
Exhibit 99.2 Corporate Presentation November 2022

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Any statement describing Acumen’s goals, expectations, financial or other projections, intentions or beliefs is a forward-looking statement and should be considered an at-risk statement. Words such as “believes,” “expects,” “anticipates,” “could,” “would,” “seeks,” “aims,” “plans,” “potential,” “will” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. Forward-looking statements include statements concerning Acumen’s business, Acumen’s ability to achieve its strategic and financial goals, including its projected use of cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities and the sufficiency of its cash resources, and the therapeutic potential of Acumen’s product candidate, ACU193, including its potential for improved safety and efficacy as compared to other monoclonal antibodies in development, as well as the expectations concerning the INTERCEPT-AD trial and Acumen’s planned Phase 2/3 clinical trial, including the expected timing of initiation, enrollment and reporting data, and risks and uncertainties relating to the progression and duration of the COVID-19 pandemic and responsive measures thereto and related effects on Acumen. These statements are based upon the current beliefs and expectations of Acumen management, and are subject to certain factors, risks and uncertainties, particularly those inherent in the process of discovering, developing and commercializing safe and effective human therapeutics. Such risks may be amplified by the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. These and other risks concerning Acumen’s programs are described in additional detail in Acumen’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), including in Acumen’s Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021, Acumen’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2022, and future filings and reports by Acumen. Copies of these and other documents are available from Acumen. Additional information will be made available in other filings that Acumen makes from time to time with the SEC. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date hereof, and Acumen expressly disclaims any obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statement, except as otherwise required by law, whether, as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. In this presentation, references to cash also include cash equivalents. 2

Advancing a Potential Best-/First-In-Class Antibody Product for Early Alzheimer’s disease (AD) $ Scientific Experienced Strong Phase 1 Clinical Alzheimer’s ACU193: First, Represents an Consensus Clinical-Stage Leadership Team Balance Sheet: Trial in Early AD Enormous Market Supports Amyloid- Monoclonal Comprised of ~$200M in cash Patients Ongoing Proof of Driven by High Beta Oligomers Antibody (mAb) to Industry Leaders at 30-Sep-22 (AβOs) as the and several with Mechanism Unmet Need and Selectively Target July 2021 IPO Most Toxic Form AD clinical Drug, Target Recent Scientific AβOs with ~$184M Gross and Regulatory of Aβ and a Novel Promising Pre- Development, and Engagement RA Capital Momentum Target for Effective Clinical Evidence Regulatory Safety Data Deep Track Topline Results AD Treatment Supporting its Expertise from Eli Sands Capital Expected Differentiation Lilly & Co. PBM Capital 2H 2023 We believe that Acumen has the organizational expertise and fiscal resources to advance ACU193 through 2025. 3

Acumen Business Strategy: 2022-2025 → Rapidly advance ACU193 through clinical development in patients with early AD; → Evaluate combination approaches to complement our core ACU193 monotherapy strategy; → Selectively explore potential of ACU193 for other diseases; → Expand our product portfolio by in-licensing and/or developing additional candidates and/or alternative formulations for, or derivatives of, ACU193; and → Optimize value of ACU193 and future drug candidates in major markets. 4

INTERCEPT-AD Trial Update – 3Q 2022 • INTERCEPT-AD: Phase 1 clinical trial of ACU193 in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (RCT) → Trial enrollment ongoing at 17 active sites ▪ Enrollment completion expected in 1Q 2023 → Topline results (proof-of-mechanism) following full database lock expected in 2H 2023 ▪ Safety / ARIA-E ▪ PK ▪ Target engagement • Phase 2/3 ‘Ready’ Activities → Chronic GLP toxicity study in-life phase completed; final study report expected in 1Q 2023 → Well-positioned to efficiently scale manufacturing to have sufficient drug supply to meet the requirements of our current development plan → Confirmation of ACU193’s IgG2 antibody subclass; maintain expectation that reduced effector function should favorably influence ACU193 safety outcomes 5

AD, Amyloid & Abeta Oligomers
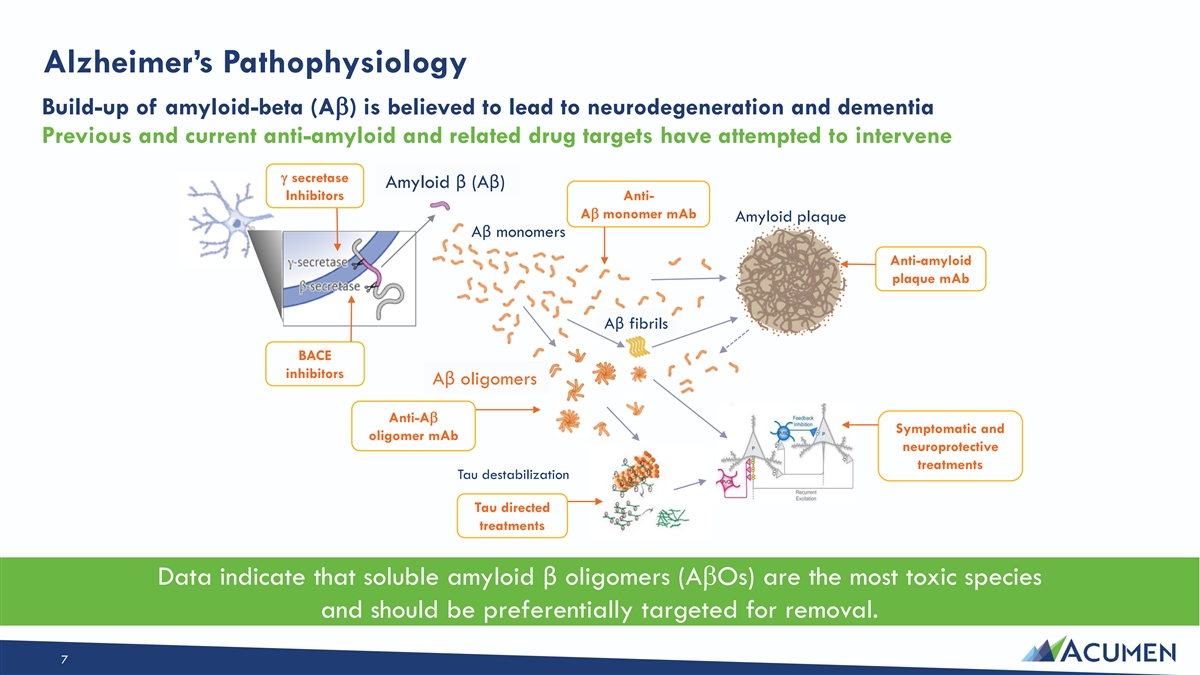
Alzheimer’s Pathophysiology Build-up of amyloid-beta (Ab) is believed to lead to neurodegeneration and dementia Previous and current anti-amyloid and related drug targets have attempted to intervene g secretase Amyloid β (Aβ) Inhibitors Anti- Ab monomer mAb Amyloid plaque Aβ monomers Anti-amyloid plaque mAb Aβ fibrils BACE inhibitors Aβ oligomers Anti-Ab Symptomatic and oligomer mAb neuroprotective treatments Tau destabilization Tau directed treatments Data indicate that soluble amyloid β oligomers (AbOs) are the most toxic species and should be preferentially targeted for removal. 7
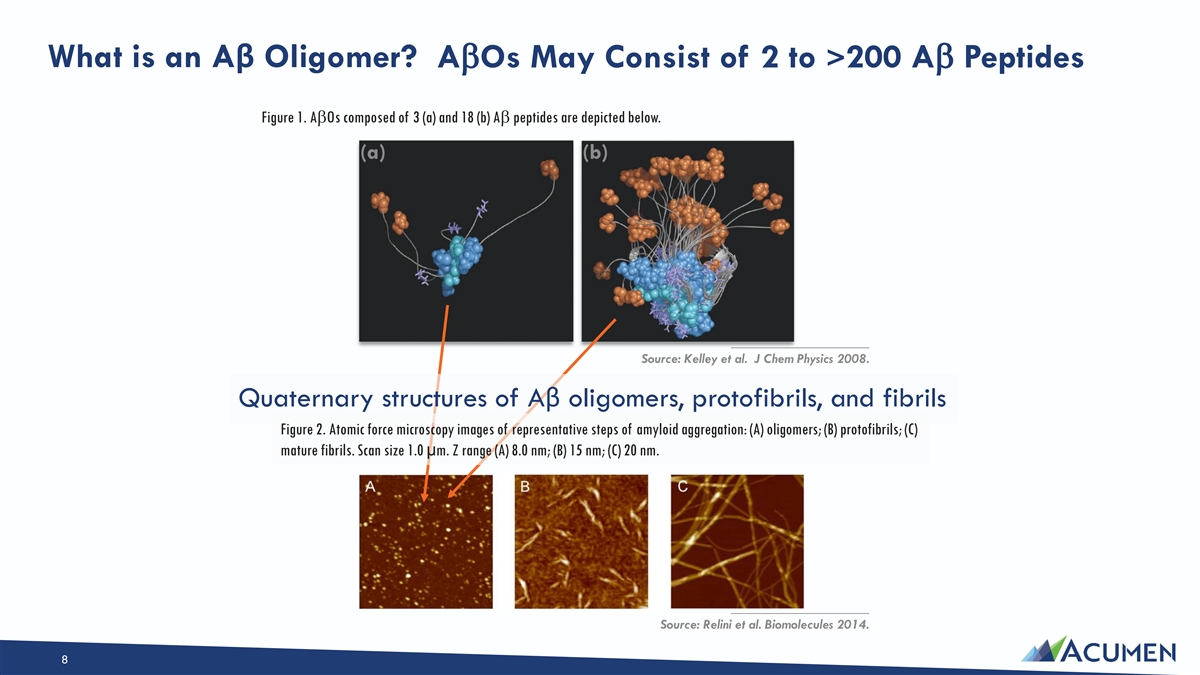
What is an Aβ Oligomer? AbOs May Consist of 2 to >200 Ab Peptides Figure 1. AbOs composed of 3 (a) and 18 (b) Ab peptides are depicted below. (a) (b) ____________________ Source: Kelley et al. J Chem Physics 2008. Quaternary structures of Aβ oligomers, protofibrils, and fibrils Figure 2. Atomic force microscopy images of representative steps of amyloid aggregation: (A) oligomers; (B) protofibrils; (C) mature fibrils. Scan size 1.0 µm. Z range (A) 8.0 nm; (B) 15 nm; (C) 20 nm. ____________________ Source: Relini et al. Biomolecules 2014. 8
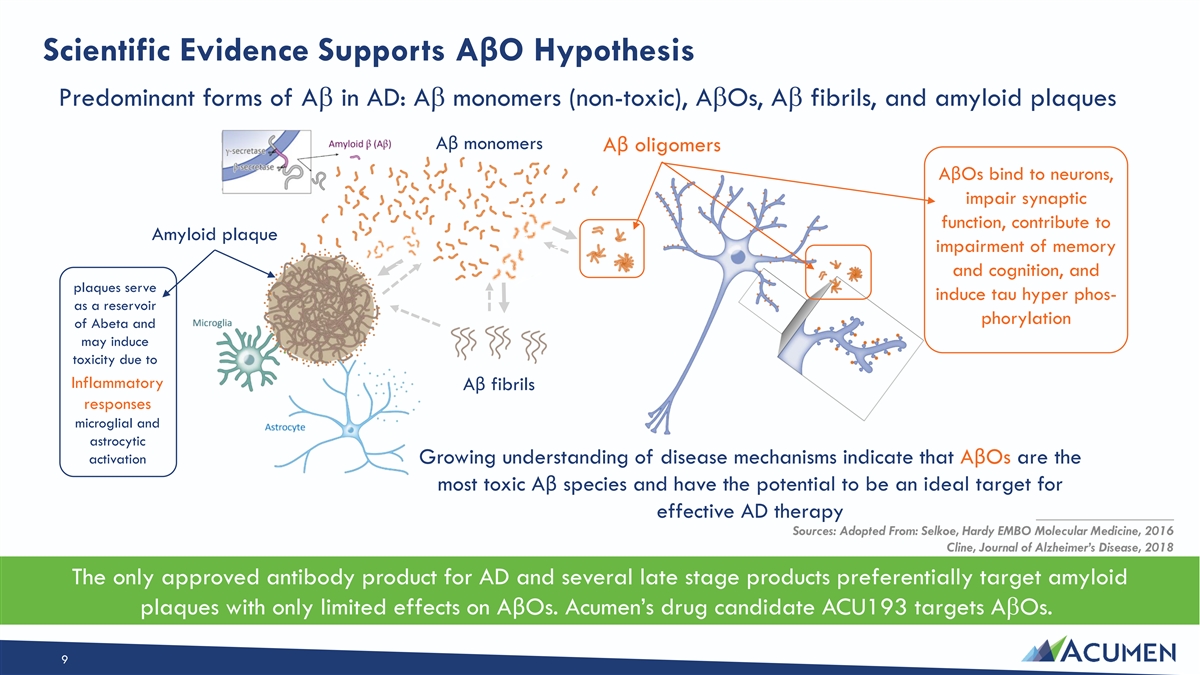
Scientific Evidence Supports AβO Hypothesis Predominant forms of Ab in AD: Ab monomers (non-toxic), AbOs, Ab fibrils, and amyloid plaques Aβ monomers Aβ oligomers AβOs bind to neurons, impair synaptic function, contribute to Amyloid plaque impairment of memory and cognition, and plaques serve induce tau hyper phos- as a reservoir phorylation of Abeta and may induce toxicity due to Inflammatory Aβ fibrils responses microglial and astrocytic activation Growing understanding of disease mechanisms indicate that AβOs are the most toxic Aβ species and have the potential to be an ideal target for effective AD therapy ____________________ Sources: Adopted From: Selkoe, Hardy EMBO Molecular Medicine, 2016 Cline, Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 2018 The only approved antibody product for AD and several late stage products preferentially target amyloid plaques with only limited effects on AβOs. Acumen’s drug candidate ACU193 targets AbOs. 9
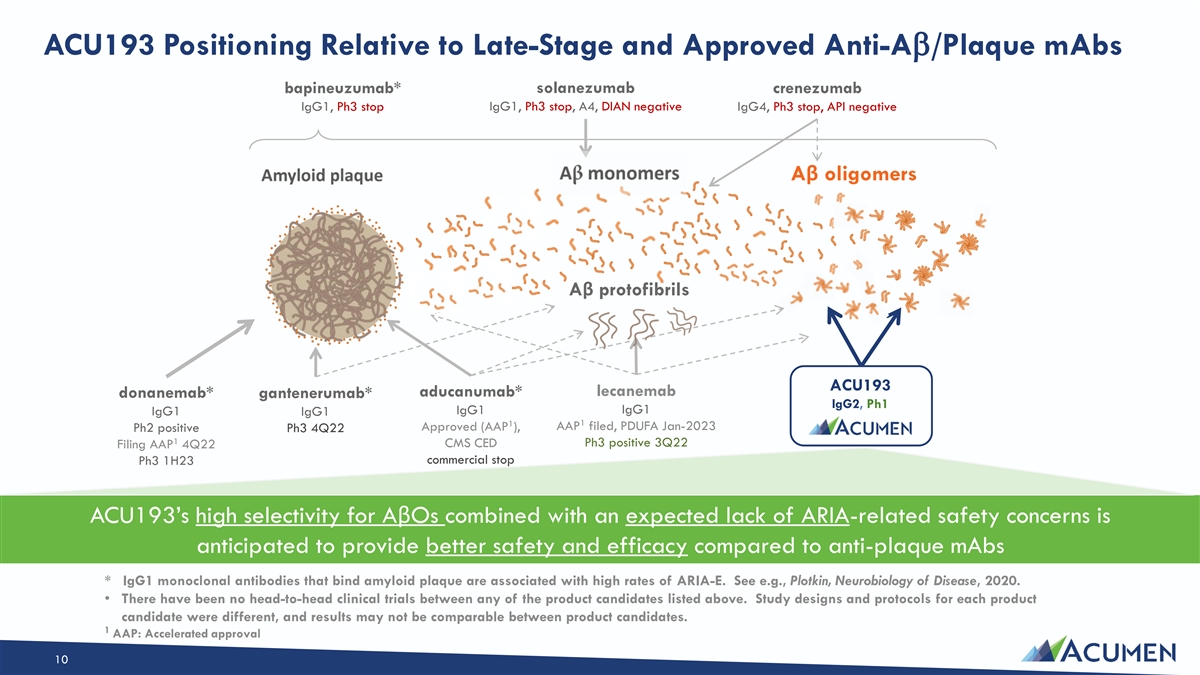
ACU193 Positioning Relative to Late-Stage and Approved Anti-Ab/Plaque mAbs bapineuzumab* solanezumab crenezumab IgG1, Ph3 stop IgG1, Ph3 stop, A4, DIAN negative IgG4, Ph3 stop, API negative Aβ oligomers Aβ protofibrils ACU193 aducanumab* lecanemab donanemab* gantenerumab* IgG2, Ph1 IgG1 IgG1 IgG1 IgG1 1 1 AAP filed, PDUFA Jan-2023 Approved (AAP ), Ph2 positive Ph3 4Q22 1 Ph3 positive 3Q22 CMS CED Filing AAP 4Q22 commercial stop Ph3 1H23 ACU193’s high selectivity for AβOs combined with an expected lack of ARIA-related safety concerns is anticipated to provide better safety and efficacy compared to anti-plaque mAbs * IgG1 monoclonal antibodies that bind amyloid plaque are associated with high rates of ARIA-E. See e.g., Plotkin, Neurobiology of Disease, 2020. • There have been no head-to-head clinical trials between any of the product candidates listed above. Study designs and protocols for each product candidate were different, and results may not be comparable between product candidates. 1 AAP: Accelerated approval 10
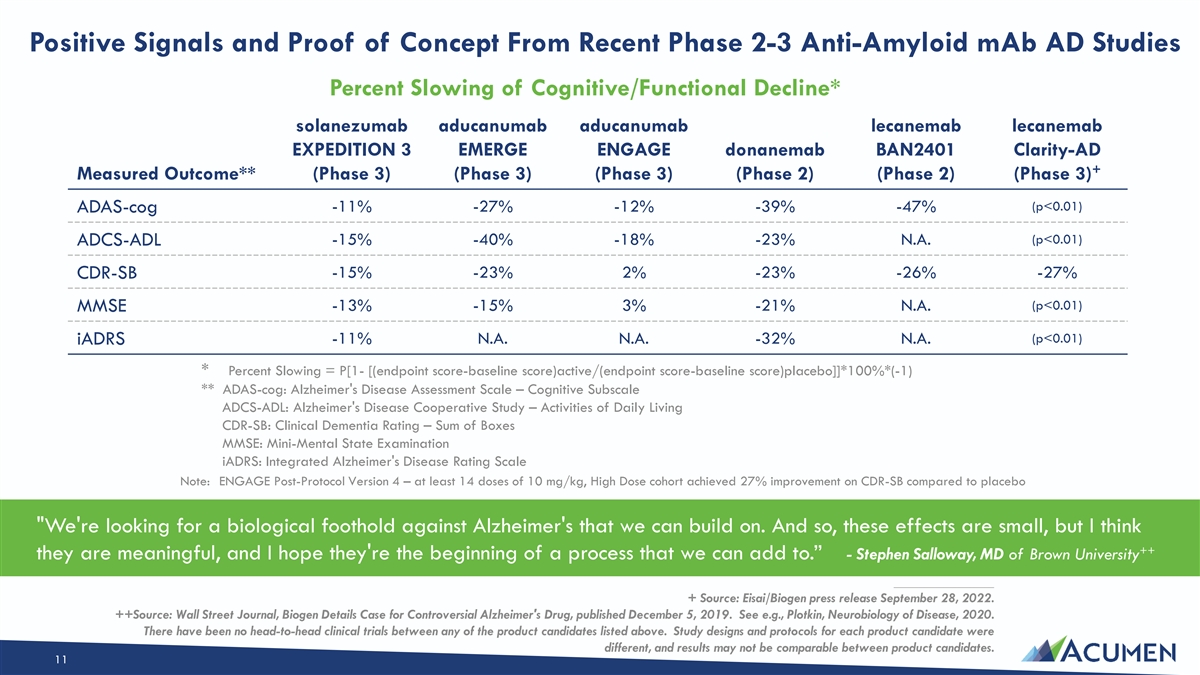
Positive Signals and Proof of Concept From Recent Phase 2-3 Anti-Amyloid mAb AD Studies Percent Slowing of Cognitive/Functional Decline* solanezumab aducanumab aducanumab lecanemab lecanemab EXPEDITION 3 EMERGE ENGAGE donanemab BAN2401 Clarity-AD + Measured Outcome** (Phase 3) (Phase 3) (Phase 3) (Phase 2) (Phase 2) (Phase 3) (p<0.01) ADAS-cog -11% -27% -12% -39% -47% (p<0.01) -15% -40% -18% -23% N.A. ADCS-ADL -15% -23% 2% -23% -26% -27% CDR-SB (p<0.01) MMSE -13% -15% 3% -21% N.A. (p<0.01) -11% N.A. N.A. -32% N.A. iADRS * Percent Slowing = P[1- [(endpoint score-baseline score)active/(endpoint score-baseline score)placebo]]*100%*(-1) ** ADAS-cog: Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale – Cognitive Subscale ADCS-ADL: Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study – Activities of Daily Living CDR-SB: Clinical Dementia Rating – Sum of Boxes MMSE: Mini-Mental State Examination iADRS: Integrated Alzheimer's Disease Rating Scale Note: ENGAGE Post-Protocol Version 4 – at least 14 doses of 10 mg/kg, High Dose cohort achieved 27% improvement on CDR-SB compared to placebo We're looking for a biological foothold against Alzheimer's that we can build on. And so, these effects are small, but I think ++ they are meaningful, and I hope they're the beginning of a process that we can add to.” - Stephen Salloway, MD of Brown University ____________________ + Source: Eisai/Biogen press release September 28, 2022. ++Source: Wall Street Journal, Biogen Details Case for Controversial Alzheimer's Drug, published December 5, 2019. See e.g., Plotkin, Neurobiology of Disease, 2020. There have been no head-to-head clinical trials between any of the product candidates listed above. Study designs and protocols for each product candidate were different, and results may not be comparable between product candidates. 11
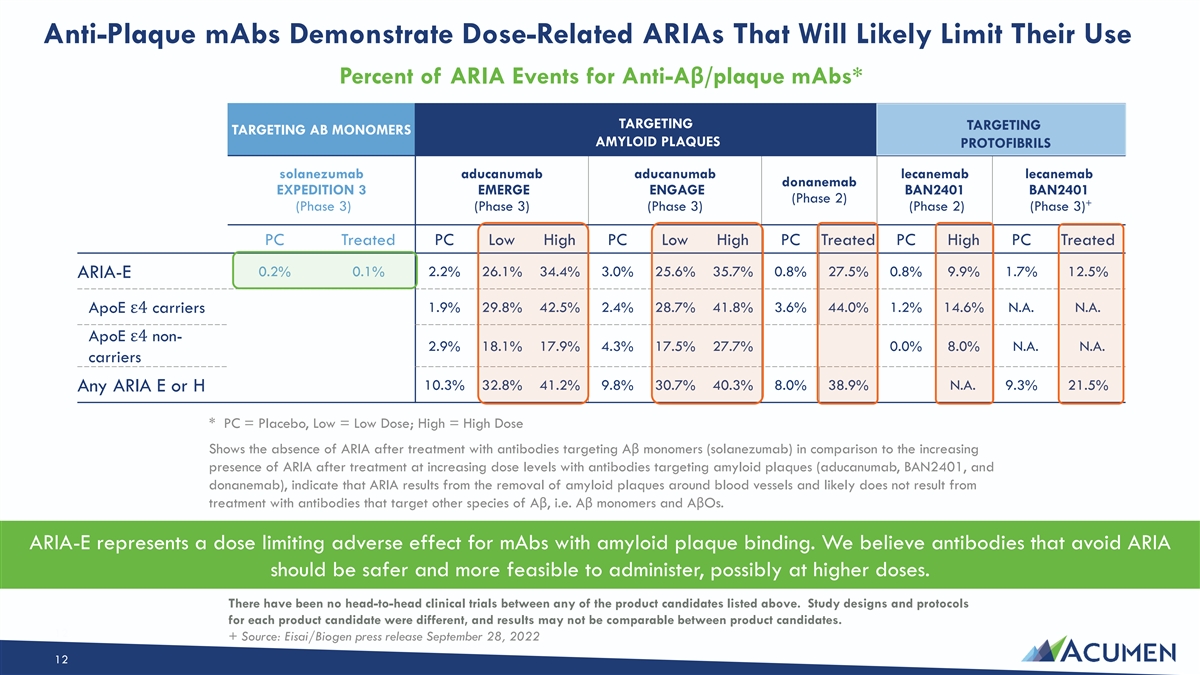
Anti-Plaque mAbs Demonstrate Dose-Related ARIAs That Will Likely Limit Their Use Percent of ARIA Events for Anti-Aβ/plaque mAbs* TARGETING TARGETING TARGETING AB MONOMERS AMYLOID PLAQUES PROTOFIBRILS solanezumab aducanumab aducanumab lecanemab lecanemab donanemab EXPEDITION 3 EMERGE ENGAGE BAN2401 BAN2401 (Phase 2) + (Phase 3) (Phase 3) (Phase 3) (Phase 2) (Phase 3) PC Treated PC Low High PC Low High PC Treated PC High PC Treated 0.2% 0.1% 2.2% 26.1% 34.4% 3.0% 25.6% 35.7% 0.8% 27.5% 0.8% 9.9% 1.7% 12.5% ARIA-E ApoE ε4 carriers 1.9% 29.8% 42.5% 2.4% 28.7% 41.8% 3.6% 44.0% 1.2% 14.6% N.A. N.A. ApoE ε4 non- 2.9% 18.1% 17.9% 4.3% 17.5% 27.7% 0.0% 8.0% N.A. N.A. carriers 10.3% 32.8% 41.2% 9.8% 30.7% 40.3% 8.0% 38.9% N.A. 9.3% 21.5% Any ARIA E or H * PC = Placebo, Low = Low Dose; High = High Dose Shows the absence of ARIA after treatment with antibodies targeting Aβ monomers (solanezumab) in comparison to the increasing presence of ARIA after treatment at increasing dose levels with antibodies targeting amyloid plaques (aducanumab, BAN2401, and donanemab), indicate that ARIA results from the removal of amyloid plaques around blood vessels and likely does not result from treatment with antibodies that target other species of Aβ, i.e. Aβ monomers and AβOs. ARIA-E represents a dose limiting adverse effect for mAbs with amyloid plaque binding. We believe antibodies that avoid ARIA should be safer and more feasible to administer, possibly at higher doses. There have been no head-to-head clinical trials between any of the product candidates listed above. Study designs and protocols for each product candidate were different, and results may not be comparable between product candidates. 12 + Source: Eisai/Biogen press release September 28, 2022 12
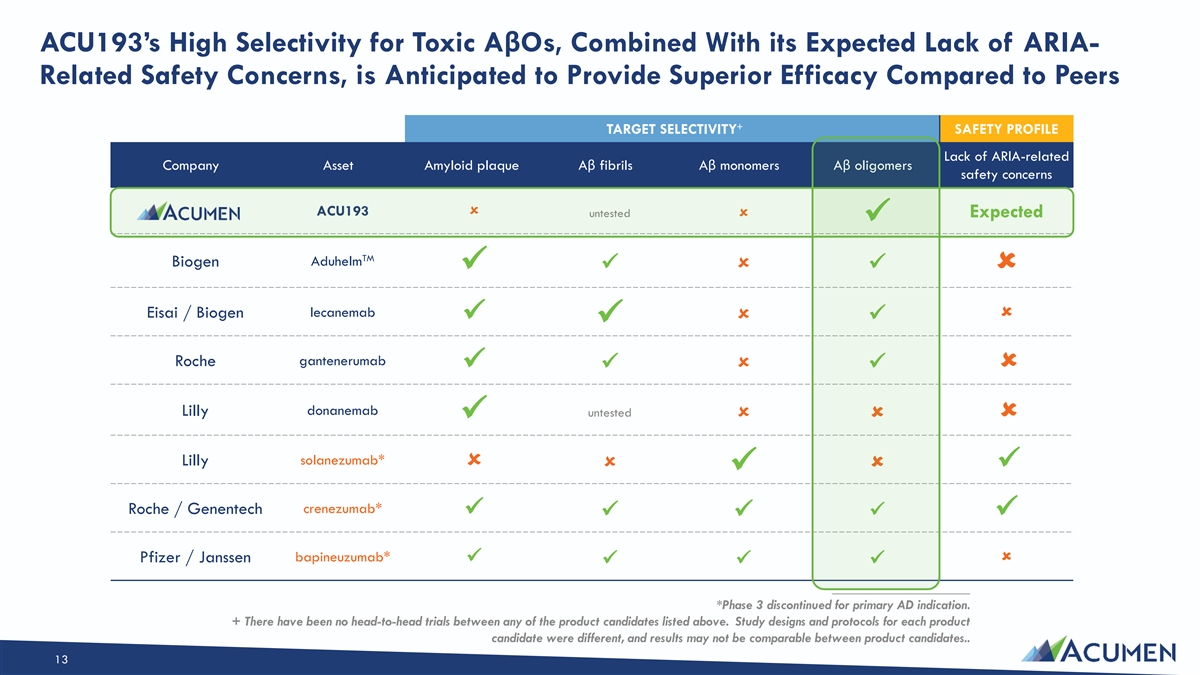
ACU193’s High Selectivity for Toxic AβOs, Combined With its Expected Lack of ARIA- Related Safety Concerns, is Anticipated to Provide Superior Efficacy Compared to Peers + TARGET SELECTIVITY SAFETY PROFILE Lack of ARIA-related Company Asset Amyloid plaque Aβ fibrils Aβ monomers Aβ oligomers safety concerns ACU193û untested Expected û ✓ TM Biogen Aduhelm ✓û✓ ✓û Eisai / Biogen lecanemab û ✓û✓ ✓ gantenerumab Roche ✓û✓ ✓û donanemab Lilly untested ûûû ✓ solanezumab* Lilly û ûû✓ ✓ Roche / Genentech crenezumab* ✓ ✓ ✓✓✓ bapineuzumab* Pfizer / Janssenû ✓ ✓✓✓ ____________________ *Phase 3 discontinued for primary AD indication. + There have been no head-to-head trials between any of the product candidates listed above. Study designs and protocols for each product candidate were different, and results may not be comparable between product candidates.. 13

ACU193: Our Differentiated Approach

ACU193 Target Product Profile: Best-in-Class, 1st Line, Anti-AβO, Disease- Modifying Immunotherapy for Early AD DRUG: ACU193 is a humanized, affinity-matured, mAb with high selectivity for toxic AβOs vs. Aβ monomers (>500x) and limited to no binding to amyloid plaques. ACU193 is an IgG2 subclass mAb which lacks inflammatory effector functions of other IgG subclasses. POPULATION: Early AD - Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Dementia due to AD (amyloid positive by PET) DOSING: IV infusion every 4 weeks DURATION: Chronic therapy for duration of Early AD VALUE Selectivity for toxic AβOs is expected to provide superior cognitive efficacy and improved PROPOSITION: safety and tolerability relative to non-selective anti-Aβ/plaque mAbs, including: • Slowing the decline of memory and cognition in Early AD • Decreasing AβO induced synaptic and neuronal network toxicity • Slowing disease progression and downstream effects on tau, neurodegeneration, and neuro- inflammation • With expected low rate of ARIA • Potentially effective as stand-alone therapy or in combination with other symptomatic, anti-inflammatory, and/or tau directed therapies 15

ACU193: Extensive Data Package Supporting Development — Nanomolar affinity for AβOs, >500-fold greater selectivity for AβOs over Aβ monomer, with limited or no discernable binding to vascular amyloid or dense core amyloid plaques SELECTIVITY — Binds broad range of endogenous AβOs present in transgenic mice and human AD samples (binds dimers to mid-sized molecular weight AβOs) — Dose-dependent effects in multiple in vitro neuroprotection assays PHARMACOLOGY — Positive memory and behavioral effects in multiple in vivo transgenic mouse models for AD — Brain penetration and biodistribution demonstrated in multiple species PK/PD — Performs like other peripherally administered CNS mAbs — IgG2 subclass lacks inflammatory effector function signaling (FcγR binding) — Nonclinical microhemorrhage studies show no SAFETY increased risk of microhemorrhage — GLP studies demonstrated acceptable safety margin for clinical dosing plans ACU193 is a promising immunotherapy for early AD expected to provide meaningful cognitive and functional benefits, slow disease progression, and offer an attractive safety profile. 16
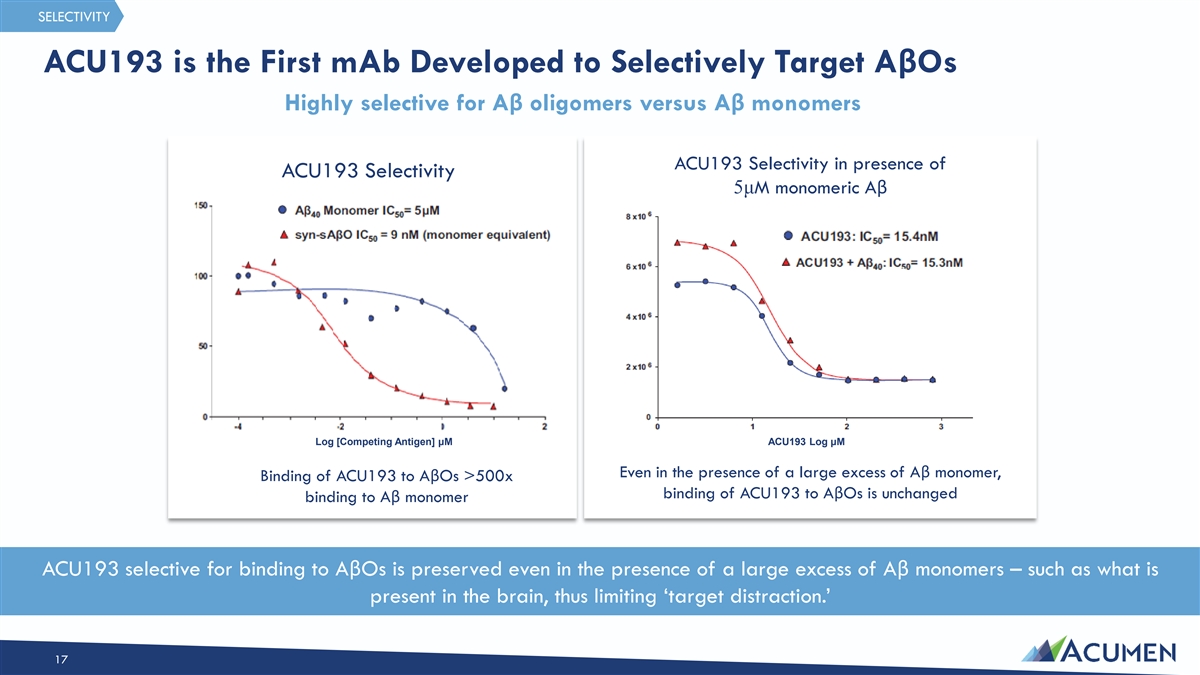
SELECTIVITY ACU193 is the First mAb Developed to Selectively Target AβOs Highly selective for Aβ oligomers versus Aβ monomers ACU193 Selectivity in presence of ACU193 Selectivity 5μM monomeric Aβ Log [Competing Antigen] μM ACU193 Log μM Even in the presence of a large excess of Aβ monomer, Binding of ACU193 to AβOs >500x binding of ACU193 to AβOs is unchanged binding to Aβ monomer ACU193 selective for binding to AβOs is preserved even in the presence of a large excess of Aβ monomers – such as what is present in the brain, thus limiting ‘target distraction.’ 17
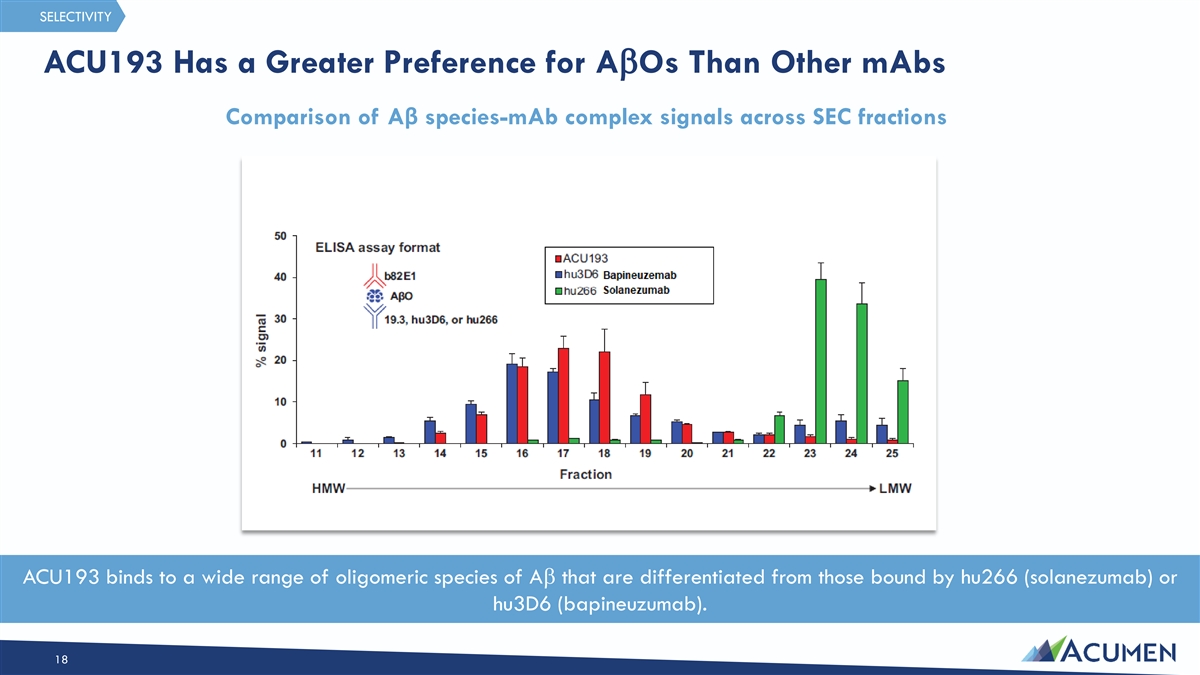
SELECTIVITY ACU193 Has a Greater Preference for AbOs Than Other mAbs Comparison of Aβ species-mAb complex signals across SEC fractions ACU193 binds to a wide range of oligomeric species of Ab that are differentiated from those bound by hu266 (solanezumab) or hu3D6 (bapineuzumab). 18
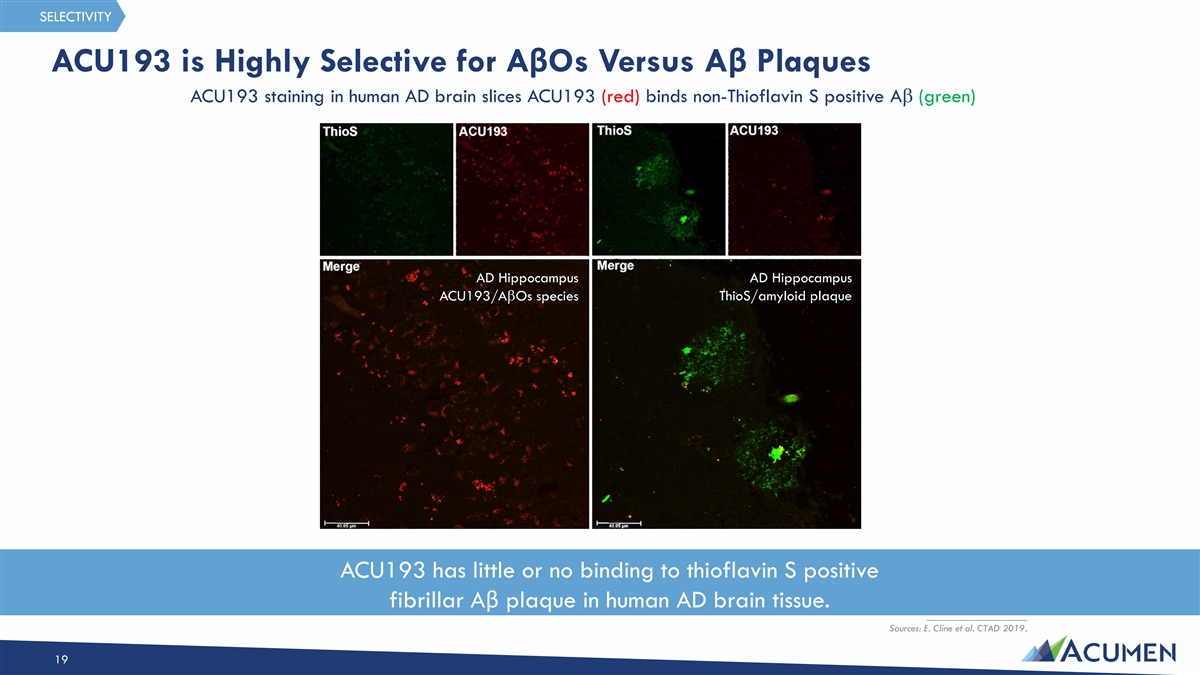
SELECTIVITY ACU193 is Highly Selective for AβOs Versus Aβ Plaques ACU193 staining in human AD brain slices ACU193 (red) binds non-Thioflavin S positive Ab (green) AD Hippocampus AD Hippocampus ThioS/amyloid plaque ACU193/AbOs species ACU193 has little or no binding to thioflavin S positive fibrillar Aβ plaque in human AD brain tissue. ____________________ Sources: E. Cline et al. CTAD 2019. 19
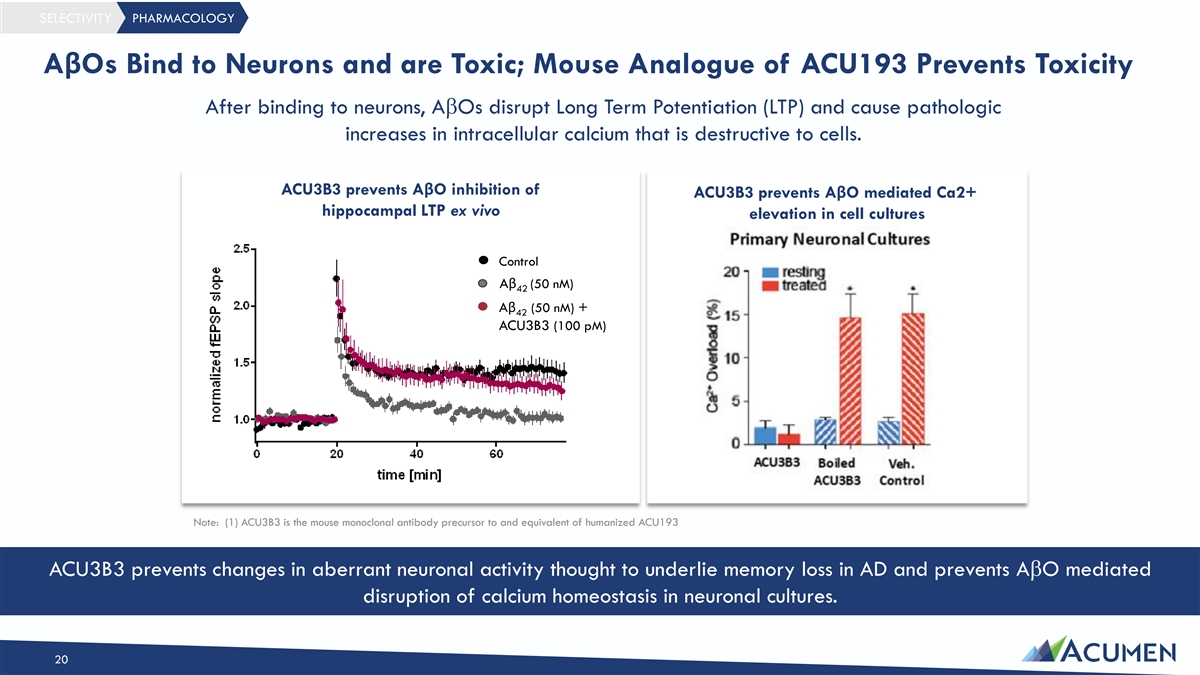
SELECTIVITY PHARMACOLOGY AβOs Bind to Neurons and are Toxic; Mouse Analogue of ACU193 Prevents Toxicity After binding to neurons, AbOs disrupt Long Term Potentiation (LTP) and cause pathologic increases in intracellular calcium that is destructive to cells. ACU3B3 prevents AβO inhibition of ACU3B3 prevents AβO mediated Ca2+ hippocampal LTP ex vivo elevation in cell cultures Control Aβ (50 nM) 42 Aβ (50 nM) + 42 ACU3B3 (100 pM) Note: (1) ACU3B3 is the mouse monoclonal antibody precursor to and equivalent of humanized ACU193 ACU3B3 prevents changes in aberrant neuronal activity thought to underlie memory loss in AD and prevents AbO mediated disruption of calcium homeostasis in neuronal cultures. 20
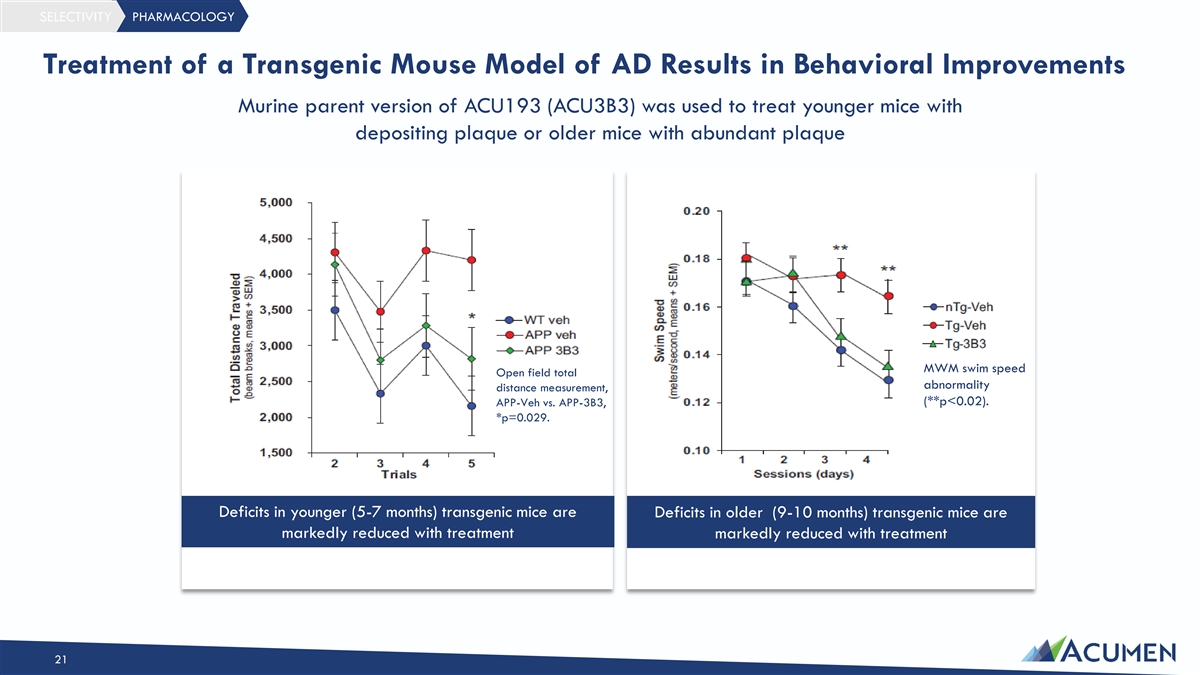
SELECTIVITY PHARMACOLOGY Treatment of a Transgenic Mouse Model of AD Results in Behavioral Improvements Murine parent version of ACU193 (ACU3B3) was used to treat younger mice with depositing plaque or older mice with abundant plaque MWM swim speed Open field total abnormality distance measurement, (**p<0.02). APP-Veh vs. APP-3B3, *p=0.029. Deficits in younger (5-7 months) transgenic mice are Deficits in older (9-10 months) transgenic mice are markedly reduced with treatment markedly reduced with treatment 21
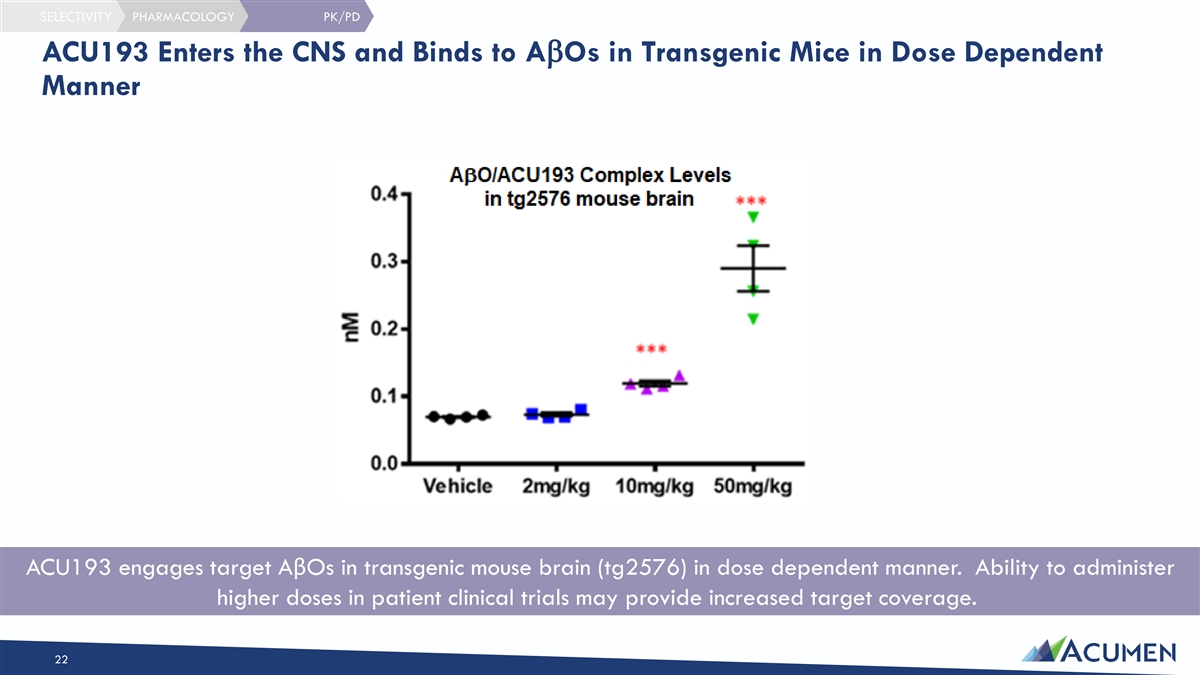
SELECTIVITY PHARMACOLOGY PK/PD ACU193 Enters the CNS and Binds to AbOs in Transgenic Mice in Dose Dependent Manner ACU193 engages target AβOs in transgenic mouse brain (tg2576) in dose dependent manner. Ability to administer higher doses in patient clinical trials may provide increased target coverage. 22

Clinical Development Plans

(ACU-001) INTERCEPT-AD Trial: Phase 1 Overview TRIAL Randomized Placebo Controlled Phase 1 DESIGN: • Part A : Single-Ascending Doses • Part B : Multiple-Ascending Doses ENROLLMENT Early AD CRITERIA: • Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Dementia due to AD (amyloid positive by PET) TRIAL Proof of Mechanism (PoM) OBJECTIVES: — Safety and tolerability — Pharmacokinetics — Target engagement — Biomarkers; cognition (exploratory) For more information on the INTERCEPT-AD trial, see https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04931459. 24
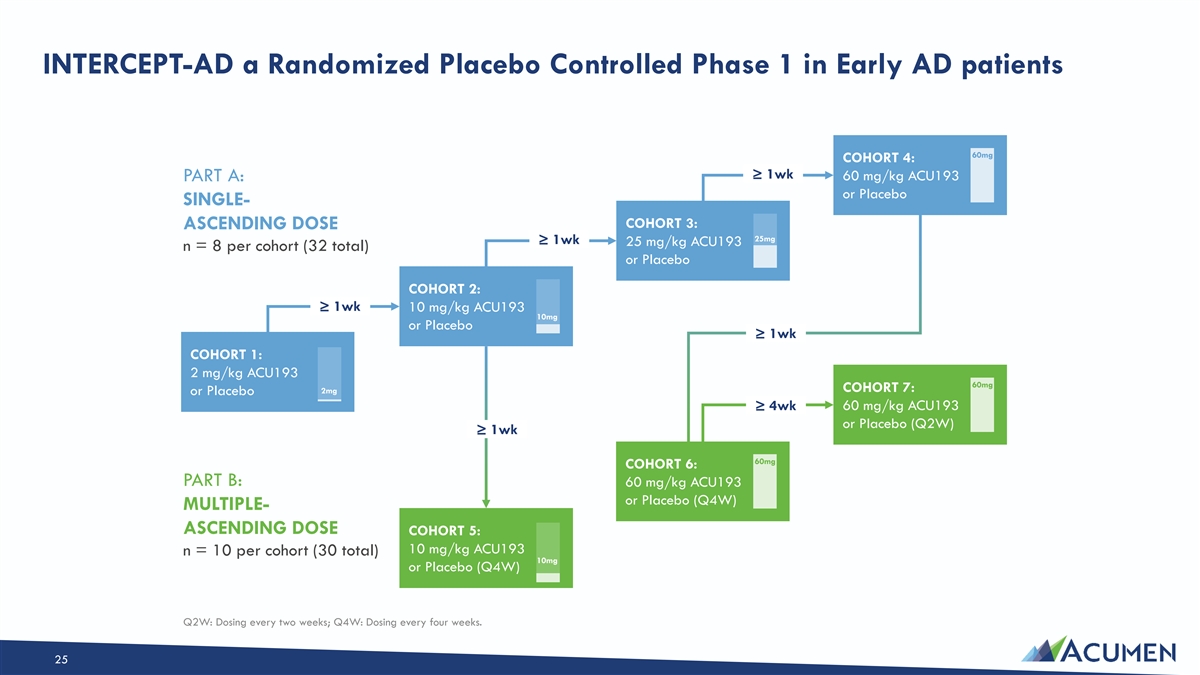
INTERCEPT-AD a Randomized Placebo Controlled Phase 1 in Early AD patients 60mg COHORT 4: ≥ 1wk 60 mg/kg ACU193 PART A: or Placebo SINGLE- COHORT 3: ASCENDING DOSE 25mg ≥ 1wk 25 mg/kg ACU193 n = 8 per cohort (32 total) or Placebo COHORT 2: ≥ 1wk 10 mg/kg ACU193 10mg or Placebo ≥ 1wk COHORT 1: 2 mg/kg ACU193 60mg COHORT 7: 2mg or Placebo ≥ 4wk 60 mg/kg ACU193 or Placebo (Q2W) ≥ 1wk 60mg COHORT 6: PART B: 60 mg/kg ACU193 or Placebo (Q4W) MULTIPLE- ASCENDING DOSE COHORT 5: 10 mg/kg ACU193 n = 10 per cohort (30 total) 10mg or Placebo (Q4W) Q2W: Dosing every two weeks; Q4W: Dosing every four weeks. 25

Phase 1 Objectives: Proof of Mechanism – Ability to Move to Phase 2/3 1. SAFETY AND TOLERABILITY • Assessment of ARIA-E • Absence of problematic immunogenicity PROOF OF MECHANISM 2. PHARMACOKINETICS Requirements for Phase 2/3 • Peripheral and Central ✓ Acceptable safety and 3. EVIDENCE OF TARGET ENGAGEMENT tolerability • CSF level of ACU193: AbO complexes (bound) ✓ Show ACU193 gets across the blood brain barrier and into 4. FLUID BIOMARKER EFFECTS central compartment • Phospho-tau, Neurofilament light, et. al. ✓ Target engagement 5. CLINICAL MEASURES (exploratory) • Assessment of clinical cognitive measures, computerized tests (Cogstate Ltd.) 6. MRI EFFECTS (exploratory) • Potential improvements in cerebral blood flow shown with MRI ASL pulse sequence Topline results anticipated in 2H 2023: primary outcomes safety/ARIA-E, PK and target engagement. Detailed study results anticipated to be presented at an Alzheimer’s medical meeting. 26
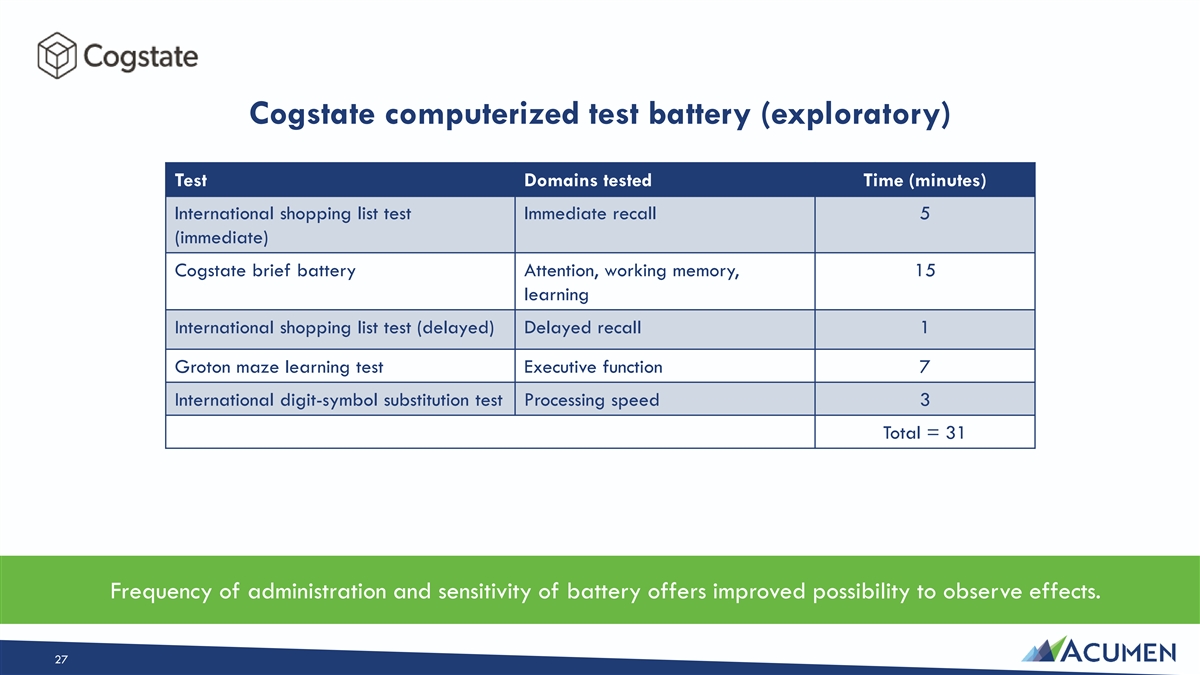
Cogstate computerized test battery (exploratory) Test Domains tested Time (minutes) International shopping list test Immediate recall 5 (immediate) Cogstate brief battery Attention, working memory, 15 learning International shopping list test (delayed) Delayed recall 1 Groton maze learning test Executive function 7 International digit-symbol substitution test Processing speed 3 Total = 31 Frequency of administration and sensitivity of battery offers improved possibility to observe effects. 27
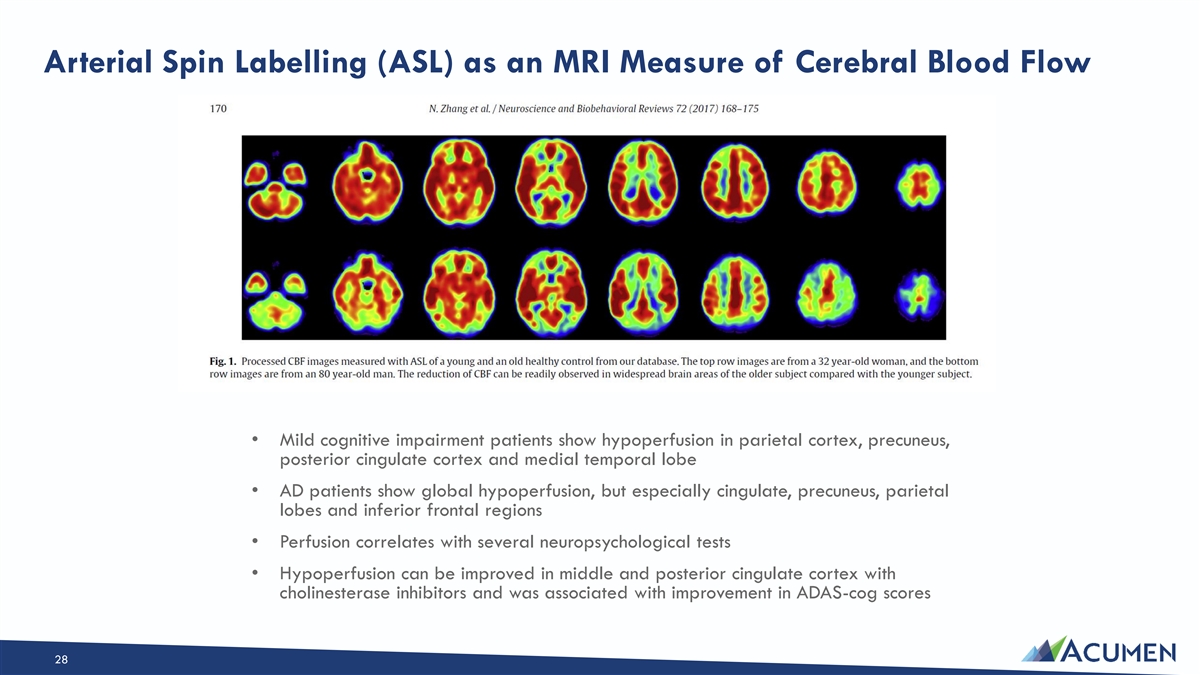
Arterial Spin Labelling (ASL) as an MRI Measure of Cerebral Blood Flow • Mild cognitive impairment patients show hypoperfusion in parietal cortex, precuneus, posterior cingulate cortex and medial temporal lobe • AD patients show global hypoperfusion, but especially cingulate, precuneus, parietal lobes and inferior frontal regions • Perfusion correlates with several neuropsychological tests • Hypoperfusion can be improved in middle and posterior cingulate cortex with cholinesterase inhibitors and was associated with improvement in ADAS-cog scores 28
ACU193 Development Summary Þ Differentiated profile: Nonclinical data consistent with toxicity of Ab oligomers and selective binding of ACU193 to Ab oligomers Þ Enrollment in a Phase1 study assessing safety, PK, and target engagement is ongoing Þ Although unlikely with this small sample size, the possibility of improvement in cognitive scales, computerized cognitive testing, and cerebral blood flow will also be assessed as exploratory outcomes in the Phase 1 study Þ Anticipate next clinical study, with success in Phase 1, starting as Phase 2 study with potential to expand to Phase 3 registration study based on interim expansion analysis 29

Business Considerations

Acumen Leadership Team Experienced in AD/Neuro Drug Development ERIC SIEMERS, MD JANICE HITCHCOCK, PHD MATT ZUGA DANIEL O'CONNELL Chief Medical Officer VP, Regulatory Affairs Chief Financial Officer & President & CEO Chief Business Officer RUSSELL BARTON ROBERT DEAN, MD, PHD LIEAN SCHENK SIEW TIN GAN Chief Operating Officer Sr. Development Advisor VP, Head of CMC Head of Clinical Operations JASNA JERECIC, PHD DEREK MEISNER, JD Analytical Methods Chief Legal Officer Leader, Research Scientist Acumen team has decades of experience in Alzheimer’s drug discovery and development. 31

ACU193 IP & Market Exclusivity • Exclusive, perpetual, irrevocable, worldwide, royalty-free license from Merck to its Amyloid Derived Diffusible Ligand (ADDL) IP including, issued ACU193 patents • ACU193 Global IP estate: ✓ Issued patents in 19 countries ✓ Composition of matter patents and methods of use run into July 2031 ✓ Patent term extensions may be available, 3-5 years depending on jurisdiction • Biologics market exclusivity is expected for ACU193 as a novel biologic drug ✓ US provides 12 years market exclusivity for novel biologics ✓ Europe provides 10 years of market exclusivity for novel biologics 32

Acumen is Well Capitalized, With Expected Cash Runway Through 2025 STATUS/ MILESTONES EXPECTED TIMING ~$200M Initiated Ph1 clinical trial INTERCEPT-AD ✓ Cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities as of September 30, 2022 INTERCEPT-AD enrollment complete 1Q 2023 Proof-of-mechanism topline results 2H 2023 We believe that Acumen has the organizational expertise and cash and marketable securities on hand to advance ACU193 through 2025. 33
ABOS: Key Takeaways Massive unmet need in AD, recent favorable trends and cumulative learnings position field for future successes Upcoming sector catalysts 2H22 - 1H23 Differentiated product candidate targeting toxic AbOs Experienced AD drug development team Blue chip investors, very strong balance sheet and cash $ runway with multiple milestones through 2025 Value-inflection clinical data 2H 2023 34

Thank you!


































