DEFINITIONS
AASB- Australian Accounting Standards Board. The term “AASB” is commonly used when identifying Australian Accounting Standards issued by the AASB.
ANZEST – ANZ Employee Share Trust.
APRA - Australian Prudential Regulation Authority.
APS - ADI Prudential Standard.
Cash and cash equivalentscomprise coins, notes, money at call, balances held with central banks, liquid settlement balances (readily convertible to known amounts of cash which are subject to insignificant risk of changes in value) and securities purchased under agreements to resell (reverse repos) in less than three months.
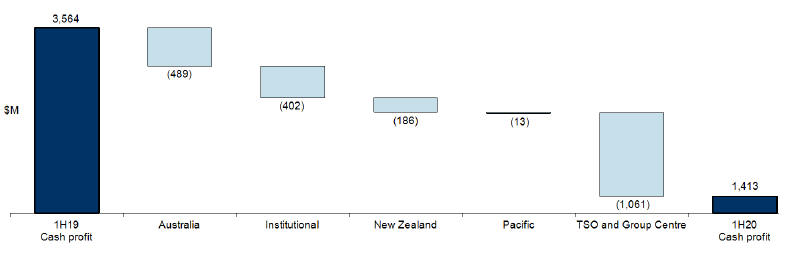
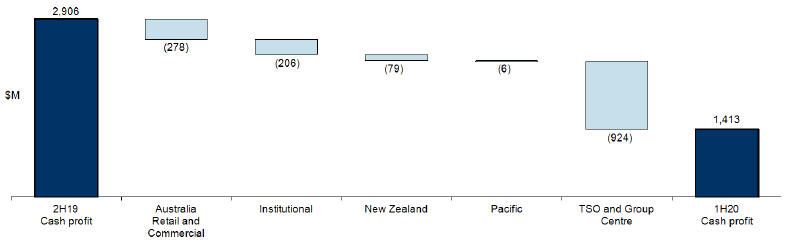
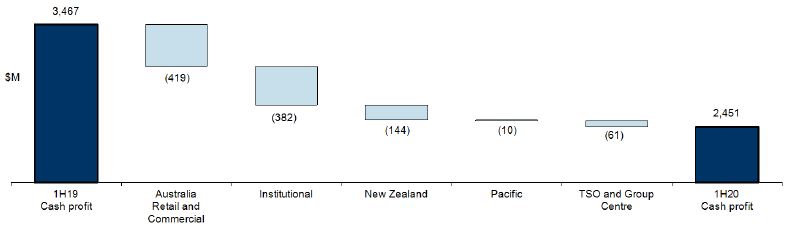
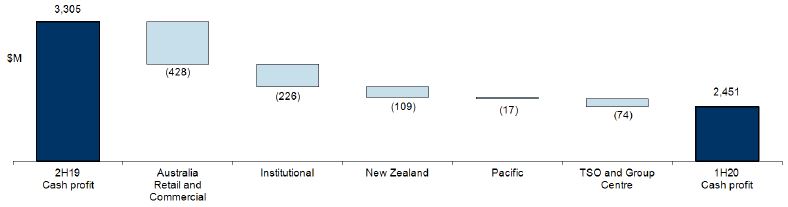
Cash profit is an additional measure of profit which is prepared on a basis other than in accordance with accounting standards. Cash profit represents ANZ’s preferred measure of the result of the core business activities of the Group, enabling readers to assess Group and Divisional performance against prior periods and against peer institutions. To calculate cash profit, the Group excludesnon-core items from statutory profit as noted below. These items are calculated consistently period on period so as not to discriminate between positive and negative adjustments.
Gains and losses are adjusted where they are significant, or have the potential to be significant in any one period, and fall into one of three categories:
| | 1. | gains or losses included in earnings arising from changes in tax, legal or accounting legislation or othernon-core items not associated with the core operations of the Group; |
| | 2. | treasury shares, revaluation of policy liabilities, economic hedging impacts and similar accounting items that represent timing differences that will reverse through earnings in the future; and |
| | 3. | accounting reclassifications between individual line items that do not impact reported results, such as policyholders tax gross up. |
Cash profit is not a measure of cash flow or profit determined on a cash accounting basis.
Collectively assessed allowance for expected credit lossrepresents the Expected Credit Loss (ECL). This incorporates forward looking information and does not require an actual loss event to have occurred for an impairment provision to be recognised.
Coronavirus(COVID-19) is a respiratory illness caused by a new virus and declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.COVID-19 was characterised as a pandemic by the World Health Organisation on 11 March 2020.
Covered bonds are bonds issued by an ADI to external investors secured against a pool of the ADI’s assets (the cover pool) assigned to a bankruptcy remote special purpose entity. The primary assets forming the cover pool are mortgage loans. The mortgages remain on the issuer’s balance sheet. The covered bond holders have dual recourse to the issuer and the cover pool assets. The mortgages included in the cover pool cannot be otherwise pledged or disposed of but may be repurchased and substituted in order to maintain the credit quality of the pool. The Group issues covered bonds as part of its funding activities.
Credit riskis the risk of financial loss resulting from the failure of ANZ’s customers and counterparties to honour or perform fully the terms of a loan or contract.
Credit risk weighted assets (CRWA)represent assets which are weighted for credit risk according to a set formula as prescribed in APS 112/113.
Customer deposits represent term deposits, other deposits bearing interest, deposits not bearing interest and borrowing corporations’ debt excluding securitisation deposits.
Customer remediation includes provisions for expected refunds to customers, remediation project costs and related customer and regulatory claims, penalties and litigation outcomes.
Derivative credit valuation adjustment (CVA) - Over the life of a derivative instrument, ANZ uses a model to adjust fair value to take into account the impact of counterparty credit quality. The methodology calculates the present value of expected losses over the life of the financial instrument as a function of probability of default, loss given default, expected credit risk exposure and an asset correlation factor. Impaired derivatives are also subject to a CVA.
Dividend payout ratiois the total ordinary dividend payment divided byprofit attributable to shareholders of the Company.
Gross loans and advances (GLA) is made up of loans and advances, capitalised brokerage/mortgage origination fees less unearned income.
Impaired assetsare those financial assets where doubt exists as to whether the full contractual amount will be received in a timely manner, or where concessional terms have been provided because of the financial difficulties of the customer. Financial assets are impaired if there is objective evidence of impairment as a result of a loss event that occurred prior to the reporting date, and that loss event has had an impact, which can be reliably estimated, on the expected future cash flows of the individual asset or portfolio of assets.
Impaired loanscomprise drawn facilities where the customer’s status is defined as impaired.
Individually assessed allowance for expected credit lossesis assessed on acase-by-case basis for all individually managed impaired assets taking into consideration factors such as the realisable value of security (or other credit mitigants), the likely return available upon liquidation or bankruptcy, legal uncertainties, estimated costs involved in recovery, the market price of the exposure in secondary markets and the amount and timing of expected receipts and recoveries.
Interest rate risk in the banking book (IRRBB) relates to the potential adverse impact of changes in market interest rates on ANZ’s future net interest income. The risk generally arises from:
| | 1. | Repricing and yield curve risk - the risk to earnings or market value as a result of changes in the overall level of interest rates and/or the relativity of these rates across the yield curve; |
| | 2. | Basis risk - the risk to earnings or market value arising from volatility in the interest margin applicable to banking book items; and |
| | 3. | Optionality risk - the risk to earnings or market value arising from the existence of stand-alone or embedded options in banking book items. |
Internationally comparable ratiosare ANZ’s interpretation of the regulations documented in the Basel Committee publications: “Basel 3: A global regulatory framework for more resilient banks and banking systems” (June 2011) and “International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards” (June 2006). They also include differences identified in APRA’s information paper entitled International Capital Comparison Study (13 July 2015).
Level 1in the context of APRA supervision, Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Limited consolidated with certain approved subsidiaries.
Level 2in the context of APRA supervision, the consolidated ANZ Group excluding associates, insurance and funds management entities, commercialnon-financial entities and certain securitisation vehicles.
139