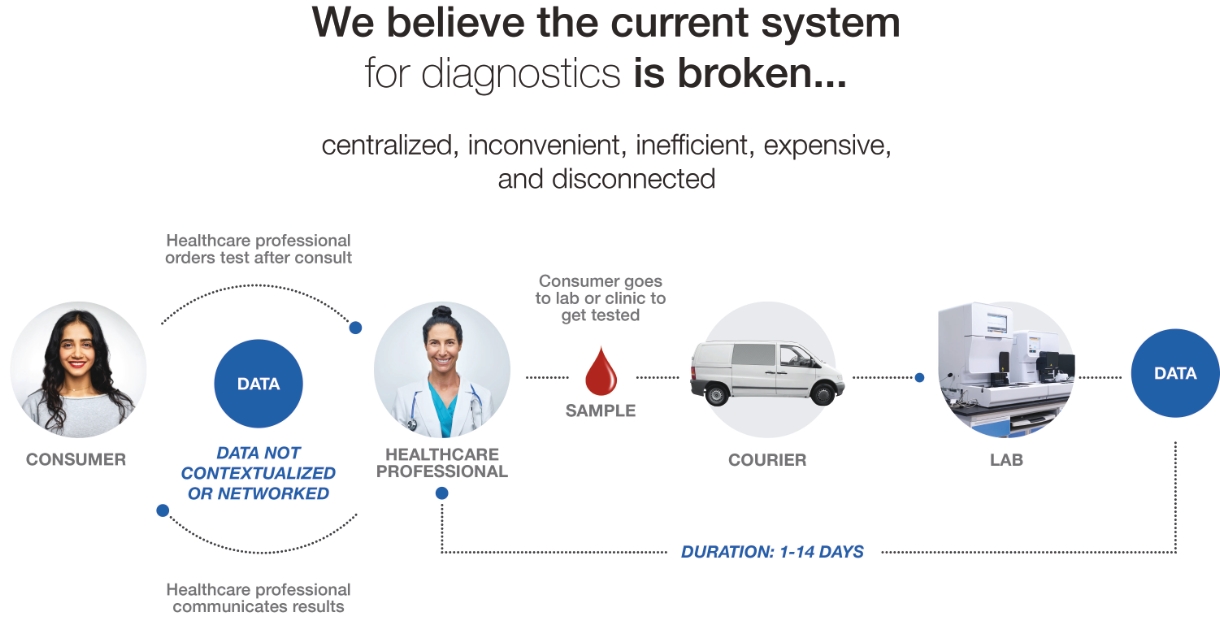
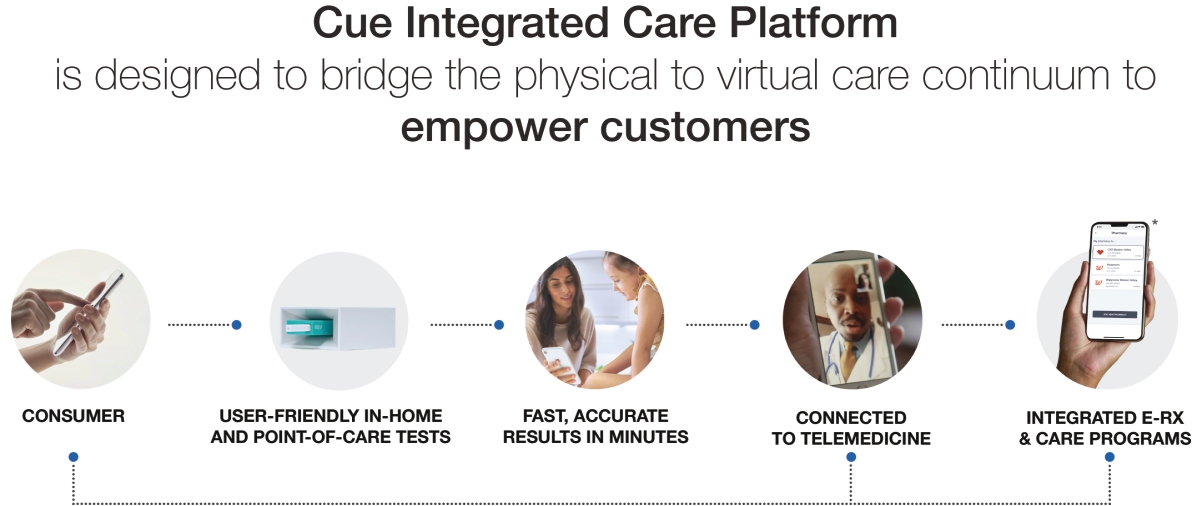
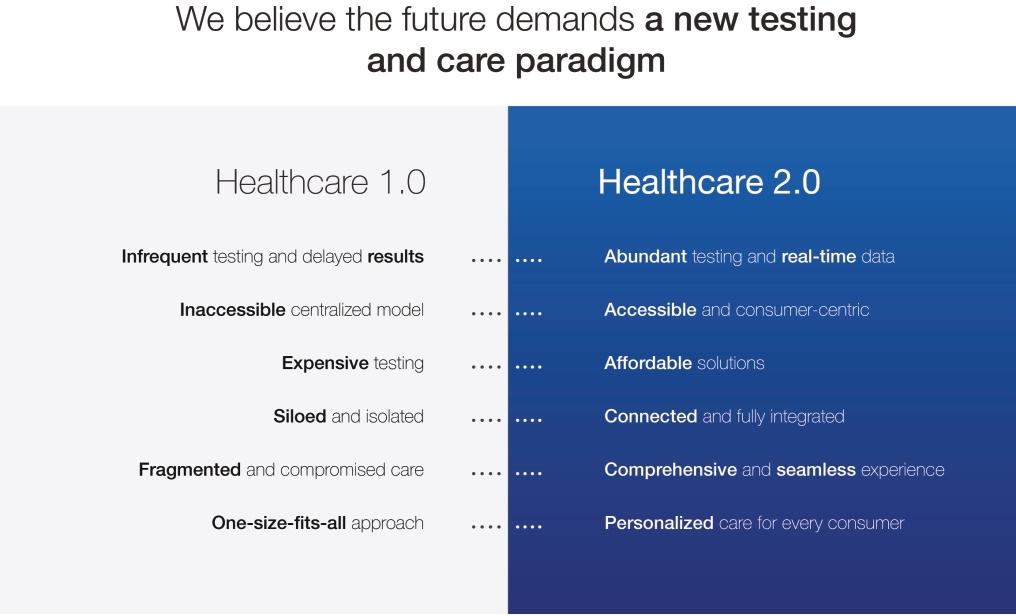
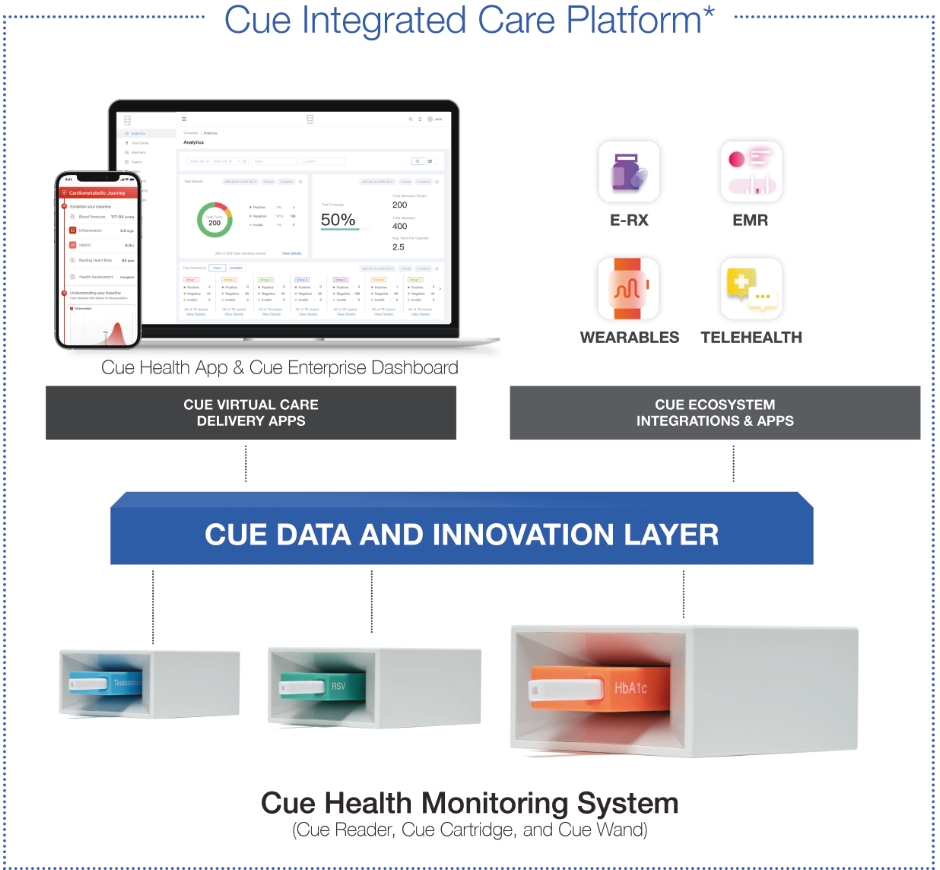
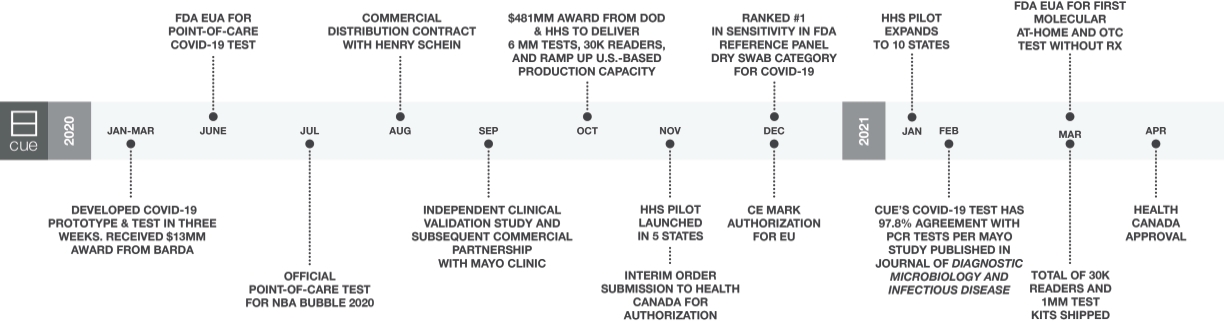
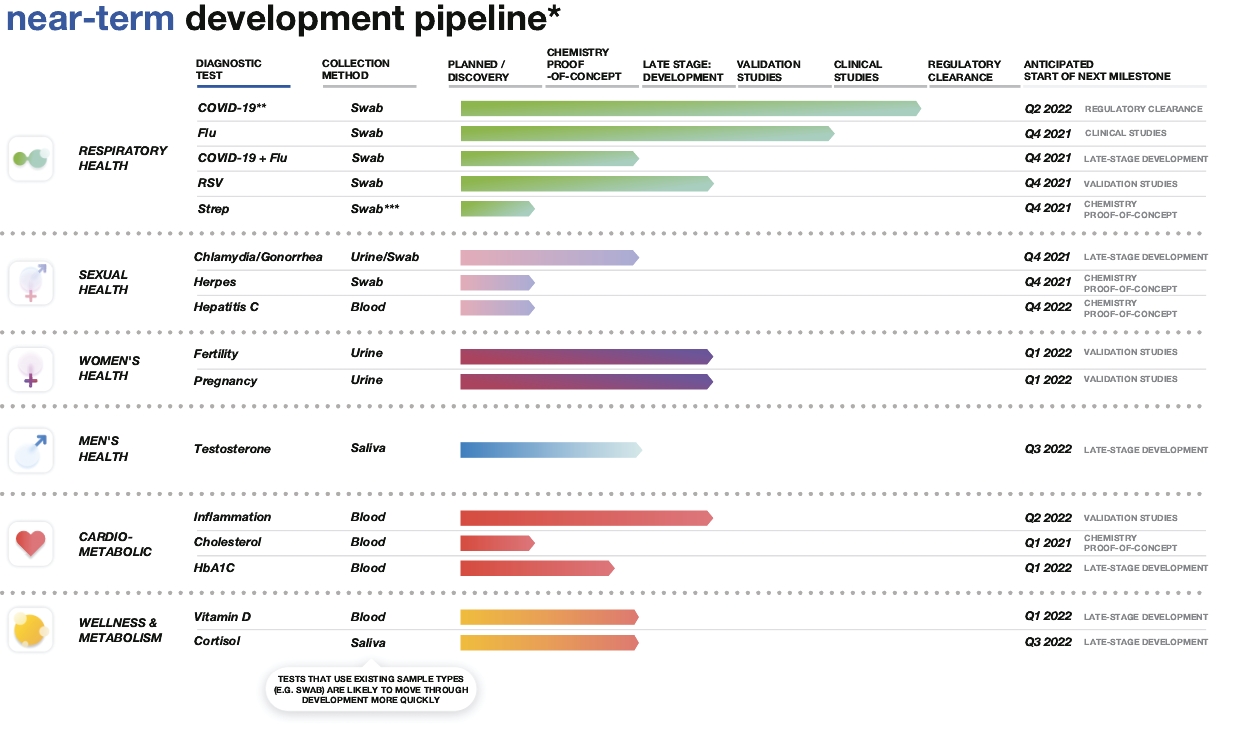
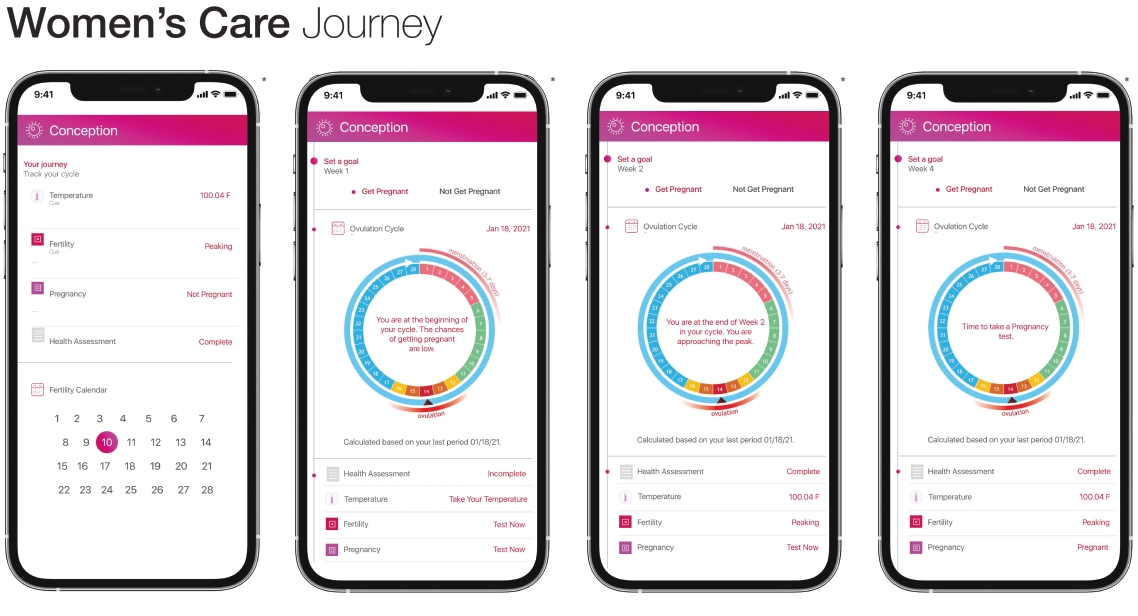
Employees and Human Capital Resources
As of August 31, 2021, we had 1,254 full-time employees. Our employees are primarily located in the San Diego, California area. None of our employees are represented by a labor union or are subject to a collective bargaining agreement. We consider our relationship with our employees to be good.
Our human capital resources objectives include, as applicable, identifying, recruiting, retaining, incentivizing and integrating our existing and new employees, advisors and consultants. The principal purposes of our equity and cash incentive plans are to attract, retain and reward personnel through the granting of stock-based and cash-based compensation awards, in order to increase stockholder value and the success of our company by motivating such individuals to perform to the best of their abilities and achieve our objectives.
Facilities
We follow Good Manufacturing Practice, or GMP, guidelines and are ISO 13485 certified, the key certification for medical device manufacturing, providing confidence and assurance in our final product. We are routinely audited to maintain our ISO 13485:2016 status.
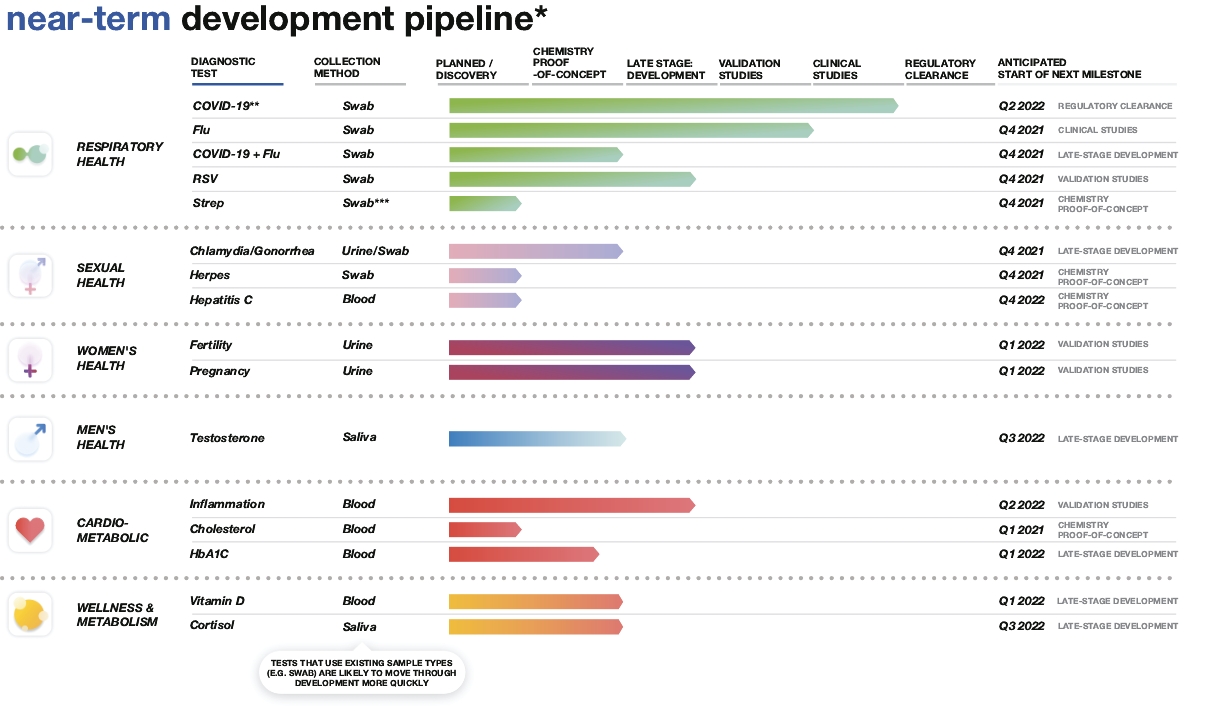
During the fall of 2020, we launched a significant expansion of our manufacturing capacity, leasing an approximately 197,000 square-foot facility in Vista, California and an approximately 63,000 square-foot facility in San Diego, California. As of August 31, 2021, the Vista facility was producing cartridges from six production pods (with space for an additional four production pods) and is serving as our warehousing and distribution hub. Our Waples facility will serve as a second reagent production hub, house certain cartridge component manufacturing, and has space for five production pods, all of which are currently in operation. Our Nancy Ridge facility is also producing cartridges from two production pods. We believe our current facilities are sufficient to meet our current needs, and that we will be able to find appropriate space for expansion when appropriate. Our Vista facility lease expires on July 1, 2026 and our Waples facility lease expires on July 1, 2031. Both leases have options to extend.
Government Regulation
Regulation of Medical Devices in the United States
Our product and operations are subject to extensive and ongoing regulation by the FDA under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act of 1938, as amended, and its implementing regulations, collectively referred to as the FDCA, as well as other federal and state regulatory bodies in the United States. The laws and regulations govern, among other things, product design and development, pre-clinical and clinical testing, manufacturing, packaging, labeling, storage, record keeping and reporting, clearance or approval, marketing, distribution, promotion, import and export and post-marketing surveillance.
The FDA regulates the development, design, pre-clinical and clinical research, manufacturing, safety, efficacy, labeling, packaging, storage, installation, servicing, recordkeeping, premarket clearance or approval, import, export, adverse event reporting, advertising, promotion, marketing and distribution of medical devices in the United States to ensure that medical devices distributed domestically are safe and effective for their intended uses and otherwise meet the requirements of the FDCA. Failure to comply with applicable requirements may subject a device and/or its manufacturer to a variety of administrative sanctions, such as FDA refusal to approve pending premarket applications, issuance of warning letters, mandatory product recalls, import detentions, civil monetary penalties, and/or judicial sanctions, such as product seizures, injunctions and criminal prosecution.
FDA Premarket Clearance and Approval Requirements
Unless an exemption applies, each medical device commercially distributed in the United States requires either FDA clearance of a 510(k) premarket notification, approval of a premarket approval, or PMA, or grant of a de novo request for classification. During public emergencies, the FDA also may grant emergency use authorizations, or EUA, to allow commercial distribution of devices intended to address the public health emergency. Under the FDCA, medical devices are classified into one of three classes—Class I, Class II or Class III—depending on the degree of risk associated with each medical device and the extent of manufacturer and regulatory control needed to provide reasonable assurance of its safety and effectiveness. Classification of a device is important because the class to which a device is assigned determines, among other things, the necessity and type of FDA review required prior to marketing the device.