deeply grateful to our dedicated team members who made this achievement possible and everyone else who has supported our work, especially our clinical trial participants and investigators. Finally, we also appreciate the continuous engagement from the FDA as they have worked with urgency to make this medicine available to populations in serious need.”
“People who are immunocompromised continue to be disproportionally impacted by COVID-19 even after receiving multiple vaccine doses,” said Cameron R. Wolfe, M.B.B.S., M.P.H., Professor of Medicine, Transplant Infectious Disease at Duke University School of Medicine. “I’m excited to have PEMGARDA as an additional COVID-19 preventive option for moderately to severely immunocompromised adult and adolescent patients, such as solid organ transplant recipients and those with hematological malignancies. These types of patients, among others, continue to have both an impaired response to vaccines and a higher risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes.”
“COVID-19 continues to pose a significant threat and major concern to those who are moderately to severely immunocompromised,” said Jorey Berry, President and CEO of the Immune Deficiency Foundation and a steering committee member of the Immunocompromised Collaborative. “As such, we are delighted that a new monoclonal antibody for pre-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 will be available soon for certain vulnerable populations.”
Multiple medical conditions or treatments may result in moderate-to-severe immune compromise and an impaired immune response to COVID-19 vaccination including, for example, hematologic malignancies (blood cancers) or treatment with immunosuppressive therapy after a solid organ or stem cell transplant.1 Observational studies have demonstrated that people with immune dysfunction have a higher risk of COVID-19-related hospitalization and death, despite vaccination, than the general population.2-3
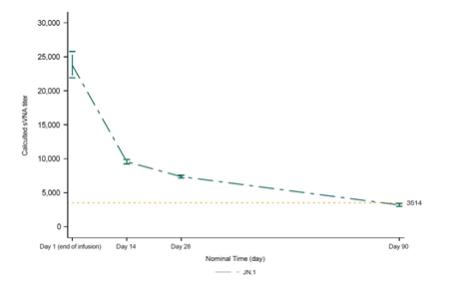
The EUA of PEMGARDA is based on the totality of scientific evidence available, such as data showing that immunobridging was established in the CANOPY clinical trial and that the calculated serum neutralizing antibody titers against JN.1 were consistent with the titer levels associated with efficacy in prior clinical trials of adintrevimab (ADG20), the parent mAb for VYD222, and other monoclonal antibody products. JN.1 is currently the dominant variant circulating in the U.S. according to estimates from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).4 PEMGARDA (pemivibart) (4500 mg) is administered as an intravenous (IV) infusion.
PEMGARDA is Invivyd’s first authorized mAb and the first mAb to receive EUA based on a rapid immunobridging trial design that is expected to be repeatable to help address the need to mitigate ongoing viral evolution. It was developed using INVYMABTM, the company’s platform approach which combines state-of-the-art viral surveillance and predictive modeling with advanced antibody engineering. INVYMAB is designed to enable the rapid, serial generation of durable mAbs targeting conserved epitopes that could be deployed to keep pace with SARS-CoV-2 viral evolution or other viral threats. With a commitment to serial innovation, Invivyd aims to ensure that vulnerable populations, such as immunocompromised people, have continuous access to innovative antibody therapies.
The Company estimates it had approximately $200.6 million of cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023. The estimated amounts are preliminary, have not been audited and are subject to change upon completion of the Company’s audited financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2023. In February 2024, the Company sold shares of common stock totaling $40.5 million in gross