
IDEAYA Biosciences Corporate Presentation August 2019 Exhibit 99.2

Safe Harbor Statement CONFIDENTIAL Certain statements in this presentation and the accompanying oral commentary are forward-looking statements. These statements relate to future events or the future financial performance of IDEAYA Biosciences, Inc. (the “Company”) and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause the actual results, levels of activity, performance or achievements of the Company or its industry to be materially different from those expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements. In some cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by terminology such as “may,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential” or other comparable terminology. All statements other than statements of historical fact could be deemed forward-looking, including any expectations regarding the Company's commercial engine as a force multiplier for research and development initiatives; any projections of financial information, market opportunities or profitability; any statements about historical results that may suggest trends for the Company's business; any statements of the plans, strategies, and objectives of management for future operations; any statements of expectation or belief regarding future events, potential markets or market size, or technology developments; and any statements of assumptions underlying any of the items mentioned. The Company has based these forward-looking statements on its current expectations, assumptions, estimates and projections. While the Company believes these expectations, assumptions, estimates and projections are reasonable, such forward-looking statements are only predictions and involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties, many of which are beyond the Company's control. These and other important factors may cause actual results, performance or achievements to differ materially from those expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements in this presentation are made only as of the date hereof. For a further description of the risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ from those expressed in these forward-looking statements, as well as risks relating to the business of the Company in general, see the Company's periodic filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC"), including its Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2019 and any current and periodic reports filed thereafter. Except as required by law, the Company assumes no obligation and does not intend to update these forward-looking statements or to conform these statements to actual results or to changes in the Company's expectations. This presentation concerns anticipated products that are under clinical investigation and which have not yet been approved for marketing by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is currently limited by Federal law to investigational use, and no representation is made as to its safety or effectiveness for the purposes for which it is being investigated.
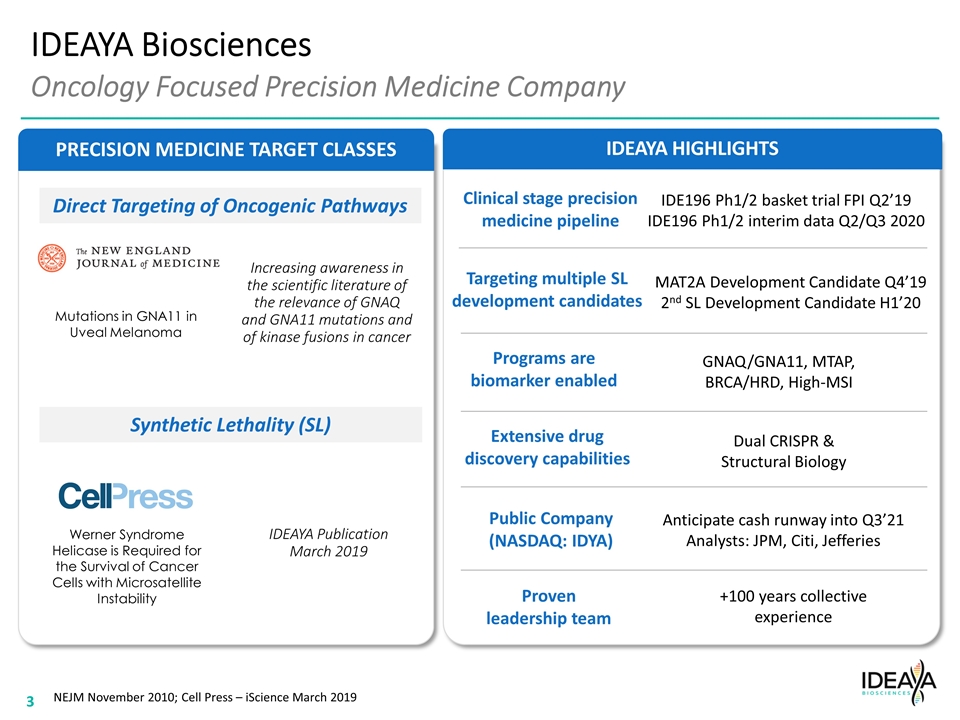
IDEAYA HIGHLIGHTS Synthetic Lethality (SL) Direct Targeting of Oncogenic Pathways PRECISION MEDICINE TARGET CLASSES IDEAYA Biosciences Oncology Focused Precision Medicine Company Werner Syndrome Helicase is Required for the Survival of Cancer Cells with Microsatellite Instability Mutations in GNA11 in Uveal Melanoma NEJM November 2010; Cell Press – iScience March 2019 Clinical stage precision medicine pipeline Programs are biomarker enabled Extensive drug discovery capabilities Public Company (NASDAQ: IDYA) Proven leadership team Targeting multiple SL development candidates IDE196 Ph1/2 basket trial FPI Q2’19 IDE196 Ph1/2 interim data Q2/Q3 2020 MAT2A Development Candidate Q4’19 2nd SL Development Candidate H1’20 GNAQ/GNA11, MTAP, BRCA/HRD, High-MSI Dual CRISPR & Structural Biology Anticipate cash runway into Q3’21 Analysts: JPM, Citi, Jefferies +100 years collective experience Increasing awareness in the scientific literature of the relevance of GNAQ and GNA11 mutations and of kinase fusions in cancer IDEAYA Publication March 2019

IDEAYA Organization Proven Leadership Team From Top Oncology Companies Michael Dillon, Ph.D. SVP, Chief Scientific Officer, Head of Research Julie Hambleton, M.D. SVP, Chief Medical Officer, Head of Development Jeff Hager, Ph.D. SVP, Chief Technology Officer, Head of Target Discovery and External Innovation Bao Truong, VP, Head of Regulatory Mark Lackner, Ph.D. SVP, Head of Biology & Translational Sciences Director and Principal Scientist, Genentech Paul Stone, J.D. SVP, Chief Financial Officer Partner, General Counsel and COO, 5AM Ventures VP Regulatory Affairs, Ignyta COO at Flexus Biosciences Global Discovery Chemistry Head, Oncology, NIBR VP, Head of US Medical Affairs, Bristol-Myers Squibb VP of Biology, Seragon; Senior Director of Biology, Aragon LEADERSHIP TEAM Yujiro Hata, M.B.A. President, Chief Executive Officer, Director Paul Barsanti, Ph.D. VP, Head of Drug Discovery Executive in Residence, 5AM Ventures
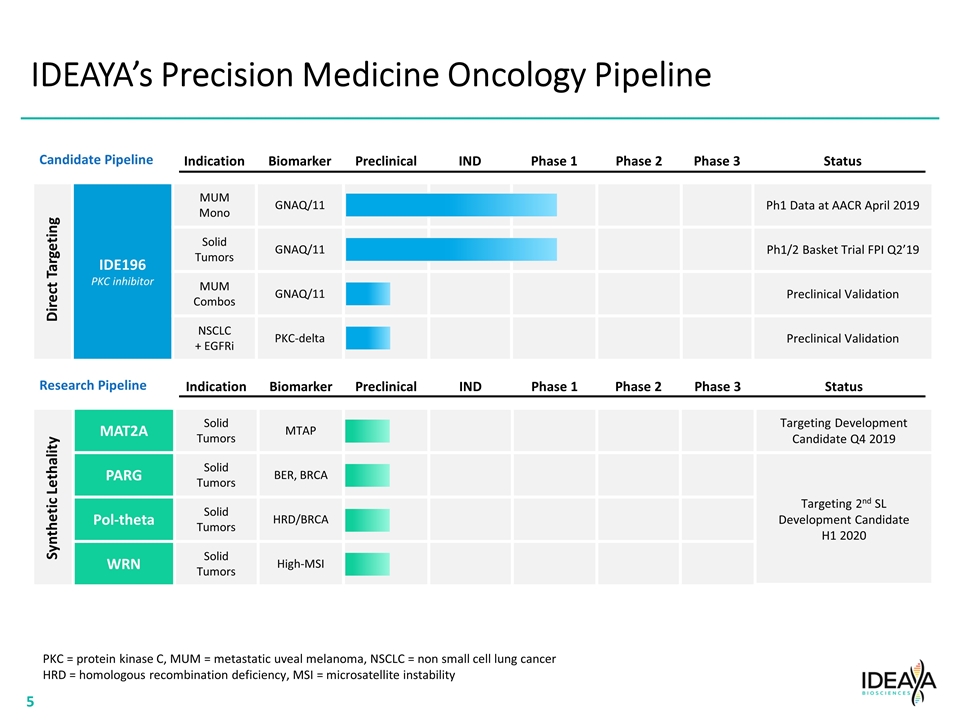
IDEAYA’s Precision Medicine Oncology Pipeline Indication Biomarker Preclinical IND Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Status IDE196 PKC inhibitor MUM Mono GNAQ/11 Ph1 Data at AACR April 2019 Solid Tumors GNAQ/11 Ph1/2 Basket Trial FPI Q2’19 MUM Combos GNAQ/11 Preclinical Validation NSCLC + EGFRi PKC-delta Preclinical Validation Direct Targeting Indication Biomarker Preclinical IND Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Status MAT2A Solid Tumors MTAP Targeting Development Candidate Q4 2019 PARG Solid Tumors BER, BRCA Targeting 2nd SL Development Candidate H1 2020 Pol-theta Solid Tumors HRD/BRCA WRN Solid Tumors High-MSI Synthetic Lethality PKC = protein kinase C, MUM = metastatic uveal melanoma, NSCLC = non small cell lung cancer HRD = homologous recombination deficiency, MSI = microsatellite instability Candidate Pipeline Research Pipeline
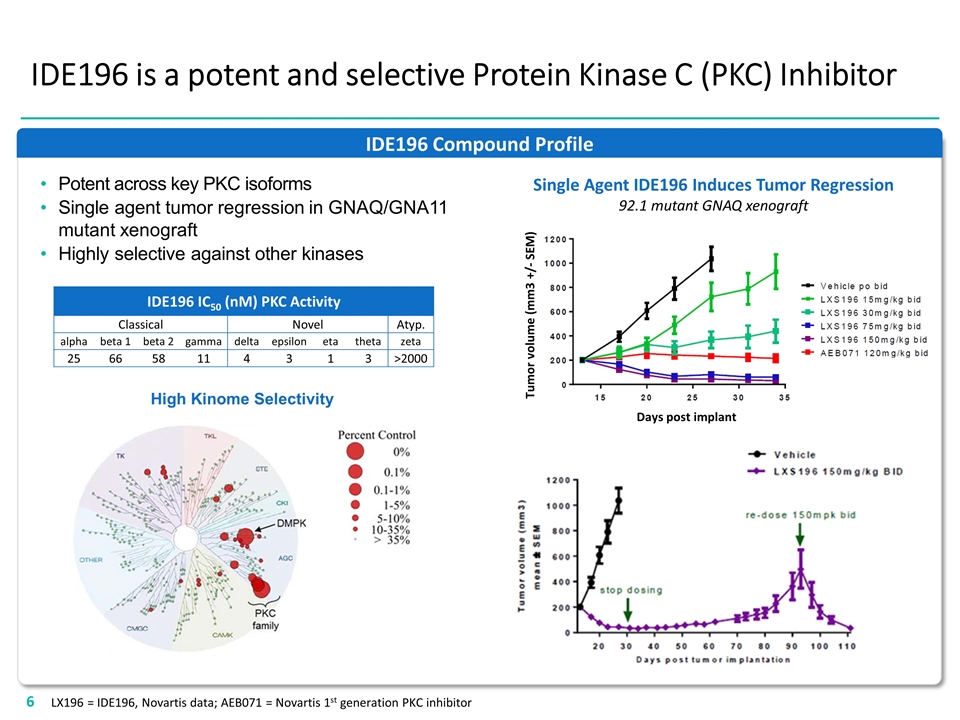
IDE196 Compound Profile IDE196 is a potent and selective Protein Kinase C (PKC) Inhibitor IDE196 IC50 (nM) PKC Activity Classical Novel Atyp. alpha beta 1 beta 2 gamma delta epsilon eta theta zeta 25 66 58 11 4 3 1 3 >2000 Single Agent IDE196 Induces Tumor Regression 92.1 mutant GNAQ xenograft Potent across key PKC isoforms Single agent tumor regression in GNAQ/GNA11 mutant xenograft Highly selective against other kinases High Kinome Selectivity Tumor volume (mm3 +/- SEM) Days post implant LX196 = IDE196, Novartis data; AEB071 = Novartis 1st generation PKC inhibitor
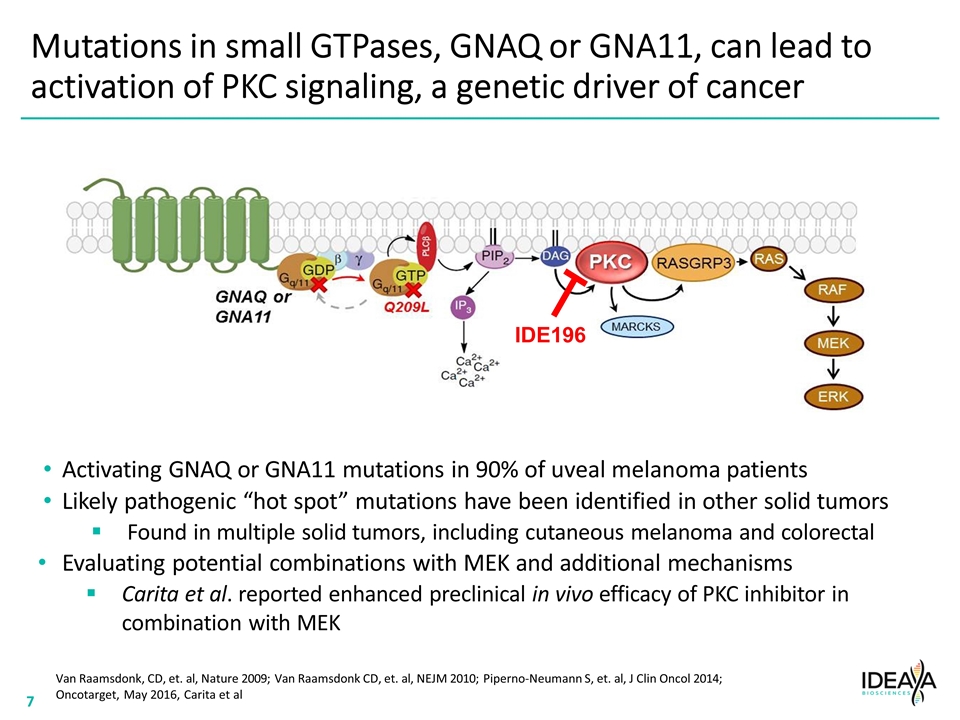
Mutations in small GTPases, GNAQ or GNA11, can lead to activation of PKC signaling, a genetic driver of cancer Van Raamsdonk, CD, et. al, Nature 2009; Van Raamsdonk CD, et. al, NEJM 2010; Piperno-Neumann S, et. al, J Clin Oncol 2014; Oncotarget, May 2016, Carita et al Activating GNAQ or GNA11 mutations in 90% of uveal melanoma patients Likely pathogenic “hot spot” mutations have been identified in other solid tumors Found in multiple solid tumors, including cutaneous melanoma and colorectal Evaluating potential combinations with MEK and additional mechanisms Carita et al. reported enhanced preclinical in vivo efficacy of PKC inhibitor in combination with MEK IDE196
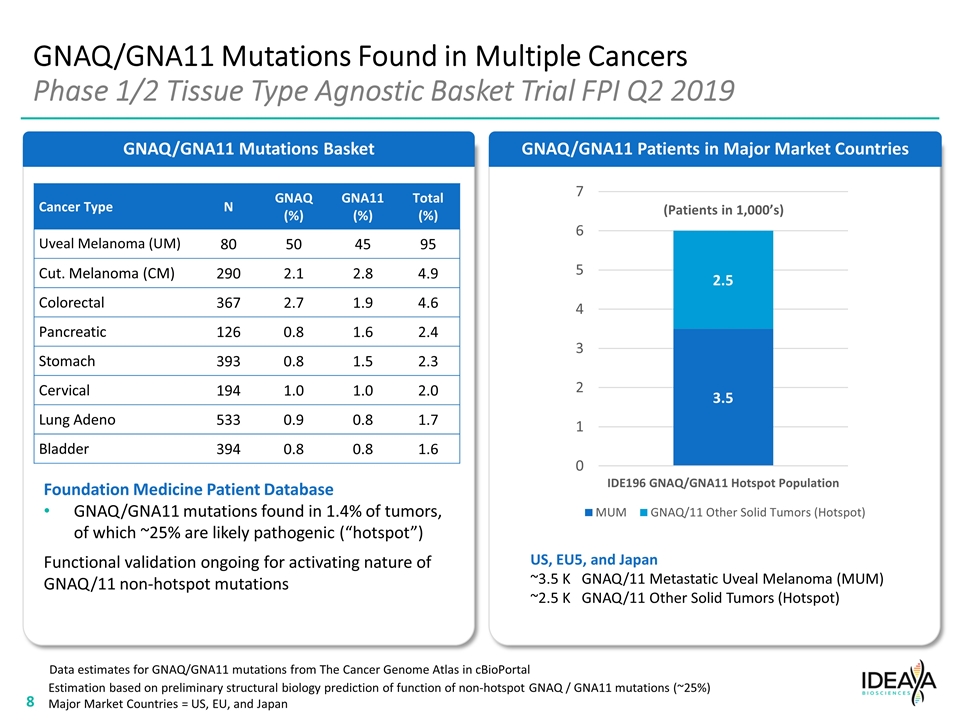
GNAQ/GNA11 Mutations Basket GNAQ/GNA11 Mutations Found in Multiple Cancers Phase 1/2 Tissue Type Agnostic Basket Trial FPI Q2 2019 Foundation Medicine Patient Database GNAQ/GNA11 mutations found in 1.4% of tumors, of which ~25% are likely pathogenic (“hotspot”) Functional validation ongoing for activating nature of GNAQ/11 non-hotspot mutations GNAQ/GNA11 Patients in Major Market Countries Data estimates for GNAQ/GNA11 mutations from The Cancer Genome Atlas in cBioPortal Cancer Type N GNAQ (%) GNA11 (%) Total (%) Uveal Melanoma (UM) 80 50 45 95 Cut. Melanoma (CM) 290 2.1 2.8 4.9 Colorectal 367 2.7 1.9 4.6 Pancreatic 126 0.8 1.6 2.4 Stomach 393 0.8 1.5 2.3 Cervical 194 1.0 1.0 2.0 Lung Adeno 533 0.9 0.8 1.7 Bladder 394 0.8 0.8 1.6 (Patients in 1,000’s) US, EU5, and Japan ~3.5 K GNAQ/11 Metastatic Uveal Melanoma (MUM) ~2.5 K GNAQ/11 Other Solid Tumors (Hotspot) Estimation based on preliminary structural biology prediction of function of non-hotspot GNAQ / GNA11 mutations (~25%) Major Market Countries = US, EU, and Japan
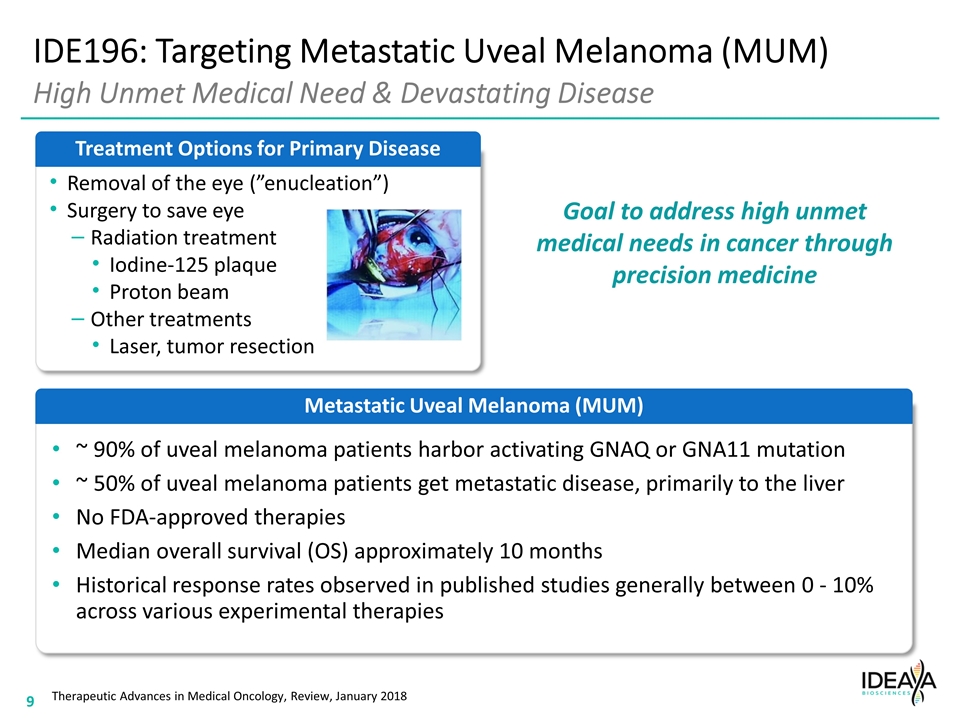
Metastatic Uveal Melanoma (MUM) Removal of the eye (”enucleation”) Surgery to save eye Radiation treatment Iodine-125 plaque Proton beam Other treatments Laser, tumor resection Treatment Options for Primary Disease ~ 90% of uveal melanoma patients harbor activating GNAQ or GNA11 mutation ~ 50% of uveal melanoma patients get metastatic disease, primarily to the liver No FDA-approved therapies Median overall survival (OS) approximately 10 months Historical response rates observed in published studies generally between 0 - 10% across various experimental therapies IDE196: Targeting Metastatic Uveal Melanoma (MUM) High Unmet Medical Need & Devastating Disease Goal to address high unmet medical needs in cancer through precision medicine Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology, Review, January 2018
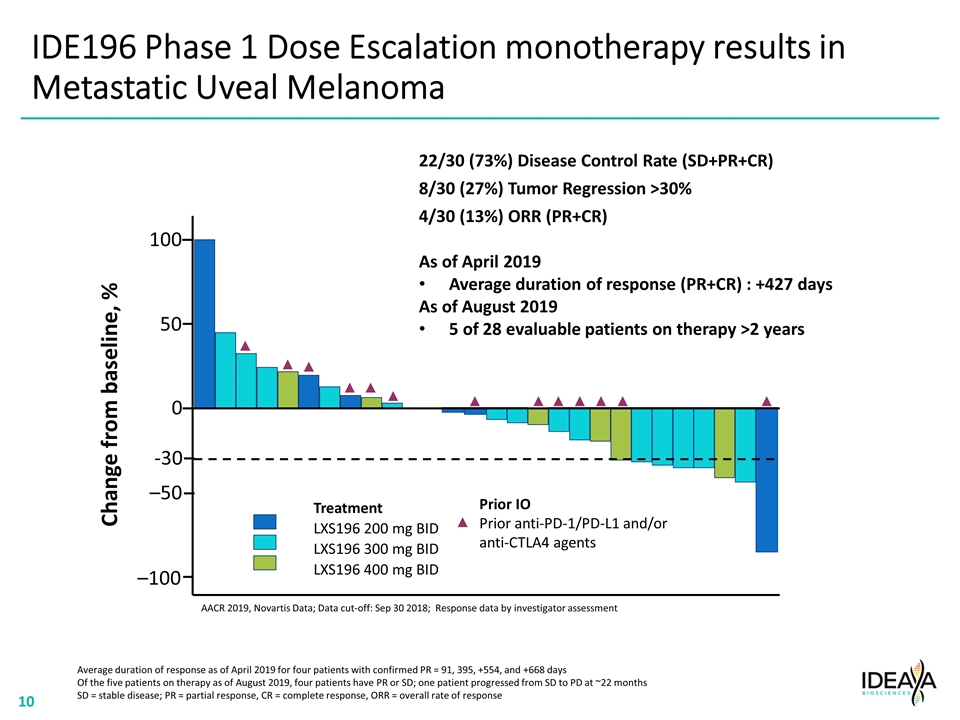
IDE196 Phase 1 Dose Escalation monotherapy results in Metastatic Uveal Melanoma AACR 2019, Novartis Data; Data cut-off: Sep 30 2018; Response data by investigator assessment Treatment LXS196 200 mg BID LXS196 300 mg BID LXS196 400 mg BID -30 22/30 (73%) Disease Control Rate (SD+PR+CR) 8/30 (27%) Tumor Regression >30% 4/30 (13%) ORR (PR+CR) Change from baseline, % –100 –50 0 50 100 Prior IO Prior anti-PD-1/PD-L1 and/or anti-CTLA4 agents As of April 2019 Average duration of response (PR+CR) : +427 days As of August 2019 5 of 28 evaluable patients on therapy >2 years Average duration of response as of April 2019 for four patients with confirmed PR = 91, 395, +554, and +668 days Of the five patients on therapy as of August 2019, four patients have PR or SD; one patient progressed from SD to PD at ~22 months SD = stable disease; PR = partial response, CR = complete response, ORR = overall rate of response
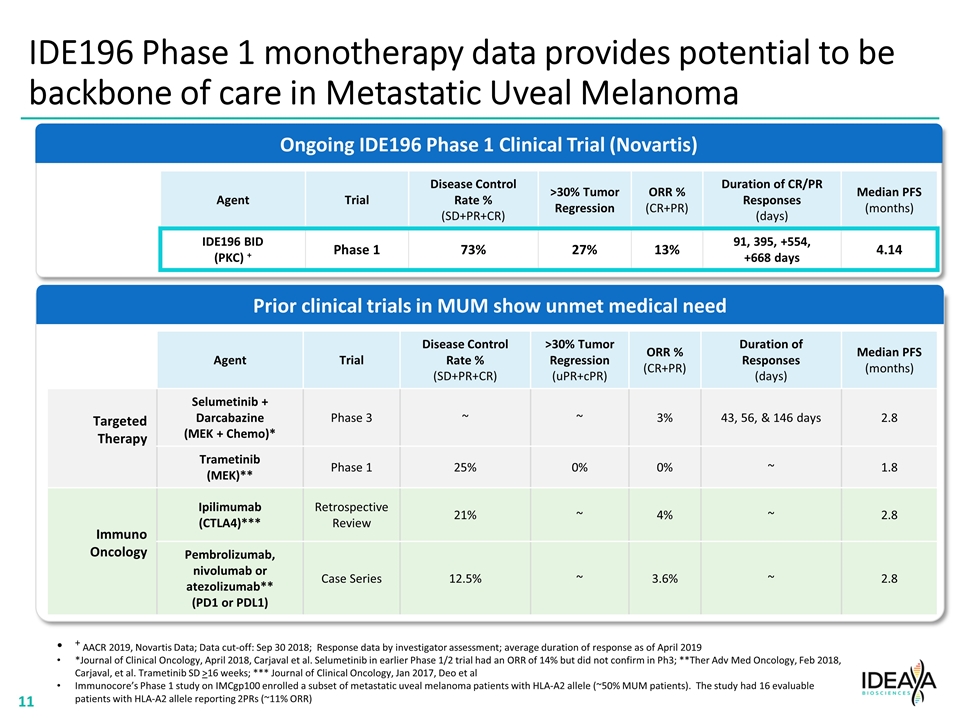
Prior clinical trials in MUM show unmet medical need IDE196 Phase 1 monotherapy data provides potential to be backbone of care in Metastatic Uveal Melanoma Agent Trial Disease Control Rate % (SD+PR+CR) >30% Tumor Regression ORR % (CR+PR) Duration of CR/PR Responses (days) Median PFS (months) IDE196 BID (PKC) + Phase 1 73% 27% 13% 91, 395, +554, +668 days 4.14 + AACR 2019, Novartis Data; Data cut-off: Sep 30 2018; Response data by investigator assessment; average duration of response as of April 2019 *Journal of Clinical Oncology, April 2018, Carjaval et al. Selumetinib in earlier Phase 1/2 trial had an ORR of 14% but did not confirm in Ph3; **Ther Adv Med Oncology, Feb 2018, Carjaval, et al. Trametinib SD >16 weeks; *** Journal of Clinical Oncology, Jan 2017, Deo et al Immunocore’s Phase 1 study on IMCgp100 enrolled a subset of metastatic uveal melanoma patients with HLA-A2 allele (~50% MUM patients). The study had 16 evaluable patients with HLA-A2 allele reporting 2PRs (~11% ORR) Agent Trial Disease Control Rate % (SD+PR+CR) >30% Tumor Regression (uPR+cPR) ORR % (CR+PR) Duration of Responses (days) Median PFS (months) Targeted Therapy Selumetinib + Darcabazine (MEK + Chemo)* Phase 3 ~ ~ 3% 43, 56, & 146 days 2.8 Trametinib (MEK)** Phase 1 25% 0% 0% ~ 1.8 Immuno Oncology Ipilimumab (CTLA4)*** Retrospective Review 21% ~ 4% ~ 2.8 Pembrolizumab, nivolumab or atezolizumab** (PD1 or PDL1) Case Series 12.5% ~ 3.6% ~ 2.8 Ongoing IDE196 Phase 1 Clinical Trial (Novartis)
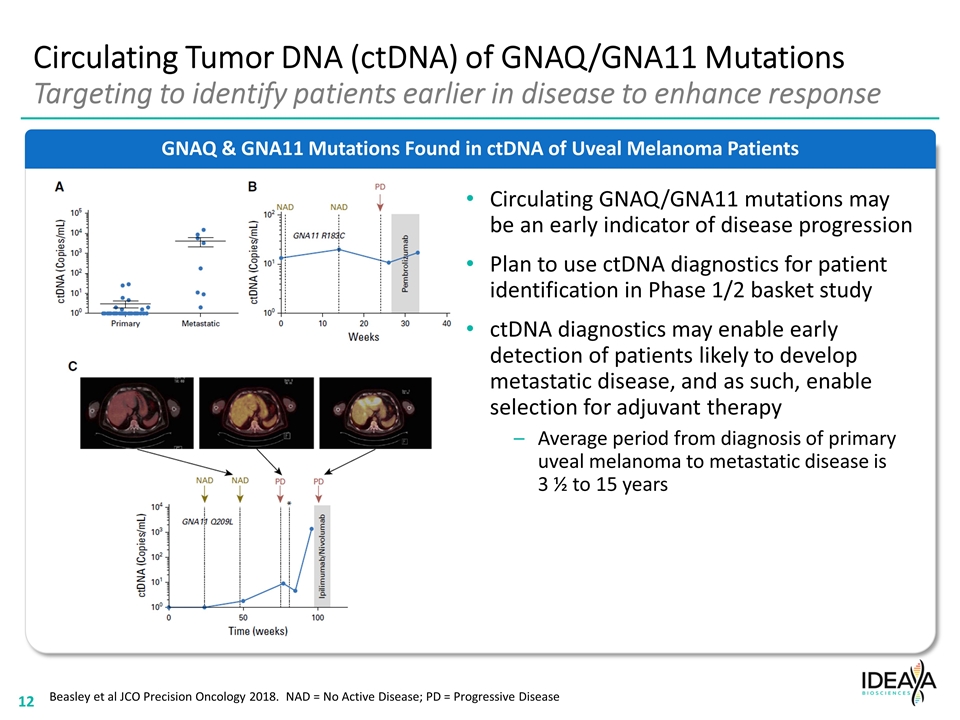
GNAQ & GNA11 Mutations Found in ctDNA of Uveal Melanoma Patients Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA) of GNAQ/GNA11 Mutations Targeting to identify patients earlier in disease to enhance response Circulating GNAQ/GNA11 mutations may be an early indicator of disease progression Plan to use ctDNA diagnostics for patient identification in Phase 1/2 basket study ctDNA diagnostics may enable early detection of patients likely to develop metastatic disease, and as such, enable selection for adjuvant therapy Average period from diagnosis of primary uveal melanoma to metastatic disease is 3 ½ to 15 years Beasley et al JCO Precision Oncology 2018. NAD = No Active Disease; PD = Progressive Disease
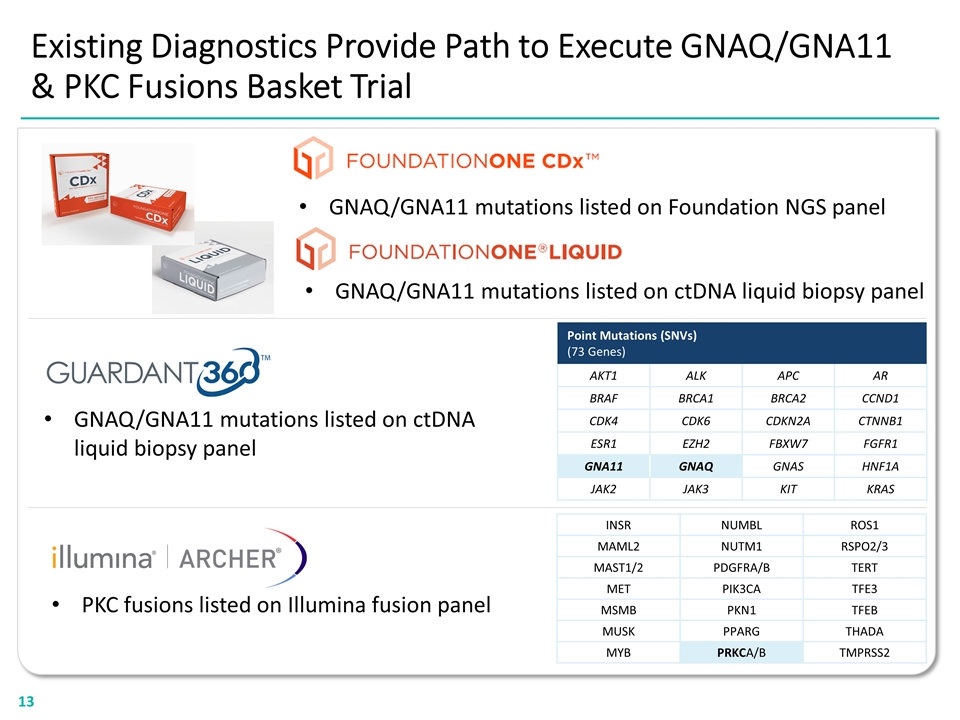
Existing Diagnostics Provide Path to Execute GNAQ/GNA11 & PKC Fusions Basket Trial GNAQ/GNA11 mutations listed on Foundation NGS panel GNAQ/GNA11 mutations listed on ctDNA liquid biopsy panel PKC fusions listed on Illumina fusion panel GNAQ/GNA11 mutations listed on ctDNA liquid biopsy panel Point Mutations (SNVs) (73 Genes) AKT1 ALK APC AR BRAF BRCA1 BRCA2 CCND1 CDK4 CDK6 CDKN2A CTNNB1 ESR1 EZH2 FBXW7 FGFR1 GNA11 GNAQ GNAS HNF1A JAK2 JAK3 KIT KRAS INSR NUMBL ROS1 MAML2 NUTM1 RSPO2/3 MAST1/2 PDGFRA/B TERT MET PIK3CA TFE3 MSMB PKN1 TFEB MUSK PPARG THADA MYB PRKCA/B TMPRSS2
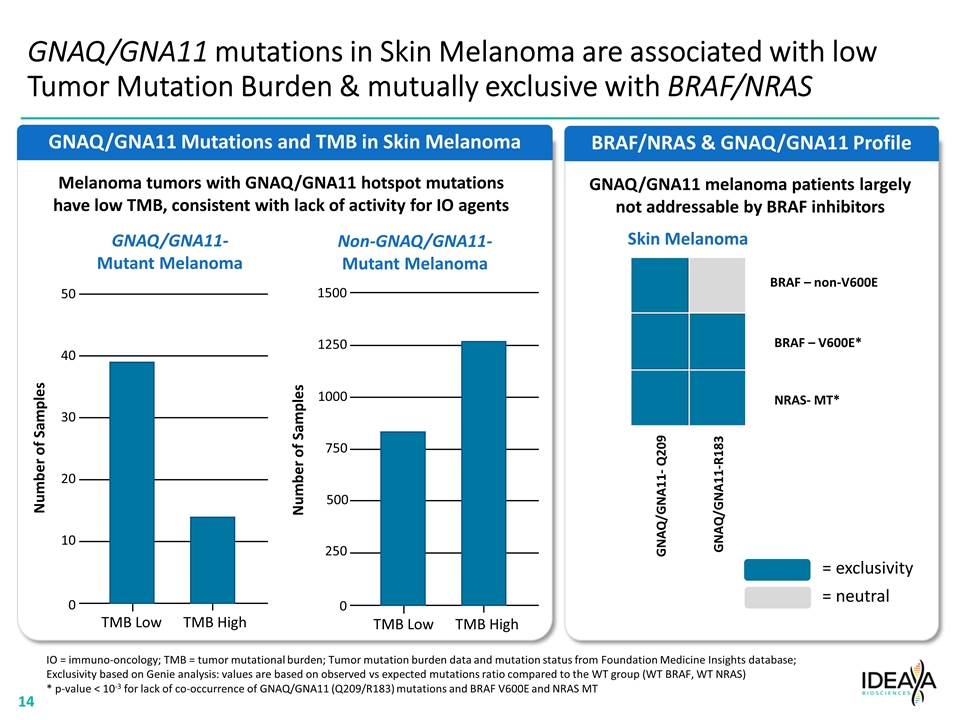
GNAQ/GNA11 Mutations and TMB in Skin Melanoma BRAF/NRAS & GNAQ/GNA11 Profile GNAQ/GNA11 mutations in Skin Melanoma are associated with low Tumor Mutation Burden & mutually exclusive with BRAF/NRAS Skin Melanoma BRAF – non-V600E BRAF – V600E* NRAS- MT* GNAQ/GNA11- Q209 GNAQ/GNA11-R183 = exclusivity = neutral GNAQ/GNA11- Mutant Melanoma Non-GNAQ/GNA11- Mutant Melanoma IO = immuno-oncology; TMB = tumor mutational burden; Tumor mutation burden data and mutation status from Foundation Medicine Insights database; Exclusivity based on Genie analysis: values are based on observed vs expected mutations ratio compared to the WT group (WT BRAF, WT NRAS) * p-value < 10-3 for lack of co-occurrence of GNAQ/GNA11 (Q209/R183) mutations and BRAF V600E and NRAS MT Melanoma tumors with GNAQ/GNA11 hotspot mutations have low TMB, consistent with lack of activity for IO agents GNAQ/GNA11 melanoma patients largely not addressable by BRAF inhibitors 50 40 30 20 10 0 Number of Samples TMB Low TMB High 1500 1250 1000 500 250 0 Number of Samples 750 TMB Low TMB High
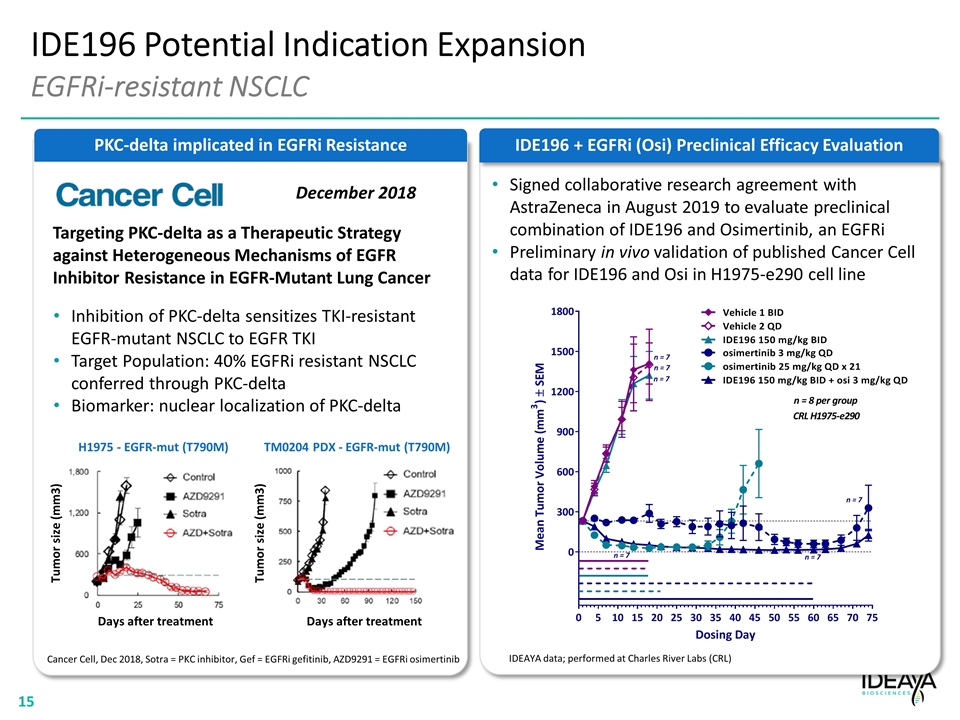
PKC-delta implicated in EGFRi Resistance IDE196 Potential Indication Expansion EGFRi-resistant NSCLC Targeting PKC-delta as a Therapeutic Strategy against Heterogeneous Mechanisms of EGFR Inhibitor Resistance in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer Inhibition of PKC-delta sensitizes TKI-resistant EGFR-mutant NSCLC to EGFR TKI Target Population: 40% EGFRi resistant NSCLC conferred through PKC-delta Biomarker: nuclear localization of PKC-delta December 2018 Tumor size (mm3) Tumor size (mm3) Days after treatment Days after treatment H1975 - EGFR-mut (T790M) TM0204 PDX - EGFR-mut (T790M) Cancer Cell, Dec 2018, Sotra = PKC inhibitor, Gef = EGFRi gefitinib, AZD9291 = EGFRi osimertinib IDE196 + EGFRi (Osi) Preclinical Efficacy Evaluation IDEAYA data; performed at Charles River Labs (CRL) Signed collaborative research agreement with AstraZeneca in August 2019 to evaluate preclinical combination of IDE196 and Osimertinib, an EGFRi Preliminary in vivo validation of published Cancer Cell data for IDE196 and Osi in H1975-e290 cell line
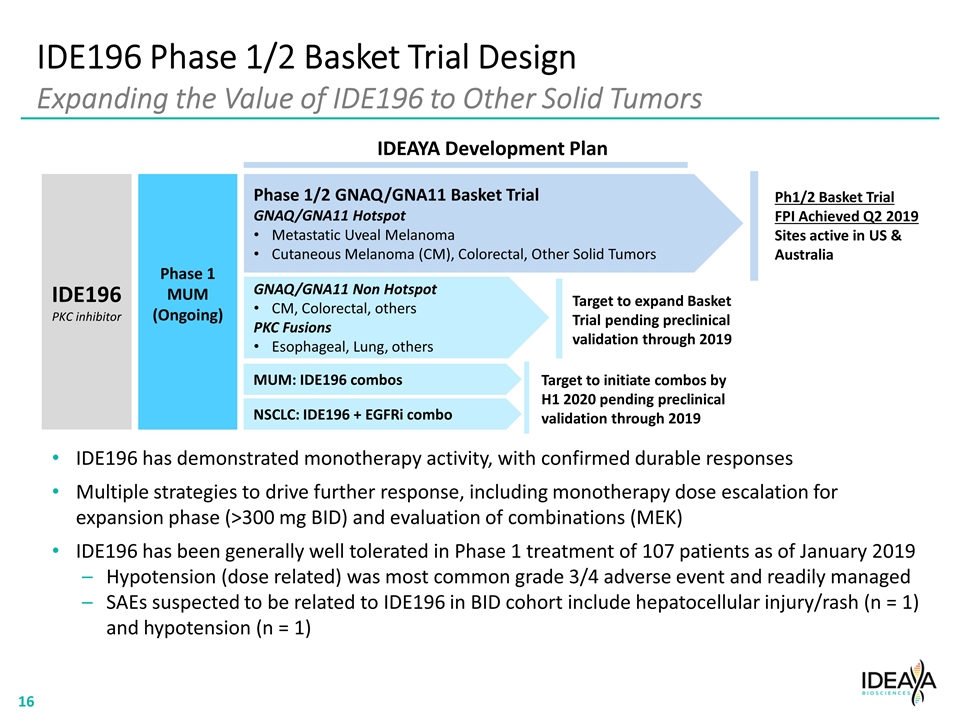
IDE196 Phase 1/2 Basket Trial Design Expanding the Value of IDE196 to Other Solid Tumors IDE196 PKC inhibitor Phase 1 MUM (Ongoing) Phase 1/2 GNAQ/GNA11 Basket Trial GNAQ/GNA11 Hotspot Metastatic Uveal Melanoma Cutaneous Melanoma (CM), Colorectal, Other Solid Tumors MUM: IDE196 combos NSCLC: IDE196 + EGFRi combo Ph1/2 Basket Trial FPI Achieved Q2 2019 Sites active in US & Australia Target to initiate combos by H1 2020 pending preclinical validation through 2019 IDEAYA Development Plan IDE196 has demonstrated monotherapy activity, with confirmed durable responses Multiple strategies to drive further response, including monotherapy dose escalation for expansion phase (>300 mg BID) and evaluation of combinations (MEK) IDE196 has been generally well tolerated in Phase 1 treatment of 107 patients as of January 2019 Hypotension (dose related) was most common grade 3/4 adverse event and readily managed SAEs suspected to be related to IDE196 in BID cohort include hepatocellular injury/rash (n = 1) and hypotension (n = 1) GNAQ/GNA11 Non Hotspot CM, Colorectal, others PKC Fusions Esophageal, Lung, others Target to expand Basket Trial pending preclinical validation through 2019
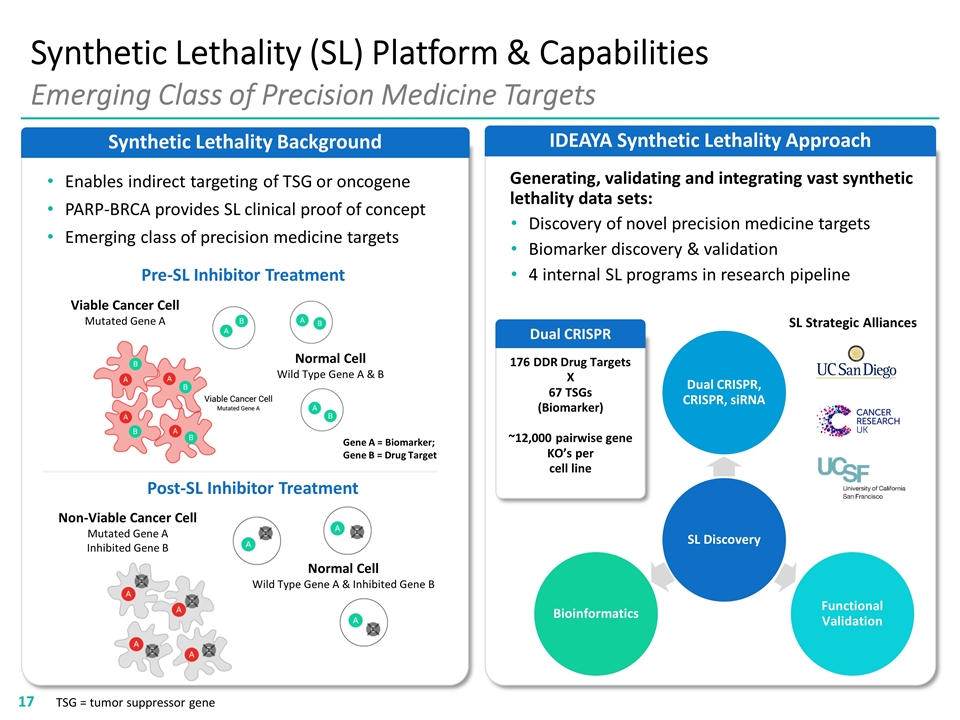
IDEAYA Synthetic Lethality Approach Synthetic Lethality Background Synthetic Lethality (SL) Platform & Capabilities Emerging Class of Precision Medicine Targets TSG = tumor suppressor gene Generating, validating and integrating vast synthetic lethality data sets: Discovery of novel precision medicine targets Biomarker discovery & validation 4 internal SL programs in research pipeline 176 DDR Drug Targets X 67 TSGs (Biomarker) ~12,000 pairwise gene KO’s per cell line Dual CRISPR SL Strategic Alliances Gene A = Biomarker; Gene B = Drug Target Pre-SL Inhibitor Treatment Post-SL Inhibitor Treatment Viable Cancer Cell Mutated Gene A Normal Cell Wild Type Gene A & B Enables indirect targeting of TSG or oncogene PARP-BRCA provides SL clinical proof of concept Emerging class of precision medicine targets Non-Viable Cancer Cell Mutated Gene A Inhibited Gene B Normal Cell Wild Type Gene A & Inhibited Gene B SL Discovery Dual CRISPR, CRISPR, siRNA Functional Validation Bioinformatics
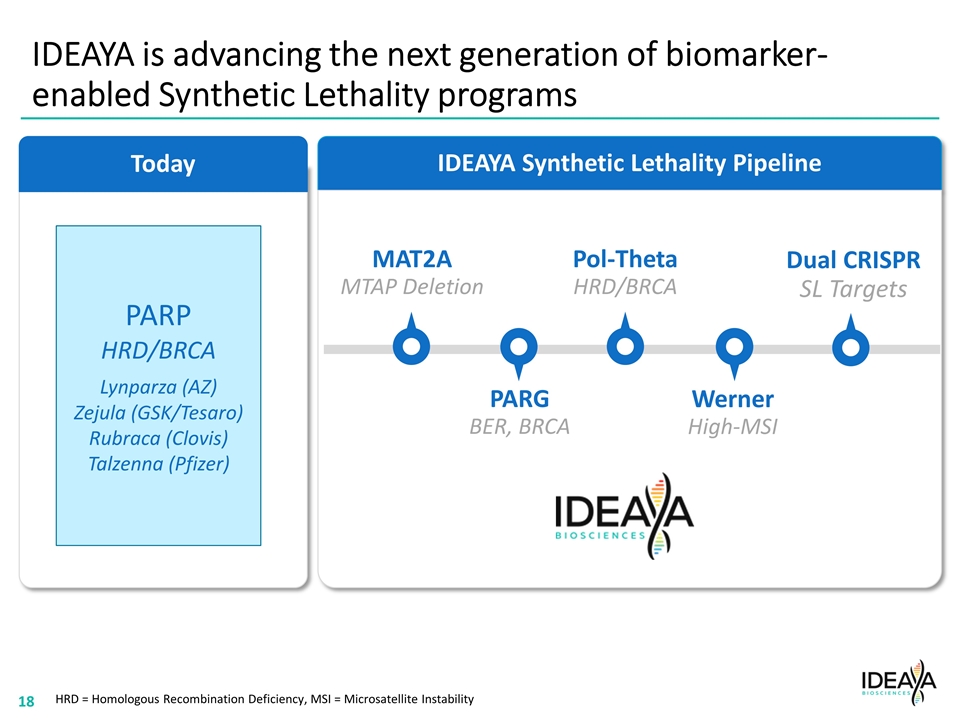
Today IDEAYA Synthetic Lethality Pipeline IDEAYA is advancing the next generation of biomarker-enabled Synthetic Lethality programs HRD = Homologous Recombination Deficiency, MSI = Microsatellite Instability MAT2A MTAP Deletion PARG BER, BRCA Pol-Theta HRD/BRCA Dual CRISPR SL Targets PARP HRD/BRCA Lynparza (AZ) Zejula (GSK/Tesaro) Rubraca (Clovis) Talzenna (Pfizer) Werner High-MSI
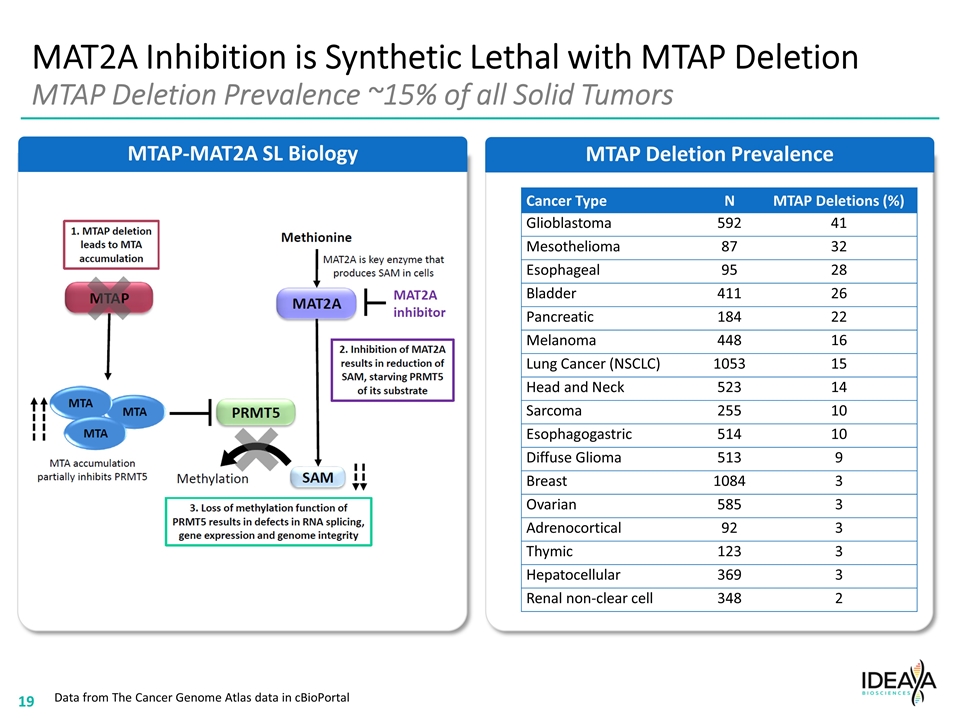
MAT2A Inhibition is Synthetic Lethal with MTAP Deletion MTAP Deletion Prevalence ~15% of all Solid Tumors MTAP Deletion Prevalence MTAP-MAT2A SL Biology Data from The Cancer Genome Atlas data in cBioPortal Cancer Type N MTAP Deletions (%) Glioblastoma 592 41 Mesothelioma 87 32 Esophageal 95 28 Bladder 411 26 Pancreatic 184 22 Melanoma 448 16 Lung Cancer (NSCLC) 1053 15 Head and Neck 523 14 Sarcoma 255 10 Esophagogastric 514 10 Diffuse Glioma 513 9 Breast 1084 3 Ovarian 585 3 Adrenocortical 92 3 Thymic 123 3 Hepatocellular 369 3 Renal non-clear cell 348 2
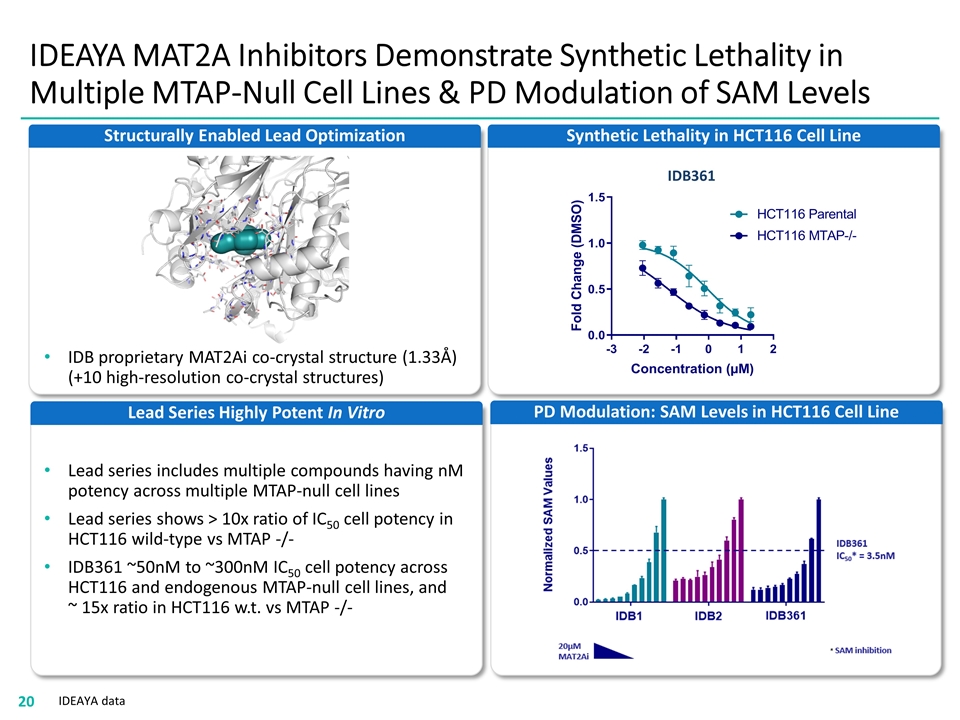
IDEAYA MAT2A Inhibitors Demonstrate Synthetic Lethality in Multiple MTAP-Null Cell Lines & PD Modulation of SAM Levels PD Modulation: SAM Levels in HCT116 Cell Line Synthetic Lethality in HCT116 Cell Line IDB361 IDEAYA data Structurally Enabled Lead Optimization IDB proprietary MAT2Ai co-crystal structure (1.33Å) (+10 high-resolution co-crystal structures) Lead Series Highly Potent In Vitro Lead series includes multiple compounds having nM potency across multiple MTAP-null cell lines Lead series shows > 10x ratio of IC50 cell potency in HCT116 wild-type vs MTAP -/- IDB361 ~50nM to ~300nM IC50 cell potency across HCT116 and endogenous MTAP-null cell lines, and ~ 15x ratio in HCT116 w.t. vs MTAP -/-
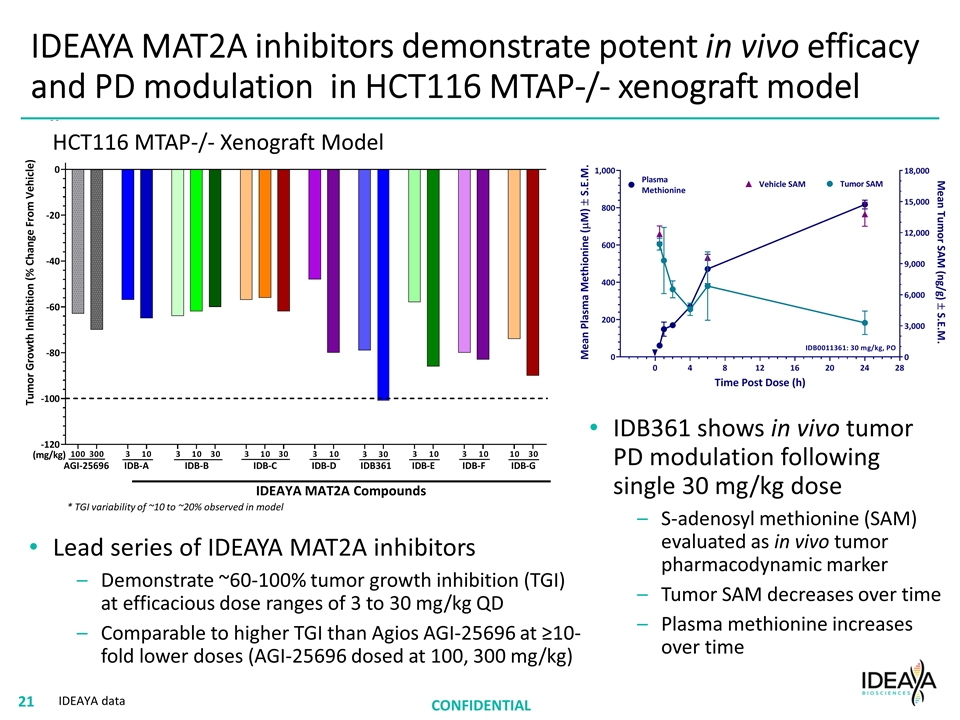
IDEAYA MAT2A inhibitors demonstrate potent in vivo efficacy and PD modulation in HCT116 MTAP-/- xenograft model Lead series of IDEAYA MAT2A inhibitors Demonstrate ~60-100% tumor growth inhibition (TGI) at efficacious dose ranges of 3 to 30 mg/kg QD Comparable to higher TGI than Agios AGI-25696 at ≥10-fold lower doses (AGI-25696 dosed at 100, 300 mg/kg) CONFIDENTIAL IDEAYA MAT2A Compounds IDB361 shows in vivo tumor PD modulation following single 30 mg/kg dose S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) evaluated as in vivo tumor pharmacodynamic marker Tumor SAM decreases over time Plasma methionine increases over time * TGI variability of ~10 to ~20% observed in model HCT116 MTAP-/- Xenograft Model IDEAYA data
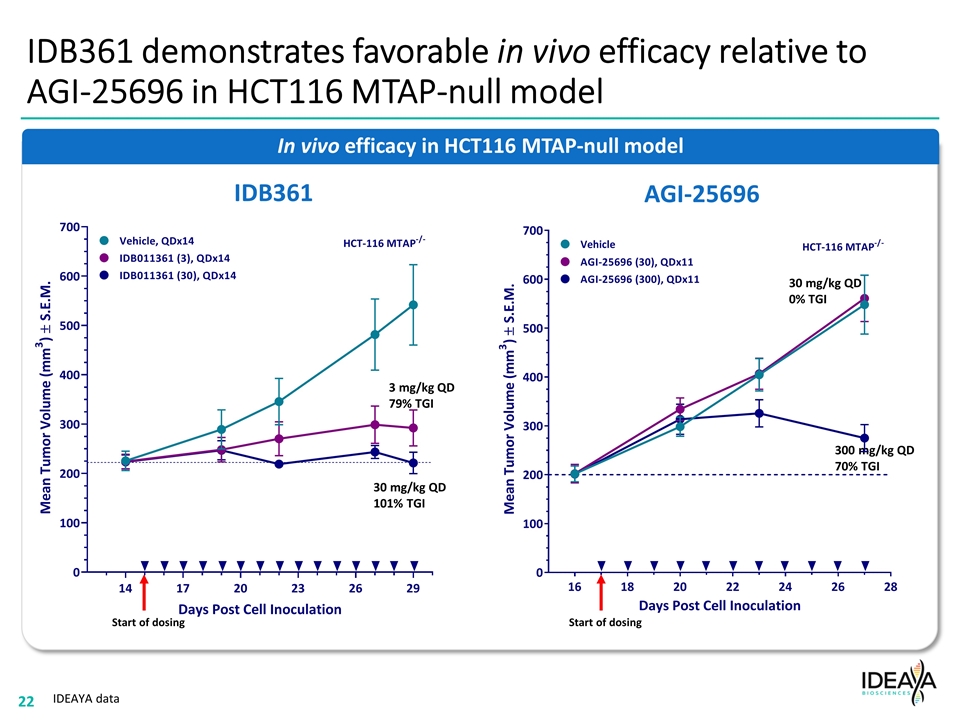
IDB361 demonstrates favorable in vivo efficacy relative to AGI-25696 in HCT116 MTAP-null model In vivo efficacy in HCT116 MTAP-null model IDEAYA data IDB361 Start of dosing 3 mg/kg QD 79% TGI 30 mg/kg QD 101% TGI 30 mg/kg QD 0% TGI 300 mg/kg QD 70% TGI Start of dosing AGI-25696
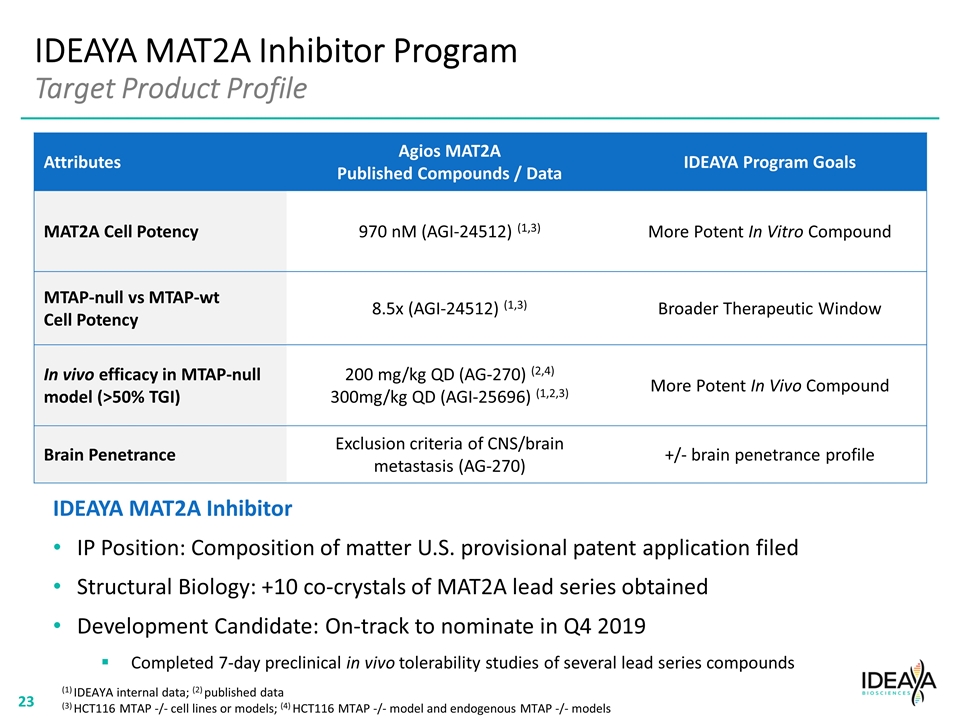
IDEAYA MAT2A Inhibitor Program Target Product Profile Attributes Agios MAT2A Published Compounds / Data IDEAYA Program Goals MAT2A Cell Potency 970 nM (AGI-24512) (1,3) More Potent In Vitro Compound MTAP-null vs MTAP-wt Cell Potency 8.5x (AGI-24512) (1,3) Broader Therapeutic Window In vivo efficacy in MTAP-null model (>50% TGI) 200 mg/kg QD (AG-270) (2,4) 300mg/kg QD (AGI-25696) (1,2,3) More Potent In Vivo Compound Brain Penetrance Exclusion criteria of CNS/brain metastasis (AG-270) +/- brain penetrance profile IDEAYA MAT2A Inhibitor IP Position: Composition of matter U.S. provisional patent application filed Structural Biology: +10 co-crystals of MAT2A lead series obtained Development Candidate: On-track to nominate in Q4 2019 Completed 7-day preclinical in vivo tolerability studies of several lead series compounds (1) IDEAYA internal data; (2) published data (3) HCT116 MTAP -/- cell lines or models; (4) HCT116 MTAP -/- model and endogenous MTAP -/- models
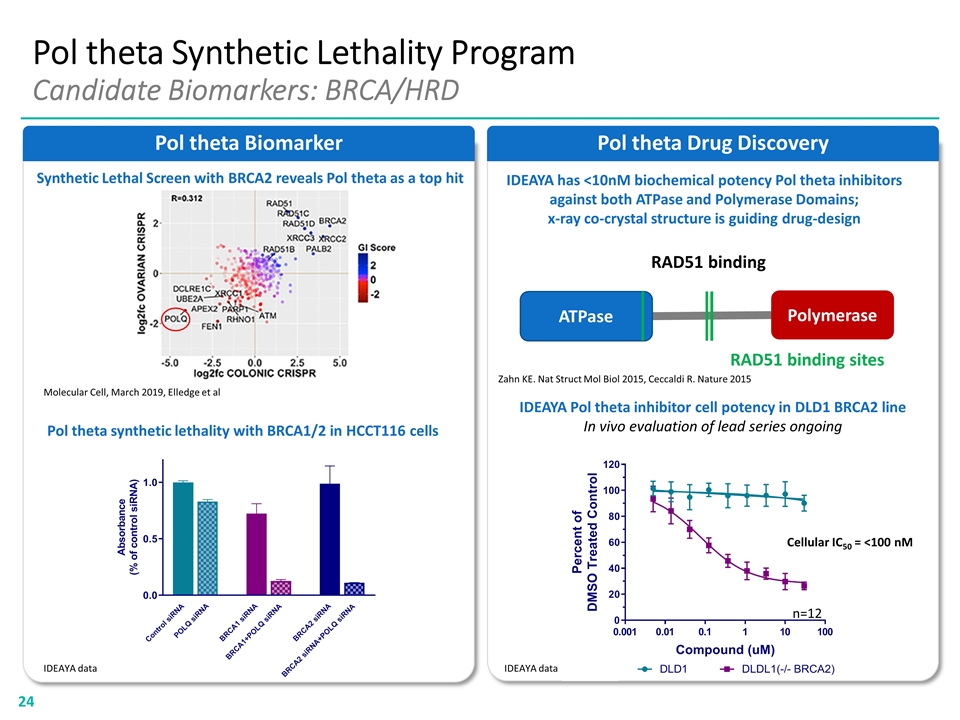
Pol theta Drug Discovery Pol theta Synthetic Lethality Program Candidate Biomarkers: BRCA/HRD Pol theta Biomarker IDEAYA Pol theta inhibitor cell potency in DLD1 BRCA2 line In vivo evaluation of lead series ongoing Pol theta synthetic lethality with BRCA1/2 in HCCT116 cells Synthetic Lethal Screen with BRCA2 reveals Pol theta as a top hit Molecular Cell, March 2019, Elledge et al ATPase Polymerase Zahn KE. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2015, Ceccaldi R. Nature 2015 RAD51 binding sites RAD51 binding IDEAYA has <10nM biochemical potency Pol theta inhibitors against both ATPase and Polymerase Domains; x-ray co-crystal structure is guiding drug-design IDEAYA data IDEAYA data Cellular IC50 = <100 nM n=12
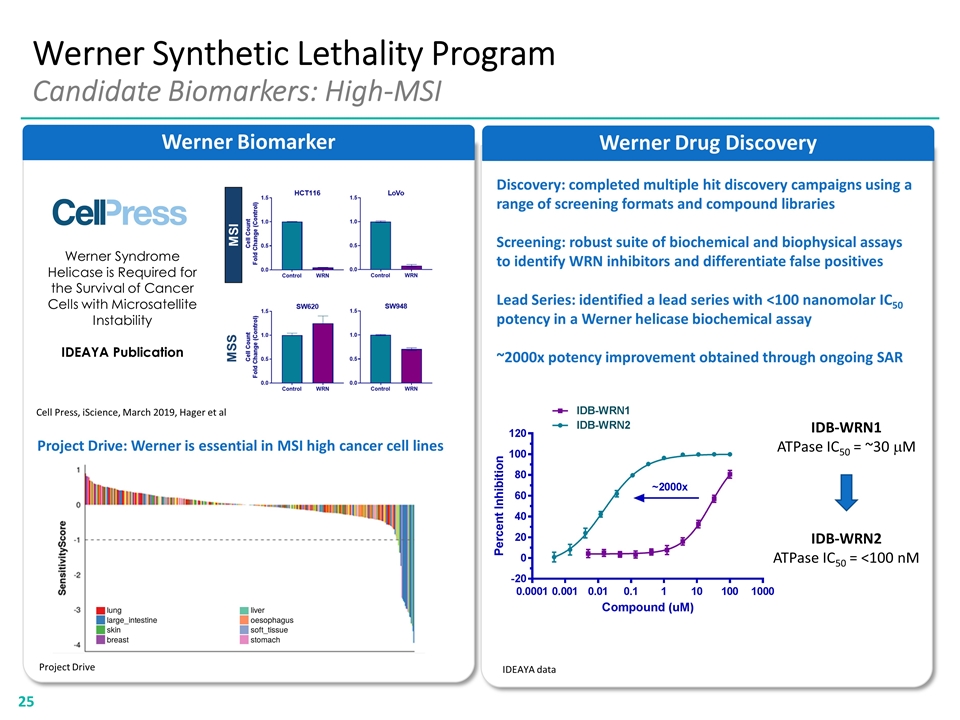
Discovery: completed multiple hit discovery campaigns using a range of screening formats and compound libraries Screening: robust suite of biochemical and biophysical assays to identify WRN inhibitors and differentiate false positives Lead Series: identified a lead series with <100 nanomolar IC50 potency in a Werner helicase biochemical assay ~2000x potency improvement obtained through ongoing SAR Werner Drug Discovery Werner Biomarker Werner Synthetic Lethality Program Candidate Biomarkers: High-MSI Werner Syndrome Helicase is Required for the Survival of Cancer Cells with Microsatellite Instability IDEAYA Publication Cell Press, iScience, March 2019, Hager et al Project Drive: Werner is essential in MSI high cancer cell lines Project Drive IDEAYA data IDB-WRN1 ATPase IC50 = ~30 mM IDB-WRN2 ATPase IC50 = <100 nM
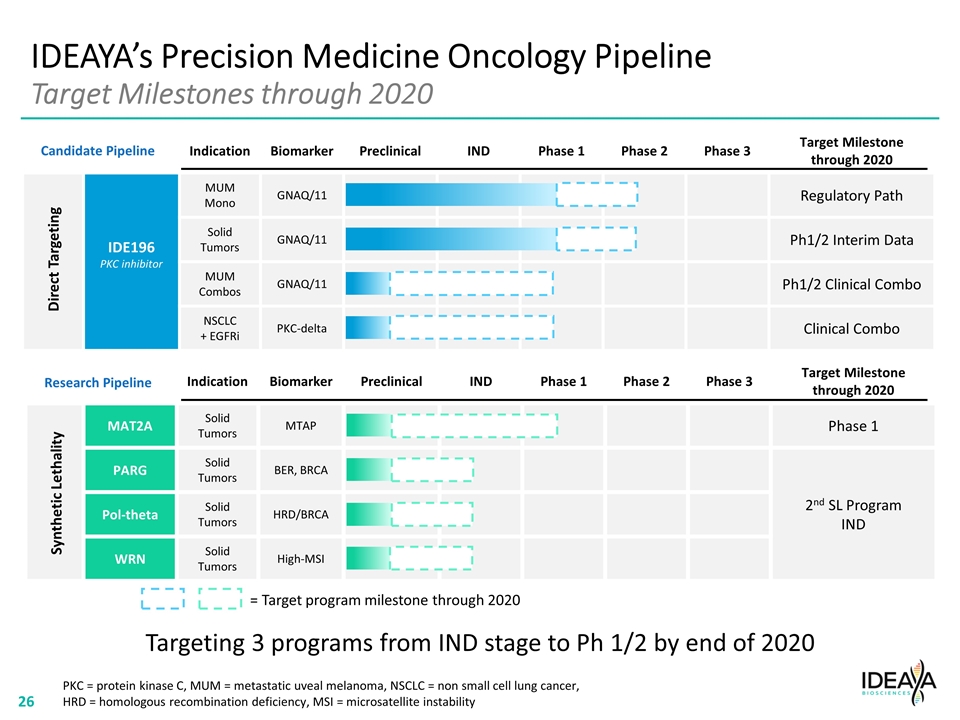
IDEAYA’s Precision Medicine Oncology Pipeline Target Milestones through 2020 Indication Biomarker Preclinical IND Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Target Milestone through 2020 IDE196 PKC inhibitor MUM Mono GNAQ/11 Regulatory Path Solid Tumors GNAQ/11 Ph1/2 Interim Data MUM Combos GNAQ/11 Ph1/2 Clinical Combo NSCLC + EGFRi PKC-delta Clinical Combo Direct Targeting Indication Biomarker Preclinical IND Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Target Milestone through 2020 MAT2A Solid Tumors MTAP Phase 1 PARG Solid Tumors BER, BRCA 2nd SL Program IND Pol-theta Solid Tumors HRD/BRCA WRN Solid Tumors High-MSI Synthetic Lethality PKC = protein kinase C, MUM = metastatic uveal melanoma, NSCLC = non small cell lung cancer, HRD = homologous recombination deficiency, MSI = microsatellite instability Targeting 3 programs from IND stage to Ph 1/2 by end of 2020 = Target program milestone through 2020 Candidate Pipeline Research Pipeline

























