UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(D) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017
or
☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(D) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 001-37794
Hilton Grand Vacations Inc.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter)
Delaware | 81-2545345 |
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
6355 MetroWest Boulevard, Suite 180, Orlando, Florida | 32835 |
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s Telephone Number, Including Area Code (407) 613-3100
(Former Name, Former Address, and Former Fiscal Year, if Changed Since Last Report)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
(Title of Class) | (Name of each exchange on which registered) |
Common Stock, $0.01 par value per share | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirement for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large Accelerated Filer | ☒ | Accelerated Filer | ☐ |
Non-Accelerated Filer | ☐ | Smaller Reporting Company | ☐ |
Emerging Growth Company | ☐ | | |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). ☐ Yes ☒ No
As of June 30, 2017, the aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was $2,471 million (based on the closing sale price of the common stock on that date on the New York Stock Exchange).
There were 99,251,898 shares of the registrant’s Common Stock outstanding as of February 23, 2018.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
The registrant has incorporated by reference into Part III of this report certain portions of its proxy statement for its 2018 annual meeting of stockholders, which is expected to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after the end of the registrant’s fiscal year ended December 31, 2017.
HILTON GRAND VACATIONS INC.
FORM 10-K TABLE OF CONTENTS
YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2017
PART I
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). These forward-looking statements are based on management’s beliefs, expectations and assumptions and information currently available to management, and are subject to risks and uncertainties. Actual results could differ materially because of factors such as: inherent business, financial and operating risks of the timeshare industry; adverse economic or market conditions that may affect the purchasing and vacationing decisions of consumers or otherwise harm our business; intense competition in the timeshare industry, which could lead to lower revenue or operating margins; the termination of material fee-for-service agreements with third parties; the ability of the Company to manage risks associated with our international activities, including complying with laws and regulations affecting our international operations; exposure to increased economic and operational uncertainties from expanding global operations, including the effects of foreign currency exchange; potential liability under anti-corruption and other laws resulting from our global operations; changes in tax rates and exposure to additional tax liabilities; the impact of future changes in legislation, regulations or accounting pronouncements; acquisitions, joint ventures, and strategic alliances that that may not result in expected benefits and that may have an adverse effect on our business; our dependence on development activities to secure inventory; cyber-attacks and security vulnerabilities that could lead to reduced revenue, increased costs, liability claims, or harm to our reputation or competitive position; disclosure of personal data that could cause liability and harm to our reputation; abuse of our advertising or social platforms that may harm our reputation or user engagement; outages, data losses, and disruptions of our online services; claims against us that may result in adverse outcomes in legal disputes; risks associated with our debt agreements and instruments, including variable interest rates, operating and financial restrictions, and our ability to service our indebtedness; the continued service and availability of key executives and employees; and catastrophic events or geo-political conditions that may disrupt our business. Forward-looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts and can be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology such as the words “outlook,” “believe,” “expect,” “potential,” “continues,” “may,” “will,” “should,” “could,” “seeks,” “approximately,” “projects,” predicts,” “intends,” “plans,” “estimates,” “anticipates” or the negative version of these words or other comparable words.
You should not put undue reliance on any forward-looking statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The risk factors discussed in “Part I—Item 1A. Risk Factors” could cause our results to differ materially from those expressed in forward-looking statements. There may be other risks and uncertainties that we are unable to predict at this time or that we currently do not expect to have a material adverse effect on our business. Any such risks could cause our results to differ materially from those expressed in forward-looking statements. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or review any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise, except as required by law.
Terms Used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K
Except where the context requires otherwise, references in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to “Hilton Grand Vacations,” “HGV,” “the Company,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to Hilton Grand Vacations Inc., together with its consolidated subsidiaries. Except where the context requires otherwise, references to our “properties” and “units” refer to the timeshare properties managed and owned. Of these resorts and units, a portion is directly owned by us or joint ventures in which we have an interest and the remaining resorts and units are owned by our third-party owners.
Reference to “Adjusted EBITDA” means earnings before interest expense (excluding interest expense on non-recourse debt), taxes and depreciation and amortization or “EBITDA,” further adjusted to exclude certain items. Refer to “Part II—Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Key Business and Financial Metrics Used by Management” for further discussion of these financial metrics.
1
Our History
Our history dates to 1992 with the joint venture between Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. (“Hilton”) and with Grand Vacations, Limited. In 1996, Hilton Grand Vacations became a wholly owned subsidiary of Hilton. During the ensuing years, we expanded our operations and established a track record of innovation in our industry. Unlike the broader timeshare industry, which experienced a contraction in 2008 and 2009 as a result of the overall economic recession, we were able to grow contract sales during the industry downturn and have continued to deliver contract sales growth in each period since, driven by our continued focus on marketing and sales activities, our strong development margins, large-market distribution model, synergies with Hilton, commitment to new owner transactions and lean organizational structure.
Our Business
We are a rapidly growing timeshare company that markets and sells vacation ownership intervals (“VOIs”), manages resorts in top leisure and urban destinations, and operates a points-based vacation club. As of December 31, 2017, we have 48 resorts, representing 8,102 units, are located in iconic vacation destinations such as the Hawaiian Islands, New York City, Orlando and Las Vegas, and feature spacious, condominium-style accommodations with superior amenities and quality service. As of December 31, 2017, we have approximately 288,000 Hilton Grand Vacations Club (the “Club”) members. Club members have the flexibility to exchange their VOIs for stays at any Hilton Grand Vacations resort or any property in the Hilton system of 14 industry-leading brands across more than 5,000 properties, as well as numerous experiential vacation options, such as cruises and guided tours.
Our compelling VOI product allows customers to advance purchase a lifetime of vacations. Because our VOI owners generally purchase only the vacation time they intend to use each year, they are able to efficiently split the full cost of owning and maintaining a vacation residence with other owners. Our customers also benefit from the high-quality amenities and service at our Hilton-branded resorts. Furthermore, our points-based platform offers members tremendous flexibility, enabling us to more effectively adapt to their changing vacation needs over time. Building on the strength of that platform, we continuously seek new ways to add value to our Club membership, including enhanced product offerings, greater geographic distribution, broader exchange networks and further technological innovation, all of which drive better, more personalized vacation experiences and guest satisfaction.
As innovators in the timeshare business, we have successfully transformed from a highly capital-intensive business to a capital-efficient model by pursuing an inventory strategy focused on fee-for-service and just-in-time inventory acquisition.
Recent Events
On October 13, 2017, we acquired the remaining unsold inventory at an 83-unit, ski-in mountain lodge in Park City, Utah, known as “The Sunrise Lodge, a Hilton Grand Vacations Club.” Prior to the acquisition, we were providing marketing, sales and resort management services to the seller, Sunrise Park City, LLC, under a fee-for-service agreement.
On November 13, 2017, we entered into an agreement with Mori Trust to construct a new mixed-used development on Sesokojima Island, Okinawa in Japan, which will be our first timeshare project in Japan. The new-build development, to be constructed by Mori Trust, will comprise a 132-unit timeshare resort that will be owned and managed by us, as well as a 300-room hotel that will be owned by Mori Trust and managed by Hilton. The hotel component is set to open in 2020, and the timeshare resort is expected to commence operations in 2021. Subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions and project milestones, we expect to make an aggregate investment of up to approximately $187 million in phases over four years commencing in 2021.
2
Our Reportable Segments
We operate our business across two segments: (1) real estate sales and financing; and (2) resort operations and club management. For more information regarding our segments, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and Note 19: Business Segments in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Our real estate sales and financing segment generates revenue from:
| • | VOI Sales—We sell our owned inventory and, through our fee-for-service agreements, we sell VOIs on behalf of third-party developers using the Hilton Grand Vacations brand in exchange for sales, marketing and brand fees. Under these agreements, we earn commission fees based on a percentage of total interval sales. See “—Inventory and Development Activities” and “—Marketing and Sales Activities” below for further information. |
| • | Financing—We provide consumer financing, which includes interest income generated from the origination of consumer loans to members to finance their purchase of VOIs owned by us. We also generate fee revenue from servicing the loans provided by third-party developers to purchasers of their VOIs. See “—Financing Activities” below for information regarding our consumer financing activities. |
Our resort operations and club management segment generates revenue from:
| • | Resort Management—Our resort management services primarily consist of operating properties under management agreements for the benefit of homeowners’ association (“HOA”s) of VOI owners at both our resorts and those owned by third parties. Our management agreements with HOAs provide for a cost-plus management fee, which means we generally earn a fee equal to 10 percent to 15 percent of the costs to operate the applicable resort. We also earn revenue from retail and spa outlets at our timeshare properties. See “—Resort and Club Management Activities” below for information regarding our resort management activities. |
| • | Club Management—We manage the Hilton Grand Vacations Club and the Hilton Club which operates for VOI owners at the Hilton New York and The District, our new resort in Washington D.C. (“The District”), receiving activation fees, annual dues and transaction fees from member exchanges for other vacation products. |
| • | Rental of Available Inventory—We generate rental revenue from unit rentals of unsold inventory and inventory made available due to ownership exchanges through our Club programs. This allows us to utilize otherwise unoccupied inventory to generate additional revenues. We also earn fee revenue from the rental of inventory owned by third parties. See “—Resort and Club Management Activities” below for further information. |
Other than the United States, there were no countries that individually represented more than 10 percent of total revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Our Products
Our primary products are fee-simple VOIs deeded in perpetuity, developed or acquired by us or by third parties. This ownership interest is an interest in real estate equivalent to annual usage rights, generally for one week, at the timeshare property where the VOI is purchased. Each Club property provides a distinctive setting, while signature elements remain consistent, such as high-quality guest service, spacious units and extensive on-property amenities. Most resorts feature studio to three-bedroom condominium-style accommodations and amenities such as full kitchens, in-unit washers and dryers, spas and kids’ clubs. Our timeshare properties are relatively concentrated in significant tourist markets, including Florida, Hawaii, Nevada, New York, Washington D.C. and South Carolina.
In addition, VOI purchasers are enrolled in our flexible, points-based Hilton Grand Vacations Club exchange program. This gives a member an annual allotment of Club points based on the value of the owned interest. Club points can be used for a priority reservation period at the home resort where a member’s VOI is deeded, and exchanged for a variety of vacation options, including stays at any Hilton Grand Vacations resort, conversion to
3
Hilton Honors® points for stays at the more than 5,000 Hilton-branded hotels and resorts, reservations for experiential travel such as cruises and guided tours, and stays at more than 4,300 resorts included in the RCI vacation exchange network. Our members also have the flexibility to choose when they will take advantage of their annual usage rights and have the option to split their time over the year. All members pay activation fees, annual dues and certain transaction fees depending on their exchange of Club points.
Inventory and Development Activities
We secure VOI inventory by developing or acquiring resorts in strategic markets, building additional phases at our existing resorts, re-acquiring inventory in the open market and sourcing inventory from third-party developers through fee-for-service and just-in-time transactions.
Our development activities involving the acquisition of real estate are followed by construction or renovation to create individual vacation ownership units. The development and construction of the units require a large upfront investment of capital and can take several years to complete in the case of a ground-up project. This investment cannot be recovered until the individual VOIs are sold to purchasers which can take several years. Traditionally, timeshare operators have funded 100 percent of the investment necessary to acquire land and construct timeshare properties.
We source VOIs through fee-for-service agreements with third-party developers. These agreements enable us to generate fees from the marketing and sale of Hilton-branded VOIs and Club memberships and from the management of the timeshare properties without requiring us to fund up-front acquisition and construction costs or incur unsold inventory maintenance costs. The capital investment we make in connection with these projects is typically limited to the cost of constructing our on-site sales centers. In just-in-time transactions, we acquire and sell inventory in transactions that are designed to closely correlate the timing of our acquisition of inventory with our sale of that inventory to purchasers. We refer to fee-for-service transactions and just-in-time sales as “capital-efficient transactions.” Over time, these capital-efficient transactions have evolved from sourcing inventory from distressed properties to sourcing from new construction projects. For the year ended December 31, 2017, sales from fee-for-service, just-in-time and developed inventory sources were 54 percent, 20 percent and 26 percent, respectively, of contract sales. Based on our 2017 sales pace, we have access to approximately five years of future inventory, with capital efficient arrangements representing approximately 89 percent of that supply. Our fee-for-service sales generally improve returns on invested capital and liquidity, while sales of owned inventory typically result in a greater contribution to the profitability of our real estate sales and financing segment. To maximize both returns on invested capital and earnings growth, we plan to sell a balanced mix of fee-for-service and owned inventory.
Owners can generally offer their VOIs for resale on the secondary market, which can create pricing pressure on the sale of developer inventory. Given the structure of our products, owners who purchase VOIs on the secondary market will also become Club members and will be responsible for paying annual Club fees, annual maintenance fees, property taxes and any assessments that are levied by the relevant HOA. While we do not have an obligation to repurchase intervals previously sold, most of our VOIs provide us with a right of first refusal on secondary market sales. We monitor sales that occur in the secondary market and exercise our right of first refusal in certain cases.
Marketing and Sales Activities
Our marketing and sales activities are based on targeted direct marketing and a highly personalized sales approach. We use targeted direct marketing to reach potential members who are identified as having the financial ability to pay for our products and have an affinity with Hilton and are frequent leisure travelers.
We sell our vacation ownership products under the Hilton Grand Vacations brand primarily through our distribution network of both in-market and off-site sales centers. Our products are currently marketed for sale throughout the United States and the Asia-Pacific region. We operate sales distribution centers in major markets and popular leisure destinations with year-round demand and a history of being a friendly environment for vacation ownership. We have sales distribution centers in Las Vegas, Myrtle Beach, Hilton Head, New York, Washington, D.C., Orlando, Park City, Oahu, Waikoloa and Japan.
4
Our Hilton Grand Vacations sales tours are designed to provide potential members with an overview of our company and our products, as well as a customized presentation to explain how our products can meet their vacationing needs. Our sales centers use proprietary sales technology to deliver a highly transparent and customized sales approach. Consumers place a great deal of trust in the Hilton brand and we believe that preserving that trust is essential. We hire our sales associates using an assessment-based, candidate screening system, which is a proprietary tool we use to uphold our selection criteria. Once hired, we emphasize training, professionalism and product knowledge, and our sales associates receive significant product and sales training before interacting with potential members. Most U.S.-based sales associates are licensed real estate agents and a real estate broker is involved with each sales center. We manage our sales associates’ consistency of presentation and professionalism using a variety of sales tools and technology and through a post-presentation survey of our tour guests that measures many aspects of each guest’s interaction with us. We do not tolerate sales activities that are not consistent with our focus on treating members and guests with the highest degree of respect.
Financing Activities
We originate loans for members purchasing our owned inventory who qualify according to our credit criteria. We generate interest income from the spread between the revenue generated on loans originated less our costs to fund and service those loans. We also earn fee revenue from servicing our own portfolio and the loans provided by third-party developers of our fee-for-service projects to purchasers of their VOIs.
We offer a wide array of financing options to members purchasing our VOIs. Our loans are collateralized by the underlying VOIs and are generally structured as ten-year, fully-amortizing loans that bear a fixed interest rate typically ranging from 9 percent to 18 percent per annum. In 2017, 65 percent of our sales were to customers who financed part of their purchase. The interest rate on our loans is determined by, among other factors, the amount of the down payment, the borrower’s credit profile and the loan term. Prepayment is permitted without penalty. As of December 31, 2017, the average loan outstanding was approximately $21 thousand with a weighted average interest rate of 12.2 percent.
As loan payments are made, the nature of these fully amortizing loans establishes an increasing level of owner financial commitment in their purchase which reduces the likelihood of default. When a member defaults, we ultimately return their VOI to inventory for resale, and that member no longer participates in our network.
We have a timeshare warehouse facility and periodically securitize timeshare financing receivables we originate in connection with the sale of VOIs to monetize receivables and achieve an efficient return on capital and manage our working capital needs.
Timeshare Financing Receivables Origination
In underwriting each loan, we obtain a credit application and review the application for completeness. We require a minimum down payment of 10 percent of the purchase price on all sales of VOIs. For U.S. and Canadian purchasers seeking financing, which represented 86 percent of the individuals we provided financing to over the last three years, we apply the credit evaluation score methodology developed by the Fair Isaac Corporation (“FICO”) to credit files compiled and maintained by Experian and Equifax. Higher credit scores equate to lower credit risk and lower credit scores equate to higher credit risk. Over the last three years, the weighted average FICO score for new loans to U.S. and Canadian borrowers at the time of origination was 742 (out of a maximum potential score of 850). For non-North American purchasers seeking financing, consisting principally of purchasers in Japan, we generally observe that these borrowers have experienced default rates comparable to U.S. and Canadian borrowers within the 725 to 774 FICO score band.
Our underwriting standards are influenced by the changing economic and financial market conditions. We have the ability to modify our down payment requirements and credit thresholds in the face of stronger or weaker market conditions. Our underwriting standards have resulted in a strong, well-seasoned consumer loan portfolio. As of December 31, 2017, our portfolio had a balance of approximately $1.2 billion with over 57,000 loans and exhibited the following characteristics:
Weighted Average Original Length of Loan: 9.9 years
Weighted Average Remaining Length of Loan: 7.7 years
5
Over 30 days past due not in default: 2.1%
Liquidity
We finance our working capital needs in part by borrowing against timeshare financing receivables. In general, we seek to use the majority of our financed VOI sales as collateral to borrow against the Timeshare Facility and subsequently transfer those loans into a term securitization after the loans have seasoned and an appropriately sized portfolio has been assembled. We target securitizations that range in size from $200 million to $400 million and we expect the timing of future securitizations will depend on our anticipated sales volume and capital needs. The strong performance of our outstanding loan securitizations demonstrates that loans originated by us are well regarded for their performance in the securitization market. In the future, we expect to regularly access the term securitization market, replenishing capacity on our Timeshare Facility in the process.
Loan Portfolio Servicing
We have a skilled, integrated consumer finance team. This team is responsible for payment processing and loan servicing, collections and default recovery and portfolio reporting and analytics. Accounts more than 30 days past due are deemed delinquent. We reserve for all loans based on our static pool method. A loan that is more than 120 days past due is reserved at 100 percent the following month and is delivered to the loss mitigation team that will make arrangements for any remaining outstanding payments or recommend recovery through a deed-in-lieu of foreclosure or foreclosure. In the deed-in-lieu of foreclosure process, the member deeds the VOI back to us. For domestic owners, this process varies from state to state and typically takes approximately 60 to 120 days, after which time we are able to resell the foreclosed VOI.
We monitor numerous metrics including collection rates, defaults and bankruptcies. Our consumer finance team also is responsible for selecting and processing loans pledged or to be pledged in our securitizations and preparing monthly servicing reports.
Resort and Club Management Activities
Resort Management
Prior to the initiation of VOI sales at a timeshare resort developed by us or by a third party with whom we have entered into a fee-for-service agreement, we enter into a management agreement with the relevant HOA. Each of the HOAs is governed by a board of directors comprising owner or developer representatives that are charged with ensuring that the resorts are well-maintained and financially stable. Our services include day-to-day operations of the resorts, maintenance of the resorts, preparation of reports, budgets and projections and employee training and oversight. Our HOA management agreements provide for a cost-plus management fee, which means we generally earn a fee equal to 10 percent to 15 percent of the costs to operate the applicable resort. As a result, the fees we earn are highly predictable, unlike traditional revenue-based hotel management fees, our management fees generally are unaffected by changes in rental rate or occupancy. Further, because maintenance fees are paid annually by owners, our management fees are recurring and less volatile than hotel management fees. We also are reimbursed for the costs incurred to perform our services, principally related to personnel providing on-site services. The original term of our management agreements is typically governed by state timeshare laws and ranges from three to five years. The agreements generally are subject to automatic renewal for one- to three-year periods unless either party provides advance notice of termination before the expiration of the term. Since our inception in 1992, none of the management agreements relating to our developed or fee-for-service properties have been terminated or lapsed.
To fund resort operations, owners are assessed an annual maintenance fee, which includes our management fee. In 2017, HOAs collected approximately $359 million in maintenance fees, including our applicable management fees. Because these funds are collected early in the year, we have substantial visibility and reliability of collection. These fees represent each owner’s allocable share of the management fee and the costs of operating and maintaining the resorts, which generally includes personnel, property taxes, insurance, a capital asset reserve to fund refurbishment and other related costs. If a VOI owner defaults on payment of its maintenance fees and there is no lien against the mortgage note, the HOA has the right to recover the defaulting owner’s VOI. As a service to HOAs at our owned resorts, subject to our inventory needs, we have the ability to reduce the bad debt expense at the HOAs
6
by assuming the defaulted owner’s obligations in exchange for an agreed purchase price. We are then able to resell those VOIs through our normal distribution channels.
A portion of the annual maintenance fees collected from owners each year is set aside for property renovations. The renovations funded by these fees enable HOAs to keep properties modern, which helps the properties consistently receive the highest quality assurance scores across the Hilton brands. HOAs engage an independent consulting firm to compile a reserve study. Typically, HOAs budget the reserve study to target property renovations on a six- and 12-year cycle. HOAs generally replace soft goods every six years and hard goods every 12 years. These reserves also benefit our members by limiting the risk of special assessments and steep increases in maintenance fees due to deferred capital expenditures.
Club Management
We also manage and operate the points-based Hilton Grand Vacations Club and Hilton Club exchange programs, which provided exclusive exchange, leisure travel and reservation services to approximately 288,000 members as of December 31, 2017. When an owner purchases a VOI, he or she is enrolled in the Club and allotted a number of points that represent his or her ownership interest and allow the member to exchange his or her annual usage rights for a number of vacation and travel options available through the club. The Hilton Club operates at the Hilton New York and the The District for its VOI owners, who also enjoy exchange benefits with the Hilton Grand Vacations Club. In addition to an annual membership fee, club members pay incremental fees depending on the type of exchange they choose within the club system.
Rental of Available Inventory
We rent unsold owned and fee-for-service VOI inventory and inventory made available due to ownership exchanges through our Club programs. By using our website, Hilton’s websites and other direct booking channels to rent available inventory, we are able to reach potential new members that may already have an affinity for and loyalty to the Hilton brands and introduce them to our products. Inventory rentals allow us to utilize otherwise unoccupied inventory to generate additional revenues and provision of ancillary services. We earn a fee from rentals of third-party inventory.
Competition
The timeshare industry has historically been highly competitive and comprised a number of national and regional companies that develop, finance and operate timeshare properties.
Our timeshare business competes with other timeshare developers for sales of VOIs based principally on location, quality of accommodations, price, service levels and amenities, financing terms, quality of service, terms of property use, reservation systems, flexibility for members to exchange into time at other timeshare properties or other travel rewards, including access to hotel loyalty programs, as well as brand name recognition and reputation. We also compete for property acquisitions and partnerships with entities that have similar investment objectives as we do. There is also significant competition for talent at all levels within the industry, in particular for sales and management. Our primary competitors in the timeshare space include Marriott Vacations Worldwide, Wyndham Vacation Ownership, Vistana Signature Experiences, Disney Vacation Club, Hyatt Vacation Ownership, Holiday Inn Club Vacations, Bluegreen Vacations and Diamond Resorts International.
In addition, our timeshare business competes with other entities engaged in the leisure and vacation industry, including resorts, hotels, cruises and other accommodation alternatives, such as condominium and single-family home rentals. We also compete with home and apartment sharing services that operate websites that market available privately owned residential properties that can be rented on a nightly, weekly or monthly basis. In certain markets, we compete with established independent timeshare operators, and it is possible that other potential competitors may develop properties near our current resort locations. In addition, we face competition from other timeshare management companies in the management of resorts on behalf of owners on the basis of quality, cost, types of services offered and relationship.
Recent and potential future consolidation in the highly fragmented timeshare industry may increase competition. For example, Interval Leisure Group, Inc., which operates the Interval International exchange program,
7
acquired Hyatt Residence Club in October 2014 and in May 2016 acquired the timeshare operations of Starwood Hotels & Resorts Worldwide, Inc. (which includes the use of Westin and Sheraton brands for timeshare purposes), known as Vistana Signature Experiences, Inc. Diamond Resorts International, Inc. completed the acquisition of the timeshare business of Gold Key Resorts in October 2015 and completed the acquisition of the timeshare business of Intrawest Resort Club Group in January 2016. Consolidation may create competitors that enjoy significant advantages resulting from, among other things, a lower cost of, and greater access to, capital and enhanced operating efficiencies.
We generally do not face competition in our consumer financing business to finance sales of our VOIs. We do face competition from financial institutions providing other forms of consumer credit, which may lead to full or partial prepayment of our timeshare financing receivables.
Seasonality and Cyclicality
We experience modest seasonality in timeshare sales at certain resorts, with stronger revenue generation during traditional vacation periods for those locations. Our business is moderately cyclical as the demand for VOIs is affected by the availability and cost of financing for purchases of VOIs, as well as general economic conditions and the relative health of the travel industry and housing market.
Intellectual Property
In connection with the spin-off, we entered into a license agreement with Hilton which grants us the right to use certain Hilton-branded trademarks, trade names and related intellectual property in our business for the term of the agreement. The license agreement provides us with, among other things, the exclusive license to design, build, manage and maintain existing and future timeshare resorts under the Hilton Grand Vacations brand throughout the world, subject to Hilton’s consent in certain circumstances. See “Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off—License Agreement” for more information. In the competitive industry in which we operate, trademarks, service marks, trade names and logos are very important to the marketing and sales of our products. We believe that the licensed marks and related intellectual property have come to represent the highest standards of quality, service and value to our members, guests, employees and those with whom we have business relationships. We have applied and will continue to apply to register our trademarks in markets in which we conduct business. We will enforce our rights against the unauthorized use of our intellectual property by third parties and otherwise protect our intellectual property through strategies and in jurisdictions we deem appropriate.
Government Regulation
Our business is subject to various international, national, federal, state and local laws, regulations and policies in jurisdictions in which we operate. Some laws, regulations and policies impact multiple areas of our business, such as securities, anti-discrimination, anti-fraud, data protection and security and anti-corruption and bribery laws and regulations or government economic sanctions, including applicable regulations under the U.S. Treasury’s Office of Foreign Asset Control and the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”). The FCPA and similar anti-corruption and bribery laws in other jurisdictions generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments to government officials for the purpose of obtaining or generating business. Other laws, regulations and policies primarily affect one of our areas of business: real estate development activities; marketing and sales activities; financial services activities; and resort management activities.
Real Estate Development Regulation
Our real estate development activities are regulated under a number of different timeshare, condominium and land sales disclosure statutes in many jurisdictions. We are generally subject to laws and regulations typically applicable to real estate development, subdivision and construction activities, such as laws relating to zoning, land use restrictions, environmental regulation, accessibility, title transfers, title insurance and taxation. In the United States, these include the Fair Housing Act and the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 and the Accessibility Guidelines promulgated thereunder, which we refer to collectively as (the “ADA”). In addition, we are subject to laws in some jurisdictions that impose liability on property developers for construction defects discovered or repairs made by future owners of property developed by the developer.
8
Marketing and Sales Regulation
Our marketing and sales activities are highly regulated. In addition to regulations implementing laws enacted specifically for the timeshare industry, a wide variety of laws and regulations govern our marketing and sales activities, including regulations implementing the USA PATRIOT Act, Foreign Investment In Real Property Tax Act, the Federal Interstate Land Sales Full Disclosure Act and fair housing statutes, U.S. Federal Trade Commission (“FTC”) and state “Little FTC Act” and other regulations governing unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices including unfair or deceptive trade practices and unfair competition, state attorney general regulations, anti-fraud laws, prize, gift and sweepstakes laws, real estate, title agency or insurance and other licensing or registration laws and regulations, anti-money laundering, consumer information privacy and security, breach notification, information sharing and telemarketing laws, home solicitation sales laws, tour operator laws, lodging certificate and seller of travel laws, securities laws, and other consumer protection laws.
We must obtain the approval of numerous governmental authorities for our marketing and sales activities. Changes in circumstances or applicable law may necessitate the application for or modification of existing approvals. In addition, many jurisdictions, including many jurisdictions in the United States, require that we file detailed registration or offering statements with regulatory authorities disclosing information regarding our VOIs, such as information concerning the intervals being offered, the project, resort or program to which the intervals relate, applicable timeshare plans, evidence of title, details regarding our business, the purchaser’s rights and obligations with respect to such intervals, and a description of the manner in which we intend to offer and advertise such intervals.
When we sell VOIs, local law grants the purchaser of a VOI the right to cancel a purchase contract during a specified rescission period following the later of the date the contract was signed or the date the purchaser received the last of the documents required to be provided by us.
In recent years, regulators in many jurisdictions have increased regulations and enforcement actions related to telemarketing operations, including requiring adherence to the federal Telephone Consumer Protection Act and “do not call” legislation. These measures have significantly increased the costs associated with telemarketing, in particular with respect to telemarketing to mobile numbers. While we continue to be subject to telemarketing risks and potential liability, we believe that our exposure to adverse effects from telemarketing legislation and enforcement is mitigated in some instances by the use of permission-based marketing in which we obtain permission to contact prospective purchasers in the future. We have also implemented procedures to comply with federal and state “do not call” regulations including subscribing to the federal do not call registry and certain state “do not call” registries as well as maintaining an internal “do not call” list.
Lending Regulation
Our lending activities are subject to a number of laws and regulations including those of applicable supervisory agencies such as, in the United States, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, the FTC, and the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network. These laws and regulations, some of which contain exceptions applicable to the timeshare industry, may include, among others, the Real Estate Settlement Procedures Act and Regulation X, the Truth In Lending Act and Regulation Z, the Federal Trade Commission Act, the Equal Credit Opportunity Act and Regulation B, the Fair Credit Reporting Act, the Fair Housing Act and implementing regulations, the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act, the Electronic Funds Transfer Act and Regulation E, unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices regulations and the Credit Practices rules, the USA PATRIOT Act, the Right to Financial Privacy Act, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, the Servicemember’s Civil Relief Act and the Bank Secrecy Act. Our lending activities are also subject to the laws and regulations of other jurisdictions, including, among others, laws and regulations related to consumer loans, retail installment contracts, mortgage lending, fair debt collection and credit reporting practices, consumer debt collection practices, mortgage disclosure, lender or mortgage loan originator licensing and registration and anti-money laundering.
Resort Management Regulation
Our resort management activities are subject to laws and regulations regarding community association management, public lodging, food and beverage services, liquor licensing, labor, employment, health care, health and safety, accessibility, discrimination, immigration, gaming and the environment (including climate change). In
9
addition, many jurisdictions in which we manage our resorts have statutory provisions that limit the duration of the initial and renewal terms of our management agreements for HOAs.
Environmental Matters
We are subject to certain requirements and potential liabilities under various U.S. federal, state and local and foreign environmental, health and safety laws and regulations and incur costs in complying with such requirements. The costs of complying with these requirements are generally covered by the HOAs that operate the affected resort property and are our responsibility for assets owned by us. These laws and regulations govern actions including air emissions, the use, storage and disposal of hazardous and toxic substances, and wastewater disposal. In addition to investigation and remediation liabilities that could arise under such laws, we may also face personal injury, property damage, fines or other claims by third parties concerning environmental compliance or contamination. We use and store hazardous and toxic substances, such as cleaning materials, pool chemicals, heating oil and fuel for back-up generators at some of our facilities, and we generate certain wastes in connection with our operations. Some of our properties include, and some of our future properties may include, older buildings, and some may have, or may historically have had, dry-cleaning facilities and underground storage tanks for heating oil and back-up generators. We have, from time to time, been responsible for investigating and remediating contamination at some of our facilities, such as contamination that has been discovered when we have removed underground storage tanks, and we could be held responsible for any contamination resulting from the disposal of wastes that we generate, including at locations where such wastes have been sent for disposal. In some cases, we may be entitled to indemnification from the party that caused the contamination pursuant to our management, construction or renovation agreements, but there can be no assurance that we would be able to recover all or any costs we incur in addressing such problems. From time to time, we may also be required to manage, abate, remove or contain mold, lead, asbestos-containing materials, radon gas or other hazardous conditions found in or on our properties. We have implemented an on-going operations and maintenance plan at each of our properties that seeks to identify and remediate these conditions as appropriate. Although we have incurred, and expect that we will continue to incur, costs relating to the investigation, identification and remediation of hazardous materials known or discovered to exist at our properties, those costs have not had, and are not expected to have, a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Employees
For more than 20 years, we have served guests on a global scale, with varied backgrounds and lifestyles, and developed personnel strategies designed to encourage effort, reward results, honor the best, celebrate careers and cultivate an inclusive work environment, including a Diversity and Inclusion Council and Team Member Resource Groups. Our talent management strategy includes ensuring that our employees feel motivated, valued and appreciated for their contributions with authentic recognition programs such as Catch Me at My Best, Daily Dividends, Team Member Appreciation Week and International Housekeeping Week, and 25 Grand, our 25th Anniversary celebration, which runs all year. Our ongoing training and development opportunities give our employees access to more than 3,000 learning programs, delivered in a variety of media to fit unique learning styles and schedules within the nonstop nature of our business. As of December 31, 2017, more than 8,000 people were employed at our timeshare and corporate locations around the world.
We pride ourselves on being an employer of choice, having won numerous awards that include:
| • | ARDA ACE Community Service Award in 2016; |
| • | ARDA ACE Employer of the Year in 2013; |
| • | top 100 places to work, Orlando Sentinel, from 2011 to 2015; |
| • | best places to work, Perspective Magazine, for 2012, 2014 and 2016; and |
| • | Southern Nevada Human Resources Association’s Best Places to Work in Southern Nevada® award for 2014 and 2015. |
As of December 31, 2017, less than 10 percent of our employees were covered by various collective bargaining agreements generally addressing pay rates, working hours, other terms and conditions of employment, certain employee benefits and orderly settlement of labor disputes.
10
Spin-Off Transactions
On February 26, 2016, Hilton announced that its Board of Directors had unanimously approved a plan to enhance long-term stockholder value by separating Hilton into three independent, publicly traded companies. Hilton subsequently executed tax-free spin-offs of HGV and Park Hotels & Resorts Inc. (“Park”), which holds a portfolio of Hilton’s owned and leased hotels and resorts.
On January 3, 2017, the spin-offs were completed, and we became a separate publicly-traded company. In connection with the completion of the spin-off, we entered into agreements with Hilton and other third parties, including licenses to use the Hilton brand, which did not exist historically. For more information regarding these agreements, see “—Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off.”
In connection with the spin-off, we entered into a registration rights agreement with Blackstone (which became effective upon the consummation of the spin-off) and a stockholders agreement with Blackstone which is substantially the same as Blackstone’s stockholders agreement with Hilton.
On October 24, 2016, Hilton, The Blackstone Group L.P. and its affiliates (“Blackstone”) and HNA Tourism Group Co., Ltd. (“HNA”) announced that affiliates of Blackstone agreed to sell to HNA 24,750,000 shares of common stock of Hilton, representing approximately 25 percent of the outstanding shares of common stock of Hilton, pursuant to a stock purchase agreement between HNA and Blackstone (the “Sale”). The Sale closed on March 15, 2017. The Sale included 25 percent of the shares of our common stock and Park’s common stock, which were received by Blackstone in the spin-off.
In connection with the Sale, we entered into a stockholders agreement and a registration rights agreement with HNA, which became effective upon the closing of the Sale. See “—Agreements with Blackstone and HNA—HNA Stockholders Agreement,” “—Blackstone Stockholders Agreement” and “—Registration Rights Agreements” for more detailed descriptions of these agreements.
Transactions with Blackstone Subsequent to Spin-off
On May 25, 2017, Blackstone filed a Registration Statement on Form S-1 and registered all of our common stock held by them. On June 14, 2017, Blackstone entered into an underwriting agreement with J.P. Morgan Securities LLC pursuant to which J.P. Morgan Securities LLC agreed to purchase from Blackstone 9,650,000 shares of our common stock at a price of $35.40 per share. The sale was completed on June 20, 2017. Subsequently, on September 25, 2017, Blackstone completed the sale of substantially all of the remaining shares of our common stock held by them to several institutional investors. We did not receive any proceeds from either of these sales. As a result of these sales, Blackstone holds only a nominal number of shares of our common stock.
In July 2017, we entered into an agreement with BRE Ace Holdings LLC, a Delaware limited liability company and an affiliate of Blackstone, and formed BRE Ace LLC. Pursuant to the agreement, we contributed $40 million in cash for a 25 percent interest in BRE Ace LLC, which owns a 1,201-key timeshare resort property and related operations, commonly known as “Elara, by Hilton Grand Vacations,” located in Las Vegas, Nevada.
Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off
This section summarizes the material agreements between us and Hilton (and, in certain cases, Park and certain affiliates of Blackstone and HNA) that govern the ongoing relationships between us and these parties which we have entered into in connection with the spin-off. Additional or modified agreements, arrangements and transactions, which would be negotiated at arm’s length, may be entered into between us and these parties in the future. These summaries are qualified in their entirety by reference to the full text of the applicable agreements, which are filed as exhibits hereto.
As of January 3, 2017 when the spin-off was completed, we and Hilton now operate independently, and neither has any ownership interest in the other. To govern certain ongoing relationships between us and Hilton and to
11
provide mechanisms for an orderly transition, we, Hilton and Park entered into agreements pursuant to which certain services and rights are provided for following the spin-off, and we, Hilton and Park will indemnify each other against certain liabilities arising from our respective businesses. We also entered into stockholders agreements and registration rights agreements with Blackstone and HNA. The following is a summary of the terms of the material agreements we have entered into with Hilton, Park, Blackstone and HNA.
The following summaries do not purport to be complete and are qualified in their entirety by reference to the full text of each agreement, which is incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K as Exhibits 2.1, 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.6, 10.7, 10.25, 10.26, 10.27, 10.28 and 10.29.
Distribution Agreement
We entered into a Distribution Agreement with Hilton and Park prior to the distribution of our shares of common stock to Hilton stockholders (the “Distribution Agreement”). The Distribution Agreement sets forth our agreements with Hilton and Park regarding the principal actions taken in connection with our spin-off from Hilton. It also sets forth other agreements that govern certain aspects of our relationship with Hilton and Park following the spin-off.
The Distribution Agreement provides for certain transfers of assets and assumptions of liabilities by each of us, Hilton and Park. The Distribution Agreement also provides for the settlement or extinguishment of certain liabilities and other obligations among us, Hilton and Park. In particular, the Distribution Agreement provides that, subject to the terms and conditions contained in the Distribution Agreement:
| • | all of the assets and liabilities (including whether accrued, contingent or otherwise, and subject to certain exceptions) associated with the timeshare business have been retained by or transferred to us or our subsidiaries; |
| • | all of the assets and liabilities (including whether accrued, contingent or otherwise, and subject to certain exceptions) associated with the separated real estate business have been retained by or transferred to Park or its subsidiaries; |
| • | all other assets and liabilities (including whether accrued, contingent or otherwise, and subject to certain exceptions) of Hilton have been retained by or transferred to Hilton or its subsidiaries; |
| • | liabilities (including whether accrued, contingent or otherwise) related to, arising out of or resulting from businesses of Hilton that were previously terminated or divested have been allocated among the parties to the extent formerly owned or managed by or associated with such parties or their respective businesses; |
| • | each of us and Park has assumed or retained any liabilities (including under applicable federal and state securities laws) relating to, arising out of or resulting from the filing of the Form 10 registration statement registering its respective common stock which was distributed by Hilton in the spin-off and from any disclosure documents that offered for sale securities in transactions related to the spin-off, subject to exceptions for certain information for which Hilton has retained liability; and |
| • | except as otherwise provided in the Distribution Agreement or any ancillary agreement, Hilton is generally be responsible for any costs or expenses incurred by each of us, Hilton and Park in connection with the transactions contemplated by the Distribution Agreement, including costs and expenses relating to legal counsel, financial advisors and accounting advisory work related to the distribution. |
In addition, notwithstanding the allocation described above, we, Park and Hilton agreed that losses related to certain contingent liabilities (and related costs and expenses) are to be apportioned among the parties according to fixed percentages of 65 percent, 26 percent, and nine percent for each of Hilton, Park, and us, respectively. Examples of shared contingent liabilities include uninsured losses arising from actions (including derivative actions) against current or former directors or officers of Hilton or its subsidiaries in respect of acts or omissions occurring prior to the completion of the spin-off, or against current or former directors or officers of any of Hilton, Park or us,
12
or of their respective subsidiaries, arising out of, in connection with, or otherwise relating to, the spin-off, subject to certain exceptions described in the Distribution Agreement. In addition, costs and expenses of, and indemnification obligations to, third party professional advisors arising out of the foregoing actions may also be subject to these provisions. Subject to certain limitations and exceptions, Hilton is generally vested with the exclusive management and control of all matters pertaining to any such shared contingent liabilities, including the prosecution of any claim and the conduct of any defense. The Distribution Agreement also provides for cross-indemnities that, except as otherwise provided in the Distribution Agreement, are principally designed to place financial responsibility for the obligations and liabilities of each business with the appropriate company.
To the extent that any transfers of assets or assumptions of liabilities contemplated by the Distribution Agreement were not consummated on or prior to the date of the distribution, the parties have agreed to cooperate with each other and use commercially reasonable efforts to effect such transfers or assumptions as promptly as practicable following the date of the distribution. In addition, each of the parties has agreed to cooperate with each other and use commercially reasonable efforts to take or to cause to be taken all actions, and to do, or to cause to be done, all things reasonably necessary under applicable law or contractual obligations to consummate and make effective the transactions contemplated by the Distribution Agreement and the ancillary agreements.
In general, neither we, Park nor Hilton made any representations or warranties regarding any assets or liabilities transferred or assumed, any consents or approvals that may have been required in connection with such transfers or assumptions, the value or freedom from any lien or other security interest of any assets transferred, the absence of any defenses relating to any claim of either party or the legal sufficiency of any conveyance documents, or any other matters. Except as expressly set forth in the Distribution Agreement or any ancillary agreement, all assets were transferred on an “as is,” “where is” basis.
The Distribution Agreement governs the rights and obligations of the parties regarding the distribution and certain actions that were required to occur prior to the distribution, such as the election of officers and directors and the adoption of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and bylaws. Prior to the distribution, we issued shares of our common stock to Hilton in a stock split, to the extent necessary to ensure that Hilton held the necessary number of shares of our common stock required to be distributed in the distribution. Hilton caused the distribution agent to distribute to Hilton stockholders that held shares of Hilton common stock as of the applicable record date all of the issued and outstanding shares of our common stock. Hilton had the sole and absolute discretion to determine (and change) the terms of, and whether to proceed with, the distribution and to determine the date of the distribution.
We, Park and Hilton agreed to broad releases pursuant to which we, Park and Hilton each released the others and certain related persons specified in the Distribution Agreement from any claims against any of them that arise out of or relate to acts or events occurring or failing to occur or alleged to occur or to have failed to occur or any conditions existing or alleged to have existed at or prior to the time of the distribution. These releases are subject to certain exceptions set forth in the Distribution Agreement and the ancillary agreements.
The Distribution Agreement provides for cross-indemnities that, except as otherwise provided in the Distribution Agreement, are principally designed to place financial responsibility for the obligations and liabilities of our business with us, financial responsibility for the obligations and liabilities of the business of Park with Park and financial responsibility for the obligations and liabilities of Hilton’s business with Hilton. Specifically, each party will, and will cause its subsidiaries and affiliates to, indemnify, defend and hold harmless each other party, its affiliates and subsidiaries and each of its officers, directors, employees and agents for any losses arising out of or otherwise in connection with:
| • | the liabilities or alleged liabilities each such party assumed or retained pursuant to the Distribution Agreement; and |
| • | any breach by such party of the Distribution Agreement or any ancillary agreement unless such ancillary agreement expressly provides for separate indemnification therein, in which case any such indemnification claims will be made thereunder. |
13
The amount of each party’s indemnification obligations is subject to reduction by any insurance proceeds received by the party being indemnified and by any proceeds received from a third party for indemnification for such liability. The Distribution Agreement also specifies procedures with respect to claims subject to indemnification and related matters. Indemnification with respect to taxes is governed solely by the Tax Matters Agreement.
In the event of any dispute arising out of the Distribution Agreement, the general counsels of the disputing parties, and/or such other representatives as such parties designate, will negotiate to resolve any disputes among such parties. If the disputing parties are unable to resolve the dispute in this manner within a specified period of time, as set forth in the Distribution Agreement, then unless agreed otherwise by such parties, the disputing parties will submit the dispute to mediation for an additional specified period of time, as set forth in the Distribution Agreement. If the disputing parties are unable to resolve the dispute in this manner, the dispute may be resolved through legal proceedings as set forth in the Distribution Agreement.
Other matters governed by the Distribution Agreement include access to financial and other information, intellectual property, confidentiality, access to and provision of records and treatment of outstanding guarantees and similar credit support.
License Agreement
Under our license arrangement with Hilton prior to the spin-off, we licensed the Hilton Grand Vacations brand and paid Hilton an annual fee based on a percentage of revenue for rights to operate under this brand. For the year ended December 31, 2017, we incurred license fee expense of $87 million. Under our Honors® program arrangement with Hilton prior to the spin-off, we purchased Hilton Honors® points from Hilton based on an estimated cost per point for the costs of future club exchanges. For the year ended December 31, 2017, we paid Hilton $59 million, respectively for Hilton Honors® points.
In connection with the spin-off, we entered into a license agreement with Hilton granting us the right to use certain Hilton trademarks and other intellectual property in our business. The license agreement grants us the exclusive right, for an initial term of 100 years, to use certain Hilton marks and intellectual property in our timeshare business.
Subject to the terms and conditions of the license agreement, Hilton has granted us the right to use the trademarks “Hilton Grand Vacations,” “HGV” and “Hilton Club” (collectively, the “Hilton Marks”) in connection with the current and future operation of a Hilton branded vacation ownership business (the “Licensed Business”). We have also received a license or right to use certain other Hilton-owned intellectual property, including promotional content and access to Hilton’s reservation system and property management software (collectively with the Hilton Marks, the “Hilton IP”). We also have the right to use Hilton’s loyalty program data and other customer information (“Hilton Data”) to promote the Licensed Business and for other internal business purposes, but may not disclose or sell such information to third parties without Hilton’s consent.
Subject to the following two sentences, Hilton will not compete or use the Hilton IP or Hilton Data in the vacation ownership business (or license others to do so) for the first 30 years of the term of the license agreement, and we may extend this exclusivity for additional 10-year terms if we achieve certain revenue targets in the last year of the initial 30-year term or any subsequent renewal term, or make a payment to cover any revenue shortfall, for a maximum of five such payments during any 10-year renewal term. If Hilton merges with or acquires a company that owns a vacation ownership business and a hotel business, Hilton shall use commercially reasonable efforts to allow us to acquire or manage the acquired vacation ownership business. If we do not do so, then after such acquisition by Hilton, notwithstanding the foregoing exclusivity, Hilton may use the Hilton IP, Hilton Data and Hilton’s loyalty program (but not the Hilton Marks) to allow such acquired vacation ownership business to compete with the Licensed Business for the remainder of the term of the license agreement.
The initial term of the license agreement will expire on December 31, 2116. After the initial term ends, we may continue to use the Hilton IP and Hilton Data on a non-exclusive basis for a “tail period” of 30 years in connection with products and projects that were using the foregoing rights, or were approved by Hilton for
14
development, when the term ended, provided that we continue to comply with the terms of the license agreement, including payment of royalty and other fees.
We pay a royalty fee of five percent of gross revenues to Hilton quarterly in arrears, as well as specified additional fees. Gross revenues include our gross sales for the initial sale or re-sale of interests in the Licensed Business (subject to certain HGV Club exceptions), property operations revenue, transient rental revenue and other certain revenues earned. We also owe Hilton an annual transition fee of $5 million for each of the first five years of the term and certain other fees and reimbursements. The license agreement contains customary requirements with respect to our record-keeping and Hilton’s audit rights.
We are required to comply with the Hilton brand standards applicable to the Licensed Business. Hilton has inspection and approval rights to monitor our compliance with these standards. Hilton brand standards include: construction and design brand standards; graphic standards for use of the Hilton IP; sales, service and operating standards; and quality assurance and customer satisfaction requirements.
During the term of the license agreement, we will participate in Hilton’s loyalty program, currently known as the Hilton Honors® program. We can purchase Hilton Honors® points at cost for the first 20 years of the term of the license agreement, and thereafter at the market rate (with a most favored nation provision, pursuant to which such market rate is no higher than the price paid by strategic partners that purchase a comparable volume of points annually on comparable business terms). All members of Hilton’s loyalty program have the right to redeem loyalty program points at our properties in the Licensed Business, consistent with the tiers and rules of Hilton’s current loyalty program. We can convert points associated with our own point-based reservations and exchange system into Hilton loyalty program points through an exchange program at a conversion rate to be determined by us. We may not participate in a loyalty program of a Hilton competitor in connection with the Licensed Business.
We are required to operate the Licensed Business in strict compliance with all of Hilton’s standards and guidelines and all applicable laws. We are responsible for obtaining and maintaining all necessary approvals, permits and licenses required and paying all taxes related to the Licensed Business. We may subcontract or delegate property-level, non-management functions, including housekeeping, security and maintenance, as long as we comply with Hilton’s standards and guidelines. Hilton has the right to enter our vacation ownership properties at any time without notice and additional permission from us in order to verify that we are complying with the license agreement and Hilton’s standards and guidelines.
We are required to comply with Hilton’s customer data privacy and security standards and protocols. We are required to notify Hilton immediately after discovering any actual or attempted circumstances that could compromise the security of our information technology systems. We are required to remedy any such breach at our own expense.
We are able to operate vacation ownership properties under other brands (with no royalty due to Hilton) if we do so without using any Hilton IP or Hilton Data and they are otherwise separate operations from the Licensed Business.
We are required to obtain Hilton’s consent to develop or operate any additional vacation ownership properties under the Hilton Marks (including on our own undeveloped parcels). Hilton may not unreasonably withhold its approval for these projects as long as they comply with existing law, do not involve a co-investor that is a competitor of Hilton or is of bad moral character, and are not reasonably likely to harm Hilton, the Licensed IP or the Hilton Data. Hilton has a right of first refusal if we want to sell an undeveloped parcel to a Hilton competitor.
We have entered into an agreement with Hilton that governs the transfer of calls from Hilton to us. Under this agreement, Hilton is required to use its reasonable best efforts to transfer calls to us at a level consistent with past practice prior to the spin-off for the first ten years. Hilton is required to provide the call transfer services at cost for the first 30 years and at market rates thereafter. We have entered into other agreements that govern other services that Hilton is required to provide us.
15
Under the license agreement, our right to use the Hilton Marks as a trade, corporate, d/b/a or similar name will automatically terminate if (i) the aggregate number of units of accommodation in our Licensed Business falls below two-thirds of the total number of units of accommodation in our entire vacation ownership business; (ii) we merge with or acquire control of the assets of Marriott International, Inc., Marriott Vacations Worldwide Corporation, Hyatt Hotels Corporation, Wyndham Worldwide Corporation and Interval Leisure Group, Inc. or their respective affiliates and we or they use their brands in any business after such acquisition; or (iii) we become an affiliate of another Hilton competitor.
Hilton has the right to terminate the license agreement as a whole if, among other things: (i) we file for bankruptcy or cease business operations; (ii) 25 percent or more of our Hilton-branded vacation ownership properties fail certain performance thresholds or the overall customer satisfaction score for all our Hilton-branded vacation ownership properties falls below a certain threshold level, and we do not promptly cure such failures; (iii) we operate the Licensed Business in a way that has a material adverse effect on Hilton; (iv) we fail to pay certain amounts due to Hilton (and in certain cases, do not promptly cure such failures); (v) we contest Hilton’s ownership of the Hilton IP or the Hilton Data; (vi) we merge with, consolidate with or are acquired by a competitor of Hilton; or (vii) we assign the agreement to a non-affiliate without Hilton’s consent.
Hilton also has the right to “deflag” (prevent use of any Hilton IP or Hilton Data at) any property in our Licensed Business in certain circumstances, including if (i) a $10 million or more final judgment is assessed against such property or a foreclosure suit is initiated against such property and not vacated; (ii) an ongoing threat or danger to public health or safety occurs at such property; (iii) such property fails to meet certain quality assurance system performance thresholds; or (iv) such property is not operated in compliance with the license agreement or Hilton’s other standards and agreements, and such breaches are not cured in accordance with the license agreement.
If we breach our obligations under the license agreement, Hilton may, in addition to terminating the license agreement, be entitled to (depending on the nature of the breach): seek injunctive relief and/or monetary damages; suspend our access to and terminate our rights to use Licensed IP and/or Hilton Data (other than the Hilton Marks and certain other content); or terminate our rights to use the Licensed IP (including the Hilton Marks) and Hilton Data at specific locations that are not in compliance with performance standards.
If the license agreement terminates due to our fault before the end of the term, we are required to cease use of the Hilton IP and Hilton Data according to a specified schedule. Hilton has the right to demand liquidated damages based upon its uncollected royalties and fees for the remainder of the term.
Hilton has registered certain of the Hilton Marks for vacation ownership services in jurisdictions in which we currently operate vacation ownership resorts and residential projects under the Hilton Marks. However, Hilton does not have affirmative trademark rights in the Hilton Marks in relation to every aspect of our business in every country around the world, and we, therefore, may not be able to use one or more of the Hilton Marks to expand various aspects of our business into one or more new countries. If we want to use a Hilton Mark in a country where it is not registered, we will have to seek Hilton’s consent, which may not be withheld if the new trademark would not reasonably be expected to harm or jeopardize the value, validity, reputation or goodwill of the Hilton Marks or subject Hilton to any risk of legal liability.
Unless we obtain Hilton’s prior written consent, we may not be able to: (i) merge with or acquire a Hilton competitor or a vacation ownership business that has entered into an operating agreement with a Hilton competitor; (ii) merge with or acquire a vacation ownership business together with a lodging business; or (iii) be acquired or combined with any entity other than an affiliate. We may acquire control of a business that is not a vacation ownership business or a lodging business without Hilton’s consent, but we are required to operate such business as a separate operation that does not use the Hilton IP or Hilton Data unless Hilton consents to such use. Without Hilton’s prior consent, we may not assign our rights under the license agreement, except to one our affiliates as part of an internal reorganization for tax or administrative purposes.
We are required to indemnify, defend and hold harmless Hilton from and against any claim or liability resulting from (i) third-party claims based on (ii) our breach of the license agreement; (iii) the operation of our vacation ownership properties; (iv) any use of the Hilton IP or Hilton Data in violation of the license agreement; or (v) claims based on any security breach of our systems and/or unauthorized use or disclosure of Hilton Data.
16
Employee Matters Agreement
We have entered into an Employee Matters Agreement with Hilton and Park that governs the respective rights, responsibilities and obligations of Hilton, Park and us after the spin-off with respect to transferred employees, defined benefit pension plans, defined contribution plans, non-qualified retirement plans, employee health and welfare benefit plans, incentive plans, equity-based awards, collective bargaining agreements and other employment, compensation and benefits-related matters (the “Employee Matters Agreement”). The Employee Matters Agreement provides for, among other things, the allocation and treatment of assets and liabilities arising out of incentive plans, retirement plans and employee health and welfare benefit plans in which our and Park’s employees participated prior to the spin-off, and continued participation by our and Park’s employees in certain of Hilton’s compensation and benefit plans for a specified period of time following the spin-off. Generally, other than with respect to certain specified compensation and benefit plans and liabilities, we and Park have assumed or retained sponsorship of, and the liabilities relating to, compensation and benefit plans and employee-related liabilities relating to its respective current and former employees. The Employee Matters Agreement also provides that then outstanding Hilton equity-based awards were equitably adjusted or converted into HGV or Park awards, as applicable, in connection with the spin-off. After the spin-off, our and Park’s employees no longer actively participate in Hilton’s benefit plans or programs (other than specified compensation and benefit plans), and we and Park have each established or will establish plans or programs for our and Park’s employees, respectively, as described in the Employee Matters Agreement. We and Park also have established or will establish or maintain plans and programs outside of the United States as may be required under applicable law or pursuant to the Employee Matters Agreement.
Tax Matters Agreement
We have entered into a Tax Matters Agreement with Hilton and Park that govern the respective rights, responsibilities and obligations of Hilton, Park and us after the spin-off with respect to tax liabilities and benefits, tax attributes, tax contests and other tax sharing regarding U.S. federal, state, local and foreign income taxes, other tax matters and related tax returns. Although binding between the parties, the Tax Matters Agreement is not binding on the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”). We and Park each will continue to have several liabilities with Hilton to the IRS for the consolidated U.S. federal income taxes of the Hilton consolidated group relating to the taxable periods in which we and Park were part of that group. The Tax Matters Agreement specifies the portion, if any, of this tax liability for which we and Park will bear responsibility, and each party has agreed to indemnify the other two parties against any amounts for which they are not responsible. The Tax Matters Agreement also provides special rules for allocating tax liabilities in the event that the spin-off is not tax-free. In general, under the Tax Matters Agreement, each party is responsible for any taxes imposed on Hilton that arise from the failure of the spin-off and certain related transactions to qualify as a tax-free transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Sections 355 and 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code, as applicable, and certain other relevant provisions of the Code, to the extent that the failure to qualify is attributable to actions taken by such party (or with respect to such party’s stock). The parties share responsibility, in accordance with sharing percentages of 65 percent for Hilton, 26 percent for Park, and nine percent for us, for any such taxes imposed on Hilton that are not attributable to actions taken by a party.
The Tax Matters Agreement also provides for certain covenants that may restrict our ability to issue equity and pursue strategic or other transactions that otherwise could maximize the value of our business, including, for two years after the spin-off:
| • | engaging in any transaction involving the acquisition of shares of our stock or in certain issuances of shares of our stock; |
| • | merging or consolidating with any other person or dissolving or liquidating in whole or in part; |
| • | selling or otherwise disposing of, or allowing the sale or other disposition of, more than 35 percent of our consolidated gross or net assets; or |
| • | repurchasing our shares, except in certain circumstances. |
17
These restrictions are generally inapplicable in the event that the IRS has granted a favorable ruling to us, Hilton or Park or in the event that we, Hilton or Park have received an opinion from a tax advisor, in either case to the effect that it can take such actions without adversely affecting the tax-free status of the spin-off and related transactions.
Transition Services Agreement
We have entered into a Transition Services Agreement with Hilton and Park under which Hilton or one of its affiliates provides us and Park with certain services for a limited time to help ensure an orderly transition following the spin-off (the “Transition Services Agreement”).
The services that Hilton has agreed to provide to us and Park under the Transition Services Agreement include certain finance, information technology, human resources and compensation, facilities, legal and compliance and other services. We and Park have agreed to pay Hilton for any such services utilized at agreed amounts as set forth in the Transition Services Agreement. In addition, for a specified term, we or Park and Hilton may mutually agree on additional services that were provided by Hilton prior to the completion of the spin-off at pricing based on market rates that are reasonably agreed to by the parties.
Agreements with Blackstone and HNA
HNA Stockholders Agreement
In connection with the Sale, we entered into a stockholders agreement with HNA (and with HNA Group Co., Ltd. for purposes of the standstill provision only) that became effective upon the closing of the Sale.
Under the HNA stockholders agreement, for so long as HNA beneficially owns at least 15 percent of our outstanding common stock, it will have the right to designate two directors to our board of directors, only one of which may be affiliated with HNA (but not its hospitality business) and the other of which must meet the independence standards of the NYSE with respect to our company and not have been, for two years, an employee, director or officer of, or consultant to, HNA or any of its affiliates. Each of HNA’s director designees must be reasonably satisfactory to our nominating and corporate governance committee. In addition, so long as HNA owns at least 20 percent of our outstanding common stock, HNA will have the right to designate an additional independent director to fill each third additional director seat above 10 directors; for example, if we were to increase the size of our board of directors in the future to 13, HNA would have the right to designate an independent director as the 13th member of the board of directors. HNA’s right to designate directors declines to one director when HNA’s ownership falls below 15 percent of our outstanding common stock and such right terminates when HNA’s ownership falls below five percent of our outstanding common stock, subject to certain exceptions. Each independent designee will be entitled to serve on at least one standing committee of the board of directors, as determined by the nominating and corporate governance committee.
Following the consummation of the Sale, we increased the size of our board of directors to ten members. Two members of our board of directors, Yasheng Huang and Kenneth Tai Lun Wong, were designated by HNA pursuant to the stockholders agreement.
The HNA stockholders agreement generally requires HNA to vote all of its shares in excess of 15 percent of our total outstanding shares in the same proportion as the shares owned by other stockholders are voted on all matters, except as follows: (i) in uncontested elections of directors, HNA is required to vote all of its shares either in favor of the board’s nominees or all of its shares in the same proportion as the shares owned by other stockholders are voted; (ii) in contested elections of directors, HNA is required to vote all of its shares in the same proportion as the shares owned by other stockholders are voted; (iii) for two years after the closing of the sale, in third-party acquisitions of our company in which both (x) shares of our common stock are exchanged for or are converted into the right to receive (A) solely cash or (B) a mixture of cash and stock of a person other than an HNA entity in which the value of the cash portion of the aggregate consideration is 60 percent or more of the value of the aggregate consideration and (y) the value of the consideration to be received per share of common stock is less than or equal to a reference price per share of our common stock calculated in accordance with the HNA stockholders agreement,
18
HNA may vote all of its shares as it chooses; (iv) for any acquisition of our company other than an acquisition described in (iii) above or an acquisition by HNA, HNA will vote all of its shares in excess of 15 percent of our total outstanding shares in proportion to the manner in which non-HNA holders vote their shares; and (v) in the case of any charter or bylaw amendment which adversely affects HNA disproportionally as compared to other stockholders, an issuance of more than 20 percent of our outstanding shares (other than for an acquisition) at a below-market price, or an acquisition of our company by HNA, HNA may vote all of its shares as it chooses. In a third-party tender offer, HNA will be required to tender its shares in excess of 15 percent of our total outstanding shares in the same proportion as shares held by non-HNA holders are tendered.
For two years after the closing of the Sale, the HNA stockholders agreement requires HNA to not transfer any shares of our common stock that it owns unless: (i) such transfer is approved in advance by a majority of the disinterested members of the board of directors or a duly-authorized committee thereof; (ii) such transfer is to an HNA affiliate, provided that such HNA affiliate agrees to be bound by the terms of the HNA stockholders agreement; such transfer is in connection with an acquisition approved by the board of directors; (iii) such transfer constitutes a tender into a tender or exchange offer commenced by us or any of our affiliates; or (iv) such transfer is in connection with a bona fide mortgage, encumbrance or pledge of capital stock to a financial institution in connection with a bona fide loan or debt transaction or enforcement thereunder. After two years, other than in an underwritten public offering, block trade or permitted transfer described above, HNA will not be permitted to transfer more than 4.9 percent of our total outstanding shares to any person or group, or any shares to certain of our competitors or, to the knowledge of HNA or its broker, a person or group who is a five percent stockholder or who would thereby become a five percent stockholder; in an underwritten public offering or a block trade, other than a permitted transfer described above, HNA will instruct the underwriter or broker not to transfer more than 4.9 percent of our total outstanding shares to any person or group or any shares to a five percent stockholder (unless the identity of the purchaser is not known to the underwriter or broker); and in a block trade, other than a permitted transfer described above, HNA will instruct its broker not to transfer shares to certain of our competitors (unless the identity of the purchaser is not known to HNA or its broker). In addition, if we propose to issue new equity securities for cash in an offering that is not an underwritten public offering or an offering pursuant to Rule 144A under the Securities Act, HNA will have a right of first refusal over its pro rata portion of such issuance, measured based on HNA’s ownership percentage (which shall be capped at 25 percent for purposes of the right of first refusal) in us at such time.
The HNA stockholders agreement requires HNA and its affiliates not to: (i) acquire, offer or agree to acquire, any beneficial interest in us, subject to certain exceptions; (ii) make any public announcement or public offer with respect to any merger, business combination or other similar transaction involving us (except when our board of directors recommends or approves such transaction); (iii) make or in any way participate in any “solicitation” of “proxies” to vote or seek to influence the voting of securities in a manner inconsistent with our board’s recommendation; (iv) seek election or removal of any director other than HNA designees or otherwise act, alone or in concert with others, to control or influence our company; (v) call a meeting of stockholders; (vi) participate in a “group” regarding our equity securities; (vii) act, alone or in concert with others, to seek to control or influence our management or policies; (viii) knowingly assist or encourage, or enter into any discussions or agreements with any third party, in connection with any of the foregoing; (ix) publicly disclose any intention, plan or arrangement inconsistent with the foregoing; provide any financing for a purchase of our equity securities or assets, subject to certain exceptions; or (x) take any actions that HNA knows or would reasonably be expected to know would require us to make a public announcement regarding the possibility of an acquisition. HNA will not be prohibited from: (a) transferring shares of our stock to HNA affiliates; (b) purchasing shares of our stock pursuant to its right of first refusal over its pro rata portion of newly issued equity securities; (c) making a non-public, confidential acquisition proposal to our board of directors; or (d) after a public announcement of a definitive agreement for the acquisition of our company by a third party, making a publicly announced alternative acquisition proposal for all of our outstanding shares, which, if a tender or exchange offer, must be on the same terms for all such shares and include a non-waivable condition that a majority of the shares held by non-HNA holders are tendered into such offer. To the extent HNA’s ownership percentage falls below 25 percent of our total outstanding shares (or a lower percentage that results from sales of shares by HNA) as a result of issuances by us, HNA may purchase our shares in the open market so as to maintain its ownership percentage at 25 percent (or such lower percentage that results from sales of shares by HNA).
Blackstone Stockholders Agreement
19
In connection with the spin-off, we entered into a stockholders agreement with Blackstone, pursuant to which Blackstone was entitled to designate a number of directors that varied depending on its level of ownership of our common stock. These provisions of the Blackstone stockholders’ agreement terminated as a result of the Sale and Blackstone’s other recent sales of substantially all of our common stock that it held. One member of our board of directors, Kenneth A. Caplan, was designated by Blackstone pursuant to the stockholders agreement prior to the sale by Blackstone of the shares of our common stock held by it.
Registration Rights Agreements
We previously entered into a registration rights agreement with Blackstone that became effective upon the completion of the spin-off. The Blackstone registration rights agreement provided Blackstone with customary “demand” and “piggyback” registration rights. The registration rights agreement also required us to pay certain expenses relating to such registrations and indemnify the registration rights holder against certain liabilities under the Securities Act. As a result of the sale during 2017 by Blackstone of substantially all of our common stock held by it, Blackstone holds only a nominal number of shares of our common stock.
In connection with the Sale, we also entered into a registration rights agreement with HNA that became effective upon the closing of the Sale. The HNA registration rights agreement provides that, beginning two years after the closing of the Sale, HNA will have customary “demand” and “piggyback” registration rights.
Tax Stockholders Agreement
We have entered into a stockholders agreement with Hilton and certain entities affiliated with Blackstone intended to preserve the tax-free status of the distributions in connection with the spin-off (the “Tax Stockholders Agreement”). The Tax Stockholders Agreement provides for certain covenants that may limit issuances or repurchases of our stock in excess of specified percentages, dispositions of our common stock by Blackstone, and transfers of interests in certain Blackstone entities that directly or indirectly own our common stock or the common stock of Hilton or Park. Additionally, the Tax Stockholders Agreement may limit issuances or repurchases of stock by Hilton in excess of specified percentages.
Where You Can Find More Information
Our website address is www.hgv.com. Information on our website is not incorporated by reference herein. We file reports with the SEC, including annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K, and certain amendments to these reports. Copies of these reports are available free of charge on our website as soon as reasonably practicable after we file the reports with the SEC. The SEC also maintains a website at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC. Additionally, you may read and copy any materials that we file with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549. You may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330.
We are subject to various risks that could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and stock price. You should carefully consider the risk factors discussed below, in addition to the other information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Further, other risks and uncertainties not presently known to management or that management currently deems less significant also may result in material and adverse effects on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and stock price. The risks below also include forward-looking information; and actual results and events may differ substantially from those discussed or highlighted in these forward-looking statements. See “Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Information.”
20
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
We are subject to the business, financial and operating risks inherent to the timeshare industry, any of which could reduce our revenues and limit opportunities for growth.
Our business is subject to a number of business, financial and operating risks inherent to the timeshare industry, including:
| • | significant competition from other timeshare businesses and hospitality providers in the markets in which we operate; |
| • | market and/or consumer perception of timeshare companies and the industry in general; |
| • | changes in operating costs, including energy, food, employee compensation and benefits and insurance; |
| • | increases in costs due to inflation or otherwise, including increases in our operating costs, that may not be fully offset by price and fee increases in our business; |
| • | changes in taxes and governmental regulations that influence or set wages, prices, interest rates or construction and maintenance procedures and costs; |
| • | the costs and administrative burdens associated with complying with applicable laws and regulations; |
| • | significant increases in cost of health care coverage for employees and potential government regulation with respect to health care coverage; |
| • | shortages of labor or labor disruptions; |
| • | increases in the use of third-party and competitor internet services to book hotel reservations, secure short-term lodging accommodations and market vacation rental properties; |
| • | the availability and cost of capital necessary for us and third-party developers with whom we do business to fund investments, capital expenditures and service debt obligations; |
| • | our ability to securitize the receivables that we originate in connection with VOI sales; |
| • | delays in or cancellations of planned or future development or refurbishment projects; |
| • | the financial condition of third-party developers with whom we do business; |
| • | relationships with third-party developers, our Club members and HOAs; |
| • | changes in desirability of geographic regions of our resorts and affiliated resorts, geographic concentration of our operations and shortages of desirable locations for development; |
| • | legal, business or regulatory issues unique to particular geographic locations that could increase the cost of or result in delays in entering into or expanding in those locations; |
| • | changes in the supply and demand for our products and services; |
| • | private resales of VOIs and the sale of VOIs in the secondary market; and |
| • | unlawful or deceptive third-party VOI resale or vacation package sales schemes. |
Any of these factors could increase our costs or limit or reduce the prices we are able to charge for our products and services or otherwise affect our ability to maintain existing properties, develop new properties or source VOI supply from third parties. As a result, any of these factors can reduce our revenues and limit opportunities for growth.
21
Macroeconomic and other factors beyond our control can adversely affect and reduce demand for our products and services.
Macroeconomic and other factors beyond our control can reduce demand for our products and services, including demand for timeshare properties. These factors include, but are not limited to:
| • | changes in general economic conditions, including low consumer confidence, unemployment levels and depressed real estate prices resulting from the severity and duration of any downturn in the U.S. or global economy; |
| • | war, political conditions or civil unrest, violence or terrorist activities or threats and heightened travel security measures instituted in response to these events; |
| • | the financial and general business condition of the travel industry; |
| • | statements, actions or interventions by governmental officials related to travel and the resulting negative public perception of such travel; |
| • | conditions that negatively shape public perception of travel, including travel-related accidents and outbreaks of pandemic or contagious diseases, such as Ebola, avian flu, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), H1N1 (swine flu) and the Zika virus; |
| • | climate change or availability of natural resources; |
| • | natural or manmade disasters, such as earthquakes, windstorms, tornadoes, hurricanes, typhoons, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, floods, drought, fires, oil spills and nuclear incidents; and |
| • | organized labor activities, which could cause a diversion of business from resorts involved in labor negotiations and loss of business generally for the resorts we manage as a result of certain labor tactics. |
Any one or more of these factors can adversely affect, and from time to time have adversely affected, individual resorts, particular regions and our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Contraction in the global economy or low levels of economic growth could adversely affect our revenues and profitability as well as limit or slow our future growth.
Consumer demand for products and services provided by the timeshare industry is closely linked to the performance of the general economy and is sensitive to business and personal discretionary spending levels. Decreased global or regional demand for products and services provided by the timeshare industry can be especially pronounced during periods of economic contraction or low levels of economic growth, and the recovery period in our industry may lag overall economic improvement. Declines in demand for our products and services due to general economic conditions could negatively affect our business by decreasing the revenues we are able to generate from our VOI sales, financing activities and Club and resort operations. In addition, many of the expenses associated with our business, including personnel costs, interest, rent, property taxes, insurance and utilities, are relatively fixed. During a period of overall economic weakness, if we are unable to meaningfully decrease these costs as demand for our products and services decreases, our business operations and financial performance may be adversely affected.
We do not own the Hilton brands and our business will be materially harmed if we breach our license agreement with Hilton or it is terminated.
Following the spin-off, Hilton retained ownership of the Hilton-branded trademarks, tradenames and certain related intellectual property used in the operation of our business. We entered into a license agreement with Hilton granting us the right to use the Hilton-branded trademarks, trade names and related intellectual property in our business for the term of the agreement. If we breach our obligations under the license agreement, Hilton may be entitled to terminate the license agreement or terminate our rights to use the Hilton brands and other Hilton intellectual property at properties that do not meet applicable standards and policies, or to exercise other remedies.
22
The termination of the license agreement or exercise of other remedies would materially harm our business and results of operations and impair our ability to market and sell our products and maintain our competitive position. For example, if we are not able to rely on the strength of the Hilton brands to attract prospective members and guests in the marketplace, our revenue and profits would decline and our marketing and sales expenses would increase. If we are not able to use Hilton’s marketing databases and corporate-level advertising channels to reach potential members and guests, including Hilton’s internet address as a channel through which to market available inventory, our member growth would be adversely affected and our revenue would materially decline, and it is uncertain whether we would be able to replace the revenue associated with those channels.
Even if the license agreement remains in effect, the termination of our rights to use the Hilton-branded trademarks, trade names and related intellectual property at properties that fail to meet applicable standards and policies, or any deterioration of quality or reputation of the Hilton brands (even deterioration not leading to termination of our rights under the license agreement or not caused by us), could also harm our reputation and impair our ability to market and sell our products at the subject properties, which could materially harm our business.
In addition, if license agreement terms relating to the Hilton Honors® loyalty program terminate, we would not be able to offer Hilton Honors® points to our members and guests. This would adversely affect our ability to sell our products, offer the flexibility associated with our Club membership and sustain our collection performance on our timeshare financing receivables portfolio. See “Item 1. Business—Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off—License Agreement.”
We will rely on Hilton to consent to our use of its trademarks at new properties we manage in the future.
Under the terms of our license agreement with Hilton, we are required to obtain Hilton’s consent to use its trademarks in circumstances specified in the license agreement. Hilton may reject a proposed project in certain circumstances. Any requirements to obtain Hilton’s consent to our expansion plans, or the need to identify and secure alternative expansion opportunities because Hilton does not allow us to use its trademarks with proposed new projects, may delay implementation of our expansion plans, cause us to incur additional expense or reduce the financial viability of our projects. Further, if Hilton does not permit us to use its trademarks in connection with our expansion plans, our ability to expand our Hilton-branded timeshare business would cease and our ability to remain competitive may be materially adversely affected.
Our business depends on the quality and reputation of the Hilton brands and affiliation with the Hilton Honors® loyalty program.
Currently, all of our products and services are offered under the Hilton brand names and affiliated with the Hilton Honors® loyalty program, and we intend to continue to develop and offer products and services under the Hilton brands and affiliated with the Hilton Honors® loyalty program in the future. In addition, the license agreement contains significant prohibitions on our ability to own or operate properties that are not Hilton brand names. The concentration of our products and services under these brands and program may expose us to risks of brand or program deterioration, or reputational decline, that are greater than if our portfolio were more diverse. Furthermore, as we are not the owner of the Hilton brands or the Hilton Honors® loyalty program, changes to these brands and program or our access to them, including our ability to buy points to offer to our members and potential members, could negatively affect our business. Any failure by Hilton to protect the trademarks, tradenames and intellectual property that we license from it could reduce the value of the Hilton brands and also harm our business. If these brands or program deteriorate or materially change in an adverse manner, or the reputation of these brands or program declines, our market share, reputation, business, financial condition or results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
23
Our dependence on development activities exposes us to project cost and completion risks.
We secure VOI inventory in part by developing new timeshare properties and new phases of existing timeshare properties. Our ongoing involvement in the development of inventory presents a number of risks, including:
| • | future weakness in the capital markets limiting our ability to raise capital for completion of projects or for development of future properties; |
| • | construction costs, to the extent they escalate faster than the pace at which we can increase the price of VOIs, adversely affecting our margins; |
| • | construction delays, zoning and other local, state or federal governmental approvals, particularly in new geographic areas with which we are unfamiliar, cost overruns, lender financial defaults, or natural or man-made disasters, such as earthquakes, tsunamis, hurricanes, floods, fires, volcanic eruptions and oil spills, increasing overall project costs, affecting timing of project completion or resulting in project cancellations; |
| • | any liability or alleged liability or resultant delays associated with latent defects in design or construction of projects we have developed or that we construct in the future adversely affecting our business, financial condition and reputation; |
| • | failure by third-party contractors to perform for any reason, exposing us to operational, reputational and financial harm; and |
| • | the existence of any title defects in properties we acquire. |
We also source inventory from third-party developers that are exposed to such risks, and the occurrence of any of these risks with respect to those third parties could have a material adverse effect on our access to the inventory sourced from these developers.
A decline in developed or acquired VOI inventory or our failure to enter into and maintain fee-for-service agreements may have an adverse effect on our business or results of operations.
In addition to VOI supply that we develop or acquire, we source VOIs through fee-for-service agreements with third-party developers. If we fail to develop timeshare properties, acquire inventory or are unsuccessful in entering into new agreements with third-party developers, we may experience a decline in VOI supply, which could result in a decrease in our revenues. Approximately 74 percent of our contract sales were from capital-efficient sources for the year ended December 31, 2017. As part of our strategy to optimize our sales mix of capital-efficient inventory, we will continue to acquire inventory and enter into additional fee-for-service agreements to source inventory. These arrangements may expose us to additional risk as we will not control development activities or timing of development completion. If third parties with whom we enter into agreements are not able to fulfill their obligations to us, the inventory we expect to acquire or market and sell on their behalf may not be available on time or at all, or may not otherwise be within agreed-upon specifications, including the specifications that we must meet in order to use Hilton’s trademarks at such properties. If our counterparties do not perform as expected and we do not have access to the expected inventory or obtain access to inventory from alternative sources on a timely basis, our ability to achieve sales goals may be adversely affected.
In addition, a decline in VOI supply could result in a decrease of financing revenues that are generated by VOI purchases and fee and rental revenues that are generated by our resort and Club management services.
A significant percentage of our revenue is derived from our fee-for-service agreements with respect to two properties that are owned by one third party, and any termination of such arrangements could have a materially adverse impact on our revenues and financial results.
We derived approximately 15 percent of our revenues for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 from fee-for-service fees with respect to two of our properties, which are owned by a single third party, and for which we have entered into fee-for-service agreements. If these fee-for-service agreements are terminated by the property owner, if one or both properties are sold to another party without the continuation of such arrangement, or if there is any occurrence or existence of any adverse economic development, adverse acts of natural or manmade disasters, or
24
any other conditions that negatively or disproportionately adversely affects either or both of these two properties, our revenues, our operating results and our financial performance could be materially adversely impacted.
We operate in a highly competitive industry.
The timeshare industry is highly competitive. The Hilton brands we use compete with the timeshare brands affiliated with major hotel chains in national and international venues, and we compete generally with other vacation options such as cruises and the vacation rental options generally offered by the lodging and travel industry (e.g., hotels, resorts and condominium rentals).
We also compete with other timeshare developers for sales of VOIs based principally on location, quality of accommodations, price, service levels and amenities, financing terms, quality of service, terms of property use, reservation systems, flexibility for VOI owners to exchange into time at other timeshare properties, or other travel rewards, including access to hotel loyalty programs, as well as brand name recognition and reputation. A number of our competitors are significantly larger than we are, and have potentially greater access to capital resources and broader marketing, sales and distribution capabilities. We also compete with numerous other smaller owners and operators of timeshare resorts, as well as home and apartment sharing services that market available privately owned residential properties that can be rented on a nightly, weekly or monthly basis. In addition, we are in competition with national and independent timeshare resale companies and members reselling existing VOIs, which could reduce demand or prices for sales of new VOIs. We also compete with other timeshare management companies in the management of resorts on behalf of owners on the basis of quality, cost, types of services offered and relationship.
We also compete for property acquisitions and partnerships with entities that have similar investment objectives as we do. This competition could limit the number of, or negatively affect the cost of, suitable investment opportunities available to us.
Recent and potential future consolidation in the highly fragmented timeshare industry may increase competition. Consolidation may create competitors that enjoy significant advantages resulting from, among other things, a lower cost of, and greater access to, capital and enhanced operating efficiencies. There is also significant competition for talent at all levels within the industry, in particular for sales and management.
Our ability to remain competitive and to attract and retain members depends on our success in distinguishing the quality and value of our products and services from those offered by others. If we cannot compete successfully in these areas or if our marketing and sales efforts are not successful and we are unable to convert customers to a sufficient number of sales, this could negatively affect our operating margins and our ability to recover the expense of our marketing programs and grow our business, diminish our market share and reduce our earnings.
The sale of VOIs in the secondary market by existing members could cause our sales revenues and profits to decline.
Existing members have offered, and are expected to continue to offer, their VOIs for sale on the secondary market. The sale of VOIs has been made easier by recent development of virtual marketplaces assisting members with the sale of their VOIs. The prices at which these intervals are sold are typically less than the prices at which we would sell the intervals. As a result, these sales create additional pricing pressure on our sale of VOIs, which could cause our sales revenues and profits to decline. In addition, if the secondary market for VOIs becomes more organized or financing for such resales becomes more available, our ability to sell VOIs could be adversely affected and/or the resulting availability of VOIs (particularly where the VOIs are available for sale at lower prices than the prices at which we would sell them) could adversely affect our sales revenues. Further, unlawful or deceptive third-party VOI resale or vacation package sales schemes could damage the reputation of the industry, our reputation and brand value, or affect our ability to collect management fees, which may adversely affect our sales revenues and results of operations.
Development of a strong secondary market may also cause a decline in the volume of VOI inventory that we are able to repurchase, which could adversely affect our development margin, as we utilize this low-cost inventory source to supplement our inventory needs and help manage our cost of vacation ownership products.
25
Partnership or joint venture investments could be adversely affected by our lack of sole decision-making authority, our reliance on partners’ or co-venturers’ financial condition, disputes between us and our partners or co-venturers and our obligation to guaranty certain obligations beyond the amount of our investments.
We have co-invested with third parties and we may in the future co-invest with other third parties through partnerships, joint ventures or other entities, acquiring non-controlling interests in, or sharing responsibility for managing the affairs, of a timeshare property, partnership, joint venture or other entity. For example, in July 2017, we entered into an agreement with BRE Ace Holdings, an affiliate of Blackstone, pursuant to which we contributed $40 million in cash for a 25 percent interest in BRE Ace LLC, which owns a 1,201-key timeshare resort property and related operations, commonly known as “Elara, by Hilton Grand Vacations,” located in Las Vegas, Nevada (the “Elara Joint Venture”). Consequently, with respect to any such third-party arrangements, we would not be in a position to exercise sole decision-making authority regarding the property, partnership, joint venture or other entity, and may, under certain circumstances, be exposed to risks not present if a third party were not involved, including the possibility that partners or co-venturers might become bankrupt or fail to fund their share of required capital contributions. In addition, we may be forced to make contributions to maintain the value of the property. Such investments may also have the potential risk of impasses on decisions, such as a sale, because neither we nor the partner or co-venturer may have full control over the partnership or joint venture. We and our respective partners or co-venturers may each have the right to trigger a buy-sell right or forced sale arrangement, which could cause us to sell our interest, or acquire our partners’ or co-venturers’ interest, or to sell the underlying asset, either on unfavorable terms or at a time when we otherwise would not have initiated such a transaction. In addition, a sale or transfer by us to a third party of our interests in the partnership or joint venture may be subject to consent rights or rights of first refusal in favor of our partners or co-venturers, which would in each case restrict our ability to dispose of our interest in the partnership or joint venture. For example, our joint venture partner in the Elara Joint Venture generally has exclusive authority to manage the business and affairs of the Elara Joint Venture, and has the discretion to call for additional capital contributions at any time. In addition, it has certain rights to transfer or sell some or all of its interests in the Elara Joint Venture and/or the property without our consent or, in certain situations, require us to sell our interests at the same time, while we are not permitted to sell or transfer our interest without their consent. Any or all of these factors could adversely affect the value of our investment, our ability to exit, sell or dispose of our investment at times that are beneficial to us, or our financial commitment to maintaining our interest in the joint ventures.
Our joint ventures may be subject to debt and the refinancing of such debt, and we may be required to provide certain guarantees or be responsible for the full amount of the debt in certain circumstances in the event of a default beyond the amount of our equity investment. Our joint venture partners may take actions that are inconsistent with the interests of the partnership or joint venture, or in violation of the financing arrangements and trigger our guaranty, which may expose us to substantial financial obligation and commitment that are beyond our ability to fund. In addition, partners or co-venturers may have economic or other business interests or goals that are inconsistent with our business interests or goals and may be in a position to take action or withhold consent contrary to our policies or objectives. In some instances, partners or co-venturers may have competing interests in our markets that could create conflict of interest issues. Disputes between us and partners or co-venturers may result in litigation or arbitration that would increase our expenses and prevent our officers from focusing their time and effort on our business. Consequently, actions by or disputes with partners or co-venturers might result in subjecting assets owned by the partnership or joint venture to additional risk. In addition, we may, in certain circumstances, be liable for the actions of our third-party partners or co-venturers.
Our business is regulated under a wide variety of laws, regulations and policies, and failure to comply with these regulations could adversely affect our business.
Our business is subject to extensive regulation, and any failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations could have a material adverse effect on our business. Our real estate development activities, for example, are subject to laws and regulations typically applicable to real estate development, subdivision and construction activities, such as laws relating to zoning, entitlement, permitting, land use restrictions, environmental regulation, title transfers, title insurance, taxation and eminent domain. Laws in some jurisdictions also impose liability on property developers for construction defects discovered or repairs made by future owners of property developed by the developer. In addition, the sales of VOIs must be registered with governmental authorities in most jurisdictions in which we do business. The preparation of VOI registrations requires time and cost, and in many jurisdictions the exact date of registration approval cannot be accurately predicted. Various laws also govern our lending
26
activities and our resort management activities, including the laws described in “Business—Government Regulation.”
A number of laws govern our marketing and sales activities, such as timeshare and land sales acts, fair housing statutes, anti-fraud laws, sweepstakes laws, real estate licensing laws, telemarketing laws, home solicitation sales laws, tour operator laws, seller of travel laws, securities laws, consumer privacy laws and consumer protection laws. In addition, laws in many jurisdictions in which we sell VOIs grant the purchaser of a VOI the right to cancel a purchase contract during a specified rescission period.
In recent years, telemarketing legislation has significantly increased the costs associated with telemarketing. We have implemented procedures that we believe will help reduce the possibility of violating such laws, however, such procedures may not be effective in ensuring regulatory compliance. In addition, because our relationship with Hilton has changed, it may be more difficult for us to utilize customer information we obtain from Hilton in the future for marketing purposes.
Under the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 and the Accessibility Guidelines promulgated thereunder, which we refer to collectively as the ADA, all public accommodations must meet various federal requirements related to access and use by disabled persons. Compliance with ADA’s requirements could require removal of access barriers, and non-compliance could result in the U.S. government imposing fines or in private litigants winning damages. Our properties also are subject to various federal, state and local regulatory requirements, such as state and local fire and life safety requirements. Furthermore, various laws govern our resort management activities, including laws and regulations regarding community association management, public lodging, food and beverage services, liquor licensing, labor, employment, health care, health and safety, accessibility, discrimination, immigration, gaming and the environment (including climate change).
Our lending activities are also subject to a number of laws and regulations, including laws and regulations related to consumer loans, retail installment contracts, mortgage lending, fair debt collection and credit reporting practices, consumer collection practices, contacting debtors by telephone, mortgage disclosure, lender licenses and money laundering.
We may not be successful in maintaining compliance with all laws, regulations and policies to which we are currently subject, and such compliance is expensive and time consuming. We do not know whether existing requirements will change or whether compliance with future requirements, including regulatory requirements in new geographic areas into which we expand would require significant unanticipated expenditures that would affect our cash flow and results of operations. Failure to comply with current or future applicable laws, regulations and policies could have a material adverse effect on our business. For example, if we do not comply with applicable laws, regulations and policies, governmental authorities in the jurisdictions where the violations occurred may revoke or refuse to renew licenses or registrations necessary to operate our business. Failure to comply with applicable laws, regulations and policies could also render sales contracts for our products void or voidable, subject us to fines or other sanctions, and increase our exposure to litigation.
We may experience financial and operational risks in connection with acquisitions and other opportunistic business ventures.
We will consider strategic acquisitions to expand our inventory options and distribution capabilities; however, we may be unable to identify attractive acquisition candidates or complete transactions on favorable terms. Future acquisitions could result in potentially dilutive issuances of equity securities and/or the assumption of contingent liabilities. These acquisitions may also be structured in such a way that we will be assuming unknown or undisclosed liabilities or obligations. Moreover, we may be unable to efficiently integrate acquisitions, management attention and other resources may be diverted away from other potentially more profitable areas of our business and in some cases these acquisitions may turn out to be less compatible with our growth and operational strategy than originally anticipated. The occurrence of any of these events could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
As part of our business strategy, we also intend to continue collaborating with Hilton on timeshare development opportunities at new and existing hotel properties and explore growth opportunities along the Hilton
27
brand spectrum, as well as expand our marketing partnerships and travel exchange partners. However, we may be unable to successfully enter into these arrangements on favorable terms or launch related products and services, or such products and services may not gain acceptance among our members or be profitable. The failure to develop and execute any such initiatives on a cost-effective basis could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, our ability to engage in acquisitions may be limited by restrictions on our ability to raise additional equity capital. See “Item 1. Business—Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off—Tax Matters Agreement,” “Business—Agreements with Blackstone and HNA—Blackstone Stockholders Agreement,” and “Business—Agreements with Blackstone and HNA—HNA Stockholders Agreement.”
The expiration, termination or renegotiation of our management agreements could adversely affect our cash flows, revenues and profits.
We enter into management agreements with the HOAs for the timeshare resorts developed by us or by third parties with whom we have entered into fee-for-service agreements. Our management agreements generally provide for a cost-plus management fee equal to 10 percent to 15 percent of the costs to operate the applicable resort. We also receive revenues that represent reimbursement for the costs incurred to perform our services, principally related to personnel providing on-site services. The original term of our management agreements is typically governed by state timeshare laws, and ranges from three to five years, and many of these agreements renew automatically for one- to three-year periods, unless either party provides advance notice of termination before the expiration of the term. Although none of the management agreements relating to our developed or fee-for-service properties have been terminated or lapsed since our inception, any of these agreements may expire at the end of its then-current term (following notice by a party of non-renewal) or be terminated, or the contract terms may be renegotiated in a manner adverse to us. If a management agreement is terminated or not renewed on favorable terms, our cash flows, revenues and profits could be adversely affected.
Disagreements with VOI owners, HOAs and other third parties may result in litigation and/or loss of management contracts.
The nature of our responsibilities in managing timeshare properties may from time to time give rise to disagreements with VOI owners and HOAs. To develop and maintain positive relations with current and potential VOI owners and HOAs, we seek to resolve any disagreements, but may not always be able to do so. Failure to resolve such disagreements may result in litigation. Further, disagreements with HOAs could also result in the loss of management contracts, a significant loss of which could negatively affect our profits or limit our ability to operate our business, and our ongoing ability to generate sales from our existing member base may be adversely affected.
In the normal course of our business, we are involved in various legal proceedings and in the future we could become the subject of claims by current or former members, persons to whom we market our products, third-party developers, guests who use our properties, our employees or contractors, our investors or regulators. The outcome of these proceedings cannot be predicted. If any such litigation results in a significant adverse judgment, settlement or court order, we could suffer significant losses, our profits could be reduced, our reputation could be harmed and our future ability to operate our business could be constrained.
We manage a concentration of properties in particular geographic areas, which exposes our business to the effects of regional events and occurrences.
A significant number, approximately 83 percent, of the resorts we manage are concentrated in significant tourist markets including Florida, Hawaii, Nevada, New York, Washington D.C. and South Carolina and are, therefore, particularly susceptible to adverse economic developments in those areas. These economic developments include regional economic downturns, significant increases in the number of our competitors’ products in these markets, and potentially higher labor, real estate, tax or other costs in the geographic markets in which we are concentrated. In addition, the properties we manage are subject to the effects of adverse acts of natural or manmade disasters, including earthquakes, windstorms, tornadoes, hurricanes, typhoons, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, floods, drought, fires, oil spills and nuclear incidents. Depending on the severity of these disasters, the damage could require closure of all or substantially all of these properties in one or more markets for a period of time while the necessary
28
repairs and renovations, as applicable, are undertaken. In addition, we cannot guarantee that the amount of insurance maintained for these properties from time to time would entirely cover damages caused by any such event.
Fear of exposure to pandemic or contagious diseases, such as Ebola, avian flu, SARs, swine flu and the Zika virus, or natural or manmade disasters, may also deter travelers from scheduling vacations or cause them to cancel vacation plans to the markets in which the properties we manage are concentrated. Actual or threatened war, political conditions or civil unrest, violence or terrorist activities or threats and heightened travel security measures instituted in response to these events, could also interrupt or deter vacation plans to our key markets.
As a result of this geographic concentration of properties, we face a greater risk of a negative effect on our revenues in the event these areas are more severely and more frequently affected by adverse economic and competitive conditions, extreme weather, manmade disasters or pandemic or contagious diseases.
Our current operations and future expansion outside of the United States make us susceptible to the risks of doing business internationally, which could lower our revenues, increase our costs, reduce our profits or disrupt our business.
We currently offer timeshare properties located in the United States, the United Kingdom and Italy. We also market both our international properties and our U.S. properties in Europe and the Asia Pacific region, primarily in Japan and South Korea. In addition, as part of our business strategy, we intend to continue the expansion of our operations in Japan, as well as explore further expansion opportunities in other countries located in the Asia Pacific region, Mexico and the Caribbean. Such activities may not be limited only to marketing efforts for existing international and U.S. properties in other countries, but also include acquiring, developing, managing, marketing, offering and/or financing timeshare properties in such countries. Current and future international operations expose us to a number of additional challenges and risks that may not be inherent in operating solely in the U.S., including, for example, the following:
| • | rapid changes in governmental, economic or political policy; |
| • | political or civil unrest, acts of terrorism or the threat of international boycotts or U.S. anti-boycott legislation; |
| • | negative impact on governmental relationships between those countries in which we currently operate or have future expansion plans, on one hand, and the U.S., on the other hand, which may result in undesirable trade, travel or similar regulations, thereby negatively affecting the tourism industry generally, and the timeshare and leisure industry specifically; |
| • | increases in anti-American sentiment and the identification of the Hilton brands as American brands; |
| • | recessionary trends or economic instability in international markets; |
| • | changes in foreign currency exchange rates or currency restructurings and hyperinflation or deflation in the countries in which we operate; |
| • | the effect of disruptions caused by severe weather, natural disasters, outbreaks of disease or other events that make travel to a particular region less attractive or more difficult; |
| • | the presence and acceptance of varying levels of business corruption in international markets and the effect of various anti-corruption and other laws; |
| • | the imposition of restrictions on currency conversion or the transfer of funds; |
| • | the ability to comply with or effect of complying with complex and changing laws, regulations and policies of foreign governments that may affect investments or operations, including foreign ownership restrictions, import and export controls, tariffs, embargoes, increases in taxes paid and other changes in applicable tax laws; |
| • | uncertain, unfamiliar and/or unpredictable regulatory environment that may adversely affect the acquisition, development, management, marketing, sales, financings, and related activities that affect the lodging, real estate, and travel industries, and, more specifically, to the timeshare industry, such as zoning laws, real estate development regulations, and consumer privacy; |
29
| • | uncertainties as to local laws regarding, and enforcement of, contract and intellectual property rights; |
| • | forced nationalization of resort properties by local, state or national governments; |
| • | different social or cultural norms and practices that are not customary in the U.S.; and |
| • | the difficulties involved in managing an organization doing business in different countries. |
These and other factors may materially adversely affect our business generally, future expansion plans, revenues from international operations, and costs and profits, as well as our financial condition, Moreover, our experience operating internationally is limited to certain markets. Expansion of our international operations into other countries and territories may result in greater inefficiencies in navigating the risks of operating internationally and could result in greater effects on our business than would be experienced by a company with greater international experience.
Further, because we market our U.S. properties and our international properties in Europe, instability of the Eurozone, including fears of sovereign debt defaults, and stagnant growth generally, and of certain Eurozone member states in particular, have resulted in concerns regarding the suitability of a shared currency for the region, which could lead to the reintroduction of individual currencies for member states. If this were to occur, certain of our Euro-denominated assets and liabilities would be re-denominated to such individual currencies, which could result in a mismatch in the values of assets and liabilities and expose us and certain of our investments to additional currency risks. Even if the Euro is maintained, continued concerns regarding the stability of the Eurozone, including potential consequences following Brexit, and the potential effects of government intervention intended to address it could materially adversely affect our business.
Similarly, we market our U.S. and international properties in Japan and we intend to continue the expansion of our operations in Japan. The Japanese economy has recently experienced periods of fiscal and economic volatility, and we may be unable to properly predict the effect of such volatility, including the actions that may be taken by the Japanese government, in a way that fully mitigates the impact of such volatility on our marketing activities and businesses in Japan.
Our insurance policies may not cover all potential losses.
We maintain insurance coverage for liability, property, business interruption and other risks with respect to business operations. While we have comprehensive property and liability insurance policies with coverage features and insured limits that we believe are customary, market forces beyond our control may limit the scope of the insurance coverage we can obtain or our ability to obtain coverage at reasonable rates. The cost of our insurance may increase and our coverage levels may decrease, which may affect our ability to maintain customary insurance coverage and deductibles at acceptable costs. There is a limit as well as various sub-limits on the amount of insurance proceeds we will receive in excess of applicable deductibles. If an insurable event occurs that affects more than one of our properties, the claims from each affected property may be considered together to determine whether the per occurrence limit, annual aggregate limit or sub-limits, depending on the type of claim, have been reached. If the limits or sub-limits are exceeded, each affected property may only receive a proportional share of the amount of insurance proceeds provided for under the policy. Further, certain types of losses, generally of a catastrophic nature, such as earthquakes, hurricanes and floods, war, terrorist acts, such as biological or chemical terrorism, political risks, some environmental hazards and/or natural or manmade disasters, may be outside the general coverage limits of our policy, subject to large deductibles, deemed uninsurable or too cost-prohibitive to justify insuring against. In addition, in the event of a substantial loss, the insurance coverage we carry may not be sufficient to pay the full market value or replacement cost of the affected resort or in some cases may not provide a recovery for any part of a loss. As a result, we could lose some or all the capital we have invested in a property, as well as the anticipated future marketing, sales or revenue opportunities from the property. Further, we could remain obligated under guarantees or other financial obligations related to the property despite the loss of product inventory, and our members could be required to contribute toward deductibles to help cover losses.
30
Failure of HOA boards to levy sufficient fees, or the failure of members to pay those fees, could lead to inadequate funds to maintain or improve the properties we manage.
Owners of our VOIs and those we sell on behalf of third-party developers must pay maintenance fees levied by HOA boards, which include reserve amounts for capital replacements and refurbishments. These maintenance fees are used to maintain and refurbish the timeshare properties and to keep the properties in compliance with applicable Hilton standards and policies. If HOA boards do not levy sufficient maintenance fees, including capital reserves required by applicable law, or fail to manage their reserves appropriately, or if members do not pay their maintenance fees, the timeshare properties could fall into disrepair and fail to comply with applicable standards and policies, and/or state regulators could impose requirements, obligations and penalties. A decline in the quality or standards of the resorts we manage would negatively affect our ability to attract new members and maintain member satisfaction. In addition, if a resort fails to comply with applicable standards and policies because maintenance fees are not paid or otherwise, Hilton could terminate our rights under the license agreement to use its trademarks at the non-compliant resort, which could result in the loss of management fees, and could decrease member satisfaction and impair our ability to market and sell our products at the non-compliant locations.
If maintenance fees at our resorts are required to be increased, our product could become less attractive and our business could be harmed.
The maintenance fees that are levied by HOA boards on VOI owners may increase as the costs to maintain and refurbish the timeshare properties and to keep the properties in compliance with Hilton brand standards increase. Increased maintenance fees could make our products less desirable, which could have a negative effect on VOI sales. Further, if our maintenance fees increase substantially year over year or are not competitive with other VOI providers, we may not be able to attract new members or retain existing members.
If purchasers default on the loans that we provide to finance their VOI purchases, our revenues, cash flows and profits could be reduced.
Providing secured financing to some purchasers of VOIs subjects us to the risk of purchaser default. As of December 31, 2017, our consumer loan portfolio had a balance of approximately $1.2 billion and experienced default rates of 4.12 percent, 3.67 percent and 2.84 percent for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. If a purchaser defaults under the financing that we provide, we could be forced to write off the loan and reclaim ownership of the VOI. We may be unable to resell the property in a timely manner or at a price sufficient to allow us to recover written-off loan balances, or at all. Also, if a purchaser of a VOI defaults on the related loan during the early part of the amortization period, we may not have recovered the marketing, selling and general and administrative costs associated with the sale of that VOI. If we are unable to recover any of the principal amount of the loan from a defaulting purchaser, or if the allowances for losses from such defaults are inadequate, our revenues and profits could be reduced.
If default rates increase beyond current projections and result in higher than expected foreclosure activity, our results of operations could be adversely affected. In addition, the transactions in which we have securitized timeshare financing receivables in the capital markets contain certain portfolio performance requirements related to default, delinquency and recovery rates, which, if not met, would result in loss or disruption of cash flow until portfolio performance sufficiently improves to satisfy the requirements.
If the default rates or other credit metrics underlying our timeshare financing receivables deteriorate, our timeshare financing receivable securitization program could be adversely affected.
Our timeshare financing receivable securitization program could be adversely affected if any pool of timeshare financing receivables fails to meet certain performance ratios, which could occur if the default rate or other credit metrics of the underlying timeshare financing receivables deteriorate. In addition, if we offer timeshare financings to our customers with terms longer than those generally offered in the industry, we may not be able to securitize those timeshare financing receivables. Our ability to sell securities backed by our timeshare financing receivables depends on the continued ability and willingness of capital market participants to invest in such securities. Asset-backed securities issued in our timeshare financing receivable securitization program could be downgraded by credit agencies in the future. If a downgrade occurs, our ability to complete other securitization transactions on acceptable terms or at all could be jeopardized, and we could be forced to rely on other potentially more expensive and less attractive funding sources, to the extent available. Similarly, if other operators of vacation
31
ownership products were to experience significant financial difficulties, or if the timeshare industry as a whole were to contract, we could experience difficulty in securing funding on acceptable terms. The occurrence of any of the foregoing would decrease our profitability and might require us to adjust our business operations, including by reducing or suspending our provision of financing to purchasers of VOIs. Sales of VOIs may decline if we reduce or suspend the provision of financing to purchasers, which may adversely affect our cash flows, revenues and profits.
A failure to keep pace with developments in technology could impair our operations, competitive position or reputation.
Our business model and competitive conditions in the timeshare industry demand the use of sophisticated technology and systems, including those used for our marketing, sales, reservation, inventory management and property management systems, and technologies we make available to our members and more generally to support our business. In particular, an increasing number of potential customers select products based on the providers’ technology and ease of interfacing with the provider. We must refine, update and/or replace these technologies and systems with more advanced systems on a regular basis. If we cannot do so as quickly as our competitors or within budgeted costs and time frames, our business could suffer. We also may not achieve the benefits that we anticipate from any new technology or system, and a failure to do so could result in higher than anticipated costs or could harm our operating results.
In addition, the proliferation and global reach of social media continue to expand rapidly and could cause us to suffer reputational harm. The continuing evolution of social media presents new challenges and requires us to keep pace with new developments, technology and trends. Negative posts or comments about us, the properties we manage or the Hilton brands, on any social networking or user-generated review website, including travel and/or vacation property websites, could affect consumer opinions of us and our products; and we cannot guarantee that we will timely or adequately redress such instances.
Our increasing reliance on information technology and other systems subjects us to risks associated with cyber-security. Cyber-attacks or our failure to maintain the integrity of internal or customer data could have a disruptive effect on our business and adversely affect our financial performance.
We rely heavily on computer, Internet-based and mobile information and communications systems operated by us or our service providers to collect, process, transmit and retain large volumes of customer data, including credit card numbers and other personally identifiable information, reservation information and mailing lists, as well as personally identifiable information of our employees. There has been an increase in the number and sophistication of criminal cyber-security attacks against companies where customer and other sensitive information has been compromised. Our information systems and records, including those we maintain with our service providers, may be subject to such cyber-attacks, which include efforts to hack or breach security measures in order to obtain or misuse information, viruses, “ransomware” or other malware. In addition, increasingly complex systems and software are subject to failure, operator error or malfeasance, or inadvertent releases of data that may materially impact our information systems and records. For instance, security breaches could result in the dissemination of member and guest credit card information, which could lead to affected members and guests experiencing fraudulent charges.
The integrity and protection of customer and employee data is critical to us. We could make faulty decisions if that data is inaccurate or incomplete. Customers and employees also have a high expectation that we and our service providers will adequately protect their personal information. A significant theft, loss, loss of access to, or fraudulent use of customer, employee, or company data could adversely impact our reputation, and could result in significant remedial and other expenses, fines, or litigation. Breaches in the security of our information systems or those of our service providers or other disruptions in data services could lead to an interruption in the operation of our systems or require us to consider changes to our customer data or payment systems, resulting in operational inefficiencies, additional expense and a loss of profits.
Our collection and use of customer information are governed by extensive and evolving privacy laws and regulations that are constantly evolving and may differ significantly depending on jurisdiction. Compliance with these laws and regulations involves significant costs, which may increase in the future and which may negatively impact our ability to provide services to our customers, and a failure by us or our service providers to comply with
32
privacy regulations may subject us to significant remedial and other expenses, fines, or litigation, as well as restrictions on our use or transfer of data. Our systems and the systems operated by our service providers may be unable to satisfy changing regulatory requirements and customer and employee expectations, or may require significant additional investments or time to do so.
The steps we take to deter and mitigate risks related to cyber-security may not provide the intended level of protection. In particular, it may be difficult to anticipate or immediately detect such incidents and the damage caused thereby. We may be required to expend significant additional resources in the future to modify and enhance our protective measures. Although we carry cyber/privacy liability insurance that is designed to protect us against certain losses related to cyber-security risks, such insurance coverage may be insufficient to cover all losses or all types of claims that may arise in connection with cyber-attacks, security breaches, and other related breaches. In addition, the third party service providers on which we rely face cyber-security risks, some of which may be different than the risks we face, and we do not directly control any of such service providers’ information security operations, including the efforts that they may take to mitigate risks or the level of cyber/privacy liability insurance that they may carry.
Changes in privacy law could adversely affect our ability to market our products effectively.
We rely on a variety of direct marketing techniques, including telemarketing, email and social media marketing and postal mailings, and we are subject to various laws and regulations in the United States and internationally that govern marketing and advertising practices. Adoption of new state or federal laws regulating marketing and solicitation, or international data protection laws that govern these activities, or changes to existing laws, such as the Telemarketing Sales Rule, the Telephone Consumer Protection Act, and the CAN-SPAM Act of 2003, could adversely affect current or planned marketing activities and cause us to change our marketing strategy. If this occurs, we may not be able to develop adequate alternative marketing strategies, which could affect the amount and timing of our VOI sales. We also obtain access to potential members and guests from travel service providers or other companies, including Hilton; and we market to some individuals on these lists directly or through other companies’ marketing materials. If access to these lists were prohibited or otherwise restricted, including access to Hilton Honors® loyalty program member information, our ability to access potential members and guests and introduce them to our products could be significantly impaired. Additionally, because our relationship with Hilton has changed, it may be more difficult for us to utilize customer information we obtain from Hilton in the future.
The growth of our business and the execution of our business strategies depend on the services of our management team and our employees.
We believe that our future growth depends, in part, on the continued services of our management team, and on our ability to attract and retain key officers and other highly qualified personnel. Competition for such personnel is intense. There can be no assurance that we will be successful in retaining and attracting management and other highly qualified personnel. The loss of any members of our management team could adversely affect our strategic, member and guest relationships and impede our ability to execute our business strategies.
In addition, insufficient numbers of talented employees at our properties could constrain our ability to maintain our current levels of business, or expand our business. We compete with other companies both within and outside of our industry for talented personnel across a diverse array of operating disciplines. If we cannot recruit, train, develop or retain sufficient numbers of talented employees, we could experience increased employee turnover, decreased member and guest satisfaction, low morale, inefficiency or internal control failures, which could materially reduce our profits.
Third-party reservation channels may negatively affect our bookings for room rental revenues.
Some stays at the properties we manage are booked through third-party internet travel intermediaries, such as expedia.com, orbitz.com and booking.com, as well as lesser-known and/or newly emerging online travel service providers. As the percentage of internet bookings increases, these intermediaries may be able to obtain higher commissions, reduced room rates or other significant contract concessions from us. Moreover, some of these internet travel intermediaries are attempting to commoditize lodging, by increasing the importance of price and general indicators of quality (such as “three-star property”) at the expense of brand identification.
33
These intermediaries also generally employ aggressive marketing strategies, including expending significant resources for online and television advertising campaigns to drive consumers to their websites. Additionally, consumers can book stays at the properties we manage through other distribution channels, including travel agents, travel membership associations and meeting procurement firms. Over time, consumers may develop loyalties to these third-party reservation systems rather than to our booking channels. Although we expect to derive most of our business from traditional channels and our websites (and those of Hilton), our business and profitability could be adversely affected if customer loyalties change significantly, diverting bookings away from our distribution channels.
Our real estate investments subject us to numerous risks.
We are subject to the risks that generally relate to investments in and the development of real property. A variety of factors affect income from properties and real estate values, including laws and regulations, insurance, interest rate levels and the availability of financing. Our license agreement or other agreements with Hilton may require us to incur unexpected costs required to cause our properties to comply with applicable standards and policies. In recent years, our financial results have been positively impacted by a lower interest rate environment. However, when interest rates increase the cost of acquiring, developing, expanding or renovating real property increases, and real property values may decrease as the number of potential buyers decrease. Similarly, as financing becomes less available, it becomes more difficult both to acquire and develop real property. Many costs of real estate investments, such as real estate taxes, insurance premiums, maintenance costs and certain operating costs, are generally more fixed than variable, and as a result are not reduced even when a property is not fully sold or occupied. If any of these risks were realized, they could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations or financial condition.
U.S. or foreign environmental laws and regulations may cause us to incur substantial costs or subject us to potential liabilities.
We are subject to certain compliance costs and potential liabilities under various U.S. federal, state and local and foreign environmental, health and safety laws and regulations. These laws and regulations govern actions including air emissions, the use, storage and disposal of hazardous and toxic substances, and wastewater disposal. Our failure to comply with such laws, including any required permits or licenses, could result in substantial fines or possible revocation of our authority to conduct some of our operations. We could also be liable under such laws for the costs of investigation, removal or remediation of hazardous or toxic substances at our currently or formerly owned real property or at third-party locations in connection with our waste disposal operations, regardless of whether or not we knew of, or caused, the presence or release of such substances. From time to time, we may be required to remediate such substances or remove, abate or manage asbestos, mold, radon gas, lead or other hazardous conditions at our properties. The presence or release of such toxic or hazardous substances could result in third-party claims for personal injury, property or natural resource damages, business interruption or other losses. Such claims and the need to investigate, remediate or otherwise address hazardous, toxic or unsafe conditions could adversely affect our operations, the value of any affected real property, or our ability to sell, lease or assign our rights in any such property, or could otherwise harm our business or reputation. Environmental, health and safety requirements have also become increasingly stringent, and our costs may increase as a result.
Some U.S. states and various countries are considering or have undertaken actions to regulate and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. New or revised laws and regulations, or new interpretations of existing laws and regulations, such as those related to climate change, could affect the operation of the properties we manage or result in significant additional expense and operating restrictions on us. The cost of such legislation, regulation or new interpretations would depend upon the specific requirements enacted and cannot be determined at this time.
Our ability to source VOI inventory and finance VOI sales may be impaired if we or the third-party developers with whom we do business are unable to access capital when necessary.
The availability of funds for new investments, primarily developing, acquiring or repurchasing VOI inventory, depends in part on liquidity factors and capital markets over which we can exert little, if any, control. Instability in the financial markets and any resulting contraction of available liquidity and leverage could constrain the capital markets for investments in timeshare products. In addition, we intend to access the securitization markets to securitize our timeshare financing receivables. Any future deterioration in the financial markets could preclude,
34
limit, delay or increase the cost to us of future securitizations. We also require the issuance of surety bonds in connection with our real estate development and VOI sales activity. The availability, terms and conditions and pricing of our bonding capacity is dependent on, among other things, continued financial strength and stability of the insurance company affiliates providing the bonding capacity, general availability of such capacity, and our corporate credit rating. If bonding capacity is unavailable, or alternatively, if the terms and conditions and pricing of such bonding capacity are unacceptable to us, our business could be negatively affected. Instability in the financial markets could also affect the timing and volume of any securitizations we undertake, as well as the financial terms of such securitizations. Any indebtedness we incur, including indebtedness under these facilities, may adversely affect our ability to obtain any additional financing necessary to develop or acquire additional VOI inventory, to make other investments in our business, or to repurchase VOIs on the secondary market. Furthermore, volatility in the financial markets, due to tightening of underwriting standards by lenders and credit rating agencies, among other things, could result in less availability of credit and increased costs for what is available. As a result, we may not be able to obtain financing on attractive terms or at all. If our overall cost of borrowing increases, the increased costs would likely reduce future cash flow available for distribution, affecting our growth and development plans.
We have and will continue to enter into fee-for-service agreements with third-party developers to source inventory. These agreements enable us to generate fees from the marketing and sales services we provide, Club memberships and from the management of the timeshare properties without requiring us to fund acquisition and construction costs. If these developers are not able to obtain or maintain financing necessary for their operations, we may not be able to enter into these arrangements, which would limit opportunities for growth and reduce our revenues.
Changes to accounting rules or regulations may adversely affect our reported financial condition and results of operations.
New accounting rules or regulations and varying interpretations of existing accounting rules or regulations have occurred and may occur in the future. A change in accounting rules or regulations may require retrospective application and affect our reporting of transactions completed before the change is effective, and future changes to accounting rules or regulations may adversely affect our reported financial condition and results of operations. See Note 2: Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a summary of accounting standards issued but not yet adopted.
Changes to estimates or projections used to assess the fair value of our assets, or operating results that are lower than our current estimates at certain locations, may cause us to incur impairment losses that could adversely affect our results of operations.
Our total assets include intangible assets with finite useful lives and long-lived assets, principally property and equipment and VOI inventory. We evaluate our intangible assets with finite useful lives and long-lived assets for impairment when circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. Our evaluation of impairment requires us to make certain estimates and assumptions including projections of future results. After performing our evaluation for impairment, including an analysis to determine the recoverability of long-lived assets, we will record an impairment loss when the carrying value of the underlying asset, asset group or reporting unit exceeds its fair value. We carry our VOI inventory at the lower of cost or estimated fair value, less costs to sell. If the estimates or assumptions used in our evaluation of impairment or fair value change, we may be required to record impairment losses on certain of these assets. If these impairment losses are significant, our results of operations would be adversely affected.
Changes in U.S. federal, state and local or foreign tax law, interpretations of existing tax law, or adverse determinations by tax authorities, could increase our tax burden or otherwise adversely affect our financial condition or results of operations.
We are subject to taxation at the federal, state and local levels in the United States and various other countries and jurisdictions. Our future effective tax rate could be affected by changes in the composition of earnings in jurisdictions with differing tax rates, changes in statutory rates and other legislative changes, changes in the valuation of our deferred tax assets and liabilities, or changes in determinations regarding the jurisdictions in which we are subject to tax. From time to time, the U.S. federal, state and local and foreign governments make
35
substantive changes to tax rules and their application, which could result in materially higher corporate taxes than would be incurred under existing tax law and could adversely affect our financial condition or results of operations. Changes in the non-income tax rates to which we are subject could also have an adverse effect on the maintenance fees charged to our members, which could result in materially lower sales and higher operating costs.
The recent U.S. tax legislation enacted on December 22, 2017 represents a significant overhaul of the U.S. federal tax code. This tax legislation significantly reduced the U.S. statutory corporate tax rate and made other changes that could have a favorable impact on our overall U.S. federal tax liability in a given period. However, the tax legislation also included a number of provisions, including, but not limited to, the limitation or elimination of various deductions or credits, the imposition of taxes on certain cross-border payments or transfers, the changing of the timing of the recognition of certain income and deductions or their character, and the limitation of asset basis under certain circumstances, that could significantly and adversely affect our U.S. federal income tax position. There can be no assurance that changes in tax laws or regulations, both within the U.S. and the other jurisdictions in which we operate, will not materially and adversely affect our effective tax rate, tax payments, financial condition and results of operations. Similarly, changes in tax laws and regulations that impact our customers and counterparties or the economy generally may also impact our financial condition and results of operations.
Tax laws and regulations are complex and subject to varying interpretations and any significant failure to comply with applicable tax laws and regulations in all relevant jurisdictions could give rise to substantial penalties and liabilities. Any changes in enacted tax laws (such as the recent U.S. tax legislation), rules or regulatory or judicial interpretations or any change in the pronouncements relating to accounting for income taxes could materially and adversely impact our effective tax rate, tax payments, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, we are subject to ongoing and periodic tax audits and disputes in U.S. federal and various state, local and foreign jurisdictions. An unfavorable outcome from any tax audit could result in higher tax costs, penalties and interest, thereby and could materially and adversely affect our financial condition or results of operations.
Failure to comply with laws and regulations applicable to our international operations may increase costs, reduce profits, limit growth or subject us to broader liability.
Our business operations in countries outside the United States are subject to a number of laws and regulations, including restrictions imposed by the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”), as well as trade sanctions administered by the Office of Foreign Assets Control (“OFAC”). The FCPA is intended to prohibit bribery of foreign officials and requires us to keep books and records that accurately and fairly reflect our transactions. OFAC administers and enforces economic and trade sanctions based on U.S. foreign policy and national security goals against targeted foreign states, organizations and individuals. Although we have policies in place designed to comply with applicable sanctions, rules and regulations, it is possible that the timeshare properties we own or manage in the countries and territories in which we operate may provide services to or receive funds from persons subject to sanctions. In addition, some of our operations may be subject to the laws and regulations of non-U.S. jurisdictions, including the U.K.’s Bribery Act of 2010, which contains significant prohibitions on bribery and other corrupt business activities, and other local anti-corruption laws in the countries and territories in which we conduct operations.
If we fail to comply with these laws and regulations, we could be exposed to claims for damages, financial penalties, reputational harm and incarceration of employees or restrictions on our operation or ownership of timeshare and other properties, including the termination of ownership and management rights. In addition, in certain circumstances, the actions of parties affiliated with us (including Hilton, third-party developers, and our and their respective employees and agents) may expose us to liability under the FCPA, U.S. sanctions or other laws. These restrictions could increase costs of operations, reduce profits or cause us to forgo development opportunities that would otherwise support growth.
In August 2012, Congress enacted the Iran Threat Reduction and Syria Human Rights Act of 2012 (“ITRSHRA”), which expands the scope of U.S. sanctions against Iran and Syria. In particular, Section 219 of the ITRSHRA amended the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), to require SEC-reporting companies to disclose in their periodic reports specified dealings or transactions involving Iran or other individuals and entities targeted by certain OFAC sanctions engaged in by the reporting company or any of its
36
affiliates. These companies are required to separately file with the SEC a notice that such activities have been disclosed in the relevant periodic report, and the SEC is required to post this notice of disclosure on its website and send the report to the U.S. President and certain U.S. Congressional committees. The U.S. President thereafter is required to initiate an investigation and, within 180 days of initiating such an investigation with respect to certain disclosed activities, to determine whether sanctions should be imposed.
Under ITRSHRA, we are required to report whether we or any of our “affiliates” knowingly engaged in certain specified activities during a period covered by one of our Annual Reports on Form 10-K or Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q. We may engage in activities that would require disclosure pursuant to Section 219 of ITRSHRA. In addition, because the SEC defines the term “affiliate” broadly, it includes any entity controlled by us as well as any person or entity that controls us or is under common control with us. Disclosure of such activities, even if such activities are permissible under applicable law, and any sanctions imposed on us or our affiliates as a result of these activities could harm our reputation and the Hilton brands we use and have a negative effect on our results of operations.
Risks Related to Our Indebtedness
Our substantial indebtedness and other contractual obligations could adversely affect our financial condition, our ability to raise additional capital to fund our operations, our ability to operate our business, our ability to react to changes in the economy or our industry and our ability to pay our debts, and could divert our cash flow from operations for debt payments.
As of December 31, 2017, our total indebtedness was approximately $1.1 billion. Our substantial debt and other contractual obligations could have important consequences, including:
| • | requiring a substantial portion of cash flow from operations to be dedicated to the payment of principal and interest on our indebtedness, thereby reducing our ability to use our cash flow to fund our operations, capital expenditures, dividends to stockholders and to pursue future business opportunities; |
| • | increasing our vulnerability to adverse economic, industry or competitive developments; |
| • | exposing us to increased interest expense, as our degree of leverage may cause the interest rates of any future indebtedness (whether fixed or floating rate interest) to be higher than they would be otherwise; |
| • | exposing us to the risk of increased interest rates because certain of our indebtedness is at variable rates of interest; |
| • | making it more difficult for us to satisfy our obligations with respect to our indebtedness, and any failure to comply with the obligations of any of our debt instruments, including restrictive covenants, could result in an event of default that accelerates our obligation to repay indebtedness; |
| • | restricting us from making strategic acquisitions or causing us to make non-strategic divestitures; |
| • | limiting our ability to obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, product development, satisfaction of debt service requirements, acquisitions and general corporate or other purposes; |
| • | limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business or market conditions and placing us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors who may be better positioned to take advantage of opportunities that our leverage prevents us from exploiting. |
For additional discussion on our indebtedness, see “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Financing Activities,” and Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse Debt in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
37
Our variable rate indebtedness subjects us to interest rate risk, which could cause our indebtedness service obligations to increase significantly.
Interest rates may increase in the future. As a result, interest rates on our revolving credit facility or other variable rate debt offerings could be higher or lower than current levels. As of December 31, 2017, we had approximately $319 million of variable rate debt, representing 30 percent, of our total debt. If interest rates increase, our debt service obligations on the variable rate indebtedness would increase, even though the amount borrowed remained the same, and our net income and cash flows, including cash available for servicing our indebtedness, would correspondingly decrease.
Servicing our indebtedness requires a significant amount of cash. Our ability to generate sufficient cash depends on many factors, some of which are not within our control.
Our ability to make payments on our indebtedness will depend on our ability to generate cash in the future. Our ability to generate cash depends on our financial and operating performance, which is subject to general economic, financial, competitive, legislative, regulatory and other factors that are beyond our control. In particular, compliance with state and local laws applicable to our business, including those relating to deeds, title transfers and certain other regulations applicable to sales of VOIs, may at times delay or hinder our ability to access cash flows generated by our VOI sales. If we are unable to generate and access sufficient cash flow to service our debt and meet our other commitments, we may need to restructure or refinance all or a portion of our debt, sell material assets or operations or raise additional debt or equity capital. We may not be able to effect any of these actions on a timely basis, on commercially reasonable terms or at all, and these actions may not be sufficient to meet our capital requirements. In addition, the terms of our existing or future debt arrangements may restrict us from effecting any of these alternatives. Finally, our ability to raise additional equity capital may be restricted because the issuance of our stock may cause the spin-off to be a taxable event for Hilton under Section 355(e) of the Code, and under the Tax Matters Agreement (as defined herein), we could be required to indemnify Hilton or Park for that tax and certain covenants may restrict issuances of our stock during the two-year period following the spin-off. See “Item 1. Business—Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off—Tax Matters Agreement.”
Certain of our debt agreements and instruments impose significant operating and financial restrictions on us, our restricted subsidiaries and the guarantors of our indebtedness, which may prevent us from capitalizing on business opportunities.
The debt agreements and instruments that govern our outstanding indebtedness impose significant operating and financial restrictions on us, certain of our subsidiaries and guarantors of our indebtedness. These restrictions limit our ability and/or the ability of our restricted subsidiaries to, among other things:
| • | incur or guarantee additional debt or issue disqualified stock or preferred stock; |
| • | pay dividends (including to us) and make other distributions on, or redeem or repurchase, capital stock; |
| • | make certain investments; |
| • | enter into transactions with affiliates; |
| • | enter into agreements that restrict the ability of restricted subsidiaries to make dividends or other payments to us; |
| • | designate restricted subsidiaries as unrestricted subsidiaries; and |
| • | transfer or sell assets. |
In addition, our credit agreement related to our senior secured credit facilities contains affirmative covenants that will require us to be in compliance with certain leverage and financial ratios.
As a result of these restrictions, we are limited as to how we conduct our business and we may be unable to raise additional debt or equity financing to compete effectively or to take advantage of new business opportunities.
38
The terms of any other future indebtedness we may incur could include more restrictive covenants. We may not be able to maintain compliance with these covenants in the future and, if we fail to do so, we may not be able to obtain waivers from the lenders and/or amend the covenants.
Our failure to comply with the restrictive covenants described above, as well as other terms of our other indebtedness and/or the terms of any future indebtedness from time to time, could result in an event of default, which, if not cured or waived, could result in our being required to repay these borrowings before their due date. If we are forced to refinance these borrowings on less favorable terms or are unable to refinance these borrowings, our financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Our failure to comply with the agreements relating to our outstanding indebtedness could result in an event of default that could materially and adversely affect our results of operations and our financial condition.
If there were an event of default under any of the agreements relating to our outstanding indebtedness, the holders of the defaulted debt could cause all amounts outstanding with respect to that debt to be due and payable immediately. We cannot assure you that our assets or cash flows would be sufficient to fully repay borrowings under our outstanding debt instruments if accelerated upon an event of default. Further, if we are unable to repay, refinance or restructure our indebtedness under our secured debt, the holders of such debt could proceed against the collateral securing that indebtedness. In addition, any event of default or declaration of acceleration under one debt instrument could also result in an event of default under one or more of our other debt instruments.
Repayment of our debt is dependent on cash flow generated by our subsidiaries, which may be subject to limitations beyond our control.
Our subsidiaries own a substantial portion of our assets and conduct a substantial portion of our operations. Accordingly, repayment of our indebtedness is dependent, to a significant extent, on the generation of cash flow by our subsidiaries and their ability to make such cash available to us, by dividend, debt repayment or otherwise.
Our subsidiaries generally do not have any obligation to pay amounts due on our indebtedness or to make funds available to us for that purpose. Our subsidiaries may not be able to, or may not be permitted to, make distributions to enable us to make payments in respect of our indebtedness. Each subsidiary is a distinct legal entity and, under certain circumstances, legal and contractual restrictions may limit our ability to obtain cash from our subsidiaries. While limitations on our subsidiaries restrict their ability to pay dividends or make other intercompany payments to us, these limitations are subject to certain qualifications and exceptions. In addition, certain of our subsidiaries are party to debt agreements that contain restrictions on their ability to pay dividends or make other intercompany payments to us and may in the future enter into agreements that include additional contractual restrictions on their ability to make any such payments to us.
In the event that we are unable to receive distributions from subsidiaries, we may be unable to make required principal and interest payments on our indebtedness.
Despite our current level of indebtedness, we may be able to incur substantially more debt and enter into other transactions, which could further exacerbate the risks to our financial condition described above.
We may be able to incur significant additional indebtedness, including secured debt, in the future. Although the agreements that govern substantially all of our indebtedness contain restrictions on the incurrence of additional indebtedness and entering into certain types of other transactions, these restrictions are subject to a number of qualifications and exceptions. Additional indebtedness incurred in compliance with these restrictions could be substantial. These restrictions also do not prevent us from incurring obligations, such as trade payables, that do not constitute indebtedness as defined under our debt instruments. To the extent new debt is added to our current debt levels, the substantial leverage risks described in the preceding six risk factors would increase.
39
Risks Related to the 2017 Spin-Off From Hilton
We may be responsible for U.S. federal income tax liabilities that relate to the distribution.
The completion of the spin-off was conditioned upon the absence of any withdrawal, invalidation or modification of the ruling (“IRS Ruling”) Hilton received from the IRS regarding certain U.S. federal income tax aspects of the spin-off in an adverse manner prior to the effective time of the spin-off. Although the IRS Ruling generally is binding on the IRS, the continued validity of the IRS Ruling is based upon and subject to the accuracy of factual statements and representations made to the IRS by Hilton.
In addition, the spin-off was conditioned on the receipt of an opinion of Simpson Thacher & Bartlett LLP, Hilton’s tax counsel (“spin-off Tax Counsel”) to the effect that the distributions of our and Park common stock would qualify as tax-free distributions under Section 355 of the Code. An opinion of spin-off Tax Counsel is not binding on the IRS. Accordingly, the IRS may reach conclusions with respect to the spin-off that are different from the conclusions reached in the opinion. The opinion was based on certain factual statements and representations, which, if incomplete or untrue in any material respect, could alter spin-off Tax Counsel’s conclusions.
We are not aware of any facts or circumstances that would cause any such factual statements or representations in the IRS Ruling or the opinion of spin-off Tax Counsel to be incomplete or untrue or cause the facts on which the IRS Ruling and legal opinion are based to be materially different from the facts at the time of the spin-off.
If all or a portion of the spin-off does not qualify as a tax-free transaction for any reason, including because any of the factual statements or representations in the IRS Ruling or the legal opinion are incomplete or untrue, because the facts upon which the IRS Ruling is based are materially different from the facts at the time of the spin-off or because one or more sales of our common stock, Hilton common stock or Park common stock by our respective stockholders after the spin-off cause the spin-off not to qualify as a tax-free transaction, Hilton may recognize a substantial gain attributable to the timeshare business for U.S. federal income tax purposes. In such case, under U.S. Treasury regulations, each member of the Hilton consolidated group at the time of the spin-off (including us and our subsidiaries) would be jointly and severally liable for the resulting entire amount of any U.S. federal income tax liability. Additionally, if the distribution of our common stock and/or the distribution of Park common stock do not qualify as tax-free under Section 355 of the Code, Hilton stockholders will be treated as having received a taxable dividend to the extent of Hilton’s current and accumulated earnings and profits, would have a tax-free basis recovery up to the amount of their tax basis in their shares, and would have taxable gain from the sale or exchange of the shares to the extent of any excess.
Even if the spin-off otherwise qualifies as a tax-free transaction for U.S. federal income tax purposes, the distribution will be taxable to Park and/or Hilton (but not to Hilton stockholders) pursuant to Section 355(e) of the Code if there are (or have been) one or more acquisitions (including issuances) of our stock, the stock of Park or the stock of Hilton, representing 50 percent or more, measured by vote or value, of the stock of any such corporation and the acquisition or acquisitions are deemed to be part of a plan or series of related transactions that include the distribution. Any acquisition of our common stock within two years before or after the distribution (with exceptions, including public trading by less-than-5 percent stockholders and certain compensatory stock issuances) generally will be presumed to be part of such a plan unless that presumption is rebutted. The resulting tax liability would be substantial, and under U.S. Treasury regulations, each member of the Hilton consolidated group at the time of the spin-off (including us and our subsidiaries) would be jointly and severally liable for the resulting U.S. federal income tax liability.
We have agreed not to enter into certain transactions that could cause any portion of the spin-off to be taxable to Hilton, including under Section 355(e) of the Code. Pursuant to the Tax Matters Agreement (as defined herein), we have also agreed to indemnify Hilton and Park for any tax liabilities resulting from such transactions or other actions we take, and Hilton and Park have agreed to indemnify us for any tax liabilities resulting from transactions entered into by Hilton or Park. These obligations may discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of our company.
40
We may be unable to take certain actions because such actions could jeopardize the tax-free status of the spin-off, and such restrictions could be significant.
To preserve the tax-free treatment of the spin-off, for the initial two-year period following the spin-off, we are prohibited, except in limited circumstances, from taking or failing to take certain actions that would prevent the spin-off and related transactions from being tax-free, including: (1) entering into any transaction pursuant to which our stock would be acquired, whether by merger or otherwise; (2) issuing any equity securities or securities that could possibly be converted into our equity securities; or (3) repurchasing our equity securities.
These restrictions may limit our ability to issue equity and to pursue strategic transactions or engage in new business or other transactions that may maximize the value of our business. In addition, if we take, or fail to take, actions that prevent the spin-off and related transactions from being tax-free, we could be liable for the adverse tax consequences resulting from such actions. For a more detailed description, see “Item 1. Business—Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off—Tax Matters Agreement” and “Business—Agreements with Blackstone and HNA—Tax Stockholders Agreement.”
The spin-off and related transactions may expose us to potential liabilities arising out of state and federal fraudulent conveyance laws and legal distribution requirements.
The spin-off could be challenged under various state and federal fraudulent conveyance laws. An unpaid creditor or an entity vested with the power of such creditor (such as a trustee or debtor-in-possession in a bankruptcy) could claim that Hilton did not receive fair consideration or reasonably equivalent value in the spin-off, and that the spin-off left Hilton insolvent or with unreasonably small capital or that Hilton intended or believed it would incur debts beyond its ability to pay such debts as they mature. If a court were to agree with such a plaintiff, then such court could void the spin-off as a fraudulent transfer and could impose a number of different remedies, including without limitation, returning our assets or your shares in our company to Hilton or providing Hilton with a claim for money damages against us in an amount equal to the difference between the consideration received by Hilton and the fair market value of our company at the time of the spin-off.
The measure of insolvency for purposes of the fraudulent conveyance laws may vary depending on which jurisdiction’s law is applied. Generally, however, an entity would be considered insolvent if the fair saleable value of its assets is less than the amount of its liabilities (including the probable amount of contingent liabilities), and such entity would be considered to have unreasonably small capital if it lacked adequate capital to conduct its business in the ordinary course and pay its liabilities as they become due. No assurance can be given as to what standard a court would apply to determine insolvency or that a court would determine that Hilton were solvent at the time of or after giving effect to the spin-off, including the distribution of our common stock.
We have a limited operating history as an independent company and our historical financial information does not predict our future results.
The historical financial information we have included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for periods prior to the spin-off has been derived in part from the consolidated financial statements of Hilton and does not necessarily reflect what our financial position, results of operations and cash flows would have been as a separate, stand-alone entity during the periods presented. Hilton did not account for us, and we were not operated, as a single stand-alone entity for periods prior to the spin-off. The costs and expenses reflected in our historical financial statements for periods prior to the spin-off include an allocation for certain corporate functions historically provided by Hilton. These allocations were based on what we and Hilton considered to be reasonable reflections of the historical utilization levels of these services required in support of our business. The historical information does not necessarily indicate what our results of operations, financial position, cash flows or costs and expenses will be in the future. For additional information, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” “Selected Financial Data,” and our audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We may incur greater costs as an independent company than we did when we were part of Hilton.
As part of Hilton, we were able to advantage of its size and purchasing power in procuring certain goods and services such as insurance and health care benefits, and technology such as computer software licenses. We were also able to rely on Hilton to provide various corporate functions. As a separate, independent entity as a result of
41
the spin-off, we may be unable to obtain these goods, services and technologies at prices or on terms as favorable to us as those we obtained prior to the distribution. We may also incur costs for functions previously performed by Hilton that are higher than the amounts reflected in our historical financial statements, which could cause our profitability to decrease.
Our accounting and other management systems and resources may not be adequately prepared to meet the financial reporting and other requirements to which we are subject as an independent company, and failure to achieve and maintain effective internal controls could have a material adverse effect on our business and the price of our common stock.
Our financial results for periods prior to the spin-off were included within the consolidated results of Hilton, and we believe that our financial reporting and internal controls were appropriate for a subsidiary of a public company. However, we were not directly subject to the reporting and other requirements of the Exchange Act. As a result of the distribution, we are directly subject to reporting and other obligations under the Exchange Act. We are required to comply with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (the “Sarbanes-Oxley Act”) which requires annual management assessments of the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting and a report by our independent registered public accounting firm as to whether we maintained, in all material respects, effective internal controls over financial reporting as of the last day of the year. These reporting and other obligations may place significant demands on our management, administrative and operational resources, including accounting systems and resources.
The Exchange Act requires that we file annual, quarterly and current reports with respect to our business and financial condition. Under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, we are required to maintain effective disclosure controls and procedures and internal controls over financial reporting. To continue to comply with these requirements, which can change over time, we may need to upgrade our systems; implement additional financial and management controls, reporting systems and procedures; and hire additional accounting and finance staff. We expect to continue to incur additional annual expenses for the purpose of addressing these requirements, and those expenses may be significant. If we are unable to upgrade our financial and management controls, reporting systems, information technology systems and procedures in a timely and effective fashion, our ability to comply with our financial reporting requirements and other rules that apply to reporting companies under the Exchange Act could be impaired.
If we are unable to conclude that we have effective internal controls over financial reporting or our independent public accounting firm is unwilling or unable to provide us with an unqualified report on the effectiveness of our internal controls as required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, we may be unable to report our financial information on a timely basis, investors may lose confidence in our operating results, the price of our common stock could decline and we may be subject to litigation or regulatory enforcement actions, which would require additional financial and management resources. This could have a material adverse effect on our business and lead to a decline in the price of our common stock.
We are dependent on Hilton to provide certain services pursuant to the Transition Services Agreement.
We have been developing the capability to provide certain corporate and administrative services such as certain information technology, financial and human resource services internally. However, to the extent that we are unable to develop such capabilities adequately in a timely manner, we will rely on Hilton to continue to provide certain services for a period of time pursuant to the Transition Services Agreement. If Hilton is unable or unwilling to provide such services pursuant to the Transition Services Agreement, or if the agreement is terminated prior to the end of its term, we may be unable to provide such services ourselves or we may have to incur additional expenditures to obtain such services from another provider.
We could be required to assume responsibility for obligations allocated to Hilton or Park under the Distribution Agreement.
We entered into a Distribution Agreement with Hilton and Park (the “Distribution Agreement”) prior to the distribution of our shares of common stock to Hilton stockholders. Under the Distribution Agreement and related ancillary agreements, each of us, Hilton and Park are generally responsible for the debts, liabilities and other obligations related to the business or businesses that they own and operate following the spin-off. Although we do not expect to be liable for any obligations that were not allocated to us under the Distribution Agreement, a court
42
could disregard the allocation agreed to among the parties, and require that we assume responsibility for obligations allocated to Hilton or Park (for example, tax and/or environmental liabilities), particularly if Hilton or Park were to refuse or were unable to pay or perform the allocated obligations. See “Item 1. Business—Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off—Distribution Agreement.”
In addition, losses in respect of certain shared contingent liabilities, which generally are not specifically attributable to any of the timeshare business, the Park business or the retained business of Hilton, were determined on or prior to the date on which the Distribution Agreement was entered (“Shared Contingent Liabilities”). The percentage of Shared Contingent Liabilities for which we are responsible has been fixed in a manner that is intended to approximate our estimated enterprise value on the distribution date relative to the estimated enterprise values of Park and Hilton. Subject to certain limitations and exceptions, Hilton is generally vested with the exclusive management and control of all matters pertaining to any such Shared Contingent Liabilities, including the prosecution of any claim and the conduct of any defense. See “Item 1. Business—Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off —Distribution Agreement.”
In connection with the spin-offs, each of Hilton and Park indemnified us for certain liabilities. These indemnities may not be sufficient to insure us against the full amount of the liabilities assumed by Hilton and Park, and Hilton and Park may be unable to satisfy their indemnification obligations to us in the future.
In connection with the spin-offs, each of Hilton and Park indemnified us with respect to such parties’ assumed or retained liabilities pursuant to the Distribution Agreement and breaches of the Distribution Agreement or other agreements related to the spin-offs. There can be no assurance that the indemnities from each of Hilton and Park will be sufficient to protect us against the full amount of these and other liabilities. Third parties also could seek to hold us responsible for any of the liabilities that Hilton and Park have agreed to assume. Even if we ultimately succeed in recovering from Hilton or Park any amounts for which we are held liable, we may be temporarily required to bear those losses ourselves. Each of these risks could negatively affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
If we are required to indemnify Hilton or Park in connection with the spin-offs, we may need to divert cash to meet those obligations, which could negatively affect our financial results.
Pursuant to the Distribution Agreement entered into in connection with the spin-offs and certain other agreements among Hilton and Park and us, we agreed to indemnify each of Hilton and Park from certain liabilities. Indemnities that we may be required to provide Hilton and/or Park may be significant and could negatively affect our business.
Risks Related to Ownership of Our Common Stock
The interests of certain of our stockholders may conflict with ours or yours in the future.
On March 15, 2017, Blackstone completed the sale of 24,750,000 shares of our common stock to HNA, representing approximately 25 percent of our outstanding common stock. Following the sale, Blackstone held approximately 15 percent of our outstanding common stock; and as of September 25, 2017, Blackstone completed the sale of substantially all of the remaining shares of our common stock held by them. As a result, Blackstone holds only a nominal number of shares of our common stock. HNA continues to hold approximately 25 percent of our outstanding common stock.
We have entered into stockholders agreements with Blackstone and HNA that, among other things, provide Blackstone and HNA the right, under certain circumstances, to designate a number of directors to our board of directors. Although Blackstone has disposed of substantially all of the shares of our common stock that it owned, and no longer has any right to appoint any directors to our board of directors, one director previously designated by Blackstone currently serves on our board of directors. Pursuant to the stockholders agreement with HNA, two members of our board of directors are HNA appointees, and for so long as HNA and its affiliates continue to own specified percentages of our common stock, HNA will be able to maintain representation on our board of directors. Accordingly, during that period of time, HNA may have influence with respect to our management, business plans and policies, including the appointment and removal of our officers. For example, for so long as HNA continues to own a significant percentage of our stock, HNA may be able to influence whether or not a change of control of our company or a change in the composition of our board of directors occurs. The concentration of ownership by HNA
43
could deprive you of an opportunity to receive a premium for your shares of common stock as part of a sale of our company and ultimately might affect the market price of our common stock.
Each of HNA and Blackstone and its respective affiliates engage in a broad spectrum of activities, including investments in real estate generally and in the hospitality industry in particular. In the ordinary course of HNA’s and Blackstone’s business activities, HNA, Blackstone and their affiliates may engage in activities where their interests conflict with our interests or those of our stockholders. For example, all of the timeshare properties that we manage as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K utilize certain Hilton-branded trademarks and Hilton trade names and related intellectual property. Each of HNA and Blackstone and its respective affiliates own a significant portion of the outstanding stock of Hilton and have significant influence with respect to the management, business plans and policies of Hilton. In addition, each of HNA and Blackstone and its respective affiliates may pursue ventures that compete directly or indirectly with us. Moreover, affiliates of HNA and Blackstone may directly and indirectly own interests in timeshare property developers or others with whom we may engage in the future, may compete with us for investment opportunities, and may enter into other transactions with us that could result in their having interests that could conflict with ours. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that none of HNA, Blackstone, any of its respective affiliates, or any director who is not employed by us (including any nonemployee director who serves as one of our officers in both his or her director and officer capacities) or his or her affiliates will have any duty to refrain from engaging, directly or indirectly, in the same business activities or similar business activities or lines of business in which we operate. HNA and Blackstone also may pursue acquisition opportunities that may be complementary to our business, and, as a result, those acquisition opportunities may be unavailable to us. In addition, each of HNA and Blackstone may have an interest in pursuing acquisitions, divestitures and other transactions that, in their judgment, could enhance their respective investments, even though such transactions might involve risks to you.
For additional information, see, “Business— Agreements with Blackstone and HNA—HNA Stockholders Agreement,” “—Blackstone Stockholders Agreement,” and “—Tax Stockholders Agreement.”
Our board of directors may change significant corporate policies without stockholder approval.
Our financing, borrowing and dividend policies and our policies with respect to all other activities, including growth, debt, capitalization and operations, will be determined by our board of directors. These policies may be amended or revised at any time and from time to time at the discretion of our board of directors without a vote of our stockholders. In addition, our board of directors may change our policies with respect to conflicts of interest provided that such changes are consistent with applicable legal requirements. A change in these policies could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, our results of operations, our cash flow, the per share trading price of our common stock and our ability to satisfy our debt service obligations and to pay dividends to our stockholders.
Anti-takeover provisions in our organizational documents and Delaware law might discourage or delay acquisition attempts for us that you might consider favorable.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and bylaws contain provisions that may make the merger or acquisition of our company more difficult without the approval of our board of directors. Among other things:
| • | although we do not have a stockholder rights plan, and would either submit any such plan to stockholders for ratification or cause such plan to expire within a year, these provisions would allow us to authorize the issuance of undesignated preferred stock in connection with a stockholder rights plan or otherwise, the terms of which may be established and the shares of which may be issued without stockholder approval, and which may include super voting, special approval, dividend, or other rights or preferences superior to the rights of the holders of common stock; |
| • | these provisions prohibit stockholder action by written consent unless such action is recommended by all directors then in office; |
| • | these provisions provide that our board of directors is expressly authorized to make, alter or repeal our bylaws and that our stockholders may only amend our bylaws with the approval of 80 percent or more of all the outstanding shares of our capital stock entitled to vote; and |
| • | these provisions establish advance notice requirements for nominations for elections to our board or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at stockholder meetings. |
44
Further, as a Delaware corporation, we are also subject to provisions of Delaware law, which may impair a takeover attempt that our stockholders may find beneficial. These anti-takeover provisions and other provisions under Delaware law could discourage, delay or prevent a transaction involving a change in control of our company, including actions that our stockholders may deem advantageous, or negatively affect the trading price of our common stock. These provisions could also discourage proxy contests and make it more difficult for you and other stockholders to elect directors of your choosing and to cause us to take other corporate actions you desire.
The market price and trading volume of our common stock may fluctuate widely.
For many reasons, including the risks identified in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the market price of our common stock may be more volatile than the market price of Hilton common stock before the spin-off. These factors may result in short-term or long-term negative pressure on the value of our common stock.
The market price of our common stock may fluctuate significantly, depending upon many factors, some of which may be beyond our control, including, but not limited to:
| • | shifts in our investor base; |
| • | our quarterly and annual earnings, or those of comparable companies; |
| • | actual or anticipated fluctuations in our operating results; |
| • | our ability to obtain financing as needed; |
| • | changes in laws and regulations affecting our business; |
| • | changes in accounting standards, policies, guidance, interpretations or principles; |
| • | announcements by us or our competitors of significant investments, acquisitions or dispositions; |
| • | the failure of securities analysts to cover our common stock; |
| • | changes in earnings estimates by securities analysts or our ability to meet those estimates; |
| • | the operating performance and stock price of comparable companies; |
| • | overall market fluctuations; |
| • | a decline in the real estate markets; and |
| • | general economic conditions and other external factors. |
Future issuances of common stock by us, and the availability for and the potential resale of shares held by HNA and its affiliates or other stockholders, may cause the market price of our common stock to decline.
None of the shares outstanding upon consummation of the spin-off were “restricted securities” within the meaning of Rule 144 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and substantially all of the outstanding shares of our common stock are freely tradable and available for resale in the public market, subject to certain restrictions in the case of control shares held by persons deemed to be our affiliates. Accordingly, the market price of our common stock could drop significantly if holders of a substantial number of shares of our common stock sell them in the public market, or if the market perceives that such sales could occur.
Pursuant to the Stockholders Agreement with HNA, for a period of two years from the Sale, HNA may not sell any of the shares of our common stock that it or its affiliates own, except pursuant to certain specified permitted transfers, including a bona fide pledge or encumbrance and a transfer or sale that has been approved in advance by a majority of disinterested members of our board of directors. See, “Business—Agreements with Blackstone and HNA—HNA Stockholders Agreement.” To date, HNA has pledged all of the shares of our common stock held by it pursuant to a margin loan agreement. If margin loan lenders foreclose upon the pledged shares and subsequently sell a substantial number of shares of our common stock in the public market, or if we allow HNA to sell all or substantial all of the shares of our common stock that it owns prior to the expiration of the lock-up period in the public market, the market price of our common stock may decline significantly.
45
We also have entered into a registration rights agreement with HNA, which provides that, beginning two years after the closing of the Sale, HNA will have customary “demand” and “piggyback” registration rights. The registration rights agreement also requires us to pay certain expenses relating to such registrations and to indemnify the registration rights holder against certain liabilities under the Securities Act. See, “Business—Agreements with Blackstone and HNA—Registration Rights Agreements.” As discussed above, if we allow HNA to sell all or substantially all of the shares of our common stock and register such sale prior to the expiration of the lock-up period, or HNA or its affiliates exercise their registration rights after the expiration of the lock-up period and sell their shares in the open market or otherwise, or are perceived by the market as intending to do so, the market price of our stock could decline substantially.
We have adopted an Omnibus Incentive Plan under which an aggregate of 10,000,000 shares of common stock are issuable. Equity-based awards that were outstanding under the Hilton Incentive Plan on the distribution date and held by our employees were converted into awards that became exercisable for or settleable in shares of our common stock; and an aggregate of 1,054,665 shares of our common stock were issued under the Omnibus Incentive Plan in respect of such converted awards. As of December 31, 2017, an aggregate of 1,718,330 shares have been issued under the Omnibus Incentive Plan.
We also adopted a Non-Employee Director Stock Plan, under which 325,000 shares of our common stock are issuable, and an Employee Stock Purchase Plan under which 2,500,000 shares of our common stock are available for issuance. As of December 31, 2017, 32,686 shares have been awarded and zero shares have been issued under the Non-Employee Director Stock Plan and the Employee Stock Purchase Plan, respectively. We filed a registration statement on Form S-8 under the Securities Act to register shares of our common stock or securities convertible into or exchangeable for shares of our common stock issued pursuant to our Omnibus Incentive Plan and our Non-Employee Director Stock Plan. In addition, we filed a registration statement on Form S-8 under the Securities Act to register shares of our common stock to be issued pursuant to our Employee Stock Purchase Plan. Accordingly, shares registered under such registration statements may be sold in the open market.
We have no current plans to pay cash dividends on our common stock, and our indebtedness could limit our ability to pay dividends in the future.
Although we expect to return capital to stockholders through dividends or otherwise in the future, we have no current plans to pay any cash dividends. The declaration, amount and payment of any future dividends on shares of common stock will be at the sole discretion of our board of directors. Our board of directors may take into account general and economic conditions, our financial condition and results of operations, our available cash, current and anticipated cash needs, capital requirements, contractual, legal, tax and regulatory restrictions on the payment of dividends by us to our stockholders or by our subsidiaries to us, and such other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant. In addition, our ability to pay dividends is limited by our credit agreement related to our senior secured credit facilities. Our ability to pay dividends may also be limited by covenants of other indebtedness that we or our subsidiaries incur in the future.
ITEM 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
None.
Timeshare Properties
As of December 31, 2017, we had 48 resorts, representing 8,102 units. We owned 47 percent of all unsold units, representing 1,104 of the 2,372 unsold units, at these resorts. We also own, manage or lease fitness, spa and sports facilities, undeveloped and partially developed land and other common area assets at some of our resorts, including resort lobbies and food and beverage outlets.
As of December 31, 2017, our resorts included the following locations and units:
Property Name | | Ownership(1) | | Location | | Units |
Hilton Grand Vacations (U.S.) | | | | | | |
HGVClub at SeaWorld Orlando | | Developed | | Orlando, FL | | 516 |
46
Property Name | | Ownership(1) | | Location | | Units |
HGVClub at Tuscany Village | | Developed | | Orlando, FL | | 440 |
Parc Soleil by HGVClub | | Developed | | Orlando, FL | | 312 |
Las Palmeras, a Hilton Grand Vacations Club | | Fee-for-service(2) | | Orlando, FL | | 226 |
HGVClub at McAlpin—Ocean Plaza | | Developed | | Miami Beach, FL | | 52 |
HGVClub at the Flamingo | | Developed | | Las Vegas, NV | | 200 |
HGVClub on Paradise | | Developed | | Las Vegas, NV | | 232 |
HGVClub on the Boulevard | | Developed | | Las Vegas, NV | | 714 |
HGVClub at Trump International Hotel Las Vegas(3) | | Developed | | Las Vegas, NV | | 205 |
Elara, a Hilton Grand Vacations Club | | Fee-for-service | | Las Vegas, NV | | 1,201 |
The Grand Islander by HGVClub | | Fee-for-service | | Honolulu, HI | | 418 |
HGVClub at Hilton Hawaiian Village—The Lagoon Tower | | Developed | | Honolulu, HI | | 236 |
HGVClub at Hilton Hawaiian Village—The Kalia Tower | | Developed | | Honolulu, HI | | 72 |
Grand Waikikian by HGVClub | | Developed | | Honolulu, HI | | 331 |
Hokulani Waikiki by HGVClub(3) | | Developed | | Honolulu, HI | | 143 |
Kohala Suites by HGVClub | | Developed | | Waikoloa, HI | | 120 |
Kings’ Land by HGVClub | | Developed | | Waikoloa, HI | | 435 |
The Bay Club at Waikoloa Beach Resort | | Collection | | Waikoloa, HI | | 172 |
The Hilton Club—New York | | Developed | | New York, NY | | 127 |
West 57th Street by Hilton Club | | Developed | | New York, NY | | 166 |
The District by Hilton Club | | Developed | | Washington, DC | | 108 |
HGVClub at Anderson Ocean Club | | Fee-for-service | | Myrtle Beach, SC | | 172 |
Ocean 22 by Hilton Grand Vacations Club | | Fee-for-service | | Myrtle Beach, SC | | 230 |
Ocean Oak Resort by Hilton Grand Vacation Club | | Fee-for-service | | Hilton Head, SC | | 65 |
Sunrise Lodge, a Hilton Grand Vacations Club | | Developed | | Park City, UT | | 83 |
Valdoro Mountain Lodge | | Collection | | Breckenridge, CO | | 70 |
HGVClub at MarBrisa(3) | | Fee-for-service | | Carlsbad, CA | | 196 |
The Cottages at South Seas Island Resort | | Collection | | Captiva, FL | | 14 |
Harbourview Villas at South Seas Island Resort | | Collection | | Captiva, FL | | 10 |
Plantation Bay Villas at South Seas Island Resort | | Collection | | Captiva, FL | | 4 |
Plantation Beach Club at South Seas Island Resort | | Collection | | Captiva, FL | | 56 |
Plantation House at South Seas Island Resort | | Collection | | Captiva, FL | | 12 |
South Seas Club at South Seas Island Resort | | Collection | | Captiva, FL | | 24 |
Casa Ybel Resort | | Collection | | Sanibel, FL | | 74 |
Hurricane House Resort | | Collection | | Sanibel, FL | | 15 |
Sanibel Cottages Resort | | Collection | | Sanibel, FL | | 28 |
Tortuga Beach Club Resort | | Collection | | Sanibel, FL | | 54 |
Seawatch On-the-Beach Resort | | Collection | | Ft. Myers Beach, FL | | 42 |
The Charter Club of Marco Beach | | Collection | | Marco Island, FL | | 80 |
Eagle’s Nest Beach Resort | | Collection | | Marco Island, FL | | 96 |
Club Regency of Marco Island | | Collection | | Marco Island, FL | | 32 |
The Surf Club of Marco | | Collection | | Marco Island, FL | | 44 |
Plantation Beach Club at Indian River Plantation Resort | | Collection | | Hutchinson Island, FL | | 30 |
Hilton International Grand Vacations (non-U.S.) | | | | | | |
HGVClub at Coylumbridge | | Developed | | Scotland | | 61 |
HGVClub at Craigendarroch Suites | | Developed | | Scotland | | 32 |
HGVClub at Craigendarroch Lodge | | Developed | | Scotland | | 99 |
HGVClub at Dunkeld | | Developed | | Scotland | | 22 |
HGVClub at Borgo alle Vigne | | Fee-for-service | | Italy | | 31 |
(1) | Fee-for-service and collection properties are properties that were funded and constructed by a third-party developer. Collection properties are properties that were contributed by a third party during Hilton’s joint venture with Grand Vacations or prior to the spin-off. A developed property is a property that was funded and constructed by Hilton Grand Vacations. Hilton Grand Vacations also manages the operation of the developed properties. |
(2) | We will acquire 20 units at this property as part of a just-in-time arrangement. As of December 31, 2017, we acquired 17 units. |
(3) | Property sub-managed by a third party. |
47
Corporate Headquarters and Sales Distribution Centers
Our corporate headquarters are located at 6355 MetroWest Boulevard, Suite 180, Orlando, Florida 32835, and consist of approximately 102,000 square feet of leased space. The lease for this property initially expires on November 30, 2021 with options to renew for two additional five-year periods. In November 2017, the initial lease was amended extending lease term through November 30, 2026 with no changes to renewal options. Our sales distribution centers are located in Las Vegas, Myrtle Beach, Hilton Head, New York, Washington, D.C., Orlando, Park City, Honolulu, Waikoloa and Tokyo. We also have other corporate offices and call centers located in Orlando, Las Vegas, Honolulu and Tokyo.
We believe that our existing office properties are in good condition and are sufficient and suitable for the conduct of our business. In the event we need to expand our operations, we believe that suitable space will be available on commercially reasonable terms.
We are involved in various claims and lawsuits arising in the ordinary course of business, some of which include claims for substantial sums, including proceedings involving tort and other general liability claims, employee claims, consumer protection claims and privacy claims. Most occurrences involving liability, claims of negligence and employees are covered by insurance with solvent insurance carriers. For those matters not covered by insurance, which include commercial matters, we recognize a liability when we believe the loss is probable and can be reasonably estimated. The ultimate results of claims and litigation cannot be predicted with certainty. We believe we have adequate reserves against such matters. We currently believe that the ultimate outcome of such lawsuits and proceedings will not, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or liquidity. However, depending on the amount and timing, an unfavorable resolution of some or all of these matters could materially affect our future results of operations in a particular period or our ability to run our business as currently conducted.
Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures |
Not applicable.
48
PART II
Item 5. | Market For Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Market Information
Our common stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbol “HGV.” Our common stock began trading on a “when-issued” basis on December 15, 2016 but did not commence regular-way trading on the NYSE until January 4, 2017, the day after the completion of our spin-off. We have not made any unregistered sales of our equity securities.
The following table sets the high and low sales prices for our common stock for the indicated period after regular way trading began:
| | Stock Price | |
| | High | | | Low | |
Year Ended December 31, 2017 | | | | | | | | |
First Quarter (January 4, 2017 through March 31, 2017) | | $ | 31.39 | | | $ | 24.60 | |
Second Quarter | | | 37.73 | | | | 28.69 | |
Third Quarter | | | 39.40 | | | | 32.20 | |
Fourth Quarter | | | 43.19 | | | | 38.56 | |
Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative share price performance since December 15, 2016 with the Russell 2500 (R2500) Index and the Dow Jones US Travel & Leisure Index GICS Level 3 (DJUSTLE). The graph assumes that the value of the investment in our common stock and each index was $100 on December 15, 2016, which was the first day our common stock began trading on a “when-issued” basis.
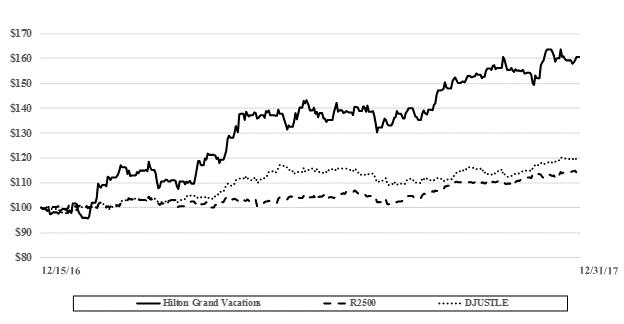
49
Holders of Record
The number of stockholders of record of our common stock as of February 23, 2018 was 23.
Dividends
Although we expect to return capital to stockholders through dividends or otherwise in the future, we have no current plans to pay dividends on our common stock. Any decision to declare and pay dividends in the future will be made at the sole discretion of our board of directors and will depend on, among other things, our results of operations, cash requirements, financial condition, contractual restrictions and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant. In addition, our Senior Secured Credit Facilities (as defined herein) and certain of our non-recourse debt includes a provision limiting our ability to make restricted payments, including dividends.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
We did not repurchase any shares of our common stock during the quarter and year ended December 31, 2017.
Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
The following selected consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The selected historical consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K but was included in our Registration Statement on Form 10. The selected historical consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2013 is derived from our unaudited consolidated financial statements that are not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K but was included in our Registration Statement on Form 10. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results expected for any future period.
The selected consolidated financial data below should be read together with the audited consolidated financial statements, including the notes thereto, and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions, except per share amounts) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
Statement of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues | | $ | 1,711 | | | $ | 1,583 | | | $ | 1,475 | | | $ | 1,317 | | | $ | 1,224 | |
Total operating expenses | | | 1,374 | | | | 1,260 | | | | 1,154 | | | | 1,004 | | | | 975 | |
Net income | | | 327 | | | | 168 | | | | 174 | | | | 167 | | | | 128 | |
Earnings per share (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 3.30 | | | $ | 1.70 | | | $ | 1.76 | | | $ | 1.69 | | | $ | 1.30 | |
Diluted | | $ | 3.28 | | | $ | 1.70 | | | $ | 1.76 | | | $ | 1.69 | | | $ | 1.30 | |
50
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | 2014 | | | 2013 (unaudited) | |
Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Securitized timeshare financing receivables, net | | $ | 444 | | | $ | 244 | | | $ | 350 | | | $ | 468 | | | $ | 221 | |
Unsecuritized timeshare financing receivables, net | | | 627 | | | | 781 | | | | 626 | | | | 460 | | | | 681 | |
Total assets | | | 2,384 | | | | 2,180 | | | | 1,724 | | | | 1,621 | | | | 1,568 | |
Debt, net | | | 482 | | | | 490 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Non-recourse debt, net(2) | | | 583 | | | | 694 | | | | 502 | | | | 625 | | | | 670 | |
Total liabilities(3) | | | 1,866 | | | | 2,013 | | | | 1,830 | | | | 1,994 | | | | 2,103 | |
(1) | For periods ending prior to the spin-off on January 3, 2017, basic and diluted earnings per share was calculated based on shares distributed our shareholders on January 3, 2017. See Note 17: Earnings Per Share in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion. |
(2) | Amounts are net of deferred financing costs. |
(3) | Includes allocated Parent debt of $634 million, $719 million, and $828 million as of December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. In November 2016, we were released from the unconditional obligation to guarantee certain debt balances and related deferred loan costs were allocated to us by Hilton. |
Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes that appear elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Overview
Our Business
We market and sell VOIs, manage vacation resorts in top leisure and urban destinations and operate a point-based vacation club. As of December 31, 2017, we had 48 resorts, representing 8,102 units, and approximately 288,000 Hilton Grand Vacations Club (the “Club”) members. Club members have the flexibility to exchange their Club points for stays at any Hilton Grand Vacations resort or any property in the Hilton system of 14 industry-leading brands across more than 5,000 properties, as well as numerous experiential vacation options, such as cruises and guided tours.
On January 3, 2017, the spin-off was completed and we entered into agreements with Hilton and other third parties, including a license agreement to use the Hilton Grand Vacations brand, that have either not existed historically, or that may be on different terms than the terms of the arrangement or agreements that existed prior to the spin-off. See Part I – “Item 1 Business - Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information.
We operate our business across two segments: (1) real estate sales and financing; and (2) resort operations and club management.
Real Estate Sales and Financing
Our primary product is the marketing and selling of fee-simple VOIs deeded in perpetuity, developed either by us or by third parties. This ownership interest is an interest in real estate generally equivalent to one week annually, at the timeshare resort where the VOI was purchased. Traditionally, timeshare operators have funded 100 percent of the investment necessary to acquire land and construct timeshare properties. In 2010, we began sourcing VOIs through fee-for-service and just-in-time agreements with third-party developers and have successfully transformed from a capital-intensive business to one that is highly capital-efficient. The fee-for-service agreements enable us to generate fees from the sales and marketing of the VOIs and Club memberships and from the management of the timeshare properties without requiring us to fund acquisition and construction costs. The just-in-time agreements enable us to source VOI inventory in a manner that allows us to correlate the timing of acquisition of the inventory
51
with the sale to purchasers. Sales of owned, including just-in-time inventory, generally result in greater Adjusted EBITDA contributions, while fee-for-service sales require less initial investment and allow us to accelerate our sales growth. Both sales of owned inventory and fee-for-service sales generate long-term, predictable fee streams, by adding to the Club membership base and properties under management, that generate strong returns on invested capital.
For the year ended December 31, 2017, sales from fee-for-service, just-in-time and developed inventory sources were 54 percent, 20 percent and 26 percent, respectively, of contract sales. See “—Real Estate Sales Metrics” for additional discussion of contract sales. Based on our 2017 sales pace, we have access to approximately five years of future inventory, with capital efficient arrangements representing approximately 89 percent of that supply. The visibility into our long-term supply allows us to efficiently manage inventory to meet predicted sales, reduce capital investments, minimize our exposure to the cyclicality of the real estate market and mitigate the risks of entering into new markets.
We originate loans for members purchasing our developed and acquired inventory and generate interest income. Our loans are collateralized by the underlying VOIs and are generally structured as 10-year, fully-amortizing loans that bear a fixed interest rate typically ranging from 9 percent to 18 percent per annum.
The interest rate on our loans is determined by, among other factors, the amount of the down payment, the borrower’s credit profile and the loan term. The weighted average FICO score for new loans to U.S. and Canadian borrowers at the time of origination were as follows:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Weighted average FICO score | | | 743 | | | | 741 | | | | 743 | |
Prepayment is permitted without penalty. When a member defaults, we ultimately return their VOI to inventory for resale and that member no longer participates in our Club. Historical default rates, which represent annual defaults as a percentage of each year’s beginning gross timeshare financing receivables balance, were as follows:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Historical default rates(1) | | | 4.12 | % | | | 3.67 | % | | | 2.84 | % |
(1) | A loan is considered to be in default if it is equal to or greater than 121 days past due as of the prior month end. |
Some of our loans have been pledged as collateral in our securitization transactions, which have in the past and may in the future provide funding for our business activities. In these securitization transactions, special purpose entities are established to issue various classes of debt securities which are generally collateralized by a single pool of assets, consisting of timeshare financing receivables that we service and related cash deposits. For additional information see Note 4: Timeshare Financing Receivables in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on form 10-K.
In addition, we earn fees from servicing our securitized loan portfolio and the loans provided by third-party developers of our fee-for-service projects to purchasers of their VOIs.
Resort Operations and Club Management
We enter into a management agreement with the HOA of the VOI owners for timeshare resorts developed by us or a third party. Each of the HOAs is governed by a board of directors comprising owner and developer representatives that are charged with ensuring the resorts are well-maintained and financially stable. Our management services include day-to-day operations of the resorts, maintenance of the resorts, preparation of reports, budgets and projections and employee training and oversight. Our HOA management agreements provide for a cost-plus management fee, which means we generally earn a fee equal to 10 percent to 15 percent of the costs to operate the applicable resort. The fees we earn are highly predictable due to the relatively fixed nature of resort operating
52
expenses and our management fees are unaffected by changes in rental rate or occupancy. We are reimbursed for the costs incurred to perform our services, principally related to personnel providing on-site services. The original term of our management agreements typically ranges from three to five years and the agreements are subject to periodic renewal for one to three year periods. Many of these agreements renew automatically unless either party provides advance notice of termination before the expiration of the term.
We also manage and operate the points-based Hilton Grand Vacations Club and Hilton Club exchange programs, which provide exclusive exchange, leisure travel and reservation services to our Club members. When an owner purchases a VOI, he or she is generally automatically enrolled in the Club and given an annual allotment of points that allow the member to exchange his or her annual usage rights in the VOI that they own for a number of vacation and travel options. In addition to an annual membership fee, Club members pay incremental fees depending on exchanges they choose within the Club system.
We rent unsold VOI inventory, third-party inventory and inventory made available due to ownership exchanges through our club programs. We earn a fee from rentals of third-party inventory. Additionally, we provide ancillary offerings including food and beverage, retail and spa offerings at these timeshare properties.
Principal Components and Factors Affecting Our Results of Operations
Principal Components of Revenues
| • | Sales of VOIs, net represents revenue recognized from the sale of owned VOIs. |
| • | Sales, marketing, brand and other fees represents sales commissions, brand fees and other fees earned on the sale of VOIs through fee-for-service agreements with third-party developers. The sales commissions and brand fees are based on the total sales price of the VOI. Also included in Sales, marketing, brand and other fees are revenues from marketing and incentive programs, including redemption of Club Bonus Points and prepaid vacation packages, excluding stays at Hilton Grand Vacations properties, which are included in Rental and ancillary services. |
| • | Financing represents revenue from the financing of sales of our owned intervals, which includes interest income and fees from servicing loans. We also earn fees from servicing the loans provided by third-party developers to purchasers of their VOIs. |
| • | Resort and club management represents revenues from Club activation fees, annual dues and transaction fees from member exchanges. Resort and club management also includes recurring management fees under our agreements with HOAs for day-to-day-management services, including housekeeping services, maintenance, and certain accounting and administrative services for HOAs, generally based on a percentage of costs to operate the resorts. |
| • | Rental and ancillary services represents revenues from transient rentals of unoccupied vacation ownership units and revenues recognized from the utilization of Club points and vacation packages when points and packages are redeemed for rental stays at one of our resorts. We also earn fees from the rental of inventory owned by third parties. Ancillary revenues include food and beverage, retail, spa offerings and other guest services provided to resort guests. |
| • | Cost reimbursements include costs that HOAs and developers reimburse to us. These costs primarily consist of payroll and payroll-related costs for management of the HOAs and other services we provide where we are the employer. The corresponding expenses are presented as Cost reimbursements expense in our consolidated statements of operations resulting in no effect on net income. |
Factors Affecting Revenues
| • | Relationships with developers. In recent years, we have entered into fee-for-service and just-in-time agreements to sell VOIs on behalf of or acquired from third-party developers. The success and sustainability of our capital-efficient business model depend on our ability to maintain good relationships with third-party developers. Our relationships with these third parties also generate new relationships with developers and opportunities for property development that can support our growth. |
53
| | We believe that we have strong relationships with our third-party developers and are committed to the continued growth and development of these relationships. These relationships exist with a diverse group of developers and are not significantly concentrated with any particular third party. |
| • | Consumer demand and global economic conditions. Consumer demand for our products and services may be affected by the performance of the general economy and is sensitive to business and personal discretionary spending levels. Declines in consumer demand due to adverse general economic conditions, risks affecting or reducing travel patterns, lower consumer confidence and adverse political conditions can subject and have subjected our revenues to significant volatility. |
| • | Interest rates. We generate interest income from consumer loans we originate and declines in interest rates may cause us to lower our interest rates on our originated loans, which would adversely affect our income generated on future loans. |
| • | Competition. We compete with other hotel and resort timeshare operators for sales of VOIs based principally on location, quality of accommodations, price, service levels and amenities, financing terms, quality of service, terms of property use, reservation systems and flexibility for VOI owners to exchange into time at other timeshare properties or other travel rewards. In addition, we compete based on brand name recognition and reputation. Our primary branded competitors in the timeshare space include Marriott Vacations Worldwide, Wyndham Vacation Ownership, Vistana Signature Experiences, Disney Vacation Club, Hyatt Residence Club, Holiday Inn Club Vacations, Bluegreen Vacations and Diamond Resorts International. |
Principal Components of Expenses
| • | Cost of VOI sales represents the costs attributable to the sales of owned VOIs recognized, as well as charges incurred related to granting credit to customers for their existing ownership when upgrading into fee-for-service projects. |
| • | Sales and marketing represents costs incurred to sell and market VOIs, including costs incurred relating to marketing and incentive programs, costs for tours, rental expense and wages and sales commissions. |
| • | Financing represents consumer financing interest expense related to our Securitized Debt and Timeshare Facility, amortization of the related deferred loan costs and other expenses incurred in providing consumer financing and servicing loans. |
| • | Resort and club management represents costs incurred to manage resorts and the Club, including payroll and related costs and other administrative costs. |
| • | Rental and ancillary services include: payroll and related costs; costs incurred from participating in the Hilton Honors loyalty program; retail, food and beverage costs; and maintenance fees on unsold inventory. |
| • | General and administrative consists primarily of compensation expense for our corporate staff and personnel supporting our business segments, professional fees (including consulting, audit and legal fees), administrative and related expenses. General and administrative also includes costs for services provided to us by Hilton. |
| • | Depreciation and amortization are non-cash expenses that primarily consist of amortization of our management agreement intangible and capitalized software, as well as depreciation of fixed assets such as buildings and leasehold improvements and furniture and equipment at our sales centers and corporate offices. |
| • | License fee expense represents the royalty fee paid to Hilton under a license agreement for the exclusive right to use the Hilton Grand Vacations mark, which is generally based on a percentage of gross sales volume. |
| • | Cost reimbursements include costs that HOAs and developers reimburse to us. These costs primarily consist of payroll and payroll-related costs for management of the HOAs and other services we provide where we are the employer. The corresponding revenues are presented as Cost reimbursements revenue in our consolidated statements of operations resulting in no effect on net income. |
54
Factors Affecting Expenses
| • | Costs of VOI sales. In periods where there is increased demand for VOIs, we may incur increased costs to acquire inventory in the short-term, which can have an adverse effect on our cash flows, margins and profits. Additionally, as we encourage owners to upgrade into other products, we incur expenses when owners upgrade from an interval in a project we developed into fee-for-service projects, on which we earn fees. In periods where more upgrades are occurring and we are not generating increased sales volume on unsold supply, we could see an adverse effect on our cash flows, margins and profits. |
| • | Sales and marketing expense. A significant portion of our costs relates to selling and marketing of our VOIs. In periods of decreased demand for VOIs, we may be unable to reduce our sales and marketing expenses quickly enough to prevent a deterioration of our profit margins on our real estate operations. |
| • | Rental and ancillary services expense. These expenses include personnel costs, rent, property taxes, insurance and utilities. We pay a portion of these costs through maintenance fees of unsold intervals and by subsidizing the costs of HOAs not covered by maintenance fees collected. If we are unable to decrease these costs significantly or rapidly when demand for our unit rentals decreases, the resulting decline in our revenues could have an adverse effect on our net cash flow, margins and profits. |
| • | General and administrative. Increases in general and administrative expenses as a result of becoming an independent publicly traded company such as costs of separation, regulatory filings and professional fees may affect our net cash flows, margins and profits. |
| • | Interest rates. Increases in interest rates would increase the consumer financing interest expense we pay on the Timeshare Facility and could adversely affect our financing operations in future securitization or other debt transactions, affecting net cash flow, margins and profits. |
Other Items
| • | Seasonality. We experience modest seasonality in VOI sales at certain resorts, with increased revenue during traditional vacation periods for those locations. |
| • | Regulation. Our business activities are highly regulated. We are subject to a wide variety of complex international, national, federal, state and local laws, regulations and policies in jurisdictions in which we operate. These laws, regulations and policies primarily affect four areas of our business: real estate development activities; marketing and sales activities; lending activities; and resort management activities. We seek to actively participate in the determination of new laws or other regulations affecting the timeshare industry. For further detail of these regulations see “Risk Factors” and “Business–Government Regulation” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
Key Business and Financial Metrics and Terms Used by Management
Real Estate Sales Metrics
| • | Contract sales represents the total amount of VOI products (fee-for-service and developed) under purchase agreements signed during the period where we have received a down payment of at least 10 percent of the contract price. Contract sales is not a recognized term under U.S. GAAP and should not be considered in isolation or as an alternative to Sales of VOIs, net or any other comparable operating measure derived in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Contract sales differ from revenues from the Sales of VOIs, net that we report in our consolidated statements of operations due to the requirements for revenue recognition as described in Note 2: Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies in our audited consolidated financial statements, as well as adjustments for incentives and other administrative fee revenues. We consider contract sales to be an important operating measure because it reflects the pace of sales in our business. |
| • | Sales revenue represents sale of VOIs, net and commissions and brand fees earned from the sale of fee-for-service intervals. |
| • | Real estate margin represents sales revenue less the cost of VOI sales and sales and marketing costs, net of marketing revenue. Real estate margin percentage is calculated by dividing real estate margin by |
55
| | sales revenue. We consider this to be an important operating measure because it measures the efficiency of our sales and marketing spending and management of inventory costs. |
| • | Tour flow represents the number of sales presentations given at our sales centers during the period. |
| • | Volume per guest (“VPG”) represents the sales attributable to tours at our sales locations and is calculated by dividing Contract sales, excluding telesales, by tour flow. We consider VPG to be an important operating measure because it measures the effectiveness of our sales process, combining the average transaction price with the closing rate. |
Resort and Club Management and Rental Metrics
| • | Transient rate represents the total rental room revenue for transient guests divided by total number of transient room nights sold in a given period and excludes room rentals associated with marketing programs, owner usage and the redemption of Club Bonus Points. See Note 2: Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion on Club Bonus Points. |
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA
EBITDA, presented herein, is a financial measure that is not recognized under U.S. GAAP that reflects net income (loss), before interest expense, a provision for income taxes and depreciation and amortization. During the first quarter of 2017, we revised our definition of EBITDA to exclude the adjustment of interest expense relating to our non-recourse debt as a reconciling item to arrive at net income (loss) in order to conform to the presentation of the timeshare industry following the consummation of the spin-off from Hilton. The revised definition was applied to prior period(s) to conform with current presentation. Adjusted EBITDA, presented herein, is calculated as EBITDA, as previously defined, further adjusted to exclude certain items, including, but not limited to, gains, losses and expenses in connection with: (i) asset dispositions; (ii) foreign currency transactions; (iii) debt restructurings/retirements; (iv) non-cash impairment losses; (v) reorganization costs, including severance and relocation costs; (vi) share-based and certain other compensation expenses; (vii) costs related to the spin-off; and (viii) other items.
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA are not recognized terms under U.S. GAAP and should not be considered as alternatives to net income (loss) or other measures of financial performance or liquidity derived in accordance with U.S. GAAP. In addition, our definitions of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA may not be comparable to similarly titled measures of other companies.
We believe that EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA provide useful information to investors about us and our financial condition and results of operations for the following reasons: (i) EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA are among the measures used by our management team to evaluate our operating performance and make day-to-day operating decisions; and (ii) EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA are frequently used by securities analysts, investors and other interested parties as a common performance measure to compare results or estimate valuations across companies in our industry.
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA have limitations as analytical tools and should not be considered either in isolation or as a substitute for net income (loss), cash flow or other methods of analyzing our results as reported under U.S. GAAP. Some of these limitations are:
| • | EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect changes in, or cash requirements for, our working capital needs; |
| • | EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect our interest expense (excluding interest expense on non-recourse debt), or the cash requirements necessary to service interest or principal payments on our indebtedness; |
| • | EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect our tax expense or the cash requirements to pay our taxes; |
56
| • | EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect historical cash expenditures or future requirements for capital expenditures or contractual commitments; |
| • | EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect the effect on earnings or changes resulting from matters that we consider not to be indicative of our future operations; |
| • | EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect any cash requirements for future replacements of assets that are being depreciated and amortized; and |
| • | EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA may be calculated differently from other companies in our industry limiting their usefulness as comparative measures. |
Because of these limitations, EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA should not be considered as discretionary cash available to us to reinvest in the growth of our business or as measures of cash that will be available to us to meet our obligations.
Recent Events
On January 18, 2018, we completed an offer to exchange up to $300 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 6.125% senior unsecured notes due 2024 that we had issued in November 2016 in a private placement offering (the “original notes”) for up to $300 million of new 6.125% senior unsecured notes due 2024 that have been registered (the “exchange notes”) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. The exchange notes, which have identical terms as the original notes, were issued pursuant to a prospectus, dated December 12, 2017, relating to our registration statement on Form S-4 that was declared effective by the SEC on December 8, 2017. Pursuant to the exchange offer, holders of an aggregate principal amount of $299.95 million of the original notes, which represented approximately 99.98% of the outstanding principal amount of such notes, tendered for an equal amount of the exchange notes.
On December 22, 2017, the United States enacted tax reform legislation commonly known as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Act”), resulting in significant modifications to existing law. HGV follows the guidance in SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin 118 (“SAB 118”), which provides additional clarification regarding the application of Accounting Standards Codification Topic 740 (“ASC 740”) in situations where we do not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the Act for the reporting period in which the Act was enacted. SAB 118 provides for a measurement period beginning in the reporting period that includes the Act’s enactment date and ending when we have obtained, prepared, and analyzed the information needed in order to complete the accounting requirements but in no circumstances should the measurement period extend beyond one year from the enactment date.
As of December 31, 2017, we have not completed our accounting for the tax effects of enactment of the Act. However, in certain cases, we have made a reasonable estimate of the effects on the one-time transition tax and our existing deferred tax balances. In other cases, we have not been able to make a reasonable estimate and continue to account for those items based on our existing accounting under ASC 740, Income Taxes, and the provisions of the tax laws that were in effect immediately prior to enactment. In all cases, we will continue to make and refine our calculations as additional analysis is completed. In addition, our estimates may also be affected as we gain a more thorough understanding of the Act. See Note 15: Income Taxes included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information.
Hurricane Irma
On September 10, 2017, Hurricane Irma hit the Florida Keys as a Category 4 hurricane, weakening somewhat as it made landfall along Florida’s southwest shoreline. Although certain of our managed Florida properties were temporarily closed during the aftermath of Hurricane Irma, neither HGV’s operations nor financial performance were significantly impacted by this storm. In the aftermath of Hurricane Irma, the IRS granted an automatic extension to individuals and businesses affected by the hurricane, which extended tax filing and payment deadlines beginning September 4, 2017. As a result, we delayed our third and fourth quarter Federal income tax payments until January 2018.
57
Results of Operations
Year Ended December 31, 2017 Compared with Year Ended December 31, 2016 and Year Ended December 31, 2016 Compared with Year Ended December 31, 2015
Segment Results
We evaluate our business segment operating performance using segment Adjusted EBITDA, as described in Note 19: Business Segments in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We do not include equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate in our measures of segment revenues. For a discussion of our definition of EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA, how management uses them to manage our business and material limitations on their usefulness, refer to “—Key Business and Financial Metrics and Terms Used by Management—EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA.” The following tables set forth revenues and Adjusted EBITDA by segment, reconciled to consolidated amounts, including net income, our most comparable U.S. GAAP financial measure:
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Real estate sales and financing | | $ | 1,239 | | | $ | 1,143 | | | $ | 1,078 | | | $ | 96 | | | | 8.4 | % | | $ | 65 | | | | 6.0 | % |
Resort operations and club management | | | 367 | | | | 339 | | | | 307 | | | | 28 | | | | 8.3 | | | | 32 | | | | 10.4 | |
Segment revenues | | | 1,606 | | | | 1,482 | | | | 1,385 | | | | 124 | | | | 8.4 | | | | 97 | | | | 7.0 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | 135 | | | | 126 | | | | 110 | | | | 9 | | | | 7.1 | | | | 16 | | | | 14.5 | |
Intersegment eliminations(1) | | | (30 | ) | | | (25 | ) | | | (20 | ) | | | (5 | ) | | | 20.0 | | | | (5 | ) | | | 25.0 | |
Total revenues | | $ | 1,711 | | | $ | 1,583 | | | $ | 1,475 | | | $ | 128 | | | | 8.1 | | | $ | 108 | | | | 7.3 | |
(1) | Refer to Note 19: Business Segments in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for details on the intersegment eliminations. |
The following table reconciles net income, our most comparable U.S. GAAP financial measure, to EBITDA and Adjusted
EBITDA:
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Net Income | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 168 | | | $ | 174 | | | $ | 159 | | | | 94.6 | % | | $ | (6 | ) | | (3.4)% | |
Interest expense | | | 27 | | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | 24 | | | NM(1) | | | | 3 | | | NM(1) | |
Allocated Parent interest expense | | | — | | | | 26 | | | | 29 | | | | (26 | ) | | | (100.0 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (10.3 | ) |
Income tax (benefit) expense | | | (16 | ) | | | 125 | | | | 118 | | | | (141 | ) | | NM(1) | | | | 7 | | | | 5.9 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 29 | | | | 24 | | | | 22 | | | | 5 | | | | 20.8 | | | | 2 | | | | 9.1 | |
Interest expense, depreciation and amortization included in equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3 | | | NM(1) | | | | — | | | NM(1) | |
EBITDA | | | 370 | | | | 346 | | | | 343 | | | | 24 | | | | 6.9 | | | | 3 | | | | 0.9 | |
Other loss, net | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | (1 | ) | | | (100.0 | ) | | | 1 | | | NM(1) | |
Share-based compensation expense | | | 15 | | | | 8 | | | | 13 | | | | 7 | | | 87.5 | | | | (5 | ) | | | (38.5 | ) |
Other adjustment items(2) | | | 10 | | | | 35 | | | | 4 | | | | (25 | ) | | | (71.4 | ) | | | 31 | | | NM(1) | |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 395 | | | $ | 390 | | | $ | 360 | | | $ | 5 | | | | 1.3 | | | $ | 30 | | | | 8.3 | |
(1) | Fluctuation in terms of percentage change is not meaningful. |
(2) For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, amounts include $8 million and $30 million, respectively, of costs associated with the spin-off transaction.
58
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Adjusted EBITDA: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Real estate sales and financing(2) | | $ | 359 | | | $ | 336 | | | $ | 316 | | | $ | 23 | | | | 6.8 | % | | $ | 20 | | | | 6.3 | % |
Resort operations and club management(2) | | | 204 | | | | 189 | | | | 162 | | | | 15 | | | | 7.9 | | | | 27 | | | | 16.7 | |
Segment Adjusted EBITDA | | | 563 | | | | 525 | | | | 478 | | | | 38 | | | | 7.2 | | | | 47 | | | | 9.8 | |
Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjusted EBITDA from unconsolidated affiliate | | | 4 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 4 | | | NM(1) | | | | — | | | NM(1) | |
License fee expense | | | (87 | ) | | | (80 | ) | | | (74 | ) | | | (7 | ) | | | 8.8 | | | | (6 | ) | | | 8.1 | |
General and administrative(3) | | | (85 | ) | | | (55 | ) | | | (44 | ) | | | (30 | ) | | | 54.5 | | | | (11 | ) | | | 25.0 | |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 395 | | | $ | 390 | | | $ | 360 | | | $ | 5 | | | | 1.3 | | | $ | 30 | | | | 8.3 | |
(1) | Fluctuation in terms of percentage change is not meaningful. |
(2) | Includes intersegment eliminations and other adjustments. |
(3) | Excludes share-based compensation and other adjustment items. |
Real Estate Sales and Financing
Real estate sales and financing segment revenues increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to a $62 million increase in sales revenue, a $23 million increase in marketing revenue and a $13 million increase in financing revenue. The increase in sales revenue was primarily due to a $40 million increase in Sales of VOIs, net, due to sales at our newly developed projects beginning the second half of 2016, in Washington, DC and New York, NY as well as a $22 million increase in commission and brand fees. The $23 million increase in marketing revenue was primarily due to a $10 million reduction of our expected redemptions of expired discounted vacation packages and an $11 million increase in other marketing revenue. The increase in financing revenue was primarily due to an increase in interest income from higher outstanding timeshare financing receivable balances. Real estate sales and financing segment Adjusted EBTIDA increased by $23 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to an increase in revenues associated with the segment, partially offset by a $69 million increase in sales and marketing and financing expenses.
Real estate sales and financing segment revenues increased for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to 2015, primarily due to a $44 million increase in sales revenue. The increase in sales revenue was primarily due to a $28 million increase in commissions and brand fees and a $16 million increase in sales of VOIs, net. The sales of VOIs, net increased primarily due to sales at our newly developed projects during the second half of 2016, partially offset by a $10 million increase in our loan loss provision. Additionally, marketing revenues and financing revenues increased $14 million and $7 million, respectively. Real estate sales and financing segment Adjusted EBITDA increased primarily due to an increase in revenues associated with the segment and a $21 million decrease in cost of VOI sales, due to a decline in existing owners upgrading into fee-for-service projects, partially offset by a $64 million increase in sales and marketing expense.
Refer to “—Real Estate” and “—Financing” for further discussion on the revenues and expenses of the real estate sales and financing segment.
Resort Operations and Club Management
Resort operations and club management segment revenues increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to (i) a $15 million increase in resort and club management revenues from the launch of new properties during and subsequent to the second quarter of 2016 and (ii) an increase of $6 million in rental and ancillary services revenues as a result of higher transient room and club inventory rentals at our developed and fee-for-service properties. Resort operations and club management segment Adjusted EBITDA increased from the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to increases in revenues associated with the segment, partially offset by a $16 million increase in segment expenses.
59
Resort operations and club management segment revenues increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily as a result of a $14 million increase in club operations revenue, a $4 million increase in resort management revenue and a $9 million increase in rental revenue. Resort operations and club management segment Adjusted EBITDA increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to increases in segment revenues, partially offset by a $4 million increase in resort operations and club management expenses.
Refer to “—Resort and Club Management” and “—Rental and Ancillary Services” for further discussion on the revenues and expenses of the resort operations and club management segment.
Real Estate Sales and Financing Segment
Real Estate
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions, except Tour flow and VPG) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Sales of VOIs, net | | $ | 548 | | | $ | 508 | | | $ | 492 | | | $ | 40 | | | | 7.9 | % | | $ | 16 | | | | 3.3 | % |
Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fee-for-service sales(1) | | | 694 | | | | 657 | | | | 611 | | | | 37 | | | | 5.6 | | | | 46 | | | | 7.5 | |
Loan loss provision | | | 58 | | | | 49 | | | | 39 | | | | 9 | | | | 18.4 | | | | 10 | | | | 25.6 | |
Reportability and other(2) | | | (25 | ) | | | (42 | ) | | | (74 | ) | | | 17 | | | | (40.5 | ) | | | 32 | | | | (43.2 | ) |
Contract sales | | $ | 1,275 | | | $ | 1,172 | | | $ | 1,068 | | | $ | 103 | | | | 8.8 | | | $ | 104 | | | | 9.7 | |
Tour flow | | | 330,775 | | | | 306,141 | | | | 287,855 | | | | 24,634 | | | | 8.0 | | | | 18,286 | | | | 6.4 | |
VPG | | $ | 3,657 | | | $ | 3,596 | | | $ | 3,508 | | | $ | 61 | | | | 1.7 | | | $ | 88 | | | | 2.5 | |
(1) | Represents contract sales from fee-for-service properties on which we earn commissions and brand fees. |
(2) | Includes adjustments for revenue recognition, including percentage-of-completion deferrals and amounts in rescission, and sales incentives, as well as adjustments related to granting credit to customers for their existing ownership when upgrading into fee-for-service projects. |
Contract sales increased for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to 2016, primarily due to an increase in tour flow, telesales and VPG. VPG increased due to a 1.9 percent increase in average transaction price, partially offset by a 0.2 percentage point decrease in the close rate.
Contract sales increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to an increase in tour flow, telesales and VPG. VPG increased due to a 0.61 percentage point increase in the close rate and a 4.3 percent increase in average transaction price.
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Sales of VOIs, net | | $ | 548 | | | $ | 508 | | | $ | 492 | | | $ | 40 | | | | 7.9 | % | | $ | 16 | | | | 3.3 | % |
Sales, marketing, brand and other fees | | | 544 | | | | 499 | | | | 457 | | | | 45 | | | | 9.0 | | | | 42 | | | | 9.2 | |
Less: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Marketing revenue and other fees | | | 145 | | | | 122 | | | | 108 | | | | 23 | | | | 18.9 | | | | 14 | | | | 13.0 | |
Sales revenue | | | 947 | | | | 885 | | | | 841 | | | | 62 | | | | 7.0 | | | | 44 | | | | 5.2 | |
Less: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of VOI sales | | | 148 | | | | 152 | | | | 173 | | | | (4 | ) | | | (2.6 | ) | | | (21 | ) | | | (12.1 | ) |
Sales and marketing expense, net(1) | | | 492 | | | | 447 | | | | 397 | | | | 45 | | | | 10.1 | | | | 50 | | | | 12.6 | |
Real estate margin | | $ | 307 | | | $ | 286 | | | $ | 271 | | | $ | 21 | | | | 7.3 | | | $ | 15 | | | | 5.5 | |
Real estate margin percentage | | | 32.4 | % | | | 32.3 | % | | | 32.2 | % | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(1) | Includes revenue recognized through our marketing programs for existing owners and prospective first-time buyers. For the year ended December 31, 2017, we revised our definition of Sales and marketing expense, net to include revenues associated with sales incentives, title service and document compliance revenue to better align with how we evaluate the |
60
| results of our real estate operations. This adjustment was retrospectively applied to prior period(s) to conform with the current presentation. |
Sales revenue increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to (i) a $40 million increase in Sales of VOIs, net, beginning the second half of 2016, as we started sales at our newly developed projects in Washington, DC and New York, NY and (ii) a $22 million increase in commission and brand fees due to the launch of one new fee-for-service property in the second quarter of 2016. Real estate margin increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily as a result of the aforementioned increase in sales revenue, partially offset by higher sales and marketing expense due to an increase in contract sales volume and research and development costs to evaluation new markets. The increase in sales and marketing expense, net, was partially offset by a $10 million reduction of our expected redemptions of expired discounted vacation packages and a $11 million increase in other marketing revenue. Real estate margin percentage was flat for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016.
Sales revenue increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to (i) a $16 million increase in Sales of VOIs, net due to higher sales volume at certain existing, owned resorts and the commencement of sales at our new resorts, (ii) a $28 million increase in commissions and brand fees due to the launch of two new fee-for-service products, one in late 2015 and one in early 2016, that resulted in higher sales volume during the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to 2015. Additionally, during the second half of 2016, we had increased sales due to our new, owned project, The District.
Sales of VOIs, net increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, due to higher sales volumes at certain existing, owned resorts and the commencement of sales at our new resorts. We have increased our percentage of fee-for-service sales compared to that of sales of developed or acquired inventory over the last three years, resulting in decreases to sales of VOIs, net and increases in sales, marketing, brand and other fees revenue.
Real estate margin increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, as a result of the increases in sales revenue and decreased cost of VOI sales, due to a decline in existing owners upgrading into fee-for-service projects, partially offset by higher sales and marketing expense based on increased contract sales volume. Real estate margin percentage was flat for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, compared to the respective prior periods. Real estate margin percentage was flat for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015.
Financing
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs. 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs. 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Interest income | | $ | 132 | | | $ | 122 | | | $ | 117 | | | $ | 10 | | | | 8.2 | % | | $ | 5 | | | | 4.3 | % |
Other financing revenue | | | 15 | | | | 12 | | | | 10 | | | | 3 | | | | 25.0 | | | | 2 | | | | 20.0 | |
Financing revenue | | | 147 | | | | 134 | | | | 127 | | | | 13 | | | | 9.7 | | | | 7 | | | | 5.5 | |
Consumer financing interest expense | | | 20 | | | | 12 | | | | 13 | | | | 8 | | | | 66.7 | | | | (1 | ) | | | (7.7 | ) |
Other financing expense | | | 23 | | | | 20 | | | | 19 | | | | 3 | | | | 15.0 | | | | 1 | | | | 5.3 | |
Financing expense | | | 43 | | | | 32 | | | | 32 | | | | 11 | | | | 34.4 | | | | — | | | — | |
Financing margin | | $ | 104 | | | $ | 102 | | | $ | 95 | | | $ | 2 | | | | 2.0 | | | $ | 7 | | | | 7.4 | |
Financing margin percentage | | | 70.7 | % | | | 76.1 | % | | | 74.8 | % | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Financing revenue increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, due to an increase of $10 million in interest income resulting from a higher outstanding timeshare financing receivables balance and a $3 million increase in fees generated from servicing the loans provided by third-party developers to purchasers their VOIs.
Financing revenue increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, due to an increase of $5 million in interest income resulting from a higher outstanding timeshare financing receivables balance and an
61
increase of $2 million in fees generated from servicing the loans provided by third-party developers to purchasers their VOIs, increased consistent with the increase in fee-for-service sales.
Financing margin increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, comparing to 2016, primarily due to an increase in the loan portfolio. Financing margin increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to an increase in the loan portfolio, a stable interest rate environment and no additional securitization transactions occurring in the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015. Financing margin percentage decreased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to higher non-recourse debt balance associated with the additional drawdown on our timeshare facility in December 2016 and our 2017 securitization. See Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse Debt in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information.
Resort and Club Management
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Club management revenue | | $ | 99 | | | $ | 92 | | | $ | 78 | | | $ | 7 | | | | 7.6 | % | | $ | 14 | | | | 17.9 | % |
Resort management revenue | | | 59 | | | | 51 | | | | 47 | | | | 8 | | | | 15.7 | | | | 4 | | | | 8.5 | |
Resort and club management revenues | | | 158 | | | | 143 | | | | 125 | | | | 15 | | | | 10.5 | | | | 18 | | | | 14.4 | |
Club management expense | | | 25 | | | | 23 | | | | 20 | | | | 2 | | | | 8.7 | | | | 3 | | | | 15.0 | |
Resort management expense | | | 18 | | | | 13 | | | | 12 | | | | 5 | | | | 38.5 | | | | 1 | | | | 8.3 | |
Resort and club management expenses | | | 43 | | | | 36 | | | | 32 | | | | 7 | | | | 19.4 | | | | 4 | | | | 12.5 | |
Resort and club management margin | | $ | 115 | | | $ | 107 | | | $ | 93 | | | $ | 8 | | | | 7.5 | | | $ | 14 | | | | 15.1 | |
Resort and club management margin percentage | | | 72.8 | % | | | 74.8 | % | | | 74.4 | % | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Resort and club management revenues increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to (i) an increase in resort management revenue from the launch of new properties during the second half of 2016 and (ii) an increase of approximately 19,300 in Club members and higher rates pertaining to annual dues and transaction fees. These increases were partially offset by higher resort and club management expenses due to an increase in costs for servicing additional Club members and properties and a one-time fee earned in 2016 on a prepaid contract.
Resort and club management revenues increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to increases in Club management revenue due to increases in net Club members, of approximately 19,200, as well as increases in transaction volume per Club member and fees earned on additional units under management. Additionally, resort management revenue increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to increases in units open and under management of seven percent as well as an increase in management services provided.
Resort and club management margin increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to the aforementioned increases in segment revenues, partially offset by a one-time fee earned in 2016 on a prepaid contract as well as a $7 million increase in segment expenses as a result of customer and company related initiatives. Rental and club management margin percentage decreased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to an increase in segment expenses as a result of customer and company related initiatives, partially offset by the aforementioned increases in segment revenues.
Resort and club management margin increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to increases in net Club members and units open and under management, partially offset by slight increases in resort and club management expenses. Resort and club management margin increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to the aforementioned increases in segment revenues, partially offset by a $4 million increase in resort and club management expenses. Resort and club management margin percentage remained flat for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015.
62
Rental and Ancillary Services
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Rental revenues | | $ | 156 | | | $ | 149 | | | $ | 140 | | | $ | 7 | | | | 4.7 | % | | $ | 9 | | | | 6.4 | % |
Ancillary services revenues | | | 23 | | | | 24 | | | | 24 | | | | (1 | ) | | | (4.2 | ) | | | — | | | — | |
Rental and ancillary services revenues | | | 179 | | | | 173 | | | | 164 | | | | 6 | | | | 3.5 | | | | 9 | | | | 5.5 | |
Rental expenses | | | 103 | | | | 90 | | | | 91 | | | | 13 | | | | 14.4 | | | | (1 | ) | | | (1.1 | ) |
Ancillary services expense | | | 19 | | | | 23 | | | | 22 | | | | (4 | ) | | | (17.4 | ) | | | 1 | | | | 4.5 | |
Rental and ancillary services expenses | | | 122 | | | | 113 | | | | 113 | | | | 9 | | | | 8.0 | | | | — | | | — | |
Rental and ancillary services margin | | $ | 57 | | | $ | 60 | | | $ | 51 | | | $ | (3 | ) | | | (5.0 | ) | | $ | 9 | | | | 17.6 | |
Rental and ancillary services margin percentage | | | 31.8 | % | | | 34.7 | % | | | 31.1 | % | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Rental and ancillary services margin decreased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to a net increase of $9 million in rental and ancillary expenses due to (i) additional owners and new properties resulting in higher travel exchange program expenses including Hilton Honors and partners perks as well as higher maintenance expense from new and existing properties with unsold inventory, (ii) a one-time insurance claim payment of $2 million received in 2016, and (iii) a reduction in access fees received due to higher quantity of access fees sold in 2016. The increase in expenses was partially offset by higher transient room and club inventory rentals at our developed and fee-for-service properties. Rental and ancillary services margin percentage decreased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, due to aforementioned increases in segment expenses.
Rental and ancillary services revenues increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to rental income at our new resort, The District, additional units available for rent in new phases at existing resorts, a 2.6 percent increase in transient rate and receipt of an insurance recovery of $2 million. Rental and ancillary services margin increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily as a result of an increase in rental revenues and marginal improvements in rental expenses.
Other Operating Expenses
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | | $ | | | % | |
Unallocated general and administrative | | $ | 104 | | | $ | 65 | | | $ | 44 | | | $ | 39 | | | | 60.0 | % | | | $ | 21 | | | | 47.7 | % |
Allocated general and administrative | | | — | | | | 27 | | | | 13 | | | | (27 | ) | | | (100.0 | ) | | | | 14 | | | NM(1) | |
General and administrative | | $ | 104 | | | $ | 92 | | | $ | 57 | | | $ | 12 | | | | 13.0 | | | | $ | 35 | | | | 61.4 | |
(1) | Fluctuation in terms of percentage change is not meaningful. |
Unallocated general and administrative expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to an increase in expenses relating to regulatory filings, professional fees and other costs as a result of becoming an independent publicly traded company. Allocated general and administrative were expenses allocated to us from Hilton relating to the spin-off which was completed on January 3, 2017.
Unallocated general and administrative expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to an increase of $15 million in spin-off related costs. Allocated general and administrative expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to an increase of $21 million in incremental expenses related to the spin-off transaction, partially offset by no longer having share-based compensation expenses related to the executive compensation plan (the “Promote plan”) in place prior to Hilton’s initial public offering as the remaining shares fully vested in 2015.
63
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Depreciation and amortization | | $ | 29 | | | $ | 24 | | | $ | 22 | | | $ | 5 | | | | 20.8 | % | | $ | 2 | | | | 9.1 | % |
License fee expense | | | 87 | | | | 80 | | | | 74 | | | | 7 | | | | 8.8 | | | | 6 | | | | 8.1 | |
Depreciation and amortization expense increased for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to asset transfers from Hilton during the fourth quarter of 2016, some of which we hold as property and equipment for future conversion into inventory. The increase for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to additional leasehold improvements and capitalized software costs placed into service.
License fee expense increased for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, compared to the respective prior periods, were as a result of increases in revenues during those periods.
Non-Operating Expenses
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Interest expense | | $ | | 27 | | | | | 3 | | | | | — | | | $ | | 24 | | | NM(1) | | | $ | | 3 | | | NM(1) | |
Allocated Parent interest expense | | | | — | | | | | 26 | | | | | 29 | | | | | (26 | ) | | | (100.0 | )% | | | | (3 | ) | | | (10.3 | )% |
Equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate | | | | (1 | ) | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | | (1 | ) | | NM(1) | | | | | — | | | NM(1) | |
Other loss, net | | | | — | | | | | 1 | | | | | — | | | | | (1 | ) | | | (100.0 | ) | | | | (1 | ) | | NM(1) | |
Income tax (benefit) expense | | | | (16 | ) | | | | 125 | | | | | 118 | | | | | (141 | ) | | NM(1) | | | | | 7 | | | | 5.9 | |
(1) | Fluctuation in terms of percentage change is not meaningful. |
The change in non-operating expenses for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, is primarily due to (i) an increase in interest expense which directly relates to the financing transactions closed during and subsequent to the fourth quarter of 2016, (ii) a decrease in allocated parent interest expense primarily due to us being released from the unconditional obligation to guarantee certain Hilton allocated debt in November 2016, (iii) equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate relates to our 25 percent interest in BRE Ace LLC (see Note 8: Investment in Unconsolidated Affiliate in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information) and (iv) a decrease in our net deferred income tax liabilities primarily as a result of the Act enacted on December 22, 2017.
The change in non-operating expenses for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to the same period in 2015, is due to (i) a decrease in allocated parent interest expense primarily due to us being released from the unconditional obligation to guarantee certain Hilton allocated debt in November 2016, (ii) an increase in interest expense which directly relates to the financing transactions closed during the fourth quarter of 2016 of which $2 million represents interest expenses to a related party (see Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse Debt in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information) and (iii) an increase in income tax expense as a result of non-deductible transaction costs.
2018 Outlook
Adoption of ASC 606
We adopted Accounting Standards Update 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (“ASC 606”) on January 1, 2018, under the modified retrospective method of adoption. Prior to the adoption of ASC 606, we recognized revenue and the related expenses from sales of VOI under construction using the percentage of completion method. As a result of the adoption of ASC 606, we will defer the recognition of revenue and the related expense until construction is completed. While we are finalizing our evaluation of the impacts of the standard, the following tables show the estimated impact that ASC 606 would have had to our quarterly and annual 2017 operating results, EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA if we had adopted ASC 606 utilizing the full retrospective
64
method of adoption based on our evaluation to date. See Note 2: Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information.
| | 2017 Results Prior to ASC 606 | |
($ in millions, except per share data) | | First Quarter | | | Second Quarter | | | Third Quarter | | | Fourth Quarter | | | Full Year | |
Total revenues | | $ | 399 | | | $ | 439 | | | $ | 426 | | | $ | 447 | | | $ | 1,711 | |
Total operating expenses | | | 316 | | | | 348 | | | | 350 | | | | 360 | | | | 1,374 | |
Net income | | | 50 | | | | 51 | | | | 43 | | | | 183 | | | | 327 | |
Earnings per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.43 | | | $ | 1.85 | | | $ | 3.30 | |
Diluted | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.43 | | | $ | 1.83 | | | $ | 3.28 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 50 | | | $ | 51 | | | $ | 43 | | | $ | 183 | | | $ | 327 | |
Interest expense | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 6 | | | | 27 | |
Income tax expense (benefit) | | | 26 | | | | 33 | | | | 28 | | | | (103 | ) | | | (16 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 8 | | | | 29 | |
Interest expense, depreciation and amortization included in equity in earnings from unconsolidated entities | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 1 | | | | 3 | |
EBITDA | | | 90 | | | | 98 | | | | 87 | | | | 95 | | | | 370 | |
Other (gain) loss, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1 | ) | | | 1 | | | | — | |
Share-based compensation expense | | | 3 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 2 | | | | 15 | |
Other adjustment items (1) | | | 1 | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | | | | 10 | |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 94 | | | $ | 106 | | | $ | 94 | | | $ | 101 | | | $ | 395 | |
(1) | For the year ended December 31, 2017, amount includes $8 million of costs associated with the spin-off transaction. |
| | 2017 Results Adjusted for ASC 606 Adoption | |
(in millions, except per share data) | | First Quarter | | | Second Quarter | | | Third Quarter | | | Fourth Quarter | | | Full Year | |
Total revenues | | $ | 388 | | | $ | 416 | | | $ | 413 | | | $ | 427 | | | $ | 1,644 | |
Total operating expenses | | | 307 | | | | 340 | | | | 342 | | | | 345 | | | | 1,334 | |
Net income | | | 48 | | | | 42 | | | | 40 | | | | 169 | | | | 299 | |
Earnings per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.49 | | | $ | 0.42 | | | $ | 0.40 | | | $ | 1.70 | | | $ | 3.01 | |
Diluted | | $ | 0.49 | | | $ | 0.42 | | | $ | 0.40 | | | $ | 1.68 | | | $ | 3.00 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 48 | | | $ | 42 | | | $ | 40 | | | $ | 169 | | | $ | 299 | |
Interest expense | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 6 | | | | 27 | |
Income tax expense (benefit) | | | 26 | | | | 27 | | | | 26 | | | | (94 | ) | | | (15 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 6 | | | | 27 | |
Interest expense, depreciation and amortization included in equity in earnings from unconsolidated entities | | | — | | | | — | | | 2 | | | | 1 | | | | 3 | |
EBITDA | | | 88 | | | | 83 | | | | 82 | | | | 88 | | | | 341 | |
Other (gain) loss, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1 | ) | | | 1 | | | | — | |
Share-based compensation expense | | | 3 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 2 | | | | 15 | |
Other adjustment items (1) | | | 1 | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | | | | 5 | | | | 12 | |
Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 92 | | | $ | 91 | | | $ | 89 | | | $ | 96 | | | $ | 368 | |
(1) | For the year ended December 31, 2017, amount includes $8 million of costs associated with the spin-off transaction. |
65
Supplemental Information Regarding the Adoption of ASC 606
The following table provides supplemental information of Sales of VOIs for project(s) under construction for the year ended December 31, 2017, but will be deferred until construction is complete.
| 2017 | |
($ in millions) | First Quarter | | | Second Quarter | | | Third Quarter | | | Fourth Quarter | | | Full Year | |
Sales of VOI | $ | 9 | | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 11 | | | $ | 17 | | | $ | 50 | |
Cost of VOI sales | | (5 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (5 | ) | | | (16 | ) |
Sales, marketing, general and administrative expense | | (1 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | (7 | ) |
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
Prior to the first quarter of 2017, any net cash generated by our business was transferred to Hilton, where it was centrally managed. Transfers of cash to and from Hilton for prior periods were reflected as a component of Net transfers (to) from Parent in our consolidated statements of cash flows.
As of December 31, 2017, we had total cash and cash equivalents of $297 million, including $51 million of restricted cash. The restricted cash balance relates to escrowed cash from our sales of our VOIs and reserves related to our non-recourse debt. See Note 11: Debt and Non-Recourse Debt included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information.
Our known short-term liquidity requirements primarily consist of funds necessary to pay for operating expenses and other expenditures, including payroll and related benefits, legal costs, operating costs associated with the operation of our resorts and sales centers, interest and scheduled principal payments on our outstanding indebtedness and capital expenditures for renovations and maintenance at our offices and sales centers. Our long-term liquidity requirements primarily consist of funds necessary to pay for scheduled debt maturities, purchase commitments and costs associated with potential acquisitions and development projects.
We finance our business activities primarily with existing cash and cash equivalents, cash generated from our operations and through securitizations of our timeshare financing receivables. We believe that this cash will be adequate to meet anticipated requirements for operating expenses and other expenditures, including payroll and related benefits, legal costs and capital expenditures for the foreseeable future. The objectives of our cash management policy are to maintain the availability of liquidity, minimize operational costs, make debt payments and fund future acquisitions and development projects. Further, we have an investment policy that is focused on the preservation of capital and maximizing the return on new and existing investments.
Sources and Uses of Our Cash
The following table summarizes our net cash flows related to our liquidity:
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Net cash provided by (used in): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating activities(2) | | $ | 356 | | | $ | 182 | | | $ | 152 | | | $ | 174 | | | | 95.6 | % | | $ | 30 | | | | 19.7 | % |
Investing activities | | | (87 | ) | | | (34 | ) | | | (18 | ) | | | (53 | ) | | NM(1) | | | | (16 | ) | | | 88.9 | |
Financing activities(2) | | | (123 | ) | | | (76 | ) | | | (119 | ) | | | (47 | ) | | | 61.8 | | | | 43 | | | | (36.1 | ) |
(1) | Fluctuation in terms of percentage change is not meaningful. |
(2) | Reflects the adoption of Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash. See Note 2: Significant Accounting Policies in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion. |
66
Operating Activities
Cash flow provided by operating activities is primarily generated from (i) sales and financing of VOIs and (ii) net cash generated from managing our resorts, Club operations and providing related ancillary services. Cash flows used in operating activities primarily include spending for the acquisition of inventory, development of new phases of existing resorts and funding our working capital needs. Our cash flows from operations generally vary due to the following factors related to the sale of our VOIs; the degree to which our owners finance their purchase and our owners’ repayment of timeshare financing receivables; the timing of management and sales and marketing services provided; and cash outlays for VOI inventory acquisition and development. Additionally, cash flow from operations will also vary depending upon our sales mix of VOIs; over time, we generally receive more cash from the sale of an owned VOI as compared to that from a fee-for-service sale.
Net cash flows provided by operating activities increased by $174 million during the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily as a result of improved operating results in both segments as well as increased sources of cash for working capital requirements along with the timing of following items: (i) a one-time $63 million deferral of estimated federal tax payments until January 2018 for regions impacted by Hurricane Irma, see Hurricane Irma section above for additional information and (ii) a reduction of inventory spending due to a deferral of certain VOI inventory expenditures until the first half of 2018. The following table exhibits our VOI inventory spending for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015.
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
VOI spending - owned properties | | $ | 45 | | | $ | 73 | | | $ | 93 | |
VOI spending - fee-for-service upgrades | | | 53 | | | | 74 | | | | 105 | |
Total VOI inventory spending | | $ | 98 | | | $ | 147 | | | $ | 198 | |
Net cash flows provided by operating activities decreased by $30 million during the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily a result of improved operating results in both segments and a decrease in VOI inventory spending, partially offset by an increase in net issuances of timeshare financing receivables.
Investing Activities
The following table summarizes our net cash used in investing activities:
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Capital expenditures for property and equipment | | $ | (35 | ) | | $ | (26 | ) | | $ | (12 | ) | | $ | (9 | ) | | | 34.6 | % | | $ | (14 | ) | | NM(1) | |
Software capitalization costs | | | (12 | ) | | | (8 | ) | | | (6 | ) | | | (4 | ) | | | 50.0 | | | | (2 | ) | | | 33.3 | % |
Investment in unconsolidated affiliate | | | (40 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (40 | ) | | NM(1) | | | | — | | | NM(1) | |
Net cash used in investing activities | | $ | (87 | ) | | $ | (34 | ) | | $ | (18 | ) | | $ | (53 | ) | | NM(1) | | | $ | (16 | ) | | | 88.9 | |
(1) | Fluctuation in terms of percentage change is not meaningful. |
Net cash used in investing activities increased by $53 million during the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, primarily due to a 25 percent investment interest in BRE Ace LLC (see Note 8: Investment in Unconsolidated Affiliate in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion) and higher capital expenditures for property and equipment. Net cash used in investing activities increased by $16 million during the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to 2015, primarily due to higher capital expenditures for property and equipment.
Our capital expenditures include spending related to technology and buildings and leasehold improvements used to support sales and marketing locations, resort operations and corporate activities. We believe the maintenance and renovations of our existing assets are necessary to stay competitive in the markets in which we operate.
67
Financing Activities
The following table summarizes our net cash used in financing activities:
| | Year Ended December 31, | | | 2017 vs 2016 Variance | | | 2016 vs 2015 Variance | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Issuance of non-recourse debt | | $ | 350 | | | $ | 300 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 50 | | | | 16.7 | % | | $ | 300 | | | NM(1) | |
Repayment of non-recourse debt | | | (459 | ) | | | (110 | ) | | | (125 | ) | | | (349 | ) | | NM(1) | | | | 15 | | | | (12.0 | )% |
Repayment of debt | | | (10 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (10 | ) | | NM(1) | | | | — | | | NM(1) | |
Issuance of debt | | | — | | | | 200 | | | | — | | | | (200 | ) | | | (100.0 | ) | | | 200 | | | NM(1) | |
Debt issuance costs | | | (5 | ) | | | (10 | ) | | | — | | | | 5 | | | | (50.0 | ) | | | (10 | ) | | NM(1) | |
Allocated debt activity | | | — | | | | 111 | | | | (87 | ) | | | (111 | ) | | | (100.0 | ) | | | 198 | | | NM(1) | |
Net transfers (to) from Parent | | | — | | | | (567 | ) | | | 95 | | | | 567 | | | | (100.0 | ) | | | (662 | ) | | NM(1) | |
Distribution to Parent | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2 | ) | | | — | | | NM(1) | | | | 2 | | | | (100.0 | ) |
Proceeds from stock option exercises | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | NM(1) | | | | — | | | NM(1) | |
Net cash used in financing activities | | $ | (123 | ) | | $ | (76 | ) | | $ | (119 | ) | | $ | (47 | ) | | | 61.8 | | | $ | 43 | | | | (36.1 | ) |
(1) | Fluctuation in terms of percentage change is not meaningful. |
The change in net cash used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2017, compared to 2016, was primarily due to our financing transactions that occurred during the first quarter of 2017. During the year ended December 31, 2017, we issued $350 million in non-recourse securitized debt and paid $5 million in debt issuance costs. The proceeds received from the non-recourse securitized debt were used to pay down a portion of our timeshare facility. We also paid $10 million of the principal amount of the senior secured term loan. See Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse Debt in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion. Additionally, following the spin-off date we no longer transfer cash to or from Hilton.
In 2016, subsequent to our guarantor obligation release of Hilton’s Allocated Parent Debt, we entered into several financing transactions including the issuance of our Senior Secured Credit Facilities (as defined herein), consisting of a $200 million variable-rate term loan facility (the “Term Loans”) and a revolving credit facility in an aggregate principal amount of up to $200 million, each with a five-year maturity, and incurred $4 million of debt issuance costs. Additionally, we issued $300 million aggregate principal amount of 6.125 percent senior unsecured notes due 2024 (the “Senior Unsecured Notes”) and recognized $8 million of debt issuance costs. See Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse Debt in our consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion.
The Timeshare Facility is a non-recourse obligation and is payable solely from the pool of timeshare financing receivables pledged as collateral to the debt and related assets. In August and December 2016, we amended the terms of the Timeshare Facility to, among other things, increase the borrowing capacity from $300 million to $450 million, allowing us to borrow up to the maximum amount until August 2018 and requiring all amounts borrowed to be repaid in August 2019. In connection with the amendments, we recognized $3 million of debt issuance costs. In December 2016, we borrowed $300 million under the Timeshare Facility. See Note 4: Timeshare Financing Receivables in our consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion.
68
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes our significant contractual obligations as of December 31, 2017:
| | Payments Due by Period | |
($ in millions) | | Total | | | Less Than 1 Year | | | 1-3 Years | | | 3-5 Years | | | More Than 5 Years | |
Debt(1) | | $ | 643 | | | $ | 35 | | | $ | 70 | | | $ | 203 | | | $ | 335 | |
Non-recourse debt(1) | | | 619 | | | | 153 | | | | 354 | | | | 64 | | | | 48 | |
Operating leases | | | 78 | | | | 14 | | | | 23 | | | | 18 | | | | 23 | |
Purchase commitments | | | 372 | | | | 3 | | | | 196 | | | | 91 | | | | 82 | |
Total contractual obligations | | $ | 1,712 | | | $ | 205 | | | $ | 643 | | | $ | 376 | | | $ | 488 | |
(1) | Includes principal, as well as estimated interest payments. For our variable-rate debt, we have assumed a constant 30-day LIBOR rate of 1.56 percent as of December 31, 2017. |
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Our off-balance sheet arrangements as of December 31, 2017, consisted of $372 million of certain commitments with developers whereby we have committed to purchase vacation ownership units at a future date to be marketed and sold under our Hilton Grand Vacations brand. The ultimate amount and timing of the acquisitions is subject to change pursuant to the terms of the respective arrangements, which could also allow for cancellation in certain circumstances, see Note 20: Commitments and Contingencies in our consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information.
Subsequent Event
In February, we entered into a commitment to acquire $41 million of inventory.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the date of the consolidated financial statements, the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods and the related disclosures in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying footnotes. We believe that of our significant accounting policies, which are described in Note 2: Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies in our audited consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the following accounting policies are critical because they involve a higher degree of judgment, and the estimates required to be made are based on assumptions that are inherently uncertain. As a result, these accounting policies could materially affect our financial position, results of operations and related disclosures. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate these estimates and judgments based on historical experiences and various other factors that are believed to reflect the current circumstances. While we believe our estimates, assumptions and judgments are reasonable, they are based on information presently available. Actual results may differ significantly from these estimates due to changes in judgments, assumptions and conditions as a result of unforeseen events or otherwise, which could have a material effect on our financial position or results of operations.
Revenue Recognition
Our revenue recognition associated with sales of VOIs requires significant estimates. Revenue is generally recognized after the period of cancellation with refund has expired, the buyer has demonstrated a sufficient level of initial and continuing investment, and the receivables are deemed collectible. We determine the portion of revenues to recognize for VOI sales using the percentage-of-completion method for sales of VOIs under construction, which requires judgments and estimates, including the total estimated costs of the project. Changes in projections of the costs could lead to adjustments to the percentage-of-completion status of a project, which may result in differences in the timing and amount of revenues and profits recognized from the projects.
69
Inventory and Cost of Sales
We use the relative sales value method of costing our VOI sales and relieving inventory, which requires us to make estimates subject to significant uncertainty. The estimates include future sales prices, timing and volume, provisions for loan losses on financed sales of VOIs, sales incentives, projected future cost and volume of recoveries, including inventory reacquired from our upgrade programs. We aggregate these factors to calculate total net cost of sales of VOIs as a percentage of net sales of VOIs and apply this ratio to allocate the cost of sales to recognized sales of VOIs. The effect of changes in these estimates over the life of a project are recognized on a retrospective basis through corresponding adjustments to inventory and cost of sales in the period in which the estimates are revised.
Due to the application of the retrospective adjustments, small changes in any of our estimates, including changes in our development and sales strategies could have a material effect on the carrying value of certain projects and inventory. We monitor our projects and inventory on an ongoing basis and complete an evaluation each reporting period to ensure that the inventory is stated at the lower of cost or fair value less cost to sell. In addition, we continually assess our VOI inventory and, if necessary, impose pricing adjustments to modify sales pace.
Allowance for Loan Losses
The allowance for loan losses is related to the receivables generated by our financing of VOI sales, which are secured by the underlying timeshare properties. We determine our timeshare financing receivables to be past due based on the contractual terms of the individual mortgage loans. We use a technique referred to as static pool analysis as the basis for determining our general reserve requirements on our timeshare financing receivables. The adequacy of the related allowance is determined by management through analysis of several factors requiring judgment, such as current economic conditions and industry trends, as well as the specific risk characteristics of the portfolio, including historic and assumed default rates.
Changes in the estimates used in developing our default rates could result in a material change to our allowance. A 0.5 percentage point increase to our default rates used in the allowance calculation would increase our allowance for loan losses by approximately $8 million.
Income Taxes
We recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of assets and liabilities using currently enacted tax rates. We regularly review our deferred tax assets to assess their potential realization and establish a valuation allowance for portions of such assets that we believe will not be ultimately realized. In performing this review, we make estimates and assumptions regarding projected future taxable income, the expected timing of reversals of existing temporary differences and the implementation of tax planning strategies. A change in these assumptions may increase or decrease our valuation allowance resulting in an increase or decrease in our effective tax rate, which could materially affect our consolidated financial statements.
We use a prescribed more-likely-than-not recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return if there is uncertainty in income taxes recognized in the financial statements. Assumptions and estimates are used to determine the more-likely-than-not designation. Changes to these assumptions and estimates can lead to an additional income tax benefit (expense), which can materially change our consolidated financial statements.
Legal Contingencies
We are subject to various legal proceedings and claims, the outcomes of which are subject to significant uncertainty. An estimated loss from a loss contingency should be accrued by a charge to income if it is probable and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. Significant judgment is required when we evaluate, among other factors, the degree of probability of an unfavorable outcome and the ability to make a reasonable estimate of the amount of loss. Changes in these factors could materially affect our consolidated financial statements.
70
ITEM 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk |
We are exposed to market risk from changes in interest rates, currency exchange rates and debt prices. We manage our exposure to these risks by monitoring available financing alternatives, through pricing policies that may take into account currency exchange rates and prior to the spin-off, through Hilton entering into derivative arrangements on our behalf. We do not foresee any significant changes in either our exposure to fluctuations in interest rates or how we manage interest rates or currency rates or how we manage such exposure in the future.
Interest Rate Risk
We are exposed to interest rate risk on our variable-rate debt, comprised of the term loans and our timeshare facility, of which the timeshare facility is without recourse to us. The interest rate is based on one-month LIBOR and we are most vulnerable to changes in this rate.
We intend to securitize timeshare financing receivables in the asset-backed financing market periodically. We expect to secure fixed-rate funding to match our fixed rate timeshare financing receivables. However, if we have floating-rate debt in the future, we will monitor the interest rate risk and evaluate opportunities to mitigate such risk through the use of derivative instruments.
To the extent we utilize variable-rate indebtedness in the future, any increase in interest rates beyond amounts covered under any corresponding derivative financial instruments, particularly if sustained, could have an adverse effect on our net income, cash flows and financial position. Hedging transactions we enter into may not adequately mitigate the adverse effects of interest rate increases or that counterparties in those transactions will honor their obligations.
The following table sets forth the contractual maturities, weighted average interest rates and the total fair values as of December 31, 2017, for our financial instruments that are materially affected by interest rate risk:
| | | | | | Maturities by Period | | | | | | | | | |
($ in millions) | | Weighted Average Interest Rate(1) | | | 2018 | | | 2019 | | | 2020 | | | 2021 | | | 2022 | | | There- after | | | Total(2) | | | Fair Value | |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fixed-rate securitized timeshare financing receivables | | | 11.919 | % | | $ | 74 | | | $ | 72 | | | $ | 70 | | | $ | 65 | | | $ | 57 | | | $ | 133 | | | $ | 471 | | | $ | 505 | |
Fixed-rate unsecuritized timeshare financing receivables | | | 12.311 | % | | | 73 | | | | 63 | | | | 69 | | | | 74 | | | | 79 | | | | 383 | | | | 741 | | | | 787 | |
Liabilities:(3) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fixed-rate debt(4) | | | 3.897 | % | | | 140 | | | | 122 | | | | 89 | | | | 34 | | | | 26 | | | | 348 | | | | 759 | | | | 777 | |
Variable-rate debt(4) | | | 3.354 | % | | | 10 | | | | 139 | | | | 10 | | | | 160 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 319 | | | | 323 | |
(1) | Weighted average interest rate as of December 31, 2017. |
(2) | Amount excludes unamortized deferred financing costs. |
(3) | Includes debt and non-recourse debt. |
(4) | Fixed-rate debt includes principal outstanding debt of $300 million and non-recourse debt of $459 million as of December 31, 2017. Variable-rate debt includes principal outstanding debt of $190 million and non-recourse debt of $129 million as of December 31, 2017. See Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse Debt in our consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information. |
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
Though the majority of our operations are conducted in United States dollar (“U.S. dollar”), we are exposed to earnings and cash flow volatility associated with changes in foreign currency exchange rates. Our principal exposure results from our timeshare financing receivables denominated in Japanese yen, the value of which could change materially in reference to our reporting currency, the U.S. dollar. A 10 percent increase in the foreign exchange rate of Japanese yen to U.S. dollar would increase our gross timeshare financing receivables by less than $1 million.
71
Item 8. | Financial Statements And Supplementary Data |
HILTON GRAND VACATIONS INC.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
72
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (the "Company") is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. The Company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of the Company’s management and directors; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of assets of the Company that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management has assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013). Based on this assessment, management determined that the Company maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017.
Ernst & Young LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm that has audited the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, has issued an attestation report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017. The report is included herein.
73
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Hilton Grand Vacations Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders' equity (deficit) and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) and our report dated March 1, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Certified Public Accountants
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2016.
Orlando, Florida
March 1, 2018
74
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Hilton Grand Vacations Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited Hilton Grand Vacations Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control— Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders' equity (deficit) and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes and our report dated March 1, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
75
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Certified Public Accountants
Orlando, Florida
March 1, 2018
76
HILTON GRAND VACATIONS INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in millions, except share data)
| | December 31, | |
| | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 246 | | | $ | 48 | |
Restricted cash | | | 51 | | | | 103 | |
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $9 and $6 | | | 112 | | | | 123 | |
Timeshare financing receivables, net | | | 1,071 | | | | 1,025 | |
Inventory | | | 509 | | | | 513 | |
Property and equipment, net | | | 238 | | | | 256 | |
Investment in unconsolidated affiliate | | | 41 | | | | — | |
Intangible assets, net | | | 72 | | | | 70 | |
Other assets | | | 44 | | | | 42 | |
TOTAL ASSETS (variable interest entities - $471 and $258) | | $ | 2,384 | | | $ | 2,180 | |
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other | | $ | 339 | | | $ | 231 | |
Advanced deposits | | | 104 | | | | 103 | |
Debt, net | | | 482 | | | | 490 | |
Non-recourse debt, net | | | 583 | | | | 694 | |
Deferred revenues | | | 109 | | | | 106 | |
Deferred income tax liabilities | | | 249 | | | | 389 | |
Total liabilities (variable interest entities - $455 and $245) | | | 1,866 | | | | 2,013 | |
Commitments and contingencies - see Note 20 | | | | | | | | |
Equity: | | | | | | | | |
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value; 300,000,000 authorized shares, none issued or outstanding as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 | | | — | | | | — | |
Common stock, $0.01 par value; 3,000,000,000 authorized shares, 99,136,304 and 98,802,597 issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively | | | 1 | | | | 1 | |
Additional paid-in capital | | | 162 | | | | 138 | |
Accumulated retained earnings | | | 355 | | | | 28 | |
Total equity | | | 518 | | | | 167 | |
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | $ | 2,384 | | | $ | 2,180 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
77
HILTON GRAND VACATIONS INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in millions, except per share amounts)
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Sales of VOIs, net | | $ | 548 | | | $ | 508 | | | $ | 492 | |
Sales, marketing, brand and other fees | | | 544 | | | | 499 | | | | 457 | |
Financing | | | 147 | | | | 134 | | | | 127 | |
Resort and club management | | | 158 | | | | 143 | | | | 125 | |
Rental and ancillary services | | | 179 | | | | 173 | | | | 164 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | 135 | | | | 126 | | | | 110 | |
Total revenues | | | 1,711 | | | | 1,583 | | | | 1,475 | |
Expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of VOI sales | | | 148 | | | | 152 | | | | 173 | |
Sales and marketing | | | 663 | | | | 605 | | | | 541 | |
Financing | | | 43 | | | | 32 | | | | 32 | |
Resort and club management | | | 43 | | | | 36 | | | | 32 | |
Rental and ancillary services | | | 122 | | | | 113 | | | | 113 | |
General and administrative | | | 104 | | | | 92 | | | | 57 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 29 | | | | 24 | | | | 22 | |
License fee expense | | | 87 | | | | 80 | | | | 74 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | 135 | | | | 126 | | | | 110 | |
Total operating expenses | | | 1,374 | | | | 1,260 | | | | 1,154 | |
Interest expense | | | (27 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | — | |
Allocated Parent interest expense | | | — | | | | (26 | ) | | | (29 | ) |
Equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Other loss, net | | | — | | | | (1 | ) | | | — | |
Income before income taxes | | | 311 | | | | 293 | | | | 292 | |
Income tax benefit (expense) | | | 16 | | | | (125 | ) | | | (118 | ) |
Net income | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 168 | | | $ | 174 | |
Earnings per share:(1) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 3.30 | | | $ | 1.70 | | | $ | 1.76 | |
Diluted | | $ | 3.28 | | | $ | 1.70 | | | $ | 1.76 | |
| (1) | For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, basic and diluted earnings per share was calculated based on shares distributed to Hilton Grand Vacations’ shareholders on January 3, 2017. See Note 17: Earnings Per Share for further discussion. |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
78
HILTON GRAND VACATIONS INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in millions)
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Operating Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 168 | | | $ | 174 | |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 29 | | | | 24 | | | | 22 | |
Amortization of deferred financing costs and other | | | 5 | | | | 5 | | | | 5 | |
Provision for loan losses | | | 58 | | | | 49 | | | | 39 | |
Other loss, net | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | — | |
Share-based compensation | | | 15 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Deferred income taxes | | | (129 | ) | | | 23 | | | | 20 | |
Equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate | | | (1 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Net changes in assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts receivables, net | | | 12 | | | | (30 | ) | | | (6 | ) |
Timeshare financing receivables, net | | | (103 | ) | | | (98 | ) | | | (88 | ) |
Inventory | | | 47 | | | | 7 | | | | (38 | ) |
Other assets | | | (4 | ) | | | (4 | ) | | | 2 | |
Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other | | | 95 | | | | 28 | | | | 18 | |
Advanced deposits | | | 1 | | | | 7 | | | | (1 | ) |
Deferred revenues | | | 3 | | | | 3 | | | | 3 | |
Other | | | 1 | | | | (1 | ) | | | 2 | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 356 | | | | 182 | | | | 152 | |
Investing Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Capital expenditures for property and equipment | | | (35 | ) | | | (26 | ) | | | (12 | ) |
Software capitalization costs | | | (12 | ) | | | (8 | ) | | | (6 | ) |
Investment in unconsolidated affiliate | | | (40 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Net cash used in investing activities | | | (87 | ) | | | (34 | ) | | | (18 | ) |
Financing Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issuance of non-recourse debt | | | 350 | | | | 300 | | | | — | |
Repayment of non-recourse debt | | | (459 | ) | | | (110 | ) | | | (125 | ) |
Repayment of debt | | | (10 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Issuance of debt | | | — | | | | 200 | | | | — | |
Debt issuance costs | | | (5 | ) | | | (10 | ) | | | — | |
Allocated debt activity | | | — | | | | 111 | | | | (87 | ) |
Net transfers (to) from Parent | | | — | | | | (567 | ) | | | 95 | |
Distribution to Parent | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2 | ) |
Proceeds from stock option exercises | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Net cash used in financing activities | | | (123 | ) | | | (76 | ) | | | (119 | ) |
Net increase in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | | | 146 | | | | 72 | | | | 15 | |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, beginning of period | | | 151 | | | | 79 | | | | 64 | |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, end of period | | $ | 297 | | | $ | 151 | | | $ | 79 | |
Supplemental Disclosures (1) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(1) | For supplemental disclosures, see Note 21: Supplemental Disclosures of Cash Flow Information. |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
79
HILTON GRAND VACATIONS INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
(in millions)
| | Common Stock | | | Parent Equity | | | Additional Paid-in | | | Accumulated Retained | | | Total | |
| | Shares | | | Amount | | | (Deficit) | | | Capital | | | Earnings | | | Equity | |
Balance as of December 31, 2014 | | | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (373 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (373 | ) |
Net income | | | — | | | | — | | | | 174 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 174 | |
Net transfers from Parent | | | — | | | | — | | | | 95 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 95 | |
Distribution to Parent | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2 | ) |
Balance as of December 31, 2015 | | | — | | | | — | | | | (106 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (106 | ) |
Net income(1) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 140 | | | | — | | | | 28 | | | | 168 | |
Net transfers to Parent | | | — | | | | — | | | | (567 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (567 | ) |
Capital contribution from Parent | | | — | | | | — | | | | 672 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 672 | |
Issuance of common stock(2) | | | 99 | | | | 1 | | | | (1 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Reclassification of Parent equity to additional paid-in capital(2) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (138 | ) | | | 138 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Balance as of December 31, 2016 | | | 99 | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 138 | | | | 28 | | | | 167 | |
Net income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 327 | | | | 327 | |
Deferred intercompany transaction(3) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 9 | | | | — | | | | 9 | |
Activity related to share-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 12 | | | | — | | | | 12 | |
Other(3) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | 3 | |
Balance as of December 31, 2017 | | | 99 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 162 | | | $ | 355 | | | $ | 518 | |
(1) | Net income earned prior to October 24, 2016, is included in Additional paid-in capital instead of Accumulated retained earnings since the accumulation of retained earnings began as of the date of issuance of the Company’s common stock to Park Hotel & Resorts. See Note 1: Organization for further discussion. |
(2) | Parent equity (deficit) was reclassified and allocated between common stock and additional paid-in capital based on the number of shares issued and outstanding as of the stock split that occurred on January 3, 2017. See Note 1: Organization for further discussion. |
(3) Includes pre-spin tax adjustment, refer to Note 15: Income Taxes for further discussion.
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
80
HILTON GRAND VACATIONS INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1: Organization
Our Spin-off from Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.
During 2016, Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. (“Former Hilton Parent” and together with its then consolidated subsidiaries “Hilton”) completed an internal reorganization to contribute to Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (“Hilton Grand Vacations,” “we,” “us,” “our,” “HGV” or the “Company”) its U.S. and non- U.S. timeshare subsidiaries, including Hilton Resorts Corporation in preparation of the tax-free spin-offs of Park Hotels & Resorts Inc. (“Park”) and HGV. We are a Delaware corporation formed on May 2, 2016. On May 4, 2016, the Company issued 100 shares of its common stock, par value $0.01 per share, to Park for $1.00 in cash. On October 24, 2016, the Company issued one share of its common stock, par value $0.01 per share, to Park in connection with the contribution by Park of all shares of common stock of Hilton Resorts Corporation owned by Park to HGV. Net income earned prior to October 24, 2016, is included in Additional paid-in capital instead of Accumulated retained earnings since the accumulation of retained earnings began as of the date of issuance of the Company’s common stock to Park. The issuance of such share of common stock was not registered under the Securities Act, because the share was issued in a transaction by the issuer not involving any public offering exempt from registration under Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. We filed a Registration Statement on Form 10 describing the transaction with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) which was declared effective on December 2, 2016.
On December 30, 2016, we filed an Amended & Restated Charter with an effective date of 4:59 p.m., Eastern time, on January 3, 2017, whereby our shares were split into 98,802,597 shares using a formula by reference to the number of Hilton shares outstanding.
On January 3, 2017, the spin-offs were completed, and we became a separate publicly-traded company on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “HGV,” and Hilton did not retain any ownership interest in our company. In connection with the completion of the spin-off, we entered into agreements with Hilton (who at the time was a related party) and other third parties, including licenses to use the Hilton brand. The audited consolidated financial statements reflect the effect of these agreements. For the year ended December 31, 2017, we incurred $178 million in costs relating to the agreements entered with Hilton. See Key Agreements Related to the Spin-Off section in Part I - Item 1. Business for further information.
Prior to the spin-off, we had a number of existing arrangements whereby Hilton and others provided services to us. See Note 18: Related Party Transactions for additional information. In addition, Hilton maintained a share-based compensation plan for the benefit of its officers, directors and employees which was presented as a component of Net transfers (to) from Parent, a financing activity, on the consolidated statements of cash flows. Subsequent to the spin-off, share-based compensation expense is presented as a component of operating activities on the consolidated statements of cash flows.
Our Business
Hilton Grand Vacations is a global timeshare company engaged in developing, marketing, selling and managing timeshare resorts primarily under the Hilton Grand Vacations brand. Our operations primarily consist of: selling vacation ownership intervals (“VOIs”) for us and third parties; operating resorts; financing and servicing loans provided to consumers for their timeshare purchases; and managing our points-based Hilton Grand Vacations Club exchange program (the “Club”). As of December 31, 2017, we had 48 resorts, comprised of 8,102 units, located in the United States (“U.S.”) and Europe.
81
Note 2: Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include 100 percent of our assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses and cash flows and all entities in which we have a controlling financial interest. Through the date of the spin-off, the consolidated financial statements presented herein were prepared on a stand-alone basis and were derived from the consolidated financial statements and accounting records of Hilton.
The determination of a controlling financial interest is based upon the terms of the governing agreements of the respective entities, including the evaluation of rights held by other interests. If the entity is considered to be a variable interest entity (“VIE”), we determine whether we are the primary beneficiary, and then consolidate those VIEs for which we have determined we are the primary beneficiary. If the entity in which we hold an interest does not meet the definition of a VIE, we evaluate whether we have a controlling financial interest through our voting interests in the entity. We consolidate entities when we own more than 50 percent of the voting shares of a company or otherwise have a controlling financial interest. All material intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation. The consolidated financial statements reflect our financial position, results of operations and cash flows as prepared in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”).
All of our significant transactions with Hilton had been included in these consolidated financial statements. The net effect of the settlement of any intercompany transactions prior to the spin-off has been included in the consolidated statements of cash flows as a financing activity within Net transfers (to) from Parent.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported and, accordingly, ultimate results could differ from those estimates.
We review our estimate of the expected redemption of expired prepaid discounted vacation packages (“packages”) on an ongoing basis. We only reduce the liability for expired packages when a package is redeemed or the likelihood of redemption is remote. This review considers factors such as historical experience, current business practices for pursuing individuals to redeem expired packages and the sufficiency and reliability of data available following a change in those redemption business practices. Previously, we concluded that redemption of an expired package was remote once a package had been expired for six months and therefore retained the liability until six months after expiration. During our review in the second quarter of 2017, we determined that we had sufficiently reliable updated information under current business practices to revise our estimate of expired packages that we expected to redeem. As a result, during the second quarter of 2017, we changed our accounting estimate for expected redemptions of expired packages to relieve a portion of the remaining liability post expiration and recorded an $11 million reduction to the Advanced Deposits liability, with corresponding increases to Sales, marketing, brand and other fees revenue of $10 million and Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other for the related sales tax liability of $1 million. As a result, for the year ended December 31, 2017, our net income increased by $10 million and basic and diluted earnings per share increased by $0.10.
Allocations
Prior to the spin-off, our consolidated financial statements included certain indirect general and administrative costs allocated to us by Hilton for certain functions and services including, but not limited to, executive office, finance and other administrative support primarily on the basis of financial and operating metrics that Hilton had historically used to allocate resources and evaluate performance against its strategic objectives. Both we and Hilton considered the basis on which expenses had been allocated to be a reasonable reflection of the utilization of services provided to or the benefit received by us during the periods presented. These costs were included in General and administrative in our consolidated statements of operations, for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015.
82
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Revenue Recognition
| • | Sales of VOIs, net—Revenue from a deeded VOI sale is recognized when the customer has executed a binding sales contract, a minimum 10 percent down payment has been received, certain minimum sales thresholds for a timeshare project have been attained, the purchaser’s period to cancel for a refund has expired and the related receivable is deemed to be collectible. In addition, before we recognize any revenues, the purchaser must have met the initial and continuing investment criteria. We defer revenue recognition for sales that do not meet these criteria. During periods of construction, revenue from VOI sales is recognized under the percentage-of-completion method, which includes judgments and estimates, including total project costs to complete. Additionally, we record an estimate of uncollectible amounts at the time of a financed sale with a charge to provision for loan loss, which we classify as a reduction of Sales of VOIs, net in our consolidated statements of operations. |
We account for rental operations of unsold VOIs, including accommodations provided through the use of our vacation sampler programs, as incidental operations. Incremental carrying costs in excess of incremental revenues are recognized in the period incurred. In all periods presented, incremental carrying costs exceeded incremental revenues and all revenues and expenses are recognized in the period earned or incurred.
We award Club Bonus Points (“Bonus Points”) to our customers. These points are valid for a maximum of two years and may be used toward reservations at Club resorts, hotel reservations within Hilton’s system and VOI interval exchanges with other third-party vacation ownership exchanges. We also take into consideration the fair value of certain incentives, including Bonus Points, provided to the purchaser when assessing the adequacy of the purchaser’s initial investment, which requires us to make certain estimates and assumptions in deriving the fair value of these incentives. We defer a portion of the VOI sales price as a liability and recognize the corresponding revenue upon the customer’s redemption of the Bonus Points.
One of our VOI products is accounted for as a long-term lease with a reversionary interest, rather than the sale of a deeded interest in real estate. In this case, sales revenue is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease.
| • | Sales, marketing, brand and other fees—We sell VOIs through fee-for-service agreements with third-party developers for which we earn sales commissions and other fees. We recognize revenue from commissions on these sales and other fees as intervals are sold and the service requirements of the respective agreements with the developers have been fulfilled. Additionally, we sell prepaid vacation packages and recognize revenue when they are redeemed for stays at properties other than our timeshare resorts; stays using these prepaid packages at our properties are included in Rental and ancillary services in our consolidated statements of operations. |
| • | Financing—VOI sales may be made for cash or we may provide financing for sales of our owned intervals. Revenue from the financing of timeshare sales is recognized on the accrual method as earned based on the outstanding principal, interest rate and terms stated in each individual financing agreement. See “—Timeshare Financing Receivables and Allowance for Loan Loss” below for further discussion of the policies applicable to our timeshare financing receivables. We also recognize revenue from servicing the loans provided by third-party developers to purchasers of their VOIs over the period services are rendered. |
| • | Resort and club management—We manage the Club, receiving activation fees, annual dues and transaction fees from member exchanges. Each purchaser of a vacation ownership unit is automatically enrolled in the Club, which gives the purchaser an annual allotment of Club points that allow the purchaser to exchange the Club points for a number of vacation options. Revenue from Club activation fees are deferred and amortized on a straight-line basis over the average inventory holding period. We recognize revenue from annual dues and transaction fees over the period services are rendered. |
We earn recurring management fees under our agreements with homeowners’ association (“HOA”s) and generally recognize these fees over the period services are rendered. We provide day-to-day-management services, including housekeeping services, operation of a reservation system, maintenance,
83
and certain accounting and administrative services for HOAs. We receive compensation for such management services which is generally based on a percentage of costs to operate the resorts.
| • | Rental and ancillary services—We offer rentals of unoccupied vacation ownership units and recognize rental revenues when occupancy has occurred. We defer advance deposits on rentals until the customer’s stay. We also recognize rental revenues from the utilization of Bonus Points and prepaid vacation packages when those points and packages are redeemed for rental stays at one of our resorts. We defer the advance payment as a liability and recognize the corresponding revenue upon the customer’s vacation stay. Ancillary revenues include food and beverage, retail, spa offerings and other guest services. |
| • | Cost reimbursements—Cost reimbursements include direct and indirect costs that HOAs and developers reimburse to us. These costs primarily consist of payroll and payroll related costs for management of the HOAs and other services we provide where we are the employer. We recognize cost reimbursements when we incur the related reimbursable costs. Cost reimbursements are based upon actual expenses with no added margin. |
Other than the United States, there were no countries that individually represented more than 10 percent of total revenues for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015.
We earn commission and other fees related to fee-for-service agreements to sell VOIs. For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, approximately 15 percent, 11 percent and 10 percent, respectively, of our total revenue was earned from one customer.
We are required to collect certain taxes and fees from customers on behalf of government agencies and remit these back to the applicable governmental agencies on a periodic basis. We have a legal obligation to act as a collection agent with respect to these taxes and fees. We do not retain these taxes and fees and, therefore, they are not included in revenues. We record a liability when the amounts are collected and relieve the liability when payments are made to the applicable taxing authority or other appropriate governmental agency.
Multiple Element Arrangements
When we enter into transactions for the sale of multiple products or services, we evaluate whether the delivered elements have value to the customer on a stand-alone basis, and if the arrangement includes a general right of return relative to the delivered items, we consider whether delivery or performance of the undelivered items is probable and substantially in our control. If these criteria are met, then we account for each deliverable in the transaction separately. We generally recognize revenue for undelivered elements on a straight-line basis over the contractual performance period for time-based elements or upon delivery to the customer.
Investments in Unconsolidated Affiliates
We account for investments in unconsolidated affiliates under the equity method of accounting when we exercise significant influence, but do not maintain a controlling financial interest over the affiliates. We evaluate our investments in affiliates for impairment when there are indicators that the fair value of our investment may be less than our carrying value.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include all highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash includes advance deposits received on VOI sales that are held in escrow until the contract is closed and cash reserves required by our non-recourse debt agreements. For purposes of our consolidated statements of cash flows, changes in restricted cash caused by changes in lender reserves due to restrictions under our loan agreements are shown as financing activities and the remaining changes in restricted cash, primarily relating to VOI sales, are the result of our normal operations and are reflected as operating activities.
84
Accounts Receivable and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Accounts receivable primarily consists of trade receivables and is reported at the customers’ outstanding balances, less any allowance for doubtful accounts. An allowance for doubtful accounts is provided on accounts receivable when losses are probable based on historical collection activity and current business conditions.
Timeshare Financing Receivables and Allowance for Loan Loss
Our timeshare financing receivables consist of loans related to our financing of VOI sales that are secured by the underlying timeshare properties. We determine our timeshare financing receivables to be past due based on the contractual terms of the individual mortgage loans. We recognize interest income on our timeshare financing receivables as earned. The interest rate charged on the notes correlates to the risk profile of the borrower at the time of purchase and the percentage of the purchase that is financed, among other factors. We record an estimate of uncollectibility as a reduction of revenue from VOI sales at the time revenue is recognized on a VOI sale.
We evaluate this portfolio collectively, since we hold a large group of homogeneous timeshare financing receivables, which are individually immaterial. We monitor the credit quality of our receivables on an ongoing basis. There are no significant concentrations of credit risk with any individual counterparty or groups of counterparties. We use a technique referred to as static pool analysis as the basis for determining our loan loss reserve requirements on our timeshare financing receivables. For static pool analysis, we use three key dimensions to stratify our portfolio: FICO scores and equity percentage at the time of sale. The adequacy of the related allowance is determined by management through analysis of several factors, such as current economic conditions and industry trends, as well as the specific risk characteristics of the portfolio including assumed default rates, aging and historical write-offs of these receivables. The allowance is maintained at a level deemed adequate by management based on a periodic analysis of the mortgage portfolio.
We apply payments we receive for loans, including those in non-accrual status, to amounts due in the following order: servicing fees; interest; principal; and late charges. Once a note is 91 days past due we cease accruing interest and reverse the accrued interest recognized up to that point. We resume interest accrual for loans for which we had previously ceased accruing interest once the loan is less than 91 days past due. We fully reserve for a timeshare financing receivable in the month following the date that the loan is 121 days past due and, subsequently, we write off the uncollectible note against the reserve once the foreclosure process is complete and we receive the deed for the foreclosed unit.
Inventory and Cost of Sales
Inventory includes unsold, completed VOIs; VOIs under construction; and land and infrastructure held for future VOI product development at our current resorts. We carry our completed VOI inventory at the lower of cost or estimated fair value, less costs to sell, which can result in impairment losses and/or recoveries of previous impairments. Projects under development, along with land and infrastructure for future development are under held and use impairment model and are reviewed for indicators of impairment quarterly.
We capitalize costs directly associated with the acquisition, development and construction of a real estate project when it is probable that the project will move forward. We capitalize salary and related costs only to the extent they directly relate to the project. We capitalize interest expense, taxes and insurance costs when activities that are necessary to get the property ready for its intended use are underway. We cease capitalization of costs during prolonged gaps in development when substantially all activities are suspended or when projects are considered substantially complete.
We account for our VOI inventory and cost of VOI sales using the relative sales value method. Also, we do not reduce inventory for the cost of VOI sales related to anticipated credit losses, and accordingly, no adjustment is made when inventory is reacquired upon default of the related receivable. This results in changes in estimates within the relative sales value calculations to be accounted for as real estate inventory true-ups, which we refer to as cost of sales true-ups, and are included in Cost of VOI sales in our consolidated statements of operations to retrospectively adjust the margin previously recognized subject to those estimates.
85
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment includes land, building and leasehold improvements and furniture and equipment at our corporate offices, sales centers and management offices. Additionally, certain property and equipment is held for future conversion into inventory. Construction-in-progress primarily relates to leasehold improvements not yet placed in service. Property and equipment are recorded at cost. Costs of improvements that extend the economic life or improve service potential are also capitalized. Capitalized costs are depreciated over their estimated useful lives. Costs for normal repairs and maintenance are expensed as incurred. Other than the United States, there were no countries that individually represented over 10 percent of total property and equipment, net as of December 31, 2017 and 2016.
Depreciation is recorded using the straight-line method over the assets’ estimated useful lives, which are generally as follows: buildings and improvements (eight to 40 years); furniture and equipment (three to eight years); and computer equipment and acquired software (three years). Leasehold improvements are depreciated over the shorter of the estimated useful life, based on the estimates above, or the lease term.
We evaluate the carrying value of our property and equipment if there are indicators of potential impairment. We perform an analysis to determine the recoverability of the asset’s carrying value by comparing the expected undiscounted future cash flows to the net book value of the asset. If it is determined that the expected undiscounted future cash flows are less than the net book value of the asset, to the extent the net book value is in excess of fair value we recognize an impairment loss. Fair value is generally estimated using valuation techniques that consider the discounted cash flows of the asset using discount and capitalization rates deemed reasonable for the type of asset, as well as prevailing market conditions, appraisals, recent similar transactions in the market and, if appropriate and available, current estimated net sales proceeds from pending offers.
If sufficient information exists to reasonably estimate the fair value of a conditional asset retirement obligation, including environmental remediation liabilities, we recognize the fair value of the obligation when the obligation is incurred.
Intangible Assets
Our intangible assets consist of management agreements and certain proprietary technologies with finite lives. We have management agreements that were recorded at their fair value at the time of the completion of a merger on October 24, 2007 where Hilton became a wholly-owned subsidiary of an affiliate of The Blackstone Group L.P. (“Blackstone”). Additionally, we capitalize direct and incremental costs to obtain management agreements and costs incurred to develop internal-use computer software, including costs incurred in connection with development of upgrades or enhancements that result in additional functionality. These capitalized costs are amortized on a straight-line basis over the term of the management agreement or the estimated useful life of the software, respectively. These capitalized costs are included in Intangible assets, net in our consolidated balance sheets.
We review all finite life intangible assets for impairment when circumstances indicate that their carrying amounts may not be recoverable. If the carrying value of an asset group is not recoverable, we recognize an impairment loss for the excess of carrying value over the fair value in our consolidated statements of operations.
Deferred Financing Costs
Deferred financing costs, including legal fees and upfront lenders fees, related to the Company’s debt and non-recourse debt are deferred and amortized over the life of the respective debt using the effective interest method. These capitalized costs are included in Other Assets or Debt, net in our consolidated balance sheets (see Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse debt for additional information. The amortization of deferred financing costs is included in interest expense in our consolidated statements of operations.
Costs Incurred to Sell VOIs
We expense indirect sales and marketing costs we incur to sell VOIs when incurred. Deferred selling and marketing expenses, which are direct selling and marketing costs related either to an unclosed contract or a contract
86
for which 100 percent of revenue has not yet been recognized, were $8 million and $9 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, and were included in Other assets in our consolidated balance sheets.
Fair Value Measurements—Valuation Hierarchy
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date (an exit price). We use the three-level valuation hierarchy for classification of fair value measurements. The valuation hierarchy is based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the measurement date. Inputs refer broadly to the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. Inputs may be observable or unobservable. Observable inputs are inputs that reflect the assumptions market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability developed based on market data obtained from independent sources. Unobservable inputs are inputs that reflect our own assumptions about the data market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability developed based on the best information available in the circumstances. The three-level hierarchy of inputs is summarized below:
| • | Level 1—Valuation is based upon quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets; |
| • | Level 2—Valuation is based upon quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, or other inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the instrument; and |
| • | Level 3—Valuation is based upon unobservable inputs that are significant to the fair value measurement. |
The classification of assets and liabilities within the valuation hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety.
Currency Translation
The U.S. dollar is our reporting currency and is the functional currency of the majority of our operations. Income and expense accounts are remeasured at the average exchange rate for the period. Gains and losses from foreign exchange rate changes related to transactions denominated in a currency other than an entity’s functional currency or intercompany receivables and payables denominated in a currency other than an entity’s functional currency that are not of a long-term investment nature are recognized as loss on foreign currency transactions included in Other loss, net our consolidated statements of operations.
Share-Based Compensation Costs
Certain of our employees participate in our 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the “Stock Plan”) which compensates eligible employees and directors with restricted stock units (“RSUs”) and nonqualified stock options (“options”). We record compensation expense based on the share-based awards granted to our employees.
Share-based compensation awards issued prior to the spin-off have been converted to reflect the separation from Hilton. Upon the separation on January 3, 2017, holders of Hilton share-based awards received an adjusted award based on our shares. The adjustments were designed to generally preserve the fair value of each award before and after the separation.
| • | RSUs vest in annual installments over three years from the date of grant, subject to the individual’s continued employment through the applicable vesting date. Vested RSUs generally will be settled for Hilton Grand Vacation’s common stock. The grant date fair value is equal to Hilton Grand Vacation’s closing stock price on the date of grant. |
| • | Options vest over three years in equal annual installments from the date of grant, subject to the individual’s continued employment through the applicable vesting date, and will terminate 10 years from the date of grant or earlier if the individual’s service terminates. The exercise price is equal to the closing price of the Hilton Grand Vacation’s common stock on the date of grant. The grant date fair value is estimated using the Black-Scholes-Merton Model. |
87
We recognize the cost of services received in share-based payment transactions with employees as services are received and recognize a corresponding change in Total Equity in our consolidated balance sheets. The measurement objective for these equity awards is the estimated fair value at the grant date of the equity instruments that we are obligated to issue when employees have rendered the requisite service and satisfied any other conditions necessary to earn the right to benefit from the instruments. Compensation expense is recognized ratably over the requisite service period. The requisite service period is the period during which an employee is required to provide service in exchange for an award.
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes using the asset and liability method. The objectives of accounting for income taxes are to recognize the amount of taxes payable or refundable for the current year, to recognize the deferred tax assets and liabilities that relate to tax consequences in future years, which result from differences between the respective tax basis of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts, and tax loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the respective temporary differences or operating loss or tax credit carryforwards are expected to be recovered or settled. The realization of deferred tax assets and tax loss and tax credit carryforwards is contingent upon the generation of future taxable income and other restrictions that may exist under the tax laws of the jurisdiction in which a deferred tax asset exists. Valuation allowances are provided to reduce such deferred tax assets to amounts more likely than not to be ultimately realized.
We use a prescribed recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken in a tax return. For all income tax positions, we first determine whether it is “more-likely-than-not” that a tax position will be sustained upon examination, including resolution of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits of the position. If it is determined that a position meets the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold, the benefit recognized in the financial statements is measured as the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50 percent likely of being realized upon settlement.
Earnings Per Share
Basic earnings per share (“EPS”) is calculated by dividing the earnings available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per common share is calculated to give effect to all potentially dilutive common shares that were outstanding during the reporting period.
88
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
Adopted Accounting Standards
In March 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2016-09 (“ASU 2016-09”), Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting. ASU 2016-09 includes provisions intended to simplify several aspects of the accounting and presentation of share-based payments. These provisions include the recognition of the income tax effects of awards in the consolidated statement of operations when the awards vest or are settled, permitting an employer to withhold shares in an amount up to the employee’s maximum individual tax rate without resulting in liability classification of the award, permitting entities to make a policy election to account for forfeitures as they occur, and changes to the classification of tax-related cash flows resulting from share-based payments and cash payments made to taxing authorities on the employee’s behalf on the statement of cash flows. This ASU 2016-09 was effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. We adopted ASU 2016-09 retrospectively as of January 1, 2017 and have applied to all periods herein with no material impact to our consolidated financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, (“ASU 2016-18”) Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash. This ASU is intended to provide guidance on the presentation of restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents and reduce the diversity in practice. This ASU requires amounts generally described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents to be included with cash and cash equivalents when reconciling beginning-of-period and end-of-period total amounts on the statement of cash flows. We elected, as permitted by the standard, to early adopt ASU 2016-18 retrospectively as of January 1, 2017 and have applied it to all periods presented herein. The adoption of ASU 2016-18 did not have a material impact to our consolidated financial statements. The effect of the adoption of ASU 2016-18 on our consolidated statements of cash flows was to include restricted cash balances in the beginning and end of period balances of cash and cash equivalent and restricted cash. The change in restricted cash was previously disclosed in operating activities and financing activities in the consolidated statements of cash flows.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-01 (“ASU 2017-01”), Business Combinations (Topic 804): Clarifying the Definition of a Business. This ASU clarifies the definition of a business with the objective of adding guidance to assist entities with evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions or disposals of assets or businesses. We elected, as permitted by the standard, to early adopt ASU 2017-01 prospectively as of January 1, 2017. The adoption of ASU 2017-01 did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
Accounting Standards Not Yet Adopted
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (ASC 606). Since its issuance, there have been several amendments to the standard prior to its adoption. The new standard, as amended, replaces all current GAAP guidance on this topic and eliminates all industry-specific guidance. The new revenue recognition guidance requires entities to recognize revenue in a way that depicts the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services.
Effective January 1, 2018, we will adopt ASC 606 using the modified retrospective approach in which the cumulative effect of applying the new standard will be recognized at the date of initial application with an adjustment to our opening balance of retained earnings. This approach applies to all contracts as of January 1, 2018. We are finalizing our evaluation of the impacts of the standard, specifically with regards to (1) the allocation of the transaction price to our identified performance obligations in VOI sales and marketing packages, (2) the historical deferral of VOI sales due to the initial and continuing investment criteria and 3) the recognition of breakage on prepaid discounted vacation packages. We do not anticipate significant changes to our consolidated financial statements aside from the following:
| • | Sales of VOIs, net – We currently recognize revenue for sales of VOIs under construction in accordance with the percentage of completion method. Upon the adoption of ASC 606, the timing of revenue recognition for Sales of VOIs under construction and all related direct costs will be deferred until the |
89
| | completion of construction activities and the permissible occupancy of the timeshare development by our customers. Compared with current accounting, this will result in a deferral of all revenues and associated expenses for sales of VOIs under construction until construction is complete. As a result, we anticipate an approximate $66 million reduction of Accumulated retained earnings as of January 1, 2018. |
| • | Sales, marketing, brand and other fees – We currently recognize revenue from prepaid discounted vacation packages when a package is redeemed or the likelihood of redemption is remote post expiration. Upon the adoption of ASC 606, using a portfolio approach, we will recognize the expected breakage on packages not expected to be redeemed as Sales, marketing, brand and other fees proportionately when our other customers redeem their packages. |
| • | Sales, marketing, brand and other fees – Certain sales incentives where we are acting as the agent (e.g., delivery of Hilton Honors points) will be recognized on a net basis in Sales, marketing, brand and other fees. This presentation change will have no impact on Accumulated retained earnings as of January 1, 2018. |
See the unaudited 2018 Outlook section of Item 8 Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02 (“ASU 2016-02”), Leases (Topic 842), which supersedes existing guidance on accounting for leases in Leases (Topic 840). Under the new provisions, all lessees will report a right-of-use asset and a liability for the obligation to make payments for all leases with the exception of those leases with a term of 12 months or less. The provisions of ASU 2016-02 are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018; early adoption is permitted. The provisions of this ASU are to be applied using a modified retrospective approach. We are currently evaluating the effect that this ASU will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, (“ASU 2016-13”), Financial Instruments-Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, which replaces the incurred loss impairment methodology in current U.S. GAAP, with a methodology that reflects expected credit losses. The update is intended to provide financial statement users with more decision-useful information about the expected credit losses on financial instruments and other commitments to extend credit held by a reporting entity at each reporting date. This update is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2018. We are currently evaluating the effect that this ASU will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15 (“ASU 2016-15”), Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments. This ASU addresses eight specific cash flow issues with the objective of reducing the existing diversity in practice. The provisions of this ASU are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017; early adoption is permitted. We are currently evaluating the effect that this ASU will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-03 (“ASU 2017-03”), Accounting Changes and Error Corrections (Topic 250) and Investments - Equity Method and Joint Ventures (Topic 323). ASU 2017-03 requires registrants to disclose the effect that recently issued accounting standards will have on their financial statements when adopted in a future period. The SEC staff expects the additional qualitative disclosures to include a description of the effect of the accounting policies that the registrant expects to apply, if determined, and a comparison to the registrant’s current accounting policies. In addition, a registrant should describe the status of its process to implement the new standards and the significant implementation matters yet to be addressed. ASU 2017-03 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, and interim periods within those fiscal years with early adoption permitted for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years. We are currently evaluating the effect that this ASU will have on our consolidated financial statements.
90
Note 3: Restricted Cash
Restricted cash was as follows:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Escrow deposits on VOI sales | | $ | 29 | | | $ | 81 | |
Reserves related to non-recourse debt(1) | | | 22 | | | | 22 | |
| | $ | 51 | | | $ | 103 | |
(1) | See Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse Debt for further discussion. |
Note 4: Timeshare Financing Receivables
Timeshare financing receivables were as follows:
| | December 31, 2017 | |
($ in millions) | | Securitized and Pledged | | | Unsecuritized | | | Total | |
Timeshare financing receivables | | $ | 471 | | | $ | 741 | | | $ | 1,212 | |
Less: allowance for loan loss | | | (27 | ) | | | (114 | ) | | | (141 | ) |
| | $ | 444 | | | $ | 627 | | | $ | 1,071 | |
| | December 31, 2016 | |
($ in millions) | | Securitized and Pledged | | | Unsecuritized | | | Total | |
Timeshare financing receivables | | $ | 253 | | | $ | 892 | | | $ | 1,145 | |
Less: allowance for loan loss | | | (9 | ) | | | (111 | ) | | | (120 | ) |
| | $ | 244 | | | $ | 781 | | | $ | 1,025 | |
The interest rate charged on the notes correlates to the risk profile of the borrower at the time of purchase and the percentage of the purchase that is financed, among other factors. As of December 31, 2017, our timeshare financing receivables had interest rates ranging from 5.3 percent to 20.5 percent, a weighted average interest rate of 12.2 percent, a weighted average remaining term of 7.7 years and maturities through 2028.
We pledge a portion of our timeshare financing receivables as collateral to secure a non-recourse revolving timeshare receivable credit facility (“Timeshare Facility”) with a borrowing capacity of $450 million. In connection with the spin-off, in December 2016, we drew down $300 million under the Timeshare Facility to primarily settle historical intercompany obligations to Hilton. See Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse Debt for further discussion. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, we had $143 million and $509 million, respectively, of gross timeshare financing receivables securing the Timeshare Facility. We recognize interest income on our timeshare financing receivables as earned. We record an estimate of uncollectibility as a reduction of revenue from VOI sales at the time revenue is recognized on a VOI sale.
In March 2017, we completed a securitization of approximately $357 million of gross timeshare financing receivables and issued approximately $291 million of 2.66 percent notes and approximately $59 million of 2.96 percent notes, which have a stated maturity date of December 2028. The securitization transaction did not qualify as sales and, accordingly, no gain or loss was recognized. The transaction is considered a secured borrowing; therefore, the proceeds from the transaction are presented as non-recourse debt (collectively, the “Securitized Debt”). The proceeds were used to pay down a portion of our timeshare facility.
91
Our timeshare financing receivables as of December 31, 2017 mature as follows:
($ in millions) | | Securitized and Pledged | | | Unsecuritized | | | Total | |
Year | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2018 | | $ | 74 | | | $ | 73 | | | $ | 147 | |
2019 | | | 72 | | | | 63 | | | | 135 | |
2020 | | | 70 | | | | 69 | | | | 139 | |
2021 | | | 65 | | | | 74 | | | | 139 | |
2022 | | | 57 | | | | 79 | | | | 136 | |
Thereafter | | | 133 | | | | 383 | | | | 516 | |
| | | 471 | | | | 741 | | | | 1,212 | |
Less: allowance for loan loss | | | (27 | ) | | | (114 | ) | | | (141 | ) |
| | $ | 444 | | | $ | 627 | | | $ | 1,071 | |
Our gross timeshare financing receivables balances by FICO score were as follows:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
FICO score | | | | | | | | |
700+ | | $ | 770 | | | $ | 725 | |
600-699 | | | 225 | | | | 211 | |
<600 | | | 28 | | | | 28 | |
No score(1) | | | 189 | | | | 181 | |
| | $ | 1,212 | | | $ | 1,145 | |
(1) | Timeshare financing receivables without a FICO score are primarily related to foreign borrowers. |
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, we had ceased accruing interest on timeshare financing receivables with an aggregate principal balance of $49 million and $38 million, respectively. The following tables detail an aged analysis of our gross timeshare financing receivables balance:
| | December 31, 2017 | |
($ in millions) | | Securitized and Pledged | | | Unsecuritized | | | Total | |
Current | | $ | 462 | | | $ | 685 | | | $ | 1,147 | |
31 - 90 days past due | | | 6 | | | | 10 | | | | 16 | |
91 - 120 days past due | | | 1 | | | | 4 | | | | 5 | |
121 days and greater past due | | | 2 | | | | 42 | | | | 44 | |
| | $ | 471 | | | $ | 741 | | | $ | 1,212 | |
| | December 31, 2016 | |
($ in millions) | | Securitized and Pledged | | | Unsecuritized | | | Total | |
Current | | $ | 248 | | | $ | 847 | | | $ | 1,095 | |
31 - 90 days past due | | | 3 | | | | 9 | | | | 12 | |
91 - 120 days past due | | | 1 | | | | 4 | | | | 5 | |
121 days and greater past due | | | 1 | | | | 32 | | | | 33 | |
| | $ | 253 | | | $ | 892 | | | $ | 1,145 | |
92
The changes in our allowance for loan loss were as follows:
($ in millions) | | Securitized and Pledged | | | Unsecuritized | | | Total | |
December 31, 2014 | | $ | 28 | | | $ | 68 | | | $ | 96 | |
Write-offs | | | — | | | | (29 | ) | | | (29 | ) |
Provision for loan loss(1) | | | (11 | ) | | | 50 | | | | 39 | |
December 31, 2015 | | | 17 | | | | 89 | | | | 106 | |
Write-offs | | | — | | | | (35 | ) | | | (35 | ) |
Provision for loan loss(1) | | | (8 | ) | | | 57 | | | | 49 | |
December 31, 2016 | | | 9 | | | | 111 | | | | 120 | |
Write-offs | | | — | | | | (37 | ) | | | (37 | ) |
Securitizations | | | 28 | | | | (28 | ) | | | — | |
Provision for loan loss(1) | | | (10 | ) | | | 68 | | | | 58 | |
December 31, 2017 | | $ | 27 | | | $ | 114 | | | $ | 141 | |
(1) | Includes activity related to repurchase of defaulted and upgraded securitized timeshare financing receivables, net of incremental provision for loan loss. |
Note 5: Inventory
Inventory was as follows:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Completed unsold VOIs | | $ | 191 | | | $ | 233 | |
Construction in process | | | 60 | | | | 20 | |
Land, infrastructure and other | | | 258 | | | | 260 | |
| | $ | 509 | | | $ | 513 | |
We benefited from $4 million and $10 million in costs of sales true-ups relating to VOI products for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, which resulted in a $4 million and $10 million increase to the carrying value of inventory as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Shown below are expenses incurred, recorded in Cost of VOI sales, related to granting credit to customers for their existing ownership when upgrading into fee-for-service projects.
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Cost of VOI sales related to fee-for-service upgrades | | $ | 36 | | | $ | 49 | | | $ | 67 | |
In 2017, we had non-cash transfers from property and equipment into inventory. See Note 21: Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information for additional information.
In 2016, Hilton transferred certain hotel assets to us for conversion to vacation ownership units. See Note 18: Related Party Transactions for further discussion.
93
Note 6: Property and Equipment
Property and equipment and related accumulated depreciation were as follows:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Land | | $ | 53 | | | $ | 71 | |
Buildings and leasehold improvements | | | 182 | | | | 185 | |
Furniture and equipment | | | 48 | | | | 44 | |
Construction-in-progress | | | 20 | | | | 12 | |
| | | 303 | | | | 312 | |
Accumulated depreciation | | | (65 | ) | | | (56 | ) |
| | $ | 238 | | | $ | 256 | |
In 2017, we had non-cash transfers from property and equipment to inventory. See Note 21: Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information for additional information.
In 2016, Hilton transferred certain property and equipment to us for future conversion to vacation ownership units. See Note 18: Related Party Transactions for further discussion.
Depreciation expense on property and equipment was $17 million, $12 million, and $10 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 respectively.
Note 7: Consolidated Variable Interest Entities
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, we consolidated three and two VIEs, respectively, that issued debt securitized by our timeshare financing receivables (the “Securitized Debt”), which is without recourse to us. We are the primary beneficiaries of these VIEs as we have the power to direct the activities that most significantly affect their economic performance. We are also the servicer of these timeshare financing receivables and we are required to replace or repurchase timeshare financing receivables that are in default at their outstanding principal amounts. Additionally, we have the obligation to absorb their losses and the right to receive benefits that could be significant to them. The assets of our VIEs are only available to settle the obligations of the respective entities.
Our consolidated balance sheets included the assets and liabilities of these entities, which primarily consisted of the following:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Restricted cash | | $ | 18 | | | $ | 10 | |
Timeshare financing receivables, net | | | 445 | | | | 244 | |
Non-recourse debt(1) | | | 454 | | | | 244 | |
(1) | Net of deferred financing costs. |
During the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, we did not provide any financial or other support to any VIEs that we were not previously contractually required to provide, nor do we intend to provide such support in the future.
Note 8: Investment in Unconsolidated Affiliate
On July 18, 2017, we entered into an agreement with BRE Ace Holdings LLC, a Delaware limited liability company (“BRE Ace Holdings”), an affiliate of The Blackstone Group L.P. (“Blackstone”) and formed BRE Ace LLC, a VIE. Because we are not the primary beneficiary, we do not consolidate BRE Ace LLC. Pursuant to the agreement, we contributed $40 million in cash for a 25 percent interest in BRE Ace LLC, which owns a 1,201-key timeshare resort property and related operations, commonly known as “Elara, by Hilton Grand Vacations,” located in Las Vegas, Nevada. Our investment interest in and equity earned from BRE Ace LLC are included in the consolidated balance sheets as Investment in unconsolidated affiliate and in the consolidated statements of operations as Equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate, respectively.
94
BRE Ace LLC had debt of $199 million and non-recourse debt of $289 million as of December 31, 2017. The debt and non-recourse debt are secured by its assets and are without recourse to us. Our maximum exposure to loss as a result of our investment interest in BRE Ace LLC is primarily limited to the carrying amount of the investment which totals $41 million as of December 31, 2017, as well as receivables for commission and other fees earned under a fee-for-service arrangement. See Note 18: Related Party Transactions for additional information.
Note 9: Intangible Assets
Intangible assets and related amortization expense were as follows:
| | December 31, 2017 | |
($ in millions) | | Gross Carrying Amount | | | Accumulated Amortization | | | Net Carrying Amount | |
Management agreements | | $ | 88 | | | $ | (37 | ) | | $ | 51 | |
Capitalized software | | | 51 | | | | (30 | ) | | | 21 | |
| | $ | 139 | | | $ | (67 | ) | | $ | 72 | |
| | December 31, 2016 | |
($ in millions) | | Gross Carrying Amount | | | Accumulated Amortization | | | Net Carrying Amount | |
Management agreements | | $ | 88 | | | $ | (33 | ) | | $ | 55 | |
Capitalized software | | | 41 | | | | (26 | ) | | | 15 | |
| | $ | 129 | | | $ | (59 | ) | | $ | 70 | |
Amortization expense on intangible assets was $12 million for each of the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015. As of December 31, 2017, the weighted average amortization period on management agreements was 14.1 years and capitalized software was 2.7 years We had approximately $15 million and $8 million of capitalized software additions for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
As of December 31, 2017, we estimated our future amortization expense for our amortizing intangible assets to be as follows:
($ in millions) | | Future Amortization Expense | |
Year | | | | |
2018 | | $ | 13 | |
2019 | | | 11 | |
2020 | | | 9 | |
2021 | | | 5 | |
2022 | | | 4 | |
Thereafter | | | 30 | |
| | $ | 72 | |
95
Note 10: Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other
Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other were as follows:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Accrued employee compensation and benefits | | $ | 70 | | | $ | 64 | |
Accounts payable | | 45 | | | 31 | |
Bonus point incentive liability | | 52 | | | 46 | |
Due to Hilton | | 23 | | | 5 | |
Income taxes payable(1) | | 64 | | | 1 | |
Other accrued expenses(2) | | 85 | | | 84 | |
| | $ | 339 | | | $ | 231 | |
(1) | During the year ended December 31, 2017, we deferred approximately $63 million in federal tax payment as permitted by the federal government pursuant to a tax relief program for regions impacted by Hurricane Irma. See Item 7 Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Result of Operations for additional information. |
(2) | Other accrued expenses consist of taxes, rent, interest and other accrued balances. |
Note 11: Debt & Non-recourse Debt
Debt
The following table details our outstanding debt balance and its associated interest rates:
| | December 31 | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Debt(1) | | | | | | | | |
Senior secured credit facilities: | | | | | | | | |
Term loans with an average rate of 3.814%, due 2021 | | $ | 190 | | | $ | 200 | |
Senior notes with a rate of 6.125%, due 2024 | | | 300 | | | | 300 | |
| | | 490 | | | | 500 | |
Less: unamortized deferred financing costs and discount(2)(3) | | | (8 | ) | | | (10 | ) |
| | $ | 482 | | | $ | 490 | |
(1) | For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, weighted average interest rates were 5.229 percent and 4.851 percent, respectively. |
(2) | Amount includes deferred financing costs of $1 million and $7 million as of December 31, 2017 and $2 million and $8 million as of December 31, 2016, relating to our term loan and senior notes, respectively. |
(3) | Amount does not include deferred financing costs of $2 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, relating to our revolving facility included in Other Assets in our consolidated balance sheets. |
Senior Secured Credit Facilities
In December 2016, we entered into the senior secured facilities (the “Senior Secured Credit Facilities”), consisting of a $200 million variable rate term loan facility (the “Term Loans”) and a revolving credit facility in an aggregate principal amount of up to $200 million (the “Revolving Facility”), each with a five-year maturity. The Revolving Facility has borrowing capacity available in an amount up to $30 million for letters of credit and $10 million for short-term borrowings. As of December 31, 2017, we had $1 million of outstanding letter of credit under the Revolving Facility.
We are required to pay an unused commitment fee of 0.35 percent per annum under the Revolving Facility for unused commitments thereunder. The Term Loans bear interest at a variable rate, which is payable monthly. The Senior Secured Credit Facilities provide the option to increase the amount available under the Term Loans and/or the Revolving Credit Facility by an aggregate of up to $300 million plus an unlimited amount subject to compliance with a first lien net leverage ratio not to exceed 0.25:1.00.
96
The obligations under the Senior Secured Credit Facility are unconditionally and irrevocably guaranteed by us and certain of our subsidiaries. We are in compliance with all applicable financial covenants as of December 31, 2017.
Senior Notes
In November 2016, we issued $300 million aggregate principal amount of 6.125 percent senior unsecured notes due 2024 (the “Senior Unsecured Notes”) and incurred $8 million of debt issuance costs. Interest on the Senior Unsecured Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on June 1 and December 1 of each year, beginning on June 1, 2017.
We may, at our sole option, redeem the Senior Unsecured Notes, in whole or in part, at any time prior to December 1, 2021, at a price equal to 100 percent of the principal amount, plus an applicable make-whole premium and accrued and unpaid interest. On and after, December 1, 2021, we may, at our sole option, redeem the Senior Unsecured Notes at 103.25 percent, 101.625 percent or 100 percent of the principal amount in 2021, 2022 or 2023, respectively, without any make-whole premium.
The Senior Unsecured Notes are guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by certain of our subsidiaries. We are in compliance with all applicable financial covenants as of December 31, 2017.
Non-recourse Debt
The following table details our outstanding non-recourse debt balance and its associated interest rates:
| | December 31 | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Non-recourse debt(1) | | | | | | | | |
Timeshare Facility with an average rate of 2.675%, due 2019 | | $ | 129 | | | $ | 450 | |
Securitized Debt with an average rate of 2.441%, due 2028 | | | 459 | | | | 246 | |
| | | 588 | | | | 696 | |
Less: unamortized deferred financing costs(2) | | | (5 | ) | | | (2 | ) |
| | $ | 583 | | | $ | 694 | |
(1) | For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, weighted average interest rates were 2.492 percent and 1.946 percent, respectively. |
(2) | Amount relates to Securitized Debt only and does not include deferred financing costs of $2 million and $3 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, relating to our Timeshare Facility included in Other Assets in our consolidated balance sheets. |
The Timeshare Facility is a non-recourse obligation and is payable solely from the pool of timeshare financing receivables pledged as collateral to the debt and related assets. In August and December 2016, we amended the terms of the Timeshare Facility to, among other things, increase the borrowing capacity from $300 million to $450 million, allowing us to borrow up to the maximum amount until August 2018 and requiring all amounts borrowed to be repaid in August 2019. In December 2016, we borrowed $300 million under the Timeshare Facility. The Timeshare Facility is secured by certain of our timeshare financing receivables. See Note 4: Timeshare Financing Receivables for further discussion.
In March 2017, we completed a securitization of approximately $357 million of gross timeshare financing receivables and issued approximately $291 million of 2.66 percent notes and approximately $59 million of 2.96 percent notes due December 2028. The Securitized Debt is backed by pledged assets, consisting primarily of a pool of timeshare financing receivables secured by first mortgages or deeds of trust on timeshare interests. The Securitized Debt is a non-recourse obligation and is payable solely from the pool of timeshare financing receivables pledged as collateral to the debt. The proceeds from the securitization were used to pay down a portion of our Timeshare Facility.
We are required to deposit payments received from customers on the timeshare financing receivables securing the Timeshare Facility and Securitized Debt into depository accounts maintained by third parties. On a monthly basis, the depository accounts are utilized to make required principal, interest and other payments due under the
97
respective loan agreements. The balances in the depository accounts were $22 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and were included in Restricted cash in our consolidated balance sheets.
Debt Maturities
The contractual maturities of our debt and non-recourse debt as of December 31, 2017 were as follows:
($ in millions) | | Debt | | | Non-recourse Debt | | | Total | |
Year | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2018 | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 140 | | | $ | 150 | |
2019 | | | 10 | | | | 251 | | | | 261 | |
2020 | | | 10 | | | | 89 | | | | 99 | |
2021 | | | 160 | | | | 34 | | | | 194 | |
2022 | | | — | | | | 26 | | | | 26 | |
Thereafter | | | 300 | | | | 48 | | | | 348 | |
| | $ | 490 | | | $ | 588 | | | $ | 1,078 | |
Note 12: Deferred Revenues
Deferred revenues were as follows:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Deferred VOI sales | | $ | 45 | | | $ | 46 | |
Club activation fees | | | 54 | | | | 45 | |
Other | | | 10 | | | | 15 | |
| | $ | 109 | | | $ | 106 | |
Deferred VOI sales include the deferred revenues associated with: the sales associated with incomplete phases or buildings that are recognized under the percentage-of-completion method; the sales of unacquired inventory; and deferred sales associated with our long-term lease product with a reversionary interest. Club activation fees are paid at closing of a VOI purchase, which grants access to our points-based Club. The revenue from these fees are deferred and amortized on a straight-line basis over the average inventory holding period. Deferred revenues do not include prepaid vacation packages or other prepayments for future stays at our resorts, which are included in Advanced deposits in our consolidated balance sheets.
98
Note 13: Fair Value Measurements
The carrying amounts and estimated fair values of our financial assets and liabilities were as follows:
| | December 31, 2017 | |
| | | | | | Hierarchy Level | |
($ in millions) | | Carrying Amount | | | Level 1 | | | Level 3 | |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Timeshare financing receivables(1) | | $ | 1,071 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,292 | |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Debt(2) | | | 482 | | | | 329 | | | | 194 | |
Non-recourse debt(2) | | | 583 | | | | — | | | | 577 | |
| | December 31, 2016 | |
| | | | | | Hierarchy Level | |
($ in millions) | | Carrying Amount | | | Level 1 | | | Level 3 | |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Timeshare financing receivables(1) | | $ | 1,025 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,147 | |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Debt(2) | | | 490 | | | | 314 | | | | 200 | |
Non-recourse debt(2) | | | 694 | | | | — | | | | 696 | |
(1) | Carrying amount includes allowance for loan loss. |
(2) | Carrying amount includes unamortized deferred financing costs and discount. |
Our estimates of the fair values were determined using available market information and appropriate valuation methods. Considerable judgment is necessary to interpret market data and develop the estimated fair values. The table above excludes cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, advance deposits and accrued liabilities, all of which had fair values approximating their carrying amounts due to the short maturities and liquidity of these instruments.
The estimated fair values of our timeshare financing receivables were determined using a discounted cash flow model. Our model incorporates default rates, coupon rates, credit quality and loan terms respective to the portfolio based on current market assumptions for similar types of arrangements.
The estimated fair values of our Level 1 debt was based on prices in active debt markets. The estimated fair value of our Level 3 debt and non-recourse debt were as follows:
| • | Debt – based on indicative quotes obtained for similar issuances and projected future cash flows discounted at risk-adjusted rates |
| • | Non-recourse debt – based on projected future cash flows discounted at risk-adjusted rates. |
We do not have any assets or liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2017 or 2016.
Note 14: Leases
We lease sales centers, office space and equipment under operating leases. Our operating leases may require minimum rent payments, contingent rent payments based on a percentage of revenue or income or rent payments equal to the greater of a minimum rent or contingent rent. Our leases expire at various dates from 2018 through 2026, with varying renewal options.
The future minimum rent payments under non-cancelable leases, due in each of the next five years and thereafter as of December 31, 2017, were as follows:
99
($ in millions) | | Operating Leases | |
Year | | | | |
2018 | | $ | 14 | |
2019 | | | 12 | |
2020 | | | 11 | |
2021 | | | 10 | |
2022 | | | 8 | |
Thereafter | | | 23 | |
Total minimum rent payments | | $ | 78 | |
Rent expense for all operating leases was as follows:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Minimum rentals | | $ | 17 | | | $ | 16 | | | $ | 12 | |
Contingent rentals | | | 3 | | | | 1 | | | | 5 | |
| | $ | 20 | | | $ | 17 | | | $ | 17 | |
Note 15: Income Taxes
On December 22, 2017, the United States enacted tax reform legislation commonly known as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Act”), resulting in significant modifications to existing law. HGV follows the guidance in SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin 118 (“SAB 118”), which provides additional clarification regarding the application of Accounting Standards Codification Topic 740 (“ASC Topic 740”) in situations where we do not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the Act for the reporting period in which the Act was enacted. SAB 118 provides for a measurement period beginning in the reporting period that includes the Act’s enactment date and ending when we have obtained, prepared, and analyzed the information needed in order to complete the accounting requirements but in no circumstances should the measurement period extend beyond one year from the enactment date.
As of December 31, 2017, we have not completed our accounting for the tax effects of enactment of the Act. However, in certain cases, as described below, we have made a reasonable estimate of the effects on the one-time repatriation tax and its existing deferred tax balances. In other cases, we have not been able to make a reasonable estimate and continue to account for those items based on our existing accounting under ASC 740, Income Taxes, and the provisions of the tax laws that were in effect immediately prior to enactment. In all cases, we will continue to make and refine our calculations as additional analysis is completed. In addition, our estimates may also be affected as we gain a more thorough understanding of the Act. Additionally, we have not yet elected an accounting policy to account for the tax upon Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income in either of the following ways: 1) as a period charge in the future period the tax arises or 2) as part of deferred taxes related to the investment or subsidiary.
One-Time Repatriation Tax: We have included a provisional current income tax payable in the amount of $1 million (net of applicable foreign tax credit) related to the one-time deemed repatriation transition tax on unrepatriated foreign earnings. The provisional amount is based on information currently available, including estimated tax earnings and profits from foreign investments. We will continue to gather and analyze information, including historical adjustments to earnings and profits of foreign subsidiaries, in order to complete the accounting for the effects of the estimated transition tax. It is our intention to complete the necessary analysis within the measurement period.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities: We have re-measured certain deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the rates at which they are expected to reverse in the future, which is generally 21%. However, we are still analyzing certain aspects of the Act and refining our calculations, which could potentially affect the measurement of these balances or potentially give rise to new deferred tax amounts. The provisional amount recorded related to the re-
100
measurement of our deferred tax balance was $132 million of deferred tax benefit, which consisted primarily of the re-measurement of deferred tax assets and liabilities from 35% to 21%.
The Company was a party to several intercompany asset transfers with Hilton prior to the spin-off. As required under U.S. tax regulations, the gain resulting from the intercompany transfer of these assets should be deferred and no deferred tax asset or liability should be recognized until a recognition event occurs. On January 3, 2017, Hilton executed a tax-free spin-off of HGV, which met the requirement of a recognition event. On the spin-off date, for the assets transferred, we recognized a stepped-up tax basis, re-measured the asset by applying applicable tax rate changes and evaluated the realizability of the asset. This resulted in a reduction to our net deferred tax liability and an increase in our Additional paid-in capital of $9 million on our consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2017. Additionally, upon Hilton’s filing of the pre spin-off income tax returns, we recorded a return-to-provision true-up, which resulted in a reduction to our net deferred tax liability and an increase in our Additional paid-in capital of $1 million on the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2017.
Our tax provision includes federal, state and foreign income taxes payable. The domestic and foreign components of income before taxes were as follows:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
U.S. income before tax | | $ | 283 | | | $ | 270 | | | $ | 275 | |
Foreign income before tax | | | 28 | | | | 23 | | | | 17 | |
Income before taxes | | $ | 311 | | | $ | 293 | | | $ | 292 | |
The components of our provision for income taxes were as follows:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Current: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 94 | | | $ | 87 | | | $ | 85 | |
State | | | 11 | | | | 8 | | | | 7 | |
Foreign | | | 8 | | | | 7 | | | | 6 | |
Total current | | | 113 | | | | 102 | | | | 98 | |
Deferred: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | | (137 | ) | | | 21 | | | | 18 | |
State | | | 8 | | | | 2 | | | | 2 | |
Total deferred | | | (129 | ) | | | 23 | | | | 20 | |
Total provision for income taxes | | $ | (16 | ) | | $ | 125 | | | $ | 118 | |
101
Reconciliations of our tax provision at the U.S. statutory rate to the provision (benefit) for income taxes were as follows:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Statutory U.S. federal income tax provision | | $ | 109 | | | $ | 102 | | | $ | 102 | |
State and local income taxes, net of U.S. federal tax benefit | | | 12 | | | | 10 | | | | 9 | |
Foreign income tax expense | | | 7 | | | | 7 | | | | 6 | |
U.S. benefit of foreign taxes | | | (7 | ) | | | (7 | ) | | | (6 | ) |
Non-deductible transactions costs | | | — | | | | 5 | | | | — | |
Interest on installment sales, net of U.S. federal tax benefit | | | 3 | | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
Interest on installment sales adjustment | | | (5 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
U.S. tax reform: one-time repatriation tax | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | — | |
U.S. tax reform: remeasurement of deferred tax | | | (132 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
U.S. tax reform: remeasurement of long-term interest liability on installment sales, net of federal tax benefit at 21% | | | (2 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Other | | | (2 | ) | | | 1 | | | | — | |
Provision for income taxes | | $ | (16 | ) | | $ | 125 | | | $ | 118 | |
Deferred income taxes represent the tax effect of the differences between the book and tax bases of assets and liabilities plus carryforward items. The compositions of net deferred tax balances were as follows:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Deferred income taxes assets | | $ | 1 | | | $ | — | |
Deferred income tax liabilities | | | (250 | ) | | | (389 | ) |
Net deferred taxes | | $ | (249 | ) | | $ | (389 | ) |
Deferred income taxes represent the tax effect of the differences between the book and tax bases of assets and liabilities plus carryforward items. The tax effects of the temporary differences and carryforwards that give rise to our net deferred tax liability were as follows:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | | | |
Compensation | | $ | 9 | | | $ | 11 | |
Other reserves | | | 42 | | | | 52 | |
Deferred tax assets | | | 51 | | | | 63 | |
Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Property and equipment | | | (54 | ) | | | (87 | ) |
Amortizable intangible assets | | | (10 | ) | | | (17 | ) |
Deferred income | | | (236 | ) | | | (347 | ) |
Other liabilities | | | — | | | | (1 | ) |
Deferred tax liabilities | | | (300 | ) | | | (452 | ) |
Net deferred taxes | | $ | (249 | ) | | $ | (389 | ) |
102
Note 16: Share-Based Compensation
Stock Plan
The share-based compensation award amounts presented below have been converted to reflect the separation from Hilton. Upon the separation on January 3, 2017, holders of Hilton stock options, RSUs and performance shares received an adjusted award based on our shares. The adjustments were designed to generally preserve the fair value of each award before and after the separation. Hilton modified the existing performance shares grant, converting the performance shares granted in 2016 and 2015 to RSUs based on a 100 percent achievement percentage with the same vesting periods as the original awards.
We issue time-vesting restricted stock units (“RSUs”) and nonqualified stock options (“options”) to certain employees. We recognized share-based compensation expense of $15 million, $8 million and $8 million during the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 respectively. The total tax benefit recognized related to this compensation was $4 million, $3 million and $3 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 respectively.
As of December 31, 2017, unrecognized compensation costs for unvested awards were approximately $11 million, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 1.9 years. As of December 31, 2017, there were 7,652,477 shares of common stock available for future issuance.
RSUs
The following table provides information about our RSU grants for the last three fiscal years:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Number of shares granted | | | 534,329 | | | | 331,227 | | | | 231,185 | |
Weighted average grant date fair value per share | | $ | 29.23 | | | $ | 18.68 | | | $ | 26.16 | |
Fair value of shares vested (in millions) | | $ | 11 | | | $ | 4 | | | $ | 8 | |
The following table summarizes the activity of our RSUs during the year ended December 31, 2017:
| | Number of Shares | | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | |
Outstanding, beginning of period | | | 721,557 | | | $ | 21.41 | |
Granted | | | 534,329 | | | | 29.23 | |
Vested | | | (330,072 | ) | | | 23.37 | |
Forfeited | | | (86,014 | ) | | | 24.54 | |
Outstanding, end of period | | | 839,800 | | | | 25.29 | |
Options
The following table provides information about our option grants for the last three fiscal years:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Number of options granted | | | 669,658 | | | | 148,929 | | | | 89,641 | |
Weighted average exercise price per share | | $ | 28.30 | | | $ | 18.69 | | | $ | 26.16 | |
Weighted average grant date fair value per share | | $ | 8.66 | | | $ | 5.21 | | | $ | 7.99 | |
103
The grant date fair value of each of these option grants was determined using the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model with the following assumptions:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Expected volatility(1) | | | 26.3 | % | | | 32.0 | % | | | 28.0 | % |
Dividend yield(2) | | | — | % | | | 1.4 | % | | | — | % |
Risk-free rate(3) | | | 2.3 | % | | | 1.4 | % | | | 1.7 | % |
Expected term (in years)(4) | | | 6.0 | | | | 6.0 | | | | 6.0 | |
(1) | Due to limited trading history for Hilton Grand Vacations’ common stock, we did not have sufficient information available on which to base a reasonable and supportable estimate of the expected volatility of its share price. As a result, we used an average historical volatility of our peer group over a time period consistent with its expected term assumption. Our peer group was determined based upon companies in our industry with similar business models and is consistent with those used to benchmark its executive compensation. |
(2) | For the 2017 and 2015 options, HGV and Hilton had no plans to pay dividends during the expected term of these options. For the 2016 options, estimated based on the expected annualized dividend payment at the date of grant. |
(3) | Based on the yields of U.S. Department of Treasury instruments with similar expected lives. |
(4) | Estimated using the average of the vesting periods and the contractual term of the options. |
The following table summarizes the activity of our options during the year ended December 31, 2017:
| | Number of Shares | | | Weighted Average Exercise Price Per Share | |
Outstanding, beginning of period | | | 333,108 | | | $ | 21.21 | |
Granted | | | 669,658 | | | | 28.30 | |
Exercised | | | (34,183 | ) | | | 21.76 | |
Forfeited, canceled or expired | | | (94,009 | ) | | | 27.36 | |
Outstanding, end of period | | | 874,574 | | | | 25.96 | |
Exercisable, end of period | | | 169,926 | | | | 21.71 | |
104
Note 17: Earnings Per Share
The following table presents the calculation of our basic and diluted earnings per share (“EPS”). The weighted average shares outstanding for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 reflect 98,802,597 shares distributed on January 3, 2017, our spin-off date, to our stockholders. See Note 1: Organization for further discussion. The weighted average shares outstanding used to compute basic and diluted EPS for the year ended December 31, 2017 is 98,934,352 and 99,621,199, respectively.
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions, except per share amounts) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Basic EPS | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Numerator: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net Income(1) | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 168 | | | $ | 174 | |
Denominator: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average shares outstanding | | | 99 | | | | 99 | | | | 99 | |
Basic EPS | | $ | 3.30 | | | $ | 1.70 | | | $ | 1.76 | |
Diluted EPS | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Numerator: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net Income(1) | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 168 | | | $ | 174 | |
Denominator: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average shares outstanding | | | 100 | | | | 99 | | | | 99 | |
Diluted EPS | | $ | 3.28 | | | $ | 1.70 | | | $ | 1.76 | |
(1) | Net income for years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015 was $326,777,744; $167,618,659 and $174,096,269, respectively. |
The dilutive effect of outstanding share-based compensation awards is reflected in diluted earnings per common share by application of the treasury stock method using average market prices during the period.
For the year ended December 31, 2017, we excluded 229,621 share-based compensation awards because their effect would have been anti-dilutive under the treasury stock method.
Note 18: Related Party Transactions
Relationship between HGV and Hilton Before and After Spin-Off
On January 3, 2017, when the spin-off was completed, Hilton and Park Hotels & Resorts Inc. ceased to be related parties of HGV. In connection with the spin-off, we entered into certain agreements with Hilton (who at the time was a related party) and other third parties. See Key Agreements Related to Spin-Off section in Part I - Item 1. Business for additional information.
Prior to the spin-off, we had a number of existing arrangements whereby Hilton and others have provided services to us. The following tables summarize amounts included in our consolidated financial statements related to the arrangements with Former Parent Hilton:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2016 | |
Consolidated Balance Sheets | | | | |
Assets: | | | | |
Accounts receivable, net | | | | |
Due from Hilton | | $ | 5 | |
Liabilities: | | | | |
Accounts payable, accrued expenses, and other | | | | |
Due to Hilton | | $ | 5 | |
105
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Consolidated Statements of Operations | | | | | | | | |
Expenses: | | | | | | | | |
General and administrative | | | | | | | | |
Allocated general and administrative | | $ | 27 | | | $ | 13 | |
Shared services | | | 12 | | | | 11 | |
Defined contribution plan | | | 7 | | | | 7 | |
Insurance | | | 2 | | | | 2 | |
License fee expense | | | 80 | | | | 74 | |
Interest expense | | | | | | | | |
Related party interest expense | | | 2 | | | | — | |
Shared Services and Corporate allocations
Our consolidated financial statements include costs for services provided to us by Hilton including, but not limited to, information technology support, financial services, human resources and other shared services. Historically, these costs were charged to us on a basis determined by Hilton to reflect a reasonable allocation of actual costs incurred to perform the services. Additionally, Hilton allocated indirect general and administrative costs to us for certain functions and services provided to us, including, but not limited to, executive office, finance and other administrative support.
Insurance
Hilton provided us with insurance coverage for general liability, group health insurance, property, business interruption and other risks with respect to business operations and charges us a fee based on estimates of claims.
Hilton Grand Vacations Brand
We licensed the Hilton Grand Vacations brand from Hilton and paid them an annual fee based on a percentage of revenue for rights to operate under this brand.
Defined Contribution Plan
Hilton administered and maintained a defined contribution plan for the benefit of Hilton employees meeting certain eligibility requirements who elect to participate in the plan. Contributions are determined based on a specified percentage of salary deferrals by participating employees.
Hilton Honors Program
We participate in Hilton’s guest loyalty program, Hilton Honors. Club members can exchange Club points for Hilton Honors points, which we purchase from Hilton. Hilton maintains and administers the program. We pay Hilton in advance based on an estimated cost per point for the costs of future club exchanges. The associated expense is included in respective operating expenses line item based on the revenue stream in our consolidated statement of operations. For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, we paid Hilton $58 million and $56 million, respectively, for Hilton Honors points. Our prepaid expenses, included in Other assets in our consolidated balance sheets, include the amount of Hilton Honors points purchased from Hilton for future redemptions. The prepaid expense is amortized into earnings evenly through the year.
Cash Management
Hilton used a centralized approach for cash management. Historically, up until October 2016, the majority of our cash was transferred to Hilton daily, and Hilton funded our operating and investing activities as needed. Accordingly, the cash and cash equivalents held by Hilton at the corporate level were not allocated to us for any of the periods presented prior to October 2016. As a result of the spin-off, beginning in the fourth quarter of 2016, we
106
no longer transferred our cash to Hilton. We reflect transfers of cash to and from Hilton’s cash management system as a component of Total equity in our consolidated balance sheets.
Net Parent Transfers
The components of Net transfers (to) from Parent in the consolidated statements of stockholders’ equity (deficit) were as follows:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Cash pooling and general financing activities | | $ | (715 | ) | | $ | (39 | ) |
Corporate allocations | | | 53 | | | | 42 | |
Income taxes | | | 95 | | | | 92 | |
Net transfers (to) from Parent | | $ | (567 | ) | | $ | 95 | |
Hotel Conversions and Other Hotel Transactions
In 2016, Hilton transferred to us certain assets and related deferred tax liabilities for conversion to vacation ownership units:
($ in millions) | | Assets | | | Deferred Tax Liabilities | | | Parent Capital Contribution | |
Certain floors at the Hilton New York(1)(2) | | $ | 33 | | | $ | 9 | | | $ | 17 | |
Certain floors at the Embassy Suites Washington, DC | | | 40 | | | | 7 | | | | 33 | |
Hotel tower and restaurant at the Hilton Waikoloa Village(2) | | | 178 | | | | 49 | | | | 129 | |
Land parcel adjacent to Hilton Waikoloa Village | | | 54 | | | | 16 | | | | 38 | |
(1) | Parent capital contribution includes the release of the $7 million included in Other assets in our consolidated balance sheets. See below for further discussion. |
(2) | Certain floors at the Hilton New York, were subject to a lease arrangement with Park whereby Park retained the right to occupy and operate those floors, which lease expired September 30, 2017. The hotel tower and restaurant at the Hilton Waikoloa Village, are subject to a lease arrangement with Park whereby Park has retained the right to occupy and operate certain floors of the properties with lease terms expiring on December 31, 2019. |
We pay rental fees and fees for other amenities to certain Hilton wholly owned hotels. During the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, we paid fees of $27 million and $25 million, respectively, included in our consolidated statements of operations.
HNA Tourism Group Co., Ltd
On March 15, 2017, Blackstone completed the previously announced sale of 24,750,000 shares of our common stock to HNA Tourism Group Co., Ltd. (“HNA”), representing approximately 25 percent of the outstanding shares of our common stock.
In connection with the consummation of the sale, we adopted our amended and restated by-laws, effective March 15, 2017, to remove references to Blackstone’s ownership of at least 40 percent of the total voting power of our common stock and revised certain provisions referencing the Blackstone Stockholders Agreement, as appropriate, to include references to the HNA Stockholder Agreement.
The Blackstone Group
Upon completion of the sale to HNA, on March 31, 2017, Blackstone held 15,008,689 shares, or approximately 15 percent of our outstanding common stock. On May 25, 2017, Blackstone filed a Registration Statement on Form S-1 and registered all of our common stock held by them. On June 14, 2017, Blackstone entered into an underwriting agreement with J.P. Morgan Securities LLC pursuant to which J.P. Morgan Securities LLC agreed to purchase from Blackstone 9,650,000 shares of our common stock at a price of $35.40 per share. The sale was completed on June 20, 2017. Subsequently, on September 25, 2017, Blackstone completed the sale of
107
substantially all of the remaining shares of our common stock held by them to several institutional investors and ceased to be a related party of HGV. We did not receive any proceeds from either of these sales. As of December 31, 2017, Blackstone holds only a nominal number of shares of our common stock.
The following table summarizes amounts included in our consolidated statements of operations related to a fee-for-service arrangement with Blackstone affiliates to sell VOIs on their behalf through September 30, 2017 were as follows:
| September 30, | | | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | 2017 | | 2016 | | 2015 | |
Commission and other fees | $ | 135 | | | $ | 177 | | | $ | 154 | |
Also related to the fee-for-service agreement, as of September 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, we have outstanding receivables of $8 and $20 million, respectively.
BRE Ace LLC
On July 18, 2017, we entered into an agreement with BRE Ace Holdings to form BRE Ace LLC. In conjunction with this agreement we acquired a 25 percent ownership interest in BRE Ace LLC. During the year ended December 31, 2017, we recorded $1 million in Equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliates, included in our consolidated statements of operations. See Note 8: Investment in Unconsolidated Affiliate for additional information. In addition, we earn commissions and other fees related to a fee-for-service agreement to sell VOIs at Elara, by Hilton Grand Vacations. These amounts are summarized in the following table and included in our consolidated statements of operations as of the date they became a related party.
| | December 31, |
($ in millions) | 2017 | | 2016 | | 2015 |
Commission and other fees | $ | | 79 | | $ | — | | $ | — |
Also related to the fee-for-service agreement, as of December 31, 2017, we have outstanding receivables of $29 million.
Note 19: Business Segments
We operate our business through the following two segments:
| • | Real estate sales and financing – We market and sell VOIs that we own. We also source VOIs through fee-for-service agreements with third-party developers. Related to the sales of the VOIs that we own, we provide consumer financing, which includes interest income generated from the origination of consumer loans to customers to finance their purchase of VOIs and revenue from servicing the loans. We also generate fee revenue from servicing the loans provided by third-party developers to purchasers of their VOIs. |
| • | Resort operations and club management – We manage the Club, earn activation fees, annual dues and transaction fees from member exchanges for other vacation products. We earn fees for managing the timeshare properties. We generate rental revenue from unit rentals of unsold inventory and inventory made available due to ownership exchanges under our Club program. We also earn revenue from food and beverage, retail and spa outlets at our timeshare properties. |
The performance of our operating segments is evaluated primarily based on adjusted earnings before interest expense, taxes, depreciation and amortization (“EBITDA”). We define Adjusted EBITDA as EBITDA which has been further adjusted to exclude certain items, including, but not limited to, gains, losses and expenses in connection with: (i) asset dispositions; (ii) foreign currency transactions; (iii) debt restructurings/retirements; (iv) non-cash impairment losses; (v) reorganization costs, including severance and relocation costs; (vi) share-based and other compensation expenses; (vii) costs related to the spin-off; and (viii) other items. During the first quarter of 2017, we revised our definition of EBITDA to exclude the adjustment of interest expense relating to our non-recourse debt as a reconciling item to arrive at net income (loss) in order to conform to the presentation of the timeshare industry
108
following the consummation of the spin-off from Hilton. This adjustment was retrospectively applied to prior period(s) to conform with the current presentation.
We do not include equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate in our measures of segment revenues. The following table presents revenues for our reportable segments reconciled to consolidated amounts:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Real estate sales and financing(1) | | $ | 1,239 | | | $ | 1,143 | | | $ | 1,078 | |
Resort operations and club management(2) | | | 367 | | | | 339 | | | | 307 | |
Total segment revenues | | | 1,606 | | | | 1,482 | | | | 1,385 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | 135 | | | | 126 | | | | 110 | |
Intersegment eliminations(1)(2)(3) | | | (30 | ) | | | (25 | ) | | | (20 | ) |
Total revenues | | $ | 1,711 | | | $ | 1,583 | | | $ | 1,475 | |
(1) | Includes charges to the resort operations and club management segment for billing and collection services provided by the real estate sales and financing segment. These charges totaled $2 million for each of the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015. There were no charges for the year ended December 31, 2017. |
(2) | Includes charges to the real estate sales and financing segment from the resort operations and club management segment for discounted stays at properties resulting from marketing packages. These charges totaled $29 million, $23 million and $17 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. |
(3) | Includes charges to the real estate sales and financing segment from the resort operations and club management segment for the rental of model units to show prospective buyers. These charges totaled $1 million for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2015. There were no charges for the year ended December 31, 2016. |
The following table presents Adjusted EBITDA for our reportable segments reconciled to net income:
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Adjusted EBITDA: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Real estate sales and financing(1) | | $ | 359 | | | $ | 336 | | | $ | 316 | |
Resort operations and club management(1) | | | 204 | | | | 189 | | | | 162 | |
Segment Adjusted EBITDA | | | 563 | | | | 525 | | | | 478 | |
General and administrative | | | (104 | ) | | | (92 | ) | | | (57 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization | | | (29 | ) | | | (24 | ) | | | (22 | ) |
License fee expense | | | (87 | ) | | | (80 | ) | | | (74 | ) |
Interest expense | | | (27 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | — | |
Allocated Parent interest expense(2) | | | — | | | | (26 | ) | | | (29 | ) |
Other loss, net | | | — | | | | (1 | ) | | | — | |
Equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate(4) | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Income tax benefit (expense)(3) | | | 16 | | | | (125 | ) | | | (118 | ) |
Other adjustment items | | | (6 | ) | | | (6 | ) | | | (4 | ) |
Net income | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 168 | | | $ | 174 | |
| (1) | Includes intersegment eliminations. Refer to our table presenting revenues by reportable segment above for additional discussion. |
| (2) | This amount represents interest expense on an unconditional obligation to guarantee certain Hilton allocated debt balances which were released in November 2016. |
| (3) | On December 22, 2017, the United States enacted tax reform legislation, the Act, resulting in significant modifications to existing law which resulted in a reduction in income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2017. See Note 15: Income Taxes for additional information. |
| (4) | This amount represents our 25 percent interest in BRE Ace LLC. See Note 8: Investment in Unconsolidated Affiliate for additional information. |
109
The following table presents total assets for our reportable segments, reconciled to consolidated amounts:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | |
Real estate sales and financing | | $ | 2,255 | | | $ | 2,067 | |
Resort operations and club management | | | 78 | | | | 80 | |
Total segment assets | | | 2,333 | | | | 2,147 | |
Corporate | | | 51 | | | | 33 | |
Total assets | | $ | 2,384 | | | $ | 2,180 | |
The following table presents capital expenditures for property and equipment for our reportable segments, reconciled to consolidated amounts:
| | December 31, | |
($ in millions) | | 2017 | | | 2016 | | | 2015 | |
Real estate sales and financing | | $ | 28 | | | $ | 19 | | | $ | 10 | |
Resort operations and club management | | | 2 | | | | 1 | | | | 1 | |
Total segment capital expenditures for property and equipment | | | 30 | | | | 20 | | | | 11 | |
Corporate | | | 5 | | | | 6 | | | | 1 | |
Total capital expenditures for property and equipment | | $ | 35 | | | $ | 26 | | | $ | 12 | |
Note 20: Commitments and Contingencies
We have entered into certain arrangements with developers whereby we have committed to purchase vacation ownership units at a future date to be marketed and sold under our Hilton Grand Vacations brand. As of December 31, 2017, we were committed to purchase approximately $372 million of inventory and land over a period of seven years. The ultimate amount and timing of the acquisitions is subject to change pursuant to the terms of the respective arrangements, which could also allow for cancellation in certain circumstances. During the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, we purchased $12 million and $14 million, respectively, of VOI inventory as required under our commitments. As of December 31, 2017, our remaining obligation pursuant to these arrangements was expected to be incurred as follows:
($ in millions) | | Purchase Obligations | |
Year | | | | |
2018 | | $ | 3 | |
2019 | | | 187 | |
2020 | | | 9 | |
2021 | | | 56 | |
2022 | | | 35 | |
Thereafter | | | 82 | |
Total | | $ | 372 | |
We are involved in litigation arising from the normal course of business, some of which includes claims for substantial sums. Management has also identified certain other legal matters where we believe an unfavorable outcome is reasonably possible and/or for which no estimate of possible losses can be made. While the ultimate results of claims and litigation cannot be predicted with certainty, we expect that the ultimate resolution of all pending or threatened claims and litigation as of December 31, 2017 will not have a material effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial position or cash flows.
110
Note 21: Supplemental Disclosures of Cash Flow Information
Cash paid for interest during the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, was $42 million, $37 million and $37 million, respectively. Cash paid for income taxes during the year ended December 31, 2017 was $57 million. Prior to 2017, we were part of Hilton’s consolidated income tax return.
The following non-cash activities were excluded from the consolidated statements of cash flows:
| • | In 2017, we had $40 million of non-cash operating activity transfer from property and equipment to inventory. |
| • | In 2016, Hilton transferred to us $72 million of net inventory and $138 million of net property and equipment for conversion into timeshare units. See Note 18: Related Party Transactions for further discussion. |
| • | In 2016, we had $300 million of a non-cash financing activity related to the issuance of our Senior Unsecured Notes and $8 million of related non-cash deferred financing costs. |
Note 22: Condensed Consolidating Guarantor Financial Information
During 2016, Hilton completed an internal reorganization to contribute to HGV its U.S. and non-U.S. timeshare subsidiaries including HRC. HGV is a Delaware corporation formed on May 2, 2016. HRC is considered our predecessor entity for periods prior to the formation of HGV. However, for the condensed consolidating information below, HRC is included in the Guarantors column to more faithfully represent the historical combined financial position and results of operations and cash flows of the subsidiaries currently serving as the guarantors of the debt. See Note 1: Organization for additional information. In November 2016, Hilton Grand Vacations Borrower LLC and Hilton Grand Vacations Borrower Inc. (the “Subsidiary Issuers”), entities formed in October 2016 which are 100 percent owned by HGV (the “Parent”), issued the Senior Unsecured Notes. The obligations of the Subsidiary Issuers are fully and unconditionally guaranteed jointly and severally on a senior unsecured basis by the Parent, and certain of the Parent’s 100 percent owned domestic subsidiaries (the “Guarantors”). The indenture that governs the Senior Unsecured Notes provides that any subsidiary of the Company that provides a guarantee of the Senior Secured Credit Facilities will guarantee the Senior Unsecured Notes. Neither of our foreign subsidiaries nor certain of our special purpose subsidiaries formed in connection with our Timeshare Facility and Securitized Timeshare Debt guarantee the Senior Unsecured Notes (collectively, the “Non-Guarantors”).
111
The following schedules present the condensed consolidating financial information as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 and for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, for the Parent, Subsidiary Issuers, Guarantors and Non-Guarantors.
| | December 31, 2017 | |
($ in millions) | | Parent | | | Issuers | | | Guarantors | | | Non- Guarantors | | | Eliminations | | | Total | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 230 | | | $ | 16 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 246 | |
Restricted cash | | | — | | | | — | | | | 29 | | | | 22 | | | | — | | | | 51 | |
Accounts receivable, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 113 | | | | 5 | | | | (6 | ) | | | 112 | |
Timeshare financing receivables, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 457 | | | | 614 | | | | — | | | | 1,071 | |
Inventory | | | — | | | | — | | | | 509 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 509 | |
Property and equipment, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 232 | | | | 6 | | | | — | | | | 238 | |
Investment in unconsolidated affiliate | | | — | | | | — | | | | 41 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 41 | |
Intangible assets, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 72 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 72 | |
Other assets | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 36 | | | | 7 | | | | (1 | ) | | | 44 | |
Investments in subsidiaries | | | 518 | | | | 999 | | | | 81 | | | | — | | | | (1,598 | ) | | | — | |
TOTAL ASSETS | | $ | 518 | | | $ | 1,001 | | | $ | 1,800 | | | $ | 670 | | | $ | (1,605 | ) | | $ | 2,384 | |
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other | | $ | — | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 338 | | | $ | 7 | | | $ | (7 | ) | | $ | 339 | |
Advance deposits | | | — | | | | — | | | | 104 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 104 | |
Debt, net | | | — | | | | 482 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 482 | |
Non-recourse debt, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 583 | | | | — | | | | 583 | |
Deferred revenues | | | — | | | | — | | | | 109 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 109 | |
Deferred income tax liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | 250 | | | | (1 | ) | | | — | | | | 249 | |
Total equity | | | 518 | | | | 518 | | | | 999 | | | | 81 | | | | (1,598 | ) | | | 518 | |
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | $ | 518 | | | $ | 1,001 | | | $ | 1,800 | | | $ | 670 | | | $ | (1,605 | ) | | $ | 2,384 | |
112
| | December 31, 2016 | |
($ in millions) | | Parent | | | Issuers | | | Guarantors | | | Non- Guarantors | | | Eliminations | | | Total | |
ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 47 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 48 | |
Restricted cash | | | — | | | | — | | | | 81 | | | | 22 | | | | — | | | | 103 | |
Accounts receivable, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 123 | | | | 18 | | | | (18 | ) | | | 123 | |
Timeshare financing receivables, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 263 | | | | 762 | | | | — | | | | 1,025 | |
Inventory | | | — | | | | — | | | | 510 | | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | 513 | |
Property and equipment, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 253 | | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | 256 | |
Intangible assets, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | 70 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 70 | |
Other assets | | | — | | | | 2 | | | | 43 | | | | 14 | | | | (17 | ) | | | 42 | |
Investments in subsidiaries | | | 167 | | | | 657 | | | | 115 | | | | — | | | | (939 | ) | | | — | |
TOTAL ASSETS | | $ | 167 | | | $ | 659 | | | $ | 1,505 | | | $ | 823 | | | $ | (974 | ) | | $ | 2,180 | |
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other | | $ | — | | | $ | 2 | | | $ | 251 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | (25 | ) | | $ | 231 | |
Advance deposits | | | — | | | | — | | | | 102 | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 103 | |
Debt, net | | | — | | | | 490 | | | | — | | | | 10 | | | | (10 | ) | | | 490 | |
Non-recourse debt, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 694 | | | | — | | | | 694 | |
Deferred revenues | | | — | | | | — | | | | 106 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 106 | |
Deferred income tax liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | 389 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 389 | |
Total equity | | | 167 | | | | 167 | | | | 657 | | | | 115 | | | | (939 | ) | | | 167 | |
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | $ | 167 | | | $ | 659 | | | $ | 1,505 | | | $ | 823 | | | $ | (974 | ) | | $ | 2,180 | |
113
| | For the Year Ended December 31, 2017 | |
($ in millions) | | Parent | | | Issuers | | | Guarantors | | | Non- Guarantors | | | Eliminations | | | Total | |
Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Sales of VOI’s, net | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 518 | | | $ | 30 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 548 | |
Sales, marketing, license and other fees | | | — | | | | — | | | | 545 | | | | 3 | | | | (4 | ) | | | 544 | |
Financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 71 | | | | 83 | | | | (7 | ) | | | 147 | |
Resort and club management | | | — | | | | — | | | | 156 | | | | 2 | | | | — | | | | 158 | |
Rental and ancillary service | | | — | | | | — | | | | 177 | | | | 2 | | | | — | | | | 179 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | — | | | | — | | | | 131 | | | | 4 | | | | — | | | | 135 | |
Total revenues | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,598 | | | | 124 | | | | (11 | ) | | | 1,711 | |
Expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of VOI sales | | | — | | | | — | | | | 145 | | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | 148 | |
Sales and marketing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 650 | | | | 17 | | | | (4 | ) | | | 663 | |
Financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 19 | | | | 31 | | | | (7 | ) | | | 43 | |
Resort and club management | | | — | | | | — | | | | 41 | | | | 2 | | | | — | | | | 43 | |
Rental and ancillary service | | | — | | | | — | | | | 120 | | | | 2 | | | | — | | | | 122 | |
General and administrative | | | — | | | | — | | | | 101 | | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | 104 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | — | | | | — | | | | 29 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 29 | |
License fee expense | | | — | | | | — | | | | 87 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 87 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | — | | | | — | | | | 131 | | | | 4 | | | | — | | | | 135 | |
Total operating expenses | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,323 | | | | 62 | | | | (11 | ) | | | 1,374 | |
Interest expense | | | — | | | | (27 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (27 | ) |
Equity in earnings from unconsolidated affiliate | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | |
Income (loss) before income taxes | | | — | | | | (27 | ) | | | 276 | | | | 62 | | | | — | | | | 311 | |
Income tax benefit (expense) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 18 | | | | (2 | ) | | | — | | | | 16 | |
Income (loss) before equity in earnings (loss) from subsidiaries | | | — | | | | (27 | ) | | | 294 | | | | 60 | | | | — | | | | 327 | |
Equity in earnings (loss) from subsidiaries | | | 327 | | | | 354 | | | | 60 | | | | — | | | | (741 | ) | | | — | |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 354 | | | $ | 60 | | | $ | (741 | ) | | $ | 327 | |
114
| | For the Year Ended December 31, 2016 | |
($ in millions) | | Parent | | | Issuers | | | Guarantors | | | Non- Guarantors | | | Eliminations | | | Total | |
Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Sales of VOI’s, net | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 495 | | | $ | 13 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 508 | |
Sales, marketing, license and other fees | | | — | | | | — | | | | 501 | | | | 2 | | | | (4 | ) | | | 499 | |
Financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 73 | | | | 66 | | | | (5 | ) | | | 134 | |
Resort and club management | | | — | | | | — | | | | 143 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 143 | |
Rental and ancillary service | | | — | | | | — | | | | 171 | | | | 2 | | | | — | | | | 173 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | — | | | | — | | | | 123 | | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | 126 | |
Total revenues | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,506 | | | | 86 | | | | (9 | ) | | | 1,583 | |
Expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of VOI sales | | | — | | | | — | | | | 150 | | | | 2 | | | | — | | | | 152 | |
Sales and marketing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 605 | | | | 4 | | | | (4 | ) | | | 605 | |
Financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 18 | | | | 19 | | | | (5 | ) | | | 32 | |
Resort and club management | | | — | | | | — | | | | 36 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 36 | |
Rental and ancillary service | | | — | | | | — | | | | 108 | | | | 5 | | | | — | | | | 113 | |
General and administrative | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | 91 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 92 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | — | | | | — | | | | 24 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 24 | |
License fee expense | | | — | | | | — | | | | 80 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 80 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | — | | | | — | | | | 123 | | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | 126 | |
Total operating expenses | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | 1,235 | | | | 33 | | | | (9 | ) | | | 1,260 | |
Interest expense | | | — | | | | (3 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3 | ) |
Allocated Parent interest expense | | | (17 | ) | | | — | | | | (9 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (26 | ) |
Other loss, net | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1 | ) |
Income (loss) before income taxes | | | (17 | ) | | | (4 | ) | | | 261 | | | | 53 | | | | — | | | | 293 | |
Income tax expense | | | — | | | | — | | | | (125 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (125 | ) |
Income (loss) before equity in earnings (loss) from subsidiaries | | | (17 | ) | | | (4 | ) | | | 136 | | | | 53 | | | | — | | | | 168 | |
Equity in earnings (loss) from subsidiaries | | | 185 | | | | 189 | | | | 53 | | | | — | | | | (427 | ) | | | — | |
Net income (loss) | | $ | 168 | | | $ | 185 | | | $ | 189 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | (427 | ) | | $ | 168 | |
115
| | For the Year Ended December 31, 2015 | |
($ in millions) | | Parent | | | Issuers | | | Guarantors | | | Non- Guarantors | | | Eliminations | | | Total | |
Revenues | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Sales of VOI’s, net | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 488 | | | $ | 4 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 492 | |
Sales, marketing, license and other fees | | | — | | | | — | | | | 457 | | | | 2 | | | | (2 | ) | | | 457 | |
Financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 60 | | | | 73 | | | | (6 | ) | | | 127 | |
Resort and club management | | | — | | | | — | | | | 125 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 125 | |
Rental and ancillary service | | | — | | | | — | | | | 161 | | | | 3 | | | | — | | | | 164 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | — | | | | — | | | | 106 | | | | 4 | | | | — | | | | 110 | |
Total revenues | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,397 | | | | 86 | | | | (8 | ) | | | 1,475 | |
Expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of VOI sales | | | — | | | | — | | | | 172 | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | 173 | |
Sales and marketing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 542 | | | | 1 | | | | (2 | ) | | | 541 | |
Financing | | | — | | | | — | | | | 16 | | | | 22 | | | | (6 | ) | | | 32 | |
Resort and club management | | | — | | | | — | | | | 32 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 32 | |
Rental and ancillary service | | | — | | | | — | | | | 108 | | | | 5 | | | | — | | | | 113 | |
General and administrative | | | — | | | | — | | | | 57 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 57 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | — | | | | — | | | | 22 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 22 | |
License fee expense | | | — | | | | — | | | | 74 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 74 | |
Cost reimbursements | | | — | | | | — | | | | 106 | | | | 4 | | | | — | | | | 110 | |
Total operating expenses | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,129 | | | | 33 | | | | (8 | ) | | | 1,154 | |
Allocated Parent interest expense | | | — | | | | — | | | | (29 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (29 | ) |
Income before income taxes | | | — | | | | — | | | | 239 | | | | 53 | | | | — | | | | 292 | |
Income tax expense | | | — | | | | — | | | | (118 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (118 | ) |
Income before equity in earnings (loss) from subsidiaries | | | — | | | | — | | | | 121 | | | | 53 | | | | — | | | | 174 | |
Equity in earnings (loss) from subsidiaries | | | — | | | | — | | | | 53 | | | | — | | | | (53 | ) | | | — | |
Net income (loss) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 174 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | (53 | ) | | $ | 174 | |
116
| | For the Year Ended December 31, 2017 | |
($ in millions) | | Parent | | | Issuers | | | Guarantors | | | Non- Guarantors | | | Eliminations | | | Total | |
Operating Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | | $ | — | | | $ | (27 | ) | | $ | 156 | | | $ | 235 | | | $ | (8 | ) | | $ | 356 | |
Investing Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Capital expenditures for property and equipment | | | — | | | | — | | | | (33 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | — | | | | (35 | ) |
Software capitalization costs | | | — | | | | — | | | | (12 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (12 | ) |
Investment in unconsolidated affiliate | | | — | | | | — | | | | (40 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (40 | ) |
Net cash used in investing activities | | | — | | | | — | | | | (85 | ) | | | (2 | ) | | | — | | | | (87 | ) |
Financing Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issuance of non-recourse debt | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 350 | | | | — | | | | 350 | |
Repayment of non-recourse debt | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (459 | ) | | | — | | | | (459 | ) |
Repayment of debt | | | — | | | | (10 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (10 | ) |
Debt issuance costs | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (5 | ) | | | — | | | | (5 | ) |
Proceeds from stock option exercises | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | |
Intercompany transfers | | | — | | | | 37 | | | | 59 | | | | (104 | ) | | | 8 | | | | — | |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | | | — | | | | 27 | | | | 60 | | | | (218 | ) | | | 8 | | | | (123 | ) |
Net increase in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | | | — | | | | — | | | | 131 | | | | 15 | | | | — | | | | 146 | |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, beginning of period | | | — | | | | — | | | | 128 | | | | 23 | | | | — | | | | 151 | |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, end of period | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 259 | | | $ | 38 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 297 | |
117
| | For the Year Ended December 31, 2016 | |
($ in millions) | | Parent | | | Issuers | | | Guarantors | | | Non- Guarantors | | | Eliminations | | | Total | |
Operating Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | | $ | — | | | $ | 4 | | | $ | 432 | | | $ | (187 | ) | | $ | (67 | ) | | $ | 182 | |
Investing Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Capital expenditures for property and equipment | | | — | | | | — | | | | (26 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (26 | ) |
Software capitalization costs | | | — | | | | — | | | | (8 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (8 | ) |
Net cash used in investing activities | | | — | | | | — | | | | (34 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (34 | ) |
Financing Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issuance of non-recourse debt | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 300 | | | | — | | | | 300 | |
Repayment of non-recourse debt | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (110 | ) | | | — | | | | (110 | ) |
Issuance of debt | | | — | | | | 200 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 200 | |
Debt issuance costs | | | — | | | | (4 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | — | | | | (10 | ) |
Allocated debt activity(1) | | | 111 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 111 | |
Net transfers to Parent(1) | | | (567 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (567 | ) |
Distribution to Parent(1) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Intercompany transfers | | | 456 | | | | (200 | ) | | | (329 | ) | | | 6 | | | | 67 | | | | — | |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | | | — | | | | (4 | ) | | | (332 | ) | | | 193 | | | | 67 | | | | (76 | ) |
Net increase in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | | | — | | | | — | | | | 66 | | | | 6 | | | | — | | | | 72 | |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, beginning of period | | | — | | | | — | | | 62 | | | | 17 | | | | — | | | | 79 | |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, end of period | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 128 | | | $ | 23 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 151 | |
(1) Amounts represent activities with Hilton.
118
| | For the Year Ended December 31, 2015 | |
($ in millions) | | Parent | | | Issuers | | | Guarantors | | | Non- Guarantors | | | Eliminations | | | Total | |
Operating Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 17 | | | $ | 117 | | | $ | 18 | | | $ | 152 | |
Investing Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Capital expenditures for property and equipment | | | — | | | | — | | | | (12 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (12 | ) |
Software capitalization costs | | | — | | | | — | | | | (6 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (6 | ) |
Net cash used in investing activities | | | — | | | | — | | | | (18 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (18 | ) |
Financing Activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Repayment of non-recourse debt | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (125 | ) | | | — | | | | (125 | ) |
Allocated debt activity(1) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (87 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (87 | ) |
Net transfers from Parent(1) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 95 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 95 | |
Distribution to Parent(1) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2 | ) |
Intercompany transfers | | | — | | | | — | | | | 18 | | | | — | | | | (18 | ) | | | — | |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | | | — | | | | — | | | | 24 | | | | (125 | ) | | | (18 | ) | | | (119 | ) |
Net increase in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | | | — | | | | — | | | | 23 | | | | (8 | ) | | | — | | | | 15 | |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, beginning of period | | | — | | | | — | | | | 39 | | | | 25 | | | | — | | | | 64 | |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, end of period | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 62 | | | $ | 17 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 79 | |
(1) | Amounts represent activities with Hilton. |
119
Note 23: Selected Quarterly Financial Information (unaudited)
The following table sets forth the historical unaudited quarterly financial data for the periods indicated. The information for each of these periods has been prepared on the same basis as the audited consolidated financial statements and, in our opinion, reflects all adjustments necessary to present fairly our financial results. Operating results for previous periods do not necessarily indicate results that may be achieved in any future period.
| | 2017 | |
| | First | | | Second | | | Third | | | Fourth | | | | | |
| | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Year | |
($ in millions, except per share data) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues | | $ | 399 | | | $ | 439 | | | $ | 426 | | | $ | 447 | | | $ | 1,711 | |
Total operating expenses | | | 316 | | | | 348 | | | | 350 | | | | 360 | | | | 1,374 | |
Income before income taxes | | | 76 | | | | 84 | | | | 71 | | | | 80 | | | | 311 | |
Net income | | | 50 | | | | 51 | | | | 43 | | | | 183 | | | | 327 | |
Basic earnings per share | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.43 | | | $ | 1.85 | | | $ | 3.30 | |
Diluted earnings per share | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.43 | | | $ | 1.83 | | | $ | 3.28 | |
| | 2016 | |
| | First | | | Second | | | Third | | | Fourth | | | | | |
| | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Quarter | | | Year | |
($ in millions, except per share data) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenues | | $ | 370 | | | $ | 391 | | | $ | 407 | | | $ | 415 | | | $ | 1,583 | |
Total operating expenses | | | 284 | | | | 304 | | | | 333 | | | | 339 | | | | 1,260 | |
Income before income taxes | | | 80 | | | | 80 | | | | 68 | | | | 65 | | | | 293 | |
Net income | | | 48 | | | | 47 | | | | 35 | | | | 38 | | | | 168 | |
Basic and diluted earnings per share(1) | | $ | 0.48 | | | $ | 0.48 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | $ | 0.38 | | | $ | 1.70 | |
(1) | Basic and diluted earnings per share was calculated based on shares distributed to our shareholders on January 3, 2017. See Note 17: Earnings Per Share for further discussion. |
Note 24: Subsequent Events
In February 2018, we entered into a commitment to acquire $41 million of inventory.
120
Item 9. | Changes In and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
There were no changes in or disagreements with our accountants on accounting and financial disclosure matters.
ITEM 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, does not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act) or our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act) will prevent all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the control system’s objectives will be met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of the controls must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within a company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error and mistake. Controls can also be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management override of the controls. The design of any system of controls is based in part on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events. Because of the inherent limitations in a cost-effective control system, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected. Also projections of any evaluation of effectiveness of controls and procedures to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls and procedures may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the controls and procedures may have deteriorated. In accordance with Rule 13a-15(b) of the Exchange Act, as of the end of the period covered by this annual report, an evaluation was carried out under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this annual report, were effective to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms and is accumulated and communicated to our management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have set forth management's report on internal control over financial reporting and the attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Management's report on internal control over financial reporting is incorporated in this Item 9A by reference.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the fourth quarter of 2017 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. | Other Information |
None.
121
PART III
Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 (the “Proxy Statement”) under the following captions: “Proposal No. 1: Election of Directors—Nominees for Election to the Board of Directors in 2018,” “Executive Officers of the Company,” “Ownership of Securities—Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance,” “The Board of Directors and Certain Governance Matters—Code of Conduct,” “—Director Nomination Process,” “—Communications with the Board,” “—Board Committees and Meetings” and “Committee Membership—Audit Committee.”
Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the Proxy Statement under the following captions: “Executive Compensation,” “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” “Compensation of Directors,” “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” and “Report of the Compensation Committee.”
Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the Proxy Statement under the following captions: “Executive Compensation—Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans” and “Ownership of Securities.”
Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the Proxy Statement under the following captions: “Transactions with Related Persons” and “The Board of Directors and Certain Governance Matters.”
Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the Proxy Statement under the following captions: “Proposal No. 2: Ratification of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm—Audit and Non-Audit Fees.”
PART IV
Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
The following documents are filed as part of this Form 10-K:
1. | All financial statements. See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements on page 75 of this Form 10-K. |
2. | Financial Statement Schedules. None required. |
3. | Exhibits. See Exhibit Index. |
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
122
EXHIBIT INDEX
Exhibit No. | | Description |
| | |
2.1 | | Distribution Agreement among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Park Hotels & Resorts Inc. and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
3.1 | | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on March 17, 2017). |
| | |
3.2 | | Amended and Restated Bylaws (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on March 17, 2017). |
| | |
4.1 | | Indenture, dated as of October 24, 2016, among Hilton Grand Vacations Borrower LLC, as the issuer, Hilton Grand Vacations Borrower Inc., as the co-issuer, the guarantors from time to time party thereto, and Wilmington Trust, National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 of the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (File No. 001-27794) filed on November 23, 2016. |
| | |
4.2 | | Form of First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of November 29, 2016, among the subsidiary guarantors party thereto and Wilmington Trust, National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (File No. 001-37794) filed on November 23, 2016). |
| | |
4.3 | | Form of 6.125% Senior Note due 2024 (included in Exhibit 4.1). |
| | |
4.4 | | Registration Rights Agreement dated as of November 29, 2016, among Hilton Grand Vacations Borrower LLC, Hilton Grand Vacations Borrower Inc., Hilton Grand Vacations Inc., the Subsidiary Guarantors, as defined therein, and Goldman, Sachs & Co. as representative of the several initial purchasers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (File No. 333-221194-02) filed on October 27, 2017). |
| | |
10.1 | | Employee Matters Agreement among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Park Hotels & Resorts Inc. and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
10.2 | | Tax Matters Agreement among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Park Hotels & Resorts Inc. and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
10.3 | | Master Transition Services Agreement between Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
10.4† | | Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
10.5† | | 2017 Declaration of Amendment to Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Appendix A of the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A (File No. 001-37794) filed on March 24, 2017). |
| | |
123
10.6 | | Indemnification Agreement entered into between Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. and each of its directors and executive officers. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (File No. 001-37794) filed on November 14, 2016). |
| | |
10.7 | | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of October 24, 2016, among Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. and the other parties thereto. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (File No. 001-37794) filed on November 14, 2016). |
| | |
10.8 | | Receivables Loan Agreement, dated as of May 9, 2013, among Hilton Grand Vacations Trust I LLC, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as paying agent and securities intermediary, the persons from time to time party thereto as conduit lenders, the financial institutions from time to time party thereto as committed lenders, the financial institutions from time to time party thereto as managing agents, and Deutsche Bank Securities, Inc., as administrative agent and structuring agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (No. 333-191110)). |
| | |
10.9 | | Amendment No. 1 to Receivables Loan Agreement, effective as of July 25, 2013, among Hilton Grand Vacations Trust I LLC, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as paying agent and securities intermediary, Deutsche Bank AG, New York Branch, as a committed lender and a managing agent, Montage Funding, LLC, as a conduit lender, Deutsche Bank Securities, Inc., as administrative agent, and Bank of America, N.A., as assignee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (No. 333-191110)). |
| | |
10.10 | | Omnibus Amendment No. 2 to Receivables Loan Agreement, Amendment No. 1 to Sale and Contribution Agreement and Consent to Custody Agreement, effective as of October 25, 2013, among Hilton Grand Vacations Trust I LLC, as borrower, Grand Vacations Services LLC, as servicer, Hilton Resorts Corporation, as seller, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as custodian, the financial institutions signatory thereto, as managing agents, and Deutsche Bank Securities, Inc., as administrative agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (No. 333-191110)). |
| | |
10.11 | | Amendment No. 3 to Receivables Loan Agreement, effective as of December 5, 2014, among Hilton Grand Vacations Trust I LLC, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as paying agent and securities intermediary, Deutsche Bank AG, New York Branch, as a committed lender and a managing agent, Bank of America, N.A., as a committed lender and a managing agent, and Deutsche Bank Securities, Inc., as administrative agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36243) filed on December 8, 2014). |
| | |
10.12 | | Omnibus Amendment No. 4 to Receivables Loan Agreement and Amendment No. 2 to Sale and Contribution Agreement, effective as of August 18, 2016, among Hilton Grand Vacations Trust I LLC, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as paying agent and securities intermediary, the financial institutions signatory thereto, as managing agents, the financial institutions signatory thereto as committed lenders and Deutsche Bank Securities, Inc., as administrative agent. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (File No. 001-37794) filed on September 16, 2016). |
| | |
124
10.13 | | Amendment No. 5 to Receivables Loan Agreement, effective as of October 4, 2016, among Hilton Grand Vacations Trust I LLC, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as paying agent and securities intermediary, Deutsche Bank AG, New York Branch, as a committed lender and a managing agent, Bank of America, N.A., as a committed lender and a managing agent, and Deutsche Bank Securities, Inc., as administrative agent. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (File No. 001-37794) filed on October 25, 2016). |
| | |
10.14† | | Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Stock Plan for Non-Employee Directors (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
10.15† | | Hilton Resorts Corporation 2017 Executive Deferred Compensation Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
10.16† | | Offer Letter, dated July 6, 2016, with James E. Mikolaichik. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (File No. 001-37794) filed on September 16, 2016). |
| | |
10.17† | | Employment Letter Agreement, dated April 17, 2017, between Mark D. Wang and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on April 17, 2017). |
| | |
10.18† | | Severance Agreement, dated April 17, 2017, between Mark D. Wang and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on April 17, 2017). |
| | |
10.19† | | Severance Agreement, dated April 17, 2017, between James E. Mikolaichik and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on April 17, 2017). |
| | |
10.20† | | Severance Agreement, dated April 17, 2017, between Stan R. Soroka and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on April 17, 2017). |
| | |
10.21† | | Severance Agreement, dated April 17, 2017, between Barbara L. Hollkamp and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on April 17, 2017). |
| | |
10.22† | | Severance Agreement, dated April 17, 2017, between Charles R. Corbin and Hilton Grand Vacations, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on August 3, 2017). |
| | |
10.23†* | | Severance Agreement, dated November 30, 2017, between Dennis A. DeLorenzo and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. |
| | |
10.24†* | | Severance Agreement, dated November 30, 2017, between Sherri A. Silver and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. |
| | |
10.25 | | License Agreement, by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
125
| | |
10.26 | | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of October 24, 2016, among Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. and HNA Tourism Group Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (File No. 001-37794) filed on November 14, 2016). |
| | |
10.27 | | Stockholders Agreement, dated as of October 24, 2016, by and among Hilton Grand Vacations, Inc., HNA Tourism Group Co., Ltd. and HNA Group Co., Ltd. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (File No. 001-37794) filed on November 14, 2016). |
| | |
10.28 | | Stockholders Agreement, dated as of January 2, 2017, among Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. and the other parties thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
10.29 | | Stockholders Agreement, dated as of January 2, 2017 by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Grand Vacations Inc., and the Blackstone Holders (as defined therein) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
10.30 | | Credit Agreement, dated as of December 28, 2016 among Hilton Grand Vacations Parent LLC, as parent, Hilton Grand Vacations Borrower LLC, as the borrower, the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch, as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and l/c issuer and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on January 4, 2017). |
| | |
10.31† | | Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (File No. 333-218056) filed on May 17, 2017). |
| | |
10.32 | | Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of BRE Ace LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, dated as of July 18, 2017 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on July 21, 2017). |
| | |
10.33(a)† | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on March 15, 2017). |
| | |
10.33(b)† | | Form of Performance Share Agreement (Converted Award – 2014 Grant) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13(b) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.33(c)† | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (Converted Award – 2014 Grant) (Time-Based) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13(c) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.33(d)† | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (Converted Award – 2015 Grant) (Performance-Based) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13(d) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
126
10.33(e)† | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (Converted Award – 2015 Grant) (Time-Based) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13(e) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.33(f)† | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (Converted Award – 2016 Grant) (Performance-Based) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13(f) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.33(g)† | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (Converted Award – 2016 Grant) (Time-Based) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13(g) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.34(a)† | | Form of Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-37794) filed on March 15, 2017). |
| | |
10.34(b)† | | Form of Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement (Converted Award – 2014 Grant) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14(b) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.34(c)† | | Form of Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement (Converted Award – 2015 Grant) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14(c) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.34(d)† | | Form of Nonqualified Stock Option Agreement (Converted Award – 2016 Grant) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14(d) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.35(a)† | | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Converted Award – 2015 Grant) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15(a) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.35(b)† | | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Converted Award – 2016 Grant) under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15(b) to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
10.36† | | Form of Stock Award Agreement for Non-Employee Directors under Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. 2017 Stock Plan for Non-Employee Directors Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-37794) filed on May 5, 2017). |
| | |
11.1* | | Statement regarding computation of earnings per share. See consolidated statements of operations on page 78 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
| | |
12.1* | | Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges. |
| | |
21.1* | | Subsidiaries of the Registrant. |
| | |
23.1* | | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
| | |
31.1* | | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
127
* | Filed herewith. |
** | Furnished not filed. |
*** | These interactive data files shall not be deemed filed for purposes of Section 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or otherwise subject to liability under those sections. |
† | Denotes management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
128
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, on this 1st day of March, 2018.
HILTON GRAND VACATIONS INC. |
| |
By: | /s/ Mark D. Wang |
Name: | Mark D. Wang |
Title: | President and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities indicated on this 1st day of March, 2018.
Signature | Title |
| |
/s/ Mark D. Wang | President and Chief Executive Officer |
Mark D. Wang | and Director (principal executive officer) |
| |
| |
/s/ James E. Mikolaichik | Chief Financial Officer |
James E. Mikolaichik | (principal financial officer) |
| |
| |
/s/ Allen J. Klingsick | Senior Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer |
Allen J. Klingsick | (principal accounting officer) |
| |
| |
/s/ Leonard A. Potter | Chairman of the Board of Directors |
Leonard A. Potter | |
| |
| |
/s/ Brenda J. Bacon | Director |
Brenda J. Bacon | |
| |
| |
/s/ Kenneth A. Caplan | Director |
Kenneth A. Caplan | |
| |
| |
/s/ Yasheng Huang | Director |
Yasheng Huang | |
| |
| |
/s/ David W. Johnson | Director |
David W. Johnson | |
| |
| |
/s/ Mark H. Lazarus | Director |
Mark H. Lazarus | |
| |
| |
/s/ Pamela H. Patsley | Director |
Pamela H. Patsley | |
| |
| |
/s/ Paul W. Whetsell | Director |
Paul W. Whetsell | |
| |
| |
/s/ Kenneth Tai Lun Wong | Director |
Kenneth Tai Lun Wong | |
129
