
Exhibit 99.2 URIROX-1 and Study 206 Topline Results November 7, 2019Exhibit 99.2 URIROX-1 and Study 206 Topline Results November 7, 2019

Allena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. These slides, and the accompanying presentation, contain forward-looking statements and information. The use of words such as “may,” “might,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “project,” “intend,” “future,” “potential,” or “continue,” and other similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. All forward-looking statements are based on estimates and assumptions by our management that, although we believe them to be reasonable, are inherently uncertain. All forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from those that we expected, including those risks and uncertainties that are described under the heading “Risk Factors” in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2019, as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties and other important factors in our subsequent filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it was made. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and us relating to market size and growth and other data about our industry. This data involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. In addition, projections, assumptions and estimates of our future performance and the future performance of the markets in which we operate are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk. 2Allena Pharmaceuticals, Inc. These slides, and the accompanying presentation, contain forward-looking statements and information. The use of words such as “may,” “might,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “project,” “intend,” “future,” “potential,” or “continue,” and other similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. All forward-looking statements are based on estimates and assumptions by our management that, although we believe them to be reasonable, are inherently uncertain. All forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from those that we expected, including those risks and uncertainties that are described under the heading “Risk Factors” in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2019, as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties and other important factors in our subsequent filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it was made. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and us relating to market size and growth and other data about our industry. This data involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. In addition, projections, assumptions and estimates of our future performance and the future performance of the markets in which we operate are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk. 2
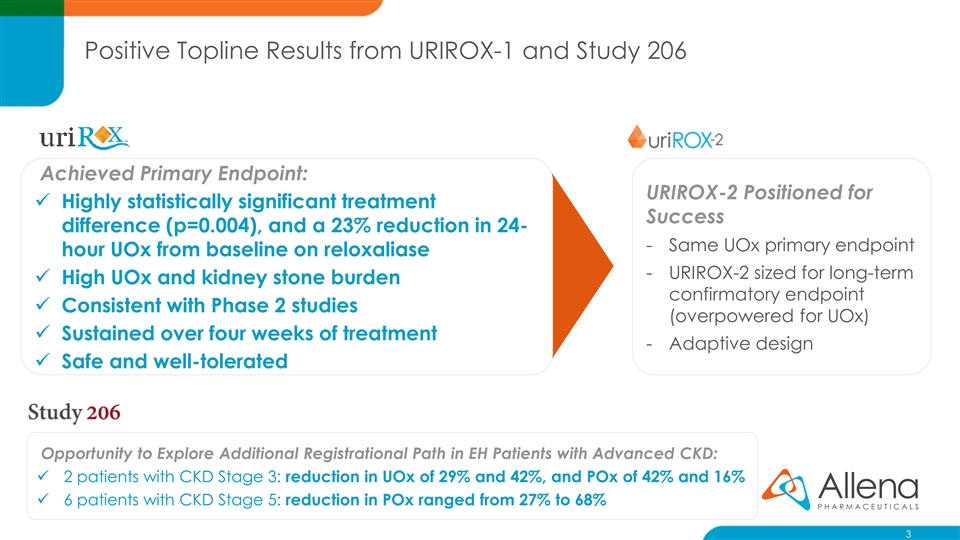
Positive Topline Results from URIROX-1 and Study 206 Achieved Primary Endpoint: URIROX-2 Positioned for ✓ Highly statistically significant treatment Success difference (p=0.004), and a 23% reduction in 24- - Same UOx primary endpoint hour UOx from baseline on reloxaliase - URIROX-2 sized for long-term ✓ High UOx and kidney stone burden confirmatory endpoint ✓ Consistent with Phase 2 studies (overpowered for UOx) ✓ Sustained over four weeks of treatment - Adaptive design ✓ Safe and well-tolerated Opportunity to Explore Additional Registrational Path in EH Patients with Advanced CKD: ✓ 2 patients with CKD Stage 3: reduction in UOx of 29% and 42%, and POx of 42% and 16% ✓ 6 patients with CKD Stage 5: reduction in POx ranged from 27% to 68% 3Positive Topline Results from URIROX-1 and Study 206 Achieved Primary Endpoint: URIROX-2 Positioned for ✓ Highly statistically significant treatment Success difference (p=0.004), and a 23% reduction in 24- - Same UOx primary endpoint hour UOx from baseline on reloxaliase - URIROX-2 sized for long-term ✓ High UOx and kidney stone burden confirmatory endpoint ✓ Consistent with Phase 2 studies (overpowered for UOx) ✓ Sustained over four weeks of treatment - Adaptive design ✓ Safe and well-tolerated Opportunity to Explore Additional Registrational Path in EH Patients with Advanced CKD: ✓ 2 patients with CKD Stage 3: reduction in UOx of 29% and 42%, and POx of 42% and 16% ✓ 6 patients with CKD Stage 5: reduction in POx ranged from 27% to 68% 3
Pioneering Technology in Formulation Oral Enzyme Therapeutics Proprietary Technology development approach Therapeutic Platform Oral Enzyme GI MOA Therapeutic candidates Leverage GI that degrade a specific tract as metabolite “auxiliary kidney” Reloxaliase ALLN-346 Non-absorbed Reduces potential for adverse events 4Pioneering Technology in Formulation Oral Enzyme Therapeutics Proprietary Technology development approach Therapeutic Platform Oral Enzyme GI MOA Therapeutic candidates Leverage GI that degrade a specific tract as metabolite “auxiliary kidney” Reloxaliase ALLN-346 Non-absorbed Reduces potential for adverse events 4
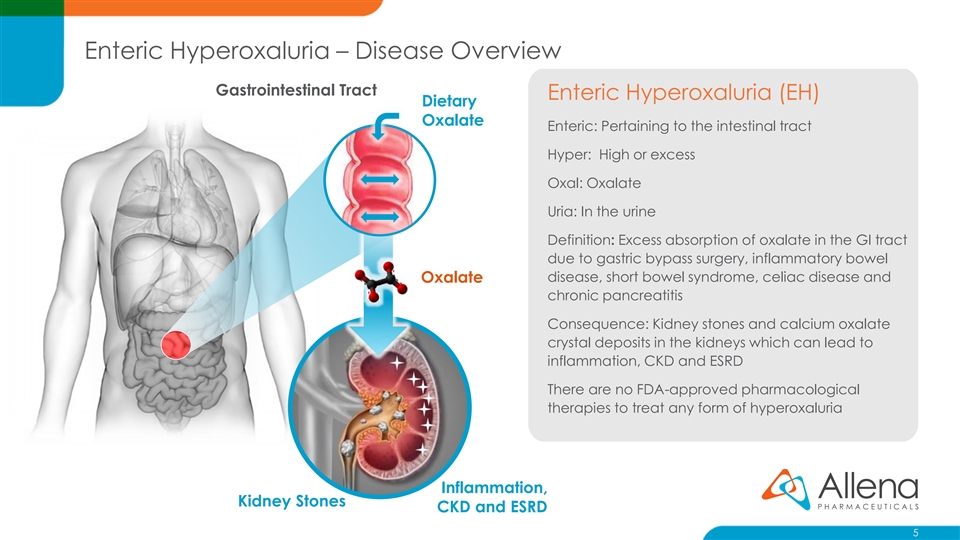
Enteric Hyperoxaluria – Disease Overview Gastrointestinal Tract Enteric Hyperoxaluria (EH) Dietary Oxalate Enteric: Pertaining to the intestinal tract Hyper: High or excess Oxal: Oxalate Uria: In the urine Definition: Excess absorption of oxalate in the GI tract due to gastric bypass surgery, inflammatory bowel disease, short bowel syndrome, celiac disease and Oxalate chronic pancreatitis Consequence: Kidney stones and calcium oxalate crystal deposits in the kidneys which can lead to inflammation, CKD and ESRD There are no FDA-approved pharmacological therapies to treat any form of hyperoxaluria Inflammation, Kidney Stones CKD and ESRD 5Enteric Hyperoxaluria – Disease Overview Gastrointestinal Tract Enteric Hyperoxaluria (EH) Dietary Oxalate Enteric: Pertaining to the intestinal tract Hyper: High or excess Oxal: Oxalate Uria: In the urine Definition: Excess absorption of oxalate in the GI tract due to gastric bypass surgery, inflammatory bowel disease, short bowel syndrome, celiac disease and Oxalate chronic pancreatitis Consequence: Kidney stones and calcium oxalate crystal deposits in the kidneys which can lead to inflammation, CKD and ESRD There are no FDA-approved pharmacological therapies to treat any form of hyperoxaluria Inflammation, Kidney Stones CKD and ESRD 5
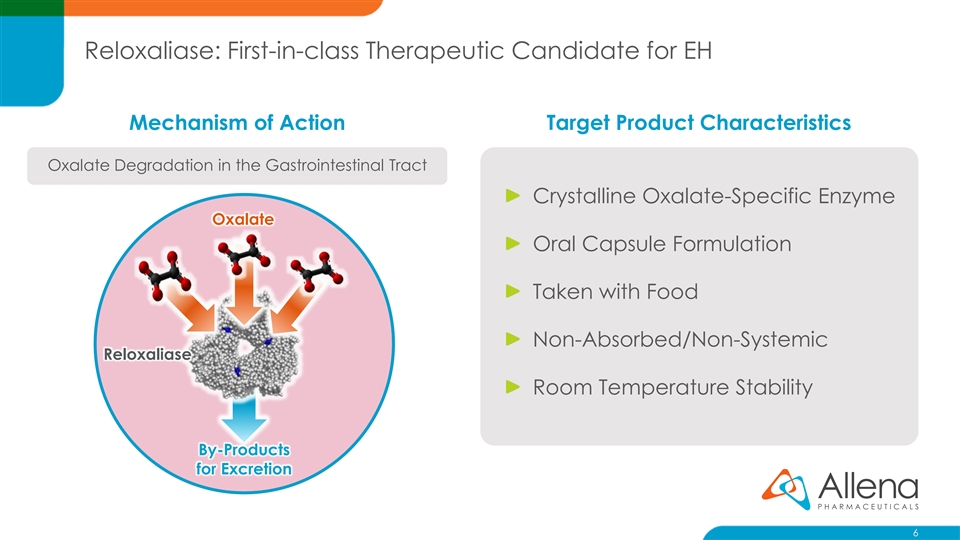
Reloxaliase: First-in-class Therapeutic Candidate for EH Mechanism of Action Target Product Characteristics Oxalate Degradation in the Gastrointestinal Tract Crystalline Oxalate-Specific Enzyme Oxalate Oral Capsule Formulation Taken with Food Non-Absorbed/Non-Systemic Reloxaliase Room Temperature Stability By-Products for Excretion 6Reloxaliase: First-in-class Therapeutic Candidate for EH Mechanism of Action Target Product Characteristics Oxalate Degradation in the Gastrointestinal Tract Crystalline Oxalate-Specific Enzyme Oxalate Oral Capsule Formulation Taken with Food Non-Absorbed/Non-Systemic Reloxaliase Room Temperature Stability By-Products for Excretion 6
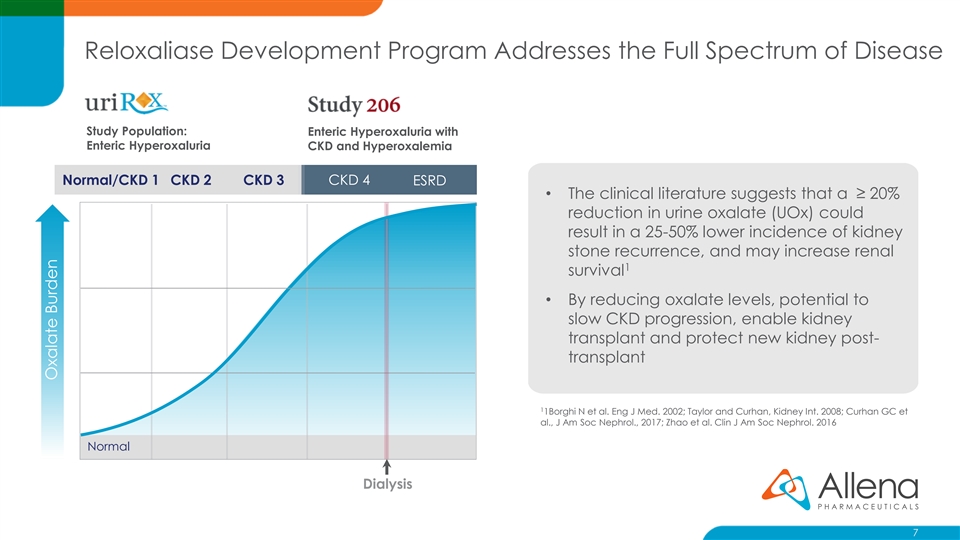
Reloxaliase Development Program Addresses the Full Spectrum of Disease Study Population: Enteric Hyperoxaluria with Enteric Hyperoxaluria CKD and Hyperoxalemia Normal/CKD 1 CKD 2 CKD 3 CKD 4 ESRD • The clinical literature suggests that a ≥ 20% reduction in urine oxalate (UOx) could result in a 25-50% lower incidence of kidney stone recurrence, and may increase renal 1 survival • By reducing oxalate levels, potential to slow CKD progression, enable kidney transplant and protect new kidney post- transplant 1 1Borghi N et al. Eng J Med. 2002; Taylor and Curhan, Kidney Int. 2008; Curhan GC et al., J Am Soc Nephrol., 2017; Zhao et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Normal Dialysis 7 Oxalate BurdenReloxaliase Development Program Addresses the Full Spectrum of Disease Study Population: Enteric Hyperoxaluria with Enteric Hyperoxaluria CKD and Hyperoxalemia Normal/CKD 1 CKD 2 CKD 3 CKD 4 ESRD • The clinical literature suggests that a ≥ 20% reduction in urine oxalate (UOx) could result in a 25-50% lower incidence of kidney stone recurrence, and may increase renal 1 survival • By reducing oxalate levels, potential to slow CKD progression, enable kidney transplant and protect new kidney post- transplant 1 1Borghi N et al. Eng J Med. 2002; Taylor and Curhan, Kidney Int. 2008; Curhan GC et al., J Am Soc Nephrol., 2017; Zhao et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Normal Dialysis 7 Oxalate Burden

URIROX-1: Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Reloxaliase in Patients with Enteric Hyperoxaluria UOx ≥ 50mg/24h Normal to Stage 3 CKD Reloxaliase Follow up (eGFR ≥ 30) 4 weeks Reloxaliase (7,500 u) or placebo 2 cap with Screening Randomization meal/snack 3 to 5 times per day x 28 days 1:1 N=115 Placebo 1x UOx 2x UOx 2x UOx 2x UOx 2x UOx 2x UOx Primary Endpoint: • Percent change from baseline in 24h UOx excretion during Weeks 1 to 4 Key Secondary Endpoint: • Proportion of subjects with a ≥ 20% reduction from baseline in 24h UOx excretion during Weeks 1 to 4 Pre-specified, Stratified Analysis • Subset analysis of the primary and lead secondary endpoint in subjects with a history of bariatric surgery 8URIROX-1: Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Reloxaliase in Patients with Enteric Hyperoxaluria UOx ≥ 50mg/24h Normal to Stage 3 CKD Reloxaliase Follow up (eGFR ≥ 30) 4 weeks Reloxaliase (7,500 u) or placebo 2 cap with Screening Randomization meal/snack 3 to 5 times per day x 28 days 1:1 N=115 Placebo 1x UOx 2x UOx 2x UOx 2x UOx 2x UOx 2x UOx Primary Endpoint: • Percent change from baseline in 24h UOx excretion during Weeks 1 to 4 Key Secondary Endpoint: • Proportion of subjects with a ≥ 20% reduction from baseline in 24h UOx excretion during Weeks 1 to 4 Pre-specified, Stratified Analysis • Subset analysis of the primary and lead secondary endpoint in subjects with a history of bariatric surgery 8

URIROX-1: Patient Demographics and Baseline Characteristics Reloxaliase Placebo High Burden of Disease Category / Statistic (N=58) (N=57) Age (years) – Mean (SD) 58.7 (10.09) 58.6 (10.18) Baseline UOx of 89.2 mg/day Gender, n (%) Female 28 (48.3) 27 (47.4) Enteric condition, n (%) Average 11 stone events in Bariatric surgery [Roux-en-Y gastric bypass] 40 (69.0) [27 (46.6)] 38 (66.7) [27 (47.4)] Inflammatory bowel disease 10 (17.2) 10 (17.5) last 5 years Short bowel syndrome 3 (5.2) 8 (14.0) Pancreatic insufficiency 3 5.2) 0 Other 2 (3.4) 1 (1.8) 16.5% reported KS events Baseline UOx (mg/24h) – Mean (SD) 87.3 (28.87) 91.1 (41.64) 1 during study Baseline UOx ≥ 90 mg/24h, n (%) 22 (37.9) 23 (40.4) Number of kidney stone episodes in past 5 years- Mean (SD) 8.8 (27.49) 14.2 (43.23) 26% CKD Stage 3 2 eGFR (mL/min/1.73m ) - Mean (SD) 76.4 (22.71) 80.5 (24.60) CKD Stage 3, n (%) 16 (27.6) 14 (24.6) 1. Kidney stone events during the study period were approximately equally distributed between treatment and placebo groups 9URIROX-1: Patient Demographics and Baseline Characteristics Reloxaliase Placebo High Burden of Disease Category / Statistic (N=58) (N=57) Age (years) – Mean (SD) 58.7 (10.09) 58.6 (10.18) Baseline UOx of 89.2 mg/day Gender, n (%) Female 28 (48.3) 27 (47.4) Enteric condition, n (%) Average 11 stone events in Bariatric surgery [Roux-en-Y gastric bypass] 40 (69.0) [27 (46.6)] 38 (66.7) [27 (47.4)] Inflammatory bowel disease 10 (17.2) 10 (17.5) last 5 years Short bowel syndrome 3 (5.2) 8 (14.0) Pancreatic insufficiency 3 5.2) 0 Other 2 (3.4) 1 (1.8) 16.5% reported KS events Baseline UOx (mg/24h) – Mean (SD) 87.3 (28.87) 91.1 (41.64) 1 during study Baseline UOx ≥ 90 mg/24h, n (%) 22 (37.9) 23 (40.4) Number of kidney stone episodes in past 5 years- Mean (SD) 8.8 (27.49) 14.2 (43.23) 26% CKD Stage 3 2 eGFR (mL/min/1.73m ) - Mean (SD) 76.4 (22.71) 80.5 (24.60) CKD Stage 3, n (%) 16 (27.6) 14 (24.6) 1. Kidney stone events during the study period were approximately equally distributed between treatment and placebo groups 9
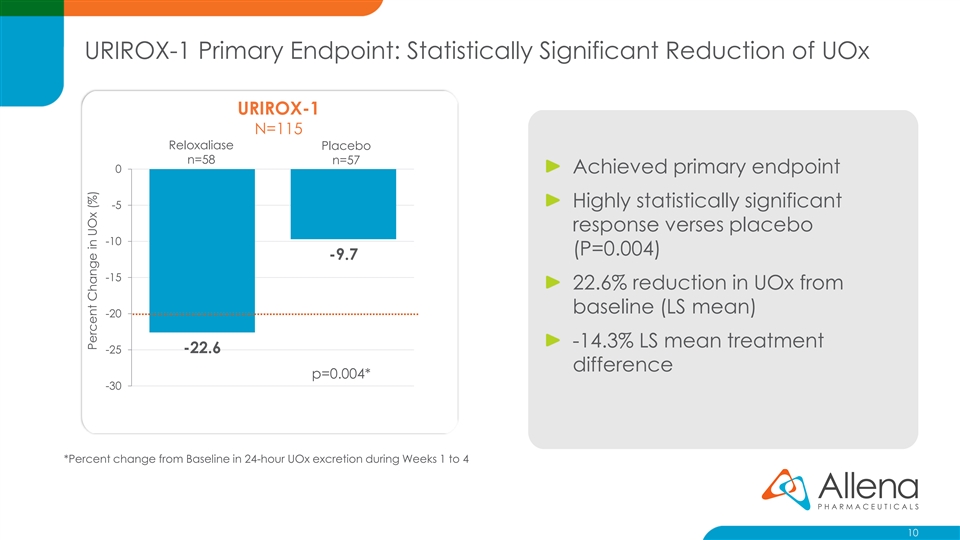
URIROX-1 Primary Endpoint: Statistically Significant Reduction of UOx URIROX-1 N=115 Reloxaliase Placebo n=58 n=57 0 Achieved primary endpoint Highly statistically significant -5 response verses placebo -10 (P=0.004) -9.7 -15 22.6% reduction in UOx from baseline (LS mean) -20 -14.3% LS mean treatment -22.6 -25 difference p=0.004* -30 *Percent change from Baseline in 24-hour UOx excretion during Weeks 1 to 4 10 Percent Change in UOx (%)URIROX-1 Primary Endpoint: Statistically Significant Reduction of UOx URIROX-1 N=115 Reloxaliase Placebo n=58 n=57 0 Achieved primary endpoint Highly statistically significant -5 response verses placebo -10 (P=0.004) -9.7 -15 22.6% reduction in UOx from baseline (LS mean) -20 -14.3% LS mean treatment -22.6 -25 difference p=0.004* -30 *Percent change from Baseline in 24-hour UOx excretion during Weeks 1 to 4 10 Percent Change in UOx (%)
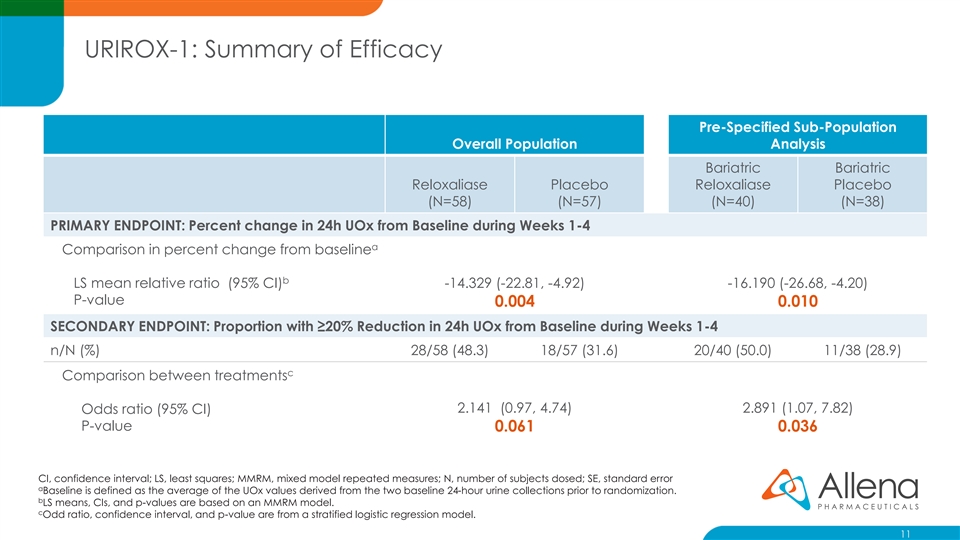
URIROX-1: Summary of Efficacy Pre-Specified Sub-Population Overall Population Analysis Bariatric Bariatric Reloxaliase Placebo Reloxaliase Placebo (N=58) (N=57) (N=40) (N=38) PRIMARY ENDPOINT: Percent change in 24h UOx from Baseline during Weeks 1-4 a Comparison in percent change from baseline b LS mean relative ratio (95% CI) -14.329 (-22.81, -4.92) -16.190 (-26.68, -4.20) P-value 0.004 0.010 SECONDARY ENDPOINT: Proportion with ≥20% Reduction in 24h UOx from Baseline during Weeks 1-4 n/N (%) 28/58 (48.3) 18/57 (31.6) 20/40 (50.0) 11/38 (28.9) c Comparison between treatments 2.141 (0.97, 4.74) 2.891 (1.07, 7.82) Odds ratio (95% CI) P-value 0.061 0.036 CI, confidence interval; LS, least squares; MMRM, mixed model repeated measures; N, number of subjects dosed; SE, standard error a Baseline is defined as the average of the UOx values derived from the two baseline 24-hour urine collections prior to randomization. b LS means, CIs, and p-values are based on an MMRM model. c Odd ratio, confidence interval, and p-value are from a stratified logistic regression model. 11URIROX-1: Summary of Efficacy Pre-Specified Sub-Population Overall Population Analysis Bariatric Bariatric Reloxaliase Placebo Reloxaliase Placebo (N=58) (N=57) (N=40) (N=38) PRIMARY ENDPOINT: Percent change in 24h UOx from Baseline during Weeks 1-4 a Comparison in percent change from baseline b LS mean relative ratio (95% CI) -14.329 (-22.81, -4.92) -16.190 (-26.68, -4.20) P-value 0.004 0.010 SECONDARY ENDPOINT: Proportion with ≥20% Reduction in 24h UOx from Baseline during Weeks 1-4 n/N (%) 28/58 (48.3) 18/57 (31.6) 20/40 (50.0) 11/38 (28.9) c Comparison between treatments 2.141 (0.97, 4.74) 2.891 (1.07, 7.82) Odds ratio (95% CI) P-value 0.061 0.036 CI, confidence interval; LS, least squares; MMRM, mixed model repeated measures; N, number of subjects dosed; SE, standard error a Baseline is defined as the average of the UOx values derived from the two baseline 24-hour urine collections prior to randomization. b LS means, CIs, and p-values are based on an MMRM model. c Odd ratio, confidence interval, and p-value are from a stratified logistic regression model. 11
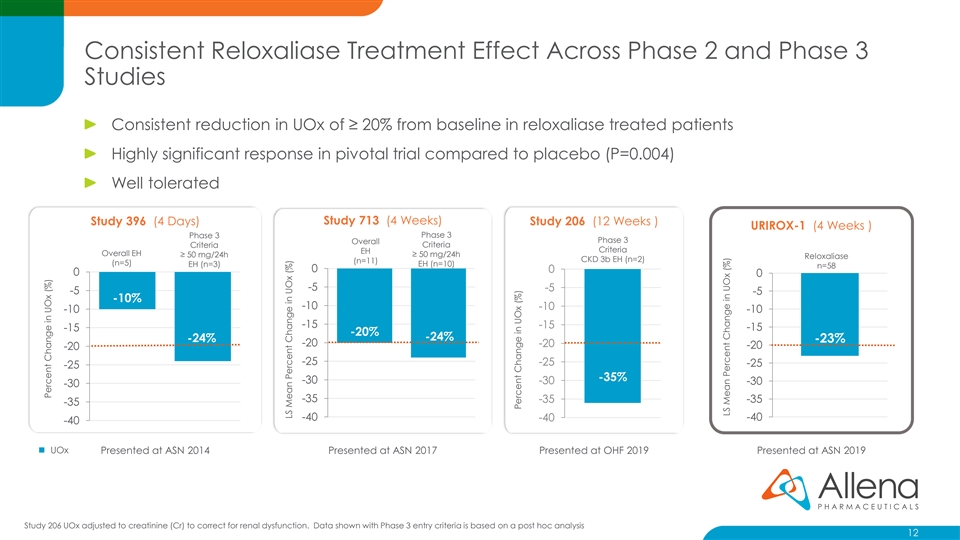
Consistent Reloxaliase Treatment Effect Across Phase 2 and Phase 3 Studies Consistent reduction in UOx of ≥ 20% from baseline in reloxaliase treated patients Highly significant response in pivotal trial compared to placebo (P=0.004) Well tolerated Study 396 (4 Days) Study 713 (4 Weeks) Study 206 (12 Weeks ) URIROX-1 (4 Weeks ) Phase 3 Phase 3 Phase 3 Overall Criteria Criteria Criteria EH Overall EH ≥ 50 mg/24h ≥ 50 mg/24h Reloxaliase CKD 3b EH (n=2) (n=11) (n=5) EH (n=3) EH (n=10) n=58 0 0 0 0 -5 -5 -5 -5 -10% -10 -10 -10 -10 -15 -15 -15 -15 -20% -24% -24% -23% -20 -20 -20 -20 -25 -25 -25 -25 -35% -30 -30 -30 -30 -35 -35 -35 -35 -40 -40 -40 -40 ◼ UOx Presented at ASN 2014 Presented at ASN 2017 Presented at OHF 2019 Presented at ASN 2019 Study 206 UOx adjusted to creatinine (Cr) to correct for renal dysfunction. Data shown with Phase 3 entry criteria is based on a post hoc analysis 12 Percent Change in UOx (%) LS Mean Percent Change in UOx (%) Percent Change in UOx (%) LS Mean Percent Change in UOx (%)Consistent Reloxaliase Treatment Effect Across Phase 2 and Phase 3 Studies Consistent reduction in UOx of ≥ 20% from baseline in reloxaliase treated patients Highly significant response in pivotal trial compared to placebo (P=0.004) Well tolerated Study 396 (4 Days) Study 713 (4 Weeks) Study 206 (12 Weeks ) URIROX-1 (4 Weeks ) Phase 3 Phase 3 Phase 3 Overall Criteria Criteria Criteria EH Overall EH ≥ 50 mg/24h ≥ 50 mg/24h Reloxaliase CKD 3b EH (n=2) (n=11) (n=5) EH (n=3) EH (n=10) n=58 0 0 0 0 -5 -5 -5 -5 -10% -10 -10 -10 -10 -15 -15 -15 -15 -20% -24% -24% -23% -20 -20 -20 -20 -25 -25 -25 -25 -35% -30 -30 -30 -30 -35 -35 -35 -35 -40 -40 -40 -40 ◼ UOx Presented at ASN 2014 Presented at ASN 2017 Presented at OHF 2019 Presented at ASN 2019 Study 206 UOx adjusted to creatinine (Cr) to correct for renal dysfunction. Data shown with Phase 3 entry criteria is based on a post hoc analysis 12 Percent Change in UOx (%) LS Mean Percent Change in UOx (%) Percent Change in UOx (%) LS Mean Percent Change in UOx (%)

Reloxaliase Demonstrates Sustained Reductions in UOx Across Weeks 1-4 URIROX-1 0 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 -5 -10 -15 -20 -25 Reloxaliase Placebo -30 13 Percent Change in UOx (%)Reloxaliase Demonstrates Sustained Reductions in UOx Across Weeks 1-4 URIROX-1 0 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 -5 -10 -15 -20 -25 Reloxaliase Placebo -30 13 Percent Change in UOx (%)
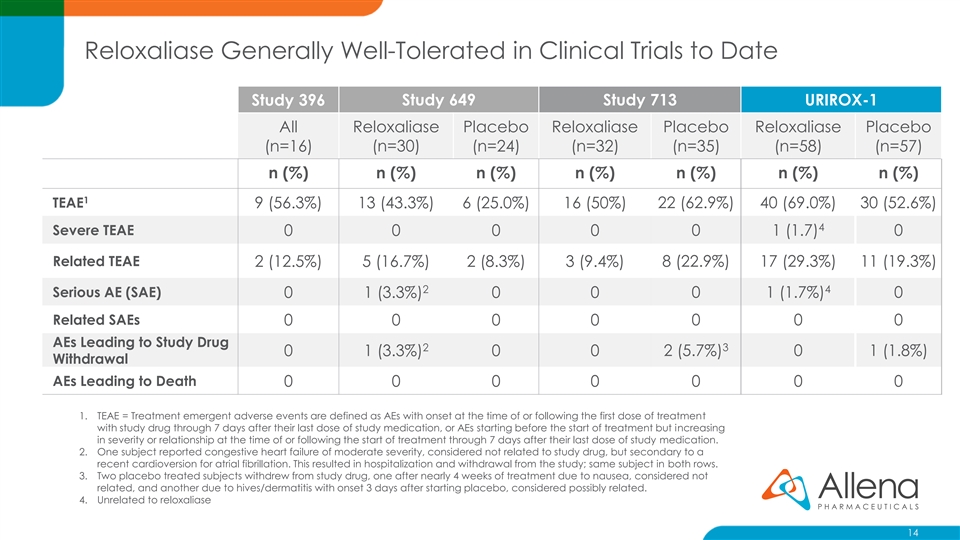
Reloxaliase Generally Well-Tolerated in Clinical Trials to Date Study 396 Study 649 Study 713 URIROX-1 All Reloxaliase Placebo Reloxaliase Placebo Reloxaliase Placebo (n=16) (n=30) (n=24) (n=32) (n=35) (n=58) (n=57) n (%) n (%) n (%) n (%) n (%) n (%) n (%) 1 TEAE 9 (56.3%) 13 (43.3%) 6 (25.0%) 16 (50%) 22 (62.9%) 40 (69.0%) 30 (52.6%) 4 Severe TEAE 0 0 0 0 0 1 (1.7) 0 Related TEAE 2 (12.5%) 5 (16.7%) 2 (8.3%) 3 (9.4%) 8 (22.9%) 17 (29.3%) 11 (19.3%) 2 4 Serious AE (SAE) 0 1 (3.3%) 0 0 0 1 (1.7%) 0 Related SAEs 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 AEs Leading to Study Drug 2 3 0 1 (3.3%) 0 0 2 (5.7%) 0 1 (1.8%) Withdrawal AEs Leading to Death 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1. TEAE = Treatment emergent adverse events are defined as AEs with onset at the time of or following the first dose of treatment with study drug through 7 days after their last dose of study medication, or AEs starting before the start of treatment but increasing in severity or relationship at the time of or following the start of treatment through 7 days after their last dose of study medication. 2. One subject reported congestive heart failure of moderate severity, considered not related to study drug, but secondary to a recent cardioversion for atrial fibrillation. This resulted in hospitalization and withdrawal from the study; same subject in both rows. 3. Two placebo treated subjects withdrew from study drug, one after nearly 4 weeks of treatment due to nausea, considered not related, and another due to hives/dermatitis with onset 3 days after starting placebo, considered possibly related. 4. Unrelated to reloxaliase 14Reloxaliase Generally Well-Tolerated in Clinical Trials to Date Study 396 Study 649 Study 713 URIROX-1 All Reloxaliase Placebo Reloxaliase Placebo Reloxaliase Placebo (n=16) (n=30) (n=24) (n=32) (n=35) (n=58) (n=57) n (%) n (%) n (%) n (%) n (%) n (%) n (%) 1 TEAE 9 (56.3%) 13 (43.3%) 6 (25.0%) 16 (50%) 22 (62.9%) 40 (69.0%) 30 (52.6%) 4 Severe TEAE 0 0 0 0 0 1 (1.7) 0 Related TEAE 2 (12.5%) 5 (16.7%) 2 (8.3%) 3 (9.4%) 8 (22.9%) 17 (29.3%) 11 (19.3%) 2 4 Serious AE (SAE) 0 1 (3.3%) 0 0 0 1 (1.7%) 0 Related SAEs 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 AEs Leading to Study Drug 2 3 0 1 (3.3%) 0 0 2 (5.7%) 0 1 (1.8%) Withdrawal AEs Leading to Death 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1. TEAE = Treatment emergent adverse events are defined as AEs with onset at the time of or following the first dose of treatment with study drug through 7 days after their last dose of study medication, or AEs starting before the start of treatment but increasing in severity or relationship at the time of or following the start of treatment through 7 days after their last dose of study medication. 2. One subject reported congestive heart failure of moderate severity, considered not related to study drug, but secondary to a recent cardioversion for atrial fibrillation. This resulted in hospitalization and withdrawal from the study; same subject in both rows. 3. Two placebo treated subjects withdrew from study drug, one after nearly 4 weeks of treatment due to nausea, considered not related, and another due to hives/dermatitis with onset 3 days after starting placebo, considered possibly related. 4. Unrelated to reloxaliase 14
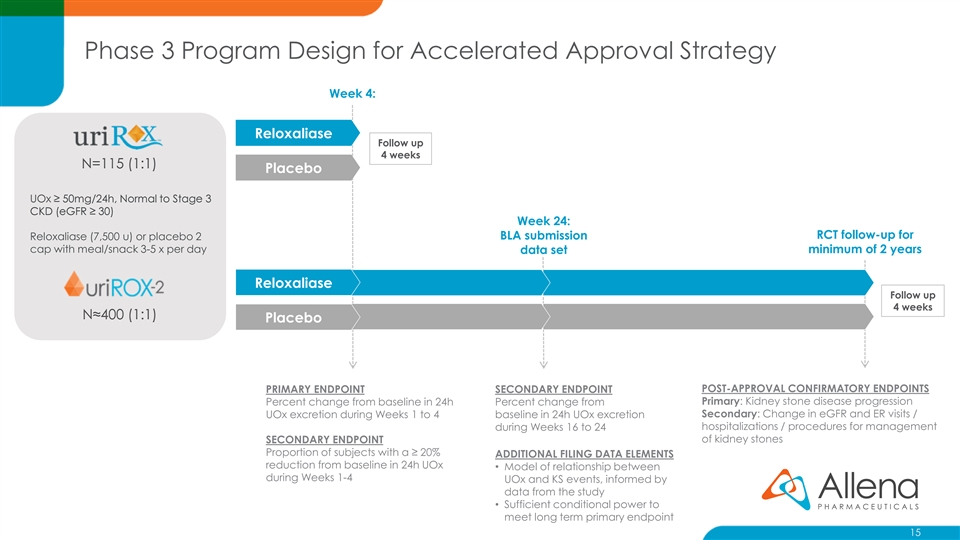
Phase 3 Program Design for Accelerated Approval Strategy Week 4: Reloxaliase Follow up 4 weeks N=115 (1:1) Placebo UOx ≥ 50mg/24h, Normal to Stage 3 CKD (eGFR ≥ 30) Week 24: RCT follow-up for Reloxaliase (7,500 u) or placebo 2 BLA submission cap with meal/snack 3-5 x per day minimum of 2 years data set Reloxaliase Follow up 4 weeks N≈400 (1:1) Placebo POST-APPROVAL CONFIRMATORY ENDPOINTS PRIMARY ENDPOINT SECONDARY ENDPOINT Primary: Kidney stone disease progression Percent change from baseline in 24h Percent change from Secondary: Change in eGFR and ER visits / UOx excretion during Weeks 1 to 4 baseline in 24h UOx excretion hospitalizations / procedures for management during Weeks 16 to 24 SECONDARY ENDPOINT of kidney stones Proportion of subjects with a ≥ 20% ADDITIONAL FILING DATA ELEMENTS reduction from baseline in 24h UOx • Model of relationship between during Weeks 1-4 UOx and KS events, informed by data from the study • Sufficient conditional power to meet long term primary endpoint 15Phase 3 Program Design for Accelerated Approval Strategy Week 4: Reloxaliase Follow up 4 weeks N=115 (1:1) Placebo UOx ≥ 50mg/24h, Normal to Stage 3 CKD (eGFR ≥ 30) Week 24: RCT follow-up for Reloxaliase (7,500 u) or placebo 2 BLA submission cap with meal/snack 3-5 x per day minimum of 2 years data set Reloxaliase Follow up 4 weeks N≈400 (1:1) Placebo POST-APPROVAL CONFIRMATORY ENDPOINTS PRIMARY ENDPOINT SECONDARY ENDPOINT Primary: Kidney stone disease progression Percent change from baseline in 24h Percent change from Secondary: Change in eGFR and ER visits / UOx excretion during Weeks 1 to 4 baseline in 24h UOx excretion hospitalizations / procedures for management during Weeks 16 to 24 SECONDARY ENDPOINT of kidney stones Proportion of subjects with a ≥ 20% ADDITIONAL FILING DATA ELEMENTS reduction from baseline in 24h UOx • Model of relationship between during Weeks 1-4 UOx and KS events, informed by data from the study • Sufficient conditional power to meet long term primary endpoint 15
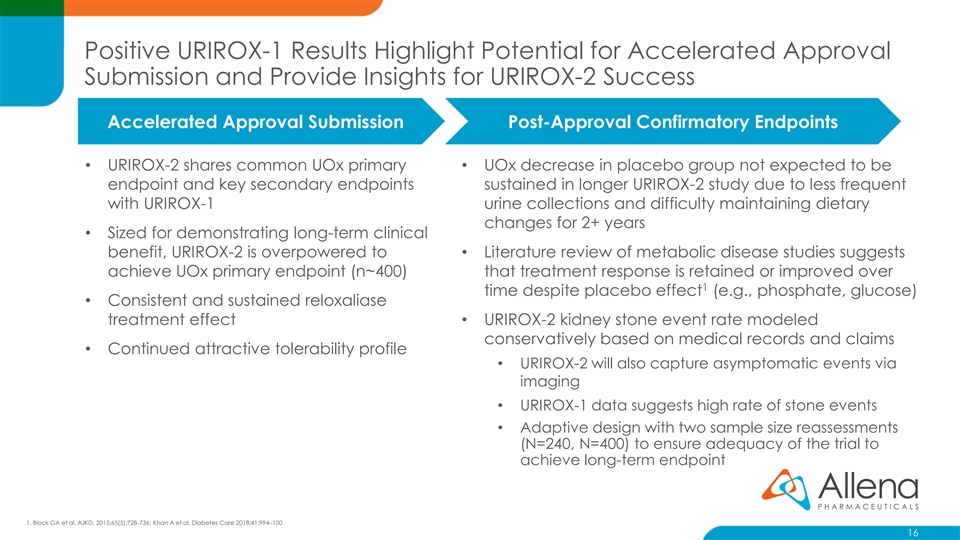
Positive URIROX-1 Results Highlight Potential for Accelerated Approval Submission and Provide Insights for URIROX-2 Success Accelerated Approval Submission Post-Approval Confirmatory Endpoints • URIROX-2 shares common UOx primary • UOx decrease in placebo group not expected to be endpoint and key secondary endpoints sustained in longer URIROX-2 study due to less frequent with URIROX-1 urine collections and difficulty maintaining dietary changes for 2+ years • Sized for demonstrating long-term clinical benefit, URIROX-2 is overpowered to • Literature review of metabolic disease studies suggests achieve UOx primary endpoint (n~400) that treatment response is retained or improved over 1 time despite placebo effect (e.g., phosphate, glucose) • Consistent and sustained reloxaliase treatment effect• URIROX-2 kidney stone event rate modeled conservatively based on medical records and claims • Continued attractive tolerability profile • URIROX-2 will also capture asymptomatic events via imaging • URIROX-1 data suggests high rate of stone events • Adaptive design with two sample size reassessments (N=240, N=400) to ensure adequacy of the trial to achieve long-term endpoint 1. Block GA et al. AJKD. 2015;65(5):728-736; Khan A et al. Diabetes Care 2018;41:994–100 16Positive URIROX-1 Results Highlight Potential for Accelerated Approval Submission and Provide Insights for URIROX-2 Success Accelerated Approval Submission Post-Approval Confirmatory Endpoints • URIROX-2 shares common UOx primary • UOx decrease in placebo group not expected to be endpoint and key secondary endpoints sustained in longer URIROX-2 study due to less frequent with URIROX-1 urine collections and difficulty maintaining dietary changes for 2+ years • Sized for demonstrating long-term clinical benefit, URIROX-2 is overpowered to • Literature review of metabolic disease studies suggests achieve UOx primary endpoint (n~400) that treatment response is retained or improved over 1 time despite placebo effect (e.g., phosphate, glucose) • Consistent and sustained reloxaliase treatment effect• URIROX-2 kidney stone event rate modeled conservatively based on medical records and claims • Continued attractive tolerability profile • URIROX-2 will also capture asymptomatic events via imaging • URIROX-1 data suggests high rate of stone events • Adaptive design with two sample size reassessments (N=240, N=400) to ensure adequacy of the trial to achieve long-term endpoint 1. Block GA et al. AJKD. 2015;65(5):728-736; Khan A et al. Diabetes Care 2018;41:994–100 16
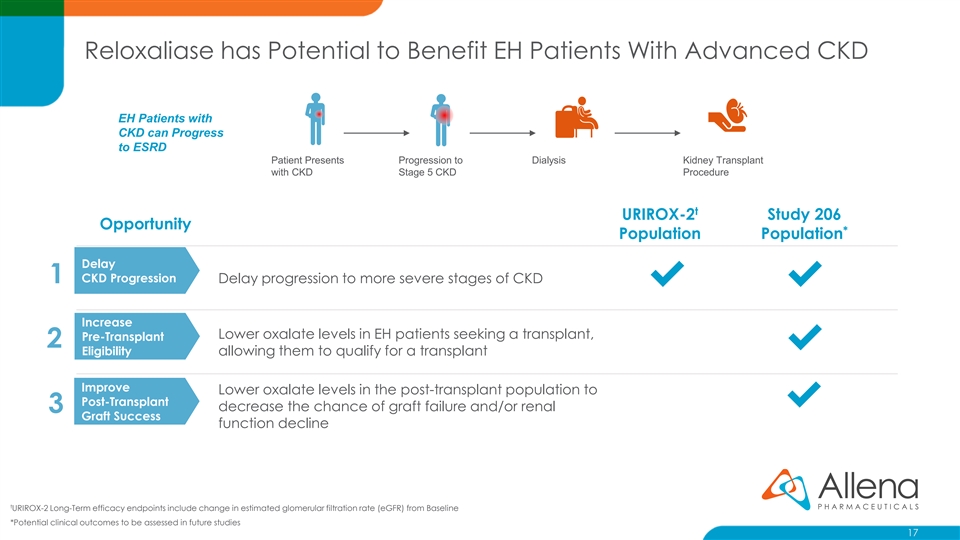
Reloxaliase has Potential to Benefit EH Patients With Advanced CKD EH Patients with CKD can Progress to ESRD Patient Presents Progression to Dialysis Kidney Transplant with CKD Stage 5 CKD Procedure t URIROX-2 Study 206 Opportunity * Population Population Delay CKD Progression 1 Delay progression to more severe stages of CKD ✔✔ Increase Lower oxalate levels in EH patients seeking a transplant, Pre-Transplant 2 ✔ Eligibility allowing them to qualify for a transplant Improve Lower oxalate levels in the post-transplant population to Post-Transplant ✔ decrease the chance of graft failure and/or renal 3 Graft Success function decline t URIROX-2 Long-Term efficacy endpoints include change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) from Baseline *Potential clinical outcomes to be assessed in future studies 17Reloxaliase has Potential to Benefit EH Patients With Advanced CKD EH Patients with CKD can Progress to ESRD Patient Presents Progression to Dialysis Kidney Transplant with CKD Stage 5 CKD Procedure t URIROX-2 Study 206 Opportunity * Population Population Delay CKD Progression 1 Delay progression to more severe stages of CKD ✔✔ Increase Lower oxalate levels in EH patients seeking a transplant, Pre-Transplant 2 ✔ Eligibility allowing them to qualify for a transplant Improve Lower oxalate levels in the post-transplant population to Post-Transplant ✔ decrease the chance of graft failure and/or renal 3 Graft Success function decline t URIROX-2 Long-Term efficacy endpoints include change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) from Baseline *Potential clinical outcomes to be assessed in future studies 17
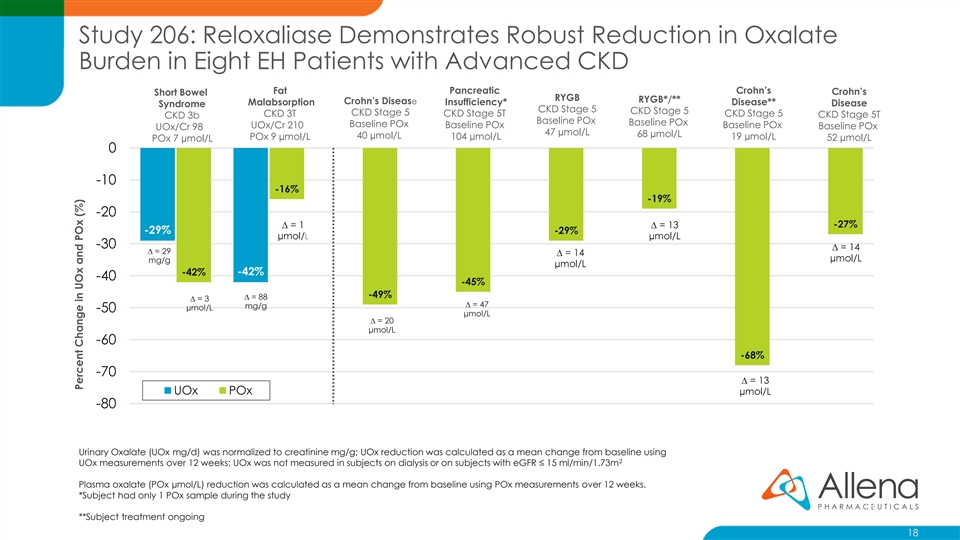
Study 206: Reloxaliase Demonstrates Robust Reduction in Oxalate Burden in Eight EH Patients with Advanced CKD Fat Pancreatic Crohn’s Crohn’s Short Bowel RYGB RYGB*/** Crohn’s Disease Malabsorption Insufficiency* Disease** Disease Syndrome CKD Stage 5 CKD Stage 5 CKD Stage 5 CKD 3T CKD Stage 5T CKD Stage 5 CKD Stage 5T CKD 3b Baseline POx Baseline POx Baseline POx UOx/Cr 210 Baseline POx Baseline POx Baseline POx UOx/Cr 98 47 µmol/L 68 µmol/L 40 µmol/L POx 9 µmol/L 104 µmol/L 19 µmol/L 52 µmol/L POx 7 µmol/L 0 -10 -16% -19% -20 ∆ = 1 ∆ = 13 -27% -29% -29% µmol/L µmol/L -30 ∆ = 14 ∆ = 29 ∆ = 14 µmol/L mg/g µmol/L -42% -42% -40 -45% -49% ∆ = 88 ∆ = 3 ∆ = 47 mg/g µmol/L -50 µmol/L ∆ = 20 µmol/L -60 -68% -70 ∆ = 13 UOx POx µmol/L -80 Urinary Oxalate (UOx mg/d) was normalized to creatinine mg/g; UOx reduction was calculated as a mean change from baseline using 2 UOx measurements over 12 weeks; UOx was not measured in subjects on dialysis or on subjects with eGFR ≤ 15 ml/min/1.73m Plasma oxalate (POx µmol/L) reduction was calculated as a mean change from baseline using POx measurements over 12 weeks. *Subject had only 1 POx sample during the study 18 **Subject treatment ongoing 18 Percent Change in UOx and POx (%)Study 206: Reloxaliase Demonstrates Robust Reduction in Oxalate Burden in Eight EH Patients with Advanced CKD Fat Pancreatic Crohn’s Crohn’s Short Bowel RYGB RYGB*/** Crohn’s Disease Malabsorption Insufficiency* Disease** Disease Syndrome CKD Stage 5 CKD Stage 5 CKD Stage 5 CKD 3T CKD Stage 5T CKD Stage 5 CKD Stage 5T CKD 3b Baseline POx Baseline POx Baseline POx UOx/Cr 210 Baseline POx Baseline POx Baseline POx UOx/Cr 98 47 µmol/L 68 µmol/L 40 µmol/L POx 9 µmol/L 104 µmol/L 19 µmol/L 52 µmol/L POx 7 µmol/L 0 -10 -16% -19% -20 ∆ = 1 ∆ = 13 -27% -29% -29% µmol/L µmol/L -30 ∆ = 14 ∆ = 29 ∆ = 14 µmol/L mg/g µmol/L -42% -42% -40 -45% -49% ∆ = 88 ∆ = 3 ∆ = 47 mg/g µmol/L -50 µmol/L ∆ = 20 µmol/L -60 -68% -70 ∆ = 13 UOx POx µmol/L -80 Urinary Oxalate (UOx mg/d) was normalized to creatinine mg/g; UOx reduction was calculated as a mean change from baseline using 2 UOx measurements over 12 weeks; UOx was not measured in subjects on dialysis or on subjects with eGFR ≤ 15 ml/min/1.73m Plasma oxalate (POx µmol/L) reduction was calculated as a mean change from baseline using POx measurements over 12 weeks. *Subject had only 1 POx sample during the study 18 **Subject treatment ongoing 18 Percent Change in UOx and POx (%)

Reloxaliase: Therapeutic Candidate with Blockbuster Potential High Unmet Need in Enteric Hyperoxaluria (EH) Novel Non-absorbed Oral Biologic URIROX-1 Trial Achieves Primary Endpoint with Highly Significant Reduction in UOx (p=0.004) Consistent Results across Phase 2 and 3 Studies Favorable Risk Benefit Profile FDA Alignment on Accelerated Approval Strategy Potential First FDA-Approved Treatment in EH Study 206 Data Supporting Further Development in EH with Advanced CKD Worldwide Marketing Rights 19Reloxaliase: Therapeutic Candidate with Blockbuster Potential High Unmet Need in Enteric Hyperoxaluria (EH) Novel Non-absorbed Oral Biologic URIROX-1 Trial Achieves Primary Endpoint with Highly Significant Reduction in UOx (p=0.004) Consistent Results across Phase 2 and 3 Studies Favorable Risk Benefit Profile FDA Alignment on Accelerated Approval Strategy Potential First FDA-Approved Treatment in EH Study 206 Data Supporting Further Development in EH with Advanced CKD Worldwide Marketing Rights 19

ALLN-346: Platform Extension Addressing Significant Opportunity in Gout Patients with Moderate-to-Severe CKD Gout Market is Incompletely Served by Existing Therapies ~375,000 gout patients with moderate to severe CKD who have uncontrolled gout on urate lowering therapy (ULT)* Gout patients with renal impairment are not optimally managed due to limitations of existing therapies ALLN-346 Therapeutic Strategy: • Gout patients with kidney and liver problems are contraindicated for allopurinol, Uloric, and • Novel urate degrading enzyme optimized for stability in the Zurampic GI tract • Current ULT’s may interact with other • MOA: orally administered, gut restricted enzyme therapeutic medications • Co-morbidities (e.g. cardiovascular) may also • Animal POC: demonstrated a robust reduction in urine and limit ULT options plasma uric acid levels in a severe animal model of hyperuricemia with advanced CKD Significant unmet need for safe and effective therapy that can be used in patients with renal impairment • Data presented at American College of Rheumatology meeting October 22, 2018 Sources: . *Lim JJ, Fu AC, and Reasner D. Prevalence of CKD and Uncontrolled Gout Among US Adults: Results from NHANES 2007- 2012. Poster presented at: The National Kidney Foundation Spring Clinical Meetings; April 18-22, 2017; Orlando Florida. Fletcher Spaght Analysis July 2016; Image: Retailleau, P., Colloc'h, N., Vivares, D., Bonnete, F., Castro, B., El Hajji, M., Prange, T. (2005) Urate oxidase from Aspergillus flavus: new crystal-packing contacts in relation to the content of the active site. Acta Crystallogr.,Sect.D, 61, 218-229; D. Grujic Urol Res 2008, 193. 20ALLN-346: Platform Extension Addressing Significant Opportunity in Gout Patients with Moderate-to-Severe CKD Gout Market is Incompletely Served by Existing Therapies ~375,000 gout patients with moderate to severe CKD who have uncontrolled gout on urate lowering therapy (ULT)* Gout patients with renal impairment are not optimally managed due to limitations of existing therapies ALLN-346 Therapeutic Strategy: • Gout patients with kidney and liver problems are contraindicated for allopurinol, Uloric, and • Novel urate degrading enzyme optimized for stability in the Zurampic GI tract • Current ULT’s may interact with other • MOA: orally administered, gut restricted enzyme therapeutic medications • Co-morbidities (e.g. cardiovascular) may also • Animal POC: demonstrated a robust reduction in urine and limit ULT options plasma uric acid levels in a severe animal model of hyperuricemia with advanced CKD Significant unmet need for safe and effective therapy that can be used in patients with renal impairment • Data presented at American College of Rheumatology meeting October 22, 2018 Sources: . *Lim JJ, Fu AC, and Reasner D. Prevalence of CKD and Uncontrolled Gout Among US Adults: Results from NHANES 2007- 2012. Poster presented at: The National Kidney Foundation Spring Clinical Meetings; April 18-22, 2017; Orlando Florida. Fletcher Spaght Analysis July 2016; Image: Retailleau, P., Colloc'h, N., Vivares, D., Bonnete, F., Castro, B., El Hajji, M., Prange, T. (2005) Urate oxidase from Aspergillus flavus: new crystal-packing contacts in relation to the content of the active site. Acta Crystallogr.,Sect.D, 61, 218-229; D. Grujic Urol Res 2008, 193. 20
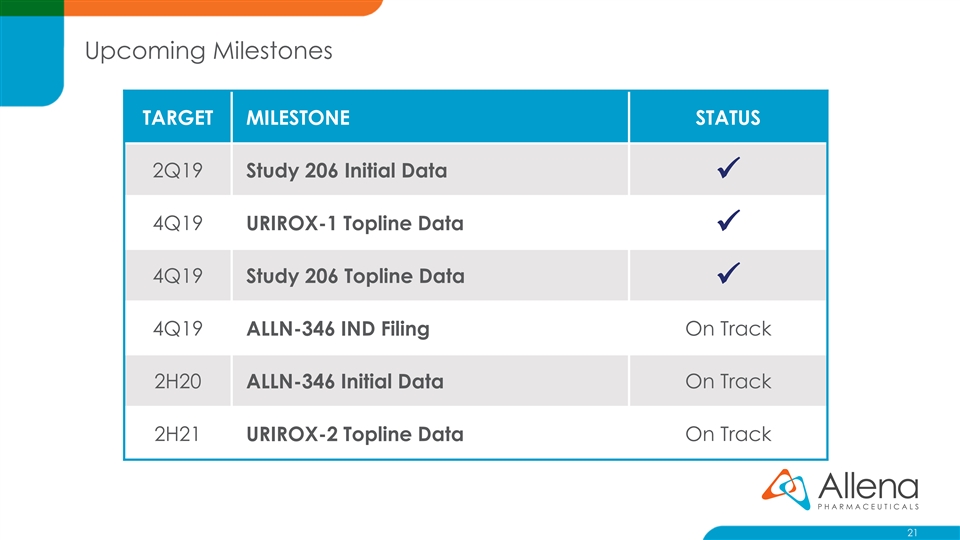
Upcoming Milestones TARGET MILESTONE STATUS 2Q19 Study 206 Initial Data ✓ 4Q19 URIROX-1 Topline Data ✓ 4Q19 Study 206 Topline Data ✓ 4Q19 ALLN-346 IND Filing On Track 2H20 ALLN-346 Initial Data On Track 2H21 URIROX-2 Topline Data On Track 21Upcoming Milestones TARGET MILESTONE STATUS 2Q19 Study 206 Initial Data ✓ 4Q19 URIROX-1 Topline Data ✓ 4Q19 Study 206 Topline Data ✓ 4Q19 ALLN-346 IND Filing On Track 2H20 ALLN-346 Initial Data On Track 2H21 URIROX-2 Topline Data On Track 21

URIROX-1 and Study 206 Topline Results November 7, 2019URIROX-1 and Study 206 Topline Results November 7, 2019





















