0000018230 cat:FinanceReceivableMember cat:CustomerMember cat:MiningMember 2019-12-31
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549

FORM 10-Q
☒ QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the quarterly period ended March 31, 2020
OR
☐ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 1-768
CATERPILLAR INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 37-0602744 | |||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation) | (IRS Employer I.D. No.) | |||
| 510 Lake Cook Road, | Suite 100, | Deerfield, | Illinois | 60015 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |||
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (224) 551-4000
Former Name, Former Address and Former Fiscal Year, if Changed Since Last Report: N/A
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol (s) | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock ($1.00 par value) | CAT | New York Stock Exchange | ¹ |
| 9 3/8% Debentures due March 15, 2021 | CAT21 | New York Stock Exchange | |
| 8% Debentures due February 15, 2023 | CAT23 | New York Stock Exchange | |
| 5.3% Debentures due September 15, 2035 | CAT35 | New York Stock Exchange | |
¹ In addition to the New York Stock Exchange, Caterpillar common stock is also listed on stock exchanges in France and Switzerland.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ☒ | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | Smaller reporting company | ☐ |
| Emerging growth company | ☐ | ||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
At March 31, 2020, 541,951,509 shares of common stock of the registrant were outstanding.
Table of Contents
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors | |
| Item 3. | Defaults Upon Senior Securities | * |
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | * |
| Item 5. | Other Information | * |
* Item omitted because no answer is called for or item is not applicable.
2
Part I. FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Item 1. Financial Statements
Caterpillar Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in millions except per share data)
| Three Months Ended March 31 | |||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | ||||||
| Sales and revenues: | |||||||
| Sales of Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 9,914 | $ | 12,724 | |||
| Revenues of Financial Products | 721 | 742 | |||||
| Total sales and revenues | 10,635 | 13,466 | |||||
| Operating costs: | |||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 7,266 | 9,003 | |||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 1,121 | 1,319 | |||||
| Research and development expenses | 356 | 435 | |||||
| Interest expense of Financial Products | 175 | 190 | |||||
| Other operating (income) expenses | 313 | 312 | |||||
| Total operating costs | 9,231 | 11,259 | |||||
| Operating profit | 1,404 | 2,207 | |||||
| Interest expense excluding Financial Products | 113 | 103 | |||||
| Other income (expense) | 222 | 160 | |||||
| Consolidated profit before taxes | 1,513 | 2,264 | |||||
| Provision (benefit) for income taxes | 425 | 387 | |||||
| Profit of consolidated companies | 1,088 | 1,877 | |||||
| Equity in profit (loss) of unconsolidated affiliated companies | 5 | 7 | |||||
| Profit of consolidated and affiliated companies | 1,093 | 1,884 | |||||
| Less: Profit (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 1 | 3 | |||||
Profit 1 | $ | 1,092 | $ | 1,881 | |||
| Profit per common share | $ | 2.00 | $ | 3.29 | |||
Profit per common share – diluted 2 | $ | 1.98 | $ | 3.25 | |||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding (millions) | |||||||
| – Basic | 546.8 | 572.4 | |||||
– Diluted 2 | 551.1 | 578.8 | |||||
1 Profit attributable to common shareholders.
2 Diluted by assumed exercise of stock-based compensation awards using the treasury stock method.
See accompanying notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
3
Caterpillar Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in millions)
| Three Months Ended March 31 | |||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | ||||||
| Profit of consolidated and affiliated companies | $ | 1,093 | $ | 1,884 | |||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | |||||||
| Foreign currency translation, net of tax (provision)/benefit of: 2020- $(10); 2019 - $(4) | (360 | ) | (22 | ) | |||
| Pension and other postretirement benefits: | |||||||
| Amortization of prior service (credit) cost, net of tax (provision)/benefit of: 2020 - $2; 2019 - $3; | (7 | ) | (7 | ) | |||
| Derivative financial instruments: | |||||||
| Gains (losses) deferred, net of tax (provision)/benefit of: 2020 - 3 ; 2019 - $(3) | (5 | ) | 10 | ||||
| (Gains) losses reclassified to earnings, net of tax (provision)/benefit of: 2020 - $15 $; 2019 - $2 | (55 | ) | (9 | ) | |||
| Available-for-sale securities: | |||||||
| Gains (losses) deferred, net of tax (provision)/benefit of: 2020 - $4; 2019 - $(6) | (18 | ) | 15 | ||||
| (Gains) losses reclassified to earnings, net of tax (provision)/benefit of: 2020 - $0; 2019 - $0 | — | 1 | |||||
| Total other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | (445 | ) | (12 | ) | |||
| Comprehensive income | 648 | 1,872 | |||||
| Less: comprehensive income attributable to the noncontrolling interests | 1 | 3 | |||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to shareholders | $ | 647 | $ | 1,869 | |||
See accompanying notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
4
Caterpillar Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Financial Position
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in millions)
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||
| Assets | |||||||
| Current assets: | |||||||
| Cash and short-term investments | $ | 7,123 | $ | 8,284 | |||
| Receivables – trade and other | 7,834 | 8,568 | |||||
| Receivables – finance | 9,120 | 9,336 | |||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 1,761 | 1,739 | |||||
| Inventories | 11,748 | 11,266 | |||||
| Total current assets | 37,586 | 39,193 | |||||
| Property, plant and equipment – net | 12,488 | 12,904 | |||||
| Long-term receivables – trade and other | 1,196 | 1,193 | |||||
| Long-term receivables – finance | 12,021 | 12,651 | |||||
| Noncurrent deferred and refundable income taxes | 1,426 | 1,411 | |||||
| Intangible assets | 1,478 | 1,565 | |||||
| Goodwill | 6,140 | 6,196 | |||||
| Other assets | 3,559 | 3,340 | |||||
| Total assets | $ | 75,894 | $ | 78,453 | |||
| Liabilities | |||||||
| Current liabilities: | |||||||
| Short-term borrowings: | |||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | — | $ | 5 | |||
| Financial Products | 4,789 | 5,161 | |||||
| Accounts payable | 5,769 | 5,957 | |||||
| Accrued expenses | 3,776 | 3,750 | |||||
| Accrued wages, salaries and employee benefits | 878 | 1,629 | |||||
| Customer advances | 1,295 | 1,187 | |||||
| Dividends payable | — | 567 | |||||
| Other current liabilities | 2,074 | 2,155 | |||||
| Long-term debt due within one year: | |||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | 143 | 16 | |||||
| Financial Products | 7,792 | 6,194 | |||||
| Total current liabilities | 26,516 | 26,621 | |||||
| Long-term debt due after one year: | |||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | 8,998 | 9,141 | |||||
| Financial Products | 15,371 | 17,140 | |||||
| Liability for postemployment benefits | 6,333 | 6,599 | |||||
| Other liabilities | 4,437 | 4,323 | |||||
| Total liabilities | 61,655 | 63,824 | |||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Notes 11 and 14) | |||||||
| Shareholders’ equity | |||||||
| Common stock of $1.00 par value: | |||||||
| Authorized shares: 2,000,000,000 Issued shares: (3/31/20 and 12/31/19 – 814,894,624) at paid-in amount | 6,046 | 5,935 | |||||
| Treasury stock (3/31/20 – 272,943,115 shares; 12/31/19 – 264,812,014 shares) at cost | (25,341 | ) | (24,217 | ) | |||
| Profit employed in the business | 35,504 | 34,437 | |||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (2,012 | ) | (1,567 | ) | |||
| Noncontrolling interests | 42 | 41 | |||||
| Total shareholders’ equity | 14,239 | 14,629 | |||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 75,894 | $ | 78,453 | |||
See accompanying notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
5
Caterpillar Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in millions)
Common stock | Treasury stock | Profit employed in the business | Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | Noncontrolling interests | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 5,827 | $ | (20,531 | ) | $ | 30,427 | $ | (1,684 | ) | $ | 41 | $ | 14,080 | |||||||||
| Adjustments to adopt new accounting guidance | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lease accounting | — | — | 235 | — | — | 235 | |||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification of certain tax effects from accumulated other comprehensive income | — | — | (108 | ) | 108 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2019 | 5,827 | (20,531 | ) | 30,554 | (1,576 | ) | 41 | 14,315 | |||||||||||||||
| Profit of consolidated and affiliated companies | — | — | 1,881 | — | 3 | 1,884 | |||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation, net of tax | — | — | — | (22 | ) | — | (22 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Pension and other postretirement benefits, net of tax | — | — | — | (7 | ) | — | (7 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial instruments, net of tax | — | — | — | 1 | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale securities, net of tax | — | — | — | 16 | — | 16 | |||||||||||||||||
| Distribution to noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | — | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Common shares issued from treasury stock for stock-based compensation: 1,859,065 | (73 | ) | 68 | — | — | — | (5 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | 45 | — | — | — | — | 45 | |||||||||||||||||
Common shares repurchased: 5,699,525 1 | — | (751 | ) | — | — | — | (751 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Other | 5 | — | — | — | (2 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2019 | $ | 5,804 | $ | (21,214 | ) | $ | 32,435 | $ | (1,588 | ) | $ | 41 | $ | 15,478 | |||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | $ | 5,935 | $ | (24,217 | ) | $ | 34,437 | $ | (1,567 | ) | $ | 41 | $ | 14,629 | |||||||||
Adjustments to adopt new accounting guidance 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Credit losses | — | — | (25 | ) | — | — | (25 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2020 | 5,935 | (24,217 | ) | 34,412 | (1,567 | ) | 41 | 14,604 | |||||||||||||||
| Profit of consolidated and affiliated companies | — | — | 1,092 | — | 1 | 1,093 | |||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation, net of tax | — | — | — | (360 | ) | — | (360 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Pension and other postretirement benefits, net of tax | — | — | — | (7 | ) | — | (7 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial instruments, net of tax | — | — | — | (60 | ) | — | (60 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale securities, net of tax | — | — | — | (18 | ) | — | (18 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Common shares issued from treasury stock for stock-based compensation: 1,197,083 | (62 | ) | 39 | — | — | — | (23 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | 47 | — | — | — | — | 47 | |||||||||||||||||
Common shares repurchased: 9,328,184 1 | — | (1,163 | ) | — | — | — | (1,163 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Other | 126 | — | — | — | — | 126 | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2020 | $ | 6,046 | $ | (25,341 | ) | $ | 35,504 | $ | (2,012 | ) | $ | 42 | $ | 14,239 | |||||||||
1 See Note 12 for additional information.
2 See Note 2 for additional information.
See accompanying notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
6
Caterpillar Inc.
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flow
(Unaudited)
(Millions of dollars)
| Three Months Ended March 31 | |||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | ||||||
| Cash flow from operating activities: | |||||||
| Profit of consolidated and affiliated companies | $ | 1,093 | $ | 1,884 | |||
| Adjustments for non-cash items: | |||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 614 | 641 | |||||
| Gain on remeasurement of a non-U.S. pension obligation | (254 | ) | — | ||||
| Provision (benefit) for deferred income taxes | 20 | (11 | ) | ||||
| Other | 534 | 88 | |||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions and divestitures: | |||||||
| Receivables – trade and other | 500 | (150 | ) | ||||
| Inventories | (541 | ) | (813 | ) | |||
| Accounts payable | 90 | 355 | |||||
| Accrued expenses | (97 | ) | 135 | ||||
| Accrued wages, salaries and employee benefits | (722 | ) | (1,185 | ) | |||
| Customer advances | 116 | 105 | |||||
| Other assets – net | (50 | ) | (7 | ) | |||
| Other liabilities – net | (173 | ) | 79 | ||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) operating activities | 1,130 | 1,121 | |||||
| Cash flow from investing activities: | |||||||
| Capital expenditures – excluding equipment leased to others | (305 | ) | (278 | ) | |||
| Expenditures for equipment leased to others | (243 | ) | (269 | ) | |||
| Proceeds from disposals of leased assets and property, plant and equipment | 216 | 209 | |||||
| Additions to finance receivables | (2,953 | ) | (2,615 | ) | |||
| Collections of finance receivables | 3,153 | 2,818 | |||||
| Proceeds from sale of finance receivables | 31 | 44 | |||||
| Investments and acquisitions (net of cash acquired) | (35 | ) | (2 | ) | |||
| Proceeds from sale of securities | 68 | 57 | |||||
| Investments in securities | (180 | ) | (107 | ) | |||
| Other – net | 35 | (38 | ) | ||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) investing activities | (213 | ) | (181 | ) | |||
| Cash flow from financing activities: | |||||||
| Dividends paid | (567 | ) | (494 | ) | |||
| Common stock issued, including treasury shares reissued | (23 | ) | (5 | ) | |||
| Common shares repurchased | (1,043 | ) | (751 | ) | |||
| Proceeds from debt issued (original maturities greater than three months): | |||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | 15 | — | |||||
| Financial Products | 2,126 | 2,665 | |||||
| Payments on debt (original maturities greater than three months): | |||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | (6 | ) | (2 | ) | |||
| Financial Products | (2,460 | ) | (2,565 | ) | |||
| Short-term borrowings – net (original maturities three months or less) | (40 | ) | (522 | ) | |||
| Other – net | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | |||
| Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities | (1,999 | ) | (1,675 | ) | |||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | (80 | ) | 3 | ||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and short-term investments and restricted cash | (1,162 | ) | (732 | ) | |||
| Cash and short-term investments and restricted cash at beginning of period | 8,292 | 7,890 | |||||
| Cash and short-term investments and restricted cash at end of period | $ | 7,130 | $ | 7,158 | |||
All short-term investments, which consist primarily of highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less, are considered to be cash equivalents.
See accompanying notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
7
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unaudited)
| 1. | A. Nature of operations |
Information in our financial statements and related commentary are presented in the following categories:
Machinery, Energy & Transportation (ME&T) – Represents the aggregate total of Construction Industries, Resource Industries, Energy & Transportation and the All Other operating segment and related corporate items and eliminations.
Financial Products – Primarily includes the company’s Financial Products Segment. This category includes Caterpillar Financial Services Corporation (Cat Financial), Caterpillar Insurance Holdings Inc. (Insurance Services) and their respective subsidiaries.
B. Basis of presentation
In the opinion of management, the accompanying unaudited financial statements include all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, necessary for a fair statement of (a) the consolidated results of operations for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, (b) the consolidated comprehensive income for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, (c) the consolidated financial position at March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, (d) the consolidated changes in shareholders’ equity for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 and (e) the consolidated cash flow for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019. The financial statements have been prepared in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (U.S. GAAP) and pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Interim results are not necessarily indicative of results for a full year. The information included in this Form 10-Q should be read in conjunction with the audited financial statements and notes thereto included in our company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019 (2019 Form 10-K).
The December 31, 2019 financial position data included herein is derived from the audited consolidated financial statements included in the 2019 Form 10-K but does not include all disclosures required by U.S. GAAP. Certain amounts for prior periods have been reclassified to conform to the current period financial statement presentation.
Unconsolidated Variable Interest Entities (VIEs)
We have affiliates, suppliers and dealers that are VIEs of which we are not the primary beneficiary. Although we have provided financial support, we do not have the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of each entity. Our maximum exposure to loss from these VIEs for which we are not the primary beneficiary was $134 million and $133 million as of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively.
Cat Financial has end-user customers that are VIEs of which we are not the primary beneficiary. Although we have provided financial support to these entities and therefore have a variable interest, we do not have the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact their economic performance. Our maximum exposure to loss from our involvement with these VIEs is limited to the credit risk inherently present in the financial support that we have provided. These risks are evaluated and reflected in our financial statements as part of our overall portfolio of finance receivables and related allowance for credit losses.
8
2. New accounting guidance
A. Adoption of new accounting standards
Credit losses (Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2016-13) – In June 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued new accounting guidance to introduce a new model for recognizing credit losses on financial instruments based on an estimate of current expected credit losses. The new guidance applies to loans, accounts receivable, trade receivables, other financial assets measured at amortized cost, loan commitments and other off-balance sheet credit exposures. The new guidance also applies to debt securities and other financial assets measured at fair value through other comprehensive income. The new guidance was effective January 1, 2020 and was applied using a modified retrospective approach through a cumulative effect adjustment to retained earnings as of January 1, 2020. Prior period comparative information has not been recast and continues to be reported under the accounting guidance in effect for those periods. The adoption did not have a material impact on our financial statements.
We adopted the following ASUs effective January 1, 2020, none of which had a material impact on our financial statements:
| ASU | Description |
| 2018-13 | Fair value measurement |
| 2018-15 | Internal-use software |
| 2018-19 | Codification improvements - Credit losses |
| 2019-04 | Codification improvements - Credit losses, Derivatives & hedging, and Financial instruments |
| 2019-05 | Financial instruments - Credit losses |
| 2019-11 | Codification improvements - Credit losses |
| 2019-12 | Simplifying accounting for income taxes |
| 2020-02 | Financial instruments - Credit losses |
| 2020-03 | Codification improvements - Financial instruments |
B. Accounting standards issued but not yet adopted
We consider the applicability and impact of all ASUs. The ASUs were assessed and either determined to be not applicable or not expected to have a material impact on our financial statements.
| 3. | Sales and revenue contract information |
Trade receivables represent amounts due from dealers and end users for the sale of our products. In addition, Cat Financial provides wholesale inventory financing for a dealer’s purchase of inventory. Wholesale inventory receivables are included in Receivables – trade and other and Long-term receivables – trade and other in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position. Trade receivables from dealers and end users were $7,645 million, $7,648 million and $7,743 million as of March 31, 2020, December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, and are recognized in Receivables – trade and other in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position. Long-term trade receivables from dealers and end users were $663 million, $693 million and $674 million as of March 31, 2020, December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively, and are recognized in Long-term receivables – trade and other in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position.
We invoice in advance of recognizing the sale of certain products. We recognize advanced customer payments as a contract liability in Customer advances and Other liabilities in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position. Contract liabilities were $1,757 million, $1,654 million and $1,680 million as of March 31, 2020, December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. We reduce the contract liability when revenue is recognized. During the three months ended March 31, 2020, we recognized $368 million of revenue that was recorded as a contract liability at the beginning of 2020. During the three months ended March 31, 2019, we recognized $507 million of revenue that was recorded as a contract liability at the beginning of 2019.
9
As of March 31, 2020, we have entered into contracts with dealers and end users for which sales have not been recognized as we have not satisfied our performance obligations and transferred control of the products. The dollar amount of unsatisfied performance obligations for contracts with an original duration greater than one year is $6.4 billion, of which $2.6 billion is expected to be completed and revenue recognized in the twelve months following March 31, 2020. We have elected the practical expedient not to disclose unsatisfied performance obligations with an original contract duration of one year or less. Contracts with an original duration of one year or less are primarily sales to dealers for machinery, engines and replacement parts.
See Note 16 for further disaggregated sales and revenues information.
4. Stock-based compensation
Accounting for stock-based compensation requires that the cost resulting from all stock-based payments be recognized in the financial statements based on the grant date fair value of the award. Our stock-based compensation primarily consists of stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs) and performance-based restricted stock units (PRSUs).
We recognized pretax stock-based compensation expense of $47 million and $45 million for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
The following table illustrates the type and fair value of the stock-based compensation awards granted during the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively:
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares Granted | Weighted-Average Fair Value Per Share | Weighted-Average Grant Date Stock Price | Shares Granted | Weighted-Average Fair Value Per Share | Weighted-Average Grant Date Stock Price | ||||||||||||||||
| Stock options | 1,913,888 | $ | 25.98 | $ | 127.60 | 1,499,524 | $ | 40.98 | $ | 138.35 | |||||||||||
| RSUs | 705,287 | $ | 127.60 | $ | 127.60 | 657,389 | $ | 138.35 | $ | 138.35 | |||||||||||
| PRSUs | 371,641 | $ | 127.60 | $ | 127.60 | 342,097 | $ | 138.35 | $ | 138.35 | |||||||||||
The following table provides the assumptions used in determining the fair value of the stock-based awards for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively:
| Grant Year | |||
| 2020 | 2019 | ||
| Weighted-average dividend yield | 2.47% | 2.56% | |
| Weighted-average volatility | 25.7% | 29.1% | |
| Range of volatilities | 24.5-29.7% | 25.1-38.7% | |
| Range of risk-free interest rates | 1.21-1.39% | 2.48-2.68% | |
| Weighted-average expected lives | 8 years | 7 years | |
As of March 31, 2020, the total remaining unrecognized compensation expense related to nonvested stock-based compensation awards was $300 million, which will be amortized over the weighted-average remaining requisite service periods of approximately 1.8 years.
5. Derivative financial instruments and risk management
Our earnings and cash flow are subject to fluctuations due to changes in foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates and commodity prices. Our Risk Management Policy (policy) allows for the use of derivative financial instruments to prudently manage foreign currency exchange rate, interest rate and commodity price exposures. Our policy specifies that derivatives are not to be used for speculative purposes. Derivatives that we use are primarily foreign currency forward, option and cross currency contracts, interest rate contracts and commodity forward and option contracts. Our derivative activities are subject to the management, direction and control of our senior financial officers. Risk management practices, including the use of financial derivative instruments, are presented to the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors at least annually.
10
All derivatives are recognized on the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position at their fair value. On the date the derivative contract is entered into, we designate the derivative as (1) a hedge of the fair value of a recognized asset or liability (fair value hedge), (2) a hedge of a forecasted transaction or the variability of cash flow (cash flow hedge) or (3) an undesignated instrument. Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is qualified, designated and highly effective as a fair value hedge, along with the gain or loss on the hedged recognized asset or liability that is attributable to the hedged risk, are recorded in current earnings. Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is qualified, designated and highly effective as a cash flow hedge are recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) (AOCI), to the extent effective, on the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position until they are reclassified to earnings in the same period or periods during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. Changes in the fair value of undesignated derivative instruments are reported in current earnings. Cash flows from designated derivative financial instruments are classified within the same category as the item being hedged on the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flow. Cash flows from undesignated derivative financial instruments are included in the investing category on the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flow.
We formally document all relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as the risk-management objective and strategy for undertaking various hedge transactions. This process includes linking all derivatives that are designated as fair value hedges to specific assets and liabilities on the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position and linking cash flow hedges to specific forecasted transactions or variability of cash flow.
We also formally assess, both at the hedge’s inception and on an ongoing basis, whether the designated derivatives that are used in hedging transactions are highly effective in offsetting changes in fair values or cash flow of hedged items. When a derivative is determined not to be highly effective as a hedge or the underlying hedged transaction is no longer probable, we discontinue hedge accounting prospectively, in accordance with the derecognition criteria for hedge accounting.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
Foreign currency exchange rate movements create a degree of risk by affecting the U.S. dollar value of sales made and costs incurred in foreign currencies. Movements in foreign currency rates also affect our competitive position as these changes may affect business practices and/or pricing strategies of non-U.S.-based competitors. Additionally, we have balance sheet positions denominated in foreign currencies, thereby creating exposure to movements in exchange rates.
Our ME&T operations purchase, manufacture and sell products in many locations around the world. As we have a diversified revenue and cost base, we manage our future foreign currency cash flow exposure on a net basis. We use foreign currency forward and option contracts to manage unmatched foreign currency cash inflow and outflow. Our objective is to minimize the risk of exchange rate movements that would reduce the U.S. dollar value of our foreign currency cash flow. Our policy allows for managing anticipated foreign currency cash flow for up to five years. As of March 31, 2020, the maximum term of these outstanding contracts was approximately 60 months.
We generally designate as cash flow hedges at inception of the contract any Australian dollar, Brazilian real, British pound, Canadian dollar, Chinese yuan, Euro, Indian rupee, Japanese yen, Mexican peso, Singapore dollar or Thailand baht forward or option contracts that meet the requirements for hedge accounting and the maturity extends beyond the current quarter-end. Designation is performed on a specific exposure basis to support hedge accounting. The remainder of ME&T foreign currency contracts are undesignated.
As of March 31, 2020, $44 million of deferred net losses, net of tax, included in equity (AOCI in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position), are expected to be reclassified to current earnings over the next twelve months when earnings are affected by the hedged transactions. The actual amount recorded in current earnings will vary based on exchange rates at the time the hedged transactions impact earnings.
In managing foreign currency risk for our Financial Products operations, our objective is to minimize earnings volatility resulting from conversion and the remeasurement of net foreign currency balance sheet positions and future transactions denominated in foreign currencies. Our policy allows the use of foreign currency forward, option and cross currency contracts to offset the risk of currency mismatch between our assets and liabilities and exchange rate risk associated with future transactions denominated in foreign currencies. Our foreign currency forward and option contracts are primarily undesignated. We designate fixed-to-fixed cross currency contracts as cash flow hedges to protect against movements in exchange rates on foreign currency fixed-rate assets and liabilities.
11
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate movements create a degree of risk by affecting the amount of our interest payments and the value of our fixed-rate debt. Our practice is to use interest rate contracts to manage our exposure to interest rate changes.
Our ME&T operations generally use fixed-rate debt as a source of funding. Our objective is to minimize the cost of borrowed funds. Our policy allows us to enter into fixed-to-floating interest rate contracts and forward rate agreements to meet that objective. We designate fixed-to-floating interest rate contracts as fair value hedges at inception of the contract, and we designate certain forward rate agreements as cash flow hedges at inception of the contract.
Financial Products operations has a match-funding policy that addresses interest rate risk by aligning the interest rate profile (fixed or floating rate and duration) of Cat Financial’s debt portfolio with the interest rate profile of our receivables portfolio within predetermined ranges on an ongoing basis. In connection with that policy, we use interest rate derivative instruments to modify the debt structure to match assets within the receivables portfolio. This matched funding reduces the volatility of margins between interest-bearing assets and interest-bearing liabilities, regardless of which direction interest rates move.
Our policy allows us to use fixed-to-floating, floating-to-fixed and floating-to-floating interest rate contracts to meet the match-funding objective. We designate fixed-to-floating interest rate contracts as fair value hedges to protect debt against changes in fair value due to changes in the benchmark interest rate. We designate most floating-to-fixed interest rate contracts as cash flow hedges to protect against the variability of cash flows due to changes in the benchmark interest rate.
We have, at certain times, liquidated fixed-to-floating and floating-to-fixed interest rate contracts at both ME&T and Financial Products. The gains or losses associated with these contracts at the time of liquidation are amortized into earnings over the original term of the previously designated hedged item.
Commodity Price Risk
Commodity price movements create a degree of risk by affecting the price we must pay for certain raw materials. Our policy is to use commodity forward and option contracts to manage the commodity risk and reduce the cost of purchased materials.
Our ME&T operations purchase base and precious metals embedded in the components we purchase from suppliers. Our suppliers pass on to us price changes in the commodity portion of the component cost. In addition, we are subject to price changes on energy products such as natural gas and diesel fuel purchased for operational use.
Our objective is to minimize volatility in the price of these commodities. Our policy allows us to enter into commodity forward and option contracts to lock in the purchase price of a portion of these commodities within a five-year horizon. All such commodity forward and option contracts are undesignated.
12
The location and fair value of derivative instruments reported in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position are as follows:
(Millions of dollars) | Consolidated Statement of Financial | Asset (Liability) Fair Value | |||||||
| Position Location | March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| Designated derivatives | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | |||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Receivables – trade and other | $ | 56 | $ | 18 | ||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Long-term receivables – trade and other | 9 | 9 | ||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Accrued expenses | (114 | ) | (20 | ) | ||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Other liabilities | (28 | ) | — | |||||
| Financial Products | Receivables – trade and other | 70 | 54 | ||||||
| Financial Products | Long-term receivables – trade and other | 82 | 13 | ||||||
| Financial Products | Accrued expenses | (1 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||
| Interest rate contracts | |||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Receivables – trade and other | 6 | — | ||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Accrued expenses | (10 | ) | — | |||||
| Financial Products | Long-term receivables – trade and other | 61 | 5 | ||||||
| Financial Products | Accrued expenses | (31 | ) | (25 | ) | ||||
| $ | 100 | $ | 51 | ||||||
| Undesignated derivatives | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | |||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Receivables – trade and other | $ | 2 | $ | 1 | ||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Accrued expenses | (7 | ) | — | |||||
| Financial Products | Receivables – trade and other | 75 | 7 | ||||||
| Financial Products | Long-term receivables – trade and other | 13 | 5 | ||||||
| Financial Products | Accrued expenses | (28 | ) | (22 | ) | ||||
| Commodity contracts | |||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Receivables – trade and other | 1 | 4 | ||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Accrued expenses | (35 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||
| $ | 21 | $ | (6 | ) | |||||
13
The total notional amounts of the derivative instruments were as follows:
| (Millions of dollars) | March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 4,784 | $ | 2,563 | ||||
| Financial Products | $ | 10,580 | $ | 8,931 | ||||
The notional amounts of the derivative financial instruments do not represent amounts exchanged by the parties. The amounts exchanged by the parties are calculated by reference to the notional amounts and by other terms of the derivatives, such as foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates or commodity prices.
The effect of derivatives designated as hedging instruments on the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations is as follows:
| Cash Flow Hedges | |||||||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||
| Recognized in Earnings | |||||||||||||
(Millions of dollars) | Amount of Gains (Losses) Recognized in AOCI | Classification of Gains (Losses) | Amount of Gains (Losses) Reclassified from AOCI | Amount of the line items in the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | |||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | (90 | ) | Sales of Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 5 | $ | 9,914 | |||||
| Cost of goods sold | (11 | ) | 7,266 | ||||||||||
| Financial Products | 101 | Interest expense of Financial Products | 11 | 175 | |||||||||
| Other income (expense) | 71 | 222 | |||||||||||
| Interest rate contracts | |||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | (4 | ) | Interest expense excluding Financial Products | (1 | ) | 113 | |||||||
| Financial Products | (15 | ) | Interest expense of Financial Products | (5 | ) | 175 | |||||||
| $ | (8 | ) | $ | 70 | |||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||
| Recognized in Earnings | |||||||||||||
| Amount of Gains (Losses) Recognized in AOCI | Classification of Gains (Losses) | Amount of Gains (Losses) Reclassified from AOCI | Amount of the line items in the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations | ||||||||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | |||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 17 | Sales of Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 1 | $ | 12,724 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | (3 | ) | 9,003 | ||||||||||
| Financial Products | 22 | Interest expense of Financial Products | 7 | 190 | |||||||||
| Other income (expense) | 6 | 160 | |||||||||||
| Interest rate contracts | |||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | — | Interest expense excluding Financial Products | (1 | ) | 103 | ||||||||
| Financial Products | (26 | ) | Interest expense of Financial Products | 1 | 190 | ||||||||
| $ | 13 | $ | 11 | ||||||||||
14
The effect of derivatives not designated as hedging instruments on the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations is as follows:
(Millions of dollars) | Classification of Gains (Losses) | Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | ||||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | |||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Other income (expense) | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 6 | |||
| Financial Products | Other income (expense) | 108 | (29 | ) | |||||
| Commodity contracts | |||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Other income (expense) | (46 | ) | 23 | |||||
| $ | 59 | $ | — | ||||||
We enter into International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA) master netting agreements within ME&T and Financial Products that permit the net settlement of amounts owed under their respective derivative contracts. Under these master netting agreements, net settlement generally permits the company or the counterparty to determine the net amount payable for contracts due on the same date and in the same currency for similar types of derivative transactions. The master netting agreements generally also provide for net settlement of all outstanding contracts with a counterparty in the case of an event of default or a termination event.
Collateral is generally not required of the counterparties or of our company under the master netting agreements. As of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, no cash collateral was received or pledged under the master netting agreements.
15
The effect of the net settlement provisions of the master netting agreements on our derivative balances upon an event of default or termination event is as follows:
| March 31, 2020 | Gross Amounts Not Offset in the Statement of Financial Position | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Gross Amount of Recognized Assets | Gross Amounts Offset in the Statement of Financial Position | Net Amount of Assets Presented in the Statement of Financial Position | Financial Instruments | Cash Collateral Received | Net Amount of Assets | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 74 | $ | — | $ | 74 | $ | (74 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| Financial Products | 301 | — | 301 | (47 | ) | — | 254 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 375 | $ | — | $ | 375 | $ | (121 | ) | $ | — | $ | 254 | |||||||||||
| March 31, 2020 | Gross Amounts Not Offset in the Statement of Financial Position | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Gross Amount of Recognized Liabilities | Gross Amounts Offset in the Statement of Financial Position | Net Amount of Liabilities Presented in the Statement of Financial Position | Financial Instruments | Cash Collateral Pledged | Net Amount of Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | (194 | ) | $ | — | $ | (194 | ) | $ | 74 | $ | — | $ | (120 | ) | |||||||||
| Financial Products | (60 | ) | — | (60 | ) | 47 | — | (13 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | (254 | ) | $ | — | $ | (254 | ) | $ | 121 | $ | — | $ | (133 | ) | |||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | Gross Amounts Not Offset in the Statement of Financial Position | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Gross Amount of Recognized Assets | Gross Amounts Offset in the Statement of Financial Position | Net Amount of Assets Presented in the Statement of Financial Position | Financial Instruments | Cash Collateral Received | Net Amount of Assets | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 32 | $ | — | $ | 32 | $ | (13 | ) | $ | — | $ | 19 | |||||||||||
| Financial Products | 84 | — | 84 | (21 | ) | — | 63 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 116 | $ | — | $ | 116 | $ | (34 | ) | $ | — | $ | 82 | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | Gross Amounts Not Offset in the Statement of Financial Position | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Gross Amount of Recognized Liabilities | Gross Amounts Offset in the Statement of Financial Position | Net Amount of Liabilities Presented in the Statement of Financial Position | Financial Instruments | Cash Collateral Pledged | Net Amount of Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | (21 | ) | $ | — | $ | (21 | ) | $ | 13 | $ | — | $ | (8 | ) | |||||||||
| Financial Products | (50 | ) | — | (50 | ) | 21 | — | (29 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | (71 | ) | $ | — | $ | (71 | ) | $ | 34 | $ | — | $ | (37 | ) | |||||||||
16
6. Inventories
Inventories (principally using the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method) are comprised of the following:
| (Millions of dollars) | March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||
| Raw materials | $ | 4,264 | $ | 4,263 | |||
| Work-in-process | 1,227 | 1,147 | |||||
| Finished goods | 6,010 | 5,598 | |||||
| Supplies | 247 | 258 | |||||
| Total inventories | $ | 11,748 | $ | 11,266 | |||
7. Intangible assets and goodwill
A. Intangible assets
Intangible assets are comprised of the following:
| March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Weighted Amortizable Life (Years) | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Net | |||||||||
| Customer relationships | 15 | $ | 2,402 | $ | (1,421 | ) | $ | 981 | |||||
| Intellectual property | 12 | 1,488 | (1,050 | ) | 438 | ||||||||
| Other | 13 | 186 | (127 | ) | 59 | ||||||||
| Total finite-lived intangible assets | 14 | $ | 4,076 | $ | (2,598 | ) | $ | 1,478 | |||||
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||
Weighted Amortizable Life (Years) | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Net | ||||||||||
| Customer relationships | 15 | $ | 2,450 | $ | (1,406 | ) | $ | 1,044 | |||||
| Intellectual property | 12 | 1,510 | (1,055 | ) | 455 | ||||||||
| Other | 13 | 191 | (125 | ) | 66 | ||||||||
| Total finite-lived intangible assets | 14 | $ | 4,151 | $ | (2,586 | ) | $ | 1,565 | |||||
Amortization expense for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 was $80 million and $82 million, respectively. Amortization expense related to intangible assets is expected to be:
| (Millions of dollars) | ||||||||||
| Remaining Nine Months of 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | Thereafter | |||||
| $226 | $288 | $271 | $214 | $157 | $322 | |||||
B. Goodwill
NaN goodwill was impaired during the three months ended March 31, 2020 or 2019.
17
The changes in carrying amount of goodwill by reportable segment for the three months ended March 31, 2020 were as follows:
| (Millions of dollars) | December 31, 2019 | Other Adjustments 1 | March 31, 2020 | |||||||||
| Construction Industries | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill | $ | 306 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 305 | |||||
| Impairments | (22 | ) | — | (22 | ) | |||||||
| Net goodwill | 284 | (1 | ) | 283 | ||||||||
| Resource Industries | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill | 4,156 | (38 | ) | 4,118 | ||||||||
| Impairments | (1,175 | ) | — | (1,175 | ) | |||||||
| Net goodwill | 2,981 | (38 | ) | 2,943 | ||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill | 2,875 | (17 | ) | 2,858 | ||||||||
All Other 2 | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill | 56 | — | 56 | |||||||||
| Consolidated total | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill | 7,393 | (56 | ) | 7,337 | ||||||||
| Impairments | (1,197 | ) | — | (1,197 | ) | |||||||
| Net goodwill | $ | 6,196 | $ | (56 | ) | $ | 6,140 | |||||
1 Other adjustments are comprised primarily of foreign currency translation.
2 Includes All Other operating segment (See Note 16).
18
8. Investments in debt and equity securities
We have investments in certain debt and equity securities, primarily at Insurance Services, which are recorded at fair value and are primarily included in Other assets in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position.
Debt securities have been classified as available-for-sale, and the unrealized gains and losses arising from the revaluation of these debt securities are included, net of applicable deferred income taxes, in equity (Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position). The unrealized gains and losses arising from the revaluation of the equity securities are included in Other income (expense) in the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations. Realized gains and losses on sales of investments are generally determined using the specific identification method for debt and equity securities and are included in Other income (expense) in the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations.
The cost basis and fair value of debt securities with unrealized gains and losses included in equity (Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position) were as follows:
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Cost Basis | Unrealized Pretax Net Gains (Losses) | Fair Value | Cost Basis | Unrealized Pretax Net Gains (Losses) | Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||
| Government debt | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. treasury bonds | $ | 9 | $ | — | $ | 9 | $ | 9 | $ | — | $ | 9 | |||||||||||
| Other U.S. and non-U.S. government bonds | 46 | 1 | 47 | 54 | — | 54 | |||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | 880 | (9 | ) | 871 | 836 | 20 | 856 | ||||||||||||||||
| Asset-backed securities | 87 | (1 | ) | 86 | 62 | — | 62 | ||||||||||||||||
| Mortgage-backed debt securities | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. governmental agency | 365 | 13 | 378 | 327 | 4 | 331 | |||||||||||||||||
| Residential | 6 | (1 | ) | 5 | 6 | — | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial | 53 | — | 53 | 46 | 1 | 47 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total debt securities | $ | 1,446 | $ | 3 | $ | 1,449 | $ | 1,340 | $ | 25 | $ | 1,365 | |||||||||||
| Available-for-sale investments in an unrealized loss position: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Less than 12 months 1 | 12 months or more 1 | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | |||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | $ | 375 | $ | 20 | $ | 42 | $ | 1 | $ | 417 | $ | 21 | |||||||||||
| Asset-backed securities | $ | 46 | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | $ | — | $ | 48 | $ | 2 | |||||||||||
| Total | $ | 421 | $ | 22 | $ | 44 | $ | 1 | $ | 465 | $ | 23 | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Less than 12 months 1 | 12 months or more 1 | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | |||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | $ | 58 | $ | 1 | $ | 50 | $ | — | $ | 108 | $ | 1 | |||||||||||
| Total | $ | 58 | $ | 1 | $ | 50 | $ | — | $ | 108 | $ | 1 | |||||||||||
1 Indicates the length of time that individual securities have been in a continuous unrealized loss position. | |||||||||||||||||||||||
19
Corporate Bonds. The unrealized losses on our investments in corporate bonds relate to changes in interest rates and credit-related yield spreads since time of purchase. We do not intend to sell the investments, and it is not likely that we will be required to sell the investments before recovery of their amortized cost basis.
The cost basis and fair value of the available-for-sale debt securities at March 31, 2020, by contractual maturity, is shown below. Expected maturities will differ from contractual maturities because borrowers may have the right to prepay and creditors may have the right to call obligations.
| March 31, 2020 | |||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Cost Basis | Fair Value | |||||
| Due in one year or less | $ | 97 | $ | 97 | |||
| Due after one year through five years | 683 | 680 | |||||
| Due after five years through ten years | 189 | 184 | |||||
| Due after ten years | 53 | 52 | |||||
| U.S. governmental agency mortgage-backed securities | 365 | 378 | |||||
| Residential mortgage-backed securities | 6 | 5 | |||||
| Commercial mortgage-backed securities | 53 | 53 | |||||
| Total debt securities – available-for-sale | $ | 1,446 | $ | 1,449 | |||
| Sales of available-for-sale securities: | |||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31 | |||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | 2020 | 2019 | |||||
| Proceeds from the sale of available-for-sale securities | $ | 58 | $ | 47 | |||
| Gross losses from the sale of available-for-sale securities | $ | — | $ | 1 | |||
For the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, the net unrealized gains (losses) for equity securities held at March 31, 2020 and 2019 were $(54) million and $38 million, respectively.
9. Postretirement benefits
A. Pension and postretirement benefit costs
U.S. Pension Benefits | Non-U.S. Pension Benefits | Other Postretirement Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||
(Millions of dollars) | March 31 | March 31 | March 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||
| For the three months ended: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of net periodic benefit cost: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Service cost | $ | — | $ | 29 | $ | 14 | $ | 21 | $ | 23 | $ | 20 | |||||||||||
| Interest cost | 121 | 150 | 19 | 23 | 26 | 34 | |||||||||||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | (198 | ) | (181 | ) | (35 | ) | (37 | ) | (3 | ) | (5 | ) | |||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service cost (credit) | — | — | — | — | (9 | ) | (10 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Gain on remeasurement of a non-U.S. pension obligation 1 | — | — | (254 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost (benefit) 2 | $ | (77 | ) | $ | (2 | ) | $ | (256 | ) | $ | 7 | $ | 37 | $ | 39 | ||||||||
1 | Total lump-sum transfers out of a non-U.S. pension plan exceeded the service and interest cost for 2020, which required us to follow settlement accounting and remeasure the plan's obligation as of March 31, 2020. |
2 | The service cost component is included in Operating costs in the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations. All other components are included in Other income (expense) in the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations. |
20
We made $98 million of contributions to our pension and other postretirement plans during the three months ended March 31, 2020. We currently anticipate full-year 2020 contributions of approximately $280 million.
B. Defined contribution benefit costs
Total company costs related to our defined contribution plans were as follows:
| Three Months Ended March 31 | ||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||
| U.S. Plans | $ | 19 | $ | 137 | ||||
| Non-U.S. Plans | 23 | 21 | ||||||
| $ | 42 | $ | 158 | |||||
The decrease in the U.S. defined contribution benefit costs for the three months ended March 31, 2020 is primarily due to the fair value adjustments related to our non-qualified deferred compensation plans.
10. Leases
Revenues from finance and operating leases, primarily included in Revenues of Financial Products on the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations, were as follows:
| (Millions of dollars) | ||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31 | ||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| Finance lease revenue | $ | 125 | $ | 119 | ||||
| Operating lease revenue | 303 | 316 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 428 | $ | 435 | ||||
Revenues are presented net of sales and other related taxes.
11. Guarantees and product warranty
Caterpillar dealer performance guarantees
We have provided an indemnity to a third-party insurance company for potential losses related to performance bonds issued on behalf of Caterpillar dealers. The bonds have varying terms and are issued to insure governmental agencies against nonperformance by certain dealers. We also provided guarantees to third-parties related to the performance of contractual obligations by certain Caterpillar dealers. These guarantees have varying terms and cover potential financial losses incurred by the third parties resulting from the dealers’ nonperformance.
In 2016, we provided a guarantee to an end user related to the performance of contractual obligations by a Caterpillar dealer. Under the guarantee, which expires in 2025, non-performance by the Caterpillar dealer could require Caterpillar to satisfy the contractual obligations by providing goods, services or financial compensation to the end user up to an annual designated cap.
Supplier consortium performance guarantee
We have provided a guarantee to a customer in Europe related to the performance of contractual obligations by a supplier consortium to which one of our Caterpillar subsidiaries is a member. The guarantee covers potential damages incurred by the customer resulting from the supplier consortium's non-performance. The damages are capped except for failure of the consortium to meet certain obligations outlined in the contract in the normal course of business. The guarantee will expire when the supplier consortium performs all of its contractual obligations, which is expected to be completed in 2022.
21
We have dealer performance guarantees and third-party performance guarantees that do not limit potential payment to end users related to indemnities and other commercial contractual obligations. In addition, we have entered into contracts involving industry standard indemnifications that do not limit potential payment. For these unlimited guarantees, we are unable to estimate a maximum potential amount of future payments that could result from claims made.
No significant loss has been experienced or is anticipated under any of these guarantees. At both March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the related recorded liability was $5 million. The maximum potential amount of future payments (undiscounted and without reduction for any amounts that may possibly be recovered under recourse or collateralized provisions) we could be required to make under the guarantees are as follows:
| (Millions of dollars) | March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||
| Caterpillar dealer performance guarantees | $ | 1,151 | $ | 1,150 | |||
| Supplier consortium performance guarantee | 238 | 238 | |||||
| Other guarantees | 209 | 221 | |||||
| Total guarantees | $ | 1,598 | $ | 1,609 | |||
Cat Financial provides guarantees to repurchase certain loans of Caterpillar dealers from a special-purpose corporation (SPC) that qualifies as a variable interest entity. The purpose of the SPC is to provide short-term working capital loans to Caterpillar dealers. This SPC issues commercial paper and uses the proceeds to fund its loan program. Cat Financial has a loan purchase agreement with the SPC that obligates Cat Financial to purchase certain loans that are not paid at maturity. Cat Financial receives a fee for providing this guarantee, which provides a source of liquidity for the SPC. Cat Financial is the primary beneficiary of the SPC as its guarantees result in Cat Financial having both the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the SPC’s economic performance and the obligation to absorb losses, and therefore Cat Financial has consolidated the financial statements of the SPC. As of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the SPC’s assets of $1,475 million and $1,453 million, respectively, were primarily comprised of loans to dealers, and the SPC’s liabilities of $1,473 million and $1,452 million, respectively, were primarily comprised of commercial paper. The assets of the SPC are not available to pay Cat Financial’s creditors. Cat Financial may be obligated to perform under the guarantee if the SPC experiences losses. No loss has been experienced or is anticipated under this loan purchase agreement.
Our product warranty liability is determined by applying historical claim rate experience to the current field population and dealer inventory. Generally, historical claim rates are based on actual warranty experience for each product by machine model/engine size by customer or dealer location (inside or outside North America). Specific rates are developed for each product shipment month and are updated monthly based on actual warranty claim experience.
| (Millions of dollars) | 2020 | ||
| Warranty liability, January 1 | $ | 1,541 | |
| Reduction in liability (payments) | (227 | ) | |
| Increase in liability (new warranties) | 219 | ||
| Warranty liability, March 31 | $ | 1,533 | |
| (Millions of dollars) | 2019 | ||
| Warranty liability, January 1 | $ | 1,391 | |
| Reduction in liability (payments) | (903 | ) | |
| Increase in liability (new warranties) | 1,053 | ||
| Warranty liability, December 31 | $ | 1,541 | |
22
12. Profit per share
| Computations of profit per share: | Three Months Ended March 31 | ||||||||
| (Dollars in millions except per share data) | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Profit for the period (A) 1 | $ | 1,092 | $ | 1,881 | |||||
| Determination of shares (in millions): | |||||||||
| Weighted-average number of common shares outstanding (B) | 546.8 | 572.4 | |||||||
| Shares issuable on exercise of stock awards, net of shares assumed to be purchased out of proceeds at average market price | 4.3 | 6.4 | |||||||
Average common shares outstanding for fully diluted computation (C) 2 | 551.1 | 578.8 | |||||||
| Profit per share of common stock: | |||||||||
| Assuming no dilution (A/B) | $ | 2.00 | $ | 3.29 | |||||
Assuming full dilution (A/C) 2 | $ | 1.98 | $ | 3.25 | |||||
| Shares outstanding as of March 31 (in millions) | 542.0 | 571.7 | |||||||
1 Profit attributable to common shareholders. | |||||||||
2 Diluted by assumed exercise of stock-based compensation awards using the treasury stock method. | |||||||||
For the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, 4.9 million and 3.0 million outstanding stock options, respectively, were excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per share because the effect would have been antidilutive.
In July 2018, the Board approved a share repurchase authorization (the 2018 Authorization) of up to $10.0 billion of Caterpillar common stock effective January 1, 2019, with no expiration. As of March 31, 2020, approximately $4.9 billion remained available under the 2018 Authorization.
During the first three months of 2020 and 2019, we repurchased 9.3 million and 5.7 million shares of Caterpillar common stock, respectively, at an aggregate cost of $1.2 billion and $0.8 billion, respectively. These purchases were made through a combination of accelerated stock repurchase agreements with third-party financial institutions and open market transactions.
23
13. Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)
Comprehensive income and its components are presented in the Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income. Changes in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax, included in the Consolidated Statement of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity, consisted of the following:
| (Millions of dollars) | Foreign currency translation | Pension and other postretirement benefits | Derivative financial instruments | Available-for-sale securities | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | $ | (1,487 | ) | $ | (3 | ) | $ | (97 | ) | $ | 20 | $ | (1,567 | ) | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | (384 | ) | — | (5 | ) | (18 | ) | (407 | ) | |||||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive (income) loss | 24 | (7 | ) | (55 | ) | — | (38 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | (360 | ) | (7 | ) | (60 | ) | (18 | ) | (445 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2020 | $ | (1,847 | ) | $ | (10 | ) | $ | (157 | ) | $ | 2 | $ | (2,012 | ) | ||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | (1,601 | ) | $ | 12 | $ | (80 | ) | $ | (15 | ) | $ | (1,684 | ) | ||||||
| Adjustment to adopt new accounting guidance related to reclassification of certain tax effects from accumulated other comprehensive income | 98 | 19 | (9 | ) | — | 108 | ||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2019 | (1,503 | ) | 31 | (89 | ) | (15 | ) | (1,576 | ) | |||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | (22 | ) | — | 10 | 15 | 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive (income) loss | — | (7 | ) | (9 | ) | 1 | (15 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | (22 | ) | (7 | ) | 1 | 16 | (12 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2019 | $ | (1,525 | ) | $ | 24 | $ | (88 | ) | $ | 1 | $ | (1,588 | ) | |||||||
24
The effect of the reclassifications out of Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) on the Consolidated Statement of Results of Operations is as follows:
| Three Months Ended March 31 | ||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Classification of income (expense) | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| Foreign currency translation | ||||||||||
| Gain (loss) on foreign currency translation | Other income (expense) | $ | (24 | ) | $ | — | ||||
| Reclassifications net of tax | $ | (24 | ) | $ | — | |||||
| Pension and other postretirement benefits: | ||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service credit (cost) | Other income (expense) | $ | 9 | $ | 10 | |||||
| Tax (provision) benefit | (2 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||
| Reclassifications net of tax | $ | 7 | $ | 7 | ||||||
| Derivative financial instruments: | ||||||||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Sales of Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 5 | $ | 1 | |||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Cost of goods sold | (11 | ) | (3 | ) | |||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Other income (expense) | 71 | 6 | |||||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Interest expense of Financial Products | 11 | 7 | |||||||
| Interest rate contracts | Interest expense excluding Financial Products | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||
| Interest rate contracts | Interest expense of Financial Products | (5 | ) | 1 | ||||||
| Reclassifications before tax | 70 | 11 | ||||||||
| Tax (provision) benefit | (15 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
| Reclassifications net of tax | $ | 55 | $ | 9 | ||||||
| Available-for-sale securities: | ||||||||||
| Realized gain (loss) | Other income (expense) | $ | — | $ | (1 | ) | ||||
| Reclassifications net of tax | $ | — | $ | (1 | ) | |||||
| Total reclassifications from Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 38 | $ | 15 | ||||||
14. Environmental and legal matters
The Company is regulated by federal, state and international environmental laws governing its use, transport and disposal of substances and control of emissions. In addition to governing our manufacturing and other operations, these laws often impact the development of our products, including, but not limited to, required compliance with air emissions standards applicable to internal combustion engines. We have made, and will continue to make, significant research and development and capital expenditures to comply with these emissions standards.
25
We are engaged in remedial activities at a number of locations, often with other companies, pursuant to federal and state laws. When it is probable we will pay remedial costs at a site, and those costs can be reasonably estimated, the investigation, remediation, and operating and maintenance costs are accrued against our earnings. Costs are accrued based on consideration of currently available data and information with respect to each individual site, including available technologies, current applicable laws and regulations, and prior remediation experience. Where no amount within a range of estimates is more likely, we accrue the minimum. Where multiple potentially responsible parties are involved, we consider our proportionate share of the probable costs. In formulating the estimate of probable costs, we do not consider amounts expected to be recovered from insurance companies or others. We reassess these accrued amounts on a quarterly basis. The amount recorded for environmental remediation is not material and is included in Accrued expenses. We believe there is no more than a remote chance that a material amount for remedial activities at any individual site, or at all the sites in the aggregate, will be required.
On January 27, 2020, the Brazilian Federal Environmental Agency (“IBAMA”) issued Caterpillar Brasil Ltda a notice of violation regarding allegations around the requirements for use of imported oils at the Piracicaba, Brazil facility. We have instituted processes to address the allegations. While we are still discussing resolution of these allegations with IBAMA, the initial notice from IBAMA included a proposed fine of approximately $370,000. We do not expect this fine or our response to address the allegations to have a material adverse effect on the Company's consolidated results of operations, financial position or liquidity.
On January 7, 2015, the Company received a grand jury subpoena from the U.S. District Court for the Central District of Illinois. The subpoena requested documents and information from the Company relating to, among other things, financial information concerning U.S. and non-U.S. Caterpillar subsidiaries (including undistributed profits of non-U.S. subsidiaries and the movement of cash among U.S. and non-U.S. subsidiaries). The Company has received additional subpoenas relating to this investigation requesting additional documents and information relating to, among other things, the purchase and resale of replacement parts by Caterpillar Inc. and non-U.S. Caterpillar subsidiaries, dividend distributions of certain non-U.S. Caterpillar subsidiaries, and Caterpillar SARL (CSARL) and related structures. On March 2-3, 2017, agents with the Department of Commerce, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation and the Internal Revenue Service executed search and seizure warrants at 3 facilities of the Company in the Peoria, Illinois area, including its former corporate headquarters. The warrants identify, and agents seized, documents and information related to, among other things, the export of products from the United States, the movement of products between the United States and Switzerland, the relationship between Caterpillar Inc. and CSARL, and sales outside the United States. It is the Company’s understanding that the warrants, which concern both tax and export activities, are related to the ongoing grand jury investigation. The Company is continuing to cooperate with this investigation. The Company is unable to predict the outcome or reasonably estimate any potential loss; however, we currently believe that this matter will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position or liquidity.
On March 20, 2014, Brazil’s Administrative Council for Economic Defense (CADE) published a Technical Opinion which named 18 companies and over 100 individuals as defendants, including 2 subsidiaries of Caterpillar Inc., MGE - Equipamentos e Serviços Ferroviários Ltda. (MGE) and Caterpillar Brasil Ltda (CBL). The publication of the Technical Opinion opened CADE’s official administrative investigation into allegations that the defendants participated in anticompetitive bid activity for the construction and maintenance of metro and train networks in Brazil. While companies cannot be held criminally liable for anticompetitive conduct in Brazil, criminal charges have been brought against 1 current employee of MGE and 2 former employees of MGE involving the same conduct alleged by CADE. On July 8, 2019, CADE found MGE, 1 of its current employees and 2 of its former employees liable for anticompetitive conduct. CBL was dismissed from the proceeding without any finding of liability. MGE intends to appeal CADE’s findings. We currently believe that this matter will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position or liquidity.
In addition, we are involved in other unresolved legal actions that arise in the normal course of business. The most prevalent of these unresolved actions involve disputes related to product design, manufacture and performance liability (including claimed asbestos exposure), contracts, employment issues, environmental matters, intellectual property rights, taxes (other than income taxes) and securities laws. The aggregate range of reasonably possible losses in excess of accrued liabilities, if any, associated with these unresolved legal actions is not material. In some cases, we cannot reasonably estimate a range of loss because there is insufficient information regarding the matter. However, we believe there is no more than a remote chance that any liability arising from these matters would be material. Although it is not possible to predict with certainty the outcome of these unresolved legal actions, we believe that these actions will not individually or in the aggregate have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial position or liquidity.
26
15. Income taxes
The provision for income taxes for the first three months of 2020 reflected a higher estimated annual tax rate of 31 percent compared with 26 percent for the first three months of 2019, excluding the discrete items discussed below. The increase in the estimated annual tax rate is primarily related to changes in the expected geographic mix of profits from a tax perspective for 2020, including the impact of U.S. tax on non-U.S. earnings as a result of U.S. tax reform.
In the first three months of 2020, a $43 million tax charge was recorded related to the $254 million remeasurement gain resulting from the settlement of a non-U.S. pension obligation. This gain and related tax were excluded from the estimated annual tax rate as the future period remeasurement impacts cannot currently be estimated. In addition, a discrete tax benefit of $8 million was recorded in the first three months of 2020, compared with $23 million in the first three months of 2019, for the settlement of stock-based compensation awards with associated tax deductions in excess of cumulative U.S. GAAP compensation expense. During the first three months of 2019, a $178 million discrete tax benefit was also recorded to adjust previously unrecognized tax benefits as a result of receipt of additional guidance related to the calculation of the mandatory deemed repatriation of non-U.S. earnings.
On January 31, 2018, we received a Revenue Agent’s Report from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) indicating the end of the field examination of our U.S. income tax returns for 2010 to 2012. In the audits of 2007 to 2012 including the impact of a loss carryback to 2005, the IRS has proposed to tax in the United States profits earned from certain parts transactions by Caterpillar SARL (CSARL), based on the IRS examination team’s application of the “substance-over-form” or “assignment-of-income” judicial doctrines. We are vigorously contesting the proposed increases to tax and penalties for these years of approximately $2.3 billion. We believe that the relevant transactions complied with applicable tax laws and did not violate judicial doctrines. We have filed U.S. income tax returns on this same basis for years after 2012. Based on the information currently available, we do not anticipate a significant change to our unrecognized tax benefits for this position within the next 12 months. We currently believe the ultimate disposition of this matter will not have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, liquidity or results of operations.
16. Segment information
| A. | Basis for segment information |
Our Executive Office is comprised of a Chief Executive Officer (CEO), 4 Group Presidents, a Chief Financial Officer (CFO), a Chief Legal Officer, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary and a Chief Human Resources Officer. The Group Presidents and CFO are accountable for a related set of end-to-end businesses that they manage. The Chief Legal Officer, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary leads the Law, Security and Public Policy Division. The Chief Human Resources Officer leads the Human Resources Organization. The CEO allocates resources and manages performance at the Group President/CFO level. As such, the CEO serves as our Chief Operating Decision Maker, and operating segments are primarily based on the Group President/CFO reporting structure.
NaN of our operating segments, Construction Industries, Resource Industries and Energy & Transportation are led by Group Presidents. NaN operating segment, Financial Products, is led by the CFO who also has responsibility for Corporate Services. Corporate Services is a cost center primarily responsible for the performance of certain support functions globally and to provide centralized services; it does not meet the definition of an operating segment. NaN Group President leads 1 smaller operating segment that is included in the All Other operating segment. The Law, Security and Public Policy Division and the Human Resources Organization are cost centers and do not meet the definition of an operating segment.
| B. | Description of segments |
We have 5 operating segments, of which 4 are reportable segments. Following is a brief description of our reportable segments and the business activities included in the All Other operating segment:
27
Construction Industries: A segment primarily responsible for supporting customers using machinery in infrastructure and building construction applications. Responsibilities include business strategy, product design, product management and development, manufacturing, marketing and sales and product support. The product portfolio includes asphalt pavers; backhoe loaders; compactors; cold planers; compact track and multi-terrain loaders; mini, small, medium and large track excavators; motor graders; pipelayers; road reclaimers; skid steer loaders; telehandlers; small and medium track-type tractors; track-type loaders; utility vehicles; wheel excavators; compact, small and medium wheel loaders; and related parts and work tools. Inter-segment sales are a source of revenue for this segment.
Resource Industries: A segment primarily responsible for supporting customers using machinery in mining, heavy construction, quarry and aggregates, waste and material handling applications. Responsibilities include business strategy, product design, product management and development, manufacturing, marketing and sales, and product support. The product portfolio includes large track-type tractors, large mining trucks, hard rock vehicles, longwall miners, electric rope shovels, draglines, hydraulic shovels, rotary drills, large wheel loaders, off-highway trucks, articulated trucks, wheel tractor scrapers, wheel dozers, landfill compactors, soil compactors, select work tools, machinery components, electronics and control systems, and related parts. In addition to equipment, Resource Industries also develops and sells technology products and services to provide customers fleet management, equipment management analytics and autonomous machine capabilities. Resource Industries also manages areas that provide services to other parts of the company, including integrated manufacturing and research and development. Inter-segment sales are a source of revenue for this segment.
Energy & Transportation: A segment primarily responsible for supporting customers using reciprocating engines, turbines, diesel-electric locomotives and related parts across industries serving Oil and Gas, Power Generation, Industrial and Transportation applications, including marine- and rail-related businesses. Responsibilities include business strategy, product design, product management and development, manufacturing, marketing and sales, and product support of the following product portfolio: turbine machinery and integrated systems and solutions and turbine-related services; reciprocating engine-powered generator sets; integrated systems used in the electric power generation industry; reciprocating engines and integrated systems and solutions for the marine and oil and gas industries; and reciprocating engines supplied to the industrial industry as well as Cat machinery. Responsibilities also include the remanufacturing of Caterpillar engines and components and remanufacturing services for other companies; the business strategy, product design, product management and development, manufacturing, remanufacturing, leasing and service of diesel-electric locomotives and components and other rail-related products and services; and product support of on-highway vocational trucks for North America. Inter-segment sales are a source of revenue for this segment.
Financial Products Segment: Provides financing alternatives to customers and dealers around the world for Caterpillar products, as well as financing for vehicles, power generation facilities and marine vessels that, in most cases, incorporate Caterpillar products. Financing plans include operating and finance leases, installment sale contracts, working capital loans and wholesale financing plans. The segment also provides insurance and risk management products and services that help customers and dealers manage their business risk. Insurance and risk management products offered include physical damage insurance, inventory protection plans, extended service coverage for machines and engines, and dealer property and casualty insurance. The various forms of financing, insurance and risk management products offered to customers and dealers help support the purchase and lease of Caterpillar equipment. The segment also earns revenues from ME&T, but the related costs are not allocated to operating segments.
All Other operating segment: Primarily includes activities such as: business strategy; product management and development; manufacturing and sourcing of filters and fluids, undercarriage, ground-engaging tools, fluid transfer products, precision seals, rubber sealing and connecting components primarily for Cat® products; parts distribution; integrated logistics solutions; distribution services responsible for dealer development and administration, including a wholly owned dealer in Japan; dealer portfolio management and ensuring the most efficient and effective distribution of machines, engines and parts; brand management and marketing strategy; and digital investments for new customer and dealer solutions that integrate data analytics with state-of-the-art digital technologies while transforming the buying experience. Results for the All Other operating segment are included as a reconciling item between reportable segments and consolidated external reporting.
| C. | Segment measurement and reconciliations |
There are several methodology differences between our segment reporting and our external reporting. The following is a list of the more significant methodology differences:
28
| • | ME&T segment net assets generally include inventories, receivables, property, plant and equipment, goodwill, intangibles, accounts payable and customer advances. Beginning in 2020, we revised how we allocate certain assets between segments. All prior period amounts have been recast to align with the current methodology. Liabilities other than accounts payable and customer advances are generally managed at the corporate level and are not included in segment operations. Financial Products Segment assets generally include all categories of assets. |
| • | Segment inventories and cost of sales are valued using a current cost methodology. |
| • | Goodwill allocated to segments is amortized using a fixed amount based on a 20-year useful life. This methodology difference only impacts segment assets; no goodwill amortization expense is included in segment profit. In addition, only a portion of goodwill for certain acquisitions made in 2011 or later has been allocated to segments. |
| • | Currency exposures for ME&T are generally managed at the corporate level and the effects of changes in exchange rates on results of operations within the year are not included in segment profit. The net difference created in the translation of revenues and costs between exchange rates used for U.S. GAAP reporting and exchange rates used for segment reporting is reported as a methodology difference. |
| • | Stock-based compensation expense is not included in segment profit. |
| • | Postretirement benefit expenses are split; segments are generally responsible for service costs, with the remaining elements of net periodic benefit cost included as a methodology difference. |
| • | ME&T segment profit is determined on a pretax basis and excludes interest expense and most other income/expense items. Financial Products Segment profit is determined on a pretax basis and includes other income/expense items. |
Reconciling items are created based on accounting differences between segment reporting and our consolidated external reporting. Please refer to pages 31 to 35 for financial information regarding significant reconciling items. Most of our reconciling items are self-explanatory given the above explanations. For the reconciliation of profit, we have grouped the reconciling items as follows:
| • | Corporate costs: These costs are related to corporate requirements primarily for compliance and legal functions for the benefit of the entire organization. |
| • | Restructuring costs: May include costs for employee separation, long-lived asset impairments and contract terminations. These costs are included in Other operating (income) expenses except for defined-benefit plan curtailment losses and special termination benefits, which are included in Other income (expense). Restructuring costs also include other exit-related costs, which may consist of accelerated depreciation, inventory write-downs, building demolition, equipment relocation and project management costs and LIFO inventory decrement benefits from inventory liquidations at closed facilities, all of which are primarily included in Cost of goods sold. Only certain restructuring costs are excluded from segment profit. A table, Reconciliation of Restructuring costs on page 33, has been included to illustrate how segment profit would have been impacted by the restructuring costs. See Note 20 for more information. |
| • | Methodology differences: See previous discussion of significant accounting differences between segment reporting and consolidated external reporting. |
| • | Timing: Timing differences in the recognition of costs between segment reporting and consolidated external reporting. For example, certain costs are reported on the cash basis for segment reporting and the accrual basis for consolidated external reporting. |
29
| Reportable Segments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External sales and revenues | Inter- segment sales and revenues | Total sales and revenues | Depreciation and amortization | Segment profit | Segment assets at March 31 | Capital expenditures | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 4,312 | $ | (6 | ) | $ | 4,306 | $ | 61 | $ | 640 | $ | 4,793 | $ | 20 | ||||||||||||
| Resource Industries | 1,979 | 105 | 2,084 | 103 | 304 | 6,278 | 17 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 3,618 | 731 | 4,349 | 146 | 602 | 8,577 | 87 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | 9,909 | 830 | 10,739 | 310 | 1,546 | 19,648 | 124 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 814 | 1 | — | 814 | 205 | 105 | 34,445 | 247 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 10,723 | $ | 830 | $ | 11,553 | $ | 515 | $ | 1,651 | $ | 54,093 | $ | 371 | |||||||||||||
| 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External sales and revenues | Inter- segment sales and revenues | Total sales and revenues | Depreciation and amortization | Segment profit | Segment assets at December 31 | Capital expenditures | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 5,852 | $ | 21 | $ | 5,873 | $ | 73 | $ | 1,085 | $ | 4,601 | $ | 28 | |||||||||||||
| Resource Industries | 2,647 | 105 | 2,752 | 112 | 576 | 6,505 | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 4,233 | 977 | 5,210 | 152 | 838 | 8,548 | 98 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | 12,732 | 1,103 | 13,835 | 337 | 2,499 | 19,654 | 149 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 850 | 1 | — | 850 | 206 | 211 | 35,813 | 246 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 13,582 | $ | 1,103 | $ | 14,685 | $ | 543 | $ | 2,710 | $ | 55,467 | $ | 395 | |||||||||||||
1 Includes revenues from Machinery, Energy & Transportation of $105 million and $131 million in the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
30
For the three months ending March 31, 2020 and 2019, sales and revenues by geographic region reconciled to consolidated sales and revenues were as follows:
| Sales and Revenues by Geographic Region | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | North America | Latin America | EAME | Asia/ Pacific | External Sales and Revenues | ||||||||||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 2,085 | $ | 265 | $ | 889 | $ | 1,073 | $ | 4,312 | |||||||||||
| Resource Industries | 696 | 320 | 395 | 568 | 1,979 | ||||||||||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 1,738 | 249 | 1,053 | 578 | 3,618 | ||||||||||||||||
| All Other operating segment | 5 | 2 | 11 | 10 | 28 | ||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (15 | ) | (2 | ) | (4 | ) | (2 | ) | (23 | ) | |||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation Sales | 4,509 | 834 | 2,344 | 2,227 | 9,914 | ||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 525 | 70 | 102 | 117 | 814 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (54 | ) | (12 | ) | (9 | ) | (18 | ) | (93 | ) | |||||||||||
| Financial Products Revenues | 471 | 58 | 93 | 99 | 721 | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Sales and Revenues | $ | 4,980 | $ | 892 | $ | 2,437 | $ | 2,326 | $ | 10,635 | |||||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 2,965 | $ | 319 | $ | 1,006 | $ | 1,562 | $ | 5,852 | |||||||||||
| Resource Industries | 951 | 423 | 468 | 805 | 2,647 | ||||||||||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 2,151 | 332 | 1,032 | 718 | 4,233 | ||||||||||||||||
| All Other operating segment | 8 | — | 11 | 18 | 37 | ||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (41 | ) | 1 | (3 | ) | (2 | ) | (45 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation Sales | 6,034 | 1,075 | 2,514 | 3,101 | 12,724 | ||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 558 | 70 | 102 | 120 | 850 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (69 | ) | (11 | ) | (9 | ) | (19 | ) | (108 | ) | |||||||||||
| Financial Products Revenues | 489 | 59 | 93 | 101 | 742 | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Sales and Revenues | $ | 6,523 | $ | 1,134 | $ | 2,607 | $ | 3,202 | $ | 13,466 | |||||||||||
1 Includes revenues from Machinery, Energy & Transportation of $105 million and $131 million in the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
For the three months ending March 31, 2020 and 2019, Energy & Transportation segment sales by end user application were as follows:
| Energy & Transportation External Sales | ||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31 | ||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||
| Oil and gas | $ | 861 | $ | 1,131 | ||||
| Power generation | 854 | 1,036 | ||||||
| Industrial | 801 | 904 | ||||||
| Transportation | 1,102 | 1,162 | ||||||
| Energy & Transportation External Sales | $ | 3,618 | $ | 4,233 | ||||
31
| Reconciliation of Consolidated profit before taxes: | |||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Financial Products | Consolidated Total | ||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||
| Total profit from reportable segments | $ | 1,546 | $ | 105 | $ | 1,651 | |||||
| All Other operating segment | 7 | — | 7 | ||||||||
| Cost centers | 32 | — | 32 | ||||||||
| Corporate costs | (161 | ) | (6 | ) | (167 | ) | |||||
| Timing | (27 | ) | — | (27 | ) | ||||||
| Restructuring costs | (28 | ) | — | (28 | ) | ||||||
| Methodology differences: | |||||||||||
| Inventory/cost of sales | 20 | — | 20 | ||||||||
| Postretirement benefit expense | 403 | — | 403 | ||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | (45 | ) | (2 | ) | (47 | ) | |||||
| Financing costs | (80 | ) | — | (80 | ) | ||||||
| Currency | (148 | ) | — | (148 | ) | ||||||
| Other income/expense methodology differences | (92 | ) | — | (92 | ) | ||||||
| Other methodology differences | (19 | ) | 8 | (11 | ) | ||||||
| Total consolidated profit before taxes | $ | 1,408 | $ | 105 | $ | 1,513 | |||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||
| Total profit from reportable segments | $ | 2,499 | $ | 211 | $ | 2,710 | |||||
| All Other operating segment | 25 | — | 25 | ||||||||
| Cost centers | 24 | — | 24 | ||||||||
| Corporate costs | (171 | ) | (5 | ) | (176 | ) | |||||
| Timing | (66 | ) | — | (66 | ) | ||||||
| Restructuring costs | (39 | ) | — | (39 | ) | ||||||
| Methodology differences: | |||||||||||
| Inventory/cost of sales | 7 | — | 7 | ||||||||
| Postretirement benefit expense | (17 | ) | — | (17 | ) | ||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense | (43 | ) | (2 | ) | (45 | ) | |||||
| Financing costs | (64 | ) | — | (64 | ) | ||||||
| Currency | 44 | — | 44 | ||||||||
| Other income/expense methodology differences | (129 | ) | — | (129 | ) | ||||||
| Other methodology differences | (12 | ) | 2 | (10 | ) | ||||||
| Total consolidated profit before taxes | $ | 2,058 | $ | 206 | $ | 2,264 | |||||
32
Reconciliation of Restructuring costs:
As noted above, certain restructuring costs are a reconciling item between Segment profit and Consolidated profit before taxes. Had we included the amounts in the segments’ results, the profit would have been as shown below:
| Reconciliation of Restructuring costs: | ||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Segment profit | Restructuring costs | Segment profit with restructuring costs | |||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 640 | $ | 2 | $ | 642 | ||||||
| Resource Industries | 304 | 29 | 333 | |||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 602 | (60 | ) | 542 | ||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 105 | — | 105 | |||||||||
| All Other operating segment | 7 | 4 | 11 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,658 | $ | (25 | ) | $ | 1,633 | |||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 1,085 | $ | (9 | ) | $ | 1,076 | |||||
| Resource Industries | 576 | (14 | ) | 562 | ||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 838 | (11 | ) | 827 | ||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 211 | — | 211 | |||||||||
| All Other operating segment | 25 | (5 | ) | 20 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 2,735 | $ | (39 | ) | $ | 2,696 | |||||
33
| Reconciliation of Assets: | |||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Financial Products | Consolidating Adjustments | Consolidated Total | |||||||||||
| March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets from reportable segments | $ | 19,648 | $ | 34,445 | $ | — | $ | 54,093 | |||||||
| All Other operating segment | 1,717 | — | — | 1,717 | |||||||||||
| Items not included in segment assets: | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and short-term investments | 6,251 | — | — | 6,251 | |||||||||||
| Intercompany receivables | 137 | — | (137 | ) | — | ||||||||||
| Investment in Financial Products | 3,999 | — | (3,999 | ) | — | ||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 1,975 | — | (645 | ) | 1,330 | ||||||||||
| Goodwill and intangible assets | 4,504 | — | — | 4,504 | |||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment – net and other assets | 2,584 | — | — | 2,584 | |||||||||||
| Inventory methodology differences | (2,554 | ) | — | — | (2,554 | ) | |||||||||
| Liabilities included in segment assets | 8,512 | — | — | 8,512 | |||||||||||
| Other | (522 | ) | 119 | (140 | ) | (543 | ) | ||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 46,251 | $ | 34,564 | $ | (4,921 | ) | $ | 75,894 | ||||||
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets from reportable segments | $ | 19,654 | $ | 35,813 | $ | — | $ | 55,467 | |||||||
| All Other operating segment | 1,728 | — | — | 1,728 | |||||||||||
| Items not included in segment assets: | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and short-term investments | 7,299 | — | — | 7,299 | |||||||||||
| Intercompany receivables | 758 | — | (758 | ) | — | ||||||||||
| Investment in Financial Products | 4,260 | — | (4,260 | ) | — | ||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 2,002 | — | (708 | ) | 1,294 | ||||||||||
| Goodwill and intangible assets | 4,435 | — | — | 4,435 | |||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment – net and other assets | 2,529 | — | — | 2,529 | |||||||||||
| Inventory methodology differences | (2,426 | ) | — | — | (2,426 | ) | |||||||||
| Liabilities included in segment assets | 8,541 | — | — | 8,541 | |||||||||||
| Other | (343 | ) | 134 | (205 | ) | (414 | ) | ||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 48,437 | $ | 35,947 | $ | (5,931 | ) | $ | 78,453 | ||||||
34
| Reconciliations of Depreciation and amortization: | |||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Financial Products | Consolidated Total | ||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||
| Total depreciation and amortization from reportable segments | $ | 310 | $ | 205 | $ | 515 | |||||
| Items not included in segment depreciation and amortization: | |||||||||||
| All Other operating segment | 62 | — | 62 | ||||||||
| Cost centers | 33 | — | 33 | ||||||||
| Other | (3 | ) | 7 | 4 | |||||||
| Total depreciation and amortization | $ | 402 | $ | 212 | $ | 614 | |||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||
| Total depreciation and amortization from reportable segments | $ | 337 | $ | 206 | $ | 543 | |||||
| Items not included in segment depreciation and amortization: | |||||||||||
| All Other operating segment | 52 | — | 52 | ||||||||
| Cost centers | 32 | — | 32 | ||||||||
| Other | 3 | 11 | 14 | ||||||||
| Total depreciation and amortization | $ | 424 | $ | 217 | $ | 641 | |||||
| Reconciliations of Capital expenditures: | |||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Financial Products | Consolidating Adjustments | Consolidated Total | |||||||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||
| Total capital expenditures from reportable segments | $ | 124 | $ | 247 | $ | — | $ | 371 | |||||||
| Items not included in segment capital expenditures: | |||||||||||||||
| All Other operating segment | 15 | — | — | 15 | |||||||||||
| Cost centers | 9 | — | — | 9 | |||||||||||
| Timing | 160 | — | — | 160 | |||||||||||
| Other | (6 | ) | 3 | (4 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||||||
| Total capital expenditures | $ | 302 | $ | 250 | $ | (4 | ) | $ | 548 | ||||||
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| Total capital expenditures from reportable segments | $ | 149 | $ | 246 | $ | — | $ | 395 | |||||||
| Items not included in segment capital expenditures: | |||||||||||||||
| All Other operating segment | 13 | — | — | 13 | |||||||||||
| Cost centers | 20 | — | — | 20 | |||||||||||
| Timing | 134 | — | — | 134 | |||||||||||
| Other | (19 | ) | 5 | (1 | ) | (15 | ) | ||||||||
| Total capital expenditures | $ | 297 | $ | 251 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 547 | ||||||
35
17. Cat Financial financing activities
Effective January 1, 2020, we implemented the new credit loss guidance using a modified retrospective approach. Prior period comparative information has not been recast and continues to be reported under the accounting guidance in effect for those periods. See Note 2 for additional information.
Allowance for credit losses
Portfolio segments
A portfolio segment is the level at which Cat Financial develops a systematic methodology for determining its allowance for credit losses. Cat Financial's portfolio segments and related methods for estimating expected credit losses are as follows:
Customer
Cat Financial provides loans and finance leases to end-user customers primarily for the purpose of financing new and used Caterpillar machinery, engines and equipment for commercial use, the majority of which operate in construction-related industries. Cat Financial also provides financing for vehicles, power generation facilities and marine vessels that, in most cases, incorporate Caterpillar products. The average original term of Cat Financial's customer finance receivable portfolio is approximately 48 months with an average remaining term of approximately 22 months.
Cat Financial typically maintains a security interest in financed equipment and requires physical damage insurance coverage on the financed equipment, both of which provide Cat Financial with certain rights and protections. If Cat Financial's collection efforts fail to bring a defaulted account current, Cat Financial generally can repossess the financed equipment, after satisfying local legal requirements, and sell it within the Caterpillar dealer network or through third party auctions.
Cat Financial estimates the allowance for credit losses related to its customer finance receivables based on loss forecast models utilizing probabilities of default and the estimated loss given default based on past loss experience adjusted for current conditions and reasonable and supportable forecasts capturing country and industry-specific macro-economic factors.
As of March 31, 2020, Cat Financial's forecasts for the markets in which it operates reflected a decline in economic conditions resulting from a contracting economy, elevated unemployment rates and an increase in the level and trend of delinquencies due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The company believes the economic forecasts employed represent reasonable and supportable forecasts, followed by a reversion to long term trends.
Dealer
Cat Financial provides financing to Caterpillar dealers in the form of wholesale financing plans. Cat Financial's wholesale financing plans provide assistance to dealers by financing their new Caterpillar equipment inventory and rental fleets and are generally secured by the financed equipment. In addition, Cat Financial provides unsecured loans to Caterpillar dealers for working capital.
Cat Financial estimates the allowance for credit losses for dealer finance receivables based on historical loss rates with consideration of current economic conditions and reasonable and supportable forecasts.
Although forecasts indicate a decline in economic conditions, Cat Financial's Dealer portfolio segment has not historically resulted in increased credit losses during prior economic downturns due to its close working relationships with the dealers and their financial strength. Therefore, no adjustments to historical loss rates were made during the three-month period ended March 31, 2020.
Classes of finance receivables
Cat Financial further evaluates portfolio segments by the class of finance receivables, which is defined as a level of information (below a portfolio segment) in which the finance receivables have the same initial measurement attribute and a similar method for assessing and monitoring credit risk. Typically, Cat Financial's finance receivables within a geographic area have similar credit risk profiles and methods for assessing and monitoring credit risk. Cat Financial's classes, which align with management reporting for credit losses, are as follows:
| • | North America - Finance receivables originated in the United States and Canada. |
36
| • | EAME - Finance receivables originated in Europe, Africa, the Middle East and the Commonwealth of Independent States. |
| • | Asia/Pacific - Finance receivables originated in Australia, New Zealand, China, Japan, Southeast Asia and India. |
| • | Mining - Finance receivables related to large mining customers worldwide. |
| • | Latin America - Finance receivables originated in Mexico and Central and South American countries. |
| • | Caterpillar Power Finance - Finance receivables originated worldwide related to marine vessels with Caterpillar engines and Caterpillar electrical power generation, gas compression and co-generation systems and non-Caterpillar equipment that is powered by these systems. |
Receivable balances, including accrued interest, are written off against the allowance for credit losses when, in the judgment of management, they are considered uncollectible (generally upon repossession of the collateral). The amount of the write-off is determined by comparing the fair value of the collateral, less cost to sell, to the amortized cost. Subsequent recoveries, if any, are credited to the allowance for credit losses when received.
An analysis of the allowance for credit losses was as follows:
(Millions of dollars) | March 31, 2020 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for Credit Losses: | Customer | Dealer | Total | ||||||||
| Balance at beginning of year | $ | 375 | $ | 45 | $ | 420 | |||||
Adjustment to adopt new accounting guidance 1 | 12 | — | 12 | ||||||||
| Receivables written off | (37 | ) | — | (37 | ) | ||||||
| Recoveries on receivables previously written off | 7 | — | 7 | ||||||||
| Provision for credit losses | 60 | — | 60 | ||||||||
| Other | (9 | ) | — | (9 | ) | ||||||
| Balance at end of period | $ | 408 | $ | 45 | $ | 453 | |||||
| Individually evaluated | $ | 176 | $ | 39 | $ | 215 | |||||
| Collectively evaluated | 232 | 6 | 238 | ||||||||
| Ending Balance | $ | 408 | $ | 45 | $ | 453 | |||||
| Finance Receivables: | |||||||||||
| Individually evaluated | $ | 570 | $ | 78 | $ | 648 | |||||
| Collectively evaluated | 17,436 | 3,500 | 20,936 | ||||||||
| Ending Balance | $ | 18,006 | $ | 3,578 | $ | 21,584 | |||||
1 See Note 2 regarding new accounting guidance related to credit losses.
37
(Millions of dollars) | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for Credit Losses: | Customer | Dealer | Total | ||||||||
| Balance at beginning of year | $ | 486 | $ | 21 | $ | 507 | |||||
| Receivables written off | (281 | ) | — | (281 | ) | ||||||
| Recoveries on receivables previously written off | 44 | — | 44 | ||||||||
| Provision for credit losses | 138 | 24 | 162 | ||||||||
| Other | (12 | ) | — | (12 | ) | ||||||
| Balance at end of year | $ | 375 | $ | 45 | $ | 420 | |||||
| Individually evaluated | $ | 178 | $ | 39 | $ | 217 | |||||
| Collectively evaluated | 197 | 6 | 203 | ||||||||
| Ending Balance | $ | 375 | $ | 45 | $ | 420 | |||||
| Finance Receivables: | |||||||||||
| Individually evaluated | $ | 594 | $ | 78 | $ | 672 | |||||
| Collectively evaluated | 18,093 | 3,632 | 21,725 | ||||||||
| Ending Balance | $ | 18,687 | $ | 3,710 | $ | 22,397 | |||||
Credit quality of finance receivables
At origination, Cat Financial evaluates credit risk based on a variety of credit quality factors including prior payment experience, customer financial information, credit-rating agency ratings, loan-to-value ratios, probabilities of default, industry trends, macroeconomic factors and other internal metrics. On an ongoing basis, Cat Financial monitors credit quality based on past-due status as there is a meaningful correlation between the past-due status of customers and the risk of loss. In determining past-due status, Cat Financial considers the entire finance receivable past due when any installment is over 30 days past due.
Customer
The table below summarizes the aging category of Cat Financial's amortized cost of finance receivables in the Customer portfolio segment by origination year:
38
| (Millions of dollars) | March 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | Prior | Revolving Finance Receivables | Total Finance Receivables | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current | $ | 931 | $ | 3,274 | $ | 2,010 | $ | 952 | $ | 455 | $ | 155 | $ | 157 | $ | 7,934 | |||||||||||||||
| 31-60 days past due | 6 | 55 | 52 | 29 | 21 | 5 | — | 168 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 61-90 days past due | — | 11 | 11 | 10 | 3 | 1 | — | 36 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 91+ days past due | — | 14 | 21 | 15 | 10 | 6 | — | 66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| EAME | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current | 249 | 1,164 | 773 | 358 | 133 | 44 | — | 2,721 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31-60 days past due | 2 | 11 | 5 | 4 | 2 | — | — | 24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 61-90 days past due | — | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | — | 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 91+ days past due | — | 8 | 22 | 23 | 53 | 61 | — | 167 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Asia/Pacific | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current | 217 | 1,021 | 570 | 163 | 21 | 9 | — | 2,001 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31-60 days past due | 2 | 26 | 25 | 9 | — | 1 | — | 63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 61-90 days past due | — | 14 | 14 | 5 | 1 | — | — | 34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 91+ days past due | — | 15 | 17 | 8 | 1 | — | — | 41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mining | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current | 72 | 701 | 413 | 235 | 139 | 215 | 199 | 1,974 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31-60 days past due | — | — | 1 | — | — | 1 | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 61-90 days past due | — | 3 | 12 | 6 | — | — | — | 21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 91+ days past due | — | 12 | 12 | 23 | — | — | 1 | 48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Latin America | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current | 175 | 483 | 253 | 88 | 23 | 49 | — | 1,071 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31-60 days past due | — | 15 | 10 | 8 | 4 | 2 | — | 39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 61-90 days past due | — | 5 | 7 | 5 | 2 | — | — | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 91+ days past due | — | 11 | 29 | 24 | 9 | 7 | — | 80 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current | 3 | 273 | 221 | 287 | 137 | 158 | 160 | 1,239 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31-60 days past due | — | — | 11 | — | 4 | 11 | — | 26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 61-90 days past due | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 91+ days past due | — | — | 20 | 11 | 37 | 149 | — | 217 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Customer | $ | 1,657 | $ | 7,123 | $ | 4,512 | $ | 2,266 | $ | 1,056 | $ | 875 | $ | 517 | $ | 18,006 | |||||||||||||||
39
Finance receivables in the Customer portfolio segment are substantially secured by collateral, primarily in the form of Caterpillar and other machinery. For those contracts where the borrower is experiencing financial difficulty, repayment of the outstanding amounts is generally expected to be provided through the operation or repossession and sale of the machinery.
Dealer
As of March 31, 2020, Cat Financial's total amortized cost of finance receivables within the Dealer portfolio segment was current, with the exception of $78 million that was 91+ days past due in Latin America. These past due receivables were originated in 2017.
The table below summarizes Cat Financial's recorded investment in finance receivables by aging category.
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(Millions of dollars) | 31-60 Days Past Due | 61-90 Days Past Due | 91+ Days Past Due | Total Past Due | Current | Total Finance Receivables | |||||||||||||||||
| Customer | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America | $ | 72 | $ | 23 | $ | 55 | $ | 150 | $ | 8,002 | $ | 8,152 | |||||||||||
| EAME | 30 | 31 | 141 | 202 | 2,882 | 3,084 | |||||||||||||||||
| Asia Pacific | 40 | 14 | 29 | 83 | 2,181 | 2,264 | |||||||||||||||||
| Mining | 5 | — | 19 | 24 | 2,266 | 2,290 | |||||||||||||||||
| Latin America | 41 | 23 | 80 | 144 | 1,089 | 1,233 | |||||||||||||||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 10 | 10 | 225 | 245 | 1,419 | 1,664 | |||||||||||||||||
| Dealer | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America | — | — | — | — | 2,136 | 2,136 | |||||||||||||||||
| EAME | — | — | — | — | 342 | 342 | |||||||||||||||||
| Asia Pacific | — | — | — | — | 437 | 437 | |||||||||||||||||
| Mining | — | — | — | — | 4 | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Latin America | — | — | 78 | 78 | 712 | 790 | |||||||||||||||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | — | — | — | — | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 198 | $ | 101 | $ | 627 | $ | 926 | $ | 21,471 | $ | 22,397 | |||||||||||
Impaired finance receivables
A finance receivable is considered impaired, based on current information and events, if it is probable that Cat Financial will be unable to collect all amounts due according to the contractual terms. Impaired finance receivables include finance receivables that have been restructured and are considered to be troubled debt restructures.
40
In Cat Financial’s Customer portfolio segment, impaired finance receivables and the related unpaid principal balances and allowance were as follows:
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Recorded Investment | Unpaid Principal Balance | Related Allowance | ||||||||
| Impaired Finance Receivables With No Allowance Recorded | |||||||||||
| North America | $ | 6 | $ | 6 | $ | — | |||||
| EAME | — | — | — | ||||||||
| Asia Pacific | — | — | — | ||||||||
| Mining | 22 | 22 | — | ||||||||
| Latin America | 8 | 8 | — | ||||||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 58 | 58 | — | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 94 | $ | 94 | $ | — | |||||
| Impaired Finance Receivables With An Allowance Recorded | |||||||||||
| North America | $ | 30 | $ | 30 | $ | 11 | |||||
| EAME | 61 | 61 | 29 | ||||||||
| Asia Pacific | 8 | 8 | 2 | ||||||||
| Mining | 37 | 36 | 9 | ||||||||
| Latin America | 58 | 58 | 20 | ||||||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 306 | 319 | 107 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 500 | $ | 512 | $ | 178 | |||||
| Total Impaired Finance Receivables | |||||||||||
| North America | $ | 36 | $ | 36 | $ | 11 | |||||
| EAME | 61 | 61 | 29 | ||||||||
| Asia Pacific | 8 | 8 | 2 | ||||||||
| Mining | 59 | 58 | 9 | ||||||||
| Latin America | 66 | 66 | 20 | ||||||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 364 | 377 | 107 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 594 | $ | 606 | $ | 178 | |||||
41
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | |||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Average Recorded Investment | Interest Income Recognized | |||||
| Impaired Finance Receivables With No Allowance Recorded | |||||||
| North America | $ | 10 | $ | — | |||
| EAME | 1 | — | |||||
| Asia Pacific | — | — | |||||
| Mining | 31 | — | |||||
| Latin America | 24 | — | |||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 60 | 1 | |||||
| Total | $ | 126 | $ | 1 | |||
| Impaired Finance Receivables With An Allowance Recorded | |||||||
| North America | $ | 40 | $ | 1 | |||
| EAME | 94 | 1 | |||||
| Asia Pacific | 7 | — | |||||
| Mining | 43 | 1 | |||||
| Latin America | 77 | 1 | |||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 451 | 3 | |||||
| Total | $ | 712 | $ | 7 | |||
| Total Impaired Finance Receivables | |||||||
| North America | $ | 50 | $ | 1 | |||
| EAME | 95 | 1 | |||||
| Asia Pacific | 7 | — | |||||
| Mining | 74 | 1 | |||||
| Latin America | 101 | 1 | |||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 511 | 4 | |||||
| Total | $ | 838 | $ | 8 | |||
There were $78 million in impaired finance receivables with a related allowance of $39 million as of December 31, 2019 for the Dealer portfolio segment, all of which was in Latin America.
Non-accrual finance receivables
Recognition of income is suspended and the finance receivable is placed on non-accrual status when management determines that collection of future income is not probable. Contracts on non-accrual status are generally more than 120 days past due or have been restructured in a troubled debt restructuring (TDR). Recognition is resumed and previously suspended income is recognized when the finance receivable becomes current and collection of remaining amounts is considered probable. Payments received while the finance receivable is on non-accrual status are applied to interest and principal in accordance with the contractual terms. Interest earned but uncollected prior to the receivable being placed on non-accrual status is written off through Provision for credit losses when, in the judgment of management, it is considered uncollectible.
42
In Cat Financial's Customer portfolio segment, finance receivables which were on non-accrual status and finance receivables over 90 days past due and still accruing income were as follows:
| March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||
| Amortized Cost | |||||||||||
(Millions of dollars) | Non-accrual With an Allowance | Non-accrual Without an Allowance | 91+ Still Accruing | ||||||||
| North America | $ | 50 | $ | — | $ | 20 | |||||
| EAME | 168 | 1 | 5 | ||||||||
| Asia Pacific | 29 | — | 12 | ||||||||
| Mining | 40 | — | 9 | ||||||||
| Latin America | 87 | — | — | ||||||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 329 | — | 7 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 703 | $ | 1 | $ | 53 | |||||
There was less than $1 million of interest income recognized during the three months ended March 31, 2020 for customer finance receivables on non-accrual status.
(Millions of dollars) | December 31, 2019 | ||||||
| Recorded Investment | |||||||
| Non-accrual Finance Receivables | 91+ Still Accruing | ||||||
| North America | $ | 44 | $ | 15 | |||
| EAME | 165 | 4 | |||||
| Asia Pacific | 21 | 8 | |||||
| Mining | 47 | — | |||||
| Latin America | 89 | 2 | |||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 361 | — | |||||
| Total | $ | 727 | $ | 29 | |||
As of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, there were $78 million in finance receivables on non-accrual status in Cat Financial's Dealer portfolio segment, all of which was in Latin America. There were 0 finance receivables in Cat Financial's Dealer portfolio segment more than 90 days past due and still accruing income as of March 31, 2020 and 0 interest income was recognized on dealer finance receivables on non-accrual status during the three months ended March 31, 2020.
Troubled debt restructurings
A restructuring of a finance receivable constitutes a TDR when the lender grants a concession it would not otherwise consider to a borrower experiencing financial difficulties. Concessions granted may include extended contract maturities, inclusion of interest only periods, below market interest rates, payment deferrals and reduction of principal and/or accrued interest.
43
There were 0 finance receivables modified as TDRs during the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 for the Dealer portfolio segment. Cat Financial’s finance receivables in the Customer portfolio segment modified as TDRs were as follows:
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
(Dollars in millions) | Number of Contracts | Pre-TDR Amortized Cost | Post-TDR Amortized Cost | Number of Contracts | Pre-TDR Recorded Investment | Post-TDR Recorded Investment | |||||||||||||||
| EAME | 0 | $ | — | $ | — | 17 | $ | 7 | $ | 7 | |||||||||||
| Latin America | 5 | 2 | 2 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Caterpillar Power Finance | 0 | — | — | 8 | 51 | 50 | |||||||||||||||
| Total | 5 | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | 25 | $ | 58 | $ | 57 | |||||||||||
TDRs in the Customer portfolio segment with a payment default (defined as 91+ days past due) which had been modified within twelve months prior to the default date, were as follows:
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 | Three Months Ended March 31, 2019 | ||||||||||
(Dollars in millions) | Number of Contracts | Post-TDR Amortized Cost | Number of Contracts | Post-TDR Recorded Investment | |||||||
| Customer | |||||||||||
| EAME | 2 | $ | 10 | — | $ | — | |||||
| Latin America | 3 | 1 | — | — | |||||||
| Total | 5 | $ | 11 | — | $ | — | |||||
18. Fair value disclosures
A. Fair value measurements
The guidance on fair value measurements defines fair value as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. This guidance also specifies a fair value hierarchy based upon the observability of inputs used in valuation techniques. Observable inputs (highest level) reflect market data obtained from independent sources, while unobservable inputs (lowest level) reflect internally developed market assumptions. In accordance with this guidance, fair value measurements are classified under the following hierarchy:
| • | Level 1 – Quoted prices for identical instruments in active markets. |
| • | Level 2 – Quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar instruments in markets that are not active; and model-derived valuations in which all significant inputs or significant value-drivers are observable in active markets. |
| • | Level 3 – Model-derived valuations in which one or more significant inputs or significant value-drivers are unobservable. |
When available, we use quoted market prices to determine fair value, and we classify such measurements within Level 1. In some cases where market prices are not available, we make use of observable market based inputs to calculate fair value, in which case the measurements are classified within Level 2. If quoted or observable market prices are not available, fair value is based upon valuations in which one or more significant inputs are unobservable, including internally developed models that use, where possible, current market-based parameters such as interest rates, yield curves and currency rates. These measurements are classified within Level 3.
44
Fair value measurements are classified according to the lowest level input or value-driver that is significant to the valuation. A measurement may therefore be classified within Level 3 even though there may be significant inputs that are readily observable.
Fair value measurement includes the consideration of nonperformance risk. Nonperformance risk refers to the risk that an obligation (either by a counterparty or Caterpillar) will not be fulfilled. For financial assets traded in an active market (Level 1 and certain Level 2), the nonperformance risk is included in the market price. For certain other financial assets and liabilities (certain Level 2 and Level 3), our fair value calculations have been adjusted accordingly.
Investments in debt and equity securities
We have investments in certain debt and equity securities, primarily at Insurance Services, that are recorded at fair value. Fair values for our U.S. treasury bonds and large capitalization value and smaller company growth equity securities are based upon valuations for identical instruments in active markets. Fair values for other government bonds, corporate bonds and mortgage-backed debt securities are based upon models that take into consideration such market-based factors as recent sales, risk-free yield curves and prices of similarly rated bonds.
In addition, Insurance Services has an equity investment in a real estate investment trust (REIT) which is recorded at fair value based on the net asset value (NAV) of the investment and is not classified within the fair value hierarchy.
See Note 8 for additional information on our investments in debt and equity securities.
Derivative financial instruments
The fair value of interest rate contracts is primarily based on models that utilize the appropriate market-based forward swap curves and zero-coupon interest rates to determine discounted cash flows. The fair value of foreign currency and commodity forward, option and cross currency contracts is based on a valuation model that discounts cash flows resulting from the differential between the contract price and the market-based forward rate.
45
Assets and liabilities measured on a recurring basis at fair value, primarily related to Financial Products, included in our Consolidated Statement of Financial Position as of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 are summarized below:
| March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||
(Millions of dollars) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Measured at NAV | Total Assets / Liabilities, at Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | |||||||||||||||||||
| Debt securities | |||||||||||||||||||
| Government debt | |||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. treasury bonds | $ | 9 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 9 | |||||||||
| Other U.S. and non-U.S. government bonds | — | 47 | — | — | 47 | ||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | |||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | — | 871 | — | — | 871 | ||||||||||||||
| Asset-backed securities | — | 86 | — | — | 86 | ||||||||||||||
| Mortgage-backed debt securities | |||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. governmental agency | — | 378 | — | — | 378 | ||||||||||||||
| Residential | — | 5 | — | — | 5 | ||||||||||||||
| Commercial | — | 53 | — | — | 53 | ||||||||||||||
| Total debt securities | 9 | 1,440 | — | — | 1,449 | ||||||||||||||
| Equity securities | |||||||||||||||||||
| Large capitalization value | 139 | — | — | — | 139 | ||||||||||||||
| Smaller company growth | 23 | — | 2 | — | 25 | ||||||||||||||
| REIT | — | — | — | 137 | 137 | ||||||||||||||
| Total equity securities | 162 | — | 2 | 137 | 301 | ||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial instruments, net | — | 121 | — | — | 121 | ||||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 171 | $ | 1,561 | $ | 2 | $ | 137 | $ | 1,871 | |||||||||
46
| December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||
(Millions of dollars) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Measured at NAV | Total Assets / Liabilities, at Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | |||||||||||||||||||
| Debt securities | |||||||||||||||||||
| Government debt | |||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. treasury bonds | $ | 9 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 9 | |||||||||
| Other U.S. and non-U.S. government bonds | — | 54 | — | — | 54 | ||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | |||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds | — | 856 | — | — | 856 | ||||||||||||||
| Asset-backed securities | — | 62 | — | — | 62 | ||||||||||||||
| Mortgage-backed debt securities | |||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. governmental agency | — | 331 | — | — | 331 | ||||||||||||||
| Residential | — | 6 | — | — | 6 | ||||||||||||||
| Commercial | — | 47 | — | — | 47 | ||||||||||||||
| Total debt securities | 9 | 1,356 | — | — | 1,365 | ||||||||||||||
| Equity securities | |||||||||||||||||||
| Large capitalization value | 187 | — | — | — | 187 | ||||||||||||||
| Smaller company growth | 29 | — | 4 | — | 33 | ||||||||||||||
| REIT | — | — | — | 126 | 126 | ||||||||||||||
| Total equity securities | 216 | — | 4 | 126 | 346 | ||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial instruments, net | — | 45 | — | — | 45 | ||||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 225 | $ | 1,401 | $ | 4 | $ | 126 | $ | 1,756 | |||||||||
In addition to the amounts above, Cat Financial impaired loans are subject to measurement at fair value on a nonrecurring basis and are classified as Level 3 measurements. A loan is considered impaired when management determines that collection of contractual amounts due is not probable. In these cases, an allowance for credit losses may be established based either on the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the receivables’ effective interest rate, the fair value of the collateral for collateral-dependent receivables, or the observable market price of the receivable. In determining collateral value, Cat Financial estimates the current fair market value of the collateral less selling costs. Cat Financial had impaired loans with a fair value of $324 million and $343 million as of March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively.
B. Fair values of financial instruments
In addition to the methods and assumptions we use to record the fair value of financial instruments as discussed in the Fair value measurements section above, we used the following methods and assumptions to estimate the fair value of our financial instruments:
Cash and short-term investments
Carrying amount approximated fair value.
Restricted cash and short-term investments
Carrying amount approximated fair value. Restricted cash and short-term investments are included in Prepaid expenses and other current assets in the Consolidated Statement of Financial Position.
Finance receivables
Fair value was estimated by discounting the future cash flows using current rates, representative of receivables with similar remaining maturities.
Wholesale inventory receivables
Fair value was estimated by discounting the future cash flows using current rates, representative of receivables with similar remaining maturities.
47
Short-term borrowings
Carrying amount approximated fair value.
Long-term debt
Fair value for fixed and floating rate debt was estimated based on quoted market prices.
Guarantees
The fair value of guarantees is based upon our estimate of the premium a market participant would require to issue the same guarantee in a stand-alone arms-length transaction with an unrelated party. If quoted or observable market prices are not available, fair value is based upon internally developed models that utilize current market-based assumptions.
Fair values of our financial instruments were as follows:
| Fair Value of Financial Instruments | ||||||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Carrying Amount | Fair Value | Carrying Amount | Fair Value | Fair Value Levels | Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and short-term investments | $ | 7,123 | $ | 7,123 | $ | 8,284 | $ | 8,284 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Restricted cash and short-term investments | $ | 7 | $ | 7 | $ | 8 | $ | 8 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Investments in debt and equity securities | $ | 1,750 | $ | 1,750 | $ | 1,711 | $ | 1,711 | 1, 2 & 3 | Note 8 | ||||||||||
Finance receivables – net (excluding finance leases 1) | $ | 14,076 | $ | 14,149 | $ | 14,473 | $ | 14,613 | 3 | Note 17 | ||||||||||
Wholesale inventory receivables – net (excluding finance leases 1) | $ | 1,104 | $ | 1,071 | $ | 1,105 | $ | 1,076 | 3 | |||||||||||
| Foreign currency contracts – net | $ | 129 | $ | 129 | $ | 62 | $ | 62 | 2 | Note 5 | ||||||||||
| Interest rate contracts – net | $ | 26 | $ | 26 | $ | — | $ | — | 2 | Note 5 | ||||||||||
| Commodity contracts – net | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 3 | $ | 3 | 2 | Note 5 | ||||||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings | $ | 4,789 | $ | 4,789 | $ | 5,166 | $ | 5,166 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Long-term debt (including amounts due within one year) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 9,141 | $ | 11,061 | $ | 9,157 | $ | 11,216 | 2 | |||||||||||
| Financial Products | $ | 23,163 | $ | 23,226 | $ | 23,334 | $ | 23,655 | 2 | |||||||||||
| Interest rate contracts – net | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 20 | $ | 20 | 2 | Note 5 | ||||||||||
| Commodity contracts – net | $ | 34 | $ | 34 | $ | �� | $ | — | 2 | Note 5 | ||||||||||
| Guarantees | $ | 5 | $ | 5 | $ | 5 | $ | 5 | 3 | Note 11 | ||||||||||
1 | Represents finance leases and failed sales leasebacks of $7,328 million and $7,800 million at March 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively. |
48
19. Other income (expense)
| Three Months Ended March 31 | ||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||
| Investment and interest income | $ | 43 | $ | 52 | ||||
Foreign exchange gains (losses) 1 | (75 | ) | 18 | |||||
| License fee income | 25 | 25 | ||||||
| Net periodic pension and OPEB income (cost), excluding service cost | 333 | 2 | 26 | |||||
| Gains (losses) on securities | (58 | ) | 39 | |||||
| Miscellaneous income (loss) | (46 | ) | — | |||||
| Total | $ | 222 | $ | 160 | ||||
1 Includes gains (losses) from foreign exchange derivative contracts. See Note 5 for further details.
2 Includes a remeasurement gain of $254 million from settlement of a non-U.S. pension obligation. See Note 9 for further details.
20. Restructuring costs
Our accounting for employee separations is dependent upon how the particular program is designed. For voluntary programs, eligible separation costs are recognized at the time of employee acceptance unless the acceptance requires explicit approval by the company. For involuntary programs, eligible costs are recognized when management has approved the program, the affected employees have been properly notified and the costs are estimable.
Restructuring costs for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 were as follows:
| (Millions of dollars) | Three Months Ended March 31 | |||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Employee separations 1 | $ | 11 | $ | 15 | ||||
Contract terminations 1 | 1 | — | ||||||
Long-lived asset impairments 1 | 9 | 7 | ||||||
Other 2 | 16 | 26 | ||||||
| Total restructuring costs | $ | 37 | $ | 48 | ||||
1 Recognized in Other operating (income) expenses. | ||||||||
2 Represents costs related to our restructuring programs, primarily for inventory write-downs, equipment relocation, building demolition and project management, all of which are primarily included in Cost of goods sold. | ||||||||
For the three months ended March 31, 2020, the restructuring costs were primarily related to a strategic action to address a certain product line, which were partially offset by a gain on the sale of a manufacturing facility that had been closed. For the three months ended March 31, 2019, the restructuring costs were primarily related to ongoing facility closures across the company.
Certain restructuring costs are a reconciling item between Segment profit and Consolidated profit before taxes. See Note 16 for more information.
49
The following table summarizes the 2019 and 2020 employee separation activity:
| (Millions of dollars) | ||||
| Liability balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 85 | ||
| Increase in liability (separation charges) | 48 | |||
| Reduction in liability (payments) | (85 | ) | ||
| Liability balance at December 31, 2019 | 48 | |||
| Increase in liability (separation charges) | 11 | |||
| Reduction in liability (payments) | (16 | ) | ||
| Liability balance at March 31, 2020 | $ | 43 | ||
Most of the liability balance at March 31, 2020 is expected to be paid in 2020 and 2021.
21. Subsequent event
As the COVID-19 global pandemic continues to evolve, Caterpillar’s financial results for the remainder of 2020 and perhaps beyond will be impacted by the continued global economic uncertainty. The magnitude of the pandemic, including the extent of any impact on Caterpillar’s business, financial position, results of operations or liquidity, which could be material, cannot be reasonably estimated at this time due to the rapid development and fluidity of the situation. The ultimate effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the company will be determined by a variety of factors beyond the company’s control, including the duration of the pandemic, its geographic spread, business disruptions and the overall impact on the global economy.
Caterpillar, as a result, has taken decisive actions to enhance our strong financial position and increase liquidity. On a consolidated basis, Caterpillar ended the first quarter with $7.1 billion of cash and available global credit facilities of $10.5 billion. In April, Caterpillar raised $2.0 billion of incremental cash by issuing new 10- and 30- year bonds. In addition, we have added an incremental $3.9 billion short-term credit facility and registered for $4.1 billion in commercial paper support programs now available in the United States and Canada. We also temporarily suspended our share repurchase program. The existing share repurchase program remains authorized by the Board, and we may resume share repurchases in the future at any time depending upon market conditions, our capital needs and other factors.
The Company has not made any drawings under any of the above mentioned credit facilities nor does it have any outstanding borrowings under either commercial paper support program as of the date of this filing.
50
Item 2. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations should be read in conjunction with our unaudited financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this report and our discussion of significant risks to the company’s business under Part I, Item 1A. Risk Factors of the 2019 Form 10-K as supplemented by Part II, Item 1A. Risk Factors of this report.
Overview
Total sales and revenues for the first quarter of 2020 were $10.635 billion, a decrease of $2.831 billion, or 21 percent, compared with $13.466 billion in the first quarter of 2019. The decline was due to lower sales volume driven by lower end-user demand and the impact from changes in dealer inventories. Dealers increased machine and engine inventories about $100 million during the first quarter of 2020, compared with about $1.3 billion during the first quarter of 2019. The changes in dealer inventories came primarily in Construction Industries, driven by North America, and Resource Industries. Sales were lower across all regions and in the three primary segments. Unfavorable currency impacts, unfavorable price realization and lower Financial Products revenues also contributed to the decrease.
First-quarter 2020 profit per share was $1.98, a decrease of $1.27, or 39 percent, compared with $3.25 profit per share in the first quarter of 2019. Profit per share in the first quarter of 2020 included a pre-tax remeasurement gain of $254 million, or $0.38 per share, resulting from the settlement of a non-U.S. pension obligation. Profit per share in the first quarter of 2019 included a discrete tax benefit related to U.S. tax reform of $178 million, or $0.31 per share. Profit was $1.092 billion in the first quarter of 2020, a decrease of $789 million, or 42 percent, compared with $1.881 billion in the first quarter of 2019. The decrease was mostly due to lower sales volume. Higher tax expense, unfavorable impacts from equity securities at Insurance Services and foreign currency exchange gains (losses) were mostly offset by a remeasurement gain resulting from the settlement of a non-U.S. pension obligation, lower selling, general and administrative (SG&A) and research and development (R&D) expenses as well as favorable manufacturing costs. Lower SG&A/R&D expenses and manufacturing costs were primarily driven by reduced short-term incentive compensation expense, a favorable change in fair value adjustments related to deferred compensation plans and other cost-reduction actions implemented in response to lower sales volumes.
Highlights for the first quarter of 2020 include:
| • | First-quarter 2020 sales and revenues were $10.635 billion, compared with $13.466 billion in the first quarter of 2019. Sales decreased across all regions and in the three primary segments. The decline was due to lower sales volume driven by lower end-user demand and the impact from changes in dealer inventories. Dealers increased machine and engine inventories about $100 million during the first quarter of 2020, compared with about $1.3 billion during the first quarter of 2019. |
| • | Operating profit margin was 13.2 percent in the first quarter of 2020, compared with 16.4 percent in the first quarter of 2019. |
| • | Profit per share was $1.98 in the first quarter of 2020, compared with $3.25 in the first quarter of 2019. Profit per share in the first quarter of 2020 included a pre-tax remeasurement gain of $254 million, or $0.38 per share, resulting from the settlement of a non-U.S. pension obligation. Profit per share in the first quarter of 2019 included a discrete tax benefit related to U.S. tax reform of $178 million, or $0.31 per share. |
| • | During the first quarter of 2020, enterprise operating cash flow was $1.130 billion. Caterpillar has taken actions to improve its strong financial position by increasing sources of liquidity. On a consolidated basis, Caterpillar ended the first quarter with $7.1 billion of cash and available global credit facilities of $10.5 billion. In April, Caterpillar raised $2.0 billion of incremental cash by issuing new 10- and 30-year bonds. In addition, we entered into an incremental $3.9 billion short-term credit facility and registered for $4.1 billion in commercial paper support programs now available in the United States and Canada. |
Response to COVID-19 and Global Business Conditions:
Operational Impacts
Caterpillar has implemented safeguards in its facilities to protect team members, including increased frequency of cleaning and disinfecting facilities, social distancing practices and other measures consistent with specific regulatory requirements and guidance from health authorities.
51
Many governments classified Caterpillar’s operations as an essential activity for support of critical infrastructure. Caterpillar has suspended operations temporarily at certain facilities during the last several months due to supply chain issues, weak customer demand or government regulations. As of mid-April 2020, globally and across the three primary segments, approximately 75 percent of the company’s primary production facilities continue to operate. Some facilities that were temporarily closed have reopened. The company will continue to monitor the situation and may suspend operations temporarily at additional facilities if warranted by business conditions.
The company has taken actions to reduce costs, including reducing discretionary expenses and suspending 2020 base salary increases and short-term incentive compensation plans for many employees and all senior executives. Caterpillar is prioritizing spending to allow continued investment in services and expanded offerings, key elements of its strategy for profitable growth introduced in 2017.
Caterpillar’s financial results for the remainder of 2020 will be impacted by continued global economic uncertainty due to the COVID-19 pandemic. We expect the impacts of the pandemic on our results to be more significant in the second quarter than in the first quarter, and to continue until global economic conditions improve.
Notes:
| • | Glossary of terms is included on pages 59 - 61; first occurrence of terms shown in bold italics. |
| • | Information on non-GAAP financial measures is included on page 66. |
52
Consolidated Results of Operations
THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2020 COMPARED WITH THREE MONTHS ENDED MARCH 31, 2019
CONSOLIDATED SALES AND REVENUES
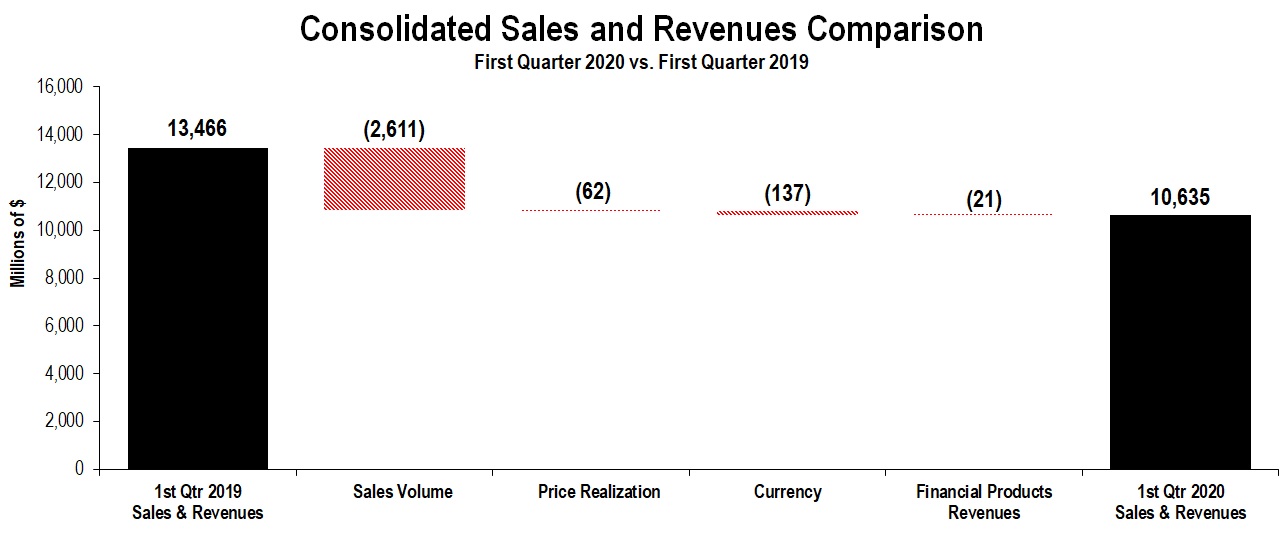
The chart above graphically illustrates reasons for the change in consolidated sales and revenues between the first quarter of 2019 (at left) and the first quarter of 2020 (at right). Caterpillar management utilizes these charts internally to visually communicate with the company’s Board of Directors and employees.
Total sales and revenues for the first quarter of 2020 were $10.635 billion, a decrease of $2.831 billion, or 21 percent, compared with $13.466 billion in the first quarter of 2019. The decline was due to lower sales volume driven by lower end-user demand and the impact from changes in dealer inventories. Dealers increased machine and engine inventories about $100 million during the first quarter of 2020, compared with about $1.3 billion during the first quarter of 2019. The changes in dealer inventories came primarily in Construction Industries, driven by North America, and in Resource Industries.
Sales were lower across all regions and in the three primary segments.
North America sales declined 25 percent driven by the impact from changes in dealer inventories and lower end-user demand. Dealers increased inventories during the first quarter of 2019 and dealer inventories were about flat during the first quarter of 2020.
Sales decreased 22 percent in Latin America due to lower demand in most countries across the region.
EAME sales decreased 7 percent due to lower demand in many countries and unfavorable currency impacts. The unfavorable currency impacts were mostly due to a weaker euro.
Asia/Pacific sales decreased 28 percent due to lower demand across most countries in the region, including unfavorable changes in dealer inventories, primarily in China. Dealers decreased inventories during the first quarter of 2020, compared with an increase during the first quarter of 2019. Decreases in China reflected lower end-user demand mostly due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Dealer machine and engine inventories increased about $100 million during the first quarter of 2020, compared with an increase of about $1.3 billion during the first quarter of 2019. Dealers are independent, and the reasons for changes in their inventory levels vary, including their expectations of future demand and product delivery times. Dealers’ demand expectations take into account seasonal changes, macroeconomic conditions, machine rental rates and other factors. Delivery times can vary based on availability of product from Caterpillar factories and product distribution centers. We expect dealer inventories to decline by at least $1.5 billion during 2020.
53
| Sales and Revenues by Segment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | First Quarter 2019 | Sales Volume | Price Realization | Currency | Inter-Segment / Other | First Quarter 2020 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 5,873 | $ | (1,418 | ) | $ | (63 | ) | $ | (59 | ) | $ | (27 | ) | $ | 4,306 | $ | (1,567 | ) | (27 | %) | |||||||||
| Resource Industries | 2,752 | (607 | ) | (21 | ) | (40 | ) | — | 2,084 | (668 | ) | (24 | %) | |||||||||||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 5,210 | (599 | ) | 21 | (37 | ) | (246 | ) | 4,349 | (861 | ) | (17 | %) | |||||||||||||||||
| All Other Segment | 121 | (9 | ) | — | — | (3 | ) | 109 | (12 | ) | (10 | %) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (1,232 | ) | 22 | 1 | (1 | ) | 276 | (934 | ) | 298 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Machinery, Energy & Transportation Sales | 12,724 | (2,611 | ) | (62 | ) | (137 | ) | — | 9,914 | (2,810 | ) | (22 | %) | |||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 850 | — | — | — | (36 | ) | 814 | (36 | ) | (4 | %) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (108 | ) | — | — | — | 15 | (93 | ) | 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Revenues | 742 | — | — | — | (21 | ) | 721 | (21 | ) | (3 | %) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Sales and Revenues | $ | 13,466 | $ | (2,611 | ) | $ | (62 | ) | $ | (137 | ) | $ | (21 | ) | $ | 10,635 | $ | (2,831 | ) | (21 | %) | |||||||||
| Sales and Revenues by Geographic Region |
| North America | Latin America | EAME | Asia/Pacific | External Sales and Revenues | Inter-Segment | Total Sales and Revenues | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | $ | % Chg | $ | % Chg | $ | % Chg | $ | % Chg | $ | % Chg | $ | % Chg | $ | % Chg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First Quarter 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 2,085 | (30 | %) | $ | 265 | (17 | %) | $ | 889 | (12 | %) | $ | 1,073 | (31 | %) | $ | 4,312 | (26 | %) | $ | (6 | ) | (129 | %) | $ | 4,306 | (27 | %) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Resource Industries | 696 | (27 | %) | 320 | (24 | %) | 395 | (16 | %) | 568 | (29 | %) | 1,979 | (25 | %) | 105 | — | % | 2,084 | (24 | %) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 1,738 | (19 | %) | 249 | (25 | %) | 1,053 | 2 | % | 578 | (19 | %) | 3,618 | (15 | %) | 731 | (25 | %) | 4,349 | (17 | %) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All Other Segment | 5 | (38 | %) | 2 | — | % | 11 | — | % | 10 | (44 | %) | 28 | (24 | %) | 81 | (4 | %) | 109 | (10 | %) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (15 | ) | (2 | ) | (4 | ) | (2 | ) | (23 | ) | (911 | ) | (934 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation Sales | 4,509 | (25 | %) | 834 | (22 | %) | 2,344 | (7 | %) | 2,227 | (28 | %) | 9,914 | (22 | %) | — | — | 9,914 | (22 | %) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 525 | (6 | %) | 70 | — | % | 102 | — | % | 117 | (3 | %) | 814 | 1 | (4 | %) | — | — | 814 | (4 | %) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (54 | ) | (12 | ) | (9 | ) | (18 | ) | (93 | ) | — | (93 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Revenues | 471 | (4 | %) | 58 | (2 | %) | 93 | — | % | 99 | (2 | %) | 721 | (3 | %) | — | — | 721 | (3 | %) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Sales and Revenues | $ | 4,980 | (24 | %) | $ | 892 | (21 | %) | $ | 2,437 | (7 | %) | $ | 2,326 | (27 | %) | $ | 10,635 | (21 | %) | $ | — | — | $ | 10,635 | (21 | %) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| First Quarter 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 2,965 | $ | 319 | $ | 1,006 | $ | 1,562 | $ | 5,852 | $ | 21 | $ | 5,873 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resource Industries | 951 | 423 | 468 | 805 | 2,647 | 105 | 2,752 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 2,151 | 332 | 1,032 | 718 | 4,233 | 977 | 5,210 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All Other Segment | 8 | — | 11 | 18 | 37 | 84 | 121 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (41 | ) | 1 | (3 | ) | (2 | ) | (45 | ) | (1,187 | ) | (1,232 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation Sales | 6,034 | 1,075 | 2,514 | 3,101 | 12,724 | — | 12,724 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 558 | 70 | 102 | 120 | 850 | 1 | — | 850 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (69 | ) | (11 | ) | (9 | ) | (19 | ) | (108 | ) | — | (108 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial Products Revenues | 489 | 59 | 93 | 101 | 742 | — | 742 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Sales and Revenues | $ | 6,523 | $ | 1,134 | $ | 2,607 | $ | 3,202 | $ | 13,466 | $ | — | $ | 13,466 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 Includes revenues from Machinery, Energy & Transportation of $105 million and $131 million in the first quarter of 2020 and 2019, respectively.
54
CONSOLIDATED OPERATING PROFIT
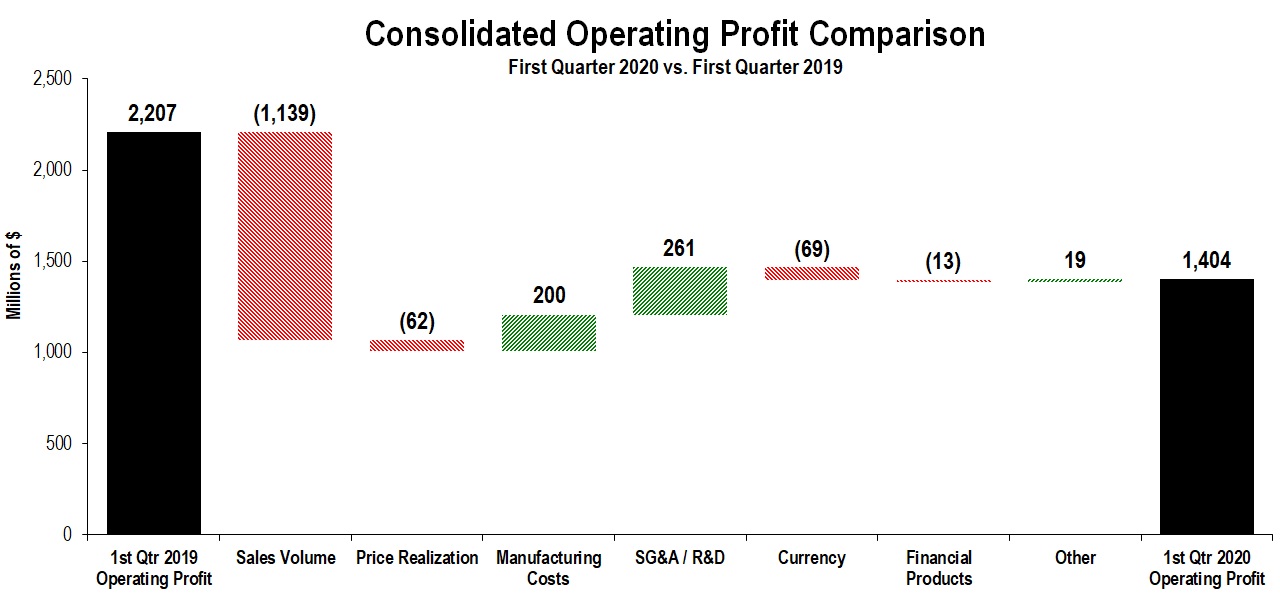
The chart above graphically illustrates reasons for the change in consolidated operating profit between the first quarter of 2019 (at left) and the first quarter of 2020 (at right). Caterpillar management utilizes these charts internally to visually communicate with the company’s Board of Directors and employees. The bar titled Other includes consolidating adjustments and Machinery, Energy & Transportation other operating (income) expenses.
Operating profit for the first quarter of 2020 was $1.404 billion, a decrease of $803 million, or 36 percent, compared with $2.207 billion in the first quarter of 2019. The decrease was mostly due to lower sales volume and unfavorable currency impacts related to the Australian dollar, partially offset by lower SG&A/R&D expenses as well as favorable manufacturing costs.
Lower SG&A/R&D expenses reflected reduced short-term incentive compensation expense, a favorable change in fair value adjustments related to deferred compensation plans and other cost-reduction actions implemented in response to lower sales volumes.
Favorable manufacturing costs were primarily driven by lower period manufacturing and material costs, partially offset by higher warranty expense. Period manufacturing costs declined mostly due to a reduction in short-term incentive compensation expense and other cost-reduction actions implemented in response to lower sales volumes.
Short-term incentive compensation expense is directly related to financial and operational performance, measured against targets set annually. In response to the continued global economic uncertainty due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Caterpillar suspended 2020 base salary increases and short-term incentive compensation plans for many employees and all senior executives. As a result, no short-term incentive compensation expense was recognized in the first quarter of 2020, compared with about $220 million in the first quarter of 2019.
Operating profit margin was 13.2 percent in the first quarter of 2020, compared with 16.4 percent in the first quarter of 2019.
55
| Profit by Segment | ||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | First Quarter 2020 | First Quarter 2019 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||
| Construction Industries | $ | 640 | $ | 1,085 | $ | (445 | ) | (41 | %) | |||||
| Resource Industries | 304 | 576 | (272 | ) | (47 | %) | ||||||||
| Energy & Transportation | 602 | 838 | (236 | ) | (28 | %) | ||||||||
| All Other Segment | 7 | 25 | (18 | ) | (72 | %) | ||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | (212 | ) | (375 | ) | 163 | |||||||||
| Machinery, Energy & Transportation | 1,341 | 2,149 | (808 | ) | (38 | %) | ||||||||
| Financial Products Segment | 105 | 211 | (106 | ) | (50 | %) | ||||||||
| Corporate Items and Eliminations | 47 | (46 | ) | 93 | ||||||||||
| Financial Products | 152 | 165 | (13 | ) | (8 | %) | ||||||||
| Consolidating Adjustments | (89 | ) | (107 | ) | 18 | |||||||||
| Consolidated Operating Profit | $ | 1,404 | $ | 2,207 | $ | (803 | ) | (36 | %) | |||||
Other Profit/Loss and Tax Items
| ▪ | Interest expense excluding Financial Products in the first quarter of 2020 was $113 million, compared with $103 million in the first quarter of 2019. The increase was due to higher average debt outstanding during the first quarter of 2020, compared with the first quarter of 2019. |
| ▪ | Other income (expense) in the first quarter of 2020 was income of $222 million, compared with income of $160 million in the first quarter of 2019. The change was primarily due to a $254 million remeasurement gain resulting from the settlement of a non-U.S. pension obligation, partially offset by unfavorable impacts from equity securities at Insurance Services and foreign currency exchange gains (losses) primarily due to the Australian dollar and Brazilian real. The unfavorable impact of equity securities was due to unrealized losses in the first quarter of 2020, compared with unrealized gains in the first quarter of 2019. The company experienced foreign currency exchange net losses in the first quarter of 2020, compared with net gains in the first quarter of 2019. |
| ▪ | The provision for income taxes for the first quarter of 2020 reflected a higher estimated annual tax rate of 31 percent compared with 26 percent for the first quarter of 2019, excluding the discrete items discussed below. The increase in the estimated annual tax rate is primarily related to changes in the expected geographic mix of profits from a tax perspective for 2020, including the impact of U.S. tax on non-U.S. earnings as a result of U.S. tax reform. |
In the first quarter of 2020, a $43 million tax charge was recorded related to the $254 million remeasurement gain resulting from the settlement of a non-U.S. pension obligation. This gain and related tax were excluded from the estimated annual tax rate as the future period remeasurement impacts cannot currently be estimated. In addition, a discrete tax benefit of $8 million was recorded in the first quarter of 2020, compared with $23 million in the first quarter of 2019, for the settlement of stock-based compensation awards with associated tax deductions in excess of cumulative U.S. GAAP compensation expense. During the first quarter of 2019, a $178 million discrete tax benefit was also recorded to adjust previously unrecognized tax benefits as a result of receipt of additional guidance related to the calculation of the mandatory deemed repatriation of non-U.S. earnings.
Construction Industries
Construction Industries’ total sales were $4.306 billion in the first quarter of 2020, a decrease of $1.567 billion, or 27 percent, compared with $5.873 billion in the first quarter of 2019. The decrease was due to lower sales volume, driven by lower end-user demand and the impact from changes in dealer inventories. Dealers increased inventories significantly more during the first quarter of 2019 than in the first quarter of 2020.
| ▪ | In North America, sales decreased due to lower demand driven by the impact from changes in dealer inventories and lower end-user demand. Dealers increased inventories more during the first quarter of 2019 than in the first quarter of 2020. The lower end-user demand was driven primarily by non-residential and pipeline construction. |
| ▪ | Sales declined in Latin America primarily due to the impact from changes in dealer inventories and unfavorable currency impacts from a weaker Brazilian real. Dealers decreased inventories more during the first quarter of 2020 than in the first quarter of 2019. |
| ▪ | In EAME, the sales decrease was primarily due to lower end-user demand across most of the region and unfavorable currency impacts from a weaker euro. |
56
| ▪ | Sales declined in Asia/Pacific due to lower end-user demand across most of the region, primarily in China. Decreases in China reflected lower end-user demand mostly due to COVID-19 pandemic-related impacts. |
Construction Industries’ profit was $640 million in the first quarter of 2020, a decrease of $445 million, or 41 percent, compared with $1.085 billion in the first quarter of 2019. The decrease was mainly due to lower sales volume, partially offset by lower manufacturing costs. Favorable manufacturing costs were primarily due to lower period manufacturing and material costs, partially offset by higher warranty expense. Lower period manufacturing costs reflected a reduction in short-term incentive compensation expense and targeted cost-reduction actions implemented in response to lower sales volumes.
Construction Industries’ profit as a percent of total sales was 14.9 percent in the first quarter of 2020, compared with 18.5 percent in the first quarter of 2019.
Resource Industries
Resource Industries’ total sales were $2.084 billion in the first quarter of 2020, a decrease of $668 million, or 24 percent, compared with $2.752 billion in the first quarter of 2019. The decrease was due to lower sales volume, driven by changes in dealer inventories and lower end-user demand. Dealers increased inventories during the first quarter of 2019, compared with a decrease during the first quarter of 2020. Mining equipment sales were lower due to weakness in certain commodities. In addition, demand decreased for equipment supporting non-residential construction and quarry and aggregates.
Resource Industries’ profit was $304 million in the first quarter of 2020, a decrease of $272 million, or 47 percent, compared with $576 million in the first quarter of 2019. The decrease was mainly due to lower sales volume. Manufacturing costs were about flat as the unfavorable impact of cost absorption and higher warranty expense were more than offset by lower period manufacturing costs, freight expense and material costs. Cost absorption was unfavorable as inventory increased more in the first quarter of 2019 than in the first quarter of 2020. Lower period manufacturing costs were primarily due to lower short-term incentive compensation expense and the favorable impact of restructuring and other cost-reduction actions.
Resource Industries’ profit as a percent of total sales was 14.6 percent in the first quarter of 2020, compared with 20.9 percent in the first quarter of 2019.
Energy & Transportation
| Sales by Application | |||||||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | First Quarter 2020 | First Quarter 2019 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
| Oil and Gas | $ | 861 | $ | 1,131 | $ | (270 | ) | (24 | %) | ||||||
| Power Generation | 854 | 1,036 | (182 | ) | (18 | %) | |||||||||
| Industrial | 801 | 904 | (103 | ) | (11 | %) | |||||||||
| Transportation | 1,102 | 1,162 | (60 | ) | (5 | %) | |||||||||
| External Sales | 3,618 | 4,233 | (615 | ) | (15 | %) | |||||||||
| Inter-segment | 731 | 977 | (246 | ) | (25 | %) | |||||||||
| Total Sales | $ | 4,349 | $ | 5,210 | $ | (861 | ) | (17 | %) | ||||||
Energy & Transportation’s total sales were $4.349 billion in the first quarter of 2020, a decrease of $861 million, or 17 percent, compared with $5.210 billion in the first quarter of 2019. Sales declined across all applications and inter-segment engine sales.
| ▪ | Oil and Gas – Sales were lower mainly in North America. The sales decline was largely due to lower demand for reciprocating engines used in gas compression and well servicing. |
| ▪ | Power Generation – Sales decreased primarily due to lower sales in Asia/Pacific and North America for both reciprocating engines and turbine-related projects. |
| ▪ | Industrial – Sales decreased due to lower demand across all regions. |
| ▪ | Transportation – Sales declined in both rail and marine applications. |
Energy & Transportation’s profit was $602 million in the first quarter of 2020, a decrease of $236 million, or 28 percent, compared with $838 million in the first quarter of 2019. The decrease was mostly due to lower sales volume. The decline was partially offset by lower SG&A/R&D expenses and manufacturing costs, both of which were mostly impacted by a reduction in short-term incentive compensation expense and other cost-reduction actions implemented in response to lower sales volumes.
57
Energy & Transportation’s profit as a percent of total sales was 13.8 percent in the first quarter of 2020, compared with 16.1 percent in the first quarter of 2019.
Financial Products Segment
Financial Products’ segment revenues were $814 million in the first quarter of 2020, a decrease of $36 million, or 4 percent, from the first quarter of 2019. The decrease was primarily due to lower average earning assets in North America.
Financial Products’ segment profit was $105 million in the first quarter of 2020, compared with $211 million in the first quarter of 2019. Most of the decrease was due to an unfavorable impact from equity securities in Insurance Services. Additionally, Cat Financial experienced lower average earning assets. These unfavorable impacts were partially offset by a reduction in SG&A expenses due to lower short-term incentive compensation expense.
At the end of the first quarter of 2020, past dues at Cat Financial were 4.13 percent, compared with 3.61 percent at the end of the first quarter of 2019. The increase was primarily due to North America, Asia/Pacific and Mining, partially offset by a decrease in Caterpillar Power Finance. Write-offs, net of recoveries, were $30 million for the first quarter of both 2020 and 2019. As of March 31, 2020, Cat Financial's allowance for credit losses totaled $457 million, or 1.69 percent of finance receivables, compared with $424 million, or 1.50 percent of finance receivables, at December 31, 2019. The increase in allowance for credit losses was driven by the forecast of deteriorating economic conditions from the COVID-19 pandemic.
Corporate Items and Eliminations
Expense for corporate items and eliminations was $165 million in the first quarter of 2020, a decrease of $256 million from the first quarter of 2019, primarily due to a favorable change in fair value adjustments related to deferred compensation plans and segment reporting methodology differences.
RESTRUCTURING COSTS
Restructuring costs for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and 2019 were as follows:
| (Millions of dollars) | Three Months Ended March 31 | |||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Employee separations 1 | $ | 11 | $ | 15 | ||||
Contract terminations 1 | 1 | — | ||||||
Long-lived asset impairments 1 | 9 | 7 | ||||||
Other 2 | 16 | 26 | ||||||
| Total restructuring costs | $ | 37 | $ | 48 | ||||
1 Recognized in Other operating (income) expenses. | ||||||||
2 Represents costs related to our restructuring programs, primarily for inventory write-downs, equipment relocation, building demolition and project management, all of which are primarily included in Cost of goods sold. | ||||||||
For the three months ended March 31, 2020, the restructuring costs were primarily related to a strategic action to address a certain product line, which were partially offset by a gain on the sale of a manufacturing facility that had been closed. For the three months ended March 31, 2019, the restructuring costs were primarily related to ongoing facility closures across the company.
Certain restructuring costs are a reconciling item between Segment profit and Consolidated profit before taxes.
The following table summarizes the 2019 and 2020 employee separation activity:
58
| (Millions of dollars) | ||||
| Liability balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 85 | ||
| Increase in liability (separation charges) | 48 | |||
| Reduction in liability (payments) | (85 | ) | ||
| Liability balance at December 31, 2019 | 48 | |||
| Increase in liability (separation charges) | 11 | |||
| Reduction in liability (payments) | (16 | ) | ||
| Liability balance at March 31, 2020 | $ | 43 | ||
Most of the liability balance at March 31, 2020 is expected to be paid in 2020 and 2021.
We expect to incur about $300 - $400 million of restructuring costs in 2020, about half for restructuring actions across the company and the remainder for strategic actions to address a small number of products. We expect that prior restructuring actions will result in an incremental benefit to operating costs, primarily Cost of goods sold and SG&A expenses of about $200 million in 2020 compared with 2019.
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
| 1. | All Other Segment – Primarily includes activities such as: business strategy; product management and development; manufacturing and sourcing of filters and fluids, undercarriage, ground engaging tools, fluid transfer products, precision seals, rubber sealing and connecting components primarily for Cat® products; parts distribution; integrated logistics solutions; distribution services responsible for dealer development and administration, including a wholly owned dealer in Japan; dealer portfolio management and ensuring the most efficient and effective distribution of machines, engines and parts; brand management and marketing strategy; and digital investments for new customer and dealer solutions that integrate data analytics with state-of-the-art digital technologies while transforming the buying experience. |
| 2. | Consolidating Adjustments – Elimination of transactions between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
| 3. | Construction Industries – A segment primarily responsible for supporting customers using machinery in infrastructure and building construction applications. Responsibilities include business strategy, product design, product management and development, manufacturing, marketing and sales and product support. The product portfolio includes asphalt pavers; backhoe loaders; compactors; cold planers; compact track and multi-terrain loaders; mini, small, medium and large track excavators; motor graders; pipelayers; road reclaimers; skid steer loaders; telehandlers; small and medium track-type tractors; track-type loaders; utility vehicles; wheel excavators; compact, small and medium wheel loaders; and related parts and work tools. |
| 4. | Corporate Items and Eliminations – Includes corporate-level expenses, timing differences (as some expenses are reported in segment profit on a cash basis), methodology differences between segment and consolidated external reporting, certain restructuring costs, and inter-segment eliminations. |
| 5. | Currency – With respect to sales and revenues, currency represents the translation impact on sales resulting from changes in foreign currency exchange rates versus the U.S. dollar. With respect to operating profit, currency represents the net translation impact on sales and operating costs resulting from changes in foreign currency exchange rates versus the U.S. dollar. Currency only includes the impact on sales and operating profit for the Machinery, Energy & Transportation lines of business; currency impacts on Financial Products revenues and operating profit are included in the Financial Products portions of the respective analyses. With respect to other income/expense, currency represents the effects of forward and option contracts entered into by the company to reduce the risk of fluctuations in exchange rates (hedging) and the net effect of changes in foreign currency exchange rates on our foreign currency assets and liabilities for consolidated results (translation). |
| 6. | EAME – A geographic region including Europe, Africa, the Middle East and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). |
| 7. | Earning Assets – Assets consisting primarily of total finance receivables net of unearned income, plus equipment on operating leases, less accumulated depreciation at Cat Financial. |
59
| 8. | Energy & Transportation – A segment primarily responsible for supporting customers using reciprocating engines, turbines, diesel-electric locomotives and related parts across industries serving Oil and Gas, Power Generation, Industrial and Transportation applications, including marine- and rail-related businesses. Responsibilities include business strategy, product design, product management and development, manufacturing, marketing and sales, and product support of the following product portfolio: turbine machinery and integrated systems and solutions and turbine-related services, reciprocating engine-powered generator sets, integrated systems used in the electric power generation industry, reciprocating engines and integrated systems and solutions for the marine and oil and gas industries, and reciprocating engines supplied to the industrial industry as well as Cat machinery. Responsibilities also include the remanufacturing of Caterpillar engines and components and remanufacturing services for other companies; the business strategy, product design, product management and development, manufacturing, remanufacturing, leasing and service of diesel-electric locomotives and components and other rail-related products and services; and product support of on-highway vocational trucks for North America. |
| 9. | Financial Products Segment – Provides financing alternatives to customers and dealers around the world for Caterpillar products, as well as financing for vehicles, power generation facilities and marine vessels that, in most cases, incorporate Caterpillar products. Financing plans include operating and finance leases, installment sale contracts, working capital loans and wholesale financing plans. The segment also provides insurance and risk management products and services that help customers and dealers manage their business risk. Insurance and risk management products offered include physical damage insurance, inventory protection plans, extended service coverage for machines and engines, and dealer property and casualty insurance. The various forms of financing, insurance and risk management products offered to customers and dealers help support the purchase and lease of Caterpillar equipment. The segment also earns revenues from ME&T, but the related costs are not allocated to operating segments. Financial Products’ segment profit is determined on a pretax basis and includes other income/expense items. |
| 10. | Latin America – A geographic region including Central and South American countries and Mexico. |
| 11. | Machinery, Energy & Transportation (ME&T) – Represents the aggregate total of Construction Industries, Resource Industries, Energy & Transportation, All Other Segment and related corporate items and eliminations with Financial Products accounted for on the equity basis. |
| 12. | Machinery, Energy & Transportation Other Operating (Income) Expenses – Comprised primarily of gains/losses on disposal of long-lived assets, gains/losses on divestitures and legal settlements, and accruals. |
| 13. | Manufacturing Costs – Manufacturing costs exclude the impacts of currency and represent the volume-adjusted change for variable costs and the absolute dollar change for period manufacturing costs. Variable manufacturing costs are defined as having a direct relationship with the volume of production. This includes material costs, direct labor and other costs that vary directly with production volume, such as freight, power to operate machines and supplies that are consumed in the manufacturing process. Period manufacturing costs support production but are defined as generally not having a direct relationship to short-term changes in volume. Examples include machinery and equipment repair, depreciation on manufacturing assets, facility support, procurement, factory scheduling, manufacturing planning and operations management. |
| 14. | Price Realization – The impact of net price changes excluding currency and new product introductions. Price realization includes geographic mix of sales, which is the impact of changes in the relative weighting of sales prices between geographic regions. |
| 15. | Resource Industries – A segment primarily responsible for supporting customers using machinery in mining, heavy construction, quarry and aggregates, waste and material handling applications. Responsibilities include business strategy, product design, product management and development, manufacturing, marketing and sales, and product support. The product portfolio includes large track-type tractors, large mining trucks, hard rock vehicles, longwall miners, electric rope shovels, draglines, hydraulic shovels, rotary drills, large wheel loaders, off-highway trucks, articulated trucks, wheel tractor scrapers, wheel dozers, landfill compactors, soil compactors, select work tools, machinery components, electronics and control systems, and related parts. In addition to equipment, Resource Industries also develops and sells technology products and services to provide customers fleet management, equipment management analytics and autonomous machine capabilities. Resource Industries also manages areas that provide services to other parts of the company, including integrated manufacturing and research and development. |
| 16. | Restructuring Costs – May include costs for employee separation, long-lived asset impairments and contract terminations. These costs are included in Other operating (income) expenses except for defined-benefit plan curtailment losses and special termination benefits, which are included in Other income (expense). Restructuring costs also include other exit-related costs, which may consist of accelerated depreciation, inventory write-downs, building demolition, equipment relocation and project management costs and LIFO inventory decrement benefits from inventory liquidations at closed facilities, all of which are primarily included in Cost of goods sold. |
60
| 17. | Sales Volume – With respect to sales and revenues, sales volume represents the impact of changes in the quantities sold for Machinery, Energy & Transportation as well as the incremental sales impact of new product introductions, including emissions-related product updates. With respect to operating profit, sales volume represents the impact of changes in the quantities sold for Machinery, Energy & Transportation combined with product mix as well as the net operating profit impact of new product introductions, including emissions-related product updates. Product mix represents the net operating profit impact of changes in the relative weighting of Machinery, Energy & Transportation sales with respect to total sales. The impact of sales volume on segment profit includes inter-segment sales. |
| 18. | Services – Enterprise services include, but are not limited to, aftermarket parts, Financial Products revenues and other service-related revenues. Machinery, Energy & Transportation segments exclude most Financial Products revenues. |
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Sources of funds
We generate significant capital resources from operating activities, which are the primary source of funding for our ME&T operations. Funding for these businesses is also available from commercial paper and long-term debt issuances. Financial Products’ operations are funded primarily from commercial paper, term debt issuances and collections from its existing portfolio. Despite lower volume in most of the industries we serve, we had positive operating cash flow in the first quarter of 2020 within both our ME&T and Financial Products' operations. On a consolidated basis, we ended the first three months of 2020 with $7.12 billion of cash, a decrease of $1.16 billion from year-end 2019. We intend to maintain a strong cash and liquidity position.
Consolidated operating cash flow for the first three months of 2020 was $1.13 billion, about flat with the same period last year. Items favorably impacting cash flow included lower payments for short-term incentive compensation and reduced working capital requirements. Favorable changes in receivables and inventory were partially offset by unfavorable changes in accounts payable and accrued expenses. Mostly offsetting these favorable changes was lower profit adjusted for non-cash items, including lower accruals for short-term incentive compensation and postemployment benefits. Higher taxes paid during the first three months of 2020 compared to the same period last year also unfavorably impacted cash flow.
Total debt as of March 31, 2020 was $37.09 billion, a decrease of $564 million from year-end 2019. Debt related to Financial Products decreased $543 million, primarily due to lower portfolio funding requirements. Debt related to ME&T decreased $21 million in the first three months of 2020.
As of March 31, 2020, we had three global credit facilities with a syndicate of banks totaling $10.50 billion (Credit Facility) available in the aggregate to both Caterpillar and Cat Financial for general liquidity purposes. Based on management’s allocation decision, which can be revised from time to time, the portion of the Credit Facility available to ME&T as of March 31, 2020 was $2.75 billion. Information on our Credit Facility is as follows:
| • | The 364-day facility of $3.15 billion (of which $0.82 billion is available to ME&T) expires in September 2020. |
| • | The three-year facility, as amended and restated in September of 2019, of $2.73 billion (of which $0.72 billion is available to ME&T) expires in September 2022. |
| • | The five-year facility, as amended and restated in September of 2019, of $4.62 billion (of which $1.21 billion is available to ME&T) expires in September 2024. |
At March 31, 2020, Caterpillar’s consolidated net worth was $14.25 billion, which was above the $9.00 billion required under the Credit Facility. The consolidated net worth is defined as the consolidated shareholders’ equity including preferred stock but excluding the pension and other postretirement benefits balance within Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss).
At March 31, 2020, Cat Financial’s covenant interest coverage ratio was 1.78 to 1. This is above the 1.15 to 1 minimum ratio calculated as (1) profit excluding income taxes, interest expense and net gain/(loss) from interest rate derivatives to (2) interest expense calculated at the end of each calendar quarter for the rolling four quarter period then most recently ended, required by the Credit Facility.
In addition, at March 31, 2020, Cat Financial’s six-month covenant leverage ratio was 7.29 to 1. This is below the maximum ratio of debt to net worth of 10 to 1, calculated (1) on a monthly basis as the average of the leverage ratios determined on the last day of each of the six preceding calendar months and (2) at each December 31, required by the Credit Facility.
61
In the event Caterpillar or Cat Financial does not meet one or more of their respective financial covenants under the Credit Facility in the future (and are unable to obtain a consent or waiver), the syndicate of banks may terminate the commitments allocated to the party that does not meet its covenants. Additionally, in such event, certain of Cat Financial’s other lenders under other loan agreements where similar financial covenants or cross default provisions are applicable may, at their election, choose to pursue remedies under those loan agreements, including accelerating the repayment of outstanding borrowings. At March 31, 2020, there were no borrowings under the Credit Facility.
Our total credit commitments and available credit as of March 31, 2020 were:
| March 31, 2020 | |||||||||||
| (Millions of dollars) | Consolidated | Machinery, Energy & Transportation | Financial Products | ||||||||
| Credit lines available: | |||||||||||
| Global credit facilities | $ | 10,500 | $ | 2,751 | $ | 7,749 | |||||
| Other external | 4,335 | 167 | 4,168 | ||||||||
| Total credit lines available | 14,835 | 2,918 | 11,917 | ||||||||
| Less: Commercial paper outstanding | (4,060 | ) | — | (4,060 | ) | ||||||
| Less: Utilized credit | (854 | ) | — | (854 | ) | ||||||
| Available credit | $ | 9,921 | $ | 2,918 | $ | 7,003 | |||||
The other external consolidated credit lines with banks as of March 31, 2020 totaled $4.34 billion. These committed and uncommitted credit lines, which may be eligible for renewal at various future dates or have no specified expiration date, are used primarily by our subsidiaries for local funding requirements. Caterpillar or Cat Financial may guarantee subsidiary borrowings under these lines.
Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 global pandemic, Caterpillar has taken actions to maintain our strong financial position and increase liquidity. In April 2020, we raised $2.0 billion of incremental cash by issuing $800 million in ten-year bonds at 2.6 percent and $1.2 billion in 30-year bonds at 3.25 percent. In addition, we entered into an incremental $3.9 billion short-term credit facility that expires on December 31, 2020 and also registered for $4.1 billion in commercial paper support programs now available in the United States and Canada. The Company has not made any drawings under any of the above mentioned credit facilities nor does it have any outstanding borrowings under either commercial paper support program as of the date of this filing.
We receive debt ratings from the major credit rating agencies. Moody’s currently rates our debt as “low-A”, while Fitch and S&P maintain a “mid-A” debt rating. To date, this split rating has not had a material impact on our borrowing costs or our overall financial health. However, a downgrade of our credit ratings by any of the major credit rating agencies would result in increased borrowing costs and could make access to certain credit markets more difficult. In the event economic conditions deteriorate such that access to debt markets becomes unavailable, ME&T’s operations would rely on cash flow from operations, use of existing cash balances, borrowings from Cat Financial and access to our committed credit facilities. Our Financial Products’ operations would rely on cash flow from its existing portfolio, existing cash balances, access to our committed credit facilities and other credit line facilities of Cat Financial, commercial paper support facilities sponsored by the U.S. Federal Reserve and the Bank of Canada, and potential borrowings from Caterpillar. In addition, we maintain a support agreement with Cat Financial, which requires Caterpillar to remain the sole owner of Cat Financial and may, under certain circumstances, require Caterpillar to make payments to Cat Financial should Cat Financial fail to maintain certain financial ratios.
Machinery, Energy & Transportation
Net cash provided by operating activities was $318 million in the first three months of 2020, compared with $860 million for the same period in 2019. The decrease was primarily due to lower profit adjusted for non-cash items, including lower accruals for short-term incentive compensation and postemployment benefits. Higher taxes paid during the first three months of 2020 compared to the same period last year also unfavorably impacted cash flow. Partially offsetting these unfavorable changes were lower payments for short-term incentive compensation.
Net cash provided by investing activities in the first three months of 2020 was $324 million, compared with net cash used of $226 million in the first three months of 2019. The change was primarily due to decreased ME&T lending with Financial Products.
Net cash used for financing activities during the first three months of 2020 was $1.63 billion, compared with net cash used of $1.25 billion in the same period of 2019. In the first three months of 2020, we repurchased $1.04 billion of Caterpillar common stock, an increase of $292 million compared to the first three months of 2019. Additionally, dividends paid increased $73 million in the first three months of 2020 compared to the same period last year.
62
While our short-term priorities for the use of cash may vary from time to time as business needs and conditions dictate, our long-term cash deployment strategy is focused on the following priorities. Our top priority is to maintain a strong financial position in support of a mid-A rating. Next, we intend to fund operational requirements and commitments. Then, we intend to fund priorities that profitably grow the company and return capital to shareholders through dividend growth and share repurchases. Additional information on cash deployment is as follows:
Strong financial position – Our top priority is to maintain a strong financial position in support of a mid-A rating. We track a diverse group of financial metrics that focus on liquidity, leverage, cash flow and margins which align with our cash deployment actions and the various methodologies used by the major credit rating agencies.
Operational excellence and commitments – Capital expenditures were $302 million during the first three months of 2020, compared to $297 million for the same period in 2019. We expect ME&T’s capital expenditures in 2020 to be about $1.0 billion. We made $98 million of contributions to our pension and other postretirement benefit plans during the first three months of 2020. We currently anticipate full-year 2020 contributions of approximately $280 million. In comparison, we made $119 million of contributions to our pension and other postretirement benefit plans during the first three months of 2019.
Fund strategic growth initiatives and return capital to shareholders – We intend to utilize our liquidity and debt capacity to fund targeted investments that drive long-term profitable growth focused in the areas of expanded offerings and services, including acquisitions.
As part of our capital allocation strategy, ME&T free cash flow is a liquidity measure we use to determine the cash generated and available for financing activities including debt repayments, dividends and share repurchases. We define ME&T free cash flow as cash from ME&T operations excluding discretionary pension and other postretirement benefit plan contributions less capital expenditures. A goal of our capital allocation strategy is to return substantially all ME&T free cash flow to shareholders in the form of dividends and share repurchases, while maintaining our mid-A rating.
Our share repurchase plans are subject to the company’s cash deployment priorities and are evaluated on an ongoing basis considering the financial condition of the company and the economic outlook, corporate cash flow, the company’s liquidity needs, and the health and stability of global credit markets. The timing and amount of future repurchases may vary depending on market conditions and investing priorities. In July 2018, the Board of Directors approved an authorization to repurchase up to $10 billion of Caterpillar common stock (the 2018 Authorization) effective January 1, 2019, with no expiration. In the first three months of 2020, we repurchased $1.04 billion of Caterpillar common stock, with $4.91 billion remaining under the 2018 Authorization as of March 31, 2020. Our basic shares outstanding as of March 31, 2020 were approximately 542 million. Due to current economic uncertainty, we have temporarily suspended our share repurchase program. The existing share repurchase program remains authorized by the Board, and we may resume share repurchases in the future at any time depending upon market conditions, our capital needs and other factors.
Each quarter, our Board of Directors reviews the company’s dividend for the applicable quarter. The Board evaluates the financial condition of the company and considers the economic outlook, corporate cash flow, the company’s liquidity needs, and the health and stability of global credit markets to determine whether to maintain or change the quarterly dividend. In April 2020, the Board of Directors approved maintaining our quarterly dividend representing $1.03 per share and we continue to expect our strong financial position to support the dividend. Dividends paid totaled $567 million in the first three months of 2020.
Financial Products
Financial Products operating cash flow was $431 million in the first three months of 2020, compared with $350 million for the same period a year ago. Net cash provided by investing activities was $444 million for the first three months of 2020, compared with net cash provided of $19 million for the same period in 2019. The change was primarily due to the impact of net intercompany purchased receivables and higher collections of finance receivables, partially offset by higher additions to finance receivables. Net cash used for financing activities was $968 million for the first three months of 2020, compared with net cash used of $489 million for the same period in 2019. The change was primarily due to lower portfolio funding requirements.
RECENT ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS
For a discussion of recent accounting pronouncements, see Part I, Item 1. Note 2 - “New accounting guidance.”
63
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
For a discussion of the company’s critical accounting policies, see Part II, Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations in our 2019 Annual Report on Form 10-K. The following critical accounting policy has been revised since our 2019 Annual Report on Form 10-K:
Allowance for credit losses - The allowance for credit losses is management’s estimate of losses inherent in our finance receivable portfolio calculated using loss forecast models that take into consideration historical credit loss experience, current economic conditions and forecasts and scenarios that capture country and industry-specific economic factors. In addition, qualitative factors not able to be fully captured in our loss forecast models, including borrower-specific and Company-specific macro-economic factors, are considered in the evaluation of the adequacy of our allowance for credit losses. These qualitative factors are subjective and require a degree of management judgment.
The allowance for credit losses is measured on a collective (pool) basis when similar risk characteristics exist and on an individual basis when it is determined that similar risk characteristics do not exist. Finance receivables are identified for individual evaluation based on past-due status and information available about the customer, such as financial statements, news reports and published credit ratings, as well as general information regarding industry trends and the economic environment in which our customers operate. The allowance for credit losses attributable to finance receivables that are individually evaluated is based on the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the receivables' effective interest rate, the fair value of the collateral for collateral-dependent receivables or the observable market price of the receivable. In determining collateral value, we estimate the current fair market value of the collateral less selling costs. We also consider credit enhancements such as additional collateral and contractual third-party guarantees.
While management believes it has exercised prudent judgment and applied reasonable assumptions, there can be no assurance that in the future, changes in economic conditions or other factors would not cause changes in the financial health of our customers. If the financial health of our customers deteriorates, the timing and level of payments received could be impacted and therefore, could result in a change to our estimated losses.
OTHER MATTERS
Environmental and Legal Matters
The Company is regulated by federal, state and international environmental laws governing its use, transport and disposal of substances and control of emissions. In addition to governing our manufacturing and other operations, these laws often impact the development of our products, including, but not limited to, required compliance with air emissions standards applicable to internal combustion engines. We have made, and will continue to make, significant research and development and capital expenditures to comply with these emissions standards.
We are engaged in remedial activities at a number of locations, often with other companies, pursuant to federal and state laws. When it is probable we will pay remedial costs at a site, and those costs can be reasonably estimated, the investigation, remediation, and operating and maintenance costs are accrued against our earnings. Costs are accrued based on consideration of currently available data and information with respect to each individual site, including available technologies, current applicable laws and regulations, and prior remediation experience. Where no amount within a range of estimates is more likely, we accrue the minimum. Where multiple potentially responsible parties are involved, we consider our proportionate share of the probable costs. In formulating the estimate of probable costs, we do not consider amounts expected to be recovered from insurance companies or others. We reassess these accrued amounts on a quarterly basis. The amount recorded for environmental remediation is not material and is included in Accrued expenses. We believe there is no more than a remote chance that a material amount for remedial activities at any individual site, or at all the sites in the aggregate, will be required.
On January 27, 2020, the Brazilian Federal Environmental Agency (“IBAMA”) issued Caterpillar Brasil Ltda a notice of violation regarding allegations around the requirements for use of imported oils at the Piracicaba, Brazil facility. We have instituted processes to address the allegations. While we are still discussing resolution of these allegations with IBAMA, the initial notice from IBAMA included a proposed fine of approximately $370,000. We do not expect this fine or our response to address the allegations to have a material adverse effect on the Company's consolidated results of operations, financial position or liquidity.
64
On January 7, 2015, the Company received a grand jury subpoena from the U.S. District Court for the Central District of Illinois. The subpoena requested documents and information from the Company relating to, among other things, financial information concerning U.S. and non-U.S. Caterpillar subsidiaries (including undistributed profits of non-U.S. subsidiaries and the movement of cash among U.S. and non-U.S. subsidiaries). The Company has received additional subpoenas relating to this investigation requesting additional documents and information relating to, among other things, the purchase and resale of replacement parts by Caterpillar Inc. and non-U.S. Caterpillar subsidiaries, dividend distributions of certain non-U.S. Caterpillar subsidiaries, and Caterpillar SARL (CSARL) and related structures. On March 2-3, 2017, agents with the Department of Commerce, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation and the Internal Revenue Service executed search and seizure warrants at three facilities of the Company in the Peoria, Illinois area, including its former corporate headquarters. The warrants identify, and agents seized, documents and information related to, among other things, the export of products from the United States, the movement of products between the United States and Switzerland, the relationship between Caterpillar Inc. and CSARL, and sales outside the United States. It is the Company’s understanding that the warrants, which concern both tax and export activities, are related to the ongoing grand jury investigation. The Company is continuing to cooperate with this investigation. The Company is unable to predict the outcome or reasonably estimate any potential loss; however, we currently believe that this matter will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position or liquidity.
On March 20, 2014, Brazil’s Administrative Council for Economic Defense (CADE) published a Technical Opinion which named 18 companies and over 100 individuals as defendants, including two subsidiaries of Caterpillar Inc., MGE - Equipamentos e Serviços Ferroviários Ltda. (MGE) and Caterpillar Brasil Ltda. The publication of the Technical Opinion opened CADE’s official administrative investigation into allegations that the defendants participated in anticompetitive bid activity for the construction and maintenance of metro and train networks in Brazil. While companies cannot be held criminally liable for anticompetitive conduct in Brazil, criminal charges have been brought against one current employee of MGE and two former employees of MGE involving the same conduct alleged by CADE. On July 8, 2019, CADE found MGE, one of its current employees and two of its former employees liable for anticompetitive conduct. CBL was dismissed from the proceeding without any finding of liability. MGE intends to appeal CADE’s findings. We currently believe that this matter will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position or liquidity.
In addition, we are involved in other unresolved legal actions that arise in the normal course of business. The most prevalent of these unresolved actions involve disputes related to product design, manufacture and performance liability (including claimed asbestos exposure), contracts, employment issues, environmental matters, intellectual property rights, taxes (other than income taxes) and securities laws. The aggregate range of reasonably possible losses in excess of accrued liabilities, if any, associated with these unresolved legal actions is not material. In some cases, we cannot reasonably estimate a range of loss because there is insufficient information regarding the matter. However, we believe there is no more than a remote chance that any liability arising from these matters would be material. Although it is not possible to predict with certainty the outcome of these unresolved legal actions, we believe that these actions will not individually or in the aggregate have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial position or liquidity.
Order Backlog
At the end of the first quarter of 2020, the dollar amount of backlog believed to be firm was approximately $14.1 billion, about $400 million higher than the fourth quarter of 2019. The increase was in Energy & Transportation and Resource Industries, while Construction Industries was about flat. Of the total backlog at March 31, 2020, approximately $4.0 billion was not expected to be filled in the following twelve months.
65
NON-GAAP FINANCIAL MEASURES
The following definitions are provided for the non-GAAP financial measures used in this report. These non-GAAP financial measures have no standardized meaning prescribed by U.S. GAAP and therefore are unlikely to be comparable to the calculation of similar measures for other companies. Management does not intend for these items to be considered in isolation or as a substitute for the related GAAP measures.
We believe it is important to separately quantify the profit impact of two significant items in order for our results to be meaningful to our readers. These items consist of (i) a remeasurement gain resulting from the settlement of a non-U.S. pension obligation in the first quarter of 2020 and (ii) a discrete tax benefit related to U.S. tax reform in the first quarter of 2019. We do not consider these items indicative of earnings from ongoing business activities and believe the non-GAAP measure provides investors with useful perspective on underlying business results and trends and aids with assessing our period-over-period results. In addition, we provide a calculation of ME&T free cash flow as we believe it is an important measure for investors to determine the cash generation available for financing activities including debt repayments, dividends and share repurchases.
Reconciliations of adjusted profit per share to the most directly comparable GAAP measure, profit per share - diluted are as follows:
| Three Months Ended March 31 | |||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | ||||||
| Profit per share - diluted | $ | 1.98 | $ | 3.25 | |||
Per share remeasurement gain of a non-US pension obligation 1 | $ | (0.38 | ) | $ | — | ||
| Per share U.S. tax reform impact | $ | — | $ | (0.31 | ) | ||
| Adjusted profit per share | $ | 1.60 | $ | 2.94 | |||
1 At statutory tax rates. | |||||||
Reconciliations of ME&T free cash flow to the most directly comparable GAAP measure, net cash provided by operating activities are as follows:
| (Millions of dollars) | Three Months Ended March 31 | ||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | ||||||
ME&T net cash provided by operating activities 1 | $ | 318 | $ | 860 | |||
| ME&T capital expenditures | $ | (302 | ) | $ | (297 | ) | |
| ME&T free cash flow | $ | 16 | $ | 563 | |||
1 See reconciliation of ME&T net cash provided by operating activities to consolidated net cash provided by operating activities on pages 72-73. | |||||||
66
Supplemental Consolidating Data
We are providing supplemental consolidating data for the purpose of additional analysis. The data has been grouped as follows:
Consolidated – Caterpillar Inc. and its subsidiaries.
Machinery, Energy & Transportation – Caterpillar defines Machinery, Energy & Transportation as it is presented in the supplemental data as Caterpillar Inc. and its subsidiaries with Financial Products accounted for on the equity basis. Machinery, Energy & Transportation information relates to the design, manufacturing and marketing of our products. Financial Products’ information relates to the financing to customers and dealers for the purchase and lease of Caterpillar and other equipment. The nature of these businesses is different, especially with regard to the financial position and cash flow items. Caterpillar management utilizes this presentation internally to highlight these differences. We also believe this presentation will assist readers in understanding our business.
Financial Products – Our finance and insurance subsidiaries, primarily Cat Financial and Insurance Services.
Consolidating Adjustments – Eliminations of transactions between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products.
Pages 68 to 73 reconcile Machinery, Energy & Transportation with Financial Products on the equity basis to Caterpillar Inc. consolidated financial information.
67
Caterpillar Inc.
Supplemental Data for Results of Operations
For the Three Months Ended March 31, 2020
(Unaudited)
(Millions of dollars)
| Supplemental Consolidating Data | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated | Machinery, Energy & Transportation 1 | Financial Products | Consolidating Adjustments | |||||||||||||
| Sales and revenues: | ||||||||||||||||
| Sales of Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 9,914 | $ | 9,914 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
| Revenues of Financial Products | 721 | — | 830 | (109 | ) | 2 | ||||||||||
| Total sales and revenues | 10,635 | 9,914 | 830 | (109 | ) | |||||||||||
| Operating costs: | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 7,266 | 7,267 | — | (1 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 1,121 | 940 | 182 | (1 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||
| Research and development expenses | 356 | 356 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense of Financial Products | 175 | — | 176 | (1 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||
| Other operating (income) expenses | 313 | 10 | 320 | (17 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||
| Total operating costs | 9,231 | 8,573 | 678 | (20 | ) | |||||||||||
| Operating profit | 1,404 | 1,341 | 152 | (89 | ) | |||||||||||
| Interest expense excluding Financial Products | 113 | 112 | — | 1 | 4 | |||||||||||
| Other income (expense) | 222 | 179 | (47 | ) | 90 | 5 | ||||||||||
| Consolidated profit before taxes | 1,513 | 1,408 | 105 | — | ||||||||||||
| Provision (benefit) for income taxes | 425 | 397 | 28 | — | ||||||||||||
| Profit of consolidated companies | 1,088 | 1,011 | 77 | — | ||||||||||||
| Equity in profit (loss) of unconsolidated affiliated companies | 5 | 5 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Equity in profit of Financial Products’ subsidiaries | — | 73 | — | (73 | ) | 6 | ||||||||||
| Profit of consolidated and affiliated companies | 1,093 | 1,089 | 77 | (73 | ) | |||||||||||
| Less: Profit (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 1 | (3 | ) | 4 | — | |||||||||||
Profit 7 | $ | 1,092 | $ | 1,092 | $ | 73 | $ | (73 | ) | |||||||
1 | Represents Caterpillar Inc. and its subsidiaries with Financial Products accounted for on the equity basis. |
2 | Elimination of Financial Products’ revenues earned from Machinery, Energy & Transportation. |
3 | Elimination of net expenses recorded by Machinery, Energy & Transportation paid to Financial Products. |
4 | Elimination of interest expense recorded between Financial Products and Machinery, Energy & Transportation. |
5 | Elimination of discount recorded by Machinery, Energy & Transportation on receivables sold to Financial Products and of interest earned between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
6 | Elimination of Financial Products’ profit due to equity method of accounting. |
7 | Profit attributable to common shareholders. |
68
Caterpillar Inc.
Supplemental Data for Results of Operations
For the Three Months Ended March 31, 2019
(Unaudited)
(Millions of dollars)
| Supplemental Consolidating Data | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated | Machinery, Energy & Transportation 1 | Financial Products | Consolidating Adjustments | |||||||||||||
| Sales and revenues: | ||||||||||||||||
| Sales of Machinery, Energy & Transportation | $ | 12,724 | $ | 12,724 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
| Revenues of Financial Products | 742 | — | 870 | (128 | ) | 2 | ||||||||||
| Total sales and revenues | 13,466 | 12,724 | 870 | (128 | ) | |||||||||||
| Operating costs: | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 9,003 | 9,003 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 1,319 | 1,127 | 192 | — | ||||||||||||
| Research and development expenses | 435 | 435 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense of Financial Products | 190 | — | 200 | (10 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||
| Other operating (income) expenses | 312 | 10 | 313 | (11 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||
| Total operating costs | 11,259 | 10,575 | 705 | (21 | ) | |||||||||||
| Operating profit | 2,207 | 2,149 | 165 | (107 | ) | |||||||||||
| Interest expense excluding Financial Products | 103 | 110 | — | (7 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||
| Other income (expense) | 160 | 19 | 41 | 100 | 5 | |||||||||||
| Consolidated profit before taxes | 2,264 | 2,058 | 206 | — | ||||||||||||
| Provision (benefit) for income taxes | 387 | 335 | 52 | — | ||||||||||||
| Profit of consolidated companies | 1,877 | 1,723 | 154 | — | ||||||||||||
| Equity in profit (loss) of unconsolidated affiliated companies | 7 | 7 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Equity in profit of Financial Products’ subsidiaries | — | 148 | — | (148 | ) | 6 | ||||||||||
| Profit of consolidated and affiliated companies | 1,884 | 1,878 | 154 | (148 | ) | |||||||||||
| Less: Profit (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 3 | (3 | ) | 6 | — | |||||||||||
Profit 7 | $ | 1,881 | $ | 1,881 | $ | 148 | $ | (148 | ) | |||||||
1 | Represents Caterpillar Inc. and its subsidiaries with Financial Products accounted for on the equity basis. |
2 | Elimination of Financial Products’ revenues earned from Machinery, Energy & Transportation. |
3 | Elimination of net expenses recorded by Machinery, Energy & Transportation paid to Financial Products. |
4 | Elimination of interest expense recorded between Financial Products and Machinery, Energy & Transportation. |
5 | Elimination of discount recorded by Machinery, Energy & Transportation on receivables sold to Financial Products and of interest earned between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
6 | Elimination of Financial Products’ profit due to equity method of accounting. |
7 | Profit attributable to common shareholders. |
69
Caterpillar Inc.
Supplemental Data for Financial Position
At March 31, 2020
(Unaudited)
(Millions of dollars)
| Supplemental Consolidating Data | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated | Machinery, Energy & Transportation 1 | Financial Products | Consolidating Adjustments | |||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||||||||||
| Cash and short-term investments | $ | 7,123 | $ | 6,251 | $ | 872 | $ | — | ||||||||
| Receivables – trade and other | 7,834 | 2,722 | 482 | 4,630 | 2,3 | |||||||||||
| Receivables – finance | 9,120 | — | 13,886 | (4,766 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 1,761 | 1,237 | 555 | (31 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||
| Inventories | 11,748 | 11,748 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Total current assets | 37,586 | 21,958 | 15,795 | (167 | ) | |||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment – net | 12,488 | 8,385 | 4,103 | — | ||||||||||||
| Long-term receivables – trade and other | 1,196 | 268 | 266 | 662 | 2,3 | |||||||||||
| Long-term receivables – finance | 12,021 | — | 12,694 | (673 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||
| Investments in Financial Products subsidiaries | — | 3,999 | — | (3,999 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Noncurrent deferred and refundable income taxes | 1,426 | 1,975 | 96 | (645 | ) | 6 | ||||||||||
| Intangible assets | 1,478 | 1,478 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill | 6,140 | 6,140 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Other assets | 3,559 | 2,048 | 1,610 | (99 | ) | 7 | ||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 75,894 | $ | 46,251 | $ | 34,564 | $ | (4,921 | ) | |||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings | $ | 4,789 | $ | — | $ | 4,789 | $ | — | ||||||||
| Short-term borrowings with consolidated companies | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Accounts payable | 5,769 | 5,672 | 233 | (136 | ) | 9 | ||||||||||
| Accrued expenses | 3,776 | 3,426 | 350 | — | ||||||||||||
| Accrued wages, salaries and employee benefits | 878 | 862 | 16 | — | ||||||||||||
| Customer advances | 1,295 | 1,295 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Dividends payable | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Other current liabilities | 2,074 | 1,500 | 626 | (52 | ) | 6,10 | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt due within one year | 7,935 | 143 | 7,792 | — | ||||||||||||
| Total current liabilities | 26,516 | 12,898 | 13,806 | (188 | ) | |||||||||||
| Long-term debt due after one year | 24,369 | 9,009 | 15,371 | (11 | ) | 8 | ||||||||||
| Liability for postemployment benefits | 6,333 | 6,332 | 1 | — | ||||||||||||
| Other liabilities | 4,437 | 3,773 | 1,387 | (723 | ) | 6 | ||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 61,655 | 32,012 | 30,565 | (922 | ) | |||||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity | ||||||||||||||||
| Common stock | 6,046 | 6,046 | 919 | (919 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Treasury stock | (25,341 | ) | (25,341 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Profit employed in the business | 35,504 | 35,504 | 4,057 | (4,057 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (2,012 | ) | (2,012 | ) | (1,152 | ) | 1,152 | 5 | ||||||||
| Noncontrolling interests | 42 | 42 | 175 | (175 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Total shareholders’ equity | 14,239 | 14,239 | 3,999 | (3,999 | ) | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 75,894 | $ | 46,251 | $ | 34,564 | $ | (4,921 | ) | |||||||
1 | Represents Caterpillar Inc. and its subsidiaries with Financial Products accounted for on the equity basis. |
2 | Elimination of receivables between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
3 | Reclassification of Machinery, Energy & Transportation’s trade receivables purchased by Financial Products and Financial Products’ wholesale inventory receivables. |
4 | Elimination of Machinery, Energy & Transportation’s insurance premiums that are prepaid to Financial Products. |
5 | Elimination of Financial Products’ equity which is accounted for by Machinery, Energy & Transportation on the equity basis. |
6 | Reclassification reflecting required netting of deferred tax assets / liabilities by taxing jurisdiction. |
7 | Elimination of other intercompany assets between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
8 | Elimination of debt between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
9 | Elimination of payables between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
10 | Elimination of prepaid insurance in Financial Products’ other liabilities. |
70
Caterpillar Inc.
Supplemental Data for Financial Position
At December 31, 2019
(Unaudited)
(Millions of dollars)
| Supplemental Consolidating Data | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated | Machinery, Energy & Transportation 1 | Financial Products | Consolidating Adjustments | |||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||||||||||
| Cash and short-term investments | $ | 8,284 | $ | 7,299 | $ | 985 | $ | — | ||||||||
| Receivables – trade and other | 8,568 | 3,737 | 451 | 4,380 | 2,3 | |||||||||||
| Receivables – finance | 9,336 | — | 14,489 | (5,153 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 1,739 | 1,290 | 529 | (80 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||
| Inventories | 11,266 | 11,266 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Total current assets | 39,193 | 23,592 | 16,454 | (853 | ) | |||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment – net | 12,904 | 8,606 | 4,298 | — | ||||||||||||
| Long-term receivables – trade and other | 1,193 | 348 | 152 | 693 | 2,3 | |||||||||||
| Long-term receivables – finance | 12,651 | — | 13,354 | (703 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||
| Investments in Financial Products subsidiaries | — | 4,260 | — | (4,260 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Noncurrent deferred and refundable income taxes | 1,411 | 2,002 | 117 | (708 | ) | 6 | ||||||||||
| Intangible assets | 1,565 | 1,565 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill | 6,196 | 6,196 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Other assets | 3,340 | 1,868 | 1,572 | (100 | ) | 7 | ||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 78,453 | $ | 48,437 | $ | 35,947 | $ | (5,931 | ) | |||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings | $ | 5,166 | $ | 5 | $ | 5,161 | $ | — | ||||||||
| Short-term borrowings with consolidated companies | — | — | 600 | (600 | ) | 8 | ||||||||||
| Accounts payable | 5,957 | 5,918 | 212 | (173 | ) | 9 | ||||||||||
| Accrued expenses | 3,750 | 3,415 | 335 | — | ||||||||||||
| Accrued wages, salaries and employee benefits | 1,629 | 1,580 | 49 | — | ||||||||||||
| Customer advances | 1,187 | 1,187 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Dividends payable | 567 | 567 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Other current liabilities | 2,155 | 1,689 | 566 | (100 | ) | 6,10 | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt due within one year | 6,210 | 16 | 6,194 | — | ||||||||||||
| Total current liabilities | 26,621 | 14,377 | 13,117 | (873 | ) | |||||||||||
| Long-term debt due after one year | 26,281 | 9,151 | 17,140 | (10 | ) | 8 | ||||||||||
| Liability for postemployment benefits | 6,599 | 6,599 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Other liabilities | 4,323 | 3,681 | 1,430 | (788 | ) | 6 | ||||||||||
| Total liabilities | 63,824 | 33,808 | 31,687 | (1,671 | ) | |||||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity | ||||||||||||||||
| Common stock | 5,935 | 5,935 | 919 | (919 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Treasury stock | (24,217 | ) | (24,217 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Profit employed in the business | 34,437 | 34,437 | 3,997 | (3,997 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (1,567 | ) | (1,567 | ) | (828 | ) | 828 | 5 | ||||||||
| Noncontrolling interests | 41 | 41 | 172 | (172 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Total shareholders’ equity | 14,629 | 14,629 | 4,260 | (4,260 | ) | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 78,453 | $ | 48,437 | $ | 35,947 | $ | (5,931 | ) | |||||||
1 | Represents Caterpillar Inc. and its subsidiaries with Financial Products accounted for on the equity basis. |
2 | Elimination of receivables between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
3 | Reclassification of Machinery, Energy & Transportation’s trade receivables purchased by Financial Products and Financial Products’ wholesale inventory receivables. |
4 | Elimination of Machinery, Energy & Transportation’s insurance premiums that are prepaid to Financial Products. |
5 | Elimination of Financial Products’ equity which is accounted for by Machinery, Energy & Transportation on the equity basis. |
6 | Reclassification reflecting required netting of deferred tax assets / liabilities by taxing jurisdiction. |
7 | Elimination of other intercompany assets between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
8 | Elimination of debt between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
9 | Elimination of payables between Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
10 | Elimination of prepaid insurance in Financial Products’ other liabilities. |
71
Caterpillar Inc.
Supplemental Data for Cash Flow
For the Three Months Ended March 31, 2020
(Unaudited)
(Millions of dollars)
| Supplemental Consolidating Data | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated | Machinery, Energy & Transportation 1 | Financial Products | Consolidating Adjustments | |||||||||||||
| Cash flow from operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Profit of consolidated and affiliated companies | $ | 1,093 | $ | 1,089 | $ | 77 | $ | (73 | ) | 2 | ||||||
| Adjustments for non-cash items: | ||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 614 | 402 | 212 | — | ||||||||||||
| Undistributed profit of Financial Products | — | (73 | ) | — | 73 | 3 | ||||||||||
| Gain on remeasurement of a non-U.S. pension obligation | (254 | ) | (254 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Provision (benefit) for deferred income taxes | 20 | 75 | (55 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| Other | 534 | 249 | 170 | 115 | 4 | |||||||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions and divestitures: | ||||||||||||||||
| Receivables – trade and other | 500 | 328 | (56 | ) | 228 | 4, 5 | ||||||||||
| Inventories | (541 | ) | (538 | ) | — | (3 | ) | 4 | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | 90 | 2 | 51 | 37 | 4 | |||||||||||
| Accrued expenses | (97 | ) | (105 | ) | 8 | — | ||||||||||
| Accrued wages, salaries and employee benefits | (722 | ) | (689 | ) | (33 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Customer advances | 116 | 116 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Other assets – net | (50 | ) | 15 | (16 | ) | (49 | ) | 4 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities – net | (173 | ) | (299 | ) | 73 | 53 | 4 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) operating activities | 1,130 | 318 | 431 | 381 | ||||||||||||
| Cash flow from investing activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures – excluding equipment leased to others | (305 | ) | (304 | ) | (1 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Expenditures for equipment leased to others | (243 | ) | 2 | (249 | ) | 4 | 4 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from disposals of leased assets and property, plant and equipment | 216 | 61 | 156 | (1 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||
| Additions to finance receivables | (2,953 | ) | — | (3,213 | ) | 260 | 5 | |||||||||
| Collections of finance receivables | 3,153 | — | 3,421 | (268 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Net intercompany purchased receivables | — | — | 376 | (376 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of finance receivables | 31 | — | 31 | — | ||||||||||||
| Net intercompany borrowings | — | 599 | 1 | (600 | ) | 6 | ||||||||||
| Investments and acquisitions (net of cash acquired) | (35 | ) | (35 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of securities | 68 | 6 | 62 | — | ||||||||||||
| Investments in securities | (180 | ) | (5 | ) | (175 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Other – net | 35 | — | 35 | — | ||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) investing activities | (213 | ) | 324 | 444 | (981 | ) | ||||||||||
| Cash flow from financing activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | (567 | ) | (567 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Common stock issued, including treasury shares reissued | (23 | ) | (23 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Common shares repurchased | (1,043 | ) | (1,043 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Net intercompany borrowings | — | (1 | ) | (599 | ) | 600 | 6 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from debt issued (original maturities greater than three months) | 2,141 | 15 | 2,126 | — | ||||||||||||
| Payments on debt (original maturities greater than three months) | (2,466 | ) | (6 | ) | (2,460 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Short-term borrowings – net (original maturities three months or less) | (40 | ) | (5 | ) | (35 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Other ��� net | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities | (1,999 | ) | (1,631 | ) | (968 | ) | 600 | |||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | (80 | ) | (59 | ) | (21 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and short-term investments and restricted cash | (1,162 | ) | (1,048 | ) | (114 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Cash and short-term investments and restricted cash at beginning of period | 8,292 | 7,302 | 990 | — | ||||||||||||
| Cash and short-term investments and restricted cash at end of period | $ | 7,130 | $ | 6,254 | $ | 876 | $ | — | ||||||||
1 | Represents Caterpillar Inc. and its subsidiaries with Financial Products accounted for on the equity basis. |
2 | Elimination of Financial Products’ profit after tax due to equity method of accounting. |
3 | Elimination of non-cash adjustment for the undistributed earnings from Financial Products. |
4 | Elimination of non-cash adjustments and changes in assets and liabilities related to consolidated reporting. |
5 | Reclassification of Financial Products’ cash flow activity from investing to operating for receivables that arose from the sale of inventory. |
6 | Elimination of net proceeds and payments to/from Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
72
Caterpillar Inc.
Supplemental Data for Cash Flow
For the Three Months Ended March 31, 2019
(Unaudited)
(Millions of dollars)
| Supplemental Consolidating Data | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated | Machinery, Energy & Transportation 1 | Financial Products | Consolidating Adjustments | |||||||||||||
| Cash flow from operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Profit of consolidated and affiliated companies | $ | 1,884 | $ | 1,878 | $ | 154 | $ | (148 | ) | 2 | ||||||
| Adjustments for non-cash items: | ||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 641 | 424 | 217 | — | ||||||||||||
| Undistributed profit of Financial Products | — | (148 | ) | — | 148 | 3 | ||||||||||
| Provision (benefit) for deferred income taxes | (11 | ) | 14 | (25 | ) | — | ||||||||||
| Other | 88 | 49 | (59 | ) | 98 | 4 | ||||||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions and divestitures: | ||||||||||||||||
| Receivables – trade and other | (150 | ) | 75 | (24 | ) | (201 | ) | 4, 5 | ||||||||
| Inventories | (813 | ) | (818 | ) | — | 5 | 4 | |||||||||
| Accounts payable | 355 | 336 | 12 | 7 | 4 | |||||||||||
| Accrued expenses | 135 | 124 | 11 | — | ||||||||||||
| Accrued wages, salaries and employee benefits | (1,185 | ) | (1,177 | ) | (8 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Customer advances | 105 | 105 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Other assets – net | (7 | ) | (6 | ) | 37 | (38 | ) | 4 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities – net | 79 | 4 | 35 | 40 | 4 | |||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) operating activities | 1,121 | 860 | 350 | (89 | ) | |||||||||||
| Cash flow from investing activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures – excluding equipment leased to others | (278 | ) | (274 | ) | (4 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Expenditures for equipment leased to others | (269 | ) | (23 | ) | (247 | ) | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| Proceeds from disposals of leased assets and property, plant and equipment | 209 | 26 | 189 | (6 | ) | 4 | ||||||||||
| Additions to finance receivables | (2,615 | ) | — | (2,971 | ) | 356 | 5 | |||||||||
| Collections of finance receivables | 2,818 | — | 3,096 | (278 | ) | 5 | ||||||||||
| Net intercompany purchased receivables | — | — | (16 | ) | 16 | 5 | ||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of finance receivables | 44 | — | 44 | — | ||||||||||||
| Net intercompany borrowings | — | 63 | — | (63 | ) | 6 | ||||||||||
| Investments and acquisitions (net of cash acquired) | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of securities | 57 | 4 | 53 | — | ||||||||||||
| Investments in securities | (107 | ) | (7 | ) | (100 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Other – net | (38 | ) | (13 | ) | (25 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) investing activities | (181 | ) | (226 | ) | 19 | 26 | ||||||||||
| Cash flow from financing activities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | (494 | ) | (494 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Common stock issued, including treasury shares reissued | (5 | ) | (5 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Common shares repurchased | (751 | ) | (751 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Net intercompany borrowings | — | — | (63 | ) | 63 | 6 | ||||||||||
| Proceeds from debt issued (original maturities greater than three months) | 2,665 | — | 2,665 | — | ||||||||||||
| Payments on debt (original maturities greater than three months) | (2,567 | ) | (2 | ) | (2,565 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Short-term borrowings – net (original maturities three months or less) | (522 | ) | 4 | (526 | ) | — | ||||||||||
| Other – net | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities | (1,675 | ) | (1,249 | ) | (489 | ) | 63 | |||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | 3 | 5 | (2 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and short-term investments and restricted cash | (732 | ) | (610 | ) | (122 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Cash and short-term investments and restricted cash at beginning of period | 7,890 | 6,994 | 896 | — | ||||||||||||
| Cash and short-term investments and restricted cash at end of period | $ | 7,158 | $ | 6,384 | $ | 774 | $ | — | ||||||||
1 | Represents Caterpillar Inc. and its subsidiaries with Financial Products accounted for on the equity basis. |
2 | Elimination of Financial Products’ profit after tax due to equity method of accounting. |
3 | Elimination of non-cash adjustment for the undistributed earnings from Financial Products. |
4 | Elimination of non-cash adjustments and changes in assets and liabilities related to consolidated reporting. |
5 | Reclassification of Financial Products’ cash flow activity from investing to operating for receivables that arose from the sale of inventory. |
6 | Elimination of net proceeds and payments to/from Machinery, Energy & Transportation and Financial Products. |
73
Forward-looking Statements
Certain statements in this Form 10-Q relate to future events and expectations and are forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Words such as “believe,” “estimate,” “will be,” “will,” “would,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “plan,” “forecast,” “target,” “guide,” “project,” “intend,” “could,” “should” or other similar words or expressions often identify forward-looking statements. All statements other than statements of historical fact are forward-looking statements, including, without limitation, statements regarding our outlook, projections, forecasts or trend descriptions. These statements do not guarantee future performance and speak only as of the date they are made, and we do not undertake to update our forward-looking statements.
Caterpillar’s actual results may differ materially from those described or implied in our forward-looking statements based on a number of factors, including, but not limited to: (i) global and regional economic conditions and economic conditions in the industries we serve; (ii) commodity price changes, material price increases, fluctuations in demand for our products or significant shortages of material; (iii) government monetary or fiscal policies; (iv) political and economic risks, commercial instability and events beyond our control in the countries in which we operate; (v) international trade policies and their impact on demand for our products and our competitive position, including the imposition of new tariffs or changes in existing tariff rates; (vi) our ability to develop, produce and market quality products that meet our customers’ needs; (vii) the impact of the highly competitive environment in which we operate on our sales and pricing; (viii) information technology security threats and computer crime; (ix) inventory management decisions and sourcing practices of our dealers and our OEM customers; (x) a failure to realize, or a delay in realizing, all of the anticipated benefits of our acquisitions, joint ventures or divestitures; (xi) union disputes or other employee relations issues; (xii) adverse effects of unexpected events; (xiii) disruptions or volatility in global financial markets limiting our sources of liquidity or the liquidity of our customers, dealers and suppliers; (xiv) failure to maintain our credit ratings and potential resulting increases to our cost of borrowing and adverse effects on our cost of funds, liquidity, competitive position and access to capital markets; (xv) our Financial Products segment’s risks associated with the financial services industry; (xvi) changes in interest rates or market liquidity conditions; (xvii) an increase in delinquencies, repossessions or net losses of Cat Financial’s customers; (xviii) currency fluctuations; (xix) our or Cat Financial’s compliance with financial and other restrictive covenants in debt agreements; (xx) increased pension plan funding obligations; (xxi) alleged or actual violations of trade or anti-corruption laws and regulations; (xxii) additional tax expense or exposure, including the impact of U.S. tax reform; (xxiii) significant legal proceedings, claims, lawsuits or government investigations; (xxiv) new regulations or changes in financial services regulations; (xxv) compliance with environmental laws and regulations; (xxvi) the duration and geographic spread of, business disruptions caused by, and the overall global economic impact of, the COVID-19 pandemic; and (xxvii) other factors described in more detail in Caterpillar’s Forms 10-Q, 10-K and other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Item 3. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
The information required by this Item is incorporated by reference from Note 5 – “Derivative financial instruments and risk management” included in Part I, Item 1 and Management’s Discussion and Analysis included in Part I, Item 2 of this Form 10-Q.
Item 4. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of disclosure controls and procedures
An evaluation was performed under the supervision and with the participation of the company’s management, including the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Chief Financial Officer (CFO), of the effectiveness of the design and operation of the company’s disclosure controls and procedures, as that term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as of the end of the period covered by this quarterly report. Based on that evaluation, the CEO and CFO concluded that the company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of the end of the period covered by this quarterly report.
Changes in internal control over financial reporting
During the first quarter of 2020, there has been no change in the company’s internal control over financial reporting that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the company’s internal control over financial reporting.
74
PART II. OTHER INFORMATION
Item 1. Legal Proceedings
The information required by this Item is incorporated by reference from Note 14 – “Environmental and legal matters” included in Part I, Item 1 of this Form 10-Q.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
This section supplements and updates certain of the information found under Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors” of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019 (the 2019 Form 10-K) and the information disclosed in the Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on March 26, 2020 (the COVID-19 8-K) based on information currently known to us and recent developments since the date of the 2019 Form 10-K and the COVID-19 8-K. The matters discussed below should be read in conjunction with the risk factors set forth in in the 2019 Form 10-K and the information disclosed in the COVID-19 8-K. However, the risks and uncertainties that we face are not limited to those described below and those set forth in the 2019 Form 10-K and the COVID-19 8-K filing. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently believe to be immaterial may also adversely affect our business.
The COVID-19 pandemic could materially adversely affect our business, financial position, results of operations and/or liquidity.
COVID-19 was identified in China in late 2019 and has spread globally. The rapid spread has resulted in weaker demand and supply constraints and the implementation of numerous measures to try to contain the virus, such as travel bans and restrictions, quarantines, shelter in place orders and shutdowns. These factors have impacted and may continue to impact all or portions of our workforce and operations, particularly as we have temporarily closed certain of our facilities and may continue to temporarily close facilities as the situation warrants.
Future restrictions on our access to our manufacturing facilities or on our support operations or workforce, any future closure of additional manufacturing facilities due to weaker demand or supply constraints, or similar limitations for our suppliers, disruptions to our supply chain or restrictions or disruptions of transportation, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position, results of operations or liquidity. The overall magnitude of the COVID-19 pandemic, including the extent of its impact on our business, financial position, results of operations or liquidity cannot be reasonably estimated due to the rapid development and fluidity of the situation.
In recent weeks, the COVID-19 pandemic has also caused, and is likely to continue to cause economic, market and other disruptions worldwide. Such volatility in the global capital markets could increase the cost of capital and could adversely impact access to capital. Risks related to negative economic conditions are described in our risk factor titled "Our business and the industries we serve are highly sensitive to global and regional economic conditions" under "Macroeconomic Risks" in our "Risk Factors" in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019.
75
Item 2. Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased2,3,4 | Average Price Paid per Share2,3,4 | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Program | Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that may yet be Purchased under the Program (in billions)1 | ||||||||||
| January 1-31, 2020 | 768,969 | $ | 142.21 | 768,969 | $ | 5.892 | ||||||||
| February 1-29, 2020 | 4,460,582 | $ | 133.84 | 4,460,582 | $ | 5.295 | ||||||||
| March 1-31, 2020 | 4,098,633 | $ | 107.56 | 4,098,633 | $ | 4.854 | ||||||||
| Total | 9,328,184 | $ | 122.98 | 9,328,184 | ||||||||||
1 In July 2018, the Board approved a share repurchase authorization of up to $10.0 billion of Caterpillar common stock effective January 1, 2019, with no expiration (the 2018 Authorization). As of March 31, 2020, approximately $4.9 billion remained available under the 2018 Authorization. | ||||||||||||||
2 During the fourth quarter of 2019, we entered into an accelerated share repurchase agreement (ASR) with a third-party financial institution to purchase $600 million of our common stock. In October 2019, upon payment of $600 million to the financial institution, we received 3.5 million shares. In January 2020, upon final settlement of the ASR, we received an additional 0.7 million shares. In total, we repurchased 4.2 million shares under this ASR at an average price per share of $142.48. | ||||||||||||||
3 During the first quarter of 2020, we entered into an ASR with a third-party financial institution to purchase $700 million of our common stock. In February 2020, upon payment of the $700 million to the financial institution, we received 4.2 million shares. In March 2020, upon final settlement of the ASR, we received an additional 1.2 million shares. In total, we repurchased 5.4 million shares under this ASR at an average price per share of $130.47. | ||||||||||||||
4 In February and March of 2020, we repurchased 0.3 million and 2.9 million shares, respectively, for an aggregate of $338 million in open market transactions at an average price per share of $134.26 and $103.08, respectively. In January of 2020, we repurchased a minimal number of shares in open market transactions as illustrated in the above table. | ||||||||||||||
Non-U.S. Employee Stock Purchase Plans
As of March 31, 2020, we had 24 employee stock purchase plans (the “EIP Plans”) that are administered outside the United States for our non-U.S. employees, which had approximately 12,000 active participants in the aggregate. During the first quarter of 2020, approximately 104,000 shares of Caterpillar common stock were purchased by the EIP Plans pursuant to the terms of such plans.
76
Item 6. Exhibits
| 3.1 | ||
| 10.1 | ||
| 10.2 | ||
| 31.1 | ||
| 31.2 | ||
| 32 | ||
| 101.INS | Inline XBRL Instance Document (the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document) | |
| 101.SCH | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |
| 101.CAL | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | |
| 101.DEF | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | |
| 101.LAB | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | |
| 101.PRE | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | |
| 104 | Cover Page Interactive File (embedded within the Inline XBRL document and included in Exhibit 101) | |
The agreements and other documents filed as exhibits to this report are not intended to provide factual information or other disclosure other than with respect to the terms of the agreements or other documents themselves, and you should not rely on them for that purpose. In particular, any representations and warranties made by us in these agreements or other documents were made solely within the specific context of the relevant agreement or document and may not describe the actual state of affairs as of the date they were made or at any other time.
77
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
| CATERPILLAR INC. | ||
| May 6, 2020 | /s/ D. James Umpleby III | Chairman of the Board & Chief Executive Officer |
| D. James Umpleby III | ||
| May 6, 2020 | /s/ Andrew R.J. Bonfield | Chief Financial Officer |
| Andrew R.J. Bonfield | ||
| May 6, 2020 | /s/ Suzette M. Long | Chief Legal Officer, General Counsel & Corporate Secretary |
| Suzette M. Long | ||
| May 6, 2020 | /s/ G. Michael Marvel | Chief Accounting Officer |
| G. Michael Marvel | ||
78