
Exhibit 99.1 Reimagining The Potential Of Human Enzyme Therapeutics Corporate Overview – September 2022 Nasdaq: AGLE

Forward Looking Statements This presentation and the accompanying oral presentation contain “forward-looking” statements that are based on our management’s beliefs and assumptions and on information currently available to management. Forward-looking statements include all statements other than statements of historical fact contained in this presentation, including information concerning our current and future financial performance, business plans and objectives, current and future clinical and preclinical development activities, timing and success of our ongoing and planned clinical trials and related data, the timing of announcements, updates, results of our clinical trials and related data, our ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approval, the potential therapeutic benefits, safety profile and economic value of our product candidates, potential growth opportunities, financing plans, use and adequacy of financing plans, the length of time that we believe our existing cash resources will fund operations, competitive position, industry environment and potential market opportunities. Forward-looking statements are subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties, assumptions and other factors including, but not limited to, those related to the success, cost and timing of our product candidate development activities and ongoing and planned clinical trials; our plans to develop and commercialize targeted therapeutics, including our lead product candidates pegzilarginase and pegtarviliase and our other product candidates; the design, progress of patient enrollment and dosing in our clinical trials; the ability of our product candidates to achieve applicable endpoints in clinical trials; the safety profile of our product candidates in clinical trials; the potential for data from our current and future clinical trials to support a marketing application, as well as the timing of these events, including data for our phase 1/2 trial of pegtarviliase (AGLE-177) in Homocystinuria; the potential for preclinical studies to be predictive of current or future clinical trials; our ability to obtain funding for our operations, development and commercialization of our product candidates; the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on our operations and clinical development activities, including on the timing of enrollment of our clinical trials; the timing of and our ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approvals; our ability to obtain regulatory approval for, and commercialize, pegzilarginase, and recognize milestone and royalty payments from our licensing and supply agreement with Immedica; the potential for expedited development and review of pegzilarginase as a result of its Breakthrough Therapy designation; the potential addressable markets of our product candidates; the rate and degree of market acceptance and clinical utility of our product candidates; the size and growth potential of the markets for our product candidates, and our ability to serve those markets; our commercialization, marketing and manufacturing capabilities and strategy; future agreements with third parties in connection with the potential commercialization of our product candidates; our expectations regarding our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection; our dependence on third party manufacturers; our ability to develop our own commercial manufacturing facility; the success of competing therapies that are or may become available; our ability to attract and retain key scientific or management personnel; our ability to identify additional product candidates with significant commercial potential consistent with our commercial objectives; and our estimates regarding expenses, future revenue, capital requirements and needs for additional financing. Moreover, we operate in a very competitive and rapidly changing environment, and new risks may emerge from time to time. It is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward- looking statements we may make. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, the forward-looking events and circumstances discussed herein may not occur and actual results could differ materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the forward-looking statements. Further information on these and other factors that could affect these forward-looking statements is contained in our most recent Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and other reports filed by the SEC. You should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. Although our management believes that the expectations reflected in our forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee that the future results, levels of activity, performance or events and circumstances described in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur. We undertake no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statements, whether written or oral, that may be made from time to time, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise. ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 2

Addressing Metabolic Imbalances to Improve the Lives of Patients Our vision is to redefine the possible, pioneer bold science with human enzymes and deliver groundbreaking medicines that transform lives. We are on a mission to change lives by bringing innovative therapies to underserved rare disease communities. ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 3

Building an Enzyme Therapy Company to Serve Patients and Drive Near and Long-Term Growth • Innovative enzyme engineering platform • Differentiated product profiles Pioneering Bold • Expertise in metabolic disease and enzyme engineering creates Science complementary opportunities in areas with limited competition • Focused on disease modifying therapies with the potential to change lives Delivering • Strong engagement with patient communities to develop products that Groundbreaking meet their needs Medicines • Efficient clinical development and commercialization model • Novel approach to unconventional targets – developing treatments for diseases others thought couldn’t be addressed with enzyme therapies Redefining the • High unmet need and limited competition drive significant commercial Possible opportunity ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 4

Aeglea’s Human Enzyme Platform for Rare Metabolic Diseases Regulatory Addressable Geographic Program Research Phase 1/2 Phase 3 Review Market Rights Pegtarviliase (AGLE-177) Worldwide >30,000 1 rights Patients Homocystinuria Retain rights outside of Europe 3 Pegzilarginase >2,500 and Middle East 2 Patients Arginase 1 Deficiency MAA Validated 5 by EMA Worldwide AGLE-325 >10,000 4 rights Patients Cystinuria Undisclosed Worldwide rights Rare Diseases 1 2 >30,000 represents estimated prevalence of Classical Homocystinuria in 38 addressable markets based on results of U.S. ICD-10 claims analysis extrapolated to global markets; all figures rounded. Sellos-Moura et al 2020 Catsburg C et al 2022 ; Diez- 3 Fernandez et al. Mutations and common variants in the human arginase 1 (ARG1) gene: impact on patients, diagnostics and protein structure considerations. Hum Mutat. 2018 Aug;39(8):1029-10502 Ex-U.S. license and supply agreement with Immedica to commercialize pegzilarginase in Europe and certain countries in the Middle East (European Economic Area, United Kingdom, Switzerland, Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, Vatican City, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, 4 Kuwait, Bahrain and Oman) Castro Pereira DJ et al 2015; Leslie and Nazzal Renal Calculi (Cystinuria, Cystine Stones) (2018) Reference; Rozanski et al, Mil Med (2005); Soucie et al, JM Kidney Int (1994); Claes & Jackson, Pediatr Nephrol (2012) 27, 2031; 5 Chillarón, J. et al. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 7, 424-34; Biyani, C.S and Cartledge, J.J. EAU-EBU Update Series, 2006, 4, 175-183; Mattoo, A. and Goldfarb D.S. 2008 Sem. Nephrol, 28, 2, 181-191 Market Authorisation Application (MAA) validated by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and currently under review; Company in dialogue with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration following Refusal to File Letter ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 5

Program Highlights and Upcoming Milestones Pegtarviliase in Homocystinuria: • Completed cohort 2, currently enrolling cohort 3 • Active clinical trial sites in UK, Australia and U.S. • Interim clinical data from Phase 1/2 clinical trial expected in fourth quarter of 2022, including data from cohort 3 Pegzilarginase in ARG1-D: • MAA under review with EMA • Continuing to engage with FDA to identify potential path to BLA resubmission Corporate: • Corporate restructuring prioritizes resources and focus on pegtarviliase • Cost saving measures put in place to extend runway into fourth quarter of 2023 • Search for permanent CEO underway; Jim Kastenmayer appointed interim CEO ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 6

Pegtarviliase (formerly AGLE-177) – Potential Best-in-Class Treatment for Homocystinuria

Classical Homocystinuria: A Rare Metabolic Disorder With Serious and Potentially Deadly Complications Serious Disease Complications Classical Homocystinuria (HCU) Eyes Cystathionine beta synthase (CBS) deficiency, also known as Lens dislocation, glaucoma, severe near-sightedness Classical Homocystinuria, is a serious and progressive metabolic disorder characterized by elevated levels of the Nervous System Intellectual and amino acid homocysteine. developmental delays, behavioral abnormalities, seizures • There are no approved treatments that address underlying driver of disease – high homocysteine levels Vascular • Uncontrolled levels of homocysteine can lead to sudden Life-threatening thrombotic events, heart attack, stroke catastrophic events, including death • Manifestations can occur in early childhood and worsen Skeletal Long bone (Marfanoid) over time features, skeletal deformities, osteoporosis ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 8

Inadequate Treatment Options to Control Homocysteine Levels and Prevent Disease Progression Favorable competitive & regulatory Current standard of care: landscape • B6 (pyridoxine) • Betaine approved on tHcy lowering alone, • Low-methionine diet + amino acid despite limited effectiveness supplements • Small number of treatments currently in clinical • Betaine development Current disease management is inadequate with an Current treatment goals focused on achievable, inability to control total homocysteine (tHcy) levels: not optimal: • Limited effectiveness • Lowering tHcy levels beyond treatment guidelines has potential to further improve outcomes and change • Difficulties with adherence the lives of patients • Periods of poor control can result in catastrophic • Strong desire among HCP and patient communities for thromboembolic events and/or life-long impairments more efficacious and less burdensome treatments • Poor tolerability of amino acid supplementation and betaine ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 9
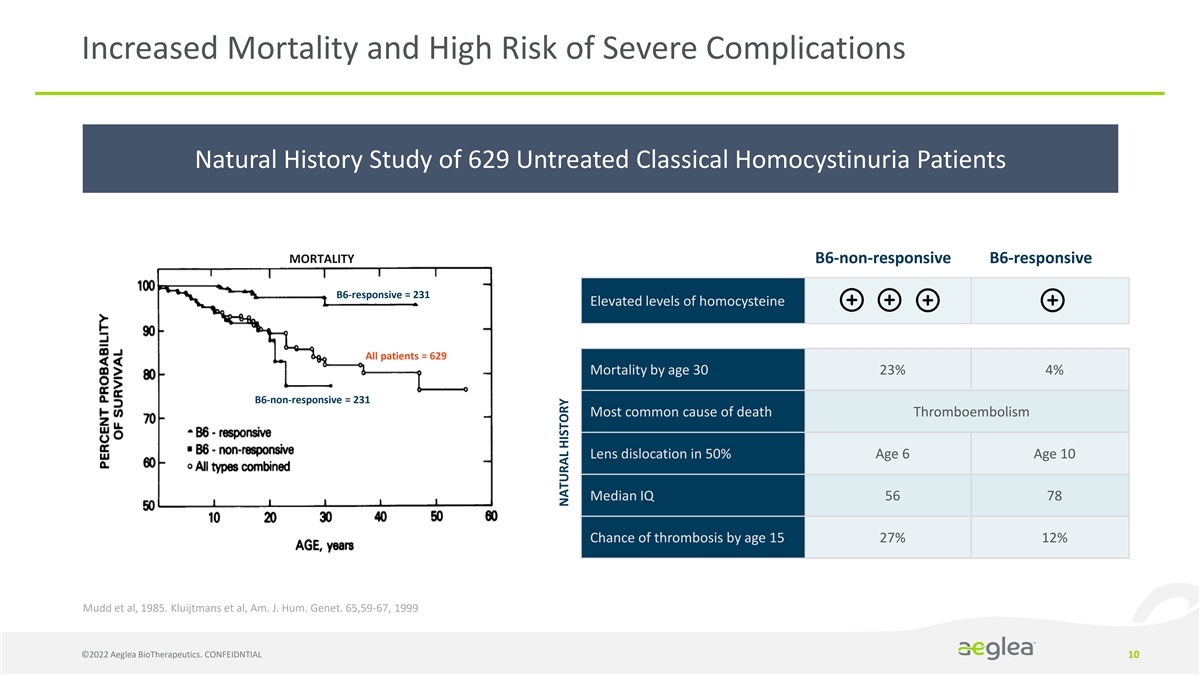
Increased Mortality and High Risk of Severe Complications Natural History Study of 629 Untreated Classical Homocystinuria Patients MORTALITY B6-non-responsive B6-responsive B6-responsive = 231 Elevated levels of homocysteine All patients = 629 Mortality by age 30 23% 4% B6-non-responsive = 231 Most common cause of death Thromboembolism Lens dislocation in 50% Age 6 Age 10 Median IQ 56 78 Chance of thrombosis by age 15 27% 12% Mudd et al, 1985. Kluijtmans et al, Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65,59-67, 1999 ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. CONFEIDNTIAL 10 NATURAL HISTORY

Sizeable Patient Population and Significant Commercial Opportunity 1 >30,000 Classical HCU patients B6-responsive • Currently available treatments work primarily for patients patients considered B6-responsive • B6-non-responsive patients and B6-partial responders Partial responders have poorer tHcy control resulting in more severe 2 disease and significantly worse outcomes B6-non-responsive • A large portion of Classical HCU population is in need of patients 2,3 more effective treatment options ~15,000 – 18,000 Significant Opportunity With Estimated 8,000-8,800 Candidates for Therapy in the U.S., U.K., and EU4 1 2 3 >30,000 represents estimated prevalence of Classical Homocystinuria (including B6-responsive and B6-non-responsive) in 38 addressable markets. Mudd et al 1985. Kožich et al, 2020. 4 ~6,000-6,600 represents estimated prevalence of B6-non-responsive Homocystinuria in the U.S (~3,300) and the EU4 plus UK (~3,300); tHcy = total homocysteine ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 11

Pegtarviliase: An Innovative Enzyme Approach to Lowering Homocysteine Depiction of Normal and Therapeutic Metabolism Pegtarviliase Mechanism Engineered Cystathionine γ-Lyase (CGL) enzyme mutated to change its native substrate specificity from cystathionine to both homocysteine and its dimer è Concentration gradient drives homocysteine out of tissue and into plasma è Equilibrium in plasma in preference of dimer è Further metabolism of both monomer and dimer Therapeutic Rationale • Elevated levels of plasma homocysteine increase risk for 1 disease manifestations • Reduction of plasma homocysteine has been correlated 2 with reduced risk of developing disease manifestations • Generally accepted aim of treatment is to lower the plasma homocysteine concentration below certain thresholds while maintaining normal nutrition 1 2 Mudd, Skovby et al. 1985, Al-Dewik, Ali et al. 2019; Mudd, Skovby et al. 1985, Wilcken and Wilcken 1997, Yap and Naughten 1998 ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 12

Pegtarviliase Treatment Resulted in Dose-Dependent Response and Statistically Significant Lowering of Homocysteine in Mouse Model Single Subcutaneous Dose in CBS Experimental Design: 1 Knockout Mouse Model • 10-day old CBS knockout mice were 375 dosed with pegtarviliase twice per week for 5 weeks to ensure they were of a 300 sufficient size • Prior to a single SC dose of pegtarviliase, 225 there was a two-week wash out Pegtarviliase (1.0 mg/kg, SC) * * AGLE-17 * * Pegtarviliase (10.0 mg/kg, SC) • To ensure accurate tHcy assessment, an 150 AGLE-17 * inhibitor of pegtarviliase was used in * * p < 0.05 by Manley Cox test * the collection tube to block metabolism * 75 2 of tHcy during sample processing 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 168 Hours 1 2 Daige C. et al. Poster presented at ASHG 2020 Virtual Meeting. Thornloe K. et al. Poster presented at ACMG 2022 Meeting’ tHcy = total homocysteine; SC = subcutaneous ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 13 Plasma tHcy (µM)

Pegtarviliase Treatment Improved Pathologies and Corrects Disease Manifestations in a Mouse Model of Homocystinuria 2 Reversal of Severe Liver Abnormalities in Beneficial Impact on Osteoporosis 1 CBS Knockout Mouse Model Disease Resolution Disease R eversa l P = 0.0407 p = 0.0407 70 Dosing Begins = Dosing Begins 65 AEB4104 25 mg/kg + AEB4104 25 mg/kg AGLE-177-HIS 25 mg/kg + Healthy liver from AGLE-177-HIS 25 mg/kg Healthy liver from Betaine Day 23 CBS -/- Day 60 CBS -/- 60 Betaine Day 23 CBS-/- wild-type animal Day 60 CBS-/- wild-type animal DD is is ea eas se P e Prro ogr ges res sis oi n on Day 10 CBS -/- : Day 10 CBS-/- 55 Macro-steatosis Macro-steatosis P P rre em ma atu ture re Death Death 50 PBS + Betaine Day 23 CBS -/- AGLE-177 Vehicle PBS + Betaine Day 23 CBS-/- Micro-steatosis and necrosis 10 mg/kg Macro-steatosis and necrosis Reductions in total plasma homocysteine leads to Increased bone mineral density (BMD) in preclinical model of Homocystinuria with multiple doses improvements in disease-related abnormalities 1 2 Daige C. et al. Poster presented at ASHG 2018; Daige C. et al. Poster presented at ASHG 2020 Virtual Meeting, CBS -/- mice were dosed SC BIW with AGLE-177 starting at D10 through Day 169 were evaluated for bone mineral density (BMD) by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; AGLE-177-HIS = AGLE-177/pegtarviliase modified to include a polyhistidine tag; CBS -/- = CBS knockout mouse model ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 14 2 BMD (mg/cm )

Preclinical Data Support Potential Advantages of Pegtarviliase Pegtarviliase demonstrated significant survival Pegtarviliase demonstrated pharmacological benefit at substantially lower dose than effect on homocysteine levels in normal animals competitor enzyme that is not seen with competitor enzyme 5 4 Pegtarviliase (10 mg/kg, BIW) V Ve eh hic icl lee Pegtarviliase (3 mg/kg, BIW) 3 A PG egt LE a-r1 v77 ilia 2 s m e 2 m g/kg g/kg Pegtarviliase 6 mg/kg AGLE-177 6 mg/kg Pegtarviliase (1.0 mg/kg, BIW) Pegtarviliase 20 mg/kg AGLE-177 20 mg/kg 2 Vehicle (BIW) 1 0 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 168 Hours • Twice weekly (BIW) subcutaneous doses pegtarviliase in CBS • Substantial decreases in homocysteine after single subcutaneous dose 1,3 knockout mouse model in toxicology studies with cynos (above) and rats (data not shown) • Significant survival benefit with pegtarviliase at total weekly • Pharmacological effect in normal animals dosed with pegtarviliase 2 dose of 2 mg/kg compared to a total weekly dose of 22.5 mg/kg differentiated from reported data for a competitor enzyme 2 reported for a competitor enzyme 1 2 3 Daige C. et al. Poster presented at ASHG 2020 Virtual Meeting. Majtan T. et al., Life Sci. 2018; May 1;200:15-25. Mice were ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 15 maintained on betaine until weaning; tHcy = total homocysteine tHcy (µM)
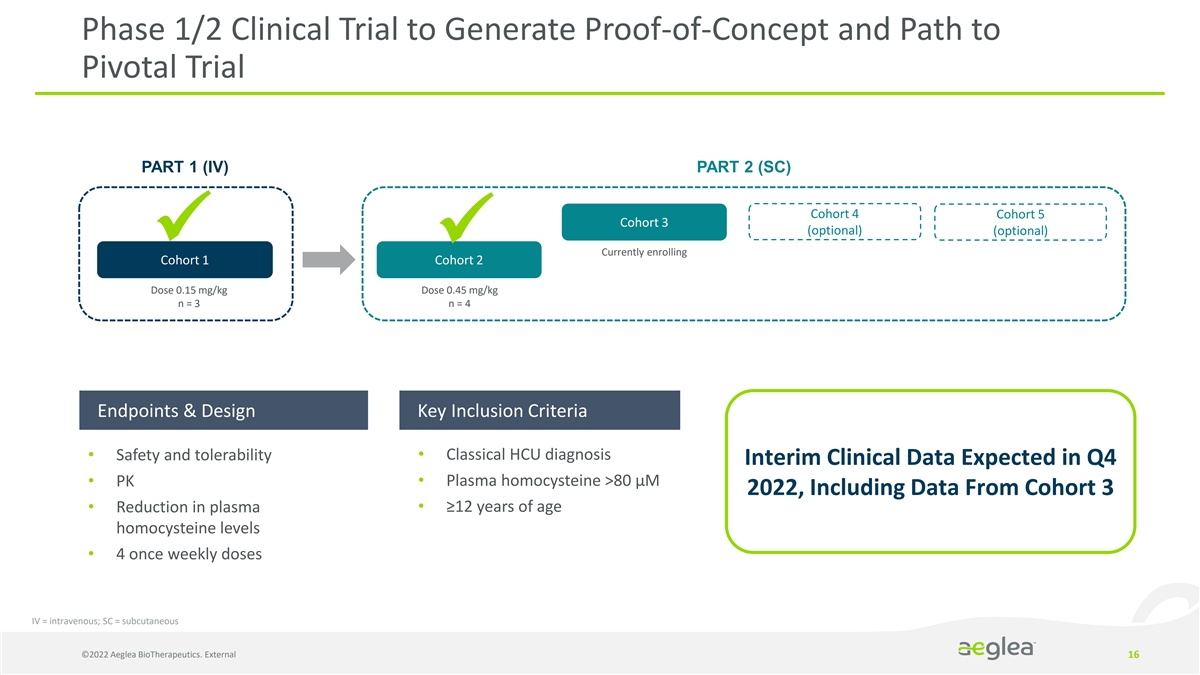
Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial to Generate Proof-of-Concept and Path to Pivotal Trial PART 1 (IV) PART 2 (SC) Cohort 4 Cohort 5 Cohort 3 (optional) (optional) ü ü Currently enrolling Cohort 1 Cohort 2 Dose 0.15 mg/kg Dose 0.45 mg/kg n = 3 n = 4 Endpoints & Design Key Inclusion Criteria • Safety and tolerability • Classical HCU diagnosis Interim Clinical Data Expected in Q4 • PK • Plasma homocysteine >80 µM 2022, Including Data From Cohort 3 • Reduction in plasma • ≥12 years of age homocysteine levels • 4 once weekly doses IV = intravenous; SC = subcutaneous ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 16
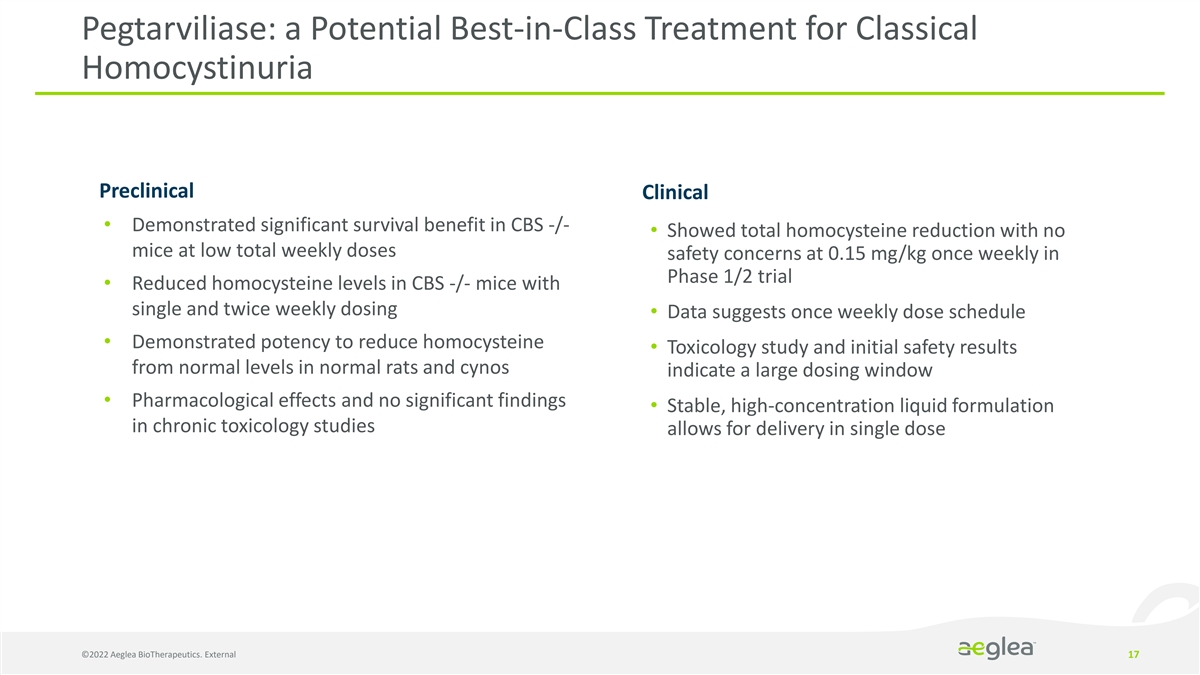
Pegtarviliase: a Potential Best-in-Class Treatment for Classical Homocystinuria Preclinical Clinical • Demonstrated significant survival benefit in CBS -/- • Showed total homocysteine reduction with no mice at low total weekly doses safety concerns at 0.15 mg/kg once weekly in Phase 1/2 trial • Reduced homocysteine levels in CBS -/- mice with single and twice weekly dosing • Data suggests once weekly dose schedule • Demonstrated potency to reduce homocysteine • Toxicology study and initial safety results from normal levels in normal rats and cynos indicate a large dosing window • Pharmacological effects and no significant findings • Stable, high-concentration liquid formulation in chronic toxicology studies allows for delivery in single dose ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 17

Pegtarviliase: Preparing to Move Rapidly into Pivotal Trial CMC Phase 3 Trial Design • Discuss interim data with FDA • Registration manufacturing campaign in process • Align on pivotal trial design and endpoints • Currently manufacturing at commercial scale • Product characterization and analytical methods in place Regulatory Designations • Stable, high-concentration liquid formulation with real-time and stressed conditions • U.S. Orphan Drug stability data • EU Orphan Drug • U.S. Rare Pediatric Disease (PRV eligible) Interim Phase 1/2 Clinical Data Expected in 4Q 2022 and Well- Positioned to Advance into Potential Pivotal Study ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 18

Pegzilarginase for Arginase 1 Deficiency

Arginase 1 Deficiency (ARG1-D) Disease Overview ARG1-D is a serious, progressive disease with early The Progressive Impact of Persistently 1-4 mortality and high unmet medical need. It is High Plasma Arginine caused by a mutation in the arginase 1 enzyme, 2-4,7,8 resulting in persistently high levels of arginine. Infancy • Initial 6-12 months may be uneventful • May present with seizures, episodes of hyperammonemia: irritability, feeding difficulties, poor appetite, nausea/vomiting, decreased alertness Current Standard of Care 2,3,7-9 Toddlerhood (2-4 years) • Focused on lowering plasma arginine levels and controlling • Spasticity in lower limbs (toe walking) hyperammonemia with: • Seizures, avoidance of protein is common and intellectual disability • Severe dietary protein restriction 2,3,5,6,9 Childhood (5-10 years) • Amino acid supplementation • Progressive spasticity and growth impairment • Declining neuromotor and intellectual capabilities • Ammonia scavengers ─ Increasing dependence on walking aids ─ Loss of mobility • Ineffective at controlling plasma arginine levels ─ Decrease/loss of vocabulary/language 2,3,5,10 Adolescence (11-17 years) Significant Unmet Need • Potential loss of ambulation and bowel/bladder control • Severe intellectual disability • High arginine levels 2,3,11,12 • Severe and progressive disease with early mortality Adulthood (18+ years) • Continued decline with increasing disability that may result in • Easily diagnosed but often missed due to lack of awareness early mortality • No approved therapies to address high arginine levels 1 2 3 4 5 Diez-Fernandez C, et al. Hum Mutat. 2018;39:1029-1050. Carvalho DR, et al. Pediatr Neurol. 2012;46:369-374. Crombez EA, Cederbaum SD. Mol Genet Metab. 2005;84:243-251. De Deyn PP, et al. Hyperargininemia: a treatable inborn error of metabolism. In: Guanidino Compounds in Biology and Medicine. London, UK: John Libbey Company Ltd.; 1997:53-69. 6 7 8 9 10 11 Prasad A, et al. J Child Neurol. 1997;12:301-309. Amayreh W, et al. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2014;56:1021-1024. Scaglia F, Lee B. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2006;142C:113-120. Sin YY, et al. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015;93:1287-1296. Cai X, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97:e9880. Schlune A, et al. J. Amino Acids. 2015;47:1751-1762. Sun A, et al. 12 Arginase deficiency. In: Adam MP, et al, eds. GeneReviews®. Seattle, WA: University of Washington, Seattle; 2020. Diaz GA, et al. Poster presented at: 13th European Paediatric Neurology Society (EPNS) Congress; September 17-21, 2019; Athens, Greece. Poster P06-34. ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 20

Pegzilarginase Program Overview First Clinical Program Ever Conducted Pegzilarginase is a novel recombinant human enzyme engineered to lower arginine levels in ARG1-D PEACE Phase 3 Clinical Trial Commercial Opportunity 1 • First placebo-controlled trial ever conducted • >2,500 patients in global addressable markets in ARG1-D • High unmet medical need – Pegzilarginase reduced arginine levels by 76.7%, • No approved therapies to address high arginine levels normalized arginine levels in 90.5% of patients – Positive trend in mobility measure Regulatory Designations – Well-tolerated • U.S. Rare Pediatric Disease (PRV eligible) • 31 patients enrolled in long-term extension study • Breakthrough Therapy • U.S. Orphan Drug Phase 1/2 and Open-Label Extension Trials • EU Orphan Drug • 13 patients remain on therapy, duration from 2-4 years • Arginine lowering was rapid and durable Ongoing Discussions with FDA on Potential • Improvements in functional measures sustained over Paths to BLA Resubmission time 1 Catsburg C et al 2022 ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 21

PEACE Phase 3 Trial: Marked and Sustained Reduction in Plasma Arginine Primary Endpoint: Reduction in Proportion of Patients Reaching * † Plasma Arginine Normal Arginine Levels (p<0.0001 ) 700 630 560 490 100% 90.5% 85.7% 420 80% 350 60% 280 47.6% 210 40% 200 µM Clinical Guideline 140 115 µM 20% Normal 70 0% 0% 0% 0% Range 0% 40 µM 0% 0 Baseline 6 Weeks 12 Weeks 24 Weeks Baseline 12 Weeks 24 Weeks Pegzilarginase (n=21) Placebo (n=11) Pegzilarginase (n=21) Placebo (n=11) Primary Endpoint Met – 24 Week Analysis • 76.7% reduction from baseline in mean plasma arginine with ǂ pegzilarginase treatment compared to placebo (p<0.0001) Enns G, et al. Poster presented at SIMD 2022 Annual Meeting; *Based on arithmetic mean of values from visit and preceding 3 visits, boxes represent ǂ ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External middle 50% with error bars depicting 95% confidence interval; Statistical analysis based on geometric mean; †Nominal p value, based on arithmetic 22 mean of values from visit and preceding 3 visits Arginine (µM)
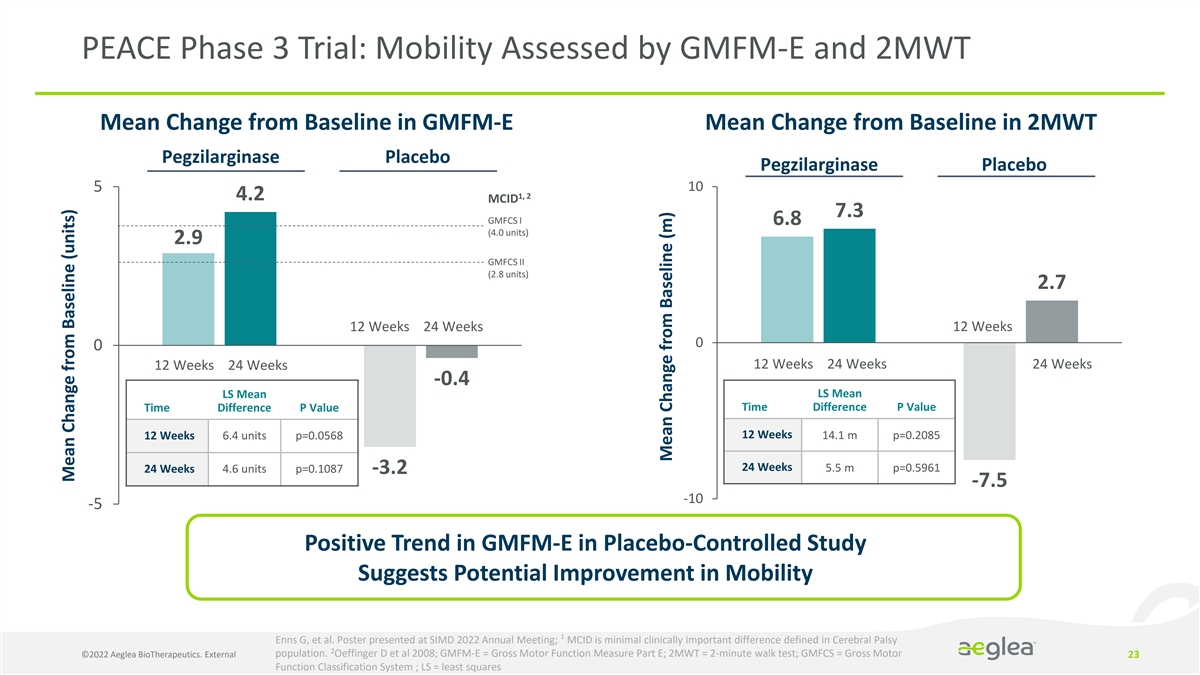
PEACE Phase 3 Trial: Mobility Assessed by GMFM-E and 2MWT Mean Change from Baseline in GMFM-E Mean Change from Baseline in 2MWT Pegzilarginase Placebo Pe Pg eg zz il ilarg arg in in asa ese PlP ala ce ceb bo o Pegzilarginase Placebo 10 5 1, 2 4.2 MCID 7.3 GMFCS I 6.8 (4.0 units) 2.9 GMFCS II (2.8 units) 2.7 12 Weeks 24 Weeks 12 Weeks 0 0 12 Weeks 24 Weeks 24 Weeks 12 Weeks 24 Weeks -0.4 LS Mean LS Mean Time Difference P Value Time Difference P Value 12 Weeks 14.1 m p=0.2085 12 Weeks 6.4 units p=0.0568 24 Weeks 5.5 m p=0.5961 24 Weeks 4.6 units p=0.1087 -3.2 -7.5 -10 -5 Positive Trend in GMFM-E in Placebo-Controlled Study Suggests Potential Improvement in Mobility 1 Enns G, et al. Poster presented at SIMD 2022 Annual Meeting; MCID is minimal clinically important difference defined in Cerebral Palsy 2 ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External population. Oeffinger D et al 2008; GMFM-E = Gross Motor Function Measure Part E; 2MWT = 2-minute walk test; GMFCS = Gross Motor 23 Function Classification System ; LS = least squares Mean Change from Baseline (units) Mean Change from Baseline (m)
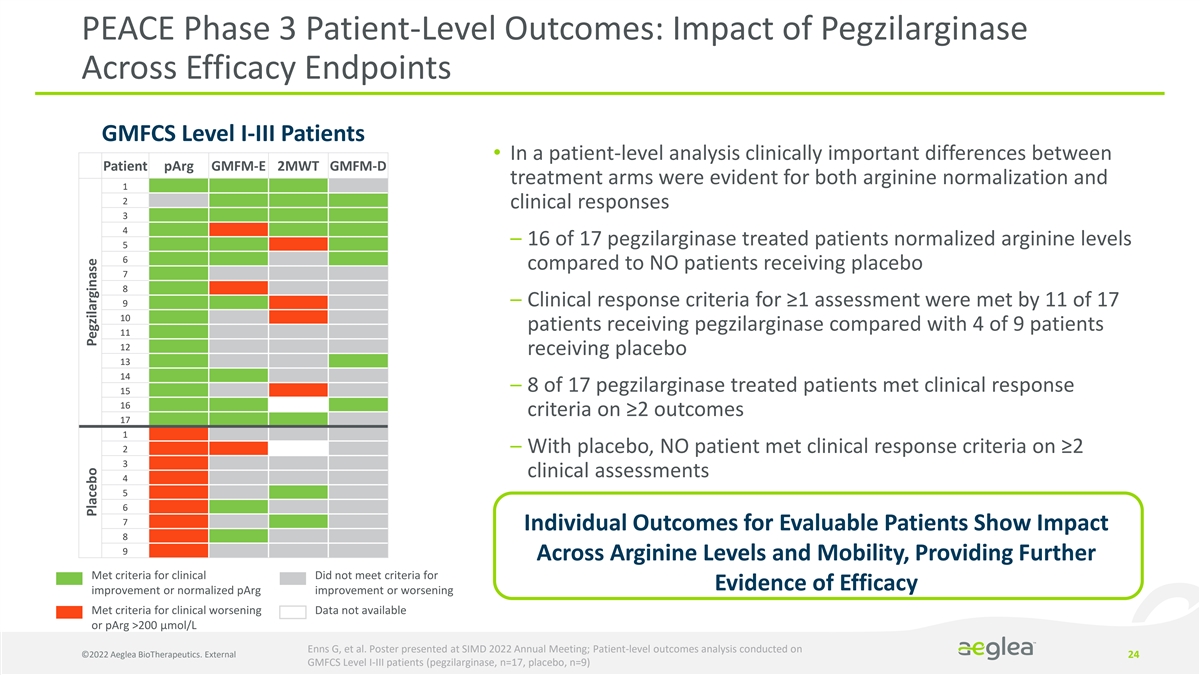
PEACE Phase 3 Patient-Level Outcomes: Impact of Pegzilarginase Across Efficacy Endpoints GMFCS Level I-III Patients • In a patient-level analysis clinically important differences between Patient pArg GMFM-E 2MWT GMFM-D treatment arms were evident for both arginine normalization and 1 2 clinical responses 3 4 – 16 of 17 pegzilarginase treated patients normalized arginine levels 5 6 compared to NO patients receiving placebo 7 8 9 – Clinical response criteria for ≥1 assessment were met by 11 of 17 10 patients receiving pegzilarginase compared with 4 of 9 patients 11 12 receiving placebo 13 14 – 8 of 17 pegzilarginase treated patients met clinical response 15 16 criteria on ≥2 outcomes 17 1 2 – With placebo, NO patient met clinical response criteria on ≥2 3 clinical assessments 4 5 6 7 Individual Outcomes for Evaluable Patients Show Impact 8 9 Across Arginine Levels and Mobility, Providing Further Met criteria for clinical Did not meet criteria for Evidence of Efficacy improvement or normalized pArg improvement or worsening Met criteria for clinical worsening Data not available or pArg >200 µmol/L Enns G, et al. Poster presented at SIMD 2022 Annual Meeting; Patient-level outcomes analysis conducted on ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 24 GMFCS Level I-III patients (pegzilarginase, n=17, placebo, n=9) Placebo Pegzilarginase
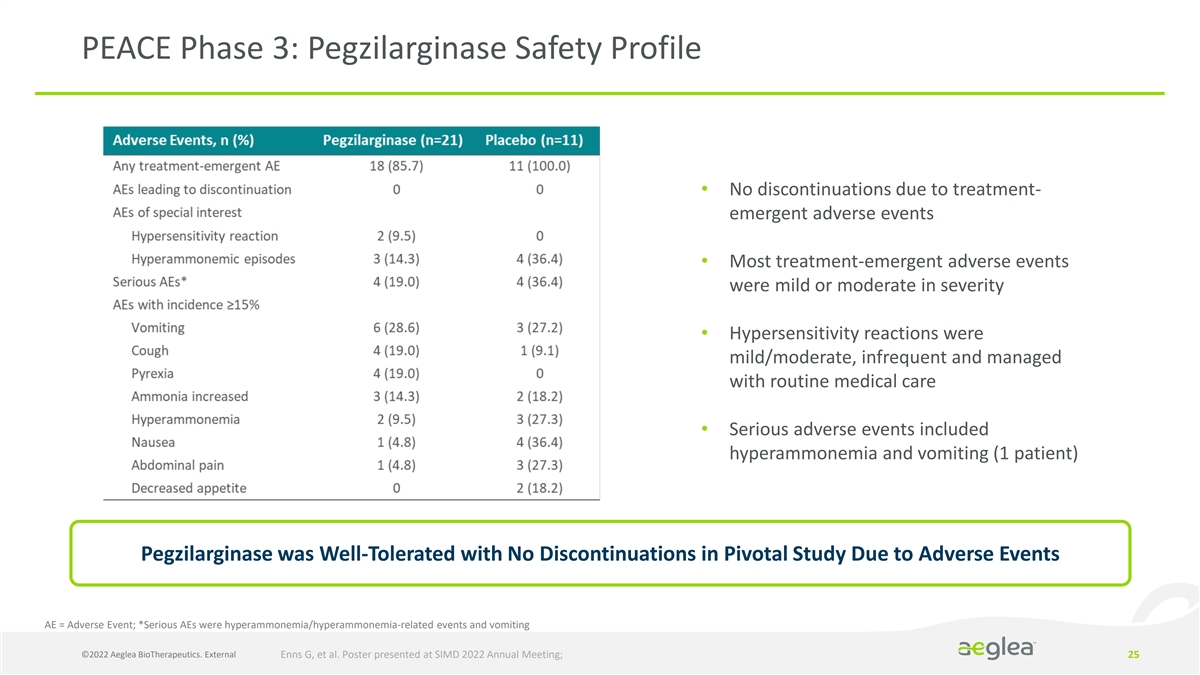
PEACE Phase 3: Pegzilarginase Safety Profile • No discontinuations due to treatment- emergent adverse events • Most treatment-emergent adverse events were mild or moderate in severity • Hypersensitivity reactions were mild/moderate, infrequent and managed with routine medical care • Serious adverse events included hyperammonemia and vomiting (1 patient) Pegzilarginase was Well-Tolerated with No Discontinuations in Pivotal Study Due to Adverse Events AE = Adverse Event; *Serious AEs were hyperammonemia/hyperammonemia-related events and vomiting ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External Enns G, et al. Poster presented at SIMD 2022 Annual Meeting; 25
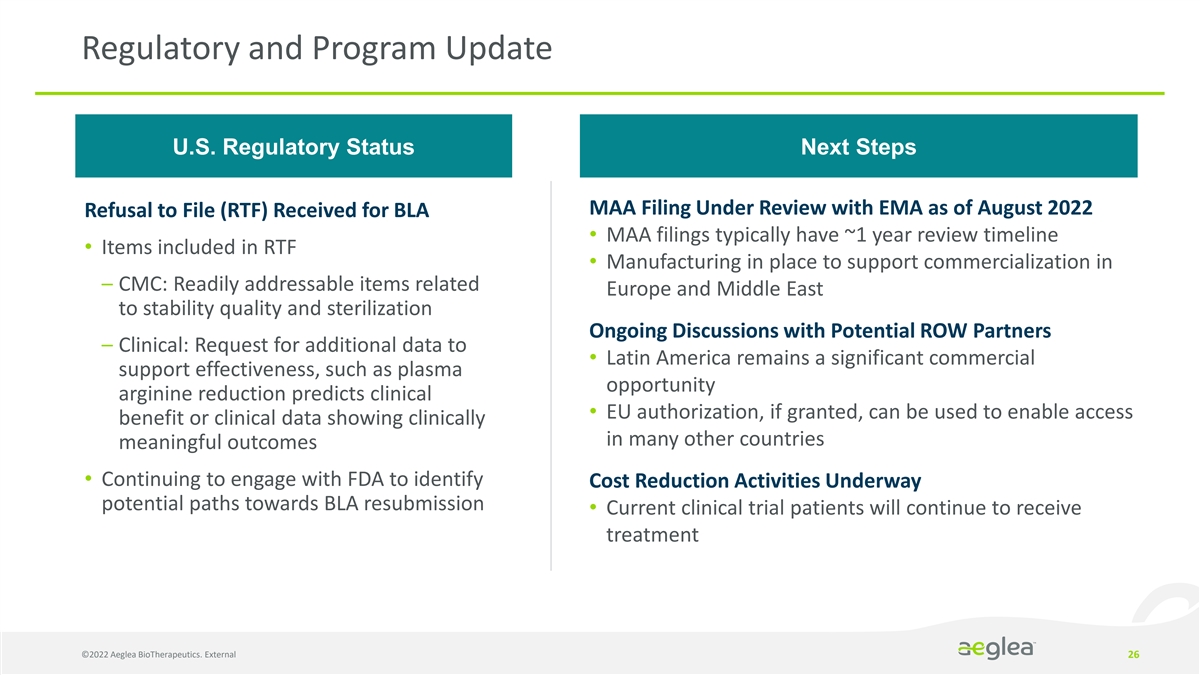
Regulatory and Program Update U.S. Regulatory Status Next Steps MAA Filing Under Review with EMA as of August 2022 Refusal to File (RTF) Received for BLA • MAA filings typically have ~1 year review timeline • Items included in RTF • Manufacturing in place to support commercialization in – CMC: Readily addressable items related Europe and Middle East to stability quality and sterilization Ongoing Discussions with Potential ROW Partners – Clinical: Request for additional data to • Latin America remains a significant commercial support effectiveness, such as plasma opportunity arginine reduction predicts clinical • EU authorization, if granted, can be used to enable access benefit or clinical data showing clinically in many other countries meaningful outcomes • Continuing to engage with FDA to identify Cost Reduction Activities Underway potential paths towards BLA resubmission • Current clinical trial patients will continue to receive treatment ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 26

Human Enzyme Engineering Platform

Cystinuria Overview Cystinuria: Cystinuria is a metabolic disorder characterized by high levels of amino acid cystine in the urine, leading to the formation of stones in the kidney, ureter and bladder. Persistent stones can result in serious damage to the kidneys, causing an increased risk of hypertension and chronic kidney failure. Addressable Market: Estimated prevalence High cystine in urine à cystine >10,000 Low cystine in urine precipitates à stone formation rate 1:15,000 Patients in addressable markets Based on literature Severe pain, surgical interventions, Healthy kidney failure Biyani and Cartledge EAU-EBU Update Series 4 (2006) 175-183, Leslie and Nazzal Renal Calculi (Cystinuria, Cystine Stones) (2018) ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 28

AGLE-325 Preclinical Advancement New candidate advanced through lead optimization with preclinical efficacy INNOVATIVE ENZYME APPROACH and PK/PD profile which support attractive clinical dosing schedule 1 1 µCT Kidney Stone Volume Kidney Pathology ** p=0.0077 5 Severe 3 4 Enzymatic Lowering of Cystine 3 in Blood 2 Moderate 2 1 0.20 Defective Transporter 0.15 Normal 1 0.10 N=16 N=32 = low cystine 0.05 0 0.00 Enzymatic reduction of plasma cystine should lower urine cystine and reduce cystine stone formation ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 1 29 Experiments performed using a clinically relevant dose range; PK = pharmacokinetics; PD = pharmacodynamics Vehicle AGLE-325 Vehicle AGLE-325 Total Kidney 3 Stone Volume per Mouse (mm )

Leveraging Aeglea’s Next Generation Human Enzyme Platform: Undisclosed Rare Disease Indication PROOF OF CONCEPT Vehicle Control Therapeutic Enzyme Pegylated enhanced human enzyme Therapeutic Approach • Enzymatic control of high levels of a metabolite considered important in disease pathogenesis • Very high - no effective therapy Unmet Medical Need • Early mortality and serious complications with continued disease progression Patient Population • >5,000 patients (Addressable Markets) • High activity human pegylated investigational enzyme • Degrades key accumulating metabolite Diagnosis • Plasma metabolite levels and mutation analysis • Results in restorative phenotypic improvements in genetically engineered mouse model ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 30

Summary

Program Highlights and Upcoming Milestones Pegtarviliase in Homocystinuria: • Completed cohort 2, currently enrolling cohort 3 • Active clinical trial sites in UK, Australia and U.S. • Interim clinical data from Phase 1/2 clinical trial expected in fourth quarter of 2022, including data from cohort 3 Pegzilarginase in ARG1-D: • MAA under review with EMA • Continuing to engage with FDA to identify potential path to BLA resubmission Corporate: • Corporate restructuring prioritizes resources and focus on pegtarviliase • Cost saving measures put in place to extend runway into fourth quarter of 2023 • Search for permanent CEO underway; Jim Kastenmayer appointed interim CEO ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 32
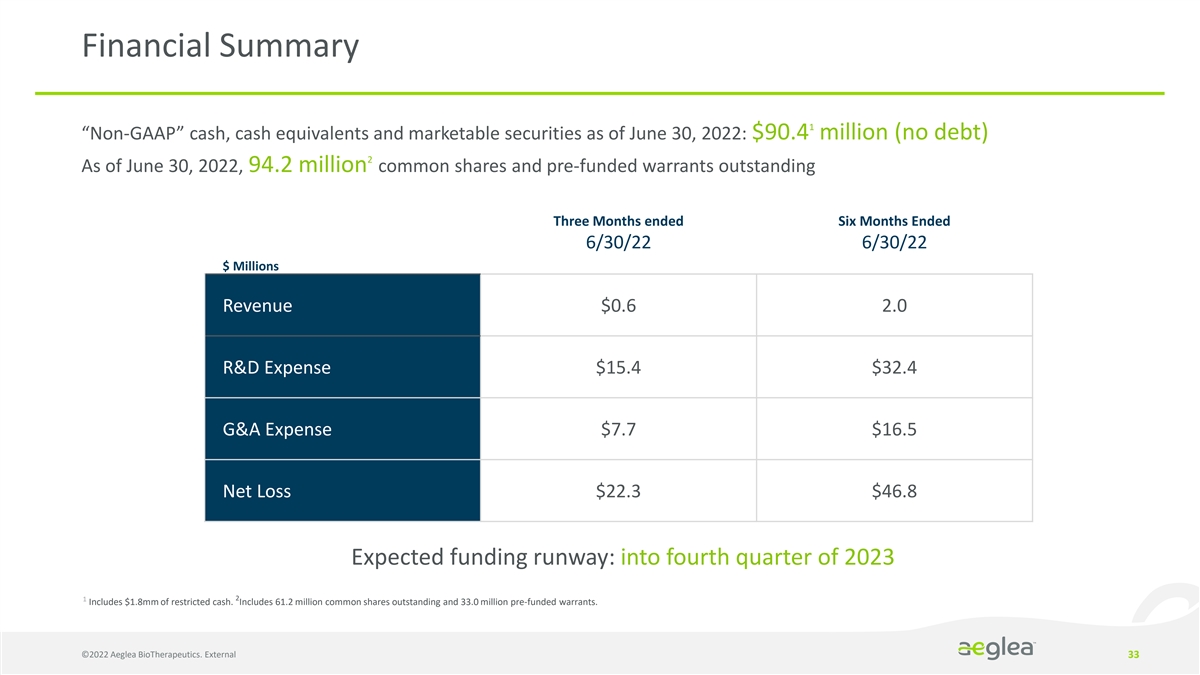
Financial Summary 1 “Non-GAAP” cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities as of June 30, 2022: $90.4 million (no debt) 2 As of June 30, 2022, 94.2 million common shares and pre-funded warrants outstanding Three Months ended Six Months Ended 6/30/22 6/30/22 $ Millions Revenue $0.6 2.0 R&D Expense $15.4 $32.4 G&A Expense $7.7 $16.5 Net Loss $22.3 $46.8 Expected funding runway: into fourth quarter of 2023 1 2 Includes $1.8mm of restricted cash. Includes 61.2 million common shares outstanding and 33.0 million pre-funded warrants. ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 33

805 Las Cimas Parkway Suite 100 Austin, TX 78746 aeglea.com

PEACE Baseline Demographics Pegzilarginase Placebo Overall Demographic Characteristic n=21 n=11 N=32 Age at Enrollment, y Mean (SD) 9.6 (6.16) 12.9 (6.77) 10.7 (6.47) Range 2-28 5-29 2-29 Age Category, n (%) 2y to less than 6y 5 (23.8) 1 (9.1) 6 (18.8) 6y to less than 12y 8 (38.1) 4 (36.4) 12 (37.5) 12y to less than 18y 7 (33.3) 4 (36.3) 11 (34.4) 18y or older 1 (4.8) 2 (18.2) 3 (9.4) Sex, n (%) Male 12 (57.1) 7 (63.6) 19 (59.4) Female 9 (42.9) 4 (36.4) 13 (40.6) Region, n (%) U.S. 8 (38.1) 6 (54.5) 14 (43.8) Ex-U.S. 13 (61.9) 5 (45.5) 18 (56.3) ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 35

PEACE Baseline Clinical Characteristics Pegzilarginase Placebo Overall Clinical Characteristic n=21 n=11 N=32 Plasma Arginine, µM/L * Mean (SD) 471.7 (79.9) 402.0 (101.8) 365.4 (93.7) Median (range) 483.7 (294-573) 398.2 (202-573) 368.2 (202-572) GMFCS level, n (%) 1 5 (45.5) 14 (43.8) 9 (42.9) ≥2 6 (54.5) 18 (56.2) 12 (57.1) GMFM-E Mean (SD) 46.5 (24.6) 47.7 (21.5) 48.3 (19.9) Median (range) 56 (0-72) 54 (0-72) 53 (5-71) 2MWT Mean (SD) 99.9 (49.0) 105.8 (52.8) 109 (55.7) Median (range) 102 (0-171) 118 (0-202) 122 (2-202) *Based on arithmetic mean ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 36
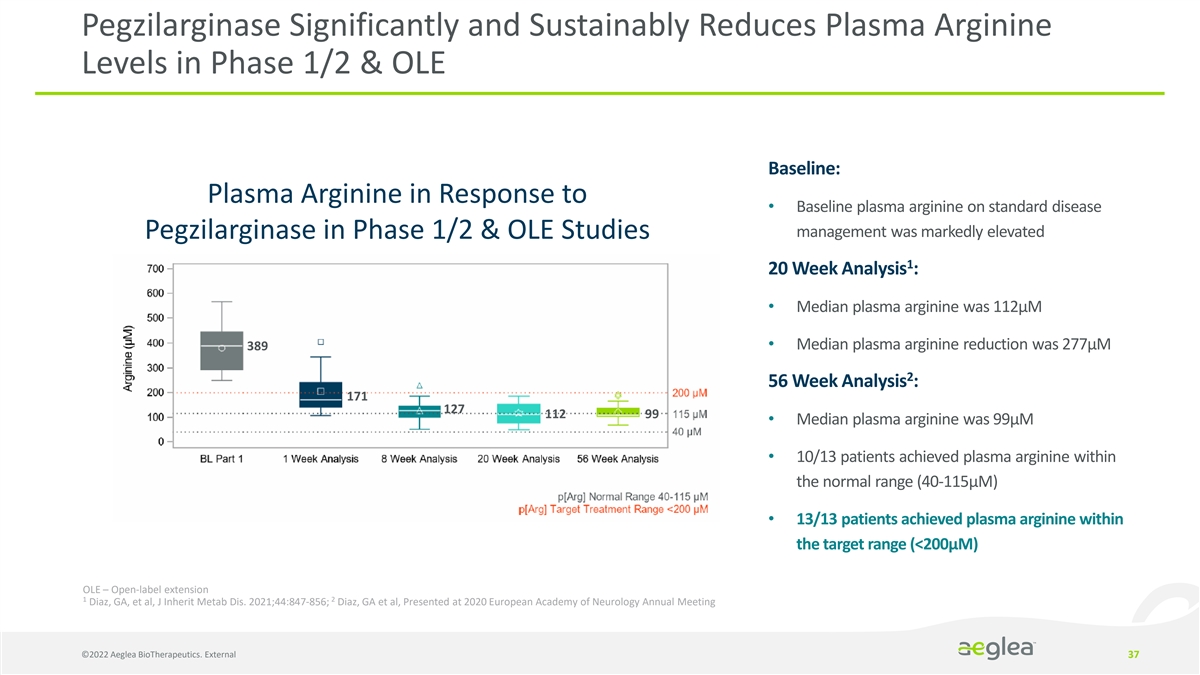
Pegzilarginase Significantly and Sustainably Reduces Plasma Arginine Levels in Phase 1/2 & OLE Baseline: Plasma Arginine in Response to • Baseline plasma arginine on standard disease management was markedly elevated Pegzilarginase in Phase 1/2 & OLE Studies 1 20 Week Analysis : • Median plasma arginine was 112µM 389 • Median plasma arginine reduction was 277µM 2 56 Week Analysis : 171 127 112 99 • Median plasma arginine was 99µM • 10/13 patients achieved plasma arginine within the normal range (40-115µM) • 13/13 patients achieved plasma arginine within the target range (<200µM) OLE – Open-label extension 1 2 Diaz, GA, et al, J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021;44:847-856; Diaz, GA et al, Presented at 2020 European Academy of Neurology Annual Meeting ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 37
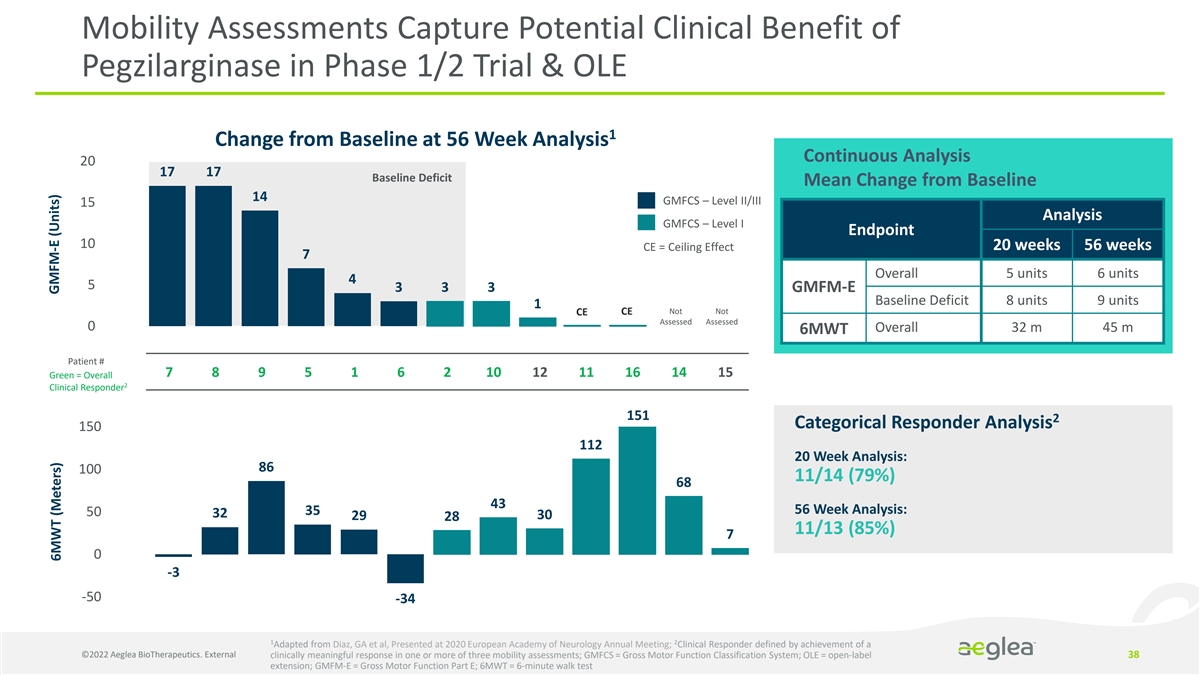
Mobility Assessments Capture Potential Clinical Benefit of Pegzilarginase in Phase 1/2 Trial & OLE 1 Change from Baseline at 56 Week Analysis Continuous Analysis 20 17 17 Baseline Deficit Mean Change from Baseline 14 GMFCS – Level II/III 15 Analysis GMFCS – Level I Endpoint 10 20 weeks 56 weeks CE = Ceiling Effect 7 Overall 5 units 6 units 4 5 3 3 3 GMFM-E Baseline Deficit 8 units 9 units 1 Not Not CE CE Assessed Assessed 0 Overall 32 m 45 m 6MWT Patient # 7 8 9 5 1 6 2 10 12 11 16 14 15 Green = Overall 2 Clinical Responder 151 2 Categorical Responder Analysis 150 112 20 Week Analysis: 86 100 11/14 (79%) 68 43 56 Week Analysis: 35 50 32 29 30 28 11/13 (85%) 7 0 -3 -50 -34 1 2 Adapted from Diaz, GA et al, Presented at 2020 European Academy of Neurology Annual Meeting; Clinical Responder defined by achievement of a ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External clinically meaningful response in one or more of three mobility assessments; GMFCS = Gross Motor Function Classification System; OLE = open-label 38 extension; GMFM-E = Gross Motor Function Part E; 6MWT = 6-minute walk test GMFM-E (Units) 6MWT (Meters)

Improvements in Mobility Measures Sustained Over Time in Phase 1/2 and OLE Mean Change from Baseline in GMFM-E 8 Change from Baseline for Phase 1/2 & OLE 7.1 3 Studies 5.8 6 1, 2 MCID Endpoint 20-week 32-week 56-week 104-week 4.2 4.1 GMFCS I 4 (4.0 units) analysis analysis analysis analysis GMFCS II 4 (N=13) (N=13) (N=13) (N=9) (2.8 units) 2 0 4.2 units 4.1 units 5.8 units 7.1 units GMFM-E 20 weeks 32 weeks 56 weeks 104 weeks 32.2 m 21.3 m 44.9 m 38.3 m 6MWT Mean Change from Baseline in 6MWT 50 44.9 38.3 40 Phase 1/2 Open-Label Extension 32.2 N=16 N=15 N=14 30 N=13 ongoing Part 2: 21.3 Weekly Open-Label Extension Part 1: 20 Doses SAD 10 Weeks Weeks 96 0 ~10 0 8 0 12 24 48 0 20 weeks 32 weeks 56 weeks 104 weeks 1 2 3 MCID is minimal clinically important difference defined in Cerebral Palsy population. Oeffinger D et al 2008; Analysis weeks are calculated by adding the 8 weeks from Part 2 of the Phase 1/2 study to the weeks of 4 treatment in the open-label extension (OLE) study (e.g., 8 weeks of Part 2 + 12 weeks of OLE is the 20-week analysis), baseline values were taken at Part 1 of the study; 13 patients remain in the OLE study, 9 of 13 patients had 96-week mobility assessments conducted; GMFM-E = Gross Motor Function Measure Part E; 6MWT = 6-minute walk test; GMFCS = Gross Motor Function Classification System; SAD = single ascending dose ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 39 Mean Change (Meters) Mean Change (Units)

Measuring the Functional Impact of Spasticity in ARG1-D Classification of Mobility: Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) Overall description of current motor function based on: • Movements such as sitting, walking Level V not pictured: adapted seating and assistance with transfers, and utilize wheeled power • Use of mobility devices mobility independently or manual mobility with assistance in most settings Measures of Change in Mobility: Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM) Part E Timed Walk Tests Evaluates aided mobility with any Assesses unaided mobility without bracing or assistive devices needed bracing or assistive devices over • 24 tasks involving walking forward/backward, running, jumping a defined period of time and ascending/descending stairs with a score range of 0-72 • 2 mins (2MWT) • 6 mins (6MWT) ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External GMFCS graphic adapted with permission from The Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne, Australia 40

PEACE Phase 3 Study Design Double-blind portion of trial complete – topline data announced December 2021 Pegzilarginase 0.1 mg/kg* IV Patients with ARG1-D R ǂ n=21 Long Term Extension N=32 2:1 • ≥2 years old N=31 Placebo IV • Plasma arginine >250 µM (mean) • Baseline deficit in clinical n=11 response assessments Up to 150 weeks 24 weeks Key Endpoints Analysis Primary: • Reduction of plasma arginine compared to placebo • Plasma arginine reduction Secondary: • Continuous analysis • GMFM-E (walking, running & jumping) • Improvement compared to placebo • 2-Minute Walk Test (distance walked in 2 min) *Dosing is weekly and, if needed, dose is modified based on plasma arginine levels with maintenance of blinding. ǂ The first 8 weeks of the open-label extension will be blinded. All study participants remain on current disease management for the duration of the trial. Dose adjustments in the double-blind treatment period can be made to optimize plasma arginine control for levels outside the range of 50-150µM. If needed, weekly doses can be increased to 0.15 and 0.2 mg/kg or reduced to 0.05mg/kg ARG1-D = Arginase 1 Deficiency; IV = intravenous; R = randomized. ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 41
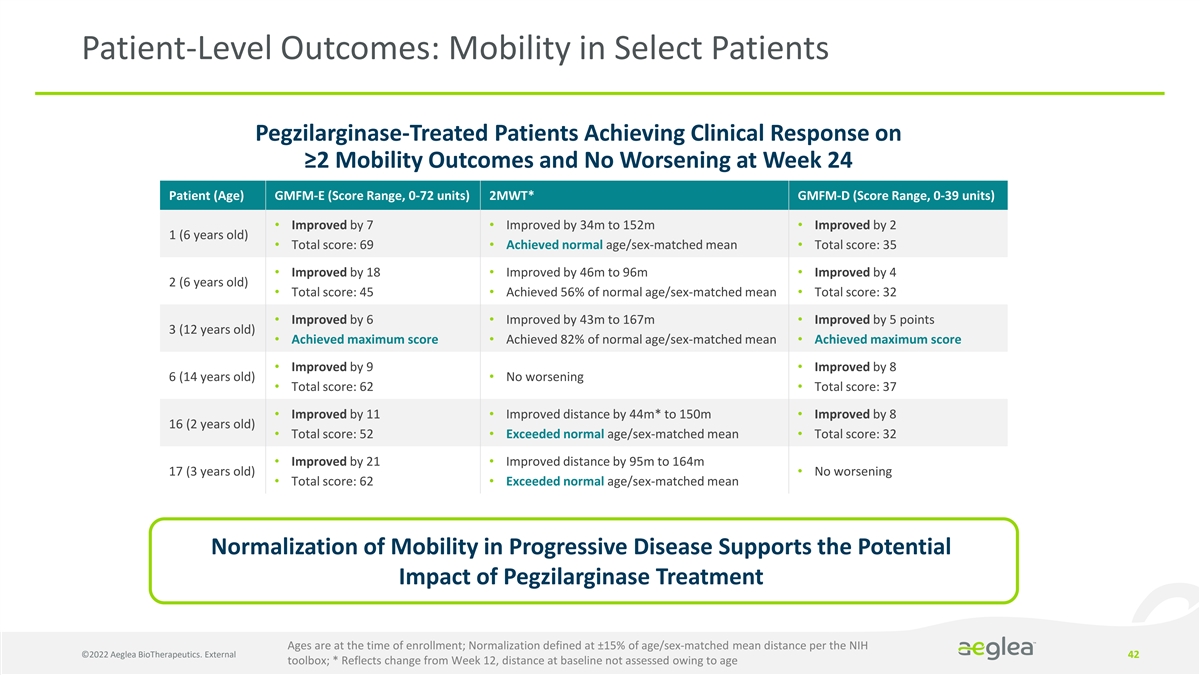
Patient-Level Outcomes: Mobility in Select Patients Pegzilarginase-Treated Patients Achieving Clinical Response on ≥2 Mobility Outcomes and No Worsening at Week 24 Patient (Age) GMFM-E (Score Range, 0-72 units) 2MWT* GMFM-D (Score Range, 0-39 units) • Improved by 7 • Improved by 34m to 152m • Improved by 2 1 (6 years old) • Total score: 69 • Achieved normal age/sex-matched mean • Total score: 35 • Improved by 18 • Improved by 46m to 96m • Improved by 4 2 (6 years old) • Total score: 45 • Achieved 56% of normal age/sex-matched mean • Total score: 32 • Improved by 6 • Improved by 43m to 167m • Improved by 5 points 3 (12 years old) • Achieved maximum score • Achieved 82% of normal age/sex-matched mean • Achieved maximum score • Improved by 9 • Improved by 8 6 (14 years old) • No worsening • Total score: 62 • Total score: 37 • Improved by 11 • Improved distance by 44m* to 150m • Improved by 8 16 (2 years old) • Total score: 52 • Exceeded normal age/sex-matched mean • Total score: 32 • Improved by 21 • Improved distance by 95m to 164m 17 (3 years old) • No worsening • Total score: 62 • Exceeded normal age/sex-matched mean Normalization of Mobility in Progressive Disease Supports the Potential Impact of Pegzilarginase Treatment Ages are at the time of enrollment; Normalization defined at ±15% of age/sex-matched mean distance per the NIH ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 42 toolbox; * Reflects change from Week 12, distance at baseline not assessed owing to age
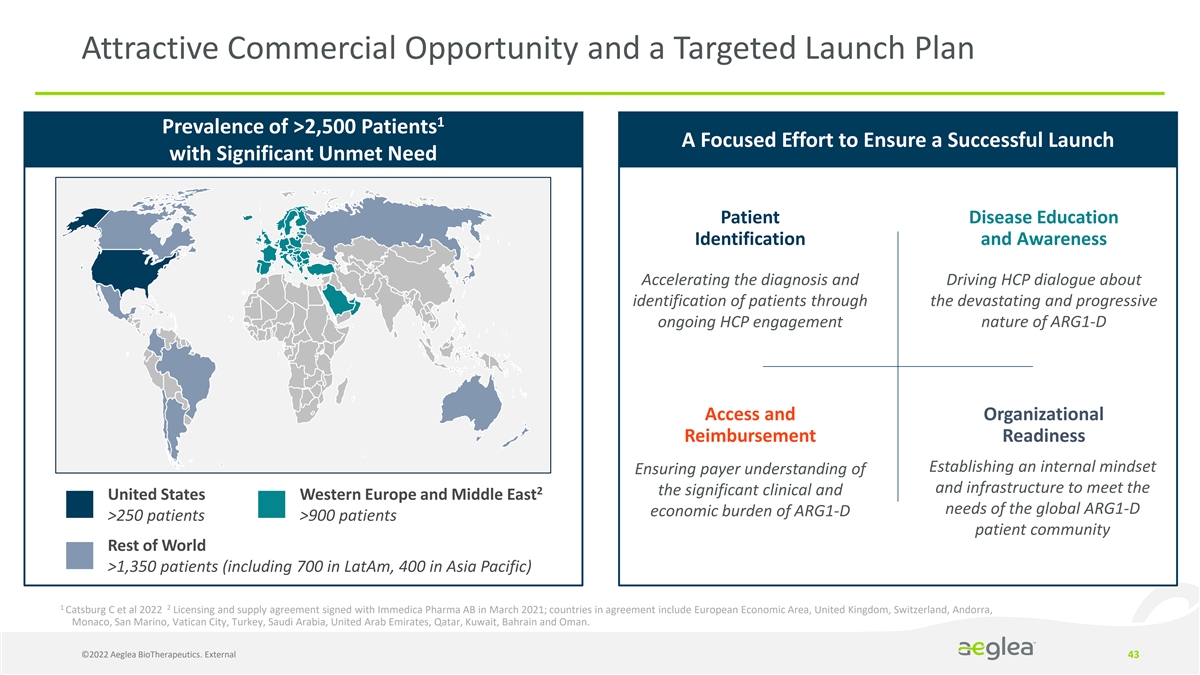
Attractive Commercial Opportunity and a Targeted Launch Plan 1 Prevalence of >2,500 Patients A Focused Effort to Ensure a Successful Launch with Significant Unmet Need Patient Disease Education Identification and Awareness Accelerating the diagnosis and Driving HCP dialogue about identification of patients through the devastating and progressive ongoing HCP engagement nature of ARG1-D Access and Organizational Reimbursement Readiness Establishing an internal mindset Ensuring payer understanding of and infrastructure to meet the 2 the significant clinical and United States Western Europe and Middle East needs of the global ARG1-D economic burden of ARG1-D >250 patients >900 patients patient community Rest of World >1,350 patients (including 700 in LatAm, 400 in Asia Pacific) 1 2 Catsburg C et al 2022 Licensing and supply agreement signed with Immedica Pharma AB in March 2021; countries in agreement include European Economic Area, United Kingdom, Switzerland, Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, Vatican City, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain and Oman. ©2022 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 43










































