AS FILED WITH THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION ON MARCH 8, 2023
Registration No. 333-
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM F-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER
THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
Midatech Pharma plc
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| England and Wales | 2834 | Not Applicable |
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | (Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) | (IRS Employer Identification No.) |
Caspian Point
Caspian Way
Cardiff, CF10 4DQ, United Kingdom
Tel: +44 29 20480 180
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of registrant’s principal executive offices)
Donald J. Puglisi
Puglisi & Associates
850 Library Ave., Suite 204
Newark, Delaware 19711
Tel: (302) 738-6680
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copies of communications to:
Jason S. McCaffrey
Mintz, Levin, Cohn, Ferris, Glovsky & Popeo, P.C.
One Financial Center
Boston, Massachusetts 02111
Telephone: (617) 542-6000
Facsimile: (617) 542-2241
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public: As soon as practicable after the effective date of this Registration Statement.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box. þ
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is an emerging growth company as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act of 1933.
Emerging growth company ¨
If an emerging growth company that prepares its financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standard provided pursuant to Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act. ¨
The Registrant hereby amends this Registration Statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the Registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this Registration Statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act or until the Registration Statement shall become effective on such date as the Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
The information in this preliminary prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This preliminary prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and we are not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state or jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted.
PRELIMINARY PROSPECTUS—SUBJECT TO COMPLETION, DATED MARCH 8, 2023

Up to 2,169,790,225 Ordinary Shares Representing 86,791,609 American Depositary Shares
___________________
This prospectus relates to the resale, by the selling shareholders identified in this prospectus, of up to an aggregate of 2,169,790,225 ordinary shares, nominal value 0.1p per share, or Ordinary Shares, of Midatech Pharma plc, or the Company, represented by 86,791,609 American Depositary Shares, or Depositary Shares, consisting of (1) 65,004,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 2,600,160 Depositary Shares issued in a private placement in February 2023, or the Private Placement, (2) 271,120,550 Ordinary Shares represented by 10,844,822 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series A warrants issued in the Private Placement or pursuant to a waiver agreement in connection with the Private Placement, (3) 387,930,900 Ordinary Shares represented by 15,517,236 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series B warrants issued in the Private Placement, (4) up to 1,434,996,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 57,399,840 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of pre-funded warrants issued in the Private Placement, (5) 10,738,775 Ordinary Shares represented by 429,551 Depositary Shares issuable upon the exercise of placement agent warrants issued in connection with the Private Placement. The issuance of the Series A warrants, Series B warrants, a portion of the pre-funded warrants, and the placement agent warrants is subject to the receipt of stockholder approval at a general meeting of the Company to be held on or about March 24, 2023.
The selling shareholders are identified in the table commencing on page 127. Each Depositary Share represents 25 Ordinary Shares. No Depositary Shares are being registered hereunder for sale by us. We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of the Depositary Shares by the selling shareholders. All net proceeds from the sale of the Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares covered by this prospectus will go to the selling shareholders. However, we may receive the proceeds from any exercise of warrants if the holders do not exercise the warrants on a cashless basis. See “Use of Proceeds.”
The selling shareholders may sell all or a portion of the Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares from time to time in market transactions through any market on which our Depositary Shares are then traded, in negotiated transactions or otherwise, and at prices and on terms that will be determined by the then prevailing market price or at negotiated prices directly or through a broker or brokers, who may act as agent or as principal or by a combination of such methods of sale. We will bear all of the expenses incurred in connection with the registration of these shares. The selling shareholders will pay any underwriting discounts and selling commissions and/or similar charges incurred in connection with the sale of the shares. See “Plan of Distribution.”
Our Depositary Shares are listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “MTP.” The last reported closing price of our Depositary Shares on the NASDAQ Capital Market on March 7, 2023 was $0.4911. Our Ordinary Shares are admitted for trading on AIM, a market operated by the London Stock Exchange plc, or AIM, under the listing code “MTPH.” The last reported closing price of our Ordinary Shares on AIM on March 7, 2023 was £0.0155.
Investing in our securities involves risks. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 5 of this prospectus for a discussion of the factors you should carefully consider before deciding to purchase these securities.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or determined if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
___________________
The date of this prospectus is , 2023
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS PROSPECTUS
This prospectus is part of a registration statement that we filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC. As permitted by the rules and regulations of the SEC, the registration statement filed by us includes additional information not contained in this prospectus. You may read the registration statement and the other reports we file with the SEC at the SEC’s website or its offices described below under the heading “Where You Can Find More Information”.
You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus. We have not authorized any person to provide you with information different from that contained in this prospectus. This prospectus is not an offer to sell, nor is it seeking an offer to buy, these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted. The information in this prospectus speaks only as of the date of this prospectus unless the information specifically indicates that another date applies, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus or of any sale of the securities offered hereby. Our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects may have changed since that date. We do not take any responsibility for, nor do we provide any assurance as to the reliability of, any information other than the information in this prospectus. Neither the delivery of this prospectus nor the sale of the Depositary Shares means that information contained in this prospectus is correct after the date of this prospectus. You should not consider this prospectus to be an offer or solicitation relating to the securities in any jurisdiction in which such an offer or solicitation relating to the securities is not authorized. Furthermore, you should not consider this prospectus to be an offer or solicitation relating to the securities if the person making the offer or solicitation is not qualified to do so, or if it is unlawful for you to receive such an offer or solicitation.
Unless the context specifically indicates otherwise, references in this prospectus supplement to “Midatech Pharma plc,” “Midatech,” “the Company,” “we,” “our,” “ours,” “us,” “the Group,” or similar terms refer to Midatech Pharma plc and its consolidated subsidiaries.
We have not taken any action to permit a public offering of the Depositary Shares outside the United States or to permit the possession or distribution of this prospectus outside the United States. Persons outside the United States who come into possession of this prospectus must inform themselves about and observe any restrictions relating to the offering of the Depositary Shares and the distribution of this prospectus outside of the United States.
PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL AND OTHER INFORMATION
Our financial statements are prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards, as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board and adopted by the European Union. We have made rounding adjustments to some of the figures included in this prospectus. Accordingly, numerical figures shown as totals in some tables may not be an arithmetic aggregation of the figures that preceded them.
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in British pounds sterling. Except as otherwise stated, all monetary amounts in this prospectus are presented in British pounds sterling.
In this prospectus, unless otherwise specified or the context otherwise requires:
| · | “$” and “U.S. dollar” each refer to the United States dollar (or units thereof); and |
| · | “£,” “pence” and “p” each refer to the British pound sterling (or units thereof). |
On March 3, 2020, following shareholder approval, we effected a one-for-20 reverse split of our Ordinary Shares and our Ordinary Shares began trading on AIM, a market operated by the London Stock Exchange plc, or AIM, on a split-adjusted basis as of such date. No fractional shares were issued in connection with the reverse stock split.
Concurrently with the reverse split, and in an effort to bring our Depositary Share price into compliance with the NASDAQ Stock Market LLC’s, or NASDAQ, minimum bid price per share requirement, on March 3, 2020 we effected a ratio change in the number of Ordinary Shares represented by our Depositary Shares from 20 Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share to five Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share.
On September 26, 2022, in an effort to bring our Depositary Share price into compliance with the NASDAQ minimum bid price per share requirement, we effected a ratio change in the number of Ordinary Shares represented by our Depositary Shares from five Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share to 25 Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share.
The change in the number of shares resulting from the reverse stock split and change in the number of Depositary Shares resulting from the changes in ratio has been applied retroactively to all share and per share amounts presented in this prospectus, to the extent applicable.
MARKET AND INDUSTRY DATA
Market data and certain industry data and forecasts used throughout this prospectus were obtained from sources we believe to be reliable, including market research databases, publicly available information, reports of governmental agencies, and industry publications and surveys. We have relied on certain data from third-party sources, including internal surveys, industry forecasts, and market research, which we believe to be reliable based on our management's knowledge of the industry. While we are not aware of any misstatements regarding the industry data presented in this prospectus, our estimates involve risks and uncertainties and are subject to change based on various factors, including those discussed under the heading “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus.
Solely for convenience, the trademarks and trade names in this prospectus may be referred to without the ® and ™ symbols, but such references should not be construed as any indicator that their respective owners will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, their rights thereto. The trademarks, trade names and service marks in this prospectus are the property of their respective owners.
PROSPECTUS SUMMARY
This summary highlights selected information that is presented in greater detail elsewhere in this prospectus. This summary does not contain all of the information that may be important to you. You should read this entire prospectus carefully, including the sections titled "Risk Factors" and "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus, before making an investment decision.
Our Business
We are focused on the research and development of medicines for rare cancers, via both in-house programs as well as partnered programs. We take existing therapies and ‘makes medicines better’, using our proprietary platform drug delivery technologies that improve the bio-delivery and bio-distribution of drugs through either sustained delivery (Q-SpheraTM ), direct delivery (MidaSolveTM ), or targeted delivery (MidaCoreTM ) of drugs:
| | · | Our Q-SpheraTM platform: Our disruptive polymer microsphere microtechnology is used for sustained delivery to prolong and control the release of therapeutics over an extended period of time, from weeks to months. |
| | · | Our MidaSolveTM platform: Our innovative nanosaccharide nanotechnology is used to solubilize drugs so that they can be administered in liquid form directly and locally into tumors. |
| | · | MidaCoreTM platform: Our leading-edge gold nanoparticle nanotechnology is used for targeting sites of disease by using either chemotherapeutic agents or immunotherapeutic agents. |
Recent Developments
February 2023 Private Placement
On February 15, 2023, we completed the closing of a private placement with certain institutional investors, for the sale of up to an aggregate of 2,169,790,225 of our Ordinary Shares represented by 86,791,609 Depositary Shares, consisting of (i) 65,004,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 2,600,160 Depositary Shares, (ii) 258,620,550 Ordinary Shares represented by 10,344,822 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series A warrants issued in the Private Placement, (iii) 387,930,900 Ordinary Shares represented by 15,517,236 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series B warrants issued in the Private Placement, and (iv) up to 1,434,996,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 57,399,840 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of pre-funded warrants issued in the Private Placement, subject to certain reset provisions set forth in the Pre-Funded Warrants, at an initial purchase price of $0.58 per Depositary Share, for aggregate gross proceeds of approximately $6.0 million. The issuance of the Series A warrants, Series B warrants and any pre-funded warrants issuable upon a reset are subject to approval of our stockholders at a general meeting.
In addition, in connection with the Private Placement, on February 9, 2023 we entered into a Waiver to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 13, 2022, or the Waiver, by and between the Company and a certain institutional investor, or the December Investor, as amended on December 16, 2022, or the December SPA, providing for a permanent waiver of certain equity issuance prohibitions and participation rights under the December SPA. In connection therewith, the Company agreed to, subject to receipt of stockholder approval, issue to the December Investor Series A Warrants exercisable for 12,500,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 500,000 Depositary Shares.
In connection with the Private Placement, we announced a general meeting of stockholders to be held on March 24, 2023. At the general meeting, our shareholders will vote on resolutions to: (i) approved the allotment of, and disapplication of preemption rights with respect to, the Ordinary Shares to be issued under the Series A warrants, the Series B warrants, certain of the pre-funded warrants, and the Ladenburg Warrants, (ii) change the name of the Company to “Biodexa Pharmaceuticals plc,” (iii) allow the allotment of up to 100% of our fully diluted share capital for future share issuances through our annual general meeting in 2025, and (iv) authorize a 1-for-20 reverse stock split of our Ordinary Shares.
Assuming the reverse stock split is approved, in order to bring the price of the Depositary Shares into compliance with NASDAQ’s minimum bid price requirement, we will change the ratio of Depositary Shares from one Depositary Share representing 25 Ordinary Shares to a new ratio of one Depositary Share representing five Ordinary Shares. This will have the effect of a one-for-four reverse split of our Depositary Shares. There can be no assurance that the ratio change, if it occurs, will be effective in achieving our goal of regaining compliance with NASDAQ’s minimum bid price requirement.
Terminated Transaction with Bioasis Technologies Inc.
On December 13, 2022, we entered into an Arrangement Agreement, or Arrangement Agreement, with Bioasis Technologies Inc., or Bioasis, pursuant to which (i) we were to acquire all of the issued and outstanding common shares of Bioasis, or the Bioasis Shares, in exchange for our Ordinary Shares (to be issued in the form of Depositary Shares), and (ii) Bioasis would become our wholly owned subsidiary.
In addition, in connection with entering into the Arrangement Agreement, Bioasis issued to the Company a promissory note, or the Note, in consideration for a loan from the Company, which loan was to be made in three tranches of $250,000 payable on each of December 19, 2022, January 3, 2023 and February 6, 2023, in each case, subject to written demand and to the terms and conditions of the Note. As of the date hereof, we have loaned Bioasis $500,000 under the Note.
On January 23, 2023, following the failure by our shareholders to approve the necessary resolutions to complete the transaction, Bioasis terminated the Arrangement Agreement and the transactions related thereto.
In connection with the termination of, and pursuant to the terms of, the Arrangement Agreement, Bioasis has demanded an expense reimbursement of $225,000. In addition, on February 27, 2023, Bioasis demanded the third payment of $250,000 under the Note. We have notified Bioasis that is in default under the terms of the Note and have demanded repayment immediately of all amounts owed to us under the Note.
Registered Direct Offering and Termination of Proposed Private Placement
On December 16, 2022, we completed the closing of a registered direct offering with the December Investor, for the sale of 9,849,325 Ordinary Shares represented by 393,973 Depositary Shares at a price per Depositary Share of $1.00, for aggregate gross proceeds of approximately $0.4 million.
On January 26, 2023, following the termination of the Arrangement Agreement by Bioasis, we terminated the December SPA, and the Registration Rights Agreement, by and between the Company and the December Investor, dated as of December 13, 2022, pursuant to which we would have sold such December Investor $9.6 million of our securities, subject to the closing of the transactions contemplated by the Arrangement Agreement.
Change in Ratio of Depositary Shares
On September 26, 2022, we effected a change in the number of our Ordinary Shares represented by our Depositary Shares, issued by The Bank of New York Mellon as depositary, from five of our Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share to 25 Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share. The change in ratio had the same effect as a one-for-five reverse stock split of the Depositary Shares, reducing the number of outstanding Depositary Shares, as of the close of business on September 26, 2022, to approximately 3,940,000.
Our Ordinary Shares, which were not affected by the change, continue to trade on AIM. The change in the number of Depositary Shares resulting from the change in ratio has been applied retroactively to all share and per share amounts presented in this prospectus; provided, however, that such changes have not been made to the financial statements and accompanying notes incorporated herein by reference.
MTX110 Developments
On June 1, 2022, we announced that upon submitting an application to the FDA, our development program of MTX110 for the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma had been granted Fast Track designation by the agency. Fast Track is a process designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of treatments for serious conditions and that potentially address unmet medical needs. Drugs that are granted this designation are given the opportunity for more frequent interactions with the FDA, as well as potential pathways for expedited approval.
On January 12, 2023, we announced that, following completion of one-month treatment with MTX110 in our first patient, our Phase I study of MTX110 in recurrent glioblastoma would continue with a planned dose escalation following positive recommendation from the study’s Data Safety Monitoring Board, or DSMB. The Phase I study, is an open-label, dose escalation study designed to assess the feasibility and safety of intermittent infusions of MTX110 administered by convection enhanced delivery (CED) via implanted refillable pump and catheter. The study aims to recruit two cohorts, each with a minimum of four patients; the first cohort will receive MTX110 only and the second cohort will receive MTX110 in combination with lomustine.
The first patient in the study was dosed at 60uM of MTX110 via direct-to-tumour delivery and has received four 48-hour infusions over a period of four weeks. No treatment-associated adverse events were noted in the patient during this period. Following successful completion of the first month of treatment, the DSMB reviewed the available data and recommended dose escalation in the study to 90uM. This dose is expected to be the optimal one of MTX110 and is the one currently being used in the ongoing Phase I study of patients with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma, or DIPG, at Columbia University.
Non-Compliance with NASDAQ Continued Listing Requirements
Our Depositary Shares are currently listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market. We are required to meet certain qualitative and financial tests to maintain the listing of our Depositary Shares on NASDAQ. On January 31, 2023, we received a letter from NASDAQ stating that, for the previous 30 consecutive business days, the bid price for our Depositary Shares had closed below the minimum $1.00 bid price per share requirement for continued listing on the NASDAQ Capital Market under NASDAQ Listing Rule 5550(a)(2). The notice has no immediate effect on the listing or trading of our Depositary Shares and the Depositary Shares will continue to trade on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “MTP.”
In accordance with NASDAQ Listing Rules, we have a grace period of 180 calendar days, or until July 31, 2023, or the Compliance Period, to regain compliance with the minimum bid price requirement. To regain compliance, the closing bid price of the Depositary Shares must meet or exceed $1.00 per share for at least 10 consecutive business days during the Compliance Period. If the Depositary Shares do not regain compliance with the minimum bid price requirement during the Compliance Period, we may be eligible for an additional grace period of 180 calendar days provided that we satisfy NASDAQ's initial listing standards for listing on the NASDAQ Capital Market, other than the minimum bid price requirement, and provide written notice to NASDAQ of its intention to cure the delinquency during the second grace period. If we do not regain compliance during the initial grace period and are not eligible for an additional grace period, NASDAQ will provide written notice that the Depositary Shares are subject to delisting from the NASDAQ Capital Market. In that event, we may appeal such determination to a hearing panel.
We intend to monitor the bid price of our Depositary Shares during the Compliance Period and will consider taking such actions as may be necessary and appropriate to achieve compliance with continued listing requirements prior to the expiration of all available grace periods, including the actions described above regarding a ratio change and reverse split of our Depositary Shares
Our Corporate Information
Our principal executive offices are located at Caspian Point, Caspian Way, Cardiff, CF10 4DQ, United Kingdom. The telephone number at our principal executive office is +44 29 20480 180. Our corporate website is located at www.midatechpharma.com. Information contained on our website is not part of, or incorporated in, this prospectus. Our authorized representative in the United States is Donald J. Puglisi of Puglisi and Associates. Our agent for service in the United States is Donald J. Puglisi of Puglisi and Associates, located at 850 Library Avenue, Suite 204, Newark, Delaware 19711. Our Ordinary Shares are traded on AIM under the symbol “MTPH,” and our Depositary Shares are traded on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “MTP.”
Implications of Being a Foreign Private Issuer
We are incorporated as a public limited company in England and Wales, are we are deemed to be a “foreign private issuer” for the purposes of the reporting rules under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act. In our capacity as a foreign private issuer, we are exempt from certain rules under the Exchange Act that would otherwise apply if we were a company incorporated in the United States, including:
| · | the requirement to file periodic reports and financial statements with the SEC as frequently or as promptly as United States companies with securities registered under the Exchange Act; |
| · | the requirement to file financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, or U.S. GAAP; |
| · | the proxy rules, which impose certain disclosure and procedural requirements for proxy solicitations; and |
| · | the requirement to comply with Regulation FD, which imposes certain restrictions on the selective disclosure of material information. |
In addition, our officers, directors and principal shareholders are exempt from the reporting and “short-swing” profit recovery provisions of Section 16 of the Exchange Act and the rules under the Exchange Act with respect to their purchases and sales of our Ordinary Shares. Accordingly, an investor may receive less information about us that it would receive about a public company incorporated in the United States.
| The Offering |
| |
| Depositary Shares offered by the Selling Shareholders | | Up to an aggregate of 2,169,790,225 Ordinary Shares of the Company represented by 86,791,609 Depositary Shares, consisting of (1) 65,004,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 2,600,160 Depositary Shares issued in the Private Placement, (2) 271,120,550 Ordinary Shares represented by 10,844,822 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series A warrants issued in the Private Placement or pursuant to the Waiver, (3) 387,930,900 Ordinary Shares represented by 15,517,236 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series B warrants issued in the Private Placement, (4) up to 1,434,996,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 57,399,840 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of pre-funded warrants issued in the Private Placement, (5) 10,738,775 Ordinary Shares represented by 429,551 Depositary Shares issuable upon the exercise of placement agent warrants issued in connection with the Private Placement. The issuance of the Series A warrants, Series B warrants, any pre-funded warrants issuable upon a reset, and the placement agent warrants are subject to approval of our stockholders at a general meeting. The selling shareholders are identified in the table commencing on page 127. |
| | | |
| Total Ordinary Shares outstanding immediately prior to this offering | | 173,346,738 Ordinary Shares (including those represented by Depositary Shares). |
| | | |
| Total Ordinary Shares to be outstanding immediately after this offering | | 2,298,249,632 Ordinary Shares (including those represented by Depositary Shares), assuming all warrants are exercised in full and the pre-funded warrant resets to the maximum amount possible thereunder. |
| | | |
| Depositary Shares | | Each Depositary Share represents 25 Ordinary Shares. The depositary (through its custodian) will hold the Ordinary Shares underlying your Depositary Shares. You will have rights as provided in the deposit agreement among us, The Bank of New York Mellon, as depositary, and all owners and holders from time to time of Depositary Shares issued thereunder. You may, among other things, cancel your Depositary Shares and withdraw the underlying Ordinary Shares against a fee paid to the depositary (which may be reimbursable by the Company). In certain limited instances described in the deposit agreement, we may amend or terminate the deposit agreement without your consent. If you continue to hold your Depositary Shares, you agree to be bound by the terms of the deposit agreement then in effect. To better understand the terms of the Depositary Shares and the deposit agreement, including applicable fees and charges, you should carefully read “Description of American Depositary Shares” in this prospectus. You should also read the deposit agreement, which is an exhibit to the registration statement that includes this prospectus. |
| | | |
| Depositary | | The Bank of New York Mellon |
| | | |
| Use of proceeds | | We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of the Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares by the selling shareholders. All net proceeds from the sale of the Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares covered by this prospectus will go to the selling shareholders. However, we may receive the proceeds from any exercise of warrants in the unlikely event the holders do not exercise the warrants on a cashless basis. See the section of this prospectus titled “Use of Proceeds.” |
| | | |
| Risk factors | | You should read the “Risk Factors” section starting on page 5 of this prospectus for a discussion of factors to consider before deciding to invest in our securities. |
| | | |
| Dividend policy | | We have never declared or paid any cash dividends to our shareholders, and we currently do not expect to declare or pay any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. See “Dividend Policy.” |
| | | |
| Listings | | Our Depositary Shares are listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “MTP.” Our Ordinary Shares are traded on AIM under the symbol “MTPH.” |
RISK FACTORS
Our business has significant risks. In addition to the other information included in this annual report, including the matters addressed in the section of the annual report entitled “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and in our financial statements and the related notes, you should consider carefully the risks described below. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only risks and uncertainties we may face. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us, or that we currently consider immaterial could also negatively affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, prospects, profits and stock prices. If any of the risks described below actually occur, our business, financial condition, results of operations, prospects, profits and stock prices could be materially adversely affected.
Summary of Risk Factors
The occurrence of one or more of the events or circumstances described in this section titled “Risk Factors,” alone or in combination with other events or circumstances, may materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and operating results. In that event, the trading price of our securities could decline, and you could lose all or part of your investment. Such risks include, but are not limited to:
| • | We have incurred significant losses since our inception and anticipate that we will continue to incur losses in the future; |
| • | Our requirement for additional financing in the short-term represents a material uncertainty that raises substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. |
| • | The effects of health epidemics, including the ongoing global coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic, in regions where we, or the third parties on which we rely, have business operations could adversely impact our business, including our clinical trials, preclinical studies and supply chains, depending on the location, duration and severity of disruptions to the systems affecting our business. |
| • | Our operations are in early-stage development with no sources of recurring revenue and there is no assurance that we will successfully develop and license our product candidates or ever become profitable. |
| • | We are exposed to political, regulatory, social and economic risk relating to the United Kingdom’s exit from the European Union. |
| • | In 2020, our license agreement related to panobinostat, the active pharmaceutical ingredient in our MTX110 product, was terminated by Secura Bio, Inc., or Secura Bio. Because of this, we believe that the relevant Secura Bio patents may delay a launch of MTX110, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. |
| • | Our future success is dependent on product development and the ability to successfully license our product candidates to partners who can seek regulatory approval and commercialization of our product candidates. |
| • | Clinical drug development involves a risky, lengthy and expensive process with an uncertain outcome, and results of earlier studies and trials may not be predictive of future trial results. |
| • | We expect to seek to establish agreements with potential licensing partners and collaborators and, if we are not able to establish them on commercially reasonable terms, we may have to alter our development and commercialization plans. |
| • | Recently enacted and future legislation in the United States and other countries may affect the prices we may obtain for our product candidates and increase the difficulty and cost for us to commercialize our product candidates. |
| • | Our success depends in part on our ability to protect rights in our intellectual property, which cannot be assured. |
| • | We rely on third parties to conduct our preclinical and clinical trials. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or commercialize our product candidates and our business could be substantially harmed. |
| • | We are dependent on third party suppliers, and if we experience problems with any of these third parties, the manufacturing of our product candidates could be delayed, which could harm our results of operations. |
| • | We recently experienced a leadership transition and this transition, along with the possibility that we may in the future be unable to retain and recruit qualified scientists, key executives, key employees or key consultants, may delay our development efforts or otherwise harm our business. |
| • | The price of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares may be volatile. |
| • | Shareholder ownership interests in the Company may be diluted as a result of future financings, additional acquisitions or the exercise of our options and warrants, and may have a material negative effect on the market price of our securities. |
| • | The rights of holders of Depositary Shares are not the same as the rights of holders of Ordinary Shares. |
| • | It may be difficult for you to bring any action or enforce any judgment obtained in the United States against us or members of our Board of Directors, which may limit the remedies otherwise available to you. |
| • | We are a “foreign private issuer” under the rules and regulations of the SEC and, as a result, are exempt from a number of rules under the Exchange Act and are permitted to file less information with the SEC than a company incorporated in the United States. |
| • | If we cannot meet NASDAQ’s continued listing requirements, NASDAQ may delist our Depositary Shares, which could have an adverse impact on the liquidity and market price of our Depositary Shares. |
Risks Related to Our Financial Operations and Capital Needs
We have incurred significant losses since our inception and anticipate that we will continue to incur losses in the future.
We are an early-stage biopharmaceutical company. Investment in biopharmaceutical product development is highly speculative because we entail substantial upfront capital expenditures and significant risk that a product candidate will fail in development, will fail to gain regulatory approval or otherwise fail to become commercially viable. We continue to incur significant development and other expenses related to our ongoing operations. As a result, we are not profitable and have incurred substantial losses since our inception. For the six months ended June 30, 2022, we had a net loss of £3.06 million and an accumulated deficit of £130.76 million. For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 we had a net loss of £5.46 million and £22.19 million, respectively.
We expect to continue to incur losses for the foreseeable future, and do not expect these losses to reduce as we continue our development of, and work with any licensing partners to seek regulatory approvals for, our product candidates.
We may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other unknown factors that may adversely affect our business. The size of our future net losses will depend, in part, on the rate of future growth of our expenses and our ability to generate revenues. If we fail to find licensing partners, if we abandon any development programs, or if any of our licensed product candidates fail in clinical trials or do not gain regulatory approval, or if approved, fail to achieve market acceptance, we may never become profitable. Even if we achieve profitability in the future, we may not be able to sustain profitability in subsequent periods. Our prior losses and expected future losses have had and will continue to have an adverse effect on our shareholders’ equity and working capital.
Our requirement for additional financing in the short-term represents a material uncertainty that raises substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
We have experienced net losses and significant cash outflows from cash used in operating activities over the past years as we develop our portfolio.
Our future viability is dependent on our ability to raise cash from financing activities to finance our development plans until commercialization, generate cash from operating activities and to successfully obtain regulatory approval to allow marketing of our development products. Our failure to raise capital as and when needed could have a negative impact on our financial condition and ability to pursue our business strategies.
Our consolidated financial statements have been presented on a going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities in the normal course of business. As at June 30, 2022, we had cash and cash equivalents of £6.42 million. We believe we currently have enough cash to fund our planned operations into December 2023.
We have prepared cash flow forecasts and considered the cash flow requirement for the next three years including the period 12 months from the date of approval of the interim financial information. These forecasts showed that further financing would be required during the first quarter of 2023 assuming, inter alia, that certain developments programs and other operating activities continue as currently planned. Following the registered direct offering in December 2022 and Private Placement in February 2023 which raised aggregate proceeds of $6.4 million, we updated our forecasts. The updated forecasts show that further financing will be required before December 2023. This requirement for additional financing in the short term represents a material uncertainty that may cast doubt upon the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
In addition to utilizing the existing cash reserves, we are evaluating a number of near-term funding options potentially available to us, including fundraising and/or the partnering of assets or technologies. After considering the uncertainties, we considered it appropriate to continue to adopt the going concern basis in preparing the financial information.
Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon our ability to obtain additional capital and/or dispose of assets, for which there can be no assurance we will be able to do on a timely basis, on favorable terms or at all.
Our operations are in early-stage development with no sources of recurring revenue and there is no assurance that we will successfully develop and license our product candidates or ever become profitable.
We are at a relatively early stage of our commercial development. To date, we have generated a minimal amount of revenue from our product candidates. Our ability to generate revenue and become and remain profitable depends, in part, on our ability to successfully find a licensing partner for our product candidates, or other product candidates we may in-license or acquire, and have such candidates successfully commercialized. Our current strategy is, once proof-of-concept of our product candidates has been established, to generate revenue via a partner, thereby earning royalty and/or milestone income; however, this is not expected to materialize in the foreseeable future, and there can be no guarantee we will be able to find a licensing partner for our product candidates. Even if our product candidates were to successfully achieve regulatory approval, we do not know when any of the product candidates will generate revenue, if at all. Our ability to generate revenue from our product candidates also depends on a number of additional factors, including our ability, and the ability of any licensing partners, to:
| • | successfully complete development activities; |
| • | complete and submit new drug applications to the European Medicines Agency, or the EMA, the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency in the United Kingdom, or the MHRA, the United States Food and Drug Administration , or the FDA, and any other foreign regulatory authorities, and obtain regulatory approval for products for which there is a commercial market; |
| • | set a commercially viable price; |
| • | obtain commercial qualities of the products at acceptable cost levels; |
| • | develop and maintain a commercial organization capable of sales, marketing and distribution in the markets where the product is to be sold; and |
| • | obtain adequate reimbursement from third-parties, including government, departments and healthcare payors. |
In addition, because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with product development, including that our product candidates may not advance through development or achieve the endpoints of applicable clinical trials, we are unable to predict the timing or amount of increased expenses, or when or if we will be able to achieve or maintain profitability. Even if we are able to complete the process described above, we anticipate incurring significant costs.
Even if we are able to generate royalty and/or milestone revenues from the sale of product candidates, we may not become profitable and may need to obtain additional funding to continue operations. If we fail to become profitable or are unable to sustain profitability on a continuing basis, then we may be unable to continue our operations at planned levels and may be forced to cease or reduce our operations.
There can be no assurance that we will operate profitably, produce a reasonable return, if any, on investment, or remain solvent. If our strategy proves unsuccessful, stockholders could lose all or part of their investment.
If we require or seek to raise additional capital to fund our operations and we fail to obtain necessary financing, we may be unable to complete the development of our product candidates.
We expect to continue to spend substantial amounts of our cash resources going forward in order to advance the development of our product candidates.
Until such time as we can generate a sufficient amount of revenue from the product candidates we license, if ever, we expect that we may finance future cash needs through, among other things, public or private equity or debt offerings. Such offerings may take place in the United Kingdom, the United States or other foreign countries. However, if we are unable to raise capital when needed, or on terms acceptable to us, our business could be significantly harmed. If we raise additional funds through the issuance of debt or additional equity securities, such issuance could result in dilution to our existing shareholders and/or increased fixed payment obligations. Furthermore, these securities may have rights senior to those of our Ordinary Shares and could contain covenants that would restrict our operations and potentially impair our competitiveness, such as limitations on our ability to incur additional debt, limitations on our ability to acquire, sell or license intellectual property rights and other operating restrictions that could adversely impact our ability to conduct our business. Any of these events could significantly harm our business, financial condition and prospects.
Our forecast of the period of time through which our financial resources will be adequate to support our operations is a forward-looking statement and involves risks and uncertainties, and actual results could vary as a result of a number of factors, including the factors discussed elsewhere in this “Risk Factors” section. We have based this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and we could utilize our available capital resources sooner than we currently expect. Our future funding requirements, both near and long-term, will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to:
| • | any acquisitions and the commercialization of other assets, including licensed assets; |
| • | the initiation, progress, timing, costs and results of clinical trials for any product candidates we advance to clinical trials; |
| • | the attainment of milestones and the need to make any royalty payments on any of our product candidates or any other future product candidates; |
| • | the number and characteristics of product candidates we in-license or acquire and develop; |
| • | the outcome, timing and cost of regulatory approvals by the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA and any other comparable foreign regulatory authorities, including the potential for such regulatory authorities to require that we perform more studies, or more costly studies, than those we currently expect; |
| • | the cost of filing, prosecuting, defending and enforcing any patent claims or other intellectual property rights; and |
| • | the effect of competing technological and market developments. |
If a lack of available capital means that we are unable to expand our operations or otherwise capitalize on our business opportunities, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
In previous years, we and our independent registered public accounting firm have identified material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting. Any failure by us to maintain an effective system of internal controls or provide reliable financial and other information in the future, may cause investors to lose confidence in our financial statements and SEC filings and the market price of our securities may be materially and adversely affected.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, or the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, requires, among other things, that we maintain effective internal controls for financial reporting and disclosure controls and procedures. We are required, under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, to furnish a report by management on, among other things, the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. This assessment includes disclosures of any material weaknesses identified by management in its internal control over financial reporting.
A material weakness is a control deficiency, or combination of control deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting that results in more than a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act also generally requires an attestation from our independent registered public accounting firm on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. However, for as long as we remain a non-accelerated filer, we are not required to comply with the independent registered public accounting firm attestation requirement.
In previous years, we and our independent registered public accounting firm have identified material weaknesses in our internal controls over financial reporting. Although we have instituted these remedial measures to address the material weaknesses identified and to continually review and evaluate our internal control systems to allow management to report on the sufficiency of our internal control over financial reporting, we cannot assure you that we will not discover additional weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting. Any such additional weaknesses or failure to adequately remediate any existing weakness could materially and adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations, as well as our ability to accurately report our financial condition and results of operations in a timely and reliable manner.
Additionally, the material weaknesses previously identified, or other material weaknesses or significant deficiencies we may become aware of in the future, could result in our determining that our controls and procedures are not effective in future periods or could result in a material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements that would not be prevented or detected.
Any failure to maintain effective internal controls over financial reporting could severely inhibit our ability to accurately report our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. If we are unable to conclude that our internal control over financial reporting is effective, or if our independent registered public accounting firm determines we have a material weakness or significant deficiency in our internal control over financial reporting once that firm begin its Section 404 reviews, we could lose investor confidence in the accuracy and completeness of our financial statements and reports, the market price of our Ordinary Shares and/or Depositary Shares could decline, and we could be subject to sanctions or investigations by NASDAQ, the SEC or other regulatory authorities. Failure to remedy any material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting, or to implement or maintain other effective control systems required of public companies, could also restrict our future access to the capital markets.
Risks Related to Our Business, Strategy and Industry
The effects of health epidemics, including the ongoing global coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic, in regions where we, or the third parties on which we rely, have business operations could adversely impact our business, including our clinical trials, preclinical studies and supply chains, depending on the location, duration and severity of disruptions to the systems affecting our business.
Our business and operations may be adversely affected by the ongoing effects of the evolving COVID-19 virus, which was declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (“WHO”).
It is not possible to accurately predict the extent of the adverse effects of the pandemic on our business. However, we have experienced certain impacts and may experience others which, if they continue for an extended period of time, could have material adverse effects on our operations and the execution of our business plans. Examples of these include the following:
| • | We have experienced some delays in our clinical trials, in particular our Phase I trials of MTX110 in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma, or DIPG, at Columbia University and in medulloblastoma at the University of Texas. Individuals defer seeking treatment, physicians have fewer in-person meetings to recruit and enroll patients, and recruited patients are hindered by restrictions in traveling to and accessing clinical sites. In addition, resources at hospitals have been diverted to dealing with the pandemic, causing delays in scheduling screening evaluations, implant procedures, and follow-up monitoring visits. As a result of the foregoing factors, the expected timeline for data readouts of our clinical trials may be negatively impacted, which would adversely affect our business. |
| • | We rely on third party service providers to assist us in managing and otherwise carrying out our nonclinical studies and clinical trials, and the outbreak may affect their ability to devote sufficient time and resources to our programs. |
| • | We rely on third party suppliers and contract manufacturers to produce materials for our clinical trials. We could experience supply chain delays or shortages with respect to these materials, which could impact our ability to meet current timetables for our clinical trials. |
| • | We previously temporarily closed our executive offices and implemented various governmental safety guidelines, including work-from-home policies for most employees. The effects of government orders and our work-from-home policies may negatively impact productivity, disrupt our business and delay our clinical programs and timelines, the magnitude of which will depend, in part, on the length and severity of the restrictions and other limitations on our ability to conduct our business in the ordinary course. |
| • | We have, from time to time, instituted work-from-home policies for certain of our employees, and this could adversely affect our operations, the productivity of our employees and our ability to conduct and complete our nonclinical studies and clinical trials. |
| • | The pandemic could cause delays in pursuing and obtaining governmental and other third-party reimbursement decisions, as the work of these organizations may be slowed due to personnel work-from-home measures and travel and other scheduling constraints. |
| • | In addition, the ability of the FDA, MHRA, EMA and other regulatory authorities or other bodies to engage in routine regulatory and oversight activities, such as the review and authorization or certification of new products and the inspection of manufacturing and clinical trial sites, may be affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. The FDA, MHRA, EMA and other regulatory authorities or other bodies may have slower response times or be under-resourced. If the global health concerns continue to disrupt or prevent regulatory authorities from conducting their regular reviews, inspections, or other regulatory activities, it could significantly impact the timely review and process our marketing applications, clinical trial authorizations, or other regulatory submissions, which could have a material adverse effect on our business. |
| • | The near- and longer-term future impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on global and national economies, and related impacts on the availability of investment capital in financial markets, continues to be uncertain. Continued economic disruptions could cause a contraction in equity capital and debt markets, making access to financing unavailable on acceptable terms or at all. |
The global COVID-19 pandemic continues to evolve rapidly. We do not yet know the full extent of potential delays or impacts on our business, our licensing efforts, our clinical studies, our research programs, healthcare systems or the global economy. However, these effects could have a material impact on our operations, and we continue to monitor the COVID-19 situation closely. The full extent to which the COVID-19 pandemic will impact our business operations, financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows will depend on future developments, including, but not limited to, the ultimate severity, scope and duration of the pandemic before it is brought under control, the pace at which governmental and private travel and other restrictions and concerns about public gatherings will ease, the rate at which historically large increases in unemployment rates will decrease, and the speed with which national economies recover, all of which are highly uncertain. To the extent the COVID-19 pandemic adversely affects our business and financial results, it may also have the effect of heightening many of the other risks described in this “Risk Factors” section.
In 2020, our license agreement related to panobinostat, the active pharmaceutical ingredient in our MTX110 product, was terminated by Secura Bio. Because of this, we believe that the relevant Secura Bio patents may delay a launch of MTX110, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We entered into a License Agreement, executed on or about June 6, 2017, or the License Agreement, by and between Midatech Limited and Novartis AG, or Novartis, which Novartis subsequently transferred to Secura Bio, or the Secura License Agreement. Pursuant to the Secura License Agreement, Midatech Limited was granted a worldwide, sublicenseable license to certain patents of panobinostat, the active pharmaceutical ingredient of Midatech’s development product MTX110. Midatech Limited’s rights are limited to the treatment of brain cancer in humans, administered by convection-enhanced delivery. We received a letter dated June 1, 2020, sent on behalf of Secura Bio purporting to terminate the Secura License Agreement “effective immediately,” the reason specified being that we were proposing to liquidate the Company. Despite our assurances to the contrary, and despite our repeated requests that Secura Bio withdraw its termination, Secura Bio reaffirmed the termination and reasons therefor and the agreement was thus terminated. We received a further letter sent on behalf of Secura Bio dated May 21, 2021 purporting to terminate the Secura License Agreement a second time for alleged material breaches of the agreement, and demanding a non-exclusive, fully paid-up, royalty-free, perpetual license to Midatech’s MTX110 intellectual property. This demand was refused based upon, among other things, Secura Bio’s previous termination of the License Agreement in 2020.
We view MTX110 as an important asset and currently have two ongoing clinical trials for MTX110 and intend to commence two further clinical trials as part of our MTX110 clinical program. While we continue to enjoy freedom to use panobinostat for research purposes and we plan to continue to pursue development of MTX110, we believe that the relevant Secura Bio patents may delay a launch of MTX110 for use in patients with DIPG. We do not, however, anticipate it would have any impact on launching MTX110 for use in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. If we are unable to launch a product candidate until the patent expires, there could be a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Further, should Secura Bio continue to interfere with our ongoing business by, among other things, challenging the legality of the termination of the Secura License Agreement, the uncertainty and diversion of time and resources associated could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and prospects, and we cannot assure you that we would be successful in resolving such dispute.
We are exposed to political, regulatory, social and economic risk relating to the United Kingdom’s exit from the European Union.
Following the result of a referendum in 2016, the United Kingdom left the European Union on January 31, 2020, commonly referred to as Brexit. Pursuant to the formal withdrawal arrangements agreed between the United Kingdom and the European Union, the United Kingdom was subject to a transition period until December 31, 2020, during which European Union rules continued to apply. The Trade and Cooperation Agreement between the United Kingdom and the European Union, which outlines the future trading relationship between the United Kingdom and the European Union, was agreed in December 2020. The impact of the new trade agreement on the general and economic conditions in the United Kingdom remains uncertain. There may be, for example, additional costs in materials and equipment sourced from the European Union and/or delays that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
From a regulatory perspective, the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the European Union could bear significant complexity and risks. A basic requirement of European Union law relating to the grant of a marketing authorization for a medicinal product in the European Union is that the applicant is established in the European Union. Following the withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the European Union, marketing authorizations previously granted to applicants established in the United Kingdom may no longer be valid. Moreover, the scope of a marketing authorization for a medicinal product granted by the European Commission pursuant to the centralized procedure might not, in the future, include the United Kingdom. In these circumstances, an authorization granted by competent United Kingdom authorities would be required to place medicinal products on the United Kingdom market. In addition, the laws and regulations that will apply after the United Kingdom withdraws from the European Union would affect the manufacturing sites that hold a certification issued by the United Kingdom competent authorities, and vice versa. Our capability to rely on these manufacturing sites for products intended for the European Union market would also depend upon the exact terms of the United Kingdom withdrawal.
Any of these factors could significantly increase the complexity of our activities in the European Union and in the United Kingdom, could depress our economic activity and restrict our access to capital, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations and reduce the price of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares.
We have undertaken in the past, and may in the future undertake, strategic acquisitions. Failure to integrate acquisitions could adversely affect our value.
One of the ways we have grown our pipeline and business in the past is through strategic acquisitions of other businesses, products, and technologies. We may, from time to time, evaluate additional acquisition opportunities, and may, in the future, strategically make further acquisitions of, and investments in, businesses, products and technologies when we believe the opportunity is advantageous to our prospects. There can be no assurance that in the future we will be able to find appropriate acquisitions or investments. In connection with these acquisitions or investments, we may:
| • | issue stock that would dilute our shareholders’ percentage of ownership; |
| • | be obligated to make milestone or other contingent or non-contingent payments; |
| • | incur debt and assume liabilities; and |
| • | incur amortization expenses related to intangible assets or incur large and immediate write-offs. |
We also may be unable to find suitable acquisition candidates and may not be able to complete acquisitions on favorable terms, if at all, or obtain adequate financing for such acquisitions. If we do complete an acquisition, this may not ultimately strengthen our competitive position or ensure that we will not be viewed negatively by customers, financial markets or investors. Further, acquisitions could also pose numerous additional risks to our operations, including:
| • | problems integrating the purchased business, products or technologies without substantial costs, delays or other problems; |
| • | increases to our expenses; |
| • | the failure to have discovered undisclosed liabilities of the acquired asset or company for which we may not be adequately indemnified; |
| • | diversion of management’s attention from their day-to-day responsibilities and our core business; |
| • | inability to enforce indemnification and non-compete agreements; |
| • | the failure to successfully incorporate acquired products or technologies into our business; |
| • | the failure of the acquired business, products or technologies to perform as well as anticipated; |
| • | the failure to realize expected synergies and cost savings; |
| • | unexpected safety issues and/or clinical trial failure of the acquisition’s products; |
| • | harm to our operating results or financial condition, particularly during the first several reporting periods after the acquisition is completed; |
| • | entrance into markets in which we have limited or no prior experience; and |
| • | potential loss of key employees or customers, particularly those of the acquired entity. |
We may not be able to complete one or more acquisitions or effectively integrate the operations, products or personnel gained through any such acquisition without a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our future success is dependent on product development and the ability to successfully license our product candidates to partners who can seek regulatory approval and commercialization of our product candidates.
We continue to conduct research and development for our product candidates and, to a lesser extent, clinical trials for certain of our product candidates; however there can be no assurance that any of our targeted developments will be successful. We must develop functional products that address specific market needs. We must therefore engage in new development activities, which may not produce innovative, commercially viable results in a timely manner or at all. In addition, we may not be able to develop new technologies or identify specific market needs that are addressable by our technologies, or technologies available to us. We may encounter delays and incur additional development and production costs and expenses, over and above those expected, in order to develop technologies and products suitable for licensing. If any of our development programs are curtailed, this may have a material adverse effect on our business and financial conditions.
Our business is dependent on our ability to complete the development of product candidates, and license our product candidates to partners who will seek to obtain regulatory approval for and commercialize our product candidates in a timely manner. Any licensing partner cannot commercialize a product without first obtaining regulatory approval from the appropriate regulatory authorities in a country. Before obtaining regulatory approvals for the commercial sale of any product candidate for a target indication, it must be demonstrated with substantial evidence gathered in preclinical and well-controlled clinical studies that the product candidate is safe and effective for use for that target indication and that the manufacturing facilities, processes and controls are adequate. The process of developing, obtaining regulatory approval for and commercializing product candidates is long, complex and costly. Even if a product candidate were to successfully obtain approval from the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA and/or comparable foreign regulatory authorities, any approval might contain significant limitations related to use restrictions for certain age groups, warnings, precautions or contraindications, or may be subject to burdensome post-approval study or risk management requirements. If our product candidates are unable to obtain regulatory approval in one or more jurisdictions, or any approval contains significant limitations, we may not be able to obtain sufficient funding or generate sufficient revenue to continue the development of any other product candidate. Furthermore, even if a product candidate obtains approval from the regulatory authorities, it is likely that, in order to obtain royalty and/or milestone revenue from any of our licensing partners, our licensing partners may need to expand their commercial operations, establish commercially viable pricing and obtain approval for adequate reimbursement from third parties and government departments and healthcare payors for such products. If our product candidates are unable to successfully be commercialized, we may not be able to earn sufficient revenues to continue our business.
Our development efforts are in the early stages. All of our product candidates are in clinical development or preclinical development phases. If we are unable to advance our product candidates through clinical development, obtain regulatory approval and ultimately commercialize our product candidates, or experience significant delays in doing so, our business will be materially harmed.
Clinical testing is expensive and can take many years to complete, and its outcome is inherently uncertain. Failure can occur at any time during the clinical trial process. The results of any preclinical studies and early clinical trials of our product candidates may not be predictive of the results of later-stage clinical trials, even after seeing promising results in earlier clinical trials. Product candidates in later stages of clinical trials may fail to show the desired safety and efficacy traits despite having progressed through preclinical studies and initial clinical trials. A number of companies in the biopharmaceutical industry, including many with greater resources and experience than us, have suffered significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials due to lack of efficacy or adverse safety profiles, notwithstanding promising results in earlier trials.
In 2018, we embarked on first-in-human clinical trial program for our MTD201 and MTX110 products, with MTD201 completing our Phase I study in the third quarter of 2018, with an additional Phase I study completed in the third quarter of 2019. The MTX110 Phase I clinical study completed in the fourth quarter of 2020. In 2020, Phase I clinical trials of MTX110 were initiated by the University of Texas in medulloblastoma, and by Columbia University in DIPG. In connection with the termination of our MTD201 program, we have determined not to conduct additional clinical trials in humans, other than pilot trials to establish proof of concept in indications other than those for which the drug is approved. We expect our licensing partners will be responsible for future clinical trials. We and any of our current or potential licensing partners may experience delays in ongoing or future clinical trials and we do not know whether planned clinical trials will begin or enroll subjects on time, need to be redesigned or be completed on schedule, if at all.
There is no assurance that clinical trials of MTX110 or any other future clinical trials our other product candidates, will be successful or will generate positive clinical data and we may not receive marketing approval from the FDA, European Commission, or other regulatory authorities for any of our product candidates. We have limited experience submitting new drug applications, or NDAs, biologics license applications, or BLAs, and investigational new drug applications, or INDs, to the FDA, as well as clinical trial applications, or CTAs, or marketing authorization applications, or MAAs, to the EMA. MTX110 is in initial clinical development, currently being studied in an ongoing investigator-initiated study. There can be no assurance that the FDA will permit any of our future NDAs, BLAs, or INDs, including the NDA for MTX110 or any future INDs for our other product candidates, to go into effect in a timely manner or at all. Without an IND or CTA for a product candidate, we will not be permitted to conduct clinical trials in the United States or the European Union, respectively, of such product candidate.
Drug or biological product development is a difficult, long, time-consuming, expensive and uncertain process, and delay or failure can occur at any stage of any of our clinical trials. Failure to obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates will prevent us from commercializing and marketing them. Clinical trials may be delayed, suspended or prematurely terminated for a variety of reasons, such as:
| • | delay or failure to complete preclinical studies; |
| • | insufficient financial and other resources to complete the necessary preclinical studies and clinical trials; |
| • | delay or failure in reaching agreement with the applicable regulatory authorities on a trial design; |
| • | delay or failure in obtaining authorization to commence a trial or inability to comply with conditions imposed by a regulatory authority regarding the scope or design of a clinical study; |
| • | delay or failure in reaching agreement on acceptable terms with prospective contract research organizations, or CROs, and clinical trial providers and sites, the terms of which can be subject to extensive negotiation and may vary significantly among different CROs and trial sites; |
| • | delay or failure in obtaining institutional review board, or IRB, or the approval of other reviewing entities, including foreign regulatory authorities, to conduct a clinical trial at each site; |
| • | failure to recruit, or subsequent withdrawal of, clinical trial sites from clinical trials as a result of changing standards of care or the ineligibility of a site to participate in our clinical trials; |
| • | delay or failure in recruiting and enrolling suitable subjects to participate in a trial; |
| • | delay or failure in having subjects complete a trial or return for post-treatment follow-up; |
| • | clinical sites and investigators deviating from trial protocol, failing to conduct the trial in accordance with regulatory requirements, or dropping out of a trial; |
| • | inability to identify and maintain a sufficient number of trial sites, many of which may already be engaged in other clinical trial programs, including some that may be for the same indication; |
| • | failure of third party clinical trial managers or clinical sites to satisfy contractual duties or meet expected deadlines; |
| • | failure to receive the recommendation of health technology assessment bodies such as the U.S. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and other relevant international bodies or agencies responsible for pricing and utilization determinations; |
| • | delay or failure in adding new clinical trial sites; |
| • | ambiguous or negative interim results, or results that are inconsistent with earlier results; |
| • | from the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA, the IRB, data safety monitoring boards, or other regulatory authority, or results from earlier stage or concurrent preclinical and clinical studies, which might require modification to the protocol for a given study; |
| • | decisions by the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA, the IRB, other regulatory authorities, or us, or recommendation by a data safety monitoring board or other regulatory authority, to suspend or terminate a clinical trial at any time for safety issues or for any other reason; |
| • | unacceptable risk-benefit profile or unforeseen safety issues or adverse side effects; |
| • | failure to demonstrate a benefit from using a drug over existing marketed products; |
| • | manufacturing issues, including problems with manufacturing or obtaining from third parties sufficient quantities of raw materials, active pharmaceutical ingredients, or API, or product candidates for use in clinical trials; and |
| • | changes in governmental regulations or administrative actions or lack of adequate funding to continue the clinical trial. |
Many of these factors are beyond our control. If we experience delays in the completion of, or termination of, any ongoing or future clinical trial of our product candidates, the commercial prospects of our product candidates will be harmed, and our ability to generate product revenues from any of these product candidates will be delayed. In addition, any delays in completing clinical trials may slow down our product candidate development and approval process and jeopardize the ability to commence product sales and generate revenues. Any of these occurrences may harm our business, financial condition and prospects significantly. In addition, many of the factors that cause, or lead to, a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical trials may also ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our product candidates. It is possible that none of our product candidates will ever complete successfully the clinical development process and obtain regulatory approval, even if we expend substantial time and resources seeking such approval.
Negative results in the development of our lead product candidates may also prevent or delay our ability to continue or conduct clinical programs or receive regulatory approvals for our other product candidates. For example, although we believe our preclinical studies and animal testing of MTX110 demonstrate indications of acceptable safety and effectiveness profiles, future clinical trials may fail to demonstrate adequate levels of safety or effectiveness. Moreover, anti-tumor activity may be different in each tumor type that we plan to evaluate in the clinical trial. Therefore, even though we plan to pursue clinical development for multiple tumor types, the tumor response may be low in patients with some cancers compared to others. As a result, we may be required to discontinue development of MTX110 for patients with those tumor types and/or mutations due to insufficient clinical benefit, while continuing development for a more limited population of patients. Consequently, in order to obtain regulatory approval, we may have to reach agreement with the FDA on defining the optimal patient population, study design, and size, any of which may require significant additional resources and delay our clinical trials and ultimately the approval, if any, of any of our product candidates.
We may experience setbacks that could delay or prevent regulatory approval of, or our ability to commercialize, our product candidates, including:
| • | negative or inconclusive results from our preclinical studies or clinical trials or positive results from the clinical trials of others for product candidates similar to ours leading to their approval, and evolving to a decision or requirement to conduct additional preclinical testing or clinical trials or abandon a program; |
| • | product-related side effects experienced by patients or subjects in our clinical trials or by individuals using drugs or therapeutics that we, the FDA, other regulators or others view as relevant to the development of to our product candidates; |
| • | delays in submitting INDs or comparable foreign applications or delays or failure in obtaining the necessary approvals from regulators to commence a clinical trial, or a suspension or termination of a clinical trial once commenced; |
| • | conditions imposed by the FDA or comparable foreign authorities regarding the scope or design of our clinical trials, including our clinical endpoints; |
| • | inability to maintain compliance with regulatory requirements, including current good manufacturing practices, or cGMP, and complying effectively with other procedures; |
| • | inadequate supply or quality of product candidates or other materials necessary for the conduct of our clinical trials; |
| • | greater than anticipated clinical trial costs; |
| • | inability to compete with other therapies; |
| • | poor efficacy of our product candidates during clinical trials; |
| • | trial results taking longer than anticipated; |
| • | trials being subjected to fraud or data capture failure or other technical mishaps leading to the invalidation of our trials; |
| • | the results of our trials not supporting application for conditional approval in the EU; |
| • | unfavorable FDA or other regulatory agency inspection and review of a clinical trial site; |
| • | failure of our third-party contractors or investigators to comply with regulatory requirements or otherwise meet their contractual obligations in a timely manner, or at all; |
| • | delays and changes in regulatory requirements, policy and guidelines, including the imposition of additional regulatory oversight around clinical development generally or with respect to our technology in particular; or |
| • | varying interpretations of data by the FDA and similar foreign regulatory agencies. |
In addition, because we have limited financial and personnel resources and are focusing primarily on developing our lead product candidates, we may forgo or delay pursuit of other future product candidates that may prove to have greater commercial potential and may fail to capitalize on viable commercial products or profitable market opportunities. If we do not accurately evaluate the commercial potential or target market for a future product candidate, we may relinquish valuable rights to those future product candidates through collaboration, licensing, or other royalty arrangements in cases in which it would have been more advantageous for us to retain sole development and commercialization rights to such future product candidates.
The results of preclinical studies and early clinical trials are not always predictive of future results. Any product candidate that we advance in clinical trials may not achieve favorable results in later clinical trials, if any, or receive marketing approval.
The research and development of drugs and biological products is expensive and extremely risky. Only a small percentage of product candidates that enter the development process ever receive marketing approval. Before obtaining marketing approval from regulatory authorities for the sale of our product candidates, we must conduct extensive clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the product candidates in humans. The outcome of clinical testing is uncertain. We may face unforeseen challenges in our product candidate development strategy, and we can provide no assurances that any of our clinical trials will be conducted as planned or completed on schedule, or at all, that we will ultimately be successful in our current and future clinical trials, or that our product candidates will be able to receive regulatory approval. A failure of one or more clinical trials can occur at any stage of testing, which may result from a multitude of factors, including, among other things, flaws in study design, dose selection issues, placebo effects, patient enrollment criteria and failure to demonstrate favorable safety or efficacy. The outcome of preclinical testing and early clinical trials may not be predictive of the success of later clinical trials, and preliminary or interim results of a clinical trial do not necessarily predict final results. For example, it is not uncommon for product candidates to exhibit unforeseen safety or efficacy issues when tested in humans despite promising results in preclinical animal models. Accordingly, we cannot assure you that any clinical trials that we may conduct will demonstrate consistent or adequate efficacy and safety to support marketing approval. In general, the FDA and regulatory authorities outside the United States require two adequate and well-controlled clinical trials demonstrating safety and effectiveness, including a Phase III clinical trial, before granting marketing approval of a drug product.
Many companies in the pharmaceutical industry have suffered significant setbacks in late-stage clinical trials even after achieving promising results in preclinical testing and earlier-stage clinical trials, and we cannot be certain that we will not face similar setbacks. Moreover, preclinical and clinical data are often susceptible to varying interpretations and analyses, and many companies that have believed their product candidates performed satisfactorily in preclinical studies and clinical trials have nonetheless failed to obtain marketing approval of their products. Furthermore, the failure of MTX110 or any other product candidates that we develop to demonstrate safety and efficacy in any clinical trial could negatively impact the perception of other product candidates that we develop or cause regulatory authorities to require additional testing before approving any of our product candidates.
If we are required to conduct additional clinical trials or other testing of MTX110 or our other product candidates, if we are unable to successfully complete clinical trials of MTX110 or our other product candidates or other testing, if the results of these trials or tests are not positive or are only modestly positive, if there are safety concerns or if we determine that the observed safety or efficacy profile would not be competitive in the marketplace, we may:
| • | be delayed in obtaining marketing approval for MTX110 or other product candidates we develop; |
| • | not obtain marketing approval at all; |
| • | obtain marketing approval in some countries and not in others; |
| • | obtain approval for indications or patient populations that are not as broad as intended or desired; |
| • | obtain approval with labeling that includes significant use or distribution restrictions or safety warnings; |
| • | be subject to additional post-marketing testing requirements; or |
| • | have the product removed from the market after obtaining marketing approval. |
Our product development costs will also increase if we experience delays in clinical trials or in obtaining marketing approvals. We do not know whether any of our clinical trials will continue or begin as planned, will need to be restructured or will be completed on schedule, or at all. We may also decide to change the design or protocol of one or more of our clinical trials, including to add additional patients or arms, which could result in increased costs and expenses or delays. Significant clinical trial delays also could shorten any periods during which we may have the exclusive right to commercialize our product candidates or allow our competitors to bring products to market before we do and impair our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates and may harm our business and results of operations.
We or our collaborators may experience delays or difficulties in the enrollment and/or retention of patients in clinical trials, which could delay or prevent our receipt of necessary regulatory approvals.
Successful and timely completion of clinical trials will require that we or our collaborators sponsoring trials for our product candidates enroll a sufficient number of patients. Patient enrollment, which is an important factor in the timing of clinical trials, is affected by many factors, including the size and nature of the patient population and competition for patients eligible for our clinical trials with competitors which may have ongoing clinical trials for product candidates that are under development to treat the same indications as one or more of our product candidates, or approved products for the conditions for which we are developing our product candidates.
Trials may be subject to delays as a result of patient enrollment taking longer than anticipated or patient withdrawal. We may not be able to initiate or continue clinical trials for our product candidates if we are unable to locate and enroll a sufficient number of eligible patients to participate in these trials as required by the FDA, EMA, or comparable foreign regulatory authorities. We cannot predict how successful we or our collaborators will be at enrolling subjects in future clinical trials. Subject enrollment is affected by other factors including:
| • | the severity and difficulty of diagnosing the disease under investigation; |
| • | the eligibility and exclusion criteria for the trial in question; |
| • | the size of the patient population and process for identifying patients; |
| • | our ability to recruit clinical trial investigators with the appropriate competencies and experience; |
| • | the design of the trial protocol; |
| • | the perceived risks and benefits of the product candidate in the trial in relation to other available therapies, including any new products that may be approved for the indications we are investigating; |
| • | the availability of competing commercially available therapies and other competing therapeutic candidates’ clinical trials for the disease or condition under investigation, including for melanoma and other cancers in a first-line setting; |
| • | the willingness of patients to be enrolled in our clinical trials; |
| • | the risk that subjects enrolled in clinical trials will drop out of our trials before completion; |
| • | our ability to obtain and maintain clinical trial subject informed consents |
| • | the efforts to facilitate timely enrollment in clinical trials; |
| • | the patient referral practices of physicians; |
| • | the ability to monitor patients adequately during and after treatment; and |
| • | the proximity and availability of clinical trial sites for prospective patients. |
Inability to enroll a sufficient number of patients for clinical trials would result in significant delays and could require us to abandon one or more clinical trials altogether. Enrollment delays in these clinical trials may result in increased development costs for our product candidates, which would cause the value of our company to decline and limit our ability to obtain additional financing. Furthermore, we expect to rely on contract research organizations (CROs) and clinical trial sites to ensure the proper and timely conduct of our clinical trials and we will have limited influence over their performance.
The regulatory approval processes in the United States and Europe are lengthy, time consuming and inherently unpredictable, and if we are ultimately unable to obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates, our business may be substantially harmed.
The time required to obtain approval for a product candidate by the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities is unpredictable, and it typically takes many years following the commencement of preclinical studies and clinical trials, if approval is obtained at all, and depends upon numerous factors, including the substantial discretion of the regulatory authorities. In addition, approval policies, regulations, or the type and amount of clinical data necessary to gain approval may change during the course of a product candidate’s clinical development and may vary among jurisdictions. We have not obtained regulatory approval for any product candidate, and it is possible that we may never obtain regulatory approval for any product candidate we may seek to develop in the future. Neither we nor any current or future collaborator is permitted to market any drug product candidates in the United States until we receive regulatory approval of a NDA from the FDA, and we cannot market it in the European Union or the United Kingdom until we receive a marketing authorization approval from the EMA or the MHRA, respectively, or in any other country until we obtain regulatory authorization as required under the laws of such country.
Our product candidates could fail to receive regulatory approval from the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities for many reasons, including:
| • | disagreement with the design or implementation of the clinical trials; |
| • | failure to demonstrate that a product candidate is safe and effective for its proposed indication; |
| • | failure of clinical trial results to meet the level of statistical significance required for approval; |
| • | failure to demonstrate that a product candidate’s clinical and other benefits outweigh its safety risks; |
| • | disagreement with our interpretation of data from preclinical studies or clinical trials; |
| • | the insufficiency of data collected from clinical trials of our product candidates to support the submission and filing of a NDA, BLA, MAA or other submission or to obtain regulatory approval; |
| • | regulatory authorities may find deficiencies in good clinical practice, or GCP, compliance or may find our record keeping, or the record keeping of our clinical trial sites, to be inadequate; |
| • | disapproval of the manufacturing processes or facilities of third party manufacturers with whom we or any licensing partner contracts with for clinical and commercial supplies; or |
| • | changes in approval policies or regulations that render the preclinical and clinical data insufficient for approval. |
Of the large number of products in development, only a small percentage successfully complete the FDA, EMA, MHRA, or other comparable regulatory approval processes and are commercialized. The lengthy approval and marketing authorization process as well as the unpredictability of future clinical trial results may result in our failing to obtain regulatory approval and marketing authorization to market our product candidates, which would significantly harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
In addition, the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities may require more information, including additional preclinical or clinical data to support approval, which may delay or prevent approval and any commercialization plans, or we or any licensing partner may decide to abandon the development program. If approval were to be obtained, regulatory authorities may approve any of our product candidates for fewer or more limited indications than is requested, may grant approval contingent on the performance of costly post-marketing clinical trials, or may approve a product candidate with a label that does not include the labeling claims necessary or desirable for the successful commercialization of that product candidate. In addition, if our product candidate produces undesirable side effects or safety issues, the regulatory authorities (the FDA, MHRA, EMA or a comparable foreign regulatory authority) may require the establishment of Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, or REMS, which may, for instance, restrict distribution of the products and impose burdensome implementation requirements on us or any licensing partner. Any of the foregoing scenarios could materially harm the commercial prospects for our product candidates.
Our product candidates may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties that could delay or prevent their regulatory approval and limit the commercial profile of an approved label, and such side effects or other properties could result in significant negative consequences following any marketing approval of any of our product candidates.
Undesirable side effects caused by any of our product candidates could cause us, our licensing partners, if any, or regulatory authorities to interrupt, delay or halt clinical trials and could result in a more restrictive label or the delay or denial of regulatory approval by the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA or other comparable foreign regulatory authority. Results of the clinical trials could reveal a high and unacceptable severity and prevalence of side effects or risks associated with a product candidate’s use. In such an event, our trials could be suspended or terminated and the regulatory authorities could order us to cease further development of or deny approval of our product candidates for any or all targeted indications. The drug-related side effects could affect patient recruitment or the ability of enrolled subjects to complete the trial or result in potential product liability claims. Any of these occurrences may harm our business, financial condition and prospects significantly.
Additionally, if undesirable side effects of our products are identified following marketing approval, a number of potentially significant negative consequences could result, including:
| • | marketing of such product may be suspended; |
| • | a product recall or product withdrawal; |
| • | regulatory authorities may withdraw approvals of such product or may require additional warnings on the label; |
| • | the requirement to develop a REMS for each product or, if a strategy is already in place, to incorporate additional requirements under the REMS, or to develop a similar strategy as required by a comparable foreign regulatory authority; |
| • | the requirement to conduct additional post-market studies; and |
| • | being sued and held liable for harm caused to subjects or patients. |
Consequently, our reputation and business operations may suffer.
Any of these events could prevent the achievement or maintaining of market acceptance of the particular product or product candidate, if approved, and could significantly harm our business, results of operations and prospects.
Even if we receive regulatory approval of any product candidates, we will be subject to ongoing regulatory oversight and continued regulatory review, which may result in significant additional expense and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or experience unanticipated problems with any of our product candidates.
Our product candidates, if they receive regulatory approval, will be subject to the ongoing requirements of the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA and other regulatory agencies governing the manufacture, quality control, further development, labeling, packaging, storage, distribution, safety surveillance, import, export, advertising, promotion, recordkeeping and reporting of safety and other post-market information. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, establishment registration and listing, as well as continued compliance with cGMP and GCP requirements for any clinical trials that we conduct post-approval. The safety profile of any product is closely monitored by the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA and other regulatory authorities after approval. If the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA or other regulatory authorities become aware of new safety information after approval of any of our products or product candidates, regulatory authorities may require labeling changes or establishment of a risk mitigation strategy or similar strategy, impose significant restrictions on a product’s indicated uses or marketing, or impose ongoing requirements for potentially costly post-approval studies or post-market surveillance.
In addition, manufacturers of drug and biological products and their facilities are subject to continual review and periodic inspections by the EMA, the MHRA, the FDA and other governmental regulatory authorities for compliance with cGMP regulations. If a previously unknown problem with a product, such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or a problem with the facility where the product is manufactured is discovered, a regulatory agency may impose restrictions on that product, the manufacturing facility or the party commercializing the product, including requiring recall or withdrawal of the product from the market or suspension of manufacturing. If our product candidates or the manufacturing facilities for our product candidates fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, a regulatory agency may:
| • | issue warning letters or untitled letters; |
| • | mandate modifications to, or the withdrawal of, marketing and promotional materials or require corrective information to be provided to healthcare practitioners; |
| • | require the violating party to enter into a consent decree, which can include the imposition of various fines, reimbursements of inspection costs, required due dates for specific actions and penalties for noncompliance; |
| • | seek an injunction or impose civil or criminal penalties or monetary fines; |
| • | require revisions to the labeling, including limitations on approved uses or the addition of additional warnings, contraindications or other safety information, including boxed warnings; |
| • | suspend, vary or withdraw regulatory approval; |
| • | require additional post-market clinical trials to assess the safety of the product; |
| • | suspend any ongoing clinical studies; |
| • | refuse to approve pending applications or supplements to applications filed by us or any licensing partner; |
| • | suspend or impose restrictions on operations, the products, manufacturing or ourselves; |
| • | require a change to the product labeling; or |
| • | seize or detain products, refuse to permit the import or export of products or require a product recall. |
In the EU, the EMA may require an equivalent risk management plan (RMP). Non-compliance with European Union requirements regarding safety monitoring or pharmacovigilance can also result in significant financial penalties. Similarly, failure to comply with the European Union’s requirements regarding the protection of personal information can also lead to significant penalties and sanctions.
The occurrence of any of these events or penalties described above may inhibit our ability to generate revenue from product candidates that are commercialized by any of our licensing partners.
The FDA’s, EMA’s, MHRA’s, and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities’ policies may change and additional government regulations may be enacted that could prevent, limit or delay regulatory approval of our product candidates. If we are slow or unable to adapt to changes in existing requirements or the adoption of new requirements or policies, or if we are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we may lose any marketing approval that we may have obtained, which would adversely affect our business, prospects and ability to achieve or sustain profitability.
Obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval of MTX110 or any of our other product candidates in one jurisdiction does not mean that we will be successful in obtaining regulatory approval of MTX110 or our other product candidates in other jurisdictions.
Obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval of MTX110 or any of our other product candidates in one jurisdiction does not guarantee that we will be able to obtain or maintain regulatory approval in any other jurisdiction, while a failure or delay in obtaining regulatory approval in one jurisdiction may have a negative effect on the regulatory approval process in others. For example, even if the FDA grants marketing approval of a product candidate, similar foreign regulatory authorities must also approve the manufacturing, marketing and promotion of the product candidate in those countries. Approval and licensure procedures vary among jurisdictions and can involve requirements and administrative review periods different from, and greater than, those in the United States, including additional studies or clinical trials as clinical trials conducted in one jurisdiction may not be accepted by regulatory authorities in other jurisdictions. In many jurisdictions outside the United States, a product candidate must be approved for reimbursement before it can be approved for sale in that jurisdiction. In some cases, the price that we intend to charge for our products is also subject to approval.
We may also submit marketing applications in other countries. Regulatory authorities in jurisdictions outside of the United States have requirements for approval of product candidates with which we must comply prior to marketing in those jurisdictions. Obtaining similar foreign regulatory approvals and compliance with similar foreign regulatory requirements could result in significant delays, difficulties and costs for us and could delay or prevent the introduction of our products in certain countries. We do not have any product candidates approved for sale in any jurisdiction, including international markets, and we do not have experience in obtaining regulatory approval in international markets. If we fail to comply with the regulatory requirements in international markets and/or receive applicable marketing approvals, our target market will be reduced and our ability to realize the full market potential of our product candidates will be harmed.
We seek to establish agreements with potential licensing partners and collaborators and, if we are not able to establish them on commercially reasonable terms, we may have to alter our development and commercialization plans.
Our current development and commercialization strategy is to deploy our proprietary drug delivery technologies to formulate a compelling portfolio of novel first-in-class sustained release formulations of products with significant commercial potential for licensing to pharmaceutical company partners at proof-of-concept stage, which would potentially result in revenue generation from product royalty and/or milestone deals. We seek to work with licensing or collaboration partners for the development and commercialization of one or more of our product candidates. For example, in January 2019, we entered into that certain Licensing, Collaboration and Distribution Agreement, or the CMS License Agreement, with China Medical Systems Holdings Limited, or CMS, as guarantor, and two of its wholly owned subsidiaries, CMS Bridging Limited, or CMS Bridging, and CMS Medical Hong Kong Limited, or CMS Medical HK, each a CMS Party, pursuant to which, among other things, we agreed to license certain of our products to the CMS Parties in exchange for, among other things, royalty revenue. In June 2020, we announced a research and development collaboration with Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd., or Dr. Reddy’s, under which we evaluated the feasibility of applying Q-Sphera technology to molecules nominated by Dr. Reddy’s. The collaboration was subsequently terminated by mutual agreement. In July 2020, we announced a similar collaboration with an unnamed European affiliate of a global healthcare company, which was subsequently extended in January 2022 and the collaboration partner disclosed as Janssen Pharmaceutical NV, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson, or Janssen. Likely future collaborators may include large and mid-size pharmaceutical companies, regional and national pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology companies.
We face significant competition in seeking appropriate licensing or collaboration partners. Whether we reach a definitive agreement will depend, among other things, upon our assessment of the partner’s resources and expertise, the terms and conditions of the proposed collaboration and the proposed partner’s evaluation of a number of factors. Those factors may include the potential differentiation of our product candidate from competing product candidates, design or results of clinical trials, the likelihood of approval by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities and the regulatory pathway for any such approval, the potential market for the product candidate, the costs and complexities of manufacturing and delivering the product to patients and the potential of competing products. The partner may also consider alternative product candidates or technologies for similar indications that may be available for collaboration and whether such collaboration could be more attractive than the one with us for our product candidate.
These agreements are complex and time consuming to negotiate and document. Further, there have been a significant number of recent business combinations among large pharmaceutical companies that have resulted in a reduced number of potential future licensing and collaboration partners.
We may not be able to negotiate agreements with these potential partners on a timely basis, on acceptable terms, or at all. If we are unable to do so, we may have to curtail the development of the product candidate for which we are seeking to collaborate, reduce or delay its development program or one or more of our other development programs.
If we enter into agreements with a licensing or collaboration partner for the development and commercialization of our product candidates, our prospects with respect to those product candidates will depend in significant part on the success of those collaborations.
Some of our revenues are currently derived from licensing or collaboration agreements with other biopharmaceutical companies, research institutes and universities, and we expect a material amount of our revenue in the future will be derived from these and similar agreement. We may enter into additional agreements with a licensing or collaboration partner for the development and commercialization of certain of our product candidates. If we enter into such agreements, we will have limited control over the amount and timing of resources that our partners will dedicate to the development or commercialization of our product candidates. Our ability to generate revenues from these arrangements will depend on any future licensing partners’ ability to successfully perform the functions assigned to them in these arrangements. In addition, any future licensing or collaboration partner may have the right to abandon research or development projects and terminate applicable agreements, including funding obligations, prior to or upon the expiration of the agreed upon terms.
Agreements involving our product candidates pose a number of risks, including:
| • | partners have significant discretion in determining the efforts and resources that they will apply to these matters; |
| • | partners may not perform their obligations as expected; |
| • | partners may not pursue development and commercialization of our product candidates or may elect not to continue or renew development or commercialization programs, based on clinical trial results, changes in the their strategic focus or available funding or external factors, such as an acquisition, that divert resources or create competing priorities; |
| • | partners may delay clinical trials, provide insufficient funding for a clinical trial, stop a clinical trial or abandon a product candidate, repeat or conduct new clinical trials or require a new formulation of a product candidate for clinical testing; |
| • | a partner with marketing and distribution rights to one or more products may not commit sufficient resources to the marketing and distribution of such product or products; |
| • | disagreements with partners, including disagreements over proprietary rights, contract interpretation or the preferred course of development, might cause delays or termination of the research, development or commercialization of product candidates, might lead to additional responsibilities for us with respect to product candidates, or might result in litigation or arbitration, any of which would be time-consuming and expensive; |
| • | partners may not properly maintain or defend our intellectual property rights or may use our proprietary information in such a way as to invite litigation that could jeopardize or invalidate our intellectual property or proprietary information or expose us to potential litigation; |
| • | partners may infringe the intellectual property rights of third parties, which may expose us to litigation and potential liability; and |
| • | agreements may be terminated and, if terminated, may result in a need for additional capital to pursue further development or commercialization of the applicable product candidates. |
Agreements may not lead to development or commercialization of product candidates in the most efficient manner, or at all. If any future partners of ours is involved in a business combination, it could decide to delay, diminish or terminate the development or commercialization of any product candidate licensed to it by us.
The commercial success of any of our product candidates is not guaranteed.
There can be no assurance that any of our product candidates currently in development will be successfully developed into any commercially viable product or products and/or be manufactured in commercial quantities at an acceptable cost or be marketed successfully and profitably. If we, or our partners, encounter delays at any stage, and fail successfully to address such delays, it may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and prospects. In addition, our success will depend on the market’s acceptance of these products and there can be no guarantee that this acceptance will be forthcoming or that our technologies will succeed as an alternative to competing products. If a market fails to develop or develops more slowly than anticipated, we may be unable to recover the costs we may have incurred in the development of particular products and may never achieve profitable royalty or licensing revenues from that product.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are highly competitive.
The development and commercialization of new drug products is highly competitive. Our business faces competition from a range of major and specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies worldwide with respect to our product candidates, and will face competition in the future with respect to any product candidates that we may seek to develop or commercialize.
There are a number of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies that currently market and sell products or are pursuing development of products similar to our technology and product candidates. With respect to our product candidates, from a technology perspective, we believe other companies in the sustained release space include Medincell S.A., GP Pharm, S.A., Peptron, Inc., Graybug Inc. and Nanomi B.V. In addition, other companies using gold nanoparticle technologies include CytImmune Sciences, Inc., and Nanospectra Biosciences, Inc.
Some of these competitive products and therapies are based on scientific approaches that are the same or similar to our approach, and others are based on entirely different approaches. Potential competitors also include academic institutions, government agencies and other public and private research organizations that conduct research, seek patent protection and establish collaborative arrangements for research, development, manufacturing and commercialization.
Our competitors in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may have superior research and development capabilities, products, manufacturing capability or sales and marketing expertise. Many of our competitors may have significantly greater financial and human resources and may have more experience in research and development.
As a result of these factors, our competitors may obtain regulatory approval of their products more rapidly than we are able to or may obtain patent protection of other intellectual property rights that limit our ability to develop or commercialize our product candidates. Our competitors may also develop products that are more effective, more widely used and less costly than our own product candidates, and may be more successful in commercializing their products.
We anticipate that we will face increased competition in the future as new companies enter our markets and alternative products and technologies become available. Mergers and acquisitions in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of our competitors. Smaller and other early-stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies. These third parties compete with us in recruiting and retaining qualified scientific, management and commercial personnel, as well as in acquiring technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs.
Changes in health care policies, laws and regulations, including legislative measures aimed at reducing health care costs, may impact our ability to obtain approval for or commercialize any of our future product candidates, if approved.
All aspects of our business, including research and development, manufacturing, marketing, pricing, sales, litigation, and intellectual property rights, are subject to extensive legislation and regulation. Changes in applicable U.S. federal and state laws and agency regulation, as well as foreign laws and regulations, could have a materially negative impact on our business. In the United States and in some other jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the health care system that could prevent or delay marketing approval of our product candidates or any potential future product candidates of ours, restrict or regulate post-approval activities, or affect our ability to profitably sell any product candidates for which we obtain marketing approval. Increased scrutiny by the U.S. Congress of the FDA’s approval process may significantly delay or prevent marketing approval, as well as subject us to more stringent product labeling and post-marketing testing and other requirements. Congress also must reauthorize the FDA’s user fee programs every five years and often makes changes to those programs in addition to policy or procedural changes that may be negotiated between the FDA and industry stakeholders as part of this periodic reauthorization process. Congress most recently reauthorized the user fee programs in September 2022 without any substantive policy changes.
Among policy makers and payors in the United States and elsewhere, there is significant interest in promoting changes in health care systems with the stated goals of containing health care costs, improving quality and/or expanding access. In the United States, the pharmaceutical industry has been a focus of these efforts and has been significantly affected by major legislative initiatives. In March 2010, Congress passed the ACA, which substantially changed the way health care is financed by both the government and private insurers, and significantly impacts the U.S. pharmaceutical industry.
There remain judicial and Congressional challenges to certain aspects of the ACA, and as a result, certain sections of the ACA have not been fully implemented or effectively repealed. However, following several years of litigation in the federal courts, in June 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld the ACA when it dismissed a legal challenge to the law’s constitutionality. Further legislative and regulatory changes under the ACA remain possible, although the new federal administration under President Biden has signaled that it plans to build on the ACA and expand the number of people who are eligible for health insurance subsidies under it. It is unknown what form any such changes or any law would take, and how or whether it may affect the pharmaceutical industry as a whole or our business in the future. We expect that changes or additions to the ACA, the Medicare and Medicaid programs, and changes stemming from other health care reform measures, especially with regard to health care access, financing or other legislation in individual states, could have a material adverse effect on the health care industry in the United States.
The uncertainty around the future of the ACA, and in particular the impact to reimbursement levels, may lead to uncertainty or delay in the purchasing decisions of our customers, which may in turn negatively impact our product sales. If there are not adequate reimbursement levels, our business and results of operations could be adversely affected.
In addition, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since the ACA was enacted. These changes include aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers of up to 2% per fiscal year pursuant to the Budget Control Act of 2011, which began in 2013 and was extended by the Consolidated Appropriations Act for 2023, and will remain in effect through 2032 unless additional Congressional action is taken.
In addition, the Drug Supply Chain Security Act, or DSCSA, enacted in 2013 imposed obligations on manufacturers of pharmaceutical products related to product tracking and tracing, and in February 2022, FDA released proposed regulations to amend the national standards for licensing of wholesale drug distributors by the states; establish new minimum standards for state licensing third-party logistics providers; and create a federal system for licensure for use in the absence of a State program, each of which is mandated by the DSCSA. Other legislative and regulatory proposals have been made to expand post-approval requirements and restrict sales and promotional activities for pharmaceutical products. We are unsure whether additional legislative changes will be enacted, or whether the current regulations, guidance or interpretations will be changed, or whether such changes will have any impact on our business.
Additionally, there has been heightened governmental scrutiny in the United States of biopharmaceutical pricing practices considering the rising cost of prescription drugs and biologics. Such scrutiny has resulted in several recent congressional inquiries and proposed and enacted federal and state legislation designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to product pricing, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs, and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for products. For example, state legislatures are increasingly passing legislation and implementing regulations designed to control pharmaceutical pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and, in some cases, designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing. In December 2020, the U.S. Supreme Court held unanimously that federal law does not preempt the states’ ability to regulate pharmaceutical benefit managers and other members of the health care and pharmaceutical supply chain, an important decision that may lead to further and more aggressive efforts by states in this area.
Most recently, in August 2022, President Biden signed into the law the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, or the IRA. Among other things, the IRA has multiple provisions that may impact the prices of drug products that are both sold into the Medicare program and throughout the United States. Starting in 2023, a manufacturer of a drug or biological product covered by Medicare Parts B or D must pay a rebate to the federal government if the product’s price increases faster than the rate of inflation. This calculation is made on a drug product by drug product basis and the amount of the rebate owed to the federal government is directly dependent on the volume of a drug product that is paid for by Medicare Parts B or D. Additionally, starting in payment year 2026, CMS will negotiate drug prices annually for a select number of single source Part D drugs without generic or biosimilar competition. CMS will also negotiate drug prices for a select number of Part B drugs starting for payment year 2028. If a drug product is selected by CMS for negotiation, it is expected that the revenue generated from such drug will decrease.
Any additional federal or state health care reform measures could limit the amounts that third-party payers will pay for future health care products and services, and, in turn, could significantly reduce the projected value of certain development projects and reduce our profitability.
Outside of the United States, particularly in the European Union, the coverage status and pricing of prescription pharmaceuticals and biologics is subject to governmental control. In these countries, pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can take considerable time after the receipt of marketing approval for a product. Furthermore, the requirements may differ across the E.U. Member States. To obtain coverage and reimbursement or pricing approval in some countries, we may be required to conduct a clinical trial that compares the cost-effectiveness of our product candidate to other available therapies. If reimbursement of our products is unavailable or limited in scope or amount, or if pricing is set at unsatisfactory levels, our business could be harmed. Also, at national level, actions have been taken to enact transparency and anti-gift laws (similar to the US Physician Payments Sunshine Act) regarding payments between pharmaceutical companies and healthcare professionals.
Coverage and adequate reimbursement may not be available for our current or any future product candidates, which could make it difficult for us to sell profitably, if approved.
Market acceptance and sales of any product candidates that we commercialize, if approved, will depend in part on the extent to which reimbursement for these products and related treatments will be available from third-party payors, including government health administration authorities, managed care organizations and private health insurers. Significant uncertainty exists as to the coverage and reimbursement status of any products for which we may obtain regulatory approval. Third-party payors decide which therapies they will pay for and establish reimbursement levels. Third-party payors in the United States often rely upon Medicare coverage policy and payment limitations in setting their own coverage and reimbursement policies. However, decisions regarding the extent of coverage and amount of reimbursement to be provided for any product candidates that we develop will be made on a payor-by-payor basis. One payor’s determination to provide coverage for a drug does not assure that other payors will also provide coverage for the drug. Additionally, a third-party payor’s decision to provide coverage for a therapy does not imply that an adequate reimbursement rate will be approved. Third-party payors are increasingly challenging the price, examining the medical necessity and reviewing the cost-effectiveness of medical products, therapies and services, in addition to questioning their safety and efficacy. We may incur significant costs to conduct expensive pharmaco-economic studies in order to demonstrate the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of our product candidates, in addition to the costs required to obtain FDA approvals. Our product candidates may not be considered medically necessary or cost-effective.
Each payor determines whether or not it will provide coverage for a therapy, what amount it will pay the manufacturer for the therapy, and on what tier of its list of covered drugs, or formulary, it will be placed. The position on a payor’s formulary, generally determines the co-payment that a patient will need to make to obtain the therapy and can strongly influence the adoption of such therapy by patients and physicians. Patients who are prescribed treatments for their conditions and providers prescribing such services generally rely on third-party payors to reimburse all or part of the associated healthcare costs. Patients are unlikely to use our products, and providers are unlikely to prescribe our products, unless coverage is provided and reimbursement is adequate to cover a significant portion of the cost of our products and their administration. Therefore, coverage and adequate reimbursement is critical to new medical product acceptance.
In the United States, no uniform policy of coverage and reimbursement for products exists among third-party payors. Therefore, coverage and reimbursement for our products can differ significantly from payor to payor. As a result, obtaining coverage and reimbursement approval of a product from a government or other third-party payor is a time-consuming and costly process that could require us to provide to each payor supporting scientific, clinical and cost-effectiveness data for the use of our products on a payor-by-payor basis, with no assurance that coverage and adequate reimbursement will be obtained. Even if we obtain coverage for a given product, the resulting reimbursement payment rates might not be adequate for us to achieve or sustain profitability or may require co-payments that patients find unacceptably high. Additionally, third-party payors may not cover, or provide adequate reimbursement for, long-term follow-up evaluations required following the use of product candidates, once approved.
A primary trend in the U.S. healthcare industry and elsewhere is cost containment. Third-party payors have attempted to control costs by limiting coverage and the amount of reimbursement for particular medications. We cannot be sure that coverage and reimbursement will be available for any product that we may commercialize and, if reimbursement is available, what the level of reimbursement will be. Even if favorable coverage and reimbursement status is attained for one or more product candidates for which we receive regulatory approval, less favorable coverage policies and reimbursement rates may be implemented in the future. Inadequate coverage and reimbursement may impact the demand for, or the price of, any drug for which we obtain marketing approval. If coverage and adequate reimbursement are not available, or are available only to limited levels, we may not be able to successfully commercialize our current and any future product candidates that we develop.
We are subject to environmental laws and regulations that govern the use, storage, handling and disposal of hazardous materials and other waste products.
We are subject to environmental laws and regulations governing the use, storage, handling and disposal of hazardous materials and other waste products. We have health and safety policies and procedures in place to assess the risks associated with use of hazardous materials, and the assessment includes information for employees on how the substances should be used to avoid contamination of the environment and inadvertent exposure to themselves and their colleagues. Despite our precautions for handling and disposing of these materials, we cannot eliminate the risk of accidental contamination or injury. In the event of a hazardous waste spill or other accident, we could be liable for damages, penalties or other forms of censure. If we fail to comply with any laws or regulations, or if an accident occurs, we may have to pay significant penalties and may be held liable for any damages that result. This liability could exceed our financial resources and could harm our reputation. We may also have to incur significant additional costs to comply with current or future environmental laws and regulations. Our failure to comply with any government regulation applicable to our laboratory and the materials used in our laboratory may adversely affect our ability to develop, produce, market or partner any products we may commercialize or develop.
Our employees, principal investigators, consultants and commercial partners may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including noncompliance with regulatory standards and requirements, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We are exposed to the risk of employee fraud or other misconduct by our employees, principal investigators, consultants and commercial partners. Misconduct by such parties could include intentional failures to comply with applicable regulations, provide accurate information to regulatory authorities, comply with manufacturing standards, comply with healthcare fraud and abuse laws and regulations, report financial information or data accurately, or disclose unauthorized activities to us. In particular, sales, marketing and business arrangements in the healthcare industry are subject to extensive laws and regulations intended to prevent fraud, kickbacks, self-dealing and other abusive practices. These laws and regulations may restrict or prohibit a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing and promotion, sales commission, customer incentive programs and other business arrangements. Such misconduct could also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of clinical trials, which could result in regulatory sanctions and serious harm to our reputation. We have adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, but it is not always possible to identify and deter employee misconduct, and the precautions we have taken to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to be in compliance with such laws or regulations. If any such actions are instituted against us and we are not successful in defending ourselves or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business and results of operations, including the imposition of significant fines or other sanctions.
Unexpected facility shutdowns or system failures may occur and our disaster recovery plans may not be sufficient.
We depend on the performance, reliability and availability of our properties, machinery, and laboratory equipment and information technology systems. We may not be able to access our facilities as a result of events beyond our control, such as extreme weather conditions, quarantines, flood, fire, theft, terrorism and acts of God.
Further, any damage to or failure of our equipment and/or systems could also result in disruptions to our operations. A complete or partial failure of our information technology systems, or those of our CROs and other third parties on which we rely, or corruption of data could result in our inability to access information that we need in order to meet our obligations to our customers or a breach of confidentiality with respect to our or our customers’ proprietary information. If such an event were to occur and cause interruptions in our operations, it could result in a material disruption of our drug development programs. For example, the loss of clinical trial data from completed or ongoing clinical trials could result in delays in our regulatory approval efforts and significantly increase our costs to recover or reproduce the data. Our disaster recovery plans may not adequately address every potential event and our insurance policies may not cover any loss in full or in part (including losses resulting from business interruptions) or damage that we suffer fully or at all. The occurrence of one or more of these events could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position, reputation or prospects, and might lead to a claim for damages.
Our business may be adversely affected by economic conditions and current economic weakness.
Any economic downturn either globally, regionally or locally in any country in which we operate may have an adverse effect on the demand for any products derived from our product candidates. A more prolonged economic downturn may lead to an overall decline in our sales, limiting our ability to generate a profit and positive cash flow. The markets in which we expect the products to be offered are directly affected by many national and international factors that are beyond our control, such as political, economic, currency, social and other factors.
Our business may be impacted by political events, war, terrorism, business interruptions and other geopolitical events and uncertainties beyond our control.
War, terrorism, geopolitical uncertainties and other business interruptions could cause damage to disrupt or cancel the conduct of our planned clinical trials on a global or regional basis, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, clinical sites or vendors with which we do business. Such events could also decrease patient demand to enroll in our clinical trials or make it difficult or impossible for us to deliver products and services to our clinical investigational sites. In addition, territorial invasions can lead to cybersecurity attacks on companies, such as ours, located far outside of the conflict zone. In the event of prolonged business interruptions due to geopolitical events, we could incur significant losses, require substantial recovery time and experience significant expenditures in order to resume our business or clinical operations. We have no operations in Russia or Ukraine, but we do not and cannot know if the current uncertainties in these geopolitical areas, which are unfolding in real-time, may escalate and result in broad economic and security conditions or rationing of medical supplies, which could limit our ability to conduct clinical trials or result in material implications for our business.
We are exposed to the risks of doing business internationally.
We have in the past, and may in the future, operate outside of the United Kingdom. These international operations are subject to a number of risks inherent in operating in different countries. These include, but are not limited to, risks regarding:
| • | currency exchange rate fluctuations; |
| • | restrictions on repatriation of earnings; |
| • | difficulty of effective enforcement of contractual provisions in local jurisdictions;’ |
| • | inadequate intellectual property (including confidentiality) protection in foreign countries; |
| • | public health epidemics or outbreaks, such as COVID-19; |
| • | trade-protection measures, import or export licensing requirements and fines, penalties or suspension or revocation of export privileges; and |
| • | changes in a specific country’s or a region’s political or economic conditions, including the implications of the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the European Union. |
The occurrence of any of these events or conditions could adversely affect our ability to increase or maintain our operations in various countries.
We are exposed to risks related to currency exchange rates.
We currently conduct a portion of our operations outside of the United Kingdom. Because we use the British pound sterling as our financial statement reporting currency, changes in currency exchange rates have had and could have a significant effect on our operating results when our operating results are translated from the local currency into the British pound sterling. Exchange rate fluctuations between local currencies and the British pound sterling create risk in several ways, including the following: weakening of the British pound sterling, as seen, for example, following the results of the Brexit referendum, may increase the British pound sterling cost of overseas research and development expenses and the cost of sourced product components outside the United Kingdom; strengthening of the British pound sterling may decrease the value of our revenues denominated in other currencies; the exchange rates on non-sterling transactions and cash deposits can distort our financial results; and commercial pricing and profit margins are affected by currency fluctuations. Future changes in currency exchange rates could have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
We are subject to cybersecurity risks and other cyber incidents, including the misappropriation of our information and other breaches of information security that may result in disruption and the incurrence of costs in an effort to minimize those risks.
In the normal course of conducting our business, we collect and store sensitive data on our networks, including intellectual property, personal information of our employees, and our proprietary business information and that of our customers, vendors and business partners. Despite the security measures we have in place and any additional measures we may implement in the future to safeguard our systems and to mitigate potential security risks, our facilities and systems, and those of our third-party service providers, could be vulnerable to security breaches, computer viruses, lost or misplaced data, programming errors, human errors, acts of vandalism or other events. Any steps we take to deter and mitigate these risks may not be successful and may cause us to incur increasing costs. Any disruption of our systems or security breach or event resulting in the misappropriation, loss or other unauthorized disclosure of confidential information, whether by us directly or by our third-party service providers, could damage our reputation, result in the incurrence of costs, expose us to the risks of litigation and liability, result in regulatory penalties under laws that protect privacy of personal information, disrupt our business or otherwise affect our results of operations.
We may incur substantial costs in our efforts to comply with evolving global data protection laws and regulations, and any failure or perceived failure by us to comply with such laws and regulations may harm our business and operations.
We maintain a large quantity of sensitive information, including confidential business and personal information in connection with the conduct of our clinical trials and related to our employees, and we are subject to laws and regulations governing the privacy and security of such information. In the United States, there are numerous federal and state privacy and data security laws and regulations governing the collection, use, disclosure and protection of personal information, including federal and state health information privacy laws, federal and state security breach notification laws, and federal and state consumer protection laws. The legislative and regulatory landscape for privacy and data protection continues to evolve, and there has been an increasing focus on privacy and data protection issues, including with respect to regulatory enforcement and private litigation, which may affect our business and is expected to increase our compliance costs and exposure to liability. In the United States, numerous federal and state laws and regulations could apply to our operations or the operations of our partners, including state data breach notification laws, state health information privacy laws, and federal and state consumer protection laws and regulations, that govern the collection, use, disclosure, and protection of health-related and other personal information. In addition, we may obtain health information from third parties (including research institutions from which we obtain clinical trial data) that are subject to privacy and security requirements under HIPAA, as amended by HITECH and regulations promulgated thereunder. Depending on the facts and circumstances, we could be subject to significant penalties if we obtain, use, or disclose, or are subject to an actual or alleged data breach regarding, individually identifiable health information in a manner that is not authorized or permitted by HIPAA.
In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (EU) 2016/679, or GDPR, lays down the legal framework for data protection and privacy. The GDPR applies directly in all European Union member states (until December 31, 2020, this included the United Kingdom) and applies to companies with an establishment in the European Economic Area, or EEA, and to certain other companies not in the EEA that offer or provide goods or services to individuals located in the EEA or monitor the behavior of individuals located in the EEA. In the United Kingdom, the GDPR has been converted into United Kingdom domestic law, pursuant to the Data Protection, Privacy and Electronic Communications (Amendments etc.)(EU Exit) Regulations 2019 (as amended), which makes some minor technical amendments to ensure the GDPR is operable in the United Kingdom, or the UK GDPR. The UK GDPR is also supplemented by the Data Protection Act 2018. United Kingdom and European Union data protection law is therefore aligned. The GDPR and UK GDPR implement stringent operational requirements for controllers of personal data, including, for example, expanded disclosures about how personal information is to be used, limitations on retention of information, increased requirements pertaining to health data and pseudonymized (i.e., key-coded) data, increased cyber security requirements, mandatory data breach notification requirements and higher standards for controllers to demonstrate that they have obtained a valid legal basis for certain data processing activities. The GDPR provides that European Union member states may make their own further laws and regulations in relation to the processing of genetic, biometric or health data, which could result in differences between member states, limit our ability to use and share personal data or could cause our costs to increase, and harm our business and financial condition.
Failure to comply with European Union laws, including failure under the GDPR and UK GDPR, Data Protection Act 2018, ePrivacy Directive and other laws relating to the security of personal data may result in fines up to €20 million (or £17.5 million under the UK GDPR) or up to 4% of the total worldwide annual turnover of the preceding financial year, if greater, and other administrative penalties including criminal liability, which may be onerous and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. The GDPR also confers a private right of action on data subjects and consumer associations to lodge complaints with supervisory authorities, seek judicial remedies, and obtain compensation for damages resulting from violations of the GDPR. In addition, the GDPR includes restrictions on cross-border data transfers. Failure to comply with the GDPR and related laws may lead to increased risk of private actions from data subjects and consumer not-for-profit organizations, including a new form of class action that is available under the GDPR. While we do not routinely handle or process personal data, we do maintain a database of employee information; however, since the GDPR and UK GDPR only came into effect recently, the potential risks associated with non-compliance therewith are uniquely difficult to predict.
We may in the future be unable to retain and recruit qualified scientists, key executives and directors, key employees or key consultants, may delay our development efforts or otherwise harm our business.
Our future development and prospects depend to a large degree on the experience, performance and continued service of our senior management team, including members of our Board of Directors. We have invested in our management team at all levels. We have entered into contractual arrangements with our directors and senior management team with the aim of securing the services of each of them. However, retention of these services or the identification of suitable replacements cannot be guaranteed. There can be no guarantee that the services of the current directors and senior management team will be retained, or that suitably skilled and qualified individuals can be identified and employed, which may adversely impact our ability to develop our technologies and/or provide our services at the time requested by our customers or our ability to market our services and technologies, and otherwise to grow our business, could be impaired. The loss of the services of any of the directors or other members of the senior management team and the costs of recruiting replacements may have a material adverse effect on us and our commercial and financial performance.
The ability to continue to attract and retain employees with the appropriate expertise and skills also cannot be guaranteed. Finding and hiring any additional personnel and replacements could be costly and might require us to grant significant equity awards or other incentive compensation, which could adversely impact our financial results, and there can be no assurance that we will have sufficient financial resources to do so. Effective product development and innovation, upon which our success is dependent, is in turn dependent upon attracting and retaining talented technical and scientific personnel, who represent a significant asset and serve as the source of our technological and product innovations. If we are unable to hire, train and retain such personnel in a timely manner, the development and introduction of our products could be delayed and our ability to sell our products and otherwise to grow our business will be impaired and the delay and inability may have a detrimental effect upon our performance.
Risks related to our intellectual property
Our success depends in part on our ability to protect rights in our intellectual property, which cannot be assured.
Our success and ability to compete effectively are in large part dependent upon exploitation of proprietary technologies and products that we have developed internally or have acquired or in-licensed. To date, we have relied on copyright, trademark and trade secret laws, as well as confidentiality procedures, non-compete and/or work for hire invention assignment agreements and licensing arrangements with our employees, consultants, contractors, customers and vendors, to establish and protect our rights to our technology and, to the best extent possible, control the access to and distribution of our technology, software, documentation and other proprietary information, all of which offer only limited protection. Where we have the right to do so under our agreements, we seek to protect our proprietary position by filing patent applications in the United States, the United Kingdom and worldwide related to our novel technologies and products that are important to our business. The patent positions of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies generally are highly uncertain, involve complex legal and factual questions and have in recent years been the subject of much litigation. As a result, the issuance, scope, validity, enforceability and commercial value of our patents, including those patent rights licensed to us by third parties, are highly uncertain. There can be no assurance that:
| • | the scope of our patents provides and will provide us with exclusivity with respect to any or all of our product candidates and technologies, as well as any other technologies and/or products that address the same problems as our technologies and product candidates by a different means, whether in the same manner as us or not; |
| • | pending or future patent applications will be issued as patents; |
| • | our patents, and/or those patents to which we are licensed, are and will remain valid and enforceable and will not be subject to invalidity or revocation proceedings and that such proceedings will not result in a complete or partial loss of rights; |
| • | our entitlement to exploit patents from time to time (including patents registered solely in our name or our affiliates’ name or in the joint names of Midatech or an affiliate and a third party or patents which are licensed to us) is and will be sufficient to protect our core intellectual property rights against third parties, our commercial activities from competition or to support comprehensively our ability to develop and market our proposed products either now or in the future; |
| • | the lack of any particular patents or rights to exploit any particular patents, and the scope of our patents, will not have a material adverse effect on our ability to develop and market our proposed product candidates, either now or in the future; |
| • | we have or will have the resources to pursue any infringer of: (i) patents registered in our name (whether solely or jointly with a third party) from time to time; or (ii) patents licensed to us where we or an affiliate have the financial responsibility to bring such infringement actions pursuant to the relevant license agreement; |
| • | we will develop technologies or product candidates which are patentable, either alone or in conjunction with third parties; |
| • | the ownership, scope or validity of any patents registered in our name (either solely or jointly) from time to time will not be challenged by third parties, including parties with whom we, or any affiliate, have entered into collaboration projects or co-ownership arrangements and that any such challenge will not be successful; |
| • | any patent or patent application owned solely or jointly by us will not be challenged on grounds that we failed to identify the correct inventors or that we failed to comply with our duty of disclosure to the United States Patent and Trademark Office or any equivalent office in a foreign jurisdiction having a disclosure requirement; |
| • | any issued patent in our sole or joint name from time to time will not be challenged in one or more post-grant proceedings, including but not limited to inter partes review, derivation proceedings, interferences, and that like; and that any such challenge will not result in a complete or partial loss of rights to such issued patent or patents; |
| • | any patent applications in our sole or joint name from time to time will not be opposed by any third party, including parties to collaboration, co-existence and any other contractual relationship with us or any of its members; |
| • | the license agreements between us and third parties are and will be valid and subsisting in the future or until their expiry dates, and that we have complied with our contractual obligations under the license agreements; |
| • | all intellectual property capable of being commercialized that is or has been generated pursuant to collaboration agreements between us and third parties will be or has been identified; |
| • | all intellectual property generated pursuant to collaboration agreements and to which we have a contractual entitlement or generated by employees has been lawfully assigned into our sole name (or to one of our subsidiaries); |
| • | in respect of all intellectual property generated pursuant to a collaboration agreement between us and a third party to which we and that third party have a joint contractual entitlement, that such intellectual property has been lawfully assigned into joint names and the rights between us and that third party are properly regulated by a co-ownership agreement; and |
| • | beyond contractual warranties, the licensors of intellectual property to us or our affiliates own the relevant patents and that those patents have not and will not be the subject of, or subject to, infringement, invalidity or revocation actions. |
The steps we have taken to protect our proprietary rights may not be adequate to preclude misappropriation of our proprietary information or infringement of our intellectual property rights, both inside and outside of the United Kingdom and United States. The rights already granted under any of our currently issued patents and those that may be granted under future issued patents may not provide us with the proprietary protection or competitive advantages we are seeking. If we are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection for our technology and products, or if the scope of the patent protection obtained is not sufficient, our competitors could develop and commercialize technology and products similar or superior to ours, and our ability to successfully commercialize our technology and products may be adversely affected.
With respect to patent rights, we do not know whether any of the pending patent applications for any of our licensed compounds will result in the issuance of patents that protect our technology or products, or which will effectively prevent others from commercializing competitive technologies and products. Although we have a number of issued patents covering our technology, our pending applications cannot be enforced against third parties practicing the technology claimed in such applications unless and until a patent issues from such applications. Further, the examination process may require us to narrow the claims, which may limit the scope of patent protection that may be obtained. Because the issuance of a patent is not conclusive as to its inventorship, scope, validity or enforceability, issued patents that we own or have licensed from third parties may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the European Union, United Kingdom, the United States and other foreign jurisdictions. Overall, such challenges may result in the loss of patent protection, the narrowing of claims in such patents, or the invalidity or unenforceability of such patents, which could limit our ability to stop others from using or commercializing similar or identical technology and products, or limit the duration of the patent protection for our technology and products. Protecting against the unauthorized use of our patented technology, trademarks and other intellectual property rights is expensive, difficult and may in some cases not be possible. In some cases, it may be difficult or impossible to detect third party infringement or misappropriation of our intellectual property rights, even in relation to issued patent claims, and proving any such infringement may be even more difficult.
The patent prosecution process is expensive and time-consuming, and we may not be able to file and prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner. It is also possible that we will fail to identify patentable aspects of inventions made in the course of our development and commercialization activities before it is too late to obtain patent protection on them. Further, given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized. We expect to seek extensions of patent terms where they are available in any countries where we are prosecuting patents. However, the applicable authorities, including the FDA in the United States, and any equivalent regulatory authority in other countries, may not agree with our assessment of whether such extensions are available, and may refuse to grant extensions to our patents, or may grant more limited extensions than we request. If this occurs, our competitors may be able to take advantage of our investment in development and clinical trials by referencing our clinical and preclinical data and launch their product earlier than might otherwise be the case. Changes in either the patent laws or interpretation of the patent laws in the European Union, the United Kingdom, the United States and other countries may diminish the value of our patents or narrow the scope of our patent protection. The laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent as the laws of the United Kingdom or the United States, and these foreign laws may also be subject to change. Publication of discoveries in the scientific literature often lag behind the actual discoveries, and patent applications typically are not published until 18 months after filing or, in some cases, not at all. Therefore, we cannot be certain that we were the first to make the inventions claimed in our owned or licensed patents or pending patent applications, or that we were the first to file for patent protection of such inventions.
Previously, in the United States, assuming the other requirements for patentability are met, the first to make the claimed invention was entitled to the patent. Outside the United States, the first to file a patent application is entitled to the patent. In March 2013, the United States transitioned to a “first to file” system in which the first inventor to file a patent application will be entitled to the patent. Under either the previous or current system, third parties will be allowed to submit prior art prior to the issuance of a patent by the United States Patent and Trademark Office, and may become involved in opposition, derivation, reexamination, inter-partes review or interference proceedings challenging our patent rights or the patent rights of others. An adverse determination in any such submission, proceeding or litigation could reduce the scope of, or invalidate, our patent rights, which could adversely affect our competitive position with respect to third parties.
Our commercial success depends, in part, upon our not infringing intellectual property rights owned by others.
Although we believe that we have proprietary platforms for our technologies and product candidates, we cannot determine with certainty whether any existing third party patents or the issuance of any third party patents in the future would require us to alter our technology, obtain licenses or cease certain activities. We may become subject to claims by third parties that our technology infringes their intellectual property rights, in which case we will have no option other than to defend the allegation, which may be possible to resolve through negotiation or which might result in court proceedings. An adverse outcome in any of these circumstances is that we might be subject to significant liabilities, be required to cease using a technology or to pay license fees (both prospectively and retrospectively); and may be subject to the payment of significant damages. We could incur substantial costs in any litigation or other proceedings relating to patent rights, even if it is resolved in our favor. If the proceedings occur in the United States, it is likely that we will be responsible for our own legal costs, no matter the outcome of the litigation. In contrast, in the United Kingdom, the losing party typically is ordered to pay the winning party’s costs, although it is rare to have a complete recovery of all costs from the losing side. Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of complex litigation more effectively or for a longer time than we can because of their substantially greater resources. In addition, uncertainties or threatened or actual disputes relating to any patent, patent application or other intellectual property right (including confidential information) could have a material adverse effect on our ability to market a product, enter into collaborations in respect of the affected products, or raise additional funds.
The policing of unauthorized use of our patented technologies and product candidates is difficult and expensive. There can be no assurance that the steps we take will prevent misappropriation of, or prevent an unauthorized third party from obtaining or using, the technologies, know-how and products we rely on. In addition, effective protection may be unavailable or limited in some jurisdictions. Any misappropriation of our proprietary technology, product candidates and intellectual property could have a negative impact on our business and our operating results. Litigation may be necessary in the future to enforce or protect our rights or to determine the validity or scope of the proprietary rights of others. Litigation could cause us to incur substantial costs and divert resources and management attention away from our daily business and there can be no guarantees as to the outcome of any such litigation. In addition, a defendant in any such litigation may counterclaim against us, resulting in additional time and expense to defend against such a counterclaim, which defense may not be successful.
We may become involved in lawsuits to protect or enforce our intellectual property, which could be expensive, time consuming and unsuccessful.
Competitors may infringe on our patents or misappropriate or otherwise violate our intellectual property rights. To counter infringement or unauthorized use, litigation may be necessary in the future to enforce or defend our intellectual property rights, to protect our trade secrets or to determine the validity and scope of our own intellectual property rights or the proprietary rights of others. This can be expensive and time consuming. Many of our current and potential competitors have the ability to dedicate substantially greater resources to defend our intellectual property rights than we can. Accordingly, despite our efforts, we may not be able to prevent third parties from infringing upon or misappropriating our intellectual property. Litigation could result in substantial costs and diversion of management resources, which could harm our business and financial results. In addition, in an infringement proceeding, a court may decide that a patent owned by or licensed to us is invalid or unenforceable, or may refuse to stop the other party from using the technology at issue on the grounds that our patents do not cover the technology in question. An adverse result in any litigation proceeding could put one or more of our patents at risk of being invalidated, held unenforceable or interpreted narrowly. Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, there is a risk that some of our confidential information could be compromised by disclosure during this type of litigation.
Third parties may initiate legal proceedings alleging that we are infringing their intellectual property rights, the outcome of which would be uncertain and could have a material adverse effect on the success of our business.
Our commercial success depends upon our ability and the ability of our collaborators and licensing partners to develop, manufacture, market and sell our product candidates, and to use our proprietary technologies without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. We may become party to, or threatened with, future adversarial proceedings or litigation regarding intellectual property rights with respect to our products and technology. Third parties may assert infringement claims against us based on existing patents or patents that may be granted in the future. If we are found to infringe a third party’s intellectual property rights, we could be required to obtain a license from such third party to continue developing and commercializing our products and technology. However, we may not be able to obtain any required license on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Even if we are able to obtain a license, it may be non-exclusive, thereby giving our competitors access to the same technologies licensed to us. We could be forced, including by court order, to cease commercializing the infringing technology or product. In addition, in any such proceeding or litigation, we could be found liable for monetary damages. A finding of infringement could prevent us from commercializing our product candidates or force us to cease some of our business operations, which could materially harm our business. Any claims by third parties that we have misappropriated our confidential information or trade secrets could have a similar negative impact on our business.
We may be subject to claims that our employees have wrongfully used or disclosed alleged trade secrets of their former employers.
Many of our employees, including our senior management, were previously employed at other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies. Some of these employees, including members of our senior management, executed proprietary rights, non-disclosure and non-competition agreements in connection with such previous employment. Although we try to ensure that our employees do not use the proprietary information or know-how of others in their work for us, we may be subject to claims that we or these employees have used or disclosed intellectual property, including trade secrets or other proprietary information, of any such employee’s former employer. We are not aware of any threatened or pending claims related to these matters or concerning the agreements with our senior management, but in the future litigation may be necessary to defend against such claims. If we fail in defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights or personnel. Even if we are successful in defending against such claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a potential distraction to management.
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our trade secrets, our business and competitive position could be harmed.
In addition to seeking patents for some of our technology and product candidates, we also rely on trade secrets, including unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary information, to maintain our competitive position. We seek to protect these trade secrets, in part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to them, such as our employees, corporate collaborators, outside scientific collaborators, contract manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties. We also enter into confidentiality and invention or patent assignment agreements with our employees and consultants. Despite these efforts, any of these parties may breach the agreements and disclose our proprietary information, including our trade secrets, and we may not be able to obtain adequate remedies for such breaches. In addition, a court may determine that we failed to take adequate steps to protect our trade secrets, in which case it may not be possible to enforce our trade secret rights. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, some may be less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets. If any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor, we would have no right to prevent such competitor from using that technology or information to compete with us, which could harm our competitive position.
We may face potential product liability, and, if successful claims are brought against us, we may incur substantial liability and costs. If the use of our product candidates harms patients or is perceived to harm patients even when such harm is unrelated to our product candidates, our regulatory approvals could be revoked or otherwise negatively impacted and we could be subject to costly and damaging product liability claims.
In carrying out our activities, we may potentially face contractual and statutory claims, or other types of claims from customers, suppliers and/or investors. In addition, we are exposed to potential product liability risks that are inherent in the research, development, production and supply of products. Subjects enrolled in our clinical trials, consumers, healthcare providers or other persons administering or selling products based on our and our collaborators’ technology may be able to bring claims against us based on the use of such products. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against claims that any product candidates commercialized caused injuries, we could incur substantial costs and liabilities. Irrespective of their merits or actual outcome, liability claims may result in:
| • | decreased demand for any product candidates that we may develop; |
| • | withdrawal of clinical trial participants; |
| • | termination of clinical trials; |
| • | significant negative media attention and injury to our reputation; |
| • | significant costs to defend the related litigation; |
| • | substantial monetary awards to trial subjects or patients; |
| • | diversion of management and scientific resources from our business operations; and |
| • | the inability to commercialize any products that we may develop. |
While we have obtained product liability coverage, our insurance coverage may not be sufficient to cover our entire product liability related expenses or losses and may not cover us for any expenses or losses we may suffer. Moreover, insurance coverage is becoming increasingly expensive and, in the future, we may not be able to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost, in sufficient amounts or upon adequate terms to protect us against losses due to product liability. If we determine that it is prudent to increase our product liability, we may be unable to obtain this increased product liability insurance on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Large judgments have been awarded in class action or individual lawsuits based on drugs that had unanticipated side effects, including side effects that may be less severe than those of our products. A successful product liability claim or series of claims brought against us could cause the price of the Ordinary Shares and/or Depositary Shares to decline and, if judgments exceed our insurance coverage, could decrease our cash and have a material adverse effect our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
Risks Related to our Relationships with Third Parties
We rely on third parties to conduct our preclinical and clinical trials. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or commercialize our product candidates and our business could be substantially harmed.
We are, and may continue to be, reliant on other parties for the successful development and commercialization of many of our product candidates. We rely upon CROs for the conduct of our clinical studies. We rely on these parties for execution of our preclinical and clinical trials, and control only certain aspects of their activities. Nevertheless, we are responsible for ensuring that each of our studies is conducted in accordance with the applicable protocol and legal, regulatory and scientific standards, and our reliance on the CROs or collaboration partners does not relieve us of our regulatory responsibilities. We also rely on third parties to assist in conducting our preclinical studies in accordance with good laboratory practices, or GLP, and requirements with respect to animal welfare. We and our CROs or collaboration or licensing partners are required to comply with GCP, which are regulations and guidelines enforced by the MHRA, the FDA, the EMA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities for all of our products in clinical development. Regulatory authorities enforce these GCP through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators and trial sites. If we or any of our CROs or partners fail to comply with applicable GCP, the clinical data generated in our clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the EMA, the MHPA, the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may require us to perform additional clinical trials before approving our marketing applications. We cannot be assured that upon inspection by a given regulatory authority, such regulatory authority will determine that any of our clinical trials comply with GCP requirements. In addition, our clinical trials must be conducted with product produced under cGMP requirements. Failure to comply with these regulations may require us to repeat preclinical and clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process.
Our CROs are not our employees, and except for remedies available to us under such agreements with such CROs, we cannot control whether or not they devote sufficient time and resources to our on-going clinical, nonclinical and preclinical programs. If CROs do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or obligations or meet expected deadlines or if the quality or accuracy of the clinical data they obtain is compromised due to the failure to adhere to our clinical protocols, regulatory requirements or for other reasons, then our clinical trials may be extended, delayed or terminated and we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or successfully commercialize our product candidates. As a result, our results of operations and the commercial prospects for our product candidates would be harmed, our costs could increase and our ability to generate revenues could be delayed.
If any of our relationships with these third parties terminate, we may not be able to enter into arrangements with alternative third parties on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. Entering into arrangements with alternative CROs, clinical trial investigators or other third parties involves additional cost and requires management focus and time, in addition to requiring a transition period when a new CRO, clinical trial investigator or other third party begins work. If third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or obligations or meet expected deadlines, if they need to be replaced or if the quality or accuracy of the clinical data they obtain are compromised due to the failure to adhere to our clinical protocols, regulatory requirements or for other reasons, any clinical trials such third parties are associated with may be extended, delayed or terminated, and we may not be able to obtain marketing approval for or successfully commercialize our product candidates. As a result, we believe that our financial results and the commercial prospects for our product candidates in the subject indication would be harmed, our costs could increase and our ability to generate revenue could be delayed.
Because we have relied on third parties, our internal capacity to perform these functions is limited. Outsourcing these functions involves risk that third parties may not perform to our standards, may not produce results in a timely manner or may fail to perform at all. In addition, the use of third party service providers requires us to disclose our proprietary information to these parties, which could increase the risk that this information will be misappropriated. We currently have a small number of employees, which limits the internal resources we have available to identify and monitor our third party providers. To the extent we are unable to identify and successfully manage the performance of third party service providers in the future, our business may be adversely affected. Though we carefully manage our relationships with our CROs, there can be no assurance that we will not encounter similar challenges or delays in the future or that these delays or challenges will not have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition and prospects.
We rely on third parties to manufacture our product candidates, and we expect to continue to rely on third parties for the clinical as well as any future commercial supply of our product candidates and other future product candidates. The development of our current and future product candidates, and the commercialization of any approved products, could be stopped, delayed or made less profitable if any such third party fails to provide us with sufficient clinical or commercial quantities of such product candidates or products, fails to do so at acceptable quality levels or prices or fails to achieve or maintain satisfactory regulatory compliance.
We do not currently have, and we do not plan to build, the infrastructure or capability internally to manufacture current product candidates or any future product candidates for use in the conduct of our clinical trials or, if approved, for commercial supply. We rely on, and expect to continue to rely on, contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs). Reliance on third-party contractors may expose us to more risk than if we were to manufacture our product candidates ourselves. We do not control the manufacturing processes of the CMOs we contract with and are dependent on those third parties for the production of our product candidates in accordance with relevant applicable regulations, such as cGMP, which include, among other things, quality control, quality assurance and the maintenance of records and documentation.
In complying with the manufacturing regulations of the FDA and other comparable foreign regulatory authorities, we and our third-party manufacturers must spend significant time, money and effort in the areas of design and development, testing, production, record-keeping and quality control to assure that the product candidates meet applicable specifications and other regulatory requirements. If either we or our CMOs fail to comply with these requirements, we may be subject to regulatory enforcement action, including the seizure of product candidates and shutting down of production.
Even if we are able to establish and maintain agreements with third-party manufacturers, reliance on third-party manufacturers entails additional risks, including:
| • | reliance on the third party for regulatory, compliance and quality assurance; |
| • | the possible breach of the manufacturing agreement by the third party; |
| • | the possible misappropriation of our proprietary information, including our trade secrets and know-how; and |
| • | the possible termination or nonrenewal of the agreement by the third party at a time that is costly or inconvenient for us. |
We or our third-party manufacturers may encounter shortages in the raw materials or APIs necessary to produce our product candidates in the quantities needed for our clinical trials or, if our product candidates are approved, in sufficient quantities for commercialization or to meet an increase in demand, as a result of capacity constraints or delays or disruptions in the market for the raw materials or active pharmaceutical ingredients, including shortages caused by the purchase of such raw materials or APIs by our competitors or others. The failure by us or our third-party manufacturers to obtain the raw materials or APIs necessary to manufacture sufficient quantities of our product candidates, may have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our third-party manufacturers are subject to inspection and approval by regulatory authorities before we can commence the manufacture and sale of any of our product candidates, and thereafter are subject to ongoing inspection from time to time. Our third-party manufacturers may not be able to comply with cGMP regulations or similar regulatory requirements outside of the United States. Our failure, or the failure of our third-party manufacturers, to comply with applicable regulations could result in regulatory actions, such as the issuance of notices of inspectional observations, warning letters or sanctions being imposed on us, including clinical holds, fines, injunctions, civil penalties, delays, suspension or withdrawal of approvals, license revocation, seizures or recalls of product candidates or drugs, operating restrictions and criminal prosecutions, any of which could significantly and adversely affect supplies of our products. If any of our third-party suppliers fails to comply with cGMP or other applicable manufacturing regulations, our ability to develop and commercialize our product candidates could suffer significant interruptions.
Any disruption, such as a fire, natural hazards or vandalism at our CMOs, or any impacts on our CMOs due to health pandemics, could significantly interrupt our manufacturing capability. We currently do not have alternative production plans in place or disaster-recovery facilities available. In case of a disruption, we will have to establish alternative manufacturing sources. This would require substantial capital on our part, which we may not be able to obtain on commercially acceptable terms or at all. Additionally, we would likely experience months of manufacturing delays as we build facilities or locate alternative suppliers and seek and obtain necessary regulatory approvals. If this occurs, we will be unable to satisfy manufacturing needs on a timely basis, if at all. If changes to CMOs occur, then there also may be changes to manufacturing processes inherent in the setup of new operations for our product candidates and any products that may obtain approval in the future. Any such changes could require the conduct of bridging studies before we can use any materials produced at new facilities or under new processes in clinical trials or, for any products reaching approval, in our commercial supply. Further, business interruption insurance may not adequately compensate us for any losses that may occur and we would have to bear the additional cost of any disruption. For these reasons, a significant disruptive event of any CMOs could have drastic consequences, including placing our financial stability at risk.
Our product candidates and any drugs that we may develop may compete with other product candidates and drugs for access to manufacturing facilities. There are no assurances we would be able to enter into similar arrangements with other manufacturers that operate under cGMP regulations and that might be capable of manufacturing for us. Any performance failure on the part of our existing or future manufacturers could delay clinical development or marketing approval.
If we were to experience an unexpected loss of supply of or if any supplier were unable to meet our clinical or commercial demand for any of our product candidates, we could experience delays in our planned clinical studies or commercialization. We could be unable to find alternative suppliers of acceptable quality and experience that can produce and supply appropriate volumes at an acceptable cost or on favorable terms. Moreover, our suppliers are often subject to strict manufacturing requirements and rigorous testing requirements, which could limit or delay production. The long transition periods necessary to switch manufacturers and suppliers, if necessary, would significantly delay our clinical trials and, for any product candidates that reach approval, the commercialization of our products, which would materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operation.
We are dependent on third party suppliers, and if we experience problems with any of these third parties, the manufacturing of our product candidates could be delayed, which could harm our results of operations.
We are dependent upon certain qualified suppliers, of which there are a limited number, for the supply of raw materials, components, devices and manufacturing equipment, some of which are manufactured or supplied by small companies with limited resources and experience to support commercial pharmaceutical and biologics production. Additionally, these suppliers may also have upstream suppliers who supply materials, components, devices and manufacturing equipment, which may indirectly impact our business operations. Thus, the success of our business may be adversely affected by the underperformance of third parties, exploitation by third parties of our commercial dependence and by unforeseen interruptions to third parties’ businesses. Although the existence of several alternative suppliers for each function mitigates the risks associated with this dependence, as does the availability of commercial insurance in respect of the impact of accidental events, the failure of a third party to properly to carry out their contractual duties or regulatory obligations could be highly disruptive to our business. Supply chain failures can result in significant clinical or commercial supply interruptions which could materially hamper our ability to conduct clinical trials or to supply adequate commercial supplies, and efforts to qualify new suppliers can be costly and time consuming. Further, any action taken by a third party that is detrimental to our reputation could have a negative impact on our ability to register our trademarks and/or market and sell our products.
For some of these raw materials, components, devices and manufacturing equipment, we rely and may in the future rely on sole source vendors or a limited number of vendors. The supply of the reagents and other specialty materials and equipment that are necessary to produce our product candidates could be reduced or interrupted at any time. In such case, identifying and engaging an alternative supplier or manufacturer could result in delay, and we may not be able to find other acceptable suppliers or manufacturers on acceptable terms, or at all. Switching suppliers or manufacturers may involve substantial costs and is likely to result in a delay in our desired clinical and commercial timelines. If we change suppliers or manufacturers for commercial production, applicable regulatory agencies may require us to conduct additional studies or trials. If key suppliers or manufacturers are lost, or if the supply of the materials is diminished or discontinued, we may not be able to develop, manufacture and market our product candidates in a timely and competitive manner, or at all. An inability to continue to source product from any of these suppliers, which could be due to a number of issues, including regulatory actions or requirements affecting the supplier, adverse financial or other strategic developments experienced by a supplier, labor disputes or shortages, unexpected demands or quality issues, could adversely affect our ability to satisfy demand for our product candidates, which could adversely and materially affect our product sales and operating results or our ability to conduct clinical trials, either of which could significantly harm our business.
As we continue to develop our product candidates and manufacturing processes, we expect that we will need to obtain rights to and supplies of certain materials and equipment to be used as part of that process. We may not be able to obtain rights to such materials on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, and if we are unable to alter our process in a commercially viable manner to avoid the use of such materials or find a suitable substitute, it would have a material adverse effect on our business. Even if we are able to alter our process so as to use other materials or equipment, such a change may lead to a delay in our clinical development and/or commercialization plans. If such a change occurs for product candidate that is already in clinical testing, the change may require us to perform both in vitro or in vivo comparability studies and to collect additional data from patients prior to undertaking more advanced clinical trials. These factors could cause the delay of studies or trials, regulatory submissions, required approvals or commercialization of product candidates that we develop, cause us to incur higher costs and prevent us from commercializing our product candidates successfully.
Our counterparties may become insolvent.
There is a risk that parties with whom we trade or have other business relationships with (including partners, joint venturers, customers, suppliers, subcontractors and other parties) may become insolvent. This may be due to general economic conditions or factors specific to that company. In the event that a party with whom we trade becomes insolvent, this could have an adverse impact on our revenues and profitability.
Our relationships with customers, healthcare providers, physicians, prescribers, purchasers, third party payors, charitable organizations and patients are subject to applicable anti-kickback, fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations, which could expose us to criminal sanctions, civil penalties, contractual damages, reputational harm and diminished profits and future earnings.
Although we do not currently have any products on the market, upon commercialization of any of our product candidates, if approved, we will be subject to additional healthcare statutory and regulatory requirements and oversight by federal and state governments in the United States as well as foreign governments in the jurisdictions in which we conduct our business. Healthcare providers, physicians and third-party payors in the United States and elsewhere play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of drug and biological products. Arrangements with third-party payors and customers can expose pharmaceutical manufacturers to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations, including, without limitation, the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, or AKS, and the False Claims Act, or FCA, which may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which such companies sell, market and distribute pharmaceutical products. In particular, the research of any of our product candidates, as well as the promotion, sales and marketing of healthcare items and services, as well as certain business arrangements in the healthcare industry, are subject to extensive laws designed to prevent fraud, kickbacks, self-dealing and other abusive practices. These laws and regulations may restrict or prohibit a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing and promotion, structuring and commission(s), certain customer incentive programs and other business arrangements generally. Activities subject to these laws also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of patient recruitment for clinical trials.
The healthcare laws that may affect us include: the federal fraud and abuse laws, including the AKS; false claims and civil monetary penalties laws, including the FCA and Civil Monetary Penalties Law; federal data privacy and security laws, including HIPAA, as amended by HITECH; and the federal Physician Payments Sunshine Act related to ownership and investment interests and payments and/or other transfers of value made to or held by physicians (including doctors, dentists, optometrists, podiatrists, and chiropractors) and teaching hospitals and, beginning in 2022, information regarding payments and transfers of value provided to other healthcare professionals, such as physician assistants and nurse practitioners among others, during the previous year. In addition, many states have similar laws and regulations that may differ from each other and federal law in significant ways, thus complicating compliance efforts. Moreover, several states require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government and may require manufacturers to report information related to payments and other transfers of value to physicians and other healthcare providers or marketing expenditures. Additionally, some state and local laws require the registration of pharmaceutical sales representatives in the jurisdiction.
The scope and enforcement of each of these laws is uncertain and subject to rapid change in the current environment of healthcare reform, especially in light of the lack of applicable precedent and regulations. Ensuring business arrangements comply with applicable healthcare laws, as well as responding to possible investigations by government authorities, can be time- and resource-consuming and can divert a company’s attention from other aspects of its business.
It is possible that governmental and enforcement authorities will conclude that our business practices may not comply with current or future statutes, regulations or case law interpreting applicable fraud and abuse or other healthcare laws and regulations. If any such actions are instituted against us, and we are not successful in defending ourselves or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business, including the imposition of significant civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, fines, disgorgement, imprisonment, reputational harm, possible exclusion from participation in federal and state funded healthcare programs, contractual damages and the curtailment or restricting of our operations, as well as additional reporting obligations and oversight if we become subject to a corporate integrity agreement or other agreement to resolve allegations of non-compliance with these laws. Further, if any of the physicians or other healthcare providers or entities with whom we expect to do business is found not to be in compliance with applicable laws, they may be subject to significant criminal, civil or administrative sanctions, including exclusions from government funded healthcare programs. Any action for violation of these laws, even if successfully defended, could cause a pharmaceutical manufacturer to incur significant legal expenses and divert management’s attention from the operation of the business. Therefore, even if we are successful in defending against any such actions that may be brought against us, our business may be impaired. Prohibitions or restrictions on sales or withdrawal of future marketed products could materially affect business in an adverse way.
Risks Related to this Offering
The sale of a substantial amount of our Ordinary Shares (represented by Depositary Shares), including resale of the Ordinary Shares (represented by Depositary Shares) issuable upon the exercise of the warrants held by the selling shareholders in the public market could adversely affect the prevailing market price of our Ordinary Shares and/or Depositary Shares.
We are registering for resale 2,169,790,225 Ordinary Shares represented by 86,791,609 Depositary Shares held by, or issuable upon the exercise of warrants held by, the selling shareholders. Sales of substantial amounts of our Ordinary Shares and/or Depositary Shares in the public market, or the perception that such sales may occur, could adversely affect the market price of our Ordinary Shares and/or Depositary Shares. We cannot predict if and when selling shareholders may sell such shares in the public markets. Furthermore, in the future, we may issue additional Ordinary Shares (including Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares). Any such issuance could result in substantial dilution to our existing shareholders and could cause our share price to decline.
Risks Related to Ownership of Our Securities and Our Status as a U.S. Listed Company
The price of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares may be volatile.
The trading price of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares in both the United Kingdom and the United States has fluctuated, and is likely to continue to fluctuate, substantially in response to various factors, some of which are beyond our control, including limited trading volume. The stock market in general, and the market for pharmaceutical and biotechnology stocks in particular, have experienced extreme volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of these companies. As a result of this volatility, investors may not be able to sell their Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares at or above the price paid for the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares, respectively.
In addition to the factors discussed in this “Risk Factors” section and elsewhere in this annual report, the factors that could cause volatility in the market price of each Ordinary Share and the Depositary Shares include:
| • | the success of competitive products or technologies; |
| • | actual or anticipated changes in our growth rate relative to our competitors; |
| • | announcements by us or our competitors of new products, significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, collaborations or capital commitments; |
| • | the progress of preclinical development, laboratory testing and clinical trials of our product candidates or those of our competitors; |
| • | the results from our clinical programs and any future trials we may conduct; |
| • | developments in the clinical trials of potentially similar competitive products; |
| • | EMA, MHRA, FDA or international regulatory or legal developments; |
| • | failure of any of our product candidates, if approved, to achieve commercial success; |
| • | developments or disputes concerning patent applications, issued patents or other proprietary intellectual property rights; |
| • | the recruitment or departure of key personnel; |
| • | the level of expenses related to any of our product candidates or clinical development programs; |
| • | litigation or public concern about the safety of our products; |
| • | actual or anticipated changes in estimates as to financial results, development timelines or recommendations by securities analysts; |
| • | actual and anticipated fluctuations in our operating results; |
| • | variations in our financial results or those of companies that are perceived to be similar to us; |
| • | share price and volume fluctuations attributable to inconsistent trading volume levels of our shares; |
| • | announcements or expectations of additional financing efforts; |
| • | rumors relating to us or our competitors; |
| • | sales of our Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares by us, our insiders or our other shareholders; |
| • | changes in the structure of healthcare payment systems; |
| • | market conditions in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors, or general volatility in the market due to other factors; |
| • | third party reimbursement policies; |
| • | Brexit and any resulting economic or currency volatility; |
| • | developments concerning current or future collaborations, strategic alliances, joint ventures or similar relationships; and |
| • | reviews of long-term values of our assets, which could lead to impairment charges that could reduce our earnings. |
These and other market and industry factors may cause the market price and demand for our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares to fluctuate substantially, regardless of our actual operating performance, which may limit or prevent investors from selling their Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares at or above the price paid for the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares, respectively, and may otherwise negatively affect the liquidity of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares. The realization of any of the above risks or any of a broad range of other risks, including those described in these “Risk Factors,” could have a dramatic and material adverse impact on the market price of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares.
If we cannot meet NASDAQ’s continued listing requirements, NASDAQ may delist our Depositary Shares, which could have an adverse impact on the liquidity and market price of our Depositary Shares.
Our Depositary Shares are currently listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market. We are required to meet certain qualitative and financial tests to maintain the listing of our Depositary Shares on NASDAQ. On January 31, 2023, we received a letter from NASDAQ stating that, for the previous 30 consecutive business days, the bid price for our Depositary Shares had closed below the minimum $1.00 bid price per share requirement for continued listing on The NASDAQ Capital Market under NASDAQ Listing Rule 5550(a)(2).
We cannot assure you that we will regain compliance, or if we do regain compliance, that we will remain in compliance with all applicable requirements for continued listing on the NASDAQ Capital Market. If we fail to sustain compliance with all applicable requirements for continued listing on NASDAQ, our Depositary Shares may be subject to delisting by NASDAQ. This could inhibit the ability of our holders of Depositary Shares to trade their shares in the open market, thereby severely limiting the liquidity of such shares. Although stockholders may be able to trade their shares of Depositary Shares on the over-the-counter market, there can be no assurance that this would occur. Further, the over-the-counter market provides significantly less liquidity than NASDAQ and other national securities exchanges, is thinly traded and highly volatile, has fewer market makers and is not followed by analysts. As a result, your ability to trade or obtain quotations for these securities may be more limited than if they were quoted on NASDAQ or other national securities exchanges.
We may be subject to securities litigation, which is expensive and could divert management attention.
The market price of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares may be volatile, and in the past, some companies that have experienced volatility in the market price of their stock have been subject to securities class action litigation. Any lawsuit to which we are a party, with or without merit, may result in an unfavorable judgment. We also may decide to settle lawsuits on unfavorable terms.
Any such negative outcome could result in payments of substantial damages or fines, damage to our reputation or adverse changes to our business practices. Defending against litigation is costly and time-consuming, and could divert our management’s attention and our resources. Furthermore, during the course of litigation, there could be negative public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments, which could have a negative effect on the market price of our Depositary Shares and our Ordinary Shares.
The liquidity of our Depositary Shares and Ordinary Shares may have an adverse effect on our share price.
Some companies that have issued American depositary shares on United States stock exchanges have experienced lower levels of liquidity in their American depositary shares than is the case for their ordinary shares listed on their domestic exchange. Our Depositary Shares are traded on the NASDAQ Capital Market and our Ordinary Shares are traded on AIM. We cannot predict the effect of this dual listing on the value of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares. However, the dual listing of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares may dilute the liquidity of these securities in one or both markets and may adversely affect the development of an active trading market for the Depositary Shares in the United States. The price of the Depositary Shares could also be adversely affected by trading in our Ordinary Shares on AIM. As a result of these and other factors, you may not be able to sell your Depositary Shares. In addition, investors may incur higher transaction costs when buying and selling Depositary Shares than they would incur in buying and selling common stock. An inactive market may also impair our ability to raise capital by selling Depositary Shares and Ordinary Shares and may impair our ability to enter into strategic partnerships or acquire companies or products by using our Ordinary Shares as consideration.
Our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares trade on two different markets, which is costly to maintain and may result in price variations.
Our Depositary Shares are listed for trading on the NASDAQ Capital Market and our Ordinary Shares are traded on AIM. As long as we are listed on these markets, we will continue to generate additional costs, including increased legal, accounting, investor relations and other expenses, in addition to the costs associated with the additional reporting requirements described elsewhere in this annual report. Trading in our securities on these markets is made in different currencies and at different times, including as a result of different time zones, different trading days and different public holidays in the U.S. and the United Kingdom. Consequently, the effective trading prices of our securities on these two markets may differ. Any decrease in the trading price of our securities on one of these markets could cause a decrease in the trading price of our securities on the other market.
Shareholder ownership interests in the Company may be diluted as a result of, among other things, future financings and/or additional acquisitions, and may have a material negative effect on the market price of our securities.
We may seek to raise additional funds from time to time in public or private issuances of equity and such financings may take place in the near future or over the longer term. Sales of our securities offered through future equity offerings may result in substantial dilution to the interests of our current shareholders. The sale of a substantial number of securities to investors, or anticipation of such sales, could make it more difficult for us to sell equity or equity-related securities in the future at a time and at a price that we might otherwise wish to effect sales.
We may also issue Ordinary Shares (and Depositary Shares underlying such Ordinary Shares) or other securities convertible into Ordinary Shares from time to time for future acquisition. The issuance of the securities underlying these instruments, or perception that issuance may occur, will have a dilutive impact on other shareholders and could have a material negative effect on the market price of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares.
If equity research analysts do not publish research or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about our business, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares will depend in part on the research and reports that equity research analysts publish about us or our business. If no or few equity research analysts cover our Company, the trading price for our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares would be negatively impacted. We do not have any control over the analysts or the content and opinions included in their reports. The price of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares could decline if one or more equity research analysts downgrade our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares or issue other unfavorable commentary or research about us. If one or more equity research analysts ceases coverage of us or fails to publish reports on us regularly, demand for our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares could decrease, which in turn could cause the trading price or trading volume of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares to decline.
The rights of holders of Depositary Shares are not the same as the rights of holders of Ordinary Shares.
We are a public limited company incorporated under the laws of England and Wales. The Depositary Shares represent a beneficial ownership interest in our Ordinary Shares. The rights of holders of Depositary Shares will be governed by English law, our constitutional documents, the listing rules of AIM, or AIM Rules, and the deposit agreement pursuant to which the Depositary Shares are issued. The rights and terms of the Depositary Shares are designed to replicate, to the extent reasonably practicable, the rights attendant to the Ordinary Shares, for which there is currently no active trading market in the United States. However, because of aspects of United Kingdom law, our constitutional documents and the terms of the deposit agreement, the rights of holders of Depositary Shares will not be identical to and, in some respects, may be less favorable than, the rights of holders of Ordinary Shares.
You may not have the same voting rights as the holders of our Ordinary Shares and may not receive voting materials in time to be able to exercise your right to vote.
Holders of our Depositary Shares do not have the same rights as shareholders who hold our Ordinary Shares directly and may only exercise their voting rights with respect to the underlying Ordinary Shares in accordance with the provisions of the deposit agreement. Holders of the Depositary Shares will appoint the depositary or its nominee as their representative to exercise the voting rights attaching to the Ordinary Shares represented by the Depositary Shares. When a general meeting is convened, if you hold Depositary Shares, you may not receive sufficient notice of a shareholders’ meeting to permit you to withdraw the Ordinary Shares underlying your Depositary Shares to allow you to vote with respect to any specific matter. Further, we cannot assure purchasers of Depositary Shares that they will receive voting materials in time to instruct the depositary to vote, and it is possible that they, or persons who hold their Depositary Shares through brokers, dealers or other third parties, will not have the opportunity to exercise a right to vote. Furthermore, the depositary will not be liable for any failure to carry out any instructions to vote, for the manner in which any vote is cast or for the effect of any such vote. As a result, purchasers of Depositary Shares may not be able to exercise their right to vote and they may lack recourse if their Depositary Shares are not voted as they request.
You may not receive distributions on Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares or any value for them if it is illegal or impractical to make them available to holders of Depositary Shares.
The depositary of the Depositary Shares has agreed to pay to you distributions with respect to cash or other distributions it or the custodian receives on Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities after deducting its agreed fees and expenses. You will receive these distributions in proportion to the number of Ordinary Shares your Depositary Shares represent. However, the depositary is not responsible if it decides that it is unlawful or impractical to make a distribution available to any holders of Depositary Shares. We have no obligation to take any other action to permit the distribution of our Depositary Shares, Ordinary Shares, rights or anything else to holders of our Depositary Shares. As a result, you may not receive the distributions made on Ordinary Shares or any value from them if it is illegal or impractical for us to make them available to you. These restrictions may have a material adverse effect on the value of your Depositary Shares.
You may be subject to limitations on transfer of your Depositary Shares.
Your Depositary Shares are transferable on the books of the depositary. However, the depositary may close its books at any time or from time to time when it deems expedient in connection with the performance of its duties. The depositary may refuse to deliver, transfer or register transfers of your Depositary Shares generally when our books or the books of the depositary are closed, or at any time if we or the depositary deems it advisable to do so because of any requirement of law or government or governmental body, or under any provision of the deposit agreement, or for any other reason.
We have no present intention to pay dividends on our Ordinary Shares in the foreseeable future and, consequently, your only opportunity to achieve a return on your investment during that time may be if the price of Depositary Shares appreciates.
We have no present intention to pay dividends on our Ordinary Shares in the foreseeable future. Any determination by our Board of Directors to pay dividends will depend on many factors, including our financial condition, results of operations, legal requirements and other factors. Accordingly, if the price of the Depositary Shares falls in the foreseeable future and you sell your Depositary Shares, you will lose money on your investment, without the likelihood that this loss will be offset in part or at all by cash dividends.
We are no longer an “emerging growth company” but remain a non-accelerated filer, and the reduced reporting obligations applicable non-accelerated filers may make our securities less attractive to investors.
We are no longer an “emerging growth company,” as defined under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act. However, for as long as we remain a “non-accelerated filer” under the rules of the SEC, our independent registered public accounting firm is not required to deliver an annual attestation report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. We will cease to be a non-accelerated filer if (a) the aggregate market value of our outstanding Ordinary Shares held by non-affiliates as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter is $75 million or more and we reported annual net revenues of greater than $100 million for our most recently completed fiscal year or (b) the aggregate market value of our outstanding Ordinary Shares held by non-affiliates as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter is $700 million or more, regardless of annual net revenues. If we cease to be a non-accelerated filer, we would be subject to the requirement for an annual attestation report by our independent registered public accounting firm on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. We cannot predict whether investors will find our securities less attractive if we rely on this exemption. If some investors find our securities less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our securities and our stock price may be more volatile and may decline.
Our disclosure controls and procedures may not prevent or detect all errors or acts of fraud.
We are subject to the periodic reporting requirements of the Exchange Act. We design our disclosure controls and procedures to reasonably assure that information we are required to disclose in reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to management, recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the SEC. We believe that any disclosure controls and procedures or internal controls and procedures, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty, and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error or mistake. Additionally, controls can be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by an unauthorized override of the controls. Accordingly, because of the inherent limitations in our control system, misstatements or insufficient disclosure due to error or fraud may occur and we may not detect them.
Any failure to maintain effective internal controls and procedures over financial reporting could severely inhibit our ability to accurately report our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
We are incurring increased costs as a result of operating as a public company, and management will be required to devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives.
As a public company in the United Kingdom and United States, we are incurring significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company, and these expenses may increase even more after we are no longer an “emerging growth company.” We are subject to the reporting requirements of, in the United Kingdom, the AIM Rules, the Market Abuse Regulation, or MAR, and the Disclosure Guidance and Transparency Rules, and in the United States, the Exchange Act, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Protection Act, as well as rules adopted, and to be adopted, by the SEC and the NASDAQ. Our management and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount of time to these compliance initiatives. Moreover, we expect these rules and regulations to substantially increase our legal and financial compliance costs and to make some activities more time-consuming and costly. For example, we expect these rules and regulations to make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance and we may be required to incur substantial costs to maintain the sufficient coverage. We cannot predict or estimate the amount or timing of additional costs we may incur to respond to these requirements. The impact of these requirements could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our Board of Directors, our board committees or as members of our senior management.
Risks Related to Investing in a Foreign Private Issuer or United Kingdom Company
We are a “foreign private issuer” under the rules and regulations of the SEC and, as a result, are exempt from a number of rules under the Exchange Act and are permitted to file less information with the SEC than a company incorporated in the United States.
We are incorporated as a public limited company in England and Wales and are deemed to be a “foreign private issuer” under the rules and regulations of the SEC. As a foreign private issuer, we are exempt from certain rules under the Exchange Act that would otherwise apply if we were a company incorporated in the United States, including:
| • | the requirement to file periodic reports and financial statements with the SEC as frequently or as promptly as United States companies with securities registered under the Exchange Act; |
| • | the requirement to file financial statements prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP; |
| • | the proxy rules, which impose certain disclosure and procedural requirements for proxy or consent solicitations; and |
| • | the requirement to comply with Regulation FD, which imposes certain restrictions on the selective disclosure of material information. |
In addition, our officers, directors and principal shareholders are exempt from the reporting and “short-swing” profit recovery provisions of Section 16 of the Exchange Act and the related rules with respect to their purchases and sales of Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares. Accordingly, you may receive less information about us than you would receive about a public company incorporated in the United States and may be afforded less protection under the United States federal securities laws than you would be if we were incorporated in the United States.
Additional reporting requirements may apply if we lose our status as a foreign private issuer.
As a foreign private issuer, we are not required to comply with all of the periodic disclosure and current reporting requirements of the Exchange Act applicable to U.S. domestic issuers. In order to maintain our current status as a foreign private issuer, either (1) a majority of our voting securities must be either directly or indirectly owned of record by non-residents of the United States or (2)(a) a majority of our executive officers or directors cannot be U.S. citizens or residents, (b) more than 50% of our assets must be located outside the United States and (c) our business must be administered principally outside the United States.
If we lose our status as a foreign private issuer, we would be required to comply with the Exchange Act reporting and other requirements applicable to U.S. domestic issuers, which are more detailed and extensive than the requirements for foreign private issuers. We may also be required to make changes in our corporate governance practices in accordance with various SEC and NASDAQ rules. The regulatory and compliance costs to us under U.S. securities laws if we are required to comply with the reporting requirements applicable to a U.S. domestic issuer may be significantly higher than the cost we would incur as a foreign private issuer. As a result, we expect that a loss of foreign private issuer status would increase our legal and financial compliance costs and would make some activities highly time consuming and costly. We also expect that if we were required to comply with the rules and regulations applicable to U.S. domestic issuers, it would make it more difficult and expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain coverage. These rules and regulations could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified members of our Board of Directors.
As a foreign private issuer, we are not required to comply with many of the corporate governance standards of NASDAQ applicable to companies incorporated in the United States.
Our Board of Directors is required to maintain an audit committee comprised solely of three or more directors satisfying the independence standards of NASDAQ applicable to audit committee members. As a foreign private issuer, however, we are not required to comply with most of the other corporate governance rules of NASDAQ, including the requirement to maintain a majority of independent directors, and nominating and compensation committees of our Board of Directors comprised solely of independent directors. Although United Kingdom corporate governance rules which we abide by have comparable requirements, holders of Depositary Shares may not be afforded the benefits of the corporate governance standards of NASDAQ to the same extent applicable to companies incorporated in the United States.
Securities traded on AIM may carry a higher risk than shares traded on other exchanges that may impact the value of your investment.
Our Ordinary Shares are currently traded on the AIM. Investment in equities traded on the AIM is perceived to carry a higher risk than an investment in equities quoted on exchanges with more stringent listing requirements, such as the Main Market of the London Stock Exchange, New York Stock Exchange or NASDAQ. This is because the AIM imposes less stringent corporate governance and ongoing reporting requirements than those other exchanges. In addition, the AIM requires only semi-annual, rather than quarterly, financial reporting. You should be aware that the value of our Ordinary Shares may be influenced by many factors, some of which may be specific to us and some of which may affect AIM-listed companies generally, including the depth and liquidity of the market, our performance, a large or small volume of trading in our Ordinary Shares, legislative changes and general economic, political or regulatory conditions, and that the prices may be volatile and subject to extensive fluctuations. Therefore, the market price of our Ordinary Shares underlying the Depositary Shares may not reflect the underlying value of the Company.
Your right to participate in any future rights offerings may be limited, which may cause dilution to your holdings.
Under English law, shareholders usually have preemptive rights to subscribe on a pro rata basis in the issuance of new shares for cash. The exercise of preemptive rights by certain shareholders not resident in the United Kingdom may be restricted by applicable law or practice in the United Kingdom and overseas jurisdictions. We may from time to time distribute rights to our shareholders, including rights to acquire our securities. However, we cannot make rights available to shareholders in the United States unless we register the rights and the securities to which the rights relate under the Securities Act or an exemption from the registration requirements is available. Also, under the deposit agreement, the depositary bank will not make rights available to Depositary Share holders unless either both the rights and any related securities are registered under the Securities Act, or the distribution of them to Depositary Share holders is exempted from registration under the Securities Act. We are under no obligation to file a registration statement with respect to any such rights or securities or to endeavor to cause such a registration statement to be declared effective. Moreover, we may not be able to establish an exemption from registration under the Securities Act. If the depositary does not distribute the rights, it may, under the deposit agreement, either sell them, if possible, or allow them to lapse. Accordingly, Depositary Share holders may be unable to participate in our rights offerings and may experience dilution in their holdings. We are also permitted under English law to disapply preemptive rights (subject to the approval of our shareholders by special resolution or the inclusion in our articles of association of a power to disapply such rights) and thereby exclude certain shareholders, such as overseas shareholders, from participating in a rights offering (usually to avoid a breach of local securities laws).
It may be difficult for you to bring any action or enforce any judgment obtained in the United States against us or members of our Board of Directors, which may limit the remedies otherwise available to you.
We are incorporated as a public limited company in England and Wales and all of our assets are located outside the United States. In addition, nearly all of the members of our Board of Directors are nationals and residents of countries, including the United Kingdom, outside of the United States. Most or all of the assets of these individuals are located outside the United States. As a result, it may not be possible for investors to effect service of process within the United States upon such persons or to enforce judgments obtained in U.S. courts against them or us, including judgments predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities laws.
The United States and the United Kingdom do not currently have a treaty providing for the reciprocal recognition and enforcement of judgments (other than arbitration awards) in civil and commercial matters. Consequently, a final judgment for payment given by a court in the United States, whether or not predicated solely upon U.S. securities laws, would not automatically be recognized or enforceable in England and Wales. In addition, uncertainty exists as to whether the English and Welsh courts would entertain original actions brought in England and Wales against us or our directors or executive officers predicated upon the securities laws of the United States or any state in the United States. Any final and conclusive monetary judgment for a definite sum obtained against us in U.S. courts would be treated by the courts of England and Wales as a cause of action in itself and sued upon as a debt so that no retrial of the issues would be necessary, provided that certain requirements are met consistent with English law and public policy. Whether these requirements are met in respect of a judgment based upon the civil liability provisions of the U.S. securities laws is an issue for the English court making such decision. If an English court gives judgment for the sum payable under a U.S. judgment, the English judgment will be enforceable by methods generally available for this purpose.
As a result, U.S. investors may not be able to enforce against us or our executive officers, board of directors or certain experts named herein who are residents of the United Kingdom or countries other than the United States any judgments obtained in U.S. courts in civil and commercial matters, including judgments under the U.S. federal securities laws.
We intend to operate so as to be treated exclusively as a resident of the United Kingdom for tax purposes, but the relevant tax authorities may treat us as also being a resident of another jurisdiction for tax purposes.
We are a public limited company incorporated under the laws of England and Wales. Under current English law, the decisions of the English courts and the published practice of His Majesty’s Revenue and Customs suggest that we are likely to be regarded as being a United Kingdom resident and should remain so if, as we intend that, (i) all major meetings of our Board of Directors and most routine meetings are held in the United Kingdom with a majority of directors present in the United Kingdom for those meetings; (ii) at those meetings there are full discussions of, and decisions are made regarding, the key strategic issues affecting us and our subsidiaries; (iii) those meetings are properly minuted; (iv) at least some of our directors, together with supporting staff, are based in the United Kingdom; and (v) we have permanent staffed office premises in the United Kingdom sufficient to discharge our functions.
Even if we are considered by His Majesty’s Revenue and Customs as resident in the United Kingdom for United Kingdom tax purposes, as expected, we would nevertheless not be treated as resident in the United Kingdom if (a) we were concurrently resident in another jurisdiction (applying the tax residence rules of that jurisdiction) that has a double tax treaty with the United Kingdom and (b) there is a tiebreaker provision in that tax treaty which allocates exclusive residence to that other jurisdiction. Because this analysis is highly factual and may depend on future changes in our management and organizational structure, there can be no assurance regarding the final determination of our tax residence. Should we be treated as resident for tax purposes in another jurisdiction other than the United Kingdom, we would be subject to taxation in such jurisdiction in accordance with such jurisdiction’s laws, which could result in additional costs and expenses.
The rights of our shareholders may differ from the rights typically offered to shareholders of a U.S. corporation.
We are incorporated under English law. The rights of holders of Ordinary Shares and, therefore, certain of the rights of holders of our Depositary ShareDepositary Sharess, are governed by English law, including the provisions of the United Kingdom Companies Act 2006, or the Companies Act, and by our articles of association. These rights differ in certain respects from the rights of shareholders in typical U.S. corporations. See “Memorandum and Articles of Association—Differences in corporate law” for a description of the principal differences between the provisions of the Companies Act applicable to us and, for example, the Delaware General Corporation Law relating to shareholders’ rights and protections.
Protections found in provisions under the United Kingdom City Code on Takeovers and Mergers may delay or discourage a takeover attempt, including attempts that may be beneficial to holders of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares.
The U.K. City Code on Takeovers and Mergers, or the Takeover Code, applies, among other things, to an offer for a public company whose registered office is in the United Kingdom and whose securities are admitted to trading on a multilateral trading facility in the United Kingdom, which includes AIM. We are therefore currently subject to the Takeover Code.
The Takeover Code provides a framework within which takeovers of certain companies organized in the United Kingdom are regulated and conducted. The following is a brief summary of some of the most important rules of the Takeover Code:
| • | In connection with a potential offer, if following an approach by or on behalf of a potential bidder, the company is “the subject of rumor or speculation” or there is an “untoward movement” in the company’s share price, there is a requirement for the potential bidder to make a public announcement about a potential offer for the company, or for the company to make a public announcement about its review of a potential offer. |
| • | When interests in shares carrying 10% or more of the voting rights of a class have been acquired by an offeror (i.e., a bidder) in the offer period (i.e., before the shares subject to the offer have been acquired) or within the previous 12 months, the offer must be in cash or be accompanied by a cash alternative for all shareholders of that class at the highest price paid by the offeror or any person acting in concert with them in that period. Further, if an offeror or any person acting in concert with them acquires any interest in shares during the offer period, the offer for the shares must be in cash or accompanied by a cash alternative at a price at least equal to the price paid for such shares during the offer period. |
| • | If after an announcement is made, the offeror or any person acting in concert with them acquires an interest in shares in an offeree company (i.e., a target) at a price higher than the value of the offer, the offer must be increased accordingly. |
| • | The board of directors of the offeree company must appoint a competent independent adviser whose advice on the financial terms of the offer must be made known to all the shareholders, together with the opinion of the board of directors of the offeree company. |
| • | Favorable deals for selected shareholders are not permitted, except in certain circumstances where independent shareholder approval is given and the arrangements are regarded as fair and reasonable in the opinion of the financial adviser to the offeree. |
| • | All shareholders must be given the same information. |
| • | Those issuing documents in connection with a takeover must include statements taking responsibility for the contents thereof. |
| • | Profit forecasts, quantified financial benefits statements and asset valuations must be made to specified standards and must be reported on by professional advisers. |
| • | Misleading, inaccurate or unsubstantiated statements made in documents or to the media must be publicly corrected immediately. |
| • | Actions during the course of an offer by the offeree company, which might frustrate the offer are generally prohibited unless shareholders approve these plans. Frustrating actions would include, for example, lengthening the notice period for directors under their service contract or agreeing to sell off material parts of the target group. |
| • | Stringent requirements are laid down for the disclosure of dealings in relevant securities during an offer, including the prompt disclosure of positions and dealing in relevant securities by the parties to an offer and any person who is interested (directly or indirectly) in 1% or more of any class of relevant securities. |
| • | Employees of both the offeror and the offeree company and the trustees of the offeree company’s pension scheme must be informed about an offer. In addition, the offeree company’s employee representatives and pension scheme trustees have the right to have a separate opinion on the effects of the offer on employment appended to the offeree board of directors’ circular or published on a website. |
If we are deemed or become a passive foreign investment company, or PFIC, for U.S. federal income tax purposes in 2023 or in any prior or subsequent year, this may result in adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences for U.S. taxpayers that are holders of our securities.
We will be treated as a PFIC for U.S. federal income tax purposes in any taxable year in which either (1) at least 75% of our gross income is “passive income” or (2) on average at least 50% of our assets by value produce passive income or are held for the production of passive income. Passive income for this purpose generally includes, among other things, certain dividends, interest, royalties, rents and gains from commodities and securities transactions and from the sale or exchange of property that gives rise to passive income. Passive income also includes amounts derived by reason of the temporary investment of funds, including those raised in a public offering. In determining whether a non-U.S. corporation is a PFIC, a proportionate share of the income and assets of each corporation in which it owns, directly or indirectly, at least a 25% interest (by value) is taken into account.
We do not believe we were a PFIC for 2022, but there can be no assurance that we will not be a PFIC in 2023 or for any other taxable year, as our operating results for any such years may cause us to be a PFIC. If we were to be characterized as a PFIC for U.S. federal income tax purposes in any taxable year during which a U.S. shareholder owns our securities, and such U.S. shareholder does not make an election to treat us as a “qualified electing fund,” or a QEF, or make a “mark-to-market” election, then “excess distributions” to a U.S. shareholder, and any gain realized on the sale or other disposition of our securities will be subject to special rules. Under these rules: (1) the excess distribution or gain would be allocated ratably over the U.S. shareholder’s holding period for the securities; (2) the amount allocated to the current taxable year and any period prior to the first day of the first taxable year in which we were a PFIC would be taxed as ordinary income; and (3) the amount allocated to each of the other taxable years would be subject to tax at the highest rate of tax in effect for the applicable class of taxpayer for that year, and an interest charge for the deemed deferral benefit would be imposed with respect to the resulting tax attributable to each such other taxable year. In addition, if the United States Internal Revenue Service, or the IRS, determines that we are a PFIC for a year with respect to which we have determined that we were not a PFIC, it may be too late for a U.S. shareholder to make a timely QEF or mark-to-market election. U.S. shareholders who hold or have held our securities during a period when we were or are a PFIC will be subject to the foregoing rules, even if we cease to be a PFIC in subsequent years, subject to exceptions for U.S. shareholders who made a timely QEF or mark-to-market election. However, because we do not intend to prepare or provide the information that would permit the making of a valid QEF election, such an election will not be available to United States holders.
Changes to U.S. and non-U.S. tax laws could materially adversely affect our Company and holders of our Ordinary Shares and the Depositary Shares.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which was legislation bringing about broad changes in the existing U.S. corporate tax system, was enacted in the United States in December 2017. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act made significant changes to the U.S. federal income tax laws. Certain provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act could have an adverse effect on the Company or holders of our Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares. The U.S. Treasury Department and the IRS continue to interpret and issue guidance on how provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act will be applied and administered. The interpretations of many provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act are still unclear. We cannot predict when or to what extent any additional U.S. federal tax laws, regulations, interpretations, or rulings clarifying the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act will be issued or the impact of any such guidance on investors or the Company. Holders of Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares are urged to consult their own tax advisors regarding the effect of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act and other potential changes to the U.S. federal tax laws.
We are unable to predict what tax changes may be enacted in the future or what effect such changes would have on our business, but such changes could affect our effective tax rates in countries where we have operations and could have an adverse effect on our overall tax position in the future, along with increasing the complexity, burden and cost of tax compliance. In addition, such changes could impact the holders of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares.
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus contains certain forward-looking information about the Company that is intended to be covered by the safe harbor for “forward-looking statements” provided by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements may be made directly in this prospectus or may be incorporated into this prospectus by reference to other documents. Our representatives may also make forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are statements that are not historical facts. Words such as “expect,” “believe,” “will,” “may,” “anticipate,” “plan,” “estimate,” “intend,” “should,” “can,” “likely,” “could” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements appear in a number of places throughout this prospectus and include statements regarding our intentions, beliefs, assumptions, projections, outlook, analyses or current expectations concerning, among other things, our intellectual property position, success integrating Midatech US and other acquisitions, research and development projects, results of operations, cash needs, capital expenditures, financial condition, liquidity, prospects, growth and strategies, regulatory approvals and clearances, the markets and industry in which we operate and the trends and competition that may affect the markets, industry or us.
These forward-looking statements are based on currently available competitive, financial and economic data together with management’s views and assumptions regarding future events and business performance as of the time the statements are made and are subject to risks and uncertainties. We wish to caution you that there are some known and unknown factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements, including but not limited to risks related to:
| · | our requirement for additional financing and our ability to continue as a going concern; |
| · | our estimates regarding losses, expenses, future revenues, capital requirements and needs for additional financing; |
| · | our ability to successfully develop, test and partner with a licensee to manufacture or commercialize products for conditions using our technology platforms; |
| · | the successful commercialization and manufacturing of our any future product we may commercialize or license; |
| · | our ability to successfully integrate the operations of Bioasis and realize the anticipated benefits of the Acquisition; |
| · | the success and timing of our preclinical studies and clinical trials; |
| · | shifts in our business and commercial strategy; |
| · | the filing and timing of regulatory filings, including Investigational New Drug applications, with respect to any of our product candidates and the receipt of any regulatory approvals; |
| · | the anticipated medical benefits of our product candidates; |
| · | the difficulties in obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval of our product candidates, and the labeling under any approval we may obtain; |
| · | the success and timing of the potential commercial development of our product candidates and any product candidates we may acquire in the future, including MTX110; |
| · | our plans and ability to develop and commercialize our product candidates and any product candidates we may acquire in the future; |
| · | the ability to manufacture products in third-party facilities; |
| · | the rate and degree of market acceptance of any of our product candidates; |
| · | the successful development of our commercialization capabilities, including our internal sales and marketing capabilities; |
| · | obtaining and maintaining intellectual property protection for our product candidates and our proprietary technology; |
| · | the success of competing therapies and products that are or become available; |
| · | the success of any future acquisitions or other strategic transactions; |
| · | the difficulties of integrating the business of any future acquisitions into our own; |
| · | cybersecurity and other cyber incidents; |
| · | the impact of government laws and regulations; |
| · | regulatory, economic and political developments in the United Kingdom, the European Union, the United States and other foreign countries, including any impact from the United Kingdom leaving the European Union; |
| · | the difficulties doing business internationally; |
| · | the ownership of our Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares; |
| · | our ability to continue to meet the listing criteria required to remain listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market; |
| · | our ability to recruit or retain key scientific or management personnel or to retain our senior management; |
| · | the impact and costs and expenses of any litigation we may be subject to now or in the future; |
| · | the performance of third parties, including joint venture partners, our current sales force, our collaborators, third-party suppliers and parties to our licensing agreements; and |
| · | other risks and uncertainties, including those described in “Risk Factors” in this prospectus. |
Any forward-looking statements that we make in this prospectus speak only as of the date of such statement, and we undertake no obligation to update such statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this prospectus or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. Comparisons of results for current and any prior periods are not intended to express any future trends or indications of future performance, unless expressed as such, and should only be viewed as historical data. You should, however, review the factors and risks we describe in the reports we will file from time to time with the SEC after the date of this prospectus. See “Where You Can Find More Information.”
You should also read carefully the factors described in “Risk Factors” in this prospectus, as well as elsewhere in this prospectus, to better understand the risks and uncertainties inherent in our business and underlying any forward-looking statements. As a result of these factors, we cannot assure you that the forward-looking statements in this prospectus will prove to be accurate. Furthermore, if our forward-looking statements prove to be inaccurate, the inaccuracy may be material. In light of the significant uncertainties in these forward-looking statements, you should not regard these statements as a representation or warranty by us or any other person that we will achieve our objectives and plans in any specified timeframe, or at all.
USE OF PROCEEDS
We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of the Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares by the selling shareholders. All net proceeds from the sale of the Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares and the warrants covered by this prospectus will go to the selling shareholders. We expect that the selling shareholders will sell their Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares as described under “Plan of Distribution.”
We may receive proceeds from the exercise of the pre-funded warrants, Series A warrants, Series B warrants, and Ladenburg Warrants, collectively the warrants, and issuance of the Depositary Shares underlying the warrants. If all of the warrants mentioned above were exercised for cash in full, the proceeds would be approximately $11.9 million if the maximum number of Depositary Shares are issued under the terms of the warrants. However, each warrant may be exercised on a cashless basis, and therefore it is likely we will not receive any proceeds from the exercise of such warrants. To the extent the warrants are exercised for cash, we currently intend to use the net proceeds of such warrant exercise, if any, to fund the clinical development program of MTX110, our product for DIPG and recurrent glioblastoma, for working capital and for general corporate purpose. Pending such uses, we intend to invest the net proceeds in short-term, interest-bearing investments.
We can make no assurances that any of the warrants will be exercised, or if exercised, the quantity which will be exercised or in the period in which they will be exercised, or that they will be exercised for cash.
DIVIDEND POLICY
Since inception, we have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our Ordinary Shares and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our Ordinary Shares or the Depositary Shares in the foreseeable future. We intend to retain all available funds and any future earnings to fund the development and expansion of our business. As a result, investors in the Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares will benefit in the foreseeable future only if the Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares appreciate in value.
Any determination to pay dividends in the future would be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend upon our results of operations, cash requirements, financial condition, contractual restrictions, and any future debt agreements and is subject to compliance with applicable laws, including the United Kingdom Companies Act of 2006, or the Companies Act, which requires English companies to have profits available for distribution equal to or greater than the amount of the proposed dividend.
CAPITALIZATION
The following table sets forth our capitalization as of June 30, 2022
| · | on a pro forma as-adjusted basis to give effect to (i) our registered direct offering that closed on December 16, 2022, whereby we issued and sold 9,849,325 Ordinary Shares represented by 393,973 Depositary Shares at a public offering price of $1.00 per Depositary Share, (ii) the loan of $500,000 to Bioasis pursuant to the Note, (iii) the Private Placement and the issuance of the Series A warrants and Series B warrants thereunder, (iv) the issuance of Series A warrants to purchase 12,500,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 500,000 Depositary Shares pursuant to the Waiver, and (v) the issuance of warrants to purchase 10,738,775 Ordinary Shares represented by 429,551 Depositary Shares to the placement agent in the Private Placement, after deducting placement agent fees and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
The adjusted amounts shown below are unaudited and represent management’s estimate. The information in this table should be read in conjunction with and is qualified by reference to the financial statements and notes thereto and other financial information contained in this prospectus.
| (£ in thousands) | | | |
| | | As of June 30, 2022 | |
| | | Actual | | | Pro Forma As-Adjusted (unaudited) (1)(2) | |
| | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 6,423 | | | | 10,480 | |
| Borrowings, non-current | | | 546 | | | | 546 | |
| Total equity | | | 7,491 | | | | 7,437 | |
| Total capitalization | | | 8,037 | | | | 7,893 | |
_______________________
| (1) | The proceeds from the registered direct offering and Private Placement have been translated into British pounds sterling at a rate of £1.00 to $1.2078. |
| (2) | The fair value of the pre-funded warrants exercisable for 7,744,662 Depositary Shares (representing 139,616,550 Ordinary Shares), the Series A warrants exercisable for 10,844,822 Depositary Shares (representing 271,120,5500 Ordinary Shares), the Series B Warrants exercisable for 15,517,236 Depositary Shares (representing 387,930,900 Ordinary Shares), has been calculated as of February 15, 2023, and recorded as a current liability of £4,615,220 and a debit to share premium of £4,615,220. |
The table above is based upon 98,493,413 Ordinary Shares outstanding as of June 30, 2022 and excludes the following as of such date:
| · | 2,945,000 Ordinary Shares issuable upon the exercise of stock options outstanding under our equity incentive plans at a weighted-average exercise price of £0.257 per share; |
| · | 2,822 Ordinary Shares issuable upon the exercise of stock options assumed in connection with the acquisition of DARA at a weighted average exercise price of $95.17 per share; |
| · | warrants exercisable for 16,892,720 Ordinary Shares at a weighted average exercise price of £0.48 per share; and |
| · | warrants issuable in connection with the Private Placement, including warrants issued pursuant to the waiver and issued to the placement agent in connection with the Private Placement. |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read together with our audited consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes thereto and our unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes thereto for the six months ended June 30, 2022, included elsewhere in this prospectus. We have prepared our consolidated financial statements in this prospectus in pounds sterling and accordance with IFRS, as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board, which may differ in material respects from generally accepted accounting principles in other jurisdictions, including generally accepted accounting principles in the United States. IFRS differs in some significant respects from U.S. GAAP. Operating results for the six months ended June 30, 2022 are not necessarily indicative of the results for the full year ending December 31, 2022, or any future period.
The following discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements. Statements that are not statements of historical fact, including expression of management’s beliefs and expectations, may be forward-looking in nature and based on current plans, estimates, projections and beliefs. Forward-looking statements are applicable only as of the date made, and we undertake no obligation to update any of them in light of new information or future events. Forward-looking statements involve inherent risks and uncertainties. A number of important factors could cause actual results or outcomes to differ materially from those expressed in any forward-looking statement. These factors include those identified under the headings “Risk Factors” and “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.”
Information pertaining to our fiscal year ended December 31, 2019 was included in our Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2020 beginning on page 70 under “Item 5. Operating and Financial Review and Prospects,” which was filed with the SEC on April 30, 2021.
Recent Developments
For information regarding our recent developments, please see “Business,” which is incorporated herein by reference.
Principal Factors Affecting Results of Operations
We consider the currency exchange rate between the British pound sterling, Euros and the United States dollar and certain other factors affecting the comparability of results of operations between periods as those most likely to influence our financial condition and results of operations.
Currency Exchange Rate
We report our financial results in British pound sterling and our cash reserves are also largely denominated in British pound sterling. Costs from our Spanish operation are denominated in Euros and revenues and costs from our former United States operations are denominated in United States dollars, which subjects us to currency exchange risks. A strong Euro or United States dollar against the British pound sterling would result in these Euros or United States dollars denominated costs needing a greater amount of cash to settle the cost.
During the periods set forth in our financial statements, incorporated herein by reference, and in particular during 2020 and 2021, there has been considerable volatility in the British pound sterling against the Euro and the United States dollar. During 2020, volatility in the British pound sterling was significant as currency markets fluctuated over the prospect of the United Kingdom and European Union reaching a deal over Brexit. At this time, we do not consider the exposure sufficient to utilize derivatives to manage the forward exchange risk. Certain other costs are denominated in other currencies; however, these are not considered material.
Components of Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income Items
Revenue
Our income streams comprise revenue derived from licensing agreements, supply of goods and services, milestone income from research and development contracts and grant revenue. Revenue is recognized in-line with that set out in Note 1 to our consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Operating Expenses
We classify our operating expenses into three categories: (i) research and development, (ii) administrative costs and (iii) distribution costs, sales and marketing. These categories correspond to different functional areas within the Company.
Our operating expenses primarily consist of personnel costs, contract research and development costs, professional service fees and depreciation. Personnel costs for each category of operating expenses include salaries, bonuses, social security, health insurance, other employee benefits and share-based compensation for personnel in that category. We allocate share-based compensation expense resulting from the amortization of the fair value of options. Central overheads, such as rent, computer and other technology costs, are not allocated out to departments.
Research and Development Cost. Research and development costs consist of costs that are directly attributable to our research and development programs associated with the products described herein, including the cost of operating our Spanish manufacturing facility, which produces material exclusively for preclinical and clinical studies. This includes costs of third party contract research organizations, research specialist professional services providers, chemicals and other consumables used in the research and manufacturing process, depreciation of assets related to the research and development function, and payroll costs of staff directly assigned to the research and manufacturing operations.
Administrative Costs. These primarily consist of personnel costs for our executive, finance, corporate development and administrative personnel, as well as legal, accounting and other professional service fees, other corporate expenses, merger and acquisition costs and initial public offering costs that are charged to the consolidated statement of comprehensive income. Administrative costs also include depreciation of administrative assets.
Impairment of Intangible Assets. As of December 31, 2020, in connection with our decision to terminate further in-house development of MTD201, our Q-Sphera formulation of octreotide, we recognized an impairment loss for in-process research and development of £9.3 million. In addition, because no other Q-Sphera products were advanced beyond the formulation stage as of December 31, 2020, we recognized an impairment of goodwill arising from our acquisition of Q Chip Limited in December 2014 of £2.3 million. Further, in connection with the purported termination of our license to panobinostat, the active ingredient for our MTX110 product, by Secura Bio in June 2020, we recognized an impairment of an intangible asset of £0.8 million as of December 31, 2020.
There was no impairment charge in 2021.
Finance Income
Finance income includes all interest receivable on cash deposits. In 2020, finance income comprised bank interest received.
In 2021, finance income also included a gain on an equity settled derivative financial liability. We issued warrants in 2020 and 2019 in connection with registered direct offerings. In 2015, we assumed fully vested warrants and share options on the acquisition of DARA. The number of Ordinary Shares to be issued when the warrants and options are exercised is fixed, however the exercise prices are denominated in United States dollars, which is different from the functional currency of the Company. Therefore, the warrants and share options are classified as equity settled derivative financial liabilities in the consolidated statement of financial position with any gains or losses being recognized through finance income or finance expense in the consolidated statement of comprehensive income.
Finance Expense
Finance expenses include all interest payable on borrowings and loan instruments. In 2021 and 2020, finance expenses were comprised primarily of interest payable on lease liabilities and other loans.
In 2020, finance expenses also included a loss on equity settled derivative financial liability.
Taxation
Taxation represents tax credits receivable by Group companies in respect of qualifying research and development costs incurred.
Results of Operations
Six Months Ended June 30, 2022 Compared to Six Months Ended June 30, 2021
The following table summarizes our consolidated results of operations for the six month periods ended June 30, 2022 and 2021:
| | | Six Months Ended June 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| | | (£ in thousands; unaudited) | |
| Revenue | | | 468 | | | | 401 | |
| Other income | | | 16 | | | | 31 | |
| Research and development costs | | | (2,413 | ) | | | (2,010 | ) |
| Administrative costs | | | (1,849 | ) | | | (1,656 | ) |
| Loss from operations | | | (3,778 | ) | | | (3,234 | ) |
| Finance income | | | 404 | | | | -- | |
| Finance expense | | | (24 | ) | | | (156 | ) |
| Loss before tax | | | (3,398 | ) | | | (3,390 | ) |
| Taxation | | | 337 | | | | 236 | |
| Loss for the period attributable to the owners of the parent | | | (3,061 | ) | | | (3,154 | ) |
Revenue. Total revenue for the six months to June 30, 2022 was £0.47 million compared to £0.40 million in the first six months of 2021, an increase of 17%. Revenue in the first half of 2022 and first half of 2021 was entirely comprised of income from R&D collaborations with Janssen. There was no grant income in 2022 or 2021.
Research and Development Costs. R&D costs for the six months ended June 30, 2022 increased by £0.40 million, or 20%, to £2.41 million, compared with £2.01 million for the six months ended June 30, 2021. The percentage of R&D costs as a percentage of operating costs also increased in the period to 57% from 55%. R&D costs for the six months ended June 30, 2022 reflected increases in MTX110 clinical costs of £0.2 million as we prepare for our Phase 1 clinical trial and an increase in staff costs of £0.4 million as we seek to increase our in-house capabilities. This was offset by a reduction of £0.1 million in R&D expense on pre-clinical programs and patent costs as we rationalized our patent portfolio.
Administrative Costs. Administrative expenses for the six months ended June 30, 2022 increased by 12% to £1.85 million from £1.66 million in the same period of the prior year. Administrative costs for the six months ended June 30, 2022 reflected an increase in legal and professional fees of £0.1 million and travel costs of £0.1 million as a result of the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions and resumption of in-person conferences.
Finance Income. Finance income during the period included a gain in respect of an equity settled derivative financial liability of £0.4 million in addition to interest earned on cash deposits. There was no interest income in the prior period.
Finance Expense. Finance expense in the period related to lease liabilities. In the prior period this included a loss in respect of an equity settled derivative financial liability of £0.1 million.
Year Ended December 31, 2021 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2020
The following table summarizes our consolidated results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020:
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| | | (£ in thousands) | |
| | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | | 578 | | | | 180 | |
| Grant revenue | | | -- | | | | 163 | |
| Total revenue | | | 578 | | | | 343 | |
| Other income | | | 24 | | | | 12 | |
| Research and development costs | | | (4,654 | ) | | | (6,068 | ) |
| Administrative costs | | | (2,946 | ) | | | (4,958 | ) |
| Impairment of intangible assets | | | -- | | | | (12,369 | ) |
| Loss from operations | | | (6,998 | ) | | | (23,040 | ) |
| Finance income | | | 936 | | | | 1 | |
| Finance expense | | | (44 | ) | | | (431 | ) |
| Loss before taxation | | | (6,106 | ) | | | (23,470 | ) |
| Taxation | | | 646 | | | | 1,281 | |
| Loss from continuing operations | | | (5,460 | ) | | | (22,189 | ) |
| Loss for the year attributable to the owners of the parent | | | (5,460 | ) | | | (22,189 | ) |
Revenue. For the year ended December 31, 2021, we generated consolidated Revenues from continuing operations of £0.58 million, compared to £0.18 million in 2020, comprising Q-Sphera formulation services under R&D collaboration agreements for customers in each year.
Research and Development Costs. We incurred research and development costs of £4.65 million in 2021, compared to £6.07 million in 2020, a decrease of 23%, primarily due to £1.81 million lower clinical development costs on MTD201 offset by a £0.48 million increase in clinical costs on MTX110 and a £1.21 million increase in preclinical costs spread across several projects, including those under R&D collaboration agreements. Personnel costs, share based payment charge and other items increased by £0.32 million, £0.21 million and £0.22 million, respectively, in 2021 compared with 2020. The prior year included certain items related to the restructuring of the Company following the previously disclosed strategic review in 2020, including redundancy costs, accelerated depreciation and foreign exchange of £0.89 million, £0.85 million and £0.31 million, respectively.
Administrative costs. For the year ended December 31, 2021, our administrative costs were £2.95 million, as opposed to £4.96 million in 2020, and included decreases in legal, professional fees, insurance and other costs of £0.95 million, and a decrease in personnel costs of £0.51 million, offset by an increase in share based payments of £0.15 million. The prior year included certain items related to the closure of our operations in Bilbao, Spain, including £0.55 million in interest on repaid Spanish soft loans and £0.17 million related to the settlement of a lawsuit.
Impairment of Intangible Assets. In connection with our decision to terminate further in-house development of MTD201, we recognized an impairment loss for in-process research and development of £9.30 million in 2020. In addition, because no other Q-Sphera products were advanced beyond the formulation stage as of December 31, 2020, we recognized an impairment of goodwill arising from our acquisition of Q Chip Limited in December 2014 of £2.30 million. In connection with the termination of our license to panobinostat by Secura Bio in June 2020, we recognized an impairment of an intangible asset of £0.78 million as of December 31, 2020.
Finance Income. Finance income generally represents interest earned on cash balances. However, in 2021, finance income of £0.94 million was credited to the income statement, compared with none in 2020, and included a gain in respect of an equity settled financial liability of £0.94 million.
Finance Expense. Finance expenses of £0.04 million were charged in 2021, compared to £0.43 million in 2020, a decrease of £0.39 million. In 2020, finance expense included a loss in respect of an equity settled financial liability of £0.40 million.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
We have incurred significant net losses and have had negative cash flows from operations during each period from inception through June 30, 2022, and had an accumulated deficit of £130.76 million as of June 30, 2022. As of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, we had cash and cash equivalents of £6.42 million and £10.06 million, respectively. We have yet to generate a profit and, excluding share issues, cash flows have been consistently negative from the date of incorporation. Management expects operating losses and negative cash flows to continue for the foreseeable future. We believe our existing balances of cash and cash equivalents will be insufficient to satisfy our working capital needs and other liquidity requirements associated with our existing operations over the next 12 months. Additional funding will have to be obtained, which may include public or private equity or debt offerings. Additional capital may not be available on reasonable terms, if at all. If we are unable to raise additional capital in sufficient amounts or on terms acceptable to us, we may have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue the development of our product candidates and formulations, as well as consider other strategic alternatives.
Our future viability is dependent on our ability to raise cash from financing activities to finance our development plans until commercialization, generate cash from operating activities and to successfully obtain regulatory approval to allow marketing of our development products. Our failure to raise capital as and when needed could have a negative impact on its financial condition and ability to pursue its business strategies.
Additional funding will have to be obtained, which may include public or private equity or debt offerings. Additional capital may not be available on reasonable terms, if at all. If we are unable to raise additional capital in sufficient amounts or on terms acceptable to us, we may have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue the development of our product candidates and formulations, as well as consider other strategic alternatives.
If we raise additional funds through the issuance of debt securities or additional equity securities, it could result in dilution to our existing stockholders, increased fixed payment obligations and these securities may have rights senior to those of our Ordinary Shares (including the Depositary Shares) and could contain covenants that would restrict our operations and potentially impair our competitiveness, such as limitations on our ability to incur additional debt, limitations on our ability to acquire, sell or license intellectual property rights and other operating restrictions that could adversely impact our ability to conduct our business. Any of these events could significantly harm our business, financial condition and prospects.
Our current strategy continues to be based on advancing our proprietary technology platforms and programs with a view to partnering these assets during the course of their development, thereby earning royalty income, or working with third party pharmaceutical companies to re-formulate their proprietary medicine on a fee-for-service basis. We continue to be subject to risks incident in the development of new biopharmaceutical products, and we may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other unknown factors that may adversely affect our business.
Our forecast of the period of time through which our financial resources will be adequate to support our operations is a forward-looking statement and involves risks and uncertainties, and actual results could vary as a result of a number of factors, including the timing of clinical trials. We have based this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and we could utilize our available capital resources sooner than we currently expect. If we lack sufficient capital to expand our operations or otherwise capitalize on our business opportunities, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Cash Flows
The following table presents a summary of the primary sources and uses of cash from continuing activities for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 and the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020:
| | | Six Months Ended June 30, | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2022 | | 2021 | | 2021 | | 2020 | | |
| | | (£ in thousands; unaudited) | | (£ in thousands) |
| Cash used in operating activities | | (3,539) | | (3,108) | | (6,008) | | (9,301) | | | |
| Cash (used in) provided by investing activities | | (17) | | (147) | | (278) | | 2,574 | | | |
| Cash (used in) provided by financing activities | | (78) | | (81) | | 8,805 | | 3,084 | | | |
| Net (decrease) increase in cash and equivalents | | (3,634) | | (3,336) | | 2,519 | | (3,643) | | | |
Operating Activities
The following table presents a summary of the cash used in operations as of the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 and years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020:
| | | Six Months Ended June 30, | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2022 | | 2021 | | 2021 | | 2020 | | |
| | | (£ in thousands; unaudited) | | (£ in thousands) |
Cash flows from operating activities before
changes in working capital | | (3,494) | | (3,063) | | (6,548) | | (9,697) | | | |
| Changes in working capital | | (45) | | (45) | | (617) | | (1,558) | | | |
| Cash used in operations | | (3,539) | | (3,108) | | (7,165) | | (11,255) | | | |
Cash flows from Operating Activities before Changes in Working Capital. Net cash outflow from operating activities before changes in working capital was £3.49 million in the first six months of 2022, as opposed to £3.06 million during the same period in 2018. The increased cash outflow of £0.43 million, or 14%, was driven by a decrease in losses attributable to the owners of the Company of £0.09 million, a decrease on loss on disposal of fixed assets of £0.04 million and increase in share based payment expense of £0.06 million offset by a net increase in finance income of £0.54 million and increased tax charge credit of £0.1 million.
Net cash outflow from operating activities before changes in working capital was £6.55 million in the year ended December 31, 2021, as opposed to £9.70 million during the same period in 2020. This decreased cash outflow of £3.15 million, or 75%, was driven by a decrease in losses attributable to the owners of the Company of £16.73 million, lower tax charge credit of £0.64 million, increased share based payment expense of £0.49 million and decrease in loss on disposal of fixed assets of £0.19 million offset by an increase in net finance income, decreases in depreciation and amortization and an increase in foreign exchange gains of £1.32 million, £0.81 million and £0.39 million, respectively. Included in cash flows from operating activities in 2020 was £12.37 million in respect of impairment of intangibles.
Cash Used in Operations. Working capital increased in cash flow terms by £0.04 million for the first six months of 2022, compared to an increase] of £0.04 million for the same period in 2021. The increase in the six months ended June 30, 2022 primarily comprised an increase in trade and other receivables of £0.22 million offset by a decrease in trade and other payables of £0.19 million.
Working capital increased in cash flow terms by £0.62 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to an increase of £1.56 million for 2020. The increase in 2021 primarily comprised of an increase in trade and other receivables of £0.49 million and a decrease in trade and other payables of £0.13 million.
Taxes Paid. Taxes paid in the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021 were £nil.
Research and development tax credits of £1.16 million were received in 2021, as opposed to £1.95 million in 2020. This related to claims submitted in the prior financial year.
Investing Activities
Purchase of property, plant and equipment of £33,000 occurred in the first six months of 2022, compared to £0.19 million in the first six months of 2022. Capital expenditures in both periods was related to the purchase of laboratory and IT equipment.
Purchase of property, plant and equipment of £0.32 million occurred in the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to £0.20 million in 2020. In 2021, capital expenditure was largely related to the purchase of laboratory equipment for our laboratories and pilot scale manufacturing facilities in Cardiff, Wales. The £2.55 million cash-backed guarantee for a Spanish government loan that was put in place in 2019 was repaid in the amount of £2.64 million in 2020.
Financing Activities
Government loans, grants and subsidies. In the six months ended June 30, 2021, we repaid £0.1 million Spanish government loans in connection with the closure of our Bilbao, Spain operations. In 2020, we repaid Spanish government loans and grants of £6.18 million and £0.22 million, respectively. All Spanish government loans were repaid in 2021.
Amounts paid on lease liabilities. In the six months ended June 30 2022 we paid £73,000 in respect of lease liabilities compared with £47,000 in the prior period. In 2021 we paid £0.11 million in respect of lease liabilities compared with £0.26 million in 2020. We entered into a lease for new corporate offices in Cardiff in 2021 and surrendered the lease on our former facilities in Cardiff in 2021. We surrendered both our property leases in Bilbao, Spain during 2020.
Shares Issues Including Warrants, Net of Costs. We did not conduct any financing transactions in the six months ended June 30, 2022. Proceeds, net of costs, of £81,000 from the exercise of warrants were received in the six months ended June 30, 2012.
We raised £9.03 million in net proceeds during the year ended December 31, 2021 in cash from the 2021 UK Placing in July 2021 and from the exercise of warrants.
On May 20, 2020, we completed the closing of a registered direct offering with certain investors for the sale of 1,818,182 Depositary Shares (representing 9,090,910 Ordinary Shares) at a price per Depositary Share of $1.65, for aggregate gross proceeds of $3.0 million. In a concurrent private placement, we sold to the investors warrants to purchase a total of 1,818,182 Depositary Shares (representing 9,090,910 Ordinary Shares) at an exercise price of $2.05 per Depositary Share. The warrants, which were immediately exercisable, will expire five and one-half years from the issuance date. The closing of the private placement occurred on May 20, 2020. As of December 31, 2020, warrants to purchase 500,000 Depositary Shares had been exercised for an aggregate exercise price of approximately $1.0 million. H.C. Wainwright & Co., LLC, or Wainright, served as the sole placement agent for the transaction. In connection therewith, we also issued to certain designees of Wainwright the warrants for the purchase of a total of 90,909 Depositary Shares (representing 454,546 Ordinary Shares) at an exercise price of $2.0625 per Depositary Share pursuant to the terms of our engagement letter agreement with Wainwright. These warrants became exercisable on May 18, 2020 and expire May 18, 2025.
Concurrently with the registered direct offering, on May 22, 2020, we, through Turner Pope Investments Limited, a United Kingdom Financial Conduct Authority registered broker, or TPI, completed a placing with certain investors in the United Kingdom of 6,666,666 units, with each unit comprising one new Ordinary Share and one warrant, at an issue price of £0.27 per unit. The exercise price of the warrants is £0.34 per share, for aggregate gross proceed of £1.8 million. The warrants expire five years and six months from the issuance date. In connection with TPI acting as the placement agent in this transaction, we issued to TPI warrants to purchase an aggregate of 333,333 Ordinary Shares.
In July 2020, we, through TPI, completed a placing with certain investors in the United Kingdom of 18,518,518 Ordinary Shares. In addition, 2,777,777 broker option shares were placed by TPI pursuant to a broker option. The shares were sold at an issue price of £0.27 per share.
In July 2021, we, through TPI, completed a placing with certain investors in the United Kingdom of 35,087,720 Ordinary Shares at an issue price of £0.285 per share.
In December 2022, we, through Ladenburg Thalmann & Co., Inc., as placement agent, completed a registered direct offering of 393,973 Depositary Shares (representing 9,849,325 Ordinary Shares) at a price per Depositary Share of $1.00 for gross proceeds of approximately US$0.4 million. In addition, 120,000 previously issued warrants over Depositary Shares with an exercise price of $31.25 per Depositary Share were re-priced with an exercise price of $1.00 per Depositary Share,
In February 2023, we, through Ladenburg Thalmann & Co., Inc., as placement agent, completed a private pacement of 10,344,822 Units, initially at an issue price of $0.58 per unit for gross proceeds of approximately $6.0 million.
For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, we issued 25,000 Ordinary Shares in each year to be purchased by the Midatech Pharma Share Incentive Plan, an employee share incentive trust.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash decreased for the six months ended June 30, 2022 by £3.63 million, compared to a decrease of £3.34 million in the corresponding period in 2021. As at June 30, 2022, we had cash and cash equivalents of £6.42 million as compared to £4.20 million as at June 30, 2021.
Cash increased for the year ended December 31, 2021 by £2.52 million, before the impact of foreign exchange movements, compared to a decrease of £3.64 million in 2020. This increase was primarily due to continuing trading losses offset by the net proceeds from share issuances and warrant exercises during the year of £9.03 million. As of December 31, 2021, we had cash and cash equivalents of £10.06 million compared to £7.55 million as at December 31, 2020.
Cash Commitments
As of June 30, 2022, our cash resources were expected to provide liquidity into the first quarter of 2023. The Company remains focused on tight control of its cash commitments at any given time. As of June 30, 2022 our cash requirements primarily relate to the following:
| | · | lease obligations, related to our office and research and development facility, which are recognized as lease liabilities in the consolidated statement of financial position; |
| | · | construction of property, plant and equipment, including leasehold improvements and dilapidations in respect of our former leased facility; |
| | · | purchase obligations, under our commercial supply agreements and related activities; and |
| | · | research and development activities related to preclinical and clinical trials for our product candidates in development. |
The lease on our office and research and development facility commenced in August 2021 and expires in August 2026. Our cash requirements for our lease obligation (on a discounted basis) are £0.17 million and £0.55 million, for the short-term (payable within twelve months after the reporting date) and long-term (payable beyond twelve months after the reporting date), respectively. Our lease obligation includes ancillary contractual commitments in relation to utilities, maintenance and other services.
We built out the office and laboratory space at our new facility in the period April through August 2021. We recognized £0.05 million in respect of leasehold improvements during 2021 and an additional £0.19 million in respect of new laboratory equipment. We expect only modest capital expenditures in the foreseeable future. We have a contingent liability in respect of dilapidations on our former office and laboratory facility expected to be around £0.05 million.
As of June 30, 2022, we believed we have sufficient cash resources to fund our commitments and operations into the first quarter of 2023. We completed a registered direct offering in December 2022 and a Private Placement in February 2023, raising in aggregate $6.4 million. We believe the Company has sufficient cash resources to fund operations until December 2023. To maintain operations beyond that date, additional funding will be required, which may include public or private equity or debt offerings. Additional capital may not be available on reasonable terms, if at all. If we are unable to raise additional capital in sufficient amounts or on terms acceptable to us, we may have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue the development of our product candidates and formulations, as well as consider other strategic alternatives.
Research and Development, Patents and Licenses, Etc.
For the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, our research and development expenses were £2.41 million and £2.01 million, respectively.
For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, our research and development expenses were £4.65 million and £6.07 million, respectively.
Trend Information
Other than as disclosed elsewhere in this prospectus, we are not aware of any trends, uncertainties, demands, commitments or events that are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on our revenues, profitability, liquidity or capital resources, or that would cause the disclosed financial information to be not necessarily indicative of future operating results or financial conditions.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of and at both June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, we did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
The preparation of our consolidated financial statements requires us to make estimates, assumptions and judgments that can have a significant impact on the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, revenue and expenses and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, at the respective dates of our financial statements. We base our estimates, assumptions and judgments on historical experience and various other factors that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. Management evaluates estimates, assumptions and judgments on a regular basis and makes changes accordingly, and discusses critical accounting estimates with the Board of Directors.
The following are considered to be critical accounting policies because they are important to the portrayal of our financial condition or results of operations and they require critical management estimates and judgments about matters that are uncertain.
Impairment of goodwill and intangible assets not yet ready for use
Goodwill and intangibles not yet ready for use are tested for impairment at the cash generating unit level on an annual basis at the year end and between annual tests if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a cash generating unit below its carrying value. These events or circumstances could include a significant change in the business climate, legal factors, operating performance indicators, competition, or sale or disposition of a significant portion of a reporting unit.
The fair value of each cash generating unit or asset is estimated using the income approach, on a discounted cash flow methodology. This analysis requires significant judgments, including estimation of future cash flows, which is dependent on internal forecasts, including for revenues and development costs, estimation of the long term rate of growth for the business, estimation of the useful life over which cash flows will occur and determination of our weighted-average cost of capital.
As of June 30, 2022, June 30 2021, December 31, 2021, and December 31, 2020 the carrying value of goodwill and intangibles not ready for use were £nil.
The estimates used to calculate the fair value of a cash generating unit change from year to year based on operating results and market conditions. Changes in these estimates and assumptions could materially affect the determination of fair value and goodwill impairment for each such unit.
In March 2020, we undertook a strategic review to re-evaluate its priorities in the context of available resources. The Board concluded that we were unlikely to conclude a license transaction or raise sufficient funds to continue the required remaining investment in MTD201 on a timely basis. The Board therefore decided to terminate further in-house development of the MTD201 program with immediate effect and, in line with that decision, to close the Company’s MTD201 dedicated manufacturing facilities in Bilbao and offer redundancy to all 42 employees. As a result of the decision to terminate this program, we recognized an impairment charge of £2.3 million in the year to December 31, 2020 against goodwill and an impairment charge against the IPRD of the Midatech Pharma (Wales) Ltd cash generating unit of £9.3 million.
In June 2020, we received a letter from Secura Bio Inc., the licensor of panobinostat, the active ingredient in our MTX110 development program, terminating our license. As a result of this termination, an impairment charge of £0.8 million was recognized in the year to December 31, 2020 against the acquired IPRD in relation to MTX110.
Share-based payments
We account for share-based payment transactions for employees in accordance with IFRS 2, Share-based Payment, which requires the measurement of the cost of employee services received in exchange for the options on our Ordinary Shares, based on the fair value of the award on the grant date.
We selected the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model as the most appropriate method for determining the estimated fair value of our share-based awards without market conditions. For performance-based options that include vesting conditions relating to the market performance of our Ordinary Shares, a Monte Carlo pricing model was used in order to reflect the valuation impact of price hurdles that have to be met as conditions to vesting.
The resulting cost of an equity incentive award is recognized as expense over the requisite service period of the award, which is usually the vesting period. Compensation expense is recognized over the vesting period using the straight-line method and classified in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income.
The assumptions used for estimating fair value for share-based payment transactions are disclosed in our annual financial statements and are estimated as follows:
| · | volatility is estimated based on the average annualised volatility of a number of publicly traded peer companies in the biotech sector; |
| · | the estimated life of the option is estimated to be until the first exercise period, which is typically the month after the option vests; and |
| · | the dividend return is estimated by reference to our historical dividend payments. Currently, this is estimated to be zero as no dividend has been paid in the prior periods. |
Financial liabilities
Fair value through profit and loss (‘FVTPL’)
We have outstanding warrants in the Ordinary Share capital of the company. The number of Ordinary Shares to be issued when exercised is fixed, however the exercise price is denominated in US Dollars being different to the functional currency of the parent company. Therefore, the warrants are classified as equity settled derivative financial liabilities recognized at fair value through the profit and loss account.
The financial liability is valued using the either the Monte Carlo model or the Black-Scholes option pricing model. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are stated at fair value, with any gains or losses arising on re-measurement recognised in profit or loss. The net gain or loss recognised in profit or loss incorporates any interest paid on the financial liability and is included in the ‘finance income’ or ‘finance expense’ lines item in the income statement. Fair value is determined in the manner described in our annual financial statements.
The following are considered to be critical accounting judgments:
Revenue
Supply of Services
There are significant management judgements and estimates involved in the recognition of revenue from the supply of services. Revenue on services is recognised over the contract term, proportionate to the progress in overall satisfaction of the performance obligations (the services performed by the Group), measured by cost incurred to date out of total estimate of costs.
Income taxes
Deferred tax assets are recognized for unused tax losses to the extent that it is probable that taxable profit will be available against which the losses can be utilized. Significant management judgment is required to determine the amount of deferred tax assets that can be recognized based upon the likely timing and the level of future taxable profits together with future tax planning strategies.
In 2021, there were approximately £67.2 million of gross unutilized tax losses carried forward (2020: £63.2 million). No deferred tax asset has been provided in respect of these losses as there was insufficient evidence to support their recoverability in future periods.
Going Concern
We are subject to a number of risks similar to those of other development and early-commercial stage pharmaceutical companies. These risks include, amongst others, generation of revenue from the development portfolio and risks associated with research, development, testing and obtaining related regulatory approvals of our pipeline products. Ultimately, the attainment of profitable operations is dependent on future uncertain events which include obtaining adequate financing to fulfill our commercial and development activities and generating a level of revenue adequate to support our cost structure.
We have experienced net losses and significant cash outflows from cash used in operating activities over the past years as it has developed its portfolio. As at June 30, 2022 we had total equity of £7.49 million (£10.45 million at December 31, 2021), incurred a net loss after tax for the six months to June 30, 2022 of £3.06 million, as compared to £3.15 million in the same period in 2021, and used cash in operating activities of £3.54 million (June 30, 2021: £3.11 million) for the same period. As at June 30, 2022, we had cash and cash equivalents of £6.42 million.
Our future viability is dependent on our ability to raise cash from financing activities to finance its development plans until commercialisation, generate cash from operating activities and to successfully obtain regulatory approval to allow marketing of its development products. Our failure to raise capital as and when needed could have a negative impact on our financial condition and ability to pursue our business strategies.
We have prepared cash flow forecasts and considered the cash flow requirement for the next three years including the period 12 months from the date of approval of the interim financial information. These forecasts showed that further financing would be required during the first quarter of 2023 assuming, inter alia, that certain developments programs and other operating activities continue as currently planned. Following the registered direct offering in December 2022 and Private Placement in February 2023 which raised aggregate proceeds of $6.4 million, we updated our forecasts. The updated forecasts show that further financing will be required before December 2023. This requirement for additional financing in the short term represents a material uncertainty that may cast doubt upon the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
We continue to evaluate near-term funding options, including fundraising and the partnering of assets and technologies of the Company. After considering the uncertainties, we consider it is appropriate to continue to adopt the going concern basis in preparing these financial statements.
Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon our ability to obtain additional capital and/or dispose of assets, for which there can be no assurance we will be able to do on a timely basis, on favorable terms or at all.
Recently Issued and Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 1 to our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this report for recently adopted accounting pronouncements and recently issued accounting pronouncements not yet adopted as of the dates of the statement of financial position included in this report.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
We are exposed to a variety of financial risks, including, but not limited to, market risk (including foreign exchange and interest rate risks), credit risks, and liquidity risks. Our overall risk management program focuses on the unpredictability of financial markets and seeks to minimize potential adverse effects on its financial performance.
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Company if a development partner or counterparty to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual obligations. We are mainly exposed to credit risk from amounts due from collaborative partners which are deemed to be low.
Credit risk also arises from cash and cash equivalents and deposits with banks and financial institutions. For banks and financial institutions, only independently rated parties with high credit status are accepted.
We do not enter into derivatives to manage credit risk.
Our total exposure to credit risk is equal to the total value of the financial assets held at year end. The consolidated entity recognizes a loss allowance for expected credit losses on financial assets which are either measured at amortized cost or fair value through other comprehensive income. The measurement of the loss allowance depends upon the consolidated entity's assessment at the end of each reporting period as to whether the financial instrument's credit risk has increased significantly since initial recognition, based on reasonable and supportable information that is available, without undue cost or effort to obtain.
Where there has not been a significant increase in exposure to credit risk since initial recognition, a 12-month expected credit loss allowance is estimated. This represents a portion of the asset’s lifetime expected credit losses that is attributable to a default event that is possible within the next 12 months. Where a financial asset has become credit impaired or where it is determined that credit risk has increased significantly, the loss allowance is based on the asset's lifetime expected credit losses. The amount of expected credit loss recognized is measured on the basis of the probability weighted present value of anticipated cash shortfalls over the life of the instrument discounted at the original effective interest rate. For financial assets measured at fair value through other comprehensive income, the loss allowance is recognized within other comprehensive income. In all other cases, the loss allowance is recognized in profit or loss.
Cash in Bank
We are continually reviewing the credit risk associated with holding money on deposit in banks and seek to mitigate this risk by holding deposits with banks with high credit status.
Foreign Exchange Risk
Foreign exchange risk arose in 2021 and prior years because we had a material operation located in Bilbao, Spain, whose functional currency was not the same as our functional currency. Due to significant currency fluctuations during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, particularly in respect of British pounds sterling against the Euro, our foreign exchange risk was significant. Our net assets arising from such overseas operations were exposed to currency risk resulting in gains or losses on retranslation into British pounds sterling. Given the closure of our Spanish operations and the levels of materiality, and despite this historical volatility, we do not hedge our net investments in overseas operations as the cost of doing so is disproportionate to the exposure.
Foreign exchange risk also arises when our individual entities enter into transactions denominated in a currency other than our functional currency. Our transactions outside the United Kingdom to Europe drive foreign exchange movements where suppliers invoice in currency other than British pounds sterling. These transactions are not hedged because the cost of doing so is disproportionate to the risk.
Interest Rate Risk
We do not hold any derivative instruments, or other financial instruments, that expose us to material interest rate risk.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk arises from our management of working capital. It is the risk that we will encounter difficulty in meeting our financial obligations as they fall due.
It is our aim to settle balances as they become due.
We have prepared cash flow forecasts and considered the cash flow requirement for the next three years including the period 12 months from the date of approval of the interim financial information. These forecasts showed that further financing would be required during the first quarter of 2023 assuming, inter alia, that certain developments programs and other operating activities continue as currently planned. Following the registered direct offering in December 2022 and Private Placement in February 2023 which raised aggregate proceeds of $6.4 million, we updated our forecasts. The updated forecasts show that further financing will be required before December 2023. This requirement for additional financing in the short term represents a material uncertainty that may cast doubt upon the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
In addition to utilizing the existing cash reserves, we are evaluating a number of near-term funding options potentially available to us, including fundraising, and the partnering of assets or technologies. After considering the uncertainties, we considered it appropriate to continue to adopt the going concern basis in preparing the financial information.
Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon our ability to obtain additional capital and/or dispose of assets, for which there can be no assurance we will be able to do on a timely basis, on favorable terms or at all.
BUSINESS
Overview
Business Overview
We are focused on the research and development of medicines which we believe would benefit from improved bio-delivery and/or bio-distribution using our using our proprietary platform drug delivery technologies:
| • | Q-Sphera™ platform: Our disruptive polymer microsphere microtechnology is used for sustained delivery to prolong and control the release of therapeutics over an extended period of time, from weeks to months. |
| • | MidaSolve™ platform: Our innovative oligosaccharide nanotechnology is used to solubilize drugs so that they can be administered in liquid form directly and locally into tumors. |
| • | MidaCore™ platform: Our leading-edge gold nanoparticle, or GNP, nanotechnology is used for targeting sites of disease by using either chemotherapeutic agents or immunotherapeutic agents |
Revenue. Revenue from continuing and discontinued operations for the whole of the Company is set out below.
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| (£ in thousands) | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| Continuing Operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue (United States) | | | -- | | | | -- | | | | 60 | |
| Revenue (Europe, including United Kingdom) | | | 578 | | | | 118 | | | | 252 | |
| Revenue (Rest of World) | | | -- | | | | 62 | | | | -- | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Discontinued Operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue (United States) | | | -- | | | | -- | | | | -- | |
| Revenue (Europe, including United Kingdom) | | | -- | | | | -- | | | | -- | |
| Total Revenue from continuing and discontinued operations | | | 578 | | | | 180 | | | | 312 | |
Recent Developments
February 2023 Private Placement
On February 15, 2023, we completed the closing of a private placement with certain institutional investors, for the sale of up to an aggregate of 2,169,790,225 of our Ordinary Shares represented by 86,791,609 Depositary Shares, consisting of (i) 65,004,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 2,600,160 Depositary Shares, (ii) 258,620,550 Ordinary Shares represented by 10,344,822 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series A warrants issued in the Private Placement, (iii) 387,930,900 Ordinary Shares represented by 15,517,236 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series B warrants issued in the Private Placement, and (iv) up to 1,434,996,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 57,399,840 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of pre-funded warrants issued in the Private Placement, subject to certain reset provisions set forth in the pre-funded warrants, at an initial purchase price of $0.58 per Depositary Share, for aggregate gross proceeds of approximately $6.0 million. The issuance of the Series A warrants, Series B warrants and any pre-funded warrants issuable upon a reset are subject to approval of our stockholders.
In addition, in connection with the Private Placement, on February 9, 2023 we entered into a Waiver to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 13, 2022, or the Waiver, by and between the Company and a certain institutional investor, or the December Investor, as amended on December 16, 2022, or the December SPA, providing for a permanent waiver of certain equity issuance prohibitions and participation rights under the December SPA. In connection therewith, the Company agreed to, subject to receipt of stockholder approval, issue to the December Investor Series A Warrants exercisable for 12,500,000 Depositary Shares represented by 500,000 Depositary Shares.
In connection with the Private Placement, we announced a general meeting of stockholders to be held on March 24, 2023. At the general meeting, our shareholders will vote on resolutions to: (i) approved the allotment of, and disapplication of preemption rights with respect to, the Ordinary Shares to be issued under the Class A warrants, the Class B warrants, certain of the pre-funded warrants, and the Ladenburg Warrants, (ii) change the name of the Company to “Biodexa Pharmaceuticals plc,” (iii) allow the allotment of up to 100% of our fully diluted share capital for future share issuances through our annual general meeting in 2025, and (iv) authorize a 1-for-20 reverse stock split of our Ordinary Shares. Following the reverse stock split of our Ordinary Shares, our Depositary Shares will also split in a corresponding amount.
Assuming the reverse stock split is approved, in order to bring the price of the Depositary Shares into compliance with NASDAQ’s minimum bid price requirement, we will change the ratio of Depositary Shares from one Depositary Share representing 25 Ordinary Shares to a new ratio of one Depositary Share representing five Ordinary Shares. This will have the effect of a one-for-four reverse split of our Depositary Shares. There can be no assurance that the ratio change, if it occurs, will be effective in achieving our goal of regaining compliance with NASDAQ’s minimum bid price requirement.
Terminated Transaction with Bioasis Technologies Inc.
On December 13, 2022, we entered into an Arrangement Agreement, or Arrangement Agreement, with Bioasis Technologies Inc., or Bioasis, pursuant to which (i) we were to acquire all of the issued and outstanding common shares of Bioasis, or the Bioasis Shares, in exchange for our Ordinary Shares (to be issued in the form of Depositary Shares), and (ii) Bioasis would become our wholly owned subsidiary.
In addition, in connection with entering into the Arrangement Agreement, Bioasis issued to the Company a promissory note, or the Note, in consideration for a loan from the Company, which loan was to be made in three tranches of $250,000 payable on each of December 19, 2022, January 3, 2023 and February 6, 2023, in each case, subject to written demand and to the terms and conditions of the Note. As of the date hereof, we have loaned Bioasis $500,000 under the Note.
On January 23, 2023, following the failure by our shareholders to approve the necessary resolutions to complete the transaction, Bioasis terminated the Arrangement Agreement and the transactions related thereto.
In connection with the termination of, and pursuant to the terms of, the Arrangement Agreement, Bioasis has demanded an expense reimbursement of $225,000. In addition, on February 27, 2023, Bioasis demanded the third payment of $250,000 under the Note. We have notified Bioasis that is in default under the terms of the Note and have demanded repayment immediately of all amounts owed to us under the Note.
Registered Direct Offering and Termination of Proposed Private Placement
On December 16, 2022, we completed the closing of a registered direct offering with the December Investor, for the sale of 9,849,325 Ordinary Shares represented by 393,973 Depositary Shares at a price per Depositary Share of $1.00, for aggregate gross proceeds of approximately $0.4 million.
On January 26, 2023, following the termination of the Arrangement Agreement by Bioasis, we terminated the December SPA, and the Registration Rights Agreement, by and between the Company and the December Investor, dated as of December 13, 2022, pursuant to which we would have sold such December Investor $9.6 million of our securities, subject to the closing of the transactions contemplated by the Arrangement Agreement.
Change in Ratio of Depositary Shares
On September 26, 2022, we effected a change in the number of our Ordinary Shares represented by our Depositary Shares, issued by The Bank of New York Mellon as depositary, from five of our Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share to 25 Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share. The change in ratio had the same effect as a one-for-five reverse stock split of the Depositary Shares, reducing the number of outstanding Depositary Shares, as of the close of business on September 26, 2022, to approximately 3,940,000.
Our Ordinary Shares, which were not affected by the change, continue to trade on AIM. The change in the number of Depositary Shares resulting from the change in ratio has been applied retroactively to all share and per share amounts presented in this prospectus; provided, however, that such changes have not been made to the financial statements and accompanying notes incorporated herein by reference.
MTX110 Developments
On June 1, 2022, we announced that upon submitting an application to the FDA, our development program of MTX110 for the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma had been granted Fast Track designation by the agency. Fast Track is a process designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of treatments for serious conditions and that potentially address unmet medical needs. Drugs that are granted this designation are given the opportunity for more frequent interactions with the FDA, as well as potential pathways for expedited approval.
On January 12, 2023, we announced that, following completion of one-month treatment with MTX110 in our first patient, our Phase I study of MTX110 in recurrent glioblastoma would continue with a planned dose escalation following positive recommendation from the study’s Data Safety Monitoring Board, or DSMB. The Phase I study, is an open-label, dose escalation study designed to assess the feasibility and safety of intermittent infusions of MTX110 administered by convection enhanced delivery (CED) via implanted refillable pump and catheter. The study aims to recruit two cohorts, each with a minimum of four patients; the first cohort will receive MTX110 only and the second cohort will receive MTX110 in combination with lomustine.
The first patient in the study was dosed at 60uM of MTX110 via direct-to-tumour delivery and has received four 48-hour infusions over a period of four weeks. No treatment-associated adverse events were noted in the patient during this period. Following successful completion of the first month of treatment, the DSMB reviewed the available data and recommended dose escalation in the study to 90uM. This dose is expected to be the optimal one of MTX110 and is the one currently being used in the ongoing Phase I study of patients with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma, or DIPG, at Columbia University.
Non-Compliance with NASDAQ Continued Listing Requirements
Our Depositary Shares are currently listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market. We are required to meet certain qualitative and financial tests to maintain the listing of our Depositary Shares on NASDAQ. On January 31, 2023, we received a letter from NASDAQ stating that, for the previous 30 consecutive business days, the bid price for our Depositary Shares had closed below the minimum $1.00 bid price per share requirement for continued listing on the NASDAQ Capital Market under NASDAQ Listing Rule 5550(a)(2). The notice has no immediate effect on the listing or trading of our Depositary Shares and the Depositary Shares will continue to trade on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “MTP.”
In accordance with NASDAQ Listing Rules, we have a grace period of 180 calendar days, or until July 31, 2023, or the Compliance Period, to regain compliance with the minimum bid price requirement. To regain compliance, the closing bid price of the Depositary Shares must meet or exceed $1.00 per share for at least 10 consecutive business days during the Compliance Period. If the Depositary Shares do not regain compliance with the minimum bid price requirement during the Compliance Period, we may be eligible for an additional grace period of 180 calendar days provided that we satisfy NASDAQ's initial listing standards for listing on the NASDAQ Capital Market, other than the minimum bid price requirement, and provide written notice to NASDAQ of its intention to cure the delinquency during the second grace period. If we do not regain compliance during the initial grace period and are not eligible for an additional grace period, NASDAQ will provide written notice that the Depositary Shares are subject to delisting from the NASDAQ Capital Market. In that event, we may appeal such determination to a hearing panel.
We intend to monitor the bid price of our Depositary Shares during the Compliance Period and will consider taking such actions as may be necessary and appropriate to achieve compliance with continued listing requirements prior to the expiration of all available grace periods, including the actions described above regarding a ratio change and reverse split of our Depositary Shares.
Our Strategy
Our development, manufacturing and commercialization strategy is based on advancing our proprietary technology platforms and programs with a view to partnering these assets during the course of their development. This is expected to drive a commercial pipeline of products with improved essential parameters, over and above the currently marketed source or parent compound, including safety, tolerability, efficacy and compliance profiles. We believe that our management team has significant industry and technical experience and is highly capable of, and committed to, building our value.
Since our announcement of a strategic review in March 2020 and the termination of further in-house development of MTD201, we have sought to broaden our research and development pipeline through technology collaborations with third party pharmaceutical companies, initiating new internal programs and adding new indications to MTX110. Our realigned strategy is to advance our development programs to proof-of-concept stage, before seeking license partners to fund further development, manufacturing scale-up and commercialization of such programs.
Development
Our intention is to build a balanced portfolio of Q-Sphera programs employing a strategy to create an:
| • | internal pipeline of long-acting, injectable products by re-formulating existing, approved therapies; and |
| • | external pipeline by entering into research collaboration with partners to formulate their proprietary products into long-acting injectable products. |
We have applied our MidaSolve technology to panobinostat to create our proprietary product MTX110. Our development strategy for MTX110 is to demonstrate its utility in a range of intractable brain cancers with a series of pilot proof-of-concept studies before seeking licensee partners. Once a licensing partner has been secured, we would expect any future development costs to be reimbursed by that partner.
Manufacturing
As part of our strategic review, we decided to close our operations in Bilbao, Spain, including our Q-Sphera dedicated manufacturing facility. To establish proof-of-concept in pre-clinical studies for potential licensees, we are able to manufacture non-GMP Q-Sphera products at pilot scale at our Cardiff, Wales facility. Our intention is to technology transfer the manufacturing of clinical trial supplies and, ultimately, full GMP commercial manufacture to a third party CMO. We would expect a licensee to assume the cost of manufacturing GMP product and commercial scale-up pursuant to a technology transfer agreement.
MTX110 is currently being manufactured to GMP standards at a CMO.
Commercialization
Once proof-of-concept has been established, we intend to seek to license our products to a partner who would complete the development, and subsequently market and sale, of the product in an agreed upon licensed territory. In addition to reimbursement of development costs, the partner would be expected to make milestone payments based on sales targets and royalty payments.
Our Platform Technologies and Pipeline
Central to our business are our three complementary platform technologies that enable the sustained release, direct local delivery, or targeted delivery improvement to previously approved therapeutic drugs. Individually, these platforms are expected to offer unique advantages that address current therapeutic challenges and needs. Our sustained release “Q-Sphera” technology platform is used for selected applications, and ensures consistently sized monodispersed polymer microparticles that may be engineered for precise and sustained release drug delivery. Our GNP “MidaCore” technology platform may provide improved targeting of chemotherapeutics agents to individual tumors using specific targeting agents in order to deliver a therapeutic payload into the tumor cell, while at the same time decreasing the side effect profile associated with off-target effects of these drugs. Our nano-inclusion technology platform, “MidaSolve,” used for local delivery of therapeutics, allows for the delivery of generally water insoluble drugs into the site of disease through the creation of water soluble complexes without the efficacy of the active drug compound being affected. Individually and collectively, we believe that these technologies provide platforms that improve bio-delivery and bio-distribution of therapeutic molecules to the right place of disease, at the right time.
In 2020, following our strategic review, we pivoted from a largely singular focus on the clinical development and manufacturing scale up of MTD201 to a strategy based on a broader, but earlier stage, pipeline designed to optimize opportunities for partnering success. Our development pipeline includes eight projects, of which two are partnered with Janssen, an affiliate of Johnson & Johnson, and as set forth in more detail below:
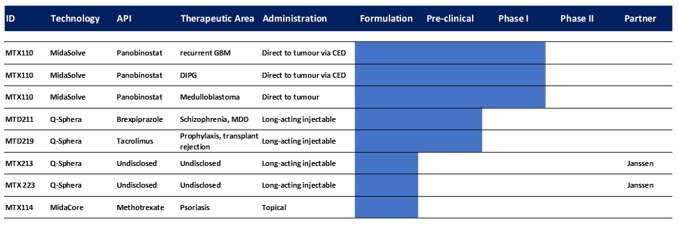
Sustained Release Technology Platform: Q-Sphera
Technology. Our Q-Sphera technology employs 3-D printing techniques to encapsulate medicines in polymer-based bioresorbable microspheres. Q-Sphera is a precise, scalable, efficient, and environmentally friendly microparticle manufacturing platform. From a clinical perspective, Q-Sphera ensures monodispersed microparticles that release active drug compounds into the body in a tightly controlled, highly predictable and linear manner over an extended period of time.
Q-Sphera is the next generation polymer microsphere technology which simplifies manufacturing, facilitates the sustained release of products and delivers formulations with significant patient, healthcare professional and payor benefits. Our polymer microsphere platform has been developed to enable sustained release delivery solutions for peptide and small-molecule therapeutics through precise definition of the properties of polymer microparticles into which active compounds can be incorporated. Microspheres are small, spherical particles that can be utilized as a time release drug capsule. This technology contributes to our oncology franchise as well as potential applications in endocrinology and other disease areas.
Current reactor-based emulsion manufacturing technology has been in use for over 20 years and, despite several issues, it continues to be used by the vast majority of the market as there are limited alternatives. Reactor-based emulsion processes, used by most existing products, require large infrastructure, are energy intensive, inefficient and wasteful, producing large quantities of unusable particles, and utilize large volumes of toxic organic solvents that are damaging to the environment.
The microspheres may be injected to form depots in the body, which release drugs over predictable, sustained periods from one week up to several months. We believe Q-Sphera offers numerous potential advantages to patients and payors compared with other immediate release products and polymer-based technologies, as set forth below:
| | | Advantages of Q-Sphera |
| Features | Benefits | For
patients | For payors | Compared
with
immediate
release
products | Compared with
other polymer-
based systems |
Biocompatible, bio-degradable microspheres | Safe, sustained release delivery of therapeutics with substantially increased dose intervals | ● | | ● | |
Homogenous, monodispersed microspheres | Lower dose to dose variability and improved injectability | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Tunable, predictable drug release | Low variability plasma levels within a targeted therapeutic window | ● | ● | ● | ● |
Easier reconstitution and adaptable to a wide range of presentations | Nurse or self-administration. Easy to use, safer pre-filled syringe and ‘pen’ presentations | ● | ● | | ● |
Low viscosity, smaller gauge needles | Reduced severity and frequency of injection site reactions. Higher doses with subcutaneous and/or self-administration | ● | ● | | ● |
Localized delivery, including intratumoral, intraocular, peritoneal and intraarticular | Reduced systemic side effects | ● | ● | ● | |
Small footprint, reliable and scalable manufacturing process | Lower cost of manufacture | | | | ● |
| Class 3 solvents in low volume | Less environmental impact and lower cost of manufacture | | | | ● |
| | | | | | | |
Pipeline. We have an internal Q-Sphera pipeline comprised of MTD211 and MTD219.
MTD211. We have developed a long-acting formulation of brexpiprazole using Q-Sphera technology. Marketed under the brand name Rexulti® by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, brexpiprazole is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia and adjunctive treatment of major depressive disorder, or MDD, and is currently only available as an immediate release oral tablet. The market for anti-psychotic drugs is shifting towards long-acting formulations for reasons of improved patient compliance and lowering of payor costs associated with patient hospitalization events. Sales of long-acting anti-psychotic products in 2020 were approximately $5.7 billion globally.
In in vivo studies, MTD211 was well tolerated and demonstrated that a single dose of MTD211 is expected to deliver therapeutic blood levels of brexpiprazole over a period of three months.
MTD201. Following the announcement of a strategic review, we ceased further in-house development of MTD201, our Q-Sphera formulation of octreotide for acromegaly and neuroendocrine tumors. We completed two clinical trials for MTD201, a 2018 first-in-human Phase I study compared MTD201 with Novartis’ Sandostatin LAR Depot, and second Phase I study of MTD201 completed in January 2020 which compared subcutaneous administration with intramuscular administration in healthy volunteers and showed similar pharmacokinetics and bioavailability in healthy volunteers. Together, the two Phase I studies of MTD201 serve as clinical validation of the Q-Sphera technology, confirming many of Q-Sphera’s features and benefits for patients, payors and licensees.
Q-Sphera Formulations of Proteins. On June 17, 2021, we announced that we had been able to successfully encapsulate a large molecule protein, specifically an exemplar monoclonal antibody, or mAb, and had preserved the functional integrity and antigen binding capacity of the mAb in vitro. We believe there are no other approved long-acting injectable formulations of biologic products such as mAbs or other high molecular weight proteins because they are delicate and easily de-natured in the manufacturing process. We further believe this to be breakthrough data, since, to our knowledge, no other commercial or academic organization has been able to successfully deliver therapeutic proteins over extended periods using methods capable of commercial scaling.
This favorable data led to the expansion of our research and development collaboration with Janssen, as announced on January 17, 2022. We will be seeking to optimize drug loading and the in vitro dissolution profile of Janssen’s proprietary development compound as project MTX213.
We believe the data from experiments on the exemplar mAb and other proteins could potentially open up opportunities for its Q-Sphera technology. A significant number of latest generation medicines are protein based and reformulation as long-acting injectables could provide significant benefits to patients, physicians and payors. In 2020, the top 10 mAbs recorded aggregate sales of $74.9 billion and all mAbs $154 billion globally.
MidaSolve: Local Delivery Technology Platform
Technology. Our MidaSolve nano inclusion technology is utilized for potent, small molecule chemotherapeutics that have minimal solubility in water at biological pH, which means they cannot normally be injected and limits them to oral administration in solid form. When reformulated with MidaSolve technology, the complexed molecules solubilize such that the molecule can be administered in liquid form into the body. This enables local infusion directly into the tumor, thus extending the available routes of administration for drugs that otherwise would be limited to oral forms only.
The complexed molecules comprise a hydrophobic (‘water-fearing’) inner surface and a hydrophilic (‘water-loving’) outer surface, and as a result are capable of forming host-guest complexes with normally water-insoluble molecules. A hydrophobic, poorly water-soluble drug can associate with the inner, more hydrophobic surface of the MidaSolve host, while the hydrophilic outer surface allows the complex to dissolve at biological pH.
MTX110. Using our MidaSolve technology in combination with panobinostat, an otherwise insoluble drug, MTX110 is designed for direct-to-tumor treatment of intractable brain cancers. The resulting complex is readily soluble in water at therapeutic concentrations, thus enabling liquid administration routes directly into the tumor that otherwise would not be possible. Panobinostat (Farydak®) is a potent, nonselective histone deacetylase inhibitor that was developed for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Given in its natural oral form, panobinostat does not cross the blood-brain barrier, and thus does not reach brain tumors. It is also a highly toxic substance and, when given orally, suffers from significant dose-limiting side effects. MidaSolve allows an alternate means of delivery in liquid form, and MTX110, our soluble form of panobinostat, is infused directly into the tumor. Direct delivery of MTX110 bypasses the blood-brain barrier and ensures adequate drug exposure to tumor cells without exposing the rest of the body to potentially toxic concentrations. MTX110’s intratumoral delivery thus provides a significant potential for treatment of DIPG and, potentially, other forms of brain cancer.
We are currently researching the utility of MTX110 to proof-of-concept stage in the following three indications.
| • | DIPG. DIPG tumors are located in the pons (middle) of the brain stem and aggressively infiltrate the brainstem such that cancer tissue typically cannot be differentiated from normal brain tissue. Occurring mostly in children, approximately 1,000 patients globally are diagnosed with DIPG per annum and median survival is approximately 10 months. There is no effective treatment as surgical resection is not possible, and radiotherapy and chemotherapy do not improve survival since anti-cancer drugs cannot cross the blood-brain barrier to access the tumor. |
On October 24, 2019, we announced that the FDA has granted orphan drug designation for MTX110. Orphan drug designation is granted to support the development of drugs that target rate diseases with high unmet needs, affecting 200,000 or fewer U.S. patients annually, and that are expected to provide significant therapeutics advantages over existing treatments. Orphan designation qualifies a company for benefits that apply across all stages of drug development, including an accelerated approval process, seven years of market exclusivity upon regulatory approval, if received, tax credits for qualified U.S. clinical trials, eligibility for orphan drug grants and exemption from certain administrative fees.
As noted above, in October 2020, we reported the first-in-man study by UCSF of MTX110 in DIPG using a CED system. The Phase I study established a recommended dose for Phase II, a good safety and tolerability profile but also encouraging survival data in the seven patients treated. We plan to initiate a Phase II study in DIPG to examine efficacy and safety in approximately 20 patients. The Phase II trial will also use a CED system, whereby MTX110 will be infused under slight pressure directly into and around the tumor. We believe the primary endpoint of the study is likely to be patient survival rates after 12 months.
| • | Glioblastoma Multiforme. GBM is one of the most aggressive forms of cancer and glioblastomas usually occur in the white matter of the cerebrum, although metastasis through the cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF, to the spinal cord is rare. Treatments include radiation, surgical resection and chemotherapy although, in most cases, tumors recur. There are approximately two to three new cases of GBM per 100,000 population per annum, with median survival of approximately 12 months. |
In December 2021, we received an IND approval for a pilot Phase I study in recurrent GBM. We are currently recruiting patients into the study.
| • | Medulloblastoma. Medulloblastomas are generally located in the fourth ventricle of the brain between the brainstem and the cerebellum. They are invasive and, unlike most brain tumors, spread through CSF and frequently metastasize to different locations in the brain and spinal cord. Treatments include resection, radiation and chemotherapy. Approximately 350 patients in the US are diagnosed with medulloblastoma per annum, and 3,800 people are living with the disease in the United States. The cumulative survival rate is 60%, 52% and 47% at five years, 10 years and 20 years, respectively. |
The University of Texas is undertaking a Phase I exploratory study in medulloblastoma using direct administration of MTX110 into the fourth ventricle of the brain, enabling it to circulate through the CSF.
In 2020, our non-exclusive worldwide, sublicenseable license to certain patents of panobinostat was terminated by Secura Bio. We view MTX110 as an important asset and currently have two ongoing clinical trials for MTX110 and intend to commence two further clinical trials as part of our MTX110 clinical program. We continue to enjoy freedom to use panobinostat for research purposes and we plan to continue to pursue development of MTX110. We believe that the relevant Secura Bio patents may delay a launch of MTX110 for use in patients with DIPG, however we do not anticipate it would have any impact on launching MTX110 for use in patients with GBM. If we are unable to launch a product candidate until the patent expires, there could be a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
For additional information regarding MTX110, see “—Recent Developments—MTX110 Developments.”
MidaCore: Targeted Delivery Platform
Technology. MidaCore is a leading innovation in ‘ultra-small’ nanomedicine and is designed for targeted delivery to enable improved delivery of therapeutics to tumor cells and the immune system. In oncology treatments MidaCore provides a nano complex (less than 5nm in size, or approximately 80,000 times smaller than the width of a hair) that carries conventional small molecule chemo-therapeutic payloads and delivers these to the tumor site in high concentrations. In immunotherapy, treatments, MidaCore acts as a nanocarrier complex for synthetic immuno-peptides that stimulate the immune system to seek out and destroy cancer cells via immune mediated vaccine processes. These small complexes can enter immune processing cells to induce T-cell mediated immune responses specifically against tumor cells, viral infected host cells or autoimmune disease.
The MidaCore technology platform is based upon ‘ultra-small’ nanoparticle drug conjugates, which at 2-4nm in size are among the smallest particles in biomedical use. They are composed of a core of gold atoms decorated with a permutation of therapeutic and/or targeting molecules. The small size and multi-functional arrangement around the gold core underpin the ability to improve biodistribution, and target tumor and/or immune sites providing a new generation of oncology drugs.
MidaCore design and synthesis GNP technology enables the production of 2nm to 5nm medications, which we believe is roughly five-to-tenfold smaller than any other delivery vehicle in clinical trials. MidaCore’s therapeutics are comprised of a core of gold atoms (approximately 100 gold atoms per GNP) surrounded by an organic layer of carbohydrates that stabilize the metallic core and make the particle water-soluble and biocompatible.
MTX114. Using MidaCore technology, we have developed a re-engineered version of methotrexate, an immuno-suppressant for topical application in psoriasis. If successful, MTX114 would be a first topical formulation of methotrexate, thus avoiding the need for potentially toxic systemic administration. Pre-clinical data suggest MTX114 may reduce inflammation in a psoriatic skin model. There are estimated to be over 100 million people who suffer from psoriasis worldwide.
Commercial Agreements, Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
We are currently collaborating with a number of biopharmaceutical companies, research institutes and universities on several of our development programs involving our core technologies.
On July 21, 2020, we announced a collaboration with the European affiliate of a global pharmaceutical company to deploy our in-house expertise and proprietary drug delivery platforms towards product candidates nominated by the collaborating company. On January 17, 2022, we announced the extension of this collaboration and disclosed the collaborator as Janssen, an affiliate of Johnson & Johnson. On March 9, 2022, we announced we had extended this collaboration to include another large molecule.
CMS License Agreement. On January 29, 2019, we entered into the CMS License Agreement with CMS, as guarantor, and the Licensees. The CMS License Agreement was effective as of February 26, 2019. Pursuant to the terms of the CMS License Agreement, we agreed to license to the Licensees the exclusive right to use our technology and our intellectual property rights and information and data related to certain of our clinical and pre-clinical products (i.e. MTD201, MTX110, MTX102, MTR103 and MTD119), together with any other pipeline products or line extensions which are in or which enter pre-clinical or clinical development in the first three years following the effective time of the CMS License Agreement, together the Products, to develop and commercialize the Products in China, including Macau, Hong Kong and Taiwan, with the same rights in certain countries in south east Asia in respect of which the Licensees notifies us that such licensee wants a license after the grant of a regulatory approval of any of the Products by the FDA, EMA or by the regulatory authorities in the United Kingdom, France, Germany or Switzerland, collectively the Territory, such activities to be conducted by the Licensee(s) and affiliates of CMS and local partners as permitted sub-licensees. The Licensees have the exclusive right to import, obtain market approvals and register, market, distribute, promote and sell the Products in the Territory at the Licensees’ sole discretion, and in the event we choose not to or fail to meet the Licensees’ binding orders for the Products under certain circumstances, will be granted the right to manufacture the Products itself. The Licensees will be restricted from supplying the Products to any customers outside of the Territory, while we will be restricted from supplying the Products into the Territory, except through the Licensees.
In addition, we agreed to assist the Licensees (and/or any affiliate of CMS) with their applications for marketing approvals for the Products in the Territory, which approvals, if granted, will be exercised by CMS Bridging or CMS Medical HK, unless it is being transferred to us when we are entitled to terminate the CMS License Agreement for material breach by CMS Bridging or CMS Medical HK. We will manufacture the Products for the Licensees and their sub-licensees, which Products will be subject to exclusive purchase and supply arrangements with the Licensees for the Territory.
Further, we agreed to permit the Licensees to identify their own product and line extension targets in respect of which, if we agree, we will carry out initial development and then will, for a technology transfer fee, the amount of which will be dependent on the circumstances, transfer the specific program know-how and data to enable the Licensees to continue to develop using our platform technologies and then to commercialize in the Territory. We will receive a low single digit royalty on the Net Sales (as such term is defined in the CMS License Agreement) in the Territory. The Licensees will own any intellectual property rights it creates and any data they collect during the development process and will license such rights and data to us for the purposes of manufacturing the products in question and also to commercialize the products outside the Territory, for which we will pay the Licensees a low double digit royalty.
The Licensees shall pay us lump sum payments on a Product-by-Product basis (in U.S. dollars) upon the achievement of certain regulatory approvals (in six, or potentially seven, figure amounts) and sales performance milestones (in seven, or potentially, eight figure amounts), as well as royalties upon Net Sales (as a low double digit percentage for the Products other than MTX110, for which the royalty will be a single digit percentage) in the Territory.
The CMS License Agreement may be terminated by either party for specific material breaches or insolvency. In particular, our rights to terminate are limited to breaches of certain non-compete restrictions, failure to pay milestones or royalties, insolvency, or a failure to develop and/or commercialize particular Products in particular countries after the grant of an FDA or EMA regulatory approval. In addition, we have the right to terminate the agreement if the Licensee directly or indirectly infringes upon our intellectual property rights or challenges their validity or, in relation to a particular Product and a particular Territory at any time, because the Licensee has made a determination that it no longer wishes to develop and/or commercialize the Product in that country in the Territory. The CMS License Agreement also includes customary indemnification for a transaction of this type.
Sales and Marketing
We do not currently have any internal sales and marketing organization or distribution capabilities.
Research and Development
We have development and pilot scale manufacturing facilities for Q-Sphera and MidaCore products in Cardiff, Wales.
Intellectual Property
Our success depends in large part on our ability to obtain and maintain proprietary protection for our product candidates (and products derived therefrom), technology and know-how, to operate without infringing the proprietary rights of others and to prevent others from infringing our proprietary rights. We strive to protect the proprietary technology that we believe is important to our business by, among other methods, seeking and maintaining patents, where available, that are intended to cover our product candidates (and products derived therefrom), compositions and formulations, their methods of use and processes for their manufacture and any other inventions that are commercially important to the development of our business. We also rely on trade secrets, know-how, continuing technological innovation and in-licensing opportunities to develop and maintain our proprietary and competitive position.
We have developed a strong intellectual property base globally, comprising patents, know-how, and trade secrets. Currently, we have 72 granted patents, 29 applications in process, in each case covering all major world markets, and 21 separate patent families covering all major regions. We continue to strengthen our patent portfolio by strategically submitting new patents and divisional patent applications based on our active research and development activities. Central to our business are our three intellectual property technologies that are designed to enable the targeted delivery, i.e. right place, and controlled sustained release, i.e. right time, of existing therapeutic drugs. These technologies have broad applications in multiple therapeutic areas and offer the potential to create multiple revenue opportunities.
Patent rights have been granted in all the major world markets, including Europe, the United States and Japan, or the Key Markets. They confer a broad position of exclusivity for metal-core glycated-nanoparticles, including our GNPs. The granted patents and pending patent applications in our patent families are owned solely by us, co-owned with other parties or in-licensed to us. These include:
| • | Sustained release technology. Eight patent families which protect devices, methods and formulations for sustained release drug delivery. |
| • | Oncology including Nano-inclusion technology. Six patent families, which have predicted expiration dates extending to 2040. These patent rights include 12 granted patents and seven pending applications in Key Markets relating to products and methods for treating and imaging cancers. |
| • | Nanoparticle technology. Five patent families, with expiration dates extending to 2039. These patent families include 12 granted patents and two pending patent applications in Key Markets. |
We also have in our portfolio several vaccine and infectious disease related patent families. These relate to GNPs for immune-based therapy and antibiotic-GNP conjugates. We acquired through the Q Chip transaction patent applications directed to the apparatus and methods of “Q-Sphera” technology, which employs a piezoelectric droplet generator to form polymeric microparticles that encapsulate a drug for sustained release. The combination of our GNP technology with Midatech Wales’ sustained release technology has provided possibilities for new formulations of GNP-drug conjugates. Our GNPs, when encapsulated in Midatech Wales’ microparticles, enjoy patent protection conferred by the existing granted patents.
The term of individual patents depends upon the legal term for patents in the countries in which they are obtained. In most countries, including the United States, the patent term is 20 years from the filing date of a non-provisional patent application. In the United States, a patent’s term may, in certain cases, be lengthened by patent term adjustment, which compensates a patentee for administrative delays by the United States Patent and Trademark Office in examining and granting a patent, or may be shortened if a patent is terminally disclaimed over an earlier filed patent.
The term of a United States patent that covers a drug, biological product or medical device approved pursuant to a pre-market approval may also be eligible for patent term extension when FDA approval is granted, provided that certain statutory and regulatory requirements are met. The length of the patent term extension is related to the length of time the drug is under regulatory review while the patent is in force. The Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984 permits a patent term extension of up to five years beyond the expiration date set for the patent. Patent extension cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the date of product approval, only one patent applicable to each regulatory review period may be granted an extension and only those claims reading on the approved drug may be extended. Similar provisions are available in Europe and certain other foreign jurisdictions to extend the term of a patent that covers an approved drug, provided that statutory and regulatory requirements are met. Thus, in the future, if and when our product candidates receive approval by the FDA or foreign regulatory authorities, we expect to apply for patent term extensions on issued patents covering those products, depending upon the length of the clinical trials for each drug and other factors. The expiration dates of our patents and patent applications referred to above are without regard to potential patent term extension or other market exclusivity that may be available to us.
In addition to patents, we may rely, in some circumstances, on trade secrets to protect our technology and maintain our competitive position. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by confidentiality agreements with our employees, corporate and scientific collaborators, consultants, scientific advisors, contractors and other third parties. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems.
Government Regulations
Government authorities in the United States, at the federal, state and local level, and in other countries and jurisdictions, including the European Union and the United Kingdom, extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, quality control, approval, packaging, storage, recordkeeping, labeling, advertising, promotion, distribution, marketing, post-approval monitoring and reporting, and import and export of pharmaceutical products. The processes for obtaining regulatory approvals in the United States and in foreign countries and jurisdictions, along with subsequent compliance with applicable statutes and regulations and other regulatory authorities, require the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources. As we have disclosed herein, we are seeking to license our product candidates and other formulations to licensing partners. While many of the rules and regulations set forth herein do and will apply to us, some are more applicable to any licensing partner who seeks to conduct clinical trials of, obtain regulatory approval for and commercialize any of our product candidates, which could have an impact on any licensing revenue received by us.
Review and Approval of Drugs in the United States
In the United States, the FDA regulates drugs under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, or the FDCA, and implementing regulations. Failure to comply with the applicable United States requirements at any time during the product development process, approval process or after approval may subject an applicant and/or sponsor to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, including refusal by the FDA to approve pending applications, withdrawal of an approval, imposition of a clinical hold, issuance of warning letters and other types of letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, refusals of government contracts, restitution, disgorgement of profits, exclusion from participation in government sponsored insurance programs such as Medicare, or civil or criminal investigations and penalties brought by the FDA and the Department of Justice, or the DOJ, or other governmental entities.
An applicant seeking approval to market and distribute a new drug product in the United States must typically undertake the following:
| • | completion of preclinical laboratory tests, animal studies and formulation studies in compliance with the FDA’s good laboratory practice, or GLP, regulations; |
| • | submission to the FDA of an IND application, which must take effect before human clinical trials may begin; |
| • | approval of clinical protocols by an independent institutional review board, or IRB, or ethics committee representing each clinical site before each site may enroll subjects; |
| • | potential initiation and completion of successive clinical trials that establish safety dose ranges; |
| • | performance of adequate and well-controlled human clinical trials in accordance with good clinical practices, or GCP, and other clinical-trial related regulations to establish the safety and efficacy of the proposed drug product for each indication; |
| • | preparation and submission to the FDA of a new drug application, or NDA, or a biologics license application, or BLA; |
| • | review of the submission by an FDA advisory committee, where appropriate or if applicable; |
| • | satisfactory completion of one or more FDA inspections of the manufacturing facility or facilities at which the product, or components thereof, are produced to assess compliance with cGMP requirements and to assure that the facilities, methods and controls are adequate to preserve the product’s identity, strength, quality and purity; |
| • | satisfactory completion of FDA audits of clinical trial sites to assure compliance with GCPs and the integrity of the clinical data; |
| • | payment of user fees and securing FDA approval of the NDA or BLA; |
| • | agree to comply with any post-approval requirements, including Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies, or REMS, and post-approval studies required by the FDA; and |
| • | FDA review and approval of the NDA or licensure of the BLA. |
Preclinical Studies
Preclinical studies include laboratory evaluation of the purity and stability of the manufactured drug substance or API and the formulated finished drug or drug product, as well as in vitro and animal studies to assess the safety and activity of the drug for initial testing in humans and to establish a rationale for therapeutic use. The conduct of preclinical studies is subject to federal and state regulations and requirements, including GLP regulations. The results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information, analytical data, any available clinical data or literature and plans for clinical trials, among other things, are submitted to the FDA as part of an IND. An IND is a request for authorization from the FDA to administer an investigational product to humans and must become effective before human clinical trials may begin. Some long-term preclinical testing, such as animal tests of reproductive adverse events and carcinogenicity, may continue after the IND is submitted.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act for 2023, signed into law on December 29, 2022, (P.L. 117-328) amended the FDCA and the Public Health Service Act to specify that nonclinical testing for drugs and biologics may, but is not required to, include in vivo animal testing. According to the amended language, a sponsor may fulfill nonclinical testing requirements by completing various in vitro assays (e.g., cell-based assays, organ chips, or microphysiological systems), in silico studies (i.e., computer modeling), other human or nonhuman biology-based tests (e.g., bioprinting), or in vivo animal tests.
Human Clinical Trials in Support of an NDA
Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational product to human subjects under the supervision of qualified investigators in accordance with GCP requirements, which include, among other things, the requirement that all research subjects provide their informed consent in writing before their participation in any clinical trial. Clinical trials are conducted under written study protocols detailing, among other things, the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the objectives of the study, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. A protocol for each clinical trial and any subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND. An IND automatically becomes effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless before that time the FDA raises concerns or questions related to a proposed clinical trial and places the clinical trial on clinical hold. In such a case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before the clinical trial can begin. Accordingly, submission of an IND may not result in the FDA allowing clinical trials to commence. A separate submission to an existing IND must also be made for each successive clinical trial conducted during product development of a product candidate, and the FDA must grant permission, either explicitly or implicitly by not objecting, before each clinical trial can begin.
Following commencement of a clinical trial, the FDA may also place a clinical hold or partial clinical hold on that trial. A clinical hold is an order issued by the FDA to the sponsor to delay a proposed clinical investigation or to suspend an ongoing investigation. A partial clinical hold is a delay or suspension of only part of the clinical work requested under the IND. No more than 30 days after imposition of a clinical hold or partial clinical hold, the FDA will provide the sponsor a written explanation of the basis for the hold. Following issuance of a clinical hold or partial clinical hold, an investigation may only resume after the FDA has notified the sponsor that the investigation may proceed.
In addition, an IRB representing each institution participating in the clinical trial must review and approve the plan for any clinical trial before it commences at that institution, and the IRB must conduct a continuing review and reapprove the study at least annually. The IRB must review and approve, among other things, the study protocol and informed consent information to be provided to study subjects. An IRB must operate in compliance with FDA regulations.
Some trials are overseen by an independent group of qualified experts organized by the trial sponsor, known as a data safety monitoring board or committee, or DSMB. This group provides authorization as to whether or not a trial may move forward at designated check points based on access that only the group maintains to available data from the study.
Information about certain clinical trials, including details of the protocol and eventually study results, must be submitted within specific timeframes to the National Institutes of Health for public dissemination on their ClinicalTrials.gov website. Information related to the product, patient population, phase of investigation, study sites and investigators and other aspects of the clinical trial is made public as part of the registration of the clinical trial. Sponsors are also obligated to disclose the results of their clinical trials after completion. Disclosure of the results of these trials can be delayed in some cases for up to two years after the date of completion of the trial. Failure to timely register a covered clinical study or to submit study results as provided for in the law can give rise to civil monetary penalties and also prevent the non-compliant party from receiving future grant funds from the federal government. The NIH’s Final Rule on ClinicalTrials.gov registration and reporting requirements became effective in 2017, and both NIH and FDA have recently begun enforcing those requirements against non-compliant clinical trial sponsors.
Human clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases, Phase I, Phase II and Phase III, which may overlap or be combined:
| • | Phase I. The product candidate is initially introduced into healthy human subjects and tested for safety, dosage tolerance, absorption, metabolism, distribution and excretion. In the case of some product candidates for severe or life-threatening diseases, especially when the product candidate may be too inherently toxic to ethically administer to healthy volunteers, the initial human testing is often conducted in patients. |
| • | Phase II. The product candidate is evaluated in a limited patient population to identify possible adverse effects and safety risks, to preliminarily evaluate the efficacy of the product candidate for specific targeted diseases and to determine dosage tolerance, optimal dosage and dosing schedule. |
| • | Phase III. Clinical trials are undertaken to further evaluate dosage, clinical efficacy, potency, and safety in an expanded patient population at geographically dispersed clinical trial sites. These clinical trials are intended to establish the overall risk/benefit ratio of the product candidate and provide, if appropriate, an adequate basis for approval and product labeling. These trials may include comparisons with placebo and/or other comparator treatments. The duration of treatment is often extended to mimic the actual use of a product during marketing. |
Post-approval clinical trials, sometimes referred to as Phase IV clinical trials, may be conducted after initial marketing approval. These clinical trials are used to gain additional experience from the treatment of patients in the intended therapeutic indication, particularly for long-term safety follow-up. In certain instances, the FDA may mandate the performance of Phase IV clinical trials as a condition of approval of an NDA or BLA.
In the Consolidated Appropriations Act for 2023, Congress amended the FDCA to require sponsors of a Phase 3 clinical trial, or other “pivotal study” of a new drug to support marketing authorization, to submit a diversity action plan for such clinical trial. The action plan must include the sponsor’s diversity goals for enrollment, as well as a rationale for the goals and a description of how the sponsor will meet them. A sponsor must submit a diversity action plan to FDA by the time the sponsor submits the trial protocol to the agency for review. The FDA may grant a waiver for some or all of the requirements for a diversity action plan. It is unknown at this time how the diversity action plan may affect Phase 3 trial planning and timing or what specific information FDA will expect in such plans, but if FDA objects to a sponsor’s diversity action plan and requires the sponsor to amend the plan or take other actions, it may delay trial initiation.
Progress reports detailing the results of the clinical trials must be submitted at least annually to the FDA and more frequently if serious adverse events occur. In addition, IND safety reports must be submitted to the FDA for any of the following: serious and unexpected suspected adverse reactions; findings from other studies or animal or in vitro testing that suggest a significant risk in humans exposed to the drug; and any clinically important increase in the case of a serious suspected adverse reaction over that listed in the protocol or investigator brochure. Phase I, Phase II and Phase III clinical trials may not be completed successfully within any specified period, or at all. Furthermore, the FDA or the sponsor may suspend or terminate a clinical trial at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the research subjects are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical trial at its institution, or an institution it represents, if the clinical trial is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB’s requirements or if the drug has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients. The FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP and the integrity of the clinical data submitted.
Submission of an NDA or BLA to the FDA
Assuming successful completion of required clinical testing and other requirements, the results of the preclinical studies and clinical trials, together with detailed information relating to the product’s chemistry, manufacture, controls and proposed labeling, among other things, are submitted to the FDA as part of an NDA or BLA requesting approval to market the product candidate for one or more indications. Data may come from company-sponsored clinical trials intended to test the safety and effectiveness of a use of a product, or from a number of alternative sources, including studies initiated by investigators. To support marketing approval, the data submitted must be sufficient in quality and quantity to establish the safety and effectiveness of the investigational drug product to the satisfaction of the FDA. In particular, a BLA must contain proof of the biological product candidate’s safety, purity, potency and efficacy for its proposed indication or indications. Under federal law, the submission of most NDAs is additionally subject to an application user fee, , and the sponsor of an approved NDA is also subject to annual product and establishment user fees. These fees are typically increased annually. Certain exceptions and waivers are available for some of these fees, such as an exception from the application fee for products with orphan designation and a waiver of the application fee for the first application filed by a qualifying small business.
The FDA conducts a preliminary review of an NDA within 60 days of its receipt and informs the sponsor by the 74th day after the FDA’s receipt of the submission whether the application is sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. The FDA may request additional information rather than accept an NDA for filing. In this event, the application must be resubmitted with the additional information. The resubmitted application is also subject to review before the FDA accepts it for filing. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins an in-depth substantive review. The FDA has agreed to specified performance goals in the review process of NDAs and BLAs. Most such applications are meant to be reviewed within ten months from the date of filing, and most applications for “priority review” products are meant to be reviewed within six months of filing. Despite these review goals, it is not uncommon for FDA review of an NDA or BLA to extend beyond the goal date. For instance, the review process may be extended by the FDA for three additional months to consider new information or clarification provided by the applicant to address an outstanding deficiency identified by the FDA following the original submission.
The FDA may refer applications for novel drug or biological products or drug or biological products which present difficult questions of safety or efficacy to an advisory committee, typically a panel that includes independent clinicians and other experts, for review, evaluation and a recommendation as to whether the application should be approved and under what conditions. The FDA is not bound by the recommendations of an advisory committee, but it considers such recommendations carefully when making decisions and typically follows the advisory committee’s recommendations.
Before approving an NDA, the FDA typically will inspect the facility or facilities where the product is or will be manufactured. These pre-approval inspections cover all facilities associated with an NDA or BLA submission, including drug or biologic component manufacturing (such as APIs), finished product manufacturing, and control testing laboratories. The FDA will not approve an application unless it determines that the manufacturing processes and facilities are in compliance with cGMP requirements and adequate to assure consistent production of the product within required specifications. Additionally, before approving an NDA, the FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP.
Fast Track, Breakthrough Therapy and Priority Review Designations
The FDA is authorized to designate certain products for expedited review if they are intended to address an unmet medical need in the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition. These programs are fast track designation, breakthrough therapy designation and priority review designation.
Specifically, the FDA may designate a product for fast track review if it is intended, whether alone or in combination with one or more other drugs, for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and it demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs by providing a therapy where none exists or a therapy that may be potentially superior to existing therapy based on efficacy or safety factors. For fast track products, sponsors may have more frequent interactions with the FDA and the FDA may initiate review of sections of a fast track product’s NDA or BLA before the application is complete. This rolling review may be available if the FDA determines, after preliminary evaluation of clinical data submitted by the sponsor, that a fast track product may be effective. The sponsor must also provide, and the FDA must approve, a schedule for the submission of the remaining information and the sponsor must pay applicable user fees. However, the FDA’s time period goal for reviewing a fast track application does not begin until the last section of the NDA is submitted. In addition, the fast track designation may be withdrawn by the FDA if the FDA believes that the designation is no longer supported by data emerging in the clinical trial process.
The FDA may grant breakthrough therapy designation to a drug or biologic meeting certain statutory criteria upon a request made by the IND sponsor. A product may be designated as a breakthrough therapy if it is intended, either alone or in combination with one or more other drugs, to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the product may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. The FDA may take certain actions with respect to breakthrough therapies, including holding meetings with the sponsor throughout the development process; providing timely advice to the product sponsor regarding development and approval; involving more senior staff in the review process; assigning a cross-disciplinary project lead for the review team; and taking other steps to design the clinical trials in an efficient manner. In addition, breakthrough therapies are eligible for accelerated approval of their respective marketing applications.
The FDA may designate a product for priority review if it is a drug that treats a serious condition and, if approved, would provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness. The FDA determines, at the time that the marketing application is submitted, on a case- by-case basis, whether the proposed drug represents a significant improvement when compared with other available therapies. Significant improvement may be illustrated by evidence of increased effectiveness in the treatment of a condition, elimination or substantial reduction of a treatment-limiting drug reaction, documented enhancement of patient compliance that may lead to improvement in serious outcomes, or evidence of safety and effectiveness in a new subpopulation. A priority designation is intended to direct overall attention and resources to the evaluation of such applications, and to shorten the FDA’s goal for taking action on a marketing application from ten months to six months for an original BLA or for an NME NDA from the date of filing.
Even if a product qualifies for one or more of these programs, the FDA may later decide that the product no longer meets the conditions for qualification or decide that the time period for FDA review or approval will not be shortened. Furthermore, fast track designation, breakthrough therapy designation, and priority review do not change the scientific or medical standards for approval or the quality of evidence necessary to support approval but may expedite the development or review process.
Accelerated Approval Pathway
The FDA may grant accelerated approval to a drug or biologic for a serious or life-threatening condition that provides meaningful therapeutic advantage to patients over existing treatments based upon a determination from well-controlled clinical trials that the drug has an effect on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit. The FDA may also grant accelerated approval for such a drug or biologic when the product has an effect on an intermediate clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality, or IMM, and that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments. Drugs and biologics granted accelerated approval must meet the same statutory standards for safety and effectiveness as those granted traditional approval.
For the purposes of accelerated approval, a surrogate endpoint is a marker, such as a laboratory measurement, radiographic image, physical sign, or other measure that is thought to predict clinical benefit, but is not itself a measure of clinical benefit. Surrogate endpoints can often be measured more easily or more rapidly than clinical endpoints. An intermediate clinical endpoint is a measurement of a therapeutic effect that is considered reasonably likely to predict the clinical benefit of a drug or biologic, such as an effect on IMM. The FDA has limited experience with accelerated approvals based on intermediate clinical endpoints, but has indicated that such endpoints generally may support accelerated approval where the therapeutic effect measured by the endpoint is not itself a clinical benefit and basis for traditional approval, if there is a basis for concluding that the therapeutic effect is reasonably likely to predict the ultimate clinical benefit of a drug or biologic.
The accelerated approval pathway is most often used in settings in which the course of a disease is long and an extended period of time is required to measure the intended clinical benefit of a drug, even if the effect on the surrogate or intermediate clinical endpoint occurs rapidly. For example, accelerated approval has been used extensively in the development and approval of drugs for treatment of a variety of cancers in which the goal of therapy is generally to improve survival or decrease morbidity and the duration of the typical disease course requires lengthy and sometimes large clinical trials to demonstrate a clinical or survival benefit.
The accelerated approval pathway is usually contingent on a sponsor’s agreement to conduct, in a diligent manner, additional post-approval confirmatory studies to verify and describe the drug’s clinical benefit. As a result, a drug candidate approved on this basis is subject to rigorous post-marketing compliance requirements, including the completion of Phase IV or post-approval clinical trials to confirm the effect on the clinical endpoint. Failure to conduct required post-approval studies, or confirm a clinical benefit during post-marketing studies, would allow the FDA to withdraw the drug from the market on an expedited basis. All promotional materials for drug candidates approved under accelerated regulations are subject to prior review by the FDA. As part of the Consolidated Appropriations Act for 2023, Congress provided FDA additional statutory authority to mitigate potential risks to patients from continued marketing of ineffective drugs previously granted accelerated approval. Under the act’s amendments to the FDCA, FDA may require the sponsor of a product granted accelerated approval to have a confirmatory trial underway prior to approval. The sponsor must also submit progress reports on a confirmatory trial every six months until the trial is complete, and such reports are published on FDA’s website. The amendments also give FDA the option of using expedited procedures to withdraw product approval if the sponsor’s confirmatory trial fails to verify the claimed clinical benefits of the product.
The FDA’s Decision on an NDA or BLA
The FDA reviews an NDA to determine, among other things, whether a product is safe and effective for its intended use and whether its manufacturing is cGMP-compliant to assure and preserve the product’s identity, strength, quality and purity. The FDA reviews a BLA to determine, among other things whether the product is safe, pure and potent and the facility in which it is manufactured, processed, packed or held meets standards designed to assure the product’s continued safety, purity and potency. The approval process is lengthy and often difficult, and the FDA may refuse to approve an NDA or BLA if the applicable regulatory criteria are not satisfied or may require additional clinical or other data and information. On the basis of the FDA’s evaluation of the NDA and accompanying information, including the results of the inspection of the manufacturing facilities, the FDA may issue an approval letter or a complete response letter. An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing of the product with specific prescribing information for specific indications. A complete response letter indicates that the review cycle of the application is complete and the application will not be approved in its present form. A complete response letter generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission and may require substantial additional testing or information in order for the FDA to reconsider the application. If and when those deficiencies have been addressed to the FDA’s satisfaction in a resubmission of the NDA, the FDA will issue an approval letter. The FDA has committed to reviewing such resubmissions in two or six months depending on the type of information included. Even with submission of this additional information, the FDA ultimately may decide that the application does not satisfy the regulatory criteria for approval.
If the FDA approves a product, it may limit the approved indications for use for the product, require that contraindications, warnings or precautions be included in the product labeling, require that post-approval studies, including Phase IV clinical trials, be conducted to further assess the drug’s safety after approval, require testing and surveillance programs to monitor the product after commercialization, or impose other conditions, including distribution restrictions or other risk management mechanisms, including REMS, which can materially affect the potential market and profitability of the product. The FDA may prevent or limit further marketing of a product based on the results of post-market studies or surveillance programs. The FDA may also require an applicant to develop a REMS as a condition of approval to ensure that the benefits of the product outweigh its risks and to assure its safe use. REMS use risk minimization strategies beyond the professional labeling to ensure that the benefits of the product outweigh the potential risks. To determine whether a REMS is needed, the FDA will consider the size of the population likely to use the product, seriousness of the disease, expected benefit of the product, expected duration of treatment, seriousness of known or potential adverse events, and whether the product is a new molecular entity. REMS can include medication guides, physician communication plans for healthcare professionals, and elements to assure safe use, or ETASU. ETASU may include, but are not limited to, special training or certification for prescribing or dispensing, dispensing only under certain circumstances, special monitoring, and the use of patient registries. The FDA may require a REMS before approval or post-approval if it becomes aware of a serious risk associated with use of the product. If the FDA concludes a REMS is needed as a condition of approval, the sponsor must submit a proposed REMS during the application review process; the FDA will not approve the NDA without an approved REMS, if required. The requirement for a REMS can materially affect the potential market and profitability of a product. After approval, many types of changes to the approved product, such as adding new indications, manufacturing changes and additional labeling claims, are subject to further testing requirements and FDA review and approval.
Post-Approval Requirements
Drugs or biologics manufactured or distributed pursuant to FDA approvals are subject to pervasive and continuing regulation by the FDA, including, among other things, requirements relating to recordkeeping, periodic reporting, product sampling and distribution, advertising and promotion and reporting of adverse experiences with the product. After approval, most changes to the approved product, such as adding new indications or other labeling claims, are subject to prior FDA review and approval. There also are continuing, annual program fee requirements for any marketed products, as well as new application fees for supplemental applications with clinical data.
In addition, drug and biologic manufacturers and other entities involved in the manufacture and distribution of approved drugs or biologics are required to register their establishments with the FDA and state agencies, and are subject to periodic prescheduled or unannounced inspections by the FDA and the relevant state agencies for compliance with cGMP and other regulatory requirements. Changes to the manufacturing process are strictly regulated and often require prior FDA approval before being implemented. FDA regulations also require investigation and correction of any deviations from cGMP and impose reporting and documentation requirements upon the sponsor and any third-party manufacturers that the sponsor may decide to use. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money and effort in the area of production and quality control to maintain cGMP compliance.
Once an approval is granted, the FDA may withdraw the approval if compliance with regulatory requirements and standards is not maintained or if problems occur after the product reaches the market. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with a product, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in revisions to the approved labeling to add new safety information; imposition of post-market studies or clinical trials to assess new safety risks; or imposition of distribution or other restrictions under a REMS program. Other potential consequences include, among other things:
| • | restrictions on the marketing or manufacturing of the product, complete withdrawal of the product from the market or product recalls; |
| • | fines, warning letters or holds on post-approval clinical trials; |
| • | refusal of the FDA to approve pending NDAs or supplements to approved NDAs, or suspension or revocation of product license approvals; |
| • | product seizure or detention, or refusal to permit the import or export of products; or |
| • | injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties. |
The FDA strictly regulates marketing, labeling, advertising and promotion of products that are placed on the market, and we must comply with the FDA’s advertising and promotion requirements, such as those related to direct-to-consumer advertising, industry-sponsored scientific and educational activities, and promotional activities involving the internet, as well as the prohibition on promoting products for uses or in patient populations that are not described in the product’s approved labeling (known as “off-label use”). Drugs and biologics may be promoted only for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved label. Although physicians may prescribe legally available products for off-label uses, manufacturers may not market or promote such uses. The FDA and other agencies actively enforce the laws and regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses, and a company that is found to have improperly promoted off-label uses may be subject to significant liability.
In addition, the distribution of prescription pharmaceutical products is subject to the Prescription Drug Marketing Act, or PDMA, which regulates the distribution of drugs and drug samples at the federal level, and sets minimum standards for the registration and regulation of drug distributors by the states. Both the PDMA and state laws limit the distribution of prescription pharmaceutical product samples and impose requirements to ensure accountability in distribution. Furthermore, the Drug Supply Chain Security Act, or DSCSA, was enacted with the aim of building an electronic system to identify and trace certain prescription drugs distributed in the United States, including most biological products. The DSCSA mandates phased-in and resource-intensive obligations for pharmaceutical manufacturers, wholesale distributors, and dispensers over a 10-year period that is expected to culminate in November 2023. From time to time, new legislation and regulations may be implemented that could significantly change the statutory provisions governing the approval, manufacturing and marketing of products regulated by the FDA. It is impossible to predict whether further legislative or regulatory changes will be enacted, or FDA regulations, guidance or interpretations changed or what the impact of such changes, if any, may be.
Abbreviated New Drug Applications for Generic Drugs
In 1984, with passage of the Hatch-Waxman amendments to the FDCA, Congress authorized the FDA to approve generic drugs that are the same as drugs previously approved by the FDA under the NDA provisions of the statute and also enacted Section 505(b)(2) of the FDCA. To obtain approval of a generic drug, an applicant must submit an abbreviated new drug application, or ANDA, to the agency. In support of such applications, a generic manufacturer may rely on the preclinical and clinical testing previously conducted for a drug product previously approved under an NDA, known as the reference listed drug, or RLD.
Specifically, in order for an ANDA to be approved, the FDA must find that the generic version is identical to the RLD with respect to the active ingredients, the route of administration, the dosage form, and the strength of the drug. At the same time, the FDA must also determine that the generic drug is “bioequivalent” to the innovator drug. Under the statute, a generic drug is bioequivalent to a RLD if “the rate and extent of absorption of the drug do not show a significant difference from the rate and extent of absorption of the listed drug.”
Upon approval of an ANDA, the FDA indicates whether the generic product is “therapeutically equivalent” to the RLD in its publication “Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations,” also referred to as the “Orange Book.” Physicians and pharmacists consider a therapeutic equivalent generic drug to be fully substitutable for the RLD. In addition, by operation of certain state laws and numerous health insurance programs, the FDA’s designation of therapeutic equivalence often results in substitution of the generic drug without the knowledge or consent of either the prescribing physician or patient.
In contrast, Section 505(b)(2) permits the filing of an NDA where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference. A Section 505(b)(2) applicant may eliminate the need to conduct certain preclinical or clinical studies, if it can establish that reliance on studies conducted for a previously-approved product is scientifically appropriate. Unlike the ANDA pathway used by developers of bioequivalent versions of innovator drugs, which does not allow applicants to submit new clinical data other than bioavailability or bioequivalence data, the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway does not preclude the possibility that a follow-on applicant would need to conduct additional clinical trials or nonclinical studies; for example, they may be seeking approval to market a previously approved drug for new indications or for a new patient population that would require new clinical data to demonstrate safety or effectiveness. The FDA may then approve the new product for all or some of the label indications for which the RLD has been approved, or for any new indication sought by the Section 505(b)(2) applicant, as applicable.
In addition, under the Hatch-Waxman amendments, the FDA may not approve an ANDA or 505(b)(2) NDA until any applicable period of non-patent exclusivity for the RLD has expired. These market exclusivity provisions under the FDCA also can delay the submission or the approval of certain applications. The FDCA provides a period of five years of non-patent data exclusivity for a new drug containing a new chemical entity. A drug is a new chemical entity if the FDA has not previously approved any other new drug containing the same active moiety, which is the molecule or ion responsible for the action of the drug substance. In cases where such exclusivity has been granted, an ANDA or 505(b)(2) NDA may not be filed with the FDA until the expiration of five years unless the submission is accompanied by a Paragraph IV certification, in which case the applicant may submit its application four years following the original product approval.
The FDCA also provides for a period of three years of exclusivity for an NDA, 505(b)(2) NDA or supplement thereto if one or more new clinical investigations, other than bioavailability or bioequivalence studies, that were conducted by or for the applicant are deemed by the FDA to be essential to the approval of the application. This three-year exclusivity period often protects changes to a previously approved drug product, such as a new dosage form, route of administration, combination or indication. This three-year exclusivity covers only the conditions of use associated with the new clinical investigations and does not prohibit the FDA from approving follow-on applications for drugs containing the original active agent. Five-year and three-year exclusivity also will not delay the submission or approval of a traditional NDA filed under Section 505(b)(1) of the FDCA. However, an applicant submitting a traditional NDA would be required to either conduct or obtain a right of reference to all of the preclinical studies and adequate and well-controlled clinical trials necessary to demonstrate safety and effectiveness.
Hatch-Waxman Patent Certification and the 30-Month Stay
Upon approval of an NDA or a supplement thereto, NDA sponsors are required to list with the FDA each patent with claims that cover the applicant’s product or an approved method of using the product. Each of the patents listed by the NDA sponsor is published in the Orange Book. When an ANDA applicant files its application with the FDA, the applicant is required to certify to the FDA concerning any patents listed for the reference product in the Orange Book, except for patents covering methods of use for which the ANDA applicant is not seeking approval. To the extent that the Section 505(b)(2) NDA applicant is relying on studies conducted for an already approved product, the applicant is required to certify to the FDA concerning any patents listed for the approved product in the Orange Book to the same extent that an ANDA applicant would.
Specifically, the applicant must certify with respect to each patent that:
| I. | the required patent information has not been filed by the original applicant; |
| II. | the listed patent has expired; |
III. the listed patent has not expired, but will expire on a particular date and approval is sought after patent expiration; or
IV. listed patent is invalid, unenforceable or will not be infringed by manufacture, use or sale of the new product.
If a Paragraph I or II certification is filed, the FDA may make approval of the application effective immediately upon completion of its review. If a Paragraph III certification is filed, the approval may be made effective on the patent expiration date specified in the application, although a tentative approval may be issued before that time. If an application contains a Paragraph IV certification, a series of events will be triggered, the outcome of which will determine the effective date of approval of the ANDA or 505(b)(2) application.
A certification that the new product will not infringe the already approved product’s listed patents or that such patents are invalid or unenforceable is called a Paragraph IV certification. If the follow-on applicant has provided a Paragraph IV certification to the FDA, the applicant must also send notice of the Paragraph IV certification to the NDA and patent holders once the follow-on application in question has been accepted for filing by the FDA. The NDA and patent holders may then initiate a patent infringement lawsuit in response to the notice of the Paragraph IV certification. The filing of a patent infringement lawsuit within 45 days after the receipt of a Paragraph IV certification automatically prevents the FDA from approving the ANDA or 505(b)(2) NDA until the earlier of 30 months after the receipt of the Paragraph IV notice, expiration of the patent or a decision in the infringement case that is favorable to the ANDA or 505(b)(2) applicant. Alternatively, if the listed patent holder does not file a patent infringement lawsuit within the required 45-day period, the follow-on applicant’s ANDA or 505(b)(2) NDA will not be subject to the 30-month stay.
Reference Product Exclusivity for Biological Products
In March 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, or ACA, was enacted in the United States and included the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009, or the BPCIA. The BPCIA amended the PHSA to create an abbreviated approval pathway for biological products that are biosimilar to or interchangeable with an FDA-licensed reference biological product. To date, the FDA has approved a number of biosimilars, and numerous biosimilars have been approved in Europe. The FDA has also issued several guidance documents outlining its approach to reviewing and approving biosimilars and interchangeable biosimilars.
A biosimilar product is defined as one that is highly similar to a reference product notwithstanding minor differences in clinically inactive components and for which there are no clinically meaningful differences between the biological product and the reference product in terms of the safety, purity and potency of the product. An interchangeable product is a biosimilar product that can be expected to produce the same clinical results as the reference product in any given patient and, for products administered multiple times to an individual, that the product and the reference product may be alternated or switched after one has been previously administered without increasing safety risks or risks of diminished efficacy relative to exclusive use of the reference biological product without such alternation or switch. Upon licensure by the FDA, an interchangeable biosimilar may be substituted for the reference product without the intervention of the healthcare provider who prescribed the reference product, although to date no such products have been approved for marketing in the United States.
The biosimilar applicant must demonstrate that the product is biosimilar based on data from (1) analytical studies showing that the biosimilar product is highly similar to the reference product; (2) animal studies (including toxicity); and (3) one or more clinical studies to demonstrate safety, purity and potency in one or more appropriate conditions of use for which the reference product is approved. In addition, the applicant must show that the biosimilar and reference products have the same mechanism of action for the conditions of use on the label, route of administration, dosage and strength, and the production facility must meet standards designed to assure product safety, purity and potency.
A reference biological product is granted 12 years of data exclusivity from the time of first licensure of the product, and the first approved interchangeable biologic product will be granted an exclusivity period of up to one year after it is first commercially marketed. As part of the Consolidated Appropriations Act for 2023, Congress amended the PHSA in order to permit multiple interchangeable products approved on the same day to receive and benefit from this one-year exclusivity period. If pediatric studies are performed and accepted by the FDA as responsive to a Written Request, the 12-year exclusivity period will be extended for an additional six months. In addition, the FDA will not accept an application for a biosimilar or interchangeable product based on the reference biological product until four years after the date of first licensure of the reference product. “First licensure” typically means the initial date the particular product at issue was licensed in the United States. Date of first licensure does not include the date of licensure of (and a new period of exclusivity is not available for) a supplement for the reference product for a subsequent application filed by the same sponsor or manufacturer of the reference product (or licensor, predecessor in interest or other related entity) for a change (not including a modification to the structure of the biological product) that results in a new indication, route of administration, dosing schedule, dosage form, delivery system, delivery device or strength or for a modification to the structure of the biological product that does not result in a change in safety, purity or potency. Therefore, one must determine whether a new product includes a modification to the structure of a previously licensed product that results in a change in safety, purity or potency to assess whether the licensure of the new product is a first licensure that triggers its own period of exclusivity. Whether a subsequent application, if approved, warrants exclusivity as the “first licensure” of a biological product is determined on a case-by-case basis with data submitted by the sponsor.
The BPCIA is complex and is still being interpreted and implemented by the FDA. In addition, recent government proposals have sought to reduce the 12-year reference product exclusivity period. Other aspects of the BPCIA, some of which may impact the BPCIA exclusivity provisions, have also been the subject of recent litigation. As a result, the ultimate impact, implementation and meaning of the BPCIA is subject to significant uncertainty.
Pediatric Studies and Exclusivity
Under the Pediatric Research Equity Act, or PREA, amendments to the FDCA, an NDA, BLA or supplement thereto must contain data that are adequate to assess the safety and effectiveness of the drug product for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations, and to support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the product is safe and effective. With enactment of the FDASIA in 2012, PREA was made permanent and sponsors are required submit pediatric study plans to FDA prior to the assessment data. In particular, a sponsor that is planning to submit a marketing application for a product that includes a new active ingredient, new indication, new dosage form, new dosing regimen or new route of administration submit an initial Pediatric Study Plan, or PSP, within 60 days of an end-of-Phase II meeting or, if there is no such meeting, as early as practicable before the initiation of the Phase III or Phase II/III study. The initial PSP must contain an outline of the proposed pediatric study or studies the applicant plans to conduct, including study objectives and design, age groups, relevant endpoints and statistical approach, or a justification for not including such detailed information and any request for a deferral of pediatric assessments or a full or partial waiver of the requirement to provide data from pediatric studies along with supporting information. The FDA and the sponsor must reach an agreement on the PSP. A sponsor can submit amendments to an agreed-upon initial PSP at any time if changes to the pediatric plan need to be considered based on data collected from preclinical studies, early phase clinical trials and/or other clinical development programs.
The FDA may, on its own initiative or at the request of the applicant, grant deferrals for submission of some or all pediatric data until after approval of the product for use in adults, or full or partial waivers from the pediatric data requirements. The law now requires the FDA to send a PREA Non-Compliance letter to sponsors who have failed to submit their pediatric assessments required under PREA, have failed to seek or obtain a deferral or deferral extension or have failed to request approval for a required pediatric formulation. It further requires the FDA to publicly post the PREA Non-Compliance letter and sponsor’s response. Unless otherwise required by regulation, the pediatric data requirements do not apply to products with orphan designation, although FDA has recently taken steps to limit what it considers abuse of this statutory exemption in PREA by announcing that it does not intend to grant any additional orphan drug designations for rare pediatric subpopulations of what is otherwise a common disease.
In addition, pediatric exclusivity is another type of non-patent marketing exclusivity in the United States that, if granted, provides for the attachment of an additional six months of marketing protection to the term of any existing regulatory exclusivity or listed patents. This six-month exclusivity may be granted if an NDA sponsor submits pediatric data that fairly respond to a Written Request from the FDA for such data. The data do not need to show the product to be effective in the pediatric population studied; rather, if the clinical trial is deemed to fairly respond to the FDA’s request, the additional protection is granted. If reports of requested pediatric studies are submitted to and accepted by the FDA within the statutory time limits, whatever statutory or regulatory periods of exclusivity or patent protection cover the product are extended by six months, including orphan drug exclusivity. This is not a patent term extension, but it effectively extends the regulatory period during which the FDA cannot approve another application. The FDA’s issuance of a Written Request does not require the sponsor to undertake the described studies.
Orphan Drug Designation and Exclusivity
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may designate a drug product as an “orphan drug” if it is intended to treat a rare disease or condition (generally meaning that it affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States, or more in cases in which there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing and making a drug product available in the United States for treatment of the disease or condition will be recovered from sales of the product). A company must request orphan product designation before submitting an NDA. If the request is granted, the FDA will disclose the identity of the therapeutic agent and its potential use. Orphan product designation does not convey any advantage in or shorten the duration of the regulatory review and approval process.
If a product with orphan designation subsequently receives the first FDA approval for the disease or condition for which it has such designation or for a select indication or use within the rare disease or condition for which it was designated, the product generally will be receiving orphan product exclusivity. Orphan product exclusivity means that the FDA may not approve any other applications for the same product for the same indication for seven years, except in certain limited circumstances, such as a showing of clinical superiority to the product with orphan exclusivity by means of greater effectiveness, greater safety or providing a major contribution to patient care or in instances of drug supply issues. Competitors, however, may receive approval of either a different product for the same indication for which the orphan product has exclusivity or for the same product but for a different indication (which could then be used off-label in the orphan indication). If a drug or drug product designated as an orphan product ultimately receives marketing approval for an indication broader than what was designated in its orphan product application, it may not be entitled to exclusivity.
Patent Term Restoration and Extension
The term of a United States patent that covers a drug, biological product or medical device approved pursuant to a PMA may also be eligible for patent term extension when FDA approval is granted, provided that certain statutory and regulatory requirements are met. The length of the patent term extension is related to the length of time the product is under regulatory review while the patent is in force. The Hatch-Waxman Act permits a patent term extension of up to five years beyond the expiration date set for the patent. Patent extension cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the date of product approval, only one patent applicable to each regulatory review period may be granted an extension and only those claims reading on the approved drug may be extended. Similar provisions are available in Europe and certain other foreign jurisdictions to extend the term of a patent that covers an approved drug, provided that statutory and regulatory requirements are met. The United States Patent and Trade Office reviews and approves the application for any patent term extension or restoration in consultation with the FDA.
Regulation Outside the United States
In order to market any product outside of the United States, a company must also comply with numerous and varying regulatory requirements of other countries and jurisdictions regarding quality, safety and efficacy and governing, among other things, clinical trials, marketing authorization, commercial sales and distribution of drug products. Whether or not it obtains FDA approval for a product, the company would need to obtain the necessary approvals by the comparable foreign regulatory authorities before it can commence clinical trials or marketing of the product in those countries or jurisdictions. The approval process ultimately varies between countries and jurisdictions and can involve additional product testing and additional administrative review periods. The time required to obtain approval in other countries and jurisdictions might differ from and be longer than that required to obtain FDA approval. Regulatory approval in one country or jurisdiction does not ensure regulatory approval in another, but a failure or delay in obtaining regulatory approval in one country or jurisdiction may negatively impact the regulatory process in others.
Regulation and Marketing Authorization in the European Union
The process governing approval of medicinal products in the European Union follows essentially the same lines as in the United States and, likewise, generally involves satisfactorily completing each of the following:
| • | preclinical laboratory tests, animal studies and formulation studies all performed in accordance with the applicable European Union good laboratory practice regulations; |
| • | submission to the relevant national authorities of a clinical trial application, or CTA, which must be approved before human clinical trials may begin; |
| • | performance of adequate and well-controlled clinical trials to establish the safety and efficacy of the product for each proposed indication; |
| • | submission to the relevant competent authorities of a marketing authorization application, or MAA, which includes the data supporting safety and efficacy as well as detailed information on the manufacture and composition of the product in clinical development and proposed labelling; |
| • | satisfactory completion of an inspection by the relevant national authorities of the manufacturing facility or facilities, including those of third parties, at which the product is produced to assess compliance with strictly enforced current cGMP; |
| • | potential audits of the non-clinical and clinical trial sites that generated the data in support of the MAA; and |
| • | review and approval by the relevant competent authority of the MAA before any commercial marketing, sale or shipment of the product. |
Preclinical Studies
Preclinical tests include laboratory evaluations of product chemistry, formulation and stability, as well as studies to evaluate toxicity in animal studies, in order to assess the potential safety and efficacy of the product. The conduct of the preclinical tests and formulation of the compounds for testing must comply with the relevant European Union regulations and requirements. The results of the preclinical tests, together with relevant manufacturing information and analytical data, are submitted as part of the CTA.
Clinical Trial Approval
The new Clinical Trials Regulation, (EU) No 536/2014, which took effect on January 31, 2022, aims to simplify and streamline the approval of clinical trials in the European Union. The main characteristics of the regulation include: a streamlined application procedure via a single entry point, the “E.U. Portal and Database”; a single set of documents to be prepared and submitted for the application as well as simplified reporting procedures for clinical trial sponsors; and a harmonized procedure for the assessment of applications for clinical trials, which is divided in two parts. Part I is assessed by the appointed reporting Member State, whose assessment report is submitted for review by the sponsor and all other competent authorities of all European Union Member States in which an application for authorization of a clinical trial has been submitted (Concerned Member States). Part II is assessed separately by each Concerned Member State. Strict deadlines have been established for the assessment of clinical trial applications. The role of the relevant ethics committees in the assessment procedure will continue to be governed by the national law of the Concerned Member State. However, overall related timelines will be defined by the Clinical Trials Regulation.
As in the United States, similar requirements for posting clinical trial information are present in the European Union (EudraCT) website: https://eudract.ema.europa.eu/ and other countries.
PRIME Designation in the European Union
In March 2016, the EMA launched an initiative to facilitate development of product candidates in indications, often rare, for which few or no therapies currently exist. The PRIority MEdicines, or PRIME, scheme is intended to encourage drug development in areas of unmet medical need and provides accelerated assessment of products representing substantial innovation reviewed under the centralized procedure. Products from small- and medium-sized enterprises, or SMEs, may qualify for earlier entry into the PRIME scheme than larger companies. Many benefits accrue to sponsors of product candidates with PRIME designation, including but not limited to, early and proactive regulatory dialogue with the EMA, frequent discussions on clinical trial designs and other development program elements, and accelerated marketing authorization application assessment once a dossier has been submitted. Importantly, a dedicated Agency contact and rapporteur from the Committee for Human Medicinal Products, or CHMP, or Committee for Advanced Therapies, or CAT, are appointed early in PRIME scheme facilitating increased understanding of the product at EMA’s Committee level. A kick-off meeting initiates these relationships and includes a team of multidisciplinary experts at the EMA to provide guidance on the overall development and regulatory strategies.
Marketing Authorization
To obtain a marketing authorization for a product under European Union regulatory systems, an applicant must submit an MAA either under a centralized procedure administered by the EMA, or one of the procedures administered by competent authorities in the European Union Member States (decentralized procedure, national procedure or mutual recognition procedure). A marketing authorization may be granted only to an applicant established in the European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1901/2006 provides that prior to obtaining a marketing authorization in the European Union, applicants have to demonstrate compliance with all measures included in an EMA-approved Paediatric Investigation Plan, or PIP, covering all subsets of the pediatric population, unless the EMA has granted (1) a product-specific waiver, (2) a class waiver or (3) a deferral for one or more of the measures included in the PIP.
The centralized procedure provides for the grant of a single marketing authorization by the European Commission that is valid across the European Economic Area (i.e., the European Union as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway). Pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 726/2004, the centralized procedure is compulsory for specific products, including for medicines produced by certain biotechnological processes, products designated as orphan medicinal products, advanced therapy medicinal products and products with a new active substance indicated for the treatment of certain diseases, including products for the treatment of cancer. For products with a new active substance indicated for the treatment of other diseases and products that are highly innovative or for which a centralized process is in the interest of patients, the centralized procedure may be optional. The centralized procedure may at the request of the applicant also be used in certain other cases.
Under the centralized procedure, the CHMP is also responsible for several post-authorization and maintenance activities, such as the assessment of modifications or extensions to an existing marketing authorization. Under the centralized procedure in the European Union., the maximum timeframe for the evaluation of an MAA is 210 days, excluding clock stops, when additional information or written or oral explanation is to be provided by the applicant in response to questions of the CHMP. Accelerated evaluation might be granted by the CHMP in exceptional cases, when a medicinal product is of major interest from the point of view of public health and in particular from the viewpoint of therapeutic innovation. If the CHMP accepts such request, the time limit of 210 days will be reduced to 150 days, but it is possible that the CHMP can revert to the standard time limit for the centralized procedure if it considers that it is no longer appropriate to conduct an accelerated assessment. At the end of this period, the CHMP provides a scientific opinion on whether or not a marketing authorization should be granted in relation to a medicinal product. Within 15 calendar days of receipt of a final opinion from the CHMP, the European Commission must prepare a draft decision concerning an application for marketing authorization. This draft decision must take the opinion and any relevant provisions of European Union law into account. Before arriving at a final decision on an application for centralized authorization of a medicinal product the European Commission must consult the Standing Committee on Medicinal Products for Human Use. The Standing Committee is composed of representatives of the European Union Member States and chaired by a non-voting European Commission representative. The European Parliament also has a related “droit de regard.” The European Parliament's role is to ensure that the European Commission has not exceeded its powers in deciding to grant or refuse to grant a marketing authorization.
The European Commission may grant a so-called “marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances.” Such authorization is intended for products for which the applicant can demonstrate that it is unable to provide comprehensive data on the efficacy and safety under normal conditions of use, because the indications for which the product in question is intended are encountered so rarely that the applicant cannot reasonably be expected to provide comprehensive evidence, or in the present state of scientific knowledge, comprehensive information cannot be provided, or it would be contrary to generally accepted principles of medical ethics to collect such information. Consequently, marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances may be granted subject to certain specific obligations, which may include the following:
| • | the applicant must complete an identified program of studies within a time period specified by the competent authority, the results of which form the basis of a reassessment of the benefit/risk profile; |
| • | the medicinal product in question may be supplied on medical prescription only and may in certain cases be administered only under strict medical supervision, possibly in a hospital and in the case of a radiopharmaceutical, by an authorized person; and |
| • | the package leaflet and any medical information must draw the attention of the medical practitioner to the fact that the particulars available concerning the medicinal product in question are as yet inadequate in certain specified respects. |
A marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances is subject to annual review to reassess the risk-benefit balance in an annual reassessment procedure. Continuation of the authorization is linked to the annual reassessment and a negative assessment could potentially result in the marketing authorization being suspended or revoked. The renewal of a marketing authorization of a medicinal product under exceptional circumstances, however, follows the same rules as a “normal” marketing authorization. Thus, a marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances is granted for an initial five years, after which the authorization will become valid indefinitely, unless the EMA decides that safety grounds merit one additional five-year renewal.
The European Commission may also grant a so-called “conditional marketing authorization” prior to obtaining the comprehensive clinical data required for an application for a full marketing authorization. Such conditional marketing authorizations may be granted for product candidates (including medicines designated as orphan medicinal products), if (i) the risk-benefit balance of the product candidate is positive, (ii) it is likely that the applicant will be in a position to provide the required comprehensive clinical trial data, (iii) the product fulfills an unmet medical need and (iv) the benefit to public health of the immediate availability on the market of the medicinal product concerned outweighs the risk inherent in the fact that additional data are still required. A conditional marketing authorization may contain specific obligations to be fulfilled by the marketing authorization holder, including obligations with respect to the completion of ongoing or new studies, and with respect to the collection of pharmacovigilance data. Conditional marketing authorizations are valid for one year, and may be renewed annually, if the risk-benefit balance remains positive, and after an assessment of the need for additional or modified conditions and/or specific obligations. The timelines for the centralized procedure described above also apply with respect to the review by the CHMP of applications for a conditional marketing authorization.
The European Union medicines rules expressly permit the European Union Member States to adopt national legislation prohibiting or restricting the sale, supply or use of any medicinal product containing, consisting of or derived from a specific type of human or animal cell, such as embryonic stem cells. While the products we have in development do not make use of embryonic stem cells, it is possible that the national laws in certain European Union Member States may prohibit or restrict us from commercializing our products, even if they have been granted a European Union marketing authorization.
Unlike the centralized authorization procedure, the decentralized marketing authorization procedure requires a separate application to, and leads to separate approval by, the competent authorities of each European Union Member State in which the product is to be marketed. This application is identical to the application that would be submitted to the EMA for authorization through the centralized procedure. The reference European Union Member State prepares a draft assessment and drafts of the related materials within 120 days after receipt of a valid application. The resulting assessment report is submitted to the concerned European Union Member States who, within 90 days of receipt, must decide whether to approve the assessment report and related materials. If a concerned European Union Member State cannot approve the assessment report and related materials due to concerns relating to a potential serious risk to public health, disputed elements may be referred to the European Commission, whose decision is binding on all European Union Member States.
The mutual recognition procedure similarly is based on the acceptance by the competent authorities of the European Union Member States of the marketing authorization of a medicinal product by the competent authorities of other European Union Member States. The holder of a national marketing authorization may submit an application to the competent authority of a European Union Member State requesting that this authority recognize the marketing authorization delivered by the competent authority of another European Union Member State.
Regulatory Data Protection in the European Union
In the European Union, innovative medicinal products approved on the basis of a complete independent data package qualify for eight years of data exclusivity upon marketing authorization and an additional two years of market exclusivity pursuant to Directive 2001/83/EC. Regulation (EC) No 726/2004 repeats this entitlement for medicinal products authorized in accordance to the centralized authorization procedure. Data exclusivity prevents applicants for authorization of generics of these innovative products from referencing the innovator’s data to assess a generic (abridged) application for a period of eight years. During an additional two-year period of market exclusivity, a generic marketing authorization application can be submitted and authorized, and the innovator’s data may be referenced, but no generic medicinal product can be placed on the European Union market until the expiration of the market exclusivity. The overall ten-year period will be extended to a maximum of 11 years if, during the first eight years of those ten years, the marketing authorization holder obtains an authorization for one or more new therapeutic indications which, during the scientific evaluation prior to their authorization, are held to bring a significant clinical benefit in comparison with existing therapies. Even if a compound is considered to be a new chemical entity so that the innovator gains the prescribed period of data exclusivity, another company nevertheless could also market another version of the product if such company obtained marketing authorization based on an MAA with a complete independent data package of pharmaceutical tests, preclinical tests and clinical trials.
Periods of Authorization and Renewals
A marketing authorization has an initial validity for five years in principle. The marketing authorization may be renewed after five years on the basis of a re-evaluation of the risk-benefit balance by the EMA or by the competent authority of the E.U. Member State. To this end, the marketing authorization holder must provide the EMA or the competent authority with a consolidated version of the file in respect of quality, safety and efficacy, including all variations introduced since the marketing authorization was granted, at least six months before the marketing authorization ceases to be valid. The European Commission or the competent authorities of the E.U. Member States may decide, on justified grounds relating to pharmacovigilance, to proceed with one further five-year period of marketing authorization. Once subsequently definitively renewed, the marketing authorization shall be valid for an unlimited period. Any authorization which is not followed by the actual placing of the medicinal product on the E.U. market (in case of centralized procedure) or on the market of the authorizing E.U. Member State within three years after authorization ceases to be valid (the so-called sunset clause).
Pediatric Studies
Prior to obtaining a marketing authorization in the European Union, applicants have to demonstrate compliance with all measures included in an EMA-approved Paediatric Investigation Plan, or PIP, covering all subsets of the pediatric population, unless the EMA has granted a product-specific waiver, a class waiver, or a deferral for one or more of the measures included in the PIP. The respective requirements for all marketing authorization procedures are set forth in Regulation (EC) No 1901/2006, which is referred to as the Paediatric Regulation. This requirement also applies when a company wants to add a new indication, pharmaceutical form or route of administration for a medicine that is already authorized. The Paediatric Committee of the EMA, or PDCO, may grant deferrals for some medicines, allowing a company to delay development of the medicine in children until there is enough information to demonstrate its effectiveness and safety in adults. The PDCO may also grant waivers when development of a medicine in children is not needed or is not appropriate, such as for diseases that only affect the elderly population.
Before a marketing authorization application can be filed, or an existing marketing authorization can be amended, the EMA determines that companies actually comply with the agreed studies and measures listed in each relevant PIP.
Regulatory Requirements after a Marketing Authorization has been Obtained
In case an authorization for a medicinal product in the European Union is obtained, the holder of the marketing authorization is required to comply with a range of requirements applicable to the manufacturing, marketing, promotion and sale of medicinal products. These include:
| • | Compliance with the European Union’s stringent pharmacovigilance or safety reporting rules must be ensured. These rules can impose post-authorization studies and additional monitoring obligations. |
| • | The manufacturing of authorized medicinal products, for which a separate manufacturer’s license is mandatory, must also be conducted in strict compliance with the applicable European Union laws, regulations and guidance, including Directive 2001/83/EC, Directive 2003/94/EC, Regulation (EC) No 726/2004 and the European Commission Guidelines for Good Manufacturing Practice. These requirements include compliance with European Union cGMP standards when manufacturing medicinal products and active pharmaceutical ingredients, including the manufacture of active pharmaceutical ingredients outside of the European Union with the intention to import the active pharmaceutical ingredients into the European Union. |
| • | The marketing and promotion of authorized drugs, including industry-sponsored continuing medical education and advertising directed toward the prescribers of drugs and/or the general public, are strictly regulated in the European Union notably under Directive 2001/83EC, as amended, and European Union Member State laws. Direct-to-consumer advertising of prescription medicines is prohibited across the European Union. |
Orphan Drug Designation and Exclusivity
The European Commission, following an evaluation by the EMA’s Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products, has designed MTX110 as an orphan medicinal product. Pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 141/2000 and Regulation (EC) No. 847/2000, the European Commission can grant orphan medicinal product designation to products for which the sponsor can establish that it is intended for the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a life-threatening or chronically debilitating condition affecting not more than five in 10,000 people in the European Union, or a life threatening, seriously debilitating or serious and chronic condition in the European Union and that without incentives it is unlikely that sales of the drug in the European Union would generate a sufficient return to justify the necessary investment. In addition, the sponsor must establish that there is no other satisfactory method approved in the European Union of diagnosing, preventing or treating the condition, or if such a method exists, the proposed orphan drug will be of significant benefit to patients.
Orphan drug designation is not a marketing authorization. It is a designation that provides a number of benefits, including fee reductions, regulatory assistance, and the possibility to apply for a centralized European Union marketing authorization, as well as ten years of market exclusivity following a marketing authorization. During this market exclusivity period, neither the EMA, the European Commission nor the member states can accept an application or grant a marketing authorization for a similar medicinal product. A “similar medicinal product” is defined as a medicinal product containing a similar active substance or substances as those contained in an authorized orphan medicinal product and that is intended for the same therapeutic indication. The market exclusivity period for the authorized therapeutic indication may be reduced to six years if, at the end of the fifth year, it is established that the orphan designation criteria are no longer met, including where it is shown that the product is sufficiently profitable not to justify maintenance of market exclusivity. In addition, a competing similar medicinal product may in limited circumstances be authorized prior to the expiration of the market exclusivity period, including if it is shown to be safer, more effective or otherwise clinically superior to the already approved orphan drug. Furthermore, a product can lose orphan designation, and the related benefits, prior to us obtaining a marketing authorization if it is demonstrated that the orphan designation criteria are no longer met.
General Data Protection Regulation
The collection, use, disclosure, transfer, or other processing of personal data regarding individuals in the European Union, including personal health data, is subject to the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, which became effective on May 25, 2018. The GDPR is wide-ranging in scope and imposes numerous requirements on companies that process personal data, including requirements relating to processing health and other sensitive data, obtaining consent of the individuals to whom the personal data relates, providing information to individuals regarding data processing activities, implementing safeguards to protect the security and confidentiality of personal data, providing notification of data breaches, and taking certain measures when engaging third-party processors. The GDPR also imposes strict rules on the transfer of personal data to countries outside the European Union, including the U.S., and permits data protection authorities to impose large penalties for violations of the GDPR, including potential fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global revenues, whichever is greater. The GDPR also confers a private right of action on data subjects and consumer associations to lodge complaints with supervisory authorities, seek judicial remedies, and obtain compensation for damages resulting from violations of the GDPR. Compliance with the GDPR will be a rigorous and time-intensive process that may increase the cost of doing business or require companies to change their business practices to ensure full compliance.
Following the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the European Union, the GDPR has been implemented in the United Kingdom (as the UK GDPR). The UK GDPR sits alongside the United Kingdom Data Protection Act 2018 which implements certain derogations in the EU GDPR into United Kingdom law. Under the UK GDPR, companies not established in the United Kingdom but who process personal data in relation to the offering of goods or services to individuals in the United Kingdom, or to monitor their behavior will be subject to the UK GDPR – the requirements of which are (at this time) largely aligned with those under the EU GDPR and as such, may lead to similar compliance and operational costs with potential fines of up to £17.5 million or 4% of global turnover. On June 28, 2021, the European Commission issued a decision that the United Kingdom ensures an adequate level of protection for personal data transferred under the EU GDPR from the European Union to the United Kingdom. In 2022, the UK government proposed and debated the Data Protection and Digital Information Bill to harmonize the 2018 Data Protection Act, UK GDPR, and the Privacy and Electronic Communications Regulations under one legislative framework. However, progress on the bill stalled as the government continues to assess the most optimal approach to data protection reform.
Pricing Decisions for Approved Products
In the European Union, pricing and reimbursement schemes vary widely from country to country. Some countries provide that products may be marketed only after a reimbursement price has been agreed. Some countries may require the completion of additional studies that compare the cost-effectiveness of a particular product candidate to currently available therapies or so-called health technology assessments, in order to obtain reimbursement or pricing approval. For example, the European Union provides options for its Member States to restrict the range of products for which their national health insurance systems provide reimbursement and to control the prices of medicinal products for human use. Member States may approve a specific price for a product or it may instead adopt a system of direct or indirect controls on the profitability of the company placing the product on the market. Other Member States allow companies to fix their own prices for products, but monitor and control prescription volumes and issue guidance to physicians to limit prescriptions. Recently, many countries in the European Union have increased the amount of discounts required on pharmaceuticals and these efforts could continue as countries attempt to manage health care expenditures, especially in light of the severe fiscal and debt crises experienced by many countries in the European Union. The downward pressure on health care costs in general, particularly prescription products, has become intense. As a result, increasingly high barriers are being erected to the entry of new products. Political, economic and regulatory developments may further complicate pricing negotiations, and pricing negotiations may continue after reimbursement has been obtained. Reference pricing used by various Member States, and parallel trade, i.e., arbitrage between low-priced and high-priced Member States, can further reduce prices. There can be no assurance that any country that has price controls or reimbursement limitations for pharmaceutical products will allow favorable reimbursement and pricing arrangements for any products, if approved in those countries.
Patent Term Extension
In order to compensate the patentee for delays in obtaining a marketing authorization for a patented product, a supplementary certificate, or SPC, may be granted extending the exclusivity period for that specific product by up to five years. Applications for SPCs must be made to the relevant patent office in each European Union member state and the granted certificates are valid only in the member state of grant. An application has to be made by the patent owner within six months of the first marketing authorization being granted in the European Union (assuming the patent in question has not expired, lapsed or been revoked) or within six months of the grant of the patent (if the marketing authorization is granted first). In the context of SPCs, the term “product” means the active ingredient or combination of active ingredients for a medicinal product and the term “patent” means a patent protecting such a product or a new manufacturing process or application for it. The duration of an SPC is calculated as the difference between the patent’s filing date and the date of the first marketing authorization, minus five years, subject to a maximum term of five years.
A six month pediatric extension of an SPC may be obtained where the patentee has carried out an agreed pediatric investigation plan, the authorized product information includes information on the results of the studies and the product is authorized in all member states of the European Union.
United Kingdom Regulation
From January 1, 2021, European Union law no longer directly applies in the United Kingdom. The United Kingdom has adopted existing European Union medicines regulation as standalone United Kingdom legislation with some amendments to reflect procedural and other requirements with respect to marketing authorizations and other regulatory provisions.
In order to market medicines in the United Kingdom, manufacturers must hold a United Kingdom authorization. On January 1, 2021, all European Union marketing authorizations were converted to United Kingdom marketing authorizations subject to a manufacturer opt-out. United Kingdom medicines legislation is subject to future regulatory change under the Medicines and Medical Devices Act 2021. This act sets out a new framework for the adoption of medicines regulation. The MHRA’s guidance states that the United Kingdom will have the power to take into account marketing authorizations made under the European Union decentralized and mutual recognition procedures. In addition, the MHRA’s guidance has been updated to refer to new national licensing procedures including new routes of evaluation for novel and biotechnological products.
Different rules will apply in Northern Ireland following implementation of the Northern Ireland Protocol. In Northern Ireland, European Union central marketing applications will continue to apply.
The Trade and Cooperation Agreement between the European Union and the United Kingdom contains an Annex in relation to medicinal products with the objective of facilitating availability of medicines, promotion of public health and consumer protection in respect of medicinal products. The Annex provides for mutual recognition of good manufacturing practice (GMP) inspections and certificates, meaning that manufacturing facilities do not need to undergo duplicate inspections for the two markets. The Annex establishes a Working Group on Medicinal Products to deal with matters under the Trade and Cooperation Agreement, facilitate co-operation and for the carrying out of technical discussions. It is expected that further bilateral discussions will continue with respect to regulatory areas not the subject of the Trade and Cooperation Agreement, including pharmacovigilance. The Trade and Cooperation Agreement also does not include reciprocal arrangements for the recognition of batch testing certification. However, the United Kingdom has listed approved countries, including the EEA which will enable UK importers and wholesales to recognize certain certification and regulatory standards. The European Commission has not adopted such recognition procedures.
Healthcare Law and Regulation
Healthcare providers, physicians and third-party payors play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of drug products that are granted marketing approval. Arrangements with third-party payors and customers are subject to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations. Such restrictions under applicable federal and state healthcare laws and regulations include the following:
| • | the federal Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among other things, persons from knowingly and willfully soliciting, offering, receiving or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, in cash or in kind, to induce or reward either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, order or recommendation of, any good or service, for which payment may be made, in whole or in part, under a federal healthcare program such as Medicare and Medicaid; |
| • | the federal False Claims Act imposes civil penalties, and provides for civil whistleblower or qui tam actions, against individuals or entities for knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, to the federal government, claims for payment that are false or fraudulent or making a false statement to avoid, decrease or conceal an obligation to pay money to the federal government. A person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the AKS or specific intent to violate it to have committed a violation. In addition, the government may assert that a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the AKS constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the FCA or federal civil money penalties statute; |
| • | the federal civil and criminal false claims laws and civil monetary penalty laws, including the federal False Claims Act, which prohibit, among other things, individuals or entities from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, false or fraudulent claims for payment to, or approval by Medicare, Medicaid, or other federal healthcare programs, knowingly making, using or causing to be made or used a false record or statement material to a false or fraudulent claim or an obligation to pay or transmit money to the federal government, or knowingly concealing or knowingly and improperly avoiding or decreasing or concealing an obligation to pay money to the federal government. Manufacturers can be held liable under the FCA even when they do not submit claims directly to government payers if they are deemed to “cause” the submission of false or fraudulent claims. The FCA also permits a private individual acting as a “whistleblower” to bring actions on behalf of the federal government alleging violations of the FCA and to share in any monetary recovery; |
| • | the anti-inducement law, which prohibits, among other things, the offering or giving of remuneration, which includes, without limitation, any transfer of items or services for free or for less than fair market value (with limited exceptions), to a Medicare or Medicaid beneficiary that the person knows or should know is likely to influence the beneficiary’s selection of a particular supplier of items or services reimbursable by a federal or state governmental program; |
| • | the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, or HIPAA, imposes criminal and civil liability for executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or making false statements relating to healthcare matters; |
| • | HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act and its implementing regulations, also imposes obligations, including mandatory contractual terms, with respect to safeguarding the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information; |
| • | the federal false statements statute prohibits knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or covering up a material fact or making any materially false statement in connection with the delivery of or payment for healthcare benefits, items or services; |
| • | the federal transparency requirements under the ACA requires manufacturers of drugs, devices, biologics and medical supplies to report to the Department of Health and Human Services information related to payments and other transfers of value to physicians and teaching hospitals or to entities or individuals at the request of, or designated on behalf of, the physicians and teaching hospitals as well as certain ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members. Beginning in 2022, applicable manufacturers also will be required to report information regarding payments and transfers of value provided to physician assistants, nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, certified nurse anesthetists, anesthesiologist assistants, and certified nurse-midwives.; and |
| • | analogous state and foreign laws and regulations, such as state anti-kickback and false claims laws, may apply to sales or marketing arrangements and claims involving healthcare items or services reimbursed by non-governmental third-party payors, including private insurers. |
Additionally, similar healthcare laws and regulations in the European Union, United Kingdom and other jurisdictions, including reporting requirements detailing interactions with and payments to healthcare providers and laws governing the privacy and security of certain protected information, such as GDPR and UK GDPR, which imposes obligations and restrictions on the collection and use of personal data relating to individuals located in the European Union (including health data).
Finally, the majority of states also have statutes or regulations similar to the aforementioned federal laws, some of which are broader in scope and apply to items and services reimbursed under Medicaid and other state programs, or, in several states, apply regardless of the payor. Some state laws require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government in addition to requiring drug manufacturers to report information related to payments to clinicians and other healthcare providers or marketing expenditures. Some states and local jurisdictions require the registration of pharmaceutical sales representatives. State and foreign laws also govern the privacy and security of health information in some circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and often are not preempted by HIPAA, thus complicating compliance efforts.
Because of the breadth of these laws and the narrowness of their exceptions and safe harbors, it is possible that business activities can be subject to challenge under one or more of such laws. The scope and enforcement of each of these laws is uncertain and subject to rapid change in the current environment of healthcare reform, especially in light of the lack of applicable precedent and regulations. Federal and state enforcement bodies have recently increased their scrutiny of interactions between healthcare companies and healthcare providers, which has led to a number of investigations, prosecutions, convictions and settlements in the healthcare industry.
Ensuring that business arrangements with third parties comply with applicable healthcare laws and regulations is costly and time consuming. If business operations are found to be in violation of any of the laws described above or any other applicable governmental regulations a pharmaceutical manufacturer may be subject to penalties, including civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, fines, disgorgement, individual imprisonment, exclusion from governmental funded healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings, additional reporting obligations and oversight if subject to a corporate integrity agreement or other agreement to resolve allegations of non-compliance with these laws, and curtailment or restructuring of operations, any of which could adversely affect a pharmaceutical manufacturer’s ability to operate its business and the results of its operations.
Coverage and Reimbursement
The future commercial success of our product candidate or any of our collaborators' ability to commercialize any approved product candidate successfully will depend in part on the extent to which governmental payor programs at the federal and state levels, including Medicare and Medicaid, private health insurers and other third-party payors provide coverage for and establish adequate reimbursement levels for our product candidate. Government health administration authorities, private health insurers and other organizations generally decide which drugs they will pay for and establish reimbursement levels for healthcare. In particular, in the United States, private health insurers and other third-party payors often provide reimbursement for products and services based on the level at which the government, through the Medicare or Medicaid programs, provides reimbursement for such treatments. In the United States, the United Kingdom, the European Union, and other potentially significant markets for our product candidate, government authorities and third-party payors are increasingly attempting to limit or regulate the price of medical products and services, particularly for new and innovative products and therapies, which often has resulted in average selling prices lower than they would otherwise be. Further, the increased emphasis on managed healthcare in the United States and on country and regional pricing and reimbursement controls in the United Kingdom and European Union will put additional pressure on product pricing, reimbursement and usage, which may adversely affect our future product sales and results of operations. These pressures can arise from rules and practices of managed care groups, judicial decisions and laws and regulations related to Medicare, Medicaid and healthcare reform, pharmaceutical coverage and reimbursement policies and pricing in general.
Third-party payors are increasingly imposing additional requirements and restrictions on coverage and limiting reimbursement levels for medical products. For example, federal and state governments reimburse covered prescription drugs at varying rates generally below average wholesale price. These restrictions and limitations influence the purchase of healthcare services and products. Third-party payors may limit coverage to specific drug products on an approved list, or formulary, which might not include all of the FDA-approved drug products for a particular indication. Third-party payors are increasingly challenging the price and examining the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of medical products and services, in addition to their safety and efficacy. We may need to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies in order to demonstrate the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of our products, in addition to the costs required to obtain the FDA approvals. Our product candidate may not be considered medically necessary or cost-effective. A payor's decision to provide coverage for a drug product does not imply that an adequate reimbursement rate will be approved. Further, one payor’s determination to provide coverage for a drug product does not assure that other payors will also provide coverage for the drug product. Adequate third-party reimbursement may not be available to enable us to maintain price levels sufficient to realize an appropriate return on our investment in drug development. Legislative proposals to reform healthcare or reduce costs under government insurance programs may result in lower reimbursement for our products and product candidate or exclusion of our product candidate from coverage. The cost containment measures that healthcare payors and providers are instituting and any healthcare reform could significantly reduce our revenues from the sale of any approved product candidates. We cannot provide any assurances that we will be able to obtain and maintain third-party coverage or adequate reimbursement for our product candidate in whole or in part.
Healthcare Reform
In the United States and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been, and continue to be, several legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the health care system that could prevent or delay marketing approval of product and therapeutic candidates, restrict or regulate post-approval activities, and affect the ability to profitably sell product and therapeutic candidates that obtain marketing approval. The FDA’s and other regulatory authorities’ policies may change and additional government regulations may be enacted that could prevent, limit or delay regulatory approval of our product and therapeutic candidates. If we are slow or unable to adapt to changes in existing requirements or the adoption of new requirements or policies, or if we are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we may lose any marketing approval that we otherwise may have obtained and we may not achieve or sustain profitability, which would adversely affect our business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, the containment of healthcare costs has become a priority of federal and state governments and the prices of therapeutics have been a focus in this effort. The U.S. government, state legislatures and foreign governments also have shown significant interest in implementing cost-containment programs to limit the growth of government-paid healthcare costs, including price controls, restrictions on reimbursement, and requirements for substitution of generic and biosimilar products for branded prescription medicines and biologics, respectively. In recent years, the U.S. Congress has considered reductions in Medicare reimbursement levels for medicines and biologics administered by physicians. CMS, the agency that administers the Medicare and Medicaid programs, also has authority to revise reimbursement rates and to implement coverage restrictions for some drugs and biologics. Cost reduction initiatives and changes in coverage implemented through legislation or regulation could decrease utilization of and reimbursement for any approved products we may market in the future. While Medicare regulations apply only to pharmaceutical benefits for Medicare beneficiaries, private payors often follow Medicare coverage policy and payment limitations in setting their own reimbursement rates. Therefore, any reduction in reimbursement that results from federal legislation or regulation may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors.
The ACA, as amended by the Health Care and Education Affordability Reconciliation Act, was enacted in 2010 and substantially changed the way health care is financed by both governmental and private insurers in the United States, and significantly impacted the pharmaceutical industry. The ACA was intended to broaden access to health insurance, reduce or constrain the growth of healthcare spending, enhance remedies against healthcare fraud and abuse, add new transparency requirements for healthcare and health insurance industries, impose new taxes and fees on pharmaceutical manufacturers, and impose additional health policy reforms. With regard to biopharmaceutical products, the ACA, among other things, addressed a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for therapeutics that are inhaled, infused, instilled, implanted or injected, increased the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and extended the rebate program to individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations, established annual fees on manufacturers of certain branded prescription medicines, created a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, and expanded the 340B drug discount program. As another example, the 2021 Consolidated Appropriations Act signed into law on December 27, 2020 incorporated extensive health care provisions and amendments to existing laws, including a requirement that all manufacturers of medicines and biological products covered under Medicare Part B report the product’s average sales price, to the DHHS beginning on January 1, 2022, subject to enforcement via civil money penalties.
There have been executive, judicial and Congressional challenges to certain aspects of the ACA since its enactment, and it is possible that there will be additional challenges and amendments to the ACA in the future.
Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since passage of the ACA that affect health care expenditures. These changes include aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers of up to 2% per fiscal year pursuant to the Budget Control Act of 2011, which began in 2013 and was extended by the Consolidated Appropriations Act for 2023, and will remain in effect through 2032 unless additional Congressional action is taken. Further legislative and regulatory changes under the ACA remain possible, but it is unknown what form any such changes or any law would take, and how or whether it may affect the biopharmaceutical industry as a whole or our business in the future. We expect that changes or additions to the ACA, the Medicare and Medicaid programs and changes stemming from other healthcare reform measures, especially with regard to healthcare access, financing or other legislation in individual states, could have a material adverse effect on the healthcare industry in the United States.
In recent years, there has been heightened governmental scrutiny over the manner in which biopharmaceutical manufacturers set prices for their marketed products. Such scrutiny has resulted in several recent U.S. Congressional inquiries and proposed and enacted federal and state legislation designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to medicine pricing, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs, reduce the cost of medicines under Medicare, and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for pharmaceutical products. Congress and the executive branch have each indicated that it will continue to seek new legislative and/or administrative measures to control the costs of medicines, making this area subject to ongoing uncertainty.
More recently, in August 2022, President Biden signed into the law the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (the “IRA”). Among other things, the IRA has multiple provisions that may impact the prices of drug products that are both sold into the Medicare program and throughout the United States. Starting in 2023, a manufacturer of a drug or biological product covered by Medicare Parts B or D must pay a rebate to the federal government if the drug product’s price increases faster than the rate of inflation. This calculation is made on a drug product by drug product basis and the amount of the rebate owed to the federal government is directly dependent on the volume of a drug product that is paid for by Medicare Parts B or D. Additionally, starting in payment year 2026, CMS will negotiate drug prices annually for a select number of single-source Part D drugs without generic or biosimilar competition. CMS will also negotiate drug prices for a select number of Part B drugs starting for payment year 2028. If a drug product is selected by CMS for negotiation, it is expected that the revenue generated from such drug will decrease.
At the state level in the United States, legislatures have also increasingly passed legislation and implemented regulations designed to control pharmaceutical product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access, and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and in some cases, designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing. In December 2020, the U.S. Supreme Court held unanimously that federal law does not preempt the states’ ability to regulate pharmaceutical benefit managers and other members of the healthcare and pharmaceutical supply chain, an important decision that may lead to further and more aggressive efforts by states in this area.
We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative or executive action, either in the United States or abroad. We expect that additional federal, state, and foreign healthcare reform measures will be adopted in the future, any of which could limit the amounts that federal and state governments will pay for healthcare products and services, which could result in limited coverage and reimbursement and reduced demand for our products, once approved, or additional pricing pressures.
Competition
Our drug conjugate platform is among the latest generation of nanomedicine technology. Liposomes, an artificially prepared spherical vehicle composed of a lipid bilayer that can be used as vehicle for the administration of nutrients and drugs, followed by various polymeric nanoparticles, were the first nanotechnologies, and now inorganic nanoparticles like our GNPs are emerging as the fastest growing sector within the nanomedicine market. The speed and nature of technological change means that physical science is always evolving and new competition and alternatives are always a possibility, however we believe that we have established competitive advantage over our peers. As a result of the combination of our platform technology, intellectual property and proprietary know-how, we have a protected position in the nanoparticle space which allows the potential for highly differentiated drugs serving high unmet needs like orphan oncology to be rapidly and independently manufactured and scaled.
Competitive Dynamics
Barriers to entry for competitors are high. The significant level of capital, scientific capabilities, and infrastructure required to achieve what we have achieved to date may deter new entrants. A high degree of specialization and expertise in equivalent drug conjugate and sustained release technologies and relevant therapeutic areas is essential for any competitor to succeed, which we have built up over many years since inception. While the power of suppliers has been relatively low given our development manufacturing capabilities, with the reduction in these capabilities the power of suppliers will likely increase. The power of buyers, i.e. pharmaceutical companies, is important insofar as they may be partners for the commercialization and distribution of our product candidates. Even for large pharmaceutical companies, the know-how, manufacturing, and effort involved in developing alternative products to us would potentially see them engage as partners rather than as competitors. Competitive pressures or substitutes for our compounds come from conventional small molecules or biologics (such as antibody drug conjugates). There is a growing trend for drugs to be produced using biotechnologies and it is likely that the main threat in the future will come from this class, albeit the costs of production and development are much higher, and the regulatory pathways more complex.
Competitive Technology
The main competing nanotechnologies are liposomes, polymers, carbon assemblies and other inorganic/metallic platforms. Carbon assemblies are not widely used in healthcare applications. Most nano activity has traditionally involved liposomes and polymers. More recently, the focus has moved to include inorganic nanoparticles using solid cores whereas ours is one of a few companies using gold. To the best of our knowledge, we are the only company using non-colloidal gold (colloidal gold is defined as larger GNPs 10-15nm and more, whereas our core GNP construct is less than 2nm) and are sufficiently progressed with the technology to have undertaken Phase II clinical trials. We believe we are therefore well positioned versus the other technologies and companies providing a differentiated platform that imparts favorable characteristics in drug delivery, including targeting and mobility, solubility (for otherwise non soluble compounds), stability (of peptides), compatibility (inert and biocompatible) and highly controlled delivery and release in the cell.
Competitive Therapeutic Areas
Much of the historical and current focus and activity of the nanomedicine market is oncology. Within this domain, we believe we are well positioned given our focus on selected orphan oncology applications where unmet needs persist, an accelerated regulatory process is possible and fewer companies compete (reflecting the challenges that need to be addressed). With our sustained release technology, the ability to address shortcomings of other controlled technologies such as burst, lag, release profile and consistency enables us to pursue unmet opportunities such as sustained release octreotide, which to date has no generic competition despite being off patent for many years. Our nano inclusion technology conjugates solubilize cancer drugs that could otherwise not be administered directly into tumors.
Competitive Companies
Our Q-Sphera technology for biodegradable sustained-release formulation takes a microsphere-based approach that is based on printing individual microspheres. It enables next-generation formulation and engineering. We believe other companies in the sustained release space include Medincell S.A., GP Pharm, S.A., Peptron, Inc., Graybug, Inc. and Nanomi B.V.
From a technology perspective, we believe other companies using GNP technologies include CytImmune Sciences, Inc., and Nanospectra Biosciences, Inc. Some companies use larger colloidal GNPs of 10 to 15nm or bigger, whereas we typically use non-colloidal gold cores smaller than 5nm.
Manufacturing
Following the closing of our Bilbao, Spain operating facilities in 2020, we no longer have our own manufacturing facilities.
To establish proof-of-concept for potential licensees, we are able to manufacture non-GMP material at pilot scale at our facility in Cardiff, Wales. We would expect a licensee to assume responsibility for manufacturing GMP material and commercial scale-up pursuant to a technology transfer agreement.
Environmental Matters and Seasonality
We may from time to time be subject to various environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing air emissions, water and wastewater discharges, noise emissions, the use, management and disposal of hazardous, radioactive and biological materials and wastes and the cleanup of contaminated sites. We believe that our business, operations and facilities are being operated in compliance in all material respects with applicable environmental and health and safety laws and regulations. Based on information currently available to us, we do not expect environmental costs and contingencies to have a material adverse effect on it. The operation of our manufacturing facility, however, entails risks in these areas. Significant expenditures could be required in the future if these facilities are required to comply with new or more stringent environmental or health and safety laws, regulations or requirements.
Our current business does not generally reflect any significant degree of seasonality.
Legal Proceedings
From time to time, we may be subject to various claims or legal proceedings that arise in the ordinary course of our business. Other than as disclosed in this annual report, we currently are not a party to any legal proceedings, which, in the opinion of management, is likely to have or could reasonably possibly have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Our current headquarters is located at 1 Caspian Point, Caspian Way, Cardiff, Wales, where we also have our laboratories and pilot scale manufacturing facility. We entered into the lease for these premises in April 2021. The new premises comprise 754 square meters (approximately 8,118 square feet). The lease expires in 2026. We believe that our new premises at this facility will be sufficient to meet our current needs.
Employees
The number of our employees by geographic location and function as of the end of the period for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 were as follows:
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| Business functional area: | | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development | | 15 | | | 13 | | | 52 | |
| General and administration | | 5 | | | 5 | | | 13 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | 20 | | | 18 | | | 65 | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| Geography: | | | | | | | | | |
| United Kingdom | | 20 | | | 18 | | | 24 | |
| Spain | | -- | | | -- | | | 41 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | 20 | | | 18 | | | 65 | |
To our knowledge, none of our employees are currently represented by labor unions or covered by collective bargaining agreements. We consider our relationship with our employees to be good.
Historical Background and Corporate Structure
We were originally formed as a limited liability company under the laws of England and Wales in 2000 under the name Midatech Limited, which acquired its base nanoparticle technology through an assignment of worldwide commercialization rights and joint ownership of patent rights from Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas, or CSIC, in Madrid, Spain. Midatech Limited was a research and development focused biotech company which subsequently advanced and developed this gold nanoparticle drug delivery platform technology to enhance the delivery of medicines for major therapeutic indications where clinical therapeutic options are limited, with a particular focus on certain cancers, such as liver and brain cancer.
To better be able to continue the commercial development of the research and development programs of Midatech Limited, Midatech Pharma PLC was incorporated on September 12, 2014 under the laws of England and Wales, to be the public holding company of Midatech Limited and Midatech Pharma (Wales) Limited, or Midatech Wales, under registered number 09216368. On December 8, 2014, we completed our initial public offering of our Ordinary Shares in the United Kingdom.
On March 31, 2020 we announced that, in the context of prevailing conditions in the capital markets, we did not expect to be able to raise capital to fund the continued development of MTD201, including scale-up of MTD201 manufacturing at our Bilbao facilities. We determined to conduct a strategic review of our operations, cease further investment in MTD201 and close our operations in Bilbao, Spain, including making all our employees in Bilbao redundant.
On April 20, 2020, we announced an update to the strategic review of operations including the appointment of Noble Capital Markets, Inc. to advise us on options for extracting value from our technologies, including partnering our clinical stage assets, partnering existing and upcoming proof of concept formulations, partnering or selling one or more of our technologies or selling the entire Company.
On January 26, 2021, we announced, among other things, that the strategic review had completed and that we were now focused on executing our realigned strategy of deploying our technologies to develop more early stage products and seeking licensing partners at proof of concept stage.
On December 13, 2022, we announced, among other things, that we had entered into the Arrangement Agreement with Bioasis and a securities purchase agreement with the December Investor to purchase an aggregate of $10.0 million of our securities in a registered direct offering and private placement. On December 19, 2022, we completed the registered direct offering and received approximately $.04 million in gross proceeds. On January 23, 2023, Bioasis terminated the Arrangement Agreement. On January 26, 2023, we terminated the securities purchase agreement with the December Investor.
Our principal executive office and registered offices are located at 1 Caspian Point, Caspian Way Cardiff, United Kingdom CF10 4DQ, and our telephone number is +44 29 2048 0180. Our authorized representative in the United States is Donald J. Puglisi of Puglisi and Associates. Our agent for service in the United States is Donald J. Puglisi of Puglisi and Associates, located at 850 Library Avenue, Suite 204, Newark, Delaware 19711. Our Ordinary Shares are traded on AIM under the symbol “MTPH,” and our Depositary Shares are traded on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “MTP.”
We file reports and other information with the SEC. The SEC maintains an Internet website that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers, including us, that file electronically with the SEC. Our filings with the SEC are available to the public through the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov. Our corporate website is located at www.midatechpharma.com. Information contained on our website is not part of, or incorporated in, this annual report.
We have four wholly owned subsidiaries, as well as several indirectly owned subsidiaries and joint ventures. The following table sets forth a description of the Group.
| Subsidiaries | Country of Incorporation | Voting Interest |
| Subsidiaries of Midatech Pharma PLC | | |
| Midatech Pharma (Wales) Limited | England and Wales | 100% |
| Midatech Limited | England and Wales | 100% |
| Midatech Pharma Pty Limited | Australia | 100% |
| Haaland Jersey Limited | Jersey | 100% |
| Joint Ventures with Midatech Limited | | |
| MidaSol Therapeutics GP (1)(3) | Cayman Islands | 50% |
| Syntara LLC (2)(3) | United States (Delaware) | 50% |
| Subsidiaries of Midatech Limited | | |
| Pharmida AG (3) | Switzerland | 100% |
_______________
| (1) | Joint venture between Midatech Limited and Aquestive Therapeutics, formerly known as MonoSol RX. |
| (2) | Joint venture between Midatech Limited and Immunotope Inc. The percentage ownership of the entity is determined by reference to the partnership agreement and varies from time to time depending on capital committed. While 50% is the economic interest, Midatech Limited can currently direct 49% of the voting rights. |
Capital Expenditures
Our capital expenditures amounted to £0.32 million and £0.21 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020.
For the year ended December 31, 2021, our principal capital expenditures largely related to investment in our laboratory and pilot-scale manufacturing facility in Cardiff, Wales.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, our principal capital expenditures largely related to investment in our laboratory and pilot-scale manufacturing facility in Cardiff, Wales.
MANAGEMENT
Directors and Senior Management
The following table sets forth certain information about our current directors and senior management. The professional address of each of the directors and officers is care of Midatech Pharma PLC, Caspian Point, 1 Caspian Way, Cardiff, CF10 4DQ, United Kingdom.
| Name (1) | | Age at 12/31/2022 | | Position/Title |
| Directors: | | | | |
| Stephen Stamp (2) | | 61 | | Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, Director |
| Stephen Parker (2)(3)(4) | | 64 | | Non-Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors |
| Simon Turton, Ph.D. (2) (3) (4) | | 55 | | Senior Independent Non-Executive Director |
| Sijmen (Simon) de Vries, M.D. (2) (3) (4) | | 63 | | Non-Executive Director |
| Senior Management (5) | | | | |
| Dmitry Zamoryakhin, M.D. | | 42 | | Chief Scientific Officer |
__________________________
| (1) | The term of the Board of Directors will expire immediately after the annual general meeting held in 2023 for Mr. Stamp and Dr. Parker, 2024 for Dr. de Vries, and 2025 for Dr. Turton. |
| (2) | Remuneration Committee member |
| (3) | Audit Committee member |
| (4) | Nominations Committee member |
| (5) | Other than directors who are also members of senior management. |
Directors
Stephen Stamp has served as our Chief Executive Officer since March 31, 2020, and our Chief Financial Officer and a member of our Board of Directors since September 2019. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Stamp served as Chief Executive Officer of Ergomed plc (AIM: ERGO) from December 2017 until January 2019 and Chief Financial Officer from January 2016 to July 2018. From March 2013 until July 2015, Mr. Stamp served as the Chief Financial Officer of Assurex Health, Inc. Mr. Stamp served as Chief Financial Officer of EZCORP Inc. (NASDAQ: EZPW) and KV Pharmaceuticals Co. from November 2010 to October 2012 and March 2010 to June 2010. Mr. Stamp has also previously served as Chief Operating Officer of Xanodyne Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and Group Finance Director of Regus PLC (now IWG plc) (LON: IWG) and Shire plc (subsequently acquired by Takeda Pharmaceuticals Company Limited). Mr. Stamp is a Chartered Accountant and qualified with KPMG LLP. Mr. Stamp has a Bachelor’s degree in economics from the University of Manchester.
Stephen Parker has served as our Non-Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors and a director since June 2022.Dr. Parker has a career in the healthcare and pharma sector that spans over 30 years, including 10 years in advisory roles. Dr. Parker has served as Managing Director of sp2 Consulting Limited since 2002, as well as an advisor to Opus Corporate Finance LLP since 2019. Dr. Parker has also served as Chairman of Sareum Holdings plc (AIM: SAR) since May 2016 and Drishti Discoveries Limited since January 2021, as Senior Independent Director of MGC Pharmaceuticals Limited (ASX, LSE:MXC) since March 2019, and as a director of Eternans Limited since July 2019 and sp2 Asset Management Limited since September 2018. Previously, Dr. Parker served as a director of Albucasis Limited from September 2013 to September 2019, as Chairman of Liverpool Chirochem Limited from July 2017 to July 2018, and as a director and Chairman of Silence Therapeutics plc (LSE: SLN) from November 2013 to April 2019. Dr. Parker also has corporate finance experience having been an investment banker focusing on pharma and biotechnology with Barings Brothers Limited, SBC Warburg Dillon Read, and Apax Partners LLP, and previously served as a director at subsidiaries of Celtic Pharma GP Limited and Chief Financial Officer of Oxford GlycoSciences. Dr. Parker received his D.Phil in Biochemistry from the University of Oxford, MBA in Business Administration from City University, London, and B.Sc. in Chemical Sciences from the University of East Anglia.
Simon Turton, Ph.D. has served as a non-executive member of our Board of Directors since December 2014. Dr. Turton served as Chairman of Q Chip and OpsiRx Pharmaceuticals from March 2014 until their acquisition by us in December 2014. Since January 2015, he has served as the Managing Director of Gensmile Limited. In 2002, Dr. Turton joined Warburg Pincus’, most recently as head of healthcare investing activities in Europe, until June 2011. Dr. Turton has previously served on the board of Archimedes Pharma, Eurand, ProStrakan Group plc and Tornier, Inc. Dr. Turton has a Master’s of Business Administration from INSEAD and a Ph.D. in pharmacy from the University of London.
Sijmen de Vries, M.D. has served as a non-executive member of our Board of Directors since October 2004 (including his service to our predecessor entity). Since November 2008, Dr. de Vries has served as of the Chief Executive Officer of Pharming Group NV (Euronext: PHARM). Prior to that, Dr. de Vries served as Chief Executive Officer of 4-Antibody and Morphochem AG. Prior to this he worked at Novartis Pharma, Novartis Ophthalmics and at SmithKline Beecham Pharmaceuticals Plc, where he held senior business and commercial positions. Dr. de Vries holds an M.D. degree from the University of Amsterdam and a Masters of Business Administration in General Management from Ashridge Management College (United Kingdom).
Senior Management
Dmitry Zamoryakhin M.D. has served as our Chief Scientific Officer since July 2021. Prior to that time, from February 2021 to July 2021 Dr. Zamoryakhin provided independent consulting services to biotech and pharmaceutical companies in the areas of gene and cell therapy, biologics and small molecules. From September 2018 to January 2021, Dr. Zamoryakhin served as the Chief Medical Officer of Oxford Biomedica plc (LON: OXB). From October 2016 to August 2018, he held positions of increasing responsibility at Grunenthal GmbH, most recently as Vice President, Head of Development and Strategy. Dr. Zamoryahkin has also held various positions at Daiichi Sankyo Company Limited (TYO: 4568), Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Limited (TYO: 4528) and GlaxoSmithKline plc (LON: GSK, NYSE: GSK). Dr. Zamoryakhin has broad experience across all phases of development of drugs and medical devices, working with regulatory authorities including the EMA, FDA, PMDA, and NMPA He qualified as a doctor of medicine at Perm State Medical Academy, Russia, before earning a diploma in Pharmaceutical Medicine at PHARMED, Universite Libre de Bruxelles, and an MBA at Warwick Business School.
For the biographical information of Stephen Stamp, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, see “—Directors and Senior Management—Directors.”
Compensation of Non-Executive Directors
Our non-executive directors receive a fee for their services as a director, which is approved by our Board of Directors, giving due consideration to the time commitment and responsibilities of their roles and of current market rates for comparable organizations and appointments. Non-executive directors are reimbursed for travelling and other incidental expenses incurred on our business in accordance with our expenses policy.
The following table summarizes the compensation paid to our non-employee directors during 2021.
| Name | | Fees Earned
or Paid in Cash (£)(1) | | | All Other Compensation (£) | | | Total £ | |
| Sijmen de Vries | | | 31,540 | | | | - | | | | 31,540 | |
| Rolf Stahel (2) | | | 24,749 | | | | 13,333 | | | | 38,082 | |
| Simon Turton | | | 31,540 | | | | - | | | | 31,540 | |
| Stephen Parker (3) | | | 43,838 | | | | - | | | | 43,848 | |
______________
| (1) | Includes annual fees, committee chairpersonship fees and meeting fees. |
| (2) | Includes fees paid to Mr. Stahel in connection with a consultancy agreement with Chesyl Pharma Limited, a company wholly owned by Mr. Stahel. Mr. Stahel resigned from the Board of Directors on June 22, 2022. |
| (3) | Dr. Parker was appointed to the Board of Directors on June 20, 2022. |
The following table sets forth, as of December 31, 2022, the aggregate number of option awards held by those individuals who served as non-executive directors during 2022:
| Name | | Number of
Options | | Grant
Date | | Exercise Price per Share (£) | | Expiration Date |
| Sijmen de Vries (1) | | | 500 | (1) | | 6/30/2014 | | 1.50 | | 6/30/2024 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
___________
| (1) | The stock options vest in the following installments: (i) 50% of the stock options vest when our share price is £106.20 a share, (ii) a further 25% of the stock options vest when our share price is £274.40 a share and (iii) the remaining 25% of the stock options vest when our share price is £377.20 a share. |
All stock options were granted with an exercise price at or above market value on the date of grant.
Deed of Indemnity
Under a deed poll declared by the Company on August 5, 2015, or a Deed of Indemnity, the Board of Directors and our Company Secretary are indemnified against costs and liabilities incurred in connection with their office, other than any liability owed by such person to the Company itself (or any of its associated entities) and other than indemnification for liabilities in certain circumstances, which are prohibited by virtue of the Companies Act. The Deed of Indemnity provides that a director may also be lent sums to finance any relevant defense costs, provided that, in the event such proceedings involve criminal or civil matters in which the person is convicted or has a judgment made against him or her, then such loan must be repaid.
Letters of Appointment
Each non-executive director (other than Dr. Parker) has been appointed to serve on our Board of Directors pursuant to a letter of appointment. The initial term of appointment for each director is three years, unless terminated earlier by either party upon one month’s prior notice or in accordance with the terms of the letters of appointment. The appointment is subject to our articles of association, and is subject to confirmation at any annual general meeting of the Company.
Each non-executive director (other than Dr. Parker) is paid an annual fee of £31,920, which covers all duties, including committee service or service on the board of a Midatech subsidiary, with the exception of committee chairmanships and certain additional responsibilities, such as taking on the role of senior independent director. This amount may be changed from time to time. In addition, we reimburse each director for reasonable and properly documented expenses incurred in performing their duties. As noted above, we also grant each director a deed of indemnity against certain liabilities that may be incurred as a result of their service, to the extent permitted by the Companies Act.
In addition, without our prior written consent, for a period of six months following a director’s termination from service, such director will not, whether as a principal or agent and whether alone or jointly with, or as a director, manager, partner, shareholder, employee consultant of, any other person, carry on or be engaged, concerned or interested in any business which is similar to or which is (or intends to be) in competition with any business being carried on by Midatech or any subsidiary, as applicable.
Dr. Parker Letter of Appointment
Pursuant to a term of appointment dated June 20, 2022, or the Appointment Agreement, Dr. Parker was appointed Non-Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors, effective as of the date thereof. The initial term of appointment for Dr. Parker expires on June 19, 2023. In addition, his appointment may be terminated:
| • | by either party giving at least three months prior written notice; |
| • | by the Board of Directors reasonably determining that Dr. Parker’s acceptance of any other employment, engagement, appointment, interest or involvement with any business or person competes or conflicts with his appointment and would result in a serious conflict of interest or Dr. Parker reasonably determines such interest would result in a serious conflict of interest, and Dr. Parker accepts such employment, engagement, appointment, interest or involvement; |
| • | in accordance with our articles of association or applicable law; or |
| • | he is not re-elected to the Board of Directors. |
Pursuant to the terms of the Appointment Agreement, Dr. Parker is paid an annual fee of £82,000, plus an additional fee of £1,750 for every day in excess of 16 days worked.
We also agreed to reimburse Dr. Parker for reasonable and documented expenses accrued in the course of performing his duties and provide him with up to £7,500 in professional advice in connection with performing his duties. The Appointment Agreement includes provisions related to the non-disclosure of information and assignment of inventions. Among other things, these provisions obligate Dr. Parker from disclosing any of our proprietary and confidential information received during the course of employment and to assign to us any inventions conceived or developed during the course of their employment.
In the event we terminate the agreement with Dr. Parker at any time in accordance with the provisions of the articles of association or applicable laws, Dr. Parker will have no right to damages or compensation if he:
| • | is found guilty of any misconduct, gross negligence or dishonesty or acts in a manner which is materially adverse to our interests; |
| • | commits any serious or repeated breach or non-observance of his obligations to the Company; |
| • | becomes bankrupt, has an interim order made against him under the United Kingdom Insolvency Act 1986 or makes any composition or enters into any deed of arrangement with his creditors or the equivalent of any of these under any other jurisdictions; |
| • | becomes of unsound mind, becomes a patient under any statute relating to mental health or is unable, due to any accident, illness or injury, to undertake his duties for the Company for a period of more than six consecutive months; |
| • | is convicted of a criminal offense (other than a motoring offense for which a non-custodial penalty is imposed); |
| • | is disqualified by law or an order of a court of competent jurisdiction from holding office; or |
| • | has failed to submit his resignation as Non-Executive Chairman and as a director of the Company when required to so pursuant to the terms of the Appointment Agreement. |
In the event we terminate the agreement at any time with immediate effect (other than pursuant to the preceding paragraph), we will pay to Dr. Parker all fees which are due to him for the following 12 months.
Dr. Parker may resign from his positions at any time if the Company (i) is guilty of any gross negligence which affects him or any dishonesty towards or concerning him or (ii) becomes insolvent, makes any composition or enters into any deed of arrangement with its creditors or the equivalent. If Dr. Parker resigns due to these reasons, we will pay to Dr. Parker all fees which are due to him for the following 12 months. Further, in the event that Dr. Parker is unable, due to an accident, illness or injury, to undertake his duties for the Company in accordance with the terms of the Stahel Appointment Agreement for a period of more than six consecutive months, he may resign at any time without any rights to damages or compensation. Dr. Parker is also required to resign in connection with the Board of Directors determination that his acceptance of any other employment, engagement, appointment, interest or involvement with any business or person competes or conflicts with his appointment and would result in a serious conflict of interest or Dr. Parker reasonably determines such interest would result in a serious conflict of interest, and Dr. Parker accepts such employment, engagement, appointment, interest or involvement, without any rights to damages or compensation. If Dr. Parker resigns for any other reason, he must provide 12 months written notice.
Compensation of Senior Management
The following table summarizes the compensation earned by our senior management during 2022 (including for any service on any our subsidiaries), including one former executive officer.
| Name | | Salary (£) | | | Bonus (£)(1) | | | All Other Compensation (2)(£) | | | Total (£) | |
| Stephen Stamp | | | 236,447 | | | | -- | | | | 1,450 | | | | 237,897 | |
| Chief Executive Officer & Chief Financial Officer | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dmitry Zamoryakhin, M.D. | | | 212,500 | | | | 2,306 | | | | 21,869 | | | | 236,675 | |
| Chief Scientific Officer (4) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| All senior management as a group (2 persons) | | | 448,947 | | | | 2,306 | | | | 23,319 | | | | 474,572 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
_____________
| (1) | Mr. Stamp and Dr. Zamoryakhin have a bonus target of 33%, and 30% respectively, of their annual base salary, which bonus is payable upon attainment of objectives as determined in the subjective judgment of the Board of Directors or a committee thereof, taking into account various factors without any preassigned weighting. Mr. Stamp did not receive a bonus for fiscal 2022. Dr. Zamoryakhin’s bonus earned in fiscal 2022 is to be paid in March 2023. |
| (2) | The amounts reflect the value of benefits payable for medical benefits (£1,450 and £619 for Mr. Stamp and Dr. Zamoryakhin, respectively) and £21,250 pursuant to a pension plan for Dr. Zamoryakhin. |
The following table sets forth, as of December 31, 2022, the aggregate number of option awards held by our senior management.
| Name | | Number of Options | | Grant Date | | Exercise Price
per Share
(£) | | Expiration Date |
| Stephen Stamp | | 30,000 (1) | | 9/9/2019 | | 1.05 | | 9/9/2029 |
| | | 300,000 (2) | | 6/17/2020 | | 0.202 | | 1/17/2030 |
| | | 500,000 (2) | | 7/15/2021 | | 0.2775 | | 7/14/2031 |
| Dmitry Zamoryakhin, M.D. | | 250,000 (2) | | 7/15/2021 | | 0/2775 | | 7/14/2031 |
| All senior management as a group (3 persons) | | 1,050,000 (3) | | (4) | | (5) | | (6) |
_________
| (1) | Of these options, 7,500 previously vested on September 9, 2020, and the remaining 22,500 options have subsequently vested, or will vest, in 12 equal quarterly tranches, over a subsequent three-year period. |
| (2) | Of these options, 25% of the options vest 12 months after the grant date, and the remaining options have subsequently vested, or will vest, in 12 equal quarterly tranches over a subsequent three-year period. |
| (3) | 446,250 stock options are fully vested. |
| (6) | The grant dates range from September 9, 2019 to July 15, 2021. |
| (7) | The exercise price of the options range from £0.202 to £1.05. |
| (8) | The stock options expire between September 9, 2029 and July 14, 2031. |
Agreements with Senior Management
Stephen Stamp. On September 9, 2019, we entered into a service agreement, or the Service Agreement, with Mr. Stamp. The Service Agreement provides for a base salary, incentive compensation benefits, and, in certain circumstances, severance benefits. The Service Agreement may be terminated, subject to certain exceptions, upon six months’ prior notice.
The Service Agreement provides for an initial base salary of £160,000. Mr. Stamp’s base salary is subject to increase each April 1 by the percentage increase, if any, in the “All Items Index of Retail Prices” published by the United Kingdom Office for National Statistics over the previous year. The base salary of Mr. Stamp is to be reviewed annually to consider any increase in salary. Mr. Stamp’s base salary was increased to £230,000 effective as of April 1, 2022.
The Service Agreements also include a bonus target for Mr. Stamp of 33% of his annual base salary, which bonus is payable upon attainment of objectives as determined in the subjective judgment of the Board of Directors or a committee thereof, taking into account various factors without any preassigned weighting. In addition to base salary and bonus, the Service Agreement provides for additional benefits, such as a 10% pension contribution, life insurance, medical insurance, vacation benefits and any other additional benefits as determined by the Board of Directors from time to time.
Pursuant to the terms of the Service Agreement, Mr. Stamp has also agreed that, for a period of six months following his termination, he will not directly or indirectly compete with the Company. The Service Agreement includes provisions related to the non-disclosure of information and assignment of inventions. Among other things, these provisions prohibit Mr. Stamp from disclosing any of our proprietary and confidential information received during the course of employment and obligates him to assign to the Company any inventions conceived or developed during the course of his employment. The Service Agreement also includes customary confidentiality, non-solicitation, non-poaching and non-disparagement provisions.
The Service Agreement also provides Mr. Stamp with certain payments and/or benefits upon certain terminations of employment. If he is terminated due to his inability to perform his duties due to illness or other incapacity for a continuous period of three months, or an aggregate period exceeding 100 working days in any period of 12-months, we may, notwithstanding any other provision of the Service Agreement, terminate Mr. Stamp’s employment upon six months’ written notice. During that period, Mr. Stamp will not be entitled to receive his salary or any bonus payment, but will be entitled to any benefits owed under the Service Agreement. Further, notwithstanding any notice requirements for termination set forth in the Service Agreements, we may, at any time and in our absolute discretion, terminate the Service Agreement and provide Mr. Stamp with a payment in lieu of any required notice. The payment will comprise of his base salary, but will not include any bonus or other benefits, and shall be subject to any tax or insurance deductions. Notwithstanding the foregoing, we may terminate the Service Agreement without notice or payment in lieu thereof if Mr. Stamp:
| • | is guilty of serious misconduct or any other misconduct which affects, or is likely to affect, prejudicially our interests; |
| • | fails or neglects to efficiently and diligently discharge his duties or commits any serious or repeated breach or non-observance of any of the provisions of the Service Agreement or any share dealing code we have adopted; |
| • | has an interim receiving order made against him, becomes bankrupt or makes any composition or enters into any deed of arrangement with his creditors; |
| • | is charged with an arrestable criminal offense (other than a road traffic offense in the United Kingdom or elsewhere for which a fine or non-custodial penalty is imposed); |
| • | is disqualified from holding office in any company by reason of an order of a court of competent jurisdiction; |
| • | becomes of unsound mind or becomes a patient under any statute relating to mental health; |
| • | is convicted of an offense under the United Kingdom’s Criminal Justice Act 1993 in relation to insider dealings or under any other present or future statutory enactment or regulations relating to insider dealings; |
| • | is in breach of the Model Code on directors’ dealings in listed securities, including securities trading on AIM, published by the London Stock Exchange (the Model Code has subsequently been replaced by provisions under the MAR, however the employment agreements have not been updated to reflect this); or |
| • | commits any other act warranting summary termination at common law including, but not limited to, any act justifying dismissal without notice in the terms of our generally applicable disciplinary rules. |
Dmitry Zamoryakhin. We have entered into a contract of employment, or the Contract of Employment, with Dr. Zamoryakhin. The Contract of Employment was effective as of July 12, 2021 and provides for Dr. Zamoryakhin’s base salary, incentive compensation benefits, and compensation surrounding a termination of his employment. The Contract of Employment may be terminated by either Dr. Zamoryakhin or the Company with six months’ prior notice.
The Contract of Employment provides for an initial base salary of £205,000, which is subject to adjustment, and also includes an initial bonus target of 30% of Dr. Zamoryakhin’s annual base salary. Dr. Zamoryakhin’s base salary was increased to £215,000 effective as of April 1, 2022. In addition to base salary and bonus, the Contract of Employment provides for additional benefits, such as a 10% pension contribution, medical insurance, vacation benefits and any other additional benefits as determined by the Board of Directors from time to time.
Dr. Zamoryakhin has also agreed that, for a period of six months following his termination (as reduced by any “garden leave” period), he will not compete with the Company, directly or indirectly, or solicit any customer, prospective customer or key employee. The Contract of Employment includes provisions related to confidentiality and the non-disclosure of information and assignment of inventions. Among other things, these provisions prohibit Dr. Zamoryakhin from disclosing any of our proprietary and confidential information received during the course of employment and require Dr. Zamoryakhin to assign to us any inventions conceived or developed during the course of his employment.
The Contract of Employment provides that we will pay Dr. Zamoryakhin his normal salary during any notice period prior to termination. We are also permitted to terminate Dr. Zamoryakhin’s employment effective immediately, without notice or payment, if Dr. Zamoryakhin is found guilty of any fundamental or repudiatory breach of contract or any breach of the disciplinary rules applicable to Dr. Zamoryakhin.
Board of Directors
Our Board of Directors is currently comprised of four directors, one of whom is an executive director and three of whom are non-executive directors, reflecting a blend of different experience and backgrounds. The roles of Chairman of the Board of Directors (which is a non-executive position) and Chief Executive Officer have been split and there is a clear division of responsibility between the two positions. With a view towards maintaining the independence of the Board of Directors, no remuneration is paid to either the Chairman or non-executive directors in the form of shares.
Effective as of September 28, 2018, all AIM listed companies were required to formally apply a recognized corporate governance code. We have chosen to adopt the principles of the Quoted Companies Alliance Corporate Governance Code for Small and Mid-Sized Quoted Companies, or the QCA Code. The QCA Code identifies ten principles to be followed in order for companies to deliver growth in long term shareholder value, encompassing and efficient, effective and dynamic management framework, accompanied by good communication, to promote confidence and trust.
The Board of Directors is responsible for inter alia, approving interim and annual financial statements, formulating and monitoring our strategy, approving financial plans and reviewing performance, as well as complying with legal, regulatory and corporate governance matters. There is a schedule of matters reserved for the Board of Directors.
The Board of Directors meets regularly to consider strategy, performance and the framework of internal controls. To enable the Board of Directors to discharge its duties, all directors receive appropriate and timely information. Briefing papers are distributed to all directors in advance of board meetings.
Board Committees
We have established audit, nomination, and remuneration committees of the Board of Directors with formally delegated duties and responsibilities. From time to time, separate committees may be set up by the Board of Directors to consider specific issues when the need arises.
Audit Committee
The Audit Committee consists of three members: Simon Turton (Chairman), Sijmen de Vries and Stephen Parker. The Board of Directors has determined that Messrs. de Vries, Turton and Parker are independent under Rule 10A-3 of the Exchange Act and the applicable rules of NASDAQ and that Mr. Turton qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” as defined under in Item 16A of Form 20-F.
The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors assists the Board of Directors in discharging its responsibilities with regard to financial reporting, external and internal audits and controls, including reviewing and monitoring the integrity of the Company’s annual and interim financial statements, advising on the appointment of external auditors, reviewing and monitoring the extent of the non-audit work undertaken by external auditors, overseeing our relationship with our external auditors, reviewing the effectiveness of the external audit process and reviewing the effectiveness of our internal control review function. The ultimate responsibility for reviewing and approving the annual report and accounts and the half-yearly reports remains with the Board of Directors.
In addition, the Audit Committee is responsible, within agreed terms of reference, for ensuring compliance with the AIM Rules, rules and regulations promulgated by the SEC and the rules of NASDAQ, and disclosure of information. The Audit Committee works closely with the Board of Directors to ensure that our nominated adviser is provided with any information it reasonably requests or requires in order for it to carry out its responsibilities under the AIM Rules and the AIM Rules for Nominated Advisers.
The Audit Committee meets not less than twice a year and otherwise as required.
Nomination Committee
The Nomination Committee is chaired by Dr. Parker and is currently comprised of all other members of the Board of Directors. The Nomination Committee assists the Board of Directors in discharging its responsibilities relating to the composition and make-up of the Board of Directors and any committees of the Board of Directors. It is responsible for periodically reviewing the Board of Director’s structure and identifying potential candidates to be appointed as directors or committee members as the need may arise. The Nomination Committee is responsible for evaluating the balance of skills, knowledge and experience and the size, structure and composition of the Board of Directors and committees of the Board of Directors, retirements and appointments of additional and replacement directors and committee members and will make appropriate recommendations to the Board of Directors on such matters.
The Nomination Committee meets not less than once a year and otherwise as required.
Remuneration Committee
The Remuneration Committee consists of three members: Sijmen de Vries (Chairman), Simon Turton and Dr. Parker. The Board of Directors has determined that Messrs. de Vries, Turton and Dr. Parker are independent under applicable rules of NASDAQ.
The Remuneration Committee of the Board of Directors is responsible, within agreed terms of reference, for establishing a formal and transparent procedure for developing policy on executive remuneration and setting the remuneration packages of individual directors. This includes agreeing with the Board of Directors on the framework for remuneration of the executive directors, the company secretary and such other members of our executive management as it is designated to consider. It is also responsible for determining the total individual remuneration packages of each director including, where appropriate, bonuses, incentive payments and share options. No director may be involved in any decision as to his/her own remuneration. The Remuneration Committee ensures compliance with the QCA Code in relation to remuneration wherever possible.
The Remuneration Committee meets not less than twice a year and otherwise as required.
Service Contracts
Except as described herein, we do not have service contracts with any member of our Board of Directors or our senior management.
Equity Benefit Plans
Midatech Pharma PLC 2014 Enterprise Management Incentive Scheme
The Board of Directors has established the Midatech Pharma PLC 2014 Enterprise Management Incentive Scheme, or 2014 Plan, to allow us to grant options to purchase Ordinary Shares to qualifying employees and directors of the Company, or Plan Participants, for the purpose of attracting, rewarding and retaining such persons.
Administration. The overall responsibility for the operation and administration of the 2014 Plan is vested in the Board of Directors.
Eligibility. In order to be eligible to participate as a Plan Participant in the 2014 Plan, a person must be an employee or director of the Company or any of its subsidiaries whose “committed time” amounts to at least 25 hours a week or, if less, 75% of his or her “working time,” as each of those terms are defined under the His Majesty’s Revenue and Customs rules set out in Schedule 5 to the Income Tax (Earnings and Pensions) Act 2003 of the United Kingdom, or Schedule 5. The Board of Directors may exercise its discretion in selecting the Plan Participants to whom stock options will be granted under the 2014 Plan.
Grant of Options. Options may be granted from time to time by the Board of Directors, other than when grants are not permitted under the applicable law or there are other restrictions with regards to the Ordinary Shares. No payment will be made for the grant of a stock option.
Form of Options. Stock options granted under the 2014 Plan may be granted either with an exercise price greater than or equal to the market value of Ordinary Share at the date of grant, but not in any event at a price less than the nominal value of such share. The stock options may be stock options to subscribe for new Ordinary Shares.
The participant will have no stockholder rights until such time as he is able to exercise the stock option and acquire Ordinary Shares.
Size of Option Grants and Plan Limits. Stock options shall be granted under, and comply with, Schedule 5. This confers tax benefits on stock options up to a certain threshold. That threshold is currently such that when an employee has received and holds stock options with a value at grant of £250,000 or more, he or she may not have any further granted options for three years. In the event that this threshold is exceeded or the Company ceases to satisfy the qualifying conditions, unapproved options may instead be granted under the terms of the 2014 Plan. The total value of shares subject to unexercised options at any time may not exceed £3.0 million. All options must be exercised within 10 years from the grant date as set out in the rules of the 2014 Plan, or as set forth in the applicable option agreement.
The Board of Directors may from time to time specify the maximum number of Ordinary Shares in respect of which options may be granted.
Vesting of Options. In the normal course, stock options will become eligible for vesting subject to the satisfaction of time and financial performance targets.
If a Plan Participant leaves the employment of the Company or its subsidiaries for any reason, his or her stock option will generally lapse unless the Board of Directors exercises its discretion to allow the exercise of the stock option.
Performance Targets. All stock options granted under the 2014 Plan will be subject to appropriate performance targets determined by the Board of Directors, which may include share price targets, with stock options vesting in part on the attainment of each performance target.
Rights Attaching to Ordinary Shares. Ordinary Shares issued in connection with the exercise of stock options will rank equally with all other Ordinary Shares then in issue (save as regards any rights attaching to Ordinary Shares by reference to a record date prior to entry of the shares on the register of stockholders). Application will be made for admission to trading on AIM of new Ordinary Shares issued under the 2014 Plan.
Adjustments. If there is any adjustment of our issued share capital, the Ordinary Shares subject to a stock option will be subject to appropriate adjustment. The Board of Directors may adjust stock options in such manner as it determines to be appropriate.
Midatech Pharma PLC Employee Share Incentive Plan
In 2017, we set up the Midatech Pharma Share Incentive Plan, or the MPSIP. Under the MPSIP, our employees and directors can acquire our Ordinary Shares via a salary sacrifice arrangement. We grant matching shares for every share bought under the MPSIP. In order to retain these shares, scheme participants must remain employed by the Group for three years from the date of acquisition. All shares purchased by the MPSIP are held by an Employee Benefit Trust that is not under our control. Shares must be left in the plan for five years to qualify for full income tax relief.
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Agreement with Chesyl Pharma Limited
In April 2014, Midatech Limited entered into a consultancy agreement, or the Consultancy Agreement, with Chesyl Pharma Limited, or Chesyl. Chesyl is wholly owned by Mr. Rolf Stahel, our former non-executive Chairman of the Board and director. The term of the Consultancy Agreement commenced on March 1, 2014, with an initial term of 12 months and continuing thereafter until terminated in accordance with its terms. Chesyl was engaged to provide management consultancy services, including support and assistance to the board of directors of Midatech Limited in relation to operational issues and the provision of advice in relation to corporate strategy, corporate activities, fund raising and mergers and acquisition opportunities, collectively the Services.
Pursuant to the terms of the Consultancy Agreement, Mr. Stahel (or a similarly qualified substitute party, approved by the Midatech Limited) was obliged to procure the Services at such times and at such locations as may be reasonably necessary for 10 full working days per year. Midatech Limited agreed to pay Chesyl £40,000 per annum for Mr. Stahel’s services (reduced from £50,000 with effect from October 1, 2017), and if engaged for any additional days, a rate of £2,000 would be paid per full working day. For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, Midatech Limited paid Chesyl £13,333.
The Consultancy Agreement was terminated in connection with Mr. Stahel’s resignation from our Board of Directors on June 20, 2022.
Agreements with the CMS Parties
CMS License Agreement
For information regarding the CMS License Agreement, see “Business—Commercial Agreements, Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations—CMS License Agreement.”
Relationship Agreement
On January 29, 2019, the Company, Panmure Gordon (UK) Limited (our former nominated advisor), the CMS Stockholders and certain affiliates of the CMS Stockholders, entered a Relationship Agreement, or the Relationship Agreement, in order to regulate our relationships with the CMS and its affiliated entities, collectively the CMS Parties, and to limit their influence over our corporate actions and activities and the outcome of general matters pertaining to the Company. The Relationship Agreement was effective from February 26, 2019. The Relationship Agreement was subsequently amended on May 12, 2020 and April 15, 2022.
Pursuant to the terms of the Relationship Agreement, the CMS Parties have agreed to (amongst other things):
| • | conduct all transactions with us on an arm’s length terms and on a normal commercial basis, including in accordance with the related party rules set out in the AIM Rules and any other applicable laws, regulations and stock exchange rules, and only with the prior approval of a majority of independent directors; |
| • | exercise their voting rights or other rights and powers so as to ensure that each member of their respective Groups is capable of carrying on its business and making decisions independently of each of the CMS Parties (and any of their group companies and associates); and |
| • | abstain from voting in respect of any resolution concerning any contract, arrangement or transaction with a related party of each of the CMS Parties (or any of their associates). |
We further agreed to conduct all transactions, agreements and relationships (whether contractual or otherwise) with the CMS Parties (and any of their group companies and associates) on arm’s length terms and on a normal commercial basis and in accordance with the related party rules set out in the AIM Rules.
The Relationship Agreement provides that any respective dispute between the Company and the CMS Parties and/or any of their respective associates relating to any existing or proposed transaction, arrangement or agreement between each of CMS Parties (or any of their associates) and the Company shall be resolved by a decision of the majority of independent directors.
The obligations of the parties under the Relationship Agreement shall automatically terminate upon:
| • | the CMS Parties (or any of their associates) ceasing to beneficially hold 10%, in aggregate, of our issued Ordinary Shares; or |
| • | the Ordinary Shares ceasing to be admitted to AIM. |
In connection with the closing of the Private Placement on February 15, 2023, the CMS Parties beneficially owned less than 10%, in aggregate, of our issued Ordinary Shares, and accordingly, the Relationship Agreement terminated in accordance with its terms.
Deed of Indemnity
We have entered into a Deed of Indemnity for the benefit of our Board of Directors and Company Secretary. For more information, see “Management—Compensation of Non-Executive Directors—Deed of Indemnity.”
Agreements with Directors and Senior Management
We have previously entered into certain agreements with directors and our senior management related to their service on our Board of Directors or employment with the Company. For more information, see “Management.”
Share Acquisitions by Related Parties
Since January 1, 2019, in addition to the transactions described elsewhere in this prospectus, we have engaged in the following transactions with our directors, senior management or holders of 3% or more of our Ordinary Shares, or affiliates of our directors, senior management or holders of more than 3% of our Ordinary Shares, that are required to be described in this prospectus pursuant to Item 7.B. of Form 20-F.
In February 2019, we completed a subscription, placement and open offer of units (each unit consisting of one Ordinary Share and one warrant to acquire Ordinary Shares, or the 2019 Units) to investors at purchase price of £0.77 per 2019 Unit. In connection with such subscription, placement and open offer:
| · | the CMS Stockholders acquired an aggregate of 10,389,610 2019 Units, equal to 10,389,610 Ordinary Shares and warrants to acquire an additional aggregate of 10,389,610 Ordinary Shares, for an aggregate purchase price of £8.0 million. Immediately following this transaction, and before the exercise of any CMS Warrants, the CMS Stockholders owned approximately 50.8% of our outstanding Ordinary Shares; and |
| · | certain of our directors and senior management purchased an aggregate of 92,989 2019 Units, equal to 92,989 Ordinary Shares and warrants to acquire 92,989 Ordinary Shares, for an aggregate purchase price of £71,602. |
PRINCIPAL SHAREHOLDERS
The following table sets forth information, to our knowledge, as of February 14, 2023, regarding the beneficial ownership of Ordinary Shares, including:
| · | each person that is known by us to be a beneficial owner of 3% or more of Ordinary Shares (based on information in our share register and information provided by such persons); |
| · | each member of our Board of Directors; |
| · | each member of our senior management; and |
| · | all members of our Board of Directors and our senior management, taken as a group. |
Beneficial ownership of shares is determined under rules of the SEC and generally includes any shares over which a person exercises sole or shared voting or investment power. Except as noted by footnote, and subject to community property laws where applicable, we believe, based upon the information provided to us, that the persons and entities named in the table below have sole voting and investment power with respect to all Ordinary Shares shown as beneficially owned by them. The percentage of beneficial ownership is based upon 108,342,738 Ordinary Shares outstanding as of February 14, 2023. Ordinary Shares subject to options or warrants currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days of February 14, 2023 are deemed to be outstanding and beneficially owned by the person holding the options for the purposes of computing the percentage of beneficial ownership of that person and any group of which that person is a member, but are not deemed outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage of beneficial ownership for any other person. Unless otherwise indicated, the address for each holder listed below is Midatech Pharma PLC, Caspian Point, 1 Caspian Way, Cardiff, CF10 4DQ, United Kingdom. All holders of Ordinary Shares, including those shareholders listed below, have the same voting rights with respect to such shares.
| Name of Beneficial Owner | | Amount and Nature
Of Ownership | | | Percent
of Class | |
| Major Stockholders: | | | | | | | | |
| Entities affiliated with Dr. Lam Kong (1) | | | 10,389,610 | | | | 9.6% | |
| Armistice Capital LLC (2) | | | 9,670,700** | | | | 8.9% | |
| Directors and Senior Management: | | | | | | | | |
| Stephen Parker | | | -- | | | | * | |
| Simon Turton | | | 55,325 | | | | * | |
| Stephen Stamp (3) | | | 501,250 | | | | * | |
| Sijmen de Vries | | | 26,441 | | | | * | |
| Dmitry Zamoryakhin (4) | | | 109,375 | | | | * | |
| Directors and senior management as a group (5 persons) (4) | | | 692,391 | | | | * | |
__________________
| * | Less than one percent of the outstanding Ordinary Shares. |
| ** | Subject to 4.99% blocker. See Footnote (2) below. |
| (1) | Information in the table and this footnote is based upon information contained in a Schedule 13D filed with the SEC on April 4, 2019 by A&B (HK) Company Limited, A&B Brother Limited, China Medical System Holdings Limited, CMS Medical Venture Investment (HK) Limited, and Dr. Lam Kong. Includes (i) for A&B (HK) Company Limited, 5,194,805 Ordinary Shares held of record and 5,194,805 Ordinary Shares issuable upon the exercise of warrants, which are exercisable at March 3, 2020, and (ii) for CMS Medical Venture Investment (HK) Limited, 5,194,805 Ordinary Shares held of record. A&B (HK) Company Limited is a wholly owned subsidiary of A&B Brother Limited, which is wholly owned by Dr. Lam Kong. CMS Medical Venture Investment (HK) Limited is a wholly owned subsidiary of China Medical System Holdings Limited, of which Dr. Lam Kong is the President, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board and maintains a 43.96% indirect ownership interest. Each of A&B (HK) Company Limited and A&B Brother Limited is deemed to be the beneficial owner with shared dispositive and voting power with respect to 5,194,805 Ordinary Shares. Each of China Medical System Holdings Limited and CMS Medical Venture Investment (HK) Limited is deemed to be the beneficial owner with shared dispositive and voting power with respect to 5,194,805 Ordinary Shares. Dr. Lam Kong is deemed to be the beneficial owner with shared dispositive and voting power with respect to 10,389,610 Ordinary Shares. The principal business address of China Medical System Holdings Limited and CMS Medical Venture Investment (HK) Limited is Unit 2106, 21/F, Island Place Tower, 510 King’s Road, North Point, Hong Kong, China. The principal place of business for A&B (HK) Company Limited is Unit A, 11/F, Chung Pont Commercial Building, 300 Hennessy Road, Wanchai, Hong Kong, China. The principal business address for A&B Brother Limited is Trident Chambers, P.O. Box 146, Road Town, Tortola, British Virgin Island. The principal business address of Dr. Lam Kong is Unit 2106, 21/F, Island Place Tower, 510 King’s Road, North Point, Hong Kong, China. |
| (2) | Information in the table and this footnote is based primarily upon information contained in a Schedule 13G/A filed with the SEC on February 14, 2023 by Armistice Capital, LLC (though amounts included in such Schedule 13G/A have been adjusted in this prospectus to give effect to the reverse stock split and Depositary Share ratio change) and information provided to us by the stockholder. Armistice Capital Master Fund Ltd., or Armistice, holds warrants issued by us in October 2019 which entitle the holder to purchase up to 600,000 Depositary Shares (representing 3,000,000 Ordinary Shares) at an exercise price of $1.00 per Depositary Share. The warrants are exercisable as at February 14, 2022. The warrants are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 4.99%, which does not permit the selling stockholder to exercise that portion of the warrants that would result in the stockholder and its affiliates owning, after exercise, a number of our Ordinary Shares in excess of the beneficial ownership limitation. The amounts and percentages in the table give effect to the 4.99% beneficial ownership limitation. Armistice Capital, LLC, the investment manager of Armistice, and Steven Boyd, the managing member of Armistice Capital, LLC, hold shared voting and dispositive power over the shares held by Armistice. Each of Armistice Capital, LLC and Steven Boyd disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein. The principal business address of Armistice is c/o Armistice Capital, LLC, 510 Madison Avenue, 7th Floor, New York, New York, 10022. |
| (3) | Shares owned by Mr. Stamp include 451,250 Ordinary Shares subject to outstanding stock options which are exercisable at February 14, 2023 or will become exercisable within 60 days after such date. |
| (4) | Shares owned by Dr. Zamoryakhin include 109,375 Ordinary Shares subject to outstanding stock options which are exercisable at February 14, 2023 or will become exercisable within 60 days after such date. |
| (5) | Shares owed by all directors and senior management as a group include 560,825 Ordinary Shares subject to outstanding stock options, each of which are exercisable at February 14, 2023, or will become exercisable within 60 days after such date. |
As of February 14, 2023, approximately 34.4% of our outstanding Ordinary Shares was held by registered shareholders with addresses in the United Kingdom (excluding shares held by the custodian under our depositary agreement with the The Bank of New York Mellon), and we had 236 holders of record in the United Kingdom. As of February 14, 2023, The Bank of New York Mellon, as depositary for the Depositary Shares, held 59,876,200 Ordinary Shares, representing 55.3% of the issued share capital held at that date. As of February 14, 2023, we had 15 holders of record with an address in the United States. The number of holders of record or registered holders in the United States or United Kingdom is not representative of the number of beneficial holders or of the residence of beneficial holders.
Based on our share register, we believe that we are not directly or indirectly controlled by another corporation or government, or by any other natural or legal persons. There are no arrangement that may result in a change of control. Our major shareholders do not have different voting rights than other holders of our Ordinary Shares.
To our knowledge, other than due to the expiration of unexercised warrants held by our shareholders or as otherwise disclosed elsewhere in this prospectus, there has been no significant change in the percentage ownership of our Ordinary Shares held by the principal shareholders listed above in the last three years.
DESCRIPTION OF SHARE CAPITAL
The following describes our issued share capital, summarizes the material provisions of our Articles of Association and highlights certain differences in corporate law in the United Kingdom and the United State. This description of our share capital and summary of our Articles of Association is not complete, and is qualified by reference to our Articles of Association. You should read our Articles of Association, which are filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, for the provisions that are important to you.
The following describes our issued share capital, summarizes the material provisions of our articles of association and highlights certain differences in corporate law in the United Kingdom and the United States. Please note that this summary is not intended to be exhaustive. For further information please refer to the full version of our articles of association, which is included as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is part.
General
We are a public limited company organized under the laws of England and Wales under registered number 09216368. Our registered office is 1 Caspian Point, Caspian Way, Cardiff, CF10 4DQ, United Kingdom. The principal legislation under which we operate and our shares are issued is the United Kingdom Companies Act of 2006, or the Companies Act.
Issued Share Capital
Our issued share capital as of March 1, 2023 and June 30, 2022 was 173,346,738 and 98,493,413 Ordinary Shares, respectively. Each Ordinary Share has a nominal value 0.1p per share. Each issued Ordinary Share is fully paid. We currently have 1,000,001 deferred shares and no preference shares in our issued share capital.
There is no limit to the number of Ordinary Shares or preference shares that we are authorized to issue, as the concept of authorized capital is no longer applicable under the provisions of the Companies Act. There are no conversion rights, redemption provisions or sinking fund provisions relating to any Ordinary Shares.
We are not permitted under English law to hold our own Ordinary Shares unless they are repurchased by us and held in treasury. We do not currently hold any of our own Ordinary Shares.
History of Share Capital
Since January 1, 2019, our issued share capital has changed as provided below.
On February 26, 2019, we issued 10,389,610 units to new investors pursuant to a subscription agreement, or the subscription, for aggregate consideration of approximately £8.0 million. Each unit consisted of one Ordinary Share and one warrant to acquire Ordinary Shares.
On February 26, 2019, we issued (i) 4,331,384 units in connection with a placing, or the 2019 Placing, to certain new and existing investors and (ii) 1,716,952 Ordinary Shares to an existing investor, for an aggregate consideration of approximately £4.7 million. Each unit consisted of one Ordinary Share and one warrant to acquire Ordinary Shares.
On February 26, 2019, we issued 972,828 units in connection with an open offer to all of our existing shareholders who did not participate in the 2019 Placing, for an aggregate consideration of approximately £0.75 million. Each unit consisted of one Ordinary Share and one warrant to acquire Ordinary Shares.
On April 8, 2019, we effected a ratio change to our Depositary Shares, pursuant to which the ratio of Ordinary Shares to Depositary Shares was changed such that one Depositary Share represented 20 Ordinary Shares. Our Ordinary Shares were not affected by this change.
On October 8, 2019, we issued 25,000 Ordinary Shares for purchase by the Midatech Pharma Share Incentive Plan.
On October 25, 2019, we sold to an institutional investor 3,000,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 120,000 Depositary Shares in a registered direct offering at $25.00 per Depositary Share, resulting in gross proceeds of $3.0 million. In addition, we issued to the investor unregistered warrants to purchase a total of 3,000,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 120,000 Depositary Shares in a private placement, or the October Private Placement Warrants. We also issued unregistered placement agent warrants to purchase a total of 150,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 6,000 Depositary Shares to affiliates of H.C. Wainwright & Co., Inc. in a private placement, or the Wainwright October Warrants.
On March 3, 2020, following shareholder approval, we effected a one-for-20 reverse split of our Ordinary Shares and our Ordinary Shares began trading on AIM, on a split-adjusted basis as of such date. No fractional shares were issued in connection with the reverse stock split. As a result of the reverse stock split, the number of issued and outstanding Ordinary Shares was reduced to 23,494,981 shares as of March 3, 2020.
Concurrently with the reverse split, on March 3, 2020 we effected a ratio change in the number of Ordinary Shares represented by our Depositary Shares from 20 Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share to five Ordinary Shares per Depositary Share.
On May 20, 2020, we sold to certain institutional investors 9,090,910 Ordinary Shares represented by 363,636 Depositary Shares in a registered direct offering at $8.25 per Depositary Share, resulting in gross proceeds of $3.0 million. In addition, we issued to the investors unregistered warrants to purchase a total of 9,090,910 Ordinary Shares represented by 363,636 Depositary Shares in a private placement, or the May Private Placement Warrants. We also issued unregistered placement agent warrants to purchase a total of 454,546 Ordinary Shares represented by 18,182 Depositary Shares to affiliates of H.C. Wainwright & Co., Inc. in a private placement, or the Wainwright May Warrants.
On May 22, 2020, we issued 6,666,666 units, or Units, to certain non-U.S. investors in a placing in the United Kingdom for aggregate gross proceeds of £1.8 million. Each Unit comprised one new Ordinary Share and one warrant to purchase Ordinary Shares, or the UK Warrants. We also issued unregistered placement agent warrants to purchase a total of 333,333 Ordinary Shares to Turner Pope Investments (TPI) Limited, or Turner Pope.
On July 27, 2020, we issued 21,296,295 Ordinary Shares, including 2,777,777 Ordinary Shares issued pursuant to a broker option, to certain non-U.S. investors in a placing in the United Kingdom for aggregate gross proceeds of £5.75 million.
On August 19, 2020, we issued 2,500,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 100,000 Depositary Shares upon the exercise of warrants issued in May 2020 at an exercise price of $10.25 per share.
On September 30, 2020, we issued 25,000 Ordinary Shares to be purchased under the Midatech Pharma Share Incentive Plan.
On February 19, 2021, we issued 306,815 Ordinary Shares represented by 12,273 Depositary Shares upon the exercise of warrants issued in May 2020 at an exercise price of $10.3125 per share.
On July 6, 2021, we issued 35,087,720 Ordinary Shares to certain non-U.S. investors in a placing in the United Kingdom for aggregate gross proceeds of £10.0 million.
On March 22, 2022, we issued 26 Ordinary Shares upon the exercise of 26 warrants issued in February 2019 at an exercise price of £10 per share.
On May 3, 2022, we issued 25,000 Ordinary Shares to be purchased under the Midatech Pharma Share Incentive Plan.
On August 3, 2022, we issued warrants to purchase 333,333 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of £0.135 per share.
On September 26, 2022, we effected a ratio change to our Depositary Shares, pursuant to which the ratio of Ordinary Shares to Depositary Shares was changed such that one Depositary Share represented 25 Ordinary Shares. Our Ordinary Shares were not affected by this change.
On December 16, 2022, we sold to an institutional investor 9,849,325 Ordinary Shares represented by 393,973 Depositary Shares in a registered direct offering at $1.00 per Depositary Share, resulting in gross proceeds of approximately $0.4 million.
On February 15, 2023, we completed the closing of a Private Placement pursuant to which we sold to certain institutional investors (1) 65,004,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 2,600,160 Depositary Shares, (2) 258,620,550 Ordinary Shares represented by 10,344,822 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series A warrants issued in the Private Placement, (3) 387,930,900 Ordinary Shares represented by 15,517,236 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series B warrants issued in the Private Placement, and (4) up to 1,434,996,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 57,399,840 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of pre-funded warrants issued in the Private Placement, for aggregate gross proceeds of approximately $6.0 million. The Series A warrants, Series B warrants, and certain of the pre-funded warrants are subject to the receipt of stockholder approval at a general meeting.
In addition, subject to the receipt of stockholder approval at a general meeting, and in connection with the Private Placement, we will issue 10,738,775 Ordinary Shares represented by 429,551 Depositary Shares upon the exercise of placement agent warrants, and a Series A warrant exercisable for 12,500,000 Ordinary Shares presented by 500,000 Depositary Shares to the December Investor in connection with the Waiver.
Options
We have established the Midatech Pharma PLC 2014 Enterprise Management Incentive Scheme pursuant to which we have issued options to purchase Ordinary Shares to employees and directors. As of June 30, 2022, there were options to purchase 2,945,000 Ordinary Shares. The options lapse after ten years from the date of the grant. As of June 30, 2022, the weighted average remaining life of the options was 8.7 years.
In connection with our acquisition of DARA BioSciences, Inc., or DARA, in December 2015, we assumed all of DARA’s outstanding options, or DARA Options. As of June 30, 2022, there were outstanding DARA Options to purchase 2,822 Ordinary Shares with a weighted average remaining life of 2.4 years.
Warrants
October 2019 and May 2020 Warrants
The following is a brief summary of the October Private Placement Warrants, Wainwright October Warrants, May Private Placement Warrants and Wainwright May Warrants issued in connection with the October Private Placement and May Private Placement, as applicable, and is subject in all respects to the provisions contained in the applicable warrants, which, with respect to the October Private Placement Warrants and Wainwright October Warrants, are filed as exhibits to our Report on Form 6-K dated October 24, 2019, and for the May Private Placement Warrants and Wainwright May Warrants, are filed as exhibits to our Report on Form 6-K dated May 20, 2020. Unless otherwise stated, references to warrants in this subsection include the October Private Placement Warrants, May Private Placement Warrants, Wainwright October Warrants and Wainwright May Warrants.
Exercisability. The October Private Placement Warrants and Wainwright October Warrants became exercisable on December 23, 2019. The May Private Placement Warrants and Wainwright May Warrants became exercisable upon issuance. The October Private Placement Warrants and May Private Placement Warrants will expire five and one-half years from the initial exercise date, and the Wainwright October Warrants and Wainwright May Warrants will expire on October 22, 2024 and May 18, 2025, respectively. The holder shall deliver the aggregate exercise price for the Depositary Shares specified in the exercise notice within two trading days following the date of exercise (subject to the ‘cashless exercise’ arrangements described below).
Cashless Exercise. With respect to the October Private Placement Warrants and Wainwright October Warrants, if, more than six months after the date of issuance of such warrants, there is no effective registration statement registering, or no current prospectus available for, the resale of the Depositary Shares underlying such warrants, the holder may exercise the warrant, in whole or in part, on a cashless basis. With respect to the May Private Placement Warrants and Wainwright May Warrants, if there is no effective registration statement registering, or no current prospectus available for, the resale of the Depositary Shares underlying such warrants, the holder may exercise the warrant, in whole or in part, on a cashless basis.
Exercise Price. The exercise price of (i) each October Private Placement Warrant and Wainwright October Warrant is $1.00 and $31.25, respectively, per Depositary Share and (ii) each May Private Placement Warrants and Wainwright May Warrant is $10.25 and $10.3125 per Depositary Share, respectively, (other than with respect to one investor, for which the exercise price is $1.00), each subject to the ‘cashless exercise’ arrangements described above and to adjustment as described below.
Beneficial Ownership Limitation. A holder shall have no right to exercise any portion of a warrant, to the extent that, after giving effect to such exercise, such holder, together with such holder’s affiliates, and any persons acting as a group together with such holder or any such affiliate, would beneficially own in excess of, at the initial option of the holder thereof, 4.99% or 9.99%, as applicable, of the number of Ordinary Shares outstanding immediately after giving effect to the issuance of the Ordinary Shares underlying the Depositary Shares upon such exercise. The holder of the warrant, upon notice to us, may increase or decrease the beneficial ownership limitation to a percentage not to exceed 9.99%, provided that any increase in the beneficial ownership limitation shall not be effective until 61 days following notice to us. Beneficial ownership of the holder and its affiliates will be determined in accordance with Section 13(d) of the Exchange Act, and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder.
Stock dividends and stock splits. If we pay a stock dividend or otherwise make a distribution payable in Depositary Shares or Ordinary Shares, or any other equity or equivalent securities, subdivide or combine outstanding Depositary Shares or Ordinary Shares, or reclassify Depositary Shares, Ordinary Shares or any shares of our capital stock, the exercise price of each warrant will be adjusted by multiplying the then exercise price by a fraction, the numerator of which shall be the number of Depositary Shares (excluding treasury shares, if any) outstanding immediately before such event, and the denominator of which shall be the number of Depositary Shares outstanding immediately after such event.
Rights Offerings; pro rata distributions. If we issue Ordinary Share equivalents or rights to purchase shares, warrants, securities or other property pro rata to holders of Depositary Shares, a holder of a warrant will be entitled to acquire, subject to the beneficial ownership limitation described above, such securities or property that such holder could have acquired if such holder had held the number of Depositary Shares issuable upon complete exercise of the warrant immediately prior to the date a record is taken for such issuance. If we declare or make any dividend or other distribution of assets or rights to acquire assets to holders of Depositary Shares or Ordinary Shares, a holder of a warrant will be entitled to participate, subject to the beneficial ownership limitation, in such distribution to the same extent that the holder would have participated therein if the holder had held the number of Depositary Shares issuable upon full exercise of the warrant.
Fundamental Transaction. If we effect a fundamental transaction, including, among other things, a merger, sale of substantially all of our assets, tender offer, exchange offer and other business combination transactions, then upon any subsequent exercise of a warrant, the holder thereof shall have the right to receive, for each Ordinary Share represented by the Depositary Shares that would have been issuable upon such exercise immediately prior to the occurrence of such fundamental transaction, the number of shares of the successor’s or acquiring corporation’s securities, if it is the surviving corporation, and any additional consideration receivable as a result of such fundamental transaction by a holder of the number of Ordinary Shares represented by the Depositary Shares for which the warrant is exercisable immediately prior to such fundamental transaction.
Transferability. Each warrant and all rights thereunder are transferable, in whole or in part, upon surrender of the warrant, together with a written assignment of the warrant subject to applicable securities laws; provided, however, that the Wainwright October Warrants and Wainwright May Warrants are subject to certain FINRA transfer restrictions. We do not intend to apply for listing of the warrants on any securities exchange or other trading system.
No Rights as Shareholder Until Exercise. Except as set forth in the warrants, the holders of the warrants do not have any voting rights, dividends or other rights as a holder of our capital stock until they exercise the warrants.
May 2020 United Kingdom Placing Warrants
On May 22, 2020, we issued 6,666,666 Units, with each Unit comprising one new Ordinary Share and one UK Warrant. The exercise price of the UK Warrants is £0.34 per share and it expires five years and six months from the issuance date. We also issued UK Warrants to purchase a total of 333,333 Ordinary Shares to Turner Pope, the placing agent, in connection with the closing of such offering, on the same terms and conditions as the other investors in the offering.
August 2022 Warrants
On August 3, 2022, we issued warrants to purchase 333,333 Ordinary Shares to Strand Hanson Limited, in payment for services rendered. The exercise price of such warrants is £0.135 per share and they expire three years from the issuance date.
Series A Warrants, Series B Warrants, Pre-Funded Warrants and Ladenburg Warrants
The following is a brief summary of the Series A warrants, Series B warrants, pre-funded warrants and the Ladenburg Warrants issued in connection with the Private Placement, and is subject in all respects to the provisions contained in the applicable warrants, which, are filed as exhibits to our Report on Form 6-K dated February 9, 2023. Unless otherwise stated, references to warrants in this subsection include the Series A warrants, the Series B warrants, pre-funded warrants and Ladenburg Warrants.
Exercisability. Other than pre-funded warrants to purchase 7,744,662 Depositary Shares, the warrants will became exercisable upon stockholder approval at a general meeting. The Series A warrants expire five years from the initial exercise date, the Series B warrants expire three years from the initial exercise date and the Ladenburg Warrants expire three years from the initial exercise date. The pre-funded warrants do not expire. The holder shall deliver the aggregate exercise price for the Depositary Shares specified in the exercise notice within two trading days following the date of exercise (subject to the ‘cashless exercise’ arrangements described below). The pre-funded warrants are exercisable at any time after the initial exercise date until exercised in full and may be exercised on a cashless basis. In addition, on the Pre-Funded Warrant Trigger Date (as defined below), the number of Depositary Shares issuable under the pre-funded warrants shall increase, and only increase, to equal a number of Depositary Shares determined by the quotient of (x) the aggregate subscription amount of the holder for the Pre-Funded Warrant divided by (y) the average of the volume weighted average price for the five trading days immediately prior to the applicable Pre-Funded Warrant Trigger Date (subject to a floor price of $0.30; provided, however, that the floor price shall be rese to $0.10 following the receipt of Stockholder Approval (subject to adjustment for forward and reverse stock splits and the like after the Initial Exercise Date)). The “Pre-Funded Warrant Trigger Date” means (i) the date a registration statement covering the securities is declared effective by the SEC, or the Resale Effective Date, (ii) in the event that the initial registration statement (as defined below) does not register all registrable securities (as defined in the registration rights agreement with the investors), the date that any subsequent registration statement is declared effective by the SEC and (iii) the date that all of the Depositary Shares issuable pursuant to the transaction documents (without giving effect to any limitations on conversion or exercise) may be sold pursuant to Rule 144 (assuming cashless exercise of the warrants with regard to the Depositary Shares), in the event that all of the registrable securities are not then registered on an effective registration statement.
Cashless Exercise. The Series A warrants and Series B warrants may be exercised on a cashless basis. In such event, the aggregate number of Depositary Shares issuable in such cashless exercise pursuant to any given notice of exercise electing to effect an alternative cashless exercise shall equal the product of (x) the aggregate number of Depositary Shares that would be issuable upon exercise of the Series A warrant or Series B warrant in accordance with the terms of thereof if such exercise were by means of a cash exercise rather than a cashless exercise and (y) 1.00.
Exercise Price. The exercise price of each (i) Series A warrant and Series B warrant is $0.67 per Depositary Share, (ii) pre-funded warrant is $0.0001 per Depositary Share, and (ii) Ladenburg Warrant is $0.8375 per Depositary Share, respectively, each subject to the ‘cashless exercise’ arrangements described above and to adjustment as described herein. In addition, on the sixth trading day immediately following the Resale Effective Date, or the Trigger Date, the exercise price of the Series A warrants and Series B warrants shall be reduced, and only reduced, to the lesser of (i) the then exercise price and (ii) 90% of the VWAP for the five trading day period immediately prior to the Trigger Date; provided, however, that the exercise price shall in no event be less than $0.10 (subject to adjustment for reverse and forward stock splits, stock dividends, stock combinations and other similar transactions of the Depositary Shares and/or the Ordinary Shares, as applicable), which shall thereafter be the new exercise price, subject to further adjustment under the terms of the Series A warrants and Series B warrants.
Beneficial Ownership Limitation. A holder shall have no right to exercise any portion of a warrant, to the extent that, after giving effect to such exercise, such holder, together with such holder’s affiliates, and any persons acting as a group together with such holder or any such affiliate, would beneficially own in excess of 9.99% (or in the case of the Ladenburg Warrants, 4.99%), of the number of Ordinary Shares outstanding immediately after giving effect to the issuance of the Ordinary Shares underlying the Depositary Shares upon such exercise. The holder of the warrant, upon notice to us, may increase or decrease the beneficial ownership limitation to a percentage not to exceed 9.99%, provided that any increase in the beneficial ownership limitation shall not be effective until 61 days following notice to us. Beneficial ownership of the holder and its affiliates will be determined in accordance with Section 13(d) of the Exchange Act, and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder.
Stock dividends and stock splits. If we pay a stock dividend or otherwise make a distribution payable in Depositary Shares or Ordinary Shares, or any other equity or equivalent securities, subdivide or combine outstanding Depositary Shares or Ordinary Shares, or reclassify Depositary Shares, Ordinary Shares or any shares of our capital stock, the exercise price of each warrant will be adjusted by multiplying the then exercise price by a fraction, the numerator of which shall be the number of Depositary Shares (excluding treasury shares, if any) outstanding immediately before such event, and the denominator of which shall be the number of Depositary Shares outstanding immediately after such event.
Rights Offerings; pro rata distributions. If we issue Ordinary Share equivalents or rights to purchase shares, warrants, securities or other property pro rata to holders of Depositary Shares, a holder of a warrant will be entitled to acquire, subject to the beneficial ownership limitation described above, such securities or property that such holder could have acquired if such holder had held the number of Depositary Shares issuable upon complete exercise of the warrant immediately prior to the date a record is taken for such issuance. If we declare or make any dividend or other distribution of assets or rights to acquire assets to holders of Depositary Shares or Ordinary Shares, a holder of a warrant will be entitled to participate, subject to the beneficial ownership limitation, in such distribution to the same extent that the holder would have participated therein if the holder had held the number of Depositary Shares issuable upon full exercise of the warrant.
Fundamental Transaction. If we effect a fundamental transaction, including, among other things, a merger, sale of substantially all of our assets, tender offer, exchange offer and other business combination transactions, then upon any subsequent exercise of a warrant, the holder thereof shall have the right to receive, for each Ordinary Share represented by the Depositary Shares that would have been issuable upon such exercise immediately prior to the occurrence of such fundamental transaction, the number of shares of the successor’s or acquiring corporation’s securities, if it is the surviving corporation, and any additional consideration receivable as a result of such fundamental transaction by a holder of the number of Ordinary Shares represented by the Depositary Shares for which the warrant is exercisable immediately prior to such fundamental transaction. In addition, with respect to the Series A warrants, Series B warrants and the Ladenburg Warrants, in the event of a fundamental transaction that is (i) an all cash or substantially all cash transaction, (ii) a “Rule 13e-3 transaction” as defined in Rule 13e-3 under the Exchange Act, or (iii) with certain limited exceptions, a fundamental transaction involving a person or entity not traded on a national securities exchange or other established trading market, including, but not limited to, the London Stock Exchange, AIM, The New York Stock Exchange, Inc., The NYSE MKT, The NASDAQ Global Select Market, The NASDAQ Global Market, The NASDAQ Capital Market, the OTC QX, the OTC QB or the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board, then the Company or any successor entity will pay at the holder’s option, exercisable at any time concurrently with or within 30 days after the consummation of the fundamental transaction, an amount of cash equal to the value of the Warrant as determined in accordance with the Black Scholes option pricing model.
Transferability. Each warrant and all rights thereunder are transferable, in whole or in part, upon surrender of the warrant, together with a written assignment of the warrant subject to applicable securities laws; provided, however, that the Ladenburg Warrants are subject to certain FINRA transfer restrictions. We do not intend to apply for listing of the warrants on any securities exchange or other trading system.
No Rights as Shareholder Until Exercise. Except as set forth in the warrants, the holders of the warrants do not have any voting rights, dividends or other rights as a holder of our capital stock until they exercise the warrants.
Articles of Association
The following is a summary of certain provisions of our articles of association. Please note that this is only a summary and is not intended to be exhaustive. For further information please refer to the full version of our articles of association, which is included as an exhibit to our most recent Annual Report on Form 20-F.
Shares and Rights Attaching to Them
Objects
The objects of our Company are unrestricted.
Share Rights
Subject to any special rights attaching to shares already in issue, our shares may be issued with or have attached to them any preferred, deferred or other special rights or privileges or be subject to such restrictions as we may resolve by ordinary resolution of the shareholders or decision of our board.
Voting Rights
Without prejudice to any rights or restrictions as to voting rights attached to any shares forming part of our share capital from time to time, the voting rights attaching to shares are as follows:
| | · | on a show of hands every shareholder who is present in person and each duly authorized representative present in person of a shareholder that is a corporation shall have one vote; |
| | · | on a show of hands, each proxy present in person has one vote for and one vote against a resolution if the proxy has been duly appointed by more than one shareholder and the proxy has been instructed by one or more of those shareholders to vote for the resolution and by one or more other of those shareholders to vote against it; |
| | · | on a show of hands, each proxy present in person has one vote for and one vote against a resolution if the proxy has been duly appointed by more than one shareholder entitled to vote on the resolution and either: (1) the proxy has been instructed by one or more of those shareholders to vote for the resolution and has been given any discretion by one or more other of those shareholders to vote and the proxy exercises that discretion to vote against it; or (2) the proxy has been instructed by one or more of those shareholders to vote against the resolution and has been given any discretion by one or more other of those shareholders to vote and the proxy exercises that discretion to vote for it; and |
| | · | on a poll every shareholder who is present in person or by proxy shall have one vote for each share of which he is the holder. |
At any general meeting a resolution put to the vote of the meeting shall be decided on a show of hands unless a poll is demanded. Subject to the provisions of the Companies Act, as described in “Differences in Corporate Law - Voting Rights” in this prospectus, a poll may be demanded by:
| | · | the chairman of the meeting; |
| | · | at least five shareholders present in person or by proxy and entitled to vote; |
| | · | any shareholder(s) present in person or by proxy and representing in the aggregate not less than 10% of the total voting rights of all shareholders having the right to vote on the resolution; or |
| | · | any shareholder(s) present in person or by proxy and holding shares conferring a right to vote on the resolution on which there have been paid up sums in the aggregate equal to not less than 10% of the total sums paid up on all shares conferring that right. |
Restrictions on Voting
No shareholder shall be entitled to vote at any general meeting or at any separate class meeting in respect of any share held by him unless all calls or other sums payable by him in respect of that share have been paid.
The Board of Directors may from time to time make calls upon the shareholders in respect of any money unpaid on their shares and each shareholder shall (subject to at least 14 days’ notice specifying the time or times and place of payment) pay at the time or times so specified the amount called on his shares. If a call remains unpaid after it has become due and payable, and the fourteen days’ notice provided by the Board of Directors has not been complied with, any share in respect of which such notice was given may be forfeited by a resolution of the Board of Directors.
A shareholder’s right to attend general or class meetings of the Company or to vote in respect of his shares may be suspended by the Board of Directors in accordance with our Articles of Association if he fails to comply with a proper request for the disclosure of interests regarding the shares. See “Other United Kingdom Law Considerations—Disclosure of Interest in Shares” in this prospectus.
Dividends
We may, by ordinary resolution, declare a dividend to be paid to the share owners according to their respective rights and interests in profits, and may fix the time for payment of such dividend. No dividend may be declared in excess of the amount recommended by the directors. The Board of Directors may from time to time declare and pay to our share owners such interim dividends as appear to the directors to be justified by our profits available for distribution. There are no fixed dates on which entitlement to dividends arises on our Ordinary Shares.
The share owners may pass, on the recommendation of the directors, an ordinary resolution to direct that all or any part of a dividend to be paid by distributing specific assets, in particular paid up shares or debentures of any other body corporate. Our articles of association also permit, with the prior authority of an ordinary resolution of shareholders, a scrip dividend scheme under which share owners may be given the opportunity to elect to receive fully paid Ordinary Shares instead of cash, or a combination of shares and cash, with respect to future dividends.
By the way of the exercise of a lien, if a share owner owes us any money relating in any way to shares, the Board of Directors may deduct any of this money from any dividend on any shares held by the share owner, or from other money payable by us in respect of the shares. Money deducted in this way may be used to pay the amount owed to us.
Unclaimed dividends and other money payable in respect of a share can be invested or otherwise used by directors for our benefit until they are claimed. A dividend or other money remaining unclaimed 12 years after it first became due for payment will be forfeited and shall revert to the Company.
A shareholder’s right to receive dividends on his shares may, if they represent more than 0.25% of the issued shares of that class, be suspended by the directors if he fails to comply with a proper request for the disclosure of interests regarding the shares. See “Other United Kingdom Law Considerations—Disclosure of Interests in Shares” in this prospectus.
Change of Control
There is no specific provision in our Articles of Association that would have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change of control. We are, however, subject to the provisions of the United Kingdom City Code on Takeovers and Mergers, or the City Code, which contains detailed provisions regulating the timing and manner of any takeover offer for those of the Company’s shares which confer voting rights. See “Other United Kingdom Law Considerations—City Code on Takeovers and Mergers” in this prospectus.
Variation of Rights
Whenever our share capital is divided into different classes of shares, all or any of the rights attached to any class may be varied or abrogated in such manner (if any) as may be provided by those rights or (in the absence of any such provision) either with the consent in writing of the holders of at least 75% of the issued shares of that class or with the authority of a special resolution passed at a separate general meeting of the holders of the shares of that class.
Alteration of Share Capital and Repurchases
Subject to the provisions of the Companies Act, and without prejudice to any relevant special rights attached to any class of shares, we may, from time to time:
| | · | increase our share capital by allotting and issuing new shares in accordance with the our articles of association and any relevant shareholder resolution; |
| | · | consolidate all or any of our share capital into shares of a larger nominal amount (i.e., par value) than the existing shares; |
| | · | subdivide any of our shares into shares of a smaller nominal amount (i.e., par value) than our existing shares; or |
| | · | redenominate our share capital or any class of share capital. |
Preemptive Rights and New Issuance of Shares
Under the Companies Act, the issuance of equity securities (except shares held under an employees’ share scheme) that are to be paid for wholly in cash must be offered first to the existing holders of equity securities in proportion to the respective nominal amounts (i.e., par values) of their holdings on the same or more favorable terms, unless a special resolution to the contrary has been passed or the articles of association otherwise provide an exclusion from this requirement (which exclusion can be for a maximum of five years after which our shareholders’ approval would be required to renew the exclusion). In this context, “equity securities” means ordinary shares (and would exclude shares that, with respect to dividends or capital, carry a right to participate only up to a specified amount in a distribution), and any and all rights to subscribe for or convert securities into such ordinary shares. This differs from U.S. law, under which shareholders generally do not have pre-emptive rights unless specifically granted in the certificate of incorporation or otherwise.
By way of resolutions passed at our general meeting held on January 23, 2023, authorities were given to the directors to allot shares in the Company, or to grant rights to subscribe for or to convert or exchange any security into shares in the Company, up to an aggregate nominal amount of £501,838.034 for a period up to the conclusion of our 2023 annual general meeting. Pre-emptive rights under the Companies Act will not apply in respect of allotment of shares for cash made pursuant to such authority, up to approximately 10% of the issued share capital. Renewal of such authorization is expected to be sought at each of our annual general meetings.
In circumstances where we allot further Ordinary Shares, we must apply for such new Ordinary Shares to be admitted to trading on AIM, which in some instances requires the publication of an admission document.
Transfer of Shares
Any certificated shareholder may transfer all or any of his shares by an instrument of transfer in the usual common form or in any other manner which is permitted by the Companies Act and approved by the Board of Directors. Any written instrument of transfer shall be signed by or on behalf of the transferor and (in the case of a partly paid share) the transferee.
All transfers of uncertificated shares shall be made in accordance with and subject to the provisions of the Uncertificated Securities Regulations 2001 and the facilities and requirements of its relevant system. The Uncertificated Securities Regulations 2001 permit shares to be issued and held in uncertificated form and transferred by means of a computer-based system.
The Board of Directors may decline to register any transfer of any share unless it is:
| | · | a share on which the Company has no lien; |
| | · | in respect of only one class of shares; |
| | · | in favor of a single transferee or not more than four transferees; |
| | · | duly stamped or duly certificated or otherwise shown the satisfaction of the Board of Directors to be exempt from any required stamp duty; or |
| | · | delivered for registration at the Company’s registered office or such other place as the Board of Directors may decide, accompanied by the certificate for the shares to which it relates (other than uncertificated shares) and any other evidence the Board of Directors may reasonably require to provide the title to such share of the transferor. |
If the Board of Directors declines to register a transfer it shall, as soon as practicable and in any event within two months after the date on which the transfer is lodged, send to the transferee notice of the refusal, together with reasons for the refusal.
CREST
To be traded on AIM, securities must be able to be transferred and settled through the CREST system. CREST is a computerized paperless share transfer and settlement system which allows securities to be transferred by electronic means, without the need for a written instrument of transfer. The Articles of Association are consistent with CREST membership and, among other things, allow for the holding and transfer of shares in uncertificated form.
Shareholder Meetings
Annual General Meetings
In accordance with the Companies Act, we are required in each year to hold an annual general meeting in addition to any other general meetings in that year and to specify the meeting as such in the notice convening it. The annual general meeting shall be convened whenever and wherever the board sees fit, subject to the requirements of the Companies Act, as described in “Differences in Corporate Law—Annual General Meeting” and “Differences in Corporate Law—Notice of General Meetings” in this prospectus.
Notice of General Meetings
The arrangements for the calling of general meetings are described in “Differences in Corporate Law—Notice of General Meetings” in this prospectus.
Subject to certain conditions, holders of Depositary Shares are entitled to receive notices under the terms of the deposit agreement relating to the Depositary Shares. See “Description of American Depositary Shares—Voting Rights” in this prospectus.
Quorum of General Meetings
No business shall be transacted at any general meeting unless a quorum is present, but the absence of a quorum shall not preclude the appointment, choice or election of a chairman which shall not be treated as part of the business of the meeting. At least two shareholders present in person or by proxy and entitled to vote shall be a quorum for all purposes.
Class Meetings
The provisions in the Articles of Association relating to general meetings apply to every separate general meeting of the holders of a class of shares except that:
| | · | no member, other than a member of the Board of Directors, shall be entitled to notice of it or attend such meeting unless he is a holder of shares of that class; |
| | · | the quorum for such class meeting shall be two holders in person or by proxy representing not less than one-third in nominal value of the issued shares of the class; |
| | · | at the class meeting, a holder of shares of the class present in person or by proxy may demand a poll and shall on a poll be entitled to one vote for every shares of the class held by him; and |
| | · | if at any adjourned meeting of such holders a quorum is not present at the meeting, one holder of shares of the class present in person or by proxy at an adjourned meeting constitutes a quorum. |
Directors
Number of Directors
We may not have less than two directors on our Board of Directors. We have no maximum number of directors, though we may fix a maximum number by ordinary resolution of the shareholders. We may, by ordinary resolution of the shareholders, vary the minimum and any maximum number of directors from time to time.
Appointment of Directors
Subject to the provisions of the Articles of Association, we may, by ordinary resolution of the shareholders, elect any person to be a director, either to fill a casual vacancy or as an addition to the existing board.
Without prejudice to the power to appoint any person to be a director by shareholder resolution, the Board of Directors has the power to appoint any person to be a director, either to fill a casual vacancy or as an addition to the existing Board of Directors. Any director appointed by the Board of Directors will hold office only until the earlier to occur of the close of the next following annual general meeting and someone being appointed in his stead at that meeting. Such a director is eligible for re-election at that meeting but shall not be taken into account in determining the directors or the number of directors who are to retire by rotation at such meeting.
Rotation of Directors
At every annual general meeting, one-third of the directors or, if their number is not a multiple of three, then the number nearest to and not exceeding one-third, shall retire from office and each director must retire from office at least once every three years. If there are fewer than three directors, one director shall make himself or herself available for re-election
The directors to retire on each occasion shall be those subject to retirement by rotation who have been longest in office since their last election, but as between persons who became or were re-elected directors on the same day those to retire shall (unless they otherwise agree amongst themselves) be determined by lot.
A director who retires at the annual general meeting shall be eligible for re-election.
The shareholders may, at the meeting at which a director retires, fill the vacated office by electing a person and in default the retiring director shall, if willing to continue to act, be deemed to have been re-elected, unless at such meeting it is expressly resolved not to fill such vacated office or unless a resolution for the re-election of such director shall have been put to the meeting and lost or such director has given notice in writing to us that he is unwilling to be re-elected or such director has attained the retirement age applicable to him as director pursuant to the Companies Act.
Director’s Interests
The Board of Directors may authorize, to the fullest extent permitted by law, any matter proposed to them which would otherwise result in a director infringing his duty to avoid a situation in which he has, or can have, a direct or indirect interest that conflicts, or possibly may conflict, with our interests and which may reasonably be regarded as likely to give rise to a conflict of interest. A director shall not, save as otherwise agreed by him, be accountable to us for any benefit which he (or a person connected with him) derives from any matter authorized by the directors and any contract, transaction or arrangement relating thereto shall not be liable to be avoided on the grounds of any such benefit.
Subject to the requirements under Sections 175, 177 and 182 of the Companies Act (which require a director to avoid a situation in which he has, or can have, a direct or indirect interest that conflicts, or possibly conflicts, with our interests, and to declare any interest that he has, whether directly or indirectly, in a proposed or existing transaction or arrangement with us), and provided that he has disclosed to the Board of Directors the nature and extent of any interest of his in accordance with the Companies Act and the Articles of Association, a director notwithstanding his office:
| | · | may be a party to, or otherwise interested in, any transaction or arrangement with us or in which we are otherwise interested; |
| | · | may be a director or other officer of, or employed by, or a party to any transaction or arrangement with, or otherwise interested in, any body corporate promoted by us or in which we are otherwise interested; and |
| | · | shall not, by reason of his office, be accountable to us for any benefit which he derives from any such office or employment or from any such transaction or arrangement or from any interest in any such body corporate and no such transaction or arrangement shall be liable to be avoided on the ground of any such interest or benefit. |
In the case of interests arising where a director is in any way, directly or indirectly, interested in (a) a proposed transaction or arrangement with us or (b) a transaction or arrangement that has been entered into by us and save as otherwise provided by the Articles of Association, such director shall not vote at a meeting of the Board of Directors or of a committee of the Board of Directors on any resolution concerning such matter in which he has a material interest (otherwise than by virtue of his interest in shares, debentures or other securities of, or otherwise in or through, us) unless his interest or duty arises only because the case falls within one or more of the following paragraphs:
| | · | the resolution relates to the giving to him or a person connected with him of a guarantee, security or indemnity in respect of money lent to, or an obligation incurred by him or such a person at the request of or for the benefit of, us or any of our subsidiaries; |
| | · | the resolution relates to the giving of a guarantee, security or indemnity in respect of a debt or obligation of ours or any of our subsidiaries for which the director or a person connected with him has assumed responsibility in whole or part under a guarantee or indemnity or by the giving of security; |
| | · | the resolution relates in any way to any other company in which he is interested, directly or indirectly and whether as an officer or shareholder or otherwise howsoever, provided that he and any persons connected with him do not to his knowledge hold an interest in shares representing one per cent or more of any class of the equity share capital of such company or of the voting rights available to shareholder of such company; |
| | · | the resolution relates in any way to an arrangement for the benefit of our employees or any employees of our subsidiaries which does not award him as such any privilege or benefit not generally awarded to the employees to whom such arrangement relates; |
| | · | the resolution relates in any way to the purchase or maintenance for the directors of insurance; or |
| | · | the resolution is in respect of any matter in which the interest of the director cannot reasonably be regarded as conflicting. |
A director shall not be counted in the quorum present at a meeting in relation to a resolution on which he is not entitled to vote.
If a question arises at a meeting of the Board of Directors or of a committee of the Board of Directors as to the right of a director to vote or be counted in the quorum, and such question is not resolved by his voluntarily agreeing to abstain from voting or not to be counted in the quorum, the question may, before the conclusion of the meeting, be referred to the chairman of the meeting and his ruling in relation to any director other than himself shall be final and conclusive except in a case where the nature or extent of the interest of the director concerned has not been fairly disclosed.
An interest of a person connected with a director shall be treated as an interest of the director and Section 252 of the Companies Act shall determine whether a person is connected with a director.
Directors’ Fees and Remuneration
Each of the directors shall be paid a fee at such rate as may from time to time be determined by the Board of Directors (or for the avoidance of doubt any duly authorized committee of the Board of Directors) provided that the aggregate of all such fees so paid to directors shall not exceed £300,000 per annum, or such higher amount as may from time to time be determined by ordinary resolution of shareholders.
Each director may be paid his reasonable traveling, hotel and other expenses of attending and returning from meetings of the Board of Directors or committees thereof of or general meetings or separate meetings of the holders class of shares or of debentures and shall be paid all expenses properly and reasonably incurred by him in the conduct of the Company’s business or in the discharge of his duties as a director. Any director who, by request, goes or resides abroad for any purposes required by us or who performs services which in the opinion of the Board of Directors go beyond the ordinary duties of a director may be paid such extra remuneration as the Board of Directors may determine.
An executive director shall receive such remuneration as the Board of Directors may determine, and either in addition to or in lieu of his remuneration as a director as detailed above.
Age Limitations and Share Ownership
We do not have any age limitations for our directors, nor do we have mandatory retirement as a result of reaching a certain age. Our directors are not required to hold any shares in the Company.
Borrowing Power
Our directors may exercise all the powers of the Company to borrow or raise money and mortgage or charge all or any part of our undertaking, property and assets (present and future), and uncalled capital. Subject to the Companies Act, the directors may also create and issue debentures, other loan stock and other securities, whether outright or as collateral security for any debt, liability or obligation of the Company or of any third party. Our directors are required to restrict the borrowings of the Company to ensure that the aggregate principal amount of borrowings at any one time outstanding and all of its subsidiary undertakings (other than intra-Group borrowing) shall not at any time, without the previous sanction of an ordinary resolution of the Company, exceed two times the gross asset value of the Company and our subsidiaries.
Liability of Midatech and its Directors and Officers
Subject to the provisions on indemnities set out in Companies Act, every director, alternate director or former director (and of any associated company) shall be entitled to be indemnified out of our assets against all costs and liabilities incurred by him or her in relation to any proceedings or any regulatory investigation or action which relate to anything done or omitted or alleged to have been done or omitted by him or her as a director so long as the indemnities do not cover liability for breach of duty to the Company or cover any fine, costs or related expense in connection with any proceedings for default on the part of the director. Lawful indemnities extend to the provision of funds to him or her by the Company to meet expenditure incurred or to be incurred by him in defending himself in any proceedings (whether civil or criminal) or in connection with an application for statutory relief or in an investigation by a regulatory authority which must however be repaid where such proceedings, application, investigation or action are in connection with any alleged negligence, default, breach of duty or breach of trust by him or her in relation to the Company (or any associated company of ours) and he or she is convicted or found in default thereof. Under English law, any provision that purports to exempt a director of a company (to any extent) from any liability that would otherwise attach to him in connection with any negligence, default, breach of duty or breach of trust in relation to the company is void.
Under a deed poll declared by us on August 5, 2015, or a Deed of Indemnity, our Board of Directors and our Company Secretary are indemnified against costs and liabilities incurred in connection with their office, other than any liability owed by such person to the Company itself (or any of our associated entities) and other than indemnification for liabilities in certain circumstances, which are prohibited by virtue of the Companies Act. The Deed of Indemnity provides that a director may also be lent sums to finance any relevant defense costs, provided that, in the event such proceedings involve criminal or civil matters in which the person is convicted or has a judgment made against him or her, then such loan must be repaid. Our total aggregate liability of Midatech under the Deed of Indemnity is £5 million.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to our directors, officers and controlling persons pursuant to a charter provision, by-law, contract, arrangements, statute or otherwise, we acknowledge that in the opinion of the SEC such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable.
Other United Kingdom Law Considerations
Notification of Voting Rights
A shareholder in a public company incorporated in the United Kingdom whose shares are admitted to trading on AIM is required pursuant to Rule 5 of the Disclosure Guidance and Transparency Rules of the United Kingdom Financial Conduct Authority to notify us of the percentage of his voting rights if the percentage of voting rights which he holds as a shareholder or through his direct or indirect holding of financial instruments (or a combination of such holdings) reaches, exceeds or falls below 3% and each 1% threshold thereafter up to 100% as a result of an acquisition or disposal of shares.
Mandatory Purchases and Acquisitions
Pursuant to Sections 979 to 991 of the Companies Act, where a takeover offer has been made for us and the offeror has acquired or unconditionally contracted to acquire not less than 90% in value of the shares to which the offer relates and not less than 90% of the voting rights carried by those shares, the offeror may give notice to the holder of any shares to which the offer relates which the offeror has not acquired or unconditionally contracted to acquire that he wishes to acquire, and is entitled to so acquire, those shares on the same terms as the general offer. The offeror would do so by sending a notice to the outstanding minority shareholders telling them that it will compulsorily acquire their shares. Such notice must be sent within three months of the last day on which the offer can be accepted in the prescribed manner. The squeeze-out of the minority shareholders can be completed at the end of six weeks from the date the notice has been given, following which the offeror can execute a transfer of the outstanding shares in its favor and pay the consideration to us, and we would hold the consideration on trust for the outstanding minority shareholders. The consideration offered to the outstanding minority shareholders whose shares are compulsorily acquired under the Companies Act must, in general, be the same as the consideration that was available under the takeover offer.
Sell Out
The Companies Act also gives our minority shareholders a right to be bought out in certain circumstances by an offeror who has made a takeover offer for all of our shares. The holder of shares to which the offer relates, and who has not otherwise accepted the offer, may require the offeror to acquire his shares if, prior to the expiry of the acceptance period for such offer, (i) the offeror has acquired or agreed to acquire not less than 90% in value of the voting shares, and (ii) not less than 90% of the voting rights carried by those shares. The offeror may impose a time limit on the rights of minority shareholders to be bought out that is not less than three months after the end of the acceptance period. If a shareholder exercises his rights to be bought out, the offeror is required to acquire those shares on the terms of this offer or on such other terms as may be agreed.
Disclosure of Interest in Shares
Pursuant to Part 22 of the Companies Act, we are empowered by notice in writing to any person whom we know or have reasonable cause to believe to be interested in our shares, or at any time during the three years immediately preceding the date on which the notice is issued has been so interested, requiring such person within a reasonable time to disclose to us particulars of that person’s interest and (so far as is within his knowledge) particulars of any other interest that subsists or subsisted in those shares. The Articles of Association specify that a response is required from such person within 14 days after service of any such notice.
Under the Articles of Association, if a person defaults in supplying us with the required particulars in relation to the shares in question, or Default Shares, the directors may by notice direct that:
| | · | in respect of the Default Shares, the relevant member shall not be entitled to attend or vote (either in person or by proxy) at any general meeting or of a general meeting of the holders of a class of shares or upon any poll or to exercise any right conferred by the Default Shares; and/or |
| | · | where the Default Shares represent at least 0.25% of their class, (a) any dividend (or any part of a dividend) payable in respect of the Default Shares shall be retained by us without liability to pay interest, (b) the shareholder may not be entitled to elect to receive shares instead of a dividend, and (c) no transfers by the relevant member of any Default Shares may be registered (unless the member himself is not in default and the transfer does not relate to Default Shares, the transfer is exempt or that the transfer is permitted under the U.K. Uncertificated Securities Regulations 2001). |
Purchase of Own Shares
Under English law, a limited company may only purchase or redeem its own shares out of the distributable profits of the company or the proceeds of a fresh issue of shares made for the purpose of financing the purchase, provided that they are not restricted from doing so by their articles. A limited company may not purchase or redeem its own shares if, as a result of the purchase, there would no longer be any issued shares of the company other than redeemable shares or shares held as treasury shares. Shares must be fully paid in order to be repurchased.
Subject to the above, we may purchase our own shares in the manner prescribed below. We may make a market purchase of our own fully paid shares pursuant to an ordinary resolution of shareholders. The resolution authorizing the purchase must:
| | · | specify the maximum number of shares authorized to be acquired; |
| | · | determine the maximum and minimum prices that may be paid for the shares; and |
| | · | specify a date, not being later than five years after the passing of the resolution, on which the authority to purchase is to expire. |
We may purchase our own fully paid shares otherwise than on a recognized investment exchange pursuant to a purchase contract authorized by resolution of shareholders before the purchase takes place. Any authority will not be effective if any shareholder from whom we propose to purchase shares votes on the resolution and the resolution would not have been passed if he had not done so. The resolution authorizing the purchase must specify a date, not being later than five years after the passing of the resolution, on which the authority to purchase is to expire.
Distributions and Dividends
Under the Companies Act, before a company can lawfully make a distribution or dividend, it must ensure that it has sufficient distributable reserves (on a non-consolidated basis). The basic rule is that a company’s profits available for the purpose of making a distribution are its accumulated, realized profits, so far as not previously utilized by distribution or capitalization, less its accumulated, realized losses, so far as not previously written off in a reduction or reorganization of capital duly made. The requirement to have sufficient distributable reserves before a distribution or dividend can be paid applies to us and to each of our subsidiaries that has been incorporated under English law.
It is not sufficient that we, as a public company, have made a distributable profit for the purpose of making a distribution. An additional capital maintenance requirement is imposed on us to ensure that the net worth of the company is at least equal to the amount of its capital. A public company can only make a distribution:
| | · | if, at the time that the distribution is made, the amount of its net assets (that is, the total excess of assets over liabilities) is not less than the total of its called up share capital and undistributable reserves; and |
| | · | if, and to the extent that, the distribution itself, at the time that it is made, does not reduce the amount of the net assets to less than that total. |
City Code on Takeovers and Mergers
As a United Kingdom incorporated public company with our registered office in the United Kingdom which is admitted to AIM, we are subject to the City Code, which is issued and administered by the United Kingdom Panel on Takeovers and Mergers, or the Panel. The City Code provides a framework within which takeovers of companies subject to it are conducted. In particular, the City Code contains certain rules in respect of mandatory offers. Under Rule 9 of the City Code, if a person:
| | · | acquires an interest in our shares which, when taken together with shares in which he or persons acting in concert with him are interested, carries 30% or more of the voting rights of our shares; or |
| | · | who, together with persons acting in concert with him, is interested in shares that in the aggregate carry not less than 30% and not more than 50% of the voting rights in us, acquires additional interests in shares that increase the percentage of shares carrying voting rights in which that person is interested, the acquirer, and depending on the circumstances, its concert parties would be required (except with the consent of the Panel) to make a cash offer for our outstanding shares at a price not less than the highest price paid for any interests in the shares by the acquirer or its concert parties during the previous 12 months. |
Exchange Controls
There are no governmental laws, decrees, regulations or other legislation in the United Kingdom that may affect the import or export of capital, including the availability of cash and cash equivalents for use by us, or that may affect the remittance of dividends, interest, or other payments by us to non-resident holders of our Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares, other than withholding tax requirements. There is no limitation imposed by English law or in the Articles of Association on the right of non-residents to hold or vote shares.
Differences in Corporate Law
The applicable provisions of the Companies Act differ from laws applicable to U.S. corporations and their shareholders. Set forth below is a summary of certain differences between the provisions of the Companies Act applicable to us and the Delaware General Corporation Law relating to shareholders’ rights and protections. This summary is not intended to be a complete discussion of the respective rights and it is qualified in its entirety by reference to English law and Delaware law.
| | | England and Wales | | Delaware |
| Number of Directors | | Under the Companies Act, a public limited company must have at least two directors and the number of directors may be fixed by or in the manner provided in a company’s articles of association. | | Under Delaware law, a corporation must have at least one director and the number of directors shall be fixed by or in the manner provided in the bylaws. |
| | | | | |
| Removal of Directors | | Under the Companies Act, shareholders may remove a director without cause by an ordinary resolution (which is passed by a simple majority of those voting in person or by proxy at a general meeting) irrespective of any provisions of any service contract the director has with the company, provided 28 clear days’ notice of the resolution has been given to the company and its shareholders. On receipt of notice of an intended resolution to remove a director, the company must forthwith send a copy of the notice to the director concerned. Certain other procedural requirements under the Companies Act must also be followed such as allowing the director to make representations against his or her removal either at the meeting or in writing. | | Under Delaware law, any director or the entire board of directors may be removed, with or without cause, by the holders of a majority of the shares then entitled to vote at an election of directors, except (a) unless the certificate of incorporation provides otherwise, in the case of a corporation whose board of directors is classified, shareholders may effect such removal only for cause, or (b) in the case of a corporation having cumulative voting, if less than the entire board of directors is to be removed, no director may be removed without cause if the votes cast against his removal would be sufficient to elect him if then cumulatively voted at an election of the entire board of directors, or, if there are classes of directors, at an election of the class of directors of which he is a part. |
| | | | | |
Vacancies on Board of
Directors | | Under English law, the procedure by which directors, other than a company’s initial directors, are appointed is generally set out in a company’s articles of association, provided that where two or more persons are appointed as directors of a public limited company by resolution of the shareholders, resolutions appointing each director must be voted on individually. | | Under Delaware law, vacancies and newly created directorships may be filled by a majority of the directors then in office (even though less than a quorum) or by a sole remaining director unless (a) otherwise provided in the certificate of incorporation or by-laws of the corporation or (b) the certificate of incorporation directs that a particular class of stock is to elect such director, in which case a majority of the other directors elected by such class, or a sole remaining director elected by such class, will fill such vacancy. |
| | | | | |
| Annual General Meeting | | Under the Companies Act, a public limited company must hold an annual general meeting in each six-month period following the company’s annual accounting reference date. | | Under Delaware law, the annual meeting of stockholders shall be held at such place, on such date and at such time as may be designated from time to time by the board of directors or as provided in the certificate of incorporation or by the bylaws. |
| | | England and Wales | | Delaware |
General Meeting | | Under the Companies Act, a general meeting of the shareholders of a public limited company may be called by the directors. Shareholders holding at least 5% of the paid-up capital of the company carrying voting rights at general meetings can require the directors to call a general meeting and, if the directors fail to do so within a certain period, may themselves convene a general meeting. | | Under Delaware law, special meetings of the stockholders may be called by the board of directors or by such person or persons as may be authorized by the certificate of incorporation or by the bylaws. |
| | | | | |
Notice of General
Meetings | | Under the Companies Act, 21 clear days’ notice must be given for an annual general meeting and any resolutions to be proposed at the meeting. Subject to a company’s articles of association providing for a longer period, at least 14 clear days’ notice is required for any other general meeting. In addition, certain matters, such as the removal of directors or auditors, require special notice, which is 28 clear days’ notice. The shareholders of a company may in all cases consent to a shorter notice period, the proportion of shareholders’ consent required being 100% of those entitled to attend and vote in the case of an annual general meeting and, in the case of any other general meeting, a majority in number of the members having a right to attend and vote at the meeting, being a majority who together hold not less than 95% in nominal value of the shares giving a right to attend and vote at the meeting. | | Under Delaware law, unless otherwise provided in the certificate of incorporation or bylaws, written notice of any meeting of the stockholders must be given to each stockholder entitled to vote at the meeting not less than ten nor more than 60 days before the date of the meeting and shall specify the place, date, hour, and purpose or purposes of the meeting. |
| | | | | |
| Proxy | | Under the Companies Act, at any meeting of shareholders, a shareholder may designate another person to attend, speak and vote at the meeting on their behalf by proxy. | | Under Delaware law, at any meeting of stockholders, a stockholder may designate another person to act for such stockholder by proxy, but no such proxy shall be voted or acted upon after three years from its date, unless the proxy provides for a longer period. A director of a Delaware corporation may not issue a proxy representing the director’s voting rights as a director. |
| | | | | |
| Pre-emptive Rights | | Under the Companies Act, “equity securities,” being (i) shares in the company other than shares that, with respect to dividends and capital, carry a right to participate only up to a specified amount in a distribution (“ordinary shares”) or (ii) rights to subscribe for, or to convert securities into, ordinary shares, proposed to be allotted for cash must be offered first to the existing equity shareholders in the company in proportion to the respective nominal value of their holdings, unless an exception applies or a special resolution to the contrary has been passed by shareholders in a general meeting or the articles of association provide otherwise in each case in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act. | | Under Delaware law, shareholders have no preemptive rights to subscribe to additional issues of stock or to any security convertible into such stock unless, and except to the extent that, such rights are expressly provided for in the certificate of incorporation. |
| | | England and Wales | | Delaware |
| Authority to Allot | | Under the Companies Act, the directors of a company must not allot shares or grant of rights to subscribe for or to convert any security into shares unless an exception applies or an ordinary resolution to the contrary has been passed by shareholders in a general meeting or the articles of association provide otherwise in each case in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act. | | Under Delaware law, if the corporation’s charter or certificate of incorporation so provides, the board of directors has the power to authorize the issuance of stock. It may authorize capital stock to be issued for consideration consisting of cash, any tangible or intangible property or any benefit to the corporation or any combination thereof. It may determine the amount of such consideration by approving a formula. In the absence of actual fraud in the transaction, the judgment of the directors as to the value of such consideration is conclusive. |
| | | | | |
Liability of Officers and
Directors | | Under the Companies Act, any provision, whether contained in a company’s articles of association or any contract or otherwise, that purports to exempt a director of a company, to any extent, from any liability that would otherwise attach to him in connection with any negligence, default, breach of duty or breach of trust in relation to the company is void. Any provision by which a company directly or indirectly provides an indemnity, to any extent, for a director of the company or of an associated company against any liability attaching to him in connection with any negligence, default, breach of duty or breach of trust in relation to the company of which he is a director is also void except as permitted by the Companies Act, which provides exceptions for the company to (a) purchase and maintain insurance against such liability; (b) provide a “qualifying third party indemnity” (being an indemnity against liability incurred by the director to a person other than the company or an associated company or criminal proceedings in which he is not convicted); and (c) provide a “qualifying pension scheme indemnity” (being an indemnity against liability incurred in connection with the company’s activities as trustee of an occupational pension plan). | | Under Delaware law, a corporation’s certificate of incorporation may include a provision eliminating or limiting the personal liability of a director to the corporation and its stockholders for damages arising from a breach of fiduciary duty as a director. However, no provision can limit the liability of a director for: · any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to the corporation or its stockholders; · acts or omissions not in good faith or that involve intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law; · intentional or negligent payment of unlawful dividends or stock purchases or redemptions; or · any transaction from which the director derives an improper personal benefit. |
| | | England and Wales | | Delaware |
| Voting Rights | | Under English law, unless a poll is demanded by the shareholders of a company or is required by the chairman of the meeting or the company’s articles of association, shareholders shall vote on all resolutions on a show of hands. Under the Companies Act, a poll may be demanded by (a) not fewer than five shareholders having the right to vote on the resolution; (b) any shareholder(s) representing not less than 10% of the total voting rights of all the shareholders having the right to vote on the resolution; or (c) any shareholder(s) holding shares in the company conferring a right to vote on the resolution being shares on which an aggregate sum has been paid up equal to not less than 10% of the total sum paid up on all the shares conferring that right. A company’s articles of association may provide more extensive rights for shareholders to call a poll, and in our case the number in clause (a) above is reduced from five to three. Under English law, an ordinary resolution is passed on a show of hands if it is approved by a simple majority (more than 50%) of the votes cast by shareholders present (in person or by proxy) and entitled to vote. If a poll is demanded, an ordinary resolution is passed if it is approved by holders representing a simple majority of the total voting rights of shareholders present, in person or by proxy, who, being entitled to vote, vote on the resolution. Special resolutions require the affirmative vote of not less than 75% of the votes cast by shareholders present, in person or by proxy, at the meeting. | | Delaware law provides that, unless otherwise provided in the certificate of incorporation, each stockholder is entitled to one vote for each share of capital stock held by such stockholder. |
| | | | | |
Shareholder Vote on
Certain
Transactions | | The Companies Act provides for schemes of arrangement, which are arrangements or compromises between a company and any class of shareholders or creditors and used in certain types of reconstructions, amalgamations, capital reorganizations or takeovers. These arrangements require: · the approval at a shareholders’ or creditors’ meeting convened by order of the court, of a majority in number of shareholders or creditors representing 75% in value of the capital held by, or debt owed to, the class of shareholders or creditors, or class thereof present and voting, either in person or by proxy; and · the approval of the court. | | Generally, under Delaware law, unless the certificate of incorporation provides for the vote of a larger portion of the stock, completion of a merger, consolidation, sale, lease or exchange of all or substantially all of a corporation’s assets or dissolution requires: · the approval of the board of directors; and · approval by the vote of the holders of a majority of the outstanding stock or, if the certificate of incorporation provides for more or less than one vote per share, a majority of the votes of the outstanding stock of a corporation entitled to vote on the matter. |
| | | England and Wales | | Delaware |
Standard of Conduct
for Directors | | Under English law, a director owes various statutory and fiduciary duties to the company, including: · to act in the way he considers, in good faith, would be most likely to promote the success of the company for the benefit of its members as a whole; · to avoid a situation in which he has, or can have, a direct or indirect interest that conflicts, or possibly conflicts, with the interests of the company; · to act in accordance with the company’s constitution and only exercise his powers for the purposes for which they are conferred; · to exercise independent judgment; · to exercise reasonable care, skill and diligence; · not to accept benefits from a third party conferred by reason of his being a director or doing, or not doing, anything as a director; and · to declare any interest that he has, whether directly or indirectly, in a proposed or existing transaction or arrangement with the company. | | Delaware law does not contain specific provisions setting forth the standard of conduct of a director. The scope of the fiduciary duties of directors is generally determined by the courts of the State of Delaware. In general, directors have a duty to act without self-interest, on a well-informed basis and in a manner they reasonably believe to be in the best interest of the stockholders. Directors of a Delaware corporation owe fiduciary duties of care and loyalty to the corporation and to its shareholders. The duty of care generally requires that a director act in good faith, with the care that an ordinarily prudent person would exercise under similar circumstances. Under this duty, a director must inform himself of all material information reasonably available regarding a significant transaction. The duty of loyalty requires that a director act in a manner he reasonably believes to be in the best interests of the corporation. He must not use his corporate position for personal gain or advantage. In general, but subject to certain exceptions, actions of a director are presumed to have been made on an informed basis, in good faith and in the honest belief that the action taken was in the best interests of the corporation. However, this presumption may be rebutted by evidence of a breach of one of the fiduciary duties. Delaware courts have also imposed a heightened standard of conduct upon directors of a Delaware corporation who take any action designed to defeat a threatened change in control of the corporation. In addition, under Delaware law, when the board of directors of a Delaware corporation approves the sale or break-up of a corporation, the board of directors may, in certain circumstances, have a duty to obtain the highest value reasonably available to the shareholders. |
| | | | | |
| Stockholder Suits | | Under English law, generally, the company, rather than its shareholders, is the proper claimant in an action in respect of a wrong done to the company or where there is an irregularity in the company’s internal management. Notwithstanding this general position, the Companies Act provides that (i) a court may allow a shareholder to bring a derivative claim (that is, an action in respect of and on behalf of the company) in respect of a cause of action arising from a director’s negligence, default, breach of duty or breach of trust and (ii) a shareholder may bring a claim for a court order where the company’s affairs have been or are being conducted in a manner that is unfairly prejudicial to some of its shareholders. | | Under Delaware law, a stockholder may initiate a derivative action to enforce a right of a corporation if the corporation fails to enforce the right itself. The complaint must: · state that the plaintiff was a stockholder at the time of the transaction of which the plaintiff complains or that the plaintiffs shares thereafter devolved on the plaintiff by operation of law; and · allege with particularity the efforts made by the plaintiff to obtain the action the plaintiff desires from the directors and the reasons for the plaintiff’s failure to obtain the action; or · state the reasons for not making the effort. Additionally, the plaintiff must remain a stockholder through the duration of the derivative suit. The action will not be dismissed or compromised without the approval of the Delaware Court of Chancery. |
DESCRIPTION OF AMERICAN DEPOSITARY SHARES
Our Depositary Shares are deposited pursuant to the Amended and Restated Deposit Agreement dated February 8, 2021, among the Company, The Bank of New York Mellon as depositary, ands owners and holders of Depositary Shares. The depositary registers and delivers the Depositary Shares. Each Depositary Share represents five Ordinary Shares (or a right to receive five Ordinary Shares) deposited with The Bank of New York Mellon, London Branch, or any successor, as custodian for the depositary. Each Depositary Share also represents any other securities, cash or other property that may be held by the depositary. The deposited Ordinary Shares together with any other securities, cash or other property held by the depositary are referred to as the deposited securities. The depositary’s office at which the Depositary Shares are administered and its principal executive office are located at 240 Greenwich Street, New York, New York 10286.
You may hold Depositary Shares either (1) directly (a) by having an American Depositary Receipt, or ADR, which is a certificate evidencing a specific number of Depositary Shares, registered in your name, or (b) by having Depositary Shares registered in your name in the Direct Registration System, or (2) indirectly by holding a security entitlement in Depositary Shares through your broker or other financial institution. If you hold Depositary Shares directly, you are a registered Depositary Share holder. This description assumes you are a Depositary Share holder. If you hold the Depositary Shares indirectly, you must rely on the procedures of your broker or other financial institution to assert the rights of Depositary Share holders described in this section. You should consult with your broker or financial institution to find out what those procedures are.
The Direct Registration System, or DRS, is a system administered by The Depository Trust Company, or DTC, pursuant to which the depositary may register the ownership of uncertificated Depositary Shares, which ownership is confirmed by periodic statements sent by the depositary to the registered holders of uncertificated Depositary Shares.
Depositary Share holders are not treated as shareholders and do not have shareholder rights. English law governs shareholder rights. The depositary is the holder of the Ordinary Shares underlying the Depositary Shares. As a holder of Depositary Shares, you will have Depositary Share holder rights. A deposit agreement among us, the depositary and you, as a Depositary Share holder, and all other persons directly and indirectly holding Depositary Shares sets out Depositary Share holder rights as well as the rights and obligations of the depositary. A copy of the deposit agreement is incorporated by reference as an exhibit to our most recent Annual Report on Form 20-F. New York law governs the deposit agreement and the Depositary Shares.
The following is a summary of the material provisions of the deposit agreement. For more complete information, you should read the entire deposit agreement and the form of Depositary Share.
Dividends and Other Distributions
How will you receive dividends and other distributions on the Ordinary Shares?
The depositary has agreed to pay you the cash dividends or other distributions it or the custodian receives on Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities, after deducting its fees and expenses. As an Depositary Share holder, you will receive these distributions in proportion to the number of Ordinary Shares your Depositary Shares represent.
Cash. We do not expect to declare or pay any cash dividends or cash distributions on our Depositary Shares for the foreseeable future. The depositary will convert any cash dividend or other cash distribution we pay on the Depositary Shares or any net proceeds from the sale of any Ordinary Shares, rights, securities or other entitlements into U.S. dollars if it can do so on a reasonable basis and at the then prevailing market rate, and can transfer the U.S. dollars to the United States. If that is not possible and lawful or if any government approval is needed and cannot be obtained, the deposit agreement allows the depositary to distribute the foreign currency only to those Depositary Share holders to whom it is possible to do so. It will hold the foreign currency it cannot convert for the account of the Depositary Share holders who have not been paid. It will not invest the foreign currency and it will not be liable for any interest. Before making a distribution, any taxes or other governmental charges, together with fees and expenses of the depositary that must be paid, will be deducted. See the section titled “Item 10 E. Additional Information—Taxation” in our most recent Annual Report on Form 20-F for a summary of certain tax consequences in respect of dividends or distributions to holders of Depositary Shares. It will distribute only whole U.S. dollars and cents and will round fractional cents to the nearest whole cent. If the exchange rates fluctuate during a time when the depositary cannot convert the foreign currency, you may lose some or all of the value of the distribution.
Ordinary Shares. The depositary may distribute additional Depositary Shares representing any Ordinary Shares we distribute as a dividend or free distribution to the extent reasonably practicable and permissible under law. The depositary will only distribute whole Depositary Shares. If the depositary does not distribute additional Depositary Shares, the outstanding Depositary Shares will also represent the new Ordinary Shares. The depositary may sell a portion of the distributed Ordinary Shares sufficient to pay its fees and expenses in connection with that distribution.
Elective Distributions in Cash or Shares. If we offer holders of our Ordinary Shares the option to receive dividends in either cash or shares, the depositary, after consultation with us, may make such elective distribution available to you as a holder of the Depositary Shares. We must first instruct the depositary to make such elective distribution available to you. As a condition of making a distribution election available to Depositary Share holders, the depositary may require satisfactory assurances from us that doing so would not require registration of any securities under the Securities Act. There can be no assurance that you will be given the opportunity to receive elective distributions on the same terms and conditions as the holders of Ordinary Shares, or at all.
Rights to Purchase Additional Ordinary Shares. If we offer holders of our securities any rights to subscribe for additional Ordinary Shares or any other rights, the depositary may make these rights available to Depositary Share holders. If the depositary decides it is not legal and practical to make the rights available but that it is practical to sell the rights, the depositary will use reasonable efforts to sell the rights and distribute the proceeds in the same way as it does with cash distributions. The depositary will allow rights that are not distributed or sold to lapse. In that case, you will receive no value for them.
If the depositary makes rights available to you, it will exercise the rights and purchase the Ordinary Shares on your behalf and in accordance with your instructions. The depositary will then deposit the Ordinary Shares and deliver Depositary Shares to you. It will only exercise rights if you pay it the exercise price and any other charges the rights require you to pay and comply with other applicable instructions.
U.S. securities laws may restrict transfers and cancellation of the Depositary Shares representing Ordinary Shares purchased upon exercise of rights. For example, you may not be able to trade these Depositary Shares freely in the United States. In this case, the depositary may deliver restricted Depositary Shares that have the same terms as the Depositary Shares described in this section except for changes needed to put the necessary restrictions in place.
Other Distributions. The depositary will send to you anything else we distribute to holders of deposited securities by any means it determines is equitable and practicable. If it cannot make the distribution proportionally among the owners, the depositary may adopt another equitable and practical method. It may decide to sell what we distributed and distribute the net proceeds, in the same way as it does with cash. Or, it may decide to hold what we distributed, in which case Depositary Shares will also represent the newly distributed property.
However, the depositary is not required to distribute any securities (other than Depositary Shares) to Depositary Share holders unless it receives satisfactory evidence from us that it is legal to make that distribution. In addition, the depositary may sell a portion of the distributed securities or property sufficient to pay its fees and expenses in connection with that distribution.
Neither we nor the depositary are responsible for any failure to determine that it may be lawful or feasible to make a distribution available to any Depositary Share holders. We have no obligation to register Depositary Shares, Ordinary Shares, rights or other securities under the Securities Act. This means that you may not receive the distributions we make on our Ordinary Shares or any value for them if it is illegal or impractical for us to make them available to you.
Deposit, Withdrawal and Cancellation
How are Depositary Shares issued?
The depositary will deliver Depositary Shares if you or your broker deposit Ordinary Shares or evidence of rights to receive Ordinary Shares with the custodian. Upon payment of its fees and expenses and of any taxes or charges, such as stamp taxes or share transfer taxes or fees, and delivery of any required endorsements, certifications or other instruments of transfer required by the depositary, the depositary will register the appropriate number of Depositary Shares in the names you request and will deliver the Depositary Shares to or upon the order of the person or persons that made the deposit.
How can Depositary Share holders withdraw the deposited securities?
You may surrender your Depositary Shares at the depositary’s corporate trust office. Upon payment of its fees and expenses and of any taxes or charges, such as stamp taxes or share transfer taxes or fees, the depositary will transfer and deliver the Ordinary Shares and any other deposited securities underlying the Depositary Shares to you or a person designated by you at the office of the custodian or through a book-entry delivery. Alternatively, at your request, risk and expense, the depositary will transfer and deliver the deposited securities at its corporate trust office, if feasible.
How do Depositary Share holders interchange between certificated Depositary Shares and uncertificated Depositary Shares?
You may surrender your ADRs to the depositary for the purpose of exchanging your ADRs for uncertificated Depositary Shares. The depositary will cancel the ADRs and will send you a statement confirming that you are the owner of uncertificated Depositary Shares. Alternatively, upon receipt by the depositary of a proper instruction from a registered holder of uncertificated Depositary Shares requesting the exchange of uncertificated Depositary Shares for certificated Depositary Shares, the depositary will execute and deliver to you an ADR evidencing those Depositary Shares.
Voting Rights
How do you vote?
You may instruct the depositary to vote the number of whole deposited Ordinary Shares your Depositary Shares represent. The depositary will notify you of shareholders’ meetings or other solicitations of consents and arrange to deliver our voting materials to you if we ask it to. Those materials will describe the matters to be voted on and explain how you may instruct the depositary how to vote. For instructions to be valid, they must reach the depositary by a date set by the depositary.
The depositary will try, as far as practical, and subject to the laws of England and Wales and our Articles of Association, to vote or to have its agents vote the Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities as instructed by Depositary Share holders.
The depositary will only vote or attempt to vote as you instruct or as described above. If we ask the depositary to solicit the Depositary Share holders’ instructions to vote and a Depositary Share holder fails to instruct the depositary as to the manner in which to vote by the specified date, such Depositary Share holder will be deemed to have given a discretionary proxy to a person designated by us to vote the number of deposited securities represented by its Depositary Shares, unless we notify the depositary that we do not wish to receive a discretionary proxy, there is substantial shareholder opposition to the particular question, or the particular question would have an adverse impact on our shareholders.
We cannot assure you that you will receive the voting materials in time to ensure that you can instruct the depositary to vote your Ordinary Shares. In addition, the depositary and its agents are not responsible for failing to carry out voting instructions or for the manner of carrying out voting instructions provided that any such failure is in good faith. This means that you may not be able to exercise your right to vote and there may be nothing you can do if your Ordinary Shares are not voted as you requested.
In order to give you a reasonable opportunity to instruct the depositary as to the exercise of voting rights relating to deposited securities, if we request the depositary to act, we will try to give the depositary notice of any such meeting and details concerning the matters to be voted upon sufficiently in advance of the meeting date.
Except as described above, you will not be able to exercise your right to vote unless you withdraw the Ordinary Shares. However, you may not know about the shareholder meeting far enough in advance to withdraw the Ordinary Shares.
Fees and Expenses
What fees and expenses am I responsible for paying?
As a Depositary Shareholder, you will be required to pay the following service fees to the depositary bank and certain taxes and governmental charges (in addition to any applicable fees, expenses, taxes and other governmental charges payable on the deposited securities represented by any of your Depositary Shares):
Persons depositing or withdrawing our ordinary
shares or Depositary Share holders must pay: | | For: |
| 5.00 USD (or less) per 100 Depositary Shares (or portion of 100 Depositary Shares) | | Issue of Depositary Shares, including issues resulting from a distribution of our Ordinary Shares or rights or other property |
| | | |
| | | Cancellation of Depositary Shares for the purpose of withdrawal, including if the deposit agreement terminates |
| | | |
| 0.05 USD (or less) per Depositary Share | | Any cash distribution to Depositary Share holders |
| | | |
| A fee equivalent to the fee that would be payable if securities distributed to Depositary Share holders had been our Ordinary Shares and the Depositary Shares had been deposited for issuance of Depositary Shares | | Distribution of securities distributed to holders of deposited securities (including rights) that are distributed by the depositary to Depositary Share holders |
| | | |
| 0.05 USD (or less) per Depositary Share per calendar year | | Depositary services |
| | | |
| Registration or transfer fees | | Transfer and registration of shares of our Ordinary Shares on our share register to or from the name of the depositary or its agent when persons deposit or withdraw our Ordinary Shares |
| | | |
| Expenses of the Depositary | | Cable and facsimile transmissions (when expressly provided in the deposit agreement) |
| | | |
| | | Converting foreign currency to U.S. dollars |
| | | |
| Taxes and other governmental charges the depositary or the custodian has to pay on any Depositary Share or our Ordinary Shares underlying Depositary Shares, such as stock transfer taxes, stamp duty or withholding taxes | | As necessary |
| | | |
| Any charges incurred by the depositary or its agents for servicing the deposited securities | | As necessary |
The depositary collects its fees for delivery and surrender of Depositary Shares directly from investors depositing our Ordinary Shares or surrendering Depositary Shares for the purpose of withdrawal or from intermediaries acting for them. The depositary collects fees for making distributions to investors by deducting those fees from the amounts distributed or by selling a portion of distributable property to pay the fees. The depositary may collect its annual fee for depositary services by deduction from cash distributions or by directly billing investors or by charging the book-entry system accounts of participants acting for them. The depositary may collect any of its fees by deduction from any cash distribution payable (or by selling a portion of securities or other property distributable) to Depositary Share holders that are obligated to pay those fees. The depositary may generally refuse to provide fee-attracting services until its fees for those services are paid.
In performing its duties under the deposit agreement, the depositary may use brokers, dealers, foreign currency dealers or other service providers that are owned by or affiliated with the depositary and that may earn or share fees, spreads or commissions.
The depositary may convert currency itself or through any of its affiliates and, in those cases, acts as principal for its own account and not as agent, advisor, broker or fiduciary on behalf of any other person and earns revenue, including, without limitation, transaction spreads, that it will retain for its own account. The revenue is based on, among other things, the difference between the exchange rate assigned to the currency conversion made under the deposit agreement and the rate that the depositary or its affiliate receives when buying or selling foreign currency for its own account. The depositary makes no representation that the exchange rate used or obtained in any currency conversion under the deposit agreement will be the most favorable rate that could be obtained at the time or that the method by which that rate will be determined will be the most favorable to Depositary Share holders, subject to the depositary’s obligations under the deposit agreement. The methodology used to determine exchange rates used in currency conversions is available upon request.
The depositary has agreed to reimburse us for a portion of certain expenses it incurs that are related to establishment and maintenance of the ADR program. There are limits on the amount of expenses for which the depositary will reimburse us, but the amount of reimbursement available to us is not related to the amounts of fees the depositary collects from investors. Further, the depositary has agreed to reimburse us certain fees payable to the depositary by holders of Depositary Shares. Neither we nor the depositary can determine the exact amount to be made available to us because (i) the number of Depositary Shares that will be issued and outstanding, (ii) the level of service fees to be charged to holders of Depositary Shares and (iii) its reimbursable expenses related to the program are not known at this time.
Payment of Taxes
Depositary Share holders will be responsible for any taxes or other governmental charges payable on their Depositary Shares or on the deposited securities represented by any of their Depositary Shares. The depositary may refuse to register any transfer of Depositary Shares or allow a Depositary Share holder to withdraw the deposited securities represented by his or her Depositary Shares until those taxes or other charges are paid. It may apply payments owed to such Depositary Share holder or sell deposited securities represented by such D Depositary Share holder’s Depositary Shares to pay any taxes owed and such Depositary Share holder will remain liable for any deficiency. If the depositary sells deposited securities, it will, if appropriate, reduce the number of Depositary Shares to reflect the sale and pay to Depositary Share holders any proceeds, or send to Depositary Share holders any property, remaining after it has paid the taxes.
Reclassifications, Recapitalizations and Mergers, etc.
| If we: | | Then: |
| ·Change the nominal or par value of our Ordinary Shares | | The cash, Ordinary Shares or other securities received by the depositary will become deposited securities. |
| | | |
| ·Reclassify, split up or consolidate any of the deposited securities | | Each Depositary Share will automatically represent its equal share of new deposited securities. |
| | | |
| ·Distribute securities on the Ordinary Shares that are not distributed to you | | The depositary may also deliver new Depositary Shares or ask you to surrender your outstanding ADRs in exchange for new ADRs identifying the new deposited securities. The depositary may also sell the new deposited securities and distribute the net proceeds if we are unable to assure the depositary that the distribution (a) does not require registration under the Securities Act or (b) is exempt from registration under the Securities Act. |
| | | |
| ·Recapitalize, reorganize, merge, liquidate, sell all or substantially all of our assets, or take any similar action | | Any replacement securities received by the depositary shall be treated as newly deposited securities and either the existing Depositary Shares or, if necessary, replacement Depositary Shares distributed by the depositary will represent the replacement securities. The depositary may also sell the replacement securities and distribute the net proceeds if the replacement securities may not be lawfully distributed to all Depositary Share holders. |
Amendment and Termination
How may the deposit agreement be amended?
We may agree with the depositary to amend the deposit agreement and the ADRs without your consent for any reason. If an amendment adds or increases fees or charges, except for taxes and other governmental charges or expenses of the depositary for registration fees, facsimile costs, delivery charges or similar items, or prejudices a substantial right of Depositary Share holders, it will not become effective for outstanding Depositary Shares until 30 days after the depositary notifies Depositary Share holders of the amendment. At the time an amendment becomes effective, you are considered, by continuing to hold your Depositary Shares, to agree to the amendment and to be bound by the ADRs and the deposit agreement as amended.
How may the deposit agreement be terminated?
The depositary will terminate the deposit agreement at our direction by mailing notice of termination to the Depositary Share holders then outstanding at least 30 days prior to the date fixed in such notice for such termination. The depositary may also terminate the deposit agreement by mailing a notice of termination to us and the Depositary Share holders if 60 days have passed since the depositary told us it wants to resign but a successor depositary has not been appointed and accepted its appointment.
After termination, the depositary and its agents will do the following under the deposit agreement but nothing else: collect distributions on the deposited securities, sell rights and other property, and deliver Ordinary Shares and other deposited securities upon cancellation of Depositary Shares. Four months after termination, the depositary may sell any remaining deposited securities by public or private sale. After that, the depositary will hold the money it received on the sale, as well as any other cash it is holding under the deposit agreement for the pro rata benefit of the Depositary Share holders that have not surrendered their Depositary Shares. It will not invest the money and has no liability for interest. The depositary’s only obligations will be to account for the money and other cash. After termination our only obligations under the deposit agreement will be to indemnify the depositary and to pay fees and expenses of the depositary that we agreed to pay and we will not have any obligations thereunder to current or former Depositary Share holders.
Limitations on Obligations and Liability
Limits on our Obligations and the Obligations of the Depositary; Limits on Liability to Holders of Depositary Shares
The deposit agreement expressly limits our obligations and the obligations of the depositary. It also limits our liability and the liability of the depositary. We and the depositary:
| | · | are only obligated to take the actions specifically set forth in the deposit agreement without negligence or bad faith; |
| | · | are not liable if we are or it is prevented or delayed by law or by events or circumstances beyond our or its ability to prevent or counteract with reasonable care or effort from performing our or its obligations under the deposit agreement; |
| | · | are not liable if we or it exercises discretion permitted under the deposit agreement; |
| | · | are not liable for the inability of any holder of Depositary Shares to benefit from any distribution on deposited securities that is not made available to holders of Depositary Shares under the terms of the deposit agreement, or for any special, consequential or punitive damages for any breach of the terms of the deposit agreement; |
| | · | have no obligation to become involved in a lawsuit or other proceeding related to the Depositary Shares or the deposit agreement on your behalf or on behalf of any other person; |
| | · | may rely upon any documents we believe or it believes in good faith to be genuine and to have been signed or presented by the proper person; |
| | · | are not liable for the acts or omissions of any securities depository, clearing agency or settlement system; and |
| | · | the depositary has no duty to make any determination or provide any information as to our tax status, or any liability for any tax consequences that may be incurred by Depositary Share holders as a result of owning or holding Depositary Shares or be liable for the inability or failure of an Depositary Share holder to obtain the benefit of a foreign tax credit, reduced rate of withholding or refund of amounts withheld in respect of tax or any other tax benefit. |
In the deposit agreement, we and the depositary agree to indemnify each other under certain circumstances. Additionally, we, the depositary and each owner and holder, to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law, waive the right to a jury trial in an action against us or the depositary arising out of or relating to the deposit agreement.
Requirements for Depositary Actions
Before the depositary will deliver or register a transfer of Depositary Shares, make a distribution on Depositary Shares, or permit withdrawal of Ordinary Shares, the depositary may require:
| | · | payment of stock transfer or other taxes or other governmental charges and transfer or registration fees charged by third parties for the transfer of any Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities; |
| | · | satisfactory proof of the identity and genuineness of any signature or other information it deems necessary; and |
| | · | compliance with regulations it may establish, from time to time, consistent with the deposit agreement, including presentation of transfer documents. |
The depositary may refuse to deliver Depositary Shares or register transfers of Depositary Shares when the transfer books of the depositary or our transfer books are closed or at any time if the depositary or we think it advisable to do so.
Your Right to Receive the Ordinary Shares Underlying your Depositary Shares
Depositary Share holders have the right to cancel their Depositary Shares and withdraw the underlying Ordinary Shares at any time except:
| | · | when temporary delays arise because: (i) the depositary has closed its transfer books or we have closed our transfer books; (ii) the transfer of Ordinary Shares is blocked to permit voting at a shareholders’ meeting; or (iii) we are paying a dividend on our Ordinary Shares; |
| | · | when you owe money to pay fees, taxes and similar charges; or |
| · | when it is necessary to prohibit withdrawals in order to comply with any laws or governmental regulations that apply to Depositary Shares or to the withdrawal of Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities. |
This right of withdrawal may not be limited by any other provision of the deposit agreement.
Pre-release of Depositary Shares
The deposit agreement permits the depositary to deliver Depositary Shares before deposit of the underlying Ordinary Shares. This is called a pre-release of the Depositary Shares. The depositary may also deliver Ordinary Shares upon cancellation of pre-released Depositary Shares (even if the Depositary Shares are canceled before the pre-release transaction has been closed out). A pre-release is closed out as soon as the underlying Ordinary Shares are delivered to the depositary.
The depositary may receive Depositary Shares instead of Ordinary Shares to close out a pre-release. The depositary may pre-release Depositary Shares only under the following conditions: (1) before or at the time of the pre-release, the person to whom the pre-release is being made represents to the depositary in writing that it or its customer owns the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares to be deposited; (2) the pre-release is fully collateralized with cash or other collateral that the depositary considers appropriate; and (3) the depositary must be able to close out the pre-release on not more than five business days’ notice. In addition, the depositary will limit the number of Depositary Shares that may be outstanding at any time as a result of prerelease to 30% of the number of deposited shares, although the depositary may disregard this limit from time to time if it determines it is appropriate to do so.
Direct Registration System
In the deposit agreement, all parties to the deposit agreement acknowledge that the DRS and Profile Modification System, or Profile, will apply to uncertificated Depositary Shares upon acceptance thereof to DRS by DTC. DRS is the system administered by DTC under which the depositary may register the ownership of uncertificated Depositary Shares and such ownership will be evidenced by periodic statements sent by the depositary to the registered holders of uncertificated Depositary Shares. Profile is a required feature of DRS that allows a DTC participant, claiming to act on behalf of a registered holder of Depositary Shares, to direct the depositary to register a transfer of those Depositary Shares to DTC or its nominee and to deliver those Depositary Shares to the DTC account of that DTC participant without receipt by the depositary of prior authorization from the Depositary Share holder to register that transfer.
In connection with and in accordance with the arrangements and procedures relating to DRS/Profile, the parties to the deposit agreement understand that the depositary will not determine whether the DTC participant that is claiming to be acting on behalf of an Depositary Share holder in requesting registration of transfer and delivery described in the paragraph above has the actual authority to act on behalf of the Depositary Share holder (notwithstanding any requirements under the Uniform Commercial Code). In the deposit agreement, the parties agree that the depositary’s reliance on and compliance with instructions received by the depositary through the DRS/Profile System and in accordance with the deposit agreement will not constitute negligence or bad faith on the part of the depositary.
Shareholder Communications; Inspection of Register of Holders of Depositary Shares
The depositary will make available for your inspection at its office all communications that it receives from us as a holder of deposited securities that we make generally available to holders of deposited securities. The depositary will send you copies of those communications or otherwise make those communications available to you if we ask it to. You have a right to inspect the register of holders of Depositary Shares, but not for the purpose of contacting those holders about a matter unrelated to our business or the Depositary Shares.
TAXATION
The following summary contains a description of the material U.S. federal income tax and United Kingdom tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership and disposition of Ordinary Shares and Depositary Shares, but it does not purport to be a comprehensive description of all the tax considerations that may be relevant to a decision to purchase Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares. The summary is based upon the on the tax laws of the United States and regulations thereunder and the tax laws of the United Kingdom and regulations thereunder as of the date hereof, which are subject to change.
Certain United Kingdom Tax Considerations
The following is a general summary of certain United Kingdom tax considerations relating to the ownership and disposal of our Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares and does not address all possible tax consequences relating to an investment in our Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares. It is based on United Kingdom tax law and generally published His Majesty’s Revenue & Customs, or HMRC, practice as of the date of this prospectus, both of which are subject to change, possibly with retrospective effect. A United Kingdom tax year runs from April 6th in any year to April 5th in the following year.
Save as provided otherwise, this summary applies only to a person who is the absolute beneficial owner of our Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares and who is resident (and, in the case of an individual, domiciled) in the United Kingdom for tax purposes and who is not resident for tax purposes in any other jurisdiction and does not have a permanent establishment or fixed base in any other jurisdiction with which the holding of our Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares is connected, or a U.K. Holder. A person who is not a U.K. Holder, including a person (a) who is not resident (or, if resident, is not domiciled) in the United Kingdom for tax purposes, including an individual and company who trades in the United Kingdom through a branch, agency or permanent establishment in the United Kingdom to which an Ordinary Share or Depositary Share is attributable, or (b) who is resident or otherwise subject to tax in a jurisdiction outside the United Kingdom, is recommended to seek the advice of professional advisors in relation to their taxation obligations.
This summary is for general information only and is not intended to be, nor should it be considered to be, legal or tax advice to any particular investor. It does not address all of the tax considerations that may be relevant to specific investors in light of their particular circumstances or to investors subject to special treatment under United Kingdom tax law. In particular this summary:
| · | only applies to an absolute beneficial owner of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares and any dividend paid in respect of that Ordinary Share where the dividend is regarded for United Kingdom tax purposes as that person’s own income (and not the income of some other person); and |
| · | (a) only addresses the principal United Kingdom tax consequences for an investor who holds Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares as a capital asset, (b) does not address the tax consequences that may be relevant to certain special classes of investor such as a dealer, broker or trader in shares or securities and any other person who holds Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares otherwise than as an investment, (c) does not address the tax consequences for a holder that is a financial institution, insurance company, collective investment scheme, pension scheme, charity or tax-exempt organization, (d) assumes that a holder is not an officer or employee of the company (nor of any related company) and has not (and is not deemed to have) acquired the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares by virtue of an office or employment, and (e) assumes that a holder does not control or hold (and is not deemed to control or hold), either alone or together with one or more associated or connected persons, directly or indirectly (including through the holding of Depositary Shares), an interest of 10% or more in the issued share capital (or in any class thereof), voting power, rights to profits or capital of the company, and is not otherwise connected with the company. |
This summary further assumes that a holder of Depositary Shares is the beneficial owner of the underlying Ordinary Shares for United Kingdom direct tax purposes.
POTENTIAL INVESTORS IN THE DEPOSITARY SHARES SHOULD SATISFY THEMSELVES PRIOR TO INVESTING AS TO THE OVERALL TAX CONSEQUENCES, INCLUDING, SPECIFICALLY, THE CONSEQUENCES UNDER UNITED KINGDOM TAX LAW AND HMRC PRACTICE OF THE ACQUISITION, OWNERSHIP AND DISPOSAL OF THE ORDINARY SHARES OR DEPOSITARY SHARES, IN THEIR OWN PARTICULAR CIRCUMSTANCES BY CONSULTING THEIR OWN TAX ADVISERS.
Taxation of Dividends
Withholding Tax. A dividend payment in respect of an Ordinary Share may be made without withholding or deduction for or on account of United Kingdom tax.
Income Tax. An individual holder of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares who is not a U.K. Holder will not be chargeable to United Kingdom income tax on a dividend paid by the Company, unless such holder carries on (whether solely or in partnership) a trade, profession or vocation in the United Kingdom through a branch or agency in the United Kingdom to which the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares are attributable. In these circumstances, such holder may, depending on his or her individual circumstances, be chargeable to United Kingdom income tax on a dividend received from the Company.
A dividend received by individual U.K. Holders will be subject to United Kingdom income tax. The rate of United Kingdom income tax that is chargeable on dividends received in the tax year 2022/2023 by an individual U.K. Holder who is (i) an additional rate taxpayer is 39.35%, (ii) a higher rate taxpayer is 33.75%, and (iii) a basic rate taxpayer is 8.75%. An individual U.K. Holder may be entitled to a tax-free dividend allowance (in addition to their personal allowance) of £2,000 for the tax year 2022/2023. This means that the relevant individual does not need to pay United Kingdom income tax on their first £2,000 of dividend income received. Dividends within the dividend allowance will still count towards the relevant individual's basic, higher or additional rate bands however. An individual’s dividend income is treated as the top slice of their total income that is chargeable to United Kingdom income tax. Dividends which are covered by an individual’s personal income tax allowance do not count towards and are ignored for the dividend allowance.
Corporation Tax. A U.K. Holder within the charge to United Kingdom corporation tax may be entitled to exemption from United Kingdom corporation tax in respect of dividend payments in respect of an Ordinary Share. If the conditions for the exemption are not satisfied or such U.K. Holder elects for an otherwise exempt dividend to be taxable, United Kingdom corporation tax will be chargeable on the dividend. The rate of United Kingdom corporation tax is currently 19% (and due to increase to a top rate of 25% from April 1, 2023). If potential investors are in any doubt as to their position, they should consult their own professional advisers.
A corporate holder of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares that is not a U.K. Holder will not be subject to United Kingdom corporation tax on a dividend received from the company, unless it carries on a trade in the United Kingdom through a permanent establishment to which the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares are attributable. In these circumstances, such holder may, depending on its individual circumstances and if the exemption from United Kingdom corporation tax discussed above does not apply, be chargeable to United Kingdom corporation tax on dividends received from the Company.
Taxation of Disposals
U.K. Holders. A disposal or deemed disposal of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares by an individual U.K. Holder may, depending on his or her individual circumstances, give rise to a chargeable gain or to an allowable loss for the purpose of United Kingdom capital gains tax. The principal factors that will determine the capital gains tax position on a disposal of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares are the extent to which the holder realizes any other capital gains in the tax year in which the disposal is made, the extent to which the holder has incurred capital losses in that or any earlier tax year and the level at which the annual exempt amount for United Kingdom capital gains tax (the “annual exempt amount”) is set by the United Kingdom government for that tax year. The annual exempt amount for the 2022/2023 tax year is £12,300. If, after all allowable deductions, an individual U.K. Holder’s total taxable income for the relevant tax year exceeds the basic rate income tax limit, a taxable capital gain accruing on a disposal of an Ordinary Share or a Depositary Shares is taxed at the rate of 20%. In other cases, a taxable capital gain accruing on a disposal of our Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares may be taxed at the rate of 10% or the rate of 20% or at a combination of both rates.
An individual U.K. Holder who ceases to be resident in the United Kingdom (or who fails to be regarded as resident in a territory outside the United Kingdom for the purposes of double taxation relief) for a period of less than five calendar years and who disposes of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares during that period of temporary non-United Kingdom residence may be liable to United Kingdom capital gains tax on a chargeable gain accruing on such disposal on his or her return to the United Kingdom (or upon ceasing to be regarded as resident outside the United Kingdom for the purposes of double taxation relief) (subject to available exemptions or reliefs).
A disposal (or deemed disposal) of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares by a corporate U.K. Holder may give rise to a chargeable gain or an allowable loss for such holder for the purpose of United Kingdom corporation tax.
Any gain or loss in respect of currency fluctuations over the period of holding Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares is also brought into account on a disposal.
Non-U.K. Holders. An individual holder who is not a U.K. Holder will not be liable to United Kingdom capital gains tax on capital gains realized on the disposal of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares unless such holder carries on (whether solely or in partnership) a trade, profession or vocation in the U.K. through a branch or agency in the United Kingdom to which the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares are attributable. In these circumstances, such holder may, depending on his or her individual circumstances, be chargeable to United Kingdom capital gains tax on chargeable gains arising from a disposal of his or her Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares.
A corporate holder of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares that is not a U.K. Holder will not be liable for United Kingdom corporation tax on chargeable gains realized on the disposal of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares unless it carries on a trade in the United Kingdom through a permanent establishment to which the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares are attributable. In these circumstances, a disposal (or deemed disposal) of Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares by such holder may give rise to a chargeable gain or an allowable loss for the purposes of United Kingdom corporation tax.
Inheritance Tax
If for the purposes of the Double Taxation Relief (Taxes on Estates of Deceased Persons and on Gifts) Treaty United States of America Order 1979 (SI 1979/1454) between the United States and the United Kingdom an individual holder is at the time of their death or a transfer made during their lifetime, domiciled in the United States and is not a national of the United Kingdom, any Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares beneficially owned by that holder should not generally be subject to United Kingdom inheritance tax, provided that any applicable United States federal gift or estate tax liability is paid, except where (i) the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares are part of the business property of a United Kingdom permanent establishment or pertains to a United Kingdom fixed base used for the performance of independent personal services; or (ii) the Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares are comprised in a settlement unless, at the time the settlement was made, the settlor was domiciled in the United States and not a national of the United Kingdom (in which case no charge to United Kingdom inheritance tax should apply).
Stamp Duty and Stamp Duty Reserve Tax
The United Kingdom stamp duty, or stamp duty, and United Kingdom stamp duty reserve tax, or SDRT, treatment of the issue and transfer of, and the agreement to transfer, an ordinary share outside a depositary receipt system or a clearance service is discussed in the paragraphs under “General” below. The stamp duty and SDRT treatment of such transactions in relation to such systems is discussed in the paragraphs under “Depositary Receipt Systems and Clearance Services” below.
General
An agreement to transfer an ordinary share would normally give rise to a charge to SDRT at the rate of 0.5% of the amount or value of the consideration payable for the transfer. SDRT is, in general, payable by the purchaser. However, since April 28, 2014, no SDRT or stamp duty is chargeable in respect of shares that are admitted to trading on a ‘recognized growth market’ and not listed on any ‘recognized stock exchange’, or the AIM Exemption. As our Ordinary Shares are admitted to trading on AIM (which qualifies as a ‘recognized growth market’) and not listed on any market that would qualify as a ‘recognized stock exchange,’ a transfer of an ordinary share is presently exempt from the charge to SDRT.
Subject to the above noted AIM Exemption, a transfer of an Ordinary Share would be subject to stamp duty at the rate of 0.5% of the consideration given for the transfer (rounded up to the next £5). The purchaser is liable to HMRC for the payment of the stamp duty (if any). Under current HMRC guidance, no stamp duty should be payable on a written instrument transferring a Depositary Share or on a written agreement to transfer a Depositary Share, on the basis that the Depositary Share is not regarded as either “stock” or a “marketable security” for United Kingdom stamp duty purposes.
If a duly stamped transfer completing an agreement to transfer is produced within six years of the date on which the agreement is made (or, if the agreement is conditional, the date on which the agreement becomes unconditional) any SDRT already paid is generally repayable, normally with interest, and any SDRT charge yet to be paid is canceled to avoid a double charge as the stamp duty has been paid.
Depositary Receipt Systems and Clearance Services
The Court of Justice of the European Union in C-569/07 HSBC Holdings Plc, Vidacos Nominees Limited v The Commissioners of Her Majesty’s Revenue & Customs and the First-tier Tax Tribunal decision in HSBC Holdings Plc and the Bank of New York Mellon Corporation v The Commissioners of Her Majesty’s Revenue & Customs, have considered the provisions of the European Union Council Directive 69/335/EEC, which was subsequently substituted by the European Union Council Directive 2008/7/EEC, or the E.U. Directives. Following these decisions HMRC has publicly confirmed that issues or transfers of shares of United Kingdom incorporated companies, such as us, to a clearance service (such as, in our understanding, DTC) or a depositary receipt system will not be charged to United Kingdom SDRT at 1.5% where that issue or transfer is an integral part of a raising of new capital.
It was announced as part of the United Kingdom Budget 2017 by the United Kingdom government that the 1.5% stamp duty and SDRT charge will not be enforced on the issue of shares by United Kingdom incorporated companies (and transfers of such shares where the transfer is integral to new capital raising) into clearance services and depositary receipt systems following Brexit. However, following Brexit, the United Kingdom government could potentially introduce new United Kingdom legislation with the effect that a future issue or transfer of our Ordinary Shares following (i) Brexit and (ii) any such change of United Kingdom law into a clearance service or depositary receipt system (even where such an issue or transfer is an integral part of the raising of new capital by the company) may potentially become chargeable to 1.5% stamp duty or SDRT. However, as long as the Company’s Ordinary Shares continue to be admitted to trading on AIM and not to be listed on any market that would qualify as a ‘recognized stock exchange,’ it is our understanding that the AIM Exemption should continue to exempt future issues and transfers of the company’s Ordinary Shares into clearance services or depositary receipt systems from any 1.5% stamp duty and SDRT charge.
Subject to the AIM exemption, where an Ordinary Share is transferred (i) to, or to a nominee for, a person whose business is or includes the provision of clearance services or (ii) to, or to a nominee for a person whose business is or includes issuing depositary receipts and that transfer is not integral to the raising of new capital by the company, stamp duty or SDRT would generally be chargeable at the rate of 1.5% of the amount or value of the consideration given or, in certain circumstances, the value of the shares.
There is an exception from the 1.5% charge on the transfer to, or to a nominee , a clearance service where the clearance service has made and maintained an election under section 97A(1) of the Finance Act 1986, which has been approved by HMRC. If such an election were made by a clearance service, subject to the AIM exemption, SDRT at the rate of 0.5% of the amount or value of the consideration payable for the transfer would arise on any transfer of an ordinary share into such a clearance service and on subsequent agreements to transfer such share within such clearance service. It is our understanding that DTC has not to date made an election under section 97A(1) of the Finance Act of 1986.
Any liability for stamp duty or SDRT in respect of a transfer into a clearance service or depositary receipt system, or in respect of a transfer within such a service, which does arise, will strictly be accountable to HMRC by the clearance service or depositary receipt system operator or their nominee, as the case may be, but will, in practice, be payable by the participants in the clearance service or depositary receipt system.
Certain United States Taxation Matters
The following is a summary of material United States federal income tax consequences of the ownership and disposition of Depositary Shares by United States holders (as defined below). This summary is for general information only and is not tax advice. Each investor should consult its tax advisor with respect to the tax consequences of the ownership and disposition of our securities, including the impact of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act enacted on December 22, 2017.
This summary is based on provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, United States Treasury regulations promulgated thereunder (whether final, temporary, or proposed), administrative rulings, and judicial interpretations thereof, and the Convention Between the Government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and the Government of the United States of America for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and the Prevention of Fiscal Evasion with Respect to Taxes on Income and on Capital Gains of 2001, as amended, or the United States-U.K. Treaty, all as in effect on the date hereof, and all of which are subject to change, possibly with retroactive effect.
For purposes of this discussion, the term “United States holder” means a holder of our Ordinary Shares or Depositary Shares that is, for United States federal income tax purposes:
| · | an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States; |
| · | a corporation or other entity taxable as a corporation that is created or organized in the United States or under the laws of the United States or any state thereof or the District of Columbia; |
| · | an estate the income of which is subject to United States federal income taxation regardless of its source; or |
| · | any trust if (a) a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over the administration of the trust and one or more United States persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust, or (b) such trust has a valid election in effect under applicable United States Treasury regulations to be treated as a United States person. |
This summary addresses only the United States federal income tax considerations for United States holders that acquire and hold the Depositary Shares as capital assets within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code (generally, property held for investment). This discussion does not address all aspects of United States federal income taxation that may be relevant to a holder in light of its particular circumstances, or that may apply to holders that are subject to special treatment under the United States federal income tax laws (including, for example, banks, financial institutions, underwriters, insurance companies, dealers in securities or foreign currencies, traders in securities who elect the mark-to-market method of accounting for their securities, persons subject to the alternative minimum tax, persons that have a functional currency other than the United States dollar, tax-exempt organizations (including private foundations), mutual funds, subchapter S corporations, partnerships or other pass-through entities for United States federal income tax purposes, certain expatriates, corporations that accumulate earnings to avoid United States federal income tax, persons who hold Depositary Shares as part of a hedge, straddle, constructive sale, conversion or other integrated transaction, persons who acquire Depositary Shares through the exercise of options or other compensation arrangements, persons who own (or are treated as owning) 10% or more of the total combined voting power or value of our outstanding shares, or persons who are not United States holders). In addition, this discussion does not address any aspect of state, local, foreign, estate, gift or other tax law that may apply to holders of Depositary Shares.
The United States federal income tax treatment of a partner in a partnership (including any entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for United States federal income tax purposes) (or owner of another “pass-through entity”) generally will depend on the status of the partner (or owner) and the activities of the partnership (or other pass-through entity). A partner (or owner) in such a partnership (or other pass-through entity) should consult its tax advisor regarding the associated tax consequences.
Consequences Relating to Ownership and Disposition of Depositary Shares
Ownership of Depositary Shares. For United States federal income tax purposes, a holder of Depositary Shares will generally be treated as if such holder directly owned the Ordinary Shares represented by such Depositary Shares.
Distributions on Depositary Shares. Subject to the discussion below under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules,” the gross amount of any distribution on Depositary Shares (including withheld taxes, if any) made out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits (as determined for United States federal income tax purposes) will generally be taxable to a United States holder as dividend income on the date such distribution is actually or constructively received. Any such dividends paid to corporate United States holders generally will not qualify for the dividends received deduction that may otherwise be allowed under the Code. Distributions in excess of our current and accumulated earnings and profits would generally be treated first as a non-taxable return of capital to the extent of the United States holder’s basis in the Depositary Shares, and thereafter as capital gain. However, since we do not calculate our earnings and profits under United States federal income tax principles, it is expected that any distribution on Depositary Shares will be reported as a dividend even if that distribution would otherwise be treated as a non-taxable return of capital or as capital gain under the rules described above.
Dividends paid in currencies other than the United States dollar, if any, will generally be taxable to a United States holder as ordinary dividend income in an amount equal to the United States dollar value of the currency received on the date such distribution is actually or constructively received. Such United States dollar value must be determined using the spot rate of exchange on such date, regardless of whether the non-United States currency is actually converted into United States dollars on such date. The United States holder may realize exchange gain or loss if the currency received is converted into United States dollars after the date on which it is actually or constructively received. In general, any such gain or loss will be ordinary and will be treated as from sources within the United States for United States foreign tax credit purposes.
Subject to the discussion below under “—3.8% Medicare Tax on Net Investment Income,” dividends received by certain non-corporate United States holders (including individuals) from a “qualified foreign corporation” may be eligible for reduced rates of taxation, currently at a maximum rate of 20%, provided that certain holding period requirements and other conditions are satisfied. For these purposes, a foreign corporation will generally be treated as a qualified foreign corporation with respect to dividends paid by that corporation on shares that are readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States. United States Treasury Department guidance indicates that the Depositary Shares, which are listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market, would be considered readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States. However, there can be no assurance that the Depositary Shares will be considered readily tradable on an established securities market in future years. A foreign corporation is also treated as a qualified foreign corporation if it is eligible for the benefits of a comprehensive income tax treaty with the United States which is determined by the United States Treasury Department to be satisfactory for purposes of these rules and which includes an exchange of information provision. The United States Treasury Department has determined that the United States-U.K. Treaty meets these requirements. We would not constitute a qualified foreign corporation for purposes of these rules if we are a passive foreign investment company for the taxable year in which we pay a dividend or for the preceding taxable year, as discussed below under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules.”
Subject to certain conditions and limitations, non-United States taxes, if any, withheld on dividends paid by the Company may be treated as foreign taxes eligible for a credit against a United States holder’s United States federal income tax liability under the United States foreign tax credit rules. The rules governing the United States foreign tax credit are complex, and United States holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the availability of the United States foreign tax credit under their particular circumstances.
Sale of Depositary Shares, Warrants, or Pre-funded Warrants
A United States holder will generally recognize gain or loss on any sale, exchange, redemption, or other taxable disposition of Depositary Shares in an amount equal to the difference between the amount realized on the disposition and such holder’s tax basis in such securities. Subject to the discussion below under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules,” any gain or loss recognized by a United States holder on a taxable disposition of Depositary Shares will generally be capital gain or loss and will be long-term capital gain or loss if the holder’s holding period in such share exceeds one year at the time of the disposition. The deductibility of capital losses is subject to limitations.
For a cash basis taxpayer, units of foreign currency received will generally be translated into United States dollars at the spot rate on the settlement date of the sale. In that case, no foreign currency exchange gain or loss will result from currency fluctuations between the trade date and the settlement date of such sale. An accrual basis taxpayer may elect to apply the same rules applicable to cash basis taxpayers with respect to the sale of ADRs that are traded on an established securities market, provided that the election must be applied consistently from year to year and cannot be changed without the consent of the IRS. For an accrual method taxpayer who does not make such an election, units of foreign currency received will generally be translated into United States dollars at the spot rate on the trade date of the sale. Such an accrual basis taxpayer may recognize foreign currency exchange gain or loss based on currency fluctuations between the trade date and the settlement date of such sale. In general, any such gain or loss will be ordinary and will be treated as from sources within the United States for United States foreign tax credit purposes.
Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules
A foreign corporation is a PFIC if either (1) 75% or more of its gross income for the taxable year is passive income or (2) the average percentage of assets held by such corporation during the taxable year that produce passive income or that are held for the production of passive income is at least 50%. For purposes of applying the tests in the preceding sentence, the foreign corporation is deemed to own its proportionate share of the assets, and to receive directly its proportionate share of the income, of any other corporation of which the foreign corporation owns, directly or indirectly, at least 25% by value of the stock.
Based upon estimates with respect to its income, assets, and operations, it is expected that we will not be a PFIC for the current taxable year. However, because the determination of PFIC status must be made on an annual basis after the end of the taxable year and will depend on the composition of the income and assets, as well as the nature of the activities, of our activities and those of our subsidiaries from time to time, there can be no assurance that we will not be considered a PFIC for any taxable year.
If we were to be classified as a PFIC for any taxable year in which a United States holder held the Depositary Shares, various adverse United States tax consequences could result to such United States holders, including taxation of gain on a sale or other disposition of the shares of the corporation, Depositary Shares at ordinary income rates and imposition of an interest charge on gain or on distributions with respect to the shares, Depositary Shares. Unless a United States holder of PFIC shares elects, in either case if eligible, to be taxed annually on a mark-to-market basis or makes a QEF election and certain other requirements are met, gain realized on the sale or other disposition of PFIC shares, Depositary Shares would generally not be treated as capital gain. Instead, the United States holder would be treated as if the United States holder had realized such gain ratably over the holder’s holding period for such securities. The amounts allocated to the taxable year of sale or other disposition and to any year before the foreign corporation became a PFIC would be taxed as ordinary income. The amount allocated to each other taxable year would be subject to tax at the highest rate in effect for such year, together with an interest charge in respect of the tax attributable to each such year. Similar rules apply to the extent any distribution in respect of PFIC shares, Depositary Shares exceeds 125% of the average annual distribution on such PFIC securities received by the shareholder during the preceding three years or holding period, whichever is shorter. With certain exceptions, a foreign corporation is treated as a PFIC with respect to a shareholder (or warrant holder, as applicable) if the corporation was a PFIC with respect to such holder at any time during the holder’s holding period of the foreign corporation’s stock or warrants. Dividends paid to with respect to shares of a PFIC are not eligible for the special tax rates applicable to qualified dividend income of certain non-corporate holders. Instead, such dividend income is taxable at rates applicable to ordinary income.
If we were to be treated as a PFIC, the tax consequences described above could be avoided by a “mark-to-market” election with respect to the Depositary Shares. A United States holder making a “mark-to-market” election (assuming the requirements for such an election are satisfied) generally would (i) be required to include as ordinary income the excess of the fair market value of the Depositary Shares on the last day of the United States holder’s taxable year over the United States holder’s adjusted tax basis in such Depositary Shares and (ii) be allowed a deduction in an amount equal to the lesser of (A) the excess, if any, of the United States holder’s adjusted tax basis in the Depositary Shares over the fair market value of such Depositary Shares on the last day of the United States holder’s taxable year or (B) the excess, if any, of the amount included in income because of the election for prior taxable years over the amount allowed as a deduction because of the election for prior taxable years. In addition, upon a sale or other taxable disposition of Depositary Shares, a United States holder would recognize ordinary income or loss (which loss could not be in excess of the amount included in income because of the election for prior taxable years over the amount allowed as a deduction because of the election for prior taxable years).
We do not intend to prepare or provide the information necessary for United States shareholders to make a QEF election.
United States holders are urged to consult their own tax advisors about the PFIC rules, including the availability of the “mark-to-market” election.
3.8% Medicare Tax on “Net Investment Income”
A 3.8% tax, or “Medicare Tax,” is imposed on all or a portion of “net investment income,” which may include any gain realized or amounts received with respect to Depositary Shares received by (i) United States holders that are individuals with modified adjusted gross income in excess of certain thresholds, and (ii) certain estates and trusts. United States holders should consult their own tax advisors with respect to the applicability of the Medicare Tax resulting from ownership or disposition of Depositary Shares.
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
United States holders may be subject to information reporting requirements and may be subject to backup withholding with respect to dividends on Depositary Shares and on the proceeds from the sale, exchange, or disposition of Depositary Shares unless the United States holder provides an accurate taxpayer identification number and complies with certain certification procedures or otherwise establishes an exemption from backup withholding. Backup withholding is not an additional tax and amounts withheld may be allowed as a credit against the United States holder’s United States federal income tax liability and may entitle the United States holder to a refund, provided that certain required information is timely furnished to the IRS.
Foreign Asset Reporting
United States holders who are individuals and who own “specified foreign financial assets” with an aggregate value in excess of $50,000 are generally required to file an information statement along with their tax returns, currently on IRS Form 8938, with respect to such assets. “Specified foreign financial assets” include securities issued by a non-United States issuer (which would include an investment in our securities) that are not held in accounts maintained by financial institutions. Higher reporting thresholds apply to certain individuals living abroad and to certain married individuals. Individuals who fail to report the required information could be subject to substantial penalties, and such individuals should consult their own tax advisors concerning the application of these rules to their investment in Depositary Shares
SELLING SHAREHOLDERS
This prospectus covers the possible resale from time to time by the selling shareholders identified in the table below of Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares, including Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares issuable upon the exercise of the Series A warrants, Series B warrants, pre-funded warrants and Ladenburg Warrants (referred to in this prospectus collectively and individually as the warrants). The selling shareholders may sell some, all or none of their Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares. We do not know how long the selling shareholders will hold the warrants, whether any will exercise the warrants, and upon such exercise, how long such selling shareholders will hold the Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares before selling them, and we currently have no agreements, arrangements or understandings with the selling shareholders regarding the sale of any of the shares.
The table below lists the selling shareholders and other information regarding the beneficial ownership of the Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares by each of the selling shareholders. The second column lists the number of Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares beneficially owned by each selling shareholder, based on its ownership of Depositary Shares and warrants to purchase Depositary Shares, as of March 1, 2023, assuming exercise of the warrants held by the selling shareholders on that date, without regard to any limitations on conversions or exercises and assuming receipt of all necessary stockholder approvals at a general meeting. The third column lists the maximum number of Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares being offered in this prospectus by the selling shareholders. The fourth and fifth columns list the amount of Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares owned after the offering, by number of Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares and percentage of outstanding Ordinary Shares, assuming in both cases (i) the receipt of all necessary stockholder approval at a general meeting, and (ii) the sale of all of the Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares offered by the selling shareholders pursuant to this prospectus, and without regard to any limitations on conversions or exercises.
In accordance with the terms of a registration rights agreement with the selling shareholders, this prospectus generally covers the resale of the sum of (i) the number of Ordinary Shares issued to the selling shareholders in connection with the Private Placement and the Waiver described herein and (ii) the maximum number of Ordinary Shares upon exercise of the related warrants, determined as if the outstanding warrants were exercised in full as of the trading day immediately preceding the date this registration statement was initially filed with the SEC, each as of the trading day immediately preceding the applicable date of determination and all subject to adjustment as provided in the registration right agreement, without regard to any limitations on the exercise of the warrants.
Under the terms of the warrants, a selling shareholder may not exercise the warrants to the extent such exercise would cause such selling shareholder, together with its affiliates and attribution parties, to beneficially own a number of Ordinary Shares which would exceed 9.99% of our then outstanding Ordinary Shares following such exercise, excluding for purposes of such determination Ordinary Shares issuable upon exercise of such warrants which have not been exercised. The beneficial ownership limitation may be increased or decreased, provided that in no event shall it exceed 9.99%, upon notice to us, provided that any increase in the beneficial ownership limitation shall not be effective until 61 days following the receipt of such notice by us. The number of shares in the table below does not reflect this limitation. See “Plan of Distribution.” The selling shareholders may sell all, some or none of their Ordinary Shares in this offering. See "Plan of Distribution."
| Name of Selling Shareholder (1) | | Number of Ordinary
Shares Owned Prior to
Offering * | | | Maximum Number of
Ordinary Shares to be Sold
Pursuant to this Prospectus * | | | Number of Ordinary
Shares Owned After
Offering (2) | |
| Armistice Capital Master Fund Limited (3) | | | 18,755,000† | | | | 12,500,000† | | | | 6,255,000† | |
| Anson Investments Master Fund LP (4) | | | 357,758,575 | | | | 357,758,575 | | | | -- | |
| CVI Investments Inc. (5) | | | 357,758,575 | | | | 357,758,575 | | | | -- | |
| Ionic Ventures, LLC (6) | | | 357,758,575 | | | | 357,758,575 | | | | -- | |
L1 Capital Global Opportunities Master
Fund (7) | | | 358,523,730† | | | | 357,758,575† | | | | 765,155† | |
| Ladenburg Thalmann & Co. Inc. (8) | | | 10,738,775 | | | | 10,738,775 | | | | -- | |
| Walleye Opportunities Master Fund Ltd. (9) | | | 357,758,575 | | | | 357,758,575 | | | | -- | |
| S.H.N. Financial Investments Ltd. (10) | | | 357,758,575 | | | | 357,758,575 | | | | -- | |
__________________
* Subject to beneficial ownership blocker of 9.99%.
† Subject to a beneficial ownership blocker of 4.99%.
| (1) | All information as of March 1, 2023. |
| (2) | Assumes that all Ordinary Shares being registered under the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part are sold in this offering, and that none of the selling stockholders acquire additional Ordinary Shares after the date of this prospectus and prior to completion of this offering. |
| (3) | The selling shareholder holds (i) warrants issued by us in prior transactions, or the Prior Armistice Warrants, which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 6,255,000 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which were previously registered, and (ii) warrants issued by us pursuant to the Waiver, or the Waiver Warrants, which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 12,500,000 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which we are registering hereby. The Prior Armistice Warrants and the Waiver Warrants are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 4.99% and 9.99%, respectively, which does not permit the selling shareholder to exercise that portion of the warrants that would result in the selling shareholder and its affiliates owning, after exercise, a number of our Ordinary Shares in excess of the beneficial ownership limitation. The amounts and percentages in the table do not give effect to the beneficial ownership limitation, if applicable. Armistice Capital, LLC, the investment manager of Armistice Capital Master Fund Ltd., or Armistice, and Steven Boyd, the managing member of Armistice Capital, LLC, hold shared voting and dispositive power over the shares held by Armistice. Each of Armistice Capital, LLC and Steven Boyd disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein. The principal business address of Armistice is c/o Armistice Capital, LLC, 510 Madison Avenue, 7th Floor, New York, New York, 10022. |
| (4) | The selling shareholder holds (i) 10,834,000 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) issued by us in the Private Placement and which we are registering hereby, and (ii) warrants issued by us in the private placement which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 346,924,575 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which we are registering hereby. The warrants are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 9.99%, which does not permit the selling shareholder to exercise that portion of the warrants that would result in the selling shareholder and its affiliates owning, after exercise, a number of our Ordinary Shares in excess of the beneficial ownership limitation. The amounts and percentages in the table do not give effect to the beneficial ownership limitation, if applicable. Anson Advisors Inc. and Anson Funds Management LP, the co-investment advisers of Anson Investments Master Fund LP, or Anson, hold voting and dispositive power over the Ordinary Shares held by Anson. Bruce Winson is the managing member of Anson Management GP LLC, which is the general partner of Anson Funds Management LP. Moez Kassam and Amin Nathoo are directors of Anson Advisors Inc. Mr. Winston, Mr. Kassam and Mr. Nathoo each disclaim beneficial ownership of these Ordinary Shares except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein. The principal business address of Anson is Maples Corporate Services Limited, PO Box 309, Ugland House, Grand Cayman, KY1-1104, Cayman Islands. |
| (5) | The selling shareholder holds (i) 10,834,000 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) issued by us in the Private Placement and which we are registering hereby, and (ii) warrants issued by us in the private placement which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 346,924,575 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which we are registering hereby. The warrants are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 9.99%, which does not permit the selling shareholder to exercise that portion of the warrants that would result in the selling shareholder and its affiliates owning, after exercise, a number of our Ordinary Shares in excess of the beneficial ownership limitation. The amounts and percentages in the table do not give effect to the beneficial ownership limitation, if applicable. Heights Capital Management, Inc., the authorized agent of CVI Investments, Inc., or CVI, has discretionary authority to vote and dispose of the shares held by CVI and may be deemed to be the beneficial owner of these shares. Martin Kobinger, in his capacity as Investment Manager of Heights Capital Management, Inc., may also be deemed to have investment discretion and voting power over the shares held by CVI. Mr. Kobinger disclaims any such beneficial ownership of the shares. CVI Investments, Inc. is affiliated with one or more FINRA member, none of whom are currently expected to participate in the sale pursuant to the prospectus contained in the registration statement of shares purchased by the investor in this offering. The principal business address of CVI Investments, Inc. is c/o Heights Capital Management, Inc., 101 California Street, Suite 3250, San Francisco CA 94111. |
| (6) | The selling shareholder holds (i) 10,834,000 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) issued by us in the Private Placement and which we are registering hereby, and (ii) warrants issued by us in the private placement which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 346,924,575 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which we are registering hereby. The warrants are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 9.99%, which does not permit the selling shareholder to exercise that portion of the warrants that would result in the selling shareholder and its affiliates owning, after exercise, a number of our Ordinary Shares in excess of the beneficial ownership limitation. The amounts and percentages in the table do not give effect to the beneficial ownership limitation, if applicable. Brendan O’Neil and Keith Coulston are the managers of Ionic Ventures, LLC and in such capacity have joint voting and dispositive power over shares held by Ionic Ventures, LLC. Mr. O’Neil and Mr. Coulston each disclaim beneficial ownership of the reported securities except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein. Ionic Ventures, LLC is not a licensed broker dealer or an affiliate of a licensed broker dealer. The principal business address of Ionic Ventures, LLC is 3053 Fillmore Street, Ste. 256, San Francisco, CA 94123. |
| (7) | The selling shareholder holds (i) warrants issued by us in prior transactions which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 765,155 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which were previously registered and are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 4.99%, (ii) 10,834,000 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) issued by us in the Private Placement and which we are registering hereby, and (iii) warrants issued by us in the Private Placement which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 346,924,575 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which we are registering hereby. The warrants are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 9.99%, which does not permit the selling shareholder to exercise that portion of the warrants that would result in the selling shareholder and its affiliates owning, after exercise, a number of our Ordinary Shares in excess of the beneficial ownership limitation. The amounts and percentages in the table do not give effect to the beneficial ownership limitations, if applicable. David Feldman and Joel Arber are both the directors the selling shareholder, and as such they each individually have sole dispositive and voting power. To the extent Mr. Feldman and Mr. Arber are deemed to beneficially own such shares, Mr. Feldman and Mr. Arber disclaim beneficial ownership of these securities for all other purposes. The principal business address of the selling shareholder is 161A Shedden Road, 1 Artillery Court, P.O. Box 10085, Grand Cayman, Cayman Islands KY1-1001, Cayman Islands. |
| (8) | The selling shareholder holds Ladenburg Warrants issued by us in connection with the Private Placement which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 10,738,775 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which we are registering hereby. The warrants are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 9.99%, which does not permit the selling shareholder to exercise that portion of the warrants that would result in the selling shareholder and its affiliates owning, after exercise, a number of our Ordinary Shares in excess of the beneficial ownership limitation. The amounts and percentages in the table do not give effect to the beneficial ownership limitation, if applicable. Ladenburg Thalmann & Co. Inc., or Ladenburg, is a registered broker-dealer that received the Ladenburg Warrants pursuant to investment banking services. David Rosenburg has voting and dispositive control with respect to the securities being offered. The address forLadenburg is 277 Park Avenue, 26th Floor, New York, New York 10172. |
| (9) | The selling shareholder holds (i) 10,834,000 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) issued by us in the Private Placement and which we are registering hereby, and (ii) warrants issued by us in the private placement which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 346,924,575 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which we are registering hereby. The warrants are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 9.99%, which does not permit the selling shareholder to exercise that portion of the warrants that would result in the selling shareholder and its affiliates owning, after exercise, a number of our Ordinary Shares in excess of the beneficial ownership limitation. The amounts and percentages in the table do not give effect to the beneficial ownership limitation, if applicable. Walleye Capital LLC is the investment manager of Walleye Opportunities Master Fund Ltd, or the Walleye Fund, and may be deemed to beneficially own the securities owned by the Walleye Fund. Roger Masi is a Portfolio Manager of Walleye Capital LLC and may be deemed to have voting and dispositive power over the securities owned by the Walleye Fund. Walleye Capital LLC and Roger Masi each disclaim any beneficial ownership of these securities. The address for Walleye Capital LLC and U.S. address for the Walleye Fund is 2800 Niagara Lane N, Plymouth MN 55447. |
| (10) | The selling shareholder holds (i) 10,834,000 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) issued by us in the Private Placement and which we are registering hereby, and (ii) warrants issued by us in the private placement which entitle the holder to purchase up to an aggregate of 346,924,575 Ordinary Shares (in the form of Depositary Shares) and which we are registering hereby. The warrants are subject to a beneficial ownership limitation of 9.99%, which does not permit the selling shareholder to exercise that portion of the warrants that would result in the selling shareholder and its affiliates owning, after exercise, a number of our Ordinary Shares in excess of the beneficial ownership limitation. The amounts and percentages in the table do not give effect to the beneficial ownership limitation, if applicable. The shares will be directly held by S.H.N. Financial Investments Ltd., an Israeli corporation, or S.H.N., and may be deemed to be indirectly beneficially owned by Mr. Hadar Shamir and Mr. Nir Shamir who each own 50% of the company and have shared voting and dispositive power over the common shares. Mr. Hadar Shamir and Mr. Nir Shamir disclaim beneficial ownership of the securities except to the extent of their respective pecuniary interests therein. The address of S.H.N. is c/o S.H.N. Financial Investments Ltd., 3 Arik Einstein Street, Herzilya, Israel. |
PLAN OF DISTRIBUTION
Each selling shareholder and any of their pledgees, assignees and successors-in-interest may, from time to time, sell any or all of their Ordinary Shares represented by Depositary Shares covered by this prospectus on the principal trading market or any other stock exchange, market or trading facility on which the securities are traded or in private transactions. These sales may be at fixed or negotiated prices. A selling shareholder may use any one or more of the following methods when selling securities:
| · | ordinary brokerage transactions and transactions in which the broker-dealer solicits purchasers; |
| · | block trades in which the broker-dealer will attempt to sell the securities as agent but may position and resell a portion of the block as principal to facilitate the transaction; |
| · | purchases by a broker-dealer as principal and resale by the broker-dealer for its account; |
| · | an exchange distribution in accordance with the rules of the applicable exchange; |
| · | privately negotiated transactions; |
| · | settlement of short sales; |
| · | in transactions through broker-dealers that agree with the selling shareholders to sell a specified number of such securities at a stipulated price per security; |
| · | through the writing or settlement of options or other hedging transactions, whether through an options exchange or otherwise; |
| · | a combination of any such methods of sale; or |
| · | any other method permitted pursuant to applicable law. |
The selling shareholders may also sell securities under Rule 144 or any other exemption from registration under the Securities Act, if available, rather than under this prospectus.
Broker-dealers engaged by the selling shareholders may arrange for other brokers-dealers to participate in sales. Broker-dealers may receive commissions or discounts from the selling shareholders (or, if any broker-dealer acts as agent for the purchaser of securities, from the purchaser) in amounts to be negotiated, but, except as set forth in a supplement to this Prospectus, in the case of an agency transaction not in excess of a customary brokerage commission in compliance with FINRA Rule 2440; and in the case of a principal transaction a markup or markdown in compliance with FINRA IM-2440.
In connection with the sale of the securities or interests therein, the selling shareholders may enter into hedging transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions, which may in turn engage in short sales of the securities in the course of hedging the positions they assume. The selling shareholders may also sell securities short and deliver these securities to close out their short positions, or loan or pledge the securities to broker-dealers that in turn may sell these securities. The selling shareholders may also enter into option or other transactions with broker-dealers or other financial institutions or create one or more derivative securities which require the delivery to such broker-dealer or other financial institution of securities offered by this prospectus, which securities such broker-dealer or other financial institution may resell pursuant to this prospectus (as supplemented or amended to reflect such transaction).
The selling shareholders and any broker-dealers or agents that are involved in selling the securities may be deemed to be “underwriters” within the meaning of the Securities Act in connection with such sales. In such event, any commissions received by such broker-dealers or agents and any profit on the resale of the securities purchased by them may be deemed to be underwriting commissions or discounts under the Securities Act. Each selling shareholders has informed the Company that it does not have any written or oral agreement or understanding, directly or indirectly, with any person to distribute the securities.
The Company is required to pay certain fees and expenses incurred by the Company incident to the registration of the securities. The Company has agreed to indemnify the selling shareholders against certain losses, claims, damages and liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act.
We agreed to keep this prospectus effective until the earlier of (i) the date on which the securities may be resold by the selling shareholders without registration and without regard to any volume or manner-of-sale limitations by reason of Rule 144, without the requirement for the Company to be in compliance with the current public information under Rule 144 under the Securities Act or any other rule of similar effect or (ii) all of the securities have been sold pursuant to this prospectus or Rule 144 under the Securities Act or any other rule of similar effect. The resale securities will be sold only through registered or licensed brokers or dealers if required under applicable state securities laws. In addition, in certain states, the resale securities covered hereby may not be sold unless they have been registered or qualified for sale in the applicable state or an exemption from the registration or qualification requirement is available and is complied with.
Under applicable rules and regulations under the Exchange Act, any person engaged in the distribution of the resale securities may not simultaneously engage in market making activities with respect to the Depositary Shares for the applicable restricted period, as defined in Regulation M, prior to the commencement of the distribution. In addition, the selling shareholders will be subject to applicable provisions of the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations thereunder, including Regulation M, which may limit the timing of purchases and sales of the Depositary Shares by the selling shareholders or any other person. We will make copies of this prospectus available to the selling shareholders and have informed them of the need to deliver a copy of this prospectus to each purchaser at or prior to the time of the sale (including by compliance with Rule 172 under the Securities Act).
EXPENSES OF THE OFFERING
The following table sets forth the expenses payable by us in connection with the sale and distribution of the securities being registered hereby. All amounts shown, other than the SEC registration fee and FINRA filing fee, are estimates:
| SEC registration fee | $ | 4,830 |
| FINRA filing fee | | * |
| Printing and engraving | | * |
| Accounting services | | * |
| Legal fees and expenses | | * |
| Depositary fees | | * |
| Miscellaneous | | * |
| Total | $ | * |
* To be completed by amendment
LEGAL MATTERS
Certain legal matters in connection with the securities offered hereby will passed upon for us by Brown Rudnick LLP.
EXPERTS
The financial statements as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and for the each of the two years in the period then ended, included in this prospectus and in the registration statement have been so included in reliance on a report of Mazars LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting. The report contains an explanatory paragraph regarding our ability to continue as a going concern.
Mazars LLP, London, United Kingdom, is a member of the Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales.
The financial statements as of December 31, 2019 and for the year then ended, included in this prospectus and in the registration statement have been so included in reliance on the report of BDO LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, incorporated herein by reference, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting. The report on the financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2019 contains an explanatory paragraph regarding the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
BDO LLP, Reading, United Kingdom, is a member of the Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales.
ENFORCEMENT OF CIVIL LIABILITIES
We are incorporated under the laws of England and Wales. All of our directors and officers of are residents of jurisdictions outside the United States. Our corporate headquarters is located in the United Kingdom and all or a substantial portion of our assets, and all or a substantial portion of the assets of our directors and officers, are located outside of the United States. As a result, it may be difficult for you to serve legal process on us or our directors or have any of them appear in a U.S. court.
We have appointed Donald J. Puglisi of Puglisi & Associates as our authorized agent upon whom process may be served in any action instituted in any U.S. federal or state court having subject matter jurisdiction arising out of or based upon the securities offered by this prospectus.
We understand that in England it may not be possible to bring proceedings or enforce a judgment of a U.S. court in respect of civil liabilities based solely on the federal securities laws of the United States. In addition, awards of punitive damages in actions brought in the United States or elsewhere may be unenforceable in England. An award of damages is usually considered to be punitive if it does not seek to compensate the claimant for loss or damage suffered and is instead intended to punish the defendant. In addition to public policy aspects of enforcement, such as the aforementioned, the enforceability of any judgment in England will depend on the particular facts of the case and the relevant circumstances, for example (and expressly without limitation), whether there are any relevant insolvency proceedings which may affect the ability to enforce a judgment. In addition, the United States and the United Kingdom have not currently entered into a treaty (or convention) providing for the reciprocal recognition and enforcement of judgments (although both are contracting states to the New York Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards).
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We are subject to periodic reporting and other informational requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, as applicable to foreign private issuers. Accordingly, we are required to file reports, including annual reports on Form 20-F, and other information with the SEC. As a foreign private issuer, we are exempt from the rules of the Exchange Act prescribing the furnishing and content of proxy statements to shareholders under the federal proxy rules contained in Sections 14(a), (b) and (c) of the Exchange Act, and our “insiders” are exempt from the reporting and short-swing profit recovery provisions contained in Section 16 of the Exchange Act. The SEC maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy, information statements and other information regarding issuers at http://www.sec.gov. Copies of certain information filed by us with the SEC are also available on our website at http://www.midatechpharma.com. Our website is not a part of this prospectus and is not incorporated by reference in this prospectus.
This prospectus is part of a registration statement we filed with the SEC. This prospectus omits some information contained in the registration statement in accordance with SEC rules and regulations. You should review the information and exhibits in the registration statement for further information on us and our consolidated subsidiaries and the securities we are offering. Statements in this prospectus concerning any document we filed as an exhibit to the registration statement or that we otherwise filed with the SEC are not intended to be comprehensive and are qualified by reference to these filings. You should review the complete document to evaluate these statements. You can obtain a copy of the registration statement from the SEC at the address listed above or from the SEC’s website.
MIDATECH PHARMA PLC
Index to Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements for the Six-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2022 and 2021
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
For the six month period ended 30 June
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Note | | | 2022 unaudited £’000 | | | 2021 unaudited £’000 | |
| Revenue | | | | | | | 468 | | | | 401 | |
| Other income | | | | | | | 16 | | | | 31 | |
| Research and development costs | | | | | | | (2,413 | ) | | | (2,010 | ) |
| Administrative costs | | | | | | | (1,849 | ) | | | (1,656 | ) |
| Loss from operations | | | | | | | (3,778 | ) | | | (3,234 | ) |
| Finance income | | | 2 | | | | 404 | | | | - | |
| Finance expense | | | 2 | | | | (24 | ) | | | (156 | ) |
| Loss before tax | | | | | | | (3,398 | ) | | | (3,390 | ) |
| Taxation | | | 3 | | | | 337 | | | | 236 | |
| Loss for the period attributable to the owners of the parent | | | | | | | (3,061 | ) | | | (3,154 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Items that will or may be reclassified subsequently to profit or loss: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total other comprehensive gain net of tax | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total comprehensive loss attributable to the owners of the parent | | | | | | | (3,061 | ) | | | (3,154 | ) |
| Loss per share | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted loss per ordinary share - pence | | | 4 | | | | (3 | )p | | | (5 | )p |
The accompanying notes form part of these financial statements
Distribution costs, sales and marketing are immaterial in 2022 and 2021 and have been included within administrative costs.
Consolidated Statements of Financial Position
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Note | | | As at 30 June 2022
unaudited £’000 | | | As at 31 December
2021 £’000 | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | | | | | 993 | | | | 1,152 | |
| Total Non-Current Assets | | | | | | | 993 | | | | 1,152 | |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other receivables | | | | | | | 1,243 | | | | 1,034 | |
| Taxation | | | | | | | 1,023 | | | | 670 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 6,423 | | | | 10,057 | |
| Total Current Assets | | | | | | | 8,689 | | | | 11,761 | |
| Total assets | | | | | | | 9,682 | | | | 12,913 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Borrowings | | | 5 | | | | 546 | | | | 620 | |
| Total Non-Current Liabilities | | | | | | | 546 | | | | 620 | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | | | | | 1,280 | | | | 1,092 | |
| Borrowings | | | 5 | | | | 167 | | | | 146 | |
| Provisions | | | 6 | | | | 43 | | | | 50 | |
| Derivative financial liability | | | 7 | | | | 155 | | | | 553 | |
| Total current Liabilities | | | | | | | 1,645 | | | | 1,841 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | | | | 2,191 | | | | 2,461 | |
| Issued capital and reserves attributable to owners of the parent | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | | 8 | | | | 1,098 | | | | 1,098 | |
| Share premium | | | | | | | 83,434 | | | | 83,434 | |
| Merger reserve | | | | | | | 53,003 | | | | 53,003 | |
| Warrant reserve | | | | | | | 720 | | | | 720 | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | | | | | (130,764 | ) | | | (127,803 | ) |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 7,491 | | | | 10,452 | |
| Total equity and liabilities | | | | | | | 9,682 | | | | 12,913 | |
The accompanying notes form part of these financial statements
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
For the six month period ended 30 June
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Note | | | 2022 unaudited £’000 | | | 2021 unaudited £’000 | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | | (3,061 | ) | | | (3,154 | ) |
| Adjustments for: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation of property, plant and equipment | | | | | | | 96 | | | | 117 | |
| Depreciation of right of use asset | | | | | | | 86 | | | | 62 | |
| (Profit)/Loss on disposal of fixed assets | | | | | | | 2 | | | | (42 | ) |
| Finance income | | | 2 | | | | (404 | ) | | | - | |
| Finance expense | | | 2 | | | | 24 | | | | 156 | |
| Share-based payment expense/(credit) | | | | | | | 100 | | | | 37 | |
| Taxation | | | 3 | | | | (337 | ) | | | (236 | ) |
| Foreign exchange (gains)/losses | | | | | | | - | | | | (3 | ) |
| Cash flows from operating activities before changes in working capital | | | | | | | (3,494 | ) | | | (3,063 | ) |
| Increase in trade and other receivables | | | | | | | (224 | ) | | | (859 | ) |
| Increase in trade and other payables | | | | | | | 187 | | | | 814 | |
| Decrease in provisions | | | | | | | (8 | ) | | | - | |
| Cash used in operations | | | | | | | (3,539 | ) | | | (3,108 | ) |
| Taxes payments | | | | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | | | | | | (3,539 | ) | | | (3,108 | ) |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (continued)
For the six month period ended 30 June
| | | Note | | | 2022 unaudited £’000 | | | 2021 unaudited £’000 | |
| Investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchases of property, plant and equipment | | | | | | | (33 | ) | | | (189 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of fixed assets | | | | | | | 9 | | | | 42 | |
| Interest received | | | | | | | 7 | | | | - | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | | | | | | (17 | ) | | | (147 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (5 | ) | | | (11 | ) |
| Amounts paid on lease liabilities | | | | | | | (73 | ) | | | (47 | ) |
| Repayment of Government loan | | | | | | | - | | | | (104 | ) |
| Share issues including warrants, net of costs | | | 8 | | | | - | | | | 81 | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | | | | | | | (78 | ) | | | (81 | ) |
| Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (3,634 | ) | | | (3,336 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | | | | | | | 10,057 | | | | 7,546 | |
| Exchange (losses)/gains on cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | - | | | | (6 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | | | | | | | 6,423 | | | | 4,204 | |
The accompanying notes form part of these financial statements
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity (unaudited)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Share capital £’000 | | | Share premium £’000 | | | Merger
reserve £’000 | | | Warrant
reserve
£’000 | | | Foreign exchange reserve £’000 | | | Accumulated deficit £’000 | | | Total equity £’000 | |
| At 1 January 2022 | | | 1,098 | | | | 83,434 | | | | 53,003 | | | | 720 | | | | - | | | | (127,803 | ) | | | 10,452 | |
| Loss for the period | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,061 | ) | | | (3,061 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,061 | ) | | | (3,061 | ) |
| Transactions with owners: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exercise of warrants on 22 March 2022 | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Shares issued on 3 May 2022 | | | - | | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Share-based payment charge | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100 | | | | 100 | |
| Total contribution by and distributions to owners | | | - | | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 100 | | | | 100 | |
| At 30 June 2022 | | | 1,098 | | | | 83,434 | | | | 53,003 | | | | 720 | | | | - | | | | (130,764 | ) | | | 7,491 | |
| | | Share capital £’000 | | | Share premium £’000 | | | Merger
reserve £’000 | | | Warrant
reserve
£’000 | | | Foreign exchange reserve £’000 | | | Accumulated deficit £’000 | | | Total equity £’000 | |
| At 1 January 2021 | | | 1,063 | | | | 74,364 | | | | 53,003 | | | | 720 | | | | - | | | | (122,432 | ) | | | 6,718 | |
| Loss for the period | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,154 | ) | | | (3,154 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,154 | ) | | | (3,154 | ) |
| Transactions with owners: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exercise of warrants on 16 February 2021 | | | - | | | | 161 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 161 | |
| Costs associated with share issue on 16 February 2021 | | | - | | | | (10 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (10 | ) |
| Share-based payment charge | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 37 | | | | 37 | |
| Total contribution by and distributions to owners | | | - | | | | 151 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 37 | | | | 188 | |
| At 30 June 2021 | | | 1,063 | | | | 74,515 | | | | 53,003 | | | | 720 | | | | - | | | | (125,549 | ) | | | 3,752 | |
The accompanying notes form part of these financial statements
Notes Forming Part of The Consolidated Unaudited Interim Financial Information
For the six month period ended 30 June 2022
The unaudited interim consolidated financial information for the six months ended 30 June 2022 has been prepared following the recognition and measurement principles of the International Financial Reporting Standards, International Accounting Standards and Interpretations (collectively IFRS) issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), and as adopted by the UK and in accordance with International Accounting Standard 34 Interim Financial Reporting (‘IAS 34’). The interim consolidated financial information does not include all the information and disclosures required in the annual financial information and should be read in conjunction with the audited financial statements for the year ended 31 December 2021.
The condensed interim financial information contained in this interim statement does not constitute statutory financial statements as defined by section 434(3) of the Companies Act 2006. The condensed interim financial information has not been audited. The comparative financial information for the six months ended 30 June 2021 and the year ended 31 December 2021 in this interim financial information does not constitute statutory accounts for that year. The statutory accounts for 31 December 2021 have been delivered to the UK Registrar of Companies. The auditor’s report on those accounts was unqualified and did not contain a statement under section 498(2) or 498(3) of the Companies Act 2006. The auditor’s report did draw attention to a material uncertainty related to going concern and the requirement, as of the date of the report, for additional funding to be raised by the Company by the first quarter of 2023.
Midatech Pharma’s annual reports may be downloaded from the Company’s website at https://www.midatechpharma.com/investors/financial-reports-accounts or a copy may be obtained from 1 Caspian Point, Caspian Way, Cardiff CF10 4DQ.
Going Concern
Midatech has experienced net losses and significant cash outflows from cash used in operating activities over the past years as it has developed its portfolio. As at 30 June 2022 the Group had total equity of £7.49m 7,491 (£10.45m at 31 December 2021),10,452 it incurred a net loss after tax for the six months to 30 June 2022 of £3.06m 3,061 (1H 21: £3.15m) 3,154 and used cash in operating activities of £3.54m 3,539 (1H21: £3.11m) 3,108 for the same period. As at 30 June 2022, the Company had cash and cash equivalents of £6.42m 6,423.
The Group’s future viability is dependent on its ability to raise cash from financing activities to finance its development plans until commercialisation, generate cash from operating activities and to successfully obtain regulatory approval to allow marketing of its development products. The group’s failure to raise capital as and when needed could have a negative impact on its financial condition and ability to pursue its business strategies.
The Directors have prepared cash flow forecasts and considered the cash flow requirement for the Company for the next three years including the period 12 months from the date of approval of this interim financial information. These forecasts show that further financing will be required during the first quarter of 2023 assuming, inter alia, that certain developments programs and other operating activities continue as currently planned. This requirement for additional financing in the short term represents a material uncertainty that may cast doubt upon the Group and Parent Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
The Directors are evaluating a number of near-term funding options potentially available to the Group, including fundraising and the partnering of assets and technologies of the Company. After considering the uncertainties, the Directors consider it is appropriate to continue to adopt the going concern basis in preparing these financial statements.
| 2. | Finance income and expense |
The gain on the equity settled derivative financial liability in 2022 arose as a result of the reduction in the Midatech share price.
| | | Six months
ended 30
June 2022 unaudited £’000 | | | Six months
ended 30
June 2021 unaudited £’000 | |
| Finance expense | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense on lease liabilities | | | 24 | | | | 13 | |
| Other loans | | | - | | | | 9 | |
| Loss on equity settled derivative financial liability | | | - | | | | 134 | |
| Total finance expense | | | 24 | | | | 156 | |
The loss on the equity settled derivative financial liability in 2021 arose as a result of the increase in the Midatech share price.
Income tax is recognised or provided at amounts expected to be recovered or to be paid using the tax rates and tax laws that have been enacted or substantively enacted at the Group Statement of Financial Position date. Research and development tax credits are recognised on an accruals basis and are included as an income tax credit under current assets. The research and development tax credit recognised is based on management’s estimate of the expected tax claim for the period and is recorded within taxation under the Small and Medium-sized Enterprise Scheme.
Basic loss per share amounts are calculated by dividing the net loss for the period from continuing operations, attributable to ordinary equity holders of the parent company, by the weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding during the period. As the Group made a loss for the period the diluted loss per share is equal to the basic loss per share.
The Group has made a loss in the current and previous years presented, and therefore the options and warrants are anti-dilutive. As a result, diluted earnings per share is presented on the same basis for all periods shown.
Book values approximate to fair value at 30 June 2022 and 31 December 2021.
Obligations under finance leases are secured by a fixed charge over the fixed assets to which they relate.
The provision relates to the ‘making good’ clause on the Cardiff office which was vacated during the fourth quarter of 2021. Management reached agreement with the landlord; this was settled in July 2022. The provision as at 31 December 2021 was managements best estimate.
| 7. | Derivative financial liability – current |
| Schedule of derivative financial liability | | As at 30
June 2022
unaudited £’000 | | | As at 31
December
2021 £’000 | |
| At 1 January | | | 553 | | | | 1,559 | |
| Transfer to share premium on exercise of warrants | | | - | | | | (70 | ) |
| Gain recognised in finance income within the consolidated statement of comprehensive income | | | (398 | ) | | | (936 | ) |
| | | | 155 | | | | 553 | |
Equity settled derivative financial liability is a liability that is not to be settled for cash.
On 16 February 2021 306,815 pre-existing warrants were exercised at $0.41. The gross proceeds received by the company was $126,561. The fair value of the warrants on the date of exercise was £70,339.
May 2020 warrants
In May 2020 the Company issued 9,545,456 warrants in the ordinary share capital of the Company as part of a registered direct offering in the US. The number of ordinary shares to be issued when exercised is fixed, however the exercise price is denominated in US Dollars being different to the functional currency of the Company. Therefore, the warrants are classified as equity settled derivative financial liabilities recognised at fair value through the profit and loss account (‘FVTPL’). The financial liability is valued using the Monte Carlo model. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are stated at fair value, with any gains or losses arising on re-measurement recognised in profit or loss. The net gain or loss recognised in profit or loss incorporates any interest paid on the financial liability and is included in the ‘finance income’ or ‘finance expense’ lines item in the income statement. A key input in the valuation of the instrument is the Company share price. Exercise price per ADR is $2.05 and $2.0625.
October 2019 warrants
In October 2019 the Company issued 3,150,000 warrants in the ordinary share capital of the Company as part of a registered direct offering in the US. The number of ordinary shares to be issued when exercised is fixed, however the exercise price is denominated in US Dollars. The warrants are classified equity settled derivative financial liabilities and accounted for in the same way as those issued in May 2020. The financial liability is valued using the Monte Carlo model. The exercise price per ADR is $6.25.
DARA warrants and share options
The Group also assumed fully vested warrants and share options on the acquisition of DARA Biosciences, Inc. (which took place in 2015). The number of ordinary shares to be issued when exercised is fixed, however the exercise prices are denominated in US Dollars. The warrants are classified equity settled derivative financial liabilities and accounted for in the same way as those detailed above. The financial liability is valued using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The exercise price of the warrants and options is $61.03 and $95.17 respectively.
The following table details the outstanding warrants as at 30 June 2022, 31 December 2021 and also the movement in the period:
| Schedule of warrants outstanding | At 1
January
2021 | Lapsed | Exercised | At 31
December
2021 | Lapsed | Exercised | At 30 June
2022 |
| May 2020 grant | 7,045,456 | – | (306,815) | 6,738,641 | – | – | 6,738,641 |
| October 2019 grant | 3,150,000 | – | – | 3,150,000 | – | – | 3,150,000 |
| DARA Warrants | 4,624 | (544) | – | 4,080 | – | – | 4,080 |
| DARA Options | 2,835 | – | – | 2,835 | (13) | – | 2,822 |
Fair value hierarchy
The Group uses the following hierarchy for determining and disclosing the fair value of financial instruments by valuation technique:
Level 1: quoted (unadjusted) prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities;
Level 2: other techniques for which all inputs which have a significant effect on the recorded fair value are observable, either directly or indirectly; and
Level 3: techniques which use inputs that have a significant effect on the recorded fair value that are not based on observable market data.
The fair value of the Group’s derivative financial liability is measured at fair value on a recurring basis. The following table gives information about how the fair value of this financial liability is determined.
| Schedule of consolidated financial assets and liabilities at fair value | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Financial
liabilities | | Fair value as at 30 June 2022 | | Fair value as
at 31
December 2021 | | Fair value
hierarchy | | Valuation
technique(s)
and key input(s) | | Significant unobservable input(s) | | Relationship of unobservable
inputs to fair value |
| Equity settled financial derivative liability – May 2020 Warrants | | £146,000 | | £467,000 | | Level 3 | | Monte Carlo simulation model | | Volatility rate of 105% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 0.1 and 3.39 years determined using the remaining life of the share options. | | The shorter the expected life the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate between a range of 1.68% determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate the higher the fair value. |
| Equity settled financial derivative liability – October 2019 Warrants | | £9,000 | | £86,000 | | Level 3 | | Monte Carlo simulation model | | Volatility rate of 108.5% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 0.1 and 3.00 years determined using the remaining life of the share options. | | The shorter the expected life the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate between a range of 1.68% determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate the higher the fair value. |
| Equity settled financial derivative liability – DARA Bioscience warrants and options | | – | | – | | Level 3 | | Black-Scholes option pricing model | | Volatility rate of 108.5%% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 0.1 and 0.4 years determined using the remaining life of the share options | | The shorter the expected life the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate between a range of 1.68% determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate the higher the fair value. |
| Total | | £155,000 | | £553,000 | | | | | | | | |
Changing the unobservable risk free rate input to the valuation model by 10% higher while all other variables were held constant, would not impact the carrying amount of shares (2021: nil).
There were no transfers between Level 1 and 2 in the period.
The financial liability measured at fair value on Level 3 fair value measurement represents consideration relating to warrants issued in May 2020 and October 2019 as part of Registered Direct offerings and also a business combination.
| Schedule of detailed information about share capital | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Authorised, allotted and
fully
paid – classified as equity | | As at 30 June
2022
unaudited Number | | | As at 30 June
2022
unaudited £ | | | As at 31
December
2021 Number | | | As at 31
December
2021 £ | |
Ordinary shares of
£0.001 each | | | 98,493,413 | | | | 98,493 | | | | 98,468,387 | | | | 98,468 | |
| Deferred shares of £1 each | | | 1,000,001 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | 1,000,001 | |
| Total | | | | | | | 1,098,494 | | | | | | | | 1,098,469 | |
Ordinary and deferred shares were recorded as equity.
| Schedule Of Ordinary and Deferred Shares | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2022 | | | | | Ordinary
Shares Number | | | Deferred
Shares Number | | | Share
Price £ | | | Total
consideration £’000 | |
| At 1 January 2022 | | | | | | 98,468,387 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | | | | | 106,517 | |
| 22 March 2022 | | | Exercise of warrants | | | 26 | | | | – | | | | 10.000 | | | | – | |
| 3 May 2022 | | | Share issue to SIPP trustee* | | | 25,000 | | | | – | | | | 0.001 | | | | – | |
| At 30 June 2022 (unaudited) | | | | | | 98,493,413 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | | | | | 106,517 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2021 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At 1 January 2021 | | | | | | 63,073,852 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | | | | | 96,426 | |
| 19 February 2021 | | | Exercise of warrants | | | 306,815 | | | | – | | | | 0.298 | | | | 91 | |
| 6 July 2021 | | | Placing | | | 35,087,720 | | | | – | | | | 0.285 | | | | 10,000 | |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | | | | 98,468,387 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | | | | | 106,517 | |
| * | Share issued to Midatech Pharma Plc employee benefit trust |
| 9. | Related party transaction |
The Directors consider there to be no related party transactions during the periods reported other than Directors Remuneration.
| 10. | Contingent liabilities |
The Group had no contingent liabilities as at 30 June 2022 (30 June 2021: Nil).
MIDATECH PHARMA PLC
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM (MAZARS LLP, LONDON, UNITED KINGDOM, PCAOB ID 1401)
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of Midatech Pharma plc
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position of Midatech Pharma plc and its subsidiaries (“the Group”) as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the related consolidated statements of comprehensive income, changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2021, including the related notes (collectively, the Consolidated Financial Statements). In our opinion, the Consolidated Financial Statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Group as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2021, in conformity with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Going Concern Uncertainty
The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared assuming that the Group will continue as a going concern. As discussed in note 1 to the financial statements the Group has suffered recurring losses from operations and has a net capital deficiency that raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to these matters are also described in note 1. The Consolidated Financial Statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These Consolidated Financial Statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these Consolidated Financial Statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Group in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the Consolidated Financial Statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the Consolidated Financial Statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the Consolidated Financial Statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the Consolidated Financial Statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the Consolidated Financial Statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the Consolidated Financial Statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
We have identified one critical audit matter, being the going concern basis of preparation. The nature of the critical audit matter, together with our conclusion, is set out above in the going concern uncertainty paragraph. The circumstances described led us to conclude that the going concern basis of preparation is a critical audit matter.
Our evaluation of the Directors’ assessment of the appropriateness of the going concern basis of preparation of these financial statements included, but was not limited to:
| ● | Undertaking an initial assessment at the planning stage of the audit to identify events or conditions that may cast significant doubt on the Group’s ability to continue as a going concern; |
| ● | Obtaining an understand of the relevant controls relating to the Directors’ going concern assessment; |
| ● | Reviewing the Directors’ formal going concern assessment, including the supporting cash flow projections that included the twelve months; |
| ● | Evaluating the Directors’ assessment of the impact of the invasion of Ukraine by the Russian Federation military; |
| ● | Evaluating the key assumptions used and judgements applied by the directors in forming their conclusions on going concern; |
| ● | Reviewing the appropriateness of the disclosures made by the Directors in the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
We have served as the Group’s auditor since 2020.
/s/ Mazars LLP
Mazars LLP
London, England
April 25, 2022
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Shareholders and Board of Directors
Midatech Pharma plc
Cardiff, United Kingdom
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statement of financial position of Midatech Pharma plc (the “Company”) as of 31 December 2019, the related consolidated statements of comprehensive income, changes in equity, and cash flows for the year ended 31 December 2019, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at 31 December 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended 31 December 2019 in conformity with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Going Concern Uncertainty
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has suffered recurring losses from operations and has a net capital deficiency that raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s plans in regard to these matters are also described in Note 1. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Adoption of New Accounting Standard
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, effective on 1 January 2019, the Company changed its method of accounting for leases due to the adoption of IFRS 16, Leases.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audit we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ BDO LLP
BDO LLP
We have served as the Company's auditor from 2014 through 2020.
Reading, United Kingdom
15 June 2020
Consolidated StatementS of Comprehensive Income
For the year ended 31 December
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Note | | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Revenue | | | 3 | | | | 578 | | | | 180 | | | | 312 | |
| Grant revenue | | | | | | | – | | | | 163 | | | | 362 | |
| Total revenue | | | | | | | 578 | | | | 343 | | | | 674 | |
| Other income | | | | | | | 24 | | | | 12 | | | | 15 | |
| Research and development costs | | | | | | | (4,654 | ) | | | (6,068 | ) | | | (7,843 | ) |
| Distribution costs, sales and marketing | | | | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (323 | ) |
| Administrative costs | | | | | | | (2,946 | ) | | | (4,958 | ) | | | (3,841 | ) |
| Impairment of intangible assets | | | 12,13 | | | | – | | | | (12,369 | ) | | | – | |
| Loss from operations | | | 5 | | | | (6,998 | ) | | | (23,040 | ) | | | (11,318 | ) |
| Finance income | | | 7 | | | | 936 | | | | 1 | | | | 492 | |
| Finance expense | | | 7 | | | | (44 | ) | | | (431 | ) | | | (97 | ) |
| Loss before tax | | | | | | | (6,106 | ) | | | (23,470 | ) | | | (10,923 | ) |
| Taxation | | | 8 | | | | 646 | | | | 1,281 | | | | 1,785 | |
| Loss from continuing operations | | | | | | | (5,460 | ) | | | (22,189 | ) | | | (9,138 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations net of tax | | | 4 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (947 | ) |
| Loss for the year attributable to the owners of the parent | | | | | | | (5,460 | ) | | | (22,189 | ) | | | (10,085 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Items that will or may be reclassified subsequently to profit or loss: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exchange gains/(losses) arising on translation of foreign operations | | | | | | | – | | | | 508 | | | | (207 | ) |
| Total other comprehensive income/(loss ) net of tax | | | | | | | – | | | | 508 | | | | (207 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss attributable to the owners of the parent | | | | | | | (5,460 | ) | | | (21,681 | ) | | | (10,292 | ) |
| Loss per share | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted loss per ordinary share - pence | | | 9 | | | | (7 | )p | | | (52 | )p | | | (50 | )p |
| Discontinued operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted loss per ordinary share - pence | | | 9 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (5 | )p |
The notes form an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Distribution costs, sales and marketing are immaterial for 2021 and 2020 and have been included within Administrative costs
Consolidated statements of financial position
At 31 December
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Company number 09216368 | | Note | | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | 10 | | | | 1,152 | | | | 542 | | | | 2,154 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 12 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 12,379 | |
| Other receivables due in greater than one year | | | 15 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 2,625 | |
| Total Non-Current Assets | | | | | | | 1,152 | | | | 542 | | | | 17,158 | |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other receivables | | | 15 | | | | 1,034 | | | | 572 | | | | 992 | |
| Taxation | | | | | | | 670 | | | | 1,157 | | | | 1,817 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 16 | | | | 10,057 | | | | 7,546 | | | | 10,928 | |
| Total Current Assets | | | | | | | 11,761 | | | | 9,275 | | | | 13,737 | |
| Total assets | | | | | | | 12,913 | | | | 9,817 | | | | 30,895 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Borrowings | | | 18 | | | | 620 | | | | 60 | | | | 5,670 | |
| Provisions | | | 19 | | | | – | | | | 50 | | | | – | |
| Total Non-Current Liabilities | | | | | | | 620 | | | | 110 | | | | 5,670 | |
| Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | 17 | | | | 1,092 | | | | 1,230 | | | | 4,494 | |
| Borrowings | | | 18 | | | | 146 | | | | 200 | | | | 412 | |
| Provisions | | | 19 | | | | 50 | | | | – | | | | 97 | |
| Derivative financial liability | | | 20 | | | | 553 | | | | 1,559 | | | | 664 | |
| Total current Liabilities | | | | | | | 1,841 | | | | 2,989 | | | | 5,667 | |
| Total liabilities | | | | | | | 2,461 | | | | 3,099 | | | | 11,337 | |
The notes form an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL POSITION
(continued)
At 31 December
| | | Note | | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Issued capital and reserves attributable to owners of the parent | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital | | | 23 | | | | 1,098 | | | | 1,063 | | | | 1,023 | |
| Share premium | | | 24 | | | | 83,434 | | | | 74,364 | | | | 65,879 | |
| Merger reserve | | | 24 | | | | 53,003 | | | | 53,003 | | | | 53,003 | |
| Warrant reserve | | | 24 | | | | 720 | | | | 720 | | | | – | |
| Foreign exchange reserve | | | 24 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (508 | ) |
| Accumulated deficit | | | 24 | | | | (127,803 | ) | | | (122,432 | ) | | | (99,839 | ) |
| Total equity | | | | | | | 10,452 | | | | 6,718 | | | | 19,558 | |
| Total equity and liabilities | | | | | | | 12,913 | | | | 9,817 | | | | 30,895 | |
The notes form an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Consolidated statements of cash flows
For the year ended 31 December
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Note | | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the year | | | | | | | (5,460 | ) | | | (22,189 | ) | | | (10,085 | ) |
| Adjustments for: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation of property, plant and equipment | | | 10 | | | | 213 | | | | 1,089 | | | | 979 | |
| Depreciation of right of use asset | | | 10 | | | | 190 | | | | 118 | | | | 303 | |
| Amortisation of intangible fixed assets | | | 12 | | | | – | | | | 10 | | | | 3 | |
| Profit on disposal of fixed assets | | | | | | | (39 | ) | | | (226 | ) | | | – | |
| Impairment of intangible assets | | | 12,13 | | | | – | | | | 12,369 | | | | – | |
| Finance income | | | 7 | | | | (936 | ) | | | (1 | ) | | | (492 | ) |
| Finance expense | | | 7 | | | | 44 | | | | 431 | | | | 97 | |
| Share-based payment charge/(credit) | | | 5 | | | | 89 | | | | (404 | ) | | | (34 | ) |
| Taxation | | | 8 | | | | (646 | ) | | | (1,281 | ) | | | (1,785 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | | | 4 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 947 | |
| Foreign exchange (gains)/losses | | | | | | | (3 | ) | | | 387 | | | | (140 | ) |
Cash flows from operating activities before changes in working
capital | | | | | | | (6,548 | ) | | | (9,697 | ) | | | (10,207 | ) |
| Decrease in trade and other receivables | | | | | | | (487 | ) | | | 493 | | | | 725 | |
| (Decrease)/Increase in trade and other payables | | | | | | | (130 | ) | | | (2,004 | ) | | | 1,141 | |
| Decrease in provisions | | | | | | | – | | | | (47 | ) | | | (68 | ) |
| Cash used in operations | | | | | | | (7,165 | ) | | | (11,255 | ) | | | (8,409 | ) |
| Taxes received | | | | | | | 1,157 | | | | 1,954 | | | | 1,920 | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | | | | | | (6,008 | ) | | | (9,301 | ) | | | (6,489 | ) |
The notes form an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Consolidated statements of cash flows(continued)
For the year ended 31 December
| | | Note | | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchases of property, plant and equipment | | | 10 | | | | (320 | ) | | | (209 | ) | | | (310 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of fixed assets | | | | | | | 42 | | | | 143 | | | | – | |
| Purchase of intangibles | | | 12 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (9 | ) |
| Long term deposit for guarantee for Government loan | | | | | | | – | | | | 2,639 | | | | (2,549 | ) |
| Deposit paid in connection with disposed subsidiary | | | 4 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (947 | ) |
| Interest received | | | | | | | – | | | | 1 | | | | 8 | |
| Net cash (used in)/generated from investing activities | | | | | | | (278 | ) | | | 2,574 | | | | (3,807 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest paid | | | | | | | (15 | ) | | | (34 | ) | | | (30 | ) |
| Receipts from sub-lessee on onerous lease | | | | | | | – | | | | 45 | | | | 107 | |
| Amounts paid on lease liabilities | | | | | | | (112 | ) | | | (258 | ) | | | (450 | ) |
| Repayment of Government grants on closure of Spanish operation | | | | | | | – | | | | (229 | ) | | | – | |
| Repayment of borrowings | | | | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (577 | ) |
| (Repayment)/Proceeds from Government loan | | | 18 | | | | (103 | ) | | | (6,182 | ) | | | 4,436 | |
| Proceeds from Government subsidy | | | | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1,139 | |
| Share issues including warrants, net of costs | | | 16 | | | | 9,035 | | | | 9,742 | | | | 14,108 | |
| Net cash generated from financing activities | | | | | | | 8,805 | | | | 3,084 | | | | 18,733 | |
| Net increase/(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | 2,519 | | | | (3,643 | ) | | | 8,437 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | | | | | | | 7,546 | | | | 10,928 | | | | 2,343 | |
| Exchange (losses)/gains on cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (8 | ) | | | 261 | | | | 148 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | | | 16 | | | | 10,057 | | | | 7,546 | | | | 10,928 | |
The notes form an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Consolidated statements of changes in equity
For the year ended 31 December
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Share capital £’000 | | | Share premium £’000 | | | Merger
reserve £’000 | | | Warrant
reserve
£’000 | | | Foreign exchange reserve £’000 | | | Accumulated deficit £’000 | | | Total equity £’000 | |
| At 1 January 2021 | | | 1,063 | | | | 74,364 | | | | 53,003 | | | | 720 | | | | – | | | | (122,432 | ) | | | 6,718 | |
| Loss for the year | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (5,460 | ) | | | (5,460 | ) |
| Foreign exchange translation | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Total comprehensive loss | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (5,460 | ) | | | (5,460 | ) |
| Transactions with owners | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Shares issued on 19 February 2021 – notes 16,
23 | | | – | | | | 161 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 161 | |
Costs associated with share issue on 19
February 2021 – notes 16, 23 | | | – | | | | (10 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (10 | ) |
| Shares issued on 6 July 2021 – notes 16,23 | | | 35 | | | | 9,965 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 10,000 | |
Costs associated with share issue on 6 July
2021 – notes 16, 23 | | | – | | | | (1,046 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (1,046 | ) |
| Share-based payment charge | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 89 | | | | 89 | |
Total contribution by and distributions to
owners | | | 35 | | | | 9,070 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 89 | | | | 9,194 | |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | 1,098 | | | | 83,434 | | | | 53,003 | | | | 720 | | | | – | | | | (127,803 | ) | | | 10,452 | |
The notes form an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Consolidated statements of changes in equity(cONTINUED)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Share capital £’000 | | | Share premium £’000 | | | Merger
reserve £’000 | | | Warrant
reserve
£’000 | | | Foreign exchange reserve £’000 | | | Accumulated deficit £’000 | | | Total equity £’000 | |
| At 1 January 2020 | | | 1,023 | | | | 65,879 | | | | 53,003 | | | | – | | | | (508 | ) | | | (99,839 | ) | | | 19,558 | |
| Loss for the year | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (22,189 | ) | | | (22,189 | ) |
| Foreign exchange translation | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 508 | | | | – | | | | 508 | |
| Total comprehensive loss | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (508 | ) | | | (22,189 | ) | | | (21,681 | ) |
| Transactions with owners | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Shares issued with warrants on 18 May 2020 –
notes 16,23 | | | 16 | | | | 2,527 | | | | – | | | | 720 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 3,263 | |
Costs associated with shares issued with
warrants on 18 May 2020 – notes 16, 23 | | | | | | | (544 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (544 | ) |
| Shares issued on 27 July 2020 – notes 16, 23 | | | 21 | | | | 5,729 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 5,750 | |
Costs associated with share issue on 27 July
2020 – notes 16, 23 | | | | | | | (489 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (489 | ) |
Shares issued on 19 August 2020 – notes 16,
23 | | | 3 | | | | 1,278 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1,281 | |
Costs associated with share issue on 19 August
2020 – notes 16, 23 | | | | | | | (16 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (16 | ) |
| Share-based payment credit | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (404 | ) | | | (404 | ) |
Total contribution by and distributions to
owners | | | 40 | | | | 8,485 | | | | – | | | | 720 | | | | – | | | | (404 | ) | | | 8,841 | |
| At 31 December 2020 | | | 1,063 | | | | 74,364 | | | | 53,003 | | | | 720 | | | | – | | | | (122,432 | ) | | | 6,718 | |
The notes form an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Consolidated statements of changes in equity(cONTINUED)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Share capital £’000 | | | Share premium £’000 | | | Merger
reserve £’000 | | | Foreign exchange reserve £’000 | | | Accumulated deficit £’000 | | | Total equity £’000 | |
| At 1 January 2019 | | | 1,003 | | | | 52,939 | | | | 53,003 | | | | (301 | ) | | | (89,720 | ) | | | 16,924 | |
| Loss for the year | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (10,085 | ) | | | (10,085 | ) |
| Foreign exchange translation | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (207 | ) | | | – | | | | (207 | ) |
| Total comprehensive loss | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (207 | ) | | | (10,085 | ) | | | (10,292 | ) |
| Transactions with owners | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Shares issued on 26 February 2019 – note 16 | | | 17 | | | | 13,388 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 13,405 | |
Costs associated with share issue on 26
February 2019 – note 16 | | | – | | | | (1,120 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (1,120 | ) |
| Shares issued on 29 October 2019 – note 16 | | | 3 | | | | 1,211 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1,214 | |
Costs associated with share issue on 29
October 2019 – note 16 | | | – | | | | (539 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (539 | ) |
| Share-based payment credit | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (34 | ) | | | (34 | ) |
Total contribution by and distributions to
owners | | | 20 | | | | 12,940 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (34 | ) | | | 12,926 | |
| At 31 December 2019 | | | 1,023 | | | | 65,879 | | | | 53,003 | | | | (508 | ) | | | (99,839 | ) | | | 19,558 | |
The notes form an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
Notes forming part of the financial statements
For the years ended 31 December 2021, 2020 and 2019
General information
Midatech Pharma plc (the ‘Company’) is a company registered and domiciled in England and Wales. The Company was incorporated on 12 September 2014.
The Company is a public limited company, which has been listed on the Alternative Investment Market (‘AIM’), which is a submarket of the London Stock Exchange, since 8 December 2014.
In addition, since 4 December 2015 the Company has American Depository Receipts (‘ADRs’) registered with the US Securities and Exchange Commission (‘SEC’) and is listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market.
The financial statements were approved and authorised for issue by the Board of Directors on 25 April 2022.
Basis of preparation
The Group was formed on 31 October 2014 when Midatech Pharma plc entered into an agreement to acquire the entire share capital of Midatech Limited and its wholly owned subsidiaries through the issue equivalent of shares in the Company which took place on 13 November 2014.
The financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
The principal accounting policies adopted in the preparation of the financial statements are set out below. The policies have been consistently applied to all the periods presented.
On 2 March 2020 a resolution was passed at a general meeting of shareholders of the Company to consolidate its ordinary shares on a one for 20 basis into new ordinary shares of 0.1p each in the capital of the Company. At the same meeting a resolution was passed to change the ratio of the Company's American Depositary Receipts ("ADRs"). This changed from one ADR representing 20 Existing Ordinary Shares to one ADR representing five new ordinary shares. Comparative numbers of shares and share options/warrants and related exercise/issue prices and earnings per share reflect the impact of the March 2020 share consolidation.
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a historical cost basis, except for the following item (refer to individual accounting policies for details):
- Certain financial instruments – fair value through profit or loss.
Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current period presentation with no impact on previously reported net loss or cash flows, and no material impact on financial position
Adoption of new and revised standards
New standards, interpretations and amendments effective from 1 January 2021
The Group in reviewed the new standards, interpretations and amendments effective from 1 January 2021 and deemed none were applicable to the annual financial statements for the year ended 31 December 2021.
New standards, interpretations and amendments not yet effective
There are a number of standards, amendments to standards, and interpretations which have been issued by the IASB that are effective in future accounting periods that the group has decided not to adopt early.
The following amendments are effective for the period beginning 1 January 2022:
| • | Onerous Contracts – Cost of Fulfilling a Contract (Amendments to IAS 37); |
| • | Property, Plant and Equipment: Proceeds before Intended Use (Amendments to IAS 16); |
| • | Annual Improvements to IFRS Standards 2018-2020 (Amendments to IFRS 1, IFRS 9, IFRS16 and IAS 41); and |
| • | References to Conceptual Framework (Amendments to IFRS 3). |
The following amendments are effective for the period beginning 1 January 2023:
| • | Disclosure of Accounting Policies (Amendments to IAS 1 and IFRS Practice Statement 2); |
| • | Definition of Accounting Estimates (Amendments to IAS 8); and |
| • | Deferred Tax Related to Assets and Liabilities arising from a Single Transaction (Amendments to IAS 12). |
These new accounting standards and amendments are not expected to have a material impact on the Group.
The Group does not expect any other standards issued by the IASB, but not yet effective, to have a material impact on the group.
| 1 | Accounting policies (continued) |
Basis for consolidation
The Group financial statements consolidate those of the parent company and all of its subsidiaries. The parent controls a subsidiary if it has power over the investee to significantly direct the activities, exposure, or rights to variable returns from its involvement with the investee, and the ability to use its power over the investee to affect the amount of the investor’s returns. All subsidiaries have a reporting date of 31 December.
All transactions and balances between Group companies are eliminated on consolidation, including unrealised gains and losses on transactions between Group companies. Where unrealised losses on intra-Group asset sales are reversed on consolidation, the underlying asset is also tested for impairment from a Group perspective. Amounts reported in the financial statements of subsidiaries have been adjusted where necessary to ensure consistency with the accounting policies adopted by the Group.
The consolidated financial statements consist of the results of the following entities:
Schedule of entities
| Entity | Summary description |
| Midatech Pharma plc | Ultimate holding company |
| Midatech Limited | Trading company |
| Midatech Pharma (Espana) SL (formerly Midatech Biogune SL) | Liquidated - 2021 |
| PharMida AG | Dormant |
| Midatech Pharma (Wales) Limited (formerly Q Chip Limited) | Trading company |
| Midatech Pharma Pty | Dissolved - 2020 |
Going concern
The Group and Company are subject to a number of risks similar to those of other development and early-commercial stage pharmaceutical companies. These risks include, amongst others, generation of revenue from the development portfolio and risks associated with research, development, testing and obtaining related regulatory approvals of our pipeline products. Ultimately, the attainment of profitable operations is dependent on future uncertain events which include obtaining adequate financing to fulfill our commercial and development activities and generating a level of revenue adequate to support our cost structure.
We have experienced net losses and significant cash outflows from cash used in operating activities over the past years as we develops our portfolio. For the year ended December 31, 2021 the Company incurred a consolidated loss from operations of £5.5million and negative cash flows from operating activities of £6.0million. As of December 31, 2021 the Group had an accumulated deficit of £127.8million.
Our future viability is dependent on our ability to raise cash from financing activities to finance our development plans until commercialisation, generate cash from operating activities and to successfully obtain regulatory approval to allow marketing of our development products. Our failure to raise capital as and when needed could have a negative impact on our financial condition and ability to pursue our business strategies.
Our Group's consolidated financial statements have been presented on a going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities in the normal course of business.
As at 31 December 2021, we had cash and cash equivalents of £10.1million. We forecast we currently has enough cash to fund its planned operations into the first quarter of 2023.
We have prepared cash flow forecasts and considered the cash flow requirement for the Company for the next three years including the period twelve months from the date of approval of the consolidated financial statements. These forecasts show that further financing will be required during the course of the next 12 months, assuming, inter alia, that certain development programs and other operating activities continue as currently planned. This requirement for additional financing represents a material uncertainty raises substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. As a result, our independent registered public accounting firm included an explanatory paragraph in its report on our financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2021 with respect to this uncertainty.
In addition, the global pandemic COVID-19 virus places increased uncertainty over the Directors’ forecasts. The restrictions that have been placed on the movement of people caused delays to some of the Group’s plans. The Directors have established a COVID-19 task force internally to monitor the impact of COVID-19 on the business and prioritize activities to minimize its continuing effect.
In addition to utilizing the existing cash reserves, we and our advisors are evaluating a number of near-term funding options potentially available to us, including fundraising and the partnering of assets and technologies of the Company. After considering the uncertainties, we considered it is appropriate to continue to adopt the going concern basis in preparing these financial information.
Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon our ability to obtain additional capital and/or dispose of assets, for which there can be no assurance we will be able to do on a timely basis, on favorable terms or at all.
| 1 | Accounting policies (continued) |
Revenue
Revenue is accounted for in line with principles of IFRS 15 ‘Revenue from contracts with customers’
Revenue from licensing agreements
The Group entered into a Licence Agreement during 2019. The licence consists of two distinct performance conditions, which is the grant of the license to use of its intellectual property (“IP”) and the supply of Product. After the Company has granted the license, and the Product is granted applicable marketing authorizations in the EU, the US, or the UK, France, Germany or Switzerland and China, there are no further obligations to participate in, or provide additional services to its customer. The transaction price for the grant of the license to use the Company’s IP comprises of fixed and variable payment streams and the grant of the license is considered to be a right to use IP. Upfront fees earned, are recognised as revenue at a point in time, upon transfer of control over the license to the licensee and the grant of the applicable marketing authorisation by the relevant statutory authority. For future royalty payments associated with a license, the Company applies the IFRS 15 exception for sales-based royalties and recognises the revenue only when the subsequent sale occurs.
Supply of Goods
Revenue from sales of goods to customer are recognised when all performance obligations are met. These criteria are considered to be met when the goods are delivered to the customer. Revenue represents the full list price of products shipped to wholesalers and other customers less product returns, discounts, rebates and other incentives based on the sales price.
Supply of Services
Revenue from the supply of services is subject to specific agreement. This is recognised over the contract term, proportionate to the progress in overall satisfaction of the performance obligations (the services performed by the Group), measured by cost incurred to date out of total estimate of costs. The primary input of substantially all work performed under these arrangements is labour. There is normally a direct relationship between costs incurred and the proportion of the contract performed to date.
Where the Group supplies services to a client it generally bills an agreed percentage in advance of the commencement of any work and the balance on completion. Invoices to clients are payable under normal commercial terms.
Grant revenue
Where grant income is received, which is not a direct re-imbursement of related costs, revenue is recognised at the point at which the conditions have been met, this has been recognised within grant revenue. Where grants are received as a re-imbursement of directly related costs they are credited to research and development expense in the same period as the expenditure towards which they are intended to contribute.
The Group previously received government loans that had a below-market rate of interest. These loans were recognised and measured in accordance with IFRS 9. The benefit of the below-market rate of interest was measured as the difference between the initial carrying value of the loan discounted at a market rate of interest and the proceeds received.
The difference was held within deferred revenue as a government grant and released as a credit to grant income or to research and development expense in line with the expenditure to which it related. In a situation where the proceeds were invested in plant and equipment, the deferred revenue was credited to research and development within the income statement in line with the depreciation of the acquired asset.
Business combinations and externally acquired intangible assets
Business combinations are accounted for using the acquisition method at the acquisition date, which is the date at which the Group obtains control over the entity. The cost of an acquisition is measured as the amount of the consideration transferred to the seller, measured at the acquisition date fair value, and the amount of any non-controlling interest in the acquiree. The Group measures goodwill initially at cost at the acquisition date, being:
| • | the fair value of the consideration transferred to the seller, plus; |
| • | the amount of any non-controlling interest in the acquiree, plus; |
| • | if the business combination is achieved in stages, the fair value of the existing equity interest in the acquiree re-measured at the acquisition date, less; |
| • | the fair value of the net identifiable assets acquired and assumed liabilities. |
Acquisition costs incurred are expensed and included in administrative costs. Any contingent consideration to be transferred by the acquirer is recognised at fair value at the acquisition date. Subsequent changes to the fair value of the contingent consideration, whether it is an asset or liability, will be recognised through the consolidated statement of comprehensive income. If the contingent consideration is classified as equity, it is not re-measured.
| 1 | Accounting policies (continued) |
Business combinations and externally acquired intangible assets (continued)
An intangible asset, which is an identifiable non-monetary asset without physical substance, is recognised to the extent that it is probable that the expected future economic benefits attributable to the asset will flow to the Group and that its cost can be measured reliably. The asset is deemed to be identifiable when it is separable or when it arises from contractual or other legal rights.
Externally acquired intangible assets other than goodwill are initially recognised at cost and subsequently amortised on a straight-line basis over their useful economic lives where they are in use. Goodwill is stated at cost less any accumulated impairment losses.
The amounts ascribed to intangibles recognised on business combinations are arrived at by using appropriate valuation techniques.
In-process research and development (‘IPRD’) programmes acquired in business combinations are recognised as assets even if subsequent expenditure is written off because the criteria specified in the policy for development costs below are not met. IPRD is subject to annual impairment testing until the completion or abandonment of the related project. No further costs are capitalised in respect of this IPRD unless they meet the criteria for research and development capitalisation as set out below.
As per IFRS 3, once the research and development of each defined project is completed, the carrying value of the acquired IPRD is reclassified as a finite-lived asset and amortised over its useful life.
The significant intangibles recognised by the Group and their useful economic lives are as follows:
Schedule of intangibles assets useful economic lives
| Goodwill | – Indefinite life |
| | |
| IPRD | – In process, not yet amortising |
| | |
| IT and website costs | – 4 years |
The useful economic life of IPRD will be determined when the in-process research projects are completed.
Internally generated intangible assets (development costs)
Expenditure on the research phase of an internal project is recognised as an expense in the period in which it is incurred. Development costs incurred on specific projects are capitalised when all the following conditions are satisfied:
| • | completion of the asset is technically feasible so that it will be available for use or sale; |
| • | the Group intends to complete the asset and use or sell it; |
| • | the Group has the ability to use or sell the asset and the asset will generate probable future economic benefits (over and above cost); |
| • | there are adequate technical, financial and other resources to complete the development and to use or sell the asset; and |
| • | the expenditure attributable to the asset during its development can be measured reliably. |
All internal activities related to the research and development of new projects are continuously monitored by the Directors. The Directors consider that the criteria to capitalise development expenditure are not met for a product prior to that product receiving regulatory approval in at least one country.
Development expenditure not satisfying the above criteria, and expenditure on the research phase of internal projects are included in research and development costs recognised in the Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income as incurred. No projects have yet reached the point of capitalisation.
Impairment of non-financial assets
Assets that have an indefinite useful life, for example goodwill, or intangible assets not ready for use, such as IPRD, are not subject to amortisation and are tested annually for impairment. Assets that are subject to amortisation are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. An impairment loss is recognised for the amount by which the asset’s carrying amount exceeds its recoverable amount. The recoverable amount is the higher of an asset’s fair value less costs to sell and value in use.
For the purposes of assessing impairment, assets are grouped at the lowest levels for which there are separately identifiable cash flows (cash-generating units). The Group at 31 December 2021 had only one cash generating unit (2020: one, 2019: one), as set out in note 13. Non-financial assets other than goodwill that suffered impairment are reviewed for possible reversal of impairment at each reporting date.
Impairment charges are included in profit or loss, except, where applicable, to the extent they reverse gains previously recognised in other comprehensive income. An impairment loss recognised for goodwill is not reversed.
Patents and trademarks
The costs incurred in establishing patents and trademarks are either expensed in accordance with the corresponding treatment of the development expenditure for the product to which they relate or capitalised if the development expenditure to which they relate has reached the point of capitalisation as an intangible asset.
| 1 | Accounting policies (continued) |
Foreign currency
Transactions entered into by subsidiary entities in a currency other than the currency of the primary economic environment, in which they operate, are recorded at the rates ruling when the transactions occur. Foreign currency monetary assets and liabilities are translated at the rates ruling at the reporting date. Exchange differences arising on the retranslation of unsettled monetary assets and liabilities are recognised immediately in profit or loss.
The presentational currency of the Group is Pounds Sterling. Foreign subsidiaries use the local currencies of the country where the operate. On consolidation, the results of overseas operations are translated into Pounds Sterling at rates approximating to those ruling when the transactions took place. All assets and liabilities of overseas operations, including goodwill arising on the acquisition of those operations, are translated at the rate ruling at the reporting date. Exchange differences arising on translating the opening net assets at opening rate and the results of overseas operations at actual rate are recognised in other comprehensive income and accumulated in the foreign exchange reserve.
Exchange differences recognised in the profit or loss of Group entities on the translation of long-term monetary items forming part of the Group’s net investment in the overseas operation concerned are reclassified to other comprehensive income and accumulated in the foreign exchange reserve on consolidation.
On disposal of a foreign operation, the cumulative exchange differences recognised in the foreign exchange reserve relating to that operation up to the date of disposal are transferred to the consolidated statement of comprehensive income as part of the gain or loss on disposal.
Financial assets and liabilities
Assets at amortised cost
The Group does not have any financial assets which it would classify as fair value through profit or loss. Therefore, all financial assets are classed as assets at amortised cost as defined below.
These assets are non-derivative financial assets with fixed or determinable payments that are not quoted in an active market. They arise principally through the provision of goods and services to customers (e.g. trade receivables), but also incorporate other types of contractual monetary asset. They are initially recognised at fair value plus transaction costs that are directly attributable to their acquisition or issue, and are subsequently carried at amortised cost using the effective interest rate method, less provision for impairment.
For impairment provisions, the Group applies the IFRS 9 simplified approach to measure expected credit losses using a lifetime expected credit loss provision for trade receivables to measure expected credit losses on a collective basis. Trade receivables are grouped based on a similar credit risk and ageing
The expected loss rates are based on the Group’s historic credit losses experienced over the three-year period prior to the period end. The historic loss rates are then adjusted for current and forward-looking information on macroeconomic factors.
Assets at amortised cost (continued)
The Group’s assets at amortised costs comprise trade and other receivables and cash and cash equivalents in the consolidated statement of financial position.
Cash and cash equivalents include cash in hand, deposits held at call with original maturities of three months or less.
| 1 | Accounting policies (continued) |
Financial liabilities
The Group classifies its financial liabilities into one of two categories, depending on the purpose for which the liability was acquired.
Fair value through profit and loss (‘FVTPL’)
The Group has outstanding warrants in the ordinary share capital of the company. The number of ordinary shares to be issued when exercised is fixed, however the exercise price is denominated in US Dollars being different to the functional currency of the parent company. Therefore, the warrants are classified as equity settled derivative financial liabilities recognised at fair value through the profit and loss account.
The financial liability is valued using the either the Monte Carlo model or the Black-Scholes option pricing model. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are stated at fair value, with any gains or losses arising on re-measurement recognised in profit or loss. The net gain or loss recognised in profit or loss incorporates any interest paid on the financial liability and is included in the ‘finance income’ or ‘finance expense’ lines item in the income statement. Fair value is determined in the manner described in note 20.
Other financial liabilities include the following items:
| • | Borrowings are initially recognised at fair value net of any transaction costs directly attributable to the issue of the instrument. Such interest-bearing liabilities are subsequently measured at amortised cost using the effective interest rate method, which ensures that any interest expense over the period to repayment is at a constant rate on the balance of the liability carried in the consolidated statement of financial position. Interest expense in this context includes initial transaction costs and premium payable on redemption, as well as any interest or coupon payable while the liability is outstanding. |
| • | Government loans received on favourable terms below market rate are discounted at a market rate of interest. The difference between the present value of the loan and the proceeds is held as a government grant within deferred revenue and is released to research and development expenditure or grant income in line with when the asset or expenditure is recognised in the income statement. |
| • | Trade payables and other short-term monetary liabilities are initially recognised at fair value and subsequently carried at amortised cost using the effective interest method. |
Share capital
Financial instruments issued by the Group are classified as equity only to the extent that they do not meet the definition of a financial liability or financial asset. The Group has two classes of share in existence:
| • | ordinary shares of £0.001 each are classified as equity instruments; |
| • | deferred shares of £1 each are classified as equity instruments. |
On 2 March 2020 a resolution was passed at a general meeting of shareholders of the Company to consolidate its ordinary shares on a one for 20 basis into new ordinary shares of £0.001 each in the capital of the Company.
Comparative figures in these financial statements reflect the impact of the share consolidation.
Retirement benefits: defined contribution schemes
Contributions to defined contribution pension schemes are charged to the consolidated statement of comprehensive income in the year to which they relate.
Provisions
Provisions are recognised when the Group has a present obligation (legal or constructive) as a result of a past event; it is probable that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation and a reliable estimate can be made of the amount of the obligation.
Share-based payments
The Group operates a number of equity-settled, share-based compensation plans, under which the entity receives services from employees as consideration for equity instruments (options) of the Group. The fair value of the employee services received in exchange for the grant of the options is recognised as an expense. The total amount to be expensed is determined by reference to the fair value of the options granted:
| • | including any market performance conditions (including the share price); |
| • | excluding the impact of any service and non-market performance vesting conditions (for example, remaining an employee of the entity over a specified time period); and |
| • | including the impact of any non-vesting conditions (for example, the requirement for employees to save). |
Non-market performance and service conditions are included in assumptions about the number of options that are expected to vest. The total expense is recognised over the vesting period, which is the period over which all of the specified vesting conditions are to be satisfied. Where vesting conditions are
| 1 | Accounting policies (continued) |
Share-based payments (continued)
accelerated on the occurrence of a specified event, such as a change in control or initial public offering, such remaining unvested charge is accelerated
to the income statement.
In addition, in some circumstances employees may provide services in advance of the grant date and therefore the grant date fair value is estimated for the purposes of recognising the expense during the period between service commencement period and grant date.
At the end of each reporting period, the Group revises its estimates of the number of options that are expected to vest based on the non-market vesting conditions. It recognises the impact of the revision to original estimates, if any, in the income statement, with a corresponding adjustment to equity. When the options are exercised, the Company issues new shares. The proceeds received net of any directly attributable transaction costs are credited to share capital (nominal value) and share premium.
Leases
Identifying Leases
The Group accounts for a contract, or a portion of a contract, as a lease when it conveys the right to use an asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration. Leases are those contracts that satisfy the following criteria:
(a) There is an identified asset;
(b) The Group obtains substantially all the economic benefits from use of the asset; and
(c) The Group has the right to direct use of the asset.
The Group considers whether the supplier has substantive substitution rights. If the supplier does have those rights, the contract is not identified as giving rise to a lease.
In determining whether the Group obtains substantially all the economic benefits from use of the asset, the Group considers only the economic benefits that arise from the use of the asset, not those incidental to legal ownership or other potential benefits.
In determining whether the Group has the right to direct use of the asset, the Group considers whether it directs how and for what purpose the asset is used throughout the period of use. If there are no significant decisions to be made because they are pre-determined due to the nature of the asset, the Group considers whether it was involved in the design of the asset in a way that predetermines how and for what purpose the asset will be used throughout the period of use. If the contract or portion of a contract does not satisfy these criteria, the Group applies other applicable IFRSs rather than IFRS 16.
All leases are accounted for by recognising a right-of-use asset and a lease liability except for:
| | Leases of low value assets; and |
| | Leases with a duration of 12 months or less. |
Lease liabilities are measured at the present value of the contractual payments due to the lessor over the lease term, with the discount rate determined by reference to the group’s incremental borrowing rate on commencement of the lease.
Right of use assets are initially measured at the amount of the lease liability, reduced for any lease incentives received, and increased for lease payments made at or before commencement of the lease. The Group has taken advantage of the practical expedient to ignore the requirement to separate non-lease components and instead account for the entire contract as a single lease.
Subsequent to initial measurement lease liabilities increase as a result of interest charged at a constant rate on the balance outstanding and are reduced for lease payments made. Right-of-use assets are amortised on a straight-line basis over the remaining term of the lease.
When the group revises its estimate of the term of any lease (because, for example, it re-assesses the probability of a lessee extension or termination option being exercised), it adjusts the carrying amount of the lease liability to reflect the payments to make over the revised term, which are discounted using a revised discount rate. An equivalent adjustment is made to the carrying value of the right-of-use asset, with the revised carrying amount being amortised over the remaining (revised) lease term. If the carrying amount of the right-of-use asset is adjusted to zero, any further reduction is recognised in profit or loss.
In 2018 the Group entered into a sublease agreement to mitigate the impact of an otherwise onerous lease on the closure of its Abingdon site. This has been recognised as a lease receivable as the Group determined that the sublease meets the definition of a finance lease under the transitional provisions of IFRS16 and therefore, no right-of-use asset is recognised. During 2020 the lease and sub-lease ended.
Nature of leasing activities (in the capacity as lessee)
The group leased a number of properties in the jurisdictions from which it operates. In some jurisdictions it is customary for lease contracts to provide for payments to increase each year by inflation or and in others to be reset periodically to market rental rates. As at 31 December 2021 the Group had one property lease in place in the UK.
1 Accounting policies (continued)
Deferred taxation
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognised where the carrying amount of an asset or liability in the consolidated statement of financial position differs from its tax base, except for differences arising on:
| • | the initial recognition of goodwill; |
| • | the initial recognition of an asset or liability in a transaction which is not a business combination and at the time
of the transaction affects neither accounting or taxable profit; and |
| • | investments in subsidiaries and jointly controlled entities where the Group is able to control the timing of the reversal of the difference and it is probable that the difference will not reverse in the foreseeable future. |
Recognition of deferred tax assets is restricted to those instances where it is probable that taxable profit will be available against which the difference can be utilised.
The amount of the asset or liability is determined using tax rates that have been enacted or substantively enacted by the reporting date and are expected to apply when the deferred tax assets or liabilities are recovered or settled.
Property, plant and equipment
Items of property, plant and equipment are initially recognised at cost. As well as the purchase price, cost includes directly attributable costs.
Depreciation is provided on all items of property, plant and equipment so as to write off their carrying value over their expected useful economic lives. It is provided at the following rates:
Schedule of depreciation rates of property, plant and equipment
| Fixtures and fittings | – 20%- 25% per annum straight line |
| | |
| Leasehold improvements | – the shorter of 10% per annum straight line or over the lease term |
| | |
| Computer equipment | – 25% per annum straight line |
| | |
| Laboratory equipment | – 15% – 25% per annum straight line |
| | |
| Right of use asset | – Economic life of contractual relationship |
| 2 | Critical accounting estimates and judgements |
The preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires the Group to make estimates, assumptions and judgments that can have a significant impact on the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, revenue and expenses and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, at the respective dates of our financial statements. The Group bases its estimates, assumptions and judgments on historical experience and various other factors that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. Management evaluates estimates, assumptions and judgments on a regular basis and makes changes accordingly, and discusses critical accounting estimates with the board of Directors.
The following are considered to be critical accounting estimates:
Impairment of goodwill and intangible assets not yet ready for use
Goodwill and intangibles not yet ready for use are tested for impairment at the cash generating unit level on an annual basis at the year end and between annual tests if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a cash generating unit below its carrying value. These events or circumstances could include a significant change in the business climate, legal factors, operating performance indicators, competition, or sale or disposition of a significant portion of a reporting unit.
The fair value of each cash generating unit or asset is estimated using the income approach, on a discounted cash flow methodology. This analysis requires significant judgments, including estimation of future cash flows, which is dependent on internal forecasts, including for revenues and development costs, estimation of the long term rate of growth for the business, estimation of the useful life over which cash flows will occur and determination of our weighted-average cost of capital.
The carrying value of goodwill was £Nil (2020: £Nil; 2019: £2.3m) and intangibles not yet ready for use was £Nil (2020: £Nil; 2019:£10.1m) as at 31 December 2021 (note 12).
The estimates used to calculate the fair value of a cash generating unit change from year to year based on operating results and market conditions. Changes in these estimates and assumptions could materially affect the determination of fair value and goodwill impairment for each such unit.
In March 2020 the Group undertook a Strategic Review to re-evaluate its priorities in the context of available resources. The Board concluded that the Company was unlikely to conclude a license transaction or raise sufficient funds to continue the required remaining investment in MTD201 on a timely basis. The Board therefore decided to terminate further in-house development of the MTD201 programme with immediate effect and, in line with that decision, to close the Company’s MTD201 dedicated manufacturing facilities in Bilbao and offer redundancy to all 42 employees. As a result of the decision to terminate this program the Group recognised an impairment charge of £2.3m in the year to 31 December 2020 (2019: £Nil) against goodwill and an impairment charge against the IPRD of the Midatech Pharma (Wales) Ltd cash generating unit of £9.3m (2019:£Nil).
In June 2020 the Group received a letter from Secura Bio Inc., the licensor of Panobinostat, the active ingredient in the Group’s MTX110 development program, purporting to terminate our license. As a result of this purported termination an impairment charge of £0.8m was recognised in the year to 31 December 2020 against the acquired IPRD in relation to MTX110. See note 12 and 13.
Share-based payments
The Group accounts for share-based payment transactions for employees in accordance with IFRS 2 Share-based Payment, which requires the measurement of the cost of employee services received in exchange for the options on our ordinary shares, based on the fair value of the award on the grant date.
The Directors selected the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model as the most appropriate method for determining the estimated fair value of our share-based awards without market conditions. For performance-based options that include vesting conditions relating to the market performance of our ordinary shares, a Monte Carlo pricing model was used in order to reflect the valuation impact of price hurdles that have to be met as conditions to vesting.
The resulting cost of an equity incentive award is recognised as expense over the requisite service period of the award, which is usually the vesting period. Compensation expense is recognised over the vesting period using the straight-line method and classified in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income.
The assumptions used for estimating fair value for share-based payment transactions are disclosed in note 26 to our consolidated financial statements and are estimated as follows:
| • | volatility is estimated based on the average annualised volatility of a number of publicly traded peer companies in the biotech sector; |
| • | the estimated life of the option is estimated to be until the first exercise period, which is typically the month after the option vests; and |
| • | the dividend return is estimated by reference to our historical dividend payments. Currently, this is estimated to be zero as no dividend has been paid in the prior periods. |
| 2 | Critical accounting estimates and judgements (continued) |
Financial liabilities
Fair value through profit and loss (‘FVTPL’)
The Group has outstanding warrants in the ordinary share capital of the company. The number of ordinary shares to be issued when exercised is fixed, however the exercise price is denominated in US Dollars being different to the functional currency of the parent company. Therefore, the warrants are classified as equity settled derivative financial liabilities recognised at fair value through the profit and loss account.
The financial liability is valued using the either the Monte Carlo model or the Black-Scholes option pricing model. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are stated at fair value, with any gains or losses arising on re-measurement recognised in profit or loss. The net gain or loss recognised in profit or loss incorporates any interest paid on the financial liability and is included in the ‘finance income’ or ‘finance expense’ lines item in the income statement. Fair value is determined in the manner described in note 20.
The following are considered to be critical accounting judgments:
Revenue
Supply of Services
There are significant management judgements and estimates involved in the recognition of revenue from the supply of services. Revenue on services is recognised over the contract term, proportionate to the progress in overall satisfaction of the performance obligations (the services performed by the Group), measured by cost incurred to date out of total estimate of costs.
Income taxes
Deferred tax assets are recognised for unused tax losses to the extent that it is probable that taxable profit will be available against which the losses can be utilised. Significant management judgment is required to determine the amount of deferred tax assets that can be recognised based upon the likely timing and the level of future taxable profits together with future tax planning strategies.
In 2021, there were approximately £67.2m of gross unutilised tax losses carried forward (2020: £63.2m; 2019: £49.6m). No deferred tax asset has been provided in respect of these losses as there was insufficient evidence to support their recoverability in future periods.
Going Concern
We have has experienced net losses and significant cash outflows from cash used in operating activities over the past years as it develops its portfolio. For the year ended December 31, 2021 the Group incurred a consolidated loss from operations of £5.5million and negative cash flows from operations of £6.0million. As of December 31, 2021 the Group had an accumulated deficit of £127.8million.
Our future viability is dependent on our ability to raise cash from financing activities to finance our development plans until commercialisation, to generate cash from operating activities and to successfully obtain regulatory approval to allow marketing of our development products. Our failure to raise capital as and when needed could have a negative impact on our financial condition and ability to pursue our business strategies.
Our Group's consolidated financial statements have been presented on a going concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities in the normal course of business.
As at December 31, 2021, the Group had cash and cash equivalents of £10.1million. We forecast that we currently have enough cash to fund our planned operations into the first quarter of 2023.
We have prepared cash flow forecasts and considered the cash flow requirement for the Company for our next three years including the period twelve months from the date of the approval of the financial statements. These forecasts show that further financing will be required during the course of the next 12 months, assuming, inter alia, that certain development programs and other operating activities continue as currently planned. This requirement for additional financing represents a material uncertainty that raises substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
In addition, the global pandemic COVID-19 virus places increased uncertainty over the Directors’ forecasts. The restrictions that have been placed on the movement of people caused delays to some of the Group’s plans. The Directors have established a COVID-19 task force internally to monitor the impact of COVID-19 on the business and prioritize activities to minimize its continuing effect.
In addition to utilizing the existing cash reserves, we and our advisors are evaluating a number of near-term funding options potentially available to us, including fundraising and the partnering of assets and technologies of the Company. After considering the uncertainties, we considered it is appropriate to continue to adopt the going concern basis in preparing these financial information.
Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon our ability to obtain additional capital and/or dispose of assets, for which there can be no assurance we will be able to do on a timely basis, on favorable terms or at all.
Revenue from contracts with customers
Geographical analysis of revenue by destination of customer
Schedule of revenue by geographical analysis
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Revenue from continuing operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| United Kingdom | | | – | | | | 4 | | | | 197 | |
| Belgium | | | 578 | | | | 114 | | | | – | |
| Rest of Europe | | | – | | | | – | | | | 55 | |
| Rest of the World | | | – | | | | 62 | | | | 60 | |
| | | | 578 | | | | 180 | | | | 312 | |
All revenue from continuing operations came from the sale of services in 2021, 2020 and 2019.
In 2021, all revenue from continuing operations came from 1 customer (2020: 3 customers; 2019: 3 customers). Within revenue from discontinued operations for 2018, reported in the consolidated statement of comprehensive income under loss from discontinued operations, four customers each accounted for at least 10% of revenue from discontinued operations:
Schedule of commercial segment
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Customer A | | | 100 | % | | | 64 | % | | | 63 | % |
| Customer B | | | – | | | | 34 | % | | | 19 | % |
| Customer C | | | – | | | | 2 | % | | | 18 | % |
The Group contains one reportable operating segment, Pipeline Research and Development (‘Pipeline R&D’). This segment seeks to develop products using the Group’s nanomedicine and sustained release technology platforms.
The accounting policies of the reportable segments are consistent with the Group’s accounting policies described in note 1. Segment results represent the result of each segment without the allocation of head office expenses, interest expense, interest income and tax.
No measures of segment assets and segment liabilities are reported to the Group’s Board of Directors in order to assess performance and allocate resources. There is no intersegment activity and all revenue is generated from external customers.
Both the UK and Spanish entities meet the aggregation criteria and have therefore been presented as a single reportable segment under Pipeline R&D. The research and development activities involve the discovery and development of pharmaceutical products in the field of nanomedicine and sustained release technology.
The cost recognised in the year to 31 December 2019 as a discontinued operation relate to a claim made by Midatech Pharma US, Inc. (“MPUS”) under the warranties provided by Midatech under the Stock Purchase Agreement entered into in connection with the disposal of MPUS, see note 4.
In the following segmented results tables, depreciation and amortisation allocated to research and development costs, and administrative costs in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income, are presented separately.
| 3 | Segment Information (continued) |
Segmented results for the year ended 31 December 2021
Schedule of segment
| | | Pipeline R&D £’000 | |
| Revenue | | | 578 | |
| Total revenue | | | 578 | |
| Other income | | | 24 | |
| Research and development costs (excluding depreciation) | | | (4,291 | ) |
| Administrative costs (excluding depreciation) | | | (2,906 | ) |
| Depreciation | | | (403 | ) |
| Loss from operations | | | (6,998 | ) |
| Finance income | | | 936 | |
| Finance expense | | | (44 | ) |
| Loss before tax | | | (6,106 | ) |
| Taxation | | | 646 | |
| Loss for the year from continuing operations | | | (5,460 | ) |
Depreciation in year allocated as follows:
| | | Depreciation £’000 | |
| Research and development costs | | | 363 | |
| Administrative costs | | | 40 | |
| Total | | | 403 | |
| 3 | Segment Information (continued) |
Segmented results for the year ended 31 December 2020
| | | Pipeline R&D £’000 | |
| Revenue | | | 180 | |
| Grant revenue | | | 163 | |
| Total revenue | | | 343 | |
| Other income | | | 12 | |
| Research and development costs (excluding depreciation and amortisation) | | | (4,886 | ) |
| Administrative costs (excluding depreciation and amortisation) | | | (4,923 | ) |
| Depreciation | | | (1,207 | ) |
| Amortisation | | | (10 | ) |
| Impairment | | | (12,369 | ) |
| Loss from operations | | | (23,040 | ) |
| Finance income | | | 1 | |
| Finance expense | | | (431 | ) |
| Loss before tax | | | (23,470 | ) |
| Taxation | | | 1,281 | |
| Loss for the year from continuing operations | | | (22,189 | ) |
Depreciation and amortisation in year allocated as follows:
| | | Depreciation £’000 | | | Amortisation
£000 | |
| Research and development costs | | | 1,174 | | | | 8 | |
| Administrative costs | | | 33 | | | | 2 | |
| Total | | | 1,207 | | | | 10 | |
| 3 | Segment Information (continued) |
Segmented results for the year ended 31 December 2019
| | | Pipeline R&D £’000 | | | Commercial
(discontinued) £’000 | | | Consolidated
(including
discontinued
operations) £’000 | |
| Revenue | | | 312 | | | | – | | | | 312 | |
| Grant revenue | | | 362 | | | | – | | | | 362 | |
| Total revenue | | | 674 | | | | – | | | | 674 | |
| Other income | | | 15 | | | | – | | | | 15 | |
Research and development costs (excluding depreciation and
amortisation) | | | (6,624 | ) | | | – | | | | (6,624 | ) |
| Distribution costs, sales and marketing | | | (323 | ) | | | – | | | | (323 | ) |
| Administrative costs (excluding depreciation) | | | (3,775 | ) | | | – | | | | (3,775 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | | | – | | | | (947 | ) | | | (947 | ) |
| Depreciation | | | (1,282 | ) | | | – | | | | (1,282 | ) |
| Amortisation | | | (3 | ) | | | – | | | | (3 | ) |
| Loss from operations | | | (11,318 | ) | | | (947 | ) | | | (12,265 | ) |
| Finance income | | | 492 | | | | – | | | | 492 | |
| Finance expense | | | (97 | ) | | | – | | | | (97 | ) |
| Loss before tax | | | (10,923 | ) | | | (947 | ) | | | (11,870 | ) |
| Taxation | | | 1,785 | | | | – | | | | 1,785 | |
| Loss for the year | | | (9,138 | ) | | | (947 | ) | | | (10,085 | ) |
| Loss from continuing operations | | | | | | | | | | | (9,138 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations | | | | | | | | | | | (947 | ) |
All material additions to non-current assets in 2021, 2020 and 2019 were in the Pipeline R&D segment.
Non-current assets by location of assets
Schedule of non-current assets by location of assets
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| United Kingdom | | | 1,152 | | | | 542 | | | | 12,775 | |
| Spain | | | – | | | | – | | | | 4,383 | |
| | | | 1,152 | | | | 542 | | | | 17,158 | |
During 2018, the Group made the decision to sell MPUS, its Commercial business based in the US. The sale completed on 1 November 2018 to an affiliate of Barings LLC, a member of the MassMutual Financial Group, for total consideration of up to $19m. This included $6m of consideration contingent payable on the achievement of various net revenue milestones for the MPUS business for the financial years 2018 and 2019. MPUS did not achieve the net revenue milestones in either 2018 or 2019, as a result no contingent consideration was received during 2019.
Under the terms of the Stock Purchase Agreement, the Group agreed to indemnify the Purchaser against, inter alia, any liability related to any prescription drug user fee amounts owed to the United States Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) under the Prescription Drug Fee User Act (“PDUFA”) by MPUS for the United States government’s fiscal year ended 30 September 2018.
MPUS had successfully obtained waivers for user fees for all prior fiscal periods in which it was liable under PDUFA and entered into the Stock Purchase Agreement with the Purchaser confident that a further waiver would be obtained. However, during 2019 MPUS sought approval from the FDA for a filing relating to one of its commercial products and was informed by the FDA that the approval would not be forthcoming whilst the PDUFA fee remained unpaid. Consequently, MPUS paid the PDUFA fee of £0.95m and then, in accordance with the terms of the Stock Purchase Agreement, Midatech deposited the same amount with MPUS, pending completion of the waiver application process.
At 31 December 2019 Management considered the recoverability of the sum paid under the warranty, and although the waiver process was still on-going, Management concluded, based on third party advice, that the probability of successfully achieving the waiver had diminished and therefore took the decision to expense the cost of the warranty claim in 2019. As a result of Fortovia Theraputics Inc (formerly MPUS) filing for bankruptcy during 2020 the waiver claim is no longer being pursued.
The post-tax loss on disposal of discontinued operations was determined as follows:
Schedule of post-tax loss on disposal of discontinued operations
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Result of discontinued operations | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Revenue | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Expenses other than finance costs | | | – | | | | – | | | | (947 | ) |
| Finance costs | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Impairment | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Loss from discontinued operations before tax | | | – | | | | – | | | | (947 | ) |
| Taxation | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Loss on disposal of discontinued operations | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Loss for the year from discontinued operations after tax | | | – | | | | – | | | | (947 | ) |
Schedule of amounts related to discontinued operations
| Statement of cash flows | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
The statement of cash flows includes the following amounts relating to
discontinued operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Investing activities | | | – | | | | – | | | | (947 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Net cash flow from discontinued operations | | | – | | | | – | | | | (947 | ) |
Schedule of loss from operations
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Loss from operations is stated after charging/(crediting): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation of property, plant and equipment | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| – From continuing operations | | | 213 | | | | 1,089 | | | | 979 | |
| Depreciation of right of use asset | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| – From continuing operations | | | 190 | | | | 118 | | | | 303 | |
| Amortisation of intangible assets – product and marketing rights | | | – | | | | | | | | | |
| – From continuing operations | | | – | | | | 10 | | | | 3 | |
| Impairment of intangible assets | | | – | | | | 12,369 | | | | – | |
Fees payable to the Company’s auditor for the audit of the parent
Company | | | 88 | | | | 87 | | | | 110 | |
Fees payable to the Company’s subsidiary auditors for the audits of the
subsidiary accounts | | | 44 | | | | 43 | | | | 48 | |
| Fees payable to the Company’s auditor for: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| – Other services | | | – | | | | 7 | | | | 66 | |
Fees payable to the Company’s previous auditor for the audit of the
parent Company | | | – | | | | 15 | | | | – | |
| Fees payable to the Company’s previous auditor for: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| - Other services | | | 41 | | | | 171 | | | | – | |
| Foreign exchange(gain)/loss | | | 12 | | | | 96 | | | | 131 | |
Profit/(Loss)
on disposal of property, plant and equipment | | | (42 | ) | | | (226 | ) | | | – | |
| Equity settled share-based payment* | | | 89 | | | | (404 | ) | | | (34 | ) |
| * | credit recognised in prior years due to employees leaving the company and the subsequent reversal of the cumulative share based payment charge relating to share options under the 2014 Midatech Pharma plc Enterprise Management Incentive Scheme. |
Staff costs (including Directors), for continuing and discontinued operations, comprise:
Schedule of staff costs
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Wages and salaries | | | 1,354 | | | | 2,727 | | | | 2,762 | |
| Defined contribution pension cost (note 25) | | | 71 | | | | 75 | | | | 90 | |
| Social security contributions and similar taxes | | | 152 | | | | 397 | | | | 565 | |
| Share-based payment charge/(credit) | | | 89 | | | | (404 | ) | | | (34 | ) |
| Staff costs gross | | | 1,666 | | | | 2,795 | | | | 3,383 | |
| Continuing operations | | | 1,666 | | | | 2,795 | | | | 3,383 | |
| Discontinued operations | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Staff costs | | | 1,666 | | | | 2,795 | | | | 3,383 | |
Employee numbers
The average number of staff employed by the Group during the financial year, for continuing and discontinued operations, amounted to:
Schedule for average number of employed staff
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| Research and development | | | 15 | | | | 31 | | | | 52 | |
| General and administration | | | 5 | | | | 9 | | | | 13 | |
| | | | 20 | | | | 40 | | | | 65 | |
Key management personnel compensation
Schedule of Management Personnel Compensation
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Short term employee benefits | | | 658 | | | | 472 | | | | 812 | |
| Wages and salaries | | | – | | | | – | | | | 656 | |
| Payments made to third parties | | | – | | | | – | | | | 82 | |
| Social security contributions and similar taxes | | | – | | | | – | | | | 72 | |
| Benefits in kind | | | – | | | | – | | | | 2 | |
| Post-employment benefits | | | 27 | | | | 24 | | | | 42 | |
| Defined contribution pension cost | | | – | | | | – | | | | 42 | |
| Termination benefits | | | – | | | | 30 | | | | – | |
| Share-based payment | | | 61 | | | | (472 | ) | | | (58 | ) |
| Total | | | 746 | | | | 54 | | | | 796 | |
Key management personnel are those persons having authority and responsibility for planning, directing and controlling the activities of the Group, including the Directors of the Company, Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Scientific Officer .
None of the Directors have exercised share options during the year (2020: nil, 2019: nil).
During the year 1 Directors (2020:2; 2019: 3) participated in a defined contribution pension scheme.
| 7 | Finance income and expense |
Schedule of finance income
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Finance income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest received on bank deposits | | | – | | | | 1 | | | | 8 | |
| Gain on equity settled derivative financial liability | | | 936 | | | | – | | | | 484 | |
| Total finance income | | | 936 | | | | 1 | | | | 492 | |
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Finance expense | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense on lease liabilities | | | 36 | | | | 20 | | | | 30 | |
| Other loans | | | 8 | | | | 14 | | | | 67 | |
| Loss on equity settled derivative financial liability | | | – | | | | 397 | | | | – | |
| Total finance expense | | | 44 | | | | 431 | | | | 97 | |
The gain/(loss) on the equity settled derivative financial liability in 2021, 2020 and 2019 arose as a result of the movement in share price (note 20).
Schedule of components of income tax expense (benefit)
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Current tax credit | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current tax credited to the income statement | | | 646 | | | | 1,144 | | | | 1,782 | |
| Taxation payable in respect of foreign subsidiary | | | – | | | | (21 | ) | | | – | |
| Adjustment in respect of prior year | | | – | | | | 158 | | | | 3 | |
| Total current tax credit | | | 646 | | | | 1,281 | | | | 1,785 | |
| Deferred tax credit | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Reversal of temporary differences | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Total tax credit | | | 646 | | | | 1,281 | | | | 1,785 | |
There was no tax charge relating to discontinued operations for 2021, 2020 and 2019.
The reasons for the difference between the actual tax charge for the year and the standard rate of corporation tax in the United Kingdom applied to losses for the year are as follows:
Schedule of difference between actual tax charge and the standard rate of corporation tax
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Loss before tax | | | (6,106 | ) | | | (23,470 | ) | | | (11,870 | ) |
Expected tax credit based on the standard rate of United Kingdom
corporation tax at the domestic rate of 19% | | | (1,160 | ) | | | (4,459 | ) | | | (2,255 | ) |
| Expenses not deductible for tax purposes | | | 75 | | | | 596 | | | | 1,087 | |
| Income not taxable | | | (2 | ) | | | (75 | ) | | | – | |
| Unrelieved tax losses and other deductions | | | – | | | | – | | | | (114 | ) |
| Adjustment in respect of prior period | | | – | | | | (158 | ) | | | (3 | ) |
| Surrender of tax losses for R&D tax refund | | | (280 | ) | | | (491 | ) | | | (1,810 | ) |
| Foreign exchange differences | | | | | | | – | | | | 1 | |
| Deferred tax not recognised | | | 721 | | | | 3,306 | | | | 1,309 | |
| Total tax credited to the income statement | | | (646 | ) | | | (1,281 | ) | | | (1,785 | ) |
The taxation credit arises on the enhanced research and development tax credits accrued for the respective periods.
An adjustment has been recognised in 2020 in respect of the prior period of £158k, this is as a result of a more detailed review of cost classification prior to the submission of tax returns to HMRC in 2020.
Schedule of loss per share
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Numerator | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss used in basic EPS and diluted EPS: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | | (5,460 | ) | | | (22,189 | ) | | | (9,138 | ) |
| Discontinued operations | | | – | | | | – | | | | (947 | ) |
| Denominator | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average number of ordinary shares used in basic EPS: | | | 80,546,881 | | | | 42,839,961 | | | | 18,330,588 | |
| Basic and diluted loss per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations – pence | | | (7 | )p | | | (52 | )p | | | (50 | )p |
| Discontinued operations – pence | | | – | | | | – | | | | (5 | )p |
On 2 March 2020 a resolution was passed at a general meeting of shareholders of the Company to consolidate its ordinary shares on a one for 20 basis into new ordinary shares of 0.1p each in the capital of the Company. The comparative denominator has been calculated to reflect the share consolidation.
The Group has made a loss in the current and previous years presented, and therefore the options and warrants are anti-dilutive. As a result, diluted earnings per share is presented on the same basis for all periods shown.
| 10 | Property, plant and equipment |
Schedule of detailed information about property, plant and equipment
| | | Fixtures and fittings £’000 | | | Leasehold improvements £’000 | | | Computer equipment £’000 | | | Laboratory equipment £’000 | | | Right of use asset £’000 | | | Total £’000 | |
| Cost | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At 1 January 2019 | | | 253 | | | | 2,013 | | | | 383 | | | | 3,651 | | | | – | | | | 6,300 | |
| Adoption of IFRS 16 Leases | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 395 | | | | 395 | |
| Additions | | | 4 | | | | 137 | | | | 23 | | | | 223 | | | | 822 | | | | 1,209 | |
| Effect of modification to lease terms | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (82 | ) | | | (82 | ) |
| Exchange differences | | | (9 | ) | | | (112 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (136 | ) | | | (11 | ) | | | (271 | ) |
| At 31 December 2019 | | | 248 | | | | 2,038 | | | | 403 | | | | 3,738 | | | | 1,124 | | | | 7,551 | |
| Additions | | | – | | | | 58 | | | | 16 | | | | 135 | | | | – | | | | 209 | |
| Effect of modification to lease terms | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (678 | ) | | | (678 | ) |
| Disposal | | | (202 | ) | | | (2,184 | ) | | | (185 | ) | | | (2,323 | ) | | | (316 | ) | | | (5,210 | ) |
| Exchange differences | | | 7 | | | | 92 | | | | 2 | | | | 112 | | | | 58 | | | | 271 | |
| At 31 December 2020 | | | 53 | | | | 4 | | | | 236 | | | | 1,662 | | | | 188 | | | | 2,143 | |
| Additions | | | 57 | | | | 53 | | | | 16 | | | | 194 | | | | 720 | | | | 1,040 | |
| Transfer | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (155 | ) | | | 155 | | | | – | |
| Effect of modification to lease terms | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (24 | ) | | | (24 | ) |
| Disposal | | | (50 | ) | | | (4 | ) | | | (10 | ) | | | (138 | ) | | | (164 | ) | | | (366 | ) |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | 60 | | | | 53 | | | | 242 | | | | 1,563 | | | | 875 | | | | 2,793 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Fixtures and fittings £’000 | | | | Leasehold improvements £’000 | | | | Computer equipment £’000 | | | | Laboratory equipment £’000 | | | | Right of use asset £’000 | | | | Total £’000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At 1 January 2019 | | | 241 | | | | 1,485 | | | | 265 | | | | 2,326 | | | | – | | | | 4,317 | |
| Charge for the year | | | 2 | | | | 400 | | | | 70 | | | | 507 | | | | 303 | | | | 1,282 | |
| Exchange differences | | | (8 | ) | | | (91 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (93 | ) | | | (7 | ) | | | (202 | ) |
| At 31 December 2019 | | | 235 | | | | 1,794 | | | | 332 | | | | 2,740 | | | | 296 | | | | 5,397 | |
| Charge for the year | | | 9 | | | | 310 | | | | 50 | | | | 720 | | | | 118 | | | | 1,207 | |
| Disposals | | | (202 | ) | | | (2,183 | ) | | | (185 | ) | | | (2,300 | ) | | | (316 | ) | | | (5,186 | ) |
| Exchange differences | | | 7 | | | | 81 | | | | 2 | | | | 79 | | | | 14 | | | | 183 | |
| At 31 December 2020 | | | 49 | | | | 2 | | | | 199 | | | | 1,239 | | | | 112 | | | | 1,601 | |
| Transfer | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (74 | ) | | | 74 | | | | – | |
| Charge for the year | | | 8 | | | | 5 | | | | 22 | | | | 178 | | | | 190 | | | | 403 | |
| Disposals | | | (50 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (8 | ) | | | (138 | ) | | | (164 | ) | | | (363 | ) |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | 7 | | | | 4 | | | | 213 | | | | 1,205 | | | | 212 | | | | 1,641 | |
| Net book value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | 53 | | | | 49 | | | | 29 | | | | 358 | | | | 663 | | | | 1,152 | |
| At 31 December 2020 | | | 4 | | | | 2 | | | | 37 | | | | 423 | | | | 76 | | | | 542 | |
| At 31 December 2019 | | | 13 | | | | 244 | | | | 71 | | | | 998 | | | | 828 | | | | 2,154 | |
Schedule of market rental rates
| Lease Liabilities | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| At 1 January | | | 76 | | | | 907 | | | | 546 | |
| Additions | | | 720 | | | | – | | | | 822 | |
| Transfer | | | 77 | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Effect of modification to lease terms | | | (24 | ) | | | (788 | ) | | | (82 | ) |
| Interest expenses | | | 29 | | | | 15 | | | | 24 | |
| Lease payments | | | (112 | ) | | | (105 | ) | | | (391 | ) |
| Exchange differences | | | – | | | | 47 | | | | (12 | ) |
| At 31 December | | | 766 | | | | 76 | | | | 907 | |
The right of use asset is disclosed in note 10.
In April 2021 the Group signed an agreement to lease new premises in Cardiff, Wales, to house its corporate offices and laboratories. The agreement to lease allowed the Group to carry out the Cat A works and fit out prior to completion of the lease and its occupation in August 2021. The lease agreed was for a 5 year period with no break clause. The lease has been recognised as a right of use asset during the year from the date of the agreement to lease.
In May 2021 the Group provided notice to terminate its property lease on its historical building in Cardiff. The lease required 6 month’s notice.
During 2020 as a result of the closure of the Group’s operations in Spain two property leases were terminated early, this impacted both the right of use asset and the lease liability.
Management considered the appropriate life of a lease in the UK in 2021, 2020 and 2019 and adjusted the right of use asset and lease liability accordingly.
Low value leases expensed in year:
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Low value leases expensed | | | 2 | | | | 10 | | | | 29 | |
| Total | | | 2 | | | | 10 | | | | 29 | |
Schedule of reconciliation of changes in intangible assets and goodwill
| | | In-process
research and
development £’000 | | | Goodwill £’000 | | | IT/Website
costs £’000 | | | Total £’000 | |
| Cost | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At 1 January 2019 | | | 13,378 | | | | 2,291 | | | | 28 | | | | 15,697 | |
| Additions | | | – | | | | – | | | | 9 | | | | 9 | |
| Foreign exchange | | | – | | | | – | | | | (2 | ) | | | (2 | ) |
| At 31 December 2019 | | | 13,378 | | | | 2,291 | | | | 35 | | | | 15,704 | |
| Disposal | | | – | | | | – | | | | (36 | ) | | | (36 | ) |
| Foreign exchange | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | |
| At 31 December 2020 | | | 13,378 | | | | 2,291 | | | | – | | | | 15,669 | |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | 13,378 | | | | 2,291 | | | | – | | | | 15,669 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | In-process research and development £’000 | | | | Goodwill £’000 | | | | IT/Website Costs £’000 | | | | Total £’000 | |
| Accumulated amortisation and impairment | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At 1 January 2019 | | | 3,300 | | | | – | | | | 23 | | | | 3,323 | |
| Amortisation charge for the year | | | – | | | | – | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | |
| Foreign exchange | | | – | | | | – | | | | (1 | ) | | | (1 | ) |
| At 31 December 2019 | | | 3,300 | | | | – | | | | 25 | | | | 3,325 | |
| Amortisation charge for the year | | | – | | | | – | | | | 10 | | | | 10 | |
| Disposal | | | – | | | | – | | | | (36 | ) | | | (36 | ) |
| Impairment | | | 10,078 | | | | 2,291 | | | | – | | | | 12,369 | |
| Foreign exchange | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | |
| At 31 December 2020 | | | 13,378 | | | | 2,291 | | | | – | | | | 15,669 | |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | 13,378 | | | | 2,291 | | | | – | | | | 15,669 | |
| Net book value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| At 31 December 2020 | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| At 31 December 2019 | | | 10,078 | | | | 2,291 | | | | 10 | | | | 12,379 | |
| 12 | Intangible assets (continued) |
The individual intangible assets, excluding goodwill, which are material to the financial statements are:
Schedule of individual intangible assets
| | Carrying amount | | | Remaining amortisation
period | |
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | | | 2021 (years) | | | 2020 (years) | | | 2019 (years) | |
| Midatech Pharma (Wales) Limited acquired IPRD | | | – | | | | – | | | | 9,300 | | | | n/a | | | | n/a | | | | n/a in process | |
| MTX110 acquired IPRD | | | – | | | | – | | | | 778 | | | | n/a | | | | n/a | | | | n/a in process | |
| | | | – | | | | – | | | | 10,078 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
In 2020 an impairment charge of £0.8m was recorded in relation to the acquire IPRD on MTX110. The impairment was as a result of the termination of a License Agreement between the Company and Secura Bio Inc. Pursuant to the License Agreement, Midatech Limited was granted a non-exclusive worldwide, sub-licenseable license to certain patents of Panobinostat, the active pharmaceutical ingredient of the Company’s development product MTX110.
Midatech Pharma (Wales) Ltd
Details of goodwill and IPRD allocated to the acquired cash generating unit and the valuation basis are as follows:
Schedule of cash generating unit
| | Indefinite lived | | | | |
| | IPRD carrying amount | | | Goodwill carrying amount | | | | |
| Name | | | 2021 £’000 | | | | 2020 £’000 | | | | 2019 £’000 | | | | 2021 £’000 | | | | 2020 £’000 | | | | 2019 £’000 | | | Valuation Basis | |
| CGU – Midatech Pharma (Wales) Ltd | | | – | | | | – | | | | 9,300 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 2,291 | | | | Value in use | |
As a result of the Board’s decision to terminate its MTD201 program in March 2020 an impairment charge of £11.6m was recorded in that year in the assets of Midatech Pharma (Wales) Ltd (‘MPW’) CGU. The impairment charge was £9.3m of IPRD and £2.3m acquired goodwill. See note 2.
The assets of MPW were valued as at 31 December 2019 were found to support the IPRD and goodwill carrying amounts set out above. The IPRD was valued using 12-13 year risk adjusted cash flow forecasts, in line with patent life, that had been approved by the Board. A period longer than 5 years was appropriate on the basis that the investment was long term and the development and commercialisation process is typically in excess of 5 years. Beyond the period from product launch and initial market penetration, a long term growth rate of Nil was used.
The key assumptions used in the valuation model examining the MPW Ltd cash generating unit include the following:
Schedule of key assumptions used
| Assumptions | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| Pre-tax discount rate | | | n/a | | | | n/a | | | | 18.4 | % |
| Cumulative probability of success of projects | | | n/a | | | | n/a | | | | 81 | % |
The discount rate is an estimated market-based weighted average cost of capital for the MPW business, determined at the date of acquisition. Cumulative probability of success of projects is the product of the probability of success of each remaining major phase of development for each individual IPRD component. These phase probabilities were determined by management with reference to the risks associated with each remaining development stage.
| 13 | Impairment testing (continued) |
Sensitivity analysis
If any one of the following changes were made to the above key assumptions, the carrying value and recoverable amount would be equal.
Schedule of key assumptions used for carrying value and recoverable amount
| Assumptions | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| Pre-tax discount rate for all projects | | | n/a | | | | n/a | | | | increase to 21% | |
| Cumulative probability of success of project | | | n/a | | | | n/a | | | | 59 | % |
The subsidiaries of Midatech Pharma plc, all of which are 100% owned, either directly or through subsidiaries where indicated, and have been included in these financial statements in accordance with the details set out in the basis of preparation and basis of consolidation note 1, are as follows:
Schedule of subsidiaries
| Name | | Registered Office | | Nature of Business | | Notes |
| Midatech Limited | | 1 Caspian Point, Caspian Way, Cardiff, CF10 4DQ | | Trading company | | |
| PharMida AG | | c/o Kellerhals, Hirschgässlein 11, 4051 Basel, Switzerland | | Dormant | | (a) (b) |
Midatech Pharma (Wales)
Limited | | 1 Caspian Point, Caspian Way, Cardiff, CF10 4DQ | | Trading company | | |
Notes:
(a) Wholly owned subsidiary of Midatech Limited.
(b) PharMida AG became dormant in January 2016.
(c) Midatech Pharma PTY was incorporated on 16 February 2015 and dissolved November 2020.
| 15 | Trade and other receivables |
Schedule of trade and other receivables
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Trade receivables | | | 33 | | | | 95 | | | | 22 | |
| Prepayments | | | 607 | | | | 258 | | | | 151 | |
| Other receivables | | | 394 | | | | 219 | | | | 3,444 | |
| Total trade and other receivables | | | 1,034 | | | | 572 | | | | 3,617 | |
| Less: non-current portion (rental deposit and on bond) | | | – | | | | – | | | | (2,625 | ) |
| Current portion | | | 1,034 | | | | 572 | | | | 992 | |
Trade and other receivables do not contain any impaired assets. The Group does not hold any collateral as security and the maximum exposure to credit risk at the consolidated statement of financial position date is the fair value of each class of receivable.
Book values approximate to fair value at 31 December 2021, 2020 and 2019.
During 2019 a cash-backed guarantee was provided to the Spanish Government in relation to a loan provided to the Group under its Reindustrialization programme, see note 18. As a result of the closure of Midatech Pharma (España) SL during 2020 the cash-back guarantee was released on the repayment of the loan to the Spanish Government.
| 16 | Cash and cash equivalents and cash flow supporting notes |
Cash and cash equivalents for purposes of the consolidated statement of cash flows comprises:
Schedule of cash and cash equivalents
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Cash at bank available on demand | | | 10,057 | | | | 7,546 | | | | 10,928 | |
During 2021, 2020 and 2019, cash inflows arose from equity financing transactions, included within financing activities on the face of the cash flow statement. As part of the equity transaction in July 2021 warrants to the value of £Nil (May 2020: £1.0m; October 2019 : £1.1m) were issued as disclosed in note 20.
Schedule of cash inflows from an equity financing transaction
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Gross proceeds | | | 10,091 | | | | 10,792 | | | | 15,767 | |
| Transaction costs | | | (1,056 | ) | | | (1,050 | ) | | | (1,659 | ) |
| Proceeds from issuing shares | | | 9,035 | | | | 9,742 | | | | 14,108 | |
The following changes in loans and borrowings arose as a result of financing activities during the year:
Schedule of changes in bank loan liabilities
| | | Non-current
liabilities £’000 | | | Current
liabilities £’000 | | | Total £’000 | |
| At 1 January 2021 | | | 60 | | | | 200 | | | | 260 | |
| Cash flows | | | – | | | | (215 | ) | | | (215 | ) |
| Non-cashflows: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign Exchange | | | – | | | | (4 | ) | | | (4 | ) |
| New leases | | | 715 | | | | 5 | | | | 720 | |
| Effect of modification to lease term – IFRS 16 | | | – | | | | (24 | ) | | | (24 | ) |
Loans and borrowings classified as non-current 31 December 2020
becoming current in 2021 | | | (178 | ) | | | 178 | | | | – | |
| Interest accruing in period | | | 23 | | | | 6 | | | | 29 | |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | 620 | | | | 146 | | | | 766 | |
| 16 | Cash and cash equivalents and cash flow supporting notes(continued) |
| | | Non-current
liabilities £’000 | | | Current
liabilities £’000 | | | Total £’000 | |
| At 1 January 2020 | | | 5,670 | | | | 412 | | | | 6,082 | |
| Cash flows | | | (6,182 | ) | | | (258 | ) | | | (6,440 | ) |
| Non-cashflows: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign Exchange | | | 252 | | | | 23 | | | | 275 | |
| Fair value changes | | | 1,176 | | | | – | | | | 1,176 | |
| Effect of modification to lease term – IFRS 16 | | | (877 | ) | | | 89 | | | | (788 | ) |
| Reclassification portion government loan to non-current | | | 51 | | | | (51 | ) | | | – | |
| Interest accruing in period | | | (30 | ) | | | (15 | ) | | | (45 | ) |
| At 31 December 2020 | | | 60 | | | | 200 | | | | 260 | |
| | | Non-current
liabilities £’000 | | | Current
liabilities £’000 | | | Total £’000 | |
| At 1 January 2019 | | | 884 | | | | 368 | | | | 1,252 | |
| Cash flows | | | 5,575 | | | | (1,027 | ) | | | 4,548 | |
| Non-cashflows: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign Exchange | | | (42 | ) | | | (29 | ) | | | (71 | ) |
| Fair value changes | | | (1,139 | ) | | | – | | | | (1,139 | ) |
| Adoption of IFRS16 leases | | | 163 | | | | 383 | | | | 546 | |
| Effect of modification to lease term – IFRS 16 | | | – | | | | (82 | ) | | | (82 | ) |
| New leases | | | 805 | | | | 95 | | | | 900 | |
Loans and borrowings classified as non-current 31 December 2018
becoming current in 2019 | | | (685 | ) | | | 685 | | | | – | |
| Transfer to grant income | | | – | | | | (14 | ) | | | (14 | ) |
| Interest accruing in period | | | 108 | | | | 34 | | | | 142 | |
| At 31 December 2019 | | | 5,670 | | | | 412 | | | | 6,082 | |
| 17 | Trade and other payables |
Schedule of trade and other payables
| Current | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Trade payables | | | 485 | | | | 337 | | | | 725 | |
| Other payables | | | 5 | | | | 26 | | | | 13 | |
| Accruals | | | 546 | | | | 768 | | | | 1,765 | |
Total financial liabilities, excluding loans and borrowings,
classified as financial liabilities measured at amortised cost | | | 1,036 | | | | 1,131 | | | | 2,503 | |
| Tax and social security | | | 56 | | | | 31 | | | | 86 | |
| Deferred revenue and government grants | | | – | | | | 68 | | | | 1,905 | |
| Total trade and other payables | | | 1,092 | | | | 1,230 | | | | 4,494 | |
Book values approximate to fair value at 31 December 2021, 2020 and 2019.
All current trade and other payables are payable within 3 months of the period end date shown above.
Government grants
The Group received development grant funding from the European Union under the Horizon 2020 ‘Nanofacturing’ project, a European Union funded programme to develop a scalable manufacturing platform for the production of nanopharmaceutical products. Midatech participated in this programme, along with seven other entities, through two Group companies, Midatech Pharma España SL (‘MPE’), which acted as project coordinator, and Midatech Limited (‘MTL’). The project commenced in February 2015 and completed in January 2019. During the year £nil (2020: £nil, 2019: £124k) revenue was recognised in relation to this project and the deferred revenue balance as at 31 December 2021 was £nil (2020: £nil, 2019: £nil).
Schedule of borrowings
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Current | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 146 | | | | 93 | | | | 233 | |
| Government and research loans | | | – | | | | 107 | | | | 179 | |
| Total | | | 146 | | | | 200 | | | | 412 | |
| Non-current | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 620 | | | | 60 | | | | 912 | |
| Government and research loans | | | – | | | | – | | | | 4,758 | |
| Total | | | 620 | | | | 60 | | | | 5,670 | |
During 2021 a euro denominated government and research loan of £103k (2020: £6.2m) was repaid. This amount includes £ nil (2020: £1.2m) of government grants, which is included in the amounts disclosed in note 17. This amount translated at year end rate was £107k (2020: £4.8m).
Book values approximate to fair value at 31 December 2021, 2020 and 2019.
Obligations under finance leases are secured by a fixed charge over the fixed assets to which they relate.
Government loans in Spain
MPE previously had four Spanish government loans, three were repaid in 2020 with the final loan repaid in February 2021 prior to the liquidation of MPE.
Three of the loans were provided for the finance of research, technical innovation and the construction of their laboratory. The loan were term loans which carried an interest rate below the market rate and were repayable over periods through to 2024. As a result of the Group’s decision on 31 March 2020 to terminate further in-house development of MTD201 and the subsequent closure of its dedicated manufacturing facilities in Bilbao two of these loans were repaid in 2020, with the final loan being repaid in 2021.
The fourth loan received by MPE in September 2019 for €6.6m was awarded under the Spanish Government Reindustrialization programme. The Spanish Government required the company to provide a €2.9 million cash-backed guarantee as security for the loan. The funds were to be used to support Midatech’s manufacturing scale-up facilities construction. This loan was terminated and repaid early in 2020 as a result of the Group’s decision on 31 March 2020. As a result of the early termination interest was charged at market rates up to the date of satisfaction of the loan.
The loans carried default interest rates in the event of scheduled repayments not being met. On initial recognition, the loans are discounted at a market rate of interest with the credit being classified as a grant within deferred revenue. The deferred grant revenue is released to the consolidated statement of comprehensive income within research and development costs in the period to which the expenditure is recognised.
The deferred revenue element of the government loans is designated within note 17 as deferred revenue and Government grants, the gross contractual repayment of the loans is disclosed in note 21. As a result of the repayment of the loans these were fully amortised during 2020.
Schedule of provisions
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Opening provision at 1 January | | | 50 | | | | 97 | | | | 165 | |
| Utilisation of provision | | | – | | | | (97 | ) | | | | |
| Provision recognised/(released) in the year | | | – | | | | 50 | | | | (68 | ) |
| At 31 December | | | 50 | | | | 50 | | | | 97 | |
| Less: non-current portion | | | – | | | | (50 | ) | | | – | |
| Current portion | | | 50 | | | | – | | | | 97 | |
The provision as at 31 December 2021 and 2020 represents management’s best estimate of the ‘making good’ clause on the Cardiff office which was vacated during the fourth quarter of 2021.
The provision as at 31 December 2019 relates to the ‘making good’ clause on the Abingdon office which was vacated in December 2018. The Abingdon office was sub-let for the remaining period of the lease, which terminated in February 2020.
| 20 | Derivative financial liability – current |
Schedule of derivative financial liability
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Equity settled derivative financial liability | | | | | | | | | |
| At 1 January | | | 1,559 | | | | 664 | | | | – | |
| Warrants issued | | | – | | | | 997 | | | | 1,148 | |
| Transfer to share premium on exercise of warrants | | | (70 | ) | | | (499 | ) | | | – | |
Gain recognised in finance income within the consolidated statement
of comprehensive income | | | (936 | ) | | | 397 | | | | (484 | ) |
| At 31 December | | | 553 | | | | 1,559 | | | | 664 | |
Equity settled derivative financial liability is a liability that is not to be settled for cash.
May 2020 warrants
In May 2020 the Company issued 9,545,456 warrants in the ordinary share capital of the Company as part of a registered direct offering in the US. The number of ordinary shares to be issued when exercised is fixed, however the exercise price is denominated in US Dollars being different to the functional currency of the Company. Therefore, the warrants are classified as equity settled derivative financial liabilities recognised at fair value through the profit and loss account (‘FVTPL’). The financial liability is valued using the Monte Carlo model. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are stated at fair value, with any gains or losses arising on re-measurement recognised in profit or loss. The net gain or loss recognised in profit or loss incorporates any interest paid on the financial liability and is included in the ‘finance income’ or ‘finance expense’ lines item in the income statement. Fair value is determined in the manner described in note 21. A key input in the valuation of the instrument is the Company share price. Exercise price per ADR is $2.05 and $2.0625.
October 2019 warrants
In October 2019 the Company issued 3,150,000 warrants in the ordinary share capital of the Company as part of a registered direct offering in the US. The number of ordinary shares to be issued when exercised is fixed, however the exercise price is denominated in US Dollars. The warrants are classified equity settled derivative financial liabilities and accounted for in the same way as those issued in May 2020. The financial liability is valued using the Monte Carlo model. The exercise price per ADR is $6.25.
DARA warrants and share options
The Group also assumed fully vested warrants and share options on the acquisition of DARA Biosciences, Inc. (which took place in 2015). The number of ordinary shares to be issued when exercised is fixed, however the exercise prices are denominated in US Dollars. The warrants are classified equity settled derivative financial liabilities and accounted for in the same way as those detailed above. The financial liability is valued using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The exercise price of the warrants and options is $61.03 and $95.17 respectively.
The following table details the outstanding warrants as at 31 December and also the movement in the year:
| | | At 1
January
2019 | | | Granted | | | Lapsed | | | At 31
December
2019 | | | Granted | | | Exercised | | | At 31
December
2020 | | | Lapsed | | | Exercised | | | At 31
December
2021 | |
May
2020
grant | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 7,545,456 | | | | (2,500,000 | ) | | | 7,045,456 | | | | – | | | | (306,815 | ) | | | 6,738,641 | |
October
19 grant | | | – | | | | 3,150,000 | | | | – | | | | 3,150,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 3,150,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 3,150,000 | |
| DARA Warrants | | | 116,206 | | | | – | | | | (111,582 | ) | | | 4,624 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 4,624 | | | | (544 | ) | | | – | | | | 4,080 | |
DARA
Options | | | 6,167 | | | | – | | | | (3,332 | ) | | | 2,835 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 2,835 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 2,835 | |
| 21 | Financial instruments – risk management |
The Group is exposed through its operations to the following financial risks:
This note describes the Group’s policies and processes for managing those risks. The policy for managing these risks is reviewed and agreed with the Board, however it has delegated the authority for designing and operating processes that ensure the effective management of the risks to the Group’s management. .
Principal financial instruments
The principal financial instruments used by the Group, from which financial instrument risk arises, are as follows:
| • | Trade and other receivables |
| • | Cash and cash equivalents |
| • | Trade and other payables |
| • | Derivative financial liability |
A summary of the financial instruments held by category is provided below:
Financial assets – amortised cost
Schedule of consolidated derivative financial instruments
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 10,057 | | | | 7,546 | | | | 10,928 | |
| Trade receivables | | | 33 | | | | 95 | | | | 22 | |
| Other receivables | | | – | | | | – | | | | 2,625 | |
| Total financial assets | | | 10,090 | | | | 7,641 | | | | 13,575 | |
Financial liabilities – amortised cost
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Trade payables | | | 485 | | | | 337 | | | | 725 | |
| Other payables | | | 5 | | | | 26 | | | | 13 | |
| Accruals | | | 546 | | | | 768 | | | | 1,765 | |
| Borrowings | | | 766 | | | | 260 | | | | 6,082 | |
| Total financial liabilities – amortised cost | | | 1,802 | | | | 1,391 | | | | 8,585 | |
Financial liabilities – fair value through profit and loss – current
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Equity settled derivative financial liability | | | 553 | | | | 1,559 | | | | 664 | |
| 21 | Financial instruments – risk management (continued) |
Fair value hierarchy
The Group uses the following hierarchy for determining and disclosing the fair value of financial instruments by valuation technique:
| • | Level 1: quoted (unadjusted) prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities; |
| • | Level 2: other techniques for which all inputs which have a significant effect on the recorded fair value are observable, either directly or indirectly; and |
| • | Level 3: techniques which use inputs that have a significant effect on the recorded fair value that are not based on observable market data. |
The fair value of the Group’s derivative financial liability is measured at fair value on a recurring basis. The following table gives information about how the fair value of this financial liability is determined, additional disclosure is given in note 20:
Schedule of consolidated financial assets and liabilities at fair value
Financial
liabilities | | Fair value as
at
31/12/2021 | | | Fair
value
hierarchy | | | Valuation
technique(s)
and key input(s) | | Significant unobservable input(s) | | Relationship of
unobservable inputs to
fair value |
Equity settled
financial derivative
liability | | £ | 467,000 | | | Level 3 | | | Monte Carlo simulation model | | Volatility rate of 95.0% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 0.1 and 3.88 years determined using the remaining life of the share options. | | The shorter the expected life the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate of 0.31% determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate
the higher the fair value. |
Equity settled
financial derivative
liability | | £ | 86,000 | | | Level 3 | | | Monte Carlo simulation model | | Volatility rate of 85.0% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 0.1 and 3.5 years determined using the remaining life of the share options. | | The shorter the expected life the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate of 0.71% determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate
the higher the fair value. |
Equity settled
financial derivative
liability | | | – | | | Level 3 | | | Black-Scholes option pricing model | | Volatility rate of 85.0% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 0.10 and 0.9 years determined using the remaining life of the share options. | | The shorter the expected life
the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate of 0.71% determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate
the higher the fair value. |
| Total | | £ | 553,000 | | | | | | | | | | |
| 21 | Financial instruments – risk management (continued) |
Financial
liabilities | | Fair value as
at
31/12/2020 | | | Fair
value
hierarchy | | | Valuation
technique(s)
and key input(s) | | Significant unobservable input(s) | | Relationship of
unobservable inputs to
fair value |
Equity settled
financial derivative
liability | | £ | 1,187,000 | | | Level 3 | | | Monte Carlo simulation model | | Volatility rate of 105.0% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 0.1 and 4.49 years determined using the remaining life of the share options. | | The shorter the expected life the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate of 0.07% determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate
the higher the fair value. |
Equity settled
financial derivative
liability | | £ | 372,000 | | | Level 3 | | | Monte Carlo simulation model | | Volatility rate of 105.0% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 0.1 and 4.888 years determined using the remaining life of the share options. | | The shorter the expected life the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate of 0.08% determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate
the higher the fair value. |
Equity settled
financial derivative
liability | | | – | | | Level 3 | | | Black-Scholes option pricing model | | Volatility rate of 105.0% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 1.0 and 1.9 years determined using the remaining life of the share options. | | The shorter the expected life
the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate of 0.8% determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate
the higher the fair value. |
| Total | | £ | 1,559,000 | | | | | | | | | | |
| 21 | Financial instruments – risk management (continued) |
Financial
liabilities | | Fair value
as at
31/12/2019 | | | Fair value
hierarchy | | | Valuation
technique(s)
and key input(s) | | Significant unobservable input(s) | | Relationship of
unobservable inputs to
fair value |
Equity settled
financial derivative
liability | | £ | 664,000 | | | Level 3 | | | Monte Carlo simulation model | | Volatility rate of 78.4% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 0.1 and 5.68 years determined using the remaining life of the share options.
| | The shorter the expected life the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate between a range of 0.59% and 1.69 % determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate
the higher the fair value. |
Equity settled
financial derivative
liability | | | – | | | Level 3 | | | Black-Scholes option pricing model | | Volatility rate of 78.3% determined using historical volatility of comparable companies. | | The higher the volatility the higher the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Expected life between a range of 2.0 and 2.9 years determined using the remaining life of the share options. | | The shorter the expected life
the lower the fair value. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | Risk-free rate between a range of 0.0% and 0.26 % determined using the expected life assumptions. | | The higher the risk-free rate
the higher the fair value. |
| Total | | £ | 664,000 | | | | | | | | | | |
Changing the unobservable risk free rate input to the valuation model by 10% higher while all other variables were held constant, would not impact the carrying amount of shares (2020 : nil ; 2019: nil).
There were no transfers between Level 1 and 2 in the period.
The financial liability measured at fair value on Level 3 fair value measurement represents consideration relating to warrants issued in May 2020 and October 2019 as part of Registered Direct offerings and also a business combination.
Credit risk
The Group is exposed to credit risk from amounts due from collaborative partners and from cash and cash equivalents and deposits with banks and financial institutions. The risk from collaborative partners is deemed to be low. For banks and financial institutions, only independently rated parties with high credit status are accepted. The Group does not enter into derivatives to manage credit risk. The gross carrying amount of a financial asset is written off (either partially or in full) to the extent that there is no realistic prospect of recovery.
The total exposure to credit risk of the Group is equal to the total value of the financial assets held at each year end as noted above.
| 21 | Financial instruments – risk management (continued) |
Foreign exchange risk
Foreign exchange risk arose because the Group had a material operation located in Bilbao, Spain. Given the levels of materiality, the Group did not hedge its net investments in overseas operations as the cost of doing so would be disproportionate to the exposure.
The table below shows analysis of the Pounds Sterling equivalent of year-end cash and cash equivalent balances by currency:
Schedule of foreign exchange risk
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pounds Sterling | | | 10,057 | | | | 7,247 | | | | 3,153 | |
| US Dollar | | | – | | | | 120 | | | | 2,021 | |
| Euro | | | – | | | | 179 | | | | 5,750 | |
| Other | | | – | | | | – | | | | 4 | |
| Total | | | 10,057 | | | | 7,546 | | | | 10,928 | |
The table below shows the foreign currency exposure that gives rise to net currency gains and losses recognised in the consolidated statement of comprehensive income. As at 31 December, these exposures were as follows:
| | | 2021 £’000 | | | 2020 £’000 | | | 2019 £’000 | |
| Net Foreign Currency Assets/(Liabilities): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| US Dollar | | | – | | | | 120 | | | | 2,021 | |
| Euro | | | 22 | | | | 54 | | | | 1,460 | |
| Other | | | – | | | | 1 | | | | 7 | |
| Total | | | 22 | | | | 175 | | | | 3,488 | |
Foreign exchange risk also arises when individual Group entities enter into transactions denominated in a currency other than their functional currency; the Group’s transactions outside the UK to the US and Europe drive foreign exchange movements where suppliers invoice in currency other than sterling. These transactions are not hedged because the cost of doing so is disproportionate to the risk.
| 21 | Financial instruments – risk management (continued) |
Foreign currency sensitivity analysis
The most significant currencies in which the Group transacts, other than Pounds Sterling, are the US Dollar and the Euro. The Group also trades in other currencies in small amounts as necessary.
The following table details the Group’s sensitivity to a 10% change in year-end exchange rates, which the Group feels is the maximum likely change in rate based upon recent currency movements, in the key foreign currency exchange rates against Pounds Sterling:
Schedule of foreign currency exchange rates
| Year ended 31 December 2021 | | US Dollar £’000 | | | Euro £’000 | | | Other £’000 | |
| Loss before tax | | | – | | | | 2 | | | | – | |
| Total equity | | | – | | | | 2 | | | | – | |
| Year ended 31 December 2020 | | US Dollar £’000 | | | Euro £’000 | | | Other £’000 | |
| Loss before tax | | | 12 | | | | (293 | ) | | | (4 | ) |
| Total equity | | | 12 | | | | (293 | ) | | | (4 | ) |
| Year ended 31 December 2019 | | US Dollar £’000 | | | Euro £’000 | | | Other £’000 | |
| Loss before tax | | | 202 | | | | 54 | | | | – | |
| Total equity | | | 202 | | | | 31 | | | | 1 | |
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk arises from the Group’s management of working capital. It is the risk that the Group will encounter difficulty in meeting its financial obligations as they fall due. It is the Group’s aim to settle balances as they become due.
In February 2021, previously issued warrants were exercised resulting in the Company receiving £0.13m before expenses. In July 2021, the Company completed a UK placing which raised £10.0m before expenses.
The Directors have prepared cash flow forecasts and considered the cash flow requirement for the Company for the next three years including the period twelve months from the date of approval of the consolidated financial statements. These forecasts show that further financing will be required during the first quarter of 2023 assuming, inter alia, that certain development programs and other operating activities continue as currently planned. This requirement for additional financing in the short term represents a material uncertainty that may cast significant doubt upon the Group and parent company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
In addition, the global pandemic COVID-19 virus places increased uncertainty over the Directors’ forecasts. The restrictions that have been placed on the movement of people caused delays to some of the Group’s plans. The Directors have established a COVID-19 task force internally to monitor the impact of COVID-19 on the business and prioritize activities to minimize its continuing effect.
The Directors are evaluating a number of near-term funding options potentially available to the Group, including fundraising and the partnering of assets and technologies of the Company. After considering the uncertainties, the Directors consider it is appropriate to continue to adopt the going concern basis in preparing these financial statements.
| 21 | Financial instruments – risk management (continued) |
The following table sets out the contractual maturities (representing undiscounted contractual cash-flows) of financial liabilities:
Schedule of contractual maturities of financial liabilities
| 2021 | | Up to 3
months £’000 | | | Between 3 and 12 months £’000 | | | Between
1 and 2 years £’000 | | | Between
2 and 5
years £’000 | | | Over
5 years £’000 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | 1,036 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 46 | | | | 171 | | | | 195 | | | | 442 | | | | – | |
| Total | | | 1,082 | | | | 171 | | | | 195 | | | | 442 | | | | – | |
| 2020 | | Up to 3
months £’000 | | | Between 3 and 12 months £’000 | | | Between
1 and 2 years £’000 | | | Between
2 and 5
years £’000 | | | Over
5 years £’000 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | 1,131 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 25 | | | | 75 | | | | 61 | | | | 8 | | | | – | |
| Government research loans | | | 107 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Total | | | 1,263 | | | | 75 | | | | 61 | | | | 8 | | | | – | |
| 2019 | | Up to 3
months £’000 | | | Between 3 and 12 months £’000 | | | Between
1 and 2 years £’000 | | | Between
2 and 5
years £’000 | | | Over
5 years £’000 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | 2,503 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| Lease liabilities | | | 79 | | | | 165 | | | | 317 | | | | 735 | | | | – | |
| Government research loans | | | – | | | | 272 | | | | 238 | | | | 2,851 | | | | 3,317 | |
| Total | | | 2,582 | | | | 437 | | | | 555 | | | | 3,586 | | | | 3,317 | |
More details with regard to the line items above are included in the respective notes:
| • | Trade and other payables – note 17 |
As a result of the Strategic Review undertaken in March 2020 the Group repaid all Government Research loans during 2020 and 2021.
| 21 | Financial instruments – risk management (continued) |
Capital risk management
The Group monitors capital which comprises all components of equity (i.e. share capital, share premium, foreign exchange reserve and accumulated deficit).
The Group’s objectives when maintaining capital are:
| • | to safeguard the entity’s ability to continue as a going concern; and |
| • | to have sufficient resource to take development projects forward towards commercialisation. |
The Group continues to incur substantial operating expenses. Until the Group generates positive net cash inflows from the commercialisation of its products it remains dependent upon additional funding through the injection of equity capital and government funding. The Group may not be able to generate positive net cash inflows in the future or to attract such additional required funding at all, or on suitable terms. In such circumstances the development programmes may be delayed or cancelled, and business operations cut back.
The Group seeks to reduce this risk by keeping a tight control on expenditure, avoiding long term supplier contracts (other than clinical trials), prioritising development spend on products closest to potential revenue generation, obtaining government grants (where applicable), maintaining a focussed portfolio of products under development and keeping shareholders informed of progress.
There have been no changes to the Group’s processes for managing capital risk since the previous year.
Deferred tax is calculated in full on temporary differences under the liability method using tax rates applicable in the tax jurisdictions where the tax asset or liability would arise.
The movement on the deferred tax account in 2021 is £nil (2020: £nil, 2019: £nil) as the net credit arising on the amortisation of intangible assets and other timing differences has been matched by a reduction in the deferred tax asset recognised on the losses offsetting the liability remaining.
Unused tax losses carried forward, subject to agreement with local tax authorities, were as follows:
Schedule of unused tax losses carried forward
| | | Gross losses £’000 | | | Potential
deferred tax
asset £’000 | |
| 31 December 2021 | | | 67,210 | | | | 16,925 | |
| 31 December 2020 | | | 63,183 | | | | 13,076 | |
| 31 December 2019 | | | 49,565 | | | | 8,426 | |
During 2020 the remaining deferred tax asset and liability arising on the business combination of Midatech Pharma (Wales) Ltd (2019: £1.6m) was de-recognised as a result of the impairment of the assets through the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income.
The deferred tax asset which qualifies for offset against the deferred tax liability, mainly arising on the acquisitions of Midatech Pharma (Wales) Limited in 2021 is £nil (2020: £nil, 2019: £1.6m). The remaining potential deferred tax asset of £16.9m (2020 £13.1m, 2019: £9.0m) has not been provided in these accounts due to uncertainty as to whether the asset would be recovered. The losses have arisen as a result of accumulated trading losses.
Deferred tax asset balances disclosed as at 31 December 2021 have been calculated at 25%. The Finance Bill 2021 enacts an increase in the tax rate to 25% from 1 April 2023.
| 22 | Deferred tax (continued) |
Details of the deferred tax liability are as follows:
Schedule of deferred tax liability
| 2021 | | | Asset £’000 | | | | Liability £’000 | | | | Net £’000 | |
| Business Combinations | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| 2020 | | | Asset £’000 | | | | Liability £’000 | | | | Net £’000 | |
| Business Combinations | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | |
| 2019 | | Asset £’000 | | | Liability £’000 | | | Net £’000 | |
| Business Combinations | | | 1,581 | | | | (1,581 | ) | | | – | |
Schedule of detailed information about share capital
Authorised, allotted and fully
paid – classified as equity | | 2021 Number | | | 2021 £ | | | 2020 Number | | | 2020 £ | | | 2019 Number | | | 2019 £ | |
| At 31 December | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ordinary shares of
£0.001 each | | | 98,468,387 | | | | 98,468 | | | | 63,073,852 | | | | 63,074 | | | | 23,494,981 | | | | 23,495 | |
| Deferred shares of £1 each | | | 1,000,001 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | 1,000,001 | |
| Total | | | | | | | 1,098,469 | | | | | | | | 1,063,075 | | | | | | | | 1,023,496 | |
On 2 March 2020 a resolution was passed at a general meeting of shareholders of the Company to consolidate its ordinary shares on a one for 20 basis into new ordinary shares of 0.1p each in the capital of the Company. The above table reflects the share consolidation in the comparative figures.
In accordance with the Articles of Association for the Company adopted on 13 November 2014, the share capital of the Company consists of an unlimited number of ordinary shares of nominal value £0.001 each. Ordinary and deferred shares were recorded as equity.
Rights attaching to the shares following the incorporation of Midatech Pharma plc
Shares classified as equity
The holders of ordinary shares in the capital of the Company have the following rights:
(a) to receive notice of, to attend and to vote at all general meetings of the Company, in which case shareholders shall have one vote for each share of which he is the holder; and,
(b) to receive such dividend as is declared by the Board on each share held.
The holders of deferred shares in the capital of the Company:
(a) shall not be entitled to receive notice of or to attend or speak at any general meeting of the Company or to vote on any resolution to be proposed at any general meeting of the Company; and
(b) shall not be entitled to receive any dividend or other distribution of out of the profits of the Company.
In the event of a distribution of assets, the deferred shareholders shall receive the nominal amount paid up on such share after the holder of each ordinary share shall have received (in cash or specie) the amount paid up or credited as paid up on such ordinary share together with an additional payment of £100 per share. The Company has the authority to purchase the deferred shares and may require the holder of the deferred shares to sell them for a price not exceeding 1p for all the deferred shares.
| 23 | Share capital (continued) |
Schedule Of Ordinary and Deferred Shares
| | | | | | Ordinary Shares Number | | | Deferred Shares Number | | | Share
Price £ | | | Total
consideration £’000 |
| At 1 January 2019 | | | | | | 3,059,207 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | | | | 69,870 |
| 2019 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 26 February 2019 | | | Subscription, Placing and Open Offer | | | 17,410,774 | | | | | | | | 0.77 | | | 13,406 |
| 8 October 2019 | | | Share issue to SIPP trustee (see note 26) | | | 25,000 | | | | | | | | 0.001 | | | – |
| 29 October 2019 | | | Registered Direct Offering | | | 3,000,000 | | | | | | | | 0.7874 | | | 2,362 |
| At 31 December 2019 | | | | | | 23,494,981 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | | | | 85,638 |
| 2020 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 18 May 2020 | | | Placing & Registered Direct Offering | | | 15,757,576 | | | | | | | | 0.27 | | | 4,255 |
| 27 July 2020 | | | Placing | | | 21,296,295 | | | | | | | | 0.27 | | | 5,750 |
| 19 August 2020 | | | Exercise of warrants | | | 2,500,000 | | | | | | | | | | | 783 |
| 30 September 2020 | | | Share issue to SIPP trustee (see note 26) | | | 25,000 | | | | | | | | 0.001 | | | – |
| At 31 December 2020 | | | | | | 63,073,852 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | | | | 96,426 |
| 19 February 2021 Exercise of warrants | | | | | | 306,815 | | | | | | | | 0.298 | | | 91 |
| 6 July 2021 Placing | | | | | | 35,087,720 | | | | | | | | 0.285 | | | 10,000 |
| At 31 December 2021 | | | | | | 98,468,387 | | | | 1,000,001 | | | | | | | 106,517 |
The following describes the nature and purpose of each reserve within equity:
Schedule of reserves
| Reserve | Description and purpose |
| Share premium | Amount subscribed for share capital in excess of nominal value. |
| Merger reserve | Represents the difference between the fair value and nominal value of shares issued on the acquisition of subsidiary companies where the Company has elected to take advantage of merger accounting. |
| Foreign exchange reserve | Gains/losses arising on retranslating the net assets of overseas operations into sterling. |
| Warrant reserve | Represents the fair value of warrants denominated in £ at the date of grant |
| Accumulated deficit | All other net gains and losses and transactions with owners (e.g. dividends) not recognised elsewhere. |
The Group operates a defined contribution pension scheme for the benefit of its employees. The assets of the scheme are administered by trustees in funds independent from those of the Group.
Share Options
The Group has issued options over ordinary shares under the 2014 Midatech Pharma plc Enterprise Management Incentive Scheme, the Midatech Pharma plc 2016 U.S. Option Plan, which is a sub-plan of the approved UK plan, and unapproved share options awarded to non-UK or non-US staff. In addition, certain share options originally issued over shares in Midatech Limited under the Midatech Limited 2008 unapproved share option scheme or Midatech Limited 2013 approved Enterprise Incentive scheme were reissued in 2015 over shares in Midatech Pharma plc under the 2014 Midatech Pharma plc Enterprise Management Incentive Scheme. Exercise of an option is subject to continued employment.
On 2 March 2020 a resolution was passed at a general meeting of shareholders of the Company to consolidate it ordinary shares on a one for 20 basis into new ordinary shares of 0.1p each in the capital of the Company. The following tables reflect the share consolidation in the comparative tables.
Details of all share options granted under the Schemes are set out below:
| Date of grant | | At 1 January
2021 | | | Granted in 2021 | | | Expired 2021 | | | Forfeited in
2021 | | | At 31 December
2021 | | | Exercise Price | |
| 13 September 2011 | | | 150 | | | | – | | | | (150 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 83.80 | |
| 20 April 2012 | | | 1,589 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1,589 | | | £ | 83.80 | |
| 9 May 2014 | | | 10,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 10,000 | | | £ | 1.50 | |
| 30 June 2014 | | | 500 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 500 | | | £ | 1.50 | |
| 31 October 2016 | | | 7,921 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (890 | ) | | | 7,031 | | | £ | 53.60 | |
| 19 December 2016 | | | 10,018 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (2,062 | ) | | | 7,956 | | | £ | 24.20 | |
| 15 December 2017 | | | 3,300 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (2,100 | ) | | | 1,200 | | | £ | 9.20 | |
| 24 April 2019 | | | 45,500 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (33,000 | ) | | | 12,500 | | | £ | 1.46 | |
| 2 October 2019 | | | 30,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 30,000 | | | £ | 1.05 | |
| 17 April 2020 | | | 100,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 100,000 | | | £ | 0.24 | |
| 17 June 2020 | | | 1,274,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (410,500 | ) | | | 863,500 | | | £ | 0.202 | |
| 15 July 2021 | | | – | | | | 1,709,000 | | | | – | | | | (280,000 | ) | | | 1,429,000 | | | £ | 0.28 | |
| 2 August 2021 | | | – | | | | 50,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 50,000 | | | £ | 0.27 | |
| 1 September 2021 | | | – | | | | 120,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 120,000 | | | £ | 0.26 | |
| | | | 1,482,978 | | | | 1,879,000 | | | | (150 | ) | | | (728,552 | ) | | | 2,633,276 | | | | | |
| Options exercisable at 31 December 2021 | | | 179,632 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of outstanding options at 31 December 2021 | | £ | 0.538 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options exercised in 2021 | | | n/a | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options lapsed in 2021 | | £ | 83.30 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options forfeited in 2021 | | £ | 0.447 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options granted in 2021 | | £ | 0.276 | |
| Weighted average remaining contractual life of outstanding options at 31 December 2021 | | | 9.0 years | |
| 26 | Share-based payments (continued) |
| Date of grant | | At 1 January
2020 | | | Granted in 2020 | | | Expired in 2020 | | | Forfeited in
2020 | | | At 31 December
2020 | | | Exercise Price | |
| 1 April 2010 | | | 1,255 | | | | – | | | | (1,255 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 80.00 | |
| 20 August 2010 | | | 2,088 | | | | – | | | | (2,088 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 83.80 | |
| 13 September 2011 | | | 150 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 150 | | | £ | 83.80 | |
| 20 April 2012 | | | 1,589 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1,589 | | | £ | 83.80 | |
| 9 May 2014 | | | 10,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 10,000 | | | £ | 1.50 | |
| 30 June 2014 | | | 18,500 | | | | | | | | – | | | | (18,000 | ) | | | 500 | | | £ | 1.50 | |
| 11 July 2014 | | | 100 | | | | – | | | | (50 | ) | | | (50 | ) | | | – | | | £ | 1.50 | |
| 31 October 2016 | | | 16,271 | | | | – | | | | (850 | ) | | | (7,500 | ) | | | 7,921 | | | £ | 53.60 | |
| 14 December 2016 | | | 400 | | | | – | | | | (400 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 31.00 | |
| 14 December 2016 | | | 500 | | | | – | | | | (500 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 34.00 | |
| 14 December 2016 | | | 2,000 | | | | – | | | | (2,000 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 37.40 | |
| 14 December 2016 | | | 1,625 | | | | – | | | | (1,625 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 37.60 | |
| 15 December 2016 | | | 4,600 | | | | – | | | | (4,600 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 24.20 | |
| 19 December 2016 | | | 22,391 | | | | – | | | | (1,562 | ) | | | (10,811 | ) | | | 10,018 | | | £ | 24.20 | |
| 15 December 2017 | | | 29,560 | | | | – | | | | (13,310 | ) | | | (12,950 | ) | | | 3,300 | | | £ | 9.20 | |
| 2 April 2018 | | | 997 | | | | – | | | | (997 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 16.60 | |
| 2 April 2018 | | | 4,500 | | | | – | | | | (4,500 | ) | | | – | | | | – | | | £ | 24.20 | |
| 24 April 2019 | | | 169,500 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (124,000 | ) | | | 45,500 | | | £ | 1.46 | |
| 2 October 2019 | | | 50,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (20,000 | ) | | | 30,000 | | | £ | 1.05 | |
| 17 April 2020 | | | – | | | | 100,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 100,000 | | | £ | 0.24 | |
| 17 June 2020 | | | – | | | | 1,363,000 | | | | – | | | | (89,000 | ) | | | 1,274,000 | | | £ | 0.202 | |
| | | | 336,026 | | | | 1,463,000 | | | | (33,737 | ) | | | (282,311 | ) | | | 1,482,978 | | | | | |
| Options exercisable at 31 December 2020 | | | 195,171 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of outstanding options at 31 December 2020 | | £ | 0.835 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options exercised in 2020 | | | n/a | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options lapsed in 2020 | | £ | 26.183 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options forfeited in 2020 | | £ | 3.648 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options granted in 2020 | | £ | 0.205 | |
| Weighted average remaining contractual life of outstanding options at 31 December 2020 | | | 9.2 years | |
| 26 | Share-based payments (continued) |
| Date of grant | | At 1 January
2019 | | | Granted in 2019 | | | Exercised in
2019 | | | Forfeited in
2019 | | | At 31 December
2019 | | | Exercise Price | |
| 1 April 2010 | | | 1,255 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1,255 | | | £ | 80.00 | |
| 20 August 2010 | | | 2,088 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 2,088 | | | £ | 83.80 | |
| 13 September 2011 | | | 150 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 150 | | | £ | 83.80 | |
| 20 April 2012 | | | 1,589 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1,589 | | | £ | 83.80 | |
| 9 May 2014 | | | 10,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 10,000 | | | £ | 1.50 | |
| 30 June 2014 | | | 21,500 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (3,000 | ) | | | 18,500 | | | £ | 1.50 | |
| 11 July 2014 | | | 100 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 100 | | | £ | 1.50 | |
| 31 October 2016 | | | 2,500 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (2,500 | ) | | | – | | | £ | 34.20 | |
| 31 October 2016 | | | 23,411 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (7,140 | ) | | | 16,271 | | | £ | 53.60 | |
| 14 December 2016 | | | 400 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 400 | | | £ | 31.00 | |
| 14 December 2016 | | | 500 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 500 | | | £ | 34.00 | |
| 14 December 2016 | | | 2,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 2,000 | | | £ | 37.40 | |
| 14 December 2016 | | | 1,625 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 1,625 | | | £ | 37.60 | |
| 15 December 2016 | | | 4,600 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 4,600 | | | £ | 24.20 | |
| 19 December 2016 | | | 35,866 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (13,475 | ) | | | 22,391 | | | £ | 24.20 | |
| 15 December 2017 | | | 45,885 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | (16,325 | ) | | | 29,560 | | | £ | 9.20 | |
| 2 April 2018 | | | 997 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 997 | | | £ | 16.60 | |
| 2 April 2018 | | | 4,500 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 4,500 | | | £ | 24.20 | |
| 24 April 2019 | | | – | | | | 219,000 | | | | – | | | | (49,500 | ) | | | 169,500 | | | £ | 1.46 | |
| 2 October 2019 | | | – | | | | 50,000 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 50,000 | | | £ | 1.05 | |
| | | | 158,966 | | | | 269,000 | | | | – | | | | (91,940 | ) | | | 336,026 | | | | | |
| Options exercisable at 31 December 2019 | | | 131,094 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of outstanding options at 31 December 2019 | | £ | 8.48 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options exercised in 2019 | | | n/a | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options forfeited in 2019 | | £ | 13.26 | |
| Weighted average exercise price of options granted in 2019 | | £ | 1.38 | |
| Weighted average remaining contractual life of outstanding options at 31 December 2019 | | | 7.9 years | |
| 26 | Share-based payments (continued) |
The following information is relevant in the determination of the fair value of options granted during the year 2021 under the equity share based remuneration schemes operated by the Group.
| | | July 2021 | | | August 2021 | | | September 2021 | |
| Number of options | | | 1,709,000 | | | | 50,000 | | | | 120,000 | |
| Option pricing models used | | | Black-Scholes | | | | Black-Scholes | | | | Black-Scholes | |
| Share price | | £ | 0.2775 | * | | £ | 0.265 | * | | £ | 0.255 | * |
| Exercise price of options issued in year | | £ | 0.2775 | | | £ | 0.265 | | | £ | 0.255 | |
| Contractual life | | | 10 years | | | | 10 years | | | | 10 years | |
| Expected life | | | 5 years | | | | 5 years | | | | 5 years | |
| Volatility | | | 88.63 | %** | | | 88.59 | %** | | | 88.11 | %** |
| Expected dividend yield | | | 0 | % | | | 0 | % | | | 0 | % |
| Risk free rate | | | 0.38 | % | | | 0.26 | % | | | 0.32 | % |
* The share price used in the determination of the fair value of the options granted in 2021 was the share price on the date of grant.
** Volatility was calculated with reference to the historic share price volatility of comparable companies measured over a five-year period.
The following information is relevant in the determination of the fair value of options granted during the year 2020 under the equity share based remuneration schemes operated by the Group.
| | | April 2020 | | | June 2020 | |
| Number of options | | | 100,000 | | | | 1,363,000 | |
| Option pricing models used | | | Black-Scholes | | | | Black-Scholes | |
| Share price | | £ | 0.24 | * | | £ | 0.213 | * |
| Exercise price of options issued in year | | £ | 0.24 | | | £ | 0.202 | |
| Contractual life | | | 10 years | | | | 10 years | |
| Expected life | | | 5 years | | | | 5 years | |
| Volatility | | | 84.76 | %** | | | 92.55 | %** |
| Expected dividend yield | | | 0 | % | | | 0 | % |
| Risk free rate | | | 0.11 | % | | | 0.10 | % |
* The share price used in the determination of the fair value of the options granted in 2020 was the share price on the date of grant.
** Volatility was calculated with reference to the historic share price volatility of comparable companies measured over a five-year period.
| 26 | Share-based payments (continued) |
The following information is relevant in the determination of the fair value of options granted during the year 2019 under the equity share based remuneration schemes operated by the Group.
| | | April 2019 | | | October 2019 | |
| Number of options | | | 219,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
| Option pricing models used | | | Black-Scholes | | | | Black-Scholes | |
| Share price | | £ | 2.30 | * | | £ | 1.126 | * |
| Exercise price of options issued in year | | £ | 1.46 | | | £ | 1.05 | |
| Contractual life | | | 10 years | | | | 10 years | |
| Expected life | | | 5 years | | | | 5 years | |
| Volatility | | | 75.3 | %** | | | 78.3 | %** |
| Expected dividend yield | | | 0 | % | | | 0 | % |
| Risk free rate | | | 0.85 | % | | | 0.26 | % |
* The share price used in the determination of the fair value of the options granted in 2019 was the share price on the date of grant.
** Volatility was calculated with reference to the historic share price volatility of comparable companies measured over a five-year period.
All other share options relate to the Midatech Limited 2008 unapproved share option scheme.
Share Incentive Plan
In April 2017 the Group set up the Midatech Pharma Share Incentive Plan (MPSIP). Under the MPSIP, Group employees and Directors can acquire ordinary shares in the Company via a salary sacrifice arrangement. Midatech grants matching shares for every share bought. In order to retain these shares, scheme participants must remain employed by the Group for three years from the date of acquisition. All shares purchased by the MPSIP are held by an Employee Benefit Trust that is not under the control of Midatech. Shares must be left in the plan for 5 years to qualify for full income tax and NIC relief.
The Group had no capital commitments at 31 December 2021, 31 December 2020 and 31 December 2019.
| 28 | Related party transactions |
Trading Transactions
The Directors consider BioConnection BV to be a related party by virtue of the fact that there is a common Director with the Company and the Director is identified as having significant influence over the entity. 2019 was the first year where this relationship existed.
During the year Group companies entered into the following transactions with related parties who are not members of the Group.
Schedule of related party transactions
| | | Purchase of good | | | Amounts owed by related parties | |
| | | 2021 €’000 | | | 2020 €’000 | | | 2019 €’000 | | | 2021 €’000 | | | 2020 €£’000 | | | 2019 €’000 | |
| BioConnection BV | | | – | | | | 296 | | | | 18 | | | | – | | | | – | | | | 8 | |
During 2019 Midatech Pharma (Espana) SL entered into a commercial contract with BioConnection BV in connection with the Group’s MTD201 program, this contract was subsequently terminated in 2020 as a result of the termination of the program.
The Group has not made any allowances for bad or doubtful debts in respect of related party debtors nor has any guarantee been given or received during 2021,2020 or 2019 regarding related party transactions.
As at 31 December 2019 the Group was party to a claim by the estate of a former employee for unfair dismissal. The claim comprised various elements totalling €258,000. During 2020 the case was settled by the Group for €190,000. This has been recognised in Administrative costs in the Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income in 2020.
The Group had no contingent liabilities at 31 December 2021 and 31 December 2020.
| 30 | Ultimate controlling party |
The Directors do not consider that there is an ultimate controlling party.
| 31 | Results of Midatech Pharma (España) SL |
Included within the Group Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the year to 31 December 2021 and 2020 are the results of the Group’s Spanish operation that was closed on 3 June 2020. The Group appointed a Liquidator to liquidate the company with documentation submitted to the Spanish Authorities in February 2021.
Management assessed whether Midatech Pharma (España) SL should be accounted for as a discontinued operation under IFRS 5 and concluded that it did not meet the criteria as it did not meet the definition of a cash generating unit.
The unaudited results of Midatech Pharma (España) SL for the year to 31 December are as follows:
Schedule Of Unaudited Results Explanatory
| | | Year ended 31 December 2021 £’000 | | | Year ended 31 December 2020 £’000 | |
| Grant revenue | | | – | | | | 163 | |
| Total revenue | | | – | | | | 163 | |
| Research and development costs | | | – | | | | (2,820 | ) |
| Administrative costs | | | – | | | | (1,146 | ) |
| Loss from operations | | | – | | | | (3,803 | ) |
| Finance expense | | | – | | | | (11 | ) |
| Loss before tax | | | – | | | | (3,814 | ) |
| Taxation | | | – | | | | (21 | ) |
| Loss from operations after tax | | | – | | | | (3,835 | ) |

PRELIMINARY PROSPECTUS
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
| Item 6. | Indemnification of Directors and Officers. |
The Registrant’s articles of association provide that, subject to the United Kingdom Companies Act 2006, every person who is or was at any time a director, alternate director, or former director of the Registrant or of any of its subsidiaries may be indemnified out of the assets of the Registrant against all costs, charges, expenses, losses, damages and liabilities incurred by him or her in performing his duties or the exercise of his or her powers or otherwise in relation to such company. Generally, under the United Kingdom Companies Act 2006, a company may not indemnify its directors against personal liability covering: liability to the company in cases where the company sues the director (i.e., only liability to third parties can be the subject of an indemnity); liability for fines for criminal conduct or fines imposed by a regulator; or other liabilities, such as legal costs, in criminal cases where the director is convicted, or in civil cases brought by the company where the final judgment goes against the director.
The Registrant has entered into a deed of indemnity with each of its directors and officers. Except as prohibited by applicable law, these deeds of indemnity may require Midatech, among other things, to indemnify its directors and officers for certain expenses, including attorneys’ fees, judgments, fines and settlement amounts incurred by such directors and officers in any action or proceeding arising out of their service as a director or officer of the Registrant, or one of its subsidiaries, or arising out of the services provided to another company or enterprise at the Registrant’s request.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, may be permitted to directors, officers or persons controlling us pursuant to the foregoing provisions, we have been informed that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable.
| Item 7. | Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities |
The following information is furnished with regard to all securities issued by the registrant within the last three years that were not registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. Unless otherwise indicated below, the issuance of such shares was deemed exempt from registration requirements of the Securities Act, of 1933, as amended, as such securities were offered and sold outside of the United States to persons who were neither citizens nor residents of the United States, pursuant to Regulation S, or such sales were exempt from registration under Section 4(2) of Securities Act of 1933, as amended and Rule 506 of Regulation D promulgated thereunder.
On May 20, 2020, we sold to certain institutional investors 9,090,910 Ordinary Shares represented by 363,636 Depositary Shares in a registered direct offering at $8.25 per Depositary Share, resulting in gross proceeds of $3.0 million. In addition, we issued to the investors unregistered warrants to purchase a total of 9,090,910 Ordinary Shares represented by 363,636 Depositary Shares in a private placements. We also issued unregistered placement agent warrants to purchase a total of 454,546 Ordinary Shares represented by 18,182 Depositary Shares to affiliates of H.C. Wainwright & Co., Inc. in a private placement.
On May 22, 2020, we issued 6,666,666 units, or Units, to certain non-U.S. investors in a placing in the United Kingdom for aggregate gross proceeds of £1.8 million. Each Unit comprised one new Ordinary Share and one warrant to purchase Ordinary Shares. We also issued unregistered placement agent warrants to purchase a total of 333,333 Ordinary Shares to Turner Pope Investments (TPI) Limited.
On July 27, 2020, we issued 21,296,295 ordinary shares, including 2,777,777 Ordinary Shares issued pursuant to a broker option, to certain non-U.S. investors in a placing in the United Kingdom for aggregate gross proceeds of £5.75 million.
On August 19, 2020, we issued 2,500,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 100,000 Depositary Shares upon the exercise of warrants issued in May 2020 at an exercise price of $10.25 per share.
On September 30, 2020, we issued 25,000 Ordinary Shares to be purchased under the Midatech Pharma Share Incentive Plan.
On February 19, 2021, we issued 306,815 Ordinary Shares represented by 12,273 Depositary Shares upon the exercise of warrants issued in May 2020 at an exercise price of $10.3125 per share.
On July 6, 2021, we issued 35,087,720 Ordinary Shares to certain non-U.S. investors in a placing in the United Kingdom for aggregate gross proceeds of £10.0 million.
On March 22, 2022, we issued 26 Ordinary Shares upon the exercise of 26 warrants issued in February 2019 at an exercise price of £10 per share.
On May 3, 2022, we issued 25,000 Ordinary Shares to be purchased under the Midatech Pharma Share Incentive Plan.
On August 3, 2022, we issued warrants to purchase 333,333 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of £0.135 per share.
On February 15, 2023, we completed the closing of a private placement pursuant to which we sold to certain institutional investors (1) 65,004,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 2,600,160 Depositary Shares, (2) 258,620,550 Ordinary Shares represented by 10,344,822 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series A warrants issued in the Private Placement, (3) 387,930,900 Ordinary Shares represented by 15,517,236 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of Series B warrants issued in the Private Placement, and (4) up to 1,434,996,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 57,399,840 Depositary Shares, issuable upon the exercise of pre-funded warrants issued in the Private Placement, for aggregate gross proceeds of approximately $6.0 million. We also issued unregistered placement agent warrants to purchase a total of 10,738,775 Ordinary Shares represented by 429,551 Depositary Shares to Ladenburg Thalman & Co. Inc., and Series A warrants to purchase 12,500,000 Ordinary Shares represented by 500,000 Depositary Shares to an investor pursuant to a waiver agreement.The Series A warrants, Series B warrants, certain of the pre-funded warrants and the placement agent warrants are subject to the receipt of stockholder approval at a general meeting.
| Item 8. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
| (a) | The Exhibit Index is incorporated herein by reference. |
See the Exhibit Index attached to this registration statement, which is incorporated herein by reference.
| (b) | Financial Statement Schedules. |
Schedules not listed above have been omitted because the information required to be set forth therein is not applicable or is shown in the financial statements or the notes thereto.
The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes:
| (1) | To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this registration statement: |
| (i) | to include any prospectus required by section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act; |
| (ii) | to reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the registration statement. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of prospectus filed with the Commission pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent no more than a 20% change in the maximum aggregate offering price set forth in the “Calculation of Registration Fee” table in the effective registration statement; and |
| (iii) | to include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to such information in the registration statement; |
| (2) | That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. |
| (3) | To remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering. |
| (4) | To file a post-effective amendment to the registration statement to include any financial statements required by Item 8.A. of Form 20-F at the start of any delayed offering or throughout a continuous offering. Financial statements and information otherwise required by Section 10(a)(3) of the Act need not be furnished, provided that the registrant includes in the prospectus, by means of a post-effective amendment, financial statements required pursuant to this paragraph (a)(4) and other information necessary to ensure that all other information in the prospectus is at least as current as the date of those financial statements. |
| (5) | That, for the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser: |
| (i) | Each prospectus filed by the registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(3) shall be deemed to be part of the registration statement as of the date the filed prospectus was deemed part of and included in the registration statement; and |
| (ii) | Each prospectus required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424(b)(2), (b)(5), or (b)(7) as part of a registration statement in reliance on Rule 430B relating to an offering made pursuant to Rule 415(a)(1)(i), (vii), or (x) for the purpose of providing the information required by section 10(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the earlier of the date such form of prospectus is first used after effectiveness or the date of the first contract of sale of securities in the offering described in the prospectus. As provided in Rule 430B, for liability purposes of the issuer and any person that is at that date an underwriter, such date shall be deemed to be a new effective date of the registration statement relating to the securities in the registration statement to which that prospectus relates, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such effective date, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such effective date. |
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the Registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the Registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the Registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the Registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the Registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question of whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes that:
| (1) | For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b) (1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective. |
| (2) | For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the registrant certifies that it has reasonable grounds to believe that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form F-1 and has duly caused this Registration Statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in Cardiff, Wales, on this 8th day of March, 2023.
| | MIDATECH PHARMA PLC |
| | | |
| | By: | /s/ Stephen Stamp |
| | | Stephen Stamp |
| | | Chief Executive Officer |
We, the undersigned, hereby severally constitute and appoint each of Stephen Stamp and Stephen Parker, each in their individual capacity, our true and lawful attorney-in-fact and agent, with full power of substitution and resubstitution, for him and his name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to execute any and all amendments (including post-effective amendments) to this registration statement, to sign any registration statement filed pursuant to Rule 462(b) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and to cause the same to be filed with all exhibits thereto, and all documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorney-in-fact and agent, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and desirable to be done in and about the premises as fully and to all intents and purposes as we might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all facts and things that said attorney-in-fact and agent, or his substitute may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue thereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, this Registration Statement on Form F-1 has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the date indicated.
| Name and Signature | | Title(s) | | Date |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Stephen Stamp | | Chief Executive Officer, Director, | | March 8, 2023 |
| Stephen Stamp | | Principal Executive Officer, Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Stephen Parker | | Non-Executive Chairman of the Board | | March 8, 2023 |
| Stephen Parker | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Simon Turton, Ph.D. | | Senior Independent Non-Executive Director | | March 8, 2023 |
| Simon Turton, Ph.D. | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ Sijmen de Vries, M.D. | | Non-Executive Director | | March 8, 2023 |
| Sijmen de Vries, M.D. | | | | |
AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, this Registration Statement on Form F-1 has been signed by the undersigned on this 8th day of March, 2023.
| By: | /s/ Donald J. Puglisi | |
| Name: | Donald J. Puglisi | |
| Title: | Authorized Representative in the United States | |
Exhibit Index
Exhibit Number | Title |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| 3.1 | Articles of Association of Midatech Pharma PLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-206305), originally filed with the SEC on August 11, 2015, as amended). |
| 4.1 | Description of Securities Registered Under Section 12 of the Exchange Act (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2021, filed with the SEC on April 26, 2022). |
| 4.2 | Specimen certificate representing ordinary shares of Midatech Pharma PLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-206305), originally filed with the SEC on August 11, 2015, as amended). |
| 4.3 | Form of Amended and Restated Deposit Agreement by and among Midatech Pharma PLC, The Bank of New York Mellon, as depositary, and all owners and holders from time to time of American Depositary Shares thereunder (incorporated by reference to Exhibit A to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-6 (File No. 333-252507), filed with the SEC on January 28, 2021). |
| 4.4 | Form of American Depositary Receipt (included in Exhibit 2.3 as Exhibit A thereto). |
| 4.5 | Form of Warrant issued on October 25, 2019 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on October 24, 2019). |
| 4.6 | Form of Placement Agent Warrant issued on October 25, 2019 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on October 24, 2019). |
| 4.7 | Form of Warrant issued on May 20, 2020 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on May 19, 2020). |
| 4.8 | Form of Placement Agent Warrant issued on May 20, 2020 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on May 19, 2020). |
| 4.9 | Form of Warrant Instrument issued on May 22, 2020 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on May 19, 2020). |
| 4.10 | Form of Series A Warrant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on February 9, 2023). |
| 4.11 | Form of Series B Warrant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on February 9, 2023). |
| 4.12 | Form of Pre-Funded Warrant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on February 9, 2023). |
| 4.13 | Form of Placement Agent Warrant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on February 9, 2023). |
| 5.1* | Opinion of Brown Rudnick LLP. |
| 10.1# | Midatech Pharma PLC 2014 Enterprise Management Incentive Scheme (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-206305), originally filed with the SEC on August 11, 2015, as amended). |
| 10.2# | Form of Option Agreement (included in Exhibit 10.1). |
| 10.3# | Consultancy Agreement, dated as of April 15, 2014, by and between Midatech Limited and Chesyl Pharma Limited (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-206305), originally filed with the SEC on August 11, 2015, as amended). |
| 10.4# | Appointment Agreement, dated as of April 15, 2014, by and between Midatech Limited and Rolf Stahel (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-206305), originally filed with the SEC on August 11, 2015, as amended). |
| 10.5# | Revised Appointment Agreement, dated as of December 2, 2014, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC and Rolf Stahel (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-206305), originally filed with the SEC on August 11, 2015, as amended). |
| 10.6# | Form of Appointment Letter between Midatech Pharma PLC and certain directors of Midatech Pharma PLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-206305), originally filed with the SEC on August 11, 2015, as amended). |
| 10.7# | Deed of Indemnity dated August 5, 2015 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form F-4 (File No. 333-206305), originally filed with the SEC on August 11, 2015, as amended). |
| 10.8† | License, Collaboration and Distribution Agreement, dated as of January 29, 2019, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC, CMS Bridging Limited, CMS Medical Hong Kong Limited and China Medical System Holdings Limited (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.17 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2018, as amended, filed with the SEC on May 28, 2019). |
| 10.9 | Relationship Agreement, dated January 29, 2019, by and among the Company, certain CMS Concert Party Members and Panmure Gordon (UK) Limited (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.18 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2018, filed with the SEC on April 30, 2019). |
| 10.10 | Deed of Variation of Relationship Agreement, dated May 12, 2020, between Midatech Pharma PLC, Certain CMS Concert Party Members and Panmure Gordon (UK) Limited (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.15 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2020, filed with the SEC on April 30, 2021). |
| 10.11# | The Midatech Pharma Share Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.27 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2018, filed with the SEC on April 24, 2018). |
| 10.12†# | Service Agreement dated as of September 9, 2019, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC and Stephen Stamp (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on September 19, 2019). |
10.13 | Form of Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 13, 2022, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC and the purchaser identified on the signature page thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on December 13, 2022). |
| 10.14 | First Amendment to the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 16, 2022, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC and the purchaser identified on the signature page thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on December 19, 2022). |
| 10.15 | Form of Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of February 9, 2023, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC and the purchasers identified on the signature page thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on February 9, 2023. |
| 10.16# | Service Agreement, dated as of July 12, 2021, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC and Dmitry Zamoryakhin (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.15 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2021, filed with the SEC on April 26, 2022). |
| 10.17# | Terms of Appointment as Director, dated June 20, 2022, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC and Stephen Barry Parker (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on June 21, 2022). |
| 10.18 | Form of Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of February 9, 2023, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC and the investors identified on the signature pages thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on February 9, 2023). |
| 10.19 | Form of Waiver, dated as of February 9, 2023, by and between Midatech Pharma PLC and a certain institutional investor (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of the Company’s Report on Form 6-K, filed with the SEC on February 9, 2023). |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of Midatech Pharma PLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 8.1 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2021, filed with the SEC on April 26, 2022). |
| 23.1* | Consent of Mazars LLP, independent registered public accounting firm. |
| 23.2* | Consent of BDO LLP, independent registered public accounting firm. |
| 23.3* | Consent of Brown Rudnick LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1). |
| 101. INS | Inline XBRL Instance Document |
| 101.SCH | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Documents |
| 101.CAL | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
| 101.DEF | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
| 101.LAB | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
| 101.PRE | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
| 104 | Cover Page Interactive Data File (embedded within Inline XBRL document) |
| 107 | Filing Fee Table |
___________
* Filed herewith.
| # | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| † | Certain portions of this exhibit (indicated by asterisks) have been omitted because they are not material and would likely cause competitive harm to Midatech Pharma PLC if publicly disclosed. |
II-8

