announce, or at all, could have a negative impact on investor sentiment, ratings outcomes for evaluating our approach to sustainability matters, stock price, and cost of capital and expose us to government enforcement actions and private litigation, among other possible material adverse impacts.
Cyberattacks and any failure to comply with related laws could negatively impact us.
We rely extensively on technology, both internal and outsourced, to process transactions and manage our business, making our business increasingly at risk from cyberattacks. These threats, which continue to increase in number, intensity and sophistication, include malware, ransomware, computer viruses, phishing, unauthorized access, and other vectors used by hackers, terrorists, foreign governments, and other actors. Cyber threats and attacks on our Company have included and could in the future include internal and external attempts to gain unauthorized access to our data and computer systems to disrupt our operations or the operations of our tenants and residents, destroy property, or steal confidential information. There is no guarantee that our controls or measures to prevent or mitigate such attacks will be successful. A cyberattack could compromise the confidential information of our employees, tenants, residents, customers, and vendors, and disrupt our business operations and relationships. Such a security breach could require us to expend significant resources to remediate any damage that result. Additionally, such a breach may subject us to litigation, damages, penalties, fines, governmental investigations and enforcement actions or termination of leases. These consequences could damage our reputation with tenants, residents, customers, and investors, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business. Any compromise of our security could also result in a violation of applicable privacy laws (e.g., Observatory customer data, Company employee data, or residential data at multifamily properties), which could result in negative legal consequences as well as significant damage to our financial condition, reputation, business, records, and confidence of our business partners in our business relationships. New laws and regulations related to data privacy and security pose increasingly complex compliance challenges and costs across multiple jurisdictions, which could negatively impact our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The adoption of, or changes, in rent control or rent stabilization regulations and eviction regulations in our markets could have an adverse effect on our operations and property values.
A growing number of state and local governments have enacted and may continue to consider enacting and/or expanding rent control or rent stabilization regulations, which have limited and could continue to limit in broadening ways our ability to raise rents or charge certain fees, either of which could have a retroactive effect. We continue to see increases in governments considering or being urged by advocacy groups to consider rent forgiveness, rent control or rent stabilization regulations or expand coverage of existing regulations in our markets. These regulations may also make changes to and/or expand eviction and other tenants’ rights regulations that may limit our ability to enforce residents’ or tenants’ contractual rental obligations (such as eviction moratoriums), pursue collections or charge certain fees, which could have an adverse impact on our operations and property values.
Government housing regulations may limit opportunities at the multifamily properties in which we invest, and failure to comply with resident qualification requirements may result in financial penalties or loss of benefits.
We own, and may acquire additional equity interests in properties that benefit from governmental programs intended to provide housing to individuals with low or moderate incomes. These governmental programs typically provide mortgage insurance, favorable financing terms, tax credits or rental assistance payments to property owners. As a condition of the initial receipt and potential extensions of assistance under these programs, the properties must comply with various requirements, which typically limit rents to pre-approved amounts and impose restrictions on resident incomes. Failure to comply with these requirements and restrictions may result in financial penalties or loss of benefits. In addition, we will typically need to obtain the approval of the applicable government agency in order to acquire or dispose of a significant interest in or manage such property. We may not always receive such approval.
Risks Related to Our Organization and Structure
If our board revokes our REIT election or we fail to remain qualified as a REIT, we may be required to pay U.S. federal income taxes at corporate rates, which may cause adverse consequences to our securityholders.
Although we believe that we will remain organized and will continue to operate so as to qualify as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes, our Board may revoke our REIT election, without stockholder approval, if the Board determines that it is no longer in our best interest to continue to qualify as a REIT or we may fail to remain so qualified. Qualifications are governed by highly technical and complex provisions of the Code for which there are only limited judicial or administrative interpretations and depend on various facts and circumstances that are not entirely within our control. In addition, legislation, new regulations, administrative interpretations or court decisions may significantly change the relevant tax laws and/or the U.S. federal income tax consequences of qualifying as a REIT. If, with respect to any taxable year, we fail to maintain our qualification as a REIT and do not qualify under statutory relief provisions, we could not deduct distributions to shareholders in computing our taxable income and would have to pay U.S. federal income tax on our taxable income at regular corporate rates and thus reduce funds available for distribution and debt service, and we would not be required to make distributions until we re-qualified as a REIT which would not be permitted for the four taxable years following our disqualification, unless we gained relief under relevant statutory provisions. Refer to Part I, ITEM 1, “Business – Our Tax Status” for more information.
Failure to qualify as a domestically controlled REIT could subject our non-U.S. securityholders to adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences.
While we intend to continue to qualify as a “domestically controlled” REIT for purposes of the Foreign Investment in Real Property Tax Act of 1980, we cannot assure that result, as our Class A common stock is publicly traded, QIA (a non-U.S. holder) owns approximately 18.45% of our common stock and other non-U.S. holders may now or in the future hold additional shares. If we were to fail to qualify, gain realized by a foreign investor (other than a “qualified shareholder,” a “qualified foreign pension fund” or a “qualified controlled entity”) on a sale of our common stock would be subject to FIRPTA unless (a) our common stock was traded on an established securities market and the foreign investor did not at any time during a specific testing period directly or indirectly own more than 10% of the value of our outstanding common stock, or (b) another exemption from FIRPTA were applicable.
Complying with the REIT requirements may cause us to forego and/or liquidate otherwise attractive investments.
If we fail to comply with the income and asset requirements for a REIT at the end of any calendar quarter, we must correct the failure within 30 days after the end of the calendar quarter or qualify for certain other statutory relief provisions to avoid losing our REIT qualification and suffering adverse tax consequences. Refer to Part I, ITEM 1, “Business – Our Tax Status” for more information. In order to satisfy the gross income or asset tests applicable to REITs under the Code, we may be required to forego investments that we otherwise would make or liquidate otherwise attractive investments. This could have the effect of reducing our income and amounts available for distribution.
The REIT distribution requirements could require us to borrow funds during unfavorable market conditions or subject us to tax, which would reduce the cash available for distribution to our securityholders.
We intend to distribute our taxable net income to our securityholders in a manner intended to satisfy the REIT 90% distribution requirement and to avoid U.S. federal income tax and the 4% nondeductible excise tax. Refer to Part I, ITEM 1, “Business – Our Tax Status” for more information. Any failure to do so will incur substantial entity level tax and/or disqualification as a REIT with the adverse tax consequences and limits on re-qualification described above in this "Risk Factors" section. In addition, our taxable income may exceed our net income as determined by GAAP. As a result of the foregoing, we may generate less cash flow than taxable income in a particular year, and we may incur U.S. federal income tax and the 4% nondeductible excise tax on that income if we do not distribute such income to securityholders in that year. In that event, we may be required to use cash reserves, incur debt or liquidate assets at rates or times that we regard as unfavorable or make a taxable distribution of our shares in order to satisfy such REIT requirements and avoid such taxes.
If our operating partnership is treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we will cease to qualify as a REIT.
In order for our publicly traded operating partnership to be treated and taxed as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, 90% or more of its gross income must consist of certain passive type income such as rent, interest, dividends, etc. If our operating partnership were to fail to meet the gross income requirement for treating a publicly traded partnership as a partnership or the IRS were to successfully challenge our operating partnership’s status as a partnership, we would fail to meet the gross income tests and certain of the asset tests applicable to REITs and, therefore, cease to qualify as a REIT and our operating partnership would become subject to U.S. federal, state and local income tax. The payment by our operating partnership of income tax would reduce significantly the amount of cash available to our operating partnership to satisfy obligations to make principal and interest payments on its debt and to make distributions to its partners, including us.
If we are unable to continue to lease the Empire State Building Observatory to a TRS or to maintain our broadcast licenses, in each case in a manner consistent with the IRS ruling that we have received, we would be required to restructure our operations in a manner that could adversely affect the value of our stock.
We rely upon private letter rulings from the IRS that income from our Observatory and broadcast facilities is qualifying rent for our REIT qualification. See Part I, ITEM 1, “Business – Our Tax Status.” We are entitled to rely upon these private letter rulings only to the extent that we did not misstate or omit a material fact in the ruling request and that we continue to operate in accordance with the material facts described in such request, and no assurance can be given that we will always be able to do so. If we were not able to treat the rent that our operating partnership receives from Observatory TRS as qualifying income for purposes of the REIT gross income tests, we would be required to restructure the manner in which we operate the Observatory, which would likely require us to cede operating control of the Observatory by leasing the Observatory to an affiliate or third-party operator. If we were not able to treat the license fees that our operating partnership will receive from the license agreements described above as qualifying income for purposes of the REIT gross income tests, we would be required to enter into the license agreements described above through a TRS, which would cause the license fees to be subject to U.S. federal income tax and accordingly reduce the amount of our cash flow available to be distributed to our securityholders. In either case, if we are not able to appropriately restructure our operations in a timely manner, we would likely realize significant income that does not qualify for the REIT gross income tests, which could cause us to fail to qualify as a REIT.
Our TRSs are subject to U.S. federal, state and local income tax, there are limits on our ability to own TRSs, and a failure to comply with the limits would jeopardize our REIT qualification and may result in the application of a 100% excise tax.
A REIT may own up to 100% of the stock of one or more TRSs. A TRS may hold assets and earn income that would not be qualifying assets or income if held or earned directly by a REIT. A corporation of which a TRS directly or indirectly owns more than 35% of the voting power or value of the stock will automatically be treated as a TRS. Overall, no more than 20% of the value of a REIT’s assets may consist of securities of one or more TRSs. TRSs are subject to U.S. federal, state and local income taxation, as applicable. The rules also impose a 100% excise tax on certain transactions between a TRS and its parent REIT that are not conducted on an arm’s-length basis.
We have jointly elected with each of Observatory TRS and Holding TRS, for each of Observatory TRS and Holding TRS to be treated as a TRS under the Code for U.S. federal income tax purposes in 2013. Observatory TRS, Holding TRS, and any other TRSs that we form pay U.S. federal, state and local income tax on their taxable income, and their after-tax net income is available for distribution to us but is not required to be distributed to us unless necessary to maintain our REIT qualification. Although we monitor the aggregate value of the securities of such TRSs and intend to conduct our affairs so that such securities will represent less than 20% of the value of our total assets, and such securities taken together with other non-qualifying assets will represent less than 25% of the value of our total assets, at the end of each calendar quarter, there can be no assurance that we will be able to comply with the TRS limitations in all market conditions.
Our state and local taxes could increase due to property tax rate changes, reassessment and/or changes in state and local tax laws, which could materially and adversely affect us.
We are required to pay state and local taxes on our properties. From time to time changes in state and local tax laws or regulations are enacted, which may result in an increase in our tax liability. A shortfall in tax revenues for states and municipalities in which we operate may lead to an increase in the frequency and size of such changes. In particular, the federal government has recently limited the ability of individuals to deduct state and local taxes on their federal tax returns, potentially leading many high-tax states to make significant changes to their own state and local tax laws. In addition, the pandemic has left many state and local governments with reduced tax revenue, which may lead such governments to increase taxes or otherwise make significant changes to their state and local tax laws. If such changes occur, we may be required to pay additional taxes on our assets or income. The real property taxes on our properties may increase as property tax rates change or as our properties are assessed or reassessed by taxing authorities. Therefore, the amount of property taxes we pay in the future may increase substantially from what we have paid in the past. If the property taxes we pay increase, our financial condition could be materially and adversely affected.
U.S. federal, state and local legislative, judicial or regulatory tax changes could have a material adverse effect on our shareholders and us.
The present U.S. federal income tax treatment of REITs and their shareholders may be modified, possibly with retroactive effect, by legislative, judicial or administrative action at any time, which could affect the U.S. federal income tax treatment of an investment in us. The U.S. federal income tax rules dealing with REITs are constantly under review by persons involved in the legislative process, the IRS and the U.S. Department of the Treasury, which results in statutory changes as well as frequent revisions to regulations and interpretations. We cannot predict how changes in the tax laws might affect our investors or us. Revisions in U.S. federal income tax laws and interpretations thereof could significantly and negatively affect our ability to qualify as a REIT and the tax considerations relevant to an investment in us, or could cause us to change our investments and commitments.
Our tax protection agreements could limit our ability either to sell certain properties or to engage in a strategic transaction, or to reduce our level of indebtedness, which could materially and adversely affect us.
In connection with the formation transactions, we entered into a tax protection agreement with certain Malkin family members, including Anthony E. Malkin and Peter L. Malkin, pursuant to which we have agreed to indemnify the Malkin Group and one additional third-party investor in Metro Center, and in connection with our sale of a 9.9% fully diluted interest in our Company to QIA in 2016, we agreed, subject to certain minimum thresholds and conditions, to indemnify QIA, in each case, against certain tax liabilities that may arise from certain property transactions. See “Financial Statements – Note 11 Related Party Transactions – Excluded Properties and Businesses” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information. If we were to trigger such tax indemnification obligations, we would be required to pay the resulting tax liability to the Malkin Group, the additional third-party investor in Metro Center and/or QIA, as applicable. These obligations may restrict our ability to engage in a strategic transaction, require us to maintain more or different debt, and/or inhibit our disposing of a property that we might judge to be otherwise be in the best interest of the securityholders.
Holders of our Class B common stock have a significant vote in matters submitted to a vote of our securityholders.
As part of our formation, we sought to give each contributing investor an option to hold equity interests which would allow such investor to vote on Company matters in proportion to such investor’s economic ownership in the consolidated entity, whether such investor elected taxable Class A common stock or tax-deferred operating partnership units. Thus, the original investors were offered the opportunity to contribute their interests to us in exchange for a mix of one share of Class B common stock and 49 operating partnership units for each 50 operating partnership units to which an investor was otherwise entitled. Each outstanding share of Class B common stock, when accompanied by 49 operating partnership units, entitles the holder thereof to 50 votes on all matters on which Class A common securityholders are entitled to vote, including the election of directors. Holders of our Class B common stock may have interests that differ from holders of our Class A common stock and may accordingly vote in ways that may not be consistent with the interests of holders of our Class A common stock. This significant voting influence over certain matters may have the effect of delaying, preventing or deterring a change of control of our Company, or could deprive holders of our Class A common stock of an opportunity to receive a premium for their Class A common stock as part of a sale of our Company.
The concentration of our voting power may adversely affect the ability of new investors to influence our policies.
As of December 31, 2023, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Anthony E. Malkin, together with the Malkin Group, has the right to vote 40,859,706 shares of our common stock, which represents approximately 19.3% of the voting power of our outstanding common stock. Consequently, Mr. Malkin has the ability to influence the outcome of matters presented to our securityholders, including the election of our board and approval of significant corporate transactions,
including business combinations, consolidations and mergers and the determination of our day-to-day corporate and management policies.
As of December 31, 2023, QIA had a 11.03% fully diluted interest in us, which represented 18.45% of the outstanding Class A common stock. Pursuant to the terms of our stockholders agreement with QIA, QIA generally has the right (but not the obligation) to maintain its fully diluted economic interest in us by purchasing additional shares of our Class A common stock when we or our operating partnership issue additional common equity securities from time to time. While QIA has agreed to limit its voting power on all matters presented to our securityholders to no more than 9.9% of total number of votes entitled to be cast, QIA has also agreed to vote its shares in favor of the election of all director nominees recommended by our board. The interests of Mr. Malkin and QIA could conflict with or differ from your interests as a holder of our common stock, and these large securityholders may exercise their right as securityholders to restrict our ability to take certain actions that may otherwise be in the best interests of our securityholders. This concentration of voting power might also have the effect of delaying or preventing a change of control that our securityholders may view as beneficial.
Tax consequences to holders of operating partnership units upon a sale or refinancing of our properties may cause the interests of certain members of our senior management team to differ from your own.
As a result of the unrealized built-in gain attributable to a property at the time of contribution, some holders of operating partnership units, including our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Anthony E. Malkin, and our Chairman Emeritus, Peter L. Malkin, may suffer different and more adverse tax consequences than holders of our Class A common stock upon the sale or refinancing of the properties owned by our operating partnership, including disproportionately greater allocations of items of taxable income and gain upon a realization event. As those holders will not receive a correspondingly greater distribution of cash proceeds, they may have different objectives regarding the appropriate pricing, timing, transaction structure and other material terms of any sale, exchange or refinancing of certain properties, or whether to sell, exchange or refinance such properties at all. As a result, the effect of certain transactions on Messrs. Malkin may influence their decisions affecting these properties and may cause such members of our senior management team to attempt to delay, defer or prevent a transaction that might otherwise be in the best interests of our other securityholders, or to structure such transactions in ways that would mitigate the above tax consequences to Messrs. Malkin. Additionally, in connection with the formation transactions, we entered into a tax protection agreement with Messrs. Malkin pursuant to which we have agreed to indemnify the Malkin Group and one additional third-party investor in Metro Center against certain tax liabilities if those tax liabilities arise from a transaction involving one of four properties. Refer to “Financial Statements – Note 11 Related Party Transactions – Excluded Properties and Businesses” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for more information. As a result of entering into the tax protection agreement, Messrs. Malkin may have an incentive to cause us to enter into transactions from which they may personally benefit.
Conflicts of interest exist or could arise in the future between the interests of our securityholders and OP unit holders.
Conflicts of interest exist or could arise in the future as a result of the relationships between us and our affiliates, on the one hand, and our operating partnership or any partner thereof, on the other. For example, a potential acquisition or disposition opportunity could be opportunistic to the REIT while tax disadvantageous to certain OP holders. Our directors and officers have duties to our Company and its shareholders under applicable Maryland law in connection with their management of our Company. At the same time, we, as the general partner in our operating partnership, have fiduciary duties and obligations to our operating partnership and its limited partners under Delaware law and the partnership agreement of our operating partnership in connection with the management of our operating partnership. If there is a conflict between the interests of such stockholders and the interests of such limited partners, such operating agreement provides that our Company will fulfill its fiduciary duties as general partner to such limited partners by acting in the best interest of such stockholders.
Our rights and the rights of our securityholders to take action against our directors and officers are limited, which could limit your recourse in the event of actions not in your best interest.
Our charter limits the liability of our present and former directors and officers to us and our securityholders for money damages to the maximum extent permitted under Maryland law. Under current Maryland law, our present and former directors and officers will not have any liability to us or our securityholders for money damages other than liability resulting from (1) actual receipt of an improper benefit or profit in money, property or services or (2) active and deliberate dishonesty by the director or officer that was established by a final judgment and is material to the cause of action. Additionally, the partnership agreement of our operating partnership provides for certain limitations on liability and indemnification obligations for us and our directors and officers and certain present and former members, managers, shareholders, directors, limited partners, general partners, officers or controlling persons of our predecessor. As a result, we and our securityholders may have limited rights against all such persons, which could limit your recourse in the event of actions not in your best interest.
Limits on changes in control may discourage takeover attempts beneficial to securityholders.
Provisions in our charter and the partnership agreement of our operating partnership, may delay or prevent a change of control over the Company or a tender offer, even if such action might be beneficial to the Company’s stockholders. Additionally, our board could establish a class or series of preferred stock that could, depending on the terms of such series, delay, defer or prevent a transaction or a change of control.
To facilitate maintenance of the Company’s qualification as a REIT and to otherwise address concerns relating to concentration of stock ownership, our charter generally prohibits any person from directly or indirectly owning more than 9.8% in value or number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the outstanding shares of our capital stock or more than 9.8% in value or number of shares, whichever is more restrictive, of the outstanding shares of our common stock. Our charter also provides that no person can directly or indirectly own shares of our capital stock to the extent such ownership would result in us owning (directly or indirectly) an interest in one of our tenants if the income derived by us from such tenant would reasonably be expected to equal or exceed the lesser of 1% of our gross income or an amount that would cause us to fail to satisfy any of the REIT gross income tests. Shares owned in violation of the ownership limit will be subject to the loss of rights to distributions and voting and other penalties. These ownership limitations could have the effect of discouraging a takeover or other transaction in which holders of our common stock might receive a premium for their shares over the then prevailing market price or which holders might believe to be otherwise in their best interests.
Our board may waive, in its sole discretion, or modify the ownership limit with respect to one or more persons if it is satisfied that ownership in excess of this limit will not jeopardize the Company’s status as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes. For example, we have entered into such a waiver with QIA, which permits QIA to own up to 15% of the outstanding shares of our Class A common stock and an aggregate amount of Class A common stock equal to a 9.9% fully diluted economic interest in the Company (inclusive of all outstanding common OP units and LTIP units), which currently equals approximately 18.45% of our outstanding Class A common stock, all subject to a supplementary waiver which may adjust the foregoing limits to the extent QIA’s ownership percentage increases solely as a result the Company’s share buybacks.
Certain provisions in the partnership agreement of our operating partnership may also delay or make more difficult unsolicited acquisitions of us or changes of our control, including, among others: redemption rights of qualifying parties; transfer restrictions on operating partnership units; our ability, as general partner, in some cases, to amend the partnership agreement and to cause the operating partnership to issue units with terms that could delay, defer or prevent a merger or other change of control of us or our operating partnership without the consent of the limited partners; the right of the limited partners to consent to transfers of the general partnership interest and mergers or other transactions involving us under specified circumstances; and a redemption premium payable to the holders of our operating partnership’s preferred units if our operating partnership decides, at its option, to redeem preferred units for cash upon the occurrence of certain fundamental transactions, such as a change of control.
Risks Related to our Common Stock and Traded OP Units
Our cash available for distribution may not be sufficient to make distributions at expected levels, and the market price of shares of our Class A common stock and traded OP units could be adversely affected by our level of cash distributions.
We intend to make distributions to holders of shares of our common stock and holders of operating partnership units. All dividends and distributions will be made at the discretion of our board and will depend on our earnings, financial condition, maintenance of REIT qualification and other factors as our board may deem relevant from time to time. If sufficient cash is not available for distribution from our operations, we may have to fund distributions from working capital or to borrow to provide funds for such distribution, or to reduce the amount of such distribution. We cannot assure you that our distributions will be made or sustained. Our failure to meet the market’s expectations with regard to future earnings and cash distributions likely would adversely affect the market price of our Class A common stock and traded OP units.
Changes in market conditions could adversely affect the market price of our Class A Common Stock and traded OP Units.
As with other publicly traded equity securities, the value of our Class A Common Stock and traded OP units depends on various market conditions, which may change from time to time. In addition to the current economic environment and future volatility in the securities and credit markets, the following market conditions may affect the value of our Class A Common Stock and traded OP units:
•the general reputation of REITs and the attractiveness of our equity securities in comparison to other equity securities, including securities issued by other real estate-based companies;
•our financial performance; and
•general stock market conditions.
The market value of our common stock is based on a number of factors, including, but not limited to, the market’s perception of the current and future value of our assets, our growth potential and our current and potential future earnings and distributions.
The future exercise of registration rights may adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
In August 2016, we entered into a registration rights agreement with QIA in connection with its purchase of our Class A common stock, which requires us, subject to certain conditions, to maintain an effective shelf registration statement with the SEC providing for the resale of QIA’s shares. The current registration statement filed on July 31, 2023, registers up to 29,894,869 shares. If QIA decides to sell all or a substantial portion of its shares, or there is market perception that it may intend to do so, it could have a material adverse impact on the market price of our Class A common stock.
Future issuances of debt or equity securities or preferred units may be dilutive to current securityholders and may materially adversely affect the market price of our traded securities.
In the future, we may issue debt or equity securities or make other borrowings. Our board, without stockholder approval, has the power under our charter to cause the Company to issue additional shares of capital stock or debt securities, and our operating partnership may also issue additional operating partnership units without the consent of our securityholders. Upon liquidation, holders of our debt securities, preferred units and other loans and preferred shares will receive a distribution of our available assets before holders of shares of our common stock. We are not required to offer any such additional debt or equity securities to existing securityholders on a preemptive basis. Therefore, additional shares of our common stock issuances, directly or through convertible or exchangeable securities (including operating partnership units), warrants or options, will dilute the holdings of our existing common securityholders and such issuances or the perception of such issuances may reduce the market price of shares of our common stock. Additionally, our preferred units or shares, if issued, would likely have a preference on distribution payments, periodically or upon liquidation, which could limit our ability to make distributions to holders of shares of our common stock.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
As of December 31, 2023, we did not have any unresolved comments from the staff of the SEC.
ITEM 1C. CYBERSECURITY
Risk Management and Strategy
We regularly assess risks from cybersecurity threats, monitor our information systems for potential vulnerabilities and test those systems pursuant to our cybersecurity policies and procedures, which are integrated into the Company’s overall risk management framework. To protect our information systems from cybersecurity threats, we use various security tools that help us identify, escalate, investigate, resolve, and recover from security incidents in a timely manner.
We partner with third parties to implement and assess the effectiveness of our cybersecurity prevention and response systems and processes. We have a Managed Security Services provider (MSSP) that provides a 24 x 7 x 365 Security Operations Center (SOC) and works with our information technology (IT) team to employ a variety of monitoring technologies to detect and be alerted to potential cyber threats, as well as establish and implement procedures for the mitigation and remediation of any cybersecurity incidents. We conduct an annual penetration test, regular phishing tests, and annual cybersecurity training for our employees.
Additionally, the management team of the Company has developed a cyber incident response plan to deploy in the event of a cyber threat. This plan is reviewed and updated at least annually and tested from time to time through tabletop exercises involving management and other key personnel, and may also include participation from the Board and outside experts. As part of regular business continuity planning, department heads are required to consider key technology systems used by their respective teams and the impact to the Company and other stakeholders in the event that such systems become compromised or unavailable. Additionally, we monitor and identify cybersecurity risks posed by third-party vendors who provide software and/or hardware to the Company or otherwise have access to our Company systems and have a cyber review process that is part of vendor onboarding.
To date, cybersecurity threats, including as a result of any previous cybersecurity incidents, have not materially affected and we believe are not reasonably likely to materially affect the Company, including our business strategy, results of operations or financial condition. Refer to the risk factor captioned “Cyberattacks and any failure to comply with related laws could negatively impact us.” in Part I, ITEM 1A. “Risk Factors” for additional description of cybersecurity risks and potential related impacts on the Company.
Governance
Our Board of Directors oversees our risk management process, including with respect to cybersecurity risks, directly and through its committees. The Audit Committee of the Board oversees our risk management program, which focuses on the most significant risks we face in the short-, intermediate-, and long-term timeframe. Audit Committee meetings include discussions of specific risk areas throughout the year, including, among others, those relating to cybersecurity, and reports on our enterprise risk profile on a quarterly basis. Our Chief Technology Officer is responsible for leading the assessment and management of cybersecurity risks and reports at least quarterly or more frequently as needed to the Audit Committee on cybersecurity strategy and risks.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
Summary of Office, Retail, and Multifamily Portfolio
As of December 31, 2023, our office and retail portfolio was comprised of approximately 8.6 million rentable square feet of office space and 0.7 million rentable square feet of retail space and was approximately 86.3% occupied and 90.6% leased, yielding approximately $536.0 million of annualized rent. We have 11 office properties and our retail properties are comprised of retail space at the base of our New York City office and multifamily properties, and five standalone retail properties predominantly located in Manhattan. All properties are located in dynamic retail corridors with convenient access to mass transportation, a diverse tenant base and high pedestrian traffic. Our real estate segment includes all activities related to the ownership, management, operation, acquisition, repositioning and disposition of all of our real estate assets other than the 86th and 102nd floor observatories at the Empire State Building, which are operated by our Observatory segment.
The tables below present an overview as of December 31, 2023.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | Annualized | |
| | | Rentable | | | | | | | Rent per | |
| | | Square | Percent | | Percent | | Annualized | | Occupied | Number of |
| Property Name | Location or Sub-Market | Feet (1) | Occupied (2) | | Leased (3) | | Rent (4) | | Square Foot (5) | Leases (6) |
| Office - Manhattan | | | | | | | | | | |
| The Empire State Building | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 2,713,783 | | 84.6 | % | | 91.8 | % | | $ | 149,146,291 | | | $ | 64.98 | | 144 | |
| One Grand Central Place | Grand Central | 1,241,235 | | 85.2 | % | | 90.7 | % | | 64,495,396 | | | 61.01 | | 148 | |
1400 Broadway (7) | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 917,281 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 51,543,523 | | | 56.19 | | 20 | |
111 West 33rd Street (8) | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 639,496 | | 94.2 | % | | 95.7 | % | | 40,779,657 | | | 67.68 | | 21 | |
| 250 West 57th Street | Columbus Circle - West Side | 472,707 | | 80.6 | % | | 84.5 | % | | 23,990,288 | | | 62.98 | | 28 | |
| 501 Seventh Avenue | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 461,209 | | 88.4 | % | | 88.4 | % | | 20,432,035 | | | 50.09 | | 19 | |
| 1359 Broadway | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 456,004 | | 83.5 | % | | 91.4 | % | | 22,376,656 | | | 58.75 | | 32 | |
1350 Broadway (9) | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 372,599 | | 85.5 | % | | 86.4 | % | | 19,076,631 | | | 59.90 | | 50 | |
| 1333 Broadway | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 296,349 | | 84.4 | % | | 94.4 | % | | 14,545,148 | | | 58.12 | | 13 | |
| Office - Manhattan | | 7,570,663 | | 87.3 | % | | 92.1 | % | | 406,385,625 | | | 61.47 | | 475 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Office - Greater New York Metropolitan Area | | | | | | | | | | |
First Stamford Place (10) | Stamford, CT | 781,731 | | 78.7 | % | | 82.3 | % | | 26,691,177 | | | 43.38 | | 48 | |
| Metro Center | Stamford, CT | 281,510 | | 70.9 | % | | 70.9 | % | | 10,914,848 | | | 54.71 | | 20 | |
| Office - Greater New York Metropolitan Area | | 1,063,241 | | 76.6 | % | | 79.3 | % | | 37,606,025 | | | 46.15 | | 68 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total/Weighted Average Office Properties | | 8,633,904 | | 86.0 | % | | 90.5 | % | | 443,991,650 | | | 59.79 | | 543 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Retail Properties | | | | | | | | | | |
112 West 34th Street (8) | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 93,057 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 24,825,569 | | | 266.78 | | 4 | |
| The Empire State Building | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 90,670 | | 71.9 | % | | 76.4 | % | | 7,032,389 | | | 107.93 | | 10 | |
| One Grand Central Place | Grand Central | 68,733 | | 99.4 | % | | 99.4 | % | | 8,977,805 | | | 131.41 | | 12 | |
| 1333 Broadway | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 67,001 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 10,155,485 | | | 151.57 | | 4 | |
| 250 West 57th Street | Columbus Circle - West Side | 65,526 | | 91.4 | % | | 91.4 | % | | 9,111,860 | | | 152.07 | | 7 | |
| 10 Union Square | Union Square | 58,006 | | 91.9 | % | | 91.9 | % | | 8,181,304 | | | 153.49 | | 10 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 1542 Third Avenue | Upper East Side | 56,135 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 2,542,042 | | | 45.28 | | 4 | |
| 1010 Third Avenue | Upper East Side | 38,235 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 3,460,188 | | | 90.50 | | 2 | |
| 501 Seventh Avenue | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 35,859 | | 50.8 | % | | 59.6 | % | | 1,310,333 | | | 71.94 | | 5 | |
1350 Broadway (9) | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 30,710 | | 77.8 | % | | 77.8 | % | | 5,962,833 | | | 249.70 | | 5 | |
| 1359 Broadway | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 29,247 | | 83.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 1,668,652 | | | 68.73 | | 5 | |
561 10th Avenue (11) | Hudson Yards | 28,266 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 2,007,748 | | | 71.03 | | 3 | |
| 77 West 55th Street | Midtown | 25,388 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 1,978,407 | | | 77.93 | | 3 | |
1400 Broadway (7) | Penn Station -Times Sq. South | 17,879 | | 78.2 | % | | 78.2 | % | | 1,538,836 | | | 110.07 | | 6 | |
298 Mulberry Street (12) | NoHo | 10,365 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 1,802,507 | | | 173.90 | | 1 | |
Williamsburg Retail (13) | Brooklyn | 6,538 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 1,158,422 | | | 177.18 | 3 |
345 East 94th Street (14) | Upper East Side | 3,700 | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 263,134 | | | 71.12 | | 1 | |
| Total/Weighted Average Retail Properties | | 725,315 | | 90.4 | % | | 92.1 | % | | 91,977,514 | | | 140.27 | | 85 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Portfolio Total | | 9,359,219 | | 86.3 | % | | 90.6 | % | | $ | 535,969,164 | | | $ | 66.32 | | 628 | |
(1)Excludes (i) 189,148 square feet of space across the Company's portfolio attributable to building management use and tenant amenities and (ii) 83,190 square feet of space attributable to the Company's Observatory.
(2)Based on leases signed and commenced as of December 31, 2023.
(3)Includes occupied space plus leases signed but not commenced as of December 31, 2023.
(4)Represents annualized base rent and current reimbursement for operating expenses and real estate taxes.
(5)Represents annualized rent under leases commenced as of December 31, 2023 divided by occupied square feet.
(6)Represents the number of leases at each property or on a portfolio basis. If a tenant has more than one lease, whether or not at the same property, but with different expirations, the number of leases is calculated equal to the number of leases with different expirations.
(7)Denotes a ground leasehold interest in the property with a remaining term, including unilateral extension rights available to the Company, of approximately 40 years (expiring December 31, 2063).
(8)Denotes a ground leasehold interest in the property with a remaining term, including unilateral extension rights available to the Company, of approximately 54 years (expiring June 10, 2077).
(9)Denotes a ground leasehold interest in the property with a remaining term, including unilateral extension rights available to the Company, of approximately 27 years (expiring July 31, 2050).
(10)First Stamford Place consists of three buildings.
(11)Does not include the square footage related to the 417 residential units at this property.
(12)Does not include the square footage related to the 96 residential units at this property.
(13)Does not include the square footage related to the 6 residential units at this property.
(14)Does not include the square footage related to the 208 residential units at this property.
Tenant Diversification
As of December 31, 2023, our office and retail portfolios were leased to a diverse tenant base consisting of approximately 628 leases. Our tenants represent a broad array of industries as follows:
| | | | | |
| Diversification by Industry | Percent (1) |
| Arts and entertainment | 3.2 | % |
| Broadcast | 1.0 | % |
| Consumer goods | 15.8 | % |
| Finance, insurance, real estate | 16.9 | % |
| Government entity | 2.1 | % |
| Healthcare | 1.8 | % |
| Legal services | 5.2 | % |
| Non-profit | 4.2 | % |
| Professional services (not including legal services) | 9.2 | % |
| Retail | 18.2 | % |
| | | | | |
| Technology, media and advertising | 18.0 | % |
| Others | 4.4 | % |
| Total | 100.0 | % |
| |
(1) Based on annualized rent. | |
The following table sets forth information regarding the 20 largest tenants in our commercial portfolio based on annualized rent as of December 31, 2023.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Weighted | | Percent of | | | |
| | | Average | Total | Portfolio | | | Percent of |
| | | Remaining | Occupied | Rentable | | | Portfolio |
| | Lease | Lease | Square | Square | | Annualized | Annualized |
| Tenant | Property | Expiration (1) | Term (2) | Feet (3) | Feet (4) | | Rent (5) | Rent (6) |
| LinkedIn | Empire State Building | Aug. 2036 | 12.7 years | 501,409 | | 5.4 | % | | $ | 33,465,435 | | 6.2 | % |
| Flagstar Bank | 1400 Broadway | Aug. 2039 | 15.7 years | 313,109 | | 3.3 | % | | 18,285,046 | | 3.4 | % |
| Centric Brands Inc. | Empire State Building | Oct. 2028 | 4.8 years | 221,365 | | 2.4 | % | | 11,952,833 | | 2.2 | % |
| PVH Corp. | 501 Seventh Avenue | Oct. 2028 | 4.8 years | 237,281 | | 2.5 | % | | 11,519,383 | | 2.1 | % |
| Sephora | 112 West 34th Street | Jan. 2029 | 5.1 years | 11,334 | | 0.1 | % | | 10,533,585 | | 2.0 | % |
| Target | 112 West 34th St., 10 Union Sq. | Jan. 2038 | 14.1 years | 81,340 | | 0.9 | % | | 9,341,224 | | 1.7 | % |
| Coty Inc. | Empire State Building | Jan. 2030 | 6.1 years | 156,187 | | 1.7 | % | | 8,497,458 | | 1.6 | % |
| Macy's | 111 West 33rd Street | May 2030 | 6.4 years | 131,117 | | 1.4 | % | | 8,451,562 | | 1.6 | % |
| Urban Outfitters | 1333 Broadway | Sept. 2029 | 5.8 years | 56,730 | | 0.6 | % | | 8,185,595 | | 1.5 | % |
| Li & Fung | 1359 Broadway, ESB | Oct. 2027 - Oct. 2028 | 4.5 years | 149,061 | | 1.6 | % | | 7,954,806 | | 1.5 | % |
| Footlocker | 112 West 34th Street | Sept. 2031 | 7.8 years | 34,192 | | 0.4 | % | | 7,745,828 | | 1.4 | % |
| Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. | Empire State Building | Dec. 2025 | 2.0 years | 119,226 | | 1.3 | % | | 7,578,004 | | 1.4 | % |
| HNTB Corporation | Empire State Building | Feb. 2029 | 5.2 years | 105,143 | | 1.1 | % | | 7,000,733 | | 1.3 | % |
| Institutional Capital Network, Inc. | One Grand Central Place | Feb. 2024 - Oct. 2035 | 10.6 years | 94,331 | | 1.0 | % | | 6,351,680 | | 1.2 | % |
| The Michael J. Fox Foundation | 111 West 33rd Street | Nov. 2029 | 5.9 years | 86,492 | | 0.9 | % | | 6,267,495 | | 1.2 | % |
| Shutterstock | Empire State Building | Apr. 2029 | 5.3 years | 104,386 | | 1.1 | % | | 6,096,096 | | 1.1 | % |
| Fragomen | 1400 Broadway | Feb. 2035 | 11.2 years | 107,680 | | 1.2 | % | | 5,959,656 | | 1.1 | % |
| Burlington Merchandising Corp. | 1400 Broadway | Jan. 2038 | 14.1 years | 102,898 | | 1.1 | % | | 5,932,832 | | 1.1 | % |
| ASCAP | 250 West 57th Street | Aug. 2034 | 10.7 years | 87,943 | | 0.9 | % | | 5,384,628 | | 1.0 | % |
| Duane Reade | Empire State Building, 1350 Broadway | May 2025 - Sept. 2027 | 2.5 years | 39,142 | | 0.4 | % | | 4,941,165 | | 0.9 | % |
| Total | | | | 2,740,366 | | 29.3 | % | | $ | 191,445,044 | | 35.5 | % |
(1)Expiration dates are per lease and do not assume exercise of renewal or extension options. For tenants with more than two leases, the lease expiration is shown as a range.
(2)Represents the weighted average remaining lease term, based on annualized rent.
(3)Based on leases signed and commenced as of December 31, 2023.
(4)Represents the percentage of rentable square feet of the Company's office and retail portfolios in the aggregate.
(5)Represents annualized base rent and current reimbursement for operating expenses and real estate taxes.
(6)Represents the percentage of annualized rent of the Company's office and retail portfolios in the aggregate.
Lease Expirations
The following table sets forth new and renewal leases entered into at our properties, the weighted average annualized cash rent per square foot for new and renewal leases executed during the year, the previous weighted average annualized cash rent prior to the renewal or re-leasing of these leases and the percent increase (decrease) in mark-to-market rent. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| New and renewal leases entered into during the year (square feet) | 950,746 | | | 1,118,579 | | | 1,005,630 | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average annualized cash rent per square foot for new and renewal leases executed during the year | $ | 65.30 | | | $ | 59.42 | | | $ | 57.55 | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average annualized cash rent per square foot for previous leases | $ | 61.25 | | | $ | 58.58 | | | $ | 58.04 | |
| | | | | |
| Increase (decrease) in mark-to-market rent | 6.6 | % | | 1.4 | % | | (0.8) | % |
The following tables set forth a summary schedule of expirations for leases in place as of December 31, 2023 plus available space for each of the ten calendar years beginning with the year ended December 31, 2023 at the office and retail properties in our commercial portfolio. The information set forth in the table assumes that tenants exercise no renewal options and all early termination rights.
Office and Retail Portfolio
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Percent of | | | | | |
| | Rentable | Portfolio | | | | | Annualized |
| Number | Square | Rentable | | | Percent of | | Rent Per |
| of Leases | Feet | Square Feet | | Annualized | Annualized | | Rentable |
| Year of Lease Expiration | Expiring (1) | Expiring (2) | Expiring | | Rent (3) | Rent | | Square Foot |
| Available | — | | 875,777 | | 9.4 | % | | $ | — | | — | % | | $ | — | |
| Signed leases not commenced | 28 | | 402,268 | | 4.3 | % | | — | | — | % | | — | |
Fourth quarter 2023(4) | 15 | | 143,627 | | 1.5 | % | | 7,522,786 | | 1.4 | % | | 52.38 | |
| 2024 | 89 | | 509,671 | | 5.4 | % | | 30,075,202 | | 5.6 | % | | 59.01 | |
| 2025 | 85 | | 594,946 | | 6.4 | % | | 40,363,625 | | 7.5 | % | | 67.84 | |
| 2026 | 72 | | 628,943 | | 6.7 | % | | 37,384,704 | | 7.0 | % | | 59.44 | |
| 2027 | 87 | | 713,569 | | 7.6 | % | | 47,192,095 | | 8.8 | % | | 66.14 | |
| 2028 | 63 | | 945,077 | | 10.1 | % | | 52,486,474 | | 9.8 | % | | 55.54 | |
| 2029 | 50 | | 981,952 | | 10.5 | % | | 73,521,837 | | 13.7 | % | | 74.87 | |
| 2030 | 38 | | 745,546 | | 8.0 | % | | 50,024,340 | | 9.3 | % | | 67.10 | |
| 2031 | 23 | | 174,491 | | 1.9 | % | | 20,214,026 | | 3.8 | % | | 115.85 | |
| 2032 | 29 | | 368,694 | | 3.9 | % | | 26,223,606 | | 4.9 | % | | 71.13 | |
| 2033 | 29 | | 329,711 | | 3.5 | % | | 21,332,708 | | 4.0 | % | | 64.70 | |
| Thereafter | 48 | | 1,944,947 | | 20.8 | % | | 129,627,759 | | 24.2 | % | | 66.65 | |
| Total | 656 | | 9,359,219 | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 535,969,162 | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 66.32 | |
Manhattan Office Properties (5)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Percent of | | | | | |
| | Rentable | Portfolio | | | | | Annualized |
| Number | Square | Rentable | | | Percent of | | Rent Per |
| of Leases | Feet | Square Feet | | Annualized | Annualized | | Rentable |
| Year of Lease Expiration | Expiring (1) | Expiring (2) | Expiring | | Rent (3) | Rent | | Square Foot |
| Available | — | | 597,862 | | 7.9 | % | | $ | — | | — | % | | $ | — | |
| Signed leases not commenced | 20 | | 362,213 | | 4.8 | % | | — | | — | % | | — | |
Fourth quarter 2023(4) | 12 | | 124,643 | | 1.6 | % | | 7,044,490 | | 1.7 | % | | 56.52 | |
| 2024 | 76 | | 431,339 | | 5.7 | % | | 25,204,397 | | 6.2 | % | | 58.43 | |
| 2025 | 67 | | 495,292 | | 6.5 | % | | 32,205,906 | | 7.9 | % | | 65.02 | |
| 2026 | 57 | | 485,929 | | 6.4 | % | | 29,511,170 | | 7.3 | % | | 60.73 | |
| 2027 | 71 | | 600,450 | | 7.9 | % | | 36,782,006 | | 9.1 | % | | 61.26 | |
| 2028 | 47 | | 854,943 | | 11.3 | % | | 47,465,773 | | 11.7 | % | | 55.52 | |
| 2029 | 35 | | 738,291 | | 9.8 | % | | 44,821,337 | | 11.0 | % | | 60.71 | |
| 2030 | 27 | | 599,150 | | 7.9 | % | | 37,243,747 | | 9.2 | % | | 62.16 | |
| 2031 | 12 | | 86,541 | | 1.1 | % | | 6,076,449 | | 1.5 | % | | 70.21 | |
| 2032 | 21 | | 334,698 | | 4.4 | % | | 23,105,190 | | 5.7 | % | | 69.03 | |
| 2033 | 15 | | 141,599 | | 1.9 | % | | 8,587,282 | | 2.1 | % | | 60.65 | |
| Thereafter | 35 | | 1,717,713 | | 22.8 | % | | 108,337,878 | | 26.6 | % | | 63.07 | |
| Total | 495 | | 7,570,663 | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 406,385,625 | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 61.47 | |
Greater New York Metropolitan Area Office Properties
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Percent of | | | | | |
| | Rentable | Portfolio | | | | | Annualized |
| Number | Square | Rentable | | | Percent of | | Rent Per |
| of Leases | Feet | Square Feet | | Annualized | Annualized | | Rentable |
| Year of Lease Expiration | Expiring (1) | Expiring (2) | Expiring | | Rent (3) | Rent | | Square Foot |
| Available | — | | 220,593 | | 20.7 | % | | $ | — | | — | % | | $ | — | |
| Signed leases not commenced | 3 | | 27,802 | | 2.5 | % | | — | | — | % | | — | |
Fourth quarter 2023(4) | 2 | | 2,540 | | 0.2 | % | | 63,701 | | 0.2 | % | | 25.08 | |
| 2024 | 7 | | 52,728 | | 5.0 | % | | 2,222,975 | | 5.9 | % | | 42.16 | |
| 2025 | 13 | | 76,903 | | 7.2 | % | | 3,597,773 | | 9.6 | % | | 46.78 | |
| 2026 | 8 | | 71,784 | | 6.8 | % | | 3,508,404 | | 9.3 | % | | 48.87 | |
| 2027 | 10 | | 58,730 | | 5.5 | % | | 2,801,695 | | 7.5 | % | | 47.70 | |
| 2028 | 11 | | 84,915 | | 8.0 | % | | 3,735,230 | | 9.9 | % | | 43.99 | |
| 2029 | 5 | | 128,271 | | 12.1 | % | | 5,907,668 | | 15.7 | % | | 46.06 | |
| 2030 | 4 | | 78,033 | | 7.3 | % | | 3,562,425 | | 9.5 | % | | 45.65 | |
| 2031 | 2 | | 16,560 | | 1.6 | % | | 843,885 | | 2.2 | % | | 50.96 | |
2032(6) | 1 | | — | | — | % | | 6,180 | | — | % | | — | |
| 2033 | 3 | | 151,754 | | 14.3 | % | | 7,494,005 | | 19.9 | % | | 49.38 | |
| Thereafter | 2 | | 92,628 | | 8.8 | % | | 3,862,084 | | 10.3 | % | | 41.69 | |
| Total | 71 | | 1,063,241 | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 37,606,025 | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 46.15 | |
Retail Properties
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Percent of | | | | | |
| | Rentable | Portfolio | | | | | Annualized |
| Number | Square | Rentable | | | Percent of | | Rent Per |
| of Leases | Feet | Square Feet | | Annualized | Annualized | | Rentable |
| Year of Lease Expiration | Expiring (1) | Expiring (2) | Expiring | | Rent (3) | Rent | | Square Foot |
| Available | — | | 57,322 | | 7.9 | % | | $ | — | | — | % | | $ | — | |
| Signed leases not commenced | 5 | | 12,253 | | 1.7 | % | | — | | — | % | | — | |
Fourth quarter 2023(4) | 1 | | 16,444 | | 2.3 | % | | 414,595 | | 0.5 | % | | 25.21 | |
| 2024 | 6 | | 25,604 | | 3.5 | % | | 2,647,830 | | 2.9 | % | | 103.41 | |
| 2025 | 5 | | 22,751 | | 3.1 | % | | 4,559,946 | | 5.0 | % | | 200.43 | |
| 2026 | 7 | | 71,230 | | 9.8 | % | | 4,365,130 | | 4.7 | % | | 61.28 | |
| 2027 | 6 | | 54,389 | | 7.5 | % | | 7,608,394 | | 8.3 | % | | 139.89 | |
| 2028 | 5 | | 5,219 | | 0.7 | % | | 1,285,471 | | 1.4 | % | | 246.31 | |
| 2029 | 10 | | 115,390 | | 15.9 | % | | 22,792,832 | | 24.8 | % | | 197.53 | |
| 2030 | 7 | | 68,363 | | 9.4 | % | | 9,218,168 | | 10.0 | % | | 134.84 | |
| 2031 | 9 | | 71,390 | | 9.8 | % | | 13,293,692 | | 14.5 | % | | 186.21 | |
| 2032 | 7 | | 33,996 | | 4.7 | % | | 3,112,236 | | 3.4 | % | | 91.55 | |
| 2033 | 11 | | 36,358 | | 5.0 | % | | 5,251,421 | | 5.7 | % | | 144.44 | |
| Thereafter | 11 | | 134,606 | | 18.7 | % | | 17,427,798 | | 18.8 | % | | 129.47 | |
| Total | 90 | | 725,315 | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 91,977,514 | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 140.27 | |
(1)If a tenant has more than one lease, whether or not at the same property, but with different expirations, the number of leases is calculated equal to the number of leases with different expirations.
(2)Excludes (i) 189,148 rentable square feet across the Company's portfolio attributable to building management use and tenant amenities and (ii)
83,190 square feet of space attributable to the Company's Observatory.
(3)Represents annualized base rent and current reimbursement for operating expenses and real estate taxes.
(4)Represents leases that are included in occupancy as of December 31, 2023 and expire on December 31, 2023.
(5)Excludes (i) retail space in our Manhattan office properties and (ii) the Empire State Building broadcasting licenses and Observatory operations.
(6)Represents a telecom lease with no square footage.
Portfolio Transaction Activity
On February 1, 2023, we closed on the sale of 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street in Westport, Connecticut at a gross asset valuation of $40.0 million. Refer to "Financial Statements - Note 11 Related Party Transactions" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
On April 5, 2023, we closed on the sale of 500 Mamaroneck Avenue in Harrison, New York at a gross asset valuation of $53.0 million.
On September 14, 2023, we closed on the acquisition of a Williamsburg retail property located on the corner of North 6th Street and Wythe Avenue in Brooklyn, New York, for a purchase price of $26.4 million.
Refer to "Financial Statements - Note 3 Acquisitions and Dispositions" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
Refer to “Financial Statements - Note 9 Commitments and Contingencies” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a description of any pending legal proceedings.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURE
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information
Our Class A common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange (the "NYSE"), under the symbol "ESRT." Our Class B common stock is not listed on any exchange and is not traded. Each share of Class B common stock may be converted to one share of Class A common stock at any time.
Our operating partnership has four series of partnership units ("OP Units") - Series PR OP Units, Series ES OP Units, Series 60 OP Units and Series 250 OP Units. The Series ES OP Units, Series 60 OP Units and Series 250 OP Units (together, the "traded OP units") are listed on the NYSE Arca, Inc. exchange ("NYSE Arca") under the symbols "ESBA," "OGCP," and "FISK," respectively. The Series PR OP Units are not listed on any exchange and are not traded.
On February 22, 2024, the last sales price for our Class A common stock on the NYSE was $9.96 per share.
Holders
As of February 22, 2024, we had 570 registered holders of our Class A common stock and 550 registered holders of our Class B common stock. As of February 22, 2024, we had approximately 574 registered holders of Series PR OP Units, 1,225 registered holders of Series ES OP Units, 357 registered holders of Series 60 OP Units and 279 registered holders of Series 250 OP Units. Certain shares of common stock and OP Units are held in "street" name and accordingly, the number of beneficial owners of such shares of common stock and OP Units is not known or included in the foregoing totals.
Dividends
We intend to pay regular quarterly dividends to holders of our Class A common stock and Class B common stock, at least to the extent of our taxable income or as required to maintain our qualification as a REIT. Any distributions we pay in the
future will depend upon our taxable income, actual results of operations, economic conditions and other factors that could differ materially from our current expectations. Our actual results of operations will be affected by a number of factors, including the revenue we receive from our properties, our operating expenses, interest expense, the ability of our tenants to meet their obligations and unanticipated expenditures.
We declared dividends of $0.035 per share for each quarter of 2023, which equates to an annualized rate of $0.14 per share.
Our board will continue our regular review of dividend and capital allocation policies. Distributions declared by us will be authorized by our board in its sole discretion out of funds legally available therefore and will be dependent upon a number of factors, including restrictions under applicable law, our capital requirements and the distribution requirements necessary to maintain our qualification as a REIT. See ITEM 1A, "Risk Factors," and ITEM 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Conditions and Results of Operations," of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for information regarding the sources of funds used for dividends and for a discussion of factors, if any, which may adversely affect our ability to make distributions to our securityholders.
Earnings and profits, which determine the tax treatment of distributions to securityholders, will differ from income reported for financial reporting purposes due to the differences for federal income tax purposes, including, but not limited to, treatment of loss on extinguishment of debt, revenue recognition, compensation expense, and basis of depreciable assets and estimated useful lives used to compute depreciation. Dividends paid in 2023 of $0.14 per share are classified for income tax purposes 89.2% as taxable ordinary dividends eligible for the Section 199A deduction and 10.8% as a return of capital.
Stockholder Return Performance
The following graph is a comparison of the cumulative total stockholder return on our Class A common stock, the Standard & Poor's 500 Index (the "S&P 500 Index"), the MSCI US REIT Index and the FTSE NAREIT Equity REIT Office Index. The graph assumes that $100.00 was invested on December 31, 2018 and dividends were reinvested without the payment of any commissions. There can be no assurance that the performance of our Class A common stock will continue in line with the same or similar trends depicted in the graph below.
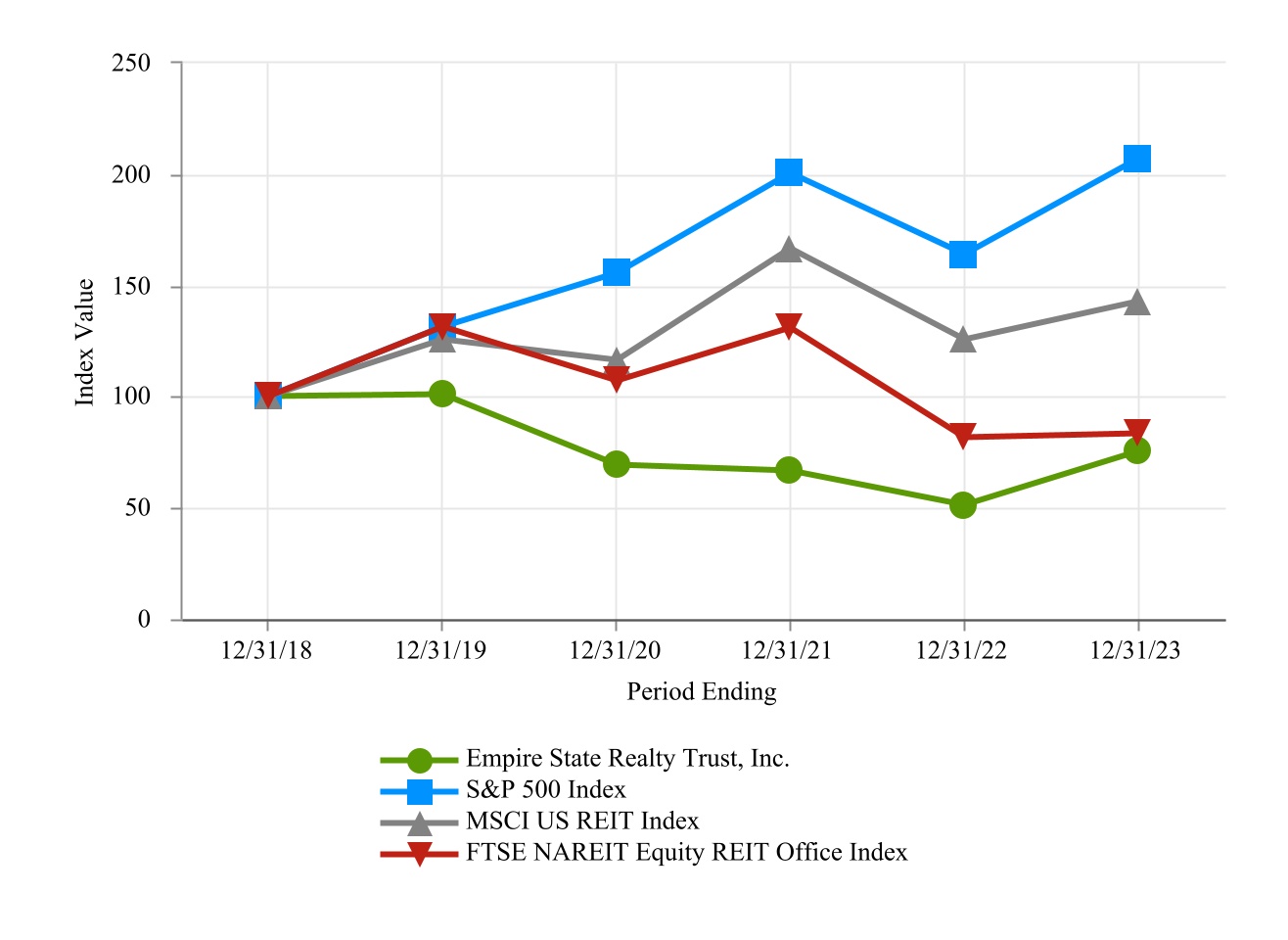
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2018 | | December 31, 2019 | | December 31, 2020 | | December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 100.92 | | | $ | 69.12 | | | $ | 66.68 | | | $ | 51.47 | | | $ | 75.33 | |
| S&P 500 Index | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 131.49 | | | $ | 155.68 | | | $ | 200.37 | | | $ | 164.08 | | | $ | 207.21 | |
| MSCI US REIT Index | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 125.84 | | | $ | 116.31 | | | $ | 166.39 | | | $ | 125.61 | | | $ | 142.87 | |
| FTSE NAREIT Equity REIT Office Index | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 131.42 | | | $ | 107.19 | | | $ | 130.77 | | | $ | 81.58 | | | $ | 83.23 | |
The graph is not deemed incorporated by reference into any filing made under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the "Securities Act"), or the Exchange Act regardless of any general statement regarding incorporation by reference in any such filing, and is not otherwise deemed filed under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act.
Securities Authorized For Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
On May 16, 2019, our shareholders approved the Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. Empire State Realty OP, L.P. 2019 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2019 Plan”). The 2019 Plan provides for grants to directors, employees and consultants of our Company and operating partnership, including options, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock appreciation rights, performance awards, dividend equivalents and other equity-based awards, including LTIP units. An aggregate of approximately 11.0 million shares of our common stock are authorized for issuance under awards granted pursuant to the 2019 Plan. Following adoption by our shareholders of the 2019 Plan, we agreed not to issue any new equity awards under the First Amended and Restated Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. and Empire State Realty OP, L.P. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan ("2013 Plan", and collectively with the 2019 Plan, "the Plans"), which we adopted upon our IPO in 2013. The shares of Class A common stock underlying any awards under the 2019 Plan and the 2013 Plan that are forfeited, canceled or otherwise terminated, other than by exercise, will be added back to the shares of Class A common stock available for issuance under the 2019 Plan. For a further discussion of the Plans, see "Financial Statements - Note 10 Equity" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The following table presents certain information about our equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2023:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Plan Category | | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights | | Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights | | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in the first column of this table) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Equity compensation plans approved by securityholders (1) | | N/A | | N/A | | 4,162,516 | | (2) |
| Equity compensation plans not approved by securityholders | | — | | | — | | | — | | |
| Total | | N/A | | N/A | | 4,162,516 | | |
______________
(1)These consist of the Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. Empire State Realty OP, L.P. 2019 Equity Incentive Plan and the First Amended and Restated Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. and Empire State Realty OP, L.P. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan.
(2)The number of securities remaining available for future issuance consists of shares remaining available for issuance under the Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. Empire State Realty OP, L.P. 2019 Equity Incentive Plan adjusted for awards that have been forfeited, canceled or otherwise terminated, other than by exercise under the Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. Empire State Realty OP, L.P. 2019 Equity Incentive Plan and the First Amended and Restated Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. and Empire State Realty OP, L.P. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan.
As of December 31, 2023, we have issued 1,147,005 shares of restricted stock and 15,052,177 LTIP units under the Plans since 2013.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities Use of Proceeds from Registered Securities
Not applicable.
Repurchases of Equity Securities Stock and Publicly Traded Operating Partnership Unit Repurchase Program
Our Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $500 million of our Class A common stock and the Operating Partnership’s Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units during the period from January 1, 2022 through December 31, 2023. Upon expiration of this program, the Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $500 million of our Class A common stock and the Operating Partnership’s Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units during the period from January 1, 2024 through December 31, 2025. Under the program, we may purchase our Class A common stock and the Operating Partnership’s Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units in accordance with applicable securities laws from time to time in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions. The timing, manner, price and amount of any repurchases will be determined by us and will be subject to stock price, availability, trading volume, general market conditions, and applicable securities laws. The authorization does not obligate us to acquire any particular amount of securities, and the program may be suspended or discontinued at our discretion without prior notice. At December 31, 2023, we had used approximately $103.3 million of the authorized repurchase amount for the 2022-2023 period.
There were no repurchases of equity securities in the three-month period ended December 31, 2023 under this repurchase program. See "Financial Statements - Note 10 Equity" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. There have also been no repurchases of equity securities yet under the new repurchase program. ITEM 6. [RESERVED]
Not applicable.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Unless the context otherwise requires or indicates, references in this section to "we," "our," and "us" refer to our Company and its consolidated subsidiaries. The following discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 and for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 and the notes related thereto which are included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
��
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act, and Section 21E of the Exchange Act. We intend these forward-looking statements to be covered by the safe harbor provisions for forward-looking statements contained in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 and are including this statement for purposes of complying with those safe harbor provisions. You can identify forward-looking statements by the use of forward-looking terminology such as “aims," "anticipates," "approximately," "believes," "contemplates," "continues," "estimates," "expects," "forecasts," "hope," "intends," "may," "plans," "seeks," "should," "thinks," "will," "would" or the negative of these words and phrases. In particular, statements pertaining to our capital resources, portfolio performance, dividend policy and results of operations contain forward-looking statements. Likewise, all of our statements regarding anticipated growth in our portfolio from operations, acquisitions and anticipated market conditions, demographics and results of operations are forward-looking statements.
Forward-looking statements are subject to substantial risks and uncertainties, many of which are difficult to predict and are generally beyond our control, and you should not rely on them as predictions of future events. Forward-looking statements depend on assumptions, data or methods which may be incorrect or imprecise, and we may not be able to realize them. We do not guarantee that the transactions and events described will happen as described (or that they will happen at all).
Many important factors could cause actual results and future events to differ materially from those set forth or contemplated in the forward-looking statements, including, among other things: (i) economic, market, political and social impact of, and uncertainty relating to, any catastrophic events, including pandemics, epidemics or other outbreaks of disease, climate-related risks such as natural disasters and extreme weather events, terrorism and other armed hostilities, as well as cybersecurity threats and technology disruptions; (ii) a failure of conditions or performance regarding any event or transaction described herein; (iii) resolution of legal proceedings involving the Company; (iv) reduced demand for office, multifamily or retail space, including as a result of the changes in the use of office space and remote work; (v) changes in our business strategy; (vi) a decline in Observatory visitors due to changes in domestic or international tourism, including due to health crises, geopolitical events, currency exchange rates, and/or competition from other observatories; (vii) defaults on, early terminations of, or non-renewal of, leases by tenants; (viii) increases in the Company’s borrowing costs as a result of changes in interest rates and other factors; (ix) declining real estate valuations and impairment charges; (x) termination of our ground leases; (xi) limitations on our ability to pay down, refinance, restructure or extend our indebtedness or borrow additional funds; (xii) decreased rental rates or increased vacancy rates; (xiii) difficulties in executing capital projects or development projects successfully or on the anticipated timeline or budget; (xiv) difficulties in identifying and completing acquisitions; (xv) impact of changes in governmental regulations, tax laws and rates and similar matters; (xvi) our failure to qualify as a REIT; (xvii) incurrence of taxable capital gain on disposition of an asset due to failure of use or compliance with a 1031 exchange program; and (xviii) failure to achieve sustainability metrics and goals, including as a result of tenant collaboration, and impact of governmental regulation on our sustainability efforts. For a further discussion of these and other factors that could impact the Company's future results, performance or transactions, see the section entitled “Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
While forward-looking statements reflect the Company's good faith beliefs, they do not guarantee future performance. Any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it was made, and we assume no obligation to update or revise publicly any forward-looking statement to reflect changes in underlying assumptions or factors, new information, data or methods, future events, or other changes after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, except as required by applicable law. Prospective investors should not place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements, which are based only on information currently available to the Company (or to third parties making the forward-looking statements).
Overview
2023 Highlights
•Net income attributable to the Company of $49.0 million.
•Core FFO of $245.8 million.
•Signed a total of 950,746 rentable square feet of new, renewal and expansion leases.
•Completed the acquisition of a retail asset located in Williamsburg, Brooklyn in the third quarter.
•Completed the dispositions of retail assets located in Westport, Connecticut in the first quarter, and an office asset located in Harrison, New York in the second quarter.
Results of Operations
Overview
The discussion below relates to the financial condition and results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. For a discussion of our 2021 financial results as compared to our 2022 financial results, please see our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022.
Year Ended December 31, 2023 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2022
The following table summarizes the historical results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | Change | % |
| Real Estate Segment | Observatory Segment | Total | | Real Estate Segment | Observatory Segment | Total | | | |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | |
Rental revenue | $ | 597,319 | | $ | — | | $ | 597,319 | | | $ | 591,048 | | $ | — | | $ | 591,048 | | | $ | 6,271 | | 1.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Observatory revenue | — | | 129,366 | | 129,366 | | | — | | 105,978 | | 105,978 | | | 23,388 | | 22.1 | % |
| Lease termination fees | — | | — | | — | | | 20,032 | | — | | 20,032 | | | (20,032) | | (100.0) | % |
| Third-party management and other fees | 1,351 | | — | | 1,351 | | | 1,361 | | — | | 1,361 | | | (10) | | (0.7) | % |
| Other revenues and fees | 11,536 | | — | | 11,536 | | | 8,622 | | — | | 8,622 | | | 2,914 | | 33.8 | % |
| Total revenues | 610,206 | | 129,366 | | 739,572 | | | 621,063 | | 105,978 | | 727,041 | | | 12,531 | | 1.7 | % |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property operating expenses | 167,324 | | — | | 167,324 | | | 157,935 | | — | | 157,935 | | | (9,389) | | (5.9) | % |
| Ground rent expenses | 9,326 | | — | | 9,326 | | | 9,326 | | — | | 9,326 | | | — | | — | % |
| General and administrative expenses | 63,939 | | — | | 63,939 | | | 61,765 | | — | | 61,765 | | | (2,174) | | (3.5) | % |
| Observatory expenses | — | | 35,265 | | 35,265 | | | — | | 31,036 | | 31,036 | | | (4,229) | | (13.6) | % |
| Real estate taxes | 127,101 | | — | | 127,101 | | | 123,057 | | — | | 123,057 | | | (4,044) | | (3.3) | % |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 189,762 | | 149 | | 189,911 | | | 216,707 | | 187 | | 216,894 | | | 26,983 | | 12.4 | % |
| Total operating expenses | 557,452 | | 35,414 | | 592,866 | | | 568,790 | | 31,223 | | 600,013 | | | 7,147 | | 1.2 | % |
| Operating income | 52,754 | | 93,952 | | 146,706 | | | 52,273 | | 74,755 | | 127,028 | | | 19,678 | | 15.5 | % |
| Intercompany rent income (expense) | 80,514 | | (80,514) | | — | | | 65,005 | | (65,005) | | — | | | — | | — | % |
| Other income (expense): | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | 14,936 | | 200 | | 15,136 | | | 4,901 | | 47 | | 4,948 | | | 10,188 | | 205.9 | % |
| Interest expense | (101,484) | | — | | (101,484) | | | (101,206) | | — | | (101,206) | | | (278) | | (0.3) | % |
| Gain on sale/disposition of properties | 26,764 | | — | | 26,764 | | | 33,988 | | — | | 33,988 | | | (7,224) | | (21.3) | % |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Income before income taxes | 73,484 | | 13,638 | | 87,122 | | | 54,961 | | 9,797 | | 64,758 | | | 22,364 | | 34.5 | % |
| Income tax expense | (552) | | (2,163) | | (2,715) | | | (584) | | (962) | | (1,546) | | | (1,169) | | (75.6) | % |
| Net income | 72,932 | | 11,475 | | 84,407 | | | 54,377 | | 8,835 | | 63,212 | | | 21,195 | | 33.5 | % |
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-controlling interests in the Operating Partnership | (31,094) | | — | | (31,094) | | | (22,812) | | — | | (22,812) | | | (8,282) | | (36.3) | % |
| Non-controlling interests in other partnerships | (68) | | — | | (68) | | | 243 | | — | | 243 | | | (311) | | (128.0) | % |
| Private perpetual preferred unit distributions | (4,201) | | — | | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | | — | | (4,201) | | | — | | — | % |
| Net income attributable to common shareholders | $ | 37,569 | | $ | 11,475 | | $ | 49,044 | | | $ | 27,607 | | $ | 8,835 | | $ | 36,442 | | | $ | 12,602 | | 35.0 | % |
Real Estate Segment
Rental Revenue
The increase in rental revenue was primarily attributable to a $13.7 million increase in base rent from new or renewed tenants and higher rents and higher tenant escalations, partially offset by a net $7.4 million decrease in revenue from our recent transaction activity as disclosed in "Financial Statements - Note 3. Acquisitions and Dispositions" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Other Revenues and Fees
The increase in other revenues and fees relates to prior period real estate tax refunds and abatements, and bad debt recovery income during the year ended December 31, 2023.
Property Operating Expenses
The increase in property operating expenses was primarily due to higher repair and maintenance costs, higher cleaning costs, and higher payroll costs in 2023 relating to increased building utilization.
Real Estate Taxes
The increase in real estate taxes was primarily attributable to a $4.5 million increase in real estate tax expense due to higher assessed values for multiple properties, partially offset by a net $0.5 million decrease from our recent transaction activity as disclosed in "Financial Statements - Note 3. Acquisitions and Dispositions" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation and amortization is lower for the year ended December 31, 2023 than for the year ended December 31, 2022 because the latter included accelerated depreciation from the disposition of 383 Main Avenue and depreciation expense on properties that were sold prior to December 31, 2023.
Interest Income
The increase in interest income reflects higher interest rates on larger cash balances in the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022.
Gain on Sale/Disposition of Property
The gain on disposition activity for the year ended December 31, 2023 relates to the dispositions of 500 Mamaroneck in Harrison, New York in April 2023 and 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street in Westport, Connecticut in February 2023. The gain on disposition activity for the year ended December 31, 2022 relates to the dispositions of 10 Bank Street in White Plains, New York in December 2022 and 383 Main Avenue in Norwalk, Connecticut in April 2022.
Observatory Segment
Observatory Revenue
Observatory revenues were higher driven by increased visitation and revenue per visitor during the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2022.
Observatory Expenses
The increase in Observatory expenses was driven by increased operating hours, which increased variable costs such as marketing, labor and maintenance costs.
Income Taxes
The increase in income tax expense was attributable to higher taxable income for the Observatory segment for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Liquidity is a measure of our ability to meet potential cash requirements, including ongoing commitments to repay borrowings, fund and maintain our assets and operations, including lease-up costs, fund our redevelopment and repositioning programs, acquire properties, make distributions to our securityholders and fulfill other general business needs. Based on the historical experience of our management and our business strategy, in the foreseeable future we anticipate we will generate positive cash flows from operations. In order to qualify as a REIT, we are required under the Code to distribute to our stockholders, on an annual basis, at least 90% of our REIT taxable income, determined without regard to the deduction for dividends paid and excluding net capital gains. We expect to make quarterly distributions, as required, to our securityholders.
While we may be able to anticipate and plan for certain liquidity needs, there may be unexpected increases in uses of cash that are beyond our control and which would affect our financial condition and results of operations. For example, we may be required to comply with new laws or regulations that cause us to incur unanticipated capital expenditures for our properties, thereby increasing our liquidity needs. Even if there are no material changes to our anticipated liquidity requirements, our sources of liquidity may be fewer than, and the funds available from such sources may be less than, anticipated or needed. Our primary sources of liquidity will generally consist of cash on hand, cash generated from our operating activities, debt issuances and unused borrowing capacity under our unsecured revolving credit facility. We expect to meet our short-term liquidity requirements, including distributions, operating expenses, working capital, debt service, and capital expenditures from cash flows from operations, cash on hand, debt issuances, and available borrowing capacity under our unsecured revolving credit facility. The availability of these borrowings is subject to the conditions set forth in the applicable loan agreements. We expect to meet our long-term capital requirements, including acquisitions, redevelopments and capital expenditures through our cash flows from operations, cash on hand, our unsecured revolving credit facility, mortgage financings, debt issuances, common and/or preferred equity issuances and asset sales. Our properties require periodic investments of capital for individual lease related tenant improvements allowances, general capital improvements and costs associated with capital expenditures. Our overall leverage will depend on our mix of investments and the cost of leverage. Our charter does not restrict the amount of leverage that we may use. See ITEM 1A. "Risk Factors - Risks Relating to Our Indebtedness and Liquidity" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for more information.
At December 31, 2023, we had approximately $346.6 million available in cash and cash equivalents and there was $850.0 million available under our unsecured revolving credit facility.
At December 31, 2023, we had approximately $2.2 billion of total consolidated indebtedness outstanding, with a weighted average interest rate of 3.9% and a weighted average maturity of 5.4 years. As of December 31, 2023, excluding debt amortization, we have a debt maturity of $77.7 million in November 2024, $315.0 million in 2025, $225.0 million in 2026, $319.0 million in 2027 and $1.3 billion thereafter. As of December 31, 2023, interest expense obligations and debt amortization from 2024 through 2028 and thereafter amount to $487.4 million and $51.6 million, respectively.
In connection with our three ground leases (i.e. long-term leaseholds of the land and the improvements) at 1350 Broadway, 111 West 33rd Street and 1400 Broadway, we also have contractual rent obligations totaling $68.3 million as of December 31, 2023, of which $7.5 million is due within the next five years.
Portfolio Transaction Activity
On February 1, 2023, we closed on the sale of 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street in Westport, Connecticut at a gross asset valuation of $40.0 million. Refer to "Financial Statements - Note 11 Related Party Transactions" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
On April 5, 2023, we closed on the sale of 500 Mamaroneck Avenue in Harrison, New York at a gross asset valuation of $53.0 million.
On September 14, 2023, we closed on the acquisition of a Williamsburg retail property located on the corner of North 6th Street and Wythe Avenue in Brooklyn, New York, for a purchase price of $26.4 million.
Refer to "Financial Statements - Note 3 Acquisitions and Dispositions" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Unsecured Revolving Credit and Term Loan Facilities
See "Financial Statements - Note 5 Debt" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a summary of our unsecured revolving credit and term loan facilities.
Financial Covenants
As of December 31, 2023, we were in compliance with the following financial covenants related to our unsecured facilities:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial Covenant | Required | December 31, 2023 | In Compliance |
| Maximum total leverage | < 60% | 31.5 | % | Yes |
| Maximum secured leverage | < 40% | 12.3 | % | Yes |
| Minimum fixed charge coverage | > 1.50x | 3.3x | Yes |
| Minimum unencumbered interest coverage | > 1.75x | 5.7x | Yes |
| Maximum unsecured leverage | < 60% | 23.4 | % | Yes |
| | | |
Mortgage Debt
As of December 31, 2023, mortgage notes payable, net, amounted to $877.4 million. The next mortgage debt maturity is November 2024. See "Financial Statements - Note 5 Debt" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for more information on mortgage debt.
Senior Unsecured Notes
The terms of the senior unsecured notes include customary covenants, including limitations on liens, investment, distributions, debt, fundamental changes, and transactions with affiliates and require certain customary financial reports. The terms also require compliance with financial ratios including a maximum leverage ratio, a maximum secured leverage ratio, a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio, a minimum unencumbered interest coverage ratio, and a maximum unsecured leverage ratio. The agreement also contains customary events of default (subject in certain cases to specified cure periods), including but not limited to non-payment, breach of covenants, representations or warranties, cross defaults, bankruptcy or other insolvency events, judgments, ERISA events, the occurrence of certain change of control transactions and loss of real estate investment trust qualification. As of December 31, 2023, we were in compliance with the covenants under the outstanding senior unsecured notes.
Leverage Policies
We expect to employ leverage in our capital structure in amounts determined from time to time by our Board of Directors. Although our Board of Directors has not adopted a policy that limits the total amount of indebtedness that we may incur, we anticipate that our Board of Directors will consider a number of factors in evaluating our level of indebtedness from time to time, as well as the amount of such indebtedness that will be either fixed or floating rate. Our charter and bylaws do not limit the amount or percentage of indebtedness that we may incur nor do they restrict the form in which our indebtedness will be taken (including, but not limited to, recourse or non-recourse debt and cross-collateralized debt). Our overall leverage will depend on our mix of investments and the cost of leverage. Our Board of Directors may from time to time modify our leverage policies in light of the then-current economic conditions, relative costs of debt and equity capital, market values of our properties, general market conditions for debt and equity securities, fluctuations in the market price of our common stock, growth and acquisition opportunities and other factors. See ITEM 1A. "Risk Factors - Risks Relating to Our Indebtedness and Liquidity" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for more information.
Capital Expenditures
The following tables summarize our tenant improvement costs, leasing commission costs and our capital expenditures for each of the periods presented (dollars in thousands, except per square foot amounts).
Office Properties(1)(5)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| Total New Leases, Expansions, and Renewals | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
Number of leases signed(2) | 82 | | 130 | | 118 |
| | | | | |
| Total square feet | 929,031 | | 1,071,426 | | 983,182 |
| | | | | |
Leasing commission costs per square foot(3) | $ | 19.80 | | | $ | 18.23 | | | $ | 20.14 | |
Tenant improvement costs per square foot(3) | 81.86 | | | 56.72 | | | 66.25 | |
Total leasing commissions and tenant improvement costs per square foot(3) | $ | 101.66 | | | $ | 74.95 | | | $ | 86.39 | |
Retail Properties(4)(5)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| Total New Leases, Expansions, and Renewals | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
Number of leases signed(2) | 8 | | | 14 | | | 11 | |
| | | | | |
| Total Square Feet | 21,715 | | | 47,153 | | | 22,448 | |
| | | | | |
Leasing commission costs per square foot(3) | $ | 54.62 | | | $ | 62.30 | | | $ | 57.27 | |
Tenant improvement costs per square foot(3) | 38.57 | | | 55.13 | | | 61.75 | |
Total leasing commissions and tenant improvement costs per square foot(3) | $ | 93.19 | | | $ | 117.43 | | | $ | 119.02 | |
_______________
(1)Excludes an aggregate of 498,682, 499,012 and 507,276 rentable square feet of retail space in our Manhattan office properties in 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Includes the Empire State Building broadcasting licenses and Observatory operations.
(2)Presents a renewed and expansion lease as one lease signed.
(3)Presents all tenant improvement and leasing commission costs as if they were incurred in the period in which the lease was signed, which may be different than the period in which they were actually paid.
(4)Includes an aggregate of 498,682, 499,012 and 507,276 rentable square feet of retail space in our Manhattan office properties in 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Excludes the Empire State Building broadcasting licenses and Observatory operations.
(5)The tables above exclude our multifamily properties.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Total Commercial Portfolio | | | | | |
Capital expenditures (1) | $ | 55,385 | | | $ | 38,445 | | | $ | 24,279 | |
_______________
(1)Includes all capital expenditures, excluding tenant improvements and leasing commission costs.
As of December 31, 2023, we expect to incur additional costs relating to obligations under signed new leases of approximately $101.2 million for tenant improvements and leasing commissions. We intend to fund the tenant improvements and leasing commission costs through a combination of operating cash flow, cash on hand and borrowings.
Capital expenditures are considered part of both our short-term and long-term liquidity requirements. We intend to fund the capital improvements through a combination of operating cash flow, cash on hand and borrowings.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2023, we did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Distribution Policy
We intend to distribute our net taxable income to our securityholders in a manner intended to satisfy REIT distribution requirements and to avoid U.S. federal income tax liability.
Before we pay any distribution, whether for U.S. federal income tax purposes or otherwise, we must first meet both our operating requirements and obligations to make payments of principal and interest, if any. However, under some circumstances, we may be required to use cash reserves, incur debt or liquidate assets at rates or times that we regard as unfavorable or make a taxable distribution of our shares in order to satisfy REIT distribution requirements.
We declared dividends of $0.035 per share for each quarter of 2023, which equates to an annualized rate of $0.14 per share. The Board of Directors will continue its regular review of its dividend and capital allocation policies at each Board meeting.
Distribution to Equity Holders
Distributions and dividends have been made to equity holders in 2021, 2022 and 2023 as follows (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2021 | 32,764 | |
| Year ended December 31, 2022 | 42,786 | |
| Year ended December 31, 2023 | 41,323 | |
Stock and Publicly Traded Operating Partnership Unit Repurchase Program
Our Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $500 million of our Class A common stock and the Operating Partnership’s Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units during the period from January 1, 2022 through December 31, 2023. Upon expiration of this program, the Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $500 million of our Class A common stock and the Operating Partnership's Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units during the period from January 1, 2024 through December 31, 2025. Under the program, we may purchase our Class A common stock and the Operating Partnership’s Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units in accordance with applicable securities laws from time to time in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions. The timing, manner, price and amount of any repurchases will be determined by us at our discretion and will be subject to stock price, availability, trading volume, general market conditions, and applicable securities laws. The authorization does not obligate us to acquire any particular amount of securities, and the program may be suspended or discontinued at our discretion without prior notice. At December 31, 2023, we had used approximately $103.3 million of the authorized repurchase amount for the 2022-2023 period.
The following table summarizes our purchases of equity securities for the year ended December 31, 2023 under the previous repurchase program.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | | Total Number of Shares Purchased | | Average Price Paid per Share | | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plan | | Maximum Approximate Dollar Value Available for Future Purchase |
| Year ended December 31, 2023 | | 2,150,857 | | | $ | 6.09 | | | 2,150,857 | | | $500,000,000 | | (a) |
(a) Represents the new board authorization for the January 1, 2024 - December 31, 2025 period. As of the date of this filing, we have used $0 of such $500 million authorization.
Cash Flows
Comparison of Year Ended December 31, 2023 to the Year Ended December 31, 2022
Net cash. Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash were $407.0 million and $314.7 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The increase was primarily due to net proceeds from the disposition of 500 Mamaroneck in April 2023 and 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street in February 2023 and from less share repurchase activity during the year ended December 31, 2023. We also had less acquisition activity in the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared with the year ended December 31, 2022.
Operating activities. Net cash provided by operating activities increased by $21.3 million to $232.5 million due to increased Observatory operating income and changes in working capital.
Investing activities. Net cash used in investing activities decreased by $153.6 million to $77.3 million primarily due to the net proceeds from the disposition of 500 Mamaroneck in April 2023 and 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street in February 2023. We also had less acquisition activity in the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared with the year ended December 31, 2022.
Financing activities. Net cash used in financing activities decreased by $80.9 million to $62.9 million primarily due to lower repurchases of common shares in 2023.
Net Operating Income
Net operating income ("NOI") is a non-GAAP financial measure of performance. NOI is used by our management to evaluate and compare the performance of our properties and to determine trends in earnings and to compute the fair value of our properties as it is not affected by: (i) the cost of funds of the property owner, (ii) the impact of depreciation and amortization expenses as well as gains or losses from the sale of operating real estate assets that are included in net income computed in accordance with GAAP, (iii) acquisition expenses, loss on early extinguishment of debt, impairment charges and loss from derivative financial instruments, or (iv) general and administrative expenses and other gains and losses that are specific to the property owner. The cost of funds is eliminated from NOI because it is specific to the particular financing capabilities and constraints of the owner. The cost of funds is eliminated because it is dependent on historical interest rates and other costs of capital as well as past decisions made by us regarding the appropriate mix of capital which may have changed or may change in the future. Depreciation and amortization expenses as well as gains or losses from the sale of operating real estate assets are eliminated because they may not accurately represent the actual change in value in our office or retail properties that result from use of the properties or changes in market conditions. While certain aspects of real property do decline in value over time in a manner that is reasonably
captured by depreciation and amortization, the value of the properties as a whole have historically increased or decreased as a result of changes in overall economic conditions instead of from actual use of the property or the passage of time. Gains and losses from the sale of real property vary from property to property and are affected by market conditions at the time of sale which will usually change from period to period. These gains and losses can create distortions when comparing one period to another or when comparing our operating results to the operating results of other real estate companies that have not made similarly-timed purchases or sales. We believe that eliminating these costs from net income is useful to investors because the resulting measure captures the actual revenue generated and actual expenses incurred in operating our properties as well as trends in occupancy rates, rental rates and operating costs.
However, the usefulness of NOI is limited because it excludes general and administrative costs, interest expense, depreciation and amortization expense and gains or losses from the sale of properties, and other gains and losses as stipulated by GAAP, the level of capital expenditures and leasing costs necessary to maintain the operating performance of our properties, all of which are significant economic costs. NOI may fail to capture significant trends in these components of net income which further limits its usefulness.
NOI is a measure of the operating performance of our properties but does not measure our performance as a whole. NOI is therefore not a substitute for net income as computed in accordance with GAAP. This measure should be analyzed in conjunction with net income computed in accordance with GAAP and discussions elsewhere in this Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations regarding components of net income that are eliminated in the calculation of NOI. Other companies may use different methods for calculating NOI or similarly titled measures and, accordingly, our NOI may not be comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies that do not define the measure exactly as we do.
The following table presents a reconciliation of our net income, the most directly comparable GAAP measure, to NOI for the periods presented (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 84,407 | | | $ | 63,212 | | | $ | (13,037) | |
| Add: | | | | | |
| General and administrative expenses | 63,939 | | | 61,765 | | | 55,947 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 189,911 | | | 216,894 | | | 201,806 | |
| Interest expense | 101,484 | | | 101,206 | | | 94,394 | |
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | — | | | — | | | 214 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 2,715 | | | 1,546 | | | (1,734) | |
| Impairment charges | — | | | — | | | 7,723 | |
| | | | | |
| Less: | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Gain on sale/disposition of properties | (26,764) | | | (33,988) | | | — | |
| Interest income | (15,136) | | | (4,948) | | | (704) | |
| Third-party management and other fees | (1,351) | | | (1,361) | | | (1,219) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Net operating income | $ | 399,205 | | | $ | 404,326 | | | $ | 343,390 | |
| | | | | |
| Other Net Operating Income Data | | | | | |
| Straight line rental revenue | $ | 19,563 | | | $ | 24,562 | | | $ | 21,078 | |
| Net increase in rental revenue from the amortization of above and below-market lease assets and liabilities | $ | 2,416 | | | $ | 4,758 | | | $ | 5,895 | |
| Amortization of acquired below-market ground leases | $ | 7,831 | | | $ | 7,831 | | | $ | 7,831 | |
Funds from Operations ("FFO")
We present below a discussion of FFO. We compute FFO in accordance with the “White Paper” on FFO published by the National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts, or NAREIT, which defines FFO as net income (loss) (determined in accordance with GAAP), excluding impairment write-off of investments in depreciable real estate and investments in in-substance real estate investments, gains or losses from debt restructurings and sales of depreciable operating properties, plus real estate-related depreciation and amortization (excluding amortization of deferred financing costs), less distributions to non-controlling interests and gains/losses from discontinued operations and after adjustments for unconsolidated partnerships and joint ventures. FFO is a widely recognized non-GAAP financial measure for REITs that we believe, when considered with financial statements determined in accordance with GAAP, is useful to investors in understanding financial performance and providing a relevant basis for comparison among REITs. In addition, we believe FFO is useful to investors as it captures features particular to real estate performance by recognizing that real estate has generally appreciated over time or maintains
residual value to a much greater extent than do other depreciable assets. Investors should review FFO, along with GAAP net income, when trying to understand an equity REIT’s operating performance. We present FFO because we consider it an important supplemental measure of our operating performance and believe that it is frequently used by securities analysts, investors and other interested parties in the evaluation of REITs. However, because FFO excludes depreciation and amortization and captures neither the changes in the value of our properties that result from use or market conditions nor the level of capital expenditures and leasing commissions necessary to maintain the operating performance of our properties, all of which have real economic effect and could materially impact our results of operations, the utility of FFO as a measure of performance is limited. There can be no assurance that FFO presented by us is comparable to similarly titled measures of other REITs. FFO does not represent cash generated from operating activities and should not be considered as an alternative to net income (loss) determined in accordance with GAAP or to cash flow from operating activities determined in accordance with GAAP. FFO is not indicative of cash available to fund ongoing cash needs, including the ability to make cash distributions. Although FFO is a measure used for comparability in assessing the performance of REITs, as the NAREIT White Paper only provides guidelines for computing FFO, the computation of FFO may vary from one company to another.
Modified Funds From Operations ("Modified FFO")
Modified FFO adds back an adjustment for any above or below-market ground lease amortization to traditionally defined FFO. We believe this is a useful supplemental measure in evaluating our operating performance due to the non-cash accounting treatment under GAAP, which stems from the third quarter 2014 acquisition of two option properties following our formation transactions as they carry significantly below market ground leases, the amortization of which is material to our overall results. We present Modified FFO because we believe it is an important supplemental measure of our operating performance in that it adds back the non-cash amortization of below-market ground leases. There can be no assurance that Modified FFO presented by us is comparable to similarly titled measures of other REITs. Modified FFO does not represent cash generated from operating activities and should not be considered as an alternative to net income (loss) determined in accordance with GAAP or to cash flow from operating activities determined in accordance with GAAP. Modified FFO is not indicative of cash available to fund ongoing cash needs, including the ability to make cash distributions.
Core Funds From Operations ("Core FFO")
Core FFO adds back to Modified FFO the following item: loss on early extinguishment of debt. The Company believes Core FFO is an important supplemental measure of its operating performance because it excludes non-recurring items. There can be no assurance that Core FFO presented by the Company is comparable to similarly titled measures of other REITs. Core FFO does not represent cash generated from operating activities and should not be considered as an alternative to net income (loss) determined in accordance with GAAP or to cash flow from operating activities determined in accordance with GAAP. Core FFO is not indicative of cash available to fund ongoing cash needs, including the ability to make cash distributions. In future periods, we may also exclude other items from Core FFO that we believe may help investors compare our results.
The following table presents a reconciliation of our net income (loss), the most directly comparable GAAP measure, to FFO, Modified FFO and Core FFO for the periods presented (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 84,407 | | | $ | 63,212 | | | $ | (13,037) | |
| Non-controlling interests in other partnerships | (68) | | | 243 | | | — | |
| Private perpetual preferred unit distributions | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | |
| Real estate depreciation and amortization | 184,633 | | | 210,522 | | | 196,360 | |
| Impairment charges | — | | | — | | | 7,723 | |
| Gain on sale/disposition of properties | (26,764) | | | (33,988) | | | — | |
| Funds from operations attributable to common stockholders and non-controlled interests | 238,007 | | | 235,788 | | | 186,845 | |
| Amortization of below-market ground leases | 7,831 | | | 7,831 | | | 7,831 | |
| Modified funds from operations attributable to common stockholders and non-controlled interests | 245,838 | | | 243,619 | | | 194,676 | |
| | | | | |
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | — | | | — | | | 214 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Core funds from operations attributable to common stockholders and non-controlled interests | $ | 245,838 | | | $ | 243,619 | | | $ | 194,890 | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average shares and Operating Partnership units |
| Basic | 263,226 | | | 268,337 | | | 277,420 | |
| Diluted | 265,633 | | | 269,948 | | | 277,420 | |
Critical Accounting Estimates
Basis of Presentation and Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements, have been prepared in conformity with GAAP and with the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC"), represent our assets and liabilities and operating results. The consolidated financial statements include our accounts and our partially owned and wholly owned subsidiaries as well as our Operating Partnership and its subsidiaries. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
We consolidate entities in which we have a controlling financial interest. In determining whether we have a controlling financial interest in a partially owned entity and the requirement to consolidate the accounts of that entity, we consider factors such as ownership interest, board representation, management representation, authority to make decisions, and contractual and substantive participating rights of the partners/members. For variable interest entities ("VIE"), we consolidate the entity if we are deemed to have a variable interest in the entity and through that interest we are deemed the primary beneficiary. The primary beneficiary of a VIE is the entity that has (i) the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the entity's economic performance and (ii) the obligation to absorb losses of the VIE or the right to receive benefits from the VIE that could be significant to the VIE. The primary beneficiary is required to consolidate the VIE. The Operating Partnership is a VIE of ESRT. As the Operating Partnership is already consolidated in the financial statements of ESRT, the identification of this entity as a VIE has no impact on our consolidated financial statements. At December 31, 2022, the Operating Partnership was the primary beneficiary of a variable interest in the intermediary entity which held title to 298 Mulberry Street, the multifamily asset acquired in December 2022. The intermediary entity was utilized to execute a like-kind exchange and subsequent to March 31, 2023, the like-kind exchange was completed and the Operating Partnership took title to 298 Mulberry Street. Therefore, the Operating Partnership had no VIEs at December 31, 2023.
We will assess the accounting treatment for each investment we may have in the future. This assessment will include a review of each entity’s organizational agreement to determine which party has what rights and whether those rights are protective or participating. For all VIEs, we will review such agreements in order to determine which party has the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance and benefit. In situations where we or our partner could approve, among other things, the annual budget, or leases that cover more than a nominal amount of space relative to the total rentable space at each property, we would not consolidate the investment as we consider these to be substantive participation rights that result in shared power of the activities that would most significantly impact the performance and benefit of such joint venture investment.
A non-controlling interest in a consolidated subsidiary is defined as the portion of the equity (net assets) in a subsidiary not attributable, directly or indirectly, to a parent. Non-controlling interests are required to be presented as a separate component of equity in the
consolidated balance sheets and in the consolidated statements of income by requiring earnings and other comprehensive income to be attributed to controlling and non-controlling interests.
Goodwill
Goodwill is tested annually for impairment and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. An impairment loss is recognized to the extent that the carrying amount, including goodwill, exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value and the implied fair value of goodwill is less than the carrying amount of that goodwill. Non-amortizing intangible assets, such as trade names and trademarks, are subject to an annual impairment test based on fair value and amortizing intangible assets are tested whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable.
We performed our annual goodwill testing in October 2023, where we bypassed the optional qualitative goodwill impairment assessment and proceeded directly to a quantitative assessment of the Observatory reportable segment and engaged a third-party valuation consulting firm to perform the valuation process. The quantitative analysis used a combination of the discounted cash flow method (a form of the income approach) utilizing Level 3 unobservable inputs and the guideline company method (a form of the market approach). Significant assumptions under the former included revenue and cost projections, weighted average cost of capital, long-term growth rate and income tax considerations while the latter included guideline company enterprise values, revenue multiples, EBITDA multiples and control premium rates. Our methodology to review goodwill impairment, which included a significant amount of judgment and estimates, provided a reasonable basis to determine whether impairment had occurred. The quantitative analysis performed concluded the fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value. Many of the factors employed in determining whether or not goodwill is impaired are outside of our control, and it is reasonably likely that assumptions and estimates will change in future periods. We will continue to assess the impairment of the Observatory reporting unit goodwill going forward.
Income Taxes
We elected to be subject to tax as a REIT under sections 856 through 860 of the Code commencing with the taxable year ended December 31, 2013 and believe that our intended manner of operation will enable us to continue to meet the requirements for qualification and taxation as a REIT. REITs are subject to a number of organizational and operational requirements, including a requirement that 90% of ordinary “REIT taxable income” (as determined without regard to the dividends paid deduction or net capital gains) be distributed. As a REIT, we will generally not be subject to U.S. federal income tax to the extent that we meet the organizational and operational requirements and our distributions equal or exceed REIT taxable income. For all periods subsequent to the effective date of our REIT election, we have met the organizational and operational requirements and distributions have exceeded net taxable income. Accordingly, no provision has been made for federal income taxes.
We have elected to treat ESRT Observatory TRS, L.L.C., our subsidiary that holds our Observatory operations, and ESRT Holdings TRS, L.L.C., our subsidiary that holds our third-party management, restaurant, cafeterias, health clubs and certain cleaning operations, as taxable REIT subsidiaries. Taxable REIT subsidiaries may participate in non-real estate activities and/or perform non-customary services for tenants and their operations are generally subject to regular corporate income taxes. Our taxable REIT subsidiaries account for their income taxes in accordance with GAAP, which includes an estimate of the amount of taxes payable or refundable for the current year and deferred tax liabilities and assets for the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in our consolidated financial statements or tax returns. The calculation of the taxable REIT subsidiaries' tax provisions may require interpreting tax laws and regulations and could result in the use of judgments or estimates which could cause its recorded tax liability to differ from the actual amount due. Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. The taxable REIT subsidiaries periodically assess the realizability of deferred tax assets and the adequacy of deferred tax liabilities, including the results of local, state, or federal tax audits or estimates and judgments used.
As of December 31, 2023, ESRT had $103.0 million of net operating loss ("NOL") carryforwards that may be used in the future to reduce the amount otherwise required to be distributed by ESRT to meet REIT requirements. However, for federal income tax purposes, the NOL will not be able to offset more than 80% of ESRT’s REIT taxable income and, therefore, may not be able to reduce the amount required to be distributed by ESRT to meet REIT requirements to zero. The federal NOL may be carried forward indefinitely. Other limitations may apply to ESRT’s ability to use its NOL to offset taxable income.
As of December 31, 2023, the Observatory TRS had a federal income tax receivable of $2.5 million. This receivable reflects an anticipated refund resulting from the carryback of 2020 NOL to previous tax years. The Observatory TRS has $1.5 million of federal NOL carryforward that may be used to offset future taxable income, if any. The federal NOL may be carried forward indefinitely.
We apply provisions for measuring and recognizing tax benefits associated with uncertain income tax positions. Penalties and interest, if incurred, would be recorded as a component of income tax expense. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, we do not have a liability for uncertain tax positions. As of December 31, 2023, the tax years ended December 31, 2020 through December 31, 2023 remain open for an audit by the Internal Revenue Service, state or local authorities.
Share-Based Compensation
Share-based compensation for time-based equity awards is measured at the fair value of the award on the date of grant and recognized as an expense on a straight-line basis over the shorter of (i) the stated vesting period, which is generally three, four or five years, or (ii) the period from the date of grant to the date the employee becomes retirement eligible, which may occur upon grant. An employee is retirement eligible when the employee attains the (i) age of 65 for awards granted in 2020 and after and age of 60 for awards granted before 2020 and (ii) the date on which the employee has first completed the requisite years of continuous service with us or our affiliates. Share-based compensation for market-based equity awards and performance-based equity awards is measured at the fair value of the award on the date of grant and recognized as an expense on a straight-line basis over three or four years. Additionally, for the performance-based equity awards, we assess, at each reporting period, whether it is probable that the performance conditions will be satisfied. We recognize expense respective to the number of awards we expect to vest at the conclusion of the measurement period. Changes in estimate are accounted for in the period of change through a cumulative catch-up adjustment. Any forfeitures of share-based compensation awards are recognized as they occur.
The determination of fair value of these awards is subjective and involves significant estimates and assumptions including expected volatility of our stock, expected dividend yield, expected term, and assumptions of whether these awards will achieve parity with other Operating Partnership units or achieve performance thresholds. We believe that the assumptions and estimates utilized are appropriate based on the information available to management at the time of grant.
Accounting Standards Update
See "Financial Statements - Note 2 Summary of Significant Accounting Policies" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for information about recently issued and recently adopted accounting standards.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Our future income, cash flows and fair values relevant to financial instruments are dependent upon prevalent market interest rates. Market risk refers to the risk of loss from adverse changes in market prices and interest rates. We are exposed to interest rate changes primarily on our unsecured revolving credit facility and debt refinancings. Our objectives with respect to interest rate risk are to limit the impact of interest rate changes on operations and cash flows, and to lower our overall borrowing costs. To achieve these objectives, we may borrow at fixed rates and may enter into derivative financial instruments such as interest rate swaps or caps in order to mitigate our interest rate risk. We do not enter into derivative or interest rate transactions for speculative purposes.
Subject to maintaining our qualification as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we may mitigate the risk of interest rate volatility through the use of hedging instruments, such as interest rate swap agreements and interest rate cap agreements. Our primary objectives when undertaking hedging transactions and derivative positions will be to reduce our floating rate exposure and to fix a portion of the interest rate for anticipated financing and refinancing transactions. This in turn will reduce the risk that the variability of cash flows will impose on floating rate debt. However, we can provide no assurances that our efforts to manage interest rate volatility will successfully mitigate the risks of such volatility on our commercial portfolio. We are not subject to foreign currency risk.
As of December 31, 2023, we have interest rate SOFR swap and cap agreements with an aggregate notional value of $573.2 million and which mature between October 1, 2024 and November 1, 2033. These "variable to fixed" interest rate swaps have been designated as cash flow hedges and are deemed highly effective with fair values of $11.8 million that is included in prepaid expenses and other assets and ($0.1 million) that is included in accounts payable and accrued expenses on the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2023.
As of December 31, 2023, the weighted average interest rate on the $2.2 billion of fixed-rate indebtedness outstanding was 3.9% per annum, each with maturities at various dates through March 17, 2035.
As of December 31, 2023, the fair value of our outstanding debt was approximately $2.0 billion which was approximately $194.0 million less than the book value as of such date. Interest risk amounts were determined by considering the impact of hypothetical interest rates on our financial instruments. These analyses do not consider the effect of any change in overall economic activity that could occur in that environment. Further, in the event of a change of that magnitude, we may take actions to further mitigate our exposure to the change. However, due to the uncertainty of the specific actions that would be taken and their possible effects, these analyses assume no changes in our financial structure.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The financial statements beginning on Page F-1 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports under the Exchange Act is processed, recorded, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and regulations and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including our Chief Executive Officer, our President, and our Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer & Chief Accounting Officer, as appropriate, to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, and management is required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
As of December 31, 2023, the end of the period covered by this report, we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of management, including our Chief Executive Officer, our President, and our Chief
Financial Officer & Chief Accounting Officer, regarding the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures at the end of the period covered by this report. Based on the foregoing, our Chief Executive Officer, our President, and our Chief Financial Officer & Chief Accounting Officer concluded, as of that time, that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective in ensuring that information required to be disclosed by us in reports filed or submitted under the Exchange Act (i) is processed, recorded, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms and (ii) is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer, our President, and our Chief Financial Officer & Chief Accounting Officer, as appropriate to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
No significant changes to our internal control over financial reporting were identified in connection with the evaluation referenced above that occurred during the period covered by this report that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
(a) Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 Rule 13(a)-15(f). Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer, President and Chief Financial Officer & Chief Accounting Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023 as required by the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 Rule 13(a)-15(c). In making this assessment, we used the criteria set forth in the framework in Internal Control–Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (the "COSO criteria"). Based on our evaluation under the COSO criteria, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2023 to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm that audited our Financial Statements included in this Annual Report, has issued an attestation report on our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, which appears in paragraph (b) of this ITEM 9A.
(b) Attestation report of the independent registered public accounting firm
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the 2023 consolidated financial statements of the Company and our report dated February 28, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
New York, New York
February 28, 2024
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
(a) None.
(b) During the three months ended December 31, 2023, none of our directors or officers (as defined in Rule 16a-1(f) of the Exchange Act) adopted, terminated or modified a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement or non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement (as such terms are defined in Item 408 of Regulation S-K).
ITEM 9C. DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS
Not applicable.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The information required by ITEM 10 will be set forth in our definitive proxy statement for our 2023 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (which is scheduled to be held on May 9, 2024), to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or our Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required by ITEM 11 will be set forth in our Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information required by ITEM 12 will be set forth in our Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
The information under ITEM 5 of this Form 10-K under the heading “Securities Authorized For Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans” is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The information required by ITEM 13 will be set forth in our Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
The information required by ITEM 14 will be set forth in our Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SCHEDULES
(a) The following documents are filed as part of this report:
1.The consolidated financial statements are set forth in ITEM 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
2.The following financial statement schedules should be read in conjunction with the financial statements included in ITEM 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Schedule III-Real Estate and Accumulated Depreciation as of December 31, 2023 on page F-42.
Schedules other than those listed are omitted as they are not applicable or the required or equivalent information has been included in the financial statements or notes thereto.
(b) The exhibits required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K (§229.601 of this chapter) are listed below:
Exhibit Index
| | | | | |
| Representation, Warranty and Indemnity Agreement among Empire Realty Trust, Inc., Empire Realty Trust, L.P., Anthony E. Malkin, Cynthia M. Blumenthal and Scott D. Malkin, dated November 28, 2011, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to the Registrant's Form S-11 (Registration No. 333-179485), filed with the SEC on February 13, 2012. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| | | | | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Empire State Realty OP, L.P.,Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. $100,000,000 3.61% Series G Senior Notes due March 17, 2032, $75,000,000 3.73% Series H Senior Notes due March 17, 2035 Note Purchase Agreement dated March 17, 2020 incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed with the SEC on March 23, 2020. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Second Amendment, dated as of August 29, 2022, to that certain Credit Agreement, dated as of March 19, 2020, among Empire State Realty Trust, Inc., Empire State Realty OP, L.P., the subsidiary guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.62 to the Empire State Realty Trust Form 10-Q filed with the SEC on November 3, 2022. |
| Third Amendment, dated as of August 29, 2022, to that certain Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated August 29, 2017, among Empire State Realty Trust, Inc., Empire State Realty OP, L.P. , the subsidiary guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, and Bank of America, N.A. , as administrative agent incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.62 to the Empire State Realty Trust Form 10-Q filed with the SEC on November 3, 2022. |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| | | | | |
| |
| |
| |
| 101.INS* | XBRL Instance Document - the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document. |
| 101.SCH* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
| 101.CAL* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Document |
| 101.DEF* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definitions Document |
| 101.LAB* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels Document |
| 101.PRE* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Document |
| 104* | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as inline XBRL with applicable taxonomy extension information contained in Exhibits 101.) |
| Notes: | |
| * Filed herewith. |
| + Indicates management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement required to be filed or incorporated by reference as an exhibit to this Form 10-K pursuant to Item 15(b) of Form 10-K. |
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
EMPIRE STATE REALTY TRUST, INC.
Date: February 28, 2024 By:/s/ Stephen V. Horn
Stephen V. Horn
Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer & Chief Accounting Officer
(Principal Financial and Accounting Officer)
Pursuant to the requirements of the Exchange Act, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | | | |
| /s/ Anthony E. Malkin | | Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer | | February 28, 2024 |
| Anthony E. Malkin | | | |
| | (Principal Executive Officer) | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Christina Chiu | | President | | February 28, 2024 |
| Christina Chiu | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Stephen V. Horn | | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer & Chief Accounting Officer | | February 28, 2024 |
| Stephen V. Horn | | | |
| | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Thomas J. DeRosa | | Director | | February 28, 2024 |
| Thomas J. DeRosa | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Steven J. Gilbert | | Lead Independent Director | | February 28, 2024 |
| Steven J. Gilbert | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ S. Michael Giliberto | | Director | | February 28, 2024 |
| S. Michael Giliberto | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Patricia S. Han | | Director | | February 28, 2024 |
| Patricia S. Han | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Grant H. Hill | | Director | | February 28, 2024 |
| Grant H. Hill | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ R. Paige Hood | | Director | | February 28, 2024 |
| R. Paige Hood | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ James D. Robinson IV | | Director | | February 28, 2024 |
| James D. Robinson IV | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Christina Van Tassell | | Director | | February 28, 2024 |
| Christina Van Tassell | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Hannah Yang | | Director | | February 28, 2024 |
| Hannah Yang | | | | |
EMPIRE STATE REALTY TRUST
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | PAGE |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PCAOB ID: 42) | | |
| | | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | | |
| | | |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | | |
| | | |
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | | |
| | | |
| Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | | |
| | | |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | | |
| | | |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | | |
| | | |
| Financial Statement Schedule: | | |
| | | |
| Schedule III - Real Estate and Accumulated Depreciation | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes and financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15(a) (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 28, 2024, expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
| | | | | | | | |
| | Valuation of goodwill – observatory |
| Description of the Matter | | At December 31, 2023, the Company’s goodwill related to the observatory reporting unit was $227.5 million as disclosed in Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements. As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, goodwill is tested for impairment at least annually or more frequently if there are indicators of impairment. |
| | |
| | The Company performed its annual impairment testing as of October 1, 2023 and engaged a third-party valuation specialist to perform valuation procedures. |
| | |
| | Auditing management’s goodwill impairment test was complex due to the highly judgmental nature of the assumptions used. The fair value estimates were sensitive to significant assumptions such as revenue and cost projections and the weighted average cost of capital, which are affected by expectations about future market and economic conditions. |
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design, and tested the operating effectiveness of controls over the Company’s goodwill impairment process, including controls over management’s review of the significant assumptions described above. |
| |
| | To test the implied fair value of the Company’s observatory reporting unit, we performed audit procedures that included, among other procedures, assessing the methodologies and testing the significant assumptions and underlying data used by the Company. We utilized internal valuation specialists in assessing the fair value methodologies applied and evaluating the reasonableness of certain assumptions selected by management. We compared the significant assumptions used by management to current industry and economic trends, recent historical performance, and other relevant factors, and performed sensitivity analyses of significant assumptions to evaluate the changes in the fair value of the observatory reporting unit that would result from changes in the assumptions. |
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2010.
New York, New York
February 28, 2024
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(amounts in thousands, except share and per share amounts) | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ASSETS | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Commercial real estate properties, at cost: | | | |
| Land | $ | 366,357 | | | $ | 365,540 | |
| Development costs | 8,178 | | | 8,166 | |
| Building and improvements | 3,280,657 | | | 3,177,743 | |
| 3,655,192 | | | 3,551,449 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (1,250,062) | | | (1,137,267) | |
| Commercial real estate properties, net | 2,405,130 | | | 2,414,182 | |
| Assets held for sale | — | | | 35,538 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 346,620 | | | 264,434 | |
| Restricted cash | 60,336 | | | 50,244 | |
| | | |
| Tenant and other receivables | 39,836 | | | 24,102 | |
| Deferred rent receivables | 255,628 | | | 240,188 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 98,167 | | | 98,114 | |
| Deferred costs, net | 172,457 | | | 187,570 | |
| Acquired below-market ground leases, net | 321,241 | | | 329,073 | |
| Right of use assets | 28,439 | | | 28,670 | |
| Goodwill | 491,479 | | | 491,479 | |
| Total assets | $ | 4,219,333 | | | $ | 4,163,594 | |
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | |
| Liabilities: | | | |
| Mortgage notes payable, net | $ | 877,388 | | | $ | 883,705 | |
| Senior unsecured notes, net | 973,872 | | | 973,659 | |
| Unsecured term loan facilities, net | 389,286 | | | 388,773 | |
| Unsecured revolving credit facility | — | | | — | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 99,756 | | | 80,729 | |
| Acquired below-market leases, net | 13,750 | | | 17,849 | |
| Ground lease liabilities | 28,439 | | | 28,670 | |
| Deferred revenue and other liabilities | 70,298 | | | 76,091 | |
| Tenants’ security deposits | 35,499 | | | 25,084 | |
| Liabilities related to assets held for sale | — | | | 5,943 | |
| Total liabilities | 2,488,288 | | | 2,480,503 | |
| Commitments and contingencies | | | |
| Equity: | | | |
| Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. stockholders' equity: | | | |
| Preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share, 50,000 shares authorized, none issued or outstanding | — | | | — | |
| Class A common stock, $0.01 par value per share, 400,000 shares authorized, 162,062 and 160,139 shares issued and outstanding in 2023 and 2022, respectively | 1,621 | | | 1,601 | |
| Class B common stock, $0.01 par value per share, 50,000 shares authorized, 984 and 990 shares issued and outstanding in 2023 and 2022, respectively | 10 | | | 10 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 1,060,969 | | | 1,055,184 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | 6,026 | | | 7,048 | |
| Retained deficit | (83,108) | | | (109,468) | |
| Total Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.'s stockholders' equity | 985,518 | | | 954,375 | |
| Non-controlling interests in Operating Partnership | 700,180 | | | 683,310 | |
| Non-controlling interests in other partnerships | 15,407 | | | 15,466 | |
| Private perpetual preferred units: | | | |
| Series 2019 preferred units, $13.52 per unit liquidation preference, 4,664 issued and outstanding in 2023 and 2022 | 21,936 | | | 21,936 | |
| Series 2014 preferred units, $16.62 per unit liquidation preference, 1,560 issued and outstanding in 2023 and 2022 | 8,004 | | | 8,004 | |
| Total equity | 1,731,045 | | | 1,683,091 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 4,219,333 | | | $ | 4,163,594 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(amounts in thousands, except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Rental revenue | $ | 597,319 | | | $ | 591,048 | | | $ | 559,690 | |
| | | | | |
| Observatory revenue | 129,366 | | | 105,978 | | | 41,474 | |
| | | | | |
| Lease termination fees | — | | | 20,032 | | | 16,230 | |
| Third-party management and other fees | 1,351 | | | 1,361 | | | 1,219 | |
| Other revenue and fees | 11,536 | | | 8,622 | | | 5,481 | |
| Total revenues | 739,572 | | | 727,041 | | | 624,094 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
| Property operating expenses | 167,324 | | | 157,935 | | | 126,986 | |
| Ground rent expenses | 9,326 | | | 9,326 | | | 9,326 | |
| General and administrative expenses | 63,939 | | | 61,765 | | | 55,947 | |
| Observatory expenses | 35,265 | | | 31,036 | | | 23,206 | |
| | | | | |
| Real estate taxes | 127,101 | | | 123,057 | | | 119,967 | |
| | | | | |
| Impairment charges | — | | | — | | | 7,723 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 189,911 | | | 216,894 | | | 201,806 | |
| Total operating expenses | 592,866 | | | 600,013 | | | 544,961 | |
| Total operating income | 146,706 | | | 127,028 | | | 79,133 | |
| Other income (expense): | | | | | |
| Interest income | 15,136 | | | 4,948 | | | 704 | |
| Interest expense | (101,484) | | | (101,206) | | | (94,394) | |
| Gain on sale/disposition of properties | 26,764 | | | 33,988 | | | — | |
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | — | | | — | | | (214) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 87,122 | | | 64,758 | | | (14,771) | |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | (2,715) | | | (1,546) | | | 1,734 | |
| Net income (loss) | 84,407 | | | 63,212 | | | (13,037) | |
| Private perpetual preferred unit distributions | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests: | | | | | |
| Non-controlling interests in the Operating Partnership | (31,094) | | | (22,812) | | | 6,527 | |
| Non-controlling interests in other partnerships | (68) | | | 243 | | | — | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders | $ | 49,044 | | | $ | 36,442 | | | $ | (10,711) | |
| | | | | |
| Total weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 161,122 | | | 165,039 | | | 172,445 | |
| Diluted | 265,633 | | | 269,948 | | | 277,420 | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to common stockholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 0.30 | | | $ | 0.22 | | | $ | (0.06) | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.30 | | | $ | 0.22 | | | $ | (0.06) | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(amounts in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 84,407 | | | $ | 63,212 | | | $ | (13,037) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | |
| Unrealized gain on valuation of interest rate swap agreements | 5,581 | | | 40,044 | | | 348 | |
| Amount reclassified into interest expense | (7,819) | | | 7,230 | | | 11,653 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | (2,238) | | | 47,274 | | | 12,001 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | 82,169 | | | 110,486 | | | (1,036) | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests and private perpetual preferred unitholders | (35,363) | | | (26,770) | | | 2,326 | |
| Other comprehensive (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests | 1,060 | | | (19,573) | | | (4,536) | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to common stockholders | $ | 47,866 | | | $ | 64,143 | | | $ | (3,246) | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity
(amounts in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of Class A Common Shares | | Class A Common Stock | | Number of Class B Common Shares | | Class B Common Stock | | Additional Paid-In Capital | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | | Retained Deficit | | Total Stockholders' Equity | | Non-controlling Interests | | | | Private Perpetual Preferred Units | | Total Equity |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2020 | 170,555 | | | $ | 1,705 | | | 1,010 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 1,147,527 | | | $ | (28,320) | | | $ | (65,673) | | | $ | 1,055,249 | | | $ | 646,118 | | | | | $ | 29,940 | | | $ | 1,731,307 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Conversion of operating partnership units and Class B shares to Class A shares | 3,512 | | | 35 | | | (14) | | | — | | | 10,384 | | | 7 | | | — | | | 10,426 | | | (10,426) | | | | | — | | | — | |
| Repurchases of common shares | (4,887) | | | (49) | | | — | | | — | | | (7,539) | | | — | | | (39,116) | | | (46,704) | | | — | | | | | — | | | (46,704) | |
| Contributions to consolidated joint venture interests | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 13,269 | | | | | — | | | 13,269 | |
| Equity compensation: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LTIP Units, net of forfeitures | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 19,747 | | | | | — | | | 19,747 | |
| Restricted stock, net of forfeitures | 41 | | | 1 | | | — | | | — | | | 512 | | | — | | | — | | | 513 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 513 | |
| Dividends and distributions | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (18,110) | | | (18,110) | | | (10,453) | | | | | (4,201) | | | (32,764) | |
| Net income (loss) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (10,711) | | | (10,711) | | | (6,527) | | | | | 4,201 | | | (13,037) | |
| Other comprehensive income | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 7,465 | | | — | | | 7,465 | | | 4,536 | | | | | . | | 12,001 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | 169,221 | | | $ | 1,692 | | | 996 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 1,150,884 | | | $ | (20,848) | | | $ | (133,610) | | | $ | 998,128 | | | $ | 656,264 | | | | | $ | 29,940 | | | $ | 1,684,332 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Conversion of operating partnership units and Class B shares to Class A shares | 2,304 | | | 23 | | | (6) | | | — | | | 4,277 | | | 195 | | | — | | | 4,495 | | | (4,495) | | | | | — | | | — | |
| Repurchases of common shares | (11,571) | | | (116) | | | — | | | — | | | (100,869) | | | — | | | 10,809 | | | (90,176) | | | — | | | | | — | | | (90,176) | |
| Contributions to consolidated joint venture interests | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 224 | | | | | — | | | 224 | |
| Equity compensation: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LTIP Units, net of forfeitures | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 20,117 | | | | | — | | | 20,117 | |
| Restricted stock, net of forfeitures | 185 | | | 2 | | | — | | | — | | | 892 | | | — | | | — | | | 894 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 894 | |
| Dividends and distributions | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (23,109) | | | (23,109) | | | (15,476) | | | | | (4,201) | | | (42,786) | |
| Net income | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 36,442 | | | 36,442 | | | 22,569 | | | | | 4,201 | | | 63,212 | |
| Other comprehensive income | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 27,701 | | | — | | | 27,701 | | | 19,573 | | | | | — | | | 47,274 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | 160,139 | | | $ | 1,601 | | | 990 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 1,055,184 | | | $ | 7,048 | | | $ | (109,468) | | | $ | 954,375 | | | $ | 698,776 | | | | | $ | 29,940 | | | $ | 1,683,091 | |
| Conversion of operating partnership units and Class B shares to Class A shares | 3,762 | | | 38 | | | (6) | | | — | | | 17,477 | | | 156 | | | — | | | 17,671 | | | (17,671) | | | | | — | | | — | |
| Repurchases of common shares | (2,151) | | | (21) | | | — | | | — | | | (13,084) | | | — | | | — | | | (13,105) | | | — | | | | | — | | | (13,105) | |
| Contributions to consolidated joint venture interests | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 187 | | | | | — | | | 187 | |
| Equity compensation: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LTIP Units, net of forfeitures | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 18,631 | | | | | — | | | 18,631 | |
| Restricted stock, net of forfeitures | 312 | | | 3 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,392 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,395 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 1,395 | |
| Dividends and distributions | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (22,684) | | | (22,684) | | | (14,438) | | | | | (4,201) | | | (41,323) | |
| Net income | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 49,044 | | | 49,044 | | | 31,162 | | | | | 4,201 | | | 84,407 | |
| Other comprehensive loss | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (1,178) | | | — | | | (1,178) | | | (1,060) | | | | | — | | | (2,238) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | 162,062 | | | $ | 1,621 | | | 984 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 1,060,969 | | | $ | 6,026 | | | $ | (83,108) | | | $ | 985,518 | | | $ | 715,587 | | | | | $ | 29,940 | | | $ | 1,731,045 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(amounts in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 84,407 | | | $ | 63,212 | | | $ | (13,037) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 189,911 | | | 216,894 | | | 201,806 | |
| Gain on sale/disposition of properties | (26,764) | | | (33,988) | | | — | |
| Impairment charges | — | | | — | | | 7,723 | |
| Amortization of non-cash items within interest expense | 9,089 | | | 9,799 | | | 10,862 | |
| Amortization of acquired above- and below-market leases, net | (2,415) | | | (4,759) | | | (5,896) | |
| Amortization of acquired below-market ground leases | 7,831 | | | 7,831 | | | 7,831 | |
| Straight-lining of rental revenue | (19,563) | | | (24,562) | | | (21,078) | |
| Equity based compensation | 20,026 | | | 21,011 | | | 20,260 | |
| | | | | |
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | — | | | — | | | 214 | |
| | | | | |
| Increase (decrease) in cash flows due to changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | |
| Security deposits | 10,486 | | | (828) | | | (1,052) | |
| Tenant and other receivables | (15,643) | | | (5,306) | | | 2,894 | |
| Deferred leasing costs | (17,669) | | | (36,909) | | | (16,090) | |
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | (5,186) | | | (2,263) | | | 5,814 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 746 | | | 4,705 | | | (99) | |
| Deferred revenue and other liabilities | (2,765) | | | (3,664) | | | 12,334 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 232,491 | | | 211,173 | | | 212,486 | |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities | | | | | |
| Acquisition of real estate property | (26,910) | | | (115,593) | | | (117,540) | |
| Net proceeds from disposition of real estate | 88,910 | | | 11,005 | | | — | |
| Additions to building and improvements | (139,328) | | | (126,268) | | | (95,037) | |
| Development costs | (12) | | | (35) | | | (165) | |
| | | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (77,340) | | | (230,891) | | | (212,742) | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (continued)
(amounts in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Repayment of mortgage notes payable | (8,632) | | | (7,504) | | | (4,091) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Contributions from consolidated joint ventures | 187 | | | 224 | | | — | |
| Deferred financing costs | — | | | — | | | (9,486) | |
| | | | | |
| Repurchases of common shares | (13,105) | | | (90,176) | | | (46,704) | |
| Private perpetual preferred unit distributions | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | |
| Dividends paid to common stockholders | (22,684) | | | (23,109) | | | (18,110) | |
| Distributions paid to non-controlling interests in the operating partnership | (14,438) | | | (15,476) | | | (10,453) | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (62,873) | | | (140,242) | | | (93,045) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash | 92,278 | | | (159,960) | | | (93,301) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash—beginning of period | 314,678 | | | 474,638 | | | 567,939 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash—end of period | $ | 406,956 | | | $ | 314,678 | | | $ | 474,638 | |
| | | | | |
| Reconciliation of Cash and Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash: | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | $ | 264,434 | | | $ | 423,695 | | | $ | 526,714 | |
| Restricted cash at beginning of period | 50,244 | | | 50,943 | | | 41,225 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash at beginning of period | $ | 314,678 | | | $ | 474,638 | | | $ | 567,939 | |
| | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 346,620 | | | $ | 264,434 | | | $ | 423,695 | |
| Restricted cash at end of period | 60,336 | | | 50,244 | | | 50,943 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash at end of period | $ | 406,956 | | | $ | 314,678 | | | $ | 474,638 | |
| | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | | | | | |
| Cash paid for interest | $ | 92,000 | | | $ | 91,012 | | | $ | 77,610 | |
| | | | | |
| Cash paid for income taxes | $ | 1,390 | | | $ | 200 | | | $ | 644 | |
| | | | | |
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | | | | | |
| Building and improvements included in accounts payable and accrued expenses | $ | 51,815 | | | $ | 44,293 | | | $ | 49,247 | |
| Write-off of fully depreciated assets | 33,391 | | | 35,124 | | | 31,341 | |
| Derivative instruments at fair values included in prepaid expenses and other assets | 11,800 | | | 17,902 | | | — | |
| Derivative instruments at fair values included in accounts payable and accrued expenses | 85 | | | — | | | 25,308 | |
| Conversion of operating partnership units and Class B shares to Class A shares | 17,671 | | | 4,495 | | | 10,426 | |
| Transfer of assets related to assets held for sale | — | | | 35,538 | | | — | |
| Transfer of liabilities related to assets held for sale | — | | | 5,943 | | | — | |
| Mortgage assumed in connection with sale of real estate | — | | | 30,117 | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Debt assumed with the acquisition of real estate properties | — | | | — | | | 177,453 | |
| Contribution from other partnerships | — | | | — | | | 13,269 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1. Description of Business and Organization
As used in these consolidated financial statements, unless the context otherwise requires, “we,” “us,” "our," the "Company,” and "ESRT" mean Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries.
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. (NYSE: ESRT) is a NYC-focused REIT that owns and operates a portfolio of modernized, amenitized, and well-located office, retail, and multifamily assets. The Company is a recognized leader in energy efficiency and indoor environmental quality. ESRT’s flagship Empire State Building – the “World’s Most Famous Building” – includes its Observatory, the #1 attraction in the U.S. in Tripadvisor’s Travelers’ Choice Awards: Best of the Best for two consecutive years.
As of December 31, 2023, our portfolio was comprised of approximately 8.6 million rentable square feet of office space, 0.7 million rentable square feet of retail space and 727 residential units. Our office portfolio included 11 properties (including three long-term ground leasehold interests) encompassing approximately 8.6 million rentable square feet. Nine of these office properties are located in midtown Manhattan and encompass approximately 7.6 million rentable square feet, including the Empire State Building. The remaining two office properties encompass approximately 1.1 million rentable square feet and are located in Stamford, Connecticut, with immediate access to mass transportation. Additionally, we have entitled land adjacent to one of the Stamford office properties that can support the development of either office or residential per local zoning. Our multifamily portfolio included 727 residential units in New York City.
We were organized as a Maryland corporation on July 29, 2011 and commenced operations upon completion of our initial public offering and related formation transactions on October 7, 2013 (the "IPO"). Our operating partnership, Empire State Realty OP, L.P. (the "Operating Partnership"), holds substantially all of our assets and conducts substantially all of our business. As of December 31, 2023, we owned approximately 60.2% of the aggregate operating partnership units in the Operating Partnership. We, as the sole general partner in the Operating Partnership, have responsibility and discretion in the management and control of the Operating Partnership, and the limited partners in the Operating Partnership, in such capacity, have no authority to transact business for, or participate in the management activities of, the Operating Partnership. Accordingly, the Operating Partnership has been consolidated by us. We elected to be subject to tax as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes commencing with our taxable year ended December 31, 2013.
We have two entities that elected to be treated as taxable REIT subsidiaries, or TRSs, and are owned by our Operating Partnership. The TRSs, through several wholly owned limited liability companies, conduct third-party services businesses, which include the Empire State Building Observatory, cleaning services, cafeterias, restaurant and health clubs, and asset and property management services.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation and Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America ("GAAP") and with the rules and regulations of the SEC, represent our assets and liabilities and operating results. The consolidated financial statements include our accounts and our partially owned and wholly owned subsidiaries as well as our Operating Partnership and its subsidiaries. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
We consolidate entities in which we have a controlling financial interest. In determining whether we have a controlling financial interest in a partially owned entity and the requirement to consolidate the accounts of that entity, we consider factors such as ownership interest, board representation, management representation, authority to make decisions, and contractual and substantive participating rights of the partners/members. For variable interest entities ("VIE"), we consolidate the entity if we are deemed to have a variable interest in the entity and through that interest we are deemed the primary beneficiary. The primary beneficiary of a VIE is the entity that has (i) the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the entity's economic performance and (ii) the obligation to absorb losses of the VIE or the right to receive benefits from the VIE that could be significant to the VIE. The primary beneficiary is required to consolidate the VIE. The Operating Partnership is a VIE of ESRT. As the Operating Partnership is already consolidated in the financial statements of ESRT, the identification of this entity
as a VIE has no impact on our consolidated financial statements. At December 31, 2022, the Operating Partnership was the primary beneficiary of a variable interest in the intermediary entity which held title to 298 Mulberry Street, the multifamily asset acquired in December 2022. The intermediary entity was utilized to execute a like-kind exchange and subsequent to March 31, 2023, the like-kind exchange was completed and the Operating Partnership took title to 298 Mulberry Street. Therefore, the Operating Partnership had no VIEs at December 31, 2023.
We will assess the accounting treatment for each investment we may have in the future. This assessment will include a review of each entity’s organizational agreement to determine which party has what rights and whether those rights are protective or participating. For all VIEs, we will review such agreements in order to determine which party has the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance and benefit. In situations where we or our partner could approve, among other things, the annual budget, or leases that cover more than a nominal amount of space relative to the total rentable space at each property, we would not consolidate the investment as we consider these to be substantive participation rights that result in shared power of the activities that would most significantly impact the performance and benefit of such joint venture investment.
A non-controlling interest in a consolidated subsidiary is defined as the portion of the equity (net assets) in a subsidiary not attributable, directly or indirectly, to a parent. Non-controlling interests are required to be presented as a separate component of equity in the consolidated balance sheets and in the consolidated statements of income by requiring earnings and other comprehensive income to be attributed to controlling and non-controlling interests.
Accounting Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to use estimates and assumptions that in certain circumstances affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, and the reported revenues and expenses. Significant items subject to such estimates and assumptions include allocation of the purchase price of acquired real estate properties among tangible and intangible assets, determination of the useful life of real estate properties and other long-lived assets, valuation and impairment analysis of commercial real estate properties, goodwill, right-of-use assets and other long-lived and indefinite-lived assets, estimate of tenant expense reimbursements, valuation of the allowance for doubtful accounts, and valuation of derivative instruments, ground lease liabilities, senior unsecured notes, mortgage notes payable, unsecured revolving credit and term loan facilities, and equity based compensation. These estimates are prepared using management’s best judgment, after considering past, current, and expected events and economic conditions. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition
Rental Revenue
Rental revenue includes base rents that each tenant pays in accordance with the terms of its respective lease and is reported on a straight-line basis over the non-cancellable term of the lease which includes the effects of rent steps and rent abatements under the leases. In general, we commence rental revenue recognition when the tenant takes possession of the leased space or controls the physical use of the leased space and the leased space is substantially ready for its intended use. We account for all of our leases as operating leases. Deferred rent receivables, including free rental periods and leasing arrangements allowing for increased base rent payments, are accounted for in a manner that provides an even amount of fixed lease revenues over the respective non-cancellable lease terms. Differences between rental income recognized and amounts due under the respective lease agreements are recognized as an increase or decrease to deferred rent receivables.
In addition to base rent, our tenants also generally will pay their pro rata share of increases in real estate taxes and operating expenses for the building over a base year. In some leases, in lieu of paying additional rent based upon increases in building operating expenses, the tenant will pay additional rent based upon increases in an index such as the Consumer Price Index over the index value in effect during a base year, or contain fixed percentage increases over the base rent to cover escalations.
We recognize rental revenue of acquired in-place above- and below-market leases at their fair values over the terms of the respective leases, including, for below-market leases, fixed option renewal periods, if any.
Lease termination fees are recognized when the fees are determinable, tenant vacancy has occurred, collectability is reasonably assured, we have no continuing obligation to provide services to such former tenants and the payment is not subject to any conditions that must be met or waived.
Observatory Revenue
Revenues from the sale of Observatory tickets are recognized upon admission or ticket expirations. Deferred revenue related to unused and unexpired tickets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 was $1.7 million and $1.4 million, respectively, and is included in deferred revenue and other liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets.
Gains on Sale/Disposition of Real Estate
We record a gain on sale of real estate pursuant to provisions under Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 610-20, Gains and Losses from the Derecognition of Nonfinancial Assets. Under ASC 610-20, we must first determine whether the transaction is a sale to a customer or non-customer. We do not sell real estate within the ordinary course of our business and therefore, expect that sale transactions will not be contracts with customers. We will next determine whether we would have a controlling financial interest in the property after the sale. If we determine that we do not have a controlling financial interest in the real estate, we would evaluate whether a contract exists under ASC 606 Revenue from Contracts with Customers and whether the buyer has obtained control of the asset that was sold. We recognize the full gain on sale of real estate when the derecognition criteria under ASC 610-20 have been met.
Third-Party Management and Other Fees
We earn revenue arising from contractual agreements with related party entities for asset and property management services. This revenue is recognized as the related services are performed under the respective agreements in place.
Other Revenues and Fees
Other revenues and fees includes parking income, legal, tax and insurance settlements, demand response energy use earnings and sales from our restaurant at the Empire State Building.
Advertising and Marketing Costs
Advertising and marketing costs are expensed as incurred. The expense for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021 was $10.9 million, $10.8 million and $7.9 million, respectively, and is included within operating expenses in our consolidated statements of operations.
Real Estate Properties and Related Intangible Assets
Land and buildings and improvements are recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. The recorded cost includes cost of acquisitions, development and construction and tenant allowances and improvements. Expenditures for ordinary repairs and maintenance are charged to property operating expense as incurred. Significant replacements and betterments which improve or extend the life of the asset are capitalized. Tenant improvements which improve or extend the life of the asset are capitalized. If a tenant vacates its space prior to the contractual termination of its lease, the unamortized balance of any tenant improvements are written off if they are replaced or have no future value. For developed properties, direct and indirect costs that clearly relate to projects under development are capitalized. Costs include construction costs, professional services such as architectural and legal costs, capitalized interest and direct payroll costs. We begin capitalization when the project is probable. The assets relating to the project are stated at cost and are not depreciated. Once construction is completed and the assets are placed in service, the assets are reclassified to the appropriate asset class and depreciated in accordance with the useful lives as indicated below. Capitalization of interest ceases when the asset is ready for its intended use, which is generally near the date that a certificate of occupancy is obtained. There was no capitalized interest for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Depreciation and amortization are computed using the straight-line method for financial reporting purposes. Buildings and improvements are depreciated over the shorter of 39 years, the useful life, or the remaining term of any leasehold interest. Tenant improvement costs, which are included in building and improvements in the consolidated balance sheets, are depreciated over the shorter of (i) the related remaining lease term or (ii) the life of the improvement. Corporate and other equipment is depreciated over three to seven years.
Acquisitions of properties are accounted for utilizing the acquisition method and accordingly the purchase cost is allocated to tangible and intangible assets and liabilities based on their fair values. The fair value of tangible assets acquired is determined by valuing the property as if it were vacant, applying methods similar to those used by independent appraisers of income-producing property. The resulting value is then allocated to land, buildings and improvements, and tenant
improvements based on our determination of the fair value of these assets. The assumptions used in the allocation of fair values to assets acquired are based on our best estimates at the time of evaluation.
Fair value is assigned to above-market and below-market leases based on the difference between (a) the contractual amounts to be paid by the tenant based on the existing lease and (b) our estimate of current market lease rates for the corresponding in-place leases, over the remaining terms of the in-place leases. Capitalized above-market lease amounts are amortized as a decrease to rental revenue over the remaining terms of the respective leases. Capitalized below-market lease amounts are amortized as an increase to rental revenue over the remaining terms of the respective leases. If a tenant vacates its space prior to the contractual termination of the lease and no rental payments are being made on the lease, any unamortized balance of the related intangible will be written off.
The aggregate value of other acquired intangible assets consists of acquired ground leases and acquired in-place leases and tenant relationships. The fair value allocated to acquired in-place leases consists of a variety of components including, but not necessarily limited to: (a) the value associated with avoiding the cost of originating the acquired in-place leases (i.e. the market cost to execute a lease, including leasing commissions, if any); (b) the value associated with lost revenue related to tenant reimbursable operating costs estimated to be incurred during the assumed lease-up period (i.e. real estate taxes, insurance and other operating expenses); (c) the value associated with lost rental revenue from existing leases during the assumed lease-up period; and (d) the value associated with any other inducements to secure a tenant lease.
We assess the potential for impairment of our long-lived assets, including real estate properties, annually or whenever events occur or a change in circumstances indicate that the recorded value might not be fully recoverable. We determine whether impairment in value has occurred by comparing the estimated future undiscounted cash flows expected from the use and eventual disposition of the asset to its carrying value. If the undiscounted cash flows do not exceed the carrying value, the real estate is adjusted to fair value and an impairment loss is recognized. Assets held for sale are recorded at the lower of cost or fair value less costs to sell and depreciation expense is no longer recorded.
During the fourth quarter 2021, we concluded that the cost basis of 383 Main Avenue, Norwalk, Connecticut exceeded its fair value when we reduced our hold period given our intent to transfer property ownership to the lender. As such, we incurred a $7.7 million impairment charge in the year ended December 31, 2021. Our methodology to calculate the fair value of the property involved a combination of the discounted cash flow method, utilizing Level 3 unobservable inputs such as market capitalization rates obtained from external sources, and the market-based approach utilizing recent sales comparables. In April 2022, we transferred this asset back to the lender in a consensual foreclosure. Refer to Note 3 Acquisitions and Dispositions. We do not believe that the value of any of our other properties and intangible assets were impaired during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents consist of cash on hand, government money markets, demand deposits with financial institutions and short-term liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less when purchased. Cash and cash equivalents held at major commercial banks may at times exceed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation limit. To date, we have not experienced any losses on our invested cash.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash consists of amounts held for tenants in accordance with lease agreements such as security deposits and amounts held by lenders and/or escrow agents to provide for future real estate tax expenditures and insurance expenditures, tenant vacancy related costs and debt service obligations.
Short-term Investments
Short-term investments include time deposits with original maturities of greater than three months and remaining
maturities of less than one year.
Tenant and Other Receivables
Tenant and other receivables, other than deferred rent receivable, are generally expected to be collected within one year.
Deferred Leasing Costs
Deferred leasing costs consist of fees incurred to initiate and renew leases, are amortized on a straight-line basis over the related lease term and the expense is included in depreciation and amortization in our consolidated statements of income. Upon the early termination of a lease, unamortized deferred leasing costs are charged to expense.
Deferred Financing Costs
Fees and costs incurred to obtain long-term financing have been deferred and are amortized as a component of interest expense in our consolidated statements of income over the life of the respective long-term financing on the straight-line method which approximates the effective interest method. Unamortized deferred financing costs are expensed when the associated debt is refinanced or repaid before maturity. Costs incurred in seeking debt, which do not close, are expensed in the period in which it is determined that the financing will not close.
Equity Method Investments
We account for investments under the equity method of accounting where we do not have control but have the ability to exercise significant influence. Under this method, investments are recorded at cost, and the investment accounts are adjusted for our share of the entities’ income or loss and for distributions and contributions. Equity income (loss) is allocated based on the portion of the ownership interest that is controlled by us. The agreements may designate different percentage allocations among investors for profits and losses; however, our recognition of the entity’s income or loss generally follows the entity’s distribution priorities, which may change upon the achievement of certain investment return thresholds.
To the extent that we contributed assets to an entity, our investment in the entity is recorded at cost basis in the assets that were contributed to the entity. Upon contributing assets to an entity, we make a judgment as to whether the economic substance of the transaction is a sale. In accordance with the provisions of ASC 610-20, we will recognize a full gain on both the retained and sold portions of real estate contributed or sold to an entity by recognizing our new equity method investment interest at fair value.
To the extent that the carrying amount of these investments on our combined balance sheets is different than the basis reflected at the entity level, the basis difference would be amortized over the life of the related asset and included in our share of equity in net income of the entity.
On a periodic basis, we assess whether there are any indicators that the carrying value of our investments in entities may be impaired on an other than temporary basis. An investment is impaired only if management’s estimate of the fair value of the investment is less than the carrying value of the investment on an other than temporary basis. To the extent impairment has occurred, the loss shall be measured as the excess of the carrying value of the investment over the fair value of the investment.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, we had no equity method investments.
Goodwill
Goodwill is tested annually for impairment and more frequently if events and circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. An impairment loss is recognized to the extent that the carrying amount, including goodwill, exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value and the implied fair value of goodwill is less than the carrying amount of that goodwill. Non-amortizing intangible assets, such as trade names and trademarks, are subject to an annual impairment test based on fair value and amortizing intangible assets are tested whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable.
Fair Value
Fair value is a market-based measurement, not an entity-specific measurement, and should be determined based on the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability. As a basis for considering market participant assumptions in fair value measurements, the FASB guidance establishes a fair value hierarchy that distinguishes between market participant assumptions based on market data obtained from sources independent of the reporting entity (observable inputs that are classified within levels one and two of the hierarchy) and the reporting entity's own assumptions about market participant assumptions (unobservable inputs classified within Level 3 of the hierarchy).
The methodologies used for valuing financial instruments have been categorized into three broad levels as follows:
Level 1 - Quoted prices in active markets for identical instruments.
Level 2 - Valuations based principally on other observable market parameters, including:
•Quoted prices in active markets for similar instruments;
•Quoted prices in less active or inactive markets for identical or similar instruments;
•Other observable inputs (such as risk free interest rates, yield curves, volatilities, prepayment speeds, loss severities, credit risks and default rates); and
•Market corroborated inputs (derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data).
Level 3 - Valuations based significantly on unobservable inputs, including:
•Valuations based on third-party indications (broker quotes or counterparty quotes) which were, in turn, based significantly on unobservable inputs or were otherwise not supportable; and
•Valuations based on internal models with significant unobservable inputs.
These levels form a hierarchy. We follow this hierarchy for our financial instruments measured or disclosed at fair value on a recurring and nonrecurring basis and other required fair value disclosures. The classifications are based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
We use the following methods and assumptions in estimating fair value disclosures for financial instruments.
Cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, short term investments, tenant and other receivables, prepaid expenses and other assets, deferred revenue, tenant security deposits, accounts payable and accrued expenses carrying values approximate their fair values due to the short term maturity of these instruments.
The fair value of derivative instruments is determined using widely accepted valuation techniques, including discounted cash flow analysis on the expected cash flows of each derivative. Although the majority of the inputs used to value our derivatives fall within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy, the credit valuation adjustments associated with our derivatives utilize Level 3 inputs, such as estimates of current credit spreads to evaluate the likelihood of default by ourselves and our counterparties. The impact of such credit valuation adjustments, determined based on the fair value of each individual contract, was not significant to the overall valuation. As a result, all of our derivatives were classified as Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy.
The fair value of our mortgage notes payable, senior unsecured notes (Series A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H), unsecured term loan facilities and unsecured revolving credit facility which are determined using Level 3 inputs are estimated by discounting the future cash flows using current interest rates at which similar borrowings could be made by us.
Derivative Instruments
We are exposed to the effect of interest rate changes and manage these risks by following policies and procedures including the use of derivatives. To manage exposure to interest rates, derivatives are used primarily to fix the rate on debt based on floating-rate indices. We record all derivatives on the balance sheet at fair value. We incorporate credit valuation adjustments to appropriately reflect both our own nonperformance risk and the respective counterparty’s nonperformance risk in the fair value measurements. We measure the credit risk of our derivative instruments that are subject to master netting agreements on a net basis by counterparty portfolio. For derivatives that qualify as cash flow hedges, we report the gain or loss on the derivative designated as a hedge as part of other comprehensive income (loss) and subsequently reclassify the gain or loss into income in the period that the hedged transaction affects income.
Income Taxes
We elected to be subject to tax as a REIT under sections 856 through 860 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, (the "Code"), commencing with the taxable year ended December 31, 2013 and believe that our intended manner of operations will enable us to continue to meet the requirements for qualification and taxation as a REIT. REITs are subject to a number of organizational and operational requirements, including a requirement that 90% of ordinary “REIT taxable income” (as determined without regard to the dividends paid deduction or net capital gains) be distributed. As a REIT, we will generally not be subject to U.S. federal income tax to the extent that we meet the organizational and operational requirements and our distributions equal or exceed REIT taxable income. For all periods subsequent to the effective date of our REIT
election, we have met the organizational and operational requirements and distributions have exceeded net taxable income. Accordingly, no provision has been made for federal income taxes.
We have elected to treat ESRT Observatory TRS, L.L.C., our subsidiary that holds our Observatory operations, and ESRT Holdings TRS, L.L.C., our subsidiary that holds our third-party management, restaurant, cafeterias, health clubs and certain cleaning operations, as taxable REIT subsidiaries. Taxable REIT subsidiaries may participate in non-real estate activities and/or perform non-customary services for tenants and their operations are generally subject to regular corporate income taxes. Our taxable REIT subsidiaries accounts for its income taxes in accordance with GAAP, which includes an estimate of the amount of taxes payable or refundable for the current year and deferred tax liabilities and assets for the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in our consolidated financial statements or tax returns. The calculation of the taxable REIT subsidiaries' tax provisions may require interpreting tax laws and regulations and could result in the use of judgments or estimates which could cause its recorded tax liability to differ from the actual amount due. Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. The taxable REIT subsidiaries periodically assess the realizability of deferred tax assets and the adequacy of deferred tax liabilities, including the results of local, state, or federal statutory tax audits or estimates and judgments used.
We apply provisions for measuring and recognizing tax benefits associated with uncertain income tax positions. Penalties and interest, if incurred, would be recorded as a component of income tax expense. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, we do not have a liability for uncertain tax positions. As of December 31, 2023, the tax years ended December 31, 2020 through December 31, 2023 remain open for an audit by the Internal Revenue Service, state or local authorities.
Share-Based Compensation
Share-based compensation for time-based equity awards is measured at the fair value of the award on the date of grant and recognized as an expense on a straight-line basis over the shorter of (i) the stated vesting period, which is generally three, four or five years, or (ii) the period from the date of grant to the date the employee becomes retirement eligible, which may occur upon grant. An employee is retirement eligible when the employee attains the (i) age of 65 for awards granted in 2020 and after and age of 60 for awards granted before 2020 and (ii) the date on which the employee has first completed the requisite years of continuous service with us or our affiliates. Share-based compensation for market-based equity awards and performance-based equity awards is measured at the fair value of the award on the date of grant and recognized as an expense on a straight-line basis over three or four years. Additionally, for the performance-based equity awards, we assess, at each reporting period, whether it is probable that the performance conditions will be satisfied. We recognize expense respective to the number of awards we expect to vest at the conclusion of the measurement period. Changes in estimate are accounted for in the period of change through a cumulative catch-up adjustment. Any forfeitures of share-based compensation awards are recognized as they occur.
The determination of fair value of these awards is subjective and involves significant estimates and assumptions including expected volatility of our stock, expected dividend yield, expected term, and assumptions of whether these awards will achieve parity with other Operating Partnership units or achieve performance thresholds. We believe that the assumptions and estimates utilized are appropriate based on the information available to management at the time of grant.
Per Share Data
Basic and diluted earnings per share are computed based upon the weighted average number of shares outstanding during the respective period.
Segment Reporting
We have identified two reportable segments: (1) Real Estate and (2) Observatory. Our real estate segment includes all activities related to the ownership, management, operation, acquisition, repositioning and disposition of our real estate assets. Our Observatory segment operates the 86th and 102nd floor observatories at the Empire State Building. These two lines of businesses are managed separately because each business requires different support infrastructures, provides different services and has dissimilar economic characteristics such as investments needed, stream of revenues and different marketing strategies. We account for intersegment sales and rent as if the sales or rent were to third parties, that is, at current market prices.
Recently Issued or Adopted Accounting Standards
During March 2020, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2020-04, Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848). ASU 2020-04 contains practical expedients for reference rate reform related activities that impact debt, leases, derivatives and other contracts. The guidance in ASU 2020-04 is optional and may be elected over time as reference rate reform activities
occur. During the first quarter 2020, we elected to apply the hedge accounting expedients related to probability and the assessments of effectiveness for future LIBOR-indexed cash flows to assume that the index upon which future hedged transactions will be based matches the index on the corresponding derivatives. Application of these expedients preserves the presentation of derivatives consistent with past presentation. In December 2022, the FASB issued ASU 2022-06, Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848) Deferral of the Sunset Date of Topic 848 which deferred the sunset date of ASU 2022-04, Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848): Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform to December 31, 2024. As of December 31, 2023, we have transitioned all of our LIBOR-indexed debt and derivatives to SOFR and applied the practical expedient allowed under the guidance.
During November 2023, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, to improve the disclosures about reportable segments and add more detailed information about a reportable segment’s expenses. The amendments in the ASU require public entities to disclose on an annual and interim basis significant segment expenses that are regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker (“CODM”) and included within each reported measure of segment profit or loss, other segment items and a description of its composition by reportable segment, the title and position of the CODM, and an explanation of how the CODM uses the reported measures of segment profit or loss in assessing segment performance and deciding how to allocate resources. The ASU does not change the definition of a segment, the method for determining segments, the criteria for aggregating operating segments into reportable segments, or the current specifically enumerated segment expenses that are required to be disclosed. The amendments in this ASU are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. We are evaluating the impact of adopting this new accounting standard on our consolidated financial statements.
3. Acquisitions and Dispositions
Property Acquisitions
On September 14, 2023, we closed on the acquisition of a retail property in Williamsburg, Brooklyn, located on the corner of North 6th Street and Wythe Avenue for a purchase price of $26.4 million. The property has three retail tenants and six residential units and was fully leased as of December 31, 2023. The transaction was executed as an exchange under Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended. The purchase price is the fair value at the date of acquisition.
On December 20, 2022, we closed on the acquisition of a multifamily asset located at 298 Mulberry Street in Manhattan for a purchase price of $114.9 million. In addition to the 96 residential units, the property also contains retail space leased to CVS and a garage. The purchase price is the fair value at the date of acquisition.
On December 22, 2021, we acquired 90% of two multifamily assets located in Manhattan, the Victory (561 10th Avenue) and 345 East 94th Street. The total transaction value was $307.0 million, inclusive of $134.0 million of debt on the Victory, that matures in 2033 and has an effective interest rate of 3.85%, and $52.0 million of debt on 345 East 94th Street, that matures in 2030 and has an effective interest rate of 3.56%. The previous owner retained a 10% equity stake. We asset manage the properties and have control over all decision making through our voting interests in each entity. We currently use a third-party manager, but we have the right to assume day-to-day property management for no additional consideration. The fair value of the non-controlling interest was equivalent to 10% of the gross purchase price less the pro-rata share of the debt assumed. The purchase price of the non-controlling interest is its fair value at the date of acquisition.
The Victory is a 417 unit, 45-story apartment building with an 11,000 square foot retail space leased to CVS through 2040. It is a participant in an extendable 421a tax abatement program.
345 East 94th Street is a 208 unit, 30-story, apartment building. It is a participant in an extendable 421a tax abatement program.
The following table summarizes properties acquired during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Intangibles | | |
| Property | Date Acquired | Land | Building and Improvements | Assets | Liabilities | Total* | |
| Williamsburg Retail, Brooklyn | 9/14/2023 | $ | 4,851 | | $ | 20,936 | | $ | 1,573 | | $ | (300) | | $ | 27,060 | | |
| 298 Mulberry Street, Manhattan | 12/20/2022 | $ | 40,935 | | $ | 69,508 | | $ | 5,300 | | $ | (150) | | $ | 115,593 | | |
| The Victory | 12/21/2021 | 91,437 | | 124,997 | | 13,573 | | (19,895) | | $ | 210,112 | | |
| 345 East 94th St. | 12/21/2021 | 44,228 | | 55,766 | | 4,824 | | (5,491) | | $ | 99,327 | | |
| *Includes total capitalized transaction costs of $3.8 million. | |
Property Dispositions
The following table summarizes properties disposed of during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property | Date of Disposal | Sales Price | Gain on Disposition |
| 500 Mamaroneck Avenue, Harrison, New York* | 4/5/2023 | $ | 53,000 | | $ | 11,075 | |
| 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street, Westport, Connecticut | 2/1/2023 | $ | 40,000 | | $ | 15,689 | |
| 10 Bank Street, White Plains, New York | 12/7/2022 | $ | 42,000 | | $ | 6,818 | |
| 383 Main Avenue, Norwalk, Connecticut** | 4/1/2022 | $ | 30,000 | | $ | 27,170 | |
| *The gain is net of approximately $4.5 million of post-closing costs we accrued related to expected contaminated soil remediation costs and our commitment to reimburse the buyer for a delay in rent commencement from a tenant impacted by the soil remediation efforts. Subsequent to December 31, 2023, we funded the buyer for these costs and we have no further obligations or contingencies that relate to this property. |
| **We transferred the property, which was encumbered by a $30.0 million mortgage, back to the lender in a consensual foreclosure and recognized a non-cash gain upon the disposition. |
There were no property dispositions for the year ended December 31, 2021.
4. Deferred Costs, Acquired Lease Intangibles and Goodwill
Deferred costs, net, consisted of the following at December 31, 2023 and 2022 (amounts in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Leasing costs | $ | 224,295 | | | $ | 218,707 | |
| Acquired in-place lease value and deferred leasing costs | 158,267 | | | 160,683 | |
| Acquired above-market leases | 23,918 | | | 27,833 | |
| 406,480 | | | 407,223 | |
| Less: accumulated amortization | (236,900) | | | (223,246) | |
| Total deferred costs, net, excluding net deferred financing costs | $ | 169,580 | | | $ | 183,977 | |
At December 31, 2023 and 2022, $2.9 million and $5.0 million, respectively, of net deferred financing costs associated with the unsecured revolving credit facility was included in deferred costs, net on the consolidated balance sheets.
Amortization expense related to deferred leasing and acquired deferred leasing costs was $23.6 million, $25.4 million, and $28.6 million, for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively. Amortization expense related to acquired lease intangibles was $7.4 million, $11.8 million and $10.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Amortizing acquired intangible assets and liabilities consisted of the following at December 31, 2023 and 2022 (amounts in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Acquired below-market ground leases | $ | 396,916 | | | $ | 396,916 | |
| Less: accumulated amortization | (75,675) | | | (67,843) | |
| Acquired below-market ground leases, net | $ | 321,241 | | | $ | 329,073 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Acquired below-market leases | $ | (55,155) | | | $ | (64,656) | |
| Less: accumulated amortization | 41,405 | | | 46,807 | |
| Acquired below-market leases, net | $ | (13,750) | | | $ | (17,849) | |
Rental revenue related to the amortization of below market leases, net of above market leases was $2.4 million, $4.8 million and $5.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. The remaining weighted-average amortization period as of December 31, 2023 is 22.2 years, 3.4 years, 3.5 years and 2.9 years for below-market ground leases, in-place leases and deferred leasing costs, above-market leases and below-market leases, respectively. We expect to recognize amortization expense and rental revenue from the acquired intangible assets and liabilities as follows (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the year ending: | Future Ground Rent Amortization | | Future Amortization Expense | | Future Rental Revenue (Expense) |
| 2024 | $ | 7,831 | | | $ | 7,430 | | | $ | 1,977 | |
| 2025 | 7,831 | | | 6,481 | | | 1,914 | |
| 2026 | 7,831 | | | 5,593 | | | 1,116 | |
| 2027 | 7,831 | | | 4,930 | | | 882 | |
| 2028 | 7,831 | | | 4,297 | | | 854 | |
| Thereafter | 282,086 | | | 4,110 | | | (124) | |
| $ | 321,241 | | | $ | 32,841 | | | $ | 6,619 | |
As of December 31, 2023, we had goodwill of $491.5 million. In 2013, we acquired the interests in Empire State Building Company, L.L.C. and 501 Seventh Avenue Associates, L.L.C. for an amount in excess of their net tangible and identified intangible assets and liabilities and as a result we recorded goodwill related to the transaction. Goodwill was allocated $227.5 million to the Observatory operations of the Empire State Building, $250.8 million to Empire State Building, and $13.2 million to 501 Seventh Avenue.
We performed our annual goodwill testing in October 2023, where we bypassed the optional qualitative goodwill impairment assessment and proceeded directly to a quantitative assessment of the Observatory reportable segment and engaged a third-party valuation consulting firm to perform the valuation process. The quantitative analysis used a combination of the discounted cash flow method (a form of the income approach) utilizing Level 3 unobservable inputs and the guideline company method (a form of the market approach). Significant assumptions under the former included revenue and cost projections, weighted average cost of capital, long-term growth rate and income tax considerations while the latter included guideline company enterprise values, revenue multiples, EBITDA multiples and control premium rates. Our methodology to review goodwill impairment, which included a significant amount of judgment and estimates, provided a reasonable basis to determine whether impairment had occurred. The quantitative analysis performed concluded the fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value. Many of the factors employed in determining whether or not goodwill is impaired are outside of our control, and it is reasonably likely that assumptions and estimates will change in future periods. We will continue to assess the impairment of the Observatory reporting unit goodwill going forward.
5. Debt
Debt consisted of the following as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | As of December 31, 2023 | |
| Principal Balance as
of December 31, 2023 | | Principal Balance as
of December 31, 2022 | | Stated
Rate | | Effective
Rate(1) | | Maturity
Date(2) | |
| Fixed rate mortgage debt | | | | | | | | | | |
| Metro Center | $ | 80,070 | | | $ | 82,596 | | | 3.59 | % | | 3.67 | % | | 11/5/2024 | |
| 10 Union Square | 50,000 | | | 50,000 | | | 3.70 | % | | 3.97 | % | | 4/1/2026 | |
| 1542 Third Avenue | 30,000 | | | 30,000 | | | 4.29 | % | | 4.53 | % | | 5/1/2027 | |
First Stamford Place (3) | 175,860 | | | 178,823 | | | 4.28 | % | | 4.73 | % | | 7/1/2027 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 1010 Third Avenue and 77 West 55th Street | 34,958 | | | 35,831 | | | 4.01 | % | | 4.21 | % | | 1/5/2028 | |
| 250 West 57th Street | 180,000 | | | 180,000 | | | 2.83 | % | | 3.21 | % | | 12/1/2030 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| 1333 Broadway | 160,000 | | | 160,000 | | | 4.21 | % | | 4.29 | % | | 2/5/2033 | |
| 345 East 94th Street - Series A | 43,600 | | | 43,600 | | | 70.0% of SOFR plus 0.95% | | 3.56 | % | | 11/1/2030 | |
| 345 East 94th Street - Series B | 7,209 | | | 7,865 | | | SOFR plus 2.24% | | 3.56 | % | | 11/1/2030 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| 561 10th Avenue - Series A | 114,500 | | | 114,500 | | | 70.0% of SOFR plus 1.07% | | 3.85 | % | | 11/1/2033 | |
| 561 10th Avenue - Series B | 15,801 | | | 17,415 | | | SOFR plus 2.45% | | 3.85 | % | | 11/1/2033 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Total fixed rate mortgage debt | 891,998 | | | 900,630 | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Senior unsecured notes: (4) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Series A | 100,000 | | | 100,000 | | | 3.93 | % | | 3.96 | % | | 3/27/2025 | |
| Series B | 125,000 | | | 125,000 | | | 4.09 | % | | 4.12 | % | | 3/27/2027 | |
| Series C | 125,000 | | | 125,000 | | | 4.18 | % | | 4.21 | % | | 3/27/2030 | |
| Series D | 115,000 | | | 115,000 | | | 4.08 | % | | 4.11 | % | | 1/22/2028 | |
| Series E | 160,000 | | | 160,000 | | | 4.26 | % | | 4.27 | % | | 3/22/2030 | |
| Series F | 175,000 | | | 175,000 | | | 4.44 | % | | 4.45 | % | | 3/22/2033 | |
| Series G | 100,000 | | | 100,000 | | | 3.61 | % | | 4.89 | % | | 3/17/2032 | |
| Series H | 75,000 | | | 75,000 | | | 3.73 | % | | 5.00 | % | | 3/17/2035 | |
Unsecured revolving credit facility (4) | — | | | — | | | SOFR plus 1.30% | | — | % | | 3/31/2025 | |
Unsecured term loan facility (4) | 215,000 | | | 215,000 | | | SOFR plus 1.20% | | 4.22 | % | | 3/19/2025 | |
Unsecured term loan facility (4) | 175,000 | | | 175,000 | | | SOFR plus 1.50% | | 4.51 | % | | 12/31/2026 | |
| Total principal | 2,256,998 | | | 2,265,630 | | | | | | | | |
| Deferred financing costs, net | (9,488) | | | (11,748) | | | | | | | | |
| Unamortized debt discount | (6,964) | | | (7,745) | | | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 2,240,546 | | | $ | 2,246,137 | | | | | | | | |
______________
(1)The effective rate is the yield as of December 31, 2023 and includes the stated interest rate, deferred financing cost amortization and interest associated with variable to fixed interest rate swap agreements.
(2)Pre-payment is generally allowed for each loan upon payment of a customary pre-payment penalty.
(3)Represents a $164.0 million mortgage loan bearing interest of 4.09% and a $11.9 million loan bearing interest at 6.25%.
(4)At December 31, 2023, we were in compliance with all debt covenants.
Principal Payments
Aggregate required principal payments at December 31, 2023 are as follows (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year | Amortization | | Maturities | | Total |
| 2024 | $ | 8,861 | | | $ | 77,675 | | | $ | 86,536 | |
| 2025 | 6,893 | | | 315,000 | | | 321,893 | |
| 2026 | 7,330 | | | 225,000 | | | 232,330 | |
| 2027 | 6,461 | | | 319,000 | | | 325,461 | |
| 2028 | 3,556 | | | 146,092 | | | 149,648 | |
| Thereafter | 18,523 | | | 1,122,607 | | | 1,141,130 | |
| Total principal maturities | $ | 51,624 | | | $ | 2,205,374 | | | $ | 2,256,998 | |
Deferred Financing Costs
Deferred financing costs, net, consisted of the following at December 31, 2023 and 2022 (amounts in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Financing costs | $ | 43,473 | | | $ | 43,473 | |
| Less: accumulated amortization | (31,108) | | | (26,753) | |
| Total deferred financing costs, net | $ | 12,365 | | | $ | 16,720 | |
Amortization expense related to deferred financing costs was $4.4 million, $4.9 million, and $4.5 million, for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively, and was included in interest expense.
Unsecured Revolving Credit and Term Loan Facilities
On August 29, 2022, through our Operating Partnership, we entered into a third amendment to our amended and restated credit agreement dated August 29, 2017 with Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent and the other lenders party thereto, which governs our senior unsecured revolving credit facility and term loan facility (collectively, the “BofA Credit Facility”). The BofA Credit Facility is in the initial maximum principal amount of up to $1.065 billion, which consists of a $850.0 million revolving credit facility that matures on March 31, 2025, and a $215.0 million term loan facility that matures on March 19, 2025. The third amendment revised the terms of the BofA Credit Facility to (i) replace LIBOR with SOFR given the phase out of LIBOR and (ii) permit the addition of multifamily assets as Unencumbered Eligible Property (as defined therein) and add a capitalization rate for such assets. As of December 31, 2023, we had no borrowings under the revolving credit facility and $215.0 million under the term loan facility.
On August 29, 2022, through our Operating Partnership, we entered into a second amendment to our credit agreement dated March 19, 2020 with Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, and the other lenders party thereto, which governs a senior unsecured term loan facility (the “Wells Term Loan Facility”). The Wells Term Loan Facility is in the original principal amount of $175 million and matures on December 31, 2026. The second amendment revised the terms of the Wells Term Loan Facility to (i) replace LIBOR with SOFR given the phase out of LIBOR and (ii) permit the addition of multifamily assets as Unencumbered Eligible Property (as defined therein) and add a capitalization rate for such assets. We may request the Wells Term Loan Facility be increased through one or more increases or the addition of new pari passu term loan tranches, for a maximum aggregate principal amount not to exceed $225 million. As of December 31, 2023, our borrowings amounted to $175.0 million under the Wells Term Loan Facility.
The terms of both the BofA Credit Facility and the Wells Term Loan Facility include customary covenants, including limitations on liens, investment, distributions, debt, fundamental changes, and transactions with affiliates and require certain customary financial reports. Both facilities also require compliance with financial ratios including a maximum leverage ratio, a maximum secured leverage ratio, a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio, a minimum unencumbered interest coverage ratio, and a maximum unsecured leverage ratio. The agreements governing both facilities also contain customary events of default (subject in certain cases to specified cure periods), including but not limited to non-payment, breach of covenants, representations or warranties, cross defaults, bankruptcy or other insolvency events, judgments, ERISA events, invalidity of loan documents, loss of real estate investment trust qualification, and occurrence of a change of control. As of December 31, 2023, we were in compliance with these covenants.
Senior Unsecured Notes
The terms of the senior unsecured notes include customary covenants, including limitations on liens, investment, distributions, debt, fundamental changes, and transactions with affiliates and require certain customary financial reports. It also requires compliance with financial ratios including a maximum leverage ratio, a maximum secured leverage ratio, a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio, a minimum unencumbered interest coverage ratio, and a maximum unsecured leverage ratio. The agreements also contain customary events of default (subject in certain cases to specified cure periods), including but not limited to non-payment, breach of covenants, representations or warranties, cross defaults, bankruptcy or other insolvency events, judgments, ERISA events, the occurrence of certain change of control transactions and loss of real estate investment trust qualification. As of December 31, 2023, we were in compliance with these covenants.
6. Accounts Payable and Accrued Expenses
Accounts payable and accrued expenses consist of the following as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Accrued capital expenditures | $ | 51,815 | | | $ | 44,293 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 44,169 | | | 32,927 | |
| | | |
| Interest rate swap agreements liability | 85 | | | — | |
| Accrued interest payable | 3,687 | | | 3,509 | |
| | | |
| Total accounts payable and accrued expenses | $ | 99,756 | | | $ | 80,729 | |
7. Financial Instruments and Fair Values
Derivative Financial Instruments
We use derivative financial instruments primarily to manage interest rate risk and such derivatives are not considered speculative. These derivative instruments are typically in the form of interest rate swap and forward agreements, and the primary objective is to minimize interest rate risks associated with investing and financing activities. The counterparties of these arrangements are major financial institutions with which we may also have other financial relationships. We are exposed to credit risk in the event of non-performance by these counterparties; however, we currently do not anticipate that any of the counterparties will fail to meet their obligations.
We have agreements with our derivative counterparties that contain a provision where if we either default or are capable of being declared in default on any of our indebtedness, then we could also be declared in default on our derivative obligations. As of December 31, 2023, the fair value of derivatives in a net liability position, which includes accrued interest but excludes any adjustment for nonperformance risk, related to these agreements was $0.1 million. If we had breached any of these provisions at December 31, 2023, we could have been required to settle our obligations under the agreements at their termination value of $0.1 million.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, we had interest rate swaps and caps with an aggregate notional value of $573.2 million and $574.8 million, respectively. The notional value does not represent exposure to credit, interest rate or market risks. As of December 31, 2023, the fair values of our derivative instruments amounted to $11.8 million which is included in prepaid expenses and other assets, and ($0.1 million) which is included in accounts payable and accrued expenses on the consolidated balance sheet. As of December 31, 2022, the fair value of our derivative instruments amounted to $17.9 million which is included in prepaid expenses and other assets on the consolidated balance sheet. These interest rate swaps have been designated as cash flow hedges and hedge the variability in future cash flows associated with our existing variable-rate term loan facilities. Interest rate caps not designated as hedges are not speculative and are used to manage our exposure to interest rate movements, but do not meet the strict hedge accounting requirements.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, our cash flow hedges are deemed highly effective and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, net unrealized gains (losses) of $(2.2) million and $47.3 million, respectively, are reflected in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss) relating to both active and terminated cash flow hedges of interest rate risk. Amounts reported in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) related to derivatives will be reclassified to interest expense as interest payments are made on the debt. We estimate that $5.6 million net gain of the current balance held in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) will be reclassified into interest expense within the next 12 months.
The table below summarizes the terms of agreement and the fair value of our derivative financial instruments as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (dollar amounts in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Derivative | | Notional Amount | Receive Rate | Pay Rate | Effective Date | Expiration Date | | Asset | Liability | | Asset | Liability |
| Interest rate swap | | $ | 36,820 | | 70% of 1 Month SOFR | 2.5000 | % | December 1, 2021 | November 1, 2030 | | $ | 64 | | $ | — | | | $ | 256 | | $ | — | |
| Interest rate swap | | 103,790 | | 70% of 1 Month SOFR | 2.5000 | % | December 1, 2021 | November 1, 2033 | | — | | (85) | | | 365 | | — | |
| Interest rate swap | | 10,710 | | 70% of 1 Month SOFR | 1.7570 | % | December 1, 2021 | November 1, 2033 | | 546 | | — | | | 643 | | — | |
| Interest rate swap | | 15,942 | | 1 Month SOFR | 2.2540 | % | December 1, 2021 | November 1, 2030 | | 782 | | — | | | 1,070 | | — | |
| Interest rate cap | | 6,780 | | 70% of 1 Month SOFR | 4.5000 | % | December 1, 2021 | October 1, 2024 | | — | | — | | | 8 | | — | |
| Interest rate cap | | 9,188 | | 1 Month SOFR | 5.5000 | % | December 1, 2021 | October 1, 2024 | | 4 | | — | | | 26 | | — | |
| Interest rate swap | | 175,000 | | SOFR Compound | 2.5620 | % | August 31, 2022 | December 31, 2026 | | 5,637 | | — | | | 8,040 | | — | |
| Interest rate swap | | 107,500 | | SOFR Compound | 2.6260 | % | August 19, 2022 | March 19, 2025 | | 2,384 | | — | | | 3,766 | | — | |
| Interest rate swap | | 107,500 | | SOFR OIS Compound | 2.6280 | % | August 19, 2022 | March 19, 2025 | | 2,383 | | — | | | 3,762 | | — | |
| | | | | | | | $ | 11,800 | | $ | (85) | | | $ | 17,936 | | $ | — | |
The table below shows the effect of our derivative financial instruments designated as cash flow hedges on accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 (amounts in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Effects of Cash Flow Hedges | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| Amount of gain recognized in other comprehensive income (loss) | | $ | 5,581 | | | $ | 40,044 | | | $ | 348 | |
| Amount of loss (gain) reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) into interest expense | | 7,819 | | | (7,230) | | | (11,653) | |
The table below shows the effect of our derivative financial instruments designated as cash flow hedges on the consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Effects of Cash Flow Hedges | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| Total interest expense presented on the consolidated statements of income in which the effects of cash flow hedges are recorded | | $ | (101,484) | | | (101,206) | | | (94,394) | |
| Amount of loss (gain) reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) into interest expense | | 7,819 | | | (7,230) | | | (11,653) | |
Fair Valuation
The estimated fair values at December 31, 2023 and 2022 were determined by management, using available market information and appropriate valuation methodologies. Considerable judgment is necessary to interpret market data and develop estimated fair value. Accordingly, the estimates presented herein are not necessarily indicative of the amounts we could realize on disposition of the financial instruments. The use of different market assumptions and/or estimation methodologies may have a material effect on the estimated fair value amounts.
The following tables summarize the carrying and estimated fair values of our financial instruments as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 |
| | Carrying Value | | Estimated Fair Value |
| | | | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate swaps included in prepaid expenses and other assets | | $ | 11,800 | | | $ | 11,800 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 11,800 | | | $ | — | |
| Interest rate swaps included in accounts payable and accrued expenses | | 85 | | | 85 | | | — | | | 85 | | | — | |
| Mortgage notes payable | | 877,388 | | | 774,280 | | | — | | | — | | | 774,280 | |
| Senior unsecured notes - Series A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H | | 973,872 | | | 882,242 | | | — | | | — | | | 882,242 | |
| Unsecured term loan facilities | | 389,286 | | | 390,000 | | | — | | | — | | | 390,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2022 |
| | Carrying Value | | Estimated Fair Value |
| | | | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Interest rate swaps included in prepaid expenses and other assets | | $ | 17,936 | | | $ | 17,936 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 17,936 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Mortgage notes payable | | 883,705 | | | 783,648 | | | — | | | — | | | 783,648 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Senior unsecured notes - Series A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H | | 973,659 | | | 865,292 | | | — | | | — | | | 865,292 | |
| Unsecured term loan facility | | 388,773 | | | 390,000 | | | — | | | — | | | 390,000 | |
Disclosure about the fair value of financial instruments is based on pertinent information available to us as of December 31, 2023 and 2022. Although we are not aware of any factors that would significantly affect the reasonable fair value amounts, such amounts have not been comprehensively revalued for purposes of these consolidated financial statements since that date and current estimates of fair value may differ significantly from the amounts presented herein.
8. Leases
Lessor
We lease various commercial spaces to tenants over terms ranging from one to 22 years. Certain leases have renewal options for additional terms. The leases provide for base monthly rentals and reimbursements for real estate taxes, escalations linked to the consumer price index or common area maintenance known as operating expense escalation. Operating expense reimbursements are reflected in our December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 consolidated statements of operations as rental revenue.
Rental revenue includes fixed and variable payments. Fixed payments primarily relate to base rent and variable payments primarily relate to tenant expense reimbursements for certain property operating costs. The components of rental revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 are as follows (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| Rental revenue | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Fixed payments | $ | 529,965 | | | $ | 531,740 | | | $ | 500,847 | |
| Variable payments | 67,354 | | | 59,308 | | | 58,843 | |
| Total rental revenue | $ | 597,319 | | | $ | 591,048 | | | $ | 559,690 | |
As of December 31, 2023, we were entitled to the following future contractual minimum lease payments (excluding operating expense reimbursements) on non-cancellable operating leases to be received which expire on various dates through 2040 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | |
| 2024 | $ | 513,589 | |
| 2025 | 499,154 | |
| 2026 | 453,645 | |
| 2027 | 434,447 | |
| 2028 | 395,858 | |
| Thereafter | 1,646,769 | |
| $ | 3,943,462 | |
The above future minimum lease payments exclude tenant recoveries and the net accretion of above-market leases and below-market lease intangibles. Some leases are subject to termination options generally upon payment of a termination fee. The preceding table is prepared assuming such options are not exercised.
Lessee
We determine if an arrangement is a lease at inception. Our operating lease agreements relate to three ground lease assets and are reflected in right-of-use assets of $28.4 million and lease liabilities of $28.4 million in our consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2023. Right-of-use assets represent our right to use an underlying asset for the lease term and lease liabilities represent our obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease. Right-of-use assets and liabilities are recognized at the commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. Variable lease payments are excluded from the right-of-use assets and lease liabilities and are recognized in the period in which the obligation for those payments is incurred.
The ground leases are due to expire between the years 2050 and 2077, inclusive of extension options, and have no variable payments or residual value guarantees. As our leases do not provide an implicit rate, we determined our incremental borrowing rate based on information available at the date of adoption of ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842), in determining the present value of lease payments. The weighted average incremental borrowing rate used to calculate the right-of-use assets and lease liabilities as of December 31, 2023 was 4.5%. Rent expense for lease payments related to our operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the non-cancellable term of the leases. The weighted average remaining lease term as of December 31, 2023 was 46.5 years.
As of December 31, 2023, the following table summarizes our future minimum lease payments discounted by our incremental borrowing rates to calculate the lease liabilities of our leases (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | |
| 2024 | $ | 1,518 | |
| 2025 | 1,518 | |
| 2026 | 1,503 | |
| 2027 | 1,482 | |
| 2028 | 1,482 | |
| Thereafter | 60,795 | |
| Total undiscounted lease payments | 68,298 | |
| Present value discount | (39,859) | |
| Ground lease liabilities | $ | 28,439 | |
9. Commitments and Contingencies
Legal Proceedings
Litigation
Except as described below, as of December 31, 2023, we were not involved in any material litigation, nor, to our knowledge, was any material litigation threatened against us or our properties, other than routine litigation arising in the ordinary course of business such as disputes with tenants. We believe that the costs and related liabilities, if any, which may result from such actions will not materially affect our consolidated financial position, operating results or liquidity.
As previously disclosed, in October 2014, 12 former investors (the "Claimants") in Empire State Building Associates L.L.C. (“ESBA”), which prior to the initial public offering of our Company (the "Offering"), owned the fee title to the Empire State Building, filed an arbitration with the American Arbitration Association against Peter L. Malkin, Anthony E. Malkin, Thomas N. Keltner, Jr., and our subsidiary ESRT MH Holdings LLC, the former supervisor of ESBA, (the "Respondents"). The statement of claim (also filed later in federal court in New York for the expressed purpose of tolling the statute of limitations) alleged breach of fiduciary duty and related claims in connection with the Offering and formation transactions and sought monetary damages and declaratory relief. Claimants had opted out of a prior class action bringing similar claims that was settled with court approval. Respondents filed an answer and counterclaims. In March 2015, the federal court action was stayed on consent of all parties pending the arbitration. Arbitration hearings started in May 2016 and concluded in August 2018. On August 26, 2020, the arbitration panel issued an award that denied all Claimants’ claims with one exception, on which it awarded Claimants approximately $1.2 million, inclusive of seven years of interest through October 2, 2020. This amount was recorded as an IPO litigation expense in the consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2020.
Respondents believe that such award in favor of the Claimants is entirely without merit and sought to vacate that portion of the award. On September 27, 2021, a federal district court denied Respondents' petition to vacate and entered judgement in the aforementioned amount, inclusive of accumulated interest. Respondents appealed that ruling. On May 10, 2022, Respondents moved to dismiss the appeal and judgment on the grounds that a recent decision of the United States Supreme Court held that the federal courts have no subject matter jurisdiction over the case. On April 20, 2023, the federal appeals court granted the motion and the federal court action challenging the award was dismissed. On April 21, 2023, the Respondents filed a petition to vacate in part and otherwise confirm in New York State court. On April 28, 2023, the Claimants filed a petition to confirm in that same court. On July 31, 2023, the New York State court denied the Respondents’ petition to vacate in part and confirmed the award. On January 22, 2024, that court entered judgment in favor of the Claimants (save for one Claimant, whose petition to confirm is still pending in New York state court) in an amount of approximately $1.26 million, inclusive of interest. The Respondents believe those rulings are incorrect and have appealed them. In addition, certain of the Claimants in the federal court action brought to toll the statute of limitations sought to pursue claims in that case against Respondents. Respondents believe that any such claims are meritless. The magistrate judge assigned to the action issued a Report and Recommendation rejecting Claimants’ claims; the district judge will decide whether to adopt the Report and Recommendation.
Pursuant to indemnification agreements which were made with our directors, executive officers and chairman emeritus as part of our formation transactions, Anthony E. Malkin, Peter L. Malkin and Thomas N. Keltner, Jr. have defense and indemnity rights from us with respect to this arbitration.
Unfunded Capital Expenditures
At December 31, 2023, we estimate that we will incur approximately $101.2 million of capital expenditures (including tenant improvements and leasing commissions) on our properties pursuant to existing lease agreements. We expect to fund these capital expenditures with operating cash flow, cash on hand and other borrowings. Future property acquisitions may require substantial capital investments for refurbishment and leasing costs. We expect that these financing requirements will be met in a similar fashion.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that subject us to credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, short-term investments, tenant and other receivables and deferred rent receivables. At December 31, 2023, we held on deposit at various major financial institutions cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash balances in excess of amounts insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
Real Estate Investments
Our properties are located in Manhattan and Brooklyn, New York; and Stamford, Connecticut. The ability of the tenants to honor the terms of their respective leases is dependent upon the economic, regulatory and social factors affecting the markets in which the tenants operate. We perform ongoing credit evaluations of our tenants for potential credit losses.
Tenant Credit Evaluations
Our investments in real estate properties are subject to risks incidental to the ownership and operation of commercial real estate. These risks include, among others, the risks normally associated with changes in general economic conditions, trends in the real estate industry, creditworthiness of tenants, competition of tenants and customers, changes in tax laws, interest rate levels, the availability and cost of financing, and potential liability under environmental and other laws.
We may require tenants to provide some form of credit support such as corporate guarantees and/or other financial guarantees and we perform ongoing credit evaluations of tenants. Although the tenants operate in a variety of industries, to the extent we have a significant concentration of rental revenue from any single tenant, the inability of that tenant to make its lease payments could have an adverse effect on our Company.
Major Customers and Other Concentrations
For the year ended December 31, 2023, other than four tenants who accounted for 6.8%, 2.5%, 2.1%, and 2.1% of rental revenues, no other tenant in our portfolio accounted for more than 2.0% of rental revenues. For the year ended December 31, 2022, other than two tenants who accounted for 6.4% and 2.0% of rental revenues, no other tenant in our portfolio accounted for more than 2.0% of rental revenues. For the year ended December 31, 2021, other than four tenants who accounted for 4.6%, 3.3%, 2.8% and 2.1% of rental revenues, no other tenant in our commercial portfolio accounted for more than 2.0% of rental revenues.
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, the three properties listed below each exceeded 10% of total rental revenues.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Empire State Building | | 29.6 | % | | 29.9 | % | | 31.7 | % |
| One Grand Central Place | | 12.8 | % | | 12.4 | % | | 12.6 | % |
| 111 West 33rd Street | | 10.8 | % | | 11.2 | % | | 11.3 | % |
Asset Retirement Obligations
We are required to accrue costs that we are legally obligated to incur on retirement of our properties which result from acquisition, construction, development and/or normal operation of such properties. Retirement includes sale, abandonment or disposal of a property. Under that standard, a conditional asset retirement obligation represents a legal obligation to perform an asset retirement activity in which the timing and/or method of settlement is conditional on a future event that may or may not be within a company’s control and a liability for a conditional asset retirement obligation must be recorded if the fair value of the obligation can be reasonably estimated. Environmental site assessments and investigations have identified asbestos or asbestos-containing building materials in certain of our properties. As of December 31, 2023, management has no plans to remove or alter these properties in a manner that would trigger federal and other applicable regulations for asbestos removal, and accordingly, the obligations to remove the asbestos or asbestos-containing building materials from these properties have
indeterminable settlement dates. As such, we are unable to reasonably estimate the fair value of the associated conditional asset retirement obligation. However ongoing asbestos abatement, maintenance programs and other required documentation are carried out as required and related costs are expensed as incurred.
Other Environmental Matters
Under various federal, state and/or local laws, ordinances and regulations, as a current or former owner or operator of real property, we may be liable for costs and damages resulting from the presence or release of hazardous substances, waste, or petroleum products at, on, in, under or from such property, including costs for investigation or remediation, natural resource damages, or third-party liability for personal injury or property damage. These laws often impose liability without regard to whether the owner or operator knew of, or was responsible for, the presence or release of such materials, and the liability may be joint and several. Some of our properties have been or may be impacted by contamination arising from current or prior uses of the property or adjacent properties for commercial, industrial or other purposes. Such contamination may arise from spills of petroleum or hazardous substances or releases from tanks used to store such materials. We also may be liable for the costs of remediating contamination at off-site disposal or treatment facilities when we arrange for disposal or treatment of hazardous substances at such facilities, without regard to whether we comply with environmental laws in doing so. The presence of contamination or the failure to remediate contamination on our properties may adversely affect our ability to attract and/or retain tenants, and our ability to develop or sell or borrow against those properties. In addition to potential liability for cleanup costs, private plaintiffs may bring claims for personal injury, property damage or for similar reasons. Environmental laws also may create liens on contaminated sites in favor of the government for damages and costs it incurs to address such contamination. Moreover, if contamination is discovered on our properties, environmental laws may impose restrictions on the manner in which that property may be used or how businesses may be operated on that property.
Some of our properties are adjacent to or near other properties which are used for industrial or commercial purposes or have contained or currently contain underground storage tanks used to store petroleum products or other hazardous or toxic substances. Releases from these properties could impact our properties. In addition, some of our properties have previously been used by former owners or tenants for commercial or industrial activities, e.g., gas stations and dry cleaners, and a portion of the Metro Tower site is currently used for automobile parking and was formerly leased to a fueling facility that may release petroleum products or other hazardous or toxic substances at such properties or to surrounding properties. While certain properties contain or contained uses that could have or have impacted our properties, we are not aware of any liabilities related to environmental contamination that we believe will have a material adverse effect on our operations.
We have post-closing obligations related to the 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street, Westport, Connecticut properties that we sold in February 2023 to (i) close out a voluntary remediation program at 69-97 Main Street to address residual impacts of prior presence of underground storage tanks and (ii) comply with a consent order issued by the Connecticut Department of Environmental Protection to investigate soil conditions at 103-107 Main Street. We believe any expenses incurred to close out and comply with the remediation program and consent order, respectively, will be immaterial to the results of our operations.
Our property situated at 500 Mamaroneck Avenue in Harrison, New York was the subject of a voluntary remedial action work cleanup plan under an agreement with the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, but we sold this property in April 2023 and the obligations have been transferred to the buyer. Refer to Note 3 Acquisitions and Dispositions.
In addition, our properties are subject to various federal, state and local environmental and health and safety laws and regulations. Noncompliance with these laws and regulations could subject us or our tenants to liability. These liabilities could affect a tenant’s ability to make rental payments to us. Moreover, changes in laws could increase the potential costs of compliance with such laws and regulations or increase liability for noncompliance. This may result in significant unanticipated expenditures. We sometimes require our tenants to comply with environmental and health and safety laws and regulations and to indemnify us for any related liabilities in our leases with them. But in the event of the bankruptcy or inability of any of our tenants to satisfy such obligations, we may be required to satisfy such obligations. We are not presently aware of any instances of material non-compliance with environmental or health and safety laws or regulations at our properties, and we believe that we and/or our tenants have all material permits and approvals necessary under current laws and regulations to operate our properties.
In addition, we may become subject to new compliance requirements and/or new costs or taxes associated with natural resource or energy usage and related emissions (such as a carbon tax), which could increase our operating costs. In particular, as the owner of large commercial buildings in New York City, we are subject to Local Law 97 passed by the New York City Council in April 2019, which for each such building establishes annual limits for greenhouse gas emissions, requires yearly emissions reports beginning in May 2025, and imposes penalties for emissions above such limits. Based upon our present
understanding of the law and calculations related thereto, we expect to pay no fine on any building in our commercial portfolio in the 2024-2029 first period of enforcement.
As the owner or operator of real property, we may also incur liability based on various building conditions. For example, environmental site assessments and investigations have identified asbestos or asbestos-containing material ("ACM") in certain of our properties, and it is possible that other properties that we currently own or operate or those we acquire or operate in the future contain, may contain, or may have contained ACM. Environmental and health and safety laws require that ACM be properly managed and maintained and may impose fines or penalties on owners, operators or employers for non-compliance with those requirements. These requirements include special precautions, such as removal, abatement or air monitoring, if ACM would be disturbed during maintenance, redevelopment or demolition of a building, potentially resulting in substantial costs. In addition, we may be subject to liability for personal injury or property damage sustained as a result of releases of ACM into the environment. We are not presently aware of any material liabilities related to building conditions, including any instances of material non-compliance with asbestos requirements or any material liabilities related to asbestos.
Our properties may contain or develop harmful mold or suffer from other indoor air quality issues, which could lead to liability for adverse health effects or property damage or costs for remediation. When excessive moisture accumulates in buildings or on building materials, mold growth may occur, particularly if the moisture problem remains undiscovered or is not addressed over a period of time. Some molds may produce airborne toxins or irritants. Indoor air quality issues can also stem from inadequate ventilation, chemical contamination from indoor or outdoor sources, and other biological contaminants such as pollen, viruses and bacteria. Indoor exposure to airborne toxins or irritants above certain levels can be alleged to cause a variety of adverse health effects and symptoms, including allergic or other reactions. As a result, the presence of significant mold or other airborne contaminants at any of our properties could require us to undertake a costly remediation program to contain or remove the mold or other airborne contaminants from the affected property or increase indoor ventilation. In addition, the presence of significant mold or other airborne contaminants could expose us to liability from our tenants, employees of our tenants or others if property damage or personal injury occurs. We are not presently aware of any material adverse indoor air quality issues at our properties.
As of December 31, 2023, with the exception of the Westport assets, management believes that there are no obligations related to environmental remediation other than maintaining the affected sites in conformity with the relevant authority’s mandates and filing the required documents. All such maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. However, we cannot be certain that we have identified all environmental liabilities at our properties, that all necessary remediation actions have been or will be undertaken at our properties or that we will be indemnified, in full or at all, in the event that such environmental liabilities arise.
Insurance Coverage
We carry insurance coverage on our properties of types and in amounts with deductibles that we believe are in line with coverage customarily obtained by owners of similar properties.
Multiemployer Pension and Defined Contribution Plans
We contribute to a number of multiemployer defined benefit pension plans under the terms of collective bargaining agreements that cover our union-represented employees. The risks of participating in these multiemployer plans are different from single-employer plans in the following respects:
•Assets contributed to the multiemployer plan by one employer may be used to provide benefits to employees of other participating employers.
•If a participating employer stops contributing to the plan, the unfunded obligations of the plan may be borne by the remaining participating employers.
•If we no longer employ union members, we may be required to pay those plans an amount based on the underfunded status of the plan, referred to as a withdrawal liability.
We participate in various unions. The union in which we have significant employees and costs is 32BJ.
32BJ
We participate in the Building Service 32BJ ("Union") Pension Plan and Health Plan. The Pension Plan is a multi-employer, non-contributory defined benefit pension plan that was established under the terms of collective bargaining
agreements between the Service Employees International Union, Local 32BJ, the Realty Advisory Board on Labor Relations, Inc. and certain other employers. This Pension Plan is administered by a joint board of trustees consisting of union trustees and employer trustees and operates under employer identification number 13-1879376. The Pension Plan year runs from July 1 to June 30. Employers contribute to the Pension Plan at a fixed rate on behalf of each covered employee. Separate actuarial information regarding such pension plans is not made available to the contributing employers by the union administrators or trustees, since the plans do not maintain separate records for each reporting unit. On September 28, 2021, the actuary certified that for the plan year beginning July 1, 2021, the Pension Plan was in critical status under the Pension Protection Act of 2006. The Pension Plan trustees adopted a rehabilitation plan consistent with this requirement. However, on September 28, 2022 and September 28, 2023, the actuary certified that for the plan year beginning July 1, 2022 and July 1, 2023, respectively, the Pension Plan was in endangered status under the Pension Protection Act of 2006. The Pension Plan trustees adopted a funding improvement plan consistent with this requirement. For the plan years ended June 30, 2021, 2022 and 2023, the Pension Plan received contributions from employers totaling $290.1 million, $305.7 million and $317.9 million, respectively.
The Health Plan was established under the terms of collective bargaining agreements between the Union, the Realty Advisory Board on Labor Relations, Inc. and certain other employers. The Health Plan provides health and other benefits to eligible participants employed in the building service industry who are covered under collective bargaining agreements, or other written agreements, with the Union. The Health Plan is administered by a Board of Trustees with equal representation by the employers and the Union and operates under employer identification number 13-2928869. The Health Plan receives contributions in accordance with collective bargaining agreements or participation agreements. Generally, these agreements provide that the employers contribute to the Health Plan at a fixed rate on behalf of each covered employee. For the plan years ended June 30, 2021, 2022 and 2023, the Health Plan received contributions from employers totaling $1.5 billion, $1.6 billion and $1.9 billion, respectively.
Term of Collective Bargaining Agreements
Our collective bargaining agreement for Service Employees International Union Local 32BJ relating to commercial properties in New York City was renewed and commenced effective January 1, 2024 through December 31, 2027. We are in the process of negotiating a successor agreement to the collective bargaining agreement for Service Employees International Union Local 32BJ relating to our operations in the greater New York metropolitan area. We are also a signatory to another collective bargaining agreement for Service Employees International Union Local 32BJ with a term from April 21, 2022 through April 20, 2026 for our residential properties.
Contributions
Contributions we made to the multi-employer plans for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 are included in the table below (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Year Ended December 31, |
| Benefit Plan | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Pension Plans (pension and annuity)* | | $ | 3,671 | | | $ | 2,958 | | | $ | 2,165 | |
| Health Plans** | | 8,812 | | | 8,618 | | | 6,214 | |
| Other*** | | 434 | | | 460 | | | 305 | |
Total plan contributions | | $ | 12,917 | | | $ | 12,036 | | | $ | 8,684 | |
* Pension plans include $0.8 million, $0.8 million and $0.7 million for the years ended 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively, to multiemployer plans not discussed above.
** Health plans include $1.6 million, $1.5 million and $1.4 million for the years ended 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively, to multiemployer plans not discussed above.
*** Other consists of union costs which were not itemized between pension and health plans. Other includes $0.3 million, $0.2 million and $0.2 million for the years ended 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively, in connection with other multiemployer plans not discussed above.
The increase in plan contributions in 2023 is mainly due to higher payroll levels with the increased building utilization at our various properties. Benefit plan contributions are included in operating expenses in our consolidated statements of operations.
10. Equity
Shares and Units
An operating partnership unit ("OP Unit") and a share of our common stock have essentially the same economic characteristics as they receive the same per unit profit distributions of the Operating Partnership. On the one-year anniversary of issuance, an OP Unit may be tendered for redemption for cash; however, we have sole and absolute discretion, and sufficient authorized common stock, to exchange OP Units for shares of common stock on a one-for-one basis instead of cash. As of December 31, 2023, there were 162,061,947 shares of Class A common stock, 984,317 shares of Class B common stock and 107,900,200 OP Units outstanding. The REIT holds a 60.2% controlling interest in the OP. The other 39.8% noncontrolling interest in the OP is diversified among various limited partners, some of whom include Company directors, senior management and employees. We have two classes of common stock as a means to give our OP Unit holders voting rights in the public company that correspond to their economic interest in the combined entity. A one-time option was created at our formation transactions for any pre-IPO OP Unit holder to exchange one OP Unit out of every 50 OP Units they owned for one Class B share, and such Class B share carries 50 votes per share.
Stock and Publicly Traded Operating Partnership Unit Repurchase Program
Our Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $500 million of our Class A common stock and the Operating Partnership’s Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units from January 1, 2022 through December 31, 2023. Upon expiration of this program, the Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $500 million of our Class A common stock and the Operating Partnership's Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units during the period from January 1, 2024 through December 31, 2025. Under the program, we may purchase our Class A common stock and the Operating Partnership’s Series ES, Series 250 and Series 60 operating partnership units in accordance with applicable securities laws from time to time in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions. The timing, manner, price and amount of any repurchases will be determined by us at our discretion and will be subject to stock price, availability, trading volume, general market conditions, and applicable securities laws. The authorization does not obligate us to acquire any particular amount of securities, and the program may be suspended or discontinued at our discretion without prior notice. At December 31, 2023, we had used approximately $103.3 million of the authorized repurchase amount for the 2022-2023 period.
The following table summarizes our purchases of equity securities for the year ended December 31, 2023 under the previous repurchase program. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased | | Average Price Paid Per Share | | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plan | | Maximum Approximate Dollar Value Available for Future Purchase |
| Year ended December 31, 2023 | 2,150,857 | | | $ | 6.09 | | | 2,150,857 | | | $500,000,000 | | (a) |
(a) Represents the new board authorization for the January 1, 2024 - December 31, 2025 period. As of the date of this filing, we have used $0 of such $500 million authorization.
Private Perpetual Preferred Units
As of December 31, 2023, there were 4,664,038 Series 2019 Preferred Units ("Series 2019 Preferred Units") and 1,560,360 Series 2014 Private Perpetual Preferred Units ("Series 2014 Preferred Units"). The Series 2019 Preferred Units have a liquidation preference of $13.52 per unit and are entitled to receive cumulative preferential annual cash distributions of $0.70 per unit payable in arrears on a quarterly basis. The Series 2014 Preferred Units which have a liquidation preference of $16.62 per unit and are entitled to receive cumulative preferential annual cash distributions of $0.60 per unit payable in arrears on a quarterly basis. Both series are not redeemable at the option of the holders and are redeemable at our option only in the case of specific defined events.
Dividends and Distributions
The following table summarizes the dividends paid on our Class A common stock and Class B common stock for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Record Date | | Payment Date | | Amount per Share |
| December 18, 2023 | | December 29, 2023 | | $0.035 |
| September 15, 2023 | | September 29, 2023 | | $0.035 |
| June 15, 2023 | | June 30, 2023 | | $0.035 |
| March 15, 2023 | | March 31, 2023 | | $0.035 |
| | | | |
| December 19, 2022 | | December 31, 2022 | | $0.035 |
| September 15, 2022 | | September 30, 2022 | | $0.035 |
| June 15, 2022 | | June 30, 2022 | | $0.035 |
| March 15, 2022 | | March 31, 2022 | | $0.035 |
| | | | |
| December 20, 2021 | | December 31, 2021 | | $0.035 |
| September 15, 2021 | | September 30, 2021 | | $0.035 |
| June 15, 2021 | | June 30, 2021 | | $0.035 |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
Total dividends paid to common securityholders during 2023, 2022 and 2021 were $22.7 million, $23.1 million and $18.1 million, respectively. Total distributions paid to OP unitholders, excluding inter-company distributions, during 2023, 2022 and 2021 totaled $14.4 million, $15.5 million and $10.5 million, respectively. Total distributions paid to Preferred unitholders during 2023, 2022 and 2021 were $4.2 million, $4.2 million, and $4.2 million, respectively.
Earnings and profits, which determine the tax treatment of distributions to securityholders, will differ from income reported for financial reporting purposes due to the differences for federal income tax purposes, including, but not limited to, treatment of revenue recognition, compensation expense, and basis of depreciable assets and estimated useful lives used to compute depreciation. The 2023 dividends of $0.14 per share are classified for income tax purposes 89.2% as taxable ordinary dividends eligible for the Section 199A deduction and 10.8% as a return of capital. The 2022 dividends of $0.14 per share are classified for income tax purposes 100% as taxable ordinary dividends eligible for the Section 199A deduction and 0% as a return of capital. The 2021 dividends of $0.105 per share are classified for income tax purposes 16.2% as taxable ordinary dividends eligible for the Section 199A deduction and 83.8% as a return of capital.
Incentive and Share-Based Compensation
On May 16, 2019, the Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. Empire State Realty OP, L.P. 2019 Equity Incentive Plan (“2019 Plan”) was approved by our shareholders. The 2019 Plan provides for grants to directors, employees and consultants of our Company and Operating Partnership, including options, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock appreciation rights, performance awards, dividend equivalents and other equity-based awards, and replaced the First Amended and Restated Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. and Empire State Realty OP, L.P. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan ("2013 Plan", and collectively with the 2019 Plan, "the Plans"). The shares of Class A common stock underlying any awards under the 2019 Plan and the 2013 Plan that are forfeited, canceled or otherwise terminated, other than by exercise, will be added back to the shares of Class A common stock available for issuance under the 2019 Plan. Shares tendered or held back upon exercise of a stock option or settlement of an award under the 2019 Plan or the 2013 Plan to cover the exercise price or tax withholding and shares subject to a stock appreciation right that are not issued in connection with the stock settlement of the stock appreciation right upon exercise thereof, will not be added back to the shares of Class A common stock available for issuance under the 2019 Plan. In addition, shares of Class A common stock repurchased on the open market will not be added back to the shares of Class A common stock available for issuance under the 2019 Plan.
An aggregate of approximately 11.0 million shares of our common stock was authorized for issuance under awards granted pursuant to the 2019 Plan, and as of December 31, 2023, approximately 4.2 million shares of common stock remain available for future issuance under the Plans.
Long-term incentive plan ("LTIP") units are a special class of partnership interests in the Operating Partnership. Each LTIP unit awarded will be deemed equivalent to an award of one share of stock under the Plans, reducing the availability for other equity awards on a one-for-one basis. The vesting period for LTIP units, if any, will be determined at the time of issuance. Under the terms of the LTIP units, the Operating Partnership will revalue for tax purposes its assets upon the occurrence of certain specified events, and any increase in valuation from the time of one such event to the next such event will be allocated first to the holders of LTIP units to equalize the capital accounts of such holders with the capital accounts of OP unitholders.
Subject to any agreed upon exceptions, once vested and having achieved parity with OP unitholders, LTIP units are convertible into OP Units in the Operating Partnership on a one-for-one basis.
LTIP units subject to time-based vesting, whether vested or not, receive the same per unit distributions as OP Units, which equal per share dividends (both regular and special) on our common stock. Market and performance-based LTIPs receive 10% of such distributions currently, unless and until such LTIP units are earned based on performance, at which time they will receive the accrued and unpaid 90% and will commence receiving 100% of such distributions thereafter.
In March 2023, we made grants of LTIP units to executive officers under the 2019 Plan, including a total of 552,412 LTIP units that are subject to time-based vesting, 834,456 LTIP units that are subject to market-based vesting and 679,969 units that are subject to performance-based vesting with fair market values of $3.2 million, $3.9 million and $3.9 million, respectively. In March 2023, we made grants of LTIP units and restricted stock to certain other employees under the 2019 Plan, including a total of 229,308 LTIP units and 370,465 shares of restricted stock that are subject to time-based vesting, 111,942 LTIP units that are subject to market-based vesting and 91,211 LTIP units that are subject to performance-based vesting, with fair market values of $1.5 million and $2.6 million, respectively, for the time-based vesting awards, $0.6 million for the market-based vesting awards and $0.6 million for the performance-based vesting awards. The awards subject to time-based vesting vest ratably over four years, subject generally to the grantee's continued employment, with the first installment vesting on January 1, 2024. The vesting of the LTIP units subject to market-based vesting is based on the achievement of relative total stockholder return hurdles over a three-year performance period, commencing on January 1, 2023. The vesting of the LTIP units subject to performance-based vesting is based on the achievement of (i) operational metrics over a one-year performance period, subject to a three-year absolute TSR modifier, and (ii) environmental, social and governance metrics over a three-year performance period, in each case, commencing on January 1, 2023. Following the completion of the respective performance periods, our Compensation and Human Capital Committee will determine the number of LTIP units to which the grantee is entitled based on our performance relative to the performance hurdles set forth in the LTIP unit award agreements the grantee entered in connection with the award grant. These LTIP units then vest in two equal installments, on January 1, 2025 and December 31, 2026, subject generally to the grantee's continued employment on those dates.
In March 2023, we also made one-time additional grants of LTIP units to certain non-executive employees under the 2019 Plan. At such time, we granted to certain other employees a total of 152,542 LTIP units that are subject to time-based vesting, with a fair market value of $1.0 million that vest over four and five year periods.
In 2023, our named executive officers could elect to receive their annual incentive bonus in any combination of (i) cash or vested LTIPs at the face amount of such bonus or (ii) time-vesting LTIPs which would vest over three years, subject to continued employment, at a premium over such face amount (120% for awards granted in 2021, 2022, and 2023; 125% for years prior to 2021). In March 2023, we made grants of LTIP units to executive officers under the 2019 Plan in connection with the 2022 bonus election program. We granted to executive officers a total of 521,571 LTIP units that are subject to time-based vesting with a fair market value of $3.0 million. Of these LTIP units, 446,376 LTIP units vest ratably over three years from January 1, 2023, subject generally to the grantee's continued employment. The first installment vests on January 1, 2024, and the remainder will vest thereafter in two equal annual installments on January 1, 2025 and January 1, 2026. We also granted to our retired general counsel 75,195 LTIP units that vested immediately on the grant date.
Annually, we make grants of LTIP units to our non-employee directors under the 2019 Plan. In May 2023, each of our directors received 60% of their $200,000 annual base retainer in the form of equity vesting ratably over four years, and could elect to receive the remaining 40% of such base retainer in (i) cash at the face value of the award, (ii) immediately vesting equity at the face value of the award, or (iii) equity vesting ratably over three years at 120% of the face amount. Each director could elect to receive any equity portion of the base retainer in either (i) LTIP units or (ii) restricted shares of our Class A common stock. In accordance with each director's election, in May 2023, we granted a total of 237,856 LTIP units that are subject to time-based vesting with fair market values of $1.2 million. The LTIP units vest ratably over three or four years from the date of the grant, based on grantee election, subject generally to the director's continued service on our Board of Directors.
During July 2023, we granted our two new directors, Christina Van Tassell and Hannah Yang, a total of 27,000 LTIP units which are subject to time-based vesting with a combined fair market value of $0.2 million. One-fourth of the units will vest on May 12, 2024, and the remainder shall vest in substantially equal installments on each subsequent anniversary for a period of three years thereafter.
Share-based compensation for time-based equity awards is measured at the fair value of the award on the date of grant and recognized as an expense on a straight-line basis over the shorter of (i) the stated vesting period, which is generally three, four or five years, or (ii) the period from the date of grant to the date the employee becomes retirement eligible, which may occur upon grant. An employee is retirement eligible when the employee attains the (i) age of 65 for awards granted in 2020 and after, and age of 60 for awards granted before 2020 and (ii) the date on which the employee has first completed the
requisite years of continuous service with us or our affiliates. Share-based compensation for market-based equity awards and performance-based equity awards is measured at the fair value of the award on the date of grant and recognized as an expense on a straight-line basis over three or four years. Additionally, for the performance-based equity awards, we assess, at each reporting period, whether it is probable that the performance conditions will be satisfied. We recognize expense respective to the number of awards we expect to vest at the conclusion of the measurement period. Changes in estimate are accounted for in the period of change through a cumulative catch-up adjustment. Any forfeitures of share-based compensation awards are recognized as they occur.
For the market-based LTIP units, the fair value of the awards was estimated using a Monte Carlo Simulation model and discounted for the restriction period during which the LTIP units cannot be redeemed or transferred and the uncertainty regarding if, and when, the book capital account of the LTIP units will equal that of the common units. Our stock price, along with the prices of the comparative indexes, is assumed to follow the Geometric Brownian Motion Process. Geometric Brownian Motion is a common assumption when modeling in financial markets, as it allows the modeled quantity (in this case the stock price) to vary randomly from its current value and take any value greater than zero. The volatilities of the returns on our stock price and the comparative indexes were estimated based on implied volatilities and historical volatilities using an appropriate look-back period. The expected growth rate of the stock prices over the performance period is determined with consideration of the risk-free rate as of the grant date. For LTIP unit awards that are time or performance based, the fair value of the awards was estimated based on the fair value of our stock at the grant date discounted for the restriction period during which the LTIP units cannot be redeemed or transferred and the uncertainty regarding if, and when, the book capital account of the LTIP units will equal that of the common units. For restricted stock awards, the fair value of the awards are based on the market price of our stock at the grant date.
LTIP units and restricted stock issued during the year ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 were valued at $21.7 million, $22.4 million and $20.0 million, respectively. The weighted-average per unit or share fair value was $5.67, $7.21 and $8.52 for grants issued in 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. The fair value per unit or share granted in 2023 was estimated on the respective dates of grant using the following assumptions: an expected life from 2.0 to 5.3 years, a dividend rate of 1.7%, a risk-free interest rate from 4.4% to 5.0%, and an expected price volatility from 35.0% to 46.0%. The fair value per unit or share granted in 2022 was estimated on the respective dates of grant using the following assumptions: an expected life from 2.0 to 5.3 years, a dividend rate of 2.0%, a risk-free interest rate from 1.4% to 2.0%, and an expected price volatility from 37.0% to 53.0%. The fair value per unit or share granted in 2021 was estimated on the respective dates of grant using the following assumptions: an expected life from 2.0 to 5.3 years, a dividend rate of 2.60%, a risk-free interest rate from 0.12% to 0.32%, and an expected price volatility from 36.0% to 53.0%. No other stock options, dividend equivalents, or stock appreciation rights were issued or outstanding in 2023, 2022 and 2021.
The following is a summary of restricted stock and LTIP unit activity for the year ended December 31, 2023: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Restricted Stock | | Time-based LTIPs | | Market-based LTIPs | | Performance-based LTIPs | | Weighted Average Grant Fair Value |
| Unvested balance at December 31, 2022 | 359,293 | | | 2,713,522 | | | 4,070,537 | | | 510,989 | | | $ | 6.69 | |
| Vested | (121,128) | | | (1,148,987) | | | (582,800) | | | (2,011) | | | 7.17 | |
| Granted | 370,465 | | | 1,733,015 | | | 946,398 | | | 771,180 | | | 5.67 | |
| Forfeited or unearned | (10,341) | | | — | | | (1,695,323) | | | (3,795) | | | 4.30 | |
| Unvested balance at December 31, 2023 | 598,289 | | | 3,297,550 | | | 2,738,812 | | | 1,276,363 | | | $ | 6.60 | |
The total fair value of LTIP units and restricted stock that vested during 2023, 2022 and 2021 was $13.3 million, $14.1 million and $12.3 million, respectively.
The time-based LTIPs and restricted stock awards are treated for accounting purposes as immediately vested upon the later of (i) the date the grantee attains the age of 60 or 65, as applicable, and (ii) the date on which grantee has first completed the requisite years of continuous service with our Company or its affiliates. For award agreements that qualify, we recognize noncash compensation expense on the grant date for the time-based awards and ratably over the vesting period for the market-based and performance-based awards, and accordingly, we recognized $2.8 million, $2.3 million and $1.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Unrecognized compensation expense was $3.2 million at December 31, 2023, which will be recognized over a weighted average period of 2.4 years.
For the remainder of the LTIP unit awards, we recognized noncash compensation expense ratably over the vesting period, and accordingly, we recognized $17.2 million, $18.7 million and $19.0 million in noncash compensation expense for
the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Unrecognized compensation expense was $24.1 million at December 31, 2023, which will be recognized over a weighted average period of 2.4 years.
Earnings Per Share
Earnings per share is calculated by dividing the net income attributable to common shareholders by the weighted average number of shares outstanding during the respective period. Unvested share-based payment awards that contain non-forfeitable rights to dividends, whether paid or unpaid, are accounted for as participating securities. Share-based payment awards are included in the calculation of diluted income using the treasury stock method if dilutive.
Earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 is computed as follows (amounts in thousands, except per share amounts):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Numerator - Basic: | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 84,407 | | | $ | 63,212 | | | $ | (13,037) | |
| Private perpetual preferred unit distributions | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interest in operating partnership | (31,094) | | | (22,812) | | | 6,527 | |
| | | | | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests in other partnerships | (68) | | | 243 | | | — | |
| Earnings allocated to unvested shares | — | | | — | | | (26) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders - basic | $ | 49,044 | | | $ | 36,442 | | | $ | (10,737) | |
| | | | | |
| Numerator - Diluted: | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 84,407 | | | $ | 63,212 | | | $ | (13,037) | |
| Private perpetual preferred unit distributions | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | | | (4,201) | |
| | | | | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests in other partnerships | (68) | | | 243 | | | — | |
| Earnings allocated to unvested shares | — | | | — | | | (26) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders - diluted | $ | 80,138 | | | $ | 59,254 | | | $ | (17,264) | |
| | | | | |
| Denominator: | | | | | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding - basic | 161,122 | | | 165,039 | | | 172,445 | |
| Operating partnership units | 102,104 | | | 103,298 | | | 104,975 | |
| Effect of dilutive securities: | | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation plans | 2,407 | | | 1,611 | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding - diluted | 265,633 | | | 269,948 | | | 277,420 | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings per share - basic | $ | 0.30 | | | $ | 0.22 | | | $ | (0.06) | |
| Earnings per share - diluted | $ | 0.30 | | | $ | 0.22 | | | $ | (0.06) | |
There were zero antidilutive shares for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. There were 1,052,390 antidilutive shares for the year ended December 31, 2021.
11. Related Party Transactions
Sale of Westport Retail Properties
On February 1, 2023, we closed on the disposition of our retail assets located at 69-97 and 103-107 Main Street in Westport, Connecticut, for total consideration of $40.0 million, to an entity affiliated with our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Anthony E. Malkin (the “Westport Transaction”). The Company determined to make the sale to the related party entity
after a marketed sale process conducted from February 2022 through August 2022 through a broker in which it received several third-party bids. Deals with third-party purchasers failed to materialize due to adverse changes in capital market conditions during that time. The Westport Transaction materialized due to timing because the related party entity had recently completed a sale of property and was in the market for exchange property to defer tax in a 1031 exchange, and the Company recently executed on the acquisition of 298 Mulberry Street. The $40.0 million valuation for the Westport Transaction is in the range of the bids the Company received during the marketed sale process.
In connection with the Westport Transaction, we advanced a loan to the buyer to facilitate closing with a maximum principal amount of up to $1.0 million, which bore interest at SOFR plus 3.5% and required repayment of principal to the extent of available cash flow of the property. As of December 31, 2023, the loan has been fully paid.
The Company has a written Related Party Transactions Policy (the “Policy”) which requires the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee to review the material facts of all related party transactions and consider all relevant factors in approving any related party transaction. Further, the Policy provides that a director or executive officer shall not participate in any consideration, discussion or approval of such related party transaction in which he or she is a related party. The Westport Transaction process was completed in compliance with the Policy.
The independent members of the Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee conducted an independent review under the guidance of outside counsel and then approved the transaction. The Company reviewed with outside counsel best practices for the specific Westport Transaction and took additional precautions to ensure an arms-length process. There were separate counsels and appraisals for both buyer and seller.
Tax Protection Agreements
In 2013, we entered into a tax protection agreement with Anthony E. Malkin and Peter L. Malkin that is intended to protect to a limited extent the Malkin Group and an additional third-party investor in Metro Center (who was one of the original landowners and was involved in the development of the property) against certain tax consequences arising from a transaction involving one of four properties, which we refer to in this section as the protected assets.
First, this agreement provides that our operating partnership will not sell, exchange, transfer or otherwise dispose of such protected assets, or any interest in a protected asset, until (i) October 7, 2025, with respect to one protected asset, First Stamford Place, and (ii) the later of (x) October 7, 2021 and (y) the death of both Peter L. Malkin and Isabel W. Malkin, who are 90 and 87 years old, respectively, for the three other protected assets, Metro Center, 298 Mulberry Street (“substituted basis property” as contemplated by the tax protection agreement for 10 Bank Street, which was sold on December 7, 2022) and 1542 Third Avenue, unless:
(1)Anthony E. Malkin consents to the sale, exchange, transfer or other disposition; or
(2)our operating partnership delivers to each protected party thereunder a cash payment intended to approximate the tax liability arising from the recognition of the pre-contribution built-in gain resulting from the sale, exchange, transfer or other disposition of such protected asset (with the pre-contribution “built-in gain” being not more than the taxable gain that would have been recognized by such protected party if the protected asset been sold for fair market value in a taxable transaction at the time of the consolidation) plus an additional amount so that, after the payment of all taxes on amounts received pursuant to the agreement (including any tax liability incurred as a result of receiving such payment), the protected party retains an amount equal to such protected party’s total tax liability incurred as a result of the recognition of the pre-contribution built-in gain pursuant to such sale, exchange, transfer or other disposition; or
(3)the disposition does not result in a recognition of any built-in gain by the protected party.
Second, with respect to the Malkin Group, including Anthony E. Malkin and Peter L. Malkin, and one additional third-party investor in Metro Center (who was one of the original landowners and was involved in the development of the property), to protect against gain recognition resulting from a reduction in such continuing investor’s share of the operating partnership liabilities, the agreement provides that during the period from October 7, 2013 until such continuing investor owns less than the aggregate number of operating partnership units and shares of common stock equal to 50% of the aggregate number of such units and shares such investor received in the formation transactions, which we refer to in this section as the tax protection period, our operating partnership will (i) refrain from prepaying any amounts outstanding under any indebtedness secured by the protected assets and (ii) use its commercially reasonable efforts to refinance such indebtedness at or prior to maturity at its
current principal amount, or, if our operating partnership is unable to refinance such indebtedness at its current principal amount, at the highest principal amount possible. The agreement also provides that, during the tax protection period, our operating partnership will make available to such continuing investors the opportunity (i) to enter into a “bottom dollar” guarantee of their allocable share of $160.0 million of aggregate indebtedness of our operating partnership meeting certain requirements or (ii) in the event our operating partnership has recourse debt outstanding and such a continuing investor agrees, in lieu of guaranteeing debt pursuant to clause (i) above, to enter into a deficit restoration obligation, in each case, in a manner intended to provide an allocation of operating partnership liabilities to the continuing investor. In the event that a continuing investor guarantees debt of our operating partnership, such continuing investor will be responsible, under certain circumstances, for the repayment of the guaranteed amount to the lender in the event that the lender would otherwise recognize a loss on the loan, such as, for example, if property securing the loan was foreclosed and the value was not sufficient to repay a certain amount of the debt. A deficit restoration obligation is a continuing investor’s obligation, under certain circumstances, to contribute a designated amount of capital to our operating partnership upon our operating partnership’s liquidation in the event that the assets of our operating partnership are insufficient to repay our operating partnership liabilities.
Because we expect that our operating partnership will at all times have sufficient liabilities to allow it to meet its obligations to allocate liabilities to its partners that are protected parties under the tax protection agreement, our operating partnership’s indemnification obligation with respect to “certain tax liabilities” would generally arise only in the event that the operating partnership disposes in a taxable transaction of a protected asset within the period specified above in a taxable transaction. In the event of such a disposition, the amount of our operating partnership’s indemnification obligation would depend on several factors, including the amount of “built-in gain,” if any, recognized and allocated to the indemnified partners with respect to such disposition and the effective tax rate to be applied to such gain at the time of such disposition. Our disposition of the 10 Bank Street asset on December 7, 2022 did not trigger any obligation of payment pursuant to the tax protection agreement.
The operating partnership agreement requires that allocations with respect to such acquired property be made in a manner consistent with Section 704(c) of the Code. Treasury Regulations issued under Section 704(c) of the Code provide partnerships with a choice of several methods of allocating book-tax differences. Under the tax protection agreement, our operating partnership has agreed to use the “traditional method” for accounting for book-tax differences for the properties acquired by our operating partnership in the consolidation. Under the traditional method, which is the least favorable method from our perspective, the carryover basis of the acquired properties in the hands of our operating partnership (i) may cause us to be allocated lower amounts of depreciation and other deductions for tax purposes than would be allocated to us if all of the acquired properties were to have a tax basis equal to their fair market value at the time of acquisition and (ii) in the event of a sale of such properties, could cause us to be allocated gain in excess of its corresponding economic or book gain (or taxable loss that is less than its economic or book loss), with a corresponding benefit to the partners transferring such properties to our operating partnership for interests in our operating partnership.
In 2016, we entered into a tax protection agreement with Q REIT Holding LLC, a Qatar Financial Centre limited liability company and a wholly owned subsidiary of the Qatar Investment Authority, a governmental authority of the State of Qatar ("QREIT", and together with any eligible transferee, "QIA"). Subject to certain minimum thresholds and conditions, we will indemnify QIA for certain applicable U.S. federal and state taxes payable by QIA in connection with dividends paid by us on the QIA shares that are attributable to capital gains from the sale or exchange of any U.S. real property interests. Our obligation to indemnify QIA will terminate one year following the date on which the sum of the QIA shares then owned by QIA falls below 10% of our outstanding common shares.
Registration Rights
We entered into a registration rights agreement with certain persons receiving shares of our common stock or operating partnership units in the formation transactions, including certain members of our senior management team and our other continuing investors. In connection therewith, we have filed, and are obligated to maintain the effectiveness of, an automatically effective shelf registration statement, along with a prospectus supplement, with respect to, among other things, shares of our Class A common stock that may be issued upon redemption of operating partnership units or issued upon conversion of shares of Class B common stock to continuing investors in the public existing entities. Pursuant to the registration rights agreement, under certain circumstances, we will also be required to undertake an underwritten offering upon the written request of the Malkin Group, which we refer to as the holder, provided (i) the registrable shares to be registered in such offering will have a market value of at least $150.0 million, (ii) we will not be obligated to effect more than two underwritten offerings during any 12-month period; and (iii) the holder will not have the ability to effect more than four underwritten offerings. In addition, if we file a registration statement with respect to an underwritten offering for our own account or on behalf of the holder, the holder will have the right, subject to certain limitations, to register such number of registrable shares held by him, her or it as each such
holder requests. With respect to underwritten offerings on behalf of the holder, we will have the right to register such number of primary shares as we request; provided, however, that if cut backs are required by the managing underwriters of such an offering, our primary shares shall be cutback first (but in no event will our shares be cut back to less than $25.0 million).
We have also agreed to indemnify the persons receiving rights against specified liabilities, including certain potential liabilities arising under the Securities Act, or to contribute to the payments such persons may be required to make in respect thereof. We have agreed to pay all of the expenses relating to the registration and any underwritten offerings of such securities, including, without limitation, all registration, listing, filing and stock exchange or FINRA fees, all fees and expenses of complying with securities or “blue sky” laws, all printing expenses and all fees and disbursements of counsel and independent public accountants retained by us, but excluding underwriting discounts and commissions, any out-of-pocket expenses (except we will pay any holder’s out-of-pocket fees (including disbursements of such holder’s counsel, accountants and other advisors) up to $25,000 in the aggregate for each underwritten offering and each filing of a resale shelf registration statement or demand registration statement), and any transfer taxes.
Employment Agreement and Change in Control Severance Agreements
We entered into an employment agreement with Anthony E. Malkin, which provides for salary, bonuses and other benefits, including among other things, severance benefits upon a termination of employment under certain circumstances and the issuance of equity awards. In addition, we entered into change in control severance agreements with Thomas P. Durels and Christina Chiu.
Indemnification of Our Directors and Officers
We entered into indemnification agreements with each of our directors, executive officers, chairman emeritus and certain other parties, providing for the indemnification by us for certain liabilities and expenses incurred as a result of actions brought, or threatened to be brought, against (i) our directors, executive officers and chairman emeritus and (ii) our executive officers, chairman emeritus and certain other parties who are former members, managers, securityholders, directors, limited partners, general partners, officers or controlling persons of our predecessor in such capacities.
Excluded Properties and Businesses
The Malkin Group, including Anthony E. Malkin, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, owns non-controlling interests in, and Anthony E. Malkin and Peter L. Malkin control the general partners or managers of, the entities that own interests in seven multi-family properties and five net leased retail properties, (including one single tenant retail property in Greenwich, Connecticut). The Malkin Group also owns non-controlling interests in one Manhattan office property, two Manhattan retail properties and several retail properties outside of Manhattan, none of which were contributed to us in the formation transactions, and two retail properties in Westport, Connecticut acquired from ESRT in February 2023 (see Sale of Westport Retail Properties above). We refer to the non-controlling interests described above collectively as the excluded properties. In addition, the Malkin Group owns interests in one senior equity fund and three property managers, which we refer to collectively as the excluded businesses. We do not believe that the excluded properties or the excluded businesses are consistent with our current commercial portfolio or strategic direction.
Pursuant to management and/or service agreements with the owners of interests in those excluded properties and businesses, we are designated as the asset manager (supervisor) and/or property manager of the excluded properties, provide services to certain of the excluded properties and the other excluded businesses. As the manager or service provider, we are paid a management or other fee with respect to those excluded properties and businesses where our predecessor had previously received a management fee, and reimbursed for our costs in providing the management and other services to those excluded properties and businesses where our predecessor had not previously received a management fee. Our management of the excluded properties and provision of services to the three residential property managers and the existing managers of the other excluded businesses represent a minimal portion of our overall business. There is no established time period in which we will continue to provide such services; and Peter L. Malkin and Anthony E. Malkin expect to sell certain properties or unwind these businesses over time. We are not precluded from acquiring all or certain interests in the excluded properties or businesses. If we were to attempt any such acquisition, we anticipate that Anthony E. Malkin, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, will not participate in the negotiation process on our behalf with respect to our potential acquisition of any of these excluded properties or businesses, and the approval of a majority of our independent directors will be required to approve any such acquisition.
Services are and were provided by us to excluded properties and businesses. These transactions are reflected in our consolidated statements of operations as third-party management and other fees.
We earned asset management (supervisory) and service fees from excluded properties and businesses of $0.9 million, $1.0 million and $1.0 million during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
We earned property management fees from excluded properties of $0.3 million, $0.3 million and $0.2 million during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Other
We receive rent generally at market rental rate for 5,447 square feet of leased space from entities affiliated with Anthony E. Malkin at one of our properties. Under the lease, the tenant has the right to cancel such lease without special payment on 90 days’ notice. We also have a shared use agreement with such tenant to occupy a portion of the leased premises as the office location for Peter L. Malkin, our chairman emeritus and employee, utilizing approximately 15% of the space, for which we pay to such tenant an allocable pro rata share of the cost. We also have agreements with these entities and excluded properties and businesses to provide them with general computer-related support services. Total aggregate revenue was $0.2 million, $0.3 million and $0.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
12. Income Taxes
Holdings TRS and Observatory TRS are taxable entities and their consolidated provision for income taxes consisted of the following for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Current: | | | | | |
| Federal | $ | (783) | | | $ | (319) | | | $ | (266) | |
| State and local | (695) | | | (227) | | | (347) | |
| Total current | (1,478) | | | (546) | | | (613) | |
| Deferred: | | | | | |
| Federal | (710) | | | (264) | | | 1,206 | |
| State and local | (527) | | | (736) | | | 1,141 | |
| Total deferred | (1,237) | | | (1,000) | | | 2,347 | |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | $ | (2,715) | | | $ | (1,546) | | | $ | 1,734 | |
As of December 31, 2023, Empire State Realty Trust, Inc. had $103.0 million of NOL carryforwards that may be used in the future to reduce the amount otherwise required to be distributed by ESRT to meet REIT requirements. However, for federal income tax purposes, the NOL will not be able to offset more than 80% of ESRT’s REIT taxable income and may not be able to reduce the amount required to be distributed by ESRT to meet REIT requirements to zero. The federal NOL may be carried forward indefinitely. Other limitations may apply to ESRT’s ability to use its NOL to offset taxable income.
As of December 31, 2023, the Observatory TRS had a federal income tax receivable of $2.5 million. This receivable reflects an anticipated refund resulting from the carryback of 2020 NOL to previous tax years. The Observatory TRS has $1.5 million of federal NOL carryforward that may be used to offset future taxable income, if any. The federal NOL may be carried forward indefinitely.
We measure deferred tax assets using enacted tax rates that will apply in the years in which the temporary differences are expected to be recovered or paid.
The effective income tax rate is 44.5%, 33.6% and 26.0% for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. The actual tax provision differed from that computed at the federal statutory corporate rate as follows (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Federal tax benefit (expense) at statutory rate | $ | (1,494) | | | $ | (583) | | | $ | 940 | |
| State income tax benefit (expense), net of federal benefit | (1,221) | | | (963) | | | 794 | |
| | | | | |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | $ | (2,715) | | | $ | (1,546) | | | $ | 1,734 | |
The income tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to deferred tax assets are presented below as of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 (amounts in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | | |
| Deferred revenue on unredeemed Observatory admission ticket sales | $ | 616 | | | $ | 535 | | | $ | 383 | |
| Federal net operating loss carryforward credit | 328 | | | 969 | | | 1,393 | |
| New York State net operating loss carryforward credit | — | | | 250 | | | 612 | |
| New York City net operating loss carryforward credit | — | | | 233 | | | 704 | |
| Other deferred tax assets | 161 | | | 261 | | | — | |
| Deferred tax assets | $ | 1,105 | | | $ | 2,248 | | | $ | 3,092 | |
Deferred tax assets at December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 are included in prepaid expenses and other assets on the consolidated balance sheets. The deferred tax assets at December 31, 2023 are mainly attributable to a timing difference in recognizing income on unredeemed Observatory admission tickets and the inclusion of the Federal net operating loss to be carried forward and utilized during income years indefinitely. No valuation allowance has been recorded against the deferred tax asset because the Company believes it is more likely than not that the deferred tax asset will be realized. This determination is based on the Observatory TRS’s anticipated future taxable income and the reversal of the deferred tax asset.
As of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, the TRS entities have no amount of unrecognized tax benefits. As of December 31, 2023, the tax years ended December 31, 2020 through December 31, 2023 remain open for an audit by the Internal Revenue Service, state or local authorities.
13. Segment Reporting
We have identified two reportable segments: (1) real estate and (2) Observatory. Our real estate segment includes all activities related to the ownership, management, operation, acquisition, redevelopment, repositioning and disposition of our traditional real estate assets. Our Observatory segment operates the 86th and 102nd floor observatories at the Empire State Building. These two lines of businesses are managed separately because each business requires different support infrastructures, provides different services and has dissimilar economic characteristics such as investments needed, stream of revenues and marketing strategies. We account for intersegment sales and rents as if the sales or rents were to third parties, that is, at current market prices.
The following tables provide components of segment profit for each segment for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 (amounts in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | |
| | Real Estate | | Observatory | | Intersegment Elimination | | Total | | |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Rental revenue | | $ | 597,319 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 597,319 | | | |
| Intercompany rental revenue | | 80,514 | | | — | | | (80,514) | | | — | | | |
| Observatory revenue | | — | | | 129,366 | | | — | | | 129,366 | | | |
| Lease termination fees | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | |
| Third-party management and other fees | | 1,351 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,351 | | | |
| Other revenue and fees | | 11,536 | | | — | | | — | | | 11,536 | | | |
| Total revenues | | 690,720 | | | 129,366 | | | (80,514) | | | 739,572 | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property operating expenses | | 167,324 | | | — | | | — | | | 167,324 | | | |
| Intercompany rent expense | | — | | | 80,514 | | | (80,514) | | | — | | | |
| Ground rent expenses | | 9,326 | | | — | | | — | | | 9,326 | | | |
| General and administrative expenses | | 63,939 | | | — | | | — | | | 63,939 | | | |
| Observatory expenses | | — | | | 35,265 | | | — | | | 35,265 | | | |
| Real estate taxes | | 127,101 | | | — | | | — | | | 127,101 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 189,762 | | | 149 | | | — | | | 189,911 | | | |
| Total operating expenses | | 557,452 | | | 115,928 | | | (80,514) | | | 592,866 | | | |
| Total operating income | | 133,268 | | | 13,438 | | | — | | | 146,706 | | | |
| Other income (expense): | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | 14,936 | | | 200 | | | — | | | 15,136 | | | |
| Interest expense | | (101,484) | | | — | | | — | | | (101,484) | | | |
| Gain on sale/disposition of properties | | 26,764 | | | — | | | — | | | 26,764 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Income before income taxes | | 73,484 | | | 13,638 | | | — | | | 87,122 | | | |
| Income tax expense | | (552) | | | (2,163) | | | — | | | (2,715) | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 72,932 | | | $ | 11,475 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 84,407 | | | |
| Segment assets | | $ | 3,957,659 | | | $ | 261,674 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4,219,333 | | | |
| Expenditures for segment assets | | $ | 169,044 | | | $ | 111 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 169,155 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2022 |
| | Real Estate | | Observatory | | Intersegment Elimination | | Total |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | |
| Rental revenue | | $ | 591,048 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 591,048 | |
| Intercompany rental revenue | | 65,005 | | | — | | | (65,005) | | | — | |
| Observatory revenue | | — | | | 105,978 | | | — | | | 105,978 | |
| Lease termination fees | | 20,032 | | | — | | | — | | | 20,032 | |
| Third-party management and other fees | | 1,361 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,361 | |
| Other revenue and fees | | 8,622 | | | — | | | — | | | 8,622 | |
| Total revenues | | 686,068 | | | 105,978 | | | (65,005) | | | 727,041 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | |
| Property operating expenses | | 157,935 | | | — | | | — | | | 157,935 | |
| Intercompany rent expense | | — | | | 65,005 | | | (65,005) | | | — | |
| Ground rent expenses | | 9,326 | | | — | | | — | | | 9,326 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | 61,765 | | | — | | | — | | | 61,765 | |
| Observatory expenses | | — | | | 31,036 | | | — | | | 31,036 | |
| Real estate taxes | | 123,057 | | | — | | | — | | | 123,057 | |
| Impairment charge | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 216,707 | | | 187 | | | — | | | 216,894 | |
| Total operating expenses | | 568,790 | | | 96,228 | | | (65,005) | | | 600,013 | |
| Total operating income (loss) | | 117,278 | | | 9,750 | | | — | | | 127,028 | |
| Other income (expense): | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | 4,901 | | | 47 | | | — | | | 4,948 | |
| Interest expense | | (101,206) | | | — | | | — | | | (101,206) | |
| Gain on sale/disposition of properties | | 33,988 | | | — | | | — | | | 33,988 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Income before income taxes | | 54,961 | | | 9,797 | | | — | | | 64,758 | |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | | (584) | | | (962) | | | — | | | (1,546) | |
| Net income | | $ | 54,377 | | | $ | 8,835 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 63,212 | |
| Segment assets | | $ | 3,909,299 | | | $ | 254,295 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4,163,594 | |
| Expenditures for segment assets | | $ | 85,646 | | | $ | 315 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 85,961 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2021 |
| | Real Estate | | Observatory | | | | Intersegment Elimination | | Total |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Rental revenue | | $ | 559,690 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | — | | | $ | 559,690 | |
| Intercompany rental revenue | | 23,413 | | | — | | | | | (23,413) | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Observatory revenue | | — | | | 41,474 | | | | | — | | | 41,474 | |
| Lease termination fees | | 16,230 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 16,230 | |
| Third-party management and other fees | | 1,219 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 1,219 | |
| Other revenue and fees | | 5,343 | | | 138 | | | | | — | | | 5,481 | |
| Total revenues | | 605,895 | | | 41,612 | | | | | (23,413) | | | 624,094 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property operating expenses | | 126,986 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 126,986 | |
| Intercompany rent expense | | — | | | 23,413 | | | | | (23,413) | | | — | |
| Ground rent expenses | | 9,326 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 9,326 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | 55,947 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 55,947 | |
| Observatory expenses | | — | | | 23,206 | | | | | — | | | 23,206 | |
| Real estate taxes | | 119,967 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 119,967 | |
| Impairment charges | | 7,723 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 7,723 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 201,676 | | | 130 | | | | | — | | | 201,806 | |
| Total operating expenses | | 521,625 | | | 46,749 | | | | | (23,413) | | | 544,961 | |
| Total operating income (loss) | | 84,270 | | | (5,137) | | | | | — | | | 79,133 | |
| Other income (expense): | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | 701 | | | 3 | | | | | — | | | 704 | |
| Interest expense | | (94,292) | | | (102) | | | | | — | | | (94,394) | |
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt | | (214) | | | — | | | | | — | | | (214) | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss before income taxes | | (9,535) | | | (5,236) | | | | | — | | | (14,771) | |
| Income tax (expense) benefit | | (613) | | | 2,347 | | | | | — | | | 1,734 | |
| Net loss | | $ | (10,148) | | | $ | (2,889) | | | | | $ | — | | | $ | (13,037) | |
| Segment assets | | $ | 4,037,122 | | | $ | 245,325 | | | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4,282,447 | |
| Expenditures for segment assets | | $ | 398,368 | | | $ | 4 | | | | | $ | — | | | $ | 398,372 | |
During the fourth quarter 2021, we incurred a $7.7 million impairment charge relating to our property in Norwalk, Connecticut. Refer to Note 2 Summary of Significant Accounting Policies. Our methodology to calculate the fair value of the property involved a combination of the discounted cash flow method, utilizing Level 3 unobservable inputs such as market capitalization rates obtained from external sources, and the market based approach utilizing recent sales comparables.
14. Subsequent Events
None.
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Schedule III—Real Estate and Accumulated Depreciation
(amounts in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | Initial Cost to
the Company | | Cost Capitalized
Subsequent to
Acquisition | | Gross Amount at which Carried at 12/31/23 | | | | | | |
| Development | | Type | | Encumbrances | | Land and Development Costs | | Building &
Improvements | | Improvements | | Carrying
Costs | | Land and Development Costs | | Buildings &
Improvements | | Total | | Accumulated
Depreciation | | Date of
Construction | | Date
Acquired | | Life on
which
depreciation
in latest
income
statement is
computed |
| 111 West 33rd Street, New York, NY | | office /
retail | | $ | — | | | $ | 13,630 | | | $ | 244,461 | | | $ | 129,859 | | | n/a | | $ | 13,630 | | | $ | 374,320 | | | $ | 387,950 | | | $ | (118,371) | | | 1954 | | 2014 | | various |
| 1400 Broadway, New York, NY | | office /
retail | | — | | | — | | | 96,338 | | | 102,241 | | | n/a | | — | | | 198,579 | | | 198,579 | | | (72,907) | | | 1930 | | 2014 | | various |
| 1333 Broadway, New York, NY | | office /
retail | | 159,039 | | | 91,434 | | | 120,190 | | | 17,239 | | | n/a | | 91,435 | | | 137,429 | | | 228,864 | | | (43,811) | | | 1915 | | 2013 | | various |
| 1350 Broadway, New York, NY | | office /
retail | | — | | | — | | | 102,518 | | | 48,815 | | | n/a | | — | | | 151,333 | | | 151,333 | | | (55,169) | | | 1929 | | 2013 | | various |
| 250 West 57th Street, New York, NY | | office/
retail | | 175,755 | | | 2,117 | | | 5,041 | | | 179,876 | | | n/a | | 2,117 | | | 184,917 | | | 187,034 | | | (74,936) | | | 1921 | | 1953 | | various |
| 501 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY | | office/
retail | | — | | | 1,100 | | | 2,600 | | | 107,812 | | | n/a | | 1,100 | | | 110,412 | | | 111,512 | | | (58,775) | | | 1923 | | 1950 | | various |
| 1359 Broadway, New York, NY | | office/
retail | | — | | | 1,233 | | | 1,809 | | | 83,221 | | | n/a | | 1,233 | | | 85,029 | | | 86,262 | | | (33,438) | | | 1924 | | 1953 | | various |
| 350 Fifth Avenue (Empire State Building), New York, NY | | office/
retail | | — | | | 21,551 | | | 38,934 | | | 1,060,121 | | | n/a | | 21,551 | | | 1,099,055 | | | 1,120,606 | | | (428,926) | | | 1930 | | 2013 | | various |
One Grand Central Place,
New York, NY | | office/
retail | | — | | | 7,240 | | | 17,490 | | | 310,522 | | | n/a | | 7,222 | | | 328,030 | | | 335,252 | | | (164,248) | | | 1930 | | 1954 | | various |
| First Stamford Place, Stamford, CT | | office | | 177,181 | | | 22,952 | | | 122,738 | | | 86,494 | | | n/a | | 24,860 | | | 207,324 | | | 232,184 | | | (113,916) | | | 1986 | | 2001 | | various |
| One Station Place, Stamford, CT (Metro Center) | | office | | 80,117 | | | 5,313 | | | 28,602 | | | 40,955 | | | n/a | | 5,313 | | | 69,557 | | | 74,870 | | | (41,494) | | | 1987 | | 1984 | | various |
| 10 Union Square, New York, NY | | retail | | 49,762 | | | 5,003 | | | 12,866 | | | 5,742 | | | n/a | | 5,003 | | | 18,608 | | | 23,611 | | | (10,102) | | | 1987 | | 1996 | | various |
| 1542 Third Avenue, New York, NY | | retail | | 29,804 | | | 2,239 | | | 15,266 | | | 485 | | | n/a | | 2,239 | | | 15,751 | | | 17,990 | | | (9,937) | | | 1991 | | 1999 | | various |
| 1010 Third Avenue, New York, NY and 77 West 55th Street, New York, NY | | retail | | 34,697 | | | 4,462 | | | 15,819 | | | 4,211 | | | n/a | | 4,462 | | | 20,030 | | | 24,492 | | | (10,937) | | | 1962 | | 1998 | | various |
| 345 E 94th Street, New York, NY | | multi-family | | 48,646 | | | 44,228 | | | 55,766 | | | 4,237 | | | n/a | | 44,228 | | | 60,003 | | | 104,231 | | | (3,485) | | | 2000 | | | 2021 | | | various |
| Victory 561 10th Ave, New York, NY | | multi-family | | 124,194 | | | 91,437 | | | 124,997 | | | 3,461 | | | n/a | | 91,437 | | | 128,458 | | | 219,895 | | | (7,491) | | | 2004 | | | 2021 | | | various |
| 298 Mulberry, New York, NY | | multi-family | | — | | | 40,935 | | | 69,509 | | | 1,475 | | | n/a | | 41,125 | | | 70,794 | | | 111,919 | | | (1,923) | | | 1986 | | 2022 | | various |
| Williamsburg Retail, Brooklyn, NY | | retail | | — | | | 4,851 | | | 20,936 | | | 101 | | | n/a | | 4,860 | | | 21,028 | | | 25,888 | | | (196) | | | 1910, 1945 | | 2023 | | various |
| Property for development at the Transportation Hub in Stamford, CT | | land | | — | | | 4,541 | | | — | | | 8,179 | | | n/a | | 12,720 | | | — | | | 12,720 | | | — | | | n/a | | n/a | | n/a |
| Totals | | | | $ | 879,195 | | | $ | 364,266 | | | $ | 1,095,880 | | | $ | 2,195,046 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 374,535 | | | $ | 3,280,657 | | | $ | 3,655,192 | | | $ | (1,250,062) | | | | | | | |
Empire State Realty Trust, Inc.
Notes to Schedule III—Real Estate and Accumulated Depreciation
(amounts in thousands)
1. Reconciliation of Investment Properties
The changes in our investment properties for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 3,551,449 | | | $ | 3,500,917 | | | $ | 3,133,966 | |
| Acquisition of new properties | 25,787 | | | 110,444 | | | 316,428 | |
| Improvements | 106,792 | | | 79,070 | | | 89,426 | |
| Property classified as held for sale | — | | | (61,965) | | | — | |
| Disposals | (28,836) | | | (77,017) | | | (38,903) | |
| Balance, end of year | $ | 3,655,192 | | | $ | 3,551,449 | | | $ | 3,500,917 | |
The unaudited aggregate cost of investment properties for federal income tax purposes as of December 31, 2023 was $3.8 billion.
2. Reconciliation of Accumulated Depreciation
The changes in our accumulated depreciation for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Balance, beginning of year | | $ | 1,137,267 | | | $ | 1,072,938 | | | $ | 941,612 | |
| Depreciation expense | | 158,879 | | | 179,872 | | | 162,667 | |
| Property classified as held for sale | | — | | | (30,315) | | | — | |
| Disposals | | (46,084) | | | (85,228) | | | (31,341) | |
| Balance, end of year | | $ | 1,250,062 | | | $ | 1,137,267 | | | $ | 1,072,938 | |
Depreciation of investment properties reflected in the combined statements of income is calculated over the estimated original lives of the assets as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | 39 years or useful life |
| Building improvements | | 39 years or useful life |
| Tenant improvements | | Term of related lease |
