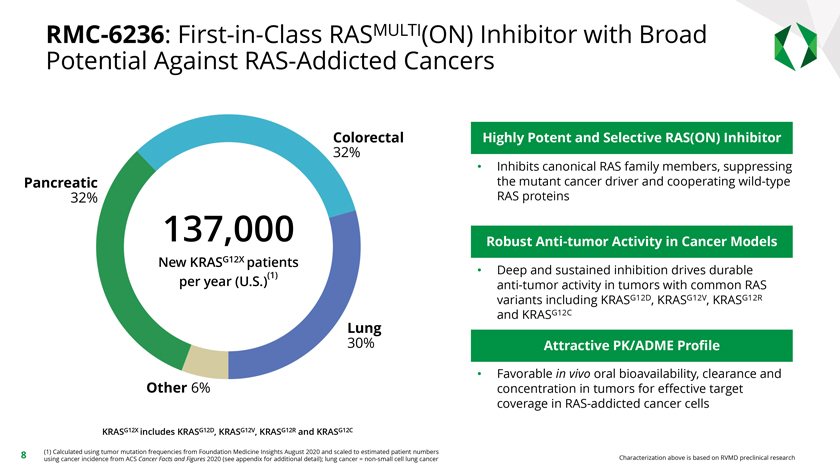
Appendix RAS cancer epidemiology statistics are estimated using tumor mutation frequencies from Foundation Medicine Insights August 2020 and scaled to estimated patient numbers using cancer incidence from ACS Cancer Facts and Figures 2020: RAS mutations include: KRAS G12(A,C,D,R,S,V), KRAS G13(C,D), KRAS Q61(H, K, L), KRAS A146T, KRAS wild-type amplification, NRAS G12C, NRAS Q61(K,L,R,P), HRAS mutations of known/likely function, BRAF class 3 mutations, NF1 loss of function mutations, PTPN11 mutations of known/likely function. NF1 LOF mutations = 50% of all NF1 mutations of known/likely function. BRAF class 3 mutations = D287H, D594(A,E,G,H,N,V,Y), F595L, G466(A,E,R,V,E,D,R), N581(I,S), S467L,T599I, V459L. Includes 12 major types: non-small cell lung cancer, colorectal, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, renal, gastroesophageal, head and neck squamous cell, ovarian and biliary cancers, acute myeloid leukemia, and advanced melanoma, bladder and uterine/endometrial cancers causing mortality. Est. worldwide annual incidence of RAS-mutated cancers is 3.4 million per Prior et al., Cancer Research 2020 RAS mutations drive 30% of human cancers per Prior et al., Cancer Research 2020 KRASG12X includes KRASG12D, KRASG12V, KRASG12R and KRASG12C Mouse tumor responses on slides 9 and 14 assigned according to mRECIST (modified from Gao et al. Nat Med. 2015): mPD = progressive disease; mSD = stable disease; mPR = partial response; mCR = complete response Kaplan-Meier progression on slide 10 defined as tumor doubling from baseline over 28 days: KRASG12X Tumors, where X = D,V,C, A or R: n = 207 RAS Pathway Mutant Tumors includes KRASG12X and other RAS and RAS pathway mutant tumors: KRASG13C, KRASG13D, KRASK117N, KRASQ61H, NF1LOF, PTPN11E76K or G503V, BRAFClass 3-mutant, and KRASWT-Amp: n = 332 PDX = patient-derived xenograft; CDX = cell line-derived xenograft