Exhibit 99.3
PART IV
Item 15 — Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules
(a)(1) Financial Statements
The following consolidated financial statements of NRG Yield LLC and related notes thereto, together with the reports thereon of KPMG LLP, are included herein:
Consolidated Statements of Income — Years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income — Years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
Consolidated Balance Sheets — As of December 31, 2016 and 2015
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows — Years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
Consolidated Statements of Members' Equity — Years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(a)(2) Not applicable
(a)(3) Exhibits: See Exhibit Index submitted as a separate section of this report
(b) Exhibits
See Exhibit Index submitted as a separate section of this report
(c) Not applicable
1
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Members
NRG Yield LLC:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of NRG Yield LLC and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive (loss) income, members’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of NRG Yield LLC and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three‑year period ended December 31, 2016, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
(signed) KPMG LLP
Philadelphia, PA
May 9, 2017
2
NRG YIELD LLC
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
| Year ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| (In millions) | 2016 (a) | 2015 (a) | 2014 (a) | ||||||||
| Operating Revenues | |||||||||||
| Total operating revenues | $ | 1,021 | $ | 953 | $ | 828 | |||||
| Operating Costs and Expenses | |||||||||||
| Cost of operations | 306 | 321 | 277 | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 297 | 297 | 233 | ||||||||
| Impairment losses | 183 | — | — | ||||||||
| General and administrative | 14 | 10 | 8 | ||||||||
| Acquisition-related transaction and integration costs | 1 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 801 | 631 | 522 | ||||||||
| Operating Income | 220 | 322 | 306 | ||||||||
| Other Income (Expense) | |||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliates | 60 | 31 | 22 | ||||||||
| Other income, net | 3 | 3 | 6 | ||||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment | — | (9 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||
| Interest expense | (268 | ) | (254 | ) | (211 | ) | |||||
| Total other expense, net | (205 | ) | (229 | ) | (184 | ) | |||||
| Net Income | 15 | 93 | 122 | ||||||||
| Less: Net (loss) income attributable to noncontrolling interests | (142 | ) | (51 | ) | 3 | ||||||
| Net Income Attributable to NRG Yield LLC | $ | 157 | $ | 144 | $ | 119 | |||||
(a) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
3
NRG YIELD LLC
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| Year ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 (a) | 2015 (a) | 2014 (a) | |||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||
| Net Income | $ | 15 | $ | 93 | $ | 122 | |||||
| Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | |||||||||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives | 13 | (17 | ) | (65 | ) | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | 13 | (17 | ) | (65 | ) | ||||||
| Comprehensive Income | 28 | 76 | 57 | ||||||||
| Less: Comprehensive (loss) income attributable to noncontrolling interests | (142 | ) | (52 | ) | 1 | ||||||
| Comprehensive Income Attributable to NRG Yield LLC | $ | 170 | $ | 128 | $ | 56 | |||||
(a) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
4
NRG YIELD LLC
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2016 (a) | December 31, 2015 (a) | ||||||
| ASSETS | (In millions) | ||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 321 | $ | 110 | |||
| Restricted cash | 165 | 131 | |||||
| Accounts receivable — trade | 92 | 101 | |||||
| Accounts receivable — affiliates | 1 | 4 | |||||
| Inventory | 39 | 36 | |||||
| Derivative instruments | 2 | — | |||||
| Notes receivable — current | 16 | 17 | |||||
| Prepayments and other current assets | 20 | 20 | |||||
| Total current assets | 656 | 419 | |||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 5,460 | 5,878 | |||||
| Other Assets | |||||||
| Equity investments in affiliates | 1,152 | 797 | |||||
| Notes receivable — non-current | 14 | 30 | |||||
| Intangible assets, net | 1,286 | 1,362 | |||||
| Derivative instruments | 1 | — | |||||
| Other non-current assets | 51 | 136 | |||||
| Total other assets | 2,504 | 2,325 | |||||
| Total Assets | $ | 8,620 | $ | 8,622 | |||
| LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS' EQUITY | |||||||
| Current Liabilities | |||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt — external | $ | 291 | $ | 264 | |||
| Accounts payable — trade | 23 | 23 | |||||
| Accounts payable — affiliate | 40 | 86 | |||||
| Derivative instruments | 32 | 39 | |||||
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | 85 | 76 | |||||
| Total current liabilities | 471 | 488 | |||||
| Other Liabilities | |||||||
| Long-term debt — external | 5,098 | 4,743 | |||||
| Long-term debt — affiliate | 618 | 618 | |||||
| Accounts payable — affiliate | 9 | — | |||||
| Derivative instruments | 44 | 61 | |||||
| Other non-current liabilities | 76 | 72 | |||||
| Total non-current liabilities | 5,845 | 5,494 | |||||
| Total Liabilities | 6,316 | 5,982 | |||||
| Commitments and Contingencies | |||||||
| Members' Equity | |||||||
| Contributed capital | 1,995 | 2,176 | |||||
| Retained earnings | 79 | 100 | |||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (83 | ) | (96 | ) | |||
| Noncontrolling interest | 313 | 460 | |||||
| Total Members' Equity | 2,304 | 2,640 | |||||
| Total Liabilities and Members’ Equity | $ | 8,620 | $ | 8,622 | |||
(a) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
5
NRG YIELD LLC
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| Year ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 (a) | 2015 (a) | 2014 (a) | |||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities | |||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 15 | $ | 93 | $ | 122 | |||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliates | (60 | ) | (31 | ) | (22 | ) | |||||
| Distributions from unconsolidated affiliates | 58 | 60 | 21 | ||||||||
| Depreciation, amortization and ARO accretion | 300 | 299 | 235 | ||||||||
| Amortization of financing costs | 8 | 7 | 6 | ||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles and out-of-market contracts | 75 | 54 | 28 | ||||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment | — | 9 | 1 | ||||||||
| Impairment losses | 183 | — | — | ||||||||
| Changes in derivative instruments | (15 | ) | (43 | ) | (12 | ) | |||||
| Loss on disposal of asset components | 6 | 3 | — | ||||||||
| Cash provided by (used in) changes in other working capital: | |||||||||||
| Changes in prepaid and accrued capacity payments | (8 | ) | (12 | ) | — | ||||||
| Changes in other working capital | 7 | (18 | ) | (17 | ) | ||||||
| Net Cash Provided by Operating Activities | 569 | 421 | 362 | ||||||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities | |||||||||||
| Acquisition of businesses, net of cash acquired | — | (37 | ) | (901 | ) | ||||||
| Acquisition of Drop Down Assets, net of cash acquired | (77 | ) | (698 | ) | (311 | ) | |||||
| Capital expenditures | (20 | ) | (29 | ) | (60 | ) | |||||
| Receipt of indemnity from supplier | — | — | 57 | ||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in restricted cash | (34 | ) | (1 | ) | 25 | ||||||
| Cash receipts from notes receivable | 17 | 17 | 14 | ||||||||
| Proceeds from renewable energy grants | — | — | 422 | ||||||||
| Return of investment from unconsolidated affiliates | 28 | 42 | 4 | ||||||||
| Investments in unconsolidated affiliates | (83 | ) | (402 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||
| Other | 4 | — | 11 | ||||||||
| Net Cash Used in Investing Activities | (165 | ) | (1,108 | ) | (741 | ) | |||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities | |||||||||||
| Contributions from tax equity investors, net of distributions | 5 | 122 | 190 | ||||||||
| Capital contributions from NRG | — | — | 2 | ||||||||
| Distributions and return of capital to NRG prior to the acquisition of Drop Down Assets | (170 | ) | (76 | ) | (333 | ) | |||||
| Proceeds from the issuance of class A and class C units | — | 599 | 630 | ||||||||
| Payments of distributions | (183 | ) | (139 | ) | (101 | ) | |||||
| Proceeds from the revolving credit facility | 60 | 551 | 500 | ||||||||
| Payments for the revolving credit facility | (366 | ) | (245 | ) | — | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt — external | 740 | 6 | 178 | ||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt — affiliate | — | 281 | 337 | ||||||||
| Payments of debt issuance costs | (15 | ) | (7 | ) | (28 | ) | |||||
| Payments for long-term debt — external | (264 | ) | (724 | ) | (626 | ) | |||||
| Net Cash (Used in) Provided by Financing Activities | (193 | ) | 368 | 749 | |||||||
| Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash and Cash Equivalents | 211 | (319 | ) | 370 | |||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Period | 110 | 429 | 59 | ||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at End of Period | $ | 321 | $ | 110 | $ | 429 | |||||
| Supplemental Disclosures | |||||||||||
| Interest paid, net of amount capitalized | $ | (266 | ) | $ | (274 | ) | $ | (192 | ) | ||
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | |||||||||||
| Additions (reductions) to fixed assets for accrued capital expenditures | 3 | 1 | (21 | ) | |||||||
| Decrease to fixed assets for accrued grants | — | — | 34 | ||||||||
| Increase in debt due to accrued interest converted to debt | — | — | 11 | ||||||||
| Net contributions from NRG (net distributions/return of capital to NRG), non cash | $ | 66 | $ | (13 | ) | $ | 1,058 | ||||
(a) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
6
NRG YIELD LLC
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF MEMBERS' EQUITY
| (In millions) | Contributed Capital | Retained Earnings | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss | Noncontrolling Interest | Total Members' Equity | |||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2013 (a) | $ | 1,302 | $ | 101 | $ | (17 | ) | $ | 58 | $ | 1,444 | |||||||||
| Members' equity - March 2017 Drop Down Assets | 91 | 14 | — | — | 105 | |||||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2013 | $ | 1,393 | $ | 115 | $ | (17 | ) | $ | 58 | $ | 1,549 | |||||||||
Net income (c) | — | 119 | — | 3 | 122 | |||||||||||||||
Unrealized loss on derivatives (c) | — | — | (63 | ) | (2 | ) | (65 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Payment for June 2014 Drop Down Assets | (357 | ) | — | — | — | (357 | ) | |||||||||||||
Capital contributions from NRG, non-cash (b)(c) | 922 | — | — | 136 | 1,058 | |||||||||||||||
Distributions and returns of capital to NRG, net of contributions (c) | (280 | ) | — | — | (51 | ) | (331 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Capital contributions from tax equity investors | — | — | — | 190 | 190 | |||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from the issuance of Class A units | 630 | — | — | — | 630 | |||||||||||||||
| Distributions paid to NRG on Class B and Class D units | — | (60 | ) | — | — | (60 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Distributions paid to Yield, Inc. | — | (41 | ) | — | — | (41 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2014 | $ | 2,308 | $ | 133 | $ | (80 | ) | $ | 334 | $ | 2,695 | |||||||||
Net income (loss) (c) | — | 144 | — | (51 | ) | 93 | ||||||||||||||
Unrealized loss on derivatives (c) | — | — | (16 | ) | (1 | ) | (17 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Payment for January 2015 and November 2015 Drop Down Assets | (698 | ) | — | — | — | (698 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Capital contributions from tax equity investors | — | — | — | 122 | 122 | |||||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest acquired in Spring Canyon acquisition | — | — | — | 74 | 74 | |||||||||||||||
Distributions paid to NRG, net of contributions(c) | (28 | ) | (38 | ) | — | (10 | ) | (76 | ) | |||||||||||
Distributions paid to NRG, net of contributions, non-cash (c) | (5 | ) | — | (8 | ) | (13 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from the issuance of Class C Common Stock | 599 | — | — | — | 599 | |||||||||||||||
| Distributions paid to NRG on Class B and Class D units | — | (70 | ) | — | — | (70 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Distributions paid to Yield, Inc. | — | (69 | ) | — | — | (69 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2015 | $ | 2,176 | $ | 100 | $ | (96 | ) | $ | 460 | $ | 2,640 | |||||||||
| Net income (loss) | — | 157 | — | (142 | ) | 15 | ||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain on derivatives | — | — | 13 | — | 13 | |||||||||||||||
| Payment for CVSR Drop Down Asset | (77 | ) | — | — | — | (77 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Distribution to Yield, Inc., non-cash | — | (5 | ) | — | — | (5 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Capital contributions from tax equity investors, net of distributions | — | — | — | 5 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Distributions paid to NRG | (170 | ) | — | — | (10 | ) | (180 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Contributions from NRG, net of distributions, non-cash | 66 | — | — | — | 66 | |||||||||||||||
| Distributions paid to NRG on Class B and Class D units | — | (81 | ) | — | — | (81 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Distributions paid to Yield, Inc. | — | (92 | ) | — | — | (92 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2016 | $ | 1,995 | $ | 79 | $ | (83 | ) | $ | 313 | $ | 2,304 | |||||||||
(a) As previously reported in the Company's audited financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2016, included in the Company's 2016 Form 10-K.
(b) Capital contributions from NRG, non-cash, primarily represent Drop Down Assets' equity transferred from NRG to the Company in accordance with guidance on business combinations between entities under common control, as further described in Note 1, Nature of Business.
(c) Retrospectively adjusted, as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
7
NRG YIELD LLC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1 — Nature of Business
NRG Yield LLC, together with its consolidated subsidiaries, or the Company, is the primary vehicle through which NRG owns, operates and acquires contracted renewable and conventional generation and thermal infrastructure assets. NRG owns 100% of the Company's Class B units and Class D units and receives distributions through its ownership of these units. NRG Yield, Inc., or Yield, Inc., owns 100% of the Company's Class A units and Class C units. NRG Yield LLC, through its wholly owned subsidiary, NRG Yield Operating LLC, or Yield Operating LLC, holds a portfolio of renewable and conventional generation and thermal infrastructure assets, primarily located in the Northeast, Southwest, Midwest and California regions of the U.S.
Yield, Inc. closed its initial public offering of Class A common stock in July 2013, which was then followed by a Class A common stock offering in July 2014, a Recapitalization in May 2015, as described below, and a Class C common stock offering in June 2015.
Effective May 14, 2015, Yield, Inc. amended its certificate of incorporation to create two new classes of capital stock, Class C common stock and Class D common stock, and distributed shares of the Class C common stock and Class D common stock to holders of Yield, Inc.'s outstanding Class A common stock and Class B common stock, respectively, through a stock split. The stock split is referred to as the Recapitalization. The Company also amended its operating agreement to reflect the Recapitalization. Effective May 14, 2015, each Class A unit of the Company was automatically reclassified into one Class A unit and one Class C unit and each Class B unit of the Company was automatically reclassified into one Class B unit and one Class D unit.
The following table represents the structure of the Company as of December 31, 2016:
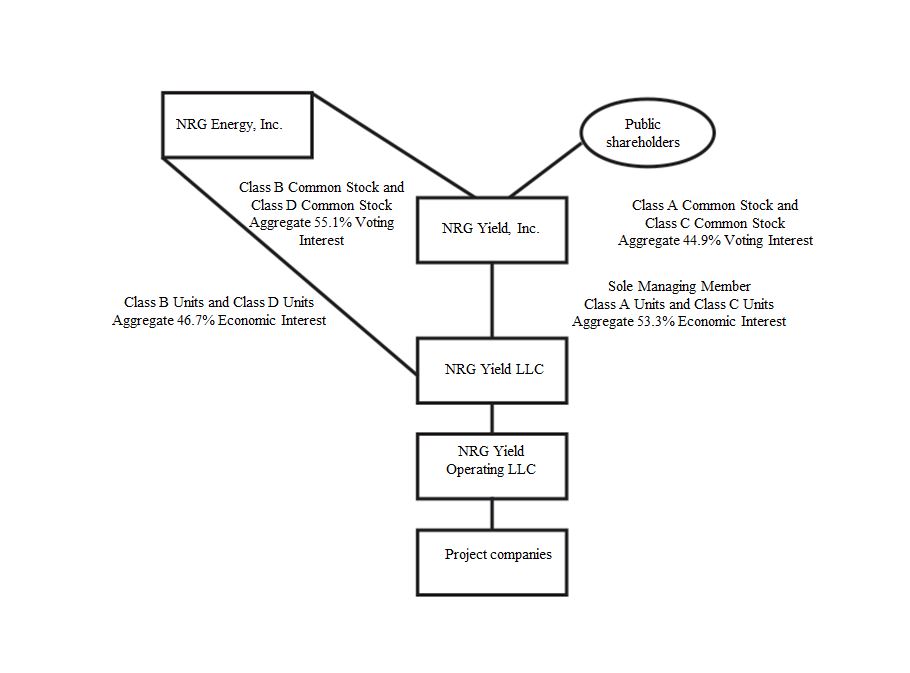
8
As of December 31, 2016, the Company's operating assets are comprised of the following projects:
| Projects | Percentage Ownership | Net Capacity (MW) (a) | Offtake Counterparty | Expiration | ||||||
| Conventional | ||||||||||
| El Segundo | 100 | % | 550 | Southern California Edison | 2023 | |||||
| GenConn Devon | 50 | % | 95 | Connecticut Light & Power | 2040 | |||||
| GenConn Middletown | 50 | % | 95 | Connecticut Light & Power | 2041 | |||||
| Marsh Landing | 100 | % | 720 | Pacific Gas and Electric | 2023 | |||||
| Walnut Creek | 100 | % | 485 | Southern California Edison | 2023 | |||||
| 1,945 | ||||||||||
| Utility Scale Solar | ||||||||||
| Agua Caliente | 16 | % | 46 | Pacific Gas and Electric | 2039 | |||||
| Alpine | 100 | % | 66 | Pacific Gas and Electric | 2033 | |||||
| Avenal | 50 | % | 23 | Pacific Gas and Electric | 2031 | |||||
| Avra Valley | 100 | % | 26 | Tucson Electric Power | 2032 | |||||
| Blythe | 100 | % | 21 | Southern California Edison | 2029 | |||||
| Borrego | 100 | % | 26 | San Diego Gas and Electric | 2038 | |||||
| CVSR | 100 | % | 250 | Pacific Gas and Electric | 2038 | |||||
| Desert Sunlight 250 | 25 | % | 63 | Southern California Edison | 2035 | |||||
| Desert Sunlight 300 | 25 | % | 75 | Pacific Gas and Electric | 2040 | |||||
| Kansas South | 100 | % | 20 | Pacific Gas and Electric | 2033 | |||||
| Roadrunner | 100 | % | 20 | El Paso Electric | 2031 | |||||
| TA High Desert | 100 | % | 20 | Southern California Edison | 2033 | |||||
Utah Solar Portfolio (e) | 50 | % | 265 | PacifiCorp | 2036 | |||||
| 921 | ||||||||||
| Distributed Solar | ||||||||||
| AZ DG Solar Projects | 100 | % | 5 | Various | 2025 - 2033 | |||||
| PFMG DG Solar Projects | 51 | % | 4 | Various | 2032 | |||||
| 9 | ||||||||||
| Wind | ||||||||||
| Alta I | 100 | % | 150 | Southern California Edison | 2035 | |||||
| Alta II | 100 | % | 150 | Southern California Edison | 2035 | |||||
| Alta III | 100 | % | 150 | Southern California Edison | 2035 | |||||
| Alta IV | 100 | % | 102 | Southern California Edison | 2035 | |||||
| Alta V | 100 | % | 168 | Southern California Edison | 2035 | |||||
Alta X (b) | 100 | % | 137 | Southern California Edison | 2038 | |||||
Alta XI (b) | 100 | % | 90 | Southern California Edison | 2038 | |||||
| Buffalo Bear | 100 | % | 19 | Western Farmers Electric Co-operative | 2033 | |||||
Crosswinds (b) | 74.3 | % | 16 | Corn Belt Power Cooperative | 2027 | |||||
Elbow Creek (b) | 75 | % | 92 | NRG Power Marketing LLC | 2022 | |||||
Elkhorn Ridge (b) | 50.3 | % | 41 | Nebraska Public Power District | 2029 | |||||
Forward (b) | 75 | % | 22 | Constellation NewEnergy, Inc. | 2017 | |||||
Goat Wind (b) | 74.9 | % | 113 | Dow Pipeline Company | 2025 | |||||
Hardin (b) | 74.3 | % | 11 | Interstate Power and Light Company | 2027 | |||||
| Laredo Ridge | 100 | % | 80 | Nebraska Public Power District | 2031 | |||||
Lookout (b) | 75 | % | 29 | Southern Maryland Electric Cooperative | 2030 | |||||
Odin (b) | 74.9 | % | 15 | Missouri River Energy Services | 2028 | |||||
| Pinnacle | 100 | % | 55 | Maryland Department of General Services and University System of Maryland | 2031 | |||||
San Juan Mesa (b) | 56.3 | % | 68 | Southwestern Public Service Company | 2025 | |||||
9
| Projects | Percentage Ownership | Net Capacity (MW) (a) | Offtake Counterparty | Expiration | ||||||
Sleeping Bear (b) | 75 | % | 71 | Public Service Company of Oklahoma | 2032 | |||||
| South Trent | 100 | % | 101 | AEP Energy Partners | 2029 | |||||
Spanish Fork (b) | 75 | % | 14 | PacifiCorp | 2028 | |||||
Spring Canyon II (b) | 90.1 | % | 29 | Platte River Power Authority | 2039 | |||||
Spring Canyon III (b) | 90.1 | % | 25 | Platte River Power Authority | 2039 | |||||
| Taloga | 100 | % | 130 | Oklahoma Gas & Electric | 2031 | |||||
Wildorado (b) | 74.9 | % | 121 | Southwestern Public Service Company | 2027 | |||||
| 1,999 | ||||||||||
| Thermal | ||||||||||
Thermal equivalent MWt(c) | 100 | % | 1,319 | Various | Various | |||||
| NRG Energy Center Dover LLC | 100 | % | 103 | NRG Power Marketing LLC | 2018 | |||||
| Thermal generation | 100 | % | 20 | Various | Various | |||||
| 1,442 | ||||||||||
Total net capacity (excluding equivalent MWt) (d) | 4,997 | |||||||||
(a) Net capacity represents the maximum, or rated, generating capacity of the facility multiplied by the Company's percentage ownership in the facility as of December 31, 2016.
(b) Projects are part of tax equity arrangements.
(c) For thermal energy, net capacity represents MWt for steam or chilled water and excludes 134 MWt available under the right-to-use provisions contained in agreements between two of the Company's thermal facilities and certain of its customers.
(d) NRG Yield's total generation capacity is net of 6 MWs for noncontrolling interest for Spring Canyon II and III. NRG Yield's generation capacity including this noncontrolling interest was 5,003 MWs.
(e) Represents interests in Four Brothers Solar, LLC, Granite Mountain Holdings, LLC, and Iron Springs Holdings, LLC, all acquired as part of the March 2017 Drop Down Assets acquisition (ownership percentage is based upon cash to be distributed).
In addition to the facilities owned or leased in the table above, the Company entered into partnerships to own or purchase solar power generation projects, as well as other ancillary related assets from a related party via intermediate funds. The Company does not consolidate these partnerships and accounts for them as equity method investments. The Company's net interest in these projects is 131 MW based on cash to be distributed. For further discussions, refer to Note 5, Investments Accounted for by the Equity Method and Variable Interest Entities to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Substantially all of the Company's generation assets are under long-term contractual arrangements for the output or capacity from these assets. The thermal assets are comprised of district energy systems and combined heat and power plants that produce steam, hot water and/or chilled water and, in some instances, electricity at a central plant. Three out of the fourteen district energy systems are subject to rate regulation by state public utility commissions while the other district energy systems have rates determined by negotiated bilateral contracts.
As described in Note 13, Related Party Transactions, the Company has a management services agreement with NRG for various services, including human resources, accounting, tax, legal, information systems, treasury, and risk management.
During the years ending December 31, 2016 and 2015 the Company completed three acquisitions of Drop Down Assets from NRG. The accounting guidance requires retrospective combination of the entities for all periods presented as if the combination has been in effect from the beginning of the financial statement period or from the date the entities were under common control (if later than the beginning of the financial statement period). For further discussion, see Note 3, Business Acquisitions.
In addition, as further described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions, on March 27, 2017, the Company acquired the following from NRG, referred to as the March 2017 Drop Down Assets: (i) Agua Caliente Borrower 2 LLC, which owns a 16% interest in the Agua Caliente solar farm, one of the NRG ROFO assets and (ii) NRG's interests in seven utility-scale solar farms located in Utah that were part of NRG's November 2, 2016 acquisition of projects from SunEdison, or Utah Solar Portfolio. The Company paid total cash consideration of $130 million, plus a $1 million working capital adjustment, and assumed non-recourse debt of $ $328 million, which is consolidated, as well as its pro-rata share of non-recourse project-level debt of $135 million. The acquisition was funded with cash on hand. The acquisition of the March 2017 Drop Down Assets was accounted for as a transfer of entities under common control. In connection with the retrospective adjustment of prior periods, the Company adjusted its financial statements to reflect its results of operations, financial position and cash flows as if it recorded its interests in the Aqua Caliente Borrower 2 LLC from the beginning of the financial statement period, and its interests in the Utah Solar Portfolio from November 2, 2016.
10
Note 2 — Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation and Principles of Consolidation
The Company's consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. The ASC is the source of authoritative GAAP to be applied by nongovernmental entities. In addition, the rules and interpretative releases of the SEC under authority of federal securities laws are also sources of authoritative GAAP for SEC registrants.
The consolidated financial statements include the Company's accounts and operations and those of its subsidiaries in which it has a controlling interest. All significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation. The usual condition for a controlling financial interest is ownership of a majority of the voting interests of an entity. However, a controlling financial interest may also exist through arrangements that do not involve controlling voting interests. As such, the Company applies the guidance of ASC 810, Consolidations, or ASC 810, to determine when an entity that is insufficiently capitalized or not controlled through its voting interests, referred to as a variable interest entity, or VIE, should be consolidated.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less at the time of purchase. Cash and cash equivalents held at project subsidiaries was $110 million and $93 million as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash consists primarily of funds held to satisfy the requirements of certain debt agreements and funds held within the Company's projects that are restricted in their use. Of these funds as of December 31, 2016, approximately $25 million is designated for current debt service payments, $13 million is designated to fund operating expenses and $37 million is designated for distributions to the Company, with the remaining $90 million restricted for reserves including debt service, performance obligations and other reserves, as well as capital expenditures.
Trade Receivables and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Trade receivables are reported on the balance sheet at the invoiced amount adjusted for any write-offs and the allowance for doubtful accounts. The allowance for doubtful accounts is reviewed periodically based on amounts past due and significance. The allowance for doubtful accounts was immaterial as of December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Inventory
Inventory consists principally of spare parts and fuel oil. Spare parts inventory is valued at weighted average cost, unless evidence indicates that the weighted average cost will not be recovered with a normal profit in the ordinary course of business. Fuel oil inventory is valued at the lower of weighted average cost or market. The Company removes fuel inventories as they are used in the production of steam, chilled water or electricity. Spare parts inventory are removed when they are used for repairs, maintenance or capital projects.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost or, in the case of third party business acquisitions, fair value; however impairment adjustments are recorded whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that their carrying values may not be recoverable. See Note 3, Business Acquisitions, for more information on acquired property, plant and equipment. Significant additions or improvements extending asset lives are capitalized as incurred, while repairs and maintenance that do not improve or extend the life of the respective asset are charged to expense as incurred. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives. Certain assets and their related accumulated depreciation amounts are adjusted for asset retirements and disposals with the resulting gain or loss included in cost of operations in the consolidated statements of operations.
Asset Impairments
Long-lived assets that are held and used are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate carrying values may not be recoverable. Such reviews are performed in accordance with ASC 360. An impairment loss is indicated if the total future estimated undiscounted cash flows expected from an asset are less than its carrying value. An impairment charge is measured by the difference between an asset's carrying amount and fair value with the difference recorded in operating costs and expenses in the statements of operations. Fair values are determined by a variety of valuation methods, including appraisals, sales prices of similar assets and present value techniques. For further discussion of the Company's long-lived asset impairments, refer to Note 9, Asset Impairments.
11
Investments accounted for by the equity method are reviewed for impairment in accordance with ASC 323, Investments-Equity Method and Joint Ventures, which requires that a loss in value of an investment that is an other-than-temporary decline should be recognized. The Company identifies and measures losses in the value of equity method investments based upon a comparison of fair value to carrying value.
Debt Issuance Costs
Debt issuance costs are capitalized and amortized as interest expense on a basis which approximates the effective interest method over the term of the related debt. Debt issuance costs related to the long term debt are presented as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of the related debt in both the current and prior periods. Debt issuance costs related to the senior secured revolving credit facility line of credit are recorded as a non-current asset on the balance sheet and are amortized over the term of the loan.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets represent contractual rights held by the Company. The Company recognizes specifically identifiable intangible assets including power purchase agreements, leasehold improvements, customer relationships, customer contracts, and development rights when specific rights and contracts are acquired. These intangible assets are amortized primarily on a straight-line basis.
Notes Receivable
Notes receivable consist of receivables related to the financing of required network upgrades. The notes issued with respect to network upgrades will be repaid within a 5-year period following the date each facility reached commercial operations.
Income Taxes
The Company is classified as a partnership for federal and state income tax purposes. Therefore, federal and state income taxes are assessed at the partner level. Accordingly, no provision has been made for federal or state income taxes in the accompanying financial statements.
Revenue Recognition
Thermal Revenues
Steam and chilled water revenue is recognized based on customer usage as determined by meter readings taken at month-end. Some locations read customer meters throughout the month, and recognize estimated revenue for the period between meter read date and month-end. The Thermal Business subsidiaries collect and remit state and local taxes associated with sales to their customers, as required by governmental authorities. These taxes are presented on a net basis in the income statement.
Power Purchase Agreements, or PPAs
The majority of the Company’s revenues are obtained through PPAs or other contractual agreements, which are accounted for as operating leases under ASC 840. ASC 840 requires the minimum lease payments received to be amortized over the term of the lease and contingent rentals are recorded when the achievement of the contingency becomes probable. Judgment is required by management in determining the economic life of each generating facility, in evaluating whether certain lease provisions constitute minimum payments or represent contingent rent and other factors in determining whether a contract contains a lease and whether the lease is an operating lease or capital lease.
Certain of these leases have no minimum lease payments and all of the rental income under these leases is recorded as contingent rent on an actual basis when the electricity is delivered. The contingent rental income recognized in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $553 million, $416 million and $296 million, respectively.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company accounts for derivative financial instruments under ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging, or ASC 815, which requires the Company to record all derivatives on the balance sheet at fair value unless they qualify for a NPNS exception. Changes in the fair value of non-hedge derivatives are immediately recognized in earnings. Changes in the fair value of derivatives accounted for as hedges, if elected for hedge accounting, are either:
| • | Recognized in earnings as an offset to the changes in the fair value of the related hedged assets, liabilities and firm commitments; or |
12
| • | Deferred and recorded as a component of accumulated OCI until the hedged transactions occur and are recognized in earnings. |
The Company's primary derivative instruments are power purchase or sale contracts used to mitigate variability in earnings due to fluctuations in market prices, fuels purchase contracts used to control customer reimbursable fuel cost, and interest rate instruments used to mitigate variability in earnings due to fluctuations in interest rates. On an ongoing basis, the Company assesses the effectiveness of all derivatives that are designated as hedges for accounting purposes in order to determine that each derivative continues to be highly effective in offsetting changes in fair values or cash flows of hedged items. Internal analyses that measure the statistical correlation between the derivative and the associated hedged item determine the effectiveness of such a contract designated as a hedge. If it is determined that the derivative instrument is not highly effective as a hedge, hedge accounting will be discontinued prospectively. In this case, the gain or loss previously deferred in accumulated OCI would be frozen until the underlying hedged item is delivered unless the transaction being hedged is no longer probable of occurring in which case the amount in OCI would be immediately reclassified into earnings. If the derivative instrument is terminated, the effective portion of this derivative deferred in accumulated OCI will be frozen until the underlying hedged item is delivered.
Revenues and expenses on contracts that qualify for the NPNS exception are recognized when the underlying physical transaction is delivered. While these contracts are considered derivative financial instruments under ASC 815, they are not recorded at fair value, but on an accrual basis of accounting. If it is determined that a transaction designated as NPNS no longer meets the scope exception, the fair value of the related contract is recorded on the balance sheet and immediately recognized through earnings.
Concentrations of Credit Risk
Financial instruments which potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of accounts receivable, notes receivable and derivative instruments, which are concentrated within entities engaged in the energy and financial industry. These industry concentrations may impact the overall exposure to credit risk, either positively or negatively, in that the customers may be similarly affected by changes in economic, industry or other conditions. In addition, many of the Company's projects have only one customer. However, the Company believes that the credit risk posed by industry concentration is offset by the diversification and creditworthiness of its customer base. See Note 6, Fair Value of Financial Instruments, for a further discussion of derivative concentrations and Note 12, Segment Reporting, for concentration of counterparties.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying amount of cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, accounts receivable, accounts receivable - affiliate, accounts payable, current portion of account payable - affiliate, and accrued expenses and other current liabilities approximate fair value because of the short-term maturity of these instruments. See Note 6, Fair Value of Financial Instruments, for a further discussion of fair value of financial instruments.
Asset Retirement Obligations
Asset retirement obligations, or AROs, are accounted for in accordance with ASC 410-20, Asset Retirement Obligations, or ASC 410-20. Retirement obligations associated with long-lived assets included within the scope of ASC 410-20 are those for which a legal obligation exists under enacted laws, statutes, and written or oral contracts, including obligations arising under the doctrine of promissory estoppel, and for which the timing and/or method of settlement may be conditional on a future event. ASC 410-20 requires an entity to recognize the fair value of a liability for an ARO in the period in which it is incurred and a reasonable estimate of fair value can be made.
Upon initial recognition of a liability for an ARO, the asset retirement cost is capitalized by increasing the carrying amount of the related long-lived asset by the same amount. Over time, the liability is accreted to its future value, while the capitalized cost is depreciated over the useful life of the related asset. The Company's AROs are primarily related to the future dismantlement of equipment on leased property and environmental obligations related to site closures and fuel storage facilities. The Company records AROs as part of other non-current liabilities on its balance sheet.
The following table represents the balance of ARO obligations as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, along with the additions and accretion related to the Company's ARO obligations for the year ended December 31, 2016:
| (In millions) | |||
| Balance as of December 31, 2015 | $ | 43 | |
| Revisions in estimates for current obligations | 2 | ||
| Accretion — expense | 3 | ||
| Balance as of December 31, 2016 | $ | 48 | |
13
Guarantees
The Company enters into various contracts that include indemnification and guarantee provisions as a routine part of its business activities. Examples of these contracts include operation and maintenance agreements, service agreements, commercial sales arrangements and other types of contractual agreements with vendors and other third parties, as well as affiliates. These contracts generally indemnify the counterparty for tax, environmental liability, litigation and other matters, as well as breaches of representations, warranties and covenants set forth in these agreements. Because many of the guarantees and indemnities the Company issues to third parties and affiliates do not limit the amount or duration of its obligations to perform under them, there exists a risk that the Company may have obligations in excess of the amounts agreed upon in the contracts mentioned above. For those guarantees and indemnities that do not limit the liability exposure, the Company may not be able to estimate what the liability would be, until a claim is made for payment or performance, due to the contingent nature of these contracts.
Investments Accounted for by the Equity Method
The Company has investments in various energy projects accounted for by the equity method, seven of which are VIEs, where the Company is not a primary beneficiary, and two of which are owned by a subsidiary that is consolidated as a VIE, as described in Note 5, Investments Accounted for by the Equity Method and Variable Interest Entities. The equity method of accounting is applied to these investments in affiliates because the ownership structure prevents the Company from exercising a controlling influence over the operating and financial policies of the projects. Under this method, equity in pre-tax income or losses of the investments is reflected as equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliates. Distributions from equity method investments that represent earnings on the Company's investment are included within cash flows from operating activities and distributions from equity method investments that represent a return of the Company's investment are included within cash flows from investing activities.
Sale Leaseback Arrangements
The Company is party to sale-leaseback arrangements that provide for the sale of certain assets to a third party and simultaneous leaseback to the Company. In accordance with ASC 840-40, Sale-Leaseback Transactions, if the seller-lessee retains, through the leaseback, substantially all of the benefits and risks incident to the ownership of the property sold, the sale-leaseback transaction is accounted for as a financing arrangement. An example of this type of continuing involvement would include an option to repurchase the assets or the buyer-lessor having the option to sell the assets back to the Company. This provision is included in most of the Company’s sale-leaseback arrangements. As such, the Company accounts for these arrangements as financings.
Under the financing method, the Company does not recognize as income any of the sale proceeds received from the lessor that contractually constitutes payment to acquire the assets subject to these arrangements. Instead, the sale proceeds received are accounted for as financing obligations and leaseback payments made by the Company are allocated between interest expense and a reduction to the financing obligation. Interest on the financing obligation is calculated using the Company’s incremental borrowing rate at the inception of the arrangement on the outstanding financing obligation. Judgment is required to determine the appropriate borrowing rate for the arrangement and in determining any gain or loss on the transaction that would be recorded either at the end of or over the lease term.
Business Combinations
The Company accounts for its business combinations in accordance with ASC 805, Business Combinations, or ASC 805. For third party acquisitions, ASC 805 requires an acquirer to recognize and measure in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree at fair value at the acquisition date. It also recognizes and measures the goodwill acquired or a gain from a bargain purchase in the business combination and determines what information to disclose to enable users of an entity's financial statements to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the business combination. In addition, transaction costs are expensed as incurred. For acquisitions that relate to entities under common control, ASC 805 requires retrospective combination of the entities for all periods presented as if the combination has been in effect from the beginning of the financial statement period of from the date the entities were under common control (if later than the beginning of the financial statement period). The difference between the cash paid and historical value of the entities' equity is recorded as a distribution/contribution from/to NRG with the offset to contributed capital. Transaction costs are expensed as incurred.
14
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions. These estimates and assumptions impact the reported amount of assets and liabilities and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the consolidated financial statements. They also impact the reported amount of net earnings during the reporting period. Actual results could be different from these estimates.
In recording transactions and balances resulting from business operations, the Company uses estimates based on the best information available. Estimates are used for such items as plant depreciable lives, uncollectible accounts, environmental liabilities, acquisition accounting and legal costs incurred in connection with recorded loss contingencies, among others. In addition, estimates are used to test long-lived assets for impairment and to determine the fair value of impaired assets. As better information becomes available or actual amounts are determinable, the recorded estimates are revised. Consequently, operating results can be affected by revisions to prior accounting estimates.
Tax Equity Arrangements
Certain portions of the Company’s noncontrolling interests in subsidiaries represent third-party interests in the net assets under certain tax equity arrangements, which are consolidated by the Company, that have been entered into to finance the cost of wind facilities eligible for certain tax credits. Additionally, certain portions of the Company’s investments in unconsolidated affiliates reflect the Company’s interests in tax equity arrangements, that are not consolidated by the Company, that have been entered into to finance the cost of distributed solar energy systems under operating leases or PPAs eligible for certain tax credits. The Company has determined that the provisions in the contractual agreements of these structures represent substantive profit sharing arrangements. Further, the Company has determined that the appropriate methodology for calculating the noncontrolling interest and investment in unconsolidated affiliates that reflects the substantive profit sharing arrangements is a balance sheet approach utilizing the hypothetical liquidation at book value, or HLBV, method. Under the HLBV method, the amounts reported as noncontrolling interests and investment in unconsolidated affiliates represent the amounts the investors to the tax equity arrangements would hypothetically receive at each balance sheet date under the liquidation provisions of the contractual agreements, assuming the net assets of the funding structures were liquidated at their recorded amounts determined in accordance with GAAP. The investors’ interests in the results of operations of the funding structures are determined as the difference in noncontrolling interests and investment in unconsolidated affiliates at the start and end of each reporting period, after taking into account any capital transactions between the structures and the funds’ investors. The calculations utilized to apply the HLBV method include estimated calculations of taxable income or losses for each reporting period.
Reclassifications
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified for comparative purposes.
Recent Accounting Developments
ASU 2016-18 — In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230), Restricted Cash, or ASU No. 2016-18. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-18 were issued to address the diversity in classification and presentation of changes in restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents on the statement of cash flows which is currently not addressed under Topic 230. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-18 would require an entity to include amounts generally described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents with cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning of period and end of period total amounts on the statement of cash flows. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-18 are effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those annual periods. Early adoption is permitted and the adoption of ASU No. 2016-18 should be applied retrospectively. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the standard on the Company’s statement of cash flows.
ASU 2016-16 — In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-16, Income Taxes (Topic 740), Intra-Entity Transfers of Assets Other Than Inventory, or ASU No. 2016-16. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-16 were issued to improve the accounting for the income tax consequences of intra-entity transfers of assets other than inventory. Current GAAP prohibits the recognition of current and deferred income taxes for an intra-entity asset transfer until the asset has been sold to an outside party which has resulted in diversity in practice and increased complexity within financial reporting. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-16 would require an entity to recognize the income tax consequences of an intra-entity transfer of an asset other than inventory when the transfer occurs and do not require new disclosure requirements. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-16 are effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those annual periods. Early adoption is permitted and the adoption of ASU No. 2016-16 should be applied on a modified retrospective basis through a cumulative-effect adjustment directly to retained earnings as of the beginning of the period of adoption. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the standard on the Company's results of operations, cash flows and financial position.
15
ASU 2016-15 — In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230), Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments, or ASU No. 2016-15. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-15 were issued to address eight specific cash flow issues for which stakeholders have indicated to the FASB that a diversity in practice existed in how entities were presenting and classifying these items in the statement of cash flows. The issues addressed by ASU No. 2016-15 include but are not limited to the classification of debt prepayment and debt extinguishment costs, payments made for contingent consideration for a business combination, proceeds from the settlement of insurance proceeds, distributions received from equity method investees and separately identifiable cash flows and the application of the predominance principle. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-15 are effective for public entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017 and interim periods in those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim fiscal period with all amendments adopted in the same period. The adoption of ASU No. 2016-15 is required to be applied retrospectively. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the standard on the Company's statement of cash flows.
ASU 2016-07 — In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-07, Investments - Equity Method and Joint Ventures (Topic 323), or ASU No. 2016-07. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-07 eliminate the requirement that when an investment qualifies for use of the equity method as a result of an increase in the level of ownership interest or degree of influence, an investor must adjust the investment, results of operations, and retained earnings retroactively on a step-by-step basis as if the equity method had been in effect during all previous periods that the investment had been held. The amendments require that the equity method investor add the cost of acquiring the additional interest in the investee to the current basis of the investor's previously held interest and adopt the equity method of accounting with no retroactive adjustment to the investment. In addition, ASU No. 2016-07 requires that an entity that has an available-for-sale equity security that becomes qualified for the equity method of accounting recognize through earnings the unrealized holding gain or loss in accumulated other comprehensive income at the date the investment becomes qualified for use of the equity method. The Company adopted this standard effective January 1, 2017. The adoption of ASU No. 2016-07 is required to be applied prospectively. The Company does not expect the standard to have a material impact on its results of operations, cash flows and financial position.
ASU 2016-02 — In 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842), or Topic 842, with the objective to increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and to improve financial reporting by expanding the related disclosures. The guidance in Topic 842 provides that a lessee that may have previously accounted for a lease as an operating lease under current GAAP should recognize the assets and liabilities that arise from a lease on the balance sheet. In addition, Topic 842 expands the required quantitative and qualitative disclosures with regards to lease arrangements. The Company expects to adopt the standard effective January 1, 2019 utilizing the required modified retrospective approach for the earliest period presented. The Company expects to elect certain of the practical expedients permitted, including the expedient that permits the Company to retain its existing lease assessment and classification. The Company is currently working through an adoption plan and evaluating the anticipated impact on the Company's results of operations, cash flows and financial position. While the Company is currently evaluating the impact the new guidance will have on its financial position and results of operations, the Company expects to recognize lease liabilities and right of use assets. The extent of the increase to assets and liabilities associated with these amounts remains to be determined pending the Company’s review of its existing lease contracts and service contracts which may contain embedded leases. As this review is still in process, it is currently not practicable to quantify the impact of adopting the ASU at this time.
ASU 2016-01 — In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-01, Financial Instruments - Overall (Subtopic 825-10): Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities, or ASU No. 2016-01. The amendments of ASU No. 2016-01 eliminate available-for-sale classification of equity investments and require that equity investments (except those accounted for under the equity method of accounting, or those that result in consolidation of the investee) to be generally measured at fair value with changes in fair value recognized in net income. Further, the amendments require that financial assets and financial liabilities to be presented separately in the notes to the financial statements, grouped by measurement category and form of financial asset. The guidance in ASU No. 2016-01 is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those annual periods. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the standard on the Company's results of operations, cash flows and financial position.
16
ASU 2015-16 — In September 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-16, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Simplifying the Accounting for Measurement-Period Adjustments, or ASU No. 2015-16. The amendments of ASU No. 2015-16 require that an acquirer recognize measurement period adjustments to the provisional amounts recognized in a business combination in the reporting period during which the adjustments are determined. Additionally, the amendments of ASU No. 2015-16 require the acquirer to record in the same period's financial statements the effect on earnings of changes in depreciation, amortization or other income effects, if any, as a result of the measurement period adjustment, calculated as if the accounting had been completed at the acquisition date as well as disclosing on either the face of the income statement or in the notes the portion of the amount recorded in current period earnings that would have been recorded in previous reporting periods. The guidance in ASU No. 2015-16 is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2015, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The amendments should be applied prospectively. The Company adopted ASU No. 2015-16 for the year ended December 31, 2016, and the adoption did not have a material impact on the Company's results of operations, cash flows and financial position.
ASU 2014-09 — In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606), or ASU No. 2014-09, which was further amended through various updates issued by the FASB thereafter. The amendments of ASU No. 2014-09 completed the joint effort between the FASB and the IASB, to develop a common revenue standard for GAAP and IFRS, and to improve financial reporting. The guidance under Topic 606 provides that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled to in exchange for the goods or services provided and establishes a five step model to be applied by an entity in evaluating its contracts with customers. The Company expects to adopt the standard effective January 1, 2018 and apply the guidance retrospectively to contracts at the date of adoption. The Company will recognize the cumulative effect of applying Topic 606 at the date of initial application, as prescribed under the modified retrospective transition method. The Company also expects to elect the practical expedient available under Topic 606 for measuring progress toward complete satisfaction of a performance obligation and for disclosure requirements of remaining performance obligations. The practical expedient allows an entity to recognize revenue in the amount to which the entity has the right to invoice such that the entity has a right to the consideration in an amount that corresponds directly with the value to the customer for performance completed to date by the entity. The majority of the Company's revenues are obtained through PPAs, which are currently accounted for as operating leases. In connection with the implementation of Topic 842, as described above, the Company expects to elect certain of the practical expedients permitted, including the expedient that permits the Company to retain its existing lease assessment and classification. As leases are excluded from the scope of Topic 606, the Company expects the standard to have an immaterial impact on the Company's results of operations, cash flows and financial position, however, the Company continues to assess the impact in connection with its plan of adoption.
Note 3 — Business Acquisitions
2017 Acquisitions
March 2017 Drop Down Assets — On March 27, 2017, the Company acquired the following from NRG: (i) Agua Caliente Borrower 2 LLC, which owns a 16% interest (approximately 31% of NRG's 51% interest) in the Agua Caliente solar farm, one of the NRG ROFO assets, representing ownership of approximately 46 net MW of capacity and (ii) NRG's interests in the Utah Solar Portfolio. Agua Caliente is located in Yuma County, AZ and sells power subject to a 25-year PPA with Pacific Gas and Electric, with 22 years remaining on that contract. The seven utility-scale solar farms in the Utah Solar Portfolio are owned by the following entities: Four Brothers Capital, LLC, Iron Springs Capital, LLC, and Granite Mountain Capital, LLC. These utility-scale solar farms achieved commercial operations in 2016, sell power subject to 20-year PPAs with PacifiCorp, a subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway and are part of a tax equity structure with Dominion Solar Projects III, Inc., or Dominion, through which the Company is entitled to receive 50% of cash to be distributed, as further described below. The Company paid cash consideration of $130 million, plus $1 million of working capital. The acquisition of the March 2017 Drop Down Assets was funded with cash on hand and is referred to as March 2017 Drop Down Assets. The Company recorded the acquired interests as equity method investments. The Company also assumed debt of $41 million and $287 million on Agua Caliente Borrower 2 LLC and the Utah Solar Portfolio, respectively, as further described in Note 10, Long-term Debt.
The assets and liabilities transferred to the Company relate to interests under common control by NRG and were recorded at historical cost in accordance with ASC 805-50, Business Combination - Related Issues. The difference between the cash paid and the historical value of the entities' equity of $8 million was recorded as an adjustment to the Company's contributed capital. Since the transaction constituted a transfer of entities under common control, the accounting guidance requires retrospective combination of the entities for all periods presented as if the combination has been in effect from the beginning of the financial statement period or from the date the entities were under common control (if later than the beginning of the financial statement period).
17
2016 Acquisitions
CVSR Drop Down — Prior to September 1, 2016, the Company had a 48.95% interest in CVSR, which was accounted for as an equity method investment. On September 1, 2016, the Company acquired from NRG the remaining 51.05% interest of CVSR Holdco LLC, which indirectly owns the CVSR solar facility, CVSR Drop Down, for total cash consideration of $78.5 million, plus an immaterial working capital adjustment. The acquisition was funded with cash on hand. The Company also assumed additional debt of $496 million, which represents 51.05% of the CVSR project level debt and 51.05% of the notes issued under the CVSR Holdco Financing Agreement, as further described in Note 10, Long-term Debt. In connection with the retrospective adjustment of prior periods, the Company now consolidates CVSR and 100% of its debt, consisting of $771 million of project level debt and $200 million of notes issued under the CVSR Holdco Financing Agreement as of September 1, 2016.
The assets and liabilities transferred to the Company relate to interests under common control by NRG and were recorded at historical cost in accordance with ASC 805-50, Business Combinations - Related Issues. The difference between the cash paid and historical value of the entities' equity was recorded as a distribution to NRG with the offset to contributed capital. Because the transaction constituted a transfer of net assets under common control, the guidance requires retrospective combination of the entities for all periods presented as if the combination has been in effect since the inception of common control. In connection with the retrospective adjustment of prior periods, the Company has removed the equity method investment from all prior periods and adjusted its financial statements to reflect its results of operations, financial position and cash flows as if it had consolidated CVSR from the beginning of the financial statement period. As of June 30, 2016, the Company's recast consolidated balance sheet included a net receivable of $67 million related to current litigation with SunPower pursuant to indemnities in the project. The agreement between NRG and the Company for the CVSR Drop Down acquisition specified that all amounts related to the litigation with SunPower were excluded from the acquisition. Accordingly, prior to close of the transaction, the net receivable was transferred to NRG as a net reduction to its ownership interest in CVSR.
The following is the summary of historical net liabilities assumed in connection with the CVSR Drop Down as of September 1, 2016:
| CVSR | |||
| (In millions) | |||
| Current assets | $ | 95 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | 826 | ||
| Non-current assets | 13 | ||
| Total assets | 934 | ||
Debt (a) | 966 | ||
| Other current and non-current liabilities | 12 | ||
| Total liabilities | 978 | ||
Net liabilities assumed | (44 | ) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (25 | ) | |
| Historical net liabilities assumed | $ | (19 | ) |
(a) Net of deferred financing costs of $5 million.
The Company incurred and expensed acquisition-related transaction costs related to the acquisition of CVSR of $1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. Since the acquisition date, CVSR has contributed $22 million in operating revenues and a $2 million in net loss to the Company.
18
The following tables present the Company's historical information summary combining the financial information for the CVSR Drop Down and March 2017 Drop Down Assets transferred in connection with the acquisitions
| As of December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||
| As Previously Reported | March 2017 Drop Down Assets | As Currently Reported | |||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||
| Current assets | $ | 645 | $ | 11 | $ | 656 | |||||
| Property, plant and equipment | 5,460 | — | 5,460 | ||||||||
| Non-current assets | 2,062 | 442 | 2,504 | ||||||||
| Total assets | 8,167 | 453 | 8,620 | ||||||||
| Debt | 5,728 | 279 | 6,007 | ||||||||
| Other current and non-current liabilities | 304 | 5 | 309 | ||||||||
| Total liabilities | 6,032 | 284 | 6,316 | ||||||||
| Net assets | $ | 2,135 | $ | 169 | $ | 2,304 | |||||
| As of December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| As Previously Reported | CVSR | March 2017 Drop Down Assets | As Currently Reported (a) | ||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||
| Current assets | $ | 321 | $ | 98 | $ | — | $ | 419 | |||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | 5,056 | 822 | — | 5,878 | |||||||||||
| Non-current assets | 2,231 | (6 | ) | 100 | 2,325 | ||||||||||
| Total assets | 7,608 | 914 | 100 | 8,622 | |||||||||||
| Debt | 4,835 | 843 | — | 5,678 | |||||||||||
| Other current and non-current liabilities | 339 | (35 | ) | — | 304 | ||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 5,174 | 808 | — | 5,982 | |||||||||||
| Net assets | $ | 2,434 | $ | 106 | $ | 100 | $ | 2,640 | |||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||
| As Previously Reported | March 2017 Drop Down Assets | As Currently Reported | |||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||
| Total operating revenues | $ | 1,021 | $ | — | $ | 1,021 | |||||
| Operating income | 220 | — | 220 | ||||||||
| Net (loss) income | (2 | ) | 17 | 15 | |||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| As Previously Reported | CVSR | March 2017 Drop Down Assets | As Currently Reported | ||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||
| Total operating revenues | $ | 869 | $ | 84 | $ | — | $ | 953 | |||||||
| Operating income | 279 | 43 | — | 322 | |||||||||||
| Net income | 78 | 10 | 5 | 93 | |||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
As Previously Reported (a) | CVSR | March 2017 Drop Down Assets | As Currently Reported | ||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||
| Total operating revenues | $ | 746 | $ | 82 | $ | — | $ | 828 | |||||||
| Operating income | 266 | 40 | — | 306 | |||||||||||
| Net income | 108 | 9 | 5 | 122 | |||||||||||
19
2015 Acquisitions
November 2015 Drop Down Assets from NRG — On November 3, 2015, the Company acquired the November 2015 Drop Down Assets, a portfolio of 12 wind facilities totaling 814 net MW, from NRG for cash consideration of $209 million, subject to working capital adjustments. In February 2016, NRG made a final working capital payment of $2 million, reducing total cash consideration to $207 million. The Company is responsible for its pro-rata share of non-recourse project debt of $193 million and noncontrolling interest associated with a tax equity structure of $159 million (as of the acquisition date).
The Company funded the acquisition with borrowings from its revolving credit facility. The assets and liabilities transferred to the Company relate to interests under common control by NRG and were recorded at historical cost. The difference between the cash paid and historical value of the entities' equity was recorded as a distribution from NRG with the offset to contributed capital.
The Class A interests of NRG Wind TE Holdco are owned by a tax equity investor, or TE Investor, who receives 99% of allocations of taxable income and other items until the flip point, which occurs when the TE Investor obtains a specified return on its initial investment, at which time the allocations to the TE Investor change to 8.53%. The Company generally receives 75% of CAFD until the flip point, at which time the allocations to the Company of CAFD change to 68.60%. If the flip point has not occurred by a specified date, 100% of CAFD is allocated to the TE Investor until the flip point occurs. NRG Wind TE Holdco is a VIE and the Company is the primary beneficiary, through its position as managing member, and consolidates NRG Wind TE Holdco.
The following is a summary of assets and liabilities transferred in connection with the acquisition as of November 3, 2015:
| NRG Wind TE Holdco | |||
| (In millions) | |||
| Current assets | $ | 30 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | 669 | ||
| Non-current assets | 177 | ||
| Total assets | 876 | ||
| Debt | 193 | ||
| Other current and non-current liabilities | 32 | ||
| Total liabilities | 225 | ||
| Less: noncontrolling interest | 282 | ||
| Net assets acquired | $ | 369 | |
Desert Sunlight — On June 29, 2015, the Company acquired 25% of the membership interest in Desert Sunlight Investment Holdings, LLC, which owns two solar photovoltaic facilities that total 550 MW, located in Desert Center, California from EFS Desert Sun, LLC, an affiliate of GE Energy Financial Services for a purchase price of $285 million. Power generated by the facilities is sold to Southern California Edison and Pacific Gas and Electric under long-term PPAs with approximately 20 years and 25 years of remaining contract life, respectively. The Company accounts for its 25% investment as an equity method investment.
Spring Canyon — On May 7, 2015, the Company acquired a 90.1% interest in Spring Canyon II, a 32 MW wind facility, and Spring Canyon III, a 28 MW wind facility, each located in Logan County, Colorado, from Invenergy Wind Global LLC. The purchase price was funded with cash on hand. Power generated by Spring Canyon II and Spring Canyon III is sold to Platte River Power Authority under long-term PPAs, each with approximately 24 years of remaining contract life.
University of Bridgeport Fuel Cell — On April 30, 2015, the Company completed the acquisition of the University of Bridgeport Fuel Cell project in Bridgeport, Connecticut from FuelCell Energy, Inc. The project added an additional 1.4 MW of thermal capacity to the Company's portfolio, with a 12-year contract, with the option for a 7-year extension. The acquisition is reflected in the Company's Thermal segment.
20
January 2015 Drop Down Assets from NRG — On January 2, 2015, the Company acquired the following projects from NRG: (i) Laredo Ridge, an 80 MW wind facility located in Petersburg, Nebraska, (ii) Tapestry, which includes Buffalo Bear, a 19 MW wind facility in Buffalo, Oklahoma; Taloga, a 130 MW wind facility in Putnam, Oklahoma; and Pinnacle, a 55 MW wind facility in Keyser, West Virginia, and (iii) Walnut Creek, a 485 MW natural gas facility located in City of Industry, California, for total cash consideration of $489 million, including $9 million for working capital, plus assumed project-level debt of $737 million. The Company funded the acquisition with cash on hand and drawings under its revolving credit facility. The assets and liabilities transferred to the Company relate to interests under common control by NRG and were recorded at historical cost. The difference between the cash paid and the historical value of the entities' equity of $61 million was recorded as a distribution to NRG and reduced the balance of its contributed capital.
2014 Acquisitions
Alta Wind Portfolio Acquisition — On August 12, 2014, the Company acquired 100% of the membership interests of Alta Wind Asset Management Holdings, LLC, Alta Wind Company, LLC, Alta Wind X Holding Company, LLC and Alta Wind XI Holding Company, LLC, which collectively own seven wind facilities that total 947 MW located in Tehachapi, California and a portfolio of associated land leases, or the Alta Wind Portfolio. Power generated by the Alta Wind Portfolio is sold to Southern California Edison under long-term PPAs with 21 years of remaining contract life for Alta I-V. The Alta Wind X and XI PPAs began in 2016 with a term of 22 years and sold energy and renewable energy credits on a merchant basis during the years ending December 31, 2015 and 2014.
The purchase price for the Alta Wind Portfolio was $923 million, which consisted of a base purchase price of $870 million, as well as a payment for working capital of $53 million, plus the assumption of $1.6 billion of non-recourse project-level debt. In order to fund the purchase price, the Company completed an equity offering of 12,075,000 shares of its Class A common stock at an offering price of $54.00 per share on July 29, 2014, which resulted in net proceeds of $630 million, after underwriting discounts and expenses. In addition, on August 5, 2014, NRG Yield Operating LLC issued $500 million of Senior Notes, which bear interest at a rate of 5.375% and mature in August 2024.
The acquisition was recorded as a business combination under ASC 805-50, with identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed provisionally recorded at their estimated fair values on the acquisition date. The accounting for the business combination was completed as of August 11, 2015, at which point the fair values became final. The following table summarizes the provisional amounts recognized for assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of December 31, 2014, as well as adjustments made through August 11, 2015, when the allocation became final.
21
The purchase price of $923 million was allocated as follows:
| Acquisition Date Fair Value at December 31, 2014 | Measurement period adjustments | Revised Acquisition Date | ||||||||||
| Assets | (In millions) | |||||||||||
| Cash | $ | 22 | $ | — | $ | 22 | ||||||
| Current and non-current assets | 49 | (2 | ) | 47 | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | 1,304 | 6 | 1,310 | |||||||||
| Intangible assets | 1,177 | (6 | ) | 1,171 | ||||||||
| Total assets acquired | 2,552 | (2 | ) | 2,550 | ||||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Debt | 1,591 | — | 1,591 | |||||||||
| Current and non-current liabilities | 38 | (2 | ) | 36 | ||||||||
| Total liabilities assumed | 1,629 | (2 | ) | 1,627 | ||||||||
| Net assets acquired | $ | 923 | $ | — | $ | 923 | ||||||
The Company incurred and expensed acquisition-related transaction costs related to the acquisition of the Alta Wind Portfolio of $2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014.
June 2014 Drop Down Assets — On June 30, 2014, the Company acquired from NRG: (i) El Segundo, a 550 MW fast-start, gas-fired facility located in Los Angeles County, California; (ii) TA High Desert, a 20 MW solar facility located in Los Angeles County, California; and (iii) Kansas South, a 20 MW solar facility located in Kings County, California. The Company paid total cash consideration of $357 million, which represents a base purchase price of $349 million and $8 million of working capital adjustments. In addition, the acquisition included the assumption of $612 million of project- level debt. The assets and liabilities transferred to the Company relate to interests under common control by NRG and were recorded at historical cost in accordance with ASC 805-50. The difference between the cash proceeds and the historical value of the net assets was recorded as a distribution to NRG and reduced the balance of its contributed capital. Since the transaction constituted a transfer of entities under common control, the guidance requires retrospective combination of the entities for all periods presented as if the combination has been in effect since the beginning of the financial statements period or the inception of common control (if later than the beginning of the financial statements period). Accordingly, the Company prepared its consolidated financial statements to reflect the transfer as if it had taken place from the beginning of the financial statements period.
22
Note 4 — Property, Plant and Equipment
The Company’s major classes of property, plant, and equipment were as follows:
| December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | Depreciable Lives | |||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||
| Facilities and equipment | $ | 6,215 | $ | 6,480 | 2 - 40 Years | ||||
| Land and improvements | 171 | 171 | |||||||
Construction in progress (a) | 25 | 9 | |||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | 6,411 | 6,660 | |||||||
| Accumulated depreciation | (951 | ) | (782 | ) | |||||
| Net property, plant and equipment | $ | 5,460 | $ | 5,878 | |||||
(a) As of December 31, 2016, construction in progress includes $20 million of capital expenditures that relate to prepaid long-term service agreements primarily in the Conventional segment.
Note 5 — Investments Accounted for by the Equity Method and Variable Interest Entities
Equity Method Investments
The following table summarizes the Company's equity method investments as of December 31, 2016:
| Name | Economic Interest | Investment Balance | ||
| (In millions) | ||||
Utah Solar Portfolio (a) | 50% | $346 | ||
| Desert Sunlight | 25% | 282 | ||
GenConn (b) | 50% | 106 | ||
| Agua Caliente Borrower 2 | 16% | 96 | ||
Elkhorn Ridge (c) | 50.3% | 85 | ||
San Juan Mesa(c) | 56.3% | 74 | ||
NRG DGPV Holdco 1 LLC (d) | 95% | 75 | ||
NRG DGPV Holdco 2 LLC (d) | 95% | 24 | ||
NRG RPV Holdco 1 LLC (d) | 95% | 71 | ||
| Avenal | 50% | (7) | ||
| Total equity investments in affiliates | $1,152 | |||
(a) Economic interest based on cash to be distributed. Four Brothers Solar, LLC, Granite Mount Holdings, LLC and Iron Spring Holdings, LLC are tax equity structures and VIEs. The related allocations are described below.
(b) GenConn is a variable interest entity.
(c) San Juan Mesa and Elkhorn Ridge are part of the Wind TE Holdco tax equity structure, as described below. San Juan Mesa and Elkhorn Ridge are owned 75% and 66.7%, respectively, by Wind TE Holdco. The Company owns 75% of the Class B interests in Wind TE Holdco.
(d) Economic interest based on cash to be distributed. NRG DGPV Holdco 1 LLC, NRG DGPV Holdco 2 LLC, and NRG RPV Holdco 1 LLC are tax equity structures and VIEs. The related allocations are described below.
23
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company had $51 million and $45 million, respectively, of undistributed earnings from its equity method investments.
The Company acquired its interest in Desert Sunlight on June 30, 2015, for $285 million, which resulted in a difference between the purchase price and the basis of the acquired assets and liabilities of $171 million. The difference is attributable to the fair value of the property, plant and equipment and power purchase agreements. In addition, the difference between the basis of the acquired assets and liabilities and the purchase price for the Utah Solar Portfolio (Four Brothers Solar, LLC, Granite Mountain Holdings, LLC and Iron Springs Holdings, LLC) of $106 million is attributable to the fair value of the property, plant and equipment. The Company is amortizing the related basis differences to equity in earnings (losses) over the related useful life of the underlying assets acquired.
Non-recourse project-level debt of unconsolidated affiliates
The Company's pro-rata share of non-recourse debt held by unconsolidated affiliates was approximately $589 million as of December 31, 2016.
Agua Caliente Financing — As described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions, the Company acquired a 16% interest in the Agua Caliente solar facility through its acquisition of Agua Caliente Borrower 2 LLC. As of December 31, 2016, Agua Caliente Solar LLC, the direct owner of the Agua Caliente solar facility, had $849 million outstanding under the Agua Caliente financing agreement with the Federal Financing Bank, or FFB, borrowed to finance the costs of constructing the facility. The Company's pro-rata share of Agua Caliente Financing was approximately $136 million as of December 31, 2016. Amounts borrowed under the Agua Caliente financing agreement accrue interest at a fixed rate based on U.S. Treasury rates plus a spread of 0.375%, mature in 2037 and are secured by the assets of Agua Caliente Solar LLC. The loans provided by the FFB are guaranteed by the U.S. DOE.
Avenal — The Company owns a 50% equity interest in Avenal, which consists of three solar PV projects in Kings County, California totaling approximately 45 MWs. Eurus Energy owns the remaining 50% of Avenal. Power generated by the projects is sold under a 20-year PPA. On September 22, 2010, Avenal entered into a $35 million promissory note facility with the Company. Amounts drawn under the promissory note facility accrue interest at 4.5% per annum. Also, on September 22, 2010, Avenal entered into a $209 million financing arrangement with a syndicate of banks, or the Avenal Facility. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, Avenal had outstanding $134 million and $143 million, respectively, under the Avenal Facility.
Desert Sunlight — Desert Sunlight 250 and Desert Sunlight 300 each entered into three distinct tranches of debt. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, Desert Sunlight had total debt outstanding of $1.1 billion under the three tranches.
GenConn — GenConn has a $237 million project note with an interest rate of 4.73% and a maturity date of July 2041 and a 5-year, $35 million working capital facility that matures in 2018 which can be used to issue letters of credit at an interest rate of 1.875% per annum. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, $212 million and $220 million, respectively, were outstanding under the note. As of December 31, 2016, $14 million was drawn on the working capital facility. The note is secured by all of the GenConn assets. The Company's maximum exposure to loss is limited to its equity investment in GenConn, which was $106 million as of December 31, 2016.
NRG DGPV Holdco 2 LLC — On June 30, 2016, NRG DGPV4 Borrower LLC, a direct subsidiary of NRG DGPV Holdco 2 LLC entered into a financing agreement to fund the acquisition of projects by the tax equity fund. As of December 31, 2016, there was $21 million outstanding under the facility.
24
Summarized Financial Information
The following tables present summarized financial information for the Company's significant equity method investments:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Income Statement Data: | (In millions) | ||||||||||
| GenConn | |||||||||||
| Operating revenues | $ | 72 | $ | 78 | $ | 82 | |||||
| Operating income | 38 | 40 | 40 | ||||||||
| Net income | 26 | 28 | 28 | ||||||||
| Desert Sunlight | |||||||||||
| Operating revenues | $ | 211 | $ | 206 | 134 | ||||||
| Operating income | 129 | 124 | 74 | ||||||||
| Net income | 80 | 73 | 37 | ||||||||
Utah Solar Portfolio (a) | |||||||||||
| Operating revenues | $ | 13 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| Operating loss | (6 | ) | (1 | ) | — | ||||||
| Net loss | (6 | ) | (1 | ) | — | ||||||
| As of December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: | (In millions) | ||||||||||
| GenConn | |||||||||||
| Current assets | $ | 36 | $ | 36 | |||||||
| Non-current assets | 389 | 416 | |||||||||
| Current liabilities | 16 | 16 | |||||||||
| Non-current liabilities | 196 | 215 | |||||||||
| Desert Sunlight | |||||||||||
| Current assets | $ | 281 | $ | 310 | |||||||
| Non-current assets | 1,401 | 1,435 | |||||||||
| Current liabilities | 64 | 82 | |||||||||
| Non-current liabilities | 1,043 | 1,086 | |||||||||
Utah Solar Portfolio (a) | |||||||||||
| Current assets | $ | 20 | $ | 11 | |||||||
| Non-current assets | 1,105 | 705 | |||||||||
| Current liabilities | 14 | 229 | |||||||||
| Non-current liabilities | 38 | — | |||||||||
(a) Utah Solar Portfolio was acquired by NRG on November 2, 2016.
25
Variable Interest Entities, or VIEs
Entities that are Consolidated
NRG Wind TE Holdco — On November 3, 2015, the Company acquired 75% of the Class B interests of NRG Wind TE Holdco, or the November 2015 Drop Down Assets, which owns a portfolio of 12 wind facilities totaling 814 net MW, from NRG for total cash consideration of $209 million, as described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions. In February 2016, NRG made a final working capital payment of $2 million, reducing total cash consideration to $207 million. NRG retained a 25% ownership of the Class B interest. The Class A interests of NRG Wind TE Holdco are owned by a tax equity investor, or TE Investor, who receives 99% of allocations of taxable income and other items until the flip point, which occurs when the TE Investor obtains a specified return on its initial investment, at which time the allocations to the TE Investor change to 8.53%. The Company generally receives 75% of CAFD until the flip point, at which time the allocations to the Company of CAFD change to 68.60%. If the flip point has not occurred by a specified date, 100% of CAFD is allocated to the TE Investor until the flip point occurs. NRG Wind TE Holdco is a VIE and the Company is the primary beneficiary, through its position as managing member, and consolidates NRG Wind TE Holdco. The Company utilizes the HLBV method to determine the net income or loss allocated to the TE Investor noncontrolling interest. Net income or loss attributable to the Class B interests is allocated to NRG's noncontrolling interest based on its 25% ownership interest.
Alta TE Holdco — On June 30, 2015, the Company sold an economic interest in Alta TE Holdco to a financial institution in order to monetize certain cash and tax attributes, primarily PTCs. The financial institution, or Alta Investor, receives 99% of allocations of taxable income and other items until the flip point, which occurs when the Alta Investor obtains a specified return on its initial investment, at which time the allocations to the Alta Investor change to 5%. The Company received 100% of CAFD through December 31, 2015, and subsequently will receive 94.34% until the flip point, at which time the allocations to the Company of CAFD will change to 97.12%, unless the flip point will not have occurred by a specified date, which would result in 100% of CAFD allocated to the Alta Investor until the flip point occurs. Alta TE Holdco is a VIE and the Company is the primary beneficiary through its position as managing member, and therefore consolidates Alta TE Holdco, with the Alta Investor's interest shown as noncontrolling interest. The Company utilizes the HLBV method to determine the net income or loss allocated to the noncontrolling interest. The net proceeds of $119 million were reflected as noncontrolling interest in the Company's balance sheet.
Spring Canyon — On May 7, 2015, the Company acquired a 90.1% of the Class B interests in Spring Canyon II, a 32 MW wind facility, and Spring Canyon III, a 28 MW wind facility, each located in Logan County, Colorado, from Invenergy Wind Global LLC. Invenergy owns 9.9% of the Class B interests. Prior to the acquisition date, the projects were financed with a partnership flip tax-equity structure with a financial institution, who owns the Class A interests, to monetize certain cash and tax attributes, primarily PTCs. Until the flip point, the Class A member will receive 34.81% of the cash distributions based on the projects’ production level and the Company and Invenergy will receive 65.19%. After the flip point, cash distributions are allocated 5% to the Class A member and 95% to the Company and Invenergy. Spring Canyon is a VIE and the Company is the primary beneficiary through its position as managing member, and therefore consolidates Spring Canyon. The Class A member and Invenergy's interests are shown as noncontrolling interest. The Company utilizes the HLBV method to determine the net income or loss allocated to the Class A member. Net income or loss attributable to the Class B interests is allocated to Invenergy's noncontrolling interest based on its 9.9% ownership interest.
26
Summarized financial information for the Company's consolidated VIEs consisted of the following as of December 31, 2016:
| (In millions) | NRG Wind TE Holdco | Alta TE Holdco | Spring Canyon | ||||||||
| Other current and non-current assets | $ | 193 | $ | 17 | $ | 4 | |||||
| Property, plant and equipment | 441 | 461 | 100 | ||||||||
| Intangible assets | 2 | 274 | — | ||||||||
| Total assets | 636 | 752 | 104 | ||||||||
| Current and non-current liabilities | 209 | 9 | 6 | ||||||||
| Total liabilities | 209 | 9 | 6 | ||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest | 139 | 107 | 67 | ||||||||
| Net assets less noncontrolling interests | $ | 288 | $ | 636 | $ | 31 | |||||
Entities that are not Consolidated
The Company has interests in entities that are considered VIEs under ASC 810, Consolidation, but for which it is not considered the primary beneficiary. The Company accounts for its interests in these entities under the equity method of accounting.
Utah Solar Portfolio — As described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions, on March 27, 2017, as part of the March 2017 Drop Down Assets acquisition the Company acquired from NRG 100% of the Class A equity interests in the Utah Solar Portfolio, comprised of Four Brothers Solar, LLC, Granite Mountain Holdings, LLC, and Iron Springs Holdings, LLC. The Class B interests of the Utah Solar Portfolio are owned by a tax equity investor, or TE Investor, who receives 99% of allocations of taxable income and other items until the flip point, which occurs when the TE Investor obtains a specified return on its initial investment, at which time the allocations to the TE Investor change to 50%. The Company generally receives 50% of distributable cash throughout the term of the tax-equity arrangements. The three entities comprising the Utah Solar Portfolio are VIEs. As the Company is not the primary beneficiary, the Company uses the equity method of accounting to account for its interests in the Utah Solar Portfolio. The Company utilizes the HLBV method to determine its share of the income or losses in the investees. The Company’s maximum exposure to loss is limited to its equity method investments in the Utah Solar Portfolio, which was $346 million on a combined basis as of December 31, 2016.
NRG DGPV Holdco 1 LLC — On May 8, 2015, the Company and NRG entered into a partnership by forming NRG DGPV Holdco 1 LLC, or DGPV Holdco 1, the purpose of which is to own or purchase solar power generation projects and other ancillary related assets from NRG Renew LLC or its subsidiaries via intermediate funds, including: (i) a tax equity-financed portfolio of 10 recently completed community solar projects representing approximately 8 MW with a weighted average remaining PPA term of 19 years; (ii) a tax equity-financed portfolio of approximately 12 commercial photovoltaic systems representing approximately 37 MW with a weighted average remaining PPA term of 18 years; and (iii) a tax equity-financed portfolio of approximately 3 commercial photovoltaic systems representing approximately 1 MW with a weighted average remaining PPA term of 20 years. All of these investments relate to the Company's $100 million commitment to distributed solar projects in partnership with NRG.
NRG DGPV Holdco 2 LLC — On February 29, 2016, the Company and NRG entered into an additional partnership by forming NRG DGPV Holdco 2 LLC, or DGPV Holdco 2, to own or purchase solar power generation projects as well as other ancillary related assets from NRG Renew LLC or its subsidiaries, via intermediate funds including: (i) a tax equity-financed portfolio of 18 projects representing approximately 28 MW with a weighted average remaining PPA term of 21 years; and (ii) a tax equity-financed portfolio of 21 projects representing approximately 18 MW with a weighted average remaining PPA term of 20 years. Under this partnership, the Company committed to fund up to $50 million of capital.
The Company's maximum exposure to loss is limited to its equity investment in DGPV Holdco 1 and DGPV Holdco 2, which was $99 million on a combined basis, of which $14 million was payable to NRG, as of December 31, 2016.
NRG RPV Holdco 1 LLC — On April 9, 2015, the Company and NRG entered into a partnership by forming NRG RPV Holdco 1 LLC, or RPV Holdco, that holds operating portfolios of residential solar assets developed by NRG's residential solar business, including: (i) an existing, unlevered portfolio of over 2,200 leases across nine states representing approximately 15 MW with a weighted average remaining lease term of approximately 19 years that was acquired outside of the partnership; and (ii) a tax equity-financed portfolio of approximately 5,400 leases representing approximately 31 MW, with a weighted average remaining lease term for the existing and new leases of approximately 19 years.
27
In addition to the acquisition of the unlevered portfolio of leases, the Company had previously committed to fund up to $150 million of capital to invest in the tax equity financed portfolio. On February 29, 2016, the Company and NRG amended the RPV Holdco partnership agreement to reduce the aggregate commitment of $150 million to $100 million in connection with the formation of DGPV Holdco 2. On August 5, 2016, the Company and NRG amended the RPV Holdco partnership agreement to further reduce that capital commitment of $100 million to $60 million in connection with NRG’s change in business model approach in the residential solar business. As of December 31, 2016, the Company had contributed $59 million of this amount.
The Company's maximum exposure to loss is limited to its equity investment, which was $71 million as of December 31, 2016.
Note 6 — Fair Value of Financial Instruments
For cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, accounts receivable — affiliate, accounts receivable, accounts payable, current portion of accounts payable — affiliate, accrued expenses and other liabilities, the carrying amount approximates fair value because of the short-term maturity of those instruments and are classified as Level 1 within the fair value hierarchy.
The estimated carrying amounts and fair values of the Company’s recorded financial instruments not carried at fair market value are as follows:
| As of December 31, 2016 | As of December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
| Carrying Amount | Fair Value | Carrying Amount | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||
| Assets: | |||||||||||||||
| Notes receivable, including current portion | $ | 30 | $ | 30 | $ | 47 | $ | 47 | |||||||
| Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt, including current portion — affiliate | 618 | 608 | 618 | 553 | |||||||||||
| Long-term debt, including current portion — external | $ | 5,451 | $ | 5,435 | $ | 5,060 | $ | 4,974 | |||||||
Fair Value Accounting under ASC 820
ASC 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three levels as follows:
| • | Level 1—quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the Company has the ability to access as of the measurement date. |
| • | Level 2—inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are directly observable for the asset or liability or indirectly observable through corroboration with observable market data. |
| • | Level 3—unobservable inputs for the asset or liability only used when there is little, if any, market activity for the asset or liability at the measurement date. |
In accordance with ASC 820, the Company determines the level in the fair value hierarchy within which each fair value measurement in its entirety falls, based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
28
The fair value of the Company's publicly-traded long-term debt is based on quoted market prices and is classified as Level 2 within the fair value hierarchy. The fair value of non-publicly traded long-term debt, affiliate debt and certain notes receivable of the Company are based on expected future cash flows discounted at market interest rates, or current interest rates for similar instruments with equivalent credit quality and are classified as Level 3 within the fair value hierarchy. The following table presents the level within the fair value hierarchy for long-term debt, including current portion as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
| As of December 31, 2016 | As of December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
| Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt, including current portion | $ | 833 | $ | 5,210 | $ | 413 | $ | 5,114 | |||||||
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
The Company records its derivative assets and liabilities at fair market value on its consolidated balance sheet. There were no asset positions as of December 31, 2015. The following table presents assets and liabilities measured and recorded at fair value on the Company's consolidated balance sheets on a recurring basis and their level within the fair value hierarchy:
| As of December 31, 2016 | As of December 31, 2016 | As of December 31, 2015 | |||||||||
Fair Value (a) | Fair Value (a) | Fair Value (a) | |||||||||
| (In millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 2 | ||||||||
| Derivative assets: | |||||||||||
| Commodity contracts | $ | 1 | $ | 1 | $ | — | |||||
| Interest rate contracts | — | 1 | — | ||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 1 | $ | 2 | $ | — | |||||
| Derivative liabilities: | |||||||||||
| Commodity contracts | $ | — | $ | 1 | $ | 2 | |||||
| Interest rate contracts | — | 75 | 98 | ||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | — | $ | 76 | $ | 100 | |||||
(a) There were no assets or liabilities classified as Level 1 as of December 31, 2015. There were no assets or liabilities classified Level 3 as of December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Derivative Fair Value Measurements
The Company's contracts are non-exchange-traded and valued using prices provided by external sources. For the Company’s energy markets, management receives quotes from multiple sources. To the extent that multiple quotes are received, the prices reflect the average of the bid-ask mid-point prices obtained from all sources believed to provide the most liquid market for the commodity.
The fair value of each contract is discounted using a risk free interest rate. In addition, a credit reserve is applied to reflect credit risk, which for interest rate swaps, is calculated based on credit default swaps utilizing the bilateral method. For commodities, to the extent that NRG's net exposure under a specific master agreement is an asset, the Company uses the counterparty's default swap rate. If the exposure under a specific master agreement is a liability, the Company uses NRG's default swap rate. For interest rate swaps and commodities, the credit reserve is added to the discounted fair value to reflect the exit price that a market participant would be willing to receive to assume the liabilities or that a market participant would be willing to pay for the assets. As of December 31, 2016, the credit reserve resulted in a $1 million increase in fair value in OCI. It is possible that future market prices could vary from those used in recording assets and liabilities and such variations could be material.
Concentration of Credit Risk
In addition to the credit risk discussion as disclosed in Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, the following item is a discussion of the concentration of credit risk for the Company's financial instruments. Credit risk relates to the risk of loss resulting from non-performance or non-payment by counterparties pursuant to the terms of their contractual obligations. The Company monitors and manages credit risk through credit policies that include: (i) an established credit approval process; (ii) daily monitoring of counterparties' credit limits; (iii) the use of credit mitigation measures such as margin, collateral, prepayment arrangements, or volumetric limits; (iv) the use of payment netting agreements; and (v) the use of master netting agreements that allow for the netting of positive and negative exposures of various contracts associated with a single counterparty. Risks surrounding counterparty performance and credit could ultimately impact the amount and timing of expected cash flows. The Company seeks to mitigate counterparty risk by having a diversified portfolio of counterparties.
29
Counterparty credit exposure includes credit risk exposure under certain long-term agreements, including solar and other PPAs. As external sources or observable market quotes are not available to estimate such exposure, the Company estimates the exposure related to these contracts based on various techniques including but not limited to internal models based on a fundamental analysis of the market and extrapolation of observable market data with similar characteristics. Based on these valuation techniques, as of December 31, 2016, credit risk exposure to these counterparties attributable to the Company's ownership interests was approximately $2.8 billion for the next five years. The majority of these power contracts are with utilities with strong credit quality and public utility commission or other regulatory support. However, such regulated utility counterparties can be impacted by changes in government regulations, which the Company is unable to predict.
Note 7 — Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
ASC 815 requires the Company to recognize all derivative instruments on the balance sheet as either assets or liabilities and to measure them at fair value each reporting period unless they qualify for a NPNS exception. The Company may elect to designate certain derivatives as cash flow hedges, if certain conditions are met, and defer the effective portion of the change in fair value of the derivatives to accumulated OCI/OCL, until the hedged transactions occur and are recognized in earnings. The ineffective portion of a cash flow hedge is immediately recognized in earnings. For derivatives that are not designated as cash flow hedges or do not qualify for hedge accounting treatment, the changes in the fair value will be immediately recognized in earnings. Certain derivative instruments may qualify for the NPNS exception and are therefore exempt from fair value accounting treatment. ASC 815 applies to the Company's energy related commodity contracts and interest rate swaps.
Energy-Related Commodities
To manage the commodity price risk associated with its competitive supply activities and the price risk associated with wholesale power sales, the Company may enter into derivative hedging instruments, namely, forward contracts that commit the Company to sell energy commodities or purchase fuels/electricity in the future. The objectives for entering into derivatives contracts designated as hedges include fixing the price for a portion of anticipated future electricity sales and fixing the price of a portion of anticipated fuel/electricity purchases for the operation of its subsidiaries. As of December 31, 2016, the Company had forward contracts for the purchase of fuel commodities relating to the forecasted usage of the Company’s district energy centers extending through 2018 and electricity contracts to supply retail power to the Company's district energy centers extending through 2020. At December 31, 2016, these contracts were not designated as cash flow or fair value hedges.
Also, as of December 31, 2016, the Company had other energy-related contracts that did not meet the definition of a derivative instrument or qualified for the NPNS exception and were therefore exempt from fair value accounting treatment as follows:
| • | Power tolling contracts through 2039, and |
| • | Natural gas transportation contracts through 2028. |
Interest Rate Swaps
The Company is exposed to changes in interest rates through the issuance of variable rate debt. In order to manage interest rate risk, it enters into interest rate swap agreements.
As of December 31, 2016, the Company had interest rate derivative instruments on non-recourse debt extending through 2036, most of which are designated as cash flow hedges.
Volumetric Underlying Derivative Transactions
The following table summarizes the net notional volume buy/(sell) of the Company's open derivative transactions broken out by commodity as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
| Total Volume | |||||||||
| December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||||
| Commodity | Units | (In millions) | |||||||
| Natural Gas | MMBtu | 3 | 4 | ||||||
| Interest | Dollars | $ | 2,070 | $ | 1,991 | ||||
30
Fair Value of Derivative Instruments
There were no derivative asset positions on the balance sheet as of December 31, 2015. The following table summarizes the fair value within the derivative instrument valuation on the balance sheet:
| Fair Value | |||||||||||
| Derivative Assets | Derivative Liabilities | ||||||||||
| December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||
| Derivatives Designated as Cash Flow Hedges: | |||||||||||
| Interest rate contracts current | $ | — | $ | 26 | $ | 34 | |||||
| Interest rate contracts long-term | 1 | 39 | 56 | ||||||||
| Total Derivatives Designated as Cash Flow Hedges | 1 | 65 | 90 | ||||||||
| Derivatives Not Designated as Cash Flow Hedges: | |||||||||||
| Interest rate contracts current | — | 5 | 3 | ||||||||
| Interest rate contracts long-term | — | 5 | 5 | ||||||||
| Commodity contracts current | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||
| Total Derivatives Not Designated as Cash Flow Hedges | 2 | 11 | 10 | ||||||||
| Total Derivatives | $ | 3 | $ | 76 | $ | 100 | |||||
The Company has elected to present derivative assets and liabilities on the balance sheet on a trade-by-trade basis and does not offset amounts at the counterparty master agreement level. As of December 31, 2016, there was no outstanding collateral paid or received. As of December 31, 2015, there were no offsetting amounts at the counterparty master agreement level or outstanding collateral paid or received. The following table summarizes the offsetting of derivatives by counterparty master agreement level as of December 31, 2016:
| Gross Amounts Not Offset in the Statement of Financial Position | |||||||||||
| As of December 31, 2016 | Gross Amounts of Recognized Assets/Liabilities | Derivative Instruments | Net Amount | ||||||||
| Commodity contracts: | (In millions) | ||||||||||
| Derivative assets | $ | 2 | $ | — | $ | 2 | |||||
| Derivative liabilities | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | ||||||
| Total commodity contracts | 1 | — | 1 | ||||||||
| Interest rate contracts: | |||||||||||
| Derivative assets | 1 | (1 | ) | — | |||||||
| Derivative liabilities | (75 | ) | 1 | (74 | ) | ||||||
| Total interest rate contracts | (74 | ) | — | (74 | ) | ||||||
| Total derivative instruments | $ | (73 | ) | $ | — | $ | (73 | ) | |||
31
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss
The following table summarizes the effects on the Company’s accumulated OCL balance attributable to interest rate swaps designated as cash flow hedge derivatives:
| Year ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||
| Accumulated OCL beginning balance | $ | (99 | ) | $ | (82 | ) | $ | (17 | ) | ||
| Reclassified from accumulated OCL to income due to realization of previously deferred amounts | 17 | 17 | 15 | ||||||||
| Mark-to-market of cash flow hedge accounting contracts | (4 | ) | (34 | ) | (80 | ) | |||||
| Accumulated OCL ending balance | (86 | ) | (99 | ) | (82 | ) | |||||
| Accumulated OCL attributable to noncontrolling interests | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||
| Accumulated OCL attributable to NRG Yield LLC | $ | (83 | ) | $ | (96 | ) | $ | (80 | ) | ||
| Losses expected to be realized from OCL during the next 12 months | $ | 19 | |||||||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated OCL into income and amounts recognized in income from the ineffective portion of cash flow hedges are recorded to interest expense. There was no ineffectiveness for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014.
Accounting guidelines require a high degree of correlation between the derivative and the hedged item throughout the period in order to qualify as a cash flow hedge. As of December 31, 2016, the Company's regression analysis for Viento Funding II interest rate swaps, while positively correlated, did not meet the required threshold for cash flow hedge accounting. As a result, the Company de-designated the Viento Funding II cash flow hedges as of December 31, 2016, and will prospectively mark these derivatives to market through the income statement.
Impact of Derivative Instruments on the Statements of Income
The Company has interest rate derivative instruments that are not designated as cash flow hedges. The effect of interest rate hedges is recorded to interest expense. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 the impact to the consolidated statements of income was a loss of $2 million, a gain of $16 million, and a loss of $22 million, respectively.
A portion of the Company’s derivative commodity contracts relates to its Thermal Business for the purchase of fuel/electricity commodities based on the forecasted usage of the thermal district energy centers. Realized gains and losses on these contracts are reflected in the costs that are permitted to be billed to customers through the related customer contracts or tariffs and, accordingly, no gains or losses are reflected in the consolidated statements of income for these contracts.
In 2015 and 2014, commodity contracts also hedged the forecasted sale of power for the Elbow Creek until the start of the PPA with NRG Power Marketing LLC, or Power Marketing, with effective date of November 1, 2015. The effect of these commodity hedges was recorded to operating revenues. For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the impact to the consolidated statements of income was an unrealized loss of $2 million and a gain of $2 million, respectively.
See Note 6, Fair Value of Financial Instruments, for a discussion regarding concentration of credit risk.
Note 8 — Intangible Assets
Intangible Assets — The Company's intangible assets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 primarily reflect intangible assets established from its business acquisitions and are comprised of the following:
| • | PPAs — Established predominantly with the acquisitions of the Alta Wind Portfolio, Walnut Creek, Tapestry and Laredo Ridge, these represent the fair value of the PPAs acquired. These will be amortized, generally on a straight-line basis, over the term of the PPA. |
| • | Leasehold Rights — Established with the acquisition of the Alta Wind Portfolio, this represents the fair value of contractual rights to receive royalty payments equal to a percentage of PPA revenue from certain projects. These will be amortized on a straight-line basis. |
| • | Customer relationships — Established with the acquisition of NRG Energy Center Phoenix and NRG Energy Center Omaha, these intangibles represent the fair value at the acquisition date of the businesses' customer base. The customer relationships are amortized to depreciation and amortization expense based on the expected discounted future net cash flows by year. |
32
| • | Customer contracts — Established with the acquisition of NRG Energy Center Phoenix, these intangibles represent the fair value at the acquisition date of contracts that primarily provide chilled water, steam and electricity to its customers. These contracts are amortized to revenues based on expected volumes. |
| • | Emission Allowances — These intangibles primarily consist of SO2 and NOx emission allowances established with the El Segundo and Walnut Creek acquisitions. These emission allowances are held-for-use and are amortized to cost of operations, with NOx allowances amortized on a straight-line basis and SO2 allowances amortized based on units of production. |
| • | Development rights — Arising primarily from the acquisition of solar businesses in 2010 and 2011, these intangibles are amortized to depreciation and amortization expense on a straight-line basis over the estimated life of the related project portfolio. |
| • | Other — Consists of the acquisition date fair value of the contractual rights to a ground lease for South Trent and to utilize certain interconnection facilities for Blythe, as well as land rights acquired in connection with the acquisition of Elbow Creek. |
The following tables summarize the components of intangible assets subject to amortization:
| Year ended December 31, 2016 | PPAs | Leasehold Rights | Customer Relationships | Customer Contracts | Emission Allowances | Development Rights | Other | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2016 | $ | 1,264 | $ | 86 | $ | 66 | $ | 15 | $ | 15 | $ | 3 | $ | 6 | $ | 1,455 | |||||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | — | — | (6 | ) | — | — | (6 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2016 | 1,264 | 86 | 66 | 15 | 9 | 3 | 6 | 1,449 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Less accumulated amortization | (138 | ) | (9 | ) | (4 | ) | (7 | ) | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | (163 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Net carrying amount | $ | 1,126 | $ | 77 | $ | 62 | $ | 8 | $ | 7 | $ | 2 | $ | 4 | $ | 1,286 | |||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2015 | PPAs | Leasehold Rights | Customer Relationships | Customer Contracts | Emission Allowances | Development Rights | Other | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2015 | $ | 1,270 | $ | 86 | $ | 66 | $ | 15 | $ | 16 | $ | 3 | $ | 6 | $ | 1,462 | |||||||||||||||
| Other | (6 | ) | — | — | — | (1 | ) | — | — | (7 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2015 | 1,264 | 86 | 66 | 15 | 15 | 3 | 6 | 1,455 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Less accumulated amortization | (75 | ) | (5 | ) | (3 | ) | (6 | ) | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | (93 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Net carrying amount | $ | 1,189 | $ | 81 | $ | 63 | $ | 9 | $ | 14 | $ | 2 | $ | 4 | $ | 1,362 | |||||||||||||||
The Company recorded amortization expense of $70 million, $55 million and $30 million during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014. Of these amounts, $69 million, $54 million and $29 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, were recorded to contract amortization expense and reduced operating revenues in the consolidated statements of income. The Company estimates the future amortization expense for its intangibles to be $71 million for the next five years through 2021.
Out-of-market contracts — The out-of-market contract liability represents the out-of-market value of the PPAs for the Blythe solar project and Spring Canyon wind projects and the out-of-market value of the land lease for Alta Wind XI Holding Company, LLC, as of their respective acquisition dates. The Blythe solar project's liability of $4 million is recorded to other non-current liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet and is amortized to revenue in the consolidated statements of income on a units-of-production basis over the twenty-year term of the agreement. Spring Canyon's liability of $3 million is recorded to other non-current liabilities and is amortized to revenue on a straight-line basis over the twenty-five year term of the agreement. The Alta Wind XI Holding Company, LLC's liability of $5 million is recorded to other non-current liabilities and is amortized to cost of operations on a straight-line basis over the term of the land lease. At December 31, 2016, accumulated amortization of out-of-market contracts was $3 million and amortization expense was $1 million for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015.
33
Note 9 — Asset Impairments
During the fourth quarter of 2016, as the Company updated its estimated cash flows in connection with the preparation and review of the Company's annual budget, the Company determined that the cash flows for the Elbow Creek and Goat Wind projects located in Texas and the Forward project in Pennsylvania were below the carrying value of the related assets, primarily driven by declining merchant power prices in post-contract periods, and that the assets were considered impaired. These projects were acquired in connection with the acquisition of the November 2015 Drop Down Assets and were recorded in the Renewables segment of the Company. The projects were recorded at historical cost at acquisition date as they were related to interests under common control by NRG. The fair value of the facilities was determined using an income approach by applying a discounted cash flow methodology to the long-term budgets for each respective plant. The income approach utilized estimates of discounted future cash flows, which were Level 3 fair value measurement and include key inputs, such as forecasted power prices, operations and maintenance expense, and discount rates. The Company measured the impairment loss as the difference between the carrying amount and the fair value of the assets and recorded impairment losses of $117 million, $60 million and $6 million for Elbow Creek, Goat Wind, and Forward, respectively.
34
Note 10 — Long-term Debt
The Company's borrowings, including short term and long term portions consisted of the following:
| December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | Interest rate % (a) | Letters of Credit Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||
| (In millions, except rates) | |||||||||||||
| 2026 Senior Notes | $ | 350 | $ | — | 5.000 | ||||||||
| 2024 Senior Notes | 500 | 500 | 5.375 | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt - affiliate, due 2020 | 281 | 281 | 3.325 | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt - affiliate, due 2019 | 337 | 337 | 3.580 | ||||||||||
NRG Yield LLC and NRG Yield Operating LLC Revolving Credit Facility, due 2019 (b) | — | 306 | L+2.500 | 60 | |||||||||
| Project-level debt: | |||||||||||||
| Alpine, due 2022 | 145 | 154 | L+1.750 | 37 | |||||||||
| Alta Wind I, lease financing arrangement, due 2034 | 242 | 252 | 7.015 | 16 | |||||||||
| Alta Wind II, lease financing arrangement, due 2034 | 191 | 198 | 5.696 | 27 | |||||||||
| Alta Wind III, lease financing arrangement, due 2034 | 198 | 206 | 6.067 | 27 | |||||||||
| Alta Wind IV, lease financing arrangement, due 2034 | 128 | 133 | 5.938 | 19 | |||||||||
| Alta Wind V, lease financing arrangement, due 2035 | 206 | 213 | 6.071 | 30 | |||||||||
| Alta Realty Investments, due 2031 | 31 | 33 | 7.000 | — | |||||||||
| Alta Wind Asset Management, due 2031 | 18 | 19 | L+2.375 | — | |||||||||
| Avra Valley, due 2031 | 57 | 60 | L+1.750 | 3 | |||||||||
| Blythe, due 2028 | 19 | 21 | L+1.625 | 6 | |||||||||
| Borrego, due 2025 and 2038 | 69 | 72 | L+ 2.500/5.650 | 5 | |||||||||
| CVSR, due 2037 | 771 | 793 | 2.339 - 3.775 | — | |||||||||
| CVSR Holdco Notes, due 2037 | 199 | — | 4.680 | 13 | |||||||||
| El Segundo Energy Center, due 2023 | 443 | 485 | L+1.625 - L+2.250 | 82 | |||||||||
| Energy Center Minneapolis, due 2017 and 2025 | 96 | �� | 108 | 5.950 -7.250 | — | ||||||||
| Energy Center Minneapolis Series D Notes, due 2031 | 125 | — | 3.550 | — | |||||||||
| Kansas South, due 2031 | 30 | 33 | L+2.000 | 4 | |||||||||
| Laredo Ridge, due 2028 | 100 | 104 | L+1.875 | 10 | |||||||||
| Marsh Landing, due 2017 and 2023 | 370 | 418 | L+1.750 - L+1.875 | 22 | |||||||||
| PFMG and related subsidiaries financing agreement, due 2030 | 27 | 29 | 6.000 | — | |||||||||
| Roadrunner, due 2031 | 37 | 40 | L+1.625 | 5 | |||||||||
| South Trent Wind, due 2020 | 57 | 62 | L+1.625 | 10 | |||||||||
| TA High Desert, due 2020 and 2032 | 49 | 52 | L+2.500/5.150 | 8 | |||||||||
| Tapestry, due 2021 | 172 | 181 | L+1.625 | 20 | |||||||||
| Utah Solar Portfolio, due 2022 | 287 | — | L+2.625 | 13 | |||||||||
| Viento, due 2023 | 178 | 189 | L+2.750 | 27 | |||||||||
| Walnut Creek, due 2023 | 310 | 351 | L+1.625 | 41 | |||||||||
| WCEP Holdings, due 2023 | 46 | 46 | L+3.000 | — | |||||||||
| Other | — | 2 | various | — | |||||||||
| Subtotal project-level debt | 4,601 | 4,254 | |||||||||||
| Total debt | 6,069 | 5,678 | |||||||||||
| Less current maturities | (291 | ) | (264 | ) | |||||||||
| Less deferred financing costs | (62 | ) | (53 | ) | |||||||||
| Total long-term debt | $ | 5,716 | $ | 5,361 | |||||||||
(a) As of December 31, 2016, L+ equals 3 month LIBOR plus x%, except for the Alpine term loan, Marsh Landing term loan, Walnut Creek term loan, Utah Solar Portfolio debt, and NRG Yield LLC and NRG Yield Operating LLC Revolving Credit Facility, where L+ equals 1 month LIBOR plus x% and Kansas South and Viento, where L+ equals 6 month LIBOR plus x%.
(b) Applicable rate is determined by the Borrower Leverage Ratio, as defined in the credit agreement.
35
The financing arrangements listed above contain certain covenants, including financial covenants, that the Company is required to be in compliance with during the term of the arrangement. As of December 31, 2016, the Company was in compliance with all of the required covenants.
NRG Yield Operating LLC 2026 Senior Notes
On August 18, 2016, Yield Operating LLC issued $350 million of senior unsecured notes, or the 2026 Senior Notes. The 2026 Senior Notes bear interest at 5.00% and mature on September 15, 2026. Interest on the notes is payable semi-annually on March 15 and September 15 of each year, and interest payments will commence on March 15, 2017. The 2026 Senior Notes are senior unsecured obligations of Yield Operating LLC and are guaranteed by the Company, and by certain of Yield Operating LLC's wholly owned current and future subsidiaries. A portion of the proceeds of the 2026 Senior Notes were used to repay the Company's revolving credit facility, as described below.
NRG Yield Operating LLC 2024 Senior Notes
On August 5, 2014, Yield Operating LLC issued $500 million of senior unsecured notes, or the 2024 Senior Notes. The 2024 Senior Notes bear interest at 5.375% and mature in August 2024. Interest on the notes is payable semi-annually on February 15 and August 15 of each year. The 2024 Senior Notes are senior unsecured obligations of Yield Operating LLC and are guaranteed by the Company, and by certain of Yield Operating LLC’s wholly owned current and future subsidiaries.
Yield, Inc. 2020 Convertible Senior Notes and Related Intercompany Note
On June 29, 2015, Yield, Inc. closed on its offering of $287.5 million aggregate principal amount of 3.25% Convertible Senior Notes due 2020, or the 2020 Convertible Notes. The 2020 Convertible Notes are convertible, under certain circumstances, into Yield, Inc.'s Class C common stock, cash or a combination thereof at an initial conversion price of $27.50 per Class C common share, which is equivalent to a conversion rate of approximately 36.3636 shares of Class C common stock per $1,000 principal amount of 2020 Convertible Notes. The Company and Yield Operating LLC provided a guarantee to Yield, Inc. with respect to the 2020 Convertible Notes. In addition, Yield Operating LLC and Yield, Inc. entered into an intercompany borrowing arrangement, under which Yield Operating LLC received $281 million of the proceeds of the 2020 Convertible Notes. The intercompany note bears interest at a rate of 3.325% and matures in 2020.
Yield, Inc. 2019 Convertible Senior Notes and Related Intercompany Note
During the first quarter of 2014, Yield, Inc. closed on its offering of $345 million aggregate principal amount of 3.50% Convertible Senior Notes due 2019, or the 2019 Convertible Notes. The 2019 Convertible Notes were convertible, under certain circumstances, into Yield, Inc.’s Class A common stock, cash or a combination thereof at an initial conversion price of $46.55 per Class A common share, which is equivalent to a conversion rate of approximately 42.9644 shares of Class A common stock per $1,000 principal amount of 2019 Convertible Notes in accordance with the terms of the related indenture. The Company and Yield Operating LLC provided a guarantee to Yield, Inc. with respect to the 2019 Convertible Notes. In addition, Yield Operating and Yield, Inc. entered into an intercompany borrowing arrangement, under which Yield Operating borrowed $337 million of the proceeds of the 2019 Convertible Notes. The intercompany note bears interest at a rate of 3.580% and matures in 2019.
NRG Yield LLC and NRG Yield Operating LLC Revolving Credit Facility
In connection with the Yield, Inc. initial public offering in July 2013, as further described in Note 1, Nature of Business, the Company and Yield Operating LLC entered into a senior secured revolving credit facility, or the Yield Credit Facility, which was amended on June 26, 2015, to, among other things, increase the availability to $495 million. The Company's revolving credit facility can be used for cash or for the issuance of letters of credit.
During 2015, the Company borrowed $254 million from the revolving credit facility to finance the acquisition of the November 2015 Drop Down Assets as discussed in Note 3, Business Acquisitions, as well as fund dividend payments and tax equity contributions.
The Company borrowed $60 million from the revolving credit facility and repaid $366 million during the year ended December 31, 2016. The Company used its pro rata proceeds of $97.5 million from the CVSR Holdco Financing Arrangement in July 2016, a portion of its proceeds from the issuance of the 2026 Senior Notes in August 2015, as well as its cash on hand to repay the outstanding borrowings under the revolving credit facility.
As of December 31, 2016, there were no outstanding borrowings and the Company had $60 million of letters of credit outstanding under the revolving credit facility.
36
Project - level Debt
Agua Caliente Borrower 2, due 2038
On February 17, 2017, Agua Caliente Borrower 1 LLC, an indirect subsidiary of NRG, and Agua Caliente Borrower 2 LLC, issued $130 million of senior secured notes under the Agua Caliente Holdco financing agreement that bear interest at 5.43% and mature on December 31, 2038. As described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions, on March 27, 2017, the Company acquired Agua Caliente Borrower 2 LLC from NRG. Agua Caliente Borrower 2 LLC owns a 16% interest in the Agua Caliente solar farm and holds $41 million of the Agua Caliente Holdco debt. The debt is joint and several with respect to Agua Caliente Borrower 1 LLC and Agua Caliente Borrower 2 LLC and is secured by the equity interests of each borrower in the Agua Caliente solar facility. Concurrent with the February 2017 borrowing, the Company entered into a letter of credit commitment of $17 million and issued same to support the Company's debt service requirement obligations. The Company pays semi-annual related fees of 2.25% on the outstanding balance.
Utah Solar Portfolio, due 2022
As part of its March 2017 Drop Down Assets acquisition, the Company assumed non-recourse debt of $287 million relating to the Utah Solar Portfolio at interest rate of LIBOR plus 2.625%. The debt matures on December 16, 2022. The $287 million consisted of $222 million outstanding at the time of the NRG acquisition in November 2016, and additional borrowings of $65 million incurred during 2016. The Company also entered into letter agreements for a commitment of $13 million to support the Company's debt service requirement obligations. The Company pays an availability fee of 2.625% on the amount on a quarterly basis. On March 27, 2017, the letters of credit were amended, reducing the issued amount to$11 million.
Energy Center Minneapolis LLC Series D Notes
On October 31, 2016, NRG Energy Center Minneapolis LLC, a subsidiary of the Company, received proceeds of $125 million from the issuance of 3.55% Series D notes due October 31, 2031, or the Series D Notes, and entered into a shelf facility for the anticipated issuance of an additional $70 million of notes at a 4.80% fixed rate. The Series D Notes will be secured by substantially all of the assets of NRG Energy Center Minneapolis LLC. NRG Thermal LLC has guaranteed the indebtedness and its guarantee is secured by a pledge of the equity interests in all of NRG Thermal LLC’s subsidiaries. NRG Energy Center Minneapolis LLC distributed the proceeds of the Series D Notes to NRG Thermal LLC, which in turn distributed the proceeds to NRG Yield Operating LLC to be utilized for general corporate purposes, including potential acquisitions.
CVSR Holdco Notes, due 2037
On July 15, 2016, CVSR Holdco, the indirect owner of the CVSR solar facility, issued $200 million of senior secured notes under the CVSR Holdco Financing Agreement, or 2037 CVSR Holdco Notes, that bear interest at 4.68% and mature on March 31, 2037. Net proceeds were distributed to the Company and NRG based on their respective ownership as of July 15, 2016, and, accordingly, the Company received net proceeds of $97.5 million.
As described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions, on September 1, 2016, the Company acquired the remaining 51.05% of CVSR, and assumed additional debt of $496 million, which represents 51.05% of the CVSR project level debt and 51.05% of the 2037 CVSR Holdco Notes. In connection with the retrospective adjustment of prior periods, as described in Note 1, Nature of Business, the Company now consolidates CVSR and 100% of its debt, consisting of $771 million of project level debt and $200 million of 2037 CVSR Holdco Notes as of September 1, 2016.
Avenal
On March 18, 2015, Avenal, one of the Company's equity method investments, amended its credit agreement to increase its borrowings by $43 million and to reduce the related interest rate from 6 month LIBOR plus an applicable margin of 2.25% to 6 month LIBOR plus 1.75% from March 18, 2015, through March 17, 2022, 6 month LIBOR plus 2.00% from March 18, 2022, through March 17, 2027, and 6 month LIBOR plus 2.25% from March 18, 2027, through the maturity date. As a result of the credit agreement amendment, the Company received net proceeds of $20 million after fees from its 49.95% ownership in Avenal. Effective September 30, 2015, the Company increased its ownership to 50% by acquiring an additional 0.05% membership interest in Avenal.
37
Lease financing arrangements
Alta Wind Holdings (Alta Wind II - V) and Alta I (operating entities) have finance lease obligations issued under lease transactions whereby the respective operating entities sold and leased back undivided interests in specific assets of the project. The sale and related lease transactions are accounted for as financing arrangements as the operating entities have continued involvement with the property. The terms and conditions of each facility lease are substantially similar. Each operating entity makes rental payments as stipulated in the facility lease agreements on a semiannual basis every June 30 and December 30 through the final maturity dates. In addition, the operating entities have a credit agreement with a group of lenders that provides for the issuance of letters of credit to support certain operating and debt service obligations. Certain operations and maintenance, as well as rent reserve requirements are satisfied by letters of credit issued under the Yield Operating agreement. As of December 31, 2016, $965 million was outstanding under the finance lease obligations, and $119 million of letters of credit were issued under the credit agreement and $23 million were issued under the Yield Credit Facility.
Interest Rate Swaps — Project Financings
Many of the Company's project subsidiaries entered into interest rate swaps, intended to hedge the risks associated with interest rates on non-recourse project level debt. These swaps amortize in proportion to their respective loans and are floating for fixed where the project subsidiary pays its counterparty the equivalent of a fixed interest payment on a predetermined notional value and will receive quarterly the equivalent of a floating interest payment based on the same notional value. All interest rate swap payments by the project subsidiary and its counterparty are made quarterly and the LIBOR is determined in advance of each interest period. In connection with the acquisition of the Alta Wind Portfolio in 2015, as described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions, the Company acquired thirty-one additional interest rate swaps, thirty of which were settled during 2015. During 2015, the Company acquired thirty-two additional interest rate swaps in connection with the January 2015 and November 2015 Drop Downs, as described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions.
The following table summarizes the swaps, some of which are forward starting as indicated, related to the Company's project level debt as of December 31, 2016:
| % of Principal | Fixed Interest Rate | Floating Interest Rate | Notional Amount at December 31, 2016 (In millions) | Effective Date | Maturity Date | |||||||||||
| Alpine | 85 | % | 2.744 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | $ | 115 | various | December 31, 2029 | |||||||
| Alpine | 85 | % | 2.421 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 8 | June 24, 2014 | June 30, 2025 | ||||||||
| Avra Valley | 85 | % | 2.333 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 49 | November 30, 2012 | November 30, 2030 | ||||||||
| AWAM | 100 | % | 2.47 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 18 | May 22, 2013 | May 15, 2031 | ||||||||
| Blythe | 75 | % | 3.563 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 14 | June 25, 2010 | June 25, 2028 | ||||||||
| Borrego | 75 | % | 1.125 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 7 | April 3, 2013 | June 30, 2020 | ||||||||
| El Segundo | 75 | % | 2.417 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 330 | November 30, 2011 | August 31, 2023 | ||||||||
| Kansas South | 75 | % | 2.368 | % | 6-Month LIBOR | 23 | June 28, 2013 | December 31, 2030 | ||||||||
| Laredo Ridge | 75 | % | 2.31 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 79 | March 31, 2011 | March 31, 2026 | ||||||||
| Marsh Landing | 75 | % | 3.244 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 342 | June 28, 2013 | June 30, 2023 | ||||||||
| Roadrunner | 75 | % | 4.313 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 28 | September 30, 2011 | December 31, 2029 | ||||||||
| South Trent | 75 | % | 3.265 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 43 | June 15, 2010 | June 14, 2020 | ||||||||
| South Trent | 75 | % | 4.95 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 21 | June 30, 2020 | June 14, 2028 | ||||||||
| Tapestry | 75 | % | 2.21 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 155 | December 30, 2011 | December 21, 2021 | ||||||||
| Tapestry | 50 | % | 3.57 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 60 | December 21, 2021 | December 21, 2029 | ||||||||
| Utah Solar Portfolio | 80 | % | various | 1-Month LIBOR | 231 | December 15, 2016 | September 30, 2036 | |||||||||
| Viento Funding II | 90 | % | various | 6-Month LIBOR | 160 | various | various | |||||||||
| Viento Funding II | 90 | % | 4.985 | % | 6-Month LIBOR | 65 | July 11, 2023 | June 30, 2028 | ||||||||
| Walnut Creek Energy | 75 | % | various | 3-Month LIBOR | 276 | June 28, 2013 | May 31, 2023 | |||||||||
| WCEP Holdings | 90 | % | 4.003 | % | 3-Month LIBOR | 46 | June 28, 2013 | May 31, 2023 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 2,070 | ||||||||||||||
38
Annual Maturities
Annual payments based on the maturities of the Company's debt, for the years ending after December 31, 2016, are as follows:
| (In millions) | |||
| 2017 | $ | 291 | |
| 2018 | 304 | ||
| 2019 | 657 | ||
| 2020 | 647 | ||
| 2021 | 452 | ||
| Thereafter | 3,718 | ||
| Total | $ | 6,069 | |
Note 11 — Members' Equity
The following table lists the distributions paid on the Company's Class A, Class B, Class C and Class D units during the year ended December 31, 2016:
| Fourth Quarter 2016 | Third Quarter 2016 | Second Quarter 2016 | First Quarter 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Distributions per Class A and Class B units | $ | 0.25 | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.225 | |||||||
| Distributions per Class C and Class D units | $ | 0.25 | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.225 | |||||||
On February 15, 2017, the Company declared a quarterly distribution on its Class A, Class B, Class C and Class D units of $0.26 per share, payable on March 15, 2017.
During the first quarter of 2017 and the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company acquired the Drop Down Assets from NRG, as described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions. The difference between the cash paid and historical value of the March 2017 Drop Down Assets of $8 million was recorded as a contribution from NRG and increased the balance of its contributed capital in 2017. The difference between the cash paid and historical value of the CVSR Drop Down of $112 million was recorded as a distribution to NRG and reduced the balance of its contributed capital in 2016. The difference between the cash paid and historical value of the January 2015 and November 2015 Drop Down Assets of $109 million was recorded as a contribution from NRG and increased the balance of its contributed capital in 2015. The difference between the cash paid and historical value of the June 2014 Drop Down Assets of $113 million was recorded as a distribution to NRG and reduced the balance of its contributed capital in 2014. Prior to the date of acquisition, certain of the projects made distributions to NRG and NRG made contributions into certain projects. These amounts are reflected within the Company’s statement of stockholders’ equity as changes in the contributed capital balance. In addition, NRG maintained a 25% ownership interest in the Class B interests of NRG Wind TE Holdco. This 25% interest is also reflected within the Company’s noncontrolling interest balance.
Note 12 — Segment Reporting
The Company’s segment structure reflects how management currently operates and allocates resources. The Company's businesses are segregated based on conventional power generation, renewable businesses which consist of solar and wind, and the thermal and chilled water business. The Corporate segment reflects the Company's corporate costs. The Company's chief operating decision maker, its Chief Executive Officer, evaluates the performance of its segments based on operational measures including adjusted earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, or Adjusted EBITDA, and CAFD, as well as economic gross margin and net income (loss).
The Company generated more than 10% of its revenues from the following customers for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Customer | Conventional (%) | Renewables (%) | Conventional (%) | Renewables (%) | Conventional (%) | Renewables (%) | |||||
| SCE | 21% | 21% | 23% | 17% | 24% | 7% | |||||
| PG&E | 12% | 11% | 13% | 12% | 15% | 13% | |||||
39
| Year ended December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | Conventional Generation | Renewables | Thermal | Corporate | Total | ||||||||||||||
| Operating revenues | $ | 333 | $ | 518 | $ | 170 | $ | — | $ | 1,021 | |||||||||
| Cost of operations | 66 | 126 | 114 | — | 306 | ||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 80 | 197 | 20 | — | 297 | ||||||||||||||
| Impairment losses | — | 183 | — | — | 183 | ||||||||||||||
| General and administrative | — | — | — | 14 | 14 | ||||||||||||||
| Acquisition-related transaction and integration costs | — | — | — | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) | 187 | 12 | 36 | (15 | ) | 220 | |||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliates | 13 | 47 | — | — | 60 | ||||||||||||||
| Other income, net | 1 | 2 | — | — | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (48 | ) | (147 | ) | (7 | ) | (66 | ) | (268 | ) | |||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $ | 153 | $ | (86 | ) | $ | 29 | $ | (81 | ) | $ | 15 | |||||||
| Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||||||||
| Equity investment in affiliates | $ | 106 | $ | 1,046 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,152 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures (a) | 7 | 2 | 14 | — | 23 | ||||||||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 1,993 | $ | 5,988 | $ | 426 | $ | 213 | $ | 8,620 | |||||||||
(a) Includes accruals.
| Year ended December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | Conventional Generation | Renewables | Thermal | Corporate | Total | ||||||||||||||
| Operating revenues | $ | 336 | $ | 443 | $ | 174 | $ | — | $ | 953 | |||||||||
| Cost of operations | 59 | 136 | 126 | — | 321 | ||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 81 | 197 | 19 | — | 297 | ||||||||||||||
| General and administrative | — | — | — | 10 | 10 | ||||||||||||||
| Acquisition-related transaction and integration costs | — | — | — | 3 | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) | 196 | 110 | 29 | (13 | ) | 322 | |||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliates | 14 | 17 | — | — | 31 | ||||||||||||||
| Other income, net | 1 | 2 | — | — | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment | (7 | ) | (2 | ) | — | — | (9 | ) | |||||||||||
| Interest expense | (48 | ) | (147 | ) | (7 | ) | (52 | ) | (254 | ) | |||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $ | 156 | $ | (20 | ) | $ | 22 | $ | (65 | ) | $ | 93 | |||||||
| Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||||||||
| Equity investments in affiliates | $ | 110 | $ | 687 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 797 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures (a) | 4 | 6 | 20 | — | 30 | ||||||||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 2,102 | $ | 6,070 | $ | 428 | $ | 22 | $ | 8,622 | |||||||||
(a) Includes accruals.
40
| Year ended December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | Conventional Generation | Renewables | Thermal | Corporate | Total | ||||||||||||||
| Operating revenues | $ | 317 | $ | 316 | $ | 195 | $ | — | $ | 828 | |||||||||
| Cost of operations | 55 | 83 | 139 | — | 277 | ||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 82 | 133 | 18 | — | 233 | ||||||||||||||
| General and administrative | — | — | — | 8 | 8 | ||||||||||||||
| Acquisition-related transaction and integration costs | — | — | — | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) | 180 | 100 | 38 | (12 | ) | 306 | |||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliates | 14 | 8 | — | — | 22 | ||||||||||||||
| Other income, net | — | 5 | — | 1 | 6 | ||||||||||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment | — | (1 | ) | — | — | (1 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (53 | ) | (126 | ) | (7 | ) | (25 | ) | (211 | ) | |||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $ | 141 | $ | (14 | ) | $ | 31 | $ | (36 | ) | $ | 122 | |||||||
41
Note 13 — Related Party Transactions
In addition to the transactions and relationships described elsewhere in the notes to the consolidated financial statements, certain subsidiaries of NRG provide services to the Company's project entities. Amounts due to NRG subsidiaries are recorded as accounts payable — affiliate and amounts due to the Company from NRG subsidiaries are recorded as accounts receivable — affiliate in the Company's balance sheet. The disclosures below summarize the Company's material related party transactions with NRG and its subsidiaries that are included in the Company's operating revenues, operating costs and other income and expense.
Power Hedge Contracts by and between Renewable Entities and NRG Texas Power LLC
Certain NRG Wind TE Holdco entities, which are subsidiaries in the Renewables segment, entered into power hedge contracts with NRG Texas Power LLC, a subsidiary of NRG, and generated $16 million and $12 million of revenues during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Included in the revenues for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are unrealized losses and gains, respectively, on forward contracts with NRG Texas Power LLC hedging the sale of power from Elbow Creek, extending through the end of 2015, as further described in Note 7, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities. Effective October 2015, Elbow Creek entered into a PPA with NRG Power Marketing LLC, or NRG Power Marketing, a wholly-owned subsidiary of NRG, as further described below, and the hedge agreement between Elbow Creek and NRG Texas Power LLC was terminated.
PPA by and between Elbow Creek and NRG
In October 2015, Elbow Creek, the Company's subsidiary in the Renewables segment, entered into a PPA with NRG Power Marketing for the sale of energy and environmental attributes with the effective date of November 1, 2015, and an expiration date of October 31, 2022. Elbow Creek generated $8 million of revenue during the year ended December 31, 2016.
PPA by and between NRG Energy Center Dover LLC and NRG
In February 2016, NRG Energy Center Dover LLC, or NRG Dover, a subsidiary of the Company, entered into a PPA with NRG Power Marketing for the sale of energy and environmental attributes with an effective date of February 1, 2016 and expiration date of December 31, 2018. NRG Dover generated $5 million of revenue during the year ended December 31, 2016. The agreement in place is in addition to the existing Power Sales and Services Agreement described further below.
Power Sales and Services Agreement by and between NRG Energy Center Dover LLC and NRG
NRG Dover is party to a Power Sales and Services Agreement with NRG Power Marketing. The agreement is automatically renewed on a month-to-month basis unless terminated by either party upon at least 30 day written notice. Under the agreement, NRG Power Marketing has the exclusive right to (i) manage, market and sell power, (ii) procure fuel and fuel transportation for operation of the Dover generating facility, to include for purposes other than generating power, (iii) procure transmission services required for the sale of power and (iv) procure and market emissions credits for operation of the Dover generating facility.
In addition, NRG Power Marketing has the exclusive right and obligation to direct the output from the generating facility, in accordance with and to meet the terms of any power sales contracts executed against the power generation of the Dover facility. Under the agreement, NRG Power Marketing pays NRG Dover gross receipts generated through sales, less costs incurred by NRG Power Marketing related to providing such services as transmission and delivery costs, as well as fuel costs. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, NRG Dover purchased approximately $1 million, $5 million and $10 million, respectively, of natural gas from NRG Power Marketing under the Power Sales and Services Agreement.
Energy Marketing Services Agreement by and between NRG Energy Center Minneapolis LLC and NRG
NRG Energy Center Minneapolis LLC, or NRG Minneapolis, a subsidiary of the Company is party to an Energy Marketing Services Agreement with NRG Power Marketing. The agreement commenced in August 2014 and is automatically renewed annually unless terminated by either party upon at least 90 day written notice prior to the end of any term. Under the agreement, NRG Power Marketing will procure fuel and fuel transportation for the operation of the Minneapolis generating facility. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, NRG Minneapolis purchased approximately $7 million, $8 million and $2 million, respectively, of natural gas from NRG Power Marketing.
42
Operations and Maintenance (O&M) Services Agreements by and between Thermal Entities and NRG
On October 1, 2014, NRG entered into Plant O&M Services Agreements with certain wholly-owned subsidiaries of the Company. NRG provides necessary and appropriate services to operate and maintain the subsidiaries' plant operations, businesses and thermal facilities. NRG is to be reimbursed for the provided services, as well as for all reasonable and related expenses and expenditures, and payments to third parties for services and materials rendered to or on behalf of the parties to the agreements. NRG is not entitled to any management fee or mark-up under the agreements. Prior to October 1, 2014, NRG provided the same services to Thermal entities on an informal basis. For each of the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, total fees incurred under the agreements were $29 million. For the year ended December 31, 2014, total fees incurred were $27 million. There was a balance of $20 million and $29 million due to NRG in accounts payable — affiliate as of December 31, 2016, and 2015, respectively. As of December 31, 2016, $11 million of the balance was recorded in the current liabilities of the consolidated balance sheet and $9 million was recorded in non-current liabilities of the consolidated balance sheet.
O&M Services Agreements by and between GenConn and NRG
GenConn incurs fees under two O&M agreements with wholly-owned subsidiaries of NRG. The fees incurred under the agreements were $5 million, $4 million and $6 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
O&M Services Agreements by and between El Segundo and NRG El Segundo Operations
El Segundo incurs fees under an O&M agreement with NRG El Segundo Operations, Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of NRG. Under the O&M agreement, NRG El Segundo Operations, Inc. manages, operates and maintains the El Segundo facility for an initial term of ten years following the commercial operations date. For each of the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the costs incurred under the agreement were approximately $4 million. There was a balance of $1 million due to NRG El Segundo in accounts payable — affiliate as of December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Administrative Services Agreement by and between Marsh Landing and GenOn Energy Services, LLC and related Assignment and Assumption Agreement
Marsh Landing was a party to an administrative services agreement with GenOn Energy Services, LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of NRG, through December 18, 2016. Under the agreement, GenOn Energy Services, LLC provided processing and invoice payment services on behalf of Marsh Landing. Marsh Landing reimbursed GenOn Energy Services, LLC for the amounts it paid. The Company reimbursed costs under this agreement of approximately $14 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, and $13 million for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2014, $2 million was capitalized. There was a balance of $1 million and $6 million due to GenOn Energy Services, LLC in accounts payable — affiliate as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Marsh Landing had the right to terminate the agreement for convenience upon thirty days prior written notice. In lieu of a termination of the agreement, Marsh Landing requested that GenOn Energy Services LLC enter into an assignment and assumption agreement with NRG West Coast LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of NRG. The administrative services agreement was assigned to NRG West Coast LLC on December 19, 2016.
Administrative Services Agreement by and between CVSR and NRG
CVSR was a party to an administrative services agreement with NRG Energy Services, a wholly-owned subsidiary of NRG, which was subsequently assigned to NRG Renew Operations & Maintenance LLC, or RENOM, on July 15, 2015. The Company reimbursed a total of $4 million and $7 million to NRG Energy Services for the expenses incurred for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. See below for further discussions of the costs incurred by CVSR under the administrative services agreement with RENOM in 2016.
Administrative Services Agreement by and between the Company and NRG Renew Operations & Maintenance LLC
Various wholly-owned subsidiaries of the Company in the Renewables segment are party to an administrative services agreement with RENOM, a wholly-owned subsidiary of NRG, which provides O&M services on behalf of these entities. The Company incurred total expenses for these services in the amount of $13 million and $7 million for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. There was a balance of $5 million and $1 million due to RENOM as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
43
O&M Services Agreements by and between Walnut Creek and NRG
Walnut Creek incurs fees under an O&M agreement with NRG Energy Services LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of NRG. Under the O&M agreement, NRG Energy Services LLC manages, operates and maintains the Walnut Creek facility and is reimbursed for the services provided. The Company incurred total expenses for these services in the amount of $3 million for each of the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 and $2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Management Services Agreement by and between the Company and NRG
NRG provides the Company with various operational, management, and administrative services, which include human resources, accounting, tax, legal, information systems, treasury, and risk management, as set forth in the Management Services Agreement. As of December 31, 2016, the base management fee was approximately $7.5 million per year, subject to an inflation-based adjustment annually, at an inflation factor based on the year-over-year U.S. consumer price index. The fee is also subject to adjustments following the consummation of future acquisitions and as a result of a change in the scope of services provided under the Management Services Agreement. During the year ended December 31, 2016, the fee was increased by approximately $0.5 million per year, primarily due to the acquisition of the CVSR Drop Down. In addition to the base management fee, the Company is also responsible for any expenses that are directly incurred and paid for by NRG on behalf of the Company. Costs incurred under this agreement were approximately $10 million, $8 million and $6 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. There was a balance of $3 million in accounts payable — affiliate due to NRG as of December 31, 2016.
Administrative Services Agreements by and between Wind TE Holdco LLC and NRG
NRG Asset Services LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of NRG, provides support services to NRG Wind TE Holdco LLC project entities pursuant to various support services agreements. The agreements provide for administrative and support services and reimbursements of certain insurance, consultant and credit costs. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the costs incurred under the agreements were $2 million, $3 million and $1 million, respectively.
Accounts Payable to NRG Repowering Holdings LLC
During 2013, NRG Repowering Holdings, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of NRG, made payments to BA Leasing BSC, LLC, or BA Leasing, of $18 million, which were expected to be repaid with the proceeds of the cash grant received by BA Leasing with respect to the PFMG DG Solar Projects, in connection with a sale-leaseback arrangement between the PFMG DG Solar Projects and BA Leasing. As of December 31, 2014, PFMG DG Solar Projects had a corresponding receivable for the reimbursement of the cash grant from BA Leasing and related payable to NRG Repowering Holdings, LLC. In the first quarter of 2014, the PFMG DG Solar Projects received $11 million from BA Leasing and reduced the remaining receivable with an offset to the deferred liability recorded in connection with the sale - leaseback arrangement. The PFMG DG Solar Projects utilized the $11 million to repay NRG Repowering Holdings LLC. There was a balance of $7 million in accounts payable — affiliate as of December 31, 2015 which was settled in October 2016 with an offset to contributed capital in the equity section of the consolidated balance sheet.
EPC Agreement by and between NECP and NRG
On October 31, 2016, NRG Business Services LLC, a subsidiary of NRG, and NECP, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, entered into an EPC agreement for the construction of a 73 MWt district energy system for NECP to provide 150 kpph of steam, 6,750 tons of chilled water and 7.5 MW of emergency backup power service to UPMC Mercy. The initial term of the energy services agreement with UPMC Mercy will be for a period of twenty years from the service commencement date. Pursuant to the terms of the EPC agreement, NECP agreed to pay NRG Business Services LLC $79 million, subject to adjustment based upon certain conditions in the EPC agreement, upon substantial completion of the project. The project is expected to reach COD in the first quarter of 2018. On January 5, 2017, the parties amended the EPC Agreement, based on a customer change order, to increase the capacity of the district energy system from 73 MWt to 80 MWt, which also increased the payment from $79 million to $87 million.
Note 14 — Commitments and Contingencies
Operating Lease Commitments
The Company leases certain facilities and equipment under operating leases, some of which include escalation clauses, expiring on various dates through 2048. The effects of these scheduled rent increases, leasehold incentives, and rent concessions are recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term unless another systematic and rational allocation basis is more representative of the time pattern in which the leased property is physically employed. Lease expense under operating leases was $15 million, $10 million and $9 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
44
Future minimum lease commitments under operating leases for the years ending after December 31, 2016, are as follows:
| Period | (In millions) | ||
| 2017 | $ | 9 | |
| 2018 | 9 | ||
| 2019 | 10 | ||
| 2020 | 9 | ||
| 2021 | 9 | ||
| Thereafter | 152 | ||
| Total | $ | 198 | |
Gas and Transportation Commitments
The Company has entered into contractual arrangements to procure power, fuel and associated transportation services. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company purchased $32 million, $40 million and $55 million, respectively, under such arrangements. As further described in Note 13 Related Party Transactions, these balances include intercompany purchases in the amount of $8 million, $13 million, and $12 million, respectively.
As of December 31, 2016, the Company's commitments under such outstanding agreements are estimated as follows:
| Period | (In millions) | ||
| 2017 | $ | 13 | |
| 2018 | 5 | ||
| 2019 | 2 | ||
| 2020 | 3 | ||
| 2021 | 3 | ||
| Thereafter | 19 | ||
| Total | $ | 45 | |
Contingencies
The Company's material legal proceedings are described below. The Company believes that it has valid defenses to these legal proceedings and intends to defend them vigorously. The Company records reserves for estimated losses from contingencies when information available indicates that a loss is probable and the amount of the loss, or range of loss, can be reasonably estimated. In addition, legal costs are expensed as incurred. Management assesses such matters based on current information and makes a judgment concerning its potential outcome, considering the nature of the claim, the amount and nature of damages sought and the probability of success. The Company is unable to predict the outcome of the legal proceedings below or reasonably estimate the scope or amount of any associated costs and potential liabilities. As additional information becomes available, management adjusts its assessment and estimates of such contingencies accordingly. Because litigation is subject to inherent uncertainties and unfavorable rulings or developments, it is possible that the ultimate resolution of the Company's liabilities and contingencies could be at amounts that are different from its currently recorded reserves and that such difference could be material.
In addition to the legal proceedings noted below, the Company and its subsidiaries are party to other litigation or legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business. In management's opinion, the disposition of these ordinary course matters will not materially adversely affect the Company's consolidated financial position, results of operations, or cash flows.
Braun v. NRG Yield, Inc. — On April 19, 2016, plaintiffs filed a putative class action lawsuit against NRG Yield, Inc., the current and former members of its board of directors individually, and other parties in California Superior Court in Kern County, CA. Plaintiffs allege various violations of the Securities Act due to the defendants’ alleged failure to disclose material facts related to low wind production prior to NRG Yield, Inc.'s June 22, 2015 Class C common stock offering. Plaintiffs seek compensatory damages, rescission, attorney’s fees and costs. On August 3, 2016, the court approved a stipulation entered into by the parties. The stipulation provided that the plaintiffs would file an amended complaint by August 19, 2016, which they did on August 18, 2016. The defendants filed demurrers and a motion challenging jurisdiction on October 18, 2016. On February 24, 2017, the court approved the parties' stipulation which provides the plaintiffs' opposition is due on June 15, 2017 and defendants' reply is due on August 14, 2017.
45
Ahmed v. NRG Energy, Inc. and the NRG Yield Board of Directors — On September 15, 2016, plaintiffs filed a putative class action lawsuit against NRG Energy, Inc., the directors of NRG Yield, Inc., and other parties in the Delaware Chancery Court. The complaint alleges that the defendants breached their respective fiduciary duties with regard to the recapitalization of NRG Yield, Inc. common stock in 2015. The plaintiffs generally seek economic damages, attorney’s fees and injunctive relief. The defendants filed a motion to dismiss the lawsuit on December 21, 2016. Plaintiffs filed their objection to the motion to dismiss on February 15, 2017. Oral argument is scheduled for June 20, 2017.
46
Note 15 — Unaudited Quarterly Data
Refer to Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies and Note 3, Business Acquisitions for a description of the effect of unusual or infrequently occurring events during the quarterly periods. Summarized unaudited quarterly financial data is as follows:
| Quarter Ended | |||||||||||||||
| December 31, | September 30, | June 30, | March 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||
| Operating Revenues | $ | 232 | $ | 272 | $ | 283 | $ | 234 | |||||||
| Operating (Loss) Income | (99 | ) | 118 | 128 | 73 | ||||||||||
Net (Loss) Income (a) | (139 | ) | 67 | 81 | 6 | ||||||||||
Net (Loss) Income (b) | (149 | ) | 64 | 79 | 4 | ||||||||||
| Change | 10 | $ | 3 | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | ||||||||
(a) The Company's unaudited quarterly financial data was recast for the effect of the March 2017 Drop Down Assets acquisition.
(b) As previously reported.
| Quarter Ended | |||||||||||||||
| December 31, | September 30, | June 30, | March 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||
| Operating Revenues | $ | 224 | $ | 256 | $ | 259 | $ | 214 | |||||||
| Operating Income | 71 | 102 | 99 | 50 | |||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) (a) | 20 | 47 | 50 | (24 | ) | ||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) (b) | 20 | 44 | 48 | (24 | ) | ||||||||||
| Change | $ | — | $ | 3 | $ | 2 | $ | — | |||||||
(a) The Company's unaudited quarterly financial data was recast for the effect of the March 2017 Drop Down Assets acquisition.
(b) As previously reported.
47
Note 16 — Condensed Consolidating Financial Information
As of December 31, 2016, Yield Operating LLC had outstanding $500 million of the 2024 Senior Notes and $350 million of the 2026 Senior Notes, collectively Senior Notes, as described in Note 10, Long-term Debt. These Senior Notes are guaranteed by the Company, as well as certain of the Company's subsidiaries, or guarantor subsidiaries. These guarantees are both joint and several. The non-guarantor subsidiaries include the rest of the Company's subsidiaries, including the ones that are subject to project financing.
Unless otherwise noted below, each of the following guarantor subsidiaries fully and unconditionally guaranteed the Senior Notes as of December 31, 2016:
| NRG Yield LLC |
| Alta Wind 1-5 Holding Company, LLC |
| Alta Wind Company, LLC |
| NRG Energy Center Omaha Holdings LLC |
| NRG Energy Center Omaha LLC |
| NYLD Fuel Cell Holdings LLC |
| UB Fuel Cell, LLC |
| NRG South Trent Holdings LLC |
| NRG Yield DGPV Holding LLC |
| NRG Yield RPV Holding LLC |
Yield Operating LLC conducts much of its business through and derives much of its income from its subsidiaries. Therefore, its ability to make required payments with respect to its indebtedness and other obligations depends on the financial results and condition of its subsidiaries and Yield Operating LLC's ability to receive funds from its subsidiaries. There are no restrictions on the ability of any of the guarantor subsidiaries to transfer funds to Yield Operating LLC. However, there may be restrictions for certain non-guarantor subsidiaries.
The following condensed consolidating financial information presents the financial information of Yield LLC, Yield Operating LLC, the issuer of the Senior Notes, the guarantor subsidiaries and the non-guarantor subsidiaries in accordance with Rule 3-10 under the SEC Regulation S-X. The financial information may not necessarily be indicative of results of operations or financial position had the guarantor subsidiaries or non-guarantor subsidiaries operated as independent entities.
In this presentation, Yield LLC consists of parent company operations. Guarantor subsidiaries and non-guarantor subsidiaries of Yield LLC are reported on an equity basis. For companies acquired, the fair values of the assets and liabilities acquired have been presented on a push-down accounting basis. As described in Note 3, Business Acquisitions, the Company completed the acquisitions of the March 2017 Drop Down Assets, CVSR Drop Down and November 2015 Drop Down Assets from NRG on March 27, 2017, September 1, 2016 and November 3, 2015, respectively. The guidance requires retrospective combination of the entities for all periods presented as if the combination has been in effect since the inception of common control. Accordingly, the Company prepared its condensed consolidating financial statements to reflect the transfers as if they had taken place from the beginning of the financial statements period. The Company has recorded all minority interests in NRG Wind TE Holdco as noncontrolling interest in the Consolidated Financial Statements for all periods presented.
In addition, the condensed parent company financial statements are provided in accordance with Rule 12-04, Schedule I of Regulation S-X, as the restricted net assets of Yield LLC’s subsidiaries exceed 25 percent of the consolidated net assets of Yield LLC. These statements should be read in conjunction with the consolidated statements and notes thereto of NRG Yield LLC. For a discussion of Yield LLC's long-term debt, see Note 10, Long-term Debt. For a discussion of Yield LLC's commitments and contingencies, see Note 14, Commitments and Contingencies. For a discussion of Yield LLC's distributions to Yield, Inc. and NRG Energy, see Note 11, Members' Equity.
48
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2016
NRG Yield LLC (a) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) | Eliminations(b) | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating Revenues | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating revenues | $ | — | $ | 22 | $ | 999 | $ | 1 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 1,021 | ||||||||||
| Operating Costs and Expenses | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of operations | — | 14 | 292 | 1 | (1 | ) | 306 | ||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | — | 5 | 292 | — | — | 297 | |||||||||||||||||
| Impairment losses | — | — | 183 | — | — | 183 | |||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative | 2 | — | — | 12 | — | 14 | |||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition-related transaction and integration costs | — | — | — | 1 | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | 2 | 19 | 767 | 14 | (1 | ) | 801 | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating (Loss) Income | (2 | ) | 3 | 232 | (13 | ) | — | 220 | |||||||||||||||
| Other Income (Expense) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of consolidated affiliates | 159 | 10 | — | 66 | (235 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings (losses) of unconsolidated affiliates | — | 9 | 21 | 30 | — | 60 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other income, net | — | — | 3 | — | — | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | — | — | (202 | ) | (66 | ) | — | (268 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Total other income (expense), net | 159 | 19 | (178 | ) | 30 | (235 | ) | (205 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | 157 | 22 | 54 | 17 | (235 | ) | 15 | ||||||||||||||||
| Less: Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | (1 | ) | (142 | ) | 1 | (142 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Net Income Attributable to NRG Yield LLC | $ | 157 | $ | 22 | $ | 55 | $ | 159 | $ | (236 | ) | $ | 157 | ||||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
49
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Year Ended December 31, 2016
NRG Yield LLC (a) | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) | Eliminations(b) | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Income | $ | 157 | $ | 22 | $ | 54 | $ | 17 | $ | (235 | ) | $ | 15 | ||||||||||
| Other Comprehensive Income | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain on derivatives | 13 | 1 | 10 | 13 | (24 | ) | 13 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | 13 | 1 | 10 | 13 | (24 | ) | 13 | ||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income | 170 | 23 | 64 | 30 | (259 | ) | 28 | ||||||||||||||||
| Less: Comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | (1 | ) | (142 | ) | 1 | (142 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income Attributable to NRG Yield LLC | $ | 170 | $ | 23 | $ | 65 | $ | 172 | $ | (260 | ) | $ | 170 | ||||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
50
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2016
NRG Yield LLC (a) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) | Eliminations(b) | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||
| ASSETS | (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 211 | $ | — | $ | 110 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 321 | ||||||||||||
| Restricted cash | — | — | 165 | — | — | 165 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable — trade | — | 2 | 90 | — | — | 92 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable — affiliates | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Inventory | — | 2 | 37 | — | — | 39 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative instruments | — | — | 2 | — | — | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Notes receivable — current | — | — | 16 | — | — | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Prepayments and other current assets | — | — | 19 | 1 | — | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total current assets | 211 | 4 | 440 | 1 | — | 656 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | — | 59 | 5,401 | — | — | 5,460 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment in consolidated subsidiaries | 1,780 | 527 | — | 3,212 | (5,519 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Equity investments in affiliates | — | 171 | 600 | 381 | — | 1,152 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Notes receivable — non-current | — | — | 14 | — | — | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Intangible assets, net | — | 56 | 1,230 | — | — | 1,286 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative instruments | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other non-current assets | — | — | 50 | 1 | — | 51 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total other assets | 1,780 | 754 | 1,895 | 3,594 | (5,519 | ) | 2,504 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 1,991 | $ | 817 | $ | 7,736 | $ | 3,595 | $ | (5,519 | ) | $ | 8,620 | |||||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
51
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING BALANCE SHEETS
(Continued)
December 31, 2016
NRG Yield LLC (a) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) | Eliminations(b) | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS' EQUITY | (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt — external | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 291 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 291 | ||||||||||||
| Accounts payable — trade | — | 2 | 18 | 3 | — | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable — affiliate | — | 7 | 15 | 18 | — | 40 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative instruments | — | — | 32 | — | — | 32 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | — | 1 | 60 | 24 | — | 85 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total current liabilities | — | 10 | 416 | 45 | — | 471 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt — external | — | — | 4,259 | 839 | — | 5,098 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt — affiliate | — | — | — | 618 | — | 618 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable — affiliate | — | — | 9 | — | — | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative instruments | — | — | 44 | — | — | 44 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other non-current liabilities | — | — | 76 | — | — | 76 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total non-current liabilities | — | — | 4,388 | 1,457 | — | 5,845 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Liabilities | — | 10 | 4,804 | 1,502 | — | 6,316 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commitments and Contingencies | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Members' Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contributed capital | 1,995 | 874 | 2,920 | 1,971 | (5,765 | ) | 1,995 | |||||||||||||||||
| Retained earnings (accumulated deficit) | 79 | (65 | ) | 35 | (108 | ) | 138 | 79 | ||||||||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (83 | ) | (2 | ) | (87 | ) | (83 | ) | 172 | (83 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest | — | — | 64 | 313 | (64 | ) | 313 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total Members' Equity | 1,991 | 807 | 2,932 | 2,093 | (5,519 | ) | 2,304 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total Liabilities and Members’ Equity | $ | 1,991 | $ | 817 | $ | 7,736 | $ | 3,595 | $ | (5,519 | ) | $ | 8,620 | |||||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
52
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2016
NRG Yield LLC (a) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Cash Provided by (Used in) Operating Activities | $ | — | $ | 62 | $ | 546 | $ | (39 | ) | $ | 569 | |||||||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Changes in investments in consolidated subsidiaries | 325 | — | (21 | ) | (304 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
| Acquisition of Drop Down Assets, net of cash acquired | — | — | — | (77 | ) | (77 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures | — | — | (20 | ) | — | (20 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Increase in restricted cash | — | — | (34 | ) | — | (34 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Cash receipts from notes receivable | — | — | 17 | — | 17 | |||||||||||||||
| Return of investment from unconsolidated affiliates | — | 16 | — | 12 | 28 | |||||||||||||||
| Net investments in unconsolidated affiliates | — | (80 | ) | (3 | ) | — | (83 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | 4 | — | 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Cash Provided by (Used in) Investing Activities | 325 | (64 | ) | (57 | ) | (369 | ) | (165 | ) | |||||||||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Contributions from tax equity investors, net of distributions | — | — | — | 5 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Distributions and return of capital to NRG prior to the acquisition of Drop Down Assets | — | — | (170 | ) | — | (170 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Transfer of funds under intercompany cash management arrangement | 54 | 2 | — | (56 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
| (Payments of) proceeds from distributions | (183 | ) | — | (420 | ) | 420 | (183 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from the revolving credit facility | — | — | — | 60 | 60 | |||||||||||||||
| Payments for the revolving credit facility | — | — | — | (366 | ) | (366 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | — | — | 390 | 350 | 740 | |||||||||||||||
| Payment of debt issuance costs | — | — | (10 | ) | (5 | ) | (15 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Payments for long-term debt | — | — | (264 | ) | — | (264 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net Cash (Used in) Provided by Financing Activities | (129 | ) | 2 | (474 | ) | 408 | (193 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net Increase in Cash and Cash Equivalents | 196 | — | 15 | — | 211 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Period | 15 | — | 95 | — | 110 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at End of Period | $ | 211 | $ | — | $ | 110 | $ | — | $ | 321 | ||||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
53
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2015
NRG Yield LLC (a) (c) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries (c) | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) (c) | Eliminations(b) (c) | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating Revenues | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating revenues | $ | — | $ | 21 | $ | 922 | $ | 10 | $ | — | $ | 953 | |||||||||||
| Operating Costs and Expenses | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of operations | — | 14 | 307 | — | — | 321 | |||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | — | 4 | 293 | — | — | 297 | |||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative | — | — | — | 10 | — | 10 | |||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition-related transaction and integration costs | — | — | — | 3 | — | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | — | 18 | 600 | 13 | — | 631 | |||||||||||||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) | — | 3 | 322 | (3 | ) | — | 322 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other Income (Expense) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings (losses) of consolidated affiliates | 144 | (43 | ) | — | 123 | (224 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||
| Equity in (losses) earnings of unconsolidated affiliates | — | (2 | ) | 8 | 25 | — | 31 | ||||||||||||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment | — | — | (9 | ) | — | — | (9 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Other income, net | — | — | 3 | — | — | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | — | — | (202 | ) | (52 | ) | — | (254 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Total other income (expense) | 144 | (45 | ) | (200 | ) | 96 | (224 | ) | (229 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | 144 | (42 | ) | 122 | 93 | (224 | ) | 93 | |||||||||||||||
| Less: Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | (2 | ) | (51 | ) | 2 | (51 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) Attributable to NRG Yield LLC | $ | 144 | $ | (42 | ) | $ | 124 | $ | 144 | $ | (226 | ) | $ | 144 | |||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
(c) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
54
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
For the Year Ended December 31, 2015
NRG Yield LLC (a) (c) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries (c) | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) (c) | Eliminations(b) (c) | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $ | 144 | $ | (42 | ) | $ | 122 | $ | 93 | $ | (224 | ) | $ | 93 | |||||||||
| Other Comprehensive Income | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on derivatives | (16 | ) | — | (18 | ) | (17 | ) | 34 | (17 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss | (16 | ) | — | (18 | ) | (17 | ) | 34 | (17 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income (Loss) | 128 | (42 | ) | 104 | 76 | (190 | ) | 76 | |||||||||||||||
| Less: Comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | (2 | ) | (52 | ) | 2 | (52 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income (Loss) Attributable to NRG Yield LLC | $ | 128 | $ | (42 | ) | $ | 106 | $ | 128 | $ | (192 | ) | $ | 128 | |||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
(c) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
55
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2015
NRG Yield LLC (a)(c) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries (c) | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) (c) | Eliminations(b)(c) | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||
| ASSETS | (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 15 | $ | — | $ | 95 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 110 | ||||||||||||
| Restricted cash | — | — | 131 | — | — | 131 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable — trade | — | 1 | 100 | — | — | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable — affiliates | 55 | 4 | 6 | 10 | (71 | ) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Inventory | — | 2 | 34 | — | — | 36 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Notes receivable — current | — | — | 17 | 3 | (3 | ) | 17 | |||||||||||||||||
| Prepayments and other current assets | — | 1 | 19 | — | — | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total current assets | 70 | 8 | 402 | 13 | (74 | ) | 419 | |||||||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | — | 61 | 5,817 | — | — | 5,878 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment in consolidated subsidiaries | 2,110 | 548 | — | 3,635 | (6,293 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Equity investments in affiliates | — | 128 | 276 | 393 | — | 797 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Notes receivable — non-current | — | — | 30 | — | — | 30 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Intangible assets, net | — | 57 | 1,305 | — | — | 1,362 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other non-current assets | — | — | 134 | 2 | — | 136 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total other assets | 2,110 | 733 | 1,745 | 4,030 | (6,293 | ) | 2,325 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 2,180 | $ | 802 | $ | 7,964 | $ | 4,043 | $ | (6,367 | ) | $ | 8,622 | |||||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
(c) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
56
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING BALANCE SHEETS
(Continued)
December 31, 2015
NRG Yield LLC (a) (c) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries (c) | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) (c) | Eliminations (b) (c) | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS' EQUITY | (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt — external | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 267 | $ | — | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 264 | |||||||||||
| Accounts payable — trade | — | 1 | 19 | 3 | — | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable — affiliate | — | 8 | 46 | 104 | (72 | ) | 86 | |||||||||||||||||
| Derivative instruments | — | 1 | 38 | — | — | 39 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | — | 1 | 58 | 17 | — | 76 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total current liabilities | — | 11 | 428 | 124 | (75 | ) | 488 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt — external | — | — | 3,943 | 800 | — | 4,743 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt — affiliate | — | — | — | 618 | — | 618 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative instruments | — | — | 61 | — | — | 61 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other non-current liabilities | — | — | 72 | — | — | 72 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total non-current liabilities | — | — | 4,076 | 1,418 | — | 5,494 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Liabilities | — | 11 | 4,504 | 1,542 | (75 | ) | 5,982 | |||||||||||||||||
| Commitments and Contingencies | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Members' Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contributed capital | 2,176 | 879 | 3,491 | 2,108 | (6,478 | ) | 2,176 | |||||||||||||||||
| Retained earnings (accumulated deficit) | 100 | (85 | ) | (5 | ) | 100 | (10 | ) | 100 | |||||||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (96 | ) | (3 | ) | (97 | ) | (96 | ) | 196 | (96 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest | — | — | 71 | 389 | — | 460 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Members' Equity | 2,180 | 791 | 3,460 | 2,501 | (6,292 | ) | 2,640 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total Liabilities and Members’ Equity | $ | 2,180 | $ | 802 | $ | 7,964 | $ | 4,043 | $ | (6,367 | ) | $ | 8,622 | |||||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
(c) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
57
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2015
NRG Yield LLC (a) (b) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries (b) | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) (b) | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Cash Provided by (Used in) Operating Activities | $ | — | $ | 19 | $ | 420 | $ | (18 | ) | $ | 421 | |||||||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of businesses, net of cash acquired | — | — | — | (37 | ) | (37 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Changes in investments in consolidated subsidiaries | (464 | ) | — | 285 | 179 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of Drop Down Assets, net of cash acquired | — | — | — | (698 | ) | (698 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures | — | — | (29 | ) | — | (29 | ) | |||||||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in restricted cash | — | — | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Decrease in notes receivable | — | — | 17 | — | 17 | |||||||||||||||
| Return of investment from unconsolidated affiliates | — | — | — | 42 | 42 | |||||||||||||||
| Investments in unconsolidated affiliates | — | (28 | ) | — | (374 | ) | (402 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net Cash Used in Investing Activities | (464 | ) | (28 | ) | 272 | (888 | ) | (1,108 | ) | |||||||||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Transfer of funds under intercompany cash management arrangement | (309 | ) | 9 | — | 300 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Net contributions from noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | 122 | 122 | |||||||||||||||
| Distributions to NRG for NRG Wind TE Holdco and CVSR | — | — | (76 | ) | — | (76 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from the issuance of Class C and Class A units | 599 | — | — | — | 599 | |||||||||||||||
| (Payments of) proceeds from distributions | (139 | ) | — | (392 | ) | 392 | (139 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from the revolving credit facility | — | — | — | 551 | 551 | |||||||||||||||
| Payments for the revolving credit facility | — | — | — | (245 | ) | (245 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt - external | — | — | 6 | — | 6 | |||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt affiliate | — | — | — | 281 | 281 | |||||||||||||||
| Payment of debt issuance costs | — | — | (6 | ) | (1 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Payments for long-term debt | — | — | (230 | ) | (494 | ) | (724 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net Cash Provided by (Used in) Financing Activities | 151 | 9 | (698 | ) | 906 | 368 | ||||||||||||||
| Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash and Cash Equivalents | (313 | ) | — | (6 | ) | — | (319 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Period | 328 | — | 101 | — | 429 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at End of Period | $ | 15 | $ | — | $ | 95 | $ | — | $ | 110 | ||||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
58
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2014
NRG Yield LLC (a) (c) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries (c) | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) (c) | Eliminations(b) (c) | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating Revenues | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating revenues | $ | — | $ | 24 | $ | 804 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 828 | |||||||||||
| Operating Costs and Expenses | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of operations | — | 16 | 261 | — | — | 277 | |||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | — | 4 | 229 | — | — | 233 | |||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative | — | — | — | 8 | — | 8 | |||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition-related transaction and integration costs | — | — | — | 4 | — | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total operating costs and expenses | — | 20 | 490 | 12 | — | 522 | |||||||||||||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) | — | 4 | 314 | (12 | ) | — | 306 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other Income (Expense) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings (losses) of consolidated affiliates | 118 | (22 | ) | — | 139 | (235 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||
| Equity in (losses) earnings of unconsolidated affiliates | — | — | 3 | 19 | — | 22 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other income, net | 1 | — | 5 | — | — | 6 | |||||||||||||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment | — | — | (1 | ) | — | — | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | — | — | (186 | ) | (25 | ) | — | (211 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Total other income (expense), net | 119 | (22 | ) | (179 | ) | 133 | (235 | ) | (184 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | 119 | (18 | ) | 135 | 121 | (235 | ) | 122 | |||||||||||||||
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | 3 | — | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) Attributable to NRG Yield LLC | $ | 119 | $ | (18 | ) | $ | 135 | $ | 118 | $ | (235 | ) | $ | 119 | |||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
(c) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
59
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
For the Year Ended December 31, 2014
NRG Yield LLC (a) (c) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries (c) | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) (c) | Eliminations (b) (c) | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $ | 119 | $ | (18 | ) | $ | 135 | $ | 121 | $ | (235 | ) | $ | 122 | |||||||||
| Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on derivatives | (63 | ) | — | (63 | ) | (65 | ) | 126 | (65 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss | (63 | ) | — | (63 | ) | (65 | ) | 126 | (65 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income (Loss) | 56 | (18 | ) | 72 | 56 | (109 | ) | 57 | |||||||||||||||
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | 1 | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income (Loss) Attributable to NRG Yield LLC | $ | 56 | $ | (18 | ) | $ | 72 | $ | 55 | $ | (109 | ) | $ | 56 | |||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
(c) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
60
NRG YIELD LLC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2014
NRG Yield LLC (a) (b) | Other Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries (b) | NRG Yield Operating LLC (Note Issuer) (b) | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Cash Provided by (Used in) Operating Activities | $ | — | $ | 12 | $ | 357 | $ | (7 | ) | $ | 362 | |||||||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Changes in investments in consolidated subsidiaries | (530 | ) | — | 36 | 494 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of businesses, net of cash acquired | — | — | — | (901 | ) | (901 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Acquisition of Drop Down Assets, net of cash acquired | — | — | 46 | (357 | ) | (311 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures | — | — | (60 | ) | — | (60 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Receipt of indemnity from supplier | — | — | 57 | — | 57 | |||||||||||||||
| Decrease in restricted cash, net | — | — | 25 | — | 25 | |||||||||||||||
| Decrease in notes receivable | — | — | 12 | 2 | 14 | |||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from renewable energy grants | — | — | 422 | — | 422 | |||||||||||||||
| Return of investment from unconsolidated affiliates | — | — | — | 4 | 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Investments in unconsolidated affiliates | — | — | (2 | ) | — | (2 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | 11 | — | 11 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Cash (Used in) Provided by Investing Activities | (530 | ) | — | 547 | (758 | ) | (741 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Transfer of funds under intercompany cash management arrangement | 326 | (12 | ) | — | (314 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
| Contributions from tax equity investors | — | — | 190 | — | 190 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital contributions from NRG | — | — | 2 | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Distributions and return of capital to NRG prior to the acquisition of Drop Down Assets | — | — | (333 | ) | — | (333 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock | 630 | — | — | — | 630 | |||||||||||||||
| (Payments of) proceeds from distributions | (101 | ) | — | (232 | ) | 232 | (101 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net borrowings from the revolving credit facility | — | — | — | 500 | 500 | |||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt — external | — | — | 178 | — | 178 | |||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt — affiliate | — | — | — | 337 | 337 | |||||||||||||||
| Payments of long-term debt — external | — | — | (626 | ) | — | (626 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Payment of debt issuance costs | — | — | (18 | ) | (10 | ) | (28 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Net Cash Provided by (Used in) Financing Activities | 855 | (12 | ) | (839 | ) | 745 | 749 | |||||||||||||
| Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash and Cash Equivalents | 325 | — | 65 | (20 | ) | 370 | ||||||||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Period | 3 | — | 36 | 20 | 59 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at End of Period | $ | 328 | $ | — | $ | 101 | $ | — | $ | 429 | ||||||||||
(a) Shown separately from the other guarantors in lieu of preparing Schedule I pursuant to the requirements of Rule 5-04(c) of Regulation S-X.
(b) Retrospectively adjusted as discussed in Note 1, Nature of Business.
61
Item 16 — Form 10-K Summary
None.
62