| This presentation is made by Applied Therapeutics, Inc.(the “Company”). Nothing contained in this presentation is, or should be construed as, a recommendation, promise or representation by the presenter or the Company or any director, employee, agent, or adviser of the Company. This presentation does not purport to be all- inclusive or to contain all of the information you may desire. This presentation shall not constitute an offer to sell or the solicitation of an offer to buy the Company's securities, nor shall there be any sale of the Company's securities in any state or jurisdiction in which such offer, solicitation or sale would be unlawful prior to registration or qualification under the securities laws of any such state or jurisdiction. Various statements in this presentation concerning the Company’s future expectations, plans and prospects, including without limitation, the Company’s current expectations regarding its strategy, its product candidate selection and development timing, its management team capabilities, and the ability of the Company’s product candidates to have a clinically meaningful effect on the target patient populations, constitute forward-looking statements. The use of words such as “may,” “might,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “project,” “intend,” “future,” “potential,” or “continue,” the negative of these and other similar expressions are intended to identify such forward looking statements. Such statements, based as they are on the current analysis and expectations of management, inherently involve numerous risks and uncertainties, known and unknown, many of which are beyond the Company’s control. Such risks include, but are not limited to: the impact of general economic conditions, general conditions in the biopharmaceutical industries, changes in the global and regional regulatory environments in the jurisdictions in which the Company does or plans to do business, market volatility, fluctuations in costs and changes to the competitive environment. Consequently, actual future results may differ materially from the anticipated results expressed in the forward-looking statements. In the case of forward-looking statements regarding investigational product candidates and continuing further development efforts, specific risks which could cause actual results to differ materially from the Company’s current analysis and expectations include: failure to demonstrate the safety, tolerability and efficacy of our product candidates; final and quality controlled verification of data and the related analyses; the expense and uncertainty of obtaining regulatory approval, including from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency; the possibility of having to conduct additional clinical trials and our reliance on third parties such as our licensors and collaboration partners regarding our suite of technologies and product candidates. Further, even if regulatory approval is obtained, biopharmaceutical products are generally subject to stringent on-going governmental regulation, challenges in gaining market acceptance and competition. These risks and uncertainties are described more fully under the caption ”Risk Factors” in the Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Other risks and uncertainties of which the Company is not currently aware may also affect Company’s forward-looking statements. The reader should not place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements included in this presentation. These statements speak only as of the date made and the Company is under no obligation and disavows any obligation to update or revise such statements as a result of any event, circumstances or otherwise, unless required by applicable legislation or regulation. 2 Disclaimer |










 0.01 (20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg vs. placebo)
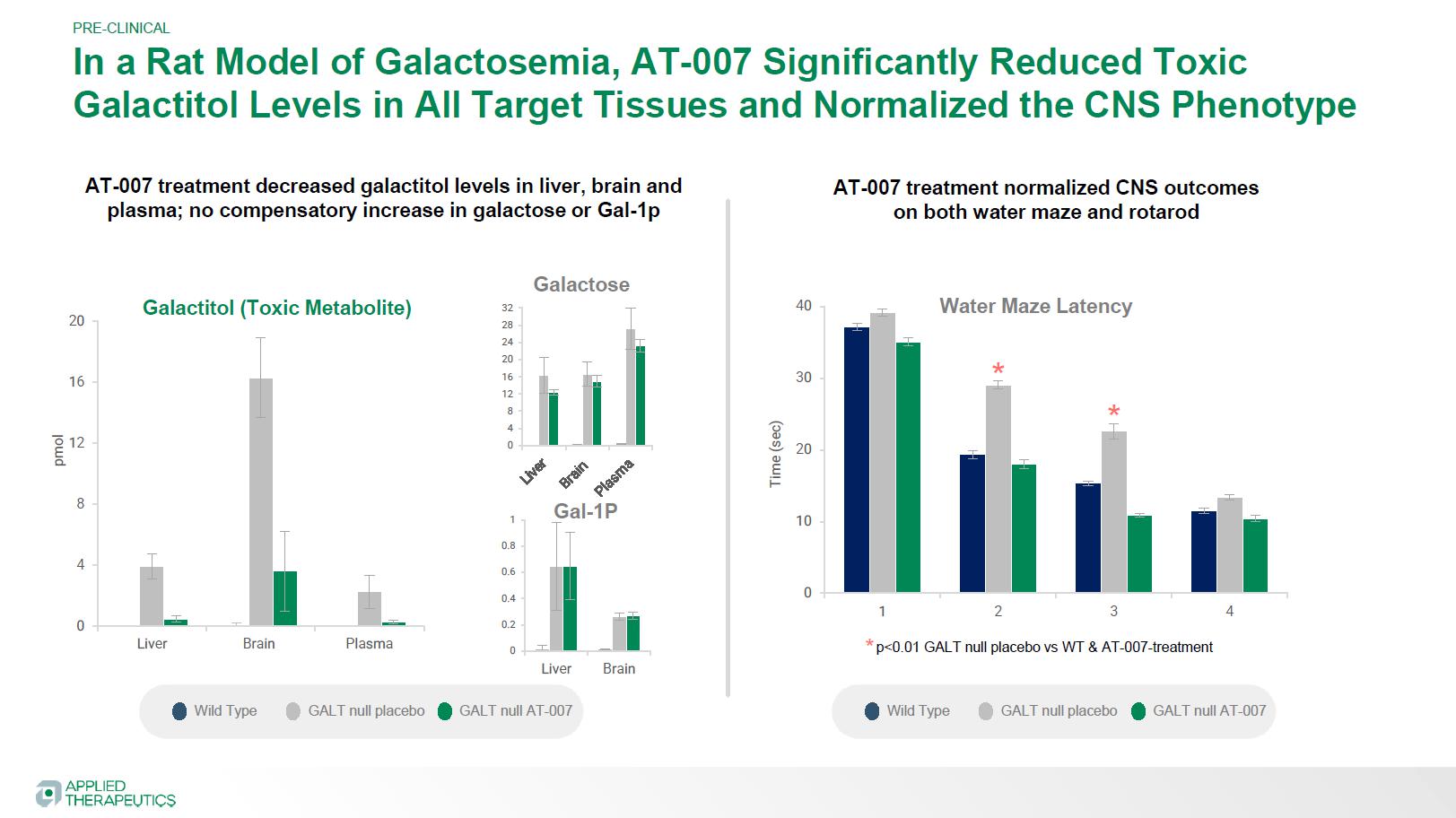
0.01 (20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg vs. placebo)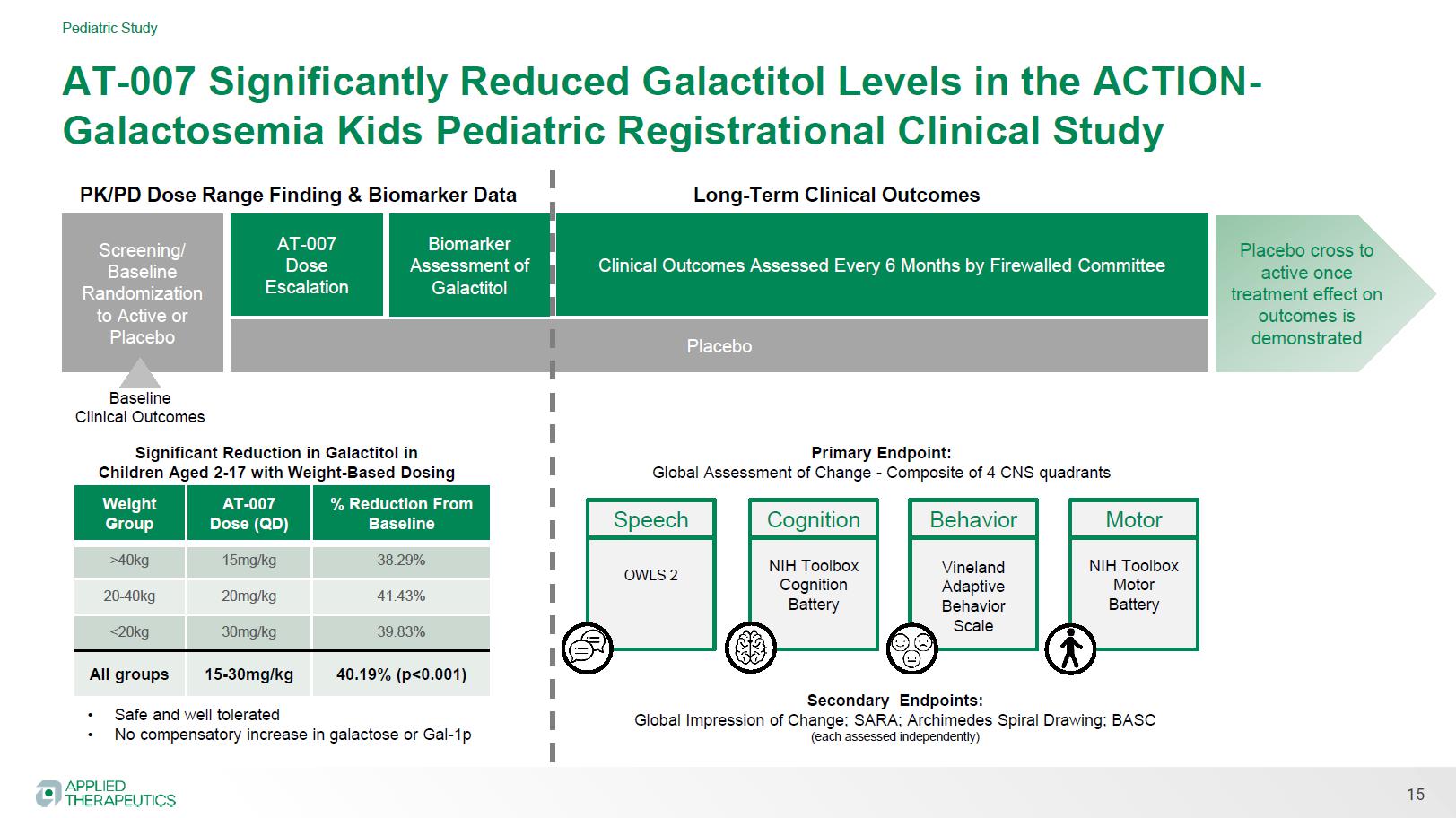 No compensatory increase in galactose or Gal-1p
No compensatory increase in galactose or Gal-1p

 Orphan Drug Designation
Orphan Drug Designation Aldose Reductase Inhibitor
Aldose Reductase Inhibitor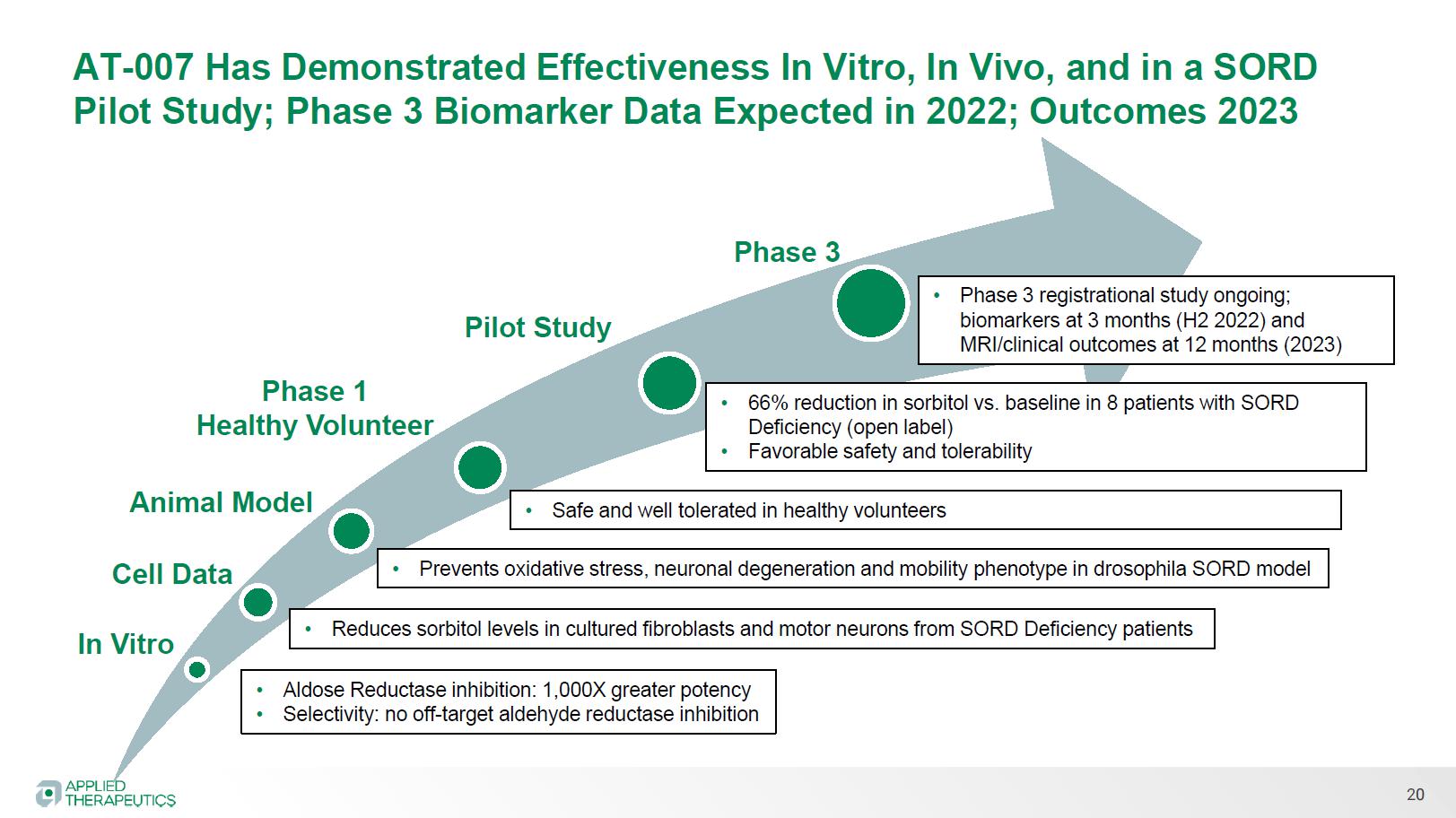 Reduces sorbitol levels in cultured fibroblasts and motor neurons from SORD Deficiency patients
Reduces sorbitol levels in cultured fibroblasts and motor neurons from SORD Deficiency patients