
Exhibit 99.2 Company Overview December 2019 1 ©2 ©201 019 K 9 KA ALE LEIDO IDO™ ™Exhibit 99.2 Company Overview December 2019 1 ©2 ©201 019 K 9 KA ALE LEIDO IDO™ ™

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended, including, without limitation, statements regarding the anticipated use of our existing cash resources, the duration for which our existing capital resources will fund our operations, the therapeutic potential of our Microbiome Metabolic Therapy (MMT) candidates, the timing of initiation, completion and reporting of results of our clinical studies and our strategy, business plans and focus. The words “may,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “project,” “potential,” “continue,” “target” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. Any forward-looking statements in this presentation are based on management’s current expectations and beliefs and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and important factors that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation, including, without limitation, those related to the Phase 2 clinical trial for KB195 for the treatment of UCD, including timeline for completion and reporting of results, the preclinical and clinical development and safety profile of our MMT candidates and timelines associated with the programs for such MMT candidates, whether and when, if at all, our MMT candidates will receive approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or other applicable regulatory agencies, if any, competition from other biotechnology companies, and other risks identified in our SEC filings, including the most recently filed 10-Q. We caution you not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date they are made. We disclaim any obligation to publicly update or revise any such statements to reflect any change in expectations or in events, conditions or circumstances on which any such statements may be based, or that may affect the likelihood that actual results will differ from those set forth in the forward-looking statements. 2 ©2019 KALEIDO™Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended, including, without limitation, statements regarding the anticipated use of our existing cash resources, the duration for which our existing capital resources will fund our operations, the therapeutic potential of our Microbiome Metabolic Therapy (MMT) candidates, the timing of initiation, completion and reporting of results of our clinical studies and our strategy, business plans and focus. The words “may,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “project,” “potential,” “continue,” “target” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. Any forward-looking statements in this presentation are based on management’s current expectations and beliefs and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and important factors that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation, including, without limitation, those related to the Phase 2 clinical trial for KB195 for the treatment of UCD, including timeline for completion and reporting of results, the preclinical and clinical development and safety profile of our MMT candidates and timelines associated with the programs for such MMT candidates, whether and when, if at all, our MMT candidates will receive approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or other applicable regulatory agencies, if any, competition from other biotechnology companies, and other risks identified in our SEC filings, including the most recently filed 10-Q. We caution you not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date they are made. We disclaim any obligation to publicly update or revise any such statements to reflect any change in expectations or in events, conditions or circumstances on which any such statements may be based, or that may affect the likelihood that actual results will differ from those set forth in the forward-looking statements. 2 ©2019 KALEIDO™
The Kaleido Opportunity Human-Centric Faster, More Broad Pipeline Proprietary Discovery & Cost-Efficient with Large Market Chemistry Development Clinical Model Opportunity Platform First Company with Novel Chemistry to Systematically Drive Functional Outputs of the Microbiome and Rapidly Translate its Promise into Solutions for Patients 3 ©2019 KALEIDO™The Kaleido Opportunity Human-Centric Faster, More Broad Pipeline Proprietary Discovery & Cost-Efficient with Large Market Chemistry Development Clinical Model Opportunity Platform First Company with Novel Chemistry to Systematically Drive Functional Outputs of the Microbiome and Rapidly Translate its Promise into Solutions for Patients 3 ©2019 KALEIDO™
Delivered Positive Clinical Data in 2019 to Support Lead Programs Further Validation of MMT Platform • KB195 – Urea Cycle Disorders 15 – RESULTS: Small open label clinical study of KB195 showed reduction in urinary N Pathologies Resulting from an excretion (biomarker of ammonia production) in 2 out of 3 well-controlled UCD patients Excess of Ammonia in the Blood – NEXT TRIAL: Phase 2 clinical trial underway in inadequately controlled UCD patients to evaluate KB195 on plasma ammonia levels; data expected in mid-2020 Decrease Production of • KB174 – Cirrhosis Ammonia – RESULTS: Controlled clinical study of 29 cirrhotic patients treated with KB174 and 15 maltodextrin; KB174 demonstrated a 26% median reduction in urinary N excretion compared to baseline. • In ex vivo testing, KB174 demonstrated a decrease in MDR pathogens; patients with cirrhosis have an increased risk of developing infections – NEXT STUDY: Plan to initiate clinical study 2H 2020 evaluating KB174 in patients Significant Unmet Medical Need with HE Urea Cycle Disorders (UCD) KB195 and KB174 were generally well tolerated with no clinically significant or serious treatment-related adverse events observed Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) Note(s): 4 ©2019 KALEIDO™ 1. See following slide for definitions of clinical trials and clinical studies.Delivered Positive Clinical Data in 2019 to Support Lead Programs Further Validation of MMT Platform • KB195 – Urea Cycle Disorders 15 – RESULTS: Small open label clinical study of KB195 showed reduction in urinary N Pathologies Resulting from an excretion (biomarker of ammonia production) in 2 out of 3 well-controlled UCD patients Excess of Ammonia in the Blood – NEXT TRIAL: Phase 2 clinical trial underway in inadequately controlled UCD patients to evaluate KB195 on plasma ammonia levels; data expected in mid-2020 Decrease Production of • KB174 – Cirrhosis Ammonia – RESULTS: Controlled clinical study of 29 cirrhotic patients treated with KB174 and 15 maltodextrin; KB174 demonstrated a 26% median reduction in urinary N excretion compared to baseline. • In ex vivo testing, KB174 demonstrated a decrease in MDR pathogens; patients with cirrhosis have an increased risk of developing infections – NEXT STUDY: Plan to initiate clinical study 2H 2020 evaluating KB174 in patients Significant Unmet Medical Need with HE Urea Cycle Disorders (UCD) KB195 and KB174 were generally well tolerated with no clinically significant or serious treatment-related adverse events observed Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) Note(s): 4 ©2019 KALEIDO™ 1. See following slide for definitions of clinical trials and clinical studies.
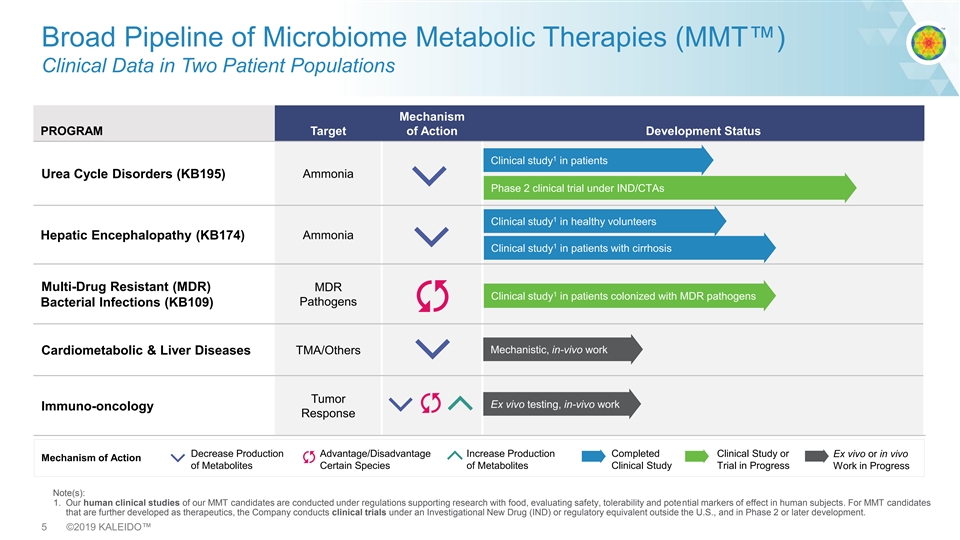
Broad Pipeline of Microbiome Metabolic Therapies (MMT™) Clinical Data in Two Patient Populations Mechanism PROGRAM Target of Action Development Status 1 Clinical study in patients Urea Cycle Disorders (KB195) Ammonia Phase 2 clinical trial under IND/CTAs 1 Clinical study in healthy volunteers Ammonia Hepatic Encephalopathy (KB174) 1 Clinical study in patients with cirrhosis Multi-Drug Resistant (MDR) MDR 1 Clinical study in patients colonized with MDR pathogens Pathogens Bacterial Infections (KB109) Mechanistic, in-vivo work TMA/Others Cardiometabolic & Liver Diseases Tumor Ex vivo testing, in-vivo work Immuno-oncology Response Decrease Production Advantage/Disadvantage Increase Production Completed Clinical Study or Ex vivo or in vivo Mechanism of Action of Metabolites Certain Species of Metabolites Clinical Study Trial in Progress Work in Progress Note(s): 1. Our human clinical studies of our MMT candidates are conducted under regulations supporting research with food, evaluating safety, tolerability and potential markers of effect in human subjects. For MMT candidates that are further developed as therapeutics, the Company conducts clinical trials under an Investigational New Drug (IND) or regulatory equivalent outside the U.S., and in Phase 2 or later development. 5 ©2019 KALEIDO™Broad Pipeline of Microbiome Metabolic Therapies (MMT™) Clinical Data in Two Patient Populations Mechanism PROGRAM Target of Action Development Status 1 Clinical study in patients Urea Cycle Disorders (KB195) Ammonia Phase 2 clinical trial under IND/CTAs 1 Clinical study in healthy volunteers Ammonia Hepatic Encephalopathy (KB174) 1 Clinical study in patients with cirrhosis Multi-Drug Resistant (MDR) MDR 1 Clinical study in patients colonized with MDR pathogens Pathogens Bacterial Infections (KB109) Mechanistic, in-vivo work TMA/Others Cardiometabolic & Liver Diseases Tumor Ex vivo testing, in-vivo work Immuno-oncology Response Decrease Production Advantage/Disadvantage Increase Production Completed Clinical Study or Ex vivo or in vivo Mechanism of Action of Metabolites Certain Species of Metabolites Clinical Study Trial in Progress Work in Progress Note(s): 1. Our human clinical studies of our MMT candidates are conducted under regulations supporting research with food, evaluating safety, tolerability and potential markers of effect in human subjects. For MMT candidates that are further developed as therapeutics, the Company conducts clinical trials under an Investigational New Drug (IND) or regulatory equivalent outside the U.S., and in Phase 2 or later development. 5 ©2019 KALEIDO™
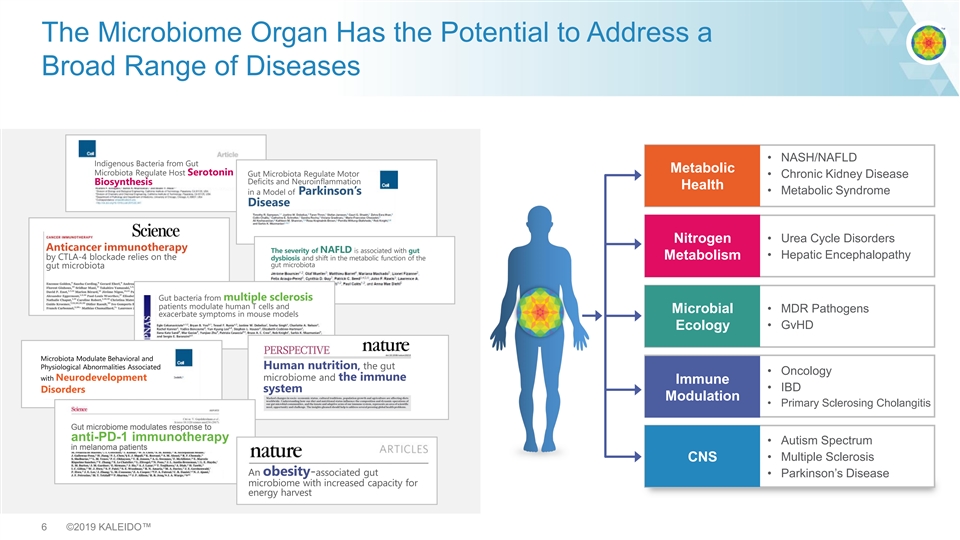
The Microbiome Organ Has the Potential to Address a Broad Range of Diseases • NASH/NAFLD Indigenous Bacteria from Gut Metabolic Microbiota Regulate Host Serotonin Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor • Chronic Kidney Disease Deficits and Neuroinflammation Biosynthesis Health • Metabolic Syndrome in a Model of Parkinson’s Disease • Urea Cycle Disorders Nitrogen Anticancer immunotherapy The severity of NAFLD is associated with gut • Hepatic Encephalopathy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on the dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the Metabolism gut microbiota gut microbiota Gut bacteria from multiple sclerosis patients modulate human T cells and Microbial • MDR Pathogens exacerbate symptoms in mouse models • GvHD Ecology Microbiota Modulate Behavioral and Human nutrition, the gut Physiological Abnormalities Associated • Oncology with Neurodevelopment microbiome and the immune Immune • IBD system Disorders Modulation • Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy • Autism Spectrum in melanoma patients • Multiple Sclerosis CNS An obesity-associated gut • Parkinson’s Disease microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest 6 ©2019 KALEIDO™The Microbiome Organ Has the Potential to Address a Broad Range of Diseases • NASH/NAFLD Indigenous Bacteria from Gut Metabolic Microbiota Regulate Host Serotonin Gut Microbiota Regulate Motor • Chronic Kidney Disease Deficits and Neuroinflammation Biosynthesis Health • Metabolic Syndrome in a Model of Parkinson’s Disease • Urea Cycle Disorders Nitrogen Anticancer immunotherapy The severity of NAFLD is associated with gut • Hepatic Encephalopathy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on the dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the Metabolism gut microbiota gut microbiota Gut bacteria from multiple sclerosis patients modulate human T cells and Microbial • MDR Pathogens exacerbate symptoms in mouse models • GvHD Ecology Microbiota Modulate Behavioral and Human nutrition, the gut Physiological Abnormalities Associated • Oncology with Neurodevelopment microbiome and the immune Immune • IBD system Disorders Modulation • Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy • Autism Spectrum in melanoma patients • Multiple Sclerosis CNS An obesity-associated gut • Parkinson’s Disease microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest 6 ©2019 KALEIDO™
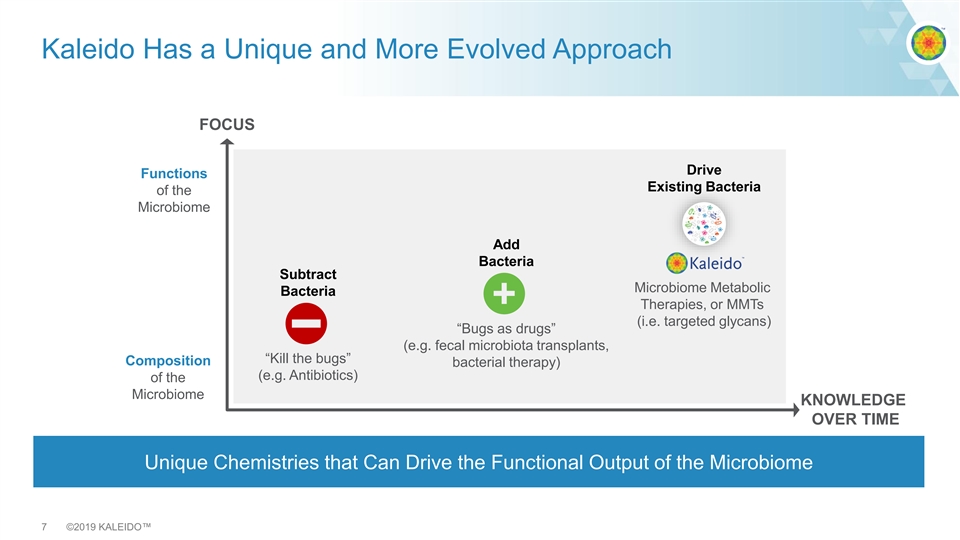
Kaleido Has a Unique and More Evolved Approach FOCUS Drive Functions Existing Bacteria of the Microbiome Add Bacteria Subtract Microbiome Metabolic Bacteria Therapies, or MMTs (i.e. targeted glycans) “Bugs as drugs” (e.g. fecal microbiota transplants, “Kill the bugs” Composition bacterial therapy) (e.g. Antibiotics) of the Microbiome KNOWLEDGE OVER TIME Unique Chemistries that Can Drive the Functional Output of the Microbiome 7 ©2019 KALEIDO™Kaleido Has a Unique and More Evolved Approach FOCUS Drive Functions Existing Bacteria of the Microbiome Add Bacteria Subtract Microbiome Metabolic Bacteria Therapies, or MMTs (i.e. targeted glycans) “Bugs as drugs” (e.g. fecal microbiota transplants, “Kill the bugs” Composition bacterial therapy) (e.g. Antibiotics) of the Microbiome KNOWLEDGE OVER TIME Unique Chemistries that Can Drive the Functional Output of the Microbiome 7 ©2019 KALEIDO™

Glycans are a Major Modality Shaping the Gut Microbiome Kaleido is Using Novel Chemistry to Develop Proprietary, Synthetic Glycans CREATION OF LIBRARIES OF SYNTHETIC GLYCANS (MMTs) Mono- Humans: + Multiple Oligo- 17 bond types, Poly- and branching glycosidases saccharide Microbiome: >3000 carbohydrate- active enzymes (CAZYmes) 1,500+ MMTs in our library: Natural glycans from multiple sources e.g. • Novel and proprietary: structurally plant, mucus, meat, microbial, milk complex & distinct ensembles • Related to a class that is Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), enabling rapid advancement into human clinical studies 8 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Source: Koropatkin et al., Nature Reviews Microbiology, 10, 323–335 (2012)Glycans are a Major Modality Shaping the Gut Microbiome Kaleido is Using Novel Chemistry to Develop Proprietary, Synthetic Glycans CREATION OF LIBRARIES OF SYNTHETIC GLYCANS (MMTs) Mono- Humans: + Multiple Oligo- 17 bond types, Poly- and branching glycosidases saccharide Microbiome: >3000 carbohydrate- active enzymes (CAZYmes) 1,500+ MMTs in our library: Natural glycans from multiple sources e.g. • Novel and proprietary: structurally plant, mucus, meat, microbial, milk complex & distinct ensembles • Related to a class that is Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), enabling rapid advancement into human clinical studies 8 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Source: Koropatkin et al., Nature Reviews Microbiology, 10, 323–335 (2012)

Our Microbiome Metabolic Therapies (MMTs) Provide Unique Advantages CHARACTERISTICS ADVANTAGES Metabolic output of microbiome not attainable Targeted, disease-specific activity from commercially available glycans Directional taxonomic changes are translated Ex vivo assay predicts response in humans from ex vivo to in human Translates from healthy subjects to patients Target genes and enzymes across taxa rather 1 Broader impact than LBPs (single strains or than only in specific species consortia) Potentially minimizes off-target Limited systemic exposure biological effects 9 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Note(s): 1. Lahti, L. et al. 013. Peer Journal 1:e32; Company data on fileOur Microbiome Metabolic Therapies (MMTs) Provide Unique Advantages CHARACTERISTICS ADVANTAGES Metabolic output of microbiome not attainable Targeted, disease-specific activity from commercially available glycans Directional taxonomic changes are translated Ex vivo assay predicts response in humans from ex vivo to in human Translates from healthy subjects to patients Target genes and enzymes across taxa rather 1 Broader impact than LBPs (single strains or than only in specific species consortia) Potentially minimizes off-target Limited systemic exposure biological effects 9 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Note(s): 1. Lahti, L. et al. 013. Peer Journal 1:e32; Company data on file
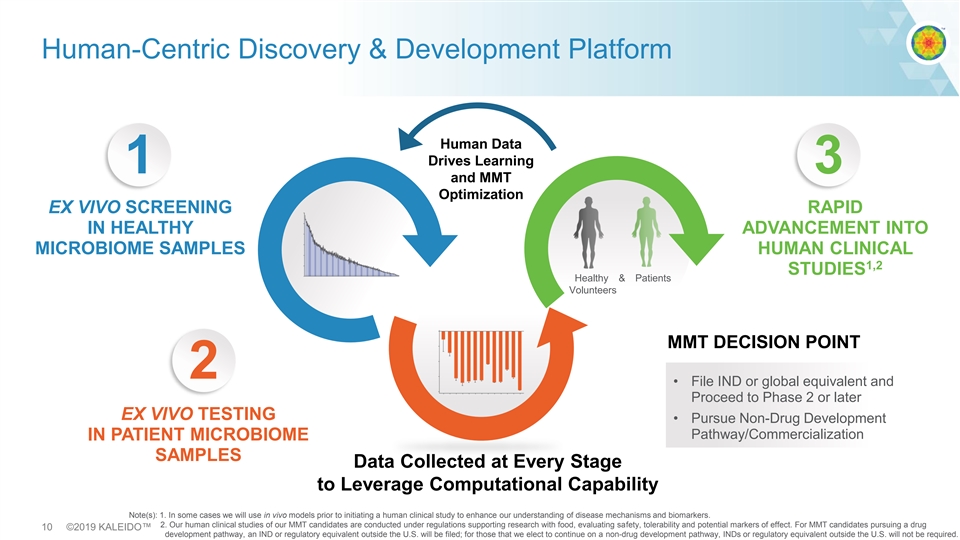
Human-Centric Discovery & Development Platform Human Data Drives Learning 1 3 and MMT Optimization EX VIVO SCREENING RAPID IN HEALTHY ADVANCEMENT INTO MICROBIOME SAMPLES HUMAN CLINICAL 1,2 STUDIES Healthy & Patients Volunteers MMT DECISION POINT 2 • File IND or global equivalent and Proceed to Phase 2 or later EX VIVO TESTING • Pursue Non-Drug Development Pathway/Commercialization IN PATIENT MICROBIOME SAMPLES Data Collected at Every Stage to Leverage Computational Capability Note(s): 1. In some cases we will use in vivo models prior to initiating a human clinical study to enhance our understanding of disease mechanisms and biomarkers. 2. Our human clinical studies of our MMT candidates are conducted under regulations supporting research with food, evaluating safety, tolerability and potential markers of effect. For MMT candidates pursuing a drug 10 ©2019 KALEIDO™ development pathway, an IND or regulatory equivalent outside the U.S. will be filed; for those that we elect to continue on a non-drug development pathway, INDs or regulatory equivalent outside the U.S. will not be required. Human-Centric Discovery & Development Platform Human Data Drives Learning 1 3 and MMT Optimization EX VIVO SCREENING RAPID IN HEALTHY ADVANCEMENT INTO MICROBIOME SAMPLES HUMAN CLINICAL 1,2 STUDIES Healthy & Patients Volunteers MMT DECISION POINT 2 • File IND or global equivalent and Proceed to Phase 2 or later EX VIVO TESTING • Pursue Non-Drug Development Pathway/Commercialization IN PATIENT MICROBIOME SAMPLES Data Collected at Every Stage to Leverage Computational Capability Note(s): 1. In some cases we will use in vivo models prior to initiating a human clinical study to enhance our understanding of disease mechanisms and biomarkers. 2. Our human clinical studies of our MMT candidates are conducted under regulations supporting research with food, evaluating safety, tolerability and potential markers of effect. For MMT candidates pursuing a drug 10 ©2019 KALEIDO™ development pathway, an IND or regulatory equivalent outside the U.S. will be filed; for those that we elect to continue on a non-drug development pathway, INDs or regulatory equivalent outside the U.S. will not be required.

Our MMTs Enable Faster, More Cost-Efficient Discovery & Development Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Year 7 Kaleido’s Human- IND Start Centric Discovery Discovery Human Clinical Studies 1 1 Year 2 Years Phase 2/3 and Development <3 Years Traditional Start IND Discovery, Preclinical Phase 1 Pharmaceutical Phase 2 ~5 Years ~1.5 Years 2 R&D or later 5-7 Years Chemistry & Human-Centric 1 Kaleido IND Traditional IND Model Advantages Start Phase 2/3 Start Phase 1 ✓ Rapid advancement into human clinical ✓ Discovery (human ex vivo)✓ Dose-response studies: ~2 years to Phase 2 trial with KB195✓ Discovery Data ✓ Abbreviated preclinical data✓ Biomarkers may also ✓ Small molecule unit manufacturing is efficient ✓ Animal Data be a surrogate for ✓ Scale for Phase 2/3 and scalable ✓ Scale to Phase 1 efficacy th ✓ Human clinical safety, ✓ 1/10 of cost to IND compared to traditional tolerability model Note(s): 1. To date with respect to KB195, which we have decided to develop as a drug candidate 11 ©2019 KALEIDO™ 2. DiMasi, Joseph, et al., Journal of Health Economics, 2016, 47, 20-23.Our MMTs Enable Faster, More Cost-Efficient Discovery & Development Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Year 7 Kaleido’s Human- IND Start Centric Discovery Discovery Human Clinical Studies 1 1 Year 2 Years Phase 2/3 and Development <3 Years Traditional Start IND Discovery, Preclinical Phase 1 Pharmaceutical Phase 2 ~5 Years ~1.5 Years 2 R&D or later 5-7 Years Chemistry & Human-Centric 1 Kaleido IND Traditional IND Model Advantages Start Phase 2/3 Start Phase 1 ✓ Rapid advancement into human clinical ✓ Discovery (human ex vivo)✓ Dose-response studies: ~2 years to Phase 2 trial with KB195✓ Discovery Data ✓ Abbreviated preclinical data✓ Biomarkers may also ✓ Small molecule unit manufacturing is efficient ✓ Animal Data be a surrogate for ✓ Scale for Phase 2/3 and scalable ✓ Scale to Phase 1 efficacy th ✓ Human clinical safety, ✓ 1/10 of cost to IND compared to traditional tolerability model Note(s): 1. To date with respect to KB195, which we have decided to develop as a drug candidate 11 ©2019 KALEIDO™ 2. DiMasi, Joseph, et al., Journal of Health Economics, 2016, 47, 20-23.

Urea Cycle Disorders: Rare Inborn Errors of Metabolism Resulting in Inability to Clear Ammonia Urea Cycle Disorders (UCD) LIVER KB195 Main Site of Ammonia Clearance • Inability to metabolize ammonia due to inborn deficiency of enzymes in the urea cycle GUT ‒ A significant proportion of ammonia is produced by the microbiome Ammonia and absorbed from the gut Production − Results in ammonia accumulation in the brain where it can cause irreversible brain damage, coma and/or death NH 3 • Rare disease with ~3,000 patients in U.S.; ~4,500 in E.U. – Liver transplant is a practical cure although does not revert preexisting neurological damage; performed in <40 patients per year in U.S. NH 3 • Limited available treatment options to: BRAIN – Lower chronic ammonia levels Main Site of Ammonia Toxicity – Reduce the risk of life-threatening hyperammonemic crises 12 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Sources: Batshaw, M. L., et. al. (2014). Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 113(0), 127-130; Häberle, J, et al. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disorders, 2019;1-39; Company reportsUrea Cycle Disorders: Rare Inborn Errors of Metabolism Resulting in Inability to Clear Ammonia Urea Cycle Disorders (UCD) LIVER KB195 Main Site of Ammonia Clearance • Inability to metabolize ammonia due to inborn deficiency of enzymes in the urea cycle GUT ‒ A significant proportion of ammonia is produced by the microbiome Ammonia and absorbed from the gut Production − Results in ammonia accumulation in the brain where it can cause irreversible brain damage, coma and/or death NH 3 • Rare disease with ~3,000 patients in U.S.; ~4,500 in E.U. – Liver transplant is a practical cure although does not revert preexisting neurological damage; performed in <40 patients per year in U.S. NH 3 • Limited available treatment options to: BRAIN – Lower chronic ammonia levels Main Site of Ammonia Toxicity – Reduce the risk of life-threatening hyperammonemic crises 12 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Sources: Batshaw, M. L., et. al. (2014). Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 113(0), 127-130; Häberle, J, et al. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disorders, 2019;1-39; Company reports
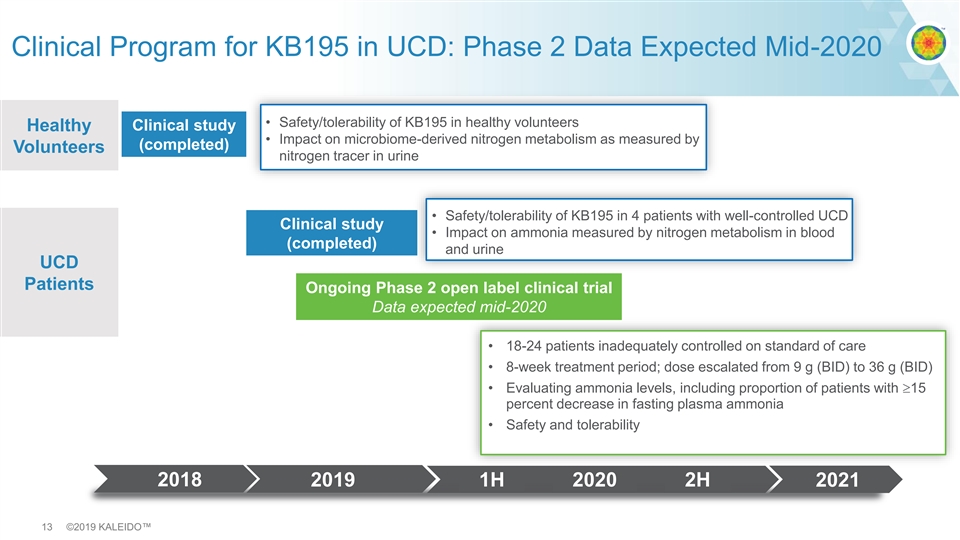
Clinical Program for KB195 in UCD: Phase 2 Data Expected Mid-2020 • Safety/tolerability of KB195 in healthy volunteers Healthy Clinical study • Impact on microbiome-derived nitrogen metabolism as measured by (completed) Volunteers nitrogen tracer in urine • Safety/tolerability of KB195 in 4 patients with well-controlled UCD Clinical study • Impact on ammonia measured by nitrogen metabolism in blood (completed) and urine UCD Patients Ongoing Phase 2 open label clinical trial Data expected mid-2020 • 18-24 patients inadequately controlled on standard of care • 8-week treatment period; dose escalated from 9 g (BID) to 36 g (BID) • Evaluating ammonia levels, including proportion of patients with ³15 percent decrease in fasting plasma ammonia • Safety and tolerability 2018 2019 1H 2020 2H 2021 13 ©2019 KALEIDO™Clinical Program for KB195 in UCD: Phase 2 Data Expected Mid-2020 • Safety/tolerability of KB195 in healthy volunteers Healthy Clinical study • Impact on microbiome-derived nitrogen metabolism as measured by (completed) Volunteers nitrogen tracer in urine • Safety/tolerability of KB195 in 4 patients with well-controlled UCD Clinical study • Impact on ammonia measured by nitrogen metabolism in blood (completed) and urine UCD Patients Ongoing Phase 2 open label clinical trial Data expected mid-2020 • 18-24 patients inadequately controlled on standard of care • 8-week treatment period; dose escalated from 9 g (BID) to 36 g (BID) • Evaluating ammonia levels, including proportion of patients with ³15 percent decrease in fasting plasma ammonia • Safety and tolerability 2018 2019 1H 2020 2H 2021 13 ©2019 KALEIDO™
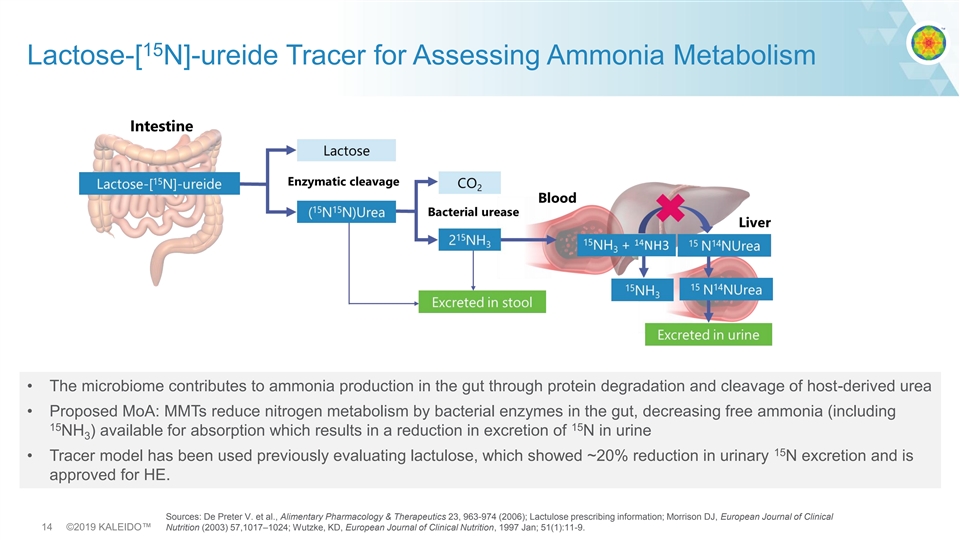
15 Lactose-[ N]-ureide Tracer for Assessing Ammonia Metabolism • The microbiome contributes to ammonia production in the gut through protein degradation and cleavage of host-derived urea • Proposed MoA: MMTs reduce nitrogen metabolism by bacterial enzymes in the gut, decreasing free ammonia (including 15 15 NH ) available for absorption which results in a reduction in excretion of N in urine 3 15 • Tracer model has been used previously evaluating lactulose, which showed ~20% reduction in urinary N excretion and is approved for HE. Sources: De Preter V. et al., Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 23, 963-974 (2006); Lactulose prescribing information; Morrison DJ, European Journal of Clinical 14 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Nutrition (2003) 57,1017–1024; Wutzke, KD, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 1997 Jan; 51(1):11-9.15 Lactose-[ N]-ureide Tracer for Assessing Ammonia Metabolism • The microbiome contributes to ammonia production in the gut through protein degradation and cleavage of host-derived urea • Proposed MoA: MMTs reduce nitrogen metabolism by bacterial enzymes in the gut, decreasing free ammonia (including 15 15 NH ) available for absorption which results in a reduction in excretion of N in urine 3 15 • Tracer model has been used previously evaluating lactulose, which showed ~20% reduction in urinary N excretion and is approved for HE. Sources: De Preter V. et al., Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 23, 963-974 (2006); Lactulose prescribing information; Morrison DJ, European Journal of Clinical 14 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Nutrition (2003) 57,1017–1024; Wutzke, KD, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 1997 Jan; 51(1):11-9.
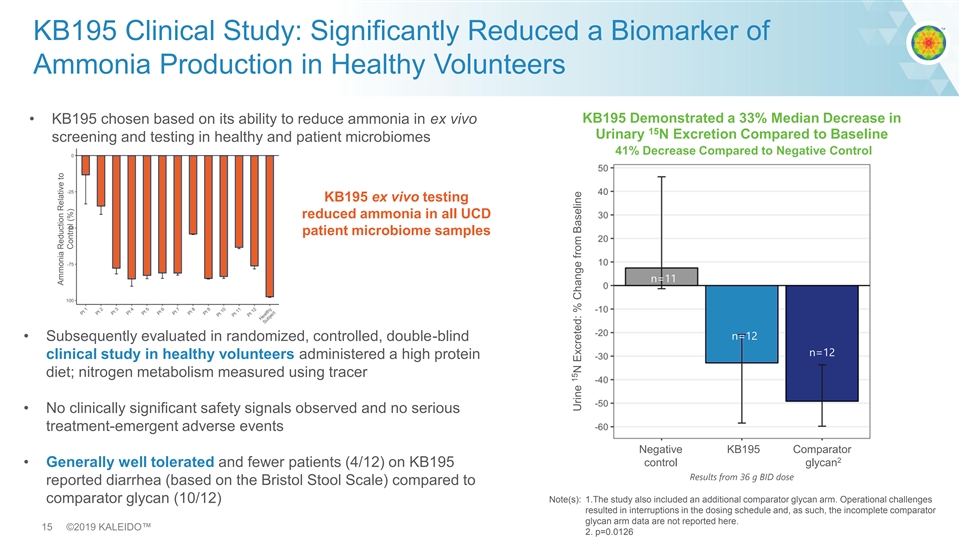
KB195 Clinical Study: Significantly Reduced a Biomarker of Ammonia Production in Healthy Volunteers KB195 Demonstrated a 33% Median Decrease in • KB195 chosen based on its ability to reduce ammonia in ex vivo 15 Urinary N Excretion Compared to Baseline screening and testing in healthy and patient microbiomes 41% Decrease Compared to Negative Control KB195 ex vivo testing reduced ammonia in all UCD patient microbiome samples n=11 n=12 • Subsequently evaluated in randomized, controlled, double-blind n=12 clinical study in healthy volunteers administered a high protein diet; nitrogen metabolism measured using tracer • No clinically significant safety signals observed and no serious treatment-emergent adverse events Negative KB195 Comparator 2 control glycan • Generally well tolerated and fewer patients (4/12) on KB195 Results from 36 g BID dose reported diarrhea (based on the Bristol Stool Scale) compared to comparator glycan (10/12) Note(s): 1.The study also included an additional comparator glycan arm. Operational challenges resulted in interruptions in the dosing schedule and, as such, the incomplete comparator glycan arm data are not reported here. 15 ©2019 KALEIDO™ 2. p=0.0126 Ammonia Reduction Relative to Control (%) 15 Urine N Excreted: % Change from BaselineKB195 Clinical Study: Significantly Reduced a Biomarker of Ammonia Production in Healthy Volunteers KB195 Demonstrated a 33% Median Decrease in • KB195 chosen based on its ability to reduce ammonia in ex vivo 15 Urinary N Excretion Compared to Baseline screening and testing in healthy and patient microbiomes 41% Decrease Compared to Negative Control KB195 ex vivo testing reduced ammonia in all UCD patient microbiome samples n=11 n=12 • Subsequently evaluated in randomized, controlled, double-blind n=12 clinical study in healthy volunteers administered a high protein diet; nitrogen metabolism measured using tracer • No clinically significant safety signals observed and no serious treatment-emergent adverse events Negative KB195 Comparator 2 control glycan • Generally well tolerated and fewer patients (4/12) on KB195 Results from 36 g BID dose reported diarrhea (based on the Bristol Stool Scale) compared to comparator glycan (10/12) Note(s): 1.The study also included an additional comparator glycan arm. Operational challenges resulted in interruptions in the dosing schedule and, as such, the incomplete comparator glycan arm data are not reported here. 15 ©2019 KALEIDO™ 2. p=0.0126 Ammonia Reduction Relative to Control (%) 15 Urine N Excreted: % Change from Baseline

KB195 Clinical Study in Patients with Well-Controlled UCD Reinforce Results in Healthy Subjects that KB195 Reduces Biomarker of Ammonia Production 15 1 • N tracer data suggestive of KB195 activity • Open-label, single-arm, clinical study enrolled 4 in reducing nitrogen metabolism, a biomarker patients with well-controlled UCD who received of ammonia production KB195 in addition to standard of care 15 – Decrease in urinary N in 2 of 3 evaluable • No clinically significant safety signals observed and patients no serious treatment-emergent adverse events 15 – Increase in N in stool in 4 of 4 patients • Generally well tolerated based on measures that 20 included Gastrointestinal Tolerability Questionnaire 10 (GITQ) and Bristol Stool Scale (BSS) 0 -10 -20 -30 • Plasma ammonia levels were within the normal -40 range at baseline and remained normal -50 -60 -70 -80 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Results from 36 g BID dose 15 Note(s): 1. In the process of analyzing the data for the KB174 studies, errors were found in the prior reporting of N tracer data. These data have been updated and 15 do not change the clinical interpretation. The mean decrease (n=3) previously reported for urinary N was 15% vs. 45% (corrected). The median decrease is 68%. 16 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Patient 1 was excluded from urine analysis due to missing urine collection hours 0 to 24. Percent Change from Baseline (%) 15 in Urine Labelled ( N-nitrogen) ExcretionKB195 Clinical Study in Patients with Well-Controlled UCD Reinforce Results in Healthy Subjects that KB195 Reduces Biomarker of Ammonia Production 15 1 • N tracer data suggestive of KB195 activity • Open-label, single-arm, clinical study enrolled 4 in reducing nitrogen metabolism, a biomarker patients with well-controlled UCD who received of ammonia production KB195 in addition to standard of care 15 – Decrease in urinary N in 2 of 3 evaluable • No clinically significant safety signals observed and patients no serious treatment-emergent adverse events 15 – Increase in N in stool in 4 of 4 patients • Generally well tolerated based on measures that 20 included Gastrointestinal Tolerability Questionnaire 10 (GITQ) and Bristol Stool Scale (BSS) 0 -10 -20 -30 • Plasma ammonia levels were within the normal -40 range at baseline and remained normal -50 -60 -70 -80 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Results from 36 g BID dose 15 Note(s): 1. In the process of analyzing the data for the KB174 studies, errors were found in the prior reporting of N tracer data. These data have been updated and 15 do not change the clinical interpretation. The mean decrease (n=3) previously reported for urinary N was 15% vs. 45% (corrected). The median decrease is 68%. 16 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Patient 1 was excluded from urine analysis due to missing urine collection hours 0 to 24. Percent Change from Baseline (%) 15 in Urine Labelled ( N-nitrogen) Excretion
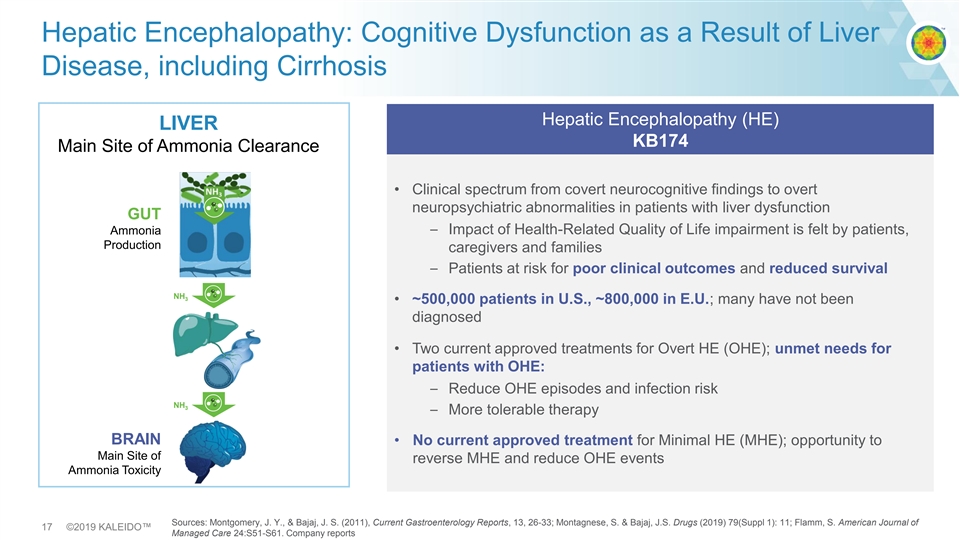
Hepatic Encephalopathy: Cognitive Dysfunction as a Result of Liver Disease, including Cirrhosis Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) LIVER KB174 Main Site of Ammonia Clearance • Clinical spectrum from covert neurocognitive findings to overt neuropsychiatric abnormalities in patients with liver dysfunction GUT – Impact of Health-Related Quality of Life impairment is felt by patients, Ammonia Production caregivers and families – Patients at risk for poor clinical outcomes and reduced survival NH 3 • ~500,000 patients in U.S., ~800,000 in E.U.; many have not been diagnosed • Two current approved treatments for Overt HE (OHE); unmet needs for patients with OHE: – Reduce OHE episodes and infection risk NH 3 – More tolerable therapy BRAIN • No current approved treatment for Minimal HE (MHE); opportunity to Main Site of reverse MHE and reduce OHE events Ammonia Toxicity Sources: Montgomery, J. Y., & Bajaj, J. S. (2011), Current Gastroenterology Reports, 13, 26-33; Montagnese, S. & Bajaj, J.S. Drugs (2019) 79(Suppl 1): 11; Flamm, S. American Journal of 17 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Managed Care 24:S51-S61. Company reportsHepatic Encephalopathy: Cognitive Dysfunction as a Result of Liver Disease, including Cirrhosis Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) LIVER KB174 Main Site of Ammonia Clearance • Clinical spectrum from covert neurocognitive findings to overt neuropsychiatric abnormalities in patients with liver dysfunction GUT – Impact of Health-Related Quality of Life impairment is felt by patients, Ammonia Production caregivers and families – Patients at risk for poor clinical outcomes and reduced survival NH 3 • ~500,000 patients in U.S., ~800,000 in E.U.; many have not been diagnosed • Two current approved treatments for Overt HE (OHE); unmet needs for patients with OHE: – Reduce OHE episodes and infection risk NH 3 – More tolerable therapy BRAIN • No current approved treatment for Minimal HE (MHE); opportunity to Main Site of reverse MHE and reduce OHE events Ammonia Toxicity Sources: Montgomery, J. Y., & Bajaj, J. S. (2011), Current Gastroenterology Reports, 13, 26-33; Montagnese, S. & Bajaj, J.S. Drugs (2019) 79(Suppl 1): 11; Flamm, S. American Journal of 17 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Managed Care 24:S51-S61. Company reports
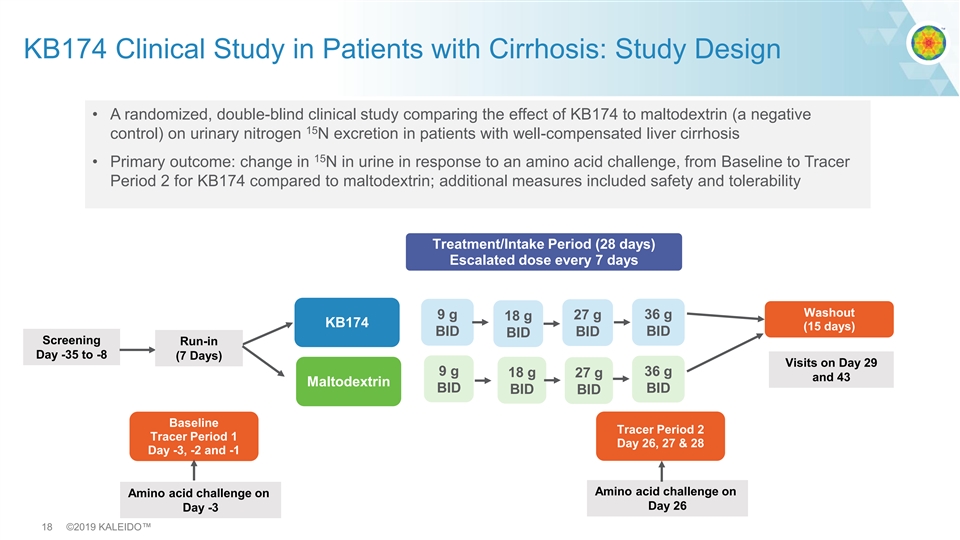
KB174 Clinical Study in Patients with Cirrhosis: Study Design • A randomized, double-blind clinical study comparing the effect of KB174 to maltodextrin (a negative 15 control) on urinary nitrogen N excretion in patients with well-compensated liver cirrhosis 15 • Primary outcome: change in N in urine in response to an amino acid challenge, from Baseline to Tracer Period 2 for KB174 compared to maltodextrin; additional measures included safety and tolerability Treatment/Intake Period (28 days) Escalated dose every 7 days Washout 9 g 36 g 27 g 18 g KB174 (15 days) BID BID BID BID Screening Run-in Day -35 to -8 (7 Days) Visits on Day 29 9 g 36 g 18 g 27 g and 43 Maltodextrin BID BID BID BID Baseline Tracer Period 2 Tracer Period 1 Day 26, 27 & 28 Day -3, -2 and -1 Amino acid challenge on Amino acid challenge on Day 26 Day -3 18 ©2019 KALEIDO™KB174 Clinical Study in Patients with Cirrhosis: Study Design • A randomized, double-blind clinical study comparing the effect of KB174 to maltodextrin (a negative 15 control) on urinary nitrogen N excretion in patients with well-compensated liver cirrhosis 15 • Primary outcome: change in N in urine in response to an amino acid challenge, from Baseline to Tracer Period 2 for KB174 compared to maltodextrin; additional measures included safety and tolerability Treatment/Intake Period (28 days) Escalated dose every 7 days Washout 9 g 36 g 27 g 18 g KB174 (15 days) BID BID BID BID Screening Run-in Day -35 to -8 (7 Days) Visits on Day 29 9 g 36 g 18 g 27 g and 43 Maltodextrin BID BID BID BID Baseline Tracer Period 2 Tracer Period 1 Day 26, 27 & 28 Day -3, -2 and -1 Amino acid challenge on Amino acid challenge on Day 26 Day -3 18 ©2019 KALEIDO™
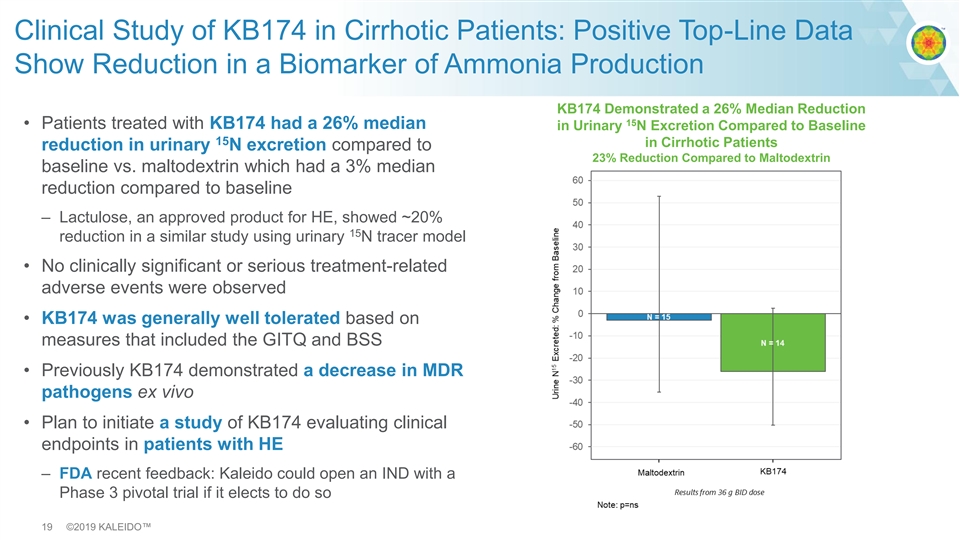
Clinical Study of KB174 in Cirrhotic Patients: Positive Top-Line Data Show Reduction in a Biomarker of Ammonia Production KB174 Demonstrated a 26% Median Reduction 15 • Patients treated with KB174 had a 26% median in Urinary N Excretion Compared to Baseline 15 in Cirrhotic Patients reduction in urinary N excretion compared to 23% Reduction Compared to Maltodextrin baseline vs. maltodextrin which had a 3% median reduction compared to baseline – Lactulose, an approved product for HE, showed ~20% 15 reduction in a similar study using urinary N tracer model • No clinically significant or serious treatment-related adverse events were observed • KB174 was generally well tolerated based on measures that included the GITQ and BSS • Previously KB174 demonstrated a decrease in MDR pathogens ex vivo • Plan to initiate a study of KB174 evaluating clinical endpoints in patients with HE – FDA recent feedback: Kaleido could open an IND with a Phase 3 pivotal trial if it elects to do so 19 ©2019 KALEIDO™Clinical Study of KB174 in Cirrhotic Patients: Positive Top-Line Data Show Reduction in a Biomarker of Ammonia Production KB174 Demonstrated a 26% Median Reduction 15 • Patients treated with KB174 had a 26% median in Urinary N Excretion Compared to Baseline 15 in Cirrhotic Patients reduction in urinary N excretion compared to 23% Reduction Compared to Maltodextrin baseline vs. maltodextrin which had a 3% median reduction compared to baseline – Lactulose, an approved product for HE, showed ~20% 15 reduction in a similar study using urinary N tracer model • No clinically significant or serious treatment-related adverse events were observed • KB174 was generally well tolerated based on measures that included the GITQ and BSS • Previously KB174 demonstrated a decrease in MDR pathogens ex vivo • Plan to initiate a study of KB174 evaluating clinical endpoints in patients with HE – FDA recent feedback: Kaleido could open an IND with a Phase 3 pivotal trial if it elects to do so 19 ©2019 KALEIDO™

Microbiome Impact on Pathogens and Immune Function Opportunity to Progress Development for Multi-drug Resistant Infections and Additional Diseases Caused by Imbalance of Immune Function Resulting from Dysbiosis Potential in Other Diseases Multi Drug Resistant Pathogens KB109 • Multi-drug resistant (MDR) infections are a global health crisis MMT Therapy • CDC has estimated that in the U.S. each year, more GOAL: Reduce infection or than 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occur and Pathobiont Overactive/inappropriate decrease inflammation, expansion more than 35,000 people die from these infections immune response driven by for improved disease pathogens/pathobionts outcomes • Patients undergoing liver or hematopoietic stem cell (e.g., MDR pathogens) Reducing transplantation (HSCT) at high risk of infections inflammatory Dysbiosis responses • Beyond MDR infections, have broader potential Loss of beneficial applications of immune homeostasis GOAL: microbes Increase immune cell − Potential to address certain bacteria that are Decreased/exhausted activation & improved implicated in immune-modulated diseases immune response disease outcomes (e.g., immuno- oncology) Immune cell Decreased ‘boost’ diversity 20 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Source: CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019Microbiome Impact on Pathogens and Immune Function Opportunity to Progress Development for Multi-drug Resistant Infections and Additional Diseases Caused by Imbalance of Immune Function Resulting from Dysbiosis Potential in Other Diseases Multi Drug Resistant Pathogens KB109 • Multi-drug resistant (MDR) infections are a global health crisis MMT Therapy • CDC has estimated that in the U.S. each year, more GOAL: Reduce infection or than 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occur and Pathobiont Overactive/inappropriate decrease inflammation, expansion more than 35,000 people die from these infections immune response driven by for improved disease pathogens/pathobionts outcomes • Patients undergoing liver or hematopoietic stem cell (e.g., MDR pathogens) Reducing transplantation (HSCT) at high risk of infections inflammatory Dysbiosis responses • Beyond MDR infections, have broader potential Loss of beneficial applications of immune homeostasis GOAL: microbes Increase immune cell − Potential to address certain bacteria that are Decreased/exhausted activation & improved implicated in immune-modulated diseases immune response disease outcomes (e.g., immuno- oncology) Immune cell Decreased ‘boost’ diversity 20 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Source: CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019
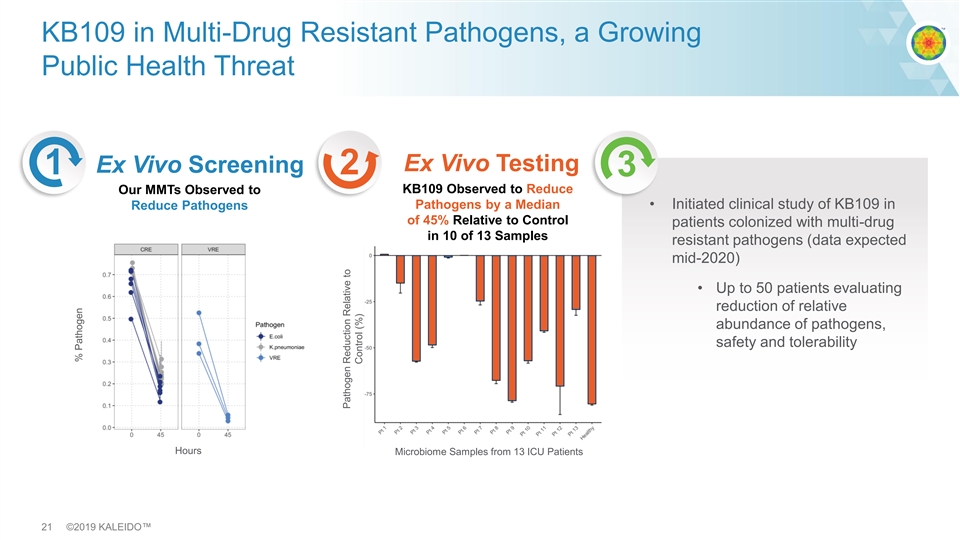
KB109 in Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens, a Growing Public Health Threat Ex Vivo Testing Ex Vivo Screening 1 2 3 KB109 Observed to Reduce Our MMTs Observed to Pathogens by a Median • Initiated clinical study of KB109 in Reduce Pathogens of 45% Relative to Control patients colonized with multi-drug in 10 of 13 Samples resistant pathogens (data expected mid-2020) • Up to 50 patients evaluating reduction of relative abundance of pathogens, safety and tolerability Hours Microbiome Samples from 13 ICU Patients 21 ©2019 KALEIDO™ % Pathogen Pathogen Reduction Relative to Control (%)KB109 in Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens, a Growing Public Health Threat Ex Vivo Testing Ex Vivo Screening 1 2 3 KB109 Observed to Reduce Our MMTs Observed to Pathogens by a Median • Initiated clinical study of KB109 in Reduce Pathogens of 45% Relative to Control patients colonized with multi-drug in 10 of 13 Samples resistant pathogens (data expected mid-2020) • Up to 50 patients evaluating reduction of relative abundance of pathogens, safety and tolerability Hours Microbiome Samples from 13 ICU Patients 21 ©2019 KALEIDO™ % Pathogen Pathogen Reduction Relative to Control (%)

Research Pipeline: New Disease Opportunities & Enhancing Knowledge of MMTs AREA OF FOCUS Collaborator Status • Two lead MMTs identified in ex vivo testing Cardiometabolic and Liver Diseases • Mechanistic work ongoing to evaluate MMTs in validated preclinical models N/A – Related metabolic pathways e.g. TMA • Pending results from mechanistic work prepare for clinical study by YE 2020 • Collaboration with Gustave Roussy initiated in September 2019 • Ex vivo screen to identify MMTs that drive changes in microbial communities associated with favorable response to treatment Immuno-oncology • Gustave Roussy to utilize advanced preclinical models to identify MMTs that – Enhancing response to checkpoint therapy stimulate targeted therapeutic responses • In vivo results from collaboration expected in Q4 2020 Jeffrey Gordon, MD • WUSL collaboration initiated in October 2019 Glycan chemistry and utilization • Gnotobiotic preclinical models combined with computational methods to further identify molecular pathways of how MMTs can modify functional – Physiology & metabolism of MMTs configuration of the gut microbiome and its metabolic outputs 22 ©2019 KALEIDO™Research Pipeline: New Disease Opportunities & Enhancing Knowledge of MMTs AREA OF FOCUS Collaborator Status • Two lead MMTs identified in ex vivo testing Cardiometabolic and Liver Diseases • Mechanistic work ongoing to evaluate MMTs in validated preclinical models N/A – Related metabolic pathways e.g. TMA • Pending results from mechanistic work prepare for clinical study by YE 2020 • Collaboration with Gustave Roussy initiated in September 2019 • Ex vivo screen to identify MMTs that drive changes in microbial communities associated with favorable response to treatment Immuno-oncology • Gustave Roussy to utilize advanced preclinical models to identify MMTs that – Enhancing response to checkpoint therapy stimulate targeted therapeutic responses • In vivo results from collaboration expected in Q4 2020 Jeffrey Gordon, MD • WUSL collaboration initiated in October 2019 Glycan chemistry and utilization • Gnotobiotic preclinical models combined with computational methods to further identify molecular pathways of how MMTs can modify functional – Physiology & metabolism of MMTs configuration of the gut microbiome and its metabolic outputs 22 ©2019 KALEIDO™

Manufacturing is a Core Strategic Advantage Proprietary Methods Standard Small Molecule Unit Operations Scalable and Transferable rd Internal Manufacturing 3 Party Manufacturers Production for ex vivo, toxicology, Large scale production for clinical trials and future and human clinical studies commercial supply (Thermo Fisher Scientific) Efficient and scalable process Internal capability to manufacture 12 MMTs per year; potential to double by early 2020 Completed tech transfer to Thermo Fisher in ~6 months, scaled to 1,000 kg with capability to increase by >40X 4 metric tons of KB195 manufactured for Phase 2 trial and toxicology 23 ©2019 KALEIDO™Manufacturing is a Core Strategic Advantage Proprietary Methods Standard Small Molecule Unit Operations Scalable and Transferable rd Internal Manufacturing 3 Party Manufacturers Production for ex vivo, toxicology, Large scale production for clinical trials and future and human clinical studies commercial supply (Thermo Fisher Scientific) Efficient and scalable process Internal capability to manufacture 12 MMTs per year; potential to double by early 2020 Completed tech transfer to Thermo Fisher in ~6 months, scaled to 1,000 kg with capability to increase by >40X 4 metric tons of KB195 manufactured for Phase 2 trial and toxicology 23 ©2019 KALEIDO™

Robust Global IP Portfolio 9 U.S. Patents + 2 EPO Patents: • Glycan pharmaceutical compositions (Europe) • Methods to reduce ammonia (U.S.) • Methods to treat pathogen colonization (U.S.) • Methods to treat diarrhea (U.S.) • Methods to treat dysbiosis (U.S.) • Catalyst compositions (U.S. and Europe) 100+ Non-Provisional Applications Pending, Worldwide in 20+ Regions/Countries • Glycan compositions • Methods to treat immune imbalances (e.g. cancer) • Methods to modulate short chain fatty acids • Methods of making glycans Continued IP Expansion by Filing Patent Applications Directed to Pharmaceutical Compositions, Methods of Treatment and Methods of Manufacture 24 ©2019 KALEIDO™Robust Global IP Portfolio 9 U.S. Patents + 2 EPO Patents: • Glycan pharmaceutical compositions (Europe) • Methods to reduce ammonia (U.S.) • Methods to treat pathogen colonization (U.S.) • Methods to treat diarrhea (U.S.) • Methods to treat dysbiosis (U.S.) • Catalyst compositions (U.S. and Europe) 100+ Non-Provisional Applications Pending, Worldwide in 20+ Regions/Countries • Glycan compositions • Methods to treat immune imbalances (e.g. cancer) • Methods to modulate short chain fatty acids • Methods of making glycans Continued IP Expansion by Filing Patent Applications Directed to Pharmaceutical Compositions, Methods of Treatment and Methods of Manufacture 24 ©2019 KALEIDO™

Significant Progress During 2019 ✓ Raised $75 million in February IPO and began trading on NASDAQ (KLDO) Corporate✓ Bolstered manufacturing capabilities, tech transfer to large-scale manufacturing partner ✓ Strengthened leadership team with appointments of CSO, CBO, new CFO; expanded SAB & new Board members ✓ 5 clinical studies initiated for 3 MMT candidates in 3 different patient populations, including: − Positive results from KB195 and KB174 in patients with UCD and cirrhosis − Phase 2 trial of KB195 in UCD & clinical study of KB109 in MDR pathogens enrolling patients Progressed Pipeline ✓ Further confirmation of regulatory support for development pathway − IND cleared and 6 CTAs approved for KB195 − FDA feedback allowing for initiation of Phase 3 pivotal trial upon decision to file an IND ✓ Ex vivo & clinical study data for lead programs and MMT platform presented at scientific meetings ✓ Established I/O collaboration with Gustave Roussy, Europe’s largest cancer treatment center Advanced ✓ Initiated research collaboration with Dr. Jeffrey Gordon, Washington University, founder of the Science modern microbiome field ✓ Initiated in vivo mechanistic work for lead MMTs in cardiometabolic/liver diseases 25 ©2019 KALEIDO™Significant Progress During 2019 ✓ Raised $75 million in February IPO and began trading on NASDAQ (KLDO) Corporate✓ Bolstered manufacturing capabilities, tech transfer to large-scale manufacturing partner ✓ Strengthened leadership team with appointments of CSO, CBO, new CFO; expanded SAB & new Board members ✓ 5 clinical studies initiated for 3 MMT candidates in 3 different patient populations, including: − Positive results from KB195 and KB174 in patients with UCD and cirrhosis − Phase 2 trial of KB195 in UCD & clinical study of KB109 in MDR pathogens enrolling patients Progressed Pipeline ✓ Further confirmation of regulatory support for development pathway − IND cleared and 6 CTAs approved for KB195 − FDA feedback allowing for initiation of Phase 3 pivotal trial upon decision to file an IND ✓ Ex vivo & clinical study data for lead programs and MMT platform presented at scientific meetings ✓ Established I/O collaboration with Gustave Roussy, Europe’s largest cancer treatment center Advanced ✓ Initiated research collaboration with Dr. Jeffrey Gordon, Washington University, founder of the Science modern microbiome field ✓ Initiated in vivo mechanistic work for lead MMTs in cardiometabolic/liver diseases 25 ©2019 KALEIDO™

Important Catalysts Expected in 2020 ❑ Data from Phase 2 clinical trial of KB195 in patients with UCD (mid-year) ❑ Data from clinical study of KB109 in patients colonized with multi-drug resistant pathogens (mid-year) ❑ Finalize development plan and trial design for HE program; initiate clinical study in patients (2H) ❑ Ready to initiate clinical study, pending results from ongoing cardiometabolic/liver diseases mechanistic work (Q4) ❑ In vivo results from immuno-oncology collaboration with Gustave Roussy (Q4) 26 ©2019 KALEIDO™Important Catalysts Expected in 2020 ❑ Data from Phase 2 clinical trial of KB195 in patients with UCD (mid-year) ❑ Data from clinical study of KB109 in patients colonized with multi-drug resistant pathogens (mid-year) ❑ Finalize development plan and trial design for HE program; initiate clinical study in patients (2H) ❑ Ready to initiate clinical study, pending results from ongoing cardiometabolic/liver diseases mechanistic work (Q4) ❑ In vivo results from immuno-oncology collaboration with Gustave Roussy (Q4) 26 ©2019 KALEIDO™

27 ©2 ©201 019 K 9 KA ALE LEIDO IDO™ ™27 ©2 ©201 019 K 9 KA ALE LEIDO IDO™ ™

World-Class Leadership Team Alison Lawton Former GM, Genzyme Biosurgery, President & Chief Executive Officer COO Aura & OvaScience Katharine Knobil, M.D. Former CMO, GlaxoSmithKline Chief Medical Officer, Head of R&D Johan van Hylckama Vlieg, Ph.D. Former VP for Microbiome & Human Chief Scientific Officer Health Innovation, Chr. Hansen William Duke Former CFO, Pulmatrix and Valeritas Chief Financial Officer Clare Fisher Former Group VP, Global Head of Chief Business Officer Transactions & Business Development, Shire Jerald Korn, J.D. Former Senior Vice President, Chief Legal and General Counsel & Corporate Secretary Administrative Officer, TESARO Mike Bonney Former CEO, Cubist Pharmaceuticals Executive Chair THERAPEUTIC AREA BREADTH CLINICAL DEVELOPMENT COMPANY BUILDING MANUFACTURING & TECHNOLOGY DEPTH & REGULATORY 28 ©2019 KALEIDO™World-Class Leadership Team Alison Lawton Former GM, Genzyme Biosurgery, President & Chief Executive Officer COO Aura & OvaScience Katharine Knobil, M.D. Former CMO, GlaxoSmithKline Chief Medical Officer, Head of R&D Johan van Hylckama Vlieg, Ph.D. Former VP for Microbiome & Human Chief Scientific Officer Health Innovation, Chr. Hansen William Duke Former CFO, Pulmatrix and Valeritas Chief Financial Officer Clare Fisher Former Group VP, Global Head of Chief Business Officer Transactions & Business Development, Shire Jerald Korn, J.D. Former Senior Vice President, Chief Legal and General Counsel & Corporate Secretary Administrative Officer, TESARO Mike Bonney Former CEO, Cubist Pharmaceuticals Executive Chair THERAPEUTIC AREA BREADTH CLINICAL DEVELOPMENT COMPANY BUILDING MANUFACTURING & TECHNOLOGY DEPTH & REGULATORY 28 ©2019 KALEIDO™
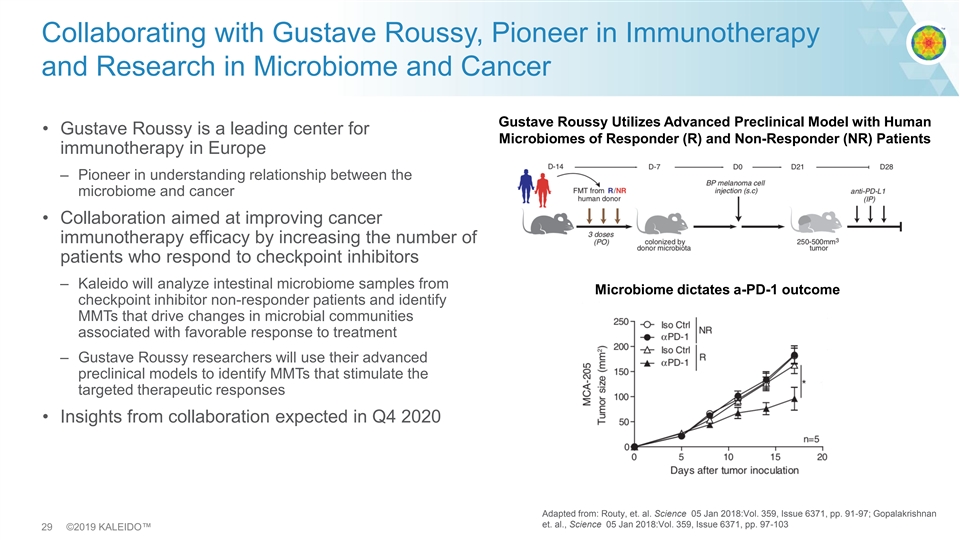
Collaborating with Gustave Roussy, Pioneer in Immunotherapy and Research in Microbiome and Cancer Gustave Roussy Utilizes Advanced Preclinical Model with Human • Gustave Roussy is a leading center for Microbiomes of Responder (R) and Non-Responder (NR) Patients immunotherapy in Europe – Pioneer in understanding relationship between the microbiome and cancer • Collaboration aimed at improving cancer immunotherapy efficacy by increasing the number of patients who respond to checkpoint inhibitors – Kaleido will analyze intestinal microbiome samples from Microbiome dictates a-PD-1 outcome checkpoint inhibitor non-responder patients and identify MMTs that drive changes in microbial communities associated with favorable response to treatment – Gustave Roussy researchers will use their advanced preclinical models to identify MMTs that stimulate the targeted therapeutic responses • Insights from collaboration expected in Q4 2020 Adapted from: Routy, et. al. Science 05 Jan 2018:Vol. 359, Issue 6371, pp. 91-97; Gopalakrishnan et. al., Science 05 Jan 2018:Vol. 359, Issue 6371, pp. 97-103 29 ©2019 KALEIDO™Collaborating with Gustave Roussy, Pioneer in Immunotherapy and Research in Microbiome and Cancer Gustave Roussy Utilizes Advanced Preclinical Model with Human • Gustave Roussy is a leading center for Microbiomes of Responder (R) and Non-Responder (NR) Patients immunotherapy in Europe – Pioneer in understanding relationship between the microbiome and cancer • Collaboration aimed at improving cancer immunotherapy efficacy by increasing the number of patients who respond to checkpoint inhibitors – Kaleido will analyze intestinal microbiome samples from Microbiome dictates a-PD-1 outcome checkpoint inhibitor non-responder patients and identify MMTs that drive changes in microbial communities associated with favorable response to treatment – Gustave Roussy researchers will use their advanced preclinical models to identify MMTs that stimulate the targeted therapeutic responses • Insights from collaboration expected in Q4 2020 Adapted from: Routy, et. al. Science 05 Jan 2018:Vol. 359, Issue 6371, pp. 91-97; Gopalakrishnan et. al., Science 05 Jan 2018:Vol. 359, Issue 6371, pp. 97-103 29 ©2019 KALEIDO™
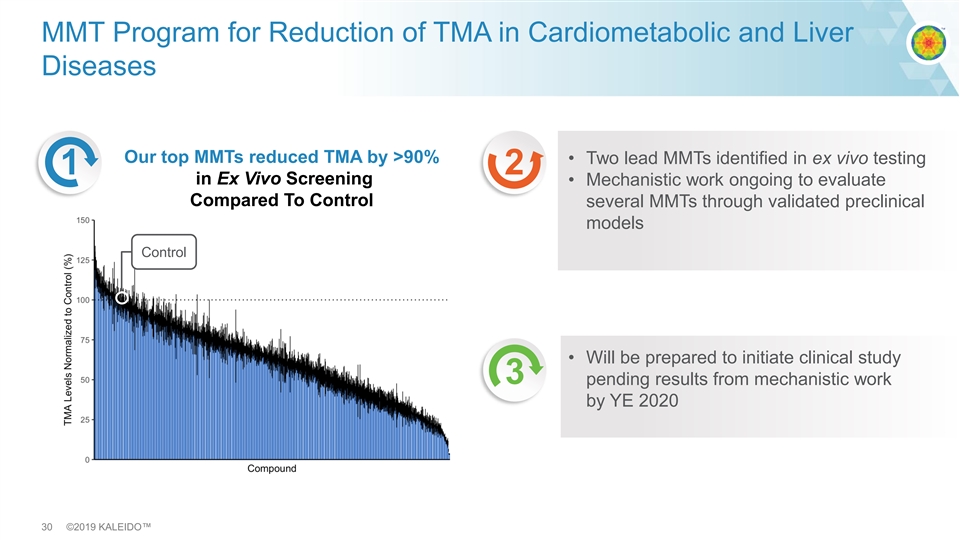
MMT Program for Reduction of TMA in Cardiometabolic and Liver Diseases Our top MMTs reduced TMA by >90% • Two lead MMTs identified in ex vivo testing 1 2 in Ex Vivo Screening • Mechanistic work ongoing to evaluate Compared To Control several MMTs through validated preclinical models Control • Will be prepared to initiate clinical study 3 pending results from mechanistic work by YE 2020 30 ©2019 KALEIDO™MMT Program for Reduction of TMA in Cardiometabolic and Liver Diseases Our top MMTs reduced TMA by >90% • Two lead MMTs identified in ex vivo testing 1 2 in Ex Vivo Screening • Mechanistic work ongoing to evaluate Compared To Control several MMTs through validated preclinical models Control • Will be prepared to initiate clinical study 3 pending results from mechanistic work by YE 2020 30 ©2019 KALEIDO™
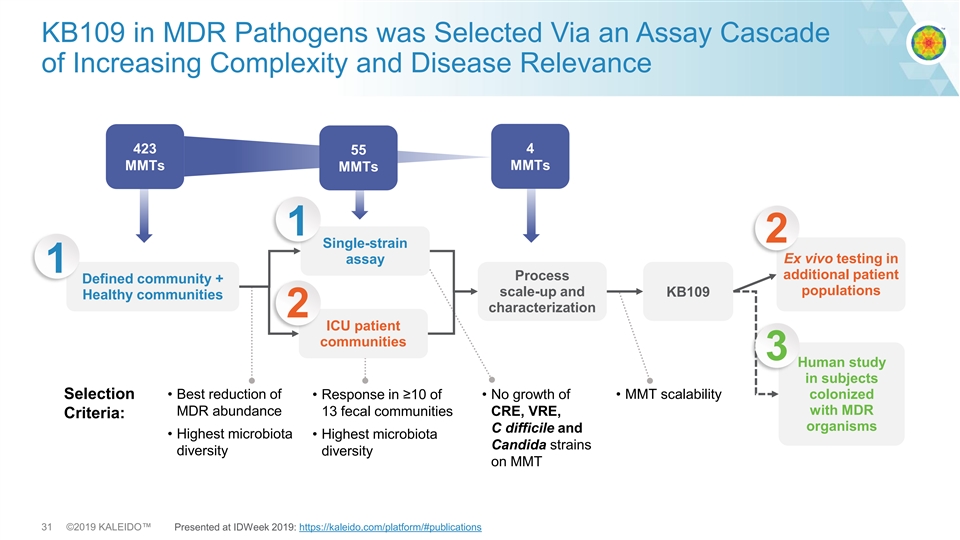
KB109 in MDR Pathogens was Selected Via an Assay Cascade of Increasing Complexity and Disease Relevance 4 423 55 MMTs MMTs MMTs 1 2 Single-strain Ex vivo testing in assay 1 additional patient Process Defined community + populations scale-up and KB109 Healthy communities characterization 2 ICU patient communities 3 Human study in subjects Selection • Best reduction of • Response in ≥10 of • No growth of • MMT scalability colonized with MDR MDR abundance 13 fecal communities CRE, VRE, Criteria: organisms C difficile and • Highest microbiota • Highest microbiota Candida strains diversity diversity on MMT 31 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Presented at IDWeek 2019: https://kaleido.com/platform/#publicationsKB109 in MDR Pathogens was Selected Via an Assay Cascade of Increasing Complexity and Disease Relevance 4 423 55 MMTs MMTs MMTs 1 2 Single-strain Ex vivo testing in assay 1 additional patient Process Defined community + populations scale-up and KB109 Healthy communities characterization 2 ICU patient communities 3 Human study in subjects Selection • Best reduction of • Response in ≥10 of • No growth of • MMT scalability colonized with MDR MDR abundance 13 fecal communities CRE, VRE, Criteria: organisms C difficile and • Highest microbiota • Highest microbiota Candida strains diversity diversity on MMT 31 ©2019 KALEIDO™ Presented at IDWeek 2019: https://kaleido.com/platform/#publications

32 ©2 ©201 019 K 9 KA ALE LEIDO IDO™ ™32 ©2 ©201 019 K 9 KA ALE LEIDO IDO™ ™