
Slowing the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease Through the Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis

Forward Looking Statements Any statements in this presentation that are not statements of historical facts may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. Examples of such statements include our plans, beliefs, intentions, expectations and projections regarding, among other things: anticipated milestones, future product development and regulatory events, goals and timing, anticipated clinical trial results and strategies, potential safety, efficacy and other benefits and market opportunities of our product candidate, our intellectual property position, our business plan, commercialization efforts, including potential cost savings and launch price recognizing predicted long-term value, and financial estimates and results. These statements are based on management’s current expectations, estimates, forecasts, and projections about our business, our product candidate and the industry in which we operate and management’s beliefs and assumptions and are not guarantees of future performance or development and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors that may be beyond our control and which could cause actual results, performance or achievements expressed or implied to differ materially from such statements. This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market size and growth and other data about our industry. This data involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. In addition, projections, assumptions, and estimates of our future performance and the future performance of the markets in which we operate are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk. These statements are also subject to a number of material risks and uncertainties that are discussed in the section entitled "Risk Factors" in our quarterly report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2018, as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties, and other important factors in our subsequent filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it was made. Neither we, nor our affiliates, advisors, or representatives, undertake any obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. 2

First-in-Class Drug Candidate - TRC101 Disease Modifying – Our Goal is to Slow CKD Progression through the Treatment of Metabolic Acidosis Improve How the Patient Feels and Functions – We Believe TRC101 has the Potential to Enhance Health-Related Quality of Life for Patients with Metabolic Acidosis 3

2018 Achievements JUNE JUNE OCTOBER DECEMBER Positive Successful Initiated Disease Completed Phase 3 IPO Awareness New HEOR Results Campaign Linking and Payer Metabolic Acidosis Survey and CKD Progression HEOR: Health Economics Outcomes Research. 4

Anticipated 2019 Milestones 1H 2019 Mid-2019 2H 2019 2H 2019 + + = TRCA-301E Stability VALOR-CKD NDA Results Data Enrollment Submission Completion of the Availability of NDA- Completion or near- Submitting under the 40-week safety enabling 12-month completion of enrollment Accelerated Approval extension trial registration stability in postmarketing trial Program data for TRC101 5

Metabolic Acidosis is Caused by Inability of the Kidneys to Excrete Excess Acid Kidneys Lose Capacity to Excrete Acid Blood Bicarbonate Levels Fall acid Normal 22 – 29 mEq/L icarbonate Range Blood B Acid is generated Diseased kidneys An increase in acid leads Metabolic 12 – <22 from dietary lose capacity to a decrease in blood Acidosis mEq/L sources and daily to excrete bicarbonate, worsening metabolism excess acid metabolic acidosis Acute/Severe <12 Metabolic mEq/L Acidosis Source: Kraut. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6(5):274; KDIGO Clinical Practice Guidelines 2012. 6

Metabolic Acidosis Poses a Significant Health Risk to ~3 Million Patients with CKD in the US ~ 22 Million US Patients with Stage 3 to 5 CKD* ~3 Million with Metabolic Acidosis Potential Consequences Muscle Breakdown & Increased Mortality CKD Progression Bone Disease CKD 3a/b (9-18%) ~2.2 M with Metabolic Acidosis CKD 4/5/ESRD* (>30%) ~ 850K with Metabolic Acidosis Source: NHANES 1999 - 2010; CDC Report 2017; USRDS 2017 Annual Report; Ryan. Am J Med. 2007;120: 981; Inker. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22(12):2322. *Non-dialysis patients with eGFR<60. 7

Eleven Studies have Established the Link between Metabolic Acidosis and CKD Progression Seven Prospective Studies Four Retrospective Studies 8

Reduced Risk of ESRD with Normal Blood Bicarbonate: Tangri Kidney Failure Risk Equation Tangri Metabolic Normal Blood Eight Variables Acidosis* Bicarbonate Age 62 62 Sex M M Relative Reduction in eGFR 26 ml/min 26 ml/min Risk of Progression ACR 250 mg/g 250 mg/g to ESRD with Normal ** Albumin 3.8 g/dL 3.8 g/dL Blood Bicarbonate Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L 22 mEq/L Two years Calcium 8.9 mg/dL 8.9 mg/dL Phosphorous 4.7 mg/dL 4.7 mg/dL 25% Five years Two years Two years Risk of 20% 15% 20% Progression Five years Five years to ESRD 51% 41% ACR: albumin creatinine ratio. Source: Tangri. JAMA, January 2016, 164-174. *Data represent actual patient data. **Changing blood bicarbonate level from 18 to 22 mEq/L illustrates the relative reduction in risk of progression to ESRD of 20% to 15% in 2 years and from 51% to 41% in 5 years. This represents a 25% and 20% reduction, respectively. 9

Prospective Data Provide Evidence of Direct Link Between Treating Metabolic Acidosis and Slowing the Progression of Kidney Disease In a Randomized, Controlled Study, Normalization of … Associated with Slower Decline in Renal Function* Blood Bicarbonate Concentration … /L) 25 ( mEq Normal Metabolic Acidosis 18 Blood Bicarbonate 0 12 24 Months of Follow-up Months of Follow-up Treated for Metabolic Not Treated for Metabolic Treated for Metabolic Not Treated for Metabolic Acidosis Acidosis Acidosis Acidosis Over two years in the treated group, 6.5% of subjects progressed to ESRD versus 33% of subjects in the control group Source: de Brito-Ashurst, Yaqoob, et al., JASN. 2009;20:2075-2084, ©2009 by American Society of Nephrology. Reprinted with permission. *Kaplan-Meier analysis to assess the probability of reaching ESRD between oral alkali supplement intervention and control. 10

Unmet Medical Need for an FDA-Approved Chronic Treatment for Metabolic Acidosis to Slow CKD Progression Oral alkali supplementation is the most common option for managing blood bicarbonate levels as established in academic clinical trials, HOWEVER… Not FDA-Approved Oral alkali supplements are available over-the-counter Limited Efficacy Oral alkali supplements have been primarily studied in mild metabolic acidosis Large Sodium Load Daily dose of oral alkali supplements may exceed the guidelines for recommended sodium intake Primarily Limited to Patients without Common Comorbidities ~ 85% to 95% of patients with Stage 3 to 5 CKD suffer from one or more sodium sensitive comorbid conditions (hypertension, CVD, HF, edema) and require a sodium-restricted diet CVD: cardiovascular disease. HF: heart failure. Source: de Brito-Ashurst, Yaqoob, et al., JASN. 2009;20:2075-2084; Garneata et al., JASN. 2016;27(7):2164-76; Phisitkul et al., Kidney Int. 2010;77(7):617; Abramowitz et al., Clin JASN. 2013;8(5):714; FDA Draft Guidance Voluntary Sodium Reduction Goals, July 2016; Rao et al., Am J of Kidney Disease. 2008;51(4)S30-S37. 11

Transforming the Treatment of Patients with CKD and Metabolic Acidosis TRC101 NH2 NH2 NH2 NH2 Designed Does not Appropriate for chronic, oral deliver sodium for all metabolic treatment (once a day or other acidosis patients, sachet) of counterions including mild to severe to the patient those with common metabolic acidosis comorbidities 12
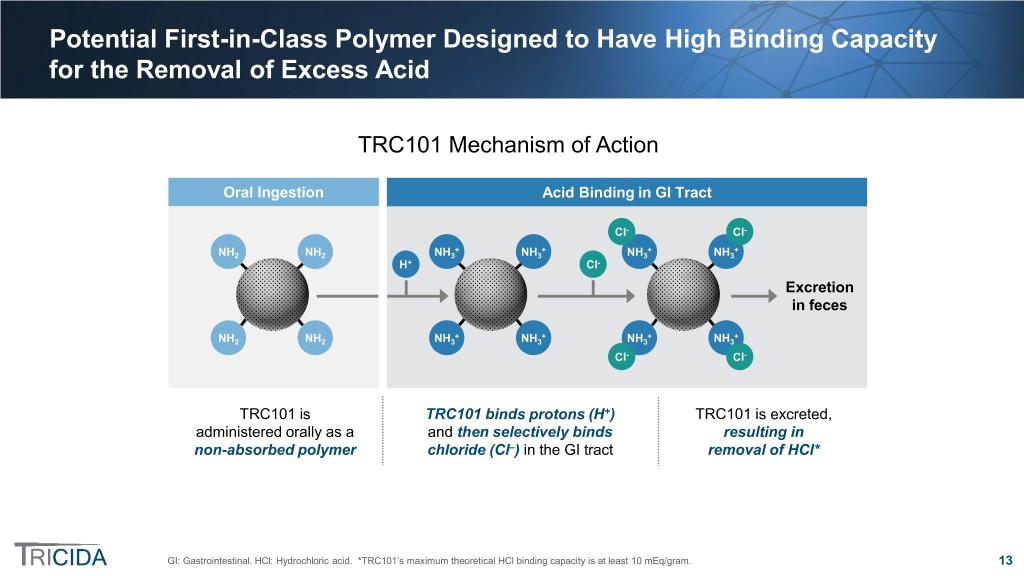
Potential First-in-Class Polymer Designed to Have High Binding Capacity for the Removal of Excess Acid TRC101 Mechanism of Action Oral Ingestion Acid Binding in GI Tract Cl- Cl- + + + + NH2 NH2 NH3 NH3 NH3 NH3 H+ Cl- Excretion in feces + + + + NH2 NH2 NH3 NH3 NH3 NH3 Cl- Cl- TRC101 is TRC101 binds protons (H+) TRC101 is excreted, administered orally as a and then selectively binds resulting in non-absorbed polymer chloride (Cl–) in the GI tract removal of HCl* GI: Gastrointestinal. HCl: Hydrochloric acid. *TRC101’s maximum theoretical HCl binding capacity is at least 10 mEq/gram. 13

TRC101: High Selectivity for Chloride Ions Derived from Built-In Size Exclusion Mechanism GI Anions Ranked by Size Bile Acids The high degree of crosslinking in TRC101 provides a size Fatty Acids exclusion mechanism that TRC101 leads to high selectivity Citrate for binding chloride (the smallest anion) over larger anions Phosphate Chloride 14

Plan to Submit NDA Under the FDA Accelerated Approval Program in 2H 2019 Accelerated Approval Program Requirements Treats a Serious Condition Meaningful Advantage Reasonably Predictive Over Standard of Care Surrogate Endpoint Treatment of metabolic There are no FDA- Increasing blood acidosis may slow approved therapies for bicarbonate has been progression to ESRD for the chronic treatment of linked to the slowing patients with CKD and metabolic acidosis of CKD progression metabolic acidosis ESRD: End stage renal disease. Source: FDA Guidance for Industry—Expedited Programs for Serious Conditions—Drugs and Biologics. 15

TRCA-301 Phase 3 Trial Design Phase 3 Clinical Trial: TRCA-301 (4:3 Randomization) TRC101 QD (n=124) 217 subjects with Placebo QD (n=93) Safety blood bicarbonate of 12 – 20 Screening Follow-up mEq/L, eGFR of 20 – 40 2-week 2-week 2 Fixed dose (6 grams QD) until week 4 with blinded 12 Weeks ml/min/1.73m Period Treatment Period dose adjustments thereafter to maintain blood bicarbonate within normal range (22 – 29 mEq/L)* Primary Endpoint: Having a change from baseline (CFB) in blood bicarbonate ≥ 4 mEq/L or having blood bicarbonate in the normal range (22 to 29 mEq/L) at the end of treatment Secondary Endpoint: CFB in blood bicarbonate at the end of treatment Exploratory Endpoints: 1) CFB in Physical Function Subpart of the Kidney Disease and Quality of Life Short Form survey (KDQOL-SF survey) 2) CFB in repeated chair stand test duration Safety: AEs, SAEs, withdrawal of study treatment due to AE, confirmed blood bicarbonate > 30 mEq/L CFB: Change from baseline. QD: Once-daily. *Doses range from 0 to 9 grams QD. 16

TRCA-301 Trial Met Primary and Secondary Efficacy Endpoints 59.2% of TRC101-Treated Subjects Experienced TRC101-Treated Subjects Experienced a Mean Increase from an Increase of ≥4 mEq/L or Reached Normal Baseline in Blood Bicarbonate of 4.5 mEq/L (p<0.0001) Blood Bicarbonate at End of Treatment (p<0.0001) 70% 22 22.0 21.7 21.6 21.6 21.7 60% 59.2% 21 50% 20.8 4.5 20.2 40% 20 mEq/L 30% 22.5% 19 19.0 18.6 18.9 18.6 20% 18.4 18.5 18 18.1 10% 17.3 17.3 0% 17 BL W1 W2 W4 W6 W8 W10 W12 Placebo (n=93) TRC101 (n=123) Placebo (n=93) TRC101 (n=123) BL: Baseline. W: Week. Error bars = Standard error of the mean. 17
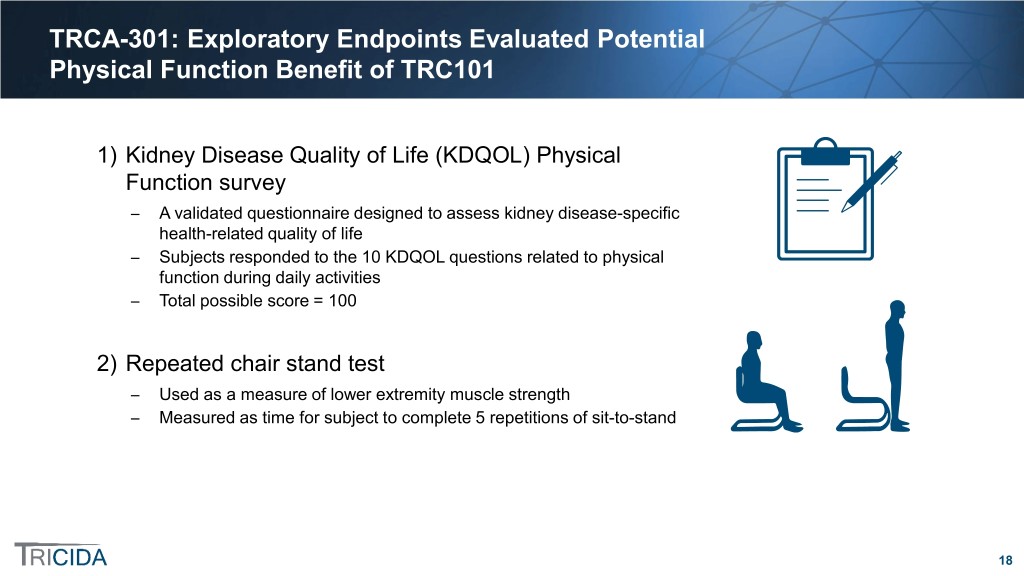
TRCA-301: Exploratory Endpoints Evaluated Potential Physical Function Benefit of TRC101 1) Kidney Disease Quality of Life (KDQOL) Physical Function survey ̶ A validated questionnaire designed to assess kidney disease-specific health-related quality of life ̶ Subjects responded to the 10 KDQOL questions related to physical function during daily activities ̶ Total possible score = 100 2) Repeated chair stand test ̶ Used as a measure of lower extremity muscle strength ̶ Measured as time for subject to complete 5 repetitions of sit-to-stand 18
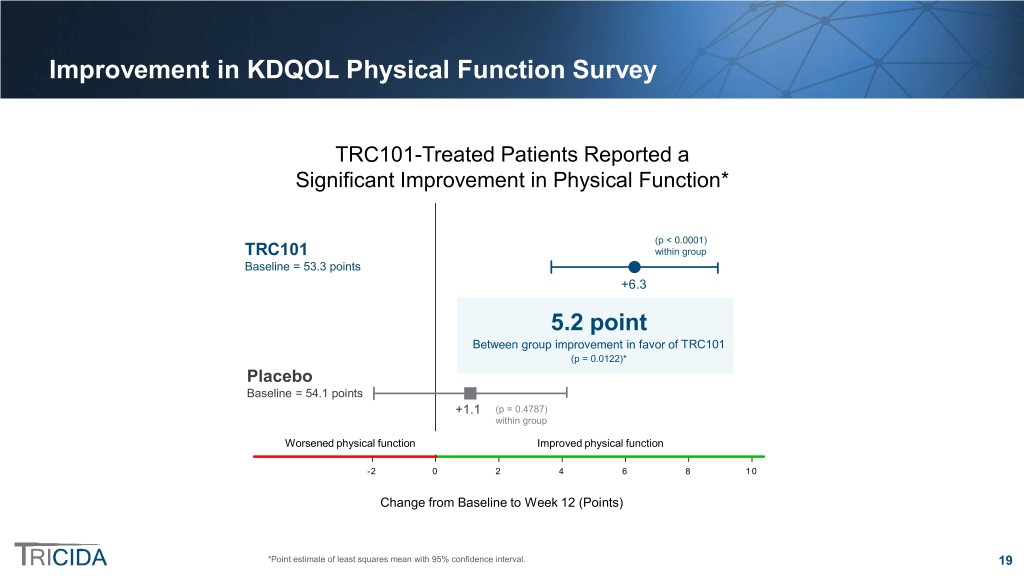
Improvement in KDQOL Physical Function Survey TRC101-Treated Patients Reported a Significant Improvement in Physical Function* p(p << 0.00010.0001) TRC101 within group TRC101 within group Baseline = 53.3 points Baseline = 53.3 +6.3 Statistically significant between-group5.2 difference point Between(p group = 0.0122) improvement in favor of TRC101 (p = 0.0122)* Placebo Baseline = 54.1 points Baseline = 54.1 +1.1 (pp == 0.4787) 0.48 withinwithin group Worsened physicalphysical function function Improved physical functionfunction -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 ChangeChange from fromBaseline Baseline to Week to Week12 (Points) 12 *Point estimate of least squares mean with 95% confidence interval. 19

Improvement in Repeated Chair Stand Test TRC101-Treated Patients Experienced a Significant Improvement in Physical Function TRC101TRC101 Baseline =Baseline 17.3 seconds = 17.3 seconds -1.17 Statistically significant between-group1.52 difference:seconds Between1.52 group seconds* improvement in favor of TRC101 (p = 0.0027)(p = 0.0027)* PlaceboPlacebo Baseline =Baseline 15.5 seconds = 15.5 seconds +0.35 ImprovedImproved chair stand stand time time WorsenedWorsened chair stand stand time time -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 ChangeChange from Baselinefrom Baseline to Weekto Week 12 12 (Seconds)(Seconds) *Based on post-hoc rank-based analysis due to non-normal distribution of data. 20

Positive TRCA-301 Safety Results • Over 95% of patients in both groups completed the study • SAE incidence low and balanced between the 2 treatment groups – 2 SAEs resulted in death; both occurred in placebo subjects – All SAEs were assessed as not related to study drug • Overall GI tolerability was very good – GI reported adverse events were 5.4% in placebo versus 12.9% in TRC101-treated subjects – These events were generally mild and none required dose discontinuation • No apparent off-target effects (e.g., on electrolytes) SAE: Serious adverse event. GI: Gastrointestinal. 21

TRCA-301E Phase 3 Extension Trial Design Phase 3 Nine-Month Extension Trial: TRCA-301E (90% of TRCA-301 subjects elected to participate) TRC101 QD (n=114) Placebo QD (n=82) Subjects from TRCA-301 trial Safety with blood bicarbonate ≥ 12 Follow-up mEq/L who completed Week 12 2-week 40 Weeks Treatment Maintain blood bicarbonate Period within normal range (22 – 29 mEq/L)* Primary Endpoint: Incidence of AEs, SAEs, and AEs leading to withdrawal Secondary Endpoints: 1) CFB in blood bicarbonate of ≥ 4 mEq/l or in the normal range 2) CFB in blood bicarbonate at Week 52 3) CFB in total score of the KDQOL Physical Function survey 4) CFB in the repeated chair stand test duration Current Status: Fully enrolled, on target for top-line results in 1H 2019 CFB: Change from baseline. QD: Once daily. *Doses range from 0 to 9 grams QD. 22

VALOR-CKD Confirmatory Postmarketing Trial Design Time-to-Event Postmarketing Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of TRC101 in Delaying CKD Progression TRC101 QD (n~800) ~1,600 patients with Screening blood bicarbonate of 12 – 20 mEq/L, eGFR of 20 – 40 mL/min/1.73m2 ~4 years ~4 Treatment Placebo QD (n~800) Primary endpoint: Progression of renal disease, defined by time to first occurrence of any event in the composite renal endpoint consisting of ≥ 40% reduction in eGFR, ESRD or renal death Secondary endpoints: 1) Time to ESRD 2) eGFR slope 3) Change from baseline in the total score of the KDQOL Physical Functioning Survey 4) Time to first occurrence of the primary composite endpoint or cardiovascular (CV) death 5) Frequency of all-cause hospitalization The study terminates when the independent blinded Clinical Endpoint Committee (CEC) has positively adjudicated the targeted number of primary efficacy endpoint events 23

We Plan to File the TRC101 NDA Under the Accelerated Approval Program in 2H 2019 TRCA101 Clinical Trials Postmarketing Trial TRCA-101*: Successful 2-week, randomized, double-blind, Initiated enrollment in Q4 2018 placebo-controlled Phase 1/2 trial, 3 doses and 2 dosing regimens of TRC101 or placebo Evaluate the efficacy and safety of TRC101 in Blood bicarbonate endpoint 135 subjects delaying CKD progression in pre-dialysis patients with metabolic acidosis TRCA-301: Successful 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 3 trial 3 – 9 g TRC101 or placebo ~1,600 subjects to be randomized by 2H 2019 Blood bicarbonate endpoint 217 subjects Time to event trial: randomized double-blind, TRCA-301E: Ongoing blinded 40-week Phase 3 extension placebo-controlled study anticipated to take trial approximately 4 years 3 – 9 g TRC101 or placebo 196 subjects * Published TRCA-101 Results, Completed TRCA-301 Data Readout Expected Post Initial Approval and TRCA-301E Ongoing * Bushinsky et al., Clin JASN. 2018;13:26. 24

We Plan to Launch TRC101 in the United States for Patients with CKD and Metabolic Acidosis Treated by Nephrologists 25

Positive Payer Feedback From 15 Payers Covering Over 200 Million Lives Key Value Drivers First-in-class • Signaled a formulary ‘must-add’ versus an ‘optional add’ • Recognized unique, meaningful attributes of TRC101 mechanism Disease modifying of action • Phase 3 results on blood bicarbonate confirmed efficacy Efficacy expectations were within range for disease modifying effects • Non-absorbed Safety • Lack of sodium allows use in ~90% of target population who have one or more sodium-sensitive CKD comorbidities Reduced health • Health Economic Outcomes Research (HEOR) model shows potential resource for significant cost reduction based on actual EMR events and claims utilization data Sources: 2018 Tricida-sponsored Payer Survey; Tangri et al., JAMA. 2011;305(15):1553. 26

Retrospective Study of Pre-Dialysis Patients with CKD Stages 3-5 Using a National De-identified Electronic Medical Record Dataset (2007 – 2016) Medical Record Data Medical Claims • Step 1: Observed DD40 renal • Step 3: All-cause costs evaluated for two years in outcomes for patients with Modeled confirmed CKD and metabolic subgroup with cost data. acidosis; evaluated for 2 Predicted costs established via potential consecutive years statistical modeling were applied to EMR study patients. savings • Step 2: Treatment effects per patient modeled as an average 4 • Step 4: Direct cost savings per year mEq/L improvement over equals difference in total all-cause baseline blood bicarbonate costs between groups with from Step 1 across full baseline blood bicarbonate levels population ~ 4 mEq/L apart or reaching the normal range EMR: Electronic medical record. DD40: Composite outcome of death, dialysis/transplantation or ≥40% decline in eGFR. 27

Improvement in Blood Bicarbonate by ~ 4 mEq/L was Associated with Potential for Measurable Cost and Renal Outcome Benefits in Commercial Patients Observed in patients with Estimated benefit of metabolic acidosis in the 4 mEq/L increase in EMR data study blood bicarbonate (N = 5,178) (N = 5,178) N % N % Total two-year adverse renal outcomes 2,650 51% 1,791 35% (DD40) Cost per patient per year ~ $90K ~ $53K Estimated Reduction in Mortality over 2 Years = 592 lives* Estimated Savings Per Patient Per Year = $37K** DD40: Composite outcome of death, dialysis/transplantation or ≥40% decline in eGFR. *Difference in 2 year mortality in observed study population and estimated mortality after a 4 mEq/L improvement in baseline blood bicarbonate. **Assumes 100% treatment response rate. 28

Significant US Market Opportunity for TRC101* Increased awareness drives higher metabolic 3,000,000 acidosis diagnosis and treatment CKD patients with metabolic acidosis Expansion beyond nephrologists 1,100,000 provides additional opportunity Diagnosed patients 600,000 Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) may be appropriate for <10% of nephrology- Focus on ~600,000 nephrologist-treated treated CKD patients (i.e., patients provides initial opportunity for those without sodium TRC101 ~540,000 sensitive comorbidities) Nephrologist- ~90% of patients have sodium treated patients sensitive comorbidities with sodium- sensitive Includes ~25% to 30% commercially comorbidities insured patient population Commercial Strategy Includes a Specialty Sales Force of 80 to 100 People *All numbers are approximate and estimates. 29

Tricida is Raising Awareness about Metabolic Acidosis and CKD Progression Major Presence at ASN Kidney Week 2018 New Educational Neph+ App Videos and Designed By MetabolicAcidosis and For Insights.com Nephrologists Website 30

Comprehensive Worldwide IP Strategy United States Europe Rest of World • Issued composition of • Issued European • Corresponding matter and method of patents applications in other treatment patents commercially significant • Several pending countries • Several pending applications applications Patent protection expected to provide exclusivity for TRC101 through at least 2034 in the United States, and the European Union. Corresponding applications are pending in Japan, China, India and certain other markets* *Exclusivity does not include extensions related to Hatch-Waxman. 31

Financial Highlights • $260.5 million cash, cash equivalents and short term investments at September 30, 2018 • $40 million drawn down on a $100 million Hercules term loan at December 31, 2018 – $25 million and $15 million drawn down in February and December 2018, respectively – Additional draw down availability of: • $35 million upon NDA submission and acceptance • $10 million upon U.S. approval • $15 million upon approval by Hercules • 42,106,604 total shares outstanding as of November 1, 2018 32

THANK YOU
































