- TCRR Dashboard
- Financials
- Filings
-
Holdings
- Transcripts
-
ETFs
- Insider
- Institutional
- Shorts
-
S-1/A Filing
Tcr2 Therapeutics (TCRR) S-1/AIPO registration (amended)
Filed: 1 Feb 19, 3:20pm
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 1, 2019
Registration No. 333–229066
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Amendment No. 1
to
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER
THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
TCR2 Therapeutics Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 2836 | 47-4152751 | ||
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
TCR2 Therapeutics Inc.
100 Binney Street
Suite 710
Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142
(617) 949-5200
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of registrant’s principal executive offices)
Garry E. Menzel, Ph.D.
President and Chief Executive Officer
TCR2 Therapeutics Inc.
100 Binney Street
Suite 710
Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142
(617) 949-5200
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copies to:
Mitchell S. Bloom, Esq. William D. Collins, Esq. Goodwin Procter LLP 100 Northern Avenue Boston, Massachusetts 02210 (617) 570-1000 | Lisa Firenze, Esq. Steven D. Singer, Esq. Scott N. Lunin, Esq. Wilmer Cutler Pickering Hale and Dorr LLP 7 World Trade Center 250 Greenwich Street New York, New York 10007 (212) 230-8800 |
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public: As soon as practicable after the effective date of this registration statement.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box. ☐
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, please check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large Accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ☒ | Smaller reporting company | ☒ | |||
| Emerging growth company | ☒ | |||||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
| ||||||||
| TITLE OF EACH CLASS OF SECURITIES TO BE REGISTERED | AMOUNT TO BE | PROPOSED | PROPOSED MAXIMUM AGGREGATE | AMOUNT OF REGISTRATION FEE (3) | ||||
Common stock, $0.0001 par value per share | 5,750,000 | $16.00 | $92,000,000 | $11,151 | ||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| (1) | Estimated solely for the purpose of computing the registration fee in accordance with Rule 457(a) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. Includes 750,000 shares that the underwriters have an option to purchase to cover over-allotments, if any. |
| (2) | Includes the offering price of shares that the underwriters have an option to purchase to cover over-allotments. |
| (3) | Previously paid by the Registrant in connection with the filing of its registration statement on Form S-1 on December 28, 2018. |
The registrant hereby amends this registration statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant files a further amendment which specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or until the registration statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
The information in this prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not sell these securities until the Securities and Exchange Commission declares our registration statement effective. This prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted.
SUBJECT TO COMPLETION, DATED FEBRUARY 1, 2019
Preliminary Prospectus
5,000,000 Shares

Common Stock
We are offering 5,000,000 shares of common stock. This is our initial public offering of our common stock. Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our shares. We expect that the initial public offering price will be between $14.00 and $16.00 per share. We have applied to list our common stock on The Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “TCRR”.
We are an “emerging growth company” under the federal securities laws and, as such, we have elected to comply with certain reduced public company reporting requirements for this prospectus and for future filings.
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. Before buying any shares, you should read carefully the discussion of the material risks of investing in our common stock under the heading “Risk Factors” starting on page 13 of this prospectus.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission approved or disapproved of the securities that may be offered under this prospectus, nor have any of these organizations determined if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
| PER SHARE | TOTAL | |||||||
Public offering price | $ | $ | ||||||
Underwriting discount(1) | $ | $ | ||||||
Proceeds, before expenses, to TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. | $ | $ | ||||||
| (1) | We refer you to “Underwriting” beginning on page 181 of this prospectus for additional information regarding underwriting compensation. |
Delivery of the shares of common stock is expected to be made on or about , 2019.
Certain of our existing stockholders (or their affiliates), including those affiliated with certain of our directors, have indicated an interest in purchasing an aggregate of approximately $30.0 million of shares of our common stock in this offering at the initial public offering price. However, because indications of interest are not binding agreements or commitments to purchase, the underwriters may determine to sell more, less or no shares in this offering to such stockholders, and such stockholders could determine to purchase more, less or no shares in this offering.
We have granted the underwriters an option for a period of 30 days to purchase an additional 750,000 shares of our common stock. If the underwriters exercise the option in full, the total underwriting discounts and commissions payable by us will be $ , and the total proceeds to us, before expenses, will be $ .
| Jefferies | SVB Leerink | BMO Capital Markets | ||
| Wedbush PacGrow | China Renaissance | |||
The date of this prospectus is , 2019.
| PAGE | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 9 | ||||
| 11 | ||||
| 13 | ||||
| 68 | ||||
| 70 | ||||
| 71 | ||||
| 72 | ||||
| 74 | ||||
| 76 | ||||
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS | 78 | |||
| 90 | ||||
| 145 | ||||
| 153 | ||||
| 162 | ||||
| 164 | ||||
| 168 | ||||
| 171 | ||||
| 176 | ||||
MATERIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS FOR NON-U.S. HOLDERS | 178 | |||
| 181 | ||||
| 189 | ||||
| 190 | ||||
| 191 | ||||
| F-1 | ||||
Neither we nor the underwriters have authorized anyone to provide you with information different from, or in addition to, that contained in this prospectus, any amendment or supplement to this prospectus and any related free writing prospectus prepared by or on behalf of us or to which we have referred you. We and the underwriters take no responsibility for, and can provide no assurances as to the reliability of, any information that others may give you. This prospectus is not an offer to sell, nor is it seeking an offer to buy, these securities in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted. The information contained in this prospectus or in any free writing prospectus is only accurate as of its date, regardless of its time of delivery or the time of any sale of our common stock. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth prospects may have changed since that date. No action is being taken in any jurisdiction outside the United States to permit a public offering of our common stock or possession or distribution of this prospectus in that jurisdiction. Persons who come into possession of this prospectus in jurisdictions outside the United States are required to inform themselves about and to observe any restrictions as to this offering and the distribution of this prospectus applicable to that jurisdiction.
We own or have rights to various trademarks, service marks and trade names that we use in connection with the operation of our business. This prospectus may also contain trademarks, service marks and trade names of third parties, which are the property of their respective owners. Our use or display of third parties’ trademarks, service marks, trade names or products in this prospectus is not intended to, and does not imply a relationship with, or endorsement or sponsorship by us. Solely for convenience, the trademarks, service marks and trade names referred to in this prospectus may appear without the®, TM or SM symbols, but the omission of such references is not intended to indicate, in any way, that we will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights or the right of the applicable owner of these trademarks, service marks and trade names.
Until and including , 2019 (25 days after the date of this prospectus), all dealers that buy, sell or trade our common stock, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This delivery requirement is in addition to the obligation of dealers to deliver a prospectus when acting as underwriters and with respect to their unsold allotments or subscriptions.
This summary highlights information contained in greater detail elsewhere in this prospectus. This summary does not contain all of the information that you should consider in making your investment decision. Before investing in our common stock, you should carefully read this entire prospectus, including our financial statements and the related notes thereto and the information set forth under the sections titled “Risk Factors,” “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements,” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” in each case included in this prospectus. Unless the context otherwise requires, we use the terms “TCR2,” “TCRR,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” “our,” and similar designations in this prospectus to refer to TCR2 Therapeutics Inc.
Overview
We are a clinical-stage immunotherapy company developing the next generation of novel T cell therapies for patients suffering from cancer. Our proprietary TCR Fusion Construct T cells (TRuC-T cells) specifically recognize and kill cancer cells by harnessing the entire T cell receptor (TCR) signaling complex, which we believe is essential for T cell therapies to be effective in patients with solid tumors. We have also designed our TRuC-T cells so that tumor cell recognition does not require human leukocyte antigens (HLA), which provides two important additional benefits. First, in contrast to current engineered T cell therapies that use the full TCR (TCR-T cells), our technology is designed so that it can be applied to all patients that express the cancer surface antigen irrespective of HLA subtype, which we believe will allow us to address a significantly larger patient population. Second, HLA is downregulated or lost in many tumors which can prevent their recognition by T cells and lead to diminished response rates and higher relapse rates. We therefore believe our approach will allow us to deliver the first HLA-independent TCR-T cell therapy for patients with solid tumors. We also believe that our product candidates have the potential to improve upon the efficacy and safety of currently approved chimeric antigenreceptor T (CAR-T) cell therapies inCD19-positive B-cell hematological malignancies. This belief is based on preclinical studies comparing our product candidates toCAR-T cells that we engineered.
In January 2019, the investigational new drug application (IND) for our lead solid tumor product candidate, TC-210, to treat patients with mesothelin-positive solid tumors was cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). We plan to initiate our Phase 1/2 clinical trial for TC-210 in early 2019. We estimate the patient population for TC-210 is up to 81,000 in the United States alone. We expect to generate our first clinical data for TC-210 in the second half of 2019. We expect to file an IND in the second half of 2019 for our lead hematology product candidate, TC-110, to treat patients with CD19-positive B-cell hematological malignancies and expect to generate our first clinical data for TC-110 in the second half of 2020. In addition, we plan to file an IND for our second solid tumor product candidate, TC-220, to treat MUC16-positive solid tumors, in early 2020 and we expect to generate our first clinical data for TC-220 in the first half of 2021.
A Revolution in T Cell Therapies
According to a 2017 press release from the FDA on the licensure of the first engineered T cell therapy for cancer, the field is “entering a new frontier in medical innovation with the ability to reprogram a patient’s own cells to attack a deadly cancer.” We founded our company to build on these early T cell therapy innovations while addressing their limitations and making our product candidates available to a broader patient population.
The immune system is responsible for protecting the human body by eliminating agents that threaten our health, including cancer cells. One of the key components of the immune system are sentinels called T cells that are able to target these agents for elimination by using TCR recognition of cell surface markers known as antigens. When a T cell recognizes a tumor antigen through the TCR, it kills the malignant cell on which it resides. Existing T cell therapies for cancer, including CAR-T cells and engineered TCR-T cells, attempt to replicate this mechanism. While current T cell therapies have shown encouraging efficacy data, they have limitations that we believe our product candidates can address.
CAR-T cell therapies have been approved for use in certain CD19-positive B-cell hematological malignancies on the basis of encouraging efficacy data. However, the durable benefit of these therapies has been limited to
1
a subset of cancer patients, while the risk of potentially fatal side effects for patients is high. In solid tumors, CAR-T cells have not shown meaningful patient benefit. We believe these limitations are a consequence of the CAR construct using only one subunit of the entire TCR signaling complex and operating independently of the normal signaling mechanisms in the T cell. As a result, CAR-T cells do not benefit from all of the activation and regulatory elements of the natural TCR complex. This results in CAR-T cells overproducing cytokines that frequently lead to severe toxicities, including cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity. CAR-T cells are also limited in their ability to persist and overcome the hostile tumor microenvironment.
TCR-T cell approaches were developed in an attempt to leverage the power of the entire TCR signaling complex. TCR-T cells have produced clinical responses in patients with solid tumors. However, recognition of the tumor antigen by existing TCR-T cell approaches occurs in the context of HLA. This significantly limits the number of patients that can be treated with each specific TCR-T cell therapy because they can only be used for one specific HLA subtype, of which there are many. In addition, the downregulation or loss of HLA in many tumors can prevent tumor antigen recognition by TCR-T cells and lead to diminished response rates and higher relapse rates.
Our Novel Platform
We are pioneering the development of a novel, transformative T cell engineering platform which, based on its design and our preclinical studies, we believe has the potential to address the shortcomings of CAR-T cells and TCR-T cells and is fundamentally different from existing approaches. Research over more than two decades has shown that each of the TCR subunits makes distinct contributions to the activation and regulation of T cells and only the sum of the TCR subunits can adequately activate and control all functions of T cells. We believe that engaging the entire TCR signaling complex is required to fully leverage T cells in their fight against cancer.
Our T cell engineering approach relies upon natural TCR elements to produce therapeutic T cells that function independent of HLA restriction. To that end, we fuse a cancer antigen recognition domain directly to a subunit of the TCR and use a lentiviral vector to transfer the genetic information for the TRuC construct into a patient’s own T cells. This modified subunit then naturally integrates into the native TCR complex. The result is the generation of an engineered T cell equipped with a new “homing device” to detect and engage a specific antigen on the surface of cancer cells. Upon antigen engagement, these T cells harness the entire TCR to produce a more powerful yet controlled T cell response against cancer. We refer to T cells engineered with our TCR fusion constructs as TRuC-T cells. In preclinical studies of both solid tumors and hematological malignancies, we have observed greater anti-tumor activity, longer persistence and less cytokine release compared to CAR-T cells we have engineered to target the same cancer antigen. We believe that these properties could translate into more durable responses with potentially fewer adverse events for patients with cancer.
2
The figure below describes the natural HLA-restricted TCR complex as compared to the HLA-independent TRuC-T cell.
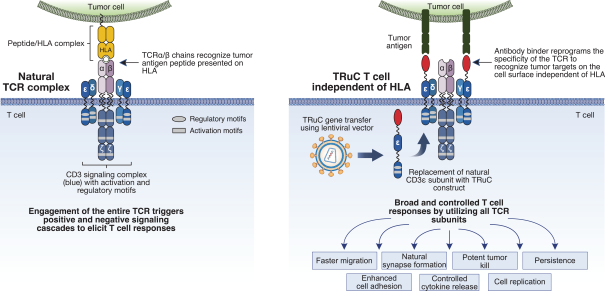
We are using our TRuC-T cell platform to target many different cancer antigens. Our core format, in which we target a single cancer antigen, is known as a mono TRuC-T cell. Our mono TRuC-T cell product candidates have shown promising anti-tumor activity and persistence in our preclinical studies. We are supplementing our core format with a series of next-generation enhancements that may further improve clinical outcomes. These fall into two broad categories. First, we are developing formats that target two antigens, known as dual TRuC-T cells, which could improve tumor response in patients who express more than one cancer antigen and combat potential antigen escape which is a leading mechanism of cancer relapse in patients receiving CAR-T cell therapy. Second, we are developing several strategies to counter the immunosuppressive microenvironment of solid tumors including mechanisms to block a key cancer defense known as the programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) checkpoint pathway.
We are also evaluating multiple proprietary designs for allogeneic, or off-the-shelf, TRuC-T cells.
3
Our Pipeline
The versatility of our platform is highlighted by the multiple programs and multiple formats of the product candidates in our pipeline. In preclinical studies with multiple TRuC-T cell product candidates, we have shown better anti-tumor activity, longer persistence and lower cytokine release compared to CAR-T cells we have engineered to bear the same tumor antigen binding domains as our product candidates. We have generated a broad pipeline with assets that address both solid tumors and hematological malignancies. Our product candidates are listed in the figure below.
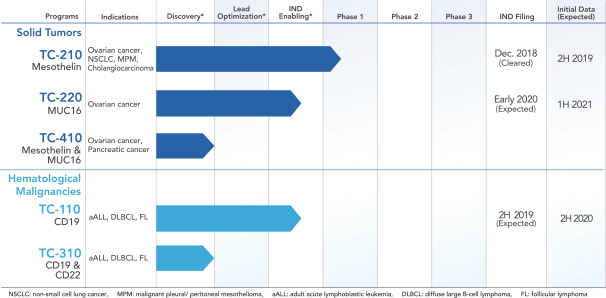
*In the Discovery stage, we identify the antigen-specific binders, tether these to a TCR subunit via a linker and then, upon introduction into T cells, test the killing activity and cytokine releasein vitro. Thereafter, the programs enter Lead Optimization stage, where we optimize the antigen binder sequence and linker length and re-test T cells expressing the enhanced TRuC sequences in cellular assays for functional activity and specificity. At this stage, we also investigate the anti-tumor activity, cytokine release, pharmacodynamics and phenotype of TRuC-T cells in mouse studies. The IND-Enabling stage is defined by the nomination of a product candidate. At this stage of drug development, we initiate the GMP production of lentiviral vector and process development of TRuC-T cells. In addition, we conduct studies addressing the specificity and toxicity to support the submission of an IND application.
| ∎ | TC-210:Our Lead Mono TRuC-T CellsTargeting Mesothelin Positive Solid Tumors.Our most advanced mono TRuC-T cell product candidate is TC-210, which targets mesothelin-positive solid tumors. While its expression in normal tissues is low, mesothelin is highly expressed on many solid tumors. The cancer types that we intend to treat in our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial include non-small cell lung cancer, ovarian cancer, malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma and cholangiocarcinoma. These cancers represent a patient population of up to 81,000 in the United States alone. By comparison, the addressable U.S. patient population with hematological malignancies for approved CD19-directed CAR-T therapies is estimated to be approximately 8,000. In our preclinical studies we have observed better anti-tumor activity and persistence of TRuC-T cells compared toCAR-T cells we engineered to target mesothelin while also exhibiting lower levels of cytokine release. The FDA cleared our IND for TC-210 in January 2019 and we plan to initiate our Phase 1/2 clinical trial in early 2019. We have submitted an FDA Orphan Drug Designation application for the treatment of malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma with TC-210 and also plan to apply for FDA Fast Track designation for TC-210. |
| ∎ | TC-110: Our Lead Mono TRuC-T Cells Targeting CD19-Positive B-Cell Hematological Malignancies.We are developing a mono TRuC-T cell, TC-110, targeting CD19-positive B-cell hematological malignancies. The clinical development plan for TC-110 will initially focus on three specific areas: adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL). These are indications for which CAR-T cells have either been approved but faced clinical outcome limitations (specifically, DLBCL), proven to be too toxic for use (specifically, adult ALL), or have not been approved at all (specifically, FL). In our preclinical studies we have observed |
4
better tumor clearance and persistence of TRuC-T cells compared to CAR-T cells we engineered to target CD19 while also exhibiting lower levels of cytokine release. We expect to file an IND for TC-110 in the second half of 2019 and seek FDA Fast Track designation. |
| ∎ | TC-220: Our Mono TRuC-T Cells Targeting MUC16 Positive Solid Tumors.We are conducting IND-enabling studies for our mono TRuC-T cell product candidate, TC-220, targeting MUC16-positive solid tumors. While its expression in normal tissues is low, MUC16 is highly expressed in many solid tumors, including ovarian, pancreatic, gastric and colorectal cancers. We plan to develop TC-220 initially for the treatment of MUC16 overexpressing ovarian cancer, which represents a patient population of up to 17,000 in the United States alone. TC-220 has shown strong anti-tumor activity in preclinical models of MUC16-positive ovarian cancers. Our goal is to file an IND for TC-220 in early 2020. |
| ∎ | TC-310 and TC-410: Our Dual TRuC-T Cell Programs Targeting CD19/22 and MSLN/MUC16.We have developed dual TRuC-T cells designed to reduce the potential for antigen escape in solid tumors or hematological malignancies by targeting more than one cancer antigen. These second generation TRuC-T cells are also able to integrate platform enhancements to counter the hostile tumor microenvironment. We are currently developing these for preclinical studies and will determine their clinical indications based on the outcome of those studies. |
Manufacturing
We are currently producing good manufacturing practices (GMP) grade materials in preparation for our Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210. Our process is semi-automated and functionally closed to ensure quality product. We have scaled and refined our technology to allow all of our product candidates to be manufactured on the same platform. While we have transferred our current capabilities to various partners for our Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210, we plan to develop our own manufacturing capabilities. We believe this will help us to meet our anticipated demand from a large patient population while allowing direct oversight of quality.
Our Strategy
Our goal is to cure cancer with our TRuC-T cell therapies. We intend to make a difference in the lives of patients by building a fully integrated cancer immunotherapy company offering the first HLA-independent TCR-T cell therapies. The key components of our strategy are:
| ∎ | Rapidly advance our solid tumor pipeline. The FDA cleared the IND for TC-210, our lead mono TRuC-T cell targeting patients with mesothelin-expressing solid tumors in January 2019. We expect to generate data from this first clinical trial in the second half of 2019. Our goal is to obtain FDA Fast Track designations for malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma and cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer), and we believe this will provide the potential for FDA Accelerated Approval based on Phase 2 clinical data. We anticipate filing an IND for our second mono TRuC-T cell, TC-220, targeting patients withMUC16-positive solid tumors, in early 2020. We are also developing product candidates targeting other cancer antigens expressed on solid tumors. |
| ∎ | Rapidly advance our hematological malignancy pipeline. We intend to file an IND for TC-110, our lead mono TRuC-T cell targeting patients with CD19-positive B-cell hematological malignancies, in the second half of 2019. Our goal is to obtain FDA Fast Track designations for both adult ALL and DLBCL and we believe this will provide the potential for FDA Accelerated Approval based on Phase 2 clinical data. |
| ∎ | Exploit the versatility of our platform to broaden our pipeline. We have developed several additional tools that may be incorporated into our future product candidates to overcome tumor defense mechanisms, including dual-antigen targeting TRuC-T cells to minimize potential for antigen escape and cancer relapse. Our most advanced dual-antigen targeting programs include a dual mesothelin/MUC16 TRuC-T cell for solid tumors and a dual CD19/CD22 TRuC-T cell for hematological malignancies. We are also evaluating multiple proprietary designs for allogeneic, or off-the-shelf,TruC-T cells. |
5
| ∎ | Scale our manufacturing capacity to match our future product needs. We plan to develop our own manufacturing capabilities. We are currently manufacturing GMP-grade clinical lots forTC-210 through third-party contractors. We have also entered into an agreement with Cell Therapy Catapult Limited (Catapult), which will allow us to manufacture our TRuC-T cells using our own personnel at Catapult’s facility, while also expanding our capacity to supply future clinical trials. If our clinical trials are successful, given the size of the patient population that can potentially be targeted by our product candidates, we plan to build our own manufacturing plant. |
| ∎ | Retain significant economic and commercial rights to our product candidates.We currently own all rights to our product candidates and programs and intend to build a fully integrated cancer immunotherapy company. We intend to maintain product rights in key geographies, in particular for TC-210. We believe the versatility of our platform presents an opportunity for us to selectively form collaborations and strategic partnerships to expand our capabilities and product offerings into other therapeutic areas and potentially accelerate the development and maximize the commercial potential of our product candidates. |
Our Management Team and Founders
Our company was founded by MPM Capital executive partner Dr. Patrick Baeuerle, a world-renowned immunologist who previously developed the first commercial bi-specific antibody at Micromet, Inc. (subsequently acquired by Amgen Inc.), currently being used for patients with Philadelphia chromosome negative relapsed or refractory ALL under the tradename Blincyto. We have also benefited from working closely with Dr. Mitchell Finer, an MPM Capital executive partner who has three decades of cell therapy manufacturing experience, including the design of GMP processes for bluebird bio, Inc. and Cell Genesys, Inc. The development of our TRuC-T cell platform has been further supported by the collective expertise and know-how of MPM Capital and its breadth of oncology portfolio companies.
Our strategy will be executed by a management team with a strong track record of relevant accomplishments as well as the experience necessary to build a fully integrated cancer immunotherapy company. This includes leading edge scientific innovation and design, process development, clinical development, manufacturing, commercial expertise and business acumen. Key employees include:
| ∎ | Our Chief Scientific Officer, Dr. Robert Hofmeister, who developed Bavencio, one of the first PD-L1 inhibitors, while at EMD Serono, Inc., currently being used for patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma and metastatic urothelial carcinoma. |
| ∎ | Our Chief Medical Officer, Dr. Alfonso Quintás Cardama, who has extensive experience with both CAR-T and TCR-T therapies and was pivotal in the approval process for Kymriah (Novartis) which is one of only two licensed T cell therapies for hematological malignancies. |
| ∎ | Our Chief Financial Officer, Mr. Ian Somaiya, who was a Wall Street research analyst for two decades with coverage of numerous leading immunotherapy companies. |
| ∎ | Our Chief Executive Officer, Dr. Garry Menzel, who has extensive operational and transactional expertise having previously served in the C-suite of three healthcare companies and led the biotechnology practices for two leading Wall Street firms, Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC and Credit Suisse Group AG. |
We have been well-funded to date raising approximately $170 million in capital from investors including founding investors MPM Capital and F2 Ventures and other investors including 6 Dimensions Capital, ArrowMark Partners, Cathay Fortune Corporation, Curative Ventures, Hillhouse Capital Group, MiraeAsset Financial Group and Redmile Group.
6
Risks Associated with Our Business
Our ability to implement our business strategy is subject to numerous risks that you should be aware of before making an investment decision. These risks are described more fully in the section entitled “Risk Factors” in this prospectus. These risks include, among others:
| ∎ | we are a clinical-stage company with a limited operating history, have incurred significant losses since our inception, and anticipate that we will continue to incur significant losses for the foreseeable future; |
| ∎ | even if this offering is successful, we will need to raise additional funding before we can expect to generate any revenues from product sales; |
| ∎ | if we are unable to successfully develop our current programs into a portfolio of product candidates, or experience significant delays in doing so, we may not realize the full commercial potential of our current and future product candidates; |
| ∎ | we are heavily dependent upon the success of our lead product candidates, TC-210 and TC-110, and if we are unable to conduct clinical trials or obtain regulatory approval for our lead product candidates or any other product candidates that we are developing or may identify or develop, our business will be substantially harmed; |
| ∎ | we are very early in our development efforts and, other than TC-210, all of our product candidates are still in preclinical development. If we are unable to advance our product candidates through clinical development, obtain regulatory approval and ultimately commercialize our product candidates, or experience significant delays in doing so, our business will be materially harmed; |
| ∎ | results of earlier studies may not be predictive of future study or trial results, and we may fail to establish an adequate safety and efficacy profile to conduct clinical trials or obtain regulatory approval for TC-210, TC-110 or any other product candidates that we may pursue; |
| ∎ | if serious adverse events, undesirable side effects, or unexpected characteristics are identified during the development of any of our product candidates, we may need to delay, abandon or limit our further clinical development of those product candidates; |
| ∎ | manufacturing and administering our product candidates is complex and we may encounter difficulties in production, particularly with respect to process development or scaling up of our manufacturing capabilities, whether we do so ourselves or through the engagement of third parties; |
| ∎ | we may acquire and establish our own manufacturing facility and infrastructure in addition to or in lieu of relying on third parties for the manufacture of our product candidates, which will be costly, time-consuming, and which may not be successful; |
| ∎ | we are highly dependent on intellectual property licensed from third parties and termination of any of these licenses could result in the loss of significant rights, which would harm our business; |
| ∎ | if we are unable to obtain and maintain sufficient intellectual property protection for TC-210, TC-110, our other product candidates and technologies or any future product candidates, we may not be able to compete effectively in our markets; and |
| ∎ | our future success depends in part upon our ability to retain our key employees, consultants and advisors and to attract, retain and motivate other qualified personnel. |
Corporate Information
We were incorporated in May 2015 under the laws of the State of Delaware under the name TCR2, Inc. On November 14, 2016, we changed our name to TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. Our principal executive offices are located at 100 Binney Street, Suite 710, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142, and our telephone number is (617) 949-5200. Our website address is http://www.tcr2.com. The information contained in or accessible from our website is not incorporated into this prospectus, and you should not consider it part of this prospectus. We have included our website address in this prospectus solely as an inactive textual reference.
7
Implications of Being an Emerging Growth Company
We qualify as an “emerging growth company” as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, as amended. As an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of specified reduced disclosure and other requirements that are otherwise applicable generally to public companies. These provisions include:
| ∎ | being permitted to provide only two years of audited financial statements in addition to any required unaudited interim financial statements with correspondingly reduced “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” disclosure; |
| ∎ | reduced disclosure about our executive compensation arrangements; |
| ∎ | not being required to hold advisory votes on executive compensation or to obtain stockholder approval of any golden parachute arrangements not previously approved; and |
| ∎ | an exemption from the auditor attestation requirement in the assessment of our internal control over financial reporting. |
We may take advantage of these exemptions for up to five years or such earlier time that we are no longer an emerging growth company. We would cease to be an emerging growth company on the date that is the earliest of (i) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenues of $1.07 billion or more; (ii) the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the completion of this offering; (iii) the date on which we have issued more than $1.0 billion in nonconvertible debt during the previous three years; or (iv) the date on which we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer under the rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). We may choose to take advantage of some but not all of these exemptions. We have taken advantage of reduced reporting requirements in this prospectus. Accordingly, the information contained herein may be different from the information you receive from other public companies in which you hold stock.
8
Shares of common stock offered by us | 5,000,000 shares |
Shares of our common stock to be outstanding after this offering | 23,189,901 shares (or 23,939,901 shares if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full). |
Option to purchase additional shares | We have granted the underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to 750,000 additional shares of our common stock at the public offering price, less underwriting discounts and commissions on the same terms as set forth in this prospectus. |
Use of proceeds | We estimate that the net proceeds to us from the sale of shares of our common stock in this offering will be approximately $67.3 million, or $77.7 million if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full, assuming an initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. We intend to use the net proceeds of this offering, together with our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, for (i) developing TC-210 through the completion of our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial, (ii) developing TC-110 through a Phase 1 clinical trial and TC-220 through a Phase 1/2 clinical trial, (iii) funding continued development of our TRuC-T cell platform, (iv) funding manufacturing activities to support our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210, Phase 1 clinical trial of TC-110 and Phase 1/2 clinical trial ofTC-220 and (v) funding new and ongoing research and development activities, working capital and other general corporate purposes. See “Use of Proceeds.” |
Proposed Nasdaq Global Market symbol | “TCRR” |
Risk Factors | Investment in our common stock involves substantial risks. You should read this prospectus carefully, including the section entitled “Risk Factors” and the financial statements and the related notes to those statements included in this prospectus, before investing in our common stock. |
Certain of our existing stockholders (or their affiliates), including those affiliated with certain of our directors, have indicated an interest in purchasing an aggregate of approximately $30.0 million of shares of our common stock in this offering at the initial public offering price. However, because indications of interest are not binding agreements or commitments to purchase, the underwriters may determine to sell more, less or no shares in this offering to such stockholders, and such stockholders could determine to purchase more, less or no shares in this offering.
9
The number of shares of our common stock outstanding after this offering is based on 18,189,901 shares of our common stock outstanding as of December 31, 2018, which includes 187,608 shares of unvested restricted stock subject to repurchase by us, after giving effect to the automatic conversion of all outstanding shares of our preferred stock into an aggregate of 17,275,299 shares of common stock upon the completion of this offering and excludes:
| ∎ | 2,094,816 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of options outstanding under our 2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan (2015 Plan) at a weighted-average exercise price of $3.79 per share as of December 31, 2018; |
| ∎ | 8,017 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of outstanding options issued outside of our 2015 Plan at an exercise price of $0.74 per share as of December 31, 2018; |
| ∎ | 203,676 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of warrants to purchase common stock at a weighted-average exercise price of $0.74 per share as of December 31, 2018; |
| ∎ | 268,393 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2015 Plan as of December 31, 2018; |
| ∎ | 2,731,607 shares of common stock to be reserved for future issuance under our 2018 Stock Option and Incentive Plan to be effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part; and |
| ∎ | 300,000 shares of common stock to be reserved for future issuance under our 2018 Employee Stock Purchase Plan to be effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. |
Except as otherwise noted, all information in this prospectus:
| ∎ | gives effect to a one for 6.1938 reverse stock split of our common stock effected on February 1, 2019; |
| ∎ | assumes no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase up to 750,000 additional shares of common stock in this offering; |
| ∎ | assumes no exercise of the outstanding options and warrants described above; |
| ∎ | gives effect to the automatic conversion upon the completion of this offering of all of our outstanding shares of preferred stock into an aggregate of 17,275,299 shares of common stock; and |
| ∎ | assumes the filing of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and the effectiveness of our amended and restated bylaws, which will occur upon the closing of this offering. |
10
The following tables summarize our financial and operating data for the periods indicated. The summary statements of operations and comprehensive loss data for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017 have been derived from our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The summary statements of operations and comprehensive loss data for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018 and the summary balance sheet data as of September 30, 2018 have been derived from our unaudited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus and have been prepared on the same basis as the audited financial information in those statements. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected in the future, and results for the nine-month period ended September 30, 2018 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year ending December 31, 2018.
The summary financial information below should be read in conjunction with the information contained in “Selected Financial Information,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” our financial statements and notes thereto, and other financial information included elsewhere in this prospectus.
| YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||
| (In thousands, except share and per share data) | 2016 | 2017 | 2017 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss Data: | ||||||||||||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||
Research and development | $ | 7,670 | $ | 9,569 | $ | 6,822 | $ | 13,454 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 2,260 | 3,611 | 2,321 | 4,558 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Total operating expenses and loss from operations | (9,930 | ) | (13,180 | ) | (9,143 | ) | (18,012 | ) | ||||||||
Other income, net | 15 | 110 | 85 | 1,451 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net loss | (9,915 | ) | (13,070 | ) | (9,058 | ) | (16,561 | ) | ||||||||
Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value | (787 | ) | (1,794 | ) | (1,272 | ) | (33,568 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (10,702 | ) | $ | (14,864 | ) | $ | (10,330 | ) | $ | (50,129 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Other Comprehensive Loss: | ||||||||||||||||
Net loss | $ | (9,915 | ) | $ | (13,070 | ) | $ | (9,058 | ) | $ | (16,561 | ) | ||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments | (2 | ) | 2 | 2 | (3 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Total comprehensive loss | $ | (9,917 | ) | $ | (13,068 | ) | $ | (9,056 | ) | $ | (16,564 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net loss per share of common stock—basic and diluted (1) | $ | (38.64 | ) | $ | (39.94 | ) | $ | (28.78 | ) | $ | (83.83 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding—basic and diluted(1) | 276,976 | 372,116 | 358,914 | 597,964 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Pro forma net loss per share of common stock—basic and diluted (unaudited)(1) | $ | (2.90 | ) | $ | (3.34 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Pro forma weighted average shares of common stock outstanding—basic and diluted (unaudited)(1) | 5,132,506 | 15,014,479 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
11
| AS OF SEPTEMBER 30, 2018 | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ACTUAL | PRO FORMA (2) | PRO FORMA AS ADJUSTED (3) | |||||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | ||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 107,769 | $ | 107,769 | $ | 175,044 | ||||||
Short-term investments | 23,229 | 23,229 | 23,229 | |||||||||
Working capital(4) | 127,598 | 127,598 | 194,873 | |||||||||
Total assets | 134,668 | 134,668 | 201,943 | |||||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock | 205,500 | — | — | |||||||||
Common stock | — | 2 | 2 | |||||||||
Additional paid-in capital | — | 205,498 | 272,773 | |||||||||
Accumulated deficit | (75,033 | ) | (75,033 | ) | (75,033 | ) | ||||||
Total stockholders’ (deficit) equity | (75,036 | ) | 130,464 | 197,739 | ||||||||
| (1) | See Note 3 to our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus for an explanation of the calculations of our basic and diluted net loss per share, basic and diluted pro forma net loss per share and the shares used in computing basic and diluted net loss per share and basic and diluted pro forma net loss per share. |
| (2) | Pro forma amounts give effect to the automatic conversion of all of our outstanding shares of preferred stock into an aggregate of 17,275,299 shares of common stock upon the closing of this offering. |
| (3) | Pro forma as adjusted amounts reflect the pro forma adjustments described in footnote 2 above as well as the sale of 5,000,000 shares of our common stock in this offering at the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
| (4) | We define working capital as current assets less current liabilities. See our financial statements for further details regarding our current assets and current liabilities. |
The pro forma as adjusted information discussed above is illustrative only and will change based on the actual initial public offering price and other terms of this offering determined at pricing. A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted amount of each of cash and cash equivalents, working capital, total assets and total stockholders’ (deficit) equity by approximately $4.7 million, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. Similarly, each increase (decrease) of 1.0 million shares in the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted amount of each of cash and cash equivalents, working capital, total assets and total stockholders’ (deficit) equity by approximately $14.0 million, assuming the assumed initial public offering price remains the same and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
12
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risks described below, as well as the other information in this prospectus, including our financial statements and the related notes and the section of this prospectus titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” before you make an investment decision. The occurrence of any of the events or developments described below could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and growth prospects. As a result, the market price of our common stock could decline, and you may lose all or part of your investment in our common stock.
Risks Related to Our Financial Condition and Capital Requirements
Our limited operating history may make it difficult for you to evaluate the success of our business to date and to assess our future viability.
We are a clinical-stage immunotherapy company with a limited operating history. We commenced operations in May 2015, and our operations to date have been limited to organizing and staffing our company, business planning, raising capital, conducting discovery and research activities, filing patent applications, identifying potential product candidates, undertaking preclinical studies and establishing arrangements with third parties for the manufacture of initial quantities of our product candidates and component materials. Most of our product candidates are still in preclinical development. We have not yet demonstrated our ability to successfully initiate, conduct or complete any clinical trials, obtain marketing approvals, manufacture a commercial-scale product or arrange for a third party to do so on our behalf, or conduct sales, marketing and distribution activities necessary for successful product commercialization. Consequently, any predictions you make about our future success or viability may not be as accurate as they could be if we had a longer operating history.
In addition, as a young business, we may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other known and unknown factors. We will need to transition at some point from a company with a research and development focus to a company capable of supporting commercial activities. We may not be successful in such a transition.
We expect our financial condition and operating results to continue to fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter and year to year due to a variety of factors, many of which are beyond our control. Accordingly, you should not rely upon the results of any quarterly or annual periods as indications of future operating performance.
We have incurred significant losses since inception, and we expect to incur losses over the next several years and may not be able to achieve or sustain revenues or profitability in the future.
Investment in biopharmaceutical product development is a highly speculative undertaking and entails substantial upfront capital expenditures and significant risk that any potential product candidate will fail to demonstrate adequate effect or an acceptable safety profile, gain regulatory approval and become commercially viable. We are still in the early stages of development of our product candidates, and have not yet initiated our first clinical trial. We have no products licensed for commercial sale and have not generated any revenue from product sales to date, and we continue to incur significant research and development and other expenses related to our ongoing operations. We have financed our operations primarily through private placements of our preferred stock.
We have incurred significant net losses in each period since our inception in May 2015. For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, we reported net losses of $9.9 million and $13.1 million, respectively. For the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018, we reported net losses of $9.1 million and $16.5 million, respectively. As of September 30, 2018, we had an accumulated deficit of $75.0 million. We expect to continue to incur significant losses for the foreseeable future, and we expect these losses to increase substantially if and as we:
| ∎ | continue our research and development efforts and submit investigational new drug applications (INDs) for our lead product candidates; |
| ∎ | conduct preclinical studies and clinical trials for our current and future product candidates based on our TRuC-T cell platform; |
| ∎ | seek marketing approvals for any product candidates that successfully complete clinical trials; |
13
| ∎ | build commercial infrastructure to support sales and marketing for our product candidates; |
| ∎ | expand, maintain and protect our intellectual property portfolio; |
| ∎ | hire additional clinical, regulatory and scientific personnel; and |
| ∎ | operate as a public company. |
Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with pharmaceutical product development, we are unable to accurately predict the timing or amount of increased expenses we will incur or when, if ever, we will be able to achieve profitability. Even if we succeed in commercializing one or more of our product candidates, we will continue to incur substantial research and development and other expenditures to develop, seek regulatory approval for, and market additional product candidates. We may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other unknown factors that may adversely affect our business. The size of our future net losses will depend, in part, on the rate of future growth of our expenses and our ability to generate revenue. Our prior losses and expected future losses have had and will continue to have an adverse effect on our stockholders’ equity and working capital.
We have not generated any revenue from our product candidates and may never be profitable.
Our ability to become profitable depends upon our ability to generate revenue. To date, we have not generated any revenue from any of our product candidates. We do not expect to generate significant revenue unless or until we successfully complete clinical development and obtain regulatory approval of, and then successfully commercialize, at least one of our product candidates. Other than TC-210, all of our product candidates are in the preclinical stages of development and will require additional preclinical studies, clinical development, regulatory review and approval, substantial investment, access to sufficient commercial manufacturing capacity and significant marketing efforts before we can generate any revenue from product sales. TC-210, our most advanced mono TRuC-T cell product candidate targeting mesothelin-positive solid tumors, is in the early stages of clinical development and has not yet been evaluated in clinical trials and will require additional regulatory review and approval, substantial investment, access to sufficient commercial manufacturing capacity and significant marketing efforts before we can generate any revenue from product sales. TC-110, our monoTRuC-T cell product candidate targeting CD19-positive B-cell hematological malignancies, and TC-220 have yet to complete IND-enabling studies. Our other TRuC-T cell product candidates are in early preclinical stages. We have not yet administered any of our product candidates in humans and, as such, we face significant translational risk as our product candidates advance to the clinical stage. Our ability to generate revenue depends on a number of factors, including, but not limited to:
| ∎ | timely completion of our preclinical studies and clinical trials, which may be significantly slower or cost more than we currently anticipate and will depend substantially upon the performance of third-party contractors; |
| ∎ | our ability to complete IND-enabling studies and successfully submit INDs or comparable applications; |
| ∎ | whether we are required by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or similar foreign regulatory authorities to conduct additional clinical trials or other studies beyond those planned to support the approval and commercialization of our product candidates or any future product candidates; |
| ∎ | our ability to demonstrate to the satisfaction of the FDA and similar foreign regulatory authorities the safety, potency, purity and acceptable risk to benefit profile of our product candidates or any future product candidates; |
| ∎ | the prevalence, duration and severity of potential side effects or other safety issues experienced with our product candidates or future product candidates, if any; |
| ∎ | the timely receipt of necessary marketing approvals from the FDA and similar foreign regulatory authorities; |
| ∎ | the willingness of physicians, operators of clinics and patients to utilize or adopt any of product candidates or future product candidates to treat solid tumors and hematological malignancies; |
| ∎ | our ability and the ability of third parties with whom we contract to manufacture adequate clinical and commercial supplies of our product candidates or any future product candidates, remain in good standing with regulatory authorities and develop, validate and maintain commercially viable manufacturing processes that are compliant with current good manufacturing practices (cGMP); |
| ∎ | our ability to successfully develop a commercial strategy and thereafter commercialize our product candidates or any future product candidates in the United States and internationally, if licensed for |
14
marketing, reimbursement, sale and distribution in such countries and territories, whether alone or in collaboration with others; |
| ∎ | patient demand for our product candidates and any future product candidates, if licensed; and |
| ∎ | our ability to establish and enforce intellectual property rights in and to our product candidates or any future product candidates. |
Many of the factors listed above are beyond our control, and could cause us to experience significant delays or prevent us from obtaining regulatory approvals or commercialize our product candidates. Even if we are able to commercialize our product candidates, we may not achieve profitability soon after generating product sales, if ever. If we are unable to generate sufficient revenue through the sale of our product candidates or any future product candidates, we may be unable to continue operations without continued funding.
If we fail to obtain additional financing, we may be unable to continue our research and product development programs.
Our operations have consumed substantial amounts of cash since inception. We expect to continue to spend substantial amounts to continue the clinical development of our product candidates, including our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210 and ongoing and planned IND-enabling studies for our other product candidates. If licensed, we will require significant additional amounts in order to launch and commercialize our product candidates.
We had cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of approximately $131.0 million as of September 30, 2018. We estimate that our net proceeds from this offering will be approximately $67.3 million, based on an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, which is the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. The net proceeds of this offering and our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments may not be sufficient to fund all of our efforts that we plan to undertake.
We believe that net proceeds from this offering, together with our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, will be sufficient to fund our operations at least into 2022. However, we have based this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be wrong. Additionally, changing circumstances may cause us to consume capital significantly faster than we currently anticipate, and we may need to spend more money than currently expected because of circumstances beyond our control. Accordingly, we will need to obtain substantial additional funding in connection with our continuing operations. We cannot be certain that additional funding will be available on acceptable terms, or at all. If we are unable to raise additional capital in sufficient amounts or on terms acceptable to us, we may have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue our research and development initiatives. We could be required to seek collaborators for our product candidates at an earlier stage than otherwise would be desirable or on terms that are less favorable than might otherwise be available or relinquish or license on unfavorable terms our rights to our product candidates in markets where we otherwise would seek to pursue development or commercialization ourselves.
Any of the above events could significantly harm our business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations and cause the price of our common stock to decline.
Risks Related to the Development of Our Product Candidates
Our approach to the discovery and development of product candidates based on our TRuC-T cell platform represents a novel approach to cancer treatment, which creates significant challenges for us.
Our future success depends on the successful development of our product candidates, which target solid tumors and hematologic malignancies using the complete T cell receptor (TCR) complex without the need for human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching. Advancing our product candidates based on our innovative TRuC-T cell platform creates significant challenges for us, including:
| ∎ | educating medical personnel about the administration of TRuC-T cell therapies on a stand-alone basis or in combination with built-in immune and tumor modulators; |
| ∎ | educating medical personnel regarding the potential side effect profile of our product candidates, such as the potential adverse side effects related to cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurotoxicity or autoimmune or rheumatologic disorders; |
15
| ∎ | administering chemotherapy to patients in advance of administering our product candidates, which may increase the risk of adverse side effects; |
| ∎ | sourcing clinical and, if licensed, commercial, supplies for the materials used to manufacture and process our product candidates; |
| ∎ | manufacturing viral vectors to deliver TRuC constructs to T cells; |
| ∎ | developing a robust and reliable TRuC-T cell manufacturing process as well as a complete shipment lifecycle and supply chain, including efficiently managing shipment of patient cells from and to clinical sites, minimizing potential contamination to the cell product and effectively scaling manufacturing capacity to meet demand; |
| ∎ | managing costs of inputs and other supplies while scaling production; |
| ∎ | using medicines to manage adverse side effects of our product candidates, which may not adequately control the side effects and/or may have a detrimental impact on the potency of the treatment; |
| ∎ | obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval from the FDA for our product candidates; and |
| ∎ | establishing sales and marketing capabilities upon obtaining any regulatory approval to gain market acceptance of a novel therapy. |
In developing our product candidates, we have not exhaustively explored different options in the design of the TRuC construct and in the method for manufacturing TRuC-T cells. We may find our existing TRuC-T cells and manufacturing process may be substantially improved with future design or process changes, necessitating development of new or additional TRuC constructs and further clinical testing and delaying commercial launch of our first products. For example:
| ∎ | We have made several TRuC constructs and used preclinical studies to select product candidates to advance into clinical trials. The preclinical studies are limited in their ability to predict behavior in patients. As we gain experience working with TRuC constructs, we may decide to select other TRuC constructs for clinical development. |
| ∎ | We have used a lentiviral vector to deliver the TRuC construct to T cells. In the future, we may find that another viral vector or non-viral transfer process offers advantages. Switching from lentiviral to another delivery system would necessitate additional process development and clinical testing and delay the development of existing product candidates. |
| ∎ | The process by which patient cells are converted into a TRuC-T cell has many steps that can influence quality and activity. We have explored a subset of variables and expect to continue to improve and optimize the manufacturing process. Depending upon the nature of the process changes, we may be compelled to perform bridging studies and/or to re-start clinical development, causing delays in time to market and potentially introducing a risk of failure if new processes do not perform as expected. |
We are very early in our development efforts. Most of our product candidates are still in preclinical development. If we are unable to advance our product candidates through clinical development, obtain regulatory approval and ultimately commercialize our product candidates, or experience significant delays in doing so, our business will be materially harmed.
We are very early in our development efforts. Most of our product candidates are still in preclinical development, andTC-210, our most advanced product candidate, is still in the early stages of clinical development. Our ability to generate product revenues, which we do not expect will occur for many years, if ever, will depend heavily on the successful development and eventual commercialization of one or more of our product candidates. The success of our product candidates will depend on several factors, including the following:
| ∎ | successful completion of preclinical studies; |
| ∎ | successful initiation of clinical trials; |
| ∎ | successful patient enrollment in and completion of clinical trials; |
| ∎ | receipt and related terms of marketing approvals and licensures from applicable regulatory authorities; |
| ∎ | obtaining and maintaining patent and trade secret protection and regulatory exclusivity for our product candidates; |
| ∎ | making arrangements with third-party manufacturers, or establishing manufacturing capabilities, for both clinical and commercial supplies of our product candidates; |
16
| ∎ | establishing sales, marketing and distribution capabilities and launching commercial sales of our products, if and when approved, whether alone or in collaboration with others; |
| ∎ | acceptance of our products, if and when approved, by patients, the medical community and third-party payors; |
| ∎ | effectively competing with other cancer therapies; |
| ∎ | obtaining and maintaining third-party coverage and adequate reimbursement; |
| ∎ | maintaining a continued acceptable safety profile of our products following licensure; and |
| ∎ | effectively competing with other therapies. |
If we do not achieve one or more of these factors in a timely manner or at all, we could experience significant delays or be unable to successfully commercialize our product candidates, which would materially harm our business.
We have no experience as a company in conducting clinical trials.
We have no experience as a company in conducting clinical trials. In part because of this lack of experience, we cannot be certain that our ongoing preclinical studies will be completed on time or if the planned preclinical studies and clinical trials will begin or be completed on time, if at all. Large-scale clinical trials would require significant additional financial and management resources and reliance on third-party clinical investigators, contract research organizations (CROs) and consultants. Relying on third-party clinical investigators, CROs and consultants may force us to encounter delays that are outside of our control.
Our business is highly dependent on our lead product candidates, TC-210 and TC-110, and we must complete IND-enabling studies and clinical testing before we can seek regulatory approval and begin commercialization of any of our product candidates.
There is no guarantee that any of our product candidates will proceed in preclinical or clinical development or achieve regulatory approval. The process for obtaining marketing approval for any product candidate is very long and risky and there will be significant challenges for us to address in order to obtain marketing approval as planned or, if at all.
There is no guarantee that the results obtained in current preclinical studies or our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210 or TC-110 will be sufficient to obtain regulatory approval or marketing authorization for such product candidates. Negative results in the development of our lead product candidates may also impact our ability to obtain regulatory approval for our other product candidates, either at all or within anticipated timeframes because, although other product candidates may target different indications, the underlying technology platform, manufacturing process and development process is the same for all of our product candidates. Accordingly, a failure in any one program may affect the ability to obtain regulatory approval to continue or conduct clinical programs for other product candidates.
In addition, because we have limited financial and personnel resources and are placing significant focus on the development of our lead product candidates, we may forgo or delay pursuit of opportunities with other future product candidates that later prove to have greater commercial potential. Our resource allocation decisions may cause us to fail to capitalize on viable commercial products or profitable market opportunities. Our spending on current and future research and development programs and other future product candidates for specific indications may not yield any commercially viable future product candidates. If we do not accurately evaluate the commercial potential or target market for a particular future product candidate, we may relinquish valuable rights to those future product candidates through collaboration, licensing or other royalty arrangements in cases in which it would have been more advantageous for us to retain sole development and commercialization rights to such future product candidates.
Our preclinical studies and clinical trials may fail to demonstrate adequately the safety, potency and purity of any of our product candidates, which would prevent or delay development, regulatory approval and commercialization.
Before obtaining regulatory approvals for the commercial sale of our product candidates, including TC-210 andTC-110, we must demonstrate through lengthy, complex and expensive preclinical studies and clinical trials that our product candidates are both safe and effective for use in each target indication. Preclinical and clinical testing is expensive and can take many years to complete, and its outcome is inherently uncertain. Failure can occur at any time during the preclinical study and clinical trial processes, and, because our product candidates are in an early stage of development, there is a high risk of failure and we may never succeed in developing marketable products.
17
The results of preclinical studies and early clinical trials of our product candidates may not be predictive of the results of later-stage clinical trials. There is typically an extremely high rate of attrition from the failure of product candidates proceeding through preclinical studies and clinical trials. Product candidates in later stages of clinical trials may fail to show the desired safety, potency and purity profile despite having progressed through preclinical studies and initial clinical trials. A number of companies in the biopharmaceutical industry have suffered significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials due to lack of potency or efficacy, insufficient durability of potency or efficacy or unacceptable safety issues, notwithstanding promising results in earlier trials. Most product candidates that commence preclinical studies and clinical trials are never approved as products.
Any preclinical studies or clinical trials that we may conduct may not demonstrate the safety, potency and purity necessary to obtain regulatory approval to market our product candidates. If the results of our ongoing or future preclinical studies and clinical trials are inconclusive with respect to the safety, potency and purity of our product candidates, if we do not meet the clinical endpoints with statistical and clinically meaningful significance, or if there are safety concerns associated with our product candidates, we may be prevented or delayed in obtaining marketing approval for such product candidates. In some instances, there can be significant variability in safety, potency or purity results between different preclinical studies and clinical trials of the same product candidate due to numerous factors, including changes in trial procedures set forth in protocols, differences in the size and type of the patient populations, changes in and adherence to the clinical trial protocols and the rate of dropout among clinical trial participants. Additionally, our preclinical studies comparing our product candidates to chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells utilized CAR-T cells that we engineered, rather than the CAR-T cell therapies that are currently approved by the FDA. Although we believe, based on the results we observed in these preclinical studies, that our product candidates have the potential to improve upon the safety and efficacy of currently approved CAR-T cell therapies, these results may not be predictive of the outcome of our future preclinical studies and clinical trials, including any potential preclinical studies and clinical trials that may compare our product candidates to FDA-approved CAR-T cells.
Clinical development involves a lengthy and expensive process with an uncertain outcome, and results of earlier studies and trials may not be predictive of future clinical trial results. If our preclinical studies and clinical trials are not sufficient to support regulatory approval of any of our product candidates, we may incur additional costs or experience delays in completing, or ultimately be unable to complete, the development of such product candidate.
We cannot be certain that our preclinical study and clinical trial results will be sufficient to support regulatory approval of our product candidates. Clinical testing is expensive and can take many years to complete, and its outcome is inherently uncertain. Human clinical trials are expensive and difficult to design and implement, in part because they are subject to rigorous regulatory requirements. Failure or delay can occur at any time during the clinical trial process.
We may experience delays in obtaining the FDA’s authorization to initiate clinical trials under future INDs, completing ongoing preclinical studies of our other product candidates, and initiating our planned preclinical studies and clinical trials. Additionally, we cannot be certain that preclinical studies or clinical trials for our product candidates will begin on time, not require redesign, enroll an adequate number of subjects on time, or be completed on schedule, if at all. Clinical trials can be delayed or terminated for a variety of reasons, including delays or failures related to:
| ∎ | the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities disagreeing as to the design or implementation of our clinical trials; |
| ∎ | delays in obtaining regulatory approval to commence a clinical trial; |
| ∎ | reaching agreement on acceptable terms with prospective CROs and clinical trial sites, the terms of which can be subject to extensive negotiation and may vary significantly among different CROs and clinical trial sites; |
| ∎ | obtaining institutional review board (IRB) approval at each clinical trial site; |
| ∎ | recruiting an adequate number of suitable patients to participate in a clinical trial; |
| ∎ | having subjects complete a clinical trial or return for post-treatment follow-up; |
| ∎ | clinical trial sites deviating from clinical trial protocol or dropping out of a clinical trial; |
18
| ∎ | addressing subject safety concerns that arise during the course of a clinical trial; |
| ∎ | adding a sufficient number of clinical trial sites; or |
| ∎ | obtaining sufficient product supply of product candidate for use in preclinical studies or clinical trials from third-party suppliers. |
We may experience numerous adverse or unforeseen events during, or as a result of, preclinical studies and clinical trials that could delay or prevent our ability to receive marketing approval or commercialize our product candidates, including:
| ∎ | we may receive feedback from regulatory authorities that requires us to modify the design of our clinical trials; |
| ∎ | clinical trials of our product candidates may produce negative or inconclusive results, and we may decide, or regulators may require us, to conduct additional clinical trials or abandon our research efforts for our other product candidates; |
| ∎ | the number of patients required for clinical trials of our product candidates may be larger than we anticipate, enrollment in these clinical trials may be slower than we anticipate or participants may drop out of our clinical trials at a higher rate than we anticipate; |
| ∎ | our third-party contractors may fail to comply with regulatory requirements, fail to maintain adequate quality controls or be unable to provide us with sufficient product supply to conduct and complete preclinical studies or clinical trials of our product candidates in a timely manner, or at all; |
| ∎ | we or our investigators might have to suspend or terminate clinical trials of our product candidates for various reasons, including non-compliance with regulatory requirements, a finding that our product candidates have undesirable side effects or other unexpected characteristics or a finding that the participants are being exposed to unacceptable health risks; |
| ∎ | the cost of clinical trials of our product candidates may be greater than we anticipate; |
| ∎ | the quality of our product candidates or other materials necessary to conduct preclinical studies or clinical trials of our product candidates may be insufficient or inadequate; |
| ∎ | regulators may revise the requirements for approving our product candidates, or such requirements may not be as we anticipate; and |
| ∎ | future collaborators may conduct clinical trials in ways they view as advantageous to them but that are suboptimal for us. |
If we are required to conduct additional clinical trials or other testing of our product candidates beyond those that we currently contemplate, if we are unable to successfully complete clinical trials of our product candidates or other testing, if the results of these trials or tests are not positive or are only moderately positive or if there are safety concerns, our business and results of operations may be adversely affected and we may incur significant additional costs. In addition, costs to treat patients with relapsed or refractory cancer and to treat potential side effects that may result from our product candidates can be significant. Accordingly, our clinical trial costs are likely to be significantly higher than those for more conventional therapeutic technologies or drug product candidates.
We could also encounter delays if a clinical trial is suspended or terminated by us, by the IRBs of the institutions in which such clinical trials are being conducted, by the Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) for such clinical trial or by the FDA or other regulatory authorities. Such authorities may suspend or terminate a clinical trial due to a number of factors, including failure to conduct the clinical trial in accordance with regulatory requirements or our clinical trial protocols, inspection of the clinical trial operations or trial site by the FDA or other regulatory authorities resulting in the imposition of a clinical hold, unforeseen safety issues or adverse side effects, failure to demonstrate a benefit from the product candidates, changes in governmental regulations or administrative actions or lack of adequate funding to continue the clinical trial.
If we experience delays in the completion, or termination, of any preclinical study or clinical trial of our product candidates, the commercial prospects of our product candidates may be harmed, and our ability to generate revenues from any of these product candidates will be delayed or not realized at all. In addition, any delays in completing our preclinical studies or clinical trials may increase our costs, slow down our product candidate
19
development and approval process and jeopardize our ability to commence product sales and generate revenues. Any of these occurrences may significantly harm our business, financial condition and prospects. In addition, many of the factors that cause, or lead to, a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical trials may also ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our product candidates. If one or more of our product candidates generally prove to be ineffective, unsafe or commercially unviable, our entire pipeline and TRuC-T cell platform would have little, if any, value, which would have a material and adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We may rely on third parties to manufacture our clinical product supplies, and we may rely on third parties to produce and process our product candidates, if licensed.
We do not currently own any facility that may be used as our clinical scale manufacturing and processing facility and expect to rely on outside vendors to manufacture supplies and process our product candidates. We have not yet caused any product candidates to be manufactured or processed on a commercial scale and may not be able to do so for any of our product candidates. We plan to make changes as we work to optimize the manufacturing process. For example, we may switch or be required to switch from research-grade materials to commercial-grade materials in order to get regulatory approval of our product candidates. We cannot be sure that even minor changes in the process will result in therapies that are safe and effective and licensed for commercial sale.
The facilities used by our contract manufacturers to manufacture our product candidates must be approved by the FDA or other foreign regulatory authorities following inspections that will be conducted after we submit an application to the FDA or other foreign regulatory authorities. We may not control the manufacturing process of, and may be completely dependent on, our contract manufacturing partners for compliance with cGMPs and any other regulatory requirements of the FDA or other regulatory authorities for the manufacture of our product candidates. We have no control over the ability of our contract manufacturers to maintain adequate quality control, quality assurance and qualified personnel. If the FDA or a comparable foreign regulatory authority does not approve these facilities for the manufacture of our product candidates or if it withdraws any approval in the future, we may need to find alternative manufacturing facilities, which would significantly impact our ability to develop, obtain regulatory approval for or market our product candidates, if licensed.
We cannot guarantee that our product candidates will show any functionality in the solid tumor microenvironment.
There are no approvedCAR-T or engineered TCR-T cell immunotherapies for solid tumors. We believe our TruC-T cell product candidates will be effective against solid tumors. While we plan to develop product candidates for use in solid tumors, including TC-210, we cannot guarantee that our product candidates will show any functionality in the solid tumor microenvironment. The cellular environment in which solid tumor cells thrive is generally hostile to T cells due to factors such as the presence of immunosuppressive cells, humoral factors and limited access to nutrients. Our TRuC-T cell-based product candidates may not be able to access the solid tumor, and even if they do, they may not be able to exert anti-tumor effects in a hostile tumor microenvironment. In addition, the safety profile of our product candidates may differ in a solid tumor setting. As a result, our product candidates may not demonstrate potency in solid tumors. If we are unable to make our product candidates function in solid tumors, our development plans and business may be significantly harmed.
Since the number of patients that we plan to dose in our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210 is small, the results from such clinical trial, once completed, may be less reliable than results achieved in larger clinical trials, which may hinder our efforts to obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates.
In our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210, we plan to evaluate the safety profile of TC-210 and establish the recommended Phase 2 dose in approximately 50 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), ovarian cancer, malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma and cholangiocarcinoma. The preliminary results of clinical trials with smaller sample sizes, such as our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210, can be disproportionately influenced by various biases associated with the conduct of small clinical trials, such as the potential failure of the smaller sample size to accurately depict the features of the broader patient population, which limits the ability to generalize the results across a broader community, thus making the clinical trial results less reliable than clinical trials with a larger number of patients. As a result, there may be less certainty that such product candidates would achieve a statistically significant effect in any future clinical trials. If we conduct any future clinical trials of TC-210, we may not achieve a statistically significant result or the same level of statistical significance, if any, that we might have anticipated based on the results observed in our initial Phase 1/2 clinical trial.
20
We may not be able to file INDs or IND amendments to commence additional clinical trials on the timelines we expect, and even if we are able to, the FDA may not permit us to proceed.
We expect to submit an IND for TC-110 in the second half of 2019 and for TC-220 in early 2020. However, we may not be able to file such INDs on the timelines we expect. For example, we may experience manufacturing delays or other delays with IND-enabling studies. In July 2018, for example, a power failure that occurred during a manufacturing run to produce virus for our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210 caused us to abandon that manufacturing run and resulted in a month-long delay in the process of manufacturing the requisite virus to support our IND filing for TC-210 and consequently a delay in the IND filing itself. Moreover, we cannot be sure that submission of an IND will result in the FDA allowing further clinical trials to begin, or that, once begun, issues will not arise that suspend or terminate clinical trials. Additionally, even if such regulatory authorities agree with the design and implementation of the clinical trials set forth in an IND, we cannot guarantee that such regulatory authorities will not change their requirements in the future. These considerations also apply to new clinical trials we may submit as amendments to existing INDs.
Our product candidates may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties that could halt their clinical development, prevent their regulatory approval, require expansion of the trial size, limit their commercial potential, or result in significant negative consequences.
Undesirable side effects caused by our product candidates could cause us or regulatory authorities, including IRBs, to interrupt, delay, or halt clinical trials and could result in a more restrictive label or the delay or denial of regulatory approval by the FDA or other comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Further, clinical trials by their nature utilize a sample of the potential patient population. With a limited number of subjects and limited duration of exposure, rare and severe side effects of our product candidates may only be uncovered with a significantly larger number of patients exposed to the drug. Because of our planned dose escalation design for our clinical trials, undesirable side effects could also result in an expansion in the size of our clinical trials, increasing the expected costs and timeline of our clinical trials. Additionally, results of our clinical trials could reveal a high and unacceptable severity and prevalence of side effects or unexpected characteristics, which may stem from our therapies specifically or may be due to an illness from which the clinical trial subject is suffering.
Autoimmunity may occur after TRuC-T cell treatment. TRuC-T cells are generated from a patient’s own T cells isolated from their peripheral blood. There is a theoretical risk that this process will expand a patient’s own T cell that has autoreactivity, or that may recognize healthy cells, and upon re-infusion may trigger an autoimmune reaction resulting in damage to normal tissues and potentially even death.
Autoimmune reaction triggered by an interaction between a patient’s naturally occurring antibodies and engineered T cells is a theoretical safety risk of product candidates we develop using our TRuC-T cell platform. If a patient’s self-generated antibodies were directed to a target expressed on the surface of cells in normal tissue (autoantibodies), engineered T cells would be directed to attack these same tissues, potentially resulting in off-tumor effects. These autoantibodies may be present whether or not the patient has an active autoimmune disease. In our clinical testing, we plan to take steps to minimize the likelihood that this occurs, for example by excluding patients with a history of severe autoimmune disease from our trials. There is no guarantee, however, that we will not observe autoimmune reactions in the future and no guarantee that if we do, that we will be able to implement interventions to address the risk.
Immunogenicity, which is the reaction between a patient’s immune system and a foreign protein outside of the autoimmune context, is an additional theoretical safety risk of product candidates we develop using our TRuC-T cell platform. Patients’ immune systems may recognize the TRuC construct on the TRuC-T cell as a foreign protein and fight against it, potentially rendering it ineffective, or even provoking an allergic/anaphylactoid response or other adverse side effects. The immunogenic potential of novel therapeutics like TRuC-T cells is difficult to predict. There is no guarantee that we will not observe immunogenic reactions in the future and no guarantee that if we do, that we will be able to implement interventions to address the risk.
If unacceptable toxicities arise in the development of our product candidates, we could suspend or terminate our clinical trials or the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities, or local regulatory authorities such as IRBs, could order us to cease clinical trials. Competent national health authorities, such as the FDA, could also deny approval of our product candidates for any or all targeted indications. Treatment-related side effects could also affect patient recruitment or the ability of enrolled patients to complete the clinical trial or result in potential product
21
liability claims. In addition, these side effects may not be appropriately recognized or managed by the treating medical staff, as toxicities resulting from T cell therapy are not normally encountered in the general patient population and by medical personnel. We expect to have to train medical personnel using our product candidates to understand the side effect profile of our product candidates for both our planned clinical trials and upon any commercialization of any product candidates, if licensed. Inadequate training in recognizing or managing the potential side effects of our product candidates could result in patient deaths. Any of these occurrences may significantly harm our business, financial condition and prospects.
Our product candidates may target healthy cells expressing target antigens leading to potentially fatal adverse effects.
Our product candidates target specific antigens that are also expressed on healthy cells. For example, our lead product candidate, TC-210, targets mesothelin, an antigen commonly found on mesotheliomas, ovarian cancers, and NSCLC, as well in healthy cells that line the pleura, pericardium and peritoneum. TC-110 targets CD19, which is overexpressed in several cancers includingB-cell leukemias and lymphomas, but is also expressed by normalB-cells. Our product candidates may target healthy cells, leading to serious and potentially fatal adverse effects. In our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial of TC-210, we plan to use a dose escalation model to closely monitor the effect of TC-210 on vital organs and other potential side effects. In clinical testing of TC-110, we also plan to closely monitor the effect of TC-110 on normalB-cells that express CD19 and for other side effects. Even though we intend to closely monitor the side effects of our product candidates in both preclinical studies and clinical trials, we cannot guarantee that products will not target and kill healthy cells.
Our product candidates may have serious and potentially fatal cross-reactivity to other peptides or protein sequences within the body.
Our product candidates may recognize and bind to a peptide unrelated to the target antigen to which it is designed to bind. If this peptide is expressed within normal tissues, our product candidates may target and kill the normal tissue in a patient, leading to serious and potentially fatal adverse effects. Detection of any cross-reactivity may halt or delay any ongoing clinical trials for any TRuC-T cell based product candidate and prevent or delay regulatory approval. Unknown cross-reactivity of the TRuC-T cell binding domain to related proteins could also occur. We have also developed a preclinical screening process to identify cross-reactivity of the TRuC-T cell binders. Any cross-reactivity that impacts patient safety could materially impact our ability to advance our product candidates into clinical trials or to proceed to marketing approval and commercialization.
The viral vectors used to manufacture our TRuC-T cells may incorrectly modify the genetic material of a patient’s T cells, potentially triggering the development of a new cancer or other adverse events.
Our TRuC-T cells are manufactured by using a viral vector to insert genetic information encoding the TRuC construct into the patient’s T cells. The TRuC construct is then integrated into the natural TCR complex and transported to the surface of the patient’s T cells. Because the viral vector modifies the genetic information of the T cell, there is a theoretical risk that modification will occur in the wrong place in the T cell’s genetic code, leading to vector-related insertional oncogenesis, and causing the T cell to become cancerous. If the cancerous T cell is then administered to the patient with the TRuC-T cells, the cancerous T cell could trigger the development of a new cancer in the patient. We use lentiviral vectors to insert genetic information into T cells, which we believe have a lower risk of insertional oncogenesis as opposed to other types of viral vectors. However, the risk of insertional oncogenesis remains a concern for gene therapy and we cannot assure that it will not occur in any of our ongoing or planned preclinical studies or clinical trials. There is also the potential risk of delayed adverse events following exposure to gene therapy products due to persistent biological activity of the genetic material or other components of vectors used to carry the genetic material. The FDA has stated that lentiviral vectors possess characteristics that may pose high risks of delayed adverse events. If any such adverse events occur, further advancement of our preclinical studies or clinical trials could be halted or delayed, which would have a material adverse effect on our business and operations.
22
If we encounter difficulties enrolling patients in our clinical trials, our clinical development activities could be delayed or otherwise adversely affected.
We may experience difficulties in patient enrollment in our clinical trials for a variety of reasons. The timely completion of clinical trials in accordance with their protocols depends on, among other things, our ability to enroll a sufficient number of patients who remain in the clinical trial until its conclusion. The enrollment of patients depends on many factors, including:
| ∎ | the patient eligibility criteria defined in the clinical trial protocol; |
| ∎ | the size of the patient population required for analysis of the clinical trial’s primary endpoints; |
| ∎ | the proximity of patients to clinical trial sites; |
| ∎ | the design of the clinical trial; |
| ∎ | our ability to recruit clinical trial investigators with the appropriate competencies and experience; |
| ∎ | our ability to obtain and maintain patient consents; |
| ∎ | reporting of the preliminary results of any of our clinical trials; and |
| ∎ | the risk that patients enrolled in clinical trials will drop out of the clinical trials before the manufacturing and infusion of our product candidates or clinical trial completion. |
In addition, our clinical trials will compete with other clinical trials for product candidates that are in the same therapeutic areas as our product candidates, and this competition will reduce the number and types of patients available to us because some patients who might have opted to enroll in our clinical trials may instead opt to enroll in a clinical trial being conducted by one of our competitors. Since the number of qualified clinical investigators is limited, we expect to conduct some of our clinical trials at the same clinical trial sites that some of our competitors use, which will reduce the number of patients who are available for our clinical trials at such clinical trial sites. Moreover, because our product candidates represent a departure from more commonly used methods for cancer treatment, potential patients and their doctors may be inclined to use conventional therapies, such as chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, rather than enroll patients in any future clinical trial. Additionally, because some of our clinical trials are in patients with relapsed/refractory cancer, the patients are typically in the late stages of their disease and may experience disease progression independent from our product candidates, making them unevaluable for purposes of the clinical trial and requiring additional patient enrollment.
Delays in completing patient enrollment may result in increased costs or may affect the timing or outcome of our ongoing and planned clinical trials, which could prevent completion or commencement of these clinical trials and adversely affect our ability to advance the development of our product candidates.
Manufacturing and administering our product candidates is complex and we may encounter difficulties in production, particularly with respect to process development or scaling up of our manufacturing capabilities. If we encounter such difficulties, our ability to provide supply of our TRuC-T cells for clinical trials or for commercial purposes could be delayed or stopped.
The process of manufacturing and administering our product candidates is complex and highly regulated. The manufacture of our product candidates involves complex processes, including the manufacture of a lentiviral delivery vector containing the genetic information for our TRuC construct and manufacturing T cells containing the TRuC construct for the final product candidates. More specifically, the manufacture of our product candidates includes harvesting white blood cells from the patient, isolating certain T cells from the white blood cells, combining patient T cells with our lentiviral delivery vector through a process known as transduction, expanding the transduced T cells to obtain the desired dose, and ultimately infusing the modified T cells back into the patient’s body. As a result of the complexities entailed in this process, our manufacturing and supply costs are likely to be higher than those at more traditional manufacturing processes and the manufacturing process is less reliable and more difficult to reproduce. Additionally, the number of facilities that are capable of harvesting patients’ cells for the manufacture of our product candidates and other autologous cell therapy products and product candidates is limited. As the number of autologous cell therapy products and product candidates increases, the limited number of facilities capable of harvesting patients’ cells could result in delays in the manufacture and administration of our product candidates.
We rely on third parties for the manufacture of our lentiviral vectors and our product candidates. These third party manufacturers may incorporate their own proprietary processes into our lentiviral vector and product candidate
23
manufacturing processes. We have limited control and oversight of a third party’s proprietary process, and a third party may elect to modify its process without our consent or knowledge. These modifications could negatively impact our manufacturing, including product loss or failure that requires additional manufacturing runs or a change in manufacturer, both of which could significantly increase the cost of and significantly delay the manufacture of our product candidates.
Our manufacturing process is and will be susceptible to product loss or failure due to logistical issues, including manufacturing issues associated with the differences in patients’ white blood cells, interruptions in the manufacturing process, contamination, equipment or reagent failure, power failures, supplier error and variability in patient characteristics. For example, in July 2018, a power failure that occurred during a manufacturing run to produce virus for our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial ofTC-210 caused us to abandon that run, and resulted in a month-long delay in the process of manufacturing the requisite virus to support our IND filing forTC-210 and consequently a delay in the IND filing itself. Even minor deviations from normal manufacturing processes could result in reduced production yields, product defects and other supply disruptions. If for any reason we lose a patient’s white blood cells, or such material gets contaminated or processing steps fail at any point, the manufacturing process of the TRuC-T cells for that patient will need to be restarted and the resulting delay may adversely affect that patient’s outcome. If microbial, viral or other contaminations are discovered in our product candidates or in the manufacturing facilities in which our product candidates are made or administered, such manufacturing facilities may need to be closed for an extended period of time to investigate and remedy the contamination.
As our product candidates progress through preclinical studies and clinical trials towards licensure and commercialization, it is expected that various aspects of the manufacturing and administration process will be altered in an effort to optimize processes and results. We have already identified some improvements to our manufacturing and administration processes, but these changes may not achieve the intended objectives, and could cause our product candidates to perform differently and affect the results of planned clinical trials or other future clinical trials. In addition, such changes may require amendments to be made to regulatory applications which may further delay the timeframes under which modified manufacturing processes can be used for any of our product candidates.
Developing a commercially viable process is a difficult and uncertain task, and there are risks associated with scaling to the level required for advanced clinical trials or commercialization, including, among others, increased costs, potential problems with process scale-out, process reproducibility, stability issues, lot consistency, and timely availability of reagents or raw materials. Competitors have had difficulty reliably producing T-cell therapies in the commercial setting. If we experience similar challenges manufacturing product candidates to approved specifications, this may limit our product candidates’ utilization and our ability to receive payment for these product candidates once approved. We may ultimately be unable to reduce the expenses associated with our product candidates to levels that will allow us to achieve a profitable return on investment.
We do not have our own clinical-scale manufacturing facility and are currently reliant on a limited number of manufacturers for our lentiviral vector and a single manufacturer to provide our needs for producing our TRuC-T cell product candidates. We are in the process of adding manufacturing capacity to support larger clinical trials for our product candidates and have contracted with Cell Therapy Catapult Limited (Catapult) to occupy a suite in their GMP manufacturing center in Stevenage, United Kingdom, which we expect to be operational in the second half of 2019. We plan to pursue additional manufacturing capacity in the United States and in Europe to meet our future demands and may build our own manufacturing capabilities to meet the patient demand for our product candidates. These third-party manufacturing providers may not be able to provide adequate resources or capacity to meet our needs.
We plan to establish our own manufacturing facility and infrastructure in addition to or in lieu of relying on third parties for the manufacture of our product candidates and the use of third party manufacturing suites, which will be costly, time-consuming, and which may not be successful.
We are in the process of adding manufacturing capacity within Catapult’s GMP manufacturing center for our larger clinical trials and we may establish our own commercial manufacturing facility to mitigate our reliance on third-party vendors and ensure we can manage the supply chain, change control and reduction of costs and other benefits. The establishment of our own commercial manufacturing facility would be a costly and time-consuming process that we expect to require additional capital to fund and take several years before becoming operational.
24
We have no experience as a company in setting up, building or managing a manufacturing facility or manufacturing suite, and may never be successful in developing our own manufacturing suite, manufacturing facility or manufacturing capability. We will need to hire additional personnel to manage our operations and facilities and develop the necessary infrastructure to continue the research and development, and eventual commercialization, if licensed, of our product candidates. If we fail to recruit the required personnel and generally manage our growth effectively or fail to select the correct location, the development and production of our product candidates could be curtailed or delayed. Even if we are successful in establishing a manufacturing suite or manufacturing facility, our manufacturing capabilities could be affected by cost-overruns, unexpected delays, equipment failures, labor shortages, natural disasters, power failures and numerous other factors that could prevent us from realizing the intended benefits of our manufacturing strategy and have a material adverse effect on our business.
In addition, the FDA, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and other foreign regulatory authorities may require us to submit samples of any lot of any licensed product together with the protocols showing the results of applicable tests at any time. Under some circumstances, the FDA, the EMA or other foreign regulatory authorities may require that we not distribute a lot until the relevant agency authorizes its release. Slight deviations in the manufacturing process, including those affecting quality attributes and stability, may result in unacceptable changes in the product that could result in lot failures or product recalls. Lot failures or product recalls could cause us to delay product launches or clinical trials, which could be costly to us and otherwise harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. Problems in our manufacturing process could restrict our ability to meet market demand for our products.
We also may encounter problems hiring and retaining the experienced scientific, quality-control and manufacturing personnel needed to operate our manufacturing processes, which could result in delays in production or difficulties in maintaining compliance with applicable regulatory requirements.
Any problems in our manufacturing process or facilities could make us a less attractive collaborator for potential partners, including larger pharmaceutical companies and academic research institutions, which could limit our access to additional attractive development programs.
We may have difficulty validating our manufacturing process as we manufactureTRuC-T cells from an increasingly diverse patient population for our clinical trials.
During our development of the manufacturing process, our TRuC-T cells have demonstrated consistency from lot to lot and from donor to donor. However, our sample size is small and the starting material is from healthy donors. Once we have experience with working with white blood cells taken from our patient population, we may encounter unforeseen difficulties due to starting with material from donors who are not healthy, including challenges inherent in harvesting white blood cells from unhealthy patients.
Although we believe our current manufacturing process is scalable for commercialization, we may encounter challenges in validating our process due to the heterogeneity of the product starting material. However, we anticipate that during the early phases of our clinical trials we will be able to adapt our process to account for these differences resulting in a more robust process. We cannot guarantee that any other issues relating to the heterogeneity of the starting material will not impact our ability to commercially manufacturing our product candidates.
The market opportunities for our product candidates may be relatively small as it will be limited to those patients who are ineligible for or have failed prior treatments and our estimates of the prevalence of our target patient populations may be inaccurate.
Cancer therapies are sometimes characterized as first line, second line, or third line, and the FDA often approves new therapies initially only for a particular line of use. When cancer is detected early enough, first line therapy is sometimes adequate to cure the cancer or prolong life without a cure. Whenever first line therapy, usually chemotherapy, antibody drugs, tumor-targeted small molecules, hormone therapy, radiation therapy, surgery, or a combination of these, proves unsuccessful, second line therapy may be administered. Second line therapies often consist of more chemotherapy, radiation, antibody drugs, tumor-targeted small molecules, or a combination of these. Third line therapies can include hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in certain cancers, chemotherapy, antibody drugs and small molecule tumor-targeted therapies, more invasive forms of surgery and new technologies. We expect to initially seek approval of our product candidates in most instances at least as a second or third line therapy, for use in patients with relapsed or refractory metastatic cancer. Subsequently, for those product candidates that prove
25
to be sufficiently safe and beneficial, if any, we would expect to seek approval as a second line therapy and potentially as a first line therapy, but there is no guarantee that our product candidates, even if licensed as a second or third or subsequent line of therapy, would be licensed for an earlier line of therapy, and, prior to any such approvals, we may have to conduct additional clinical trials. Consequently, the potentially addressable patient population for our product candidates may be extremely limited or may not be amenable to treatment with our product candidates.
Our projections of both the number of people who have the cancers we are targeting, as well as the subset of people with these cancers in a position to receive a particular line of therapy and who have the potential to benefit from treatment with our product candidates, are based on our beliefs and estimates. These estimates have been derived from a variety of sources, including scientific literature, surveys of clinics, patient foundations or market research, and may prove to be incorrect. Further, new therapies may change the estimated incidence or prevalence of the cancers that we are targeting. Consequently, even if our product candidates are approved for a second or third line of therapy, the number of patients that may be eligible for treatment with our product candidates may turn out to be much lower than expected.
Our product candidates rely on the use of protein binding domains, or binders, to target specific cancers, which we may develop or which may be developed by third parties. We are limited in our ability to apply our product candidates to a wider range of potential target cancers by our ability to develop, partner for or acquire these binders on commercially reasonable terms.
TRuC-T cell therapies require the use of antigen-specific protein binding domains, or binders, which guide the TRuC-T cells and bind to the antigens on the surface of a tumor to target specific types of cancers. Our ability to develop and commercialize our product candidates will depend on our ability to develop these binders or partner for such binders on commercially reasonable terms for use in clinical trials as well as the availability of such binders for use in commercialized products, if licensed. For example, we have a non-exclusive license for the mesothelin binder incorporated into the TRuC construct for TC-210 from Harpoon Therapeutics, Inc. (Harpoon). However, we cannot be certain that our Harpoon license or potential future collaborations will provide us with a steady supply of binders that we can utilize in combination with the TRuC construct to develop future product candidates. If we are unable to enter into such collaborations on commercially reasonable terms or fail to realize the benefits of any such collaboration, we may be limited to using antibody fragments that we are able to independently develop which may limit the ability of our product candidates to target and kill cancer cells.
The failure to enter into a successful collaboration or to develop our own binders may delay our development timelines, increase our costs and jeopardize our ability to develop future product candidates as a commercially viable drug, which could result in delays in product development and harm our business.
We currently have no marketing and sales organization and have no experience in marketing products. If we are unable to establish marketing and sales capabilities or enter into agreements with third parties to market and sell our product candidates, if licensed, we may not be able to generate product revenue.
We currently have no sales, marketing or distribution capabilities and have no experience in marketing products. We intend to develop an in-house marketing organization and sales force, which will require significant capital expenditures, management resources and time. We will have to compete with other pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies to recruit, hire, train and retain marketing and sales personnel.
If we are unable or decide not to establish internal sales, marketing and distribution capabilities, we will pursue collaborative arrangements regarding the sales and marketing of our products, if licensed. However, there can be no assurance that we will be able to establish or maintain such collaborative arrangements, or if we are able to do so, that they will have effective sales forces. Any revenue we receive will depend upon the efforts of such third parties, which may not be successful. We may have little or no control over the marketing and sales efforts of such third parties and our revenue from product sales may be lower than if we had commercialized our product candidates ourselves. We also face competition in our search for third parties to assist us with the sales and marketing efforts of our product candidates.
There can be no assurance that we will be able to develop in-house sales and distribution capabilities or establish or maintain relationships with third-party collaborators to commercialize any product in the United States or overseas.
26
A variety of risks associated with marketing our product candidates internationally could materially adversely affect our business.
We plan to seek regulatory approval of our product candidates outside of the United States and, accordingly, we expect that we will be subject to additional risks related to operating in foreign countries if we obtain the necessary approvals, including:
| ∎ | differing regulatory requirements in foreign countries; |
| ∎ | unexpected changes in tariffs, trade barriers, price and exchange controls and other regulatory requirements; |
| ∎ | economic weakness, including inflation, or political instability in particular foreign economies and markets; |
| ∎ | compliance with tax, employment, immigration and labor laws for employees living or traveling abroad; |
| ∎ | foreign taxes, including withholding of payroll taxes; |
| ∎ | foreign currency fluctuations, which could result in increased operating expenses and reduced revenue, and other obligations incident to doing business in another country; |
| ∎ | difficulties staffing and managing foreign operations; |
| ∎ | workforce uncertainty in countries where labor unrest is more common than in the United States; |
| ∎ | potential liability under the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977 or comparable foreign regulations; |
| ∎ | challenges enforcing our contractual and intellectual property rights, especially in those foreign countries that do not respect and protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as the United States; |
| ∎ | production shortages resulting from any events affecting raw material supply or manufacturing capabilities abroad; and |
| ∎ | business interruptions resulting from geo-political actions, including war and terrorism. |
These and other risks associated with international operations may materially adversely affect our ability to attain or maintain profitable operations.
We face significant competition, and our operating results will suffer if we fail to compete effectively.
The biopharmaceutical industry is characterized by intense competition and rapid innovation. Our competitors may be able to develop other products or drugs that are able to achieve similar or better results. Our potential competitors include larger biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies with greater resources than us, academic institutions, governmental agencies, public and private research institutions and early stage or smaller companies. Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial, technical and other resources, such as larger research and development staff, experienced marketing and manufacturing organizations and well-established sales forces. In addition, many of these competitors are active in seeking patent protection and licensing arrangements in anticipation of collecting royalties for use of technology that they have developed. Mergers and acquisitions in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated in our competitors. Competition may increase further as a result of advances in the commercial applicability of technologies and greater availability of capital for investment in these industries. Our competitors, either alone or with collaborative partners, may succeed in developing, acquiring or licensing on an exclusive basis drug or biologic products that are more effective, safer, more easily commercialized or less costly than our product candidates or may develop proprietary technologies or secure patent protection that we may need for the development of our technologies and products. We believe the key competitive factors that will affect the development and commercial success of our product candidates are safety, potency, purity, tolerability, reliability, convenience of use, price and reimbursement.
Specifically, by genetically engineering T cell products, we face significant competition in both the chimeric antigen receptor technology and TCR space from multiple companies, including Novartis AG, Kite Pharma Inc. (recently acquired by Gilead Sciences, Inc.), Adaptimmune Therapeutics PLC, Juno Therapeutics, Inc. (recently acquired by Celgene Corporation), bluebird bio, Inc., Bayer AG, Selecta Biosciences, Inc. and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Even if we obtain regulatory approval of our product candidates, the availability and price of our competitors’ products could limit the demand and the price we are able to charge for our product candidates. We may not be able to implement our business plan if the acceptance of our product candidates is inhibited by price competition or the reluctance of physicians to switch from existing methods of treatment to our product candidates, or if physicians
27
switch to other new drug or biologic products or choose to reserve our product candidates for use in limited circumstances. For additional information regarding our competition, see “Business—Competition.”
Risks Related to Government Regulation
The FDA regulatory approval process is lengthy and time-consuming, and we may experience significant delays in the clinical development and regulatory approval of our product candidates.
We have not previously submitted a Biologics License Application (BLA) to the FDA or similar licensure applications to comparable foreign regulatory authorities. A BLA must include extensive preclinical and clinical data and supporting information to establish the product candidate’s safety, purity and potency for each desired indication. The BLA must also include significant information regarding the manufacturing controls for the product. We expect the novel nature of our product candidates to create further challenges in obtaining regulatory approval. Accordingly, the regulatory approval pathway for our product candidates may be uncertain, complex, expensive and lengthy, and licensure may not be obtained.
We may also experience delays in completing planned clinical trials for a variety of reasons, including delays related to:
| ∎ | the availability of financial resources to commence and complete the planned trials; |
| ∎ | reaching agreement on acceptable terms with prospective CROs and clinical trial sites, the terms of which can be subject to extensive negotiation and may vary significantly among different CROs and clinical trial sites; |
| ∎ | obtaining approval at each clinical trial site by an IRB or ethics committee; |
| ∎ | recruiting suitable patients to participate in a clinical trial; |
| ∎ | having patients complete a clinical trial or return for post-treatment follow-up; |
| ∎ | clinical trial sites deviating from trial protocol or dropping out of a trial; |
| ∎ | adding new clinical trial sites; or |
| ∎ | manufacturing sufficient quantities of qualified materials under cGMPs, including current Good Tissue Practices (cGTPs), and applying them on a subject by subject basis for use in clinical trials. |
We could also experience delays if physicians encounter unresolved ethical issues associated with enrolling patients in clinical trials of our product candidates in lieu of prescribing existing treatments that have established safety, efficacy, potency and purity profiles. Further, a clinical trial may be suspended or terminated by us, the IRBs for the institutions in which such trials are being conducted, the Data Monitoring Committee for such trial, or by the FDA or other regulatory authorities due to a number of factors, including failure to conduct the clinical trial in accordance with regulatory requirements or our clinical protocols, inspection of the clinical trial operations or trial site by the FDA or other regulatory authorities resulting in the imposition of a clinical hold, unforeseen safety issues or adverse side effects, failure to demonstrate a benefit from using a product candidate, changes in governmental regulations or administrative actions or lack of adequate funding to continue the clinical trial. If we experience termination of, or delays in the completion of, any clinical trial of our product candidates, the commercial prospects for our product candidates will be harmed, and our ability to generate product revenue will be delayed. In addition, any delays in completing our clinical trials will increase our costs, slow down our product development and approval process and jeopardize our ability to commence product sales and generate revenue.
Securing regulatory approval also requires the submission of information about the biologic manufacturing process and inspection of manufacturing facilities by the relevant regulatory authority. The FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may fail to approve our manufacturing processes or facilities, whether run by us or our commercial manufacturing organizations (CMOs). In addition, if we make manufacturing changes to our product candidates in the future, we may need to conduct additional preclinical studies to bridge our modified product candidates to earlier versions.
Many of the factors that cause, or lead to, a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical trials may ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our product candidates.
28
We may be unable to obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates under applicable regulatory requirements. The denial or delay of any such approval would delay commercialization of our product candidates and adversely impact our potential to generate revenue, our business and our results of operations.
The research, testing, manufacturing, labeling, licensure, sale, marketing and distribution of biologic products are subject to extensive regulation by the FDA and other regulatory authorities in the United States and other countries, and such regulations differ from country to country. We are not permitted to market our product candidates in the United States or in any foreign countries until they receive the requisite licensure from the applicable regulatory authorities of such jurisdictions.
The FDA or any foreign regulatory authorities can delay, limit or deny licensure of our product candidates for many reasons, including:
| ∎ | our inability to demonstrate to the satisfaction of the FDA or the applicable foreign regulatory authority that any of our product candidates are safe, potent and pure; |
| ∎ | the FDA’s or the applicable foreign regulatory agency’s disagreement with our trial protocol or the interpretation of data from preclinical studies or clinical trials; |
| ∎ | our inability to demonstrate that the clinical and other benefits of any of our product candidates outweigh any safety or other perceived risks; |
| ∎ | the FDA’s or the applicable foreign regulatory agency’s requirement for additional preclinical studies or clinical trials; |
| ∎ | the results of clinical trials may not meet the level of statistical significance required by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities for licensure; |
| ∎ | the FDA’s or the applicable foreign regulatory agency’s failure to approve the manufacturing processes or facilities of third-party manufacturers upon which we rely; |
| ∎ | the potential for approval policies or regulations of the FDA or the applicable foreign regulatory authorities to significantly change in a manner rendering our clinical data insufficient for licensure; |
| ∎ | the data collected from clinical trials of our product candidates may not be sufficient to the satisfaction of the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities to support the submission of a BLA or other comparable submission in foreign jurisdictions or to obtain licensure of our product candidates in the United States or elsewhere; or |
| ∎ | the approval policies or regulations of the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may significantly change in a manner rendering our clinical data insufficient for approval. |
Any of these factors, many of which are beyond our control, may result in our failing to obtain regulatory approval to market any of our product candidates, which would significantly harm our business, results of operations, and prospects. Of the large number of biological products in development, only a small percentage successfully complete the FDA or other regulatory approval processes and are commercialized. Even if we eventually complete clinical testing and receive licensure from the FDA or applicable foreign regulatory authorities for any of our product candidates, the FDA or the applicable foreign regulatory agency may grant licensure contingent on the performance of costly additional clinical trials which may be required after licensure. The FDA or the applicable foreign regulatory agency also may license our product candidates for a more limited indication or a narrower patient population than we originally requested, and the FDA, or applicable foreign regulatory agency, may not license our product candidates with the labeling that we believe is necessary or desirable for the successful commercialization of such product candidates.
In addition, even if the trials are successfully completed, preclinical and clinical data are often susceptible to varying interpretations and analyses, and we cannot guarantee that the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities will interpret the results as we do, and more clinical trials could be required before we submit our product candidates for approval. To the extent that the results of the clinical trials are not satisfactory to the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities for support of a marketing application, approval of our product candidates may be significantly delayed, or we may be required to expend significant additional resources, which may not be available to us, to conduct additional clinical trials in support of potential approval of our product candidates.
29
Any delay in obtaining, or inability to obtain, applicable regulatory approval would delay or prevent commercialization of our product candidates and would materially adversely impact our business and prospects.
We may seek orphan drug status for TC-210, TC-110 and some of our other future product candidates, but we may be unable to obtain such designations or to maintain the benefits associated with orphan drug status, including market exclusivity, which may cause our revenue, if any, to be reduced.
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant orphan designation to a drug or biologic intended to treat a rare disease or condition, defined as a disease or condition with a patient population of fewer than 200,000 in the United States, or a patient population greater than 200,000 in the United States when there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing and making available the drug or biologic in the United States will be recovered from sales in the United States for that drug or biologic. Orphan drug designation must be requested before submitting a BLA. In the United States, orphan drug designation entitles a party to financial incentives such as opportunities for grant funding towards clinical trial costs, tax advantages and user-fee waivers. After the FDA grants orphan drug designation, the generic identity of the drug and its potential orphan use are disclosed publicly by the FDA. Orphan drug designation does not convey any advantage in, or shorten the duration of, the regulatory review and approval process.
If a product that has orphan drug designation subsequently receives the first FDA approval for a particular active ingredient for the disease for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to orphan product exclusivity, which means that the FDA may not approve any other applications, including a BLA, to market the same biologic for the same indication for seven years, except in limited circumstances such as a showing of clinical superiority to the product with orphan drug exclusivity or if FDA finds that the holder of the orphan drug exclusivity has not shown that it can assure the availability of sufficient quantities of the orphan drug to meet the needs of patients with the disease or condition for which the drug was designated. As a result, even if one of our product candidates receives orphan exclusivity, the FDA can still approve other drugs that have a different active ingredient for use in treating the same indication or disease. Furthermore, the FDA can waive orphan exclusivity if we are unable to manufacture sufficient supply of our product.
We have applied for orphan drug designation for the treatment of malignant mesothelioma with TC-210 and we may seek orphan drug designation for TC-210, TC-110 and some or all of our other future product candidates in additional orphan indications in which there is a medically plausible basis for the use of these products, including cholangiocarcinoma. Even when we obtain orphan drug designation, exclusive marketing rights in the United States may be limited if we seek licensure for an indication broader than the orphan designated indication and may be lost if the FDA later determines that the request for designation was materially defective or if the manufacturer is unable to assure sufficient quantities of the product to meet the needs of patients with the rare disease or condition. In addition, although we intend to seek orphan drug designation for other product candidates, we may never receive such designations.
On August 3, 2017, the Congress passed the FDA Reauthorization Act of 2017 (FDARA). FDARA, among other things, codified the FDA’s pre-existing regulatory interpretation, to require that a drug sponsor demonstrate the clinical superiority of an orphan drug that is otherwise the same as a previously approved drug for the same rare disease in order to receive orphan drug exclusivity. The new legislation reverses prior precedent holding that the Orphan Drug Act unambiguously requires that the FDA recognize the orphan exclusivity period regardless of a showing of clinical superiority. The FDA may further reevaluate the Orphan Drug Act and its regulations and policies. We do not know if, when, or how the FDA may change the orphan drug regulations and policies in the future, and it is uncertain how any changes might affect our business. Depending on what changes the FDA may make to its orphan drug regulations and policies, our business could be adversely impacted.
A Breakthrough Therapy designation by the FDA, even if granted for any of our product candidates, may not lead to a faster development or regulatory review or approval process and it does not increase the likelihood that our product candidates will receive marketing approval.
We plan to seek a Breakthrough Therapy designation for TC-210 and TC-110 and may seek Breakthrough Therapy designation for some or all of our future product candidates. A breakthrough therapy is defined as a drug or biologic that is intended, alone or in combination with one or more other drugs or biologics, to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug, or biologic, may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as
30
substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. For product candidates that have been designated as breakthrough therapies, interaction and communication between the FDA and the sponsor of the trial can help to identify the most efficient path for clinical development while minimizing the number of patients placed in ineffective control regimens. Biologics designated as breakthrough therapies by the FDA may also be eligible for other expedited approval programs, including Accelerated Approval.
Designation as a breakthrough therapy is within the discretion of the FDA. Accordingly, even if we believe one of our product candidates meets the criteria for designation as a breakthrough therapy, the FDA may disagree and instead determine not to make such designation. In any event, the receipt of a Breakthrough Therapy designation for a product candidate may not result in a faster development process, review or licensure compared to candidate products considered for licensure under non-expedited FDA review procedures and does not assure ultimate approval by the FDA. In addition, even if one or more of our product candidates qualify as breakthrough therapies, the FDA may later decide that the product no longer meets the conditions for qualification. Thus, even though we intend to seek Breakthrough Therapy designation for TC-210 and some or all of our future product candidates for the treatment of various cancers, there can be no assurance that we will receive breakthrough therapy designation.
A Fast Track designation by the FDA, even if granted for TC-210, TC-110 or any other future product candidate(s), may not lead to a faster development or regulatory review or approval process, and does not increase the likelihood that our product candidates will receive marketing approval.
If a drug is intended for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening condition and the drug demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for this condition, the drug sponsor may apply for FDA Fast Track designation for a particular indication. We plan to seek Fast Track designation for TC-210 and TC-110 and may seek Fast Track designation for certain of our future product candidates, but there is no assurance that the FDA will grant this status to any of our proposed product candidates. Marketing applications filed by sponsors of products in Fast Track development may qualify for priority review under the policies and procedures offered by the FDA, but the Fast Track designation does not assure any such qualification or ultimate marketing approval by the FDA. The FDA has broad discretion whether or not to grant Fast Track designation, so even if we believe a particular product candidate is eligible for this designation, there can be no assurance that the FDA would decide to grant it. Even if we do receive Fast Track designation, we may not experience a faster development process, review or licensure compared to conventional FDA procedures, and receiving a Fast Track designation does not provide assurance of ultimate FDA approval. In addition, the FDA may withdraw Fast Track designation if it believes that the designation is no longer supported by data from our clinical development program. In addition, the FDA may withdraw any Fast Track designation at any time.
Accelerated approval by the FDA, even if granted for TC-210 and TC-110 or any other future product candidates, may not lead to a faster development or regulatory review or approval process and it does not increase the likelihood that our product candidates will receive marketing approval.
We plan to seek approval of TC-210 and TC-110, and may seek approval of future product candidates using FDA’s accelerated approval pathway. A product may be eligible for accelerated approval if it treats a serious or life-threatening condition and generally provides a meaningful advantage over available therapies. In addition, it must demonstrate an effect on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit or on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality (IMM) that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on IMM or other clinical benefit. As a condition of approval, the FDA may require that a sponsor of a drug or biologic receiving accelerated approval perform adequate and well-controlled post-marketing clinical trials. These confirmatory trials must be completed with due diligence. In addition, the FDA currently requires as a condition for accelerated approval pre-approval of promotional materials, which could adversely impact the timing of the commercial launch of the product. Even if we do receive accelerated approval, we may not experience a faster development or regulatory review or approval process, and receiving accelerated approval does not provide assurance of ultimate FDA approval.
Obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval of our product candidates in one jurisdiction does not mean that we will be successful in obtaining regulatory approval of our product candidates in other jurisdictions.
Obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval of our product candidates in one jurisdiction does not guarantee that we will be able to obtain or maintain regulatory approval in any other jurisdiction, while a failure or delay in obtaining regulatory approval in one jurisdiction may have a negative effect on the regulatory approval process in
31
others. For example, even if the FDA grants marketing approval of a product candidate, comparable regulatory authorities in foreign jurisdictions must also approve the manufacturing, marketing and promotion of the product candidate in those countries. Approval and licensure procedures vary among jurisdictions and can involve requirements and administrative review periods different from, and greater than, those in the United States, including additional preclinical studies or clinical trials as clinical trials conducted in one jurisdiction may not be accepted by regulatory authorities in other jurisdictions. In many jurisdictions outside the United States, a product candidate must be approved for reimbursement before it can be approved for sale in that jurisdiction. In some cases, the price that we intend to charge for our products is also subject to approval.
We may also submit marketing applications in other countries. Regulatory authorities in jurisdictions outside of the United States have requirements for approval of product candidates with which we must comply prior to marketing in those jurisdictions. Obtaining foreign regulatory approvals and compliance with foreign regulatory requirements could result in significant delays, difficulties and costs for us and could delay or prevent the introduction of our products in certain countries. If we fail to comply with the regulatory requirements in international markets and/or receive applicable marketing approvals, our target market will be reduced and our ability to realize the full market potential of our product candidates will be harmed.
Even if we receive regulatory approval of our product candidates, we will be subject to ongoing regulatory obligations and continued regulatory review, which may result in significant additional expense and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or experience unanticipated problems with our product candidates.
Any regulatory approvals that we receive for our product candidates will require surveillance to monitor the safety, potency and purity of the product candidate. The FDA may also require a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy in order to license our product candidates, which could entail requirements for a medication guide, physician communication plans or additional elements to ensure safe use, such as restricted distribution methods, patient registries and other risk minimization tools. In addition, if the FDA or a comparable foreign regulatory authority approves our product candidates, the manufacturing processes, labeling, packaging, distribution, adverse event reporting, storage, advertising, promotion, import, export and recordkeeping for our product candidates will be subject to extensive and ongoing regulatory requirements. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, registration, as well as continued compliance with cGMPs, cGTPs and good clinical practices (GCPs) for any clinical trials that we conduct post-licensure. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with our product candidates, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with our third-party manufacturers or manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in, among other things:
| ∎ | restrictions on the marketing or manufacturing of our product candidates, withdrawal of the product from the market or voluntary or mandatory product recalls; |
| ∎ | revisions to the labeling, including limitation on approved uses or the addition of additional warnings, contraindications or other safety information, including boxed warnings; |
| ∎ | imposition of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS), which may include distribution or use restrictions; |
| ∎ | requirements to conduct additional post-market clinical trials to assess the safety of the product; |
| ∎ | fines, warning letters or holds on clinical trials; |
| ∎ | refusal by the FDA to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications filed by us or suspension or revocation of license approvals; |
| ∎ | product seizure or detention, or refusal to permit the import or export of our product candidates; and |
| ∎ | injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties. |
The FDA’s and other regulatory authorities’ policies may change and additional government regulations may be enacted that could prevent, limit or delay regulatory approval of our product candidates. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action, either in the United States or abroad. If we are slow or unable to adapt to changes in existing requirements or the adoption of new requirements or policies, or if we are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we may lose any marketing approval that we may have obtained and we may not achieve or sustain profitability.
32
Coverage and reimbursement may be limited or unavailable in certain market segments for our product candidates, which could make it difficult for us to sell our product candidates, if licensed, profitably.
In both domestic and foreign markets, successful sales of our product candidates, if licensed, will depend on the availability of adequate coverage and reimbursement from third-party payors. In addition, because our product candidates represent new approaches to the treatment of cancer, we cannot accurately estimate the potential revenue from our product candidates.
Patients who are provided medical treatment for their conditions generally rely on third-party payors to reimburse all or part of the costs associated with their treatment. Adequate coverage and reimbursement from governmental healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, and commercial payors is critical to new product acceptance.
Government authorities and third-party payors, such as private health insurers and health maintenance organizations, decide which drugs and treatments they will cover and the amount of reimbursement. Reimbursement by a third-party payor may depend upon a number of factors, including, but not limited to, the third-party payor’s determination that use of a product is:
| ∎ | a covered benefit under its health plan; |
| ∎ | safe, effective and medically necessary; |
| ∎ | appropriate for the specific patient; |
| ∎ | cost-effective; and |
| ∎ | neither experimental nor investigational. |
Obtaining coverage and reimbursement approval of a product from a government or other third-party payor is a time-consuming and costly process that could require us to provide to the payor supporting scientific, clinical and cost-effectiveness data for the use of our products. Even if we obtain coverage for a given product, the resulting reimbursement payment rates might not be adequate for us to achieve or sustain profitability or may require co-payments that patients find unacceptably high. Patients are unlikely to use our product candidates unless coverage is provided and reimbursement is adequate to cover a significant portion of the cost of our product candidates.
In the United States, no uniform policy of coverage and reimbursement for products exists among third-party payors. Therefore, coverage and reimbursement for products can differ significantly from payor to payor. As a result, the coverage determination process is often a time-consuming and costly process that will require us to provide scientific and clinical support for the use of our product candidates to each payor separately, with no assurance that coverage and adequate reimbursement will be obtained.
We intend to seek approval to market our product candidates in both the United States and in selected foreign jurisdictions. If we obtain licensure in one or more foreign jurisdictions for our product candidates, we will be subject to rules and regulations in those jurisdictions. In some foreign countries, particularly those in the European Union (EU), the pricing of biologics is subject to governmental control. In these countries, pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can take considerable time after obtaining marketing approval of a product candidate. In addition, market acceptance and sales of our product candidates will depend significantly on the availability of adequate coverage and reimbursement from third-party payors for our product candidates and may be affected by existing and future healthcare reform measures.
Third-party payors, whether domestic or foreign, or governmental or commercial, are developing increasingly sophisticated methods of controlling healthcare costs. In both the United States and certain foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes to the healthcare system that could impact our ability to sell our products profitably. In particular, in 2010, Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (collectively, the Affordable Care Act) was enacted. The Affordable Care Act and its implementing regulations, among other things, revised the methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers to the state and federal government for covered outpatient drugs and certain biologics, including our product candidates, under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated, increased the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by most manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program, extended the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program to utilization of prescriptions of individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care
33
organizations, subjected manufacturers to new annual fees and taxes for certain branded prescription drugs and provided incentives to programs that increase the federal government’s comparative effectiveness research.
Members of the U.S. Congress and the Trump administration have expressed an intent to pass legislation or adopt executive orders to fundamentally change or repeal parts of the Affordable Care Act. While Congress has not passed repeal legislation to date, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (TCJA) repealed, effective January 1, 2019, the tax-based shared responsibility payment imposed by the Affordable Care Act on certain individuals who fail to maintain qualifying health coverage for all or part of a year that is commonly referred to as the “individual mandate.” On December 14, 2018, a federal district court in Texas ruled that upon the repeal of the shared responsibility payment, the ACA’s individual mandate will become unconstitutional. The court further ruled that the individual mandate is not severable from the remaining provisions of the Affordable Care Act, and that the remaining provisions are therefore invalid. The court, however, did not grant an injunction against enforcement of the Affordable Care Act. An appeal of the decision is expected.
Further, on January 20, 2017, President Trump signed an Executive Order directing federal agencies with authorities and responsibilities under the Affordable Care Act to waive, defer, grant exemptions from, or delay the implementation of any provision of the Affordable Care Act that would impose a fiscal burden on states or a cost, fee, tax, penalty or regulatory burden on individuals, healthcare providers, health insurers, or manufacturers of pharmaceuticals or medical devices. On October 13, 2017, President Trump signed an Executive Order terminating the cost-sharing subsidies that reimburse insurers under the Affordable Care Act. Several state Attorneys General filed suit to stop the administration from terminating the subsidies, but their request for a restraining order was denied by a federal judge in California on October 25, 2017. In addition, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has recently proposed regulations that would give states greater flexibility in setting benchmarks for insurers in the individual and small group marketplaces, which may have the effect of relaxing the essential health benefits required under the Affordable Care Act for plans sold through such marketplaces. There may be further changes to the Affordable Care Act as a result of new legislation or further executive, administrative or judicial action.
Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted in the United States since the Affordable Care Act was enacted. In August 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011, among other things, created measures for spending reductions by Congress. A Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction, tasked with recommending a targeted deficit reduction of at least $1.2 trillion for the years 2013 through 2021, was unable to reach required goals, thereby triggering the legislation’s automatic reduction to several government programs. This includes aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers up to 2% per fiscal year. In January 2013, President Obama signed into law the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (ATRA), which delayed for another two months the budget cuts mandated by these sequestration provisions of the Budget Control Act of 2011. In March 2013, President Obama signed an executive order implementing sequestration, and in April 2013, the 2% Medicare payment reductions went into effect. ATRA also, among other things, reduced Medicare payments to several providers, including hospitals, imaging centers and cancer treatment centers, and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years.
In addition, on May 11, 2018, the Trump administration issued a plan to lower drug prices. Under this blueprint for action, the Trump administration indicated that HHS will: take steps to end the use of regulatory and patent processes by drug makers to protect their products from competition; advance biosimilars and generics to boost price competition; evaluate the inclusion of prices in drug makers’ ads to enhance price competition; speed access to and lower the cost of new drugs by clarifying policies for sharing information between insurers and drug makers; avoid excessive pricing by relying more on value-based pricing by expanding outcome-based payments in Medicare and Medicaid; work to give Part D plan sponsors more negotiation power with drug makers; examine which Medicare Part B drugs could be negotiated for a lower price by Part D plans, and improving the design of the Part B Competitive Acquisition Program; update Medicare’s drug-pricing dashboard to increase transparency; prohibit Part D contracts that include “gag rules” that prevent pharmacists from informing patients when they could pay less out-of-pocket by not using insurance; and require that Part D plan members be provided with an annual statement of plan payments, out-of-pocket spending, and drug price increases.
34
At the state level, individual states are increasingly aggressive in passing legislation and implementing regulations designed to control pharmaceutical and biological product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and, in some cases, designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing. In addition, regional health care authorities and individual hospitals are increasingly using bidding procedures to determine what pharmaceutical products and which suppliers will be included in their prescription drug and other health care programs. These measures could reduce the ultimate demand for our products, once licensed, or put pressure on our product pricing.
We expect that additional state and federal healthcare reform measures will be adopted in the future, any of which could limit the amounts that federal and state governments will pay for healthcare products and services, which could result in reduced demand for our product candidates or additional pricing pressures.
The impact of recent healthcare reform legislation and other changes in the healthcare industry and in healthcare spending on us is currently unknown, and may adversely affect our business model.
Our revenue prospects could be affected by changes in healthcare spending and policy in the United States and abroad. We operate in a highly regulated industry and new laws, regulations or judicial decisions, or new interpretations of existing laws, regulations or decisions, related to healthcare availability, the method of delivery or payment for healthcare products and services could negatively impact our business, operations and financial condition.
There have been, and likely will continue to be, legislative and regulatory proposals at the foreign, federal and state levels directed at broadening the availability of healthcare and containing or lowering the cost of healthcare. We cannot predict the initiatives that may be adopted in the future, including repeal, replacement or significant revisions to the Affordable Care Act. The continuing efforts of the government, insurance companies, managed care organizations and other payors of healthcare services to contain or reduce costs of healthcare and/or impose price controls may adversely affect:
| ∎ | the demand for our product candidates, if we obtain regulatory approval; |
| ∎ | our ability to set a price that we believe is fair for our products; |
| ∎ | our ability to obtain coverage and reimbursement approval for a product; |
| ∎ | our ability to generate revenue and achieve or maintain profitability; |
| ∎ | the level of taxes that we are required to pay; and |
| ∎ | the availability of capital. |
Any reduction in reimbursement from Medicare or other government programs may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors, which may adversely affect our future profitability.
Regulatory requirements in the United States and abroad governing cell therapy products have changed frequently and may continue to change in the future, which could negatively impact our ability to complete clinical trials and commercialize our product candidates in a timely manner, if at all.
Regulatory requirements in the United States and abroad governing cell therapy products have changed frequently and may continue to change in the future. The FDA has established the Office of Tissues and Advanced Therapies within its Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research to consolidate the review of gene therapy and related products, and has established the Cellular, Tissue and Gene Therapies Advisory Committee, among others, to advise this review. Recently, the National Institutes of Health proposed to revise its guidelines for overseeing gene therapy research, including deleting the protocol registration and reporting requirements for certain therapies and eliminating Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee review and reporting requirements for human gene transfer research.
Inadequate funding for the FDA, the SEC and other government agencies could hinder their ability to hire and retain key leadership and other personnel, prevent new products and services from being developed or commercialized in a timely manner or otherwise prevent those agencies from performing normal business functions on which the operation of our business may rely, which could negatively impact our business.
The ability of the FDA to review and approve new products can be affected by a variety of factors, including government budget and funding levels, ability to hire and retain key personnel and accept the payment of user fees,
35
and statutory, regulatory, and policy changes. Average review times at the agency have fluctuated in recent years as a result. In addition, government funding of the SEC and other government agencies on which our operations may rely, including those that fund research and development activities is subject to the political process, which is inherently fluid and unpredictable.
Disruptions at the FDA and other agencies may also slow the time necessary for new drugs to be reviewed and/or approved by necessary government agencies, which would adversely affect our business. For example, over the last several years the U.S. government has shut down several times and certain regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and the SEC, have had to furlough critical FDA, SEC and other government employees and stop critical activities. If a prolonged government shutdown occurs, it could significantly impact the ability of the FDA to timely review and process our regulatory submissions, which could have a material adverse effect on our business. Further, upon completion of this offering and in our operations as a public company, future government shutdowns could impact our ability to access the public markets and obtain necessary capital in order to properly capitalize and continue our operations.
Our employees, independent contractors, consultants, commercial partners and vendors may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including noncompliance with regulatory standards and requirements.
We are exposed to the risk of employee fraud or other illegal activity by our employees, independent contractors, consultants, commercial partners and vendors. Misconduct by these parties could include intentional, reckless and/or negligent conduct that fails to: comply with the regulations of the FDA and other similar foreign regulatory authorities, provide true, complete and accurate information to the FDA and other similar foreign regulatory authorities, comply with manufacturing standards we have established, comply with healthcare fraud and abuse laws in the United States and similar foreign fraudulent misconduct laws or report financial information or data accurately or to disclose unauthorized activities to us. If we obtain FDA approval of any of our product candidates and begin commercializing those products in the United States, our potential exposure under such laws and regulations will increase significantly, and our costs associated with compliance with such laws and regulations are also likely to increase. These laws may impact, among other things, our current activities with principal investigators and research patients, as well as proposed and future sales, marketing and education programs. In particular, the promotion, sales and marketing of healthcare items and services, as well as certain business arrangements in the healthcare industry, are subject to extensive laws designed to prevent fraud, kickbacks, self-dealing and other abusive practices. These laws and regulations may restrict or prohibit a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing and promotion, structuring and commission(s), certain customer incentive programs and other business arrangements generally. Activities subject to these laws also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of patient recruitment for clinical trials. The laws that may affect our ability to operate include, but are not limited to:
| ∎ | the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, knowingly and willfully soliciting, receiving, offering or paying any remuneration (including any kickback, bribe, or rebate), directly or indirectly, overtly or covertly, in cash or in kind, to induce, or in return for, either the referral of an individual, or the purchase, lease, order or recommendation of any good, facility, item or service for which payment may be made, in whole or in part, under a federal healthcare program, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs; |
| ∎ | federal civil and criminal false claims laws and civil monetary penalty laws, which prohibit, among other things, individuals or entities from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, claims for payment or approval from Medicare, Medicaid, or other third-party payors that are false or fraudulent or knowingly making a false statement to improperly avoid, decrease or conceal an obligation to pay money to the federal government; |
| ∎ | the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), which created new federal criminal statutes that prohibit knowingly and willfully executing, or attempting to execute, a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or obtain, by means of false or fraudulent pretenses, representations, or promises, any of the money or property owned by, or under the custody or control of, any healthcare benefit program, regardless of the payor (for example, public or private) and knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or covering up by any trick or device a material fact or making any materially false statements in connection with the delivery of, or payment for, healthcare benefits, items or services relating to healthcare matters; |
36
| ∎ | HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act of 2009 (HITECH), and their respective implementing regulations, which impose requirements on certain covered healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses as well as their respective business associates that perform services for them that involve the use, or disclosure of, individually identifiable health information, relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information without appropriate authorization; |
| ∎ | the federal Physician Payment Sunshine Act, created under the Affordable Care Act and its implementing regulations, which require manufacturers of drugs, devices, biologicals and medical supplies for which payment is available under Medicare, Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (with certain exceptions) to report annually to HHS information related to payments or other transfers of value made to physicians (defined to include doctors, dentists, optometrists, podiatrists and chiropractors) and teaching hospitals, as well as ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members; and |
| ∎ | federal consumer protection and unfair competition laws, which broadly regulate marketplace activities and activities that potentially harm consumers. |
Additionally, we are subject to state and foreign equivalents of each of the healthcare laws described above, among others, some of which may be broader in scope and may apply regardless of the payor.
Effective upon the closing of this offering, we will adopt a code of business conduct and ethics, but it is not always possible to identify and deter employee misconduct, and the precautions we take to detect and prevent inappropriate conduct may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to be in compliance with such laws or regulations.
Efforts to ensure that our business arrangements with third parties will comply with applicable healthcare laws and regulations will involve substantial costs. Because of the breadth of these laws and the narrowness of the statutory exceptions and safe harbors available, it is possible that some of our business activities could be subject to challenge under one or more of such laws. It is possible that governmental authorities will conclude that our business practices may not comply with current or future statutes, regulations or case law involving applicable fraud and abuse or other healthcare laws and regulations. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of these laws or any other governmental regulations that may apply to us, we may be subject to significant criminal, civil and administrative sanctions including monetary penalties, damages, fines, disgorgement, individual imprisonment, and exclusion from participation in government funded healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, additional reporting requirements and oversight if we become subject to a corporate integrity agreement or similar agreement to resolve allegations of non-compliance with these laws, reputational harm, and we may be required to curtail or restructure our operations, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our results of operations.
The risk of our being found in violation of these laws is increased by the fact that many of them have not been fully interpreted by the regulatory authorities or the courts, and their provisions are open to a variety of interpretations. Any action against us for violation of these laws, even if we successfully defend against it, could cause us to incur significant legal expenses and divert our management’s attention from the operation of our business. The shifting compliance environment and the need to build and maintain robust and expandable systems to comply with multiple jurisdictions with different compliance and/or reporting requirements increases the possibility that a healthcare company may run afoul of one or more of the requirements.
The provision of benefits or advantages to physicians to induce or encourage the prescription, recommendation, endorsement, purchase, supply, order or use of medicinal products is also prohibited in the EU. The provision of benefits or advantages to physicians is governed by the national anti-bribery laws of EU Member States, such as the U.K. Bribery Act 2010, or the Bribery Act. Infringement of these laws could result in substantial fines and imprisonment. Payments made to physicians in certain EU Member States must be publicly disclosed. Moreover, agreements with physicians often must be the subject of prior notification and approval by the physician’s employer, his or her competent professional organization and/or the regulatory authorities of the individual EU Member States.
37
These requirements are provided in the national laws, industry codes or professional codes of conduct, applicable in the EU Member States. Failure to comply with these requirements could result in reputational risk, public reprimands, administrative penalties, fines or imprisonment.
The collection, use, disclosure, transfer, or other processing of personal data regarding individuals in the EU, including personal health data, is subject to the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which became effective on May 25, 2018. The GDPR is wide-ranging in scope and imposes numerous requirements on companies that process personal data, including requirements relating to processing health and other sensitive data, obtaining consent of the individuals to whom the personal data relates, providing information to individuals regarding data processing activities, implementing safeguards to protect the security and confidentiality of personal data, providing notification of data breaches, and taking certain measures when engaging third-party processors. The GDPR also imposes strict rules on the transfer of personal data to countries outside the EU, including the United States, and permits data protection authorities to impose large penalties for violations of the GDPR, including potential fines of up to€20 million or 4% of annual global revenues, whichever is greater. The GDPR also confers a private right of action on data subjects and consumer associations to lodge complaints with supervisory authorities, seek judicial remedies, and obtain compensation for damages resulting from violations of the GDPR. Compliance with the GDPR will be a rigorous and time-intensive process that may increase our cost of doing business or require us to change our business practices, and despite those efforts, there is a risk that we may be subject to fines and penalties, litigation, and reputational harm in connection with our European activities.
If we fail to comply with environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, we could become subject to fines or penalties or incur costs that could have a material adverse effect on the success of our business.
We are subject to numerous environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing laboratory procedures and the handling, use, storage, treatment and disposal of hazardous materials and wastes. Our operations involve the use of hazardous and flammable materials, including chemicals and biological and radioactive materials. Our operations also produce hazardous waste products. We generally contract with third parties for the disposal of these materials and wastes. We cannot eliminate the risk of contamination or injury from these materials. In the event of contamination or injury resulting from our use of hazardous materials, we could be held liable for any resulting damages, and any liability could exceed our resources. We also could incur significant costs associated with civil or criminal fines and penalties.
Although we maintain workers’ compensation insurance to cover us for costs and expenses we may incur due to injuries to our employees resulting from the use of hazardous materials, this insurance may not provide adequate coverage against potential liabilities. We do not maintain insurance for environmental liability or toxic tort claims that may be asserted against us in connection with our storage or disposal of biological, hazardous or radioactive materials.
Even if we are able to commercialize any product candidates, the products may become subject to unfavorable pricing regulations, third party reimbursement practices or healthcare reform initiatives, which would harm our business.
The regulations that govern marketing approvals, pricing, coverage and reimbursement for new drug products vary widely from country to country. Current and future legislation may significantly change the approval requirements in ways that could involve additional costs and cause delays in obtaining approvals. Some countries require approval of the sale price of a drug before it can be marketed. In many countries, the pricing review period begins after marketing or product licensing approval is granted. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval in some countries, we may be required to conduct a clinical trial that compares the cost-effectiveness of our product candidate to other available therapies. In some foreign markets, prescription pharmaceutical pricing remains subject to continuing governmental control even after initial approval is granted. As a result, we might obtain marketing approval for a product candidate in a particular country, but then be subject to price regulations that delay our commercial launch of the product, possibly for lengthy time periods, and negatively impact the revenues, if any, we are able to generate from the sale of the product in that country. Adverse pricing limitations may hinder our ability to recoup our investment in one or more product candidates, even if our product candidates obtain marketing approval.
Our ability to commercialize any product candidates successfully also will depend in part on the extent to which coverage and adequate reimbursement for these products and related treatments will be available from government
38
healthcare programs, private health insurers and other organizations. Government authorities and third party payors, such as private health insurers and health maintenance organizations, decide which medications they will pay for and establish reimbursement levels. A primary trend in the U.S. healthcare industry and elsewhere is cost containment. Government authorities and third-party payors have attempted to control costs by limiting coverage and the amount of reimbursement for particular medications. Increasingly, government authorities and third-party payors are requiring that drug companies provide them with predetermined discounts from list prices and are challenging the prices charged for medical products. Coverage and reimbursement may not be available for any product that we commercialize and, even if these are available, the level of reimbursement may not be satisfactory. Reimbursement may affect the demand for, or the price of, any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval. Obtaining and maintaining adequate reimbursement for our products may be difficult. We may be required to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies to justify coverage and reimbursement or the level of reimbursement relative to other therapies. If coverage and adequate reimbursement are not available or reimbursement is available only to limited levels, we may not be able to successfully commercialize any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval.
There may be significant delays in obtaining coverage and reimbursement for newly approved drugs, and coverage may be more limited than the purposes for which the drug is approved by the FDA or similar regulatory authorities outside of the United States. Moreover, eligibility for coverage and reimbursement does not imply that a drug will be paid for in all cases or at a rate that covers our costs, including research, development, intellectual property, manufacture, sale and distribution expenses. Interim reimbursement levels for new drugs, if applicable, may also not be sufficient to cover our costs and may not be made permanent. Reimbursement rates may vary according to the use of the drug and the clinical setting in which it is used, may be based on reimbursement levels already set for lower cost drugs and may be incorporated into existing payments for other services. Net prices for drugs may be reduced by mandatory discounts or rebates required by government healthcare programs or private payors and by any future relaxation of laws that presently restrict imports of drugs from countries where they may be sold at lower prices than in the United States. Third party payors often rely upon Medicare coverage policy and payment limitations in setting their own reimbursement policies. Our inability to promptly obtain coverage and adequate reimbursement rates from both government-funded and private payors for any approved products that we develop could have a material adverse effect on our operating results, our ability to raise capital needed to commercialize products and our overall financial condition.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
If we are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection for any products we develop and for our technology, or if the scope of the patent protection obtained is not sufficiently broad, our competitors could develop and commercialize products and technology similar or identical to ours, and our ability to commercialize any product candidates we may develop, and our technology may be adversely affected.
Our success depends in large part on our ability to obtain and maintain patent protection in the United States and other countries with respect to our product candidates, their respective components, formulations, combination therapies, methods used to manufacture them and methods of treatment and development that are important to our business. If we do not adequately protect our intellectual property rights, competitors may be able to erode or negate any competitive advantage we may have, which could harm our business and ability to achieve profitability. To protect our proprietary position, we file patent applications in the United States and abroad related to our novel product candidates that are important to our business; we may in the future also license or purchase patent applications filed by others. If we are unable to secure or maintain patent protection with respect to our antibody technology and any proprietary products and technology we develop, our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects could be materially harmed.
If the scope of the patent protection we or our potential licensors obtain is not sufficiently broad, we may not be able to prevent others from developing and commercializing technology and products similar or identical to ours. The degree of patent protection we require to successfully compete in the marketplace may be unavailable or severely limited in some cases and may not adequately protect our rights or permit us to gain or keep any competitive advantage. We cannot provide any assurances that any of our patents have, or that any of our pending patent applications that mature into issued patents will include, claims with a scope sufficient to protect our current and
39
future product candidates or otherwise provide any competitive advantage. In addition, to the extent that we license intellectual property in the future, we cannot assure you that those licenses will remain in force. In addition, the laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States. Furthermore, patents have a limited lifespan. In the United States, the natural expiration of a patent is generally 20 years after it is filed. Various extensions may be available; however, the life of a patent, and the protection it affords, is limited. Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized.
Even if they are unchallenged, our patents and pending patent applications, if issued, may not provide us with any meaningful protection or prevent competitors from designing around our patent claims to circumvent our patents by developing similar or alternative technologies or therapeutics in a non-infringing manner. For example, a third party may develop a competitive therapy that provides benefits similar to one or more of our product candidates but that uses a formulation and/or a device that falls outside the scope of our patent protection. If the patent protection provided by the patents and patent applications we hold or pursue with respect to our product candidates is not sufficiently broad to impede such competition, our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates could be negatively affected, which would harm our business. Although we currently own all of our patents and our patent applications, similar risks would apply to any patents or patent applications that we may in-license in the future.
Patent positions of life sciences companies can be uncertain and involve complex factual and legal questions. No consistent policy governing the scope of claims allowable in the field of antibodies has emerged in the United States. The scope of patent protection in jurisdictions outside of the United States is also uncertain. Changes in either the patent laws or their interpretation in any jurisdiction that we seek patent protection may diminish our ability to protect our inventions, maintain and enforce our intellectual property rights; and, more generally, may affect the value of our intellectual property, including the narrowing of the scope of our patents and any that we may license.
The patent prosecution process is complex, expensive, time-consuming and inconsistent across jurisdictions. We may not be able to file, prosecute, maintain, enforce, or license all necessary or desirable patent rights at a commercially reasonable cost or in a timely manner. In addition, we may not pursue or obtain patent protection in all relevant markets. It is possible that we will fail to identify important patentable aspects of our research and development efforts in time to obtain appropriate or any patent protection. While we enter into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to confidential or patentable aspects of our research and development efforts, including for example, our employees, corporate collaborators, external academic scientific collaborators, CROs, contract manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties, any of these parties may breach the agreements and disclose such output before a patent application is filed, thereby endangering our ability to seek patent protection. In addition, publications of discoveries in the scientific and scholarly literature often lag behind the actual discoveries, and patent applications in the United States and other jurisdictions are typically not published until 18 months after filing, or in some cases not at all. Consequently, we cannot be certain that we were the first to file for patent protection on the inventions claimed in our patents or pending patent applications.
The issuance, scope, validity, enforceability and commercial value of our patent rights are highly uncertain. Further, the scope of the invention claimed in a patent application can be significantly reduced before the patent is issued, and this scope can be reinterpreted after issuance. Even where patent applications we currently own or that we may license in the future issue as patents, they may not issue in a form that will provide us with adequate protection to prevent competitors or other third parties from competing with us, or otherwise provide us with a competitive advantage. Any patents that eventually issue may be challenged, narrowed or invalidated by third parties. Consequently, we do not know whether any of our product candidates will be protectable or remain protected by valid and enforceable patent rights. Our competitors or other third parties may be able to evade our patent rights by developing new antibodies, biosimilar antibodies, or alternative technologies or products in a non-infringing manner.
The issuance or grant of a patent is not irrefutable as to its inventorship, scope, validity or enforceability, and our patents may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the United States and abroad. There may be prior art of which we are not aware that may affect the validity or enforceability of a patent claim. There also may be prior art of which we are aware, but which we do not believe affects the validity or enforceability of a claim, which may,
40
nonetheless, ultimately be found to affect the validity or enforceability of a claim. We may in the future, become subject to a third-party pre-issuance submission of prior art or opposition, derivation, revocation, re-examination, post-grant andinter partes review, or interference proceeding and other similar proceedings challenging our patent rights or the patent rights of others in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) or other foreign patent office. An unfavorable determination in any such submission, proceeding or litigation could reduce the scope of, or invalidate, our patent rights, allow third parties to commercialize our technology or products and compete directly with us, without payment to us, or extinguish our ability to manufacture or commercialize products without infringing third-party patent rights.
In addition, given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized. As a result, our intellectual property may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing products similar or identical to ours. Moreover, some of our owned and in-licensed patents and patent applications are, and may in the future be, co-owned with third parties. If we are unable to obtain an exclusive license to any such third-party co-owners’ interest in such patents or patent applications, such co-owners may be able to license their rights to other third parties, including our competitors, and our competitors could market competing products and technology. In addition, we or our licensors may need the cooperation of any such co-owners of our owned and in-licensed patents in order to enforce such patents against third parties, and such cooperation may not be provided to us or our licensors. Any of the foregoing could have a material adverse effect on our competitive position, business, financial conditions, results of operations and prospects.
We depend on intellectual property licensed from third parties and termination of any of these licenses could result in the loss of significant rights, which would harm our business.
We are dependent on patents, know-how and proprietary technology, both our own and licensed from others. For example, we have a non-exclusive license for the mesothelin binder incorporated into the TRuC construct for TC-210 from Harpoon. Harpoon has the ability to terminate our license in the event we materially breach our agreement with Harpoon and fail to cure this breach within sixty days. If the license with Harpoon is terminated, we would need to partner for another mesothelin binder or independently develop our own mesothelin binder. In addition, we cannot prevent Harpoon from also licensing the mesothelin binder we use in TC-210 to a third-party. If Harpoon licenses the mesothelin binder to another immuno-oncology company, that company could develop a competitive product to TC-210.
We are currently, and expect in the future to be, party to material license or collaboration agreements. These agreements typically impose numerous obligations, such as diligence and payment obligations. Any termination of these licenses could result in the loss of significant rights and could harm our ability to commercialize our product candidates. These licenses do and future licenses may include provisions that impose obligations and restrictions on us. This could delay or otherwise negatively impact a transaction that we may wish to enter into.
Disputes may also arise between us and our licensors regarding intellectual property subject to a license agreement, including:
| ∎ | the scope of rights granted under the license agreement and other interpretation-related issues; |
| ∎ | whether and the extent to which our technology and processes infringe on intellectual property of the licensor that is not subject to the licensing agreement; |
| ∎ | our right to sublicense patent and other rights to third parties under collaborative development relationships; |
| ∎ | our diligence obligations with respect to the use of the licensed technology in relation to our development and commercialization of our product candidates, and what activities satisfy those diligence obligations; and |
| ∎ | the ownership of inventions and know-how resulting from the joint creation or use of intellectual property by our licensors and us and our partners. |
If disputes over intellectual property that we have licensed prevent or impair our ability to maintain our current licensing arrangements on acceptable terms, we may be unable to successfully develop and commercialize the affected product candidates.
41
We are generally also subject to all of the same risks with respect to protection of intellectual property that we license, as we are for intellectual property that we own, which are described below. If we or our licensors fail to adequately protect this intellectual property, our ability to commercialize products could suffer.
If we fail to comply with our obligations under our patent licenses with third parties, we could lose license rights that are important to our business.
We are a party to a license agreement with Harpoon, pursuant to which we in-license key patent and patent applications for use in one or more of our product candidates. This existing license imposes various diligence, milestone payment, royalty, insurance and other obligations on us. If we fail to comply with these obligations, Harpoon may have the right to terminate the license, in which event we would not be able to develop or market the products covered by such licensed intellectual property.
We rely on certain of our licensors to file and prosecute patent applications and maintain patents and otherwise protect the intellectual property we license from them and may continue to do so in the future. We have limited control over these activities or any other intellectual property that may be related to our in-licensed intellectual property. For example, we cannot be certain that such activities by these licensors have been or will be conducted in compliance with applicable laws and regulations or will result in valid and enforceable patents and other intellectual property rights. We have limited control over the manner in which our licensors initiate an infringement proceeding against a third-party infringer of the intellectual property rights, or defend certain of the intellectual property that is licensed to us. It is possible that any licensors’ infringement proceeding or defense activities may be less vigorous than had we conducted them ourselves.
Our proprietary position depends upon patents that are manufacturing, formulation or method-of-use patents, which may not prevent a competitor or other third party from using the same product candidate for another use.
Composition-of-matter patents on the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in prescription drug products are generally considered to be the strongest form of intellectual property protection for drug products because such patents provide protection without regard to any particular method of use or manufacture or formulation of the API used. We do not currently have any claims in our owned or in-licensed issued U.S. patents that cover the composition-of-matter of our other product candidates. We are pursuing claims in our pending owned or in-licensed patent applications that cover the composition-of-matter of our product candidates. We cannot be certain that claims in any future patents issuing from our pending owned or in-licensed patent applications or our future owned or in-licensed patent applications will cover the composition-of-matter of our current or future product candidates.
If our efforts to protect the proprietary nature of the intellectual property related to our technologies are not adequate, we may not be able to compete effectively in our market.
Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies generally, and we in particular, compete in a crowded competitive space characterized by rapidly evolving technologies and aggressive defense of intellectual property. The USPTO and various foreign governmental patent agencies require compliance with a number of procedural, documentary, fee payment and other provisions during the patent process. There are situations in which noncompliance can result in abandonment or lapse of a patent or patent application, resulting in partial or complete loss of patent rights in the relevant jurisdiction. In such an event, competitors might be able to enter the market earlier than would otherwise have been the case.
We rely upon a combination of patents, confidentiality agreements, trade secret protection and license agreements to protect the intellectual property related to our technologies. Any disclosure to or misappropriation by third parties of our confidential proprietary information could enable competitors to quickly duplicate or surpass our technological achievements, thus eroding our competitive position in our market. We, or any future partners, collaborators, or licensees, may fail to identify patentable aspects of inventions made in the course of development and commercialization activities before it is too late to obtain patent protection on them. Therefore, we may miss potential opportunities to strengthen our patent position.
It is possible that defects of form in the preparation or filing of our patents or patent applications may exist, or may arise in the future, for example with respect to proper priority claims, inventorship, claim scope, or requests for patent term adjustments. If we or our partners, collaborators, licensees or licensors fail to establish, maintain or protect such patents and other intellectual property rights, such rights may be reduced or eliminated. If our partners, collaborators, licensees or licensors are not fully cooperative or disagree with us as to the prosecution, maintenance
42
or enforcement of any patent rights, such patent rights could be compromised. If there are material defects in the form, preparation, prosecution, or enforcement of our patents or patent applications, such patents may be invalid and/or unenforceable, and such applications may never result in valid, enforceable patents. Any of these outcomes could impair our ability to prevent competition from third parties, which may have an adverse impact on our business.
Currently, our patents and patent applications are directed to our TRuC-T cells and accompanying technologies. We seek or plan to seek patent protection for our TRuC-T cell platform and product candidates by filing and prosecuting patent applications in the United States and other countries as appropriate. As of December 15, 2018, our patent portfolio included at least 15 pending U.S. provisional or non-provisional patent applications including one allowed U.S. nonprovisional patent application, at least five pending Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) international applications, and at least 19 pending foreign patent applications, which patent applications we owned or in-licensed. The claims of these patent applications are directed toward various aspects of our product candidates and research programs including compositions of matter, methods of use, and processes. These patent applications, if issued, are expected to expire on various dates from 2036 through 2039, in each case without taking into account any possible patent term adjustments or extensions.
We anticipate additional patent applications will be filed both in the United States and in other countries, as appropriate. However, we cannot predict:
| ∎ | if and when patents will issue; |
| ∎ | the degree and range of protection any issued patents will afford us against competitors including whether third parties will find ways to invalidate or otherwise circumvent our patents; |
| ∎ | whether any of our intellectual property will provide any competitive advantage; |
| ∎ | whether any of our patents that may be issued may be challenged, invalidated, modified, revoked, circumvented, found to be unenforceable or otherwise may not provide any competitive advantage; |
| ∎ | whether or not others will obtain patents claiming aspects similar to those covered by our patents and patent applications; or |
| ∎ | whether we will need to initiate or defend litigation or administrative proceedings which may be costly regardless of whether we win or lose. |
Additionally, we cannot be certain that the claims in our pending patent applications covering composition of matter of our product candidates will be considered patentable by the USPTO, or by patent offices in foreign countries, or that the claims in any of our issued patents will be considered patentable by courts in the United States or foreign countries.
Method of use patents protect the use of a product for the specified method. These types of patents do not prevent a competitor from making and marketing a product that is identical to our product for an indication that is outside the scope of the patented method. Moreover, even if competitors do not actively promote their product for our targeted indications, physicians may prescribe these products “off-label.” Although off-label prescriptions may induce or contribute to the infringement of method of use patents, the practice is common and such infringement is difficult to prevent or prosecute.
The strength of patents in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical field involves complex legal and scientific questions and can be uncertain. The patent applications that we own or in-license may fail to result in issued patents with claims that cover our product candidates or uses thereof in the United States or in other foreign countries. Even if the patents do successfully issue, third parties may challenge the validity, enforceability or scope thereof, which may result in such patents being narrowed, invalidated or held unenforceable. Furthermore, even if they are unchallenged, our patents and patent applications may not adequately protect our intellectual property or prevent others from designing around our claims. If the breadth or strength of protection provided by the patent applications we hold with respect to our product candidates is threatened, it could dissuade companies from collaborating with us to develop, and threaten our ability to commercialize, our product candidates. Further, if we encounter delays in our clinical trials, the period of time during which we could market our product candidates under patent protection would be reduced. Since patent applications in the United States and most other countries
43
are confidential for a period of time after filing, we cannot be certain that we were the first to file any patent application related to our product candidates. Furthermore, for U.S. applications in which all claims are entitled to a priority date before March 16, 2013, an interference proceeding can be provoked by a third-party or instituted by the USPTO to determine who was the first to invent any of the subject matter covered by the patent claims of our applications. We cannot be certain that we are the first to invent the inventions covered by pending patent applications and, if we are not, we may be subject to priority disputes. We may be required to disclaim part or all of the term of certain patents or all of the term of certain patent applications. Various post grant review proceedings, such asinter partes review and post grant review, are available for any interested third party to challenge the patentability of claims issued in patents to us. While these post grant review proceedings have been used less frequently to invalidate biotech patents, they have been successful regarding other technologies, and these relatively new procedures are still changing, and those changes might affect future results. No assurance can be given that if challenged, our patents would be declared by a court to be valid or enforceable or that even if found valid and enforceable, a competitor’s technology or product would be found by a court to infringe our patents. We may analyze patents or patent applications of our competitors that we believe are relevant to our activities, and consider that we are free to operate in relation to our product candidates, but our competitors may achieve issued claims, including in patents we consider to be unrelated, which block our efforts or may potentially result in our product candidates or our activities infringing such claims. The possibility exists that others will develop products which have the same effect as our products on an independent basis which do not infringe our patents or other intellectual property rights, or will design around the claims of patents that we have had issued that cover our products.
Recent or future patent reform legislation could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of our patent applications and the enforcement or defense of our issued patents. In March 2013, under the recently enacted Leahy-Smith America Invents Act, or America Invents Act, the United States moved from a “first to invent” to a “first-to-file” system. Under a “first-to-file” system, assuming the other requirements for patentability are met, the first inventor to file a patent application generally will be entitled to a patent on the invention regardless of whether another inventor had made the invention earlier. The America Invents Act includes a number of other significant changes to U.S. patent law, including provisions that affect the way patent applications are prosecuted, redefine prior art and establish a new post-grant review system. The effects of these changes are currently unclear as the USPTO only recently developed new regulations and procedures in connection with the America Invents Act and many of the substantive changes to patent law, including the “first-to-file” provisions, only became effective in March 2013. In addition, the courts have yet to address many of these provisions and the applicability of the act and new regulations on specific patents discussed herein have not been determined and would need to be reviewed. However, the America Invents Act and its implementation could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of our patent applications and the enforcement or defense of our issued patents, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial condition.
The degree of future protection for our proprietary rights is uncertain because legal means afford only limited protection and may not adequately protect our rights or permit us to gain or keep our competitive advantage. For example:
| ∎ | others may be able to make or use compounds or cells that are similar to the biological compositions of our product candidates but that are not covered by the claims of our patents; |
| ∎ | the active biological ingredients in our current product candidates will eventually become commercially available in biosimilar drug products, and no patent protection may be available with regard to formulation or method of use; |
| ∎ | we or our licensors, as the case may be, may fail to meet our obligations to the U.S. government in regards to any in-licensed patents and patent applications funded by U.S. government grants, leading to the loss of patent rights; |
| ∎ | we or our licensors, as the case may be, might not have been the first to file patent applications for these inventions; |
| ∎ | others may independently develop similar or alternative technologies or duplicate any of our technologies; |
| ∎ | it is possible that our pending patent applications will not result in issued patents; |
| ∎ | it is possible that there are prior public disclosures that could invalidate our or our licensors’ patents, as the case may be, or parts of our or their patents; |
44
| ∎ | it is possible that others may circumvent our owned or in-licensed patents; |
| ∎ | it is possible that there are unpublished applications or patent applications maintained in secrecy that may later issue with claims covering our products or technology similar to ours; |
| ∎ | the laws of foreign countries may not protect our or our licensors’, as the case may be, proprietary rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States; |
| ∎ | the claims of our owned or in-licensed issued patents or patent applications, if and when issued, may not cover our product candidates; |
| ∎ | our owned or in-licensed issued patents may not provide us with any competitive advantages, may be narrowed in scope, or be held invalid or unenforceable as a result of legal challenges by third parties; |
| ∎ | the inventors of our owned or in-licensed patents or patent applications may become involved with competitors, develop products or processes which design around our patents, or become hostile to us or the patents or patent applications on which they are named as inventors; |
| ∎ | it is possible that our owned or in-licensed patents or patent applications omit individual(s) that should be listed as inventor(s) or include individual(s) that should not be listed as inventor(s), which may cause these patents or patents issuing from these patent applications to be held invalid or unenforceable; |
| ∎ | we have engaged in scientific collaborations in the past and will continue to do so in the future, and such collaborators may develop adjacent or competing products to ours that are outside the scope of our patents; |
| ∎ | we may not develop additional proprietary technologies for which we can obtain patent protection; |
| ∎ | it is possible that product candidates or diagnostic tests we develop may be covered by third parties’ patents or other exclusive rights; or |
| ∎ | the patents of others may have an adverse effect on our business. |
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our trade secrets, our business and competitive position would be harmed.
In addition to the protection afforded by patents, we seek to rely on trade secret protection, confidentiality agreements, and license agreements to protect proprietary know-how that is not patentable, processes for which patents are difficult to enforce and any other elements of our product discovery and development processes that involve proprietary know-how, information, or technology that is not covered by patents. Although we require all of our employees to assign their inventions to us, and require all of our employees, consultants, advisors and any third parties who have access to our proprietary know-how, information, or technology to enter into confidentiality agreements, we cannot be certain that our trade secrets and other confidential proprietary information will not be disclosed or that competitors will not otherwise gain access to our trade secrets or independently develop substantially equivalent information and techniques. Furthermore, the laws of some foreign countries do not protect proprietary rights to the same extent or in the same manner as the laws of the United States. As a result, we may encounter significant problems in protecting and defending our intellectual property both in the United States and abroad. If we are unable to prevent unauthorized material disclosure of our intellectual property to third parties, we will not be able to establish or maintain a competitive advantage in our market, which could materially adversely affect our business, operating results and financial condition.
Courts outside the United States are sometimes less willing to protect trade secrets. If we choose to go to court to stop a third party from using any of our trade secrets, we may incur substantial costs. These lawsuits may consume our time and other resources even if we are successful. For example, significant elements of our products, including aspects of sample preparation, methods of manufacturing, cell culturing conditions, computational-biological algorithms, and related processes and software, are based on unpatented trade secrets that are not publicly disclosed. Although we take steps to protect our proprietary information and trade secrets, including through contractual means with our employees and consultants, third parties may independently develop substantially equivalent proprietary information and techniques or otherwise gain access to our trade secrets or disclose our technology.
Thus, we may not be able to meaningfully protect our trade secrets. It is our policy to require our employees, consultants, outside scientific collaborators, sponsored researchers and other advisors to execute confidentiality agreements upon the commencement of employment or consulting relationships with us. These agreements provide that all confidential information concerning our business or financial affairs developed or made known to the
45
individual or entity during the course of the party’s relationship with us is to be kept confidential and not disclosed to third parties except in specific circumstances. In the case of employees, the agreements provide that all inventions conceived by the individual, and which are related to our current or planned business or research and development or made during normal working hours, on our premises or using our equipment or proprietary information, are our exclusive property. In addition, we take other appropriate precautions, such as physical and technological security measures, to guard against misappropriation of our proprietary technology by third parties. We have also adopted policies and conduct training that provides guidance on our expectations, and our advice for best practices, in protecting our trade secrets.
Third-party claims of intellectual property infringement may prevent or delay our product discovery and development efforts.
Our commercial success depends in part on our avoiding infringement of the patents and proprietary rights of third parties. There is a substantial amount of litigation involving patents and other intellectual property rights in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, as well as administrative proceedings for challenging patents, including interference, reexamination, and post grant review proceedings before the USPTO or oppositions and other comparable proceedings in foreign jurisdictions. We may be exposed to, or threatened with, future litigation by third parties having patent or other intellectual property rights alleging that our product candidates and/or proprietary technologies infringe their intellectual property rights. Numerous U.S. and foreign issued patents and pending patent applications, which are owned by third parties, exist in the fields in which we are developing our product candidates. As the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries expand and more patents are issued, the risk increases that our product candidates may give rise to claims of infringement of the patent rights of others. Moreover, it is not always clear to industry participants, including us, which patents cover various types of drugs, products or their methods of use or manufacture. Thus, because of the large number of patents issued and patent applications filed in our fields, there may be a risk that third parties may allege they have patent rights encompassing our product candidates, technologies or methods.
If a third party claims that we infringe its intellectual property rights, we may face a number of issues, including, but not limited to:
| ∎ | infringement and other intellectual property claims which, regardless of merit, may be expensive and time-consuming to litigate and may divert our management’s attention from our core business; |
| ∎ | substantial damages for infringement, which we may have to pay if a court decides that the product candidate or technology at issue infringes on or violates the third party’s rights, and, if the court finds that the infringement was willful, we could be ordered to pay treble damages and the patent owner’s attorneys’ fees; |
| ∎ | a court prohibiting us from developing, manufacturing, marketing or selling our product candidates, or from using our proprietary technologies, unless the third party licenses its product rights to us, which it is not required to do; |
| ∎ | if a license is available from a third party, we may have to pay substantial royalties, upfront fees and other amounts, and/or grant cross-licenses to intellectual property rights for our products; and |
| ∎ | redesigning our product candidates or processes so they do not infringe third party intellectual property rights, which may not be possible or may require substantial monetary expenditures and time. |
Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than we can because they have substantially greater resources. In addition, any uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of any litigation could have a material adverse effect on our ability to raise the funds necessary to continue our operations or could otherwise have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
Third parties may assert that we are employing their proprietary technology without authorization. Generally, conducting preclinical and clinical trials and other development activities in the United States is not considered an act of infringement. If TC-210, TC-110 or another product candidate is licensed by the FDA, a third party may then seek to enforce its patent by filing a patent infringement lawsuit against us. While we do not believe that any claims that could otherwise have a materially adverse effect on the commercialization of our product candidates, if
46
licensed, are valid and enforceable, we may be incorrect in this belief, or we may not be able to prove it in litigation. In this regard, patents issued in the United States by law enjoy a presumption of validity that can be rebutted only with evidence that is “clear and convincing,” a heightened standard of proof. There may be issued third-party patents of which we are currently unaware with claims to compositions, formulations, methods of manufacture or methods for treatment related to the use or manufacture of our product candidates. Patent applications can take many years to issue. There may be currently pending patent applications which may later result in issued patents that our product candidates may infringe. In addition, third parties may obtain patents in the future and claim that use of our technologies infringes upon these patents. Moreover, we may fail to identify relevant patents or incorrectly conclude that a patent is invalid, not enforceable, exhausted, or not infringed by our activities. If any third-party patents were held by a court of competent jurisdiction to cover the manufacturing process of our product candidates, constructs or molecules used in or formed during the manufacturing process, or any final product itself, the holders of any such patents may be able to block our ability to commercialize the product candidate unless we obtained a license under the applicable patents, or until such patents expire or they are finally determined to be held invalid or unenforceable. Similarly, if any third-party patent were held by a court of competent jurisdiction to cover aspects of our formulations, processes for manufacture or methods of use, including combination therapy or patient selection methods, the holders of any such patent may be able to block our ability to develop and commercialize the product candidate unless we obtained a license or until such patent expires or is finally determined to be held invalid or unenforceable. In either case, such a license may not be available on commercially reasonable terms or at all. If we are unable to obtain a necessary license to a third-party patent on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, our ability to commercialize our product candidates may be impaired or delayed, which could in turn significantly harm our business. Even if we obtain a license, it may be non-exclusive, thereby giving our competitors access to the same technologies licensed to us. In addition, if the breadth or strength of protection provided by our patents and patent applications is threatened, it could dissuade companies from collaborating with us to license, develop or commercialize current or future product candidates.
Parties making claims against us may seek and obtain injunctive or other equitable relief, which could effectively block our ability to further develop and commercialize our product candidates. Defense of these claims, regardless of their merit, could involve substantial litigation expense and would be a substantial diversion of employee resources from our business. In the event of a successful claim of infringement against us, we may have to pay substantial damages, including treble damages and attorneys’ fees for willful infringement, obtain one or more licenses from third parties, pay royalties or redesign our infringing products, which may be impossible or require substantial time and monetary expenditure. We cannot predict whether any such license would be available at all or whether it would be available on commercially reasonable terms. Furthermore, even in the absence of litigation, we may need or may choose to obtain licenses from third parties to advance our research or allow commercialization of our product candidates. We may fail to obtain any of these licenses at a reasonable cost or on reasonable terms, if at all. In that event, we would be unable to further develop and commercialize our product candidates, which could harm our business significantly.
We may not be successful in obtaining or maintaining necessary rights to product components and processes for our development pipeline through acquisitions and in-licenses.
Presently we have rights to certain intellectual property, through licenses from third parties and under patent applications that we own or will own, related to TC-210, TC-110 and certain other product candidates. Because additional product candidates may require the use of proprietary rights held by third parties, the growth of our business will likely depend in part on our ability to acquire, in-license or use these proprietary rights. In addition, while we have patent rights directed to certain TRuC constructs we may not be able to obtain intellectual property to broad TRuC-T cell or engineered TCR-T cell constructs.
Our product candidates may also require specific formulations to work effectively and efficiently and these rights may be held by others. Similarly, efficient production or delivery of our product candidates may also require specific compositions or methods, and the rights to these may be owned by third parties. We may be unable to acquire or in-license any compositions, methods of use, processes or other third-party intellectual property rights from third parties that we identify as necessary or important to our business operations. We may fail to obtain any of these licenses at a reasonable cost or on reasonable terms, if at all, which would harm our business. We may need to cease use of the compositions or methods covered by such third-party intellectual property rights, and may need to seek to
47
develop alternative approaches that do not infringe on such intellectual property rights which may entail additional costs and development delays, even if we were able to develop such alternatives, which may not be feasible. Even if we are able to obtain a license, it may be non-exclusive, thereby giving our competitors access to the same technologies licensed to us. In that event, we may be required to expend significant time and resources to develop or license replacement technology. Moreover, the specific antibodies that will be used with our product candidates may be covered by the intellectual property rights of others.
Additionally, we sometimes collaborate with academic institutions to accelerate our preclinical research or development under written agreements with these institutions. In certain cases, these institutions provide us with an option to negotiate a license to any of the institution’s rights in technology resulting from the collaboration. Regardless of such option, we may be unable to negotiate a license within the specified timeframe or under terms that are acceptable to us. If we are unable to do so, the institution may offer the intellectual property rights to others, potentially blocking our ability to pursue our program. If we are unable to successfully obtain rights to required third-party intellectual property or to maintain the existing intellectual property rights we have, we may have to abandon development of such program and our business and financial condition could suffer.
The licensing and acquisition of third-party intellectual property rights is a competitive area, and companies, which may be more established, or have greater resources than we do, may also be pursuing strategies to license or acquire third-party intellectual property rights that we may consider necessary or attractive in order to commercialize our product candidates. More established companies may have a competitive advantage over us due to their size, cash resources and greater clinical development and commercialization capabilities.
We may be involved in lawsuits to protect or enforce our patents or the patents of our licensors, which could be expensive, time-consuming and unsuccessful.
Competitors may infringe our patents or the patents of our licensors. To counter infringement or unauthorized use, we may be required to file infringement claims, which can be expensive and time-consuming. In addition, in an infringement proceeding, a court may decide that one or more of our patents is not valid or is unenforceable, or may refuse to stop the other party from using the technology at issue on the grounds that our patents do not cover the technology in question. An adverse result in any litigation or defense proceedings could put one or more of our patents at risk of being invalidated, held unenforceable, or interpreted narrowly and could put our patent applications at risk of not issuing. Defense of these claims, regardless of their merit, would involve substantial litigation expense and would be a substantial diversion of employee resources from our business. In the event of a successful claim of infringement against us, we may have to pay substantial damages, including treble damages and attorneys’ fees for willful infringement, obtain one or more licenses from third parties, pay royalties or redesign our infringing products, which may be impossible or require substantial time and monetary expenditure.
Post-grant proceedings provoked by third parties or brought by the USPTO may be necessary to determine the validity or priority of inventions with respect to our patents or patent applications or those of our licensors. An unfavorable outcome could result in a loss of our current patent rights and could require us to cease using the related technology or to attempt to license rights to it from the prevailing party. Our business could be harmed if the prevailing party does not offer us a license on commercially reasonable terms. Litigation or post-grant proceedings may result in a decision adverse to our interests and, even if we are successful, may result in substantial costs and distract our management and other employees. We may not be able to prevent, alone or with our licensors, misappropriation of our trade secrets or confidential information, particularly in countries where the laws may not protect those rights as fully as in the United States.
Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, there is a risk that some of our confidential information could be compromised by disclosure during this type of litigation. In addition, there could be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments. If securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could have a substantial adverse effect on the price of our common stock.
48
Obtaining and maintaining our patent protection depends on compliance with various procedural, document submission, fee payment and other requirements imposed by governmental patent agencies, and our patent protection could be reduced or eliminated for non-compliance with these requirements.
Some of our patent applications have been allowed or may be allowed in the future. We cannot be certain that an allowed patent application will become an issued patent. There may be events that cause withdrawal of the allowance of a patent application. For example, after a patent application has been allowed, but prior to being issued, material that could be relevant to patentability may be identified. In such circumstances, the applicant may pull the application from allowance in order for the USPTO to review the application in view of the new material. We cannot be certain that the USPTO will re-allow the application in view of the new material. Further, periodic maintenance fees on any issued patent are due to be paid to the USPTO and foreign patent agencies in several stages over the lifetime of the patent. The USPTO and various foreign governmental patent agencies require compliance with a number of procedural, documentary, fee payment and other similar provisions during the patent application process and following the issuance of a patent. While an inadvertent lapse can in many cases be cured by payment of a late fee or by other means in accordance with the applicable rules, there are situations in which noncompliance can result in abandonment or lapse of the patent or patent application, resulting in partial or complete loss of patent rights in the relevant jurisdiction. Noncompliance events that could result in abandonment or lapse of a patent or patent application include, but are not limited to, failure to respond to official actions within prescribed time limits, non-payment of fees and failure to properly legalize and submit formal documents. In such an event, our competitors might be able to enter the market, which would have a material adverse effect on our business.
Issued patents covering our product candidates could be found invalid or unenforceable if challenged in court or the USPTO.
If we or one of our licensing partners initiate legal proceedings against a third party to enforce a patent covering one of our product candidates, the defendant could counterclaim that the patent covering our product candidate, as applicable, is invalid and/or unenforceable. In patent litigation in the United States, defendant counterclaims alleging invalidity and/or unenforceability are commonplace, and there are numerous grounds upon which a third party can assert invalidity or unenforceability of a patent. Third parties may also raise similar claims before administrative bodies in the United States or abroad, even outside the context of litigation. Such mechanisms include re-examination,inter partes review, post grant review and equivalent proceedings in foreign jurisdictions (such as opposition proceedings). Such proceedings could result in revocation or amendment to our patents in such a way that they no longer cover our product candidates. The outcome following legal assertions of invalidity and unenforceability is unpredictable. With respect to the validity question, for example, we cannot be certain that there is no invalidating prior art, of which we, our patent counsel and the patent examiner were unaware during prosecution. If a defendant were to prevail on a legal assertion of invalidity and/or unenforceability, or if we are otherwise unable to adequately protect our rights, we would lose at least part, and perhaps all, of the patent protection on our product candidates. Such a loss of patent protection could have a material adverse impact on our business and our ability to commercialize or license our technology and product candidates.
Changes to patent law in the United States and in foreign jurisdictions could diminish the value of patents in general, thereby impairing our ability to protect our products.
As is the case with other biopharmaceutical companies, our success is heavily dependent on intellectual property, particularly patents. Obtaining and enforcing patents in the biopharmaceutical industry involve both technological and legal complexity, and is therefore costly, time-consuming and inherently uncertain. In addition, the United States continues to adapt to wide-ranging patent reform legislation that became effective starting in 2012. Moreover, recent U.S. Supreme Court rulings have narrowed the scope of patent protection available in certain circumstances and weakened the rights of patent owners in certain situations. In addition to increasing uncertainty with regard to our ability to obtain patents in the future, this combination of events has created uncertainty with respect to the value of patents, once obtained. Depending on decisions by the U.S. Congress, the federal courts, and the USPTO, the laws and regulations governing patents could change in unpredictable ways that would weaken our ability to obtain new patents or to enforce our existing patents and patents that we might obtain in the future. For example, in the caseAssoc. for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics, Inc., the U.S. Supreme Court held that certain claims to DNA molecules are not patentable. While we do not believe that any of the patents owned or licensed by us will be found invalid based on this decision, we cannot predict how future decisions by the courts, Congress or the USPTO may impact the value of our patents. Similarly, any adverse changes in the patent laws of
49
other jurisdictions could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial condition. Changes in the laws and regulations governing patents in other jurisdictions could similarly have an adverse effect on our ability to obtain and effectively enforce our patent rights.
We have limited foreign intellectual property rights and may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights throughout the world.
Certain of our key patent families have been filed in the United States, however, we have less robust intellectual property rights outside the United States, and, in particular, we may not be able to pursue generic coverage of the TRuC-T cell platform outside of the United States. Filing, prosecuting and defending patents on product candidates in all countries throughout the world would be prohibitively expensive, and our intellectual property rights in some countries outside the United States can be less extensive than those in the United States. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as federal and state laws in the United States. Consequently, we may not be able to prevent third parties from practicing our inventions in all countries outside the United States, or from selling or importing products made using our inventions in and into the United States or other jurisdictions. Competitors may use our technologies in jurisdictions where we have not obtained patent protection to develop their own products and further, may export otherwise infringing products to territories where we have patent protection, but enforcement is not as strong as that in the United States. These products may compete with our products and our patents or other intellectual property rights may not be effective or sufficient to prevent them from competing. Most of our patent portfolio is at the very early stage. We will need to decide whether and in which jurisdictions to pursue protection for the various inventions in our portfolio prior to applicable deadlines.
Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting and defending intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of certain countries, particularly certain developing countries, do not favor the enforcement of patents, trade secrets and other intellectual property protection, particularly those relating to biopharmaceutical products, which could make it difficult for us to stop the infringement of our patents or marketing of competing products in violation of our proprietary rights generally. Proceedings to enforce our patent rights in foreign jurisdictions could result in substantial costs and divert our efforts and attention from other aspects of our business, could put our patents at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly and our patent applications at risk of not issuing and could provoke third parties to assert claims against us. We may not prevail in any lawsuits that we initiate and the damages or other remedies awarded, if any, may not be commercially meaningful. Accordingly, our efforts to enforce our intellectual property rights around the world may be inadequate to obtain a significant commercial advantage from the intellectual property that we develop or license.
We may be subject to claims challenging the inventorship or ownership of our patents and other intellectual property.
We generally enter into confidentiality and intellectual property assignment agreements with our employees, consultants, and contractors. These agreements generally provide that inventions conceived by the party in the course of rendering services to us will be our exclusive property. However, those agreements may not be honored and may not effectively assign intellectual property rights to us. Moreover, there may be some circumstances, where we are unable to negotiate for such ownership rights. Disputes regarding ownership or inventorship of intellectual property can also arise in other contexts, such as collaborations and sponsored research. If we are subject to a dispute challenging our rights in or to patents or other intellectual property, such a dispute could be expensive and time consuming. If we were unsuccessful, we could lose valuable rights in intellectual property that we regard as our own.
The intellectual property landscape around adoptive cell therapy is crowded, and third parties may initiate legal proceedings alleging that we are infringing, misappropriating, or otherwise violating their intellectual property rights, the outcome of which would be uncertain and could have a material adverse effect on the success of our business. We are aware of certain third-party patents and third-party patent applications in this landscape that may, if issued as patents, be asserted to encompass our technology.
We may be subject to claims that our employees, consultants or independent contractors have wrongfully used or disclosed confidential information of third parties.
We have received confidential and proprietary information from third parties. In addition, we employ individuals who were previously employed at other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies. We may be subject to claims that we or our employees, consultants or independent contractors have inadvertently or otherwise used or disclosed confidential information of these third parties or our employees’ former employers or our consultants’ or contractors’
50
current or former clients or customers. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims. Even if we are successful in defending against these claims, litigation could result in substantial cost and be a distraction to our management and employees. If we are not successful, we could lose access or exclusive access to valuable intellectual property.
We may be subject to damages resulting from claims that we or our employees have wrongfully used or disclosed alleged trade secrets of our competitors or are in breach of non-competition or non-solicitation agreements with our competitors.
Many of our employees were previously employed at other pharmaceutical companies, including our competitors or potential competitors, in some cases until recently. We may be subject to claims that we or our employees have inadvertently or otherwise used or disclosed trade secrets or other proprietary information of these former employers or competitors. In addition, we have been and may in the future be subject to claims that we caused an employee to breach the terms of his or her non-competition or non-solicitation agreement. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims. Even if we are successful in defending against these claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and could be a distraction to management. If our defense to those claims fails, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights or personnel. Any litigation or the threat thereof may adversely affect our ability to hire employees. A loss of key personnel or their work product could hamper or prevent our ability to commercialize product candidates, which could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
If we do not obtain patent term extension and data exclusivity for any of our current or future product candidates, our business may be materially harmed.
Depending upon the timing, duration and specifics of any FDA marketing approval of any of our current or future product candidates, one or more of our U.S. patents may be eligible for limited patent term extension under the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, or the Hatch-Waxman Amendments. The Hatch-Waxman Amendments permit a patent extension term of up to five years as compensation for patent term lost during the FDA regulatory review process. A patent term extension cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the date of product approval, only one patent may be extended and only those claims covering the approved drug, a method for using it, or a method for manufacturing it may be extended. However, we may not be granted an extension because of, for example, failing to exercise due diligence during the testing phase or regulatory review process, failing to apply within applicable deadlines, failing to apply prior to expiration of relevant patents, or otherwise failing to satisfy applicable requirements. Moreover, the applicable time period or the scope of patent protection afforded could be less than we request. If we are unable to obtain patent term extension or term of any such extension is less than we request, our competitors may obtain approval of competing products following our patent expiration, and our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects could be materially harmed.
If our trademarks and trade names are not adequately protected, then we may not be able to build name recognition in our marks of interest and our business may be adversely affected.
Our trademarks or trade names may be challenged, infringed, circumvented or declared generic or determined to be infringing on other marks. We rely on both registration and common law protection for our trademarks. We may not be able to protect our rights to these trademarks and trade names or may be forced to stop using these names, which we need for name recognition by potential partners or customers in our markets of interest. During the trademark registration process, we may receive Office Actions from the USPTO objecting to the registration of our trademark. Although we would be given an opportunity to respond to those objections, we may be unable to overcome such rejections. In addition, in the USPTO and in comparable agencies in many foreign jurisdictions, third parties are given an opportunity to oppose pending trademark applications and/or to seek the cancellation of registered trademarks. Opposition or cancellation proceedings may be filed against our trademarks, and our trademarks may not survive such proceedings. If we are unable to establish name recognition based on our trademarks and trade names, we may not be able to compete effectively and our business may be adversely affected.
The U.S. government may exercise its march-in rights with regards to certain patents.
Pursuant to the Bayh-Dole Act, the U.S. government has march-in rights with regards to government-funded technology. The U.S. government can exercise its march-in rights if it determines that action is necessary because we fail to achieve practical application of the government-funded technology, because action is necessary to alleviate
51
health or safety needs, to meet requirements of federal regulations, or to give preference to U.S. industry. In addition, our rights in such inventions may be subject to certain requirements to manufacture products embodying such inventions in the United States. Any exercise by the government of any of the foregoing rights could harm our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects.
Numerous factors may limit any potential competitive advantage provided by our intellectual property rights.
The degree of future protection afforded by our intellectual property rights, whether owned or in-licensed, is uncertain because intellectual property rights have limitations, and may not adequately protect our business, provide a barrier to entry against our competitors or potential competitors, or permit us to maintain our competitive advantage. Moreover, if a third party has intellectual property rights that cover the practice of our technology, we may not be able to fully exercise or extract value from our intellectual property rights. The following examples are illustrative:
| ∎ | pending patent applications that we own or license may not lead to issued patents; |
| ∎ | patents, should they issue, that we own or license, may not provide us with any competitive advantages, or may be challenged and held invalid or unenforceable; |
| ∎ | others may be able to develop and/or practice technology that is similar to our technology or aspects of our technology but that is not covered by the claims of any of our owned or in-licensed patents, should any such patents issue; |
| ∎ | third parties may compete with us in jurisdictions where we do not pursue and obtain patent protection; |
| ∎ | we (or our licensors) might not have been the first to make the inventions covered by a pending patent application that we own or license; |
| ∎ | we (or our licensors) might not have been the first to file patent applications covering a particular invention; |
| ∎ | others may independently develop similar or alternative technologies without infringing our intellectual property rights; |
| ∎ | we may not be able to obtain and/or maintain necessary licenses on reasonable terms or at all; |
| ∎ | third parties may assert an ownership interest in our intellectual property and, if successful, such disputes may preclude us from exercising exclusive rights, or any rights at all, over that intellectual property; |
| ∎ | we may not be able to maintain the confidentiality of our trade secrets or other proprietary information; |
| ∎ | we may not develop or in-license additional proprietary technologies that are patentable; and |
| ∎ | the patents of others may have an adverse effect on our business. |
Should any of these events occur, they could significantly harm our business and results of operation.
Risks Related to Our Reliance On Third Parties
We plan to rely on third parties to conduct our clinical trials. If these third parties do not properly and successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval of or commercialize our product candidates.
We plan to utilize and depend upon independent investigators and collaborators, such as medical institutions, CROs, CMOs and strategic partners to conduct our preclinical studies and clinical trials under agreements with us. We expect to have to negotiate budgets and contracts with CROs, trial sites and CMOs which may result in delays to our development timelines and increased costs. We will rely heavily on these third parties over the course of our clinical trials, and we control only certain aspects of their activities. As a result, we will have less direct control over the conduct, timing and completion of these clinical trials and the management of data developed through clinical trials than would be the case if we were relying entirely upon our own staff. Nevertheless, we are responsible for ensuring that each of our studies is conducted in accordance with applicable protocol, legal and regulatory requirements and scientific standards, and our reliance on third parties does not relieve us of our regulatory responsibilities. We and these third parties are required to comply with GCPs, which are regulations and guidelines enforced by the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities for product candidates in clinical development. Regulatory authorities enforce these GCPs through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators and trial sites. If we or any of these third parties fail to comply with applicable GCP regulations, the clinical data generated in our clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may require us to perform
52
additional clinical trials before approving our marketing applications. We cannot assure you that, upon inspection, such regulatory authorities will determine that any of our clinical trials comply with the GCP regulations. In addition, our clinical trials must be conducted with biologic product produced under cGMP regulations, including cGTP regulations, and will require a large number of test patients. Our failure or any failure by these third parties to comply with these regulations or to recruit a sufficient number of patients may require us to repeat clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process. Moreover, our business may be implicated if any of these third parties violates federal or state fraud and abuse or false claims laws and regulations or healthcare privacy and security laws.
Any third parties conducting our clinical trials are not and will not be our employees and, except for remedies available to us under our agreements with such third parties, we cannot control whether or not they devote sufficient time and resources to our ongoing, clinical and non-clinical product candidates. These third parties may also have relationships with other commercial entities, including our competitors, for whom they may also be conducting clinical trials or other drug development activities, which could affect their performance on our behalf. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or obligations or meet expected deadlines, if they need to be replaced or if the quality or accuracy of the clinical data they obtain is compromised due to the failure to adhere to our clinical protocols or regulatory requirements or for other reasons, our clinical trials may be extended, delayed or terminated and we may not be able to complete development of, obtain regulatory approval of or successfully commercialize our product candidates. As a result, our financial results and the commercial prospects for our product candidates would be harmed, our costs could increase and our ability to generate revenue could be delayed.
Switching or adding third parties to conduct our clinical trials involves substantial cost and requires extensive management time and focus. In addition, there is a natural transition period when a new third party commences work. As a result, delays occur, which can materially impact our ability to meet our desired clinical development timelines.
We may form or seek collaborations or strategic alliances or enter into additional licensing arrangements in the future, and we may not realize the benefits of such collaborations, alliances or licensing arrangements.
We may form or seek strategic alliances, create joint ventures or collaborations, or enter into additional licensing arrangements with third parties that we believe will complement or augment our development and commercialization efforts with respect to our product candidates and any future product candidates that we may develop. Any of these relationships may require us to incur non-recurring and other charges, increase our near and long-term expenditures, issue securities that dilute our existing stockholders or disrupt our management and business.
In addition, we face significant competition in seeking appropriate strategic partners and the negotiation process is time-consuming and complex. Moreover, we may not be successful in our efforts to establish a strategic partnership or other alternative arrangements for our product candidates because they may be deemed to be at too early of a stage of development for collaborative effort and third parties may not view our product candidates as having the requisite potential to demonstrate safety, potency and purity and obtain marketing approval.
Further, collaborations involving our product candidates are subject to numerous risks, which may include the following:
| ∎ | collaborators have significant discretion in determining the efforts and resources that they will apply to a collaboration; |
| ∎ | collaborators may not pursue development and commercialization of our product candidates or may elect not to continue or renew development or commercialization of our product candidates based on clinical trial results, changes in their strategic focus due to the acquisition of competitive products, availability of funding or other external factors, such as a business combination that diverts resources or creates competing priorities; |
| ∎ | collaborators may delay clinical trials, provide insufficient funding for a clinical trial, stop a clinical trial, abandon a product candidate, repeat or conduct new clinical trials or require a new formulation of a product candidate for clinical testing; |
53
| ∎ | collaborators could independently develop, or develop with third parties, products that compete directly or indirectly with our product candidates; |
| ∎ | a collaborator with marketing and distribution rights to one or more products may not commit sufficient resources to their marketing and distribution; |
| ∎ | collaborators may not properly maintain or defend our intellectual property rights or may use our intellectual property or proprietary information in a way that gives rise to actual or threatened litigation that could jeopardize or invalidate our intellectual property or proprietary information or expose us to potential liability; |
| ∎ | disputes may arise between us and a collaborator that cause the delay or termination of the research, development or commercialization of our product candidates, or that result in costly litigation or arbitration that diverts management attention and resources; |
| ∎ | collaborations may be terminated and, if terminated, may result in a need for additional capital to pursue further development or commercialization of the applicable product candidates; and |
| ∎ | collaborators may own or co-own intellectual property covering our products that results from our collaborating with them, and in such cases, we would not have the exclusive right to commercialize such intellectual property. |
As a result, if we enter into additional collaboration agreements and strategic partnerships or license our product candidates, we may not be able to realize the benefit of such transactions if we are unable to successfully integrate them with our existing operations and company culture, which could delay our timelines or otherwise adversely affect our business. We also cannot be certain that, following a strategic transaction or license, we will achieve the revenue or specific net income that justifies such transaction. Any delays in entering into new collaborations or strategic partnership agreements related to our product candidates could delay the development and commercialization of our product candidates in certain geographies for certain indications, which would harm our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
If or until we develop our own manufacturing facility, we expect to rely on the use of manufacturing suites in third-party GMP facilities or third parties to manufacture our product candidates. Our business could be harmed if we are unable to use third-party manufacturing suites or if the third party manufacturers fail to provide us with sufficient quantities of our product candidates or fail to do so at acceptable quality levels or prices.
We do not currently own any facility that may be used as our clinical-scale manufacturing and processing facility and must currently rely on outside vendors to manufacture and process our product candidates, which is and will need to be done on a patient-by-patient basis. We are in the process of adding manufacturing capacity at a suite in Catapult’s GMP manufacturing center, which we expect to be operational in the second half of 2019, but the build-out and staffing of the manufacturing suite may be delayed and the suite may never become operational. We have not yet caused our product candidates to be manufactured or processed on a commercial scale and may not be able to do so for any of our product candidates.
Although in the future we plan to build our own manufacturing facility, we also intend to use the manufacturing suite at Catapult and other third parties as part of our manufacturing process and may, in any event, never be successful in developing our own manufacturing facility. Our anticipated reliance on a limited number of third-party manufacturers exposes us to the following risks:
| ∎ | we may be unable to identify manufacturers on acceptable terms or at all because the number of potential manufacturers is limited and the FDA must inspect any manufacturers for current cGMP and cGTP compliance as part of our marketing application; |
| ∎ | a new manufacturer would have to be educated in, or develop substantially equivalent processes for, the production of our product candidates; |
| ∎ | our manufacturers may have little or no experience with autologous cell products, which are products made from a patient’s own cells, and therefore may require a significant amount of support from us in order to implement and maintain the infrastructure and processes required to manufacture our product candidates; |
| ∎ | our third-party manufacturers might be unable to timely manufacture our product candidates or produce the quantity and quality required to meet our clinical and commercial needs, if any; |
54
| ∎ | our third-party suppliers or collaborators from whom we receive our antibodies used in combination with our product candidates may be unable to timely manufacture or provide the applicable antibody or produce the quantity and quality required to meet our clinical and commercial needs; |
| ∎ | contract manufacturers may not be able to execute our manufacturing procedures and other logistical support requirements appropriately; |
| ∎ | our future contract manufacturers may not perform as agreed, may not devote sufficient resources to our product candidates or may not remain in the contract manufacturing business for the time required to supply our clinical trials or to successfully produce, store, and distribute our products, if any; |
| ∎ | manufacturers are subject to ongoing periodic unannounced inspection by the FDA and corresponding state agencies to ensure strict compliance with cGMP, cGTP and other government regulations and corresponding foreign standards. We do not have control over third-party manufacturers’ compliance with these regulations and standards; |
| ∎ | we may not own, or may have to share, the intellectual property rights to any improvements made by our third-party manufacturers in the manufacturing process for our product candidates; |
| ∎ | our third-party manufacturers could breach or terminate their agreements with us; |
| ∎ | raw materials and components used in the manufacturing process, particularly those for which we have no other source or supplier, may not be available or may not be suitable or acceptable for use due to material or component defects; |
| ∎ | our contract manufacturers and critical reagent suppliers may be subject to inclement weather, as well as natural or man-made disasters; and |
| ∎ | our contract manufacturers may have unacceptable or inconsistent product quality success rates and yields, and we have no direct control over our contract manufacturers’ ability to maintain adequate quality control, quality assurance and qualified personnel. |
Each of these risks could delay or prevent the completion of our clinical trials or the approval of any of our product candidates by the FDA, result in higher costs or adversely impact commercialization of our product candidates. In addition, we will rely on third parties to perform certain specification tests on our product candidates prior to delivery to patients. If these tests are not appropriately done and test data are not reliable, patients could be put at risk of serious harm and the FDA could place significant restrictions on our company until deficiencies are remedied.
The manufacture of biological drug products is complex and requires significant expertise and capital investment, including the development of advanced manufacturing techniques and process controls. Manufacturers of biologic products often encounter difficulties in production, particularly in scaling up or out, validating the production process and assuring high reliability of the manufacturing process (including the absence of contamination). These problems include logistics and shipping, difficulties with production costs and yields, quality control, including stability of the product, product testing, operator error and availability of qualified personnel, as well as compliance with strictly enforced federal, state and foreign regulations. Furthermore, if contaminants are discovered in our supply of our product candidates or in the manufacturing facilities, such manufacturing facilities may need to be closed for an extended period of time to investigate and remedy the contamination. We cannot assure you that any stability failures or other issues relating to the manufacture of our product candidates will not occur in the future.
We may fail to manage the logistics of collecting and shipping patient material to the manufacturing site and shipping the product candidate back to the patient. Logistical and shipment delays and problems caused by us, our vendors or other factors not in our control, such as weather, could prevent or delay the delivery of product candidates to patients. Additionally, we have to maintain a complex chain of identity and chain of custody with respect to patient material as it moves to the manufacturing facility, through the manufacturing process and back to the patient. Failure to maintain chain of identity and chain of custody could result in patient death, loss of product or regulatory action.
Our product candidates rely on the availability of specialty raw materials, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms or at all.
Our product candidates require many specialty raw materials, some of which are manufactured by small companies with limited resources and experience to support a commercial product. In addition, those suppliers normally
55
support blood-based hospital businesses and generally do not have the capacity to support commercial products manufactured under cGMP by biopharmaceutical firms. The suppliers may be ill-equipped to support our needs, especially in non-routine circumstances like an FDA inspection or medical crisis, such as widespread contamination. We also do not have contracts with many of these suppliers and may not be able to contract with them on acceptable terms or at all. Accordingly, we may experience delays in receiving key raw materials to support clinical or commercial manufacturing.
In addition, some of our raw materials are currently available from a single supplier, or a small number of suppliers. The type of cell culture media and cryopreservation buffer that we currently use in our manufacturing process for the TRuC-T cells for TC-210 and TC-110 are each only available from a single supplier. In addition, the cell processing equipment and tubing that we use in our current manufacturing process is only available from a single supplier. We also use certain biologic materials, including certain activating antibodies, that are available from multiple suppliers, but each version may perform differently, requiring us to characterize them and potentially modify some of our protocols if we change suppliers. We cannot be sure that these suppliers will remain in business, or that they will not be purchased by one of our competitors or another company that is not interested in continuing to produce these materials for our intended purpose. Accordingly, if we no longer have access to these suppliers, we may experience delays in our clinical or commercial manufacturing which could harm our business or results of operations.
Our manufacturing process needs to comply with FDA regulations relating to the quality and reliability of such processes. Any failure to comply with relevant regulations could result in delays in or termination of our clinical programs and suspension or withdrawal of any regulatory approvals.
In order to commercially produce our products either at our own facility or at a third party’s facility, we will need to comply with the FDA’s cGMP regulations and guidelines, including cGTPs. We may encounter difficulties in achieving quality control and quality assurance and may experience shortages in qualified personnel. We are subject to inspections by the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities to confirm compliance with applicable regulatory requirements. Any failure to follow cGMP, cGTP or other regulatory requirements or delay, interruption or other issues that arise in the manufacture, fill-finish, packaging, or storage of our TRuC-T cells as a result of a failure of our facilities or the facilities or operations of third parties to comply with regulatory requirements or pass any regulatory authority inspection could significantly impair our ability to develop and commercialize our TRuC-T cell programs, including leading to significant delays in the availability of our TRuC-T cells for our clinical trials or the termination of or suspension of a clinical trial, or the delay or prevention of a filing or approval of marketing applications for our TRuC-T cell product candidates. Significant non-compliance could also result in the imposition of sanctions, including warning or untitled letters, fines, injunctions, civil penalties, failure of regulatory authorities to grant marketing approvals for our TRuC-T cell product candidates, delays, suspension or withdrawal of approvals, license revocation, seizures or recalls of products, operating restrictions and criminal prosecutions, any of which could damage our reputation and our business.
If our third-party manufacturers use hazardous and biological materials in a manner that causes injury or violates applicable law, we may be liable for damages.
Our research and development activities involve the controlled use of potentially hazardous substances, including chemical and biological materials, by our third-party manufacturers. Our manufacturers are subject to federal, state and local laws and regulations in the United States governing the use, manufacture, storage, handling and disposal of medical and hazardous materials. Although we believe that our manufacturers’ procedures for using, handling, storing and disposing of these materials comply with legally prescribed standards, we cannot completely eliminate the risk of contamination or injury resulting from medical or hazardous materials. As a result of any such contamination or injury, we may incur liability or local, city, state or federal authorities may curtail the use of these materials and interrupt our business operations. In the event of an accident, we could be held liable for damages or penalized with fines, and the liability could exceed our resources. We do not have any insurance for liabilities arising from medical or hazardous materials. Compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations is expensive, and current or future environmental regulations may impair our research, development and production efforts, which could harm our business, prospects, financial condition or results of operations.
56
Risks Related to Employee Matters and Managing Growth
We are highly dependent on our key personnel, and if we are not successful in attracting and retaining highly qualified personnel, we may not be able to successfully implement our business strategy.
Our ability to compete in the highly competitive biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries depends upon our ability to attract and retain highly qualified managerial, scientific and medical personnel. We are highly dependent on our management, scientific and medical personnel, including our Chief Executive Officer and President, our Chief Financial Officer, our Chief Scientific Officer and our Chief Medical Officer. The loss of the services of any of our executive officers, other key employees and other scientific and medical advisors, and an inability to find suitable replacements could result in delays in product development and harm our business.
We conduct our operations at our facility in Cambridge, Massachusetts. This region is headquarters to many other biopharmaceutical companies and many academic and research institutions. Competition for skilled personnel in our market is intense and may limit our ability to hire and retain highly qualified personnel on acceptable terms or at all. Changes to U.S. immigration and work authorization laws and regulations, including those that restrain the flow of scientific and professional talent, can be significantly affected by political forces and levels of economic activity. Our business may be materially adversely affected if legislative or administrative changes to immigration or visa laws and regulations impair our hiring processes and goals or projects involving personnel who are not U.S. citizens.
To encourage valuable employees to remain at our company, in addition to salary and cash incentives, we have provided stock options that vest over time. The value to employees of stock options that vest over time may be significantly affected by movements in our stock price that are beyond our control, and may at any time be insufficient to counteract more lucrative offers from other companies. Despite our efforts to retain valuable employees, members of our management, scientific and development teams may terminate their employment with us on short notice. Although we have employment agreements with our key employees, these employment agreements provide for at-will employment, which means that any of our employees could leave our employment at any time, with or without notice. Our success also depends on our ability to continue to attract, retain and motivate highly skilled junior, mid-level and senior managers as well as junior, mid-level and senior scientific and medical personnel.
We will need to grow the size of our organization, and we may experience difficulties in managing this growth.
As of January 15, 2019, we had 46 full-time employees and one part-time employee. As our development and commercialization plans and strategies develop, and as we transition into operating as a public company, we expect to need additional managerial, operational, sales, marketing, financial and other personnel, as well as additional facilities to expand our operations. Future growth would impose significant added responsibilities on members of management, including:
| ∎ | identifying, recruiting, integrating, maintaining and motivating additional employees; |
| ∎ | managing our internal development efforts effectively, including the clinical and FDA review process for our product candidates, while complying with our contractual obligations to contractors and other third parties; and |
| ∎ | improving our operational, financial and management controls, reporting systems and procedures. |
Our future financial performance and our ability to commercialize our product candidates will depend, in part, on our ability to effectively manage any future growth, and our management may also have to divert a disproportionate amount of its attention away from day-to-day activities in order to devote a substantial amount of time to managing these growth activities.
We currently rely, and for the foreseeable future will continue to rely, in substantial part on certain independent organizations, advisors and consultants to provide certain services, including substantially all aspects of regulatory approval, clinical trial management and manufacturing. There can be no assurance that the services of independent organizations, advisors and consultants will continue to be available to us on a timely basis when needed, or that we can find qualified replacements. In addition, if we are unable to effectively manage our outsourced activities or if the quality or accuracy of the services provided by consultants is compromised for any reason, our clinical trials may be extended, delayed or terminated, and we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval of our product candidates or otherwise advance our business. There can be no assurance that we will be able to manage our existing consultants or find other competent outside contractors and consultants on economically reasonable terms, or at all.
57
If we are not able to effectively expand our organization by hiring new employees and expanding our groups of consultants and contractors, or we are not able to effectively build out new facilities to accommodate this expansion, we may not be able to successfully implement the tasks necessary to further develop and commercialize our product candidates and, accordingly, may not achieve our research, development and commercialization goals.
Our internal computer systems, or those used by our third-party CROs or other contractors or consultants, may fail or suffer security breaches, which could result in a material disruption of the development programs of our product candidates.
Despite the implementation of security measures, our internal computer systems and those of our current and future CROs and other contractors and consultants are vulnerable to damage from computer viruses, unauthorized access, natural disasters, and telecommunication and electrical failures. While we have not experienced any such material system failure or security breach to date, if such an event were to occur and cause interruptions in our operations, it could result in a material disruption of our development programs and our business operations. For example, the loss of data from completed or future preclinical studies and clinical trials could result in delays in our regulatory approval efforts and significantly increase our costs to recover or reproduce the data. Likewise, we rely on third parties for the manufacture of our product candidates and to conduct clinical trials, and similar events relating to their computer systems could also have a material adverse effect on our business. To the extent that any disruption or security breach were to result in a loss of, or damage to, our data or applications, or inappropriate disclosure of confidential or proprietary information, we could incur liability and the further development and commercialization of our product candidates could be delayed.
Business disruptions could seriously harm our future revenue and financial condition and increase our costs and expenses.
Our operations, and those of our CROs, CMOs and other contractors and consultants, could be subject to earthquakes, power shortages, telecommunications failures, water shortages, floods, hurricanes, typhoons, fires, extreme weather conditions, medical epidemics and other natural or man-made disasters or business interruptions, for which we are predominantly self-insured. The occurrence of any of these business disruptions could seriously harm our operations and financial condition and increase our costs and expenses. We rely on third-party manufacturers to produce and process our product candidates on a patient-by-patient basis. Our ability to obtain clinical supplies of our product candidates could be disrupted if the operations of these suppliers are affected by a man-made or natural disaster or other business interruption.
Even if we obtain regulatory approval of our product candidates, the products may not gain market acceptance among physicians, patients, hospitals, cancer treatment centers and others in the medical community.
The use of engineered T cells as a potential cancer treatment is a recent development and may not become broadly accepted by physicians, patients, hospitals, cancer treatment centers and others in the medical community. Various factors will influence whether our product candidates are accepted in the market, including:
| ∎ | the clinical indications for which our product candidates are licensed; |
| ∎ | physicians, hospitals, cancer treatment centers and patients considering our product candidates as a safe and effective treatment; |
| ∎ | the potential and perceived advantages of our product candidates over alternative treatments; |
| ∎ | our ability to demonstrate the advantages of our product candidates over other engineered TCR-T cell and CAR-T cell therapies; |
| ∎ | the prevalence and severity of any side effects; |
| ∎ | the prevalence and severity of any side effects for other adoptive cell therapies, engineered TCR-T cell and CAR-T cell products and public perception of other adoptive cell therapies, engineered TCR-T cell andCAR-T cell products; |
| ∎ | product labeling or product insert requirements of the FDA or other regulatory authorities; |
| ∎ | limitations or warnings contained in the labeling approved by the FDA; |
| ∎ | the timing of market introduction of our product candidates as well as competitive products; |
| ∎ | the cost of treatment in relation to alternative treatments; |
| ∎ | the availability of adequate coverage, reimbursement and pricing by third-party payors and government authorities; |
58
| ∎ | the willingness of patients to pay out-of-pocket in the absence of coverage by third-party payors and government authorities; |
| ∎ | relative convenience and ease of administration, including as compared to alternative treatments and competitive therapies; and |
| ∎ | the effectiveness of our sales and marketing efforts. |
In addition, although we are not utilizing embryonic stem cells or replication competent vectors, adverse publicity due to the ethical and social controversies surrounding the therapeutic use of such technologies, and reported side effects from any clinical trials using these technologies or the failure of such clinical trials to demonstrate that these therapies are safe and effective may limit market acceptance of our product candidates. If our product candidates are licensed but fail to achieve market acceptance among physicians, patients, hospitals, cancer treatment centers or others in the medical community, we will not be able to generate significant revenue.
In addition, although our product candidates differ in certain ways from other engineered TCR-T cell and CAR-T cell approaches, serious adverse events or deaths in other clinical trials involving engineered TCR, CAR-T or other T cell products or with our use of licensed engineered TCR-T cell or CAR-T cell products, even if not ultimately attributable to our product or product candidates, could result in increased government regulation, unfavorable public perception and publicity, potential regulatory delays in the testing or licensing of our product candidates, stricter labeling requirements for those product candidates that are licensed, and a decrease in demand for any such product candidates.
Even if our products achieve market acceptance, we may not be able to maintain that market acceptance over time if new products or technologies are introduced that are more favorably received than our products, are more cost effective or render our products obsolete.
If product liability lawsuits are brought against us, we may incur substantial liabilities and may be required to limit commercialization of our product candidates.
We face an inherent risk of product liability as a result of the planned clinical testing of our product candidates and will face an even greater risk if we commercialize any products. For example, we may be sued if our product candidates cause or are perceived to cause injury or are found to be otherwise unsuitable during clinical testing, manufacturing, marketing or sale. Any such product liability claims may include allegations of defects in manufacturing, defects in design, a failure to warn of dangers inherent in the product, negligence, strict liability or a breach of warranties. Claims could also be asserted under state consumer protection acts. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against product liability claims, we may incur substantial liabilities or be required to limit commercialization of our product candidates. Even successful defense would require significant financial and management resources. Regardless of the merits or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in:
| ∎ | decreased demand for our product candidates or products that we may develop; |
| ∎ | injury to our reputation; |
| ∎ | withdrawal of clinical trial participants; |
| ∎ | initiation of investigations by regulators; |
| ∎ | costs to defend the related litigation; |
| ∎ | a diversion of management’s time and our resources; |
| ∎ | substantial monetary awards to trial participants or patients; |
| ∎ | product recalls, withdrawals or labeling, marketing or promotional restrictions; |
| ∎ | loss of revenue; |
| ∎ | exhaustion of any available insurance and our capital resources; |
| ∎ | the inability to commercialize any product candidate; and |
| ∎ | a decline in our share price. |
Failure to obtain or retain sufficient product liability insurance at an acceptable cost to protect against potential product liability claims could prevent or inhibit the commercialization of products we develop, alone or with corporate collaborators. Although we have clinical trial insurance, our insurance policies also have various
59
exclusions, and we may be subject to a product liability claim for which we have no coverage. We may have to pay any amounts awarded by a court or negotiated in a settlement that exceed our coverage limitations or that are not covered by our insurance, and we may not have, or be able to obtain, sufficient capital to pay such amounts. Even if our agreements with any future corporate collaborators entitle us to indemnification against losses, such indemnification may not be available or adequate should any claim arise.
Comprehensive tax reform legislation could adversely affect our business and financial condition.
On December 22, 2017, President Trump signed into law the TCJA, which significantly reformed the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended. The TCJA, among other things, contains significant changes to corporate taxation, including reduction of the corporate tax rate from a top marginal rate of 35% to a flat rate of 21%, limitation of the tax deduction for interest expense, limitation of the deduction for net operating losses and elimination of net operating loss carrybacks, in each case, for losses arising in taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 (though any such tax losses may be carried forward indefinitely), and modifying or repealing many business deductions and credits, including reducing the business tax credit for certain clinical testing expenses incurred in the testing of certain drugs for rare diseases or conditions generally referred to as “orphan drugs”. We continue to examine the impact this tax reform legislation may have on our business. However, the effect of the TCJA on us and our affiliates, whether adverse or favorable, is uncertain and may not become evident for some period of time. You are urged to consult your tax adviser regarding the implications of the TCJA on an investment in our common stock.
Our ability to utilize our net operating loss carryforwards and certain other tax attributes may be limited.
Under Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change” (generally defined as a greater than 50% change (by value) in its equity ownership over a three-year period), the corporation’s ability to use its pre-change net operating loss carryforwards and other pre-change tax attributes to offset its post-change taxable income may be limited. As a result of our most recent private placements and other transactions that have occurred over the past three years, we may have experienced, and, upon closing of this offering, may experience, an “ownership change.” We may also experience ownership changes in the future as a result of subsequent shifts in our stock ownership. As of December 31, 2017, we had U.S. federal net operating loss carryforwards of $1.8 million and U.S. federal research and development tax credit carryforwards of $0.4 million, each of which will begin to expire in 2037 and which could be limited if we experience an “ownership change.” The reduction of the corporate tax rate under the TCJA may cause a reduction in the economic benefit of our net operating loss carryforwards and other deferred tax assets available to us. Under the TCJA, federal net operating losses generated after December 31, 2017 will not be subject to expiration.
Unstable market and economic conditions may have serious adverse consequences on our business, financial condition and stock price.
As widely reported, global credit and financial markets have experienced extreme volatility and disruptions in the past several years, including severely diminished liquidity and credit availability, declines in consumer confidence, declines in economic growth, increases in unemployment rates and uncertainty about economic stability. There can be no assurance that further deterioration in credit and financial markets and confidence in economic conditions will not occur. Our general business strategy may be adversely affected by any such economic downturn, volatile business environment or continued unpredictable and unstable market conditions. If the current equity and credit markets deteriorate, or do not improve, it may make any necessary debt or equity financing more difficult, more costly, and more dilutive. Failure to secure any necessary financing in a timely manner and on favorable terms could have a material adverse effect on our growth strategy, financial performance and stock price and could require us to delay or abandon clinical development plans. In addition, there is a risk that one or more of our current service providers, manufacturers and other partners may not survive these difficult economic times, which could directly affect our ability to attain our operating goals on schedule and on budget.
As of September 30, 2018, we had cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of $131.0 million. While we are not aware of any downgrades, material losses, or other significant deterioration in the fair value of our cash equivalents and short-term investments since September 30, 2018, no assurance can be given that further deterioration of the global credit and financial markets would not negatively impact our current portfolio of cash equivalents or our ability to meet our financing objectives. Furthermore, our stock price may decline due in part to the volatility of the stock market and the general economic downturn.
60
We currently have no marketing and sales organization and have no experience in marketing products. If we are unable to establish marketing and sales capabilities or enter into agreements with third parties to market and sell our product candidates, if licensed, we may not be able to generate product revenue.
We currently have no sales, marketing or distribution capabilities and have no experience in marketing products. We intend to develop an in-house marketing organization and sales force, which will require significant capital expenditures, management resources and time. We will have to compete with other pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies to recruit, hire, train and retain marketing and sales personnel.
If we are unable or decide not to establish internal sales, marketing and distribution capabilities, we will pursue collaborative arrangements regarding the sales and marketing of our products, if licensed. However, there can be no assurance that we will be able to establish or maintain such collaborative arrangements, or if we are able to do so, that they will have effective sales forces. Any revenue we receive will depend upon the efforts of such third parties, which may not be successful. We may have little or no control over the marketing and sales efforts of such third parties and our revenue from product sales may be lower than if we had commercialized our product candidates ourselves. We also face competition in our search for third parties to assist us with the sales and marketing efforts of our product candidates.
There can be no assurance that we will be able to develop in-house sales and distribution capabilities or establish or maintain relationships with third-party collaborators to commercialize any product in the United States or overseas.
Risks Related to This Offering and Ownership of our Common Stock
We do not know whether an active, liquid and orderly trading market will develop for our common stock or what the market price of our common stock will be and, as a result, it may be difficult for you to sell your shares of our common stock.
Prior to this offering, there was no public trading market for shares of our common stock. Although we have applied to list our common stock on The Nasdaq Global Market, an active trading market for our shares may never develop or be sustained following this offering. You may not be able to sell your shares quickly or at the market price if trading in shares of our common stock is not active. The initial public offering price for our common stock will be determined through negotiations with the underwriters, and the negotiated price may not be indicative of the market price of the common stock after the offering. As a result of these and other factors, you may be unable to resell your shares of our common stock at or above the initial public offering price. Further, an inactive market may also impair our ability to raise capital by selling shares of our common stock and may impair our ability to enter into strategic partnerships or acquire companies or products by using our shares of common stock as consideration.
The price of our stock may be volatile, and you could lose all or part of your investment.
The trading price of our common stock following this offering is likely to be highly volatile and could be subject to wide fluctuations in response to various factors, some of which are beyond our control, including limited trading volume. In addition to the factors discussed in this “Risk Factors” section and elsewhere in this prospectus, these factors include:
| ∎ | the results of our ongoing, planned or any future preclinical studies, clinical trials or clinical development programs; |
| ∎ | the commencement, enrollment, or results of clinical trials of our product candidates or any future clinical trials we may conduct, or changes in the development status of our product candidates; |
| ∎ | adverse results or delays in preclinical studies and clinical trials; |
| ∎ | our decision to initiate a clinical trial, not to initiate a clinical trial, or to terminate an existing clinical trial; |
| ∎ | any delay in our regulatory filings or any adverse regulatory decisions, including failure to receive regulatory approval of our product candidates; |
| ∎ | changes in laws or regulations applicable to our products, including but not limited to clinical trial requirements for approvals; |
| ∎ | adverse developments concerning our manufacturers or our manufacturing plans; |
| ∎ | our inability to obtain adequate product supply for any licensed product or inability to do so at acceptable prices; |
61
| ∎ | our inability to establish collaborations if needed; |
| ∎ | our failure to commercialize our product candidates; |
| ∎ | additions or departures of key scientific or management personnel; |
| ∎ | unanticipated serious safety concerns related to the use of our product candidates; |
| ∎ | introduction of new products or services offered by us or our competitors; |
| ∎ | announcements of significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital commitments by us or our competitors; |
| ∎ | our ability to effectively manage our growth; |
| ∎ | the size and growth of our initial cancer target markets; |
| ∎ | our ability to successfully treat additional types of cancers or at different stages; |
| ∎ | actual or anticipated variations in quarterly operating results; |
| ∎ | our cash position; |
| ∎ | our failure to meet the estimates and projections of the investment community or that we may otherwise provide to the public; |
| ∎ | publication of research reports about us or our industry, or immunotherapy in particular, or positive or negative recommendations or withdrawal of research coverage by securities analysts; |
| ∎ | changes in the market valuations of similar companies; |
| ∎ | overall performance of the equity markets; |
| ∎ | sales of our common stock by us or our stockholders in the future; |
| ∎ | trading volume of our common stock; |
| ∎ | changes in accounting practices; |
| ∎ | ineffectiveness of our internal controls; |
| ∎ | disputes or other developments relating to proprietary rights, including patents, litigation matters and our ability to obtain patent protection for our technologies; |
| ∎ | significant lawsuits, including patent or stockholder litigation; |
| ∎ | general political and economic conditions; and |
| ∎ | other events or factors, many of which are beyond our control. |
In addition, the stock market in general, and The Nasdaq Global Market and biopharmaceutical companies in particular, have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of these companies. Broad market and industry factors may negatively affect the market price of our common stock, regardless of our actual operating performance. If the market price of our common stock after this offering does not exceed the initial public offering price, you may not realize any return on your investment in us and may lose some or all of your investment. In the past, securities class action litigation has often been instituted against companies following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities. This type of litigation, if instituted, could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources, which would harm our business, operating results, or financial condition.
If you purchase our common stock in this offering, you will incur immediate and substantial dilution in the book value of your shares.
The initial public offering price will be substantially higher than the net tangible book value per share of our common stock. Investors purchasing common stock in this offering will pay a price per share that substantially exceeds the book value of our tangible assets after subtracting our liabilities. As a result, investors purchasing common stock in this offering will incur immediate dilution of $6.47 per share, based on the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share which is the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus. Further, investors purchasing common stock in this offering will contribute approximately 30.6% of the total amount invested by stockholders since our inception, but will own only approximately 21.8% of the total number of shares of our common stock outstanding after this offering.
This dilution is due to our investors who purchased shares prior to this offering having paid substantially less when they purchased their shares than the price offered to the public in this offering and the exercise of stock options
62
granted to our employees. To the extent that outstanding stock options or warrants are exercised, there will be further dilution to new investors. As a result of the dilution to investors purchasing common stock in this offering, investors may receive significantly less than the purchase price paid in this offering, if anything, in the event of our liquidation. For a further description of the dilution that you will experience immediately after this offering, see the section of this prospectus entitled “Dilution.”
Future sales and issuances of our common stock or rights to purchase common stock, including pursuant to our 2018 Stock Option and Incentive Plan, could result in additional dilution of the percentage ownership of our stockholders and could cause our stock price to fall.
We expect that significant additional capital may be needed in the future to continue our planned operations, including conducting clinical trials, expanded research and development activities, and costs associated with operating as a public company. To raise capital, we may sell common stock, convertible securities, or other equity securities in one or more transactions at prices and in a manner we determine from time to time. If we sell common stock, convertible securities, or other equity securities, investors may be materially diluted by subsequent sales. Such sales may also result in material dilution to our existing stockholders, and new investors could gain rights, preferences, and privileges senior to the holders of our common stock, including shares of common stock sold in this offering.
Pursuant to our 2018 Stock Option and Incentive Plan (2018 Plan), which will become effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, our management is authorized to grant stock options to our employees, directors, and consultants.
Initially, the aggregate number of shares of our common stock that may be issued pursuant to stock awards under the 2018 Plan will be 3,000,000 shares, less the shares of common stock remaining available for issuance under our 2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan as of the business day immediately prior to the effective date of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. The number of shares of our common stock reserved for issuance under the 2018 Plan shall be cumulatively increased on January 1, 2020 and each January 1 thereafter by 4% of the total number of shares of our common stock outstanding on December 31 of the preceding calendar year or a lesser number of shares determined by our board of directors. Unless our board of directors elects not to increase the number of shares available for future grant each year, our stockholders may experience additional dilution, which could cause our stock price to fall.
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our existing stockholders, restrict our operations or require us to relinquish rights to our technologies or product candidates.
We may seek additional capital through a combination of public and private equity offerings, debt financings, strategic partnerships and alliances and licensing arrangements. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, your ownership interest will be diluted, and the terms may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights as a stockholder. The incurrence of indebtedness would result in increased fixed payment obligations and could involve certain restrictive covenants, such as limitations on our ability to incur additional debt, limitations on our ability to acquire or license intellectual property rights and other operating restrictions that could adversely impact our ability to conduct our business. If we raise additional funds through strategic partnerships and alliances and licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies or product candidates, or grant licenses on terms unfavorable to us.
We have broad discretion in the use of the net proceeds from this offering and may not use them effectively.
Our management will have broad discretion in the application of the net proceeds from this offering, including for any of the purposes described in the section entitled “Use of Proceeds,” and you will not have the opportunity as part of your investment decision to assess whether the net proceeds are being used appropriately. Because of the number and variability of factors that will determine our use of the net proceeds from this offering, their ultimate use may vary substantially from their currently intended use. Our management might not apply our net proceeds in ways that ultimately increase or maintain the value of your investment.
We do not intend to pay dividends on our common stock, so any returns will be limited to the value of our stock.
We currently anticipate that we will retain future earnings for the development, operation, and expansion of our business and do not anticipate declaring or paying any cash dividends for the foreseeable future. In addition, we may enter into agreements that prohibit us from paying cash dividends without prior written consent from our contracting parties, or which other terms prohibiting or limiting the amount of dividends that may be declared or paid on our
63
common stock. Any return to stockholders will therefore be limited to the appreciation of their stock, which may never occur.
Our principal stockholders and management own a significant percentage of our stock and will be able to exert significant influence over matters subject to stockholder approval.
Prior to this offering, our executive officers, directors, and 5% stockholders beneficially owned approximately 85% of our voting stock as of December 31, 2018, and, assuming the sale by us of 5,000,000 shares of common stock in this offering, based on an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, which is the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, and not accounting for any shares purchased in this offering by certain of our existing stockholders (or their affiliates), including those affiliated with certain of our directors, who have indicated an interest in purchasing approximately $30.0 million of shares of our common stock in this offering, we anticipate that same group will hold approximately 67% of our outstanding voting stock following this offering (assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares). Therefore, even after this offering, these stockholders will have the ability to influence us through this ownership position. These stockholders may be able to determine all matters requiring stockholder approval. For example, these stockholders may be able to control elections of directors, amendments of our organizational documents, or approval of any merger, sale of assets, or other major corporate transaction. This may prevent or discourage unsolicited acquisition proposals or offers for our common stock that you may feel are in your best interest as one of our stockholders.
We are an emerging growth company, and we cannot be certain if the reduced reporting requirements applicable to emerging growth companies will make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an emerging growth company, as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (JOBS Act) enacted in April 2012. For as long as we continue to be an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies, including not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as amended (Sarbanes-Oxley Act), reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in this prospectus and our periodic reports and proxy statements, and exemptions from the requirements of holding nonbinding advisory votes on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. We could be an emerging growth company for up to five years following the year in which we complete this offering, although circumstances could cause us to lose that status earlier. We will remain an emerging growth company until the earlier of (1) the last day of the fiscal year (a) following the fifth anniversary of the closing of this offering, (b) in which we have total annual gross revenue of at least $1.07 billion or (c) in which we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer, which requires the market value of our common stock that is held by non-affiliates to exceed $700 million as of the prior June 30th, and (2) the date on which we have issued more than $1 billion in non-convertible debt during the prior three-year period.
Under the JOBS Act, emerging growth companies can also delay adopting new or revised accounting standards until such time as those standards apply to private companies. We have elected to avail ourselves of this exemption from complying with new or revised accounting standards and, therefore, will not be subject to the same new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not emerging growth companies.
Even after we no longer qualify as an emerging growth company, we may still qualify as a “smaller reporting company,” which would allow us to take advantage of many of the same exemptions from disclosure requirements, including not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in this prospectus and our periodic reports and proxy statements. We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we may rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
We will incur significant increased costs as a result of operating as a public company, and our management will be required to devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives.
As a public company, we will incur significant legal, accounting, and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. We will be subject to the reporting requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, which will require, among other things, that we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), annual, quarterly, and current reports with respect to our business and financial condition. In addition, the
64
Sarbanes-Oxley Act, as well as rules subsequently adopted by the SEC and The Nasdaq Global Market to implement provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, impose significant requirements on public companies, including requiring establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and changes in corporate governance practices. Further, in July 2010, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the Dodd-Frank Act) was enacted. There are significant corporate governance and executive compensation related provisions in the Dodd-Frank Act that require the SEC to adopt additional rules and regulations in these areas, such as “say on pay” and proxy access. Recent legislation permits emerging growth companies to implement many of these requirements over a longer period and up to five years from the pricing of this offering. We intend to take advantage of this new legislation but cannot guarantee that we will not be required to implement these requirements sooner than budgeted or planned and thereby incur unexpected expenses. Stockholder activism, the current political environment, and the current high level of government intervention and regulatory reform may lead to substantial new regulations and disclosure obligations, which may lead to additional compliance costs and impact the manner in which we operate our business in ways we cannot currently anticipate.
We expect the rules and regulations applicable to public companies to substantially increase our legal and financial compliance costs and to make some activities more time-consuming and costly. If these requirements divert the attention of our management and personnel from other business concerns, they could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. The increased costs will decrease our net income or increase our net loss and may require us to reduce costs in other areas of our business or increase the prices of our products or services. For example, we expect these rules and regulations to make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance and we may be required to incur substantial costs to maintain the same or similar coverage. We cannot predict or estimate the amount or timing of additional costs we may incur to respond to these requirements. The impact of these requirements could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our board of directors, our board committees, or as executive officers.
Sales of a substantial number of shares of our common stock by our existing stockholders in the public market could cause our stock price to fall.
If our existing stockholders sell, or indicate an intention to sell, substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market after the lock-up and other legal restrictions on resale discussed in this prospectus lapse, the trading price of our common stock could decline. Based on the number of shares of common stock outstanding as of December 31, 2018, upon the closing of this offering, we will have outstanding a total of 23,189,901 shares of common stock. Of these shares, only the shares of common stock sold in this offering by us, plus any shares sold upon exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares, will be freely tradable without restriction in the public market immediately following this offering, unless purchased by our affiliates. In connection with this offering, our officers, directors and substantially all of our stockholders have agreed to be subject to a contractual lock-up with the underwriters, which will expire 180 days after the date of this prospectus. Jefferies LLC, SVB Leerink LLC and BMO Capital Markets Corp., however, may, in their sole discretion, permit our officers, directors and other stockholders who are subject to these lock-up agreements to sell shares prior to the expiration of the lock-up agreements.
In addition, shares of common stock that are either subject to outstanding options or reserved for future issuance under our 2018 Plan and our 2018 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, each to be effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, will become eligible for sale in the public market to the extent permitted by the provisions of various vesting schedules, the lock-up agreements and Rule 144 and Rule 701 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the Securities Act). If these additional shares of common stock are sold, or if it is perceived that they will be sold, in the public market, the trading price of our common stock could decline.
After this offering, the holders of 17,276,913 shares of our common stock will be entitled to rights with respect to the registration of their shares under the Securities Act, subject to the 180-day lock-up agreements described above. See “Description of Capital Stock—Registration Rights.” Registration of these shares under the Securities Act would result in the shares becoming freely tradable without restriction under the Securities Act, except for shares held by affiliates, as defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act. Any sales of securities by these stockholders could have a material adverse effect on the trading price of our common stock.
65
Anti-takeover provisions under our charter documents and Delaware law could delay or prevent a change of control, which could limit the market price of our common stock and may prevent or frustrate attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws, which are to become effective upon the closing of this offering, will contain provisions that could delay or prevent a change of control of our company or changes in our board of directors that our stockholders might consider favorable. Some of these provisions include:
| ∎ | a board of directors divided into three classes serving staggered three-year terms, such that not all members of the board will be elected at one time; |
| ∎ | a prohibition on stockholder action through written consent, which requires that all stockholder actions be taken at a meeting of our stockholders; |
| ∎ | a requirement that special meetings of stockholders be called only by the chairperson of the board of directors, the chief executive officer, or by a majority of the total number of authorized directors; |
| ∎ | advance notice requirements for stockholder proposals and nominations for election to our board of directors; |
| ∎ | a requirement that no member of our board of directors may be removed from office by our stockholders except for cause and, in addition to any other vote required by law, upon the approval of not less than two-thirds of all outstanding shares of our voting stock then entitled to vote in the election of directors; |
| ∎ | a requirement of approval of not less than two-thirds of all outstanding shares of our voting stock to amend any bylaws by stockholder action or to amend specific provisions of our certificate of incorporation; and |
| ∎ | the authority of the board of directors to issue preferred stock on terms determined by the board of directors without stockholder approval and which preferred stock may include rights superior to the rights of the holders of common stock. |
In addition, because we are incorporated in Delaware, we are governed by the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporate Law, which may prohibit certain business combinations with stockholders owning 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock. These anti-takeover provisions and other provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws could make it more difficult for stockholders or potential acquirers to obtain control of our board of directors or initiate actions that are opposed by the then-current board of directors and could also delay or impede a merger, tender offer, or proxy contest involving our company. These provisions could also discourage proxy contests and make it more difficult for you and other stockholders to elect directors of your choosing or cause us to take other corporate actions you desire. Any delay or prevention of a change of control transaction or changes in our board of directors could cause the market price of our common stock to decline.
Our bylaws to be effective upon the consummation of this offering designate certain courts as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings that may be initiated by our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers, or employees.
Our bylaws that will become effective upon the completion of this offering provide that, unless we consent in writing to an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of fiduciary duty owed by any of our directors, officers, and employees to us or our stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or our amended and restated bylaws or (iv) any action asserting a claim that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine, in each case subject to the Court of Chancery having personal jurisdiction over the indispensable parties named as defendants therein. This exclusive forum provision will not apply to any causes of action arising under the Exchange Act. In addition, our amended and restated bylaws will provide that any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of our common stock is deemed to have notice of and consented to the foregoing provisions. We recognize that the forum selection clause in our bylaws may impose additional litigation costs on stockholders in pursuing any such claims, particularly if the stockholders do not reside in or near the State of Delaware. Additionally, the forum selection clauses in our amended and restated bylaws may limit our stockholders’ ability to bring a claim in a forum that they find favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers or employees, which may discourage such lawsuits against us and our directors, officers and employees even though an action, if successful, might benefit our stockholders. The Court of Chancery of the State
66
of Delaware may also reach different judgments or results than would other courts, including courts where a stockholder considering an action may be located or would otherwise choose to bring the action, and such judgments may be more or less favorable to us than our stockholders.
If we fail to establish and maintain proper and effective internal control over financial reporting, our operating results and our ability to operate our business could be harmed.
Ensuring that we have adequate internal financial and accounting controls and procedures in place so that we can produce accurate financial statements on a timely basis is a costly and time-consuming effort that needs to be re-evaluated frequently. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. In connection with this offering, we intend to begin the process of documenting, reviewing, and improving our internal controls and procedures for compliance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which will require annual management assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. We have begun recruiting additional finance and accounting personnel with certain skill sets that we will need as a public company.
Implementing any appropriate changes to our internal controls may distract our officers and employees, entail substantial costs to modify our existing processes, and take significant time to complete. These changes may not, however, be effective in maintaining the adequacy of our internal controls, and any failure to maintain that adequacy, or consequent inability to produce accurate financial statements on a timely basis, could increase our operating costs and harm our business. In addition, investors’ perceptions that our internal controls are inadequate or that we are unable to produce accurate financial statements on a timely basis may harm our stock price and make it more difficult for us to effectively market and sell our service to new and existing customers.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about our business, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock will depend in part on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about us or our business. Securities and industry analysts do not currently, and may never, publish research on our company. If no securities or industry analysts commence coverage of our company, the trading price for our stock would likely be negatively impacted. In the event securities or industry analysts initiate coverage, if one or more of the analysts who cover us downgrades our stock or publishes inaccurate or unfavorable research about our business, our stock price may decline. If one or more of these analysts ceases coverage of our company or fails to publish reports on us regularly, demand for our stock could decrease, which might cause our stock price and trading volume to decline.
67
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus, including the sections entitled “Prospectus Summary,” “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” and “Business,” contains express or implied forward-looking statements that are based on our management’s belief and assumptions and on information currently available to our management. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in these forward-looking statements are reasonable, these statements relate to future events or our future operational or financial performance, and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements in this prospectus include, but are not limited to, statements about:
| ∎ | the timing of preclinical studies and clinical trials of TC-210, TC-110 and any other product candidates; |
| ∎ | our need to raise additional funding before we can expect to generate any revenues from product sales; |
| ∎ | our ability to submit our planned INDs and conduct successful clinical trials or obtain regulatory approval for TC-210, TC-110 or any other product candidates that we may identify or develop; |
| ∎ | the ability of our TRuC-T cell platform to generate and advance additional product candidates; |
| ∎ | our ability to establish an adequate safety, potency and purity profile for TC-210, TC-110 or any other product candidates that we may pursue; |
| ∎ | our ability to manufacture TC-210, TC-110 or any other product candidate in conformity with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s requirements and to scale up manufacturing of our product candidates to commercial scale, if approved; |
| ∎ | the implementation of our strategic plans for our business, any product candidates we may develop and our technology; |
| ∎ | our intellectual property position, including the scope of protection we are able to establish and maintain for intellectual property rights covering our product candidates and technology; |
| ∎ | the rate and degree of market acceptance and clinical utility for any product candidates we may develop; |
| ∎ | our ability to use the proceeds of this offering in ways that increase the value of your investment; |
| ∎ | our expectations related to the use of proceeds from this offering, and estimates of our expenses, future revenues, capital requirements and our needs for additional financing; |
| ∎ | our ability to maintain and establish collaborations; |
| ∎ | our financial performance; |
| ∎ | our ability to effectively manage our anticipated growth; |
| ∎ | developments relating to our competitors and our industry, including the impact of government regulation; |
| ∎ | our estimates regarding the market opportunities for our product candidates; |
| ∎ | our ability to retain the continued service of our key professionals and to identify, hire and retain additional qualified professionals; and |
| ∎ | other risks and uncertainties, including those listed under the section titled “Risk Factors.” |
In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “may,” “should,” “expects,” “intends,” “plans,” “anticipates,” “believes,” “estimates,” “predicts,” “potential,” “continue” or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology. These statements are only predictions. You should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements because they involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors, which are, in some cases, beyond our control and which could materially affect results. Factors that may cause actual results to differ materially from current expectations include, among other things, those listed under the section titled “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus. If one or more of these risks or uncertainties occur, or if our underlying assumptions prove to be incorrect, actual events or results may vary significantly from those implied or projected by the forward-looking statements. No forward-looking statement is a guarantee of future performance. You should read this prospectus and the documents that we reference in this prospectus and have filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission as exhibits to the registration statement, of which this prospectus forms a part, completely and with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from any future results expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements.
68
The forward-looking statements in this prospectus represent our views as of the date of this prospectus. We anticipate that subsequent events and developments will cause our views to change. However, while we may elect to update these forward-looking statements at some point in the future, we have no current intention of doing so except to the extent required by applicable law. You should therefore not rely on these forward-looking statements as representing our views as of any date subsequent to the date of this prospectus.
This prospectus also contains estimates, projections and other information concerning our industry, our business and the markets for our product candidates. Information that is based on estimates, forecasts, projections, market research or similar methodologies is inherently subject to uncertainties and actual events or circumstances may differ materially from events and circumstances that are assumed in this information. Unless otherwise expressly stated, we obtained this industry, business, market, and other data from our own internal estimates and research as well as from reports, research surveys, studies, and similar data prepared by market research firms and other third parties, industry, medical and general publications, government data and similar sources. While we are not aware of any misstatements regarding any third-party information presented in this prospectus, their estimates, in particular, as they relate to projections, involve numerous assumptions, are subject to risks and uncertainties and are subject to change based on various factors, including those discussed under the section titled “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus.
69
We estimate that the net proceeds to us from the sale of 5,000,000 shares of our common stock in this offering will be approximately $67.3 million, or approximately $77.7 million if the underwriters exercise in full their option to purchase additional shares, assuming an initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the net proceeds to us from this offering by $4.7 million, assuming the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. An increase (decrease) of 1.0 million shares in the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) our net proceeds from this offering by $14.0 million, assuming no change in the assumed initial public offering price per share and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. We do not expect that a change in the offering price or the number of shares by these amounts would have a material effect on our intended uses of the net proceeds from this offering, although it may impact the amount of time prior to which we may need to seek additional capital.
As of September 30, 2018, we had cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of $131.0 million. We currently intend to use the net proceeds from this offering, together with our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, as follows:
| ∎ | approximately $25 million to $30 million to fund the development of our lead product candidate,TC-210, targeting mesothelin-positive solid tumors, through the completion of our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial in patients with mesothelin-positive non-small cell lung cancer, ovarian cancer, malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma and cholangiocarcinoma; |
| ∎ | approximately $35 million to $40 million to fund the development of our lead product candidate,TC-110, targeting CD19-positiveB-cell hematological malignancies through a Phase 1 clinical trial and the development ofTC-220 for the treatment of patients withMUC16-positive ovarian cancer through a Phase 1/2 clinical trial; |
| ∎ | approximately $10 million to $15 million to fund the continued development of our TRuC-T cell platform; |
| ∎ | approximately $30 million to $35 million to fund manufacturing activities to support our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial ofTC-210, Phase 1 clinical trial ofTC-110 and Phase 1/2 clinical trial ofTC-220; and |
| ∎ | the remaining proceeds, if any, to fund new and ongoing research and development activities, working capital and other general corporate purposes, which may include funding for the hiring of additional personnel, capital expenditures and the costs of operating as a public company. |
Based on our current plans, we believe our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, together with the net proceeds from this offering, will be sufficient to fund our operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements at least into 2022.
This expected use of the net proceeds from this offering represents our intentions based upon our current plans and business conditions, which could change in the future as our plans and business conditions evolve. For example, we may use a portion of the net proceeds for the acquisition of businesses or technologies to continue to build our pipeline, our research and development capabilities and our intellectual property position, although we currently have no agreements, commitments or understandings with respect to any such transaction. We cannot predict with certainty all of the particular uses for the net proceeds to be received upon the completion of this offering or the amounts that we will actually spend on the uses set forth above. The amounts and timing of our actual expenditures may vary significantly depending on numerous factors, including the progress of our research and development, the status of and results from non-clinical studies or clinical trials we may commence in the future, as well as any collaborations that we may enter into with third parties for our product candidates or strategic opportunities that become available to us, and any unforeseen cash needs. As a result, our management will retain broad discretion over the allocation of the net proceeds from this offering.
Pending our use of proceeds from this offering, we intend to invest the net proceeds in a variety of capital preservation instruments, including short-term, investment-grade, interest-bearing instruments and U.S. government securities.
70
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain any future earnings to fund the development and expansion of our business, and therefore we do not anticipate paying cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. Any future determination to pay dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on our results of operations, financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors deemed relevant by our board of directors.
71
The following table sets forth our cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments and our capitalization as of September 30, 2018:
| ∎ | on an actual basis; |
| ∎ | on a pro forma basis to give effect to (i) the automatic conversion of all outstanding shares of our preferred stock into an aggregate of 17,275,299 shares of common stock upon the closing of this offering, and (ii) the filing and effectiveness of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, which will occur upon the closing of this offering; and |
| ∎ | on a pro forma as adjusted basis to give further effect to the sale and issuance by us of 5,000,000 shares of our common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
You should read the information below in conjunction with the financial statements and the related notes thereto and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this prospectus.
| AS OF SEPTEMBER 30, 2018 | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands, except share and per share data) | ACTUAL | PRO FORMA | PRO FORMA AS ADJUSTED | |||||||||
Cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments | $ | 130,998 | $ | 130,998 | $ | 198,273 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series A and B), $0.0001 par value; 107,000,001 shares authorized and 107,000,001 shares issued and outstanding, actual; no shares authorized, issued or outstanding, pro forma; no shares authorized, issued or outstanding, pro forma as adjusted | 205,500 | — | — | |||||||||
Stockholders’ equity (deficit): | ||||||||||||
Common stock, $0.0001 par value; 20,988,730 shares authorized, 908,390 shares issued and 681,005 shares outstanding, actual; 150,000,000 shares authorized, 18,183,689 shares issued and 17,956,304 shares outstanding, pro forma; 150,000,000 shares authorized, 23,183,689 shares issued and 22,956,304 shares outstanding, pro forma as adjusted | — | 2 | 2 | |||||||||
Preferred stock, $0.0001 par value; no shares authorized, issued or outstanding, actual; 10,000,000 shares authorized and no shares issued and outstanding, pro forma and pro forma as adjusted | — | — | — | |||||||||
Additional paid-in capital | — | 205,498 | 272,773 | |||||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||
Accumulated deficit | (75,033 | ) | (75,033 | ) | (75,033 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) | (75,036 | ) | 130,464 | 197,739 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total capitalization | $ | 130,464 | $ | 130,464 | $ | 197,739 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted amount of cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, additional paid-in capital, total stockholders’ equity and total capitalization by approximately $4.7 million, assuming the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. Similarly, each increase (decrease) of 1.0 million
72
shares in the number of shares offered by us in this offering would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted amount of cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, additional paid-in capital, total stockholders’ equity and total capitalization by approximately $14.0 million, assuming the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same, and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
The table above excludes each of the following:
| ∎ | 1,965,705 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of options outstanding under our 2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan (2015 Plan) at a weighted-average exercise price of $3.47 per share as of September 30, 2018; |
| ∎ | 8,017 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of outstanding options issued outside of our 2015 Plan at an exercise price of $0.74 per share as of September 30, 2018; |
| ∎ | 203,676 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of warrants to purchase common stock at a weighted-average exercise price of $0.74 per share as of September 30, 2018; |
| ∎ | 403,728 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2015 Plan as of September 30, 2018; |
| ∎ | 2,731,607 shares of common stock to be reserved for future issuance under our 2018 Stock Option and Incentive Plan to be effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part; and |
| ∎ | 300,000 shares of common stock to be reserved for future issuance under our 2018 Employee Stock Purchase Plan to be effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. |
73
If you invest in our common stock in this offering, your interest will be diluted immediately to the extent of the difference between the public offering price per share of our common stock and the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share of our common stock after this offering. As of September 30, 2018, our historical net tangible book value was ($76.2) million, or ($83.92) per share. Our historical net tangible book value represents total tangible assets less total liabilities and preferred stock, all divided by the number of shares of common stock outstanding on September 30, 2018.
Our pro forma net tangible book value as of September 30, 2018 was $129.3 million, or $7.11 per share, after giving effect to the automatic conversion of all outstanding shares of our preferred stock into shares of our common stock upon the completion of this offering. After giving effect to the sale of 5,000,000 shares of common stock offered in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value as of September 30, 2018 would have been $197.7 million, or $8.53 per share. This represents an immediate increase in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value of $1.42 per share to existing stockholders and an immediate dilution of $6.47 per share to new investors in this offering, or approximately 43% of the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share. The following table illustrates this dilution on a per share basis:
Assumed initial public offering price per share | $ | 15.00 | ||||||
Historical net tangible book value per share as of September 30, 2018 | $ | (83.92 | ) | |||||
Increase per share attributable to the pro forma adjustments described above | 91.03 | |||||||
Pro forma net tangible book value per share as of September 30, 2018, before giving effect to this offering | 7.11 | |||||||
|
| |||||||
Increase in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share attributable to this offering | 1.42 | |||||||
|
| |||||||
Pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share after giving effect to this offering | 8.53 | |||||||
|
| |||||||
Dilution in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share to new investors in this offering | $ | 6.47 | ||||||
|
|
A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value by $0.20 per share and the dilution to investors participating in this offering by $0.80 per share, assuming the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same, and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated expenses payable by us. Similarly, each increase (decrease) of 1.0 million shares in the number of shares offered by us in this offering would increase (decrease) the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value by $0.22 per share and the dilution to investors participating in this offering by $(0.22) per share, assuming the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated expenses payable by us.
The following table summarizes, on a pro forma as adjusted basis as of September 30, 2018, the differences between the number of shares of common stock purchased from us on an as converted basis, the total cash consideration paid and the average price per share paid to us by existing stockholders and by new investors purchasing shares in this offering, at the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, before deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us:
74
| SHARES PURCHASED | TOTAL CONSIDERATION | AVERAGE PRICE PER SHARE | ||||||||||||||||||
| NUMBER | PERCENT | AMOUNT | PERCENT | |||||||||||||||||
Existing stockholders | 17,956,304 | 78.2 | % | $ | 169,763,017 | 69.4 | % | $ | 9.45 | |||||||||||
Investors participating in this offering | 5,000,000 | 21.8 | % | $ | 75,000,000 | 30.6 | % | $ | 15.00 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
Total | 22,956,304 | 100.0 | % | $ | 244,763,017 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
Certain of our existing stockholders (or their affiliates), including those affiliated with certain of our directors, have indicated an interest in purchasing an aggregate of approximately $30.0 million of shares of our common stock in this offering at the initial public offering price. The table above does not reflect the purchases by such stockholders in this offering.
A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) the total consideration paid by investors in this offering by approximately $5.0 million, assuming the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. Similarly, each increase (decrease) of 1.0 million shares in the number of shares offered by us in this offering would increase (decrease) the total consideration paid by investors in this offering by approximately $15.0 million, assuming the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same, and after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
The table above assumes no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares in this offering. If the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares of our common stock in full, our existing stockholders would own 76% and our new investors would own 24% of the total number of shares of our common stock outstanding after this offering.
The number of shares of our common stock outstanding after this offering is based on 18,183,689 shares of common stock outstanding as of September 30, 2018, which includes 227,385 shares of unvested restricted stock subject to repurchase by us, after giving effect to the automatic conversion of all outstanding shares of our preferred stock into an aggregate of 17,275,299 shares of common stock upon completion of this offering.
The foregoing tables and calculations exclude:
| ∎ | 1,965,705 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of options outstanding under our 2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan (2015 Plan) at a weighted-average exercise price of $3.47 per share as of September 30, 2018; |
| ∎ | 8,017 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of outstanding options issued outside of our 2015 Plan at an exercise price of $0.74 per share as of September 30, 2018; |
| ∎ | 203,676 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of warrants to purchase common stock at an exercise price of $0.74 per share as of September 30, 2018; |
| ∎ | 403,728 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2015 Plan as of September 30, 2018; |
| ∎ | 2,731,607 shares of common stock to be reserved for future issuance under our 2018 Stock Option and Incentive Plan to be effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part; and |
| ∎ | 300,000 shares of common stock to be reserved for future issuance under our 2018 Employee Stock Purchase Plan to be effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. |
To the extent that outstanding options or warrants are exercised or shares are issued under our equity incentive plans, you will experience further dilution. In addition, we may choose to raise additional capital due to market conditions or strategic considerations even if we believe we have sufficient funds for our current or future operating plans. To the extent that additional capital is raised through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the issuance of these securities may result in further dilution to our stockholders.
75
SELECTED FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The statements of operations and comprehensive loss data for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017 and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2016 and 2017 are derived from our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The statements of operations and comprehensive loss data for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018 and the balance sheet data as of September 30, 2018 are derived from our unaudited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus and have been prepared on the same basis as the audited financial statements. You should read this data together with our financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus and in the section of this prospectus titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected in the future, and results for the nine-month period ended September 30, 2018 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year ending December 31, 2018.
| YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||
| (In thousands, except share and per share data) | 2016 | 2017 | 2017 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss Data: | ||||||||||||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||
Research and development | $ | 7,670 | $ | 9,569 | $ | 6,822 | $ | 13,454 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 2,260 | 3,611 | 2,321 | 4,558 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Total operating expenses and loss from operations | (9,930 | ) | (13,180 | ) | (9,143 | ) | (18,012 | ) | ||||||||
Other income, net | 15 | 110 | 85 | 1,451 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net loss | (9,915 | ) | (13,070 | ) | (9,058 | ) | (16,561 | ) | ||||||||
Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value | (787 | ) | (1,794 | ) | (1,272 | ) | (36,568 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (10,702 | ) | $ | (14,864 | ) | $ | (10,330 | ) | $ | (50,129 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Other comprehensive loss: | ||||||||||||||||
Net loss | $ | (9,915 | ) | $ | (13,070 | ) | $ | (9,058 | ) | $ | (16,561 | ) | ||||
Unrealized (loss) gain on investments | (2 | ) | 2 | 2 | (3 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Total comprehensive loss | $ | (9,917 | ) | $ | (13,068 | ) | $ | (9,056 | ) | $ | (16,564 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net loss per share of common stock—basic and diluted (1) | $ | (38.64 | ) | $ | (39.94 | ) | $ | (28.78 | ) | $ | (83.83 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding—basic and diluted (1) | 276,976 | 372,116 | 358,914 | 597,964 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Pro forma net loss per share of common stock—basic and diluted (unaudited) (1) | $ | (2.90 | ) | $ | $ | (3.34 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Pro forma weighted average shares of common stock outstanding—basic and diluted (unaudited) (1) | 5,132,506 | 15,014,479 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| (1) | See Note 3 to our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus for an explanation of the calculations of our basic and diluted net loss per share, basic and diluted pro forma net loss per share and the shares used in computing basic and diluted net loss per share and basic and diluted pro forma net loss per share. |
76
| AS OF DECEMBER 31, | AS OF SEPTEMBER 30, 2018 | |||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2016 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | ||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 7,992 | $ | 19,811 | $ | 107,769 | ||||||
Short-term investments | 8,348 | — | 23,229 | |||||||||
Working capital(1) | 16,349 | 19,472 | 127,598 | |||||||||
Total assets | 18,251 | 22,039 | 134,668 | |||||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock | 29,169 | 47,102 | 205,500 | |||||||||
Additional paid-in capital | — | — | — | |||||||||
Accumulated deficit | (11,882 | ) | (26,324 | ) | (75,033 | ) | ||||||
Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) | (11,884 | ) | (26,324 | ) | (75,036 | ) | ||||||
| (1) | We define working capital as current assets less current liabilities. See our financial statements for further details regarding our current assets and current liabilities. |
77
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with the “Selected Financial Data” section of this prospectus and our financial statements and related notes appearing elsewhere in this prospectus. Some of the information contained in this discussion and analysis or set forth elsewhere in this prospectus, including information with respect to our plans and strategy for our business and related financing, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. As a result of many factors, including those factors set forth in the “Risk Factors” section of this prospectus, our actual results could differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion and analysis.
Overview
We are a clinical-stage immunotherapy company developing the next generation of novel T cell therapies for patients suffering from cancer. Our proprietary TCR Fusion Construct T cells (TRuC-T cells) specifically recognize and kill cancer cells by harnessing the entire T cell receptor (TCR) signaling complex, which we believe is essential for T cell therapies to be effective in patients with solid tumors. We have also designed our TRuC-T cells so that tumor cell recognition does not require human leukocyte antigens (HLA), which provides two important additional benefits. First, in contrast to current engineered T cell therapies that use the full TCR(TCR-T cells), our technology is designed so that it can be applied to all patients that express the cancer surface antigen irrespective of HLA subtype, which we believe will allow us to address a significantly larger patient population. Second, HLA is downregulated or lost in many tumors which can prevent their recognition by T cells and lead to diminished response rates and higher relapse rates. We therefore believe our approach will allow us to deliver the first HLA-independent TCR-T cell therapy for patients with solid tumors. We also believe that our product candidates have the potential to improve upon the efficacy and safety of currently approved chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell therapies in CD19-positiveB-cell hematological malignancies. This belief is based on preclinical studies comparing our product candidates to CAR-T cells that we engineered.
Since our inception in May 2015, we have focused significant efforts and financial resources on developing our TRuC platform, establishing and protecting our intellectual property portfolio, conducting research and development of our product candidates, manufacturing drug product material for use in preclinical studies, staffing our company and raising capital. We do not have any products approved for sale and have not generated any revenue from product sales. To date, we have funded our operations with proceeds from the sale of our preferred stock. Through September 30, 2018 we have received gross proceeds of $169.8 million from the sale of our preferred stock, stock option exercises and warrant exercises.
Since our inception, we have incurred significant operating losses. Our ability to generate product revenue sufficient to achieve profitability will depend heavily on the successful development and eventual commercialization of one or more of our product candidates. We reported net losses of $9.9 million, $13.1 million, $9.1 million and $16.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017 and for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018, respectively. As of September 30, 2018, we had an accumulated deficit of $75.0 million. We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and increasing operating losses for at least the next several years. We expect that our expenses and capital requirements will increase substantially in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly if and as we:
| ∎ | conduct additional preclinical studies for our product candidates; |
| ∎ | initiate and conduct clinical trials for our product candidates; |
| ∎ | continue to discover and develop additional product candidates; |
| ∎ | acquire or in-license other product candidates and technologies; |
| ∎ | maintain, expand, and protect our intellectual property portfolio; |
| ∎ | hire additional clinical and scientific personnel; |
| ∎ | expand our manufacturing capabilities with third parties and establish manufacturing capabilities in-house; |
| ∎ | seek regulatory approvals for any product candidates that successfully complete clinical trials; and |
| ∎ | add operational, financial, and management information systems and personnel, including personnel to support our product development and planned future commercialization efforts, as well as to support our transition to a public reporting company. |
78
We will not generate revenue from product sales unless and until we successfully complete clinical development and obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates. If we obtain regulatory approval for any of our product candidates and do not enter into a commercialization partnership, we expect to incur significant expenses related to developing our internal commercialization capability to support product sales, marketing and distribution. Additionally, we expect to incur significant expenses if we acquire and establish our own commercial manufacturing facility, which will be a costly and time-consuming process. Further, upon the closing of this offering, we expect to incur additional costs associated with operating as a public company.
As a result, we will need substantial additional funding to support our continuing operations and pursue our growth strategy. Until such time as we can generate significant revenue from product sales, if ever, we expect to finance our operations through a combination of equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances, and marketing, distribution or licensing arrangements. We may be unable to raise additional funds or enter into such other agreements or arrangements when needed on favorable terms, or at all. If we fail to raise capital or enter into such agreements as, and when, needed, we may have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue the development and commercialization of one or more of our product candidates.
Components of Our Results of Operations
Operating Expenses
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses consist primarily of costs incurred for our research activities, including our drug discovery efforts and the development of our product candidates, which include:
| ∎ | employee-related expenses, including salaries, benefits and stock-based compensation; |
| ∎ | expenses incurred in connection with the preclinical and clinical development of our product candidates, including under agreements with third parties, such as consultants, contractors and contract research organizations (CROs); |
| ∎ | the cost of acquiring and manufacturing preclinical and clinical trial materials, including under agreements with third parties, such as consultants, contractors and contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs); |
| ∎ | consultant fees and expenses associated with outsourced professional scientific development services; |
| ∎ | facilities, depreciation and other expenses, which include direct and allocated expenses for rent and maintenance of facilities and insurance; and |
| ∎ | payments made under third-party licensing agreements. |
We expense research and development costs as incurred. Any nonrefundable advance payments that we make for goods or services to be received in the future for use in research and development activities are recorded as prepaid expenses. The prepaid amounts are expensed as the related goods are delivered or the services are performed.
We typically use our employee, consultant and infrastructure resources across our development programs. We track certain outsourced development costs by product candidate, but we do not allocate personnel costs or other internal costs to specific product candidates.
Product candidates in later stages of clinical development generally have higher development costs than those in earlier stages of clinical development, primarily due to the increased size and duration of later-stage clinical trials. We expect that our research and development expenses will increase substantially in connection with our planned preclinical and clinical development and manufacturing activities in the near term and in the future. At this time, we cannot reasonably estimate or know the nature, timing, and costs of the efforts that will be necessary to complete the preclinical and clinical development of any of our product candidates. The successful development and commercialization of our product candidates is highly uncertain. This is due to the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with product development and commercialization, including the following:
| ∎ | the timing and progress of our preclinical studies and clinical trials, which may be significantly slower or cost more than we currently anticipate and will depend substantially upon the performance of third-party contractors; |
79
| ∎ | the number and scope of preclinical and clinical programs we decide to pursue; |
| ∎ | the progress of the development efforts of parties with whom we may enter into collaboration arrangements; |
| ∎ | our ability to maintain our current research and development programs and to establish new ones; |
| ∎ | our ability to establish licensing or collaboration arrangements; |
| ∎ | our ability to complete investigational new drug application (IND)-enabling studies and successfully submit IND or comparable applications; |
| ∎ | whether we are required by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or similar foreign regulatory authorities to conduct additional clinical trials or other studies beyond those planned to support the approval and commercialization of our product candidates or any future product candidates; |
| ∎ | the timely receipt of necessary marketing approvals from the FDA and similar foreign regulatory authorities; |
| ∎ | our ability and the ability of third parties with whom we contract to manufacture adequate clinical and commercial supplies of our product candidates or any future product candidates, remain in good standing with regulatory agencies and develop, validate and maintain commercially viable manufacturing processes that are compliant with current good manufacturing practices (cGMP); |
| ∎ | our ability to demonstrate to the satisfaction of the FDA and similar foreign regulatory authorities the safety, potency, purity and acceptable risk to benefit profile of our product candidates or any future product candidates; |
| ∎ | the prevalence, duration and severity of potential side effects or other safety issues experienced with our product candidates or future product candidates, if any; |
| ∎ | our ability to establish and enforce intellectual property rights in and to our product candidates or any future product candidates; |
| ∎ | our ability to successfully develop a commercial strategy and thereafter commercialize our product candidates or any future product candidates in the United States and internationally, if licensed for marketing, reimbursement, sale and distribution in such countries and territories, whether alone or in collaboration with others; |
| ∎ | the willingness of physicians, operators of clinics and patients to utilize or adopt any of our product candidates or future product candidates to treat solid and hematologic cancers; |
| ∎ | patient demand for our product candidates and any future product candidates, if licensed; |
| ∎ | competition with other products; and |
| ∎ | continued acceptable safety profile of our therapies following approval. |
A change in the outcome of any of these variables with respect to the development of any of our product candidates could significantly change the costs and timing associated with the development of that product candidate. We may never succeed in obtaining regulatory approval for any of our product candidates.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and related costs, including stock-based compensation, for personnel in executive, finance and administrative functions. General and administrative expenses also include direct and allocated facility-related costs as well as professional fees for legal, patent, consulting, investor and public relations, accounting and audit services. We anticipate that our general and administrative expenses will increase in the future as we increase our headcount to support our continued research activities and development of our product candidates. We also anticipate that we will incur increased accounting, audit, legal, regulatory, compliance, and director and officer insurance costs as well as investor and public relations expenses associated with operating as a public company.
Other Income, Net
Other income, net consists of interest earned on our cash equivalents and short-term investment balances. Our interest income is due to interest earned on invested balances.
80
Results of Operations
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the periods indicated:
| YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||
| (In thousands, except share and per share data) | 2016 | 2017 | 2017 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss Data: | ||||||||||||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||
Research and development | $ | 7,670 | $ | 9,569 | $ | 6,822 | $ | 13,454 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 2,260 | 3,611 | 2,321 | 4,558 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Total operating expenses and loss from operations | (9,930 | ) | (13,180 | ) | (9,143 | ) | (18,012 | ) | ||||||||
Other income, net | �� | 15 | 110 | 85 | 1,451 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net loss | $ | (9,915 | ) | $ | (13,070 | ) | $ | (9,058 | ) | $ | (16,561 | ) | ||||
Comparison of the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 and 2018
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses were $6.8 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 compared to $13.4 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2018. The following table summarizes our research and development expenses for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018:
| NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2017 | 2018 | CHANGE | |||||||||
TC-210 preclinical expenses | $ | 542 | $ | 3,566 | $ | 3,024 | ||||||
Platform development (preclinical) | 1,868 | 1,630 | (238 | ) | ||||||||
Personnel expenses | 3,237 | 5,762 | 2,525 | |||||||||
Allocated facilities costs | 980 | 2,297 | 1,317 | |||||||||
Other expenses | 195 | 199 | 4 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total research and development expenses | $ | 6,822 | $ | 13,454 | $ | 6,632 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
The $6.6 million increase in expense is primarily attributable to the $3.0 million increase in expenses to third parties progressing the preclinical development of our lead solid tumor product candidate, TC-210, an increase in personnel expenses of $2.5 million due to our increase in headcount, and an increase in allocated facilities costs of $1.3 million. These increases were offset by a decrease in preclinical expenses related to our platform development of $0.2 million.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses were $2.3 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, compared to $4.6 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2018. The increase in general and administrative expenses was primarily due to an increase in personnel costs of $1.5 million due to our increase in headcount, an increase in professional service expenses of $0.3 million and an increase in facility and other expenses of $0.5 million.
Other Income, Net
Interest income, net was $0.1 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, compared to $1.5 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2018. The increase in interest income, net was due to higher interest rates and a higher average balance in our commercial and investment accounts during the nine months ended September 30, 2018 compared to the nine months ended September 30, 2017.
81
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2017
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses were $7.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared to $9.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. The following table summarizes our research and development expenses for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017:
| YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2016 | 2017 | CHANGE | |||||||||
TC-210 preclinical expenses | $ | — | $ | 929 | $ | 929 | ||||||
Platform development (preclinical) | 3,378 | 2,197 | (1,181 | ) | ||||||||
Personnel expenses | 2,925 | 4,769 | 1,844 | |||||||||
Allocated facilities costs | 1,233 | 1,422 | 189 | |||||||||
Other expenses | 134 | 252 | 118 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total research and development expenses | $ | 7,670 | $ | 9,569 | $ | 1,899 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
The $1.9 million increase in expense is primarily attributable to the $0.9 million increase in expenses to third parties progressing the preclinical development of our lead solid tumor product candidate,TC-210, during 2017, an increase in personnel expenses of $1.8 million due to our increase in headcount, an increase in allocated facilities costs of $0.2 million and an increase in other research and development expenses of $0.1 million primarily attributable to an increase in scientific advisory board fees and equipment maintenance contracts. These increases were offset by a decrease of $1.2 million in preclinical expenses related to our platform development. The decrease in platform development costs is the result of us shifting our focus and resources to the advancement of our lead product candidate,TC-210.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses for the year ended December 31, 2016 were $2.3 million, compared to $3.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. The increase in general and administrative expenses was primarily due to an increase in personnel costs of $0.7 million due to our increase in headcount, an increase in professional service expenses of $0.4 million and an increase in facility and other expenses of $0.2 million.
Other Income, Net
Other income, net for the year ended December 31, 2016 was $15,000, compared to $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. The increase was due to interest income as a result of a higher average cash balance in our commercial and investment accounts in 2017.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Since our inception, we have incurred net losses and generated negative cash flows from operations. Since inception, we have funded our operations with proceeds from the sale of our Series A and Series B preferred stock. We have received aggregate gross cash proceeds of approximately $45.0 million in connection with the sale of our Series A preferred stock and $125.0 million in connection with the sale of our Series B preferred stock. As of September 30, 2018, we had cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of $131.0 million.
Cash Flows
The following table summarizes our sources and uses of cash for each of the periods presented:
| YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | 2016 | 2017 | 2017 | 2018 | ||||||||||||
Operating activities | $ | (9,380 | ) | $ | (12,036 | ) | $ | (7,795 | ) | $ | (12,309 | ) | ||||
Investing activities | (9,219 | ) | 7,672 | 5,045 | (23,990 | ) | ||||||||||
Financing activities | 22,486 | 16,183 | 3 | 124,257 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash | $ | 3,887 | $ | 11,819 | $ | (2,747 | ) | $ | 87,958 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
82
Operating Activities
During the nine months ended September 30, 2017, we used $7.8 million of cash in operating activities, primarily resulting from our net loss of $9.1 million offset by increases in non-cash charges of $0.4 million, which primarily consisted of depreciation, accretion of investments and stock-based compensation, and a net decrease in operating assets and liabilities of $0.9 million. The net decrease in operating assets and liabilities was primarily attributable to a decrease in prepaid expenses and other current assets.
During the nine months ended September 30, 2018, we used $12.3 million of cash in operating activities, primarily resulting from our net loss of $16.5 million offset by increases in net non-cash charges of $1.3 million, which primarily consisted of depreciation, accretion of investments and stock-based compensation, and a net decrease in operating assets and liabilities. The net decrease in operating assets and liabilities was primarily attributable to an increase in accounts payable, accrued expenses and other current liabilities and a decrease in prepaid expenses and other current assets.
During the year ended December 31, 2016, we used $9.4 million of cash in operating activities, primarily resulting from our net loss of $9.9 million offset by non-cash charges of $0.3 million, which related to depreciation and amortization and stock-based compensation, and a net decrease in operating assets and liabilities of $0.2 million. The net decreases in operating assets and liabilities were primarily attributable to the timing in which we paid our vendors.
During the year ended December 31, 2017, we used $12.0 million of cash in operating activities, primarily resulting from our net loss of $13.1 million offset by non-cash charges of $0.8 million, which primarily consisted of depreciation andstock-based compensation, and a net decrease in operating assets and liabilities of $0.3 million.
Investing Activities
During the nine months ended September 30, 2017, our cash provided by investing activities was $5.0 million, consisting primarily of maturities and sales of short-term investments of $12.1 million, partially offset by purchases of short-term investments of $6.5 million, purchases of property and equipment of $0.3 million and changes in restricted cash of $0.3 million.
During the nine months ended September 30, 2018, our cash used in investing activities was $24.0 million, consisting primarily of purchases of short-term investments of $36.0 million and purchases of property and equipment of $0.9 million, partially offset by maturities of short-term investments of $12.9 million.
During the year ended December 31, 2016, cash used in investing activities was $9.2 million, consisting primarily of purchases of short-term investments of $8.3 million and purchases of property and equipment of $0.9 million.
During the year ended December 31, 2017, cash provided by investing activities was $7.7 million, consisting primarily of maturities of investments of $14.8 million, offset by related purchases of short-term investments of $6.5 million, purchases of property and equipment of $0.4 million and an increase in restricted cash of $0.3 million.
Financing Activities
During the nine months ended September 30, 2017, our cash provided by financing activities was $3,000, consisting of proceeds from the exercise of stock options.
During the nine months ended September 30, 2018, our cash provided by financing activities was $124.3 million, consisting of gross proceeds received from the sale and issuance of our Series B preferred stock. We issued and sold an aggregate 62.5 million shares of Series B preferred stock for gross proceeds of $125.0 million during the nine months ended September 30, 2018. We also paid $0.8 million in deferred offering costs, $0.2 million in Series B offering costs and received $0.2 million in connection with the exercise of stock options and warrants, including options and warrants that were unvested and remain subject to repurchase until vesting.
During the year ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, net cash provided by financing activities was $22.5 million and $16.2 million, respectively, in each case consisting of net cash proceeds from the sale and issuance of our Series A preferred stock. We also received proceeds of $44,000 during the year ended December 31, 2017 in connection with the exercise of stock options, including options that were unvested and remain subject to repurchase until vesting.
83
Funding Requirements
We expect our expenses to increase substantially in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we advance the preclinical studies and clinical trials of our product candidates in development. In addition, if we obtain marketing approval for any of our product candidates, we expect to incur significant commercialization expenses related to establishing sales, marketing, distribution and other commercial infrastructure to commercialize such products. Furthermore, upon the closing of this offering, we expect to incur additional costs associated with operating as a public reporting company.
In addition, our expenses will increase as we:
| ∎ | commence enrollment of clinical trials for our product candidates; |
| ∎ | seek regulatory approval for any product candidates that successfully complete preclinical and clinical trials; |
| ∎ | establish manufacturing capabilities in-house for the production of preclinical and clinical supply; |
| ∎ | hire additional clinical, medical, research and operational personnel; and |
| ∎ | maintain, expand, and protect our intellectual property portfolio. |
As of September 30, 2018, we had cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of $131.0 million. We believe that the net proceeds from this offering, together with our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, will enable us to fund our operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements at least into 2022. We have based this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and we could utilize our available capital resources sooner than we expect. Additionally, changing circumstances may cause us to consume capital significantly faster than we currently anticipate, and we may need to spend more money than currently expected because of circumstances beyond our control. Accordingly, we will need to obtain substantial additional funding in connection with our continuing operations.
Until such time, if ever, as we can generate substantial product revenue, we expect to finance our operations through a combination of equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances, and marketing, distribution, or licensing arrangements. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, your ownership interest will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights as a common stockholder. Debt financing and preferred equity financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making acquisitions or capital expenditures, or declaring dividends. If we raise additional funds through collaborations, strategic alliances, or marketing, distribution, or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or drug candidates, or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings or other arrangements when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce, or terminate our research, product development, or future commercialization efforts, or grant rights to develop and market drug candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2017 and the effects that such obligations are expected to have on our liquidity and cash flows in future periods:
| PAYMENTS DUE BY PERIOD | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | TOTAL | LESS THAN 1 YEAR | 1 TO 3 YEARS | 4 TO 5 YEARS | MORE THAN 5 YEARS | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease commitments (1) | $366 | $366 | $— | $— | $— | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total | $366 | $366 | $— | $— | $— | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Reflects payments due for our office and laboratory space in Cambridge, Massachusetts under an operating lease that expired in April 2018. |
84
In March 2018, we began occupying office and laboratory facilities under a new lease that expires in July 2025.
Collaboration Agreement with Cell Therapy Catapult Limited
In December 2018, we signed a collaboration agreement (the Collaboration Agreement) with Cell Therapy Catapult Limited (Catapult) to establish our manufacturing process in Catapult’s GMP manufacturing facility in the United Kingdom. We paid a £200,000 non-refundable contribution to Catapult to reserve a GMP manufacturing cleanroom in October 2018. The non-refundable contribution will be applied against our input contributions (or fees) once we and Catapult have determined the various inputs that Catapult will contribute to the collaboration in order to support our manufacturing process under the Collaboration Agreement. The initial term of the Collaboration Agreement is three years and assumes an occupancy date of March 1, 2019. We can terminate the Collaboration Agreement earlier with twelve months’ notice and continued payment for contributions during the twelve-month termination period. The only fee fixed over the three-year term is a specified facility input contribution.The total financial contribution from us under the Collaboration Agreement comprises our portion of the shared costs for the infrastructure of the center and its operation as a licensed GMP facility. Our exact costs under the Collaboration Agreement are based on input-related contributions and will change year to year, and are partially dependent on the inputs we require from Catapult to meet the collaboration aim of establishing our manufacturing of autologous cell therapies.
We enter into contracts in the normal course of business with CROs, CMOs and other third parties for clinical trials and preclinical research studies and testing. These contracts provide for termination upon notice. Payments due upon cancellation consist only of payments for services provided and expenses incurred, including non-cancelable obligations of our service providers, up to the date of cancellation.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
Our financial statements are prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (GAAP). The preparation of our financial statements and related disclosures requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, and expenses, and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities in our financial statements. We base our estimates on historical experience, known trends and events, and various other factors that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. We evaluate our estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis. Our actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
While our significant accounting policies are described in more detail in Note 3 to our audited financial statements appearing elsewhere in this prospectus, we believe that the following accounting policies are those most critical to the judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our financial statements.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses consist primarily of costs incurred in connection with the development of our product candidates. We expense research and development costs as incurred.
As part of the process of preparing our financial statements, we are required to estimate our accrued research and development expenses. This process involves reviewing open contracts and purchase orders, communicating with our applicable personnel to identify services that have been performed on our behalf, and estimating the level of service performed and the associated cost incurred for the service when we have not yet been invoiced or otherwise notified of actual costs. The majority of our service providers invoice us in arrears for services performed, on a pre-determined schedule or when contractual milestones are met; however, some require advance payments. We make estimates of our accrued expenses as of each balance sheet date in the financial statements based on facts and circumstances known to us at that time. We periodically confirm the accuracy of the estimates with the service providers and make adjustments, if necessary. Examples of estimated accrued research and development expenses include fees paid to:
| ∎ | vendors in connection with preclinical development activities; |
| ∎ | CMOs in connection with the production of preclinical and clinical trial materials; and |
| ∎ | CROs in connection with preclinical studies and clinical trials. |
85
We base our expenses related to preclinical studies and clinical trials on our estimates of the services received and efforts expended pursuant to quotes and contracts with multiple CMOs and CROs that supply, conduct, and manage preclinical studies on our behalf. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation, vary from contract to contract, and may result in uneven payment flows. There may be instances in which payments made to our vendors will exceed the level of services provided and result in a prepayment of the expense. In accruing service fees, we estimate the time period over which services will be performed and the level of effort to be expended in each period. If the actual timing of the performance of services or the level of effort varies from the estimate, we adjust the accrual or prepaid expense accordingly. Although we do not expect our estimates to be materially different from amounts actually incurred, our understanding of the status and timing of services performed relative to the actual status and timing of services performed may vary and may result in reporting amounts that are too high or too low in any particular period. To date, there have not been any material adjustments to our prior estimates of accrued research and development expenses.
Stock-Based Compensation
We measure stock options and other stock-based awards granted to employees based on their fair value on the date of the grant and recognize compensation expense of those awards over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period of the respective award. We apply the straight-line method of expense recognition to all awards with service-based vesting conditions.
For stock-based awards granted to non-employees, compensation expense is recognized over the period during which services are rendered by such non-employees until completed. At the end of each financial reporting period prior to the completion of the service, the fair value of these awards is remeasured using the then-current fair value of our common stock and updated assumption inputs in the Black-Scholes option-pricing model for options and warrants.
We estimate the fair value of restricted stock at the then-current fair value of our common stock and for other stock-based awards we use the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, which requires subjective assumptions, including the fair value of our common stock, volatility, the expected term of our common stock options, the risk-free interest rate for a period that approximates the expected term of our common stock options, and our expected dividend yield. The assumptions used in our Black-Scholes option-pricing model represent management’s best estimates and involve a number of variables, uncertainties and assumptions and the application of management’s judgment, as they are inherently subjective. If any assumptions change, our stock-based compensation expense could be materially different in the future.
These assumptions are estimated as follows:
| ∎ | Risk-Free Interest Rate.The risk-free interest rate was based on the yields of U.S. Treasury securities with maturities commensurate with the expected term of the award. |
| ∎ | Expected Dividend Yield.We have not paid dividends on our common stock nor do we expect to pay dividends in the foreseeable future. |
| ∎ | Expected Term.The expected term represents the period that our stock options are expected to be outstanding. We calculated the expected term using the simplified method based on the average of each option’s vesting term and the contractual period during which the option can be exercised, which is typically 10 years following the date of grant. |
| ∎ | Expected Volatility.The expected volatility was based on the historical stock volatility of several comparable publicly traded companies over a period of time equal to the expected term of the options, as we do not have any trading history to use the volatility of our own common stock. |
| ∎ | Fair Market Value of Common Stock.As our common stock has not historically been publicly traded, we have periodically estimated the fair market value of common stock. See “—Fair Market Value of Common and Preferred Stock.” |
86
The following table reflects the weighted average assumptions used to estimate the fair value of the options and warrants granted during the periods presented:
| YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, | NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | 2017 | 2018 | |||||||||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 2.15 | % | 2.14 | % | 1.92 | % | 2.87 | % | ||||||||
Expected dividend yield | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
Expected term (in years) | 7.06 | 6.58 | 6.23 | 6.08 | ||||||||||||
Expected volatility | 69.30 | % | 65.70 | % | 66.15 | % | 64.70 | % | ||||||||
Fair Market Value of Common and Preferred Stock
As there has been no public market for our common or preferred stock to date, the estimated fair value of our common and preferred stock has been determined by our board of directors as of the date of each option grant, with input from management, considering our most recently available third-party valuations of common stock, and our board of directors’ assessment of additional objective and subjective factors that it believed were relevant and which may have changed from the date of the most recent valuation through the date of the grant. These third-party valuations were performed in accordance with the guidance outlined in the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants’ Accounting and Valuation Guide, Valuation of Privately-Held-Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation. In addition to considering the results of these third-party valuations, our board of directors considered various objective and subjective factors to determine the fair value of our common stock as of each grant date, including:
| ∎ | the prices at which we sold shares of our preferred stock and the superior rights and preferences of the preferred stock relative to our common stock at the time of each grant; |
| ∎ | the progress of our research and development programs, including the status and results of preclinical studies for our product candidates; |
| ∎ | our stage of development and our business strategy; |
| ∎ | external market conditions affecting the biopharmaceutical industry and trends within the biopharmaceutical industry; |
| ∎ | our financial position, including cash on hand, and our historical and forecasted performance and operating results; |
| ∎ | the lack of an active public market for our common stock and our preferred stock; |
| ∎ | the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event, such as an initial public offering (IPO) or sale of our company in light of prevailing market conditions; and |
| ∎ | the analysis of IPOs and the market performance of similar companies in the biopharmaceutical industry. |
Based on an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, the intrinsic value of vested and unvested stock options outstanding as of September 30, 2018 was $1.9 million and $20.9 million, respectively.
Common and Preferred Stock Valuation Methodology
Our common and preferred stock valuations were prepared using a hybrid between the option pricing method (OPM) and the probability-weighted expected return method (PWERM), both of which used market approaches to estimate our enterprise value. The OPM treats common stock and preferred stock as call options on the total equity value of a company, with exercise prices based on the value thresholds at which the allocation among the various holders of a company’s securities changes. Under this method, the common stock has value only if the funds available for distribution to stockholders exceeded the value of the preferred stock liquidation preferences at the time of the liquidity event, such as a strategic sale, a merger or initial public offering. The common stock has a claim on the equity value at an exercise price equal to the remaining value immediately after the preferred stock is liquidated. The OPM is appropriate to use when the range of possible future outcomes is so difficult to predict that forecasts would be highly speculative. The OPM commonly uses the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the price of the call option.
87
In the OPM, the backsolve method can be used to infer the total equity value implied by the pricing and terms of our Series A and Series B preferred stock financing transactions by making assumptions regarding the expected time to liquidity, expected volatility and risk-free interest rate, and then solve for the value of equity such that the implied value for the most recent financing equals the amount paid. At certain valuation dates, the equity value inferred from the OPM backsolve method was adjusted for company and market specific events that occurred between the financing date and the valuation date.
The PWERM involves a forward-looking analysis of the possible future outcomes, estimation of ranges of future and present value under each outcome and application of a probability factor to each outcome as of the valuation date. Under this method, discrete future outcomes, including an IPO, and non-IPO scenarios, are weighted based on the estimated probability of each scenario.
The hybrid method is generally appropriate to use when the time to a liquidity event is short, making the range of possible future outcomes relatively easy to predict. In the IPO scenario, all shares of preferred stock were assumed to convert to common stock. Accordingly, the estimated equity value was allocated pro rata among our preferred stock and common stock on an as converted basis, which caused the common stock to have a higher relative value per share than under the scenarios captured by the OPM. The weighting between the PWERM and OPM employed in the hybrid method was based on our board of directors’ estimate of the probability of each scenario as of each valuation date. These third-party valuations were performed at various dates, which resulted in valuations of our common stock of $0.74 per share as of September 30, 2016, $1.73 per share as of December 31, 2017, $5.88 per share as of February 28, 2018 and $8.05 per share as of August 31, 2018. The fair value of our Series A preferred stock was $1.50 per share as of August 31, 2018 and the fair value of our Series B preferred stock was $2.22 per share as of August 31, 2018.
The assumptions underlying these valuations represented management’s best estimate, which involved inherent uncertainties and the application of management’s judgment. As a result, if we had used significantly different assumptions or estimates, the fair value of our common stock and our stock-based compensation expense could have been materially different.
Once a public trading market for our common stock has been established in connection with the closing of this offering all of our outstanding preferred stock will convert to common stock and it will no longer be necessary for our board of directors to estimate the fair value of our common stock in connection with our accounting for granted stock options and other such awards we may grant, as the fair value of our common stock will be determined based on the quoted market price of our common stock.
Options Granted
The following table summarizes by grant date the number of shares of our common stock subject to options granted between January 1, 2017 and December 15, 2018, the per share exercise price of the options, the fair value of common stock underlying the options on each grant date, and the per share estimated fair value of the options:
GRANT DATE | NUMBER OF SHARES SUBJECT TO OPTIONS GRANTED | PER SHARE EXERCISE PRICE OF OPTIONS | PER SHARE FAIR VALUE OF COMMON STOCK ON GRANT DATE | PER SHARE ESTIMATED FAIR VALUE OF OPTIONS | ||||||||||||
May 9, 2017 | 8,017 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.56 | |||||||||
June 21, 2017 | 14,915 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.43 | |||||||||
September 12, 2017 | 89,498 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.43 | |||||||||
October 10, 2017 | 74,582 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.43 | |||||||||
December 7, 2017 | 503,711 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 1.73 | (1) | $ | 1.11 | ||||||||
April 30, 2018 | 242,452 | $ | 5.88 | $ | 5.88 | $ | 3.59 | |||||||||
July 26, 2018 | 800,973 | $ | 5.88 | $ | 8.05 | (2) | $ | 5.45 | ||||||||
October 11, 2018 | 66,705 | $ | 8.05 | $ | 8.05 | $ | 5.02 | |||||||||
December 13, 2018 | 74,989 | $ | 8.05 | $ | 8.05 | $ | 5.26 | |||||||||
| (1) | In the third quarter of 2018, we undertook a retrospective valuation of the fair value of our common stock as of December 31, 2017 and this value represents our estimated fair value per common share in accordance with such retrospective valuation. |
| (2) | In the fourth quarter of 2018, we undertook a retrospective valuation of the fair value of our common stock as of July 31, 2018 and this value represents our estimated fair value per common share in accordance with such retrospective valuation. |
88
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We did not have during the periods presented, and we do not currently have, any off-balance sheet arrangements, as defined in the rules and regulations of the SEC.
Recently Issued and Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
A description of recently issued accounting pronouncements that may potentially impact our financial position and results of operations is disclosed in Note 3 to our audited financial statements appearing elsewhere in this prospectus.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risks
Interest Rate Sensitivity
As of September 30, 2018, we had cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of $131.0 million, which consisted of cash, money market funds, U.S. Treasury notes, and U.S. government agency bonds. Interest income is sensitive to changes in the general level of interest rates; however, due to the nature of these investments, an immediate 10% change in interest rates would not have a material effect on the fair market value of our investment portfolio.
Emerging Growth Company Status
We are an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (JOBS Act), and are eligible to take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company may take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act of 1933 for complying with new or revised accounting standards issued subsequent to the enactment of the JOBS Act until such time as those standards apply to private companies. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that we can elect to opt out of the extended transition period at any time, which election is irrevocable. We have elected to avail ourselves of this exemption from complying with new or revised accounting standards and, therefore, will not be subject to the same new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not emerging growth companies.
We are in the process of evaluating the benefits of relying on other exemptions and reduced reporting requirements under the JOBS Act. Subject to certain conditions, as an emerging growth company, we may rely on certain of these exemptions, including without limitation (i) providing an auditor’s attestation report on our system of internal controls over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and (ii) complying with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements, known as the auditor discussion and analysis. We will remain an emerging growth company until the earlier of (a) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenue of $1.07 billion or more; (b) the last day of the fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the completion of this offering; (c) the date on which we have issued more than $1.0 billion in nonconvertible debt during the previous three years; or (d) the date on which we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer under the rules of the SEC.
89
Overview
We are a clinical-stage immunotherapy company developing the next generation of novel T cell therapies for patients suffering from cancer. Our proprietary TCR Fusion Construct T cells(TRuC-T cells) specifically recognize and kill cancer cells by harnessing the entire T cell receptor (TCR) signaling complex, which we believe is essential for T cell therapies to be effective in patients with solid tumors. We have also designed ourTRuC-T cells so that tumor cell recognition does not require human leukocyte antigens (HLA), which provides two important additional benefits. First, in contrast to current engineered T cell therapies that use the full TCR(TCR-T cells), our technology is designed so that it can be applied to all patients that express the cancer surface antigen irrespective of HLA subtype, which we believe will allow us to address a significantly larger patient population. Second, HLA is downregulated or lost in many tumors which can prevent their recognition by T cells and lead to diminished response rates and higher relapse rates. We therefore believe our approach will allow us to deliver the first HLA-independentTCR-T cell therapy for patients with solid tumors. We also believe that our product candidates have the potential to improve upon the efficacy and safety of currently approved chimeric antigenreceptor T (CAR-T) cell therapies in CD19-positiveB-cell hematological malignancies. This belief is based on preclinical studies comparing our product candidates toCAR-T cells that we engineered.
In January 2019, the investigational new drug application (IND) for our lead solid tumor product candidate,TC-210, to treat patients with mesothelin-positive solid tumors was cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). We plan to initiate our Phase 1/2 clinical trial for TC-210 in early 2019. We estimate the patient population forTC-210 is up to 81,000 in the United States alone. We expect to generate our first clinical data for TC-210 in the second half of 2019. We expect to file an IND in the second half of 2019 for our lead hematology product candidate,TC-110, to treat patients with CD19-positiveB-cell hematological malignancies. We expect to generate our first clinical data forTC-110 in the second half of 2020. In addition, we plan to file an IND for our second solid tumor product candidate,TC-220, to treat MUC16-positive solid tumors, in early 2020 and we expect to generate our first clinical data for TC-220 in the first half of 2021.
A Revolution in T Cell Therapies
According to a 2017 press release from the FDA on the licensure of the first engineered T cell therapy for cancer, the field is “entering a new frontier in medical innovation with the ability to reprogram a patient’s own cells to attack a deadly cancer.” We founded our company to build on these early T cell therapy innovations while addressing their limitations and making our product candidates available to a broader patient population.
The immune system is responsible for protecting the human body by eliminating agents that threaten our health, including cancer cells. One of the key components of the immune system are sentinels called T cells that are able to target these agents for elimination by using TCR recognition of cell surface markers known as antigens. When a T cell recognizes a tumor antigen through the TCR, it kills the malignant cell on which it resides. Existing T cell therapies for cancer, includingCAR-T cells and engineeredTCR-T cells, attempt to replicate this mechanism. While current T cell therapies have shown encouraging efficacy data, they have limitations that we believe our product candidates can address.
CAR-T cell therapies have been approved for use in certain CD19-positiveB-cell hematological malignancies on the basis of encouraging efficacy data. However, the durable benefit of these therapies has been limited to a subset of cancer patients, while the risk of potentially fatal side effects for patients is high. In solid tumors,CAR-T cells have not shown meaningful patient benefit. We believe these limitations are a consequence of the CAR construct using only one subunit of the entire TCR signaling complex and operating independently of the normal signaling mechanisms in the T cell. As a result,CAR-T cells do not benefit from all of the activation and regulatory elements of the natural TCR complex. This results inCAR-T cells overproducing cytokines that frequently lead to severe toxicities, including cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity.CAR-T cells are also limited in their ability to persist and overcome the hostile tumor microenvironment.
TCR-T cell approaches were developed in an attempt to leverage the power of the entire TCR signaling complex.TCR-T cells have produced clinical responses in patients with solid tumors. However, recognition of the tumor
90
antigen by existingTCR-T cell approaches occurs in the context of HLA. This significantly limits the number of patients that can be treated with each specificTCR-T cell therapy because they can only be used for one specific HLA subtype, of which there are many. In addition, the downregulation or loss of HLA in many tumors can prevent tumor antigen recognition byTCR-T cells and lead to diminished response rates and higher relapse rates.
Our Novel Platform
We are pioneering the development of a novel, transformative T cell engineering platform which, based on its design and our preclinical studies, we believe has the potential to address the shortcomings ofCAR-T cells andTCR-T cells and is fundamentally different from existing approaches. Research over more than two decades has shown that each of the TCR subunits makes distinct contributions to the activation and regulation of T cells and only the sum of the TCR subunits can adequately activate and control all functions of T cells. We believe that engaging the entire TCR signaling complex is required to fully leverage T cells in their fight against cancer.
Our T cell engineering approach relies upon natural TCR elements to produce therapeutic T cells that function independently of HLA restriction. To that end, we fuse a cancer antigen recognition domain directly to a subunit of the TCR and use a lentiviral vector to transfer the genetic information for the TRuC construct into a patient’s own T cells. This modified subunit then naturally integrates into the native TCR complex. The result is the generation of an engineered T cell equipped with a new “homing device” to detect and engage a specific antigen on the surface of cancer cells. Upon antigen engagement, these T cells harness the entire TCR to produce a more powerful yet controlled T cell response against cancer. We refer to T cells engineered with our TCR fusion constructs asTRuC-T cells. In preclinical studies of both solid tumors and hematological malignancies we have observed greater anti-tumor activity, longer persistence and less cytokine release compared toCAR-T cells we have engineered to target the same cancer antigen. We believe that these properties could translate into more durable responses with potentially fewer adverse events for patients with cancer.
The figure below describes the naturalHLA-restricted TCR complex as compared to theHLA-independent TRuC TCR.

91
Our platform enables the design ofTRuC-T cells with a number of potential advantages, as described in the table below:
ATTRIBUTES | FEATURES | MECHANISMS | DESIRED PATIENT OUTCOME | |||
| Enhanced signaling | TRuC construct integrates into and utilizes the entire TCR | ∎ Naturally controlled T cell responses
∎ No requirement forbuilt-in costimulatory domain
∎ Lower cytokine production | ∎ Produce a more powerful, yet controlled T cell response
∎ Improved clinical outcomes, including lower adverse event rates | |||
| Efficient metabolism | Longer persistence and survival ofTRuC-T cells in the hostile tumor microenvironment | ∎ Enhanced tumor penetration and retention
∎ Enhanced energy production
∎ Promotion of memory T cell phenotype | ∎ Higher T cell tumor infiltration leading to improved response rates
∎ Long-term persistence reducing risk of relapse | |||
| Advanced targeting | Antibody-based tumor cell recognition | ∎ Reprogramming of T cell specificity to recognize tumor surface antigen
∎ HLA-independent binding to tumor | ∎ Access to larger patient population
∎ TRuC-T cells have the potential to improve upon existing therapies because of HLA downregulation | |||
| Dual targeting | ∎ Ability to attack tumors based on the recognition of two different antigens | ∎ Reduced risk of relapse due to antigen escape
∎ Improved response rates in tumors with heterogeneous target antigen expression | ||||
| Amenability to various tumor cell recognition modalities | ∎ Binder formats include, but are not limited to, single-chain variable fragments, single-domain antibodies and receptors
∎ Humanized binders | ∎ Improved response rates and lower relapse rates | ||||
We use ourTRuC-T cell platform to target many different cancer antigens. Our core format, in which we target a single cancer antigen, is known as a monoTRuC-T cell. Our mono TRuC-T cell product candidates have shown promising anti-tumor activity and persistence in our preclinical studies. We are supplementing our core format with a series of next-generation enhancements that may further improve clinical outcomes. These fall into two broad categories. First, we are developing formats that target two antigens, known as dualTRuC-T cells, which could improve tumor response in patients who express more than one cancer antigen and combat potential antigen escape, which is a leading mechanism of cancer relapse in patients receivingCAR-T cell therapy. Second, we are developing several strategies to counter the immunosuppressive microenvironment of solid tumors including mechanisms to
92
block a key cancer defense known as the programmed cell death 1(PD-1) and programmed death-ligand 1(PD-L1) checkpoint pathway.
OurTRuC-T cell platform is a novel, transformative approach because it incorporates the entire TCR to redirect T cells to kill cancer while operating independently of HLA. It is a flexible and versatile approach that has allowed us to continue our innovation beyond the coreTRuC-T cell format. We believe ourTRuC-T cells can be used against numerous solid tumors and hematological malignancies and can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Our Strategy
Our goal is to cure cancer with ourTRuC-T cell therapies. We intend to make a difference in the lives of patients by building a fully integrated cancer immunotherapy company offering the first HLA-independentTCR-T cell therapies. The key components of our strategy are:
| ∎ | Rapidly advance our solid tumor pipeline. The FDA cleared the IND forTC-210, our lead monoTRuC-T cell targeting patients with mesothelin-expressing solid tumors in January 2019. We expect to generate data from this clinical trial in the second half of 2019. Our plan is to begin the dose-escalation portion of our Phase 1/2 clinical trial in patients who have malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma, cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer), ovarian cancer ornon-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Our goal is to obtain FDA Fast Track designations for malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma and cholangiocarcinoma, and we believe this will provide the potential for FDA Accelerated Approval based on Phase 2 data. We anticipate filing an IND for our second monoTRuC-T cell,TC-220, targeting patients with MUC16 positive solid tumors, in early 2020. We are also developing product candidates targeting other cancer antigens expressed on solid tumors. |
| ∎ | Rapidly advance our hematological malignancy pipeline. We intend to file an IND forTC-110, our lead monoTRuC-T cell targeting patients with CD19-positiveB-cell hematological malignancies, in the second half of 2019. We are conducting preclinical studies and have developed a clinical plan for patients with adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), diffuse largeB-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), or follicular lymphoma (FL). Our goal is to obtain FDA Fast Track designations for both ALL and DLBCL, and we believe this will provide the potential for FDA Accelerated Approval based on Phase 2 clinical data. |
| ∎ | Exploit the versatility of our platform to broaden our pipeline. We have developed several additional tools that may be incorporated into our future product candidates to overcome tumor defense mechanisms, including dual-antigen targetingTRuC-T cells to minimize potential for antigen escape and cancer relapse. Our most advanced dual-antigen targeting programs include a dual mesothelin/MUC16TRuC-T cell for solid tumors and a dual CD19/CD22TRuC-T cell for hematological malignancies. We are also developing several tools to counter the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, including interference with immune checkpoint pathways. We are also evaluating multiple proprietary designs for allogeneic, or off-the-shelf, TRuC-T cells. |
| ∎ | Scale our manufacturing capacity to match our future product needs. We plan to develop our own manufacturing capabilities. We are currently manufacturingGMP-grade clinical lots forTC-210 through third-party contractors. We have also entered into an agreement with Cell Therapy Catapult Limited (Catapult), which will allow us to manufacture our TRuC-T cells using our own personnel at Catapult’s facility, while also expanding our capacity to supply future clinical trials. If our clinical trials are successful, given the size of the patient population that can potentially be targeted by our product candidates, we plan to build our own manufacturing plant. |
| ∎ | Retain significant economic and commercial rights to our product candidates.We currently own all rights to our product candidates and programs and intend to build a fully integrated cancer immunotherapy company. We intend to maintain product rights in key geographies, in particular forTC-210. We believe the versatility of our platform presents an opportunity for us to selectively form collaborations and strategic partnerships to expand our capabilities and product offerings into other therapeutic areas and potentially accelerate the development and maximize the commercial potential of our product candidates. |
Background on Cancer and Therapeutic Approaches Using T Cells
Cancer is caused by fatal changes in the genes of single cells. These mutations deregulate proteins that normally control the survival, growth and division of cells. As a result, mutated cells change their behavior and can undergo
93
unlimited growth to form tumors, a key attribute of cancer. Our immune system is an essential defense against the growth and spread of cancer cells. T cells are a special type of immune cell that patrol our body to recognize and kill cells with abnormal proteins. This recognition is based on the TCR, a large complex comprised of six different protein subunits (denoted as TCRa, TCRß, CD3e, CD3g, CD3d, CD3z). When thea and ß subunits of the TCR recognize a specific tumor antigen presented by the HLA complex on the cancer cell, a broad cascade is triggered that regulates all of the T cell’s necessary functions to perform as a killer cell, including T cell activation, survival, differentiation, migration, adhesion, chemotaxis, metabolic adaption, tumor cell killing, cytokine release and persistence. All of these functions are required to orchestrate tumor cell killing and prevent relapse. Deficiencies in the TCR signaling system allow the escape and unrestricted growth of malignant cells, which can culminate in a patient’s death. The loss of the antigen-presenting HLA complex on cancer cells makes them invisible for T cells, thereby escaping immune surveillance.
Adoptive T Cell Therapies Against Cancer
Adoptive T cell transfer (ACT) is a cancer therapy modality that involves the infusion of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes or genetically manipulated peripheral T cells to attack tumor cells. The two most common engineered T cell platforms currently being developed and/or commercialized areCAR-T cells andTCR-T cells.
CAR-T cell therapies have been shown to induce durable clinical responses in some patients whose cancers had become otherwise refractory to standard therapies. In contrast to normal T cells andTCR-T cells that signal through the entire TCR,CAR-T cells use only the CD3z subunit of the TCR, often in combination with a syntheticco-stimulatory domain, to trigger T cell activation once cancer cells have been identified by a fused antibody-derived tumor antigen recognition domain. CD19-targetingCAR-T cell therapies have shown clinical responses in ALL,B-cell lymphomas and multiple myeloma and two of them, Kymriah and Yescarta, have been approved for pediatric patients with ALL and patients with DLBCL. However,CAR-T cell therapies are limited by serious adverse events caused by high levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as CRS and neurotoxicity. These adverse events are black box warnings for both Kymriah and Yescarta, which are only available through a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) program. In solid tumors,CAR-T cells have been much less successful, with a lack of meaningful clinical activity. We believe that the severe side effects in hematological malignancies and the lack of efficacy in solid tumors are a consequence of the CAR construct being physically and functionally separate from the TCR and therefore unable to trigger the full repertoire of activation and regulatory signaling pathways.
UnlikeCAR-T cells, engineeredTCR-T cells rely on the entire TCR for signaling. In this approach, affinity matured TCRa and ß subunits that recognize tumor antigens are introduced via gene transfer into T cells isolated from a patient’s blood. Upon expression, these subunits are integrated into the natural TCR complex to activate the T cells.TCR-T cells have shown benefits in multiple myeloma and also solid tumors, such as synovial sarcoma, melanoma, esophageal and ovarian cancer. However, a primary limitation of this type of therapy is thatTCR-T cells require matching with the right HLA counterpart to kill tumor cells. More specifically, most syntheticTCR-T cell therapies currently in clinical development are directed against antigens presented on theHLA-A*02 subtype, which is present only in 40% to 45% of patients of Caucasian descent and at lower frequencies in patients of other ethnic backgrounds, thus preventing the use of these therapies in the majority of cancer patients. The use of syntheticTCR-T cells may be further limited by the loss or down-regulation of HLA molecules by cancer cells as part of the tumor escape mechanism. As a result, these T cells can no longer recognize and kill tumor cells, which leads to relapse.
We have developed a platform to address the limitations of existing T cell therapies. We believe ourTRuC-T cell platform has the potential to deliver the first HLA-independent TCR-T cell therapies to a broader population of patients with solid tumors and hematological malignancies.
Our Pipeline
The versatility of our platform is highlighted by the multiple programs and multiple formats of the product candidates in our pipeline. In preclinical studies with multipleTRuC-T cell product candidates, we have shown better anti-tumor activity, longer persistence and lower cytokine release compared toCAR-T cells we have engineered to bear the same tumor antigen binding domains as our product candidates. We have generated a broad pipeline
94
with assets that address both solid tumors and hematological malignancies. Our product candidates are listed in the figure below.

*In the Discovery stage, we identify the antigen-specific binders, tether these to a TCR subunit via a linker and then, upon introduction into T cells, test the killing activity and cytokine releasein vitro. Thereafter, the programs enter Lead Optimization stage, where we optimize the antigen binder sequence and linker length and re-test T cells expressing the enhanced TRuC sequences in cellular assays for functional activity and specificity. At this stage, we also investigate the anti-tumor activity, cytokine release, pharmacodynamics and phenotype of TRuC-T cells in mouse studies. The IND-Enabling stage is defined by the nomination of a product candidate. At this stage of drug development, we initiate the GMP production of lentiviral vector and process development of TRuC-T cells. In addition, we conduct studies addressing the specificity and toxicity to support the submission of an IND application.
OurTRuC-T Cell Product Candidates for Solid Tumors
TC-210: Our Lead MonoTRuC-T Cells Targeting Mesothelin Positive Solid Tumors
Our most advanced monoTRuC-T cell product candidate isTC-210, which targets mesothelin-positive solid tumors. Mesothelin is a cell-surface protein whose expression is mostly restricted to mesothelial cell layers lining the pleura, pericardium and peritoneum but which is not known to be expressed on any vital organs. While its expression on normal tissues is low, mesothelin is highly expressed in many solid tumors. The cancer types that we intend to treat in our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial includenon-small cell lung cancer, ovarian cancer, malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma and cholangiocarcinoma. These cancers represent a patient population of up to 81,000 in the United States alone. By comparison, the addressable U.S. patient population with hematological malignancies for approved CD19-directedCAR-T therapies is estimated to be approximately 8,000. In our preclinical studies we have observed better anti-tumor activity and persistence ofTRuC-T cells compared withCAR-T cells we engineered to target mesothelin while also exhibiting lower levels of cytokine release. The FDA cleared our IND for TC-210 in January 2019 and we plan to initiate our Phase 1/2 clinical trial in early 2019. We also plan to apply for FDA Fast Track designation forTC-210. We have submitted an FDA Orphan Drug Designation application for the treatment of malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma with TC-210 and also plan to apply for FDA Fast Track designation for TC-210.
95
Mesothelin is overexpressed in multiple cancers, including approximately 76% of malignant pleural mesotheliomas (the most common type of mesothelioma), 58% of ovarian cancers and 31% of NSCLC, among others. The following figure illustrates the proportion of cancer patients that express high levels of mesothelin and are therefore candidates forTC-210 therapy.
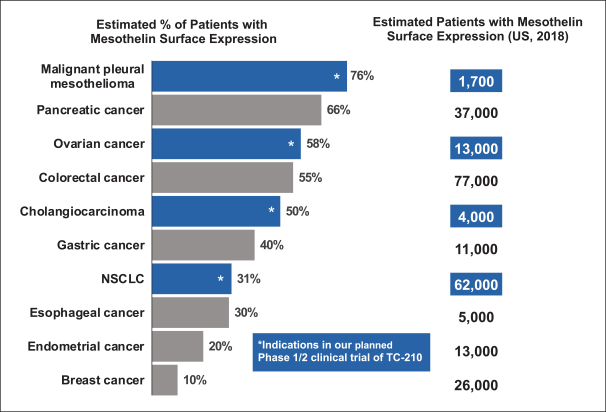
NSCLC Background
NSCLC remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, accounting for approximately 18% of all cancer deaths. There are an estimated 200,000 new cases in the United States annually with an estimated 62,000 (31%) expressing mesothelin on the cell surface.
The current standard of care for NSCLC involves the use of a platinum-based chemotherapy. Patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations or anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements can be treated with targeted agents such as EGFR inhibitors and ALK inhibitors, respectively. Patients with metastatic NSCLC have a poor prognosis with a median survival of approximately ten months and a five-year survival rate of approximately 15% to 20%. While recent advances with checkpoint inhibitors have demonstrated promising results, the majority of patients treated with these agents do not derive a long-term benefit. Notably, no standard of care is available for patients failing to respond or relapsing after checkpoint inhibitor therapy, a segment of the NSCLC market which is expected to grow in size as the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors increases in first- and second-line settings.
Ovarian Cancer Background
Epithelial ovarian cancer comprises approximately 90% of all ovarian malignancies. Approximately 22,000 patients in the United States were diagnosed with ovarian cancers in 2018 with an estimated 13,000 cases expressing mesothelin on the cell surface.
Taxane and platinum-based combinations have been the backbone of ovarian cancer treatment for the past 20 years, despite having very low efficacy rates (below 15%) in patients with advanced forms of the disease. While recently approved poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors are improving outcomes for ovarian cancer patients with
96
BRCA mutations, the use of such therapeutics is limited to the approximately 15% of ovarian cancer patients that carry those mutations. The majority of patients progressing after platinum retreatment have no approved treatment options. However, even with these subsequent treatments, ovarian cancer remains incurable with an estimated 14,000 deaths in 2018 in the United States alone.
Malignant Pleural/Peritoneal Mesothelioma Background
Malignant mesothelioma is a rare and aggressive malignancy arising from mesothelial cells lining the cavity surrounding the lungs (pleura), abdomen (peritoneum), heart (pericardium) or testes.
Malignant pleural mesothelioma is the most common form of mesothelioma, accounting for an estimated 84% of cases. Asbestos exposure causes approximately 80% of malignant pleural mesothelioma cases. There are an estimated 2,200 new cases per year of malignant pleural mesothelioma in the United States of which an estimated 1,700 express mesothelin on the cell surface.
Effective treatment options for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma are very limited. The standard of care recommended is chemotherapy that includes a platinum salt and an anti-folate. Unfortunately, the ORR is 17% to 40% and the median overall survival of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma is 12 to 19 months when systemic chemotherapy is used with or without anti-angiogenic agents or targeted therapy. Malignant pleural mesothelioma caused approximately 2,200 deaths in 2018 in the United States alone.
Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma is the second-most common form of mesothelioma, accounting for an estimated 10% of cases. While malignant peritoneal mesothelioma is less commonly studied than malignant pleural mesothelioma, similar systemic chemotherapy regimens of platinum and antifolate combinations are often used. The prognosis for patients with malignant peritoneal mesothelioma is poor as only 35% of patients survive more than two years after diagnosis.
Patients with either malignant pleural mesothelioma or malignant peritoneal mesothelioma are eligible for enrollment in our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial ofTC-210.
Cholangiocarcinoma Background
Cholangiocarcinoma is a form of cancer that is composed of mutated epithelial cells that originate in the bile ducts which drain bile from the liver into the small intestine. There are an estimated 8,000 new cholangiocarcinoma cases in the United States per year with about 50% expressing mesothelin on the cell surface. Most patients with cholangiocarcinoma have advanced-stage disease at presentation due to its aggressiveness and the difficulty of early diagnosis. While surgery is the preferred therapy, only 35% of patients have early disease amenable to surgical resection. For unresectable cholangiocarcinoma, the availablestandard-of-care chemotherapy (gemcitabine and cisplatin) renders a median overall survival of less than one year. Multiple products, including checkpoint inhibitors and others, are being tested in clinical trials, but cholangiocarcinoma remains an unmet medical need. Cholangiocarcinoma causes over 7,000 deaths per year in the United States alone.
We have submitted an FDA Orphan Drug Designation application for TC-210’s treatment of mesothelioma. In addition, we plan to apply for FDA Fast Track, FDA Breakthrough Therapy and Orphan Drug Designations, as well as Accelerated Approvals, where applicable. In addition to applying for FDA Fast Track designation for TC-210, we plan to apply for FDA Breakthrough Therapy and Orphan Drug designations, where applicable, as well as Accelerated Approval.
TC-210 Phase 1/2 Trial in Mesothelin-Positive Tumors
In January 2019, the FDA cleared our IND forTC-210, our product candidate to treat patients with mesothelin-positive solid tumors. In early 2019, we plan to initiate a Phase 1/2 clinical trial at leading cancer institutions, including Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, MD Anderson Cancer Center, The National Cancer Institute, Stanford Cancer Center, and The University of California San Francisco. We intend to conduct the Phase 1/2 trial ofTC-210 in patients with NSCLC, ovarian cancer, malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma and cholangiocarcinoma. Given the high unmet need and limited treatment options in malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma and cholangiocarcinoma, our goal is to obtain Fast Track designations forTC-210 in those indications from the FDA, which we believe will provide the potential for accelerated licensing based on Phase 2 clinical trial data.
97
Our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial consists of two parts:
| ∎ | In the Phase 1 portion of the clinical trial, patients will receiveTC-210 at four dose levels with or without lymphodepleting chemotherapy to determine the recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D). |
| ∎ | The objective of the Phase 2 portion of the clinical trial, in addition to further characterizing the safety profile ofTC-210, is to evaluate the efficacy ofTC-210 in mesothelin-expressing cancers as assessed by ORR according to standard Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1 criteria (ORR: complete response + partial response). Secondary endpoints will include time to response, duration of response, progression free survival and overall survival. A total of 50 patients will receiveTC-210 at the RP2D schedule and will be stratified according to their cancer diagnosis in four groups: NSCLC, ovarian cancer, malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma and cholangiocarcinoma. A total of ten patients per indication will be infused withTC-210 T cells, except in the NSCLC cohort where 20 patients will be treated, including eight receivingTC-210 as single agent and 12 receivingTC-210 in combination with the programmed cell death 1(PD-1) blocking antibody. |
The design of our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial, as illustrated in the figure below, will allow us to further expand individual cohorts in the Phase 2 portion of the trial to evaluate the efficacy ofTC-210 in a larger sample size, which we believe may accelerate regulatory timelines for approval in the United States.
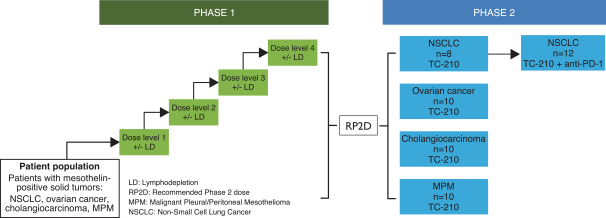
98
Design ofTC-210
The construct to generateTC-210 is comprised of a humanized single-domain antibody that specifically binds to mesothelin on the cell surface. This binding domain is tethered to the human CD3e subunit via a flexible linker to form the mesothelin-targeting TRuC construct, as shown below. We use a lentiviral vector to transfer the genetic information for the TRuC construct into a patient’s own T cells. Once in the T cell, the TRuC protein is expressed and integrated into the endogenous TCR followed by transport of the reprogrammed TCR to the cell surface. There, it redirects theTRuC-T cells to recognize mesothelin-positive tumor cells and activate them to eliminate mesothelin-positive tumors. We believe thatTC-210’s unique way of engaging and powering T cells as well as its humanized binding domain could lead to improved clinical outcomes for patients. The following figure illustrates the design ofTC-210.
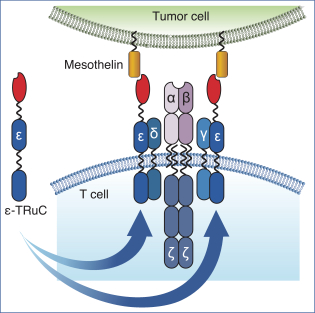
Preclinical Studies ofTC-210
TC-210 has shown robust anti-tumor activity in cellular assays and animal models of malignant pleural/peritoneal mesothelioma, lung and ovarian cancers. We have completed a number of preclinical studies that have generated data on themechanism-of-action, pharmacodynamic and pharmacology/toxicology data of TC-210. In those studies, TC-210 was comparedhead-to-head against mesothelin-targetingCAR-T cells (MSLNCAR-T cells) that we engineered with the same mesothelin binder expressed by TC-210. Our preclinical studies have highlighted the following attributes ofTC-210 that we believe to be important for solid tumor clearance:
| ∎ | Migration to and accumulation in the tumor site that was significantly faster and greater forTC-210 than that observed for the MSLNCAR-T cells; |
| ∎ | Mesothelin-dependent T cell activation, expansion and tumor clearance byTC-210 was faster than that observed for the MSLNCAR-T cells; |
| ∎ | Long-term functional persistence ofTC-210 which is critical for preventing relapse; and |
| ∎ | Systemic cytokine levels produced byTC-210 were lower compared to the MSLNCAR-T cells, which could potentially translate into lower rates of adverse events. |
TC-210 Showed Robust Mesothelioma Tumor Clearance
To compare the anti-tumor activity of TC-210 and MSLN CAR-T cells, we used a mouse xenograft model of mesothelioma. In the set of experiments shown below, we tested TC-210 against MSLN CAR-T cells that we engineered to incorporate the two most common CAR-T designs. These designs incorporate either the CD28 or 4-1BB costimulatory domains—described below as MSLN-28z CAR-T and MSLN-41BBz CAR-T, respectively. Mesothelioma
99
cells overexpressing mesothelin were injected into mice. When tumors reached approximately 200 to 300 mm3, the mice were infused with a total of 1.0x107 T cells containing either 2.0x106 TC-210 or 1.0x106 MSLN-28z CAR-T cells. A separate group of nine animals was treated with a control. Treatment of tumor-bearing animals with TC-210 showed rapid tumor control and clearance of tumors by day 25 after start of treatment in all of the nine animals tested. In contrast, while theMSLN-28z CAR-T cell treated animals showed initial tumor regression, tumor relapse was only observed in four out of the nine animals tested with MSLN CAR-T cells. These observations conform to prior published studies showing poor long-term activity of MSLN-28zCAR-T cells in similar models.
An additional mouse xenograft model of mesothelioma was also conducted to compare the activity of TC-210 to MSLN-41BBz CAR-T cells that we engineered. In this study, when tumors reached approximately 200 to 300 mm3, the mice were infused with a total of 1x107 T cells containing either 4.8x106 TC-210 or 3.9x106 MSLN-41BBz CAR-T cells. Treatment of tumor-bearing animals with TC-210 showed rapid tumor control and clearance of tumors by day 20 after start of treatment in all seven of the animals tested, while the MSLN-41BBz CAR-T cell treatment showed tumor clearance in only four of seven animals tested by day 20.
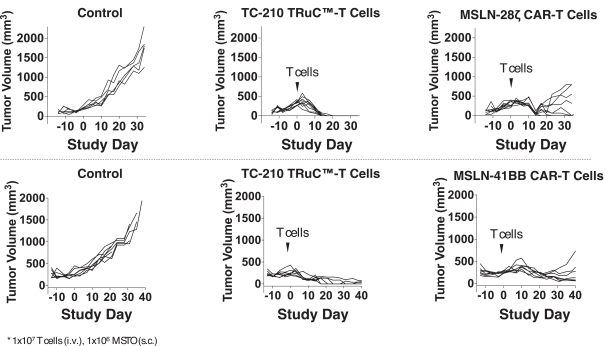
100
TC-210 showed faster trafficking to and accumulation in mesothelioma tumors
One of the major challenges forCAR-T cell therapies has been the ability ofCAR-T cells to migrate into the tumor tissue in significant numbers. In our preclinical studies, we observed thatTC-210 expressed higher levels of the chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CCR10 than MSLNCAR-T cells we engineered. We believe this is one of the major factors causing the faster migration to and greater accumulation ofTC-210 in tumors as compared to the MSLNCAR-T cells we engineered.
We investigated the ability of TC-210 to traffic to and accumulate in mesothelioma tumors. After mesothelin-overexpressing xenograft tumors reached a mean volume of approximately 200 mm3, the mice were randomized into two groups of five mice. The mice were then intravenously infused with eitherTC-210 or the MSLNCAR-T cells, which we engineered toco-express a tracing agent to analyze the migration pattern ofTC-210 and the MSLNCAR-T cells using living images. As illustrated in the figure below, imaging studies showed thatTC-210 migrated into the tumor faster and accumulated in greater number than observed for the MSLNCAR-T cells. The faster trafficking and accumulation ofTC-210 correlated with faster tumor clearance compared to the MSLNCAR-T cells. Therefore, we believe that these properties of TC-210 could translate into improved clinical outcomes in patients.
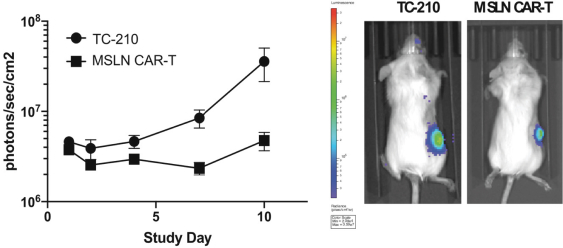
101
CXCR3 expression was higher on TC-210 compared to MSLN CAR-T cells
One of the major challenges for CAR-T cell therapies in solid tumors has been their inability to migrate into the tumor tissue in significant numbers. In our preclinical studies, we observed that TC-210 expressed higher levels of the chemokine receptors CXCR3 (shown below) and CCR10 than the MSLN CAR-T cells we engineered. We believe this higher chemokine receptor expression is one of the main factors causing the faster migration to and greater accumulation of TC-210 in tumors as compared to the MSLN CAR-T cells in our preclinical studies.
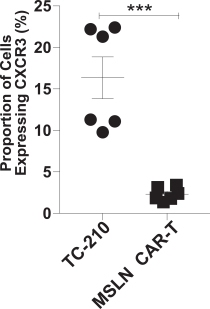
TC-210 showed mesothelin-dependent T cell activation, expansion and faster tumor cell killing in both ovarian cancer and NSCLC models when compared to MSLNCAR-T cells
We tested the ability ofTC-210 to migrate into the tumor site and then recognize and kill mesothelin-positive ovarian cancers in a mouse xenograft model. The ovarian adenocarcinoma cells in this study were engineered to express a tracing agent to monitor tumor clearance. The labeled ovarian cancer cells were injected into the peritoneal space to mirror a frequent location of metastatic ovarian cancer in humans. Five days after injection of cancer cells, mice were given eitherTC-210 or unmodified T cells. As shown below, unlike animals treated with unmodified T cells, all mice treated withTC-210 experienced a robust reduction of tumor mass, with six of seven mice showing a complete eradication.
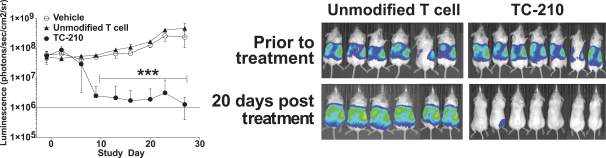
102
We further testedTC-210 in a mouse NSCLC xenograft model. Lung cancer cells were engineered to overexpress mesothelin and injected into the dorsal flank of mice. When the mean tumor volume reached 200 mm3, the mice were randomized into four groups and received either (i) the same number ofTC-210, MSLNCAR-T cells we engineered, or unmodified T cells or (ii) the vehicle phosphate buffered saline. Administration of unmodified T cells had no impact on tumor growth compared to vehicle. Both treatment withTC-210 and the MSLNCAR-T cells resulted in tumor clearance. Notably, as shown in the figure below, treatment withTC-210 led to a faster tumor clearance than the MSLNCAR-T cells. This accelerated clearance byTC-210 was also associated with less cytokine production compared to the MSLNCAR-T cells.
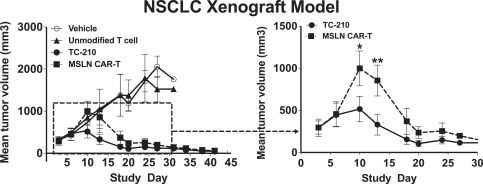
The ability ofTC-210 to eradicate mesothelin-expressing tumors was also observed in a mouse xenograft model of mesothelioma, as shown in the figure below. Primary mesothelioma cells overexpressing mesothelin were injected into mice. When tumors reached approximately 200 mm3, the mice were infused with the same number ofTC-210, the MSLNCAR-T cells, or unmodified T cells, or treated with vehicle. Treatment of tumor-bearing animals withTC-210 showed rapid tumor control and eventually clearance of tumors by day 25 after start of treatment. As observed in the NSCLC model,TC-210 cleared mesothelioma faster than the MSLNCAR-T cells. Infusion ofnon-transduced T cells had no impact on tumor growth.
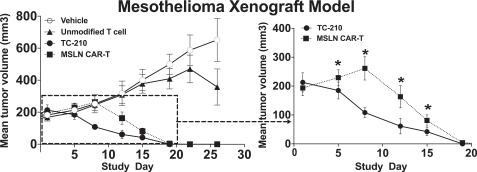
TC-210 demonstrated persistent anti-tumor activity in a mesothelioma rechallenge model
To evaluate the ability ofTC-210 to persist and maintain its anti-tumor activity, we conducted a mesothelioma xenograft mouse study. The experiment consisted of two phases. In the first phase, mice with established mesothelioma tumors were treated withTC-210 or unmodified T cells. As shown before, tumors were cleared in all mice and no relapse was observed until 56 days after treatment with a single dose ofTC-210. In the second phase,TC-210-treated mice were reinjected with mesothelioma cells to stimulate tumor recurrence. As shown in the graph below,TC-210 controlled the outgrowth of new tumors until the end of the study after 90 days. By contrast, in untreated mice, the rechallenge with mesothelioma cells caused a rapid outgrowth of tumors.
103
In this study, TC-210 showed both long-term elimination of the primary mesothelin-expressing tumor cells and lasting functional persistence. This persistence is associated with the ability to migrate to new tumor sites and recognize and kill tumor cells expressing mesothelin.
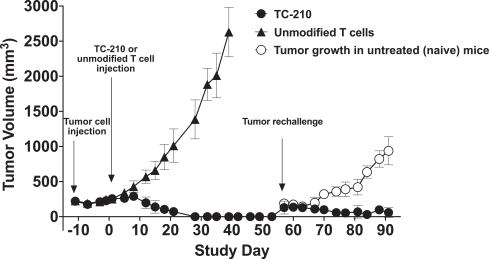
TC-210 persistence correlates with a favorable metabolic profile
To further understand potential causes of TC-210’s persistence, we investigated its metabolic profile. T cell respiratory reserve and mitochondrial activity are correlated with long-term functional persistence and resistance to exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment—properties which help T cells maintain long-term tumor control and prevent relapse. We analyzed TC-210’s respiratory reserve and mitochondrial activity as compared to the MSLN CAR-T cells we engineered to have the same mesothelin binder expressed by TC-210. As shown in the figure below, prior to exposure to tumor cells, TC-210 had a higher respiratory reserve when compared to the MSLN CAR-T cells, and, when exposed to mesothelin-positive tumors, TC-210 generated more energy through oxidative phosphorylation than the MSLN CAR-T cells, a potentially more efficient process in the hostile tumor microenvironment than glucose metabolism. Based on these observations, we believe that the metabolic profile of TC-210 may correlate with a better ability to persist and prevent relapse of mesothelin-positive tumors.
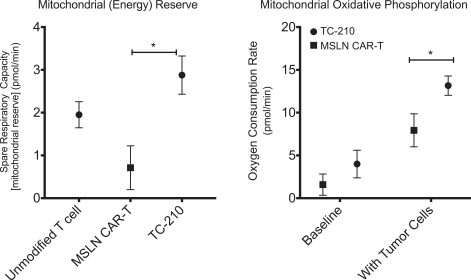
104
TC-210 showed preferential killing of high expressing mesothelin tumor cells
On-target,off-tumor activity of engineered T cells is a safety concern that may result in damage to normal tissue expressing mesothelin. We studied the potential ofTC-210 to preferentially kill cancer tissue expressing high levels of mesothelin and spare tissue expressing low levels of mesothelin. Mesothelin-high ormesothelin-low expressing tumor cells were injected into mice to establish subcutaneous tumors with a size of approximately 200 to 400 mm3. The difference in mesothelin expression between high and low expressing cells was 55-fold. As shown in the following figure,TC-210 cleared tumors formed by cells highly expressing mesothelin, but showed limited effect on the growth of tumors expressing low levels of mesothelin. This suggests thatTC-210 can spare normal tissue expressing low levels of mesothelin but eliminate tumors expressing mesothelin. We believe this property will play a critical role in the clinic as it potentially widens the therapeutic window forTC-210 and may minimize, if not completely prevent, any damage to mesothelin-expressing normal tissue.
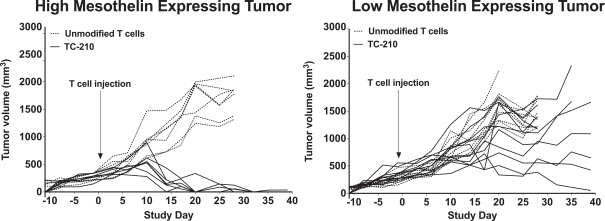
High Mesothelin Expressing Cells (MSTO-MSLN) Low Mesothelin Expressing Cells (MSTO)
105
TC-210 produced less cytokines than MSLNCAR-T cells
CRS is a life-threatening toxicity frequently associated with approved CD19-targetingCAR-T cell therapies. We compared the systemic release of cytokines in a mesothelin-positive lung cancer xenograft mouse model where one cohort was treated withTC-210 and another cohort with our engineered MSLNCAR-T cells we engineered. The serum levels of cytokines IFNyIL-2,IL-4,IL-5 andGM-CSF were measured at several time points after treatment. As shown in the figure below,TC-210 treated animals consistently produced lower circulating cytokine levels than the MSLNCAR-T cell treated animals over the time course examined. We believe this was due to natural feedback loops integrated into the entire TCR complex that could regulate overproduction of cytokines.We have observed similar results in a mesothelioma xenograft model. Based on our preclinical studies, we also believe that lower cytokine production byTC-210 and otherTRuC-T cells could translate into low levels of CRS and improved tolerability.
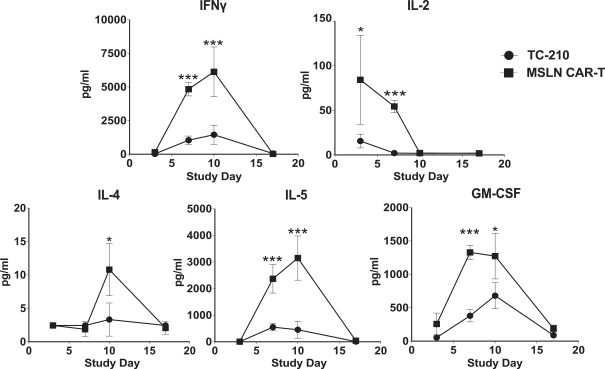
106
TC-220: Our MonoTRuC-T Cells Targeting MUC16 Positive Solid Tumors
We are conductingIND-enabling studies for our monoTRuC-T cell product candidate,TC-220, targeting MUC16-positive solid tumors. While its expression in normal tissues is low, MUC16 is highly expressed in many solid tumors, including ovarian, pancreatic, gastric and colorectal cancers. We plan to initially developTC-220 for the treatment of MUC16 overexpressing ovarian cancer, which represents a patient population of up to 17,000 in the United States alone.TC-220 has shown strong anti-tumor activity in preclinical models of MUC16-positive ovarian cancers. We plan to file an IND forTC-220 in early 2020 and we expect to generate our first clinical data in the first half of 2021.
MUC16 is a highly glycosylated transmembrane protein with a very large extracellular region. It serves as a physical mucous barrier protecting the epithelium from invasion by pathogens. In cancer, MUC16 expression increases the risk of metastases and contributes to tumor immunosuppression. When overexpressed in tumors, the large extracellular domain of the MUC16 protein, known asCA-125, is shed.CA-125 is used as a biomarker of tumor progression in patients with ovarian, pancreatic and other cancers. Previous therapeutic approaches targeting MUC16 have not proven to be effective because they bind to solubleCA-125, whereasTC-220 is activated only upon binding to MUC16 expressed on the surface of tumor cells.
Design ofTC-220
TC-220 uses a humanized single-domain antibody that specifically recognizes MUC16 fused to the human CD3e subunit via a flexible linker to form the MUC16-targeting fusion construct. We use a lentiviral vector to transfer the genetic information for the construct into a patient’s own T cells. Once in the cell, the fusion construct is integrated into the natural TCR and transported to the cell surface. The reprogramming of the TCR specificity enablesTC-220 to attack and destroy MUC16-positive tumors. The figure below illustrates the design ofTC-220.
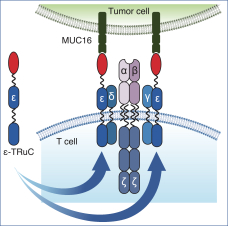
107
Preclinical Studies withTC-220
TC-220 killed ovarian cancer cells in cellular assays
We testedTC-220 in cellular assays using ovarian cell lines expressing either high or low levels of MUC16. In these studies,TC-220 killed cancer cells depending on their level of MUC16 expression on the cell surface, killing cancer cells with high levels of MUC16 but largely sparing cells expressing low levels of MUC16, providing a potential therapeutic window in patients. We believe thatTC-220 can therefore distinguish between cancer cells overexpressing the target antigen and normal tissues expressing low levels of MUC16. The graph below shows the dose-dependent killing of MUC16-positive ovarian cancer cells in our preclinical studies expressing high or low levels of the target antigen.
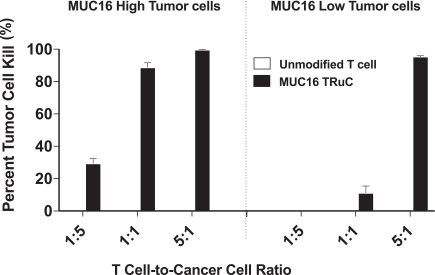
TC-220 reduced tumor burden in ovarian cancer model
We tested the ability of TC-220 to kill MUC16-positive ovarian cancers in a mouse xenograft model. The ovarian cancer cells in this study were engineered to express a tracing agent to monitor tumor clearance. The cells were injected into the peritoneal space to mirror the site where ovarian cancer is located in humans. Five days after injection of cancer cells, mice were given either vehicle control, TC-220 or unmodified T cells. As shown below, unlike mice treated with vehicle or unmodified T cells, all mice treated with TC-220 experienced a robust reduction of tumor mass. Tumors were completely cleared in five of seven mice tested.
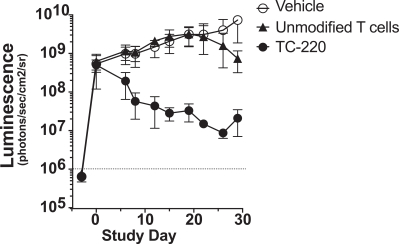
108
TC-220 showed preferential killing of tumor cells with high levels of MUC16
We further studied the potential of TC-220 to preferentially kill cancer tissue expressing high levels of MUC16 and spare tissue expressing low levels of MUC16 in a mouse model. Ovarian adenocarcinoma cells expressing high or low levels of MUC16 in this preclinical study were engineered to express a tracing agent to monitor tumor clearance. MUC16-high or MUC16-low cells were injected into the peritoneal cavity to mirror the site where ovarian cancer is located in humans. Five days after injection of cancer cells, mice were given either TC-220 or unmodified T cells. As shown in the figure below, TC-220 cleared tumors formed by cells with high MUC16 expression but showed limited effect on the growth of tumors expressing low levels of MUC16. This suggests that TC-220 can spare tissues expressing low levels of MUC16 but eliminate tumors overexpressing MUC16, which may prevent damage to MUC16-expressing normal tissue in human patients.
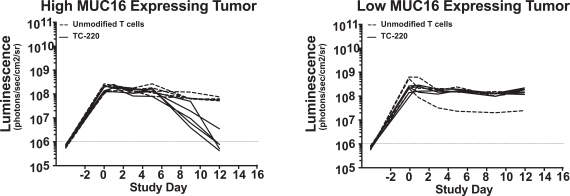
TC-410: Our DualTRuC-T Cell Program Targeting Mesothelin and MUC16
In cancer therapy, loss of antigen expression is one tumor escape mechanism that can lead to relapse. Once the antigen recognized by a T cell therapy is lost from the tumor cell surface, such cancer cells become invisible to T cells and can regrow a resistant tumor. For example, patients with glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) treated withCAR-T cells have been reported to relapse with target-negative tumor cells. Dual targeting is a means to potentially increase the response rates by binding to two target antigens. We believe that combined antigen targeting will enhance the potential ofTRuC-T cells to more broadly recognize cancer cells, which may result in fewer cases of relapse due to target loss.
We are developingTC-410, a dualTRuC-T cell designed to increase response rates and reduce the potential for antigen escape in solid tumors by targeting both mesothelin and MUC16. We are conducting preclinical studies to further characterize the expression profile of mesothelin and MUC16 in various cancers. We plan to advanceTC-410 intoIND-enabling studies in 2019.
The table below shows the prevalence of mesothelin and MUC16 expression in selected tumor types.
TUMOR TYPE | PREVALENCE OF MESOTHELIN SURFACE EXPRESSION (%) | PREVALENCE OF MUC16 EXPRESSION (%) | ||||||
Ovarian | 58 | 80 | ||||||
Pancreatic | 66 | 81 | ||||||
Colorectal | 55 | 64 | ||||||
Esophageal | 30 | 70 | ||||||
Gastric | 40 | 42 | ||||||
109
OurTRuC-T Cell Therapeutic Candidates for Hematological Malignancies
TC-110: Our Lead MonoTRuC-T Cells Targeting CD19-PositiveB-Cell Hematological Malignancies
We are developing a monoTRuC-T cell,TC-110, targeting CD19-positiveB-cell hematological malignancies. The clinical development plan forTC-110 will initially focus on three specific areas: adult ALL, DLBCL and FL. These are indications for whichCAR-T cells have either been approved but faced clinical outcome limitations (specifically, DLBCL), proven to be too toxic for use (specifically, adult ALL), or have not been approved at all (specifically, FL). In our preclinical studies, we have observed better anti-tumor activity and persistence ofTRuC-T cells compared toCAR-T cells we engineered to target CD19 while also exhibiting lower levels of cytokine release. We have a pre-IND meeting with the FDA scheduled in early 2019 and we expect to file an IND forTC-110 in the second half of 2019 and seek FDA Fast Track designation.
Background on Adult ALL
ALL is a cancer that results from the malignant proliferation of lymphoid progenitor cells in the bone marrow. It is characterized by an excess of malignant lymphoblasts, which in the vast majority of cases arise from progenitors of theB-cell lineage. In 2018, there were an estimated 3,000 cases of adult ALL and over 1,400 related deaths in the United States.
While 80% to 90% of patients with pediatric ALL can be cured with standard therapy and the remaining10-20% can be effectively treated with allogeneic stem cell transplantation or anti-CD19CAR-T cell therapy, like Kymriah, the prognosis of adults with ALL is much worse, with a five-year overall survival of 30% to 40%. Furthermore, while Kymriah has been approved for pediatric patients with ALL, noCAR-T cell therapy has been deemed safe in adults with ALL. Thus, the development of T cell therapies in adult patients with ALL will only be possible with platforms that are associated with significantly lower rates of severe CRS and neurotoxicity.
Background on Adult DLBCL
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) comprise a heterogeneous group of malignancies. DLBCL is the most common subtype of NHL, constituting up to 40% of cases globally. In 2018, there were an estimated 75,000 new cases of NHL and 20,000 related deaths in the United States. Approximatelytwo-thirds of patients with DLBCL are cured of their disease with frontline chemoimmunotherapy(R-CHOP). However, refractory patients have a median overall survival of only 6.3 months.
CD19-directedCAR-T cell therapy has shown activity in heavilypre-treated patients with CD19-positive DLBCL and twoCAR-T cell therapies, Kymriah and Yescarta, have been approved for that indication. However, the response rate six months post-infusion ranges from 37% to 41% and both therapies are associated with high rates of severe CRS (13% to 23%) and neurotoxicity (12% to 28%). Our preclinical data show better anti-tumor activity and lower cytokine release withTC-110 compared to CD28-based or4-1BB-basedCAR-T cells we engineered against CD19-expressing tumors.
Background on Follicular Lymphoma
FL is the most common indolent NHL in the Western hemisphere accounting for 20% of patients with newly diagnosed NHL. Approximately 15,000 patients were diagnosed in the United States with FL in 2018. The clinical course of patients with FL is generally indolent, with many patients remaining asymptomatic for months or even years after diagnosis. Although FL is considered incurable, the current overall survival of patients with FL approaches or exceeds ten years for many patients. However, 20% of patients with FL relapse within two years ofR-CHOP therapy and have a median five-year survival rate of only 50% compared to 90% for the remaining 80% of patients with a longer response duration. The experience withCAR-T cell therapy in FL is much more limited than in ALL or DLBCL but preliminary data indicate that CD19-directed adoptive T cell approaches are promising in high-risk FL.
In addition to applying for FDA Fast Track designation for TC-110, we plan to apply for FDA Breakthrough Therapy and Orphan Drug designations, where applicable, as well as Accelerated Approval.
110
Design ofTC-110
The construct to generateTC-110 is comprised of the single chain variable fragment, FMC63, that specifically binds to CD19 on the cell surface that is fused with a flexible linker to the human CD3e subunit. We use a lentiviral vector to introduce the genetic information ofTC-110 into a patient’s own T cells. In the cell, the fusion construct is integrated into the natural TCR and transported to the cell surface. The reprogramming of the TCR specificity enablesTC-110 to attack and destroy hematological malignancies that are CD19-positive. The following figure illustrates the design ofTC-110:
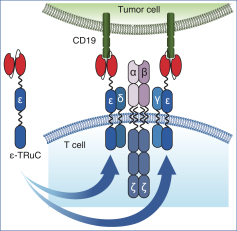
Summary of our Preclinical Data onTC-110
TC-110 showed robust activity in preclinical models where we compared the T cell signaling, cytokine production and anti-tumor activity ofTC-110 with CD19-targetingCAR-T cells, which we engineered with the same CD19 binder as TC-110. These CAR-T cells had a similar design as currently used in approved CD19 CAR-T cell therapies but are not identical. Our preclinical data support our hypothesis thatTC-110 could result in potent anti-tumor activity with lower cytokine levels than existing T cell therapies. In our preclinical studies of TC-110, we observed the following results:
| ∎ | Rapid regression and clearance of tumors in a CD19-positive leukemia model; |
| ∎ | Elimination of tumors in a subcutaneous CD19 lymphoma model; and |
| ∎ | Lower cytokine release compared to CD19-targetingCAR-T cells that we engineered. |
111
TC-110 triggered distinct gene expression compared to CAR-T cells
Initial experiments were conducted to examine the differences in gene expression between TC-110 and CAR-T cells we engineered to target CD19 and express a CD28 costimulatory domain (28z-CAR) compared to non-transduced T cells after four hours of stimulation with CD19 expressing lymphoma cells. As shown in the figure below, TC-110 had a broader set of genes both upregulated and downregulated compared to the CD19-targeting CAR-T cells we engineered.
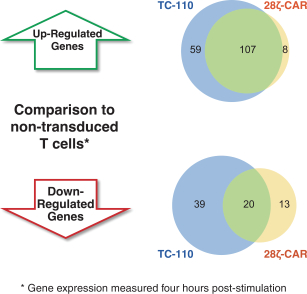
Specifically, several genes involved in TCR and chemokine signaling were significantly upregulated in TC-110 compared to the CD19-CAR T cells we engineered, as shown in the figure below. Because the expression of chemokines leads to improved trafficking of T cells to cancer cells and TCR signaling indicates broader T cell activation, we believe this differential gene expression will lead to enhanced functional activity of TC-110in vivo.
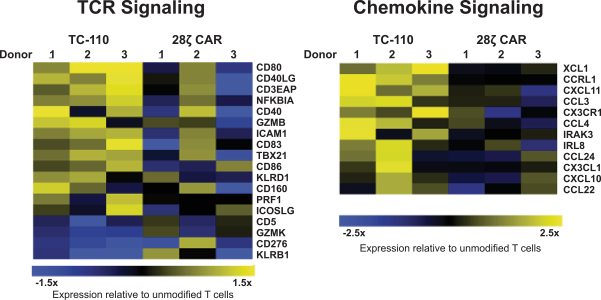
112
TC-110 cleared subcutaneous lymphoma in a mouse model more efficiently thanCAR-T cells
We compared the anti-tumor activity ofTC-110 with that of two CD19CAR-T cells that we engineered to replicate approvedCAR-T cell therapies in a subcutaneous lymphoma xenograft model (Raji cell line). Six days after lymphoma cell injection under the skin, mice were treated with similar numbers of either unmodified T cells,TC-110, our CD19 CAR-T cells with a BBz costimulatory domain or the CD19 CAR-T cells we engineered with a 28z costimulatory domain, in each case bearing an identical CD19-binding domain (FMC63). As shown below, treatment withTC-110 resulted in tumor clearance in the majority of mice at the end of the study. In contrast, the CD19CAR-T cells we engineered were not capable of eradicating the lymphoma cells and despite an initial response, a significant number of animals relapsed. We believe these data support thatTC-110 may have a higher and more sustained activity in treating lymphoma than the twoCAR-T cell variants. The following figure shows a comparison of the tumor control ofTC-110 and the twoCAR-T cell variants in the Raji NSG model.
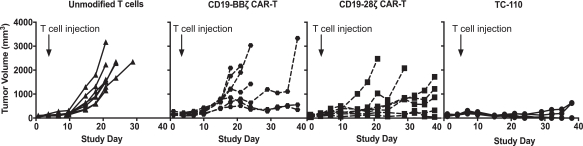
TC-110 cleared tumors in a leukemia xenograft model
We also explored the anti-tumor activity ofTC-110 in a leukemia xenograft model(Nalm-6 cell line).Nalm-6 cells lackco-stimulatory molecules. The leukemia cells were injected into the blood stream of mice with a tracing agent to monitor leukemic cell load monitored over time. As shown below, treatment withTC-110 and both variants ofCAR-T cells resulted in tumor clearance within ten days. Importantly,TC-110 showed a similar degree of leukemia cell clearance asCAR-T cells we engineered, despite not havingbuilt-in costimulatory domains derived from4-1BB or CD28.
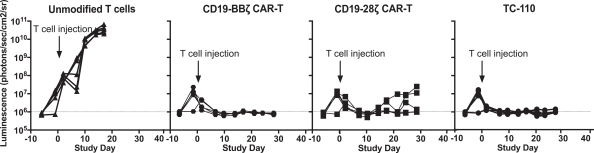
113
TC-110 releases less cytokines thanCAR-T cells
We investigated the effect ofTC-110 on cytokine release compared toCAR-T cells we engineered in a cell culture model. CRS is a major safety concern forCAR-T cell therapies. In the model, cytokine levels produced byTC-110 were significantly lower than those released by theCAR-T cells we engineered. These results, as illustrated below, are consistent with the lower levels of cytokine release observed in solid tumor models treated withTC-210 or the engineeredCAR-T cells.
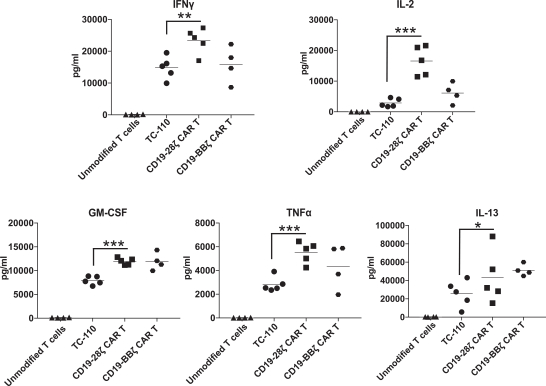
114
TC-110 showed less tonic signaling than CAR-T cells
Antigen-independent activation, referred to as tonic signaling, is the level of T cell activation that occurs in the absence of stimulation by the tumor antigen. While naturally occurring in all T cells, the high levels of tonic signaling observed in CAR-T cells have been linked to CAR-T cell exhaustion and lack of persistence. To study tonic signaling of TC-110 in comparison to CAR-T cells, we measured the phosphorylation of the CD3z subunit as a means for baseline T cell activation. We chose the CD3z subunit because both TC-110 and CAR-T cells use this subunit as an integral part of their respective signaling complexes. Compared to TC-110, the CAR-T cells we engineered with either a CD28 or4-1BB costimulatory domain showed higher levels of CD3z phosphorylation in the absence of target stimulation, indicating increased tonic signaling in the CAR-T cells. We believe that the reduced tonic signaling in TC-110 contributes to the enhanced anti-tumor activity of TC-110 and functional persistence observed in our other preclinical studies.
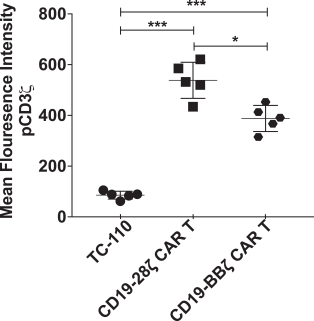
TC-310: Our DualTRuC-T Cell Program Targeting CD19/22
Antigen escape is a leading mechanism of relapse in patients treated with CD19-targetingCAR-T cells. For example, 40% of patients treated with Kymriah relapse within twelve months post-infusion, and 65% of those relapsing cases are CD19-negative. This phenomenon has also been recently identified as a mechanism whereby DLBCL can relapse post CD19-directedCAR-T cell therapy. We believe simultaneously targeting two tumor antigens on leukemia or lymphoma cells will potentially improve response rates and reduce the risk of recurrence due to antigen escape, thus leading to more durable responses.
We are developingTC-310, dualTRuC-T cells targeting both CD19 and CD22. We believe that CD22 is an ideal partner for CD19 because it is present on most cases of ALL and DLBCL and both CD19 and CD22 expression on normal cells is restricted to theB-cell lineage. In a third-party Phase 1 clinical trial of a CD22-directedCAR-T cell therapy, 73% of patients showed initial objective response rates. But similar to CD19-targetingCAR-T cell therapies, patients relapsed due to loss of CD22 expression on tumor cells, which rendered the therapy ineffective. These findings underscore the continued high medical need for patients with ALL and DLBCL and the possibility of improving clinical outcomes through the targeting of more than one antigen. We intend to advanceTC-310, which is currently at the preclinical development stage, intoIND-enabling studies in 2019.
Target Selection and Prioritization
We have systematically prioritized cancer antigens to select the targets for our lead product candidates and programs. From a list of over 40 potential targets, we assessed each antigen based on:
| ∎ | Clinical need; |
115
| ∎ | Unique expression or overexpression in tumor tissue; |
| ∎ | Little to no expression in other non-tumor associated tissues; |
| ∎ | Validation of the antigen as a potential target for cancer therapies; and |
| ∎ | Number of cell therapies and other competition targeting the antigen. |
The targets for our current programs—mesothelin, MUC16, CD19 and CD22—were the most promising based on the factors described above. We continue to actively evaluate other targets in our discovery-stage research based on these factors.
Broadening our CoreTRuC-T Cell Platform with a Series of Next-Generation Enhancements
We have developed a novel, transformative platform to address the limitations of existing T cell therapies. OurTRuC-T cell platform is designed to deliver the first HLA-independent TCR-T cell therapies to a broader population of patients with solid tumors and hematological malignancies. Our approach is to fuse a cancer antigen recognition domain directly to a subunit of the TCR, which becomes fully integrated into the natural complex. This has the effect of activating the entire TCR to produce a more powerful, yet controlled T cell response to cancer.
We are focused on continued innovation to broaden our platform through internal research and collaboration with leading academic laboratories and industry partners in the field ofT-cell immunology, cell therapy, gene editing, and process development. These innovations fall into three broad categories:
| ∎ | First, we are developing enhancements that target two antigens, or dualTRuC-T cells, to deal with potential antigen escape, a leading mechanism of cancer relapse in patients receivingCAR-T cell therapy. |
| ∎ | Second, we are developing several enhancements to controlon-target,off-tumor activity and counter the immunosuppressive microenvironment of solid tumors. These include mechanisms to block a key cancer defense known as thePD-1/PD-L1 pathway. |
| ∎ | Third, we are evaluating multiple proprietary designs foroff-the-shelfTRuC-T cells, aiming to give patients faster access to and reduce the costs ofTRuC-T cell therapies. |
116
The table below describes new platform elements to broaden and enhance the coreTRuC-T cell platform.
NEXT-GENERATION PLATFORM | MECHANISMS | DESIRED PATIENT OUTCOME | ||
| Dual antigen recognition | ∎ Ability to attack tumors based on the recognition of two different antigens | ∎ Reduced risk of relapse due to antigen escape
∎ Greater efficacy in tumors with heterogeneous target expression | ||
| Release of immune checkpoint brakes | ∎ Prevent dampening of the T cell performance by the tumor microenvironment
∎ Enhance the endogenous immune response | ∎ Greater anti-tumor efficacy
∎ Longer-lasting therapeutic benefit
∎ Decrease systemic toxicities related to immune checkpoint blockers | ||
| InducibleTRuC-T cells | ∎ Activation ofTRuC-T cells only in the tumor, which dampenson-target,off-tumor activity
∎ Controlled release of immunostimulatory factors | ∎ Improved safety profile | ||
| Off-the-shelfTRuC-T cells | ∎ UniversalTRuC-T cells for improved patient access | ∎ Ability to treat patients sooner after diagnosis
∎ Minimize risk of TRuC-T cell production failures
∎ Reduced costs of therapy | ||
DualTRuC-T Cell Programs
Antigen loss has been reported in solid tumors and CD19-positiveB-cell hematological malignancies after treatment withCAR-T cells. In each case, patients relapsed with cancer cells no longer expressing the targeted antigen. The versatility of ourTRuC-T cell platform allows us to programTRuC-T cells with more than one tumor binding domain. As illustrated in the figure below, this can be done by harnessing different subunits of the TCR complex.
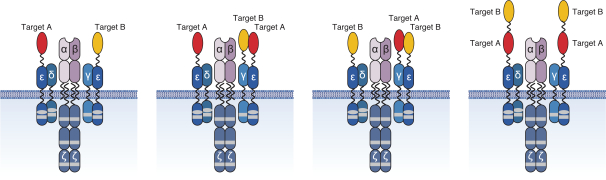
TRuC-T Cells Modulating the Hostile Tumor Microenvironment
T cells express a series of proteins that control the scale of an immune response as triggered by the TCR. One group is called checkpoint inhibitors and includes thePD-1 receptor, which is able to dampen a T cell response upon interaction with its ligandPD-L1. This important immunoregulatory mechanism has been hijacked by tumor cells, which expressPD-L1, thereby inhibiting the ability of T cells to kill cancer cells. In lung cancer and melanoma, treatment with monoclonal antibodies againstPD-1 orPD-L1 can result in long-lasting clinical responses in a
117
subgroup of patients. Because of the established role of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis in lung cancer, we intend to investigate in our planned Phase 1/2 clinical trial ofTC-210 whether the combination ofTC-210 with ananti-PD-1 antibody is safe and has the potential to improve on the activity of single-agentTC-210 in NSCLC. These results will inform the future clinical development of thePD-1TRuC-T cell enhancements.
Given the importance of thePD-1 pathway as a cancer defense mechanism, we are also engineeringTRuC-T cells with features that can intrinsically counteractPD-1. An advantage of these approaches is that they comprise two different immunotherapies (engineered T cells andanti-PD-1 therapy) in a single cell therapy, which may simplify clinical development, prevent systemic toxicities of theanti-PD-1 agent as it is delivered exclusively to the tumor, and be more cost-efficient thanco-administration of two therapeutics. In this context, we are evaluating the utility of a chimericPD-1/CD28 switch receptor designed to convert the negativePD-1 signal into an immune-activating signal via a CD28 intracellular signaling domain. Early preclinical studies have shown that theco-expressed switch receptor can enhance the expansion of ourTRuC-T cells.
InducibleTRuC-T Cells
We are developing a range of technologies designed to restrict the activation ofTRuC-T cells only in the tumor and release immune-stimulating factors only upon engagement of theTRuC-T cell complex. Such modalities have the potential to reduce the risk ofTRuC-T cell activation outside the tumor thereby protecting normal tissues.
Off-The-ShelfTRuC-T Cells
The development ofoff-the-shelfTRuC-T cells using third-party donor T cells is an attractive alternative to using a patient’s own T cells. Anoff-the-shelf therapy would enable us to treat patients immediately after diagnosis without them having to wait for production of their individual T cell products. Moreover,off-the-shelfTRuC-T cells offer an opportunity to treat patients who have too few T cells forTRuC-T cell manufacturing. We are evaluating multiple proprietaryoff-the-shelfTRuC-T cell designs. We are also exploring the use of different types of cells that are less prone to elicit a graft-versus-host-reaction, a serious complication observed in individuals who receive cells fromnon-HLA matching donors.
Competition
We believe our novelTRuC-T cell platform, its design flexibility, superior performance overCAR-T cell andTCR-T cell therapies, emerging enhancements, and our knowledge of cellular immunotherapy should enable us to successfully develop novel and highly effective treatments for cancer. However, we may face intense and increasing competition from larger biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies with greater financial resources, who are also developing immuno-oncology therapies (including cellular therapies) and more traditional treatments for cancer. In addition, academic institutions, governmental agencies, public and private research institutions, and early stage or smaller companies could also prove competitive.
The market opportunity in oncology has led to a number of collaborations (GlaxoSmithKline plc (GlaxoSmithKline)/Adaptimmune Therapeutics PLC (Adaptimmune), Janssen Biotech, Inc. (Janssen)/ Nanjing Legend Pharmaceutical & Chemical Co., Ltd (Legend), bluebird bio, Inc. (bluebird)/ Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc. (Regeneron) and bluebird/Gritstone Oncology, Inc.) and major acquisitions (Gilead Sciences, Inc. (Gilead)/Kite Pharma Inc. (Kite), Celgene Corporation (Celgene)/Juno Therapeutics, Inc. (Juno)) among companies focused on cellular cancer therapies. For example, the first CAR-T cell therapy licensed for pediatric ALL achieved a remarkable 81% ORR for patients with a minimum follow-up of three months and 76% of patients survived more than one year. Subsequently, Kite and Juno, two leading clinical-stageCAR-T cell therapy companies, were acquired for approximately $12 billion and $10 billion, respectively. If this trend continues, which we expect, we could see further consolidation of technical expertise and human capital. This potentially provides a partnership opportunity for us but could also make it more challenging for us to acquire complementary technology or products and recruit and retain qualified scientific and management personnel. In addition, this competition could impact our ability to recruit clinical trial sites and patients in a timely manner for our clinical trials. Larger companies with greater financial flexibility and global reach may be able to obtain regulatory approvals and gain widespread market acceptance before us, which could impact our commercial launch and could make our products obsolete ornon-competitive.
118
We are developing one of our lead product candidates,TC-210, in combination with an immune checkpoint inhibitor for the treatment of NSCLC. Others are evaluating these immune checkpoint inhibitor approaches in combination withCAR-T cells andTCR-T cells to enhance efficacy in the treatment of solid tumors and hematological malignancies. We therefore could experience significant direct competition from this type of combination immunotherapy. We may also face substantial competition in the future from other immunotherapies, if their use alone or in combination demonstrates a significant improvement in efficacy. Development of more effective small molecules, antibody-based approaches, cancer vaccines, oncolytic viruses and other products could lead to them preferentially being used as first- or second-line treatments, which would reduce the opportunity for our product candidates.
Despite the unique approach that we have developed to address the limitations ofCAR-T cells andTCR-T cells, we expect to face increasing competition as new more effective treatments for cancer enter the market and further advancements in technologies are made. We expect market adoption of any treatments that we develop and commercialize to be dependent on, among other things, efficacy, safety, delivery, price and the availability of reimbursement from government and other third-party payors.
We expect the commercial opportunity for our products that we take to regulatory licensing to be reduced or eliminated if competitors develop and commercialize products that are more effective, safer (have fewer or less severe side effects), are more convenient or are less expensive or better reimbursed than any products that we may commercialize. We compete with larger, better-funded companies, who may obtain regulatory approval for their products more rapidly than we may obtain licensing for ours. This could result in our competitors establishing a strong market position for either the product or a specific indication before we are able to enter the market.
Competition forTC-210
The overexpression of mesothelin by numerous solid tumors, combined with its low expression on mesothelial cells lining the pleura, peritoneum, and pericardium, has led to a number of different mesothelin-targeting agents being tested in Phase 1/2 trials. These approaches include novel antibody therapeutics, such as unconjugated monoclonal antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates, as well as vaccines. Antibody-based approaches are being pursued by F.Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Bayer AG, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Selecta Biosciences, Inc. and Morphotek, Inc., among others. Antibody-based agents in development have been limited to date by immunogenicity, poor tumor penetration and dose-limiting toxicities associated with the therapy. Novartis, Atara Biotherapeutics, Inc., Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center and several Chinese academic institutions are developinganti-mesothelinCAR-T cell therapies. Anti-mesothelinCAR-T cell therapies have been limited in the clinic by poor expansion, short persistence and immunogenicity.
Competition forTC-220
Approaches targeting tumors expressing MUC16 include antibody-based therapeutics, such as monoclonal antibodies and recombinant immunotoxins, as well as T cell-based approaches, such asCAR-T cells, and vaccines. Regeneron (in collaboration with Sanofi S.A.) is conducting a Phase 1/2 trial with a bispecific MUC16xCD3 antibody in patients with advanced platinum resistant ovarian cancer. Juno, in collaboration with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, is conducting a Phase 1 trial ofCAR-T cells against MUC16.
Competition forTC-110 andTC-310
Recent regulatory approvals of Gilead’s and Novartis’CAR-T cell therapies and clinical results for Juno’sCAR-T cell therapy have led a number of companies to increase their research and development efforts in the cell therapeutics field, including Janssen through its collaboration with Legend, as well as the entry into the field by many other companies. In addition to theseCAR-T cell therapies, many companies are developing enhancedTCR-T cells, which may compete withTC-110 andTC-310 in B-cell hematological malignancies. These include Cellectis S.A./Allogene Therapeutics, Inc., Mustang Bio, Inc., Autolus Therapeutics plc, Unum Therapeutics, Inc., Eureka Therapeutics, Inc., Triumvira Immunologics, Inc., Poseida Therapeutics, Inc. and Miltenyi Biotec GmbH, among others. Companies such asF. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Amgen Inc., Regeneron, MorphoSys AG, Forty Seven, Inc., and others are pursuing antibody based approaches. We therefore expect competition within the cell therapy field to intensify and for antibody-based approaches to more directly compete withTCR-T cell therapies in the future.
119
Manufacture and Delivery ofTRuC-T Cells to Patients
TRuC-T Cell Production and Delivery
The process of manufacturing cell and gene therapies, such asTRuC-T cells, is highly complex. As shown in the figure below, the generation of ourTRuC-T cells starts with the collection of white blood cells from patients, known as leukapheresis, at the treatment center. The blood cells are shipped to a central manufacturing facility where they are further processed. Following the enrichment of the sample T cells, they are activated, which causes them to divide. In the next step, a viral vector is used to shuttle the genetic information encoding the TRuC construct into the T cells. During the assembly process of the TCR, the TRuC construct is integrated into the natural TCR complex and transported to the cell surface. The now reprogrammedTRuC-T cells are further stimulated to replicate and produce enough quantities to administer a therapeutic dose to the patient from whom the cells were originally collected.
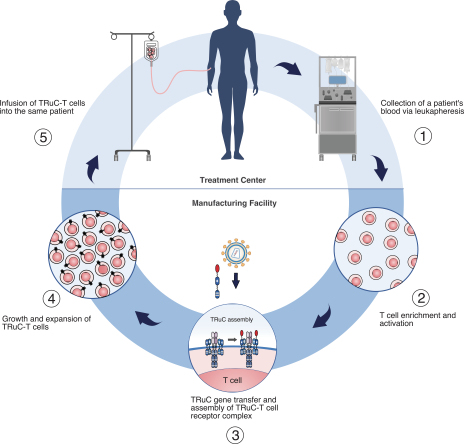
We use a next-generation cell processing platform that performs cell sample loading, cell washing, density-based cell separation, magnetic separation, cell culture and final product formulation. This is a semi-automated and functionally closed system that we believe will enable us to scale ourTRuC-T cell manufacturing and overcome the constraints associated with current processes.
TRuC-T Cell Manufacturing Strategy
We are devoting extensive resources to process development and manufacturing to optimize the reliability of our product candidates and reduce manufacturing costs and vein-to-vein time. This investment will ensure that our manufacturing and delivery process will have utility across all the product candidates in our pipeline.
The generation of a genetically-modified autologous T cell therapy suchas TRuC-T cells involves several integrated and complex steps, including the collection of T cells through apheresis, cryopreservation, manufacture of the
120
transfer vector under cGMP conditions, ex vivo selection, activation, transduction, and expansion of theTRuC-T cells, ultimately leading to infusion ofTRuC-T cells into patients. The technical, logistical, and regulatory challenges associated with the virus and cell manufacturing processes are significant. We plan to simplify the manufacturing process through the implementation of automated technologies and the development of scalable processes aimed at reducing the cost of goods.
We have already taken two critical steps geared towards simplifying our manufacturing process. First, ourTRuC-T cells are manufactured via a semi-automated and functionally closed system (CliniMACS Prodigy), which provides a common platform that will be employed in the development of all of the product candidates in our pipeline. This manufacturing process is economical, reliable, and scalable, and can support rapid development of the product candidates throughout the clinical life cycle and regulatory approvals. This system has a small footprint, which enables us to manufacture multiple products in parallel units within the same minimally controlled space, thereby reducing operating costs. Second, both the input leukapheresis material that enters the manufacturing process as well as the final TRuC-T cells are cryopreserved products, which simplifies the logistics for delivery to the patient and reduces the risk of product delivery failure. The entire vein-to-vein manufacturing process has safe-guards in place designed to ensure product identity and integrity throughout the production life-cycle.
We have entered into manufacturing agreements for the supply ofGMP-S plasmids for generation of the viral vectors, which are manufactured by third parties. The viral vectors are manufactured through established agreements with Brammer Bio, LLC, WuXi AppTec Inc. and LentiGen Technology, Inc. (a Miltenyi Biotec company). We outsource our T cell manufacturing process and we may enter into additional agreements to increase capacity for future clinical trials and commercialization if licensed. Because our starting materials are frozen, we expect to be able to base future agreements on rolling forecasts of regularly scheduled manufacturing runs, which we expect will minimize any cost overruns due to loss of reservation fees. Depending on the results of our clinical trials, we may choose to develop our own manufacturing capabilities.
As part of our manufacturing strategy, we plan to expand our capacity as we begin clinical trials and are planning for potential further expansion in anticipation of an approval for any of ourTRuC-T cell product candidates. Under our existing agreements with Miltenyi Biotec, Inc., we estimate that we have potential access to capacity to produce up to approximately 100 annual treatments per year, which we believe will be sufficient to conduct our initial planned clinical trials. We are in the process of adding manufacturing capacity to support larger clinical trials for our product candidates. To that end, in December 2018, we contracted with Cell Therapy Catapult Limited, United Kingdom to occupy a suite with our own personnel in their GMP manufacturing center in Stevenage, United Kingdom. We expect the suite to be operational in the second half of 2019, which we estimate would expand our manufacturing capacity to a total of approximately 400 treatments per year and facilitate conducting clinical trials in Europe. If our clinical trials are successful, we plan to acquire and develop our own manufacturing infrastructure to generate the additional capacity needed to support expanded clinical trials and commercial scale production. We believe our manufacturing platform can be scaled with minimal infrastructure while meeting GMP requirements, which will facilitate the design and building of a standard centralized manufacturing facility. Further into the future, however, we expect this system to be amenable to manufacturing in a controllednon-classified environment closer to or at the point of care, such as at a regional hub or hospital, resulting in a decentralized manufacturing model. We anticipate that this decentralized model would require minimal infrastructure, be led by operators that would require minimal technical training, shortenvein-to-vein time, and decrease costs.
Commercialization
We have not established a commercial organization or developed distribution capabilities given our current stage of development. However, over time we plan to create and expand our global commercial footprint as our product candidates approach regulatory licensing. As we approach the submission of a biologics license application (BLA), we plan to leverage our extensive experience with gene and cell therapy manufacturing and oncology to ensure each clinical site and manufacturer has the necessary oversight and management to support a successful launch. Overall, the main focus of our commercialization plan will be the development of our own manufacturing capacity. We believe the manufacturing platform’s efficient use of space, short utilization time and minimal foot print will facilitate commercial scaling.
121
Advisory Board
We work with a world-class Advisory Board, comprised of leaders in T cell biology and cell therapy, who provide feedback and guidance on the company’s direction. Our Advisory Board is comprised of the following individuals:
| ∎ | Mitchell Finer, Ph.D., Chairman of the Advisory Board, has over two decades of manufacturing and strategic development experience, including serving as the Chief Scientific Officer of bluebird bio, Inc. from 2010 to 2015, and is also a member of our Board of Directors. |
| ∎ | Stephan Grupp, M.D., Ph.D., is a world-renowned pediatric oncologist and cancer researcher who has pioneered CAR-T cell therapies at the University of Pennsylvania. He is the Yetta Deitch Novotny Professor of Pediatrics at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, and Chief of the Section of Cellular Therapy and Transplant at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. |
| ∎ | Marcela Maus, M.D., Ph.D., is a leading expert in CAR-T cell therapies and cancer immunotherapy. She is Director of Cellular Immunotherapy, Cancer Center, Massachusetts General Hospital and Assistant Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. |
| ∎ | Wolfgang Schamel, Ph.D., is an innovator and leader in the field of TCR signaling. He is professor and Chairman at the Institute of Biology III (Molecular Immunology) and a professor at the Centre for Biological Signaling Studies of the University of Freiburg, Germany. |
| ∎ | Kai Wucherpfennig, M.D., Ph.D., is a prominent T cell biologist and cancer immunologist and is Director of Center for the Cancer Immunotherapy Research, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Professor of Microbiology and Immunology at Harvard University. |
Intellectual Property
Intellectual property is a fundamental component of our business and of vital importance in our field. We actively seek to protect the intellectual property and proprietary technology that we believe is important to our business, including seeking, maintaining, enforcing and defending patent rights for our product candidates and processes, whether developed internally or licensed from third parties. We may additionally rely on regulatory protection afforded through orphan drug designations, data exclusivity, market exclusivity, and patent term extensions where available.
TheTRuC-T cell platform was initially conceived and developed by our scientific founder, Dr. Patrick Baeuerle. The priority patent application disclosing theTRuC-T cell platform was filed in May 2015. Our further work encompassing a broad range of TRuC concepts has been described in subsequent patent applications.
Additional patent applications filed by us since 2015 include at least the following additional technological innovations and product-related claims:
| ∎ | TRuC-T cells targeting an array of tumor antigens; |
| ∎ | TRuC-T cells targeting multiple types of antigens on the same tumor; |
| ∎ | engineeredTRuC-T cells with enhanced activity and/or modulated activity; |
| ∎ | second generationoff-the-shelfTRuC-T cells; and |
| ∎ | methods of usingTRuC-T cells to treat human diseases, including solid tumors. |
Our strategy is to pursue a variety of broad claims in the United States and foreign jurisdictions to provide multiple layers of patent protection, including:
| ∎ | pursuing broad claims in the United States for the TRuC concept; |
| ∎ | pursuing claims to specific compositions of matter in connection with particular TRuC constructs (including specific protein and nucleic acid sequences); and |
| ∎ | methods of using theTRuC-T cell platform as monotherapy or in combination with other anti-cancer or immune system enhancing therapeutics. |
All of the patent applications that we own orin-license, including our trademark filings, are still in the early stages of prosecution and no claims have yet issued. Examination of most of the patent applications that we own has not yet commenced, because they are either provisional applications or Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) applications that
122
are not examined. We will need to decide whether and where to pursue protection for the inventions disclosed in these provisional and PCT applications before applicable statutory deadlines, our applications will only be examined in jurisdictions where we elect to pursue protection, and we will only have the opportunity to attempt to obtain patents in such jurisdictions where we elect to pursue protection. We are seeking protection across a range of commercially important territories, including (but not limited to) countries in North America, Europe, and Asia. As of December 15, 2018, our patent portfolio includes at least 15 pending U.S. provisional or nonprovisional patent applications including one allowed U.S. nonprovisional patent application, at least five pending Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) international applications, and at least 19 pending foreign patent applications, which patent applications we own orin-license. The claims of these patent applications are directed toward various aspects of our product candidates and research programs including compositions of matter, methods of use, and processes. These owned and in-licensed patent applications, if issued, are expected to expire on various dates from 2036 through 2039, in each case without taking into account any possible patent term adjustments or extensions.
Within our patent portfolio, as of December 15, 2018, we owned at least six pending U.S. provisional or U.S. nonprovisional patent applications including one allowed U.S. nonprovisional patent application, at least two pending PCT international applications, and at least 14 pending foreign patent applications, and had a nonexclusive license from Harpoon Therapeutics, Inc. (Harpoon) to at least one pending U.S. provisional or U.S. nonprovisional patent application, and at least one pending PCT international application, and had an exclusive license to at least four pending foreign patent applications that include claims directed toTC-210, such as compositions of matter, manufacturing precursors or uses thereof. These owned and in-licensed patent applications, if issued, are expected to expire on various dates from 2036 through 2039, in each case without taking into account any possible patent term adjustment or extensions.
Within our patent portfolio, as of December 15, 2018, we owned at least six pending U.S. provisional or U.S. nonprovisional patent applications, at least one pending PCT international application, and at least 13 pending foreign patent applications, and had an exclusive license to at least four pending foreign patent applications that include claims directed toTC-220, such as compositions of matter, manufacturing precursors or uses thereof. These owned and in-licensed patent applications, if issued, are expected to expire on various dates from 2036 through 2039, in each case without taking into account any possible patent term adjustment or extensions.
Within our patent portfolio, as of December 15, 2018, we owned at least five pending U.S. provisional or U.S. nonprovisional patent applications, at least one pending PCT international application, and at least 13 pending foreign patent applications, and had an exclusive license to at least four pending foreign patent applications that include claims directed toTC-110, such as compositions of matter, manufacturing precursors or uses thereof. These owned and in-licensed patent applications, if issued, are expected to expire on various dates from 2036 through 2039, in each case without taking into account any possible patent term adjustment or extensions.
Within our patent portfolio, as of December 15, 2018, we owned at least nine pending U.S. provisional or U.S. nonprovisional patent applications including one allowed U.S. nonprovisional patent application, at least three pending PCT international applications, and at least 14 pending foreign patent applications; and had anon-exclusive license to at least one pending U.S. provisional or U.S. nonprovisional patent application, and at least one pending PCT international application and had an exclusive license to at least four pending foreign patent applications, that include claims directed toTC-410, such as compositions of matter, manufacturing precursors or uses thereof. These owned andin-licensed patent applications, if issued, are expected to expire on various dates from 2036 through 2039, in each case without taking into account any possible patent term adjustment or extensions.
Within our patent portfolio, as of December 15, 2018, we owned at least five pending U.S. provisional or U.S. nonprovisional patent applications, at least two pending PCT international applications, and at least 13 pending foreign patent applications and had an exclusive license to at least four pending foreign patent applications that include claims directed toTC-310, such as compositions of matter, manufacturing precursors or uses thereof. These owned and in-licensed patent applications, if issued, are expected to expire on various dates from 2036 through 2039, in each case without taking into account any possible patent term adjustment or extensions.
The term of individual patents depends upon the legal term of the patents in the countries in which they are obtained. In most countries in which we file, the patent term is 20 years from the date of filing of the first
123
non-provisional application to which priority is claimed. In the United States, a patent’s term may be lengthened by patent term adjustment, which compensates a patentee for administrative delays by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (PTO) in granting a patent or may be shortened if a patent is terminally disclaimed over an earlier-filed patent. The term of a patent that covers anFDA-approved drug may also be eligible for a patent term restoration of up to five years under the Hatch-Waxman Act, which is designed to compensate for the patent term lost during the FDA regulatory review process. The length of the patent term restoration is calculated based on the length of time the drug is under regulatory review. A patent term restoration under the Hatch-Waxman Act cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the date of product approval and only one patent applicable to an approved drug may be restored. Moreover, a patent can only be restored once, and thus, if a single patent is applicable to multiple products, it can only be extended based on one product. Similar provisions are available in Europe and certain other foreign jurisdictions to extend the term of a patent that covers an approved drug. If and when possible, we expect to apply for patent term extensions for patents covering our product candidates or their methods of use.
Our commercial success may depend in part on our ability to obtain and maintain patent and other proprietary protection for commercially important technology, inventions andknow-how related to our business; defend and enforce our patents; preserve the confidentiality of our trade secrets; and operate without infringing the valid enforceable patents and proprietary rights of third parties. Our ability to stop third parties from making, using, selling, offering to sell or importing our products may depend on the extent to which we have rights under valid and enforceable patents or trade secrets that cover these activities. With respect to bothin-licensed and company-owned intellectual property, we cannot be sure that patents will be granted with respect to any of our pending patent applications or with respect to any patent applications filed by us in the future, nor can we be sure that any of our existing patents or any patents that may be granted to us in the future will be commercially useful in protecting our commercial products and methods of manufacturing the same. Development and commercialization of products can be subject to substantial delays and it is possible that, at the time of commercialization, any patent covering the product has expired or will be in force for only a short period of time following commercialization. Numerous third-party U.S. andnon-U.S. issued patents exist in the area of programmed T cell therapies, including patents held by our competitors. We cannot predict with any certainty if any third-party U.S. or foreign patent rights, or other proprietary rights, will be deemed infringed by the use of our technology, nor can we predict with certainty which, if any, of these rights will or may be asserted against us by third parties. Should we need to defend ourselves against any such claims, substantial costs may be incurred, regardless of whether such defense is successful. Furthermore, parties making such claims may be able to obtain injunctive or other equitable relief, which could effectively block our ability to develop or commercialize some or all our product candidates in the United States, the EU and other major markets.
We may rely, in some circumstances, on trade secrets to protect our technology. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by entering into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors and contractors. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in these individuals, organizations and systems, agreements or security measures may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors. To the extent that our consultants, contractors or collaborators use intellectual property owned by others in their work for us, disputes may arise as to the rights in related or resultingknow-how and inventions.
Our trademark portfolio currently contains registration applications for TCR2, TRuC, and our logo in the United States.
License
In June 2017, we entered into a license with Harpoon (the Harpoon License) that grants us a perpetual, irrevocable, world-wide,non-exclusive, royalty free, sublicensable license to research, develop, make, use, sell, commercialize or otherwise exploit products based on Harpoon’s MSLN polypeptide binding proteins (the MSLN Binder). We have incorporated the MSLN Binder intoTC-210.
124
As consideration for the Harpoon License, we granted Harpoon a perpetual, irrevocable, world-wide,non-exclusive, royalty free, sublicensable license to research, develop, make, use, sell, commercialize or otherwise exploit products based on certain binding proteins which we had developed (theOut-Licensed Binder). We do not incorporate theOut-Licensed Binder into any of our product candidates.
Under the Harpoon License, we retain ownership of theOut-Licensed Binder and own any of our improvements to the MSLN Binder and any of our product candidates incorporating the MSLN Binder. Similarly, Harpoon retains ownership of the MSLN Binder and owns any of its improvements to theOut-Licensed Binder and any of its products incorporating theOut-Licensed Binder. Each party is responsible for the prosecution and maintenance of the patent rights owned by such party.
The Harpoon License is effective through the expiration of all patents underlying the MSLN Binder andOut-Licensed Binder and it may be terminated by either party upon a material breach that remains uncured for 60 days after receiving notice thereof, or in the event of the other party’s bankruptcy.
Cell Therapy Catapult Limited Collaboration Agreement
On December 18, 2018, we entered into a Collaboration Agreement with Cell Therapy Catapult Limited (Catapult) to establish our GMP manufacturing and supply chain at their GMP manufacturing center in Stevenage, United Kingdom. The agreement also provides us with an option to expand our collaboration area with a second GMP cleanroom suite in Catapult’s second phase of development. The agreement is for a term of three years with earlier termination available to us on provision of twelve months’ notice. Termination is also possible in the event of material breach of the Agreement that remains uncured for 90 days and insolvency of a party.
The Catapult manufacturing center is a GMP facility. The agreement will enable us to have our own dedicated manufacturing space in the Catapult manufacturing center. Catapult’s contribution to collaboration is their GMP support, expertise, and inbound and outbound logistics and supply chain, being developed at the center. We expect the GMP manufacturing to be operational in the second half of 2019. We will use our own manufacturing process and we will be responsible for the operation of the manufacturing process in the suite.
Government Regulation and Product Licensure
Government authorities in the United States, at the federal, state, and local level, and in other countries and jurisdictions, including the EU, extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, pricing, quality control, approval, packaging, storage, recordkeeping, labeling, advertising, promotion, distribution, marketing, post-approval monitoring and reporting, and import and export of biopharmaceutical products. The processes for obtaining marketing approvals in the United States and in foreign countries and jurisdictions, along with compliance with applicable statutes and regulations and other regulatory authorities, require the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources.
Licensure and Regulation of Biologics in the United States
In the United States, biological products including gene therapy products, such as our lead product candidates, are licensed for marketing by the FDA under the Public Health Service Act (PHSA), and regulated by the FDA under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDCA), as well as by other federal, state and local statute and regulations. Both the FDCA and the PHSA and their corresponding regulations govern, among other things, the testing, manufacturing, safety, potency, labeling, packaging, storage, record keeping, distribution, reporting, advertising, and other promotional practices involving biological products. Additionally, each clinical trial protocol for a gene therapy product candidate is reviewed by the FDA and, in limited situations, the National Institutes for Health (NIH) through its Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee (RAC). The FDA must license a biological product before it may be marketed within the United States.
Within the FDA, the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) regulates gene therapy products. Within the CBER, the review of gene therapy and related products is consolidated in the Office of Tissues and Advanced Therapies and the FDA has established the Cellular, Tissue and Gene Therapies Advisory Committee to advise the CBER on its reviews. The CBER works closely with the NIH and the RAC, which makes recommendations to the NIH on gene therapy issues and engages in a public discussion of scientific, safety, ethical and societal issues related to proposed and ongoing gene therapy protocols. To date, the FDA has licensed three human gene therapy products for
125
sale and the agency has provided guidance for the development of other gene therapy products. This guidance includes a growing body of guidance documents on chemistry, manufacturing and control (CMC), clinical investigations and other areas of gene therapy development, all of which are intended to facilitate the industry’s development of gene therapy products and their implementing regulations. Recently, NIH proposed to revise its guidelines overseeing gene therapy research, including deleting the protocol registration and reporting requirements for certain therapies and eliminating RAC review and reporting requirements for human gene transfer research.
The failure of an applicant to comply with the applicable regulatory requirements at any time during the product development process, includingnon-clinical testing, clinical testing, the approval process or post-approval process, may result in delays to the conduct of a study, regulatory review and approval, and/or administrative or judicial sanctions. These sanctions may include, but are not limited to, the FDA’s refusal to allow an applicant to proceed with clinical trials, refusal to approve pending applications, license suspension or revocation, withdrawal of an approval, warning letters, adverse publicity, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, and civil or criminal investigations and penalties brought by the FDA or Department of Justice (DOJ), or other government entities, including state agencies.
An applicant seeking licensing to market and distribute a new biologic in the United States generally must satisfactorily complete each of the following steps before the product candidate will be licensed by the FDA:
| ∎ | preclinical testing including laboratory tests, animal studies, and formulation studies, which must be performed in accordance with the FDA’s good laboratory practice (GLP) regulations and standards; |
| ∎ | submission to the FDA of an IND for human clinical testing, which must become effective before human clinical trials may begin; |
| ∎ | approval by an institutional review board (IRB) representing each clinical site before each clinical trial may be initiated; |
| ∎ | performance of adequate and well-controlled human clinical trials to establish the safety, potency, and purity of the product candidate for each proposed indication, in accordance with current good clinical practices (GCP); |
| ∎ | preparation and submission to the FDA of a BLA for a biological product which includes not only the results of the clinical trials, but also detailed information on the chemistry, manufacture, and quality controls for the product candidate and proposed labeling for one or more proposed indication(s) and the payment of user fees (unless exempt); |
| ∎ | FDA acceptance and substantive review of the BLA; |
| ∎ | review of the product candidate by an FDA advisory committee, where appropriate or if applicable; |
| ∎ | satisfactory completion of an FDA inspection of the manufacturing facility or facilities, including those of third parties, at which the product candidate or components thereof are manufactured to assess compliance with cGMP requirements and to assure that the facilities, methods, and controls are adequate to preserve the product’s identity, strength, quality, and purity; |
| ∎ | satisfactory completion of any FDA audits of thenon-clinical and clinical trial sites to assure compliance with GCP and the integrity of clinical data in support of the BLA; |
| ∎ | securing FDA licensure of the BLA to allow marketing of the new biological product; and |
| ∎ | compliance with any post-licensing requirements, including the potential requirement to implement a REMS and the potential requirement to conduct and any post-licensing studies required by the FDA. |
Preclinical Studies and Investigational New Drug Application
Before an applicant begins testing a product candidate with potential therapeutic value in humans, the product candidate enters preclinical testing. Preclinical tests include laboratory evaluations of product chemistry, formulation, and stability, as well as other studies to evaluate, among other things, the toxicity of the product candidate. The conduct of the preclinical tests and formulation of the compounds for testing must comply with federal regulations and requirements, including GLP regulations and standards. The results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information and analytical data, are submitted to the FDA a part of an IND. Some long-term preclinical testing, such as animal tests of reproductive adverse events and carcinogenicity, and long-term toxicity studies, may continue after the IND is submitted.
126
The IND and IRB Processes
An IND is an exemption from the FDCA that allows an unapproved product candidate to be shipped in interstate commerce for use in an investigational clinical trial and a request for FDA authorization to administer such investigational product to humans. Such authorization must be secured prior to interstate shipment and administration of any product candidate that is not the subject of an approved BLA. In support of a request for an IND, applicants must submit a protocol for each clinical trial and any subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND. In addition, the results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information, analytical data, any available clinical data or literature and plans for clinical trials, among other things, must be submitted to the FDA as part of an IND. The FDA requires a30-day waiting period after the filing of each IND before clinical trials may begin. This waiting period is designed to allow the FDA to review the IND to determine whether human research subjects will be exposed to unreasonable health risks. At any time during this30-day period, or thereafter, the FDA may raise concerns or questions about the conduct of the trials as outlined in the IND and impose a clinical hold or partial clinical hold. In this case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before clinical trials can begin.
Following commencement of a clinical trial under an IND, the FDA may also place a clinical hold or partial clinical hold on that trial. A clinical hold is an order issued by the FDA to the sponsor to delay a proposed clinical investigation or to suspend an ongoing investigation. A partial clinical hold is a delay or suspension of only part of the clinical work requested under the IND. For example, a specific protocol or part of a protocol is not allowed to proceed, while other protocols may do so. No more than 30 days after imposition of a clinical hold or partial clinical hold, the FDA will provide the sponsor a written explanation of the basis for the hold. Following issuance of a clinical hold or partial clinical hold, an investigation may only resume after the FDA has notified the sponsor that the investigation may proceed. The FDA will base that determination on information provided by the sponsor correcting the deficiencies previously cited or otherwise satisfying the FDA that the investigation can proceed.
A sponsor may choose, but is not required, to conduct a foreign clinical trial under an IND. When a foreign clinical trial is conducted under an IND, all FDA IND requirements must be met unless waived. When a foreign clinical trial is not conducted under an IND, the sponsor must ensure that the study complies with certain regulatory requirements of the FDA in order to use the study as support for an IND or application for marketing approval or licensing. In particular, such studies must be conducted in accordance with GCP, including review and approval by an independent ethics committee (IEC) and informed consent from subjects. The GCP requirements in the final rule encompass both ethical and data integrity standards for clinical studies and the FDA must be able to validate the data through an onsite inspection, if deemed necessary by the FDA. The FDA’s regulations are intended to help ensure the protection of human subjects enrolled innon-IND foreign clinical studies, as well as the quality and integrity of the resulting data. They further help ensure thatnon-IND foreign studies are conducted in a manner comparable to that required for IND studies.
If a gene therapy trial is conducted at, or sponsored by, institutions receiving NIH funding for recombinant DNA research, prior to the submission of an IND to the FDA, a protocol and related documents must be submitted to, and the study registered with, the NIH Office of Biotechnology Activities (OBA) pursuant to the NIH Guidelines for Research Involving Recombinant DNA Molecules (the NIH Guidelines). Compliance with the NIH Guidelines is mandatory for investigators at institutions receiving NIH funds for research involving recombinant DNA. However, many companies and other institutions, not otherwise subject to the NIH Guidelines, voluntarily follow them. NIH is responsible for convening the RAC that discusses protocols that raise novel or particularly important scientific, safety or ethical considerations at one of its quarterly public meetings. The OBA will notify the FDA of the RAC’s decision regarding the necessity for full public review of a gene therapy protocol. RAC proceedings and reports are posted to the OBA website and may be accessed by the public.
In addition to the foregoing IND requirements, an IRB representing each institution participating in the clinical trial must review and approve the plan for any clinical trial before it commences at that institution, and the IRB must conduct continuing review and reapprove the study at least annually. The IRB must review and approve, among other things, the study protocol and informed consent information to be provided to study subjects. An IRB must operate in compliance with FDA regulations. An IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical trial at its institution, or an institution it represents, if the clinical trial is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB’s requirements or if the product candidate has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients.
127
Additionally, some trials are overseen by an independent group of qualified experts organized by the trial sponsor, known as a data safety monitoring board or committee (DSMB). This group provides authorization as to whether or not a trial may move forward at designated check points based on access that only the group maintains to available data from the study. Suspension or termination of development during any phase of clinical trials can occur if it is determined that the participants or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Other reasons for suspension or termination may be made by us based on evolving business objectives and/or competitive climate.
Information about clinical trials must be submitted within specific timeframes to the NIH for public dissemination on its ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Additional Regulation for Gene Therapy Clinical Trials
In addition to the regulations discussed above, there are a number of additional standards that apply to clinical trials involving the use of gene therapy. The FDA has issued various guidance documents regarding gene therapies, which outline additional factors that the FDA will consider at each of the above stages of development, which relate to, among other things: the proper preclinical assessment of gene therapies; the CMC information that should be included in an IND; the proper design of tests to measure product potency in support of an IND or BLA; and measures to observe delayed adverse effects in subjects who have been exposed to investigational gene therapies when the risk of such effects is high. Further, the FDA usually recommends that sponsors observe subjects for potential gene therapy-related delayed adverse events for a15-year period, including a minimum of five years of annual examinations followed by ten years of annual queries, either in person or by questionnaire, although the FDA recently proposed updating its guidance on long-termfollow-up after administration of human gene therapy products.
The NIH and the FDA have a publicly accessible database, the Genetic Modification Clinical Research Information System, which includes information on gene therapy trials and serves as an electronic tool to facilitate the reporting and analysis of adverse events on these trials.
Human Clinical Trials in Support of a BLA
Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational product candidate to human subjects under the supervision of a qualified investigator in accordance with GCP requirements which include, among other things, the requirement that all research subjects provide their informed consent in writing before their participation in any clinical trial. Clinical trials are conducted under written clinical trial protocols detailing, among other things, the objectives of the study, inclusion and exclusion criteria, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety, and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated.
Human clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases, but the phases may overlap or be combined. Additional studies may also be required after licensing.
| ∎ | Phase 1clinical trials are initially conducted in a limited population to test the product candidate for safety, including adverse effects, dose tolerance, absorption, metabolism, distribution, excretion, and pharmacodynamics in healthy humans or in patients. During Phase 1 clinical trials, information about the investigational biological product’s pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects may be obtained to permit the design of well-controlled and scientifically valid Phase 2 clinical trials. |
| ∎ | Phase 2clinical trials are generally conducted in a limited patient population to identify possible adverse effects and safety risks, evaluate the potency or efficacy of the product candidate for specific targeted indications, and determine dose tolerance and optimal dosage. Multiple Phase 2 clinical trials may be conducted by the sponsor to obtain information prior to beginning larger and more costly Phase 3 clinical trials. Phase 2 clinical trials are well controlled, closely monitored and conducted in a limited patient population. |
| ∎ | Phase 3clinical trials proceed if the Phase 2 clinical trials demonstrate that a dose range of the product candidate is potentially potency or effective and has an acceptable safety profile. Phase 3 clinical trials are undertaken within an expanded patient population to further evaluate dosage, provide substantial evidence of clinical potency or efficacy, and further test for safety in an expanded and diverse patient population at multiple, geographically dispersed clinical trial sites. A well-controlled, statistically robust Phase 3 trial may be designed to deliver the data that regulatory authorities will use to decide whether or not to license, and, if licensed, how to appropriately label a biologic. Such Phase 3 studies are referred to as “pivotal.” |
128
In some cases, the FDA may approve a BLA for a product candidate but require the sponsor to conduct additional clinical trials to further assess the product candidate’s safety and effectiveness after approval. Such post-approval trials are typically referred to as Phase 4 clinical trials. These studies are used to gain additional experience from the treatment of a larger number of patients in the intended treatment group and to further document a clinical benefit in the case of biologics licensed under accelerated approval regulations. Failure to exhibit due diligence with regard to conducting Phase 4 clinical trials could result in withdrawal of approval for products.
Progress reports detailing the results of the clinical trials must be submitted at least annually to the FDA. In addition, IND safety reports must be submitted to the FDA for any of the following: serious and unexpected suspected adverse reactions; findings from other studies or animal orin vitro testing that suggest a significant risk in humans exposed to the product; and any clinically important increase in the case of a serious suspected adverse reaction over that listed in the protocol or investigator brochure. Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical trials may not be completed successfully within any specified period, or at all. Furthermore, the FDA or the sponsor may suspend or terminate a clinical trial at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the research subjects are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical trial at its institution, or an institution it represents, if the clinical trial is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB’s requirements or if the product has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients. The FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP and the integrity of the clinical data submitted.
Review and Approval of a BLA
In order to obtain approval to market a biological product in the United States, a marketing application must be submitted to the FDA that provides sufficient data establishing the safety, purity and potency of the proposed biological product for its intended indication. The application includes all relevant data available from pertinent preclinical and clinical trials, including negative or ambiguous results as well as positive findings, together with detailed information relating to the product’s chemistry, manufacturing, controls and proposed labeling, among other things. Data can come from company-sponsored clinical trials intended to test the safety and effectiveness of a use of a product, or from a number of alternative sources, including studies initiated by investigators. To support marketing approval, the data submitted must be sufficient in quality and quantity to establish the safety, purity and potency of the biological product to the satisfaction of the FDA.
The BLA is a vehicle through which applicants formally propose that the FDA license a new product for marketing and sale in the United States for one or more indications. Every new biological product candidate must be the subject of an approved BLA before it may be commercialized in the United States. Under federal law, the submission of most BLAs is subject to an application user fee, which for federal fiscal year 2019 is $2,588,478 for an application requiring clinical data. The sponsor of an approved BLA is also subject to an annual program fee, which for fiscal year 2019 is $309,915. Certain exceptions and waivers are available for some of these fees, such as an exception from the application fee for products with orphan designation and a waiver for certain small businesses.
Following submission of a BLA, the FDA conducts a preliminary review of the application generally within 60 calendar days of its receipt and strives to inform the sponsor by the 74th day after the FDA’s receipt of the submission whether the application is sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. The FDA may request additional information rather than accept the application for filing. In this event, the application must be resubmitted with the additional information. The resubmitted application is also subject to review before the FDA accepts it for filing. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins anin-depth substantive review. The FDA has agreed to specified performance goals in the review process of the BLAs. Under that agreement, 90% of original BLA submissions are meant to be reviewed within ten months of the60-day filing date, and 90% of original BLAs that have been designated for “priority review” are meant to be reviewed within six months of the60-day filing date. The review process and the Prescription Drug User Fee Act goal date may be extended by the FDA for three additional months to consider new information or clarification provided by the applicant to address an outstanding deficiency identified by the FDA following the original submission.
Before approving an application, the FDA typically will inspect the facility or facilities where the product is or will be manufactured. Thesepre-approval inspections may cover all facilities associated with a BLA submission, including component manufacturing, finished product manufacturing and control testing laboratories. The FDA will not
129
approve an application unless it determines that the manufacturing processes and facilities are in compliance with cGMP requirements and adequate to assure consistent production of the product within required specifications. Additionally, before approving a BLA, the FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP.
In addition, as a condition of approval, the FDA may require an applicant to develop a REMS. REMS use risk minimization strategies beyond the professional labeling to ensure that the benefits of the product outweigh the potential risks. To determine whether a REMS is needed, the FDA will consider the size of the population likely to use the product, seriousness of the disease, expected benefit of the product, expected duration of treatment, seriousness of known or potential adverse events and whether the product is a new molecular entity.
The FDA may refer an application for a novel product to an advisory committee or explain why such referral was not made. Typically, an advisory committee is a panel of independent experts, including clinicians and other scientific experts, that reviews, evaluates and provides a recommendation as to whether the application should be approved and under what conditions. The FDA is not bound by the recommendations of an advisory committee, but it considers such recommendations carefully when making decisions.
Fast Track, Breakthrough Therapy, Priority Review and Regenerative Advanced Therapy Designations
The FDA is authorized to designate certain products for expedited review if they are intended to address an unmet medical need in the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition. These programs are referred to as Fast Track designation, Breakthrough Therapy designation, Priority Review designation and Regenerative Advanced Therapy designation.
Specifically, the FDA may designate a product for Fast Track review if it is intended, whether alone or in combination with one or more other products, for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and it demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for such a disease or condition. For Fast Track products, sponsors may have greater interactions with the FDA and the FDA may initiate review of sections of a Fast Track product’s application before the application is complete. This rolling review may be available if the FDA determines, after preliminary evaluation of clinical data submitted by the sponsor, that a Fast Track product may be effective. The sponsor must also provide, and the FDA must approve, a schedule for the submission of the remaining information and the sponsor must pay applicable user fees. However, the FDA’s time period goal for reviewing a fast track application does not begin until the last section of the application is submitted. In addition, the Fast Track designation may be withdrawn by the FDA if the FDA believes that the designation is no longer supported by data emerging in the clinical trial process.
Second, a product may be designated as a Breakthrough Therapy if it is intended, either alone or in combination with one or more other products, to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the product may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. The FDA may take certain actions with respect to Breakthrough Therapies, including holding meetings with the sponsor throughout the development process; providing timely advice to the product sponsor regarding development and approval; involving more senior staff in the review process; assigning a cross-disciplinary project lead for the review team; and taking other steps to design the clinical trials in an efficient manner.
Third, the FDA may designate a product for priority review if it is a product that treats a serious condition and, if licensed, would provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness. The FDA determines, on acase-by-case basis, whether the proposed product represents a significant improvement when compared with other available therapies. Significant improvement may be illustrated by evidence of increased effectiveness in the treatment of a condition, elimination or substantial reduction of a treatment-limiting product reaction, documented enhancement of patient compliance that may lead to improvement in serious outcomes, and evidence of safety and effectiveness in a new subpopulation. A priority designation is intended to direct overall attention and resources to the evaluation of such applications, and to shorten the FDA’s goal for taking action on a marketing application from ten months to six months.
With passage of the 21st Century Cures Act (the Cures Act), in December 2016, Congress authorized the FDA to accelerate review and approval of products designated as regenerative advanced therapies. A product is eligible for
130
this designation if it is a regenerative medicine therapy that is intended to treat, modify, reverse or cure a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the product has the potential to address unmet medical needs for such disease or condition. The benefits of a regenerative advanced therapy designation include early interactions with FDA to expedite development and review, benefits available to breakthrough therapies, potential eligibility for priority review and accelerated approval based on surrogate or intermediate endpoints.
Accelerated Approval Pathway
The FDA may grant accelerated approval to a product for a serious or life-threatening condition that provides meaningful therapeutic advantage to patients over existing treatments based upon a determination that the product has an effect on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit. The FDA may also grant accelerated approval for such a condition when the product has an effect on an intermediate clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality (IMM) and that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on IMM or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments. Products granted accelerated approval must meet the same statutory standards for safety and effectiveness as those granted traditional approval.
For the purposes of accelerated approval, a surrogate endpoint is a marker, such as a laboratory measurement, radiographic image, physical sign, or other measure that is thought to predict clinical benefit, but is not itself a measure of clinical benefit. Surrogate endpoints can often be measured more easily or more rapidly than clinical endpoints. An intermediate clinical endpoint is a measurement of a therapeutic effect that is considered reasonably likely to predict the clinical benefit of a drug, such as an effect on IMM. The FDA has limited experience with accelerated approvals based on intermediate clinical endpoints, but has indicated that such endpoints generally may support accelerated approval where the therapeutic effect measured by the endpoint is not itself a clinical benefit and basis for traditional approval, if there is a basis for concluding that the therapeutic effect is reasonably likely to predict the ultimate clinical benefit of a product.
The accelerated approval pathway is most often used in settings in which the course of a disease is long and an extended period of time is required to measure the intended clinical benefit of a product, even if the effect on the surrogate or intermediate clinical endpoint occurs rapidly. Thus, accelerated approval has been used extensively in the development and approval of products for treatment of a variety of cancers in which the goal of therapy is generally to improve survival or decrease morbidity and the duration of the typical disease course requires lengthy and sometimes large trials to demonstrate a clinical or survival benefit. Thus, the benefit of accelerated approval derives from the potential to receive approval based on surrogate endpoints sooner than possible for trials with clinical or survival endpoints, rather than deriving from any explicit shortening of the FDA approval timeline, as is the case with priority review.
The accelerated approval pathway is usually contingent on a sponsor’s agreement to conduct, in a diligent manner, additional post-approval confirmatory studies to verify and describe the product’s clinical benefit. As a result, a product candidate licensed on this basis is subject to rigorous post-marketing compliance requirements, including the completion of Phase IV or post-approval clinical trials to confirm the effect on the clinical endpoint. Failure to conduct required post-approval studies, or confirm a clinical benefit during post-marketing studies, would allow the FDA to initiate expedited proceedings to withdraw approval of the product. All promotional materials for product candidates licensed under accelerated regulations are subject to prior review by the FDA.
The FDA’s Decision on a BLA
On the basis of the FDA’s evaluation of the application and accompanying information, including the results of the inspection of the manufacturing facilities, the FDA may issue an approval letter or a complete response letter. An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing of the product with specific prescribing information for specific indications. A complete response letter generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission and may require substantial additional testing or information in order for the FDA to reconsider the application. If and when those deficiencies have been addressed to the FDA’s satisfaction in a resubmission of the BLA, the FDA will issue an approval letter. The FDA has committed to reviewing such resubmissions in two or six months depending on the type of information included. Even with submission of this additional information, the FDA ultimately may decide that the application does not satisfy the regulatory criteria for licensing.
131
If the FDA licenses a new product, it may limit the licensed indications for use of the product. The agency may also require testing and surveillance programs to monitor the product after commercialization, or impose other conditions, including distribution restrictions or other risk management mechanisms, including REMS, to help ensure that the benefits of the product outweigh the potential risks. REMS can include medication guides, communication plans for health care professionals, and elements to assure safe use (ETASU). ETASU can include, but are not limited to, special training or certification for prescribing or dispensing, dispensing only under certain circumstances, special monitoring and the use of patent registries. The FDA may prevent or limit further marketing of a product based on the results of post-market studies or surveillance programs. After licensing, many types of changes to the licensed product, such as adding new indications, manufacturing changes and additional labeling claims, are subject to further testing requirements and FDA review and approval.
Post-Licensing Regulation
If regulatory licensing for marketing of a product or new indication for an existing product is obtained, the sponsor will be required to comply with all regular post-licensing regulatory requirements as well as any post-licensing requirements that the FDA may have imposed as part of the licensing process. The sponsor will be required to report, among other things, certain adverse reactions and manufacturing problems to the FDA, provide updated safety and potency or efficacy information and comply with requirements concerning advertising and promotional labeling requirements. Manufacturers and certain of their subcontractors are required to register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies, and are subject to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and certain state agencies for compliance with ongoing regulatory requirements, including cGMP regulations, which impose certain procedural and documentation requirements upon manufacturers. Changes to the manufacturing processes are strictly regulated and often require prior FDA approval before being implemented. Accordingly, the sponsor and its third-party manufacturers must continue to expend time, money, and effort in the areas of production and quality control to maintain compliance with cGMP regulations and other regulatory requirements.
A product may also be subject to official lot release, meaning that the manufacturer is required to perform certain tests on each lot of the product before it is released for distribution. If the product is subject to official release, the manufacturer must submit samples of each lot, together with a release protocol showing a summary of the history of manufacture of the lot and the results of all of the manufacturer’s tests performed on the lot, to the FDA. The FDA may in addition perform certain confirmatory tests on lots of some products before releasing the lots for distribution. Finally, the FDA will conduct laboratory research related to the safety, purity, potency, and effectiveness of pharmaceutical products.
Once a license is granted, the FDA may withdraw the license if compliance with regulatory requirements is not maintained or if problems occur after the product reaches the market. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with a product, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in revisions to the licensed labeling to add new safety information; imposition of post-market studies or clinical trials to assess safety risks; or imposition of distribution or other restrictions under a REMS program. Other potential consequences include, among other things:
| ∎ | restrictions on the marketing or manufacturing of the product, complete withdrawal of the product from the market, or product recalls; |
| ∎ | fines, warning letters, or holds on post-licensing clinical trials; |
| ∎ | refusal of the FDA to approve pending applications or supplements to licensed applications, or suspension or revocation of product license licenses; |
| ∎ | product seizure or detention, or refusal to permit the import or export of products; or |
| ∎ | injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties. |
The FDA strictly regulates the marketing, labeling, advertising and promotion of prescription drug products placed on the market. This regulation includes, among other things, standards and regulations fordirect-to-consumer advertising, communications regarding unapproved uses, industry-sponsored scientific and educational activities, and promotional activities involving the Internet and social media. Promotional claims about a drug’s safety or effectiveness are prohibited before the drug is licensed. After licensing, a drug product generally may not be promoted for uses that are not licensed by the FDA, as reflected in the product’s prescribing information. In the
132
United States, health care professionals are generally permitted to prescribe drugs for such uses not described in the drug’s labeling, known asoff-label uses, because the FDA does not regulate the practice of medicine. However, FDA regulations impose rigorous restrictions on manufacturers’ communications, prohibiting the promotion ofoff-label uses. It may be permissible, under very specific, narrow conditions, for a manufacturer to engage in nonpromotional,non-misleading communication regardingoff-label information, such as distributing scientific or medical journal information.
If a company is found to have promotedoff-label uses, it may become subject to adverse public relations and administrative and judicial enforcement by the FDA, the Department of Justice, or the Office of the Inspector General of the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), as well as state authorities. This could subject a company to a range of penalties that could have a significant commercial impact, including civil and criminal fines and agreements that materially restrict the manner in which a company promotes or distributes drug products. The federal government has levied large civil and criminal fines against companies for alleged improper promotion, and has also requested that companies enter into consent decrees or permanent injunctions under which specified promotional conduct is changed or curtailed.
In addition, the distribution of prescription pharmaceutical products is subject to the Prescription Drug Marketing Act (PDMA) and its implementing regulations, as well as the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCA), which regulate the distribution and tracing of prescription drug samples at the federal level, and set minimum standards for the regulation of distributors by the states. The PDMA, its implementing regulations and state laws limit the distribution of prescription pharmaceutical product samples, and the DSCA imposes requirements to ensure accountability in distribution and to identify and remove counterfeit and other illegitimate products from the market.
Pediatric Studies and Exclusivity
Under the Pediatric Research Equity Act, a BLA or supplement thereto for a biological product with a new active ingredient, indication, dosage form, dosing regimen or route of administration must contain data that are adequate to assess the safety and effectiveness of the product for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations, and to support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the product is safe and effective. Sponsors must also submit pediatric study plans prior to the assessment data. Those plans must contain an outline of the proposed pediatric study or studies the applicant plans to conduct, including study objectives and design, any deferral or waiver requests and other information required by regulation. The applicant, the FDA, and the FDA’s internal review committee must then review the information submitted, consult with each other and agree upon a final plan. The FDA or the applicant may request an amendment to the plan at any time.
For products intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, the FDA must, upon the request of an applicant, meet to discuss preparation of the initial pediatric study plan or to discuss deferral or waiver of pediatric assessments. In addition, FDA will meet early in the development process to discuss pediatric study plans with sponsors and FDA must meet with sponsors by no later than theend-of-Phase 1 meeting for serious or life-threatening diseases and by no later than ninety (90) days after FDA’s receipt of the study plan.
The FDA may, on its own initiative or at the request of the applicant, grant deferrals for submission of some or all pediatric data until after licensing of the product for use in adults, or full or partial waivers from the pediatric data requirements. Additional requirements and procedures relating to deferral requests and requests for extension of deferrals are contained in FDASIA. Unless otherwise required by regulation, the pediatric data requirements do not apply to products with orphan designation.
The FDA Reauthorization Act of 2017 established new requirements to govern certain molecularly targeted cancer indications. Any company that submits a BLA three years after the date of enactment of that statute must submit pediatric assessments with the BLA if the biologic is intended for the treatment of an adult cancer and is directed at a molecular target that FDA determines to be substantially relevant to the growth or progression of a pediatric cancer. The investigation must be designed to yield clinically meaningful pediatric study data regarding the dosing, safety and preliminary potency to inform pediatric labeling for the product. Deferrals and waivers as described above are also available.
Pediatric exclusivity is another type ofnon-patent marketing exclusivity in the United States and, if granted, provides for the attachment of an additional six months of marketing protection to the term of any existing regulatory
133
exclusivity, including thenon-patent and orphan exclusivity. Thissix-month exclusivity may be granted if a BLA sponsor submits pediatric data that fairly respond to a written request from the FDA for such data. The data do not need to show the product to be effective in the pediatric population studied; rather, if the clinical trial is deemed to fairly respond to the FDA’s request, the additional protection is granted. If reports of requested pediatric studies are submitted to and accepted by the FDA within the statutory time limits, whatever statutory or regulatory periods of exclusivity or patent protection cover the product are extended by six months. This is not a patent term extension, but it effectively extends the regulatory period during which the FDA cannot license another application.
Orphan Drug Designations and Exclusivity
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may designate a biological product as an “orphan drug” if it is intended to treat a rare disease or condition, generally meaning that it affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States, or more in cases in which there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing and making a product available in the United States for treatment of disease or condition will be recovered from sales of the product. A company must seek orphan drug designation before submitting a BLA for the candidate product. If the request is granted, the FDA will disclose the identity of the therapeutic agent and its potential use. Orphan drug designation does not shorten the PDUFA goal dates for the regulatory review and licensing process, although it does convey certain advantages such as tax benefits and exemption from the PDUFA application fee.
If a product with orphan designation receives the first FDA approval for the disease or condition for which it has such designation or for a select indication or use within the rare disease or condition for which it was designated, the product generally will receive orphan drug exclusivity. Orphan drug exclusivity means that the FDA may not license another sponsor’s marketing application for the same drug for the same condition for seven years, except in certain limited circumstances. Orphan exclusivity does not block the licensing of a different product for the same rare disease or condition, nor does it block the licensing of the same product for different conditions. If a biologic designated as an orphan drug ultimately receives marketing licensing for an indication broader than what was designated in its orphan drug application, it may not be entitled to exclusivity.
Orphan drug exclusivity will not bar licensing of another product under certain circumstances, including if a subsequent product with the same biologic for the same condition is shown to be clinically superior to the licensed product on the basis of greater potency, purity or safety, or providing a major contribution to patient care, or if the company with orphan drug exclusivity is not able to meet market demand. This is the case despite an earlier court opinion holding that the Orphan Drug Act unambiguously required the FDA to recognize orphan exclusivity regardless of a showing of clinical superiority.
Biosimilars and Exclusivity
The 2010 Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, which was signed into law on March 23, 2010, included a subtitle called the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009 (BPCIA). The BPCIA established a regulatory scheme authorizing the FDA to license biosimilars and interchangeable biosimilars. The FDA has licensed several biosimilar products for use in the United States. As of September 30, 2018, however, no interchangeable biosimilars, however, have been licensed. The FDA has issued several guidance documents outlining an approach to review and licensing of biosimilars. Additional guidances are expected to be proposed and finalized by the FDA in the near term.
Under the BPCIA, a manufacturer may submit an application for licensure of a biological product that is “biosimilar to” or “interchangeable with” a previously licensed biological product or “reference product.” In order for the FDA to license a biosimilar product, it must find, among other things, that the product is “highly similar” to the reference product notwithstanding minor differences in clinically inactive components and that there are no clinically meaningful differences between the reference product and proposed biosimilar product in terms of safety, purity, and potency. For the FDA to license a biosimilar product as interchangeable with a reference product, the agency must find that the biosimilar product can be expected to produce the same clinical results as the reference product, and, for products administered multiple times, that the biologic and the reference biologic may be switched after one has been previously administered without increasing safety risks or risks of diminished potency relative to exclusive use of the reference biologic.
Under the BPCIA, an application for a biosimilar or interchangeable biological product may not be submitted to the FDA until four years following the date of licensing of the reference product. The FDA may not license a biosimilar or
134
interchangeable biological product until 12 years from the date on which the reference product was licensed. Even if a product is considered to be a reference product eligible for exclusivity, another company could market a competing version of that product if the FDA licenses a full BLA for such product containing the sponsor’s own preclinical data and data from adequate and well-controlled clinical trials to demonstrate the safety, purity, and potency of their product. The BPCIA also created certain exclusivity periods for biosimilars licensed as interchangeable products. At this juncture, it is unclear whether products deemed “interchangeable” by the FDA will, in fact, be readily substituted by pharmacies, which are governed by state pharmacy law.
Patent Term Restoration and Extension
A patent claiming a new biological product may be eligible for a limited patent term extension under the Hatch-Waxman Act, which permits a patent restoration of up to five years for patent term lost during product development and FDA regulatory review. The restoration period granted on a patent covering a product is typicallyone-half the time between the effective date of an IND and the submission date of a marketing application (such as a BLA), plus the time between the submission date of a marketing application and the ultimate licensing date. Patent term restoration cannot be used to extend the remaining term of a patent past a total of 14 years from the product’s licensing date. Only one patent applicable to a licensed product is eligible for the extension, and the application for the extension must be submitted prior to the expiration of the patent in question and within 60 days after approval of the relevant marketing application. A patent that covers multiple products for which licensing is sought can only be extended in connection with one of the licenses. The USPTO reviews and licenses the application for any patent term extension or restoration in consultation with the FDA.
The 21st Century Cures Act
On December 13, 2016, President Obama signed the Cures Act into law. The Cures Act is designed to modernize and personalize healthcare, spur innovation and research, and streamline the discovery and development of new therapies through increased federal funding of particular programs. It authorizes increased funding for the FDA to spend on innovation projects. The new law also amends the PHSA to reauthorize and expand funding for the NIH. The Cures Act establishes the NIH Innovation Fund to pay for the cost of development and implementation of a strategic plan, early stage investigators and research. It also charges NIH with leading and coordinating expanded pediatric research. Further, the Cures Act directs the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to expand surveillance of neurological diseases.
With amendments to the FDCA and the PHSA, Title III of the Cures Act seeks to accelerate the discovery, development, and delivery of new medicines and medical technologies. To that end, and among other provisions, the Cures Act reauthorizes the existing priority review voucher program for certain drugs intended to treat rare pediatric diseases until 2020; creates a new priority review voucher program for drug applications determined to be material national security threat medical countermeasure applications; revises the FDCA to streamline review of combination product applications; requires FDA to evaluate the potential use of “real world evidence” to help support approval of new indications for approved drugs; provides a new “limited population” approval pathway for antibiotic and antifungal drugs intended to treat serious or life-threatening infections; and authorizes FDA to designate a drug as a “regenerative advanced therapy,” thereby making it eligible for certain expedited review and approval designations.
Healthcare Law and Regulation
Health care providers and third-party payors play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of biological products that are granted marketing licensing. Arrangements with providers, consultants, third-party payors and customers are subject to broadly applicable fraud and abuse, anti-kickback, false claims laws, patient privacy laws and regulations and other health care laws and regulations that may constrain business and/or financial arrangements. Restrictions under applicable federal and state health care laws and regulations, include the following:
| ∎ | the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, persons and entities from knowingly and willfully soliciting, offering, paying, receiving or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, in cash or in kind, to induce or reward either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, order or recommendation of, any good or service, for which payment may be made, in whole or in part, under a federal health care program such as Medicare and Medicaid; |
| ∎ | the federal civil and criminal false claims laws, including the civil False Claims Act, and civil monetary penalties laws, which prohibit individuals or entities from, among other things, knowingly presenting, or |
135
causing to be presented, to the federal government, claims for payment that are false, fictitious or fraudulent or knowingly making, using or causing to made or used a false record or statement to avoid, decrease or conceal an obligation to pay money to the federal government. |
| ∎ | the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), which created additional federal criminal laws that prohibit, among other things, knowingly and willfully executing, or attempting to execute, a scheme to defraud any health care benefit program or making false statements relating to health care matters; |
| ∎ | HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, and their respective implementing regulations, including the Final Omnibus Rule published in January 2013, which impose obligations, including mandatory contractual terms, with respect to safeguarding the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information; |
| ∎ | the federal false statements statute, which prohibits knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or covering up a material fact or making any materially false statement in connection with the delivery of or payment for health care benefits, items or services; |
| ∎ | the federal transparency requirements known as the federal Physician Payments Sunshine Act, under the 2010 Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care Education Reconciliation Act (the ACA), which requires certain manufacturers of drugs, devices, biologics and medical supplies to report annually to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) within the HHS, information related to payments and other transfers of value made by that entity to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members; and |
| ∎ | analogous state and foreign laws and regulations, such as state anti-kickback and false claims laws, which may apply to health care items or services that are reimbursed bynon-government third-party payors, including private insurers. |
Some state laws require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government in addition to requiring manufacturers to report information related to payments to physicians and other health care providers or marketing expenditures. State and foreign laws also govern the privacy and security of health information in some circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and often are not preempted by HIPAA, thus complicating compliance efforts.
Pharmaceutical Insurance Coverage and Health Care Reform
In the United States and markets in other countries, patients who are prescribed treatments for their conditions and providers performing the prescribed services generally rely on third-party payors to reimburse all or part of the associated health care costs. Significant uncertainty exists as to the coverage and reimbursement status of products licensed by the FDA and other government authorities. Thus, even if a product candidate is licensed, sales of the product will depend, in part, on the extent to which third-party payors, including government health programs in the United States such as Medicare and Medicaid, commercial health insurers and managed care organizations, provide coverage and establish adequate reimbursement levels for, the product. The process for determining whether a payor will provide coverage for a product may be separate from the process for setting the price or reimbursement rate that the payor will pay for the product once coverage is licensed. Third-party payors are increasingly challenging the prices charged, examining the medical necessity and reviewing the cost-effectiveness of medical products and services and imposing controls to manage costs. Third-party payors may limit coverage to specific products on a licensed list, also known as a formulary, which might not include all of the licensed products for a particular indication.
In order to secure coverage and reimbursement for any product that might be licensed for sale, a company may need to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies in order to demonstrate the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of the product, in addition to the costs required to obtain FDA or other comparable marketing licenses. Nonetheless, product candidates may not be considered medically necessary or cost effective. A decision by a third-party payor not to cover a product could reduce physician utilization once the product is licensed and have a material adverse effect on sales, results of operations and financial condition. Additionally, a payor’s decision to provide coverage for a product does not imply that an adequate reimbursement rate will be licensed. Further, one
136
payor’s determination to provide coverage for a product does not assure that other payors will also provide coverage and reimbursement for the product, and the level of coverage and reimbursement can differ significantly from payor to payor.
The containment of health care costs also has become a priority of federal, state and foreign governments and the prices of products have been a focus in this effort. Governments have shown significant interest in implementing cost-containment programs, including price controls, restrictions on reimbursement and requirements for substitution of generic products. Adoption of price controls and cost-containment measures, and adoption of more restrictive policies in jurisdictions with existing controls and measures, could further limit a company’s revenue generated from the sale of any licensed products. Coverage policies and third-party reimbursement rates may change at any time. Even if favorable coverage and reimbursement status is attained for one or more products for which a company or its collaborators receive marketing licenses, less favorable coverage policies and reimbursement rates may be implemented in the future.
There have been a number of federal and state proposals during the last few years regarding the pricing of pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical products, limiting coverage and reimbursement for drugs and biologics and other medical products, government control and other changes to the health care system in the United States. In March 2010, the Affordable Care Act was enacted, which includes measures that have significantly changed health care financing by both governmental and private insurers. The provisions of the Affordable Care Act of importance to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry are, among others, the following:
| ∎ | an annual, nondeductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports certain branded prescription drug agents or biologic agents, which is apportioned among these entities according to their market share in certain government health care programs; |
| ∎ | an increase in the rebates a manufacturer must pay under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program to 23.1% and 13% of the average manufacturer price for branded and generic drugs, respectively; |
| ∎ | a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50%point-of-sale discounts to negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs to be covered under Medicare Part D; |
| ∎ | extension of manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability to covered drugs dispensed to individuals who are enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations, unless the drug is subject to discounts under the 340B drug discount program; |
| ∎ | a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for drugs that are inhaled, infused, instilled, implanted or injected; |
| ∎ | expansion of eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs by, among other things, allowing states to offer Medicaid coverage to additional individuals and by adding new mandatory eligibility categories for certain individuals with income at or below 133% of the federal poverty level, thereby potentially increasing manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability; |
| ∎ | expansion of the entities eligible for discounts under the Public Health Service pharmaceutical pricing program; |
| ∎ | new requirements under the federal Physician Payments Sunshine Act for drug manufacturers to report information related to payments and other transfers of value made to physicians and teaching hospitals as well as ownership or investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members; |
| ∎ | a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research; |
| ∎ | creation of the Independent Payment Advisory Board, which, if and when impaneled, will have authority to recommend certain changes to the Medicare program that could result in reduced payments for prescription drugs; and |
| ∎ | establishment of a Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation at CMS to test innovative payment and service delivery models to lower Medicare and Medicaid spending, potentially including prescription drug spending. |
137
Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since the ACA was enacted. These changes include the Budget Control Act of 2011, which, among other things, led to aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers of up to 2% per fiscal year that started in 2013 and will stay in effect through 2024 unless additional Congressional action is taken, and the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, which, among other things, reduced Medicare payments to several types of providers and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years. These new laws may result in additional reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding and otherwise affect the prices we may obtain for any of our product candidates for which we may obtain regulatory licensing or the frequency with which any such product candidate is prescribed or used. Further, there have been several recent U.S. congressional inquiries and proposed state and federal legislation designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to drug pricing, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs, reduce the costs of drugs under Medicare and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for drug products.
These healthcare reforms, as well as other healthcare reform measures that may be adopted in the future, may result in additional reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding, more rigorous coverage criteria, new payment methodologies and additional downward pressure on the price for any licensed product and/or the level of reimbursement physicians receive for administering any licensed product. Reductions in reimbursement levels may negatively impact the prices or the frequency with which products are prescribed or administered. Any reduction in reimbursement from Medicare or other government programs may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors.
Further, since enactment of the Affordable Care Act, there have been numerous legal challenges and Congressional actions to repeal and replace provisions of the law. In May 2017, the U.S. House of Representatives passed legislation known as the American Health Care Act of 2017. Thereafter, the Senate Republicans introduced and then updated a bill to replace the Affordable Care Act known as the Better Care Reconciliation Act of 2017. The Senate Republicans also introduced legislation to repeal the Affordable Care Act without companion legislation to replace it, and a “skinny” version of the Better Care Reconciliation Act of 2017. In addition, the Senate considered proposed healthcare reform legislation known as the Graham-Cassidy Bill. None of these measures were passed by the U.S. Senate.
The Trump Administration has also taken executive actions to undermine or delay implementation of the Affordable Care Act. In January 2017, President Trump signed an Executive Order directing federal agencies with authorities and responsibilities under the Affordable Care Act to waive, defer, grant exemptions from, or delay the implementation of any provision of the Affordable Care Act that would impose a fiscal or regulatory burden on states, individuals, healthcare providers, health insurers, or manufacturers of pharmaceuticals or medical devices. In October 2017, the President signed a second Executive Order allowing for the use of association health plans and short-term health insurance, which may provide fewer health benefits than the plans sold through the Affordable Care Act exchanges. At the same time, the Administration announced that it will discontinue the payment of cost-sharing reduction (CSR) payments to insurance companies until Congress approves the appropriation of funds for such CSR payments. The loss of the CSR payments is expected to increase premiums on certain policies issued by qualified health plans under the Affordable Care Act. A bipartisan bill to appropriate funds for CSR payments was introduced in the Senate, but the future of that bill is uncertain. Further, in July 2018 following a federal district court decision form New Mexico, the Administration announced that it would be freezing payments to insurers under the Affordable Care Act to cover sicker patients until it or Congress can address the appropriate methodology for calculating and making such payments. It remains to be seen how this action will affect the implementation of the Affordable Care Act.
More recently, with enactment of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, which was signed by the President on December 22, 2017, Congress repealed the “individual mandate.” The repeal of this provision, which requires most Americans to carry a minimal level of health insurance, will become effective in 2019. According to the Congressional Budget Office, the repeal of the individual mandate will cause 13 million fewer Americans to be insured in 2027 and premiums in insurance markets may rise. Additionally, on January 22, 2018, President Trump signed a continuing resolution on appropriations for fiscal year 2018 that delayed the implementation of certain Affordable CareAct-mandated fees, including theso-called “Cadillac” tax on certain high cost employer-sponsored
138
insurance plans, the annual fee imposed on certain health insurance providers based on market share, and the medical device excise tax onnon-exempt medical devices. The Congress will likely consider other legislation to replace elements of the Affordable Care Act, during the next Congressional session.
Further, there have been several recent U.S. congressional inquiries and proposed federal and proposed and enacted state legislation designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to drug pricing, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs, reduce the costs of drugs under Medicare and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for drug products. At the federal level, Congress and the Trump administration have each indicated that it will continue to seek new legislative and/or administrative measures to control drug costs. At the state level, individual states are increasingly aggressive in passing legislation and implementing regulations designed to control pharmaceutical and biological product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and, in some cases, designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing. In addition, regional health care authorities and individual hospitals are increasingly using bidding procedures to determine what pharmaceutical products and which suppliers will be included in their prescription drug and other health care programs. These measures could reduce the ultimate demand for our product candidates, once licensed, or put pressure on our product pricing.
In addition, on May 11, 2018, the Administration issued a plan to lower drug prices. Under this blueprint for action, the Administration indicated that HHS will: take steps to end the gaming of regulatory and patent processes by drug makers to unfairly protect monopolies; advance biosimilars and generics to boost price competition; evaluate the inclusion of prices in drug makers’ ads to enhance price competition; speed access to and lower the cost of new drugs by clarifying policies for sharing information between insurers and drug makers; avoid excessive pricing by relying more on value-based pricing by expanding outcome-based payments in Medicare and Medicaid; work to give Part D plan sponsors more negotiation power with drug makers; examine which Medicare Part B drugs could be negotiated for a lower price by Part D plans, and improving the design of the Part B Competitive Acquisition Program; update Medicare’s drug-pricing dashboard to increase transparency; prohibit Part D contracts that include “gag rules” that prevent pharmacists from informing patients when they could pay lessout-of-pocket by not using insurance; and require that Part D plan members be provided with an annual statement of plan payments,out-of-pocket spending, and drug price increases.
At the state level, individual states are increasingly aggressive in passing legislation and implementing regulations designed to control pharmaceutical and biological product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and, in some cases, designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing. In addition, regional health care authorities and individual hospitals are increasingly using bidding procedures to determine what pharmaceutical products and which suppliers will be included in their prescription drug and other health care programs. These measures could reduce the ultimate demand for our product candidates, once licensed, or put pressure on our product pricing.
Review and Approval of Medicinal Products in the EU
In order to market any product outside of the United States, a company must also comply with numerous and varying regulatory requirements of other countries and jurisdictions regarding quality, safety and efficacy and governing, among other things, clinical trials, marketing authorization, commercial sales and distribution of products. Whether or not it obtains FDA licensing for a product, an applicant will need to obtain the necessary approvals by the comparablenon-U.S. regulatory authorities before it can commence clinical trials or marketing of the product in those countries or jurisdictions. Specifically, the process governing approval of medicinal products in the EU generally follows the same lines as in the United States. It entails satisfactory completion of preclinical studies and adequate and well-controlled clinical trials to establish the safety and efficacy of the product for each proposed indication. It also requires the submission to the relevant competent authorities of a marketing authorization application (MAA), and granting of a marketing authorization by these authorities before the product can be marketed and sold in the EU.
Clinical Trial Approval
The Clinical Trials Directive 2001/20/EC, the Directive 2005/28/EC on GCP and the related national implementing provisions of the individual EU Member States govern the system for the approval of clinical trials in the EU. Under
139
this system, an applicant must obtain prior approval from the competent national authority of the EU Member States in which the clinical trial is to be conducted. Furthermore, the applicant may only start a clinical trial at a specific study site after the competent ethics committee has issued a favorable opinion. The clinical trial application must be accompanied by, among other documents, an investigational medicinal product dossier (the Common Technical Document) with supporting information prescribed by Directive 2001/20/EC, Directive 2005/28/EC, where relevant the implementing national provisions of the individual EU Member States and further detailed in applicable guidance documents.
In April 2014, the new Clinical Trials Regulation, (EU) No 536/2014 (Clinical Trials Regulation) was adopted. The Regulation was published on June 16, 2014 but is not expected to apply until 2019. The Clinical Trials Regulation will be directly applicable in all the EU Member States, repealing the current Clinical Trials Directive 2001/20/EC and replacing any national legislation that was put in place to implement the Directive. Conduct of all clinical trials performed in the EU will continue to be bound by currently applicable provisions until the new Clinical Trials Regulation becomes applicable. The extent to whichon-going clinical trials will be governed by the Clinical Trials Regulation will depend on when the Clinical Trials Regulation becomes applicable and on the duration of the individual clinical trial. If a clinical trial continues for more than three years from the day on which the Clinical Trials Regulation becomes applicable the Clinical Trials Regulation will at that time begin to apply to the clinical trial.
The new Clinical Trials Regulation aims to simplify and streamline the approval of clinical trials in the EU. The main characteristics of the regulation include: a streamlined application procedure via a single entry point, the “EU Portal and Database”; a single set of documents to be prepared and submitted for the application as well as simplified reporting procedures for clinical trial sponsors; and a harmonized procedure for the assessment of applications for clinical trials, which is divided in two parts. Part I is assessed by the appointed reporting Member State, whose assessment report is submitted for review by the sponsor and all other competent authorities of all EU Member States in which an application for authorization of a clinical trial has been submitted (Concerned Member States). Part II is assessed separately by each Concerned Member State. Strict deadlines have been established for the assessment of clinical trial applications. The role of the relevant ethics committees in the assessment procedure will continue to be governed by the national law of the Concerned Member State. However, overall related timelines will be defined by the Clinical Trials Regulation.
PRIME Designation in the EU
In March 2016, the European Medicines Agency (EMA), launched an initiative to facilitate development of product candidates in indications, often rare, for which few or no therapies currently exist. The PRIority Medicines (PRIME), scheme is intended to encourage drug development in areas of unmet medical need and provides accelerated assessment of products representing substantial innovation reviewed under the centralized procedure. Products from small- andmedium-sized enterprises may qualify for earlier entry into the PRIME scheme than larger companies. Many benefits accrue to sponsors of product candidates with PRIME designation, including but not limited to, early and proactive regulatory dialogue with the EMA, frequent discussions on clinical trial designs and other development program elements, and accelerated marketing authorization application assessment once a dossier has been submitted. Importantly, a dedicated Agency contact and rapporteur from the Committee for Human Medicinal Products (CHMP) or Committee for Advanced Therapies are appointed early in PRIME scheme facilitating increased understanding of the product at EMA’s Committee level. Akick-off meeting initiates these relationships and includes a team of multidisciplinary experts at the EMA to provide guidance on the overall development and regulatory strategies.
Marketing Authorization
To obtain a marketing authorization for a product under EU regulatory systems, an applicant must submit an MAA, either under a centralized procedure administered by the EMA or one of the procedures administered by competent authorities in EU Member States (decentralized procedure, national procedure, or mutual recognition procedure). A marketing authorization may be granted only to an applicant established in the EU. Regulation (EC) No 1901/2006 provides that prior to obtaining a marketing authorization in the EU, applicants must demonstrate compliance with all measures included in anEMA-approved Pediatric Investigation Plan (PIP) covering all subsets of the pediatric population, unless the EMA has granted a product-specific waiver, class waiver, or a deferral for one or more of the measures included in the PIP.
140
The centralized procedure provides for the grant of a single marketing authorization by the European Commission that is valid across the European Economic Area. Pursuant to Regulation (EC) No. 726/2004, the centralized procedure is compulsory for specific products, including for medicines produced by certain biotechnological processes, products designated as orphan medicinal products, ATMPs and products with a new active substance indicated for the treatment of certain diseases, including products for the treatment of cancer. For products with a new active substance indicated for the treatment of other diseases and products that are highly innovative or for which a centralized process is in the interest of patients, the centralized procedure may be optional. The centralized procedure may at the request of the applicant also be used in certain other cases. We anticipate that the centralized procedure will be mandatory for the product candidates we are developing.
Under the centralized procedure, the CHMP is also responsible for several post-authorization and maintenance activities, such as the assessment of modifications or extensions to an existing marketing authorization. Under the centralized procedure in the EU, the maximum timeframe for the evaluation of an MAA is 210 days, excluding clock stops when additional information or written or oral explanation is to be provided by the applicant in response to questions of the CHMP. Accelerated evaluation may be granted by the CHMP in exceptional cases, when a medicinal product is of major interest from the point of view of public health and, in particular, from the viewpoint of therapeutic innovation. If the CHMP accepts such a request, the time limit of 210 days will be reduced to 150 days, but it is possible that the CHMP may revert to the standard time limit for the centralized procedure if it determines that it is no longer appropriate to conduct an accelerated assessment. At the end of this period, the CHMP provides a scientific opinion on whether or not a marketing authorization should be granted in relation to a medicinal product. Within 15 calendar days of receipt of a final opinion from the CHMP, the European Commission must prepare a draft decision concerning an application for marketing authorization. This draft decision must take the opinion and any relevant provisions of EU law into account. Before arriving at a final decision on an application for centralized authorization of a medicinal product the European Commission must consult the Standing Committee on Medicinal Products for Human Use. The Standing Committee is composed of representatives of the EU Member States and chaired by anon-voting European Commission representative. The European Parliament also has a related “droit de regard”. The European Parliament’s role is to ensure that the European Commission has not exceeded its powers in deciding to grant or refuse to grant a marketing authorization.
The European Commission may grant aso-called “marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances”. Such authorization is intended for products for which the applicant can demonstrate that it is unable to provide comprehensive data on the efficacy and safety under normal conditions of use, because the indications for which the product in question is intended are encountered so rarely that the applicant cannot reasonably be expected to provide comprehensive evidence, or in the present state of scientific knowledge, comprehensive information cannot be provided, or it would be contrary to generally accepted principles of medical ethics to collect such information. Consequently, marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances may be granted subject to certain specific obligations, which may include the following:
| ∎ | the applicant must complete an identified program of studies within a time period specified by the competent authority, the results of which form the basis of a reassessment of the benefit/risk profile; |
| ∎ | the medicinal product in question may be supplied on medical prescription only and may in certain cases be administered only under strict medical supervision, possibly in a hospital and in the case of a radiopharmaceutical, by an authorized person; and |
| ∎ | the package leaflet and any medical information must draw the attention of the medical practitioner to the fact that the particulars available concerning the medicinal product in question are as yet inadequate in certain specified respects. |
A marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances is subject to annual review to reassess the risk-benefit balance in an annual reassessment procedure. Continuation of the authorization is linked to the annual reassessment and a negative assessment could potentially result in the marketing authorization being suspended or revoked. The renewal of a marketing authorization of a medicinal product under exceptional circumstances, however, follows the same rules as a “normal” marketing authorization. Thus, a marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances is granted for an initial five years, after which the authorization will become valid indefinitely, unless the EMA decides that safety grounds merit one additional five-year renewal.
141
The European Commission may also grant aso-called “conditional marketing authorization” prior to obtaining the comprehensive clinical data required for an application for a full marketing authorization. Such conditional marketing authorizations may be granted for product candidates (including medicines designated as orphan medicinal products), if (i) the risk-benefit balance of the product candidate is positive, (ii) it is likely that the applicant will be in a position to provide the required comprehensive clinical trial data, (iii) the product fulfills an unmet medical need and (iv) the benefit to public health of the immediate availability on the market of the medicinal product concerned outweighs the risk inherent in the fact that additional data are still required. A conditional marketing authorization may contain specific obligations to be fulfilled by the marketing authorization holder, including obligations with respect to the completion of ongoing or new studies, and with respect to the collection of pharmacovigilance data. Conditional marketing authorizations are valid for one year, and may be renewed annually, if the risk-benefit balance remains positive, and after an assessment of the need for additional or modified conditions and/or specific obligations. The timelines for the centralized procedure described above also apply with respect to the review by the CHMP of applications for a conditional marketing authorization.
The EU medicines rules expressly permit the EU Member States to adopt national legislation prohibiting or restricting the sale, supply or use of any medicinal product containing, consisting of or derived from a specific type of human or animal cell, such as embryonic stem cells. While the product candidates we have in development do not make use of embryonic stem cells, it is possible that the national laws in certain EU Member States may prohibit or restrict us from commercializing our product candidates, even if they have been granted an EU marketing authorization.
Unlike the centralized authorization procedure, the decentralized marketing authorization procedure requires a separate application to, and leads to separate approval by, the competent authorities of each EU Member State in which the product is to be marketed. This application is identical to the application that would be submitted to the EMA for authorization through the centralized procedure. The reference EU Member State prepares a draft assessment and drafts of the related materials within 120 days after receipt of a valid application. The resulting assessment report is submitted to the concerned EU Member States who, within 90 days of receipt, must decide whether to approve the assessment report and related materials. If a concerned EU Member State cannot approve the assessment report and related materials due to concerns relating to a potential serious risk to public health, disputed elements may be referred to the European Commission, whose decision is binding on all EU Member States.
The mutual recognition procedure similarly is based on the acceptance by the competent authorities of the EU Member States of the marketing authorization of a medicinal product by the competent authorities of other EU Member States. The holder of a national marketing authorization may submit an application to the competent authority of an EU Member State requesting that this authority recognize the marketing authorization delivered by the competent authority of another EU Member State.
Regulatory Data Protection in the EU
In the EU, innovative medicinal products approved on the basis of a complete independent data package qualify for eight years of data exclusivity upon marketing authorization and an additional two years of market exclusivity pursuant to Directive 2001/83/EC. Regulation (EC) No 726/2004 repeats the entitlement for medicinal products authorized in accordance with the centralized authorization procedure. Data exclusivity prevents applicants for authorization of generics of these innovative products from referencing the innovator’s data to assess a generic (abridged) application for a period of eight years. During the additionaltwo-year period of market exclusivity, a generic marketing authorization application can be submitted and authorized, and the innovator’s data may be referenced, but no generic medicinal product can be placed on the EU market until the expiration of the market exclusivity. The overallten-year period will be extended to a maximum of 11 years if, during the first eight years of those ten years, the marketing authorization holder obtains an authorization for one or more new therapeutic indications which, during the scientific evaluation prior to their authorization, are held to bring a significant clinical benefit in comparison with existing therapies. Even if a compound is considered to be a new chemical entity so that the innovator gains the prescribed period of data exclusivity, another company may market another version of the product if such company obtained marketing authorization based on an MAA with a complete independent data package of pharmaceutical tests,non-clinical tests and clinical trials.
142
Periods of Authorization and Renewals
A marketing authorization has an initial validity for five years in principle. The marketing authorization may be renewed after five years on the basis of are-evaluation of the risk-benefit balance by the EMA or by the competent authority of the EU Member State. To this end, the marketing authorization holder must provide the EMA or the competent authority with a consolidated version of the file in respect of quality, safety, and efficacy, including all variations introduced since the marketing authorization was granted, at least six months before the marketing authorization ceases to be valid.
The European Commission or the competent authorities of the EU Member States may decide, on justified grounds relating to pharmacovigilance, to proceed with one further five-year period of marketing authorization. Once subsequently definitively renewed, the marketing authorization shall be valid for an unlimited period. Any authorization which is not followed by the actual placing of the medicinal product on the EU market (in case of centralized procedure) or on the market of the authorizing EU Member State within three years after authorization ceases to be valid (theso-called sunset clause).
Orphan Drug Designation and Exclusivity
Regulation (EC) No. 141/2000, as implemented by Regulation (EC) No. 847/2000 provides that a drug can be designated as an orphan drug by the European Commission if its sponsor can establish: that the product is intended for the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of (1) a life-threatening or chronically debilitating condition affecting not more than five in ten thousand persons in the EU when the application is made, or (2) a life-threatening, seriously debilitating or serious and chronic condition in the EU and that without incentives it is unlikely that the marketing of the drug in the EU would generate sufficient return to justify the necessary investment. For either of these conditions, the applicant must demonstrate that there exists no satisfactory method of diagnosis, prevention or treatment of the condition in question that has been authorized in the EU or, if such method exists, the drug will be of significant benefit to those affected by that condition.
Once authorized, orphan medicinal products are entitled to 10 years of market exclusivity in all EU Member States and in addition a range of other benefits during the development and regulatory review process including scientific assistance for study protocols, authorization through the centralized marketing authorization procedure covering all member countries and a reduction or elimination of registration and marketing authorization fees. However, marketing authorization may be granted to a similar medicinal product with the same orphan indication during the10-year period with the consent of the marketing authorization holder for the original orphan medicinal product or if the manufacturer of the original orphan medicinal product is unable to supply sufficient quantities. Marketing authorization may also be granted to a similar medicinal product with the same orphan indication if this product is safer, more effective or otherwise clinically superior to the original orphan medicinal product. The period of market exclusivity may, in addition, be reduced to six years if it can be demonstrated on the basis of available evidence that the original orphan medicinal product is sufficiently profitable not to justify maintenance of market exclusivity
Regulatory Requirements after a Marketing Authorization has been Obtained
In case an authorization for a medicinal product in the EU is obtained, the holder of the marketing authorization is required to comply with a range of requirements applicable to the manufacturing, marketing, promotion, and sale of the products. These include:
Regulatory Requirements after a Marketing Authorization has been Obtained
In case an authorization for a medicinal product in the EU is obtained, the holder of the marketing authorization is required to comply with a range of requirements applicable to the manufacturing, marketing, promotion and sale of medicinal products. These include:
| ∎ | Compliance with the European Union’s stringent pharmacovigilance or safety reporting rules must be ensured. These rules can impose post-authorization studies and additional monitoring obligations. |
| ∎ | The manufacturing of authorized medicinal products, for which a separate manufacturer’s license is mandatory, must also be conducted in strict compliance with the applicable EU laws, regulations and guidance, including Directive 2001/83/EC, Directive 2003/94/EC, Regulation (EC) No 726/2004 and the European Commission Guidelines for Good Manufacturing Practice. These requirements include compliance with EU cGMP standards when manufacturing medicinal products and active pharmaceutical ingredients, |
143
including the manufacture of active pharmaceutical ingredients outside of the EU with the intention to import the active pharmaceutical ingredients into the EU. |
| ∎ | The marketing and promotion of authorized drugs, including industry-sponsored continuing medical education and advertising directed toward the prescribers of drugs and/or the general public, are strictly regulated in the EU notably under Directive 2001/83EC, as amended, and EU Member State laws.Direct-to-consumer advertising of prescription medicines is prohibited across the EU. |
Brexit and the Regulatory Framework in the United Kingdom
On June 23, 2016, the electorate in the United Kingdom voted in favor of leaving the EU (commonly referred to as “Brexit”). Thereafter, on March 29, 2017, the country formally notified the EU of its intention to withdraw pursuant to Article 50 of the Lisbon Treaty. The withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the EU will take effect either on the effective date of the withdrawal agreement or, in the absence of agreement, two years after the United Kingdom provides a notice of withdrawal pursuant to the EU Treaty. Since the regulatory framework for pharmaceutical products in the United Kingdom covering quality, safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products, clinical trials, marketing authorization, commercial sales and distribution of pharmaceutical products is derived from EU directives and regulations, Brexit could materially impact the future regulatory regime which applies to products and the approval of product candidates in the United Kingdom. It remains to be seen how, if at all, Brexit will impact regulatory requirements for product candidates and products in the United Kingdom.
Pricing Decisions for Approved Products
In the EU, pricing and reimbursement schemes vary widely from country to country. Some countries provide that products may be marketed only after a reimbursement price has been agreed. Some countries may require the completion of additional studies that compare the cost-effectiveness of a particular product candidate to currently available therapies orso-called health technology assessments, in order to obtain reimbursement or pricing approval. For example, the EU provides options for its Member States to restrict the range of products for which their national health insurance systems provide reimbursement and to control the prices of medicinal products for human use. Member States may approve a specific price for a product or it may instead adopt a system of direct or indirect controls on the profitability of the company placing the product on the market. Other Member States allow companies to fix their own prices for products, but monitor and control prescription volumes and issue guidance to physicians to limit prescriptions. Recently, many countries in the EU have increased the amount of discounts required on pharmaceuticals and these efforts could continue as countries attempt to manage health care expenditures, especially in light of the severe fiscal and debt crises experienced by many countries in the EU. The downward pressure on health care costs in general, particularly prescription products, has become intense. As a result, increasingly high barriers are being erected to the entry of new products. Political, economic and regulatory developments may further complicate pricing negotiations, and pricing negotiations may continue after reimbursement has been obtained. Reference pricing used by various Member States, and parallel trade, or arbitrage, betweenlow-priced and high-priced Member States, can further reduce prices. There can be no assurance that any country that has price controls or reimbursement limitations for pharmaceutical products will allow favorable reimbursement and pricing arrangements for any products, if approved in those countries.
Employees
As of January 15, 2019, we had 46 full-time employees and one part-time employee. Twenty-three of our employees have Ph.D. or M.D. degrees and 38 of our employees are engaged in research and development activities. None of our employees are represented by labor unions or covered by collective bargaining agreements. We consider our relationship with our employees to be good.
Facilities
We lease a facility containing our research and development, laboratory and office space, which consists of approximately 23,000 square feet located at 100 Binney Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142. Our lease expires in June of 2025.
Legal Proceedings
As of the date of this prospectus, we were not party to any material legal matters or claims. In the future, we may become party to legal matters and claims arising in the ordinary course of business, the resolution of which we do not anticipate would have a material adverse impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
144
The following table sets forth information about our directors, executive officers and other key employees as of December 31, 2018.
NAME | AGE | POSITION(S) | ||||
Executive Officers | ||||||
Garry Menzel | 54 | President, Chief Executive Officer and Director | ||||
Robert Hofmeister | 51 | Chief Scientific Officer | ||||
Alfonso Quintás Cardama | 48 | Chief Medical Officer | ||||
Mayur (Ian) Somaiya | 45 | Chief Financial Officer | ||||
Non-Employee Directors | ||||||
Ansbert Gadicke(2)(3)(4) | 60 | Chairman of the Board of Directors | ||||
Andrew Allen(2) | 52 | Director | ||||
Patrick Baeuerle | 61 | Director | ||||
Morana Jovan-Embiricos(1)(2)(4) | 51 | Director | ||||
Neil Gibson(1)(2)(3) | 62 | Director | ||||
Mitchell Finer(1)(3) | 60 | Director | ||||
| (1) | Member of our audit committee |
| (2) | Member of our compensation committee |
| (3) | Member of our nominating and corporate governance committee |
| (4) | Member of our finance and strategy committee |
Executive Officers
Garry Menzel, Ph.D. Dr. Menzel joined our company in 2016 as a director and Chief Executive Officer. Dr. Menzel has also served on the board of directors of the oncology company Black Diamond Therapeutics Inc. since 2014. Previously, Dr. Menzel was the Chief Strategy Officer at Axcella Health Inc. from 2015 to 2016, the Chief Financial Officer at DaVita Healthcare Partners Inc. from 2013 to 2015, and the Chief Operating Officer at Regulus Therapeutics Inc. from 2008 to 2013. Dr. Menzel also had global leadership roles in running the biotechnology practices at Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC from 1994 to 2004 and Credit Suisse Group AG from 2004 to 2008. In addition, he was a consultant with Bain & Company and was a research assistant at SmithKline Beecham PLC (now GlaxoSmithKline PLC). Dr. Menzel received his Ph.D. from the University of Cambridge, where he studied the regulation of oncogenes in immune cells, and his M.B.A. from the Stanford University Graduate School of Business. We believe Dr. Menzel is qualified to serve as a member of our board of directors because of his scientific background and corporate leadership experience.
Robert Hofmeister, Ph.D. Dr. Hofmeister joined our company in September 2015 as Senior Vice President, Research and Development and became our Chief Scientific Officer in October 2016. From 2005 to 2015, Dr. Hofmeister held positions at EMD Serono Research and Development Institute, Inc., including as the Global Head of Translational Immunotherapy, Immuno-Oncology from 2012 to 2015. Previously, Dr. Hofmeister held positions at Micromet AG (now a part of Amgen, Inc.). Dr. Hofmeister received his Ph.D. from the University of Regensburg in Germany, where he studied the signaling of the cytokine interleukin-1.
Alfonso Quintás Cardama, M.D.Dr. Quintás joined our company in 2017 as Chief Medical Officer. Dr. Quintás was the clinical development head of the Cell & Gene Therapies Unit at GlaxoSmithKline PLC in 2017. Between 2014 and 2016, he served as Global Clinical Leader, Cell & Gene Therapy, at Novartis AG and was an Assistant Professor in the Department of Leukemia at The University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center from 2009 to 2014. Dr. Quintás received his M.D. from the Universidad de Santiago de Compostela School of Medicine in Spain. He completed an internship and residency in the Department of Medicine of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine—Yeshiva University and a hematology and oncology fellowship and a leukemia fellowship at The University of Texas, MD Anderson Cancer Center.
145
Mayur (Ian) Somaiya. Mr. Somaiya joined our company in 2018 as Chief Financial Officer. From 2015 to 2018, Mr. Somaiya was Managing Director and Head of Biotechnology Research at BMO Capital Markets Corp. Previously, he served as a Managing Director and Equity Analyst at Nomura Securities Co. Ltd. from 2013 to 2015, Piper Jaffray Companies from 2009 to 2013, Thomas Weisel Partners Group, Inc. from 2003 to 2009 and Morgan Stanley from 2000 to 2003. Mr. Somaiya received his B.A in Biology from New York University.
Non-Employee Directors
Ansbert Gadicke, M.D.Dr. Gadicke joined our board of directors in May 2015. Dr. Gadicke co-founded MPM Capital’s venture investing activities in 1997 and has since served as a Managing Director. Prior to that, Dr. Gadicke led MPM Capital’s Advisory and Investment Banking business from 1992 to 1996 and was in Boston Consulting Group’s Health Care Group from 1989 to 1992. He is a member of the board of directors of Cullinan Oncology, LLC and ElevateBio, LLC and formerly served as a member of the board of directors of Radius Health, Inc. and Chiasma, Inc. Dr. Gadicke received his M.D. from J.W. Goethe University and has held research positions at the Whitehead Institute and Harvard University. We believe Dr. Gadicke is qualified to serve as a member of our board of directors because of his extensive experience in the life sciences industry and in investment management.
Andrew Allen, M.D., Ph.D. Dr. Allen joined our board of directors in December 2018. Dr. Allen is a co-founder of Gritstone Oncology, Inc., and has served as its President and Chief Executive Officer since August 2015. Dr. Allen previously co-founded Clovis Oncology, Inc., a public pharmaceutical development company, and served as its executive vice president of clinical and preclinical development and chief medical officer from April 2009 to July 2015. Prior to that, he was chief medical officer at Pharmion Corporation from 2006 to 2008. Previously, Dr. Allen served in clinical development leadership roles at Chiron Corporation and Abbott Laboratories, and worked at McKinsey & Company, where he advised life science companies on strategic issues. He currently serves on the board of directors of Gritstone Oncology, Inc., Epizyme, Inc., Sierra Oncology, Inc., and Revitope Oncology, Inc. Dr. Allen previously served on the board of directors of Cell Design Labs, a private biotechnology company, from November 2015 until its acquisition by Gilead Sciences, Inc. in December 2017. Dr. Allen qualified in medicine at Oxford University and received a Ph.D. in immunology from Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine in London. We believe Dr. Allen is qualified to serve on our board of directors due to his educational experience and his experience as a founder and senior executive of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies.
Patrick Baeuerle, Ph.D. Dr. Baeuerle has served on our board of directors since May 2015. Since 2015, Dr. Baeuerle has been a Managing Director of MPM Capital. From 2012 to 2015 he served as Vice President, Research, and General Manager at Amgen Research (Munich) GmbH. From 1998 to 2012, Dr. Baeuerle served as Chief Scientific Officer for Micromet, Inc. Dr. Baeuerle co-founded Harpoon Therapeutics, Inc. in 2015. Dr. Baeuerle also co-founded Cullinan Oncology, LLC, of which he is Chief Scientific Officer—Biologics, Maverick Therapeutics, Inc. and iOmx AG. He currently serves on the board of directors of Harpoon Therapeutics and the advisory boards of Amphivena Therapeutics, Inc., iOmx AG and Maverick Therapeutics, Inc. He is also an Honorary Professor of Immunology of the Medical Faculty at University of Munich. Dr. Baeuerle received his Ph.D. in biology from the University of Munich and performed post-doctoral research at the Whitehead Institute. We believe Dr. Baeuerle is qualified to serve as a member of our board of directors because of his scientific background, experience in the venture capital industry, corporate leadership experience and his experience as a founder of numerous biopharmaceutical companies.
Mitchell Finer, Ph.D. Dr. Finer has served on our board of directors since October 2015. Dr. Finer has served as an Executive Partner of MPM Capital since August 2015. Dr. Finer previously served as Chief Executive Officer of Oncorus, Inc. from January 2016 to June 2018 and co-founded Adverum Biotechnologies, Inc. and CODA Biotherapeutics, Inc. Previously, he served as Chief Scientific Officer of bluebird bio, Inc., from March 2010 through July 2015. Dr. Finer serves on the boards of directors of Adverum Biotechnologies, Inc., Semma Therapeutics, Inc., Oncorus, Inc. and CODA Biotherapeutics, Inc. Dr. Finer received a Ph.D. in biochemistry and molecular biology from Harvard University and a B.A. in biochemistry and bacteriology from the University of California, Berkeley. He completed a postdoctoral fellowship at the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research. We believe Dr. Finer is qualified to serve as a member of our board of directors because of his operational, strategic and corporate leadership experience and his experience as a founder of numerous biopharmaceutical companies.
146
Morana Jovan-Embiricos, Ph.D. Dr. Jovan has served on our board of directors since October 2015. In 2003, Dr. Jovan co-founded F2 Ventures, a biotech venture capital fund and has since served as its Managing Partner. Prior to joining F2 Ventures, Dr. Jovan was a partner at MPM Capital. Dr. Jovan currently serves on the boards of directors of ElevateBio, LLC, TriNetX, Inc. and Cullinan Oncology, LLC. Dr. Jovan received her Ph.D. in biophysical chemistry from the University of Cambridge and was a post-doctoral fellow at Harvard University. We believe Dr. Jovan is qualified to serve as a member of our board of directors because of her scientific background and experience in the venture capital industry.
Neil Gibson, Ph.D. Dr. Gibson has served on our board of directors since February 2018. Since 2017, he has served as Senior Vice President to COI Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Avalon Ventures. From 2015 to 2016, Dr. Gibson served as Senior Vice President and Chief Development Officer to BioAlta LLC. From 2011 to 2015, he served as Chief Scientific Officer of Regulus Therapeutics Inc., and from 2013 to 2016 he served as Chair of Scripps Advance LLC. Previously, Dr. Gibson held management roles at Pfizer Inc. and OSI Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Dr. Gibson received his Ph.D. from the University of Aston and his B.Sc. from the University of Strathclyde. We believe Dr. Gibson is qualified to serve on our board of directors because of his extensive experience in the life sciences industry.
Board Composition
Our board of directors currently consists of seven members, each of whom is a member pursuant to the board composition provisions of our current certificate of incorporation and agreements with our stockholders, which agreements are described in the section of this prospectus titled “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions.” These board composition provisions will terminate upon the closing of this offering. Upon the termination of these provisions, there will be no further contractual obligations regarding the election of our directors. Our nominating and corporate governance committee and our board of directors may therefore consider a broad range of factors relating to the qualifications and background of nominees. Our nominating and corporate governance committee’s and our board of directors’ priority in selecting board members is identification of persons who will further the interests of our stockholders through their established record of professional accomplishment, the ability to contribute positively to the collaborative culture among board members, knowledge of our business, understanding of the competitive landscape, professional and personal experiences and expertise relevant to our growth strategy. Our directors hold office until their successors have been elected and qualified or until their earlier resignation or removal. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws that will become effective upon the closing of this offering also provide that our directors may be removed only for cause by the affirmative vote of the holders of at least two-thirds of the votes that all our stockholders would be entitled to cast in an annual election of directors, and that any vacancy on our board of directors, including a vacancy resulting from an enlargement of our board of directors, may be filled only by vote of a majority of our directors then in office.
Staggered Board
In accordance with the terms of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and our amended and restated bylaws that will become effective upon the closing of this offering, our board of directors will be divided into three staggered classes of directors and each director will be assigned to one of the three classes. At each annual meeting of the stockholders, one class of directors will be elected for a three-year term to succeed the directors of the same class whose terms are then expiring. The terms of the directors will expire upon the election and qualification of successor directors at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held during the years 2019 for Class I directors, 2020 for Class II directors and 2021 for Class III directors.
| ∎ | Our Class I directors will be Morana Jovan-Embiricos and Mitchell Finer; |
| ∎ | Our Class II directors will be Andrew Allen and Patrick Baeuerle; and |
| ∎ | Our Class III directors will be Garry Menzel, Ansbert Gadicke and Neil Gibson. |
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws that will become effective upon the closing of this offering will provide that the number of our directors shall be fixed from time to time by a resolution of the majority of our board of directors.
147
The division of our board of directors into three classes with staggered three-year terms may delay or prevent stockholder efforts to effect a change of our management or a change in control.
Director Independence
We have applied to list our common stock on The Nasdaq Global Market. Under the Nasdaq listing rules, independent directors must comprise a majority of a listed company’s board of directors within twelve months from the date of listing. In addition, the Nasdaq listing rules require that, subject to specified exceptions, each member of a listed company’s audit, compensation and nominating and governance committees be independent within twelve months from the date of listing. Audit committee members must also satisfy additional independence criteria, including those set forth in Rule 10A-3 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act), and compensation committee members must also satisfy the independence criteria set forth in Rule 10C-1 under the Exchange Act. Under Nasdaq listing rules, a director will only qualify as an “independent director” if, in the opinion of that company’s board of directors, that person does not have a relationship that would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment in carrying out the responsibilities of a director. In order to be considered independent for purposes of Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act, a member of an audit committee of a listed company may not, other than in his or her capacity as a member of the audit committee, the board of directors or any other board committee: (1) accept, directly or indirectly, any consulting, advisory or other compensatory fee from the listed company or any of its subsidiaries, other than compensation for board service; or (2) be an affiliated person of the listed company or any of its subsidiaries. In order to be considered independent for purposes of Rule 10C-1, the board of directors must consider, for each member of a compensation committee of a listed company, all factors specifically relevant to determining whether a director has a relationship to such company which is material to that director’s ability to be independent from management in connection with the duties of a compensation committee member, including, but not limited to: the source of compensation of the director, including any consulting advisory or other compensatory fee paid by such company to the director, and whether the director is affiliated with the company or any of its subsidiaries or affiliates.
In October, 2018, our board of directors undertook a review of the composition of our board of directors and its committees and the independence of each director. Based upon information requested from and provided by each director concerning his background, employment and affiliations, including family relationships, our board of directors has determined that all members of our board of directors, except Garry Menzel and Patrick Baeuerle, are independent directors, including for purposes of Nasdaq and SEC rules. In making that determination, our board of directors considered the relationships that each director has with us and all other facts and circumstances the board of directors deemed relevant in determining independence, including the potential deemed beneficial ownership of our capital stock by each director, including non-employee directors that are affiliated with certain of our major stockholders. Upon the completion of this offering, we expect that the composition and functioning of our board of directors and each of our committees will comply with all applicable requirements of Nasdaq and the rules and regulations of the SEC. There are no family relationships among any of our directors or executive officers.
We intend to adopt a policy, subject to and effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, that outlines a process for our securityholders to send communications to the board of directors.
Board Committees
Our board of directors has established an audit committee, a compensation committee and a nominating and corporate governance committee, each of which will operate pursuant to a charter to be adopted by our board of directors and will be effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. Our board of directors has also established a finance and strategy committee. We believe that the composition and functioning of all of our committees will comply with the applicable requirements of Nasdaq, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and SEC rules and regulations that will be applicable to us. We intend to comply with future requirements to the extent they become applicable to us.
Following the consummation of this offering, the full text of our audit committee charter, compensation committee charter, and nominating and corporate governance charter will be posted on the investor relations portion of our
148
website at https://www.tcr2.com/. We do not incorporate the information contained on, or accessible through, our corporate website into this prospectus, and you should not consider it a part of this prospectus.
Audit Committee
Upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, our audit committee will consist of Morana Jovan-Embiricos, Mitchell Finer and Neil Gibson and will be chaired by Morana Jovan-Embiricos. The functions of the audit committee will include:
| ∎ | appointing, approving the compensation of and assessing the independence of our independent registered public accounting firm; |
| ∎ | pre-approving auditing and permissible non-audit services, and the terms of such services, to be provided by our independent registered public accounting firm; |
| ∎ | reviewing the overall audit plan with our independent registered public accounting firm and members of management responsible for preparing our financial statements; |
| ∎ | reviewing and discussing with management and our independent registered public accounting firm our annual and quarterly financial statements and related disclosures as well as critical accounting policies and practices used by us; |
| ∎ | coordinating the oversight and reviewing the adequacy of our internal control over financial reporting; |
| ∎ | establishing policies and procedures for the receipt and retention of accounting-related complaints and concerns; |
| ∎ | recommending based upon the audit committee’s review and discussions with management and our independent registered public accounting firm whether our audited financial statements shall be included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K; |
| ∎ | monitoring the integrity of our financial statements and our compliance with legal and regulatory requirements as they relate to our financial statements and accounting matters; |
| ∎ | preparing the audit committee report required by SEC rules to be included in our annual proxy statement; |
| ∎ | reviewing all related party transactions for potential conflict of interest situations and approving all such transactions; and |
| ∎ | reviewing quarterly earnings releases. |
All members of our audit committee will meet the requirements for financial literacy under the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and the Nasdaq listing rules. Our board of directors has determined that Neil Gibson is “independent” for audit committee purposes as that term is defined in the rules of the SEC and the current listing standards of Nasdaq. The transition rules of the SEC require (1) one independent member at the time of listing, (2) a majority of independent members within 90 days of listing and (3) all independent members within one year of listing. Our board of directors intends to cause our audit committee to comply with the transition rules within the applicable time periods. There is not an “audit committee financial expert” (within the meaning of applicable SEC regulations) currently serving on our audit committee. Our board of directors does not believe that any of our current directors have the qualifications or experience to be considered an audit committee financial expert. However, the members of our board of directors individually and collectively have vast educational and business financial experience and training. Additionally, both our independent registered public accounting firm and management will periodically meet privately with our audit committee. At this time, no qualified candidates to serve on our audit committee as an “audit committee financial expert” have been identified, and there can be no assurance that we can attract and retain an independent director to act as our qualified financial expert.
Compensation Committee
Upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, our compensation committee will consist of Ansbert Gadicke, Andrew Allen and Neil Gibson, and will be chaired by Neil Gibson. The functions of the compensation committee will include:
| ∎ | annually reviewing and recommending to the board of directors the corporate goals and objectives relevant to the compensation of our Chief Executive Officer; |
| ∎ | evaluating the performance of our Chief Executive Officer in light of such corporate goals and objectives and based on such evaluation (i) reviewing and determining the cash compensation of our Chief Executive Officer and (ii) reviewing and approving grants and awards to our Chief Executive Officer under our equity-based plans; |
149
| ∎ | reviewing and approving the compensation of our other executive officers; |
| ∎ | reviewing and establishing our overall management compensation, philosophy and policy; |
| ∎ | overseeing and administering our compensation and similar plans; |
| ∎ | evaluating and assessing potential and current compensation advisors in accordance with the independence standards identified in the applicable Nasdaq listing rules; |
| ∎ | reviewing and approving our policies and procedures for the grant of equity-based awards; |
| ∎ | reviewing and recommending to the board of directors the compensation of our directors; |
| ∎ | preparing our compensation committee report if and when required by SEC rules; |
| ∎ | reviewing and discussing annually with management our “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” if and when required, to be included in our annual proxy statement; and |
| ∎ | reviewing and approving the retention or termination of any consulting firm or outside advisor to assist in the evaluation of compensation matters. |
Each member of our compensation committee will be a non-employee director, as defined in Rule 16b-3 promulgated under the Exchange Act, and an outside director, as defined pursuant to Section 162(m) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the Code).
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee
Upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, our nominating and corporate governance committee will consist of Ansbert Gadicke, Mitchell Finer and Neil Gibson and will be chaired by Ansbert Gadicke. The functions of the nominating and corporate governance committee will include:
| ∎ | developing and recommending to the board of directors criteria for board and committee membership; |
| ∎ | establishing procedures for identifying and evaluating board of director candidates, including nominees recommended by stockholders; |
| ∎ | reviewing the composition of the board of directors to ensure that it is composed of members containing the appropriate skills and expertise to advise us; |
| ∎ | identifying individuals qualified to become members of the board of directors; |
| ∎ | recommending to the board of directors the persons to be nominated for election as directors and to each of the board’s committees; |
| ∎ | developing and recommending to the board of directors a code of business conduct and ethics and a set of corporate governance guidelines; and |
| ∎ | overseeing the evaluation of our board of directors and management. |
Finance and Strategy Committee
Our finance and strategy committee will consist of Ansbert Gadicke and Morana Jovan-Embiricos and will be chaired by Ansbert Gadicke. The purpose of the finance and strategy committee is to consider and make recommendations to our board of directors regarding issues impacting our financial structure and strategic direction, including, but not limited to, our capital structure, business development activities and financing strategy, as well as the overall scope and focus of our business and operations.
Our board of directors may from time to time establish other committees.
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
None of the members of our compensation committee is, or has at any time during the prior three years been, one of our officers or employees. None of our executive officers currently serve, or have in the past fiscal year served, as a member of the board of directors or compensation committee of any entity that has one or more of its executive officers serving as a member of our board of directors or our compensation committee.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
Our board of directors intends to adopt, subject to and effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics in connection with this offering. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics will apply to all of our employees, officers (including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller or persons performing similar functions), agents and representatives, including directors and consultants.
150
We intend to disclose future amendments to certain provisions of our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and our Code of Ethics on our website identified below. Upon the completion of this offering, the full text of our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and our Code of Ethics will be posted on our website at http://www.tcr2.com. The inclusion of our website address in this prospectus does not include or incorporate by reference the information on our website into this prospectus, and you should not consider that information a part of this prospectus.
Limitations on Liability and Indemnification Agreements
As permitted by Delaware law, provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws, both of which will become effective upon the closing of this offering, limit or eliminate the personal liability of directors for a breach of their fiduciary duty of care as a director. The duty of care generally requires that, when acting on behalf of the corporation, a director exercise an informed business judgment based on all material information reasonably available to him or her. Consequently, a director will not be personally liable to us or our stockholders for monetary damages or breach of fiduciary duty as a director, except for liability for:
| ∎ | any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to us or our stockholders; |
| ∎ | any act or omission not in good faith or that involves intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law; |
| ∎ | any act related to unlawful stock repurchases, redemptions or other distributions or payments of dividends; or |
| ∎ | any transaction from which the director derived an improper personal benefit. |
These limitations of liability do not limit or eliminate our rights or any stockholder’s rights to seek non-monetary relief, such as injunctive relief or rescission. These provisions will not alter a director’s liability under other laws, such as the federal securities laws or other state or federal laws. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation that will become effective upon the closing of this offering also authorizes us to indemnify our officers, directors and other agents to the fullest extent permitted under Delaware law.
As permitted by Delaware law, our amended and restated bylaws to be effective upon the closing of this offering will provide that:
| ∎ | we will indemnify our directors, officers, employees and other agents to the fullest extent permitted by law; |
| ∎ | we must advance expenses to our directors and officers, and may advance expenses to our employees and other agents, in connection with a legal proceeding to the fullest extent permitted by law; and |
| ∎ | the rights provided in our amended and restated bylaws are not exclusive. |
If Delaware law is amended to authorize corporate action further eliminating or limiting the personal liability of a director or officer, then the liability of our directors or officers will be so eliminated or limited to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law, as so amended. Our amended and restated bylaws will also permit us to secure insurance on behalf of any officer, director, employee or other agent for any liability arising out of his or her actions in connection with their services to us, regardless of whether our bylaws permit such indemnification. We have obtained such insurance.
In addition to the indemnification that will be provided for in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws, we plan to enter into separate indemnification agreements with each of our directors and executive officers, which may be broader than the specific indemnification provisions contained in the Delaware General Corporation Law. These indemnification agreements may require us, among other things, to indemnify our directors and executive officers for some expenses, including attorneys’ fees, expenses, judgments, fines and settlement amounts incurred by a director or executive officer in any action or proceeding arising out of his service as one of our directors or executive officers or any other company or enterprise to which the person provides services at our request. We believe that these provisions and agreements are necessary to attract and retain qualified individuals to serve as directors and executive officers.
This description of the indemnification provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, our amended and restated bylaws and our indemnification agreements is qualified in its entirety by reference to these documents, each of which is attached as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
151
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the Securities Act), may be permitted to our directors, officers and controlling persons pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, we have been advised that, in the opinion of the SEC, such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act, and is, therefore, unenforceable.
There is no pending litigation or proceeding naming any of our directors or officers as to which indemnification is being sought, nor are we aware of any pending or threatened litigation that may result in claims for indemnification by any director or officer.
152
Executive Compensation Overview
As an emerging growth company, we have opted to comply with the executive compensation disclosure rules applicable to “smaller reporting companies,” as such term is defined in the rules promulgated under the Securities Act. This section provides an overview of the compensation awarded to and earned by each individual who served as our principal executive officer at any time during our fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2018 and to our next two most highly compensated executive officers in respect of their service to our company for our fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2018. We refer to these individuals as our named executive officers. Our named executive officers are:
| ∎ | Garry Menzel, our President and Chief Executive Officer; |
| ∎ | Robert Hofmeister, our Chief Scientific Officer; and |
| ∎ | Alfonso Quintás Cardama, our Chief Medical Officer. |
Our executive compensation program is based on a pay-for-performance philosophy. Compensation for our executive officers is composed primarily of the following main components: base salary, bonus and equity incentives in the form of stock options. Our executive officers, like all full-time employees, are eligible to participate in our health and welfare benefit plans. As we transition from a private company to a publicly traded company, we intend to evaluate our compensation values and philosophy and compensation plans and arrangements as circumstances require.
Summary Compensation Table
The following table sets forth information regarding compensation awarded to and earned by our named executive officers for services rendered to us in all capacities during our fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2018.
NAME AND PRINCIPAL | YEAR | SALARY ($) | BONUS ($) | OPTION AWARDS ($)(1) | NON-EQUITY PLAN COMPENSATION $(2) | ALL OTHER COMPENSATION ($) | TOTAL ($) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Garry Menzel,President andChief Executive Officer | 2018 | 435,845 | — | 2,398,230 | — (3) | — | 2,834,075 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 423,150 | — | 190,129 | 179,204 | — | 792,483 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Robert Hofmeister,Chief ScientificOfficer | 2018 | 320,114 | — | 502,304 | — (3) | — | 822,418 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 297,000 | — | 55,920 | 89,843 | — | 442,763 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Alfonso Quintás Cardama,Chief Medical Officer | 2018 | 362,484 | 60,000 | (5) | 502,273 | — (3) | — | 924,757 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 82,500 | (4) | 60,000 | (5) | 89,625 | 25,047 | (4) | — | 257,172 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | The amounts reported in the “Option Awards” column reflects the aggregate grant date fair value of share-based compensation awarded during the indicated year computed in accordance with the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 718. See Note 9 to our audited financial statements appearing elsewhere in this prospectus regarding assumptions underlying the valuation of equity awards. |
| (2) | Except where noted, the amounts reported reflect annual bonuses earned based upon achievement of company and individual performance metrics. |
| (3) | As of the date of this prospectus, the board of directors has not yet determined bonuses for the year ended December 31, 2018. |
| (4) | Dr. Quintás Cardama commenced his employment with us in October 2017. His annual salary and annual bonus for 2017 were prorated to reflect his partial year of service. |
| (5) | Dr. Quintás Cardama received a $120,000 sign-on bonus with 50% paid upon commencement of employment in October 2017 and the other 50% paid upon the six-month anniversary of his continued employment in April 2018. |
Narrative to the Summary Compensation Table
Base Salary
We use base salaries to recognize the experience, skills, knowledge and responsibilities required of all our employees, including our named executive officers. Base salaries are reviewed annually, typically in connection with our annual performance review process, and adjusted from time to time to realign salaries with market levels after taking into account individual responsibilities, performance and experience.
153
Annual Bonus
We do not have a formal performance-based bonus plan. Our employment arrangements with our named executive officers provide that the executive may be eligible to earn an annual performance bonus of up to a target percentage of the executive’s base salary, as described further below under the section entitled “––Employment Arrangements and Severance Agreements with our Named Executive Officers”. From time to time, our board of directors or compensation committee may approve additional annual bonuses for our named executive officers based on individual performance, company performance or as otherwise determined to be appropriate. In connection with this offering, we intend to adopt a senior executive cash bonus plan.
Equity Compensation
Although we do not have a formal policy with respect to the grant of equity incentive awards to our executive officers, or any formal equity ownership guidelines applicable to them, we believe that equity grants provide our executive officers with a strong link to our long-term performance, create an ownership culture and help to align the interests of our executive officers and our stockholders. In addition, we believe that equity grants with a time-based vesting feature promote executive retention because this feature incentivizes our executive officers to remain in our employment during the vesting period. Accordingly, our board of directors periodically reviews the equity incentive compensation of our executives, including our named executive officers, and from time to time may grant equity incentive awards to them in the form of stock options.
We typically grant stock option awards at the start of employment to each executive officer and our other employees as well as on an annual basis for retention purposes. We award our stock options on the date our board of directors approves the grant. We set the option exercise price equal to the fair market value of our common stock on the date of grant.
Employment Arrangements and Severance Agreements with our Named Executive Officers
We have entered into offer letters with each of our named executive officers. These offer letters set forth the initial terms and conditions of each executive’s employment with us, including base salary, target annual bonus opportunity and standard employee benefit plan participation.
Garry Menzel
We entered into an offer letter with Dr. Garry Menzel, our President and Chief Executive Officer, on July 22, 2016, pursuant to which Dr. Menzel is entitled to receive an annual base salary of $420,000, an annual target bonus of 35% of his annual base salary based upon our board of directors’ assessment of Dr. Menzel’s performance and our attainment of targeted goals approved by the board of directors. Dr. Menzel also received, pursuant to the offer letter, an equity grant equal to 4.25% of our fully-diluted capitalization as of the date Dr. Menzel commenced employment with us. The offer letter also required that Dr. Menzel sign an Employee Confidentiality and Assignment Agreement, pursuant to which Dr. Menzel agreed to refrain from disclosing our confidential information and agrees not to compete with us during the term of his employment and for two years following termination of his employment for any reason. Dr. Menzel is also eligible to participate in the employee benefit plans available to our employees, subject to the terms of those plans. Dr. Menzel’s offer letter provides that, in the event that his employment is terminated by us without “cause” or by him for “good reason” (as each term is defined in the offer letter), subject to the execution and effectiveness of a release of claims, he will be entitled to receive (in addition to accrued compensation and benefits through the date of termination) (i) salary continuation based on his then-current base salary for 12 months following termination and (ii) continuation of COBRA premium payments for 12 months following termination.
In December 2018, we entered into an employment agreement with Dr. Menzel, effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, pursuant to which Dr. Menzel is entitled to receive an annual base salary of $500,000 and an annual target bonus equal to 50% of his annual base salary based upon our board of directors’ or the compensation committee of the board of directors’ assessment of Dr. Menzel’s performance and our performance. This employment agreement also includes a reaffirmation of Dr. Menzel’s Employee Confidentiality and Assignment Agreement, which contains continuing obligations to us, including provisions on proprietary information, assignment of inventions, non-competition and non-solicitation of customers and employees. Dr. Menzel’s employment agreement provides that, in the event that his employment is terminated by us without “cause” or by him for “good reason,” then subject to the execution and effectiveness of a separation agreement and release, he will be entitled to receive (i) an amount equal to (x) 12 months of base salary payable on
154
our normal payroll cycle if such termination is not in connection with a “change in control” or (y) 18 months of base salary if such termination is in connection with a “change in control,” payable on our normal payroll cycle, provided that in either case, if Dr. Menzel commences new employment, all payments shall cease; and (ii) payment of the monthly employer COBRA premium for the same level of group health coverage as in effect for Dr. Menzel on the date of termination up to (x) 12 months if such termination is not in connection with a “change in control,” and (y) 18 months if such termination is in connection with a “change in control.” In addition, if within 12 months following a “change in control,” Dr. Menzel’s employment is terminated by us without “cause” or he resigns for “good reason,” then subject to the execution of the separation agreement and release, all time-based stock options and other time-based stock-based awards held by Dr. Menzel will accelerate and vest immediately.
Robert Hofmeister
We entered into an offer letter with Dr. Robert Hofmeister, our Chief Scientific Officer, on September 16, 2015, pursuant to which Dr. Hofmeister is entitled to receive an annual base salary of $270,000, an annual target bonus of 20% of his annual base salary based upon our board of directors’ assessment of Dr. Hofmeister’s performance and our attainment of targeted goals approved by the board of directors. Dr. Hofmeister also received, pursuant to the offer letter, an equity grant equal to 1.25% of our fully diluted capitalization at the conclusion of the first tranche of our Series A preferred stock financing. The offer letter also required that Dr. Hofmeister sign an Employee Confidentiality and Assignment Agreement, pursuant to which Dr. Hofmeister agreed to refrain from disclosing our confidential information and agrees not to compete with us during the term of his employment and for two years following termination of his employment for any reason. Dr. Hofmeister is also eligible to participate in the employee benefit plans available to our employees, subject to the terms of those plans. Dr. Hofmeister’s offer letter provides that, in the event that his employment is terminated by us without “cause” or by him for “good reason” (as each term is defined in the offer letter), subject to the execution and effectiveness of a release of claims, he will be entitled to receive (in addition to accrued compensation and benefits through the date of termination) (i) salary continuation based on his then-current base salary for nine months following termination and (ii) continuation of COBRA premium payments for six months following termination.
In December 2018, we entered into an employment agreement with Dr. Hofmeister, effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, pursuant to which Dr. Hofmeister is entitled to receive an annual base salary of $380,000 and an annual target bonus equal to 35% of his annual base salary based upon our board of directors’ or the compensation committee of the board of directors’ assessment of Dr. Hofmeister’s performance and our performance. This employment agreement also includes a reaffirmation of Dr. Hofmeister’s Employee Confidentiality and Assignment Agreement, which contains continuing obligations to us, including provisions on proprietary information, assignment of inventions, non-competition and non-solicitation of customers and employees. Dr. Hofmeister’s employment agreement provides that, in the event that his employment is terminated by us without “cause” or by him for “good reason,” then subject to the execution and effectiveness of a separation agreement and release, he will be entitled to receive (i) an amount equal to (x) nine months of base salary payable on our normal payroll cycle if such termination is not in connection with a “change in control” or (y) 12 months of base salary if such termination is in connection with a “change in control,” payable on our normal payroll cycle, provided that in either case, if Dr. Hofmeister commences new employment, all payments shall cease; and (ii) payment of the monthly employer COBRA premium for the same level of group health coverage as in effect for Dr. Hofmeister on the date of termination for up to (x) nine months if such termination is not in connection with a “change in control,” and (y) 12 months if such termination is in connection with a “change in control.” In addition, if within 12 months following a “change in control,” Dr. Hofmeister’s employment is terminated by us without “cause” or he resigns for “good reason,” then subject to the execution of the separation agreement and release, all time-based stock options and other time-based stock-based awards held by Dr. Hofmeister will accelerate and vest immediately.
Alfonso Quintás Cardama
We entered into an offer letter with Dr. Alfonso Quintás Cardama, our Chief Medical Officer, on July 20, 2017, pursuant to which Dr. Quintás Cardama is entitled to receive an annual base salary of $360,000, a one-time bonus of $120,000, with 50% awarded upon commencement of employment and the other 50% awarded upon the six-month anniversary of his continued employment, an annual target bonus of 25% of his annual base salary based upon the our board of directors’ assessment of Dr. Quintás Cardama’s performance and our attainment of targeted goals approved by the board of directors. Dr. Quintás Cardama also received, pursuant to the offer letter, an equity
155
grant equal to 1.25% of our fully-diluted capitalization on the date of grant. This offer letter also required that Dr. Quintás Cardama sign an Employee Confidentiality and Assignment Agreement, pursuant to which Dr. Quintás Cardama agreed to refrain from disclosing our confidential information and agrees not to compete with us during the term of his employment and for two years following termination of his employment for any reason. Dr. Quintás Cardama is also eligible to participate in the employee benefit plans available to our employees, subject to the terms of those plans.
In December 2018, we entered into an employment agreement with Dr. Quintás Cardama, effective upon the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, pursuant to which Dr. Quintás Cardama is entitled to receive an annual base salary of $430,000 and an annual target bonus equal to 35% of his annual base salary based upon our board of directors’ or the compensation committee of the board of directors’ assessment of Dr. Quintás Cardama’s performance and our performance. This employment agreement also includes a reaffirmation of Dr. Quintás Cardama’s Employee Confidentiality and Assignment Agreement, which contains continuing obligations to us including provisions on proprietary information, assignment of inventions, non-competition and non-solicitation of customers and employees. Dr. Quintás Cardama’s employment agreement provides that, in the event that his employment is terminated by us without “cause” or by him for “good reason,” then subject to the execution and effectiveness of a separation agreement and release, he will be entitled to receive (i) an amount equal to (x) nine months of base salary payable on our normal payroll cycle if such termination is not in connection with a “change in control” or (y) 12 months of base salary if such termination is in connection with a “change in control,” payable on our normal payroll cycle, provided that in either case, if Dr. Quintás Cardama commences new employment, all payments shall cease; and (ii) payment of the monthly employer COBRA premium for the same level of group health coverage as in effect for Dr. Quintás Cardama on the date of termination for up to (x) nine months if such termination is not in connection with a “change in control,” and (y) 12 months if such termination is in connection with a “change in control.” In addition, if within 12 months following a “change in control,” Dr. Quintás Cardama’s employment is terminated by us without “cause” or he resigns for “good reason,” then subject to the execution of the separation agreement and release, all time-based stock options and other time-based stock-based awards held by Dr. Quintás Cardama will accelerate and vest immediately.
Outstanding Equity Awards at 2018 Fiscal Year-End
The following table sets forth information concerning outstanding equity awards held by our named executive officers as of December 31, 2018.
| OPTION AWARDS | STOCK AWARDS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NAME | VESTING COMMENCE- MENT DATE | NUMBER OF SECURITIES ACQUIRED ON EXERCISE | VALUE REALIZED UPON EXERCISE | NUMBER OF SECURITIES UNDERLYING UNEXERCISED OPTIONS (#) EXERCISABLE | NUMBER OF SECURITIES UNDERLYING UNEXERCISED OPTIONS (#) UNEXERCISABLE | OPTION EXERCISE PRICE ($) | OPTION EXPIRATION DATE | NUMBER OF SHARES OR UNITS OF STOCK THAT HAVE NOT VESTED (#) | MARKET VALUE OF SHARES OR UNITS OF STOCK THAT HAVE NOT VESTED ($) (6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Garry Menzel | 10/17/16 | 84,527 | $ | 434,469 | 52,829 | (1) | 116,225 | (1) | $ | 0.74 | 12/12/2026 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12/6/17 | — | — | 35,994 | 107,983 | (2) | $ | 0.74 | 12/6/2027 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/26/18 | — | — | — | 433,037 | (3) | $ | 5.88 | 7/25/2028 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Robert Hofmeister | 12/13/16 | 14,713 | 75,625 | 10,509 | (1) | 25,223 | (1) | $ | 0.74 | 12/12/2026 | 6,036 | (5) | $ | 90,540 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12/6/17 | — | — | 10,586 | 31,760 | (2) | $ | 0.74 | 12/6/2027 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/26/18 | — | — | — | 90,720 | (3) | $ | 5.88 | 7/25/2028 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Alfonso Quintás Cardama | 10/10/17 | — | — | 21,753 | 52,829 | (4) | $ | 0.74 | 9/11/2027 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12/6/17 | — | — | 10,586 | 31,760 | (2) | $ | 0.74 | 12/6/2027 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/26/18 | — | — | — | 90,720 | (3) | $ | 5.88 | 7/25/2028 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unless otherwise specified, all option awards vest over four years, with 25% vesting on the first anniversary of the vesting commencement date, and the remainder vesting in 36 equal monthly installments thereafter, subject to continued employment with us.
156
| (1) | Represents stock option granted on December 13, 2016. |
| (2) | Represents stock option granted on December 7, 2017. |
| (3) | Represents stock option granted on July 26, 2018. |
| (4) | Represents stock option granted on October 10, 2017. |
| (5) | Represents shares of restricted stock granted on October 1, 2015, with 25% vesting on the first anniversary of the grant date, and the remainder vesting in 12 equal quarterly installments through October 1, 2019. |
| (6) | Calculated using an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus. |
Compensation Risk Assessment
We believe that although a portion of the compensation provided to our executive officers and other employees is performance-based, our executive compensation program does not encourage excessive or unnecessary risk taking.
This is primarily due to the fact that our compensation programs are designed to encourage our executive officers and other employees to remain focused on both short-term and long-term strategic goals. As a result, we do not believe that our compensation programs are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on us.
Employee Benefit and Equity Compensation Plans
2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan
Our 2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan (the 2015 Plan) was approved and adopted by our board of directors and stockholders on October 16, 2015. The 2015 Plan was most recently amended in July 2018 with the approval of our board of directors. Under the 2015 Plan, we have reserved for issuance an aggregate of 2,554,723 shares of our common stock for the issuance of stock options and other equity awards under the 2015 Plan. This number of shares of common stock reserved for issuance is subject to adjustment in the event of any merger, consolidation, sale of all or substantially all of our assets, reorganization, recapitalization, reclassification, stock dividend, stock split, reverse stock split or other similar transaction.
The shares of common stock underlying awards that are forfeited, canceled, reacquired prior to vesting, satisfied without the issuance of stock or otherwise terminated (other than by exercise), as well as shares that are withheld upon exercise of a stock option or settlement of an award to cover the exercise price or tax withholding will be added back to the shares of common stock available for issuance under the 2015 Plan. Following the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, such shares will be added to the shares of common stock available for issuance under the 2018 Stock Option and Incentive Plan (the 2018 Plan), which our board of directors intends to adopt, and we expect our stockholders will approve, prior to the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
Our board of directors has acted as administrator of the 2015 Plan. The board has full power to select, from among the individuals eligible for awards, the individuals to whom awards will be granted, and to determine the specific terms and conditions of each award, subject to the provisions of the 2015 Plan. Persons eligible to participate in the 2015 Plan are those full or part-time employees, officers and directors of, and consultants and advisors to, our company as selected from time to time by the board in its discretion. The 2015 Plan permitted us to make grants of incentive stock options to our employees and any of our subsidiary corporations’ employees, and grants ofnon-qualified stock options, restricted stock awards, unrestricted stock awards and restricted stock units to the officers, employees, directors and consultants of the company and our subsidiary corporations.
The 2015 Plan permitted the granting of (1) options to purchase common stock intended to qualify as incentive stock options under Section 422 of the Code and (2) options that do not so qualify. The option exercise price per share of our common stock underlying each stock option was determined by our board of directors, and must have been at least equal to 100% of the fair market value of a share of our common stock on the date of grant. In the case of an incentive stock option granted to a participant who, at the time of grant of such stock option, owned stock representing more than 10% of the voting power of all classes of our capital stock, or a 10% owner, the exercise price per share of our common stock underlying each such stock option must have been at least equal to 110% of the fair market value of a share of our common stock on the date of grant. The term of each stock option may not have exceeded 10 years from the date of grant (or five years for a 10% owner). The board determines the methods of payment of the exercise price of a stock option, which may include cash, if permitted by the board, by a promissory note (subject to the terms and conditions of the 2015 Plan), if permitted by the board through a net exercise arrangement fornon-qualified stock options, and, if permitted by the board of directors and an initial public offering
157
of the company has occurred, through either the delivery of shares of our common stock owned by the participant or a broker-assisted arrangement. After a participant’s termination of service (other than a termination for cause), the participant generally may exercise his or her stock options, to the extent vested as of such date of termination, for 90 days after termination or such longer period of time as specified in the applicable stock option agreement; provided, that if the termination is due to death or disability, the stock option generally will remain exercisable, to the extent vested as of such date of termination, until theone-year anniversary of such termination. However, in no event may a stock option be exercised later than the expiration of its term.
The 2015 Plan also permitted the granting of restricted shares of common stock to participants subject to such conditions and restrictions as the board determined. These conditions and restrictions, among others, included the continued employment of the participant with us through a specified vesting period.
The 2015 Plan generally does not allow for the transfer or assignment of options, other than by will or the laws of descent and distribution, or, at the discretion of the plan administrator in the case of non-qualified stock options, by gift to an immediate family member, or to a trust or partnership of which such family members are beneficiaries or the only partners, as applicable.
The 2015 Plan provides that, upon the consummation of a “sale event,” as defined in the 2015 Plan, unless provision is made in connection with the sale event for the assumption or continuation of the awards by the successor entity or substitution of the awards with new awards of the successor entity, with appropriate adjustment, the 2015 Plan and all outstanding and unexercised options issued thereunder will terminate upon the effective time of the sale event. We may make or provide for cash payment to holders of options equal to the difference between (i) the value as determined by the board of the consideration payable per share of common stock in the sale event multiplied by the number of shares subject to outstanding options being cancelled to the extent vested and exercisable, including by reason of acceleration in connection with the sale event and (ii) the aggregate exercise price to the holders of all vested and exercisable options.
Our board of directors may amend, suspend or terminate the 2015 Plan at any time, subject to stockholder approval where such approval is required by applicable law. Our board of directors may also amend, modify, or terminate any outstanding award, provided that no amendment to an award may adversely affect a participant’s rights without his or her consent.
As of December 31, 2018, options to purchase 2,094,816 shares of common stock were outstanding under the 2015 Plan. Our board of directors has determined not to make any further awards under the 2015 Plan following the closing of this offering, but all outstanding awards under the 2015 Plan will continue to be governed by their existing terms.
2018 Stock Option and Incentive Plan
Prior to the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, our board of directors intends to adopt, and we expect our stockholders will approve, our 2018 Plan. Our 2018 Plan will become effective immediately prior to the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. The 2018 Plan will allow the board of directors to make equity-based incentive awards to our officers, employees, directors and other key persons (including consultants). The 2018 Plan will replace our 2015 Plan. Our 2018 Plan will provide flexibility to our board of directors to use various equity-based incentive awards as compensation tools to motivate our workforce.
We have initially reserved 3,000,000 shares of our common stock less the shares of common stock remaining available for issuance under our 2015 Plan as of the business day immediately prior to the effective date of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part (the Initial Limit) for the issuance of awards under the 2018 Plan. The 2018 Plan will provide that the number of shares reserved and available for issuance under the plan will automatically increase each January 1, beginning on January 1, 2020, by 4% of the outstanding number of shares of our common stock on the immediately preceding December 31 or such lesser number of shares as determined by our board of directors (the Annual Increase). This number is subject to adjustment in the event of a stock split, stock dividend or other change in our capitalization.
The shares we issue under the 2018 Plan will be authorized but unissued shares reserved for issuance under the 2018 Plan. In addition, the shares of common stock underlying any awards that are forfeited, cancelled, held back upon exercise or settlement of an award to satisfy the exercise price or tax withholding, reacquired by us prior to
158
vesting, satisfied without any issuance of stock, expire or are otherwise terminated (other than by exercise) under the 2018 Plan and the 2015 Plan will be added back to the shares of common stock available for issuance under the 2018 Plan. The value of all awards issued under the 2018 Plan and all other cash compensation paid by us to any non-employee director in any calendar year cannot exceed $1,000,000.
The maximum aggregate number of shares that may be issued in the form of incentive stock options shall not exceed the Initial Limit cumulatively increased on January 1, 2020 and on each January 1 thereafter by the lesser of the Annual Increase for such year or such lesser number of shares of common stock as determined by the administrator.
Our board of directors has delegated authority to our compensation committee to administer the 2018 Plan. Our compensation committee has full power to select, from among the individuals eligible for awards, the individuals to whom awards will be granted, to make any combination of awards to participants, and to determine the specific terms and conditions of each award, subject to the provisions of the 2018 Plan. Persons eligible to participate in the 2018 Plan will be those full or part-time officers, employees, non-employee directors and other key persons (including consultants) as selected from time to time by our compensation committee in its discretion.
The 2018 Plan will permit the granting of both options to purchase common stock intended to qualify as incentive stock options under Section 422 of the Code and options that do not so qualify. The option exercise price of each option will be determined by our compensation committee but may not be less than 100% of the fair market value of our common stock on the date of grant. The term of each option will be fixed by our compensation committee and may not exceed 10 years from the date of grant. Our compensation committee will determine at what time or times each option may be exercised.
Our compensation committee may award stock appreciation rights subject to such conditions and restrictions as it may determine. Stock appreciation rights entitle the recipient to shares of common stock, or cash, equal to the value of the appreciation in our stock price over the exercise price. The exercise price of each stock appreciation right may not be less than 100% of the fair market value of the common stock on the date of grant.
Our compensation committee may award shares of restricted common stock and restricted stock units to participants subject to such conditions and restrictions as it may determine. These conditions and restrictions may include the achievement of certain performance goals and continued employment with us through a specified vesting period. Our compensation committee may also grant shares of common stock that are free from any restrictions under the 2018 Plan. Unrestricted stock may be granted to participants in recognition of past services or other valid consideration and may be issued in lieu of cash compensation due to such participant.
Our compensation committee may grant cash-denominated awards under the 2018 Plan to participants, subject to the achievement of specified performance goals.
The 2018 Plan will provide that in the case of, and subject to, the consummation of a “sale event” (as defined in the 2018 Plan), all outstanding awards may be assumed, substituted or otherwise continued by the successor entity. To the extent that the successor entity does not assume, substitute or otherwise continue such awards, then (i) all stock options and stock appreciation rights with time-based vesting conditions will automatically become fully exercisable and the restrictions and conditions on all other awards with time-based vesting conditions will automatically be deemed waived, and awards with conditions and restrictions relating to the attainment of performance goals may become vested and non-forfeitable in connection with a sale event in the compensation committee’s discretion and (ii) upon the effectiveness of a sale event, the 2018 Plan and all awards will automatically terminate. In the event of such termination, (i) individuals holding options and stock appreciation rights will be permitted to exercise such options and stock appreciation rights (to the extent exercisable) prior to the sale event or (ii) we may make or provide for a cash payment to participants holding options and stock appreciation rights equal to the difference between the per share cash consideration payable to stockholders in the sale event and the exercise price of the options or stock appreciation rights (to the extent exercisable).
Our board of directors will have the power to amend or discontinue the 2018 Plan and our compensation committee will have the power to amend the exercise price of options and amend or cancel outstanding awards for purposes of satisfying changes in law or any other lawful purpose, but no such action shall materially and adversely affect rights under an award without the holder’s consent. Certain amendments to the 2018 Plan will require the approval of our stockholders.
159
No awards may be granted under the 2018 Plan after the date that is ten years from the date of stockholder approval. No awards under the 2018 Plan have been made prior to the date of this prospectus.
2018 Employee Stock Purchase Plan
Prior to the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, our board of directors intends to adopt, and we expect our stockholders will approve, our 2018 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the ESPP). The ESPP is intended to qualify as an “employee stock purchase plan” within the meaning of Section 423(b) of the Code. The ESPP will initially reserve and authorize the issuance of up to a total of 300,000 shares of common stock to participating employees. The ESPP will provide that the number of shares reserved and available for issuance will automatically increase each January 1, beginning on January 1, 2020 and each January 1 thereafter through January 1, 2029, by the least of (i) 1% of the outstanding number of shares of our common stock on the immediately preceding December 31, (ii) 500,000 shares or (iii) such number of shares as determined by the ESPP administrator. The number of shares reserved under the ESPP will be subject to adjustment in the event of a stock split, stock dividend or other change in our capitalization.
All employees whose customary employment is for more than 20 hours per week and who have completed at least three months of employment will be eligible to participate in the ESPP. However, any participating employee who would own 5% or more of the total combined voting power or value of all classes of our stock after an option were granted under the ESPP will not be eligible to purchase shares under the ESPP.
We will make one or more offerings each year to our employees to purchase shares under the ESPP. The first offering, or the Initial Offering, will begin on the effective date of the registration statement of which this prospectus is part and, unless otherwise determined by the administrator of the ESPP, will end on August 31, 2019. Each eligible employee as of the effective date of the registration statement for the offering will be deemed to be a participant in the ESPP at that time and must authorize payroll deductions by submitting an enrollment form by the deadline specified by the plan administrator. Thereafter, unless otherwise determined by the Administrator, offerings will usually begin on each September 1 and March 1 and will continue for six-month periods, referred to as offering periods. Each eligible employee may elect to participate in any subsequent offering by submitting an enrollment form at least 15 business days before the relevant offering date.
Each employee who is a participant in the ESPP will be able to purchase shares by authorizing payroll deductions of up to 15% of his or her base compensation during an offering period. Unless the participating employee has previously withdrawn from the offering, his or her accumulated payroll deductions will be used to purchase shares on the last business day of the offering period at a price equal to 85% of the fair market value of the shares on the first business day or the last business day of the offering period, whichever is lower. Under applicable tax rules, an employee may purchase no more than $25,000 worth of shares of common stock, valued at the start of the purchase period, under the ESPP in any calendar year. The ESPP also includes limits on the number of shares participating employees may purchase in each offering period. It is a condition to the issuance of shares to an employee under the ESPP that the employee agrees that he or she may not sell, transfer or otherwise dispose of any of the shares acquired under the ESPP for three months, except in limited circumstances described in the ESPP.
The accumulated payroll deductions of any employee who is not a participant on the last day of an offering period will be refunded. An employee’s rights under the ESPP will terminate upon voluntary withdrawal from the plan or when the employee ceases employment with us for any reason.
Senior Executive Cash Incentive Bonus Plan
Prior to the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, our board of directors intends to adopt our Senior Executive Cash Incentive Bonus Plan (the Bonus Plan). The Bonus Plan will provide for cash bonus payments based upon the attainment of performance targets established by our compensation committee. The payment targets will be related to financial and operational measures or objectives with respect to our company corporate performance goals as well as individual performance objectives.
Our compensation committee may select corporate performance goals from among the following: cash flow (including, but not limited to, operating cash flow and free cash flow); research and development, publication, clinical and/or regulatory milestones; earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization; net income
160
(loss) (either before or after interest, taxes, depreciation and/or amortization); changes in the market price of our common stock; economic value-added; acquisitions or strategic transactions, including licenses, collaborations, joint ventures or promotion arrangements; operating income (loss); return on capital, assets, equity, or investment; total stockholder returns; coverage decisions; productivity; expense efficiency; margins; operating efficiency; working capital; earnings (loss) per share of our common stock; sales or market shares; number of prescriptions or prescribing physicians; revenue; corporate revenue; operating income and/or net annual recurring revenue, any of which may be (A) measured in absolute terms or compared to any incremental increase, (B) measured in terms of growth, (C) compared to another company or companies or to results of a peer group, (D) measured against the market as a whole and/or as compared to applicable market indices and/or (E) measured on a pre-tax or post-tax basis (if applicable).
Each executive officer who is selected to participate in the Bonus Plan will have a target bonus opportunity set for each performance period. The bonus formulas will be adopted in each performance period by the compensation committee and communicated to each executive. The corporate performance goals will be measured at the end of each performance period after our financial reports have been published or such other appropriate time as the compensation committee determines. If the corporate performance goals and individual performance objectives are met, payments will be made as soon as practicable following the end of each performance period. The Bonus Plan will also permits the compensation committee to approve additional bonuses to executive officers in its sole discretion. We may amend or terminate the Bonus Plan at any time in our sole discretion.
401(k) Plan
We maintain a tax-qualified retirement plan (the 401(k) Plan) that provides eligible U.S. employees with an opportunity to save for retirement on a tax advantaged basis. Eligible employees are able to defer eligible compensation subject to applicable annual Code limits. Employees’ pre-tax or Roth contributions are allocated to each participant’s individual account and are then invested in selected investment alternatives according to the participants’ directions. Employees are immediately and fully vested in their contributions. Our 401(k) Plan is intended to be qualified under Section 401(a) of the Code with our 401(k) Plan’s related trust intended to be tax exempt under Section 501(a) of the Code. As a tax-qualified retirement plan, contributions to our 401(k) Plan and earnings on those contributions are not taxable to the employees until distributed from our 401(k) Plan.
161
The following table presents the total compensation for each person who served as a non-employee member of our board of directors and received compensation for such service during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2018. Other than as set forth in the table and described more fully below, we did not pay any compensation, make any equity awards to, or pay any other compensation to any of the non-employee members of our board of directors in 2018. Dr. Menzel, our President and Chief Executive Officer, did not receive any compensation for his service as a member of our board of directors during 2018. Dr. Menzel’s compensation for service as an employee for fiscal year 2018 is presented in “Executive Compensation—2018 Summary Compensation Table.” We reimburse non-employee members of our board of directors for reasonable travel and out-of-pocket expenses incurred in connection with attending board of directors and committee meetings.
Director Compensation Table—2018
NAME | FEES EARNED OR PAID IN CASH ($) | WARRANT AWARDS ($)(1) | STOCK AWARDS ($) | OPTION AWARDS ($)(3) | ALL OTHER COMPENSATION ($) | TOTAL ($) | ||||||||||||||||||
Ansbert Gadicke(2) | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Patrick Baeuerle (4) | — | | — | | — | — | 76,134 | 76,134 | ||||||||||||||||
Mitchell Finer(2)(4) | — | | — | | — | — | 76,029 | 76,029 | ||||||||||||||||
Morana Jovan-Embiricos(2)(4) | — | | — | | — | — | 126,757 | 126,757 | ||||||||||||||||
Neil Gibson | — | — | — | 48,997 | 6,412 | 55,409 | ||||||||||||||||||
Andrew Allen | — | — | — | 48,997 | 4,634 | 53,631 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | The amounts reported in the “Warrant Awards” column reflects the aggregate grant date fair value of share-based compensation awarded during the indicated year computed in accordance with the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 718. See Note 9 to our audited financial statements appearing elsewhere in this prospectus regarding assumptions underlying the valuation of equity awards. |
| (2) | Investor-appointed directors did not receive fees or other compensation for their service on our board of directors. |
| (3) | Represents stock options granted on December 13, 2018. In accordance with SEC rules, these columns reflect the aggregate grant date fair value of the option awards granted during 2018 computed in accordance with Financial Accounting Standard Board ASC Topic 718 for stock-based compensation transactions, or ASC 718. |
| (4) | Each of Drs. Bauerle, Finer and Jovan-Embiricos provided services to us pursuant to the terms of the consulting agreements with Dr. Bauerle, Dr. Finer and Pattern Recognition Ventures, and Globeways Holdings Limited, respectively. The cash fees presented above are related to these services for the period ended December 31, 2018. For more information regarding these consulting arrangements, see “Certain Relationships and Related Person Transactions” on page 164. |
Non-Employee Director Compensation Policy
Our board of directors will adopt a non-employee director compensation policy, effective upon effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, that is designed to enable us to attract and retain, on a long-term basis, highly qualified non-employee directors. Under the policy, each director who is not an employee will be paid cash compensation from and after the completion of this offering, as set forth below:
| MEMBER ANNUAL FEE ($) | CHAIRMAN ADDITIONAL ANNUAL FEE ($) | |||||||
Board of Directors | $ | 35,000 | $ | 25,000 | ||||
Audit Committee | $ | 7,500 | $ | 7,500 | ||||
Compensation Committee | $ | 5,000 | $ | 5,000 | ||||
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee | $ | 4,000 | $ | 3,500 | ||||
Finance and Strategy Committee | — | — | ||||||
In addition, each non-employee director elected or appointed to our board of directors following the closing of this offering will be granted options to purchase 8,072 shares of common stock on the date of such director’s election
162
or appointment to the board of directors, which will vest in three equal annual installments, subject to continued service through such vesting date(s). On the date of each annual meeting of stockholders of our company, each non-employee director will be granted options to purchase shares of common stock, which will vest on the earlier of the date that is one year from the date of grant or the date of the first annual meeting of our stockholders held after the date of grant subject to continued service as a director through such vesting date(s).
163
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PERSON TRANSACTIONS
The following is a description of transactions or series of transactions since our inception on May 29, 2015, to which we were or will be a party, in which:
| ∎ | the amount involved in the transaction exceeds, or will exceed, $120,000; and |
| ∎ | in which any of our executive officers, directors or holder of five percent or more of any class of our capital stock, including their immediate family members or affiliated entities, had or will have a direct or indirect material interest. |
Compensation arrangements for our named executive officers and our directors are described elsewhere in this prospectus under “Director Compensation” and “Executive Compensation.”
On October 1, 2015, we entered into a consulting agreement with Dr. Patrick Baeuerle. Pursuant to the consulting agreement, Dr. Baeuerle agreed to perform such consulting, advisory and related services to and for us as may be reasonably requested. In exchange, we agreed to pay Dr. Baeuerle a consulting fee of€15,417 per month. On November 1, 2016, we amended the consulting agreement to revise Dr. Baeuerle’s consulting fee to be€3,838 per month. Dr. Baeuerle is also eligible for an annual bonus equal to 33% of the annual fees paid under the consulting agreement, subject to the discretion of our board of directors based on Dr. Baeuerle’s performance and our performance. The term of the agreement is one year, and automatically extends for additional one-year periods unless terminated. During the fiscal years ended December 31, 2015, 2016 and 2017, we incurred fees and travel related expenses to Dr. Baeuerle in the amount of $50,669, $239,690 and $70,831, respectively, under the consulting agreement. During the year ended December 31, 2018, we incurred consulting fees and travel-related expenses to Dr. Baeuerle in the amount of $76,134. Dr. Baeuerle is a member of our board of directors and is a managing director at MPM Capital, the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our voting securities.
On March 2, 2016, we entered into a consulting agreement with Dr. Mitchell Finer (the Original Finer Agreement), which was amended and restated on May 9, 2017 to, among other things, add Pattern Recognition Ventures as a party. Pursuant to the amended and restated consulting agreement, Pattern Recognition Ventures agreed to perform scientific consulting, advisory and related services to and for us as may be reasonably requested, including making Dr. Finer available to serve as Chairman of our Scientific Advisory Board. We paid Dr. Finer an amount equal to $37,878 for services performed and expenses incurred under the Original Finer Agreement during the six-month period from October 1, 2015 through March 31, 2016. Additionally, as compensation for services provided under the Original Finer Agreement, we granted Dr. Finer 36,371 shares of our common stock that are subject to vesting pursuant to a Founder Stock Restriction Agreement, dated as of June 1, 2015, by and between Dr. Finer and us, and granted Dr. Finer an option to purchase 8,017 shares of our common stock, which option was cancelled in connection with the execution of the amended and restated consulting agreement. Pursuant to the amended and restated consulting agreement, we agreed (i) to pay Pattern Recognition Ventures a consulting fee of $18,750 per quarter for services provided under the agreement, commencing on July 1, 2017, (ii) to pay Pattern Recognition Ventures an amount equal to $37,500 for services performed from January 1, 2017 through July 1, 2017, and (iii) to grant Pattern Recognition Ventures an option to purchase 8,017 shares of our common stock, which option is subject to vesting. During the fiscal years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, we incurred fees and travel-related expenses to Pattern Recognition Ventures in the amount of $75,378 and $77,169, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2018, we incurred consulting fees and travel-related expenses to Pattern Recognition Ventures in the amount of $76,029. Dr. Finer has a financial interest in Pattern Recognition Ventures and is its managing member. Dr. Finer is also a member of our board of directors and is an executive partner at MPM Capital, the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our voting securities.
On October 1, 2017, we entered into a consulting agreement with Globeways Holdings Limited. Dr. Morana Jovan-Embiricos has financial interests in Globeways Holdings Limited and is its founding director. Pursuant to the consulting agreement, Globeways Holdings Limited provides consulting, advisory and related services in exchange for consulting fees of $100,000 per year. During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017, we incurred fees and travel-related expenses to Globeways Holdings Limited in the amount of $72,779. During the year ended December 31, 2018, we incurred consulting fees and travel-related expenses to Globeways Holdings Limited in the
164
amount of $126,757. Dr. Jovan is also a member of our board of directors and Globeways Holdings Limited is the appointed manager of certain affiliates of F2 Capital that collectively beneficially own more than 5% of our voting securities.
On June 1, 2015, we entered into an investment letter agreement with MPM Asset Management LLC pursuant to which MPM Asset Management LLC agreed to continue to make available to us, prior to completing our Series A financing, at no charge, office space and certain incubation services. In consideration of the office space and incubation services, we agreed to issue MPM Asset Management LLC 195,902 shares of our common stock.
On May 26, 2016, in connection with our Series A preferred stock financing, we entered into a Royalty Transfer Agreement with MPM Charitable Foundation and UBS Optimus Foundation, under which we are obligated pay to each of MPM Charitable Foundation and UBS Optimus Foundation 0.5% of the global net sales of our products and income from any license arrangements. Additionally, on May 26, 2016, we entered into a Royalty Direction Letter with MPM Charitable Foundation, UBS Optimus Foundation and UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P., pursuant to which we agreed that a portion of the consideration received from by Oncology Impact Fund L.P. in our Series A preferred stock financing was to be treated as consideration for the Royalty Transfer Agreement. Affiliates of MPM Capital and UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P. that own shares of our preferred and common stock hold interests in MPM Charitable Foundation and UBS Optimus Foundation.
Private Placements of Securities
Option and Warrant Grants
On December 13, 2016, we granted MPM Asset Management LLC a warrant to purchase 42,761 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.74 per share for an aggregate exercise price of $31,643.
On December 6, 2017, we granted MPM Asset Management LLC a warrant to purchase 135,508 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.74 per share for an aggregate exercise price of $100,276.
On December 6, 2017, we granted APAK Solutions Gmbh a warrant to purchase 169,385 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.74 per share for an aggregate exercise price of $125,345. Dr. Baeuerle has a financial interest in APAK Solutions Gmbh, and he serves as the managing director of APAK Solutions Gmbh. Dr. Bauerle is a member of our board of directors and is a managing director at MPM Capital, the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our voting securities.
On December 6, 2017, we granted Pattern Recognition Ventures a warrant to purchase 25,407 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.74 per share for an aggregate exercise price of $18,801. On May 9, 2017, we entered into a Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement with Pattern Recognition Ventures pursuant to which Pattern Recognition Ventures has the option to purchase 8,017 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.74 per share for an aggregate exercise price of $5,933. Dr. Finer has a financial interest in Pattern Recognition Ventures and is its managing member. Dr. Finer is also a member of our board of directors and is an executive partner at MPM Capital, the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our voting securities.
Series A Preferred Stock Financing
In October 2015, with subsequent closings in January 2016, October 2016, and December 2017, we sold an aggregate of 44,500,001 shares of our Series A preferred stock at a purchase price of $1.00 per share for an aggregate amount of $44.5 million. The following table summarizes purchases of our Series A preferred stock by related persons:
STOCKHOLDER | SHARES OF SERIES A PREFERRED STOCK | TOTAL PURCHASE PRICE | ||||||
Entities affiliated with MPM Capital(1) | 17,500,000 | $ | 17,500,000 | |||||
Entities affiliated with F2 Capital(2) | 10,000,001 | $ | 10,000,001 | |||||
UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P. (3) | 15,000,000 | $ | 15,000,000 | |||||
165
| (1) | Represents 493,306 shares of Series A preferred stock purchased by MPM Asset Management Investors BV2014 LLC, 325,002 shares of Series A preferred stock purchased by MPM Asset Management Investors SunStates Fund LLC, 907,073 shares of Series A preferred stock purchased by MPM Bioventures 2014 (B), L.P., 13,599,621 shares of Series A preferred stock purchased by MPM BioVentures 2014, L.P., and 2,174,998 shares of Series A preferred stock purchased by MPM SunStates Fund, L.P. Each of Patrick Baeuerle, Ansbert Gadicke and Mitchell Finer serves as an officer or director of the Company and is an affiliate of MPM Capital, of which MPM Asset Management Investors BV2014 LLC, MPM Asset Management Investors SunStates Fund LLC, MPM Bioventures 2014 (B), L.P., MPM BioVentures 2014, L.P., and MPM SunStates Fund, L.P are affiliated funds. Entities affiliated with MPM Capital collectively hold more than 5% of our voting securities. |
| (2) | Represents 10,000,001 shares of Series A preferred stock purchased by F2 Capital I 2015 Limited. Dr. Morana Jovan-Embiricos serves as a director of the company and is a Managing Partner of F2 Capital, of which F2 Capital I 2015 Limited is an affiliated fund. Entities affiliated with F2 Capital collectively hold more than 5% of our voting securities. |
| (3) | Represents 15,000,000 shares of Series A preferred stock purchased by UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P. Each of Patrick Baeuerle, Ansbert Gadicke and Mitchell Finer serves as an officer or director of the Company and is an affiliate of UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P. UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P. is a holder of more than 5% of our voting securities. |
Series B Preferred Stock Financing
In February 2018, with subsequent closings in March 2018 and April 2018, we sold an aggregate of 62,500,000 shares of our Series B preferred stock at a purchase price of $2.00 per share for an aggregate amount of $125.0 million. The following table summarizes purchases of our Series B preferred stock by related persons:
STOCKHOLDER | SHARES OF SERIES B PREFERRED STOCK | TOTAL PURCHASE PRICE | ||||||
Entities affiliated with MPM Capital(1) | 2,000,000 | $ | 4,000,000 | |||||
Entities affiliated with F2 Capital (2) | 7,990,500 | $ | 15,981,000 | |||||
UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P. (3) | 1,750,000 | $ | 3,500,000 | |||||
Entities affiliated with 6 Dimensions Capital (4) | 10,000,000 | $ | 20,000,000 | |||||
Entities affiliated with Curative Ventures (5) | 4,375,000 | $ | 8,750,000 | |||||
| (1) | Represents 57,552 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by MPM Asset Management Investors BV2014 LLC, 32,500 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by MPM Asset Management Investors SunStates Fund LLC, 105,825 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by MPM Bioventures 2014 (B), L.P., 1,586,623 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by MPM BioVentures 2014, L.P., and 217,500 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by MPM SunStates Fund, L.P. Each of Patrick Baeuerle, Ansbert Gadicke and Mitchell Finer serves as an officer or director of the Company and is an affiliate of MPM Capital, of which MPM Asset Management Investors BV2014 LLC, MPM Asset Management Investors SunStates Fund LLC, MPM Bioventures 2014 (B), L.P., MPM BioVentures 2014, L.P., and MPM SunStates Fund, L.P are affiliated funds. Entities affiliated with MPM Capital collectively hold more than 5% of our voting securities. |
| (2) | Represents 1,200,000 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by F2 Bioscience II 2017 Limited, 2,540,500 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by F2 Capital I 2017 Limited, 1,750,000 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by F2 MG Limited, and 2,500,000 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by F2-TPO Investments, LLC. Morana Jovan-Embiricos serves as a director of the company and is the Managing Partner of F2 Capital, of which F2 Bioscience II 2017 Limited, F2 Capital I 2017 Limited, F2 MG Limited, and F2-TPO Investments, LLC are affiliated funds. Entities affiliated with F2 Capital collectively hold more than 5% of our voting securities. |
| (3) | Represents 1,750,000 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P. Each of Patrick Baeuerle, Ansbert Gadicke and Mitchell Finer serves as an officer or director of the Company and is an affiliate of UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P. UBS Oncology Impact Fund L.P. is a holder of more than 5% of our voting securities. |
| (4) | Represents 500,000 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by 6 Dimensions Affiliates Fund, L.P. and 9,500,000 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by 6 Dimensions Capital, L.P. Wei Li was a director of the company from February 2018 to December 2018 and is a Managing Partner of 6 Dimensions Capital, of which 6 Dimensions Affiliates Fund, L.P. and 6 Dimensions Capital, L.P. are affiliated funds. Entities affiliated with 6 Dimensions Capital collectively hold more than 5% of our voting securities. |
| (5) | Represents 4,375,000 shares of Series B preferred stock purchased by Curative Ventures CT LLC. Neil Gibson is a director of the Company and is a partner of Curative Ventures CT LLC. |
Agreements with Stockholders
In connection with our Series A preferred stock financing and our Series B preferred stock financing, we entered into investors’ rights, voting and right of first refusal and co-sale agreements containing registration rights, information rights, voting rights and rights of first refusal, among other things, with certain holders of our preferred stock and certain holders of our common stock. These stockholder agreements will terminate upon the closing of this offering, except for the registration rights granted under our investors’ rights agreement, as more fully described in “Description of Capital Stock—Registration Rights.”
166
Participation in this Offering
Certain of our existing stockholders (or their affiliates), including those affiliated with certain of our directors, have indicated an interest in purchasing an aggregate of approximately $30.0 million of shares of our common stock in this offering at the initial public offering price. However, because indications of interest are not binding agreements or commitments to purchase, the underwriters may determine to sell more, less or no shares in this offering to any of these stockholders, or any of these stockholders may determine to purchase more, less or no shares in this offering.
Harpoon Therapeutics, Inc. License Agreement
In June 2017, we entered into a license agreement with Harpoon Therapeutics, Inc. (Harpoon), under which Harpoon provides us with rights to use certain Harpoon intellectual property relating to antibody-based protein binders and related know-how developed by Harpoon. In return, we provide Harpoon with the right to use antibody-based protein binders developed by us. Each license granted under this Harpoon license agreement is non-exclusive. Affiliates of MPM Capital that own shares of our preferred and common stock are founding stockholders in Harpoon, and Dr. Patrick Baeuerle, one of our directors and co-founders, is a director and co-founder of Harpoon.
Indemnification Agreements
In connection with this offering, we intend to enter into new agreements to indemnify our directors and executive officers. These agreements will, among other things, require us to indemnify these individuals for certain expenses (including attorneys’ fees), judgments, fines and settlement amounts reasonably incurred by such person in any action or proceeding, including any action by or in our right, on account of any services undertaken by such person on behalf of our company or that person’s status as a member of our board of directors to the maximum extent allowed under Delaware law.
Policies for Approval of Related Party Transactions
Our board of directors reviews and approves transactions with directors, officers and holders of 5% or more of our voting securities and their affiliates, each a related party. Prior to this offering, the material facts as to the related party’s relationship or interest in the transaction were disclosed to our board of directors prior to their consideration of such transaction, and the transaction was not considered approved by our board of directors unless a majority of the directors who are not interested in the transaction approved the transaction. Further, when stockholders are entitled to vote on a transaction with a related party, the material facts of the related party’s relationship or interest in the transaction were disclosed to the stockholders, who must approve the transaction in good faith.
In connection with this offering, we expect to adopt a written related party transactions policy that will provide that such transactions must be approved by our audit committee. This policy will become effective on the date on which the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part is declared effective by the SEC. Pursuant to this policy, the audit committee has the primary responsibility for reviewing and approving or disapproving “related party transactions,” which are transactions between us and related persons in which the aggregate amount involved exceeds or may be expected to exceed $120,000 and in which a related person has or will have a direct or indirect material interest. For purposes of this policy, a related person will be defined as a director, executive officer, nominee for director, or greater than 5% beneficial owner of our common stock, in each case since the beginning of the most recently completed year, and their immediate family members.
167
The following table sets forth, as of December 31, 2018, information regarding the beneficial ownership of our common stock by:
| ∎ | each person, or group of affiliated persons, who is known by us to be the beneficial owner of five percent or more of our outstanding common stock (on an as-converted to common stock basis); |
| ∎ | each of our directors; |
| ∎ | each of our named executive officers; and |
| ∎ | all of our current directors and executive officers as a group. |
The information in the following table is calculated based on 18,189,901 shares of common stock deemed to be outstanding before this offering and 23,189,901 shares of common stock outstanding after this offering, assuming no exercise by the underwriters of their option to purchase additional shares of common stock. The number of shares outstanding is based on the number of shares of common stock outstanding as of December 31, 2018 as adjusted to give effect to:
| ∎ | the automatic conversion of all outstanding shares of our preferred stock into 17,275,299 shares of common stock upon the completion of this offering; and |
| ∎ | the sale of 5,000,000 shares of common stock in this offering (assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares). |
Each individual or entity shown on the table has furnished information with respect to beneficial ownership. Except as otherwise indicated below, the address of each officer, director and five percent stockholder listed below is c/o TCR2 Therapeutics Inc., 100 Binney Street, Suite 710, Cambridge, MA 02142.
We have determined beneficial ownership in accordance with the rules of the SEC, and the information is not necessarily indicative of beneficial ownership for any other purpose. These rules generally attribute beneficial ownership of securities to persons who possess sole or shared voting power or investment power with respect to those securities as well as any shares of common stock that the person has the right to acquire within 60 days of December 31, 2018 through the exercise of stock options or other rights. These shares are deemed to be outstanding and beneficially owned by the person holding those options for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of that person, but they are not treated as outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of any other person. Unless otherwise indicated, the persons or entities identified in this table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares shown as beneficially owned by them.
Certain of our existing stockholders (or their affiliates), including those affiliated with certain of our directors, have indicated an interest in purchasing an aggregate of approximately $30.0 million of shares of our common stock in this offering at the initial public offering price. The table below does not give effect to the potential purchases by such stockholders in this offering.
| SHARES OF COMMON STOCK BENEFICIALLY OWNED | PERCENTAGE OF SHARES OUTSTANDING | |||||||||||
| BEFORE OFFERING | AFTER OFFERING | |||||||||||
5% or Greater Stockholders | ||||||||||||
Entities affiliated with MPM Capital(1) | 3,522,468 | 19.18 | % | 15.07 | % | |||||||
Entities affiliated with F2 Capital(2) | 2,904,594 | 15.97 | % | 12.53 | % | |||||||
UBS Oncology Impact Fund, L.P.(3) | 2,704,315 | 14.87 | % | 11.66 | % | |||||||
Entities affiliated with Cathay Fortune Corporation (4) | 1,937,419 | 10.65 | % | 8.35 | % | |||||||
Entities affiliated with 6 Dimensions Capital(5) | 1,614,516 | 8.88 | % | 6.96 | % | |||||||
Entities affiliated with Mirae Asset(6) | 968,708 | 5.33 | % | 4.18 | % | |||||||
168
| SHARES OF COMMON STOCK BENEFICIALLY OWNED | PERCENTAGE OF SHARES OUTSTANDING | |||||||||||
| BEFORE OFFERING | AFTER OFFERING | |||||||||||
Directors, Named Executive Officers and Other Executive Officers | ||||||||||||
Garry Menzel(7) | 377,798 | 2.04 | % | 1.61 | % | |||||||
Robert Hofmeister (8) | 101,503 | * | * | |||||||||
Alfonso Quintás Cardama(9) | 92,470 | * | * | |||||||||
Ansbert Gadicke(10) | 6,226,783 | 33.90 | % | 26.65 | % | |||||||
Patrick Baeuerle(11) | 467,715 | 2.57 | % | 2.02 | % | |||||||
Mitchell Finer(12) | 51,732 | * | * | |||||||||
Morana Jovan-Embiricos(13) | 2,904,594 | 15.97 | % | 12.53 | % | |||||||
Neil Gibson(14) | 706,351 | 3.88 | % | 3.05 | % | |||||||
Andrew Allen(15) | — | — | — | |||||||||
All executive officers and directors as a group (10 persons) (16) | 10,928,946 | 58.04 | % | 45.86 | % | |||||||
| * | Less than one percent. |
| (1) | Consists of (i) 79,644 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of shares of Series A preferred stock and 9,291 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of shares of Series B preferred stock, in each case held by MPM Asset Management Investors BV2014 LLC, (ii) 52,469 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series A preferred stock and 5,247 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock, in each case held by MPM Asset Management Investors SunStates Fund LLC, (iii) 195,902 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase 178,269 shares of common stock exercisable within 60 days of December 31, 2018, in each case held by MPM Asset Management LLC, (iv) 146,447 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series A preferred stock and 17,085 shares issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock, in each case held by MPM BioVentures 2014 (B), L.P., (v) 2,195,681 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series A preferred stock and 256,163 shares issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock, in each case held by MPM BioVentures 2014, L.P., and (vi) 351,155 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series A preferred stock and 35,115 shares issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock, in each case held by MPM SunStates Fund, L.P. MPM Bioventures 2014 GP LLC is the general partner of MPM BioVentures 2014, L.P. and MPM BioVentures 2014 (B), L.P. MPM Bioventures 2014 LLC is the managing member of MPM Bioventures 2014 GP LLC and the manager of MPM Asset Management Investors BV2014 LLC. MPM SunStates Fund GP LLC is the general partner of MPM SunStates Fund, L.P. MPM SunStates GP Managing Member LLC is the managing member of MPM SunStates Fund GP LLC and the manager of MPM Asset Management Investors SunStates Fund LLC. MPM Asset Management LLC was retained as a manager to manage the operations of MPM BioVentures 2014, L.P., MPM BioVentures 2014 (B), L.P., MPM Asset Management Investors BV2014 LLC, MPM SunStates Fund, L.P., and MPM Asset Management SunStates Fund LLC. Dr. Ansbert Gadicke is a member of MPM BioVentures 2014 LLC, MPM SunStates GP Managing Member LLC, and MPM Capital, formerly known as MPM Asset Management LLC, and collectively with the other members of such entities makes investment decisions with respect to shares held by such entities. Each of the entities and individuals listed above expressly disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed above except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein. The address of these entities and individuals is 450 Kendall Street, Cambridge, MA 02142. |
| (2) | Consists of (i) 193,742 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by F2 Bioscience II 2017 Limited, (ii) 1,614,515 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series A preferred stock held by F2 Capital I 2015 Limited, (iii) 410,168 shares issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by F2 Capital I 2017 Limited, (iv) 282,540 shares issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by F2 MG Limited, and (v) 403,629 shares issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by F2-TPO Investments, LLC. Dr. Morana Jovan-Embiricos is a member of our board of directors and is the founding director of Globeways Holdings Limited, which is the appointed manager of each of F2 Bioscience II 2017 Limited, F2 Capital I 2015 Limited, F2 Capital I 2017 Limited, F2 MG Limited, and F2-TPO Investments, LLC and makes investment decisions on behalf of such entities with respect to shares held by such entities. Dr. Morana Jovan-Embiricos expressly disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed above except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein. The address of these entities and individuals for correspondence is 8, Rue Saint-Leger, 04-1205, Geneva, Switzerland. |
| (3) | Consists of 2,421,775 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series A preferred stock and 282,540 shares issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock, in each case held by UBS Oncology Impact Fund, L.P. The general partner of UBS Oncology Impact Fund, L.P. is Oncology Impact Fund (Cayman) Management L.P. The general partner of Oncology Impact Fund (Cayman) Management L.P. is MPM Oncology Impact Management LP. The general partner of MPM Oncology Impact Management LP is MPM Oncology Impact Management GP LLC. Dr. Ansbert Gadicke is a managing member and the managing director of MPM Oncology Impact Management GP LLC. Each of the entities and individuals listed above expressly disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed above except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein. The address of these entities and individuals is Durell House, 28 New Street, St Helier, Jersey, JE1 4FS. |
169
| (4) | Consists of (i) 322,902 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series A preferred stock and (ii) 1,614,517 shares issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock, in each case held by an entity affiliated with Cathay Fortune Corporation. The address of this entity is Vistra Corporate Services Centre, Wickham’s Cay II, Road Town, Tortola, VG1110, British Virgin Islands. |
| (5) | Consists of (i) 80,725 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by 6 Dimensions Affiliates Fund, L.P. and (ii) 1,533,791 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by 6 Dimensions Capital, L.P. The general partner of 6 Dimensions Affiliates Fund, L.P. and 6 Dimensions Capital, L.P. is 6 Dimensions Capital GP, LLC. Wei Li was a member of our board of directors from February 2018 to December 2018 and is a Director of 6 Dimensions Capital GP, LLC. Each of the entities and individuals listed above expressly disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed above except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein. The address of these entities and individuals is P.O. Box 309, Ugland House, Grand Cayman, Cayman Islands, KY 1-1104. |
| (6) | Consists of (i) 80,725 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by Mirae Asset Venture Investment, Co, Ltd., (ii) 161,451 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by Mirae Asset Young Start-up Investment Fund #2, and (iii) 726,532 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by Mirae Asset-Celltrion New Growth Fund I. Mirae Asset Venture Investment, Co, Ltd. is the general partner of Mirae Asset Young Start-up Investment Fund. Mr. Eung Suk Kim is the chief executive officer of Mirae Asset Venture Investment, Co, Ltd. Each of the entities and individuals listed above expressly disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed above except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein. The address of each of Mirae Asset Young Start-up Investment Fund #2, Mirae Asset Venture Investment, Co, Ltd., and Mr. Eung Suk Kim is (Glass Tower) 21F, 534, Teheran-ro Gangnam-gu, Seoul, 06181, Korea. MiraeAsset Capital co., Ltd is the general partner of Mirae Asset-Celltrion New Growth Fund I. Mr. KuBeom Lee is the chief executive officer of MiraeAsset Capital co., Ltd. The address of each of MiraeAsset Capital co., Ltd, Mirae Asset-Celltrion New Growth Fund I, and Mr. KumBeom Lee is Miraeasset Venture Tower Bild, BI, 20 Pangyoyeok-ro 241beon-gil, Bundang-gu, Seongnam-si, Gyeonggi-do, 13494, Republic of Korea. Each of the entities and individuals listed above expressly disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed above except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein. |
| (7) | Consists of (i) options to purchase 293,271 shares of common stock exercisable within 60 days of December 31, 2018 and (ii) 84,527 shares of common stock held by Dr. Garry Menzel, as Trustee of the Garry E. Menzel and Mary E. Henshall Family Trust, under instrument of trust dated July 29, 2010. Dr. Menzel is the trustee of the Garry E. Menzel and Mary E. Henshall Family Trust and may be deemed to beneficially own these securities. |
| (8) | Consists of (i) 38,850 shares of common stock, of which 13,578 will remain unvested within 60 days of December 31, 2018 and subject to a right of repurchase in our favor upon Mr. Robert Hofmeister’s cessation of service prior to vesting, and (ii) options to purchase 62,653 shares of common stock exercisable within 60 days of December 31, 2018. |
| (9) | Consists of options to purchase 92,470 shares of common stock exercisable within 60 days of December 31, 2018. |
| (10) | See notes (1) and (3) above. |
| (11) | Consists of 467,715 shares of common stock held by APAK Solutions GmbH, of which 143,318 shares will remain unvested within 60 days of December 31, 2018 and subject to a right of repurchase in our favor upon APAK Solutions GmbH’s and/or Dr. Patrick Baeuerle’s cessation of service prior to vesting. Dr. Baeuerle is a managing director of APAK Solutions GmbH and shares voting and investment power with respect to these shares. Each of the entities and individuals listed above expressly disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed above except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein. The address of these entities and individuals is c/o MPM Capital, 450 Kendall Street, Cambridge, MA 02142. |
| (12) | Consists of (i) 36,731 shares of common stock held by Dr. Mitchell Finer, of which 2,296 shares will remain unvested within 60 days of December 31, 2018 and subject to a right of repurchase in our favor upon Dr. Finer’s cessation of service prior to vesting, and (ii) options to purchase 5,121 shares of common stock exercisable within 60 days of December 31, 2018 and warrants to purchase 9,880 shares of common stock exercisable within 60 days of December 31, 2018, in each case held by Pattern Recognition Ventures. Dr. Finer is a managing member of Pattern Recognition Ventures and shares voting and investment power with respect to these shares. Each of the entities and individuals listed above expressly disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed above except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein. The address of these entities and individuals is 450 Kendall Street, Cambridge, MA 02142. |
| (13) | See note (2) above. |
| (14) | Consists of 706,351 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock held by Curative Ventures CT LLC. Mr. Neil Gibson is a partner at Curative Ventures CT LLC and shares voting and investment power with respect to these shares. Each of the entities and individuals listed above expressly disclaims beneficial ownership of the securities listed above except to the extent of any pecuniary interest therein. The address of Curative Ventures CT LLC is 5949 Sherry Lane, Suite 820, Dallas, TX 75225, and the address of Mr. Neil Gibson is c/o Curative Ventures CT LLC , 5949 Sherry Lane, Suite 820, Dallas, TX 75225. |
| (15) | Dr. Allen was appointed to our board of directors in December 2018. |
| (16) | Includes options to purchase 453,515 shares of common stock exercisable within 60 days of December 31, 2018 and warrants to purchase 188,149 shares of common stock exercisable within 60 days of December 31, 2018, held by ten executive officers, directors and entities affiliated with such executive officers and directors, as described in notes (7) through (14) above. |
170
The following descriptions are summaries of the material terms of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws, which will be effective upon the closing of this offering. The descriptions of the common stock and preferred stock give effect to changes to our capital structure that will occur upon the closing of this offering. We refer in this section to our amended and restated certificate of incorporation as our certificate of incorporation, and we refer to our amended and restated bylaws as our bylaws.
General
Upon completion of this offering, our authorized capital stock will consist of 150,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, and 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.0001 per share, all of which shares of preferred stock will be undesignated.
As of December 31, 2018, 914,602 shares of our common stock (of which 187,608 shares are subject to a right of repurchase by us pursuant to a stock restriction agreement between us and the holders of such shares) were outstanding and held of record by 19 stockholders, 44,500,001 shares of Series A preferred stock were outstanding and held of record by 8 stockholders and 62,500,000 shares of Series B preferred stock were outstanding and held of record by 41 stockholders. This amount does not take into account the conversion of all outstanding shares of our preferred stock into common stock upon the closing of this offering.
Common Stock
The holders of our common stock are entitled to one vote for each share held on all matters submitted to a vote of the stockholders. The holders of our common stock do not have any cumulative voting rights. Holders of our common stock are entitled to receive ratably any dividends declared by our board of directors out of funds legally available for that purpose, subject to any preferential dividend rights of any outstanding preferred stock. Our common stock has no preemptive rights, conversion rights or other subscription rights or redemption or sinking fund provisions.
In the event of our liquidation, dissolution or winding up, holders of our common stock will be entitled to share ratably in all assets remaining after payment of all debts and other liabilities and any liquidation preference of any outstanding preferred stock. The shares to be issued by us in this offering will be, when issued and paid for, validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable.
Preferred Stock
Upon the completion of this offering, all outstanding shares of our preferred stock will be converted into shares of our common stock. Upon the closing of this offering, our board of directors will have the authority, without further action by our stockholders, to issue up to 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock in one or more series and to fix the rights, preferences, privileges and restrictions thereof. These rights, preferences and privileges could include dividend rights, conversion rights, voting rights, terms of redemption, liquidation preferences, sinking fund terms and the number of shares constituting, or the designation of, such series, any or all of which may be greater than the rights of common stock. The issuance of our preferred stock could adversely affect the voting power of holders of common stock and the likelihood that such holders will receive dividend payments and payments upon our liquidation. In addition, the issuance of preferred stock could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change in control of our company or other corporate action. Immediately after consummation of this offering, no shares of preferred stock will be outstanding, and we have no present plan to issue any shares of preferred stock.
Options
As of December 31, 2018, options to purchase 2,094,816 shares of common stock at a weighted-average exercise price of $3.79 per share were outstanding under our 2015 Plan.
As of December 31, 2018, options to purchase 8,017 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $0.74 per share, which options were not granted pursuant to a benefits plan, were outstanding.
171
Warrants
As of December 31, 2018, warrants to purchase 203,676 shares of common stock at a weighted exercise price of $0.74 per share were outstanding, which warrants were not granted pursuant to a benefits plan.
Registration Rights
Upon the completion of this offering, the holders of 17,276,913 shares of our common stock, including those issuable upon the conversion of preferred stock, will be entitled to rights with respect to the registration of these securities under the Securities Act. These rights are provided under the terms of an amended and restated investors’ rights agreement between us, certain holders of our common stock and holders of our preferred stock. The amended and restated investors’ rights agreement includes demand registration rights, short-form registration rights and piggyback registration rights. All fees, costs and expenses of underwritten registrations under the amended and restated investors’ rights agreement will be borne by us, and all selling expenses, including underwriting discounts and selling commissions, will be borne by the holders of the shares being registered.
Demand Registration Rights
Beginning 180 days after the effective date of this registration statement, the holders of 17,276,913 shares of our common stock, including those issuable upon the conversion of shares of our preferred stock upon closing of this offering, are entitled to demand registration rights. Under the terms of the amended and restated investors’ rights agreement, we will be required, upon the written request of holders of at least a majority of the securities eligible for registration then outstanding, including at least a majority of the common stock issuable or issued upon conversion of our Series A preferred stock and at least a majority of the common stock issuable or issued upon conversion of the Series B preferred stock, to file a registration statement with respect to at least 40% of the securities eligible for registration then outstanding (or a lesser percent if the anticipated aggregate offering price, net of related fees and expenses, would exceed $5 million), we will be required to file a registration statement covering all securities eligible for registration that our stockholders request to be included in such registration. We are required to effect only two registrations pursuant to this provision of the investors’ rights agreement in any twelve-month period.
Short-Form Registration Rights
Pursuant to the amended and restated investors’ rights agreement, if we are eligible to file a registration statement on Form S-3, upon the written request of stockholders holding at least 10% of the securities eligible for registration then outstanding with respect to outstanding securities of such stockholders having an anticipated aggregate offering, net of related fees and expenses, of at least $1.0 million, we will be required to file a Form S-3 registration restatement covering all securities eligible for registration that our stockholders request to be included in such registration. We are required to effect only two registrations in any twelve-month period pursuant to this provision of the amended and restated investors’ rights agreement. The right to have such shares registered on Form S-3 is further subject to other specified conditions and limitations.
Piggyback Registration Rights
Pursuant to the amended and restated investors’ rights agreement, if we register any of our securities either for our own account or for the account of other security holders, the holders of our common stock, including those issuable upon the conversion of our preferred stock, are entitled to include their shares in the registration. Subject to certain exceptions contained in the amended and restated investors’ rights agreement, we and the underwriters may limit the number of shares included in the underwritten offering to the number of shares which we and the underwriters determine in our sole discretion will not jeopardize the success of the offering.
Indemnification
Our amended and restated investors’ rights agreement contains customary cross-indemnification provisions, under which we are obligated to indemnify holders of registrable securities in the event of material misstatements or omissions in the registration statement attributable to us, and they are obligated to indemnify us for material misstatements or omissions attributable to them.
Expiration of Registration Rights
The registration rights granted under the amended and restated investors’ rights agreement will terminate the earliest to occur of: (i) on the fifth anniversary of the completion of this offering or, (ii) at such time after this offering when the holders’ shares may be sold pursuant to Rule 144 without restriction within a three-month period or (iii) a merger, sale or liquidation of our company.
172
Anti-Takeover Effects of Delaware Law and Certain Provisions of our Certificate of Incorporation and Amended and Restated Bylaws
Our certificate of incorporation and bylaws include a number of provisions that may have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing another party from acquiring control of us and encouraging persons considering unsolicited tender offers or other unilateral takeover proposals to negotiate with our board of directors rather than pursue non-negotiated takeover attempts. These provisions include the items described below.
Board Composition and Filling Vacancies
Our certificate of incorporation provides for the division of our board of directors into three classes serving staggered three-year terms, with one class being elected each year. Our certificate of incorporation also provides that directors may be removed only for cause and then only by the affirmative vote of the holders of two-thirds or more of the shares then entitled to vote at an election of directors. Furthermore, any vacancy on our board of directors, however occurring, including a vacancy resulting from an increase in the size of our board, may only be filled by the affirmative vote of a majority of our directors then in office even if less than a quorum. The classification of directors, together with the limitations on removal of directors and treatment of vacancies, has the effect of making it more difficult for stockholders to change the composition of our board of directors.
No Written Consent of Stockholders
Our certificate of incorporation provides that all stockholder actions are required to be taken by a vote of the stockholders at an annual or special meeting, and that stockholders may not take any action by written consent in lieu of a meeting. This limit may lengthen the amount of time required to take stockholder actions and would prevent the amendment of our bylaws or removal of directors by our stockholders without holding a meeting of stockholders.
Meetings of Stockholders
Our certificate of incorporation and bylaws provide that only a majority of the members of our board of directors then in office may call special meetings of stockholders and only those matters set forth in the notice of the special meeting may be considered or acted upon at a special meeting of stockholders. Our bylaws limit the business that may be conducted at an annual meeting of stockholders to those matters properly brought before the meeting.
Advance Notice Requirements
Our bylaws establish advance notice procedures with regard to stockholder proposals relating to the nomination of candidates for election as directors or new business to be brought before meetings of our stockholders. These procedures provide that notice of stockholder proposals must be timely given in writing to our corporate secretary prior to the meeting at which the action is to be taken. Generally, to be timely, notice must be received at our principal executive offices not less than 90 days nor more than 120 days prior to the first anniversary date of the annual meeting for the preceding year. Our bylaws specify the requirements as to form and content of all stockholders’ notices. These requirements may preclude stockholders from bringing matters before the stockholders at an annual or special meeting.
Amendment to Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws
Any amendment of our certificate of incorporation must first be approved by a majority of our board of directors, and if required by law or our certificate of incorporation, must thereafter be approved by a majority of the outstanding shares entitled to vote on the amendment and a majority of the outstanding shares of each class entitled to vote thereon as a class, except that the amendment of the provisions relating to stockholder action, board composition, limitation of liability and the amendment of our bylaws and certificate of incorporation must be approved by not less than two-thirds of the outstanding shares entitled to vote on the amendment, and not less than a majority of the outstanding shares of each class entitled to vote thereon as a class. Our bylaws may be amended by the affirmative vote of a majority of the directors then in office, subject to any limitations set forth in the bylaws; and may also be amended by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the outstanding shares entitled to vote on the amendment, or, if our board of directors recommends that the stockholders approve the amendment, by the affirmative vote of the majority of the outstanding shares entitled to vote on the amendment, in each case voting together as a single class.
Undesignated Preferred Stock
Our certificate of incorporation provides for 10,000,000 authorized shares of preferred stock. The existence of authorized but unissued shares of preferred stock may enable our board of directors to discourage an attempt to
173
obtain control of us by means of a merger, tender offer, proxy contest or otherwise. For example, if in the due exercise of its fiduciary obligations, our board of directors were to determine that a takeover proposal is not in the best interests of our stockholders, our board of directors could cause shares of preferred stock to be issued without stockholder approval in one or more private offerings or other transactions that might dilute the voting or other rights of the proposed acquirer or insurgent stockholder or stockholder group. In this regard, our certificate of incorporation grants our board of directors broad power to establish the rights and preferences of authorized and unissued shares of preferred stock. The issuance of shares of preferred stock could decrease the amount of earnings and assets available for distribution to holders of shares of common stock. The issuance may also adversely affect the rights and powers, including voting rights, of these holders and may have the effect of delaying, deterring or preventing a change in control of us.
Delaware Anti-Takeover Statute
Upon completion of this offering, we will be subject to the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law. In general, Section 203 prohibits a publicly held Delaware corporation from engaging in a “business combination” with an “interested stockholder” for a three-year period following the time that this stockholder becomes an interested stockholder, unless the business combination is approved in a prescribed manner. Under Section 203, a business combination between a corporation and an interested stockholder is prohibited unless it satisfies one of the following conditions:
| ∎ | before the stockholder became interested, our board of directors approved either the business combination or the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder; |
| ∎ | upon consummation of the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested stockholder owned at least 85% of the voting stock of the corporation outstanding at the time the transaction commenced, excluding for purposes of determining the voting stock outstanding, shares owned by persons who are directors and also officers, and employee stock plans, in some instances, but not the outstanding voting stock owned by the interested stockholder; or |
| ∎ | at or after the time the stockholder became interested, the business combination was approved by our board of directors and authorized at an annual or special meeting of the stockholders by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the outstanding voting stock which is not owned by the interested stockholder. |
Section 203 defines a business combination to include:
| ∎ | any merger or consolidation involving the corporation and the interested stockholder; |
| ∎ | any sale, transfer, lease, pledge, exchange, mortgage or other disposition involving the interested stockholder of 10% or more of the assets of the corporation; |
| ∎ | subject to exceptions, any transaction that results in the issuance or transfer by the corporation of any stock of the corporation to the interested stockholder; or |
| ∎ | the receipt by the interested stockholder of the benefit of any loans, advances, guarantees, pledges or other financial benefits provided by or through the corporation. |
In general, Section 203 defines an interested stockholder as any entity or person beneficially owning 15% or more of the outstanding voting stock of the corporation and any entity or person affiliated with or controlling or controlled by the entity or person.
Choice of Forum
Our bylaws provide that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the exclusive forum for (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (ii) any action asserting a breach of fiduciary duty by one or more of our directors, officers or employees, (iii) any action asserting a claim against us arising pursuant to the Delaware General Corporation Law or (iv) any action asserting a claim against us that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine. This exclusive forum provision does not apply to any complaints asserting a cause of action arising under the Exchange Act. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of our capital stock shall be deemed to have notice of and consented to the forum provisions in our amended and restated bylaws. The enforceability of similar choice of forum provisions in other companies’ certificates of incorporation and bylaws has been challenged in legal proceedings, and it is possible that a court could find these types of provisions to be inapplicable or unenforceable.
174
Stock Exchange Listing
We have applied to list our common stock on The Nasdaq Global Market under the proposed trading symbol “TCRR.”
Transfer Agent and Registrar
The Transfer Agent and Registrar for our common stock will be American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC.
175
SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our shares. Future sales of our common stock in the public market, or the availability of such shares for sale in the public market, could adversely affect market prices prevailing from time to time. As described below, only a limited number of shares will be available for sale shortly after this offering due to contractual and legal restrictions on resale. Nevertheless, sales of shares of our common stock in the public market after such restrictions lapse, or the perception that those sales may occur, could adversely affect the prevailing market price at such time and our ability to raise equity capital in the future.
Based on the number of shares outstanding as of December 31, 2018, upon the completion of this offering, 23,189,901 shares of our common stock will be outstanding, assuming the issuance of 5,000,000 shares offered by us in this offering, no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares and no exercise of outstanding options or warrants. Of the outstanding shares, all of the shares sold in this offering will be freely tradable, except that any shares held by our affiliates, as that term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act, may only be sold in compliance with the limitations described below, and restricted shares of common stock are subject to time-based vesting terms. All remaining shares of common stock held by existing stockholders immediately prior to the completion of this offering will be “restricted securities” as such term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act. These restricted securities were issued and sold by us in private transactions and are eligible for public sale only if registered under the Securities Act or if they qualify for an exemption from registration under the Securities Act, including the exemptions provided by Rule 144 or Rule 701, summarized below.
Rule 144
In general, a person who has beneficially owned restricted stock for at least six months would be entitled to sell their securities provided that (i) such person is not deemed to have been one of our affiliates at the time of, or at any time during the 90 days preceding, a sale and (ii) we are subject to the periodic reporting requirements of the Exchange Act for at least 90 days before the sale. Persons who have beneficially owned restricted shares for at least six months but who are our affiliates at the time of, or any time during the 90 days preceding, a sale, would be subject to additional restrictions, by which such person would be entitled to sell within any three-month period only a number of securities that does not exceed the greater of either of the following:
| ∎ | 1% of the number of shares then outstanding, which will equal approximately 232,000 shares immediately after this offering, assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares, based on the number of shares outstanding as of September 30, 2018; or |
| ∎ | the average weekly trading volume of our common stock on The Nasdaq Global Market during the four calendar weeks preceding the filing of a notice on Form 144 with respect to the sale; |
provided, in each case, that we are subject to the periodic reporting requirements of the Exchange Act for at least 90 days before the sale. Such sales both by affiliates and by non-affiliates must also comply with the manner of sale, current public information and notice provisions of Rule 144.
Rule 701
Rule 701 under the Securities Act, as in effect on the date of this prospectus, permits resales of shares in reliance upon Rule 144 but without compliance with certain restrictions of Rule 144, including the holding period requirement. Most of our employees, executive officers or directors who purchased shares under a written compensatory plan or contract may be entitled to rely on the resale provisions of Rule 701, but all holders of Rule 701 shares are required to wait until 90 days after the date of this prospectus before selling their shares.
However, substantially all Rule 701 shares are subject to lock-up agreements as described below and under “Underwriting” included elsewhere in this prospectus and will become eligible for sale upon the expiration of the restrictions set forth in those agreements.
Lock-Up Agreements
We, all of our directors and officers and substantially all of our stockholders have agreed not to sell or otherwise transfer or dispose of any of our securities for a period of 180 days from the date of this prospectus, subject to
176
certain exceptions. The representatives of the underwriters in this offering may, in their sole discretion, permit early release of shares subject to the lock-up agreements. See the section entitled “Underwriting,” appearing elsewhere in this prospectus for more information.
Registration Rights
Upon completion of this offering, certain holders of our securities will be entitled to various rights with respect to registration of their shares under the Securities Act. Registration of these shares under the Securities Act would result in these shares becoming fully tradable without restriction under the Securities Act immediately upon the effectiveness of the registration. See the section entitled “Description of Capital Stock—Registration Rights” appearing elsewhere in this prospectus for more information.
Equity Incentive Plans
We intend to file one or more registration statements on Form S-8 under the Securities Act to register our shares issued or reserved for issuance under our equity incentive plans. The first such registration statement is expected to be filed soon after the date of this prospectus and will automatically become effective upon filing with the SEC. Accordingly, shares registered under such registration statement will be available for sale in the open market, unless such shares are subject to vesting restrictions with us or the lock-up restrictions described above. As of the date of this prospectus, we estimate that such registration statement on Form S-8 will cover approximately 5,100,000 shares.
177
MATERIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS FOR NON-U.S. HOLDERS
The following discussion is a summary of the material U.S. federal income tax considerations applicable to non-U.S. holders (as defined below) with respect to their ownership and disposition of shares of our common stock issued pursuant to this offering. For purposes of this discussion, a non-U.S. holder means a beneficial owner of our common stock that is for U.S. federal income tax purposes:
| ∎ | a non-resident alien individual; |
| ∎ | a corporation or other organization taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes that is created or organized in or under laws other than the laws of the United States, any state thereof, or the District of Columbia; |
| ∎ | an estate the income of which is not subject to U.S. federal income tax on a net income basis; or |
| ∎ | a trust the income of which is not subject to U.S. federal income tax on a net income basis and that (1) is not subject to the primary supervision of a court within the United States or over which no U.S. persons have authority to control all substantial decisions and (2) has not made an election to be treated as a U.S. person. |
This discussion does not address the tax treatment of partnerships or other entities that are pass-through entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes or persons that hold their common stock through partnerships or other pass-through entities. A partner in a partnership or other pass-through entity that will hold our common stock should consult his, her or its tax advisor regarding the tax consequences of acquiring, holding and disposing of our common stock through a partnership or other pass-through entity, as applicable.
This discussion is based on current provisions of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, which we refer to as the Code, existing and proposed U.S. Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder, current administrative rulings and judicial decisions, all as in effect as of the date of this prospectus and all of which are subject to change or to differing interpretation, possibly with retroactive effect. Any such change or differing interpretation could alter the tax consequences to non-U.S. holders described in this prospectus. There can be no assurance that the Internal Revenue Service, which we refer to as the IRS, will not challenge one or more of the tax consequences described herein. We assume in this discussion that a non-U.S. holder holds shares of our common stock as a capital asset within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code, generally property held for investment.
This discussion does not address all aspects of U.S. federal income taxation that may be relevant to a particular non-U.S. holder in light of that non-U.S. holder’s individual circumstances nor does it address any U.S. state, local or non-U.S. taxes, the alternative minimum tax, the Medicare tax on net investment income, the rules regarding qualified small business stock within the meaning of Section 1202 of the Code, or any other aspect of any U.S. federal tax other than the income tax. This discussion also does not consider any specific facts or circumstances that may apply to a non-U.S. holder and does not address the special tax rules applicable to particular non-U.S. holders, such as:
| ∎ | insurance companies; |
| ∎ | tax-exempt or governmental organizations; |
| ∎ | financial institutions; |
| ∎ | brokers or dealers in securities; |
| ∎ | regulated investment companies; |
| ∎ | pension plans; |
| ∎ | “controlled foreign corporations,” “passive foreign investment companies,” and corporations that accumulate earnings to avoid U.S. federal income tax; |
| ∎ | “qualified foreign pension funds,” or entities wholly owned by a “qualified foreign pension fund”; |
| ∎ | persons deemed to sell our common stock under the constructive sale provisions of the Code; |
| ∎ | persons that hold our common stock as part of a straddle, hedge, conversion transaction, synthetic security or other integrated investment; and |
| ∎ | certain U.S. expatriates. |
178
This discussion is for information only and is not tax advice. Accordingly, all prospective non-U.S. holders of our common stock should consult their tax advisors with respect to the U.S. federal, state, local and non-U.S. tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our common stock.
Distributions on Our Common Stock
Distributions, if any, on our common stock will constitute dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes to the extent paid from our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. If a distribution exceeds our current and accumulated earnings and profits, the excess will be treated as a tax-free return of the non-U.S. holder’s investment, up to such holder’s tax basis in the common stock. Any remaining excess will be treated as capital gain, subject to the tax treatment described below in “Gain on Sale or Other Taxable Disposition of Our Common Stock.” Any such distributions will also be subject to the discussions below under the sections titled “Backup Withholding and Information Reporting” and “Withholding and Information Reporting Requirements—FATCA.”
Subject to the discussion in the following two paragraphs in this section, dividends paid to a non-U.S. holder generally will be subject to withholding of U.S. federal income tax at a 30% rate or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty between the United States and such holder’s country of residence.
Dividends that are treated as effectively connected with a trade or business conducted by a non-U.S. holder within the United States and, if an applicable income tax treaty so provides, that are attributable to a permanent establishment or a fixed base maintained by the non-U.S. holder within the United States, are generally exempt from the 30% withholding tax if the non-U.S. holder satisfies applicable certification and disclosure requirements. However, such U.S. effectively connected income, net of specified deductions and credits, is taxed at the same U.S. federal income tax rates applicable to United States persons (as defined in the Code). Any U.S. effectively connected income received by a non-U.S. holder that is a corporation may also, under certain circumstances, be subject to an additional “branch profits tax” at a 30% rate or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty between the United States and such holder’s country of residence.
A non-U.S. holder of our common stock who claims the benefit of an applicable income tax treaty between the United States and such holder’s country of residence generally will be required to provide a properly executed IRS Form W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E (or successor form) to the applicable withholding agent and satisfy applicable certification and other requirements. Non-U.S. holders are urged to consult their tax advisors regarding their entitlement to benefits under a relevant income tax treaty. A non-U.S. holder that is eligible for a reduced rate of U.S. withholding tax under an income tax treaty may obtain a refund or credit of any excess amounts withheld by timely filing a U.S. tax return with the IRS.
Gain on Sale or Other Taxable Disposition of Our Common Stock
Subject to the discussions below under “Backup Withholding and Information Reporting” and “Withholding and Information Reporting Requirements—FATCA,” a non-U.S. holder generally will not be subject to any U.S. federal income tax on any gain realized upon such holder’s sale or other taxable disposition of shares of our common stock unless:
| ∎ | the gain is effectively connected with the non-U.S. holder’s conduct of a U.S. trade or business and, if an applicable income tax treaty so provides, is attributable to a permanent establishment or a fixed-base maintained by such non-U.S. holder in the United States, in which case the non-U.S. holder generally will be taxed on a net income basis at the same U.S. federal income tax rates applicable to United States persons (as defined in the Code) and, if the non-U.S. holder is a foreign corporation, the branch profits tax described above in “Distributions on Our Common Stock” also may apply; |
| ∎ | the non-U.S. holder is a nonresident alien individual who is present in the United States for 183 days or more in the taxable year of the disposition and certain other conditions are met, in which case the non-U.S. holder will be subject to a 30% tax (or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty between the United States and such holder’s country of residence) on the net gain derived from the disposition, which may be offset by certain U.S. source capital losses of the non-U.S. holder, if any (even though the individual is not considered a resident of the United States), provided that the non-U.S. holder has timely filed U.S. federal income tax returns with respect to such losses; or |
179
| ∎ | we are, or have been, at any time during the five-year period preceding such sale or other taxable disposition (or the non-U.S. holder’s holding period, if shorter) a “U.S. real property holding corporation,” unless our common stock is regularly traded on an established securities market and the non-U.S. holder holds no more than 5% of our outstanding common stock, directly or indirectly, actually or constructively, during the shorter of the 5-year period ending on the date of the disposition or the period that the non-U.S. holder held our common stock. Generally, a corporation is a U.S. real property holding corporation only if the fair market value of its U.S. real property interests equals or exceeds 50% of the sum of the fair market value of its worldwide real property interests plus its other assets used or held for use in a trade or business. Although there can be no assurance, we do not believe that we are, or have been, a U.S. real property holding corporation, or that we are likely to become one in the future. No assurance can be provided that our common stock will be regularly traded on an established securities market for purposes of the rules described above. |
Backup Withholding and Information Reporting
We must report annually to the IRS and to each non-U.S. holder the gross amount of the distributions on our common stock paid to such holder and the tax withheld, if any, with respect to such distributions. Non-U.S. holders may have to comply with specific certification procedures to establish that the holder is not a United States person (as defined in the Code) in order to avoid backup withholding at the applicable rate with respect to dividends on our common stock. Dividends paid to non-U.S. holders subject to withholding of U.S. federal income tax, as described above in “Distributions on Our Common Stock,” generally will be exempt from U.S. backup withholding.
Information reporting and backup withholding will generally apply to the proceeds of a disposition of our common stock by a non-U.S. holder effected by or through the U.S. office of any broker, U.S. or foreign, unless the holder certifies its status as a non-U.S. holder and satisfies certain other requirements, or otherwise establishes an exemption. Generally, information reporting and backup withholding will not apply to a payment of disposition proceeds to a non-U.S. holder where the transaction is effected outside the United States through a non-U.S. office of a broker. However, for information reporting purposes, dispositions effected through a non-U.S. office of a broker with substantial U.S. ownership or operations generally will be treated in a manner similar to dispositions effected through a U.S. office of a broker.
Non-U.S. holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the application of the information reporting and backup withholding rules to them. Copies of information returns may be made available to the tax authorities of the country in which the non-U.S. holder resides or is incorporated under the provisions of a specific treaty or agreement. Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules from a payment to a non-U.S. holder can be refunded or credited against the non-U.S. holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability, if any, provided that an appropriate claim is filed with the IRS in a timely manner.
Withholding and Information Reporting Requirements—FATCA
Provisions of the Code commonly referred to as the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA), generally impose a U.S. federal withholding tax at a rate of 30% on payments of dividends on our common stock paid to a foreign entity unless (i) if the foreign entity is a “foreign financial institution,” such foreign entity undertakes certain due diligence, reporting, withholding, and certification obligations, (ii) if the foreign entity is not a “foreign financial institution,” such foreign entity identifies certain of its U.S. investors, if any, or (iii) the foreign entity is otherwise exempt under FATCA. Such withholding may also apply to payments of proceeds from sales or other dispositions of our common stock, although under recently proposed U.S. Treasury Regulations no withholding would apply to payments of gross proceeds. The preamble to the proposed regulations specifies that taxpayers (including withholding agents) are permitted to rely on the proposed regulations pending finalization. Under certain circumstances, a non-U.S. holder may be eligible for refunds or credits of this withholding tax. An intergovernmental agreement between the United States and an applicable foreign country may modify the requirements described in this paragraph. Non-U.S. holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the possible implications of this legislation on their investment in our common stock and the entities through which they hold our common stock, including, without limitation, the process and deadlines for meeting the applicable requirements to prevent the imposition of the 30% withholding tax under FATCA.
180
Subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the underwriting agreement, dated , 2019 among us and Jefferies LLC, SVB Leerink LLC and BMO Capital Markets Corp., as the representatives of the underwriters named below and the joint book-running managers of this offering, we have agreed to sell to the underwriters, and each of the underwriters has agreed, severally and not jointly, to purchase from us, the respective number of shares of common stock shown opposite its name below:
UNDERWRITER | NUMBER OF SHARES | |||
Jefferies LLC | ||||
SVB Leerink LLC | ||||
BMO Capital Markets Corp. | ||||
Wedbush Securities Inc. | ||||
China Renaissance Securities (US) Inc. | ||||
|
| |||
Total | 5,000,000 | |||
|
| |||
The underwriting agreement provides that the obligations of the several underwriters are subject to certain conditions precedent such as the receipt by the underwriters of officers’ certificates and legal opinions and approval of certain legal matters by their counsel. The underwriting agreement provides that the underwriters will purchase all of the shares of common stock if any of them are purchased. If an underwriter defaults, the underwriting agreement provides that the purchase commitments of the nondefaulting underwriters may be increased or the underwriting agreement may be terminated. We have agreed to indemnify the underwriters and certain of their controlling persons against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act, and to contribute to payments that the underwriters may be required to make in respect of those liabilities.
The underwriters have advised us that, following the completion of this offering, they currently intend to make a market in the common stock as permitted by applicable laws and regulations. However, the underwriters are not obligated to do so, and the underwriters may discontinue any market-making activities at any time without notice in their sole discretion. Accordingly, no assurance can be given as to the liquidity of the trading market for the common stock, that you will be able to sell any of the common stock held by you at a particular time or that the prices that you receive when you sell will be favorable.
The underwriters are offering the shares of common stock subject to their acceptance of the shares of common stock from us and subject to prior sale. The underwriters reserve the right to withdraw, cancel or modify offers to the public and to reject orders in whole or in part.
Commission and Expenses
The underwriters have advised us that they propose to offer the shares of common stock to the public at the initial public offering price set forth on the cover page of this prospectus and to certain dealers, which may include the underwriters, at that price less a concession not in excess of $ per share of common stock. The underwriters may allow, and certain dealers may reallow, a discount from the concession not in excess of $ per share of common stock to certain brokers and dealers. After the offering, the initial public offering price, concession and reallowance to dealers may be reduced by the representatives. No such reduction will change the amount of proceeds to be received by us as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus.
181
The following table shows the public offering price, the underwriting discounts and commissions that we are to pay the underwriters and the proceeds, before expenses, to us in connection with this offering. Such amounts are shown assuming both no exercise and full exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares.
| PER SHARE | TOTAL | |||||||||||||||
| WITHOUT OPTION TO PURCHASE ADDITIONAL SHARES | WITH OPTION TO PURCHASE ADDITIONAL SHARES | WITHOUT OPTION TO PURCHASE ADDITIONAL SHARES | WITH OPTION TO PURCHASE ADDITIONAL SHARES | |||||||||||||
Public offering price | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
Underwriting discounts and commissions paid by us | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
Proceeds to us, before expenses | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
We estimate expenses payable by us in connection with this offering, other than the underwriting discounts and commissions referred to above, will be approximately $2,475,000. We have also agreed to pay the filing fees incident to, and the fees and disbursements of counsel for the underwriters in connection with the required review by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. in an amount up to $40,000.
Determination of Offering Price
Prior to this offering, there has not been a public market for our common stock. Consequently, the initial public offering price for our common stock will be determined by negotiations between us and the representatives. Among the factors to be considered in these negotiations will be prevailing market conditions, our financial information, market valuations of other companies that we and the underwriters believe to be comparable to us, estimates of our business potential, the present state of our development and other factors deemed relevant.
We offer no assurances that the initial public offering price will correspond to the price at which the common stock will trade in the public market subsequent to the offering or that an active trading market for the common stock will develop and continue after the offering.
Listing
We have applied to have our common stock listed on The Nasdaq Global Market under the trading symbol “TCRR“.
Stamp Taxes
If you purchase shares of common stock offered in this prospectus, you may be required to pay stamp taxes and other charges under the laws and practices of the country of purchase, in addition to the offering price listed on the cover page of this prospectus.
Option to Purchase Additional Shares
We have granted to the underwriters an option, exercisable for 30 days from the date of this prospectus, to purchase, from time to time, in whole or in part, up to an aggregate of 750,000 shares from us at the public offering price set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, less underwriting discounts and commissions. If the underwriters exercise this option, each underwriter will be obligated, subject to specified conditions, to purchase a number of additional shares proportionate to that underwriter’s initial purchase commitment as indicated in the table above. This option may be exercised only if the underwriters sell more shares than the total number set forth on the cover page of this prospectus.
No Sales of Similar Securities
We, our officers, directors and holders of all or substantially all our outstanding capital stock and other securities have agreed, subject to specified exceptions, not to directly or indirectly:
| ∎ | sell, offer, contract or grant any option to sell (including any short sale), pledge, transfer, establish an open “put equivalent position” within the meaning of Rule 16a-l(h) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or |
| ∎ | otherwise dispose of any shares of common stock, options or warrants to acquire shares of common stock, or securities exchangeable or exercisable for or convertible into shares of common stock currently or hereafter owned either of record or beneficially, or |
182
| ∎ | publicly announce an intention to do any of the foregoing for a period of 180 days after the date of this prospectus without the prior written consent of the representatives. |
This restriction terminates after the close of trading of the common stock on and including the 180th day after the date of this prospectus.
The representatives may, in their sole discretion and at any time or from time to time before the termination of the 180-day period release all or any portion of the securities subject to lock-up agreements. There are no existing agreements between the underwriters and any of our shareholders who will execute a lock-up agreement, providing consent to the sale of shares prior to the expiration of the lock-up period.
Stabilization
The underwriters have advised us that they, pursuant to Regulation M under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and certain persons participating in the offering may engage in short sale transactions, stabilizing transactions, syndicate covering transactions or the imposition of penalty bids in connection with this offering. These activities may have the effect of stabilizing or maintaining the market price of the common stock at a level above that which might otherwise prevail in the open market. Establishing short sales positions may involve either “covered” short sales or “naked” short sales.
“Covered” short sales are sales made in an amount not greater than the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares of our common stock in this offering. The underwriters may close out any covered short position by either exercising their option to purchase additional shares of our common stock or purchasing shares of our common stock in the open market. In determining the source of shares to close out the covered short position, the underwriters will consider, among other things, the price of shares available for purchase in the open market as compared to the price at which they may purchase shares through the option to purchase additional shares.
“Naked” short sales are sales in excess of the option to purchase additional shares of our common stock. The underwriters must close out any naked short position by purchasing shares in the open market. A naked short position is more likely to be created if the underwriters are concerned that there may be downward pressure on the price of the shares of our common stock in the open market after pricing that could adversely affect investors who purchase in this offering.
A stabilizing bid is a bid for the purchase of shares of common stock on behalf of the underwriters for the purpose of fixing or maintaining the price of the common stock. A syndicate covering transaction is the bid for or the purchase of shares of common stock on behalf of the underwriters to reduce a short position incurred by the underwriters in connection with the offering. Similar to other purchase transactions, the underwriter’s purchases to cover the syndicate short sales may have the effect of raising or maintaining the market price of our common stock or preventing or retarding a decline in the market price of our common stock. As a result, the price of our common stock may be higher than the price that might otherwise exist in the open market. A penalty bid is an arrangement permitting the underwriters to reclaim the selling concession otherwise accruing to a syndicate member in connection with the offering if the common stock originally sold by such syndicate member are purchased in a syndicate covering transaction and therefore have not been effectively placed by such syndicate member.
Neither we nor any of the underwriters make any representation or prediction as to the direction or magnitude of any effect that the transactions described above may have on the price of our common stock. The underwriters are not obligated to engage in these activities and, if commenced, any of the activities may be discontinued at any time.
Electronic Distribution
A prospectus in electronic format may be made available by e-mail or on the web sites or through online services maintained by one or more of the underwriters or their affiliates. In those cases, prospective investors may view offering terms online and may be allowed to place orders online. The underwriters may agree with us to allocate a specific number of shares of common stock for sale to online brokerage account holders. Any such allocation for online distributions will be made by the underwriters on the same basis as other allocations. Other than the prospectus in electronic format, the information on the underwriters’ web sites and any information contained in any other web site maintained by any of the underwriters is not part of this prospectus, has not been approved and/or endorsed by us or the underwriters and should not be relied upon by investors.
183
Other Activities and Relationships
The underwriters and certain of their affiliates are full service financial institutions engaged in various activities, which may include securities trading, commercial and investment banking, financial advisory, investment management, investment research, principal investment, hedging, financing and brokerage activities. The underwriters and certain of their affiliates have, from time to time, performed, and may in the future perform, various commercial and investment banking and financial advisory services for us and our affiliates, for which they received or will receive customary fees and expenses. In addition, affiliates of SVB Leerink LLC, one of the joint book-running managers, are beneficial owners of less than 1% of our outstanding capital stock prior to giving effect to the offering.
In the ordinary course of their various business activities, the underwriters and certain of their affiliates may make or hold a broad array of investments and actively trade debt and equity securities (or related derivative securities) and financial instruments (including bank loans) for their own account and for the accounts of their customers, and such investment and securities activities may involve securities and/or instruments issued by us and our affiliates. If the underwriters or their respective affiliates have a lending relationship with us, they routinely hedge their credit exposure to us consistent with their customary risk management policies. The underwriters and their respective affiliates may hedge such exposure by entering into transactions which consist of either the purchase of credit default swaps or the creation of short positions in our securities or the securities of our affiliates, including potentially the common stock offered hereby. Any such short positions could adversely affect future trading prices of the common stock offered hereby. The underwriters and certain of their respective affiliates may also communicate independent investment recommendations, market color or trading ideas and/or publish or express independent research views in respect of such securities or instruments and may at any time hold, or recommend to clients that they acquire, long and/or short positions in such securities and instruments.
Selling Restrictions
Canada
Resale Restrictions
The distribution of our shares of common stock in Canada is being made only in the provinces of Ontario, Quebec, Alberta and British Columbia on a private placement basis exempt from the requirement that we prepare and file a prospectus with the securities regulatory authorities in each province where trades of these securities are made. Any resale of the shares of common stock in Canada must be made under applicable securities laws which may vary depending on the relevant jurisdiction, and which may require resales to be made under available statutory exemptions or under a discretionary exemption granted by the applicable Canadian securities regulatory authority. Purchasers are advised to seek legal advice prior to any resale of the securities.
Representations of Canadian Purchasers
By purchasing our shares of common stock in Canada and accepting delivery of a purchase confirmation, a purchaser is representing to us and the dealer from whom the purchase confirmation is received that:
| ∎ | the purchaser is entitled under applicable provincial securities laws to purchase the shares of common stock without the benefit of a prospectus qualified under those securities laws as it is an “accredited investor” as defined under National Instrument 45-106—Prospectus Exemptions, |
| ∎ | the purchaser is a “permitted client” as defined in National Instrument 31-103—Registration Requirements, Exemptions and Ongoing Registrant Obligations, |
| ∎ | where required by law, the purchaser is purchasing as principal and not as agent, and |
| ∎ | the purchaser has reviewed the text above under Resale Restrictions. |
Conflicts of Interest
Canadian purchasers are hereby notified that the underwriters are relying on the exemption set out in section 3A.3 or 3A.4, if applicable, of National Instrument 33-105—Underwriting Conflicts from having to provide certain conflict of interest disclosure in this document.
Statutory Rights of Action
Securities legislation in certain provinces or territories of Canada may provide a purchaser with remedies for rescission or damages if the prospectus (including any amendment thereto) such as this document contains a
184
misrepresentation, provided that the remedies for rescission or damages are exercised by the purchaser within the time limit prescribed by the securities legislation of the purchaser’s province or territory. The purchaser of these securities in Canada should refer to any applicable provisions of the securities legislation of the purchaser’s province or territory for particulars of these rights or consult with a legal advisor.
Enforcement of Legal Rights
All of our directors and officers as well as the experts named herein may be located outside of Canada and, as a result, it may not be possible for Canadian purchasers to effect service of process within Canada upon us or those persons. All or a substantial portion of our assets and the assets of those persons may be located outside of Canada and, as a result, it may not be possible to satisfy a judgment against us or those persons in Canada or to enforce a judgment obtained in Canadian courts against us or those persons outside of Canada.
Taxation and Eligibility for Investment
Canadian purchasers of our shares of common stock should consult their own legal and tax advisors with respect to the tax consequences of an investment in the shares in their particular circumstances and about the eligibility of the shares for investment by the purchaser under relevant Canadian legislation.
Australia
This prospectus is not a disclosure document for the purposes of Australia’s Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) of Australia, or Corporations Act, has not been lodged with the Australian Securities & Investments Commission and is only directed to the categories of exempt persons set out below. Accordingly, if you receive this prospectus in Australia:
You confirm and warrant that you are either:
| ∎ | a “sophisticated investor” under section 708(8)(a) or (b) of the Corporations Act; |
| ∎ | a “sophisticated investor” under section 708(8)(c) or (d) of the Corporations Act and that you have provided an accountant’s certificate to the company which complies with the requirements of section 708(8)(c)(i) or (ii) of the Corporations Act and related regulations before the offer has been made; or |
| ∎ | a “professional investor” within the meaning of section 708(11)(a) or (b) of the Corporations Act. |
To the extent that you are unable to confirm or warrant that you are an exempt sophisticated investor or professional investor under the Corporations Act any offer made to you under this prospectus is void and incapable of acceptance.
You warrant and agree that you will not offer any of the shares issued to you pursuant to this prospectus for resale in Australia within 12 months of those securities being issued unless any such resale offer is exempt from the requirement to issue a disclosure document under section 708 of the Corporations Act.
European Economic Area
In relation to each member state of the European Economic Area which has implemented the Prospectus Directive, each referred to herein as a Relevant Member State, with effect from and including the date on which the Prospectus Directive is implemented in that Relevant Member State, referred to herein as the Relevant Implementation Date, no offer of any securities which are the subject of the offering contemplated by this prospectus has been or will be made to the public in that Relevant Member State other than any offer where a prospectus has been or will be published in relation to such securities that has been approved by the competent authority in that Relevant Member State or, where appropriate, approved in another Relevant Member State and notified to the relevant competent authority in that Relevant Member State in accordance with the Prospectus
Directive, except that with effect from and including the Relevant Implementation Date, an offer of such securities may be made to the public in that Relevant Member State:
| ∎ | to any legal entity which is a “qualified investor” as defined in the Prospectus Directive; |
| ∎ | to fewer than 100 or, if the Relevant Member State has implemented the relevant provision of the 2010 PD Amending Directive, 150, natural or legal persons (other than qualified investors as defined in the Prospectus Directive), as permitted under the Prospectus Directive, subject to obtaining the prior consent of the representatives of the underwriters for any such offer; or |
| ∎ | in any other circumstances falling within Article 3(2) of the Prospectus Directive, |
185
provided that no such offer of securities shall require the Company or any of the underwriters to publish a prospectus pursuant to Article 3 of the Prospectus Directive or supplement a prospectus pursuant to Article 16 of the Prospectus Directive.
For the purposes of this provision, the expression an “offer to the public” in relation to any securities in any Relevant Member State means the communication in any form and by any means of sufficient information on the terms of the offer and the securities to be offered so as to enable an investor to decide to purchase or subscribe the securities, as the same may be varied in that Relevant Member State by any measure implementing the Prospectus Directive in that Relevant Member State and the expression “Prospectus Directive” means Directive 2003/71/EC (and amendments thereto, including the 2010 PD Amending Directive, to the extent implemented in the Relevant Member State), and includes any relevant implementing measure in the Relevant Member State and the expression “2010 PD Amending Directive” means Directive 2010/73/EU.
PRC
This prospectus has not been and will not be circulated or distributed in the PRC, and no securities may be offered or sold, or will be offered or sold, to any person for re-offering or resale, directly or indirectly, to any resident of the PRC except pursuant to applicable laws and regulations of the PRC.
Hong Kong
No securities have been offered or sold, and no securities may be offered or sold, in Hong Kong, by means of any document, other than to persons whose ordinary business is to buy or sell shares or debentures, whether as principal or agent; or to “professional investors” as defined in the Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571) of Hong Kong (SFO) and any rules made under that Ordinance; or in other circumstances which do not result in the document being a “prospectus” as defined in the Companies Ordinance (Cap. 32) of Hong Kong (CO), or which do not constitute an offer to the public for the purpose of the CO or the SFO. No document, invitation or advertisement relating to the securities has been issued or may be issued or may be in the possession of any person for the purpose of issue (in each case whether in Hong Kong or elsewhere), which is directed at, or the contents of which are likely to be accessed or read by, the public of Hong Kong (except if permitted under the securities laws of Hong Kong) other than with respect to securities which are or are intended to be disposed of only to persons outside Hong Kong or only to “professional investors” as defined in the SFO and any rules made under that Ordinance.
This prospectus has not been registered with the Registrar of Companies in Hong Kong. Accordingly, this prospectus may not be issued, circulated or distributed in Hong Kong, and the securities may not be offered for subscription to members of the public in Hong Kong. Each person acquiring the securities will be required, and is deemed by the acquisition of the securities, to confirm that he is aware of the restriction on offers of the securities described in this prospectus and the relevant offering documents and that he is not acquiring, and has not been offered any securities in circumstances that contravene any such restrictions.
Israel
This document does not constitute a prospectus under the Israeli Securities Law, 5728-1968 (the Securities Law), and has not been filed with or approved by the Israel Securities Authority. In the State of Israel, this document is being distributed only to, and is directed only at, and any offer of the shares is directed only at, (i) a limited number of persons in accordance with section 15A of the Securities Law and (ii) investors listed in the first addendum (the Addendum), to the Israeli Securities Law, consisting primarily of joint investment in trust funds, provident funds, insurance companies, banks, portfolio managers, investment advisors, members of the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange, underwriters, venture capital funds, entities with equity in excess of NIS 50 million and “qualified individuals”, each as defined in the Addendum (as it may be amended from time to time), collectively referred to as qualified investors (in each case purchasing for their own account or, where permitted under the Addendum, for the accounts of their clients who are investors listed in the Addendum). Qualified investors will be required to submit written confirmation that they fall within the scope of the Addendum, are aware of the meaning of same and agree to it.
Japan
The offering has not been and will not be registered under the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law of Japan (Law No. 25 of 1948 of Japan, as amended) (FIEL) and the Initial Purchaser will not offer or sell any securities, directly or indirectly, in Japan or to, or for the benefit of, any resident of Japan (which term as used herein means, unless otherwise provided herein, any person resident in Japan, including any corporation or other entity organized
186
under the laws of Japan), or to others for re-offering or resale, directly or indirectly, in Japan or to a resident of Japan, except pursuant to an exemption from the registration requirements of, and otherwise in compliance with, the FIEL and any other applicable laws, regulations and ministerial guidelines of Japan.
Singapore
This prospectus has not been and will not be lodged or registered with the Monetary Authority of Singapore. Accordingly, this prospectus and any other document or material in connection with the offer or sale, or the invitation for subscription or purchase of the securities may not be issued, circulated or distributed, nor may the securities be offered or sold, or be made the subject of an invitation for subscription or purchase, whether directly or indirectly, to the public or any member of the public in Singapore other than (i) to an institutional investor under Section 274 of the Securities and Futures Act, Chapter 289 of Singapore (the SFA) (ii) to a relevant person as defined under Section 275(2), or any person pursuant to Section 275(1A) of the SFA, and in accordance with the conditions, specified in Section 275 of the SFA, or (iii) otherwise pursuant to, and in accordance with the conditions of any other applicable provision of the SFA.
Where the securities are subscribed or purchased under Section 275 of the SFA by a relevant person which is:
| ∎ | a corporation (which is not an accredited investor as defined under Section 4A of the SFA) the sole business of which is to hold investments and the entire share capital of which is owned by one or more individuals, each of whom is an accredited investor; or |
| ∎ | a trust (where the trustee is not an accredited investor) whose sole purpose is to hold investments and each beneficiary is an accredited investor, |
securities (as defined in Section 239(1) of the SFA) of that corporation or the beneficiaries’ rights and interest (howsoever described) in that trust shall not be transferred within six months after that corporation or that trust has acquired the shares of common stock pursuant to an offer made under Section 275 of the SFA except:
| ∎ | to an institutional investor or to a relevant person defined in Section 275(2) of the SFA, or to any person arising from an offer referred to in Section 275(1A) or Section 276(4)(i)(B) of the SFA; |
| ∎ | where no consideration is or will be given for the transfer; |
| ∎ | where the transfer is by operation of law; |
| ∎ | as specified in Section 276(7) of the SFA; or |
| ∎ | as specified in Regulation 32 of the Securities and Futures (Offers of Investments) (Shares and Debentures) Regulations 2005 of Singapore. |
Switzerland
The securities may not be publicly offered in Switzerland and will not be listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange (SIX) or on any other stock exchange or regulated trading facility in Switzerland. This prospectus has been prepared without regard to the disclosure standards for issuance prospectuses under art. 652a or art. 1156 of the Swiss Code of Obligations or the disclosure standards for listing prospectuses under art. 27 ff. of the SIX Listing Rules or the listing rules of any other stock exchange or regulated trading facility in Switzerland. Neither this prospectus nor any other offering or marketing material relating to the securities or the offering may be publicly distributed or otherwise made publicly available in Switzerland.
Neither this prospectus nor any other offering or marketing material relating to the offering, the Company or the securities have been or will be filed with or approved by any Swiss regulatory authority. In particular, this prospectus will not be filed with, and the offer of securities will not be supervised by, the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority FINMA and the offer of securities has not been and will not be authorized under the Swiss Federal Act on Collective Investment Schemes (CISA). The investor protection afforded to acquirers of interests in collective investment schemes under the CISA does not extend to acquirers of securities.
United Kingdom
This prospectus is only being distributed to, and is only directed at, persons in the United Kingdom that are qualified investors within the meaning of Article 2(1)(e) of the Prospectus Directive that are also (i) investment professionals falling within Article 19(5) of the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (Financial Promotion)
187
Order 2005, as amended, referred to herein as the Order, and/or (ii) high net worth entities falling within Article 49(2)(a) to (d) of the Order and other persons to whom it may lawfully be communicated. Each such person is referred to herein as a Relevant Person.
This prospectus and its contents are confidential and should not be distributed, published or reproduced (in whole or in part) or disclosed by recipients to any other persons in the United Kingdom. Any person in the United Kingdom that is not a Relevant Person should not act or rely on this document or any of its contents.
188
The validity of the shares of common stock offered by this prospectus will be passed upon for us by Goodwin Procter LLP, Boston, Massachusetts. Certain legal matters relating to this offering will be passed upon for the underwriters by Wilmer Cutler Pickering Hale and Dorr LLP, New York, New York.
189
The financial statements of TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. as of December 31, 2016 and 2017 and for each of the years then ended have been included herein in reliance upon the report of KPMG LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, appearing elsewhere herein and upon the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
190
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-1 (File Number 333-229066) under the Securities Act with respect to the common stock we are offering by this prospectus. This prospectus, which constitutes part of the registration statement, does not contain all of the information included in the registration statement. For further information pertaining to us and our common stock, you should refer to the registration statement and to its exhibits. Whenever we make reference in this prospectus to any of our contracts, agreements or other documents, the references are not necessarily complete, and you should refer to the exhibits attached to the registration statement for copies of the actual contract, agreement or other document.
Upon the completion of the offering, we will be subject to the informational requirements of the Exchange Act and will file annual, quarterly and current reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. You can read our SEC filings, including the registration statement, at the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov. We also maintain a website at www.tcr2.com and upon completion of the offering, you may access, free of charge, our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to those reports, as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC. The information contained in, or that can be accessed through, our website is not part of, and is not incorporated into, this prospectus.
191
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
| PAGE | ||||
Audited Financial Statements | ||||
| F-2 | ||||
| F-3 | ||||
Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2017 | F-4 | |||
| F-5 | ||||
Statements of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2017 | F-6 | |||
| F-7 | ||||
Unaudited Interim Financial Statements | ||||
Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018 | F-21 | |||
| F-22 | ||||
| F-23 | ||||
Statements of Cash Flows for the Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 and 2018 | F-24 | |||
| F-25 | ||||
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors
TCR2 Therapeutics Inc.:
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2016 and 2017, the related statements of operations and comprehensive loss, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the years then ended and the related notes (collectively, the financial statements). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2016 and 2017, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years then ended, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ KPMG LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2017.
Cambridge, Massachusetts
September 7, 2018, except as to note 12, which date is February 1, 2019
F-2
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
(amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
| DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Assets | ||||||||
Current assets: | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 7,992 | $ | 19,811 | ||||
Investments | 8,348 | — | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 975 | 892 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current assets | 17,315 | 20,703 | ||||||
Property and equipment, net | 936 | 1,026 | ||||||
Restricted cash | — | 290 | ||||||
Deferred offering costs | — | 20 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total assets | $ | 18,251 | $ | 22,039 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit) | ||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 508 | $ | 427 | ||||
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | 458 | 804 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current liabilities | 966 | 1,231 | ||||||
Other liabilities | — | 30 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities | 966 | 1,261 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Commitments (Note 7) | ||||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock, $0.0001 par value: | ||||||||
Series A preferred stock: 45,000,000 shares authorized; 28,333,334 and 44,500,001 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively (liquidation preference of $47,102 at December 31, 2017) | 29,169 | 47,102 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total redeemable convertible preferred stock | 29,169 | 47,102 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stockholders’ equity (deficit): | ||||||||
Common stock, $0.0001 par value; 13,239,045 shares authorized; 554,484 and 612,962 shares issued at December 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively; 326,870 and 435,630 shares outstanding at December 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively | — | — | ||||||
Additionalpaid-in capital | — | — | ||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (2 | ) | — | |||||
Accumulated deficit | (11,882 | ) | (26,324 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) | (11,884 | ) | (26,324 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit) | $ | 18,251 | $ | 22,039 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements
F-3
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss
(amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
| YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||
Research and development | $ | 7,670 | $ | 9,569 | ||||
General and administrative | 2,260 | 3,611 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Loss from operations | (9,930 | ) | (13,180 | ) | ||||
Other income, net | 15 | 110 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net loss | (9,915 | ) | (13,070 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value | (787 | ) | (1,794 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (10,702 | ) | $ | (14,864 | ) | ||
|
|
|
| |||||
Other comprehensive loss: | ||||||||
Net loss | $ | (9,915 | ) | $ | (13,070 | ) | ||
Unrealized (loss) gain on investments | (2 | ) | 2 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Comprehensive loss | $ | (9,917 | ) | $ | (13,068 | ) | ||
|
|
|
| |||||
Per share information: | ||||||||
Net loss per share of common stock, basic and diluted | $ | (38.64 | ) | $ | (39.94 | ) | ||
|
|
|
| |||||
Weighted average shares outstanding, basic and diluted | 276,976 | 372,116 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Pro forma net loss per share of common stock—basic and diluted (unaudited) | $ | (2.90 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Pro forma weighted average shares outstanding (unaudited) | 5,132,506 | |||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements
F-4
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
Statements of Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2017
(amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SERIES A REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK | COMMON STOCK | ADDITIONAL PAID-IN CAPITAL | ACCUMULATED DEFICIT | ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPRE- HENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) | TOTAL STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHARES | AMOUNT | SHARES | AMOUNT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at January 1, 2016 | 5,823,530 | $ | 5,896 | 237,225 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (1,273 | ) | $ | — | $ | (1,273 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Sale of Series A preferred stock, net of issuance costs of $24 | 22,509,804 | 22,486 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reclassification of shares issued and previously subject to repurchase | — | — | 89,645 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | 93 | — | — | 93 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized loss on investments | — | — | — | — | — | — | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of Series A preferred stock to redemption value | — | 787 | — | — | (93 | ) | (694 | ) | — | (787 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | (9,915 | ) | — | (9,915 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | 28,333,334 | 29,169 | 326,870 | — | — | (11,882 | ) | (2 | ) | (11,884 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Sale of Series A preferred stock, net of issuance costs of $28 | 16,166,667 | 16,139 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reclassification of shares issued and previously subject to repurchase | — | — | 89,645 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options | — | — | 19,115 | — | 14 | — | — | 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | 408 | — | — | 408 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized gain on investments | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of Series A preferred stock to redemption value | — | 1,794 | — | — | (422 | ) | (1,372 | ) | — | (1,794 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | (13,070 | ) | — | (13,070 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2017 | 44,500,001 | $ | 47,102 | 435,630 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (26,324 | ) | $ | — | $ | (26,324 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements
F-5
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
(amounts in thousands)
| YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Operating activities: | ||||||||
Net loss | $ | (9,915 | ) | $ | (13,070 | ) | ||
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 220 | 298 | ||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 93 | 408 | ||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (222 | ) | 83 | |||||
Accounts payable | 76 | (101 | ) | |||||
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | 368 | 347 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash used in operating activities | (9,380 | ) | (12,036 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Investing activities: | ||||||||
Purchase of investments | (8,350 | ) | (6,480 | ) | ||||
Proceeds from maturity of investments | — | 14,830 | ||||||
Change in restricted cash | — | (290 | ) | |||||
Purchases of equipment | (869 | ) | (388 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (9,219 | ) | 7,672 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Financing activities: | ||||||||
Proceeds from the sale of Series A preferred stock | 22,510 | 16,167 | ||||||
Proceeds from the exercise of stock options | — | 14 | ||||||
Proceeds from the exercise of unvested stock options | — | 30 | ||||||
Payment of issuance costs | (24 | ) | (28 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash provided by financing activities | 22,486 | 16,183 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 3,887 | 11,819 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 4,105 | 7,992 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 7,992 | $ | 19,811 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Supplemental disclosure of noncash financing activities: | ||||||||
Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value | $ | 787 | $ | 1,794 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Deferred offering costs included in accounts payable | $ | — | $ | 20 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements
F-6
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
December 31, 2016 and 2017
1. Organization and Description of Business
TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. (the Company), a Delaware incorporated company, is an immunotherapy company focused on developing the next generation of novel T cell treatments for patients suffering from cancer. The Company’s principal operations are located in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
2. Liquidity
The Company’s operations to date have focused on organization and staffing, business planning, raising capital, acquiring technology and assets, manufacturing and conducting preclinical studies. The Company does not have any product candidates approved for sale and has not generated any revenue from product sales. The Company’s product candidates are subject to long development cycles and the Company may be unsuccessful in its efforts to develop, obtain regulatory approval for or market its product candidates.
The Company is subject to a number of risks including, but not limited to, the need to obtain adequate additional funding for the ongoing and planned clinical development of its product candidates. Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with pharmaceutical products and development, the Company is unable to accurately predict the timing or amount of funds required to complete development of its product candidates, and costs could exceed the Company’s expectations for a number of reasons, including reasons beyond the Company’s control.
The Company is also subject to a number of other risks including possible failure of preclinical studies or clinical trials, the need to obtain marketing approval for its product candidates, the development of new technological innovations by competitors, the need to successfully commercialize and gain market acceptance of any of the Company’s products that are approved and uncertainty around intellectual property matters. If the Company does not successfully commercialize any of its products, it will be unable to generate product revenue or achieve profitability.
The Company has incurred net losses from operations since inception and has an accumulated deficit of $26.3 million as of December 31, 2017. The Company intends to raise additional capital through the issuance of equity securities, and potentially through strategic arrangements with third parties. If financing is not available at adequate levels, the Company may need tore-evaluate its operating plans. Management believes currently available resources, which include $125.0 million in gross proceeds the Company received in connection with the 2018 sale of 62.5 million shares of the Company’s Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series B stock), will be sufficient to fund its operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements through at least twelve months from the date of issuance of these financial statements. However, if the Company’s anticipated operating results are not achieved in future periods, planned expenditures may need to be reduced in order to extend the time period over which the then-available resources would be able to fund the Company’s operations.
3. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Any reference in these notes to applicable guidance is meant to refer to GAAP as found in the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) and Accounting Standards Updates (ASU) of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
Use of estimates
The preparation of the accompanying financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates and assumptions reflected in these financial statements include, but are not limited to, impairment of long-lived assets, fair value of the royalty transfer agreement obligations and the fair value of common stock, warrants issued, and options granted under the Company’s equity-based compensation plans. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Due to the uncertainty of factors surrounding the estimates
F-7
or judgments used in the preparation of the financial statements, actual results may materially vary from these estimates. Estimates and assumptions are periodically reviewed and the effects of revisions are reflected in the financial statements in the period they are determined to be necessary.
Unaudited pro forma financial information
In the accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive loss, unaudited pro forma basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock has been prepared to give effect to the automatic conversion of all outstanding shares of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series A preferred stock) as if this proposed initial public offering had occurred on the later of the beginning of the reporting period or the issuance date of the convertible preferred stock. Further, the unaudited pro forma net loss attributable to common stockholders used in the calculation of unaudited basic and diluted pro forma net loss per share of common stock excludes the effects of accretion on redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value.
Fair value of financial instruments
At December 31, 2016 and 2017, the Company’s financial instruments included investments, accounts payable and accrued expenses. The carrying amount of accounts payable and accrued expenses approximates fair value due to the short-term maturities of these instruments. The carrying value of investments is the estimated fair value.
Cash and cash equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. As of December 31, 2016 and 2017, cash equivalents consisted of U.S treasuries, corporate bonds andgovernment-backed money market funds.
Restricted cash
Cash accounts that are restricted as to withdrawal or usage are presented as restricted cash. Restricted cash includes amounts held as a security deposit in the form of a letter of credit for the Company’s leased facility.
Investments
The Company determines the appropriate classification of its investments in debt and equity securities at the time of purchase andre-evaluates such determination at each balance sheet date. As of December 31, 2016, all investments were classified as available for sale and carried at their estimated fair value. Unrealized gains and losses are recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). The Company periodically reviews its investments in equity securities for impairment and adjusts these investments to their fair value when a decline in market value is deemed to be other than temporary. If losses on these securities are considered to be other than temporary, the loss is recognized in earnings.
Property and equipment
Property and equipment are recorded at cost. Depreciation and amortization is determined using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives ranging from 3 to 5 years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the life of the lease or the estimated useful life of the assets, whichever is shorter. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred while renewals and betterments are capitalized. When property and equipment is sold or otherwise disposed of, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are eliminated from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss is reflected in operations.
Impairment of long-lived assets
Long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future undiscounted net cash flows expected to be generated. Impairment charges are recognized at the amount by which the carrying amount of an asset exceeds the fair value of the asset. Assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of the carrying amount or the fair value less costs to sell. The Company has not recognized any impairment of long-lived assets for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017.
Deferred offering costs
The Company capitalizes costs that are directly associated within-process equity financings until such financings are consummated at which time such costs are recorded against the gross proceeds of the offering. Should thein-process equity financing be abandoned, the deferred offering costs will be expensed immediately as a charge to operating expenses in the statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
F-8
Classification and accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock
The Company has classified redeemable convertible preferred stock outside of stockholders’ equity (deficit) because the shares contain certain redemption features that are not solely within the control of the Company. The carrying value of the Series A preferred stock is being accreted to redemption value at the end of each reporting period as if the end of the reporting period were the redemption date. Increases to the carrying value of redeemable convertible preferred stock are charged to additionalpaid-in capital or, in the absence of additionalpaid-in capital, charged to accumulated deficit.
Patent costs
All patent-related costs incurred in connection with filing and prosecuting patent applications are expensed as incurred due to the uncertainty about the recovery of future expenditure. Amounts incurred are classified as general and administrative expenses.
Stock-based compensation
The Company measures employee stock-based awards at grant-date fair value and records compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period of the respective award. Generally, the Company issues awards with only service-based vesting conditions. The Company accounts for forfeitures as they occur.
The Company measures the fair value of stock-based awards granted tonon-employees on the date at which the related service is complete. Compensation expense is recognized over the period during which services are rendered by suchnon-employee consultants until completed. At the end of each financial reporting period prior to completion of the service, the fair value of these awards is remeasured using the then-current fair value of its common stock and updated assumption inputs in the Black-Scholes option-pricing model for options or the then current fair value of its common stock for restricted stock. Exercised but unvested stock-based awards are subject to repurchase by the Company at the lesser of the initial exercise price and the fair market value of the Company’s common stock at the time of repurchase. The proceeds from the shares subject to repurchase are classified as a liability and reclassified to equity as the shares vest.
Estimating the fair value of stock-based awards requires the input of subjective assumptions, including the fair value of the Company’s common stock, and, for stock options, the expected life of the options and stock price volatility. The Company uses the Black-Scholes option pricing model to value its stock option awards. The assumptions used in calculating the fair value of stock-based awards represent management’s estimates and involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management’s judgment. As a result, if factors change and management uses different assumptions, stock-based compensation expense could be materially different for future awards.
The Company classifies stock-based compensation expense in its statements of operations and comprehensive loss in the same manner in which the award recipient’s payroll costs are classified or in which the award recipient’s service payments are classified.
Research and development expenses
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred and consist primarily of funds paid to third parties for the provision of services for product candidate development, clinical and preclinical development and related supply and manufacturing costs, and regulatory compliance costs. At the end of the reporting period, the Company compares payments made to third party service providers to the estimated progress toward completion of the research or development objectives. Such estimates are subject to change as additional information becomes available. Depending on the timing of payments to the service providers and the progress that the Company estimates has been made as a result of the service provided, the Company may record net prepaid or accrued expense relating to these costs.
Upfront milestone payments made to third parties who perform research and development services on the Company’s behalf are expensed as services are rendered.
Income taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the
F-9
enactment date. A reduction in the carrying value of the net deferred tax assets is required when it is not more likely than not that such deferred tax assets are realizable.
Net loss per share
Basic and diluted net loss per common share is determined by dividing net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding during the period The Company’s outstanding redeemable convertible preferred stock contractually entitles the holders of such shares to participate in distributions but contractually does not require the holders of such shares to participate in losses of the Company. Similarly, restricted stock awards granted by the Company entitle the holder of such awards to dividends declared or paid by the board of directors, regardless of whether such awards are unvested, as if such shares were outstanding shares of common stock at the time of the dividend. However, the unvested restricted stock awards are not entitled to share in the residual net assets (deficit) of the Company. Accordingly, in periods in which the Company reports a net loss attributable to common stockholders, diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is the same as basic net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, since dilutive shares of common stock are not assumed to have been issued if their effect is anti-dilutive. Therefore, the weighted-average shares used to calculate both basic and diluted loss per share are the same.
The following potentially dilutive securities, on an as converted basis have been excluded from the computation of diluted weighted-average shares outstanding as of December 31, 2016 and 2017, as they would be antidilutive:
| YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock | 4,574,455 | 7,184,588 | ||||||
Stock options | 596,141 | 1,223,744 | ||||||
Unvested shares of restricted stock | 227,614 | 137,244 | ||||||
Common stock warrants | 42,761 | 373,061 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total | 5,440,971 | 8,918,637 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Unaudited pro forma net loss per share of common stock is computed using the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding and assumes the conversion of 44,500,001 shares of Series A preferred stock as though the conversion had occurred on January 1, 2017 or the original issuance date, if later.
Comprehensive loss
Comprehensive loss is defined as the change in equity of a business enterprise during a period from transactions and other events and circumstances fromnon-owner sources (which excludes investments from owners). The Company’s only element of other comprehensive loss is unrealized gains and losses on investments.
Segment information
Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise about which separate discrete information is available for evaluation by the chief operating decision maker, or decision-making group, in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Company views its operations and manages its business in one segment.
Recently adopted accounting pronouncements
In March 2018, the FASB issued ASU2018-05, which amends Income Taxes (Topic 740) by incorporating the Securities and Exchange Commission’s (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin 118 (SAB 118) issued on December 22, 2017. SAB 118 provide guidance on accounting for the effects of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (Tax Act). The Company recognized the income tax effects of the Tax Act in the 2017 financial statements in accordance with SAB 118. See Note 11 of the financial statements for additional information.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU2016-09, Compensation-Stock Compensation: Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting. This standard will require entities to recognize all excess tax benefits and tax deficiencies in the statement of operations as a discrete item in the reporting period in which they occur. The standard also allows an employer to withhold up to the maximum statutory tax rate and still qualify for equity
F-10
classification. Classification of excess tax benefits on the statement of cash flows should be classified as an operating activity, and employee taxes paid when an employer withholds shares fortax-withholding purposes should be classified as a financing activity. The provisions that affect the statement of operations will be effective prospectively in the year of adoption and the provisions that affect the statement of cash flows will be effective retrospectively. The Company adopted this standard effective January 1, 2017 and it had no impact on the Company’s financial statements and related disclosures.
In August 2014, the FASB issued ASU2014-15, Disclosure of Uncertainties about an Entity’s Ability to Continue as a Going Concern. The amendments in this update explicitly require a company’s management to assess an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern, and to provide related footnote disclosures in certain circumstances. The standard was effective in the first annual period ending after December 15, 2016. The Company adopted this standard effective January 1, 2017 and it had no impact on the Company’s financial statements and related disclosures.
Recently issued accounting pronouncements
JOBS Act Accounting Election
The Company is an emerging growth company, as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the JOBS Act). Under the JOBS Act, emerging growth companies can delay adopting new or revised accounting standards issued subsequent to the enactment of the JOBS Act until such time as those standards apply to private companies. The Company has elected to use this extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards that have different effective dates for public and private companies until the earlier of the date that it is (i) no longer an emerging growth company or (ii) affirmatively and irrevocably opt out of the extended transition period provided in the JOBS Act. As a result, these financial statements may not be comparable to companies that comply with the new or revised accounting pronouncements as of public company effective dates.
In June 2018, the FASB issued ASU2018-07, Compensation — Stock Compensation (Topic 718) Improvements toNon-employee Share-Based Payment Accounting. The amendments in this update expand the scope of Topic 718 to include share-based payment transactions for acquiring goods and services fromnon-employees. Under this ASU, an entity should apply the requirements of Topic 718 tonon-employee awards except for specific guidance on inputs to an option pricing model and the attribution of costs (that is, the period of time over which share-based payment awards vest and the pattern of cost recognition over that period). The guidance is applicable to public business entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018 including interim periods within that fiscal year. For all other entities, the amendments are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020. The Company is currently evaluating the effect that this guidance will have on its financial statements and related disclosures.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230) Restricted Cash, which requires entities to show the changes in the total of cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents in the statement of cash flows. Entities will no longer present transfers between cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents in the statement of cash flows. The guidance is applicable to public business entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017 and interim periods within those fiscal years. For all other entities, the amendments are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019 with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect that this guidance will have on its financial statements and related disclosures.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230) Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments, which will make eight targeted changes to how cash receipts and cash payments are presented and classified in the statement of cash flows. This standard is effective for public business entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. For all other entities, the amendments are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019 and will require adoption on a retrospective basis unless it is impracticable to apply, in which case the Company would be required to apply the amendments prospectively as of the earliest date practicable. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of the adoption of this standard on its financial statements and related disclosures.
F-11
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). The FASB issued the update to require the recognition of lease assets and liabilities on the balance sheet of lessees. The standard will be effective for public business entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018 and interim periods within those fiscal years. For all other entities, the amendments are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020. This ASU requires a modified retrospective transition method with the option to elect a package of practical expedients. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of the adoption of this standard on its financial statements and related disclosures.
4. Investments and Fair Value Measurements
As of December 31, 2017, there were no investments outstanding. As of December 31, 2016, investments were comprised of the following (in thousands):
| AMORTIZED COST | UNREALIZED GAINS | UNREALIZED LOSSES | FAIR VALUE | |||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | $ | 3,867 | $ | — | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 3,866 | |||||||
Commercial paper | 3,733 | — | (1 | ) | 3,732 | |||||||||||
Asset backed securities | 750 | — | — | 750 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| $ | 8,350 | $ | — | $ | (2 | ) | $ | 8,348 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
The Company follows FASB’s accounting guidance on fair value measurements for financial assets and liabilities measured on a recurring basis. The guidance requires fair value measurements to be classified and disclosed in one of the following three categories:
Level 1—Quoted prices (unadjusted in active markets for identical assets or liabilities)
Level 2—Inputs other than quoted prices in active markets that are observable either directly or indirectly
Level 3—Unobservable inputs in which there is little or no market data, which require the Company to develop its own assumptions.
This hierarchy requires the use of observable market data when available and to minimize the use of unobservable inputs when determining fair value.
The Company has classified assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as follows (in thousands):
| DECEMBER 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENT BASED ON | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CARRYING AMOUNT | FAIR VALUE | QUOTED PRICES IN ACTIVE MARKETS (LEVEL 1) | SIGNIFICANT OTHER OBSERVABLE INPUTS (LEVEL 2) | SIGNIFICANT UNOBSERVABLE INPUTS (LEVEL 3) | ||||||||||||||||
Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash equivalents (1) | $ | 7,611 | $ | 7,611 | $ | 4,075 | $ | 3,536 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 3,866 | 3,866 | — | 3,866 | — | |||||||||||||||
Commercial paper | 3,732 | 3,732 | — | 3,732 | — | |||||||||||||||
Asset backed securities | 750 | 750 | — | 750 | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| $ | 15,959 | $ | 15,959 | $ | 4,075 | $ | 11,884 | $ | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Includes cash sweep accounts, U.S. Treasury money market mutual fund, bank certificates of deposit, U.S. Treasury bills and corporate bonds that have a maturity of three months or less from the original acquisition date. |
F-12
| DECEMBER 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENT BASED ON | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CARRYING AMOUNT | FAIR VALUE | QUOTED PRICES IN ACTIVE MARKETS (LEVEL 1) | SIGNIFICANT OTHER OBSERVABLE INPUTS (LEVEL 2) | SIGNIFICANT UNOBSERVABLE INPUTS (LEVEL 3) | ||||||||||||||||
Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash equivalents (2) | $ | 19,107 | $ | 19,107 | $ | 18,107 | $ | 1,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| $ | 19,107 | $ | 19,107 | $ | 18,107 | $ | 1,000 | $ | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (2) | Includes cash sweep accounts, U.S. Treasury money market mutual fund, bank certificates of deposit, U.S. Treasury bills and corporate bonds that have a maturity of three months or less from the original acquisition date. |
5. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, net, consisted of (in thousands):
| DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Laboratory equipment | $ | 1,086 | $ | 1,312 | ||||
Computer hardware and equipment | 79 | 105 | ||||||
Constructionin-process | — | 136 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| 1,165 | 1,553 | |||||||
Less: accumulated depreciation | (229 | ) | (527 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| $ | 936 | $ | 1,026 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Depreciation expense was $0.2 million and $0.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively.
6. Accrued Expenses and Other Current Liabilities
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities consisted of (in thousands):
| DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Employee compensation and related benefits | $ | 364 | $ | 686 | ||||
Professional fees | 15 | 37 | ||||||
Other | 79 | 81 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| $ | 458 | $ | 804 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
7. Commitments and Contingencies
Leases
The Company recognizes rent expense on a straight-line basis over the lease period and has accrued for rent expense incurred but not yet paid. Landlord allowances for tenant improvements are deferred and recognized as a reduction to rent expense on a straight-line basis and over the remaining lease term. The Company leases its office and laboratory facilities in Cambridge, Massachusetts under anon-cancelable operating lease agreement that expired in April 2018. Rent expense was $1.1 million and $1.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, respectively. The Company entered into a new lease agreement in March 2018 as discussed further in Note 12.
F-13
Employee benefit plan
The Company maintains a defined contribution 401(k) plan (the 401(k) Plan) in which employees may contribute a portion of their compensation, subject to statutory maximum contribution amounts. The Company assumes all administrative costs of the 401(k) Plan. For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, the expense relating to the matching contribution was $41,000 and $61,000, respectively.
Litigation
The Company is not currently party to any material legal proceedings. At each reporting date, the Company evaluates whether or not a potential loss amount or a potential range of loss is probable and reasonably estimable under the provisions of the authoritative guidance that addresses accounting for contingencies. The Company expenses as incurred the costs related to such legal proceedings.
Royalty transfer agreement
In connection with the sale of Series A preferred stock (see Note 8), certain investors are entitled to receive, in the aggregate, a royalty from the Company equal to one percent of (i) all global net sales of any Company products and (ii) any license income on intellectual property that was in existence at the time of the Series A preferred stock financing. The Company has elected to account for this liability at fair value with changes recognized in earnings. Given the early stage nature of the underlying technology and inherent risks associated with obtaining regulatory approval and achieving commercialization, the Company ascribed no value to the royalty agreement at inception and at December 31, 2016 and 2017. The Company currently does not have any net sales or license income and as a result has paid no royalties under this obligation as of December 31, 2017 nor has the Company accrued any liability as of December 31, 2017.
8. Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
Common stock
Each share of common stock entitles the holder to one vote on all matters submitted to a vote of the Company’s stockholders. Subject to the rights of holders of redeemable convertible preferred stock, common stockholders are entitled to receive dividends, as may be declared by the board of directors, if any. No dividends had been declared through December 31, 2017.
During the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, the Company reclassified to equity 89,645 and 89,645 shares of restricted common stock held at par that were issued upon the exercise of stock options and previously subject to repurchase, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company issued 19,115 shares of common stock in connection with the exercise of stock options. As of December 31, 2016 and 2017, there were 227,614 and 177,332 shares of common stock purchased but not presented as outstanding, respectively, as they remain subject to repurchase until they vest.
Redeemable convertible preferred stock
In 2015, the Company entered into a Series A preferred stock purchase agreement and initially sold 5,823,530 shares. During the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, the Company sold 22,509,804 and 16,166,667 shares, respectively, of its Series A preferred stock at a price of $1.00 per share in exchange for gross cash proceeds of $22.5 million and $16.2 million, respectively. Included in the Series A preferred stock purchase agreement, the investor is required to purchase additional shares upon the achievement of certain Company milestones. The Company evaluated the future commitment obligations at original issuance and determined they were not freestanding instruments as they were not legally detachable. The future commitment obligations were also evaluated as embedded derivatives and determined they did not meet the definition of a derivative instrument for which bifurcation would be required.
Conversion
Each share of Series A preferred stock is convertible, at the option of the holder, into shares of common stock, on aone-to-one basis, subject to adjustment for certain dilutive events. The conversion price may be adjusted to prevent dilution of the Series A preferred stock.
The preferred stock is also mandatorily convertible upon the closing of an initial public offering and proceeds exceeding $50.0 million or by a written election by the majority of the Series A stockholders.
F-14
Redemption
At the election of a majority of the Series A stockholders, the Series A preferred stock is redeemable at any time on or after October 16, 2020. The Series A preferred stock may be redeemed at a price equal to the greater of (a) the original issuance price, plus any cumulative dividends accrued but unpaid thereon, whether or not declared, or (b) the fair market value as of the date of the redemption.
Dividends
The holders of shares of Series A preferred stock are entitled to receive cumulative dividends of 6% from the date of issuance. Accumulated dividends are payable only when and if declared by the Board of Directors, in preference to dividends paid to holders of common stock. The dividend preference for Series A preferred stock is $0.06 per share, as adjusted for recapitalizations. No dividends have been declared through December 31, 2017.
Liquidation
In the event of a liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, either voluntary or involuntary, or in the event of a deemed liquidation event, which includes a sale of the Company as defined in the Company’s certificate of incorporation, holders of Series A preferred stock are entitled to receive, in preference to all other stockholders, an amount equal to their original investment amount plus any declared and unpaid dividends. If upon the occurrence of such event, the assets and funds available for distribution are insufficient to pay such holders the full amount to which they are entitled, then the entire assets and funds legally available for distribution shall be distributed ratably among the holders of the Series A preferred stock in proportion to the full amounts to which they would otherwise be entitled.
After payment of the liquidation preference on shares of Series A preferred stock has been made, any remaining assets would be distributed ratably to common and Series A stockholders, on anas-converted basis.
9. Stock-based Compensation
The Company issues stock-based awards pursuant to its 2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan, as amended (the “Plan”). The maximum number of authorized shares to be issued under the Plan was 1,263,110. As of December 31, 2017, there were 28,232 shares of common stock available for future issuance. The amount, terms of grants, and exercisability provisions are determined and set by the Company’s board of directors. The term of the options may be up to 10 years, and options are exercisable in cash or as otherwise determined by the board of directors. Generally, options and restricted stock awards vest over a four-year period.
The Company recorded stock-based compensation expense in the following expense categories of its accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive loss for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017 (in thousands):
| DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Research and development | $ | 7 | $ | 43 | ||||
General and administrative | 86 | 365 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| $ | 93 | $ | 408 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
F-15
Stock options
The following table summarizes the activity related to stock option grants to employees andnon-employees for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017:
| SHARES | WEIGHTED AVERAGE EXERCISE PRICE PER SHARE | WEIGHTED AVERAGE REMAINING CONTRACTUAL LIFE (IN YEARS) | ||||||||||
Balance at January 1, 2016 | — | $ | — | |||||||||
Granted | 615,830 | 0.74 | ||||||||||
Forfeited | (19,689 | ) | 0.74 | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 596,141 | 0.74 | 9.9 | |||||||||
Granted | 690,723 | 0.74 | ||||||||||
Exercised | (19,115 | ) | 0.74 | |||||||||
Forfeited | (44,005 | ) | 0.74 | |||||||||
|
| |||||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2017 | 1,223,744 | $ | 0.74 | 9.5 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2017 | 151,297 | $ | 0.74 | 8.9 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2017 | 1,223,744 | $ | 0.74 | 9.5 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
The 1,223,744 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of options outstanding as of December 31, 2017 in the table above includes 40,088 shares of common stock that have been issued upon exercise prior to vesting and are subject to repurchase by the Company and 8,017 options that were granted outside of the Plan.
The weighted average grant date fair value of options granted to employees, directors andnon-employee consultants during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017 was $0.50 and $1.11, respectively. As of December 31, 2017, there was $0.9 million in unrecognized compensation cost that is expected to be recognized over an estimatedweighted-average amortization period of 3.6 years. The aggregate intrinsic value of options outstanding and options exercisable as of December 31, 2017 was $1.2 million and $0.2 million, respectively.
The fair value of options is estimated using theBlack-Scholes option pricing model, which takes into account inputs such as the exercise price, the value of the underlying common stock at the grant date, expected term, expected volatility,risk-free interest rate and dividend yield. The fair value of each grant of options during the year ended December 31, 2016 and 2017 was determined using the methods and assumptions discussed below:
| ∎ | The expected term of employee options is determined using the “simplified” method, as prescribed in the SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) No. 107, whereby the expected life equals the arithmetic average of the vesting term and the original contractual term of the option due to the Company’s lack of sufficient historical data. The expected term ofnon-employee options is equal to the contractual term. |
| ∎ | The expected volatility is based on historical volatilities of similar entities within the Company’s industry which were commensurate with the expected term assumption as described in SAB No. 107. |
| ∎ | The estimated annual dividend yield is 0% because the Company has not historically paid, and does not expect for the foreseeable future to pay, a dividend on its common stock. |
| ∎ | The Company considered numerous objective and subjective factors in estimating the fair value of its common stock, including the estimated fair value of the Company’s Series A preferred stock. |
F-16
For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, the grant date fair value of all option grants was estimated at the time of grant using theBlack-Scholesoption-pricing model using the following weighted average assumptions:
| DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Risk free interest rate | 2.1% | 2.1% | ||||||
Expected term (in years) | 7.1 | 6.6 | ||||||
Expected volatility | 69.3% | 65.7% | ||||||
Annual dividend yield | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||||||
Fair value of common stock | $ | 0.74 | $ | 1.49 | ||||
Restricted stock
For restricted stock awards granted to employees, the fair value of the award is the current fair value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date, while fornon-employees, the fair value of the award isre-measured each reporting period using the then-current fair value of the Company’s common stock until performance is complete. All restricted stock grants were outside of the plan.
In the event of a termination of employment or consulting services arrangement, the unvested restricted stock awards are subject to repurchase by the Company at the lower of the purchase price paid by the holder and the then current fair value.
The following table summarizes the activity related to restricted stock grants to employees andnon-employees for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017:
| SHARES | ||||
Balance at January 1, 2016 | 317,259 | |||
Granted | — | |||
Vested | (89,645 | ) | ||
|
| |||
Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 227,614 | |||
Granted | — | |||
Vested | (89,645 | ) | ||
Forfeited | (725 | ) | ||
|
| |||
Outstanding at December 31, 2017 | 137,244 | |||
|
| |||
As of December 31, 2017, there was $0.2 million in unrecognized compensation cost that is expected to be recognized over an estimated weighted-average amortization period of 1.5 years.
Warrants
Warrants issued tonon-employees in connection with providing consulting services are issued outside of the Plan and are accounted for as stock-based compensation. The fair value of warrants is estimated using theBlack-Scholes option pricing model.
During the year ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, the Company issued 42,761 and 330,300 common stock warrants, respectively. The warrants have an initial exercise price of $0.74 per share and will expire at the earlier of ten years from the date of issuance or a change in control event as defined in the warrant agreements.
F-17
For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, the grant date fair value of all warrant grants was estimated at the time of grant using theBlack-Scholesoption-pricing model using the following weighted average assumptions:
| DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Risk free interest rate | 2.5% | 2.4% | ||||||
Expected term (in years) | 10.0 | 10.0 | ||||||
Expected volatility | 71.8% | 68.3% | ||||||
Annual dividend yield | 0.00% | 0.00% | ||||||
Fair value of common stock | $ | 0.74 | $ | 1.73 | ||||
As of December 31, 2017, there was $0.3 million in unrecognized compensation cost that is expected to be recognized over an estimatedweighted-average amortization period of 2.9 years.
10. Income taxes
Subject to the limitations described below, at December 31, 2017, we have cumulative net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $1.8 million and $1.4 million available to reduce federal and state taxable income, which expire through 2037. In addition, we have cumulative federal and state tax credit carryforwards of $0.4 million and $0.4 million, respectively, available to reduce federal and state income taxes which expire through 2037 and 2032, respectively.
Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the Code) provides for limitation on the use of net operating loss and research and development tax credit carryforwards following certain ownership changes (as defined in Code) that could limit the Company’s ability to utilize these carryforwards. Pursuant to Section 382 of the Code, an ownership change occurs when the stock ownership of a 5% stockholder increases by more than 50% over a three-year testing period. The Company may have experienced various ownership changes, as defined by the Code, as a result of past financings and may in the future experience an ownership change. Accordingly, the Company’s ability to utilize the aforementioned carryforwards may be limited. Additionally, U.S. tax laws limit the time during which these carryforwards may be applied against future taxes. The Company has not performed an Internal Revenue Code Section 383 study in connection with changes in control.
The components of net deferred income tax assets as of December 31, 2016 and 2017 are as follows (in thousands):
| DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
Accrued expenses and other | $ | 143 | $ | 187 | ||||
Capitalized costs | 4,077 | 5,879 | ||||||
Research and development credits | 175 | 732 | ||||||
Net operating loss carryforwards | 139 | 471 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total deferred tax assets | $ | 4,534 | $ | 7,269 | ||||
Deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||||
Depreciation | (16 | ) | (15 | ) | ||||
Other temporary differences | (34 | ) | (74 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total deferred tax liabilities | (50 | ) | (90 | ) | ||||
Less: valuation allowance | (4,484 | ) | (7,180 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total net deferred tax assets (liabilities) | $ | — | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
F-18
In assessing the realizability of the net deferred tax assets, the Company considers all relevant positive and negative evidence in determining whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred income tax assets will not be realized. The realization of the gross deferred tax assets is dependent on several factors, including the generation of sufficient taxable income prior to the expiration of the net operating loss carryforwards. Management believes that it is more likely than not that the Company’s deferred income tax assets will not be realized. As such, there is a full valuation allowance against the net deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2016 and 2017. The valuation allowance increased by approximately $4.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2016 due primarily to the increase in our capitalized costs forstart-up and research and development expenditures and increased by approximately $2.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2017 due primarily to the increase in the Company’s capitalized costs forstart-up and research and development expenditures partially offset by there-measurement of our deferred tax balance following the decrease in the federal income tax rate from 34% to 21%.
In December 2017, the Tax Act was enacted. The Tax Act includes a number of changes to existing United States tax laws that impact the Company, most notably a reduction of the United States corporate income tax rate from 35% (34% for the Company) to 21% for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. The Tax Act also provides for aone-time transition tax on certain foreign earnings and the acceleration of depreciation for certain assets placed into service after September 27, 2017, as well as prospective changes beginning in 2018, including repeal of the domestic manufacturing deduction, acceleration of tax revenue recognition, capitalization of research and development expenditures, additional limitations on executive compensation and limitations on the deductibility of interest. Due to the enactment of the Tax Act, the Company reduced both its gross deferred tax assets and the related valuation allowance by $2.8 million as of December 31, 2017, resulting in no net effect on the Company’s statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2017.
The Company did not have unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2016 or December 31, 2017. The Company recognizes interest and penalties accrued on any unrecognized tax benefits as a component of income tax expense.
A reconciliation of income tax expense (benefit) at the statutory federal income tax rate and income taxes as reflected in the financial statements is as follows:
| DECEMBER 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2017 | |||||||
Federal income tax benefit at statutory rate | 34.00 | % | 34.00 | % | ||||
State income tax, net of federal benefit | 6.02 | % | 6.12 | % | ||||
Permanent differences | (0.30 | )% | (0.93 | )% | ||||
Research and development credit benefit | 0.41 | % | 2.79 | % | ||||
Federal rate change – Tax Act | (0.0 | )% | (21.36 | )% | ||||
Change in valuation allowance | (40.13 | )% | (20.62 | )% | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Effective income tax rate | — | % | — | % | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
The Company’s income tax returns remain open and subject to examination for all tax years after 2015.
Management believes that the Company does not have any uncertain tax positions that would result in a material impact on the Company’s financial statements. The Company files income tax returns in the above jurisdictions as well as the applicable state jurisdictions in the United States. There are currently no income tax examinations ongoing. If and when applicable, the Company will recognize interest and penalties on uncertain tax positions as income tax expense.
11. Related party transactions
Consulting arrangements
The majority investor in the Company is MPM Capital (MPM). In September 2015, the Company began receiving consulting and management services pursuant to agreements with three Managing Directors at MPM. For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, the Company incurred approximately $0.6 million and $0.5 million, respectively, for management and advisory services in connection with those agreements. These amounts were recorded in general and administrative expenses in the statement of operations and comprehensive loss. As of
F-19
December 31, 2016 and 2017, the Company had amounts due to related parties of approximately $0.1 million and $19,000, respectively, for management and advisory services in connection with those agreements, which are included within accounts payable on the balance sheet.
Leasing arrangements
Following its inception, the Company began leasing office space pursuant to an unwritten shared facilities and services agreement with MPM. For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2017, the Company incurred approximately $90,000 and $7,000, respectively, for facilities costs in connection with that agreement, which were recorded in general and administrative and research and development expense in the statement of operations and comprehensive loss. As of December 31, 2016 and 2017, the Company had no outstanding obligations for facilities and other pass-through costs related to that agreement. The Company ended its lease with MPM in January 2017.
12. Subsequent Events
The Company has evaluated subsequent events from the balance sheet date through February 1, 2019, the date at which the financial statements were issued, and determined there are no other items requiring disclosure except for the following:
Sale of Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock
In 2018, the Company issued an aggregate of 62.5 million shares of Series B preferred stock in exchange for gross cash proceeds of $125.0 million.
Series A preferred stock and Series B preferred stock may be redeemed at a price equal to the greater of (a) the original issuance price, plus any cumulative dividends accrued but unpaid thereon, whether or not declared, or (b) the fair market value as of the date of the redemption, in three annual installments commencing not more than 60 days after receipt of notice by holders of the Series A preferred stock and Series B preferred stock after February 2023.
In February 2018, in conjunction with the Series B preferred stock financing, the Company amended its certificate of incorporation to authorize the issuance of 107,000,001 shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share, 44,500,001 of which are designated Series A preferred stock and 65,000,000 of which are designated Series B preferred stock. In addition, the certificate of incorporation was amended to authorize the issuance of up to 20,988,730 shares of common stock at a par value of $0.0001 per share.
Lease Agreement
In March 2018, the Company began occupying office and laboratory facilities under a new lease that expires in July 2025. Under the terms of the lease, the Company was required to place $0.3 million into a restricted cash account as security for the facility, which occurred during 2017.
Future minimum rental payments under the noncancelable operating lease are as follows (in thousands):
2018 | $ | 1,143 | ||
2019 | 1,779 | |||
2020 | 1,832 | |||
2021 | 1,887 | |||
2022 | 1,944 | |||
Thereafter | 5,118 | |||
|
| |||
| $ | 13,703 | |||
|
|
2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan
In February 2018 and July 2018, the 2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan was amended to increase the number of shares reserved for issuance under the Plan by 807,259 shares and 484,355 shares, respectively.
Reverse Stock Split
On February 1, 2019, the Company effected a 1-for-6.1938 reverse stock split of its issued and outstanding shares of common stock and a proportional adjustment to the existing conversion ratios for each series of the Company’s Preferred Stock. Accordingly, all share and per share amounts for all periods presented in the accompanying financial statements and notes thereto have been adjusted retroactively, where applicable, to reflect this reverse stock split and adjustment of the preferred stock conversion ratios.
F-20
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
(amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
| DECEMBER 31, 2017 | SEPTEMBER 30, 2018 | PRO FORMA SEPTEMBER 30, 2018 | ||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) | |||||||||||
Assets | ||||||||||||
Current assets: | ||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 19,811 | $ | 107,769 | $ | 107,769 | ||||||
Investments | — | 23,229 | 23,229 | |||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 892 | 392 | 392 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total current assets | 20,703 | 131,390 | 131,390 | |||||||||
Property and equipment, net | 1,026 | 1,791 | 1,791 | |||||||||
Restricted cash | 290 | 293 | 293 | |||||||||
Deferred offering costs | 20 | 1,194 | 1,194 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total assets | $ | 22,039 | $ | 134,668 | $ | 134,668 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ (deficit) equity | ||||||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 427 | $ | 1,509 | $ | 1,509 | ||||||
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | 804 | 2,283 | 2,283 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total current liabilities | 1,231 | 3,792 | 3,792 | |||||||||
Other liabilities | 30 | 412 | 412 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total liabilities | 1,261 | 4,204 | 4,204 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Commitments (Note 7) | ||||||||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock, $0.0001 par value: | ||||||||||||
Series A preferred stock: 45,000,000 and 44,500,001 shares authorized at December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018, respectively; 44,500,001 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018 respectively (liquidation value of $49,099 at September 30, 2018) | 47,102 | 66,750 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Series B preferred stock: No shares and 62,500,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018, respectively; No shares and 62,500,000 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018, respectively (liquidation value of $129,000 at September 30, 2018) | — | 138,750 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total redeemable convertible preferred stock | 47,102 | 205,500 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Stockholders’ (deficit) equity; | ||||||||||||
Common stock, $0.0001 par value; 13,239,045 and 20,988,730 shares authorized at December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018, respectively; 612,962 and 908,390 shares issued at December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018, respectively; 435,630 and 681,005 shares outstanding at December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018, respectively | — | — | 2 | |||||||||
Additionalpaid-in capital | — | — | 205,498 | |||||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | — | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | |||||||
Accumulated deficit | (26,324 | ) | (75,033 | ) | (75,033 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total stockholders’ (deficit) equity | (26,324 | ) | (75,036 | ) | 130,464 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ (deficit) equity | $ | 22,039 | $ | 134,668 | $ | 134,668 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
See accompanying notes to unaudited interim financial statements
F-21
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss
(amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
(unaudited)
| NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2018 | |||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||
Research and development | $ | 6,822 | $ | 13,454 | ||||
General and administrative | 2,321 | 4,558 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Loss from operations | (9,143 | ) | (18,012 | ) | ||||
Other income, net | 85 | 1,451 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net loss | (9,058 | ) | (16,561 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value | (1,272 | ) | (33,568 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (10,330 | ) | $ | (50,129 | ) | ||
|
|
|
| |||||
Other comprehensive (income) loss: | ||||||||
Net loss | $ | (9,058 | ) | $ | (16,561 | ) | ||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments | 2 | (3 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Comprehensive loss | $ | (9,056 | ) | $ | (16,564 | ) | ||
|
|
|
| |||||
Per share information: | ||||||||
Net loss per share of common stock, basic and diluted | $ | (28.78 | ) | $ | (83.83 | ) | ||
|
|
|
| |||||
Weighted average shares outstanding, basic and diluted | 358,914 | 597,964 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Pro forma net loss per share of common stock—basic and diluted | $ | (3.34 | ) | |||||
|
| |||||||
Pro forma weighted average shares outstanding | 15,014,479 | |||||||
|
| |||||||
See accompanying notes to unaudited interim financial statements
F-22
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
Statements of Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
Period ended September 30, 2017 and 2018
(amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
(unaudited)
| Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Total Stockholders' Equity (Deficit) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Series A | Common Stock | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | 28,333,334 | $ | 29,169 | 326,870 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (11,882 | ) | $ | (2 | ) | $ | (11,884 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Vesting of restricted stock | — | — | 67,235 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options and warrants | — | — | 4,615 | — | 3 | — | — | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | — | — | — | 130 | — | — | 130 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments | — | — | — | — | — | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of redeemable preferred stock to redemption value | — | 1,272 | — | (133 | ) | — | (1,139 | ) | (1,272 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | (9,058 | ) | — | (9,058 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at September 30, 2017 | 28,333,334 | $ | 30,441 | 398,720 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (20,940 | ) | $ | (1,139 | ) | $ | (22,079 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Total Stockholders' Equity (Deficit) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Series A | Series B | Common Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2017 | 44,500,001 | $ | 47,102 | — | $ | — | 435,630 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (26,324 | ) | $ | — | $ | (26,324 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Sale of Series B preferred stock, net of issuance costs of $170 | — | — | 62,500,000 | 124,830 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reclassification of shares issued and previously subject to repurchase | — | — | — | — | 66,964 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options and warrants | — | — | — | — | 178,411 | — | 132 | — | — | 132 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,288 | — | — | 1,288 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on investments | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of redeemable preferred stock to redemption value | — | 19,648 | — | 13,920 | — | — | (1,420 | ) | (32,148 | ) | — | (33,568 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (16,561 | ) | — | (16,561 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at September 30, 2018 | 44,500,001 | $ | 66,750 | 62,500,000 | $ | 138,750 | 681,005 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (75,033 | ) | $ | (3 | ) | $ | (75,036 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to unaudited interim financial statements
F-23
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
(amounts in thousands)
(unaudited)
| NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2018 | |||||||
Operating activities: | ||||||||
Net loss | $ | (9,058 | ) | $ | (16,561 | ) | ||
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 222 | 303 | ||||||
Loss on disposal of asset | — | 2 | ||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 130 | 1,288 | ||||||
Accretion of investment | 28 | (183 | ) | |||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 863 | 500 | ||||||
Accounts payable | 25 | 568 | ||||||
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | (5 | ) | 1,774 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash used in operating activities | (7,795 | ) | (12,309 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Investing activities: | ||||||||
Purchase of investments | (6,535 | ) | (36,039 | ) | ||||
Proceeds from maturity of investments | 12,110 | 12,990 | ||||||
Change in restricted cash | (291 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||
Purchases of property and equipment | (239 | ) | (938 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash provided by (used in) investing activities | 5,045 | (23,990 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Financing activities: | ||||||||
Proceeds from the sale of Series B preferred stock | — | 125,000 | ||||||
Proceeds from the exercise of stock options and warrants | 3 | 125 | ||||||
Proceeds from the exercise of unvested stock options and warrants | — | 94 | ||||||
Payment of deferred offering costs | — | (792 | ) | |||||
Payment of Series B financing costs | — | (170 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash provided by financing activities | 3 | 124,257 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents | (2,747 | ) | 87,958 | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 7,992 | 19,811 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 5,245 | $ | 107,769 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing and financing activities: | ||||||||
Property and equipment additions in accounts payable | $ | — | $ | 132 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value | $ | 1,272 | $ | 33,568 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Deferred offering costs included in accounts payable | $ | — | $ | 382 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Reclassification of early exercise liability upon vesting of options | $ | — | $ | (7 | ) | |||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to unaudited interim financial statements
F-24
TCR2 THERAPEUTICS INC.
Notes to Unaudited Interim Financial Statements
1. Organization and Description of Business
TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. (the Company), a Delaware incorporated company, is an immuno-oncology company focused onT-cell engineering. The Company’s principal operations are located in Boston, Massachusetts.
2. Liquidity
The Company’s operations to date have focused on organization and staffing, business planning, raising capital, acquiring technology and assets, and conducting preclinical studies and clinical trials. The Company does not have any product candidates approved for sale and has not generated any revenue from product sales. The Company’s product candidates are subject to long development cycles and the Company may be unsuccessful in its efforts to develop, obtain regulatory approval for or market its product candidates.
The Company is subject to a number of risks including, but not limited to, the need to obtain adequate additional funding for the ongoing and planned clinical development of its product candidates. Because of the
numerous risks and uncertainties associated with pharmaceutical products and development, the Company is unable to accurately predict the timing or amount of funds required to complete development of its product candidates, and costs could exceed the Company’s expectations for a number of reasons, including reasons beyond the Company’s control.
The Company is also subject to a number of other risks including possible failure of preclinical studies or clinical trials, the need to obtain marketing approval for its product candidates, the development of new technological innovations by competitors, the need to successfully commercialize and gain market acceptance of any of the Company’s products that are approved and uncertainty around intellectual property matters. If the Company does not successfully commercialize any of its products, it will be unable to generate product revenue or achieve profitability.
The Company has incurred net losses from operations since inception and has an accumulated deficit of $75.0 million as of September 30, 2018. The Company intends to raise additional capital through the issuance of additional equity, and potentially through strategic alliances with third parties. If financing is not available at adequate levels, the Company may need tore-evaluate its operating plans. Management believes currently available resources, which include $125.0 million in gross proceeds the Company received in connection with the March 2018 sale of 62.5 million shares of the Company’s Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series B preferred stock), will provide sufficient funds to enable the Company to meet its operating plans through 2020. However, if the Company’s anticipated operating results are not achieved in future periods, planned expenditures may need to be reduced in order to extend the time period over which the then-available resources would be able to fund the Company’s operations.
3. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The accompanying unaudited interim financial statements have been prepared in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Any reference in these notes to applicable guidance is meant to refer to GAAP as found in the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) and Accounting Standards Updates (ASU) of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
In the opinion of management, the accompanying unaudited interim financial statements include all normal and recurring adjustments (which consist primarily of accruals and estimates that impact the financial statements) which are considered necessary to present fairly the Company’s financial position as of September 30, 2018 and its results of operations and cash flows for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018. Operating results for the nine months ended September 30, 2018 are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for the year ending December 31, 2018. The unaudited interim financial statements, presented herein, do not contain the required disclosures under GAAP for annual financial statements. The accompanying unaudited interim financial statements should be read in conjunction with the annual audited financial statements and related notes as of and for the year ended December 31, 2017 found elsewhere in this prospectus.
F-25
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the accompanying financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Due to the uncertainty of factors surrounding the estimates or judgments used in the preparation of the financial statements, actual results may materially vary from these estimates. Estimates and assumptions are periodically reviewed and the effects of revisions are reflected in the financial statements in the period they are determined to be necessary.
Unaudited pro forma financial information
The accompanying unaudited pro forma balance sheet as of September 30, 2018 has been prepared to give effect to the automatic conversion of all outstanding shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock into 17,275,299 shares of common stock as if the Company’s proposed initial public offering had occurred on September 30, 2018.
In the accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive loss, unaudited pro forma basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock has been prepared to give effect to the automatic conversion of all outstanding shares of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series A preferred stock) and Series B preferred stock as if this proposed initial public offering had occurred on the later of the beginning of the reporting period or the issuance date of the convertible preferred stock. Further, the unaudited pro forma net loss attributable to common stockholders used in the calculation of unaudited basic and diluted pro forma net loss per share of common stock excludes the effects of accretion on redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value.
Fair value of financial instruments
At December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018, the Company’s financial instruments included investments, accounts payable and accrued expenses. The carrying amount of accounts payable and accrued expenses approximates fair value due to the short-term maturities of these instruments. The carrying value of investments is the estimated fair value.
Deferred offering costs
The Company capitalizes costs that are directly associated within-process equity financings until such financings are consummated at which time such costs are recorded against the gross proceeds of the offering. Should thein-process equity financing be abandoned, the deferred offering costs will be expensed immediately as a charge to operating expenses in the statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
Net loss per share
Basic and diluted net loss per common share is determined by dividing net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average common shares outstanding during the period. For all periods presented, the outstanding shares of Series A preferred stock and Series B preferred stock have been excluded from the calculation because their effects would be anti-dilutive. Therefore, the weighted-average shares used to calculate both basic and diluted loss per share are the same.
The following potentially dilutive securities, on an as converted basis, have been excluded from the computation of diluted weighted-average shares outstanding as of September 30, 2017 and 2018, as they would be antidilutive:
��
| NINE MONTHS ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2018 | |||||||
Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock | 4,574,455 | 7,184,588 | ||||||
Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | 10,090,711 | ||||||
Stock options | 667,949 | 2,013,819 | ||||||
Unvested shares of restricted stock | 159,654 | 70,280 | ||||||
Common stock warrants | 42,761 | 330,715 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total | 5,444,819 | 19,690,113 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Unaudited pro forma net loss per share of common stock is computed using the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding and assumes the conversion of 44,500,001 shares of Series A preferred stock and 62,500,000 shares of Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock as though the conversion had occurred on January 1, 2017 or the original issuance date, if later.
F-26
4. Investments and Fair Value Measurements
As of December 31, 2017, there were no investments outstanding. As of September 30, 2018, investments consisted of the following (in thousands):
| AMORTIZED COST | UNREALIZED GAINS | UNREALIZED LOSSES | FAIR VALUE | |||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | $ | 8,694 | $ | — | $ | (2 | ) | $ | 8,692 | |||||||
Commercial paper | 14,149 | 1 | (2 | ) | 14,148 | |||||||||||
Asset backed securities | 389 | — | — | 389 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| $ | 23,232 | $ | 1 | $ | (4 | ) | $ | 23,229 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
The Company follows FASB’s accounting guidance on fair value measurements for financial assets and liabilities measured on a recurring basis. The guidance requires fair value measurements to be classified and disclosed in one of the following three categories:
Level 1—Quoted prices (unadjusted in active markets for identical assets or liabilities)
Level 2—Inputs other than quoted prices in active markets that are observable either directly or indirectly
Level 3—Unobservable inputs in which there is little or no market data, which require the Company to develop its own assumptions.
This hierarchy requires the use of observable market data when available and to minimize the use of unobservable inputs when determining fair value.
The Company has classified assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as follows (in thousands):
| DECEMBER 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENT BASED ON | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CARRYING AMOUNT | FAIR VALUE | QUOTED PRICES IN ACTIVE MARKETS (LEVEL 1) | SIGNIFICANT OTHER OBSERVABLE INPUTS (LEVEL 2) | SIGNIFICANT UNOBSERVABLE INPUTS (LEVEL 3) | ||||||||||||||||
Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash equivalents(1) | $ | 19,107 | $ | 19,107 | $ | 18,107 | $ | 1,000 | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| $ | 19,107 | $ | 19,107 | $ | 18,107 | $ | 1,000 | $ | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Includes cash sweep accounts, U.S. Treasury money market mutual fund, and bank certificates of deposit and U.S. Treasury bills and corporate bonds that have a maturity of three months or less from the original acquisition date. |
| SEPTEMBER 30, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENT BASED ON | ||||||||||||||||||||
| CARRYING AMOUNT | FAIR VALUE | QUOTED PRICES IN ACTIVE MARKETS (LEVEL 1) | SIGNIFICANT OTHER OBSERVABLE INPUTS (LEVEL 2) | SIGNIFICANT UNOBSERVABLE INPUTS (LEVEL 3) | ||||||||||||||||
Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash equivalents(2) | $ | 104,954 | $ | 104,954 | $ | 102,460 | $ | 2,494 | — | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 8,692 | 8,692 | — | 8,692 | — | |||||||||||||||
Commercial paper | 14,148 | 14,148 | — | 14,148 | — | |||||||||||||||
Asset backed securities | 389 | 389 | — | 389 | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| $ | 128,183 | $ | 128,183 | $ | 102,460 | $ | 25,723 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (2) | Includes cash sweep accounts, U.S. Treasury money market mutual fund, and bank certificates of deposit and U.S. Treasury bills and corporate bonds that have a maturity of three months or less from the original acquisition date. |
F-27
5. Accrued Expenses and Other Current Liabilities
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities consisted of (in thousands):
| DECEMBER 31, 2017 | SEPTEMBER 30, 2018 | |||||||
Employee compensation and related benefits | $ | 686 | $ | 905 | ||||
Professional fees | 37 | 374 | ||||||
Contract manufacturing organization fees | — | 331 | ||||||
Contract research organization fees | — | 278 | ||||||
University partnerships | — | 97 | ||||||
Other | 81 | 298 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| $ | 804 | $ | 2,283 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
6. Commitments and Contingencies
Leases
In March 2018, the Company began occupying a new lease for larger office and laboratory facilities that expires in July 2025. Under the terms of the lease, the Company placed $0.3 million letter into a restricted cash account as security for the facility.
Future minimum rental payments under noncancelable operating leases are as follows (in thousands):
2018 | $ | 435 | ||
2019 | 1,779 | |||
2020 | 1,832 | |||
2021 | 1,887 | |||
2022 | 1,944 | |||
Thereafter | 5,118 | |||
|
| |||
| $ | 12,995 | |||
|
|
Royalty transfer agreement
In connection with the sale of Series A preferred stock (see Note 8), certain investors are entitled to receive, in the aggregate, a royalty from the Company equal to one percent of (i) all global net sales of any Company products and (ii) any license income on intellectual property that was in existence at the time of the Series A preferred stock financing. The Company has elected to account for this liability at fair value with changes recognized in earnings. Given the early stage nature of the underlying technology and inherent risks associated with obtaining regulatory approval and achieving commercialization, the Company ascribed no value to the royalty agreement at inception and at December 31, 2017 and September 30, 2018. The Company currently does not have any net sales of license income and as a result has paid no royalties under this obligation as of September 30, 2018 nor has the Company accrued any liability as of September 30, 2018.
7. Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
In February 2018, in conjunction with the Series B preferred financing, the Company amended its Certificate of Incorporation to authorize the issuance of 107,000,001 shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share, 44,500,001 of which are designated Series A preferred stock and 62,500,000 of which are designated Series B preferred stock. In addition, the Certificate of Incorporation was amended to authorize the issuance of up to 20,988,730 shares of common stock at a par value of $0.0001 per share.
The Company has elected to accrete the carrying value of the Series A and B preferred stock to redemption value at the end of each reporting period as if the end of the reporting period were the redemption date, increases to the
F-28
carrying value of redeemable convertible preferred stock are charged to additional paid-in capital or, in the absence of additional paid-in capital, charged to accumulated deficit.
Series A preferred stock and Series B preferred stock may be redeemed at a price equal to the greater of (a) the original issuance price, plus any cumulative dividends accrued but unpaid thereon, whether or not declared, or (b) the fair market value as of the date of the redemption, in three annual installments commencing not more than 60 days after receipt of notice by holders of the Series A stock and B stock after February 2023.
The fair value of the Series A preferred stock was determined to be $1.50 per share and the fair value of the Series B preferred stock was determined to be $2.22 per share as of September 30, 2018.
Series B Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock
In 2018, the Company issued an aggregate of 62.5 million shares of Series B preferred stock in exchange for gross cash proceeds of $125.0 million.
The Series B preferred stock is classified outside of stockholders’ equity (deficit) as the preferred holders may, at their option, elect to have their shares redeemed upon written notice by a majority of the preferred shareholders and at any time after February 2023.
Certain provisions of the outstanding Series B preferred stock are as follows:
Conversion
Each share of Series B preferred stock is convertible, at the option of the holder, into shares of common stock, on aone-to-one basis, subject to adjustment for certain dilutive events. The conversion price may be adjusted to prevent dilution of the Series B preferred stock.
The Series B preferred stock is also mandatorily convertible upon the closing of an initial public offering and proceeds exceeding $50.0 million or by a written election by the majority of the Series B stockholders.
Redemption
At the election of a majority of the Series B stockholders, the Series B preferred stock is redeemable at any time on or after February 2023. The Series B preferred stock may be redeemed at a price equal to the greater of (a) the original issuance price, plus any cumulative dividends accrued but unpaid thereon, whether or not declared, or (b) the fair market value as of the date of the redemption.
Dividends
The holders of shares of Series B preferred stock are entitled to receive cumulative dividends of 6% from the date of issuance. Accumulated dividends are payable only when and if declared by the Board of Directors, in preference to dividends paid to holders of Series A preferred stock and common stock. The dividend preference for Series B preferred stock is $0.12 per share, as adjusted for recapitalizations. No dividends have been declared through September 30, 2018.
Liquidation
In the event of a liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, either voluntary or involuntary, or in the event of a deemed liquidation event, which includes a sale of the Company as defined in the Company’s articles of incorporation, holders of Series B preferred stock are entitled to receive, in preference to the holders of Series A preferred stock or Common Stock, an amount equal to their original investment amount plus any declared and unpaid dividends. If upon the occurrence of such event, the assets and funds available for distribution are insufficient to pay such holders the full amount to which they are entitled, then the entire assets and funds legally available for distribution shall be distributed ratably among the holders of the Series B preferred stock in proportion to the full amounts to which they would otherwise be entitled.
After payment of the liquidation preference on shares of Series B preferred stock has been made, any remaining assets shall be distributed ratably to Series A stockholders an amount equal to their original investment amount plus any accrued dividends, whether or not declared, together with any other dividends declared but unpaid thereon.
F-29
8. Stock-based Compensation
The Company issues stock-based awards pursuant to its 2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan, as amended (the “Plan”). The maximum number of authorized shares to be issued under the Plan was 2,554,724. As of September 30, 2018, there were 403,728 shares of common stock available for future issuance. The amount, terms of grants, and exercisability provisions are determined and set by the Company’s board of directors. The term of the options may be up to 10 years, and options are exercisable in cash or as otherwise determined by the board of directors. Generally, options and restricted stock awards vest over a four-year period.
The Company measures employee andnon-employee stock-based awards at grant-date fair value and records compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the award. Stock-based awards issued tonon-employees are revalued until the award vests. The Company recorded stock-based compensation expense in the following expense categories of its accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive loss for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018 (amounts in thousands):
| SEPTEMBER 30, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2018 | |||||||
Research and development | $ | 23 | $ | 310 | ||||
General and administrative | 107 | 978 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| $ | 130 | $ | 1,288 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stock options
The following table summarizes the activity related to stock option grants to employees andnon-employees for the nine months ended September 30, 2018:
| SHARES | WEIGHTED AVERAGE EXERCISE PRICE PER SHARE | WEIGHTED AVERAGE REMAINING CONTRACTUAL LIFE (IN YEARS) | ||||||||||
Balance at January 1, 2018 | 1,223,744 | $ | 0.74 | |||||||||
Granted | 1,043,425 | $ | 5.88 | |||||||||
Exercised | (126,043 | ) | $ | 0.74 | ||||||||
Forfeited | (127,307 | ) | $ | 0.74 | ||||||||
|
| |||||||||||
Outstanding at September 30, 2018 | 2,013,819 | $ | 3.47 | 9.3 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Exercisable at September 30, 2018 | 135,298 | $ | 0.74 | 8.3 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Vested and expected to vest at September 30, 2018 | 2,013,819 | $ | 3.47 | 9.3 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
The 2,013,819 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of options outstanding as of September 30, 2018 in the table above includes 30,066 shares of common stock that have been issued upon exercise prior to vesting and are subject to repurchase by the Company.
The weighted average fair value of options granted to employees, directors andnon-employee consultants during the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018 was $0.68 and $3.59, respectively. As of September 30, 2018, there was $4.8 million in unrecognized compensation cost that is expected to be recognized over an estimatedweighted-average amortization period of 3.4 years. The aggregate intrinsic value of options outstanding and options exercisable as of September 30, 2018 was $9.1 million and $1.0 million, respectively.
F-30
The fair value of options is estimated using theBlack-Scholes option pricing model, which takes into account inputs such as the exercise price, the value of the underlying common stock at the grant date, expected term, expected volatility,risk-free interest rate and dividend yield. The fair value of each grant of options during the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018 was determined using the methods and assumptions discussed below
| ∎ | The expected term of employee options is determined using the “simplified” method, as prescribed in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s (SEC) Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) No. 107, whereby the expected life equals the arithmetic average of the vesting term and the original contractual term of the option due to the Company’s lack of sufficient historical data. The expected term ofnon-employee options is equal to the contractual term. |
| ∎ | The expected volatility is based on historical volatilities of similar entities within the Company’s industry which were commensurate with the expected term assumption as described in SAB No. 107. |
| ∎ | The estimated annual dividend yield is 0% because the Company has not historically paid, and does not expect for the foreseeable future to pay, a dividend on its common stock. |
| ∎ | The Company considered numerous objective and subjective factors in estimating the fair value of its common stock, including the estimated fair value of the Company’s Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock. |
For the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018, the grant date fair value of all option grants was estimated at the time of grant using theBlack-Scholesoption-pricing model using the following weighted average assumptions:
| SEPTEMBER 30, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2018 | |||||||
Risk free interest rate | 1.9 | % | 2.9 | % | ||||
Expected term (in years) | 6.2 | 6.1 | ||||||
Expected volatility | 66.3 | % | 64.7 | % | ||||
Annual dividend yield | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | % | ||||
Fair value of common stock | $ | 0.11 | $ | 0.58 | ||||
Restricted stock
For restricted stock awards granted to employees, the fair value of the award is the current fair value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date, while fornon-employees, the fair value of the award isre-measured each reporting period using the then-current fair value of the Company’s common stock until performance is complete. All restricted stock grants were outside of the plan.
In the event of a termination of employment or consulting services arrangement, the unvested restricted stock awards are subject to repurchase by the Company at the lower of the purchase price paid by the holder and the then current fair value. As of September 30, 2018, there was $0.5 million of unrecognized compensation related to the unvested restricted stock awards that will be recognized over a period of less than one year.
The following table summarizes the activity related to restricted stock grants to employees andnon-employees for the nine months ended September 30, 2018:
| SHARES | ||||
Balance at January 1, 2018 | 137,244 | |||
Granted | — | |||
Vested | (66,964 | ) | ||
Forfeited | — | |||
|
| |||
Outstanding at September 30, 2018 | 70,280 | |||
|
| |||
F-31
Warrants
Warrants issued tonon-employees in connection with providing consulting services are issued outside of the Plan and are accounted for as stock-based compensation. The fair value of warrants are estimated using theBlack-Scholes option pricing model and the Company records compensation expense associated with the warrants on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the warrant.
As of September 30, 2018, there was $1.1 million in unrecognized compensation cost that is expected to be recognized over an estimatedweighted-average amortization period of 2.2 years.
As of September 30, 2018, the Company had the following warrants outstanding to acquire shares of its common stock:
| SHARES | EXERCISE PRICE | EXPIRATION DATES | ||||||||||
Balance at January 1, 2018 | 373,061 | $ | 0.74 | 2026 through 2027 | ||||||||
Exercised | (169,385 | ) | $ | 0.74 | ||||||||
|
| |||||||||||
Outstanding at September 30, 2018 | 203,676 | $ | 0.74 | |||||||||
|
|
|
| |||||||||
The 169,385 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of warrants outstanding as of September 30, 2018 in the table above includes 127,039 shares of common stock that have been issued upon exercise prior to vesting and are subject to repurchase by the Company.
11. Related party transactions
Consulting agreements
The majority investor in the Company is MPM Capital (MPM). In September 2015, the Company began receiving consulting and management services pursuant to agreements with three Managing Directors at MPM. For the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018, the Company incurred approximately $0.4 million and $0.3 million, respectively, for management and advisory services in connection with those agreements. These amounts were recorded in general and administrative expenses in the statement of operations and comprehensive loss. As of September 30, 2017, the Company had amounts due to related parties of approximately $5,000, for management and advisory services in connection with those agreements, which are included within accounts payable on the balance sheet.
In October 2017, the Company entered into a consulting agreement with Globeways Holdings Limited. Dr. Morana Jovan-Embiricos is a member of our Board of Directors and has financial interests in Globeways Holdings Limited and is its founding director. Pursuant to the consulting agreement, Globeways Holdings Limited provides consulting, advisory and related services in exchange for consulting fees of $100,000 per year and reimbursement of travel-related expenses. During the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2018, the Company incurred travel-related expenses of $32,000 and incurred consulting fees and travel-related expenses of $91,000, respectively. As of September 30, 2018, the Company did not have an outstanding payable to Globeways Holdings Limited for management and advisory services, and travel-related expenses.
12. Subsequent Events
The Company has evaluated subsequent events from the balance sheet date through February 1, 2019, the date on which these financial statements were issued, and determined there are no other items requiring disclosure except for the following:
Collaboration Agreement with Cell Therapy Catapult Limited
In December 2018, the Company signed a collaboration agreement (the Collaboration Agreement) with Cell Therapy Catapult Limited (Catapult) to establish their manufacturing process in Catapult’s GMP manufacturing facility in the United Kingdom. The Company paid a £200,000 non-refundable contribution to Catapult to reserve a GMP manufacturing cleanroom in October 2018. The non-refundable contribution will be applied against the Company’s input contributions (or fees) once Catapult and the Company have determined the various inputs that Catapult will
F-32
contribute to the collaboration in order to support the Company’s manufacturing process under the Collaboration Agreement. The initial term of the Collaboration Agreement is three years and assumes an occupancy date of March 1, 2019. The Company can terminate the Collaboration Agreement earlier with twelve months’ notice and continued payment for contributions during the twelve-month termination period. The only fee fixed over the three-year term is a specified facility input contribution.The total financial contribution from the Company under the Collaboration Agreement comprises the Company’s portion of the shared costs for the infrastructure of the center and its operation as a licensed GMP facility. The Company’s exact costs under the Collaboration Agreement are based on collaboration input-related contributions and will change year to year, and are partially dependent on the inputs the Company requires from Catapult to meet the collaboration aim of establishing the Company’s manufacturing of autologous cell therapies.
In December 2018, the Company formed TRUC Securities Corporation, a wholly-owned Massachusetts corporation for the sole purpose of buying, selling, and holding securities on the Company’s behalf.
Reverse Stock Split
On February 1, 2019, the Company effected a 1-for-6.1938 reverse stock split of its issued and outstanding shares of common stock and a proportional adjustment to the existing conversion ratios for each series of the Company’s Preferred Stock. Accordingly, all share and per share amounts for all periods presented in the accompanying financial statements and notes thereto have been adjusted retroactively, where applicable, to reflect this reverse stock split and adjustment of the preferred stock conversion ratios.
F-33
Shares
Common Stock
PROSPECTUS
| Jefferies | SVB Leerink | BMO Capital Markets | ||
| Wedbush PacGrow | China Renaissance | |||
Until , 2019, all dealers that effect transactions in these securities, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This is in addition to the dealers’ obligation to deliver a prospectus when acting as underwriters and with respect to their unsold allotments or subscriptions.
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 13. Other Expenses of Issuance and Distribution
The following table sets forth the costs and expenses, other than underwriting discounts and commissions, to be paid by us in connection with the sale of the shares of common stock being registered hereby. All amounts shown are estimates except for the SEC registration fee, the FINRA filing fee and The Nasdaq Global Market initial listing fee.
SEC registration fee | $ | 11,151 | ||
FINRA filing fee | $ | 15,500 | ||
Nasdaq listing fee | $ | 25,000 | ||
Printing and engraving expenses | $ | 165,000 | ||
Legal fees and expenses | $ | 1,300,000 | ||
Accounting fees and expenses | $ | 800,000 | ||
Transfer agent and registrar fees and expenses | $ | 5,000 | ||
Miscellaneous | $ | 153,349 | ||
|
| |||
Total | $ | 2,475,000 | ||
|
|
Item 14. Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Section 145 of the Delaware General Corporation Law (the DGCL) authorizes a corporation to indemnify its directors and officers against liabilities arising out of actions, suits and proceedings to which they are made or threatened to be made a party by reason of the fact that they have served or are currently serving as a director or officer to a corporation. The indemnity may cover expenses (including attorneys’ fees) judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred by the director or officer in connection with any such action, suit or proceeding. Section 145 permits corporations to pay expenses (including attorneys’ fees) incurred by directors and officers in advance of the final disposition of such action, suit or proceeding. In addition, Section 145 provides that a corporation has the power to purchase and maintain insurance on behalf of its directors and officers against any liability asserted against them and incurred by them in their capacity as a director or officer, or arising out of their status as such, whether or not the corporation would have the power to indemnify the director or officer against such liability under Section 145.
We have adopted provisions in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws to be in effect upon the closing of this offering that limit or eliminate the personal liability of our directors to the fullest extent permitted by the DGCL, as it now exists or may in the future be amended. Consequently, a director will not be personally liable to us or our stockholders for monetary damages or breach of fiduciary duty as a director, except for liability for:
| ∎ | any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to us or our stockholders; |
| ∎ | any act or omission not in good faith or that involves intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law; |
| ∎ | any unlawful payments related to dividends or unlawful stock purchases, redemptions or other distributions; or |
| ∎ | any transaction from which the director derived an improper personal benefit. |
These limitations of liability do not alter director liability under the federal securities laws and do not affect the availability of equitable remedies such as an injunction or rescission.
II-1
In addition, our bylaws provide that:
| ∎ | we will indemnify our directors, officers and, in the discretion of our board of directors, certain employees to the fullest extent permitted by the DGCL, as it now exists or may in the future be amended; and |
| ∎ | we will advance reasonable expenses, including attorneys’ fees, to our directors and, in the discretion of our board of directors, to our officers and certain employees, in connection with legal proceedings relating to their service for or on behalf of us, subject to limited exceptions. |
We intend to enter into indemnification agreements with each of our directors and executive officers. These agreements provide that we will indemnify each of our directors, certain of our executive officers and, at times, their affiliates to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. We will advance expenses, including attorneys’ fees (but excluding judgments, fines and settlement amounts), to each indemnified director or executive officer in connection with any proceeding in which indemnification is available and we will indemnify our directors and officers for any action or proceeding arising out of that person’s services as a director or officer brought on behalf of us or in furtherance of our rights. Additionally, certain of our directors or officers may have certain rights to indemnification, advancement of expenses or insurance provided by their affiliates or other third parties, which indemnification relates to and might apply to the same proceedings arising out of such director’s or officer’s services as a director referenced herein. Nonetheless, we have agreed in the indemnification agreements that our obligations to those same directors or officers are primary and any obligation of such affiliates or other third parties to advance expenses or to provide indemnification for the expenses or liabilities incurred by those directors are secondary.
We also maintain general liability insurance which covers certain liabilities of our directors and officers arising out of claims based on acts or omissions in their capacities as directors or officers, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the Securities Act).
The underwriting agreement filed as Exhibit 1.1 to this registration statement provides for indemnification of us and our directors and officers by the underwriters against certain liabilities under the Securities Act and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Item 15. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
In the three years preceding the filing of this registration statement, we have issued the following securities that were not registered under the Securities Act:
(a) Founder Capital Stock
In June 2015 and October 2015, founders, employees and advisors purchased an aggregate of 554,484 shares of our common stock for approximately $343.44.
No underwriters were involved in the foregoing sales of securities. The sales of securities described above were deemed to be exempt from registration pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act, including Regulation D and Rule 506 promulgated thereunder, as transactions by an issuer not involving a public offering. All of the purchasers in these transactions represented to us in connection with their purchase that they were acquiring the securities for investment and not distribution, that they could bear the risks of the investment and could hold the securities for an indefinite period of time. Such purchasers received written disclosures that the securities had not been registered under the Securities Act and that any resale must be made pursuant to a registration or an available exemption from such registration. All of the foregoing securities are deemed restricted securities for the purposes of the Securities Act.
(b) Issuances of Capital Stock
In October 2015, with subsequent offerings in January 2016, October 2016, and December 2017, investors purchased an aggregate of 44,500,001 shares of our Series A preferred stock for approximately $44,500,001 at $1.00 per share.
In February 2018, with subsequent offerings in March 2018 and April 2018, investors purchased an aggregate of 62,500,000 shares of Series B preferred stock for approximately $125,000,000 at $2.00 per share.
II-2
No underwriters were involved in the foregoing sales of securities. The sales of securities described above were deemed to be exempt from registration pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act, including Regulation D and Rule 506 promulgated thereunder, as transactions by an issuer not involving a public offering. All of the purchasers in these transactions represented to us in connection with their purchase that they were acquiring the securities for investment and not distribution, that they could bear the risks of the investment and could hold the securities for an indefinite period of time. Such purchasers received written disclosures that the securities had not been registered under the Securities Act and that any resale must be made pursuant to a registration or an available exemption from such registration. All of the foregoing securities are deemed restricted securities for the purposes of the Securities Act.
(c) Grants and Exercises of Stock Options Under Equity Plans
We have granted stock options to purchase an aggregate of 2,483,655 shares of our common stock, with exercise prices ranging from $0.68 to $8.05 per share, to employees, directors and consultants pursuant to the 2015 Stock Option and Grant Plan, as amended (the 2015 Plan). Through the date of filing, 191,458 shares of common stock have been issued upon the exercise of stock options pursuant to the 2015 Plan.
The issuances of the securities described above were deemed to be exempt from registration pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act or Rule 701 promulgated under the Securities Act as transactions pursuant to compensatory benefit plans. The shares of common stock issued upon the exercise of options are deemed to be restricted securities for purposes of the Securities Act.
(d) Issuances of Warrants andNon-Plan Stock Options
In May 2017, we granted a stock option to purchase 8,017 shares of our common stock, with an exercise price of $0.74 per share to a consultant, which grant was not made pursuant to a benefits plan.
In December 2016 and December 2017, we granted warrants to purchase an aggregate of 373,061 shares of our common stock, with an exercise price of $0.74 per share, to consultants, which grants were not made pursuant to a benefits plan.
No underwriters were involved in the foregoing sales of securities. The sales of securities described above were deemed to be exempt from registration pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act, including Regulation D and Rule 506 promulgated thereunder, as transactions by an issuer not involving a public offering. All of the purchasers in these transactions represented to us in connection with their purchase that they were acquiring the securities for investment and not distribution, that they could bear the risks of the investment and could hold the securities for an indefinite period of time. Such purchasers received written disclosures that the securities had not been registered under the Securities Act and that any resale must be made pursuant to a registration or an available exemption from such registration. All of the foregoing securities are deemed restricted securities for the purposes of the Securities Act.
II-3
Item 16. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) Exhibits.
II-4
(b) Financial Statement Schedules.
None.
Item 17. Undertakings
The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes to provide to the underwriters at the closing specified in the Underwriting Agreement certificates in such denominations and registered in such names as required by the underwriters to permit prompt delivery to each purchaser.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the Registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the Registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the Registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the Registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the Registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes that:
| (1) | For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the Registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective. |
| (2) | For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. |
II-5
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. has duly caused this registration statement onForm S-1 to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Cambridge, Commonwealth of Massachusetts, on the 1st day of February, 2019.
| TCR2 Therapeutics Inc. | ||
| By: | /s/ Garry Menzel | |
Garry Menzel President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended this registration statement has been signed by the following persons in the capacities indicated on the 1st day of February, 2019.
SIGNATURE | TITLE | |
/s/ Garry Menzel Garry Menzel | President, Chief Executive Officer and Director | |
/s/ Mayur Somaiya Mayur (Ian) Somaiya | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) | |
* Ansbert Gadicke | Director | |
* Patrick Baeuerle | Director | |
* Andrew Allen | Director | |
* Morana Jovan-Embiricos | Director | |
* Neil Gibson | Director | |
* Mitchell Finer | Director | |
| By: | /s/ Garry Menzel | |
Garry Menzel Attorney-in-fact |
II-6