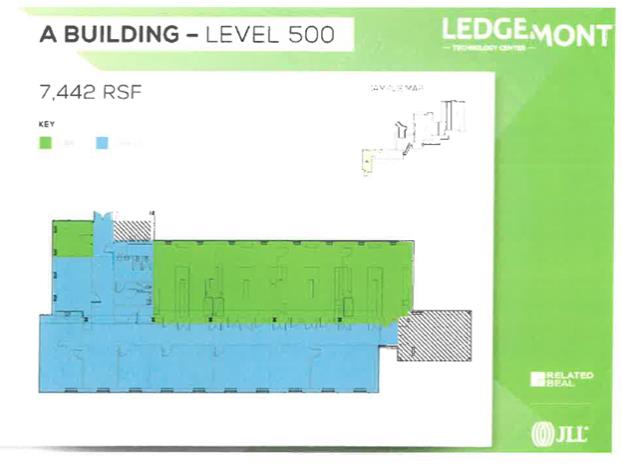
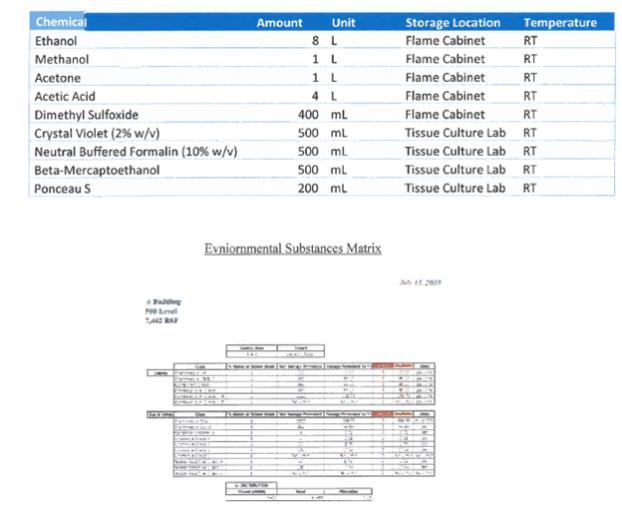
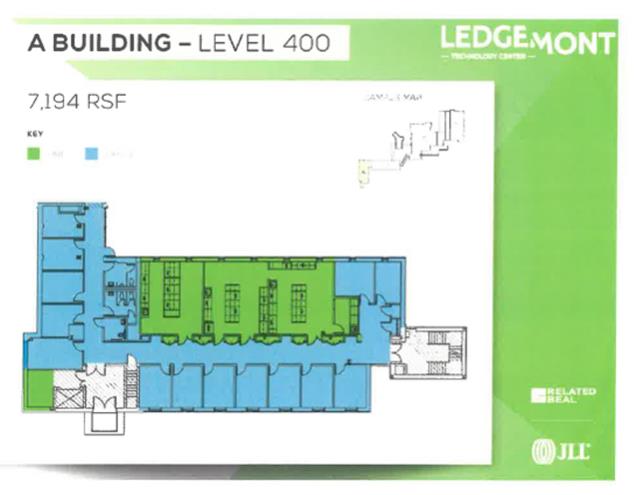
9.04. Environmental Substances. “Environmental Law(s)” means all statutes, laws, rules, regulations, codes, ordinances, standards, guidelines, authorizations and orders of federal, state and local public authorities pertaining to any of the Environmental Substances or to environmental compliance, contamination, cleanup or disclosures of any release or threat of release to the environment, of any hazardous, biological, chemical, radioactive or toxic substances, wastes or materials, any pollutants or contaminants that are included under or regulated by any municipal, county, state or federal statutes, laws, rules, regulations, codes, ordinances, standards, guidelines, authorizations or orders, including, without limitation, the Toxic Substances Control Act, 15 U.S.C. § 2601, et seq.; the Clean Water Act, 33 U.S.C. § 1251, et seq.: the Clean Air Act, 42 U.S.C. § 7401, et seq.; the Safe Drinking Water Act, 42 U.S.C. § 300f-300j, et seq.; the Federal Water Pollution Control Act, 33 U.S.C. § 1321, et seq.; the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act of 1980, 42 U.S.C. Section 9601 et seq.; the Federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, 42 U.S.C. Section 6901 et seq.; the Massachusetts Hazardous Waste Management Act, as amended, M.G.L. Chapter 21C, and the Massachusetts Oil and Hazardous Material Release Prevention Act, as amended, M.G.L., Chapter 21E, as any of the same are from time to time amended, and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder, and any judicial or administrative interpretation thereof, including any judicial or administrative orders or judgments, and all other federal, state and local statutes, laws, rules, regulations, codes, ordinances, standards, guidelines, authorizations and orders regulating the generation, storage, containment or disposal of any Environmental Substances, including, but not limited to, those relating to lead paint, radon gas, asbestos, storage and disposal of oil, biological, chemical, radioactive and hazardous wastes, substances and materials, and underground and above ground oil storage tanks; and any amendments, modifications or supplements of any of the foregoing.
“Environmental Substances” means, but shall not be limited to, any hazardous substances, hazardous waste, environmental, biological, chemical, radioactive substances, oil, petroleum products and any waste or substance, which because of its quantitative concentration, chemical, biological, radioactive, flammable, explosive, infectious or other characteristics, constitutes or may reasonably be expected to constitute or contribute to a danger or hazard to public health, safety or welfare or to the environment, or that would trigger any employee or community “right-to-know” requirements adopted by any federal, state or local governing or regulatory body, or for which any such body has adopted any requirements for the preparation or distribution of a materials safety data sheet (“MSDS”), including, without limitation, any asbestos (whether or not friable) and any asbestos- containing materials, lead paint, waste oils, solvents and chlorinated oils, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), toxic metals, etchants, pickling and plating wastes, explosives, reactive metals and compounds, pesticides, herbicides, radon gas, urea formaldehyde foam insulation and chemical, biological and radioactive wastes, or any other similar materials that are mentioned under or regulated by any Environmental Law; and the regulations adopted under these acts, and including any other products or materials subsequently found by an authority of competent jurisdiction to have adverse effects on the environment or the health and safety of persons.
-23-