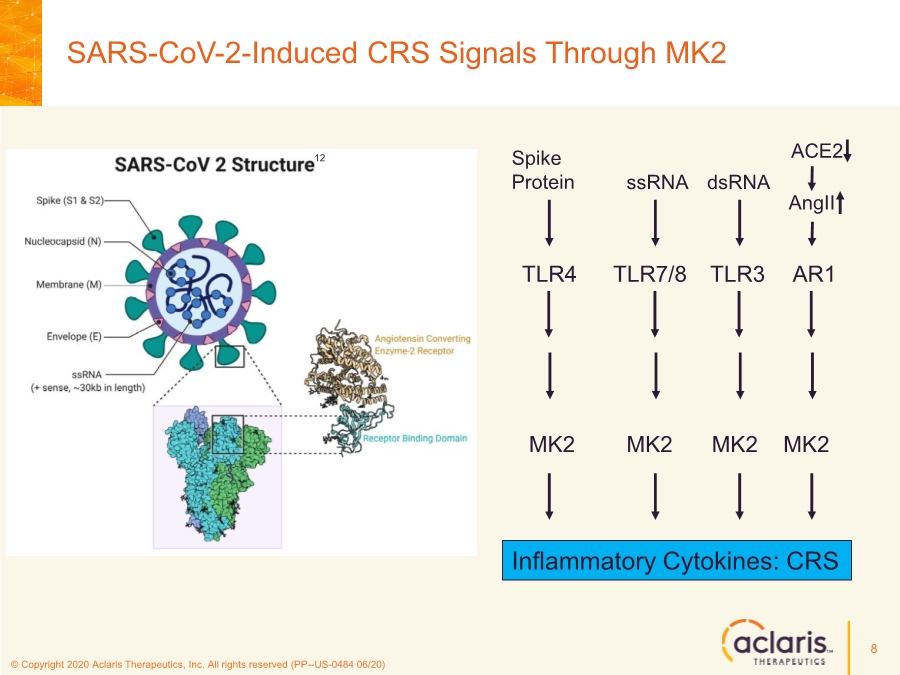
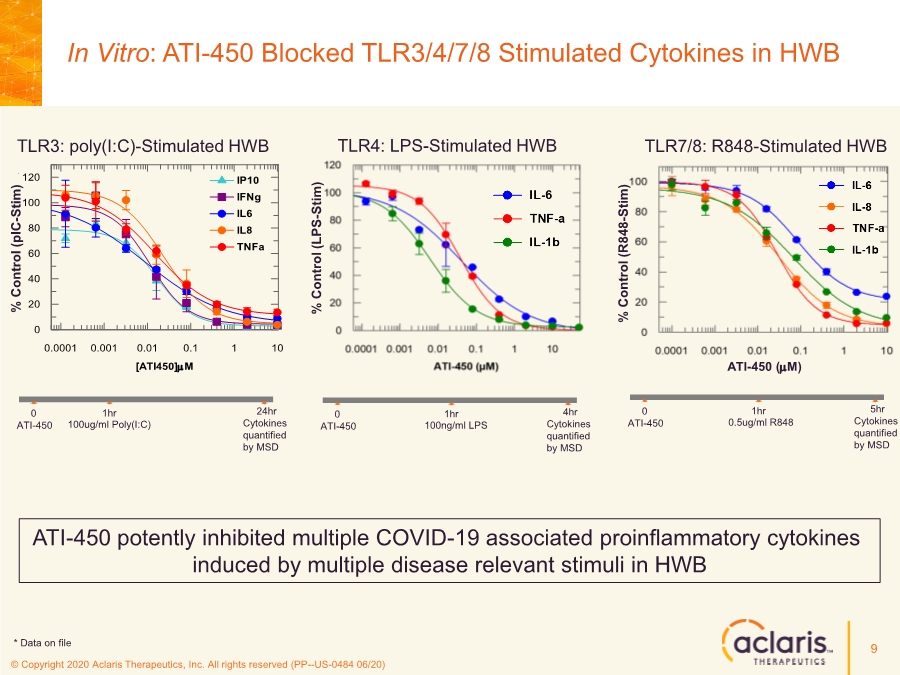
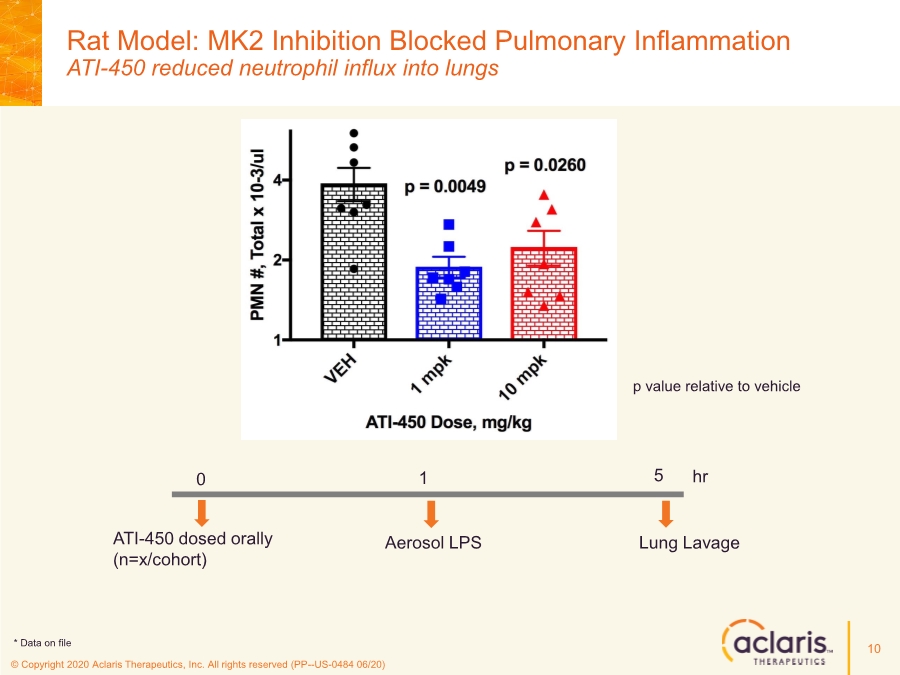
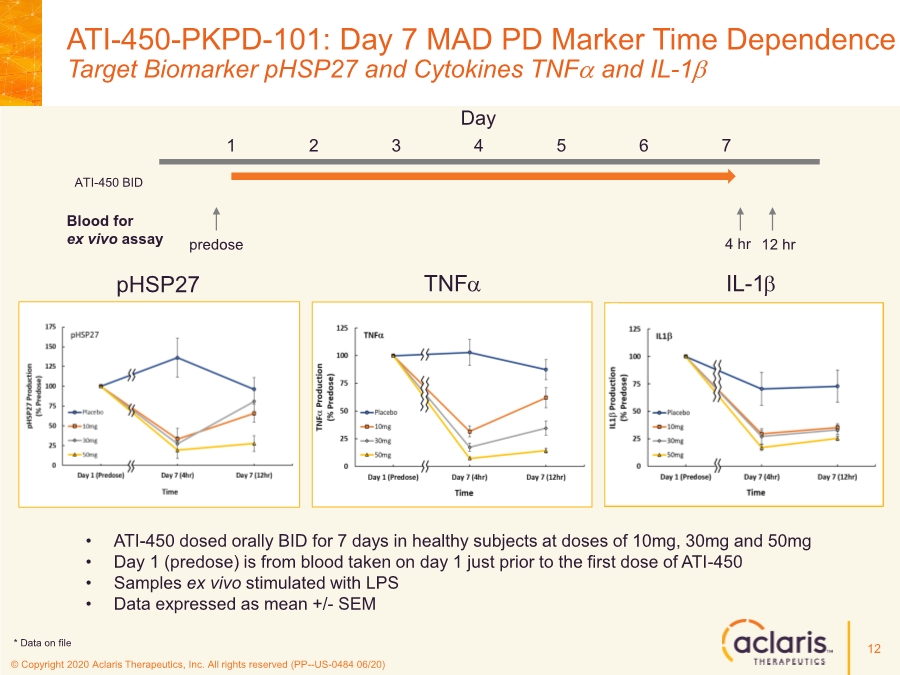
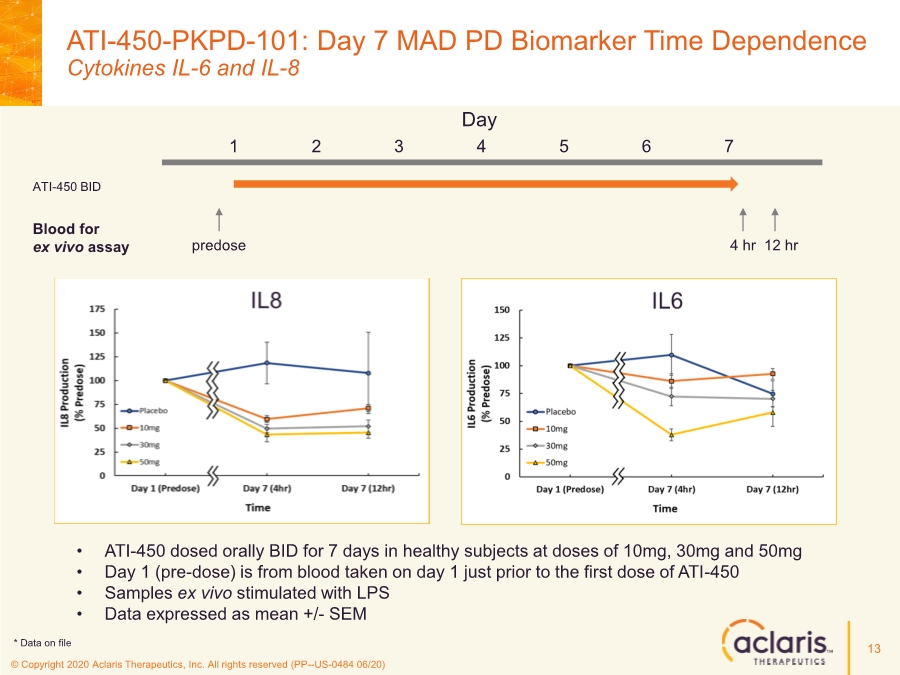
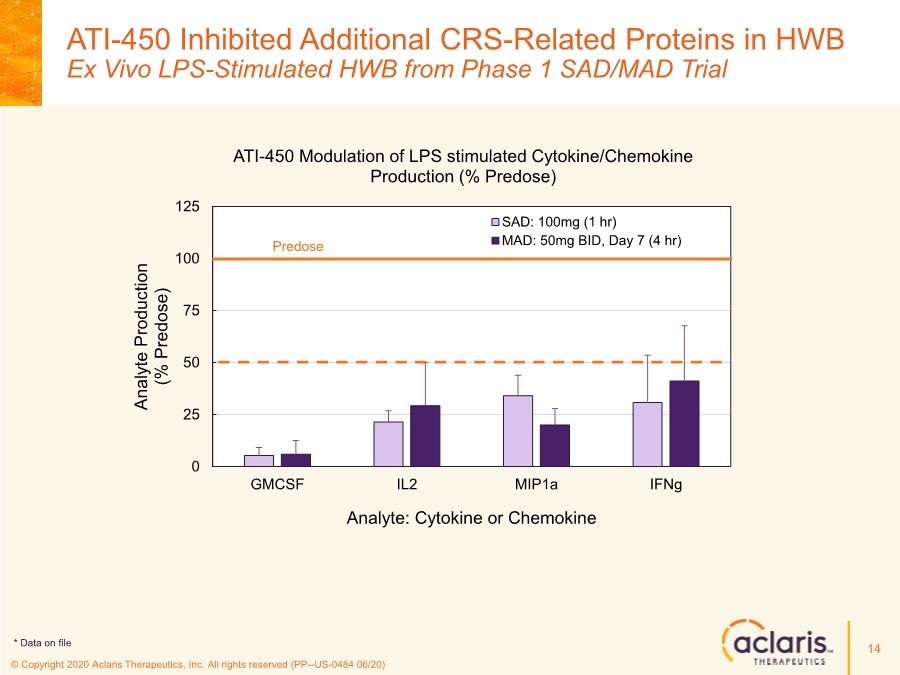
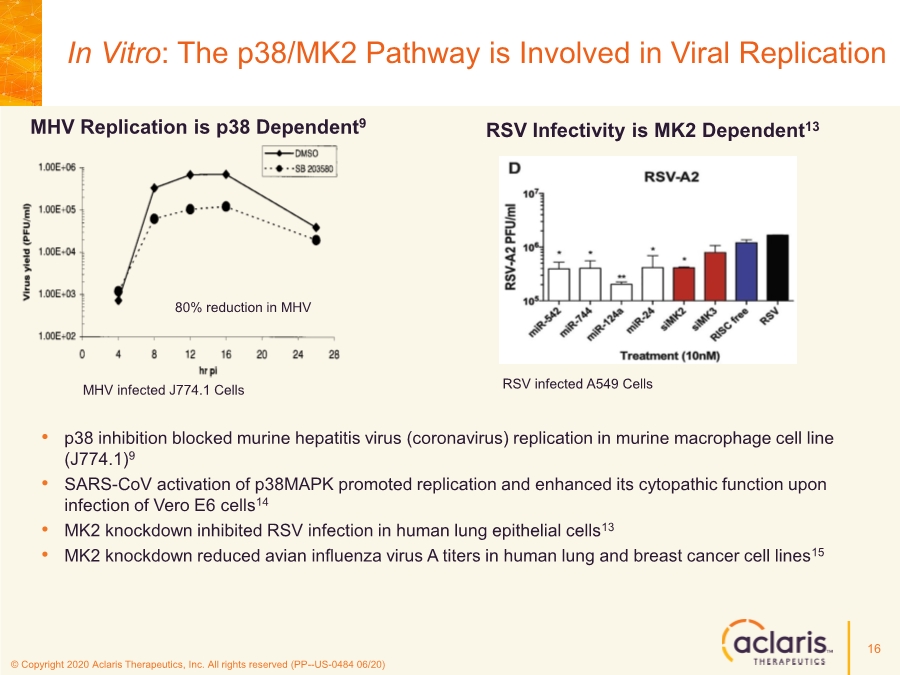
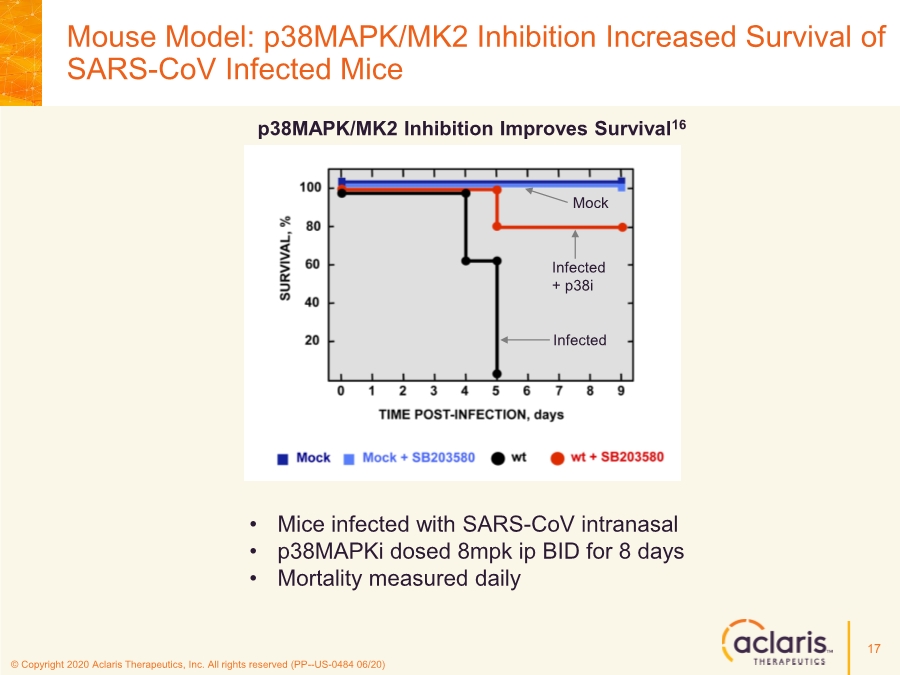
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) References 23 1. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497-506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 2. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054-1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3 3. Xu X, Han M, Li T, et al. Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(20):10970-10975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005615117 4. Investigating Otilimab in Patients With Severe Pulmonary COVID-19 Related Disease (OSCAR). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04376684. Accessed June 15, 2020. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04376684 5. Study of Efficacy and Safety of Canakinumab Treatment for CRS in Participants With COVID-19-induced Pneumonia (CAN-COVID). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04362813. Accessed June 15, 2020. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04362813 6. Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Moderate to Severe COVID-19 With Inflammatory Markers (TOCIBRAS). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04403685. Accessed June 16, 2020. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04403685 7. Anti-Interleukin-8 (Anti-IL-8) for Patients With COVID-19. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04347226. Accessed June 15, 2020. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04347226 8. Fung TS, Liao Y, Liu DX. Regulation of Stress Responses and Translational Control by Coronavirus. Viruses. 2016;8(7):184. doi: 10.3390/v8070184 9. Banerjee S, Narayanan K, Mizutani T, Makino S. Murine Coronavirus Replication-Induced p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation Promotes Interleukin-6 Production and Virus Replication in Cultured Cells. J Virol. 2002;76(12):5937-5948. doi:10.1128/JVI.76.12.5937–5948.2002 10. Regan, AD, Cohen RD, Whittaker GR. Activation of p38 MAPK by feline infectious peritonitis virus regulates pro-inflammatory cytokine production in primary blood-derived feline mononuclear cells. J Virol. 2009;384(1):135-143. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.11.006 11. Liao Y, Wang X, Huang M, Tam JP, Liu DX. Regulation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and dual-specificity phosphatase 1 feedback loop modulates the induction of interleukin 6 and 8 in cells infected with coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. J Virol. 2011;420(2):106-116. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.09.003 12. Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn S. Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19). StatPearls. Updated May 18, 2020. Accessed June 16, 2020. https://www.statpearls.com/kb/viewarticle/52171 13. McCaskill JL, Ressel S, Alber A, et al. Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of Respiratory Virus Infection by MicroRNA Mimics Targeting p38 MAPK Signaling. Mol Therapy: Nuc Acids. 2017;7:256- 266. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.03.008 14. Yoshino S, Mizutani N. Intranasal exposure to monoclonal antibody Fab fragments to Japanese cedar pollen Cry j1 suppresses Japanese cedar pollen‐induced allergic rhinitis. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173(10):1629–1638. doi: 10.1111/bph.13463 15. Luig C, Köther K, Dudek SE, et al. MAP kinase-activated protein kinases 2 and 3 are required for influenza A virus propagation and act via inhibition of PKR. FASEB J. 2010; 24:4068- 4077. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-158766 16. Jimenez-Guardeño JM, Nieto-Torres JL, DeDiego ML, et al. The PDZ-Binding Motif of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Envelope Protein Is a Determinant of Viral Pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10(8):1-20. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004320 17. Spagnolo P, Balestro E, Aliberti S, et al. Pulmonary fibrosis secondary to COVID-19: a call to arms? Lancet Respir Med. Published online May 15, 2020. doi: 10.1016/ S2213- 2600(20)30222-8 18. Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matté A, et al. Functional Disability 5 Years after Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(14):1293-1304. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1011802 19. Borthwick LA. The IL-1 Cytokine Family and Its Role in Inflammation and Fibrosis in the Lung. Semin Immunopathol. 2016;38(4):517-34. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0559-z 20. Meduri GU, Headley S, Kohler G, Stentz F, Tolley E, Umberger R, Leeper K. Persistent Elevation of Inflammatory Cytokines Predicts a Poor Outcome in ARDS. Plasma IL-1 Beta and IL-6 Levels Are Consistent and Efficient Predictors of Outcome Over Time. Chest. 1995;107(4):1062-1073. doi: 10.1378/chest.107.4.1062 21. Fang L, Karakiulakis G, Roth M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(4):e21. doi: 10.1016/S2213- 2600(20)30116-8 22. Vittal R, Fisher A, Gu H, et al. Peptide-Mediated Inhibition of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase–Activated Protein Kinase–2 Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013;49(1):47–57. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0389OC 23. Liang J, Liu N, Liu X, et al. Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase–activated Protein Kinase 2 Inhibition Attenuates Fibroblast Invasion and Severe Lung Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019;60(1):41–48. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0033OC |