
Kaleido R&D Day October 5, 2021 Exhibit 99.1 Company Logo©2021KALEIDO®1

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation also contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended, including, without limitation, statements regarding our strategy, business plans and focus, including the therapeutic potential of our Microbiome Metabolic Therapy (MMT) candidates, the timing of initiation, completion and reporting of results of our clinical studies and our strategy, business plans and focus. The words “may,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “project,” “potential,” “continue,” “target” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. Any forward-looking statements in this presentation are based on management’s current expectations and beliefs and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and important factors that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation, including, without limitation, those related to planned clinical and preclinical studies and areas of interest, the preclinical and clinical development and safety profile of our MMT candidates and timelines associated with the programs for such MMT candidates, whether and when, if at all, our MMT candidates will receive approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or other applicable regulatory agencies, if any, competition from other biotechnology companies, and other risks identified in our SEC filings, including the most recently filed 10-K. We caution you not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date they are made. We disclaim any obligation to update or revise any such statements to reflect any change in expectations or in events, conditions or circumstances on which any such statements may be based, or that may affect the likelihood that actual results will differ from those set forth in the forward-looking statements. ©2021KALEIDO®2

Today’s Agenda & Speakers Introduction to Kaleido’s MMT Platform Daniel Menichella President and CEO UC Update Preclinical Findings Johan van Hylckama Vlieg, Ph.D. CSO KB295 Clinical Data Mark Wingertzahn, Ph.D. SVP, Head of Development KOL Perspective Bruce Sands, M.D. Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai COPD Update KB109 in COPD Mark Wingertzahn, Ph.D. SVP, Head of Development Partnership with the COPD Foundation Ruth Tal-Singer, Ph.D. President and CSO, COPD Foundation Closing Remarks Daniel Menichella President and CEO Q&A ©2021 KALEIDO® 3
Kaleido Snapshot Creating immunomodulators that target the gut microbiome Loss of immune homeostasis in the gut drives both local and systemic inflammation, which can lead to GI diseases, exacerbated infections and other devastating conditions and diseases Leveraging small molecules to systematically modulate the microbiome that acts as an upstream regulator of key pathways in immune-driven conditions and diseases A clinically translatable discovery platform to rapidly generate and test NCEs and backed by a robust IP portfolio Re-establishing Gut-Immune Homeostasis To Treat Major Conditions and Diseases Drugging the Microbiome not Replacing It To Promote Microbiome-Mediated Immune Modulation Safe, Effective, and Scalable Discovery and Manufacturing Platform ©2021 KALEIDO® 4
The Untapped Therapeutic Potential of the Human Microbiome These metabolites positively impact important biological systems, like the immune system, cell division, and metabolism Only Kaleido can differentially shift the composition and functional output of the entire microbiome in a targeted manner Trillions of gut microbes exert tremendous influence on our body Microbes utilize complex carbohydrates like glycans, and produce bioactive metabolites like short chain fatty acids ©2021 KALEIDO® 5
Kaleido MMTs Modulate Immune Function Through the Microbiome Provides systematic framework for testing and candidate selection Dysbiosis Homeostasis Microbiome Metabolic Therapies Large Set of Synthetic Glycans Target The Microbiome Metabolite Modulation Butyrate Bile acids Propionate Lipids Acetate Nucleotides Ammonia Many more Alter Host Physiology Modulate Immune Function TNFα TLR activation IFNγ IFNβ Antigen presentation Tissue remodeling Chemokine receptors TNFR family activation ©2021 KALEIDO® 6

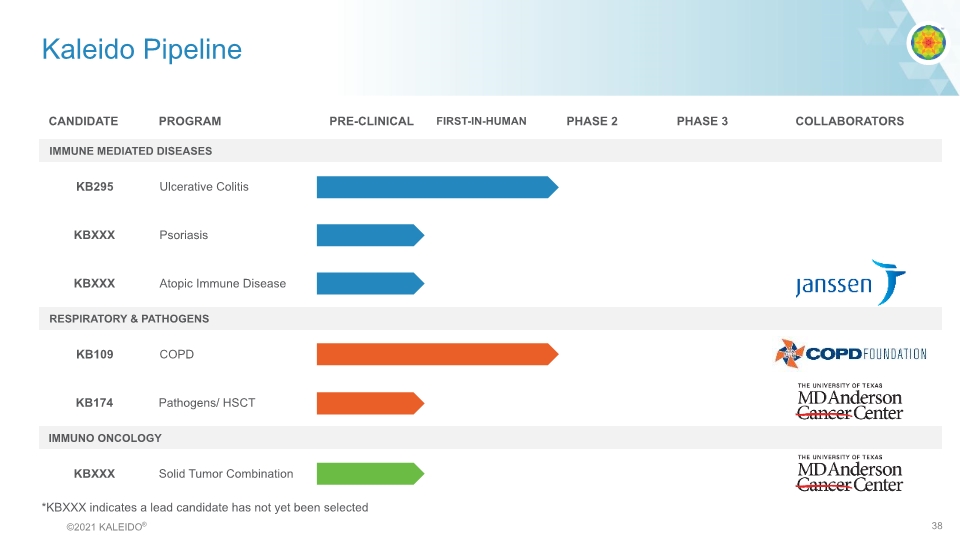
Kaleido Pipeline *KBXXX indicates a lead candidate has not yet been selected CANDIDATE PROGRAM PRE-CLINICAL FIRST-IN-HUMAN PHASE 2 PHASE 3 COLLABORATORS IMMUNE MEDIATED DISEASES KB295 Ulcerative Colitis KBXXX Psoriasis KBXXX Atopic Immune Disease RESPIRATORY & PATHOGENS KB109 COPD KB174 Pathogens/ HSCT IMMUNO ONCOLOGY KBXXX Solid Tumor Combination janssen COPD FOUNDATION THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS MD Anderson Cancer Center THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS MD Anderson Cancer Center ©2021 KALEIDO® 7
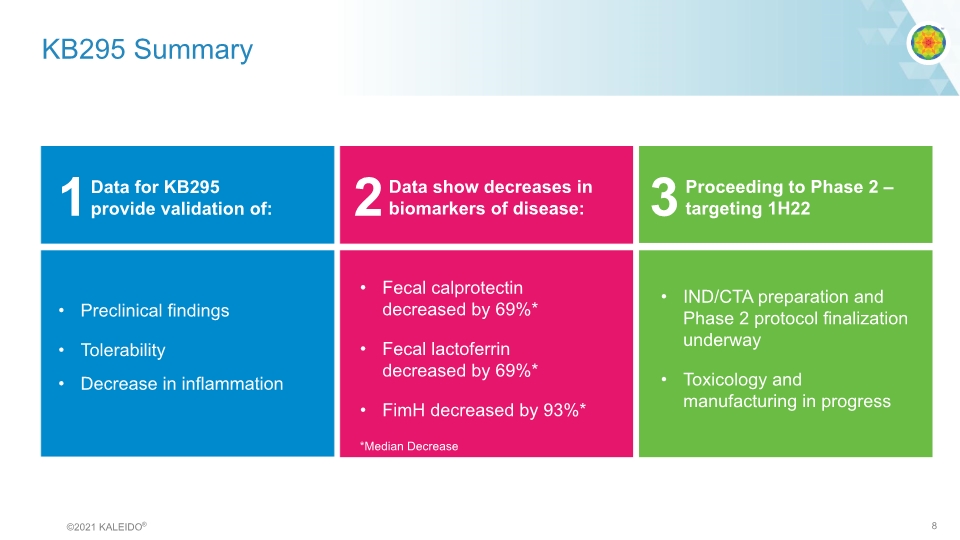
KB295 Summary 1 2 3 Data for KB295 provide validation of: Data show decreases in biomarkers of disease: Proceeding to Phase 2 – targeting 1H22 Preclinical findings Tolerability Decrease in inflammation Fecal calprotectin decreased by 69%* Fecal lactoferrin decreased by 69%* FimH decreased by 93%* IND/CTA preparation and Phase 2 protocol finalization underway Toxicology and manufacturing in progress *Median Decrease ©2021 KALEIDO® 8

Ulcerative Colitis Preclinical Data Johan van Hylckama Vlieg, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer Kaleido TM©2021 KALEIDO® 9
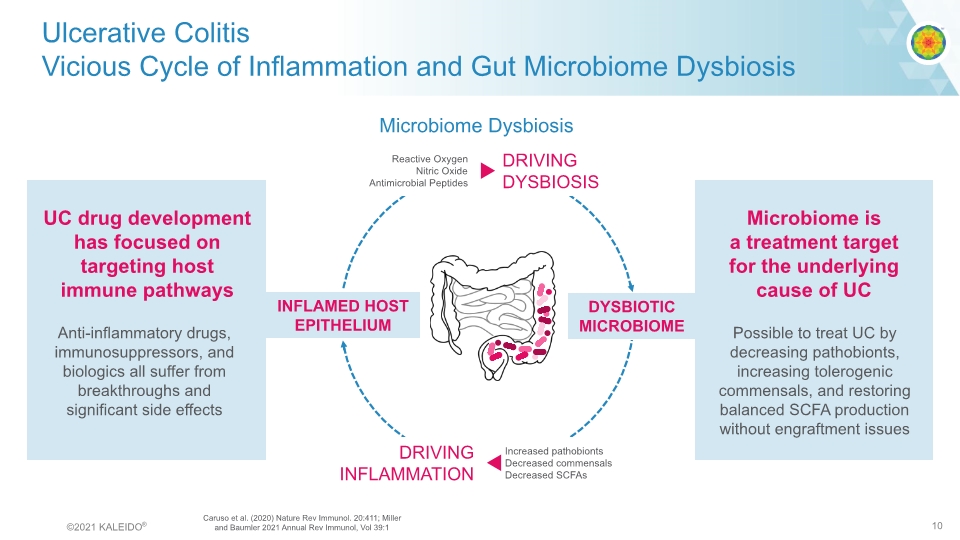
Ulcerative Colitis Vicious Cycle of Inflammation and Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis DYSBIOTIC MICROBIOME INFLAMED HOST EPITHELIUM UC drug development has focused on targeting host immune pathways Microbiome is a treatment target for the underlying cause of UC Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressors, and biologics all suffer from breakthroughs and significant side effects Possible to treat UC by decreasing pathobionts, increasing tolerogenic commensals, and restoring balanced SCFA production without engraftment issues Microbiome Dysbiosis Caruso et al. (2020) Nature Rev Immunol. 20:411; Miller and Baumler 2021 Annual Rev Immunol, Vol 39:1 ©2021 KALEIDO® 10
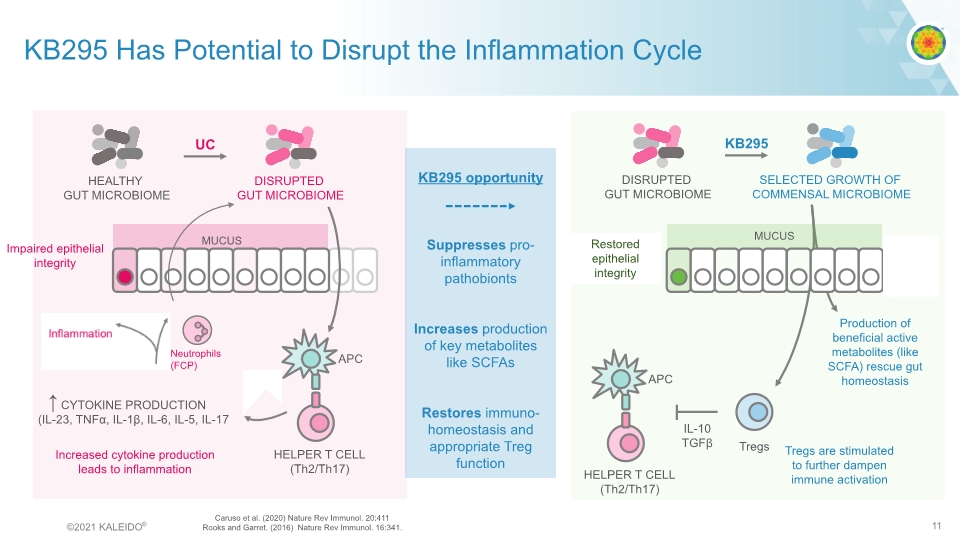
KB295 Has Potential to Disrupt the Inflammation Cycle CYTOKINE PRODUCTION (IL-23, TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-5, IL-17 Impaired epithelial integrity Increased cytokine production leads to inflammation Production of beneficial active metabolites (like SCFA) rescue gut homeostasis Tregs are stimulated to further dampen immune activation KB295 opportunity Suppresses pro-inflammatory pathobionts Increases production of key metabolites like SCFAs Restores immuno-homeostasis and appropriate Treg function INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELLS ↑ Restored epithelial integrity Caruso et al. (2020) Nature Rev Immunol. 20:411 Rooks and Garret. (2016) Nature Rev Immunol. 16:341. ©2021 KALEIDO® 11
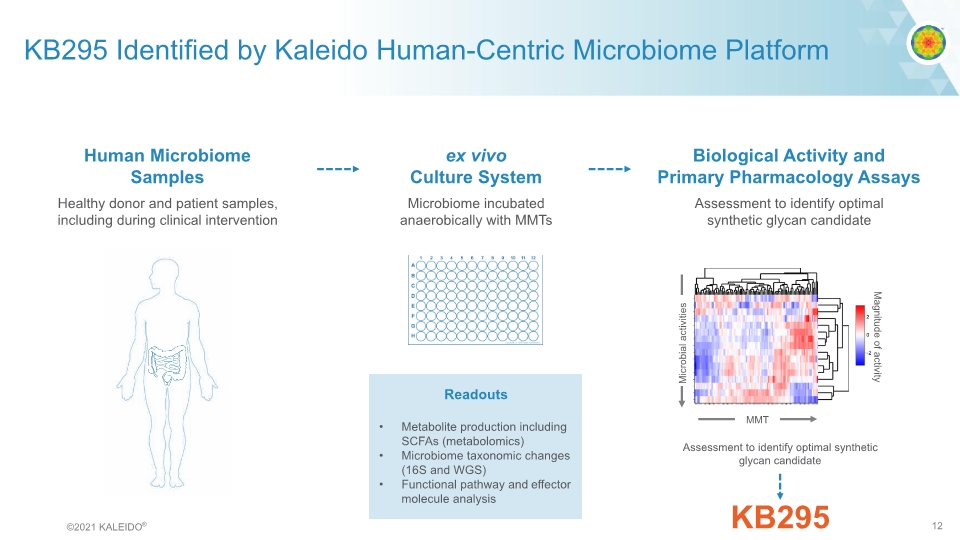
KB295 Identified by Kaleido Human-Centric Microbiome Platform Readouts Metabolite production including SCFAs (metabolomics) Microbiome taxonomic changes (16S and WGS) Functional pathway and effector molecule analysis Assessment to identify optimal synthetic glycan candidate Biological Activity and Primary Pharmacology Assays ex vivo Microbiome incubated Human Microbiome Healthy donor and patient samples, including during clinical interventionSample sanaerobically with MMTsCulture System ©2021 KALEIDO® 12
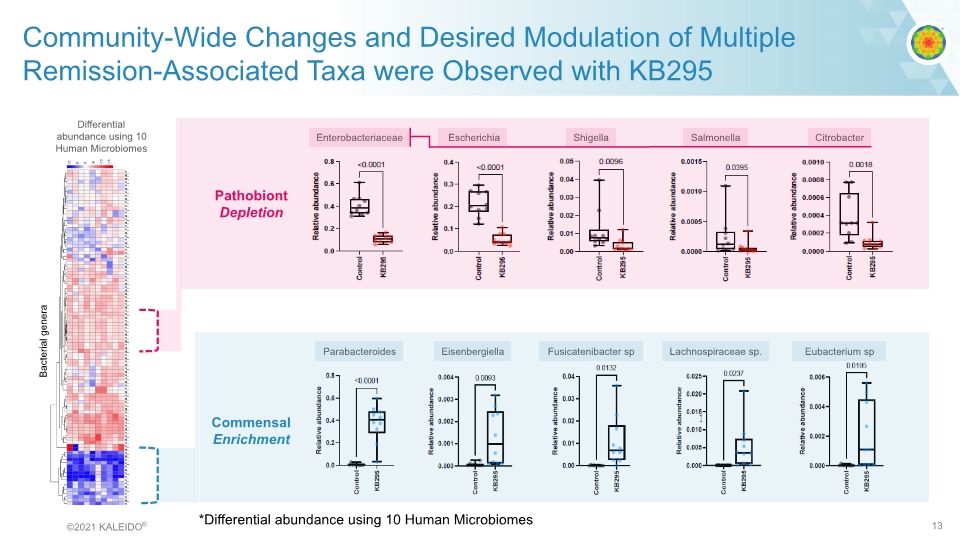
Community-Wide Changes and Desired Modulation of Multiple Remission-Associated Taxa were Observed with KB295 Enterobacteriaceae Escherichia Shigella Salmonella Citrobacter Parabacteroides Eisenbergiella Fusicatenibacter sp Lachnospiraceae sp. Eubacterium sp Pathobiont Depletion Commensal Enrichment Bacterial genera *Differential abundance using 10 Human Microbiomes ©2021 KALEIDO® 13
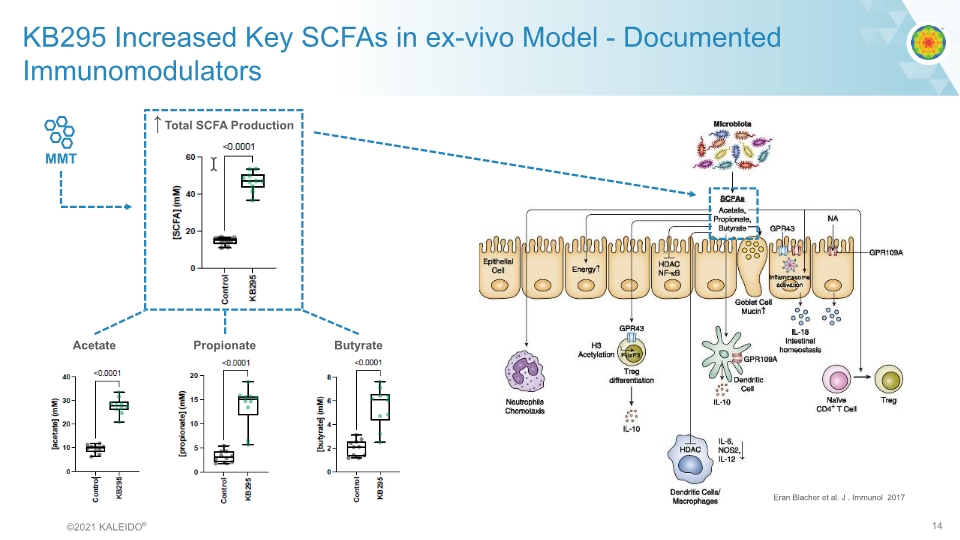
Eran Blacher et al. J . Immunol 2017 KB295 Increased Key SCFAs in ex-vivo Model - Documented Immunomodulators ©2021 KALEIDO® 14
Summary of Key Preclinical Findings 1 2 3 UC is a vicious cycle of inflammation and microbiome dysbiosis KB295 demonstrated microbiome-wide changes, including key taxa in ulcerative colitis KB295 increased key SCFAs to reduce inflammation ©2021 KALEIDO® 15

Ulcerative Colitis KB295 Data Mark Wingertzahn, Ph.D. Head of Development KaleidoTM©2021 KALEIDO® 16
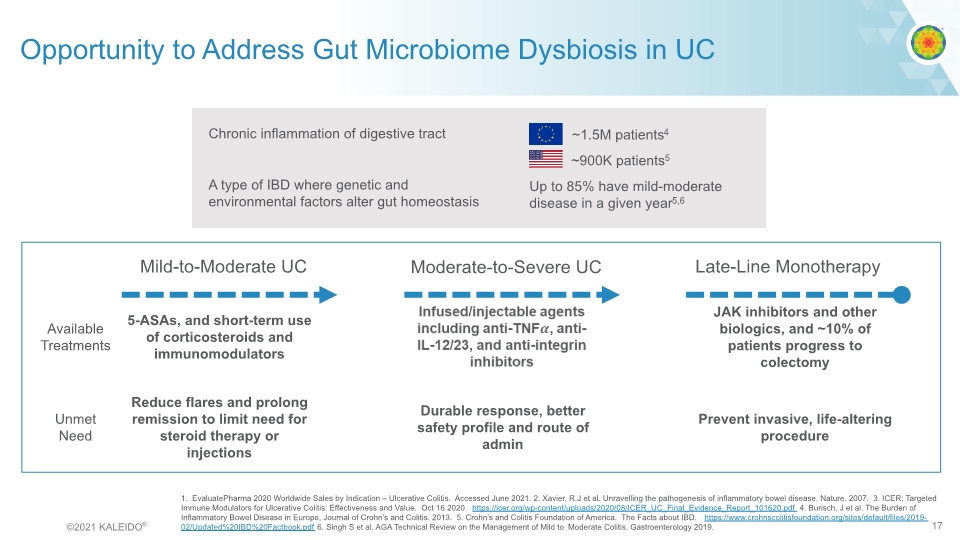
Opportunity to Address Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis in UC Mild-to-Moderate UC Moderate-to-Severe UC Late-Line Monotherapy ~1.5M patients4 ~900K patients5 Up to 85% have mild-moderate disease in a given year5,6 1. EvaluatePharma 2020 Worldwide Sales by Indication – Ulcerative Colitis. Accessed June 2021. 2. Xavier, R.J et al. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2007. 3. ICER: Targeted Immune Modulators for Ulcerative Colitis: Effectiveness and Value. Oct 16 2020. https://icer.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/ICER_UC_Final_Evidence_Report_101620.pdf 4. Burisch, J et al. The Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Europe, Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis. 2013. 5. Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation of America. The Facts about IBD. https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/sites/default/files/2019-02/Updated%20IBD%20Factbook.pdf 6. Singh S et al. AGA Technical Review on the Management of Mild to Moderate Colitis. Gastroenterology 2019. ©2021 KALEIDO® 17
KB295 Summary 1 2 3 Data for KB295 provide validation of: Data show decreases in biomarkers of disease: Proceeding to Phase 2 – targeting 1H22 Preclinical findings Tolerability Decrease in inflammation Fecal calprotectin decreased by 69%* Fecal lactoferrin decreased by 69%* FimH decreased by 93%* IND/CTA preparation and Phase 2 protocol finalization underway Toxicology and manufacturing in progress *Median Decrease ©2021 KALEIDO® 18
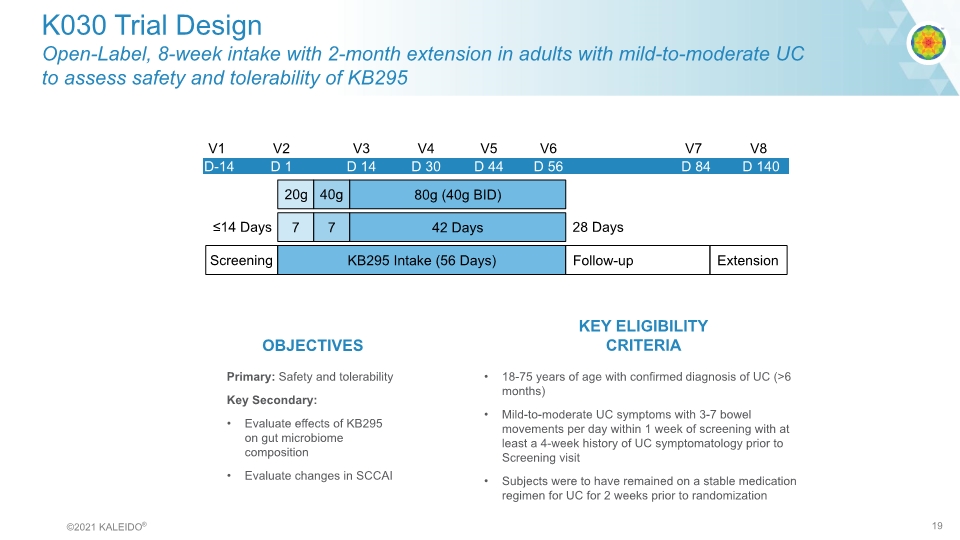
K030 Trial Design Open-Label, 8-week intake with 2-month extension in adults with mild-to-moderate UC to assess safety and tolerability of KB295 V1 V2 V3 V4 V6 D-14 D 1 D 30 D 14 D 44 D 56 D 84 V7 V5 D 140 V8 28 Days ≤14 Days Screening KB295 Intake (56 Days) 7 7 42 Days 80g (40g BID) 20g 40g Extension Follow-up Primary: Safety and tolerability Key Secondary: Evaluate effects of KB295 on gut microbiome composition Evaluate changes in SCCAI OBJECTIVES 18-75 years of age with confirmed diagnosis of UC (>6 months) Mild-to-moderate UC symptoms with 3-7 bowel movements per day within 1 week of screening with at least a 4-week history of UC symptomatology prior to Screening visit Subjects were to have remained on a stable medication regimen for UC for 2 weeks prior to randomization KEY ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA ©2021 KALEIDO® 19
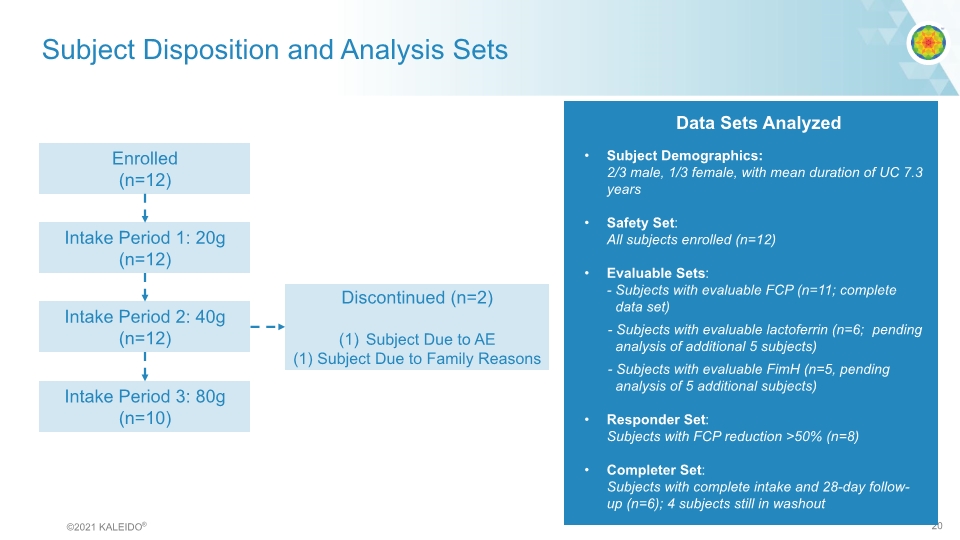
Subject Disposition and Analysis Sets Enrolled (n=12) Intake Period 1: 20g (n=12) Intake Period 2: 40g (n=12) Intake Period 3: 80g (n=10) Discontinued (n=2) Subject Due to AE (1) Subject Due to Family Reasons Data Sets Analyzed Subject Demographics: 2/3 male, 1/3 female, with mean duration of UC 7.3 years Safety Set: All subjects enrolled (n=12) Evaluable Sets: - Subjects with evaluable FCP (n=11; complete data set) - Subjects with evaluable lactoferrin (n=6; pending analysis of additional 5 subjects) - Subjects with evaluable FimH (n=5, pending analysis of 5 additional subjects) Responder Set: Subjects with FCP reduction >50% (n=8) Completer Set: Subjects with complete intake and 28-day follow-up (n=6); 4 subjects still in washout ©2021 KALEIDO® 20
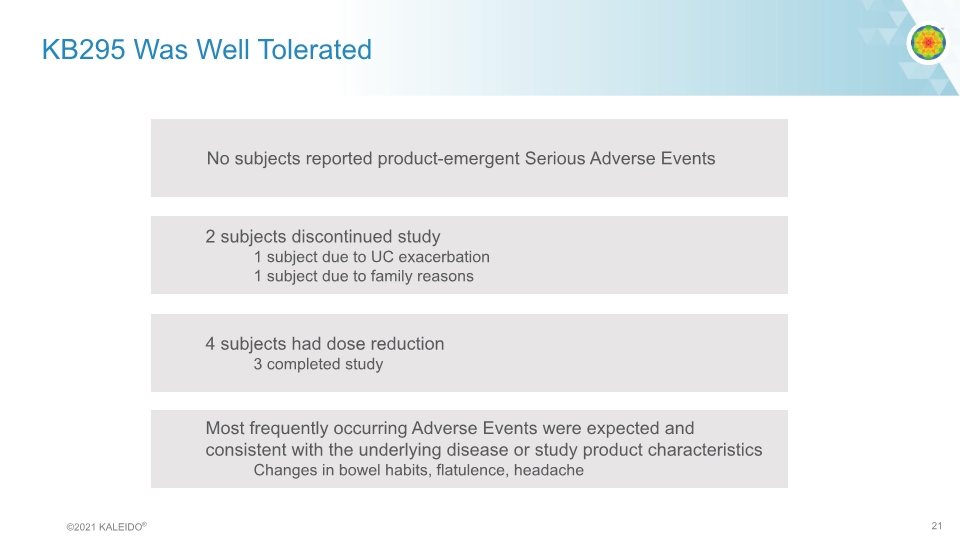
KB295 Was Well Tolerated No subjects reported product-emergent Serious Adverse Events 2 subjects discontinued study 1 subject due to UC exacerbation 1 subject due to family reasons 4 subjects had dose reduction 3 completed study Most frequently occurring Adverse Events were expected and consistent with the underlying disease or study product characteristics Changes in bowel habits, flatulence, headache ©2021 KALEIDO® 21

SCCAI (Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index) SCCAI provides relevant information on tolerability in subjects with ongoing gut inflammation Units Symptom Score Bowel frequency day 13 0 46 1 79 2 9 3 Bowel frequency night 13 1 4 6 2 urgency of defecation hurry immediately incontinence 1 2 3 blood in stool trace occasionally frank usually frank 1 2 3 general well being very well slightly below par poor very poor terrible 0 1 2 3 4 ©2021 KALEIDO® 22
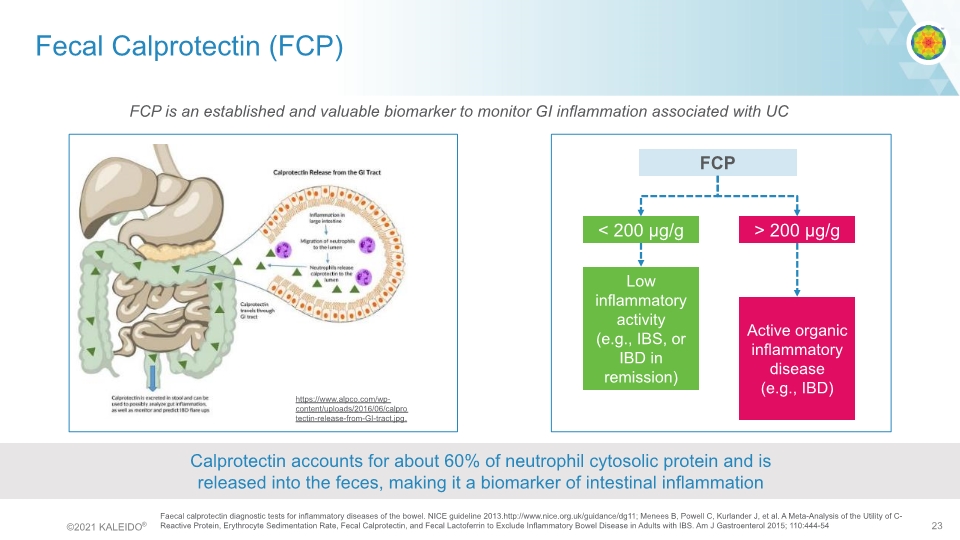
Fecal Calprotectin (FCP) Faecal calprotectin diagnostic tests for inflammatory diseases of the bowel. NICE guideline 2013.http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/dg11; Menees B, Powell C, Kurlander J, et al. A Meta-Analysis of the Utility of C-Reactive Protein, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, Fecal Calprotectin, and Fecal Lactoferrin to Exclude Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Adults with IBS. Am J Gastroenterol 2015; 110:444-54 Calprotectin accounts for about 60% of neutrophil cytosolic protein and is released into the feces, making it a biomarker of intestinal inflammation FCP < 200 μg/g > 200 μg/g Low inflammatory activity (e.g., IBS, or IBD in remission) Active organic inflammatory disease (e.g., IBD) za https://www.alpco.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/calprotectin-release-from-GI-tract.jpg. FCP is an established and valuable biomarker to monitor GI inflammation associated with UC calprotectin travels through GI tract calprotectin release from the GI tract©2021 KALEIDO® 23
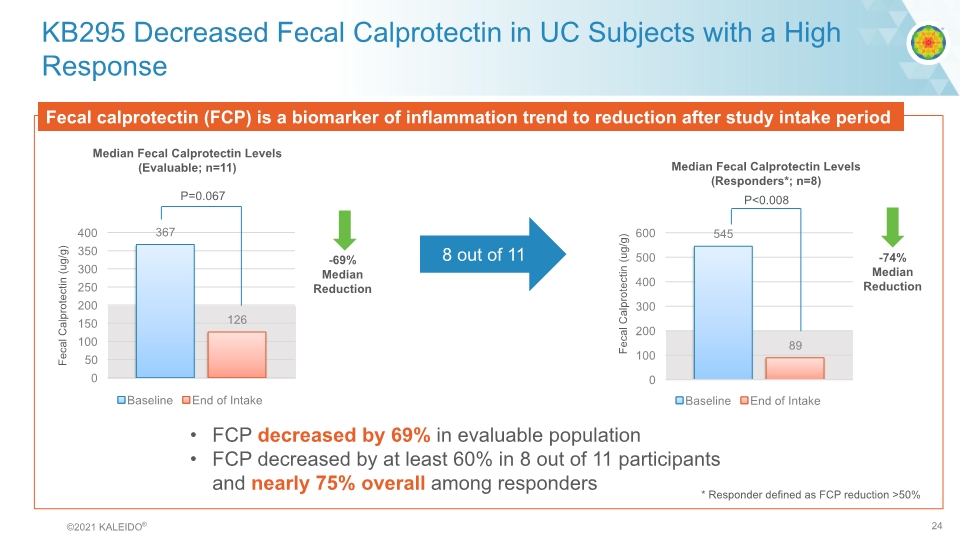
KB295 Decreased Fecal Calprotectin in UC Subjects with a High Response Fecal calprotectin (FCP) is a biomarker of inflammation trend to reduction after study intake period 8 out of 11 Median Fecal Calprotectin Levels (Evaluable; n=11) P=0.067 -69% Median Reduction Fecal Calprotectin (ug/g) Median Fecal Calprotectin Levels (Responders*; n=8) P<0.008 -74% Median Reduction Fecal Calprotectin (ug/g) * Responder defined as FCP reduction >50% FCP decreased by 69% in evaluable population FCP decreased by at least 60% in 8 out of 11 participants and nearly 75% overall among responders bar graph©2021 KALEIDO® 24
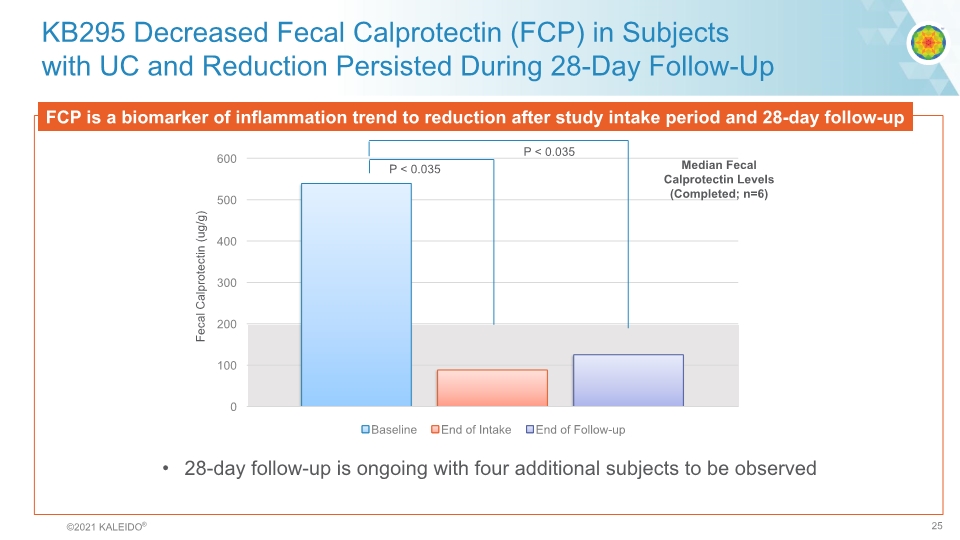
KB295 Decreased Fecal Calprotectin (FCP) in Subjects with UC and Reduction Persisted During 28-Day Follow-Up FCP is a biomarker of inflammation trend to reduction after study intake period and 28-day follow-up Median Fecal Calprotectin Levels (Completed; n=6) P < 0.035 P < 0.035 Fecal Calprotectin (ug/g) 28-day follow-up is ongoing with four additional subjects to be observed ©2021 KALEIDO® 25
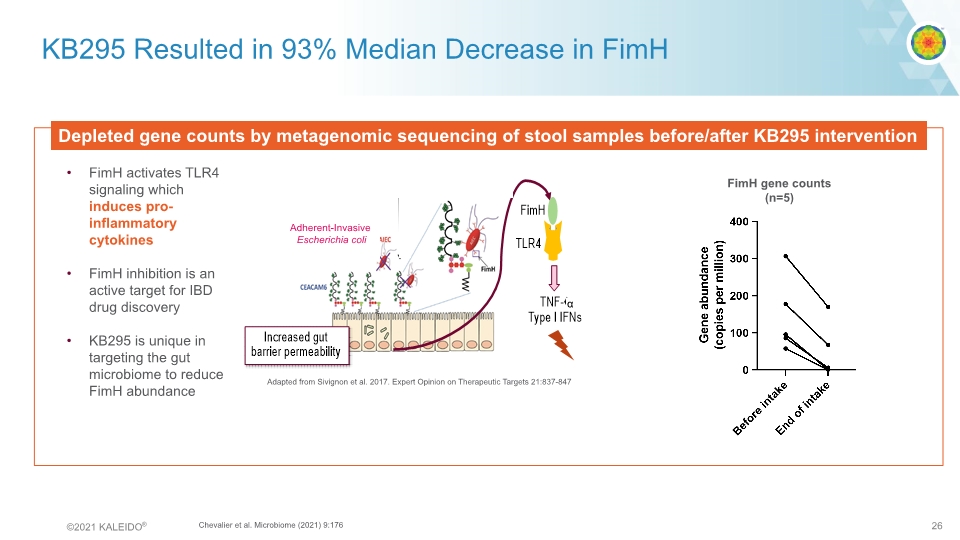
KB295 Resulted in 93% Median Decrease in FimH Depleted gene counts by metagenomic sequencing of stool samples before/after KB295 intervention FimH gene counts (n=5) FimH activates TLR4 signaling which induces pro-inflammatory cytokines FimH inhibition is an active target for IBD drug discovery KB295 is unique in targeting the gut microbiome to reduce FimH abundance Adapted from Sivignon et al. 2017. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets 21:837-847 Adherent-Invasive Escherichia coli α Chevalier et al. Microbiome (2021) 9:176 Adherent Invasive Escherichia coli graphic©2021 KALEIDO® 26
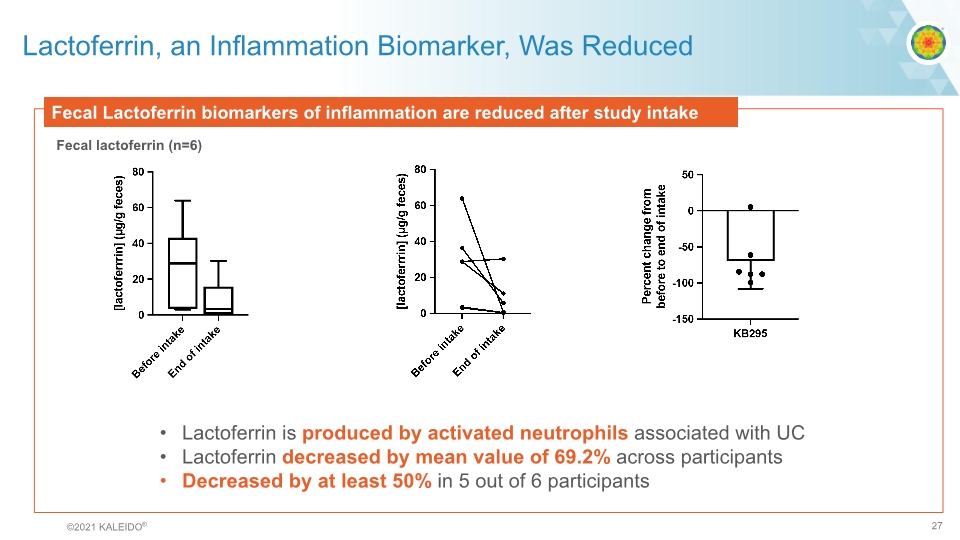
Lactoferrin, an Inflammation Biomarker, Was Reduced Fecal Lactoferrin biomarkers of inflammation are reduced after study intake Fecal lactoferrin (n=6) Lactoferrin is produced by activated neutrophils associated with UC Lactoferrin decreased by mean value of 69.2% across participants Decreased by at least 50% in 5 out of 6 participants graph©2021 KALEIDO® 27

K030 Results Bridge ex vivo Findings to UC Patients Pathobiont Enterobacteriaceae Commensal Parabacteroides KB295 enriched commensal Parabacteroides and depleted pathobionts Enterobacteriaceae Median relative abundance of Parabacteroides increased after intake in 4 out of 5 subjects Median relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae decreased after intake in all 5 subjects ©2021 KALEIDO® 28
K030 Data Encourages Move to Phase 2 Clinical Study 1 2 3 K030 data Preclinical data Proceeding to Phase 2 – targeting 1H22 KB295 was well tolerated in subjects Decrease in biomarkers including FimH, FCP, and Lactoferrin KB295 selectively enriched commensal microbiota Decreases abundance of pro-inflammatory pathobionts Supports hypothesis that KB295 enriches for taxa producing specific SCFA Production of key SCFA and other bioactive metabolites results in reduction of UC-driven inflammation ©2021 KALEIDO® 29

Bruce Sands, M.D. Dr. Burrill B. Crohn Professor of Medicine Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Chief of the Division of Gastroenterology, Mount Sinai Former Medical Co-Director of the Crohn’s & Colitis Center Massachusetts General Hospital KB295 – A KOL’s Perspective ©2021 KALEIDO® 30

COPD KB109 Program Update Mark Wingertzahn, Ph.D. Head of Development Kaleido ©2021 KALEIDO® 31
Opportunity in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD Current options offer limited benefit on inflammation No treatment targets microbiome Few oral options available have safety and tolerability issues for patients The Opportunity A maintenance treatment to reduce risk of acute exacerbations in COPD patients. Progressive, long-term disease caused by inflammation to lung airways 3rd leading cause of death worldwide ~250M suffer from COPD worldwide, exacerbations frequently results in hospitalization and increased mortality risk Current SoC include LABA/LAMA, ICS, and PDE-4 inhibitor © 2021 KALEIDO® 32
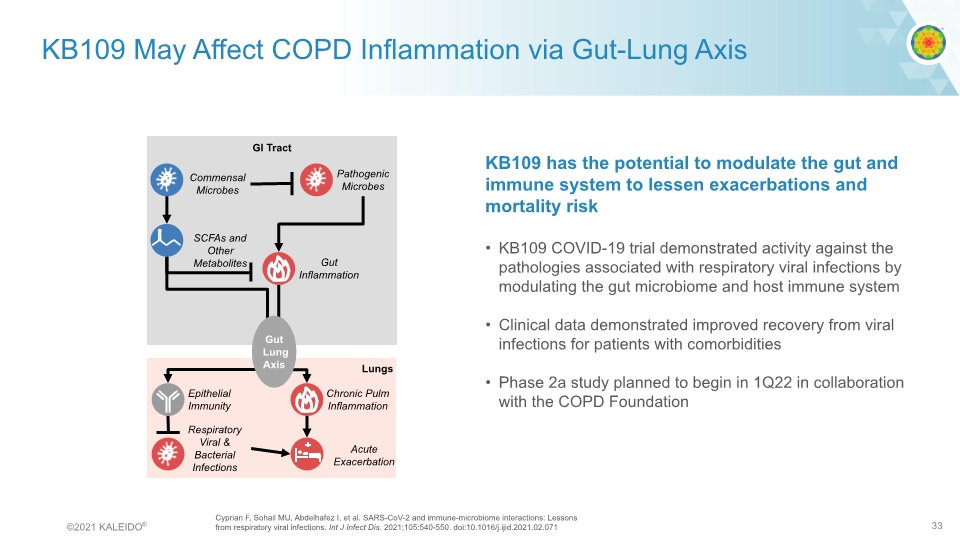
KB109 May Affect COPD Inflammation via Gut-Lung Axis KB109 has the potential to modulate the gut and immune system to lessen exacerbations and mortality risk KB109 COVID-19 trial demonstrated activity against the pathologies associated with respiratory viral infections by modulating the gut microbiome and host immune system Clinical data demonstrated improved recovery from viral infections for patients with comorbidities Phase 2a study planned to begin in 1Q22 in collaboration with the COPD Foundation Cyprian F, Sohail MU, Abdelhafez I, et al. SARS-CoV-2 and immune-microbiome interactions: Lessons from respiratory viral infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;105:540-550. doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.071 GI Tract Commensal Microbes SCFAs and Other Metabolites Acute Exacerbation Lungs Gut Inflammation © 2021 KALEIDO® 33
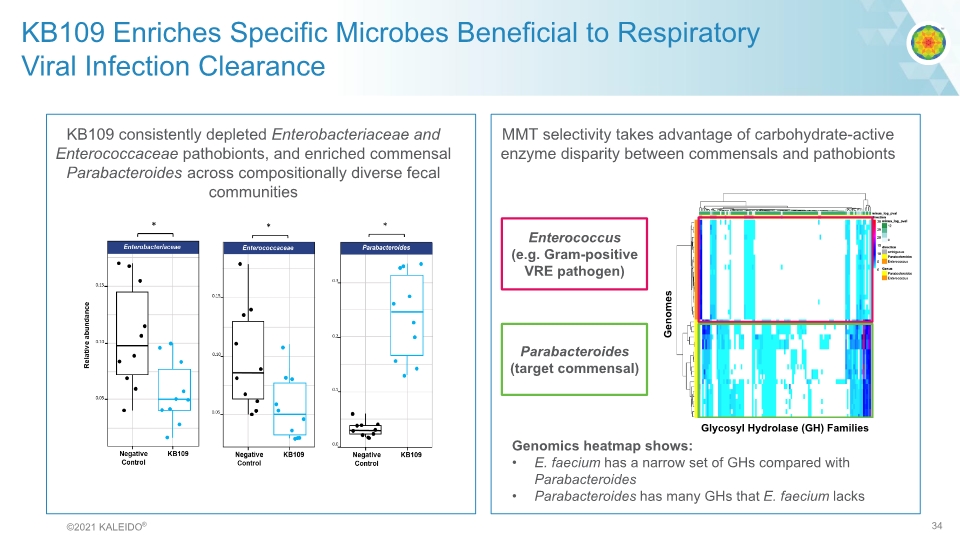
KB109 Enriches Specific Microbes Beneficial to Respiratory Viral Infection Clearance KB109 consistently depleted Enterobacteriaceae and Enterococcaceae pathobionts, and enriched commensal Parabacteroides across compositionally diverse fecal communities MMT selectivity takes advantage of carbohydrate-active enzyme disparity between commensals and pathobionts Enterococcus (e.g. Gram-positive VRE pathogen) Parabacteroides (target commensal) Genomics heatmap shows: E. faecium has a narrow set of GHs compared with Parabacteroides Parabacteroides has many GHs that E. faecium lacks Genomes Glycosyl Hydrolase (GH) Families © 2021 KALEIDO® 34
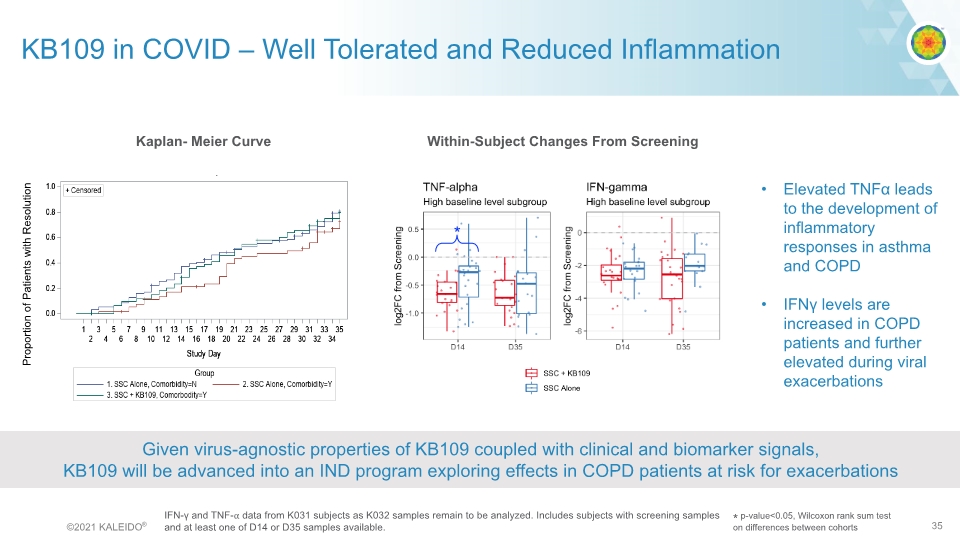
Proportion of Patients with Resolution Kaplan- Meier Curve IFN-γ and TNF-⍺ data from K031 subjects as K032 samples remain to be analyzed. Includes subjects with screening samples and at least one of D14 or D35 samples available. * p-value<0.05, Wilcoxon rank sum test on differences between cohorts Within-Subject Changes From Screening KB109 in COVID – Well Tolerated and Reduced Inflammation Given virus-agnostic properties of KB109 coupled with clinical and biomarker signals, KB109 will be advanced into an IND program exploring effects in COPD patients at risk for exacerbations Elevated TNFα leads to the development of inflammatory responses in asthma and COPD IFNγ levels are increased in COPD patients and further elevated during viral exacerbations © 2021 KALEIDO® 35

New Collaboration with the COPD Foundation Collaboration Partnership with leading experts in the Foundation and its COPD360Net® Joint clinical development support No financial obligations Advantages Leverage expertise to support trial design Provide access to top clinical sites Support trial enrollment through the Foundation’s network Collaboration to explore KB109’s potential to correct dysbiosis and prevent significant disease burden related to respiratory infections in people with COPD © 2021 KALEIDO® 36

Ruth Tal-Singer, Ph.D. President and Chief Scientific Officer COPD Foundation Former VP of Medical Innovation, GSK Value Evidence and Outcomes, at GSK Former Industry Chair of COPD Biomarker Qualification Consortium Partnership with the COPD Foundation © 2021 KALEIDO® 37
Kaleido Pipeline *KBXXX indicates a lead candidate has not yet been selected © 2021 KALEIDO® 38

Q&A © 2021 KALEIDO® 39

Kaleido in Brief An Exceptional Team Leading A Novel Approach to Targeting the Microbiome Daniel Menichella President and Chief Executive Officer Former CEO,CureVac AG Jerald Korn, J.D. Chief Operating Officer, Tesaro Johan Van Hylckama Vliag, Ph.D. Chief Scientifin Officer Former VP for Microviome & Human Health Innovation, Chr. Hansen Kimberly Hocknell SVP, Techincal Operations Former Director of GMP Facilities and systems, LFB Mark Wingertzahn, Ph.D. SVP, Head of Development Former Head of Clinical Development, GSK William Duke Chief Financial Officer Former CFO, Pulmatrix Commanding the Microbiome Small molecule approach,using synthetic MMT glycans to modulate the immune system via the gut Advancing Comprehensive Pipeline Scalable discovery and manufacturing platform supporting a robust pipeline of MMts to address Several indications including UC, COPD and psoriasis Poised For Growth New Phase 2 clinical trials in UC and COPD planned for 1h22, and continuing to grow strategic partnerships with notable instititions, companies and foundations © 2021 KALEIDO®40







































