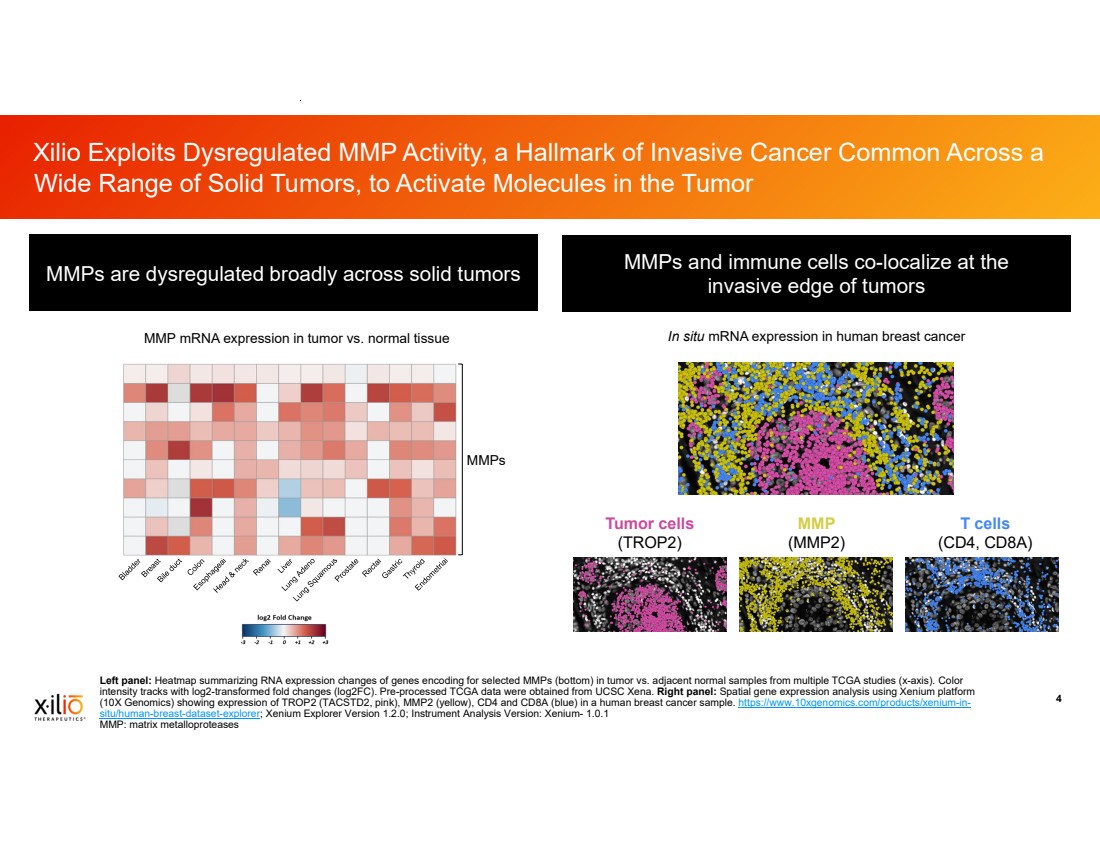
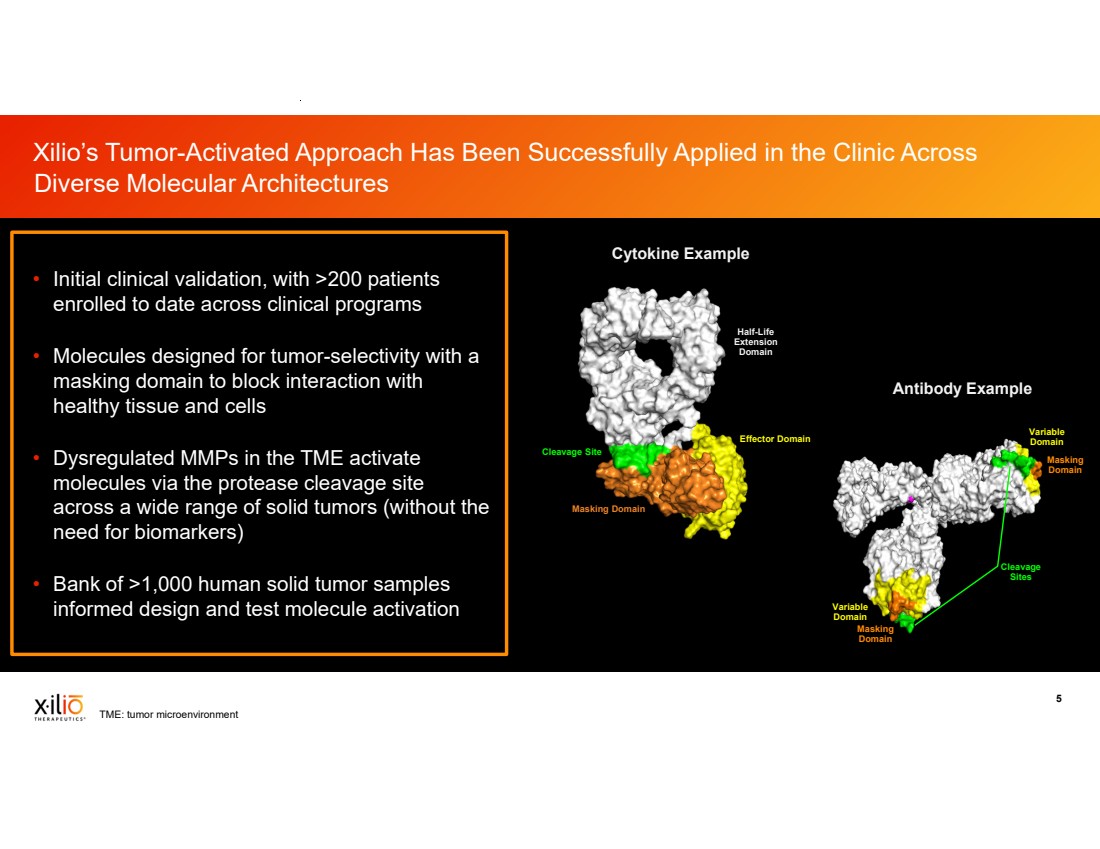
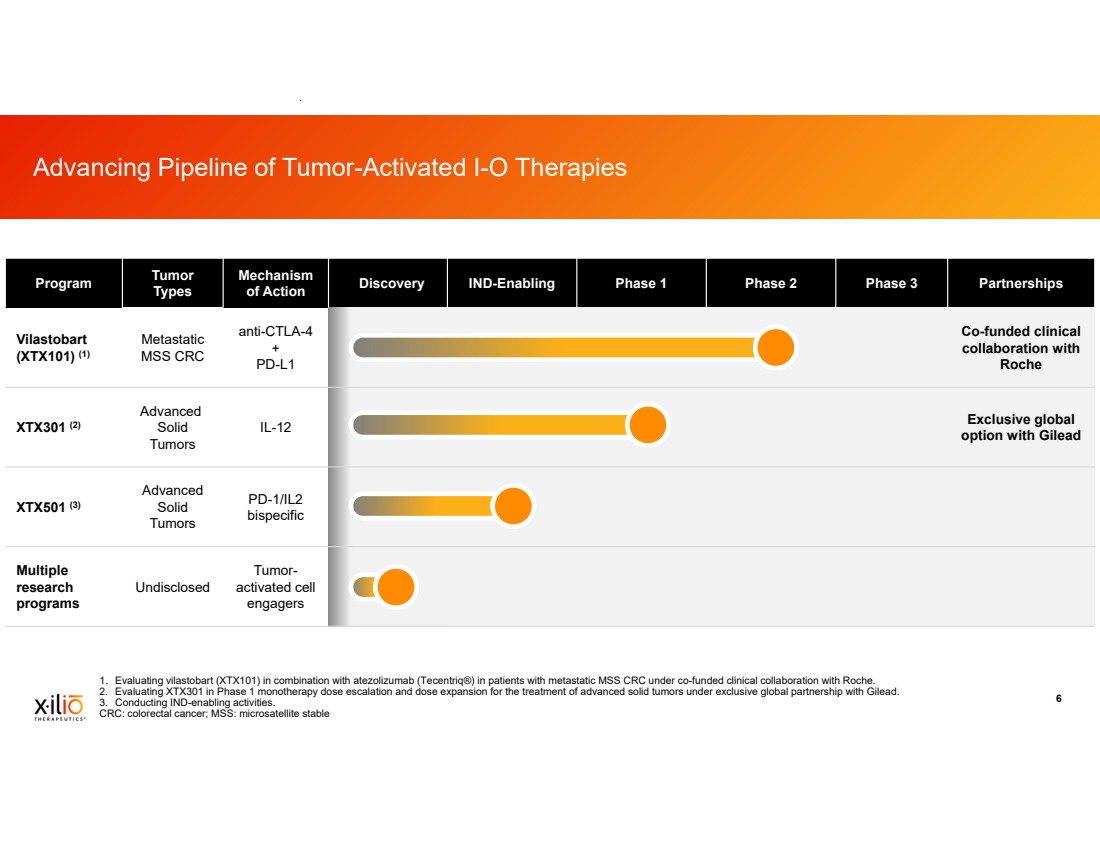
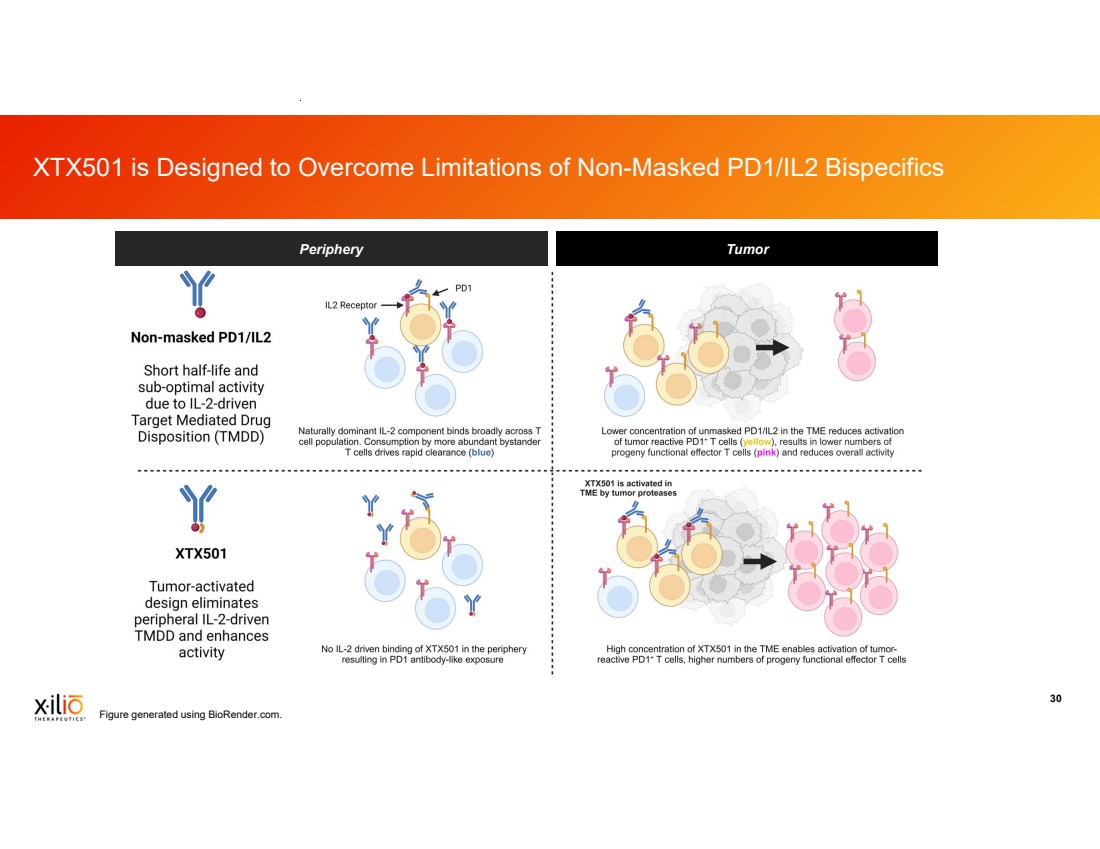
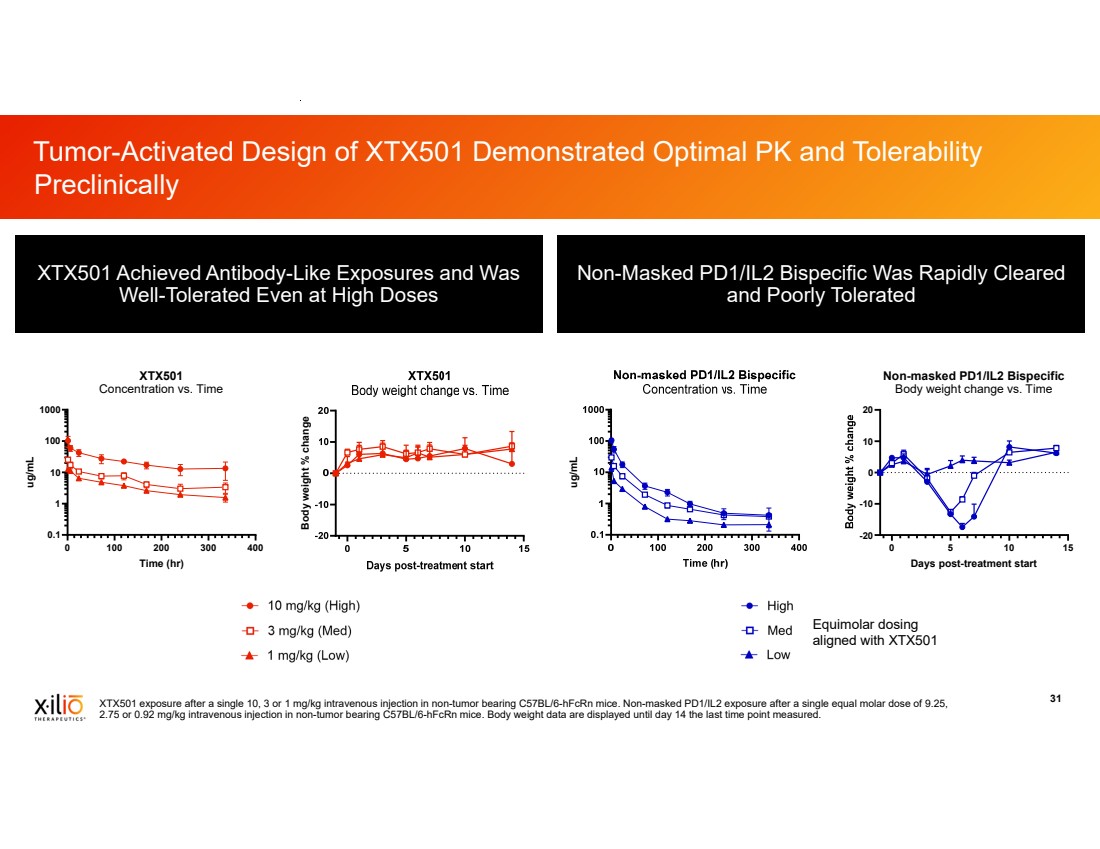
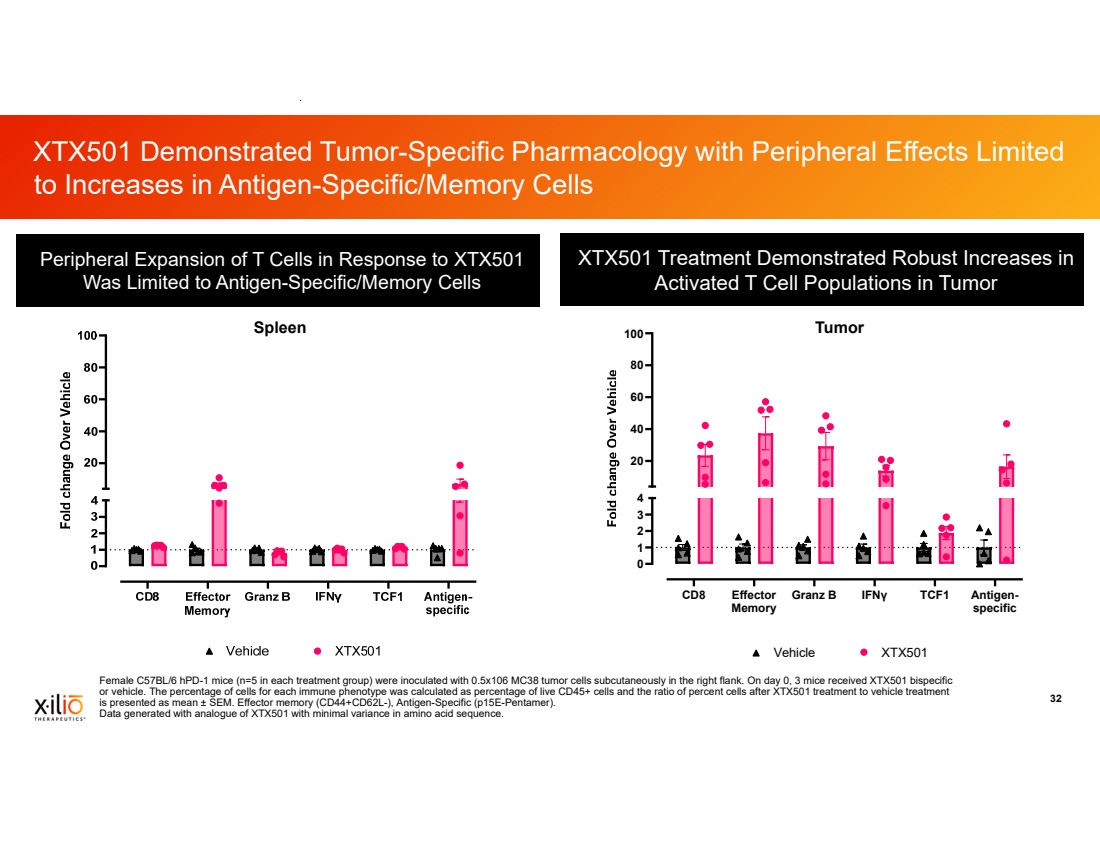
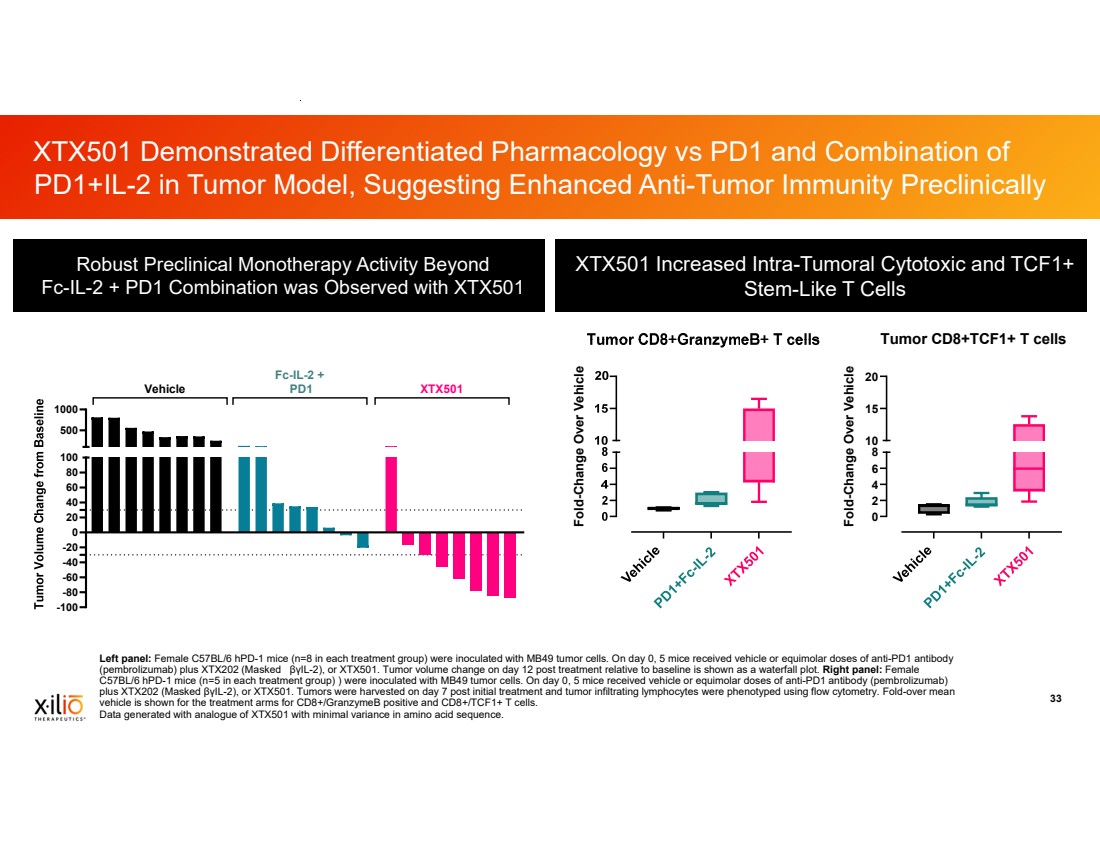
| 2 This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended, including, without limitation, statements regarding plans, timing and expectations related to: plans and anticipated milestones for vilastobart (XTX101), XTX301 and Xilio’s development candidates, including plans and timing for reporting and results of the Phase 2 clinical data for vilastobart in combination with atezolizumab in patients with microsatellite stable (MSS) colorectal cancer or any of our other clinical programs; the potential to partner vilastobart; the ultimate safety data for any of Xilio’s product candidates; the potential benefits of any of Xilio’s current or future product candidates in treating patients as a monotherapy or combination therapy; the period in which Xilio expects to have cash to fund its operations; the potential for Xilio to leverage its research platform to develop bispecific and cell engager molecules; and Xilio’s strategy, goals and anticipated financial performance, milestones, business plans and focus. The words “aim,” “may,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “project,” “potential,” “continue,” “seek,” “target” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. Any forward-looking statements in this presentation are based on management’s current expectations and beliefs and are subject to a number of important risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation, including, without limitation, general market conditions, risks and uncertainties related to ongoing and planned research and development activities, including initiating, conducting or completing preclinical studies and clinical trials and the timing and results of such preclinical studies or clinical trials; the delay of any current or planned preclinical studies or clinical trials or the development of Xilio’s current or future product candidates; Xilio’s ability to obtain and maintain sufficient preclinical and clinical supply of current or future product candidates; Xilio’s advancement of multiple early-stage immune cell engager programs, including tumor-activated immune cell engagers and tumor-activated effector-enhanced immune cell engagers; initial, preliminary or interim preclinical or clinical data or results (including, without limitation, the Phase 2 data for vilastobart and the preliminary investigator-reported response awaiting radiology confirmation), which may not be replicated in or predictive of future preclinical or clinical data or results; Xilio’s ability to successfully demonstrate the safety and efficacy of its product candidates and gain approval of its product candidates on a timely basis, if at all; results from preclinical studies or clinical trials for Xilio’s product candidates, which may not support further development of such product candidates; actions of regulatory agencies, which may affect the initiation, timing and progress of Xilio’s current or future clinical trials; Xilio’s ability to obtain, maintain and enforce patent and other intellectual property protection for current or future product candidates; Xilio’s ability to obtain and maintain sufficient cash resources to fund its operations; the impact of international trade policies on Xilio’s business, including U.S. and China trade policies; Xilio’s ability to maintain its clinical trial collaboration with Roche to develop vilastobart in combination with atezolizumab and its license agreement with Gilead to develop and commercialize XTX301. These and other risks and uncertainties are described in greater detail in the sections entitled “Risk Factor Summary” and “Risk Factors” in Xilio’s filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), including Xilio’s most recent Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q and any other filings that Xilio has made or may make with the SEC in the future. Any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation represent Xilio’s views only as of the date hereof and should not be relied upon as representing its views as of any subsequent date. Except as required by law, Xilio explicitly disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements. Certain information contained in this presentation relates to or is based on studies, publications, surveys and other data obtained from third-party sources and Xilio’s own internal estimates and research. While Xilio believes these third-party studies, publications, surveys and other data to be reliable as of the date of this presentation, Xilio has not independently verified, and makes no representation as to the adequacy, fairness, accuracy or completeness of, any information obtained from third-party sources. In addition, no independent source has evaluated the reasonableness or accuracy of Xilio’s internal estimates or research and no reliance should be made on any information or statements made in this presentation relating to or based on such internal estimates and research. This presentation contains trademarks, trade names and service marks of other companies, which are the property of their respective owners. TECENTRIQ is a registered trademark of Genentech USA Inc., a member of the Roche Group. Forward-Looking Statements and Disclaimers |