
Exhibit 99.2 CONNECT1-EDO51 5 mg/kg Clinical Data July 30, 2024

Disclaimers This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended. These statements may be identified by words such as “aims,” “anticipates,” “believes,” “could,” “estimates,” “expects,” “forecasts,” “goal,” “intends,” “may,” “plans,” “possible,” “potential,” “seeks,” “will,” and variations of these words or similar expressions that are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Any such statements in this presentation that are not statements of historical fact may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements include, without limitation, statements regarding the therapeutic potential and safety profile of PGN-EDO51 based on early data, the potential of our EDO platform to deliver higher levels of oligonucleotide to the nuclei, our expectations regarding the potential for increased levels of exon skipping and dystrophin production following dosing at 10 mg/kg with a longer treatment period, the design, initiation and conduct of clinical trials, including expected timelines for our CONNECT2 Phase 2 trial, the expected timing for additional data reports from our CONNECT1 trial, ongoing and planned regulatory interactions regarding the CONNECT2 trial, and expectations regarding our FREEDOM-DM1 and FREEDOM2-DM1 clinical trials. Any forward-looking statements in this presentation are based on current expectations, estimates and projections only as of the date of this presentation and are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially and adversely from those set forth in or implied by such forward- looking statements. These risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to: delays or failure to successfully initiate or complete our ongoing and planned development activities for our product candidates, including PGN-EDO51 and PGN-EDODM1; our ability to enroll patients in our clinical trials, including CONNECT1-EDO51, CONNECT2-EDO51 and FREEDOM-DM1; that our interpretation of clinical and preclinical study results may be incorrect, or that we may not observe the levels of therapeutic activity in clinical testing that we anticipate based on prior clinical or preclinical results; our product candidates, including PGN- EDO51 and PGN-EDODMI, may not be safe and effective or otherwise demonstrate safety and efficacy in our clinical trials; adverse outcomes from our regulatory interactions, including delays in regulatory review, clearance to proceed or approval by regulatory authorities with respect to our programs, including clearance to commence planned clinical studies of our product candidates, including CONNECT2-EDO51, or other regulatory feedback requiring modifications to our development programs; changes in regulatory framework that are out of our control; our ability to obtain, maintain and protect our intellectual property; our ability to enforce our patents against infringers and defend our patent portfolio against challenges from third parties; competition from others developing therapies for the indications we are pursuing; unexpected increases in the expenses associated with our development activities or other events that adversely impact our financial resources and cash runway; and our dependence on third parties for some or all aspects of our product manufacturing, research and preclinical and clinical testing. Additional risks concerning PepGen's programs and operations are described in our most recent annual report on Form 10-K and quarterly report on Form 10-Q that are filed with the SEC. PepGen explicitly disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements except to the extent required by law. 2

Agenda James McArthur, PhD President and Chief Executive Officer Platform, Key Takeaways, and Closing Remarks Michelle Mellion, MD Chief Medical Officer DMD Landscape and CONNECT1 Clinical Trial Design Hugh McMillan, MD, MSc 1 Pediatric Neurologist, CHEO and CONNECT1 Lead Investigator CONNECT1 5mg/kg Clinical Data and Potential Clinical Utility 1. Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario 3

Platform and Key Takeaways James McArthur, PhD President and Chief Executive Officer

Driven by our proprietary Enhanced Delivery Oligonucleotide (EDO) platform, PepGen is creating a pipeline of disease-modifying therapeutics with the potential to safely and effectively target the underlying cause of serious genetic neuromuscular and neurological disorders.

The Challenge of Oligonucleotides Naked Oligonucleotide (PMO) Naked oligonucleotides do not efficiently penetrate the muscle cells and the nucleus Red = oligo Note: 1. In vitro staining image is shown with 10µM conc. of PMO23 (naked oligonucleotide); 2. C2C12 mouse cells were differentiated for 4 days into 6 myotubes and treated with fluorescently tagged compounds for 24h. PMO: phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligonucleotide

PepGen’s EDO Platform Has Been Designed and Developed to Solve this Decades Long Problem PepGen’s EDO: Up to 25X Higher Nuclear Uptake of Oligonucleotide EDO platform results in nuclear delivery of oligonucleotide therapeutics Red = oligo Note: 1. In vitro staining image is shown with 10µM conc. of EDO23; 2. C2C12 mouse cells were differentiated for 4 days into myotubes and treated with 7 fluorescently tagged compounds for 24h.

CONNECT1 Key Takeaways • PGN-EDO51 was well tolerated at 5 mg/kg, currently dosing at 10 mg/kg • All patients demonstrated increased exon skipping and dystrophin production and have continued into the long-term extension study • PGN-EDO51 generated the highest levels of mean exon 51 skipping (2.15%) seen to date at 5 mg/kg versus all other exon 51-skipping therapies given at even 2x higher doses and 2x treatment 1 period 1 • Dystrophin production encouraging at just 3 months and 4 doses at 5 mg/kg • Increase from baseline of 0.70% in muscle content adjusted dystrophin and 0.26% unadjusted • DYNE-251 (5 mg/kg at 6 months and 6 doses): Increase from baseline of 0.44% in muscle content adjusted dystrophin and 0.28% unadjusted • Initial results support that our EDO technology delivers high levels of oligonucleotides to the nucleus 1. No head-to-head trials have been conducted comparing PGN-EDO51 to DYNE-251, eteplirsen or SRP-5051. Data from studies of these clinical candidates may not be directly comparable due to differences in molecule composition, trial protocols, methodologies for calculating muscle content adjusted dystrophin, dosing regimens, and 8 patient populations and characteristics. Accordingly, cross-trial comparisons may not be reliable.DYNE-251 DELIVER clinical data update, May 20 2024; Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases. 2021; 8(6): 989–1001; SRP-5051 MOMENTUM clinical data update, December 7, 2020.
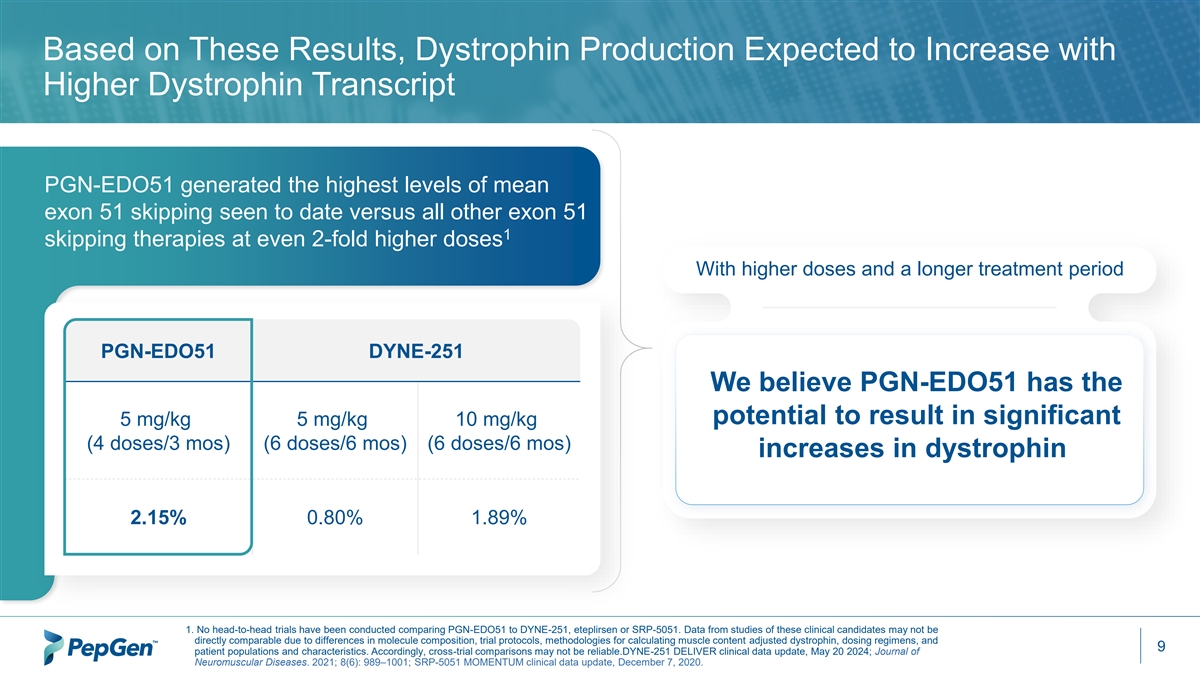
Based on These Results, Dystrophin Production Expected to Increase with Higher Dystrophin Transcript PGN-EDO51 generated the highest levels of mean exon 51 skipping seen to date versus all other exon 51 1 skipping therapies at even 2-fold higher doses With higher doses and a longer treatment period PGN-EDO51 DYNE-251 We believe PGN-EDO51 has the potential to result in significant 5 mg/kg 5 mg/kg 10 mg/kg (4 doses/3 mos) (6 doses/6 mos) (6 doses/6 mos) increases in dystrophin 2.15% 0.80% 1.89% 1. No head-to-head trials have been conducted comparing PGN-EDO51 to DYNE-251, eteplirsen or SRP-5051. Data from studies of these clinical candidates may not be directly comparable due to differences in molecule composition, trial protocols, methodologies for calculating muscle content adjusted dystrophin, dosing regimens, and 9 patient populations and characteristics. Accordingly, cross-trial comparisons may not be reliable.DYNE-251 DELIVER clinical data update, May 20 2024; Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases. 2021; 8(6): 989–1001; SRP-5051 MOMENTUM clinical data update, December 7, 2020.

DMD Overview and CONNECT1 Trial Design Michelle Mellion, MD Chief Medical Officer

More Effective Therapies are Urgently Needed to Treat DMD Living with Duchenne puts you in front of your own mortality. You’re kind of given a list of things that become impossible. Not that they necessarily do, but that’s the way it seems.” - Mallory, living with DMD 11
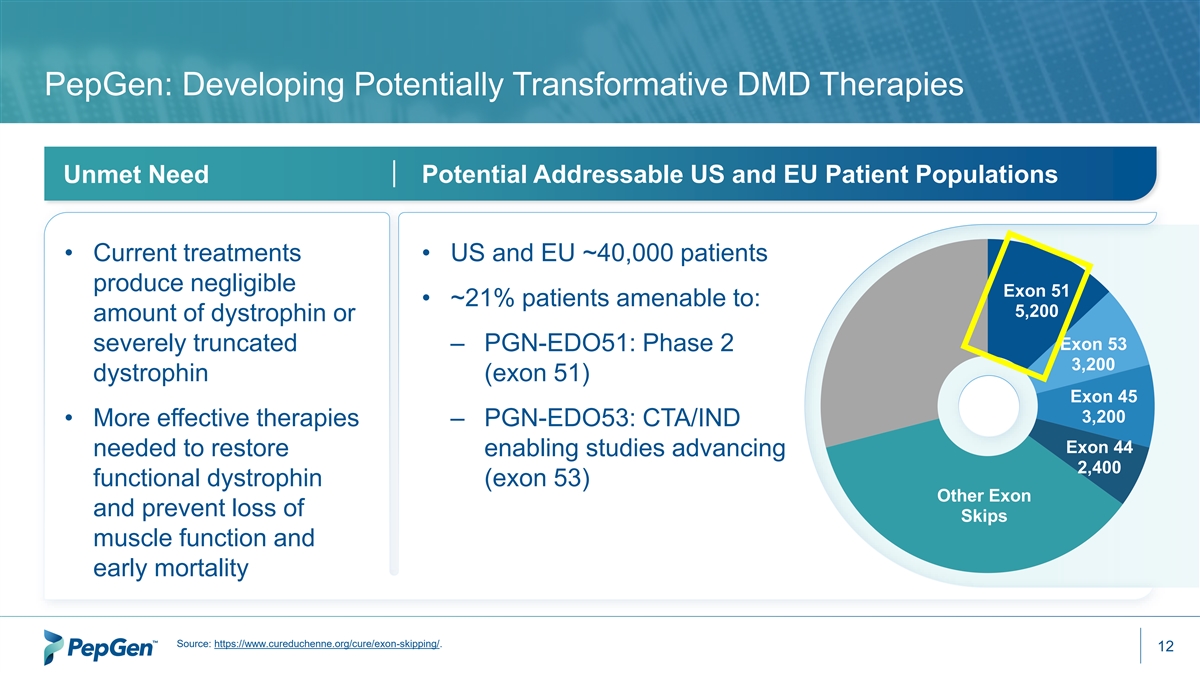
PepGen: Developing Potentially Transformative DMD Therapies Potential Addressable US and EU Patient Populations Unmet Need • Current treatments • US and EU ~40,000 patients produce negligible Exon 51 • ~21% patients amenable to: 5,200 amount of dystrophin or Exon 53 severely truncated – PGN-EDO51: Phase 2 3,200 dystrophin (exon 51) Exon 45 3,200 • More effective therapies – PGN-EDO53: CTA/IND Exon 44 needed to restore enabling studies advancing 2,400 functional dystrophin (exon 53) Other Exon and prevent loss of Skips muscle function and early mortality Source: https://www.cureduchenne.org/cure/exon-skipping/. 12
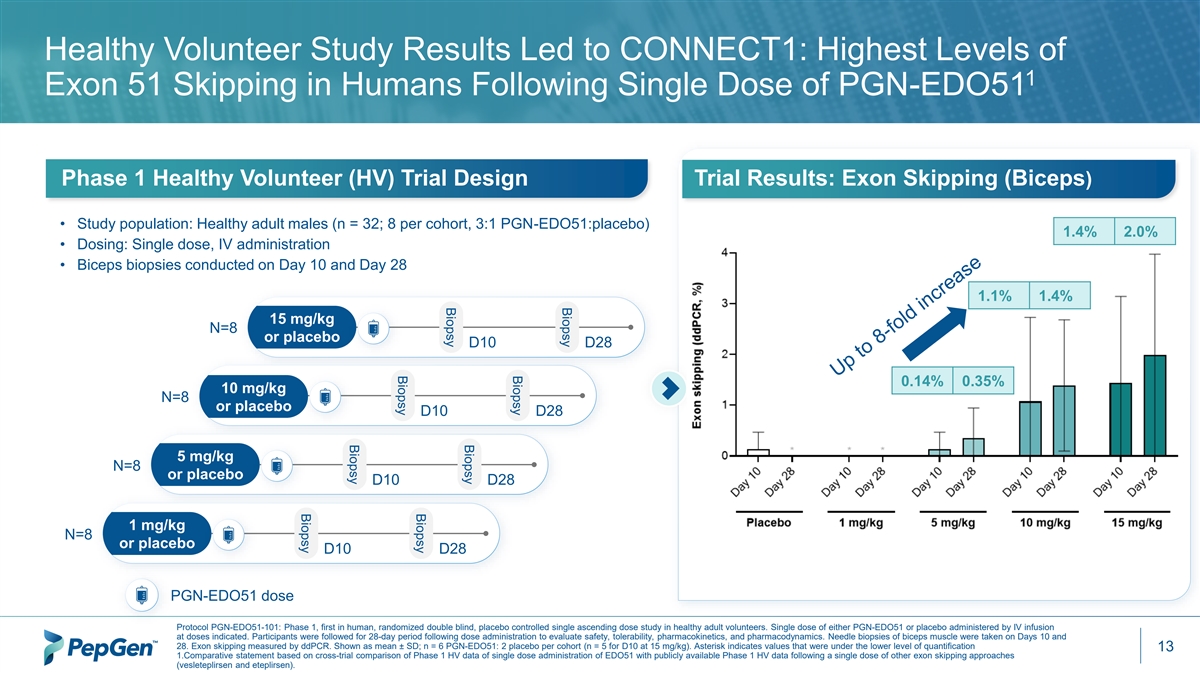
Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Healthy Volunteer Study Results Led to CONNECT1: Highest Levels of 1 Exon 51 Skipping in Humans Following Single Dose of PGN-EDO51 Phase 1 Healthy Volunteer (HV) Trial Design Trial Results: Exon Skipping (Biceps) • Study population: Healthy adult males (n = 32; 8 per cohort, 3:1 PGN-EDO51:placebo) 1.4% 2.0% • Dosing: Single dose, IV administration • Biceps biopsies conducted on Day 10 and Day 28 1.1% 1.4% 15 mg/kg N=8 or placebo D10 D28 0.14% 0.35% 10 mg/kg N=8 or placebo D10 D28 5 mg/kg N=8 or placebo D10 D28 1 mg/kg N=8 or placebo D10 D28 PGN-EDO51 dose Protocol PGN-EDO51-101: Phase 1, first in human, randomized double blind, placebo controlled single ascending dose study in healthy adult volunteers. Single dose of either PGN-EDO51 or placebo administered by IV infusion at doses indicated. Participants were followed for 28-day period following dose administration to evaluate safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Needle biopsies of biceps muscle were taken on Days 10 and 28. Exon skipping measured by ddPCR. Shown as mean ± SD; n = 6 PGN-EDO51: 2 placebo per cohort (n = 5 for D10 at 15 mg/kg). Asterisk indicates values that were under the lower level of quantification 13 1.Comparative statement based on cross-trial comparison of Phase 1 HV data of single dose administration of EDO51 with publicly available Phase 1 HV data following a single dose of other exon skipping approaches (vesleteplirsen and eteplirsen).
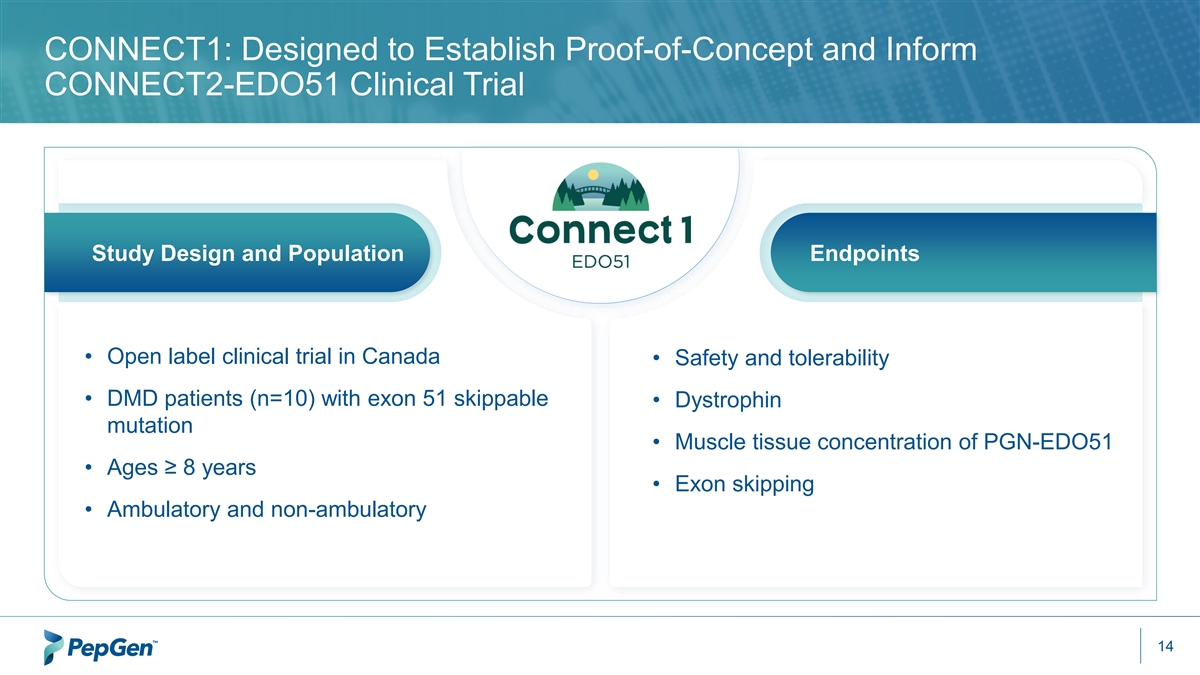
CONNECT1: Designed to Establish Proof-of-Concept and Inform CONNECT2-EDO51 Clinical Trial Study Design and Population Endpoints • Open label clinical trial in Canada • Safety and tolerability • DMD patients (n=10) with exon 51 skippable • Dystrophin mutation • Muscle tissue concentration of PGN-EDO51 • Ages ≥ 8 years • Exon skipping • Ambulatory and non-ambulatory 14
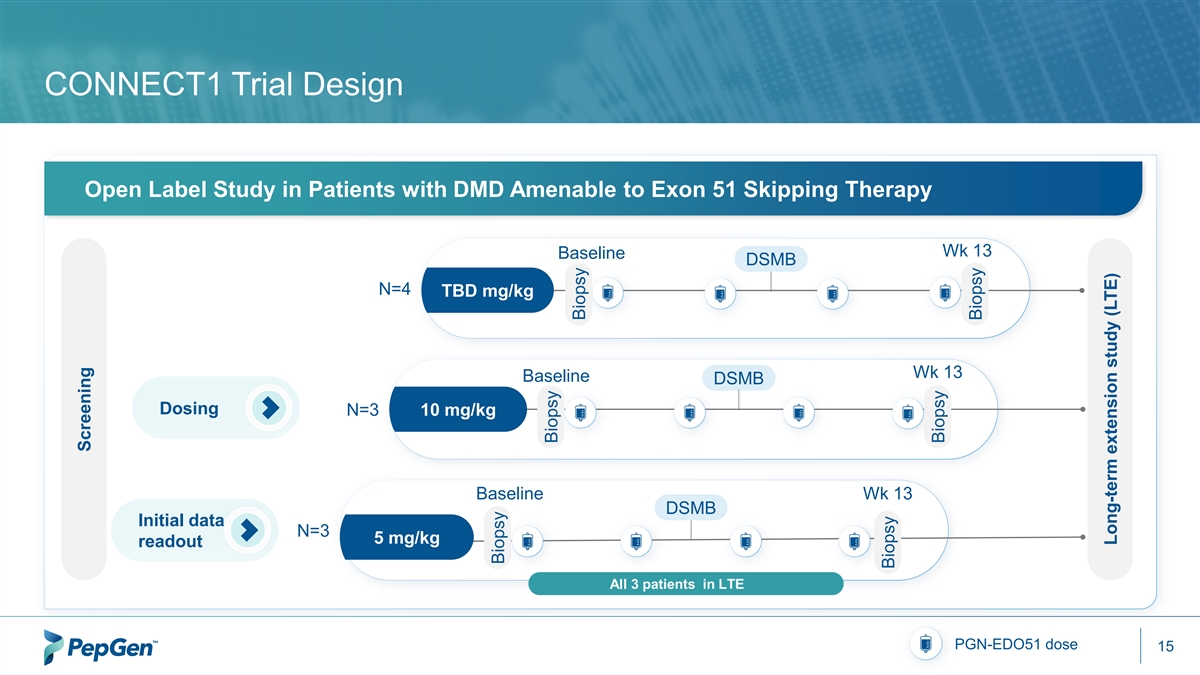
CONNECT1 Trial Design Open Label Study in Patients with DMD Amenable to Exon 51 Skipping Therapy Wk 13 Baseline DSMB N=4 TBD mg/kg Wk 13 Baseline DSMB Dosing N=3 10 mg/kg Baseline Wk 13 DSMB Initial data N=3 5 mg/kg readout All 3 patients in LTE PGN-EDO51 dose 15 Screening Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Biopsy Long-term extension study (LTE)
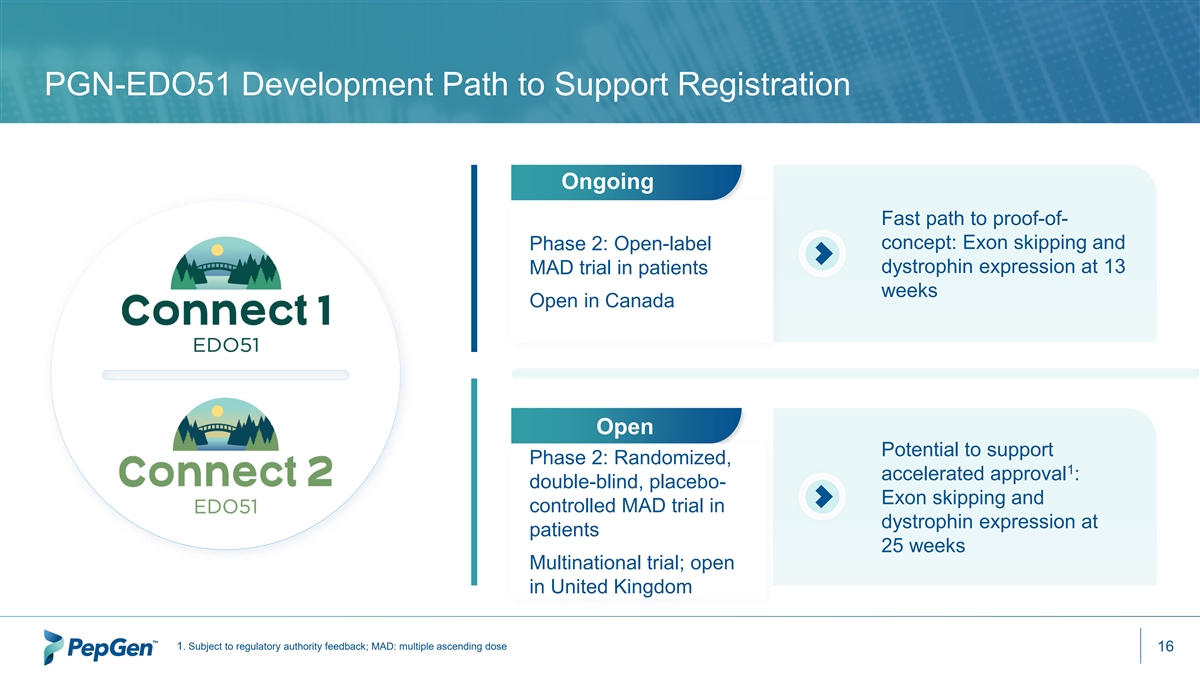
PGN-EDO51 Development Path to Support Registration Ongoing Fast path to proof-of- concept: Exon skipping and Phase 2: Open-label dystrophin expression at 13 MAD trial in patients weeks Open in Canada Open Potential to support Phase 2: Randomized, 1 accelerated approval : double-blind, placebo- Exon skipping and controlled MAD trial in dystrophin expression at patients 25 weeks Multinational trial; open in United Kingdom 1. Subject to regulatory authority feedback; MAD: multiple ascending dose 16

CONNECT1 5 mg/kg Clinical Data Hugh McMillan, MD, MSc Pediatric Neurologist, Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, and CONNECT1 Lead Investigator

Dystrophin Gene is One of the Largest Genes (~2.6 Mb, 79 exons) Full length dystrophin produced 18

Dystrophin Gene with “Out of Frame” Mutation No functional dystrophin produced 19

Mutated Dystrophin Sequence Results in Mutated Transcript Exon 51 skipping therapies bind to exon 51 allowing its exclusion 20
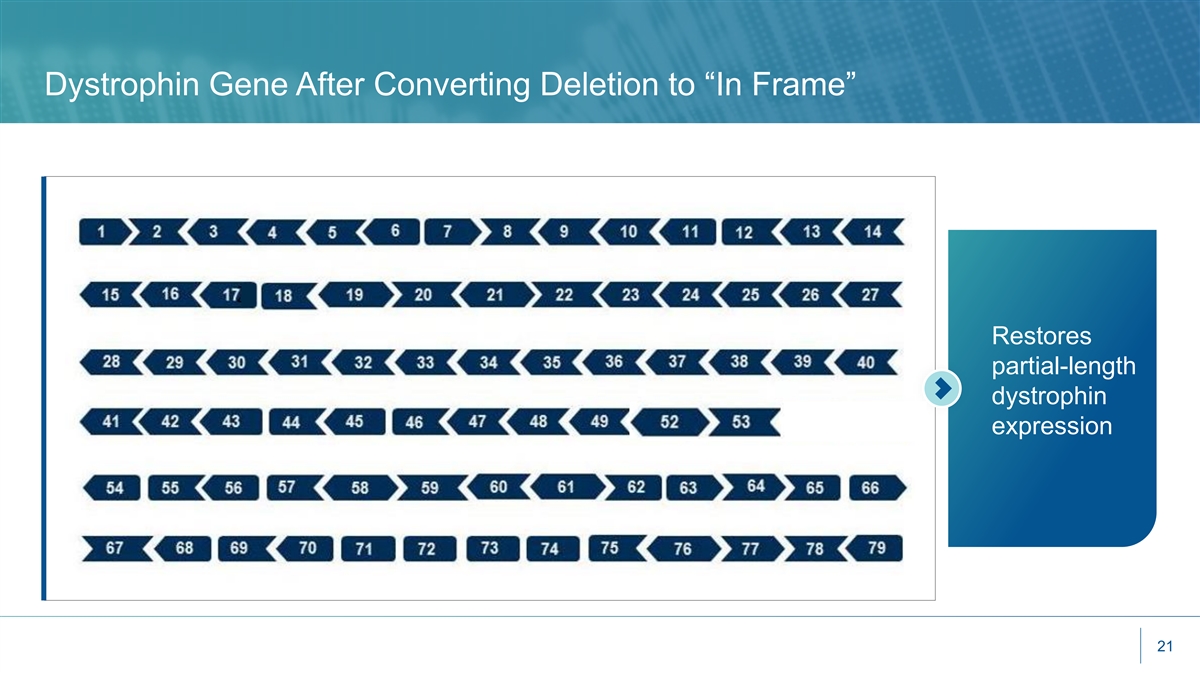
Dystrophin Gene After Converting Deletion to “In Frame” Restores partial-length dystrophin expression 21

DMD Disease Progression • Loss of muscle • Progressive • Death from • Symptom onset <6 yo • Loss of ambulation respiratory muscle cardiorespiratory weakness complications (late 20’s) –8 – 11 yo w/o • Cardiomyopathy: Risk corticosteroids increases with age –10 – 14 yo w/ corticosteroids Asher D et al, Expert Opinion Biol Therapy 2020. 20;263-7. yo: year old 22
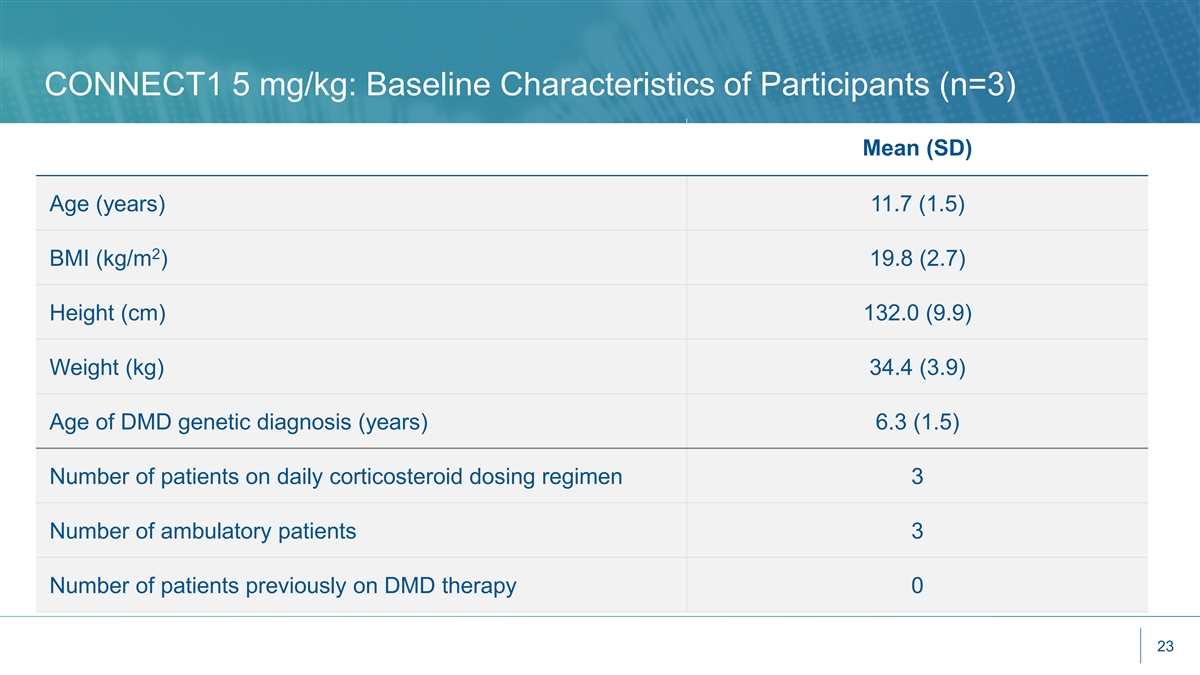
CONNECT1 5 mg/kg: Baseline Characteristics of Participants (n=3) Mean (SD) Age (years) 11.7 (1.5) 2 BMI (kg/m ) 19.8 (2.7) Height (cm) 132.0 (9.9) Weight (kg) 34.4 (3.9) Age of DMD genetic diagnosis (years) 6.3 (1.5) Number of patients on daily corticosteroid dosing regimen 3 Number of ambulatory patients 3 Number of patients previously on DMD therapy 0 23
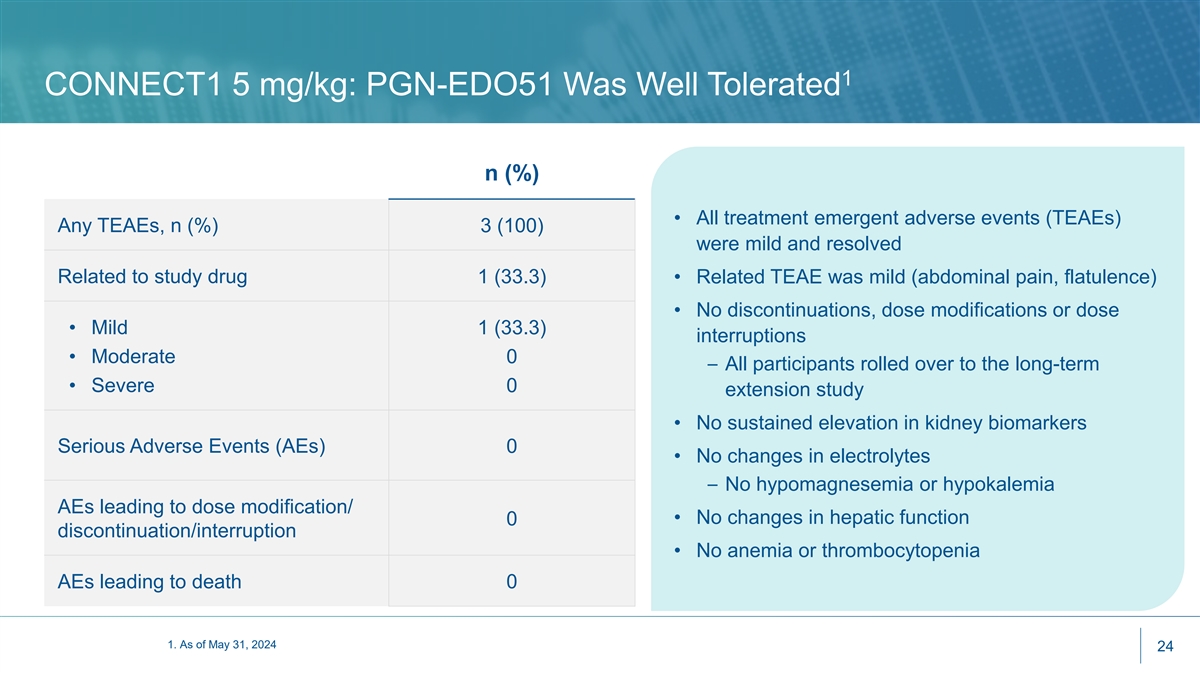
1 CONNECT1 5 mg/kg: PGN-EDO51 Was Well Tolerated n (%) • All treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) Any TEAEs, n (%) 3 (100) were mild and resolved Related to study drug 1 (33.3) • Related TEAE was mild (abdominal pain, flatulence) • No discontinuations, dose modifications or dose • Mild 1 (33.3) interruptions • Moderate 0 – All participants rolled over to the long-term • Severe 0 extension study • No sustained elevation in kidney biomarkers Serious Adverse Events (AEs) 0 • No changes in electrolytes – No hypomagnesemia or hypokalemia AEs leading to dose modification/ • No changes in hepatic function 0 discontinuation/interruption • No anemia or thrombocytopenia AEs leading to death 0 1. As of May 31, 2024 24
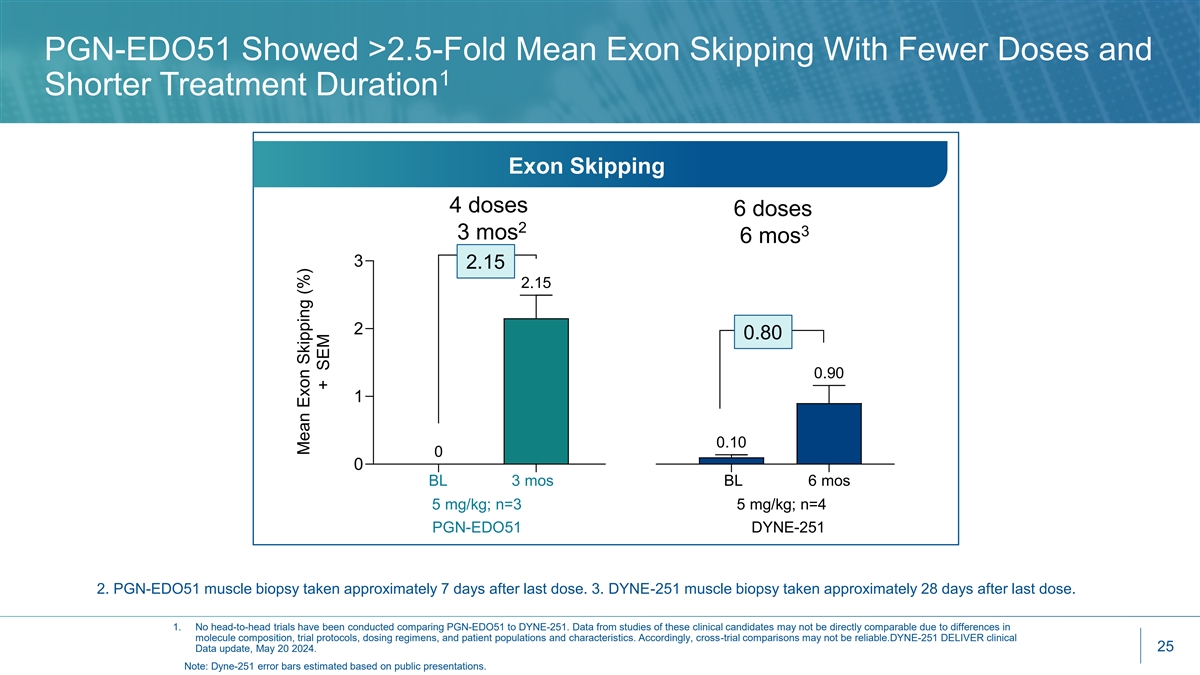
PGN-EDO51 Showed >2.5-Fold Mean Exon Skipping With Fewer Doses and 1 Shorter Treatment Duration Exon Skipping 4 doses 6 doses 2 3 3 mos 6 mos 3 2.15 2.15 2 0.80 0.90 1 0.10 0 0 BL 3 mos BL 6 mos 5 mg/kg; n=3 5 mg/kg; n=4 PGN-EDO51 DYNE-251 2. PGN-EDO51 muscle biopsy taken approximately 7 days after last dose. 3. DYNE-251 muscle biopsy taken approximately 28 days after last dose. 1. No head-to-head trials have been conducted comparing PGN-EDO51 to DYNE-251. Data from studies of these clinical candidates may not be directly comparable due to differences in molecule composition, trial protocols, dosing regimens, and patient populations and characteristics. Accordingly, cross-trial comparisons may not be reliable.DYNE-251 DELIVER clinical 25 Data update, May 20 2024. Note: Dyne-251 error bars estimated based on public presentations. Mean Exon Skipping (%) + SEM
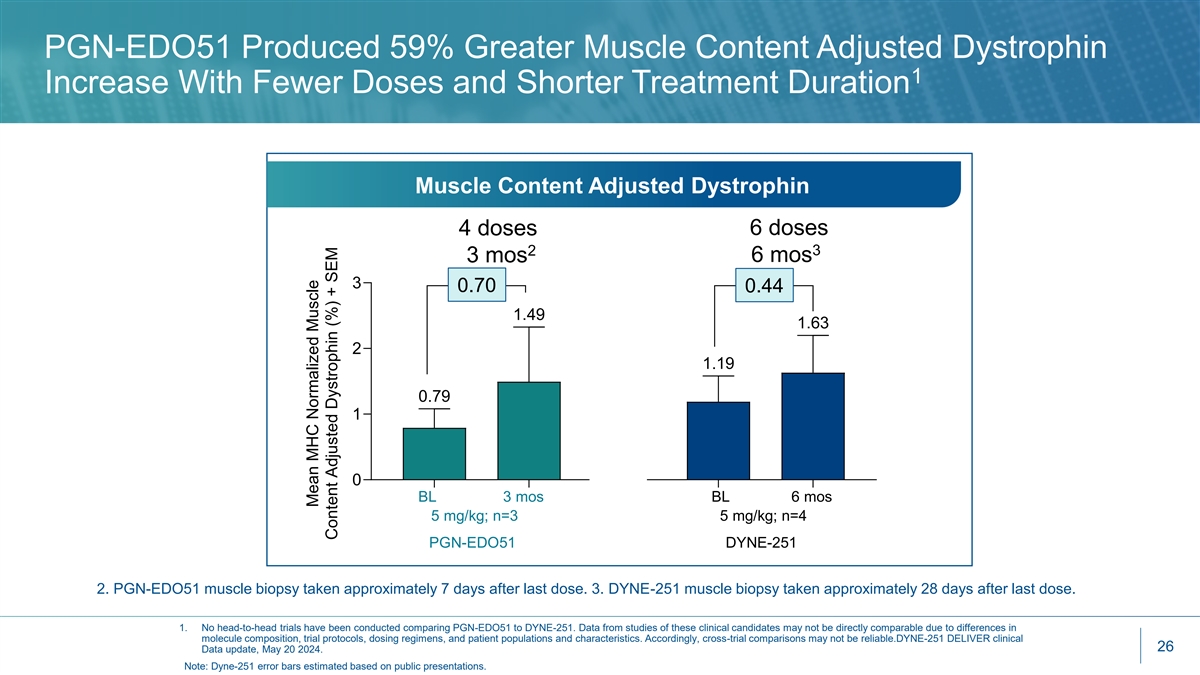
PGN-EDO51 Produced 59% Greater Muscle Content Adjusted Dystrophin 1 Increase With Fewer Doses and Shorter Treatment Duration Muscle Content Adjusted Dystrophin 4 doses 6 doses 3 2 3 mos 6 mos 3 0.70 0.44 1.49 1.63 2 1.19 0.79 1 0 BL 3 mos BL 6 mos 5 mg/kg; n=3 5 mg/kg; n=4 PGN-EDO51 DYNE-251 2. PGN-EDO51 muscle biopsy taken approximately 7 days after last dose. 3. DYNE-251 muscle biopsy taken approximately 28 days after last dose. 1. No head-to-head trials have been conducted comparing PGN-EDO51 to DYNE-251. Data from studies of these clinical candidates may not be directly comparable due to differences in molecule composition, trial protocols, dosing regimens, and patient populations and characteristics. Accordingly, cross-trial comparisons may not be reliable.DYNE-251 DELIVER clinical 26 Data update, May 20 2024. Note: Dyne-251 error bars estimated based on public presentations. Mean MHC Normalized Muscle Content Adjusted Dystrophin (%) + SEM

PGN-EDO51 Produced Similar Dystrophin Increase With Fewer Doses and 1 Shorter Treatment Duration Total (unadjusted) Dystrophin 6 doses 4 doses 3 2 6 mos 3 mos 1.5 0.26 0.28 0.88 1.0 0.61 0.60 0.34 0.5 0.0 BL 3 mos BL 6 mos 5 mg/kg; n=3 5 mg/kg; n=4 PGN-EDO51 DYNE-251 2. PGN-EDO51 muscle biopsy taken approximately 7 days after last dose. 3. DYNE-251 muscle biopsy taken approximately 28 days after last dose. 1. No head-to-head trials have been conducted comparing PGN-EDO51 to DYNE-251. Data from studies of these clinical candidates may not be directly comparable due to differences in molecule composition, trial protocols, dosing regimens, and patient populations and characteristics. Accordingly, cross-trial comparisons may not be 27 reliable.DYNE-251 DELIVER clinical Data update, May 20 2024. Note: Dyne-251 error bars estimated based on public presentations. Mean MHC Normalized Dystrophin (%) +SEM
CONNECT1 Initial 5 mg/kg Data Demonstrated Encouraging Results Given its tolerability profile to date and promising early dystrophin production, PGN-EDO51 has the potential to improve on current treatment options for DMD patients 28

Closing Remarks James McArthur, PhD President and Chief Executive Officer
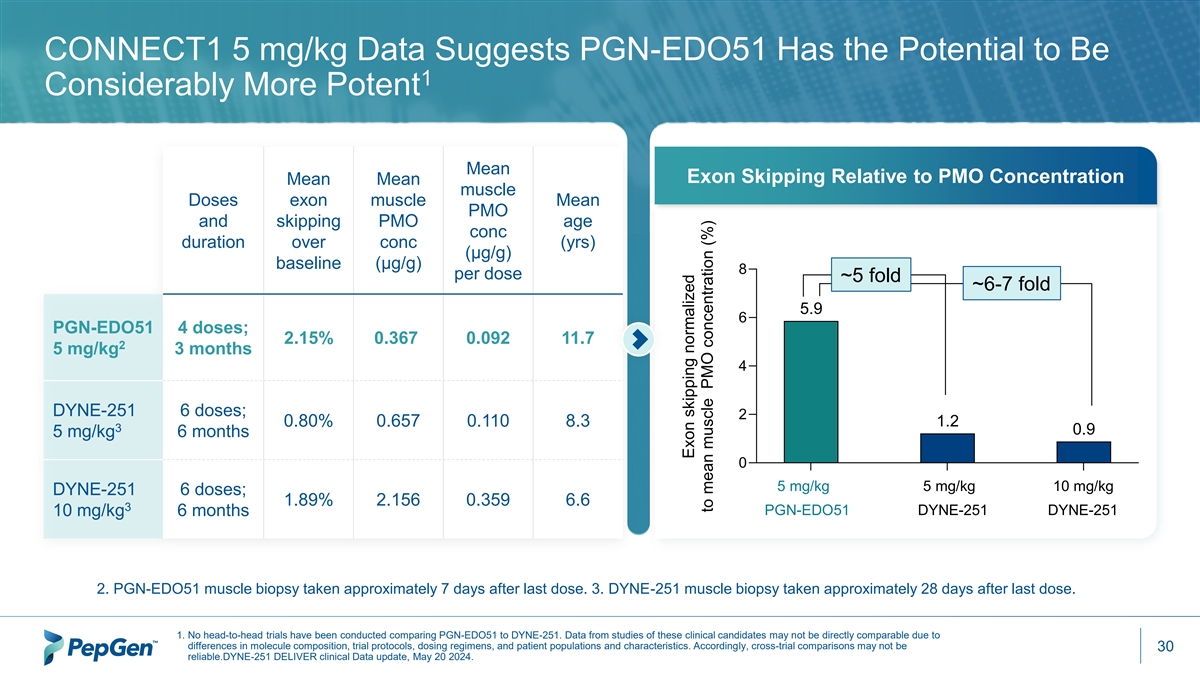
CONNECT1 5 mg/kg Data Suggests PGN-EDO51 Has the Potential to Be 1 Considerably More Potent Mean Exon Skipping Relative to PMO Concentration Mean Mean muscle Doses exon muscle Mean PMO and skipping PMO age conc duration over conc (yrs) (µg/g) baseline (µg/g) 8 per dose ~5 fold ~6-7 fold 5.9 6 PGN-EDO51 4 doses; 2.15% 0.367 0.092 11.7 2 5 mg/kg 3 months 4 DYNE-251 6 doses; 2 0.80% 0.657 0.110 8.3 1.2 3 0.9 5 mg/kg 6 months 0 5 mg/kg 5 mg/kg 10 mg/kg DYNE-251 6 doses; 1.89% 2.156 0.359 6.6 3 PGN-EDO51 DYNE-251 DYNE-251 10 mg/kg 6 months 2. PGN-EDO51 muscle biopsy taken approximately 7 days after last dose. 3. DYNE-251 muscle biopsy taken approximately 28 days after last dose. 1. No head-to-head trials have been conducted comparing PGN-EDO51 to DYNE-251. Data from studies of these clinical candidates may not be directly comparable due to differences in molecule composition, trial protocols, dosing regimens, and patient populations and characteristics. Accordingly, cross-trial comparisons may not be 30 reliable.DYNE-251 DELIVER clinical Data update, May 20 2024. Exon skipping normalized to mean muscle PMO concentration (%)

CONNECT1 Key Takeaways • PGN-EDO51 was well tolerated at 5 mg/kg, currently dosing at 10 mg/kg • All patients dosed at 5 mg/kg demonstrated increased exon skipping and dystrophin production and have continued into the long-term extension study • PGN-EDO51 generated the highest levels of mean exon 51 skipping (2.15%) seen to date at 5 mg/kg 1 versus all other exon 51-skipping therapies given at even 2x higher doses and 2x treatment period • Dystrophin production encouraging at just 3 months and 4 doses of 5 mg/kg • Initial results support that our EDO technology delivers high levels of oligonucleotides to the nucleus Potentially higher levels of dystrophin production are expected with higher doses of PGN-EDO51 over longer treatment periods 1. No head-to-head trials have been conducted comparing PGN-EDO51 to DYNE-251, eteplirsen or SRP-5051. Data from studies of these clinical candidates may not be directly comparable due to differences in molecule composition, trial protocols, methodologies for calculating muscle content adjusted dystrophin, dosing regimens, and 31 patient populations and characteristics. Accordingly, cross-trial comparisons may not be reliable.DYNE-251 DELIVER clinical data update, May 20 2024; Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases. 2021; 8(6): 989–1001; SRP-5051 MOMENTUM clinical data update, December 7, 2020.

PepGen’s Pipeline Enabled by EDO Technology INVESTIGATIONAL CLINICAL INDICATIONS PRECLINICAL PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PIVOTAL CANDIDATES PROGRAMS PGN-EDO51 DMD – Exon 51 PGN-EDODM1 DM1 – DMPK PGN-EDO53 DMD – Exon 53 • DMD Exon 45, Exon 44 • Neurological diseases Research • Additional neuromuscular diseases Note: Clinical plans are subject to alignment with regulatory authorities. 32

Key Milestones Ahead • CONNECT1 10 mg/kg initial clinical data readout expected in early 2025 • CONNECT2 − Currently open in UK EDO51 − Engaging with EU regulators − Expect to open clinical trial in US by year-end • Update on FREEDOM-DM1 clinical trial expected in Q4 2024 EDODM1 • Initiate dosing of FREEDOM2-DM1 clinical trial in 2H:2024 33

Thank you! • We sincerely thank patients, families and clinical investigators! • We now look forward to answering your questions 34

































