
Reimagining The Potential Of Human Enzyme Therapeutics PEACE Phase 3 Topline Study Results – December 6, 2021 Exhibit 99.2

Forward Looking Statements ©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 2 This presentation and the accompanying oral presentation contain “forward-looking” statements that are based on our management’s beliefs and assumptions and on information currently available to management. Forward-looking statements include all statements other than statements of historical fact contained in this presentation, including information concerning our current and future financial performance, business plans and objectives, current and future clinical and preclinical development activities, timing and success of our ongoing and planned clinical trials and related data, the timing of announcements, updates, results of our clinical trials and related data and our planned BLA submission for our lead product candidate pegzilarginase, our ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approval, the potential therapeutic benefits, safety profile and economic value of pegzilarginase and our other product candidates, potential growth opportunities, financing plans, use and adequacy of financing plans, competitive position, industry environment and potential market opportunities. Forward-looking statements are subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties, assumptions and other factors including, but not limited to, those related to the success, cost and timing of our product candidate development activities and ongoing and planned clinical trials; our plans to develop and commercialize targeted therapeutics, including our lead product candidate pegzilarginase and our product candidates for the treatment of homocystinuria and cystinuria; the design, progress of patient enrollment and dosing in our clinical trials; the ability of our product candidates to achieve applicable endpoints in clinical trials; the safety profile of our product candidates in clinical trials; the potential for data from our current and future clinical trials to support a marketing application, as well as the timing of these events; the potential for preclinical studies to be predictive of current or future clinical trials; our ability to obtain funding for our operations, development and commercialization of our product candidates; the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on our operations and clinical development activities, including on the timing of enrollment of our clinical trials; the timing of and our ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approvals; our ability to obtain regulatory approval for, and commercialize, pegzilarginase, and recognize milestone and royalty payments from our licensing and supply agreement with Immedica; the potential for expedited development and review of pegzilarginase as a result of its Breakthrough Therapy designation; the potential addressable markets of our product candidates; the rate and degree of market acceptance and clinical utility of our product candidates; the size and growth potential of the markets for our product candidates, and our ability to serve those markets; our commercialization, marketing and manufacturing capabilities and strategy; future agreements with third parties in connection with the potential commercialization of our product candidates; our expectations regarding our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection; our dependence on third party manufacturers; our ability to develop our own commercial manufacturing facility; the success of competing therapies that are or may become available; our ability to attract and retain key scientific or management personnel; our ability to identify additional product candidates with significant commercial potential consistent with our commercial objectives; and our estimates regarding expenses, future revenue, capital requirements and needs for additional financing. Moreover, we operate in a very competitive and rapidly changing environment, and new risks may emerge from time to time. It is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements we may make. In light of these risks, uncertainties and assumptions, the forward-looking events and circumstances discussed herein may not occur and actual results could differ materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the forward-looking statements. Further information on these and other factors that could affect these forward-looking statements is contained in our most recent Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and other reports filed by the SEC. You should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. Although our management believes that the expectations reflected in our forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee that the future results, levels of activity, performance or events and circumstances described in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur. We undertake no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statements, whether written or oral, that may be made from time to time, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise.

PEACE Phase 3 Study of Pegzilarginase in Patients with ARG1-D ©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 3 Thank you to all the patients, families, investigators and study staff who participated in the PEACE study

PEACE Phase 3 Topline Study Results Pegzilarginase in Arginase 1 Deficiency Draft for Internal Discussion Only
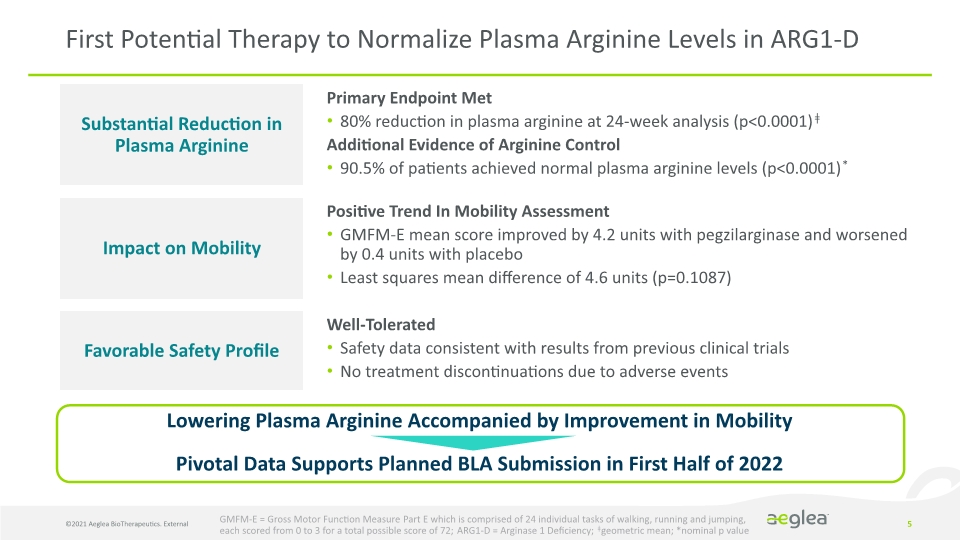
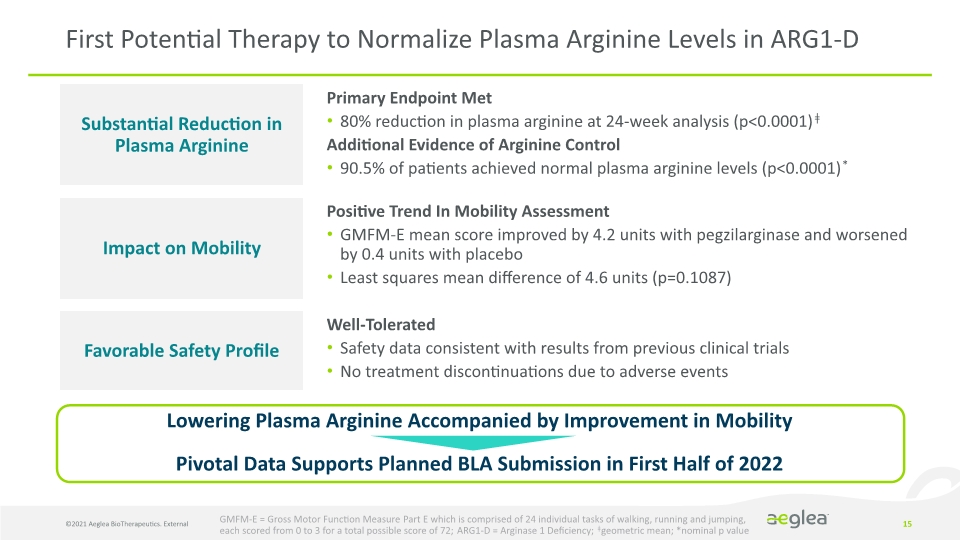
©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 5 First Potential Therapy to Normalize Plasma Arginine Levels in ARG1-D Lowering Plasma Arginine Accompanied by Improvement in Mobility Pivotal Data Supports Planned BLA Submission in First Half of 2022 Substantial Reduction in Plasma Arginine Impact on Mobility Favorable Safety Profile Primary Endpoint Met 80% reduction in plasma arginine at 24-week analysis (p<0.0001)ǂ Additional Evidence of Arginine Control 90.5% of patients achieved normal plasma arginine levels (p<0.0001)* Positive Trend In Mobility Assessment GMFM-E mean score improved by 4.2 units with pegzilarginase and worsened by 0.4 units with placebo Least squares mean difference of 4.6 units (p=0.1087) Well-Tolerated Safety data consistent with results from previous clinical trials No treatment discontinuations due to adverse events GMFM-E = Gross Motor Function Measure Part E which is comprised of 24 individual tasks of walking, running and jumping, each scored from 0 to 3 for a total possible score of 72; ARG1-D = Arginase 1 Deficiency; ǂgeometric mean; *nominal p value
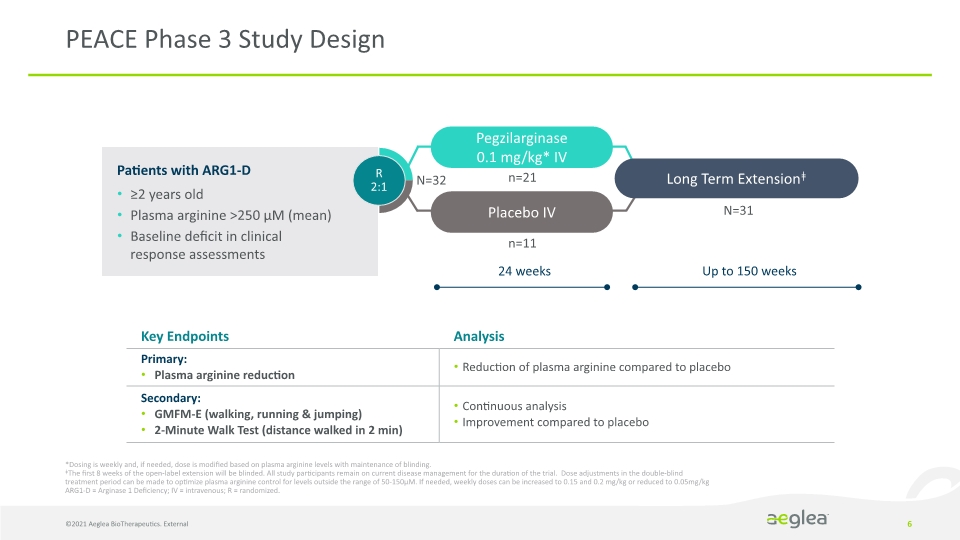
PEACE Phase 3 Study Design ©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 6 *Dosing is weekly and, if needed, dose is modified based on plasma arginine levels with maintenance of blinding. ǂThe first 8 weeks of the open-label extension will be blinded. All study participants remain on current disease management for the duration of the trial. Dose adjustments in the double-blind treatment period can be made to optimize plasma arginine control for levels outside the range of 50-150µM. If needed, weekly doses can be increased to 0.15 and 0.2 mg/kg or reduced to 0.05mg/kg ARG1-D = Arginase 1 Deficiency; IV = intravenous; R = randomized. Patients with ARG1-D ≥2 years old Plasma arginine >250 µM (mean) Baseline deficit in clinical response assessments Placebo IV R 2:1 Long Term Extensionǂ Pegzilarginase 0.1 mg/kg* IV 24 weeks Up to 150 weeks n=11 N=32 n=21 N=31
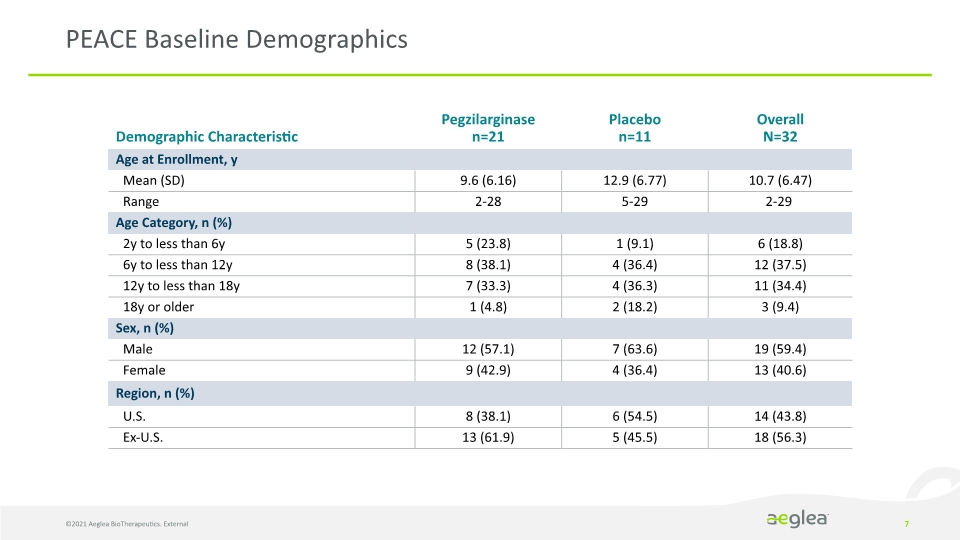
PEACE Baseline Demographics ©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 7 Demographic Characteristic Pegzilarginase n=21 Placebo n=11 Overall N=32 Age at Enrollment, y Mean (SD) 9.6 (6.16) 12.9 (6.77) 10.7 (6.47) Range 2-28 5-29 2-29 Age Category, n (%) 2y to less than 6y 5 (23.8) 1 (9.1) 6 (18.8) 6y to less than 12y 8 (38.1) 4 (36.4) 12 (37.5) 12y to less than 18y 7 (33.3) 4 (36.3) 11 (34.4) 18y or older 1 (4.8) 2 (18.2) 3 (9.4) Sex, n (%) Male 12 (57.1) 7 (63.6) 19 (59.4) Female 9 (42.9) 4 (36.4) 13 (40.6) Region, n (%) U.S. 8 (38.1) 6 (54.5) 14 (43.8) Ex-U.S. 13 (61.9) 5 (45.5) 18 (56.3)
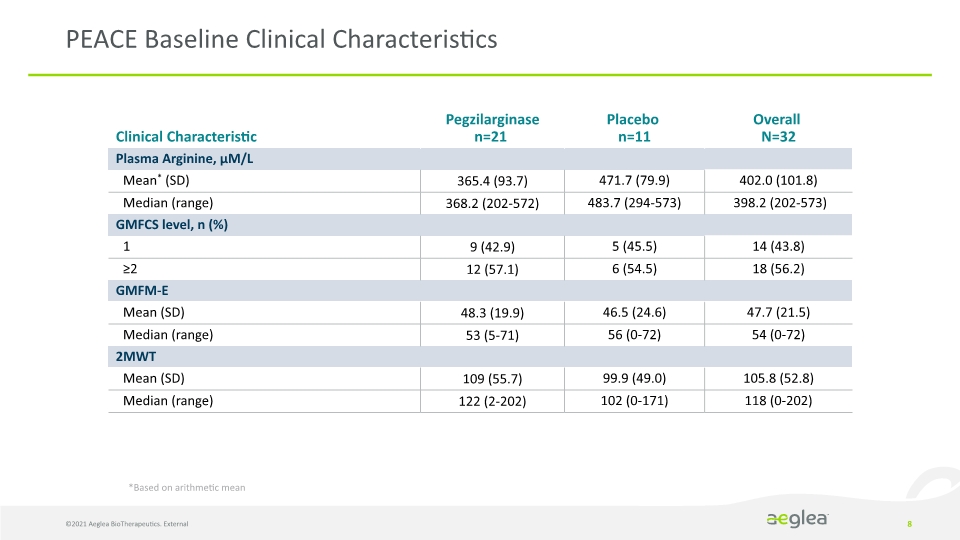
PEACE Baseline Clinical Characteristics ©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 8 *Based on arithmetic mean Clinical Characteristic Pegzilarginase n=21 Placebo n=11 Overall N=32 Plasma Arginine, µM/L Mean* (SD) 365.4 (93.7) 471.7 (79.9) 402.0 (101.8) Median (range) 368.2 (202-572) 483.7 (294-573) 398.2 (202-573) GMFCS level, n (%) 1 9 (42.9) 5 (45.5) 14 (43.8) ≥2 12 (57.1) 6 (54.5) 18 (56.2) GMFM-E Mean (SD) 48.3 (19.9) 46.5 (24.6) 47.7 (21.5) Median (range) 53 (5-71) 56 (0-72) 54 (0-72) 2MWT Mean (SD) 109 (55.7) 99.9 (49.0) 105.8 (52.8) Median (range) 122 (2-202) 102 (0-171) 118 (0-202)
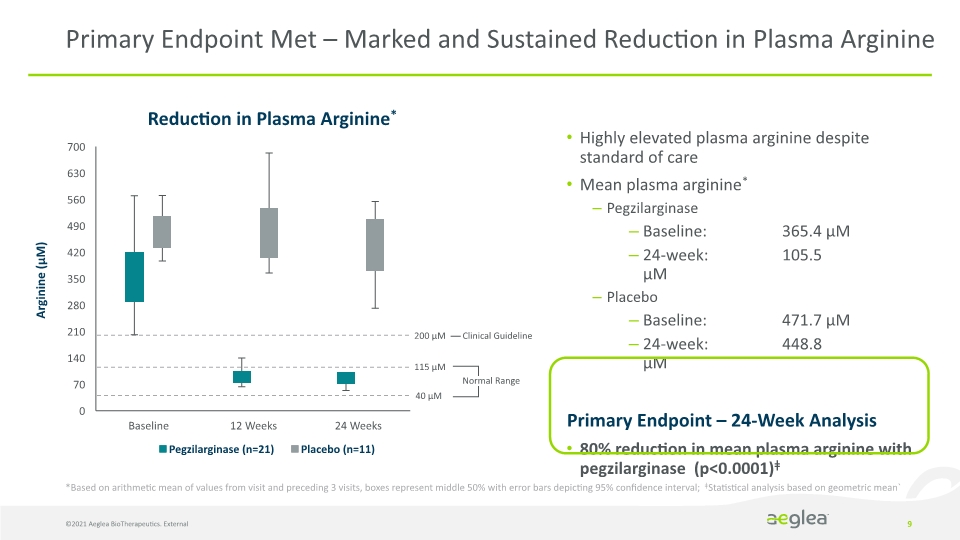
©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 9 Highly elevated plasma arginine despite standard of care Mean plasma arginine* Pegzilarginase Baseline: 365.4 µM 24-week: 105.5 µM Placebo Baseline: 471.7 µM 24-week: 448.8 µM Primary Endpoint – 24-Week Analysis 80% reduction in mean plasma arginine with pegzilarginase (p<0.0001)ǂ Primary Endpoint Met – Marked and Sustained Reduction in Plasma Arginine Reduction in Plasma Arginine* *Based on arithmetic mean of values from visit and preceding 3 visits, boxes represent middle 50% with error bars depicting 95% confidence interval; ǂStatistical analysis based on geometric mean` Clinical Guideline 0 70 140 280 350 420 490 560 630 700 Pegzilarginase (n=21) Placebo (n=11) Arginine (µM) Baseline 12 Weeks 24 Weeks
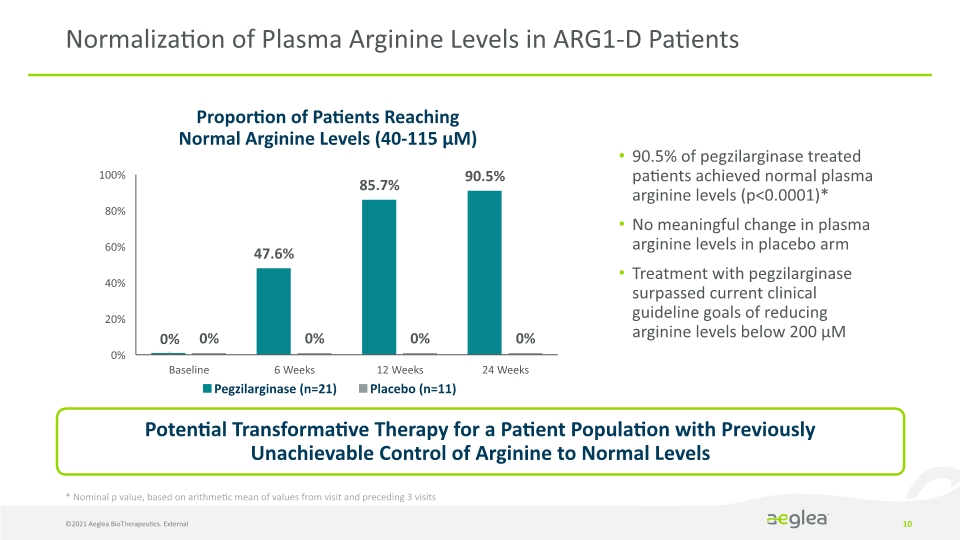
90.5% of pegzilarginase treated patients achieved normal plasma arginine levels (p<0.0001)* No meaningful change in plasma arginine levels in placebo arm Treatment with pegzilarginase surpassed current clinical guideline goals of reducing arginine levels below 200 µM ©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 10 Normalization of Plasma Arginine Levels in ARG1-D Patients Proportion of Patients Reaching Normal Arginine Levels (40-115 µM) Potential Transformative Therapy for a Patient Population with Previously Unachievable Control of Arginine to Normal Levels * Nominal p value, based on arithmetic mean of values from visit and preceding 3 visits 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% 0% 0% 47.6% 0% 85.7% 0% 90.5% 0% Baseline 6 Weeks 12 Weeks 24 Weeks Pegzilarginase (n=21) Placebo (n=11)

©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 11 Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM) Part E Assesses unaided mobility without bracing or assistive devices 24 tasks involving walking forward/backward, running, jumping and ascending/descending stairs, each scored from 0 to 3 with a total score range of 0-72 PEACE Key Mobility Measurements 2-Minute Walk Test Evaluates aided mobility with any needed bracing or assistive devices over a defined period of time
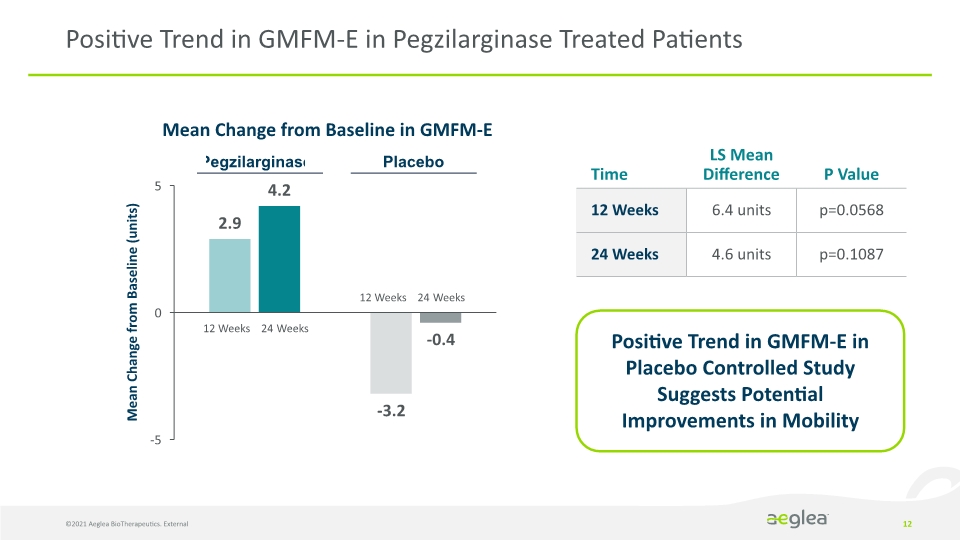
Positive Trend in GMFM-E in Pegzilarginase Treated Patients ©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 12 Mean Change from Baseline in GMFM-E Positive Trend in GMFM-E in Placebo Controlled Study Suggests Potential Improvements in Mobility Mean Change from Baseline (units) Pegzilarginase Placebo 12 Weeks 24 Weeks 12 Weeks 24 Weeks 2.9 4.2 -0.4 -3.2 -5 0 5 Time LS Mean Difference P Value 12 Weeks 6.4 units p=0.0568 24 Weeks 4.6 units p=0.1087

©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 13 Mobility Assessment by 2-Minute Walk Test 6MWT – Six Minute Walk Test 2MWT = 2-Minute Walk Test Mean Change from Baseline in 2MWT 6.8 -7.5 7.3 2.7 -10 0 10 Pegzilarginase Placebo Mean Change from Baseline (m) Pegzilarginase Placebo 12 Weeks 24 Weeks 12 Weeks 24 Weeks Mobility Assessment by 2-Minute Walk Test 6MWT –Six Minute Walk Test 2MWT = 2-Minute Walk TestTime LS Mean Difference P Value 12 Weeks 14.1 meters p=0.2085 24 Weeks 5.5 meters p=0.5961
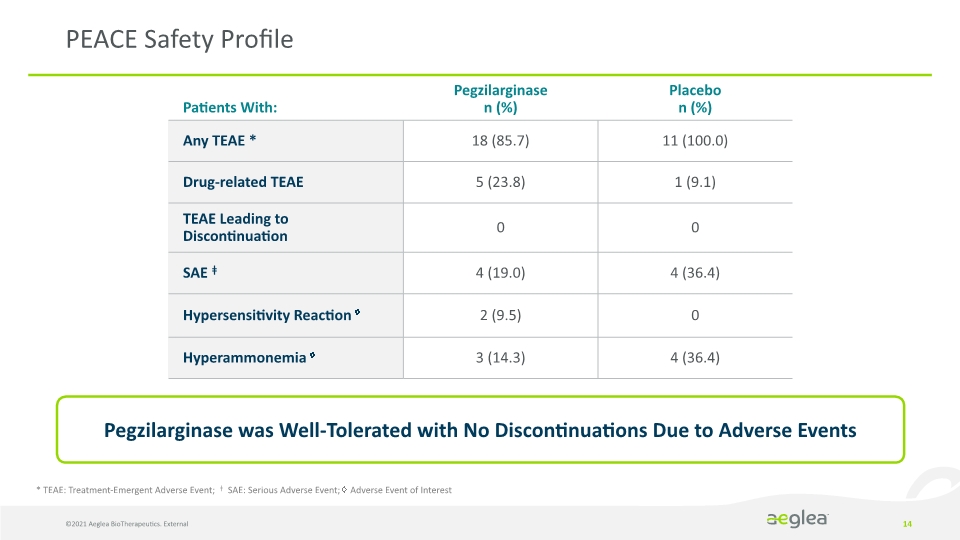
©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 14 PEACE Safety Profile * TEAE: Treatment-Emergent Adverse Event; ǂ SAE: Serious Adverse Event; ♢ Adverse Event of Interest Pegzilarginase was Well-Tolerated with No Discontinuations Due to Adverse Events Patients With: Pegzilarginase n (%) Placebo n (%) Any TEAE * 18 (85.7) 11 (100.0) Drug-related TEAE 5 (23.8) 1 (9.1) TEAE Leading to Discontinuation 0 0 SAE ǂ 4 (19.0) 4 (36.4) Hypersensitivity Reaction ♢ 2 (9.5) 0 Hyperammonemia ♢ 3 (14.3) 4 (36.4)
©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 15 First Potential Therapy to Normalize Plasma Arginine Levels in ARG1-D Lowering Plasma Arginine Accompanied by Improvement in Mobility Pivotal Data Supports Planned BLA Submission in First Half of 2022 Substantial Reduction in Plasma Arginine Impact on Mobility Favorable Safety Profile Primary Endpoint Met 80% reduction in plasma arginine at 24-week analysis (p<0.0001)ǂ Additional Evidence of Arginine Control 90.5% of patients achieved normal plasma arginine levels (p<0.0001)* Positive Trend In Mobility Assessment GMFM-E mean score improved by 4.2 units with pegzilarginase and worsened by 0.4 units with placebo Least squares mean difference of 4.6 units (p=0.1087) Well-Tolerated Safety data consistent with results from previous clinical trials No treatment discontinuations due to adverse events GMFM-E = Gross Motor Function Measure Part E which is comprised of 24 individual tasks of walking, running and jumping, each scored from 0 to 3 for a total possible score of 72; ARG1-D = Arginase 1 Deficiency; ǂgeometric mean; *nominal p value
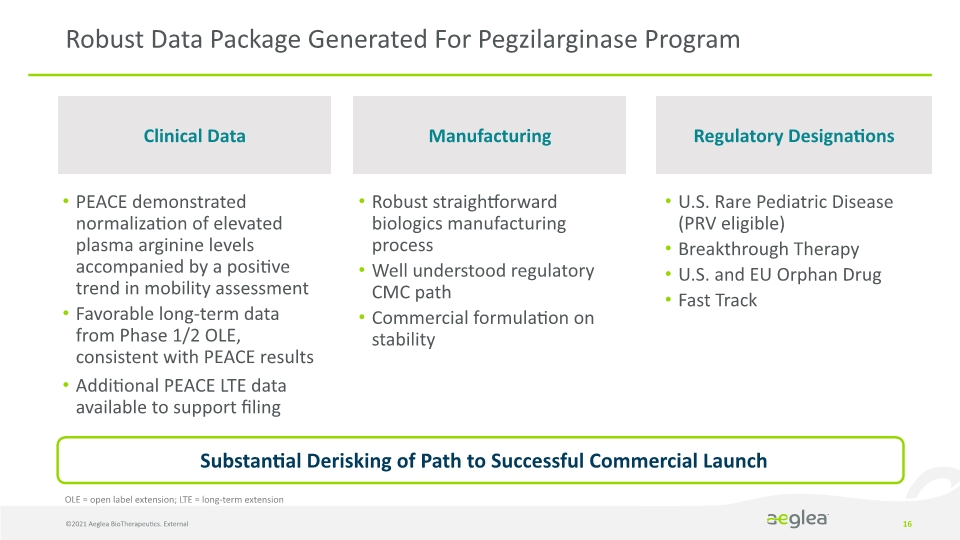
Robust Data Package Generated For Pegzilarginase Program ©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 16 Clinical Data Manufacturing Regulatory Designations PEACE demonstrated normalization of elevated plasma arginine levels accompanied by a positive trend in mobility assessment Favorable long-term data from Phase 1/2 OLE, consistent with PEACE results Additional PEACE LTE data available to support filing U.S. Rare Pediatric Disease (PRV eligible) Breakthrough Therapy U.S. and EU Orphan Drug Fast Track Robust straightforward biologics manufacturing process Well understood regulatory CMC path Commercial formulation on stability Substantial Derisking of Path to Successful Commercial Launch OLE = open label extension; LTE = long-term extension
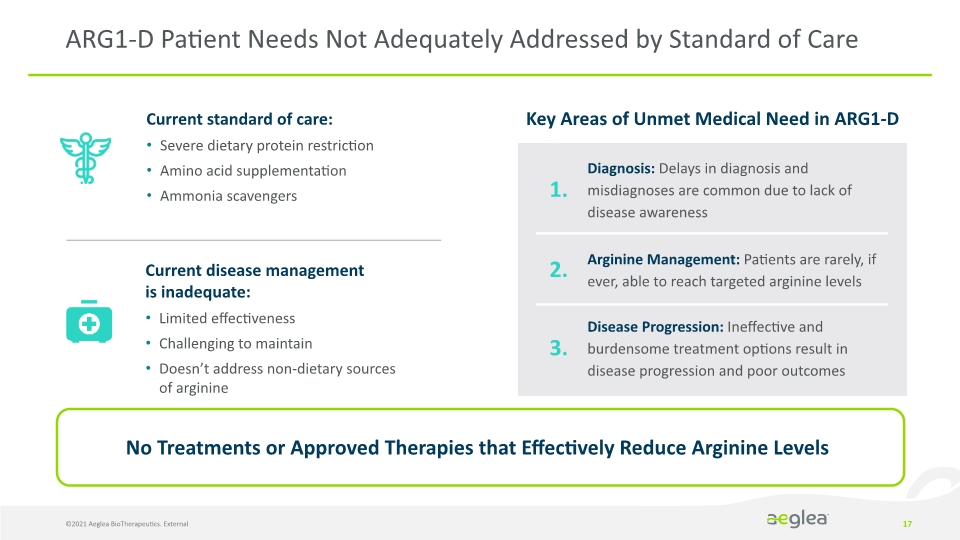
©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 17 ARG1-D Patient Needs Not Adequately Addressed by Standard of Care Current standard of care: Severe dietary protein restriction Amino acid supplementation Ammonia scavengers Current disease management is inadequate: Limited effectiveness Challenging to maintain Doesn’t address non-dietary sources of arginine Key Areas of Unmet Medical Need in ARG1-D No Treatments or Approved Therapies that Effectively Reduce Arginine Levels
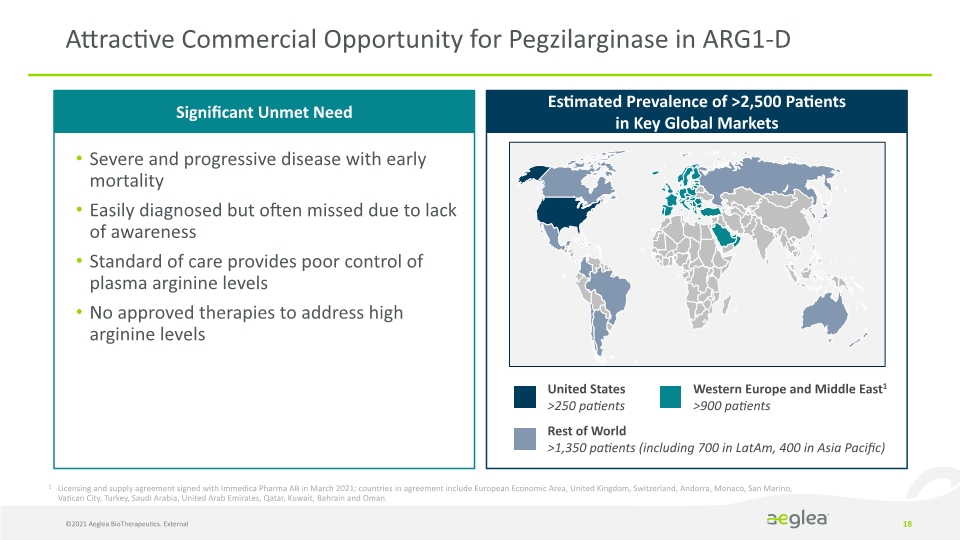
©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 18 Attractive Commercial Opportunity for Pegzilarginase in ARG1-D Severe and progressive disease with early mortality Easily diagnosed but often missed due to lack of awareness Standard of care provides poor control of plasma arginine levels No approved therapies to address high arginine levels Significant Unmet Need Estimated Prevalence of >2,500 Patients in Key Global Markets United States >250 patients Western Europe and Middle East1 >900 patients Rest of World >1,350 patients (including 700 in LatAm, 400 in Asia Pacific) 1 Licensing and supply agreement signed with Immedica Pharma AB in March 2021; countries in agreement include European Economic Area, United Kingdom, Switzerland, Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, Vatican City, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain and Oman.

©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 19 Building the Foundation for a Successful Launch and Enduring Commercial Presence Patient Identification Accelerating the diagnosis and identification of patients through ongoing HCP engagement Disease Education and Awareness Driving HCP dialogue about the devastating and progressive nature of ARG1-D Access and Reimbursement Ensuring payer understanding of the significant clinical and economic burden of ARG1-D Organizational Readiness Establishing an internal mindset and infrastructure to meet the needs of the ARG1-D patient community

©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 20 Committed to Delivering Innovative Therapies for Patients in Need Countries included in Immedica license and supply agreement – European Economic Area, United Kingdom, Switzerland, Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, Vatican City, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain and Oman. Significant Patient Need Debilitating and progressive disease with significant burden No effective treatments currently available Estimated worldwide patient prevalence of >2,500 patients in global addressable markets (including >250 in U.S.) Demonstrated Clinical Impact 80% reduction in plasma arginine in pegzilarginase treated patients at 24-week analysis 90.5% of patients achieved normal plasma arginine levels Positive trend in key mobility assessment of clinical benefit Well tolerated; safety data consistent with results from previous clinical trials Advancing Commercial Efforts Patient identification: outpacing relevant benchmarks, driving diagnosis Disease education and awareness: accelerating disease understanding among key specialties Access and reimbursement: articulating disease burden and pegzilarginase value proposition •Organizational readiness: ongoing efforts to prepare for approval and successful launch –U.S.: Building commercial infrastructure –Ex-U.S.: Continued progress in EU/ME with Immedica, ongoing ROW partnership focus

©2021 Aeglea BioTherapeutics. External 21 Aeglea’s Human Enzyme Platform for Rare Metabolic Diseases 1 Ex-U.S. license and supply agreement with Immedica to commercialize pegzilarginase in Europe and certain countries in the Middle East (European Economic Area, United Kingdom, Switzerland, Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, Vatican City, Turkey, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain and Oman) 2 ARG1-D case reports ; Diez-Fernandez et al. Mutations and common variants in the human arginase 1 (ARG1) gene: impact on patients, diagnostics and protein structure considerations. Hum Mutat. 2018 Aug;39(8):1029-10502. 3 >30,000 represents estimated prevalence of Classical Homocystinuria in 38 addressable markets based on results of U.S. ICD-10 claims analysis extrapolated to global markets; all figures rounded. Sellos-Moura et al 2020 4 Castro Pereira DJ et al 2015; Leslie and Nazzal Renal Calculi (Cystinuria, Cystine Stones) (2018) Reference; Rozanski et al, Mil Med (2005); Soucie et al, JM Kidney Int (1994); Claes & Jackson, Pediatr Nephrol (2012) 27, 2031; Chillarón, J. et al. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 7, 424-34; Biyani, C.S and Cartledge, J.J. EAU-EBU Update Series, 2006, 4, 175-183; Mattoo, A. and Goldfarb D.S. 2008 Sem. Nephrol, 28, 2, 181-191

Q&A

805 Las Cimas Parkway Suite 100 Austin, TX 78746 aeglea.com






















