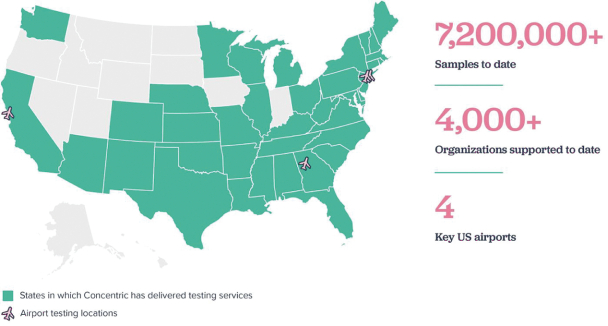
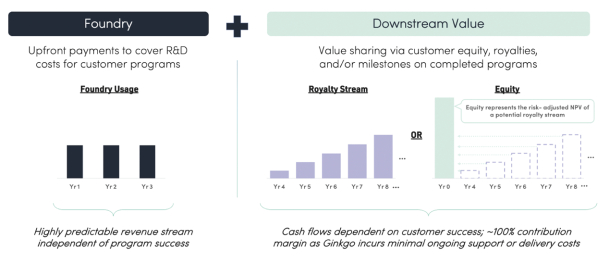
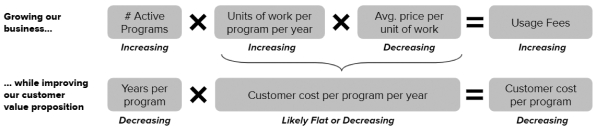
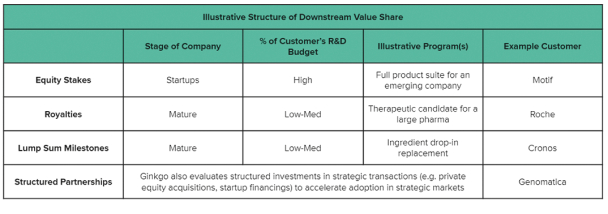
contracts contain provisions permitting unilateral termination or modification, in whole or in part, at the government’s convenience. Under general principles of government contracting law, if the government terminates a contract for convenience, the government contractor may recover only its incurred or committed costs, settlement expenses and profit on work completed prior to the termination. If the government terminates a contract for default, the government contractor is entitled to recover costs incurred and associated profits on accepted items only and may be liable for excess costs incurred by the government in procuring undelivered items from another source. Any termination for default may also adversely affect our ability to contract with other government customers, as well as our reputation, business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, changes in U.S. government budgetary priorities could lead to changes in the procurement environment, affecting availability of U.S. government contracting, subcontracting or funding opportunities, which could lead to modification, reduction or termination of our U.S. government contracts or subcontracts. If and to the extent such changes occur, they could impact our results and potential growth opportunities.
Furthermore, our U.S. government contracts grant the government the right to use technologies developed by us under the government contract or the right to share data related to our technologies, for or on behalf of the government. Under our government contracts, we may not be able to limit third parties, including our competitors, from accessing certain of these technology or data rights, including intellectual property, in providing products and services to the government.
In addition, failure by us, our employees, representatives, contractors, partners, agents, intermediaries, other customers or other third parties to comply with these regulations and requirements could result in reductions of the value of contracts, contract modifications or termination, claims for damages, refund obligations, the assessment of civil or criminal penalties and fines, loss of rights in our intellectual property and temporary suspension or permanent debarment from government contracting, all of which could negatively impact our results of operations and financial condition. Any such damages, penalties, disruptions or limitations in our ability to do business with the public sector could result in reduced sales of our products, reputational damage, penalties and other sanctions, any of which could harm our business, reputation and results of operations.
We are engaged in certain research activities involving controlled substances, including cannabinoids and other chemical intermediates, the making, use, sale, importation, exportation, and distribution of which may be subject to significant regulation by the DEA and other regulatory agencies.
We are engaged in certain research activities involving the development of microbes designed to generate cannabinoids, their precursors and other chemical intermediaries, some of which may be regulated as controlled substances in the United States. Controlled substances are subject to state, federal, and foreign laws and regulations regarding their manufacture, use, sale, importation, exportation, and distribution. Among other things, controlled substances are regulated under the federal Controlled Substances Act of 1970 (“CSA”) and implementing regulations of the DEA. The DEA regulates controlled substances as Schedule I, II, III, IV or V substances. Schedule I substances by definition have no established medicinal use and may generally not be marketed or sold in the United States. Schedule I substances are subject to the most stringent controls and Schedule V the least controls of the five schedules, based on their relative risk of abuse.
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in the cannabis plant. The cannabis plant and its derivatives are highly regulated by the DEA and the USDA. Specifically, marihuana, which is defined as all parts of the plant Cannabis sativa L., whether growing or not, the seeds thereof, the resin extracted therefrom, and every compound, manufacture, salt, derivative, mixture, or preparation, is classified as a Schedule I controlled substance. However, the term does not include “hemp,” which means the cannabis plant and any part of that plant, including the seeds and all derivatives, extracts, cannabinoids, isomers, acids, salts, and salts of isomers, whether growing or not, with a delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (“THC”) concentration of not more than 0.3% on a dry weight basis. Thus, depending on the THC concentration of the product, the product may or may not be regulated as a controlled substance. The DEA has historically regulated synthetic cannabinoids similarly to naturally-derived cannabinoids. Consequently, even though our cannabinoids that could be produced from
41